Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
116results about How to "Boost voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
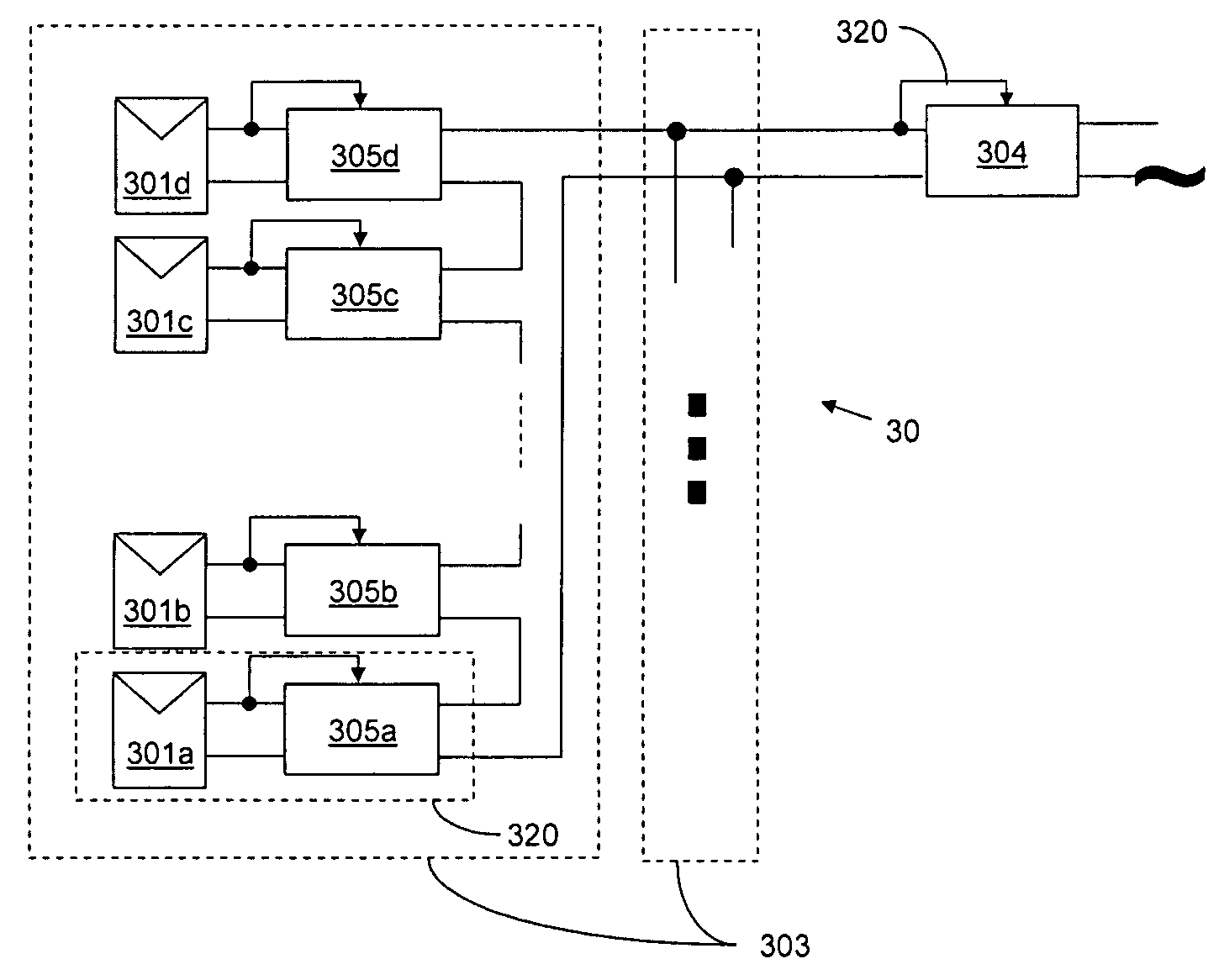
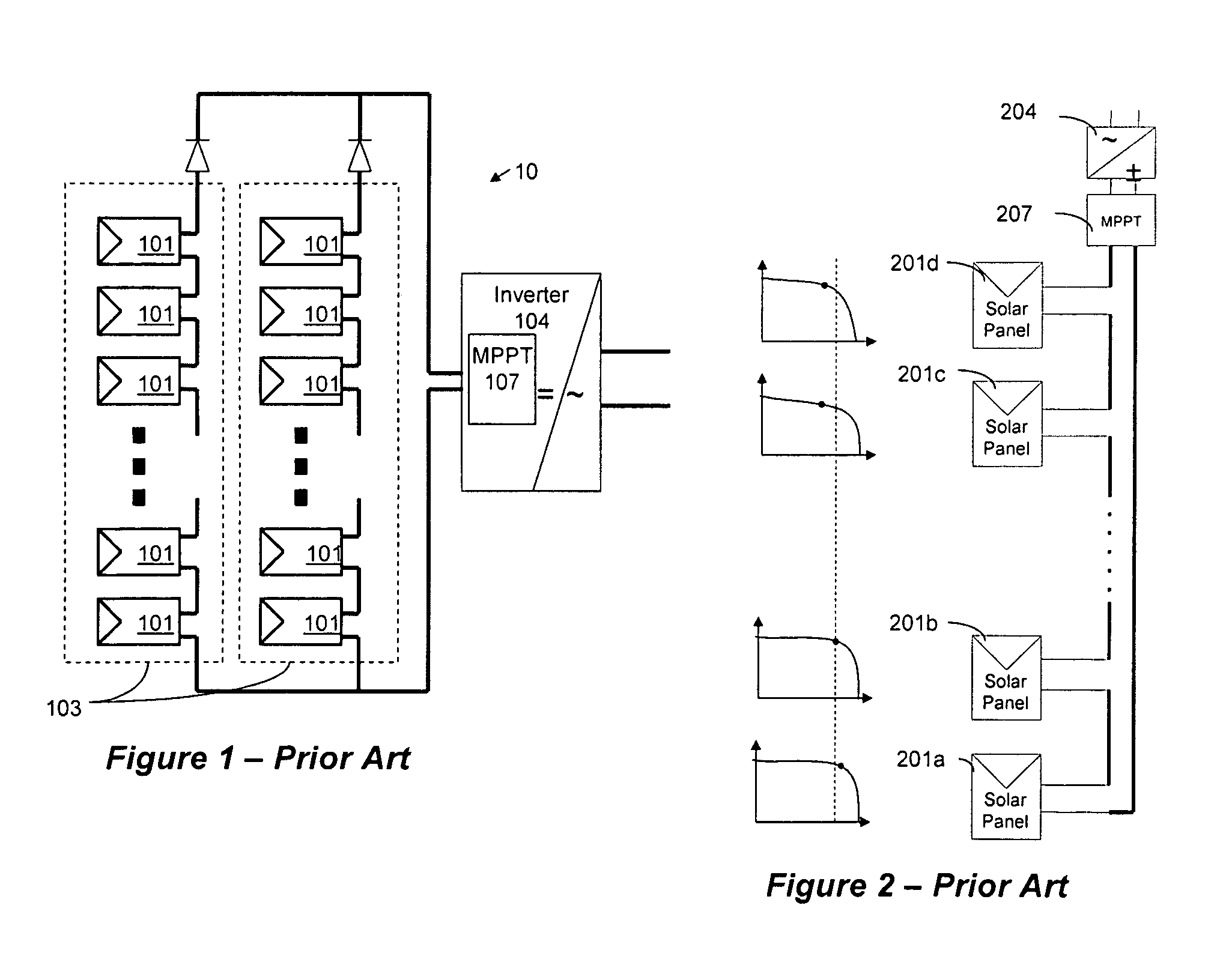
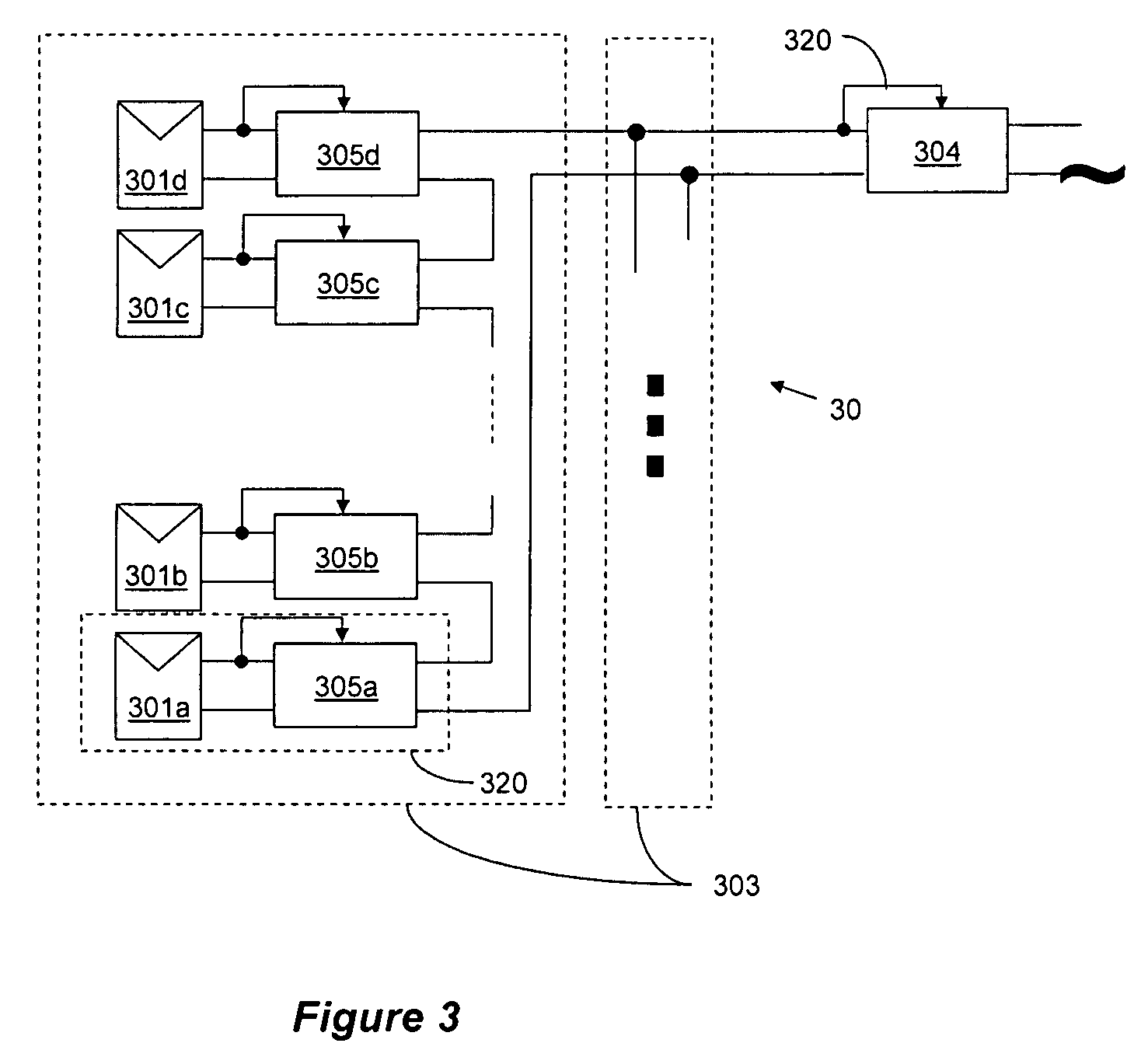
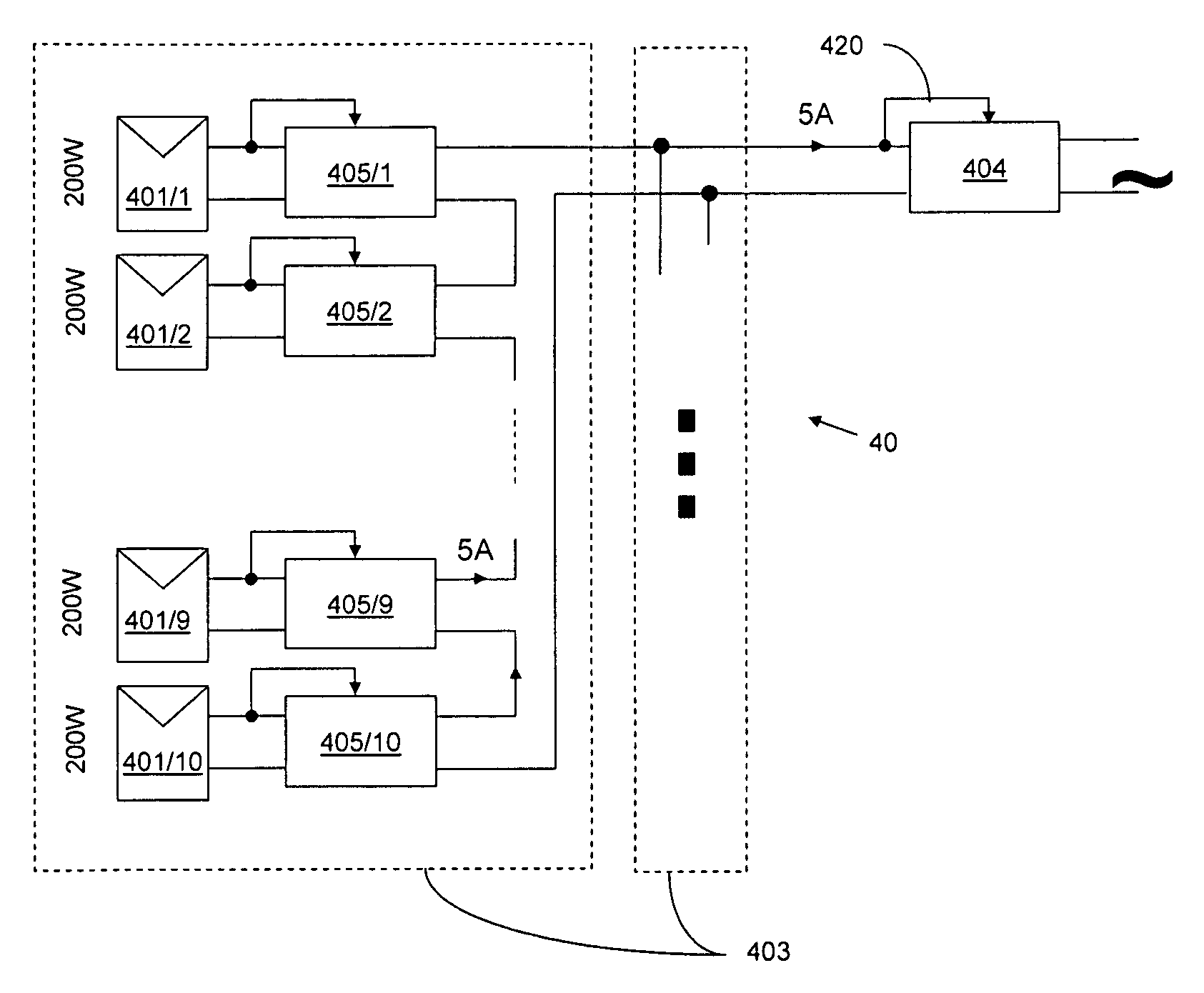
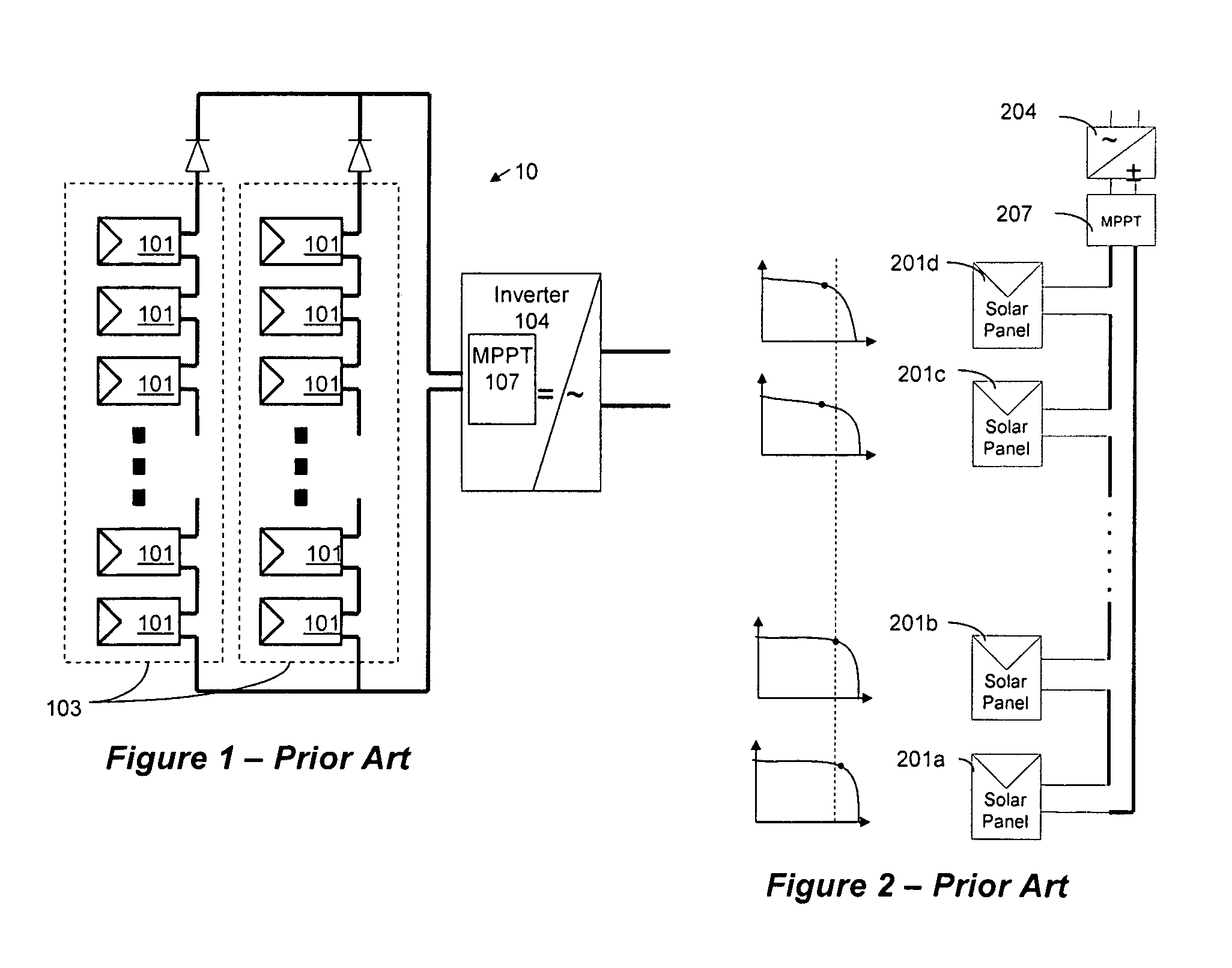
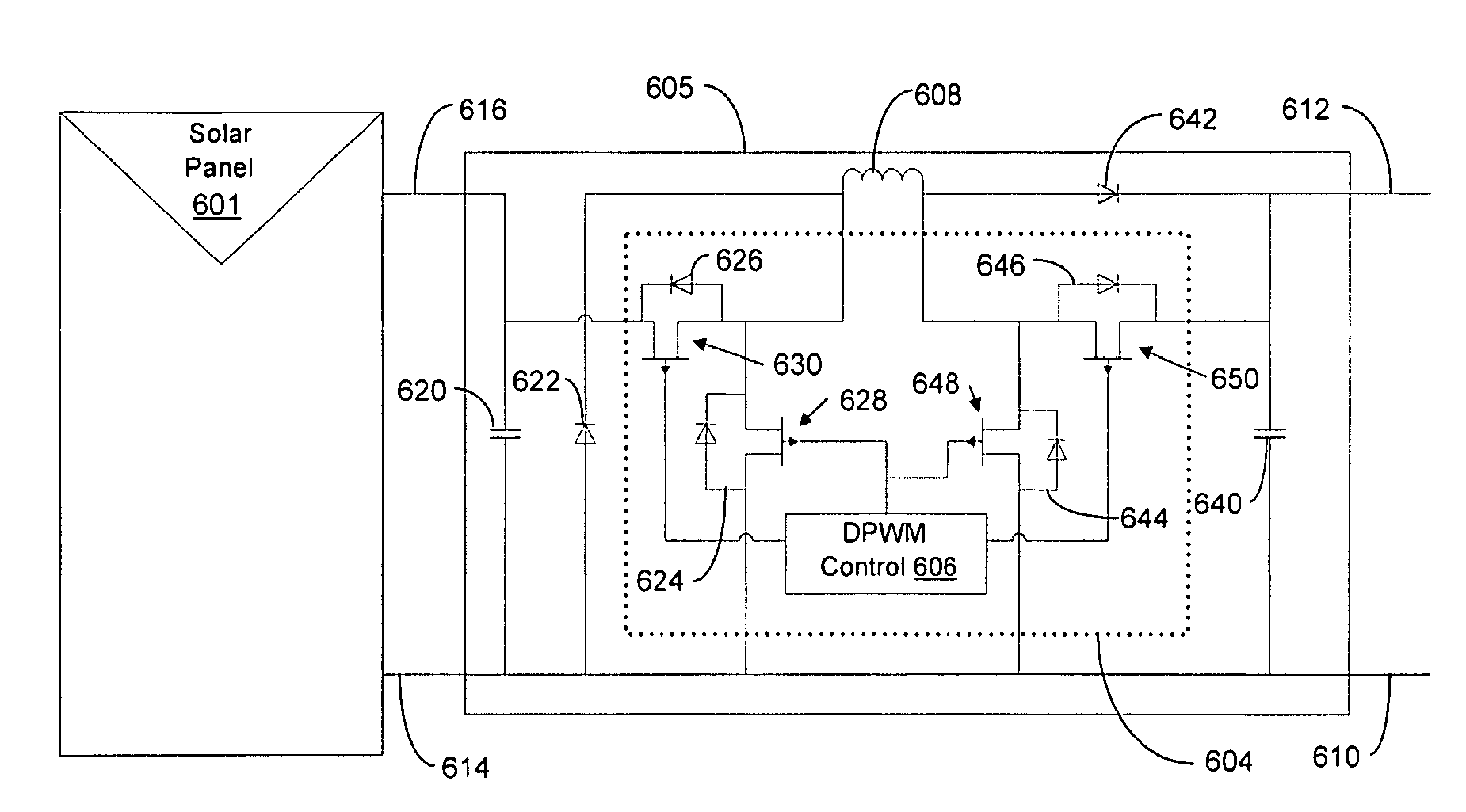
Method for distributed power harvesting using DC power sources
ActiveUS20080150366A1Improve reliabilitySafe operating voltageDc network circuit arrangementsPower network operation systems integrationTransverterVoltage variation
A system and method for combining power from DC power sources. Each power source is coupled to a converter. Each converter converts input power to output power by monitoring and maintaining the input power at a maximum power point. Substantially all input power is converted to the output power, and the controlling is performed by allowing output voltage of the converter to vary. The converters are coupled in series. An inverter is connected in parallel with the series connection of the converters and inverts a DC input to the inverter from the converters into an AC output. The inverter maintains the voltage at the inverter input at a desirable voltage by varying the amount of the series current drawn from the converters. The series current and the output power of the converters, determine the output voltage at each converter.
Owner:SOLAREDGE TECH LTD
Method for distributed power harvesting using DC power sources
ActiveUS8013472B2Improve component reliabilitySafe operating voltageDc network circuit arrangementsPower network operation systems integrationTransverterVoltage variation
A system and method for combining power from DC power sources. Each power source is coupled to a converter. Each converter converts input power to output power by monitoring and maintaining the input power at a maximum power point. Substantially all input power is converted to the output power, and the controlling is performed by allowing output voltage of the converter to vary. The converters are coupled in series. An inverter is connected in parallel with the series connection of the converters and inverts a DC input to the inverter from the converters into an AC output. The inverter maintains the voltage at the inverter input at a desirable voltage by varying the amount of the series current drawn from the converters. The series current and the output power of the converters, determine the output voltage at each converter.
Owner:SOLAREDGE TECH LTD
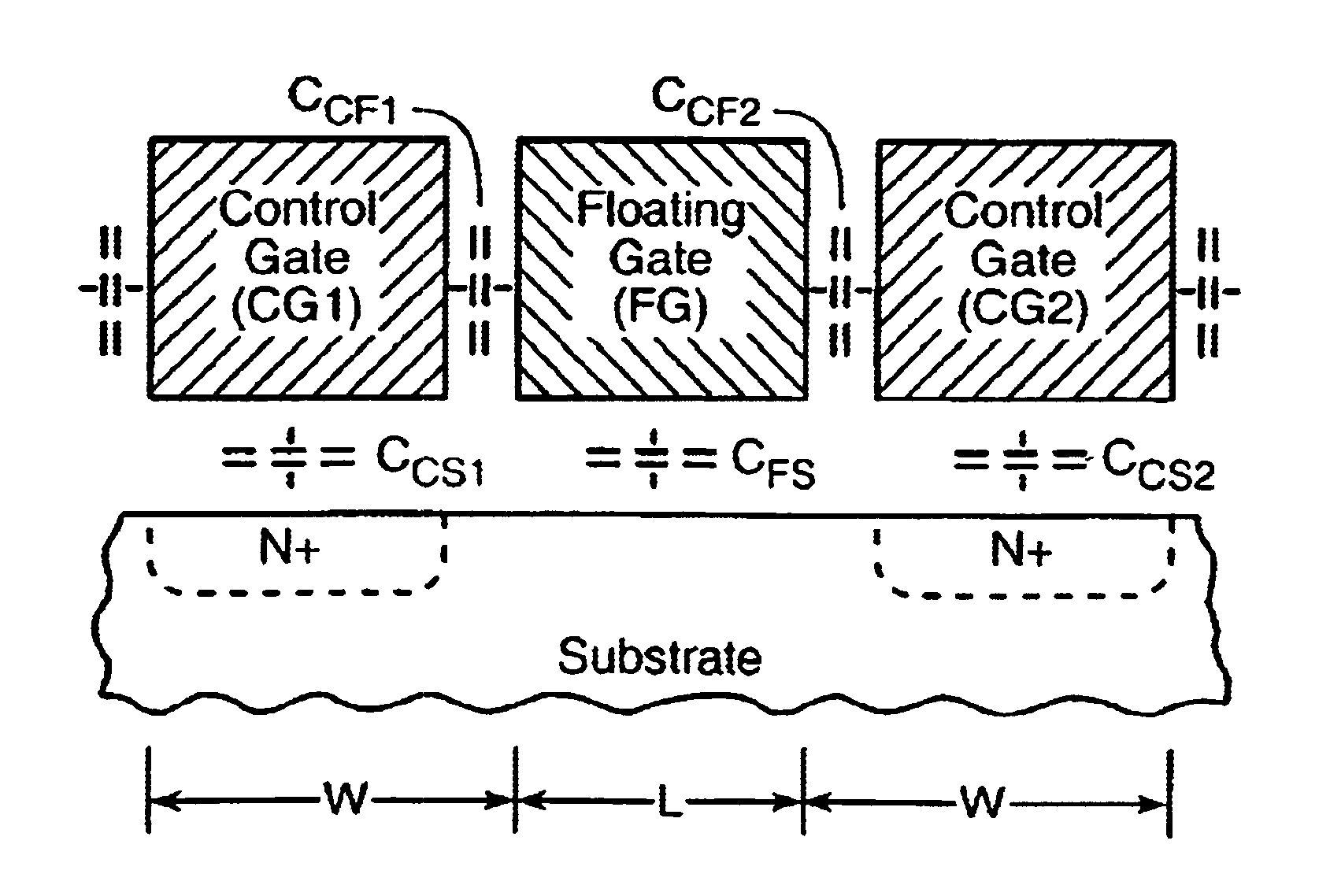
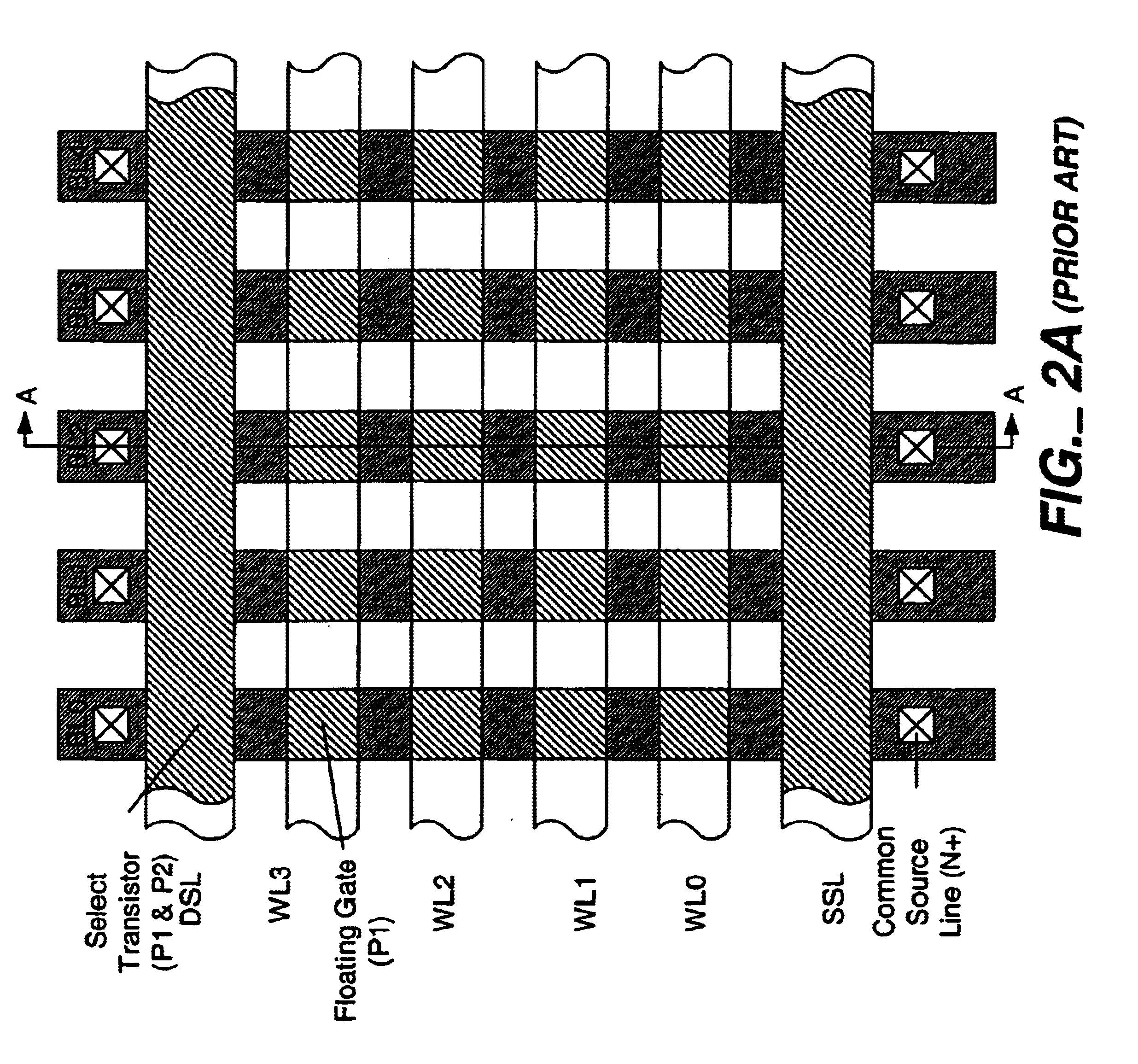
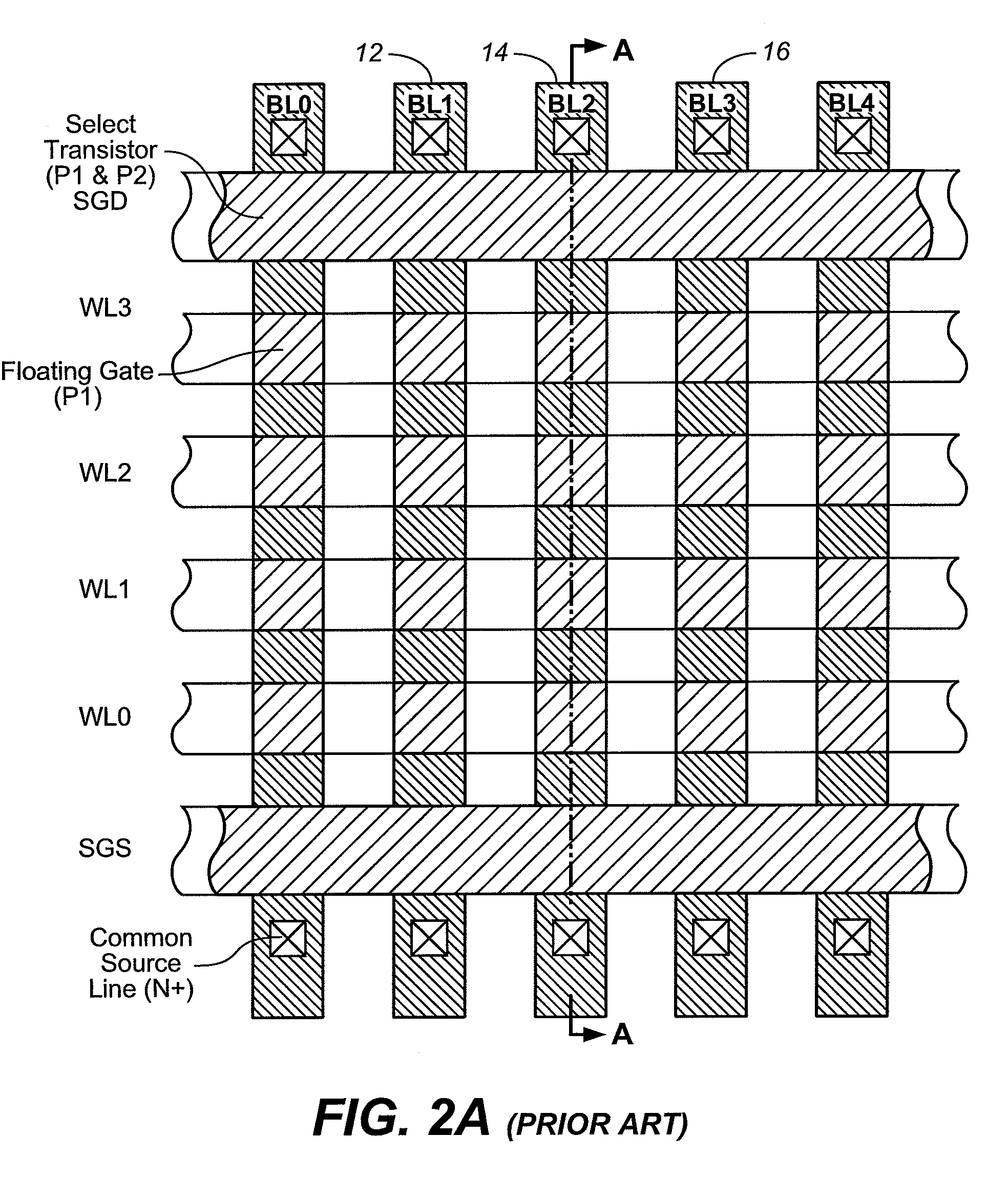
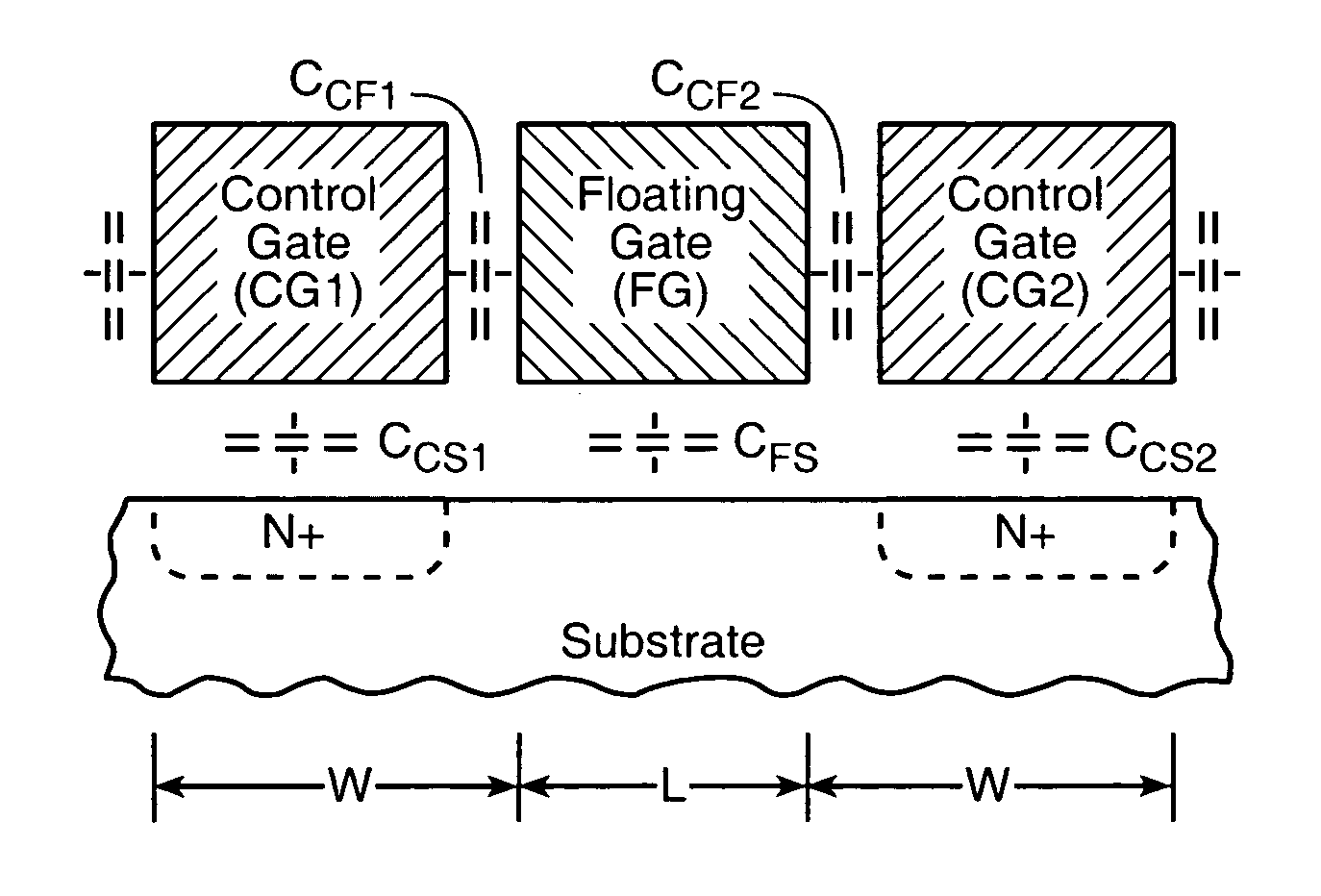
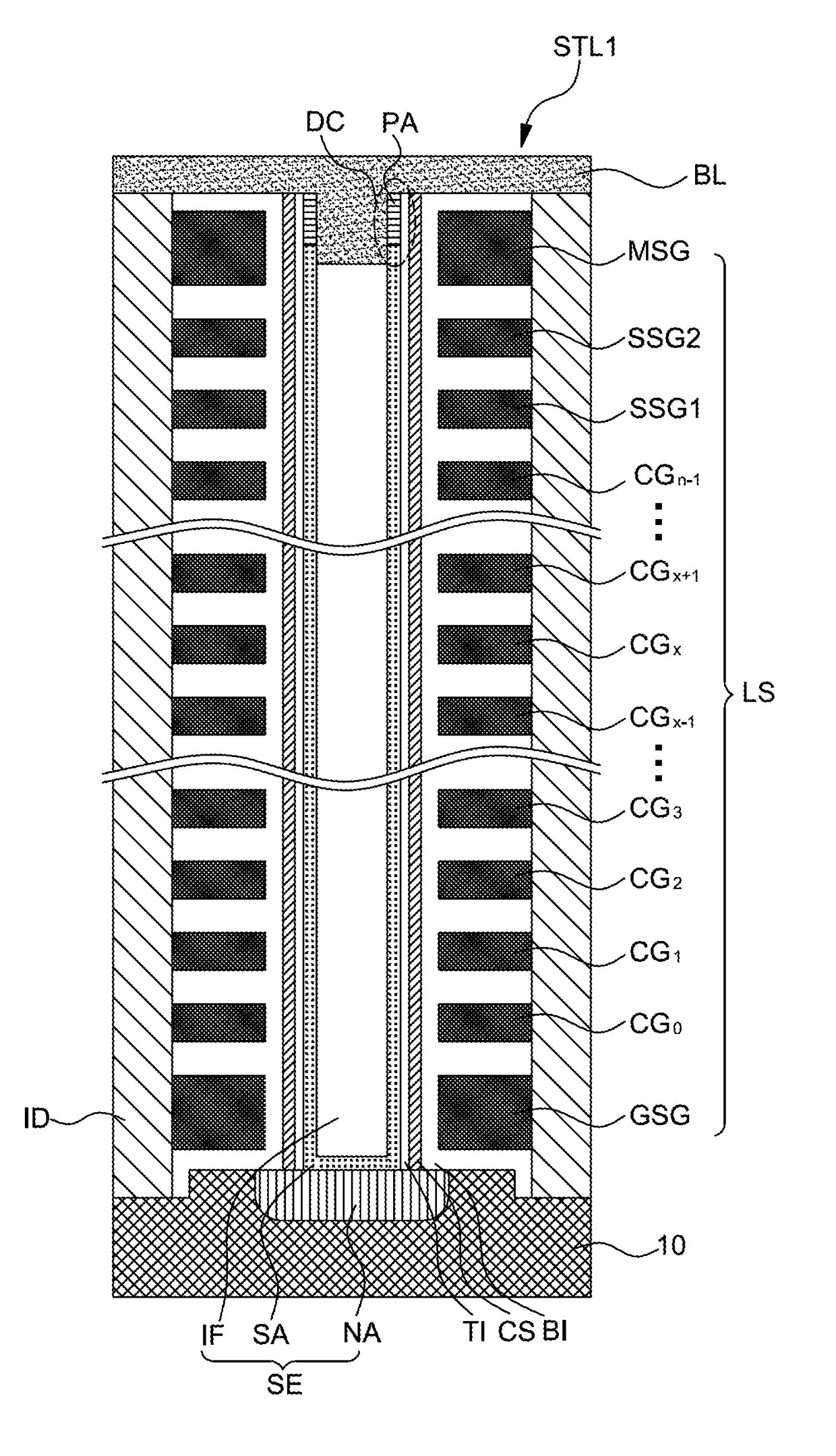
Flash memory cell arrays having dual control gates per memory cell charge storage element
InactiveUS6888755B2Increase coupling areaImprove the coupling ratioTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceImage resolution
A flash NAND type EEPROM system with individual ones of an array of charge storage elements, such as floating gates, being capacitively coupled with at least two control gate lines. The control gate lines are preferably positioned between floating gates to be coupled with sidewalls of floating gates. The memory cell coupling ratio is desirably increased, as a result. Both control gate lines on opposite sides of a selected row of floating gates are usually raised to the same voltage while the second control gate lines coupled to unselected rows of floating gates immediately adjacent and on opposite sides of the selected row are kept low. The control gate lines can also be capacitively coupled with the substrate in order to selectively raise its voltage in the region of selected floating gates. The length of the floating gates and the thicknesses of the control gate lines can be made less than the minimum resolution element of the process by forming an etch mask of spacers.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
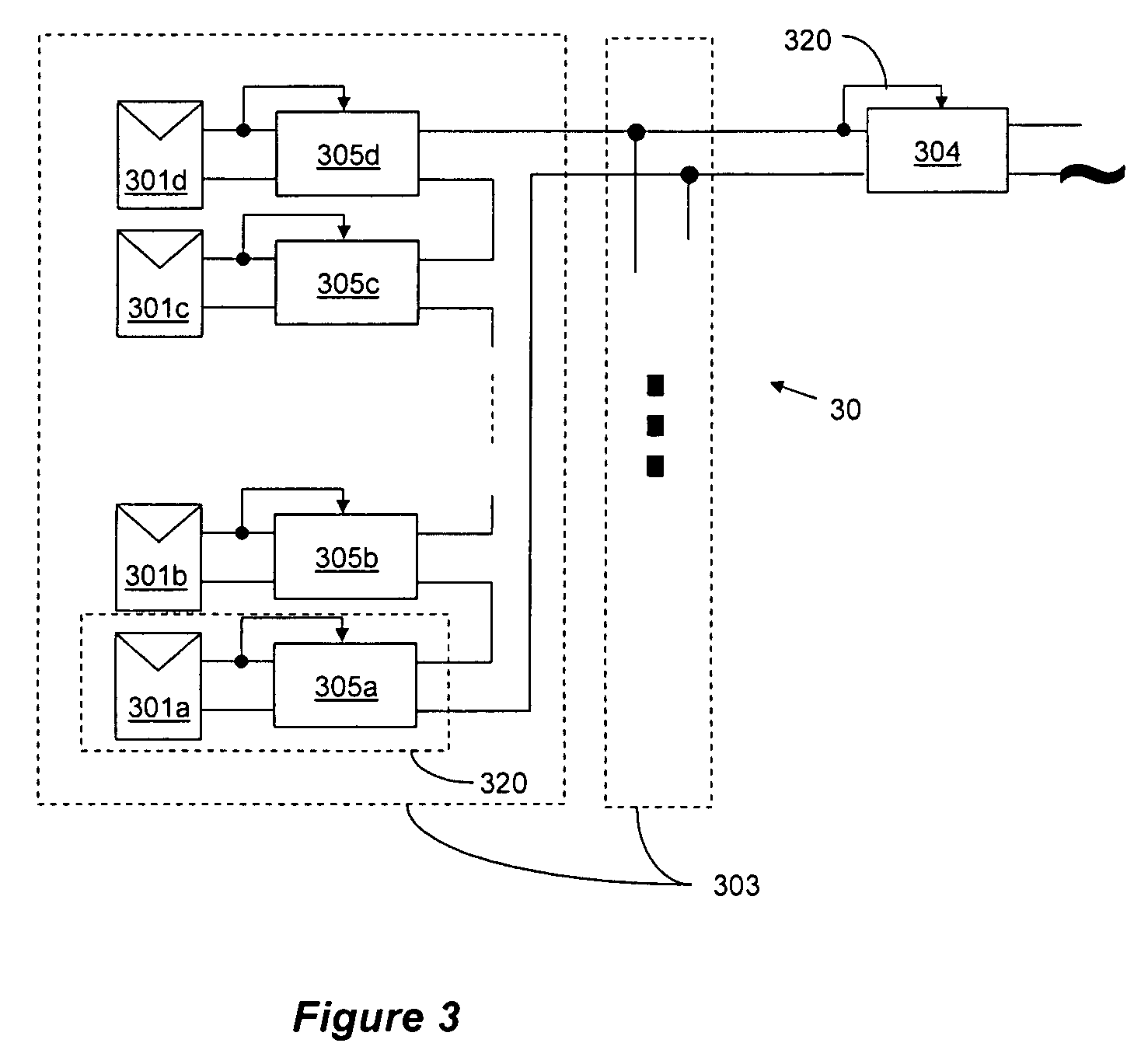
Distributed Power Harvesting Systems Using DC Power Sources
InactiveUS20120175963A1Improve component reliabilitySafe operating voltageDc network circuit arrangementsBatteries circuit arrangementsTransverterEngineering
A system and method for combining power from DC power sources. Each power source is coupled to a converter. Each converter converts input power to output power by monitoring and maintaining the input power at a maximum power point. Substantially all input power is converted to the output power, and the controlling is performed by allowing output voltage of the converter to vary. The converters are coupled in series. An inverter is connected in parallel with the series connection of the converters and inverts a DC input to the inverter from the converters into an AC output. The inverter maintains the voltage at the inverter input at a desirable voltage by varying the amount of the series current drawn from the converters. The series current and the output power of the converters, determine the output voltage at each converter.
Owner:SOLAREDGE TECH LTD
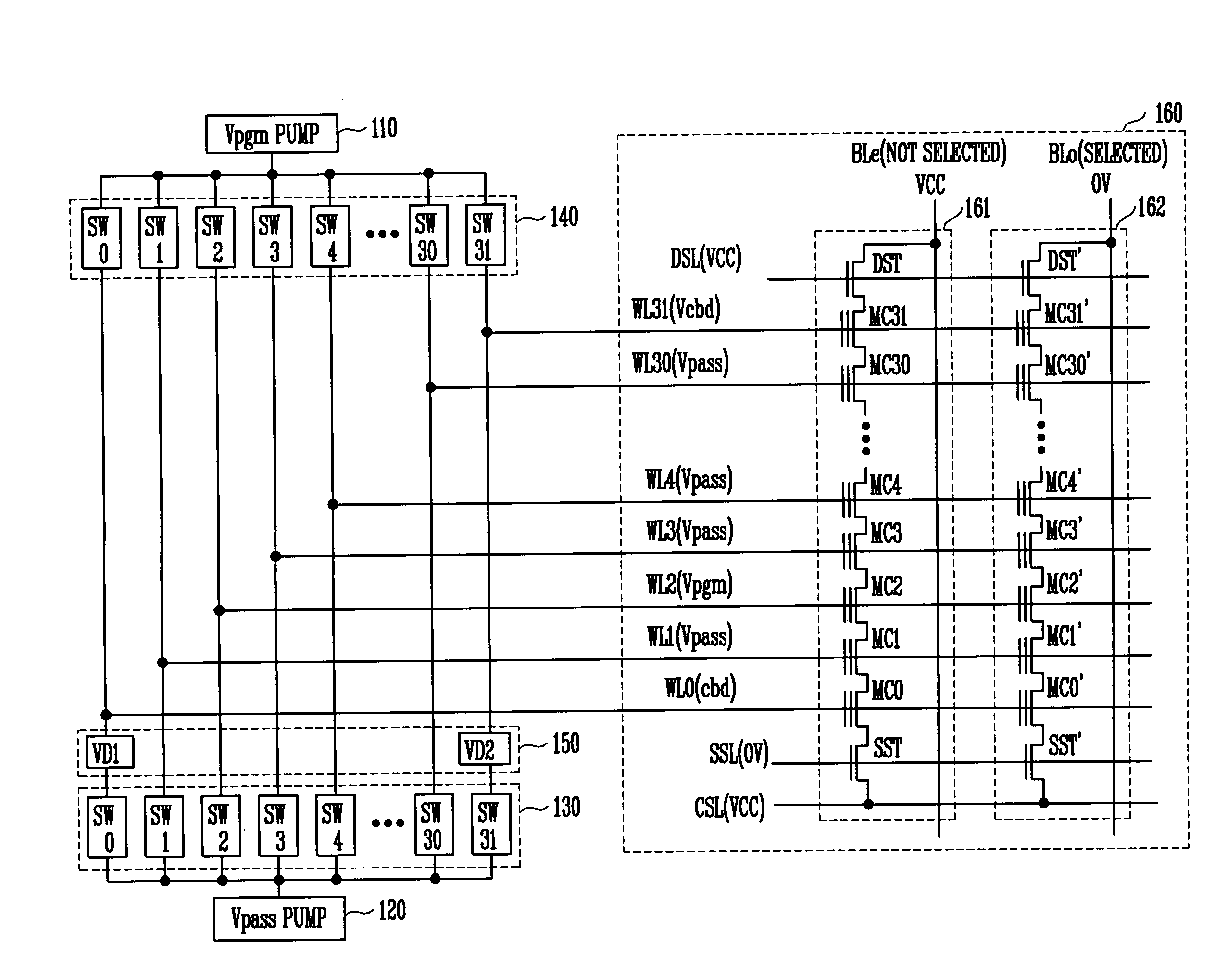
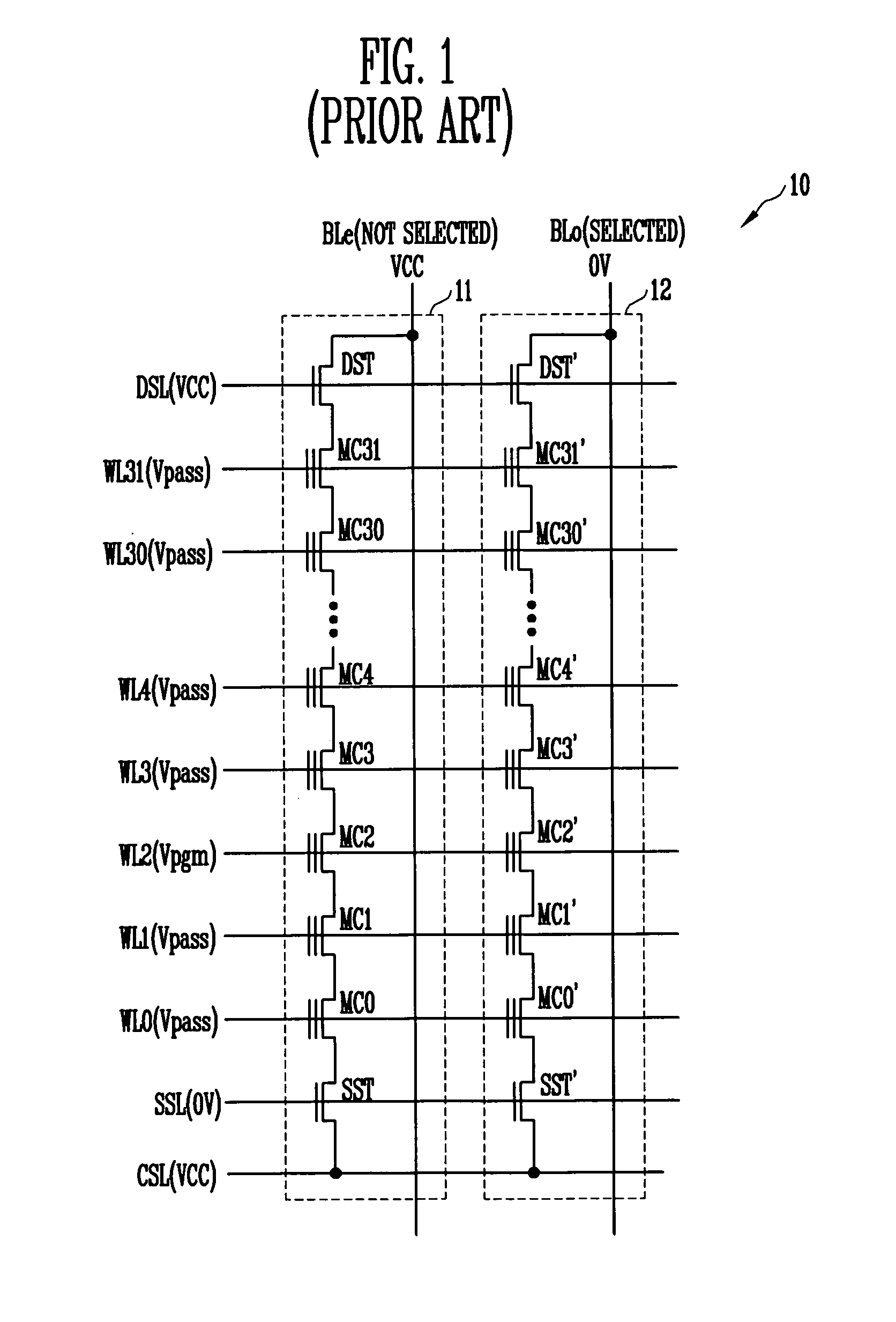
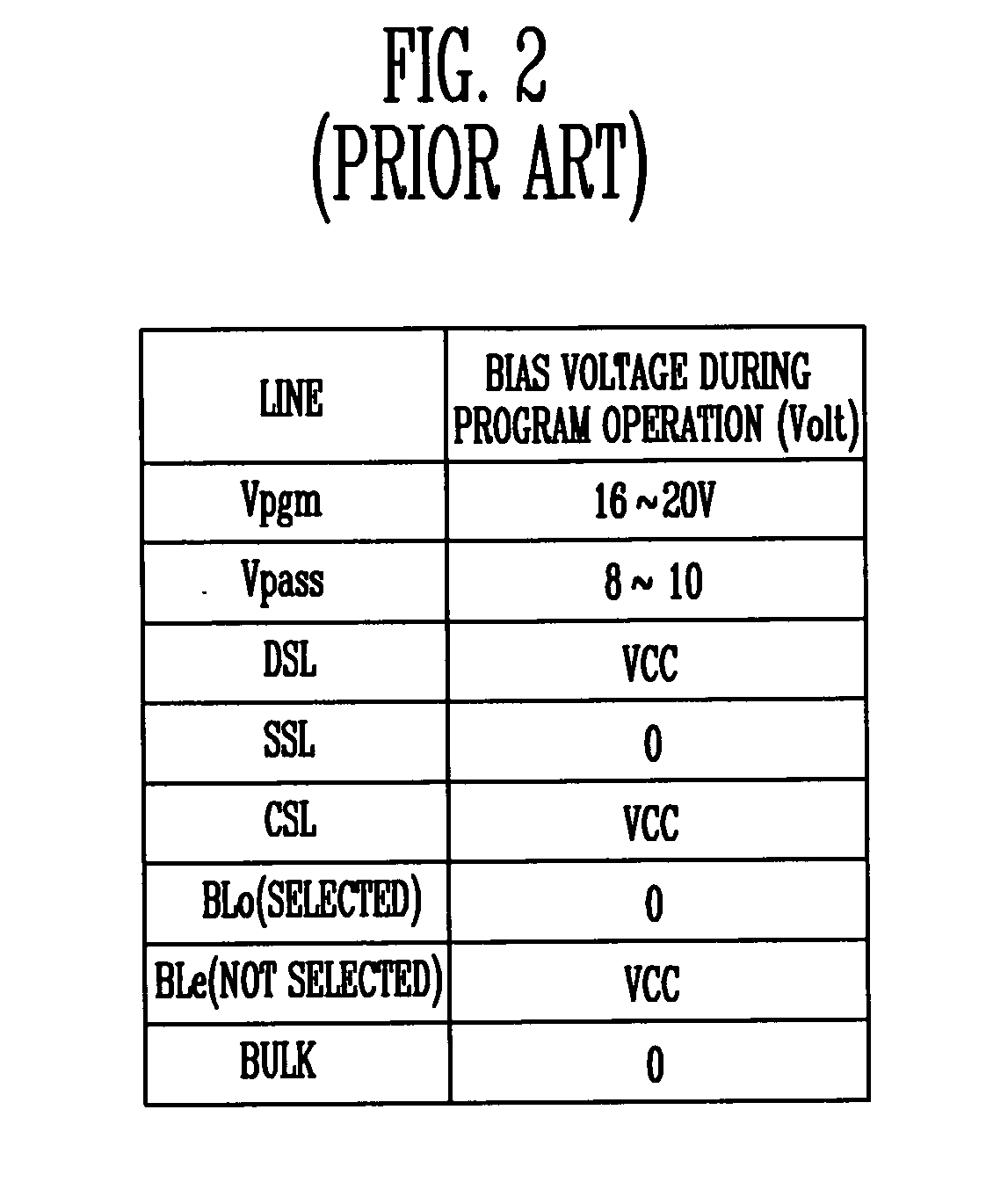
Non-volatile memory device and method of preventing hot electron program disturb phenomenon
ActiveUS20060227613A1Weak electric fieldWeaker electric fieldRead-only memoriesDigital storageComputer scienceElectric field
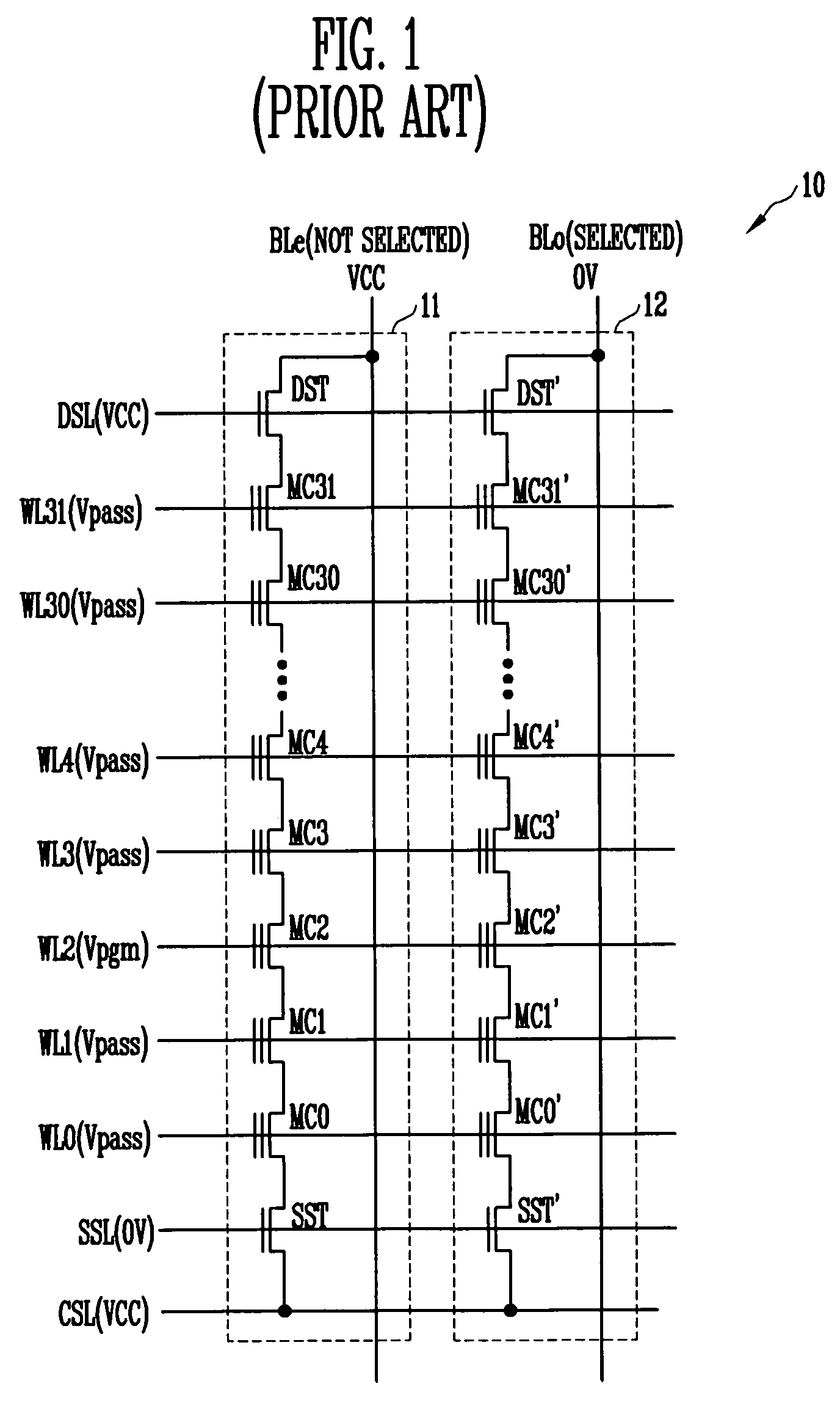
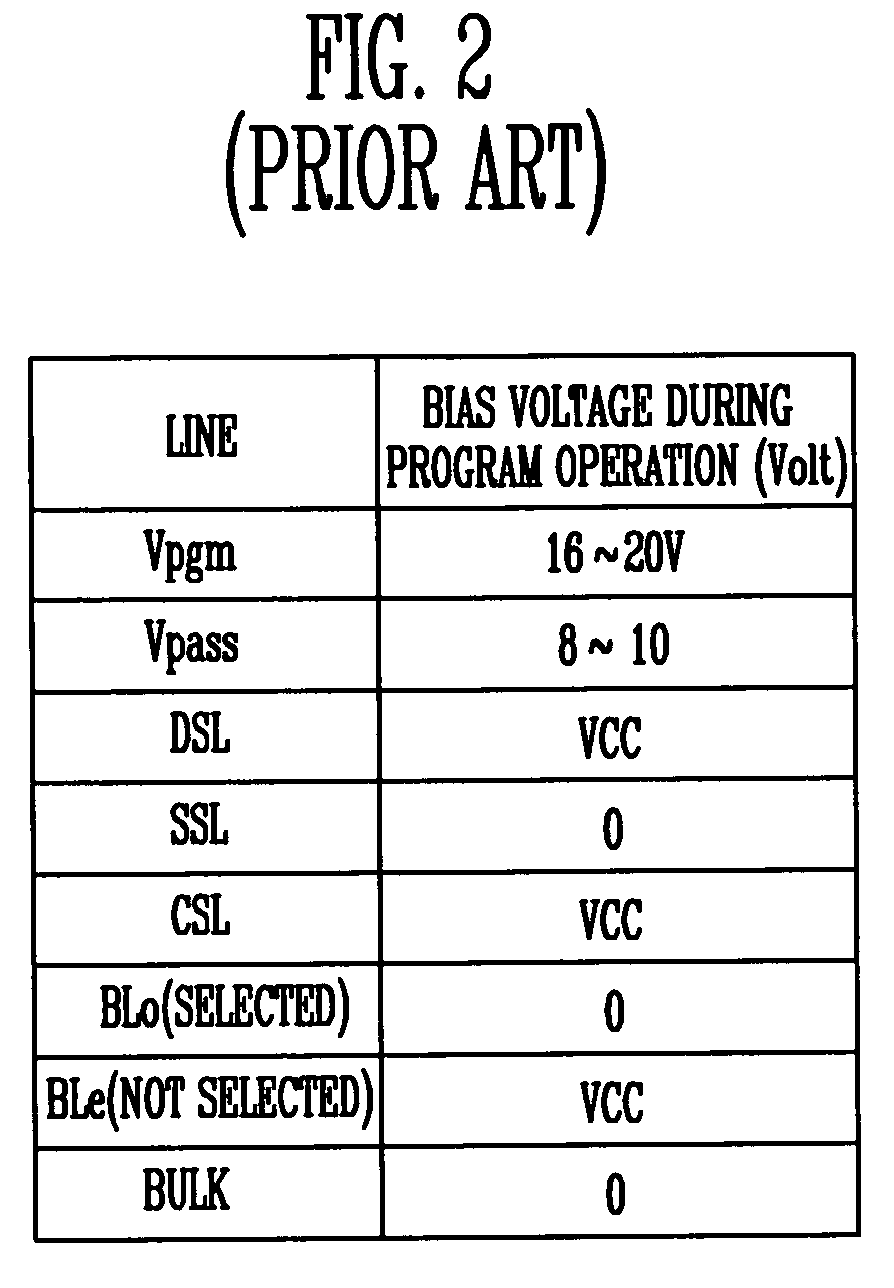
A method for preventing generation of program disturbance incurred by hot electrons in a NAND flash memory device. A channel boosting disturb-prevention voltage lower than a program-prohibit voltage applied to other word lines is applied to edge word lines coupled to memory cells that are nearest to select transistors. As a result, an electric field between the memory cells coupled to the edge word lines and the select transistors is weakened, and the energy of the hot electrons is reduced.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
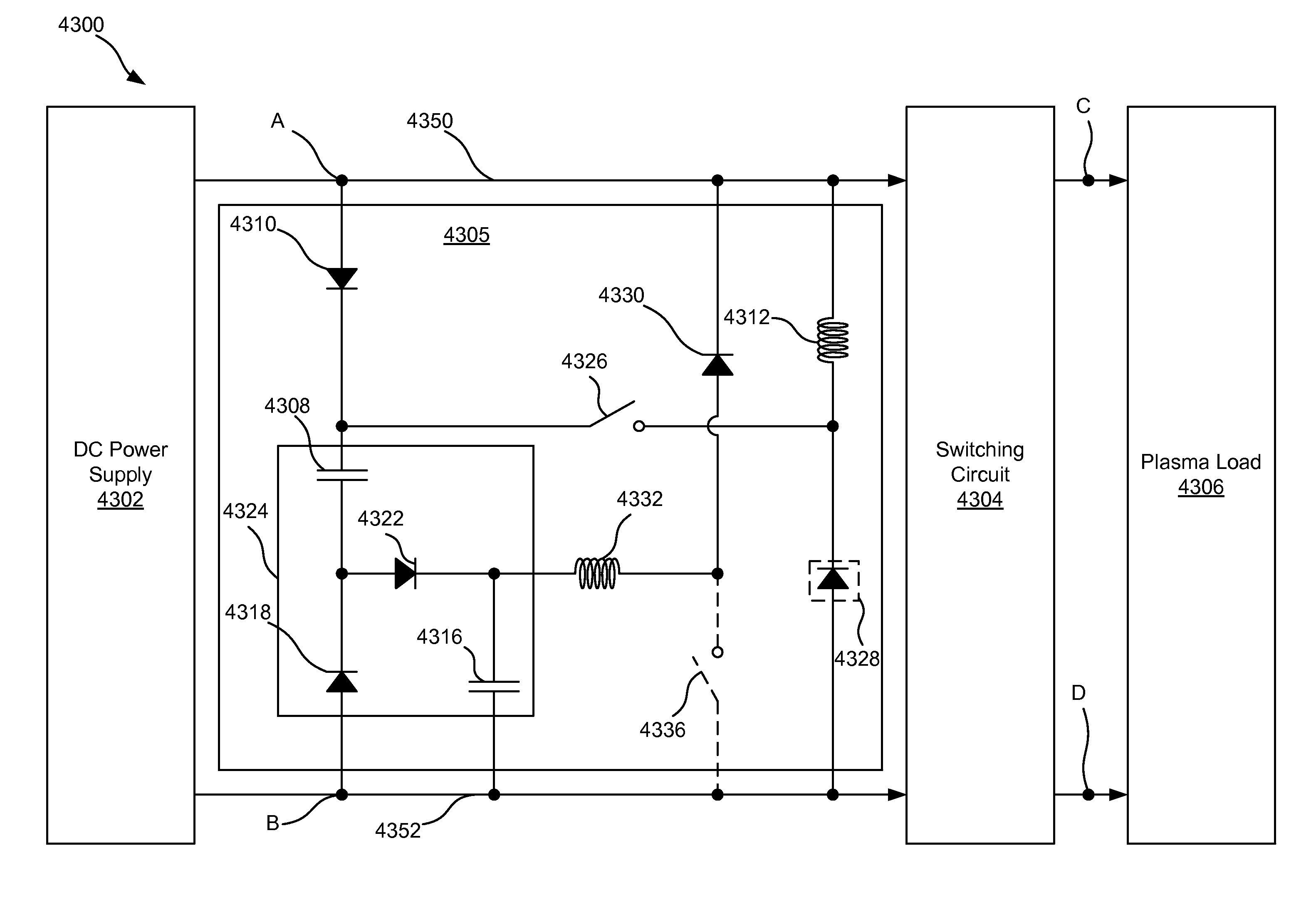
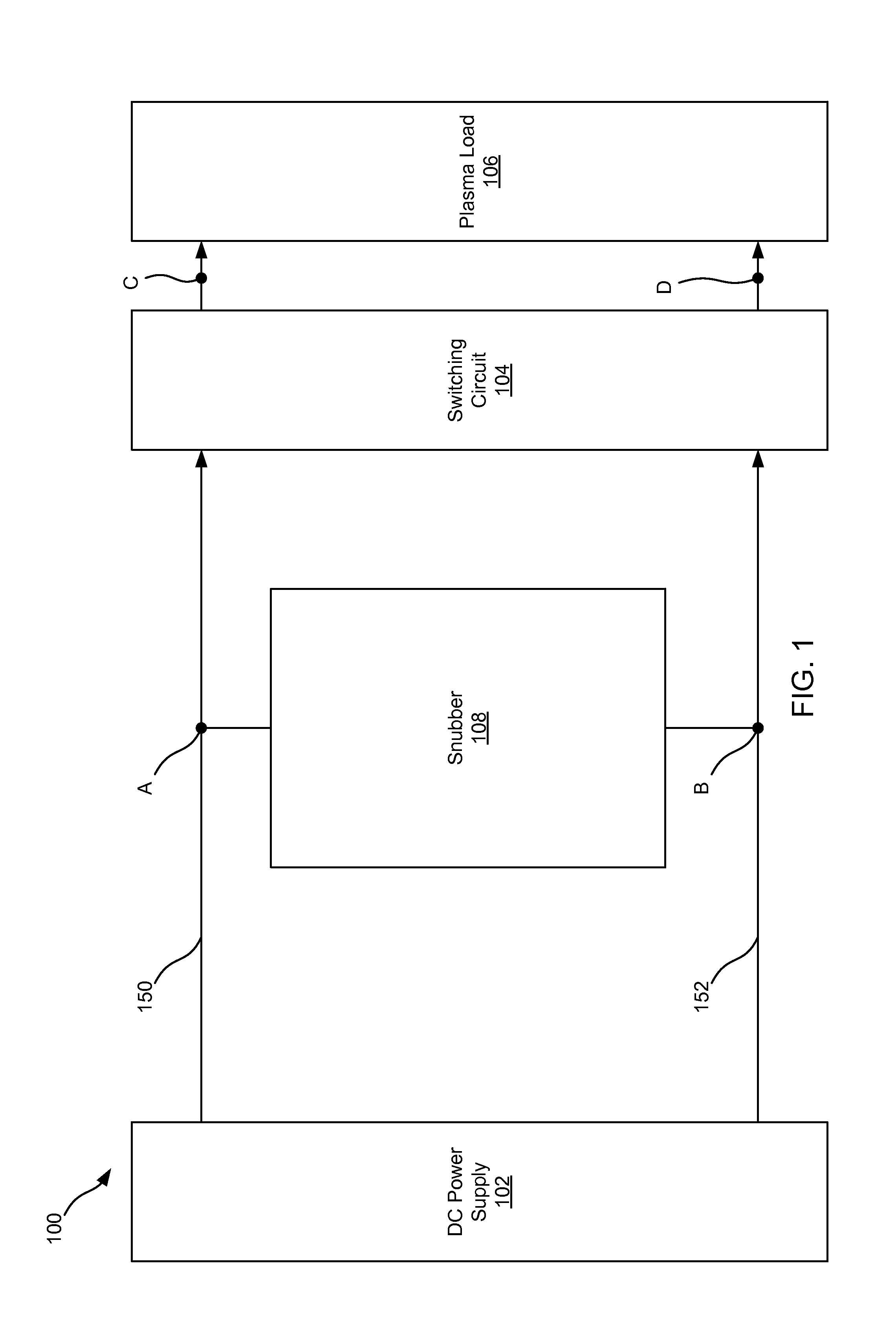
Charge removal from electrodes in unipolar sputtering system
ActiveUS20140231243A1Boost voltageReduce voltageCellsElectric discharge tubesVoltage multiplierEngineering
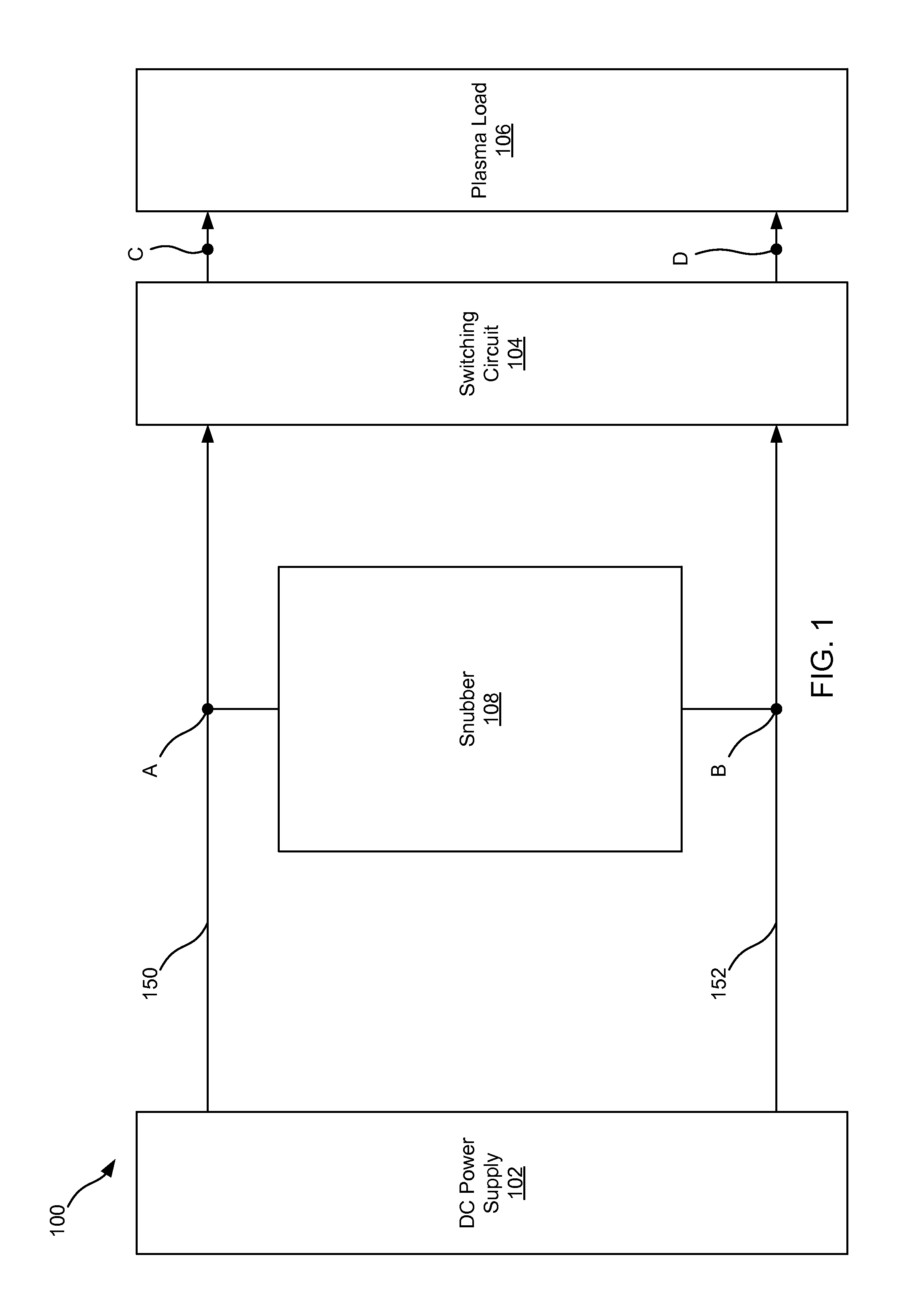
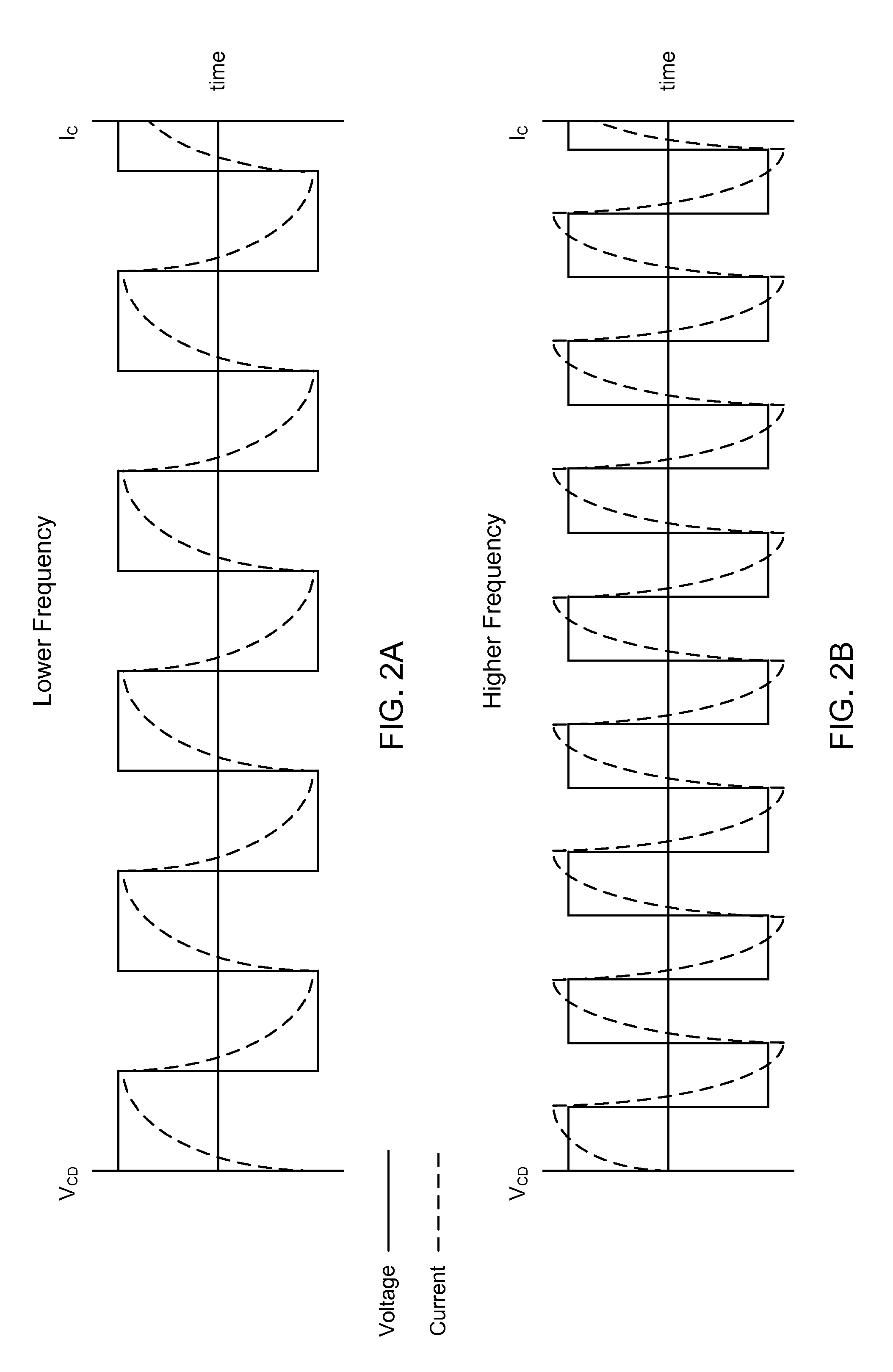
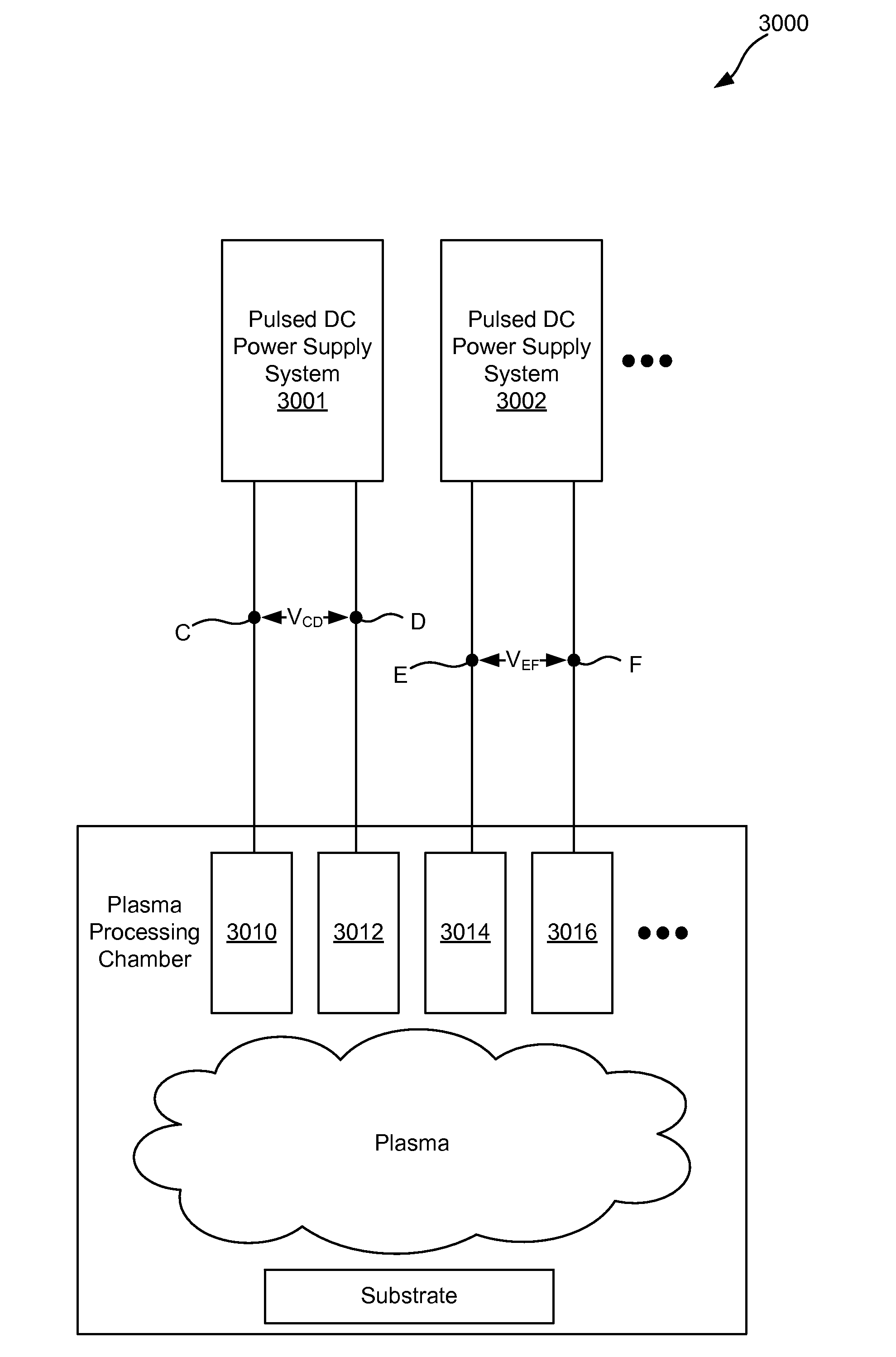
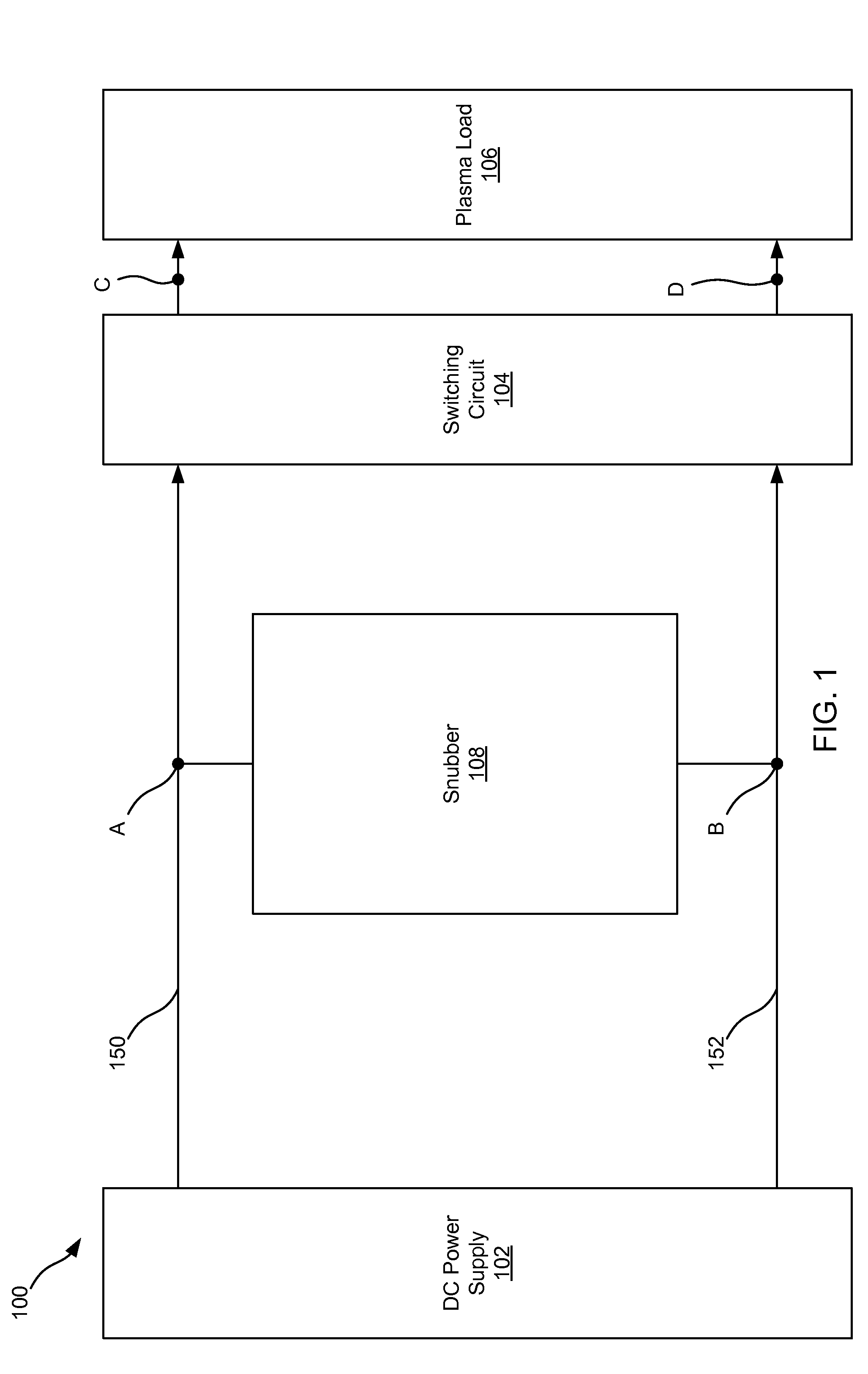
This disclosure describes a non-dissipative snubber circuit configured to boost a voltage applied to a load after the load's impedance rises rapidly. The voltage boost can thereby cause more rapid current ramping after a decrease in power delivery to the load which results from the load impedance rise. In particular, the snubber can comprise a combination of a unidirectional switch, a voltage multiplier, and a current limiter. In some cases, these components can be a diode, voltage doubler, and an inductor, respectively.
Owner:AES GLOBAL HLDG PTE LTD
Differing boost voltages applied to two or more anodeless electrodes for plasma processing
ActiveUS20140117861A1Boost voltageReduce voltageElectric discharge tubesElectric light circuit arrangementPower flowVoltage multiplier
This disclosure describes a non-dissipative snubber circuit configured to boost a voltage applied to a load after the load's impedance rises rapidly. The voltage boost can thereby cause more rapid current ramping after a decrease in power delivery to the load which results from the load impedance rise. In particular, the snubber can comprise a combination of a unidirectional switch, a voltage multiplier, and a current limiter. In some cases, these components can be a diode, voltage doubler, and an inductor, respectively.
Owner:AES GLOBAL HLDG PTE LTD
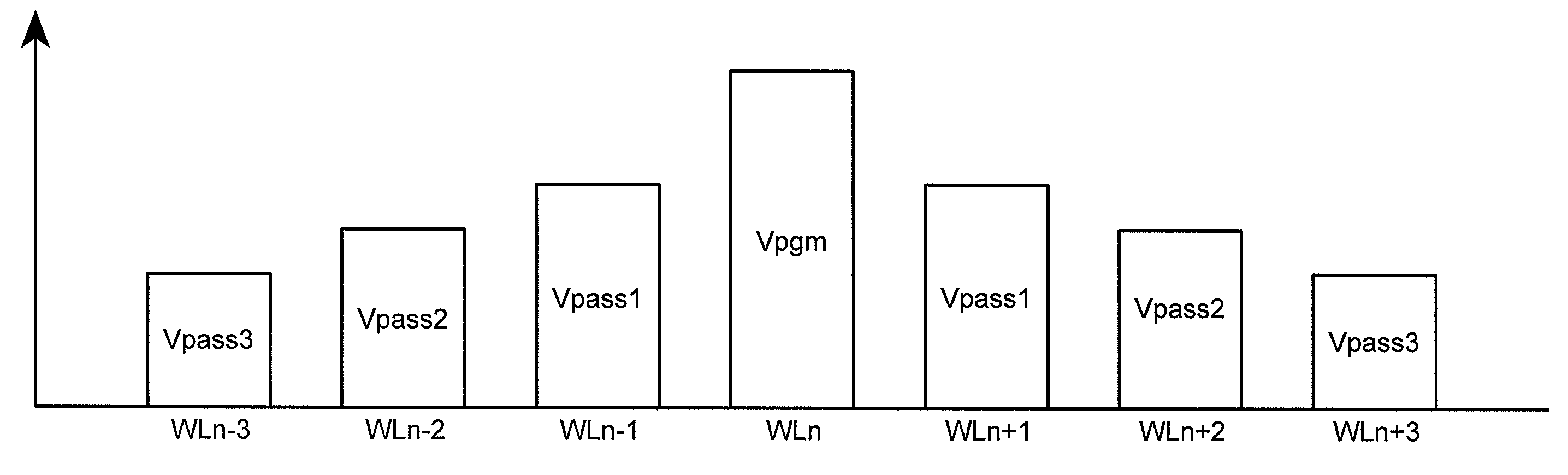
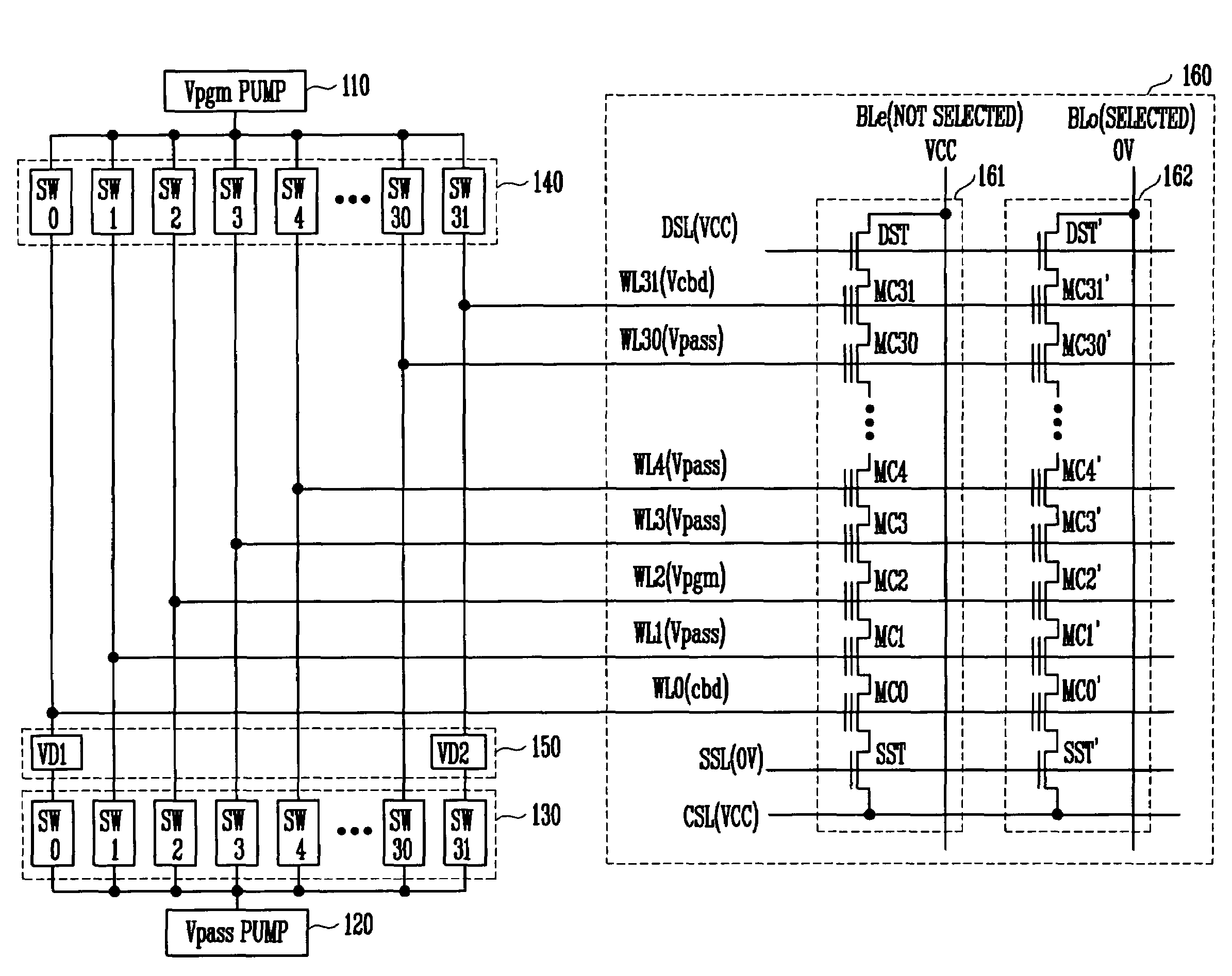
Boosting methods for NAND flash memory
InactiveUS7286408B1Reducing Vpgm-disturbsHigh boosting voltageRead-only memoriesDigital storageHemt circuitsEngineering
A floating gate memory array includes row control circuits that provide a programming voltage to a selected word line and provide a stair-like pattern of boosting voltages to unselected word lines. Boosting voltages descend with increased distance from the selected word line. Boosting voltages are increased in small increments up to their final values.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
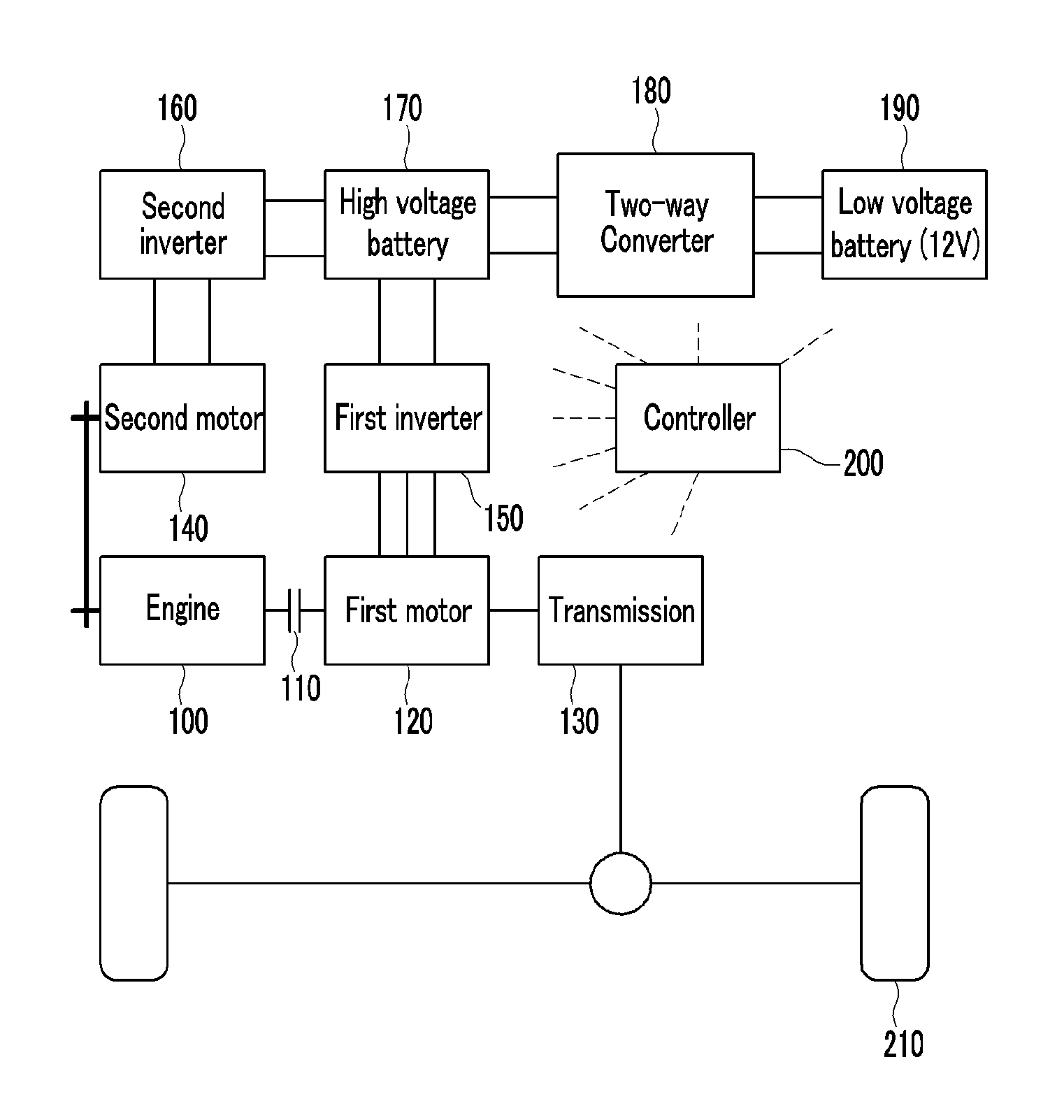
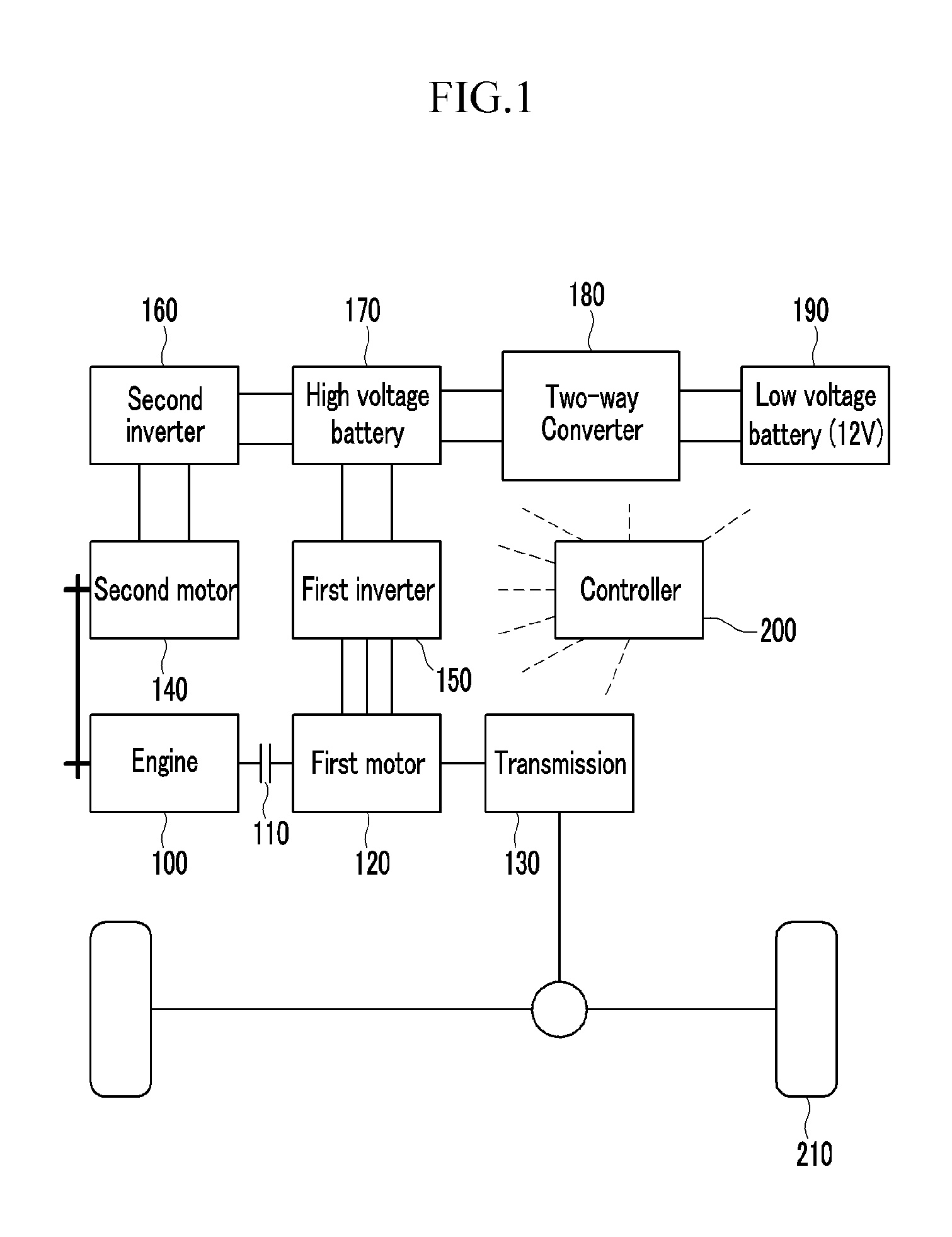
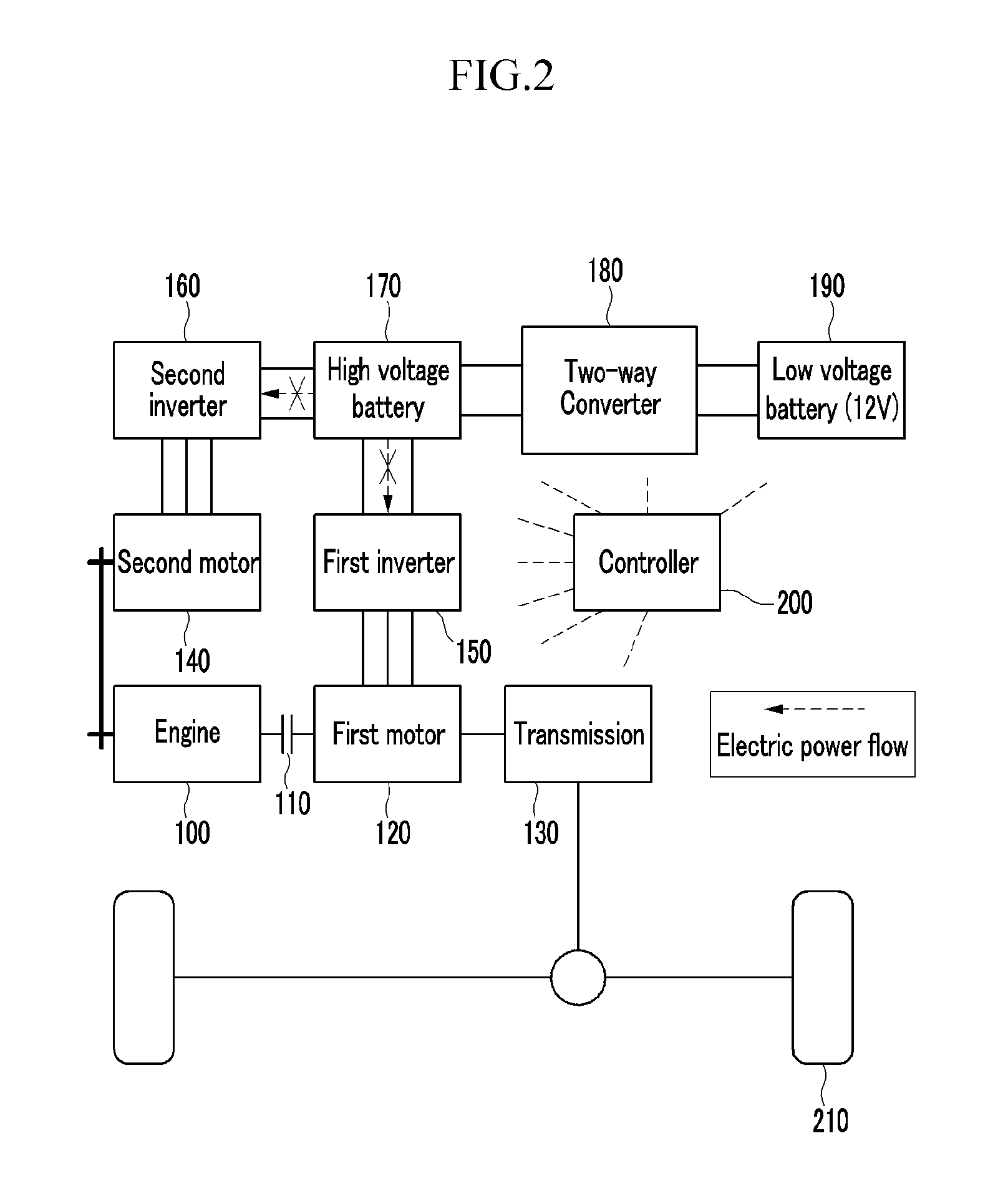
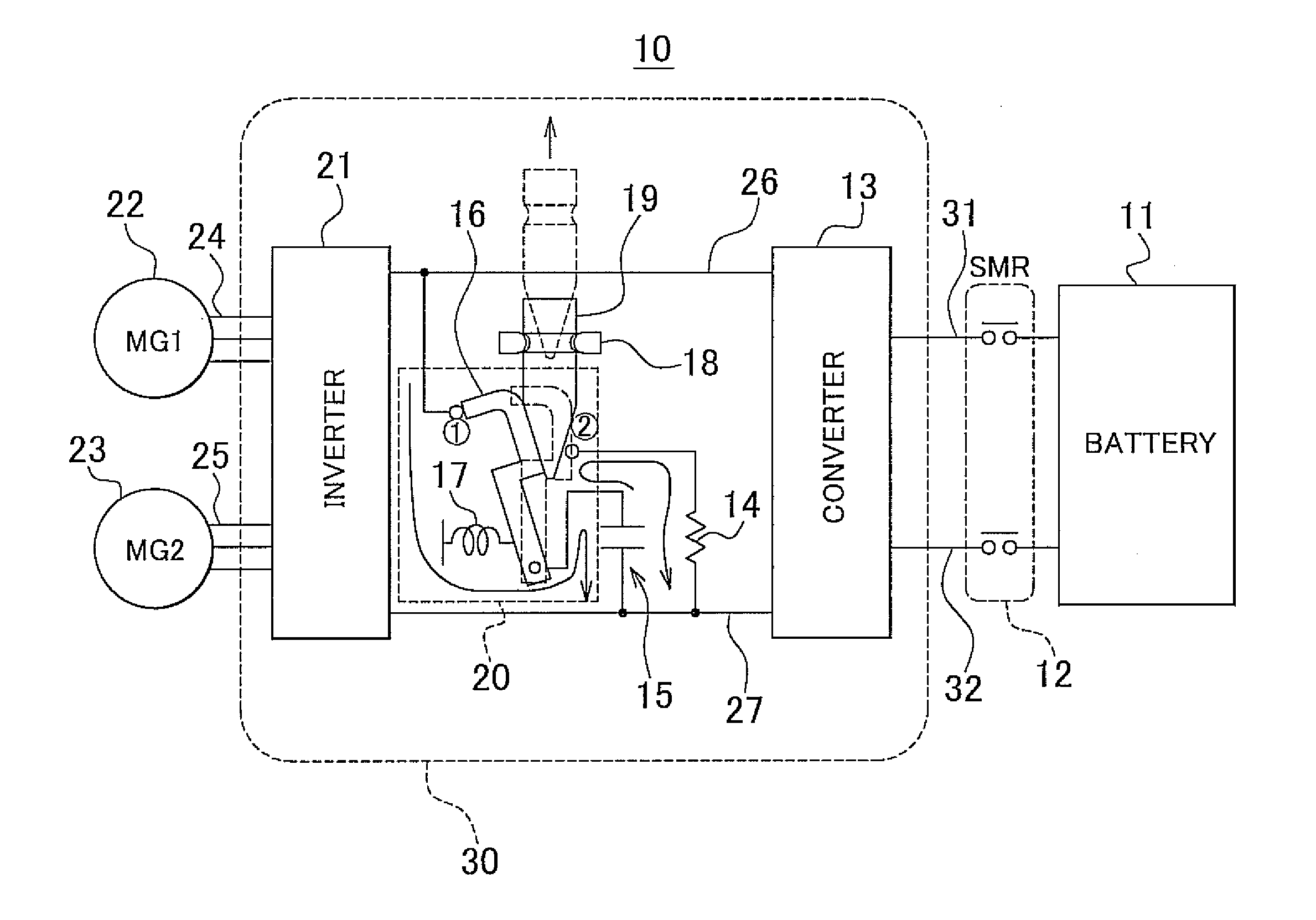
Control method of hybrid vehicle
InactiveUS20130038271A1Boost voltageHybrid vehiclesBatteries circuit arrangementsState of chargeElectrical battery
Disclosed is a system for controlling a hybrid vehicle when the state of charge of a high voltage battery is sufficiently low. In particular, a motor unit is connected to an engine via a rotation element, a high voltage battery is electrically connected to the motor unit to provide power thereto, and a low voltage battery is electrically connected to the high voltage battery through a two-way converter. Advantageously, a control portion is configured to boost voltage of the low voltage battery to supply the high voltage battery with high voltage through the two-way converter when the state of charge of the high voltage battery falls below a first predetermined value.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Adjustable non-dissipative voltage boosting snubber network for achieving large boost voltages
ActiveUS20140232266A1Boost voltageReduce voltageElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsVoltage multiplierSnubber
This disclosure describes a non-dissipative snubber circuit configured to boost a voltage applied to a load after the load's impedance rises rapidly. The voltage boost can thereby cause more rapid current ramping after a decrease in power delivery to the load which results from the load impedance rise. In particular, the snubber can comprise a combination of a unidirectional switch, a voltage multiplier, and a current limiter. In some cases, these components can be a diode, voltage doubler, and an inductor, respectively.
Owner:AES GLOBAL HLDG PTE LTD
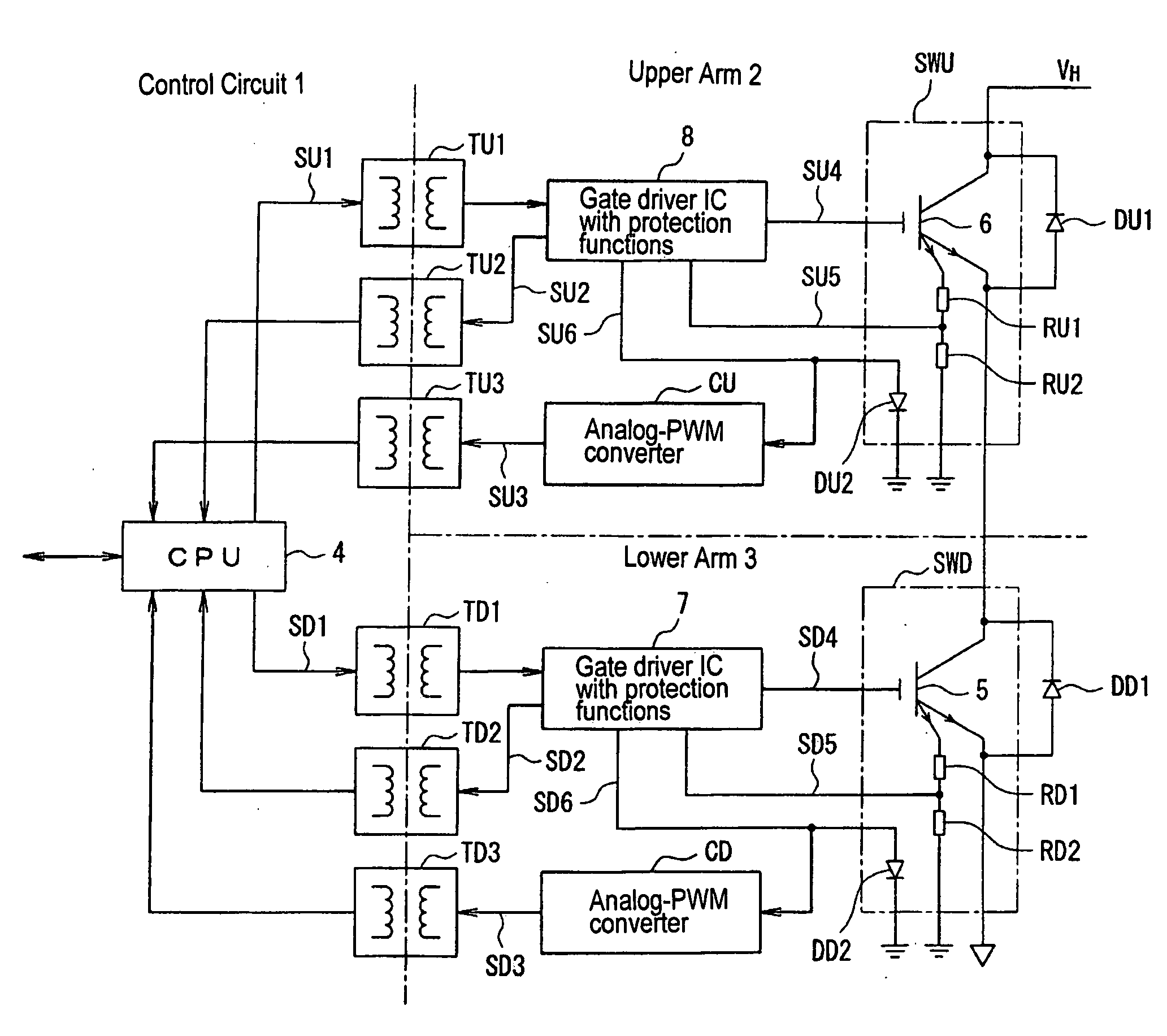
Power electronics equipments
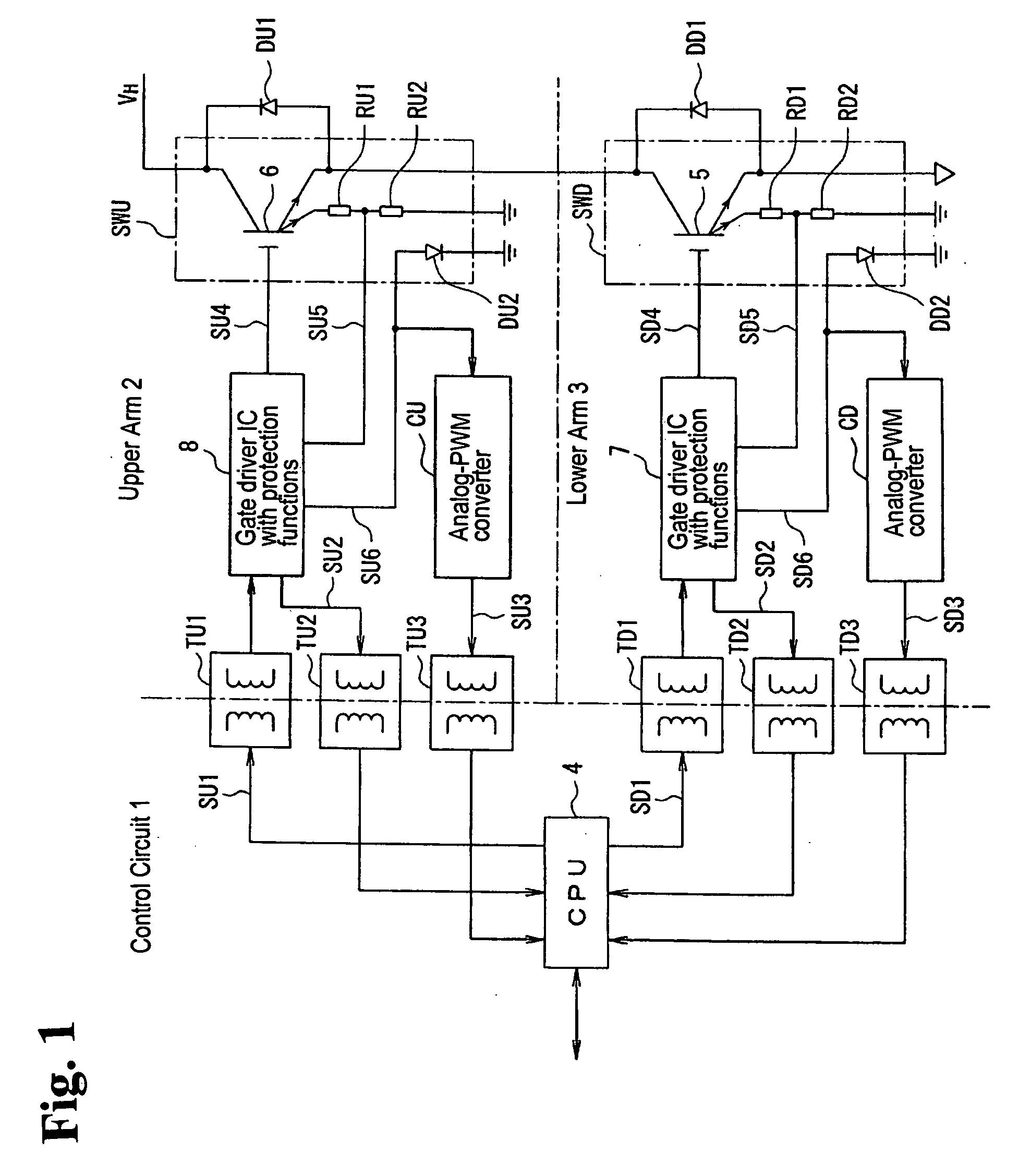
ActiveUS20070216377A1Reduce the overall diameterReduce spacingTransformersSolid-state devicesDriver circuitControl signal
Power electronics equipment includes a switching device directing current flow to a load and interrupting the current flowing to the load, a control circuit generating a control signal directing the conduction and non-conduction of the switching device, a driver circuit driving a control terminal of the switching device based on the control signal, and at least one air-cored insulating transformer insulating the control circuit and the driver circuit from each other. Each air-cored insulating transformer includes a primary winding and a secondary winding configured to generate a voltage by a change of interlinkage of a magnetic field. The secondary winding includes a plurality of coils configured such that voltages generated by external magnetic flux intersecting the secondary winding are canceled and a voltage generated by the signal magnetic flux intersecting the secondary winding is increased.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Flash memory cell arrays having dual control gates per memory cell charge storage element
InactiveUS7075823B2Increase coupling areaImprove the coupling ratioSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesCapacitanceMemory cell
A flash NAND type EEPROM system with individual ones of an array of charge storage elements, such as floating gates, being capacitively coupled with at least two control gate lines. The control gate lines are preferably positioned between floating gates to be coupled with sidewalls of floating gates. The memory cell coupling ratio is desirably increased, as a result. Both control gate lines on opposite sides of a selected row of floating gates are usually raised to the same voltage while the second control gate lines coupled to unselected rows of floating gates immediately adjacent and on opposite sides of the selected row are kept low. The control gate lines can also be capacitively coupled with the substrate in order to selectively raise its voltage in the region of selected floating gates. The length of the floating gates and the thicknesses of the control gate lines can be made less than the minimum resolution element of the process by forming an etch mask of spacers.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
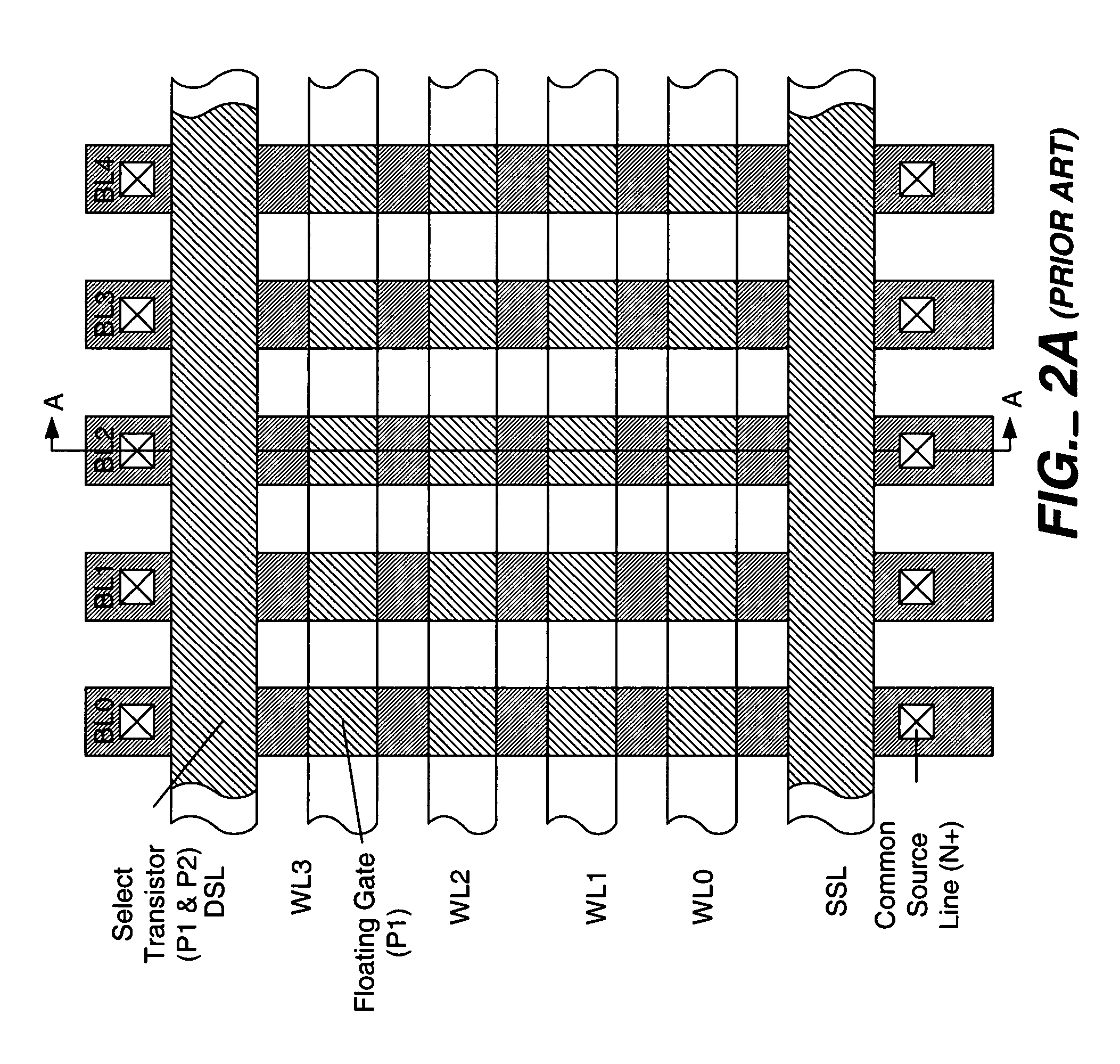
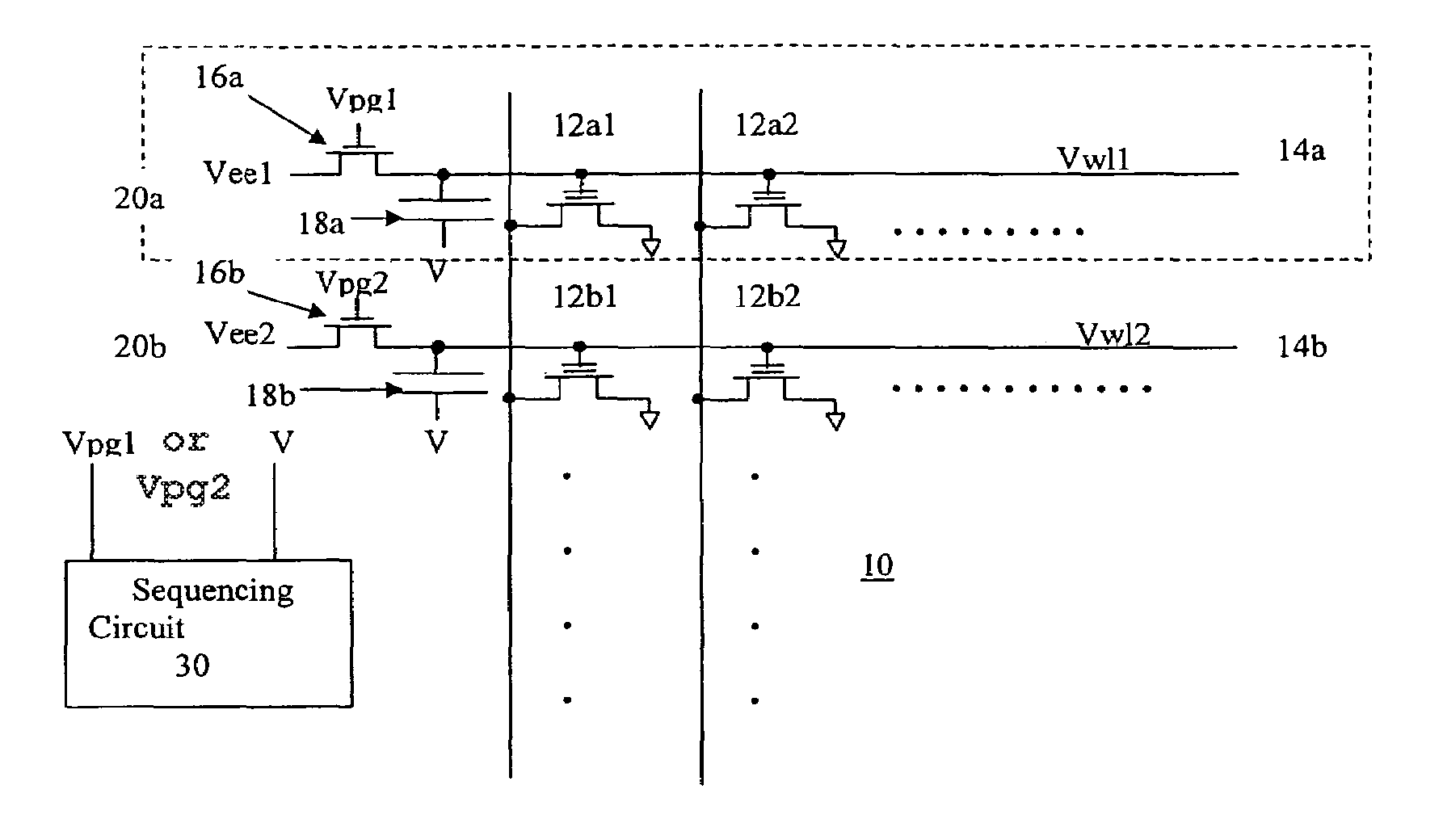
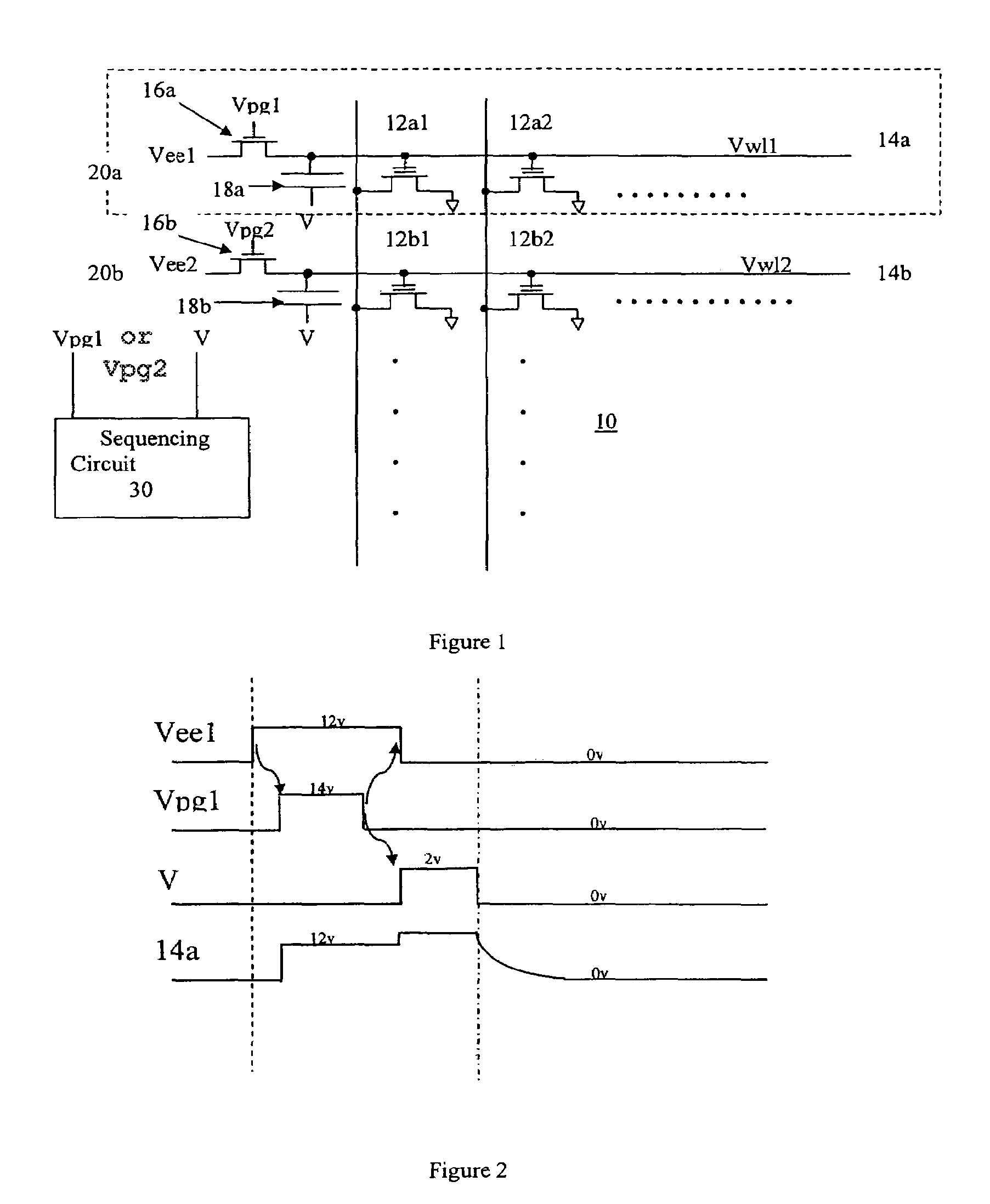
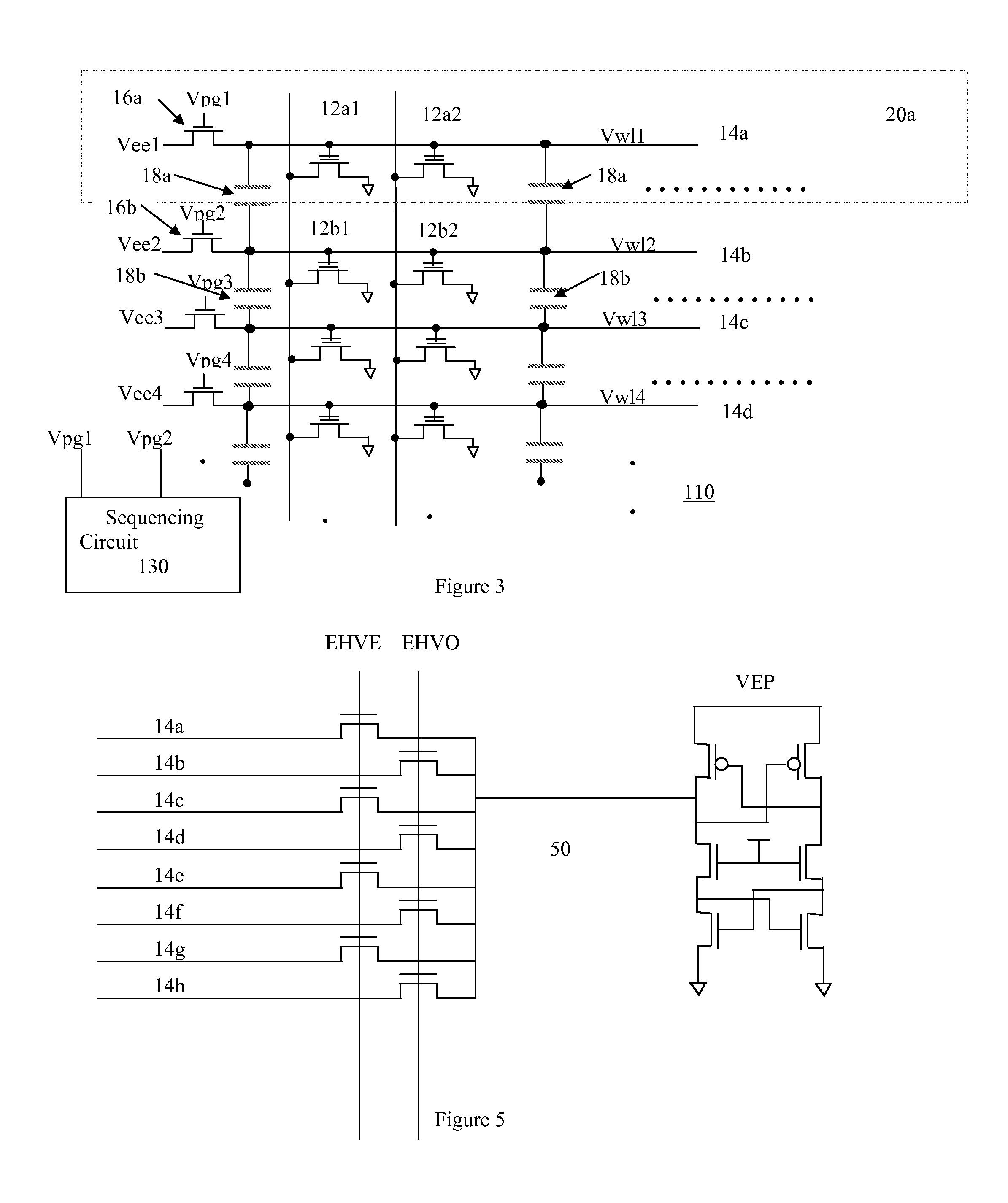
Word line voltage boosting circuit and a memory array incorporating same
A first embodiment of a word line voltage boosting circuit for use with an array of non-volatile memory cells has a capacitor, having two ends, connected to the word line. One end of the capacitor is electrically connected to the word line. The other end of the capacitor is electrically connected to a first voltage source. The word line is also connected through a switch to a second source voltage source. A sequencing circuit activates the switch such that the word line is connected to the second voltage source, and the other end of the capacitor is not connected to the first voltage source. Then the sequencing circuit causes the switch to disconnect the word line from the second voltage source, and connect the second end of the capacitor to the first voltage source. The alternate switching of the connection boosts the voltage on the word line. In a second embodiment, a first word line is electrically connected to a first switch to a first voltage source. An adjacent word line, capacitively coupled to the first word line, is electrically connected to a second switch to a second voltage source. A sequencing circuit activates the first switch and the second switch such that the first word line is connected to the first voltage source, and the second word line is disconnected from the second voltage source. Then the sequencing circuit causes the first switch to disconnect the first word line from the first voltage source, and causes the second word line to be electrically connected to the second voltage source. The alternate switching of the connection boosts the voltage on the first word line, caused by its capacitive coupling to the second word line. A boosted voltage on the word line may be used to improve cycling and yield, where the memory cells of the array are of the floating gate type and erase through the mechanism of Fowler-Nordheim tunneling from the floating gate to a control gate which is connected to the word line.
Owner:SILICON STORAGE TECHNOLOGY
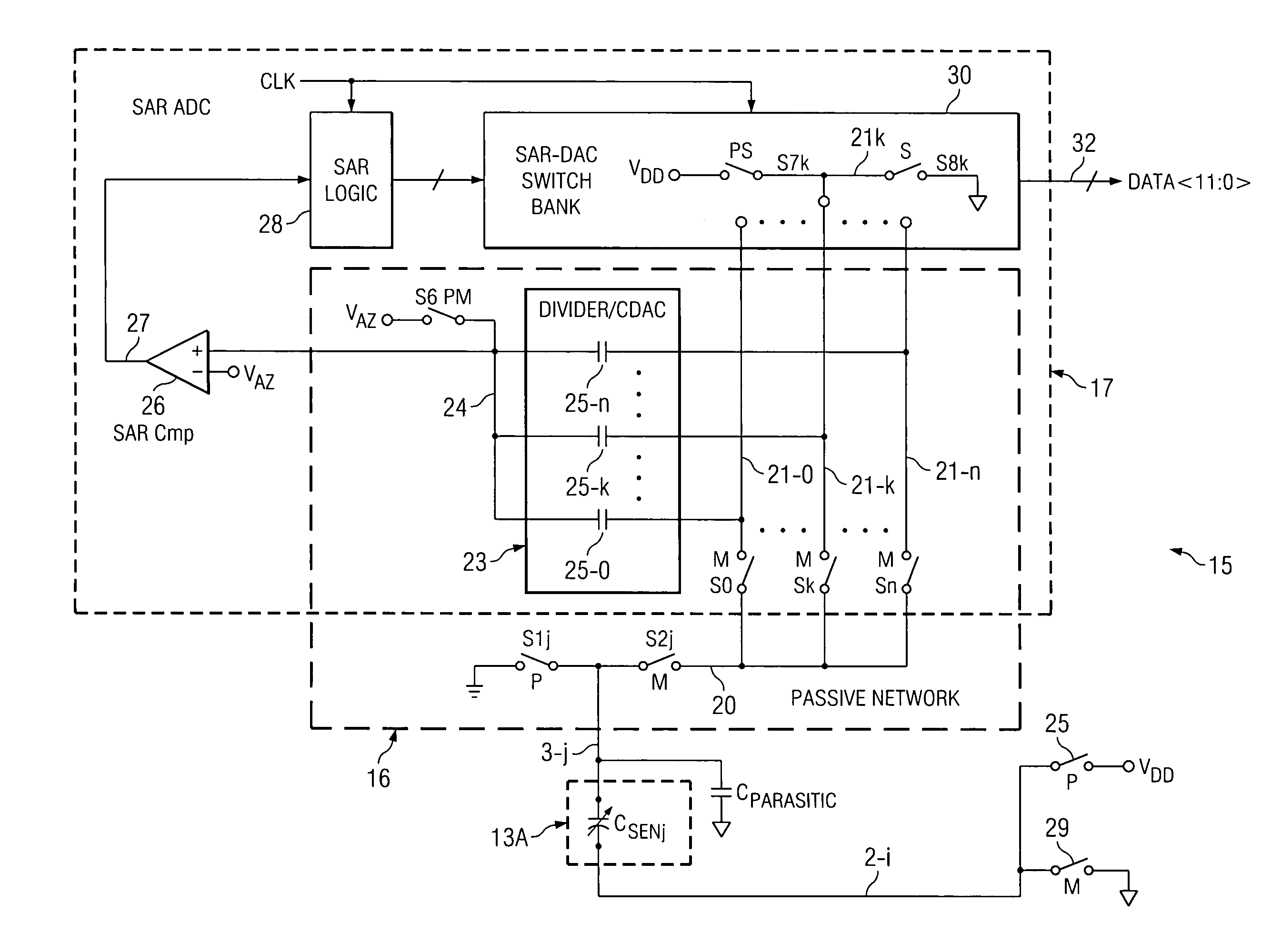
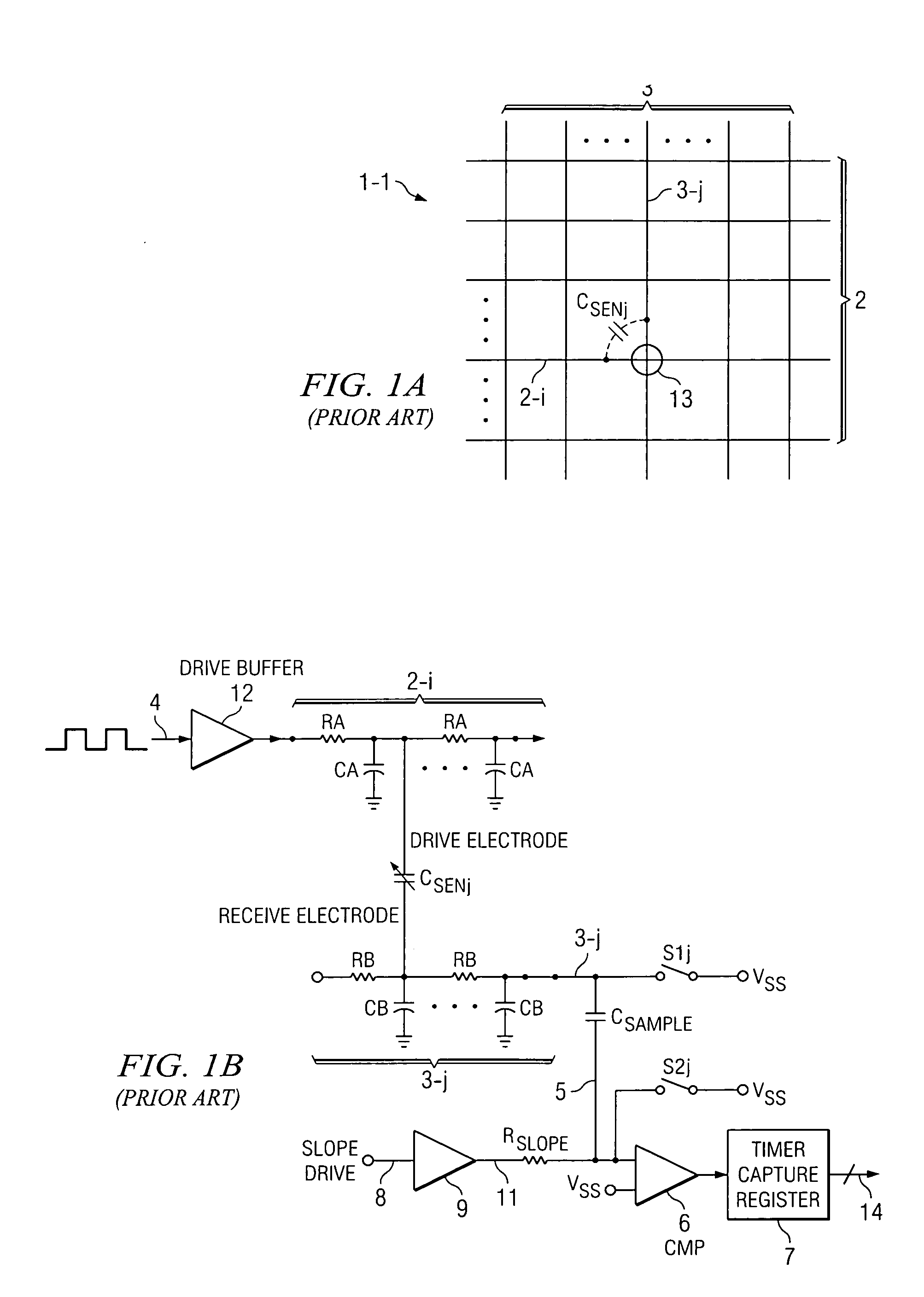
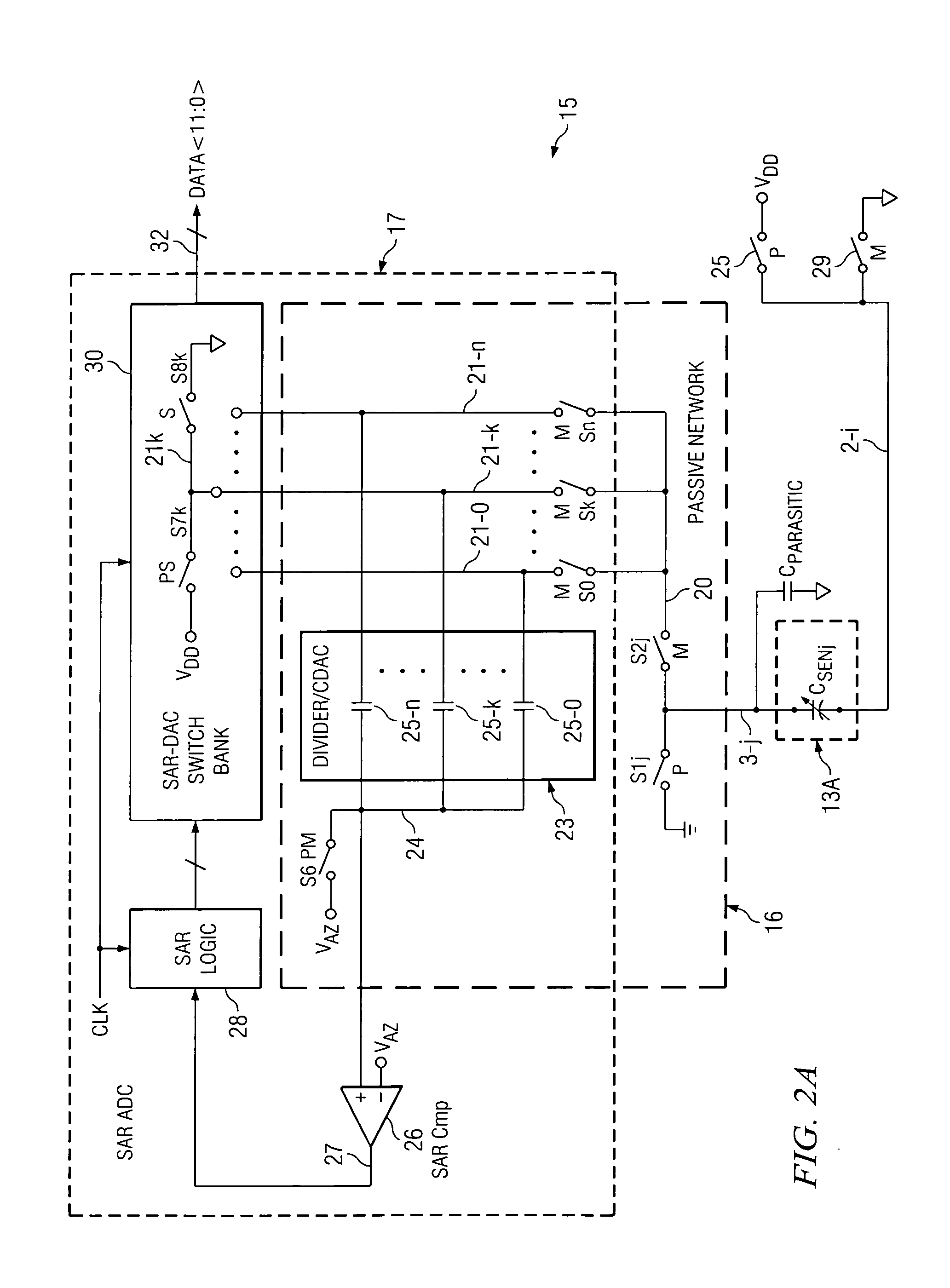
Capacitance measurement system and method
ActiveUS20100231241A1High sensitivityBoost voltageRecording apparatusCapacitance measurementsPre-chargeCapacitor
A capacitance measurement system precharges first terminals (21-0 . . . 21-k . . . 21-n) of a plurality of capacitors (25-0 . . . 25-k . . . 25), respectively, of a CDAC (capacitor digital-to-analog converter) (23) included in a SAR (successive approximation register) converter (17) to a first voltage (VDD) and pre-charges a first terminal (3-j) of a capacitor (CSENj) to a second voltage (GND). The first terminals are coupled to the first terminal of the capacitor to redistribute charges therebetween so as to generate a first voltage on the first terminals and the first terminal of the capacitor, the first voltage being representative of a capacitance of the first capacitor (CSENj). A SAR converter converts the first voltage to a digital representation (DATA) of the capacitor. The capacitance can be a touch screen capacitance.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
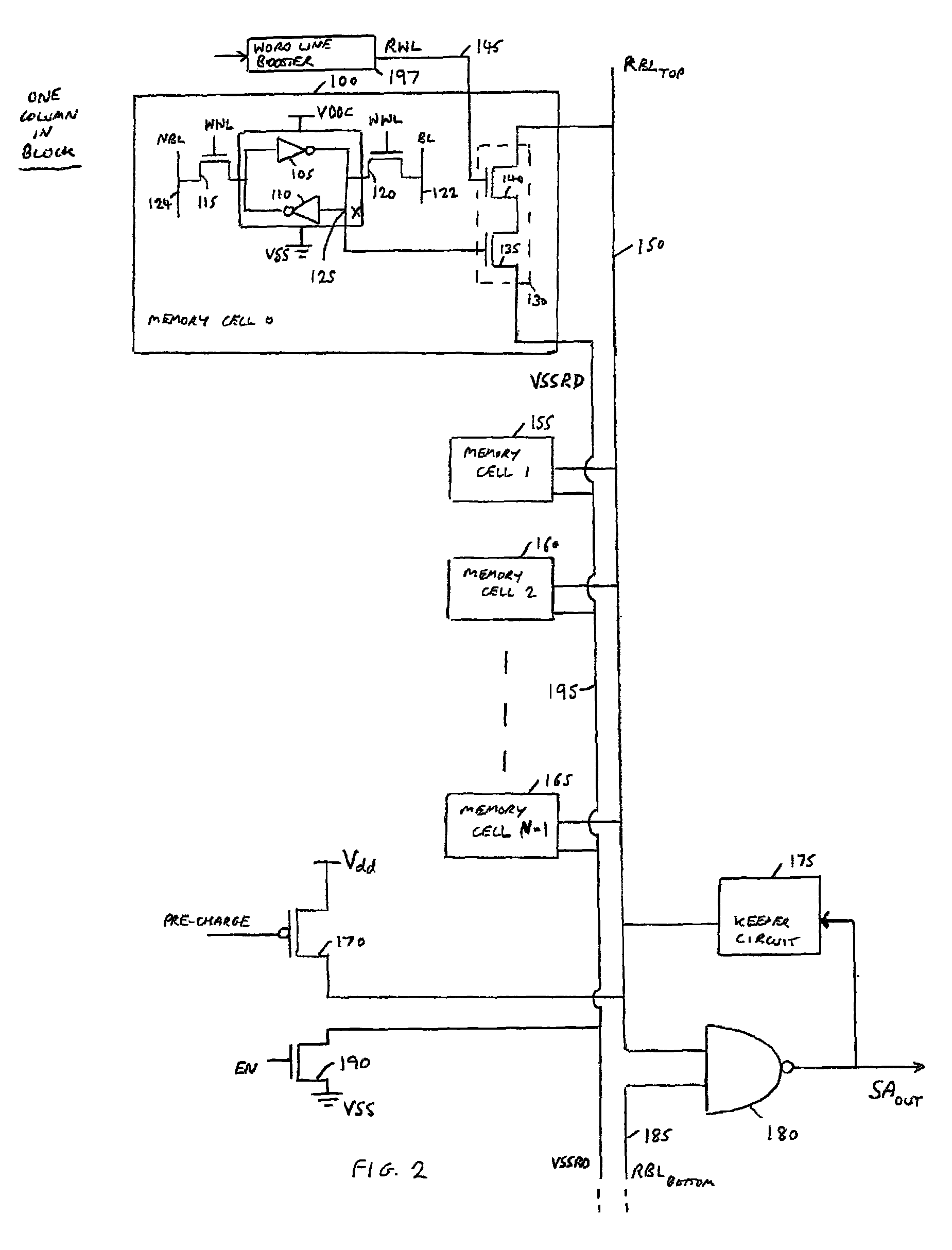
Memory device and method of controlling leakage current within such a memory device
ActiveUS9171634B2Reduce leakage currentImprove performanceRead-only memoriesDigital storageComputer architectureDrain current
A memory device includes an array of memory cells arranged as a plurality of rows and columns, each row being coupled to an associated read word line, and each column forming at least one column group, where the memory cells of each column group are coupled to an associated read bit line. Each column has an active mode of operation where a read operation may be performed on an activated memory cell within that column group, and a non-active mode of operation where the read operation is not performable. Precharge circuitry is used, for each column group, to precharge the associated read bit line to a first voltage level prior to the read operation. Each memory cell includes coupling circuitry connected between the associated read bit line and a reference line associated with the column group containing that memory cell.
Owner:ARM LTD
Charge removal from electrodes in unipolar sputtering system
ActiveUS9287098B2Boost voltageReduce voltageElectric discharge tubesElectric lighting sourcesVoltage multiplierEngineering
This disclosure describes a non-dissipative snubber circuit configured to boost a voltage applied to a load after the load's impedance rises rapidly. The voltage boost can thereby cause more rapid current ramping after a decrease in power delivery to the load which results from the load impedance rise. In particular, the snubber can comprise a combination of a unidirectional switch, a voltage multiplier, and a current limiter. In some cases, these components can be a diode, voltage doubler, and an inductor, respectively.
Owner:AES GLOBAL HLDG PTE LTD
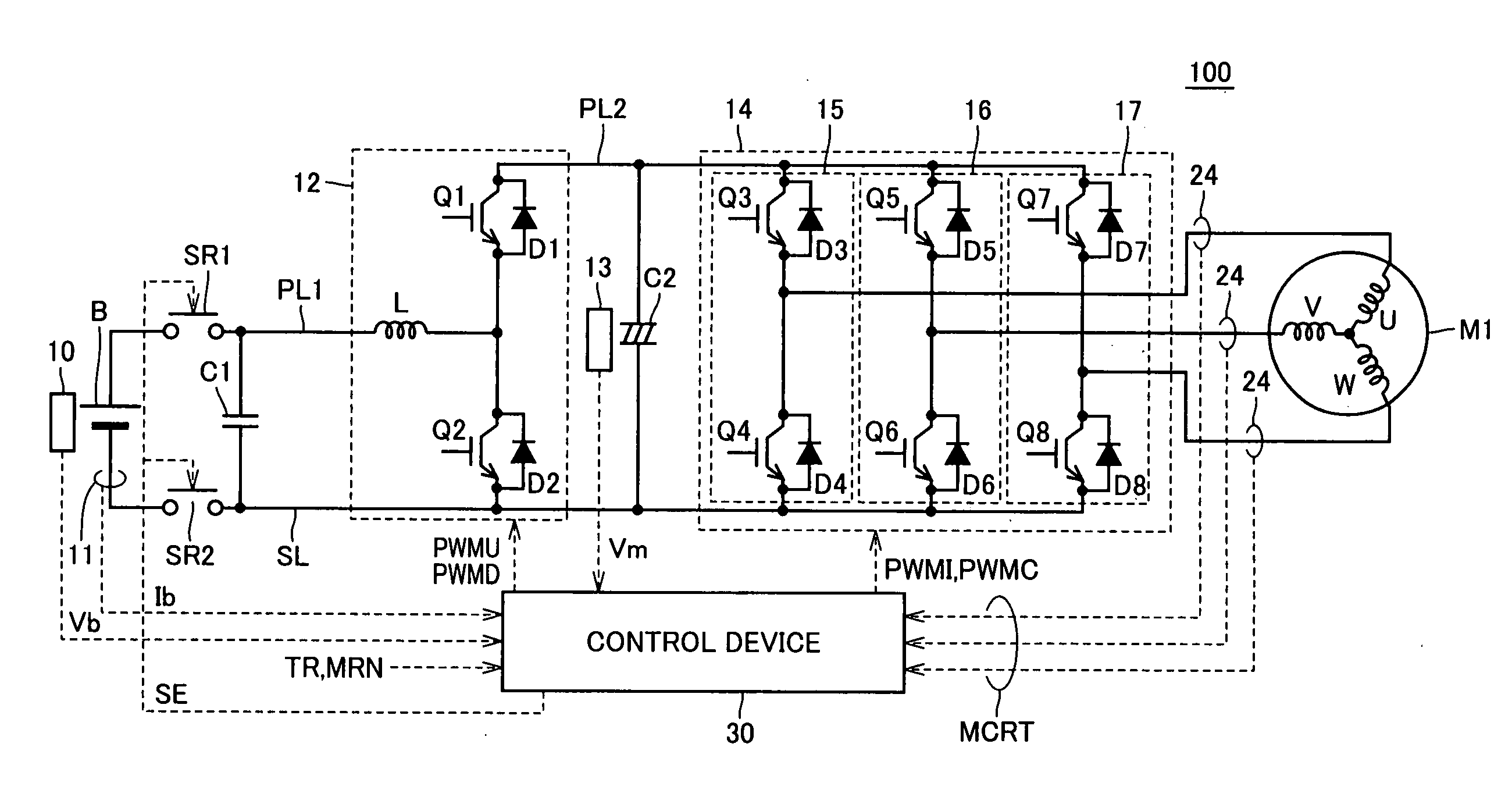
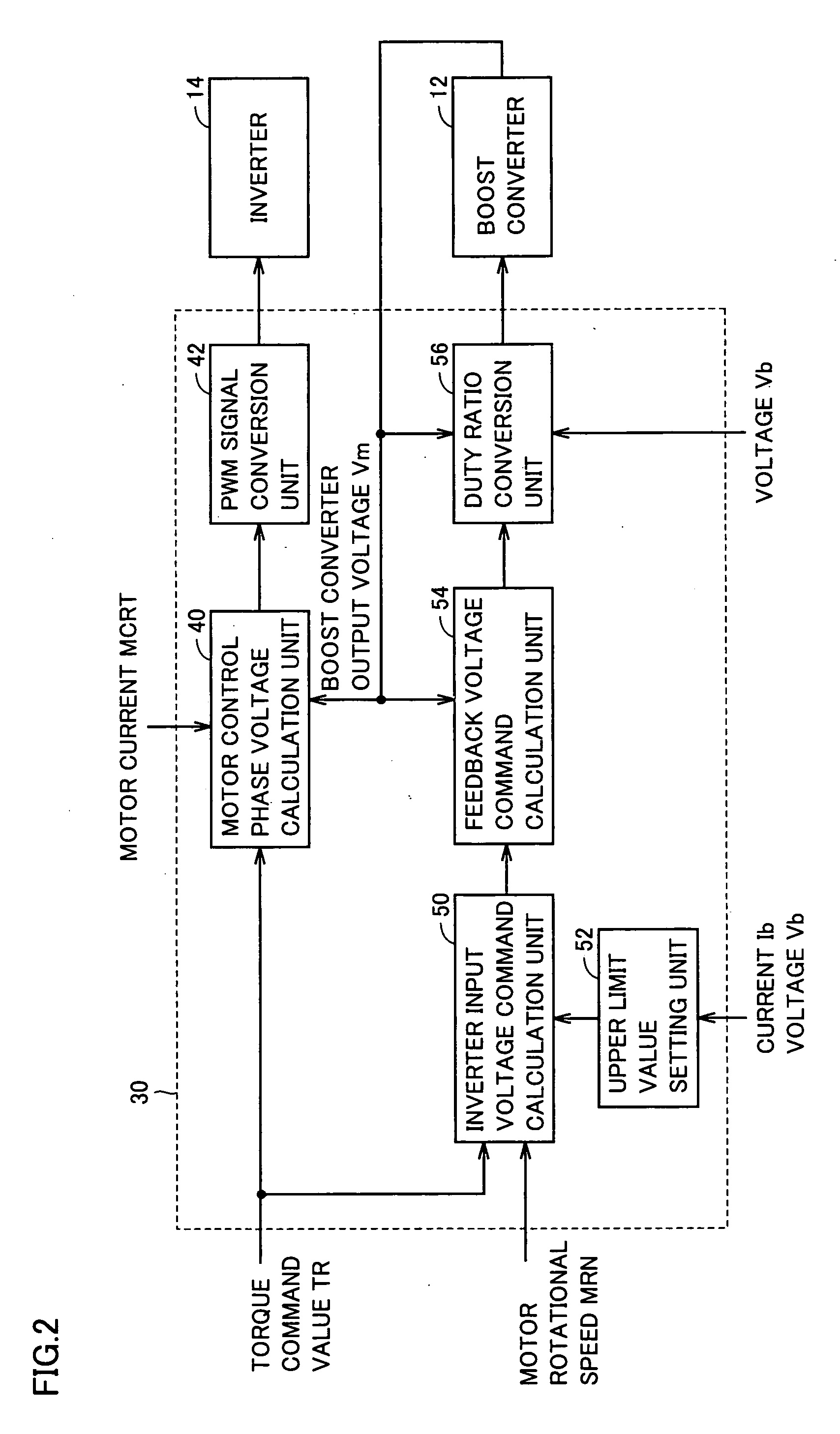
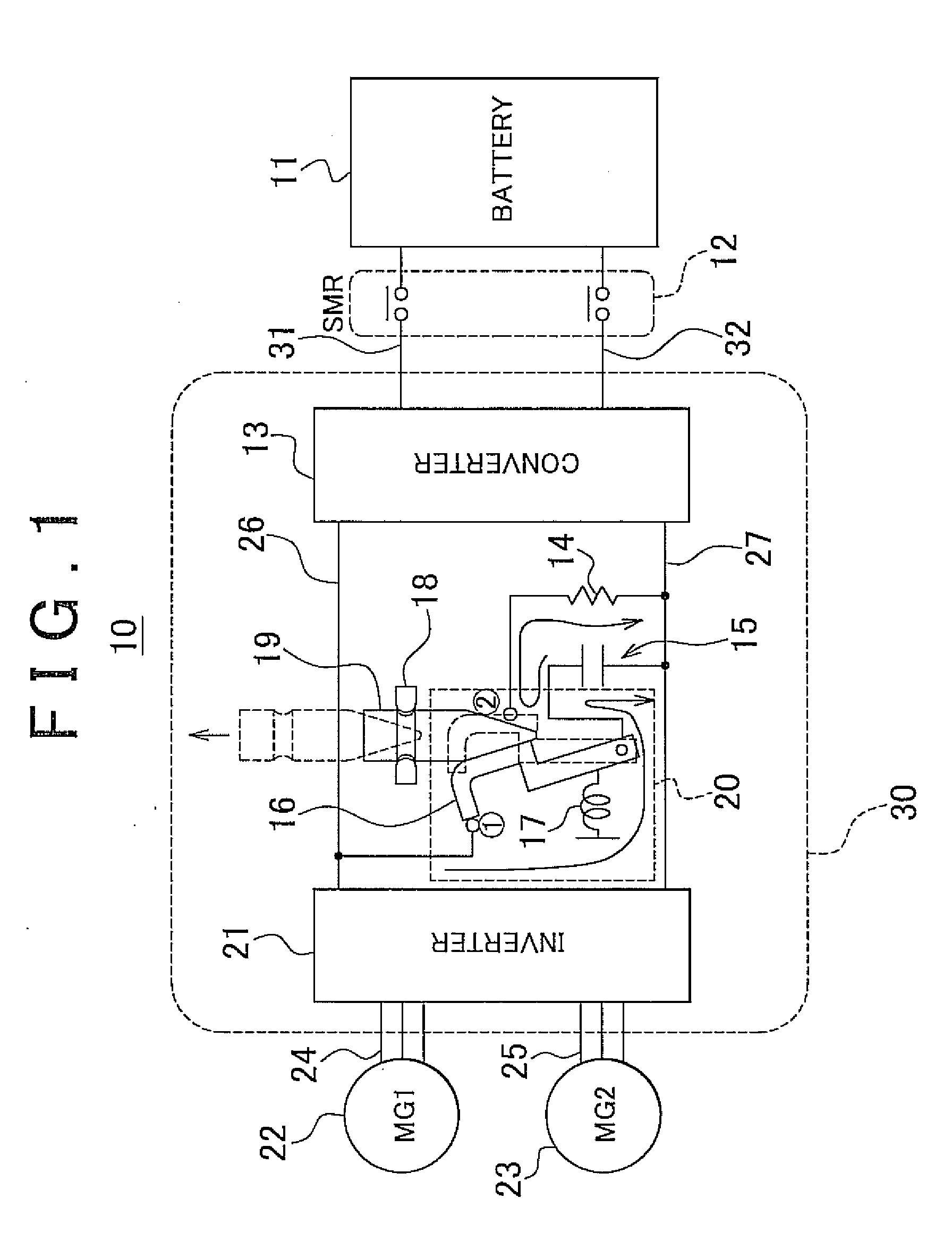
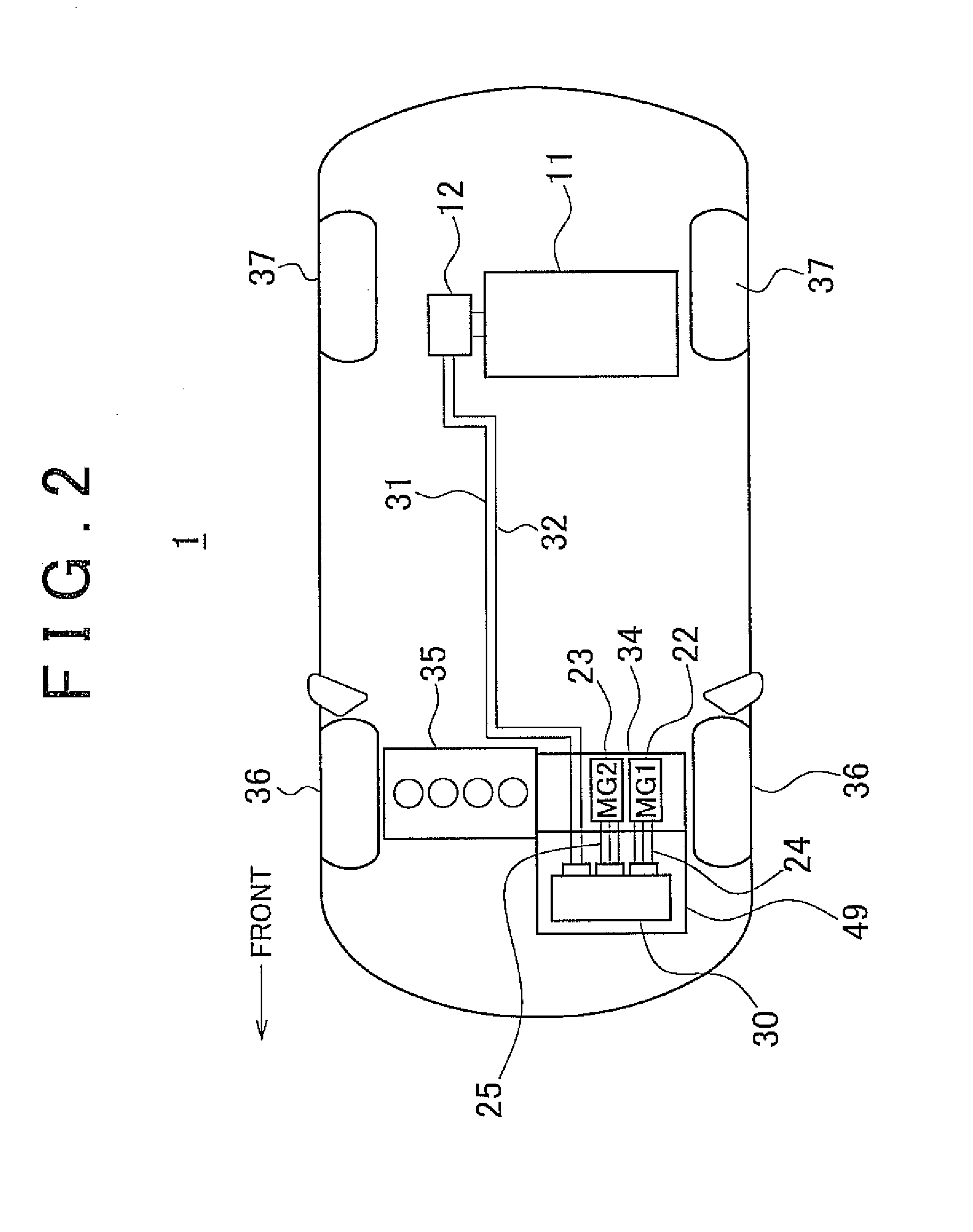
Voltage conversion apparatus, power output apparatus, and control method of voltage converter
ActiveUS20070200521A1Boost voltageReduce voltageAC motor controlMultiple dynamo-motor startersPower differenceVoltage converter
An upper limit value setting unit of a control device conducts integration on the change in battery power, and determines whether the integrated value is lower than a preset first threshold value (negative value). When determination is made that the integrated value is lower than the first threshold value, and the battery power difference is lower than the second threshold value (negative value), the upper limit value setting unit sets Vup2 that is lower than the general Vup1 as the upper limit value of the inverter input voltage command.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Non-volatile memory device and method of preventing hot electron program disturb phenomenon
ActiveUS7304894B2Weaker electric fieldPreventing hot electron program disturbance of a non-volatile memory deviceRead-only memoriesDigital storageComputer scienceElectric field
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Charge-pump circuit
ActiveUS20110241767A1Increase the output voltageLow efficiencyApparatus without intermediate ac conversionElectric variable regulationEngineeringThreshold voltage
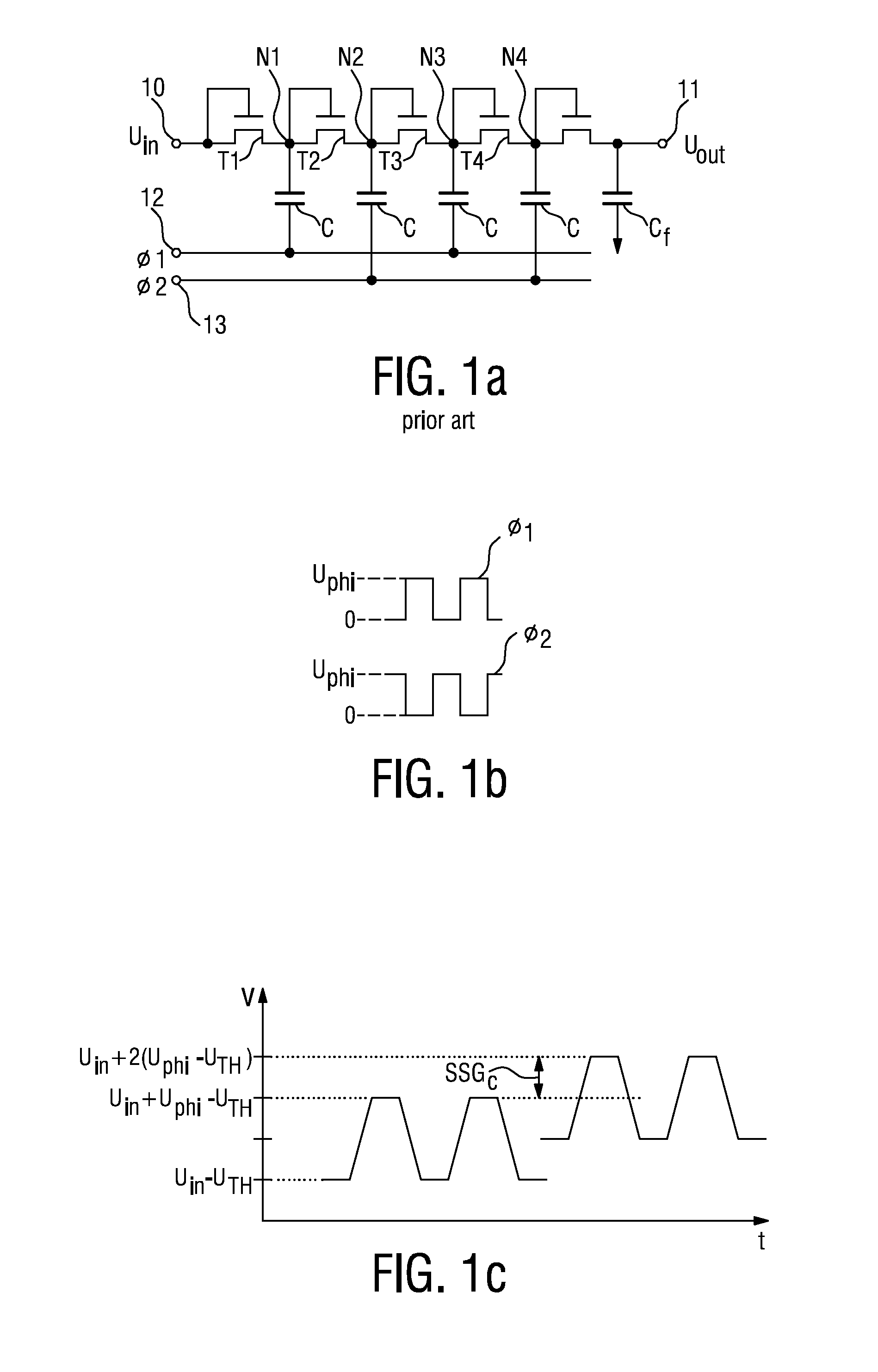
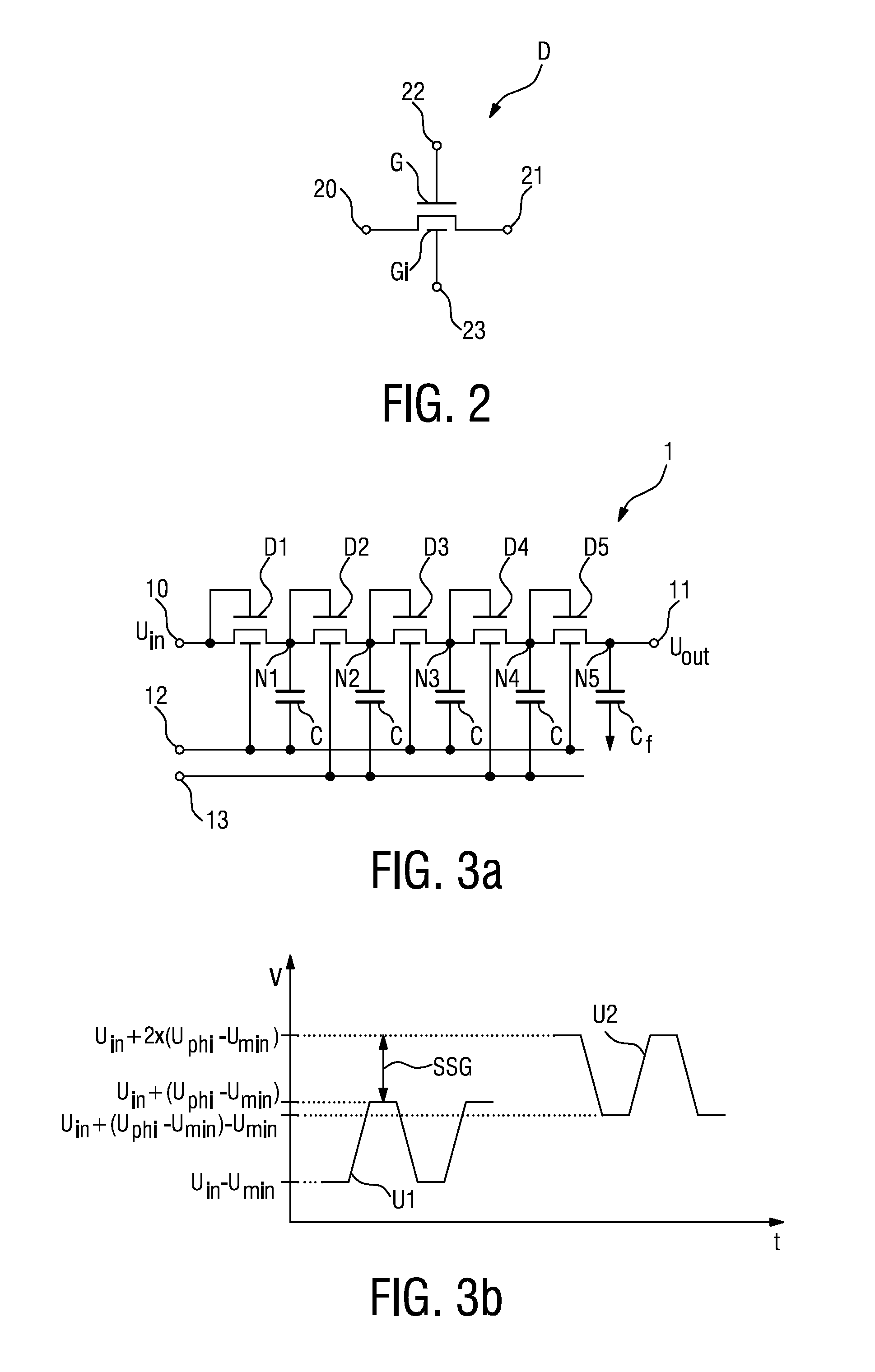
The invention describes a charge-pump circuit (1, 1′) comprising a supply voltage input node (10) for applying an input voltage (Uin) to be boosted, a boosted voltage output node (11) for outputting a boosted voltage (Uout), and a plurality of transistor stages connected in series between the supply voltage input node (10) and the boosted voltage output node (11), wherein at least one transistor stage comprises a multiple-gate transistor (D1, . . . , D5), which transistor (D1, . . . , D5) comprises at least two gates, of which one is a first gate (G) for switching the transistor (D1, . . . , D5) on or off according to a voltage applied to the first gate (G), and one is an additional second gate (Gi) for controlling the threshold voltage of the multiple-gate transistor (D1, . . . , D5), independently of the first gate (G), according to a control voltage (Φ1, Φ2) applied to the second gate (Gi). The invention further describes a method of boosting a voltage using a charge-pump circuit (1, 1′) comprising a plurality of transistor stages connected in series between a supply voltage input node (10) and a boosted voltage output node (11), wherein at least one transistor stage comprises a multiple-gate transistor (D1, . . . , D5), which method comprises applying an input voltage (Uin) to be boosted at the supply voltage input node (10); applying a control voltage, (Φ1, Φ2) to the second gate (Gi) of the multiple-gate transistor (D1, . . . , D5) to control the threshold voltage of the multiple-gate transistor (D1, . . . , D5); and outputting the boosted voltage (Uout) at the voltage output node (11).
Owner:NXP BV
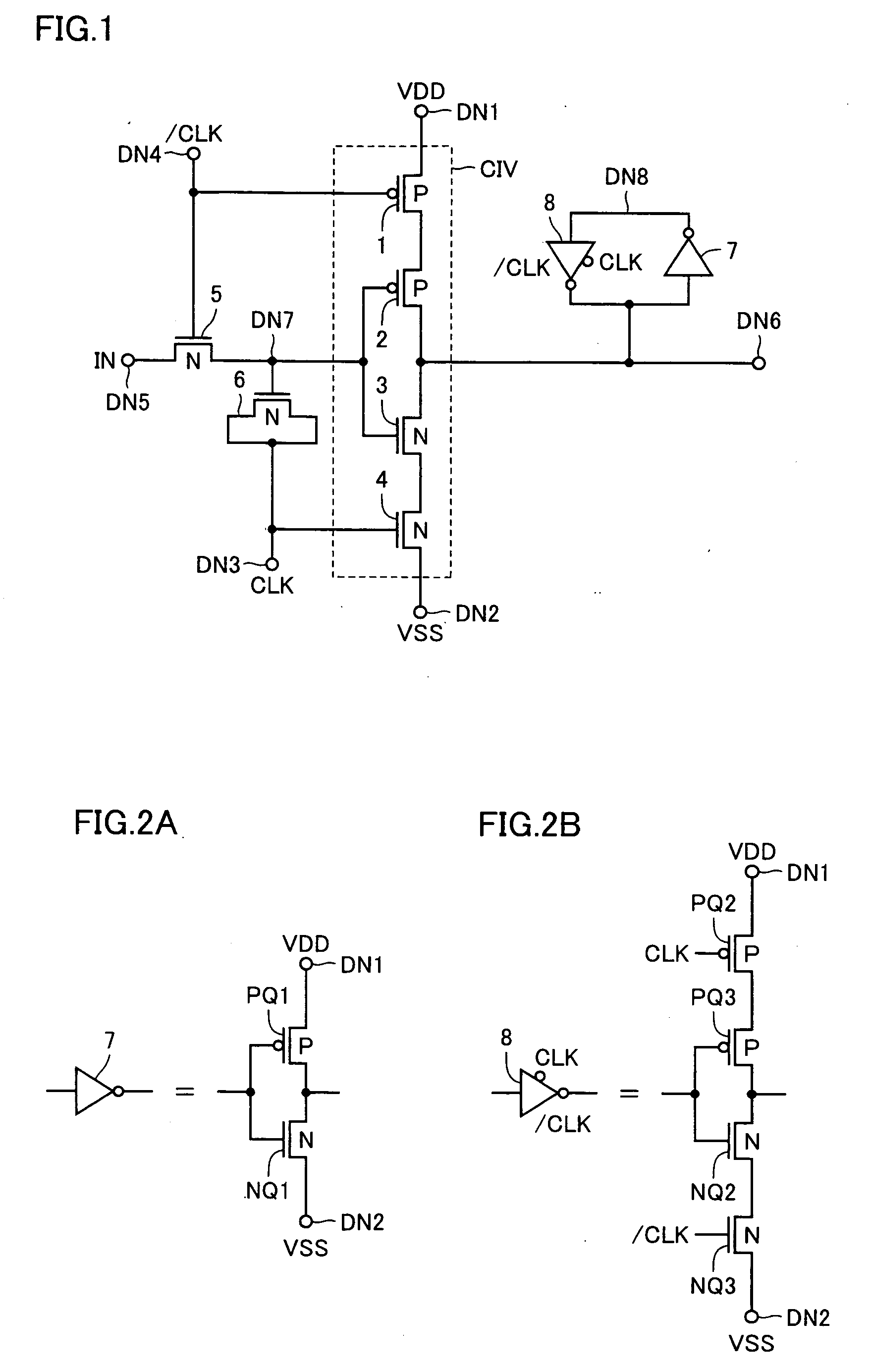
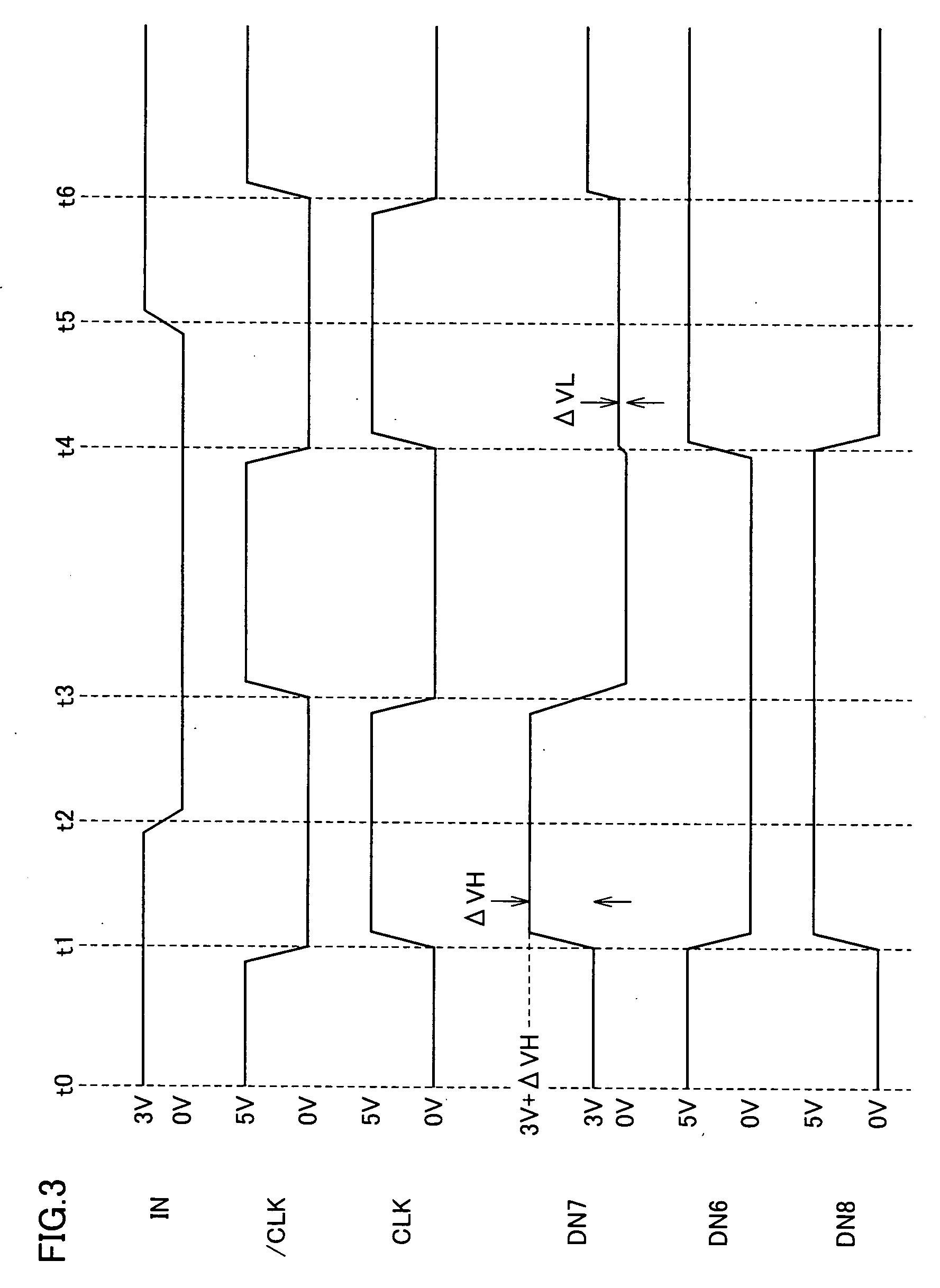
Level conversion circuit and serial/parallel conversion circuit with level conversion function
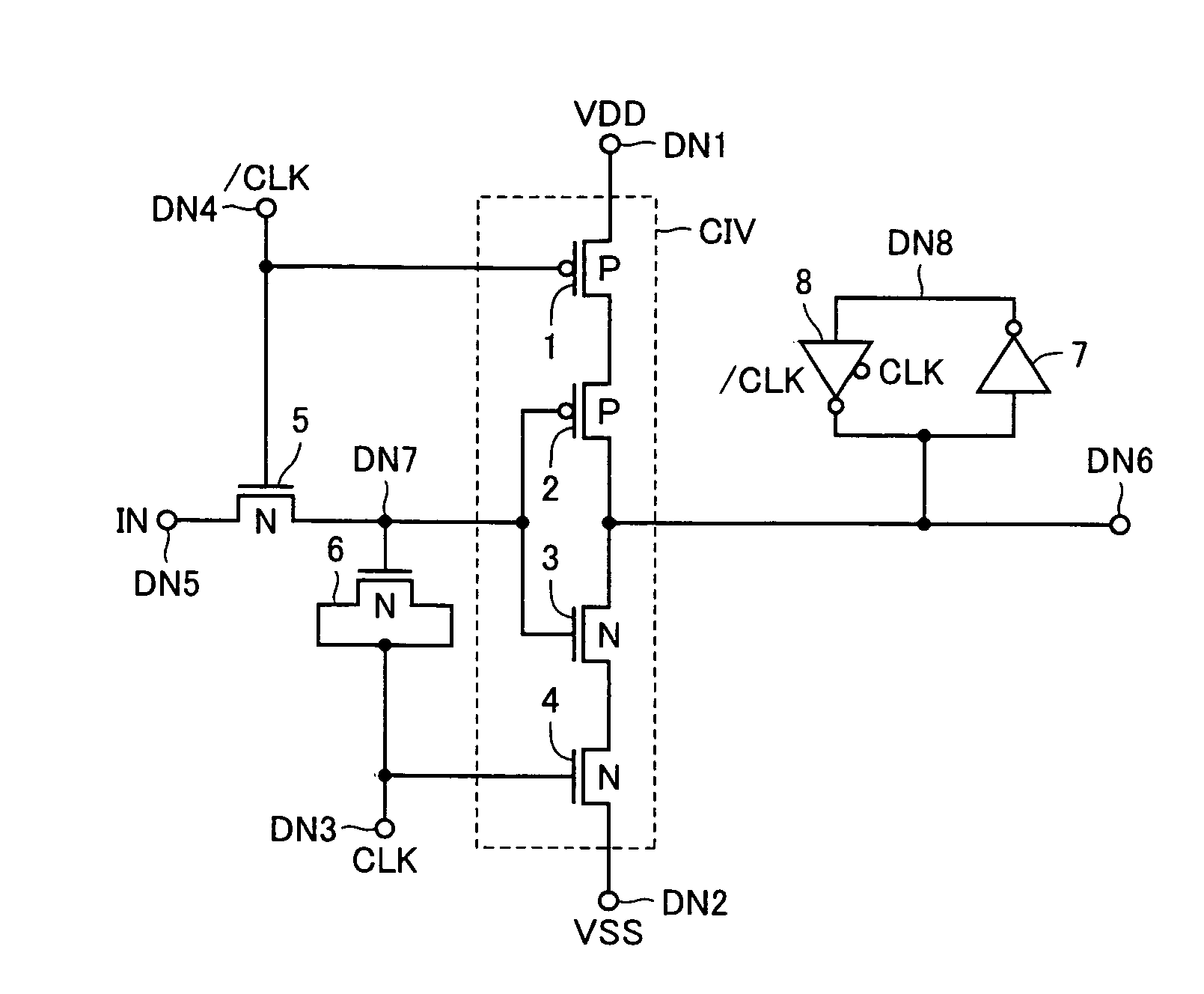
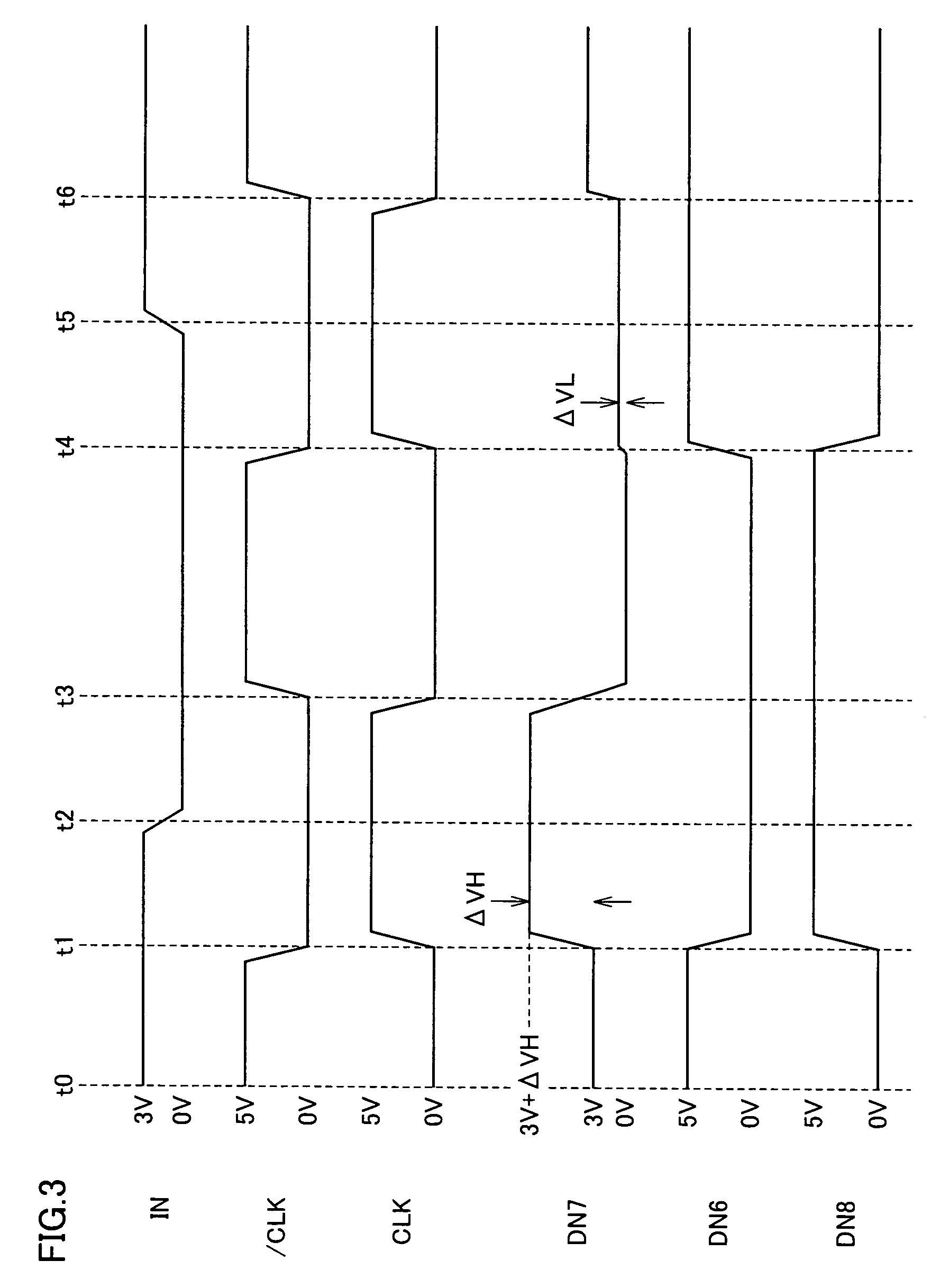
InactiveUS7138831B2Increase speedReduce power consumptionParallel/series conversionPulse automatic controlVoltage amplitudeBiological activation
A MOS capacitor receiving a clock signal complementary to a sampling clock signal is provided at an input of a clocked inverter that is activated after sampling an input signal to perform level conversion. A charge pump operation of the MOS capacitor is performed in parallel with the activation of the clocked inverter. The power consumption of and the area occupied by a level conversion circuit converting a voltage amplitude of the input signal are reduced without deteriorating a high-speed operating characteristics.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
High efficiency dc/dc converter and controller
ActiveUS20150138841A1Boost voltageEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionElectric forceElectric power transmission
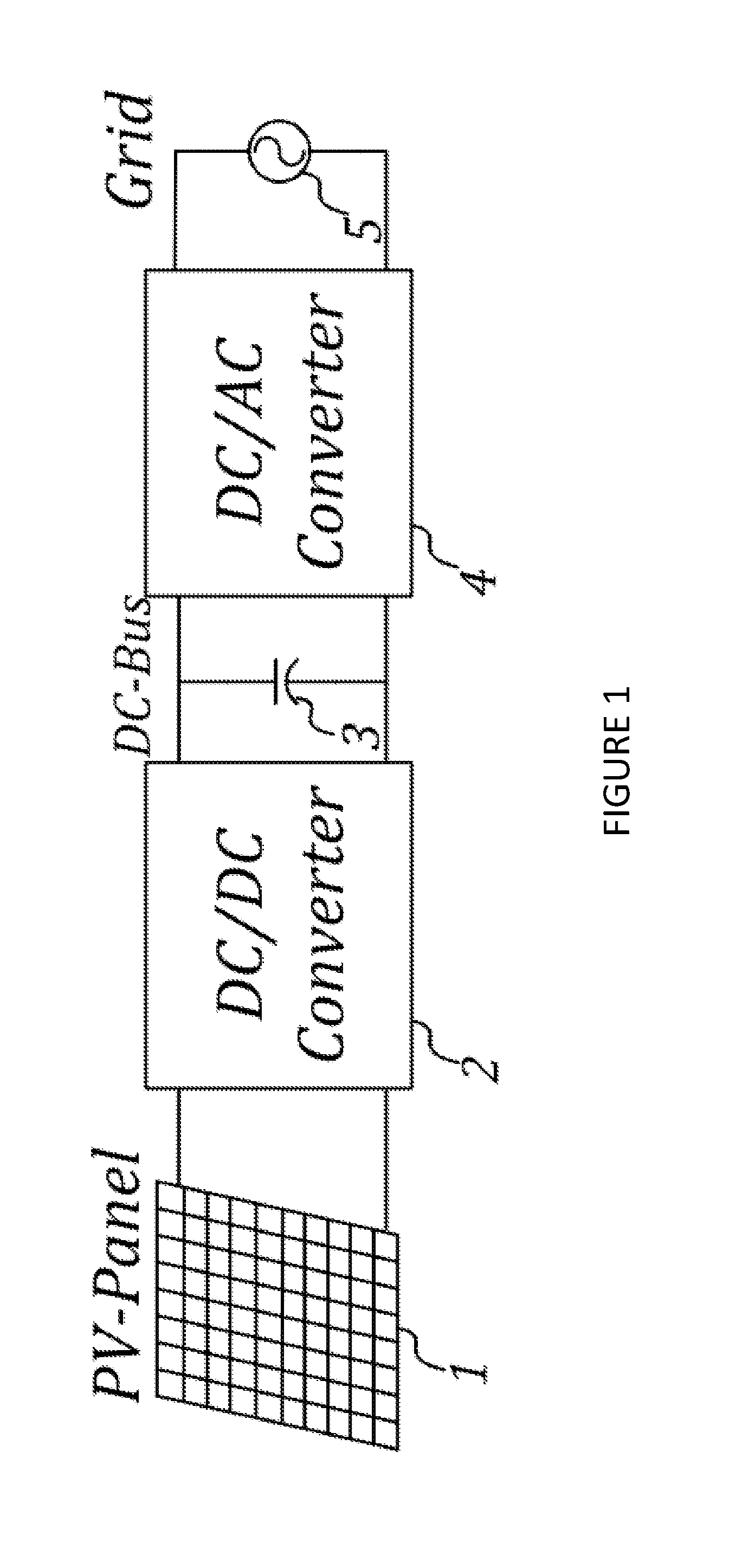
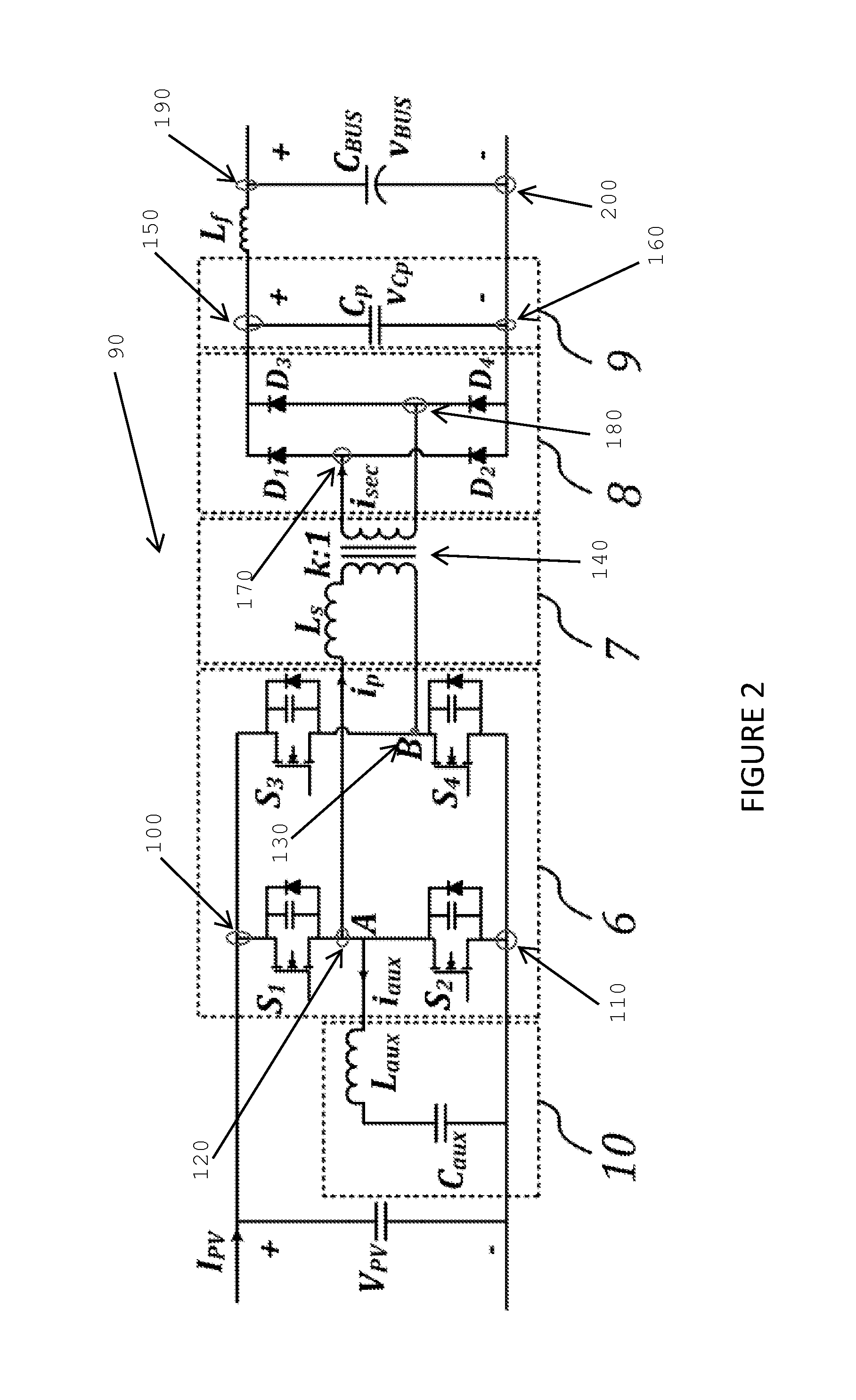
Systems, methods, and devices for use in a DC / DC converter. A circuit uses a full-bridge power semiconductor subcircuit along with a high power transformer subcircuit, a diode bridge subcircuit, and a parallel capacitor to provide galvanic isolation and boost the voltage from a power source such as a photovoltaic panel. To ensure zero voltage switching for the power semiconductors, either a passive auxiliary subcircuit or an inductor coupled in parallel to a transformer in the transformer subcircuit may be used. A controller which derives its timing signals from the transformer primary current is used to control the timing of the power semiconductors in the circuit. The circuit and its controller allows for self-adjusting regardless of load and uses the entire switching cycle to be used for power transfer.
Owner:SPARQ SYST INC
Voltage generator with reduced noise
ActiveUS7091769B2Reduce volatilityBoost voltageEmergency protective circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversionVoltage generatorLow noise
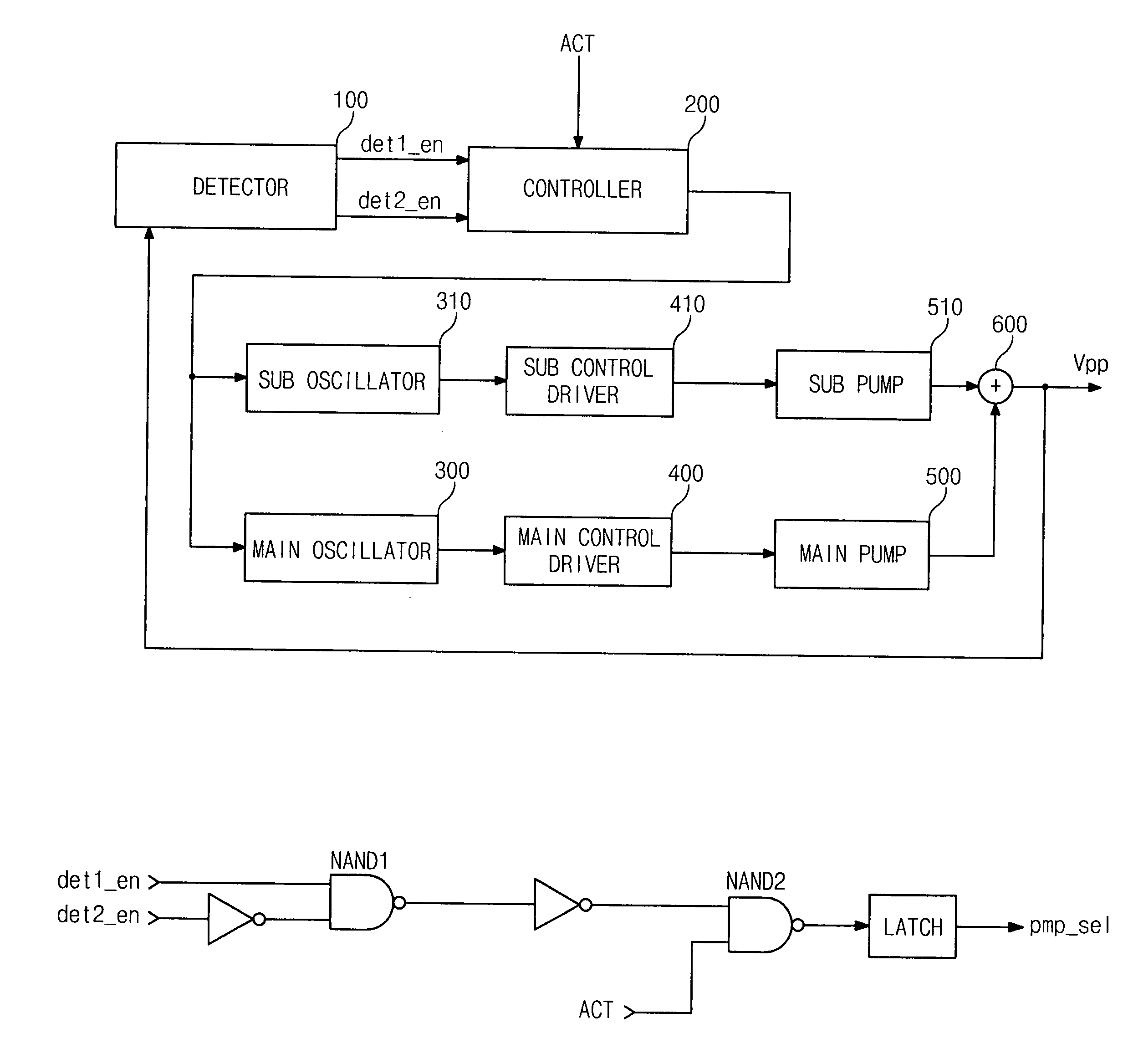
A voltage generator with reduced noise features a detector, a controller, a sub-booster, a main booster and a voltage adder. The detector receives an output voltage, a first reference voltage and a second reference voltage lower than the first reference voltage, and then outputs a first sensing signal and a second sensing signal. The controller receives the first sensing signal and the second sensing signal and an action signal to output a first control signal and a second control signal. The sub-booster boosts a voltage in response of the first control signal. The main booster boosts a voltage in response to the second control signal. The voltage adder adds output signals from the sub-booster and main booster, to provide the output voltage.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
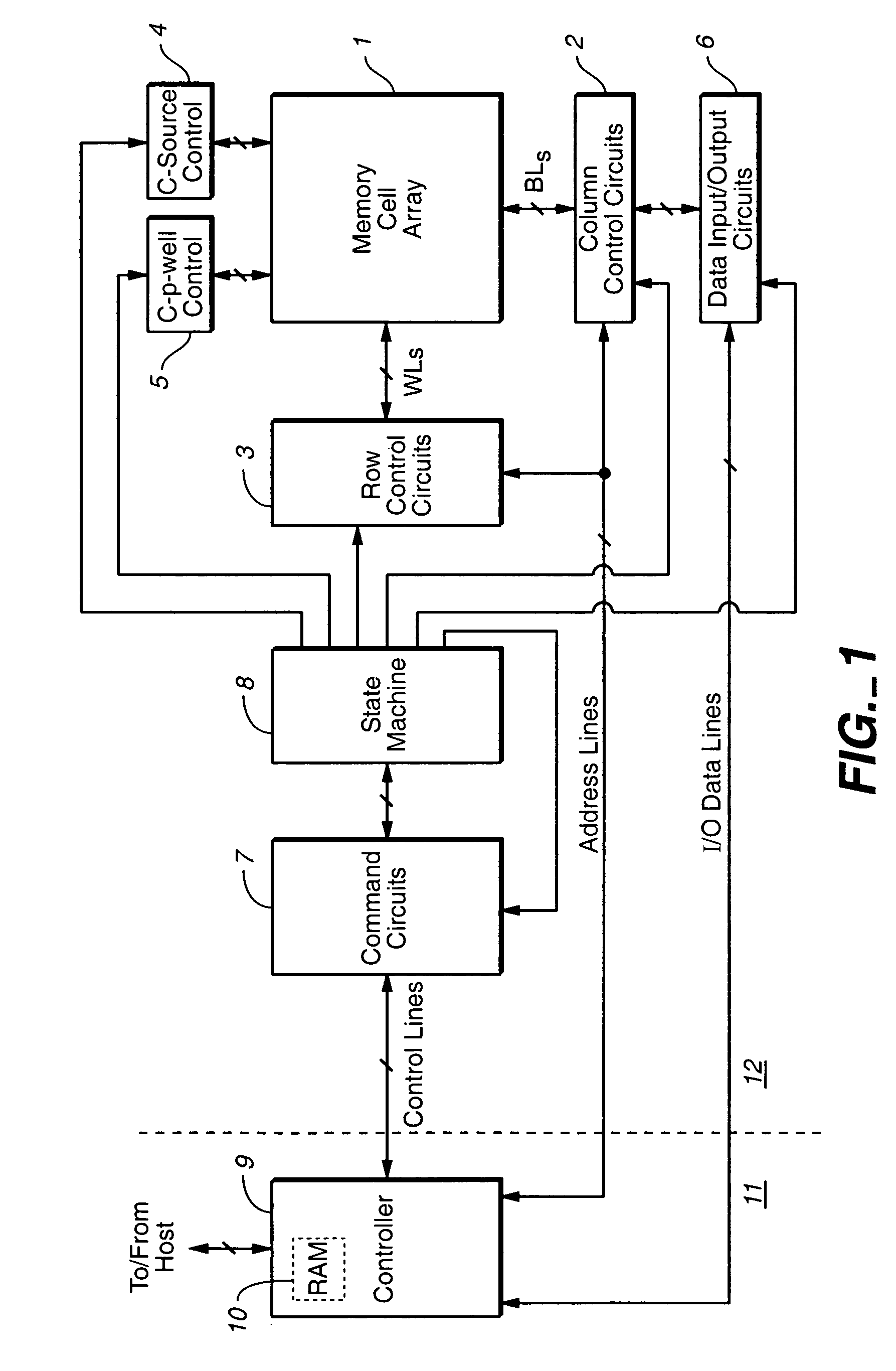
Data storage device and method of driving the same
ActiveUS20170194057A1Improve characteristicImproved operation speedSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A data storage device includes a semiconductor structure including a first conductive-type region having a first-type conductivity, a second conductive-type region spaced apart from the first conductive-type region and having a second-type conductivity opposite to the first-type conductivity, and a semiconductor region between the first conductive-type region and the second conductive-type region and including a neighbouring portion adjacent to the second conductive-type region; a mode select transistor including a gate electrode aligned with the neighbouring portion and an insulation layer between the gate electrode and the neighbouring portion; a plurality of memory cell transistors including a plurality of control gate electrodes aligned with the semiconductor region, and a data storage layer interposed between the plurality of control gate electrodes and the semiconductor region; a first wire electrically connected to the first conductive-type region; and a second wire including an ambipolar contact having a first contact between the second wire and the second conductive-type region, and a second contact between the second wire and the neighbouring portion.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC +1
Power unit
InactiveUS20110139595A1Low costImprove securityElectric devicesContact operating partsPower inverterControl system
In order to discharge electrical charges from a smoothing capacitor even if no discharge command is issued by a control system, making use of the displacement of a power unit in the event of a collision, a movable electrode is connected to a first contact connected to a high-potential bus, and the smoothing capacitor is connected with a converter and an inverter to be in parallel in the case where an engagement rod is positioned by a retaining ring. Further, when the engagement rod is disengaged from the retaining ring and removed from a relay, the movable electrode is held in contact with a second contact by a pressure spring, and the electrical charge remaining in the smoothing capacitor is discharged to a low-potential bus through a discharge portion.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Level conversion circuit and serial/parallel conversion circuit with level conversion function
InactiveUS20050206432A1Increase speedReduce power consumptionParallel/series conversionPulse automatic controlVoltage amplitudeBiological activation
A MOS capacitor receiving a clock signal complementary to a sampling clock signal is provided at an input of a clocked inverter that is activated after sampling an input signal to perform level conversion. A charge pump operation of the MOS capacitor is performed in parallel with the activation of the clocked inverter. The power consumption of and the area occupied by a level conversion circuit converting a voltage amplitude of the input signal are reduced without deteriorating a high-speed operating characteristics.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Adjustable non-dissipative voltage boosting snubber network
ActiveUS9226380B2Boost voltageReduce voltageElectric discharge tubesElectric lighting sourcesPower flowVoltage multiplier
This disclosure describes a non-dissipative snubber circuit configured to boost a voltage applied to a load after the load's impedance rises rapidly. The voltage boost can thereby cause more rapid current ramping after a decrease in power delivery to the load which results from the load impedance rise. In particular, the snubber can comprise a combination of a unidirectional switch, a voltage multiplier, and a current limiter. In some cases, these components can be a diode, voltage doubler, and an inductor, respectively.
Owner:AES GLOBAL HLDG PTE LTD
Booster circuit
ActiveUS7663427B2Reduce the numberBoost voltageAc-dc conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionEngineeringCapacitor
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
High-efficiency High Step-up Ratio Direct CurrentConverter with Interleaved Soft-switchingMechanism
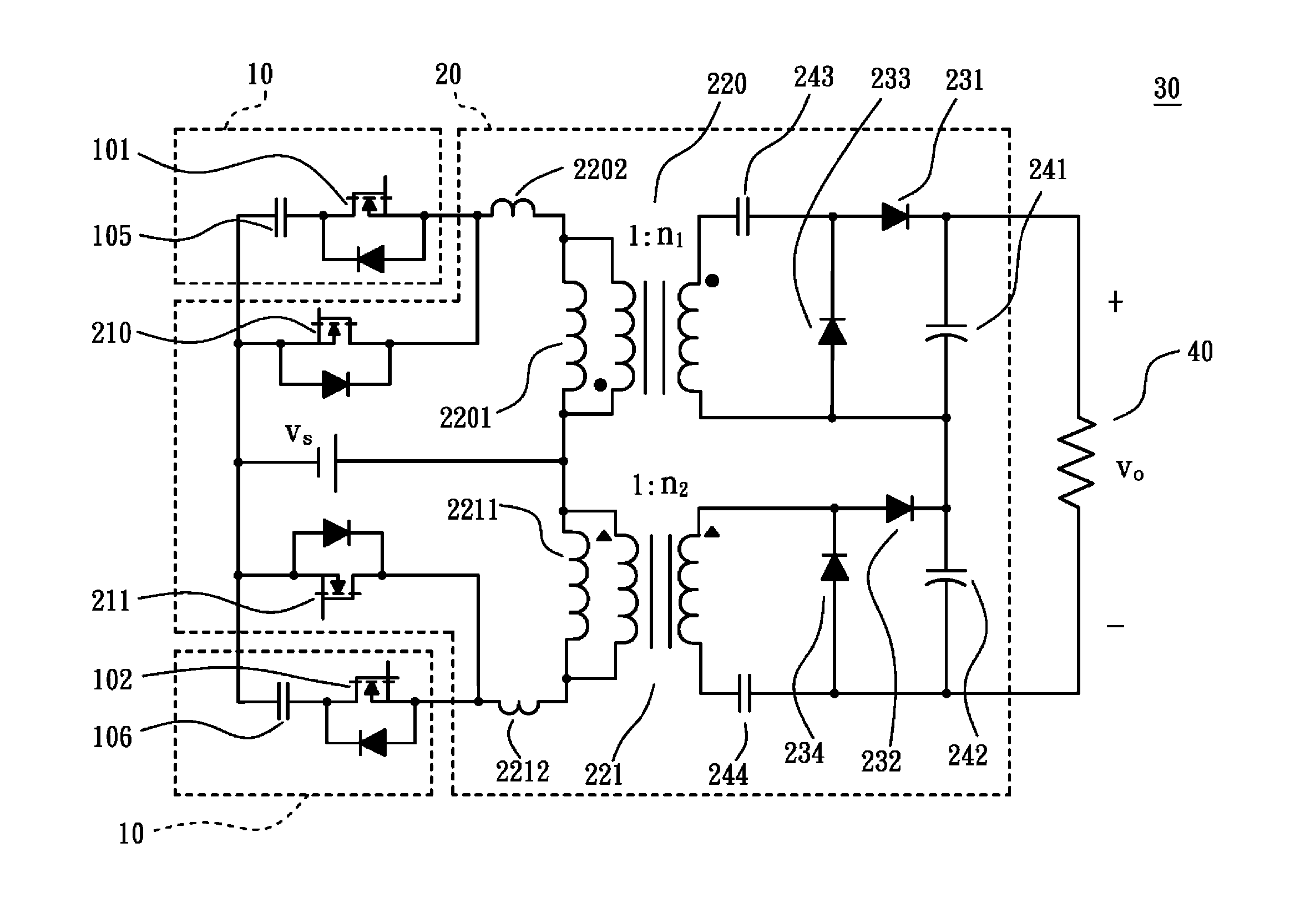
InactiveUS20140056032A1High step-up ratioPromoting efficiency of converterEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionClamp capacitorSoft switching
A high-efficiency high step-up ratio direct current converter with an interleaved soft-switching mechanism is provided. The direct current converter includes a voltage-multiplier circuit and an active clamping circuit. The voltage-multiplier circuit includes two isolating transformers, two main switches disposed on a primary side of the two isolating transformers, four diodes disposed on a secondary side of the two isolating transformers and four capacitors disposed on the secondary side of two isolating transformers, configured to boost a voltage of a direct-current power to a desired voltage value. The active clamping circuit, electrically connected to the voltage-multiplier circuit, includes two active clamp switches and a clamp capacitor to lower a voltage surge of the two main switches so that the two main switches and the two active clamp switches can be soft switched on.
Owner:ALLIS ELECTRIC
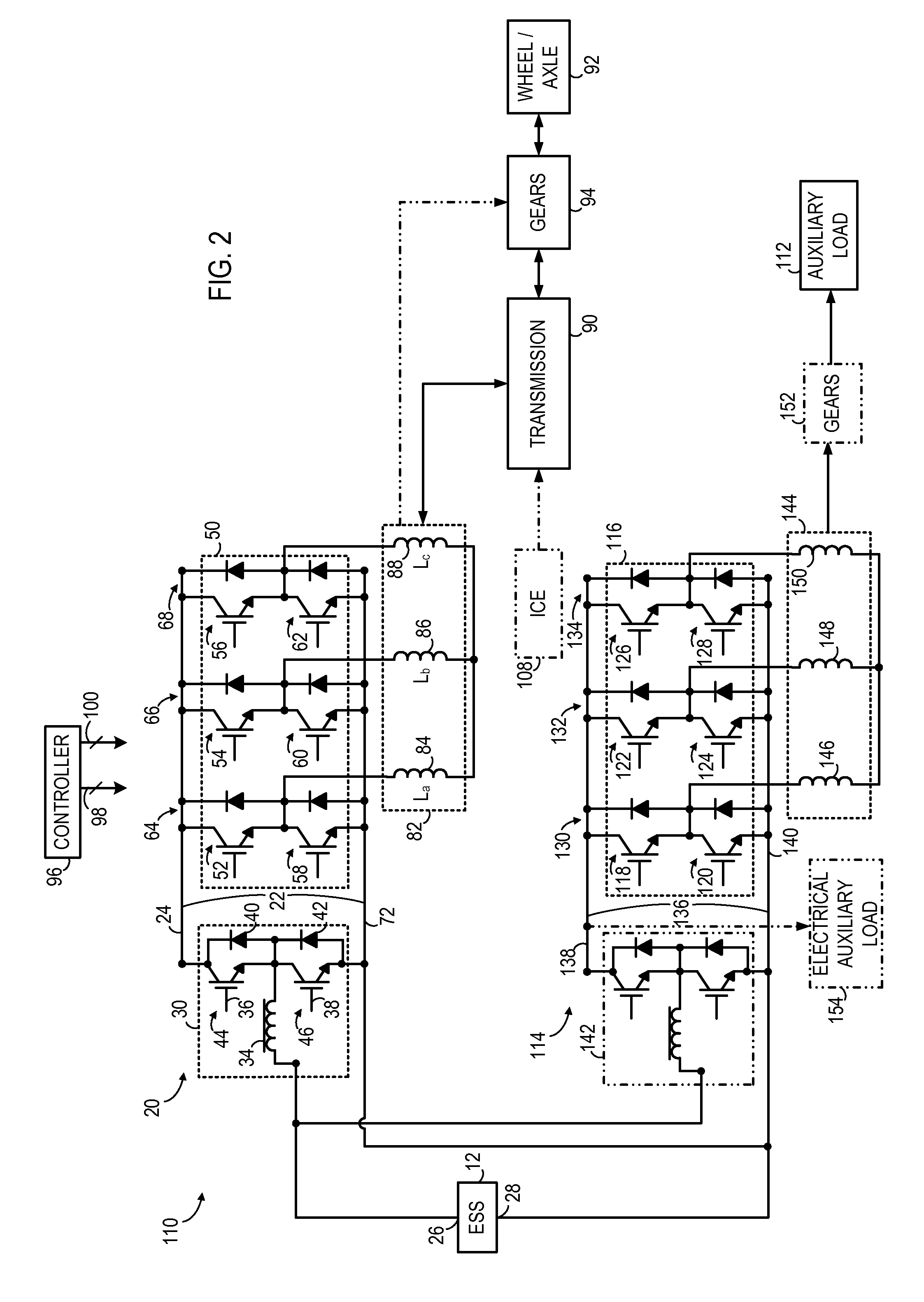
Vehicle propulsion system with multi-channel DC bus and method of manufacturing same
ActiveUS20150210171A1Boost voltageHybrid vehiclesPropulsion by batteries/cellsElectricityVoltage inverter
An apparatus includes a multi-channel DC bus assembly comprising a first channel and a second channel, a first electromechanical device coupled to a positive DC link of the first channel, and a second electromechanical device coupled to a positive DC link of the second channel. A first DC-to-AC voltage inverter is coupled to the positive DC link of the first channel and a second DC-to-AC voltage inverter is coupled to the positive DC link of the second channel. The apparatus further includes a bi-directional voltage modification assembly coupled to the positive DC link of the second channel and a first energy storage system electrically coupled to the first electromechanical device.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
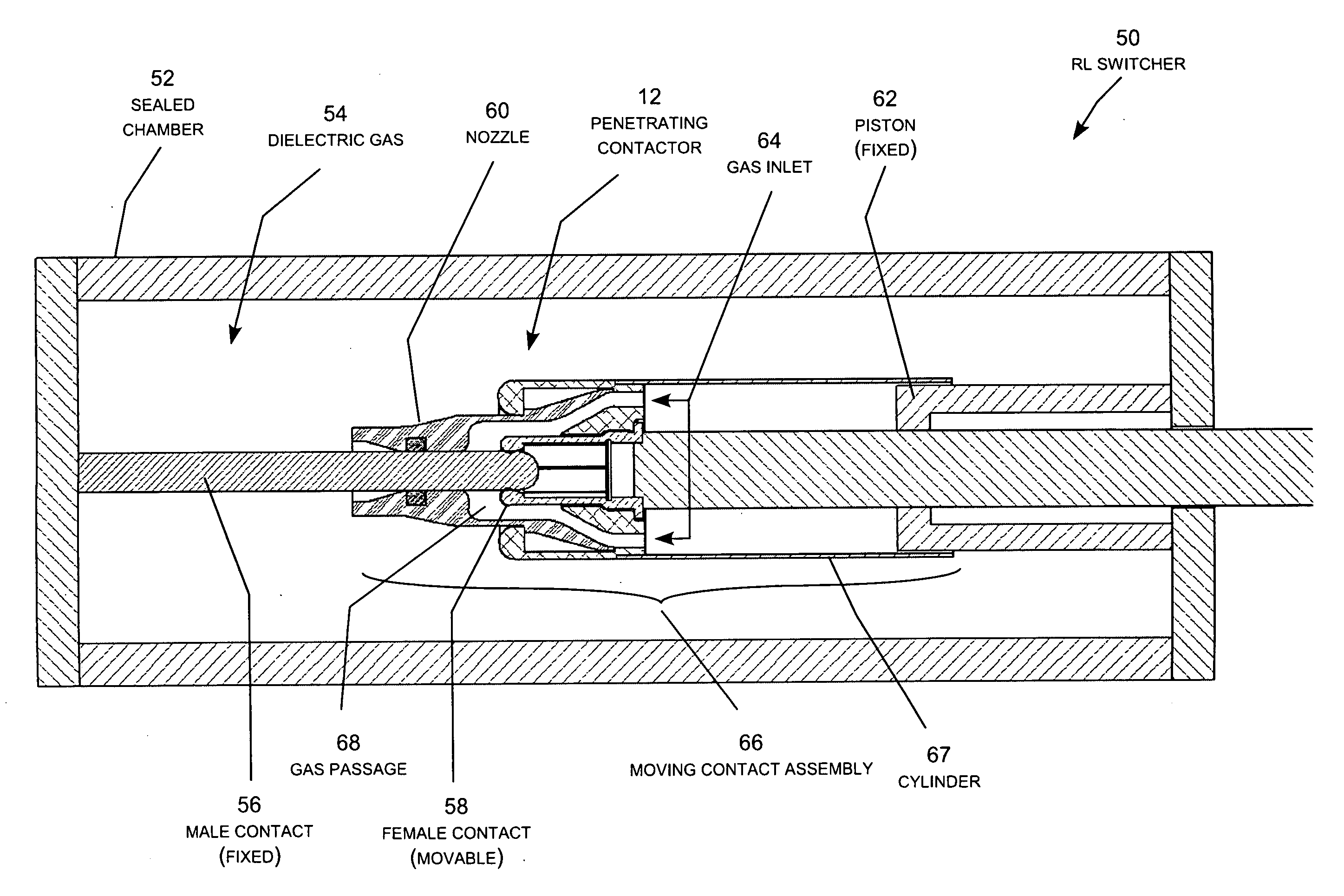
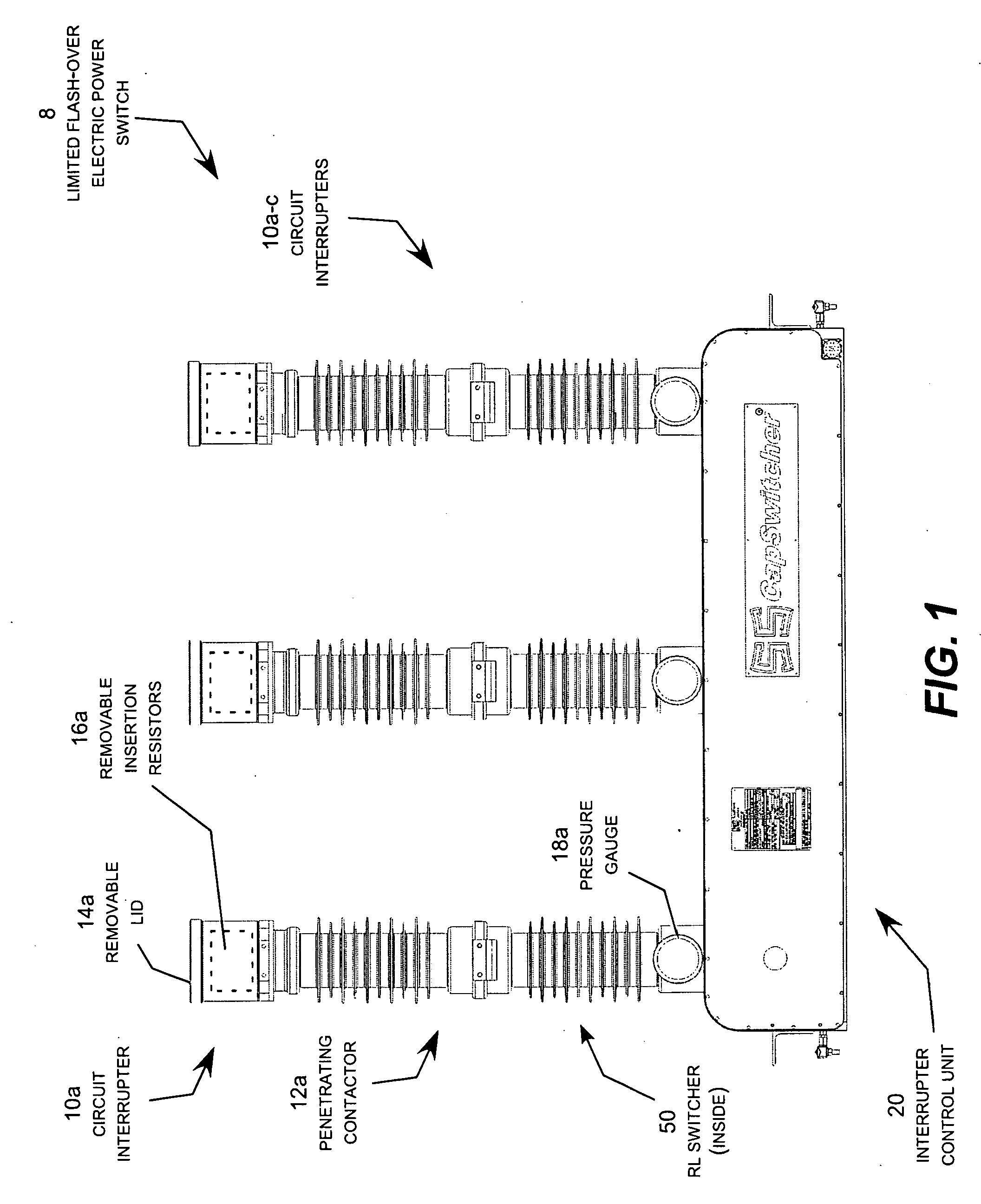
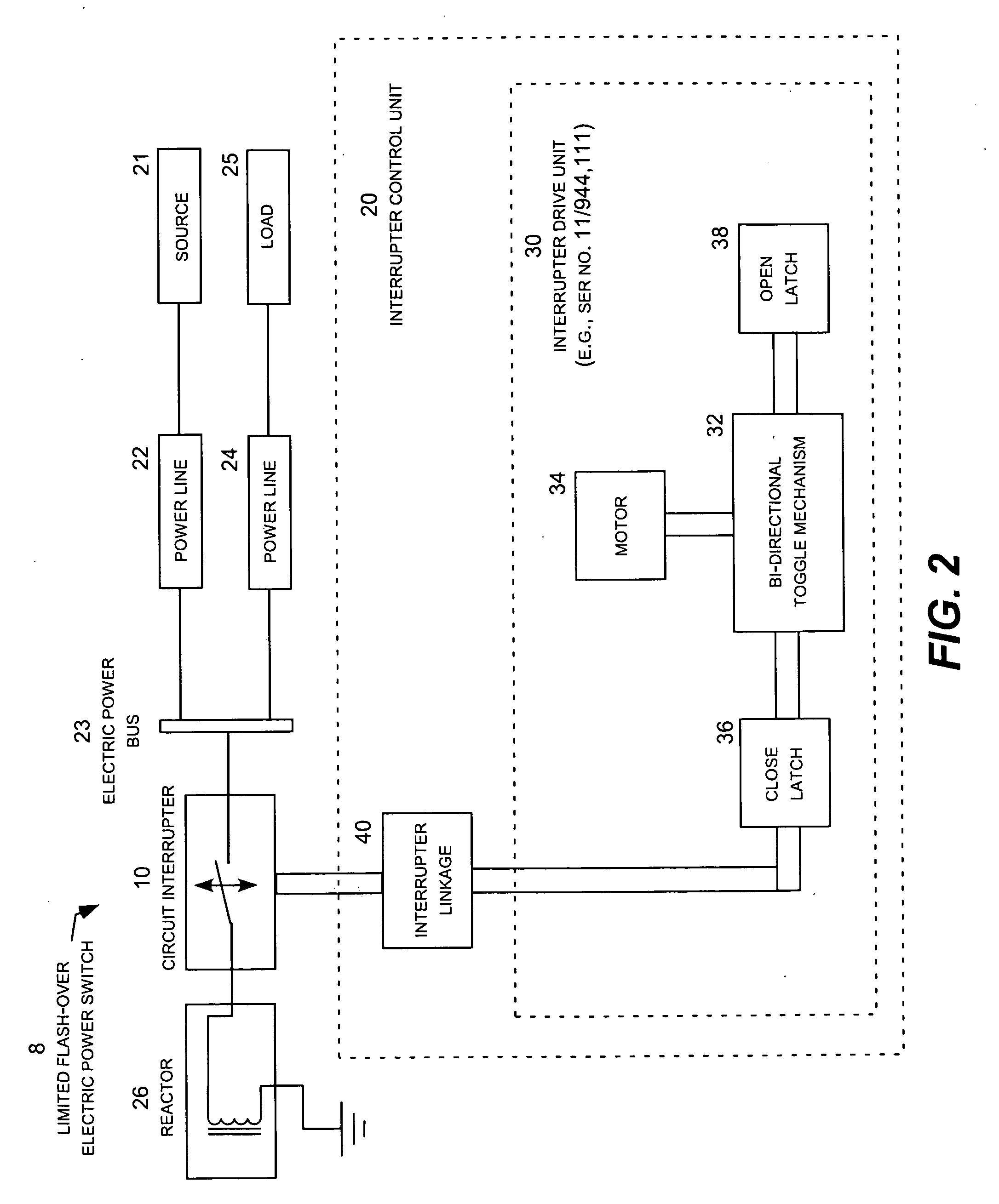
Limited flash-over electric power switch
ActiveUS20100193474A1Minimize damageProlong lifeHigh-tension/heavy-dress switchesAir-break switchesElectricityElectric power system
A limited flash-over electric power switch uses a dielectric gas regulator and a flash-over arrestor to greatly diminish the occurrences of high voltage flash-over during operation of a circuit interrupter. The dielectric gas regulator prevents the flow of the dielectric gas into the arc gap during an initial portion of the opening stroke of the interrupter contacts. Once the arc gap is sufficiently wide to greatly diminish the likelihood of a high voltage flash-over, the dielectric gas regulator allows the dielectric gas to flow into the arc gap to extinguish the arc. The flash-over arrestor snubs out incipient flash-over that may occur as the arc attempts to reform across the arc gap. The flash-over arrestor may be a conductive ring located on the interior surface of the nozzle in the region of the orifice.
Owner:SOUTHERN STATES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com