Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
804results about How to "Avoid power" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
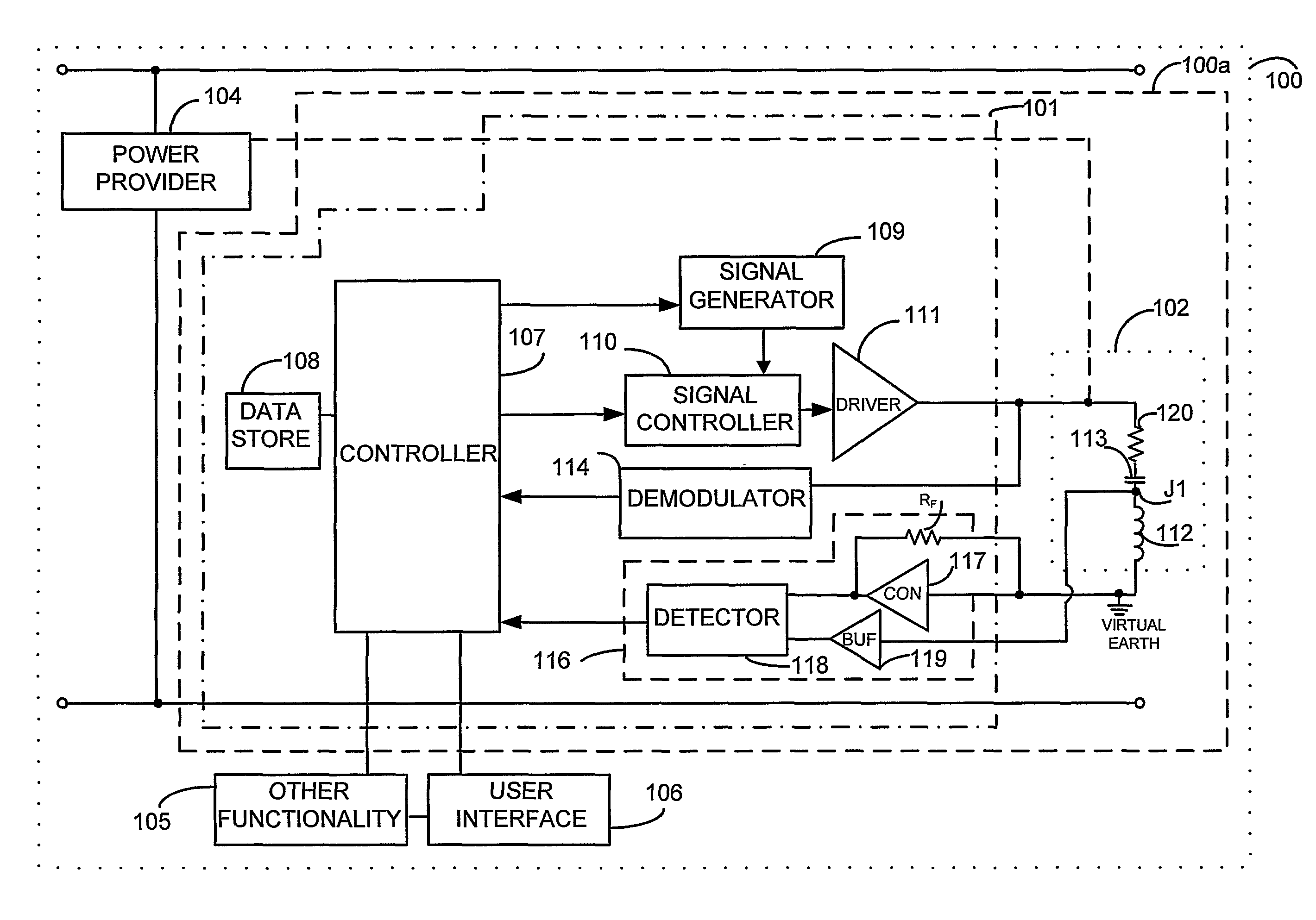
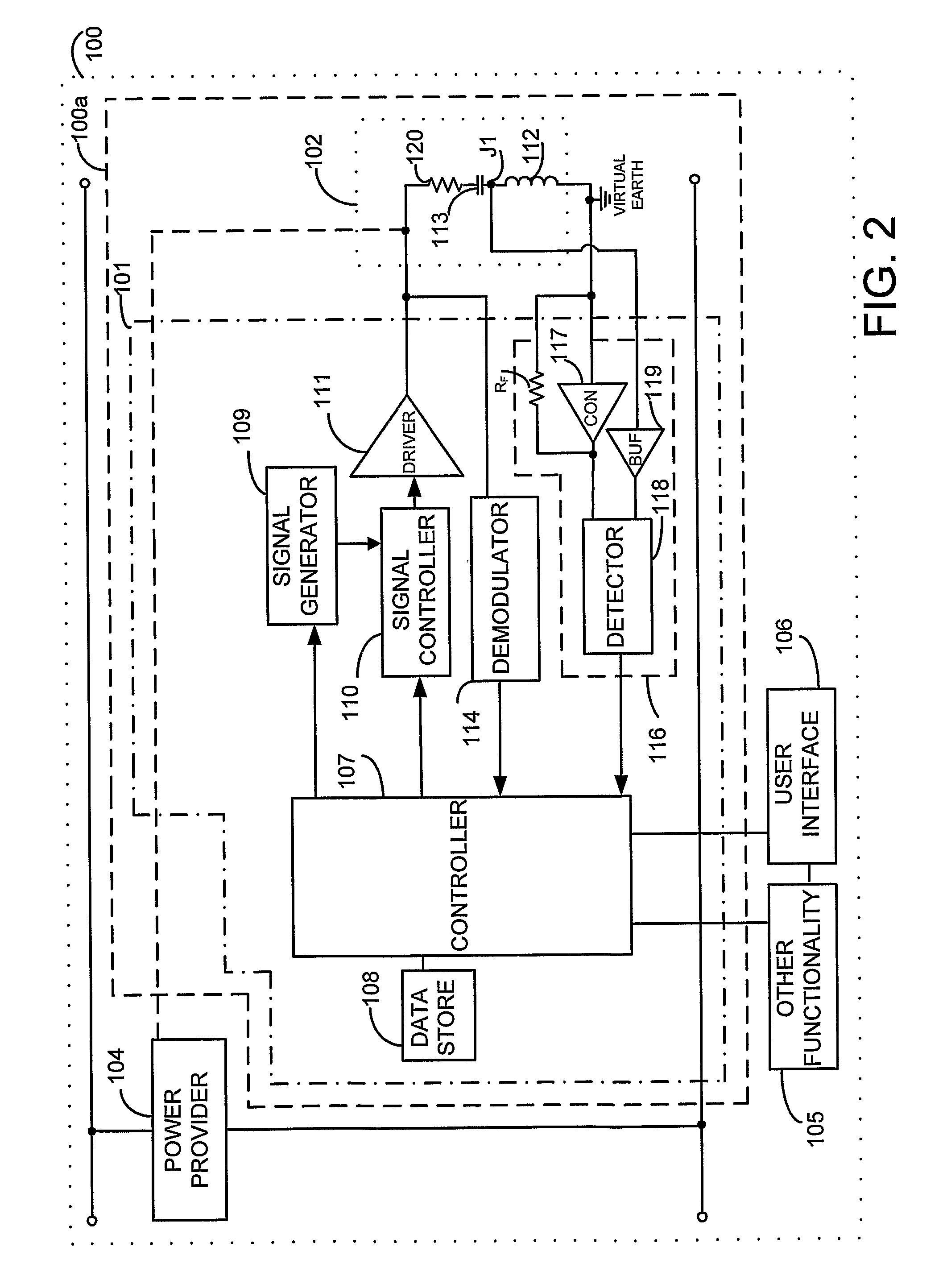
Near field RF communicators and near field RF communications enabled devices
ActiveUS8140010B2Avoid powerAvoid timeTransformersNear-field systems using receiversPhase detectorCurrent voltage
A near field RF communicator (100) has an inductive coupler (102) and a first signal provider (109, 110, 111) to cause the inductive coupler to provide a first signal that when inductively coupled to the inductive coupler of another near field RF communicator in near field range is insufficient to cause initiation of communication with that other near field RF communicator. A sensor (116) senses a change in an impedance of the inductive coupler (102) due to inductive coupling of the first signal between the inductive couplers of the said near field RF communicator and a said other near field RF communicator in near field range. A controller (107) determines whether or not another near field RF communicator is in near field range on the basis of any change in impedance sensed by the sensor and, if another near field RF communicator is determined to be in near field range, causes a second signal to be inductively coupled to the other near field RF communicator to initiate communication between the two near field RF communicators. The sensor may use a phase detector (118) to enable a change in impedance to be sensed by detecting a change in a current-voltage phase relationship resulting from a change in impedance.
Owner:NXP USA INC
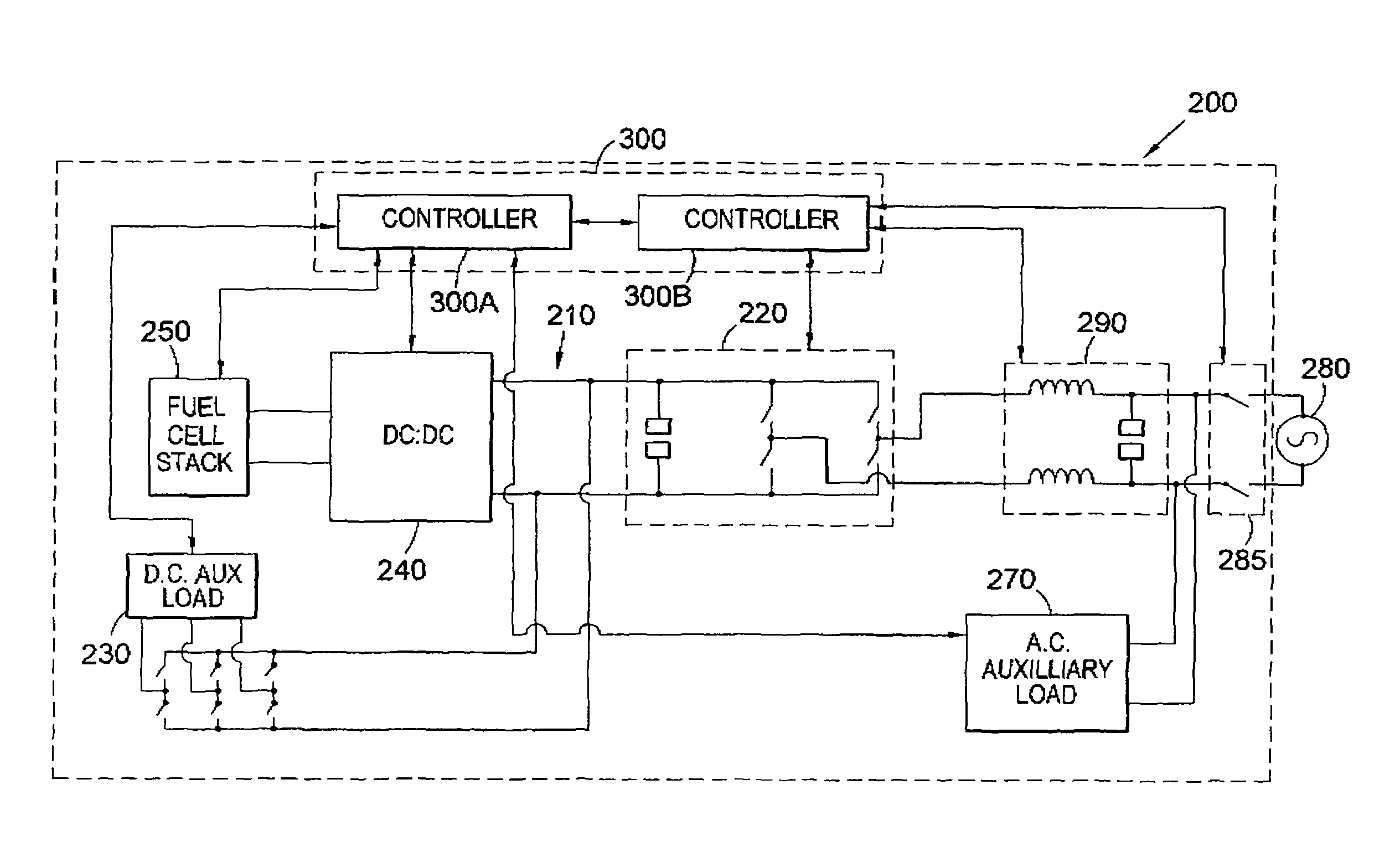
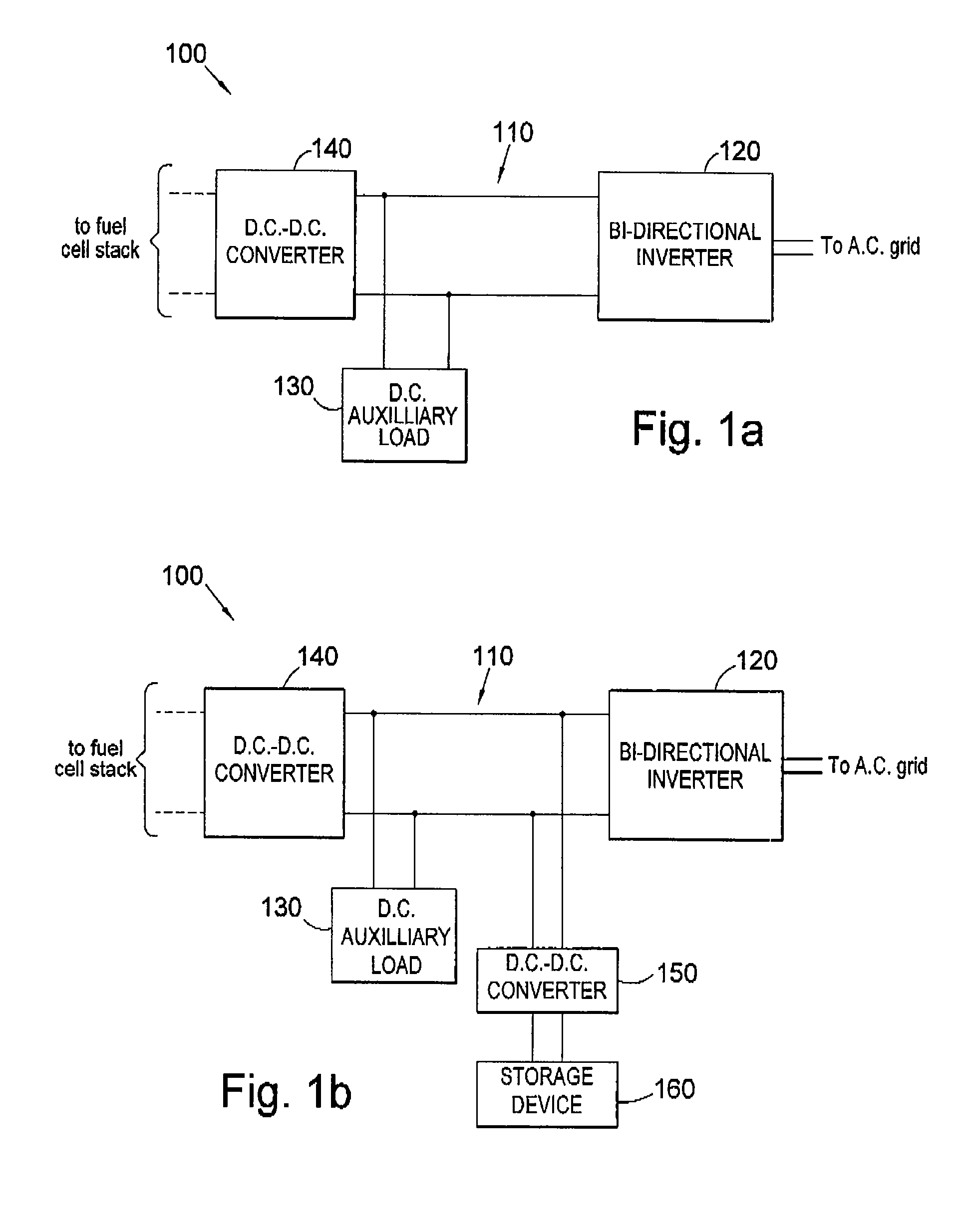
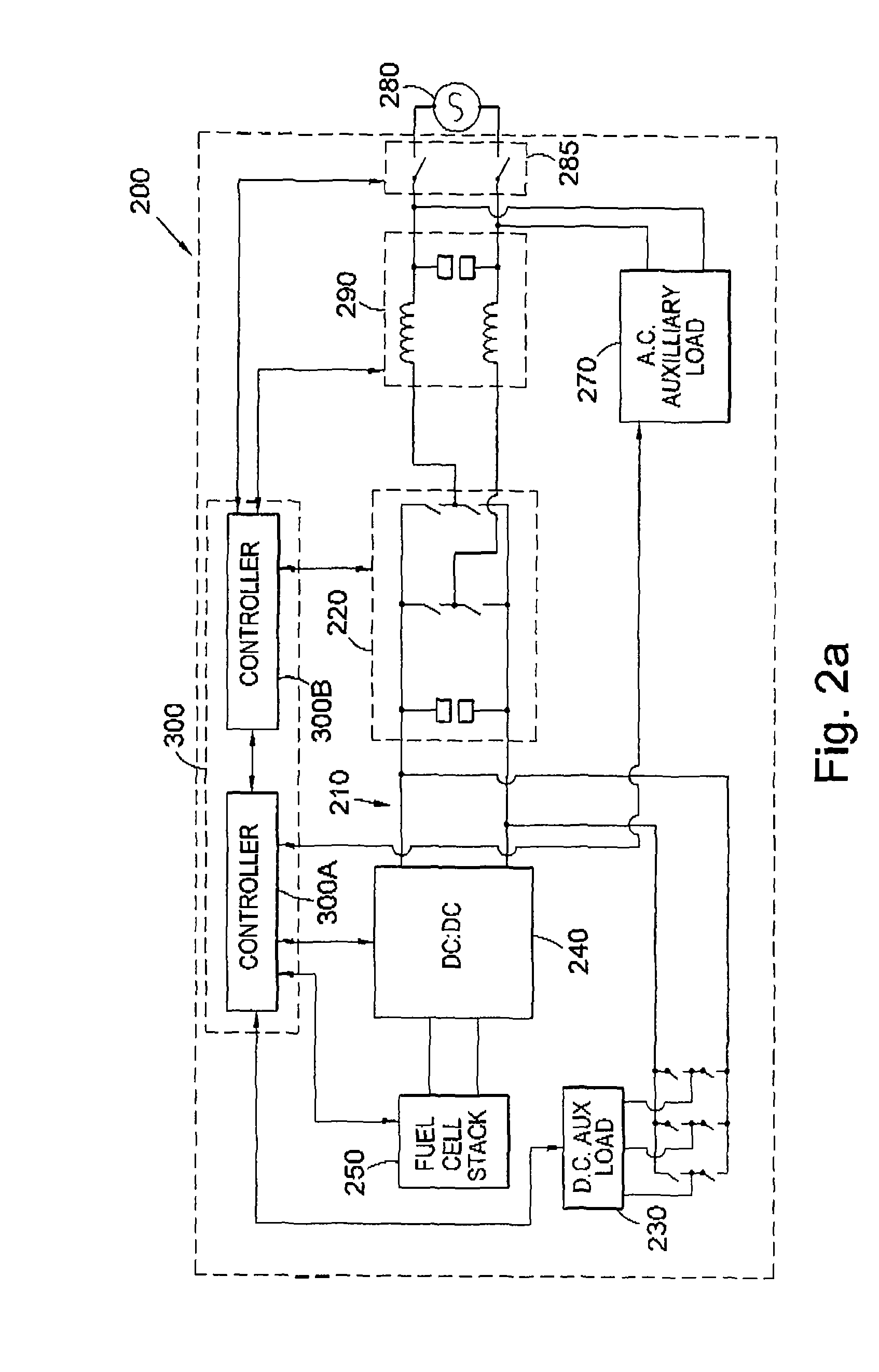
Power supply control for power generator
ActiveUS7880334B2Loss in efficiencyAvoid powerDc network circuit arrangementsBatteries circuit arrangementsFuel cellsMicro power generator
A system (100) for connecting a fuel cell stack to an A.C. grid to provide power thereto is disclosed in which a voltage regulated D.C. bus (110) is provided to be coupled to the fuel cell stack, a bidirectional inverter (120) is coupled to the D.C. bus (110), and is to be coupled between the D.C. bus (110) and the A.C. grid. At least one D.C. auxiliary load (130) of the fuel cell stack is provided coupled to the D.C. bus (110). A D.C. to D.C. converter (140) is provided between the fuel cell stack and the D.C. bus (110).
Owner:CERES INTPROP CO LTD
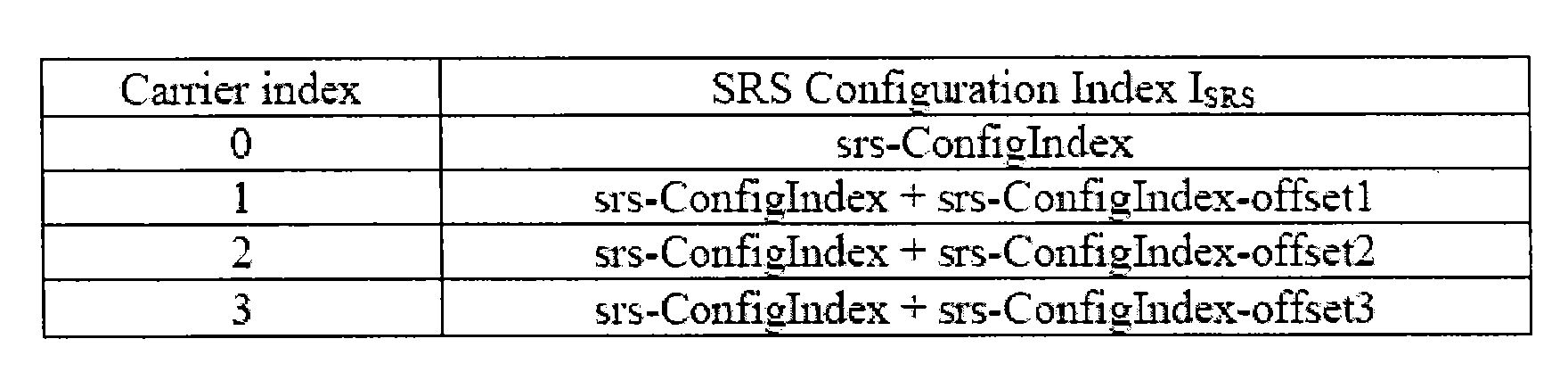
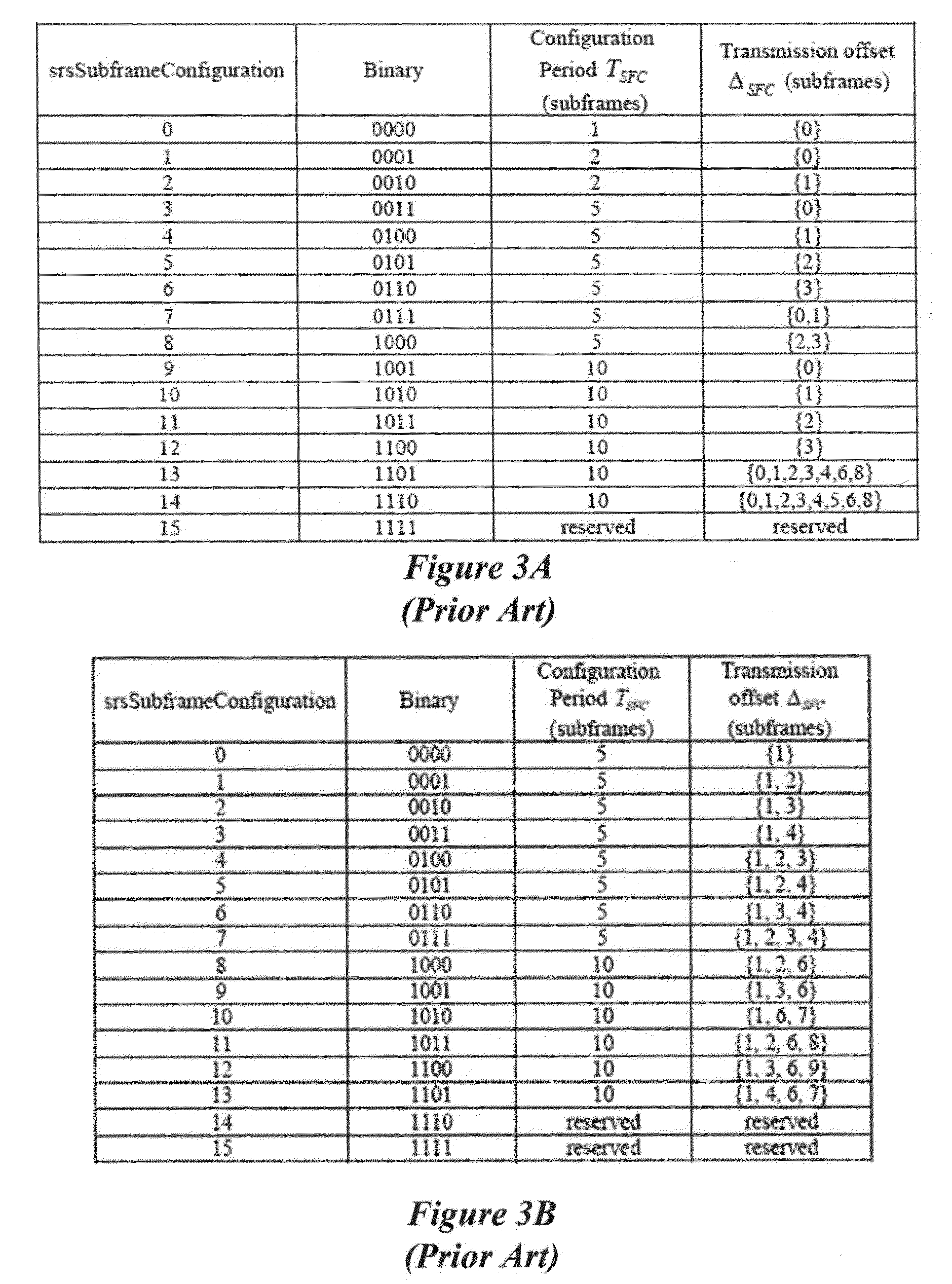
Sounding reference signal transmission in carrier aggregation
ActiveUS20130242911A1Reduce powerIncrease spectral efficiencyPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementCarrier signalPrimary component
A cell-specific sounding reference symbol (SRS) subframe configuration and UE-specific SRS configuration are defined for carrier aggregation. For the cell-specific SRS subframe configuration, the same cell-specific SRS subframes are configured for all uplink (UL) carrier components (CCs). For the UE-specific SRS configuration, different configurations are applied for UL CCs. Also, to reduce signaling overhead, the different UE-specific SRS configuration is signaled by using an offset on top of the UE-specific SRS configuration of a primary component carrier (PCC).
Owner:RES IN MOTION LTD
Method and apparatus for load management in an electric power system
InactiveUS20060049694A1Reduce system loadMinimize impactPower network operation systems integrationElectric switchesElectric power transmissionElectric power system
A system for load control in an electrical power system is described, wherein one or more load-control devices are provided to control power delivered to electrical equipment. A remote power authority, such as a power company, government agency, or power transmission company sends one or more commands to the load-control devices to adjust loading on the electrical power system. In one embodiment, the power authority sends shutdown commands. In one embodiment, the power authority sends commands to tell the electric power device to operate in a relatively low-power mode. In one embodiment, the commands are time-limited, thereby allowing the electric power device system to resume normal operation after a specified period of time. In one embodiment, the commands include query commands to cause the control device to report operating characteristics (e.g., efficiency, time of operation, etc.) back to the power authority.
Owner:KATES LAWRENCE
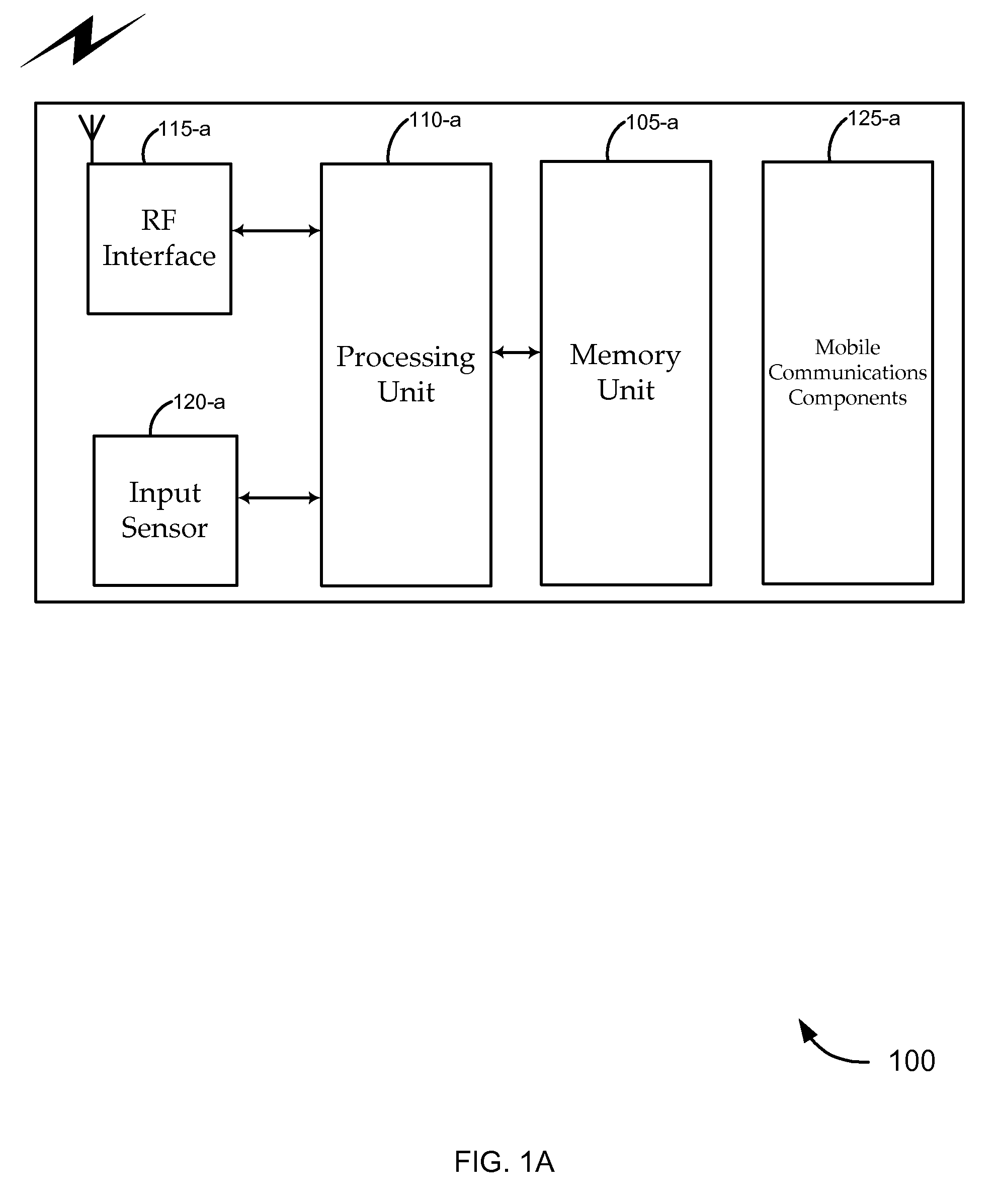
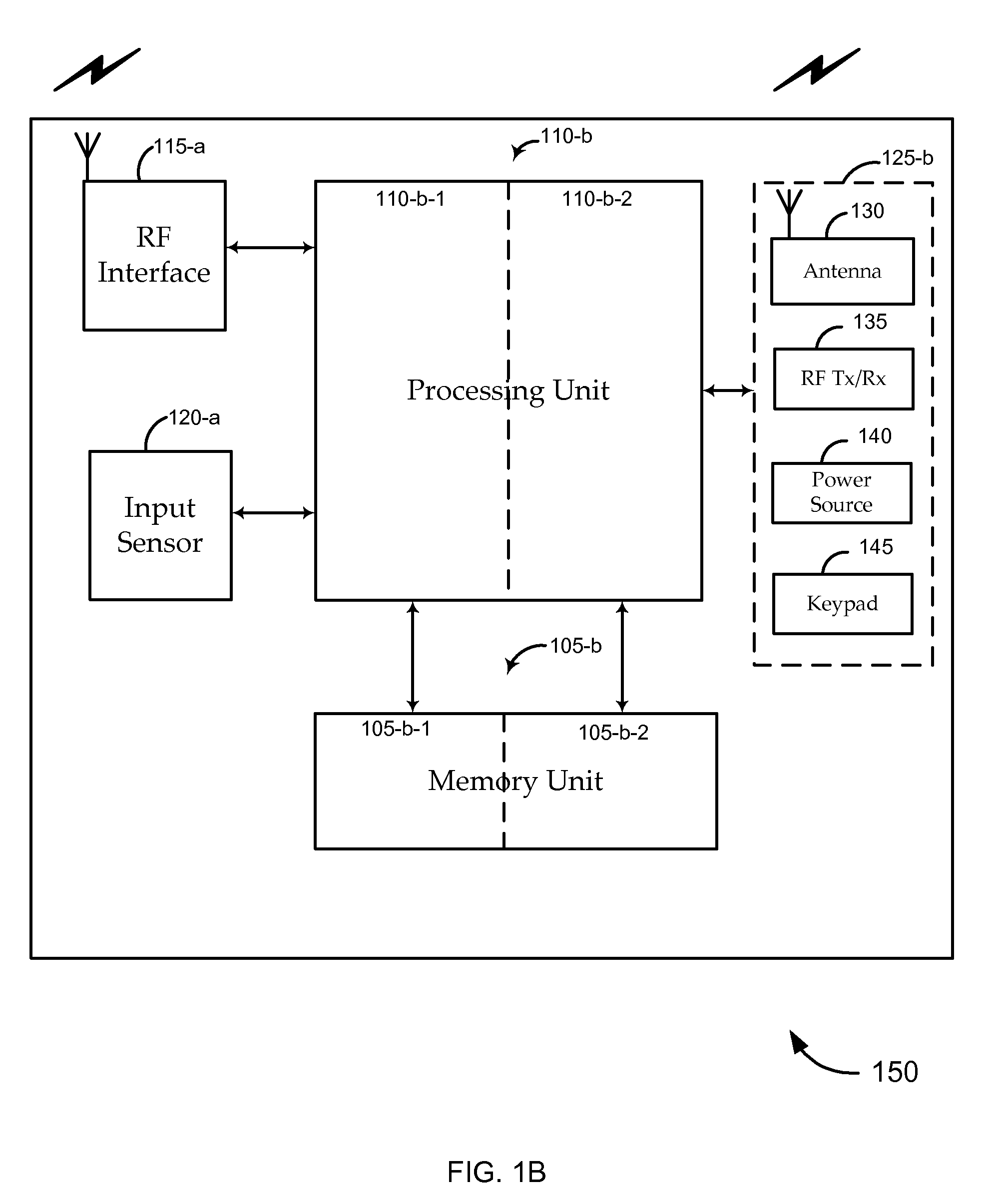
Wireless phone RF presentation instrument with sensor control
ActiveUS20070257767A1Avoid spreadingAvoid powerElectric signal transmission systemsMultiple keys/algorithms usageEngineeringData storing
A mobile communications device is described which includes an input sensor, a memory unit, processing unit, and an antenna configured to wirelessly transmit and receive financial account data for a transaction. The antenna is configured to receive a request for data stored on the memory unit, and may also be configured to induce a voltage from a magnetic field to power certain components of the device. The input sensor may control whether the components can be so powered from the magnetic field. Alternatively, input from the input sensor may otherwise control the functionality of the device. By way of example, data representative of an input received by the input sensor may be transmitted in addition to the requested data.
Owner:FIRST DATA
Dualband power amplifier control using a single power amplifier controller
InactiveUS6216012B1Avoid radiationMinimize size cost complexityPower managementTransmission control/equalisingSignal qualityAudio power amplifier
A system having dualband power amplifier control in a dualband phone is provided using a single power amplifier controller. The dualband phone includes two power amplifiers, where each power amplifier amplifies the power of a signal transmitted at a different frequency band. A power amplifier controller is provided for controlling the amount of amplification performed by both of the power amplifiers, and a power amplifier switching device is connected to the power amplifier controller for switching the connection of the power amplifier controller between the two power amplifiers. The system further includes a processing device which monitors the quality and strength of the received signal transmitted by various base stations in the transmission region of the dualband phone. The processing device instructs the power amplifier switching device to switch its connection between the two power amplifiers based upon a determination of which frequency band provides the optimal balance between signal quality and signal strength, and the dualband phone then transmits its signal within the selected optimal frequency band. The system measures the power of the signal transmitted from the power amplifier connected to the power amplifier controller and feeds the measured power value back to the power amplifier controller, so that the power amplifier controller may adjust the voltage driving the power amplifier connected thereto based upon any differences found between the desired power output of the connected power amplifier and the measured power output.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
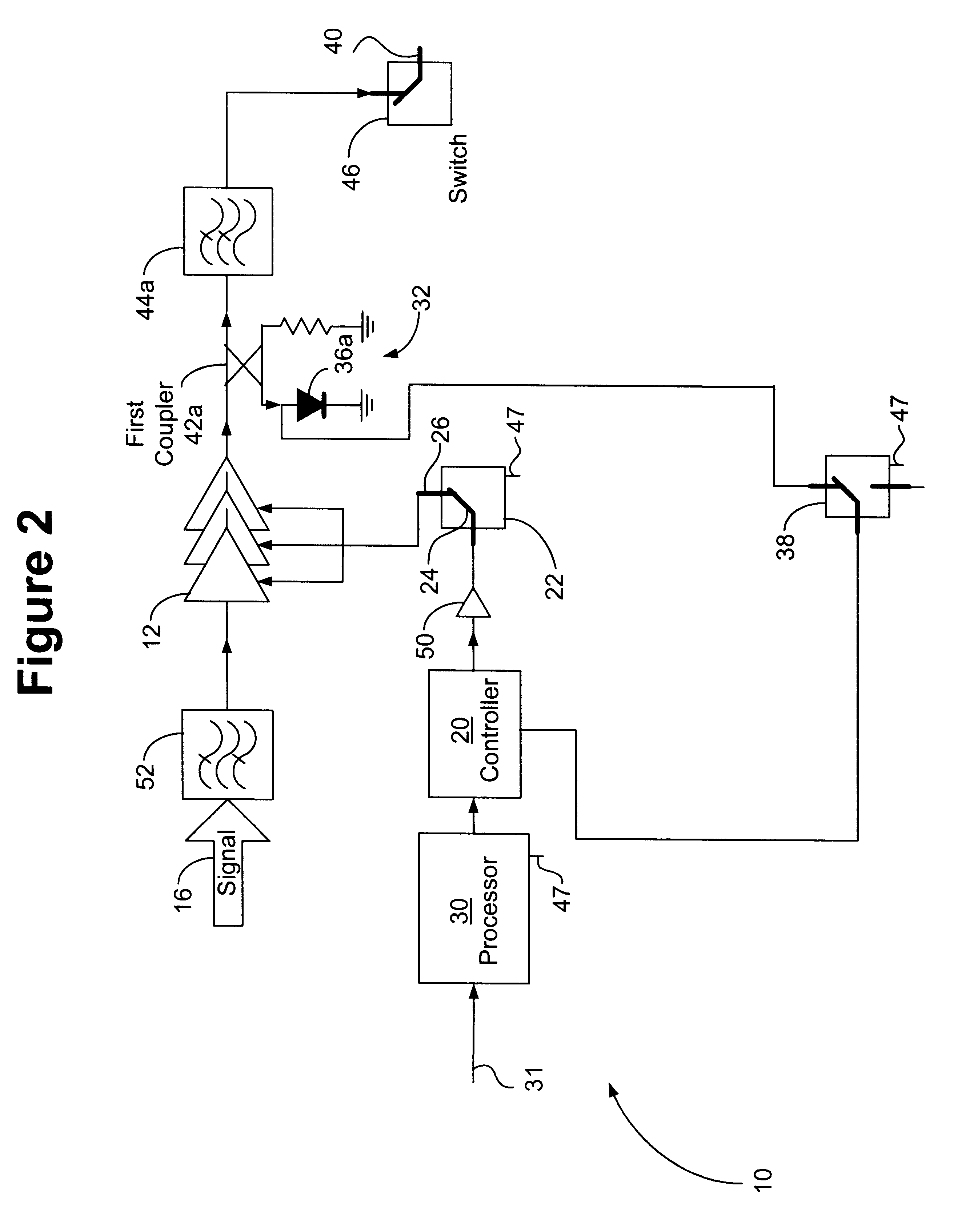
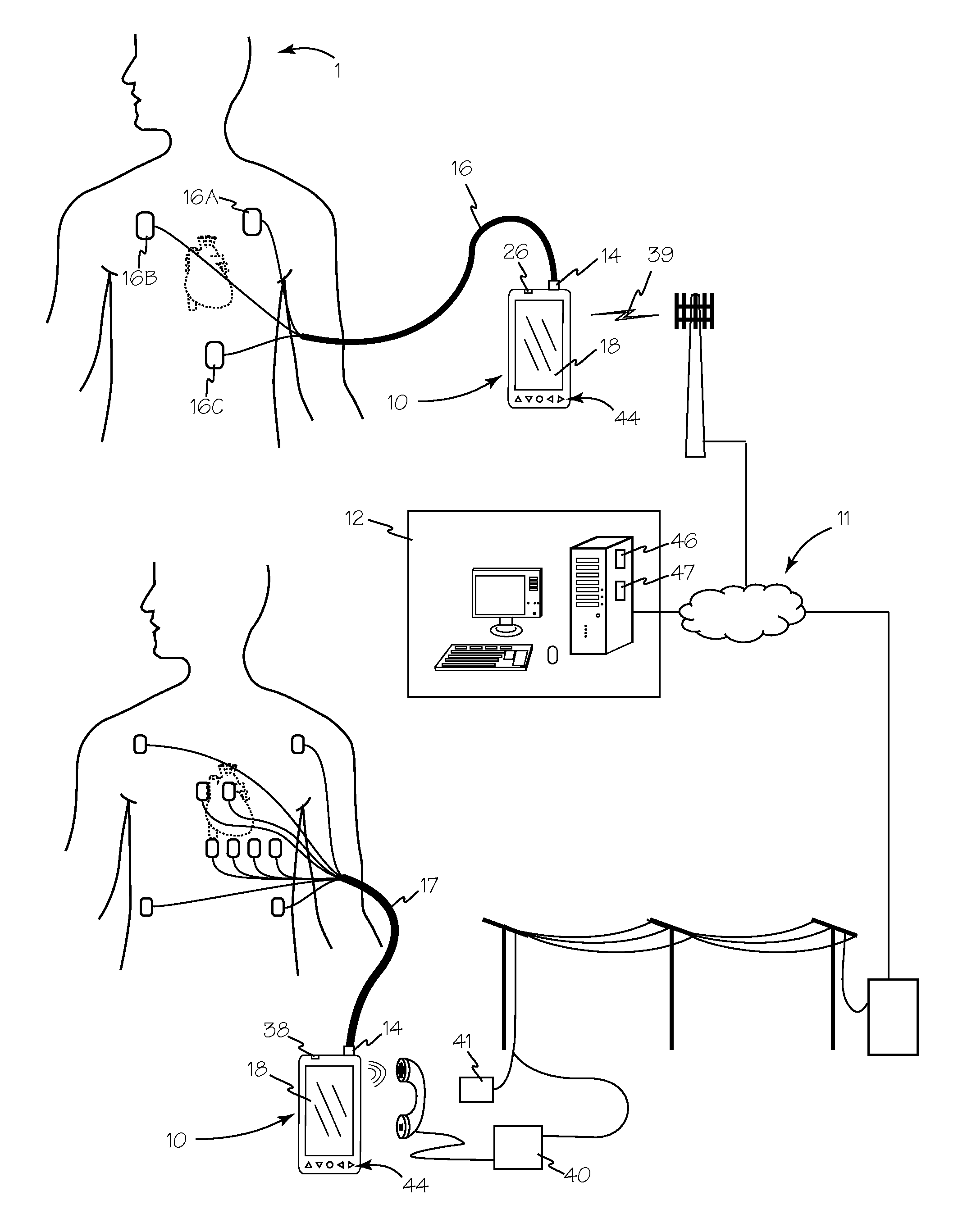
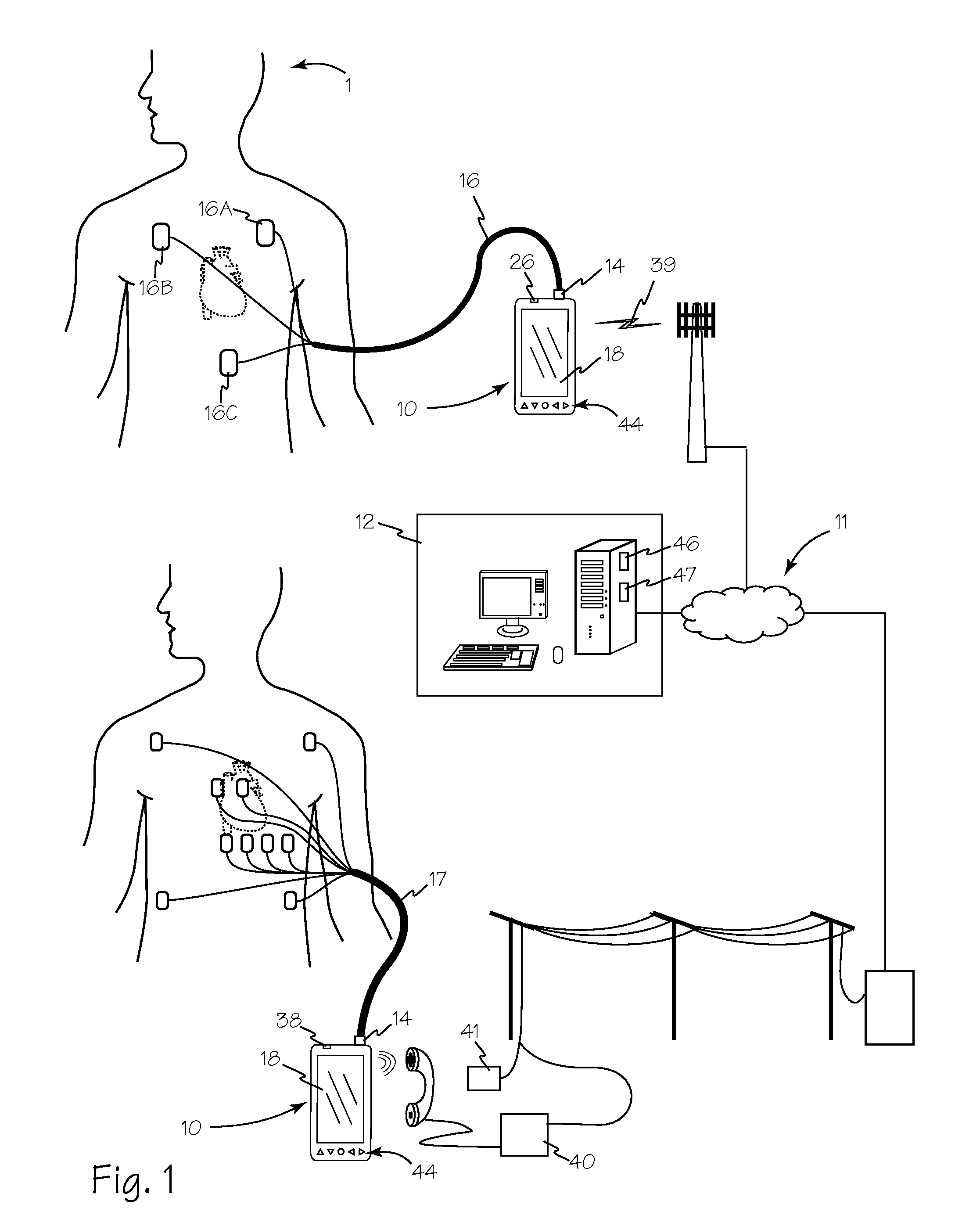
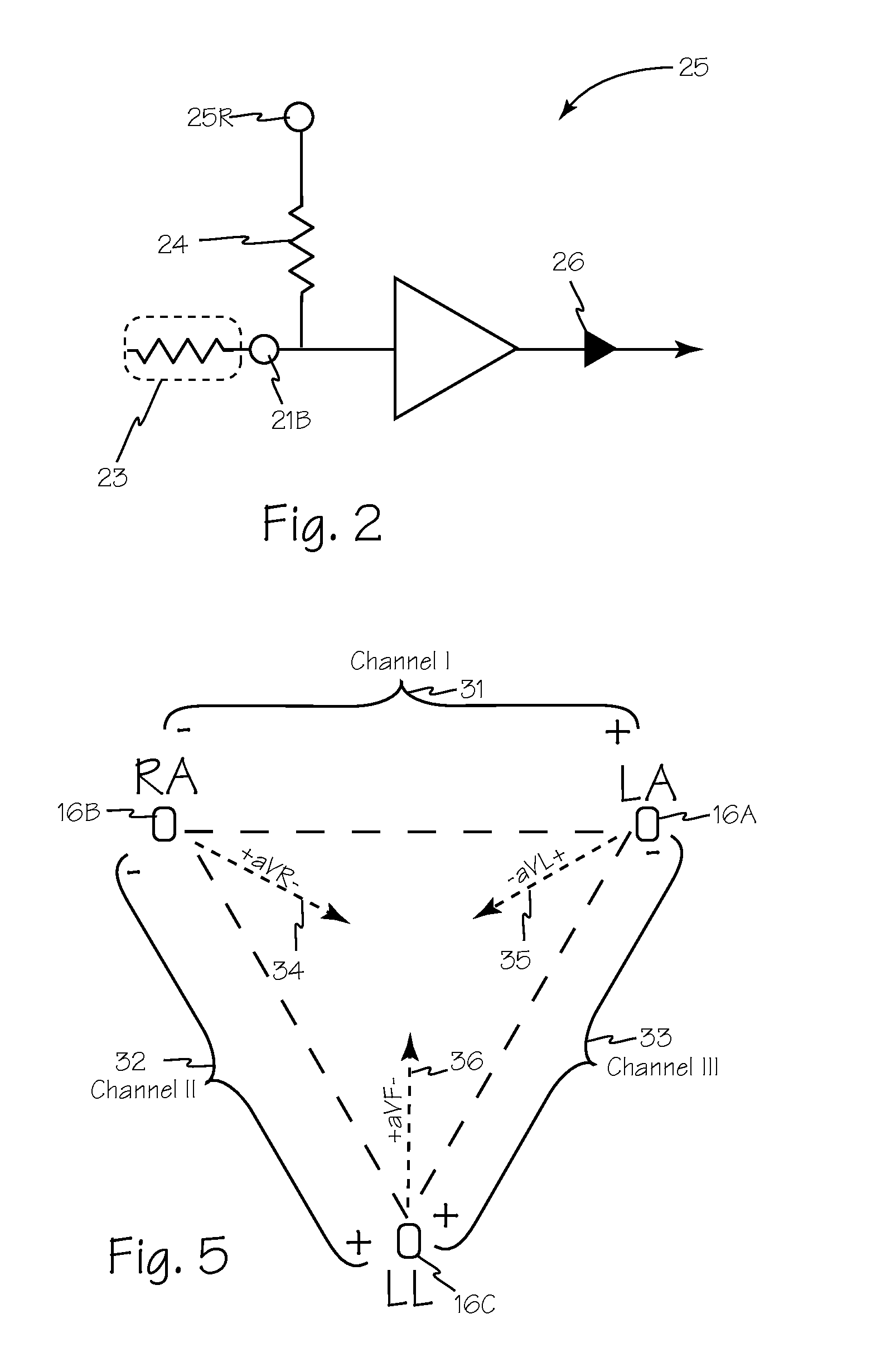
Multi-Function Health Monitor
InactiveUS20110270112A1Minimize power consumptionEasy to handleElectrocardiographySensorsHolter monitorHolter Electrocardiography
A multi-function health monitor is capable of performing a resting 12-lead ECG test, an ECG stress test, a 24-hour holter monitor evaluation and or a 30-day MCT monitoring. Using only 3 electrodes, the multifunction health monitor derives 6 channels (Limb leads & Augmented leads) of data with the noise cancellation (ground) effect of a virtual dynamic RL electrode. An electrode resistivity measurement system quantifies and may compensate for increasing resistance the electrodes and the patient that results from the length of time the electrodes are installed on a patient. The multi-function health monitor can provide data analysis through the gate array as the data is acquired. Data may also be stored for remote analysis as well as for transmission to remote stations upon occurrence of one or more threshold events. Parameters for threshold events may be adjusted remotely to obviate the need for a patient to travel for system adjustment.
Owner:ACS DIAGNOSTICS INC
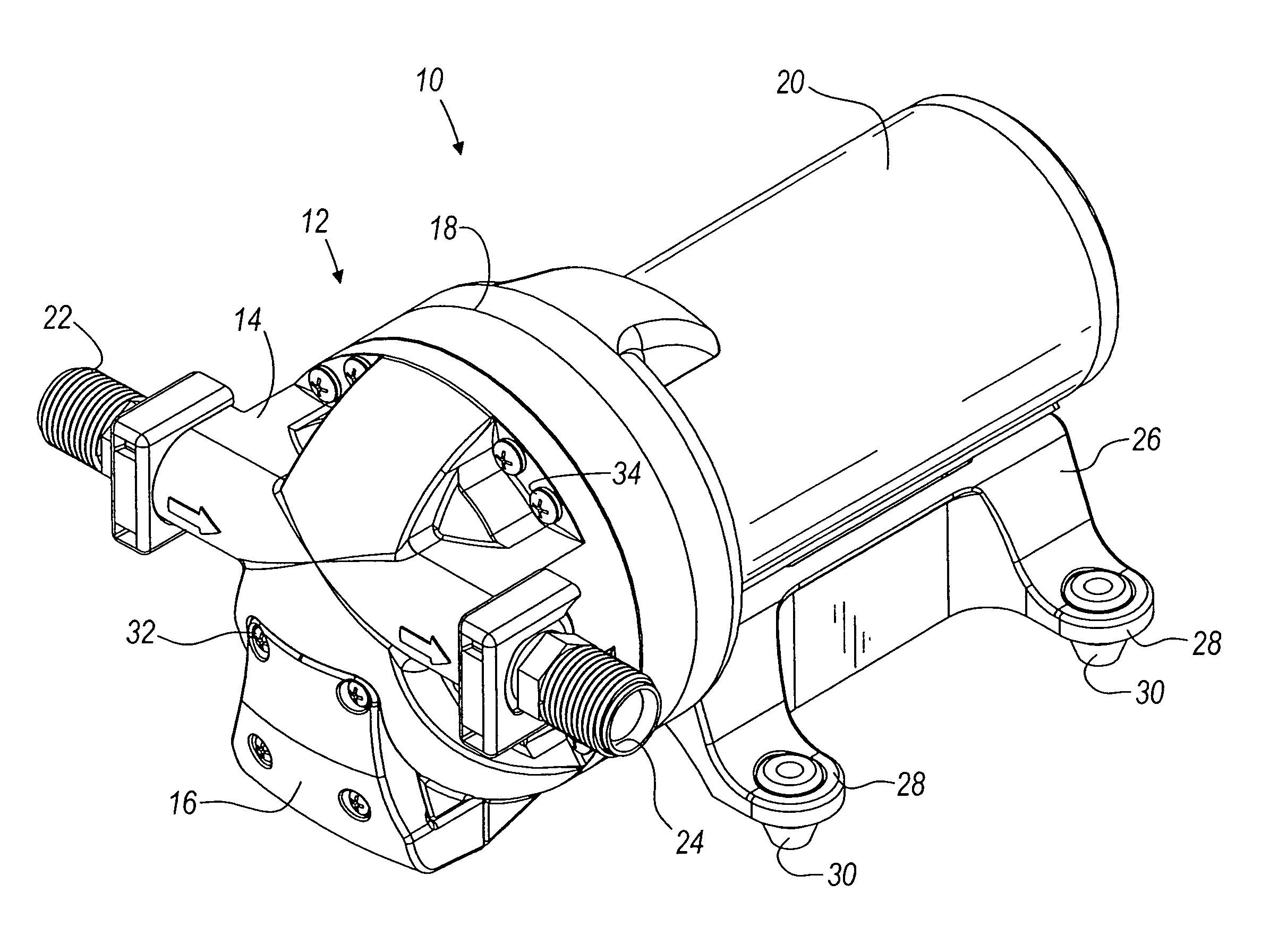
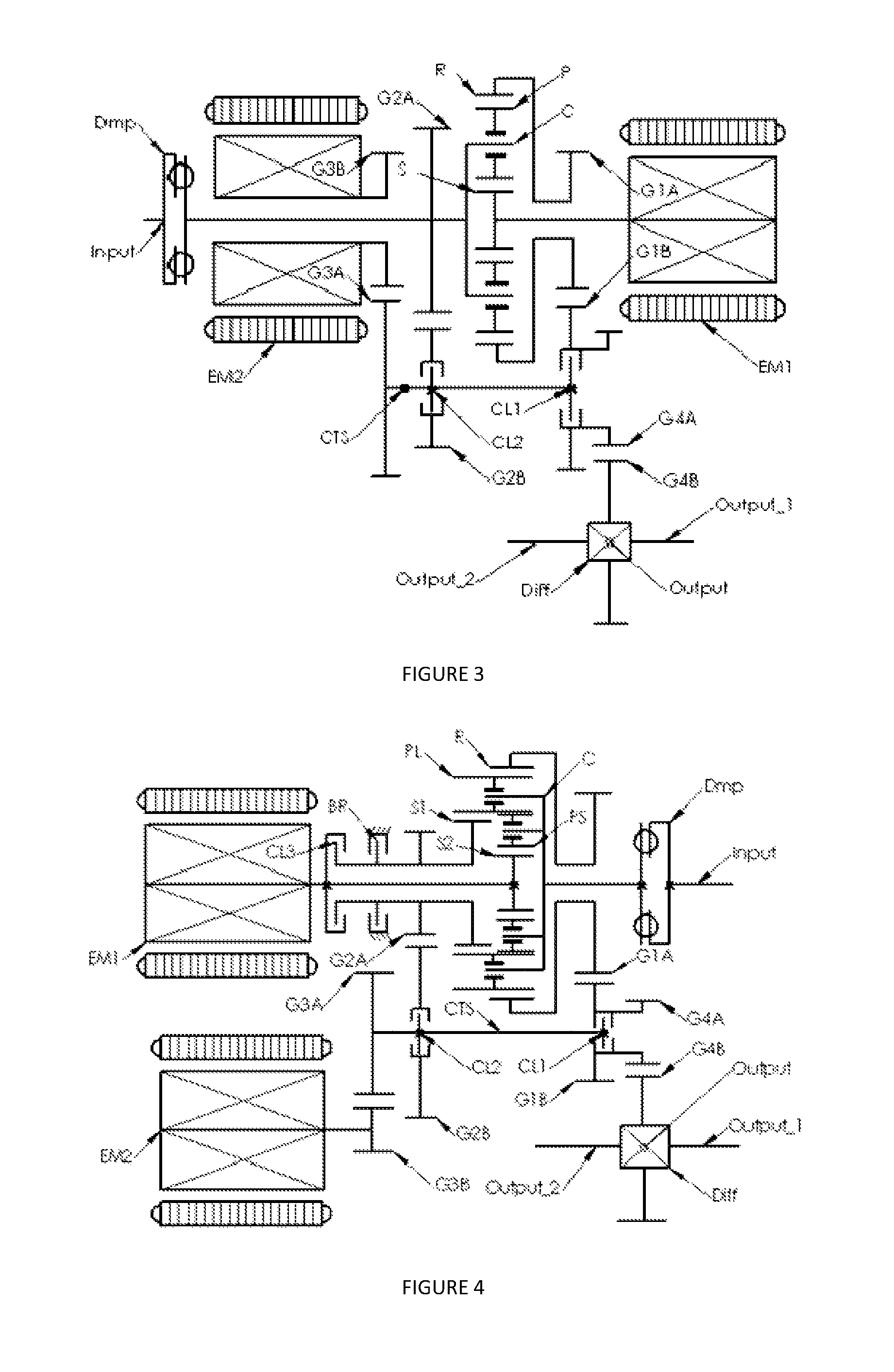
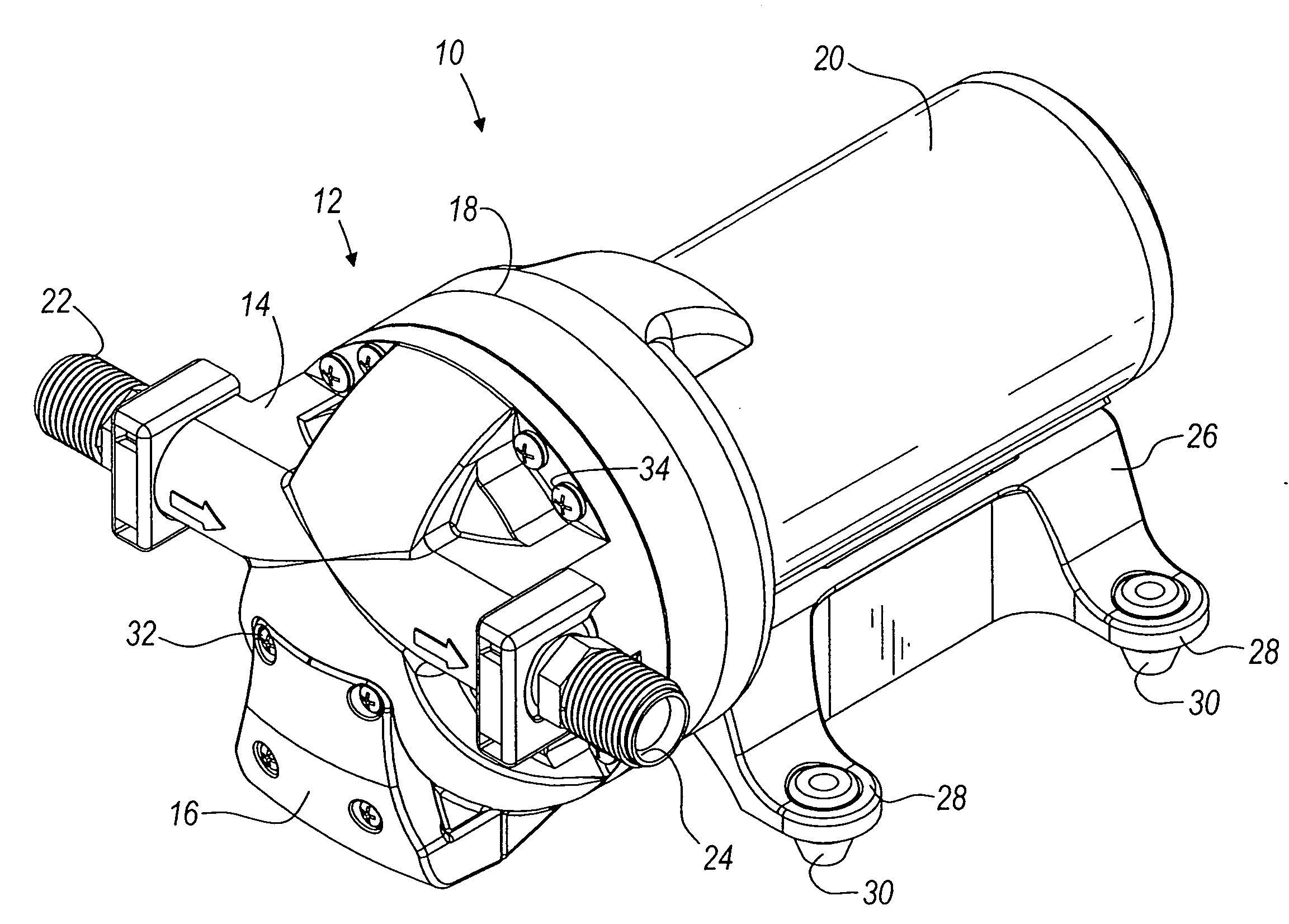
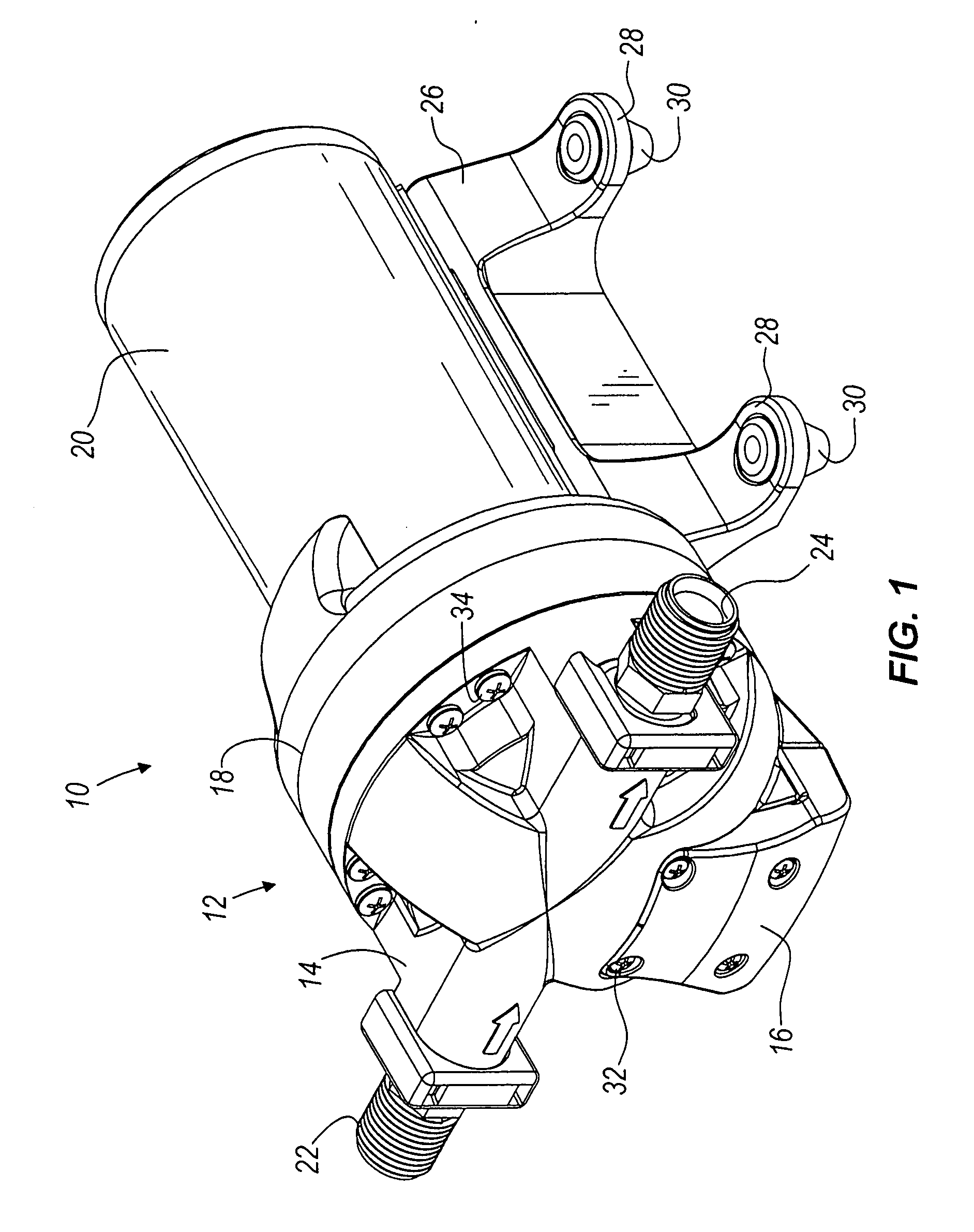
Pump and pump control circuit apparatus and method
InactiveUS7083392B2Large range of motionReduce diaphragm stressFluid parameterFlexible member pumpsMicrocontrollerControl system
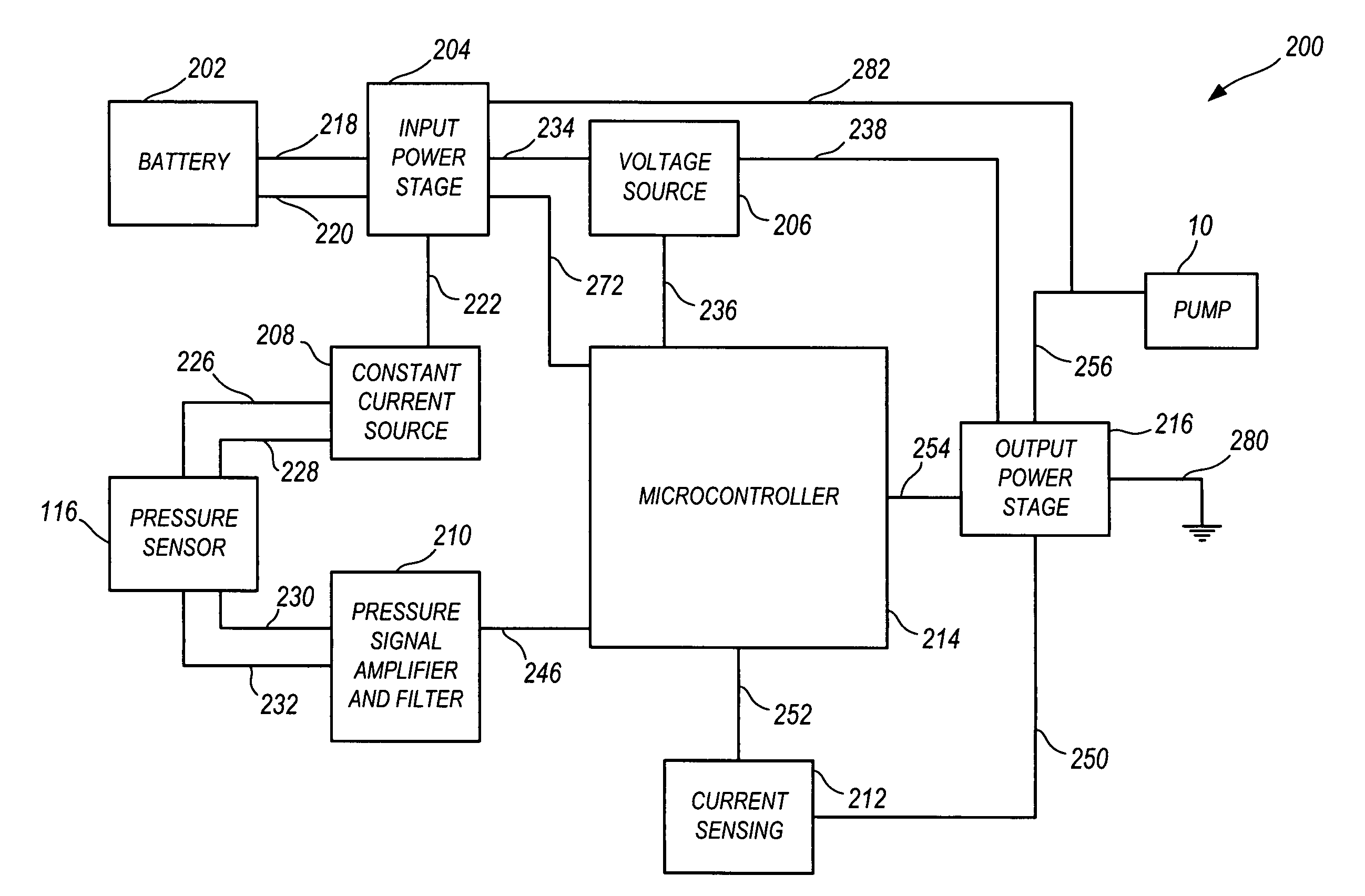
A method and apparatus for a pump and a pump control system. The apparatus includes pistons integrally formed in a diaphragm and coupled to the diaphragm by convolutes. The convolutes have a bottom surface angled with respect to a top surface of the pistons. The apparatus also includes an outlet port positioned tangentially with respect to the perimeter of an outlet chamber. The apparatus further includes a non-mechanical pressure sensor and a temperature sensor coupled to a pump control system. For the method of the invention, the microcontroller provides a pulse-width modulation control signal to an output power stage in order to selectively control the power provided to the pump. The control signal is based on the pressure within the pump, the current being provided to the pump, the voltage level of the battery, and the temperature of the pump.
Owner:SHURFLO
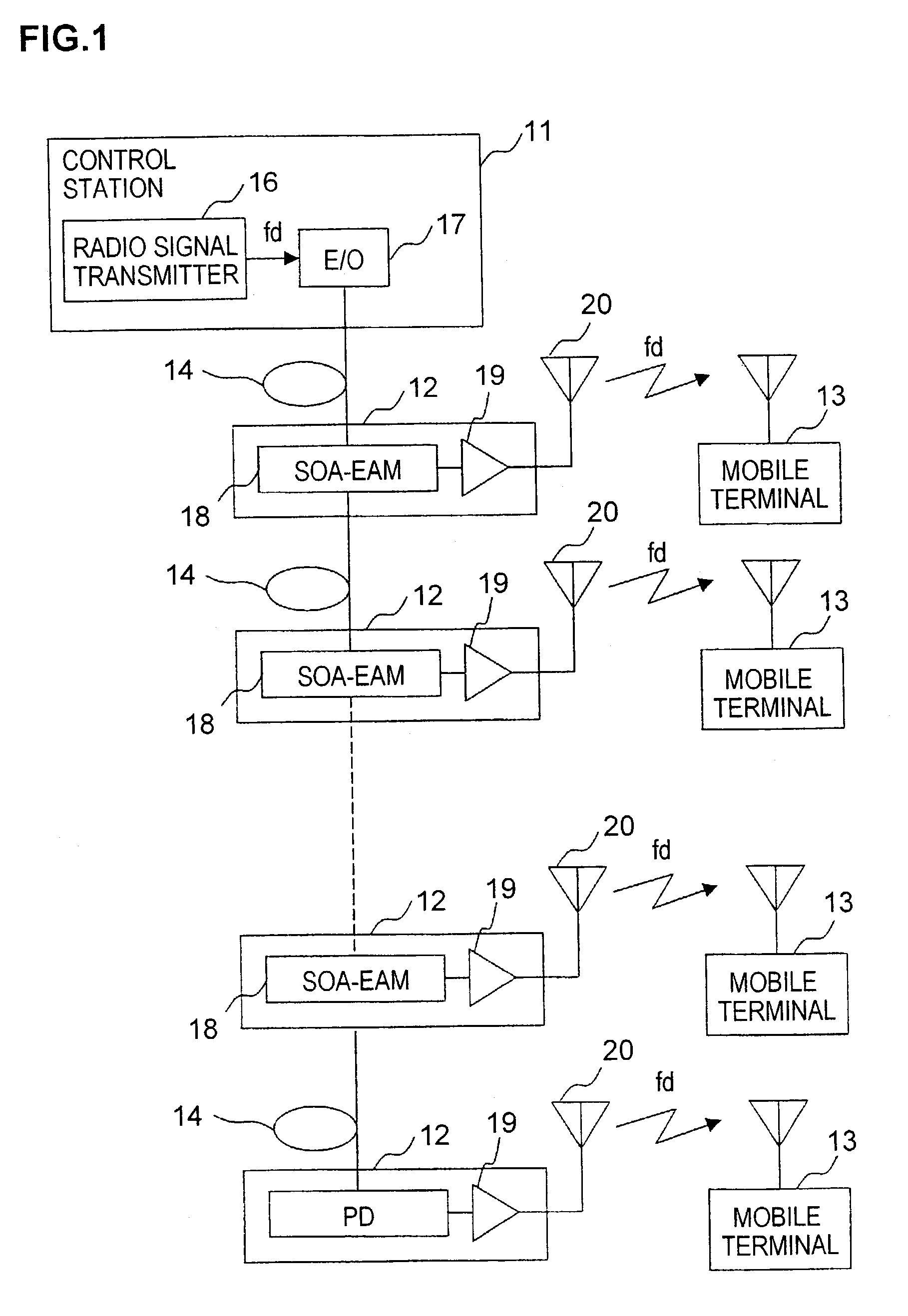
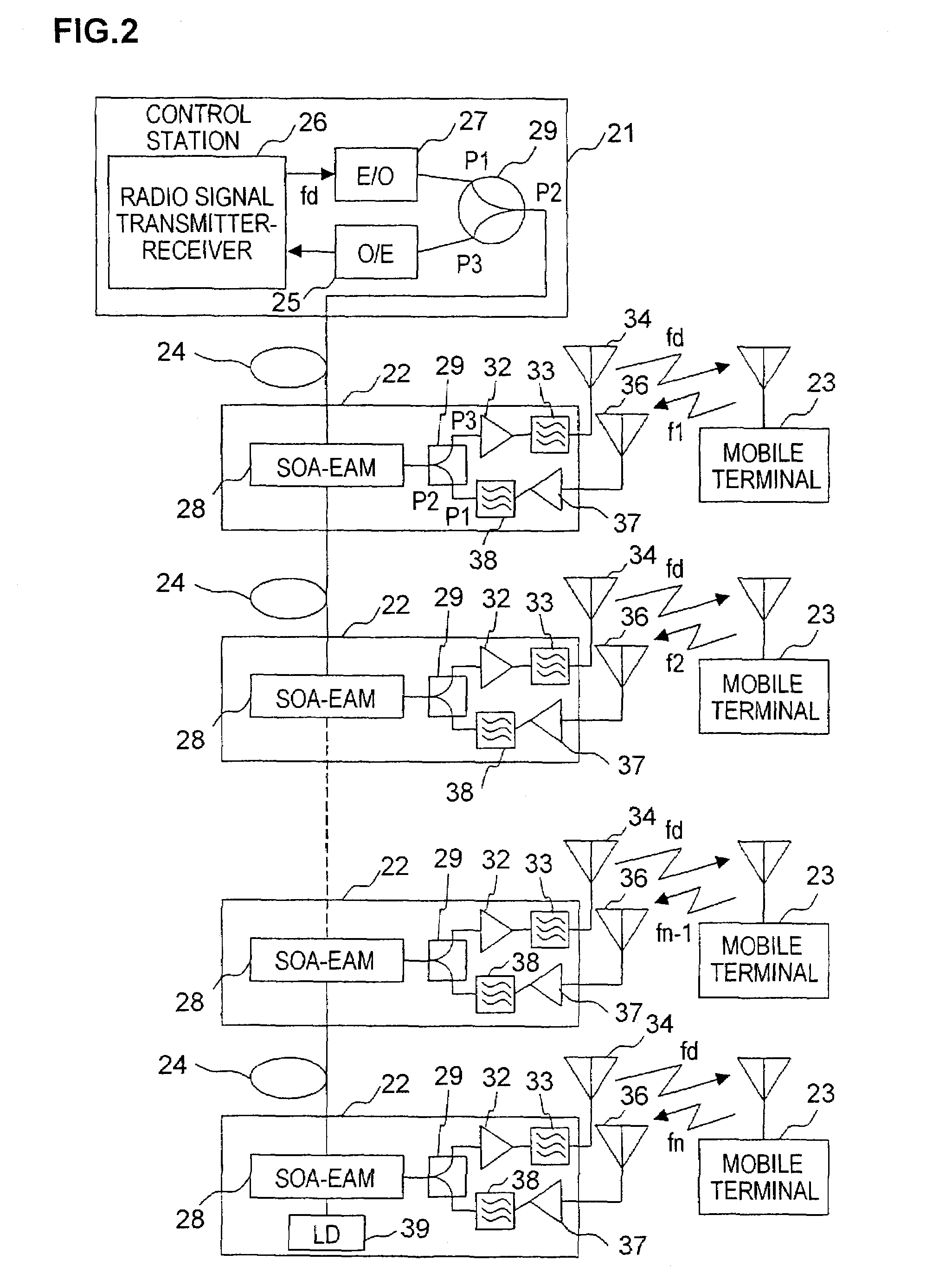
Optical transmission system of radio signal over optical fiber link
InactiveUS7127176B2Small sizeFacilitate manufacturingBus-type electromagnetic networksDistortion/dispersion eliminationOptical powerOptical coupler
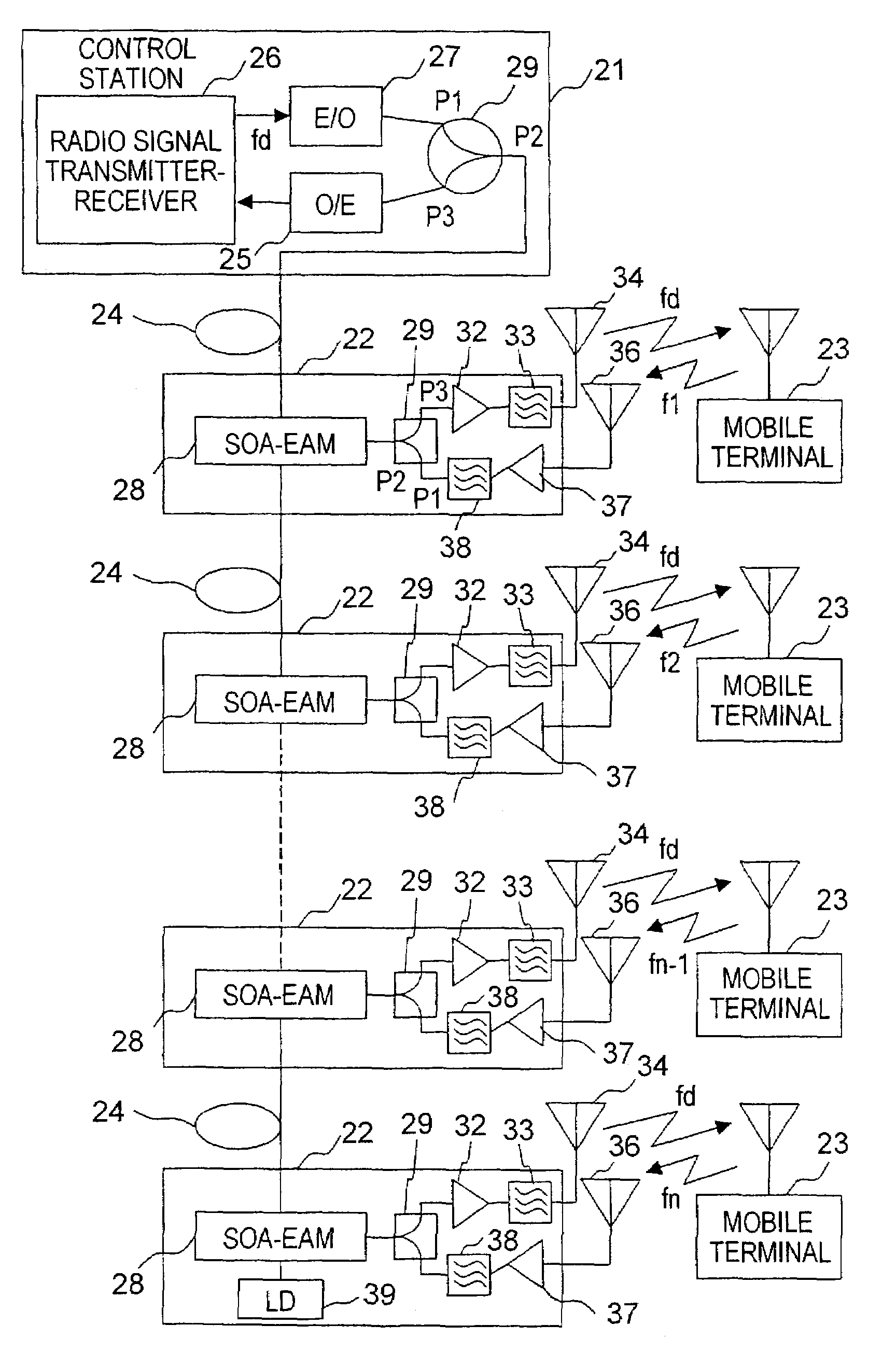
In coupling a control station transmitting a radio signal to a plurality of base stations each transmitting the radio signal to a terminal station by an optical fiber, and dependently connecting the plurality of base stations to the optical fiber, the control station includes a radio signal transmitter and an electrical-to-optical converter. Each of the base stations including an SOA-EAM comprises a semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA) and an electro-absorption modulator (EAM), a down link radio signal amplifier, and a down link antenna, the SOA-EAM receiving an optical signal from the control station. The optical transmission system can prevent optical power from lowering even if the number of base stations increases and can facilitate adding a base station since an optical coupler is not used.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
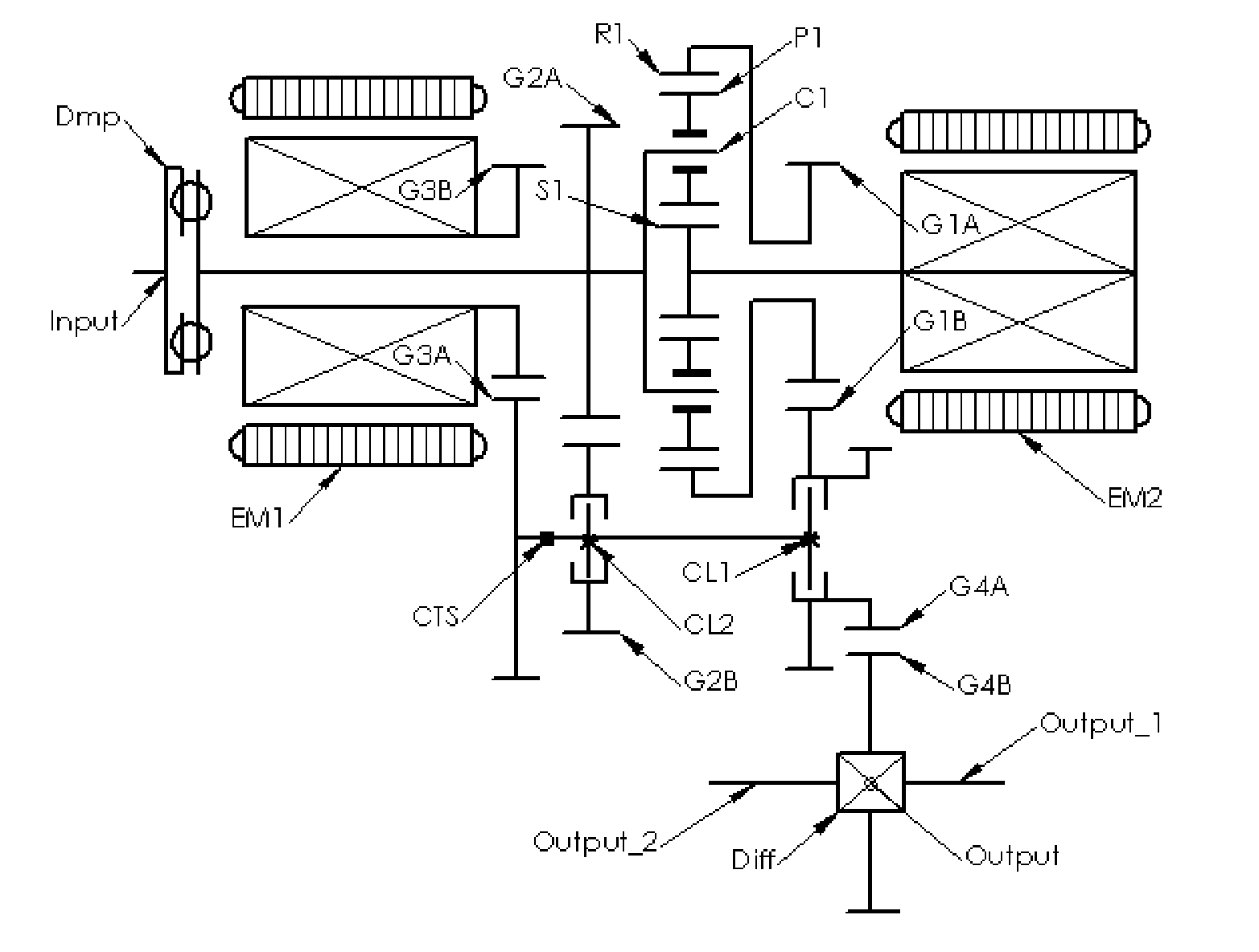
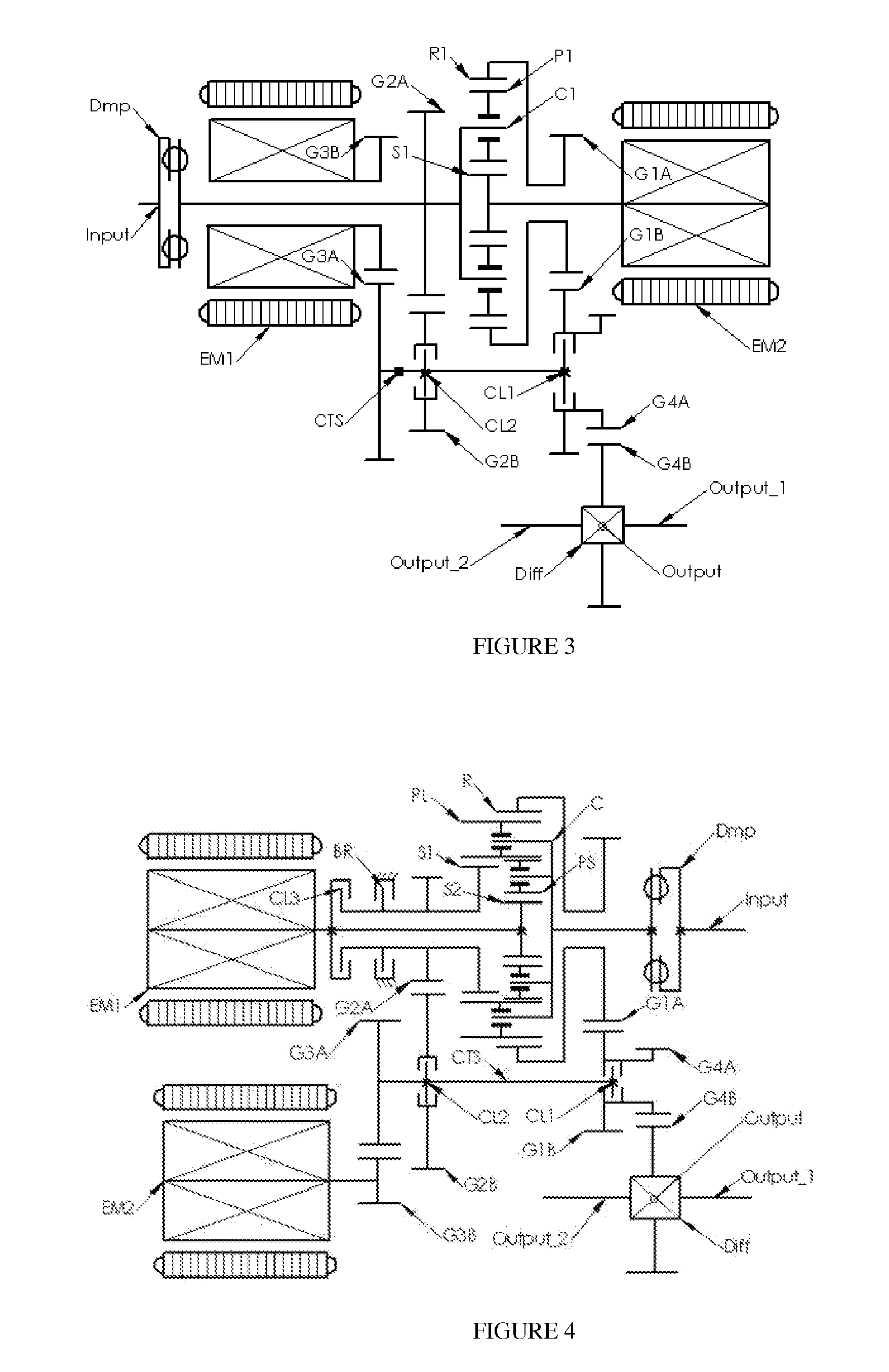
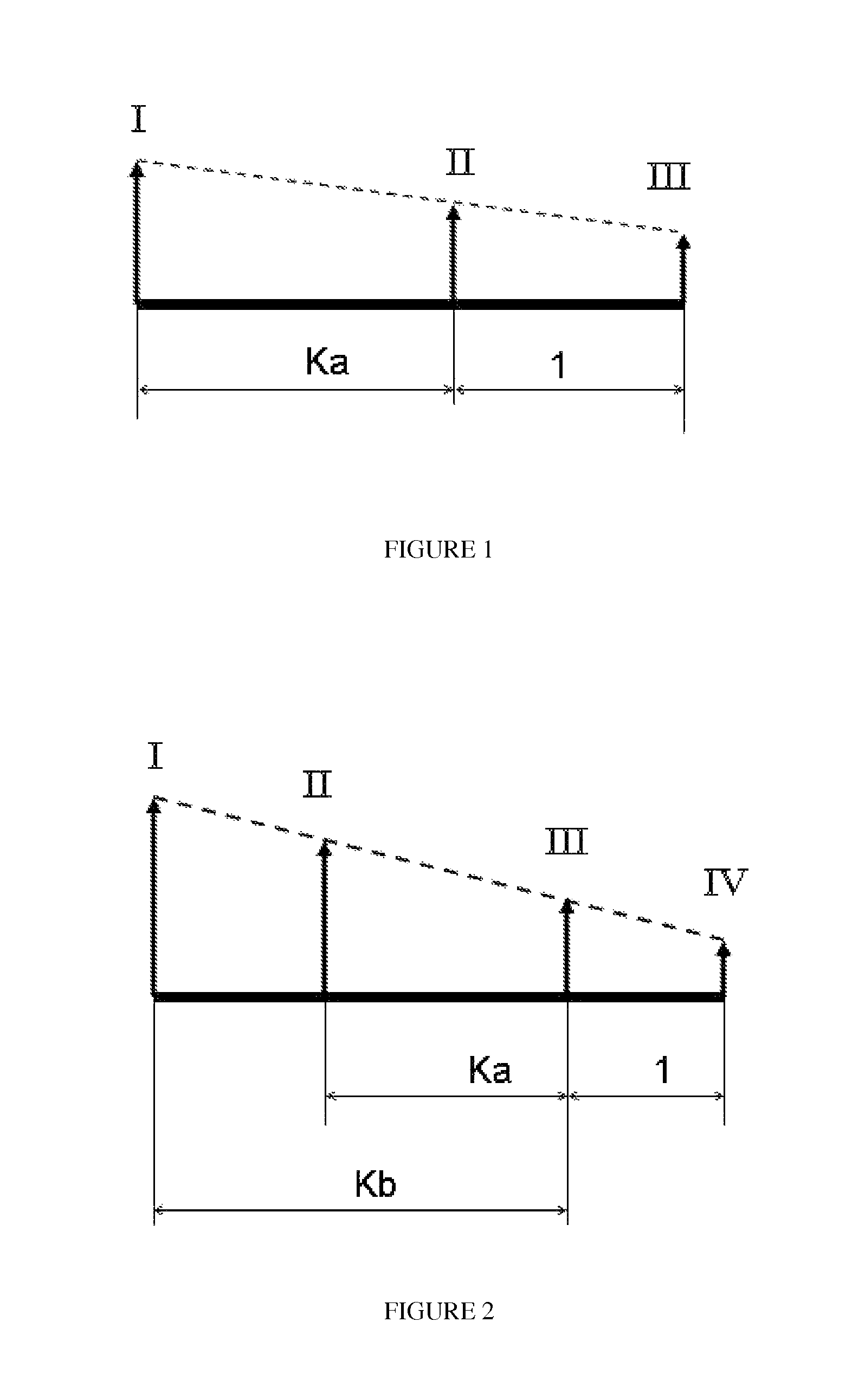
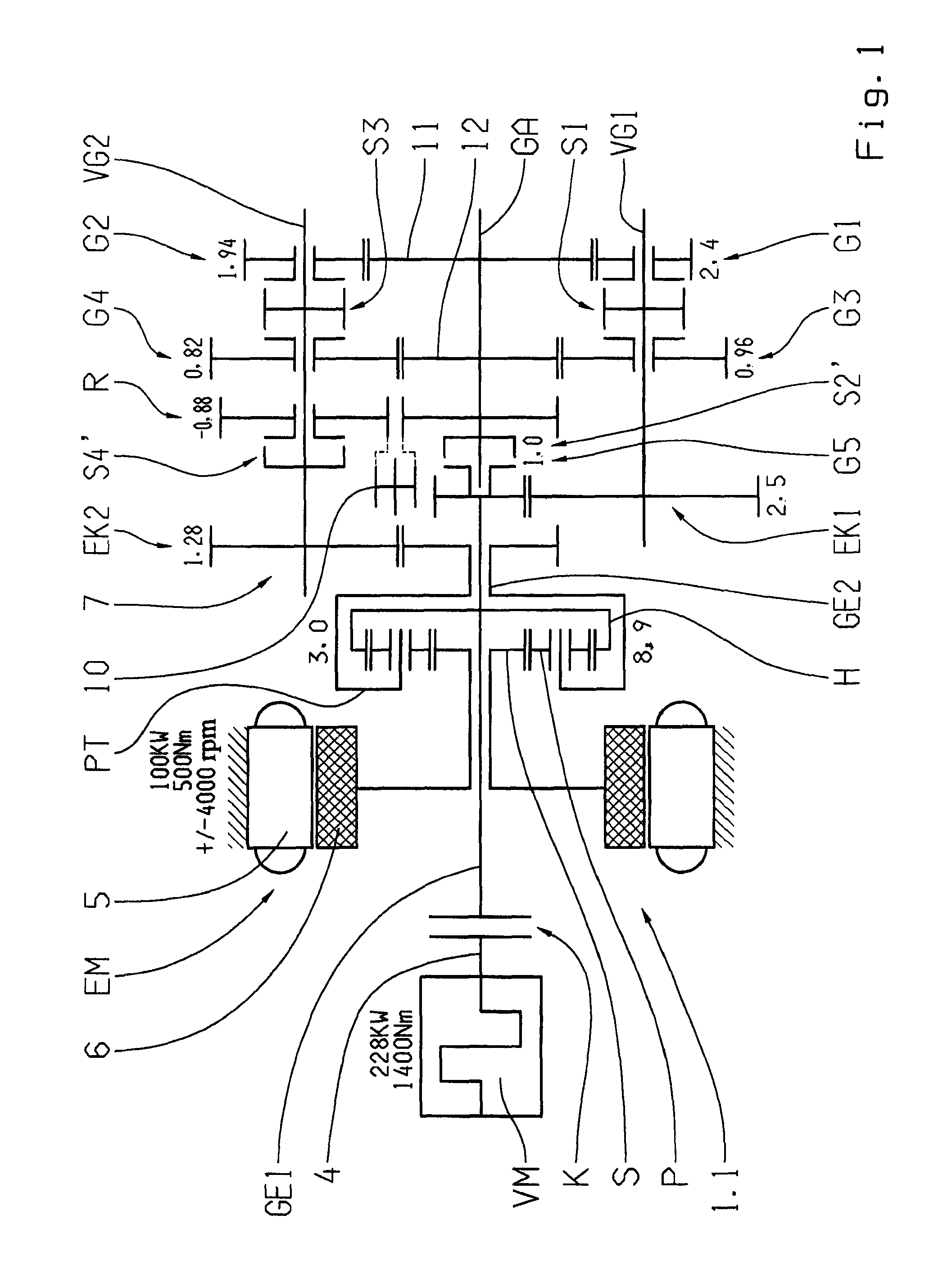
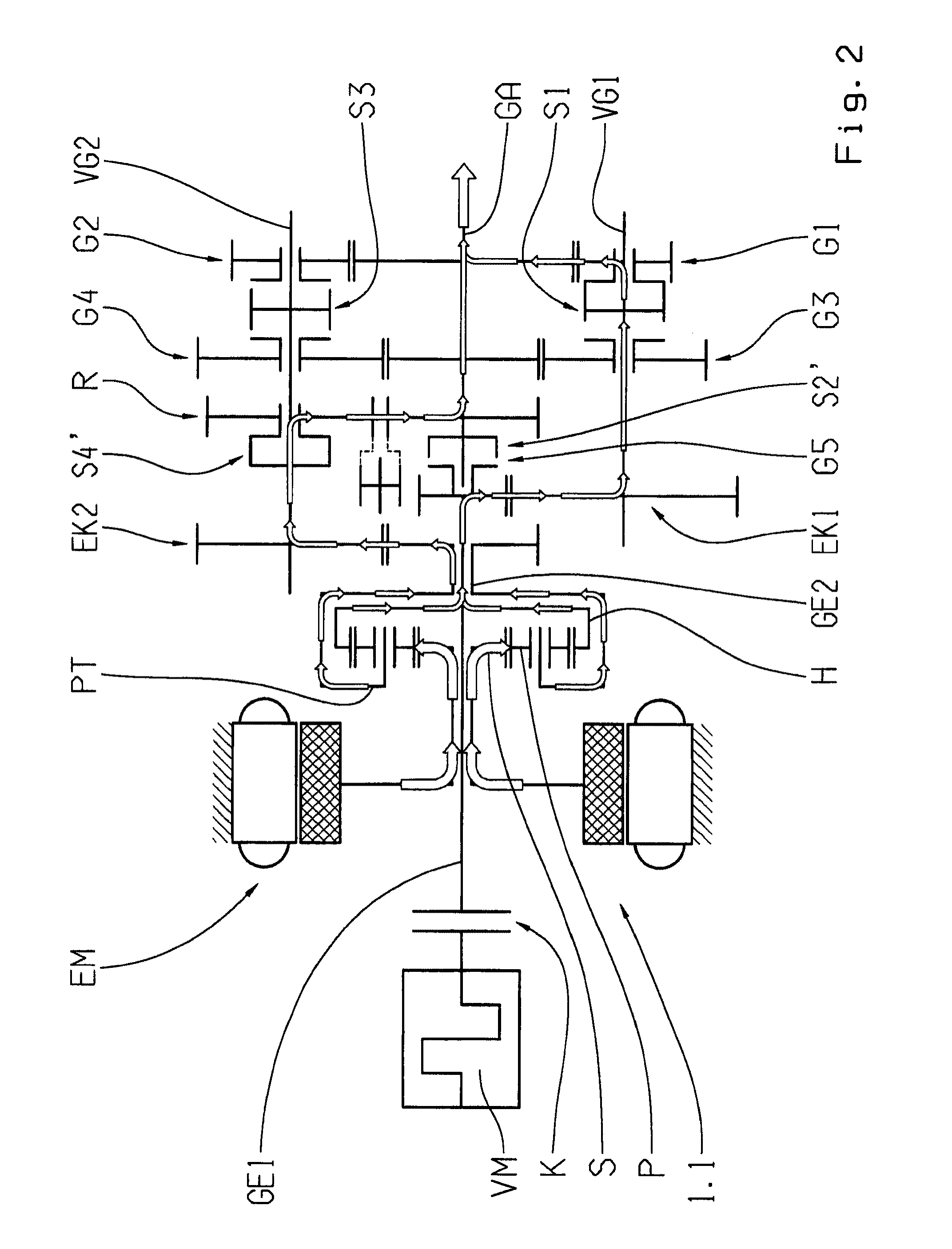
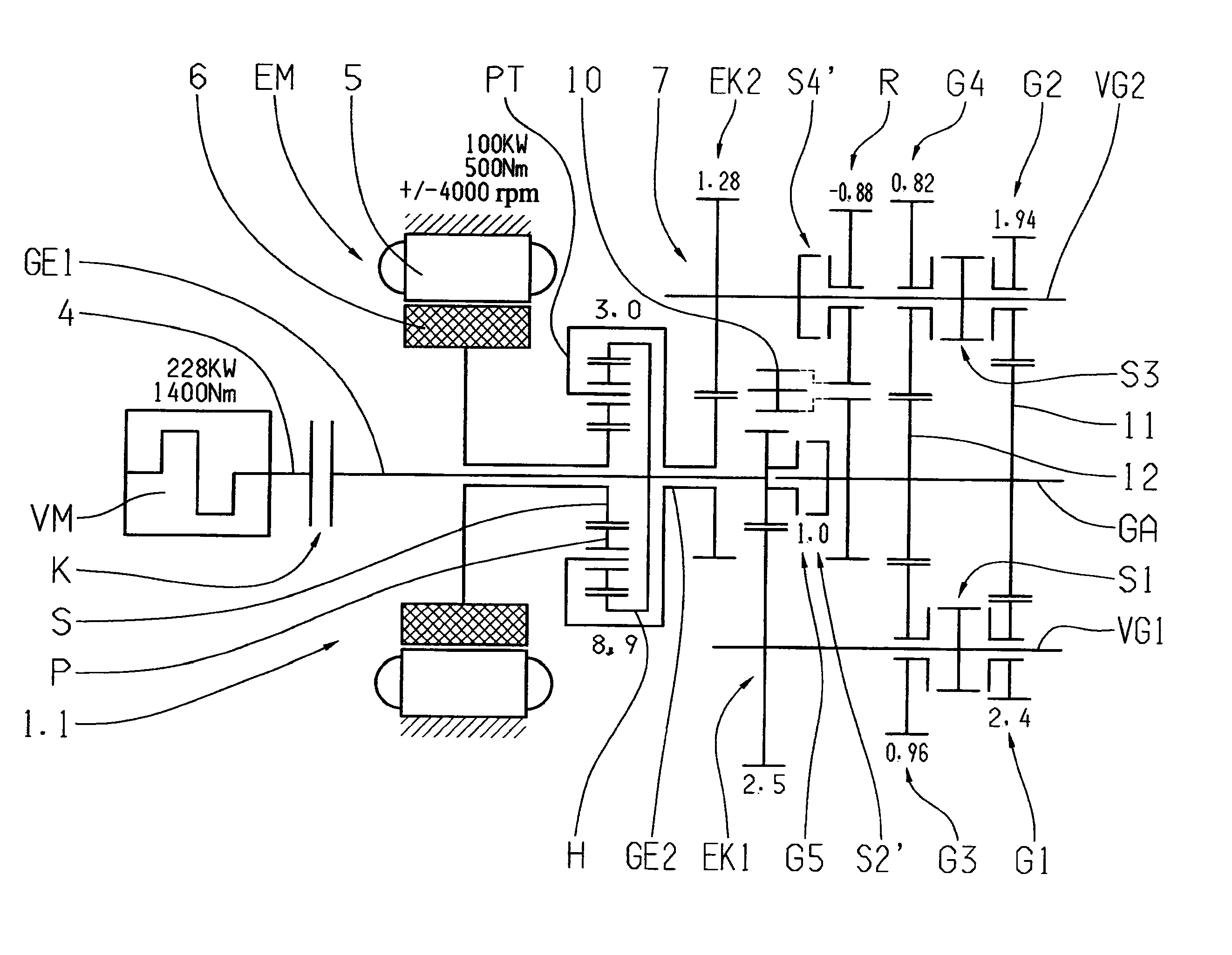
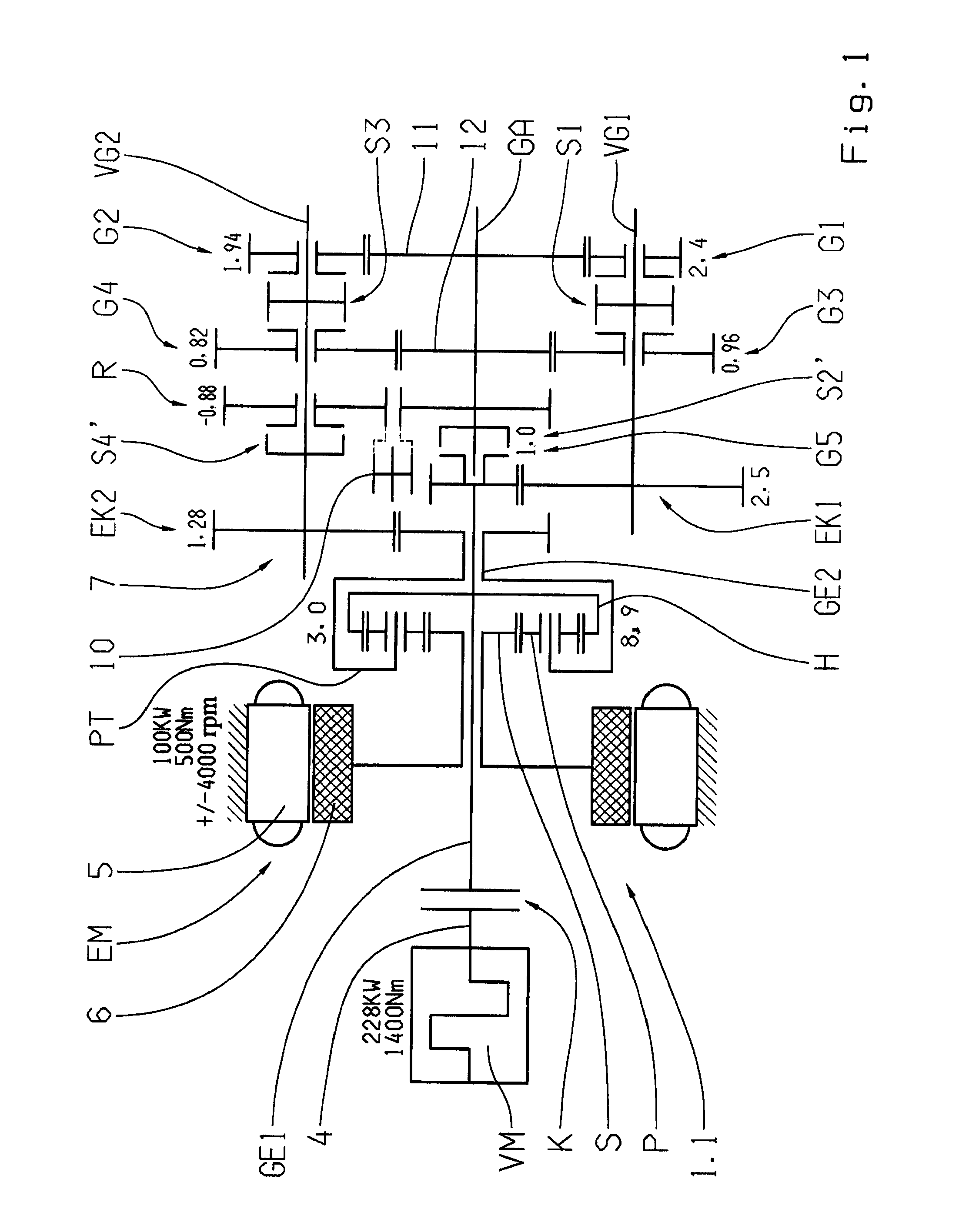
Dual-mode electromechanical variable speed transmission apparatus and method of control
InactiveUS20100261565A1Improve transmission efficiencyAvoid powerHybrid vehiclesElectric propulsion mountingDual modeElectric machine
The current invention discloses a dual-mode electro-mechanical variable speed transmission. Said transmission includes an input shaft, an output shaft system, a planetary gear system having at least three co-axial rotating members, two electric machines along with the associated controllers for the electric machines, and at least a clutch. Said planetary gear system has at least three branches; each branch corresponds to a co-axial rotating member. The first branch couples to the first electric machine with a fixed speed ratio; another branch couples to the input shaft with a fixed speed ratio; and yet anther branch couples to the output shaft system with a fixed speed ratio; the second electric machine couples selectively to two of the branches in the planetary gear system with different speed ratios. Said two branches are not the first branch and one of the said two branches is connected to the output shaft system. Said dual-mode electro-mechanical variable speed transmission is capable of providing at least two power splitting operation modes, including an output power splitting mode. Different operation modes cover different speed ratio regimes. At the mode switching point, the corresponding clutch or clutches is automatically synchronized. Thus the speeds of the rotation members of the transmission are continuous, and the transmission is free from shock loads at the operating mode switching point. In addition, said transmission is capable of providing operations with at least a fixed input-to-output speed ratio.
Owner:SHANDONG LIANCHENG GREENMAX TECH
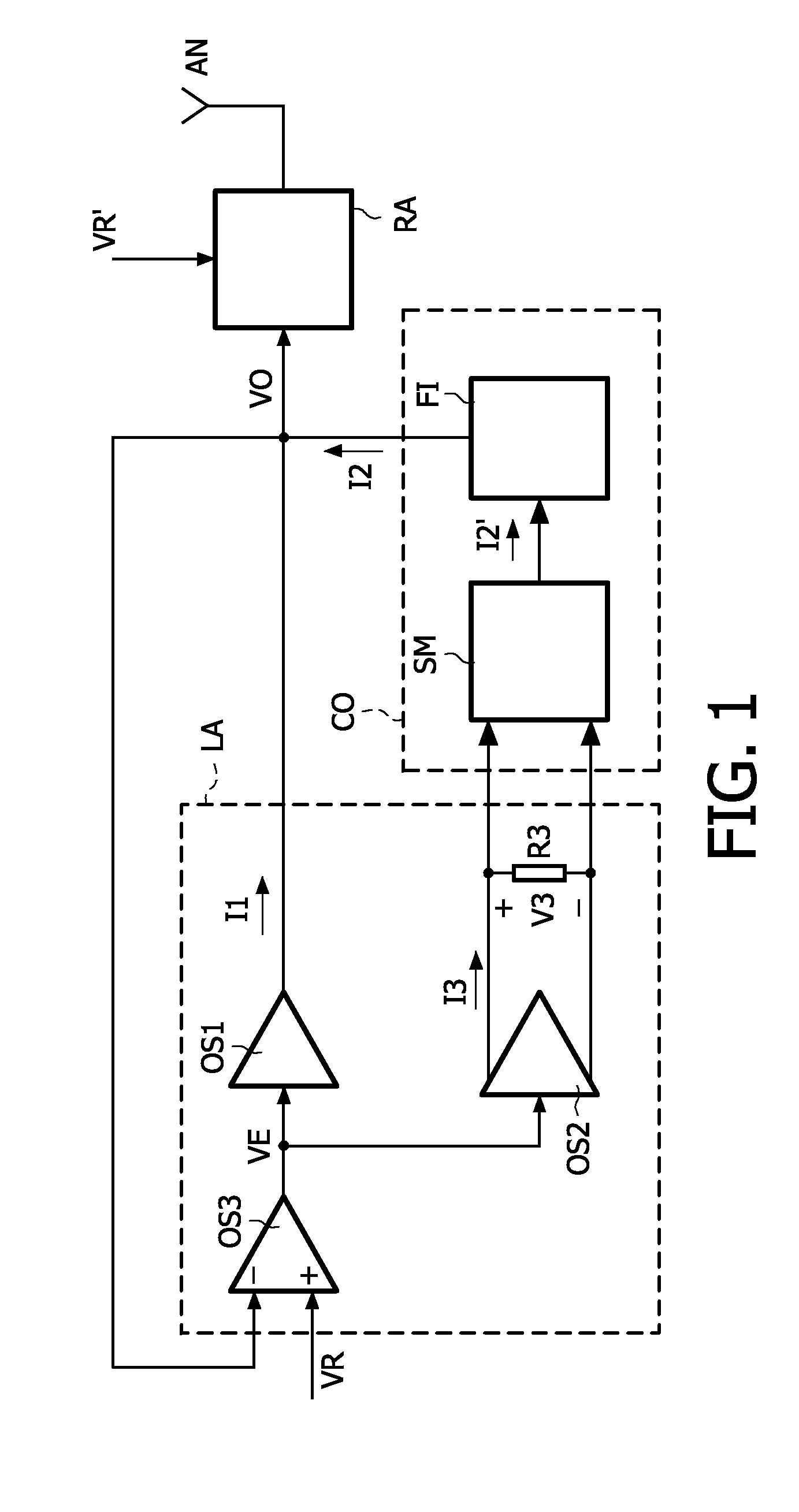
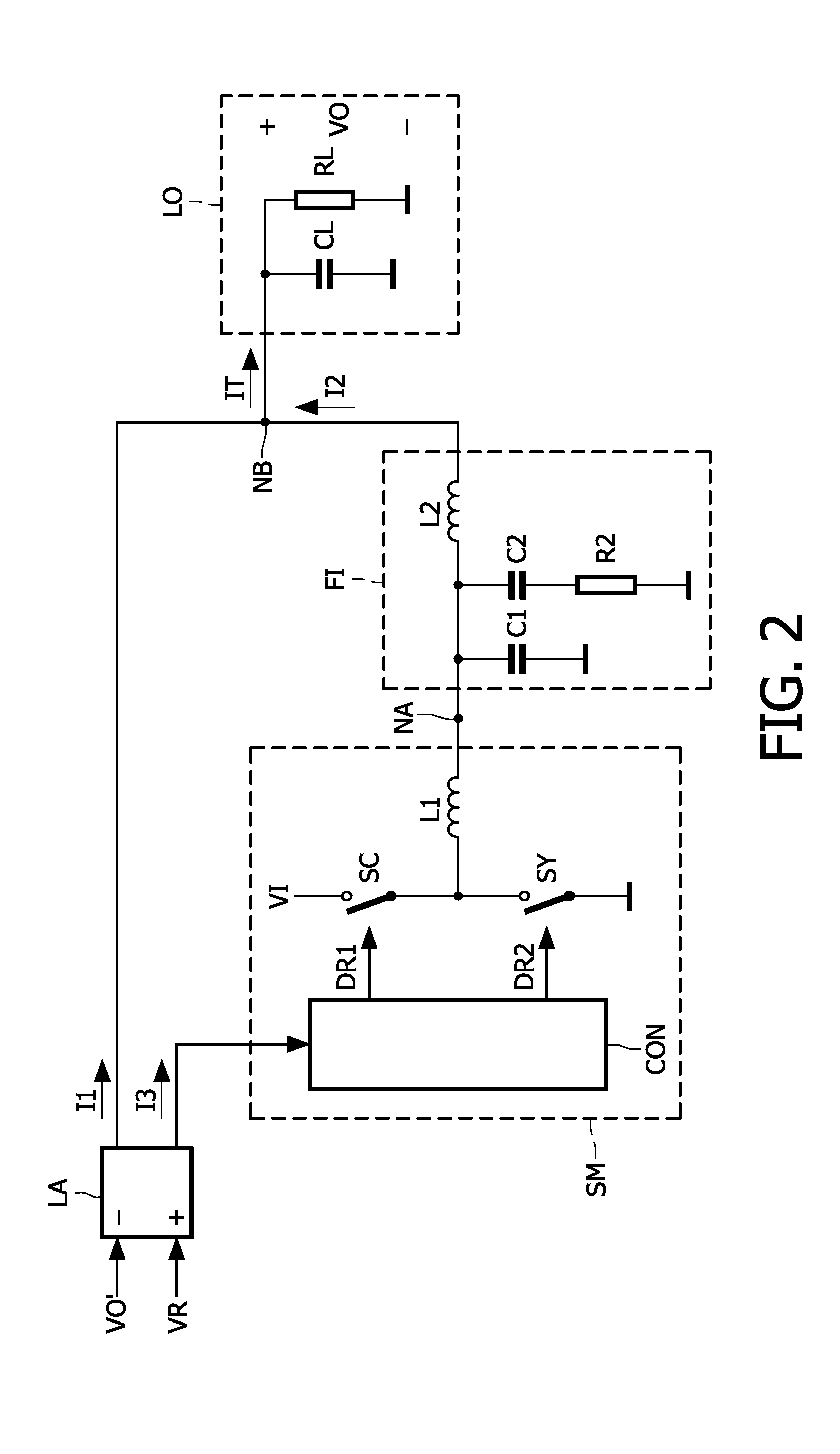
Parallel arranged linear amplifier and dc-dc converter
InactiveUS20100045247A1Enhanced inhibitory effectNot control loop stabilityAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesElectric variable regulationDc dc converterAudio power amplifier
A power supply system comprises a parallel arrangement of a linear amplifier (LA) and a DC-DC converter (CO). The linear amplifier (LA) has an amplifier output to supply a first current (II) to the load (LO). The DC-DC converter (CO) comprises: a converter output for supplying a second current (12) to the load (LO), a first inductor (L1), and a switch (SC) coupled to the first inductor (L1) for generating a current in the first inductor (L1), and a low-pass filter (FI) arranged between the first inductor (L1) and the load (LO). The low pass filter (FI) comprises a first capacitor (C1; CA) which has a first terminal coupled to the switch (SC) an a second terminal coupled to a reference voltage level (GND), and a second inductor (L2; LC) which has a first terminal coupled to the first inductor (L1) and a second terminal coupled to the load (LO). The low-pass filter further comprises, either: (i) a series arrangement of a second capacitor (C2) and a damping resistor (R2), which series arrangement is arranged in parallel with the first capacitor (C1), or (ii) a parallel arrangement of a third capacitor (CB) and a damping resistor (RB) arranged in series with the first capacitor (CA), or (iii) a series arrangement of a third inductor (L3) and a damping resistor (R3), which series arrangement is arranged in parallel with the second inductor (L2), or (iv) a parallel arrangement of a fourth inductor (LD) and a damping resistor (RD), which parallel arrangement is arranged in series with the second inductor (LC).
Owner:NXP BV
Pump and pump control circuit apparatus and method
InactiveUS20080181786A1Large range of motionRelieve pressureFluid parameterFlexible member pumpsMicrocontrollerControl system
A method and apparatus for a pump and a pump control system. The apparatus includes pistons integrally formed in a diaphragm and coupled to the diaphragm by convolutes. The convolutes have a bottom surface angled with respect to a top surface of the pistons. The apparatus also includes an outlet port positioned tangentially with respect to the perimeter of an outlet chamber. The apparatus further includes a non-mechanical pressure sensor and a temperature sensor coupled to a pump control system. For the method of the invention, the microcontroller provides a pulse-width modulation control signal to an output power stage in order to selectively control the power provided to the pump. The control signal is based on the pressure within the pump, the current being provided to the pump, the voltage level of the battery, and the temperature of the pump.
Owner:SHURFLO
Managing Power Consumption Based on Historical Average
ActiveUS20090119523A1Avoid powerEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementComputerized systemEngineering
In one embodiment, an upper power limit and an average power limit are specified for each server of a computer system. Power to each server is controlled so that the instantaneous power consumption does not exceed the upper power limit and the average power consumption does not exceed the average power limit. Servers whose average power consumption is currently less than the average power limit are identified. The instantaneous power consumption of each identified server is temporarily allowed to exceed its average power limit, to maximize server throughput. In cases where the average power limit of a device is reduced, such as may occur during peak energy pricing hours, the instantaneous power consumption of the device may be throttled down below the average power limit until the average power consumption no longer exceeds the average power limit.
Owner:LENOVO GLOBAL TECH INT LTD
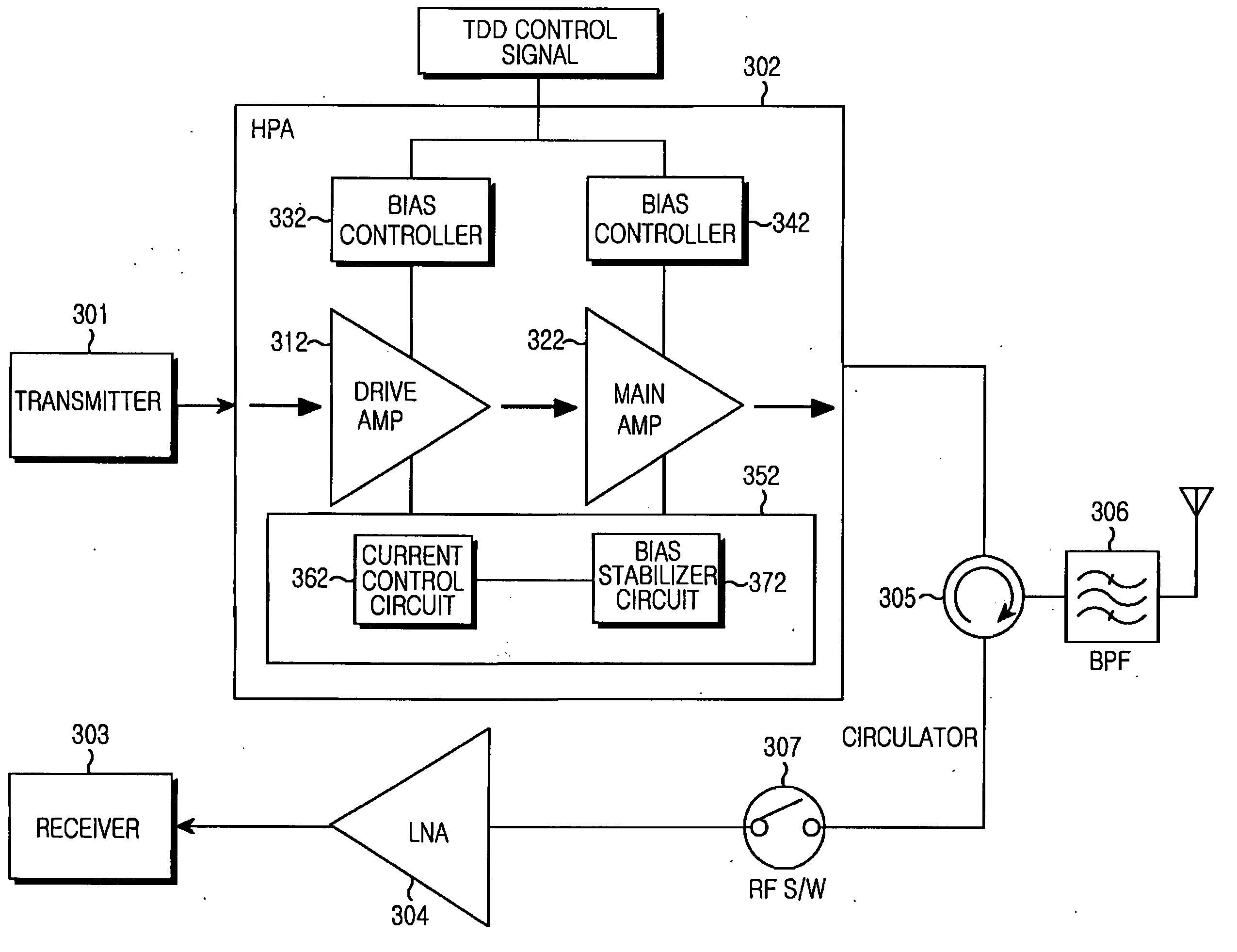
High-power amplifier apparatus for TDD wireless communication system
ActiveUS20070111686A1Avoid powerReduce leakage powerResonant long antennasHigh frequency amplifiersCommunications systemAudio power amplifier
Provided is an HPA apparatus for a TDD wireless communication system. In the HPA apparatus, a power amplifier amplifies the power of an input signal. A gate bias controller turns on / off a gate bias of the power amplifier in accordance with a TDD control signal. A constellation error optimizer circuit removes a current fluctuation and a power noise, which occur when the gate bias controller turns on / off the power amplifier in a TX mode, to stabilize a drain bias thereof.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Dual-mode electromechanical variable speed transmission apparatus and method of control
InactiveUS8734281B2Improve transmission efficiencyAvoid powerHybrid vehiclesElectric propulsion mountingElectric machineDual mode
A dual-mode electro-mechanical variable speed transmission includes an input shaft, an output shaft system, a gear system having at least three branches, two electric machines, and at least a clutch. The first electric machine couples to a branch of the gear system, the output shaft system couples to another branch of the gear system, the input shaft couples to the remaining branch or one of the remaining branches of the gear system, and the second electric machine selectively couples either to the same branch that is coupled to the output shaft system with a speed ratio or to one of the remaining branches that that is not coupled to the first electric machine with a different speed ratio. The transmission provides at least two power splitting modes to cover different speed ratio regimes. The transmission can also provide at least a fixed output shaft to input shaft speed ratio.
Owner:SHANDONG LIANCHENG GREENMAX TECH
Pump and pump control circuit apparatus and method
InactiveUS20080152508A1Large range of motionRelieve pressureFluid parameterAC motor controlMicrocontrollerControl system
A method and apparatus for a pump and a pump control system. The apparatus includes pistons integrally formed in a diaphragm and coupled to the diaphragm by convolutes. The convolutes have a bottom surface angled with respect to a top surface of the pistons. The apparatus also includes an outlet port positioned tangentially with respect to the perimeter of an outlet chamber. The apparatus further includes a non-mechanical pressure sensor and a temperature sensor coupled to a pump control system. For the method of the invention, the microcontroller provides a pulse-width modulation control signal to an output power stage in order to selectively control the power provided to the pump. The control signal is based on the pressure within the pump, the current being provided to the pump, the voltage level of the battery, and the temperature of the pump.
Owner:SHURFLO
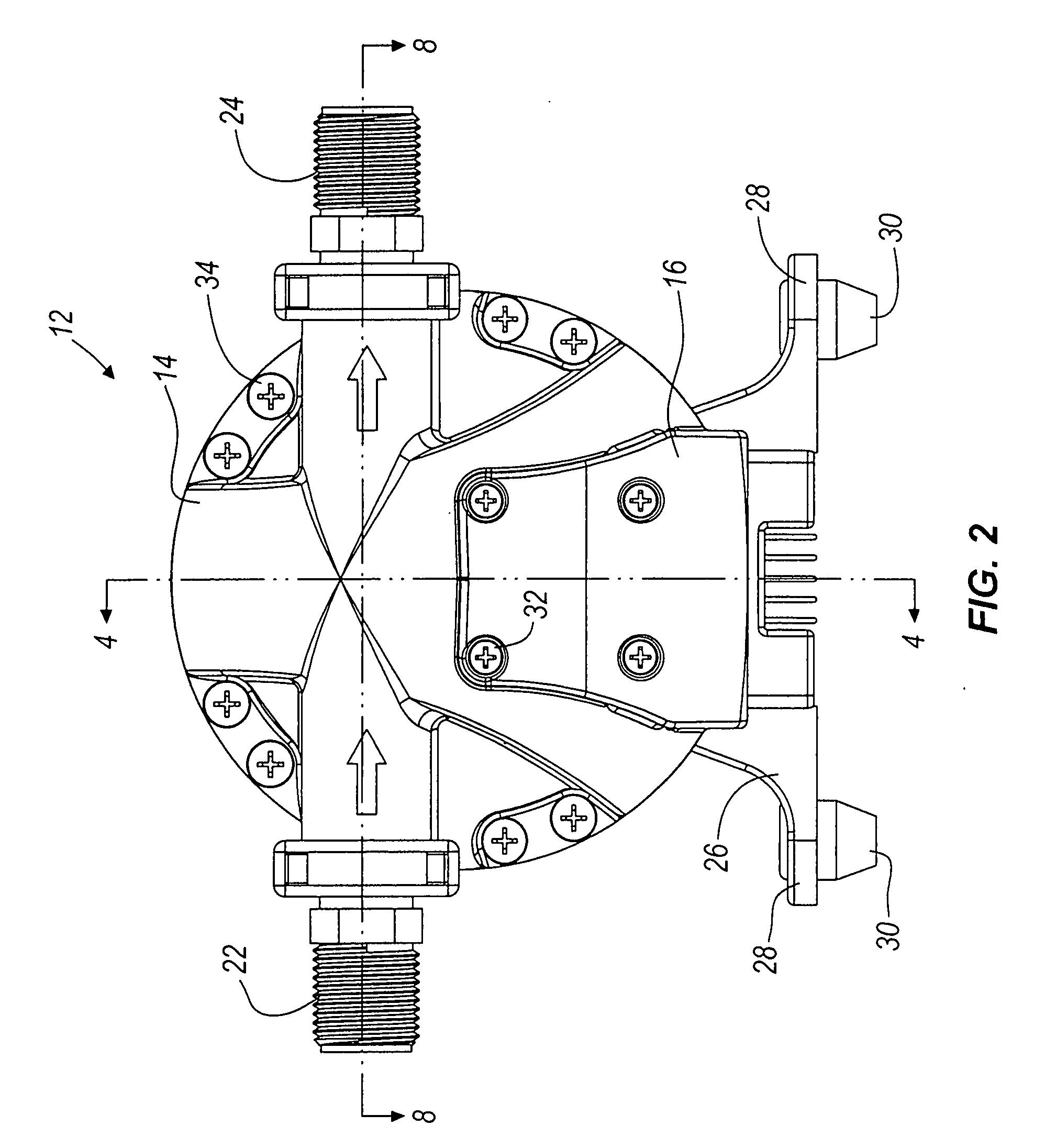
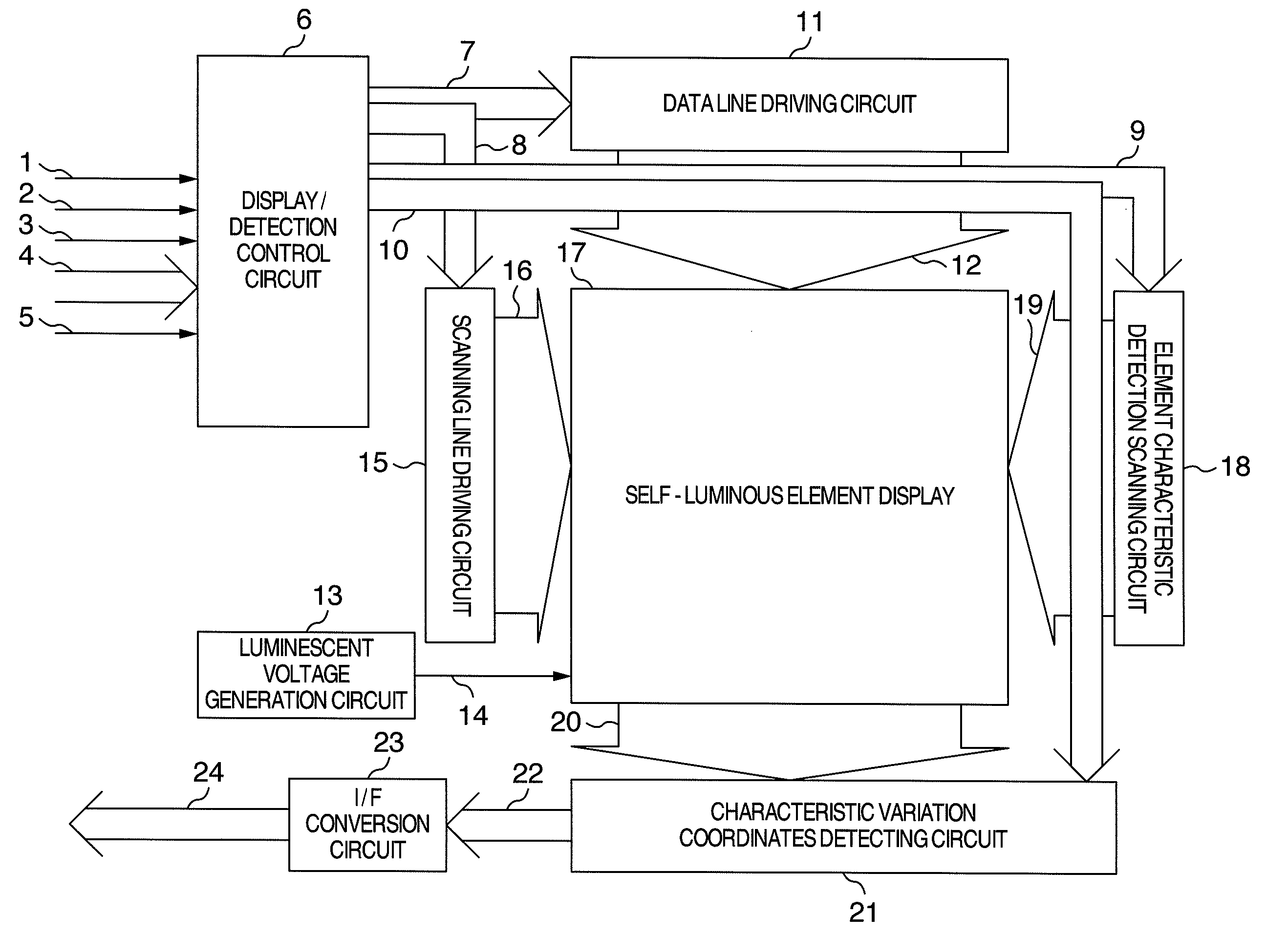
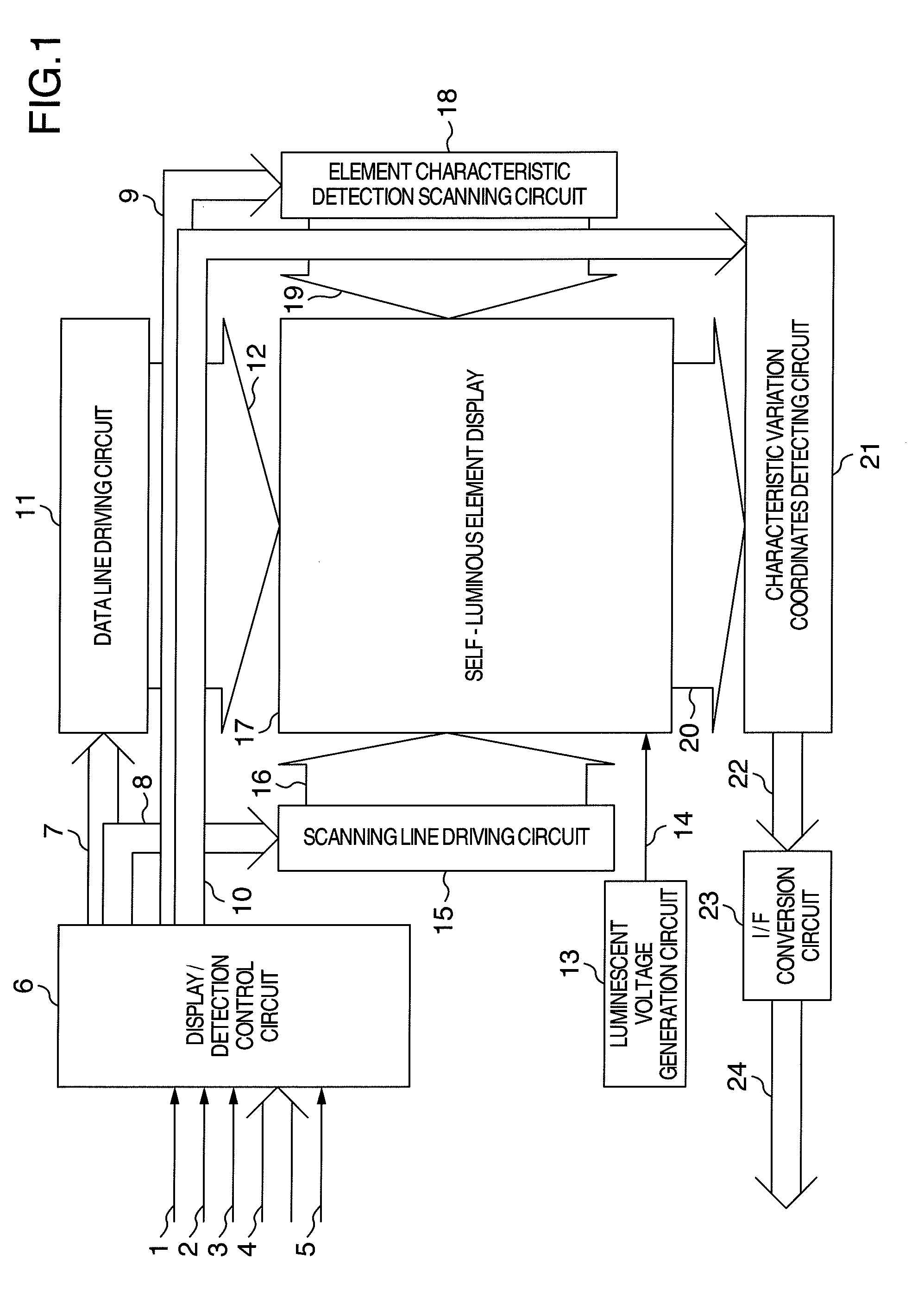
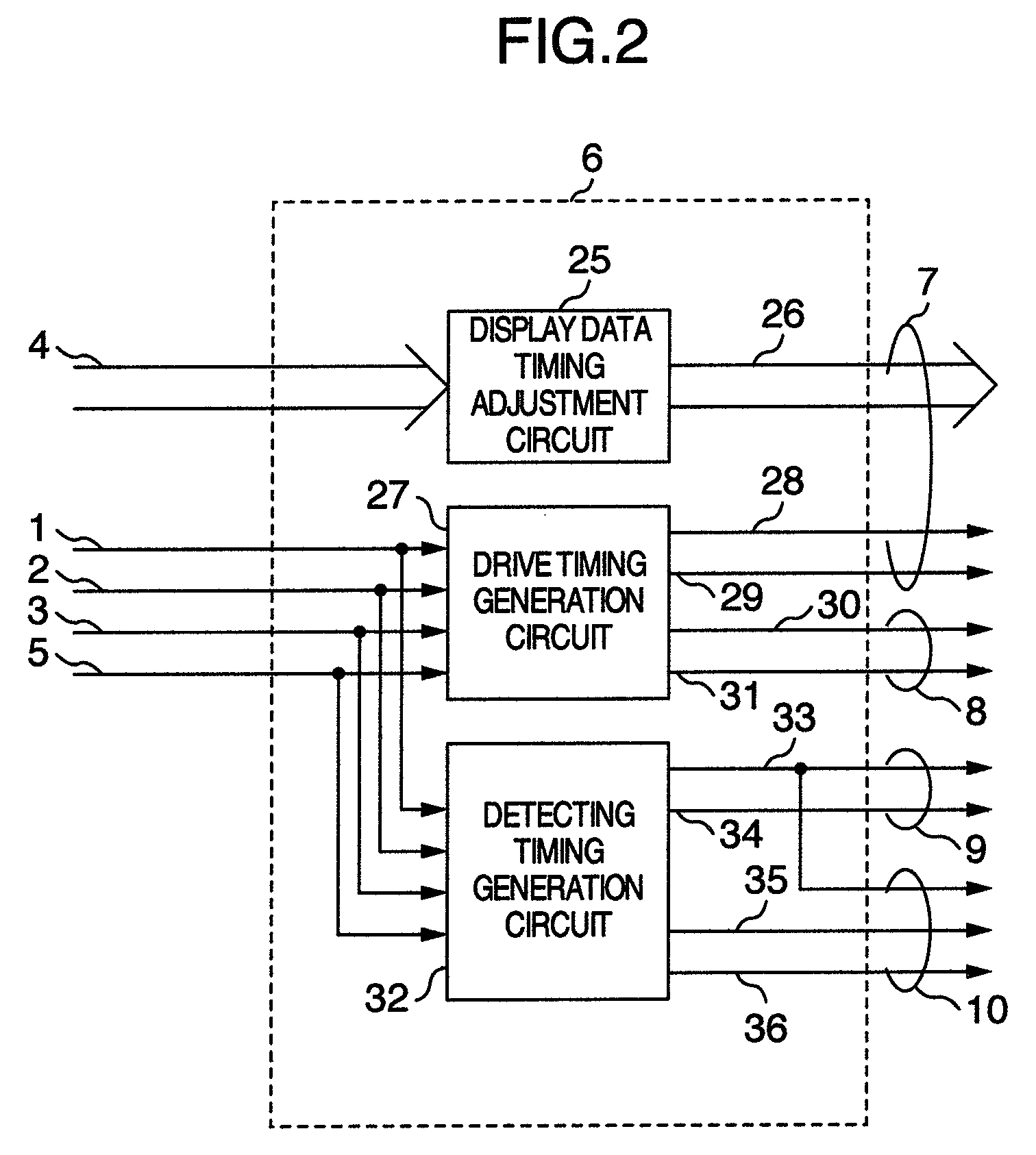
Image display device
ActiveUS20080224962A1Aperture ratio be degradeIncrease aperture ratioCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingConstant current sourceEngineering
An image display device includes switches directly connected a constant current source to a self-luminous element to be able to detect a characteristic of the self-luminous element, generate a coordinates and convert information of the characteristic and coordinates into a system communication signal, transferring an input with a temperature variation to a system side.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD +1
Charge removal from electrodes in unipolar sputtering system
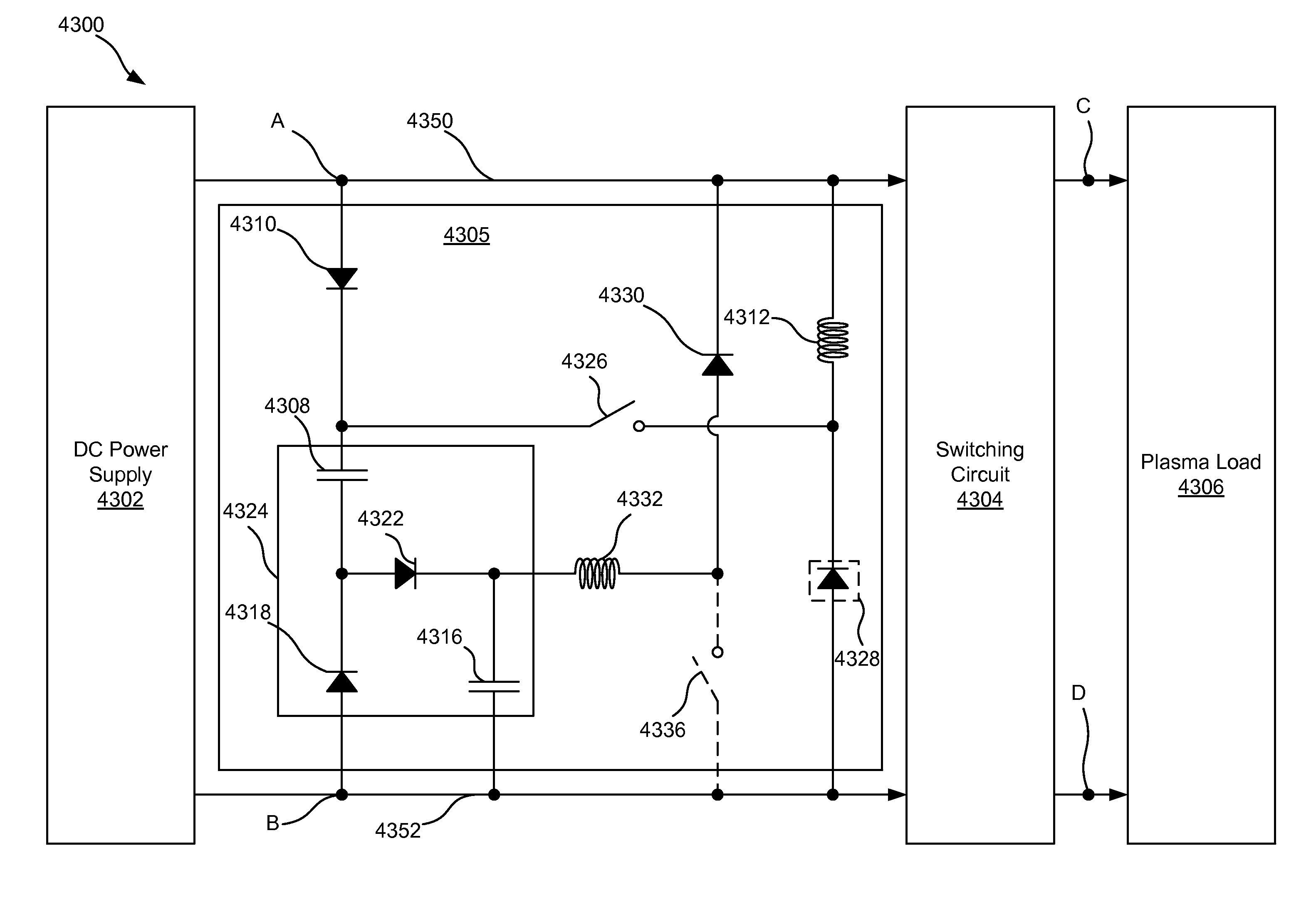
ActiveUS20140231243A1Boost voltageReduce voltageCellsElectric discharge tubesVoltage multiplierEngineering
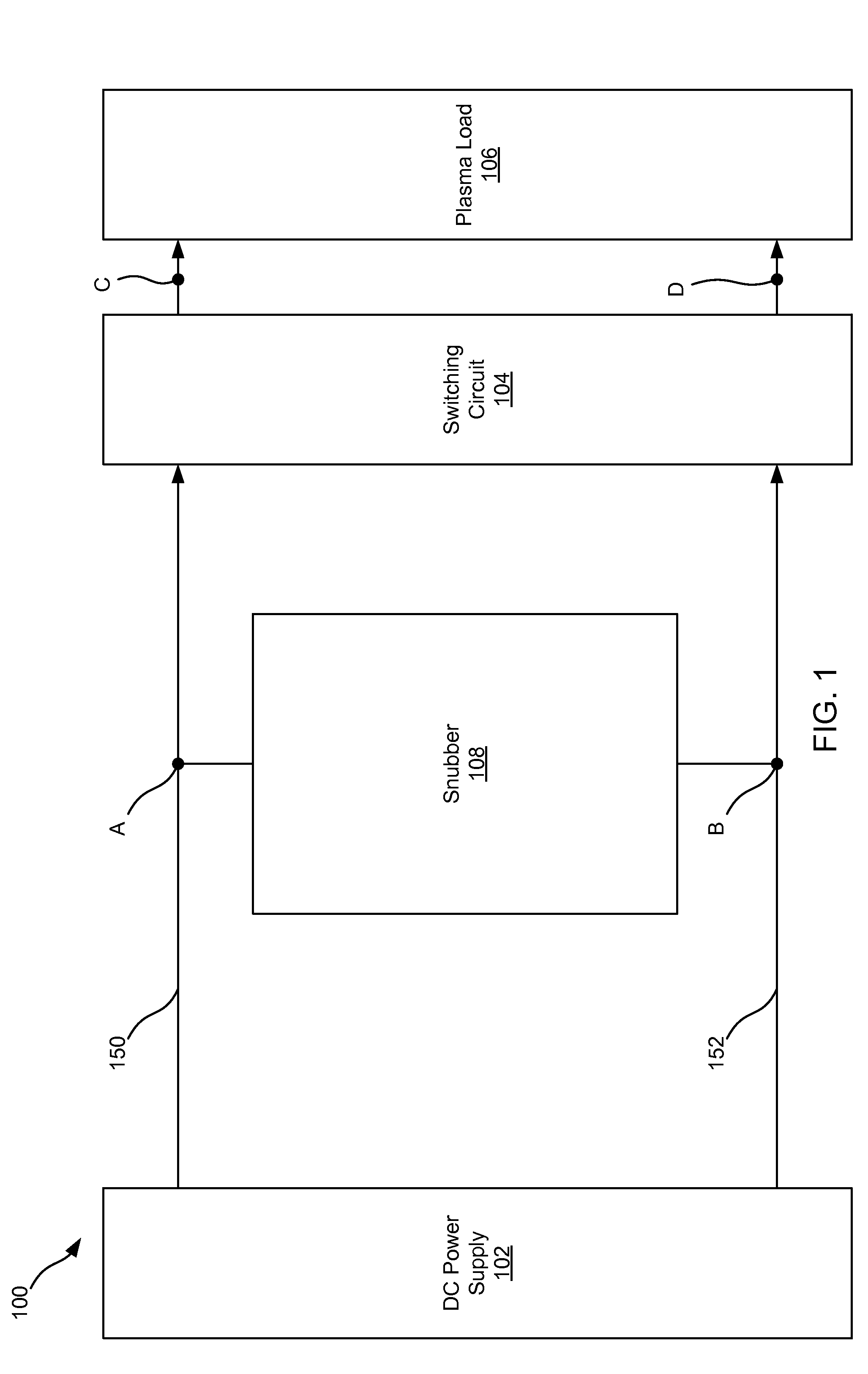
This disclosure describes a non-dissipative snubber circuit configured to boost a voltage applied to a load after the load's impedance rises rapidly. The voltage boost can thereby cause more rapid current ramping after a decrease in power delivery to the load which results from the load impedance rise. In particular, the snubber can comprise a combination of a unidirectional switch, a voltage multiplier, and a current limiter. In some cases, these components can be a diode, voltage doubler, and an inductor, respectively.
Owner:AES GLOBAL HLDG PTE LTD
Hybrid drive train of a motor vehicle
InactiveUS8075436B2Improve control characteristicsAvoid powerElectric propulsion mountingToothed gearingsGear wheelDifferential transmission
A hybrid gear train of a motor vehicle that has an internal combustion engine with a drive shaft, an electric motor with a rotor that operate as a motor and a generator, a transmission with two input shafts and an output shaft, as well as a differential transmission. At least one of the input shafts can be connected, via an assigned de-coupler, to the drive shaft, both of the input shafts can be connected by alternately assigned gearwheel sets of different ratios and in each case one assigned gear clutch to the output shaft. The differential transmission is designed as a simple planetary gearset that is coaxial with the first input shaft. The ring gear of this transmission is rotationally fixed to the one input shaft. The planet carrier is rotationally fixed to the second input shaft, and the sun gear is connected to and drives the rotor.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
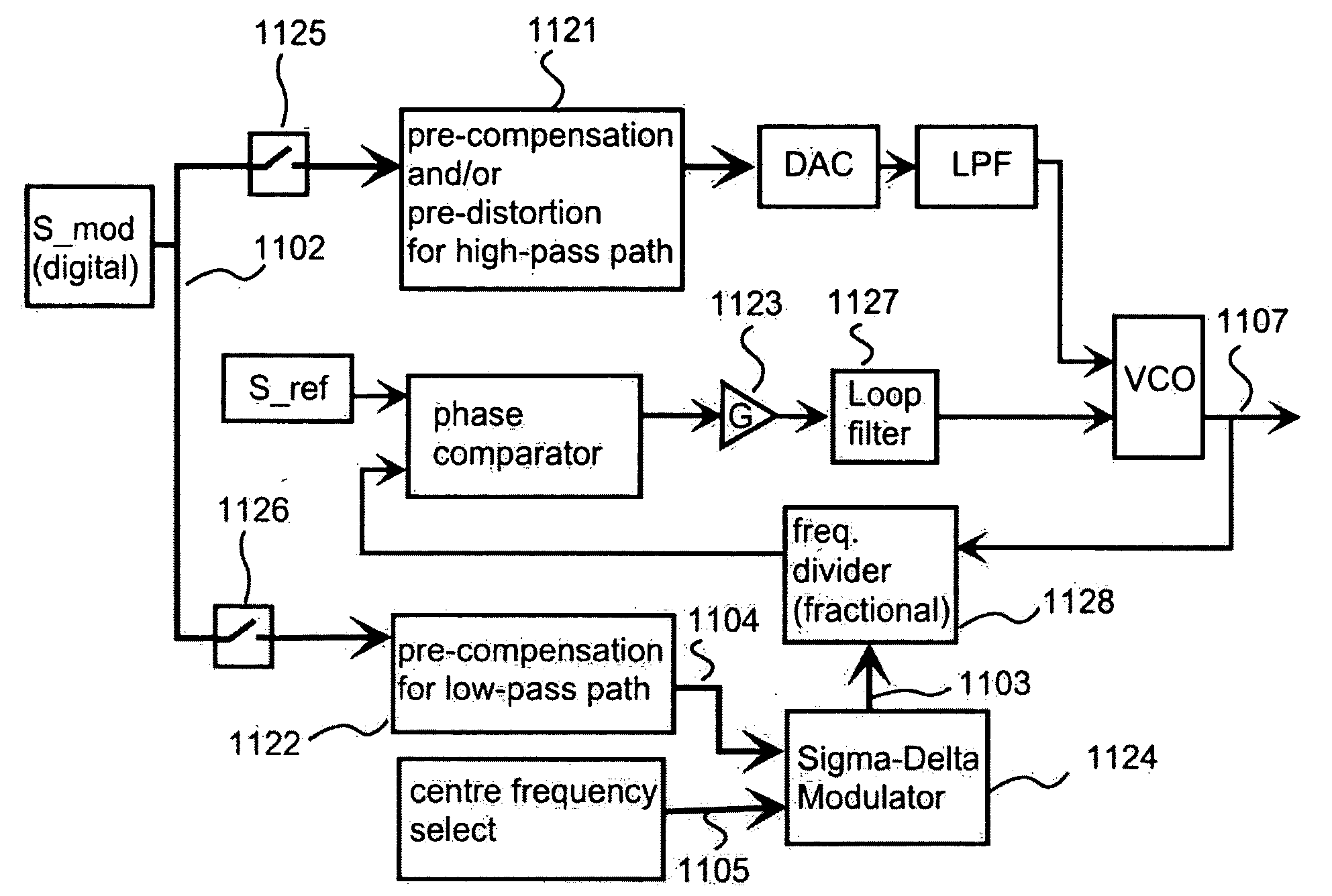
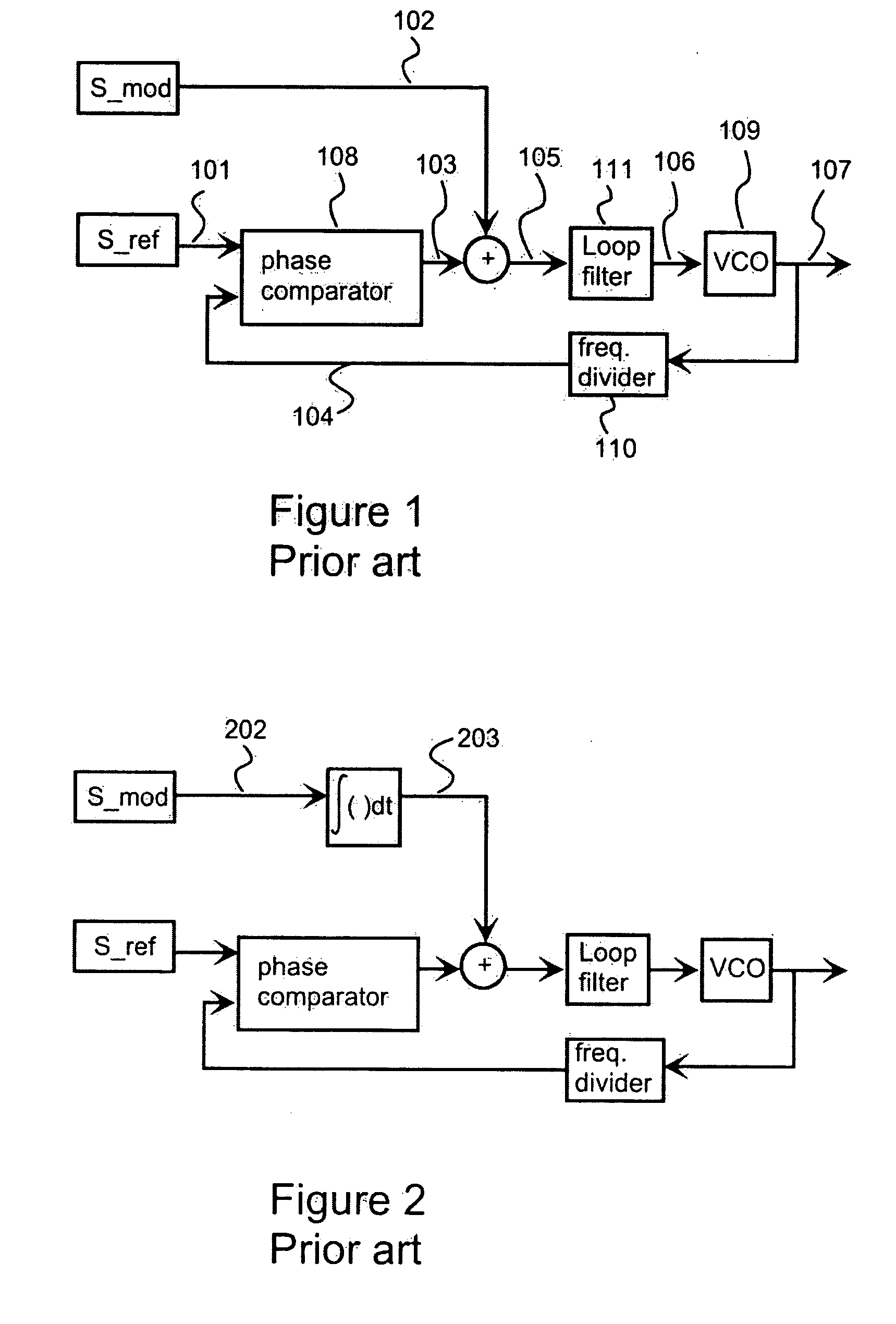
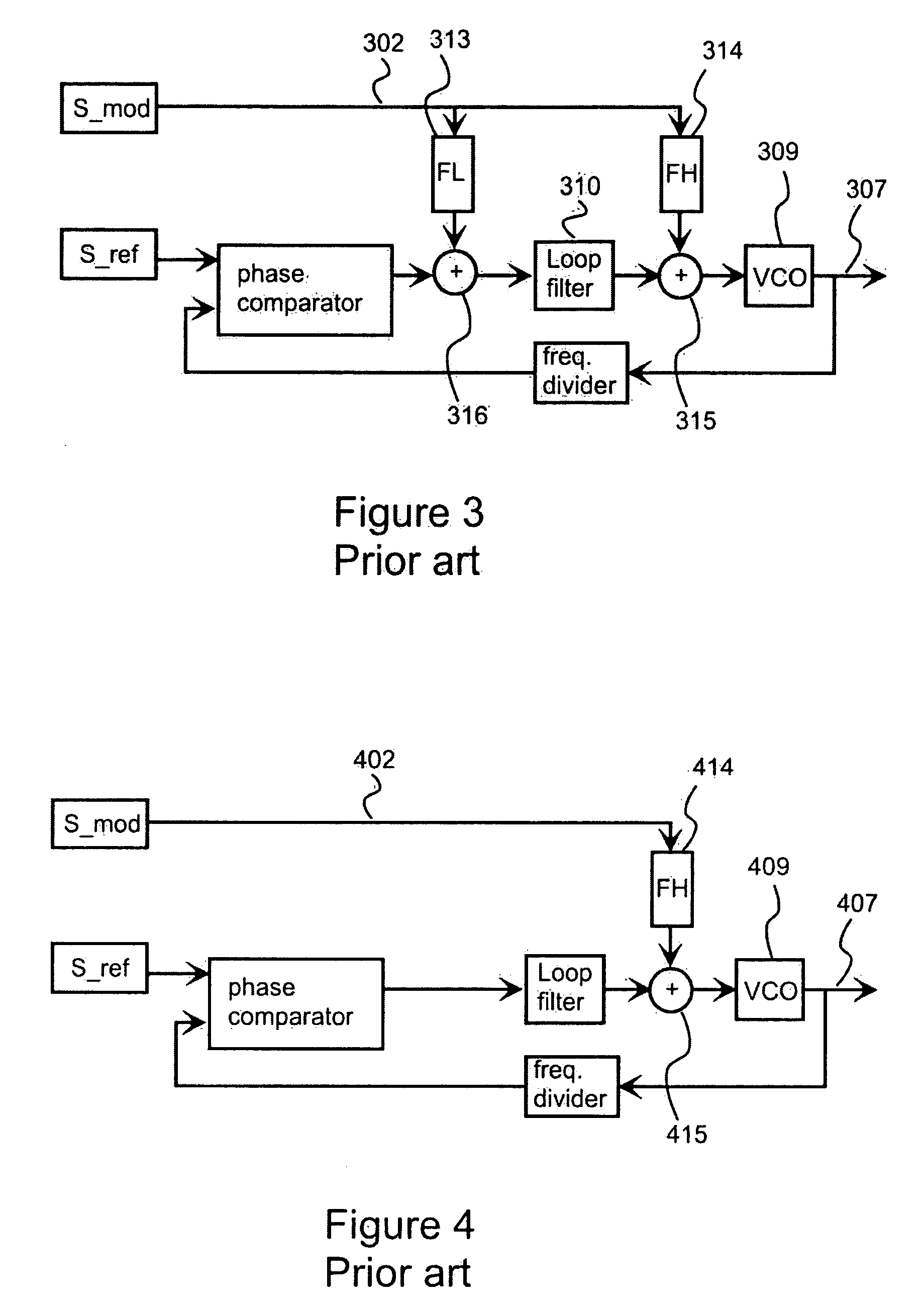
High pass modulation of a phase locked loop
ActiveUS20070036238A1Drawback and limitationCompensation effectModulated-carrier systemsAngle modulationDigital signal processingRadio frequency
A radio frequency modulator based on direct frequency / phase modulation of output signal of a controllable oscillator (724) that is a part of a phase locked loop (PLL) provides a direct modulator that is able to operate over a wide frequency range with a flat frequency response. A modulation signal is digitally processed (721, 730) before injection to a high-pass path of a direct modulator. Applicability of digital signal processing is based on the fact that the modulation signal is a base band signal. Therefore, the modulation signal (702) occupies such a band in the frequency domain so that a sufficient ratio of a sampling rate to an upper edge frequency of the modulation signal can be achieved. Digital processing is used for compensating an effect of non-flat high-pass PLL transfer function and / or to perform pre-distortion of the input signal of a controlled oscillator to compensate an effect of non-linearity of a controlled oscillator.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
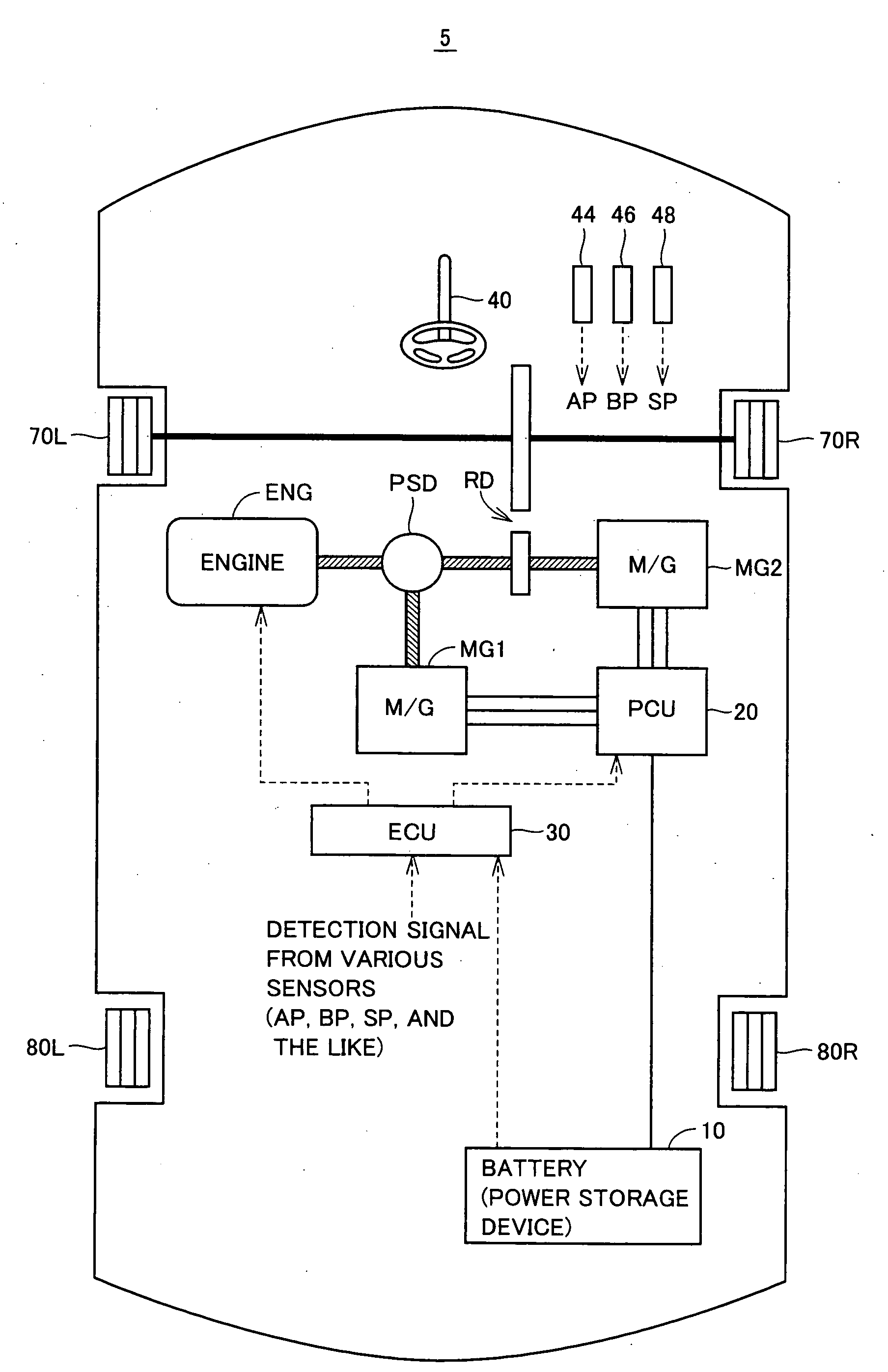
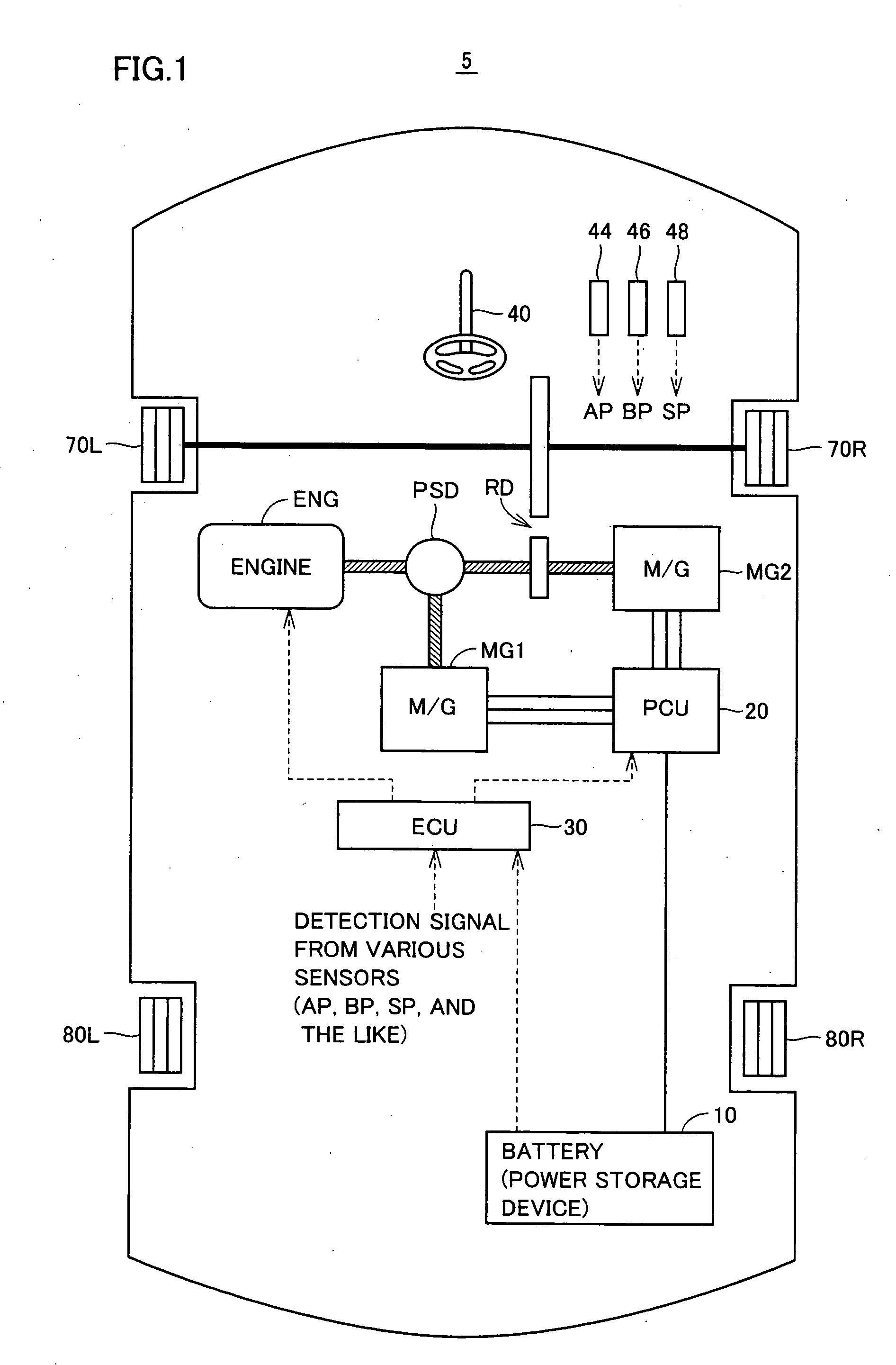
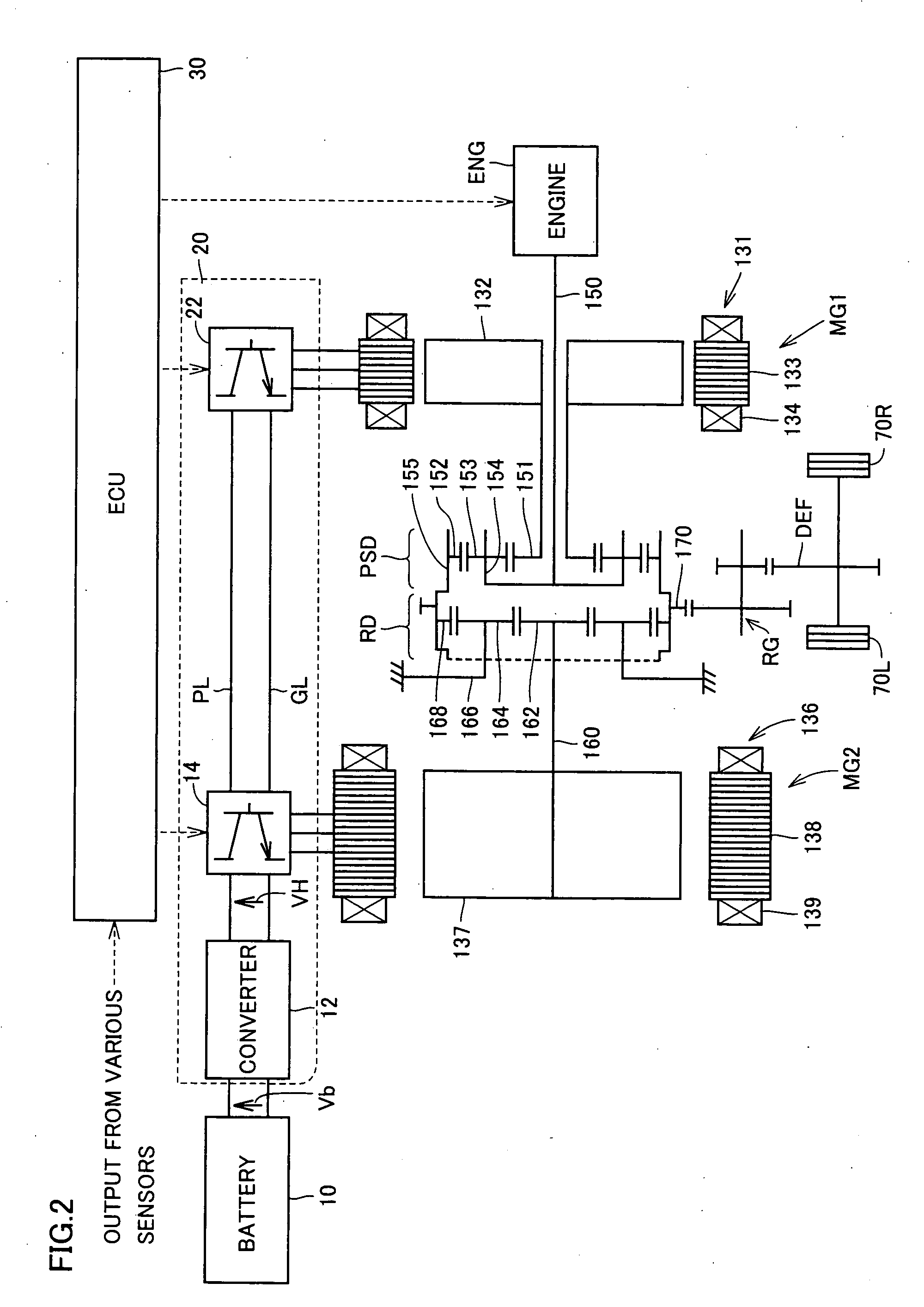
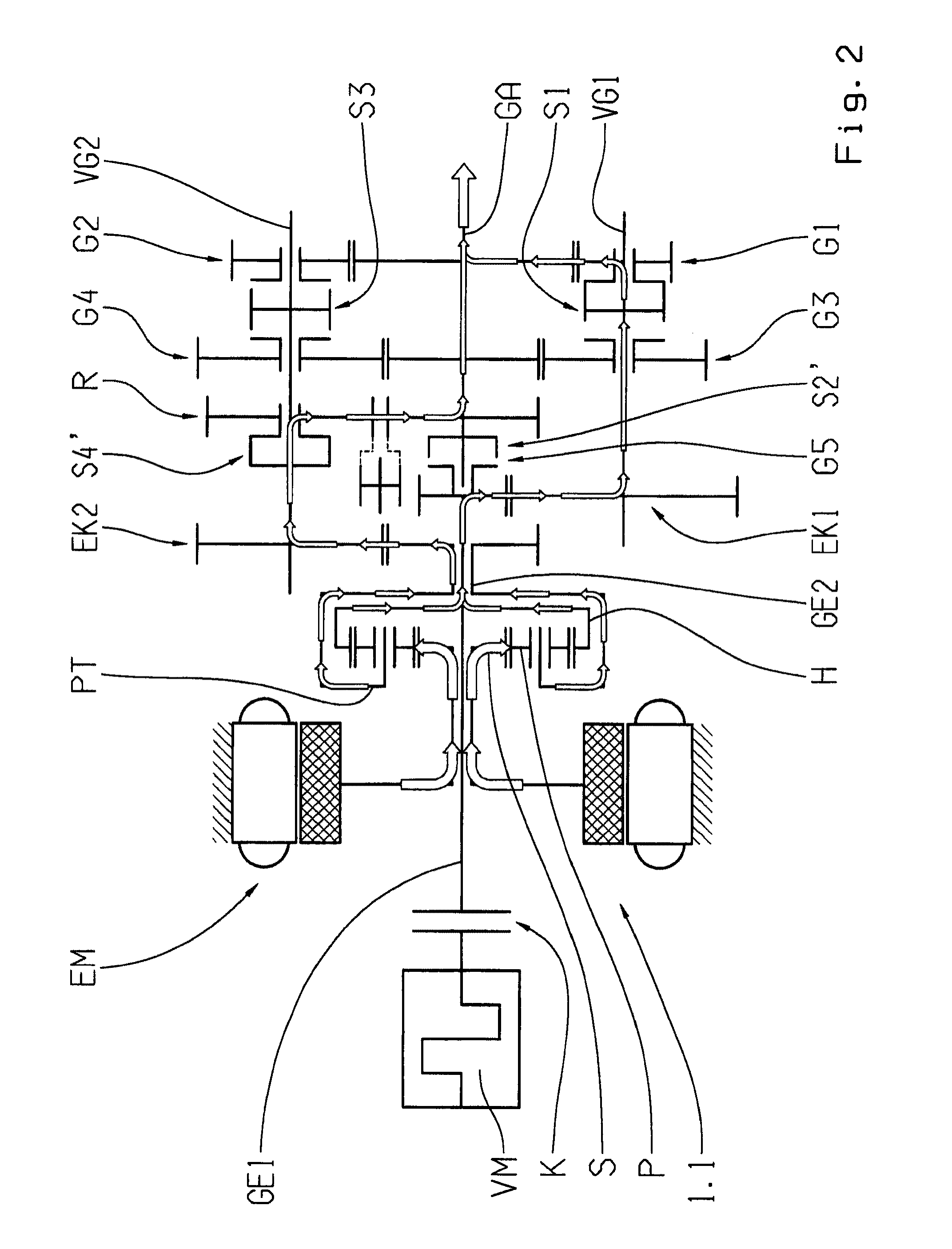
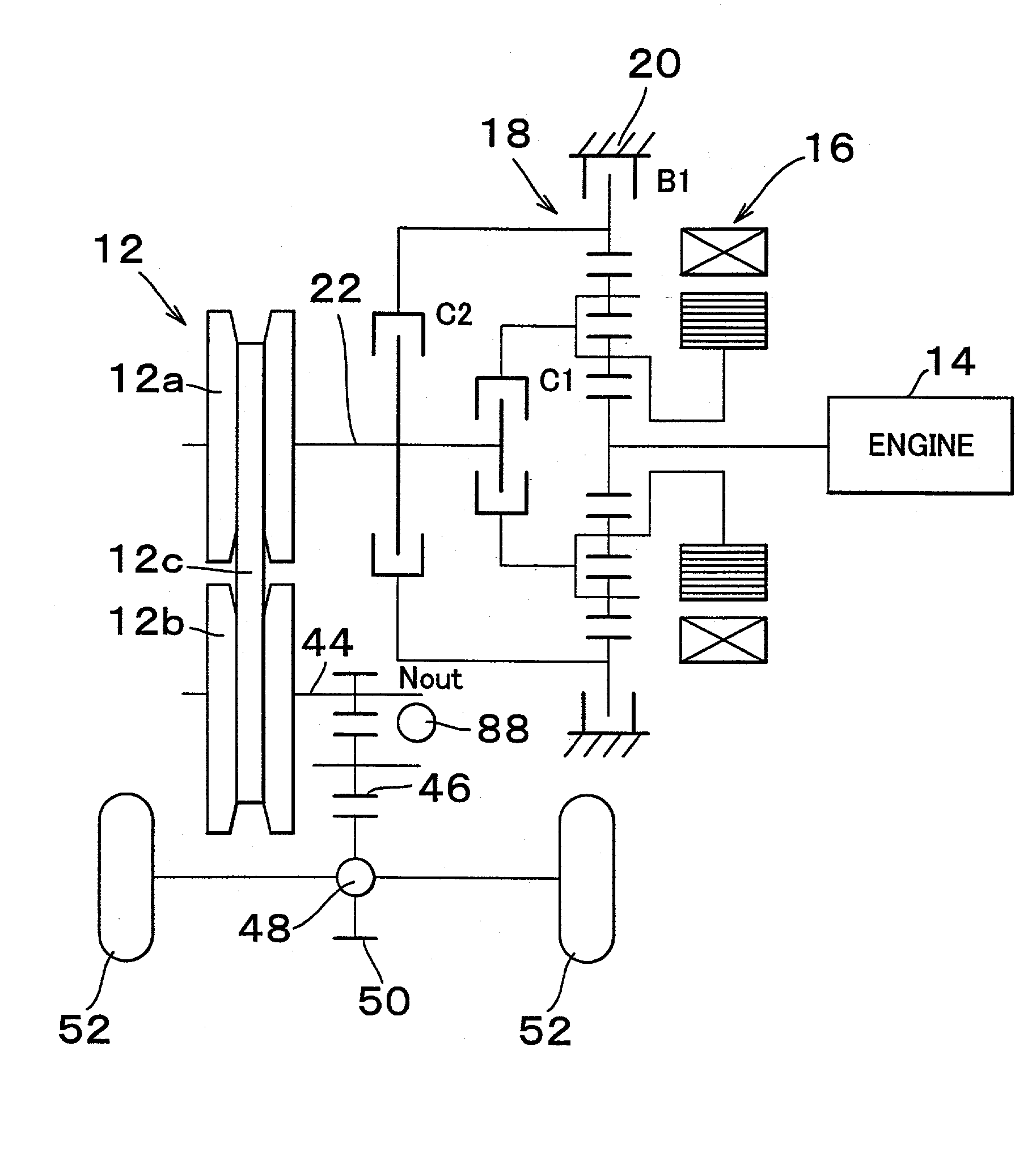
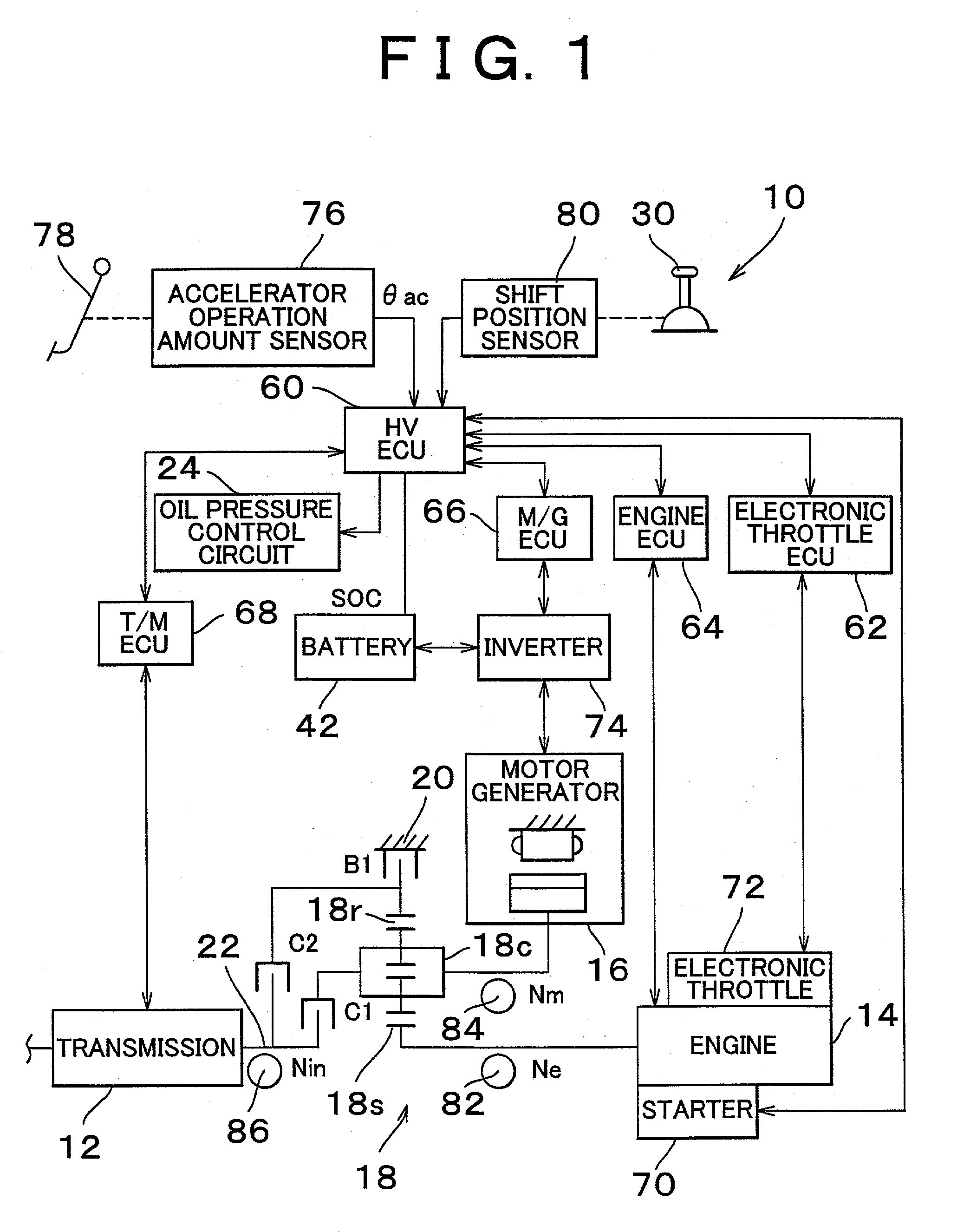
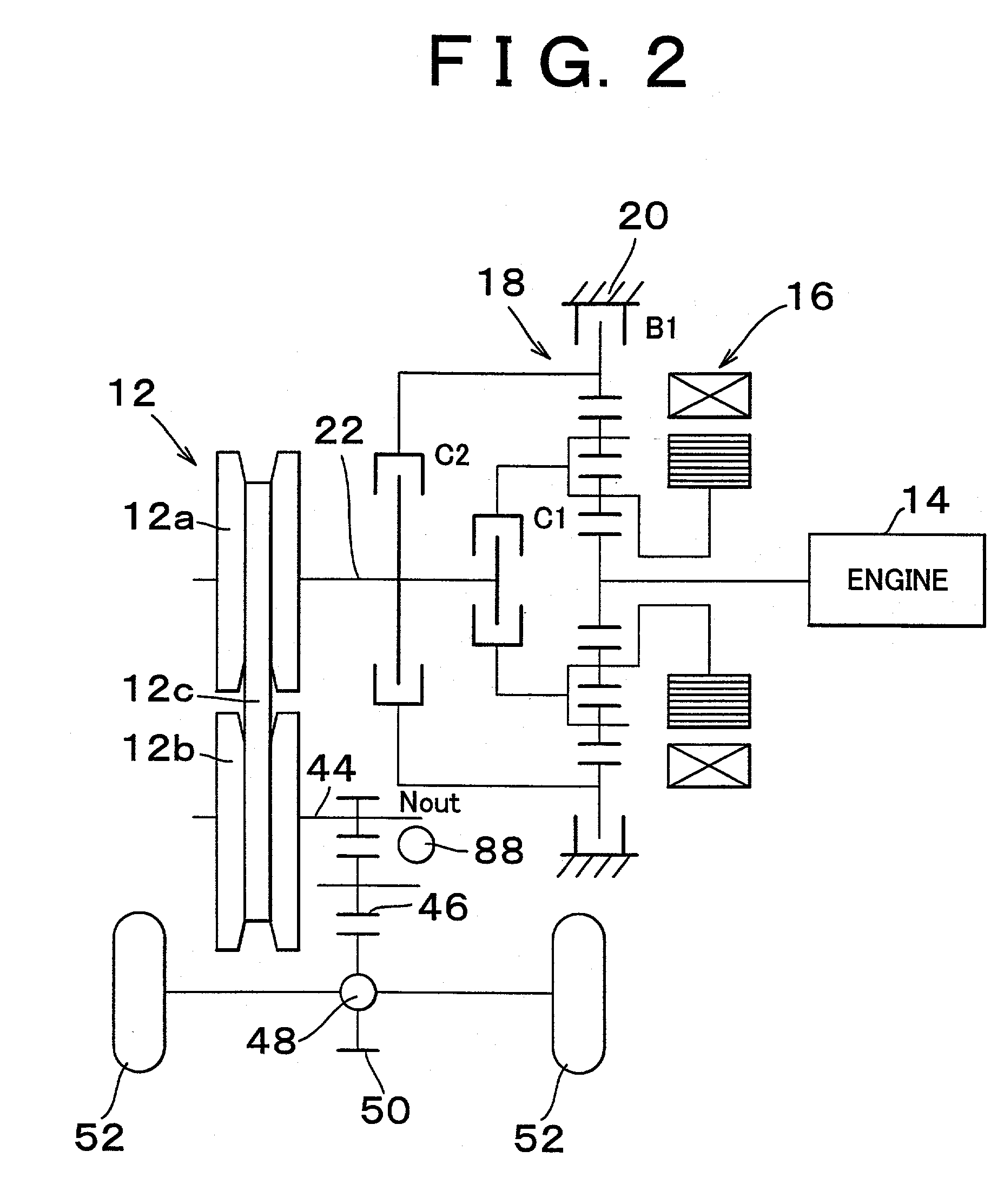
Control apparatus and control method for hybrid vehicle
ActiveUS20100051367A1Prevent overdischarging power storage devicePrevent overcurrentHybrid vehiclesGearingHybrid vehicleElectric power
The present invention is directed to solve the problem of generation of overdischarging from a power storage device according to compensation for reduction in electrical power generated by an MG1 corresponding to reduction in the revolution speed of the MG1. When detection is made of reduction in the revolution speed of the MG1 corresponding to reduction in the engine speed, any of the four following operations is carried out: (1) modifying the output torque of the MG1 such that electrical power generated by the MG1 increases; (2) modifying the output torque of an MG2 such that power consumption by the MG2 is reduced; (3) forcing the control mode of the MG1 to be changed to PWM control from one-pulse switching control; and (4) reducing the DC voltage command value for the converter.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
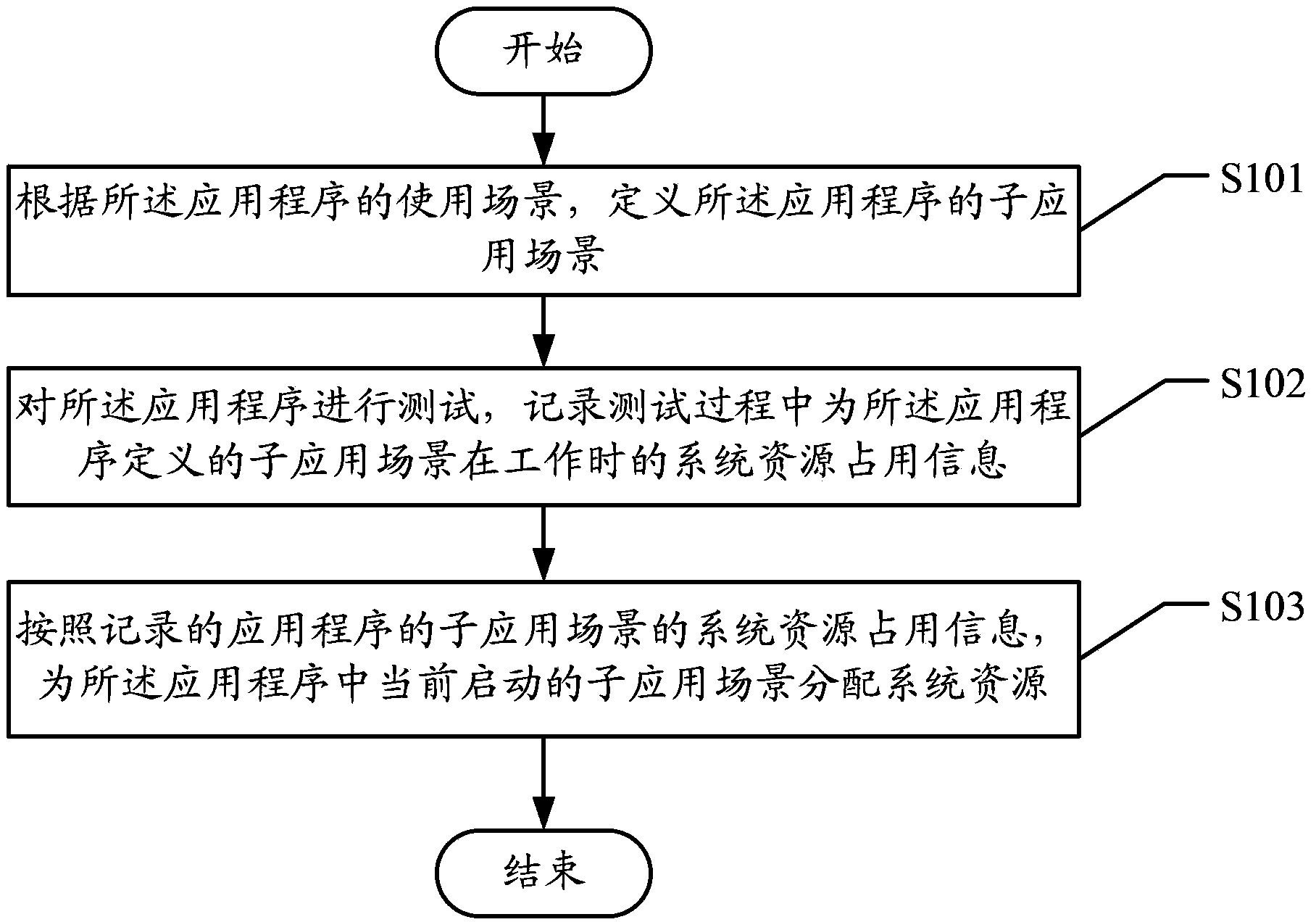
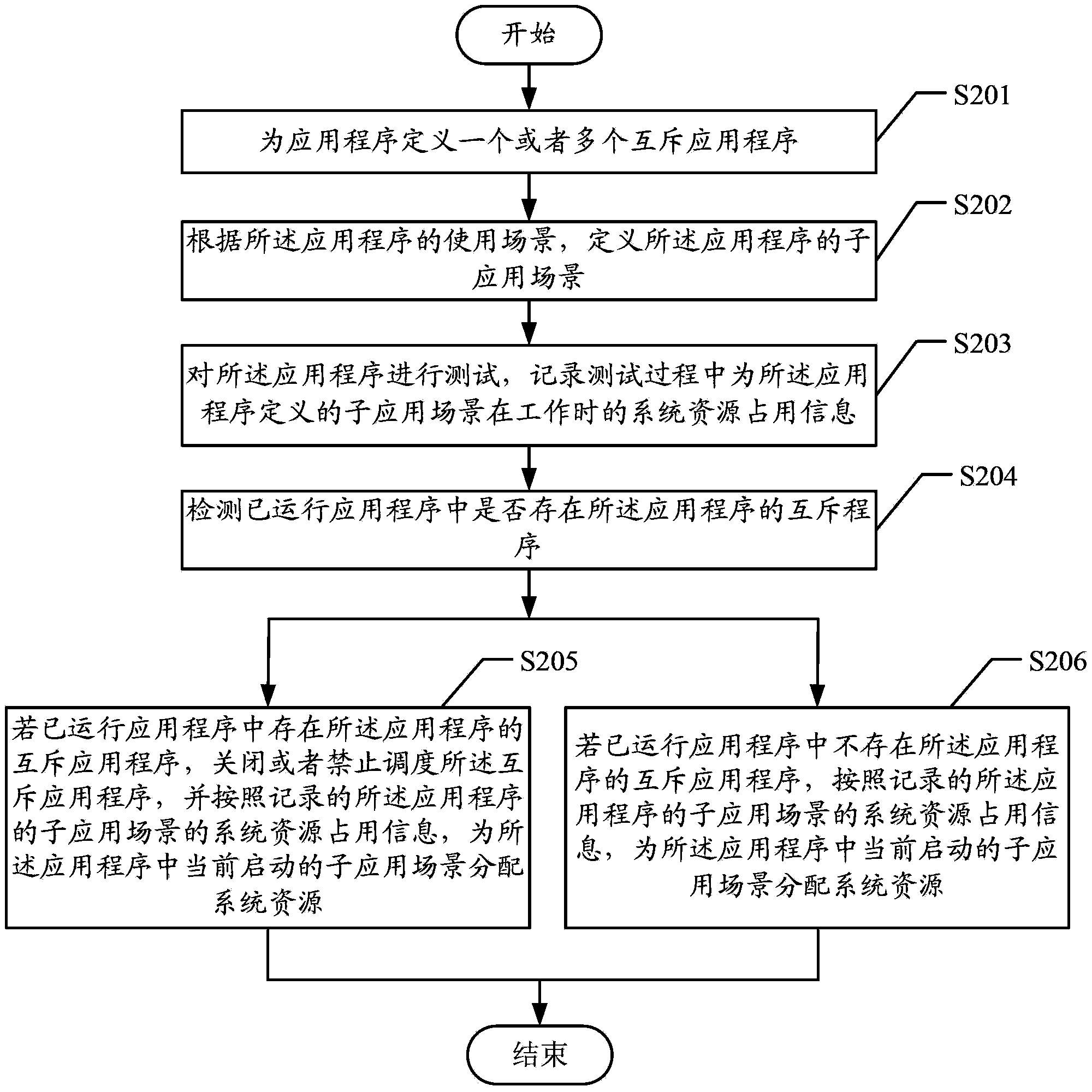
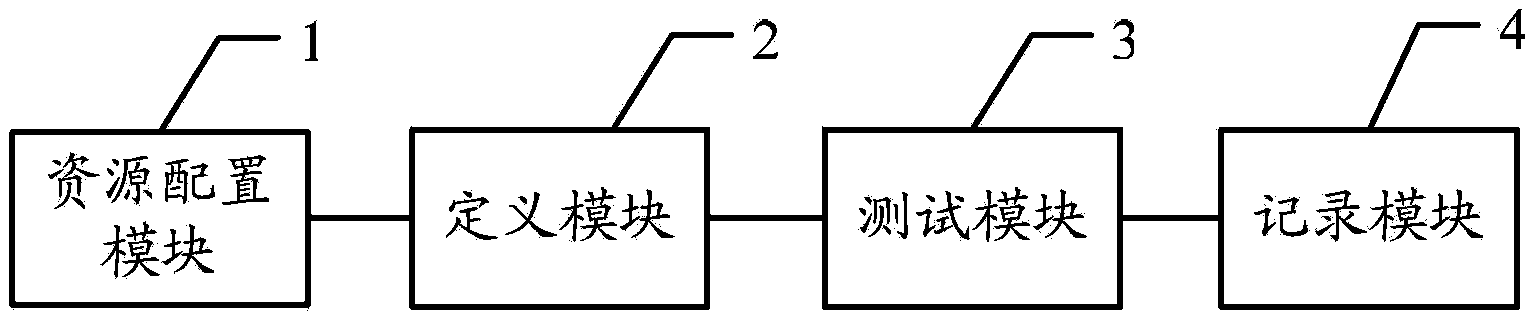
Method and apparatus for configuring resource
ActiveCN103430151AGuaranteed uptimeShorten adjustment timeEnergy efficient ICTResource allocationApplication softwareOperating system
Embodiments of the present invention disclose a method for configuring a resource and an apparatus. The method includes: allocating a system resource to a currently active application sub-scenario in an application according to recorded system resource occupation information of the application sub-scenario of the application, where the system resource occupation information of the application sub-scenario of the application includes the system resource occupation information recorded when the application sub-scenario works in a process of testing the application after the application sub-scenario of the application is defined. With the present invention, the system resource is configured for the application sub-scenario at a single attempt. Therefore, enough system resources are ensured to meet the requirements for running the currently active application sub-scenario of the application, the running performance is ensured, and the adjustment time and the power consumption are saved.
Owner:HUAWEI DEVICE CO LTD
Differing boost voltages applied to two or more anodeless electrodes for plasma processing
ActiveUS20140117861A1Boost voltageReduce voltageElectric discharge tubesElectric light circuit arrangementPower flowVoltage multiplier
This disclosure describes a non-dissipative snubber circuit configured to boost a voltage applied to a load after the load's impedance rises rapidly. The voltage boost can thereby cause more rapid current ramping after a decrease in power delivery to the load which results from the load impedance rise. In particular, the snubber can comprise a combination of a unidirectional switch, a voltage multiplier, and a current limiter. In some cases, these components can be a diode, voltage doubler, and an inductor, respectively.
Owner:AES GLOBAL HLDG PTE LTD
Vehicle power inhibiter
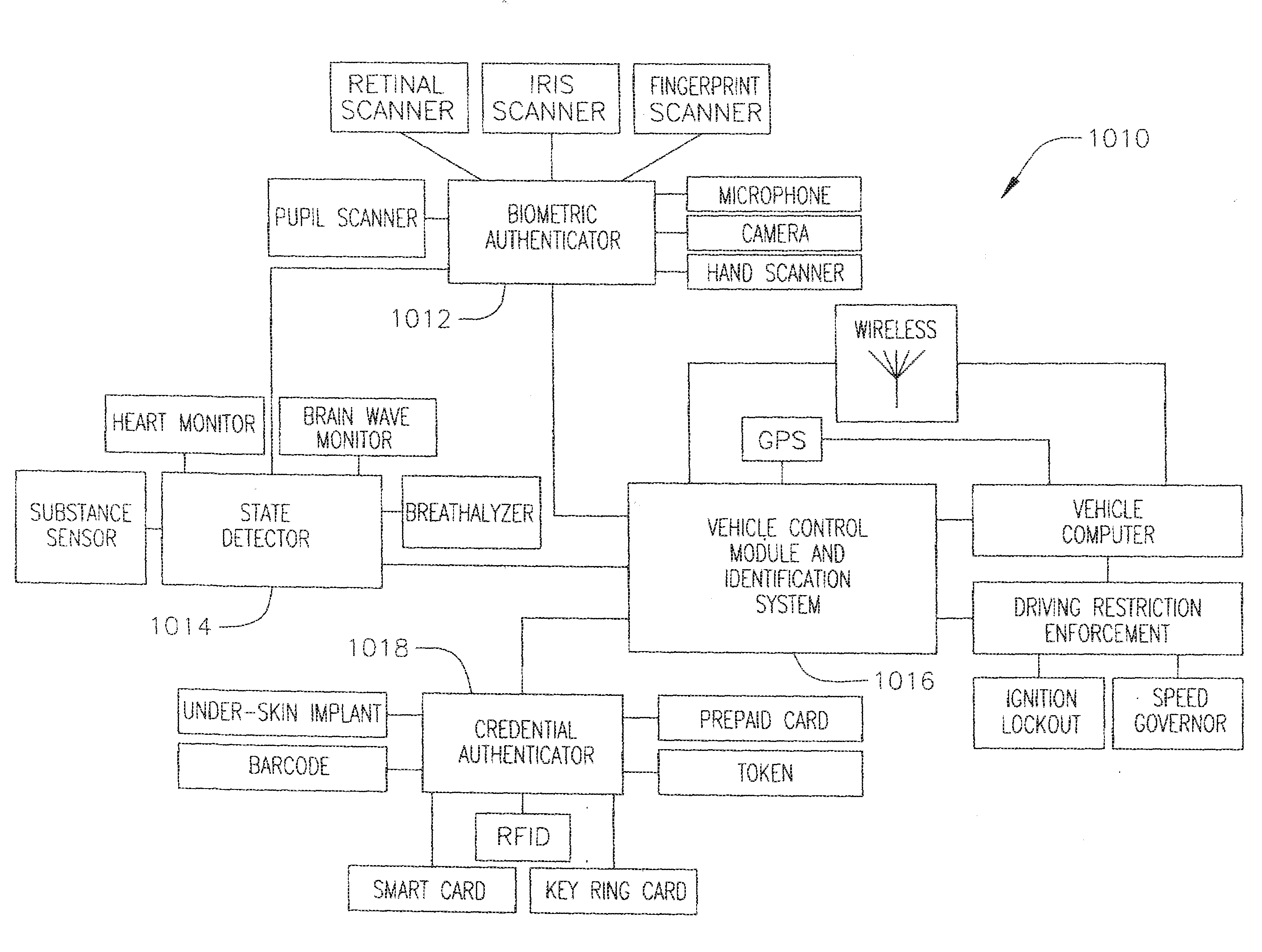
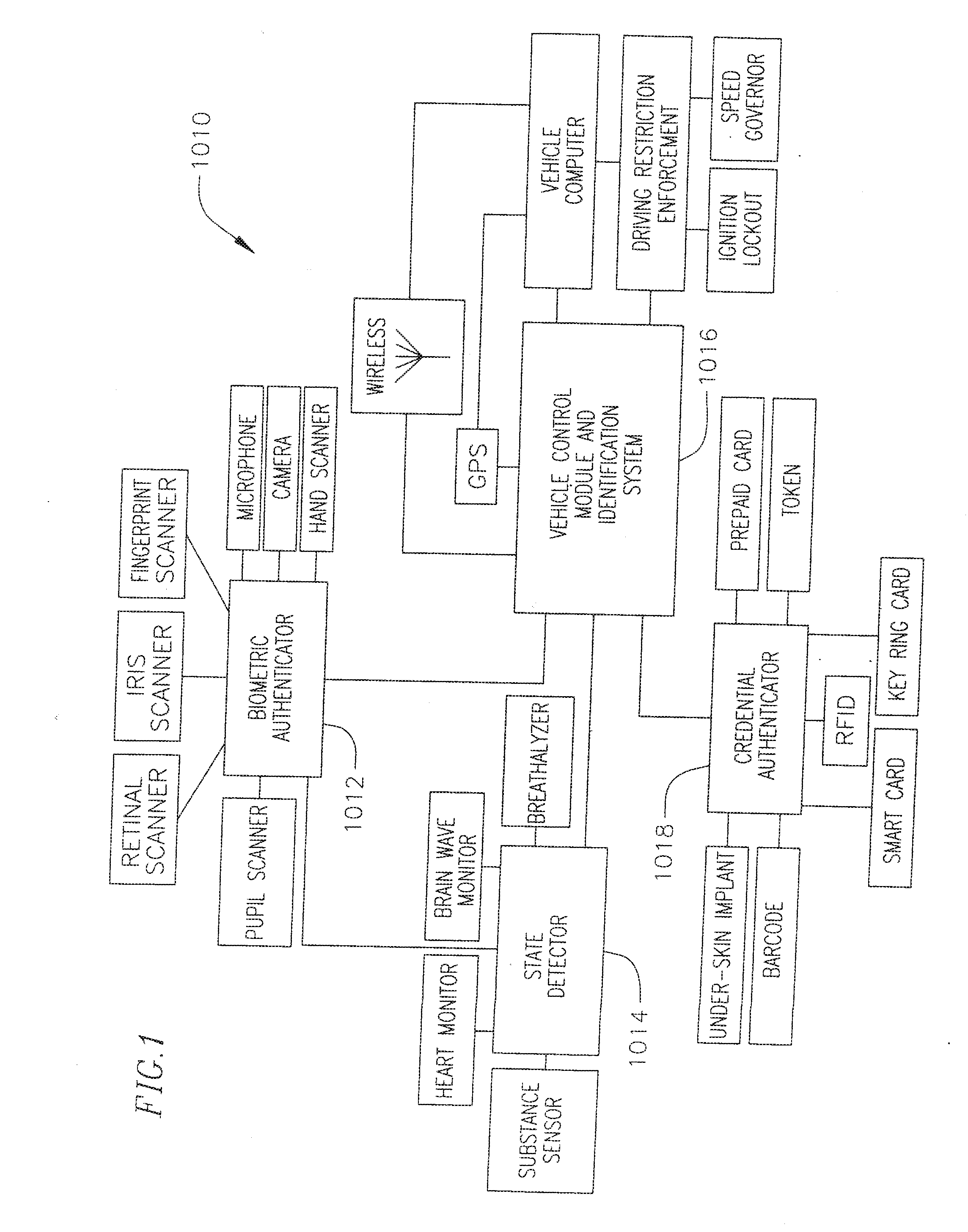
InactiveUS20080228365A1Increase powerAvoid powerAnalogue computers for trafficAnti-theft devicesThird partyBiological activation
A method and system for inhibiting power of a vehicle given to a third party. The system includes a mode-indicating, an authenticator coupled to the mode-indicating device, and a power inhibiting device coupled to the mode-indicating device and adapted to selectively inhibit the power of the vehicle. Here, the mode-indicating device is adapted to communicate a power restriction signal to the power inhibiting device to inhibit the power of the vehicle upon an activation of the mode-indicating device by an authenticated driver and until a deactivation of the mode-indicating device by the authenticated driver, and the authenticator is adapted to restrict the activation and the deactivation of the mode-indicating device unless the driver has been authenticated by the authenticator.
Owner:WHITE STEVEN C +1
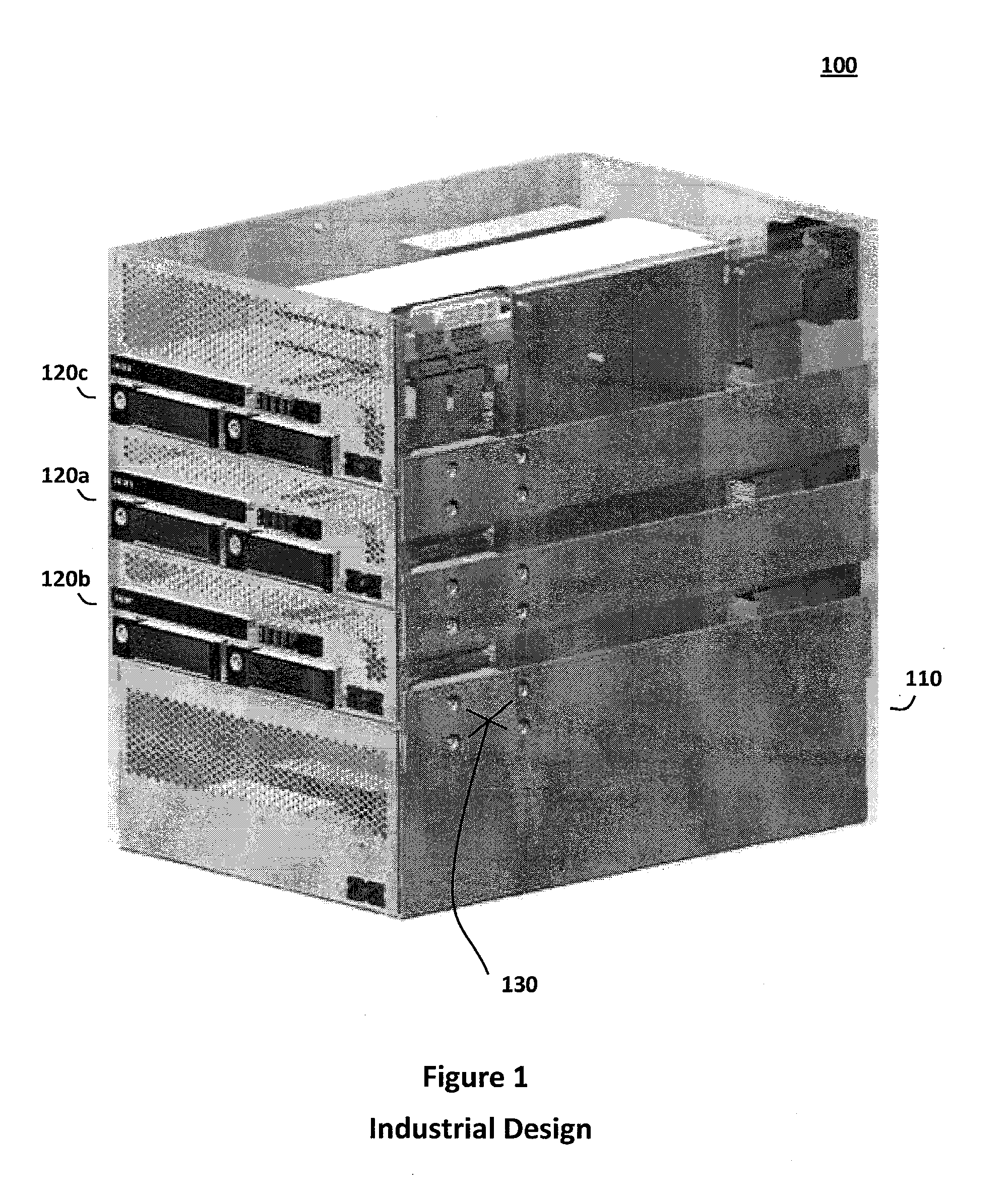
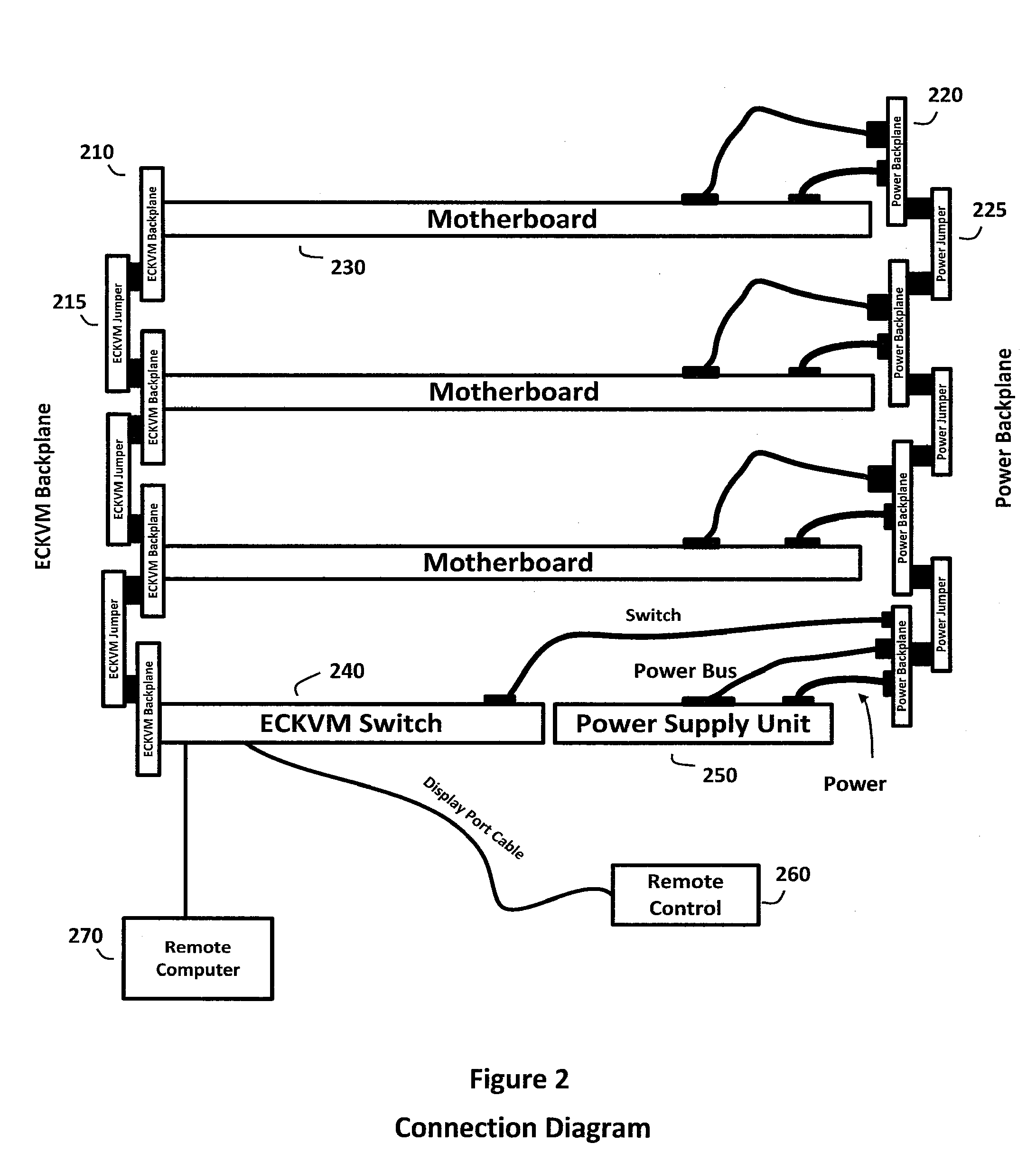
Adaptive computing system with modular control, switching, and power supply architecture
InactiveUS20120243160A1Low initial costSimple to deployCasings with display/control unitsPower supply for data processingModularityAdaptive computing
The adaptive computing system described herein may generally include a modular control, switching, and power supply architecture. In particular, the adaptive computing system may provide a platform supporting multiple independent desktop computer modules that occupy less physical space than a standalone commercial computer, provide performance density comparable to current server solutions, and address concerns relating to stability, safety, productivity, performance, assembly, service, and other factors important to diverse desktop computer user communities. Moreover, mechanical, electrical, and functional components associated with the adaptive computing system may have various certifications or otherwise be relied upon to demonstrate compliance with criteria in regulatory, environmental, consumer safety, and other contexts.
Owner:NCS TECH
Hybrid drive train of a motor vehicle
InactiveUS20100009805A1Improve control characteristicsAvoid powerElectric propulsion mountingPropulsion using engine-driven generatorsDifferential transmissionControl theory
A hybrid gear train of a motor vehicle that has an internal combustion engine with a drive shaft, an electric motor with a rotor that operate as a motor and a generator, a transmission with two input shafts and an output shaft, as well as a differential transmission. At least one of the input shafts can be connected, via an assigned de-coupler, to the drive shaft, both of the input shafts can be connected by alternately assigned gearwheel sets of different ratios and in each case one assigned gear clutch to the output shaft. The differential transmission is designed as a simple planetary gearset that is coaxial with the first input shaft. The ring gear of this transmission is rotationally fixed to the one input shaft. The planet carrier is rotationally fixed to the second input shaft, and the sun gear is connected to and drives the rotor.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Vehicle drive control apparatus and method
InactiveUS20020173391A1Solve insufficient capacityReduce power transmission lossesElectric propulsion mountingGearingDevice WheelControl theory
Methods and apparatus for a vehicle drive control apparatus changes in the transfer torque capacity of a power transfer device according to various states of operation with respect to at least one drive power source. The vehicle drive control apparatus includes a power transfer device that has a variable transfer torque capacity and the drive power sources that rotate a device wheel via the power transfer device. A controller is included that causes a vehicle to selectively run in a variety of run modes that differ in states of operation with respect to at least one of the drive power sources. The controller changes the transfer torque capacity of the power transfer device in accordance with the various run modes. According to the vehicle device control apparatus, a target oil pressure is raised by a predetermined amount when the mode of run is change, or when the vehicle descends in a direction opposite to a vehicle starting direction at the time of a hill climb start.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
System and Method for Wireless Communications
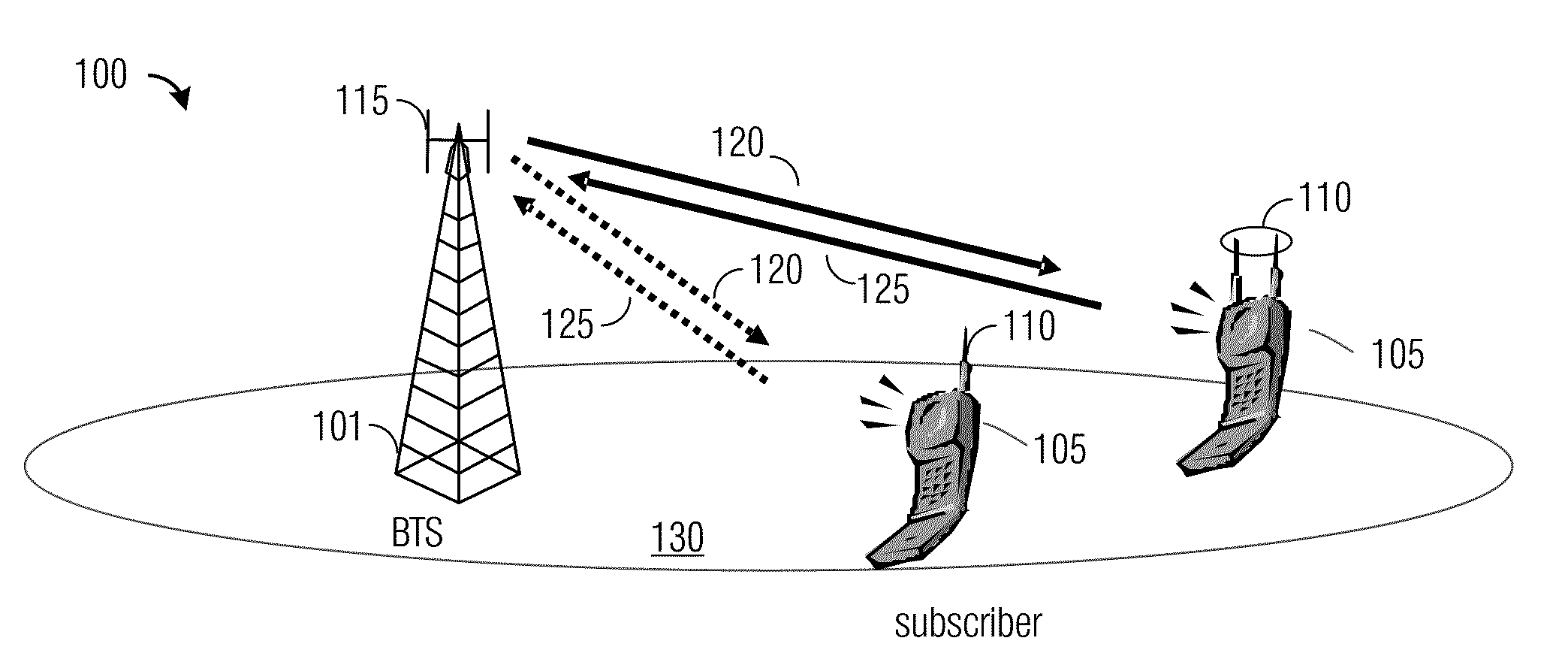
ActiveUS20100054212A1Avoid transmit power imbalanceReduce computational complexityMultiplex communicationSecret communicationComputer hardwareCommunication device
A system and method for wireless communications is provided. A method for operating in a communications network includes receiving a codebook, the codebook includes a plurality of codewords, and determining if the codebook satisfies a constant modulus property. The method also includes in response to determining that the codebook does not satisfy the constant modulus property, converting the codebook into a codebook satisfying the constant modulus property, and storing the codebook satisfying the constant modulus property. The method further includes storing the codebook in response to determining that the codebook does satisfy the constant modulus property, and causing to transmit a transmission to a communications device, wherein the transmission is encoded using a codeword in the stored codebook.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
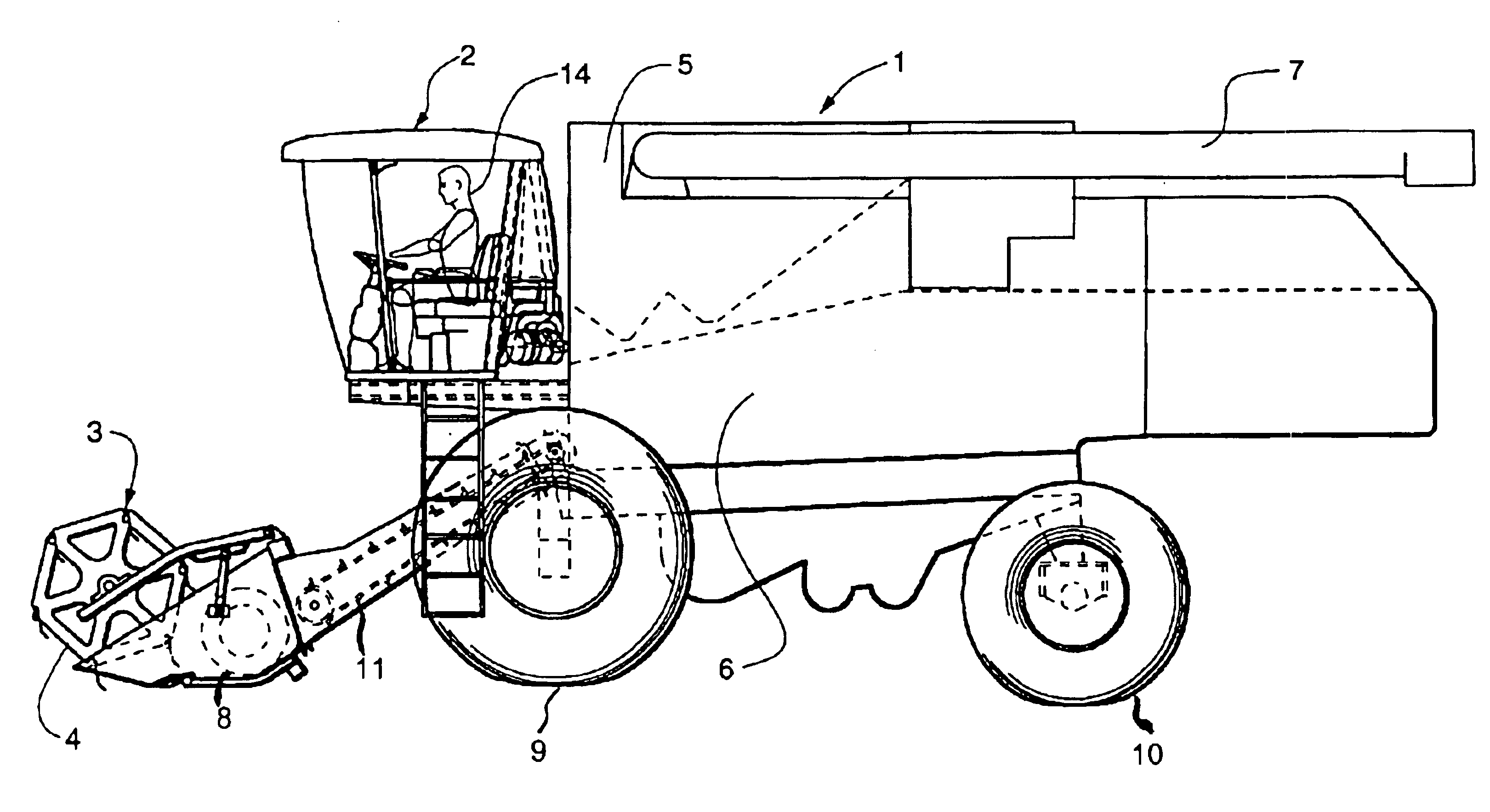
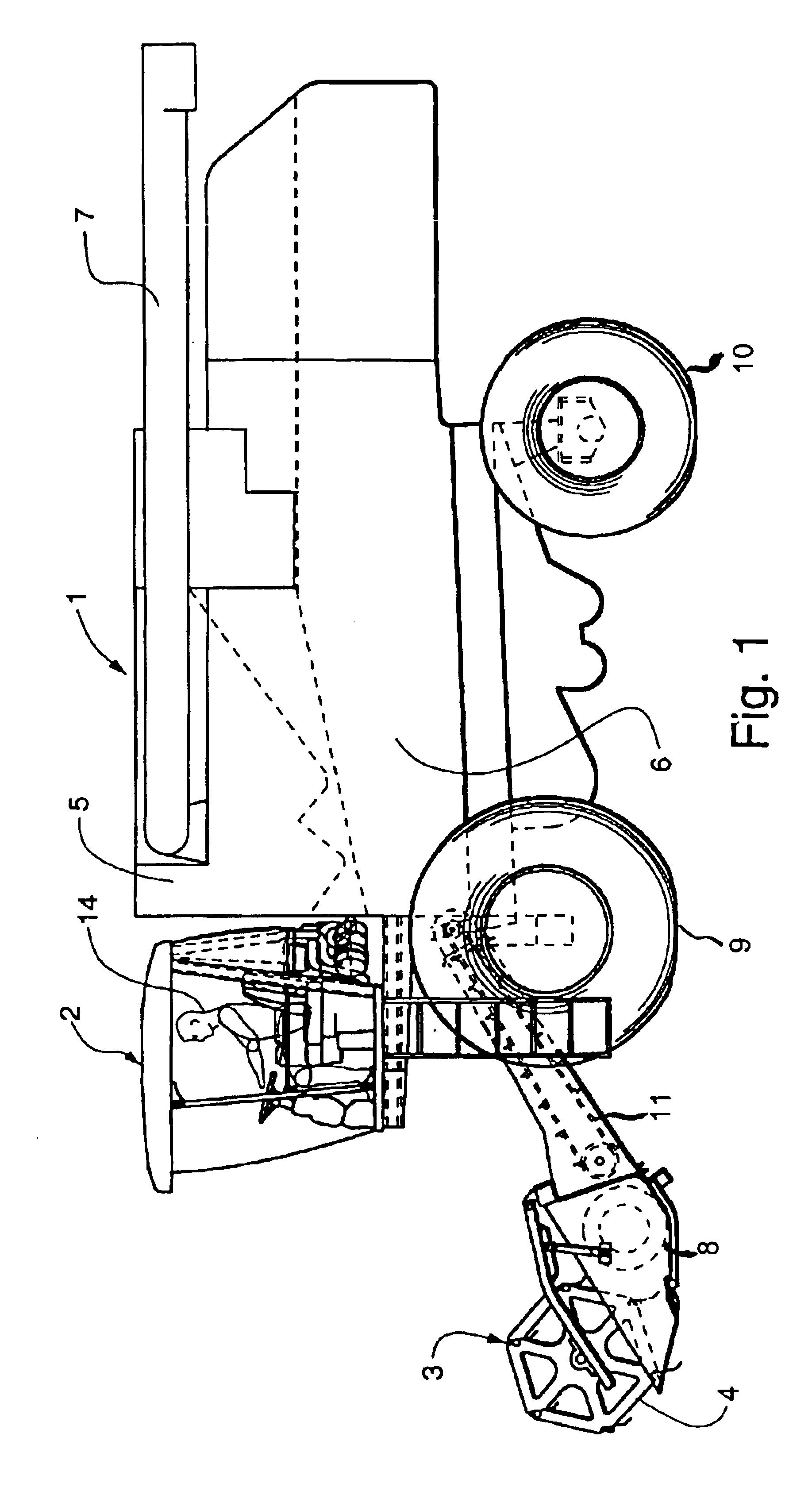
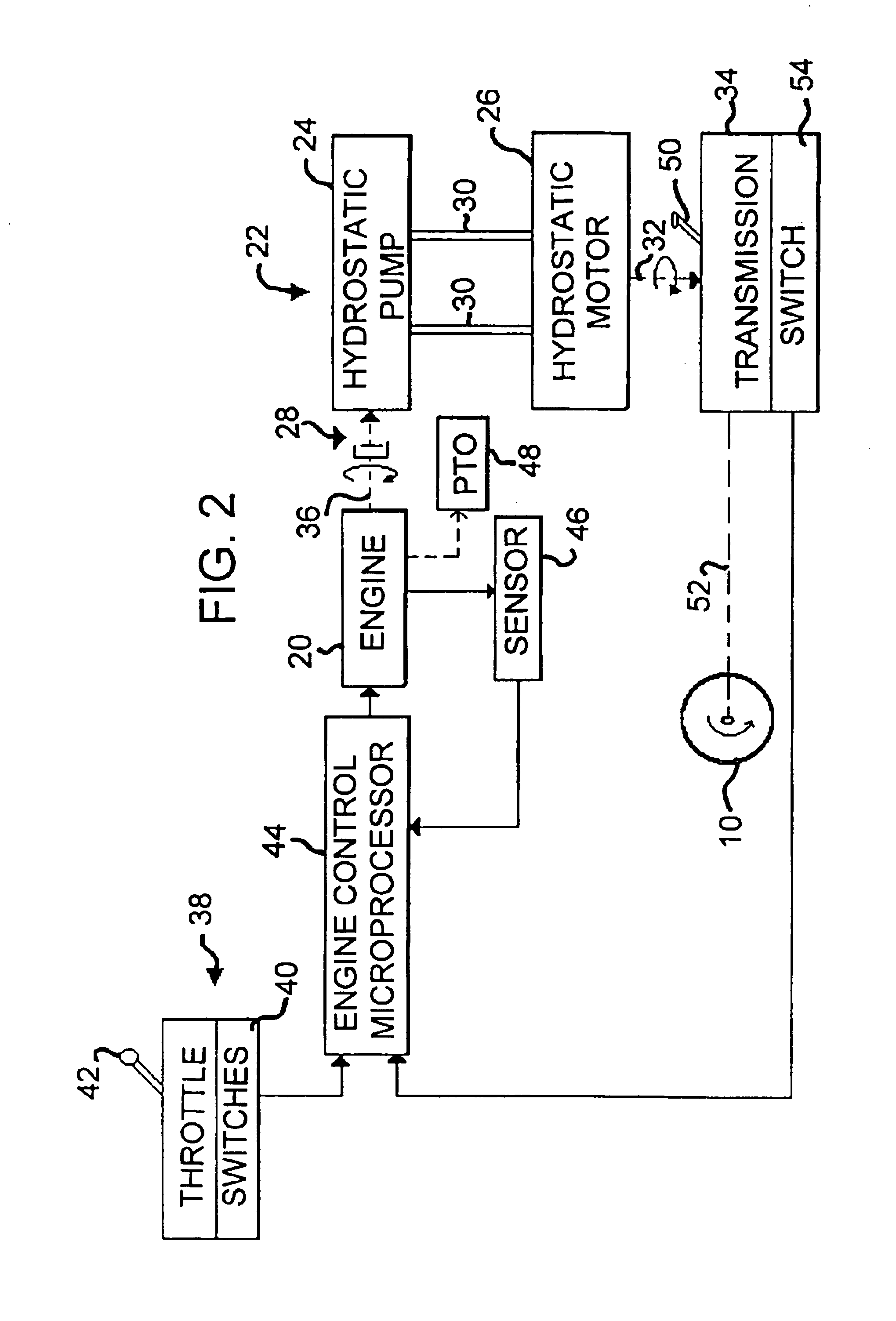
Combine power selection system
InactiveUS6865870B2Increase engine speedAvoid efficiencyAgricultural machinesVehicle fittingsThrottle controlRoad surface
A system for propelling a combine over the ground and driving other components of the combine includes an engine driving a transmission via a hydrostatic drive system. A microprocessor stores a work table and a road table for controlling engine speed. A gear selector operates a switch to select one of the tables and a throttle control operates switches to select a speed value from the selected table. When working a field, the work table is selected so that the engine runs at speeds in a range suitable for driving the other components. For transport of the combine the road table is selected so that the engine may run at a speed higher than speeds suitable for driving the other components. For a given setting of the throttle control, the engine is controlled to run at either a first or second speed depending on the setting of the gear select lever.
Owner:BLUE LEAF I P +1
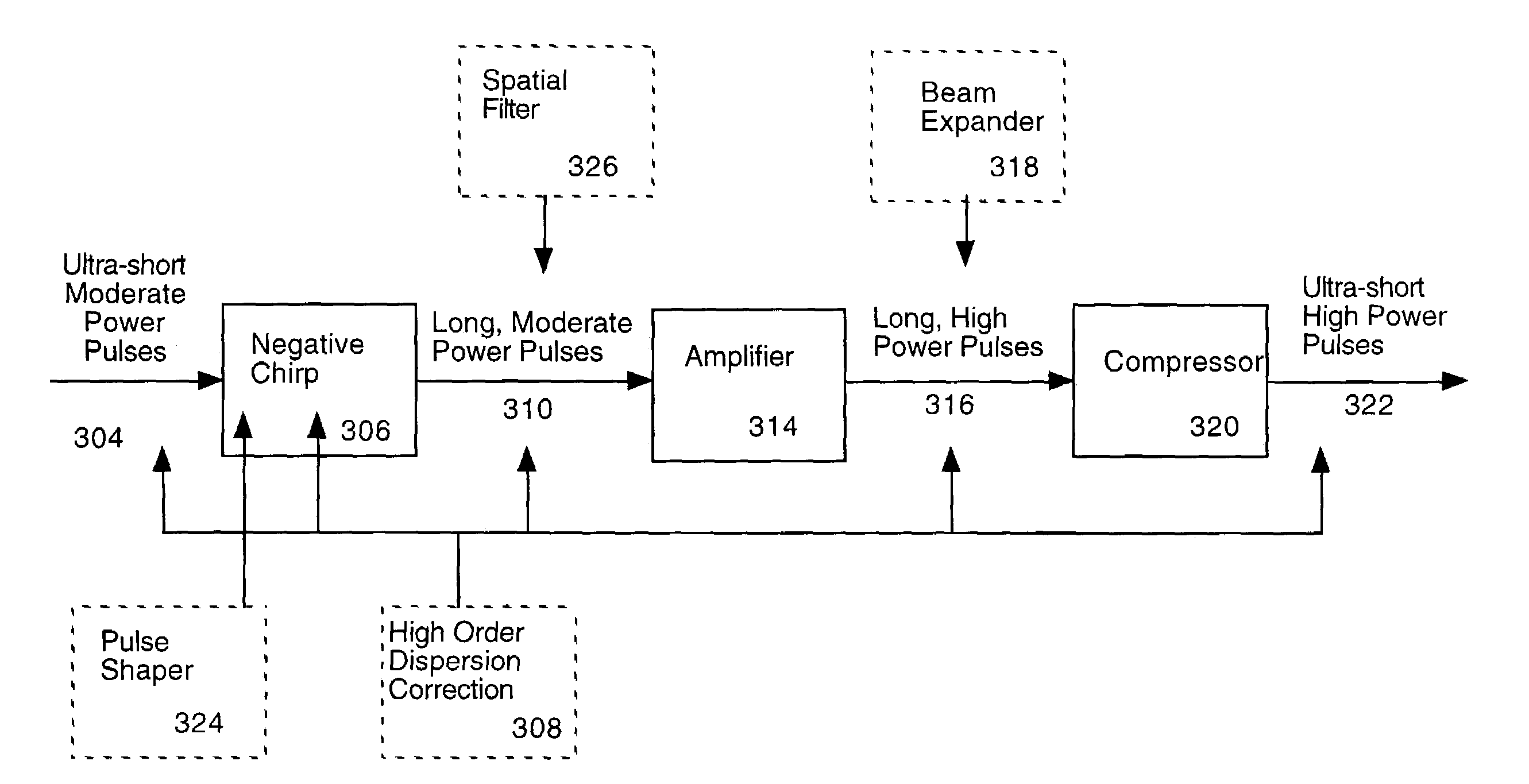
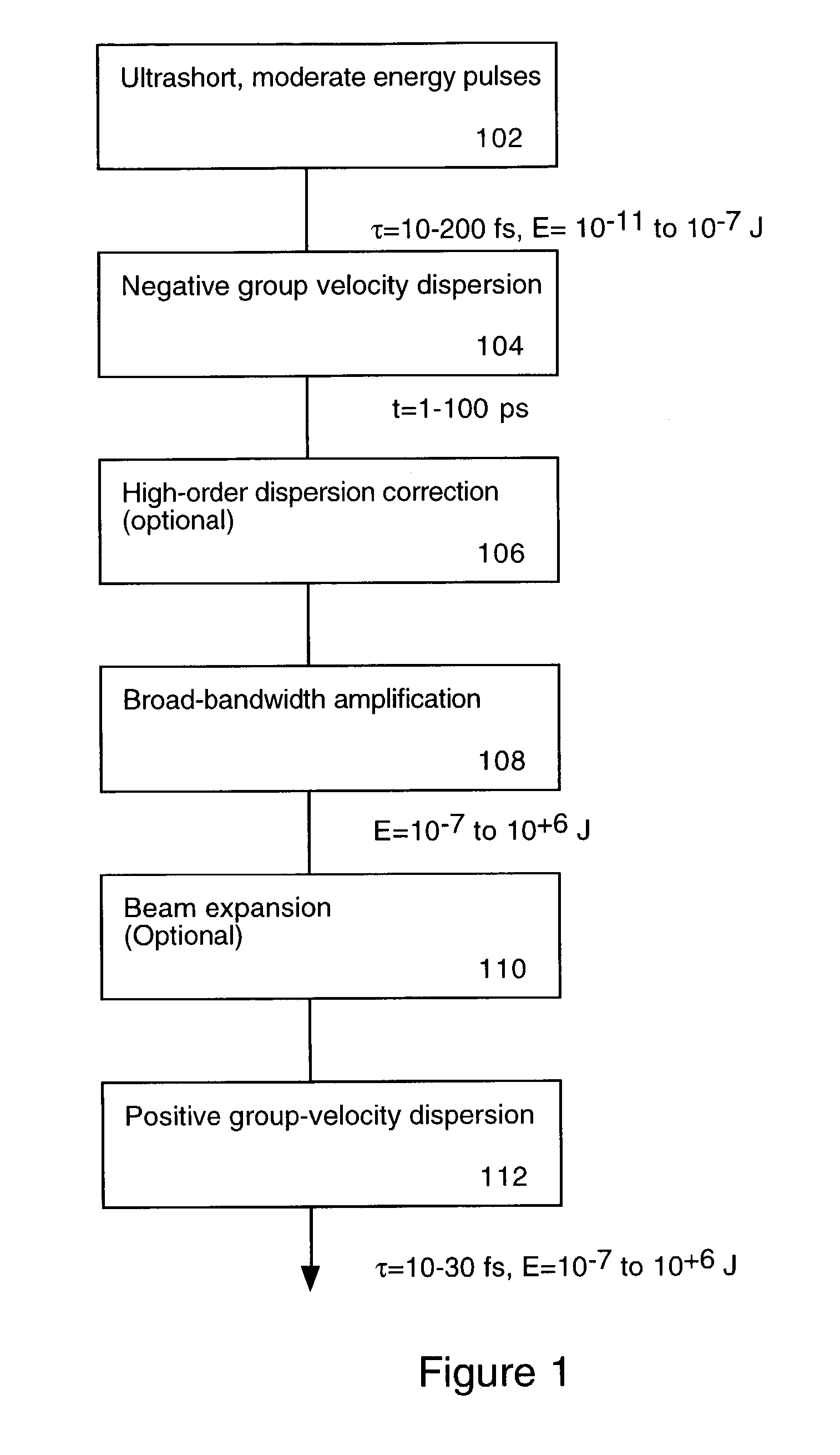
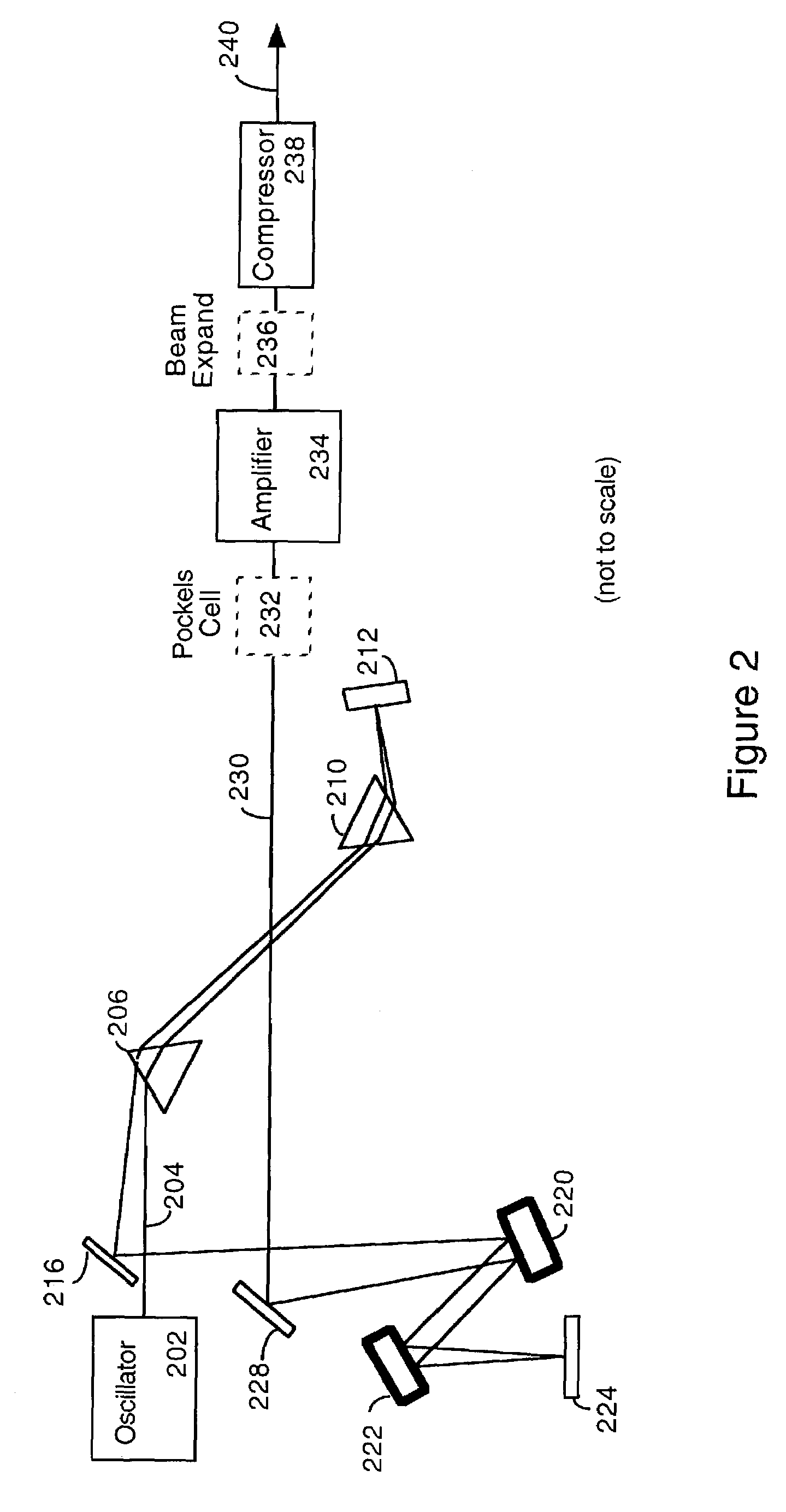
Downchirped pulse amplification
InactiveUS7072101B2High gainAvoid powerPulse automatic controlLaser arrangementsAudio power amplifierOptoelectronics
An ultrashort pulse amplifier produces high-power ultrafast laser pulses. Pulses first have net negative (i.e. blue to red) chirp applied, and are then amplified in a laser amplifier. After amplification, the pulses are compressed using propagation through a block of material or other convenient optical system with a positive sign of chromatic dispersion. High-order dispersion correction may also be included.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com