Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
395 results about "Voltage inverter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
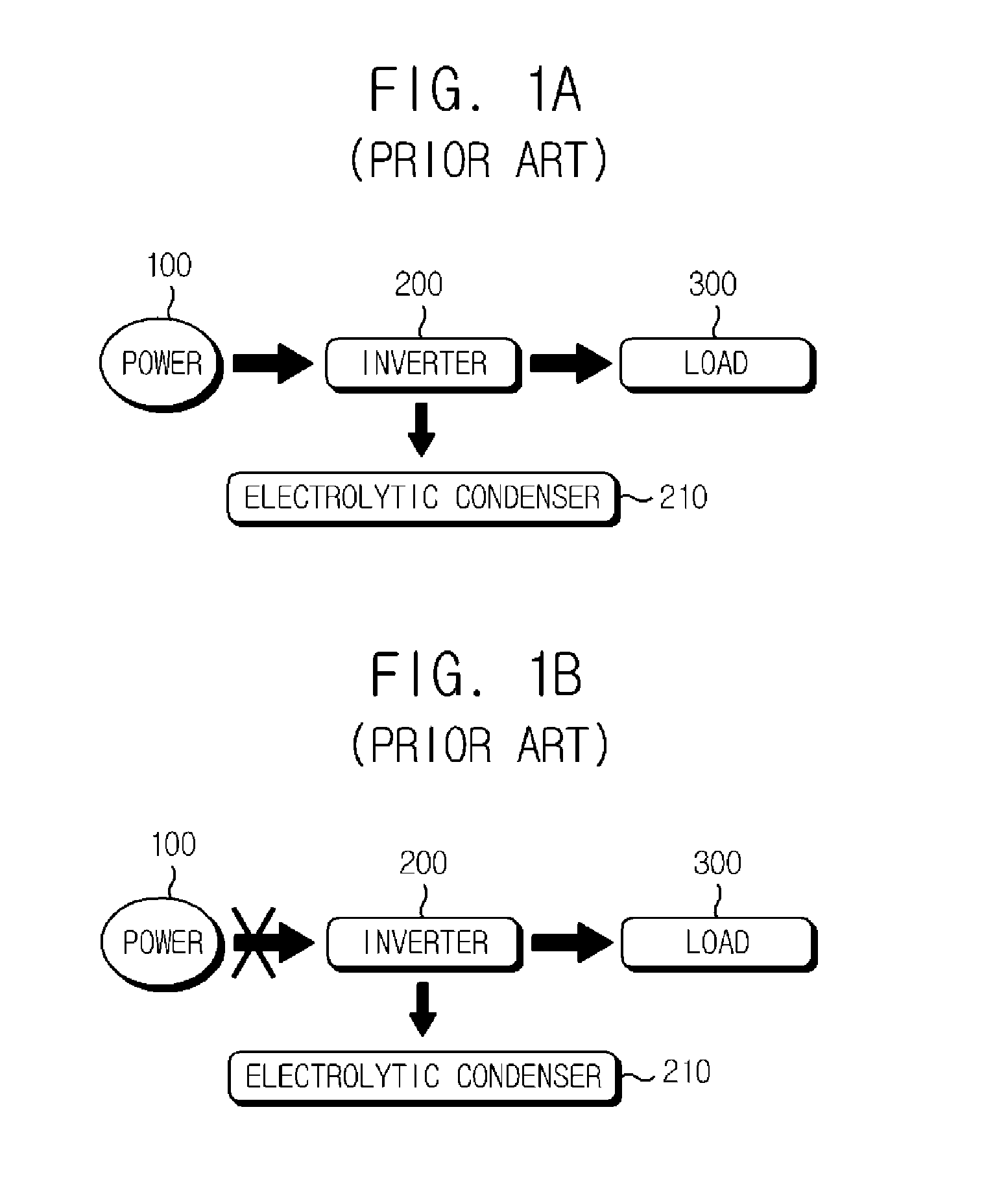
The AC output voltage of a power inverter is often regulated to be the same as the grid line voltage, typically 120 or 240 VAC at the distribution level, even when there are changes in the load that the inverter is driving. This allows the inverter to power numerous devices designed for standard line power.
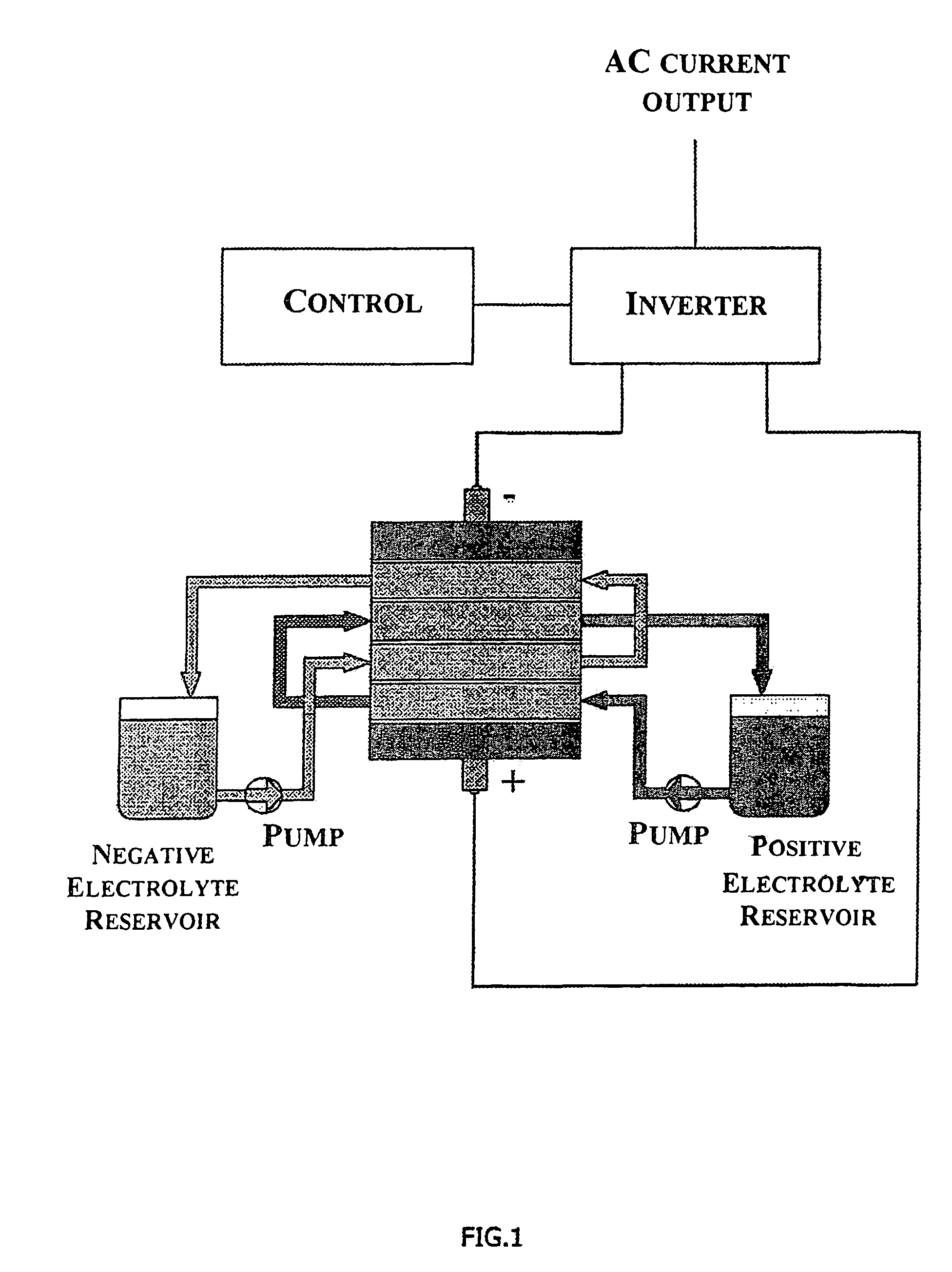
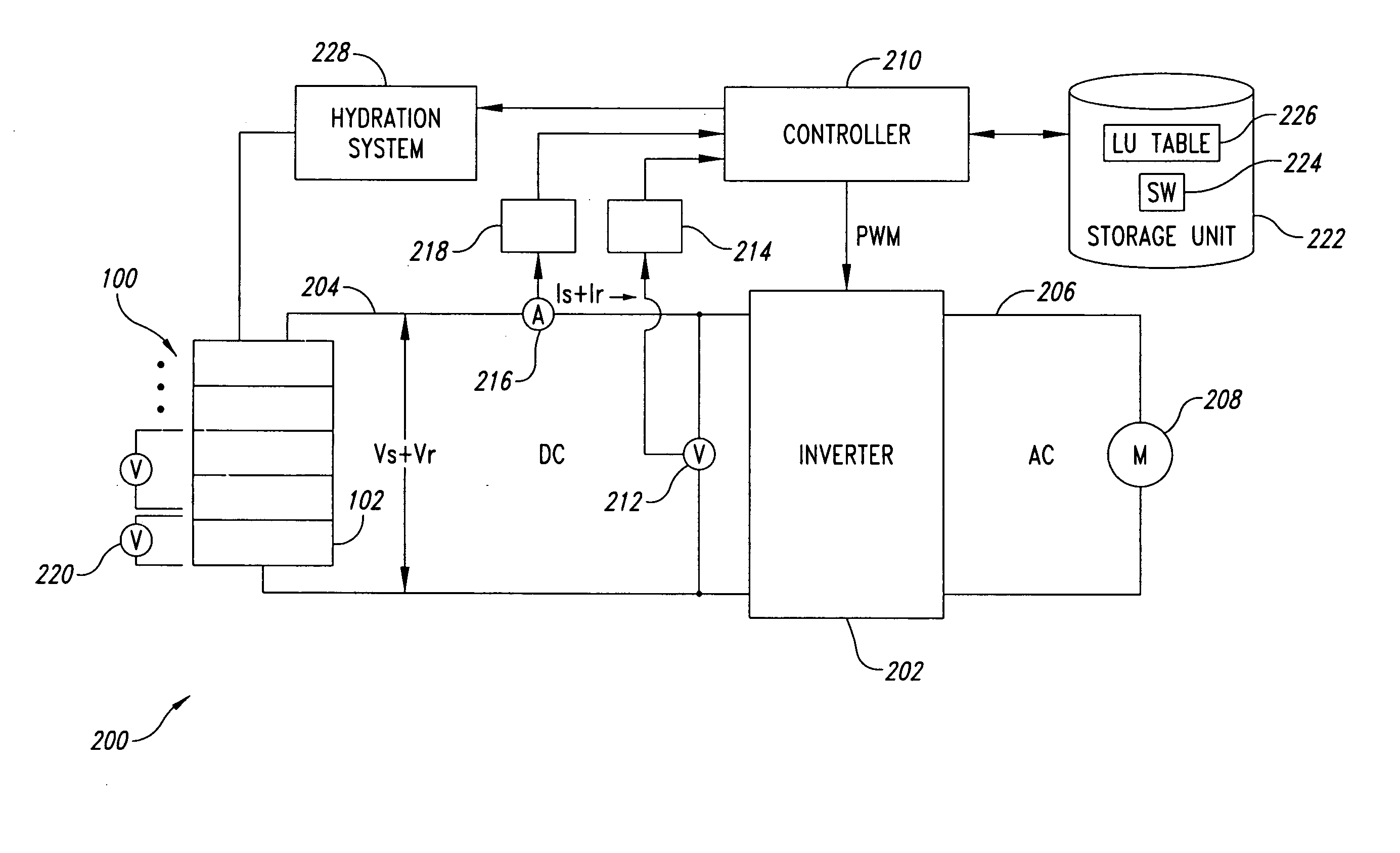
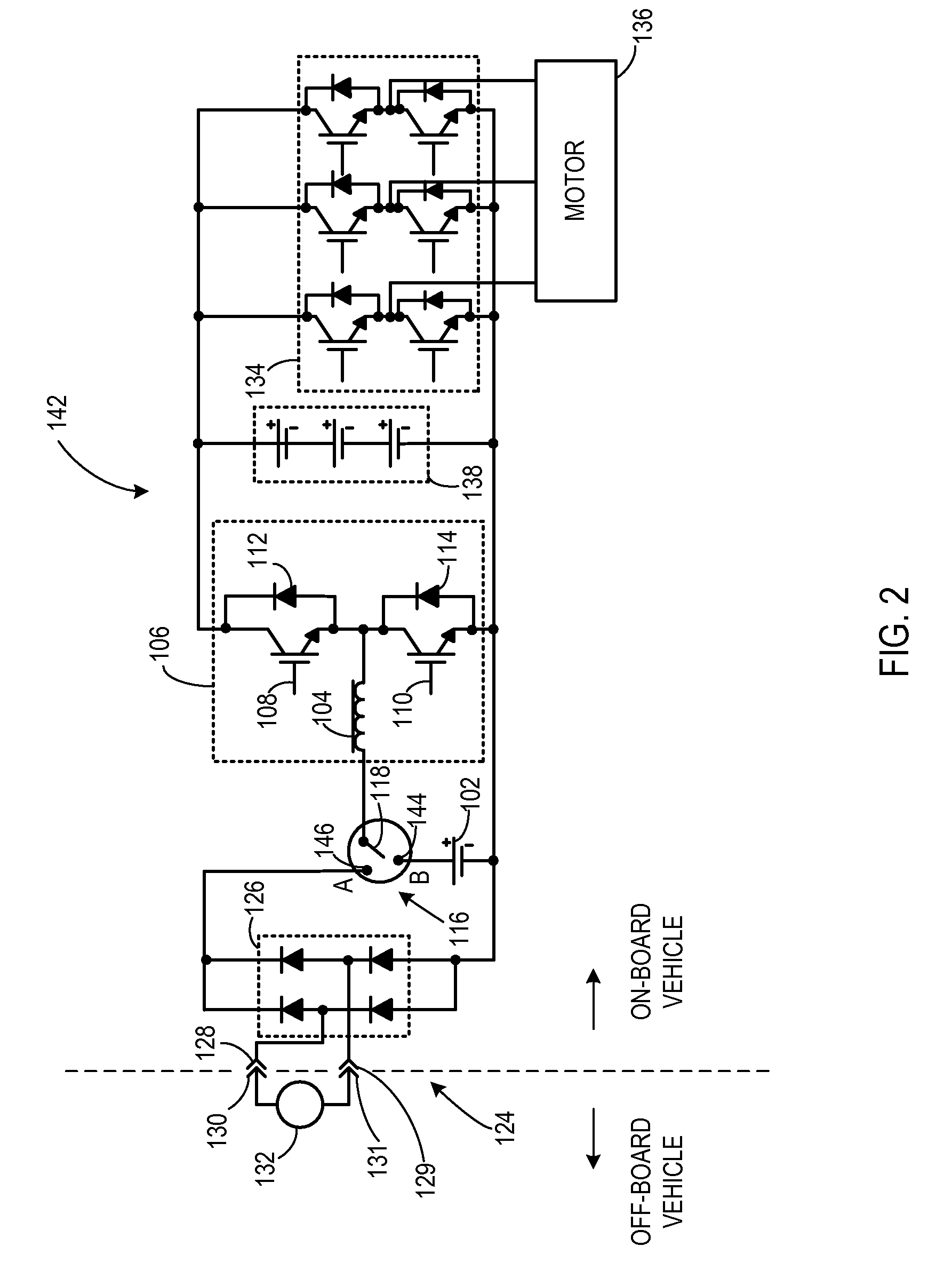
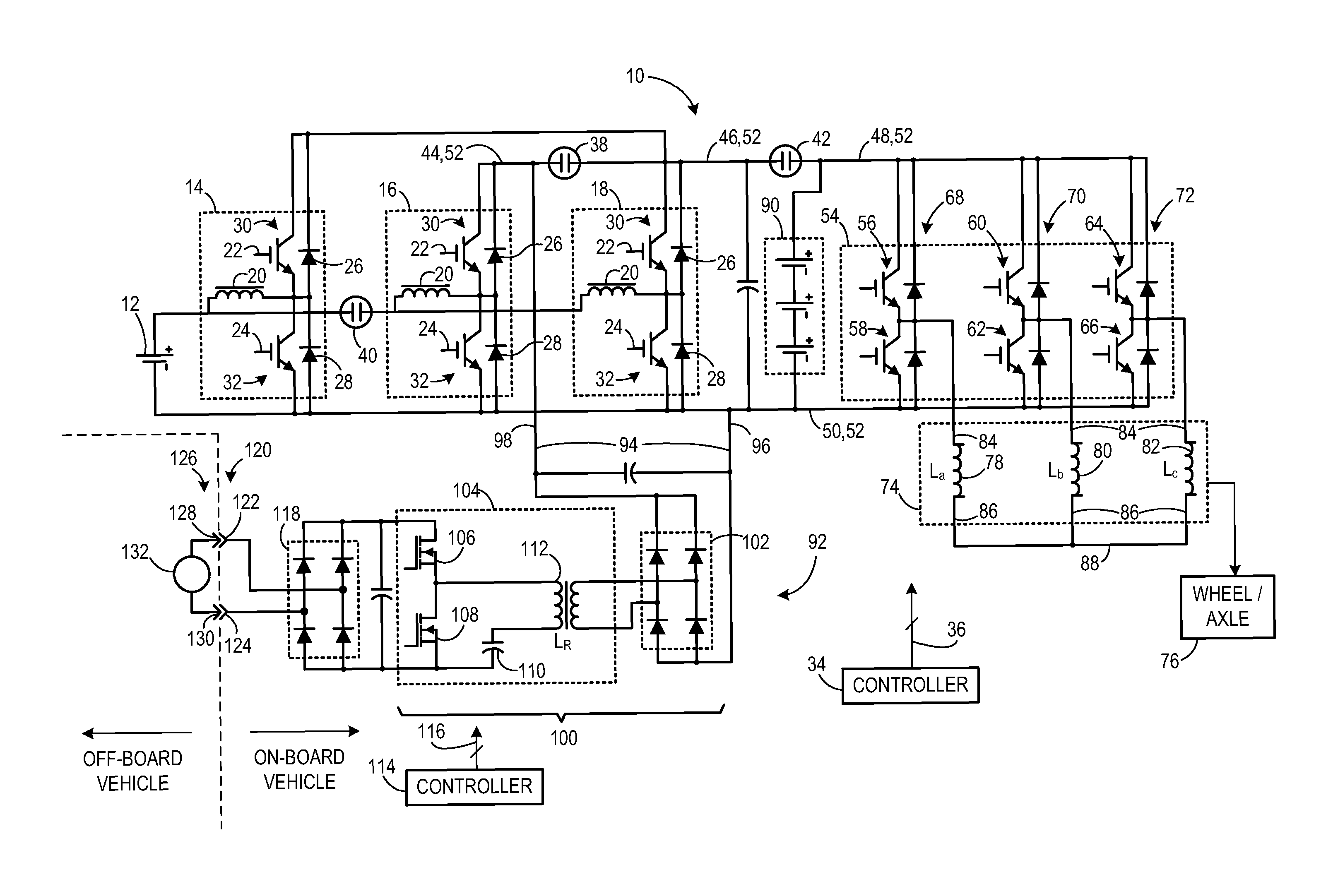
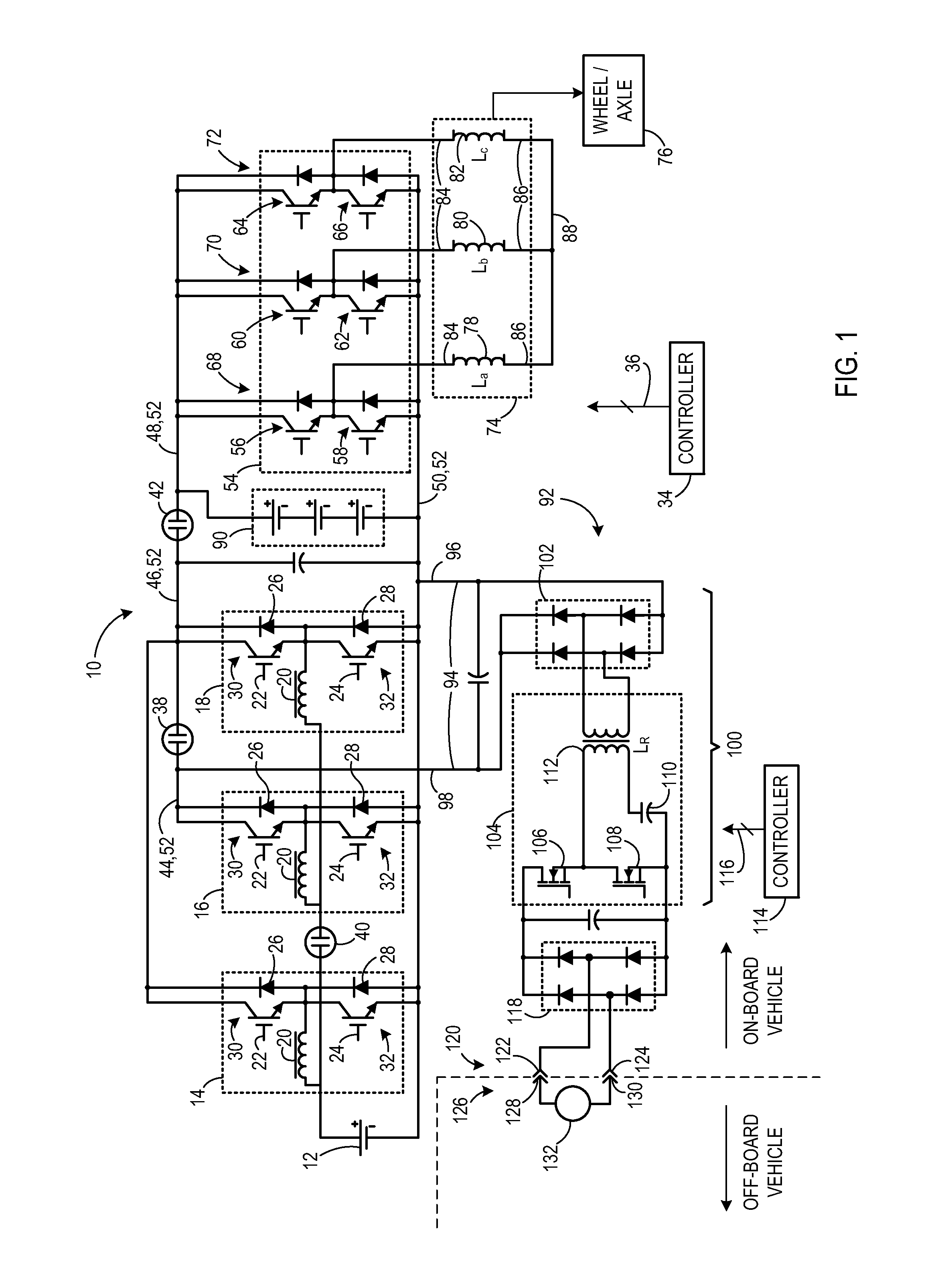
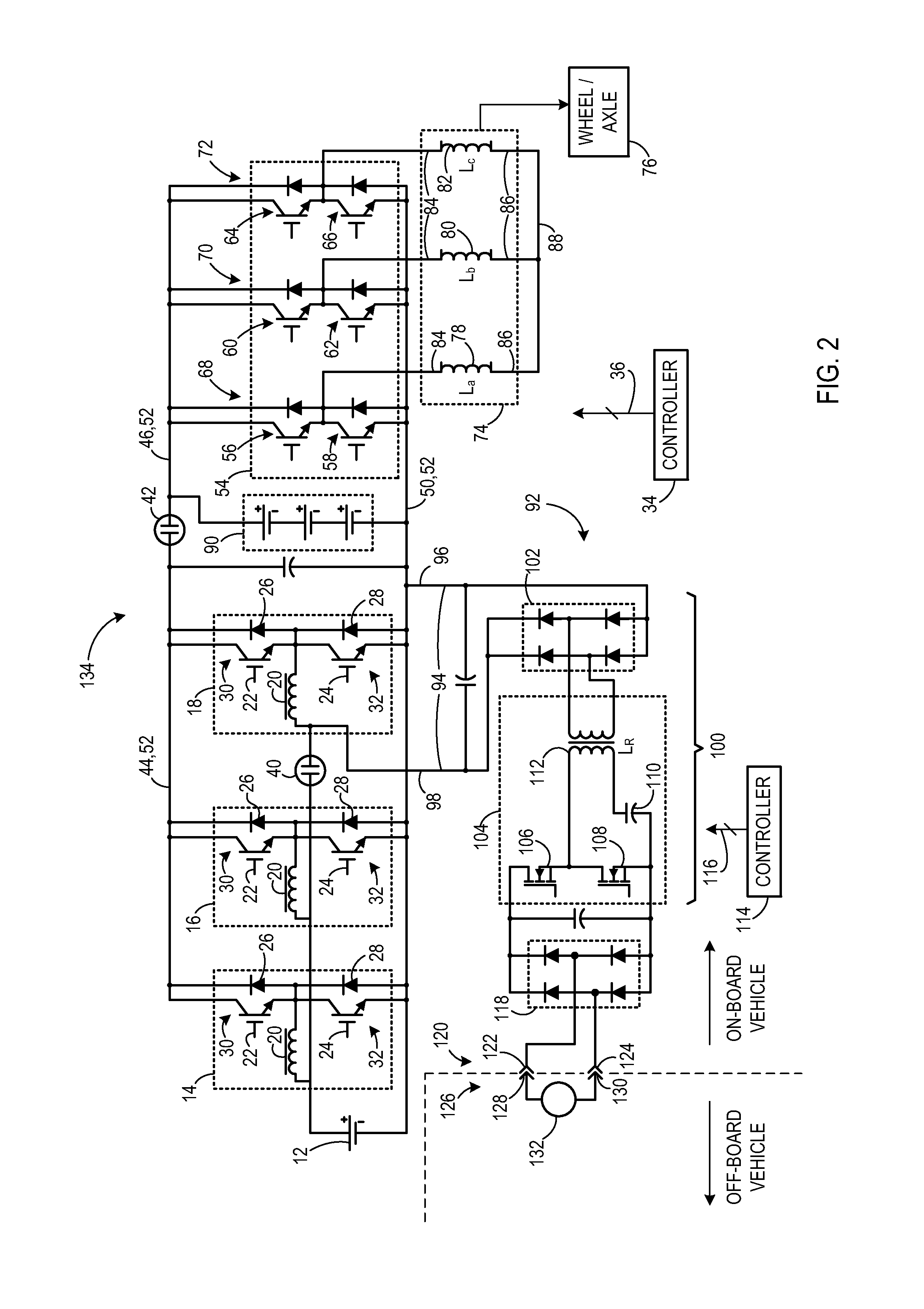
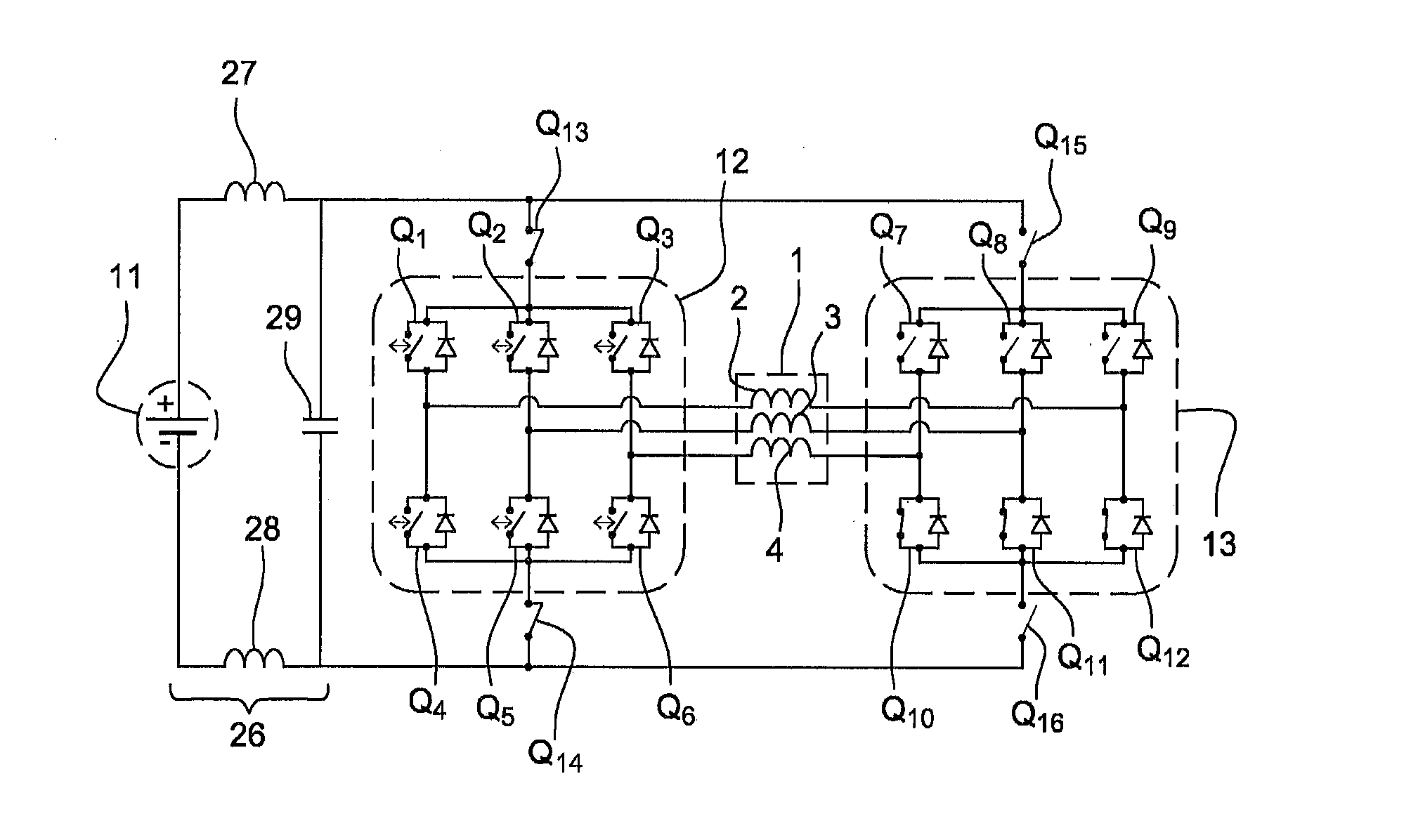
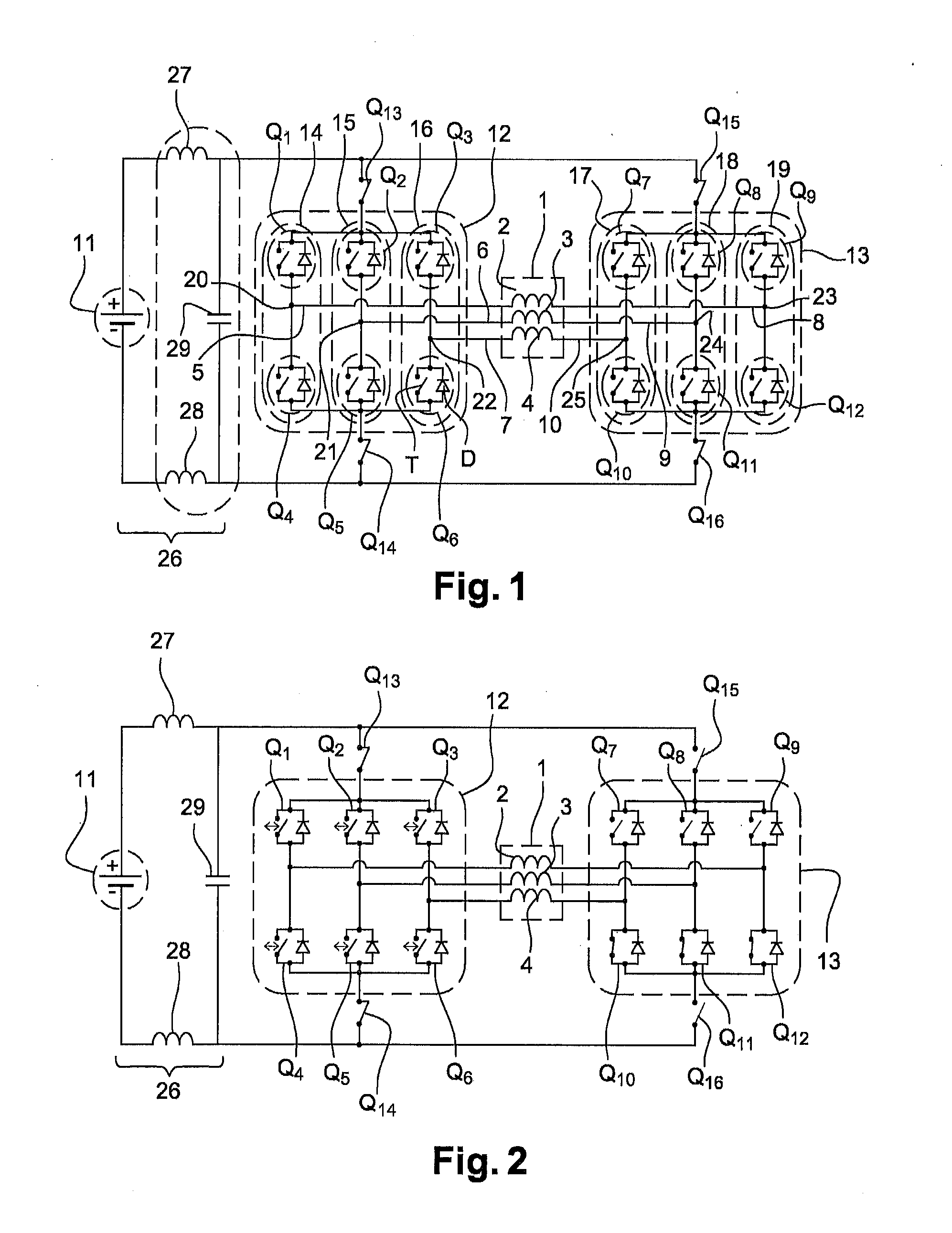
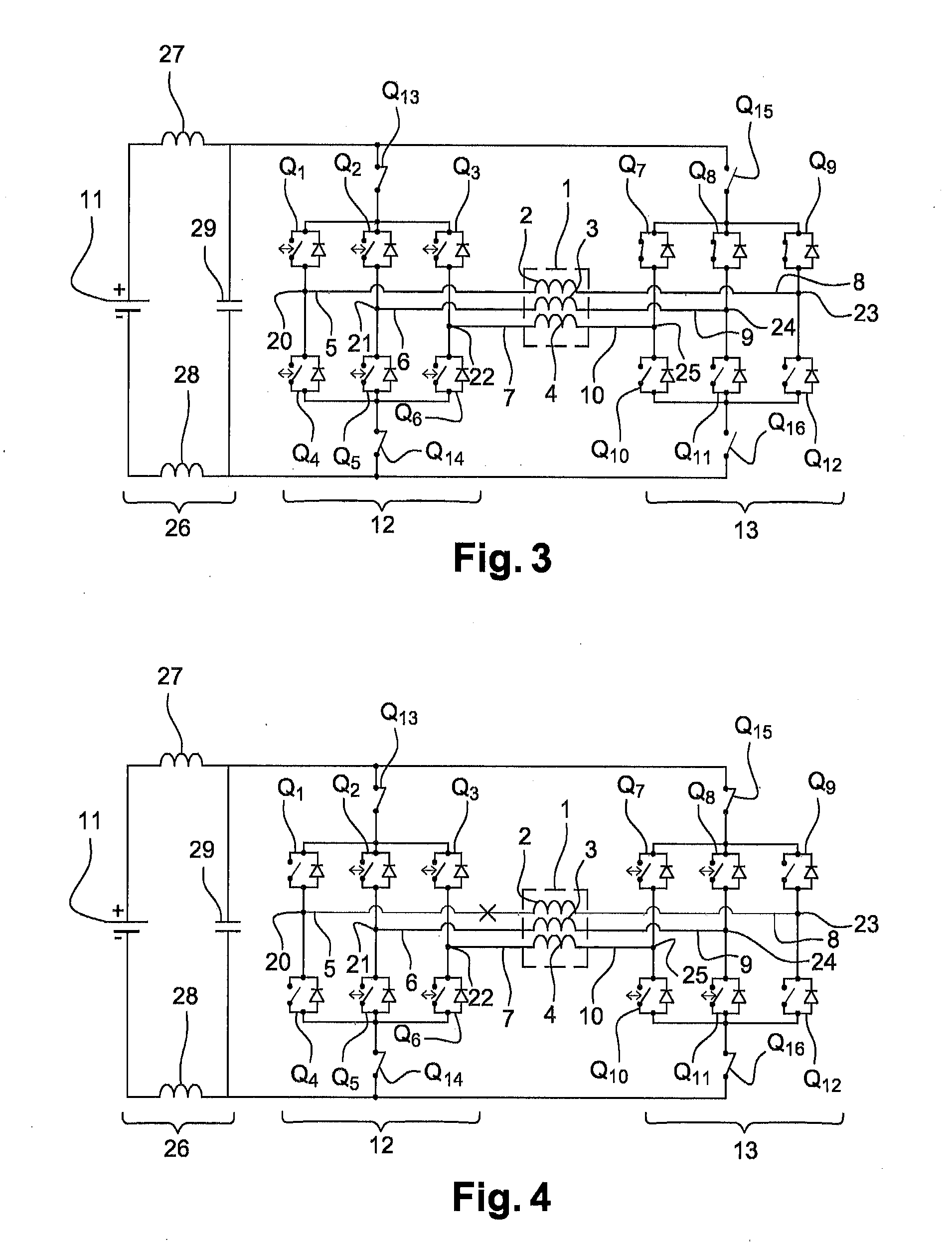
Transformerless static voltage inverter for battery systems
InactiveUS7046531B2Improve efficiencyReduce weightDc source parallel operationDc-ac conversion without reversalDc currentVoltage inverter
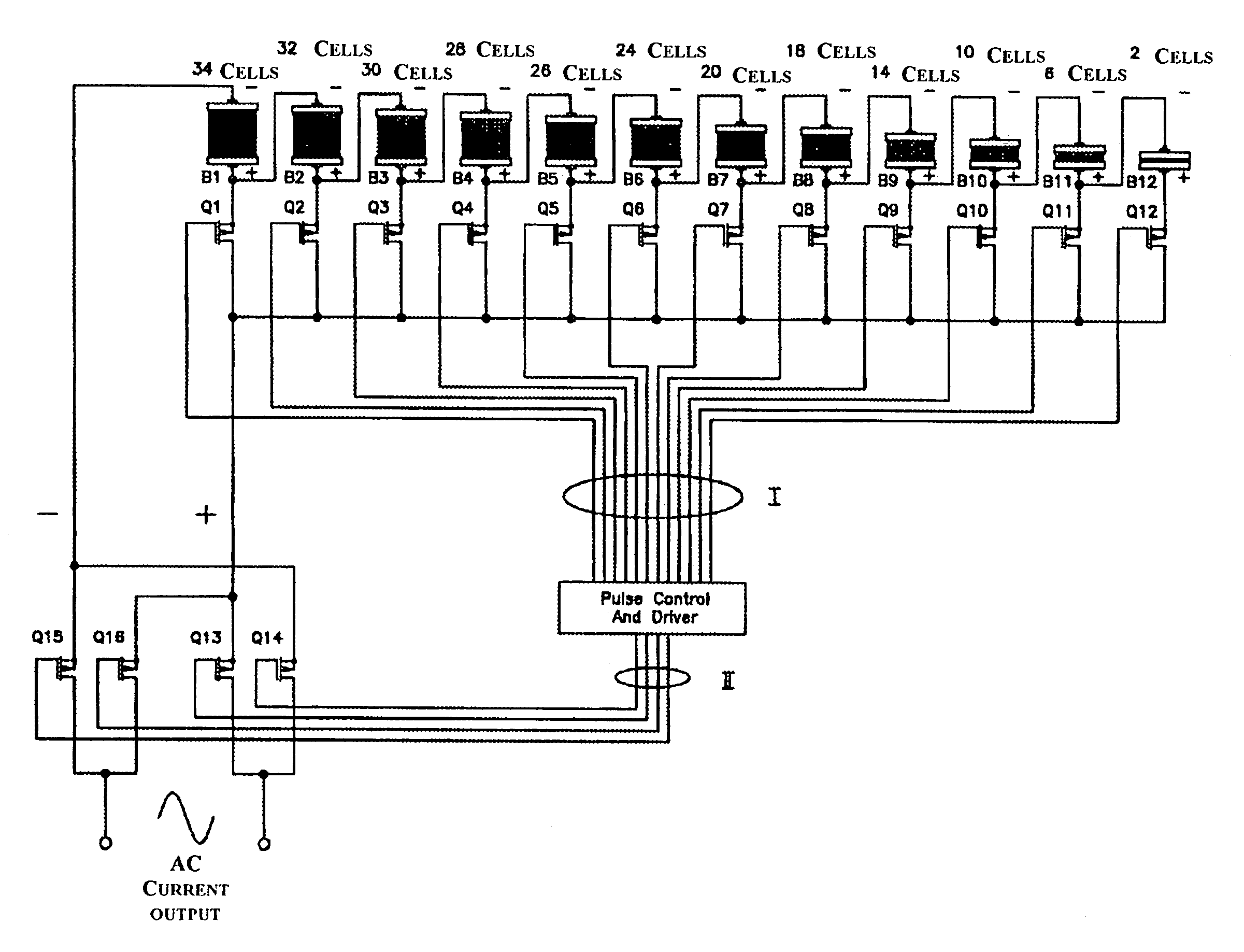
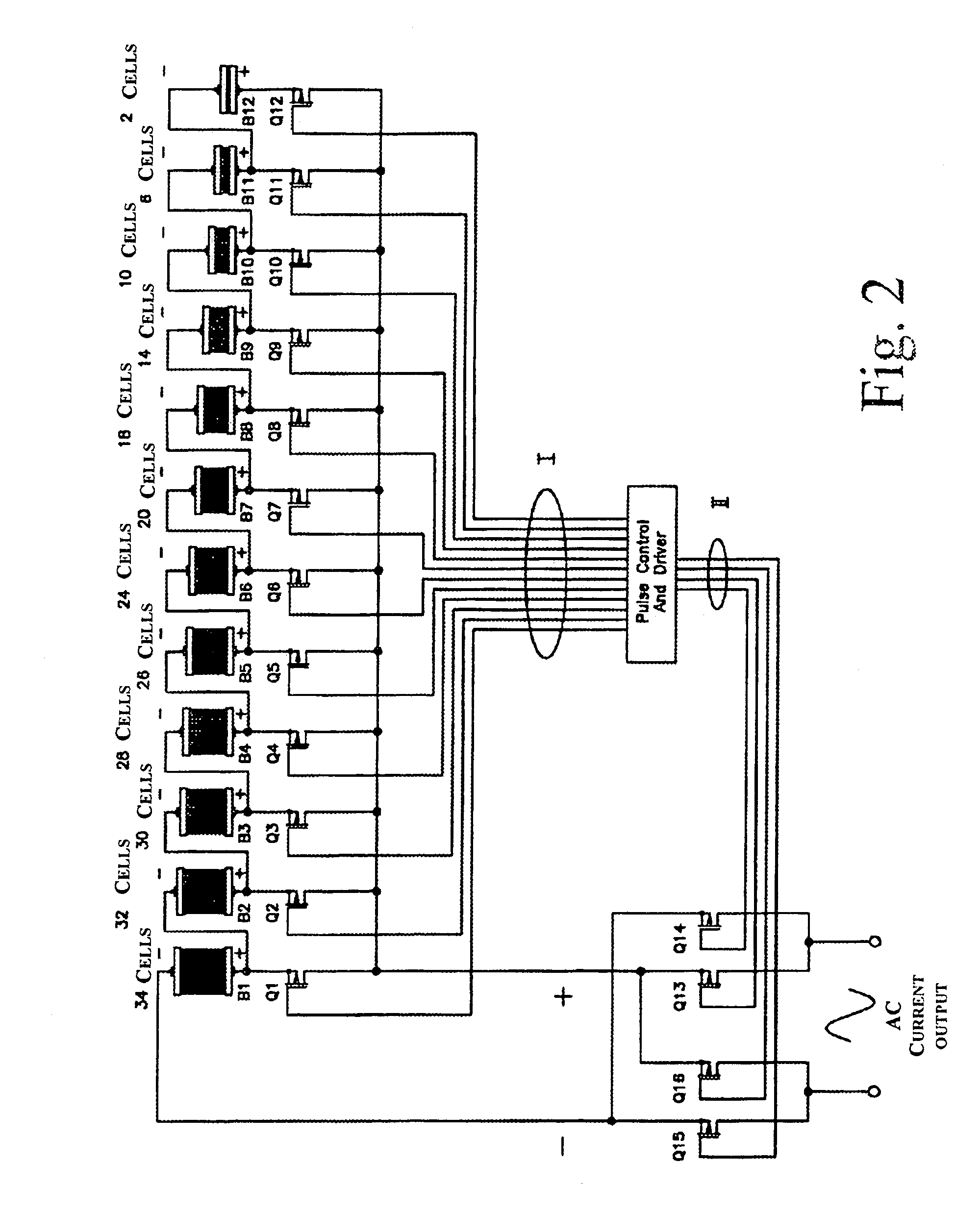
A static inverter for a battery of elementary, current sources or cells electrically in series and a number N of intermediate voltage taps along the chain of elementary DC current sources, wherein the number of elementary cells comprised between an intermediate tap and another intermediate tap adjacent to it or an end terminal of said chain is proportionate to the amplitude in the respective phase interval of a number N of discretization phases of the waveform of the AC voltage to be output in a quadrant; is implemented by arranging for: a number N of power switches each connecting a respective intermediate tap and a first end terminal of a first polarity of said chain of elementary cells in series to a common circuit node of said first polarity; an output bridge stage constituted by at least four power switches controlled in pairs for switching the current paths through the bridge stage, having a first pair of nodes coupled to said common circuit node of said first plurality and to the other end terminal of polarity opposite to said first polarity of said chain of elementary cells, respectively, and a second pair of nodes constituting an AC output; and a control circuit sequentially and cyclically turning on, in a continuous manner, one switch at the time of said N switches; each for a phase interval of 1 / (4N) times the period of said AC output, and alternately tuning on by pairs said four power switches of said output bridge stage at every half a period.
Owner:SQUIRREL HLDG
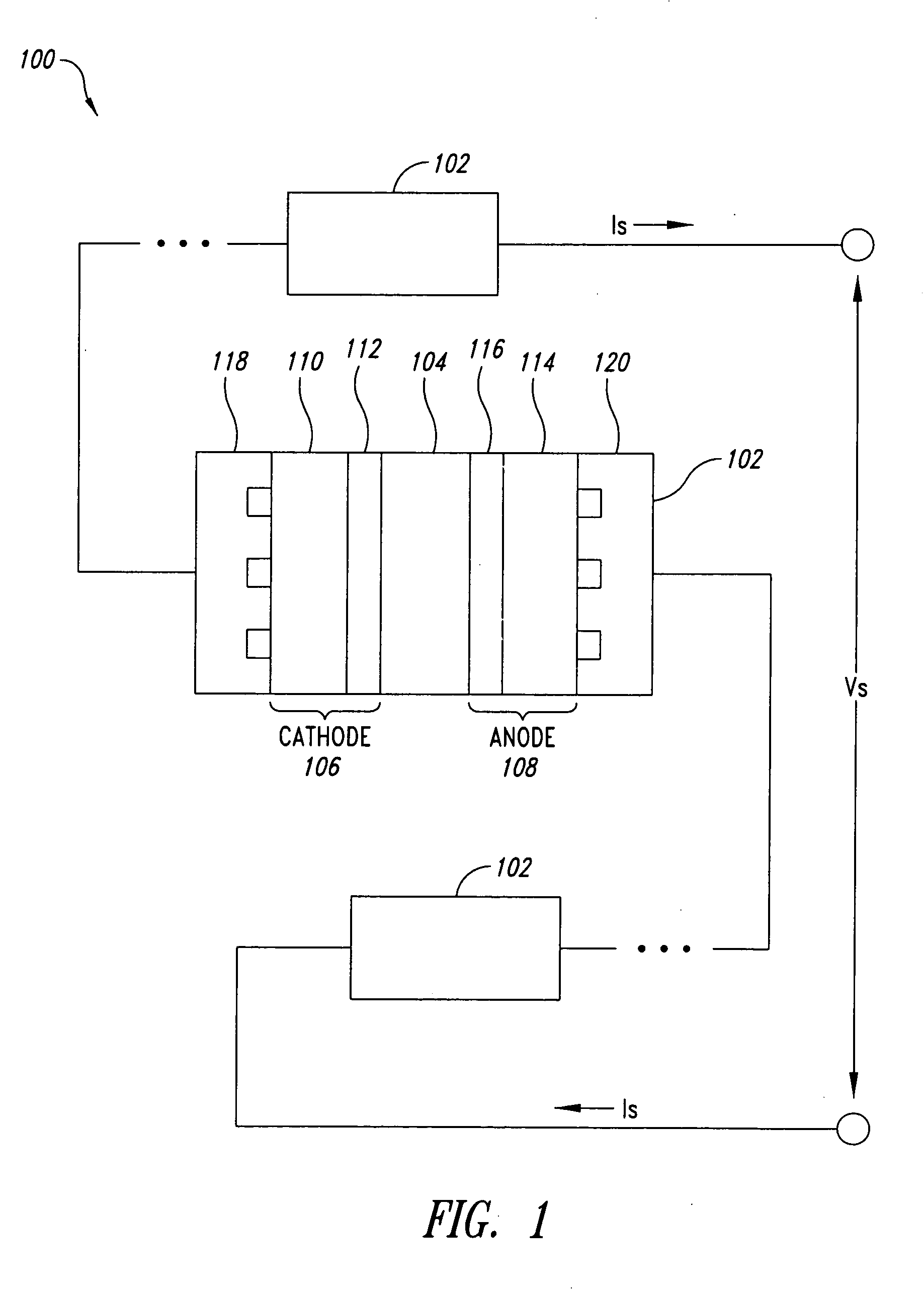
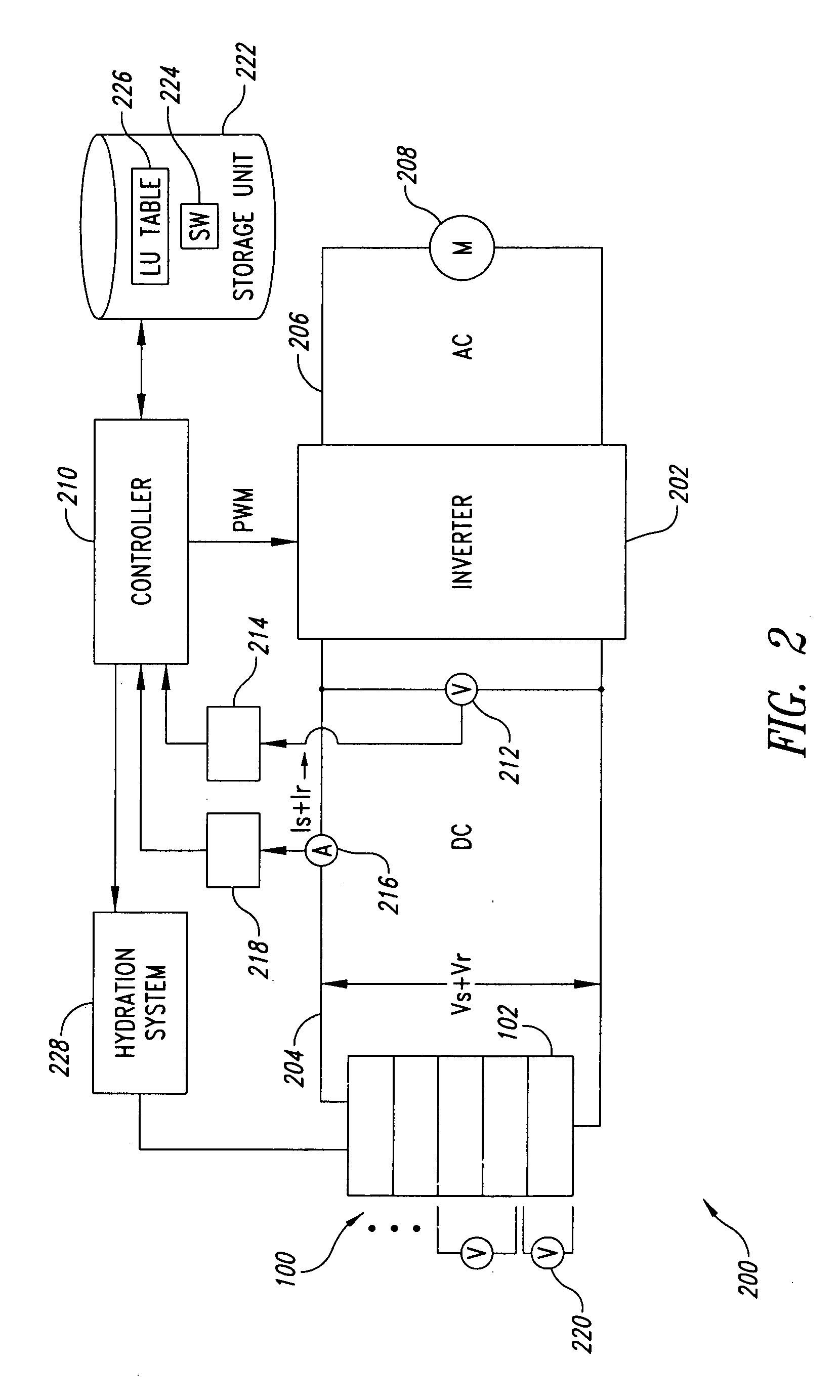
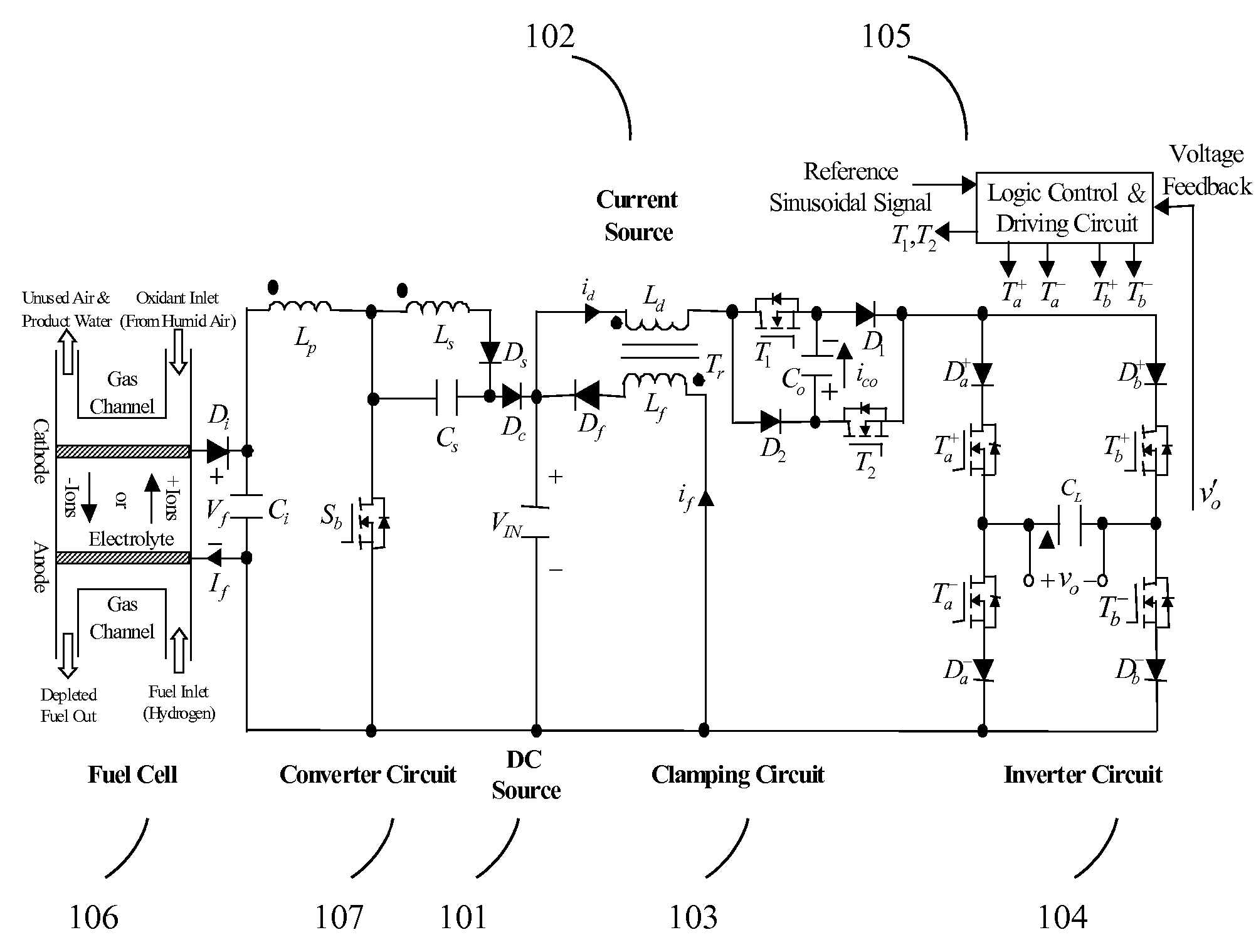
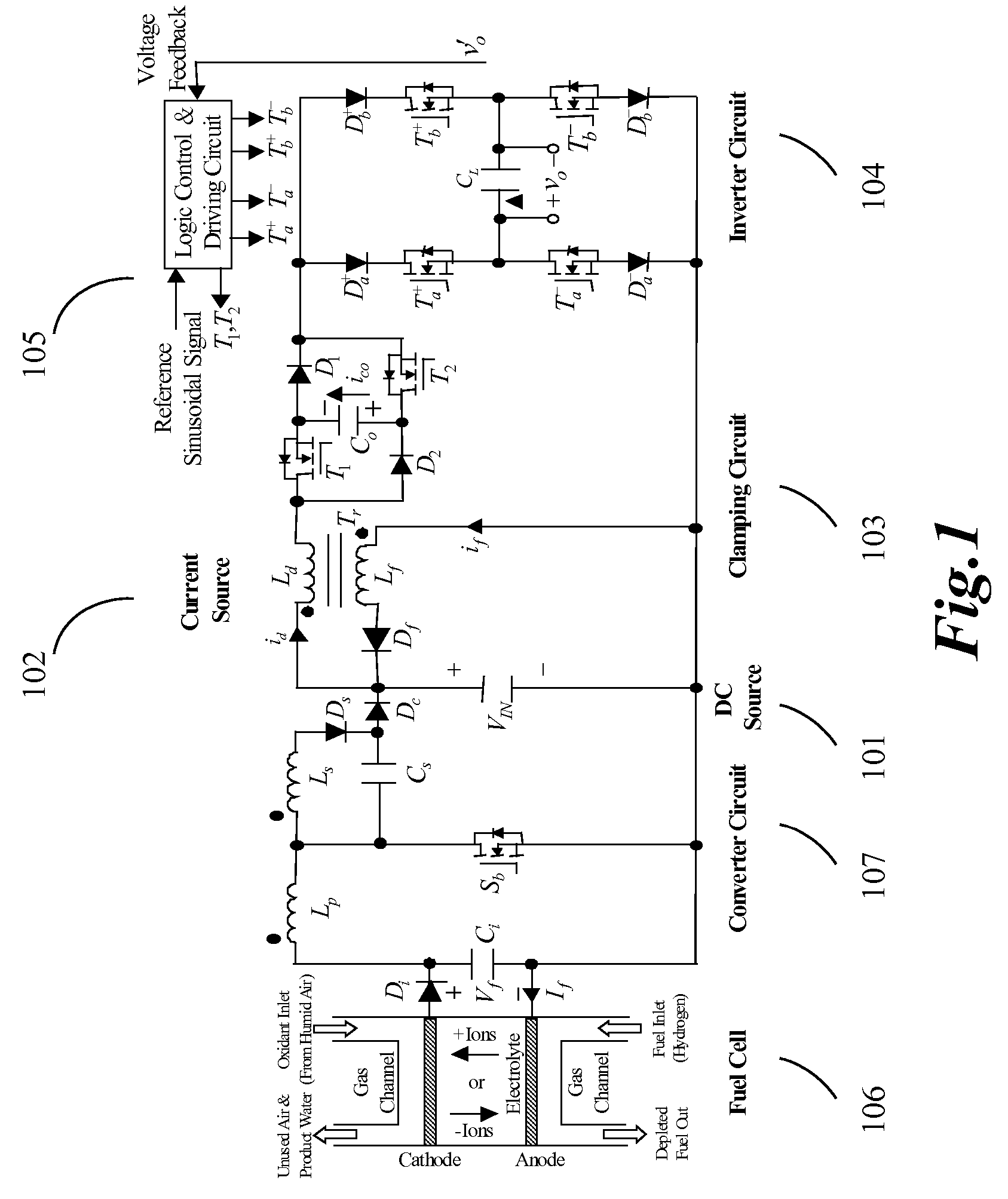
Current source wave voltage inverter voltage-clamping and soft-switching techniques, and fuel cell system using the same
ActiveUS7262979B2Lower component costsEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcSoft switchingEngineering
A current-source sine-wave voltage inverter for converting a direct current (DC) voltage to an alternating (AC) voltage includes a DC source for providing a DC voltage, a current source circuit having a primary side inductance of a transformer, a clamping circuit, an inverting circuit, and a control and driving circuit. The clamping circuit includes a first switch cascaded with a first diode, a second diode cascaded with a second switch, a first capacitor connected between an anode of the first diode and a cathode of the second diode, a secondary side inductance of the transformer cascaded with a third diode, the secondary side inductance of the transformer and the third diode connected to two ends of the DC source, and a cathode of the third diode connected to an anode of the DC source. The present invention also provides a fuel cell system.
Owner:YUAN ZE UNIV
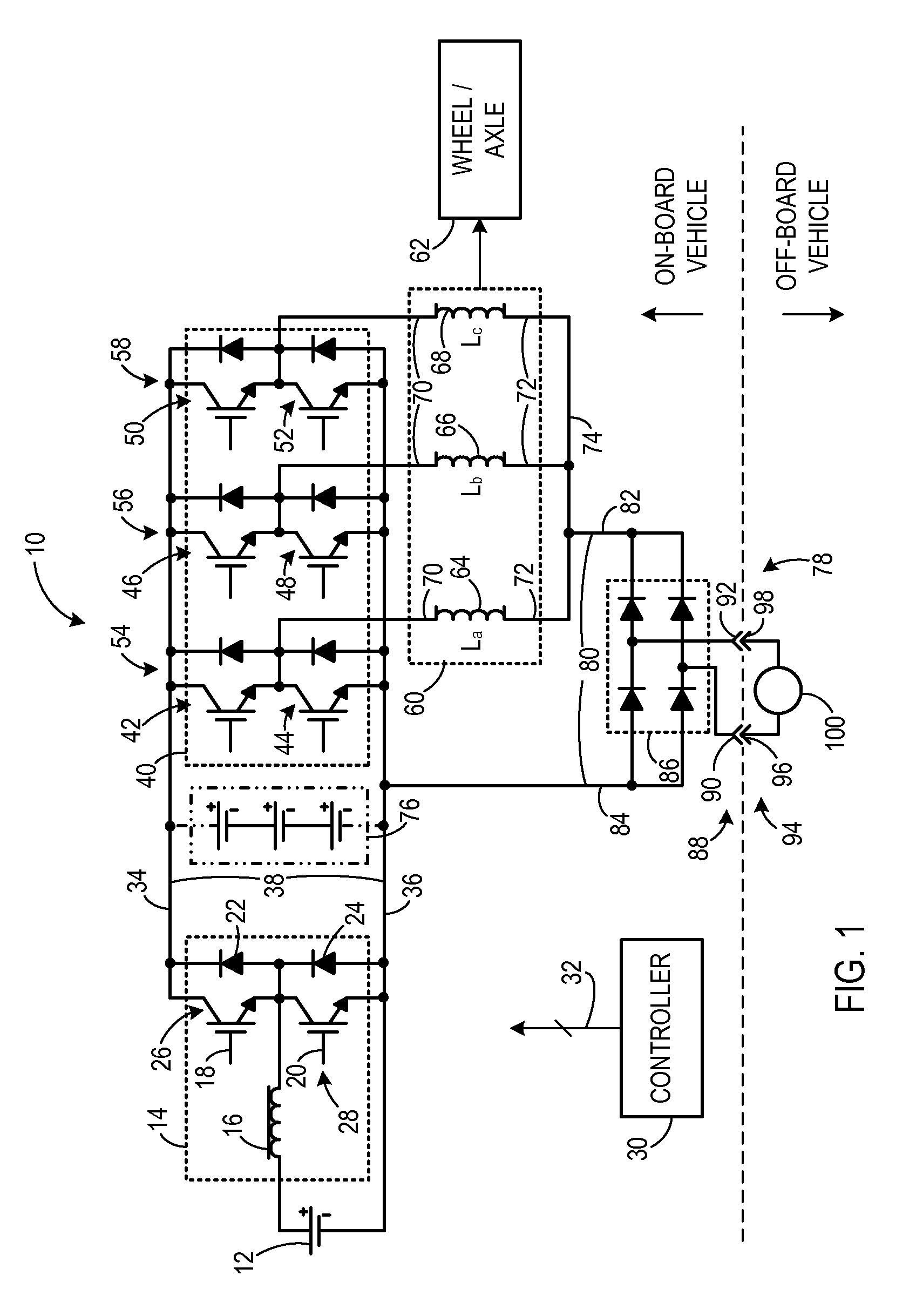
Apparatus for energy transfer using converter and method of manufacturing same
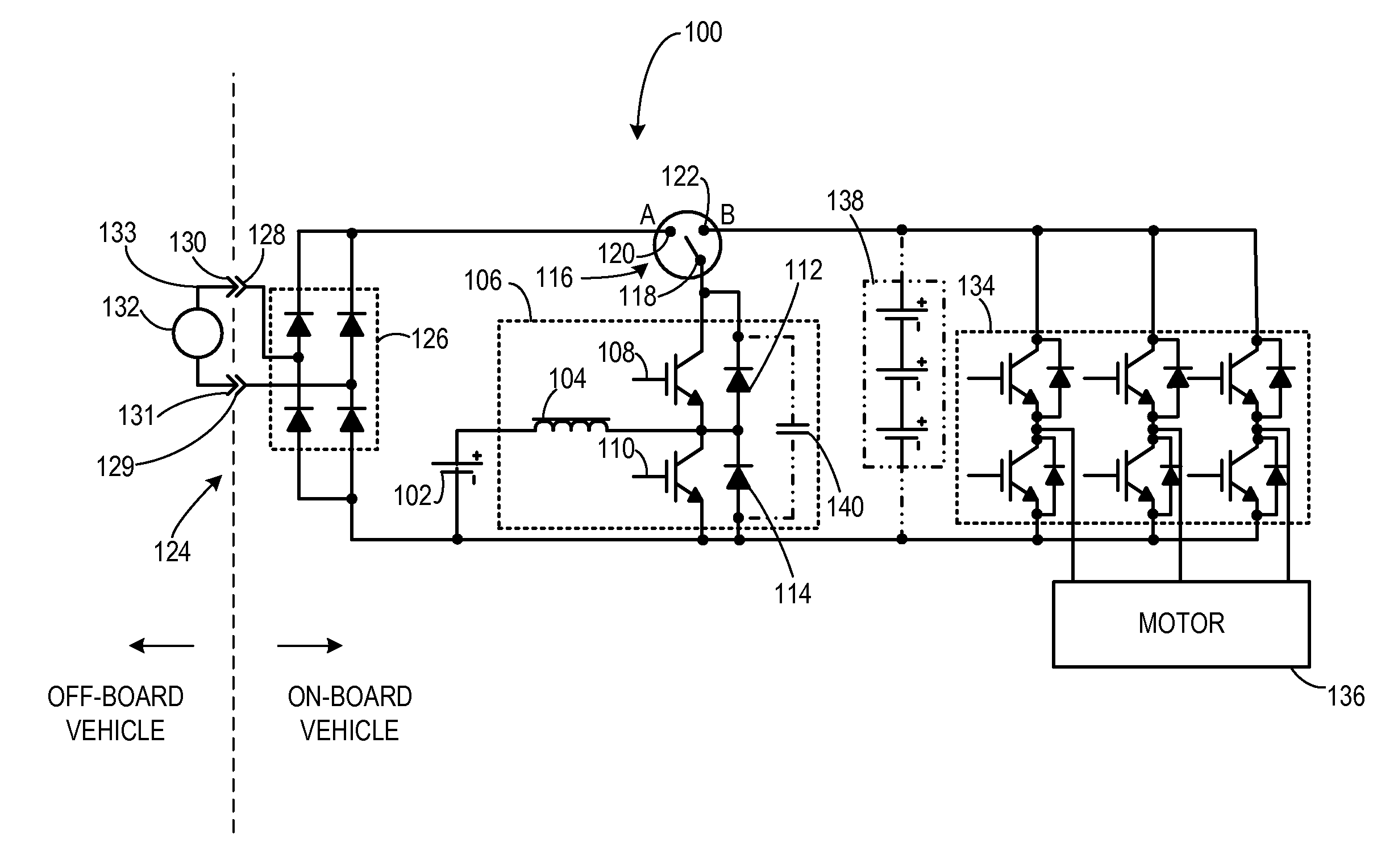
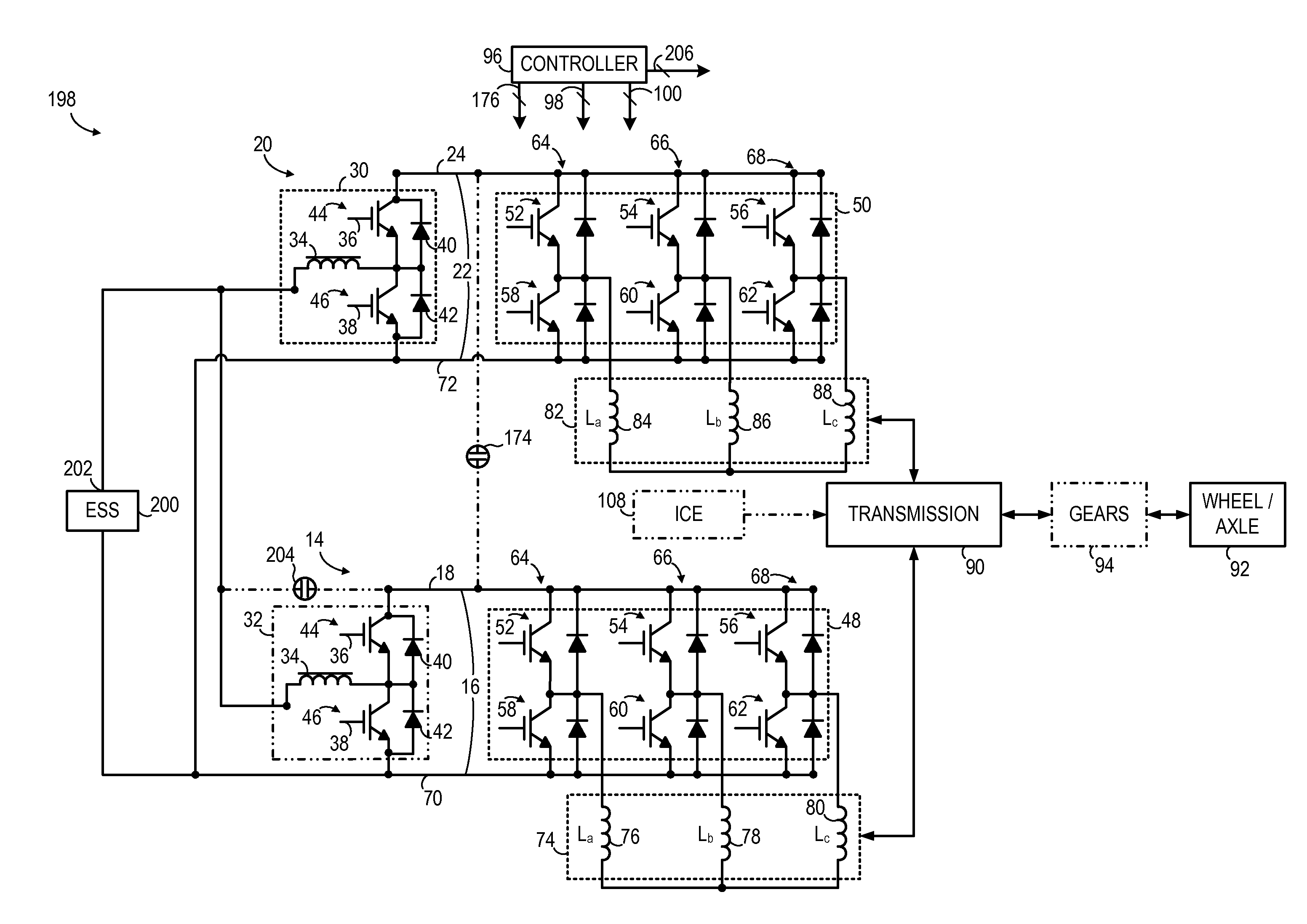
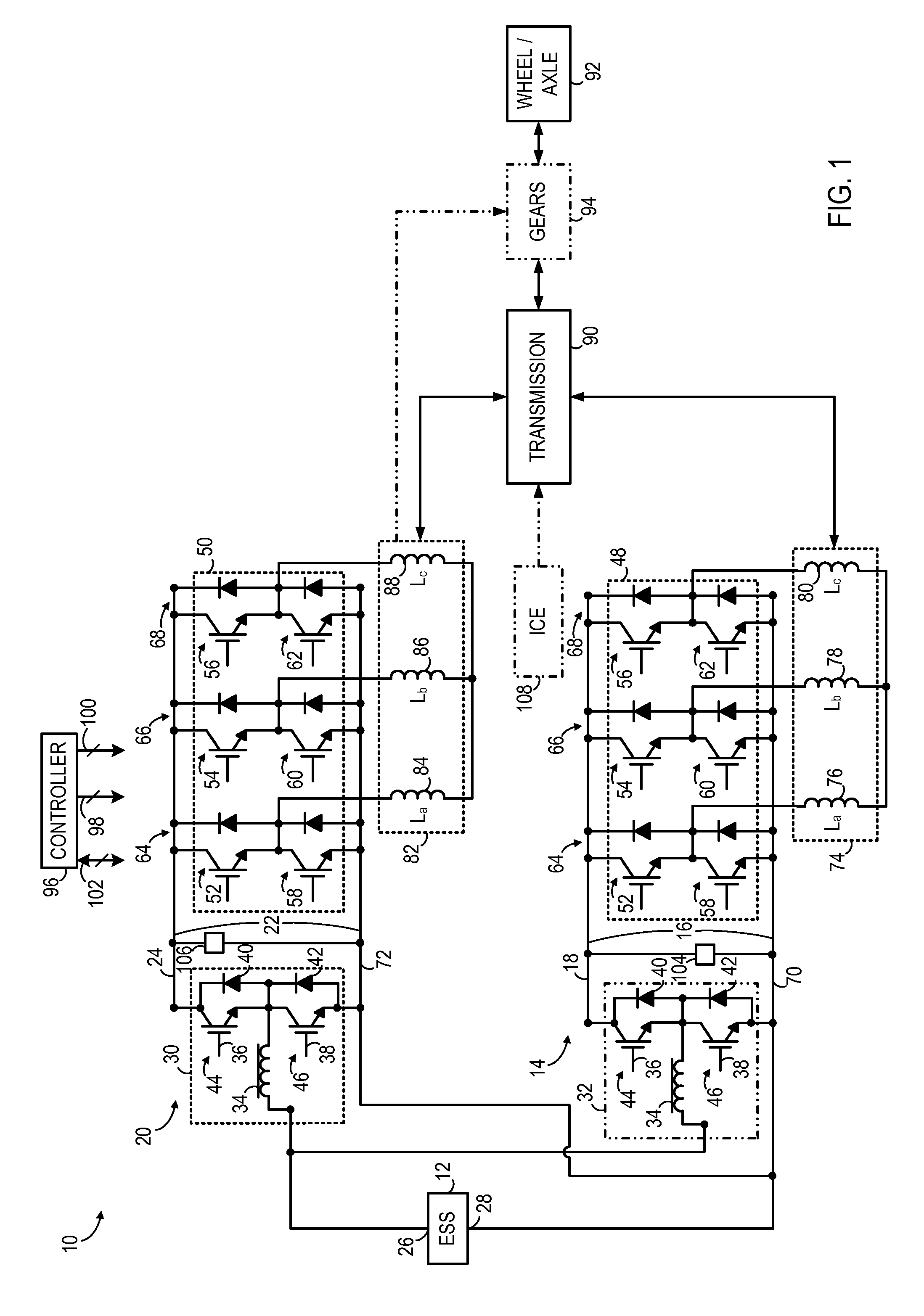
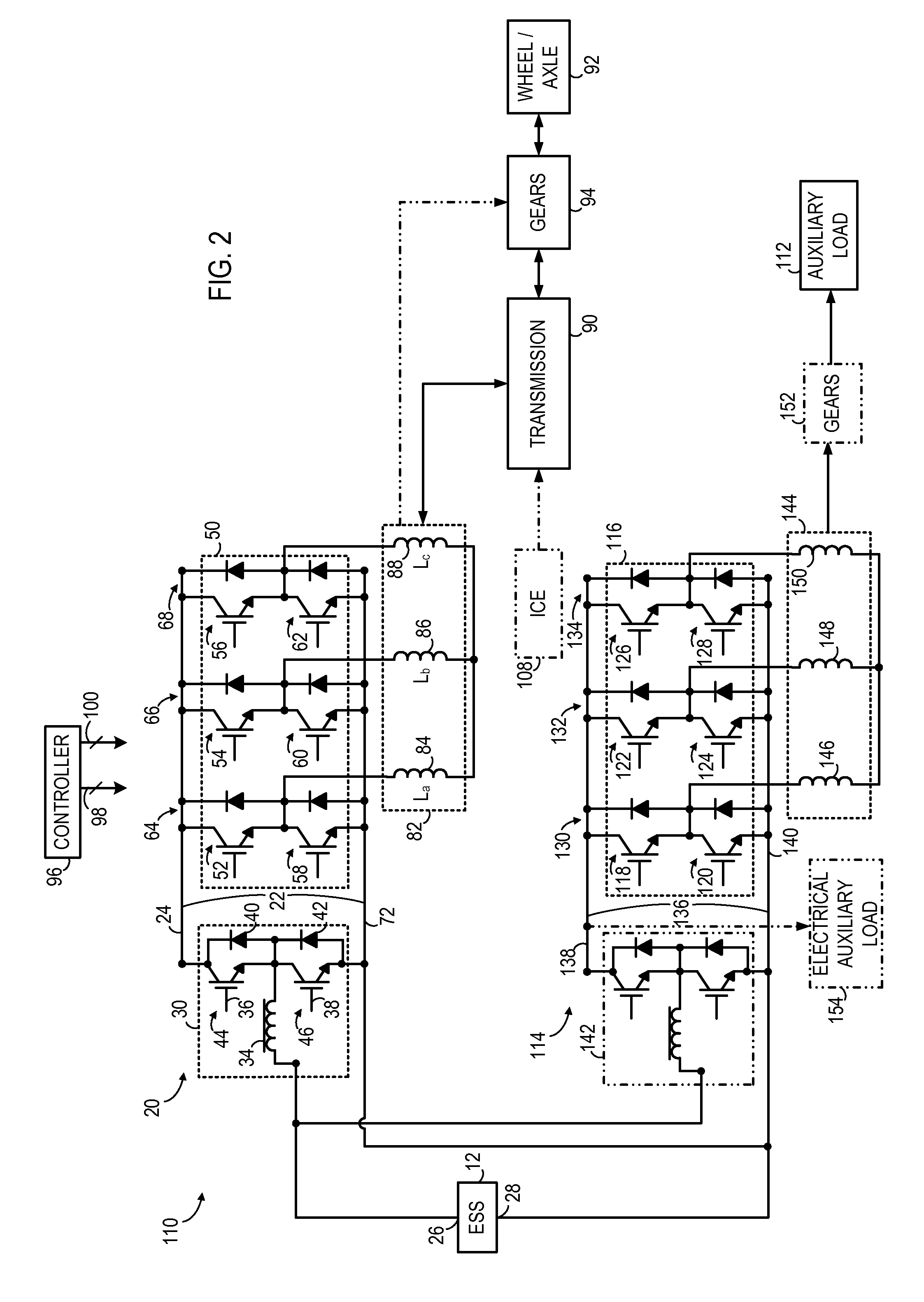
According to an aspect of the invention, a motor drive circuit includes a first energy storage device configured to supply electrical energy, a bi-directional DC-to-DC voltage converter coupled to the first energy storage device, a voltage inverter coupled to the bi-directional DC-to-DC voltage converter, and an input device configured to receive electrical energy from an external energy source. The motor drive circuit further includes a coupling system coupled to the input device, to the first energy storage device, and to the bi-directional DC-to-DC voltage converter. The coupling system has a first configuration configured to transfer electrical energy to the first energy storage device via the bi-directional DC-to-DC voltage converter, and has a second configuration configured to transfer electrical energy from the first energy storage device to the voltage inverter via the bi-directional DC-to-DC voltage converter.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
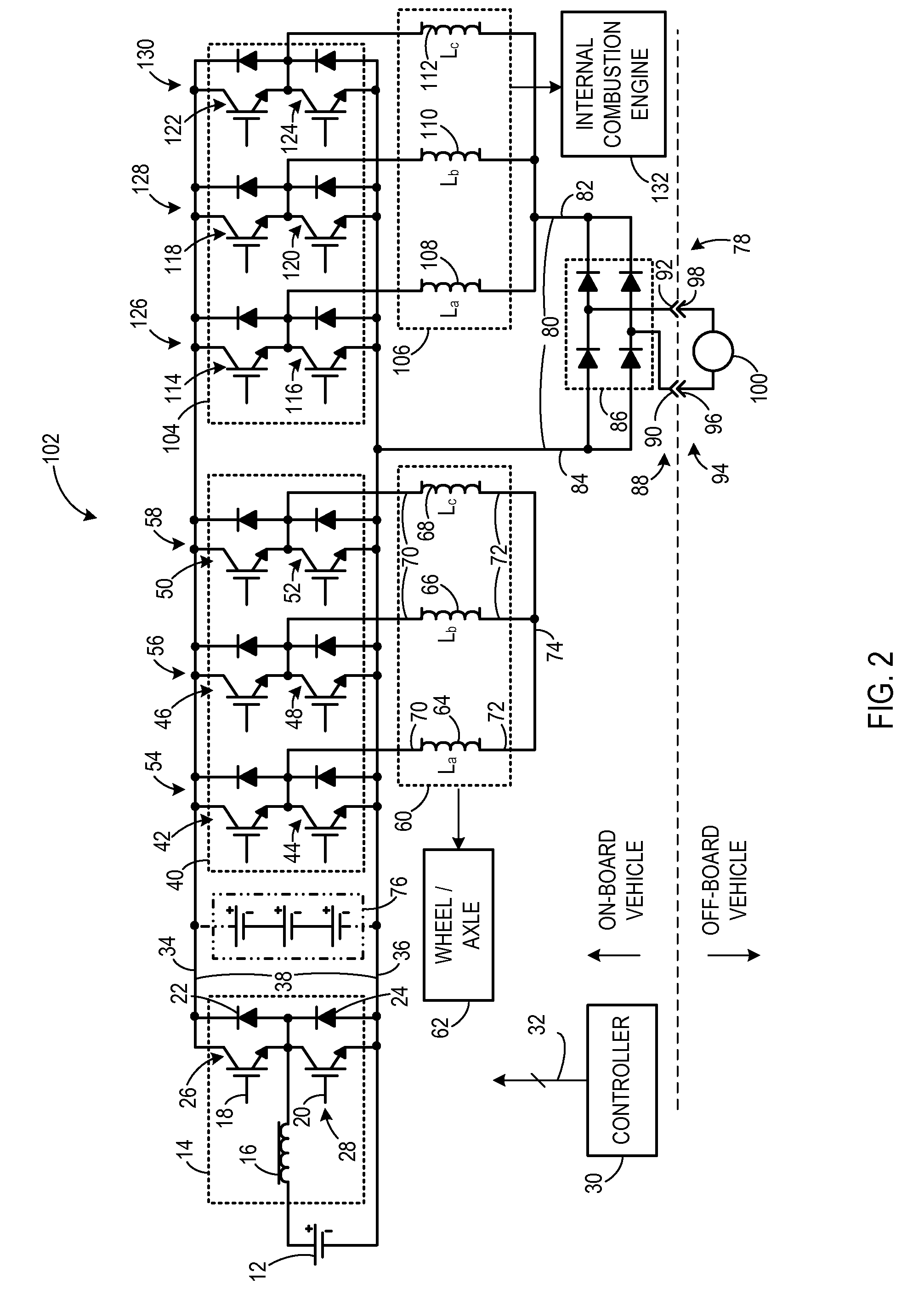
Apparatus for transferring energy using power electronics and machine inductance and method of manufacturing same
ActiveUS20100096926A1Auxillary drivesBatteries circuit arrangementsElectrical conductorCharge current
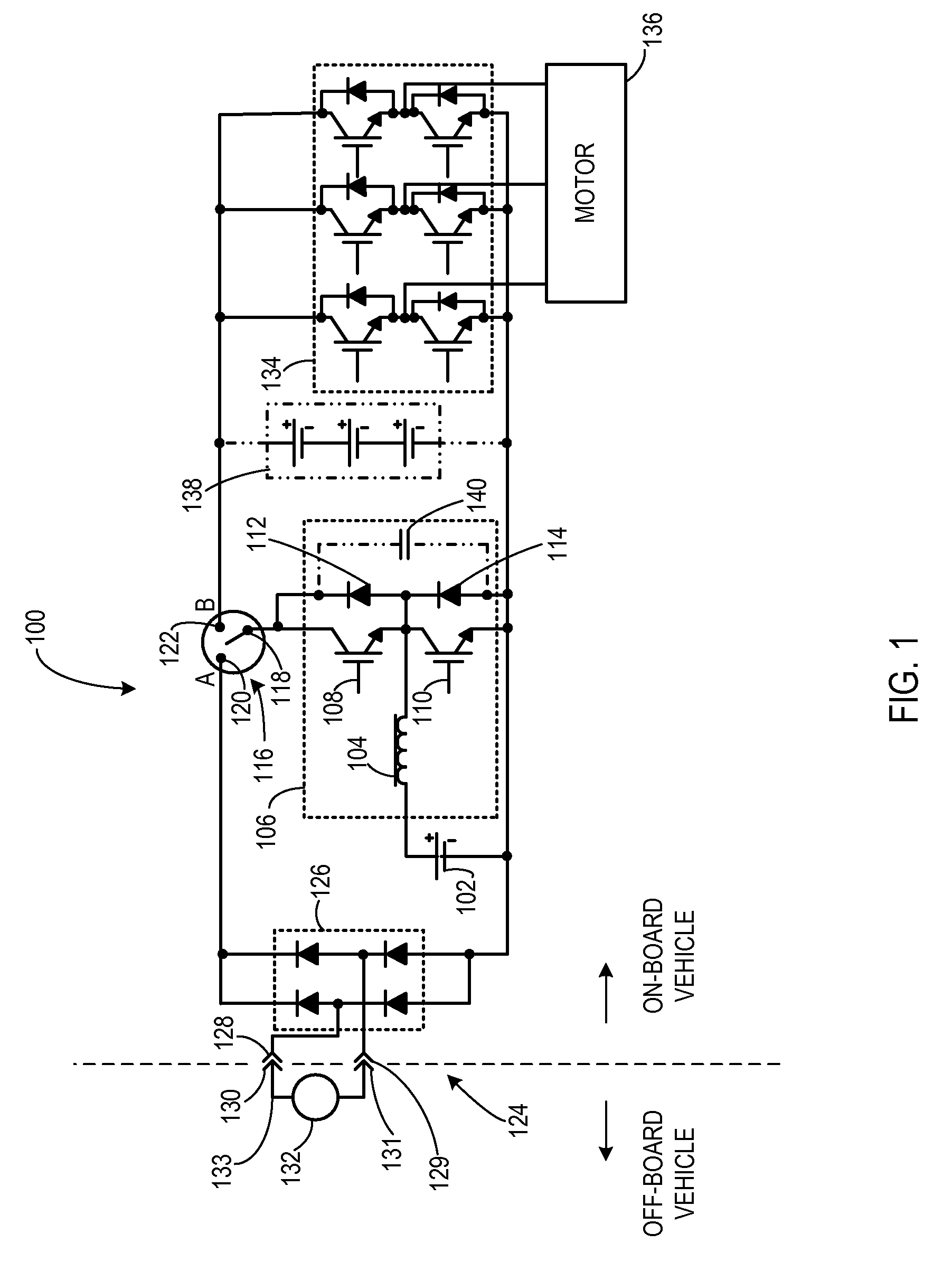
A traction inverter circuit includes a first energy storage device configured to output a DC voltage, a first bi-directional DC-to-AC voltage inverter coupled to the first energy storage device, and a first electromechanical device. The first electromechanical device includes a first plurality of conductors coupled to the first bi-directional DC-to-AC voltage inverter, a second plurality of conductors coupled together, and a plurality of windings coupled between the first plurality of conductors and the second plurality of conductors. The traction converter circuit also includes a charge bus comprising a first conductor coupled to the second plurality of conductors of the first electromechanical device, the charge bus configured to transmit a charging current to or receive a charging current from the first electromechanical device to charge the first energy storage device via the first electromechanical device and the first bi-directional DC-to-AC voltage inverter.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
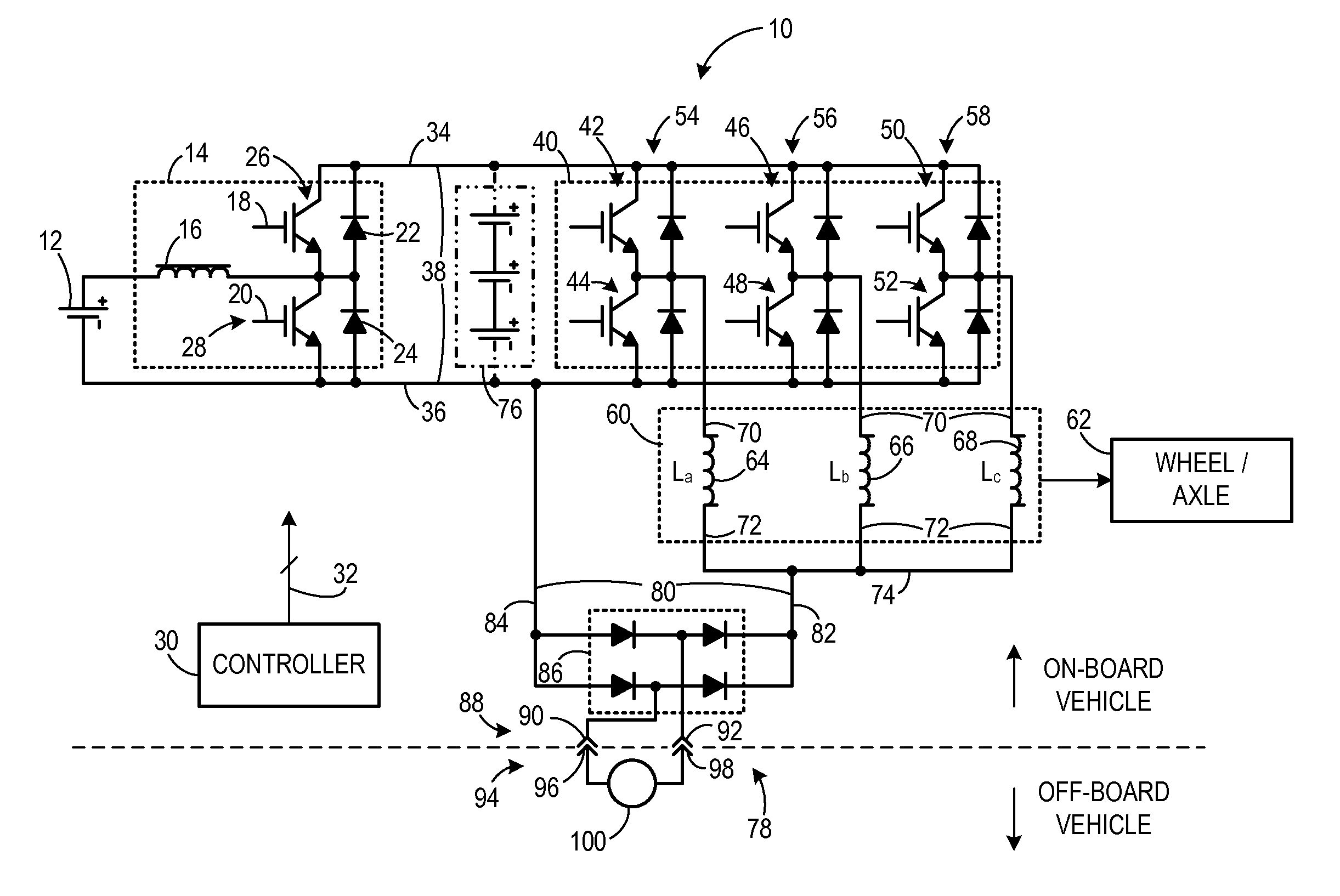
Apparatus for transferring energy using onboard power electronics with high-frequency transformer isolation and method of manufacturing same
ActiveUS20120112702A1Batteries circuit arrangementsPropulsion by batteries/cellsElectric forceEngineering
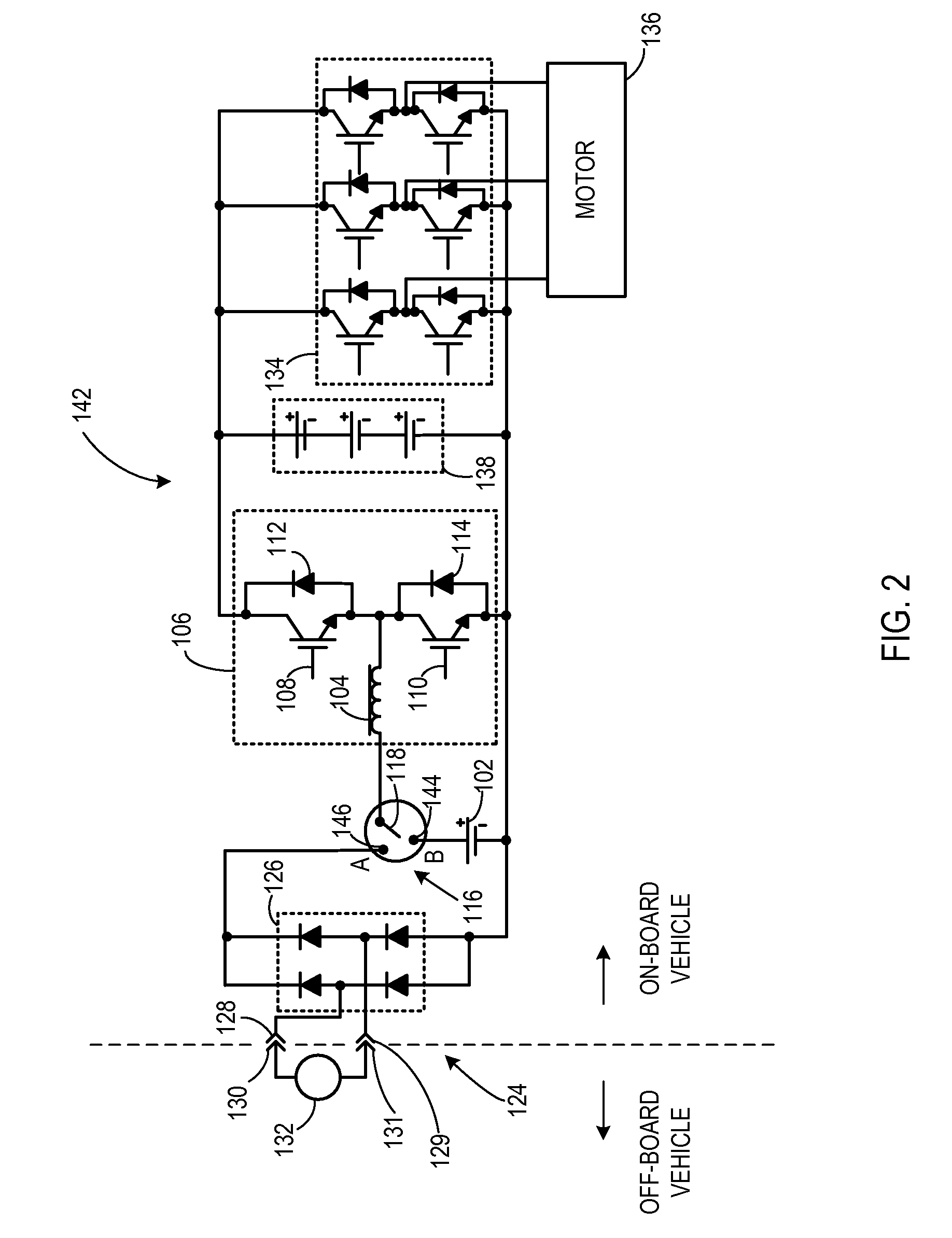
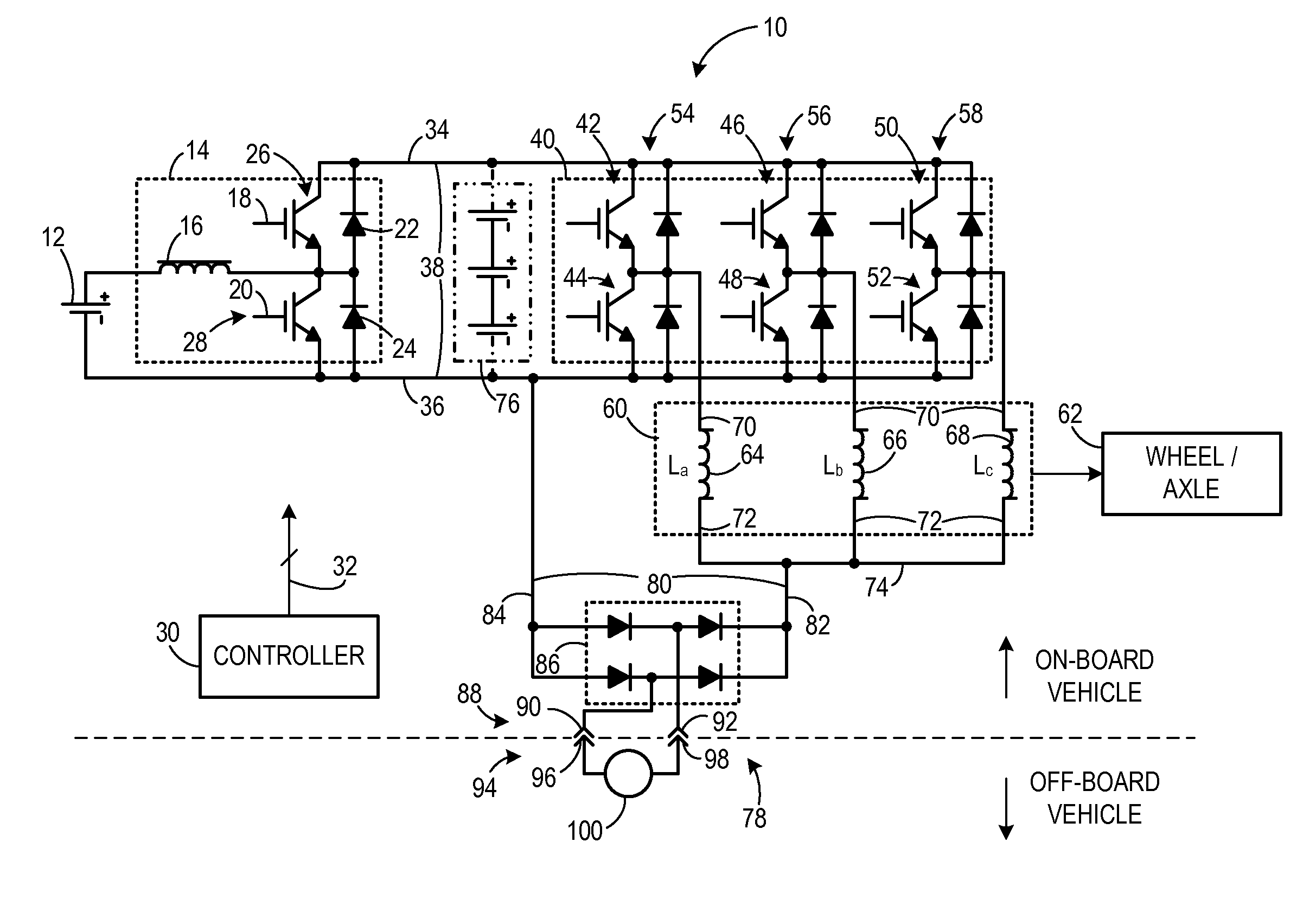
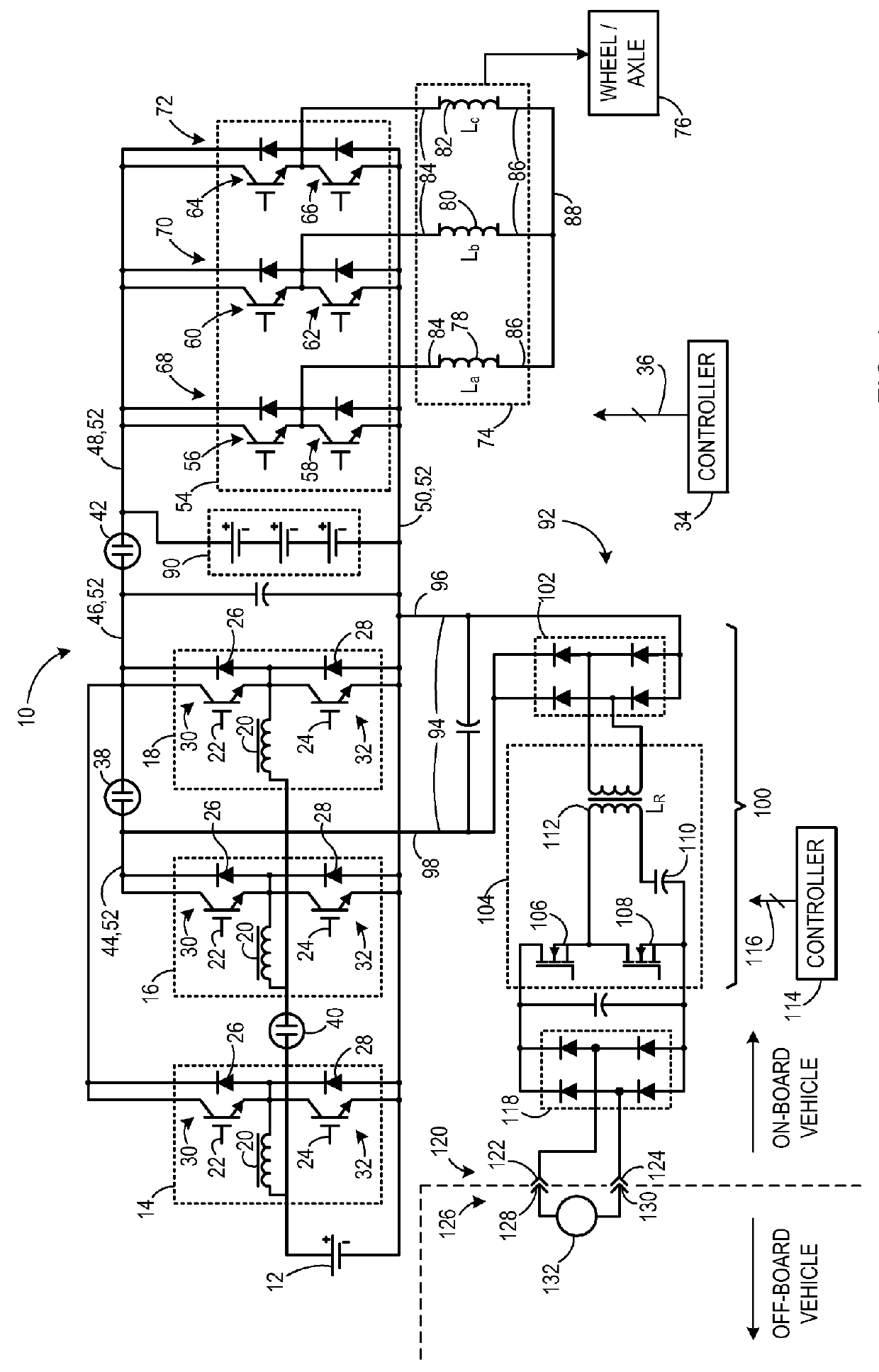
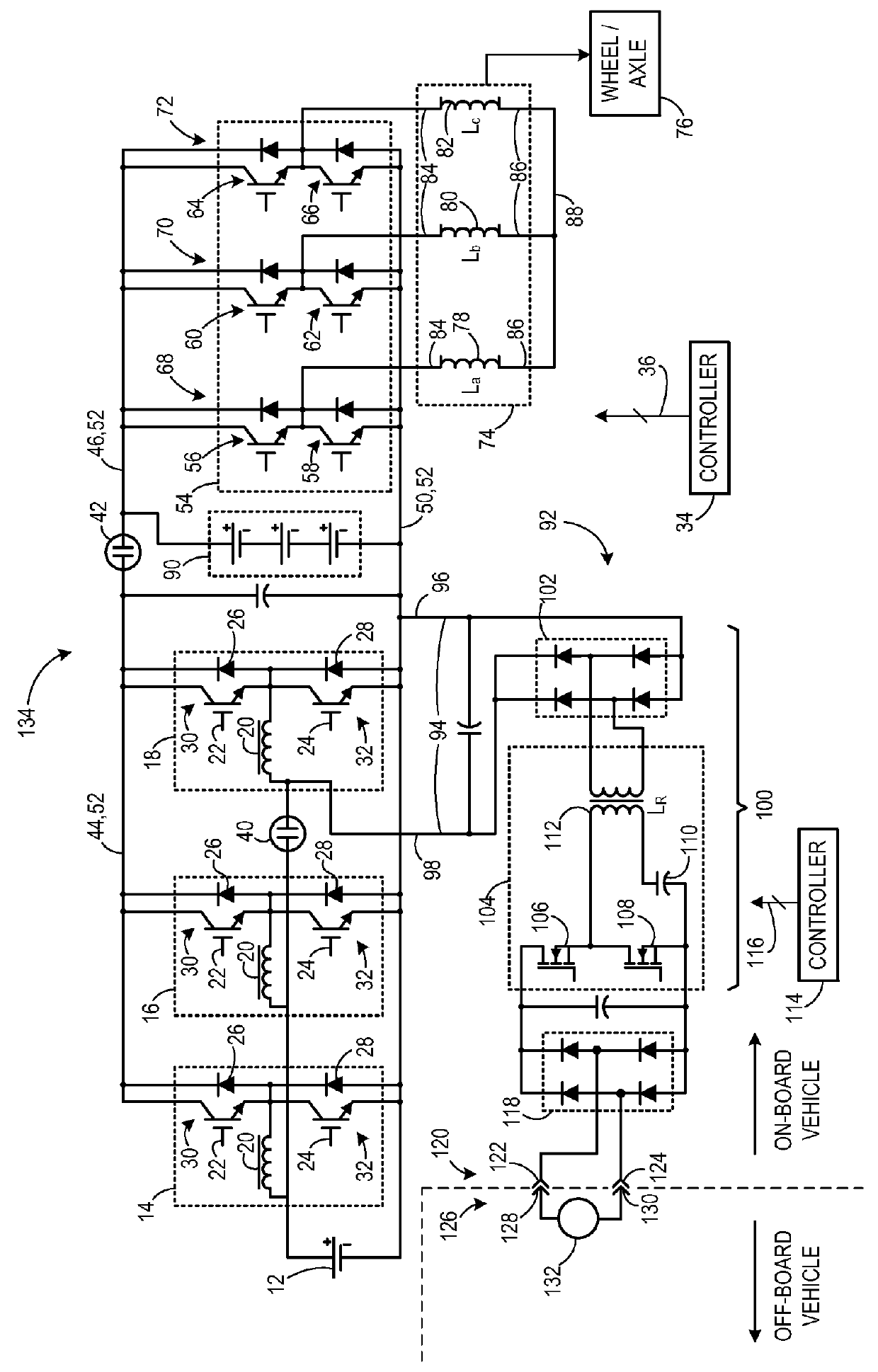
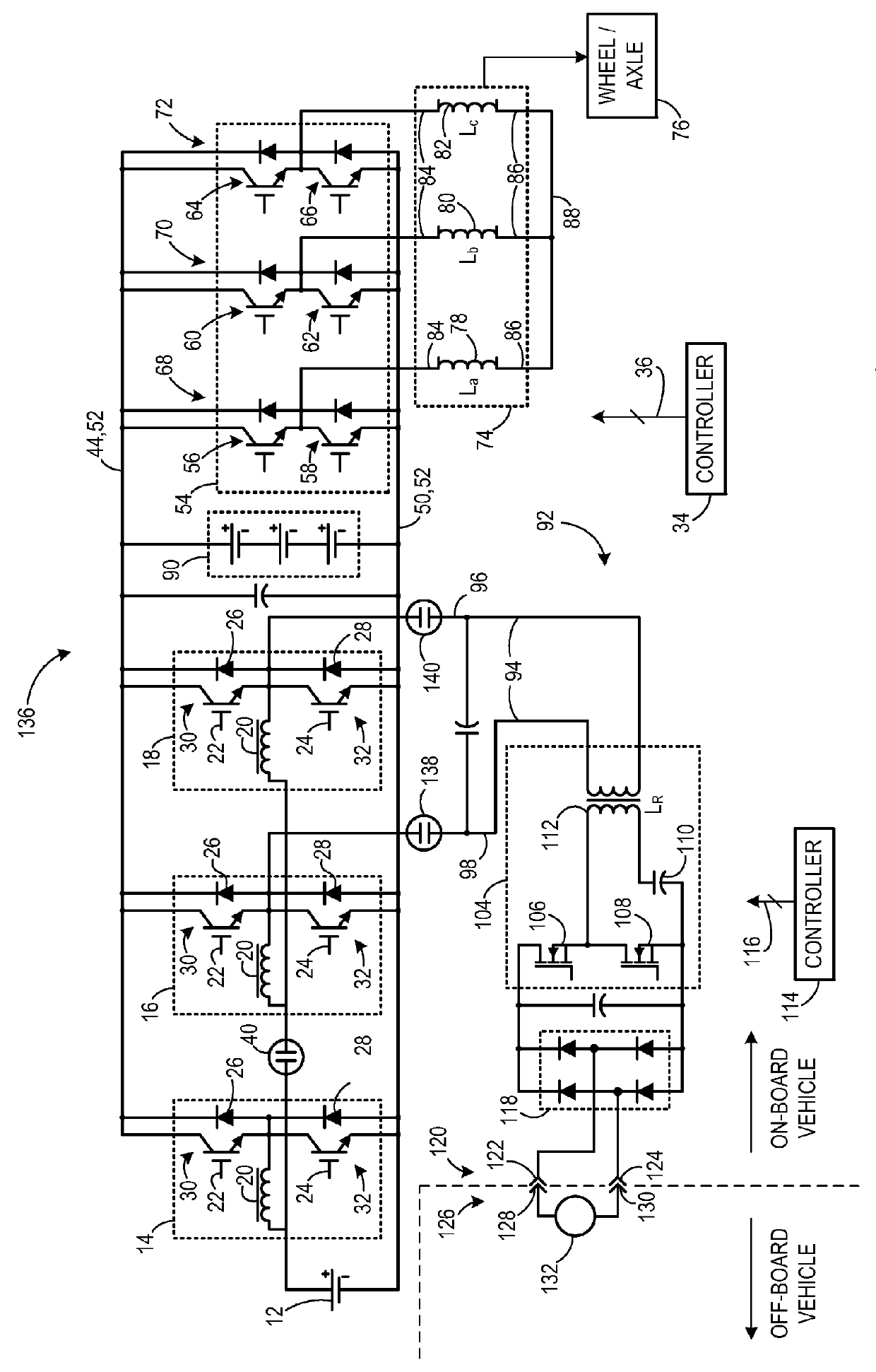
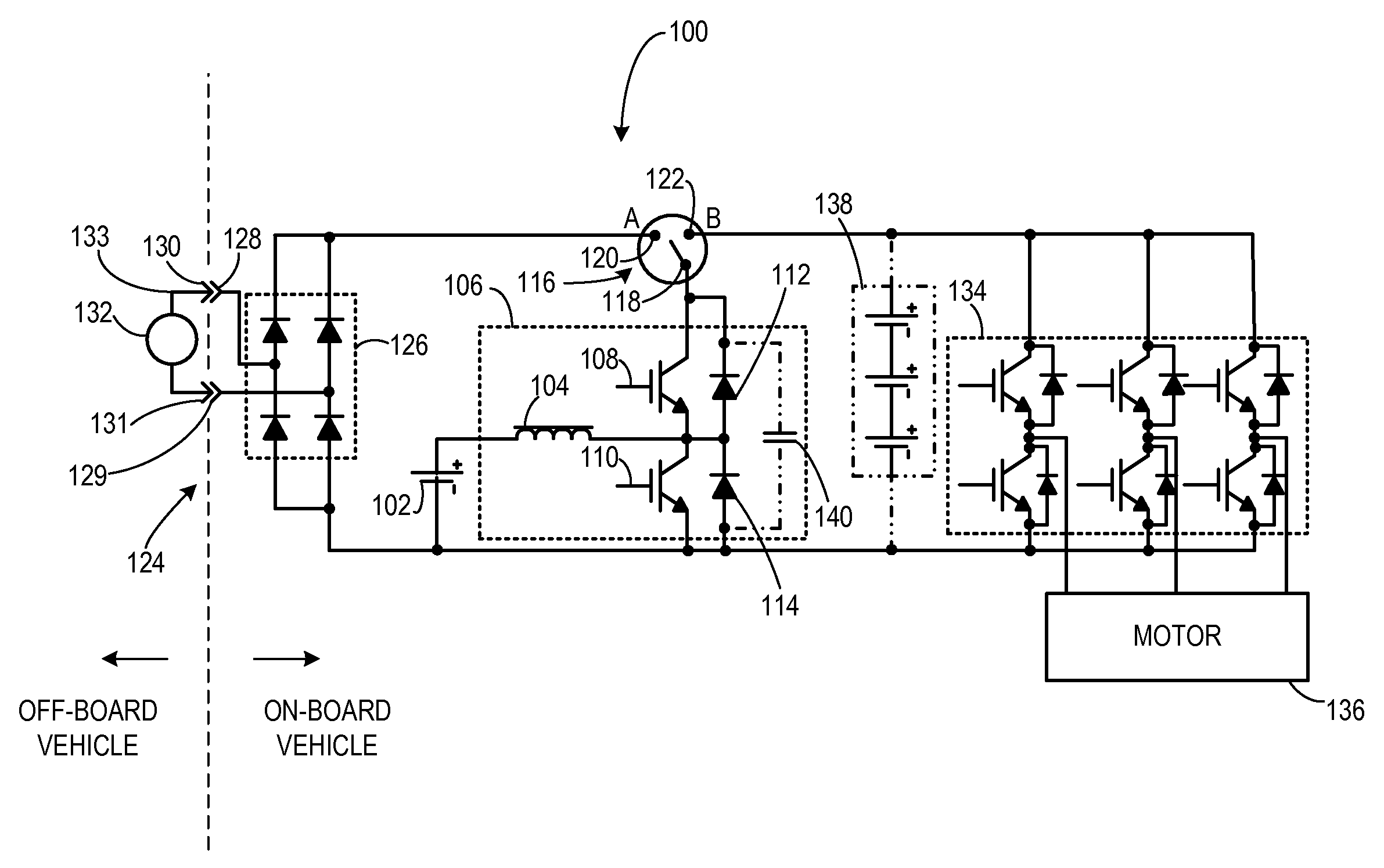
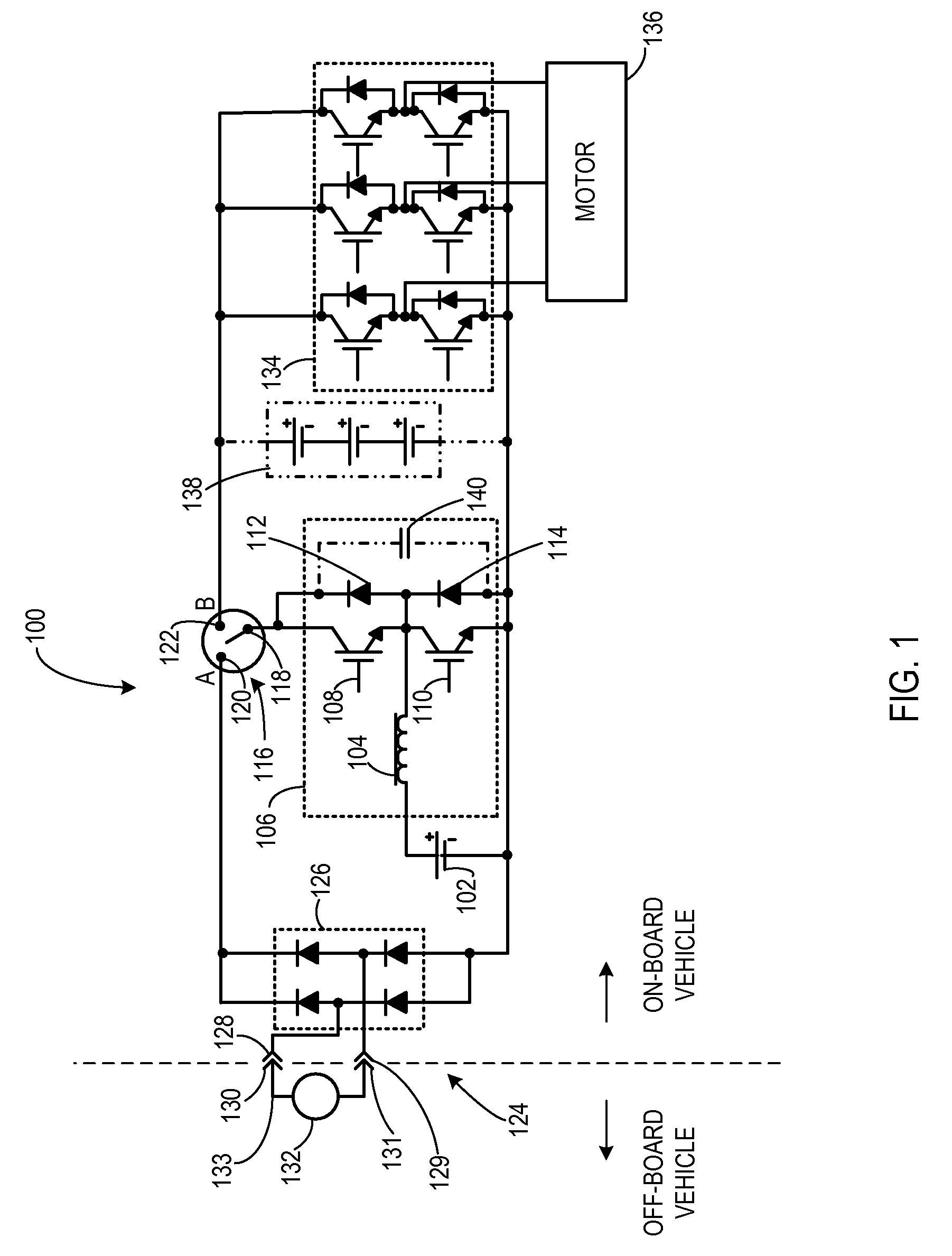
An apparatus for transferring energy using onboard power electronics with high-frequency transformer isolation includes a power electronic drive circuit comprises a dc bus and a first energy storage device coupled to the dc bus. A first bi-directional dc-to-ac voltage inverter is coupled to the first energy storage device and to the dc bus, and a first electromechanical device coupled to the first bi-directional dc-to-ac voltage inverter. A charging system coupled to the dc bus via a charge bus comprises a receptacle configured to mate with a connector coupled to a voltage source external to the power electronic drive circuit and an isolation transformer configured to electrically isolate the charge bus from the receptacle. A controller configured to cause the charging system to supply a charging voltage to the dc bus based on a voltage received from the voltage source external to the power electronic drive circuit.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Apparatus for transferring energy using power electronics and machine inductance and method of manufacturing same
A traction inverter circuit includes a first energy storage device configured to output a DC voltage, a first bi-directional DC-to-AC voltage inverter coupled to the first energy storage device, and a first electromechanical device. The first electromechanical device includes a first plurality of conductors coupled to the first bi-directional DC-to-AC voltage inverter, a second plurality of conductors coupled together, and a plurality of windings coupled between the first plurality of conductors and the second plurality of conductors. The traction converter circuit also includes a charge bus comprising a first conductor coupled to the second plurality of conductors of the first electromechanical device, the charge bus configured to transmit a charging current to or receive a charging current from the first electromechanical device to charge the first energy storage device via the first electromechanical device and the first bi-directional DC-to-AC voltage inverter.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
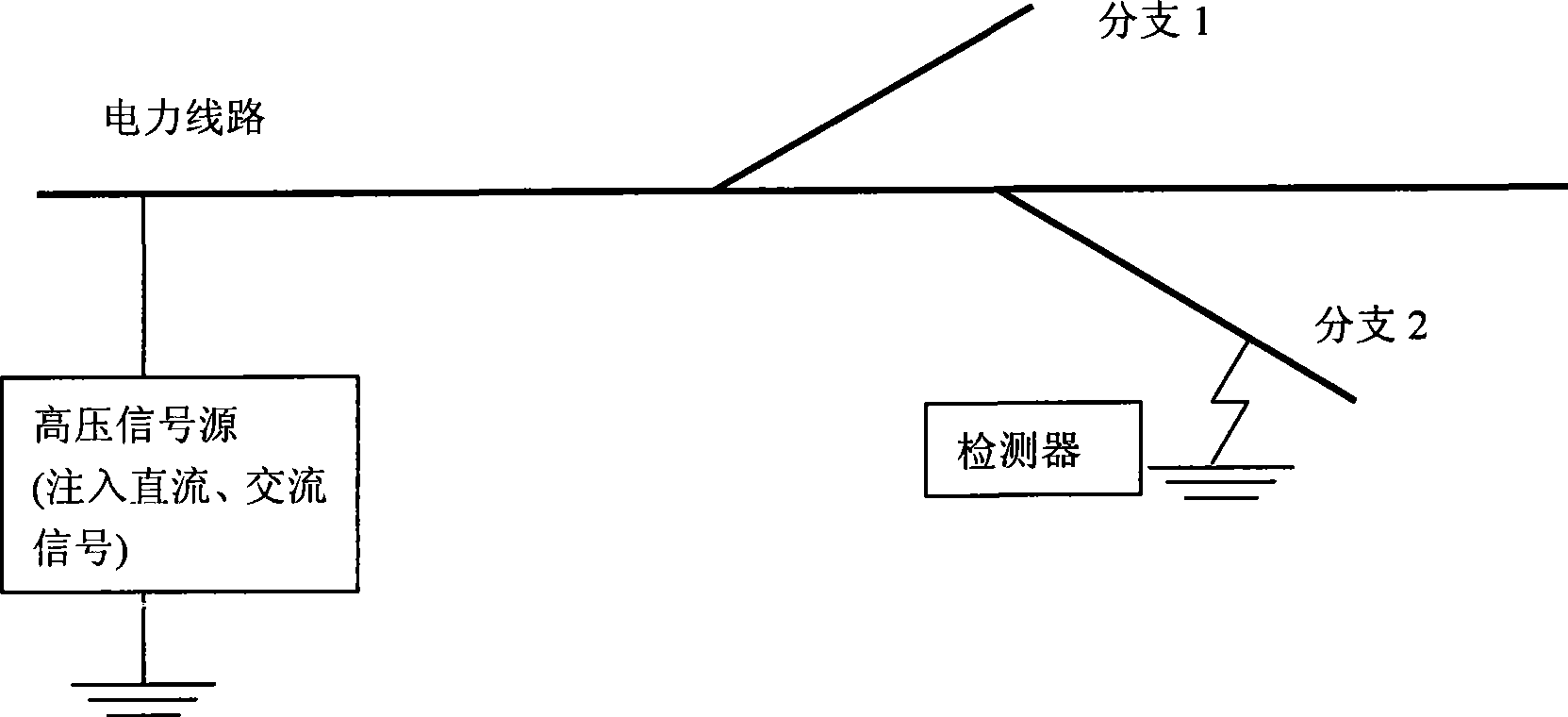
Single-phase earth fault positioning device for electrical power distribution network
InactiveCN101382577AAccurate locationSolve the positioning problemFault locationInformation technology support systemTransformerEngineering
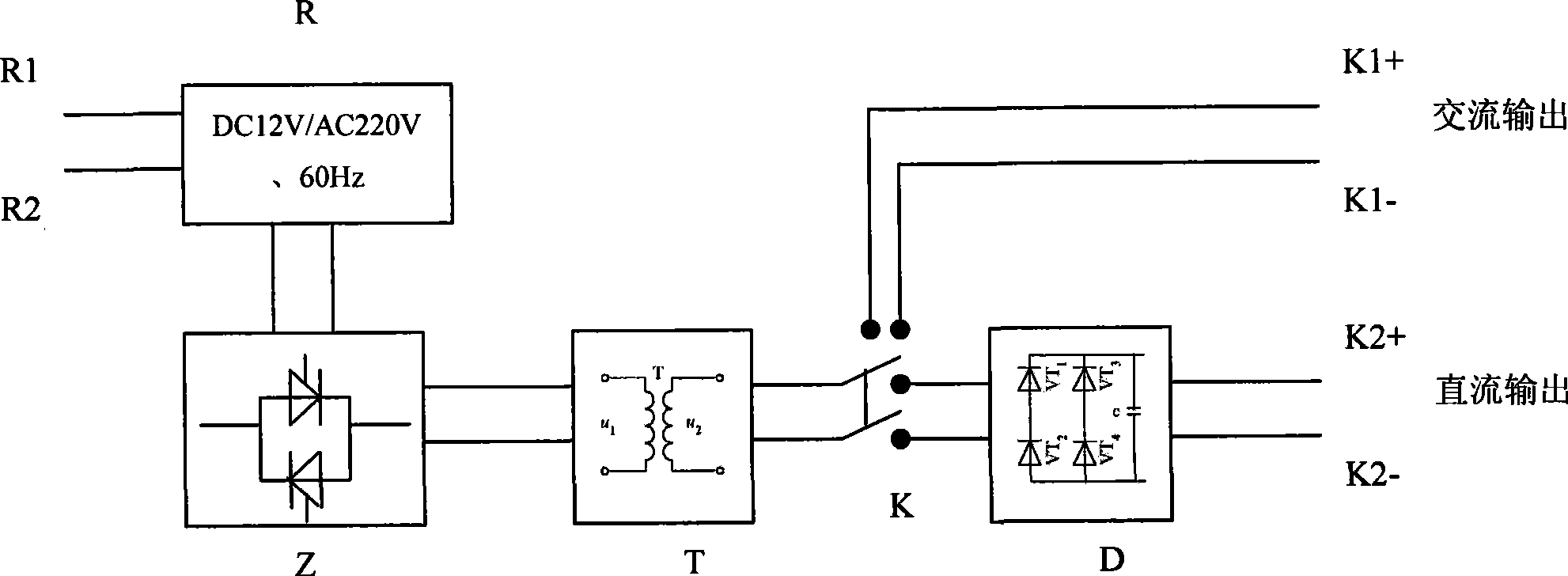
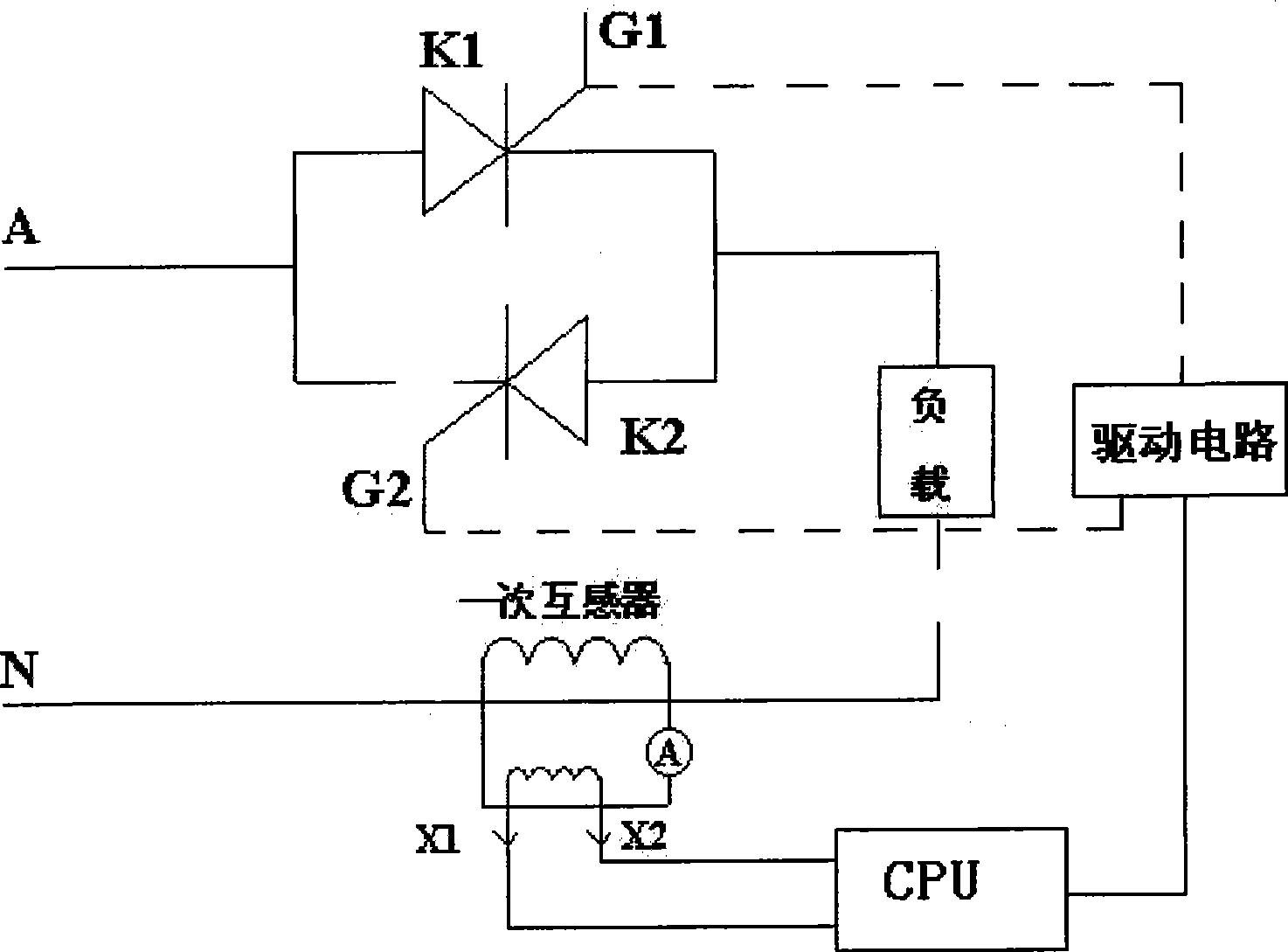
The invention disclose a new positioning method of a distribution network single-phase earth fault, which is applicable to a 3-60 kV neutral point ineffective earth grid. The principle of the positioning method is that: firstly, a high-voltage DC signal is poured into a circuit starting end and the DC signal is detected along the circuit so as to determine a fault area; then a high-voltage AC signal is poured into the circuit starting end, and the AC signal is detected along the circuit so as to determine the position of a fault point. A positioning device developed on the basis of the invention consists of two parts: a high-voltage signal source and a signal detector, wherein, the high-voltage signal source consists of a voltage inverter, a constant flow source, a transformer and a rectifier bridge and is used for pouring a high-voltage DC signal and a high-voltage AC signal; the signal detector comprises a DC detector and an AC detector, wherein, the DC detector consists of a Hall DC detector, a Bluetooth wireless sender and a Bluetooth wireless receiver and is used for measuring the DC signal; while the AC detector consists of an AC electromagnetic field inductor and a signal processing and display segment and is used for measuring the AC signal. The method and the device have mature technique and high reliability.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING) +2
Apparatus for energy transfer using converter and method of manufacturing same
According to an aspect of the invention, a motor drive circuit includes a first energy storage device configured to supply electrical energy, a bi-directional DC-to-DC voltage converter coupled to the first energy storage device, a voltage inverter coupled to the bi-directional DC-to-DC voltage converter, and an input device configured to receive electrical energy from an external energy source. The motor drive circuit further includes a coupling system coupled to the input device, to the first energy storage device, and to the bi-directional DC-to-DC voltage converter. The coupling system has a first configuration configured to transfer electrical energy to the first energy storage device via the bi-directional DC-to-DC voltage converter, and has a second configuration configured to transfer electrical energy from the first energy storage device to the voltage inverter via the bi-directional DC-to-DC voltage converter.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
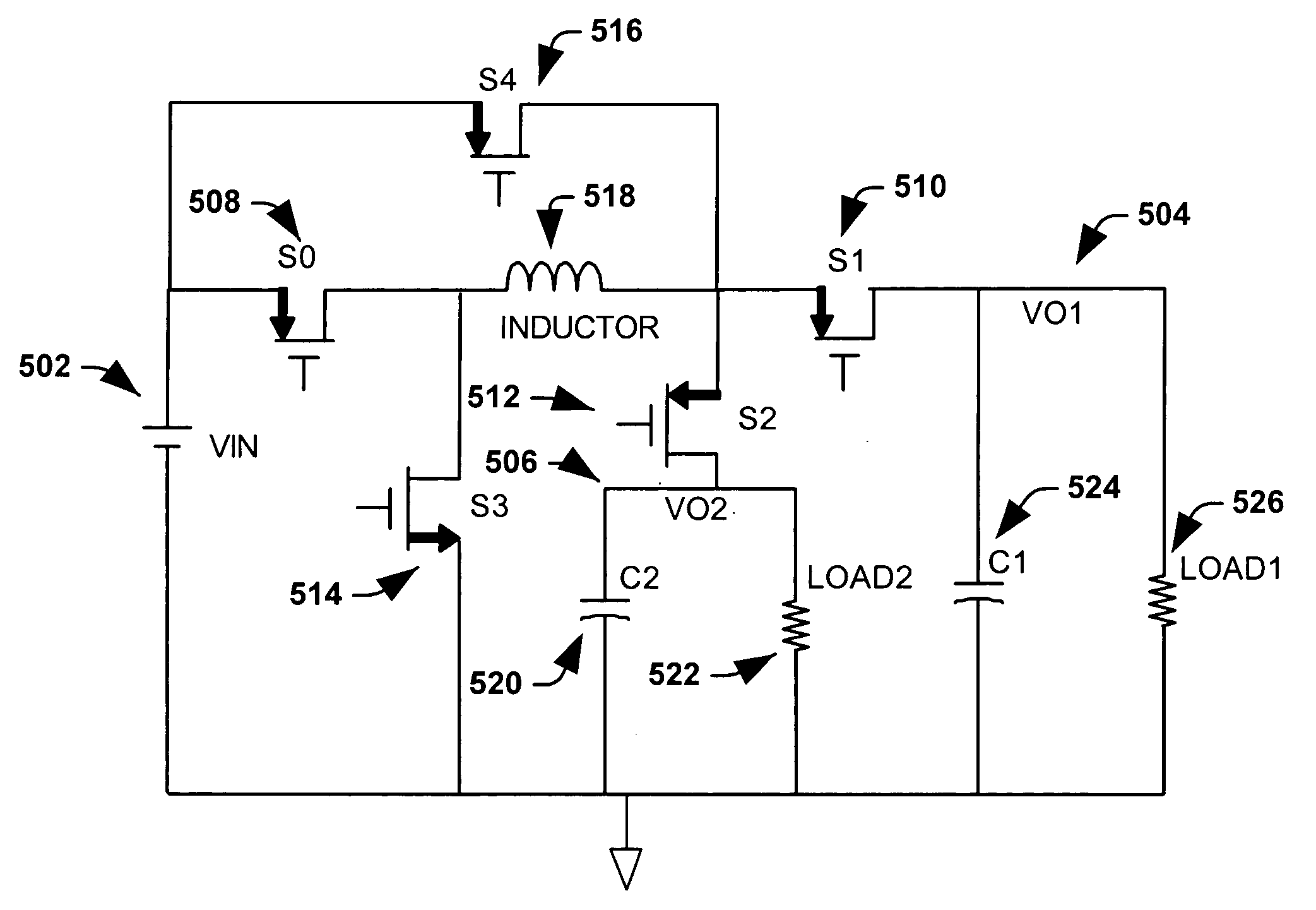
Single inductor dual output buck converter with frequency and time varying offset control
ActiveUS20050110471A1Facilitates power conversionReduce crosstalkDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationBuck converterVoltage inverter
A single-inductor dual-output buck converter and control method that facilitates power conversion by converting a single DC power source / supply into two separate DC outputs, each of which can be configured to provide a selected / desired voltage by selection of respective duty cycles. The topology of the inverter includes a pair of diodes or switches that can selectively re-circulate inductor current. The converter is generally operated at a fixed frequency with four stages of operation. A first and third stage of operation provide power to a first and second output, respectively. A second and fourth stage of operation re-circulate inductor current and can partially recharge a battery type power source. The power output for each stage (voltage and current) can be selectively obtained by computing and employing appropriate time periods for the stages of operation that correspond to appropriate duty cycles.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
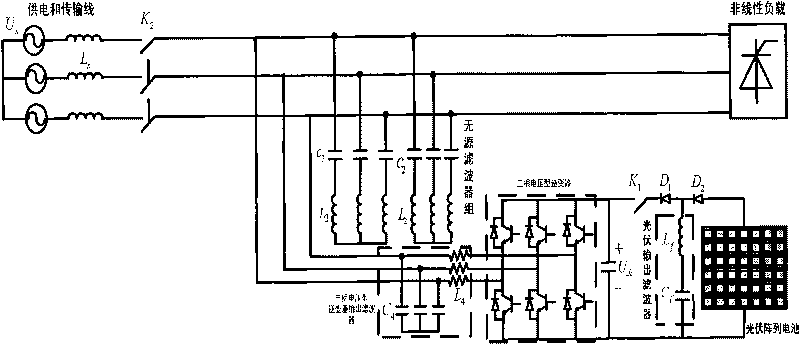
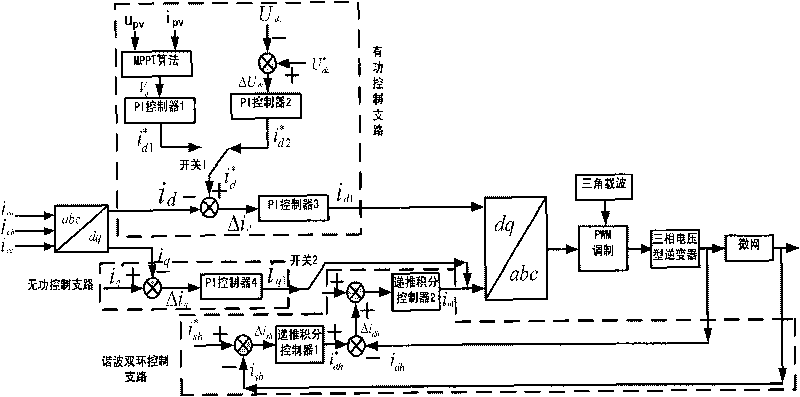
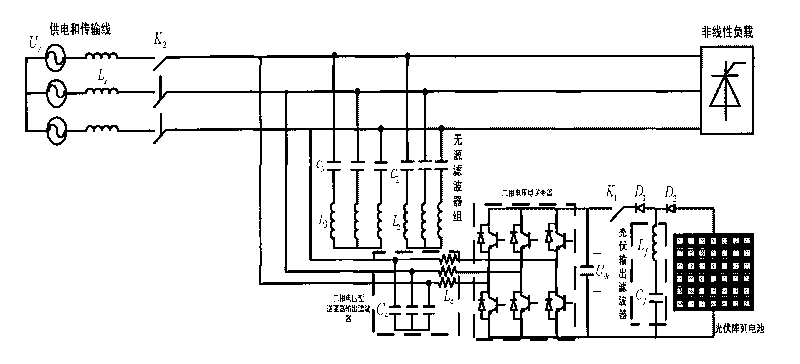
Photovoltaic inversion grid-connection and harmonic suppression hybrid system for micro grid and composite control method thereof
InactiveCN101697418AImprove stabilityLow costReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationPhotovoltaic energy generationHybrid systemVoltage inverter
The invention discloses a photovoltaic inversion grid-connection and harmonic suppression hybrid system for a micro grid and a composite control method thereof. The photovoltaic inversion grid-connection and harmonic suppression hybrid system for the micro grid comprises photovoltaic array cells, a photovoltaic output filter, a three-phase voltage inverter, an output filter and a passive filter bank. The photovoltaic inversion grid-connection and harmonic suppression hybrid system for the micro grid and the composite control method thereof realize dynamic active and passive power compensation of the micro-grid, stable system voltage, and real-time and dynamic management on harmonic waves.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
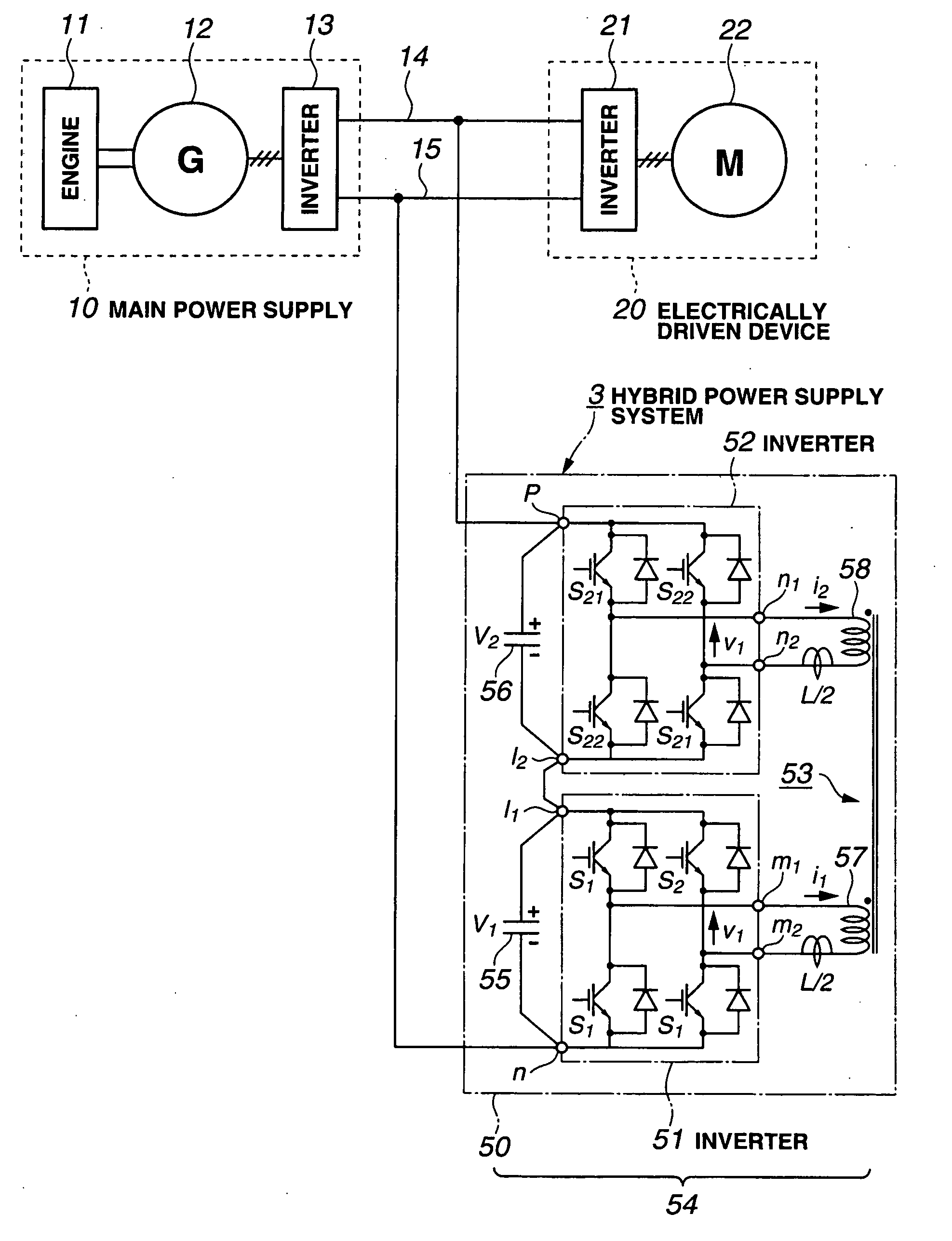
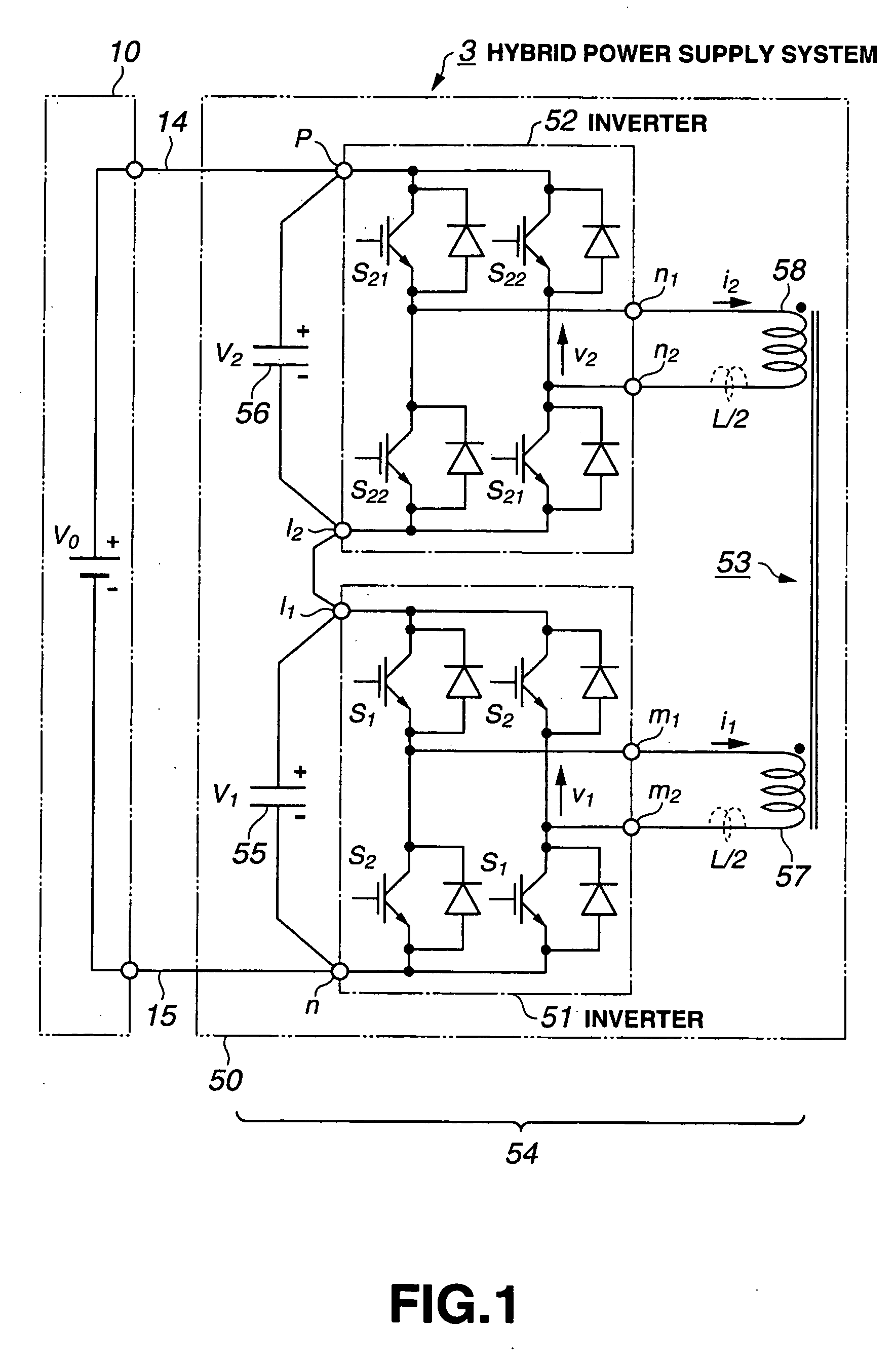
AC Link Bidirectional DC-DC Converter, Hybrid Power Supply System Using the Same and Hybrid Vehicle
InactiveUS20090171521A1Reduce the voltage ratingTotal current dropCharge equalisation circuitDigital data processing detailsPower inverterDc dc converter
In an AC link type boosting device, DC terminals of two voltage inverters are connected each other in series in additive polarity and plural AC terminals of each of the voltage inverters are connected to a transformer. The two voltage type inverters are AC linked to each other via the transformer. An external voltage applied between the DC terminals of the AC link type booster is divided by the voltage-type inverters.
Owner:KOMATSU LTD
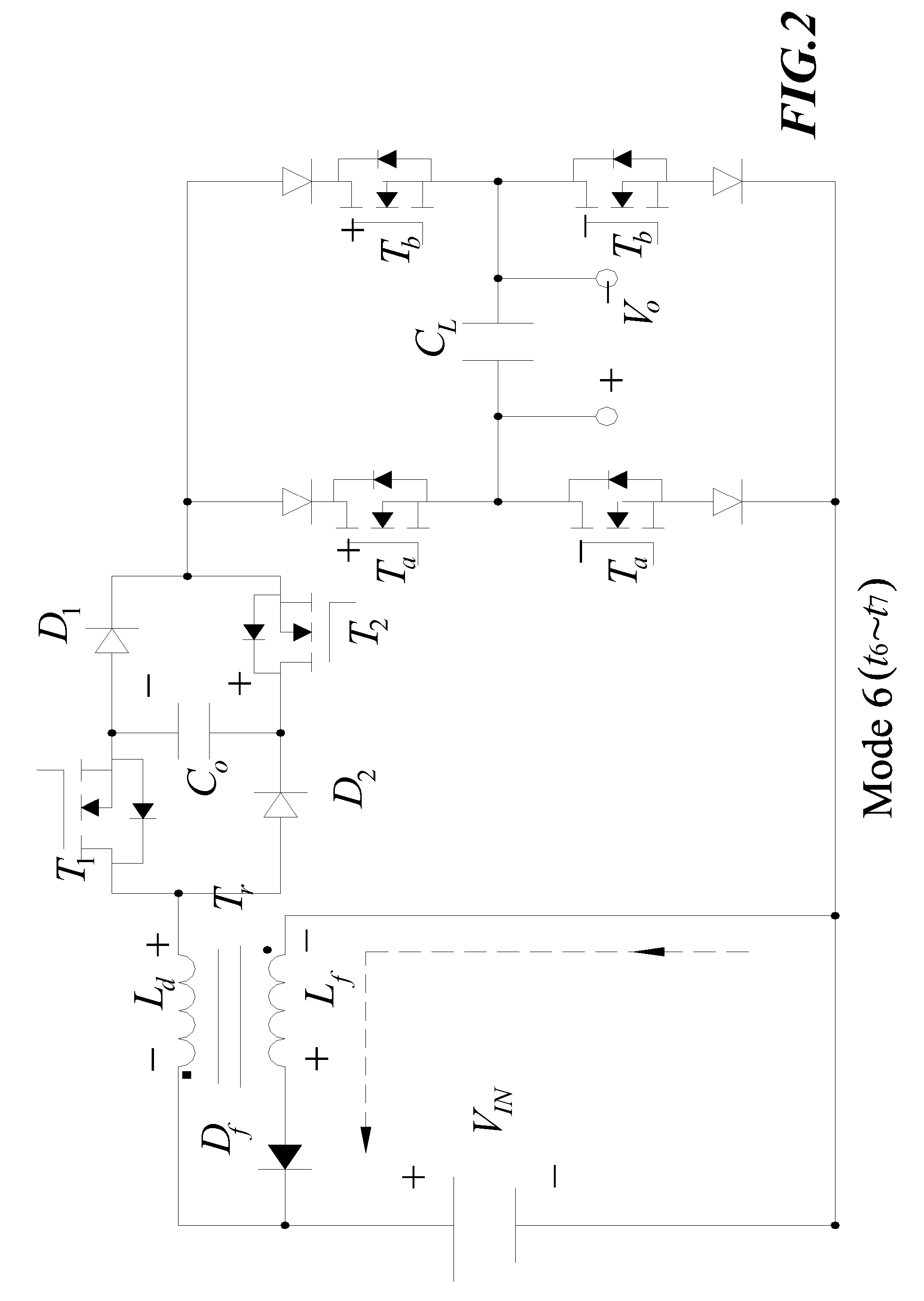
2n+1 level voltage inverter
This system for converting a direct input voltage into an alternating output voltage comprises two input terminals, two voltage generators connected in series between the input terminals and connected to one another by a middle point, as well as, for each phase of the alternating voltage, an output terminal, two switching branches each connected between the output terminal and a respective input terminal, each switching branch comprising N first switching cells connected in series and N−1 intermediate points, the first switching cells successively being connected to one another by a corresponding intermediate point, N being an integer greater than or equal to 2, and control means for controlling the first switching cells. The system includes, for each phase of the alternating voltage, N−1 pair(s) of capacitors, each pair of capacitors being connected between intermediate points of one of the two switching branches and the other of the two switching branches.
Owner:GE ENERGY POWER CONVERSION TECH
Electric actuator including two current-controlled voltage inverters powering an electric machine, and reconfigurable in the presence of a defect
ActiveUS20110181219A1Control flowMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersAviationPower inverter
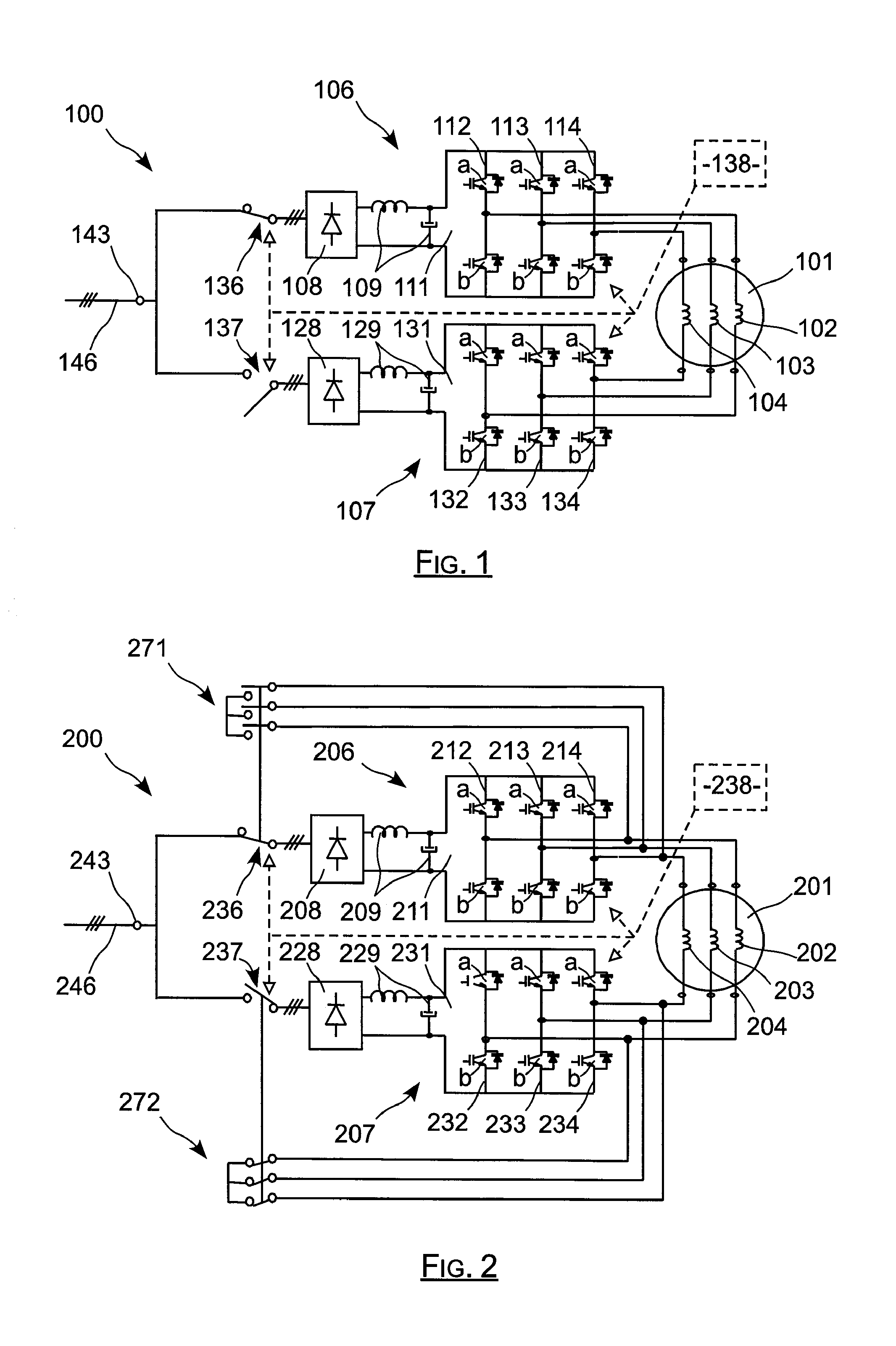
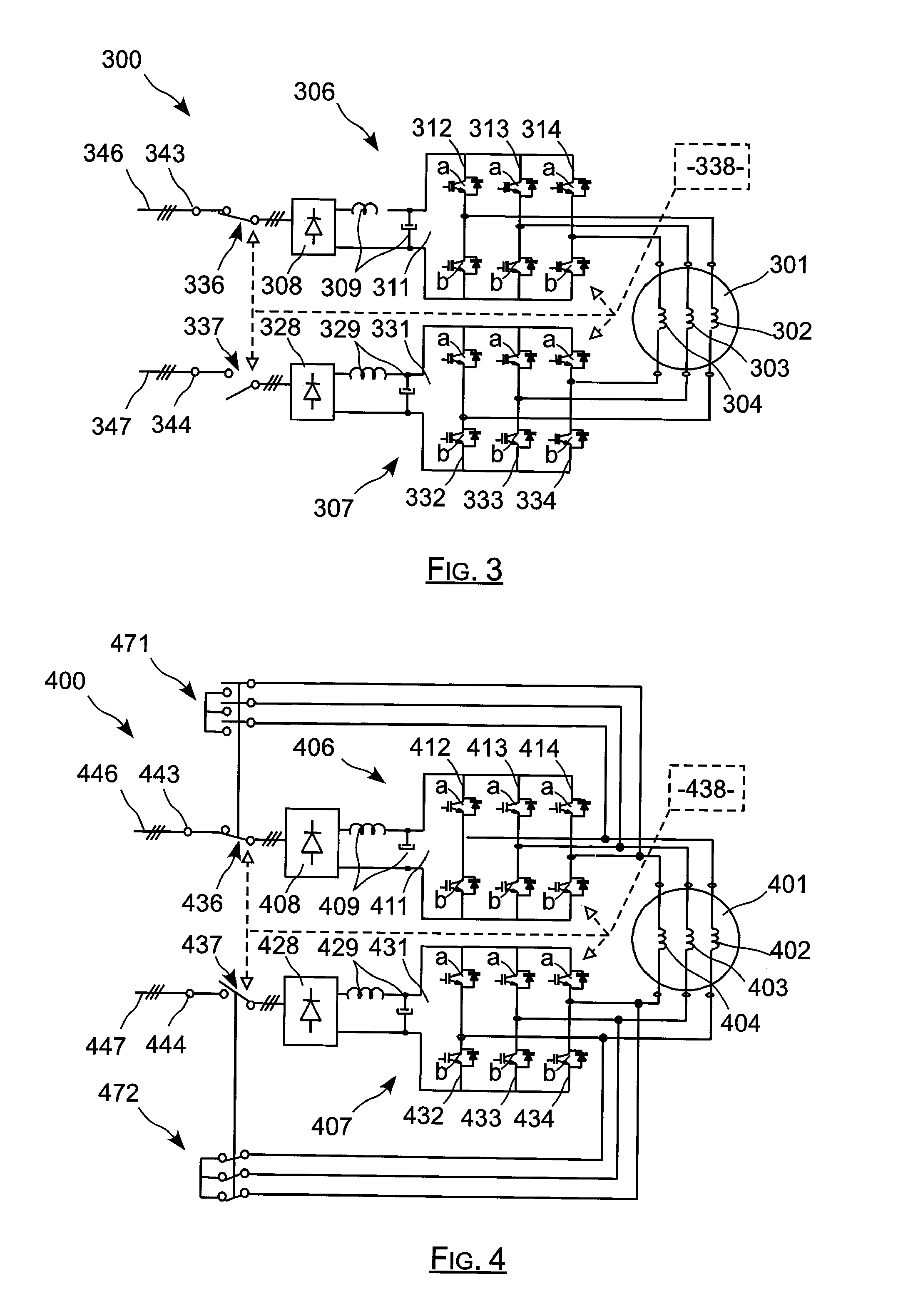
The invention relates to an actuator including an electrical machine. The electrical actuator (100) comprising: a polyphase machine (101); at least one connection member (143) for powering the actuator from at least one network (146) delivering alternating current; and first and second buses (106, 107) connected in parallel between each connection member (143) and the machine (101) for applying frequency control thereto. Each inverter (111, 131) comprises a plurality of arms each having two controlled switches, each phase of the machine (101) being connected both to the two switches of an arm of the first inverter (111) and also to the two switches of an arm of the second inverter (131). The actuator further comprises controlled connection and disconnection means interposed between each bus (106, 107) and each connection member. The invention is applicable to actuators used in aviation.
Owner:SAFRAN LANDING SYSTEMS +2
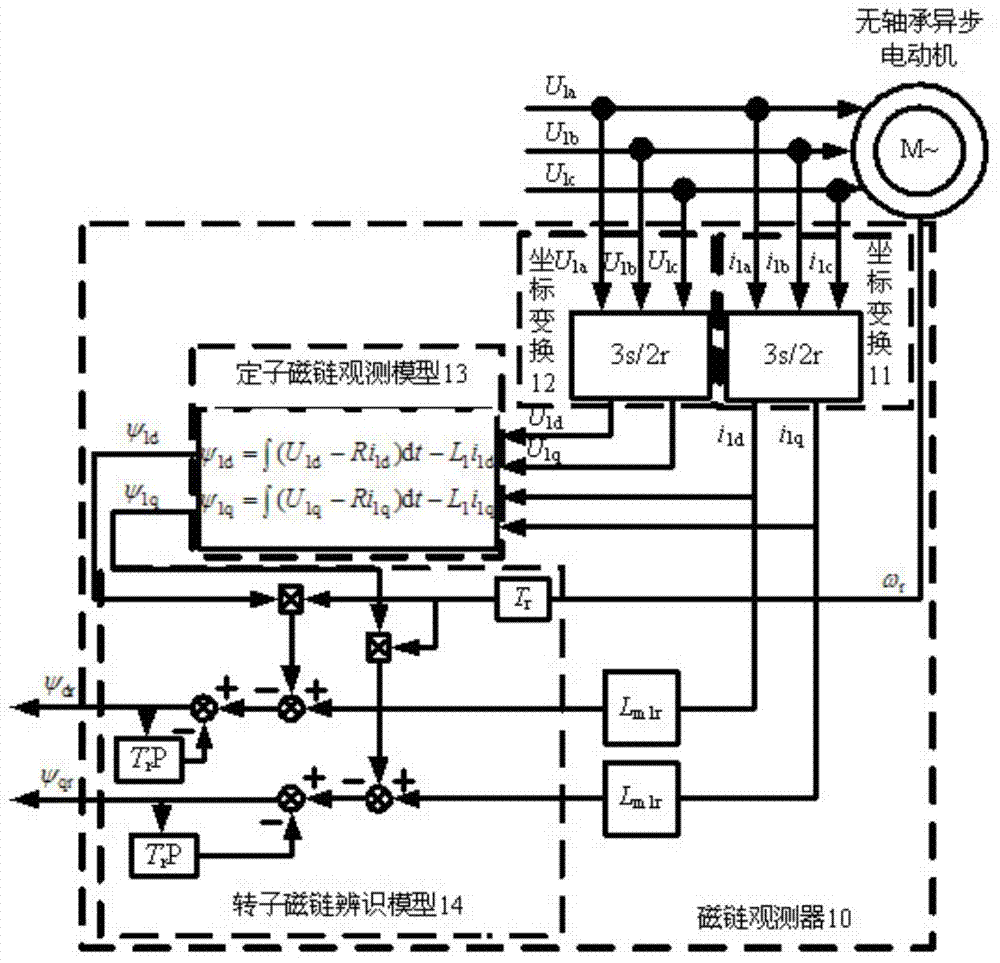
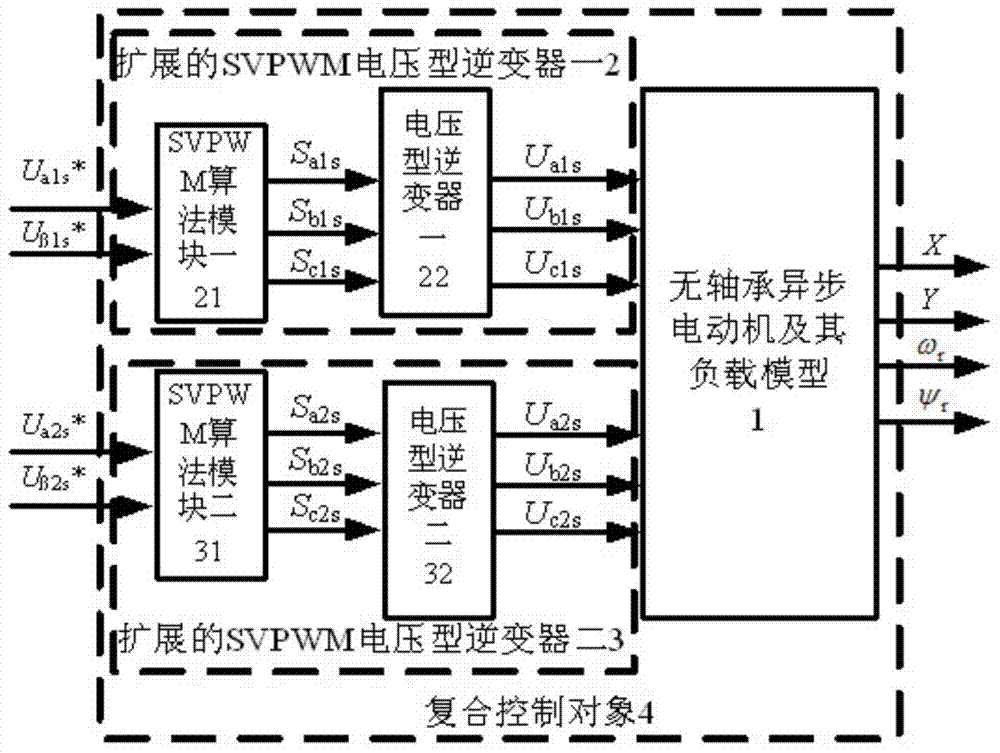
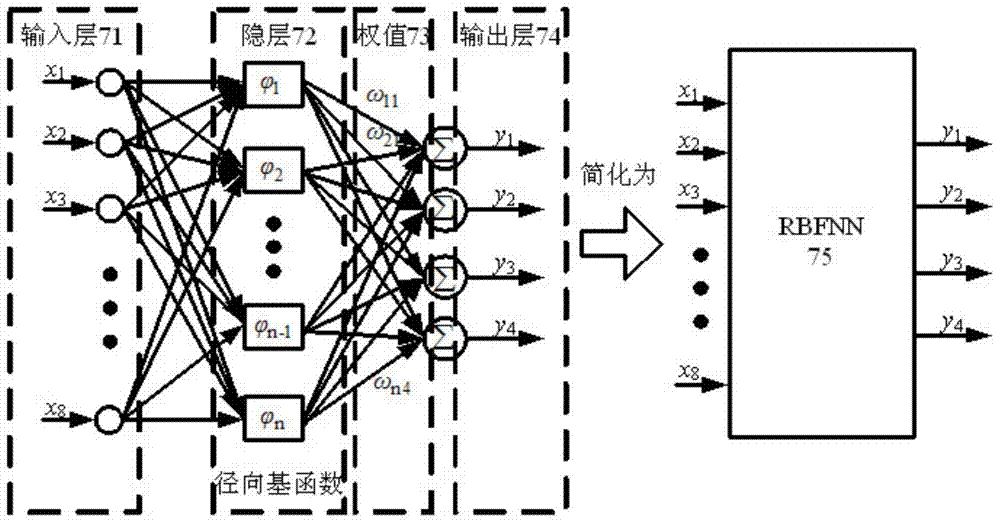
Bearing-free asynchronous motor RBF neural network self-adaptive inverse decoupling control and parameter identification method
InactiveCN104767449AFrictionlessNo wearElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsRadial basis function neuralVoltage inverter
The invention discloses a bearing-free asynchronous motor RBF neural network self-adaptive inverse decoupling control and parameter identification method. An SVPWM module, a voltage inverter, a bearing-free asynchronous motor and a load of the bearing-free asynchronous motor form a whole serving as a composite controlled object. Two radial basis function neural networks are adopted to achieve inverse control and parameter identification conducted on the composite controlled object. A self-adaptive inverse controller is formed by using an RBF neural network through learning, and is serially connected in front of the composite controlled object, errors of a feedback signal and a given signal are input into an inverse controller, and accordingly closed-loop control is formed, then a self-adaptive parameter identifier is formed by using one RBF neural network through learning and identifies output quantity speed and displacement of the composite controlled object, speed-less and displacement-free sensor control is achieved, online learning of an estimation signal is aided by means of a learning algorithm, and non-linear dynamic decoupling control of the bearing-free asynchronous motor is achieved. The bearing-free asynchronous motor RBF neural network self-adaptive inverse decoupling control and parameter identification method is high in control speed and higher in identification accuracy, and a control system is excellent.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
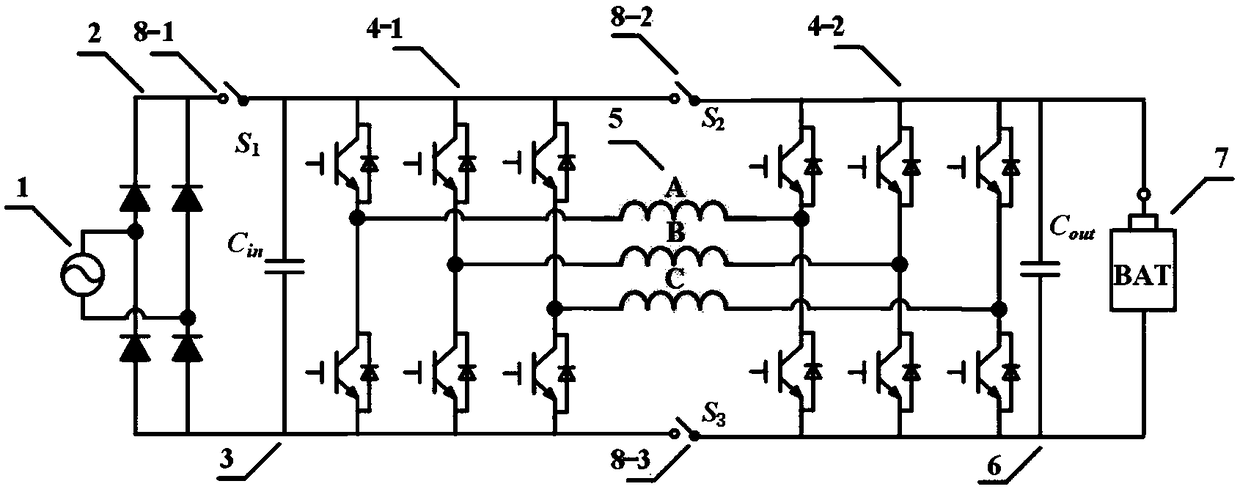
Open winding type permanent magnet motor driven reconstructed vehicle-mounted charging system for electric vehicle
ActiveCN108539833AImprove reliabilityEliminate the effects ofBatteries circuit arrangementsAC motor controlHarmonic controlElectric vehicle
The invention relates to an open winding type permanent magnet motor driven reconstructed vehicle-mounted charging system for an electric vehicle. The system comprises a single-phase AC power supply,a rectifier bridge, an input filtering capacitor, three-phase voltage inverters, a three-phase permanent magnet motor winding, an output filtering capacitor, a storage battery and mode switches. The charging system sufficiently utilizes original double three-phase inverters, the permanent magnet motor winding, control and sensor units and the like of electric vehicles, and total integration of functions such as motor driving, high-power factor charging, harmonic control and the like is realized by optimizing topology to complete rectification, inversion and power factor correction. During charging, two three-phase voltage inverters are reconstructed into a three-phase cascading Buck-Boost circuit; the permanent magnet motor winding serves as an energy storage inductor of the three-phase cascading Buck-Boost circuit. By means of the charging system, the cost of a device can be effectively reduced and high-power factor charging can be realized.
Owner:NANTONG WELL ELECTRIC MOTOR
Method for compensating instantaneous power failure in medium voltage inverter and medium voltage inverter system by using the same
ActiveUS20130076285A1Reduce output frequencyEnsure reliabilityMotor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlVoltage inverterEngineering
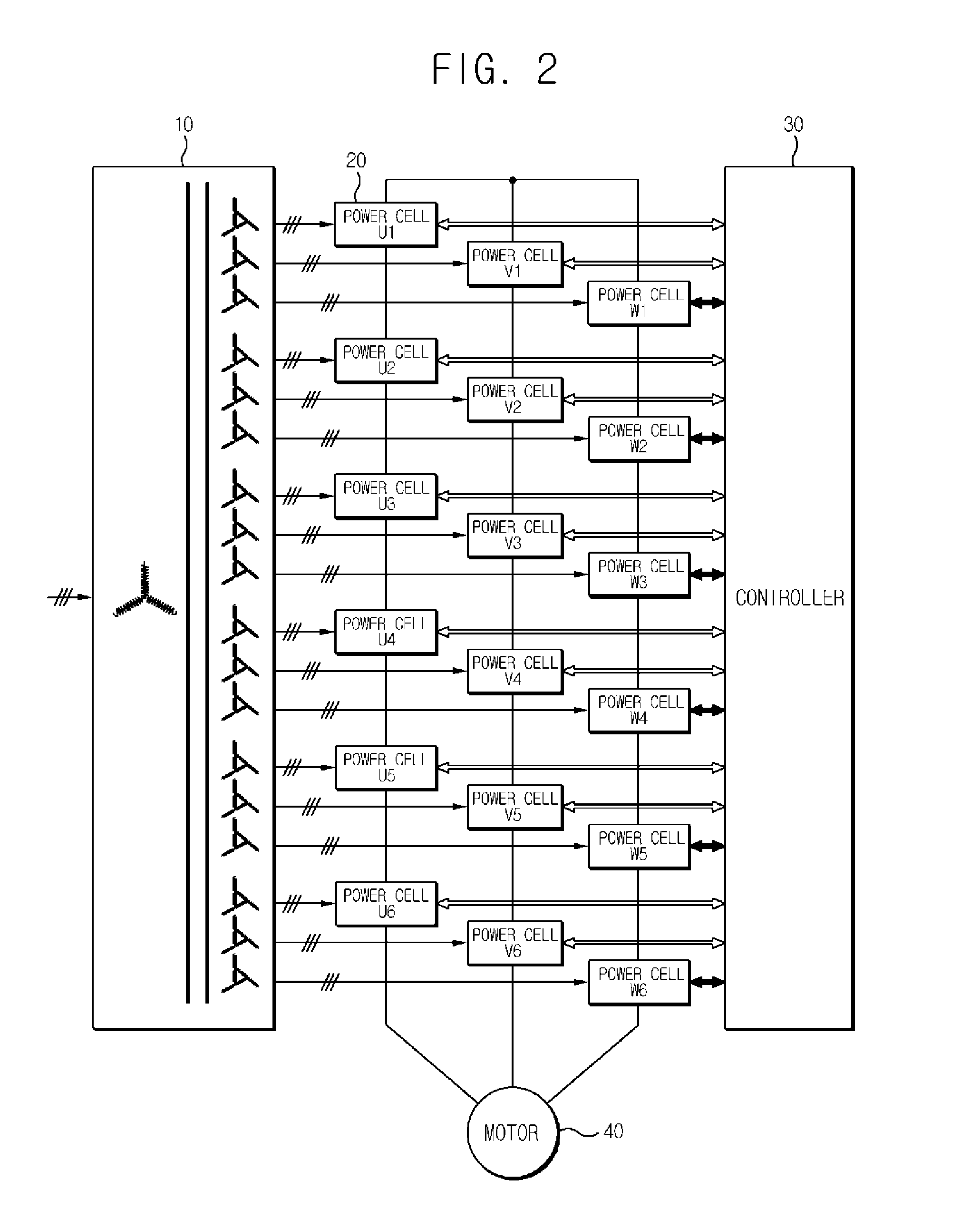
Provided are a method for compensating instantaneous power failure in medium voltage inverter and a medium voltage inverter system by using the same, the method for compensating instantaneous power failure in medium voltage inverter including a plurality of power cells supplying a phase voltage to a motor by being connected to the motor in series, the method including decreasing an output frequency of the plurality of power cells by as much as a predetermined value at a relevant point where an input voltage of the plurality of power cells is less than a reference value, decreasing the output frequency at a predetermined deceleration gradient, and maintaining the output frequency during restoration of input voltage as long as a predetermined time, in a case the input voltage is restored.
Owner:LSIS CO LTD
Common-voltage compensation circuit and compensation method for use in a liquid crystal display
ActiveUS20100277399A1Suppressing crosstalk interferenceStatic indicating devicesVoltage converterLiquid-crystal display
A common-voltage compensation circuit functions to provide a crosstalk interference suppressing mechanism for use in a liquid crystal display having a liquid-crystal capacitor and a storage capacitor. The compensation circuit includes a buffer for receiving a preliminary common voltage, a current / voltage converter, a high-pass filter and a ripple-voltage inverter. The current / voltage converter is utilized for generating a liquid-crystal capacitor common voltage furnished to the liquid-crystal capacitor according to an output current of the buffer. The high-pass filter performs a high-pass filtering operation on the liquid-crystal capacitor common voltage for extracting a ripple voltage. The ripple-voltage inverter is employed to generate a storage capacitor common voltage furnished to the storage capacitor through performing an inverting operation on the ripple voltage based on the preliminary common voltage. The ripple voltage of the storage capacitor common voltage has a phase opposite to that of the liquid-crystal capacitor common voltage for suppressing crosstalk interference.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
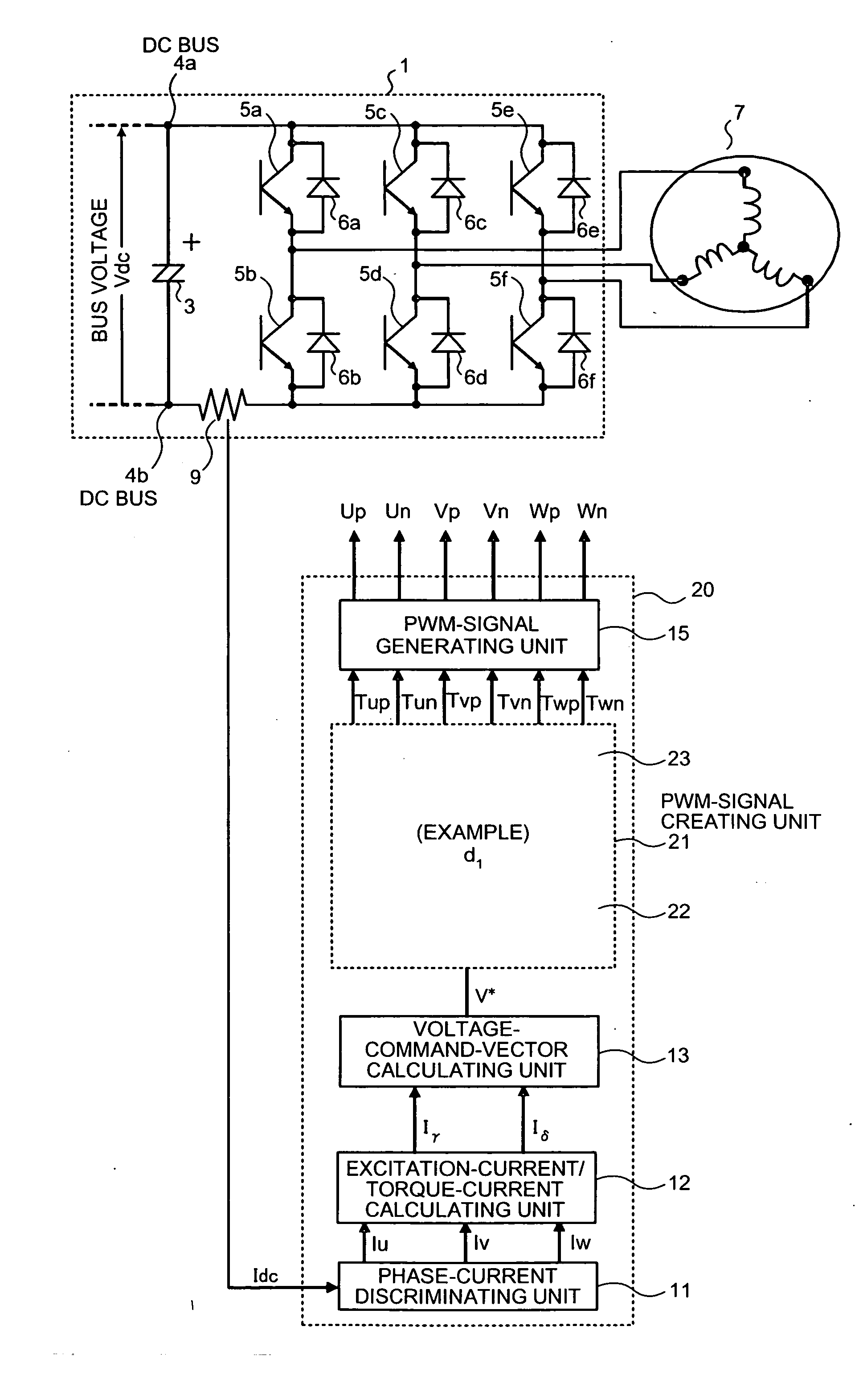
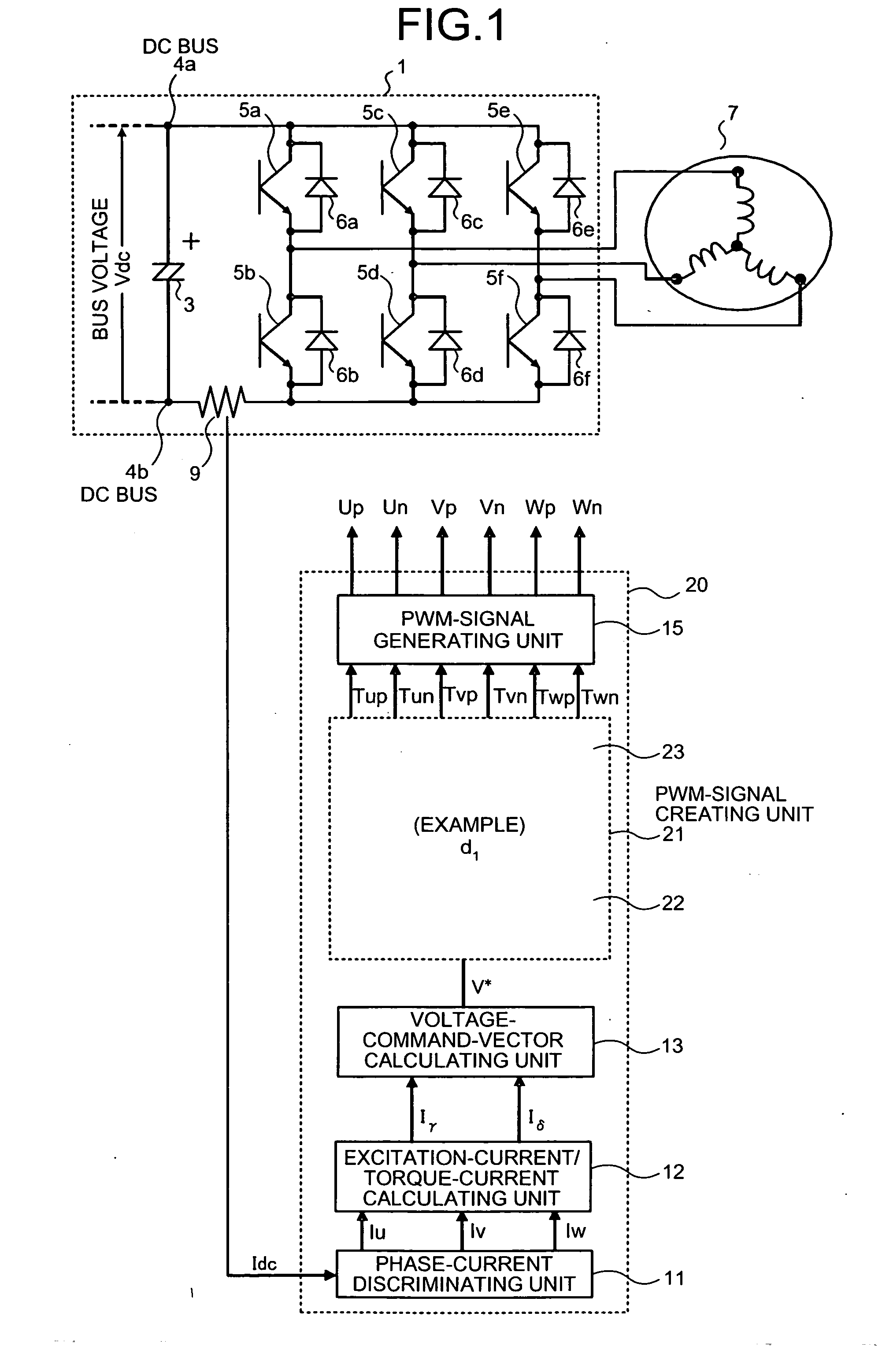
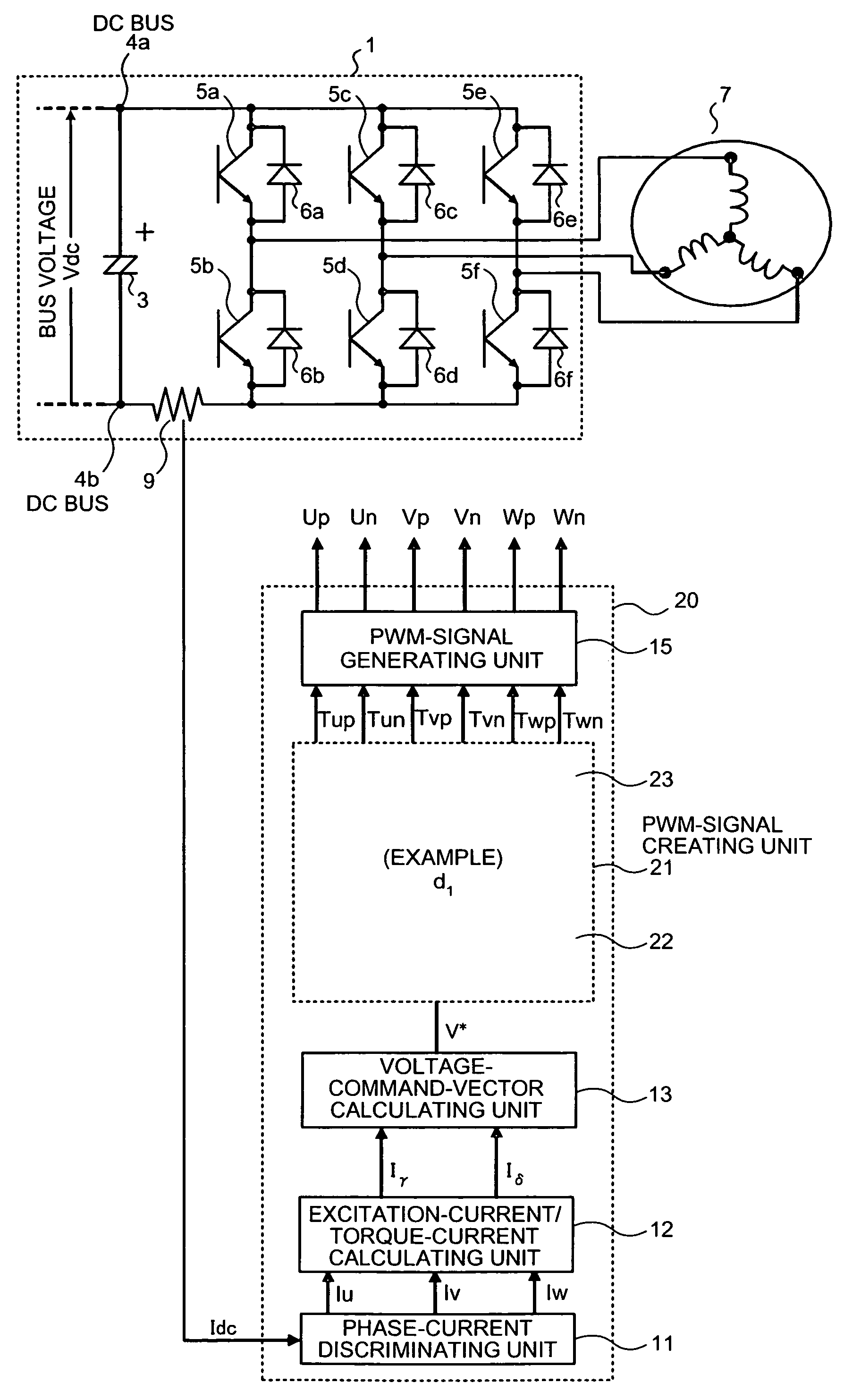
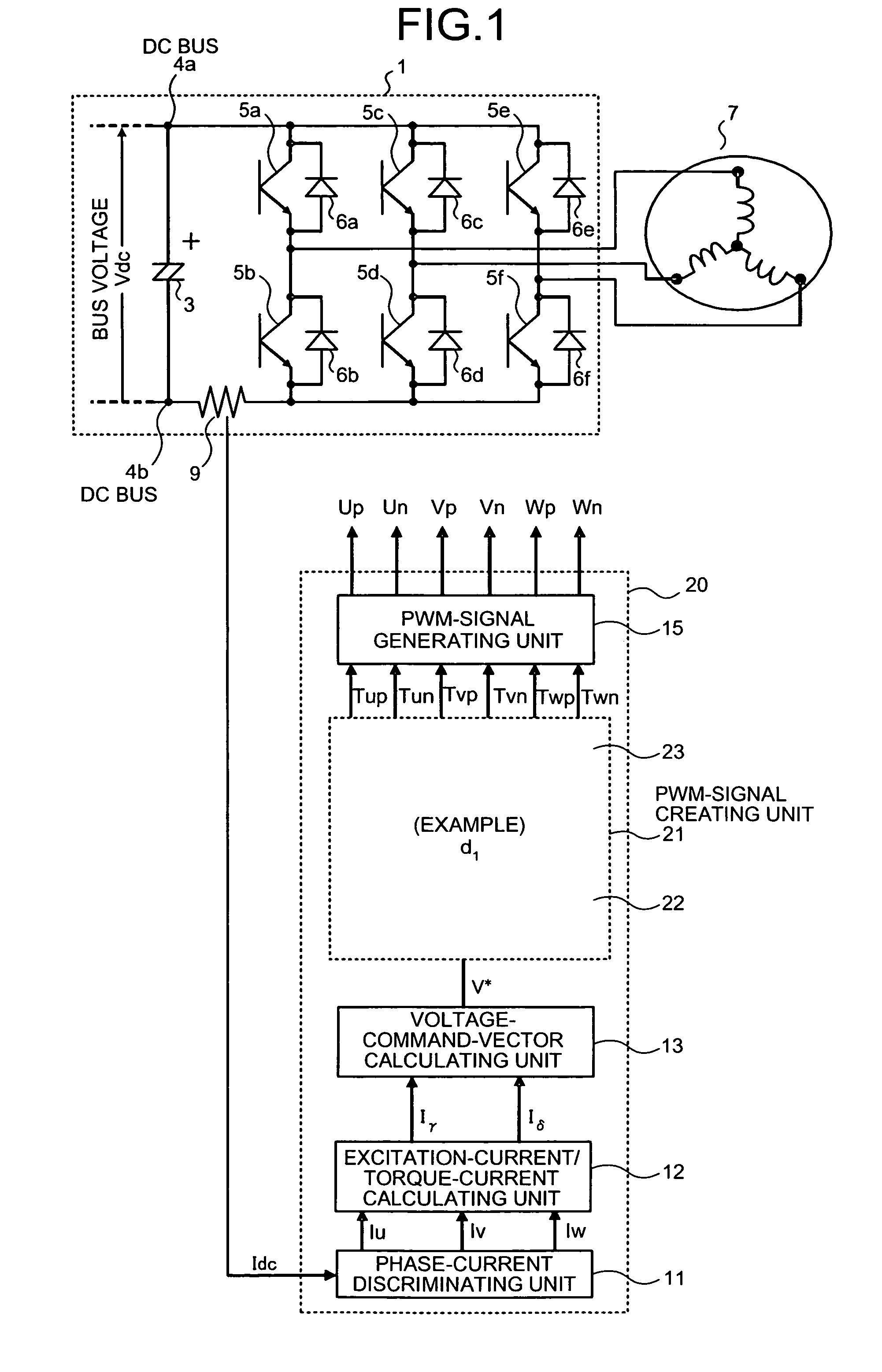
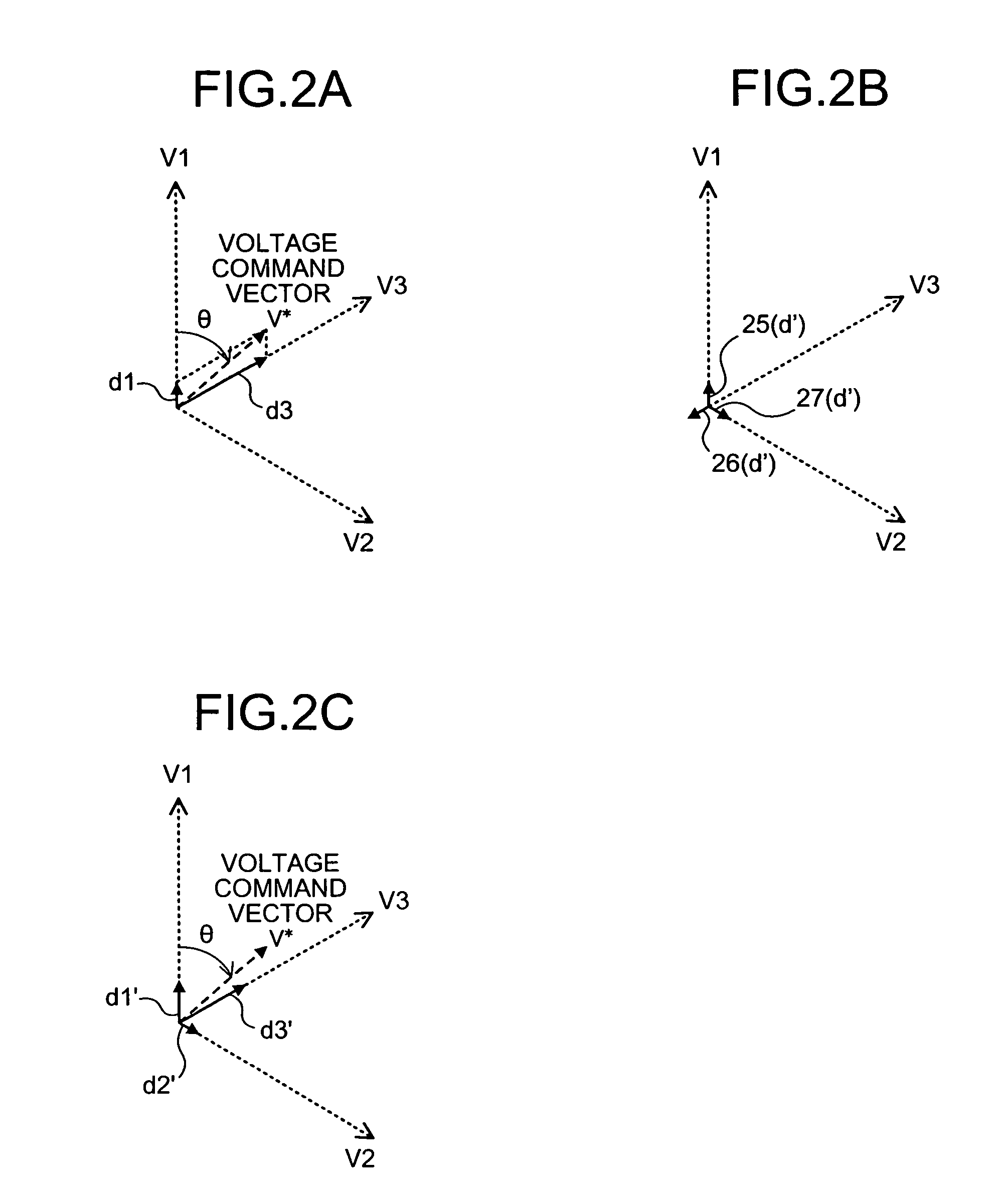
Three-phase pwm-signal generating apparatus
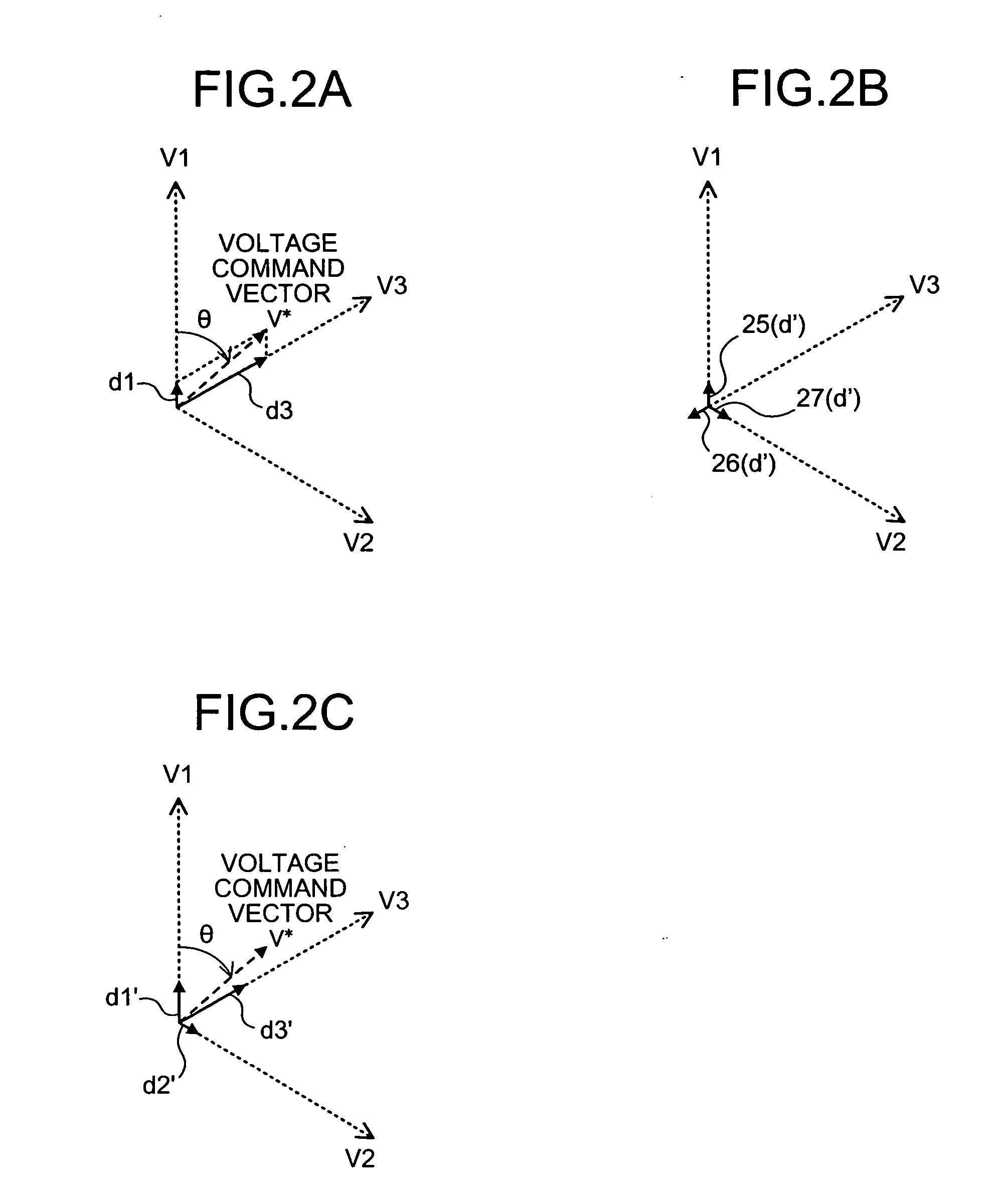
ActiveUS20070103950A1Increase time widthLess limitation of outputAc-dc conversionVoltage vectorVoltage inverter
An apparatus for generating a three-phase pulse-width-modulation signal for a three-phase voltage inverter employing a semiconductor switching element includes a generating unit that generates the three-phase pulse-width-modulation signal based on at least one combination of three basic voltage vectors and at least a zero vector.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
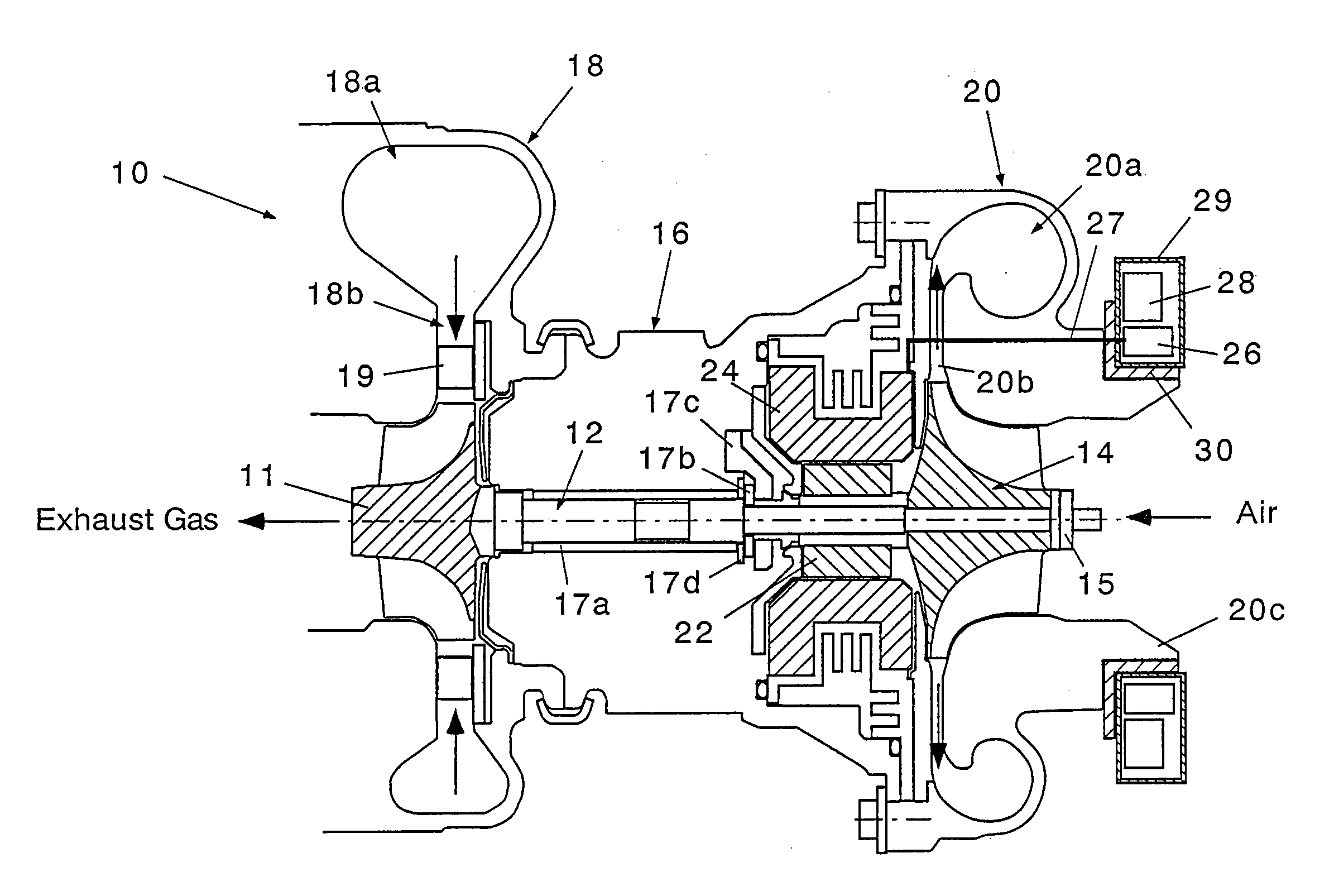
Motor-driven supercharger
ActiveUS20070108772A1Reduce power lossAvoid high temperatureInternal combustion piston enginesEngine manufactureMotor driveVoltage inverter
There are provided with a motor rotor (22) fixed to a turbine shaft (12) and rotating together with the turbine shaft, a motor stator (24) surrounding the motor rotor and fixed within a bearing housing (16), an inverted (26) converting a dc power into an ac power, and an inverter controller (28) controlling a frequency and a voltage of the ac power by the inverter. The inverter and the inverter controller are accommodated in a driver container (29), and are coupled to a compressor housing (20) by an insulating coupling member (30).
Owner:IHI CORP
Apparatus for transferring energy using onboard power electronics with high-frequency transformer isolation and method of manufacturing same
ActiveUS9290097B2Batteries circuit arrangementsPropulsion by batteries/cellsEngineeringVoltage source
An apparatus for transferring energy using onboard power electronics with high-frequency transformer isolation includes a power electronic drive circuit comprises a dc bus and a first energy storage device coupled to the dc bus. A first bi-directional dc-to-ac voltage inverter is coupled to the first energy storage device and to the dc bus, and a first electromechanical device coupled to the first bi-directional dc-to-ac voltage inverter. A charging system coupled to the dc bus via a charge bus comprises a receptacle configured to mate with a connector coupled to a voltage source external to the power electronic drive circuit and an isolation transformer configured to electrically isolate the charge bus from the receptacle. A controller configured to cause the charging system to supply a charging voltage to the dc bus based on a voltage received from the voltage source external to the power electronic drive circuit.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
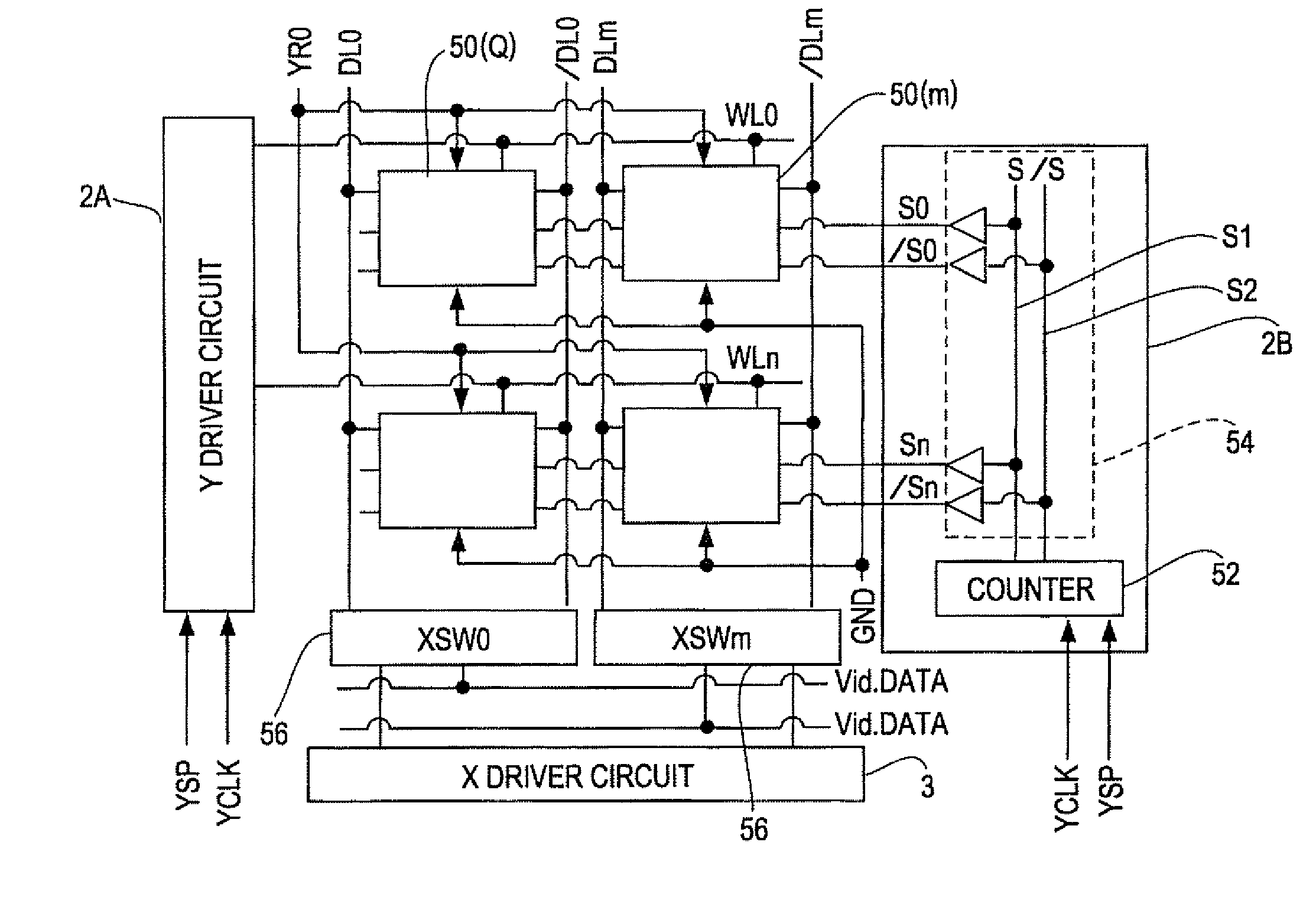
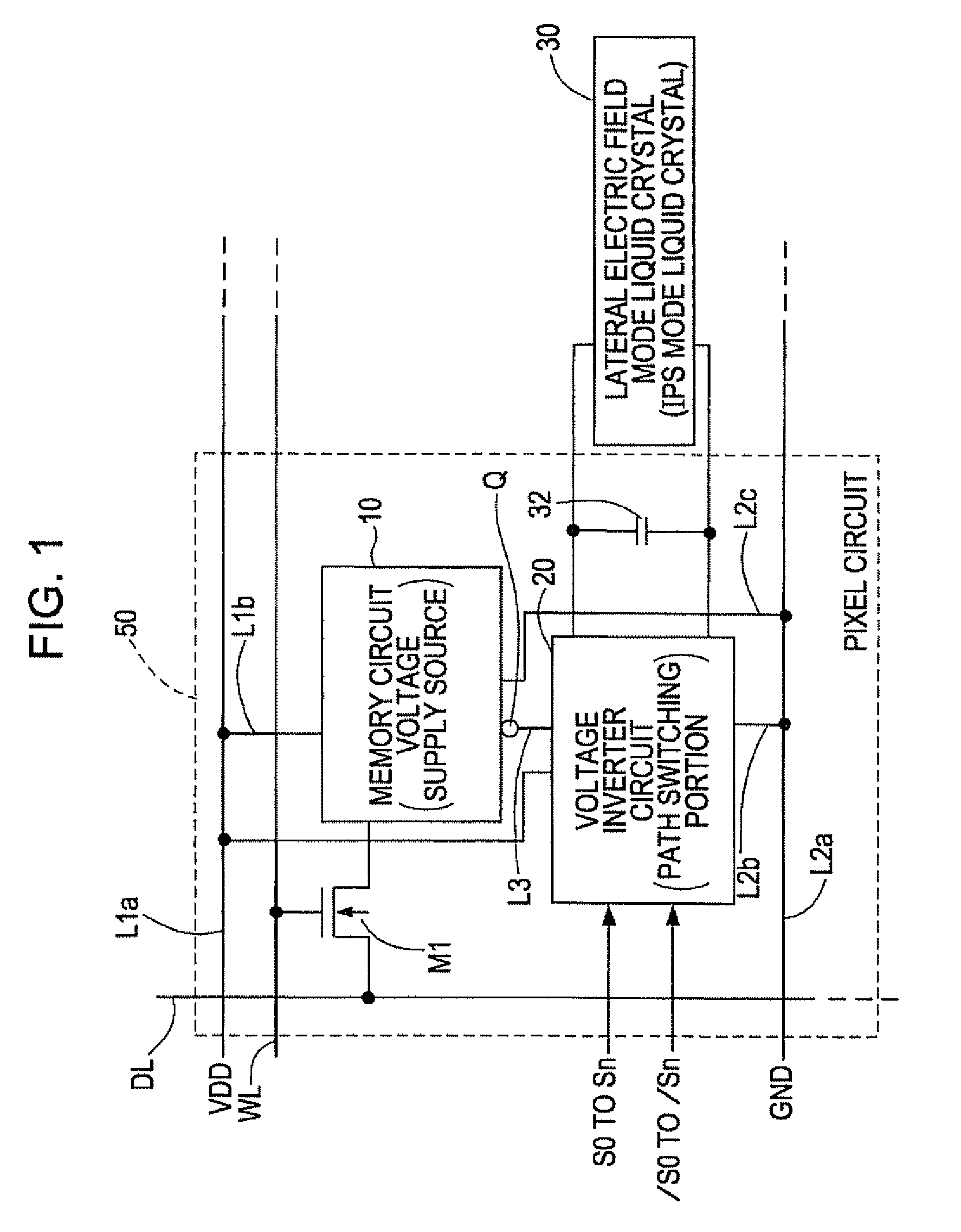
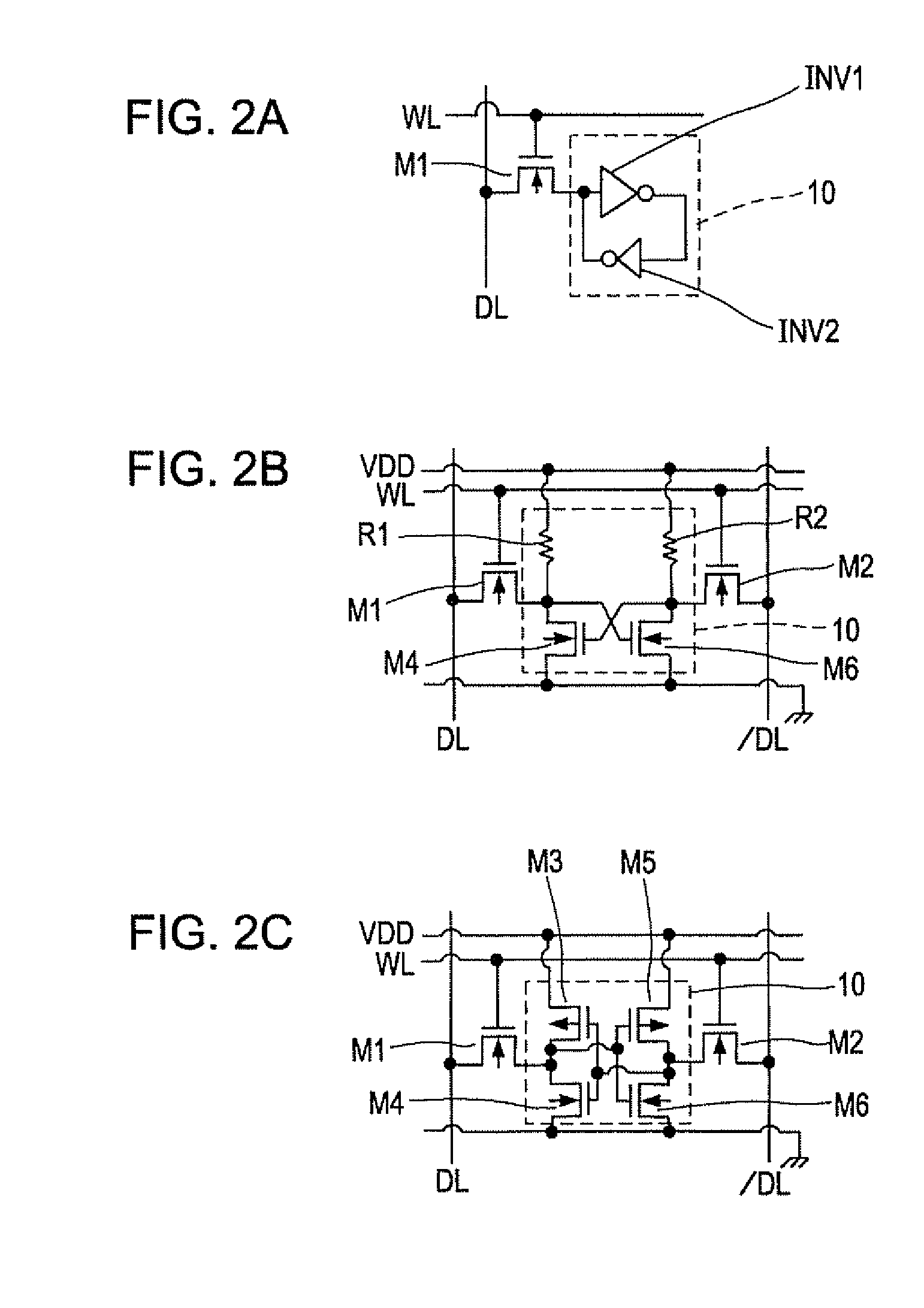
Liquid crystal device, pixel circuit, active matrix substrate, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20080238850A1Precise inversionSimple circuit configurationCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingActive matrixVoltage inverter
A liquid crystal device includes a lateral electric field mode liquid crystal element that controls alignment of liquid crystal molecules by applying an electric field in a direction of a substrate plane to a liquid crystal layer. A voltage inverter circuit is provided in each pixel circuit, and inverts a voltage applied to the liquid crystal element by switching the supply of each of the first and second voltages, supplied from a memory circuit, to between a first pixel electrode and a second pixel electrode of the liquid crystal element. A holding capacitor holds a voltage applied to the liquid crystal element. The voltage inverter circuit includes switching elements. One end of the holding capacitor is connected to at least one of a common connecting point of first and second switching elements and a connecting point of third and fourth switching elements.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
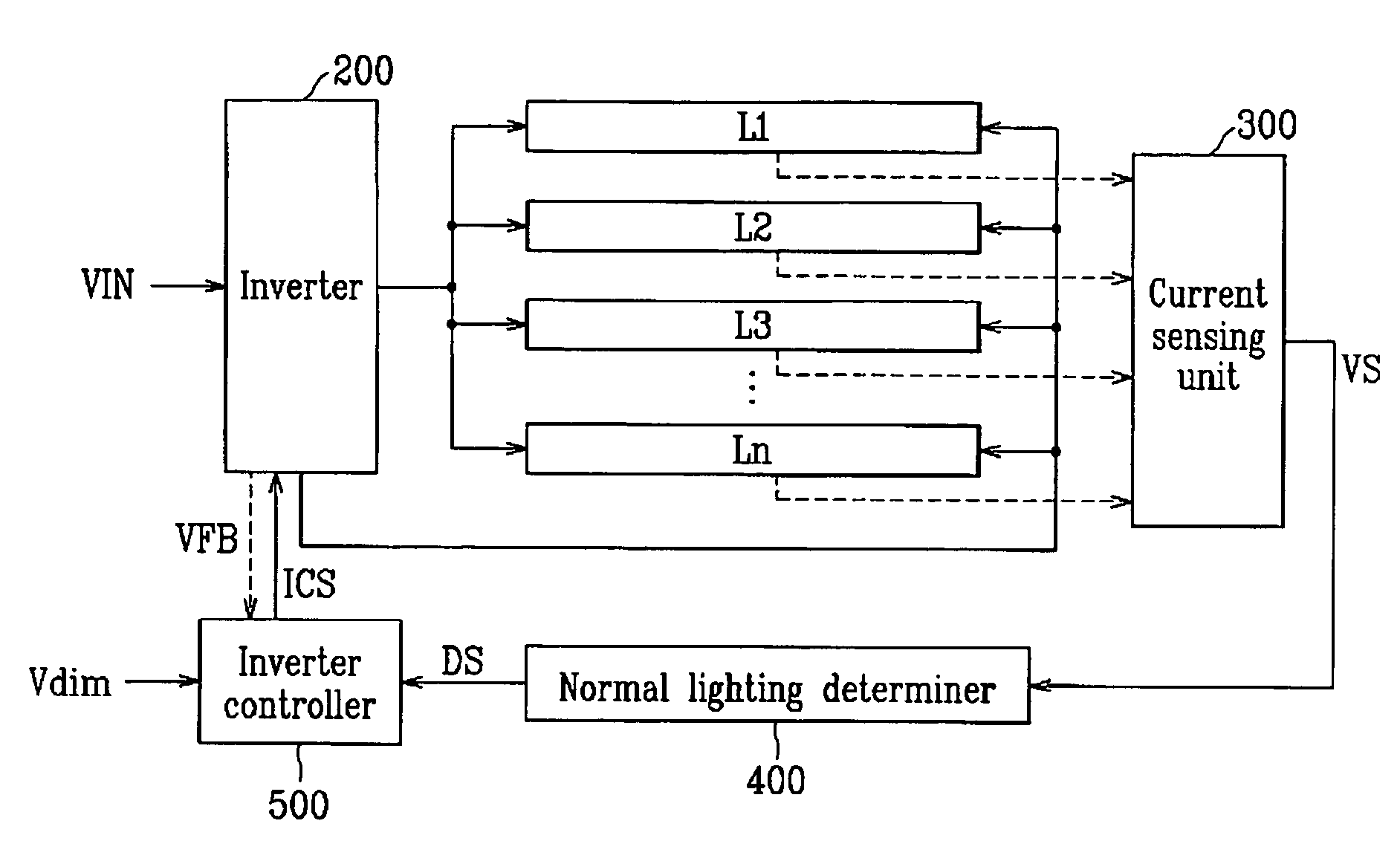
Backlight assembly, display device and driving apparatus of light source for display device
A backlight assembly device includes lamps, an inverter, a sensing unit, a normal lighting determiner and an inverter controller. The inverter applies a control signal to the lamps to control operation of the lamps. The sensing unit outputs sensing voltages in response to currents flowing in the lamps. The normal lighting determiner compares the sensing voltages to a reference voltage for determining an operating state of the lamps to output a determination signal and varies the reference voltage in response to a change in the operating state of the lamps. The inverter controller outputs the control signal in response to the determination signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
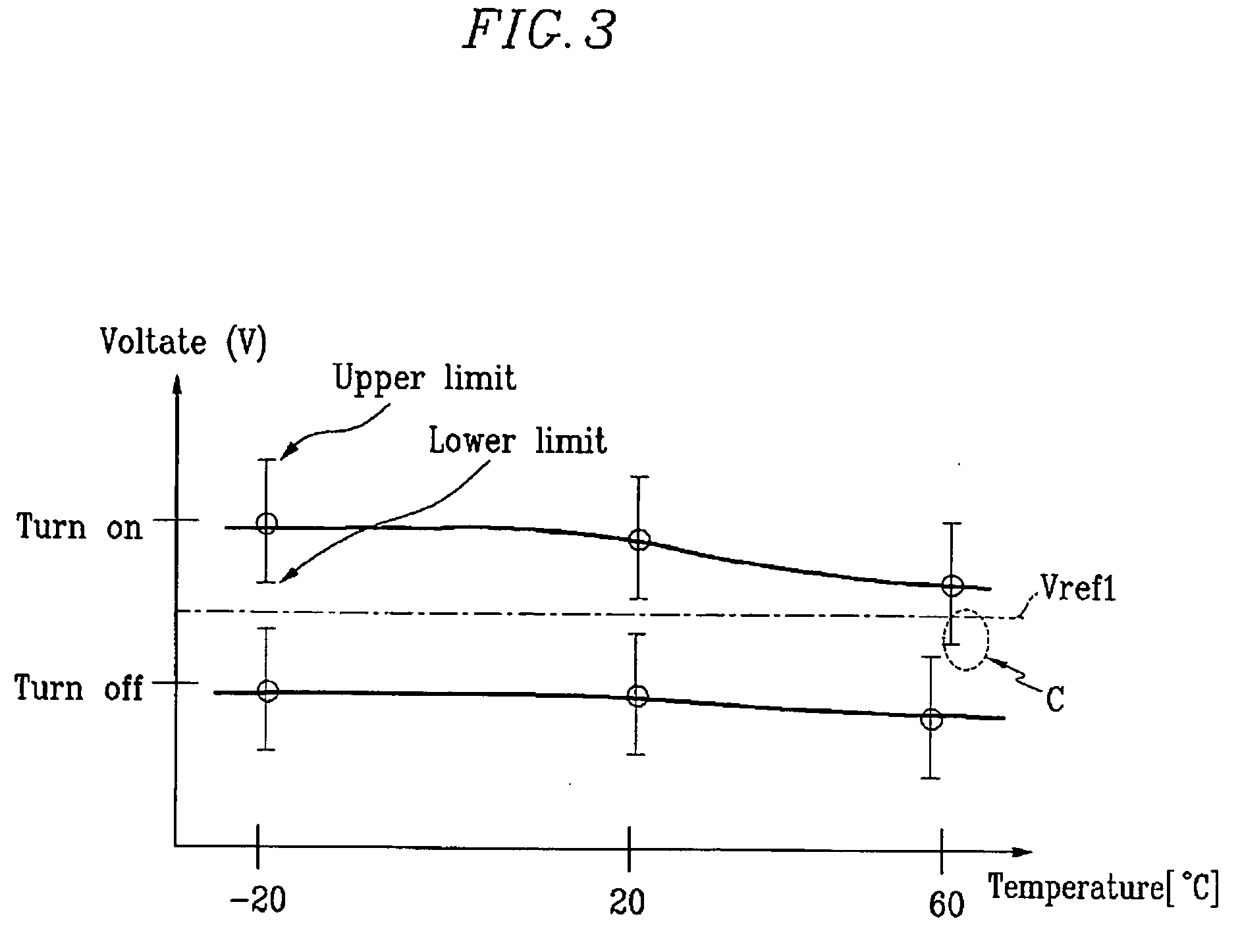
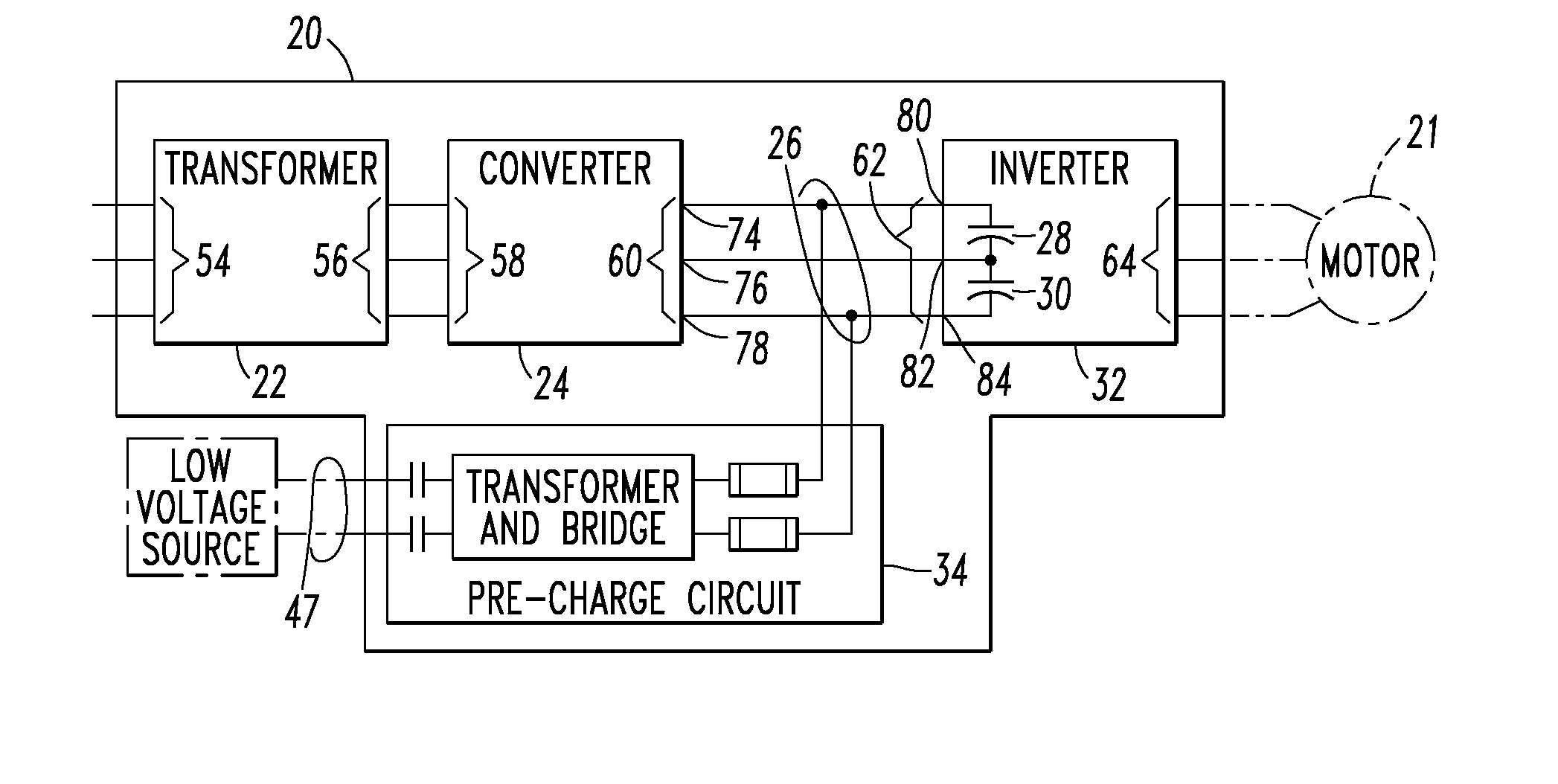
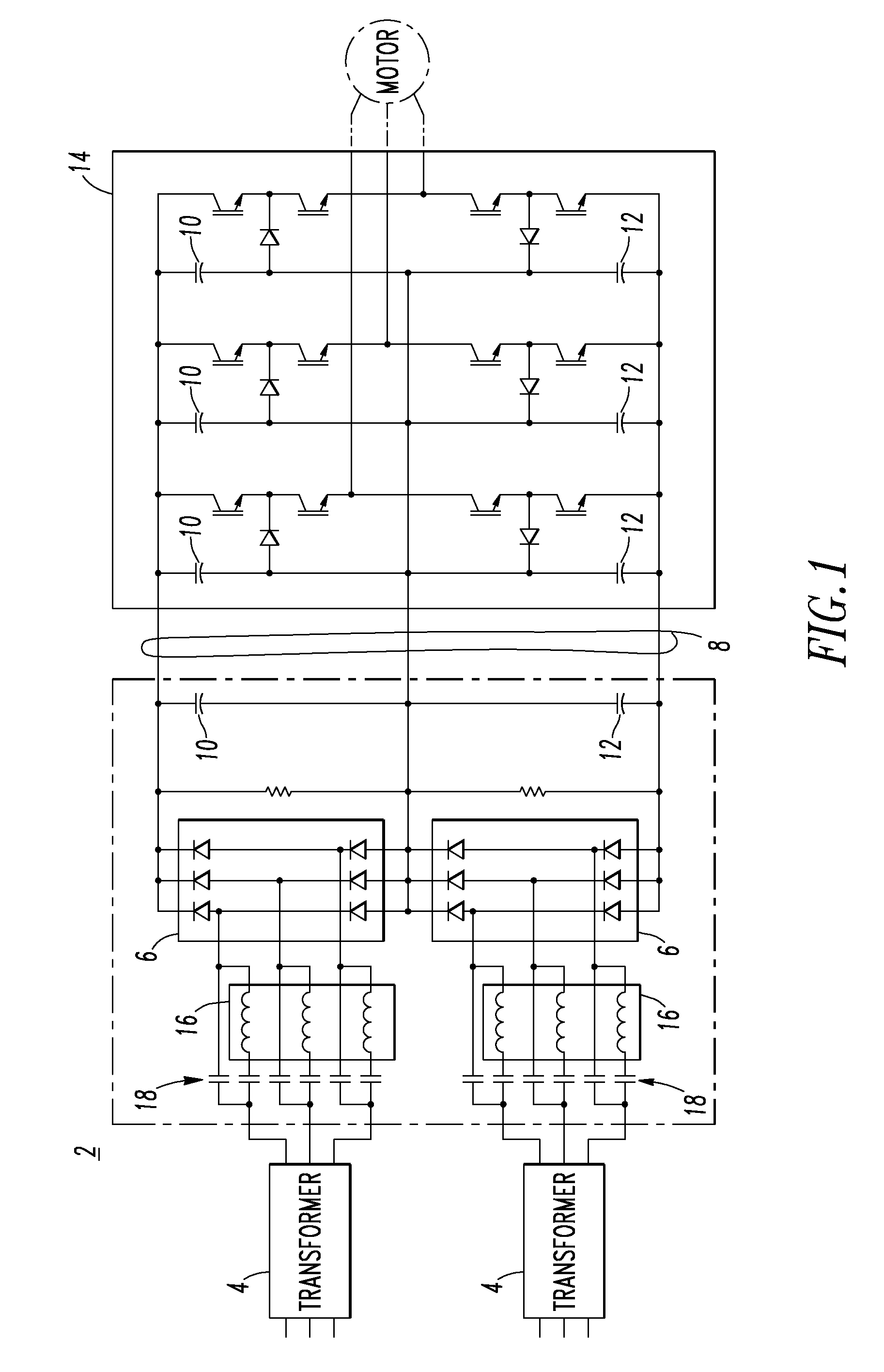
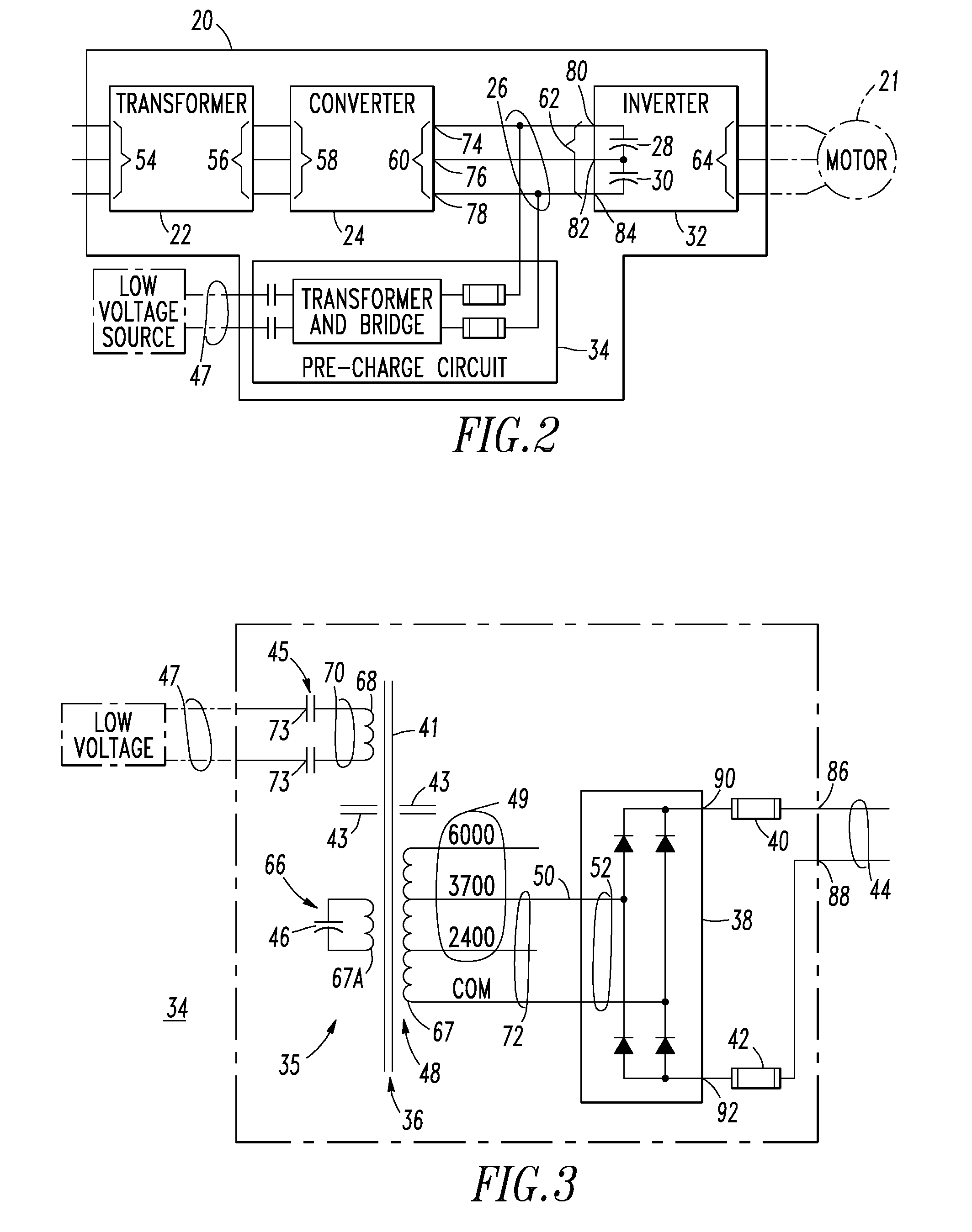
Voltage source inverter and medium voltage pre-charge circuit therefor
InactiveUS20090284999A1Ac-dc conversionElectric power transfer ac networkZ-source inverterLow voltage
A medium voltage adjustable frequency drive includes an input isolation transformer having a three-phase input and a three-phase output, a converter having a three-phase input electrically connected to the three-phase output of the input isolation transformer and an output providing a direct current bus, an inverter having an input electrically connected to the output of the converter and a three-phase output, and a pre-charge circuit. The pre-charge circuit includes a ferro-resonant transformer circuit having a primary winding structured to input a low voltage and a secondary winding structured to output a medium voltage and provide a constant current source. The pre-charge circuit also includes a medium voltage diode bridge having an input receiving the medium voltage from the secondary winding of the ferro-resonant transformer circuit and an output structured to provide the constant current source to the direct current bus.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LIMITED
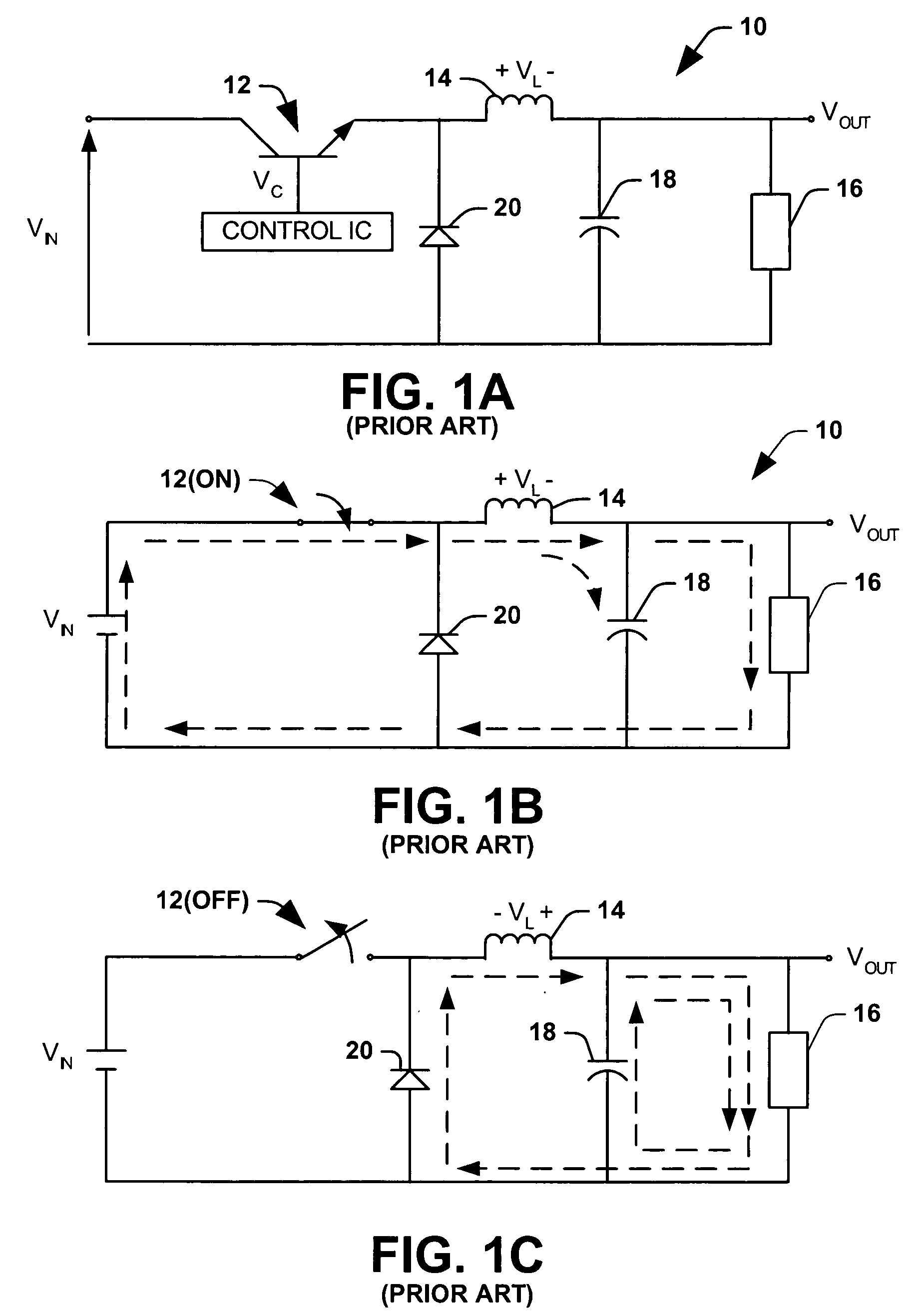
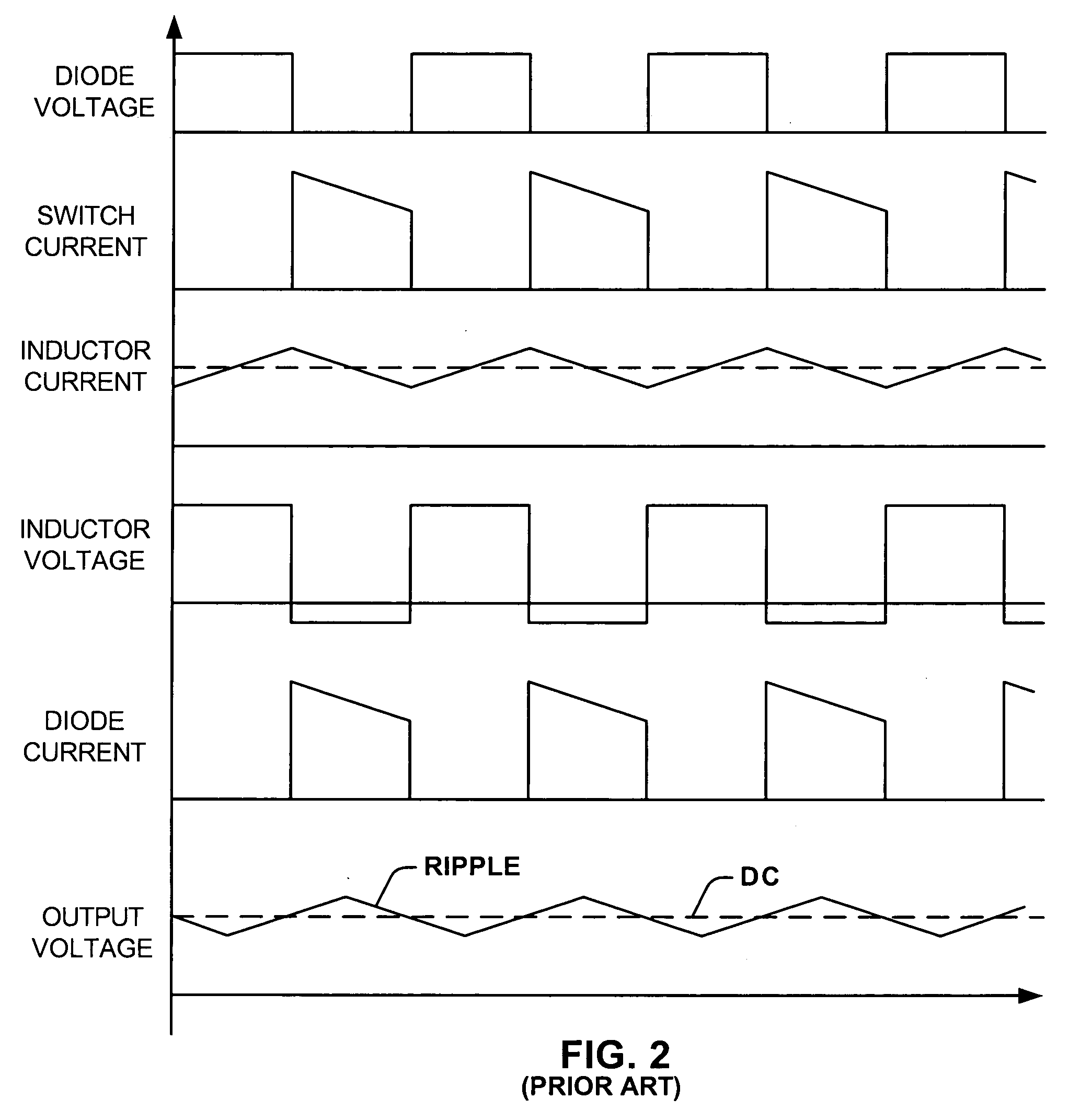
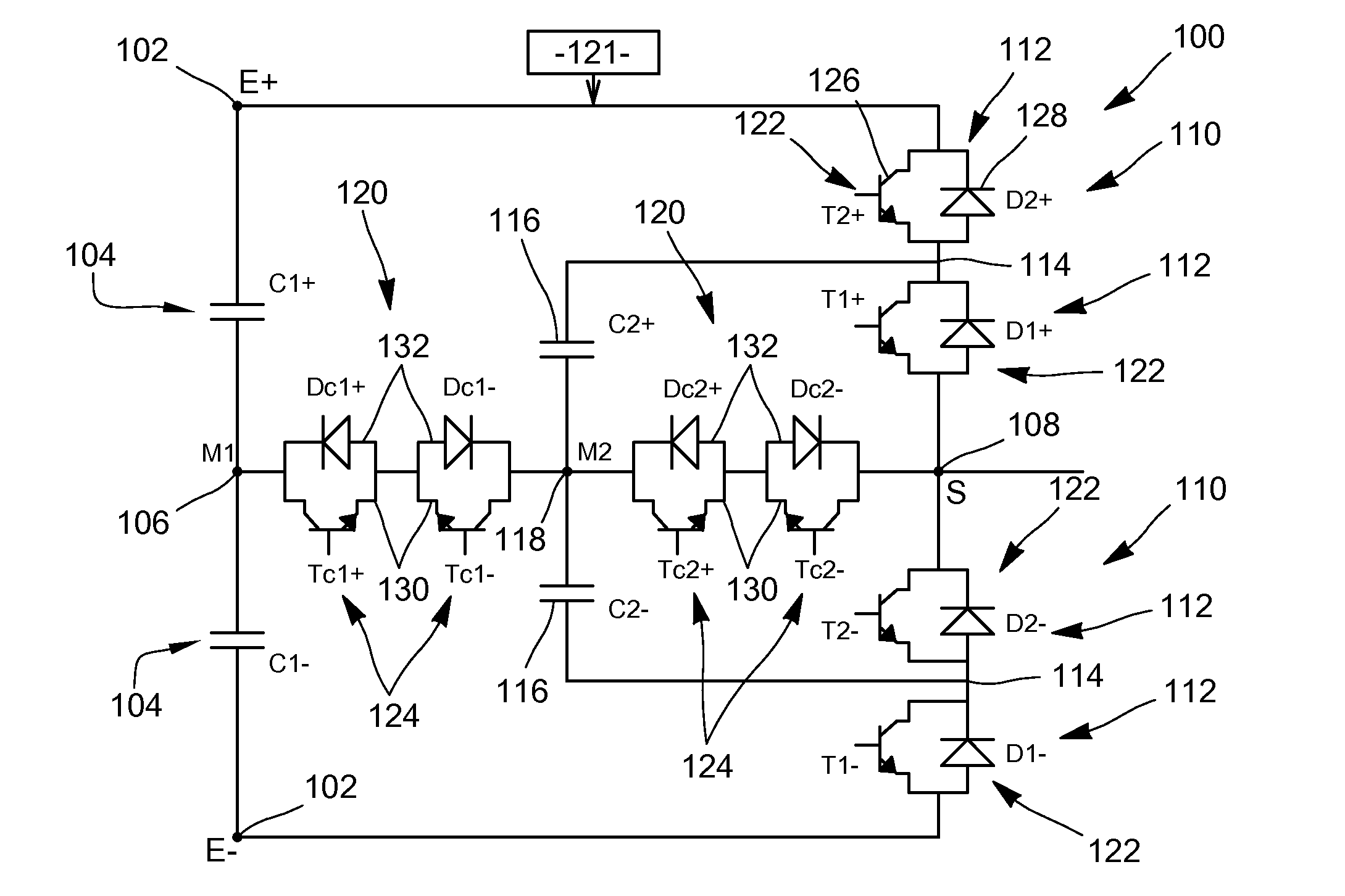
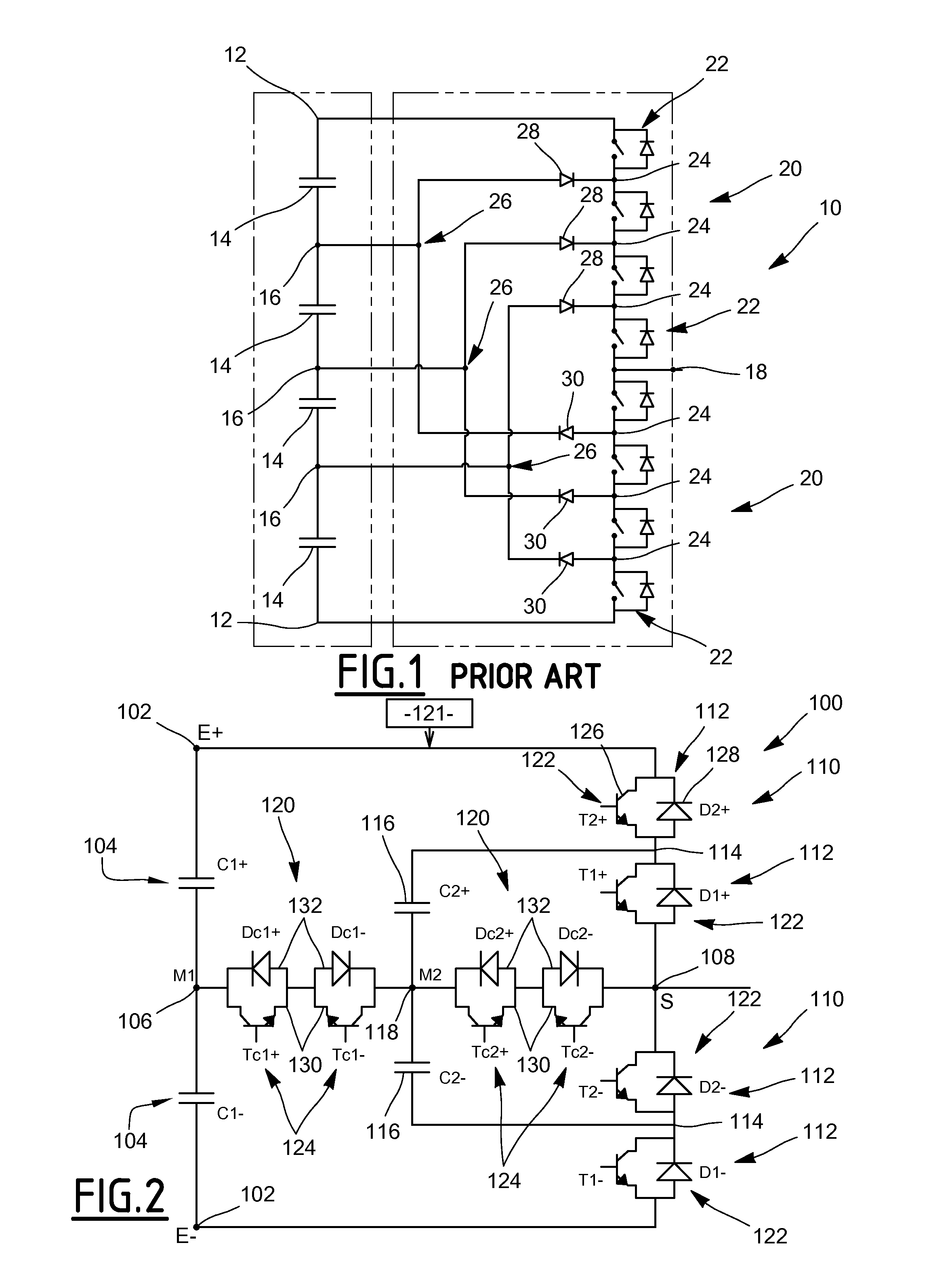
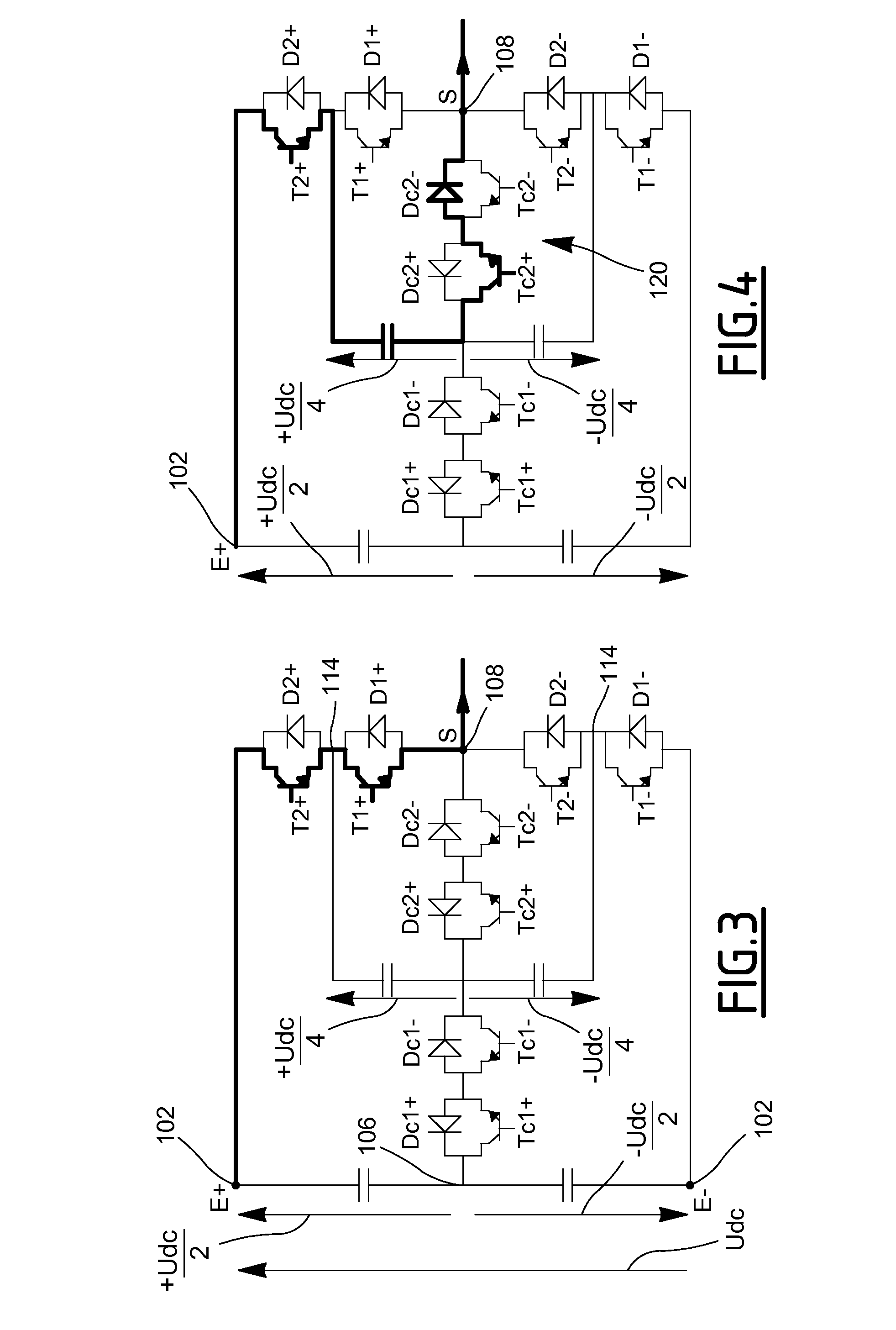
Voltage inverter and method of controlling such an inverter
ActiveUS20130094266A1Improve usabilitySmall space requirementAC motor controlElectric motor controlElectricityVoltage inverter
A voltage inverter capable of operating in the event of a short-circuit or open-circuit fault. The voltage inverter includes: a load having three phases, each phase having a first terminal and a second terminal; first and second cells each including three branches connected together in parallel, each branch including two switches connected in series and a mid-point positioned between the two switches, each first terminal of each of the phases being connected to one of the mid-points of the first cell and each second terminal of each of the phases being connected to one of the mid-points of the second cell; and a DC voltage source, the first and second cells each being connected to the DC voltage source via two electrical isolators.
Owner:SAFRAN ELECTRICAL & POWER
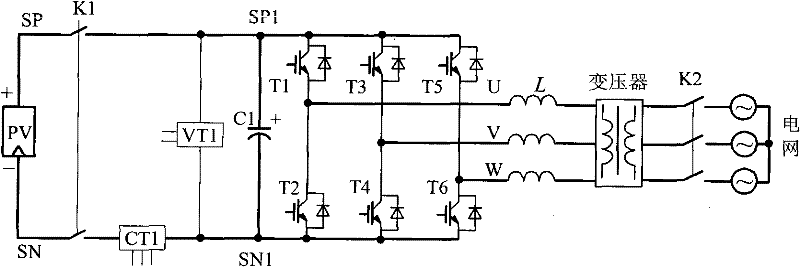
Photovoltaic synchronization inverter with photovoltaic array IV test function and test method
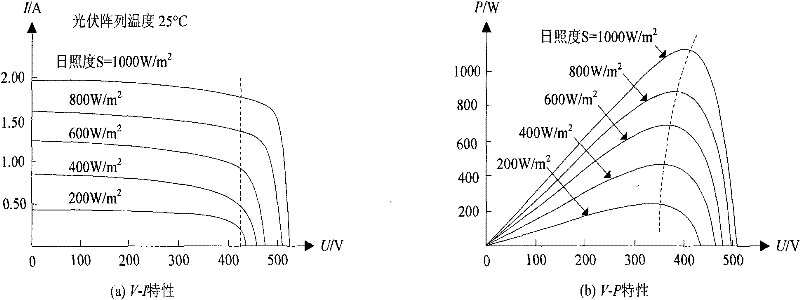
InactiveCN101752877AConvenient IV CharacteristicsEasy to testElectrical testingPhotovoltaicsCapacitanceEngineering
The invention discloses a photovoltaic synchronization inverter with a photovoltaic array IV test function, which is composed of an inverter main circuit and a system controller; the inverter main circuit adopts an adjustable-voltage inverter and comprises a one-phase and three-phase synchronization system; the photovoltaic synchronization inverter is characterized in that: a current sensor CT1 for measuring photovoltaic array input current is arranged between a photovoltaic array input port and a filter capacitor C1; a direct-current bus bar voltage sensor VT1 for measuring the voltage of the filter capacitor C1 end is arranged; a direct-current breaker K1 is arranged at the photovoltaic array output port, the photovoltaic array output general current is input to the photovoltaic synchronization inverter, the direct-current bus bar voltage sensor VT1 and the current sensor CT1 through the direct-current breaker K1; the photovoltaic synchronization inverter is suitable for the conventional synchronization inverting system, can test the photovoltaic array IV characteristics of the system conveniently, and the test data is used for analyzing and evaluating the photovoltaic array characteristics of the system and the power generating capacity.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
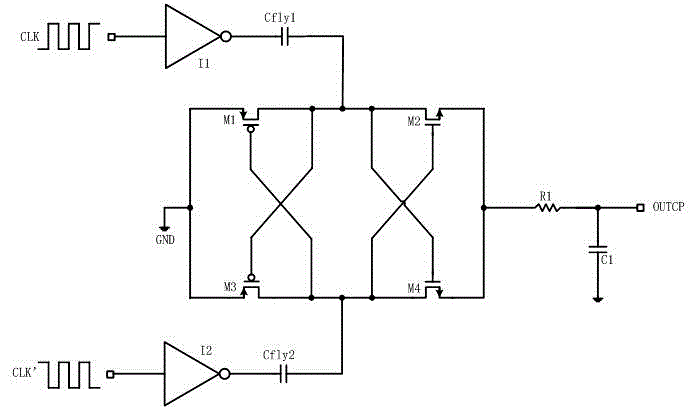
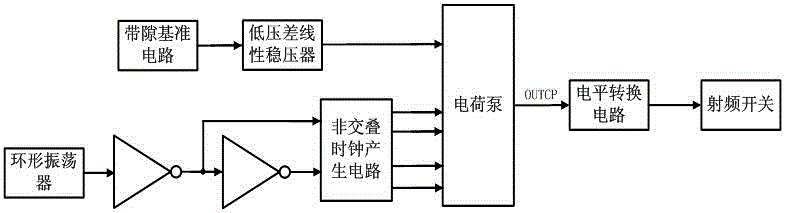
Control circuit applied to SOI (silicon on insulator) CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) radiofrequency switches
The invention discloses a control circuit applied to SOI (silicon on insulator) CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) radiofrequency switches. The control circuit comprises a band-gap reference circuit, a low-dropout linear voltage regulator, an annular oscillator, voltage inverters, a non-overlapping clock circuit, a charge pump and a level switching circuit. A core unit of the control circuit is a charge pump circuit capable of generating negative voltages. The band-gap reference circuit is connected with the low-dropout linear voltage regulator, an output end of the low-dropout linear voltage regulator is connected with the charge pump, an output end of the annular oscillator is connected with an input end of the inverter I2 by the inverter I1, an output end of the inverter I1 and an output end of the inverter I2 are connected with an input end of the non-overlapping clock generating circuit, four output ends of the non-overlapping clock generating circuit is connected with an input end of the charge pump, and the SOI CMOS radiofrequency switches can be controlled by an output end OUTPUT of the charge pump via the level switching circuit. The control circuit has the advantages that the charge pump capable of generating the negative voltages can be quickly started and has low steady-state currents, accordingly, radiofrequency switch tubes can be assuredly in excellent closed states under the conditions of high radiofrequency signals, and the linearity and the isolation of the radiofrequency switches can be improved.
Owner:广东拓思软件科学园有限公司
High-voltage inverter sharing direct current (DC) bus
InactiveCN103138675AMeet special requirementsParallel connectionAC motor controlCapacitanceFrequency changer
The invention relates to a high-voltage inverter sharing a direct current (DC) bus. The high-voltage inverter sharing the DC bus comprises a charging circuit, a phase-shifting transformer, three-phase diode rectifier bridges, a high voltage DC bus and an inverter based on multi-media card (MMC) topology. The primary side of the phase-shifting transformer is connected with a power grid through the charging circuit, each subsidiary side output winding of the phase-shifting transformer is connected with the three-phase diode rectifier bridge, the output capacitors of each diode rectifier are connected in series to form the high voltage DC bus, the high voltage DC bus is connected with the public DC end of one inverter or multiple inverters based on MMC topology, and the output ends of the inverters are connected the electric motor to be detected, and the mixed frequency test and the frequency control function of the electric motor is achieved. The topologic scheme of the high-voltage inverter sharing the DC bus meets the requirements of the electric motor test station of a weak grid end, multiple-unit output of the phase-shifting transformer with multiple windings is used, the DC bus formed by the series connection of the diode rectifying capacitors is used to store the energy extracted and fed back when the electric motor mixed frequency test is carried out, the energy is no longer loaded by the power grid, and therefore the pollution to the power grid caused by the electric motor test is eliminated.
Owner:LIAONING RONGXIN ZHONGTENG TECH
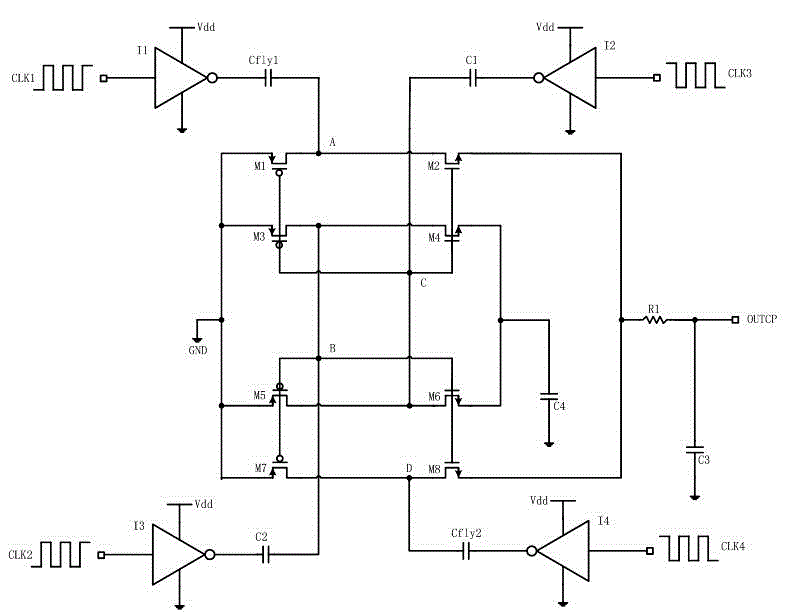
Vehicle propulsion system with multi-channel DC bus and method of manufacturing same
ActiveUS20150210171A1Boost voltageHybrid vehiclesPropulsion by batteries/cellsElectricityVoltage inverter
An apparatus includes a multi-channel DC bus assembly comprising a first channel and a second channel, a first electromechanical device coupled to a positive DC link of the first channel, and a second electromechanical device coupled to a positive DC link of the second channel. A first DC-to-AC voltage inverter is coupled to the positive DC link of the first channel and a second DC-to-AC voltage inverter is coupled to the positive DC link of the second channel. The apparatus further includes a bi-directional voltage modification assembly coupled to the positive DC link of the second channel and a first energy storage system electrically coupled to the first electromechanical device.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Three-phase PWM-signal generating apparatus
ActiveUS7548443B2Extension of timeLess limitation of outputAc-dc conversionVoltage vectorVoltage inverter
An apparatus for generating a three-phase pulse-width-modulation signal for a three-phase voltage inverter employing a semiconductor switching element includes a generating unit that generates the three-phase pulse-width-modulation signal based on at least one combination of three basic voltage vectors and at least a zero vector.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com