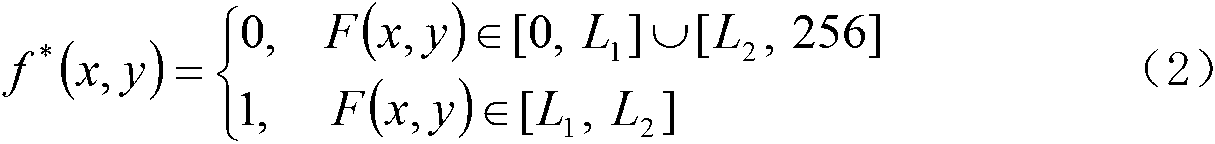Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
369 results about "Gas laser" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A gas laser is a laser in which an electric current is discharged through a gas to produce coherent light. The gas laser was the first continuous-light laser and the first laser to operate on the principle of converting electrical energy to a laser light output. The first gas laser, the Helium–neon laser (HeNe), was co-invented by Iranian-American physicist Ali Javan and American physicist William R. Bennett, Jr. in 1960. It produced a coherent light beam in the infrared region of the spectrum at 1.15 micrometres.
Method and arrangement for the efficient generation of short-wavelength radiation based on a laser-generated plasma
InactiveUS20060215712A1Losses in the main pulse (e.g., due to transmission) are minimizedLaser using scattering effectsActive medium materialIon densityElectromagnetic radiation
The invention is directed to a method and an arrangement for the efficient generation of intensive short-wavelength radiation based on a plasma. The object of the invention is to find a novel possibility for the generation of intensive short-wavelength electromagnetic radiation, particularly EUV radiation, which permits the excitation of a radiation-emitting plasma with economical gas lasers (preferably CO2 lasers). This object is met, according to the invention, in that a first prepulse for reducing the target density is followed by at least a second prepulse which generates free electrons in the target by multiphoton ionization after a virtually complete recombination of free electrons generated by the first prepulse has taken place due to a long-lasting expansion of the target for reducing the target density, and the main pulse of a gas laser with a low critical electron density typical for its wavelength is directed to the target immediately after the second prepulse when the second prepulse in the expanded target, whose ion density corresponds to the critical electron density of the gas laser, has created enough free electrons so that an efficient avalanche ionization is triggered by the main pulse of the gas laser until reaching the ionization level for the desired radiation emission of the plasma.
Owner:XTREME TECH
Instrument and method for real time monitoring optical fibre distributed multi-point mash gas
InactiveCN101281127AEliminate distractionsConcentration sensitiveColor/spectral properties measurementsData acquisitionEngineering
The invention discloses an optical fiber distributed multi-point methane real-time monitor based on the light wave modulation spectrometry and the monitoring method, a semiconductor DFB laser, an optical fiber splitter, a gas calibration pond, a laser control circuit board, a signal generative circuit board, a lock-in amplified board, a data acquisition card, a control module, a multi-channel analog signal selection switch and a driving circuit are arranged in the main case of the monitor, the main case is connected with miniature optical sensors in various underground detection optical path through dingle mode fibers. The wavelength modulation of a gas laser absorption spectrum is realized by a low frequency scanning signal and a high frequency modulation signal generated by a signal generative circuit. The laser wavelength shift is carried out adaptive adjustment by the built-in gas calibration pond so as to realize the locking of a methane absorption line. The distributed multi-point methane concentration monitoring in the underground coal mine is realized by the switching of the multi-channel analog signal selection switch.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of manufacturing a three-dimensional object
ActiveUS8303886B2Compensation deviationAdditive manufacturing apparatus3D object support structuresControl signalErbium lasers
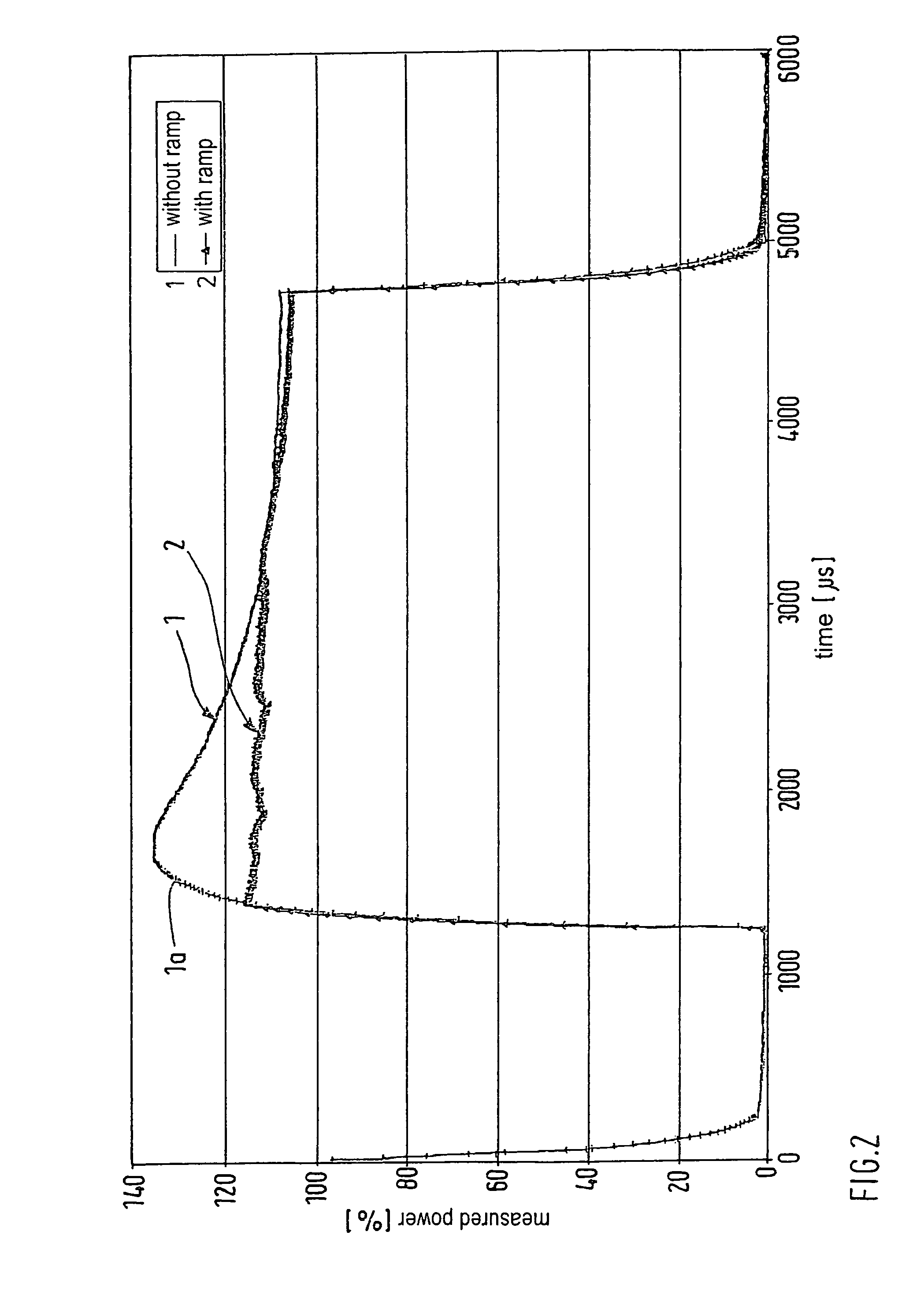
A method of manufacturing a three-dimensional object is disclosed, in which the object is solidified layer by layer by solidifying a building material by means of a beam of a gas laser at locations in each layer corresponding to the cross section of the object, wherein the power of the laser is measured and the power of the laser is controlled according to the measured value. The power measurement takes place in a time window, in which a change of the power occurs, and an input control signal of the laser is controlled according to the measured values.
Owner:EOS ELECTRO OPTICAL SYST
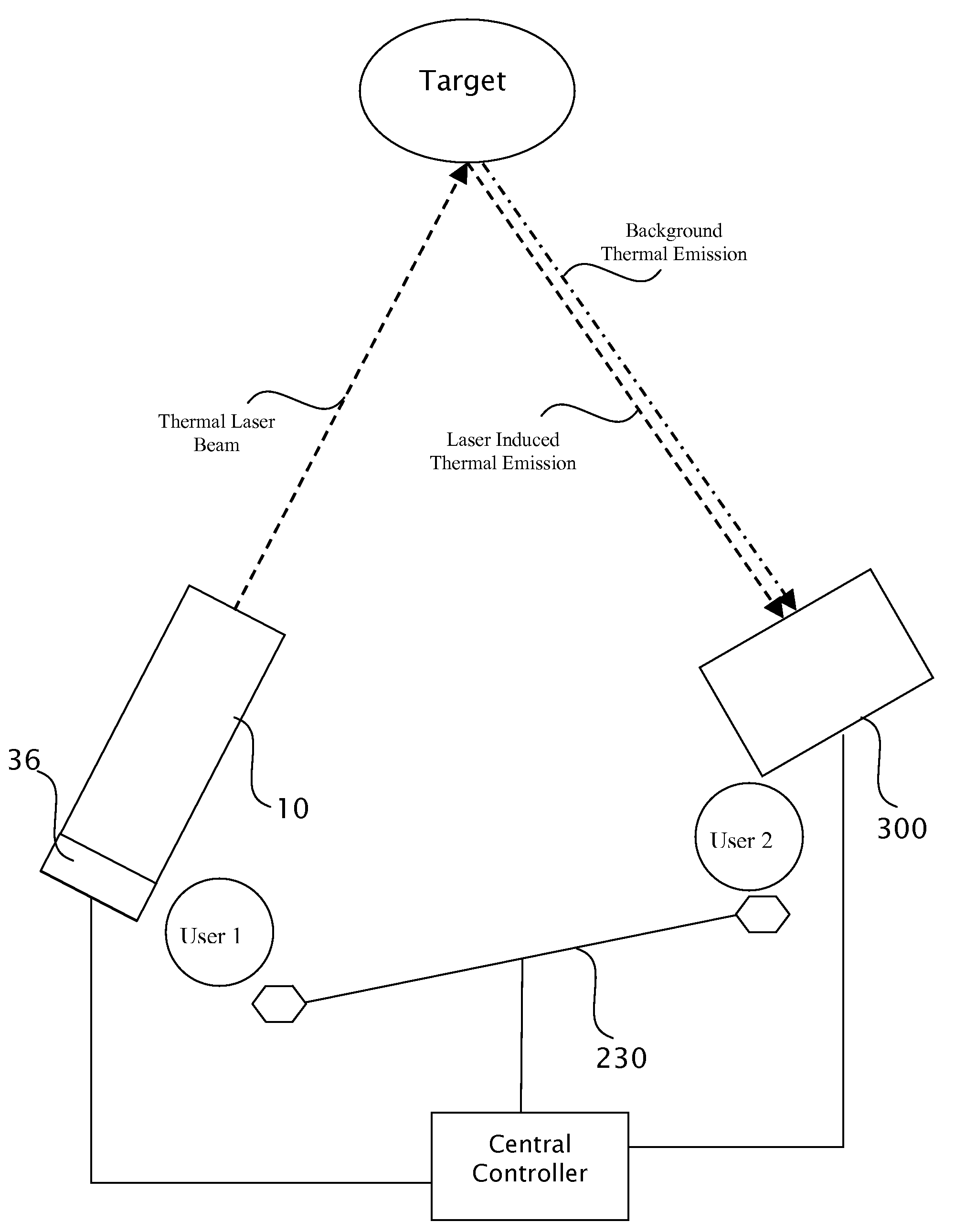
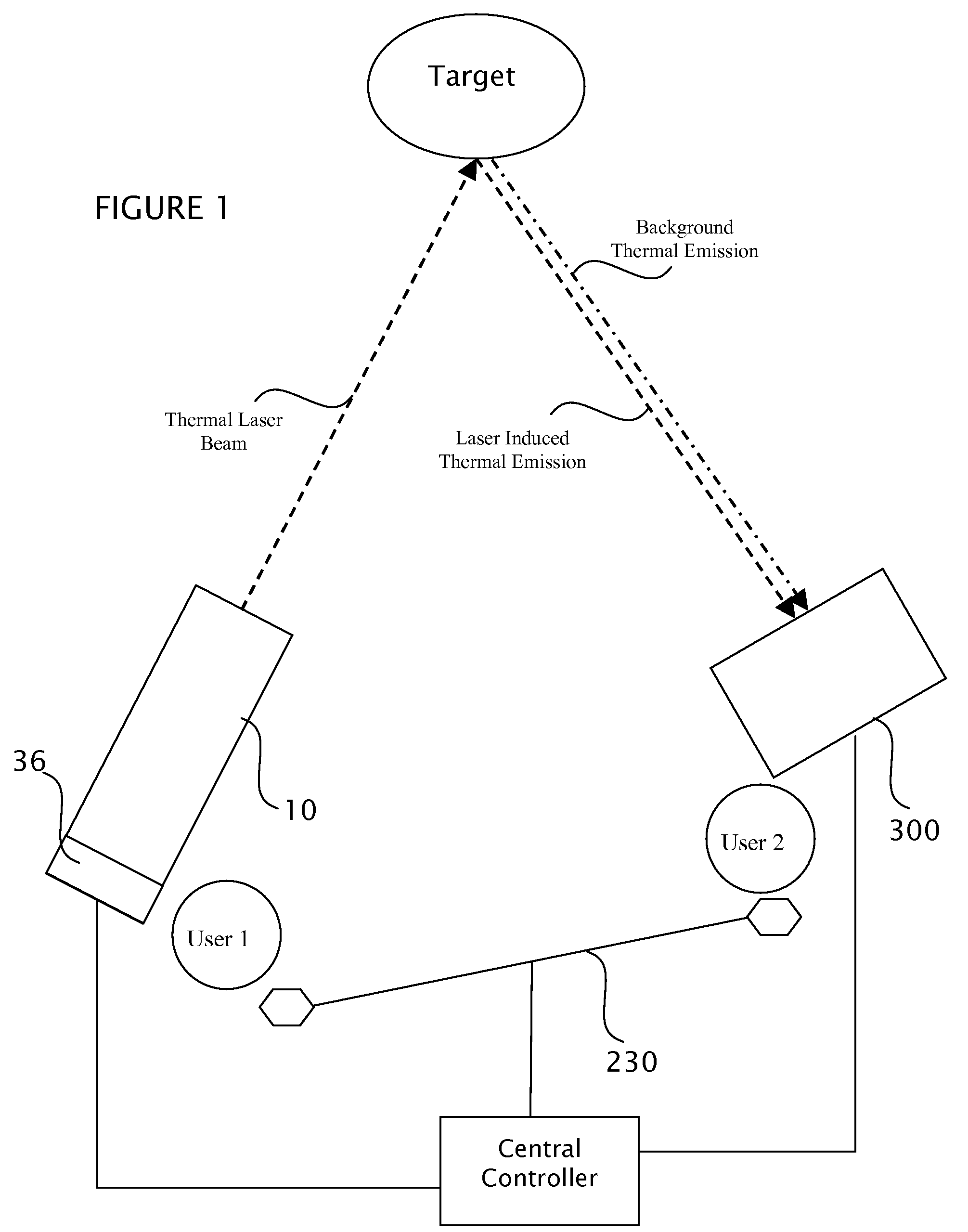
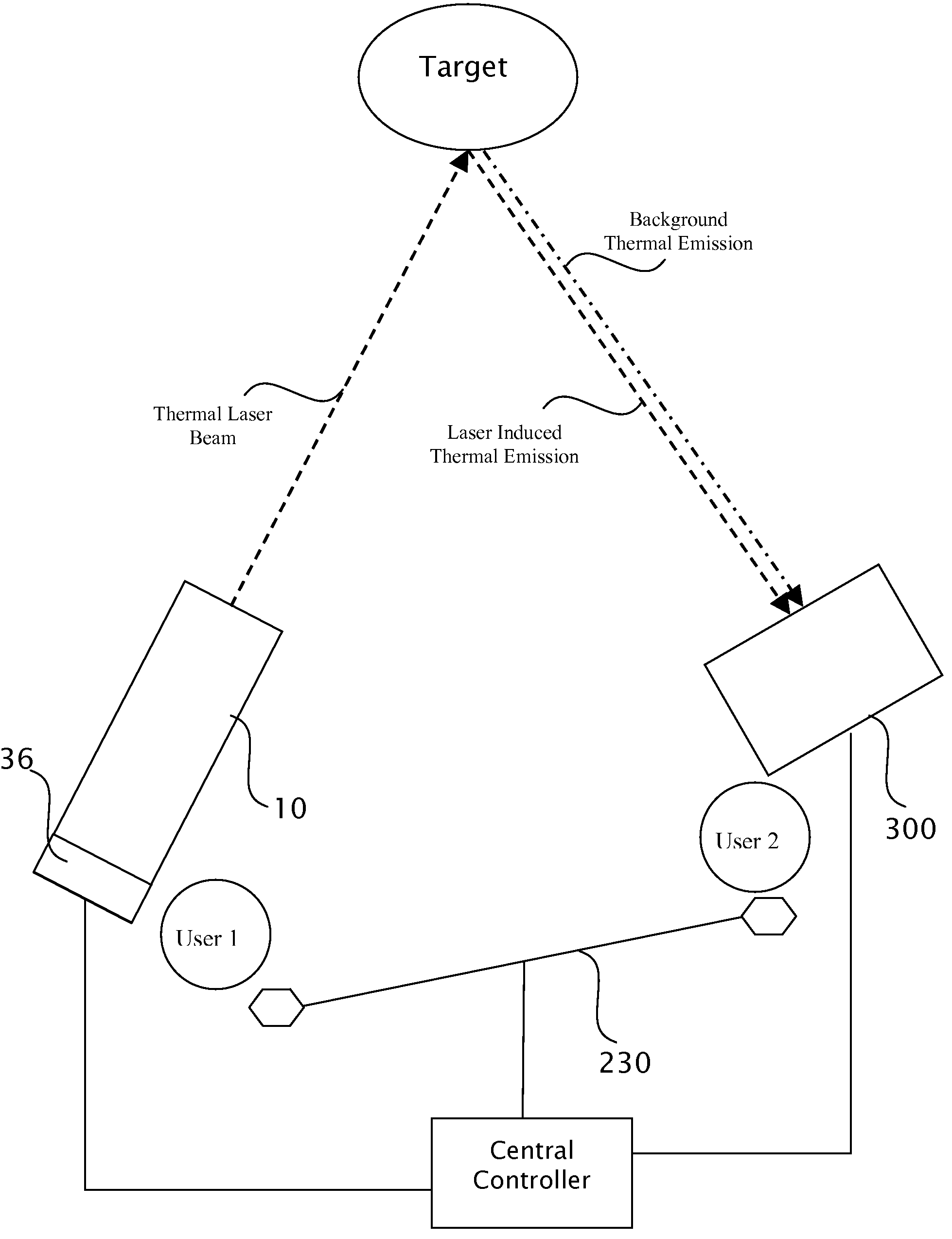
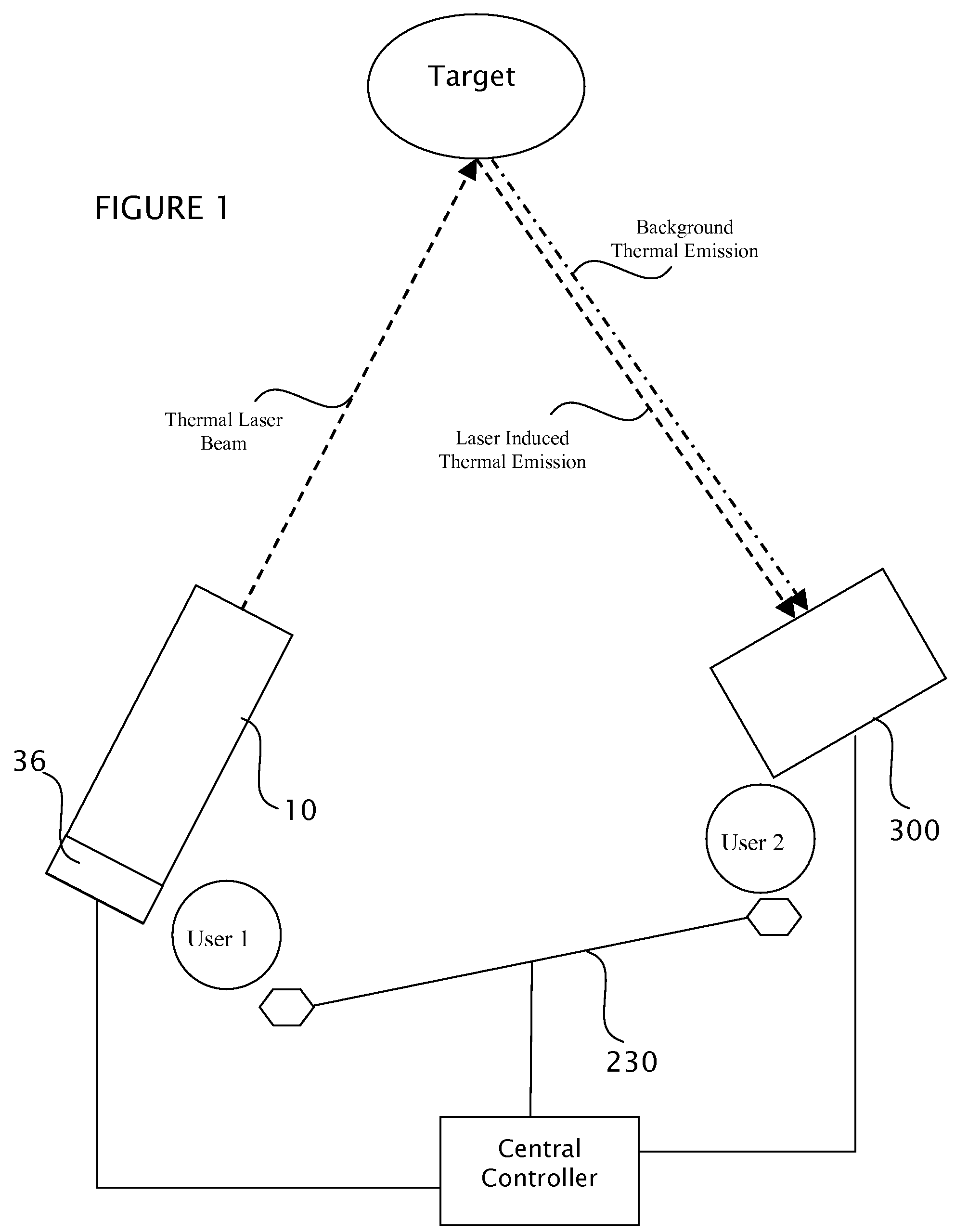
Target marking system having a gas laser assembly and a thermal imager
InactiveUS20090110019A1Robust configurationSighting devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansLight beamThermographic camera
A handheld target marker is provided, wherein the target marker includes a housing retaining a gas laser, a collimating or focusing lens, a driver and a power supply. The laser produces a thermal infrared beam which can be selectively directed to impinge upon a target. The impinging beam is viewable by a thermal imager. The handheld target marker operates at ambient temperatures and incorporates the driver and power supply necessary for operation of the laser, wherein the beam can be pulsed for enhancing imaging on the thermal imager.
Owner:LMD APPL SCI LLC
Laser assisted material deposition
Apparatus is provided for a method of forming a film on a substrate that includes activating a gas precursor to deposit a material on the substrate by irradiating the gas precursor with electromagnetic energy at a frequency tuned to an absorption frequency of the gas precursor. The electromagnetic energy can be provided by an array of lasers. The frequency of the laser beam is selected by switching from one laser in the array to another laser in the array. The laser array may include laser diodes, one or more tunable lasers, solid state lasers, or gas lasers. The frequency of the electromagnetic energy is selected to impart specific amounts of energy to a gas precursor at a specific frequency that provides point of use activation of the gas precursor.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
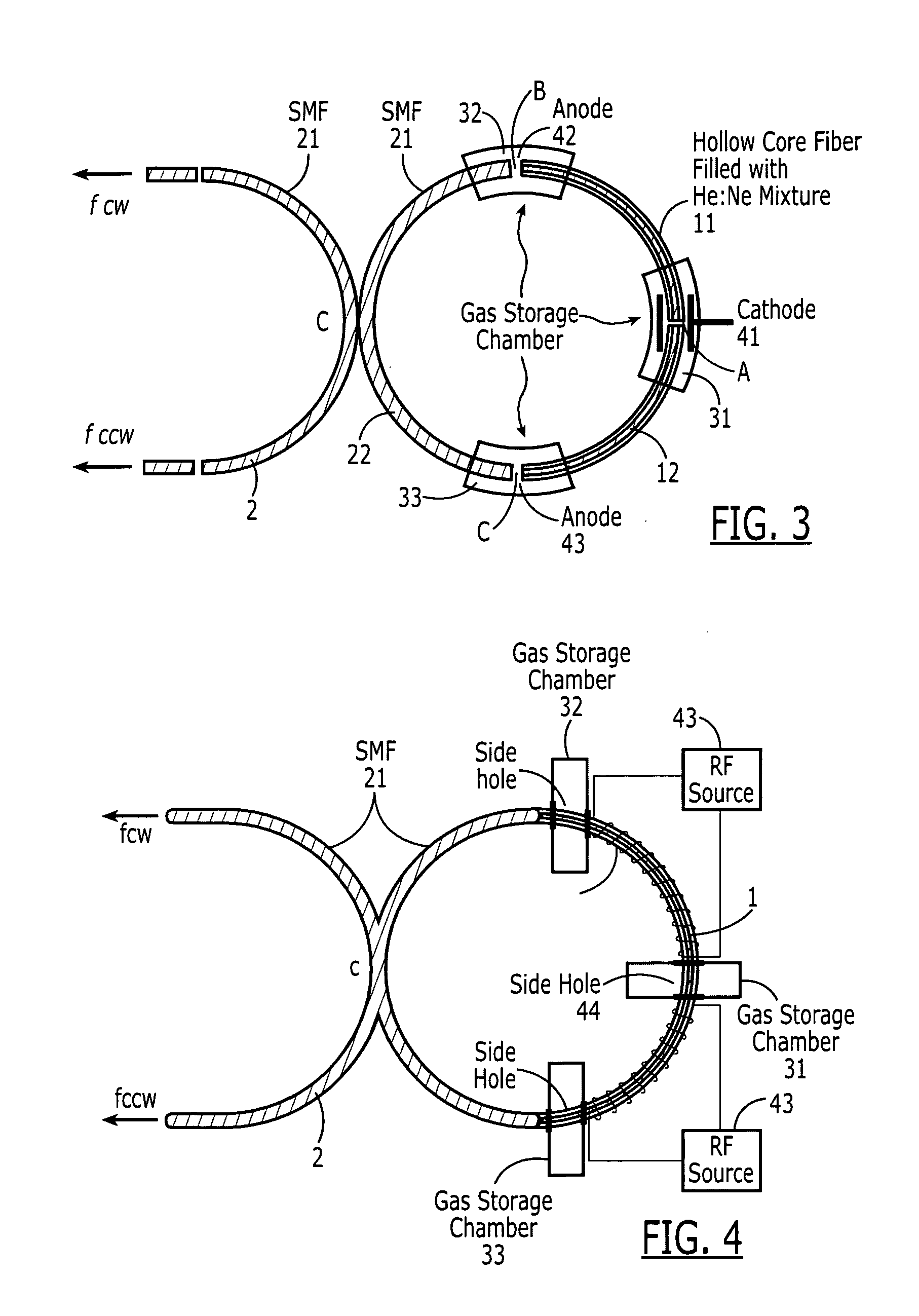
Fiber gas lasers and fiber ring laser gyroscopes based on these gas lasers
InactiveUS20080094636A1Good amplification performanceSimple structureLaser using scattering effectsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsFiber couplerGyroscope
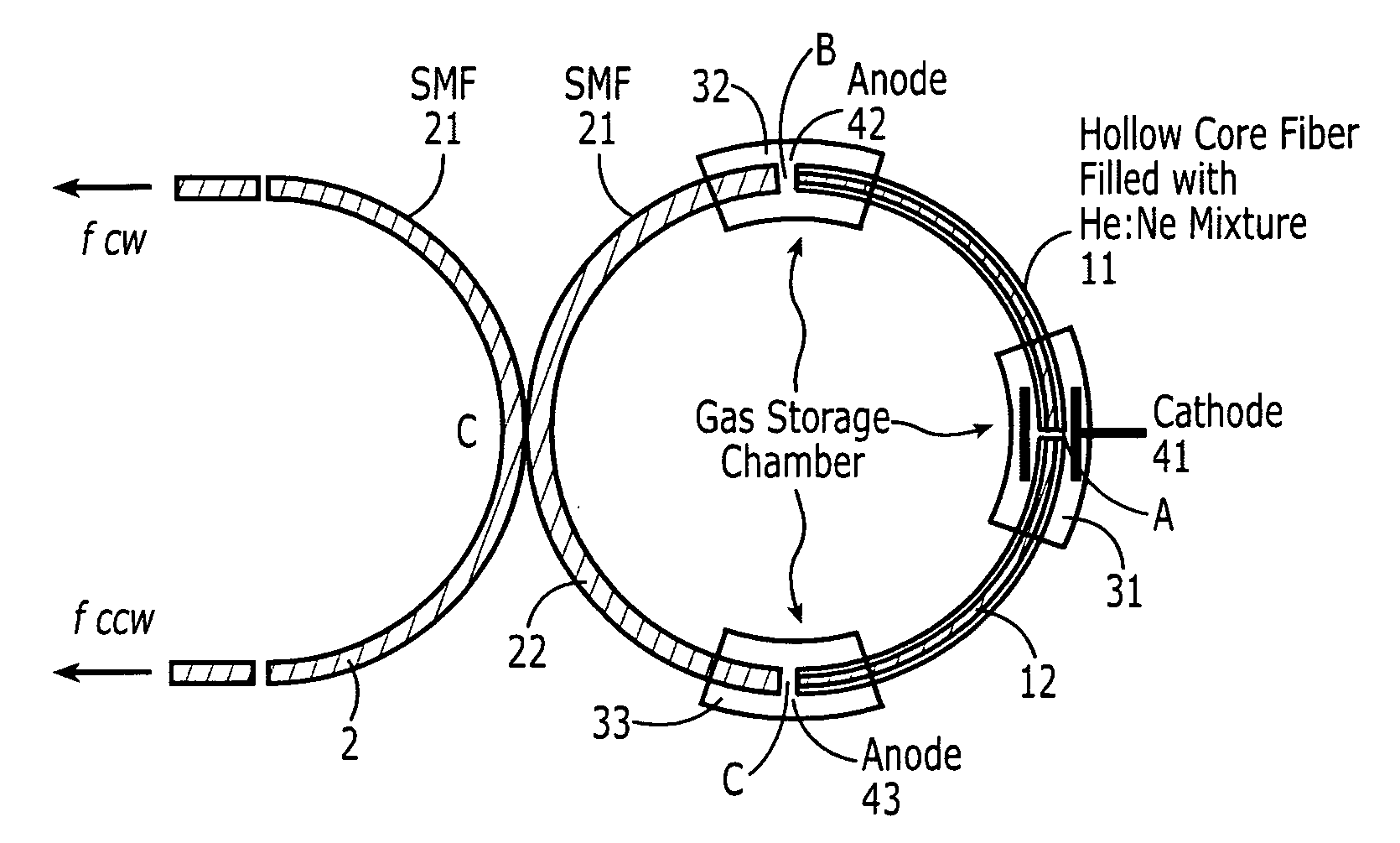
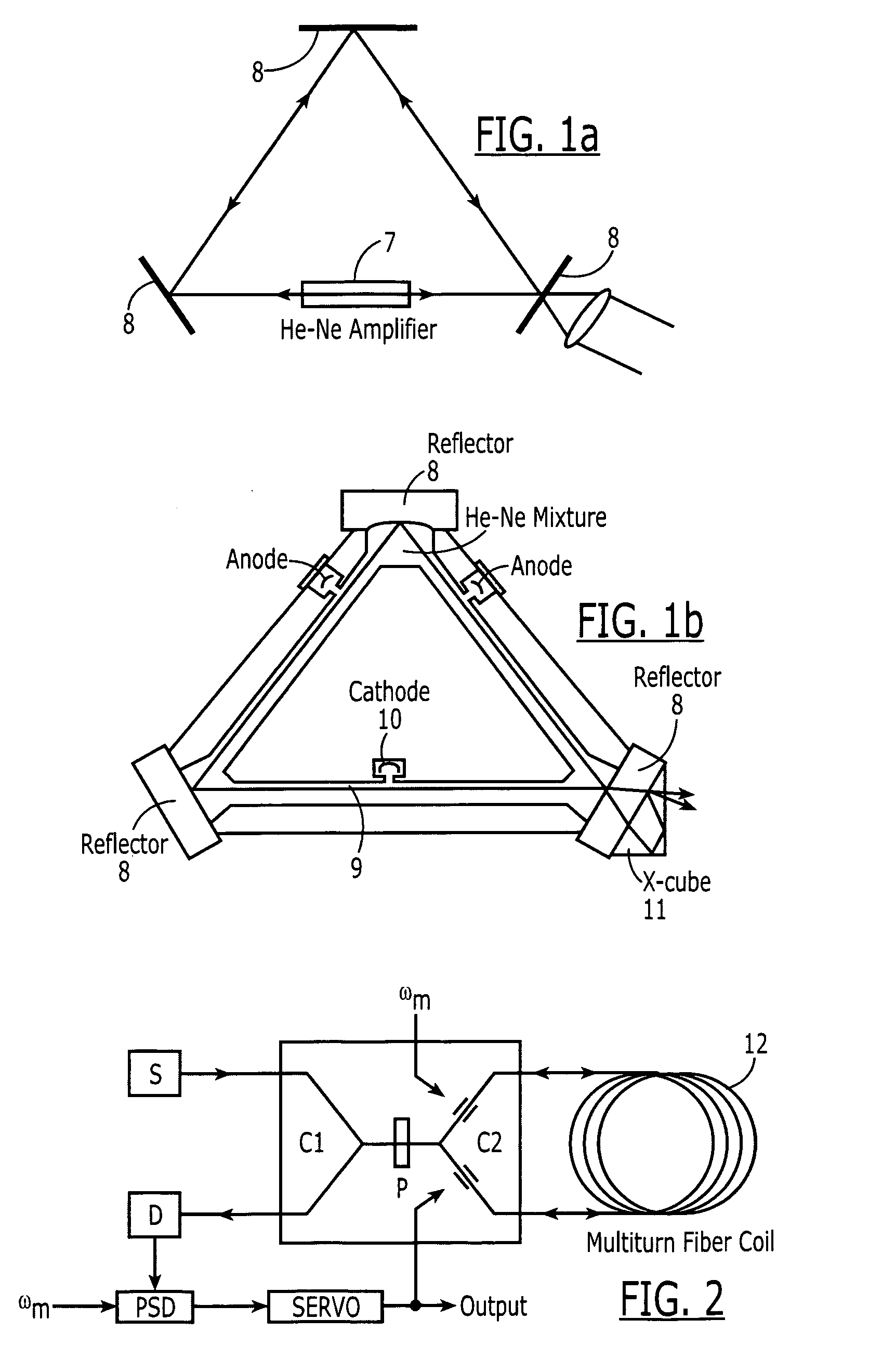
This invention discloses to a type of fiber gas lasers and fiber ring laser gyroscopes based on these fiber gas lasers. The fiber gas lasers comprise of excitation gases, optical resonator and excitation source, etc. The optical resonator is made by connecting two selected arms of a single mode fiber coupler to the two ends of hollow-core fiber to form a ring resonator. The hollow-core of the fiber is filled with excitation gases to act as gain medium. The fiber laser is simple to construct, lower cost, and has adjustable size and good amplification performance. The fiber ring laser gyroscopes based on this novel type of gas lasers can be applied on robotics, automobile navigation, etc.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
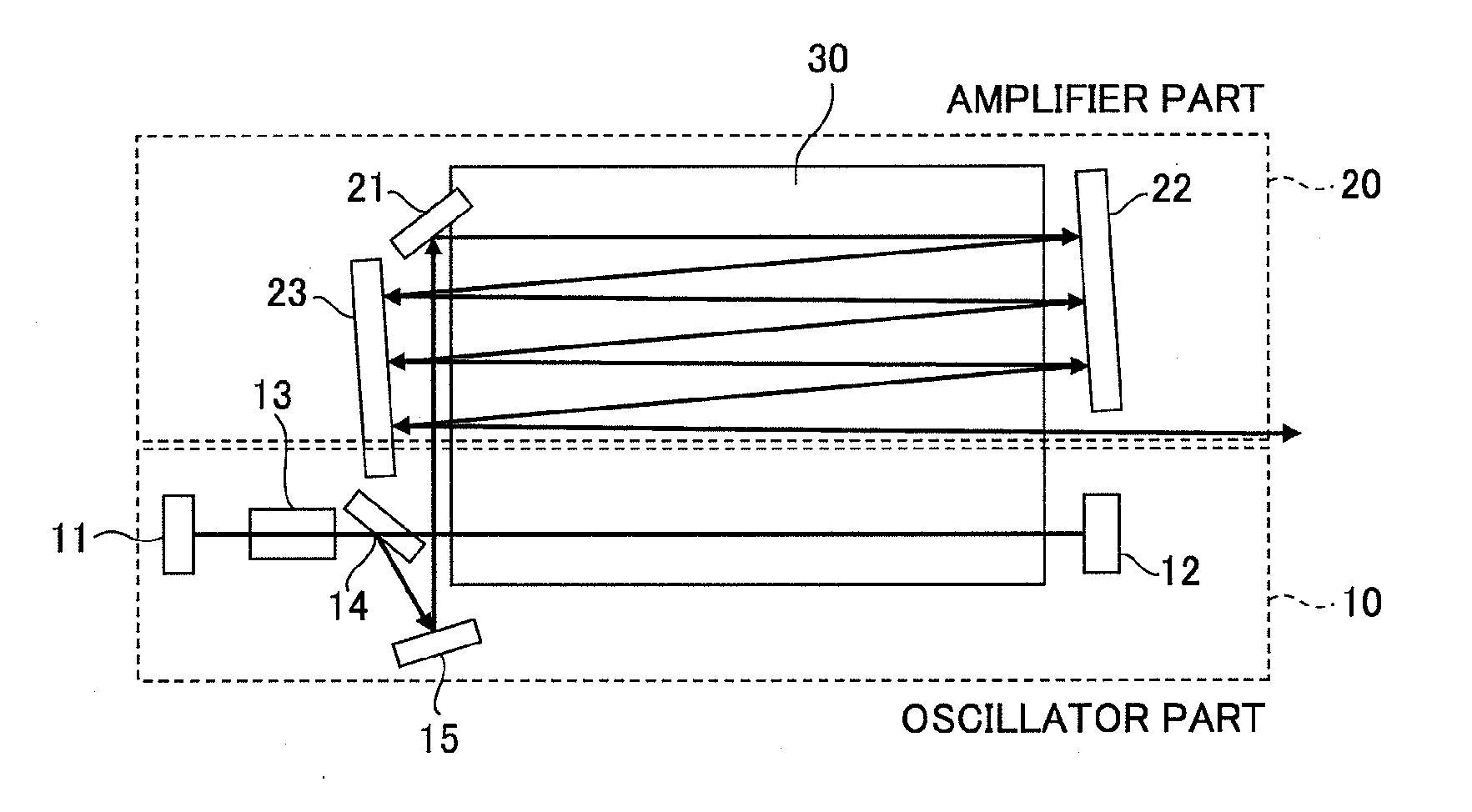
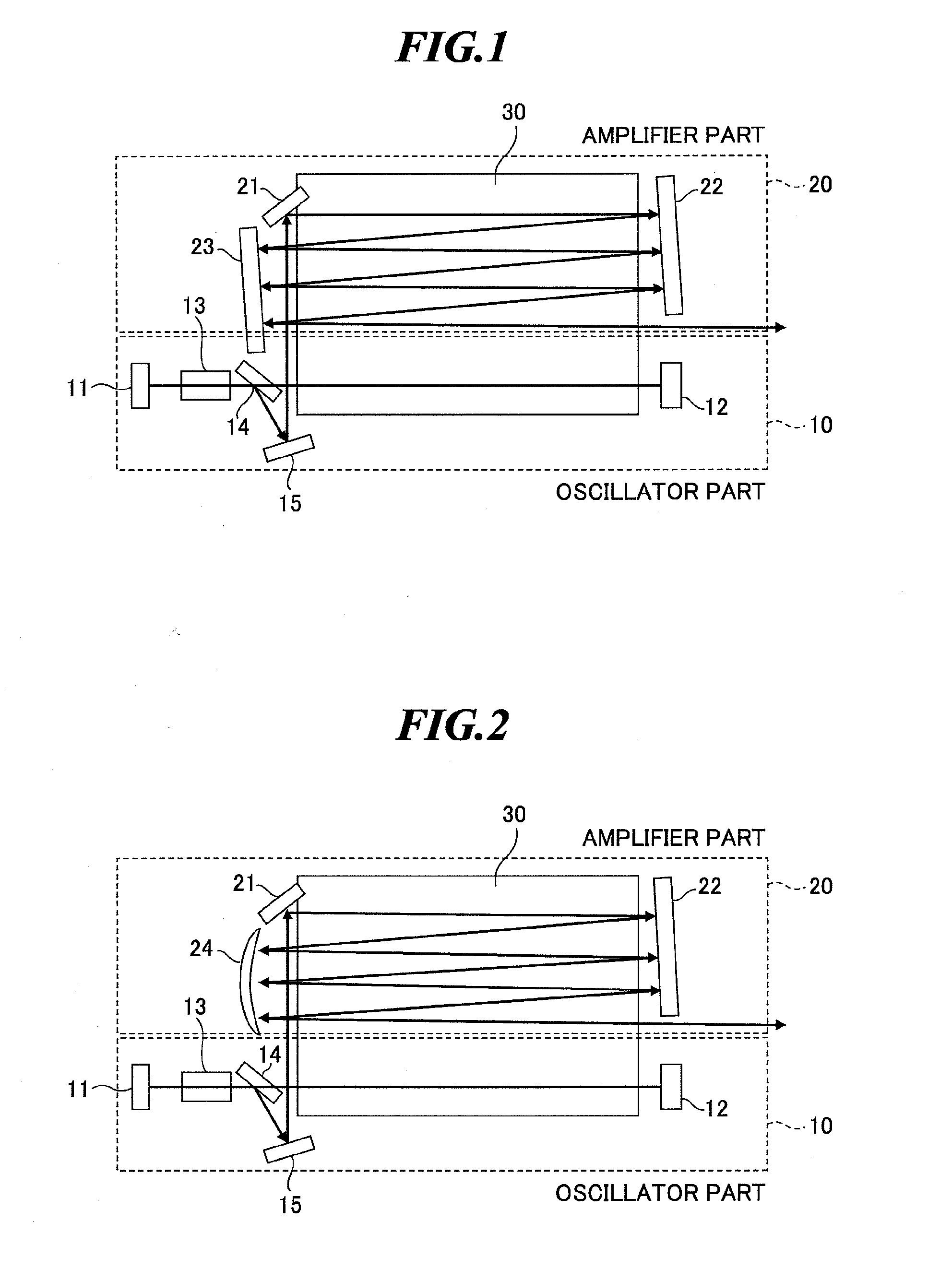
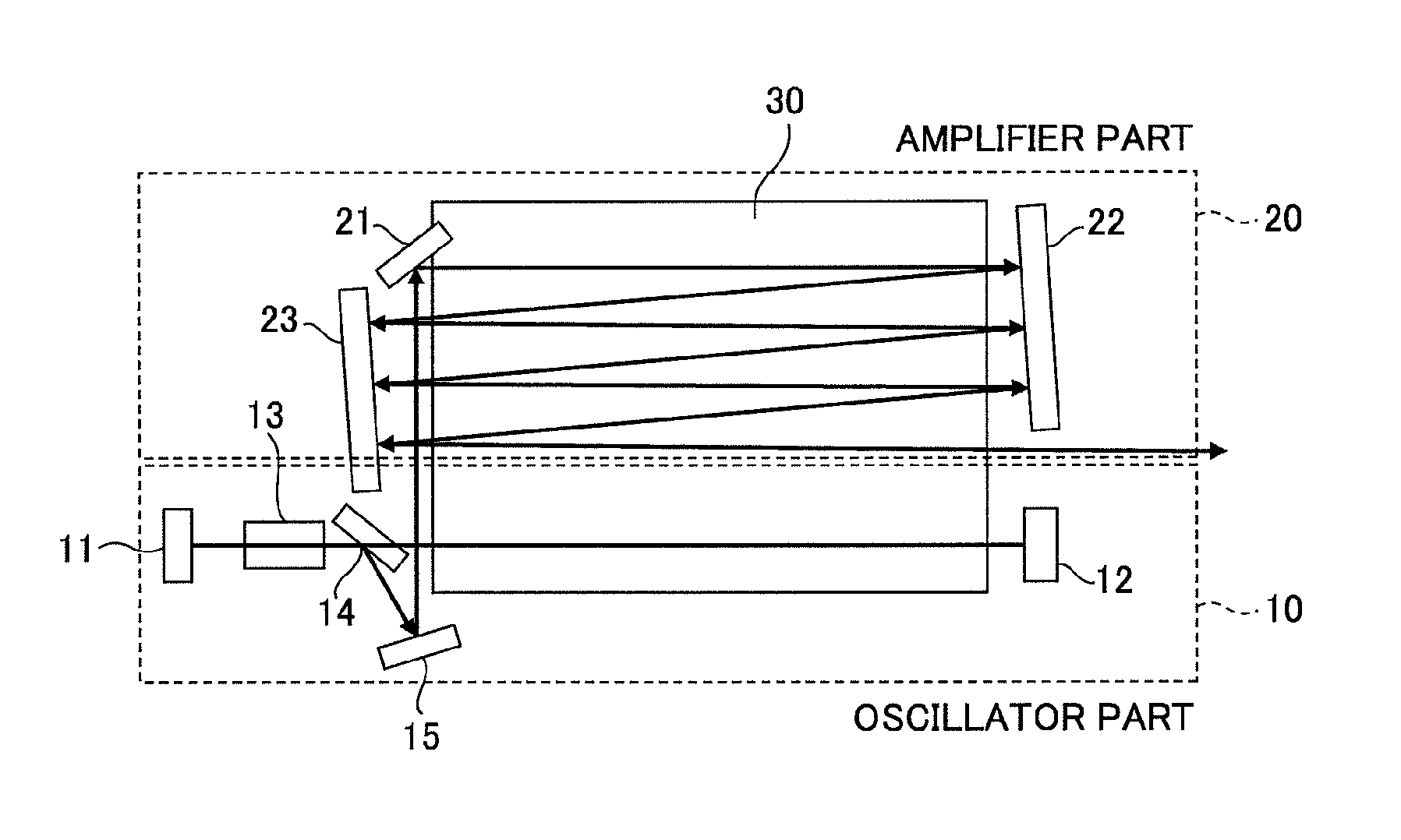
Slab type laser apparatus
ActiveUS20090316746A1Improve focus performanceInhibit swellingExcitation process/apparatusPhotomechanical apparatusAudio power amplifierGas laser
A slab type laser apparatus has a slab type gas laser medium part formed in a region defined by a pair of electrode flat plates oppositely disposed in parallel with each other in a space to be filled with a gas laser medium which is excited by high-frequency electric power. The apparatus includes an oscillator part including a pair of resonator mirrors oppositely disposed with a part of the gas laser medium part in between, and for amplifying a laser beam to have predetermined light intensity to emit the laser beam, and the amplifier part including a plurality of return mirrors oppositely disposed with a part of the gas laser medium part in between. The incident laser beam goes and returns plural times between the return mirrors, and the laser beam is amplified to have predetermined power.
Owner:GIGAPHOTON +1
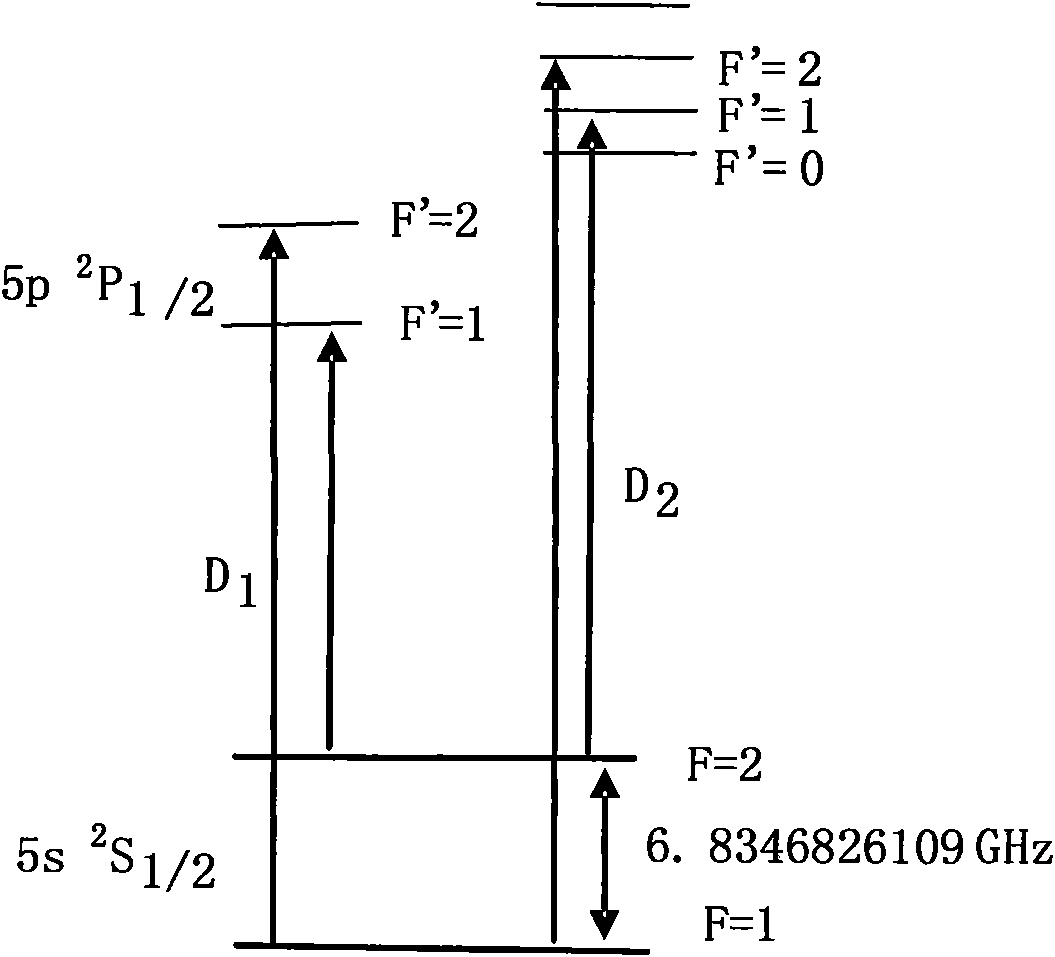
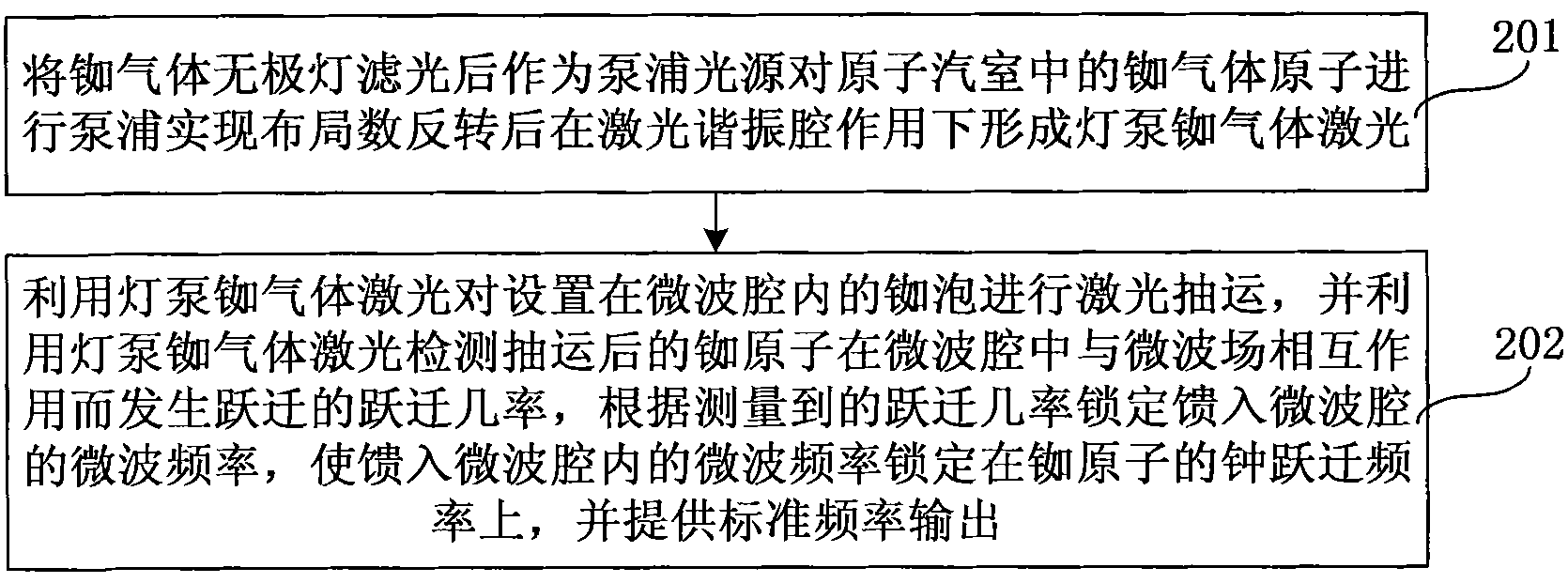
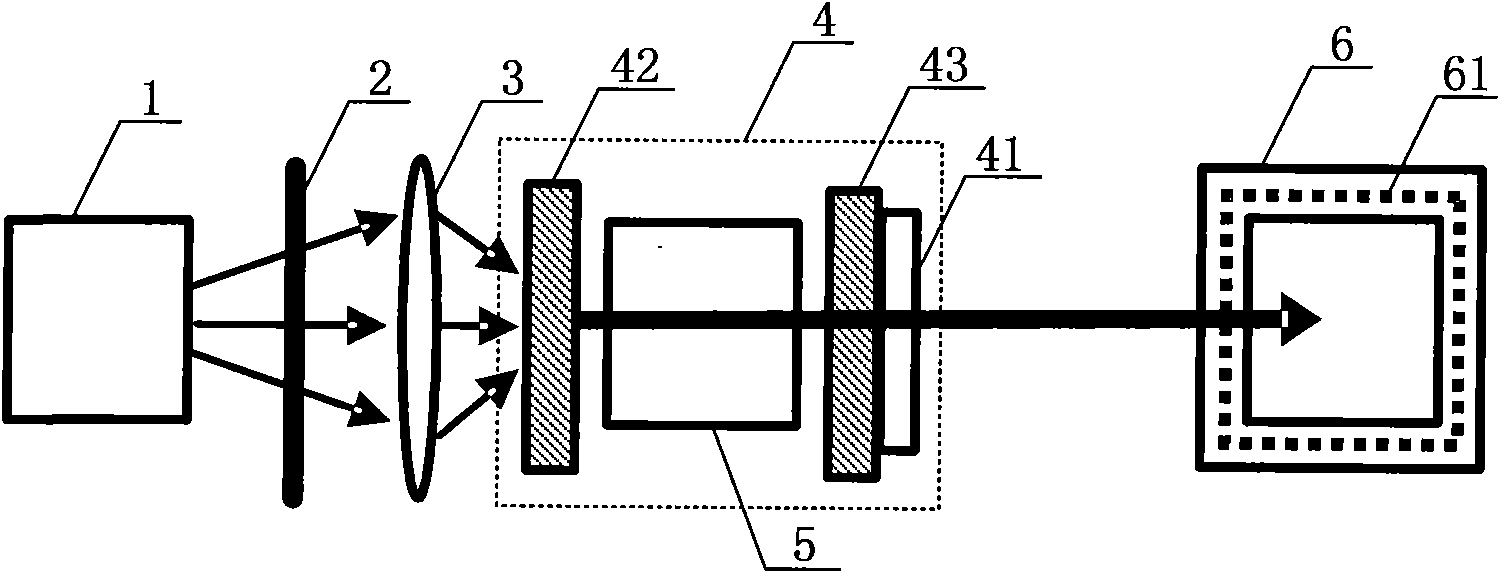
Method for pumping rubidium bubble for outputting standard frequency by lamp pump rubidium gas laser and rubidium atomic clock
ActiveCN101846965AEasy to lockQuick lockPulse automatic controlApparatus using atomic clocksMicrowave cavityResonant cavity
The invention relates to a method for pumping a rubidium bubble for outputting standard frequency by a lamp pump rubidium gas laser and a rubidium atomic clock. The method comprises the following steps of: adopting a filtered rubidium gas electrodeless lamp as a pumping light source for pumping a rubidium gas atom in an atom steam chamber, realizing distribution quantity conversion and then forming a lamp pump rubidium gas laser under the action of a laser resonant cavity; carrying out laser pumping on the rubidium bubble arranged in a microwave cavity by utilizing the lamp pump rubidium gas laser and detecting the transition probability of the pumped rubidium atom for generating transition by generating interaction with a microwave field in the microwave cavity by utilizing the lamp pump rubidium gas laser; and locking microwave frequency fed in the microwave cavity according to the detected transition probability and locking the microwave frequency fed in the microwave cavity on clock transition frequency of the atom. In the embodiment of the invention, because the frequency of the lamp pump rubidium gas laser still operates on a rubidium transition spectral line broadening spectrum in an unlocking state, even if the frequency of the lamp pump rubidium gas laser is unlocked, the lamp pump rubidium gas laser can be rapidly locked on needed laser frequency.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
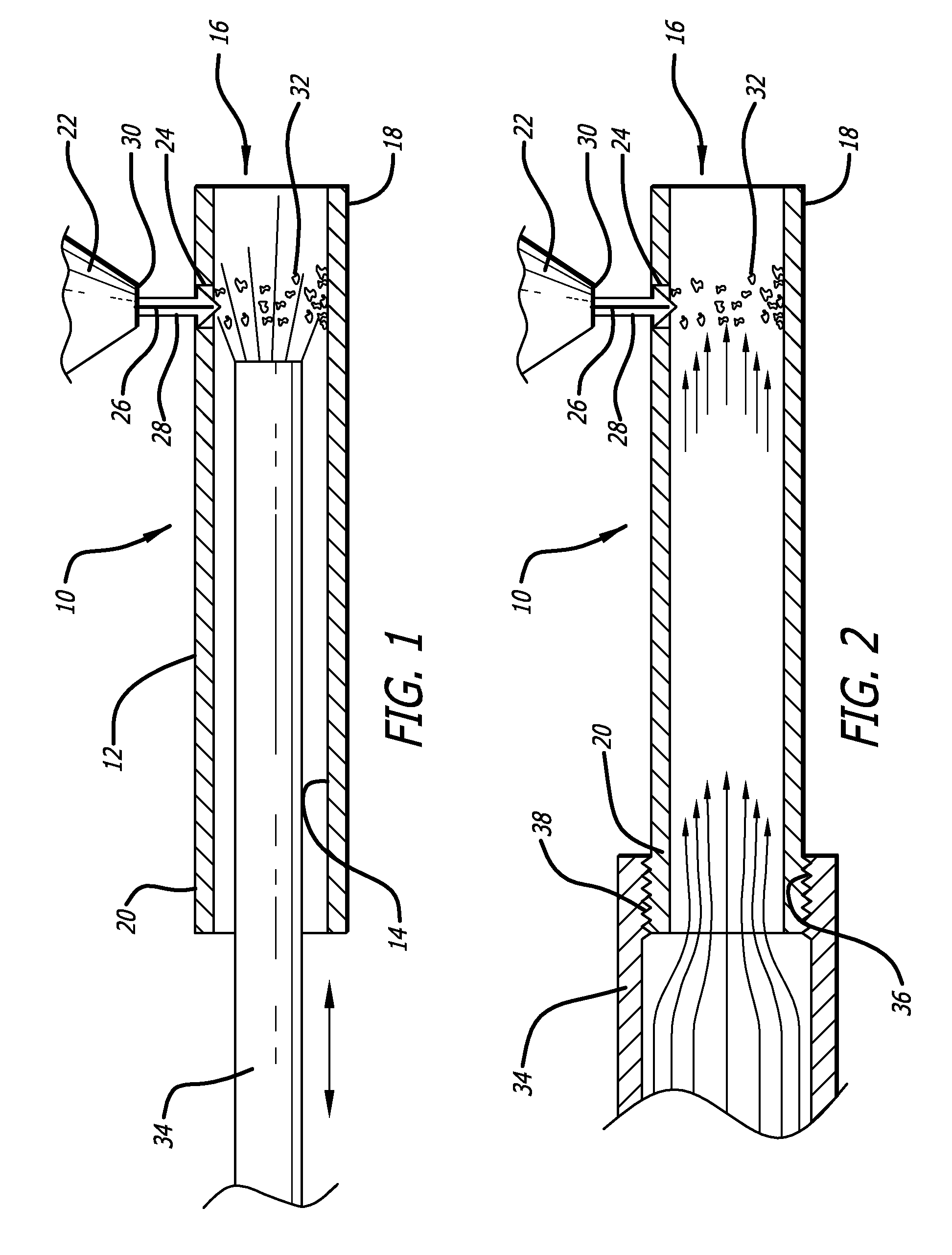
Dual gas laser cutting of medical devices
ActiveUS20100230391A1Reduce in quantityPrevent oxidationStentsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesSlagOptoelectronics
A system prevents oxidation of a laser cut workpiece by utilizing a laser source that utilizes laser source with an inert gas, such as argon or helium, rather than air or oxygen, to create the slots or kerfs which form the pattern cut into the workpiece. The system introduces oxygen gas through the workpiece as it is being laser cut to oxidize any slag or dross created during the laser cutting process. Oxygen or a mixture of oxygen with other gases cools the slag and the workpiece while at the same time oxidizing the slag to either completely burn or partial burn the slag before it strikes an exposed surface of the tubular member.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Two-dimensional flow velocity field measurement method and device of interlaced scanning CCD (charge coupled device)
ActiveCN103293333AEnables full-field velocity measurementLow priceFluid speed measurementMeasurement deviceHigh power lasers
The invention discloses a two-dimensional flow velocity field measurement method and device of an interlaced scanning CCD (charge coupled device). Trace particles are implanted into a to-be-measured flowing object (gas or liquid) and can move together with fluid due to viscidity. For the measurement device, a continuously light-emitting gas laser (such as He-Ne laser) is used as a light source, and a common interlaced scanning CCD sensor is used as an image detector. A one-frame flowing image including the trace particles is captured transiently, then the flowing image is processed by means of filtering and binaryzation, the interlacedly scanned one-frame image is separated into two images according to odd-even lines, a cross-correlation technology is adopted to perform computation processing, and accordingly a two-dimensional flow velocity field can be obtained. PIV (particle image velocimetry) full-field velocity measurement can be achieved without a high-power laser, a high-resolution CCD and a complex synchronizer; and the two-dimensional flow velocity field measurement method and device is simple in equipment, low in cost and applicable to flow field measurement on different occasions.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
RF excited gas laser
InactiveUS7145926B2Low costSimpler laser tube laserActive medium materialLaser cooling arrangementsForced-airEngineering
RF excited gas laser consists of a laser tube having external surfaces; a power supply compartment having elongated external fins and a pair of endplates on its opposite ends and wherein laser tube is placed between and is flexibly attached to the endplates; a sheet-metal cover mounted to the endplates and to power supply compartment and forming a laser assembly and having at least one pair of intake openings and at least one pair of exhaust openings for the cooling air to flow through the laser assembly by entering the laser assembly through the intake openings and flowing over power supply external fins and over laser tube external surfaces and then exiting through the exhaust openings. Present invention is characterized by lower cost and more efficient forced air cooling laser tube and RF power supply.
Owner:VITRUK PETER +2
Laser cutting apparatus
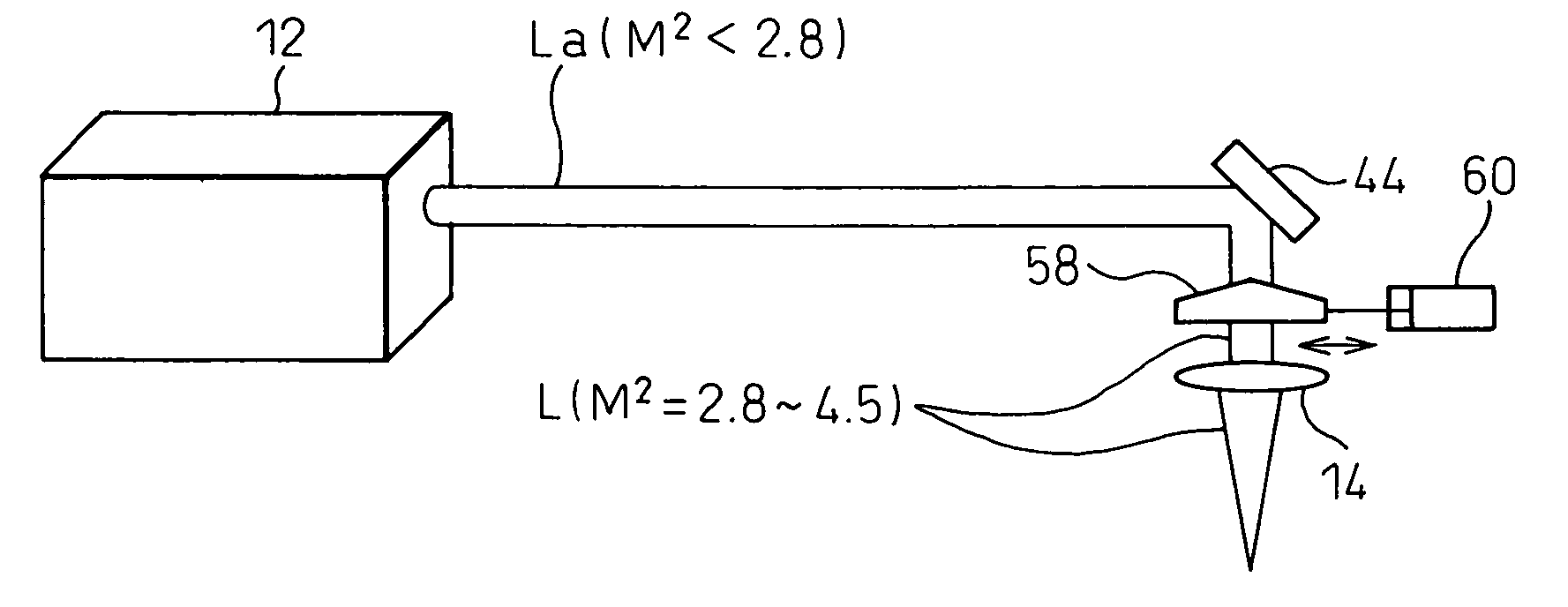
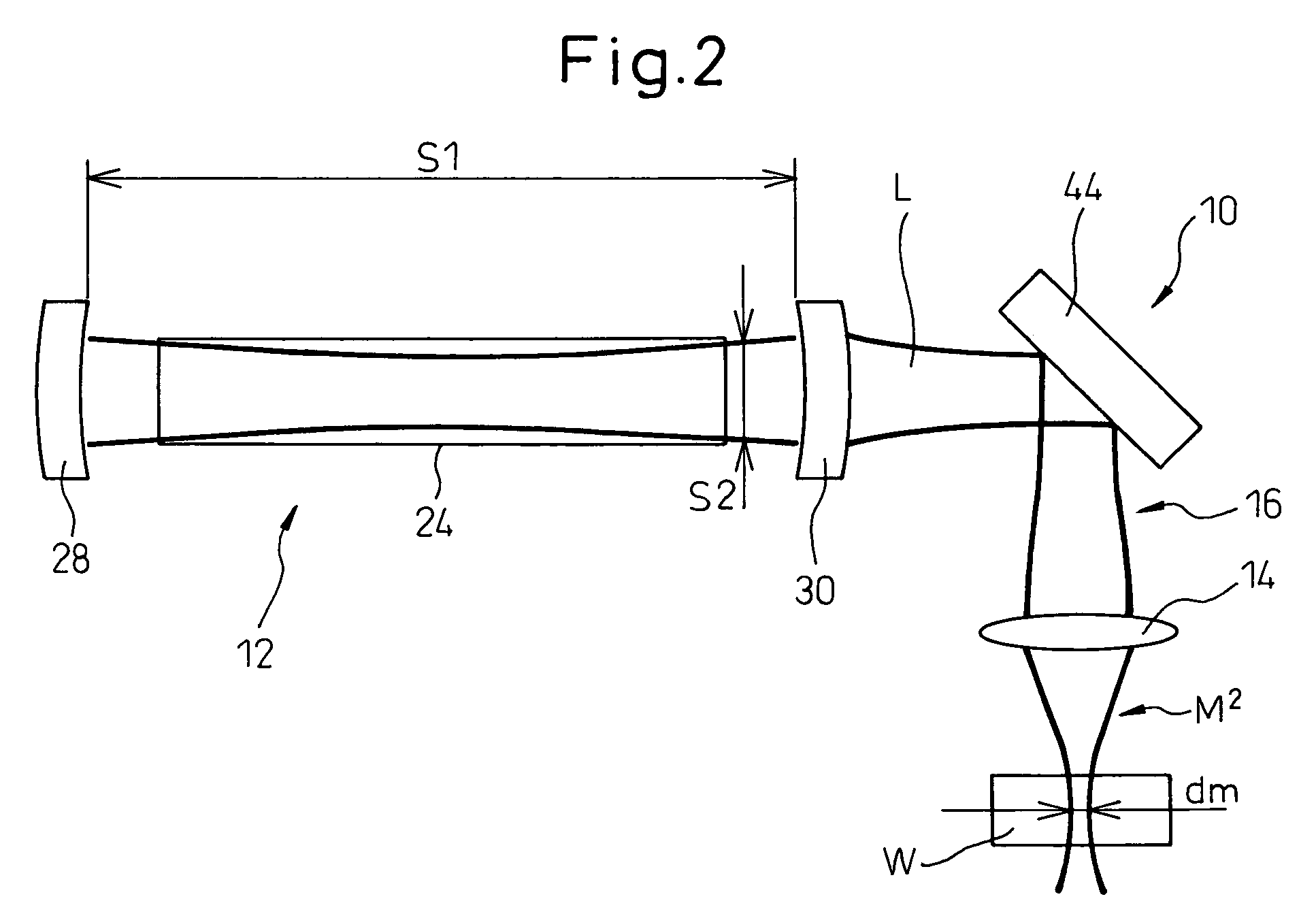
InactiveUS20060044981A1Large thicknessPrecise cuttingCombination recordingRecord information storageBeam diameterOptical axis
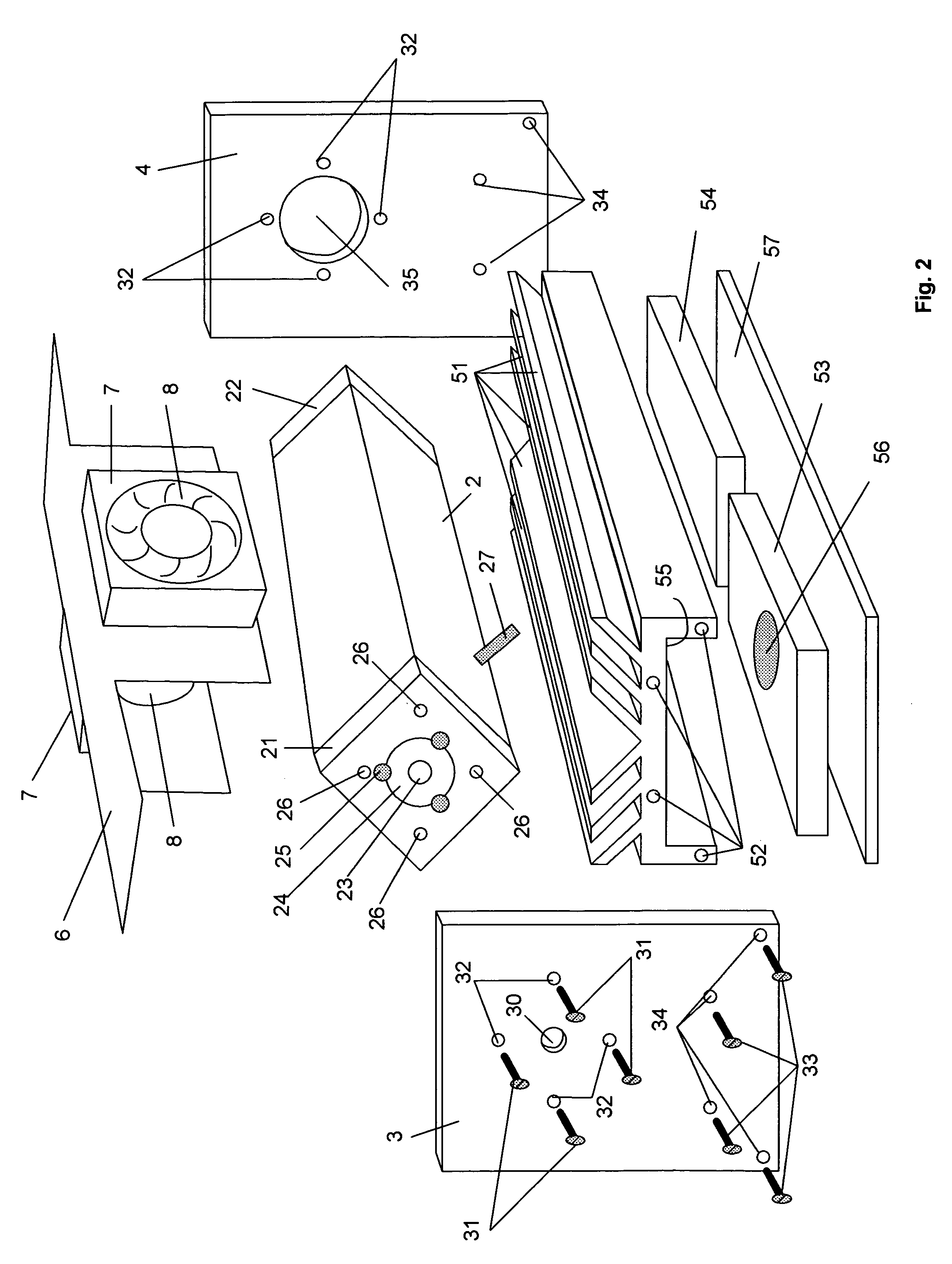
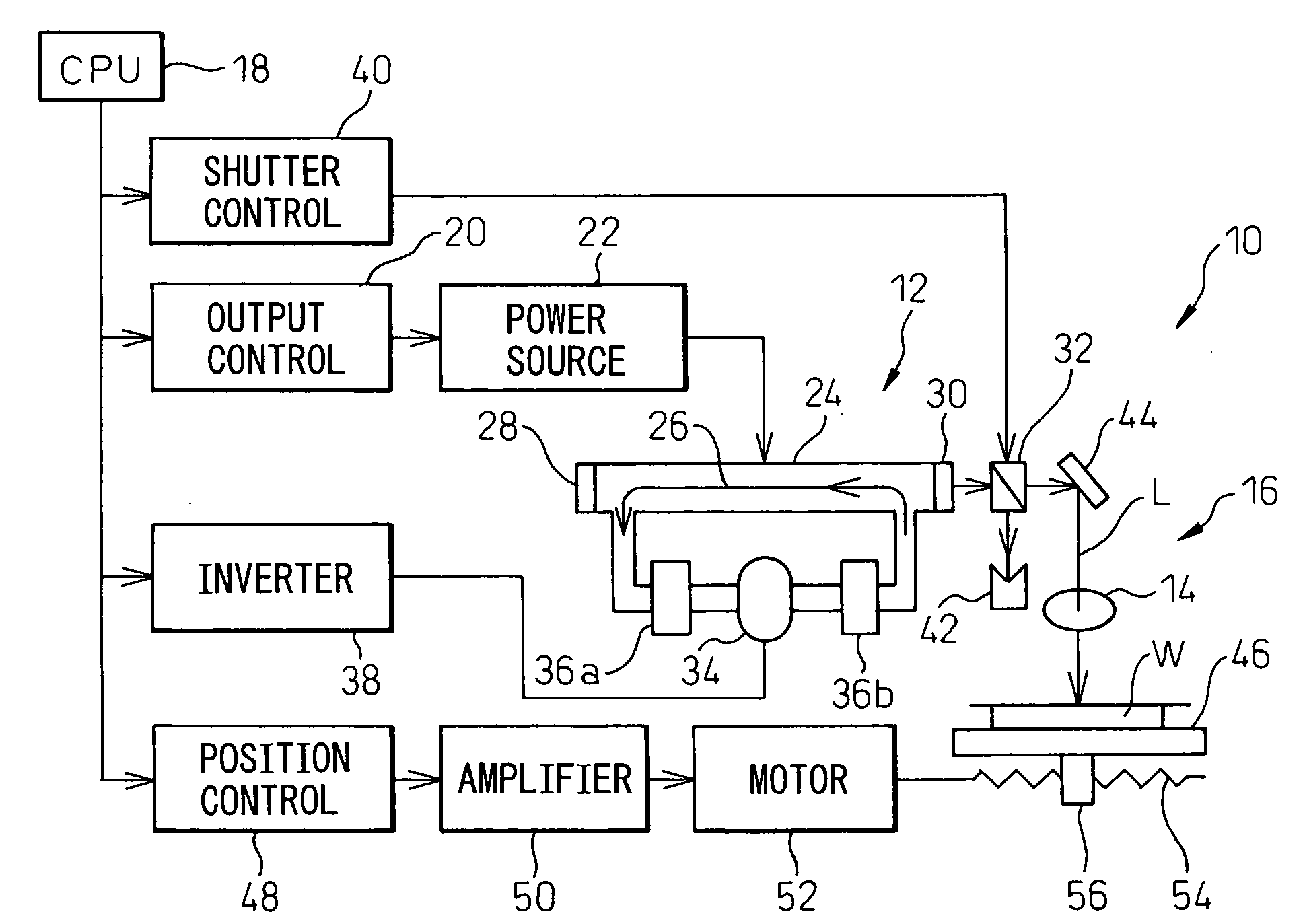
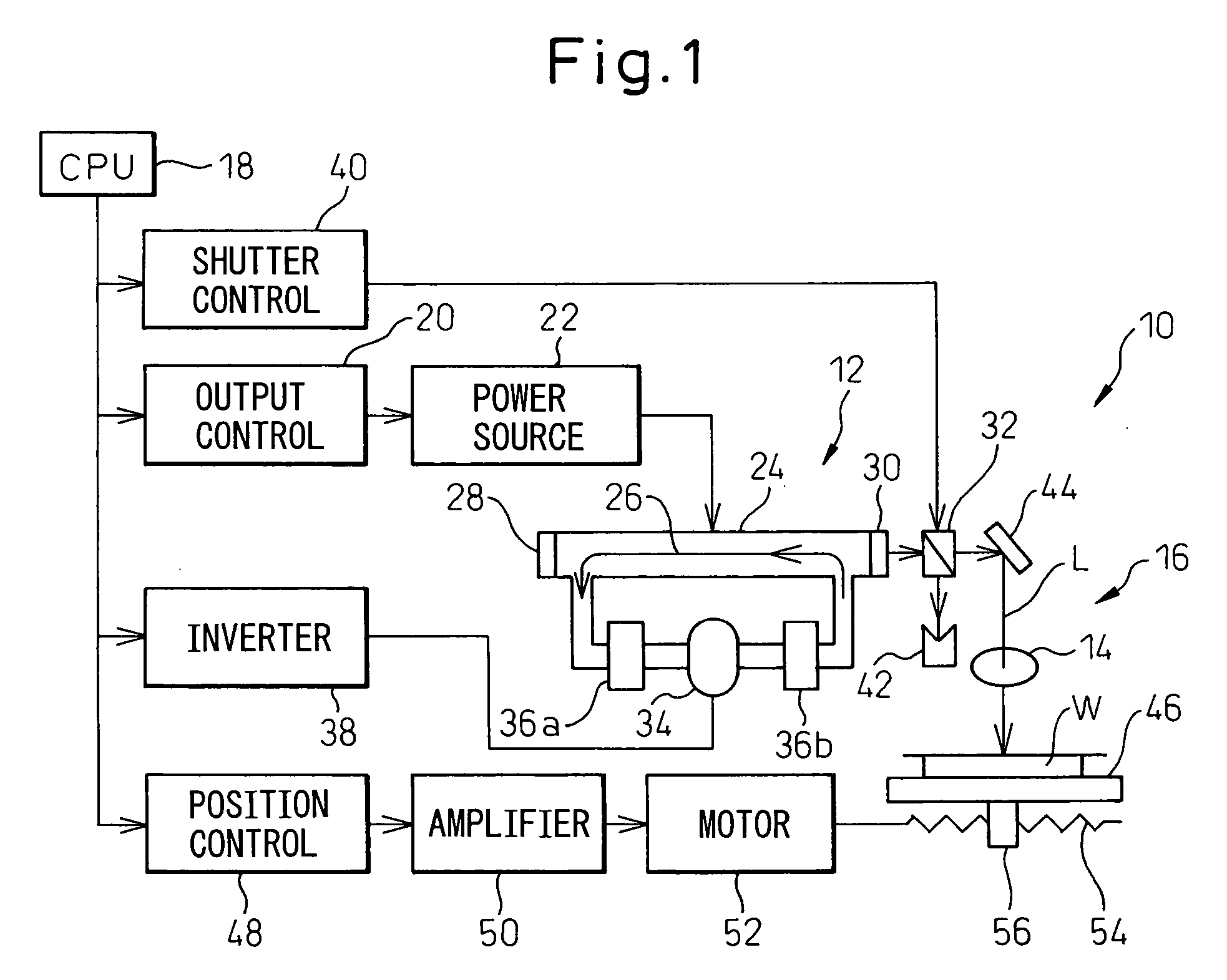
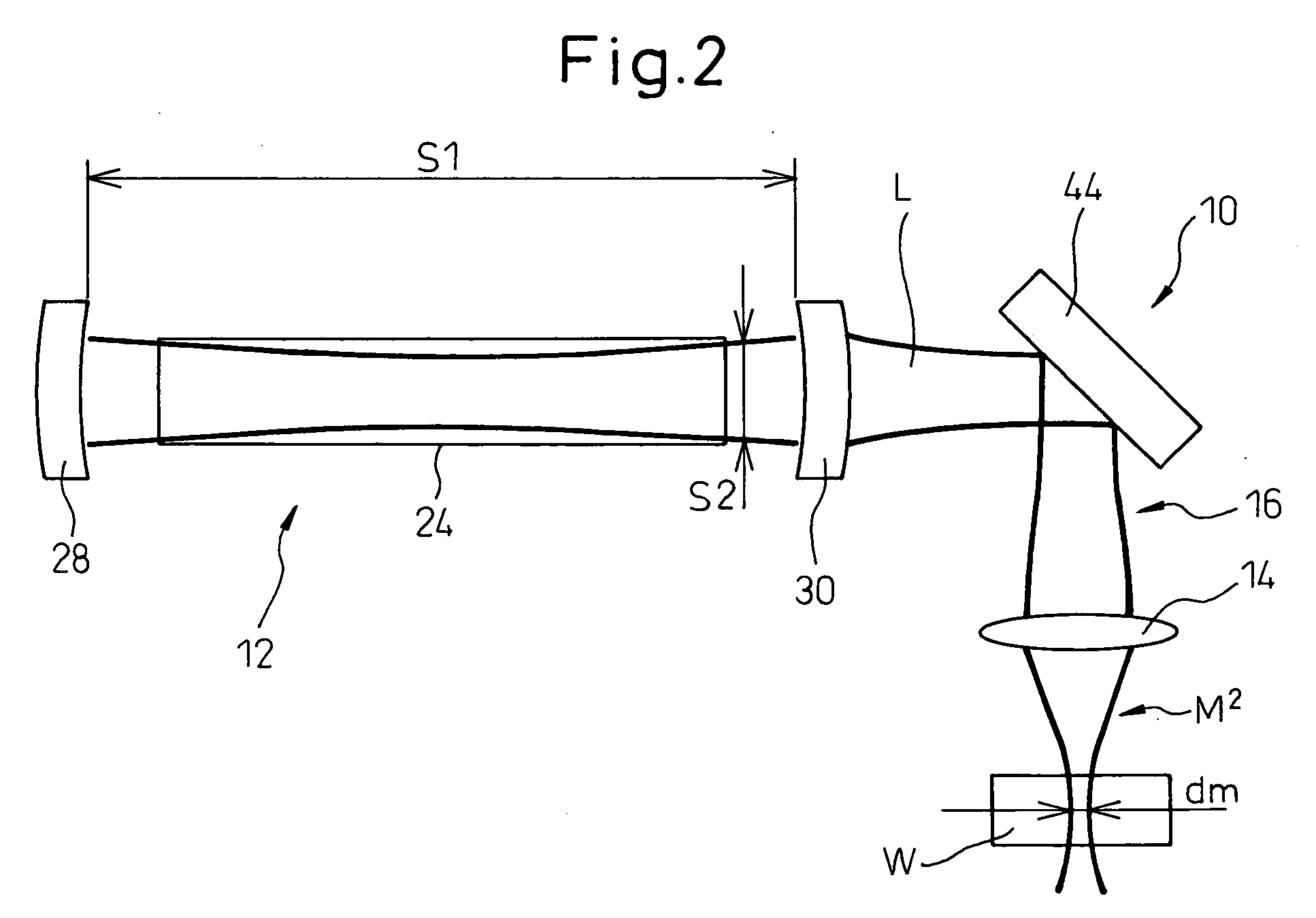
A laser cutting apparatus capable of properly cutting a workpiece having a large thickness with a laser beam. The laser cutting apparatus includes a gas laser oscillator; and an optical system including a collective lens and transmitting and collecting a laser beam generated in the gas laser oscillator to irradiate a workpiece with the laser beam. An index M2 for evaluating a beam quality of the laser beam emerging from the optical system, with which the workpiece is irradiated, is in a range of 2.8 to 4.5; while the index M2 is defined by a formula: M2=π×(dm)2 / (4×λ×Zr); in which λ is a wavelength of the laser beam; dm is a minimum beam diameter of the laser beam in a predetermined optical-path range including a focal point of the collective lens; and Zr is a distance between a first position on an optical axis, at which the minimum beam diameter dm is established, and a second position on the optical axis, at which a beam diameter “21 / 2×dm” is established, in the laser beam in the predetermined optical-path range.
Owner:FANUC LTD
High-repetition rate all-solid-state high-voltage pulse generator
InactiveCN102447213AThere is no misleading phenomenonSolution to short lifeExcitation process/apparatusElectric pulse generator circuitsCapacitanceRapid pulse
The invention discloses a high-repetition rate all-solid-state high-voltage pulse generator which comprises a direct current power supply, a resonance charging circuit, an energy storage capacitor, a step-up pulse transformer and a magnetic pulse compression switch circuit, wherein the direct current power supply is connected into the resonance charging circuit after being connected with a filter capacitor in parallel; the resonance charging circuit then is connected with the two ends of the filter capacitor after being connected with the energy storage capacitor; the two ends of a primary coil of the step-up pulse transformer are connected with the two ends of the energy storage capacitor; and a secondary coil of the step-up pulse transformer is connected into the magnetic pulse compression switch circuit. The invention has the beneficial effects that a high-pressure rapid pulse is generated by adopting a method of combining a power semiconductor switch with a magnetic pulse compression switch to replace a thyratron, is used for discharging and exciting a gas laser and can overcome the defects caused by the thyratron; and the running demands of an excimer laser at high repetition rate and long service life are satisfied.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical fibre gas laser and optical fiber type ring laser gyroscope possessing the laser
ActiveCN101165977AGood zoom effectSimple structureExcitation process/apparatusSagnac effect gyrometersFiber couplerRobotic systems
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Laser cutting apparatus with a high quality laser beam
InactiveUS7348517B2Large thicknessPrecise cuttingCombination recordingRecord information storageBeam diameterOptical axis
A laser cutting apparatus capable of properly cutting a workpiece having a large thickness with a laser beam. The laser cutting apparatus includes a gas laser oscillator; and an optical system including a collective lens and transmitting and collecting a laser beam generated in the gas laser oscillator to irradiate a workpiece with the laser beam. An index M2 for evaluating a beam quality of the laser beam emerging from the optical system, with which the workpiece is irradiated, is in a range of 2.8 to 4.5; while the index M2 is defined by a formula: M2=π×(dm)2 / (4×λ×Zr); in which λ is a wavelength of the laser beam; dm is a minimum beam diameter of the laser beam in a predetermined optical-path range including a focal point of the collective lens; and Zr is a distance between a first position on an optical axis, at which the minimum beam diameter dm is established, and a second position on the optical axis, at which a beam diameter “21 / 2×dm” is established, in the laser beam in the predetermined optical-path range.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Refractive surgery and presbyopia correction using infrared and ultraviolet lasers
InactiveUSRE40184E1Avoid smooth surfaceImprove distributionLaser surgeryLaser detailsKeratorefractive surgeryFiber
A method and surgical technique for corneal reshaping and for presbyopia correction are provided. The preferred embodiments of the system consists of a scanner, a beam spot controller and coupling fibers and the basic laser having a wavelength of (190-310) nm, (0.5-3.2) microns and (5.6-6.2) microns and a pulse duration of about (10-150) nanoseconds, (10-500) microseconds and true continuous wave. New mid-infrared gas lasers are provided for the corneal reshaping procedures. Presbyopia is treated by a method which uses ablative laser to ablate the sclera tissue and increase the accommodation of the ciliary body. The tissue bleeding is prevented by a dual-beam system having ablative and coagulation lasers. The preferred embodiments include short pulse ablative lasers (pulse duration less than 200 microseconds) with wavelength range of (0.15-3.2) microns and the long pulse (longer than 200 microseconds) coagulative lasers at (0.5-10.6) microns. Compact diode lasers of (980-2100) nm and diode-pumped solid state laser at about 2.9 microns for radial ablation patterns on the sclera ciliary body of a cornea are also disclosed for presbyopia correction using the mechanism of sclera expansion.
Owner:SURGILIGHT
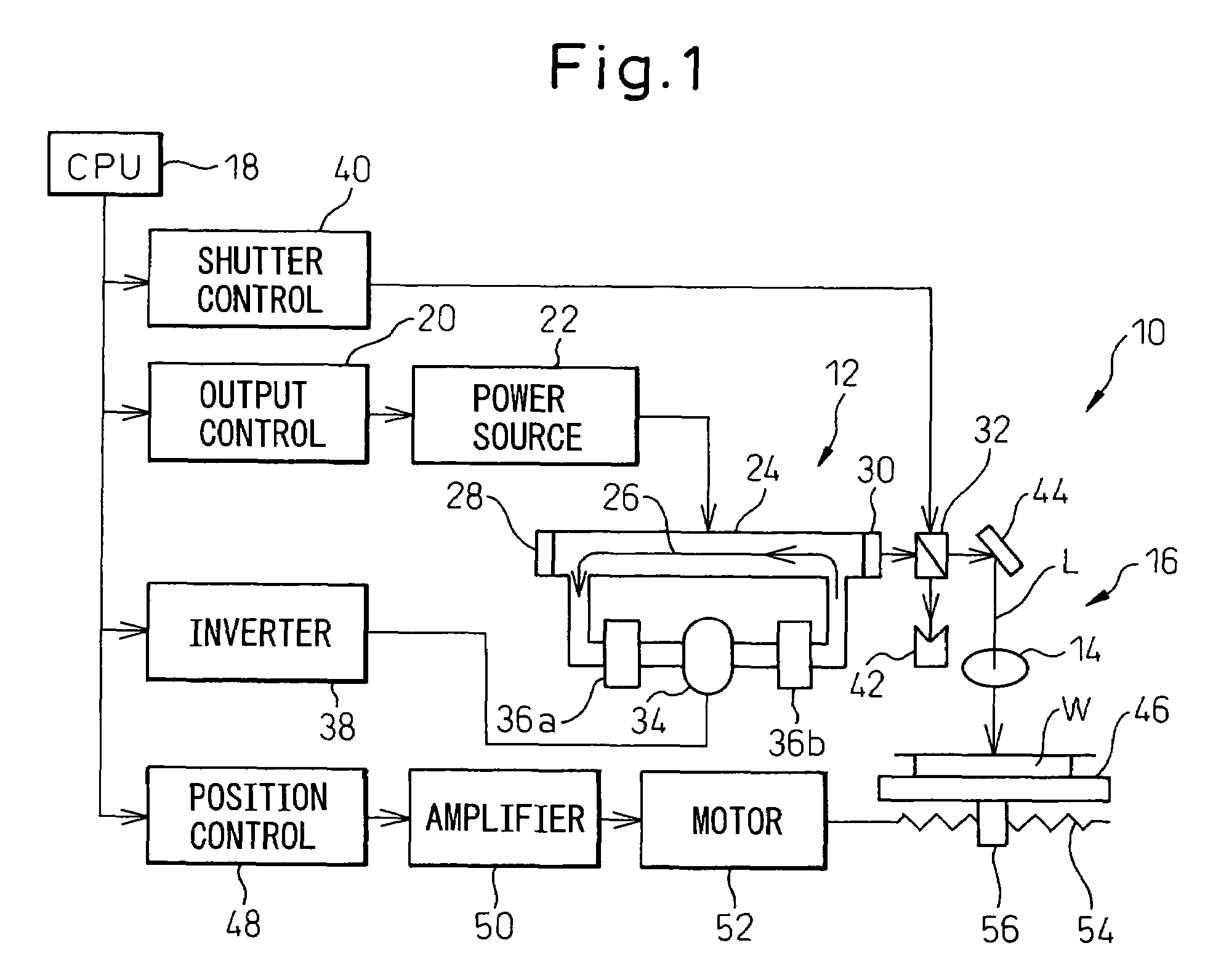
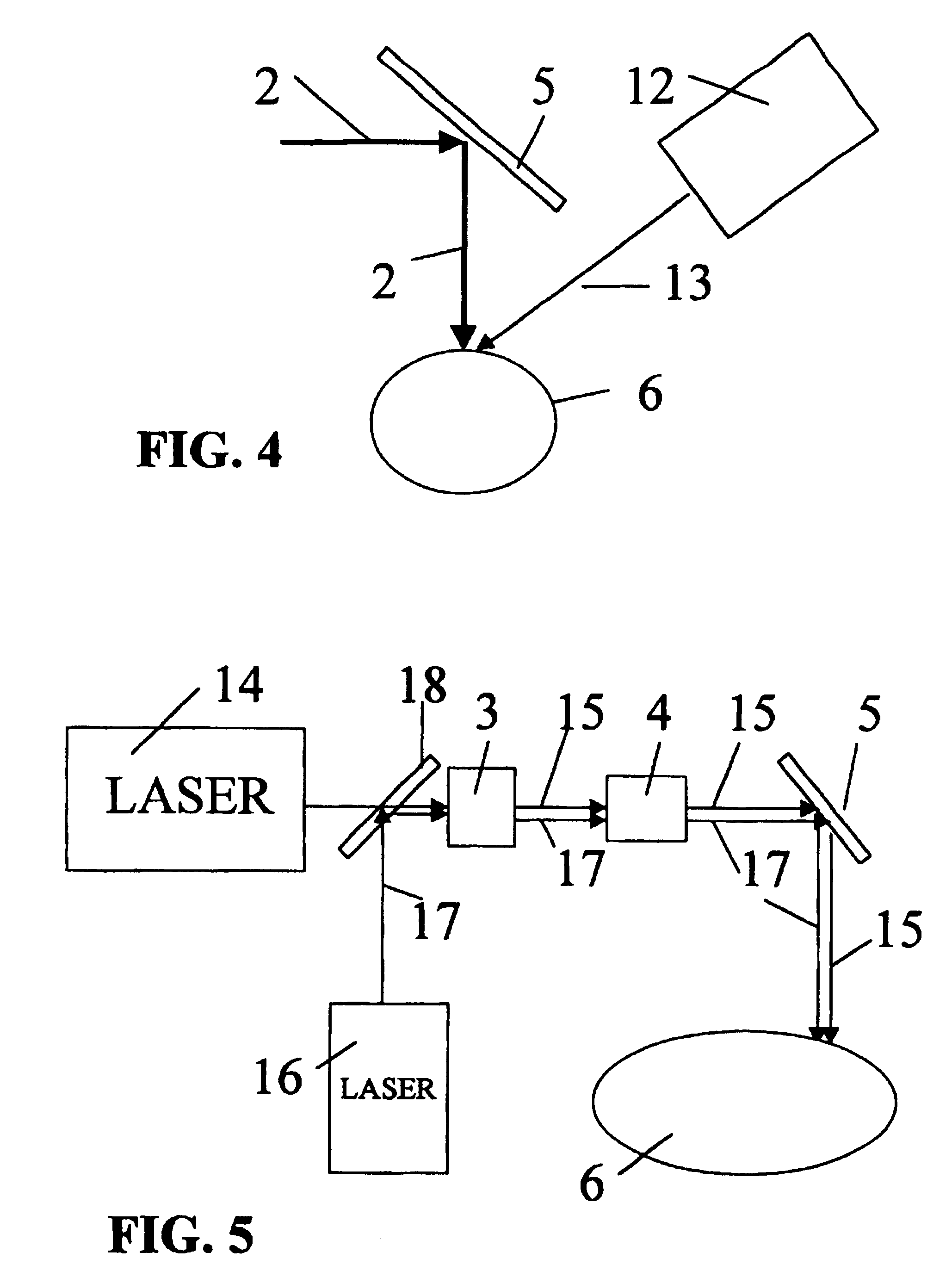
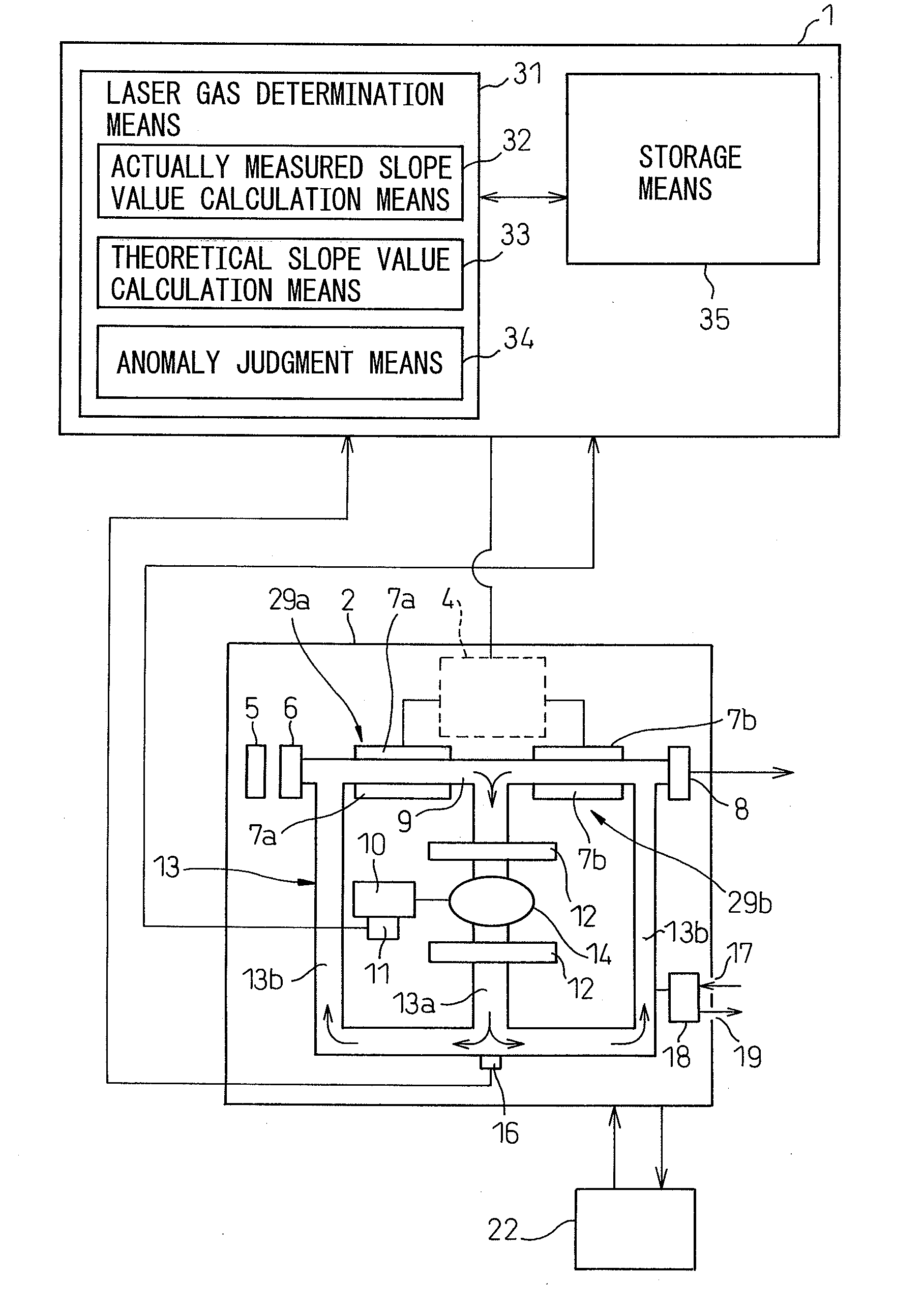
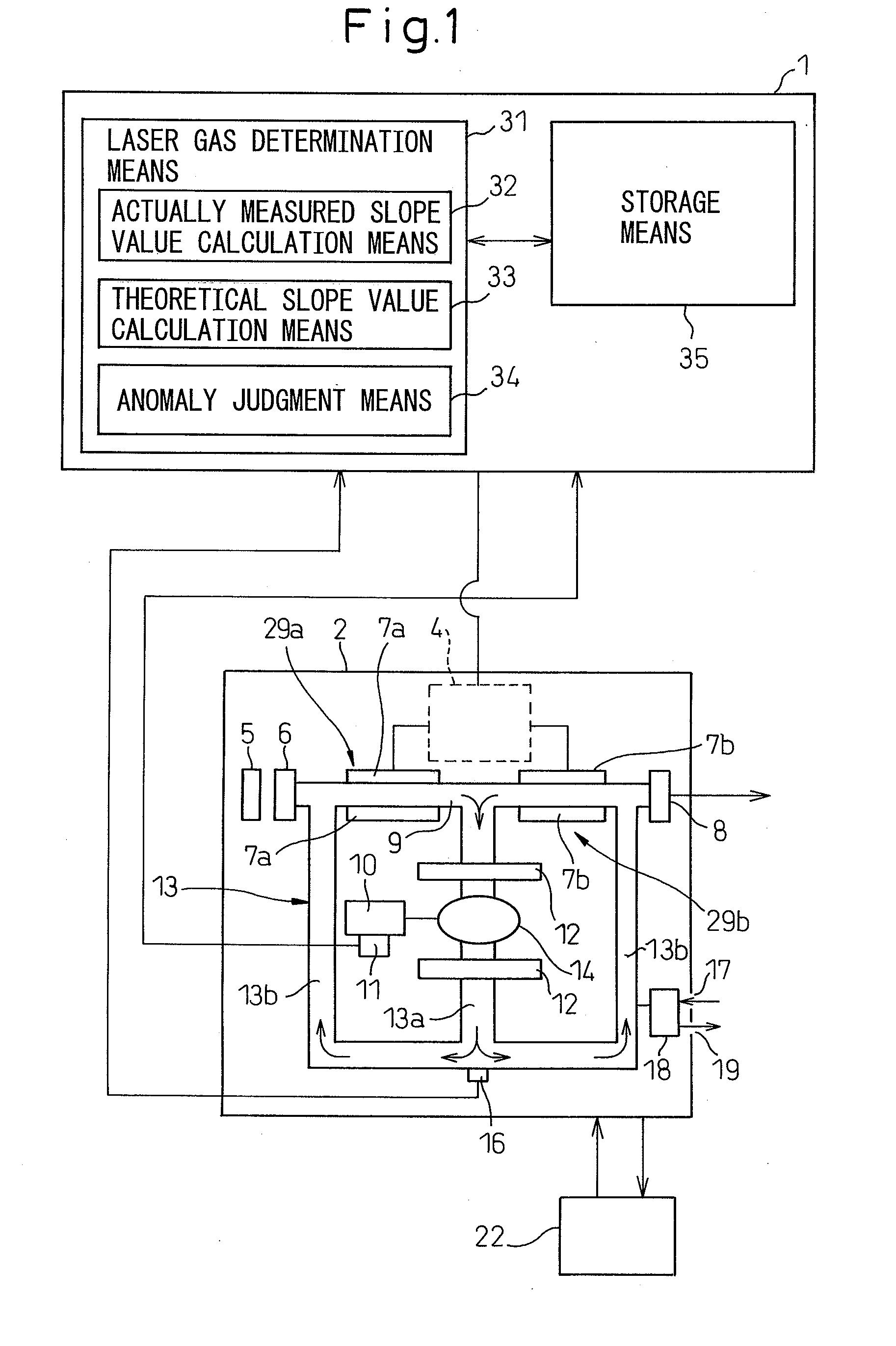
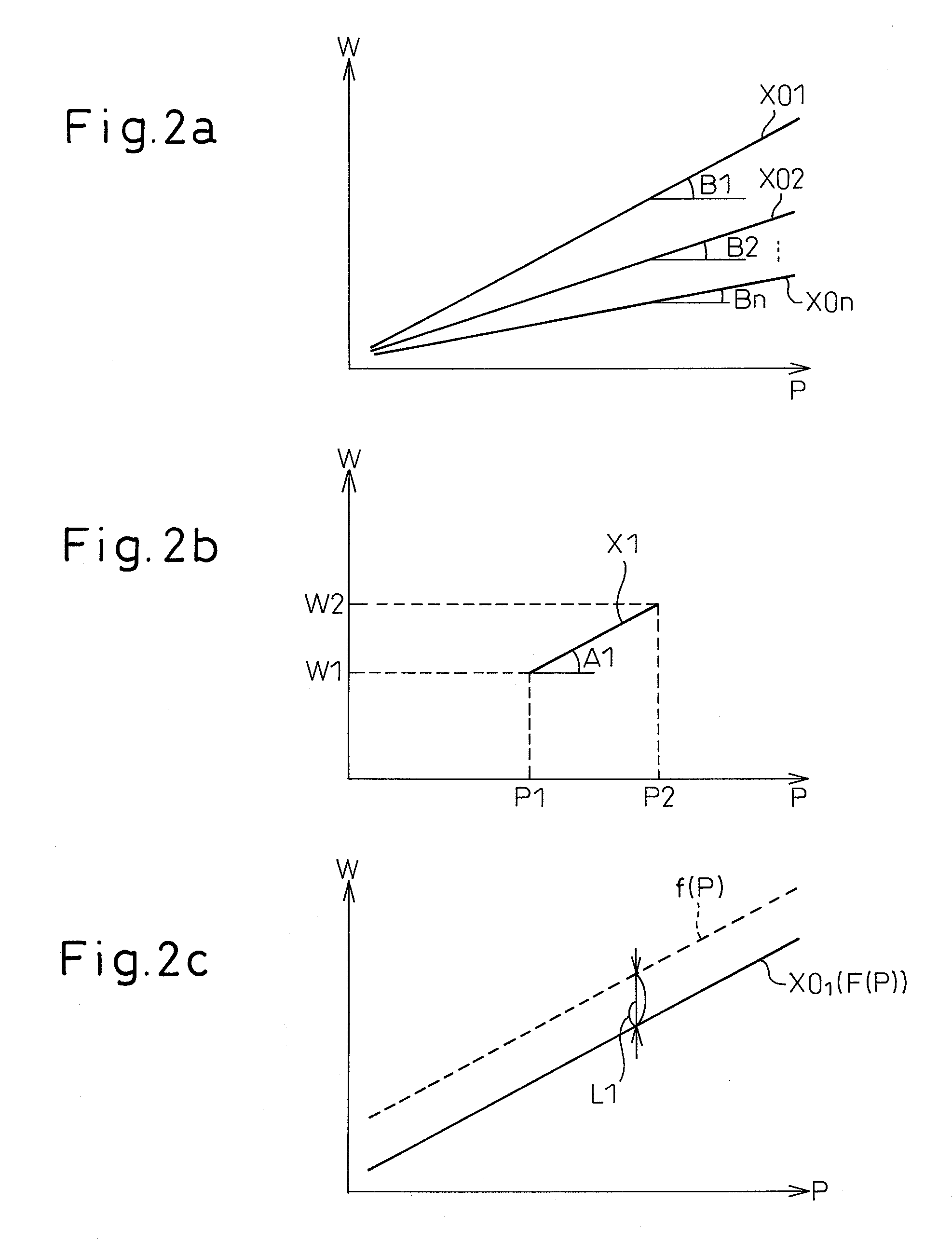
Gas laser oscillator
InactiveUS20080043799A1Reduce riskReduce usageActive medium materialElectric power systemLaser light
A gas laser oscillator (2) that excites a laser gas to generate laser light includes a circulation path (9) for the laser gas, a circulation means (14) for circulating the laser gas through the circulation path, a pressure detection means (16) for detecting the pressure of the laser gas in the circulation path, an electric power detection means (11) for detecting electric power to drive the circulation means, a storage means (35) for storing the relationship between the pressure of the laser gas and the electric power of the circulation means during the period of normal operation of the circulation means for each kind of the laser gas, and a laser gas determination means (31). The laser gas determination means determines the kind of the laser gas based on the pressure of the laser gas and the electric power of the circulation means detected during the period of normal operation of the circulation means, and the relationship between the pressure of the laser gas and the electric power of the circulation means stored in the storage means. Due to this, the laser gas is determined without generating a discharge voltage. If the laser gas cannot be determined, it may be possible to judge that the laser oscillator is anomalous.
Owner:FANUC LTD
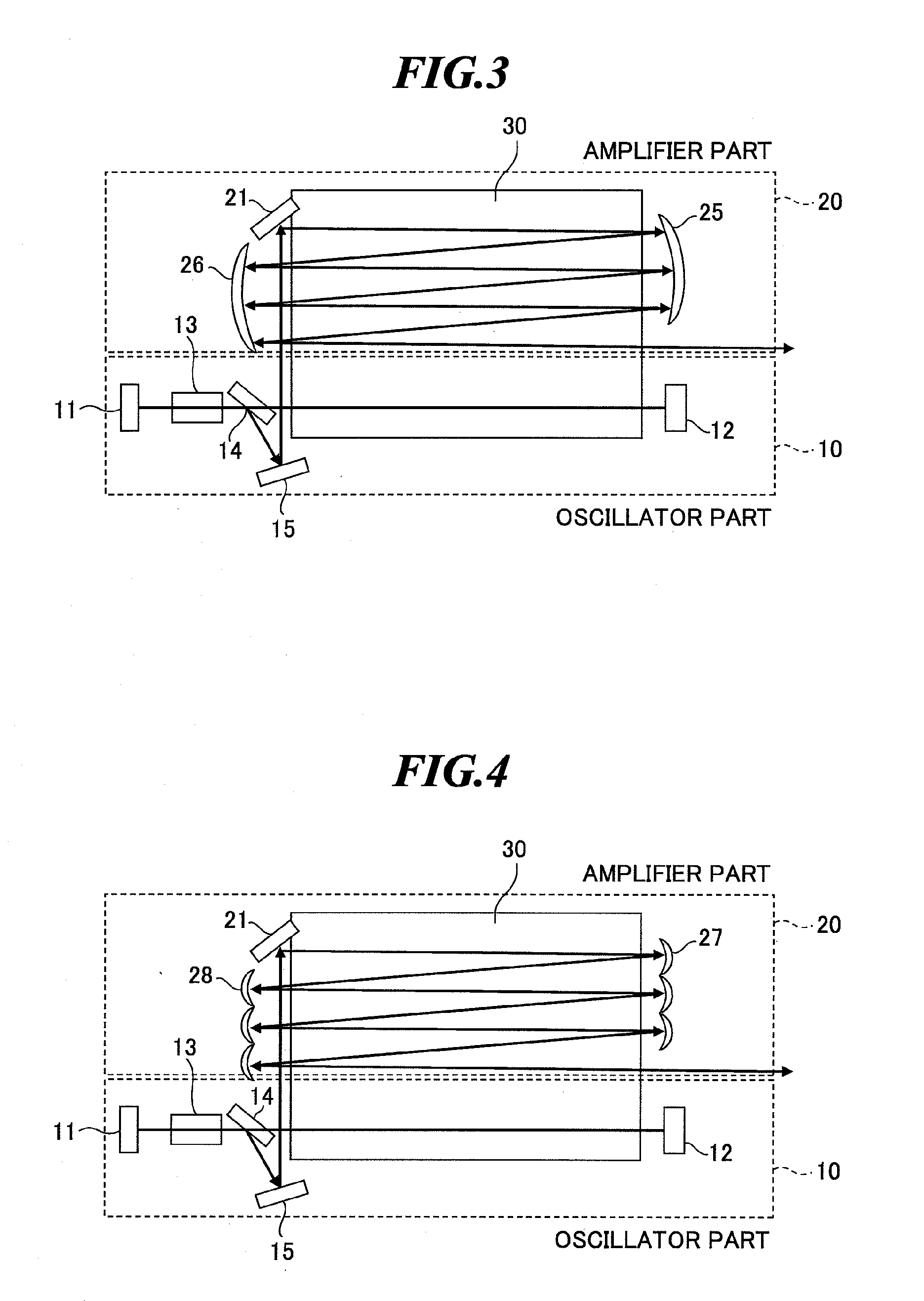
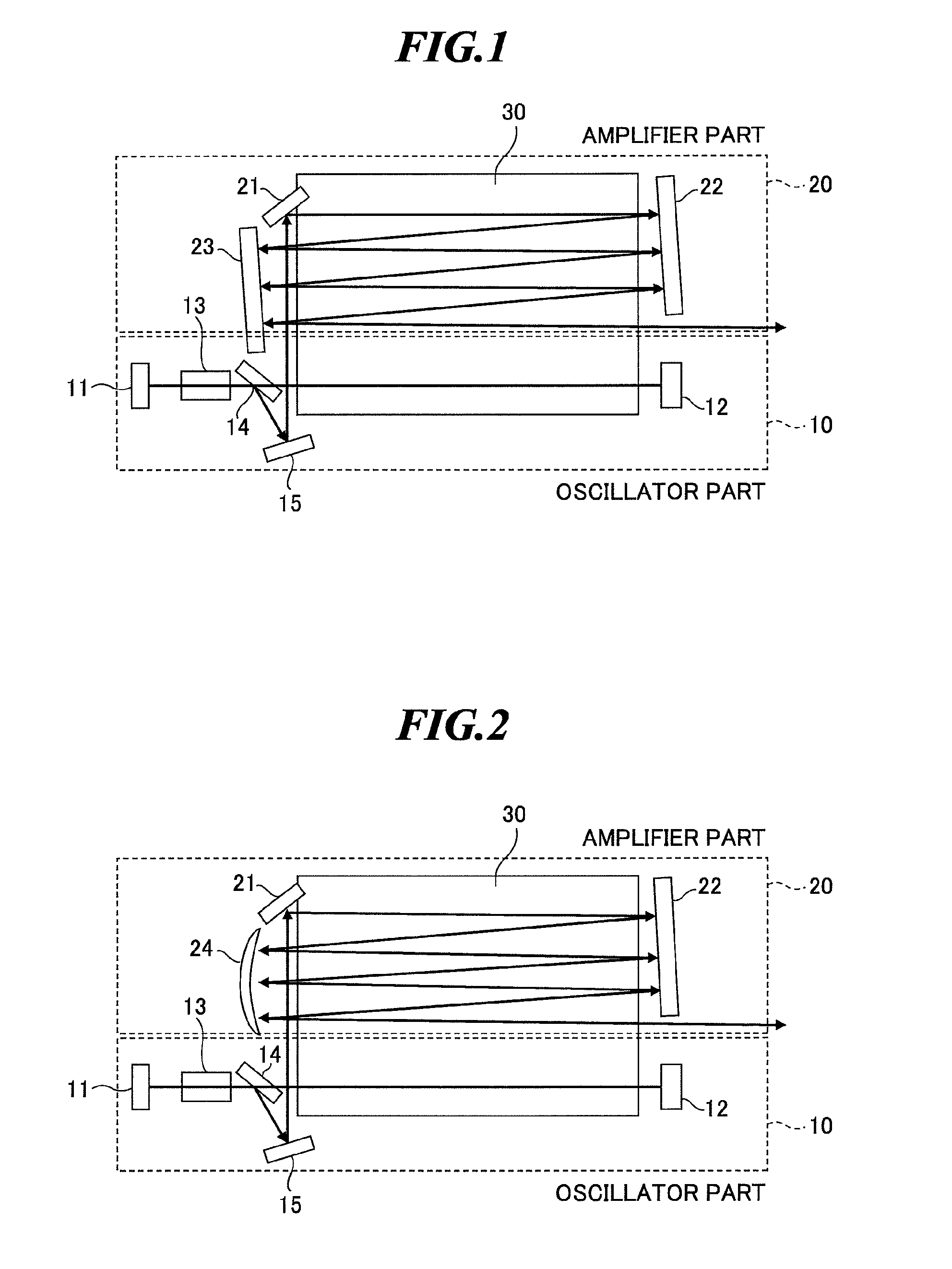
Slab type laser apparatus
ActiveUS7903715B2Improve focus performanceAmplify a laser beam efficientlyExcitation process/apparatusPhotomechanical apparatusAudio power amplifierGas laser
A slab type laser apparatus has a slab type gas laser medium part formed in a region defined by a pair of electrode flat plates oppositely disposed in parallel with each other in a space to be filled with a gas laser medium which is excited by high-frequency electric power. The apparatus includes an oscillator part including a pair of resonator mirrors oppositely disposed with a part of the gas laser medium part in between, and for amplifying a laser beam to have predetermined light intensity to emit the laser beam, and the amplifier part including a plurality of return mirrors oppositely disposed with a part of the gas laser medium part in between. The incident laser beam goes and returns plural times between the return mirrors, and the laser beam is amplified to have predetermined power.
Owner:GIGAPHOTON +1
A pulse width adjustable laser
InactiveCN101060227ASimple installation and debuggingEase of engineering promotionOptical resonator shape and constructionDye laserOptoelectronics
The disclosed laser with adjustable Q pulse width comprises: an output mirror, a laser rod, a Pockel's box together with a first full deflection mirror coaxial arranged on a straight line, a first polaroid between the Pockel's box and first deflection mirror, at least one movable 1 / 2 glass filter and polaroid (7) between former first polaroid and the first deflection mirror, a second full reflection mirror (11) near the polaroid (7) to deflect all laser from (7) backwardly. This invention is simple and convenient, and can be used in different lasers.
Owner:BEIJING GK LASER TECH
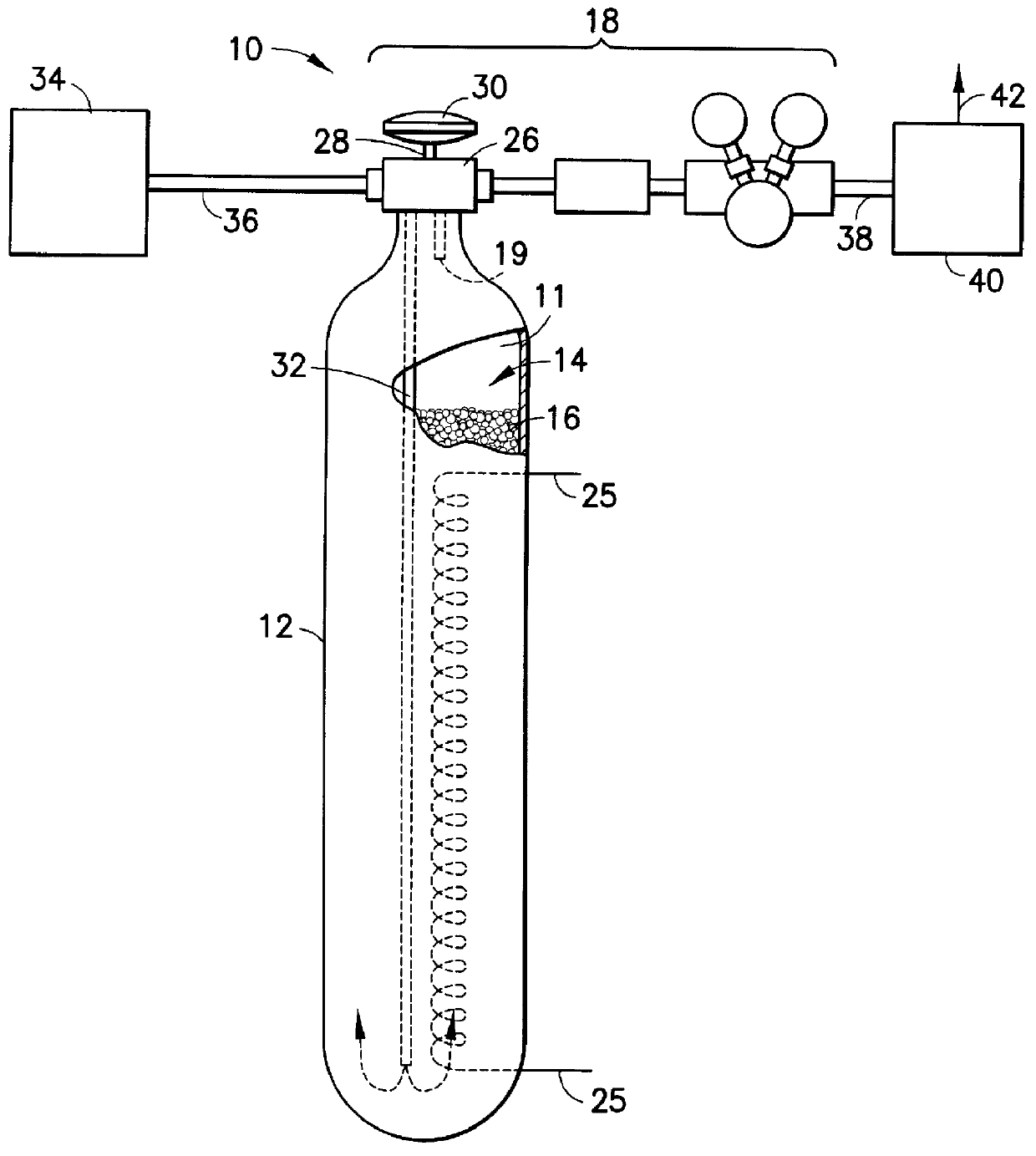
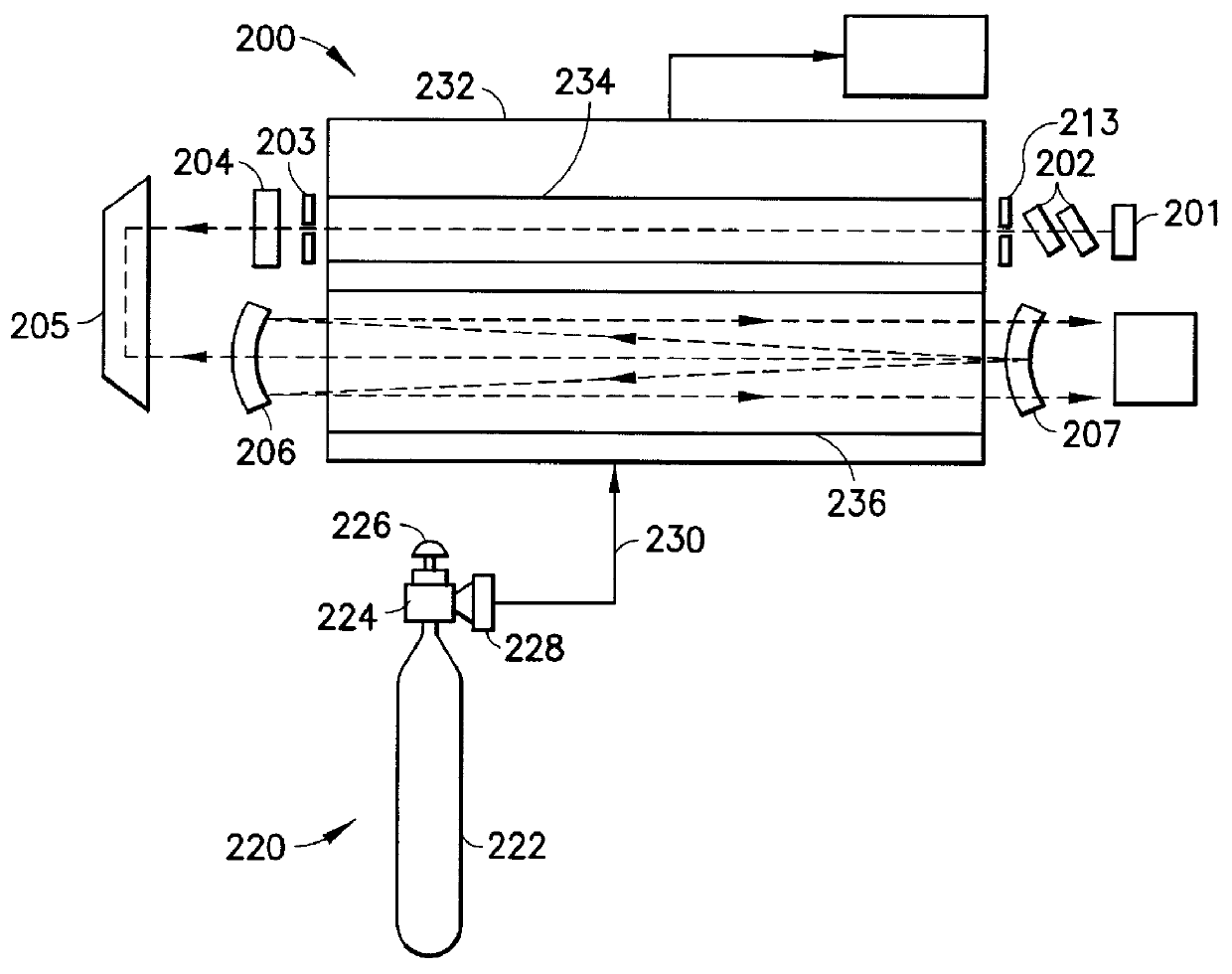
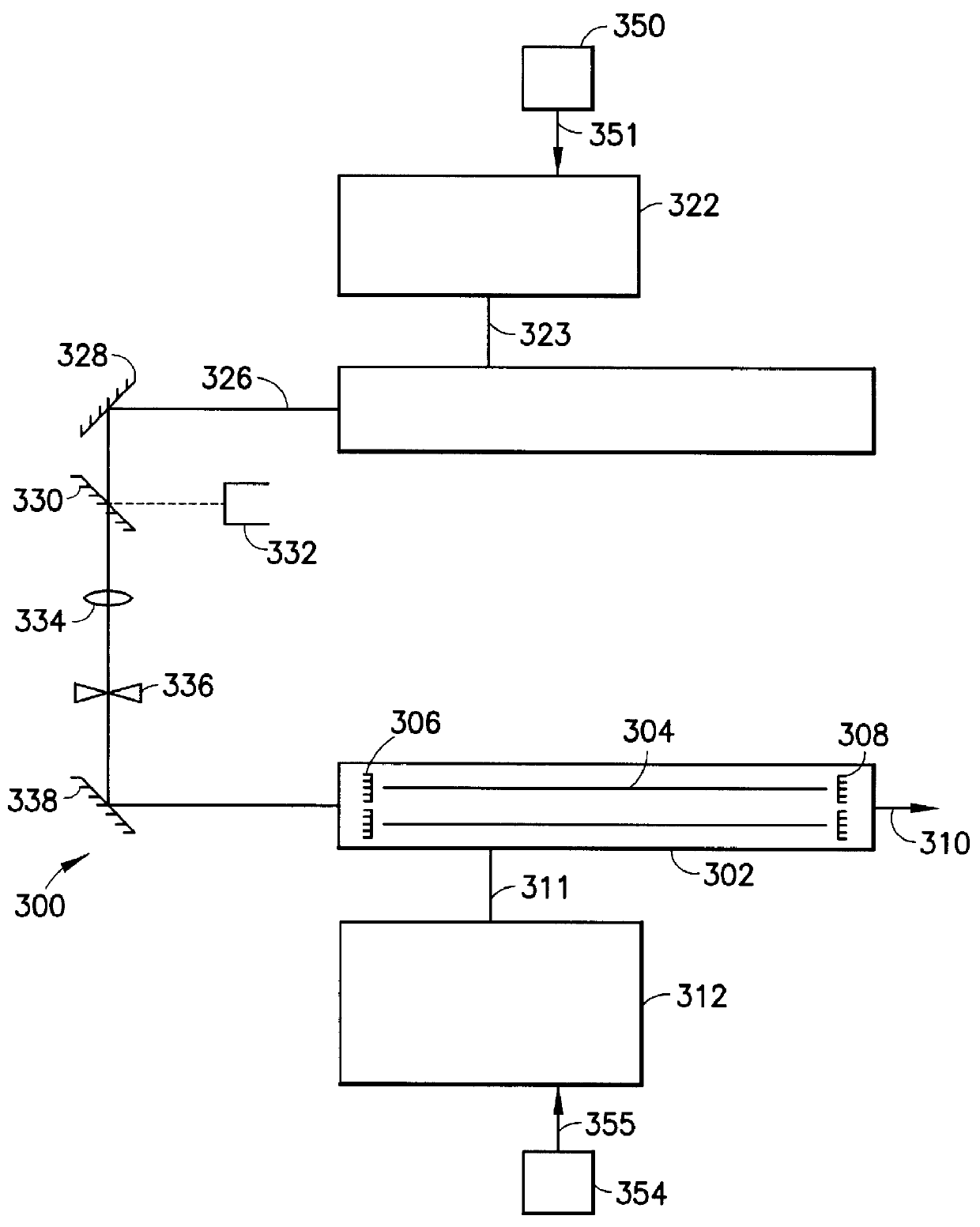
Laser system utilizing sorbent-based gas storage and delivery system
A laser system utilizing a fluid as the excitatory medium for stimulated light emission, wherein the fluid is supplied from a sorbent-based fluid storage and dispensing system coupled in fluid-supplying relationship with the laser apparatus. The laser may be an excimer laser utilizing as the laser working fluid a rare gas halide compound such as fluorides and / or chlorides of krypton, xenon and argon, as well as fluorine and / or chlorine per se. The laser system may alternatively be a far infrared gas laser utilizing a gas such as CO2, N2O, CD3OD, CH3OD, CH3OH, CH3NH2, C2H2F2, HCOOH, CD3I, CH3F, and C13H3F. Laser systems of the present invention may be utilized in applications such as materials processing, measurement and inspection, reading, writing, and recording of information, holography, communications, displays, spectroscopy and analytical chemistry, remote sensing, surveying, marking, and alignment, surgical and medical applications, plasma diagnostics, laser weaponry, laser-induced nuclear fusion, isotope enrichment and atomic physics.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
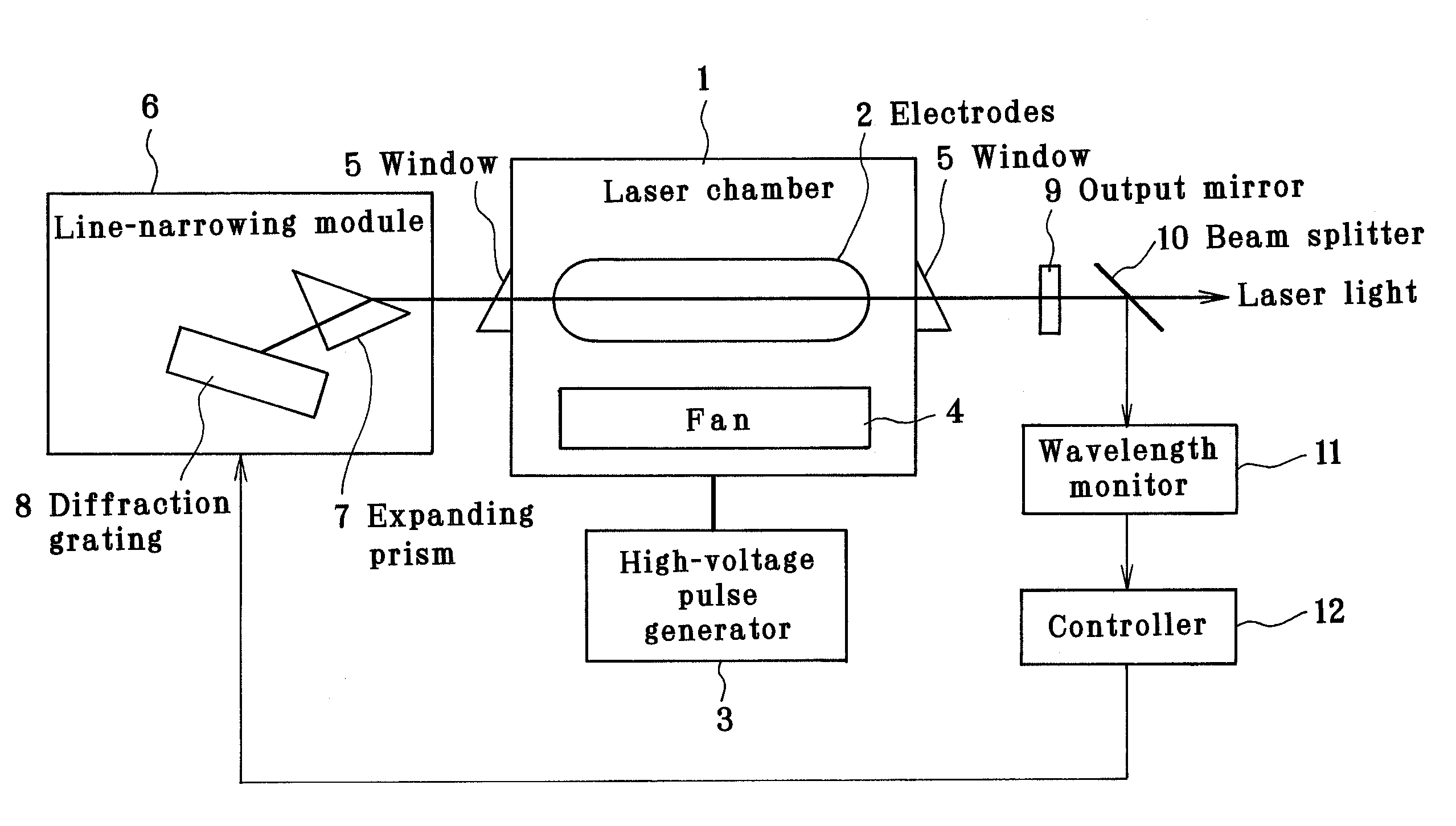
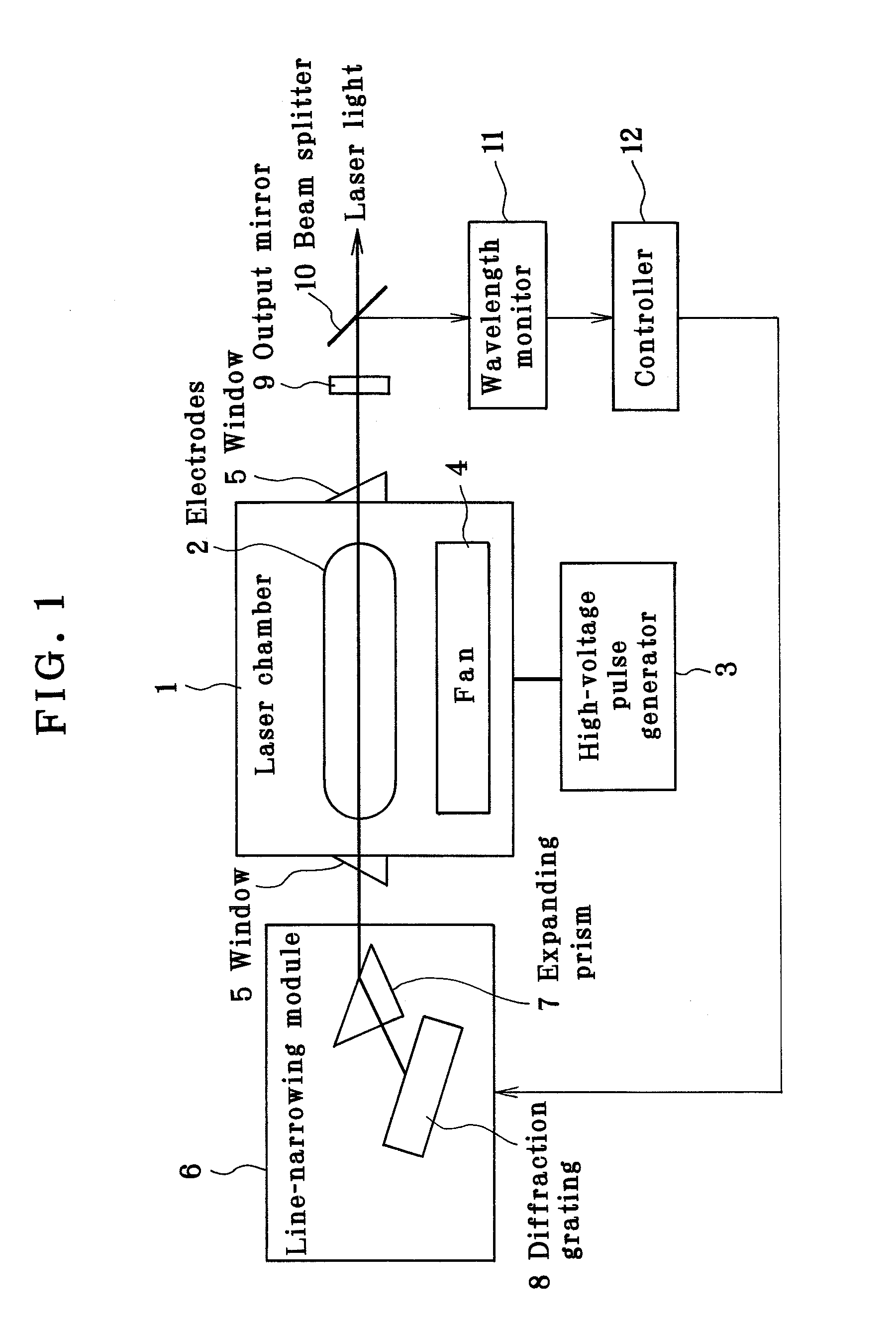
Line-narrowed gas laser system
ActiveUS7072375B2Improve abilitiesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingActive medium materialLine widthPeak value
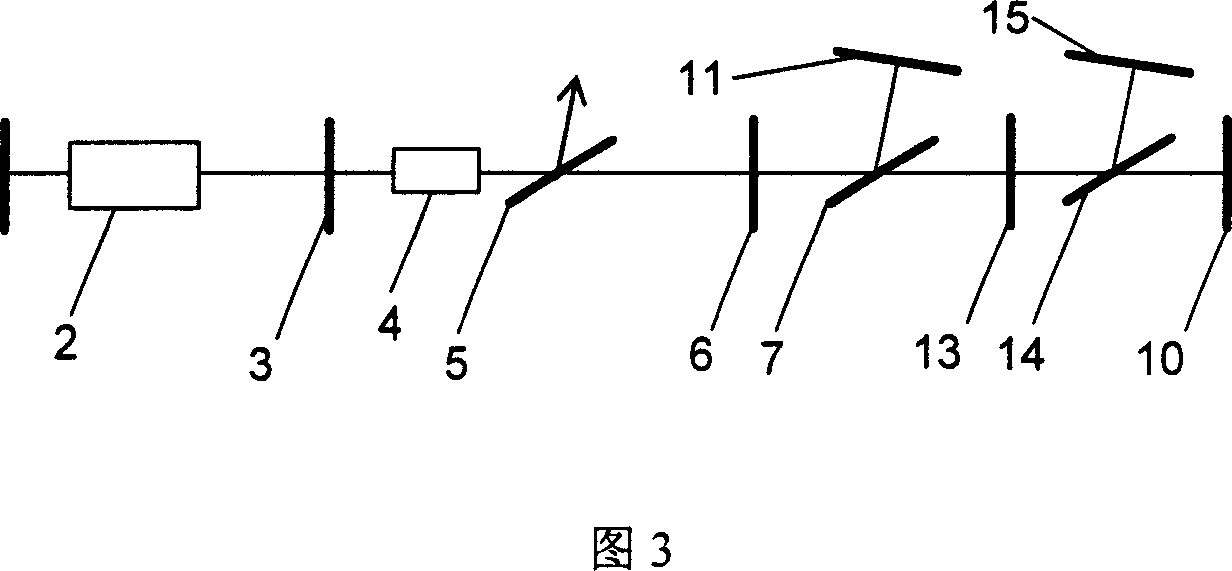
In a line-narrowed gas laser system such as a line-narrowed molecular fluorine laser system, ASE is cut off to obtain a spectral linewidth of 0.2 pm or lower and a spectral purity of 0.5 pm or lower. The laser system comprises a laser chamber filled with an F2-containing laser gas, discharge electrodes located in the laser chamber, a laser resonator and a line-narrowing module located in the laser resonator with a wavelength selection element, so that a line-narrowed laser beam emerges from the laser resonator. To cut off ASE from the laser beam emerging from the laser resonator, the duration from laser emission by discharge to generation of a laser beam is preset. Rise of the sidelight is made so gentle that the starting point of a laser pulse can exist after the time of the first sidelight peak.
Owner:GIGAPHOTON +1
Optical resonator of high-power CO2 gas laser
InactiveCN101854023ASolve the output stability problemReduce volumeLaser detailsOptical axisEffect light
The invention relates to an optical resonator of a high-power CO2 gas laser. The optical resonator comprises a total reflecting mirror, a total reflecting mirror base, a total reflecting mirror gland cover, an output reflecting mirror, an output reflecting mirror base and an output reflecting mirror gland cover. The connection relationship is as follows: the optical resonator is installed and fixed on two end plates of a high-stability optical support and is fixedly connected with both ends of a chamber passage of a working gas circularly flowing in a closed mode through elastic adjustable bellows. The axle centers of the total reflecting mirror and the output reflecting mirror are adjusted through a calibration lighting source and are coaxial with the space optical axis 0 of a laser discharge chamber. After an energy storing charge and discharge circuit supplies electrical energy, one pair of discharge electrodes of the laser discharge chamber glow discharges evenly to a large area. After multiple times of actuating resonation through the total reflecting mirror and the output reflecting mirror, pulse signals repeat multiple times and become stronger and stronger to form laser light, and the laser light is transmitted through an output window so as to form the optical resonator of the laser. The invention has high stability and reliability and compact structure, and is applicable to high-power gas lasers and pulsed gas lasers.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
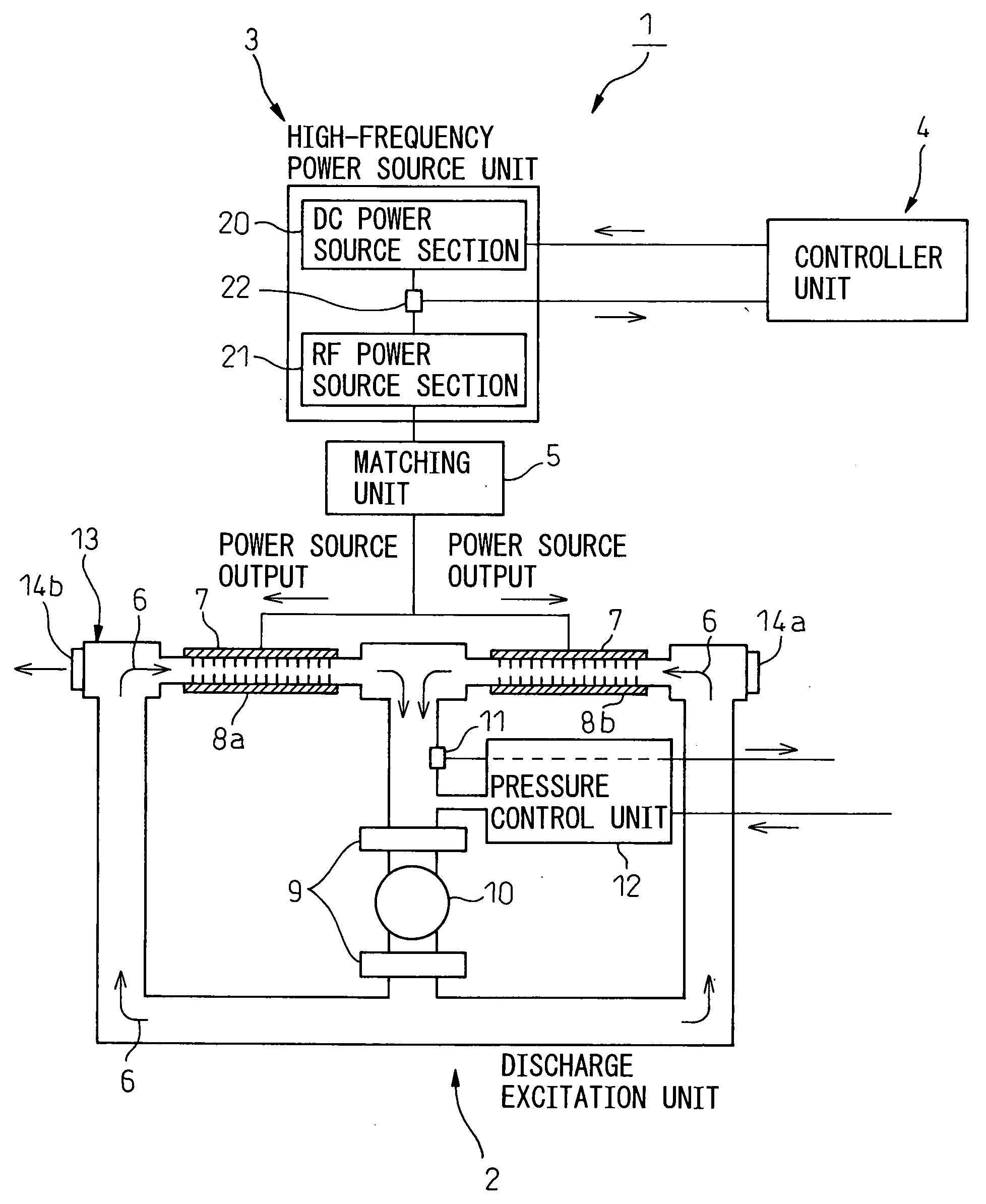
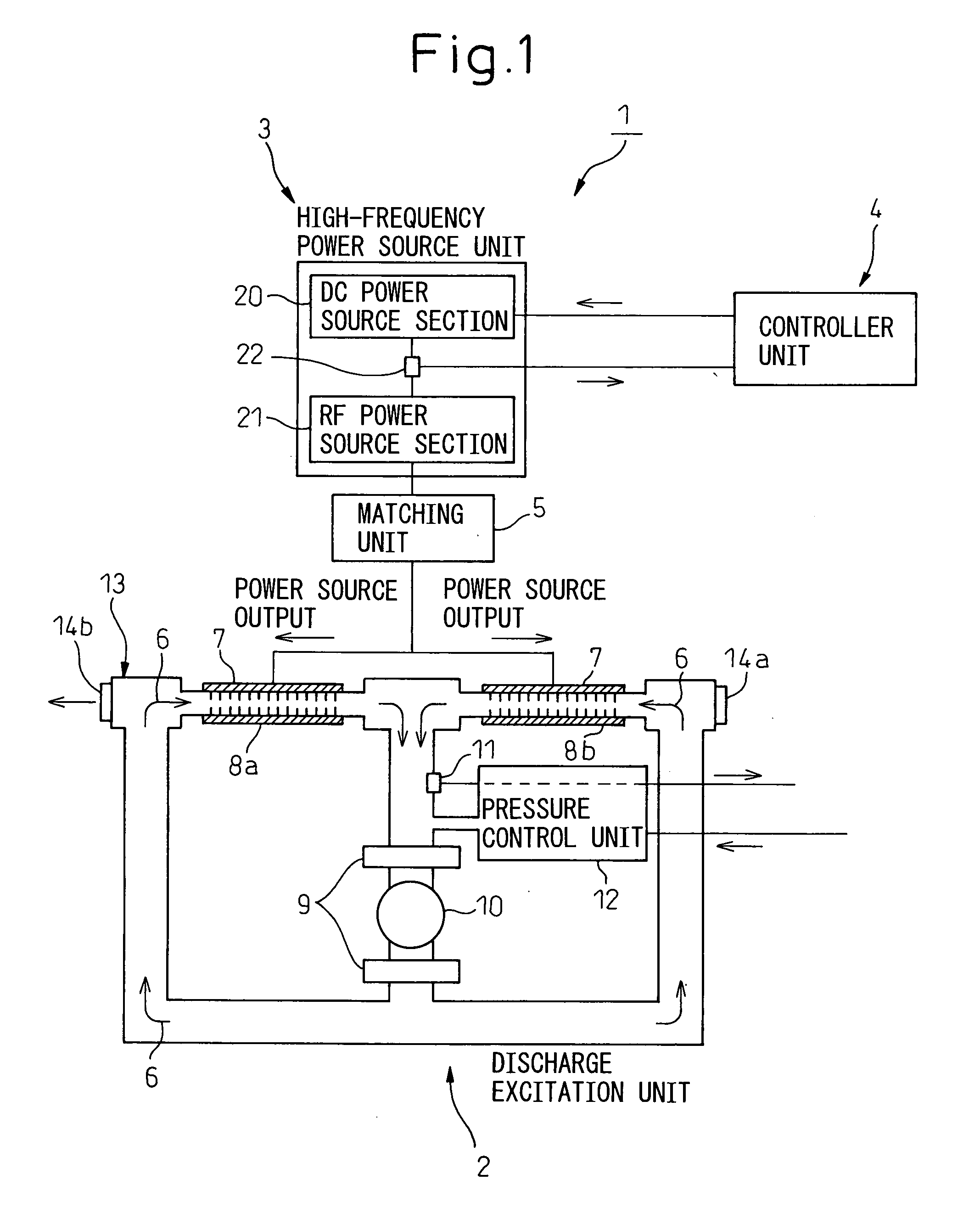
Method for discriminating anomaly in gas composition and discharge excitation type gas laser oscillator
ActiveUS20080144681A1Avoid damageDiscriminating an anomaly of gas compositionActive medium materialGas laser constructional detailsHigh frequency powerOutput compare
A discharge excitation type gas laser oscillator has a discharge excitation unit for exciting a laser gas by discharge in a discharge tube to generate induced emission of laser light, a high-frequency power supply unit for supplying power to the discharge tube, and a controller unit for controlling output current of the high-frequency power supply unit. The laser oscillator further has an output detecting section that detects actual current value of the high-frequency power supply unit supplying power to the discharge tube at an arbitrary pressure lower than the high pressure during the steady-state operation, at the start of the laser oscillator, after the laser gas begins discharge excitation at a pressure lower than the high pressure during steady-state operation, an output comparison section that compares the detected actual current value with a normal current value that has been detected when the gas composition of the laser gas is normal at the same pressure as the actual current value is detected; and a power supply control section that discriminates, if the difference between the actual current value and the normal current value is equal to or greater than a preset value, that the gas composition of the laser gas is abnormal, and stops output of the high-frequency power supply unit.
Owner:FANUC LTD
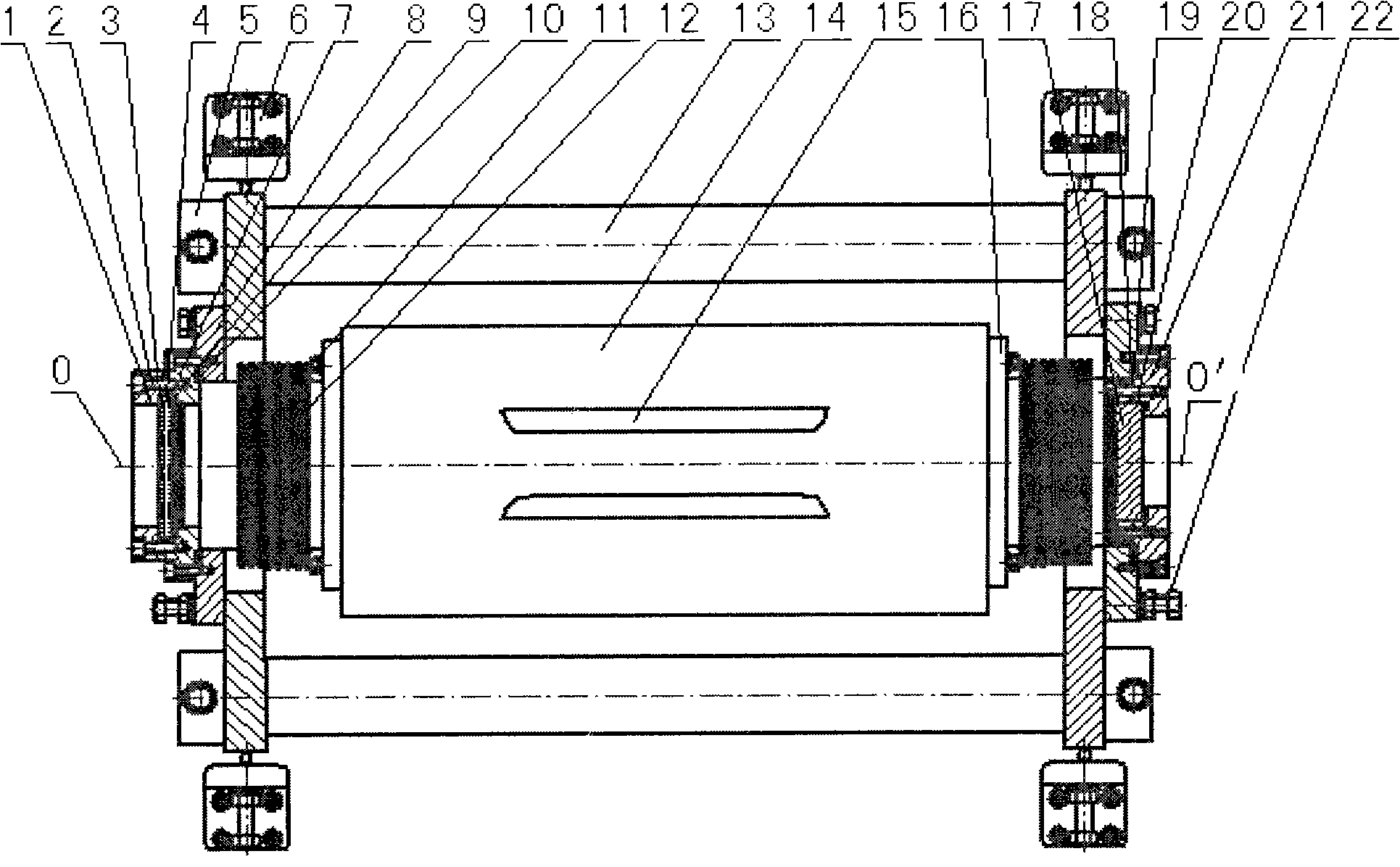
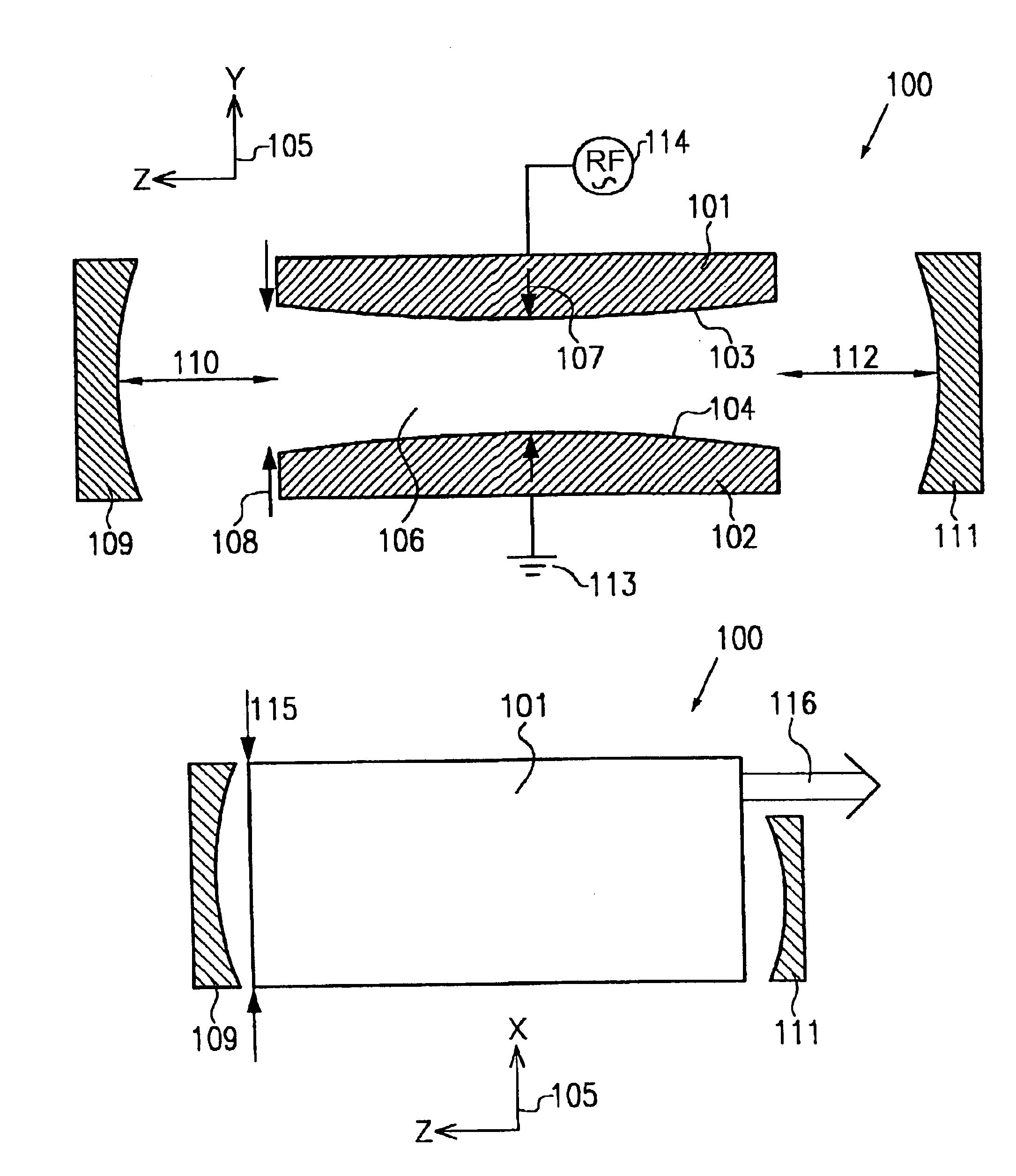
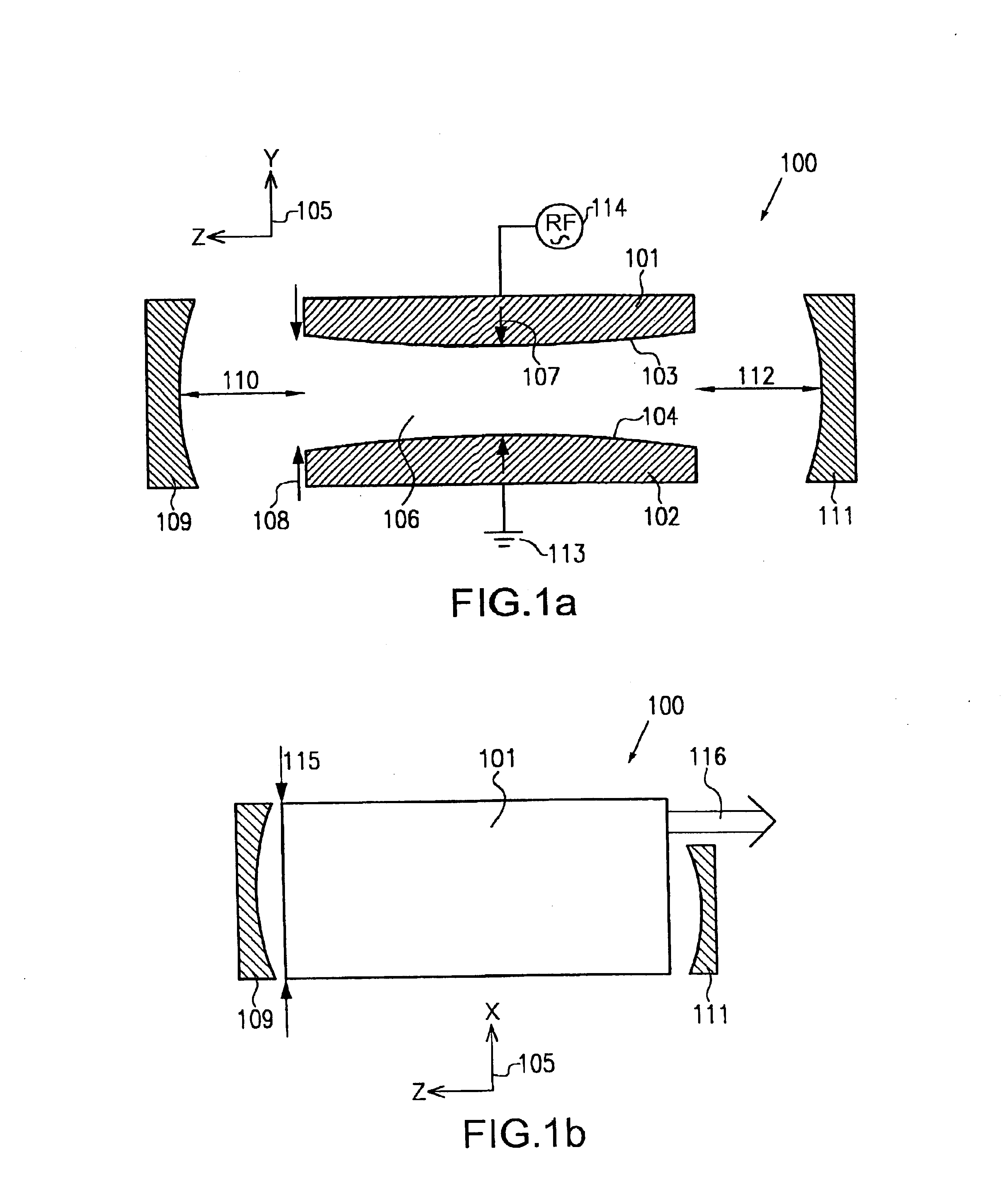
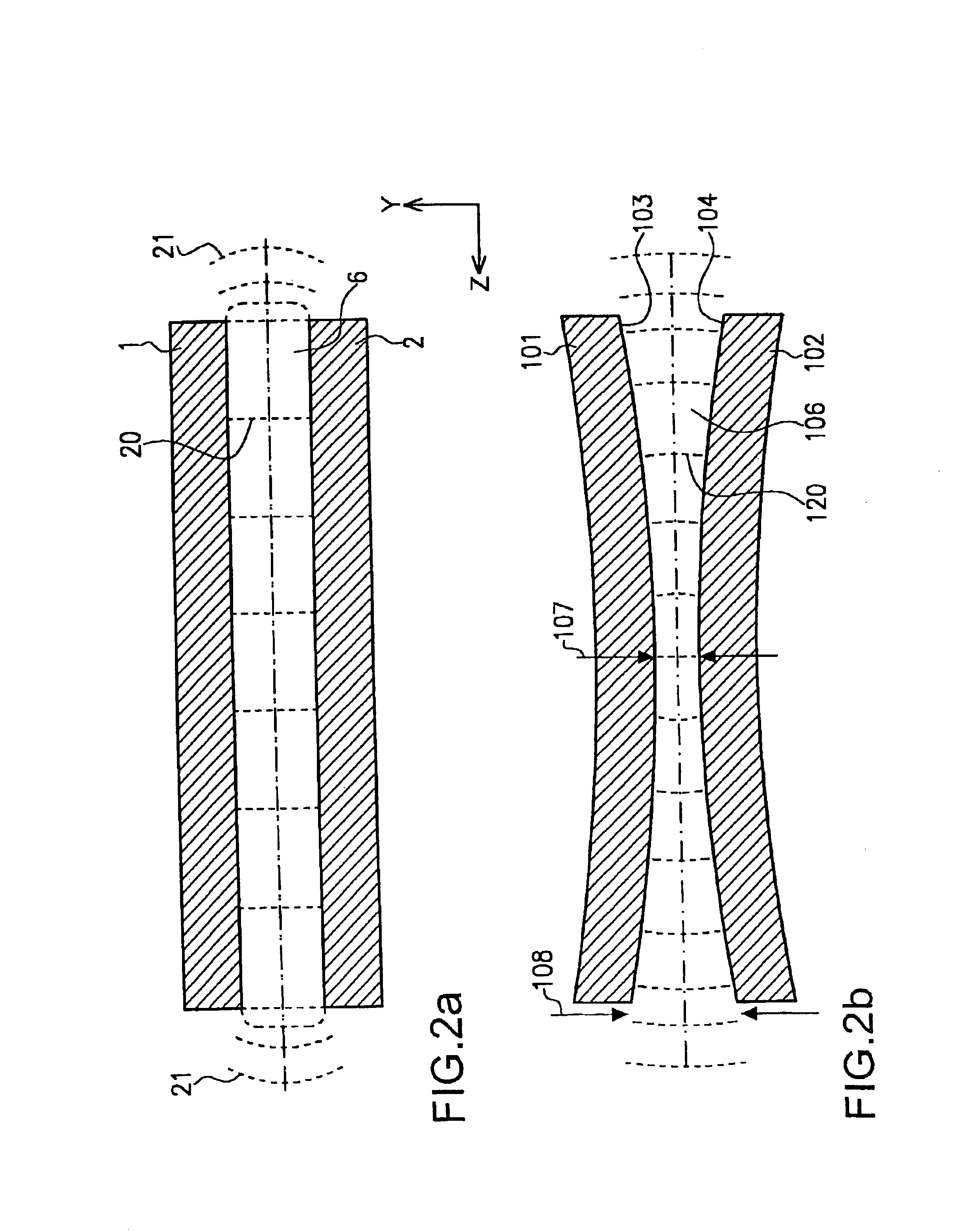
High power slab type gas laser
InactiveUS6856639B2Increase output powerHigh purityOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialRadiation modeOptoelectronics
A gas laser comprises a pair of elongated electrodes arranged to define a discharge region between two opposing surfaces of said elongated electrodes, wherein the discharge region defines a longitudinal axis, a wide axis and a narrow axis. The gas laser further includes a lasing gas disposed in said discharge region and an excitation means for energizing the electrodes to excite the lasing gas. A first mirror is arranged in front of a first end of the pair of elongated electrodes, wherein the first mirror is spaced apart from the first end along the longitudinal axis by a first distance, and a second mirror is arranged in front of a second end of the pair of elongated electrodes. Moreover, the two opposing electrode surfaces define an electrode curvature, respectively, that is adapted such that a wave front of the a fundamental transverse radiation mode with respect to the narrow axis substantially coincides with a mirror curvature of the first mirror at the first distance.
Owner:GOSUDARSTVENNOYE PREDPRIYATIE NAUCHNOISSLEDOVATELSKY INST LAZERNOY FIZIKI +1
Gas laser oscillator
InactiveUS20060114959A1Avoid insulation breakdownAvoid damageGas laser constructional detailsEngineeringGas laser
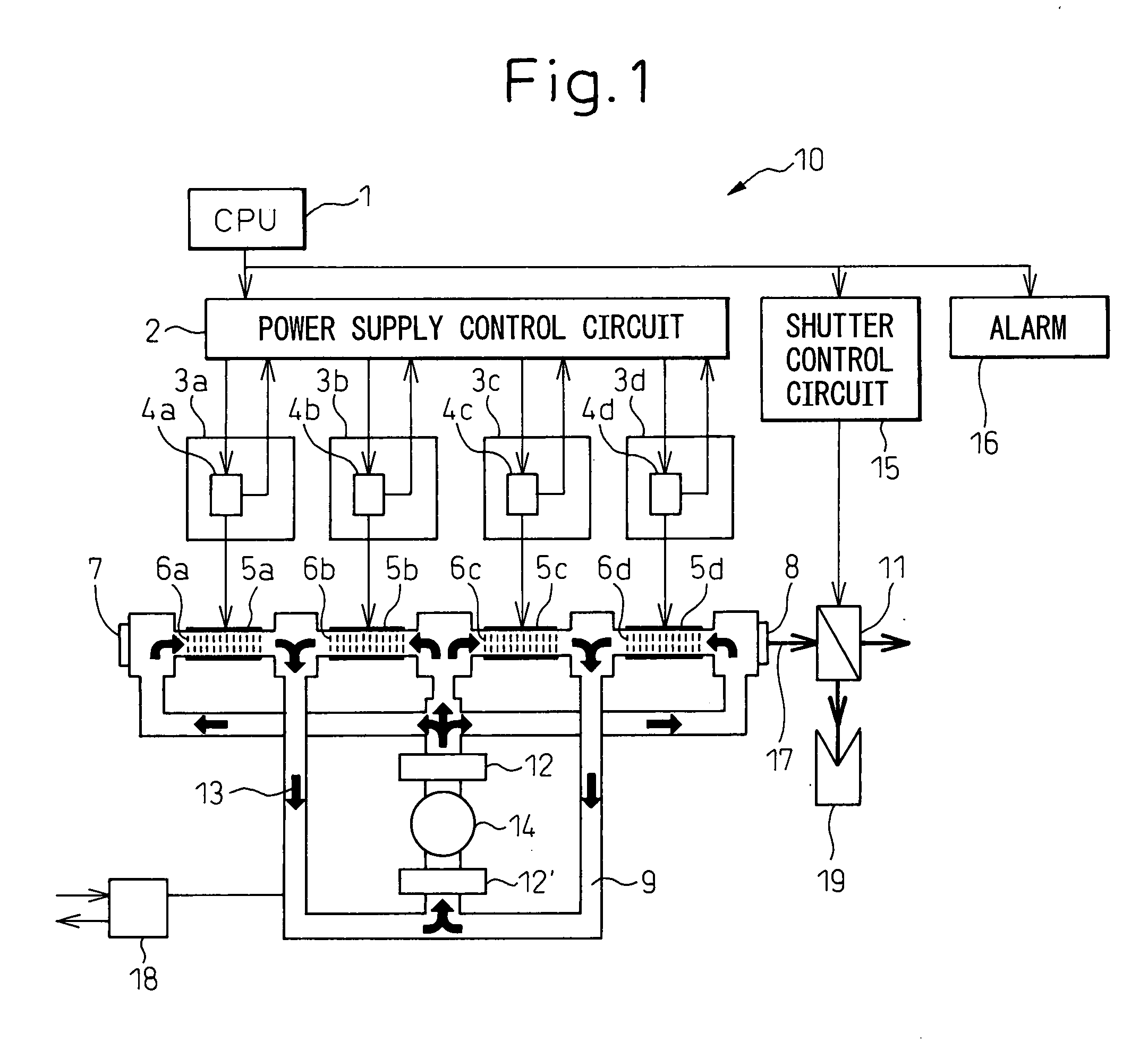
A gas laser oscillator (10) provided with voltage detecting means (4a to 4d) for detecting the voltage of each of a plurality of discharge tube segments (6a to 6d) of a discharge tube before start of discharge and a discharge tube segment start judging means (1) for judging if each of the plurality of discharge tube segments (6a to 6d) has started based on the voltage of the discharge tube segments (6a to 6d) detected by the voltage detecting means (4a to 4d), wherein the discharge tube segment start judging means (1) allows all of the plurality of discharge tube segments (6a to 6d) to start only when the voltages of all of the discharge tube segments (6a to 6d) of the plurality of discharge tube segments are smaller than a predetermined voltage (Vb) is provided. Due to this, it is possible to judge an abnormality in the laser gas before the start of discharge without any work on the part of the operator and thereby prevent the discharge tube from being damaged.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Target marking system having a gas laser assembly and a thermal imager
InactiveUS7818911B2Robust configurationSighting devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansHand heldLight beam
A handheld target marker is provided, wherein the target marker includes a housing retaining a gas laser, a collimating or focusing lens, a driver and a power supply. The laser produces a thermal infrared beam which can be selectively directed to impinge upon a target. The impinging beam is viewable by a thermal imager. The handheld target marker operates at ambient temperatures and incorporates the driver and power supply necessary for operation of the laser, wherein the beam can be pulsed for enhancing imaging on the thermal imager.
Owner:LMD APPL SCI LLC
Discharge igniter for a waveguide CO2 laser
ActiveUS6999490B2Easy to igniteIgnited faster and more predictablyActive medium materialGas laser constructional detailsLateral extensionGas laser
A waveguide gas laser includes an enclosure filled with a lasing gas. A ceramic block is provided with one or more waveguide channels. At least one of the waveguide channels includes an open region which is in fluid communication with a waveguide channel. Lasing gas in the enclosure fills the waveguide channels and the lateral extension. An electric field is applied across the lateral extension of the waveguide channel while simultaneously applying a smaller electric field across the waveguide channel. The electric field across the lateral extension ignites a discharge in the lateral extension that spreads into the lasing gas in the waveguide channel. The electric field across the waveguide channel is sufficient to sustain the discharge in the lasing in the waveguide channel.
Owner:COHERENT INC
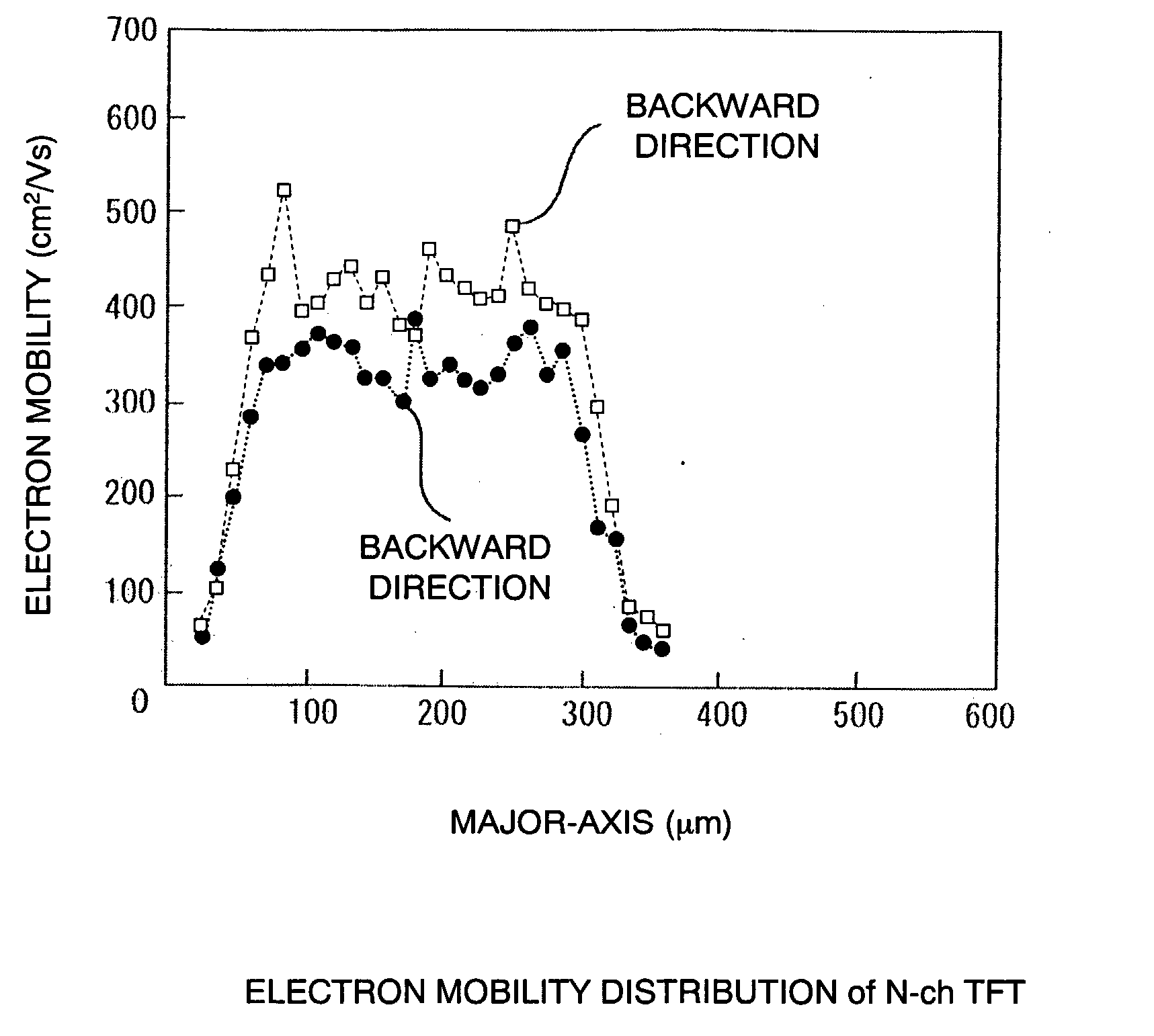
Laser irradiation apparatus and laser irradiation method
InactiveUS20070148834A1Suppress interferenceImprove mobilityTransistorSolid-state devicesLight beamOptoelectronics
It is an object of the present invention to provide a laser irradiation apparatus which can manufacture a homogenously crystallized film by varying the energy intensity of an irradiation beam in forward and backward directions of the irradiation. A laser irradiation apparatus of the present invention comprises a laser oscillator and means for varying beam intensity wherein a laser beam is obliquely incident into the irradiation surface, the laser beam is scanned relative to the irradiation surface, and the beam intensity is varied in accordance with the scanning direction. Further, the laser oscillator is a continuous wave solid-state laser, gas laser, or metal laser. A pulsed laser having a repetition frequency of 10 MHz or more can also be used.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
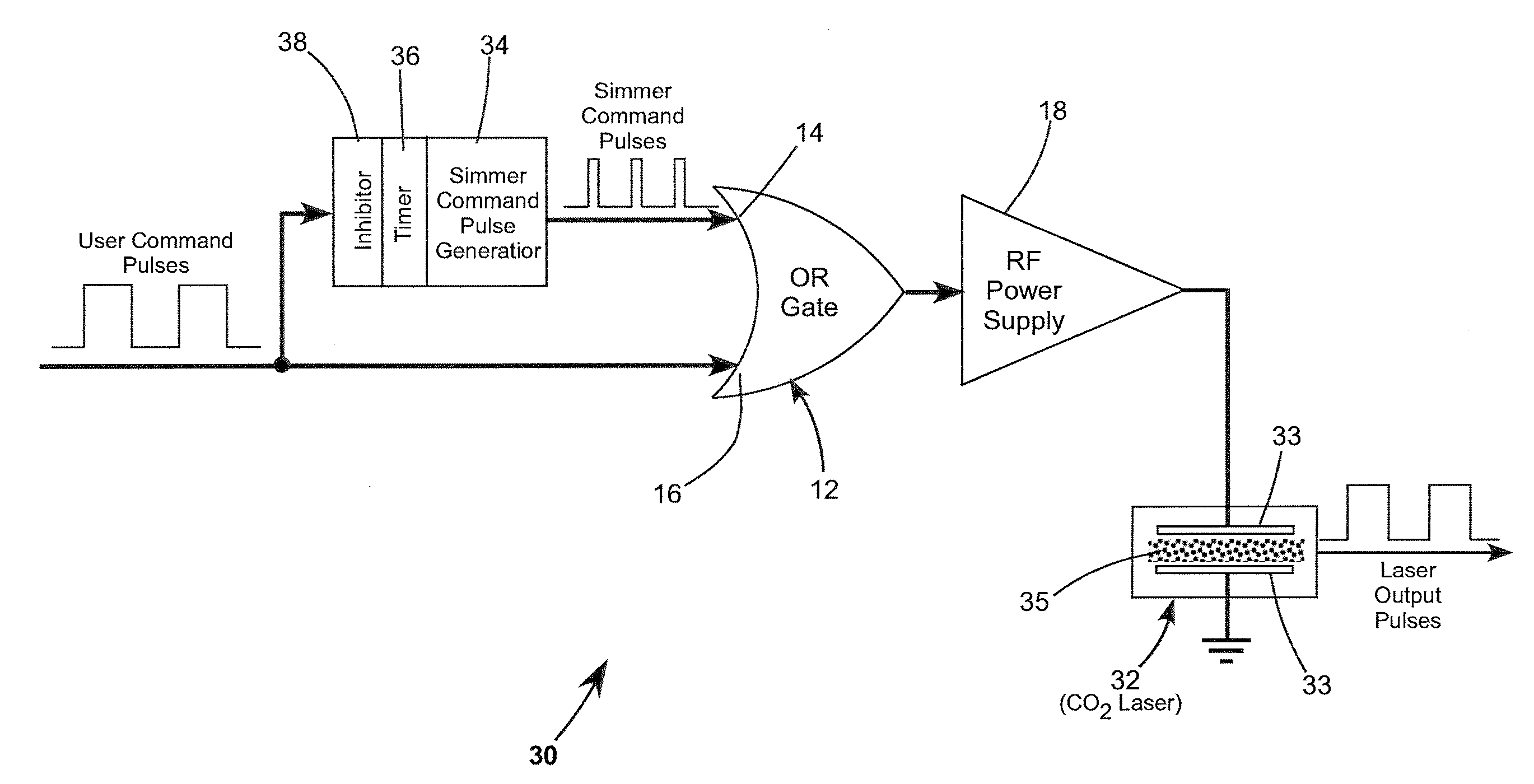
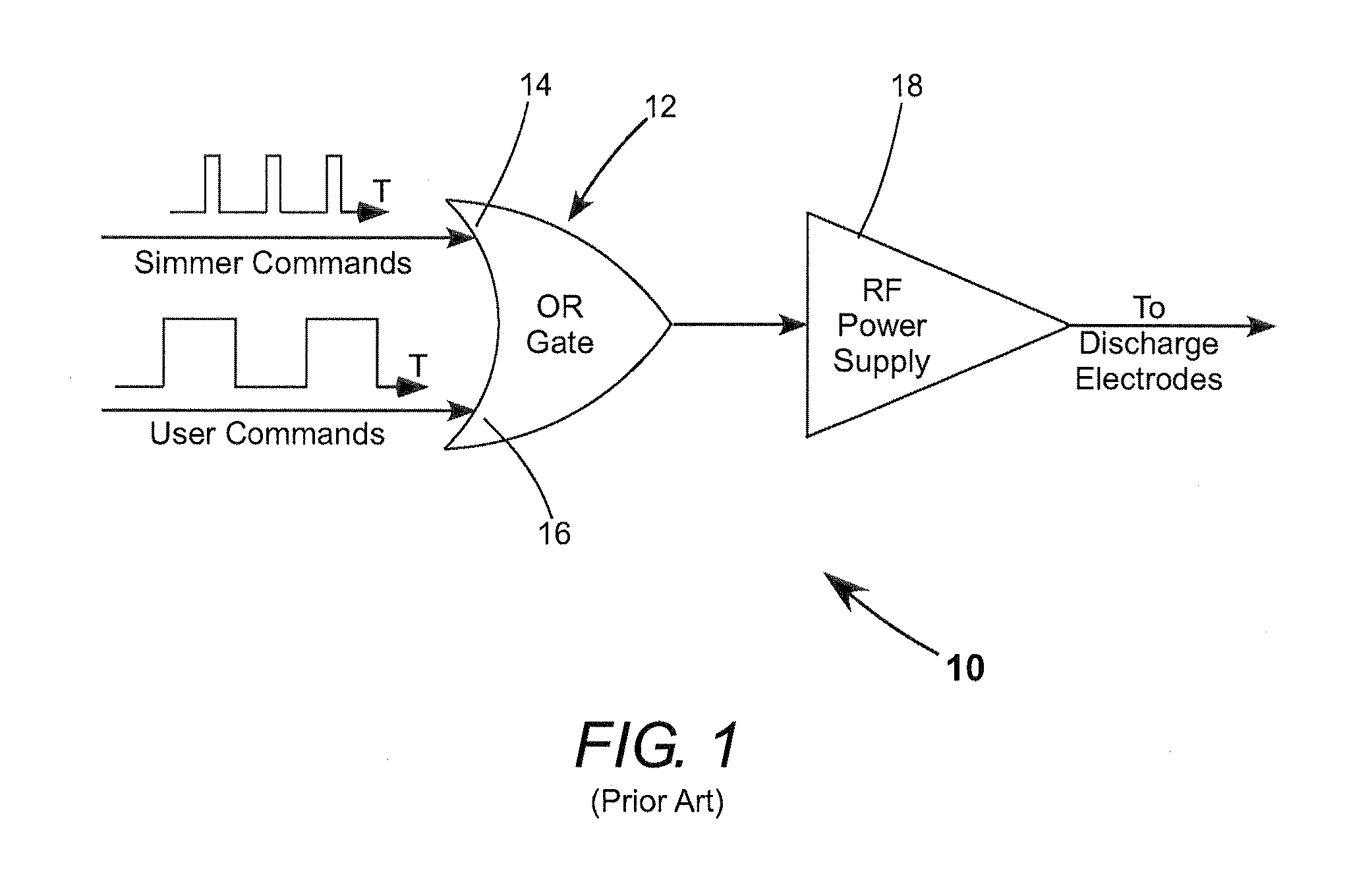
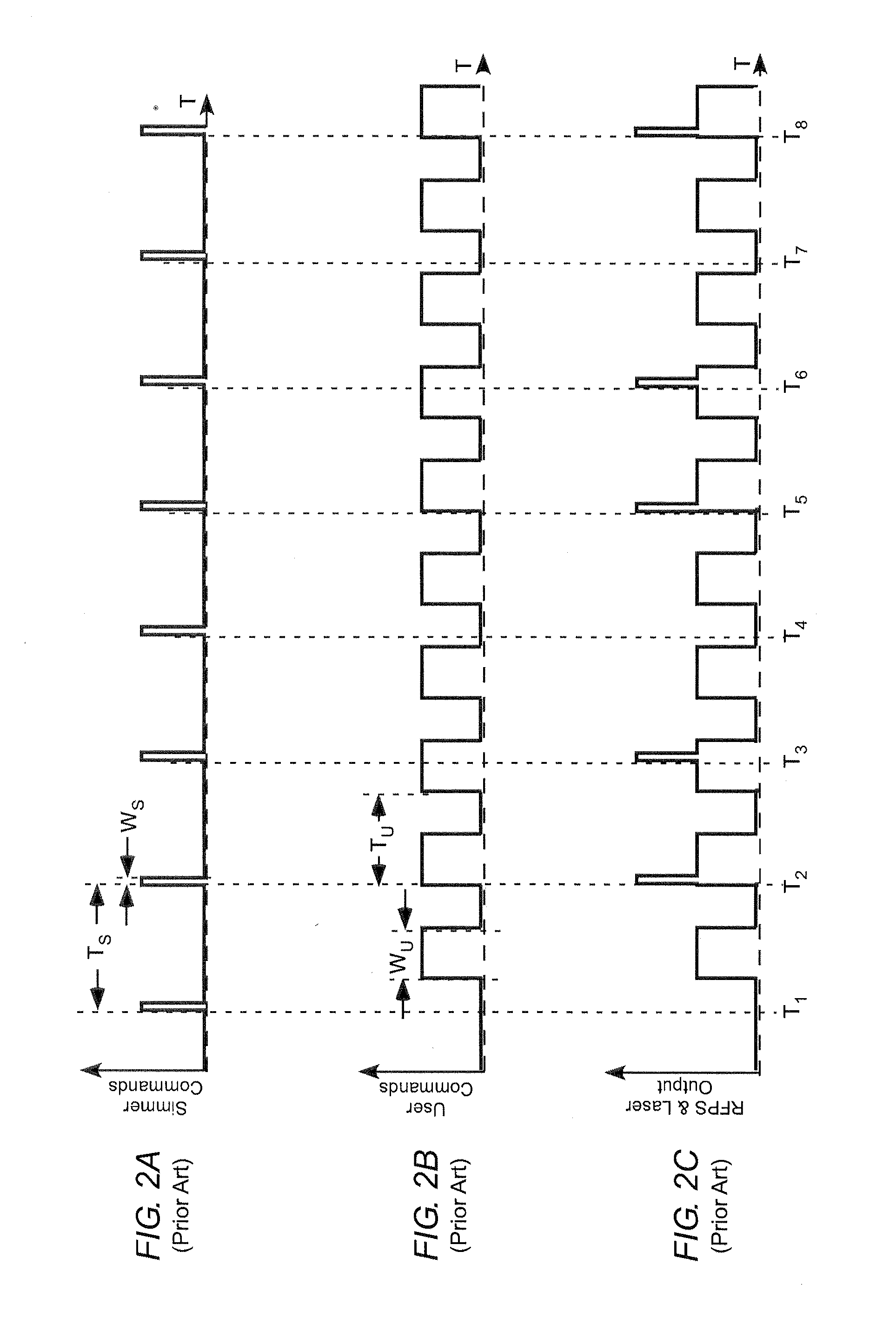
Gas laser discharge pre-ionization using a simmer-discharge
ActiveUS20120189031A1Avoids amplitude modulationParticularly effectiveActive medium materialOptoelectronicsGas laser
A gas discharge laser including a lasing gas between discharge electrodes and has a power supply for generating RF pulses to be delivered to the electrodes of the laser for energizing the lasing gas. A sequence of RF simmer pulses is delivered to the electrodes. The simmer pulses create sufficient free electrons in the lasing gas to facilitate subsequent ignition of the discharge while not causing laser action. RF lasing pulses having a longer duration than the simmer pulses are delivered to the electrodes to ignite the discharge and provide corresponding laser output pulses. Delivery of the simmer pulses is suspended during delivery of the lasing pulses to avoid amplitude or pulse-width modulation of the laser output pulses by the simmer pulses.
Owner:COHERENT INC
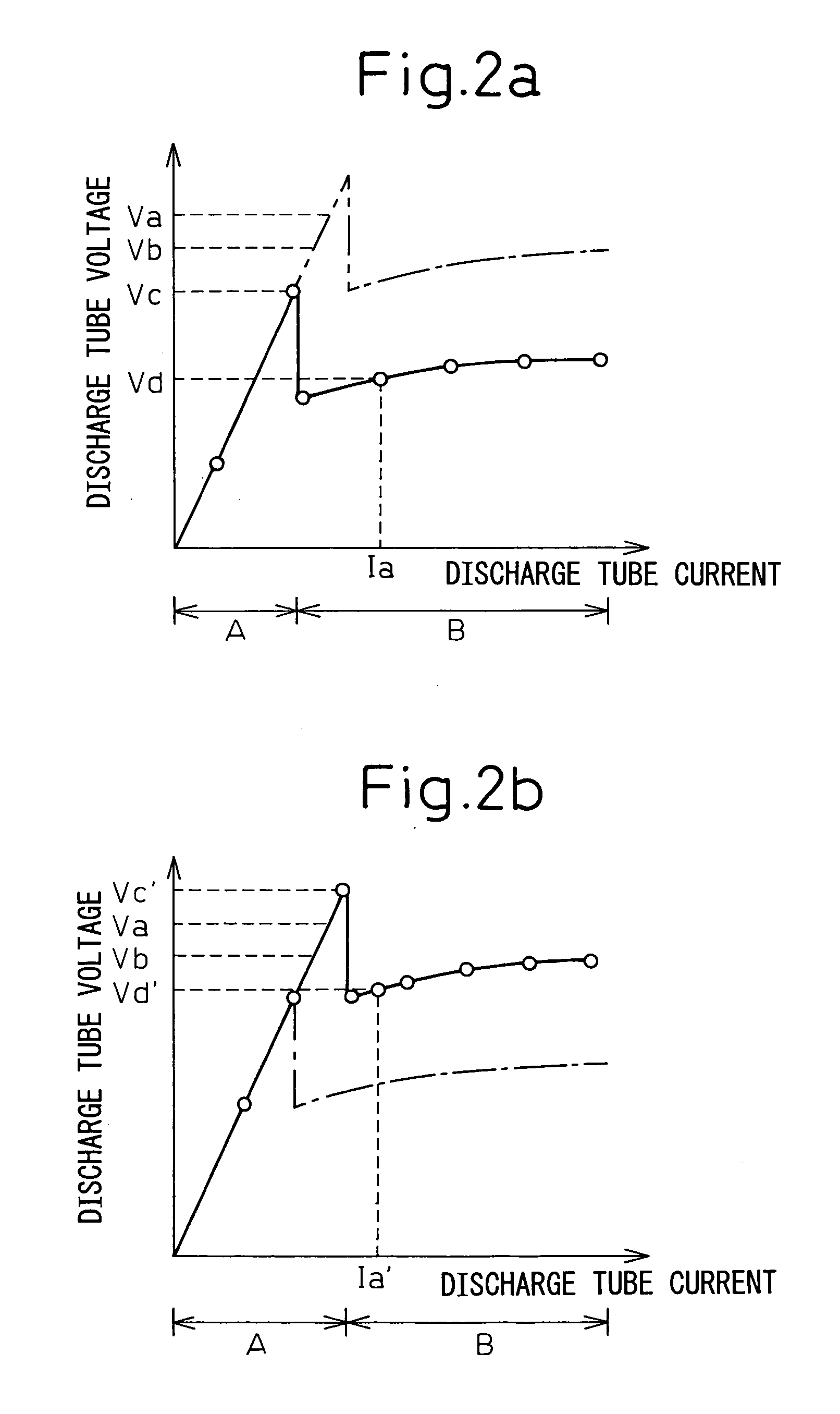
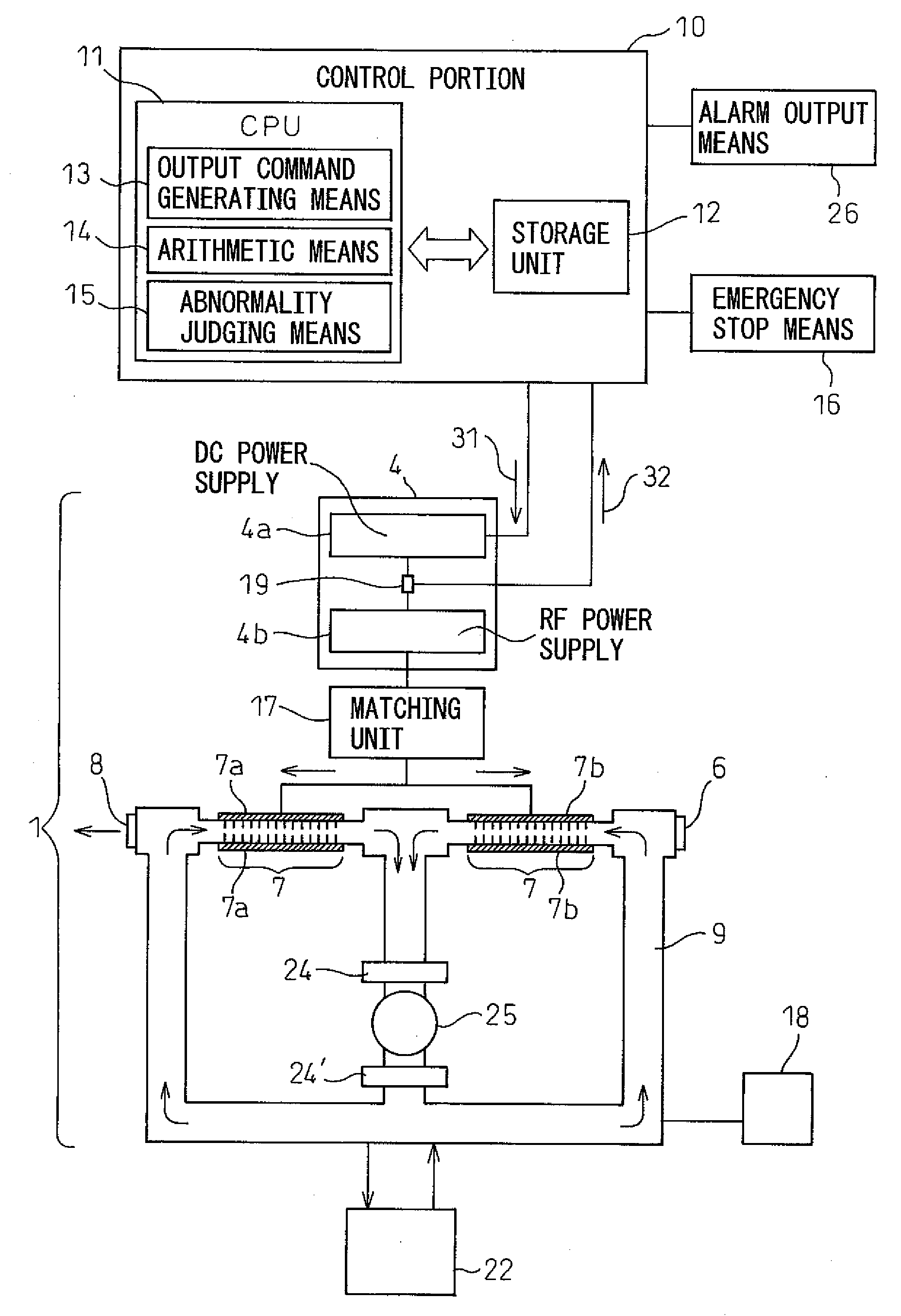
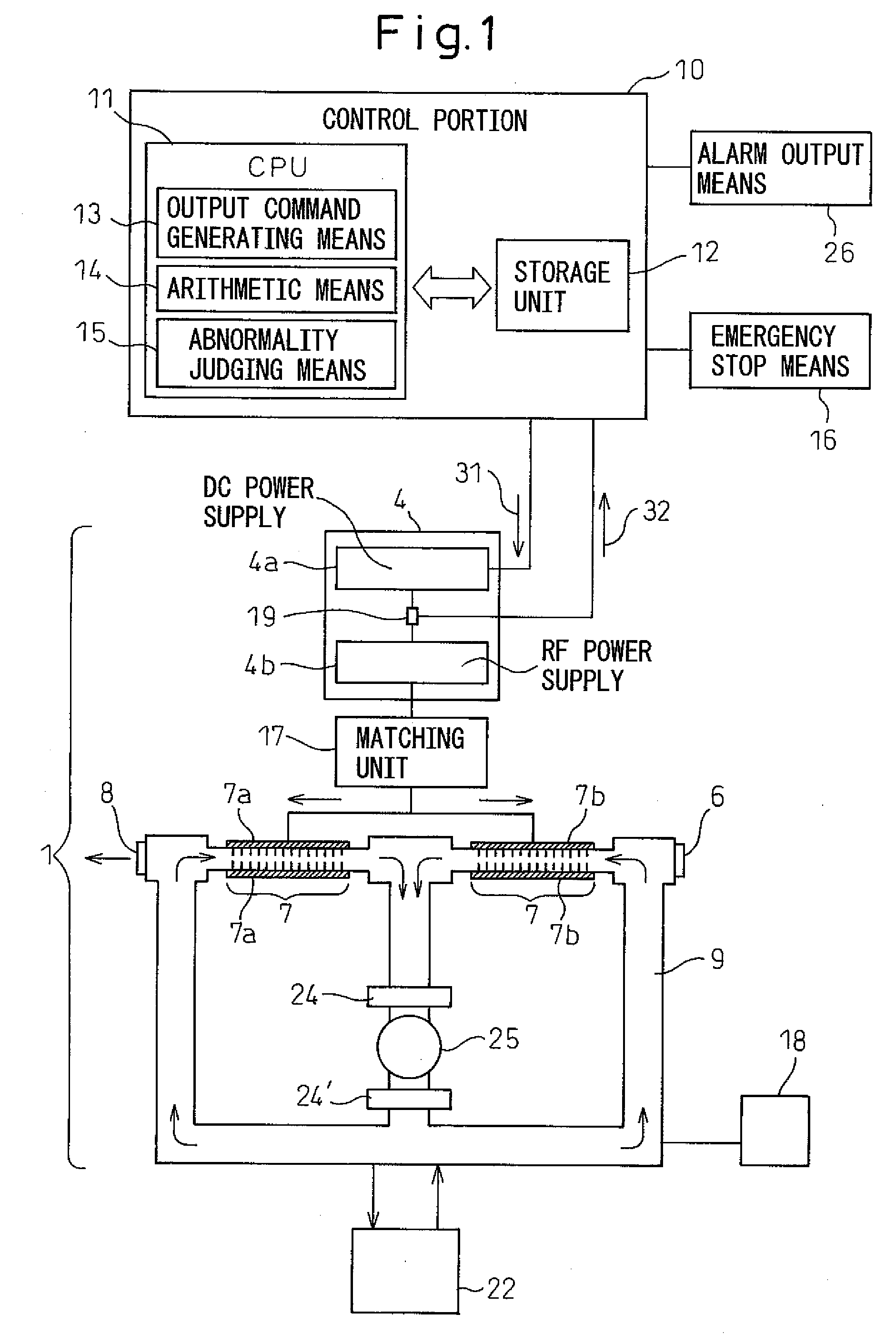
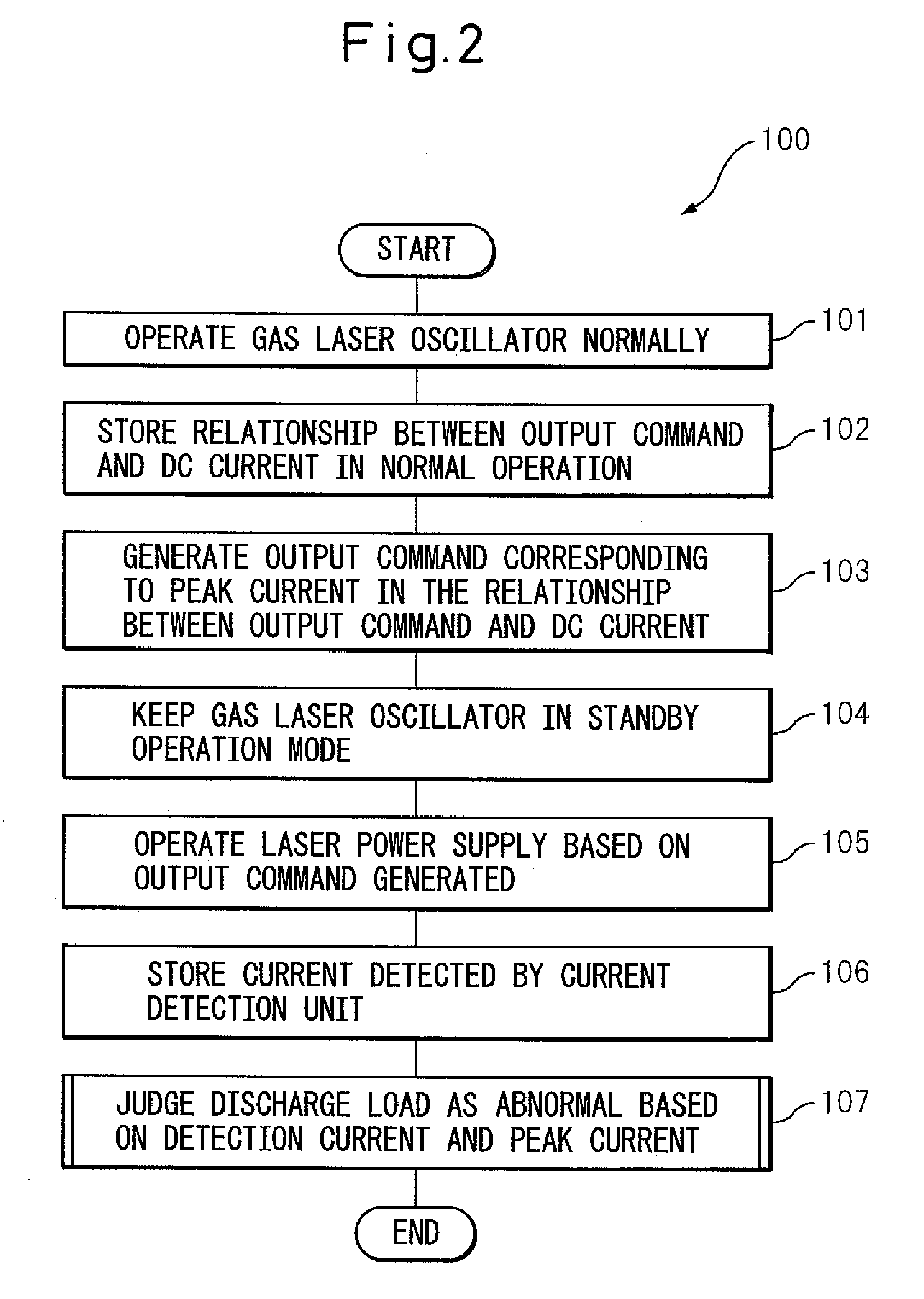
Abnormality detection method for gas laser oscillator and gas laser oscillator for implementing the method
A gas laser oscillator (1), which generates a laser beam by exciting laser gas in discharge tubes (7) with a laser power supply (4) and detecting an abnormality thereof, includes a storage unit (12) for storing the relationship between the output command and the DC current of the laser power supply (4) during the normal operation of the oscillator (1), an output command generating unit (13) for generating an output command corresponding to the peak current value in the relationship between the output command and the DC current, a current detection unit (19) for detecting the current during the operation of the laser power supply (4) based on the output command in the standby operation mode of the gas laser oscillator (1), and an abnormality judging unit (15) for judging that the discharge load of the gas laser oscillator (1) has an abnormality based on the detection current detected by the current detection unit (19) and the peak value of the current in the relationship between the output command and the DC current. In this way, the abnormality of the discharge load of the discharge tubes (7) can be easily and safely detected. The gas laser oscillator further desirably includes a stop unit for stopping the gas laser oscillator when the discharge load is judged as abnormal.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com