Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
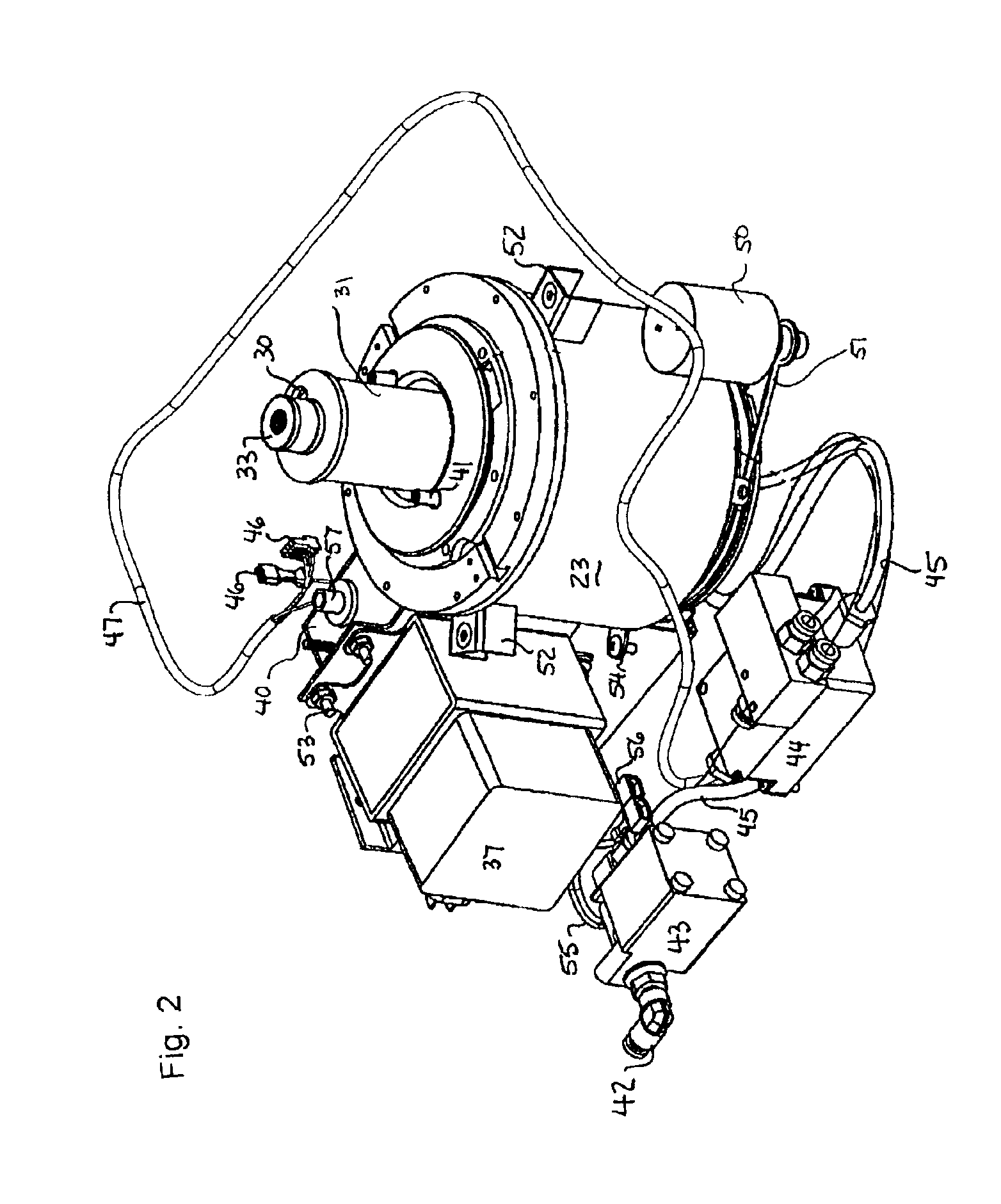
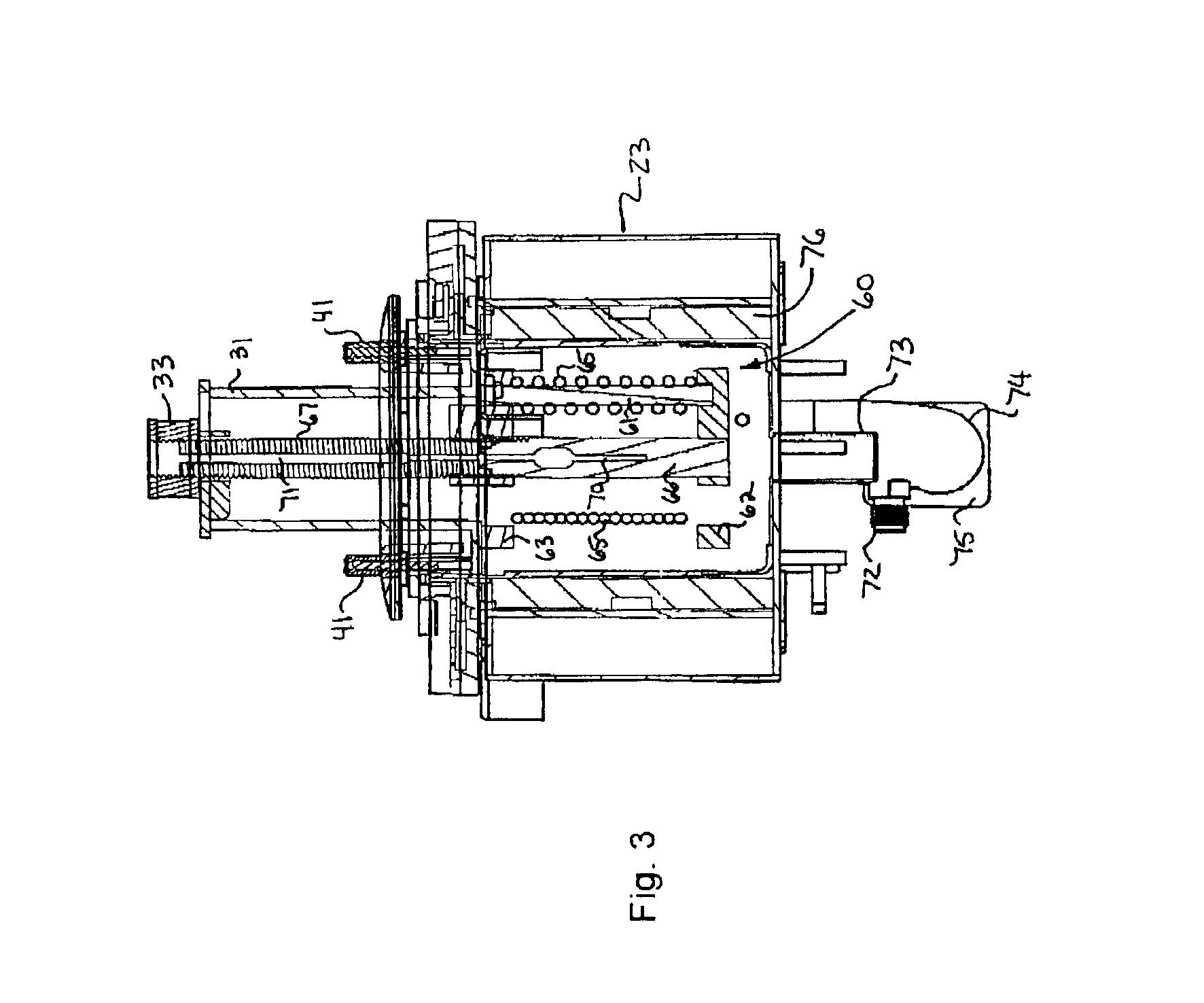
631 results about "Microwave cavity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
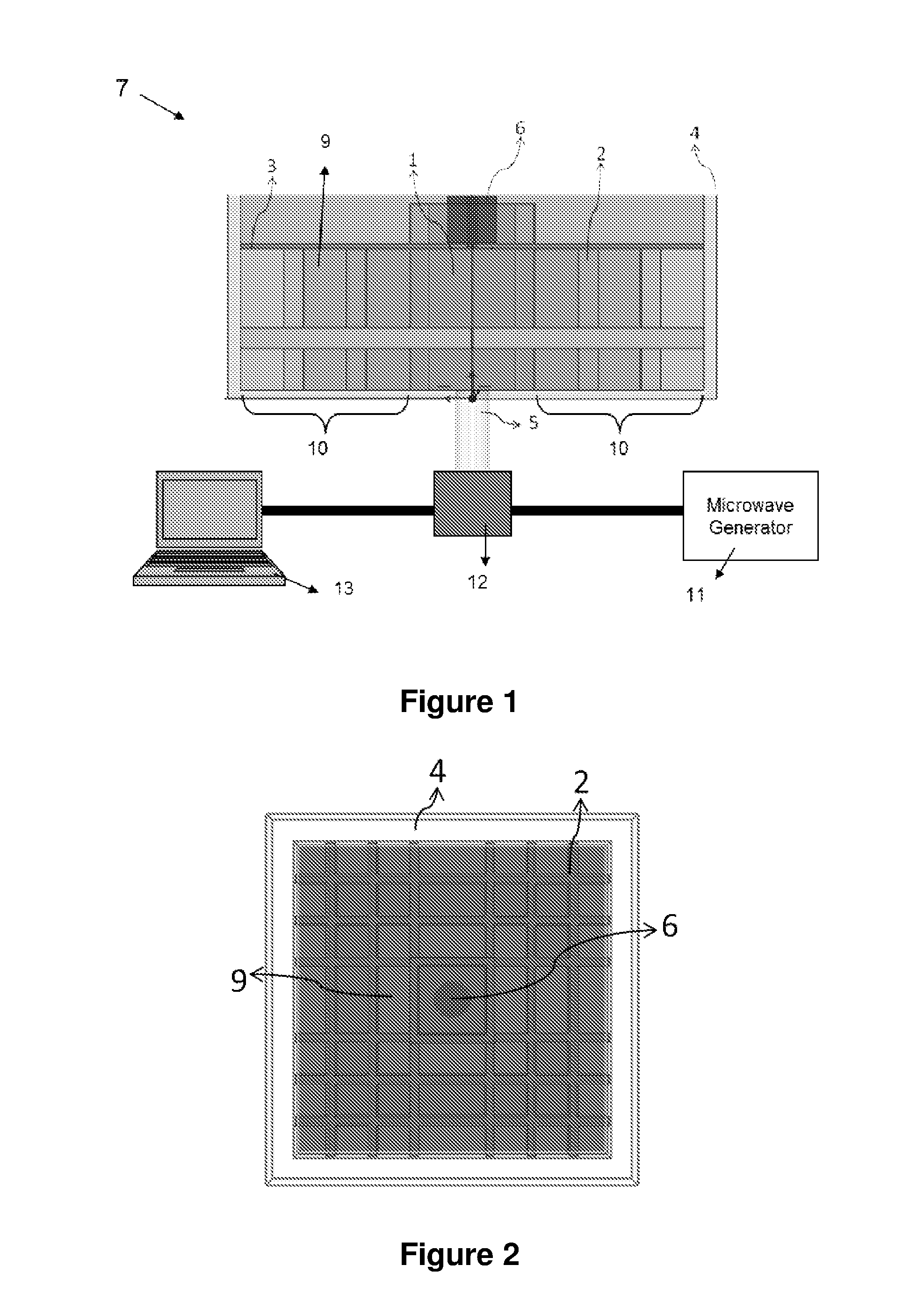
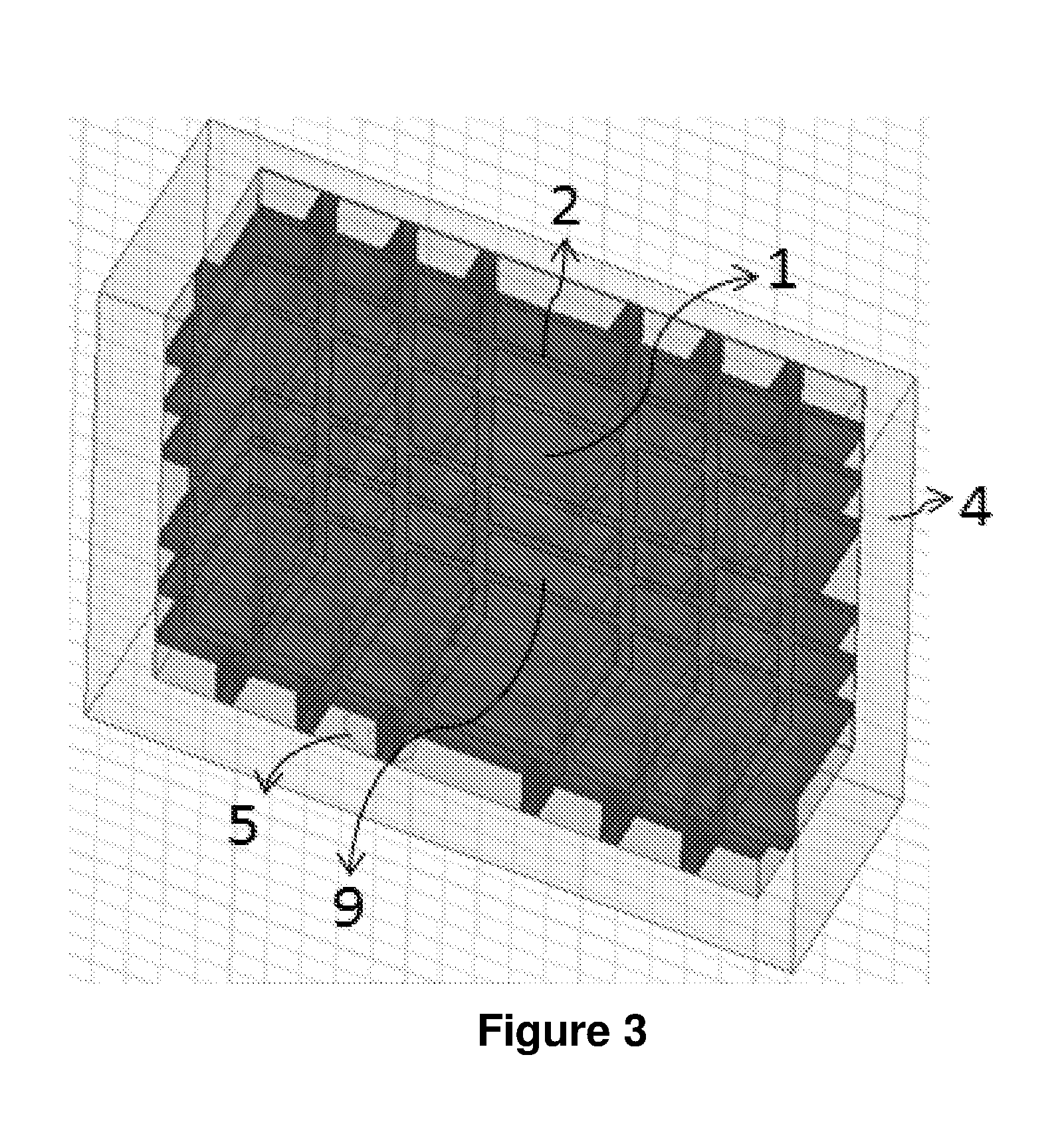
A microwave cavity or radio frequency (RF) cavity is a special type of resonator, consisting of a closed (or largely closed) metal structure that confines electromagnetic fields in the microwave region of the spectrum. The structure is either hollow or filled with dielectric material. The microwaves bounce back and forth between the walls of the cavity. At the cavity's resonant frequencies they reinforce to form standing waves in the cavity. Therefore, the cavity functions similarly to an organ pipe or sound box in a musical instrument, oscillating preferentially at a series of frequencies, its resonant frequencies. Thus it can act as a bandpass filter, allowing microwaves of a particular frequency to pass while blocking microwaves at nearby frequencies.
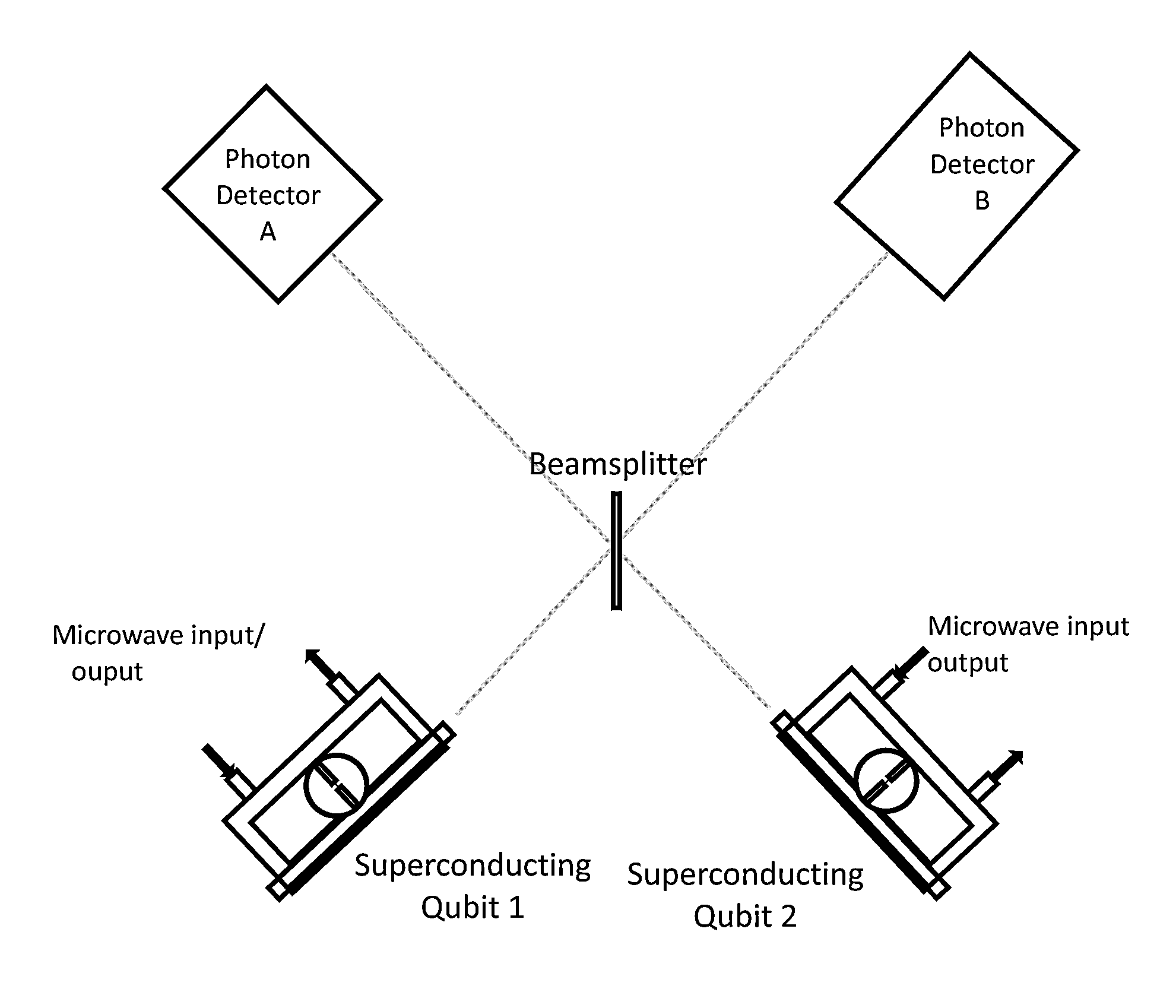
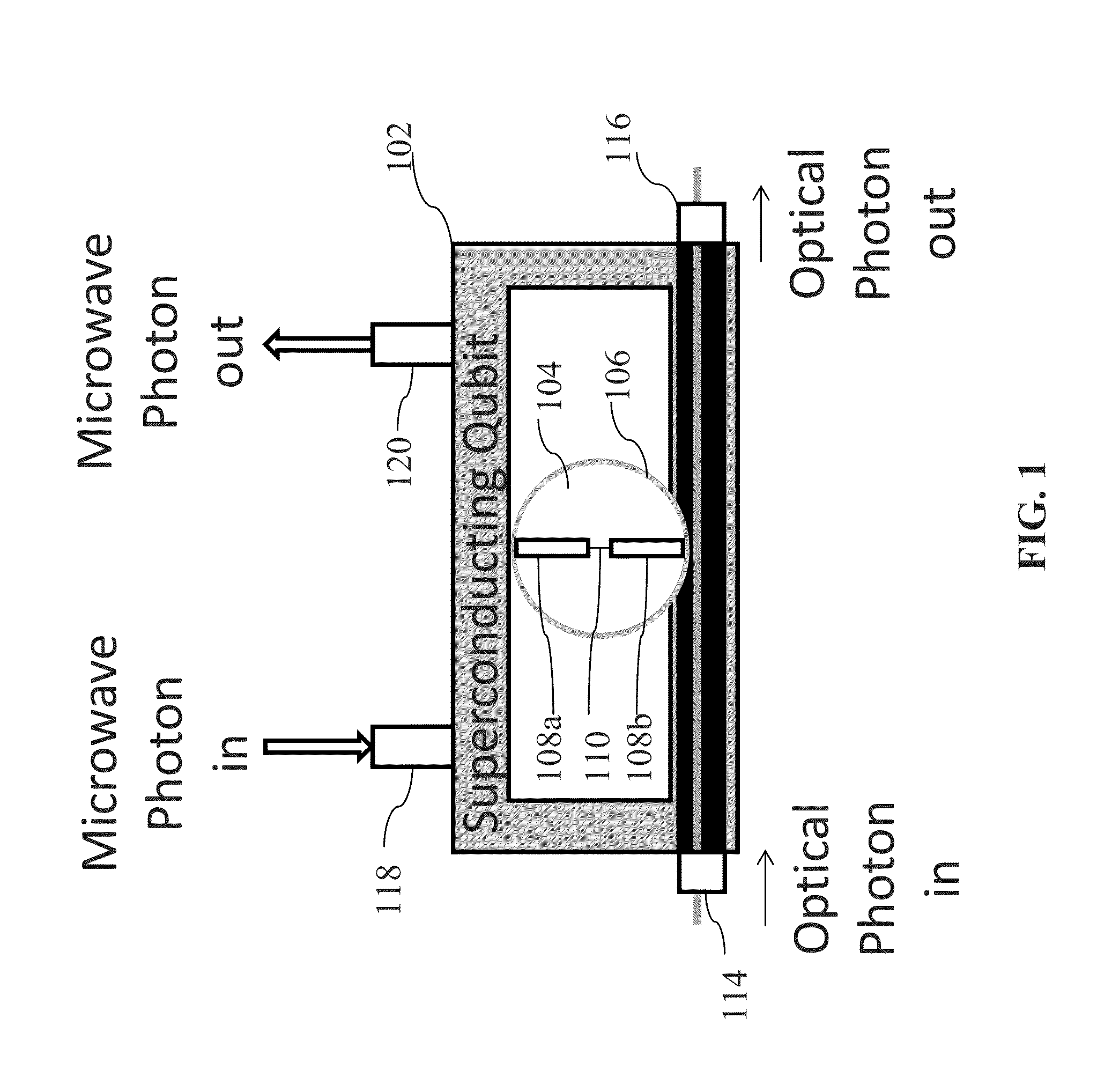
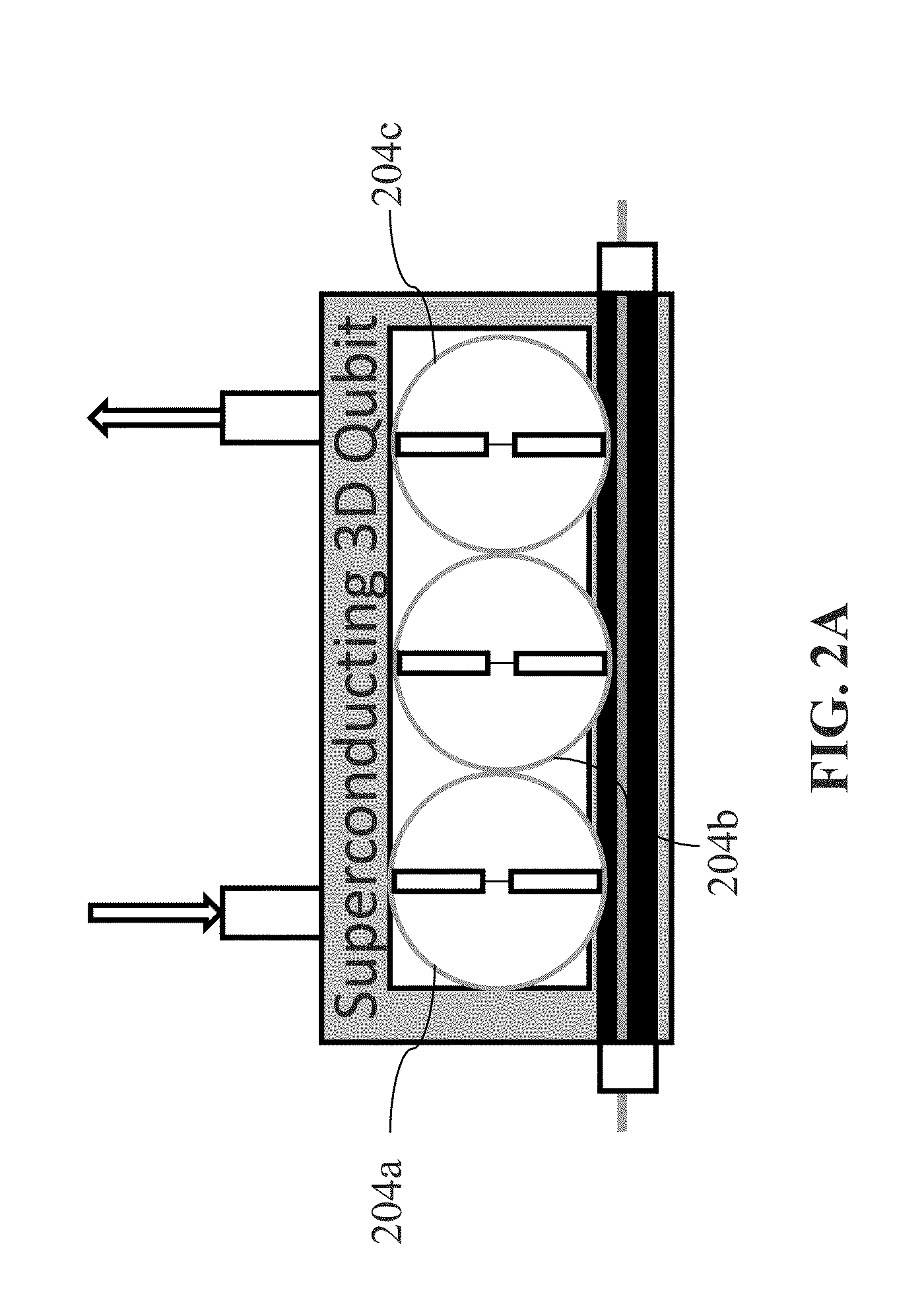
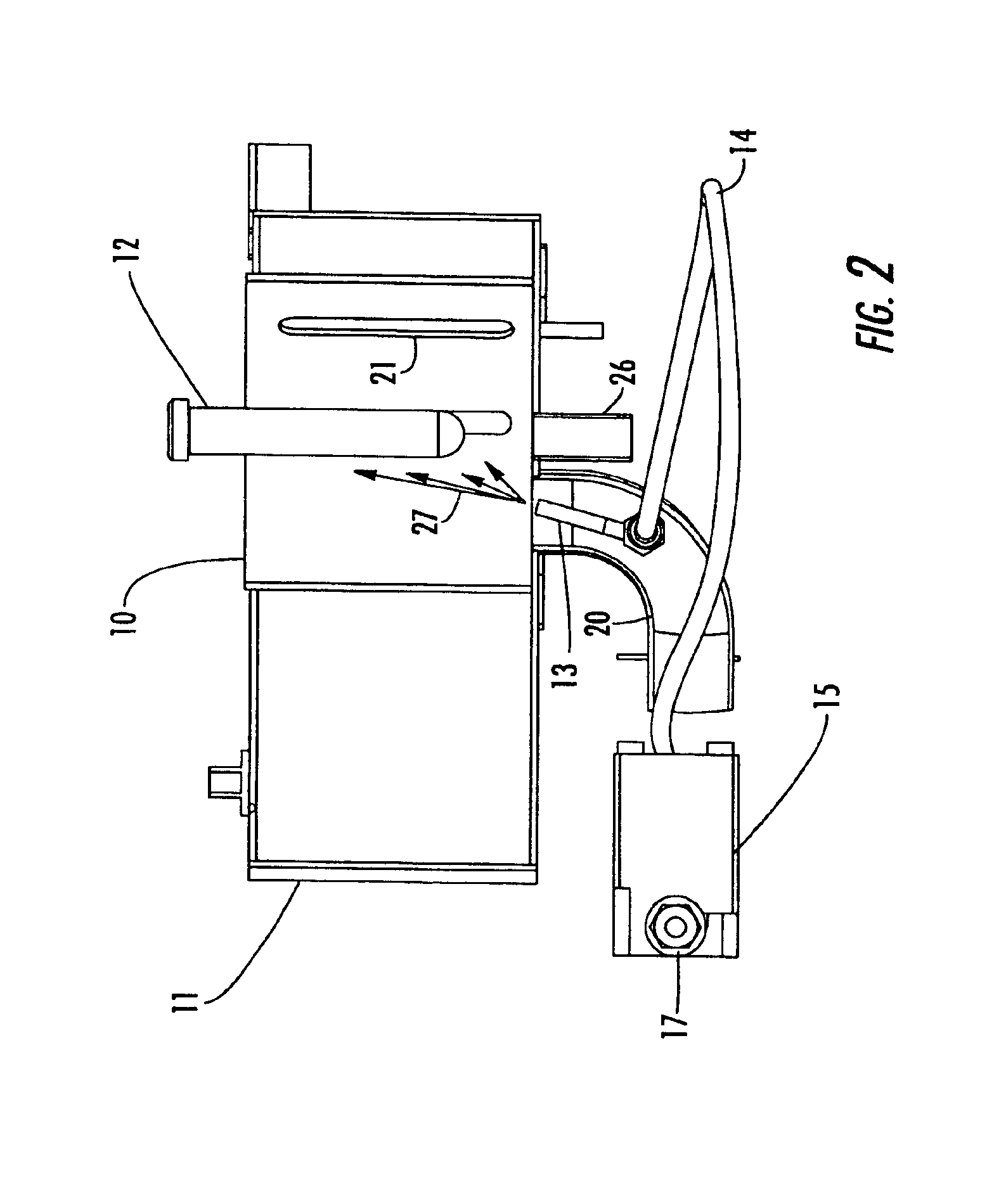
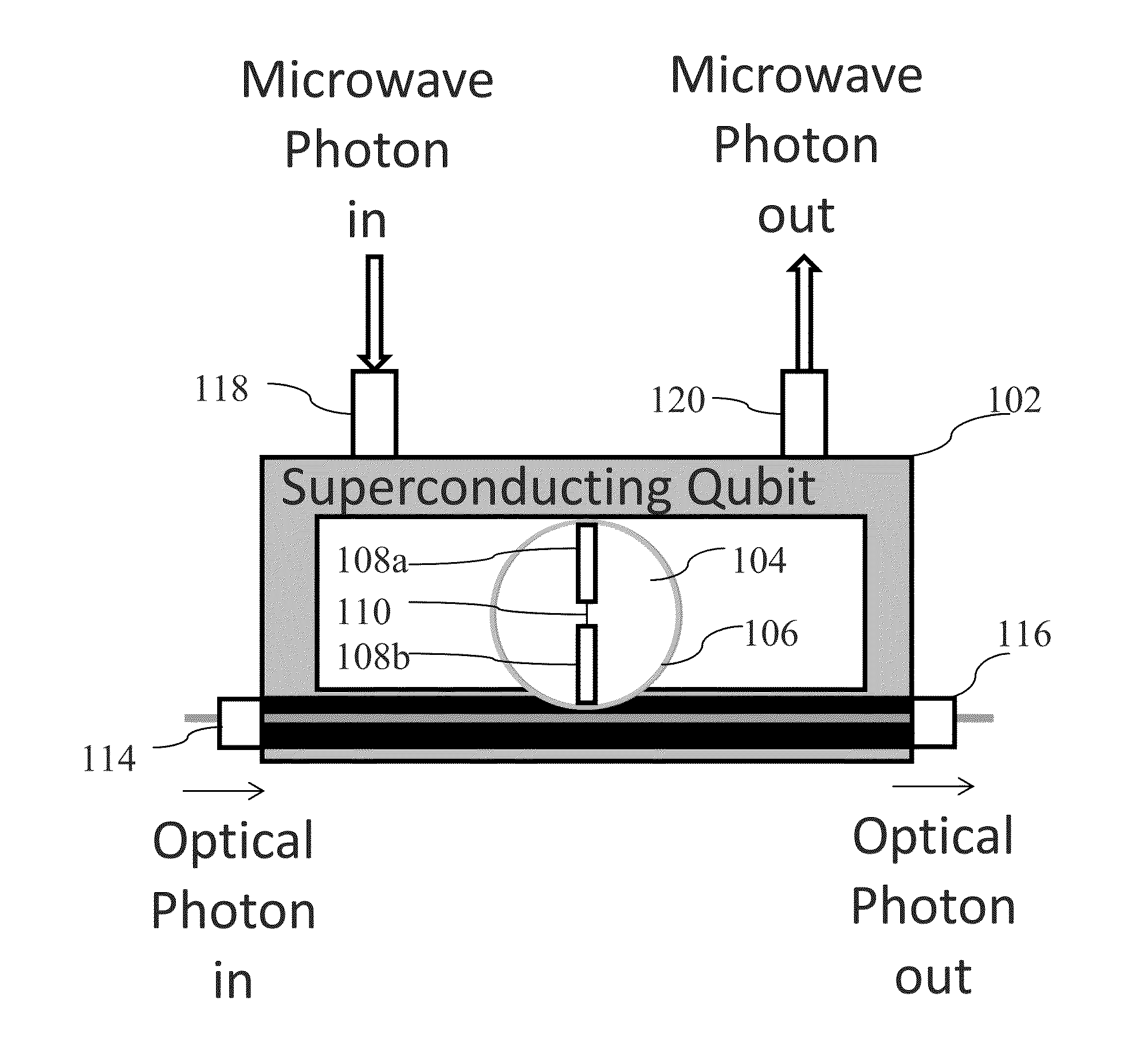
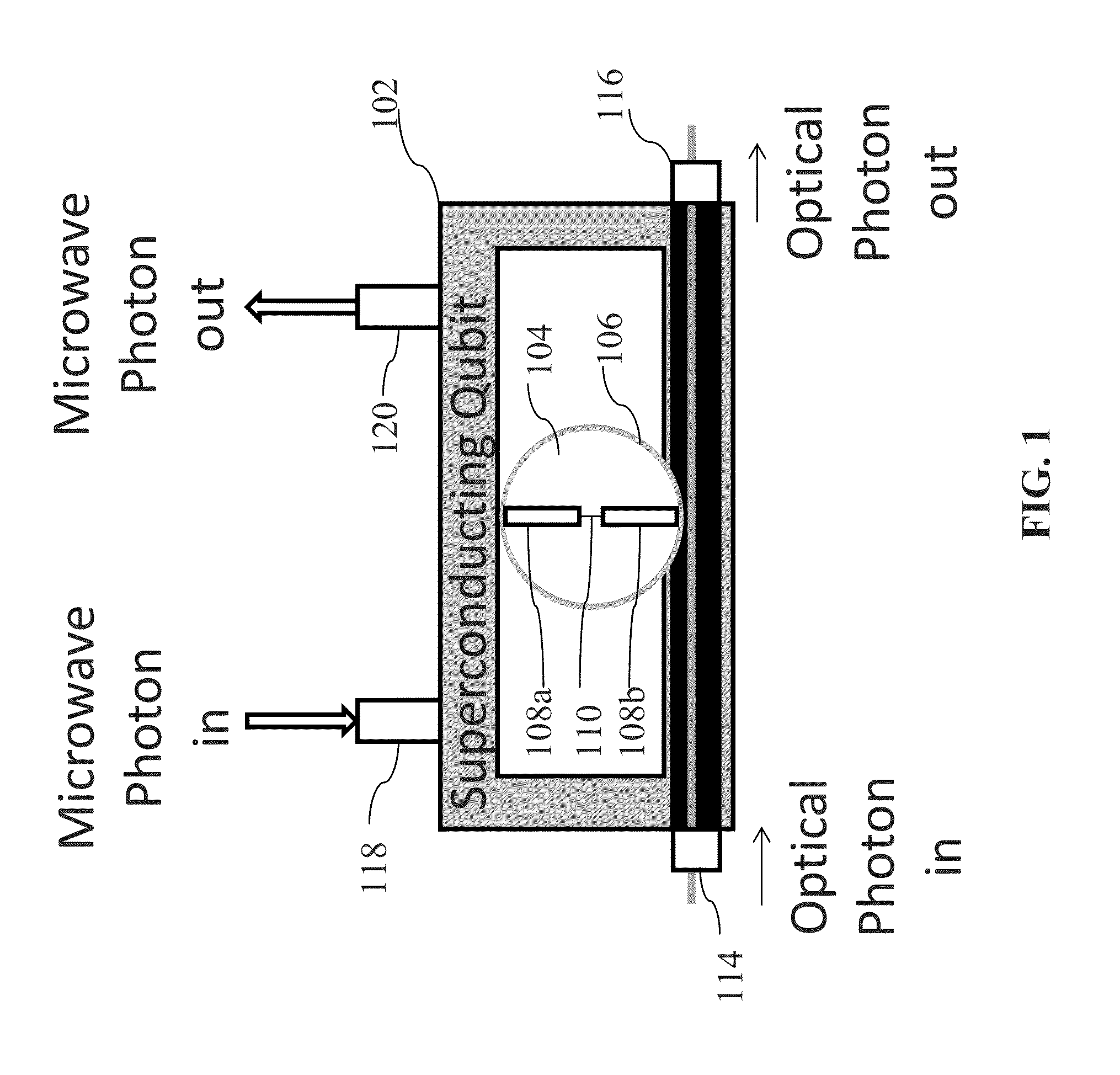
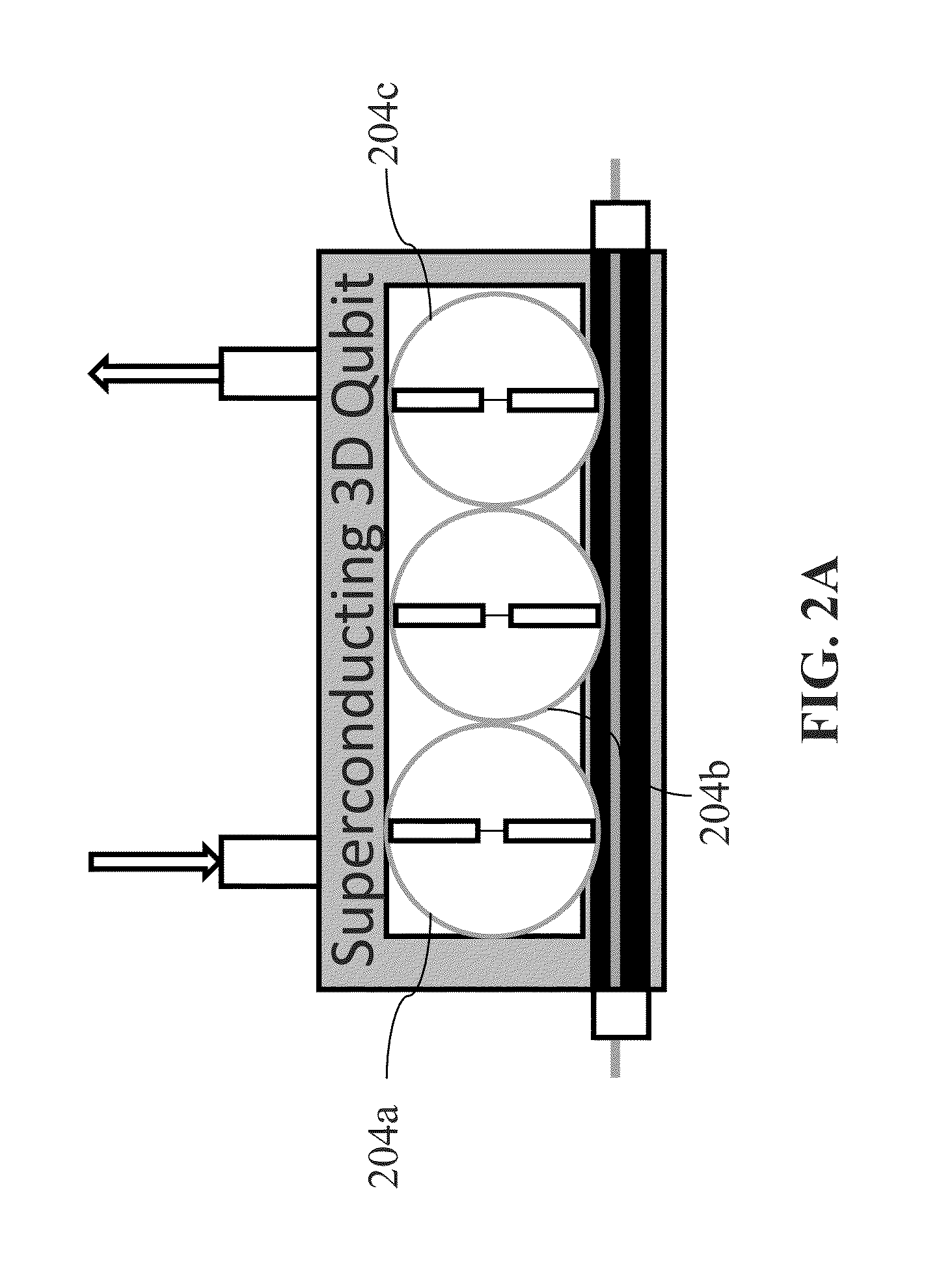
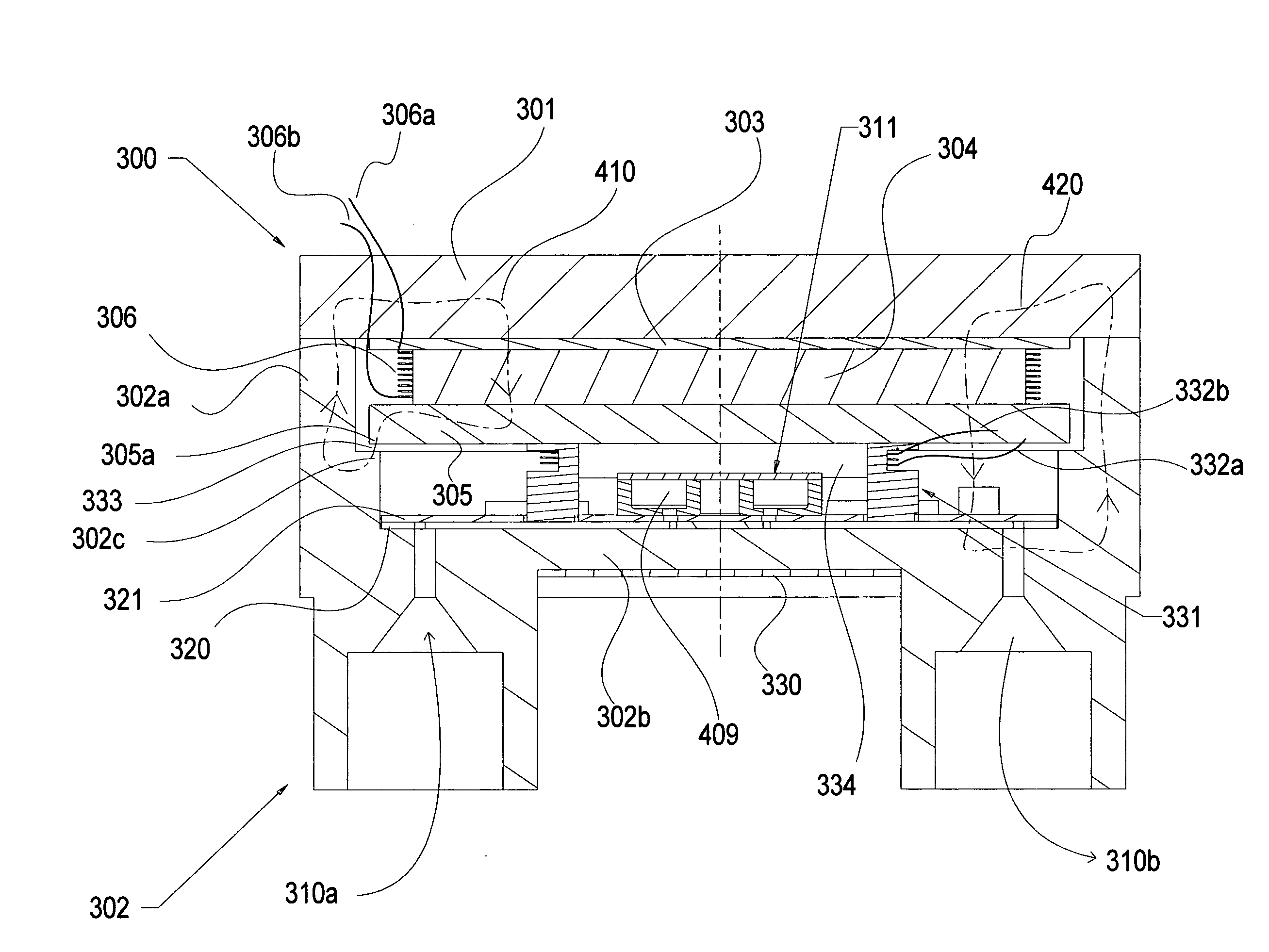
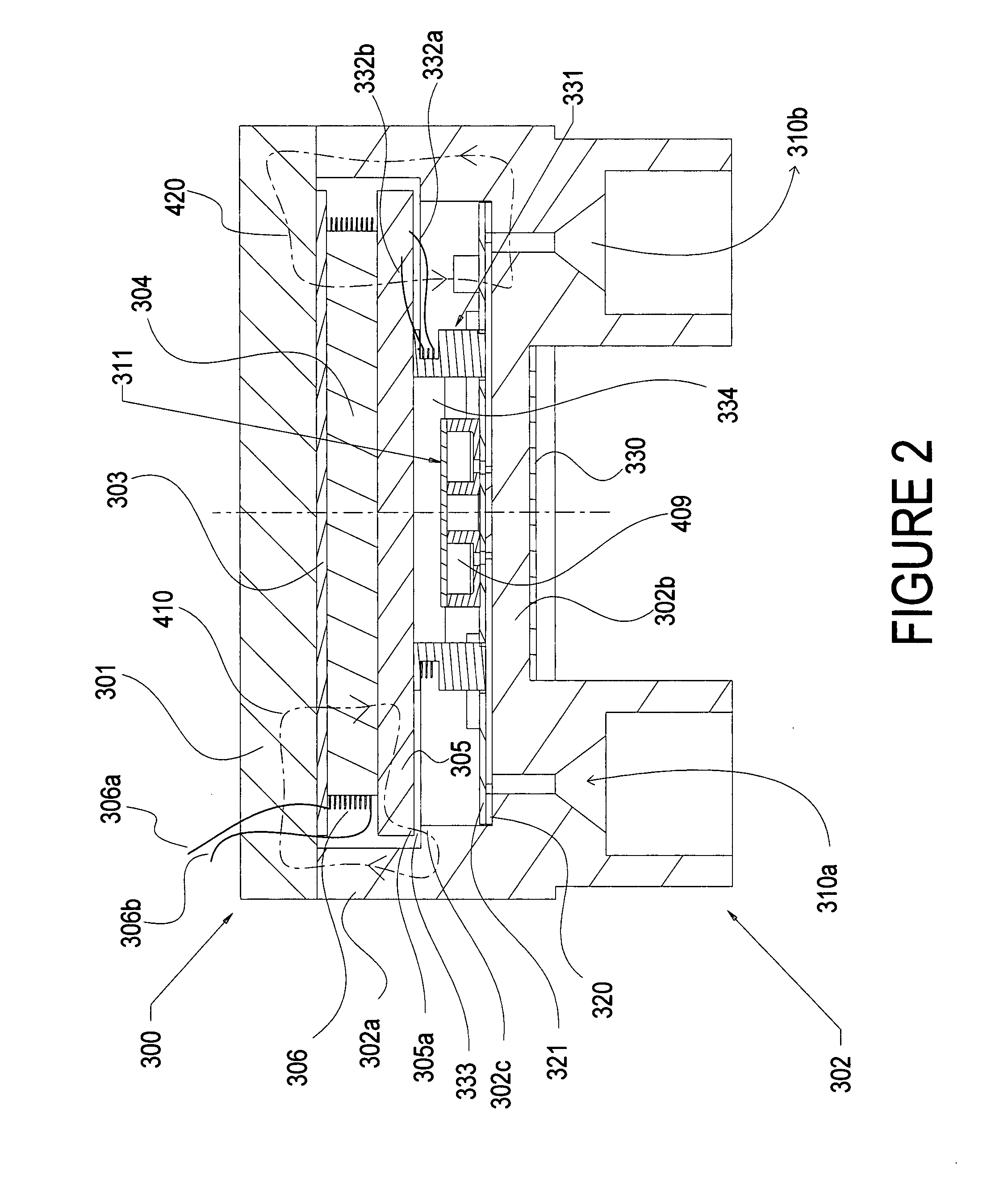
System and method for quantum information transfer between optical photons and superconductive qubits
ActiveUS20140314419A1Modulation frequencyQuantum computersNanoinformaticsMicrowave cavityDirect coupling
An electro-optical system for exchanging quantum information between optical qubits and including a superconductive microwave cavity; an electro-optical material: a superconductive qubit circuit formed on the electro-optical material including a superconductive qubit; a dipole antenna, formed on the electro-optical material for directly coupling the superconductive qubit to the superconductive microwave cavity; an optical input for receiving input optical photons; a microwave input for receiving input microwave photons; and an optical output for outputting modulated optical photons, wherein a frequency and a phase of the optical photon is modulated with a state of the superconducting qubit by the dipole antenna.
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP
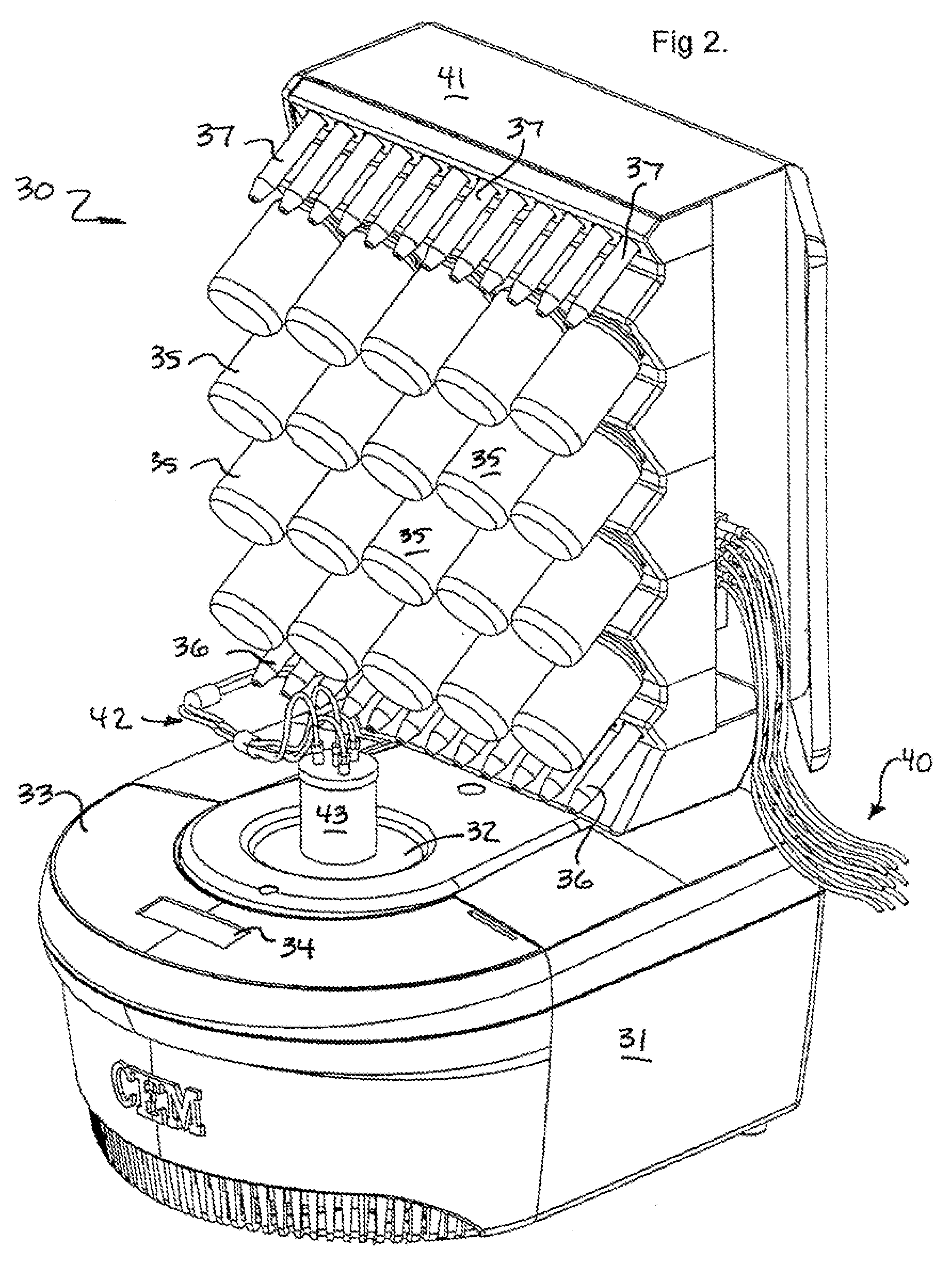
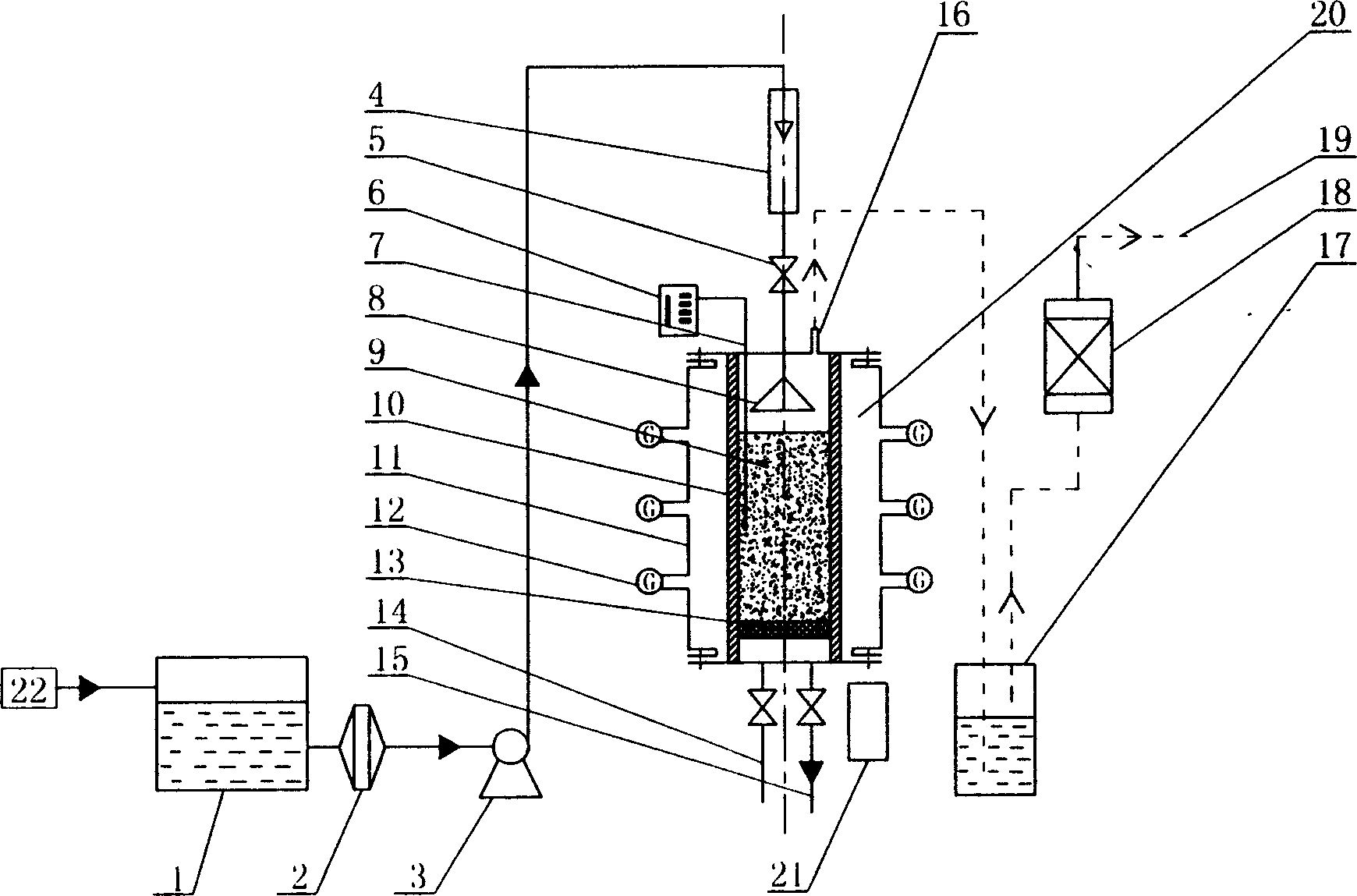
Method and apparatus for continuous flow microwave-assisted chemistry techniques
InactiveUS6867400B2Increase temperaturePreparation by ester-hydroxy reactionOrganic compound preparationMicrowave cavityContinuous flow
The invention is a method and associated instrument for microwave assisted chemistry. The invention includes the steps of directing a continuous flow of fluid through a microwave cavity while applying microwave radiation to the cavity and to the continuous flow of materials therein, monitoring the pressure of the fluid in the cavity; and cooling the fluid in the cavity when the pressure exceeds a predetermined setpoint pressure.
Owner:CEM CORP
Apparatus and method for microwave processing of materials
InactiveUS20070215612A1Uniform of microwave energyUniform power densityMicrowave heatingMicrowave cavityEngineering
A microwave heating apparatus is designed to improve distribution of the microwaves introduced into a multi-mode microwave cavity for heating or other selected applications. The microwave heating apparatus includes a microwave signal generator and a waveguide to convey microwave power to the cavity. A perforated metal plate disposed within the cavity encloses a volume adjacent to the waveguide opening, forming a leaky multimode subcavity. Through multiple processes of reflection, transmission, diffraction, and scattering, the leaky subcavity serves to smooth the microwave power distribution in the near-field region adjacent to the waveguide to better disperse the energy throughout the main applicator cavity. A more uniform level of microwave power is thereby applied to the workpiece.
Owner:HICKS KEITH R +4
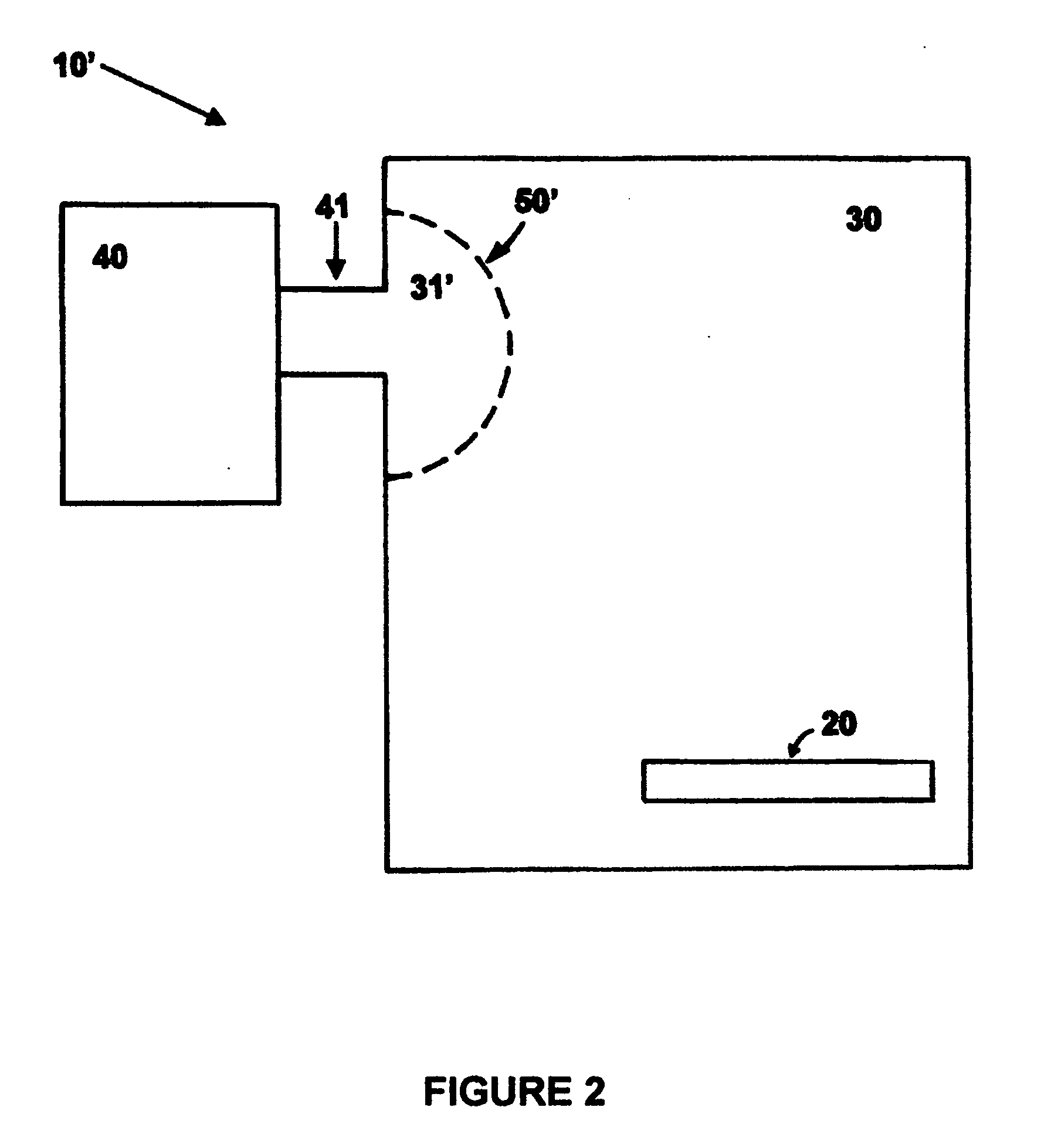
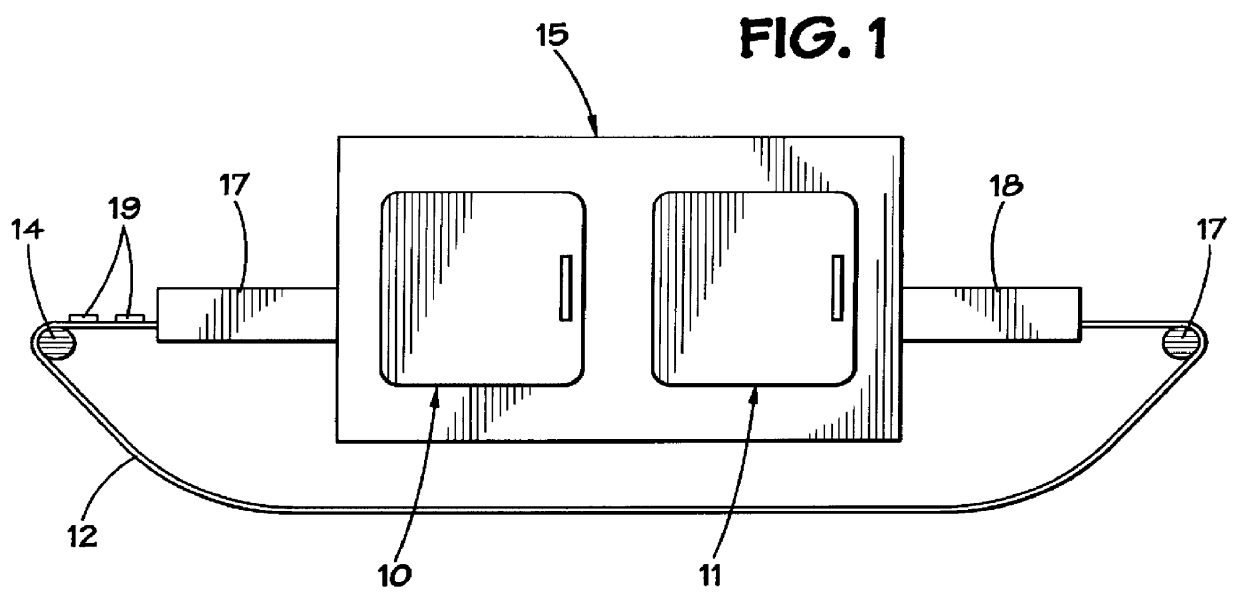
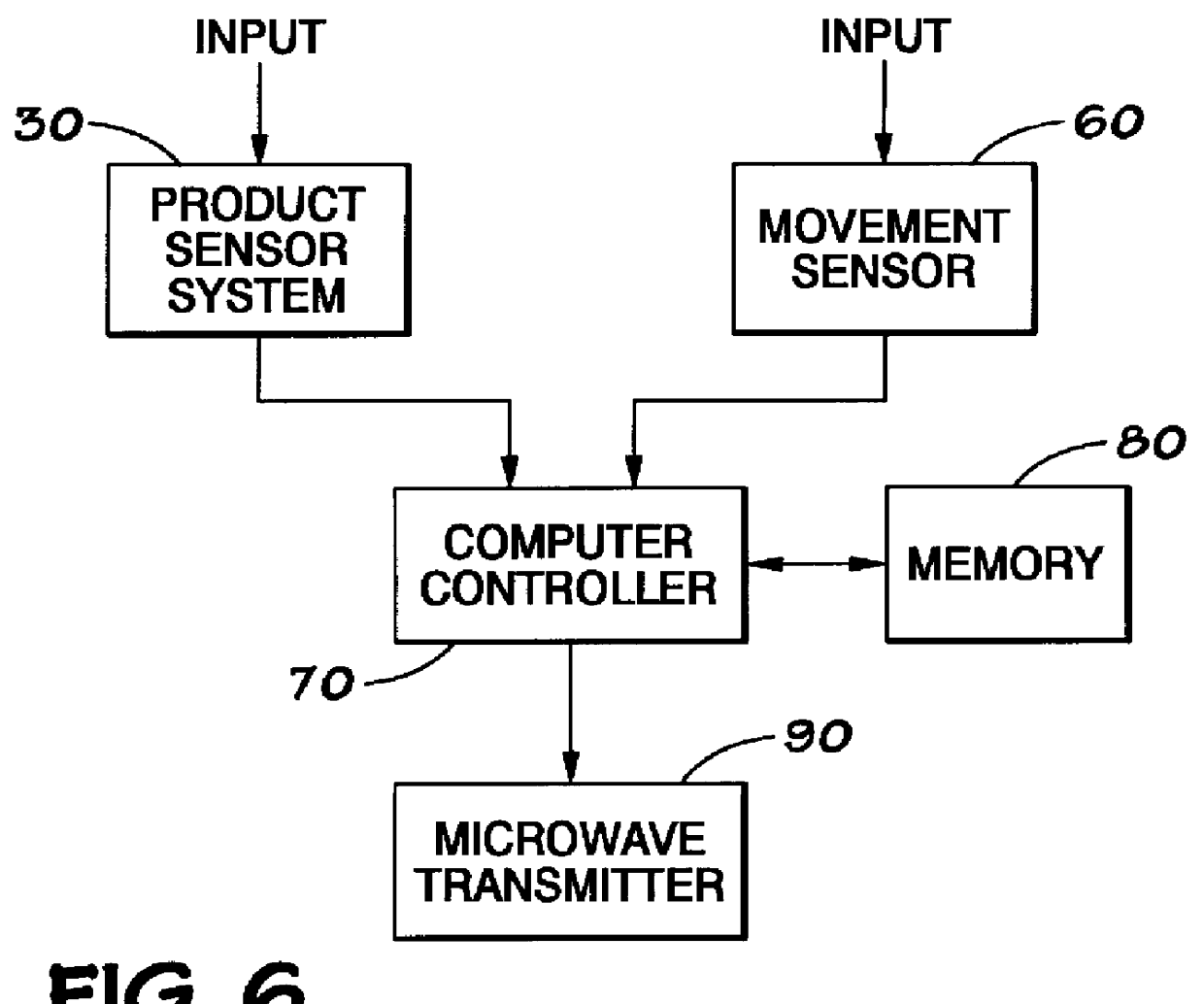
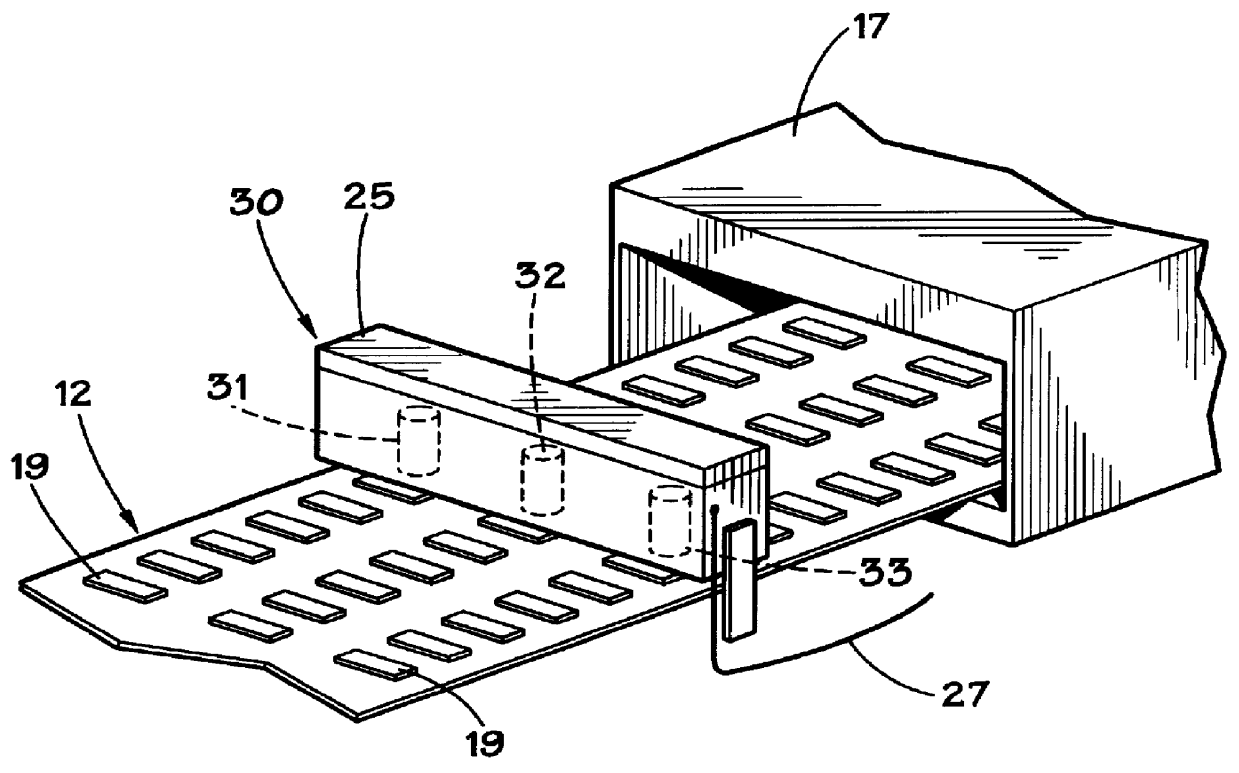
Product-based microwave power level controller
InactiveUS6157014AAdjust microwave powerAvoid powerMilk preservationDielectric heating circuitsMicrowave cavityProduct base
A microwave apparatus and system that monitors the amount of food products within a cavity and adjust the microwave power provided to the cavity. The apparatus and system uses a product sensor system and a movement sensor system to accurately determine the product load in the microwave cavity. A computer controller, based on the product load information provided by the product sensor system and the movement sensor system, operates to adjust the amount of power provide to the microwave cavities by the microwave transmitters.
Owner:AMANA +1
Apparatus and method for microwave processing of materials using field-perturbing tool
InactiveUS6222170B1Improve efficiencyReduce power densityMicrowave heatingChemical vapor deposition coatingMicrowave cavityEngineering
A variable frequency microwave heating apparatus designed to allow modulation of the frequency of the microwaves introduced into a multi-mode microwave cavity for heating or other selected applications. A field-perturbing tool is disposed within the cavity to perturb the microwave power distribution in order to apply a desired level of microwave power to the workpiece.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN ENERGY SYST INC
System and method for measuring retentate in filters
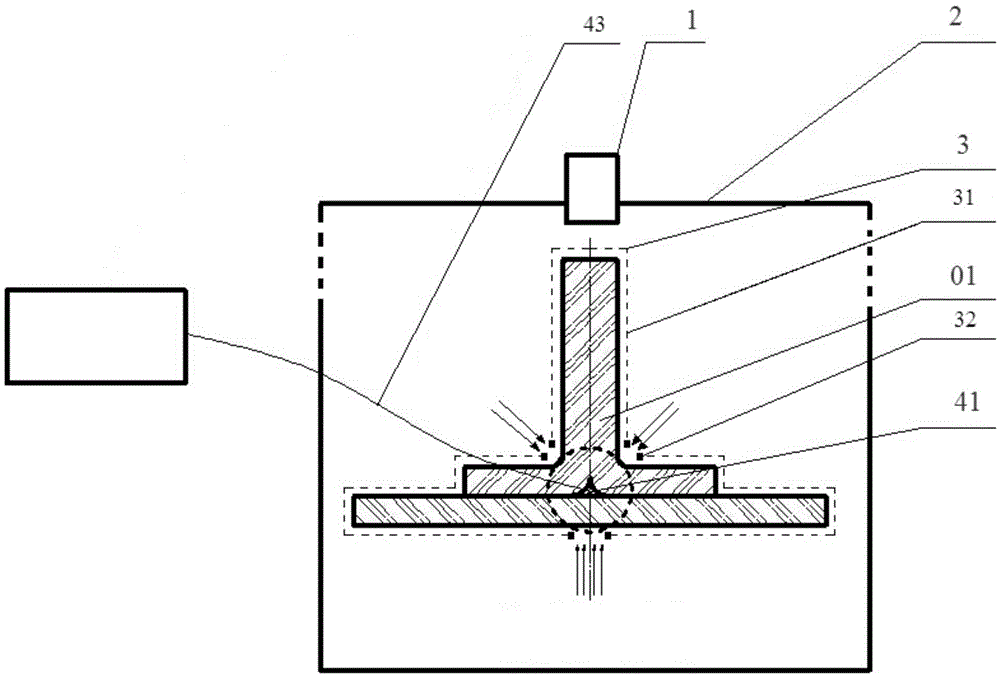
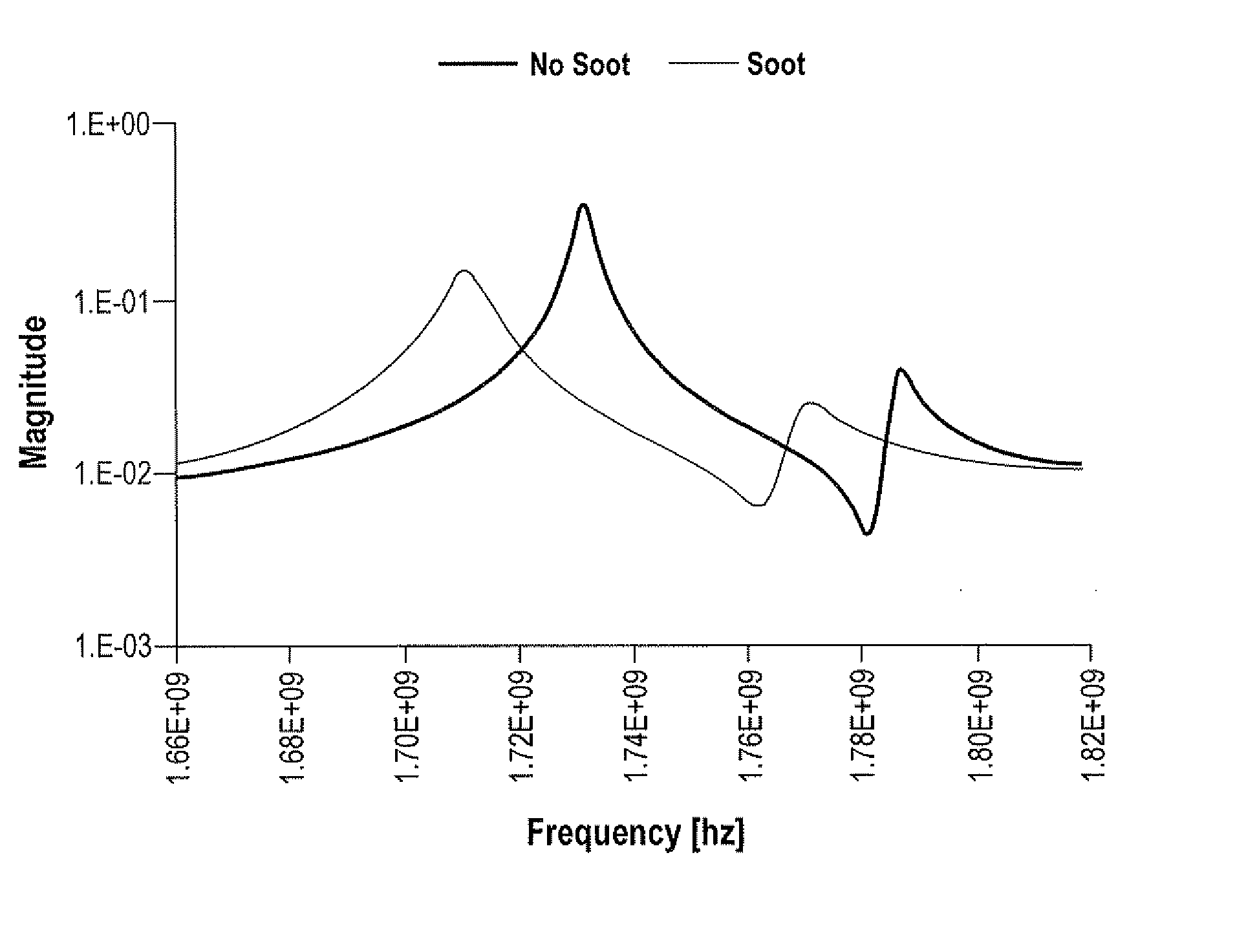
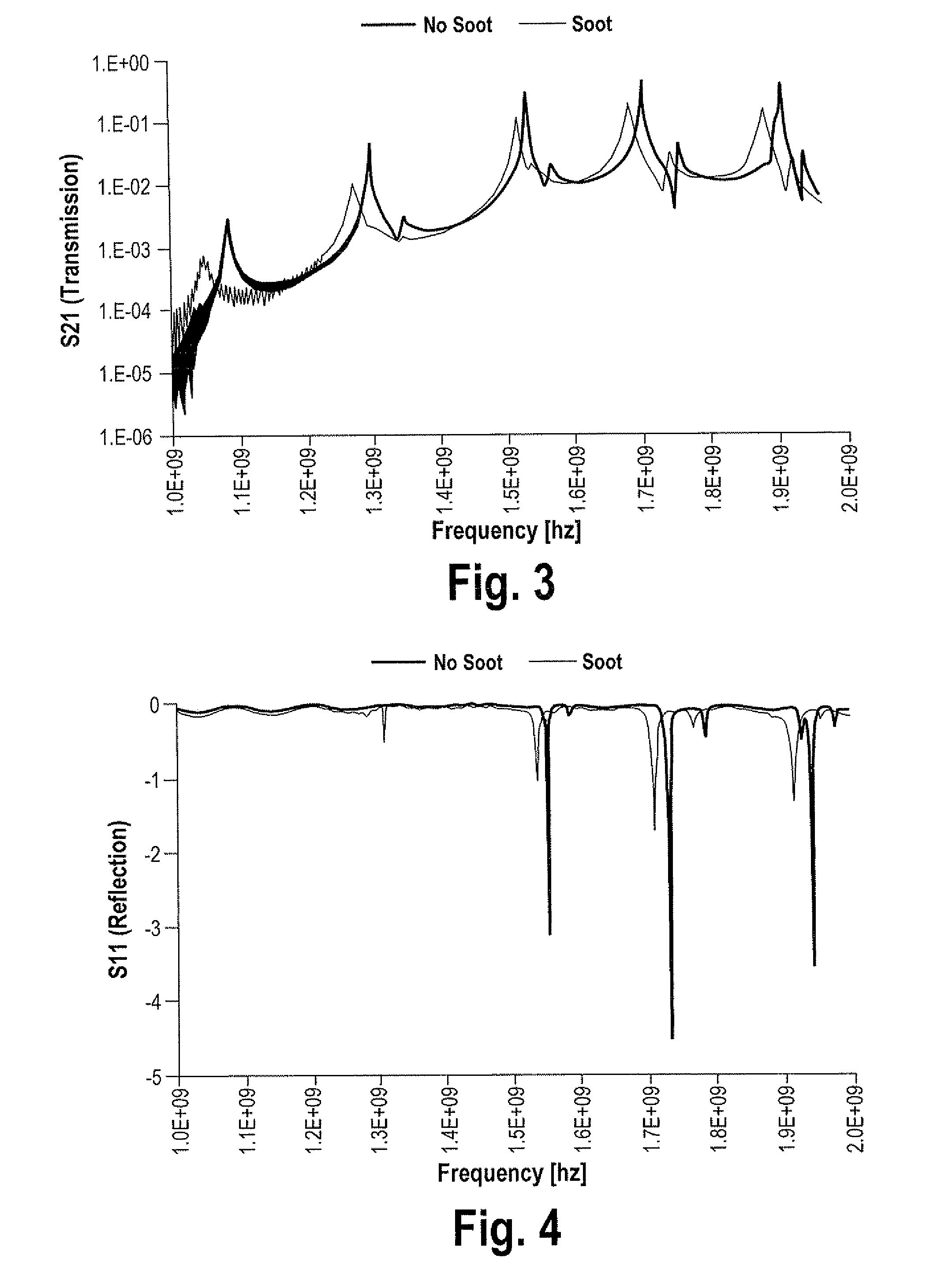
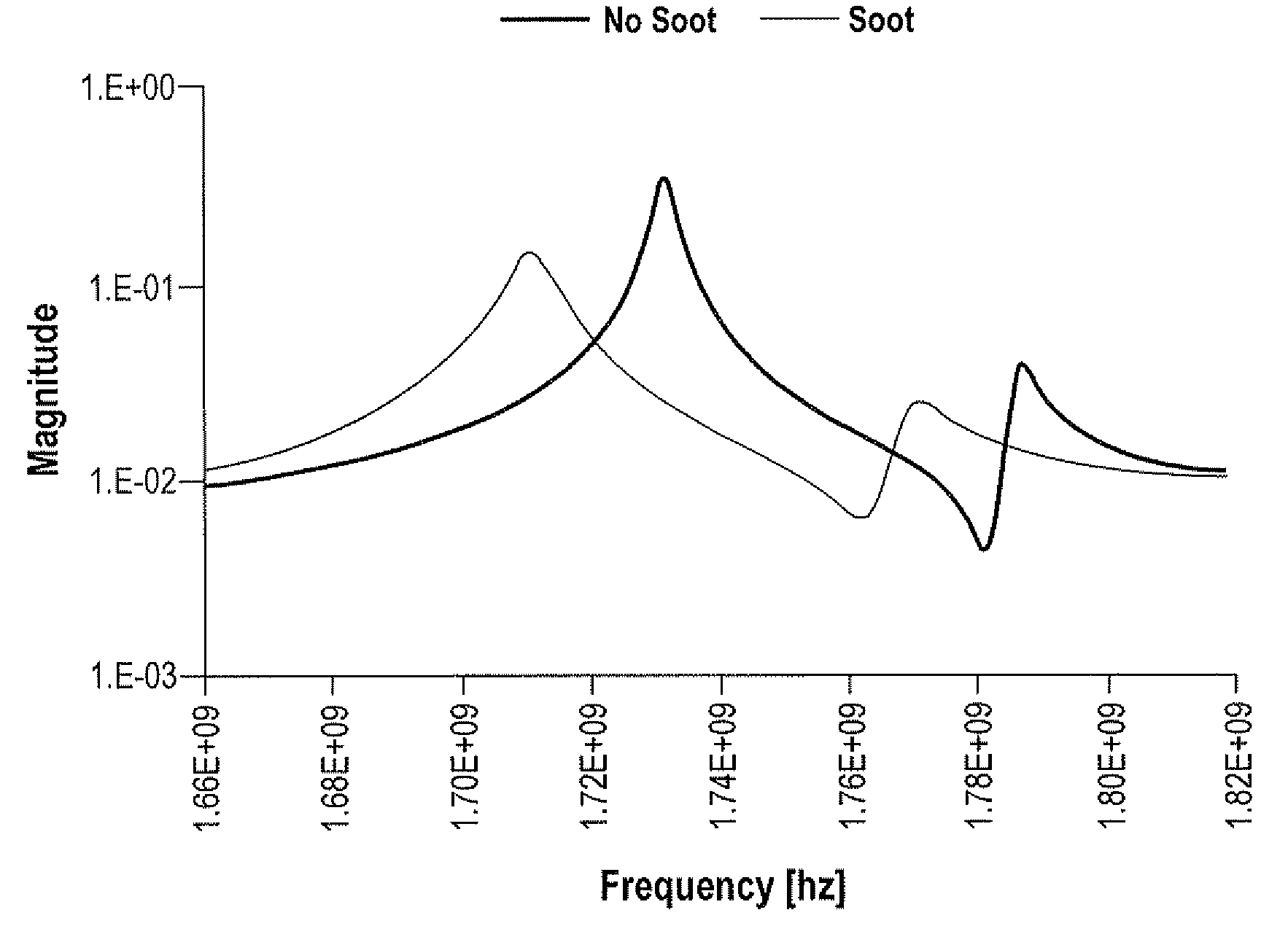
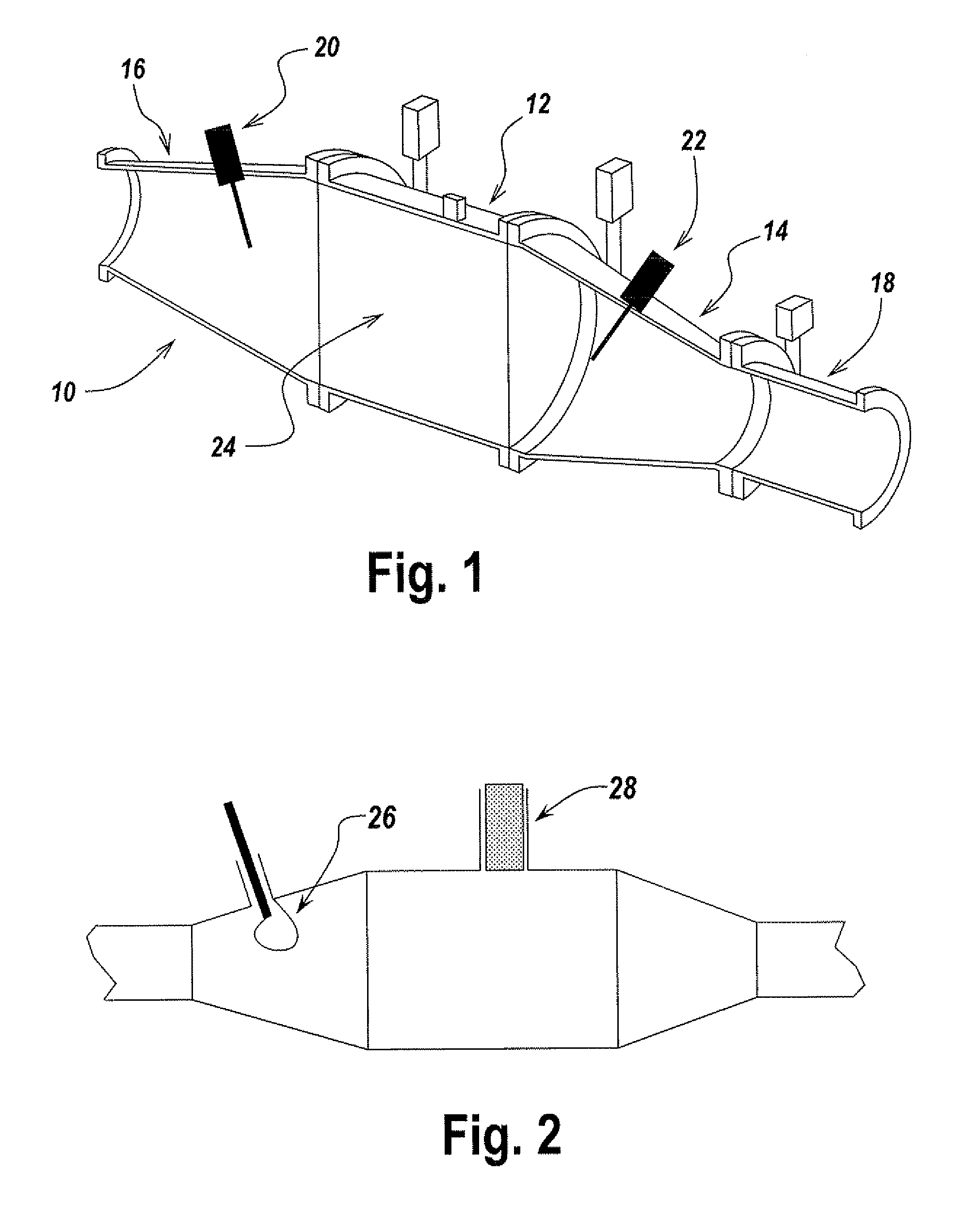
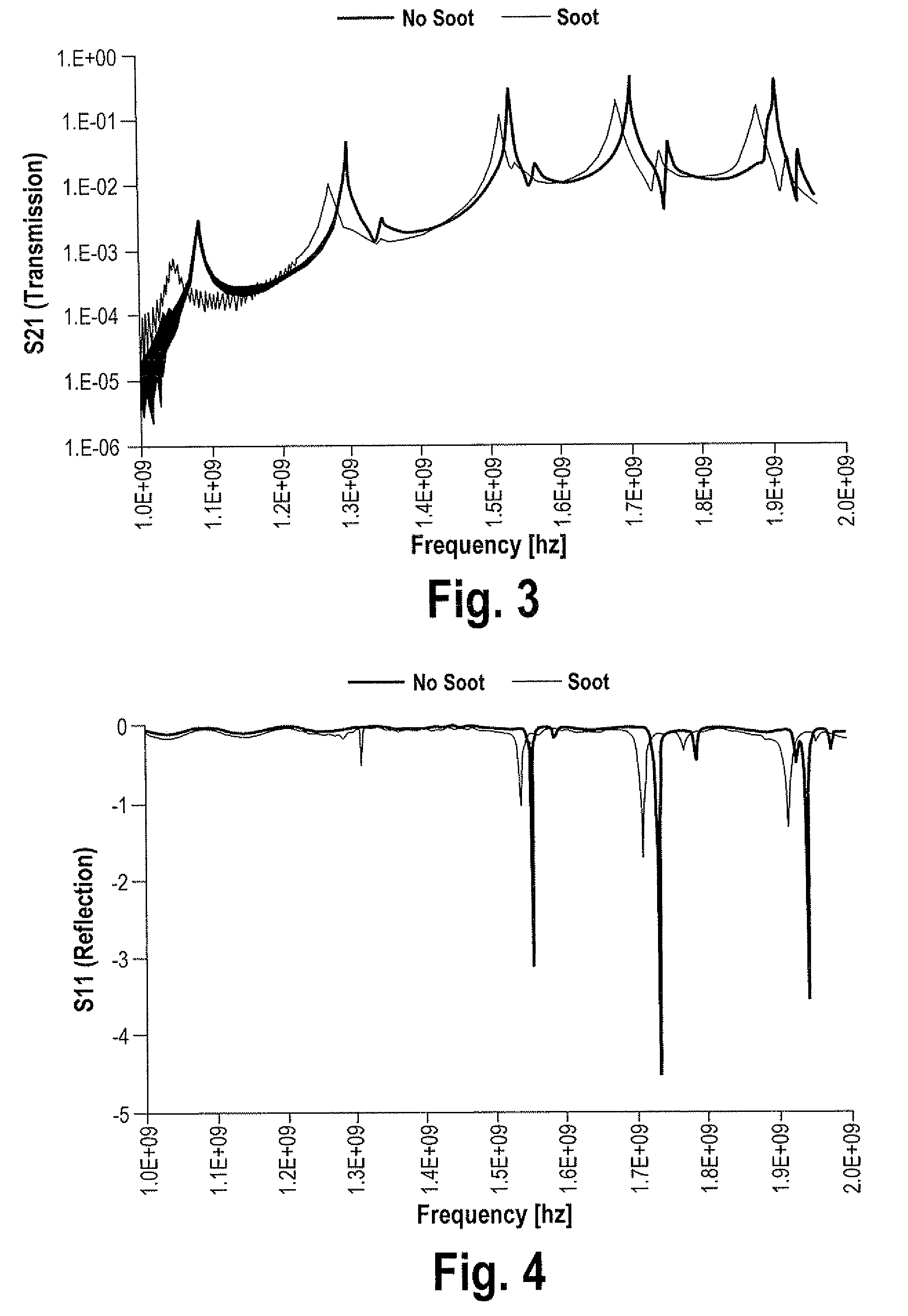
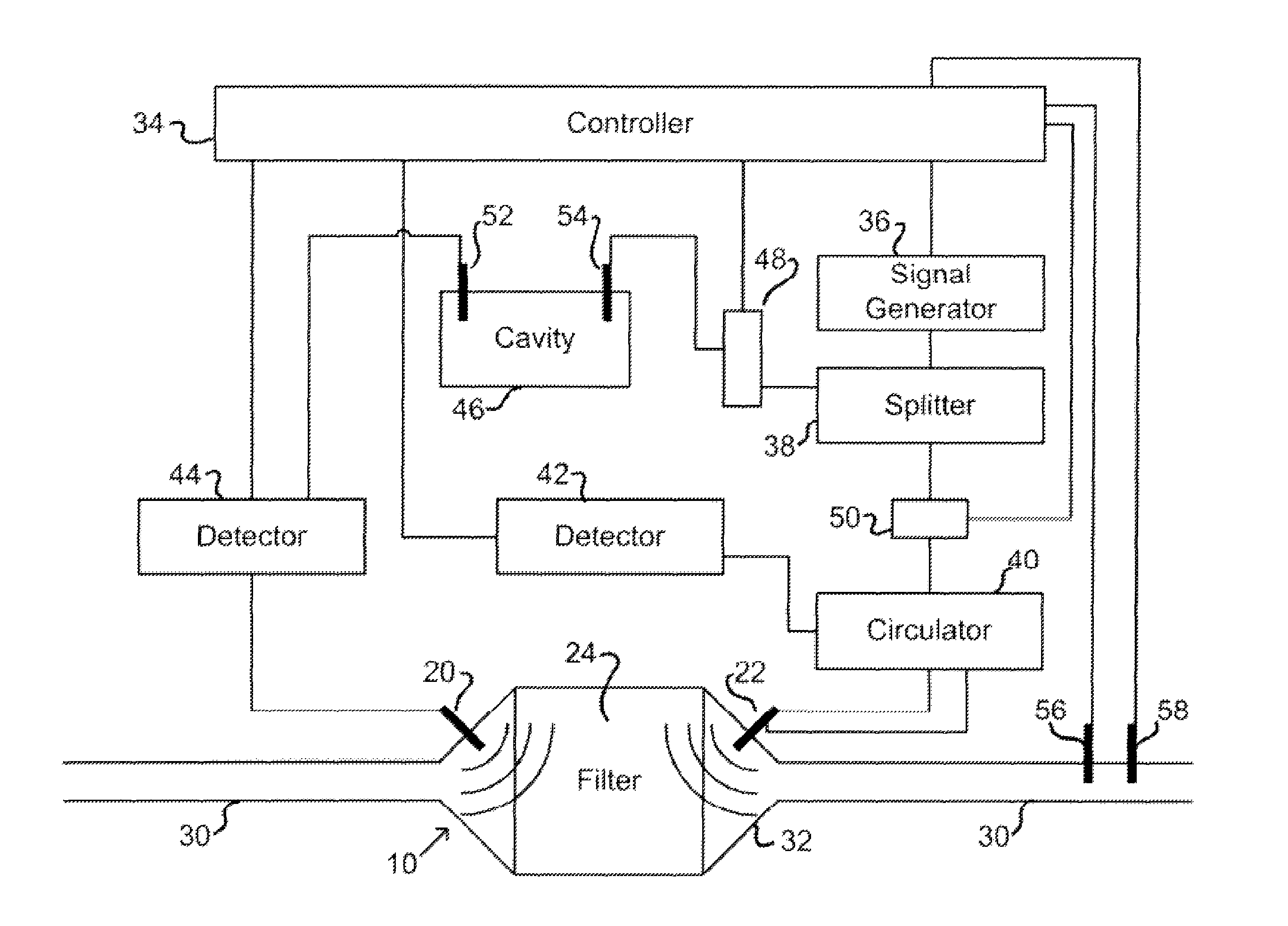
A system and method for determining loading of a filter having a first dielectric constant with a material having a different dielectric constant, is disclosed. The filter is contained within a metallic container forming a microwave cavity, and microwave or RF energy is created within the cavity and changes in the cavity microwave response are monitored. The changes in cavity microwave response are related to filter loading. In a preferred embodiment, the microwave energy includes multiple cavity modes thereby allowing determination of spatial distribution of the contaminant material loading. In one embodiment, the microwave cavity response includes a shift in frequency of a resonant mode. Alternatively, the microwave cavity response includes a shift in quality factor Q of a resonant mode. The microwave cavity response may include a shift in amplitude or peak width of the microwave's signal at resonance.
Owner:FILTER SENSING TECH
Reaction and temperature control for high power microwave-assisted chemistry techniques
InactiveUS6917023B2Organic chemistry methodsDielectric heating circuitsMicrowave cavityTemperature control
A method is disclosed for carrying out microwave assisted chemical reactions. The method includes the steps of placing reactants in a microwave-transparent vessel, placing the vessel and its contents into a microwave cavity, applying microwave radiation within the cavity and to the vessel and its contents while concurrently externally cooling the vessel conductively.
Owner:CEM CORP
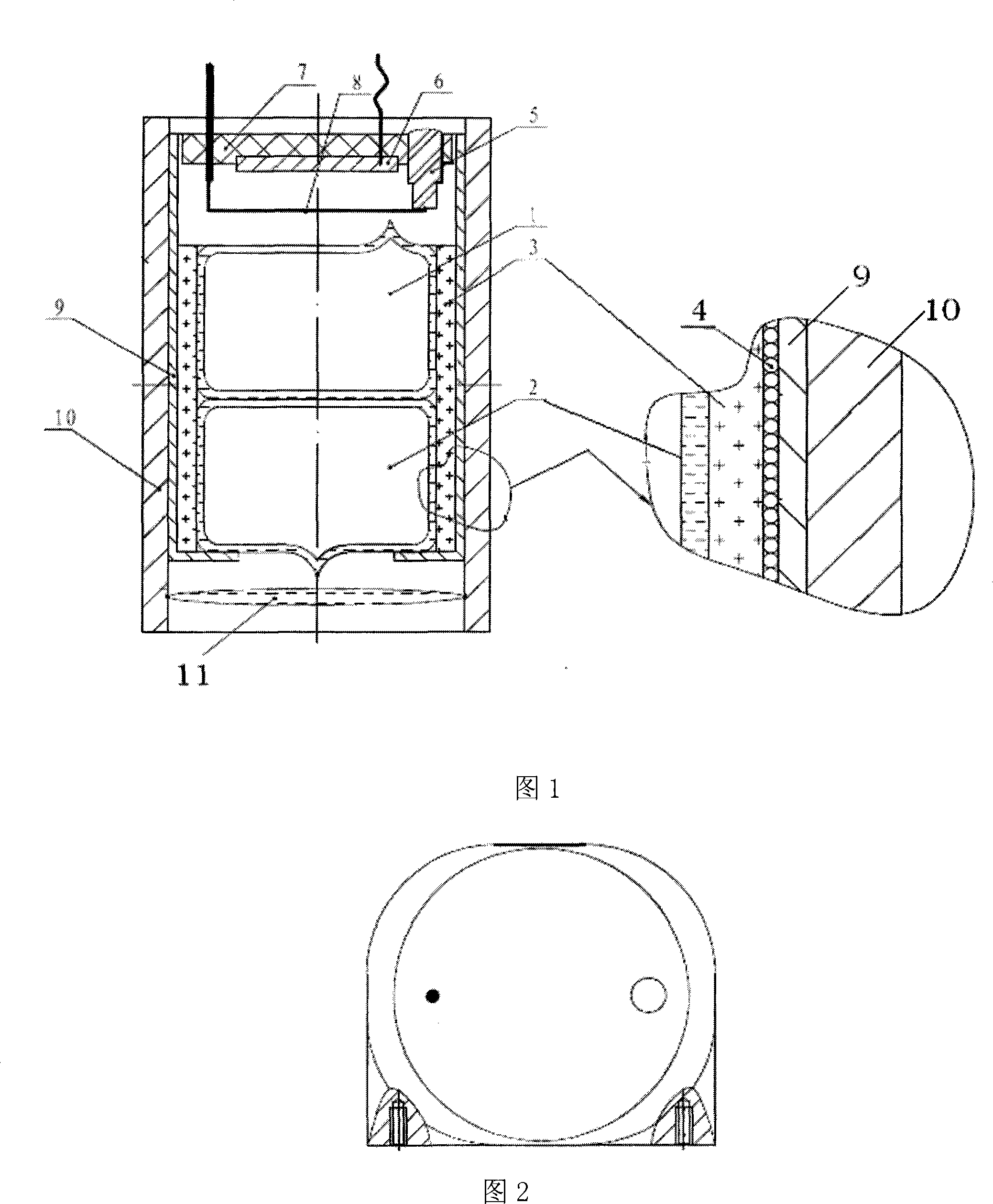
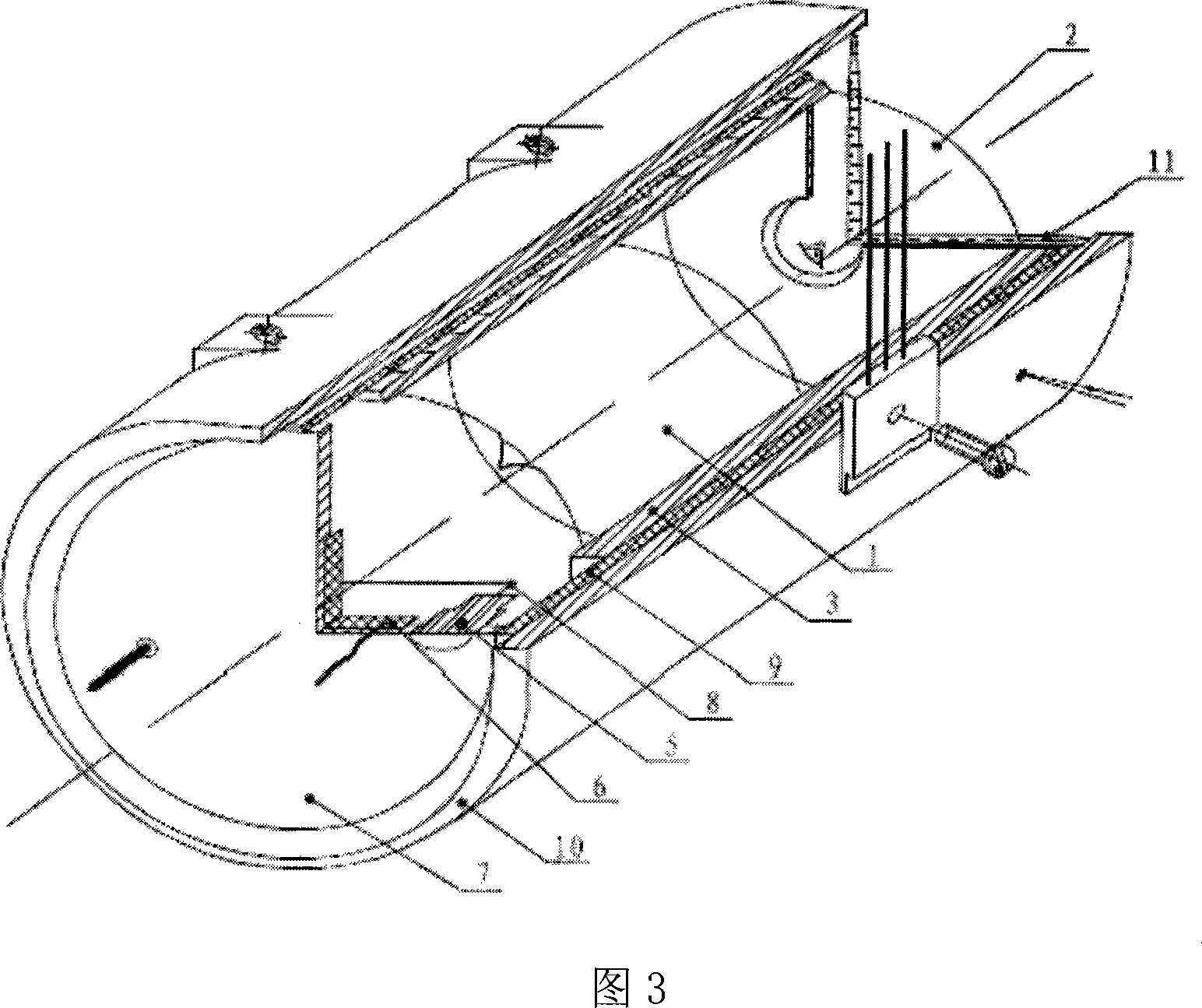
Composite energy field heating device
ActiveCN105666895AImprove performanceUniform and controllable heating and curing processMicrowave cavityAviation
The invention provides a composite energy field heating device. The composite energy field heating device comprises a microwave heating device and a hot-pressing tank, wherein the microwave heating device comprises a microwave generator, a microwave cavity and a microwave local shielding part; the microwave generator is used for sending microwaves into the microwave cavity; a wave absorbing material is arranged in the microwave cavity; the microwave local shielding part is positioned in the microwave cavity, and is used for covering the outer surface of the wave absorbing material; the microwave local shielding part is composed of a shielding microwave region and a transmission microwave region; the transmission microwave region comprises one or more seams, so that microwaves in the microwave cavity can enter the wave absorbing material through the seams for being absorbed; the microwave cavity is integrally arranged in the hot-pressing tank; a ventilating window or a ventilating wall which consists of one or more metal honeycomb plates is arranged on the microwave cavity; and the ventilating window or the ventilating wall can be used for enabling smooth air flow inside and outside the microwave cavity in the hot-pressing tank while shielding the microwaves. The composite energy field heating device can truly realize consistent temperature on all parts in the wave absorbing material, so that high-quality cured products are provided for the aviation and aerospace fields.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
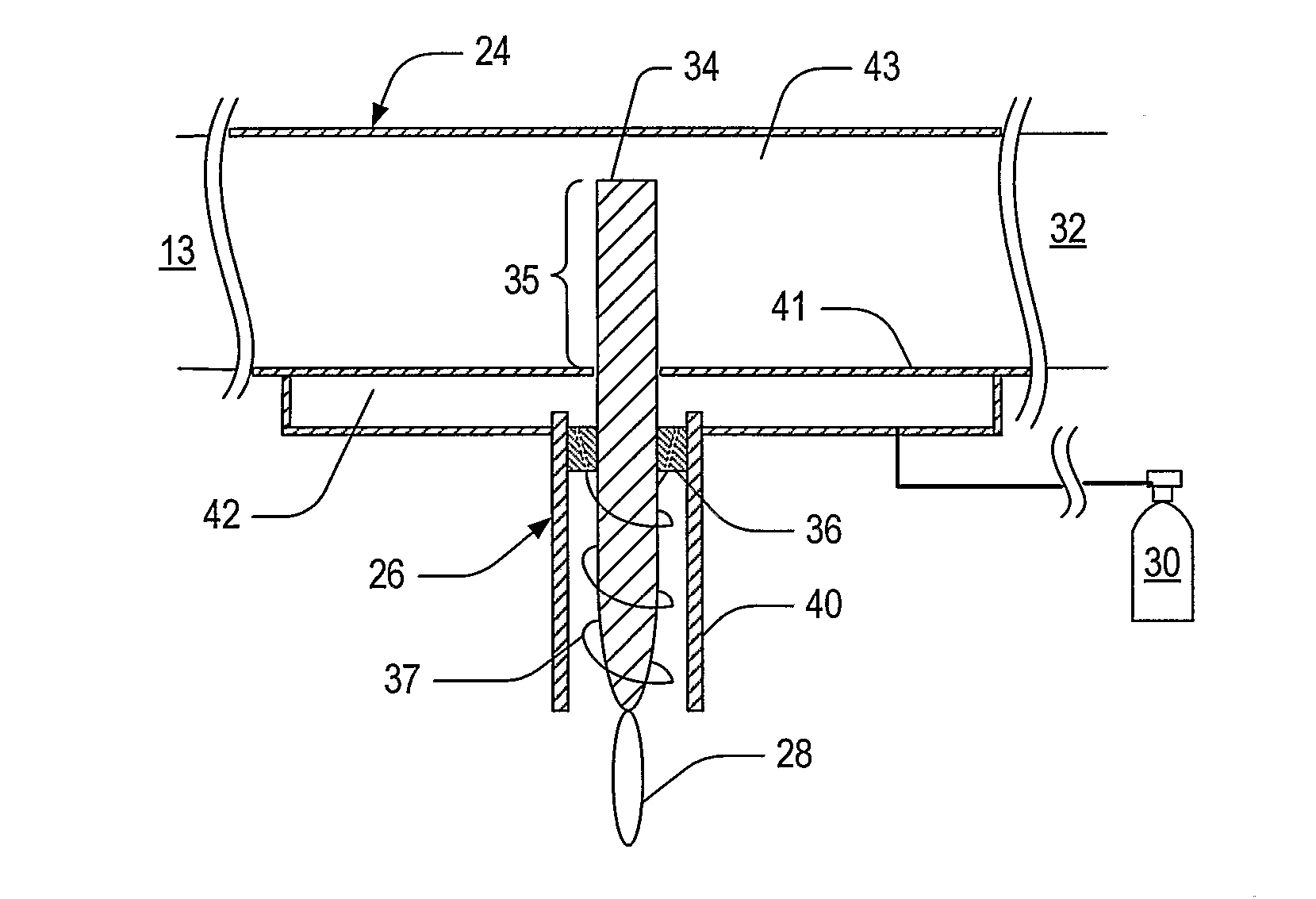
Microwave plasma nozzle with enhanced plume stability and heating efficiency
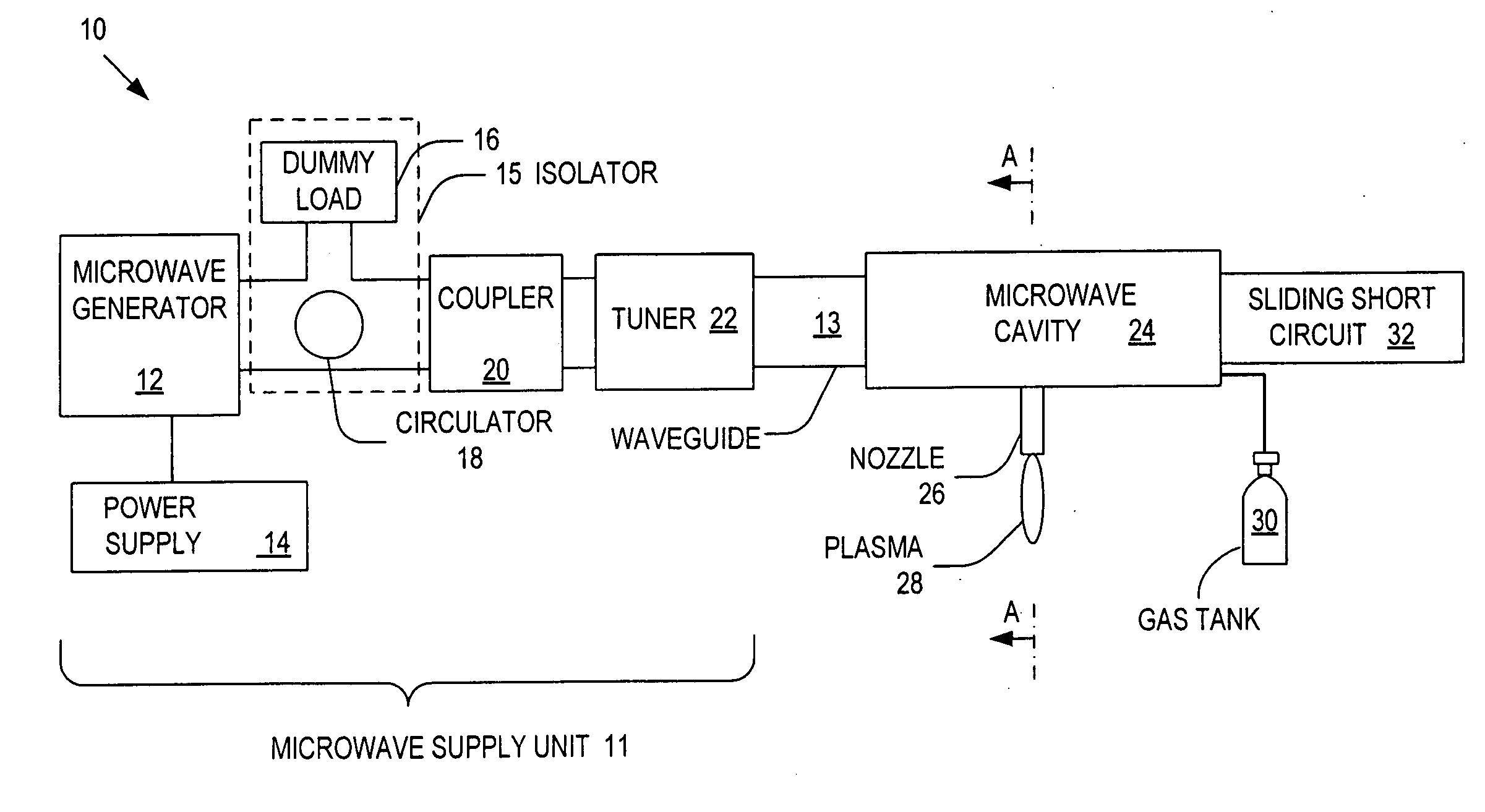
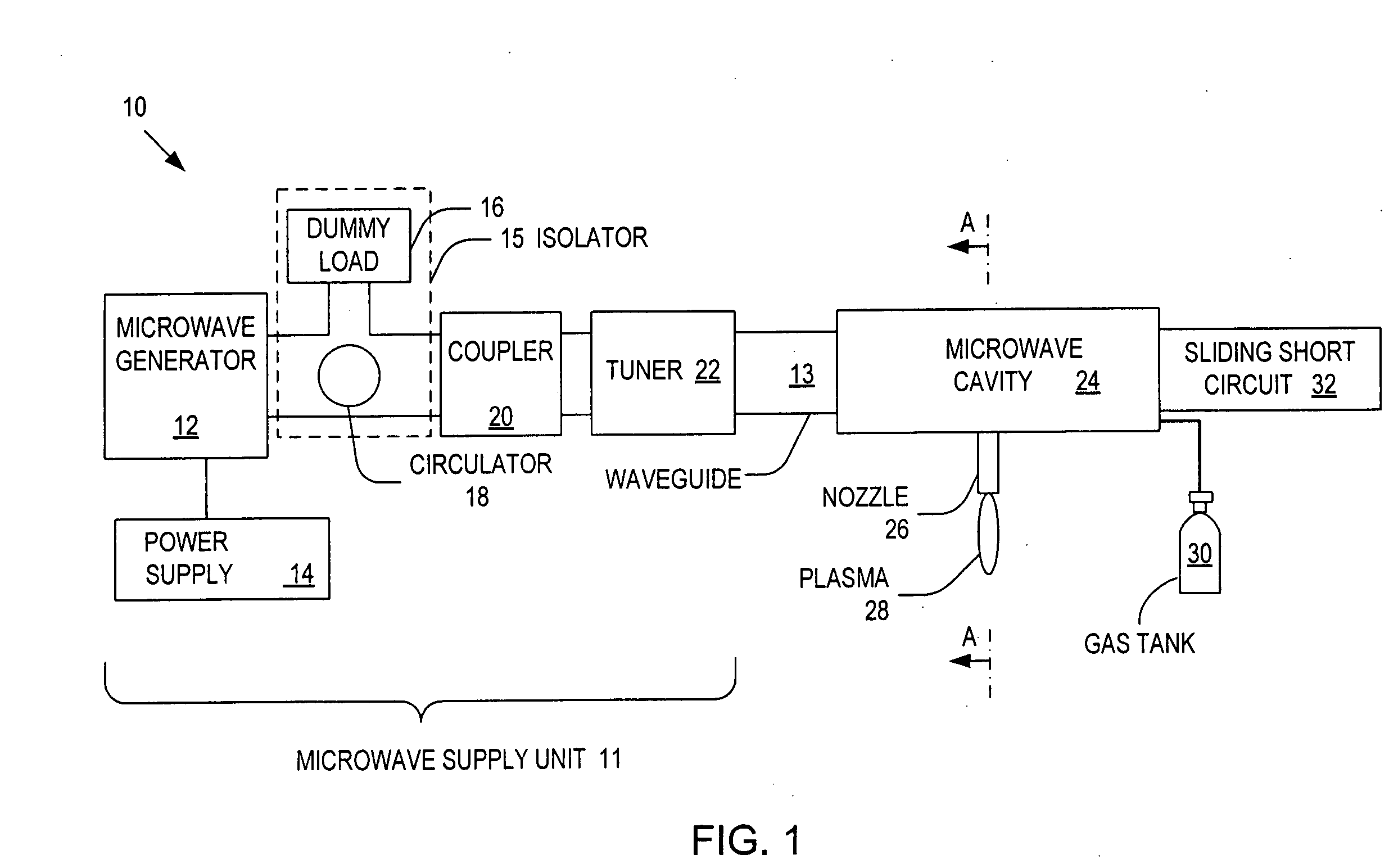
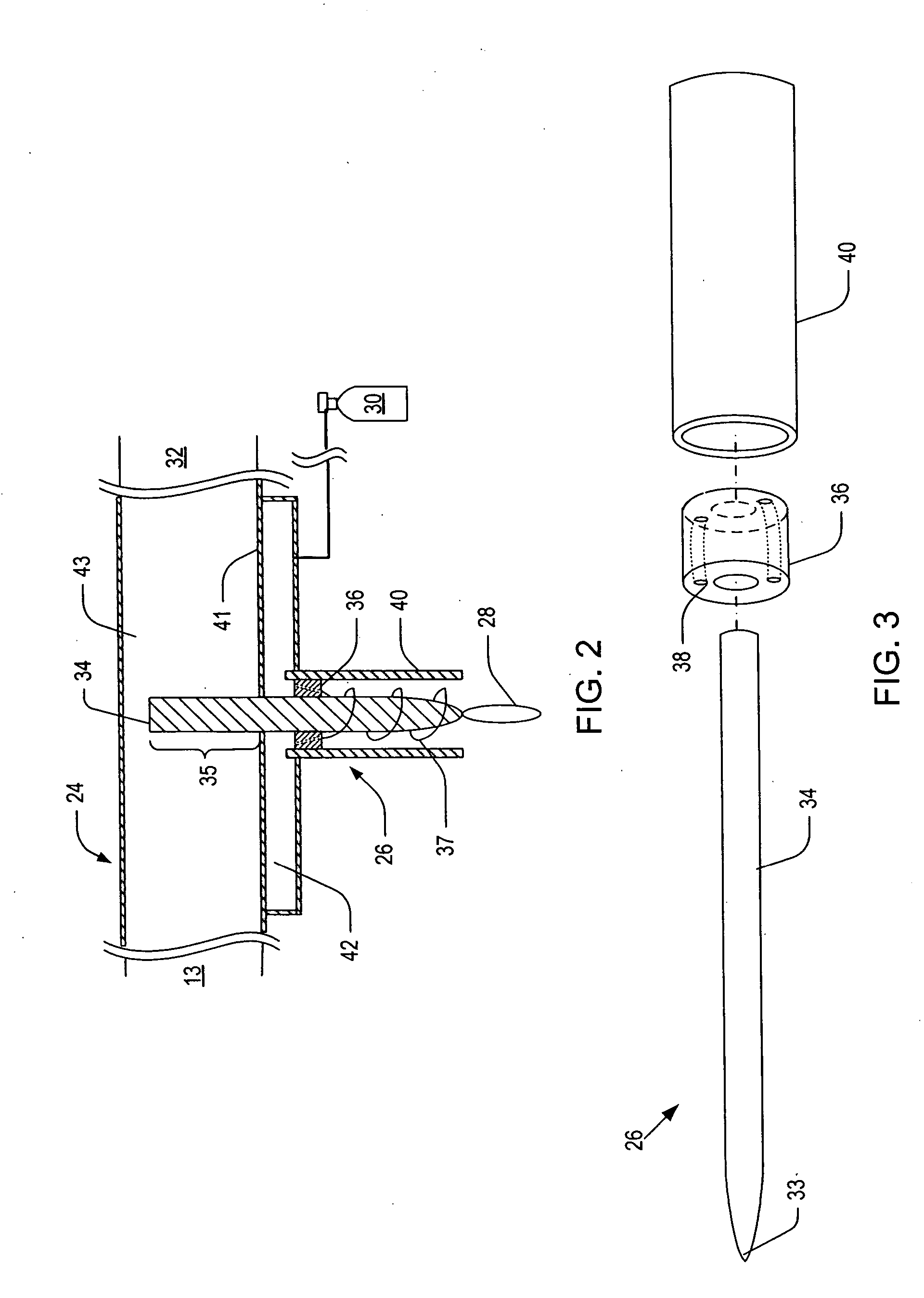
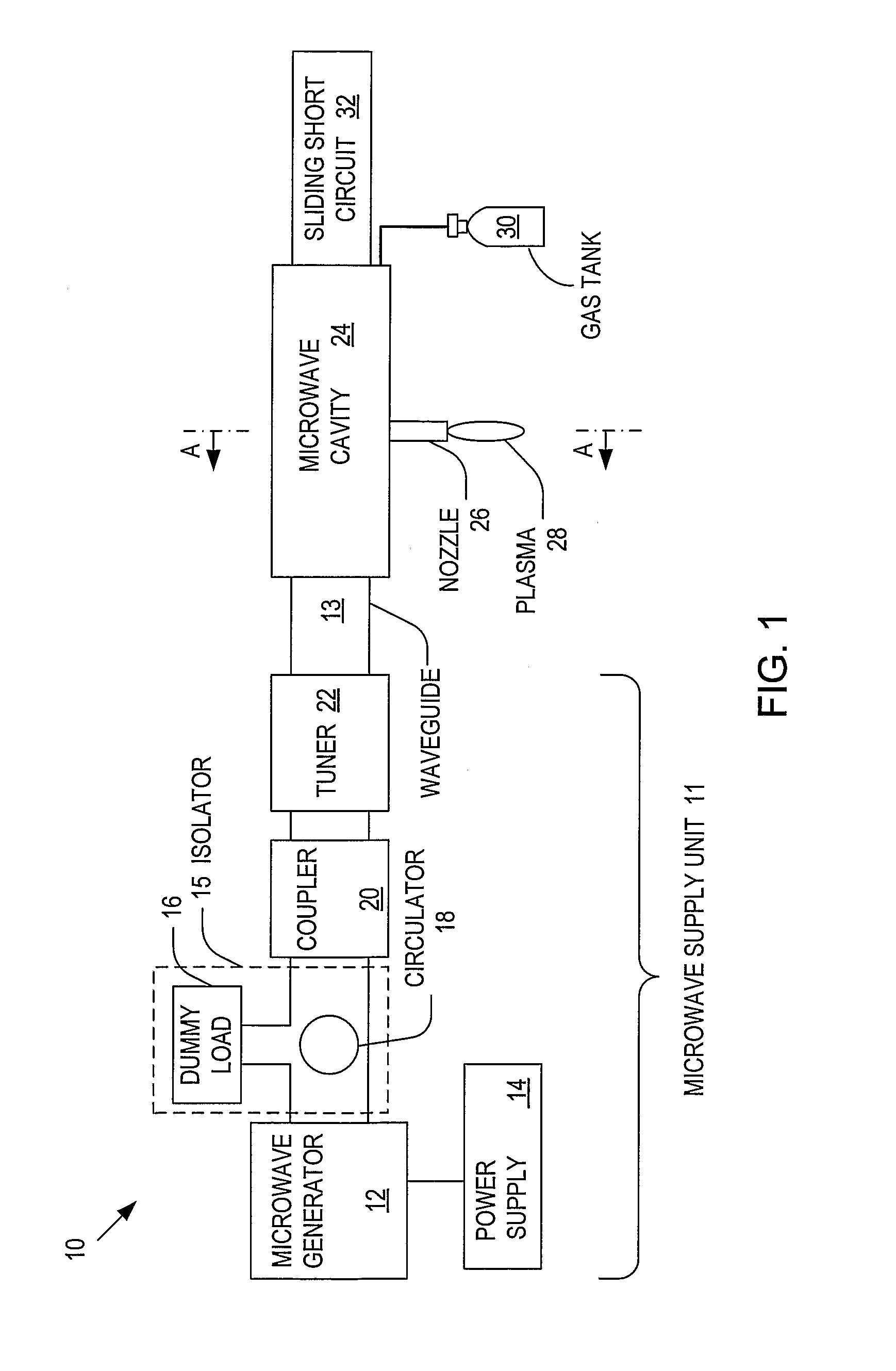
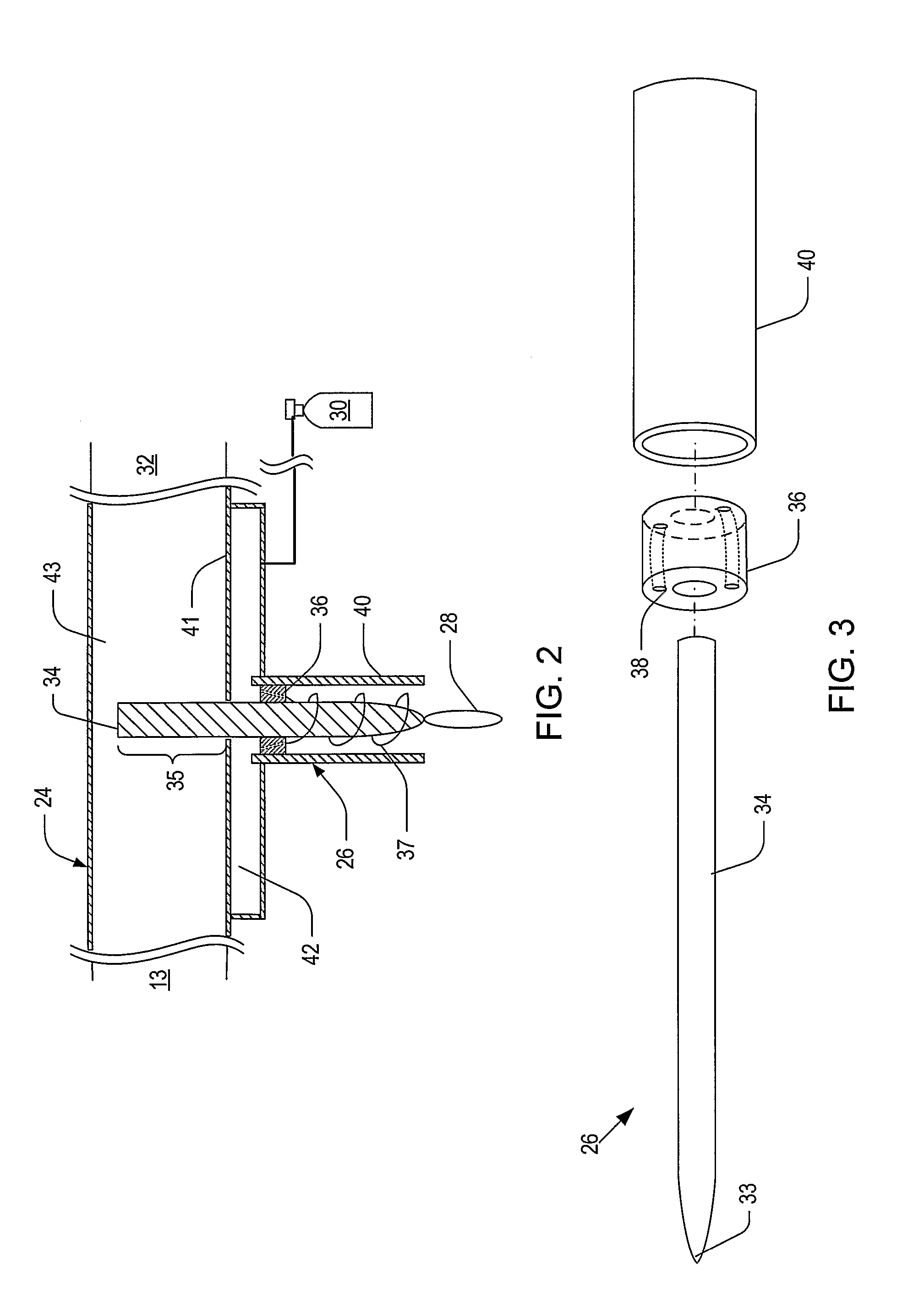
ActiveUS20060006153A1Low per unit costReduce operating costsElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsMicrowave cavityElectrical conductor
Systems and methods for generating relatively cool microwave plasma are disclosed. The present invention provides a microwave plasma nozzle that includes a gas flow tube through which a gas flows, and a rod-shaped conductor that is disposed in the gas flow tube and has a tapered tip near the outlet of the gas flow tube. A portion of the rod-shaped conductor extends into a microwave cavity to receive microwaves passing in the cavity. These received microwaves are focused at the tapered tip to heat the gas into plasma. The microwave plasma nozzle also includes a vortex guide between the rod-shaped conductor and the gas flow tube imparting a helical shaped flow direction around the rod-shaped conductor to the gas flowing through the tube. The microwave plasma nozzle further includes a mechanism for electronically exciting the gas and a shielding mechanism for reducing a microwave power loss through the gas flow tube.
Owner:NOXILIZER
System and method for quantum information transfer between optical photons and superconductive qubits
An electro-optical system for exchanging quantum information between optical qubits and including a superconductive microwave cavity; an electro-optical material; a superconductive qubit circuit formed on the electro-optical material including a superconductive qubit; a dipole antenna, formed on the electro-optical material for directly coupling the superconductive qubit to the superconductive microwave cavity; an optical input for receiving input optical photons; a microwave input for receiving input microwave photons; and an optical output for outputting modulated optical photons, wherein a frequency and a phase of the optical photon is modulated with a state of the superconducting qubit by the dipole antenna.
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP
Microwave heating device and method
The invention provides a microwave heating device. The microwave heating device comprises a microwave generator, a microwave cavity and a microwave local shielding part; the microwave generator sends microwaves into the microwave cavity; the microwave cavity is used for placing a wave sucking material; the microwave local shielding part is positioned in the microwave cavity, and is used for covering the outer surface of the wave sucking material; the microwave local shielding part consists of a microwave shielding area and a microwave passing area; and the microwave passing area includes one or more gaps, so that the microwaves in the microwave cavity can enter the wave sucking material from the gaps to be absorbed. The microwave heating device, provided by the invention,can perform fixed-point and / or fixed-direction heating for the wave sucking material.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Microwave sensing for determination of loading of filters
ActiveUS20080059093A1Avoid pollutionSpectral/fourier analysisInternal combustion piston enginesMicrowave cavityMetallic enclosure
Method for determining loading of a filter. The filter has a first dielectric constant. The filter becomes loaded with contaminant material that has a second dielectric constant. The filter, such as a diesel particulate filter, is contained within a metallic enclosure forming a microwave cavity. The method includes establishing microwave energy in the cavity and monitoring changes in the cavity microwave response, the changes being related to filter loading.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
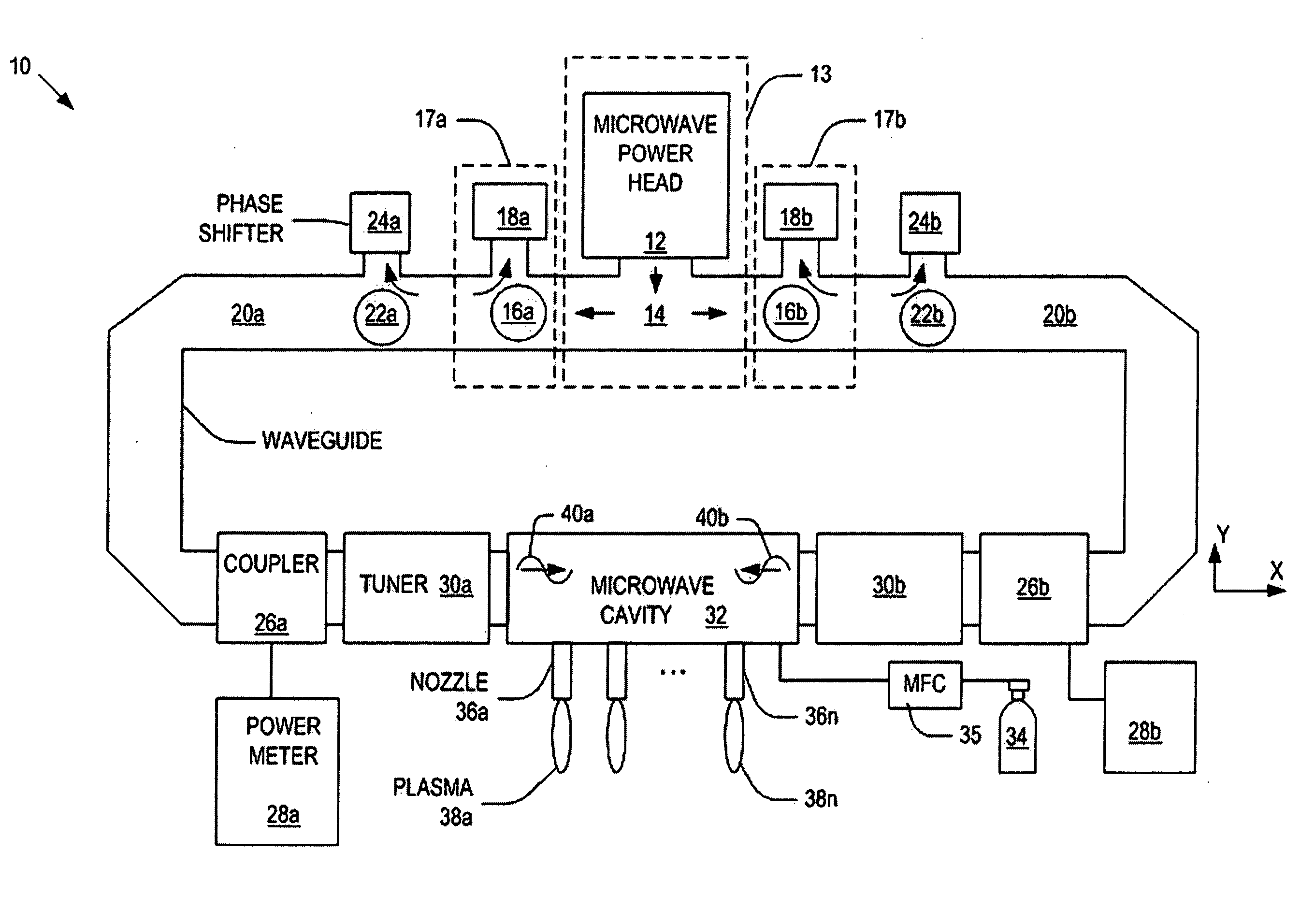
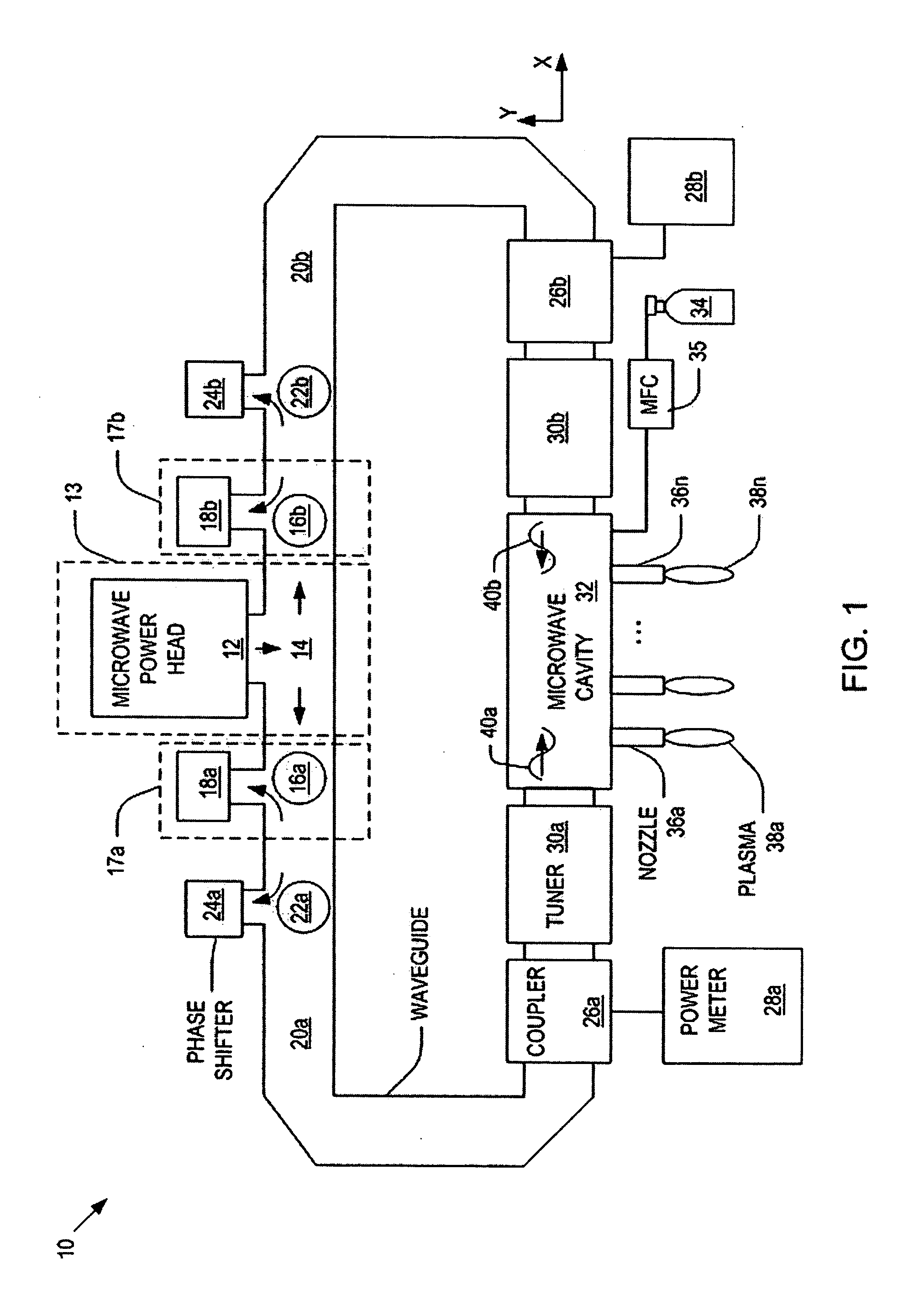
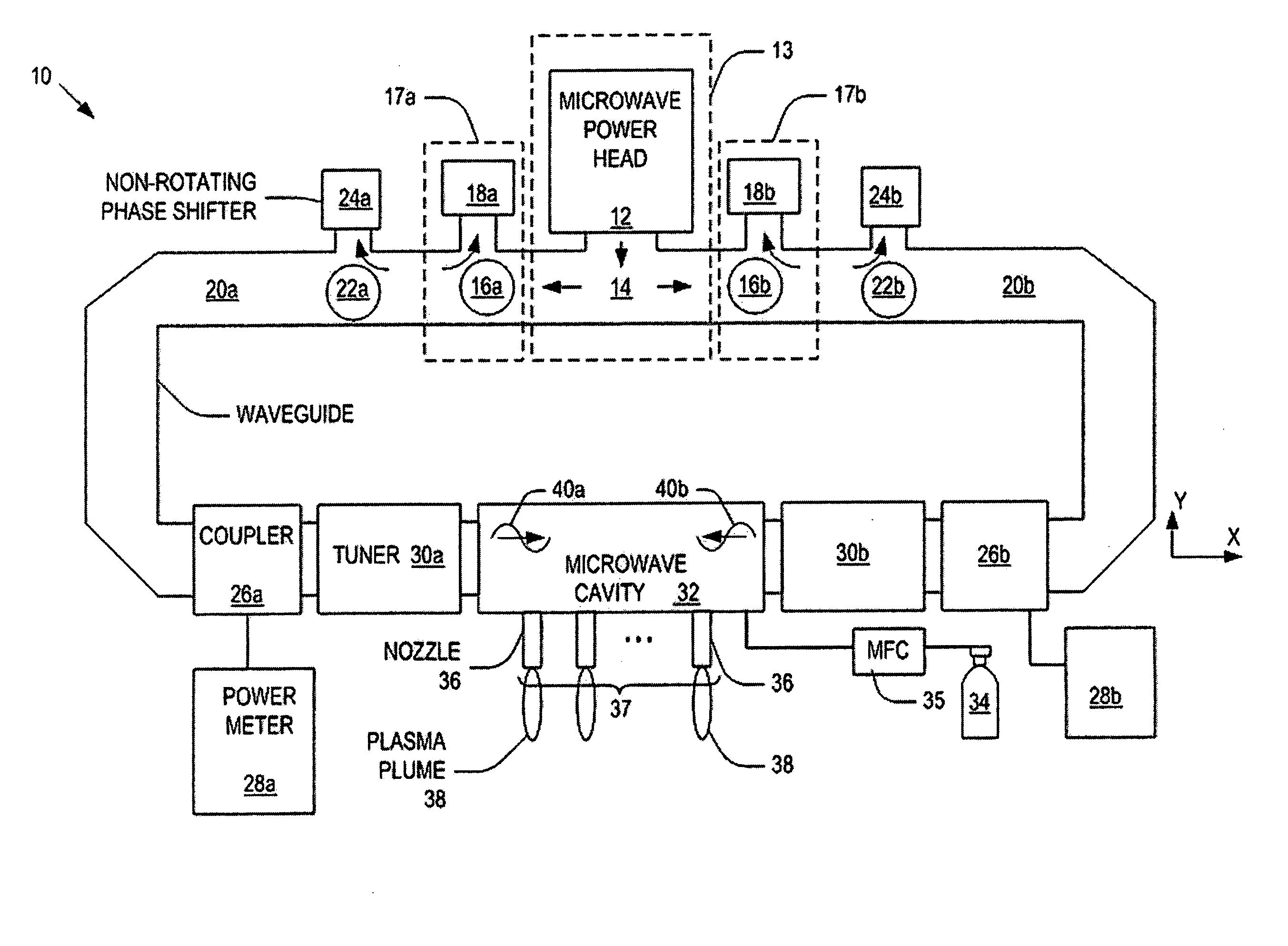
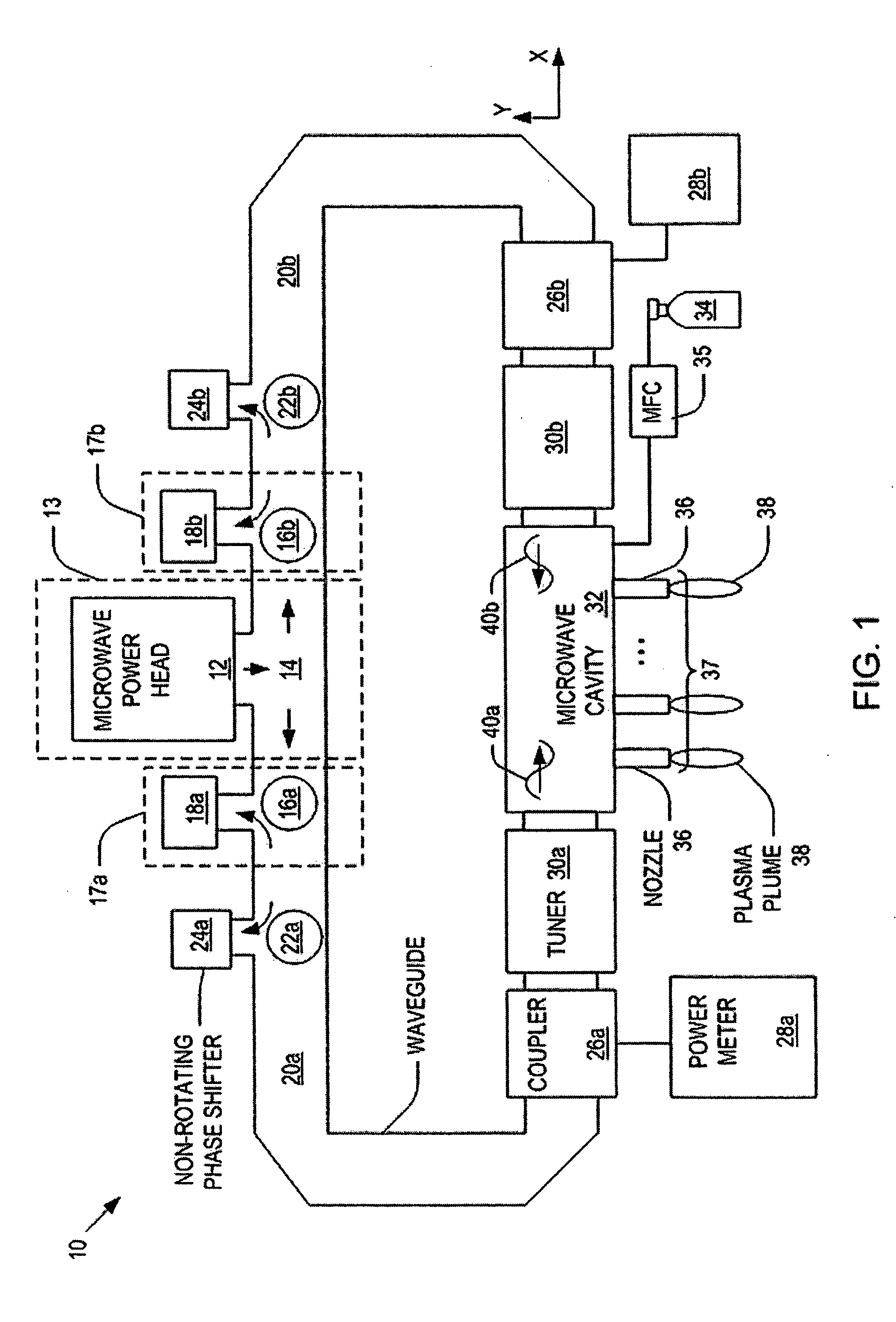
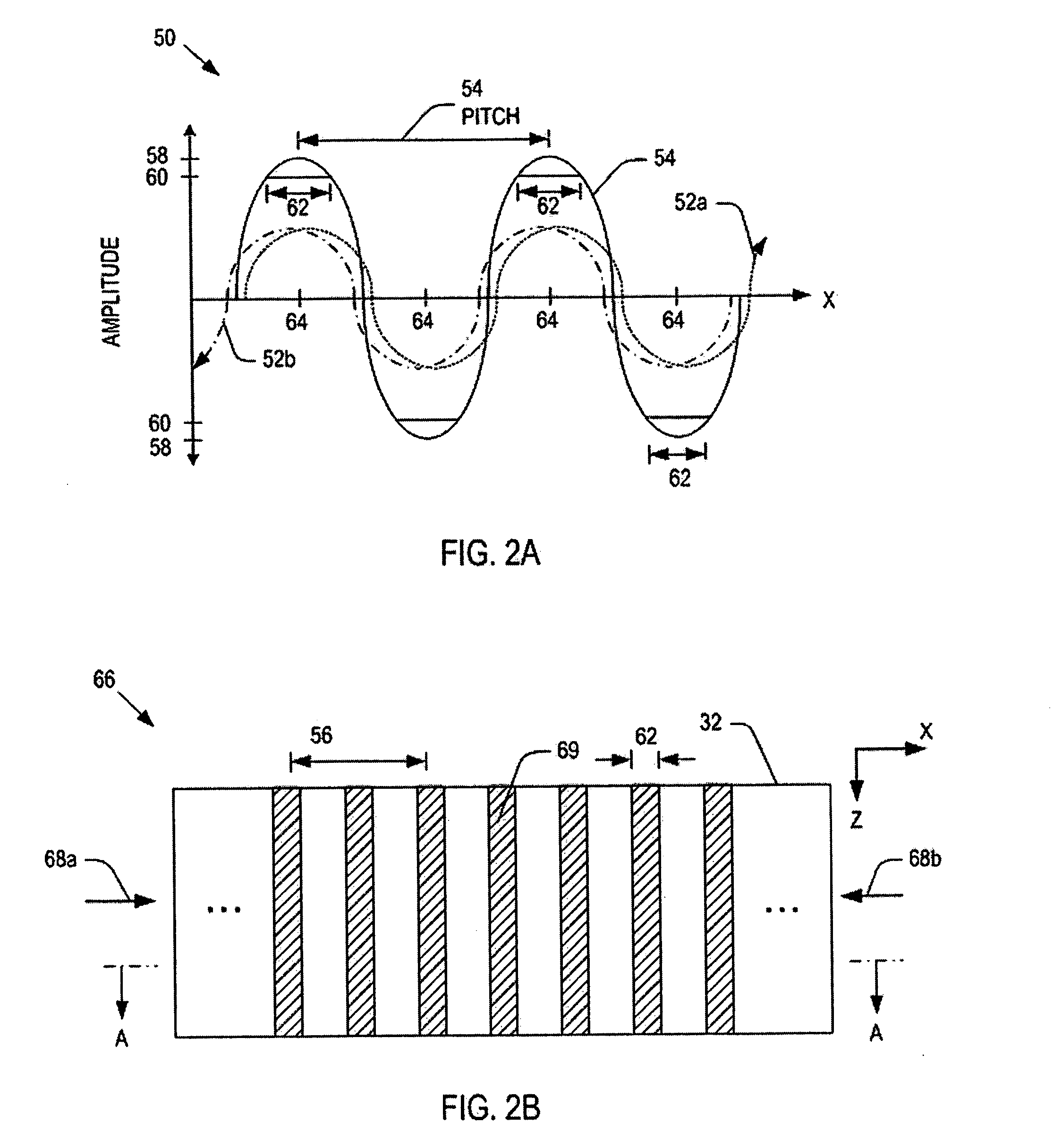
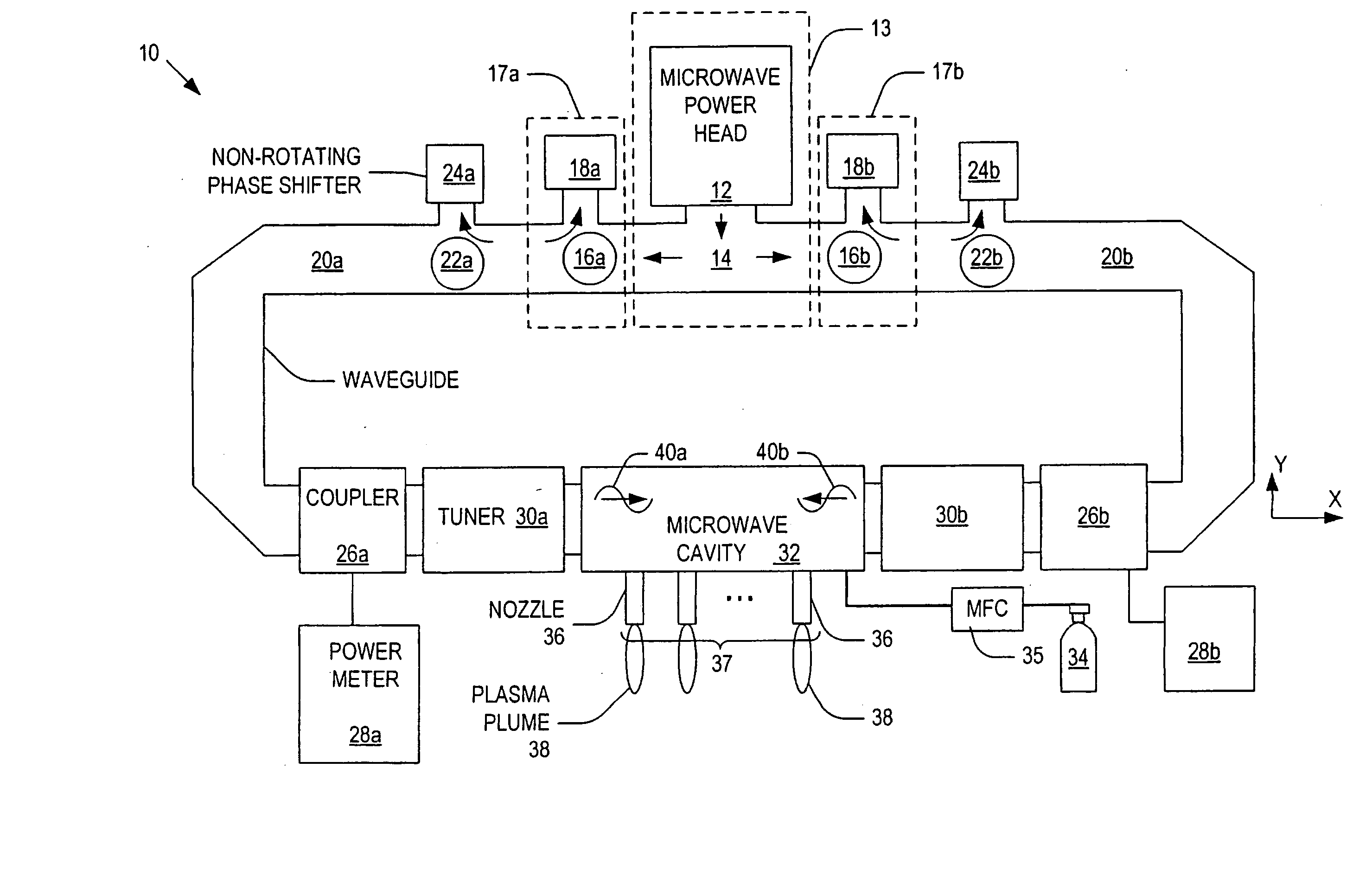
System and method for controlling a power distribution within a microwave cavity
Systems and methods for controlling a power distribution in a microwave cavity are disclosed. The present invention provides a system that includes a microwave source and a pair of isolators that dissipate retrogressing microwaves that travel toward the microwave source. The isolators are connected to the microwave source. The system also includes a microwave cavity having a pair of inlets disposed on opposite sides of the microwave cavity, a pair of waveguides operatively connected to the inlets to the isolators, respectively; a pair of non-rotating phase shifters operatively connected to the waveguides and the isolators, respectively; a pair of circulators operatively connected to the waveguides and being configured to direct the microwaves to the pair of non-rotating phase shifters, respectively. A power distribution within the microwave cavity is controlled by operation of at least one of the pair of non-rotating phase shifters.
Owner:NORITZ CORP +1
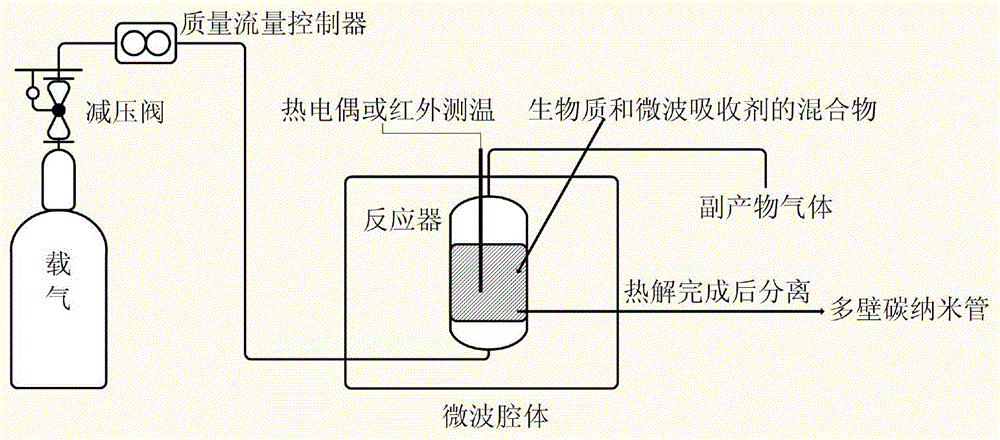
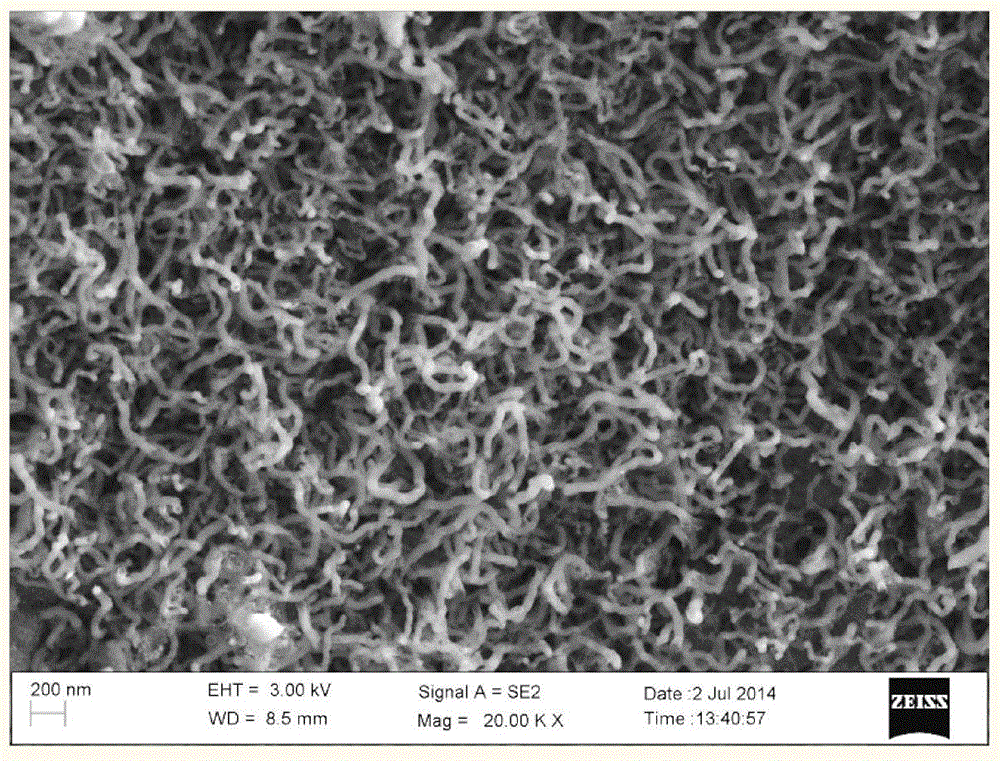
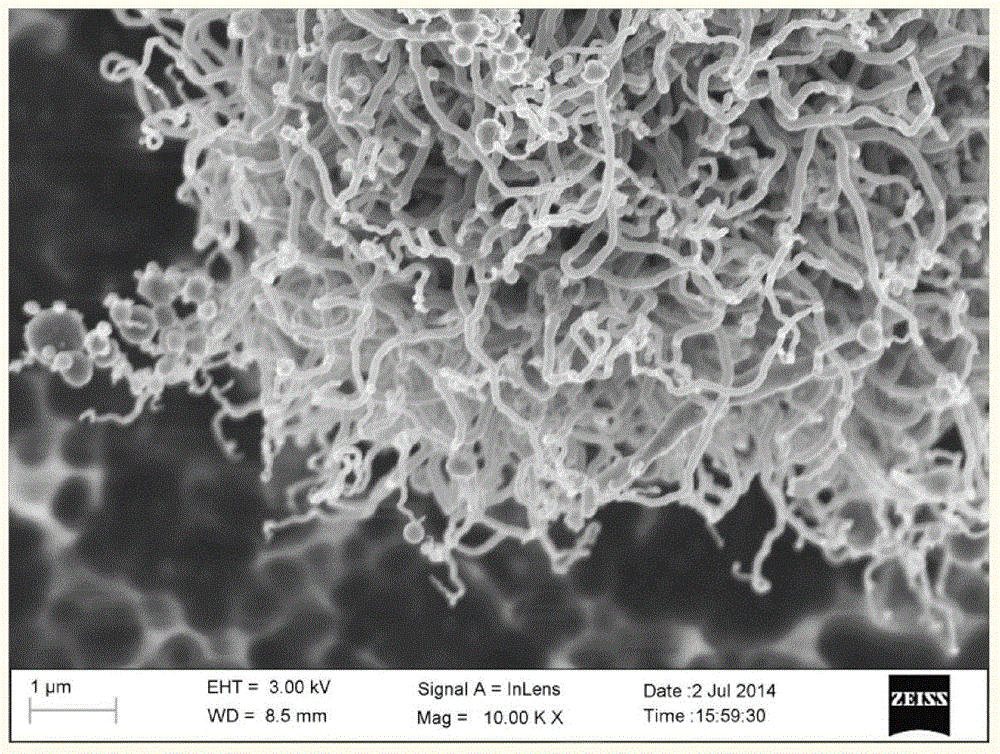
Method for preparing multiwalled carbon nanotube through microwave enhanced fast pyrolysis of biomass and/or carbonaceous organic waste
ActiveCN104787747AFast pyrolysisReduce manufacturing costMaterial nanotechnologyMean diameterMicrowave cavity
The invention discloses a method for preparing a multiwalled carbon nanotube through microwave enhanced fast pyrolysis of biomass and / or carbonaceous organic waste. The method comprises the following steps: biomass, carbonaceous organic waste, a mixture of the biomass and carbonaceous organic waste or a mixture of the biomass and carbonaceous organic waste uniformly mixed with a microwave absorbent is placed in a reaction vessel in a microwave cavity; an inert gas is introduced into the reaction vessel until an oxygen-free environment is formed; the microwave input power is adjusted to be higher than 500w, and the reaction vessel is heated to 400-1,500 DEG C for a pyrolytic reaction; the multiwalled carbon nanotube is obtained after the reaction. The method for preparing the multiwalled carbon nanotube is cheap and easy, the prepared carbon nanotube is curly, has the mean diameter of 3 nm-200 nm, can be applied to the fields of composites, electrode materials, catalyst preparation and the like and has a broad application prospect.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NOTTINGHAM NINGBO CHINA
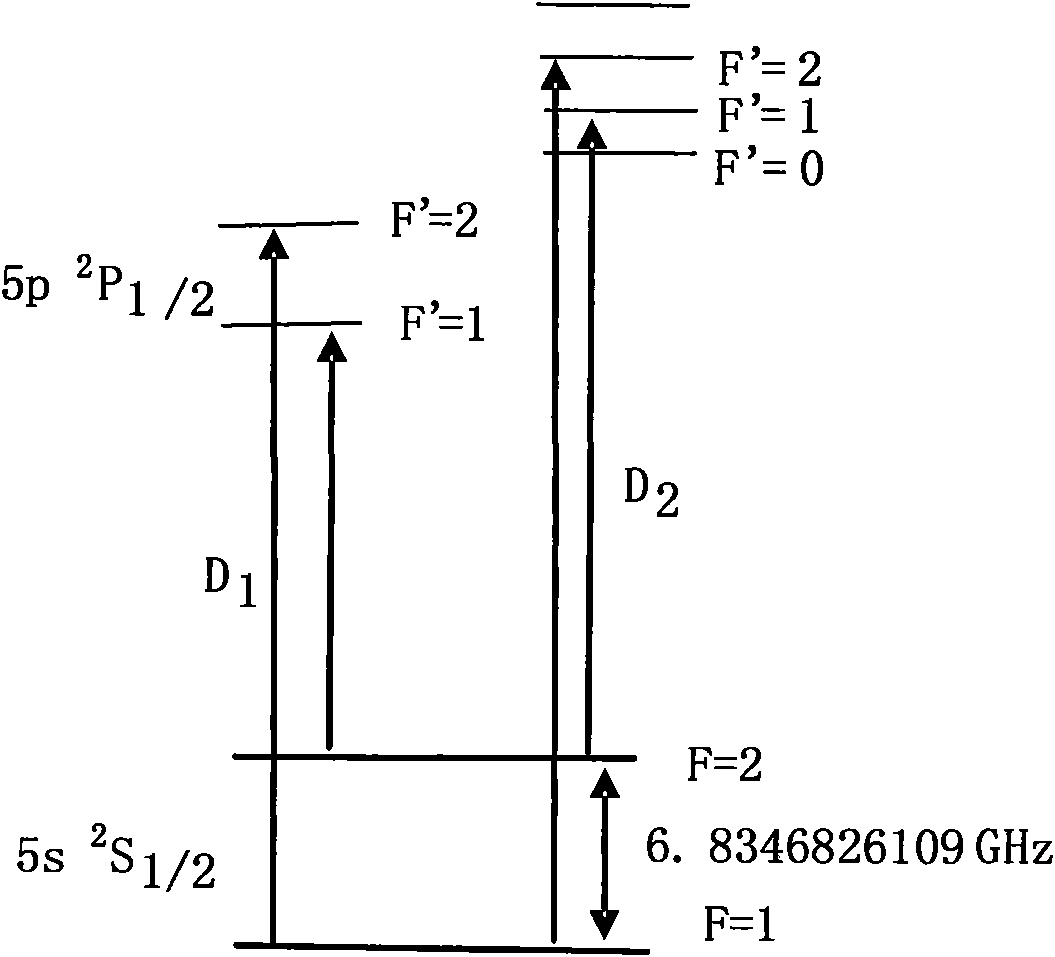
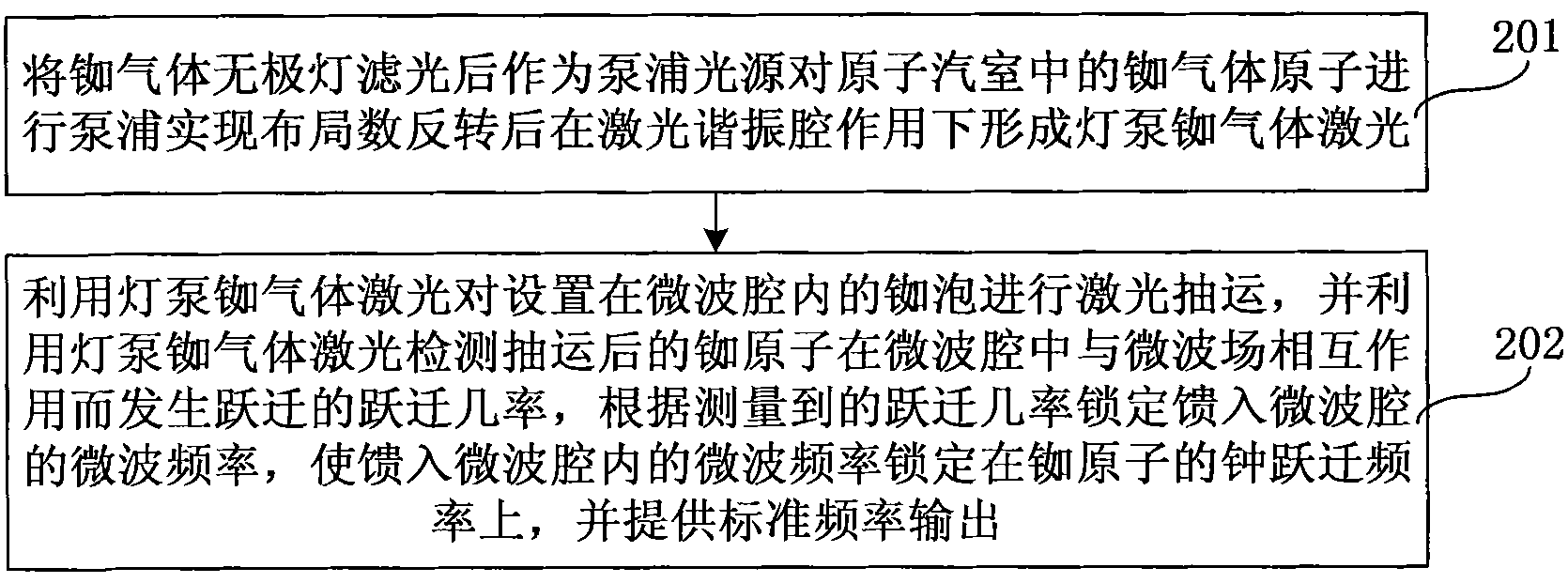
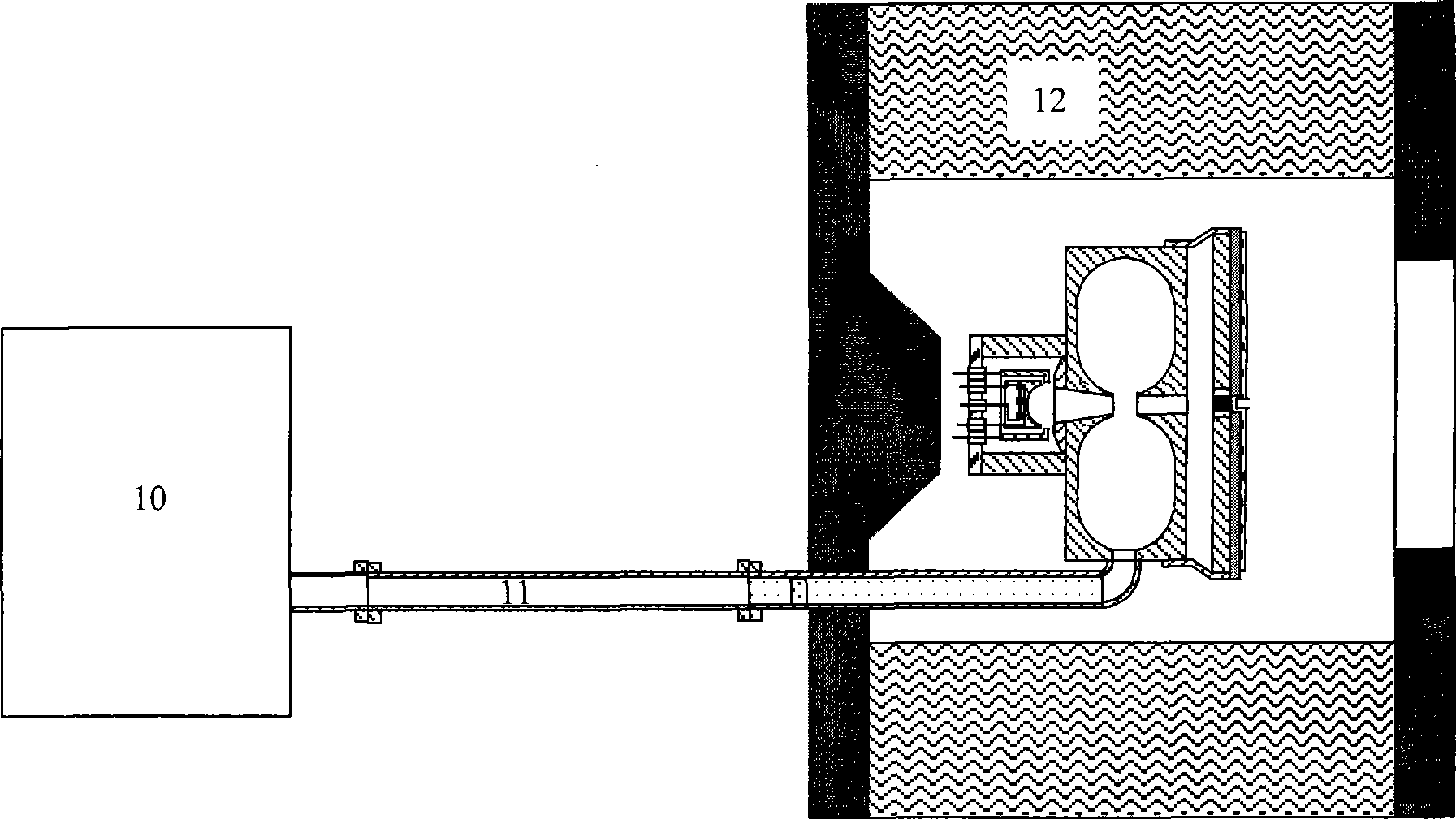
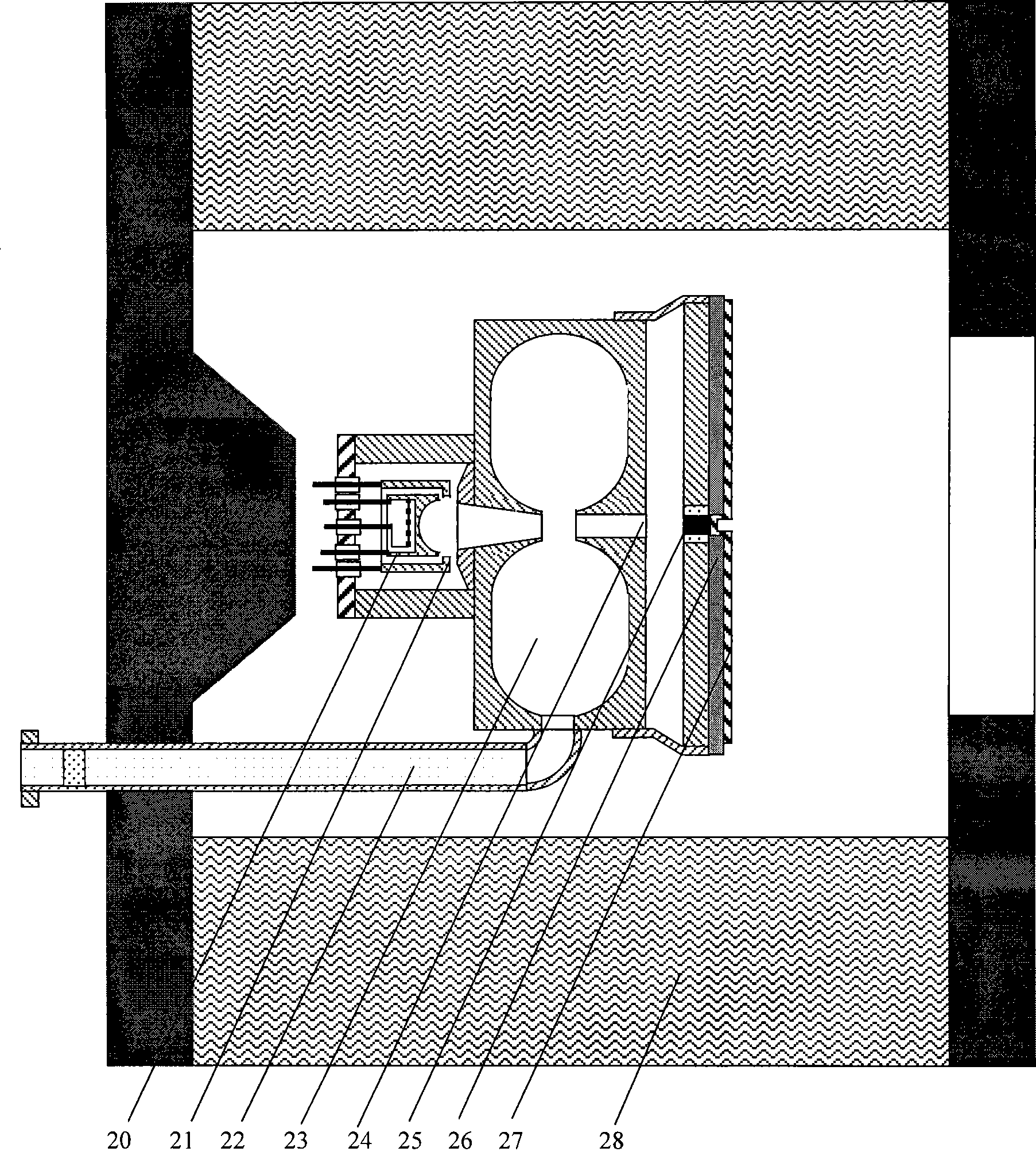
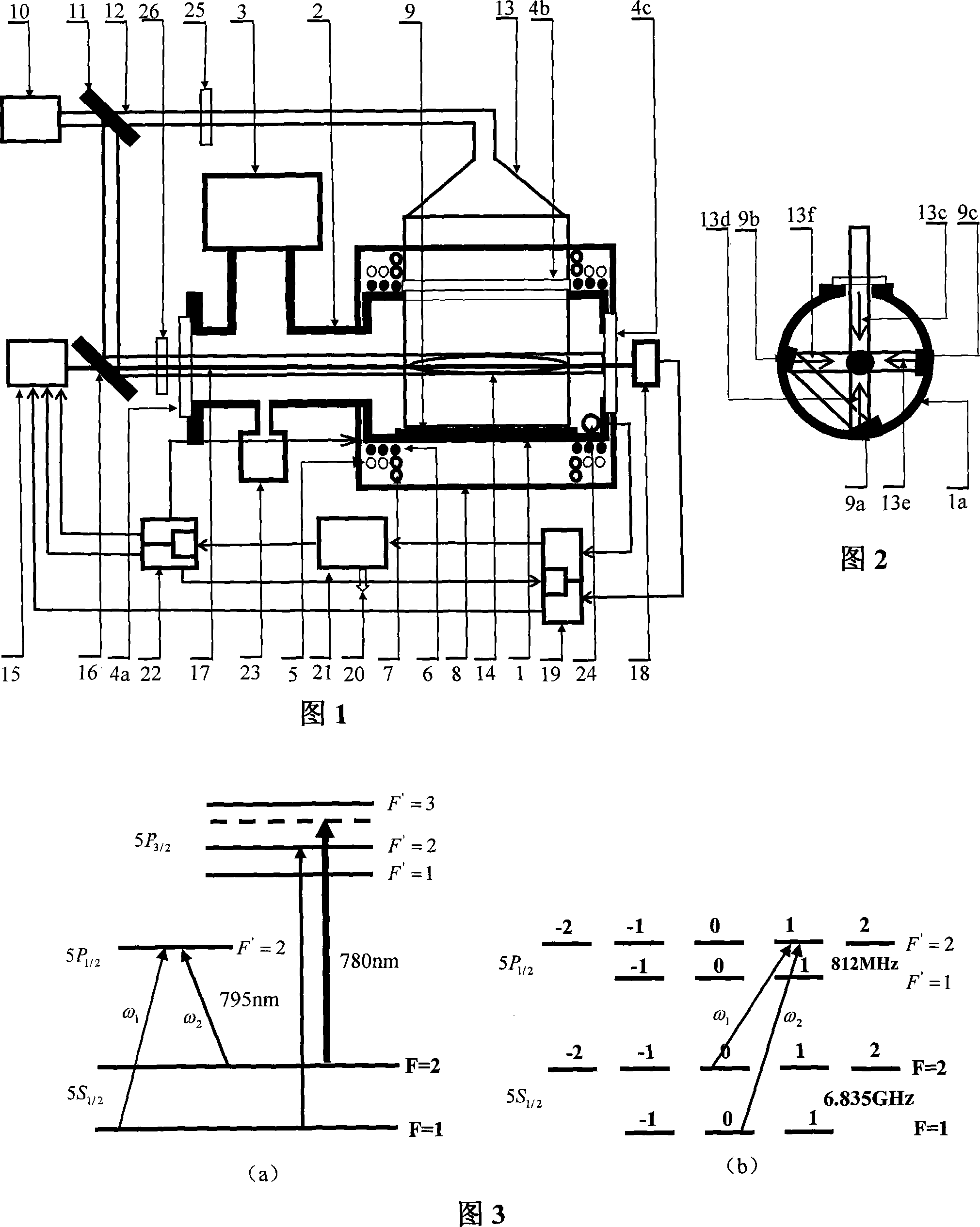
Method for pumping rubidium bubble for outputting standard frequency by lamp pump rubidium gas laser and rubidium atomic clock
ActiveCN101846965AEasy to lockQuick lockPulse automatic controlApparatus using atomic clocksMicrowave cavityResonant cavity
The invention relates to a method for pumping a rubidium bubble for outputting standard frequency by a lamp pump rubidium gas laser and a rubidium atomic clock. The method comprises the following steps of: adopting a filtered rubidium gas electrodeless lamp as a pumping light source for pumping a rubidium gas atom in an atom steam chamber, realizing distribution quantity conversion and then forming a lamp pump rubidium gas laser under the action of a laser resonant cavity; carrying out laser pumping on the rubidium bubble arranged in a microwave cavity by utilizing the lamp pump rubidium gas laser and detecting the transition probability of the pumped rubidium atom for generating transition by generating interaction with a microwave field in the microwave cavity by utilizing the lamp pump rubidium gas laser; and locking microwave frequency fed in the microwave cavity according to the detected transition probability and locking the microwave frequency fed in the microwave cavity on clock transition frequency of the atom. In the embodiment of the invention, because the frequency of the lamp pump rubidium gas laser still operates on a rubidium transition spectral line broadening spectrum in an unlocking state, even if the frequency of the lamp pump rubidium gas laser is unlocked, the lamp pump rubidium gas laser can be rapidly locked on needed laser frequency.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
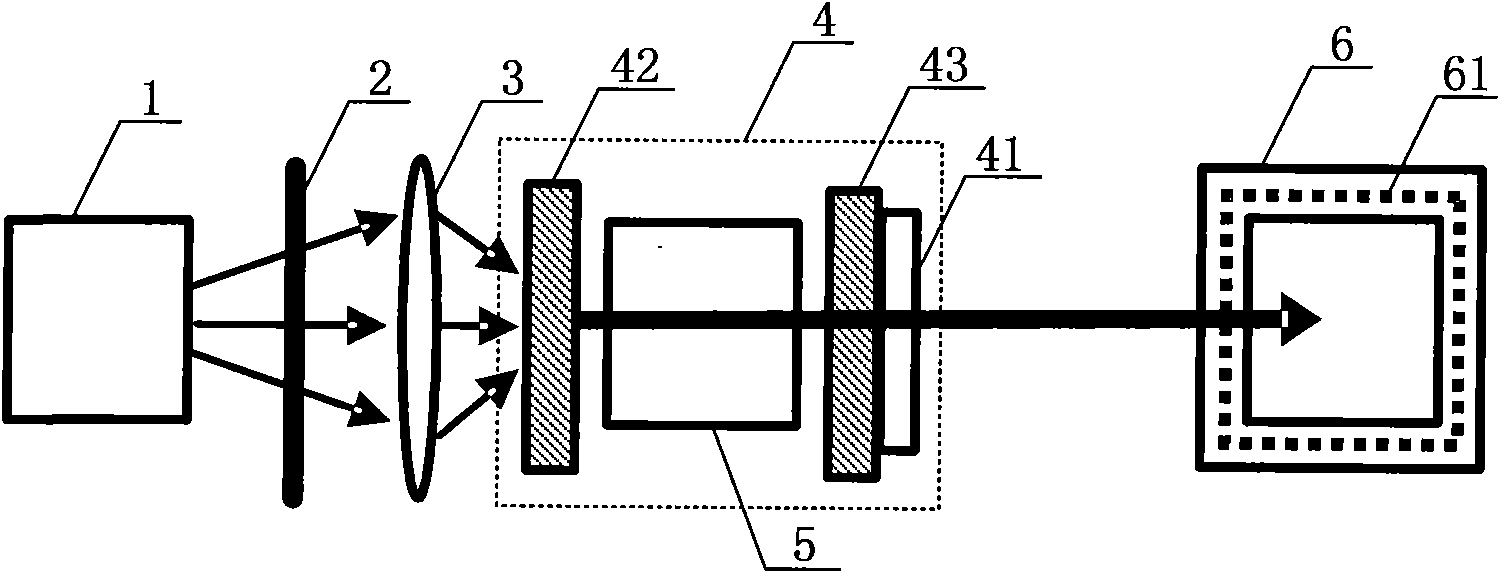
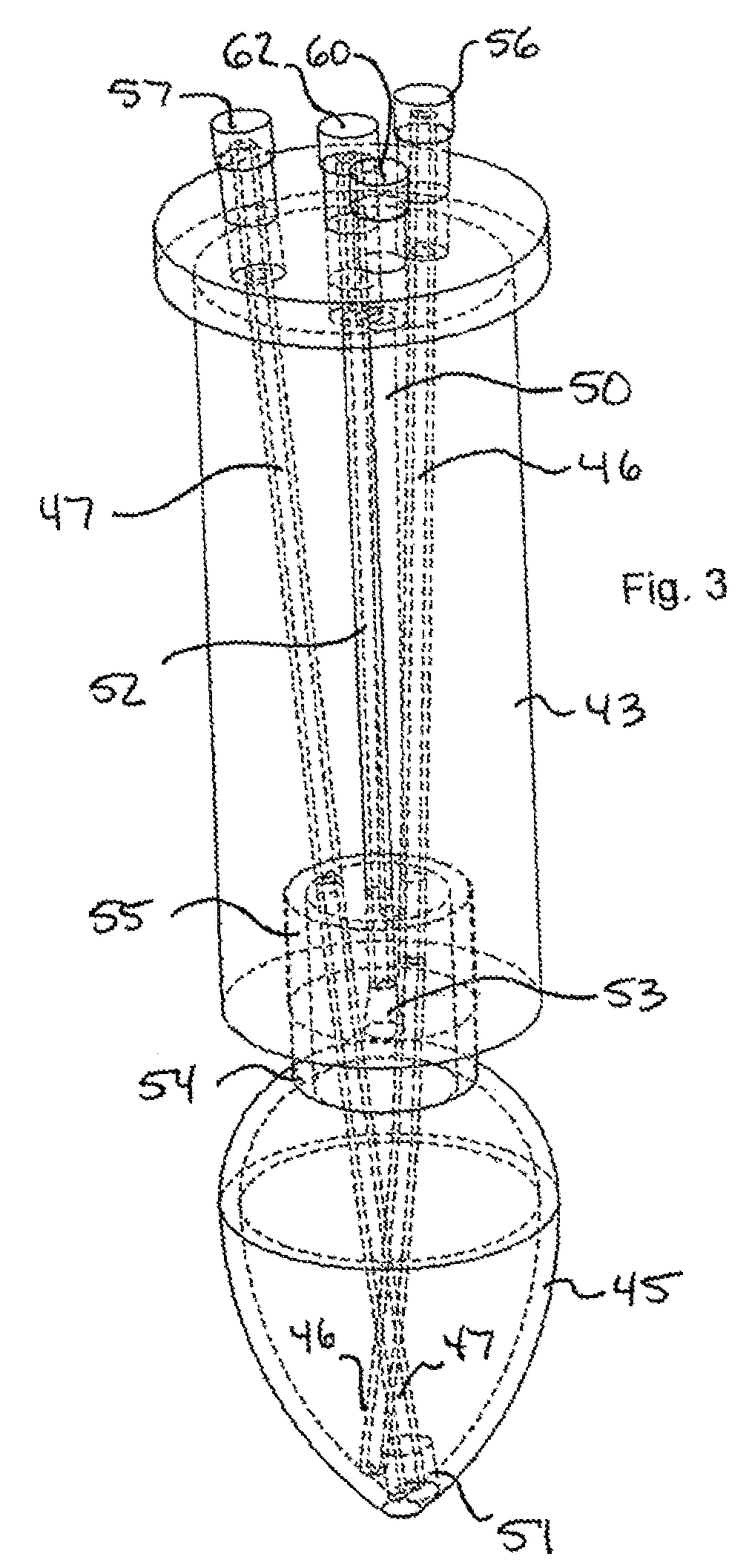
Microwave-assisted peptide synthesis
InactiveUS7902488B2Peptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsMicrowave cavityCombinatorial chemistry
An instrument and associated method are disclosed for the accelerated synthesis of peptides by the solid phase method. The instrument includes a microwave cavity, a microwave source in communication with the cavity, a column in the cavity formed of a material that is transparent to microwave radiation, a solid phase peptide support resin in the column, respective filters for maintaining the solid phase support resin in the column, a first passageway for adding starting compositions to the column, a second passageway for removing compositions from the column, and a third passageway for circulating compositions from the column into the third passageway and back to the column.
Owner:CEM CORP
Microwave sensing for determination of loading of filters
ActiveUS7679374B2Avoid pollutionSpectral/fourier analysisInternal combustion piston enginesMetallic enclosureMicrowave cavity
Method for determining loading of a filter. The filter has a first dielectric constant. The filter becomes loaded with contaminant material that has a second dielectric constant. The filter, such as a diesel particulate filter, is contained within a metallic enclosure forming a microwave cavity. The method includes establishing microwave energy in the cavity and monitoring changes in the cavity microwave response, the changes being related to filter loading.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
System and method for measuring retentate in filters
A system and method for determining loading of a filter having a first dielectric constant with a material having a different dielectric constant, is disclosed. The filter is contained within a metallic container forming a microwave cavity, and microwave or RF energy is created within the cavity and changes in the cavity microwave response are monitored. The changes in cavity microwave response are related to filter loading. In a preferred embodiment, the microwave energy includes multiple cavity modes thereby allowing determination of spatial distribution of the contaminant material loading. In one embodiment, the microwave cavity response includes a shift in frequency of a resonant mode. Alternatively, the microwave cavity response includes a shift in quality factor Q of a resonant mode. The microwave cavity response may include a shift in amplitude or peak width of the microwave's signal at resonance.
Owner:FILTER SENSING TECH
Restoring method of activated carbon for decomposing, processing and adsorbing organic substance in waste water through microwave irradiation
InactiveCN1562775AReduce lossNo frictionOther chemical processesCombustible gas purificationActivated carbonMicrowave cavity
The characteristics are: adsorption of organic substances in waste water and regeneration of active carbon are all proceeded in a microwave irradiating regenerating unit, active carbon is granular, humidity is controlled in 35-55 percent, stuffing quantity is 1 / 3-4 / 5 of volume of reactor, microwave frequency is 2450 MHz or 915 MHz, power is 0.5-64 kw, temp. is increased to 800-1200 deg.C and kept 3-5 minutes, total irradiating time is 15 minutes. The microwave irradiating regenerating unit consists of magnetron, microwave cavity resonantor and reactor, in top of which water control valve and vapour exit are set on, and there is a blow head in the reactor and sample connection and water exit on bottom of the reactor, alkali solution absorbing tank connected to vapour exit and gas adsorption column.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Small Rb atom frequency marking cavity bubble system
InactiveCN101237077AReduce volumeReduce design difficultyPulse automatic controlGaseous masersDielectric cylinderCell system
The present invention discloses a miniaturized rubidium atomic frequency standard cavity-cell system, wherein, a microwave cavity cylinder is made from high magnetic permeability material; the microwave cavity cylinder is sleeved with a heating cylinder; a pump light incident port of the heating cylinder is also provided with a convex lens which gathers and transmits rays emitted by a rubidium spectral lamp into a microwave cavity; a C field coil is directly wound on a dielectric cylinder arranged between the microwave cavity cylinder and an absorption cell; a cusp on the tail part of a light-filtering cell is concentrated at the center of a circular plane at the end of the cell; a cusp on the tail part of the absorption cell is concentrated at the edge of a circular plane at the end of the cell; a photocell and a snap-off diode are fixed on the end face of the inner wall of a cavity end cover which can be movably fixed. The present invention has no machinery regulating rod inside the cavity, uses an intracavity frequency doubling mode, adopts a cylindrical TE111 mode and a dielectric filling method to get rid of the complex structure of a magnetic shield cylinder in the prior art, and reduces the volume of the cavity-cell system. As the pump light incident port of the heating cylinder is provided with the convex lens to increase the light intensity of pump light, the performance of the cavity-cell system is guaranteed. A mobile photoelectric component is adopted for cavity frequency fine adjustment, which is convenient for debugging and cannot cause field form distortion.
Owner:SICHUAN TIANAO XINGHUA TIME & FREQUENCY
Microwave Plasma Nozzle With Enhanced Plume Stability And Heating Efficiency
ActiveUS20080017616A1Low per unit costShort turnaround timeElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsMicrowave cavityElectrical conductor
Systems and methods for generating relatively cool microwave plasma are disclosed. The present invention provides a microwave plasma nozzle that includes a gas flow tube through which a gas flows, and a rod-shaped conductor that is disposed in the gas flow tube and has a tapered tip near the outlet of the gas flow tube. A portion of the rod-shaped conductor extends into a microwave cavity to receive microwaves passing in the cavity. These received microwaves are focused at the tapered tip to heat the gas into plasma. The microwave plasma nozzle also includes a vortex guide between the rod-shaped conductor and the gas flow tube imparting a helical shaped flow direction around the rod-shaped conductor to the gas flowing through the tube. The microwave plasma nozzle further includes a mechanism for electronically exciting the gas and a shielding mechanism for reducing a microwave power loss through the gas flow tube.
Owner:RECARBON INC
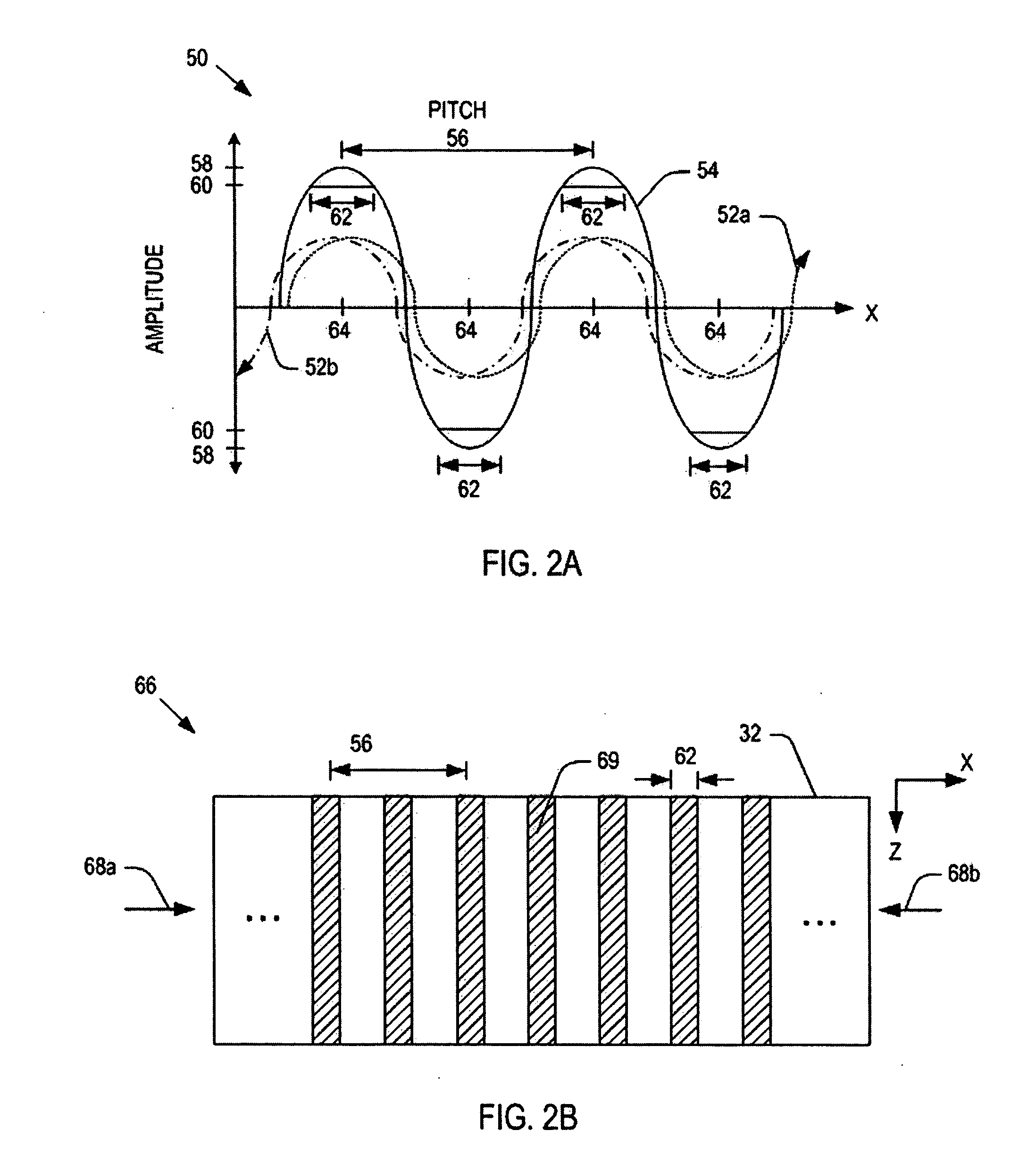
Plasma nozzle array for providing uniform scalable microwave plasma generation
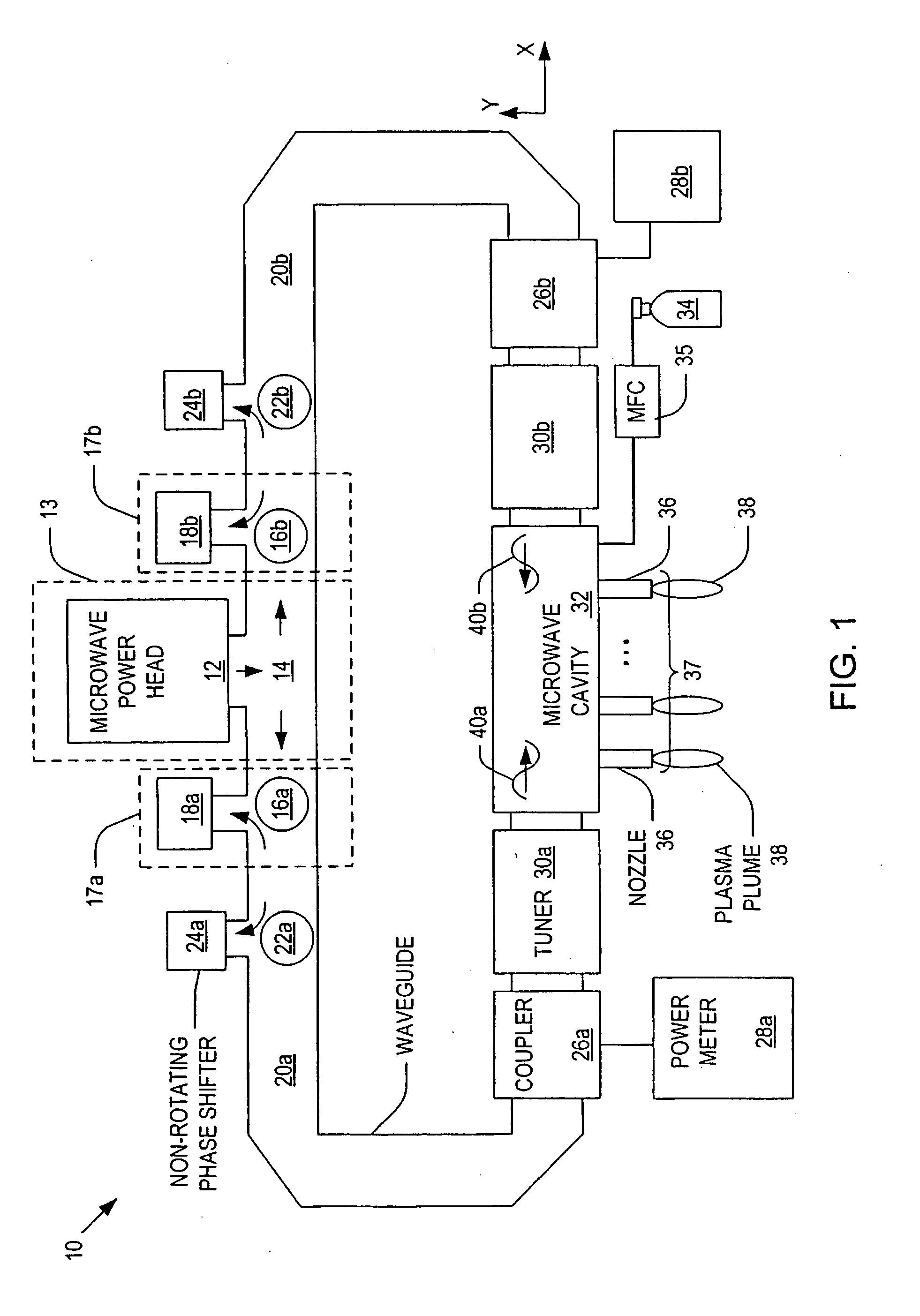
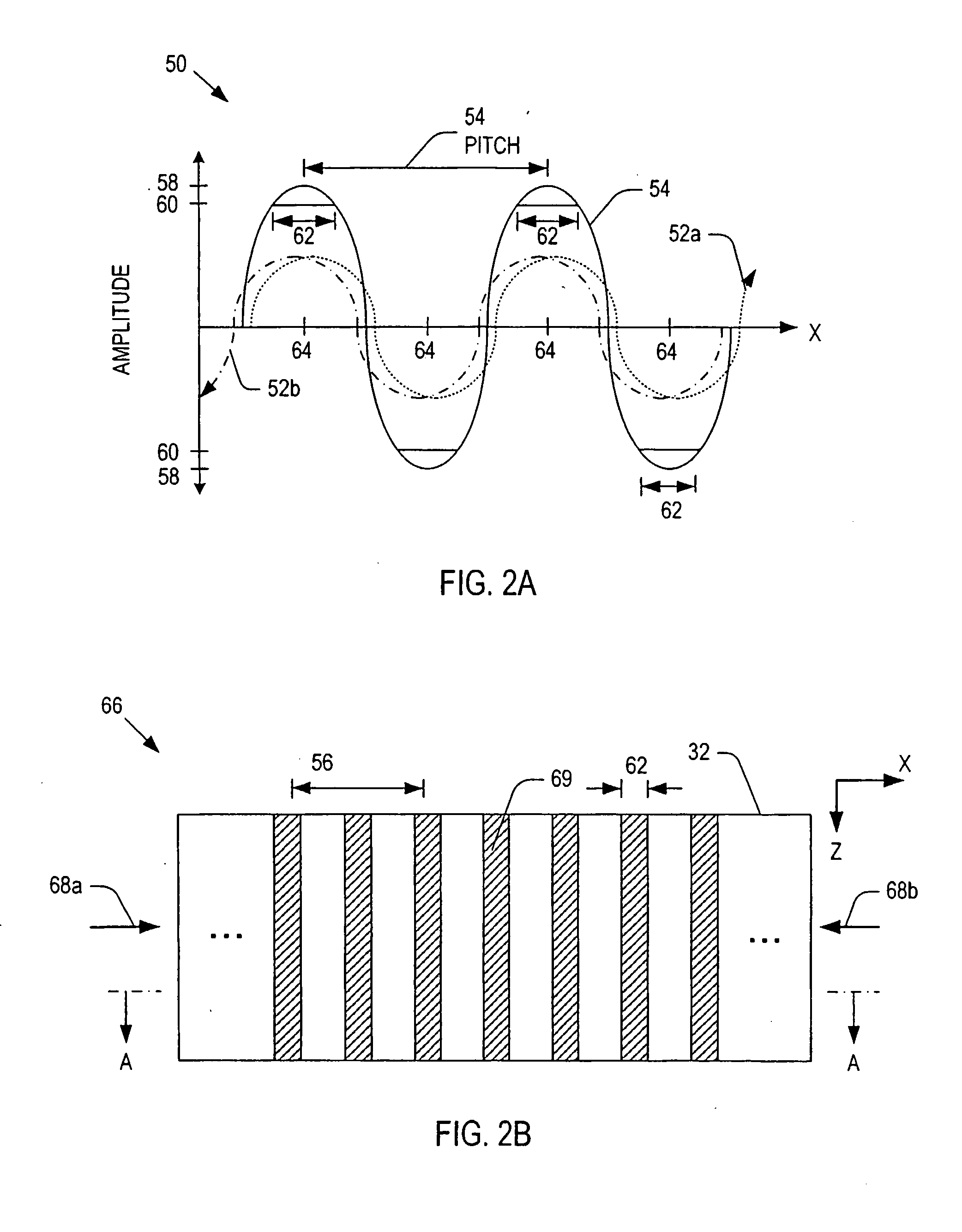
ActiveUS20060021581A1Electric discharge tubesElectrostatic cleaningMicrowave cavityElectrical conductor
Microwave plasma nozzle array systems and methods for configuring the microwave plasma nozzle arrays are disclosed. The microwaves are transmitted to a microwave cavity in a specific manner and form an interference pattern that includes high-energy regions within the microwave cavity. The high-energy regions are controlled by the phases and the wavelengths of the microwaves. A plurality of nozzle elements is provided in the array. Each of the nozzle elements has a portion partially disposed in the microwave cavity and receives a gas for passing therethrough. The nozzle elements receive microwave energy from one of the high-energy regions. Each of the nozzle elements include a rod-shaped conductor having a tip that focuses the microwaves and a plasma is then generated using the received gas.
Owner:NOXILIZER +1
Plasma Nozzle Array for Providing Uniform Scalable Microwave Plasma Generation
The present invention provides microwave plasma nozzle array systems (10, 70, 230, and 310) and methods for configuring microwave plasma nozzle arrays (37, 99, and 337). The microwaves are transmitted to a microwave cavity (323) in a specific manner and form an interference pattern (66) that includes high-energy regions (69) within the microwave cavity (32). The high-energy regions (69) are controlled by the phases and the wavelengths of the microwaves. A plurality of nozzle elements (36) is provided in the array (37). Each of the nozzle elements (36) has a portion (116) partially disposed in the microwave cavity (32) and receives a gas for passing therethrough. The nozzle elements (36) receive microwave energy from one of the high-energy regions (69). Each of the nozzle elements (36) includes a rod-shaped conductor (114) having a tip (117) that focuses on the microwaves and a plasma (38) is then generated using the received gas.
Owner:SAIAN CORP +1
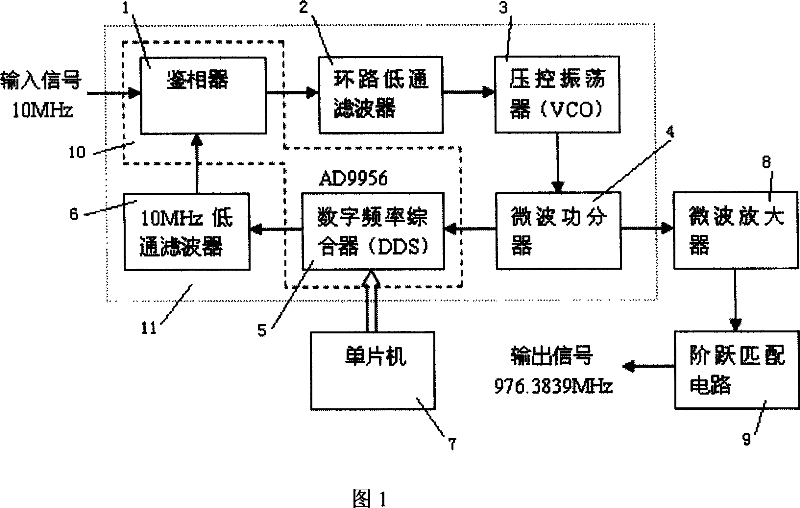
Rubidium atom frequency scale digital phase-locking frequency doubler
InactiveCN101039117AIncrease dynamicsHigh resolutionPulse automatic controlPhase noiseFrequency multiplier
The invention discloses a rubidium atom frequency standard digital phase locked frequency multiplier. The input terminal of the digital phase locked loop is connected with the output terminal of the rubidium atom frequency standard 10MHz voltage control crystal oscillatory as the output terminal of the frequency multiplier. The output terminal of the digital phase locked loop is connected with the output terminal of the microwave oven amplifier which is connected with the output terminal of the step matching circuit. The output terminal of the step matching circuit as the output terminal of the frequency multiplier is connected with the input terminal of the rubidium atom frequency standard microwave cavity. The phase detector and the digital frequency synthesizer are integrated by AD 9956. The invention adopts digital synthesizer as the fractional divider in which a digital phase locked loop is inserted, sets and modulate the fractional frequency division ratio of the digital synthesizer through the single chip computer thus enabling the direct fractional frequency multiplying and frequency modulation of the frequency multiplier. The invention with a simple structure, high degree of integration, high purity of the spectrum, low phase noise, small stray and high degree of digitalization is easy to modulate and can be used to produce miniaturized rubidium atom frequency standard.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Superconducting quantum bit chip
ActiveCN109376870APrevent Interconnect BreakpointsIncrease flexibilityQuantum computersMicrowave cavityChain structure
The invention discloses a superconducting quantum bit chip, comprising a quasi-one-dimensional network chain structure layout superconducting quantum bit array and a manipulating and reading microwavecircuit, wherein each mesh unit comprises n qubits, and m (m and n are natural numbers, n>m>=2) shared qubits between adjacent networks are used for interconnection between mesh units; Each superconducting qubit in the mesh unit is coupled to the same coplanar superconducting microwave cavity for interconnection of qubits in the network. Each qubit is coupled to a coplanar superconducting microwave cavity and further coupled to a coplanar microwave transmission line, and is connected to an external circuit for qubit state reading. The present application can effectively prevent the possibility of qubit interconnection breakpoints, greatly improve interconnection reliability, increase the flexibility of error correction coding design, effectively reduce the complexity of qubit manipulationand reading circuits, and has an important scientific research and industrial application prospect.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
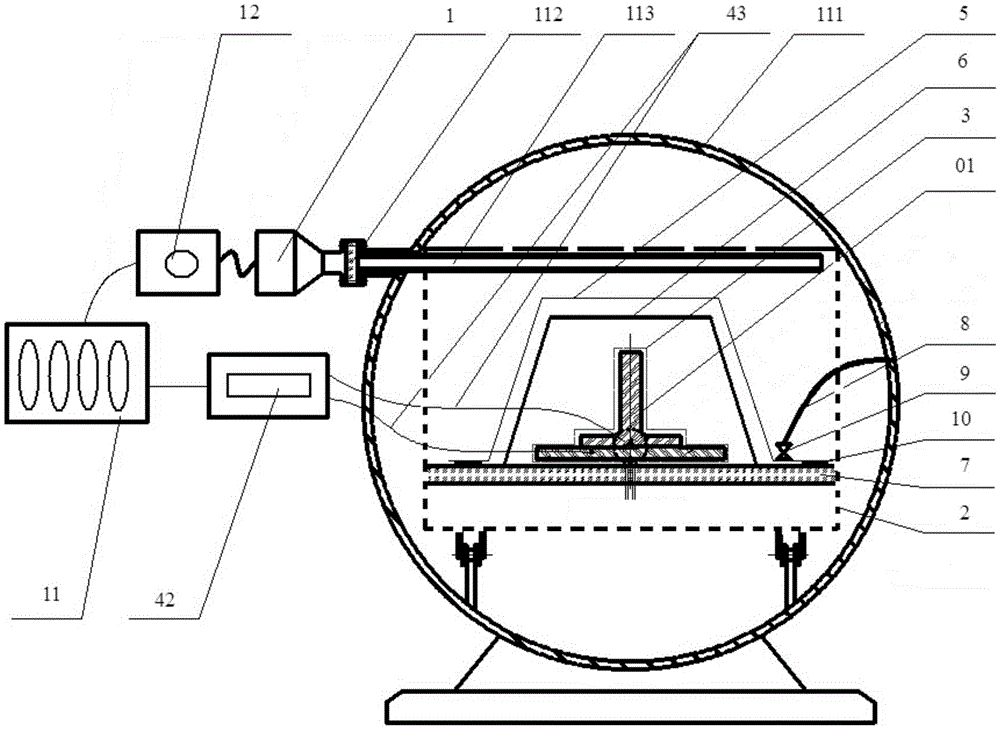
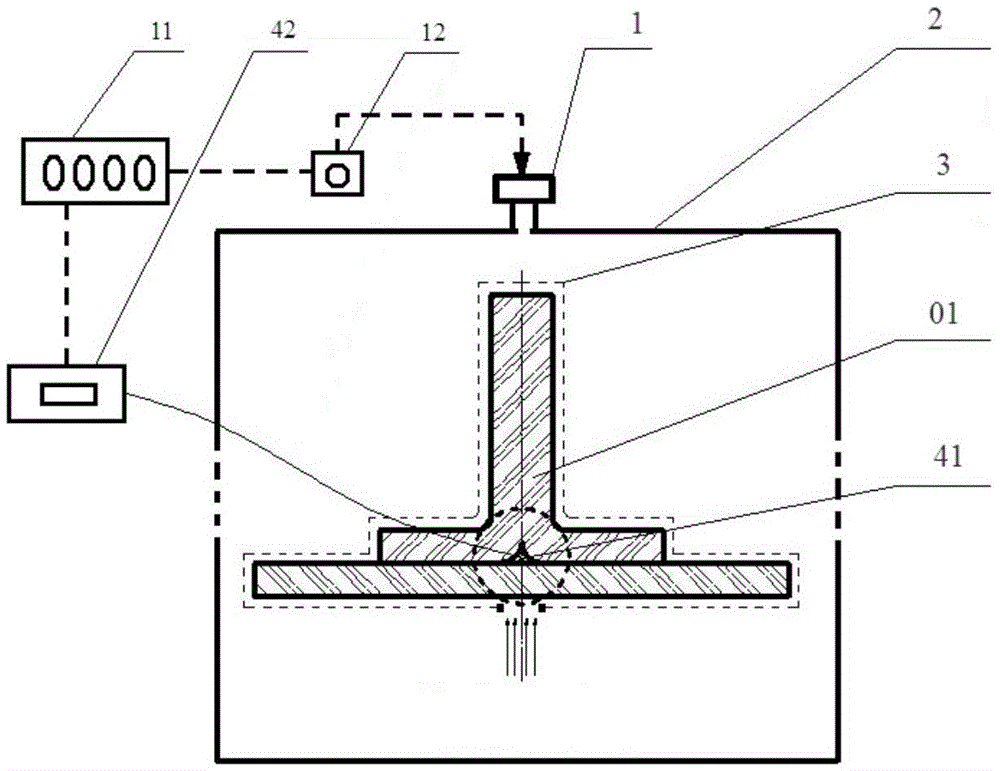
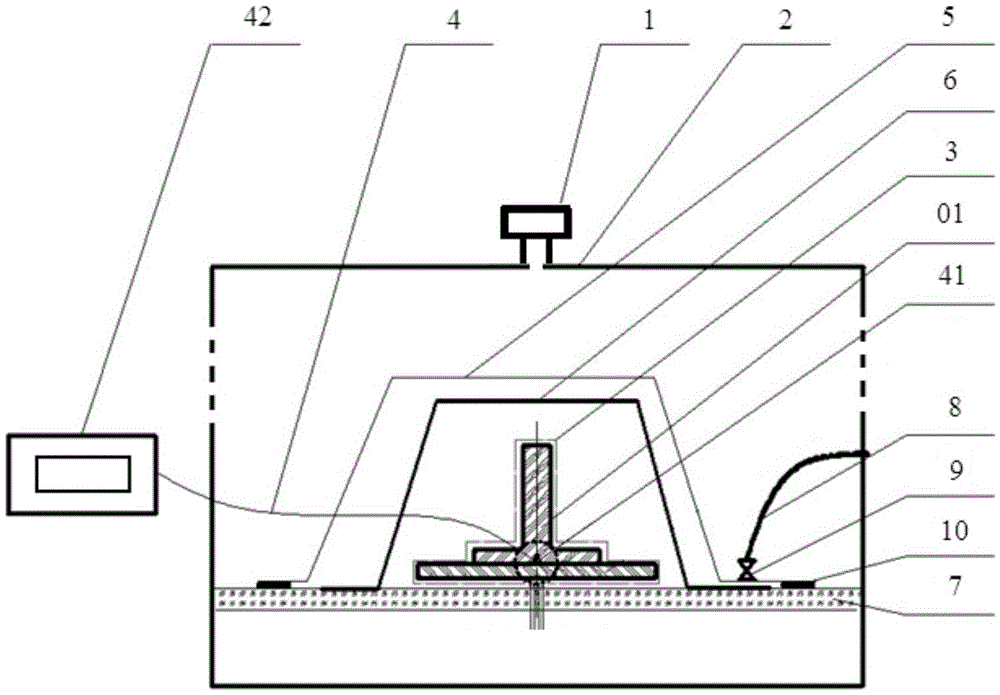
Thickness measuring apparatus and method using a microwave cavity resonator
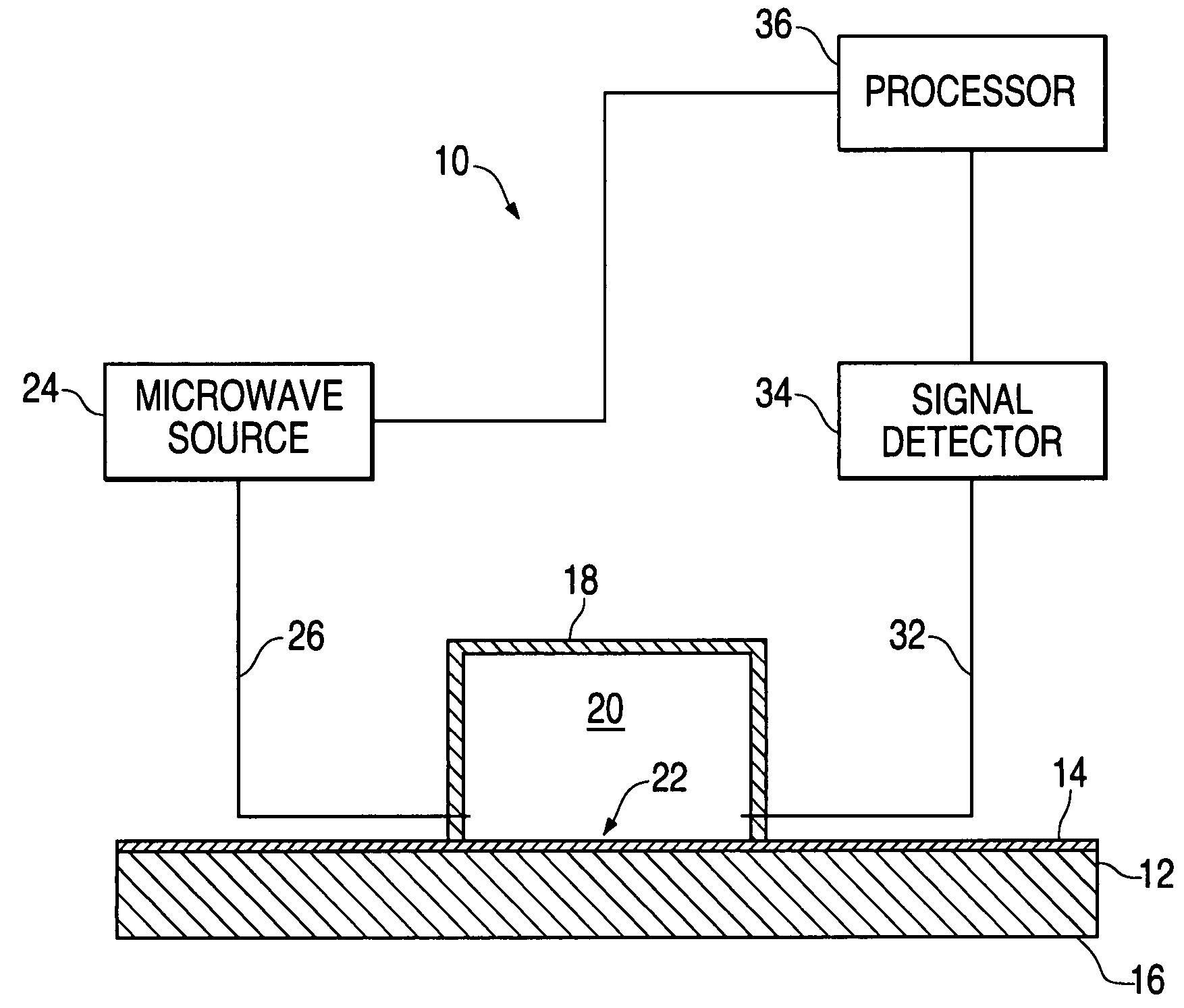
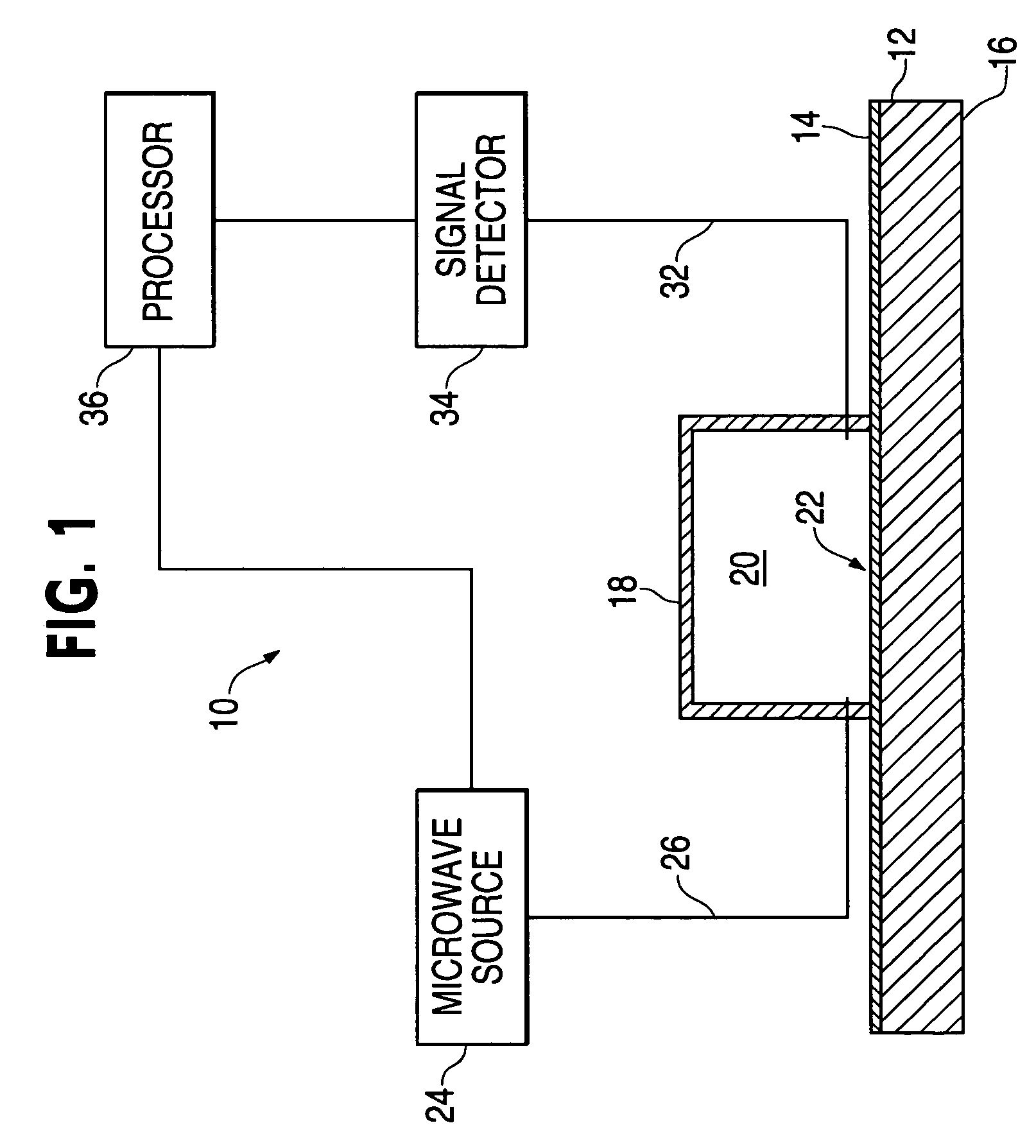
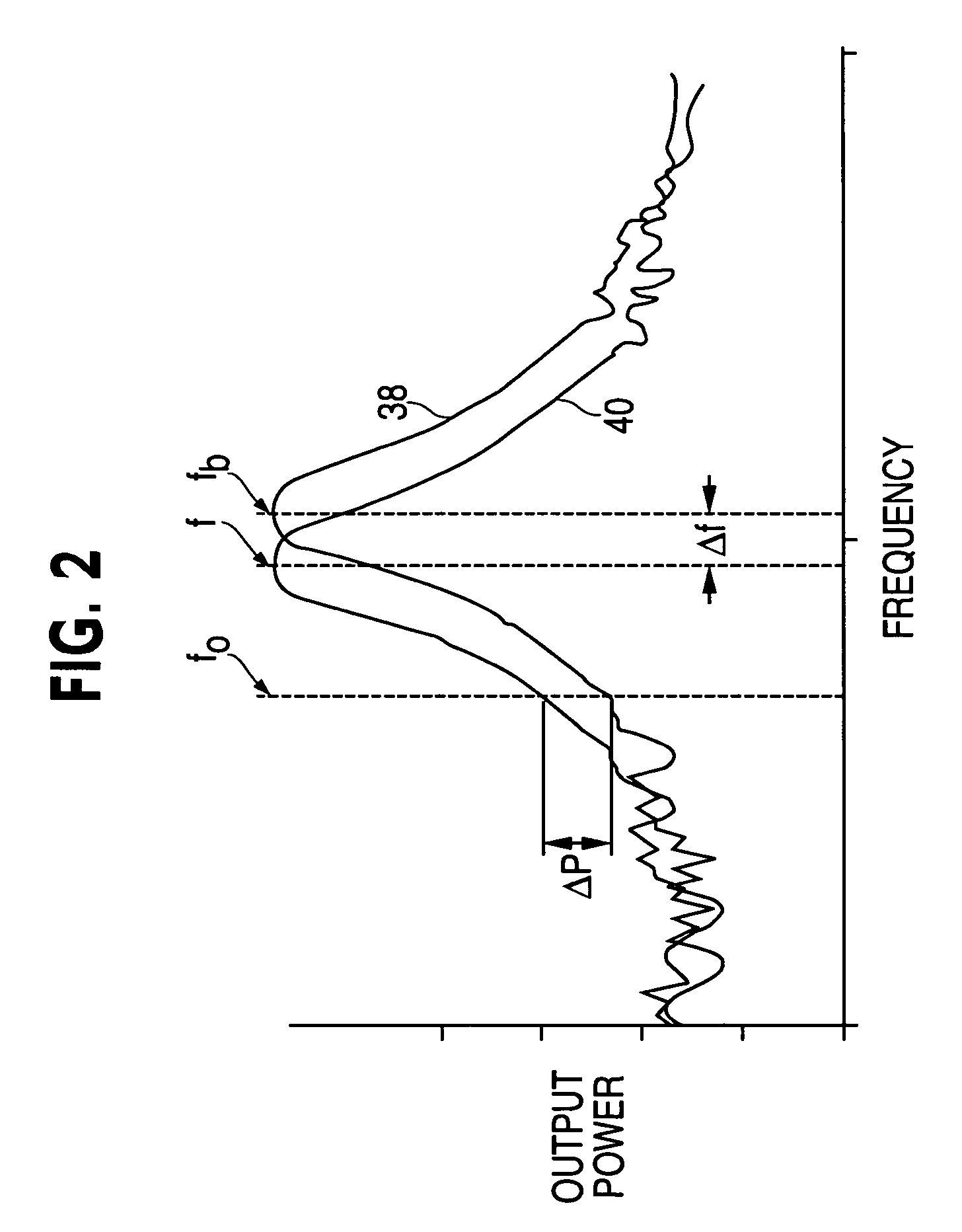
InactiveUS7173435B1Low direct-current conductivityLow magnetic permeabilityResistance/reactance/impedenceUsing wave/particle radiation meansResonant cavityMicrowave cavity
A measurement device for measuring a thickness of a film layer over a substrate utilizes a microwave source and a resonant cavity having an open side. A microwave signal is introduced at a first end of the resonant cavity with the open side against a surface measurement sample having a film layer over a substrate, and an output signal detector senses the output power of the signal at a far end of the resonant cavity. A processor uses a difference in the resulting resonant frequency of the cavity from that using a substrate without the film layer to determine the thickness of the film layer.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Terahertz radiation source
InactiveCN101364517AIncrease powerHigh power redundancyTransit-time tubesMasersCapacitanceMicrowave cavity
A Terahertz wave radiation source belongs to the technical field of Terahertz wave. The basic structure comprises a microwave source, a connecting wave guide and a Terahertz wave generator. The Terahertz wave generator works in a vacuum state in a tube, and mainly comprises a cathode for emitting electrons, a focusing electrode, a microwave input wave guide, a microwave cavity, an electron beam drifting and bunching pipe, an extraction electrode, a thick film capacitor, a thin film radiating antenna, an electron beam focusing magnet and a pole shoe. The invention has a simple structure, the output power and efficiency greatly exceeding that of the prior Terahertz wave generator, is suitable for large-scaled production, and has wide application prospect in the fields, such as material detection, human body imaging, component analysis, and the like.
Owner:李德杰
Coherent maser radiation cold atomic clock
InactiveCN101145025AReduce FWHMExtended transit timeApparatus using atomic clocksPulse automatic controlMaserHelmholtz coil
The present invention discloses a coherent microwave-radiation cold atomic clock; and an ion pump is connected with a vacuum catheter which is connected with a microwave cavity; a light window is fixed in the microwave cavity by quartz glass and three reflective mirrors; a pair of anti-Helmholtz coils and a pair of Helmholtz coils are fixed on the microwave cavity; a pair of rectangular coils are fixed on the microwave cavity; a magnetic shielding system is connected with a vacuum system; semiconductor laser provides captive light and beams of pump-back light; a semiconductor laser on the vertical cavity surface provides a plurality of beams of captive light; a voltage-controlled crystal oscillator is connected with a frequency synthesizers connected with a signal receiver and processor; the semiconductor laser on the vertical cavity surface is connected with the microwave cavity; a photoelectric detector and a microwave-power receiver are connected with the signal receiver and processor connected with the voltage-controlled crystal oscillator as well as the semiconductor laser on the vertical cavity surface. The present invention is characterized in that the structure is compact and the size is small, and has good stability, high accuracy as well as good applicability.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method of and apparatus for in-situ measurement of changes in fluid composition by electron spin resonance (ESR) spectrometry
ActiveUS20080164874A1Increasing sensitivity of instrumentEasy to identifyMeasurements using electron paramagnetic resonanceAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceElectronResonance signal
A miniaturized instrument and method of using electron spin resonance spectrometry for measuring the degradation of lubricating fluids, and the like, that includes continuously passing a sample of such fluid through a resonating RF microwave cavity resonator during the application therethrough of a uniform slowly varying uniform magnetic field that is rapidly modulated and measuring the resulting phase modulation or amplitude modulation thereof to derive an electron spin resonance signal that directly senses the molecular changes in the fluid sample resulting from fluid degradation during operation of the vehicle, such as peroxy radicals in vehicle engine oil and the like.
Owner:ACTIVE SPECTRUM
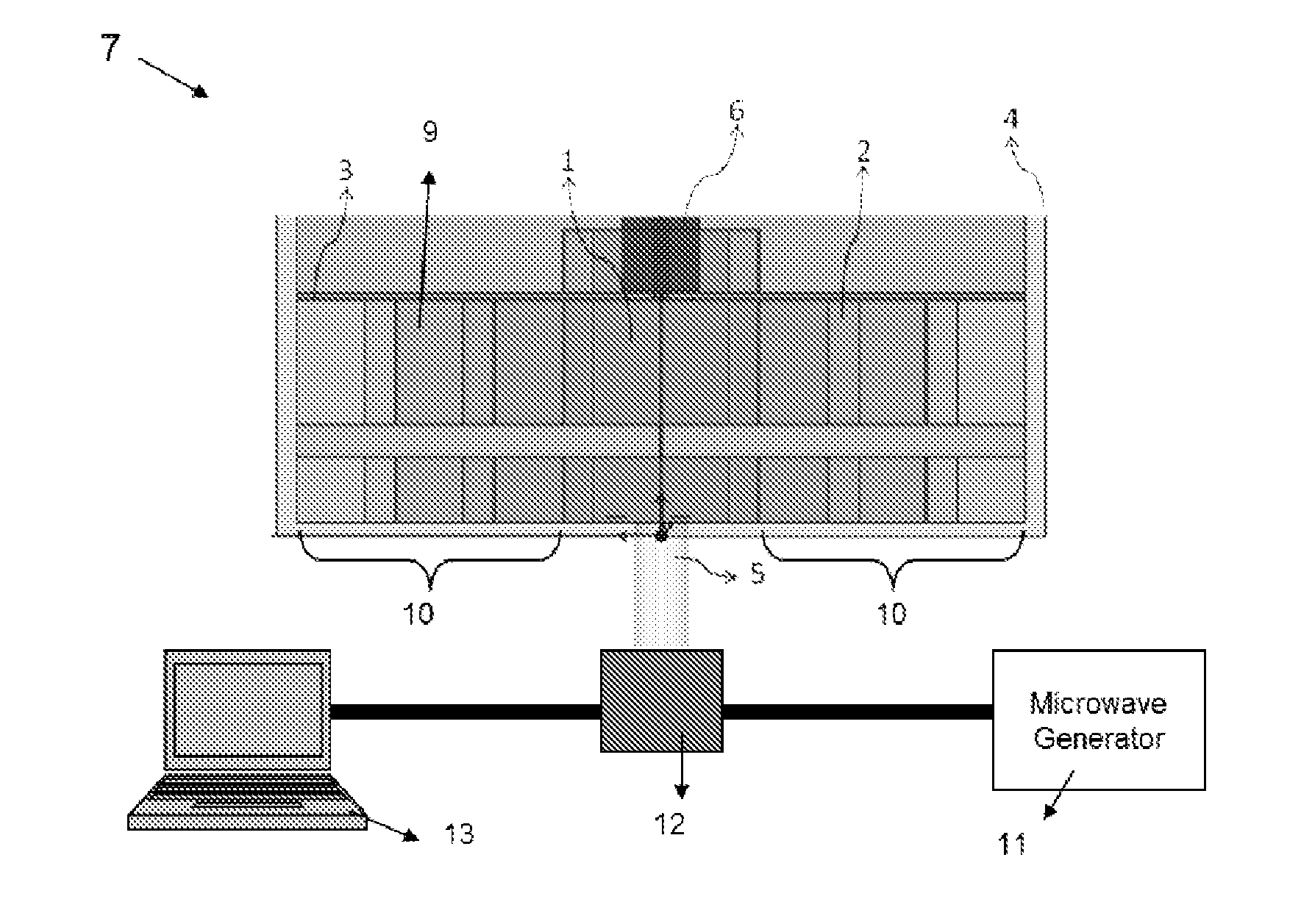
Microwave cavity sensor
ActiveUS20150097561A1Resistance/reactance/impedenceMaterial analysis using microwave meansMicrowave cavityWaveguide
A sensor comprising: a dielectric waveguide for guiding a microwave signal; and a dielectric reflector at an end of the dielectric waveguide to cause formation of a sensing field beyond an outer surface of the dielectric reflector.
Owner:HERIOT WATT UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com