Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
268 results about "Voltage multiplier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
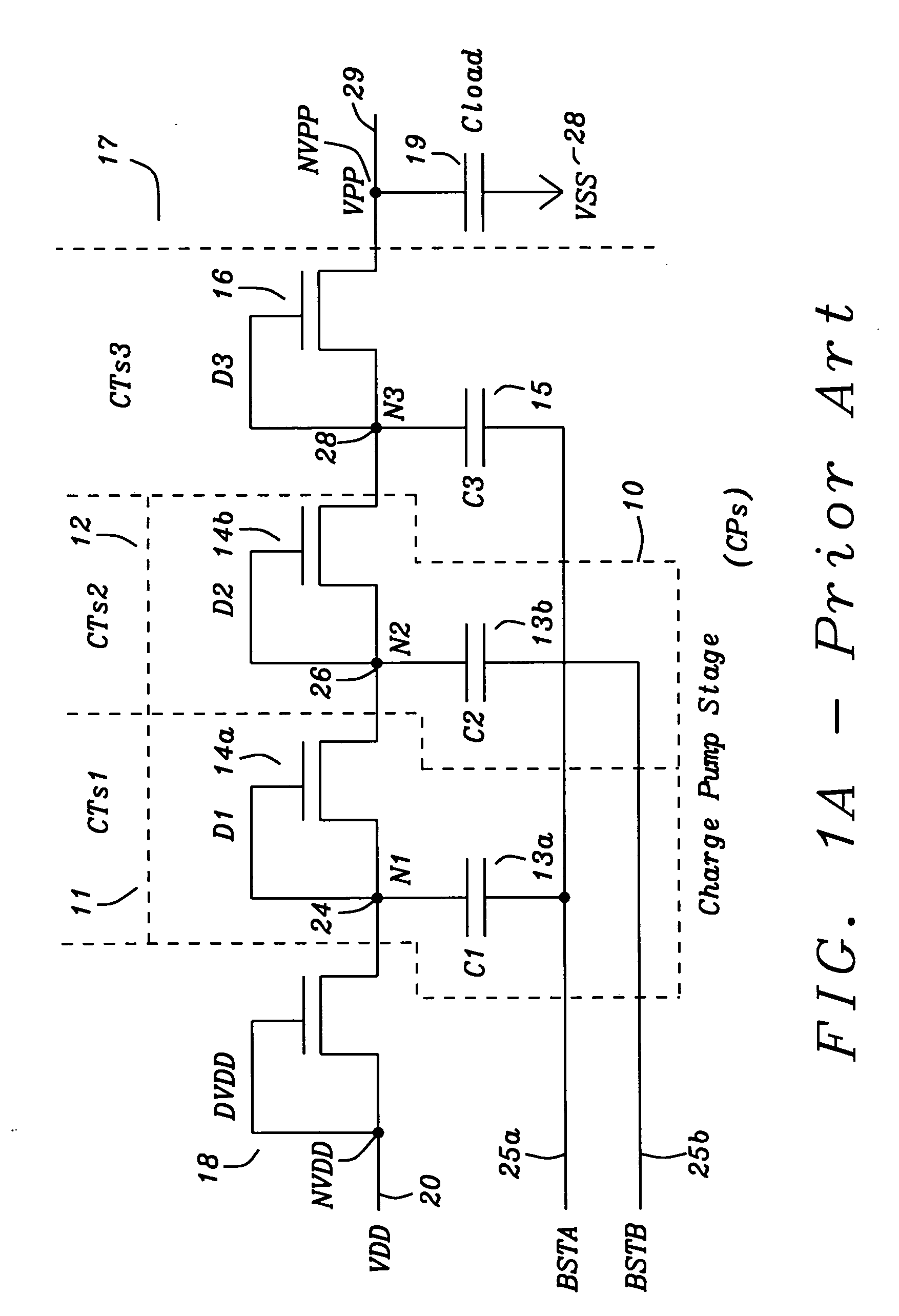
A voltage multiplier is an electrical circuit that converts AC electrical power from a lower voltage to a higher DC voltage, typically using a network of capacitors and diodes. Voltage multipliers can be used to generate a few volts for electronic appliances, to millions of volts for purposes such as high-energy physics experiments and lightning safety testing. The most common type of voltage multiplier is the half-wave series multiplier, also called the Villard cascade (but actually invented by Heinrich Greinacher).
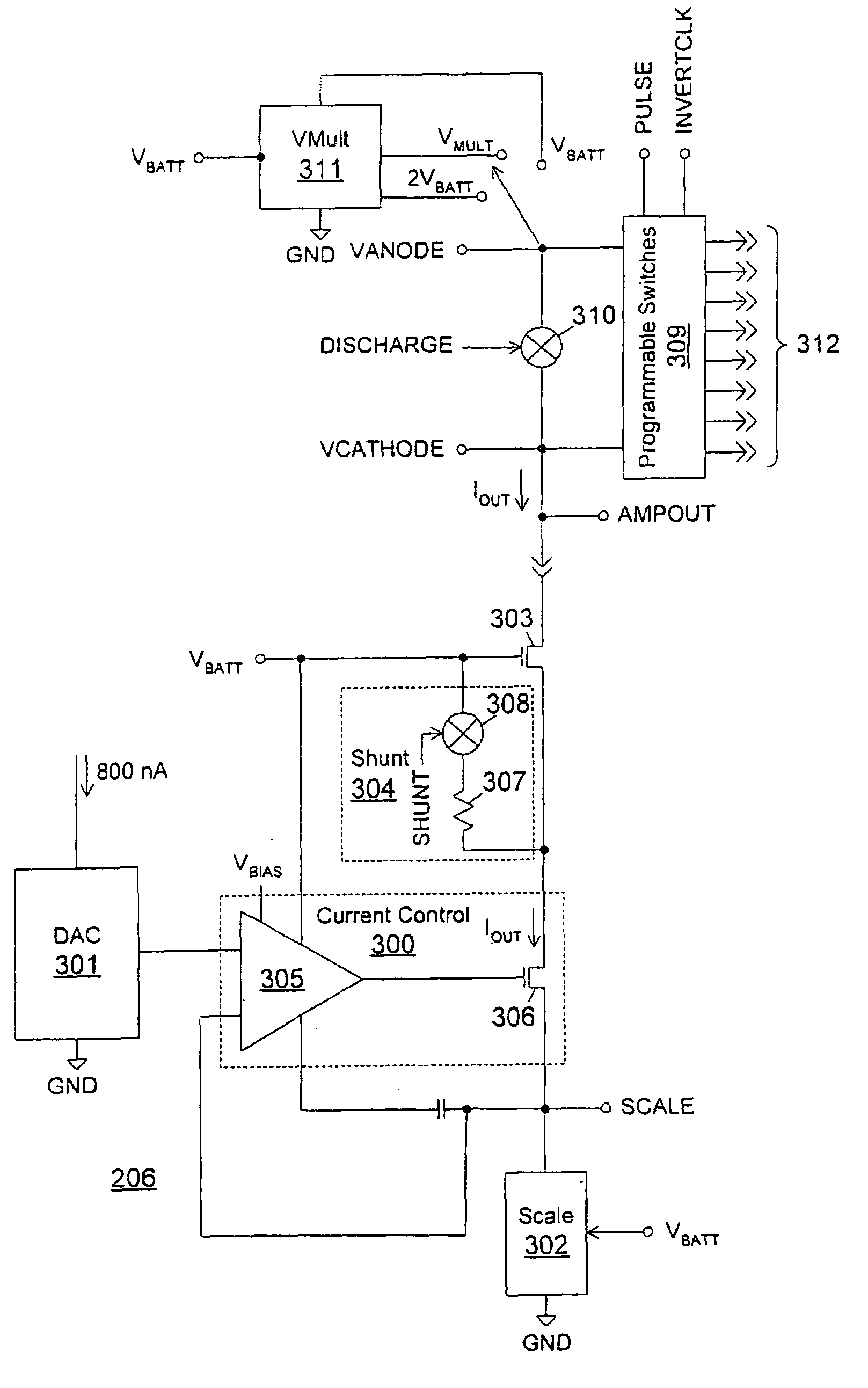
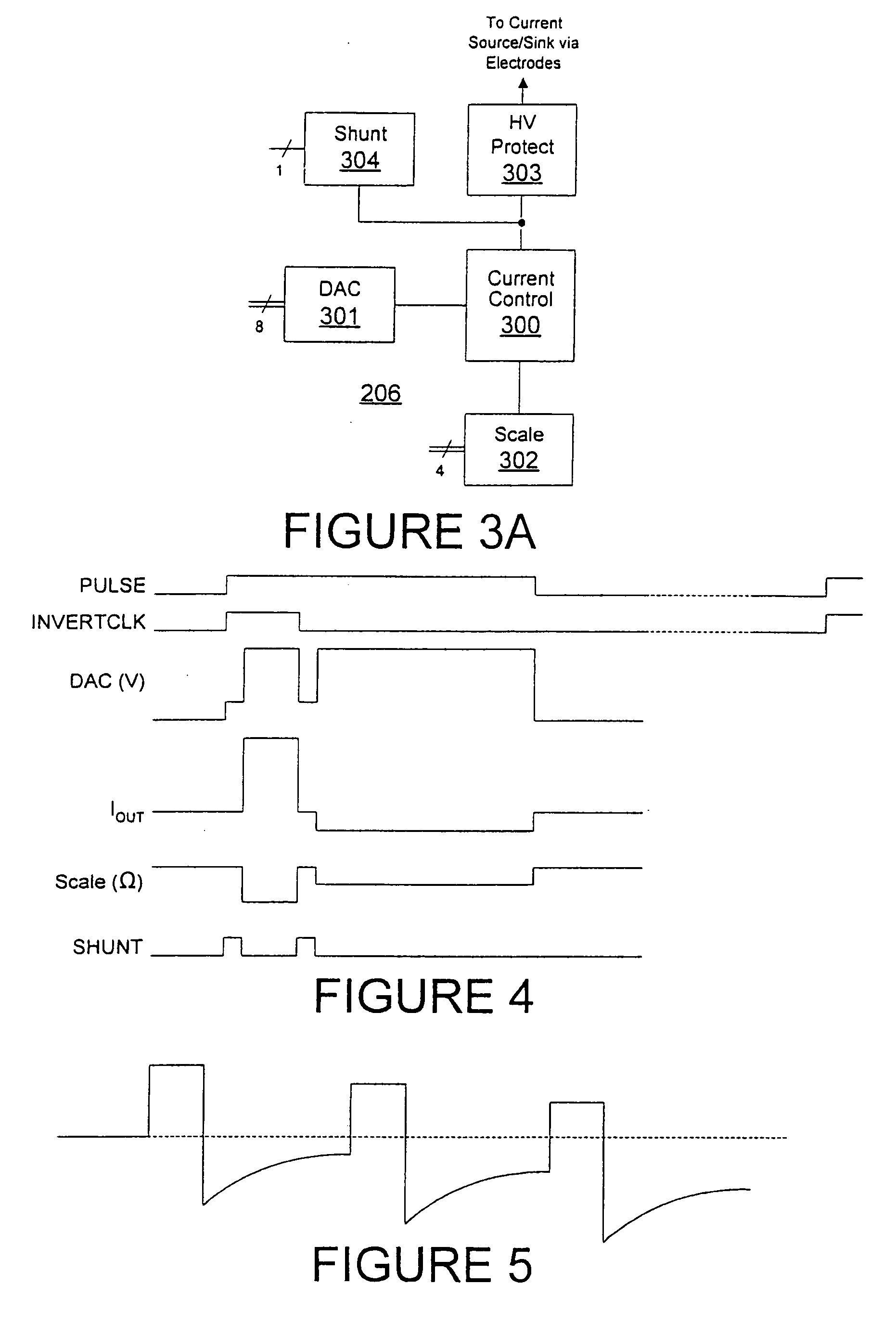
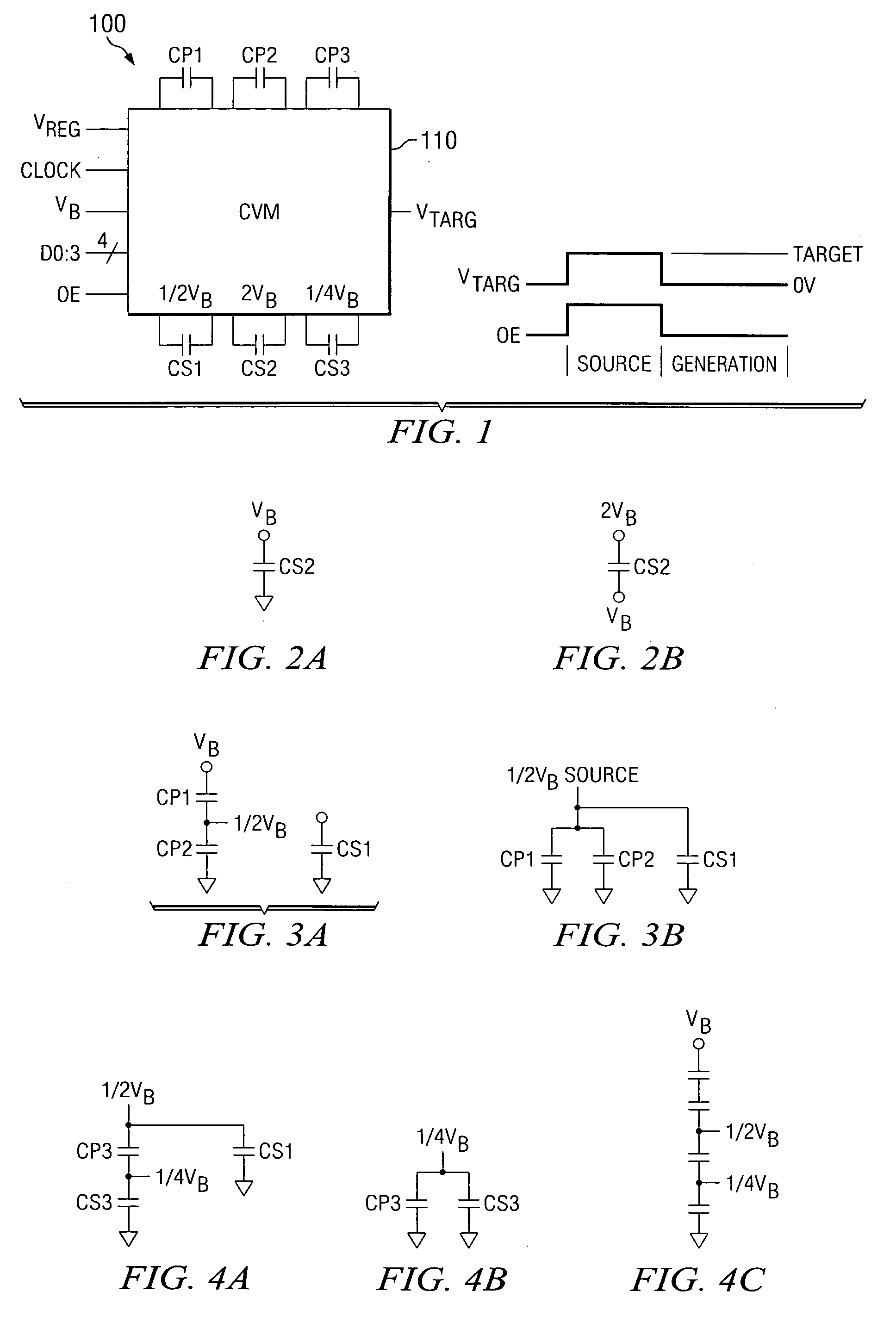
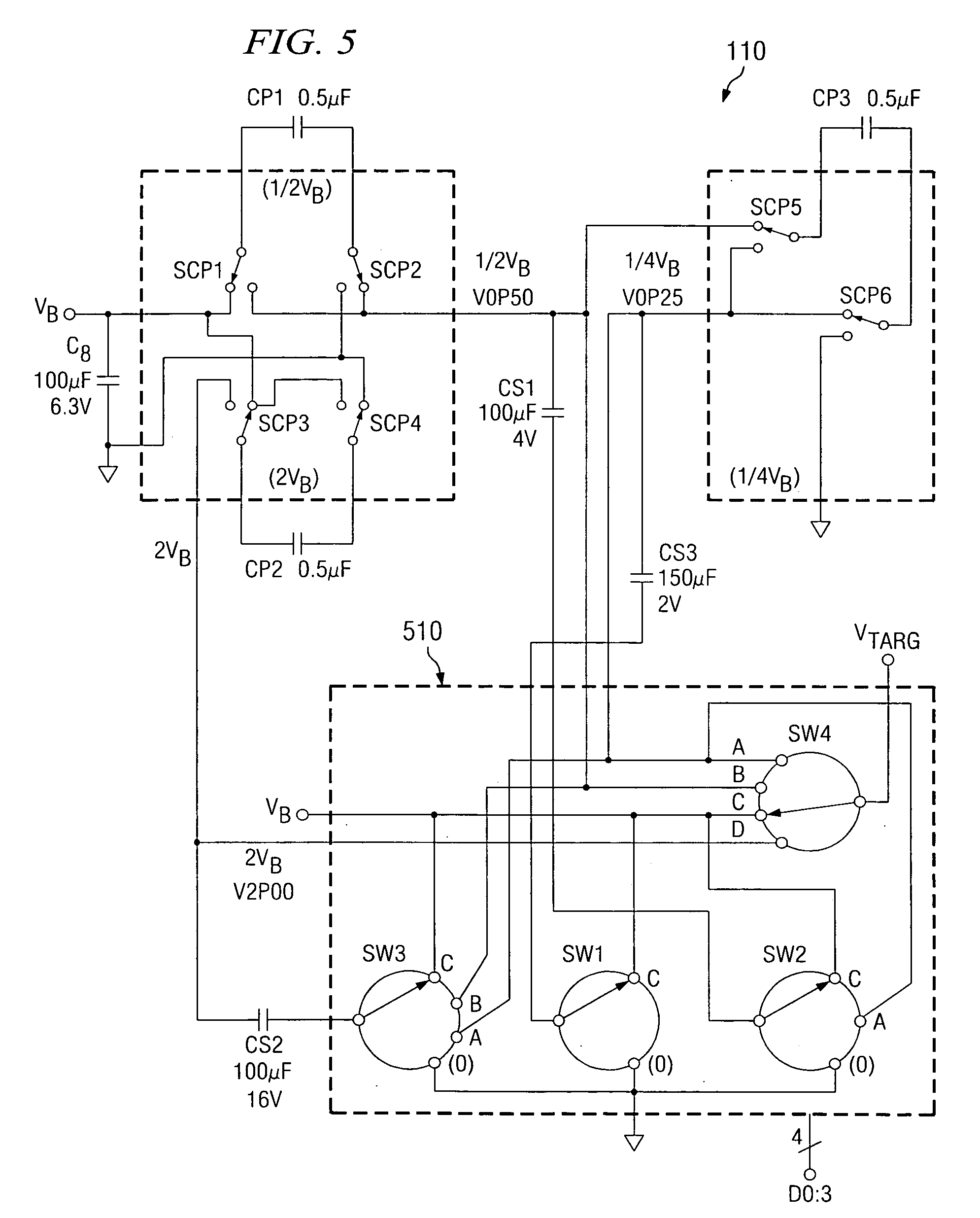
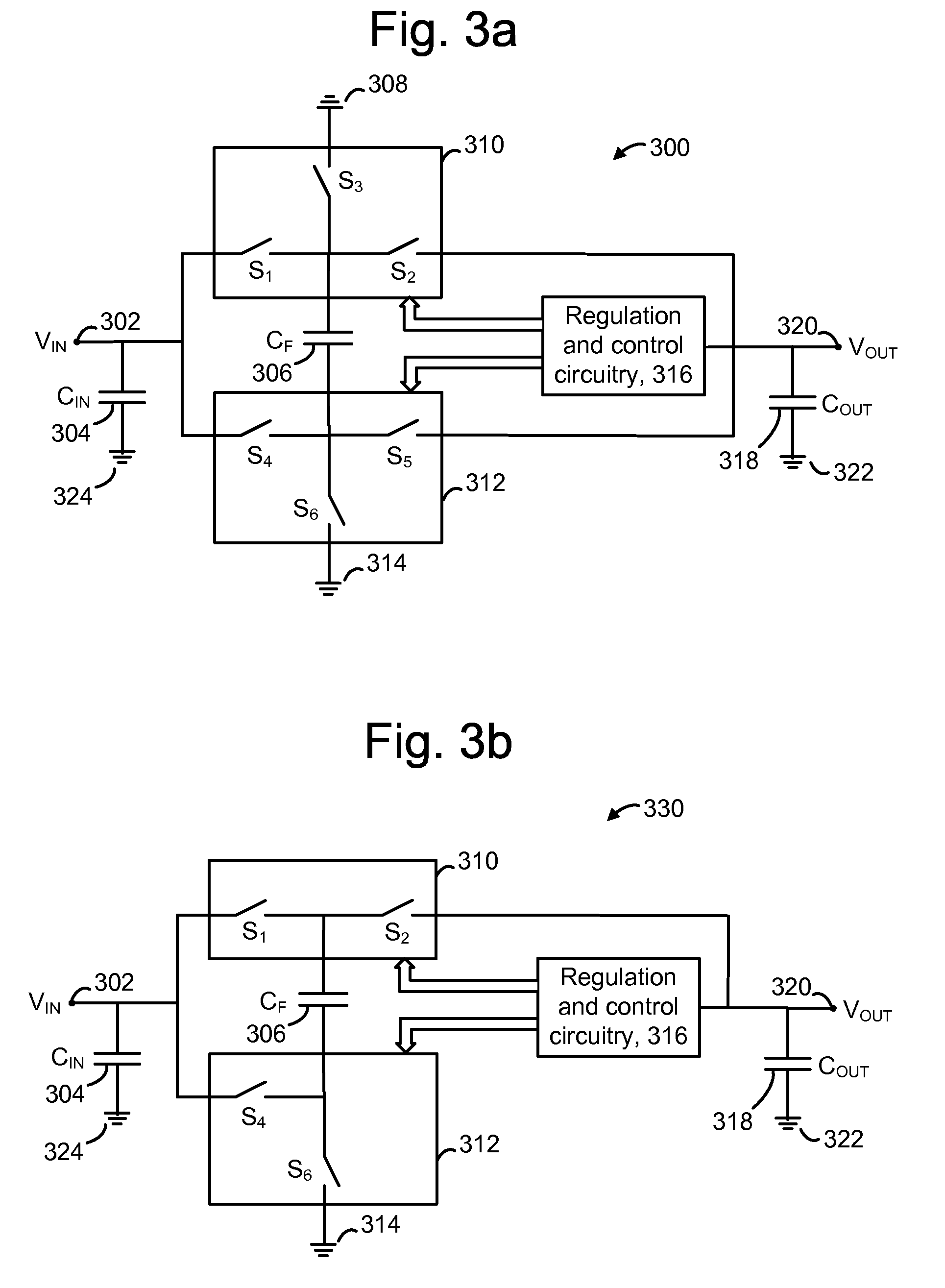
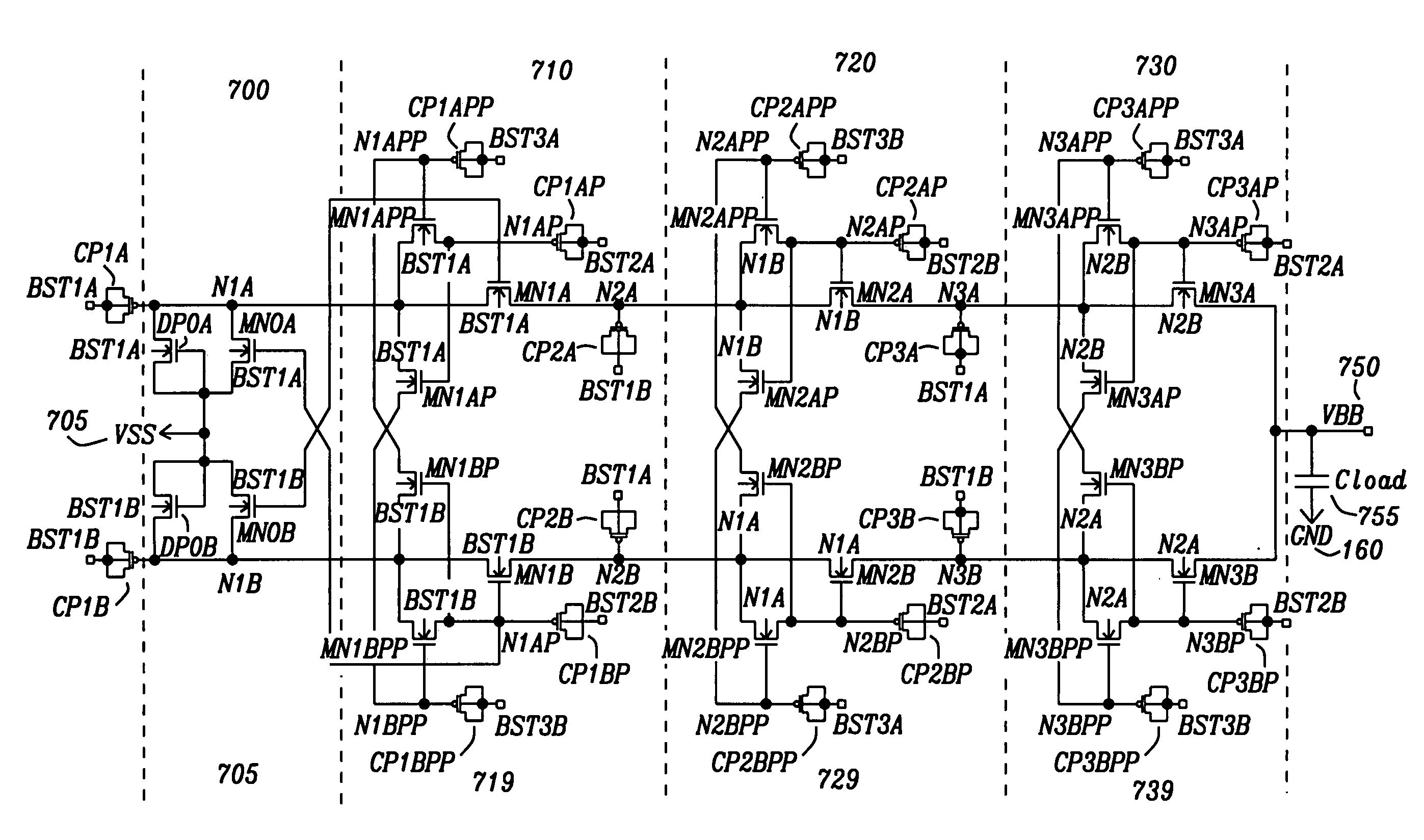
Method of efficiently performing fractional voltage conversion and system comprising efficient fractional voltage converter circuitry
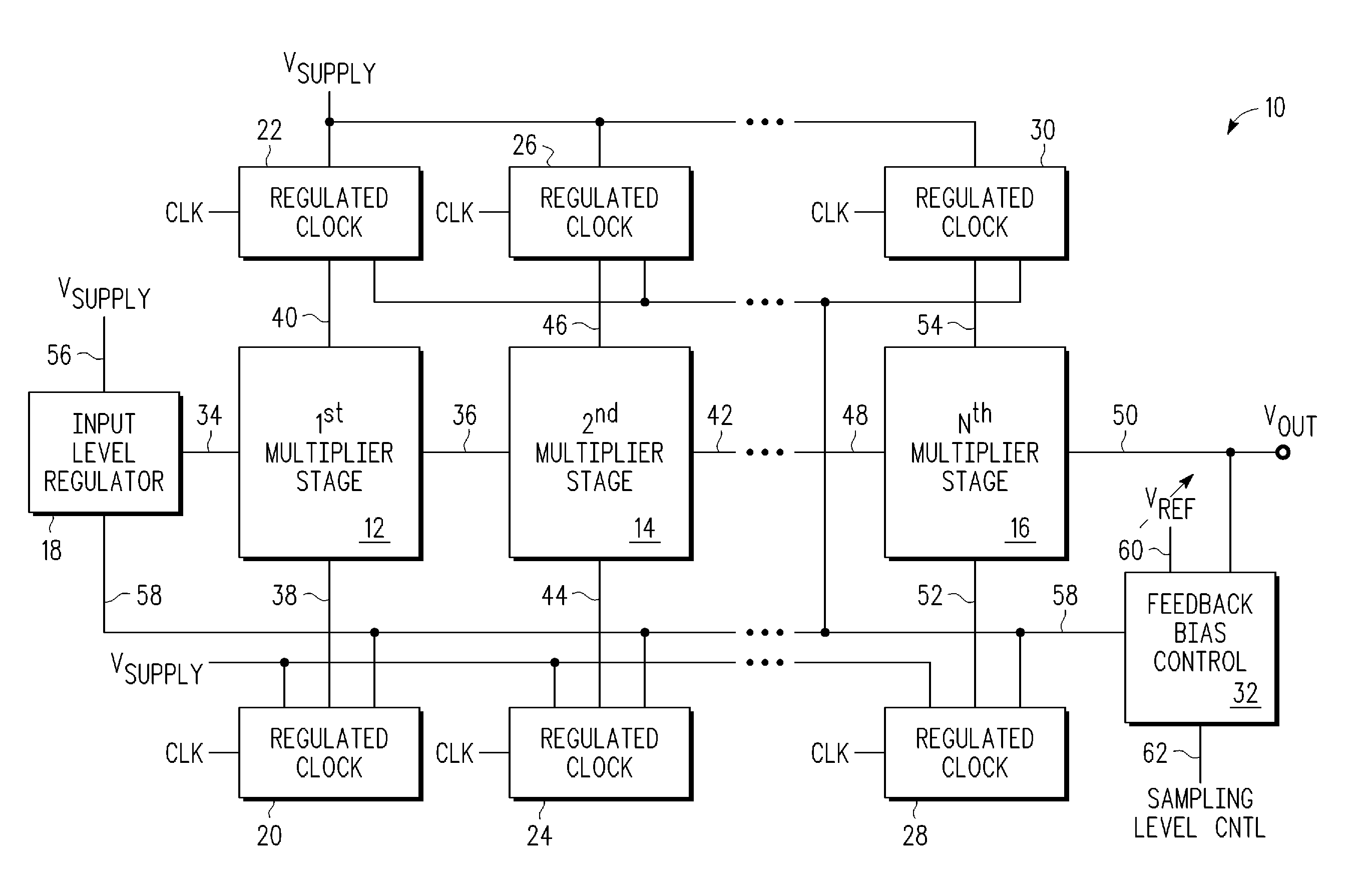
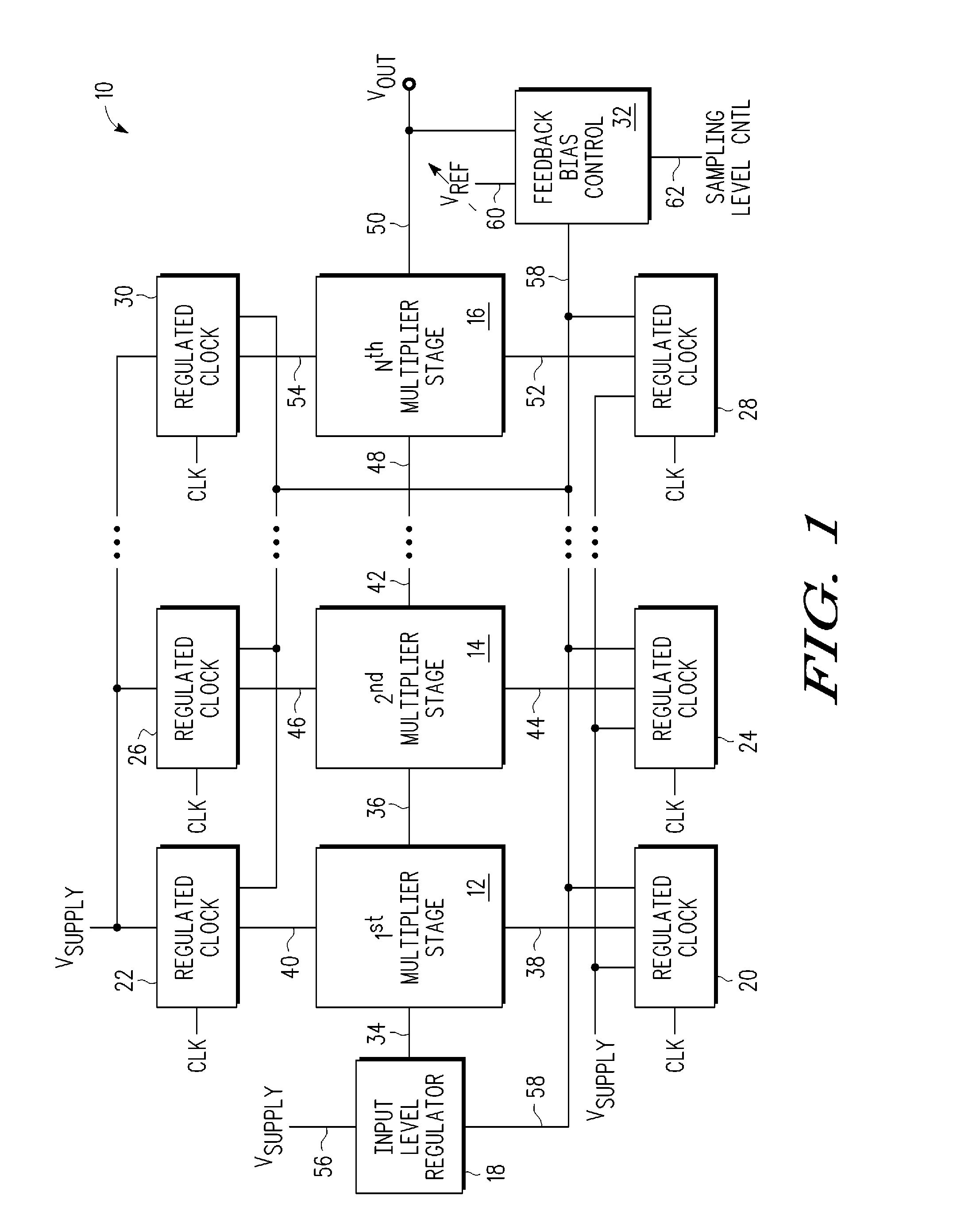
Embodiments provide a capacitive voltage multiplier for efficiently producing multiples, including fractional multiples, of a power supply voltage use high, medium and low voltage field effect transistors for switching terminals of various capacitors into and out of connection with power supply or ground voltages in charge mode and with an output or other capacitor terminals for series connection in pump mode. A single non-overlapping clock is level-shifted up to the maximum voltage level required for switching to produce a desired output, then level shifted back down to lower levels with delay added as necessary according to embodiments.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
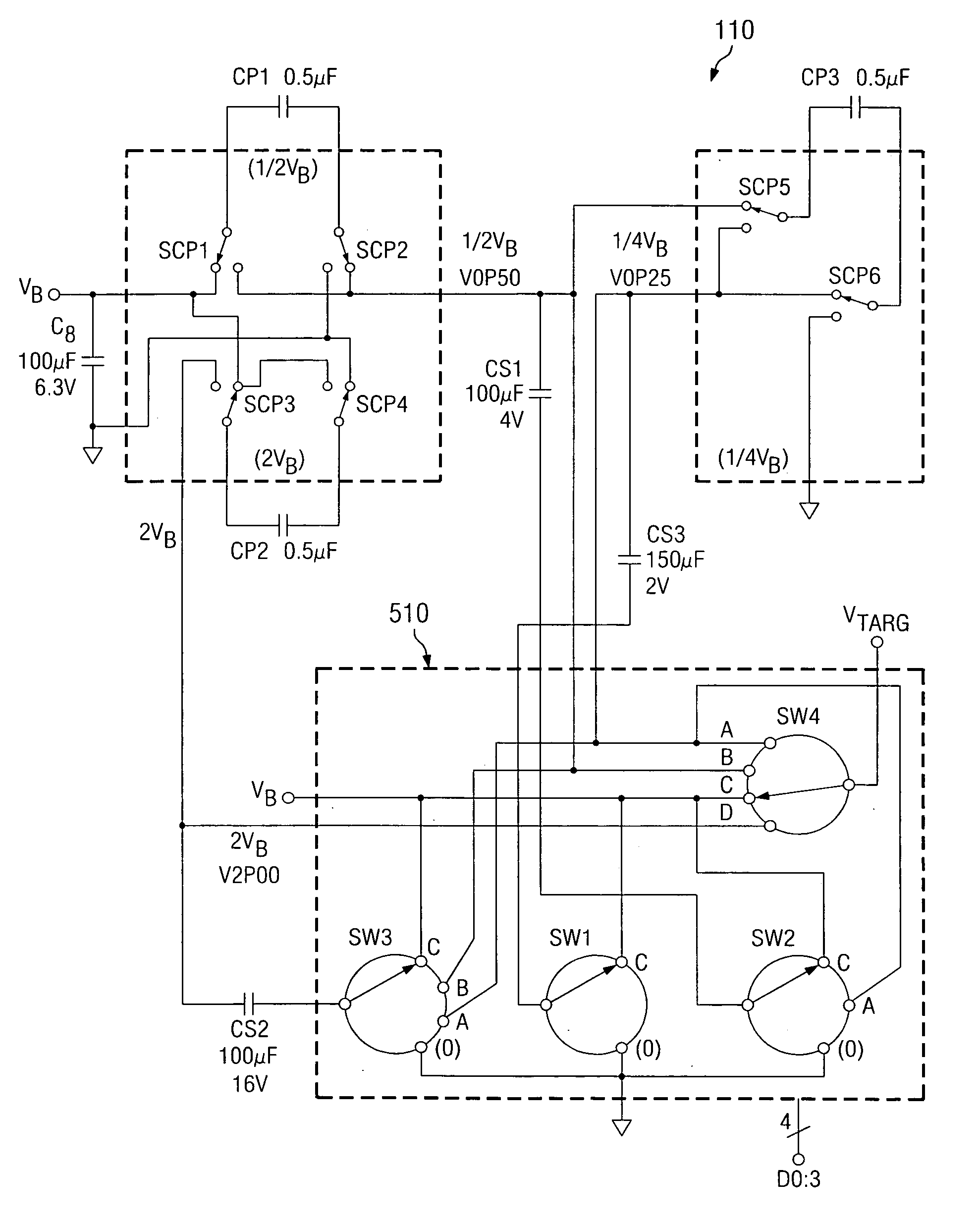
Pulse generator having an efficient fractional voltage converter and method of use
InactiveUS20060170486A1Minimize the number of componentsReduce in quantityElectrotherapyApparatus without intermediate ac conversionVoltage converterVoltage multiplier
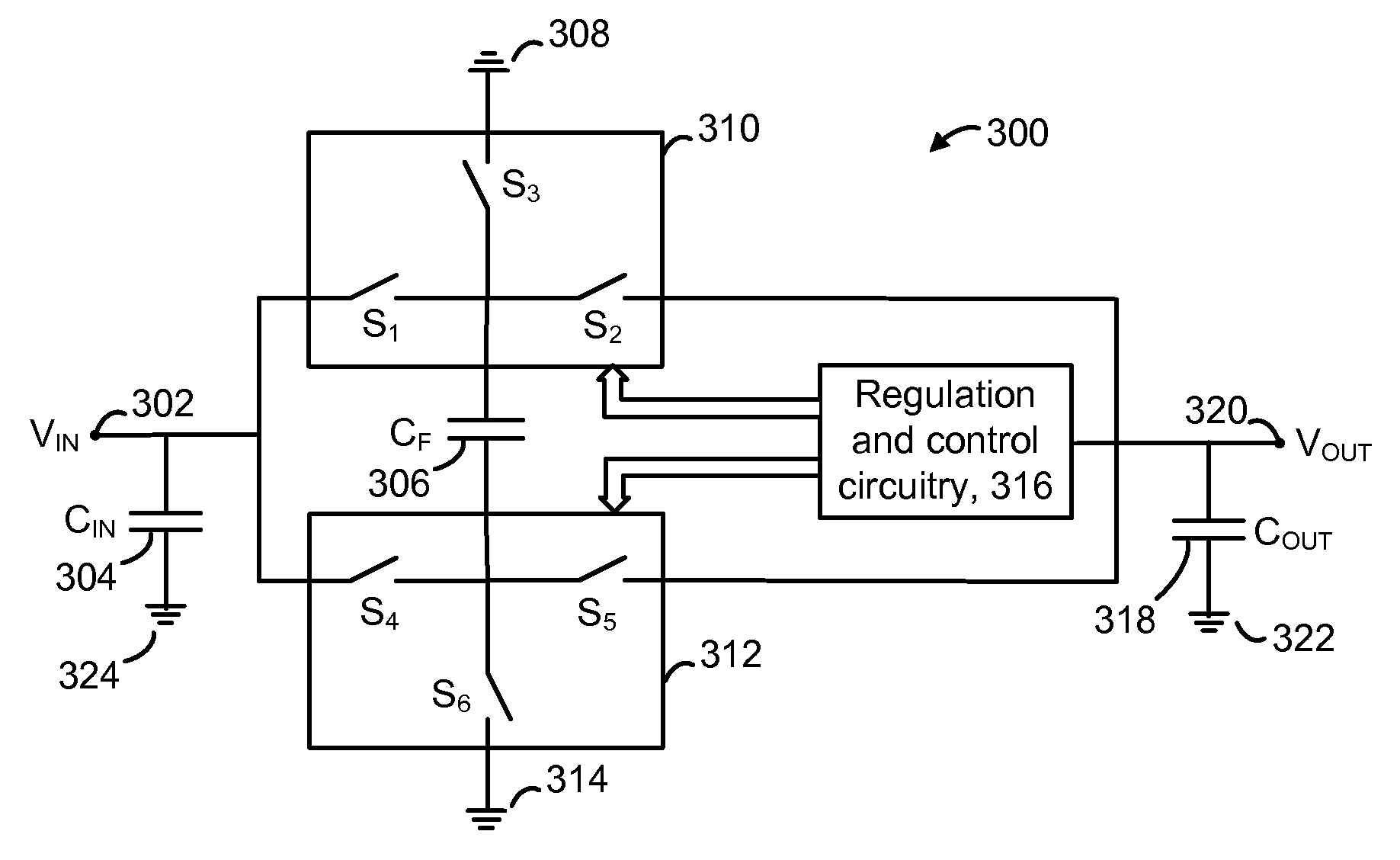
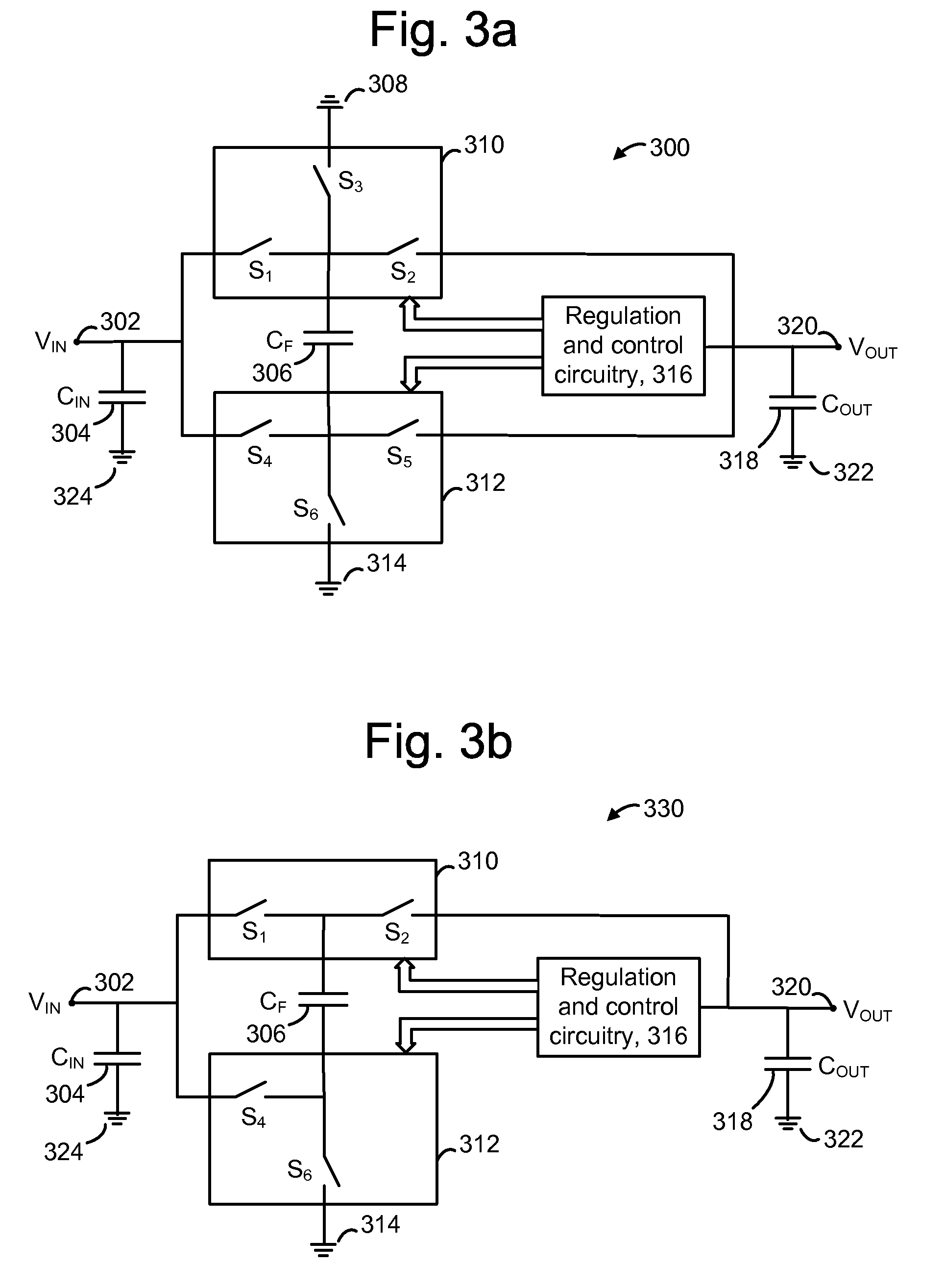
Disclosed are systems and methods which provide voltage conversion in increments less than integer multiples of a power supply (e.g., battery) voltage. A representative embodiment provides power supply voltage multipliers in a binary ladder distribution to provide a desired number of output voltage steps using a relatively uncomplicated circuit design. By using different sources in various combinations and / or by “stacking” different sources in various ways, the voltage multiplier circuit may be used to provide desired voltages. In order to minimize the number of components used in a voltage converter of an embodiment, a capacitive voltage converter circuit uses one or more storage capacitors in place of pump capacitors in a voltage generation cycle. Also, certain embodiments do not operate to generate an output voltage until the time that voltage is needed.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
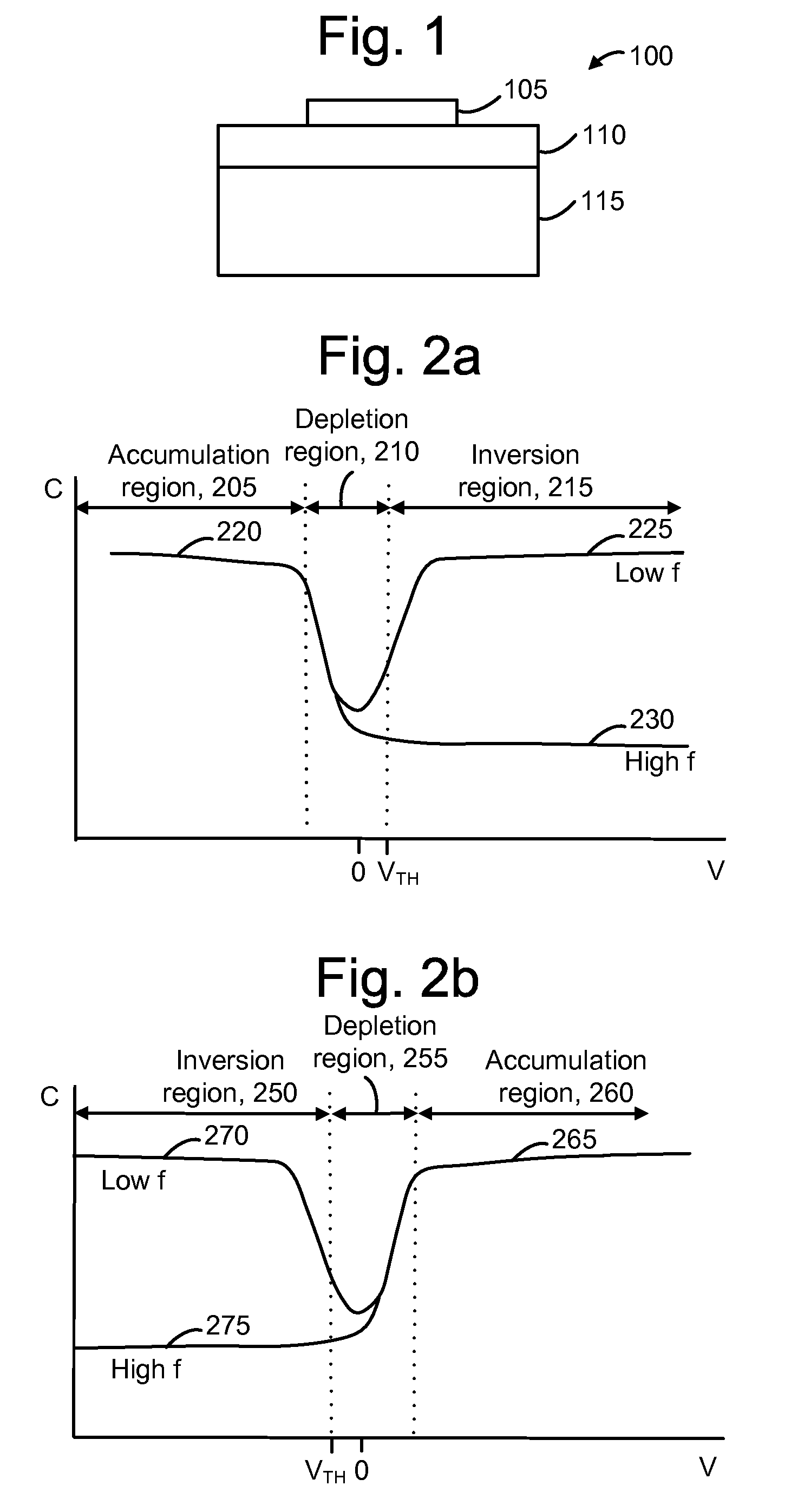
Charge coupled pump-efficient charge pump regulator with MOS capacitor
ActiveUS8040174B2Easy to operateCurrent/voltage measurementInstant pulse delivery arrangementsCapacitanceVoltage multiplier
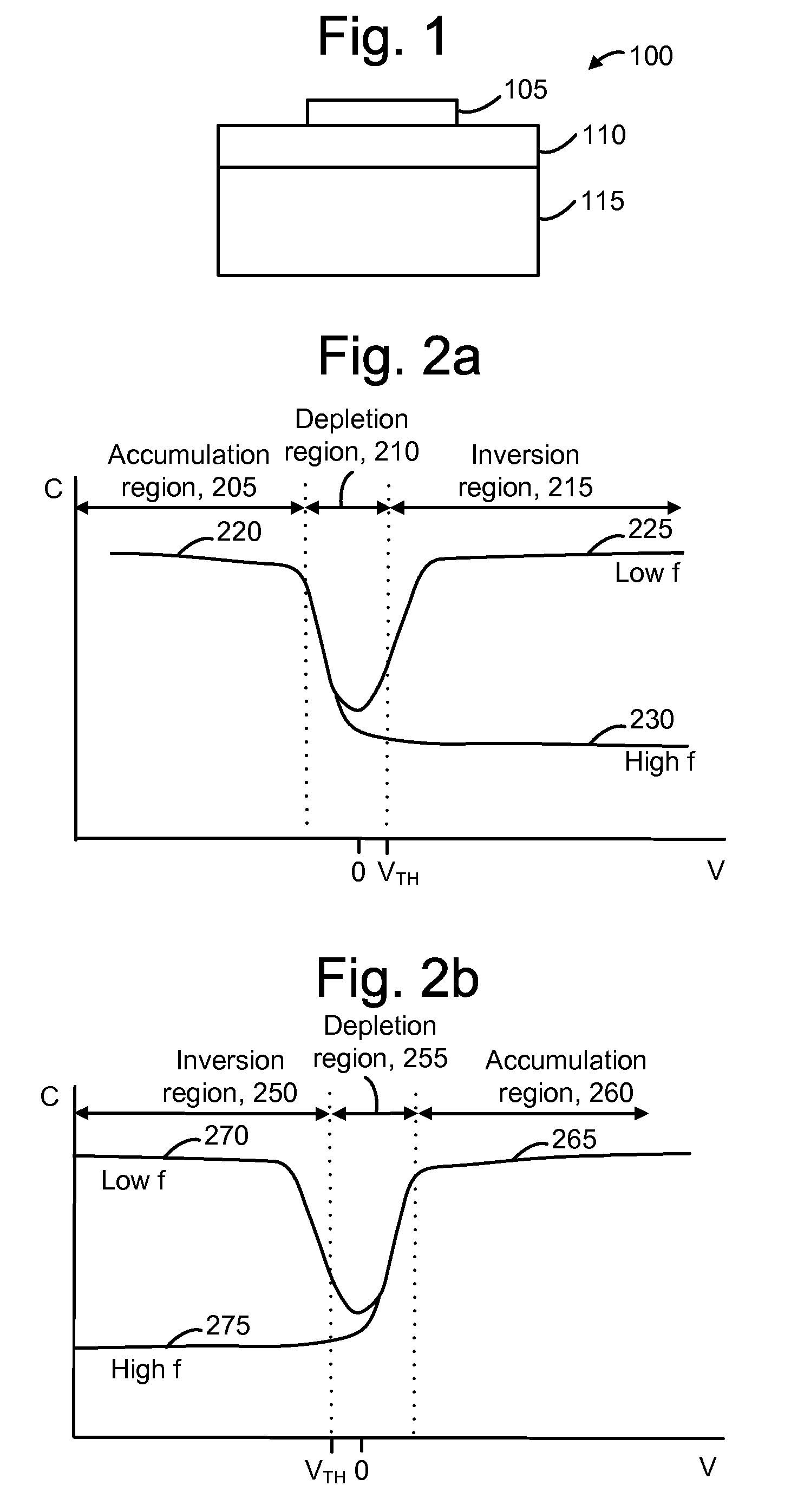
A charge pump with a MOS-type capacitor, where the MOS-type capacitor is operated in an inversion region in which capacitance varies as a function of the frequency of the applied signal. The charge pump is switched to transfer charge from an input node to the capacitor and from the capacitor to an output node. During a transition interval, a relatively high frequency switching signal is used to lower the capacitance and increase efficiency. During a settling interval, a relatively low frequency switching signal is used, in which case the capacitance is higher, but similar to a level which would be seen if the capacitor was operated in an accumulation region. MOS capacitor dimensions and switching intervals are mutually optimized to provide high efficiency and required throughput. The charge pump may be configured as a voltage multiplier, divider, inverter or follower, for instance.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL ISRAEL LTD
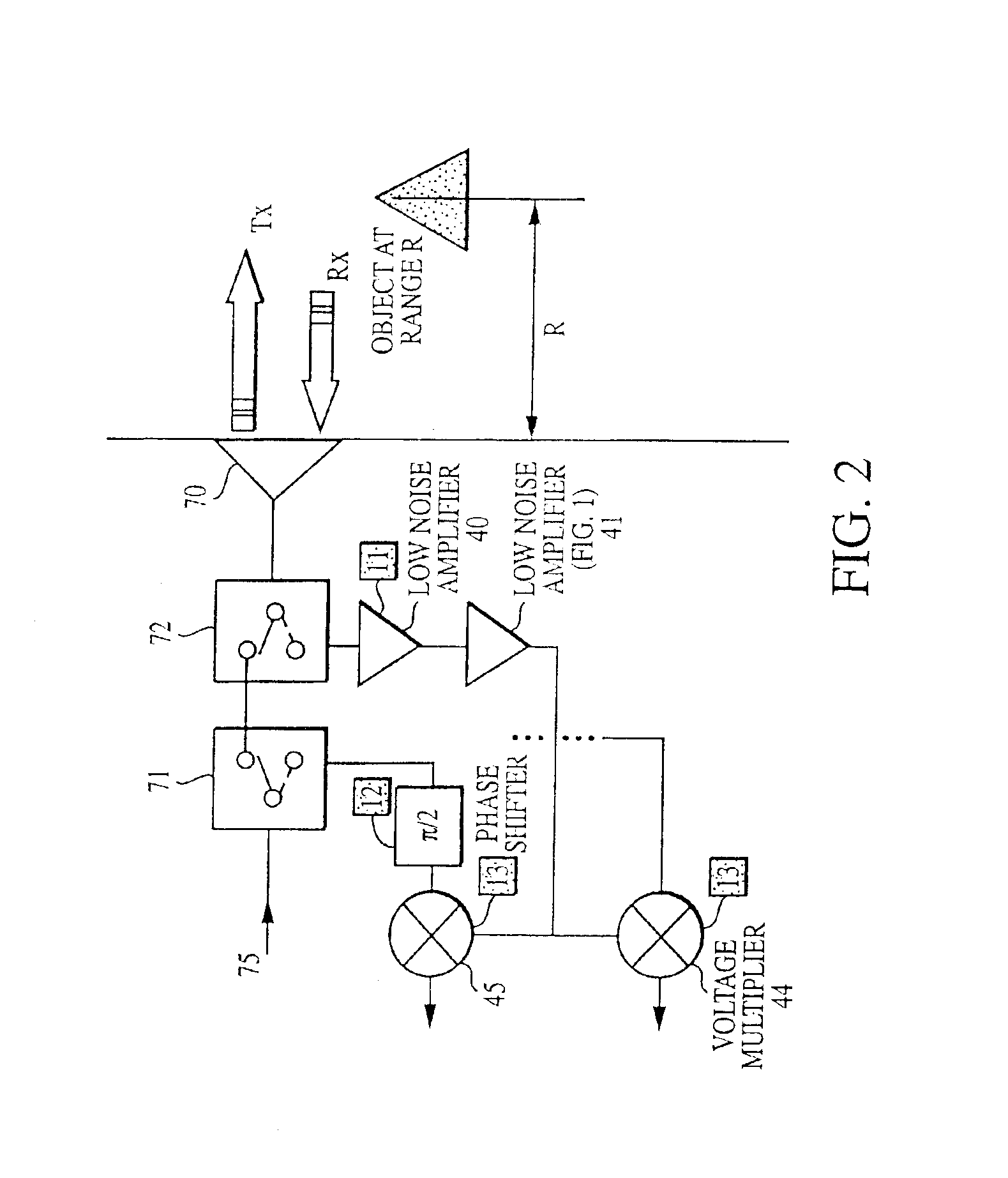
Pulse radar detection system
InactiveUS6879281B2Improve immunityShort-range discriminationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsRadar detection
A radar based sensor detection system comprises a microwave source operative to provide a continuous wave signal at an output. A pulse-former is coupled to the output of the source and is operative to provide at an output a variable length pulse that increases the transmitted energy of the radar system according to the range of object detection. A modulator is coupled to the output of the pulse-former for providing a modulated pulse signal when required. A transmit / receive switch coupled to the output of the modulator is selectively operative between a first transmit position and a second receive position. A transmit channel coupled to the transmit / receive switch transmits the pulse signal when the switch is operated in the transmit position. A receiving channel coupled to the transmit / receive switch receives the modulator signal when the switch is operated in the receive position. First and second voltage multipliers each have a local oscillator input for receiving the modulator signal in the receive position, and each have an input signal port, and an output port. A receiver channel receives a reflected transmitted signal from an object and applies the received signal to the receive signal input ports of the voltage multipliers. An autocorrelator coupled to the output ports of the voltage multipliers correlates the received signal to produce an output signal indicating the detection and position of the object.
Owner:VEONEER US LLC
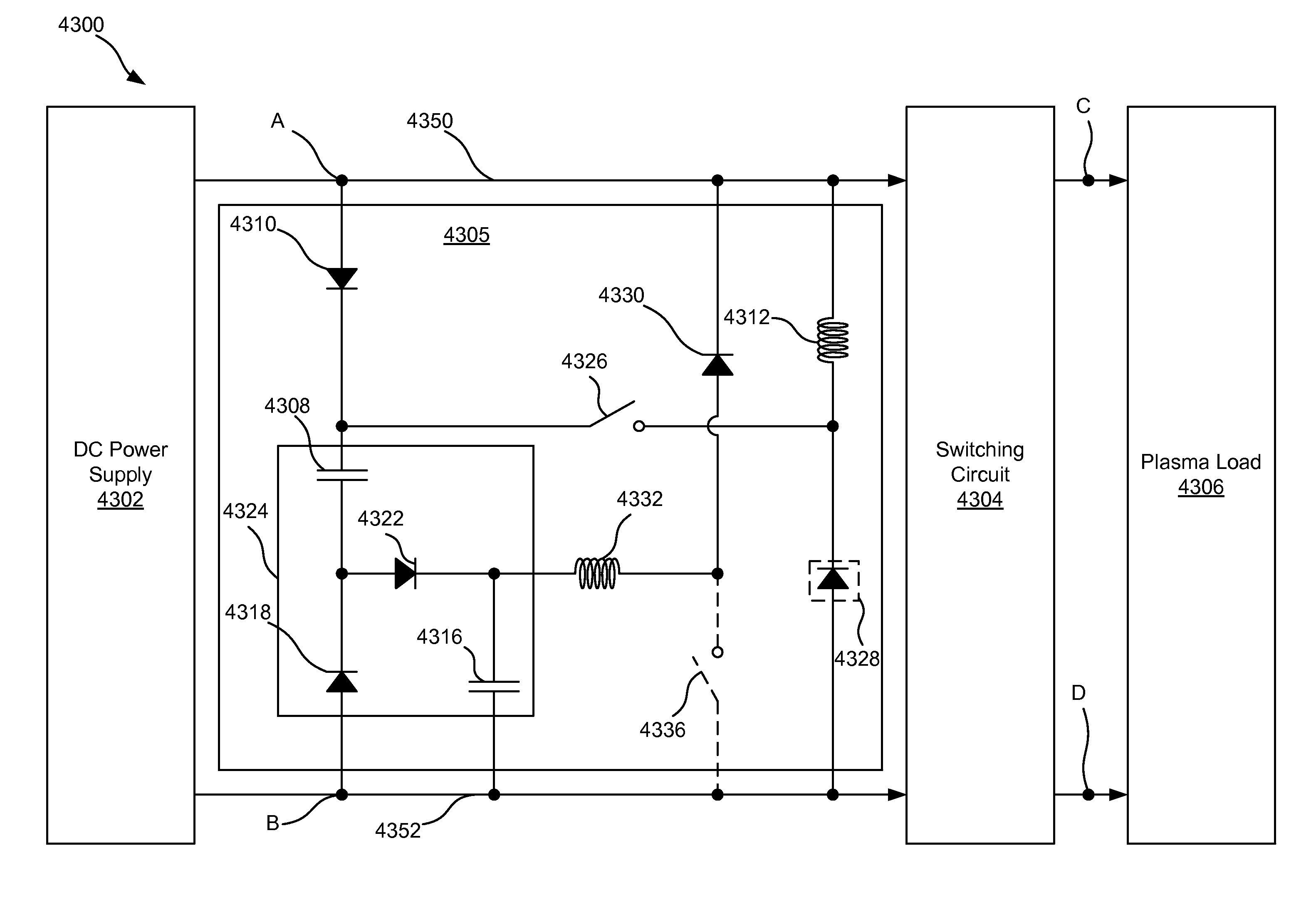
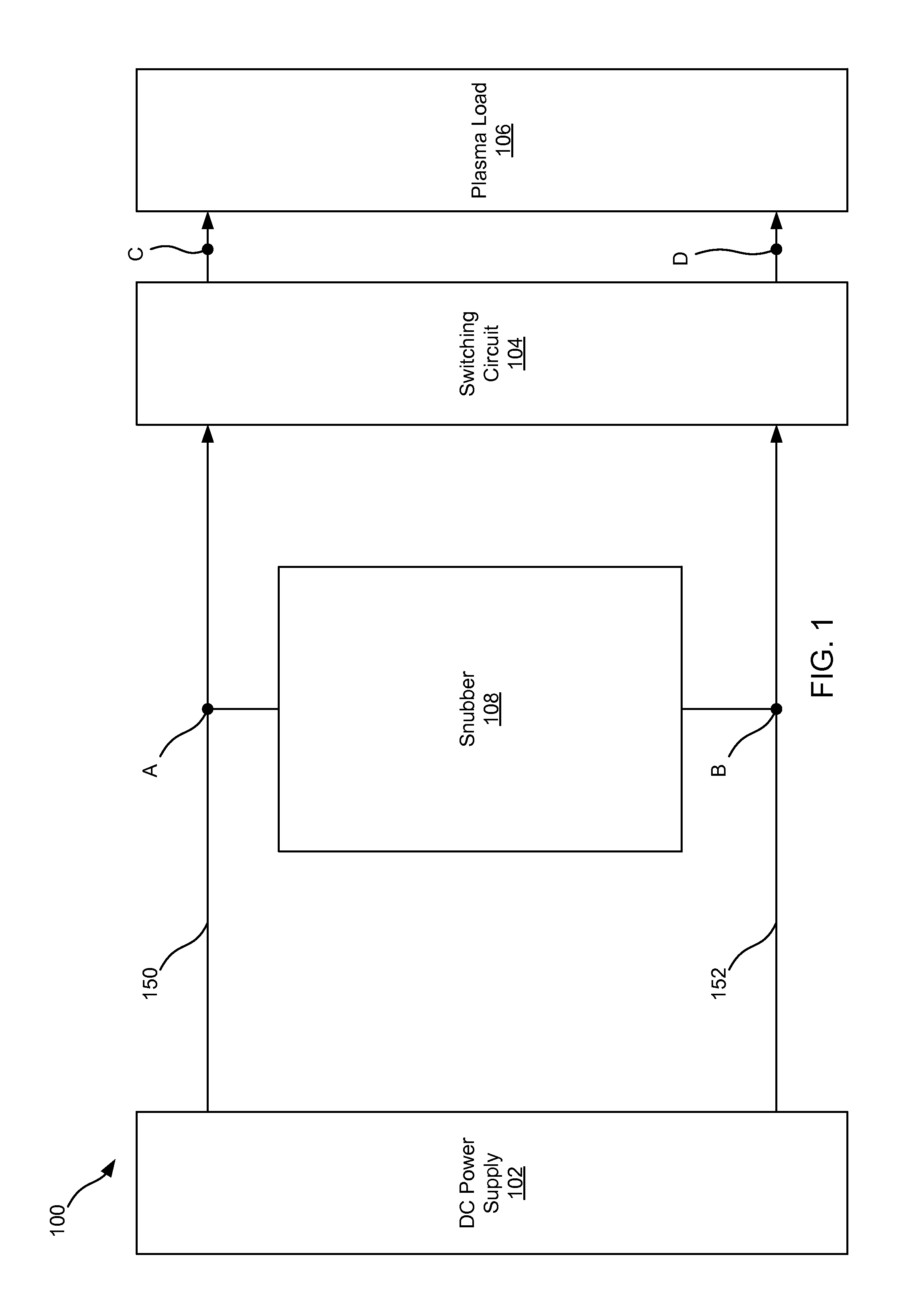
Charge removal from electrodes in unipolar sputtering system
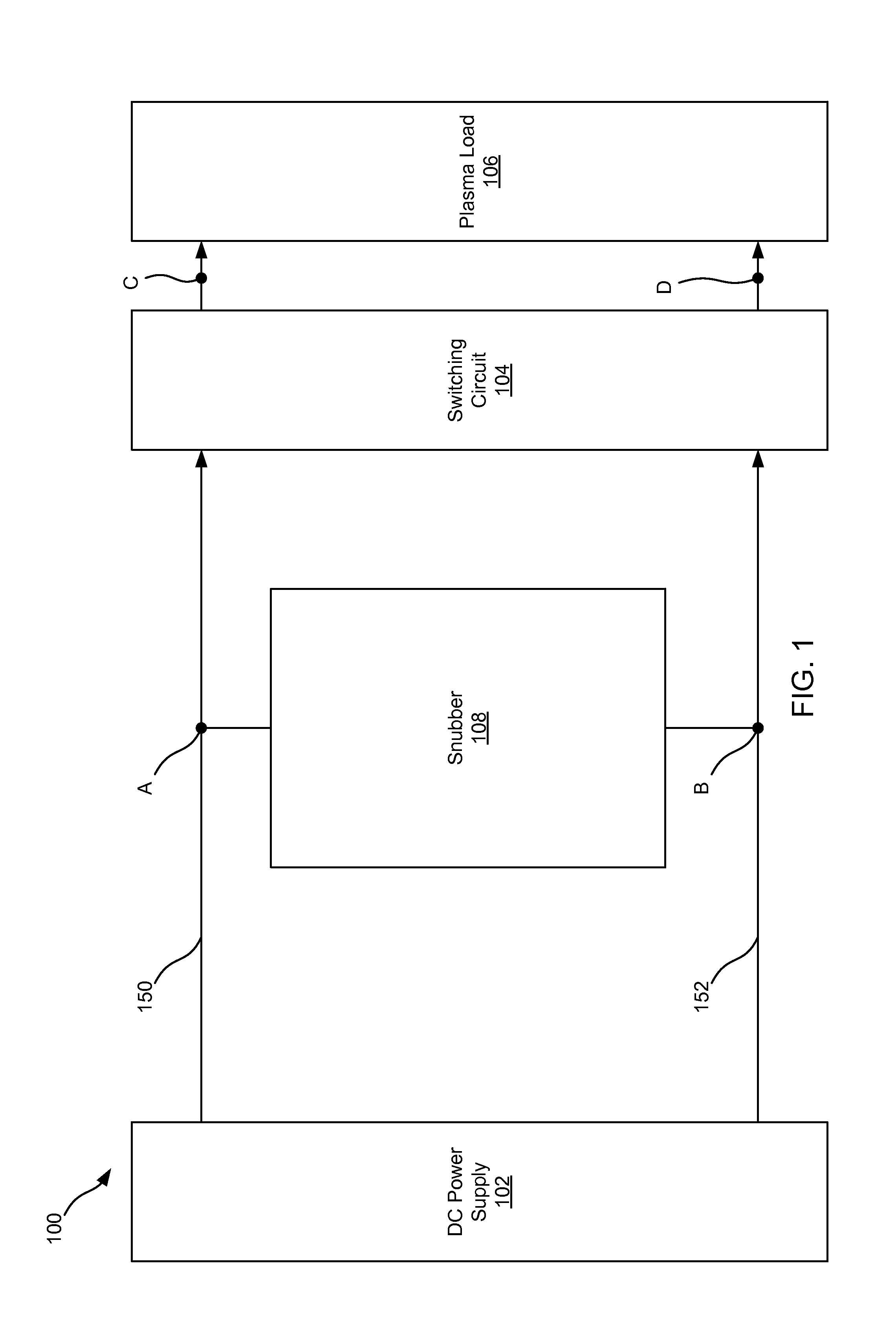
ActiveUS20140231243A1Boost voltageReduce voltageCellsElectric discharge tubesVoltage multiplierEngineering
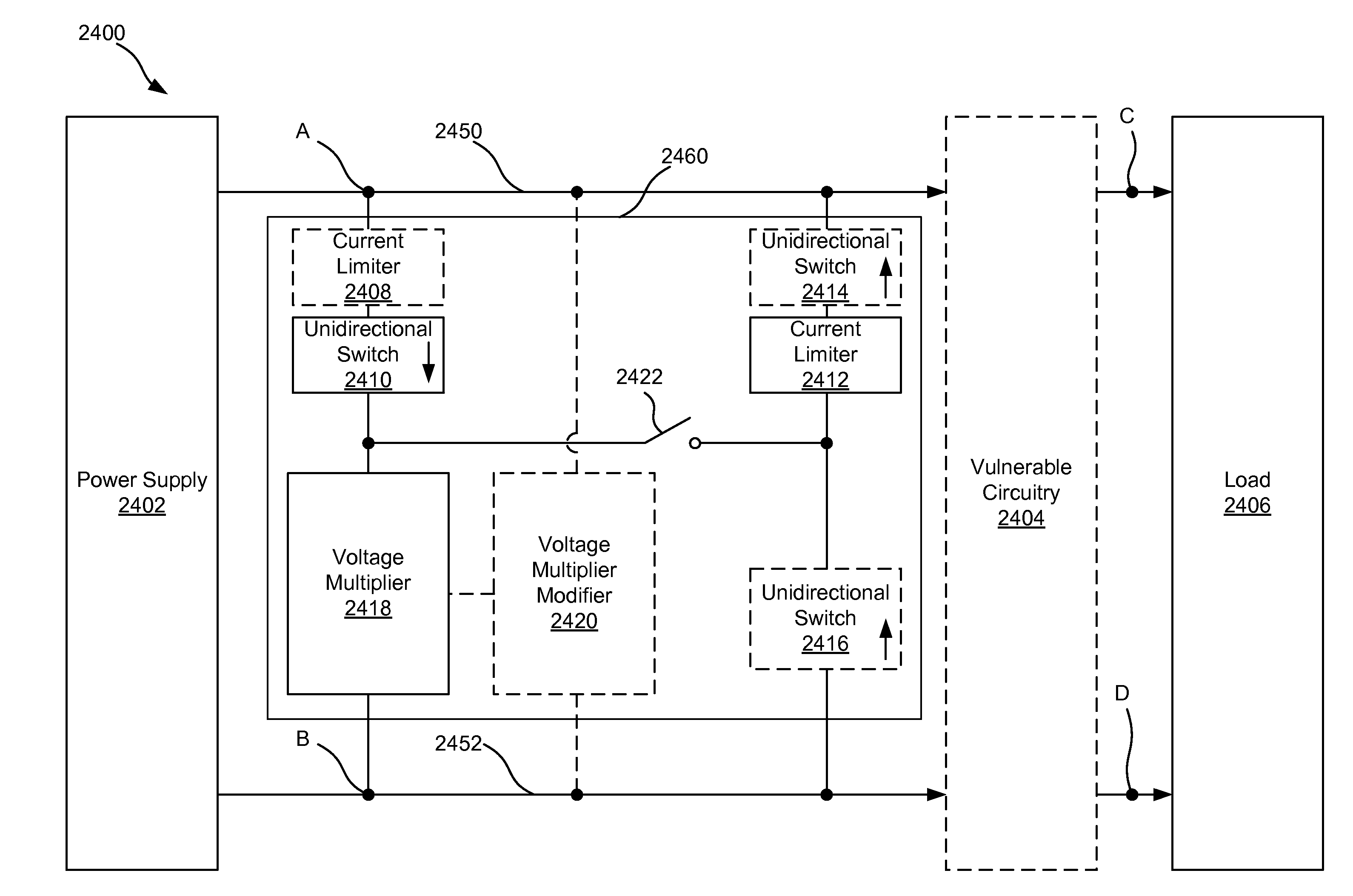
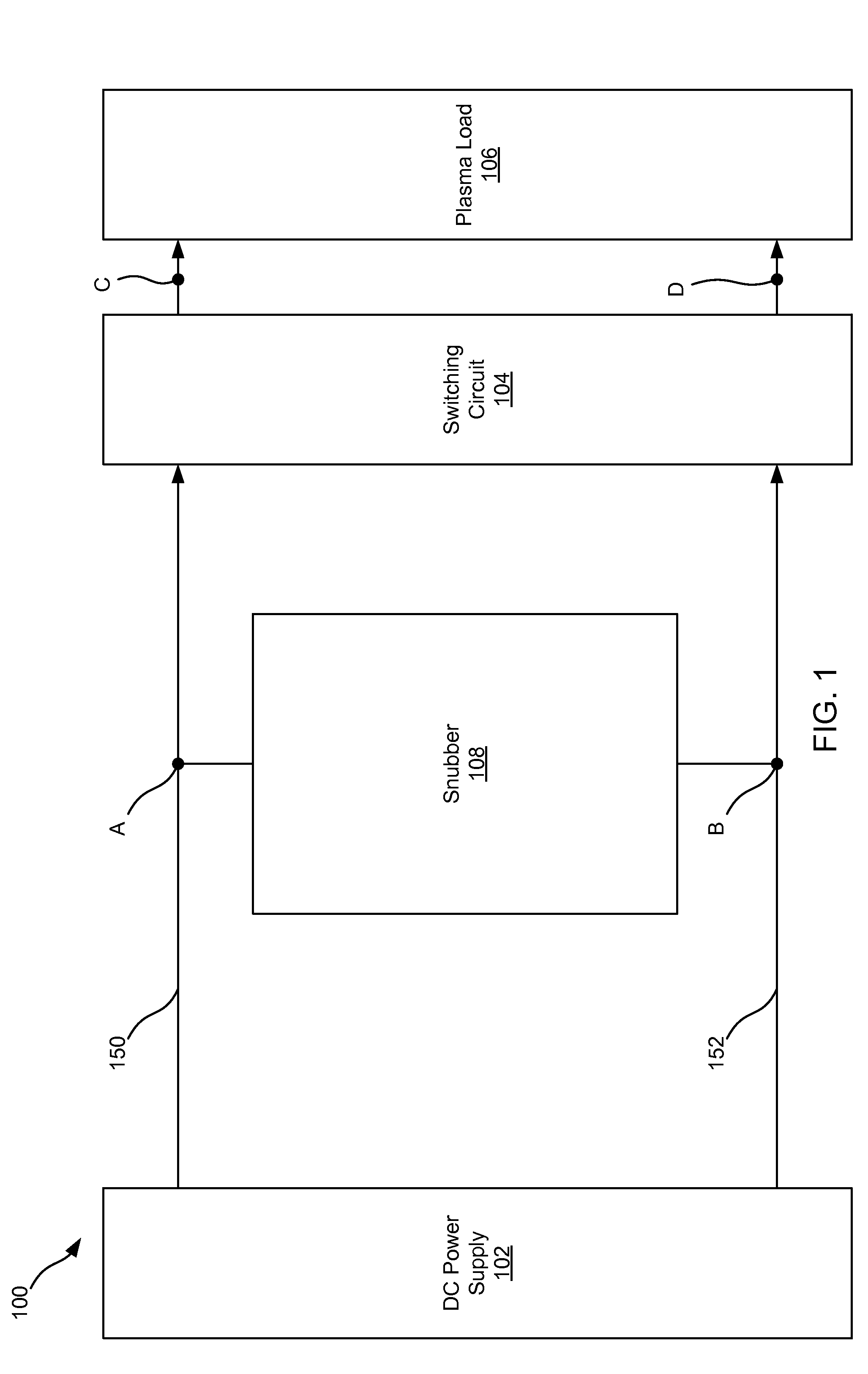
This disclosure describes a non-dissipative snubber circuit configured to boost a voltage applied to a load after the load's impedance rises rapidly. The voltage boost can thereby cause more rapid current ramping after a decrease in power delivery to the load which results from the load impedance rise. In particular, the snubber can comprise a combination of a unidirectional switch, a voltage multiplier, and a current limiter. In some cases, these components can be a diode, voltage doubler, and an inductor, respectively.
Owner:AES GLOBAL HLDG PTE LTD
Wide range power supply
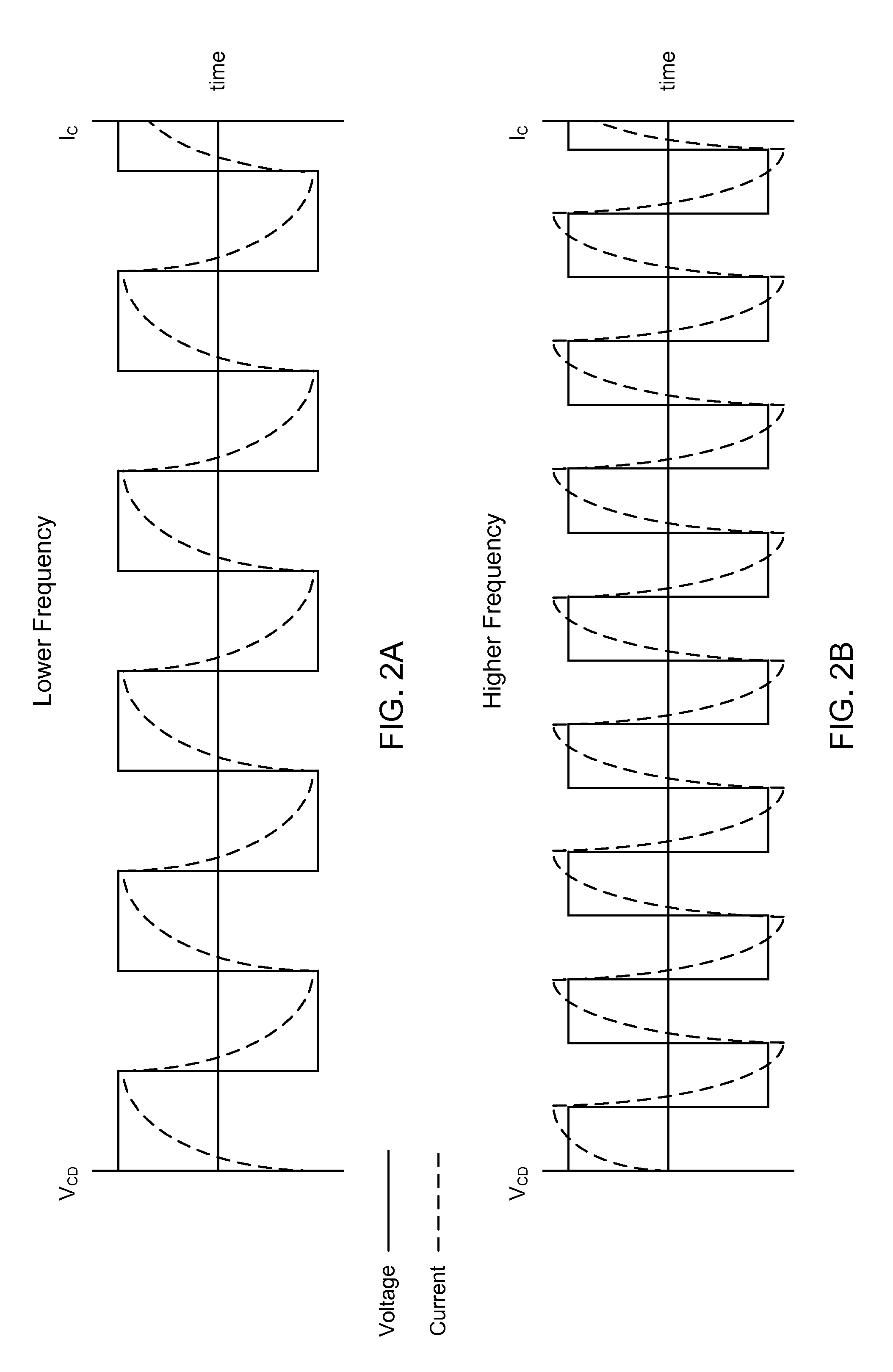
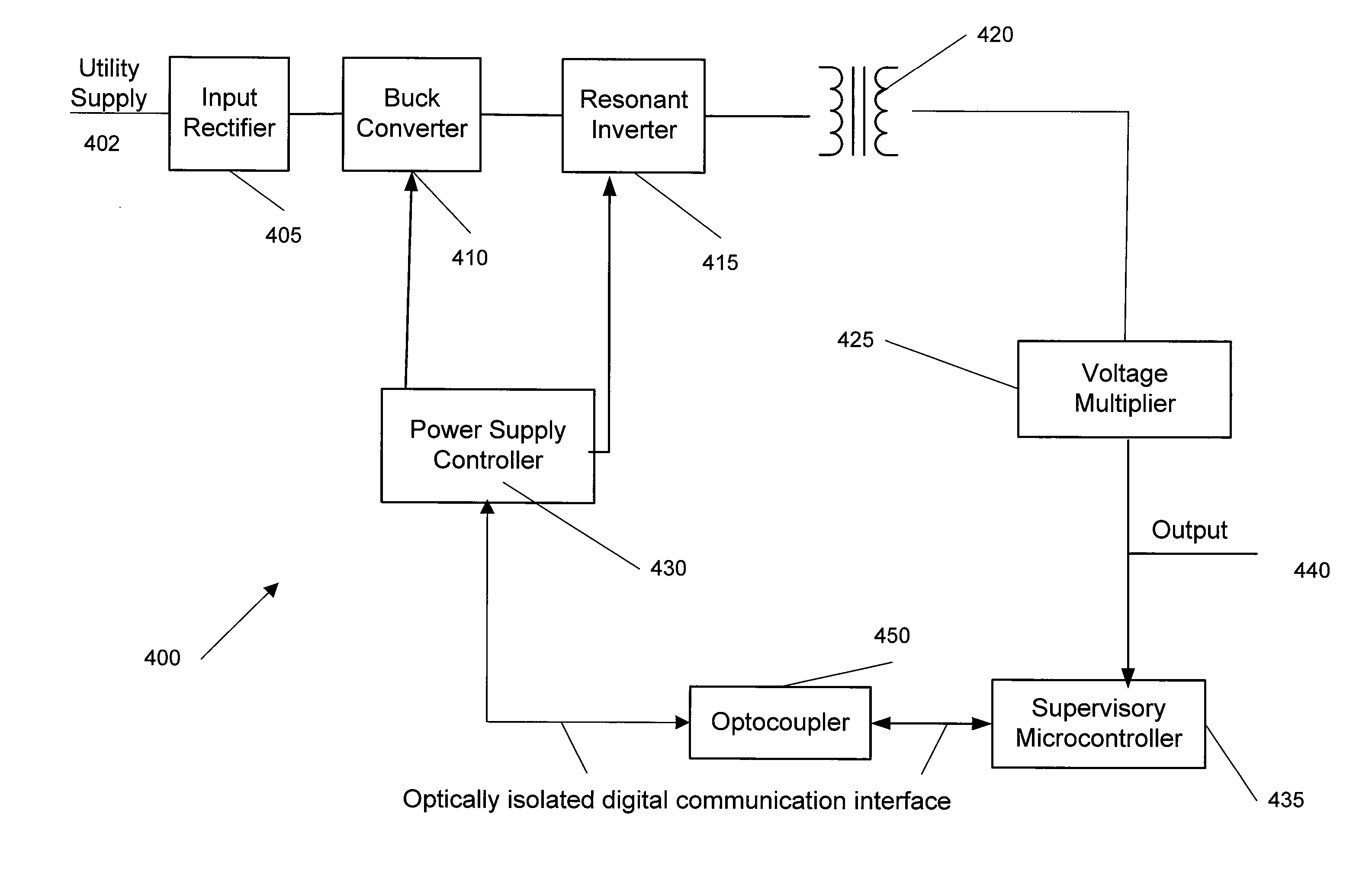
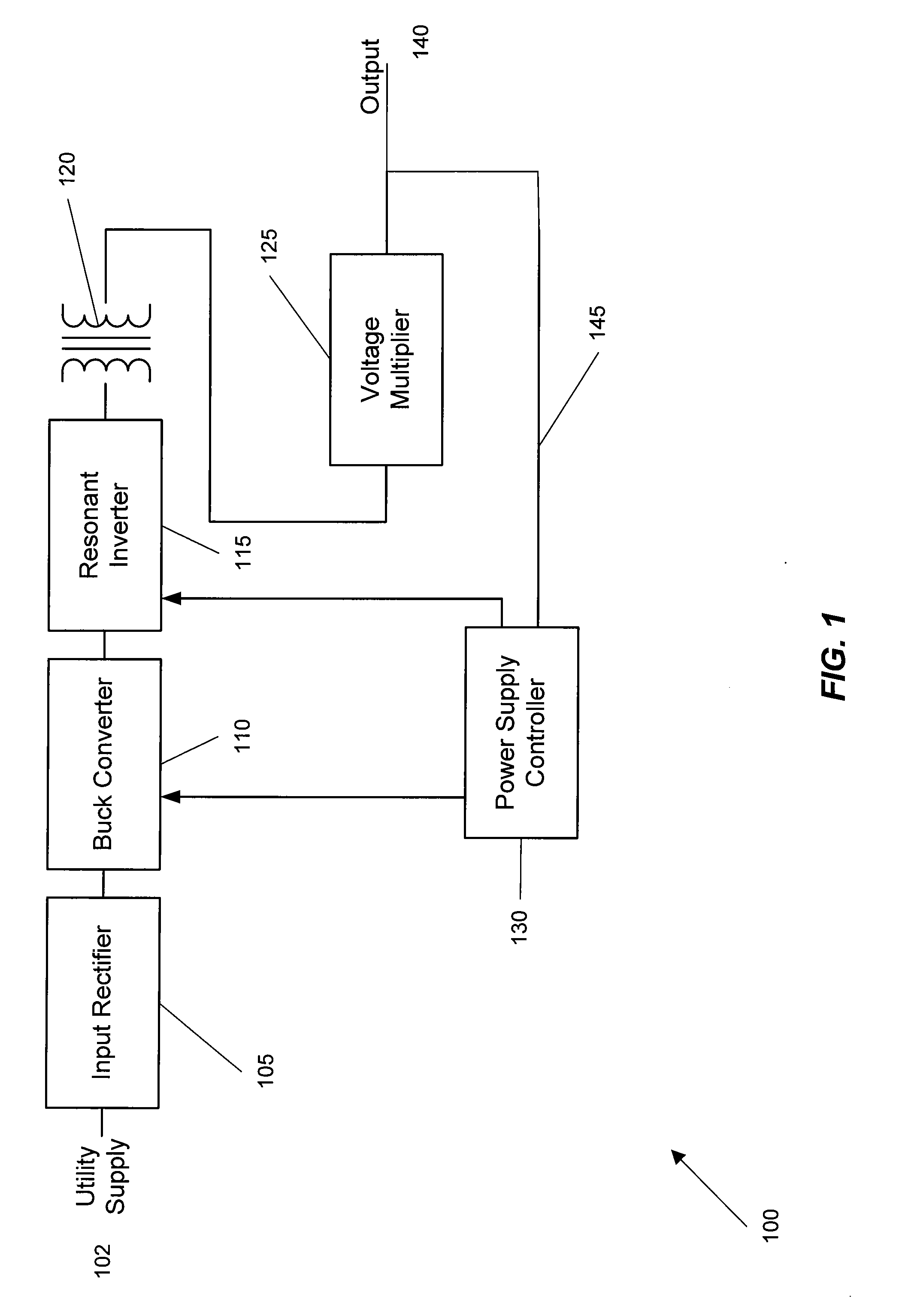
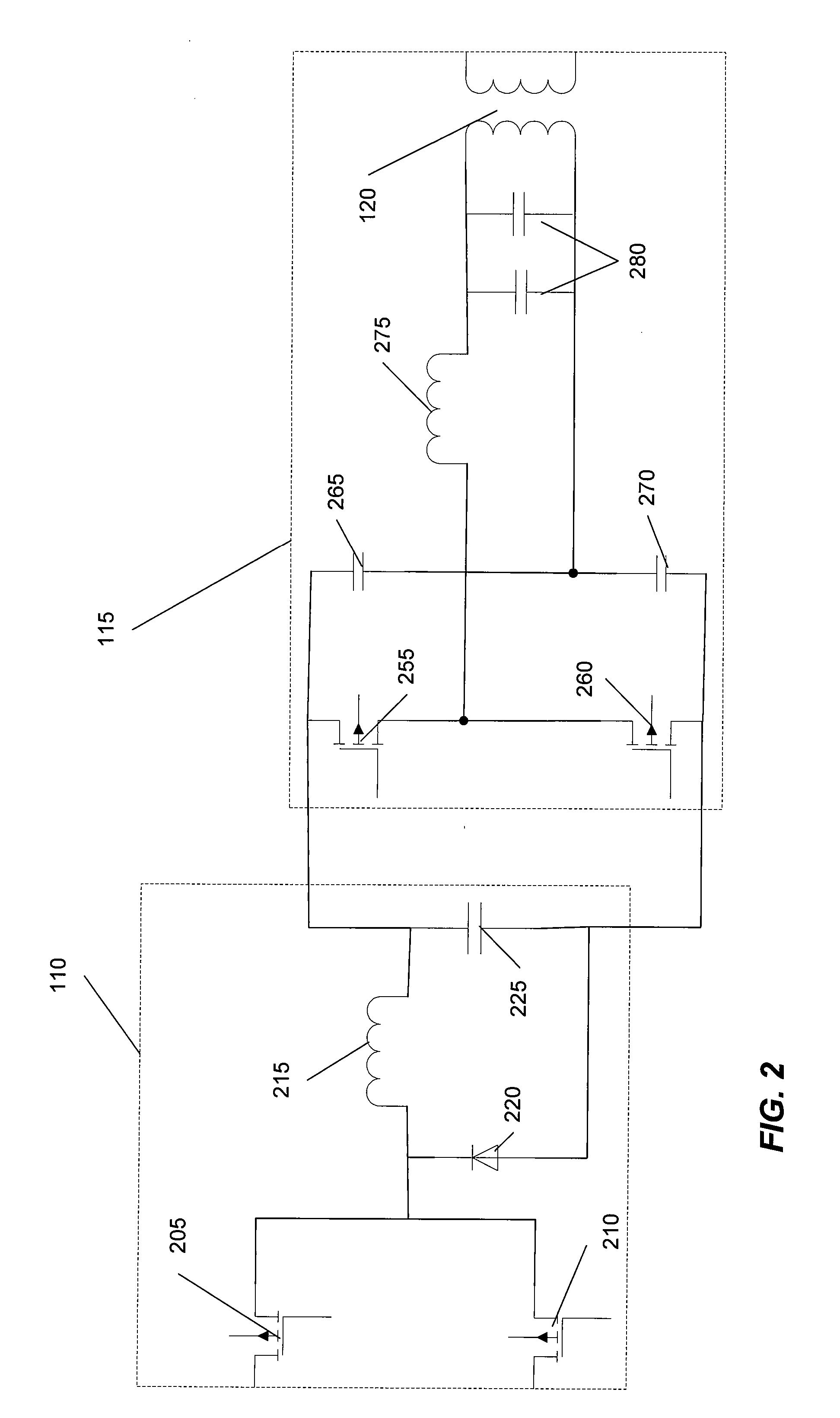
ActiveUS20070008745A1Operation efficiency is highHigh operating requirementsEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcResonant inverterAnalog feedback
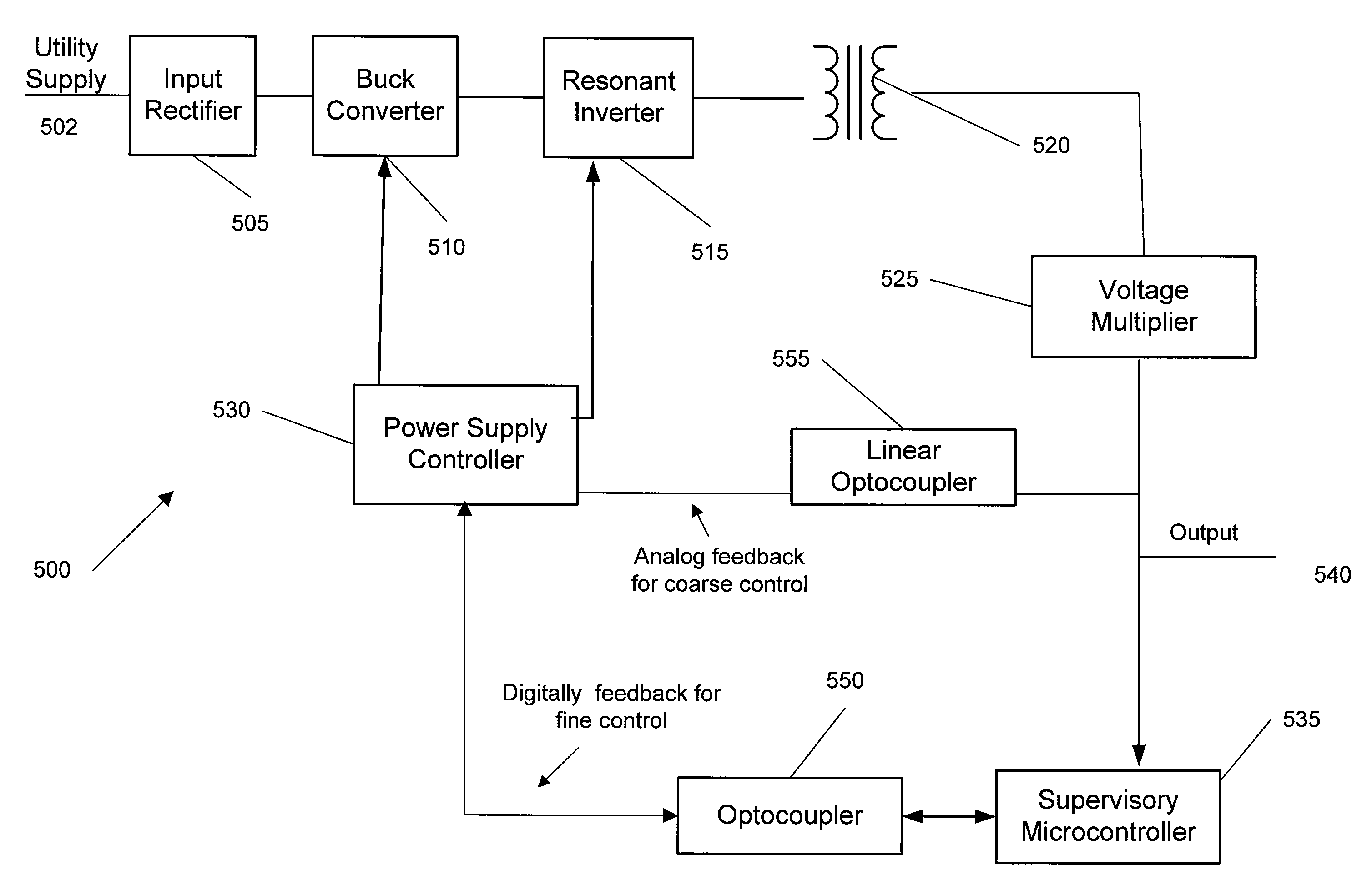
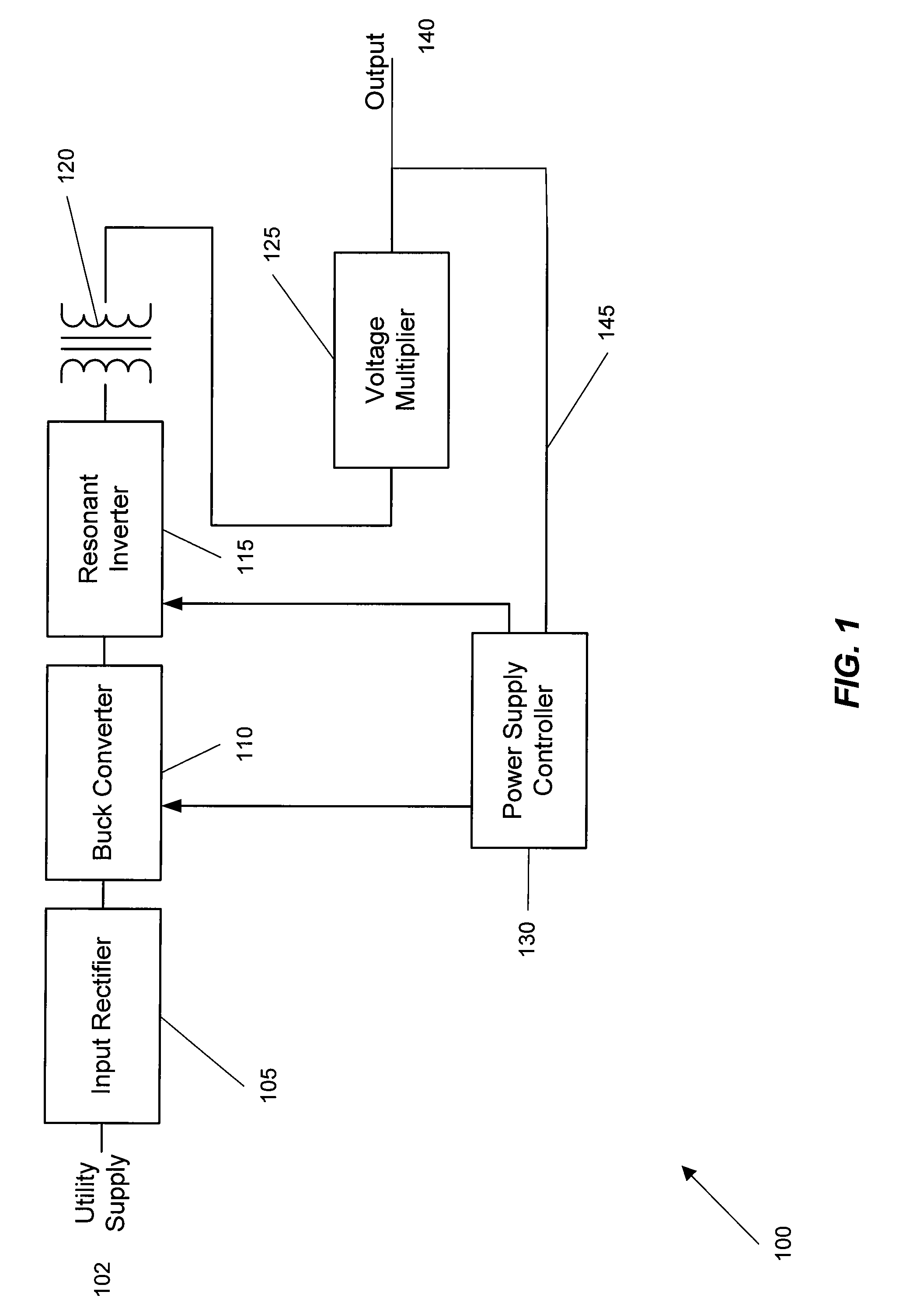
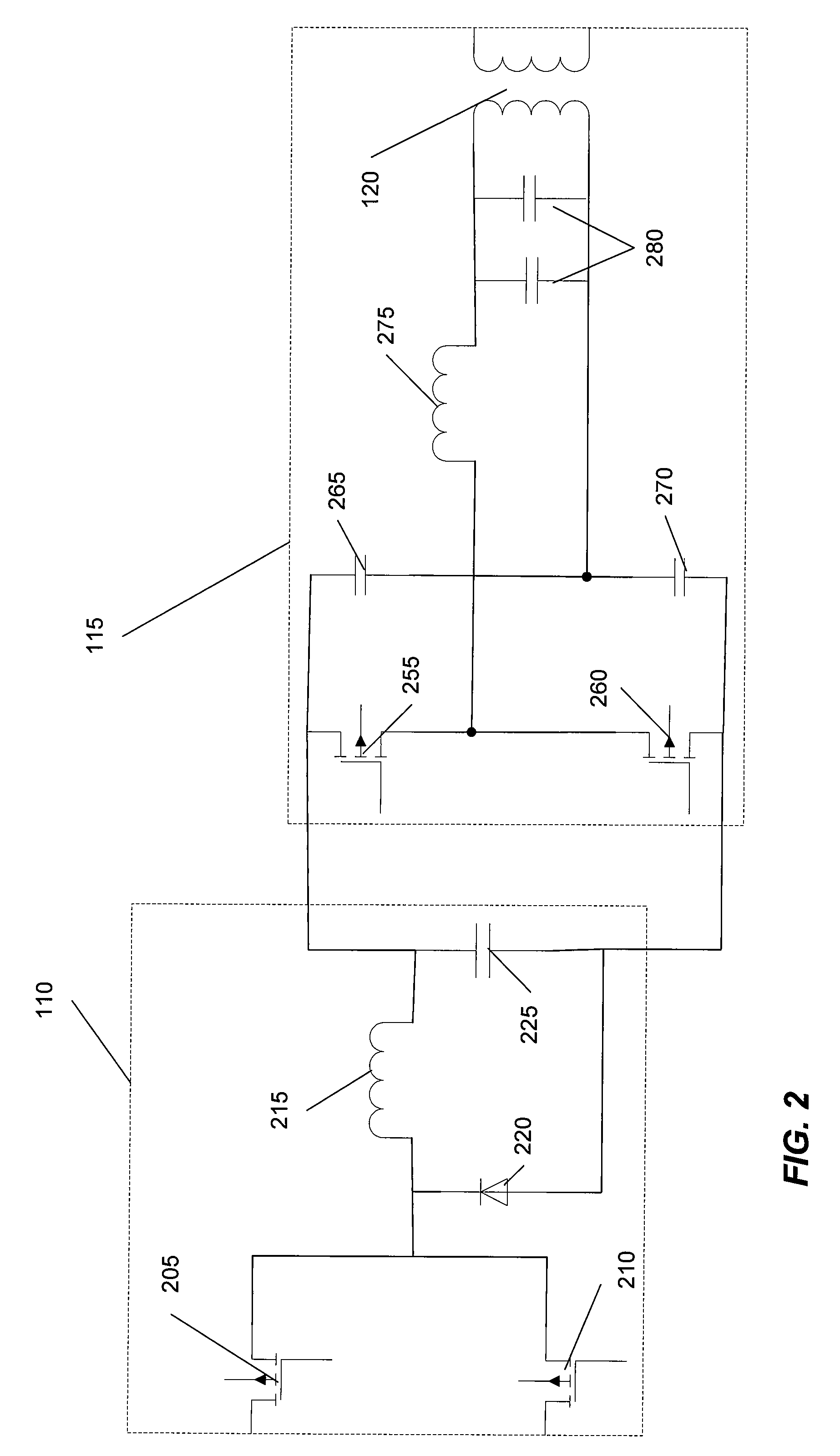
A wide range power supply capable of delivering 20V to 5000V is provided. The power supply of the present invention uses switch mode technology to achieve high overall operating efficiency and is capable of operating from no load to full load without loss of regulation. The power supply in accordance with the embodiments of the present invention operates directly from the utility supply (e.g., 110V / 220V and 50 Hz / 60 Hz). In one embodiment, the power supply's power conversion stage includes the following stages: an input rectifier; a buck converter; a quasi-resonant inverter; and a voltage multiplier. The above indicated stages are connected in series to achieve the large output voltage range. High precision is obtained from a use of a digital feedback loop, possibly in connection with an analog feedback loop.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Voltage multiplier charge pump buck
DC to DC converter circuitry includes a dual phase charge pump and at least one pair of multiplier phase circuits. The dual phase charge pump is coupled to each one of the at least one pair of multiplier circuits and adapted to receive a DC input voltage and only four control signals, and produce a stepped-up output voltage. Each one of the at least one pair of multiplier phase circuits are adapted to receive the stepped-up output voltage, a cross-coupled control signal from the other multiplier phase circuit in the pair of multiplier phase circuits, and a different one of the control signals and further multiply the stepped-up output voltage to produce a multiplied stepped-up output voltage with a magnitude that is approximately three times that of the DC input voltage or greater.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Adjustable non-dissipative voltage boosting snubber network
ActiveUS20140117872A1Boost voltageReduce voltageElectric discharge tubesElectric lighting sourcesPower flowVoltage multiplier
This disclosure describes a non-dissipative snubber circuit configured to boost a voltage applied to a load after the load's impedance rises rapidly. The voltage boost can thereby cause more rapid current ramping after a decrease in power delivery to the load which results from the load impedance rise. In particular, the snubber can comprise a combination of a unidirectional switch, a voltage multiplier, and a current limiter. In some cases, these components can be a diode, voltage doubler, and an inductor, respectively.
Owner:AES GLOBAL HLDG PTE LTD
Differing boost voltages applied to two or more anodeless electrodes for plasma processing
ActiveUS20140117861A1Boost voltageReduce voltageElectric discharge tubesElectric light circuit arrangementPower flowVoltage multiplier
This disclosure describes a non-dissipative snubber circuit configured to boost a voltage applied to a load after the load's impedance rises rapidly. The voltage boost can thereby cause more rapid current ramping after a decrease in power delivery to the load which results from the load impedance rise. In particular, the snubber can comprise a combination of a unidirectional switch, a voltage multiplier, and a current limiter. In some cases, these components can be a diode, voltage doubler, and an inductor, respectively.
Owner:AES GLOBAL HLDG PTE LTD
Power supply with a digital feedback loop
ActiveUS7324354B2High operating requirementsLow costEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcResonant inverterDigital feedback
A wide range power supply capable of delivering 20V to 5000V is provided. The power supply of the present invention uses switch mode technology to achieve high overall operating efficiency and is capable of operating from no load to full load without loss of regulation. The power supply in accordance with the embodiments of the present invention operates directly from the utility supply (e.g., 110V / 220V and 50 Hz / 60 Hz). In one embodiment, the power supply's power conversion stage includes the following stages: an input rectifier; a buck converter; a quasi-resonant inverter; and a voltage multiplier. The above indicated stages are connected in series to achieve the large output voltage range. High precision is obtained from a use of a digital feedback loop, possibly in connection with an analog feedback loop.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
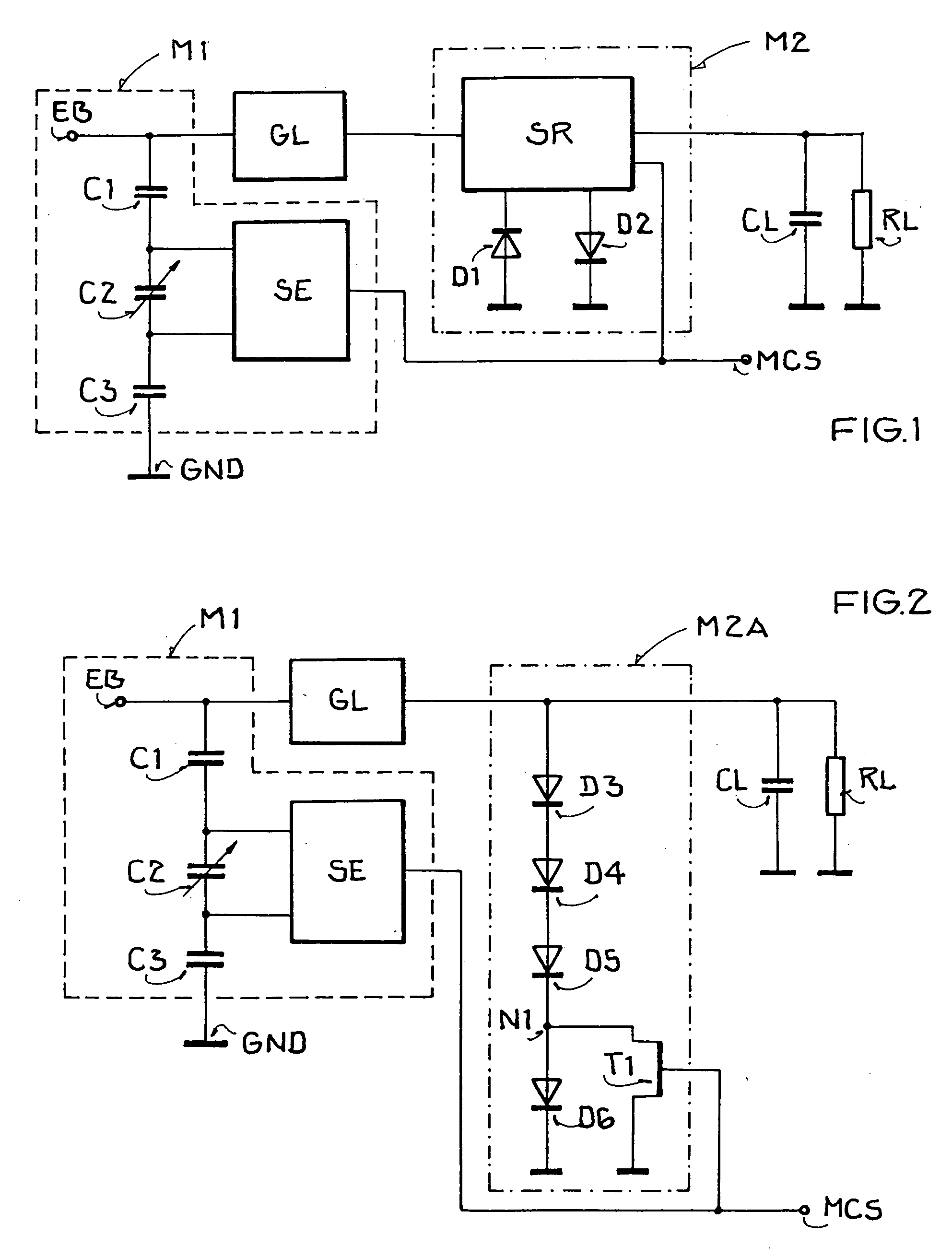
Charge pump circuit for high voltage generation
ActiveUS20080174360A1High voltage is generatedReduce power consumptionAc-dc conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionControl signalEngineering
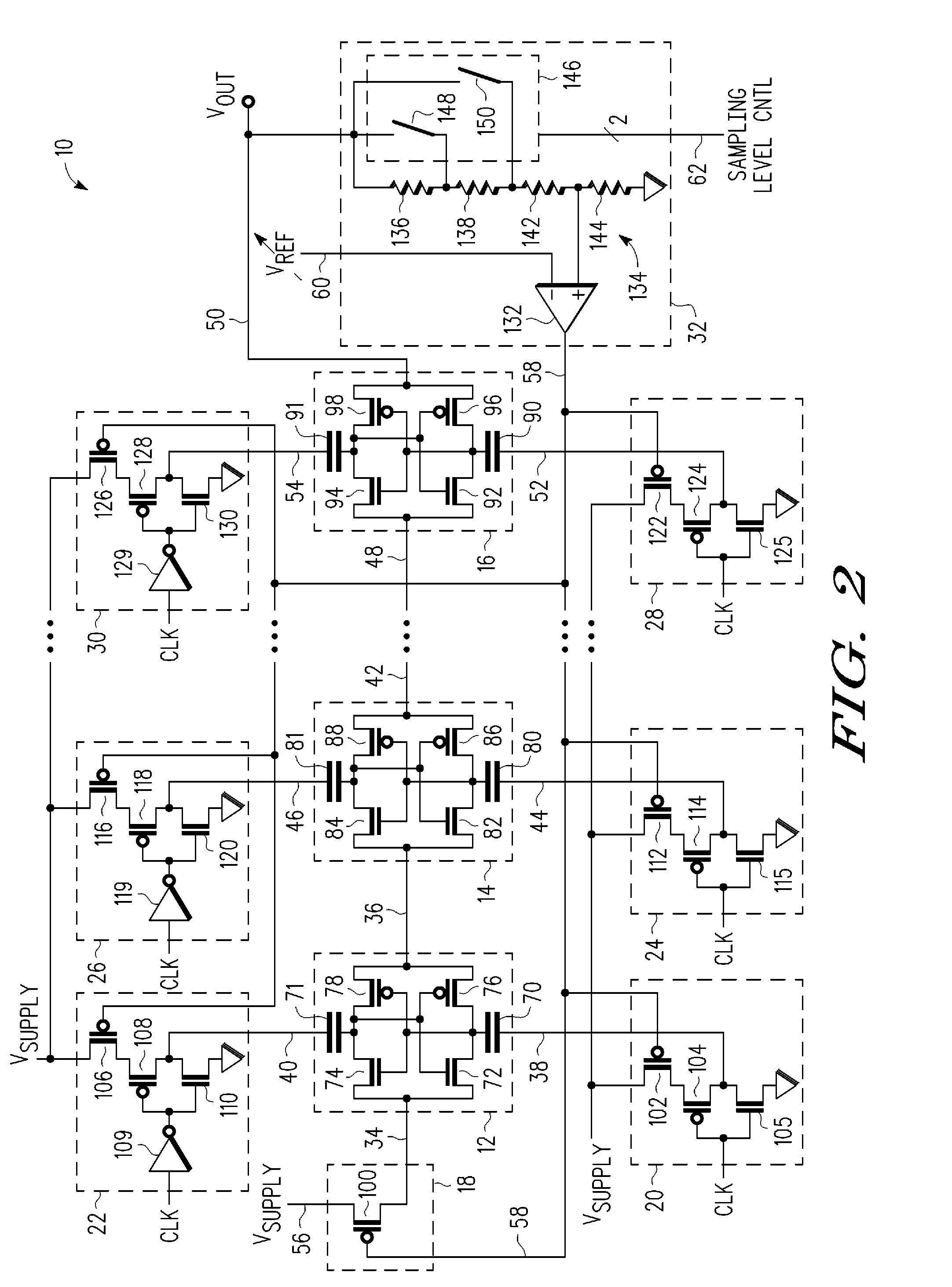
A circuit and method are given, to realize a high efficiency voltage multiplier for integrated circuits generating an internal and flexible positive or negative high voltage on-chip supply voltage from low external positive or negative supply voltages or ground. Applying multi-phase control signals to voltage boost internal nodes allows for eliminating threshold voltage drop losses and thus improves the voltage pumping gain compared to circuits with diode-configured FETs of prior art. Making use of voltage signals from antecedent stages in order to bias the bulk of MOS transistors fabricated in triple-well technology enables relaxing of the gate oxide stress within high order stage MOS transistors. Such a method, called leap-frog bulk potential tracking method, makes MOS transistors from different stages exhibit about the same body effect, which is very important because MOS transistors of higher order stages now show the same performance as MOS transistors from lower order stages. Important also in terms of efficiency as the charge sharing speed of high order MOS transistors always dominates the total charge pump performance and the driving force of pumped currents, thus also allowing for a greater number of serially connectable stages overall or a smaller number necessary for a certain targeted output voltage.
Owner:ETRON TECH INC
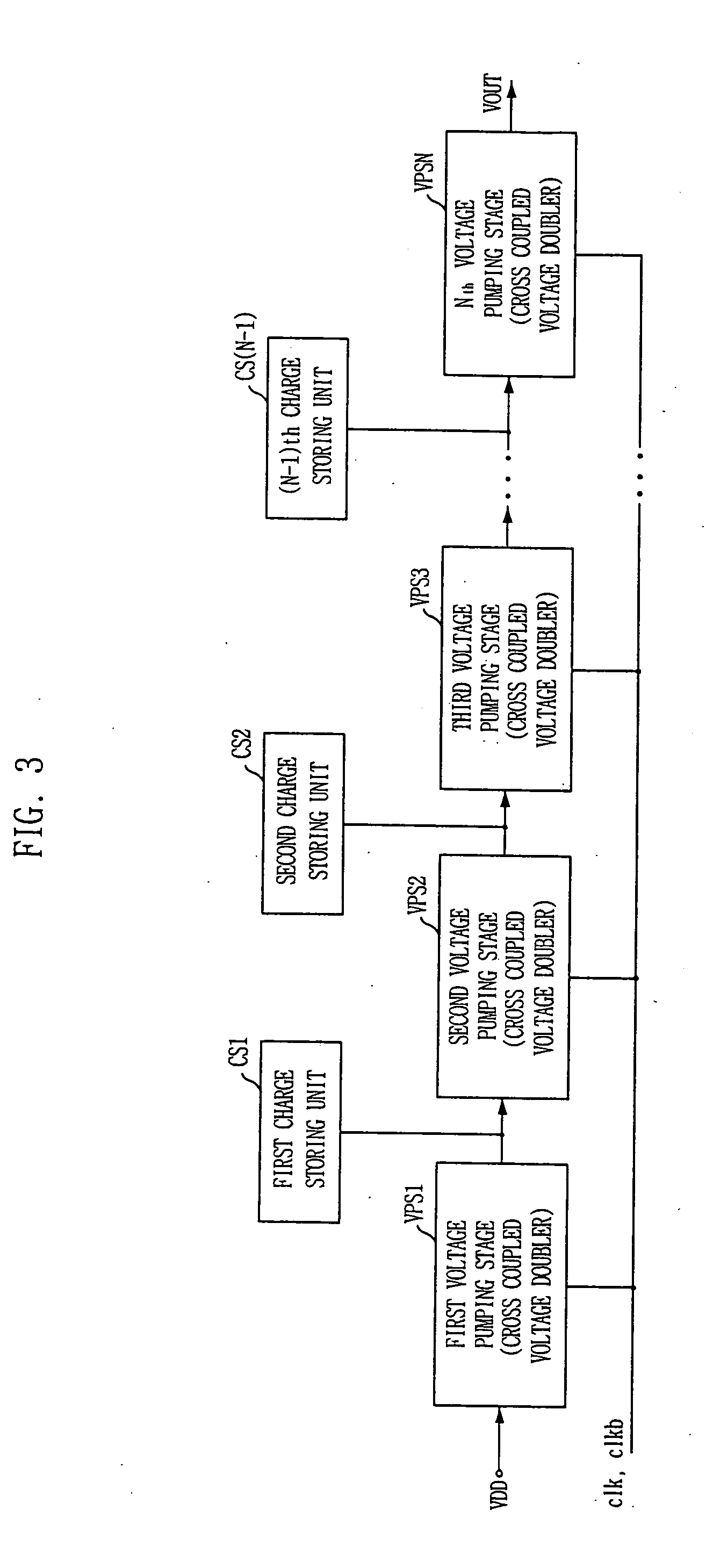
Multi stage voltage pump circuit
ActiveUS20050093614A1Avoid unnecessary power consumptionAvoid inefficiencyApparatus without intermediate ac conversionStatic storageVoltage multiplierEngineering
A multi stage voltage pumping circuit includes a plurality of voltage pumping stages each operated by a first clock signal and a second clock signal for raising a voltage level of an inputted voltage; and a plurality of charge storing means each connected to outputs of the plurality of voltage pumping stages respectively except for a last voltage pumping stage in order to store charge, wherein each of the plurality of voltage pumping stages is a cross coupled voltage doubler and an output of a previous voltage pumping stage is connected to an input of a next voltage pumping stage.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Adjustable non-dissipative voltage boosting snubber network for achieving large boost voltages
ActiveUS20140232266A1Boost voltageReduce voltageElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsVoltage multiplierSnubber
This disclosure describes a non-dissipative snubber circuit configured to boost a voltage applied to a load after the load's impedance rises rapidly. The voltage boost can thereby cause more rapid current ramping after a decrease in power delivery to the load which results from the load impedance rise. In particular, the snubber can comprise a combination of a unidirectional switch, a voltage multiplier, and a current limiter. In some cases, these components can be a diode, voltage doubler, and an inductor, respectively.
Owner:AES GLOBAL HLDG PTE LTD
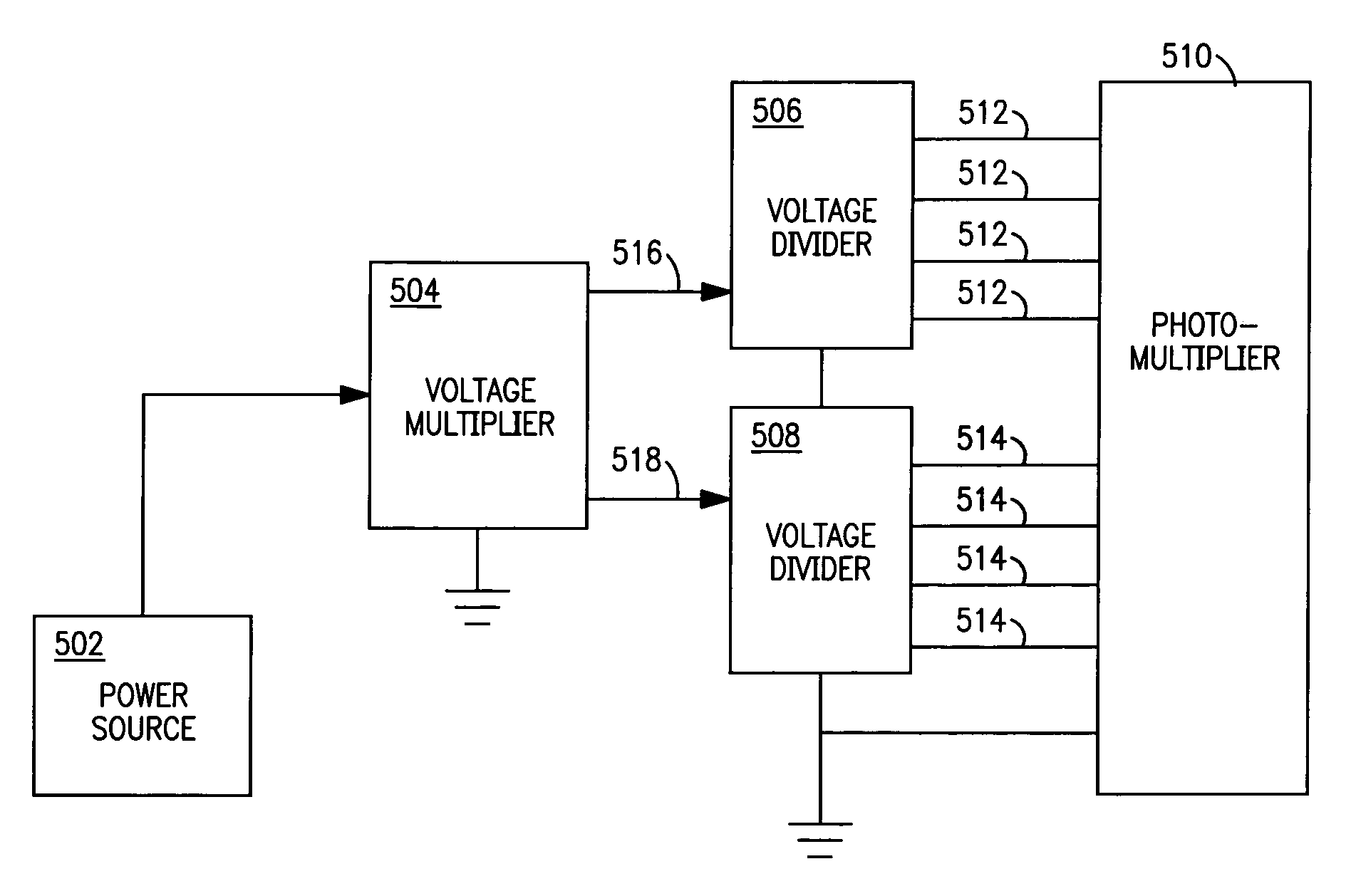
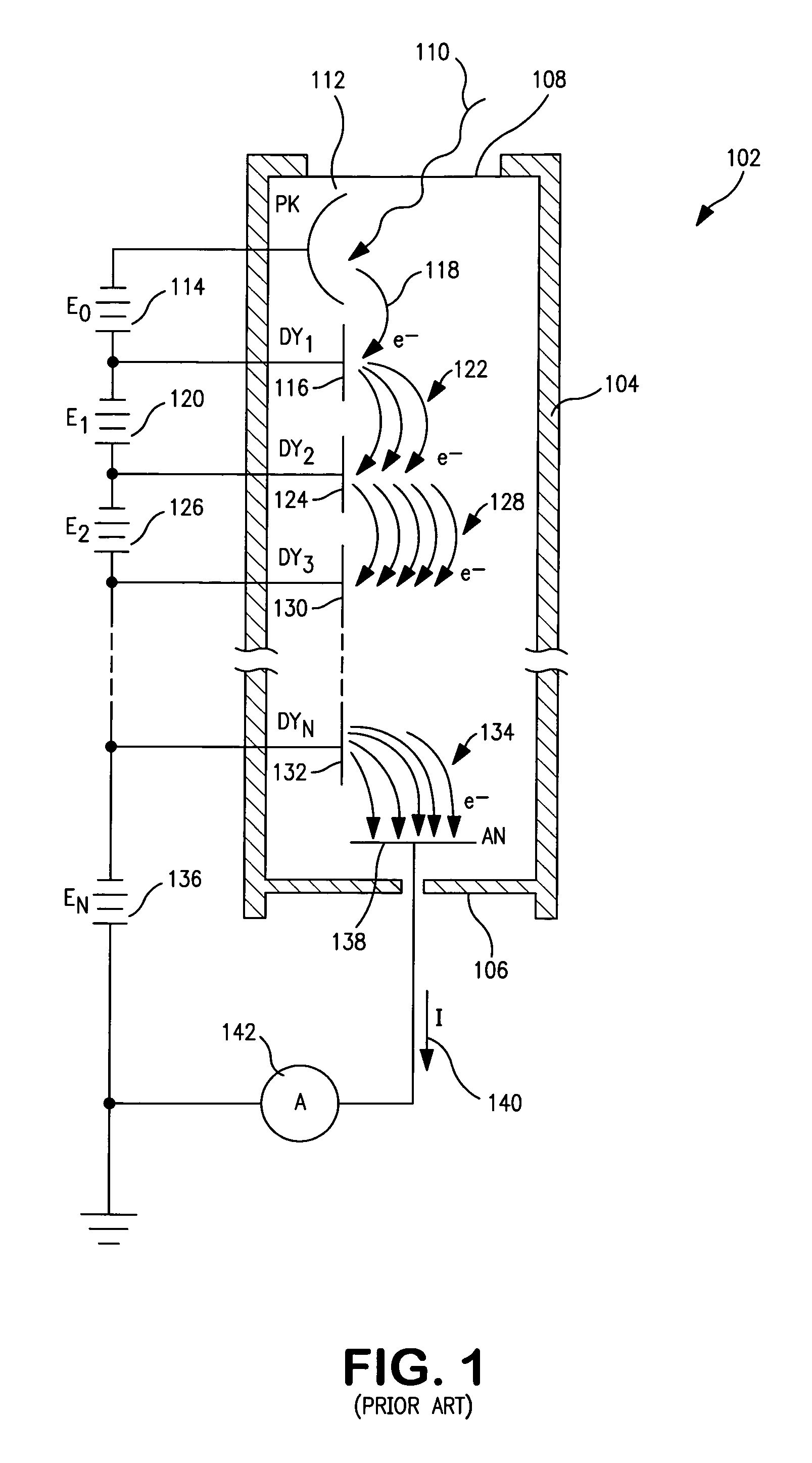
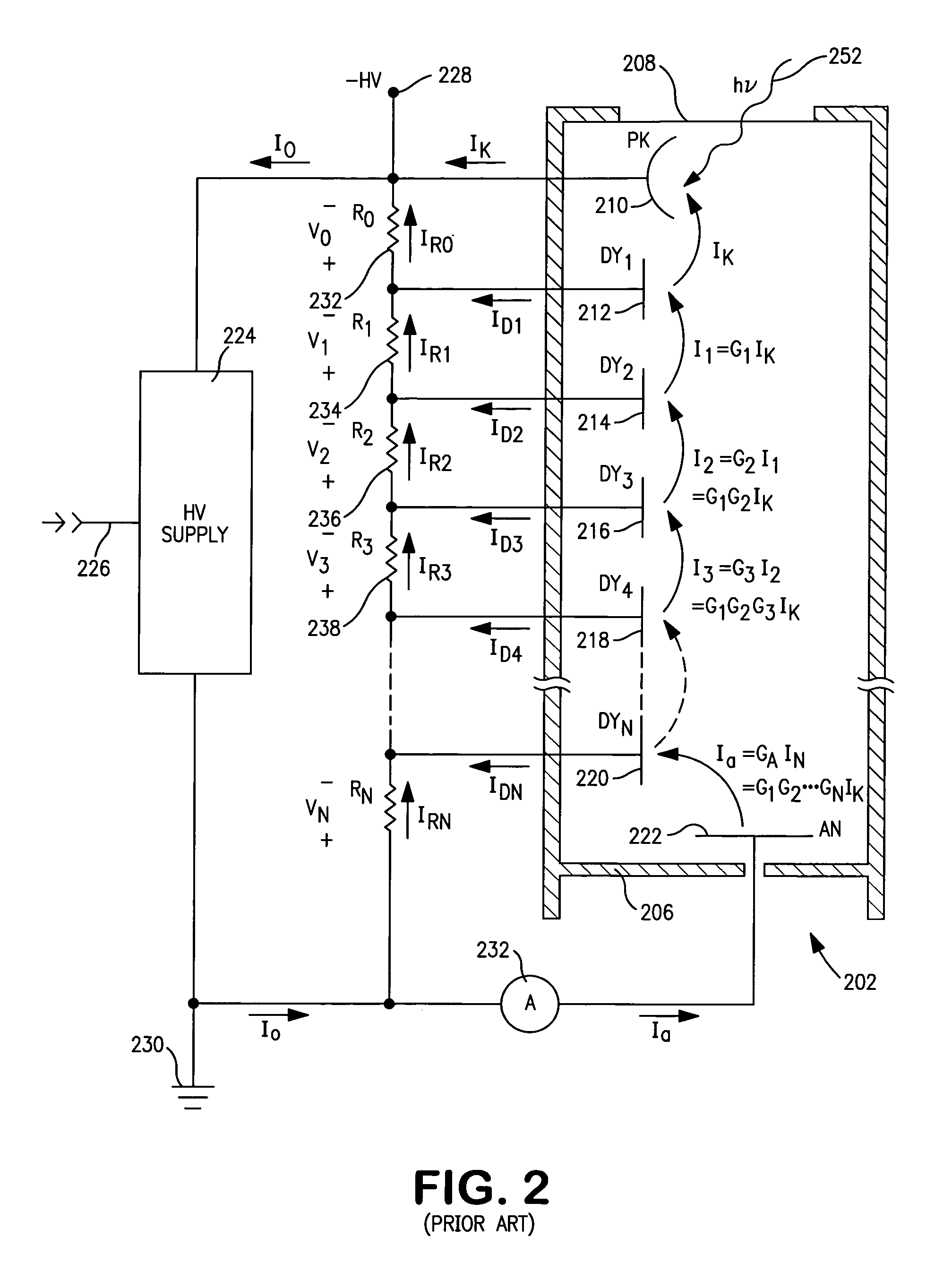
Low power stabilized voltage divider network
InactiveUS7005625B1Reduce the required powerReduce power consumptionMultiplier circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansVoltage multiplierPhotomultiplier
A voltage divider network in combination with a voltage multiplier circuit voltage biases the electrodes of a photomultiplier tubes or related device. The circuit exploits the several voltage levels produced at successive stages of a voltage multiplier circuit in order to optimize the voltage divider network with respect to power consumption, current draw from the power supply, operating stability, and linear operation of the photomultiplier tube.
Owner:LUDLUM MEASUREMENTS
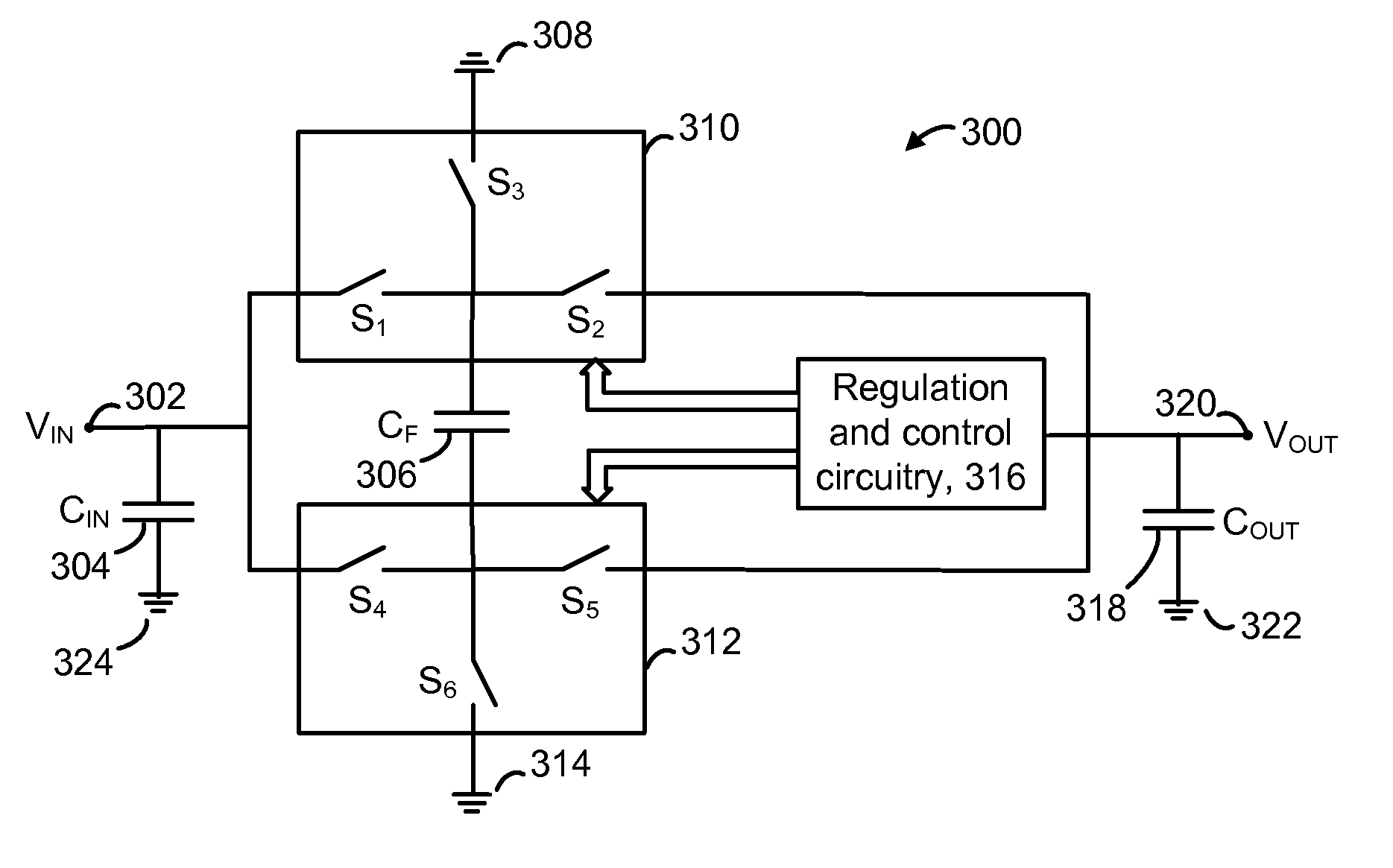
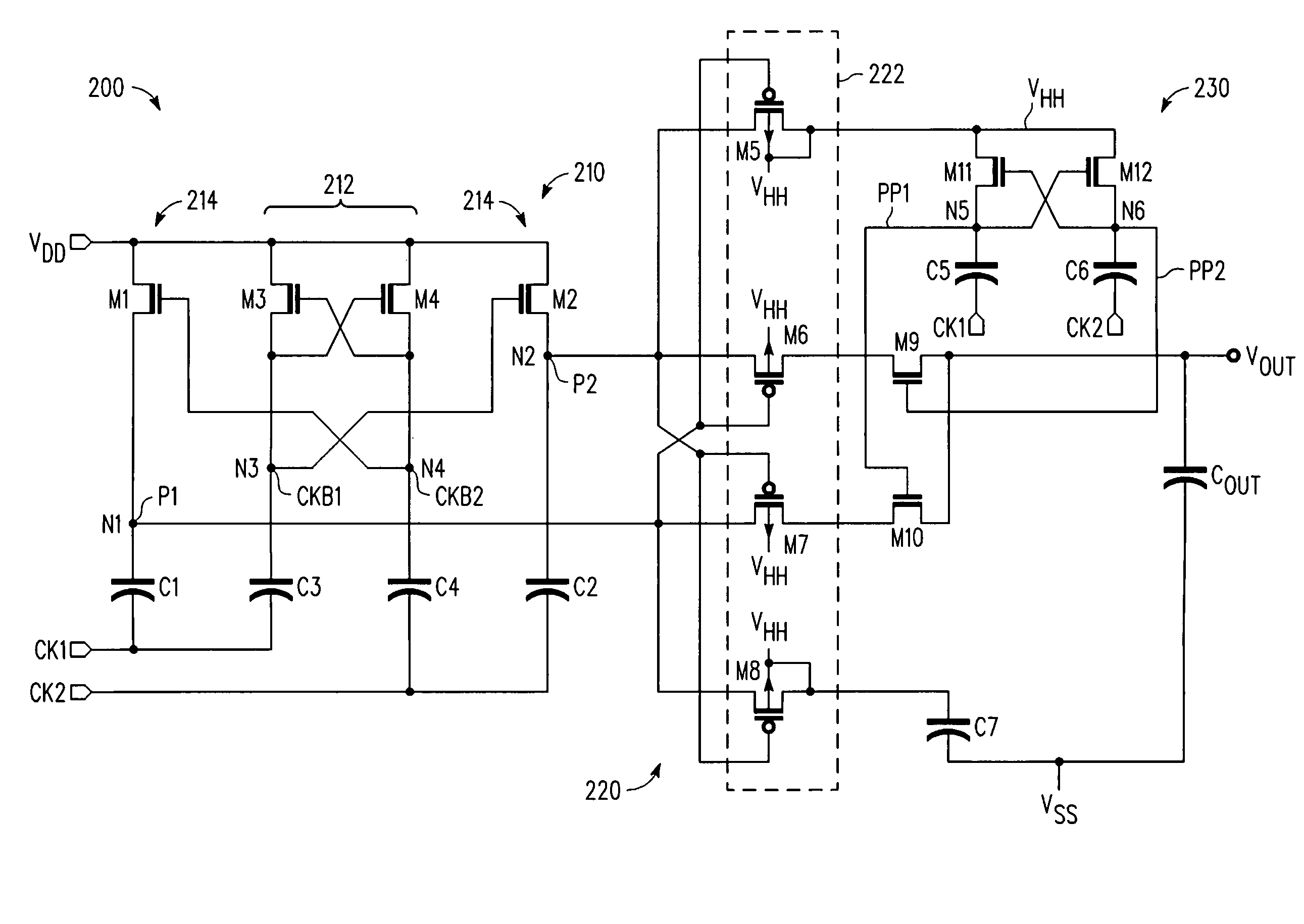
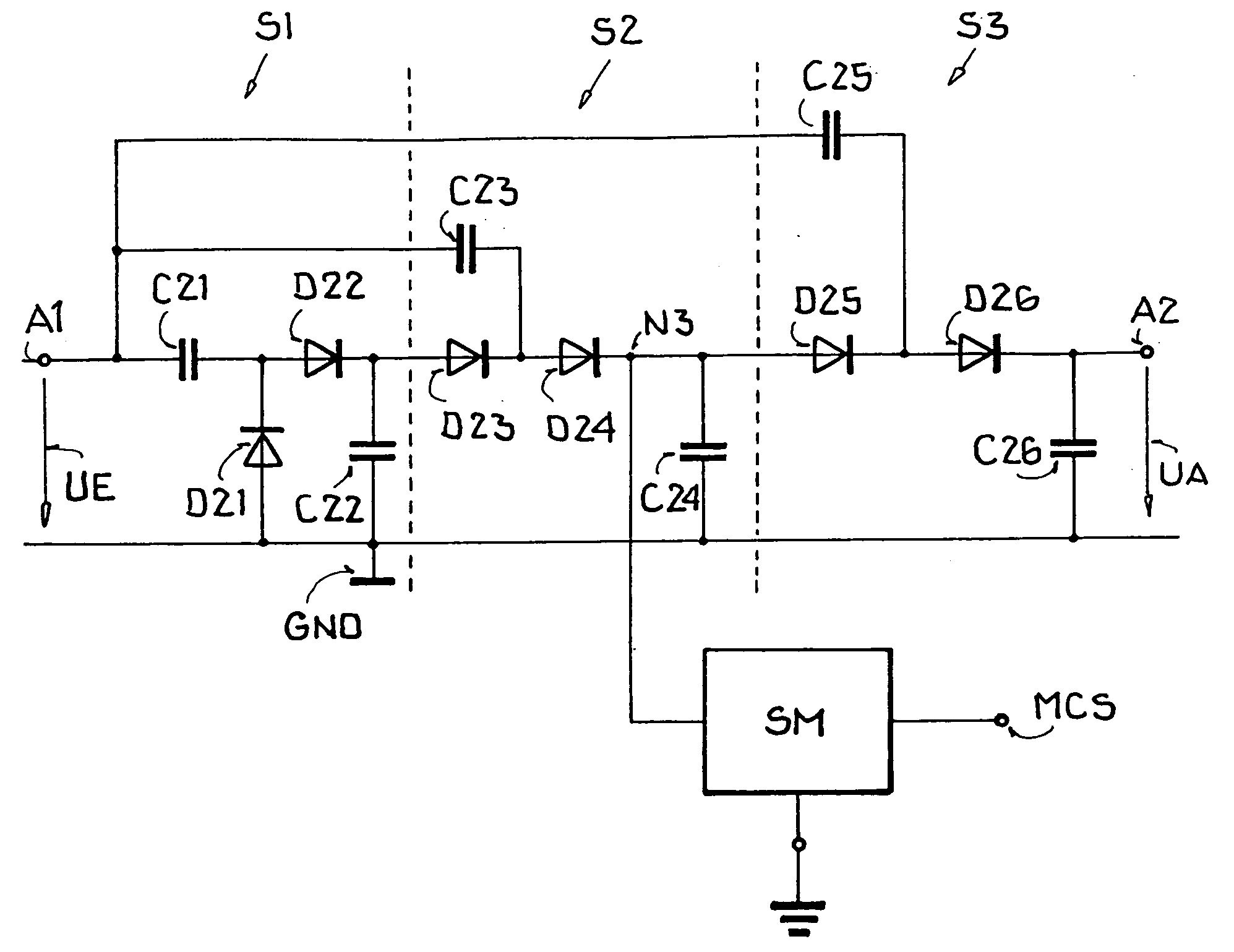
Voltage multiplier with improved efficiency
InactiveUS7602233B2Ac-dc conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionVoltage multiplierReturn current
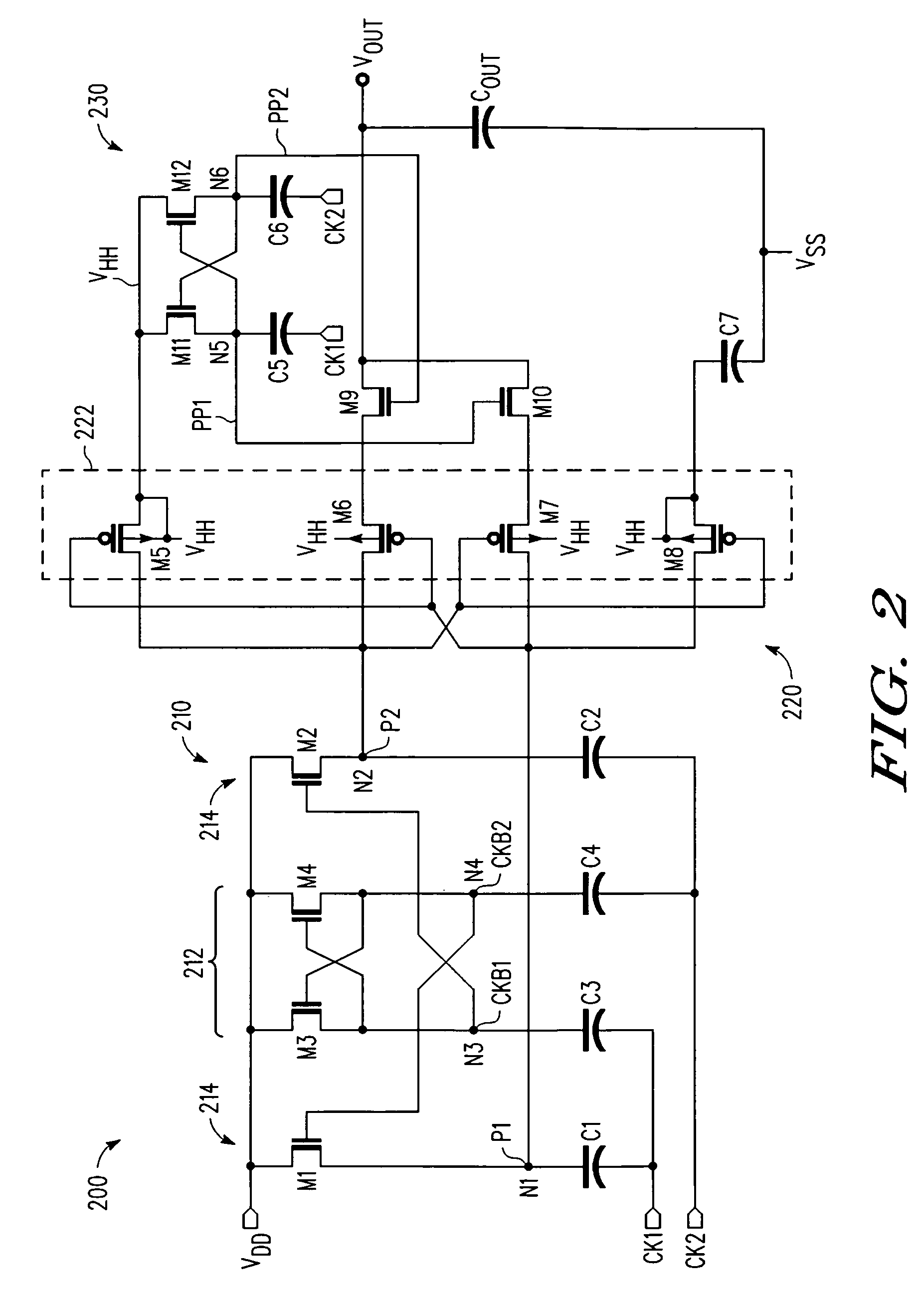
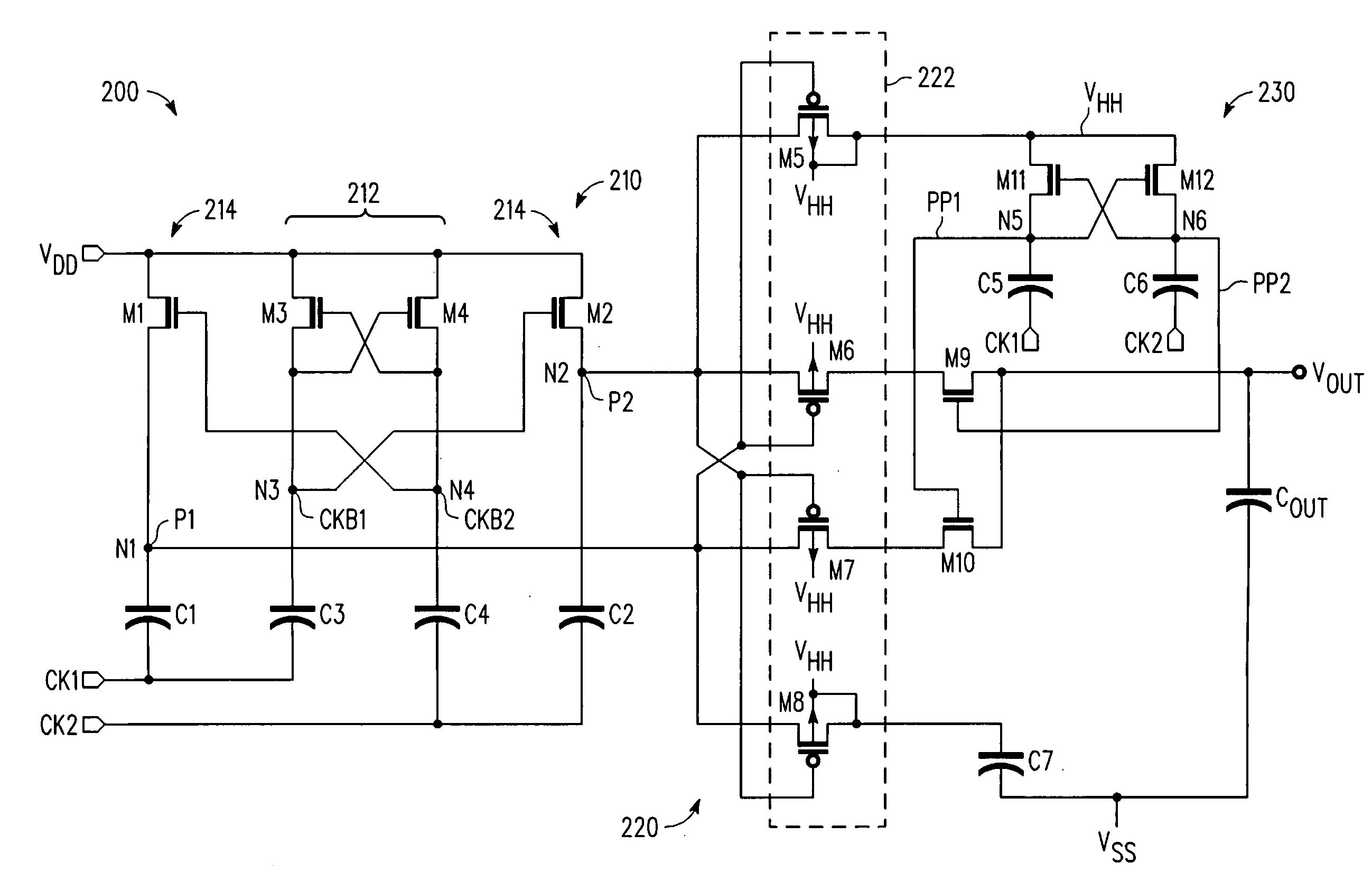
A multi-stage voltage multiplication circuit and methodology are provided which use a multi-stage charge pump boosting circuit (210) and two-stage pass gate circuit (220) having complementary power switches (M6, M9, M7, M10) to efficiently develop an output voltage (VOUT) that is higher than the input supply voltage (VDD). By using a two-stage complementary switch to connect boosted clock signals (P1, P2) from a charge pump (210) to the multiplier output (VOUT), return current from the storage capacitor (COUT) to the pumping capacitor (C1, C2) is blocked, thereby increasing power transfer efficiency, even at high clock frequencies. In addition, a boosted auxiliary voltage is generated by an additional boosting stage (230) and applied to the PMOS wells of the pass gate circuit (220), thereby preventing latch-up and backflow.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Charge coupled pump-efficient charge pump regulator with mos capacitor
ActiveUS20090315615A1Easy to operateCurrent/voltage measurementInstant pulse delivery arrangementsCapacitanceVoltage multiplier
A charge pump with a MOS-type capacitor, where the MOS-type capacitor is operated in an inversion region in which capacitance varies as a function of the frequency of the applied signal. The charge pump is switched to transfer charge from an input node to the capacitor and from the capacitor to an output node. During a transition interval, a relatively high frequency switching signal is used to lower the capacitance and increase efficiency. During a settling interval, a relatively low frequency switching signal is used, in which case the capacitance is higher, but similar to a level which would be seen if the capacitor was operated in an accumulation region. MOS capacitor dimensions and switching intervals are mutually optimized to provide high efficiency and required throughput. The charge pump may be configured as a voltage multiplier, divider, inverter or follower, for instance.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL ISRAEL LTD
High voltage ripple reduction and substrate protection
InactiveUS7116155B2Improve stabilityLower capability requirementsEfficient power electronics conversionRead-only memoriesCapacitanceVoltage multiplier
In a non-volatile memory, charge pumps are used to provide high voltages needed for programming memory cells that have floating gate structures. Charge pumps have a series of voltage multiplier stages in series to boost voltage. These charge pumps must rapidly charge a load to a high voltage and then maintain a voltage with a high degree of stability. Techniques for achieving both of these goals are presented. In one aspect, a charge pump has two operating states, one to charge a load rapidly and a second to maintain a voltage on a charged load with high stability. These states are achieved by changing the current output-from a high current during charging to a low current to maintain the voltage. This is done by changing the capacitance used in the individual voltage multiplier stages. In another aspect, two different current levels are produced by changing the voltage used to charge the capacitors of the voltage multiplier stages.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Voltage multiplier with improved efficiency
InactiveUS20090219077A1Ac-dc conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionVoltage multiplierReturn current
A multi-stage voltage multiplication circuit and methodology are provided which use a multi-stage charge pump boosting circuit (210) and two-stage pass gate circuit (220) having complementary power switches (M6, M9, M7, M10) to efficiently develop an output voltage (VOUT) that is higher than the input supply voltage (VDD). By using a two-stage complementary switch to connect boosted clock signals (P1, P2) from a charge pump (210) to the multiplier output (VOUT), return current from the storage capacitor (COUT) to the pumping capacitor (C1, C2) is blocked, thereby increasing power transfer efficiency, even at high clock frequencies. In addition, a boosted auxiliary voltage is generated by an additional boosting stage (230) and applied to the PMOS wells of the pass gate circuit (220), thereby preventing latch-up and backflow.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Low threshold current switch
ActiveUS7193428B1Current/voltage measurementElectrical measurement instrument detailsVoltage multiplierPower cable
Low threshold current switch comprising a sensing transformer, a voltage multiplier and a switch enables monitoring a very low electric current in a power cable.
Owner:VERIS INDS
Charge removal from electrodes in unipolar sputtering system
ActiveUS9287098B2Boost voltageReduce voltageElectric discharge tubesElectric lighting sourcesVoltage multiplierEngineering
This disclosure describes a non-dissipative snubber circuit configured to boost a voltage applied to a load after the load's impedance rises rapidly. The voltage boost can thereby cause more rapid current ramping after a decrease in power delivery to the load which results from the load impedance rise. In particular, the snubber can comprise a combination of a unidirectional switch, a voltage multiplier, and a current limiter. In some cases, these components can be a diode, voltage doubler, and an inductor, respectively.
Owner:AES GLOBAL HLDG PTE LTD
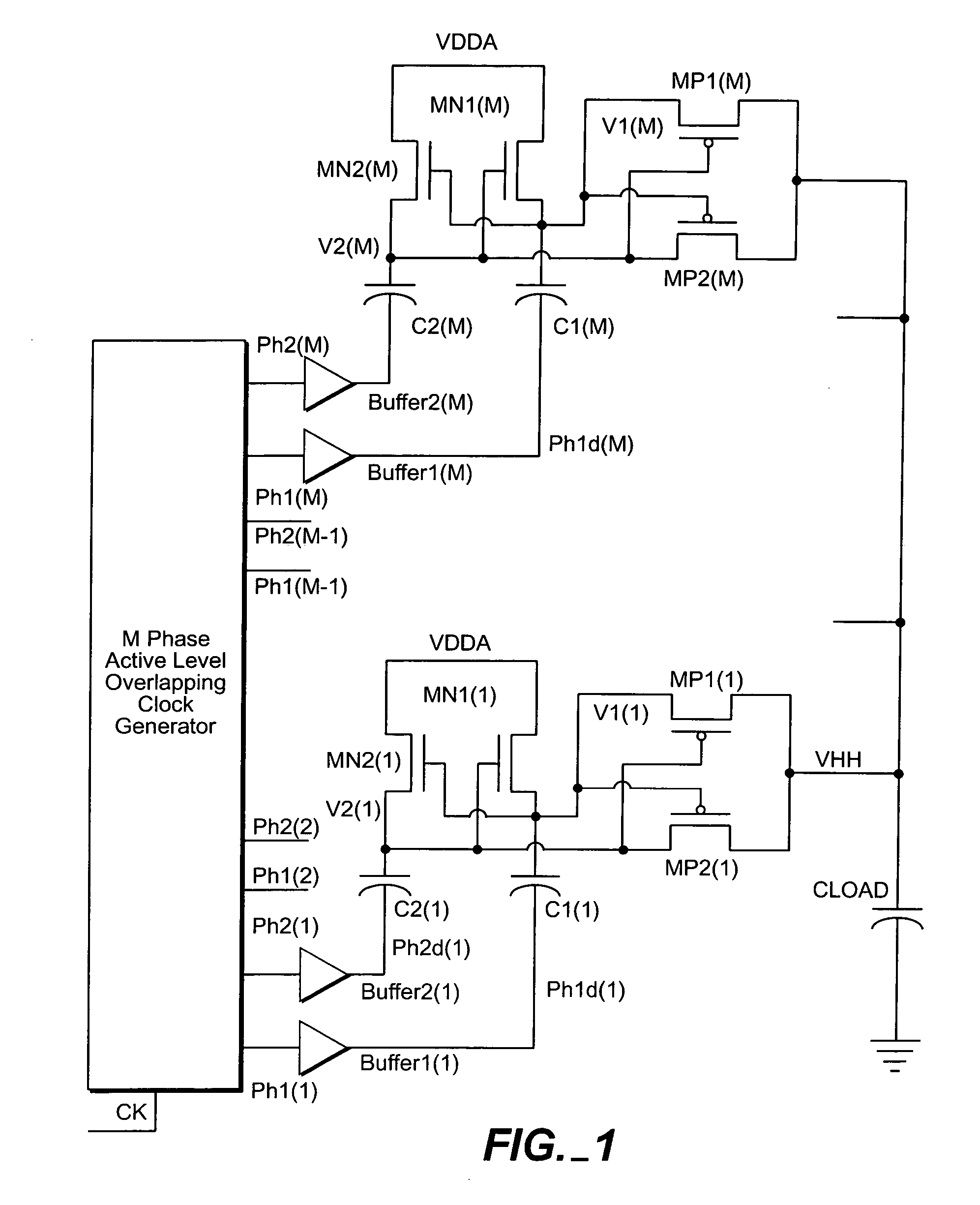
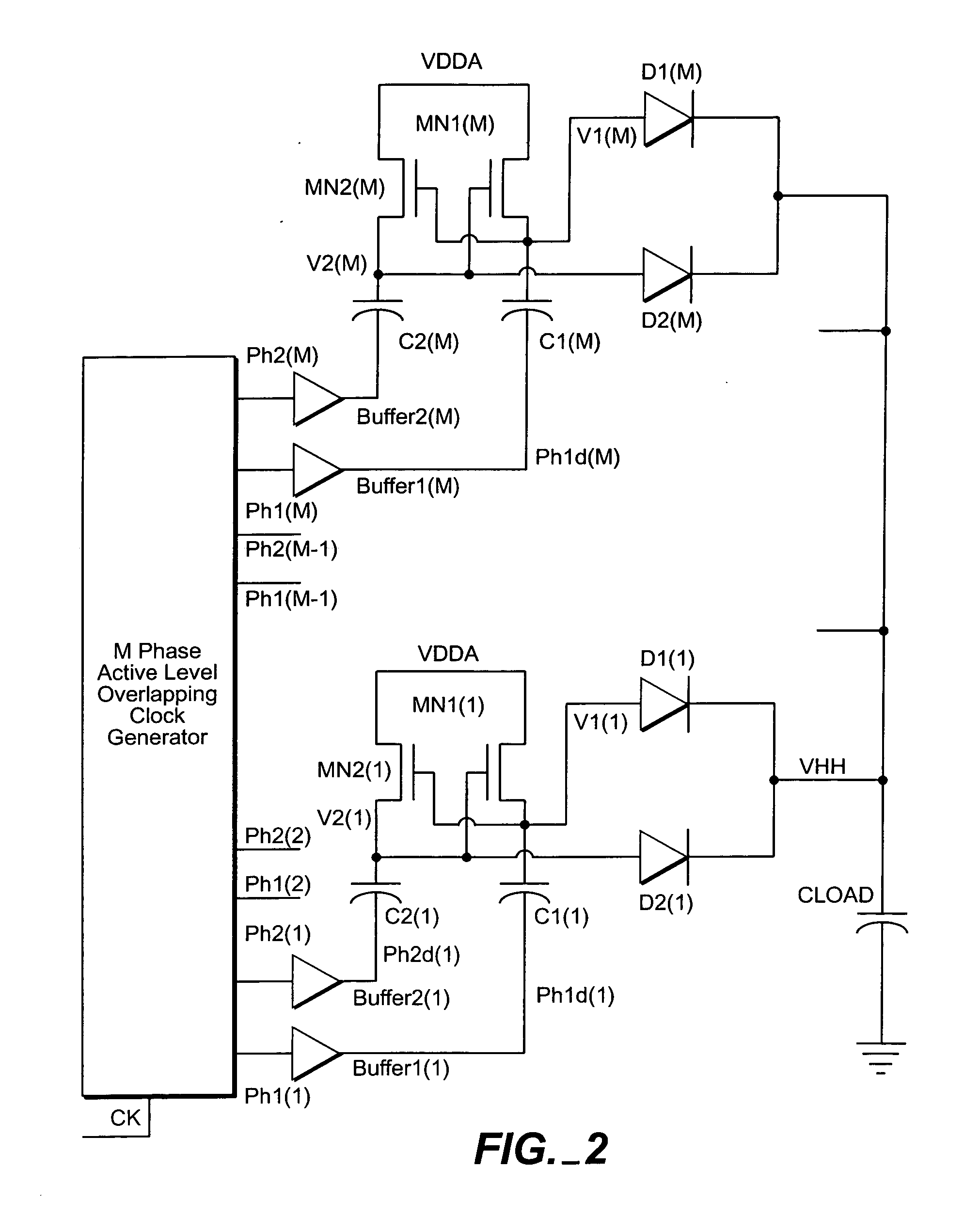
Highly efficient, high current drive, multi-phase voltage multiplier
InactiveUS20050024125A1Low efficiencyImprove efficiencyApparatus without intermediate ac conversionElectric variable regulationDriving currentVoltage multiplier
The highly efficient, high current drive, multi-phase voltage multiplier reduces the inefficiency due to the active level overlapping portion of the clock at high frequencies, reduces the inefficiency due to extremely large drive currents on the inverters supplying current to the multiplying capacitors C1(*) and C2(*), and increases the efficiency of the multiplier by allowing M-1 phases to charge the output at any given time and providing more time given to each capacitor to fully charge and discharge. The ripple on the output is much smaller than in a single dual phase multiplier. This multi-phase voltage multiplier supplies very large current to the load while remaining very efficient.
Owner:LSI CORPORATION
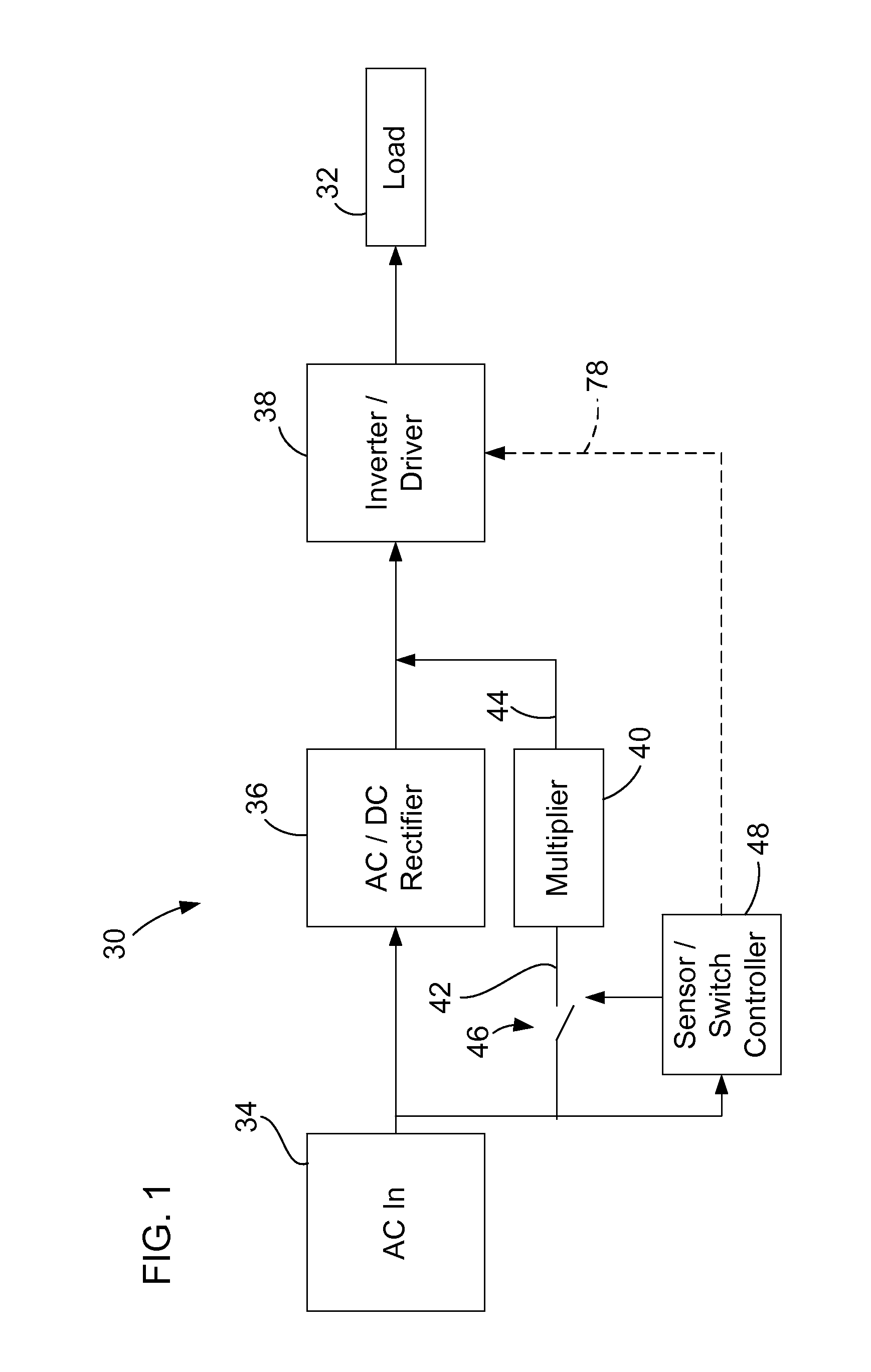
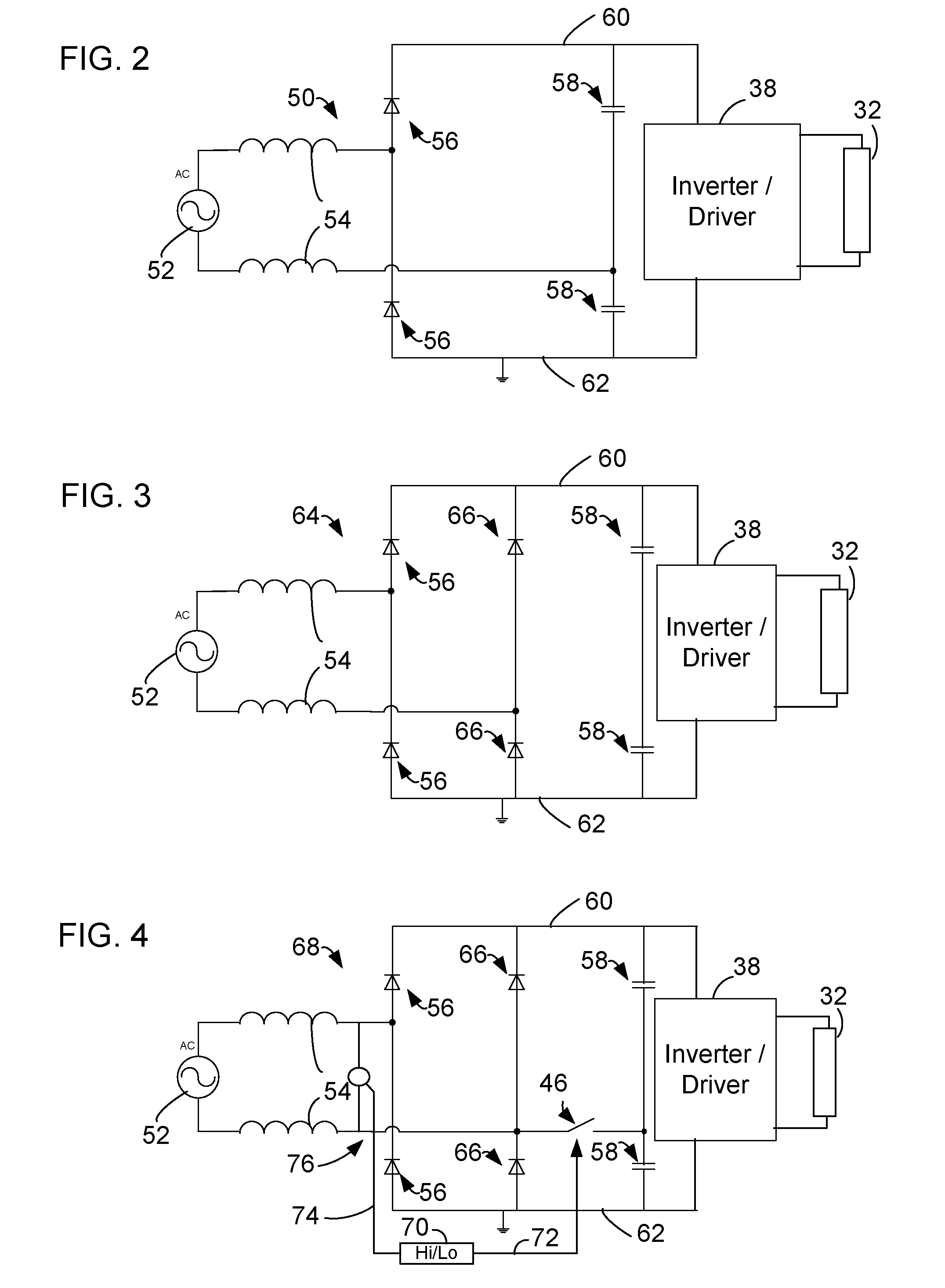
Multiple voltage ballast
ActiveUS20070217093A1Electric light circuit arrangementEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentVoltage multiplierEngineering
A ballast and method for operating a ballast includes a switch or other circuit for connecting and disconnecting a voltage multiplier to a rectifier circuit. A control circuit for controlling the switch senses an input voltage and connects the voltage multiplier to the rectifier circuit when an input voltage falls below a selected voltage level.
Owner:FULHAM CO LTD
Tire parameter monitoring system with inductive power source
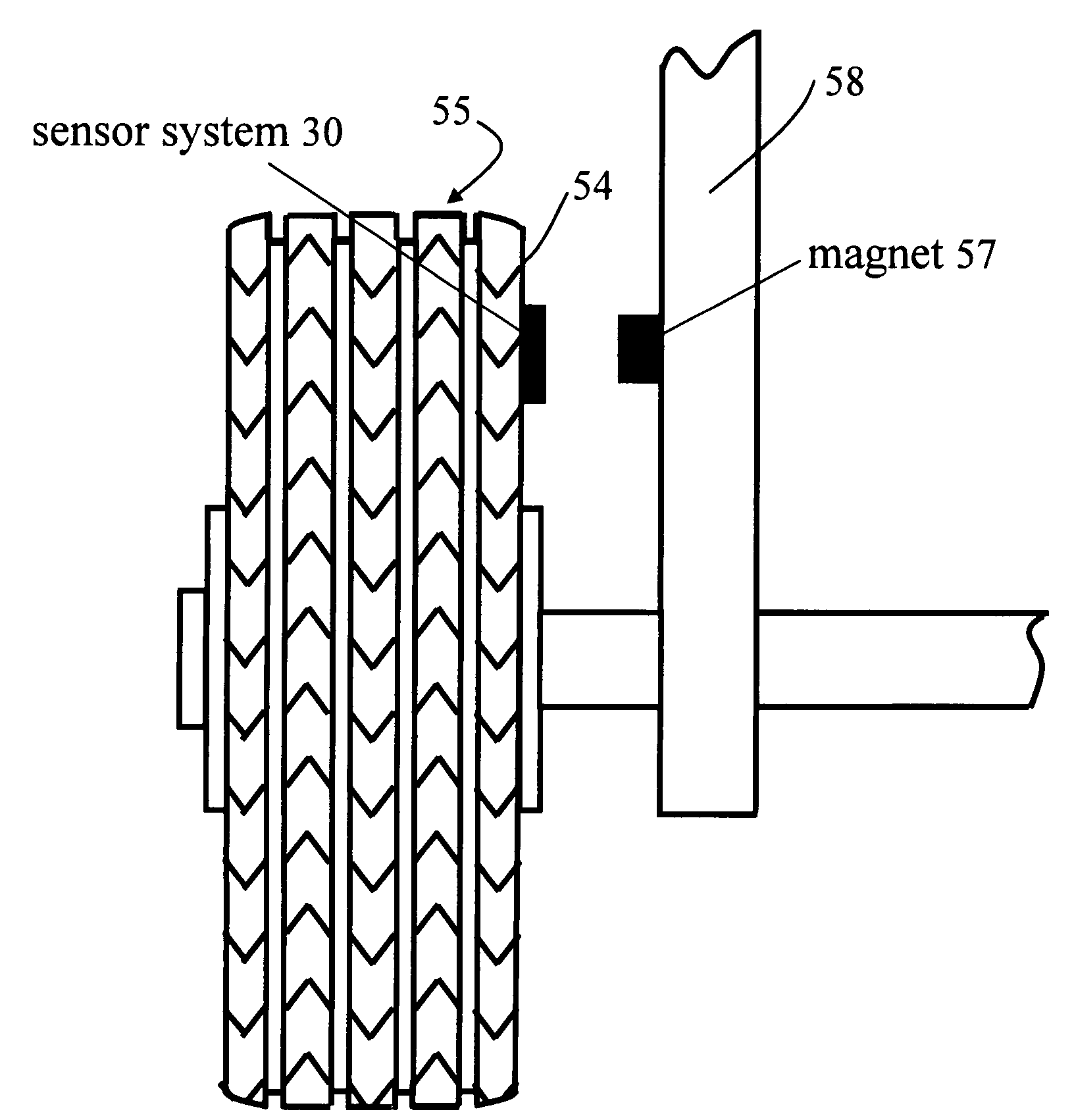
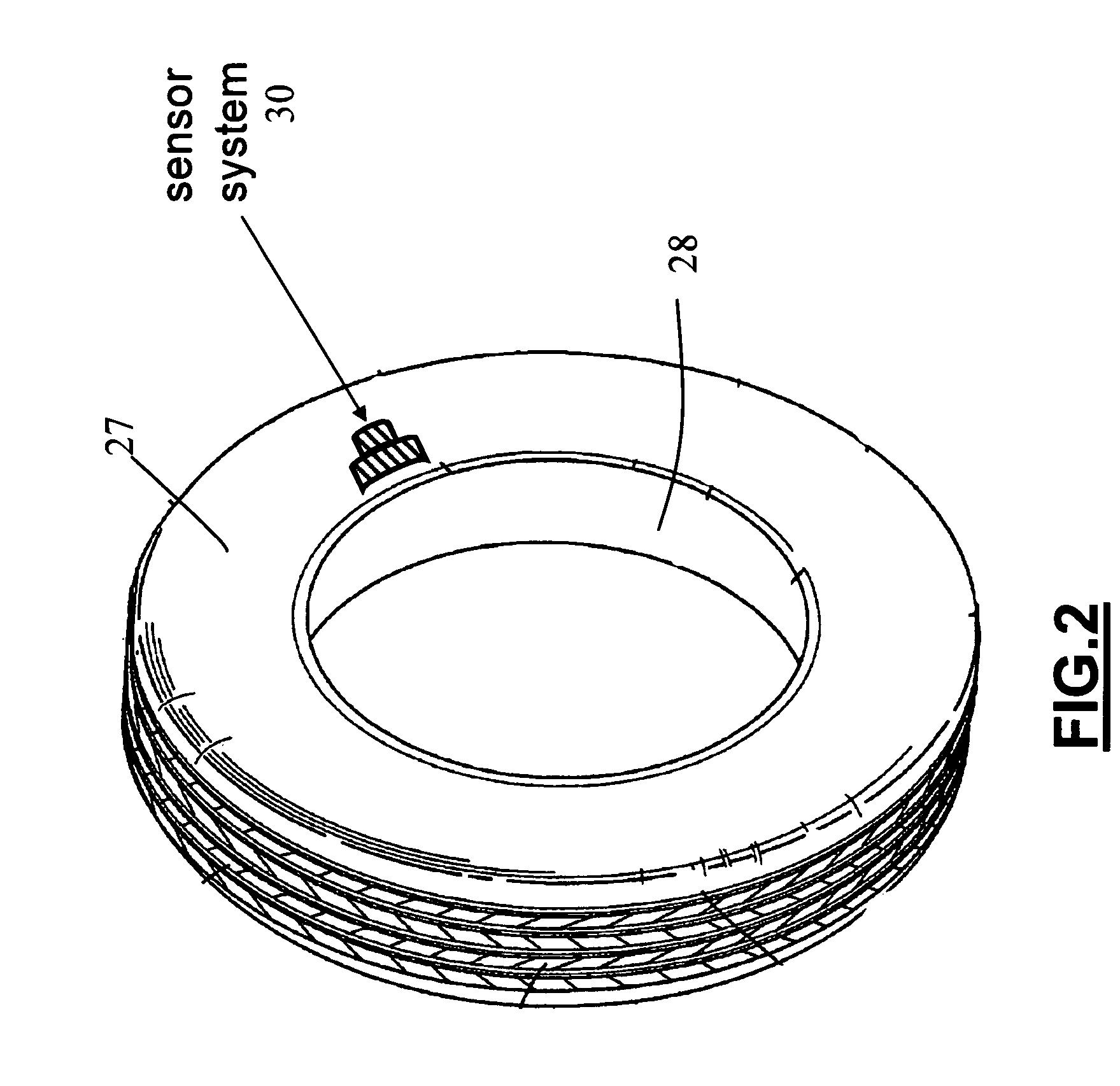
InactiveUS7363806B2Simple and inexpensive to implementEliminate needTyre measurementsRoads maintainenceVoltage multiplierMonitoring system
A battery-less tire parameter sensor system for monitoring a vehicle tire parameter such as pressure and temperature. A sensor assembly has a power system, a processor / transmitter, a sensor, and a power coil mounted on a substrate. This assembly is mounted on or in the side wall or tread wall of a tire. A magnet is mounted on the vehicle in proximity to the path of the power coil during tire rotation. The moving power coil passes through the magnetic field and generates operating voltage for the sensor assembly components. The power system includes a voltage multiplier, a voltage regulator, and a storage capacitor. Two or more sensor assemblies can be mounted on the same tire to monitor different parameters.
Owner:SILICON VALLEY MICRO C CORPORATION
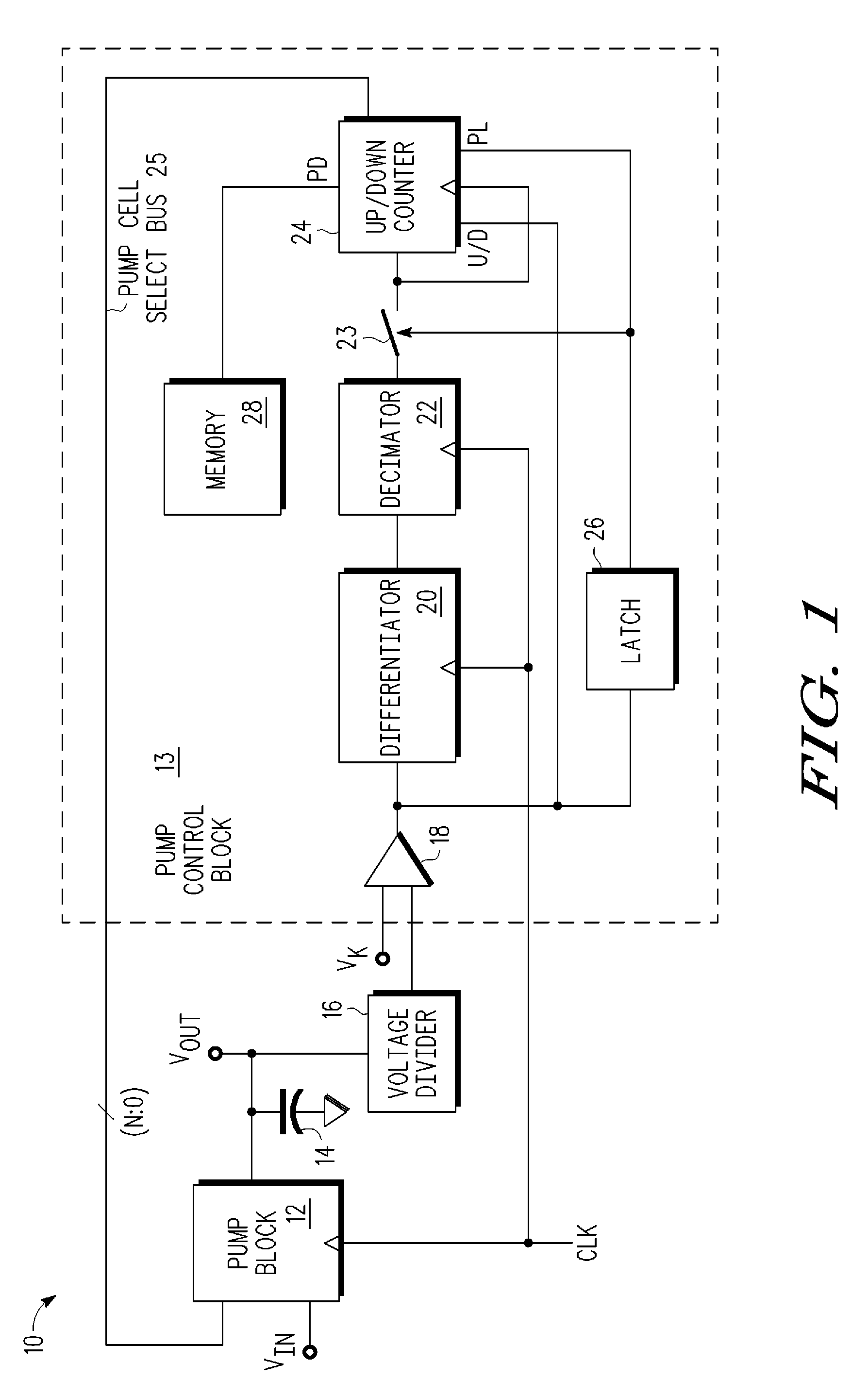
Variable load, variable output charge-based voltage multipliers
ActiveUS20090097285A1Ac-dc conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionVoltage multiplierEngineering
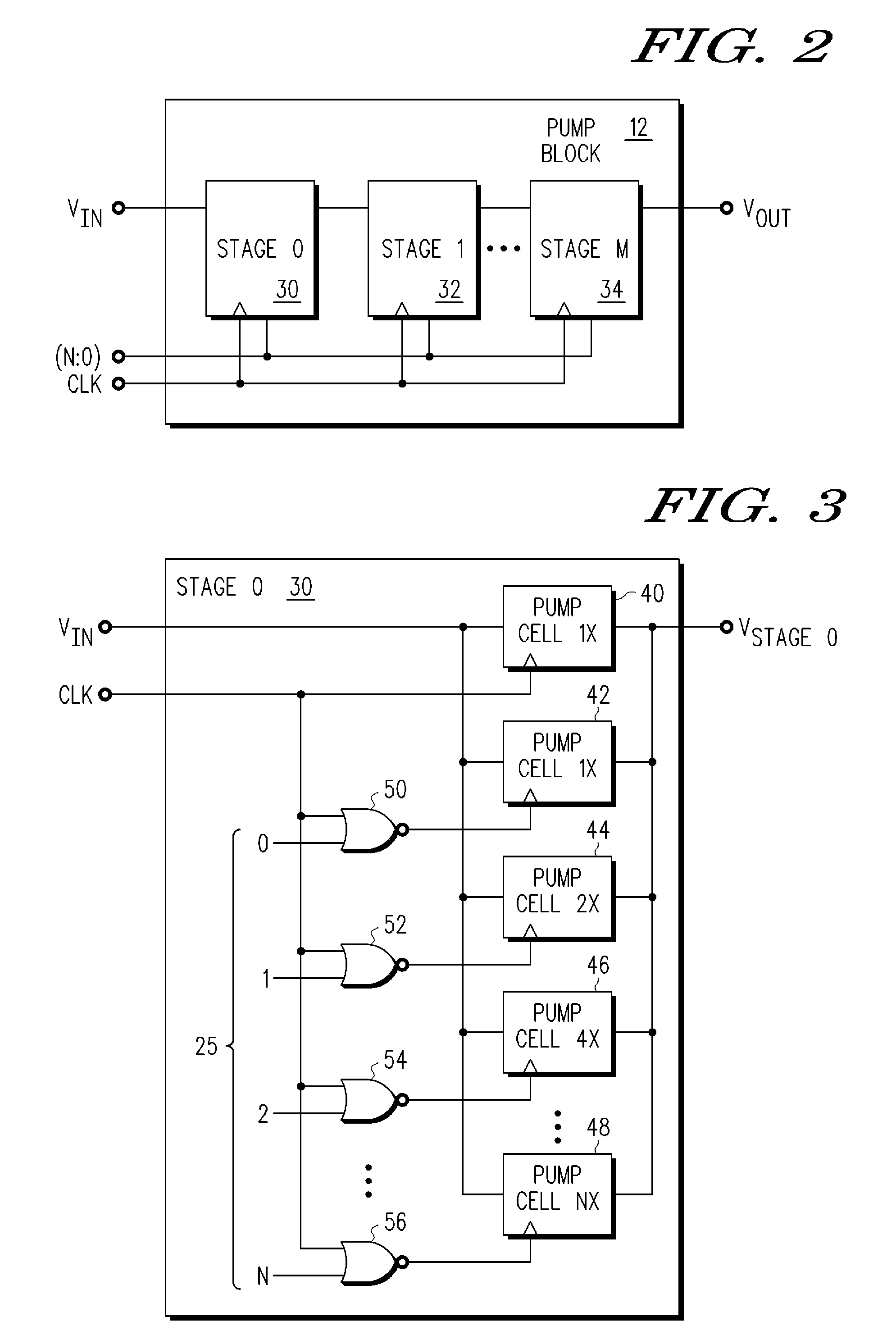
A charge-based voltage multiplier device comprising a charge-pump circuit and a charge-pump controller is provided. The charge-pump circuit is configured to multiply an input voltage signal (Vin) into an output voltage signal (Vout), the charge-pump circuit includes a plurality of charge-pump stages, wherein at least one of the charge-pump stages includes a weighted capacitor array of pump cells. The charge-pump controller is configured to provide a pump cell select to selectively control the weighted capacitor array of pump cells of the at least one of the charge-pump stages of the charge-pump circuit.
Owner:NXP USA INC
System for generating high-stability high voltage
InactiveCN101697453AReduce adverse effectsImprove high-frequency operating frequencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionOperating pointEngineering
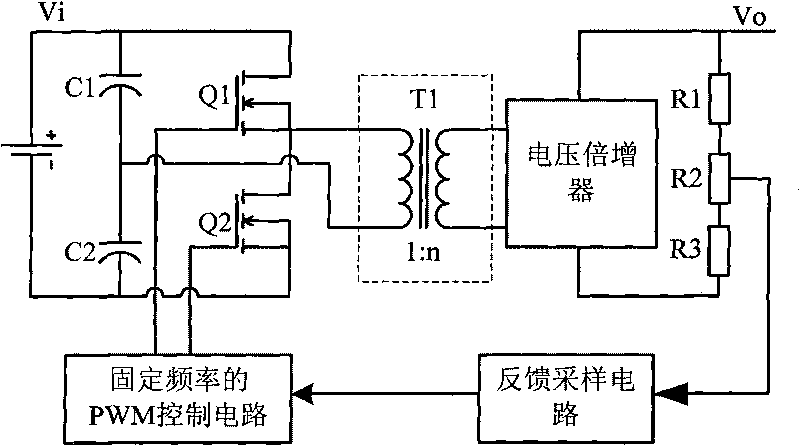
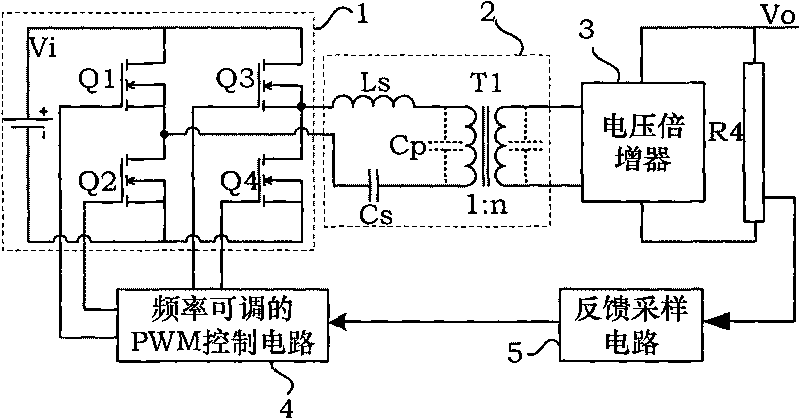
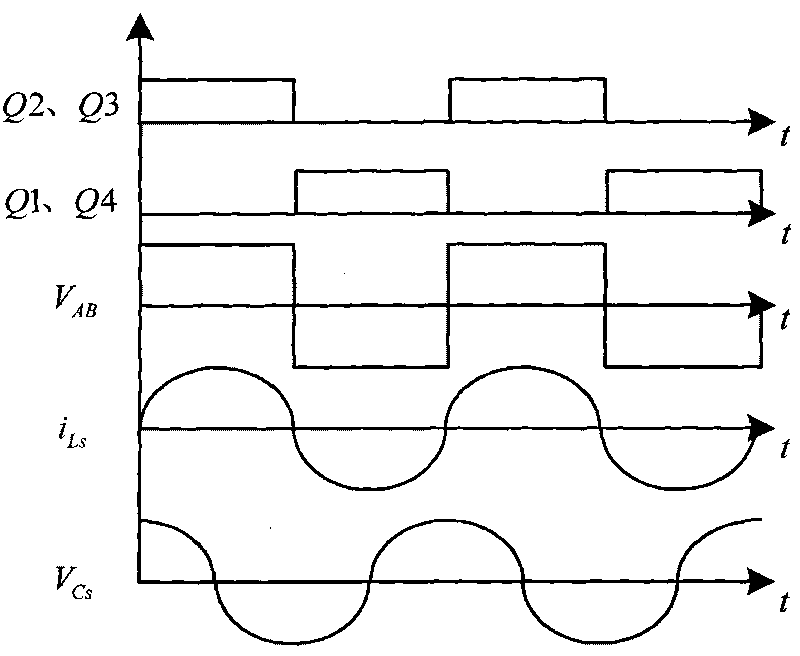
The invention discloses a system for generating high-stability high voltage, which belongs to the technical field of a high-voltage generator. A circuit structure of the system comprises a switch conversion circuit, a high-ratio transformer, a voltage multiplier, a feedback sampling circuit and a frequency-adjustable PWM control circuit, wherein the transformer is provided with a primary side and a secondary side; and the primary side is connected to a high-frequency wave output end of the switch conversion circuit, and is a series-parallel resonant circuit consisting of a resonant inductor Ls, a resonant capacitor Cs and an equivalent parallel resonant capacitor Cp of the high-ratio transformer. The system reduces the adverse impact of parasitic parameters of the transformer, improves the high-frequency operating frequency of the circuit, reduces the voltage drop of the pulsation and load of an output voltage, strengthens the stability of the output high voltage obviously, realizes a soft-switch operating mode by adjusting circuit operating points, further strengthens the stability of the output high voltage, improves operating frequency, reduces the volume of magnetic elements, and reduces the occupied space of the system obviously.
Owner:BEIJING ARITIME INTELLIGENT CONTROL
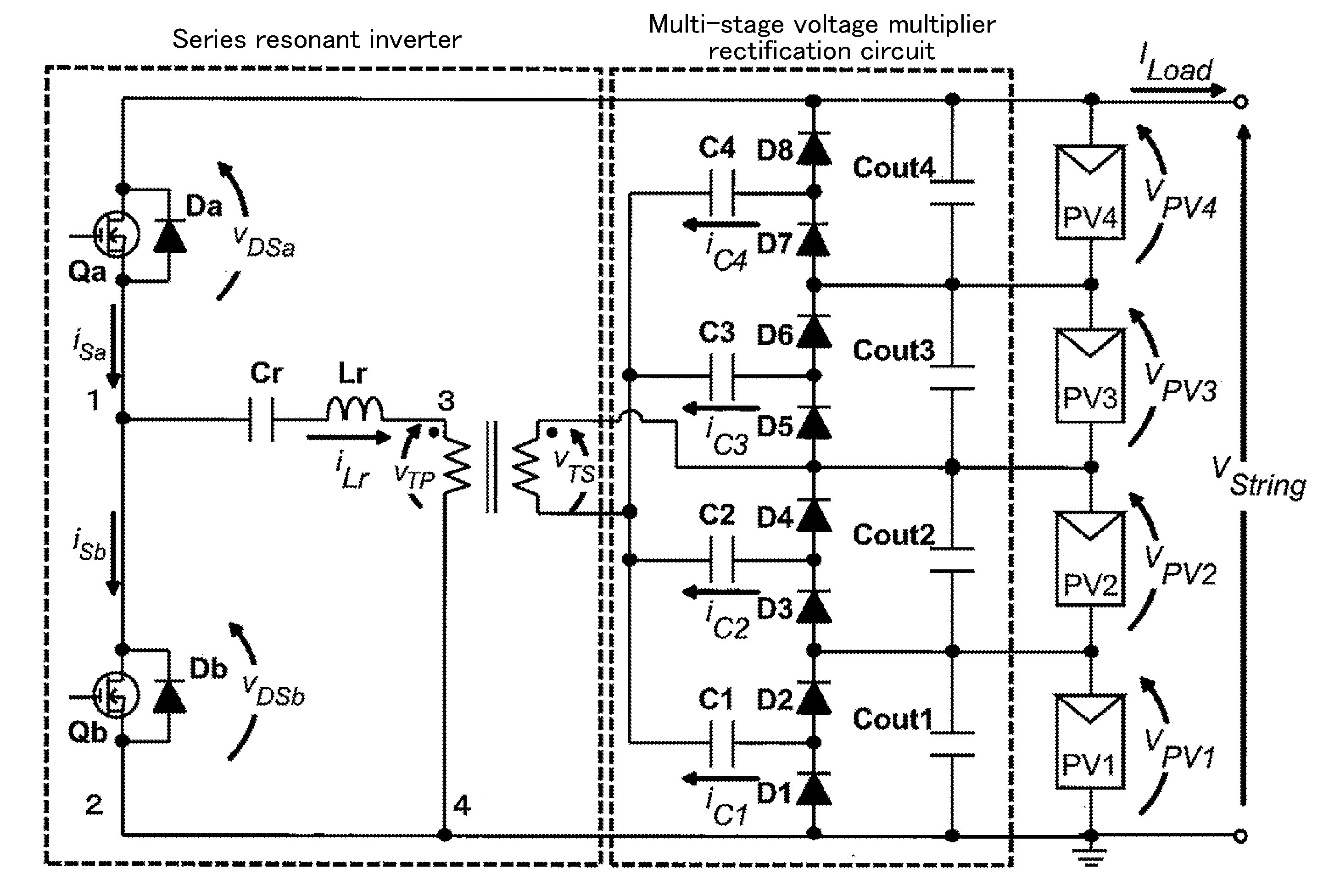
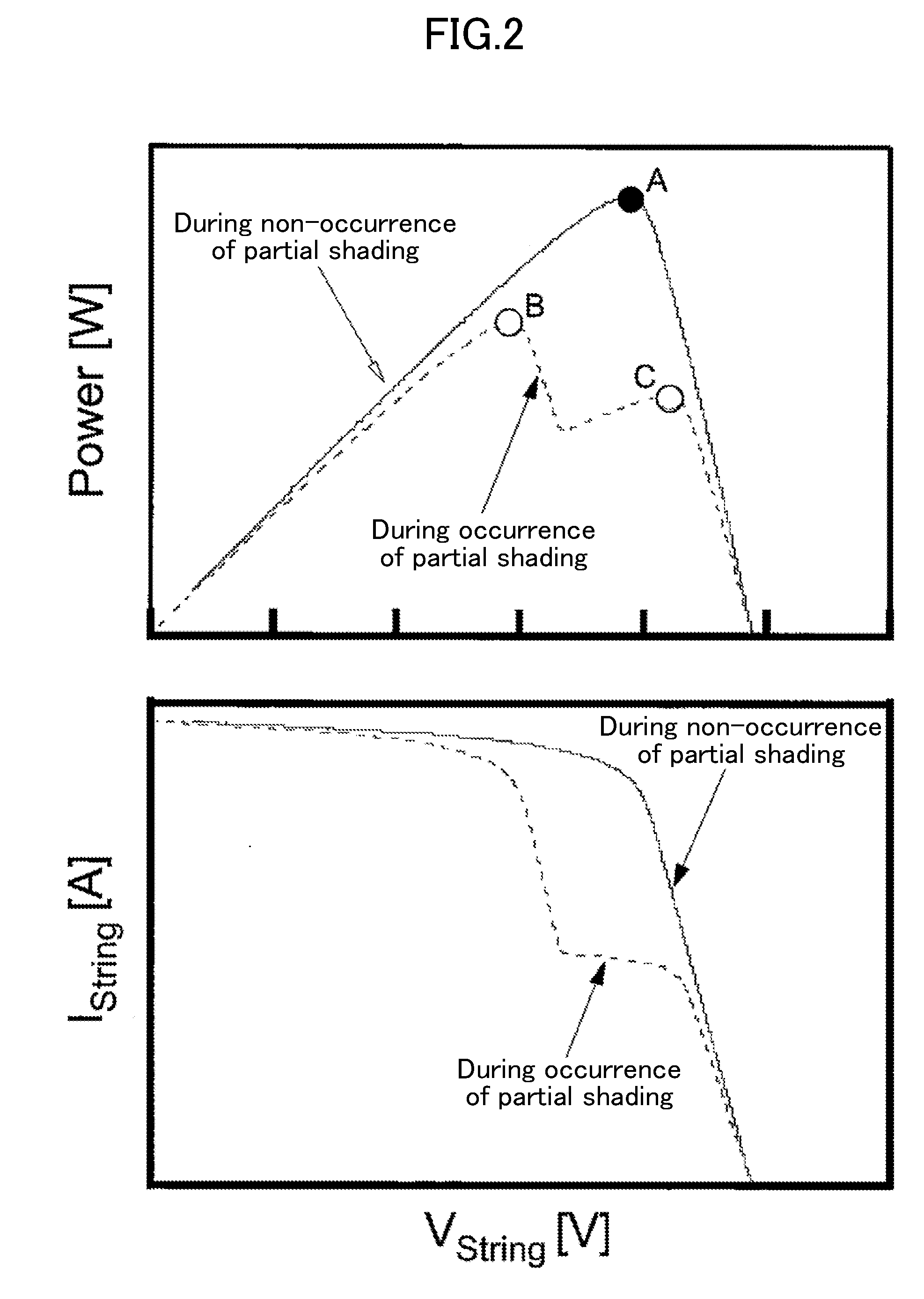
Solar cell adjustment system, related method, and minimum current detection and control system
ActiveUS20160294189A1Low working voltageSimple circuit configurationPhotovoltaic monitoringSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsVoltage multiplierControl system
[Problem] It is intended to provide a system, a related method and a minimum current detection and control system for, even when partial shading occurs in a string composed of a series connection of a plurality of solar cell modules, maintaining an output current of the whole.[Solution] By inputting an output voltage of the string into an inverter to convert the output voltage into an AC voltage and applying the AC voltage to the string via a multi-stage voltage multiplier rectification circuit, a compensation current is supplied to a shaded module on a priority basis to maintain an output current of the whole string while lowering an operating voltage of the shaded module by impedance generated on a pathway of the compensation current. Further provided are a system and the like constructed by multistage-connecting an output-side circuit section of one of various types of converters to the solar cell modules, and configured to supply a compensation current from the converter section to the shaded module on a priority basis.
Owner:JAPAN AEROSPACE EXPLORATION AGENCY
Receiving/backscattering arrangement and method with two modulation modes for wireless data transmission as well as modulation arrangement therefor
ActiveUS20040145452A1Guaranteed uptimeEfficient amplitude shiftSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationElectric signal transmission systemsVoltage multiplierMethod selection
For transmitting data, a receiving / backscattering arrangement receives, modulates and reflects or backscatters electromagnetic waves emitted by a base station. The modulation corresponds to the data to be transmitted and is carried out selectively using first and / or second different modulation methods depending on the received field strength of the received electromagnetic waves. Preferably, phase shift keying is used especially or at least at low field strengths at far range, while amplitude shift keying is used additionally or alternatively for high field strengths at close range. The two modulation methods can be superimposed. A circuit arrangement includes two different modulator arrangements to perform the two modulation methods depending on the received field strength. The second modulator arrangement preferably comprises a multi-stage voltage multiplier circuit with a modulated switching device intervening in one of the stages to achieve the modulation.
Owner:ATMEL GERMANY +1
High-dynamic range low ripple voltage multiplier
ActiveUS20090140795A1Dc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationVoltage multiplierVoltage reference
A voltage multiplier (10) including a first clocked multiplier stage (12) having an input and an output and a second clocked multiplier stage (14, 16) having an input and an output is provided. The voltage multiplier further includes an input level regulator (18) coupled to the input of the first multiplier stage. The voltage multiplier further includes a feedback bias control circuit (32) coupled to the input level regulator, wherein the feedback bias control circuit is further coupled to receive the output (50) of the second multiplier stage, and wherein the feedback bias control circuit generates a feedback signal (58) affecting an output of the input level regulator based on a comparison between a voltage proportional to a voltage at the output of the second clocked multiplier stage and a reference voltage.
Owner:NXP USA INC
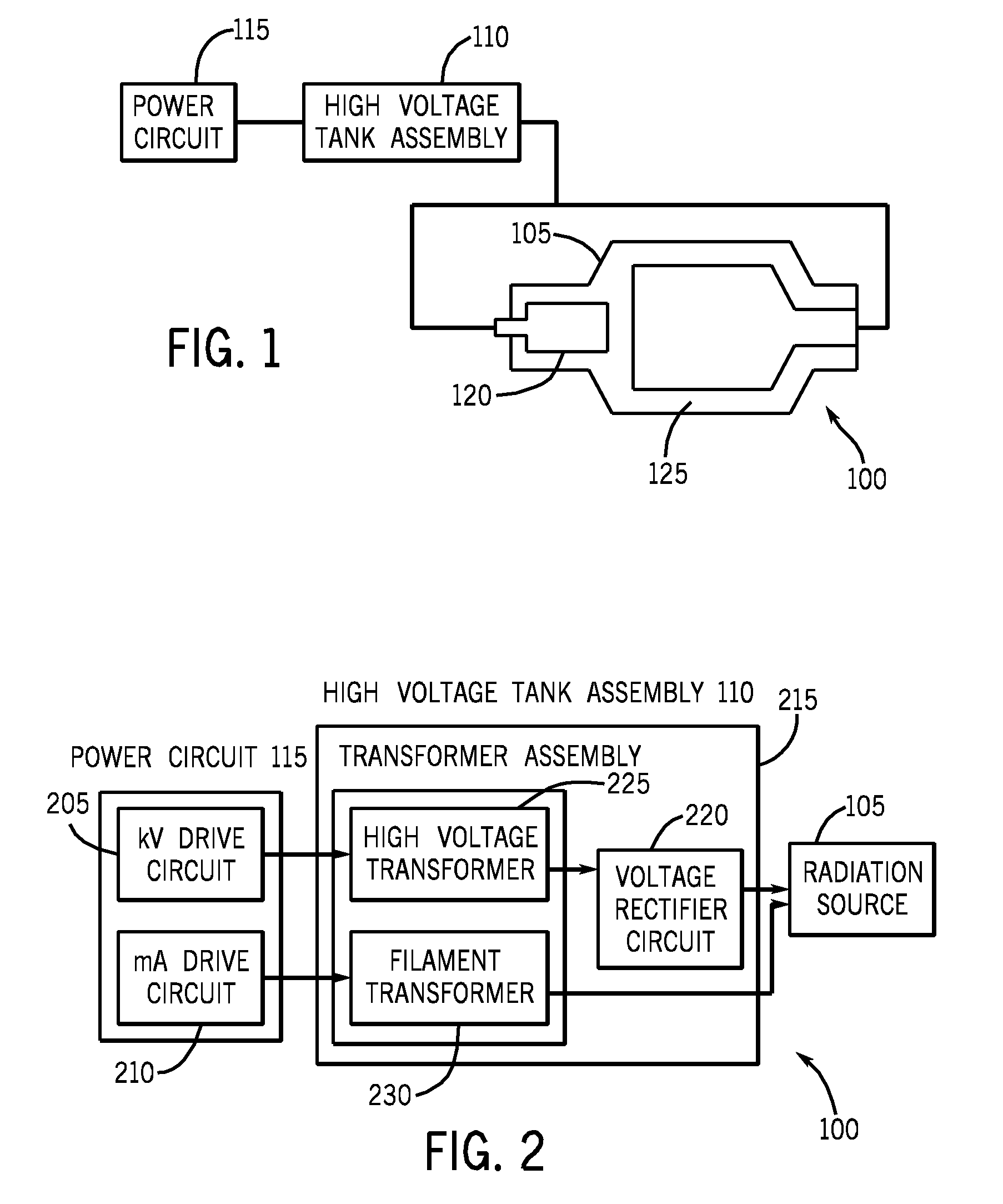
High voltage tank assembly for radiation generator
InactiveUS20090041192A1Printed circuit aspectsHigh voltage circuit adaptationsVoltage multiplierEngineering
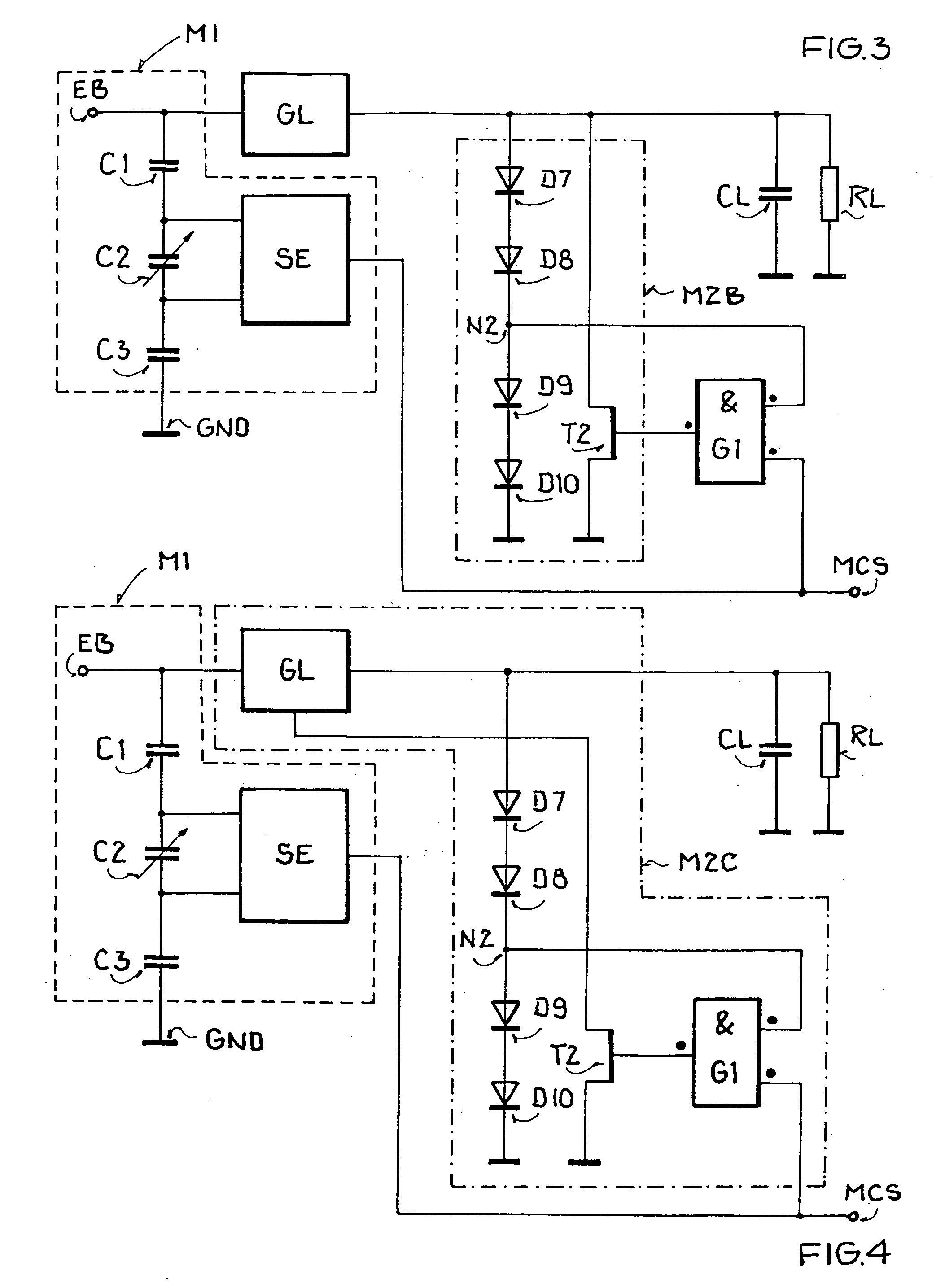
In one embodiment, a voltage rectifier circuit for a radiation generator is provided. The voltage rectifier circuit is configured to be used in a voltage multiplier circuit and a voltage doubler circuit. The voltage rectifier circuit comprises at least one first printed circuit board and at least one second printed circuit board coupled to each other using a plurality of connectors. Further, each printed circuit board comprises, a first terminal, a second terminal, a third terminal, a diode assembly externally connected between the first terminal and the second terminal and a capacitor assembly embedded between the second terminal and the third terminal.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Adjustable non-dissipative voltage boosting snubber network
ActiveUS9226380B2Boost voltageReduce voltageElectric discharge tubesElectric lighting sourcesPower flowVoltage multiplier
This disclosure describes a non-dissipative snubber circuit configured to boost a voltage applied to a load after the load's impedance rises rapidly. The voltage boost can thereby cause more rapid current ramping after a decrease in power delivery to the load which results from the load impedance rise. In particular, the snubber can comprise a combination of a unidirectional switch, a voltage multiplier, and a current limiter. In some cases, these components can be a diode, voltage doubler, and an inductor, respectively.
Owner:AES GLOBAL HLDG PTE LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com