Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2626 results about "Microwave power" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
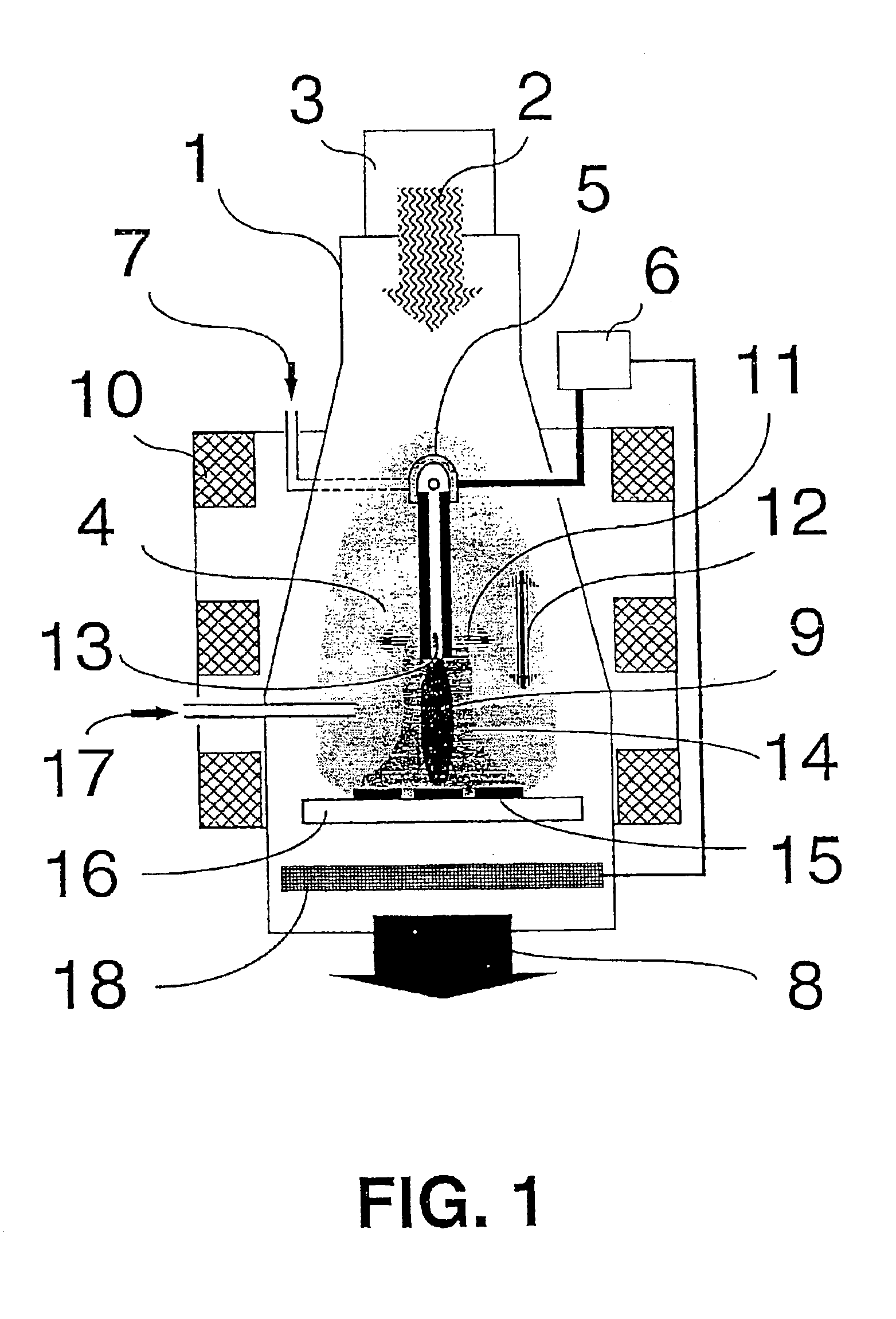
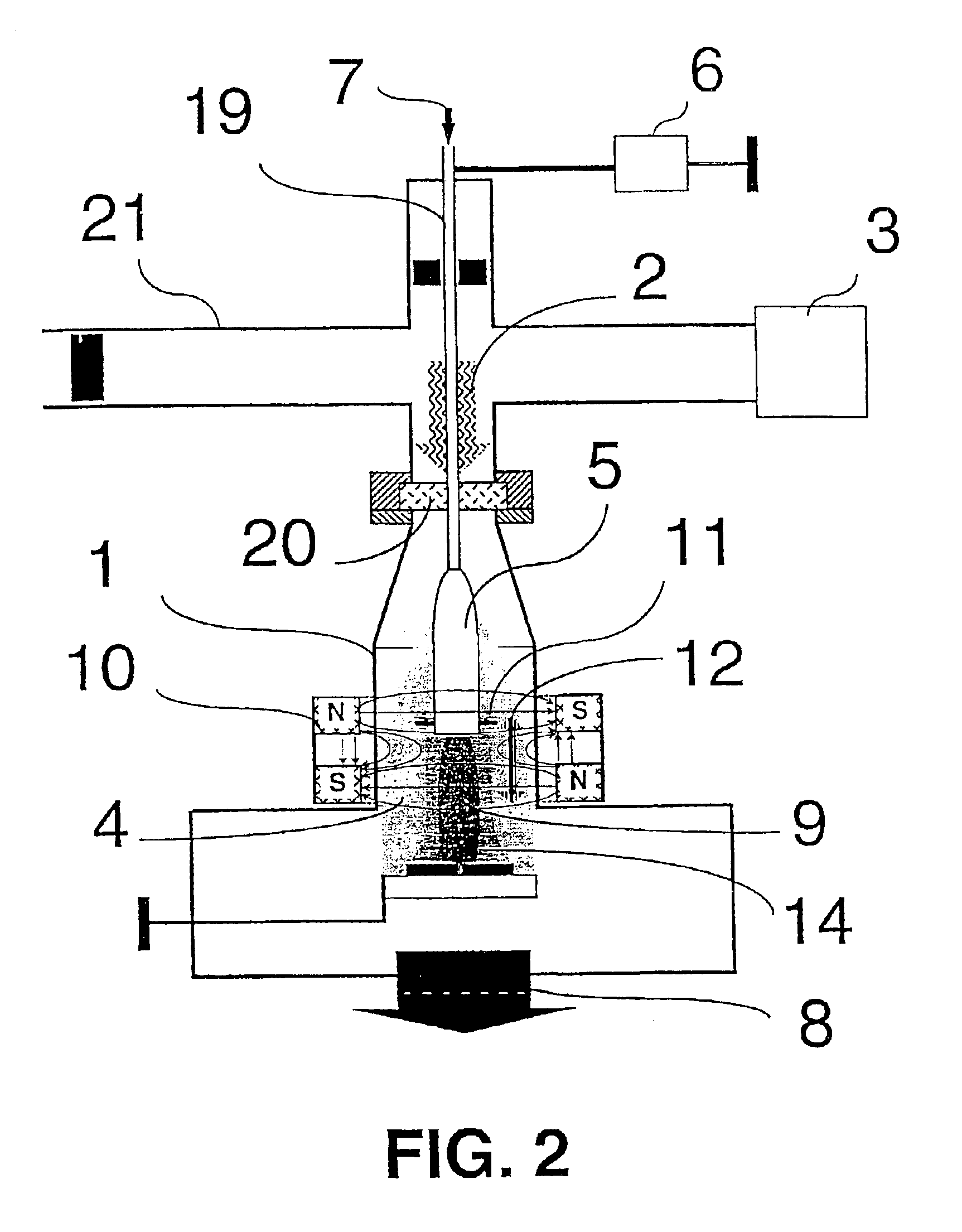
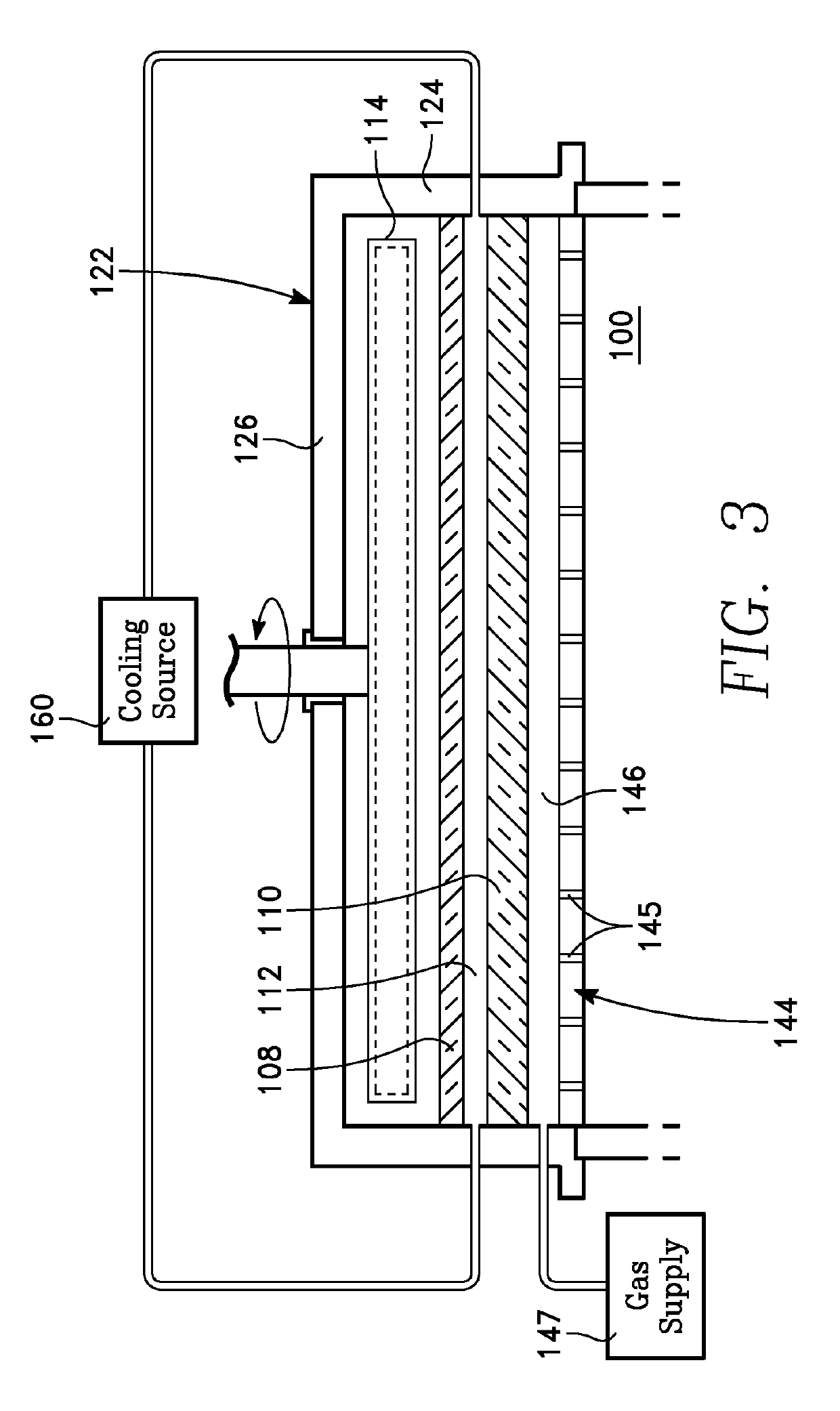
Thin film deposition using microwave plasma
InactiveUS20120171391A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCelsius DegreeEngineering
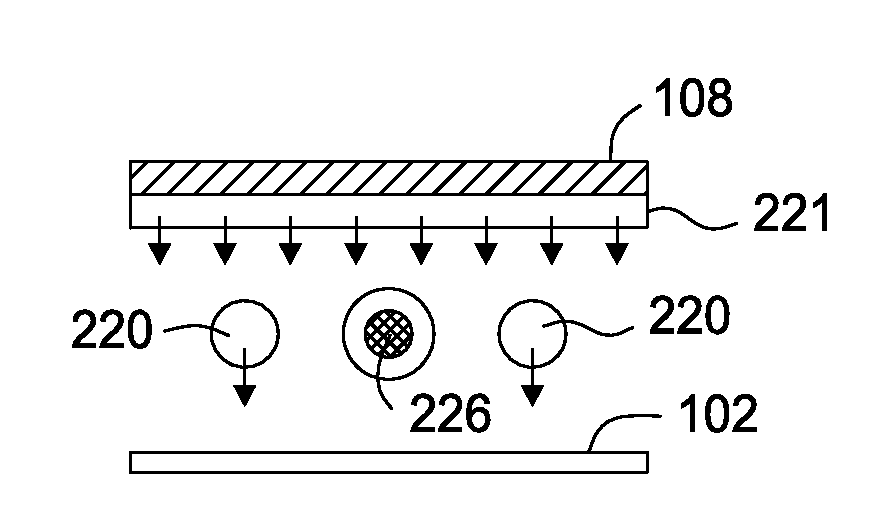
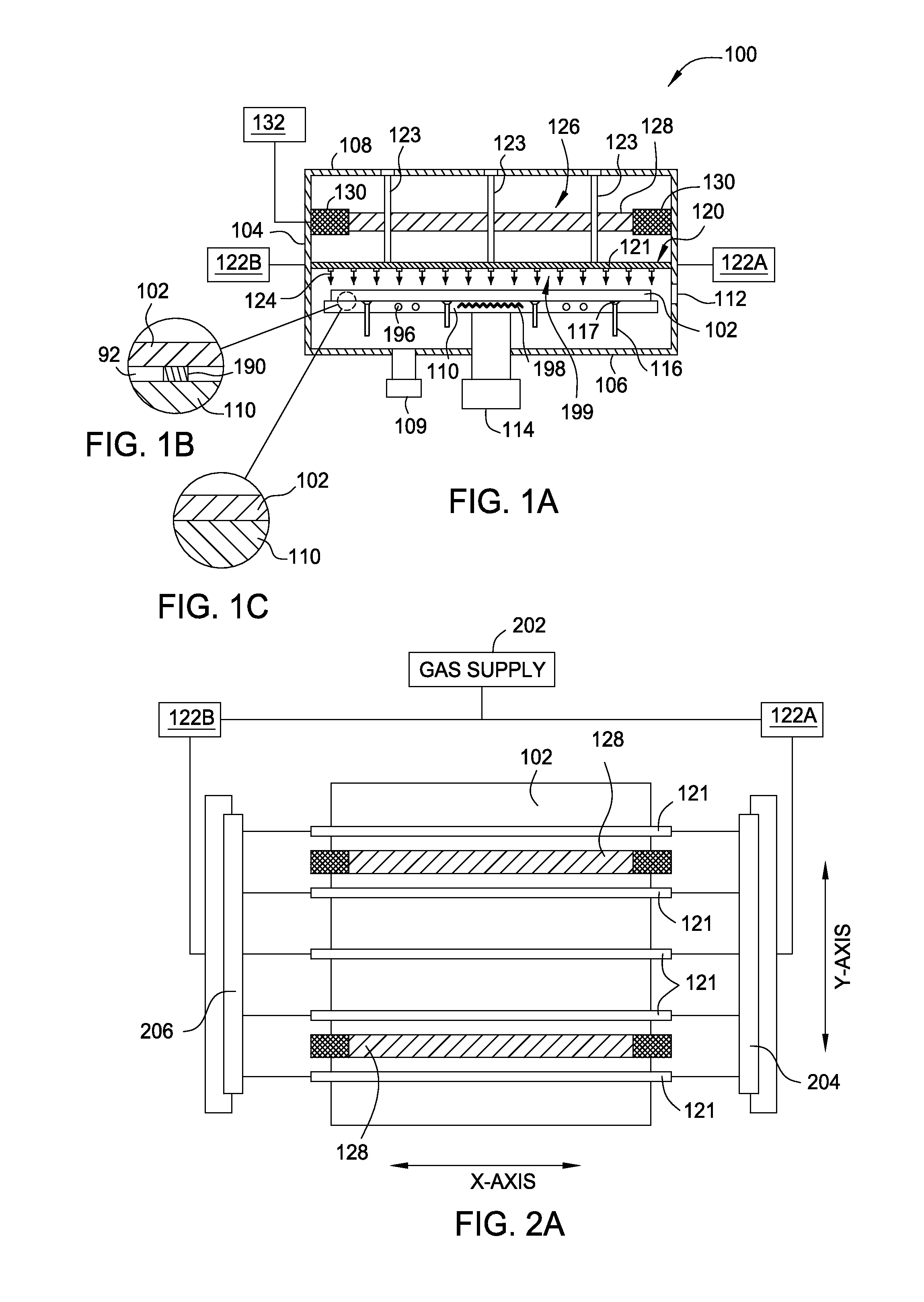
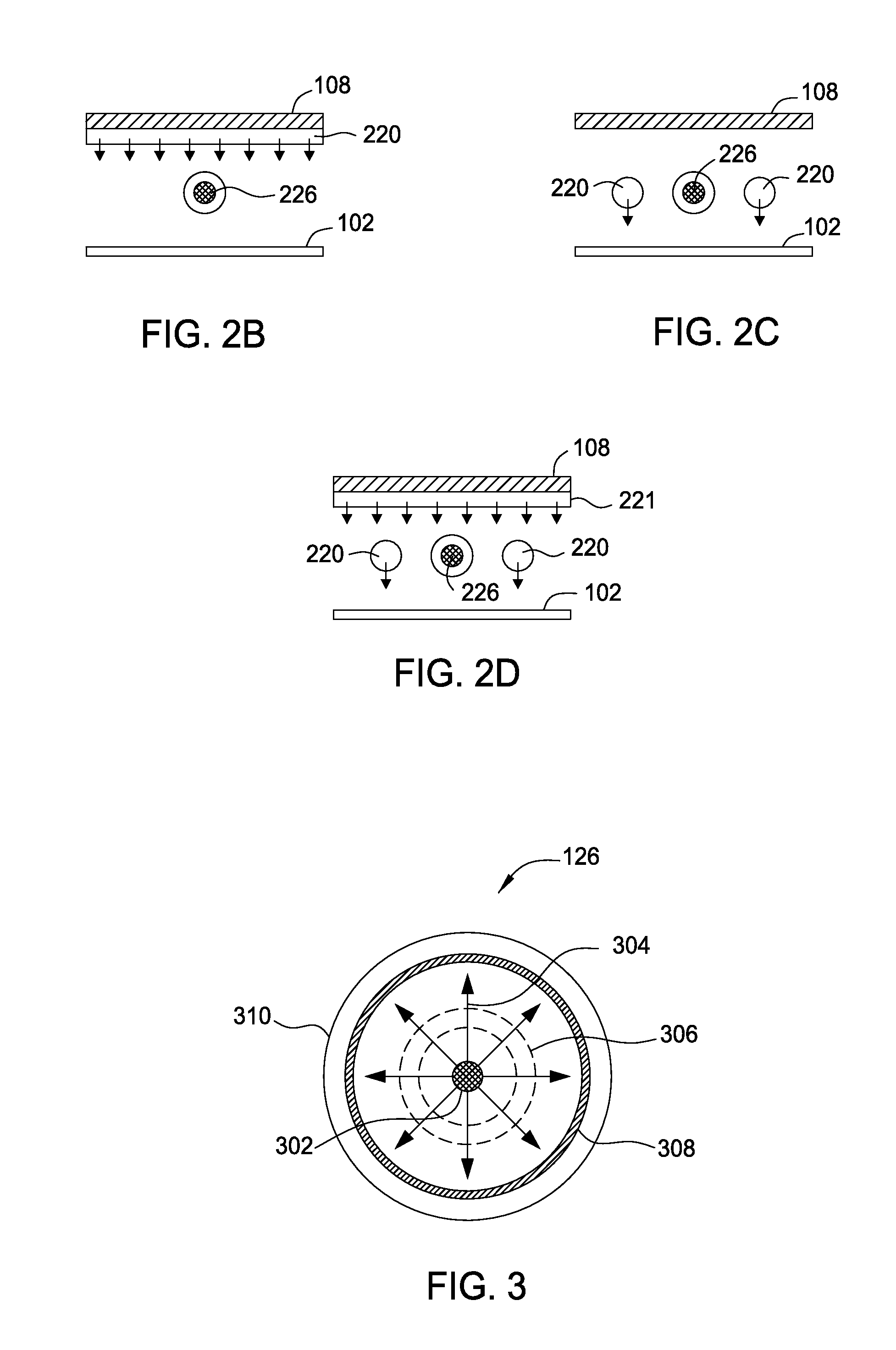
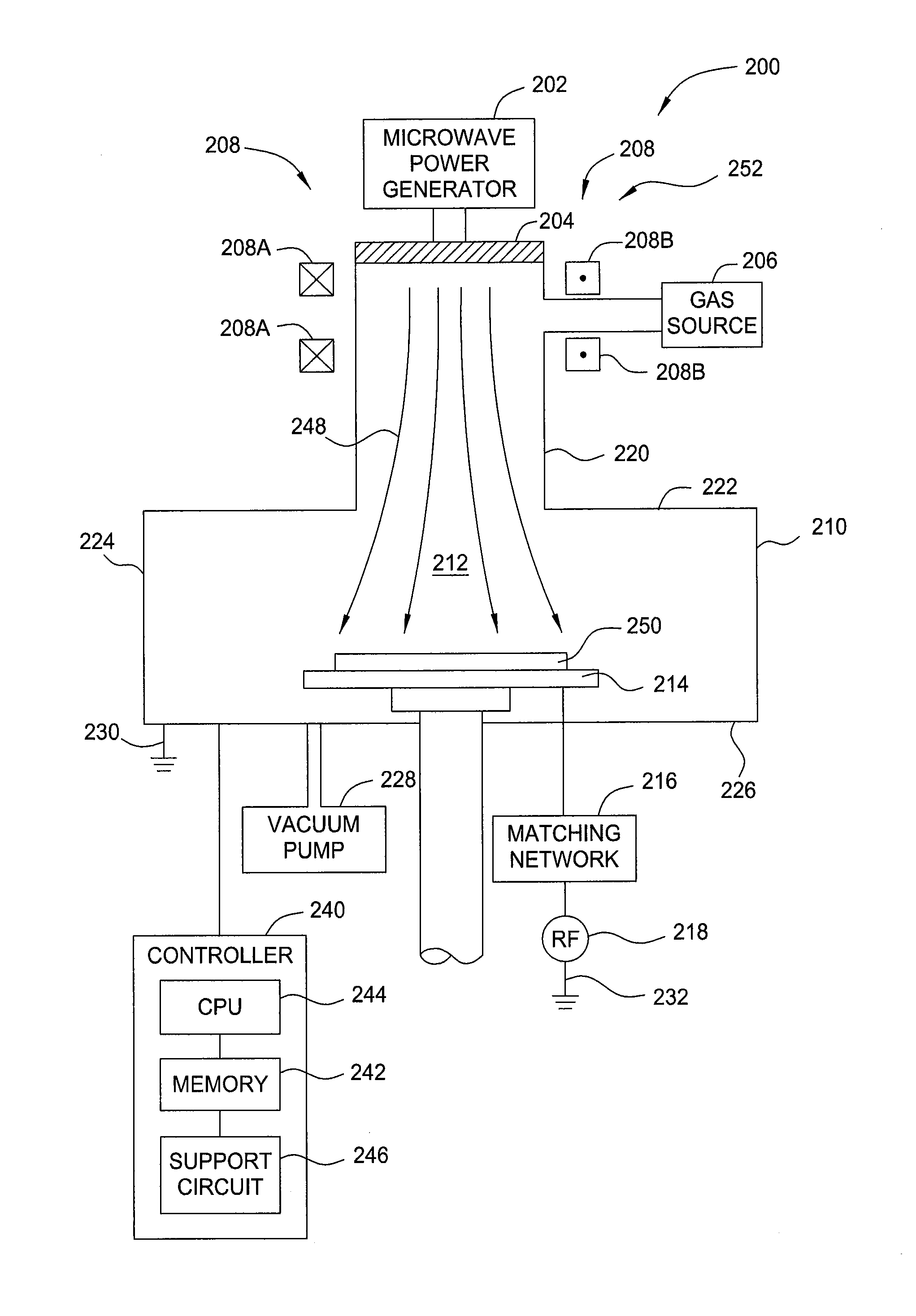
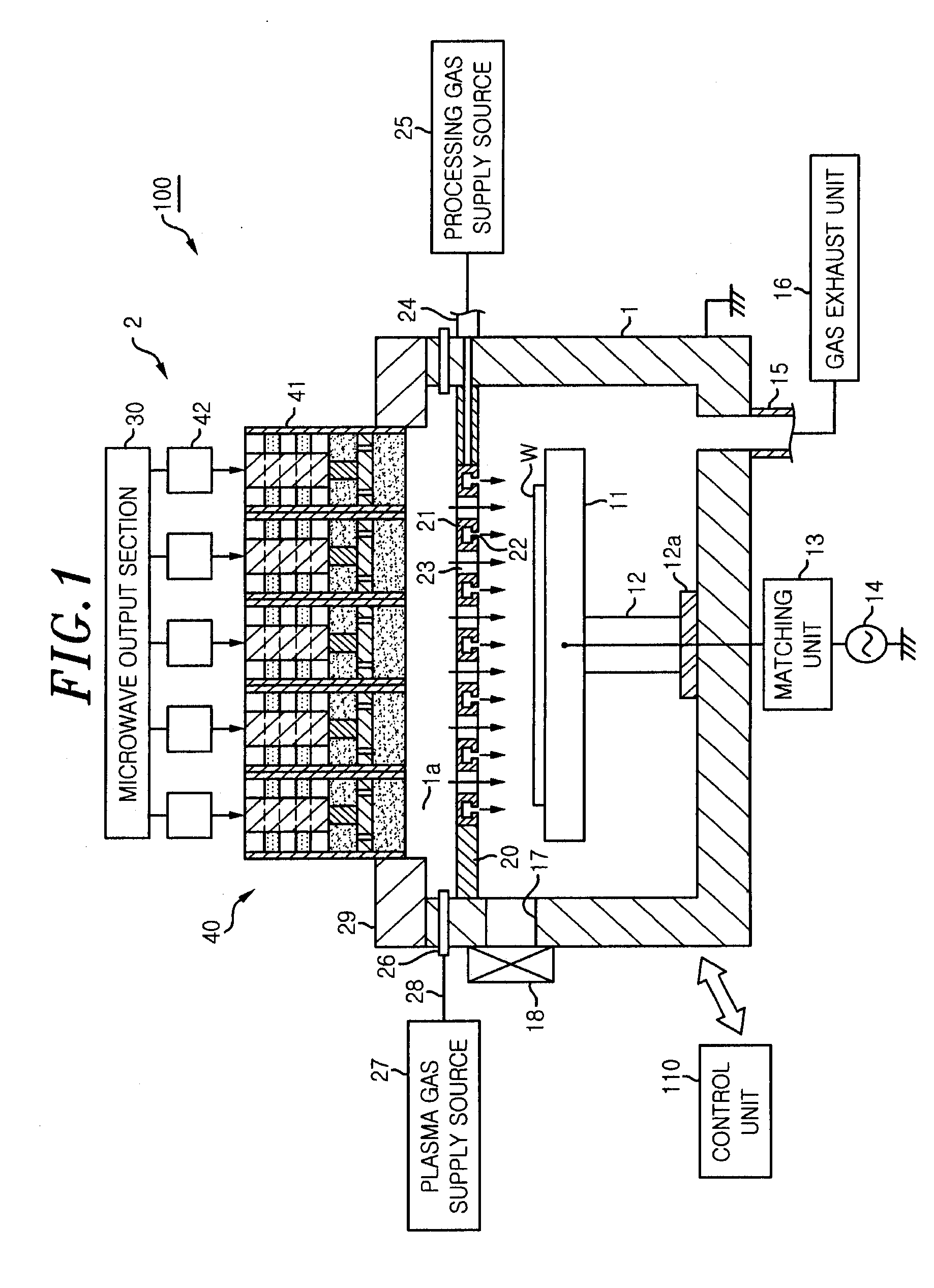
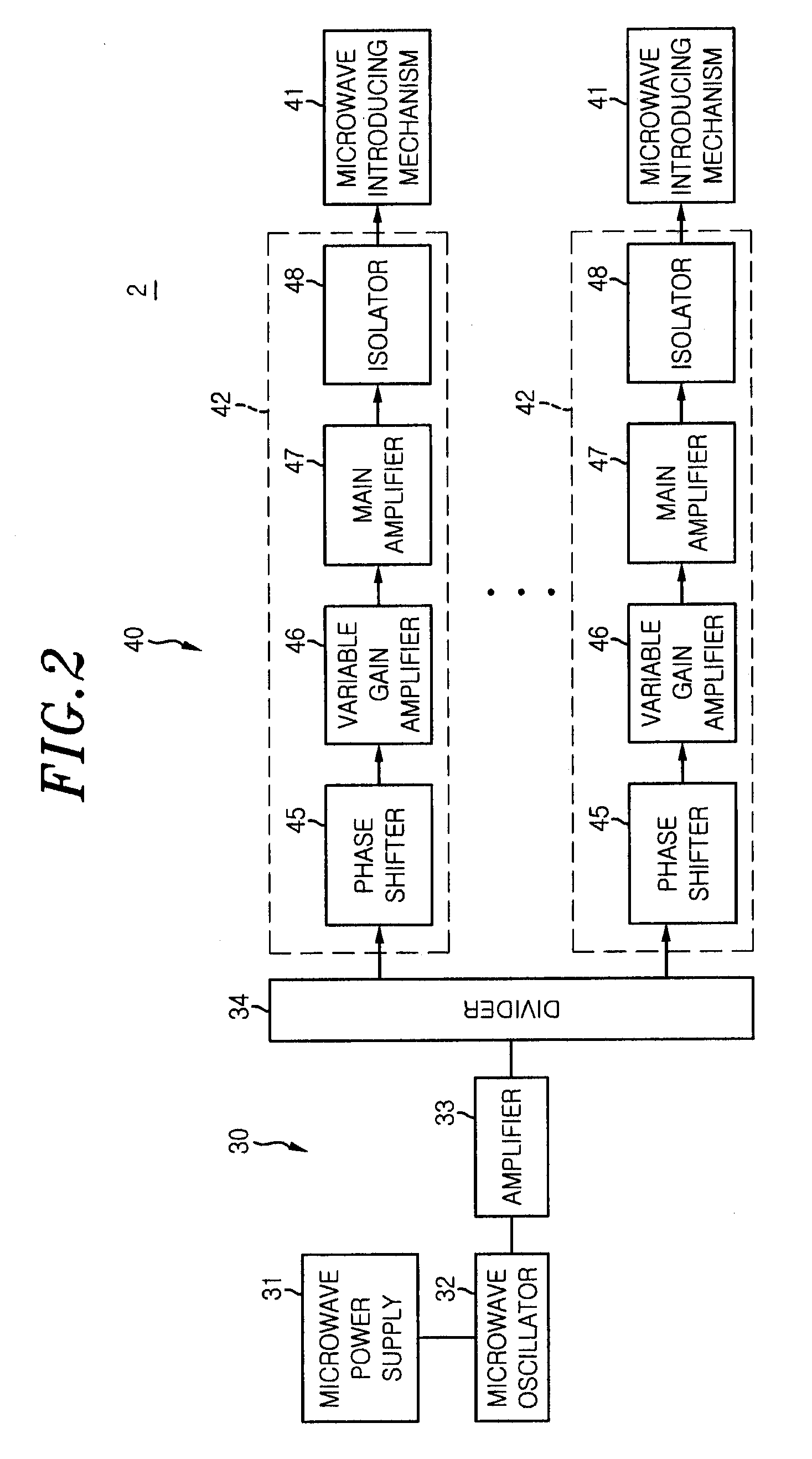
Embodiments of the present invention generally provide deposition processes for a silicon-containing dielectric layer using an improved microwave-assisted CVD chamber. In one embodiment, a method of processing a substrate in a processing chamber is provided. The method generally includes applying a microwave power to an antenna coupled to a microwave source disposed within the processing chamber, wherein the microwave source is disposed relatively above a gas feeding source configured to provide a gas distribution coverage covering substantially an entire surface of the substrate, and exposing the substrate to a microwave plasma generated from a processing gas provided by the gas feeding source to deposit a silicon-containing layer on the substrate at a temperature lower than about 200 degrees Celsius, the microwave plasma using a microwave power of about 500 milliWatts / cm2 to about 5,000 milliWatts / cm2 at a frequency of about 1 GHz to about 10 GHz.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Methods and apparatus for controlling photoresist line width roughness
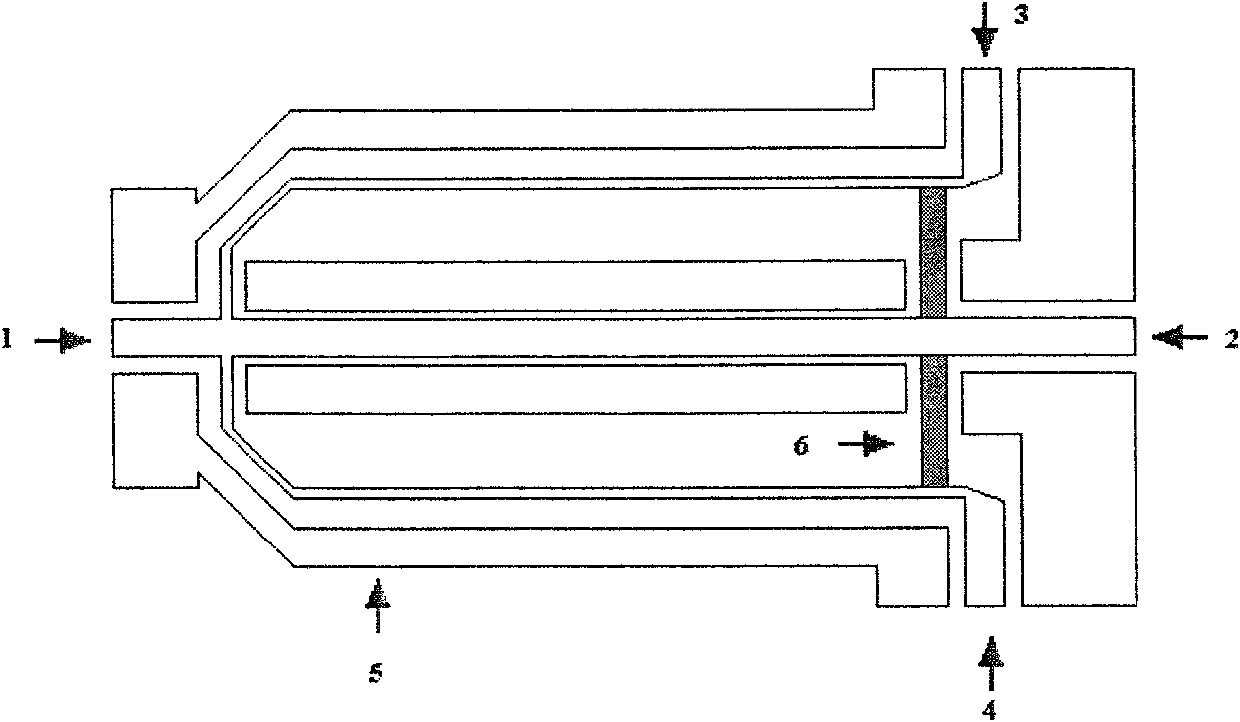
The present invention provides methods and an apparatus for controlling and modifying line width roughness (LWR) of a photoresist layer. In one embodiment, an apparatus for controlling a line width roughness of a photoresist layer disposed on a substrate includes a chamber body having a top wall, side wall and a bottom wall defining an interior processing region, a microwave power generator coupled to the to the chamber body through a waveguild, and one or more coils or magnets disposed around an outer circumference of the chamber body adjacent to the waveguide, and a gas source coupled to the waveguide through a gas delivery passageway.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Siox process chemistry development using microwave plasma CVD
InactiveUS20130302999A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSilica hydridePhysical chemistry
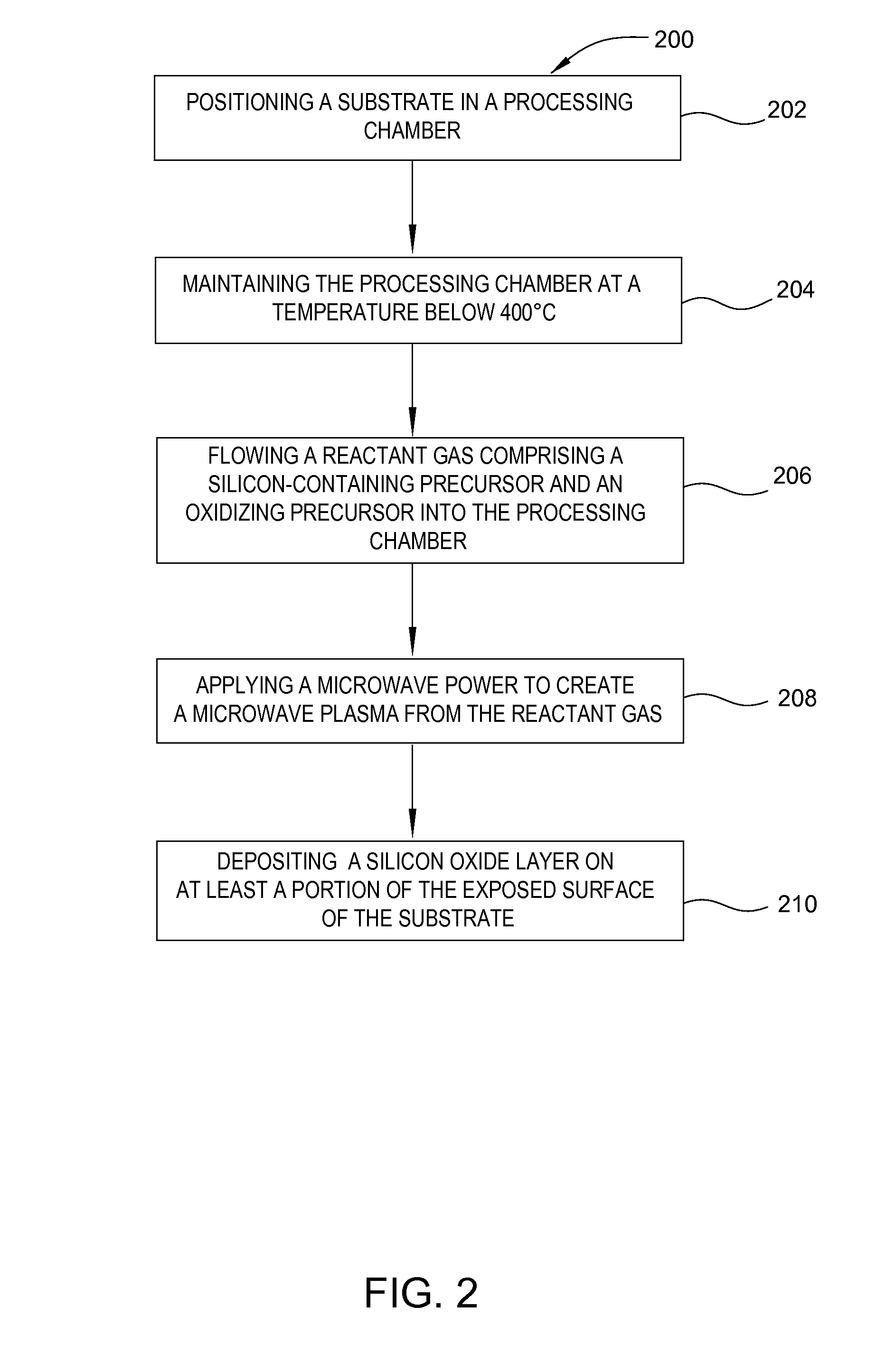
Methods for processing a substrate are described herein. Methods can include positioning a substrate in a processing chamber, maintaining the processing chamber at a temperature below 400° C., flowing a reactant gas comprising either a silicon hydride or a silicon halide and an oxidizing precursor into the process chamber, applying a microwave power to create a microwave plasma from the reactant gas, and depositing a silicon oxide layer on at least a portion of the exposed surface of a substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Electromagnetic-radiation power-supply mechanism and microwave introduction mechanism
ActiveUS20120299671A1Efficient supplyShortening an effective wavelength of an electromagnetic waveElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorCoaxial waveguides
An electromagnetic-radiation power-supply mechanism includes a microwave power introduction port provided on the side of the coaxial waveguide, a power line being connected to the microwave power introduction port; and a power supply antenna for radiating the electromagnetic wave power into the waveguide, the power supply antenna being connected to the power line. The power supply antenna includes an antenna body having a first pole connected to the power line and a second pole connected to an inner conductor of the waveguide; and a ring-shaped reflection portion extending from opposite sides of the antenna body.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Electromagnetic-radiation power-supply mechanism for exciting a coaxial waveguide by using first and second poles and a ring-shaped reflection portion
ActiveUS9072158B2Efficient supplyShortening an effective wavelength of an electromagnetic waveElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorCoaxial waveguides
An electromagnetic-radiation power-supply mechanism includes a microwave power introduction port provided on the side of the coaxial waveguide, a power line being connected to the microwave power introduction port; and a power supply antenna for radiating the electromagnetic wave power into the waveguide, the power supply antenna being connected to the power line. The power supply antenna includes an antenna body having a first pole connected to the power line and a second pole connected to an inner conductor of the waveguide; and a ring-shaped reflection portion extending from opposite sides of the antenna body.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Controlling etch rate drift and particles during plasma processing
The invention is an plasma processing system with a plasma chamber for processing semiconductor substrates, comprising: a radio frequency or microwave power generator coupled to the plasma chamber; a low pressure vacuum system coupled to the plasma chamber; and at least one chamber surface that is configured to be exposed to a plasma, the chamber surface comprising: a YxOyFz layer that comprises Y in a range from 20 to 40%, O in a range from ≦60%, and F in a range of ≦75%. Alternatively, the YxOyFz layer can comprise Y in a range from 25 to 40%, O in a range from 40 to 55%, and F in a range of 5 to 35% or Y in a range from 25 to 40%, O in a range from 5 to 40%, and F in a range of 20 to 70%.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Air-core microwave ablation antennas
ActiveUS20060276780A1Increase powerIncrease the diameterElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingElectrical conductorCoaxial cable
A method and device delivers microwave power to an antenna through a coaxial cable utilizing air or other gases as its dielectric core. The cable includes supports made of low-loss materials to keep the inner conductor centered in the cable, and defining spaces therebetween for the air or gas. Channels in the supports allow the air or gas to circulate in the cable. The gas may be chilled or cooled to provide an addition level of heat dissipation. The device enables delivery of large amounts of power to tissue without undue heating of the feed cable or peripheral tissues, and without increasing the diameter of the feeding cable or antenna, keeping the antenna safe for percutaneous use.
Owner:NEUWAVE MEDICAL
Microwave energized plasma lamp with dielectric waveguide
InactiveUS20050212456A1Electric light circuit arrangementDischarge tube/lamp detailsElectric forceDielectric
A plasma lamp including a waveguide body comprising at least one dielectric material. The body is coupled to a microwave power source which causes the body to resonate in at least one resonant mode. A lamp chamber integrated with the body contains a bulb with a fill forming a light-emitting plasma when the chamber receives power from the resonating body. A bulb either is self-enclosed or an envelope sealed by a window or lens covering the chamber aperture. Embodiments disclosed include lamps having a drive probe and a feedback probe, and lamps having a drive probe, feedback probe and start probe, which minimize power reflected from the body back to the source.
Owner:LUXIM CORP
Device for hybrid plasma processing
InactiveUS6899054B1Add deviceElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas passingPerpendicular magnetic field
A device for hybrid plasma processing, particularly for deposition of thin films and for plasma treatment of samples, in a plasma reactor with pumping system characterized in that at least one feeder of microwave power (2) is installed in the plasma reactor (1) and connected to a microwave generator (3) for generation of a microwave plasma (4) in contact with at least one hollow cathode (5) in the plasma reactor, where the hollow cathode is powered from a cathode power generator (6). At least one inlet for a processing gas (7) is installed behind the hollow cathode and the gas is admitted into the plasma reactor through the hollow cathode where a hollow cathode plasma (9) is generated. A magnetic element (10) is used for generation of a perpendicular magnetic field (11) and / or a longitudinal magnetic field (12) at an outlet (13) from the hollow cathode.
Owner:BARDOS LADISLAV +1
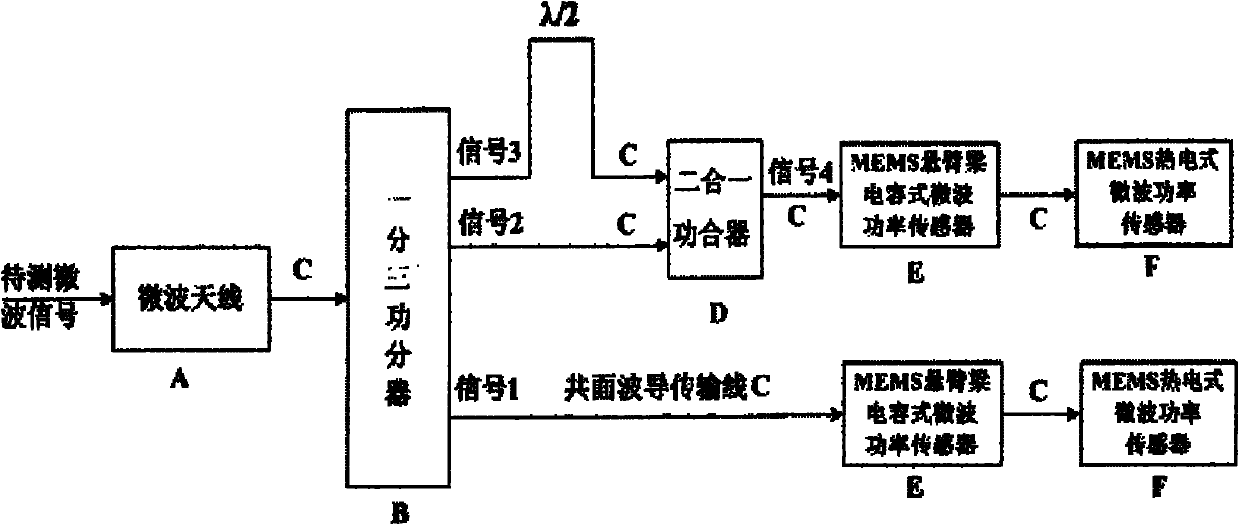
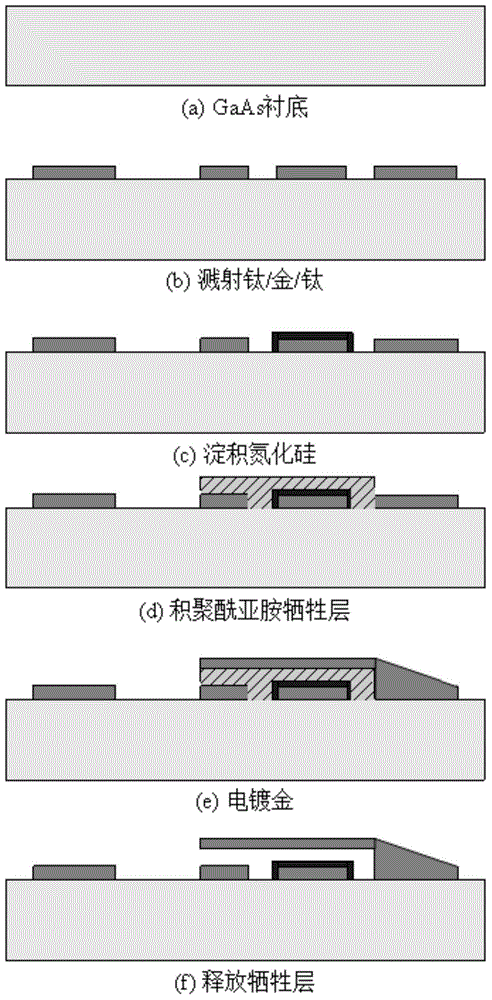
Wireless-receiving system for detecting microelectronic mechanical microwave frequency and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101788605ARealize wireless receptionTo achieve the purpose of wireless detectionTelevision system detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPower combinerPhase difference
The invention relates to a wireless-receiving system for detecting microelectronic mechanical microwave frequency and a preparation method thereof. The wireless-receiving system for detecting the microelectronic mechanical microwave frequency has quite simple structure, large measurement magnitude range, no direct-current power consumption and easy integration. In the system for detecting the microelectronic mechanical microwave frequency, gallium arsenide is used as a substrate, wherein a microwave antenna (A), a one-three power splitter (B), a coplanar waveguide transmission line (C), a two-in-one power combiner (D), an MEMS cantilever capacitive microwave power sensor (E) and an MEMS thermoelectric microwave power sensor (F) are designed on the substrate; and then a phase difference between a signal 3 and a signal 2 after the signal 3 passes through the coplanar waveguide transmission line with the length of lambda / 2 can be determined according to a law of cosines. Because the phase difference corresponds to the frequency of the signal, the frequency of the signal can be measured.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Plasma Deposition of Amorphous Semiconductors at Microwave Frequencies
InactiveUS20120040492A1Prevent and slow relaxationPrevent and slow and decayElectric discharge tubesFinal product manufacturePorosityPlasma deposition
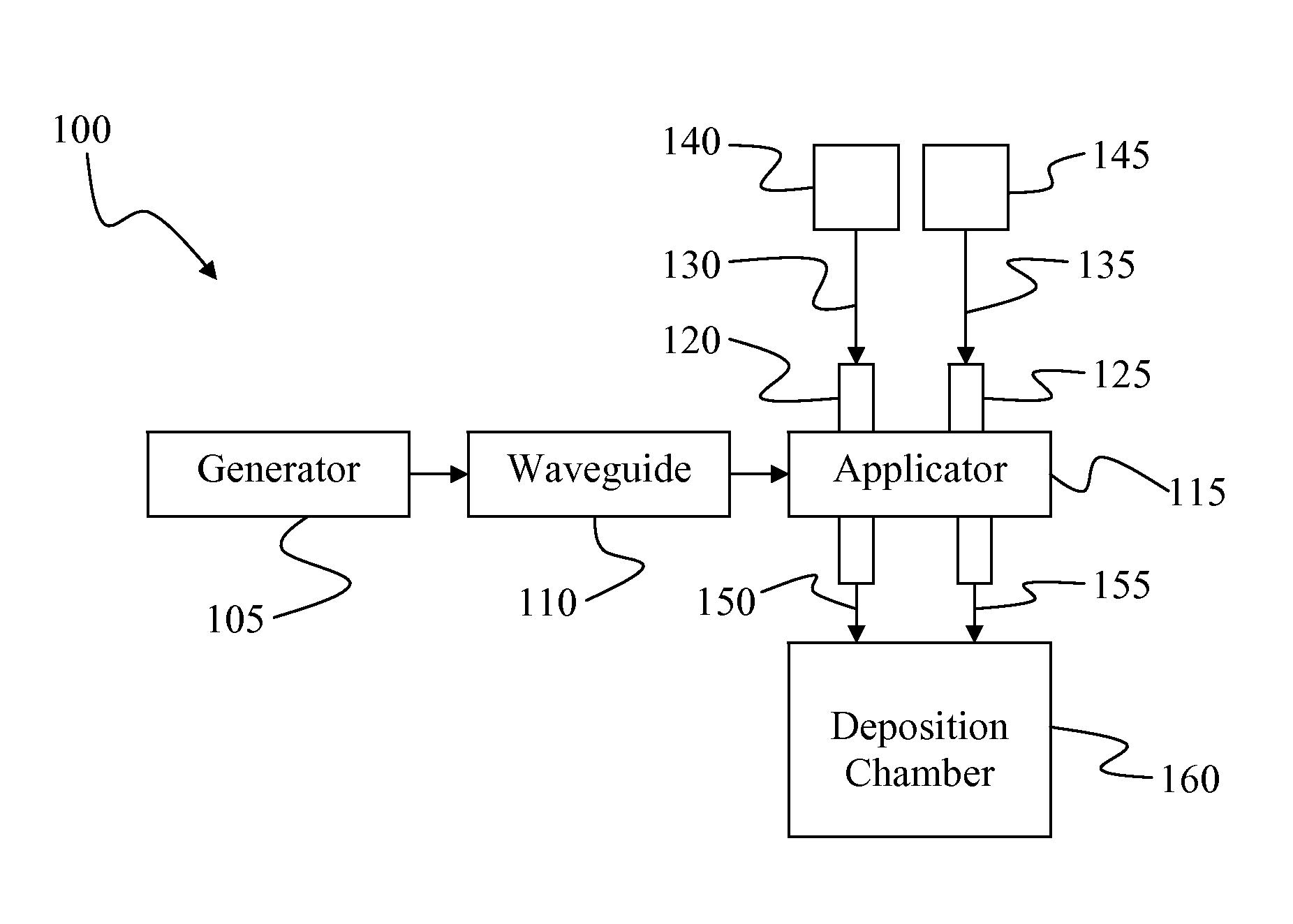
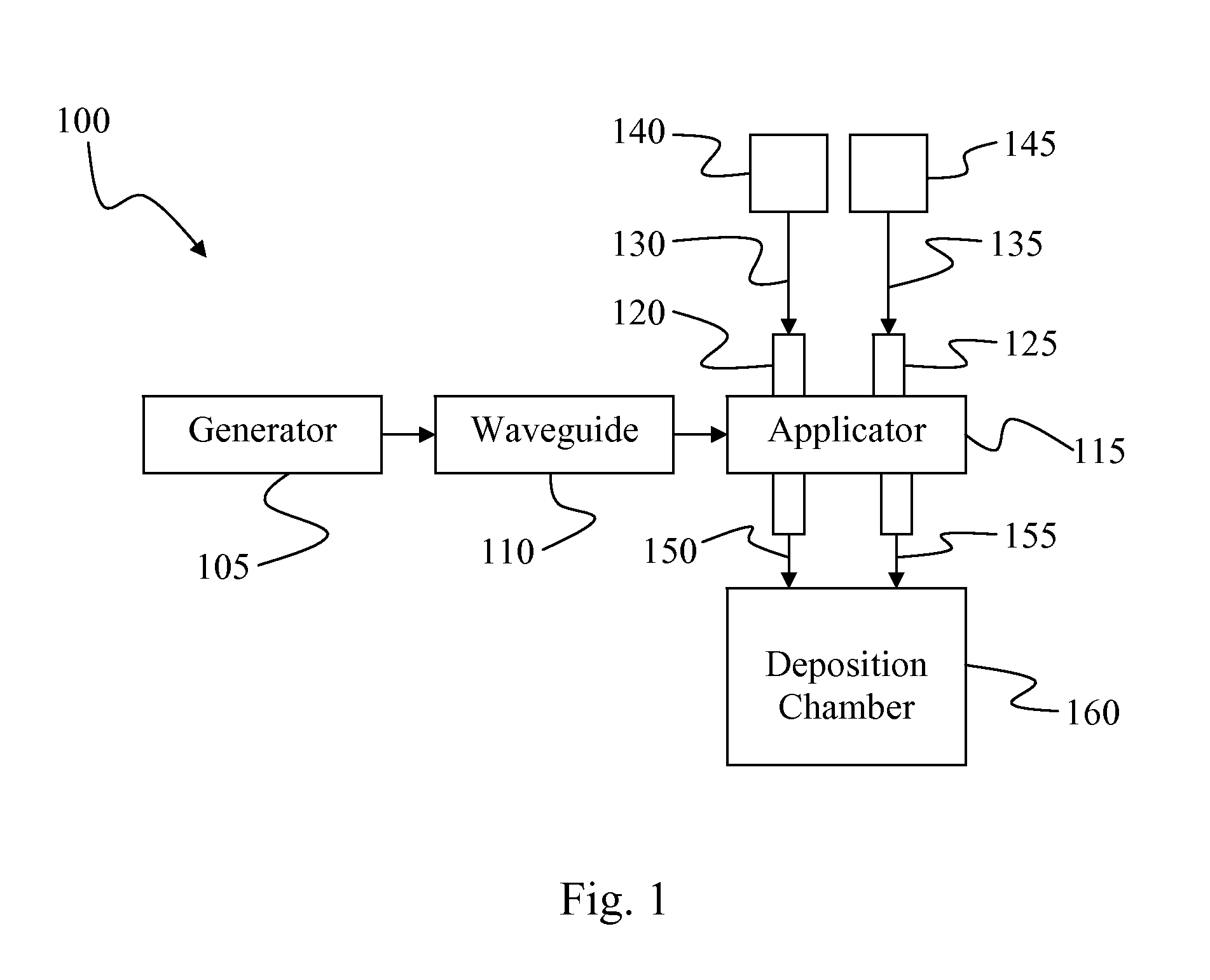
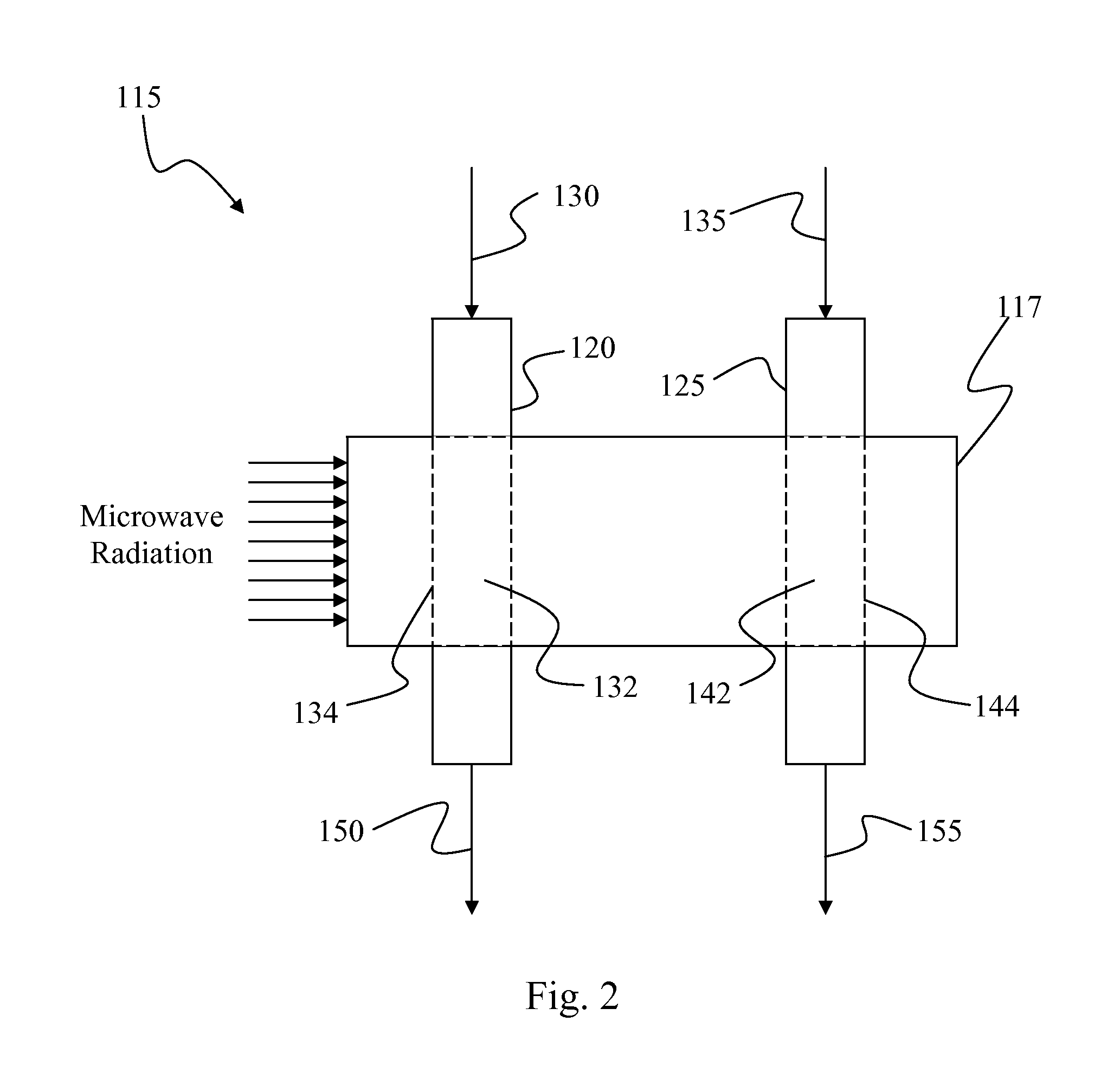
Apparatus and method for plasma deposition of thin film photovoltaic materials at microwave frequencies. The apparatus avoids unintended deposition on windows or other microwave transmission elements that couple microwave energy to deposition species. The apparatus includes a microwave applicator with conduits passing therethrough that carry deposition species. The applicator transfers microwave energy to the deposition species to activate or energize them to a reactive state conducive to formation of a thin film material. The conduits physically isolate deposition species that would react or otherwise combine to form a thin film material at the point of microwave power transfer. The deposition species are separately energized and swept away from the point of power transfer to prevent thin film deposition. Suitable deposition species include precursors that contain silicon, germanium, fluorine, and / or hydrogen. The invention allows for the ultrafast formation of silicon-containing amorphous semiconductors that exhibit high mobility, low porosity, little or no Staebler-Wronski degradation, and low defect concentration.
Owner:OVSHINSKY TECH
Multiple medical accelerators and a kV-CT incorporated radiation therapy device and semi-automated custom reshapeable blocks for all field synchronous image guided 3-D-conformal-intensity modulated radiation therapy
S-band, C-band or X-band microwave powered linear accelerators capable of delivering therapeutic photon and electron beams are mounted to a gantry with extensions to hold multiple accelerators and are combined with a kV CT for 3-D conformal—IMRT and IGRT to treat a patient by SSD or SAD methods and in a full circle. The invention's tertiary collimator system consists of semi-automated reusable custom field shaping with tungsten powder or melted Cerrobend blocks. The beam's intensity modulation is by means of simultaneous but independently operating multiple accelerators. This system's multiple accelerators enable to avoid interrupted subfractionated radiation therapy to each treatment fields. Hence its effective dose rate at the tumor site is high. The improved radiobiology reduces the total radiation dose to treat a tumor, reducing the incidence of developing second primary tumors is also minimized.
Owner:SAHADEVAN VELAYUDHAN
Microwave power sensor with multi-cantilever structure
InactiveCN103278681AError range is controllableSimple structurePower measurement by thermal methodsPower sensorCantilevered beam
The invention discloses a microwave power sensor with a multi-cantilever structure. The microwave power sensor comprises a substrate, and a micro-strip line, a cantilever anchoring region and a plurality of pressure welding blocks, which are arranged on the substrate, wherein the cantilever anchoring region and the pressure welding blocks are arranged on the two sides of the micro-strip line respectively; a plurality of cantilevers which are parallel to one another and hung in the air are arranged above the micro-strip line; the cantilevers and the micro-strip line are vertical and have different lengths; and one end of each cantilever is arranged on the cantilever anchoring region, and the other end of each cantilever are correspondingly hung above one pressure welding block. According to the microwave power sensor, the displacements of the cantilevers are caused by the attraction of the microwave power transmitted on the micro-strip line to the cantilevers of different lengths, and the measurement of the microwave power transmitted on the micro-strip line is realized by detecting the number of the cantilevers of different lengths, which are placed in parallel and contacted with the pressure welding blocks, so that the sensitivity of the power sensor can be improved, the structure can be simplified, digital output is realized, and the error range is controlled.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Online microwave frequency detector and detecting method thereof based on cantilever beam and direct-type power sensor
InactiveCN103048540ANovel structureEasy to measureFrequency to phase shift conversionPower sensorPower combiner
The invention discloses an online microwave frequency detector and a detecting method thereof based on a cantilever beam and a direct-type power sensor. The detector is prepared on a GaAs substrate and comprises coplanar waveguide (CPW) transmission lines, four micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) cantilever beam structures of the completely same structure, a power combiner and three MEMS direct-type microwave power sensors of the completely same structure. The micro-electronic mechanical online microwave frequency detector provided by the invention not only has the advantages of being novel in structure and smaller in size, but also can realize online detection on a microwave signal frequency, and can be compatible with a GaAs single wafer microwave integrated circuit.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
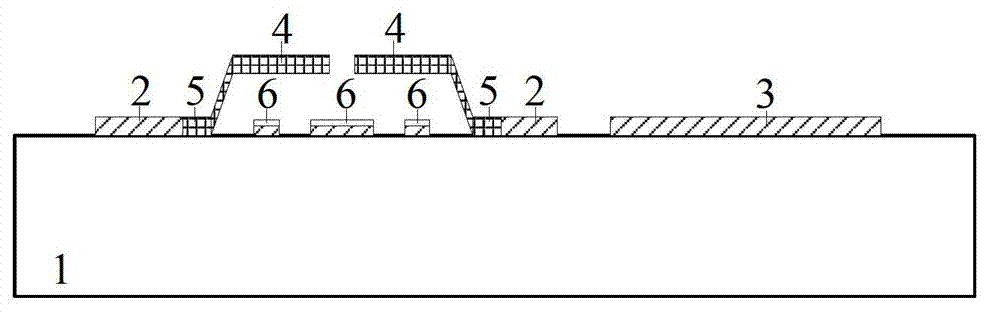
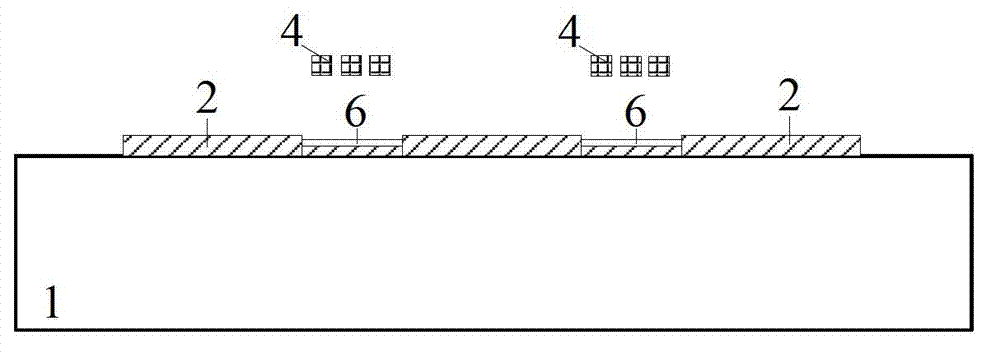
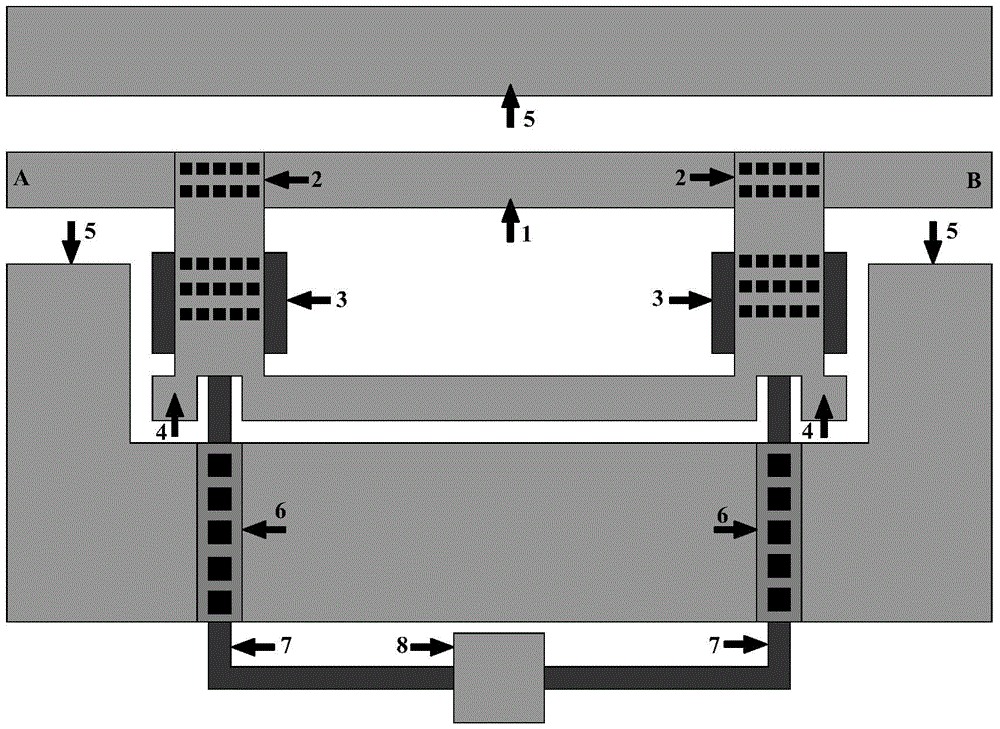
Microwave power detection system based on parallel-connected MEMS (micro-electromechanical system) cantilever beams and preparation method of microwave power detection system
ActiveCN104655921AHigh sensitivityGood compatibilityElectric devicesElectric power measurementCapacitanceMicrowave power
The invention discloses a microwave power detection system based on parallel-connected MEMS (micro-electromechanical system) cantilever beams and a preparation method of the microwave power detection system. The method is used for on-line measurement, electrostatic force can be generated between each MEMS cantilever beam and a transmission line in a center signal line transmission process, the cantilever beams are pulled downwards, and an interval between each cantilever beam and a corresponding test electrode becomes smaller, so that capacitance values are changed and microwave power in one-to-one correspondence with the capacitance values is obtained by measuring the changed capacitance values. The microwave power detection system based on the parallel-connected MEMS cantilever beams comprises a gallium arsenide substrate, wherein a plane-waveguide center signal line (A), a parallel-connected MEMS cantilever beam structure (B) and a capacitance type microwave power sensor (C) are arranged on the substrate. When a microwave signal is transmitted on the plane-waveguide center signal line, the two parallel-connected MEMS cantilever beams generate displacement under the action of the electrostatic force, and the to-be-measured power is detected by the capacitance type microwave power sensor.
Owner:南京尔芯电子有限公司
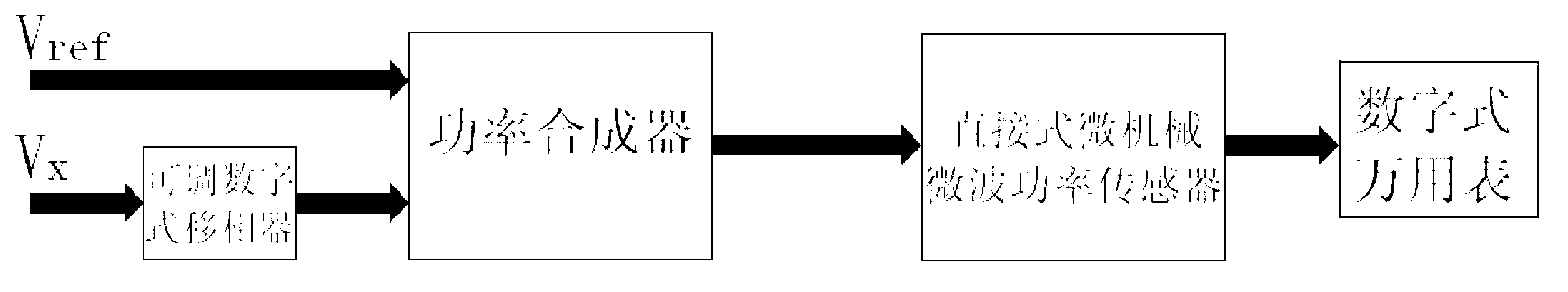
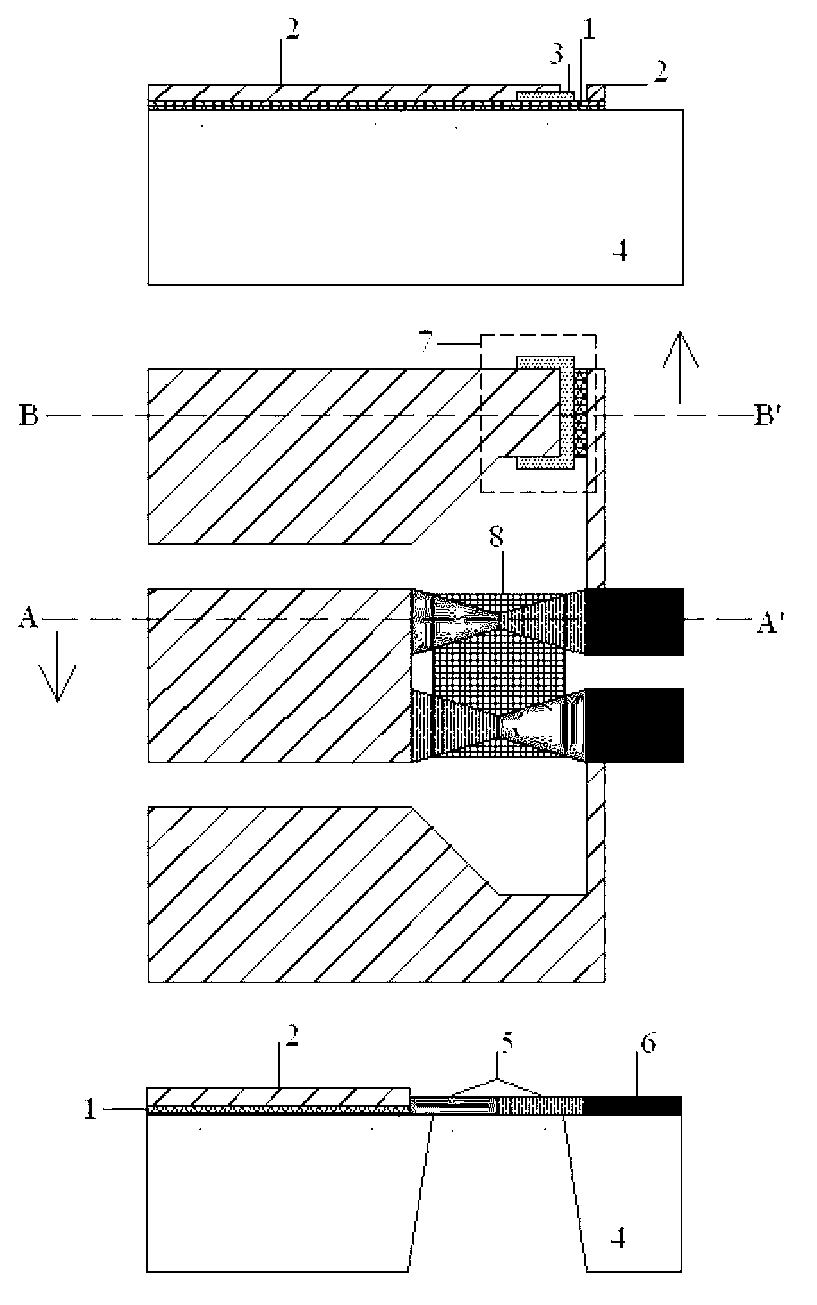
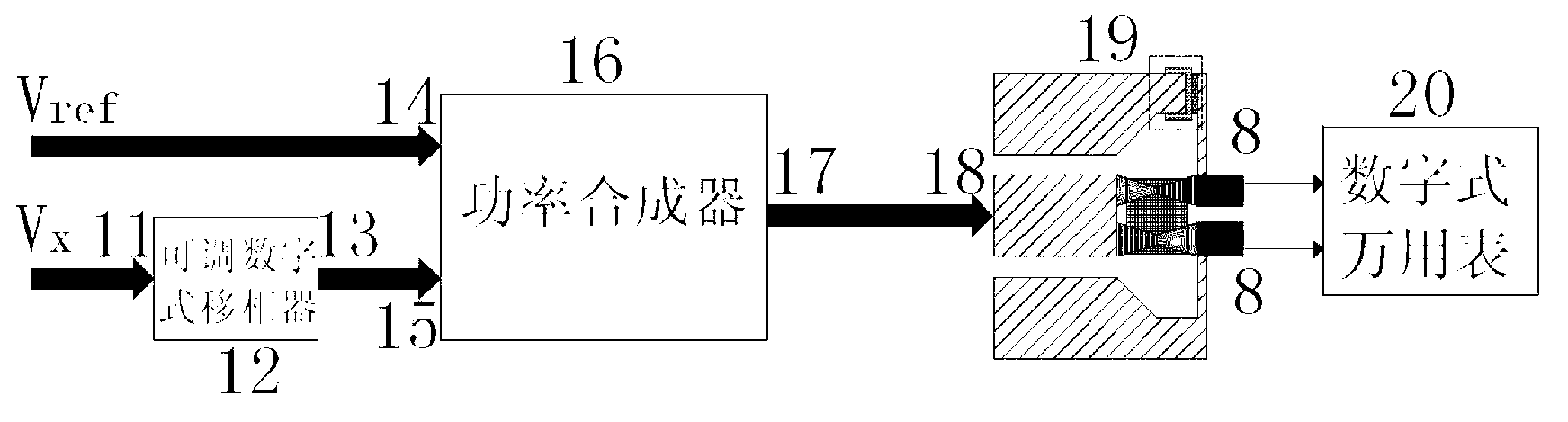
Device and method for phase detection based on indirect type micromechanical microwave power sensor
InactiveCN103018559AImprove linearityHigh bandwidthVoltage-current phase anglePower sensorPower combiner
The invention discloses a device and a method for phase detection based on a direct type micromechanical microwave power sensor. The device comprises an adjustable digital phase shifter (12), a power combiner (16), the direct type micromechanical microwave power sensor (19) and a digital multimeter (20), a reference microwave signal Vref is connected with a first input port (14) of the power combiner, a to-be-detected signal Vx is connected with an input port (11) of the adjustable digital phase shifter, an output port (13) of the adjustable digital phase shifter is connected with a second input port (15) of the power combiner, an output port (17) of the power combiner is connected with an input port (18) of the direct type micromechanical microwave power sensor, and back holes (8) on the direct type micromechanical microwave power sensor (19) are connected with the digital multimeter (20). The objective of accurate detection of microwave signal phase position is realized by utilizing the method of power after combining a measuring reference signal with the to-be-detected signal after phase shifting by the adjustable digital phase shifter.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Workpiece processing chamber having a thermal controlled microwave window
ActiveUS10269541B2Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNuclear engineeringMicrowave power
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Microwave heating using distributed semiconductor sources
Distributed high power solid state microwave sources are provided to improve the efficiency of microwave heating applications. A plurality of solid state microwave sources can be distributed throughout and / or adjacent to a microwave environment with the microwave power output of the solid state microwave sources being directed toward the chamber. The distribution of the plurality of solid state microwave devices can be customized to the specific size and shape of the microwave chamber and / or specific regions / compartments of the microwave chambers.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMAN CORP
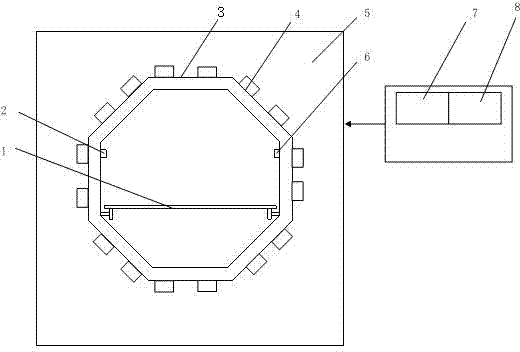
Method and device for curing fiber-reinforced resin-based composite material component by utilizing microwaves
ActiveCN103587130ASolve for uniformitySolve power problemsResin-Based CompositeFiber-reinforced composite
The invention relates to a method and a device for curing a fiber-reinforced resin-based composite material component by utilizing microwaves. The microwaves which are generated by a microwave source with linearly-adjustable power are guided into a resonant cavity, and the microwaves penetrate through and heat the composite material, so that the composite material can be quickly cured and formed. By adopting the advanced octagonal microwave-mode resonant cavity, the uniformity of an electromagnetic field inside the device can be realized; the interference of the reflection wave on the microwave source can be reduced by adopting an automatic impedance matching system, so that the optimal transmission of the microwave power can be realized. A vacuum pipe connector and a temperature sensor are arranged on the inner side wall of the octagonal multi-mode resonant cavity, a glass worktable is arranged inside the resonant cavity, and the rotation of a ball screw is controlled through a stepper motor to control the back-forth movement of the worktable. A choking groove is adopted to prevent the leakage of the microwave. By adopting the method and the device, the problems of the traditional autoclave forming method that the time for manufacturing the fiber-reinforced composite material is long, the energy consumption is high and the heat is non-uniform can be solved, the curing time can be saved, and the quality and performance of the composite material component can be improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
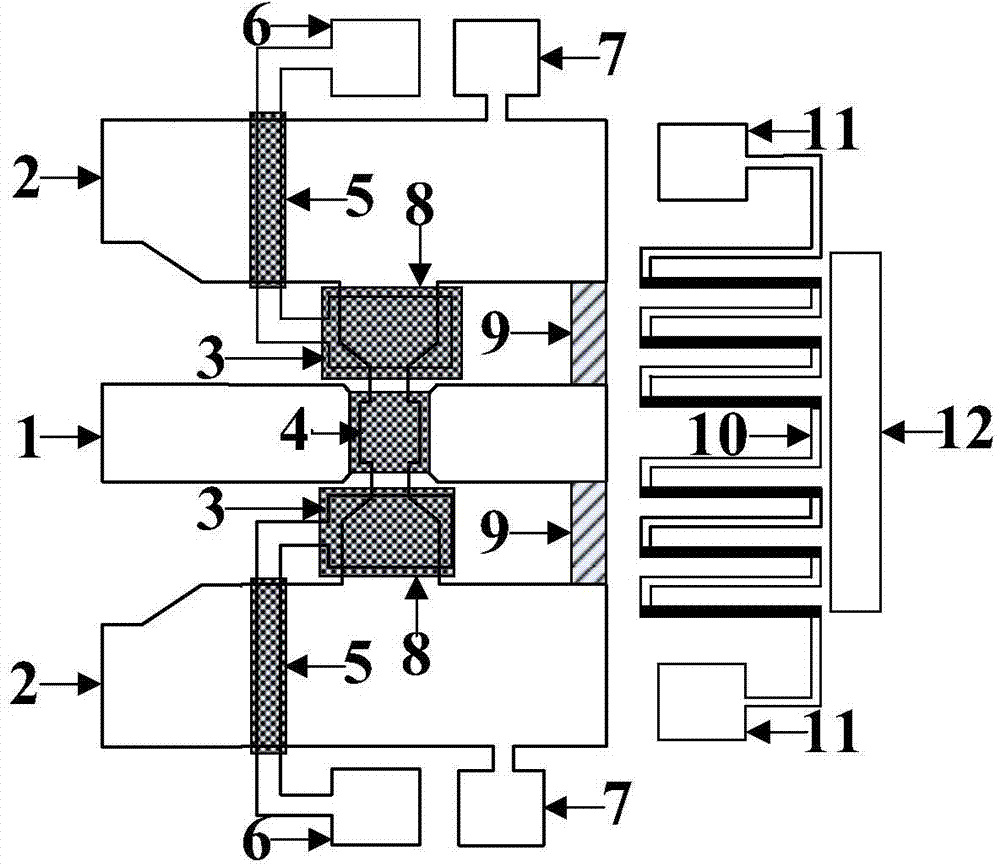
Microelectronic mechanical dual channel microwave power detection system and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103777066ALarge dynamic rangeProtection from being burnedTelevision system detailsImpedence networksPower sensorThermopile
The invention discloses a dual channel microwave power detection system based on a microelectronic mechanical microwave power sensor and a preparation method thereof. The system has the advantages of simple structure, large measurement range and no direct current power consumption. The system is based on a gallium arsenide substrate. A coplanar waveguide transmission line (A), a thermoelectric MEMS microwave power sensor (B) and an MEMS clamped beam capacitor type microwave power sensor (C) are designed on the substrate. When the power of a microwave signal is small, the thermoelectric MEMS microwave power sensor carries out detection according to the one-to-one corresponding relationship between the thermopile output voltage and the microwave power. When the power of the microwave signal is large, the MEMS clamped beam capacitor type microwave power sensor carries out detection. A square mass block is designed on an MEMS clamped beam above the coplanar waveguide transmission line. The area with the coplanar waveguide transmission line is increased, and at the same time the weight of the center position of the MEMS clamped beam is increased. Static power is more likely to cause large deformation of the MEMS clamped beam, and the system sensitivity is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
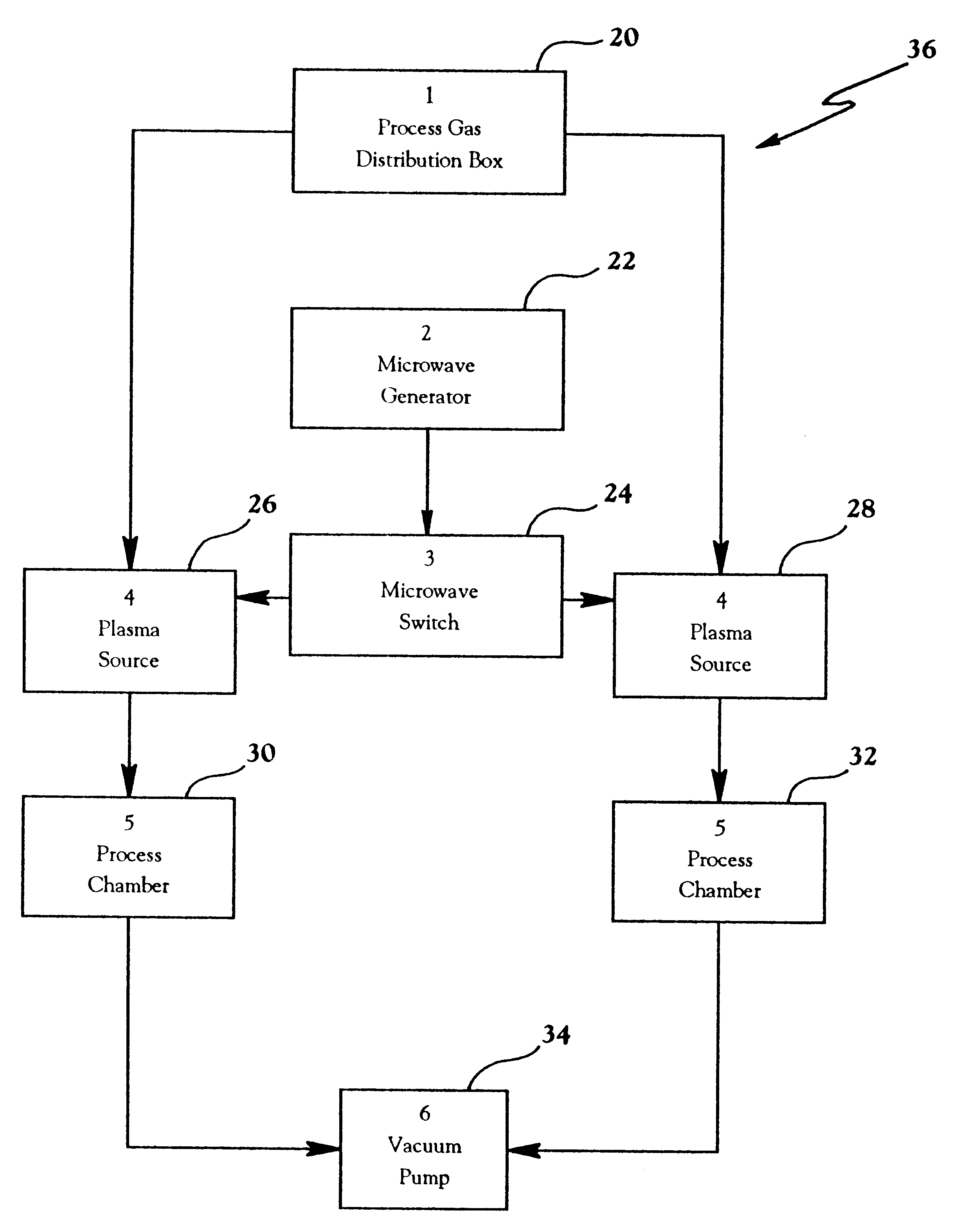
Synchronous multiplexed near zero overhead architecture for vacuum processes
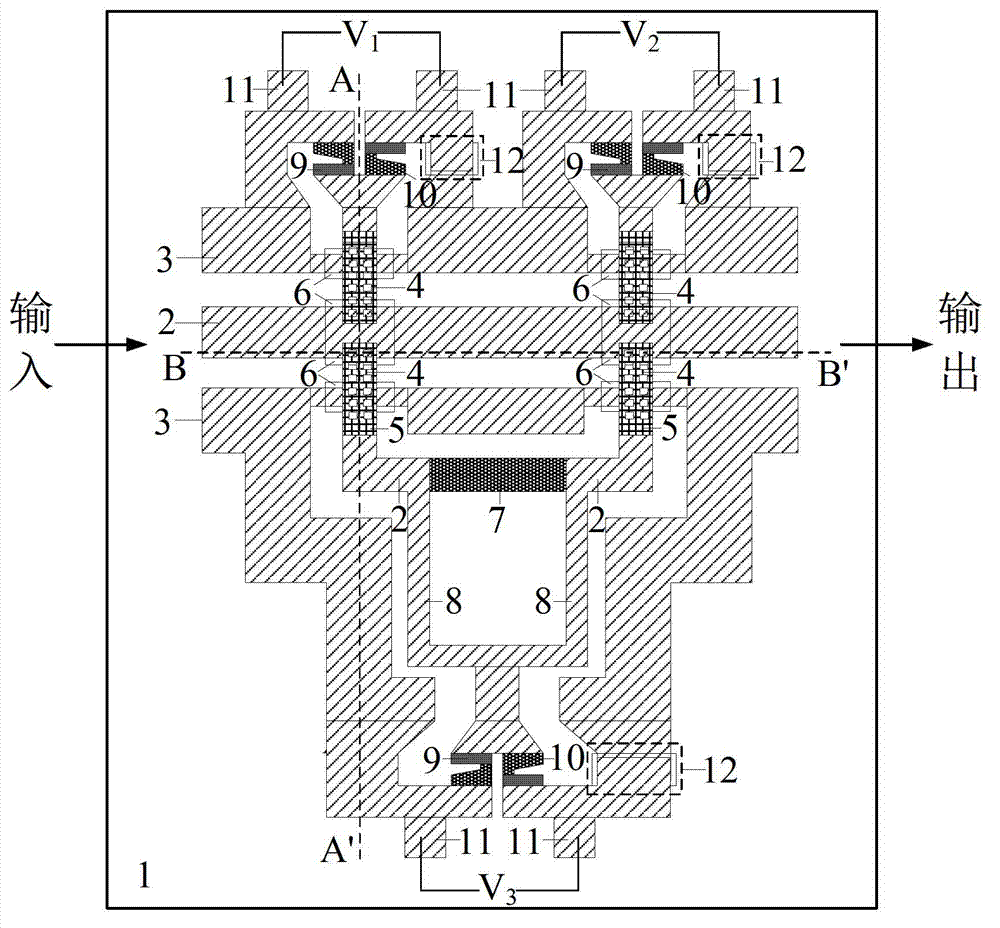
InactiveUS6228773B1Redundant partImprove throughputSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingAtmospheric airMicrowave power
Workpieces, such as, semiconductor wafers, are continuously manufactured by repetitively alternately switching a common radio frequency power source between a plurality of downstream or in-chamber processing reactors and actively processing one workpiece in a vacuum in an operating one of the processing chambers while simultaneously executing with a robot at atmospheric pressure the overhead tasks relative to next processing another workpiece in the other processing chamber. The active processing of the workpieces in alternate chambers does not overlap, and the robot starts and completes all of its preparatory tasks during the active processing step during the time when a chamber's door is closed thereby providing virtual zero overhead. System architecture allows eliminating all redundant components other than the dual chambers which operate in parallel. For a modest cost increase for the second chamber throughput is trebled and overall costs significantly reduced. Preferred modes include switching a common microwave power source between the pair of processing chambers, pumping down with a common vacuum pump, and stabilizing the chamber pressure with a common throttle valve.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Apparatus and method for microwave processing of materials
InactiveUS20070215612A1Uniform of microwave energyUniform power densityMicrowave heatingMicrowave cavityEngineering
A microwave heating apparatus is designed to improve distribution of the microwaves introduced into a multi-mode microwave cavity for heating or other selected applications. The microwave heating apparatus includes a microwave signal generator and a waveguide to convey microwave power to the cavity. A perforated metal plate disposed within the cavity encloses a volume adjacent to the waveguide opening, forming a leaky multimode subcavity. Through multiple processes of reflection, transmission, diffraction, and scattering, the leaky subcavity serves to smooth the microwave power distribution in the near-field region adjacent to the waveguide to better disperse the energy throughout the main applicator cavity. A more uniform level of microwave power is thereby applied to the workpiece.
Owner:HICKS KEITH R +4
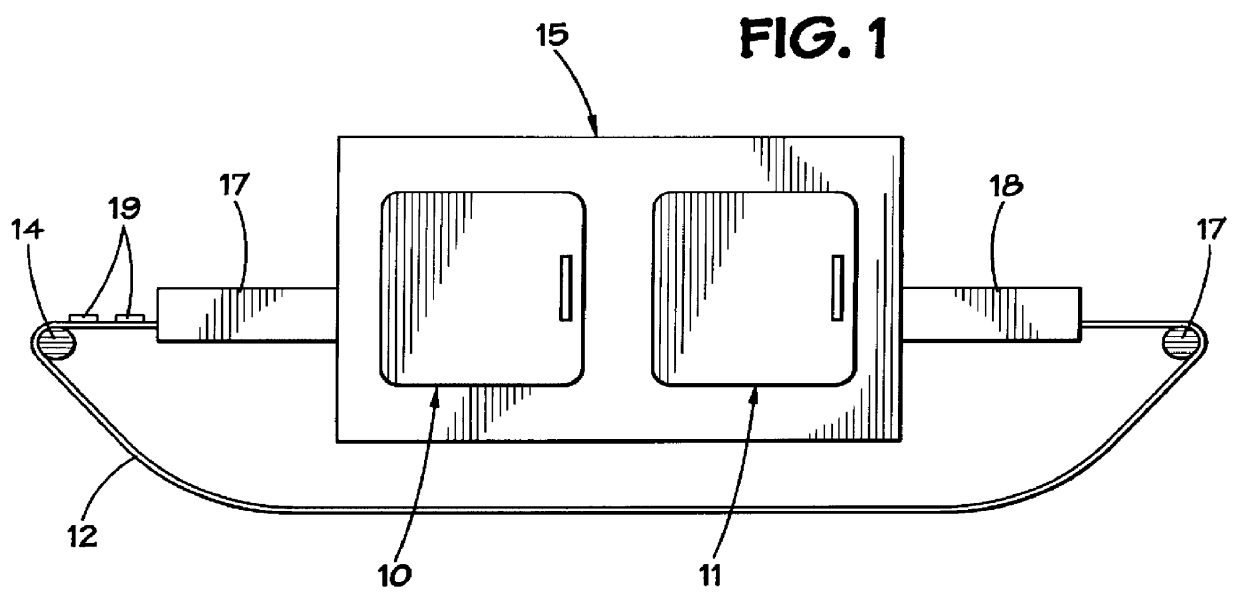
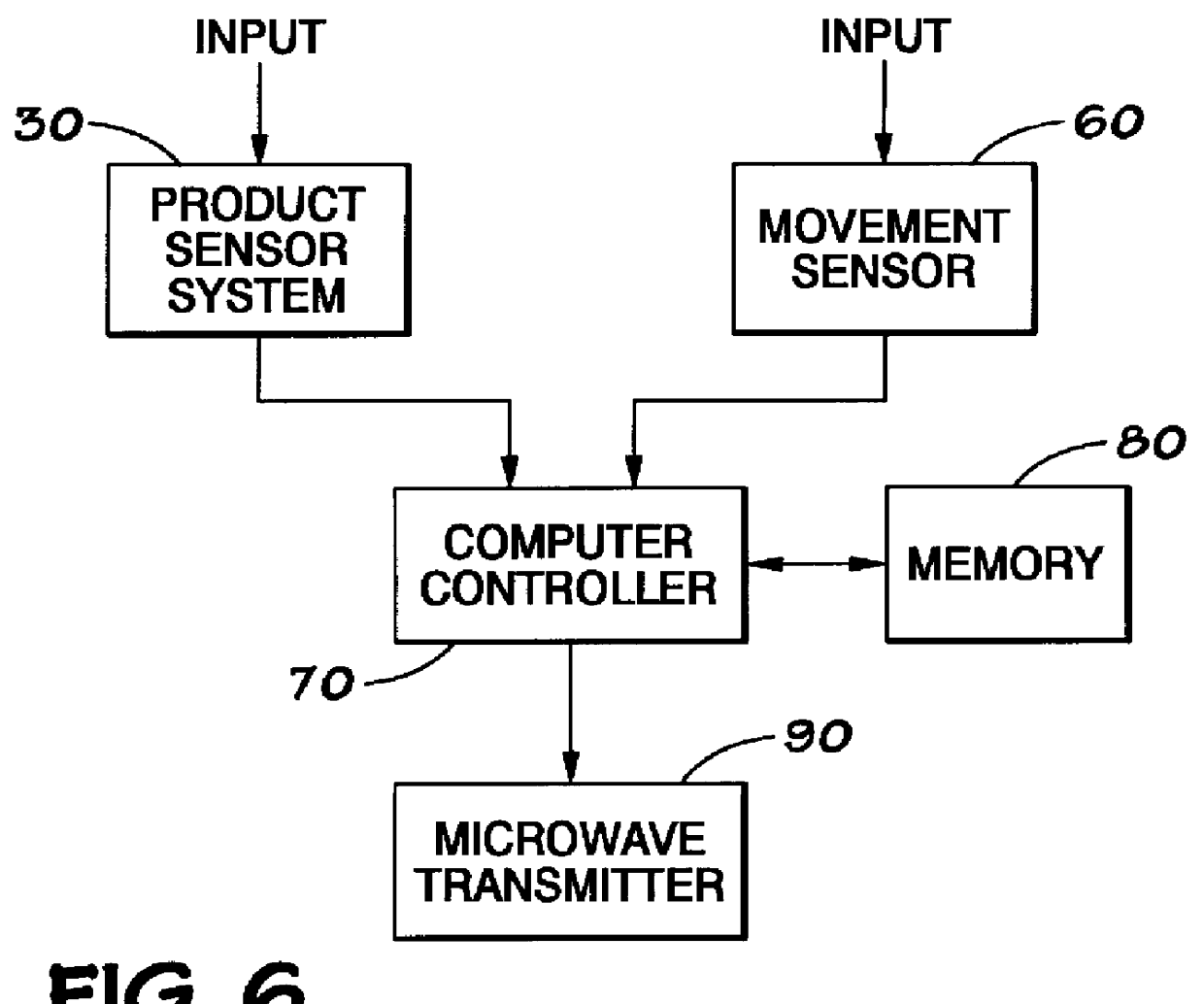
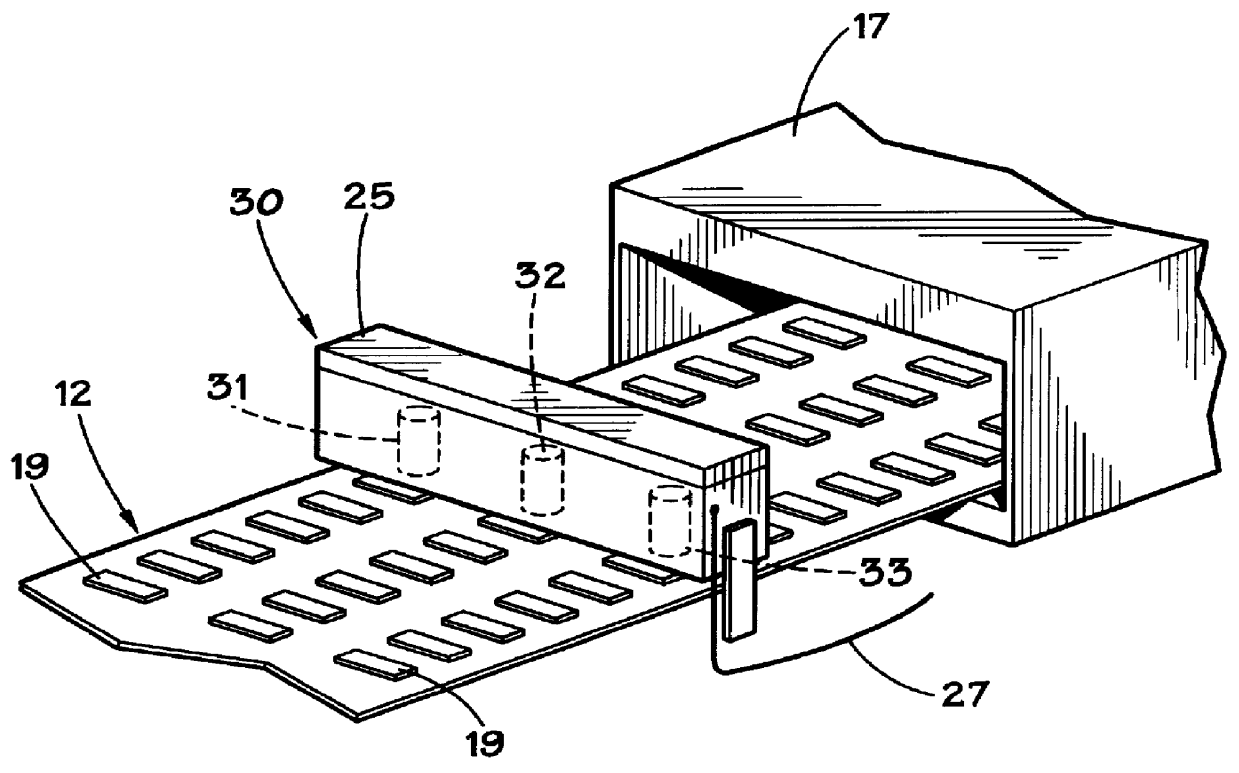
Product-based microwave power level controller
InactiveUS6157014AAdjust microwave powerAvoid powerMilk preservationDielectric heating circuitsMicrowave cavityProduct base
A microwave apparatus and system that monitors the amount of food products within a cavity and adjust the microwave power provided to the cavity. The apparatus and system uses a product sensor system and a movement sensor system to accurately determine the product load in the microwave cavity. A computer controller, based on the product load information provided by the product sensor system and the movement sensor system, operates to adjust the amount of power provide to the microwave cavities by the microwave transmitters.
Owner:AMANA +1
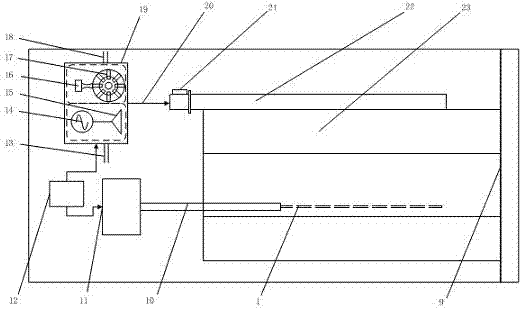
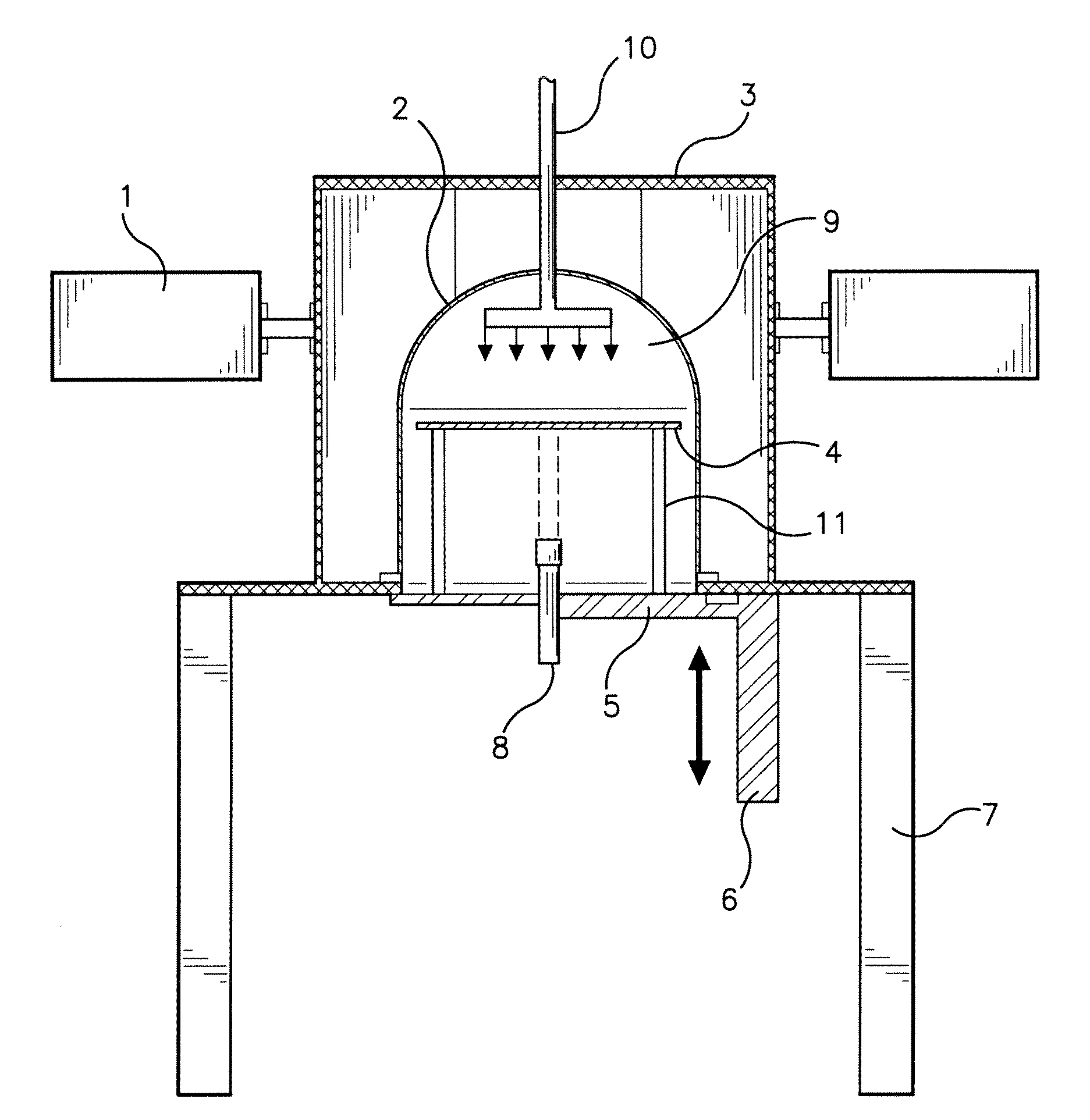
System for and method of microwave annealing semiconductor material
ActiveUS20090184399A1Inhibited DiffusionLong heating timeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicrowave heatingSusceptorSemiconductor materials
A system for and method of processing, i.e., annealing semiconductor materials. By controlling the time, frequency, variance of frequency, microwave power density, wafer boundary conditions, ambient conditions, and temperatures (including ramp rates), it is possible to repair localized damage lattices of the crystalline structure of a semiconductor material that may occur during the ion implantation of impurities into the material, electrically activate the implanted dopant, and substantially minimize further diffusion of the dopant into the silicon. The wafer boundary conditions may be controlled by utilizing susceptor plates (4) or a water chill plate (12). Ambient conditions may be controlled by gas injection (10) within the microwave chamber (3).
Owner:DSGI
Microwave energized plasma lamp with dielectric waveguide
InactiveUS20050099130A1Minimize powerElectric light circuit arrangementDischarge tube/lamp detailsDielectricStable state
A plasma lamp including a waveguide body consisting essentially of at least one solid dielectric material. The body is coupled to a microwave power source which causes the body to resonate in at least one resonant mode. A lamp chamber integrated into the body contains a fill mixture which forms a light-emitting plasma when the chamber receives microwave power from the resonating waveguide body. The chamber has an aperture sealed to the external environment by a window or lens allowing light to be transmitted. Alternatively, the fill is in a self-enclosed bulb positioned in the chamber. Embodiments disclosed include lamps having a drive probe and a feedback probe, and lamps having a drive probe, feedback probe and start probe, which minimize power reflected from the body back to the source both before the plasma is formed and after it reaches steady state.
Owner:LUXIM CORP
Apparatus and method for microwave processing of materials using field-perturbing tool
InactiveUS6222170B1Improve efficiencyReduce power densityMicrowave heatingChemical vapor deposition coatingMicrowave cavityEngineering
A variable frequency microwave heating apparatus designed to allow modulation of the frequency of the microwaves introduced into a multi-mode microwave cavity for heating or other selected applications. A field-perturbing tool is disposed within the cavity to perturb the microwave power distribution in order to apply a desired level of microwave power to the workpiece.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN ENERGY SYST INC
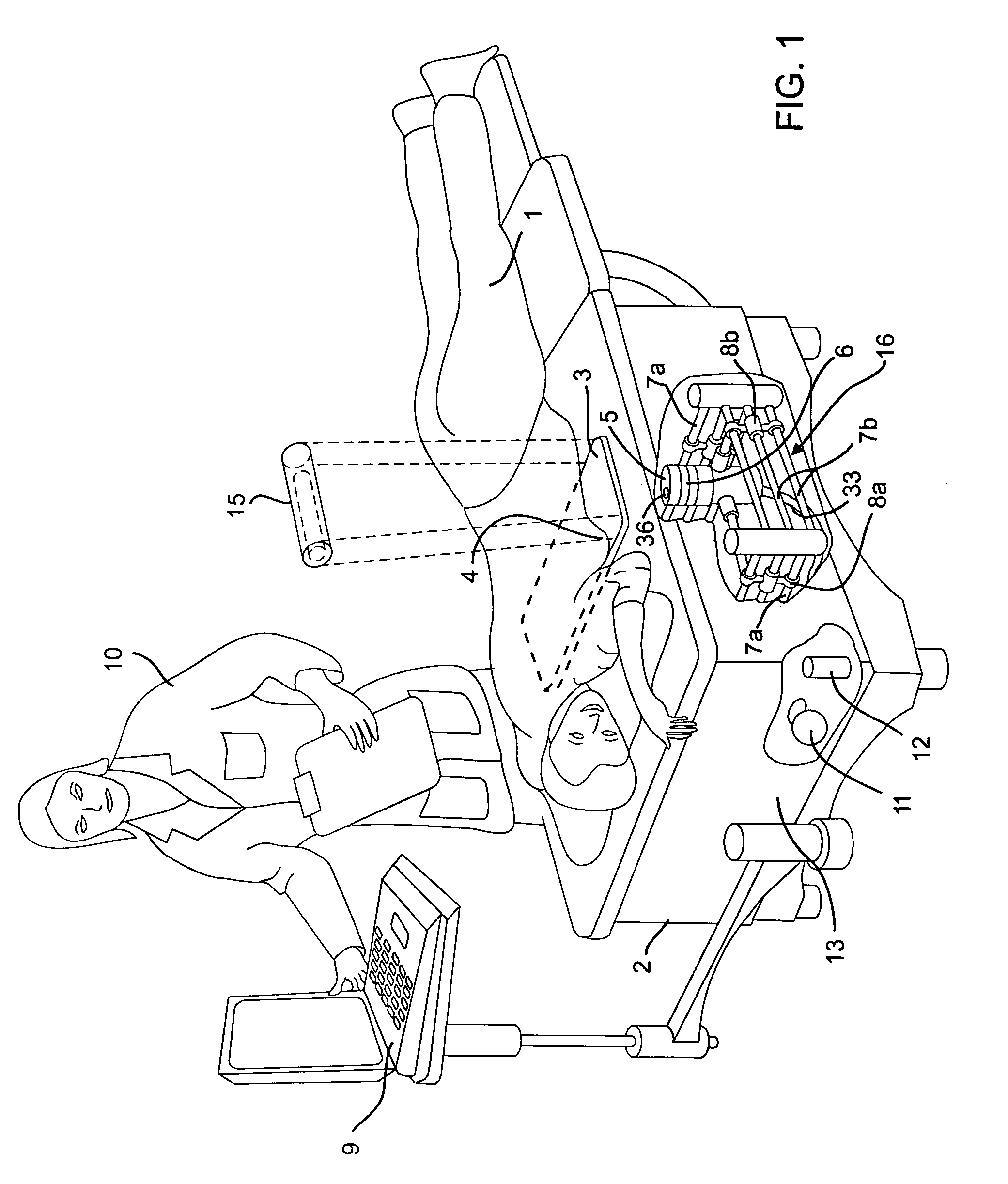
Apparatus and method for diagnosing breast cancer including examination table
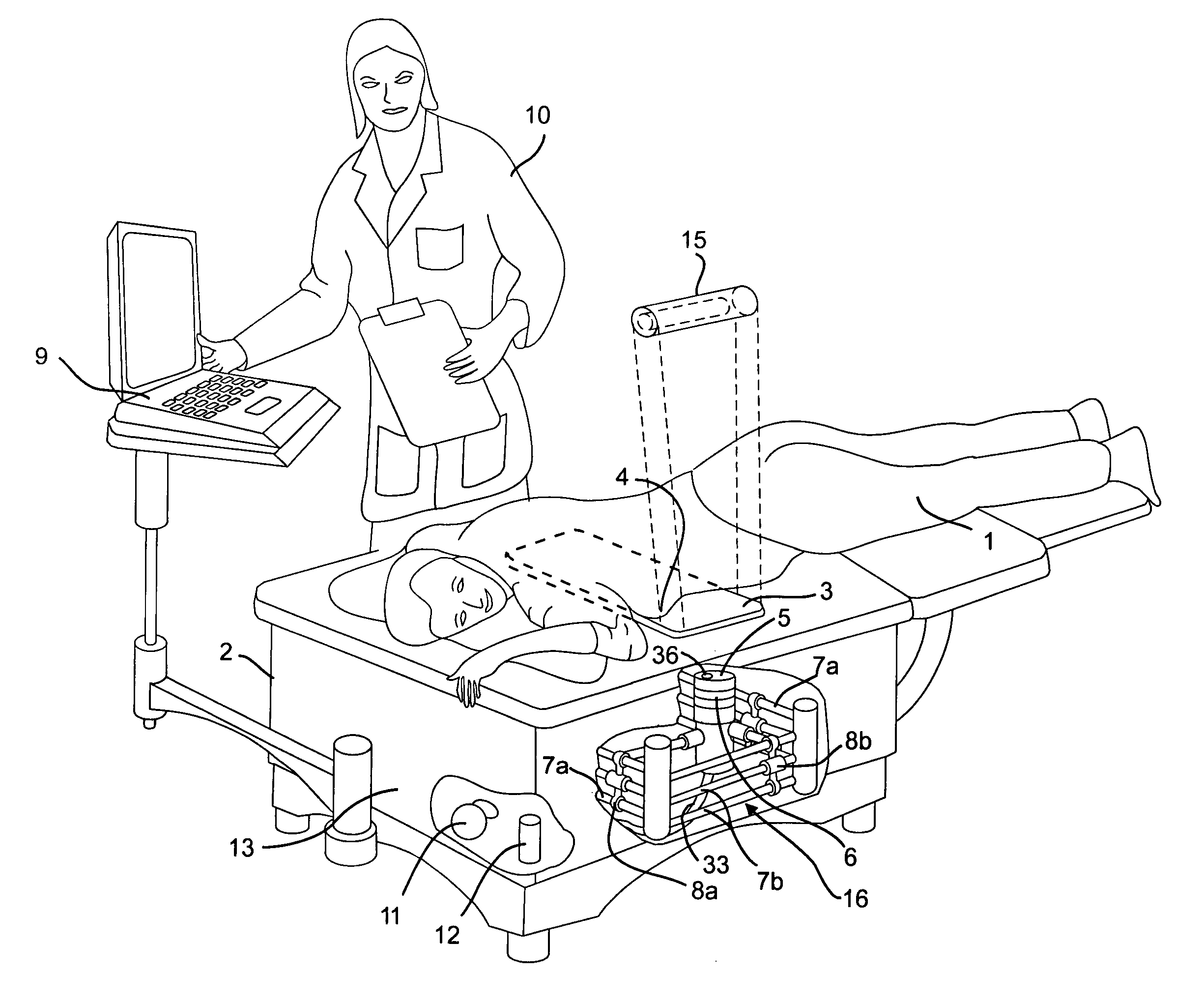
ActiveUS8095204B2Safe and simple and comfortable and convenient and effectiveComfortable supportResistance/reactance/impedenceHeart/pulse rate measurement devicesSupporting systemMedicine
A microwave breast cancer imaging method that includes an examination table that is both comfortable and reliable is provided that includes a support system and an orientation system such that breasts can remain in a fixed position to allow for scanning. A horizontal microwave and optically transparent scan plate forms part of the top of the examination table. The imprint of the breasts on the scan plate may be visually displayed to aid in the orienting of each breast such that all volumes within the breast are scanned. Microwave power is then scanned upward through the scan plate to develop a microwave response that is indicative of the presence of a lesion. After scanning, the visual imprint of the breast is recorded. As needed, microwave equipment can be included within a microwave shielded enclosure that also forms part of the scan table. Spurious leakage of microwave power may be further suppressed by use of microwave-absorbing materials, within the enclosure and, in the padding that covers the surface of the examination table and removable pads.
Owner:INTERSTITIAL SYST
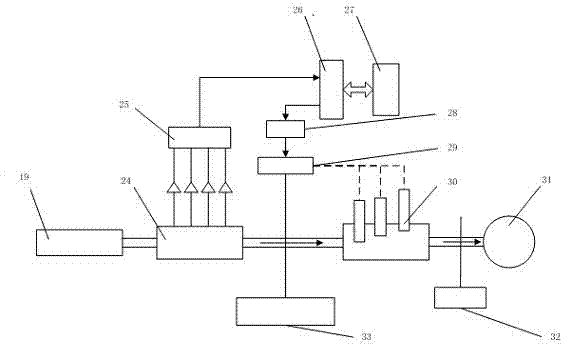
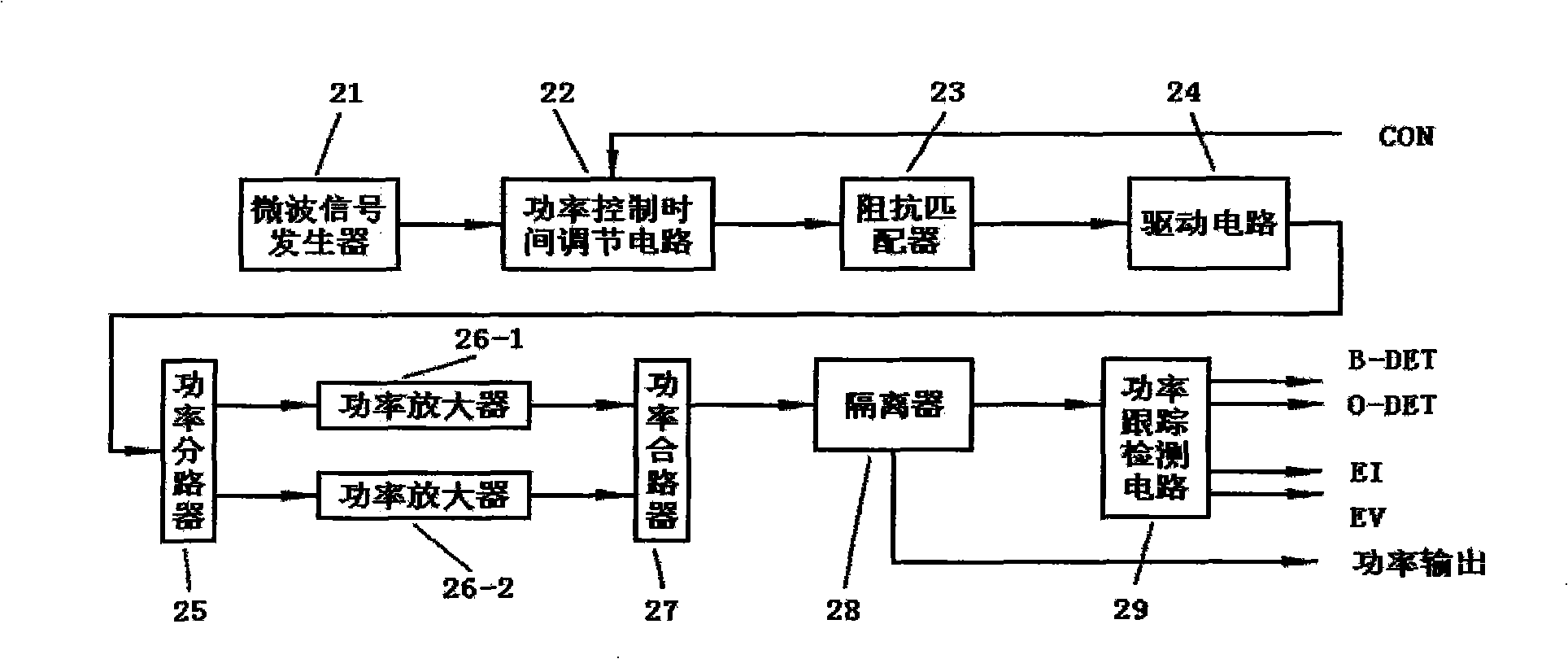
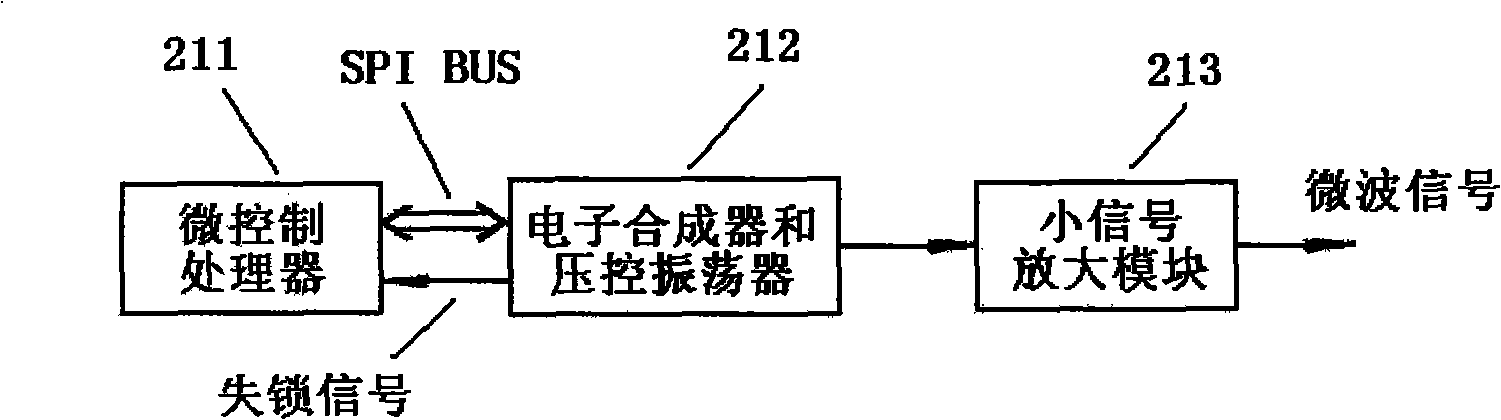
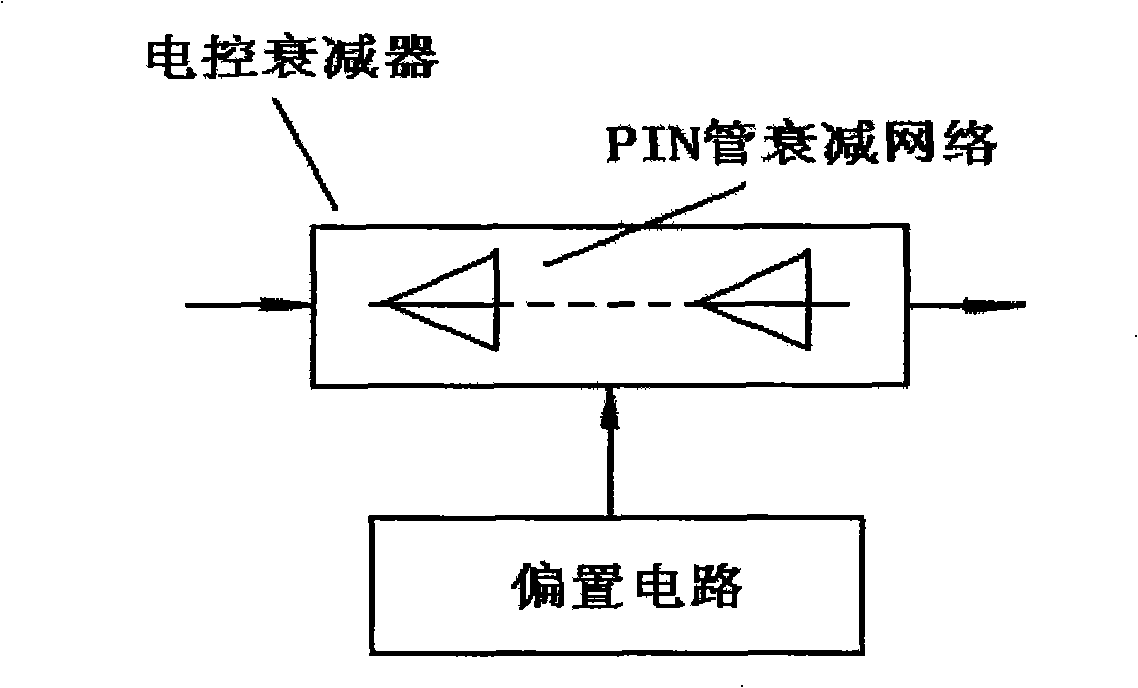
Microwave power source and microwave ablation therapeutic equipment thereof
ActiveCN101283926AExtended service lifeContinuous output powerSurgical instrument detailsMicrowave heatingLoop controlImpedance matching
The invention discloses a microwave power source and a microwave ablation therapeutic instrument, which relate to a full-solid-state microwave power generating circuit and a microwave therapeutic instrument circuit. The microwave power source adopts a full-solid-state circuit close-loop control to achieve stable microwave power output and continuous adjustable microwave power. The microwave energy can generate enough penetration depth in human tissue to enlarge the ablation range. The ablation range of 915 MHz microwave frequency band is larger than that of 2,450 MHz microwave frequency band, so that the 915 MHz microwave frequency band is more suitable for ablation therapy. The microwave power source comprises a microwave signal generator, a power control time adjusting circuit, an impedance matcher, a drive circuit, a power splitter, a plurality of power amplifiers, a power mixer, an isolator and a power tracking and detecting circuit. The microwave ablation therapeutic instrument is constituted by the microwave power source and a microwave ablation pin under control of a microprocessor.
Owner:CANYON MEDICAL INC
MEMS (Micro Electronic Mechanical System) cantilever beam type online microwave power sensor and production method thereof
InactiveCN101915870AReduce lossHigh sensitivityDecorative surface effectsPower measurement by thermal methodsCouplingMonitoring system
The invention discloses an MEMS (Micro Electronic Mechanical System) cantilever beam type online microwave power sensor and a production method thereof. The microwave power sensor comprises a gallium arsenide substrate, a mainline CPW (Co-Planer Waveguide), a subline CPW, an MEMS cantilever beam type structure and a terminal microwave power monitoring system, wherein the MEMS cantilever beam type structure comprises a cantilever beam and an anchor area; the cantilever beam stretches across the mainline CPW signal line, and the fixed end of the cantilever beam is fixed on the anchor area; the anchor area is connected with the terminal microwave power monitoring system through the subline CPW signal line; and a drive electrode is arranged below the cantilever beam type structure. The MEMS cantilever beam type online microwave power sensor not only has the advantages of the terminal type microwave power sensor, such as low loss and high sensitivity, but also has the advantages of online microwave power measurement, realization of monitoring and not monitoring, integration of the online microwave power sensors with various kinds of coupling factors, and compatibility with the gallium arsenide monolithic microwave integrated circuit.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
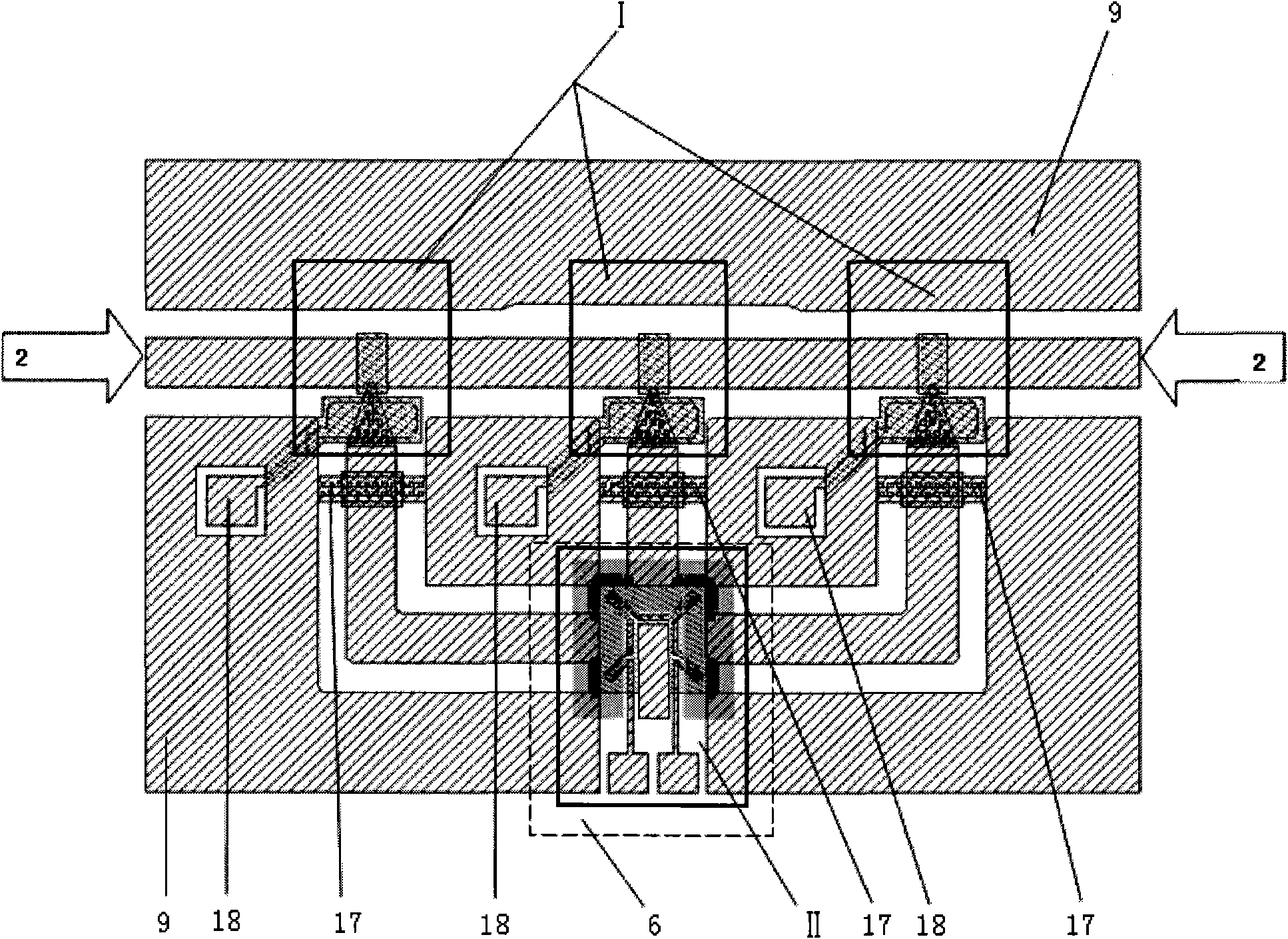
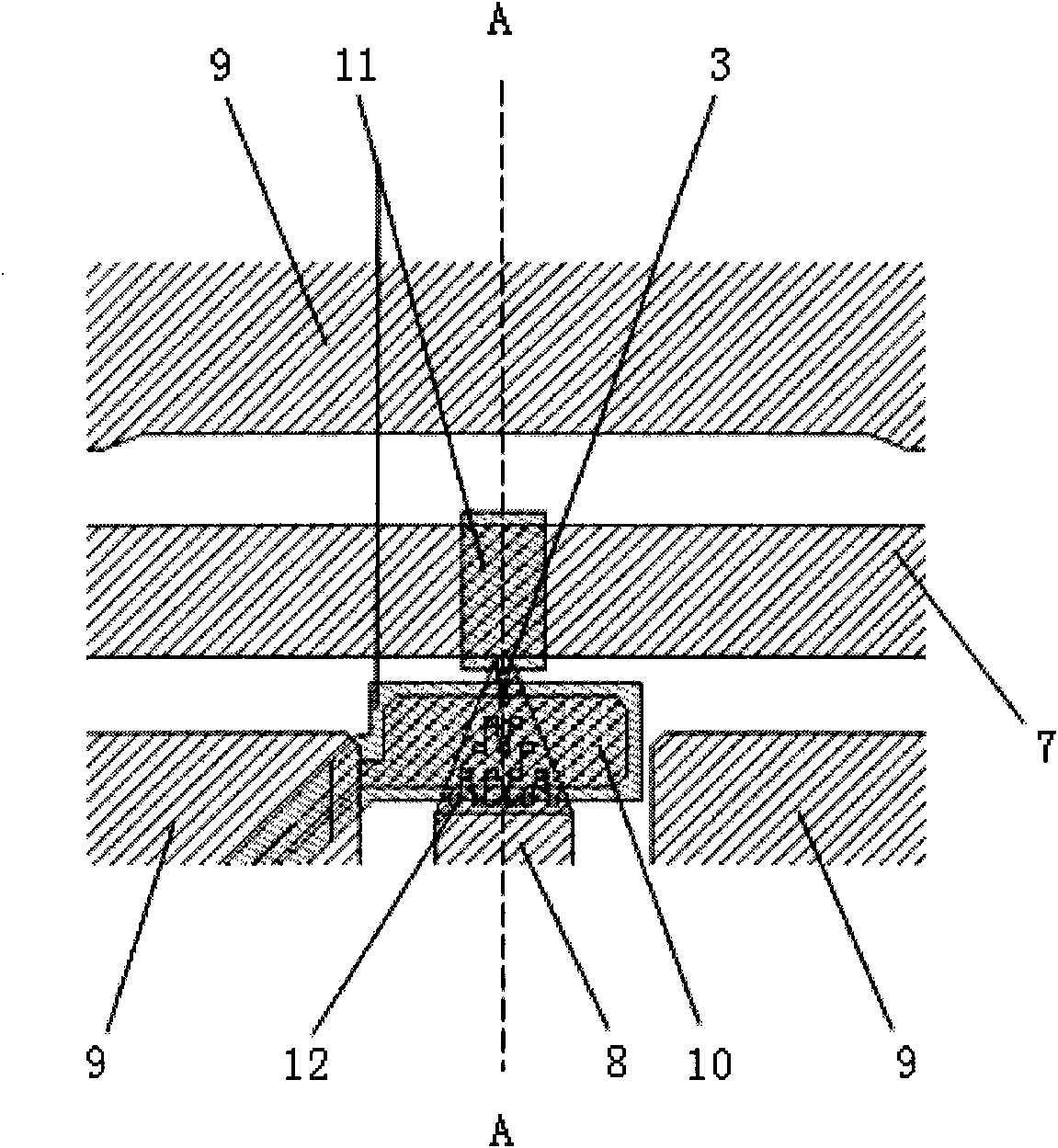
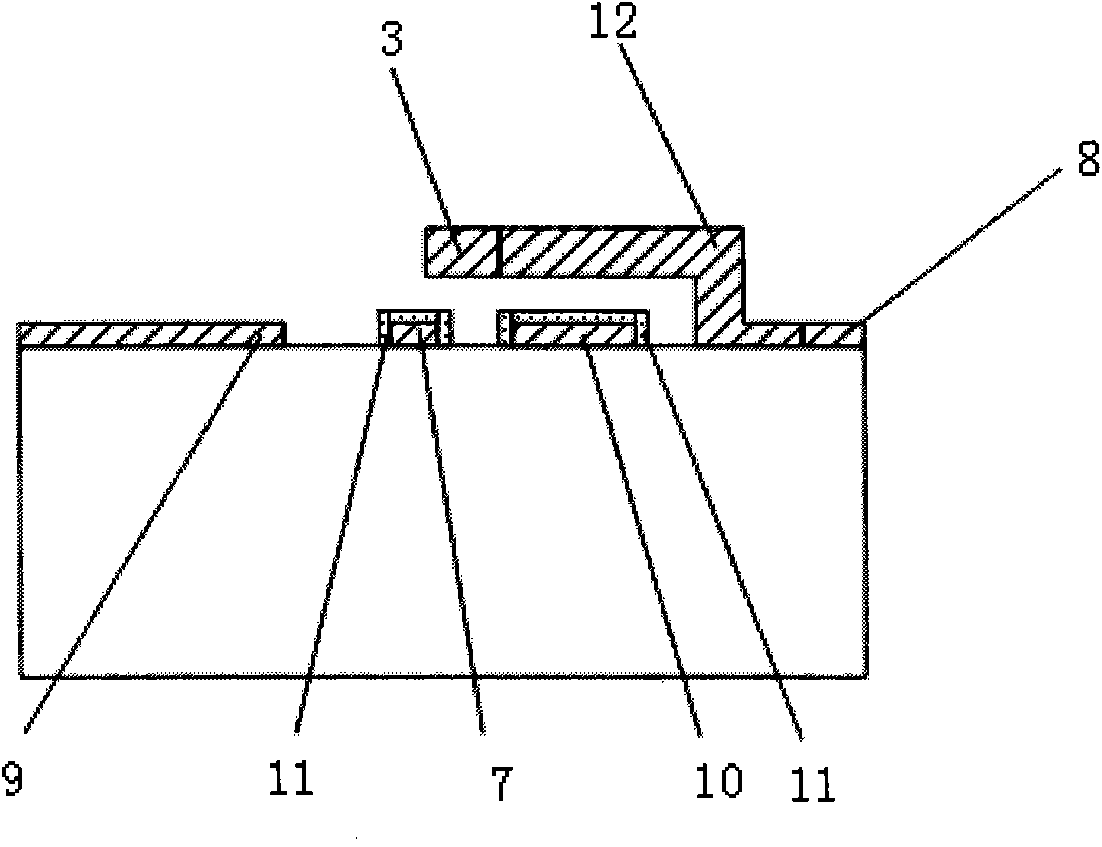
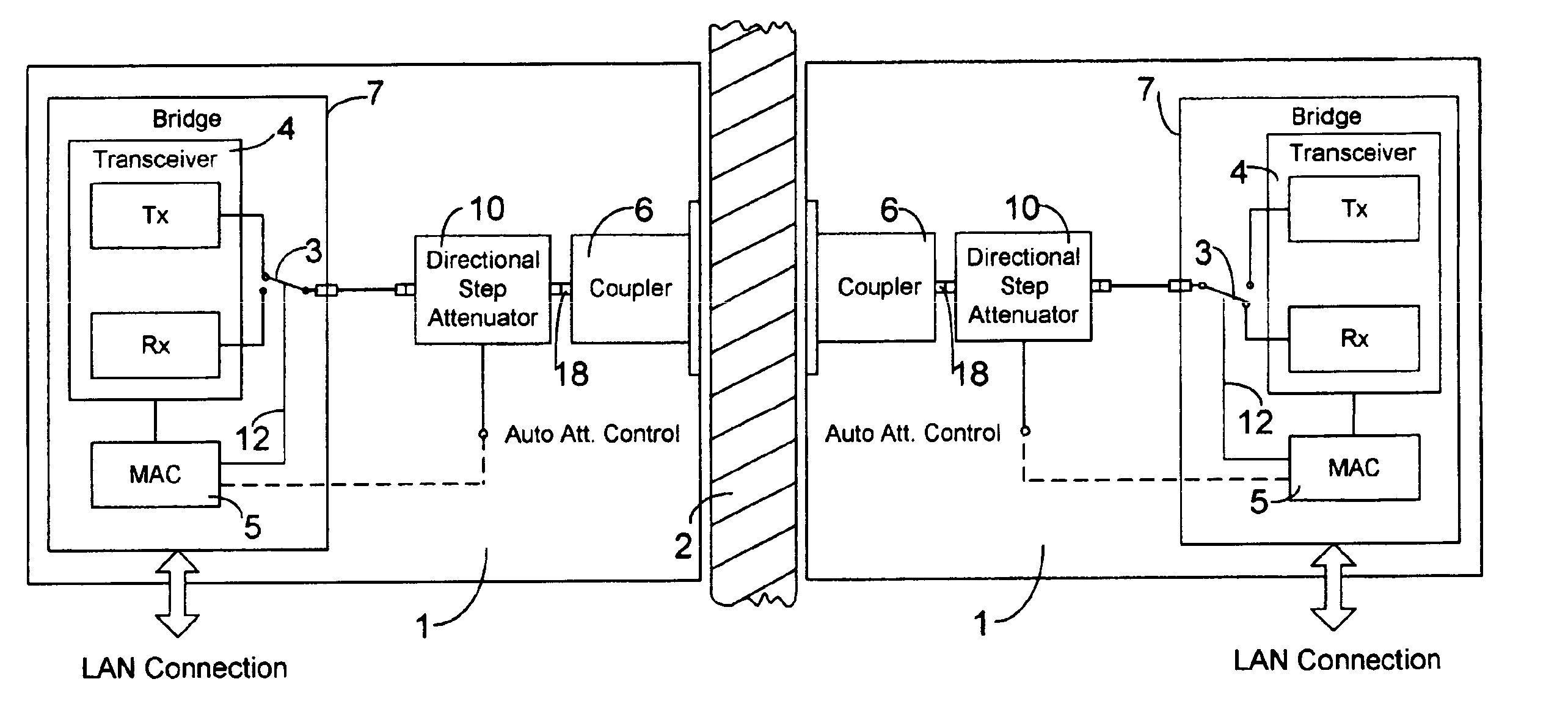
Electromagnetic coupler system
InactiveUS6963305B2Simplify and optimize operationLow powerMultiple-port networksEnergy efficient ICTElectromagnetic couplingEngineering
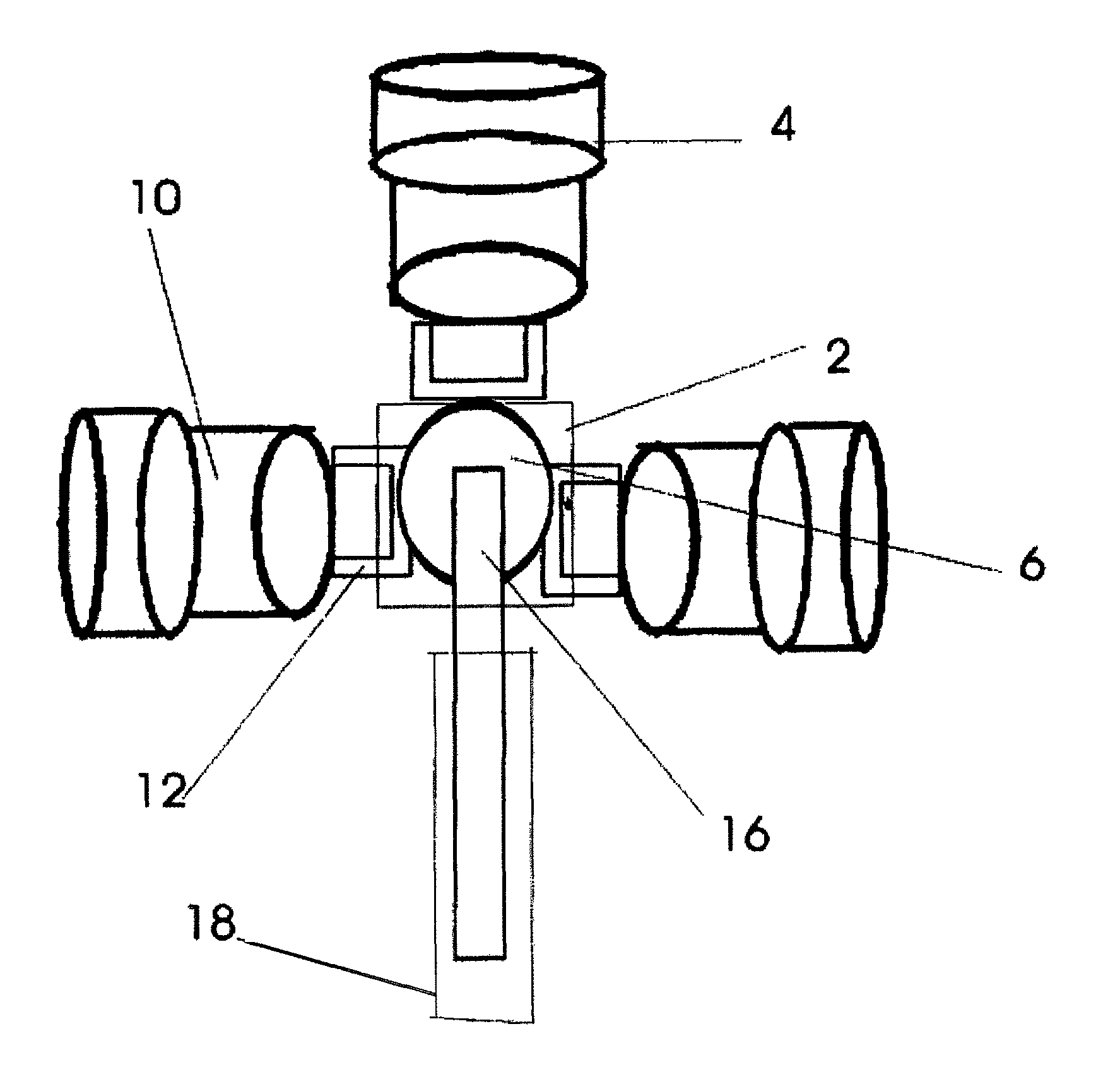
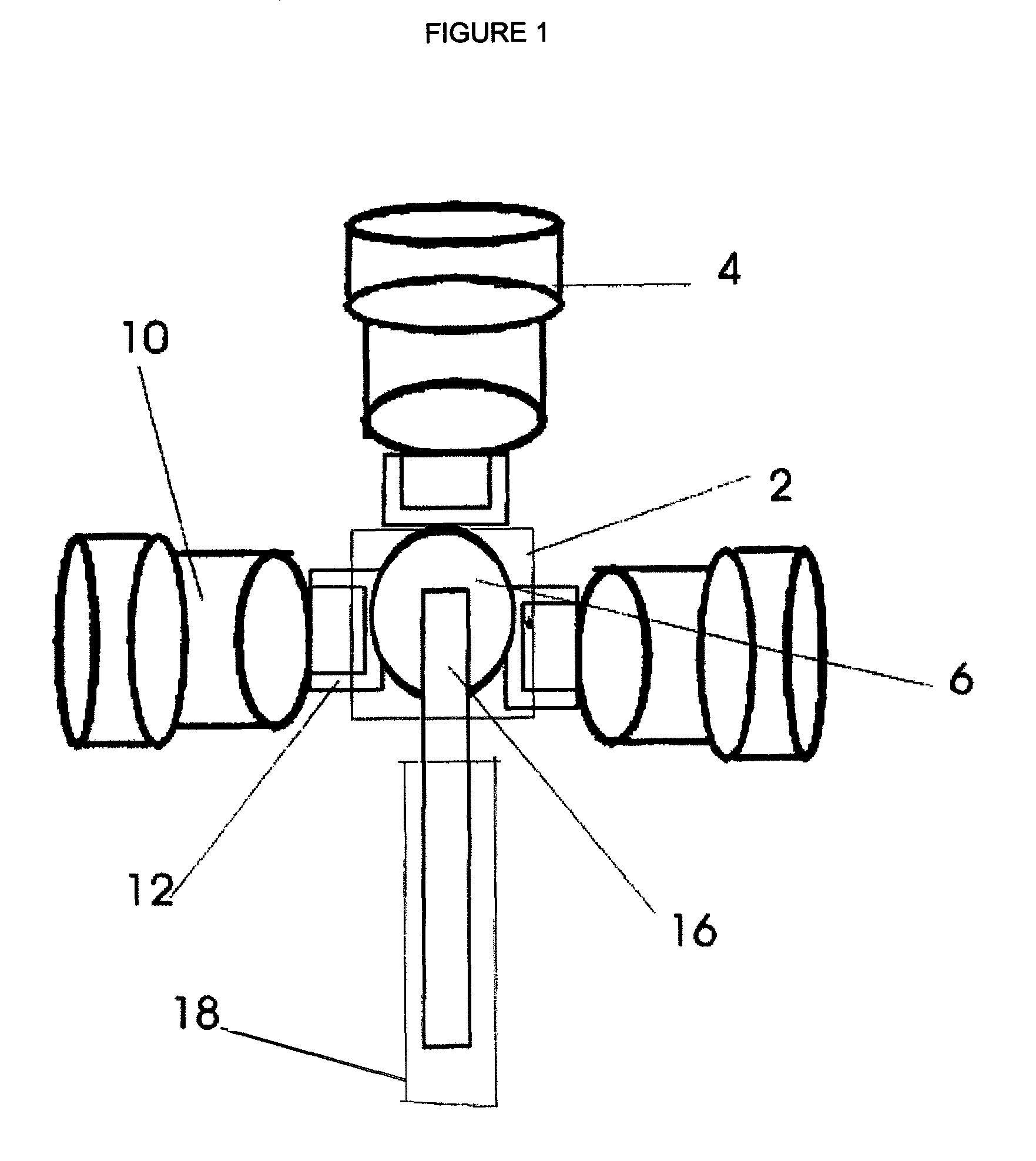
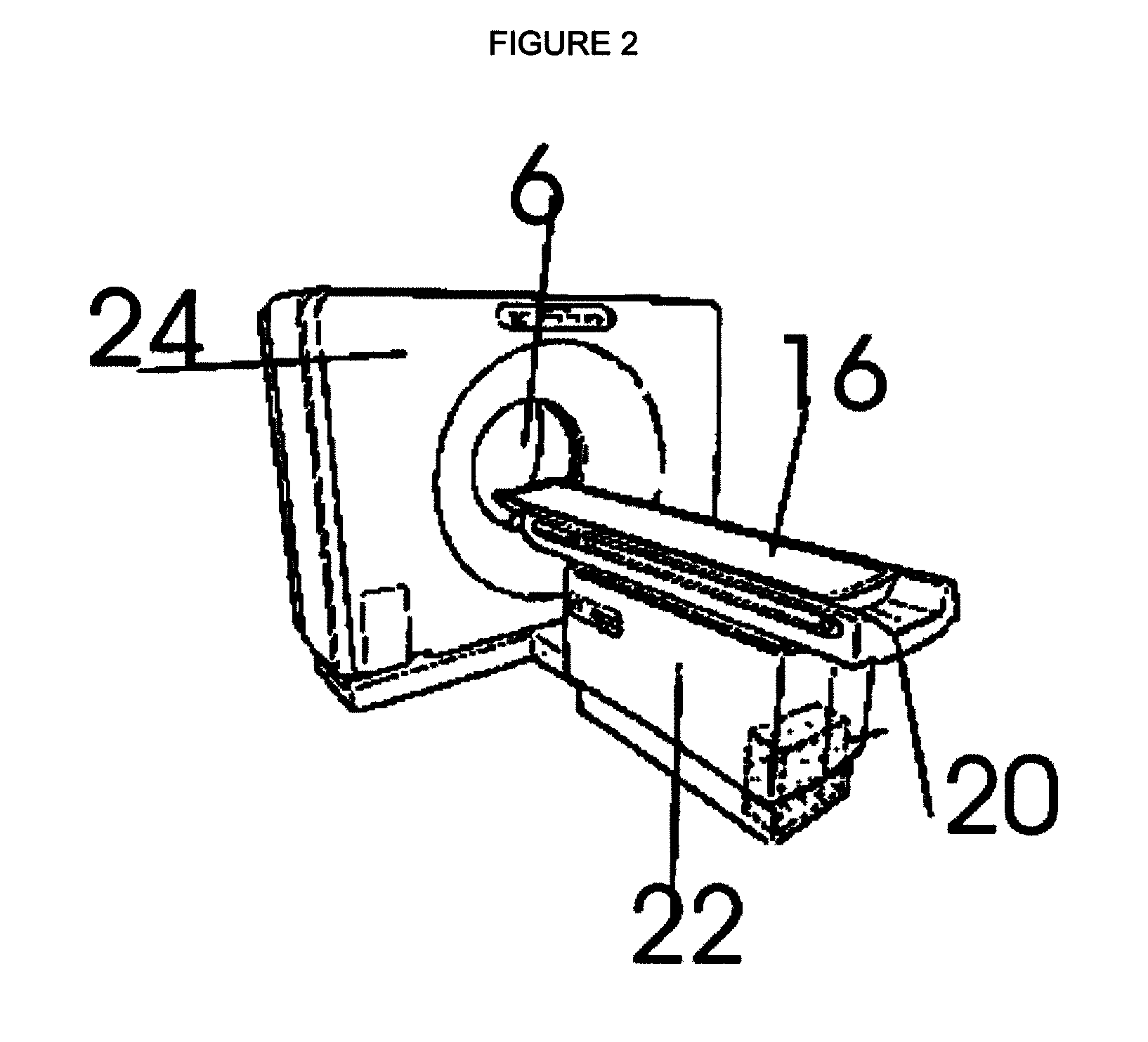
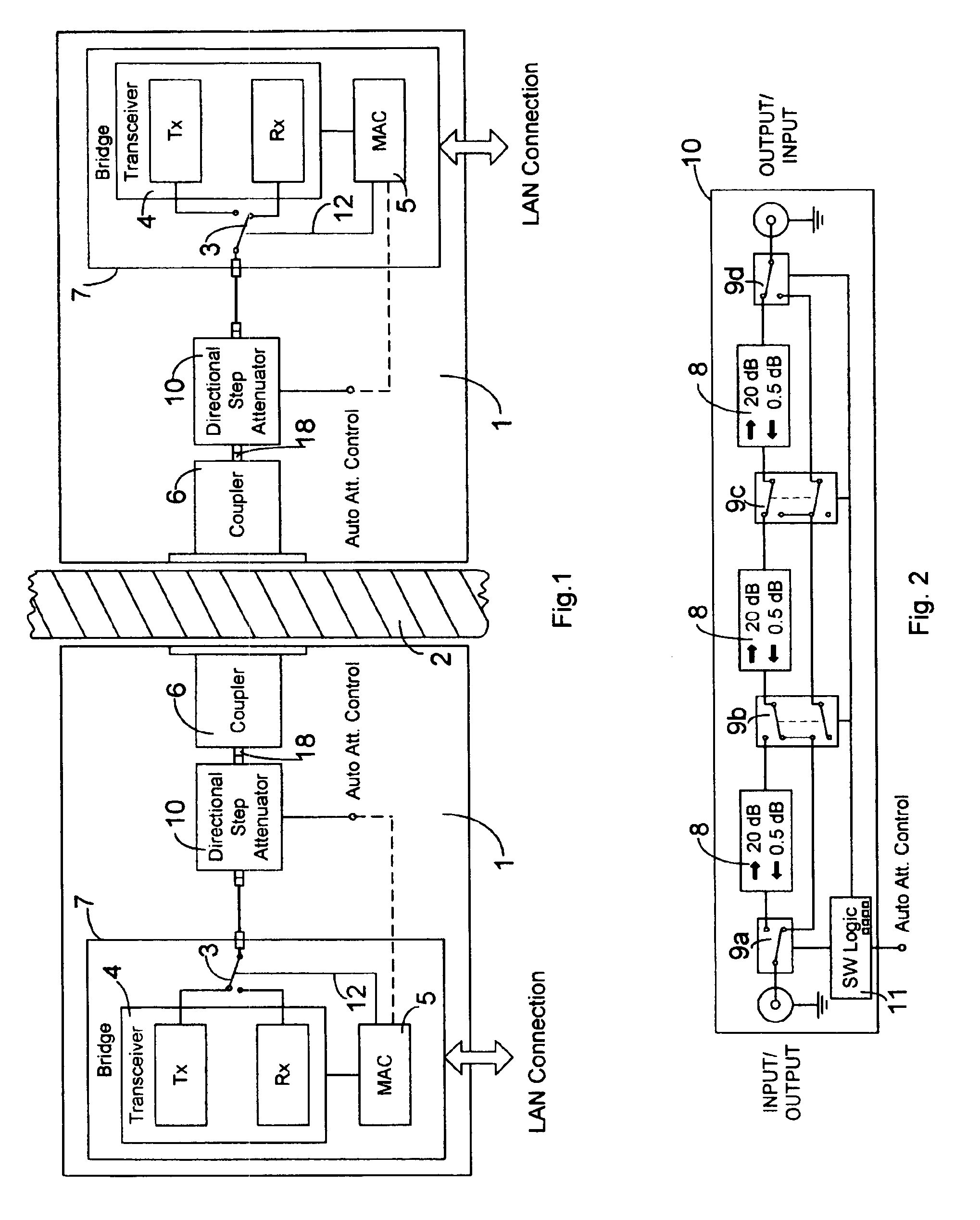
This invention makes it possible to communicate through solid non-metallic walls or ceilings with low microwave power levels. RF beam forming couplers are driven by common networks.For connection to a LAN segment at the other side of a wall or ceiling, transceiver 4 transmits data modulated microwave RF to coupler 6 through a directional step attenuator 10. The reduced signal is received by the coupler system at the other side with a power level low enough to eliminate wireless detection from the outside. However, the directional step attenuator on the receive side reduces the signal power only by an insignificant amount due to its low directional losses during receive signal flow. Each coupler's geometry is minimizing the radiation exposed material volume by RF field concentration, therefore, enabling transmission through thick concrete walls at microwave frequencies without compromising privacy. When used as wireless access point, coupler transmits through a floor to wireless devices below. The preferred embodiment operates in the 5-GHz ISM band.
Owner:KNAPP GUENTHER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com