Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
473 results about "Frequency wave" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
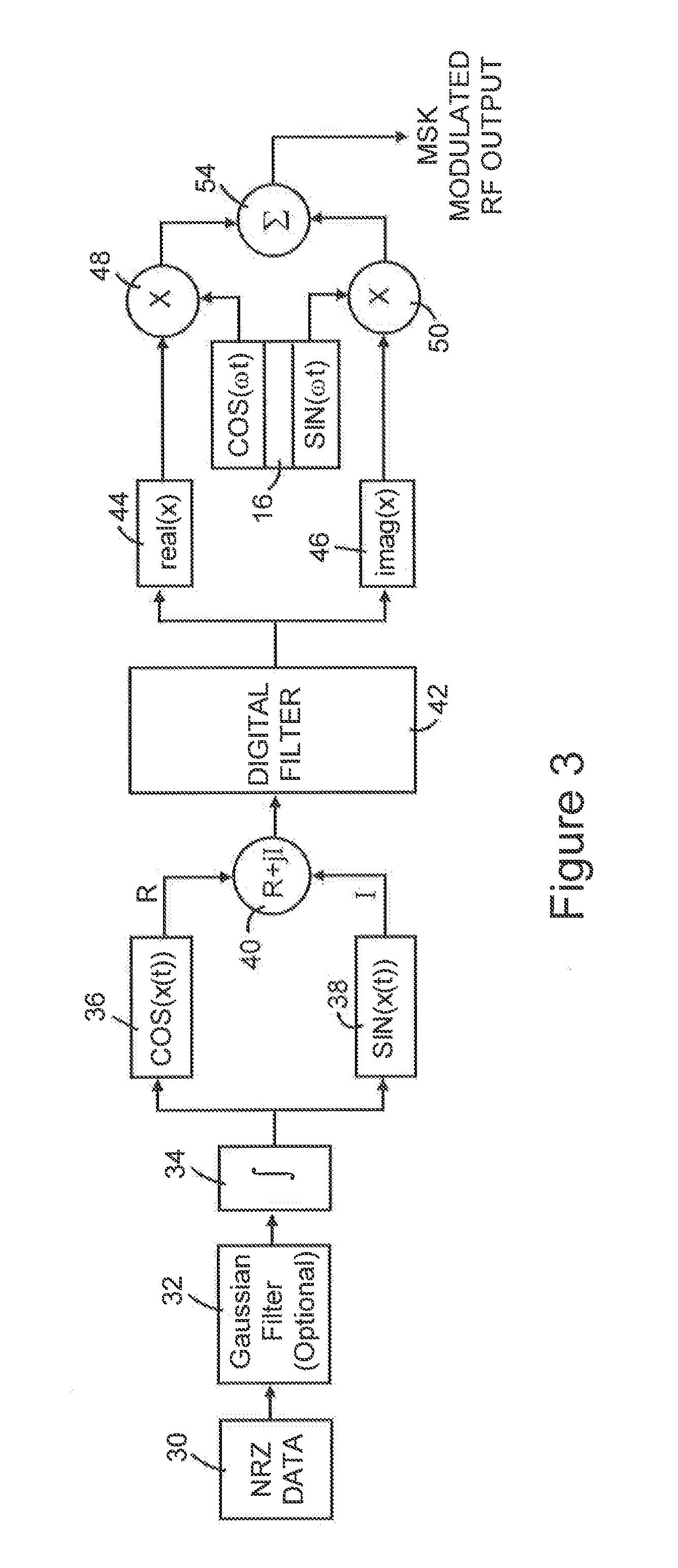
Frequency (wave motion) The number of times which sound pressure, electrical intensity, or other quantities specifying a wave vary from their equilibrium value through a complete cycle in unit time. The most common unit of frequency is the hertz (Hz), which is equal to 1 cycle per second.
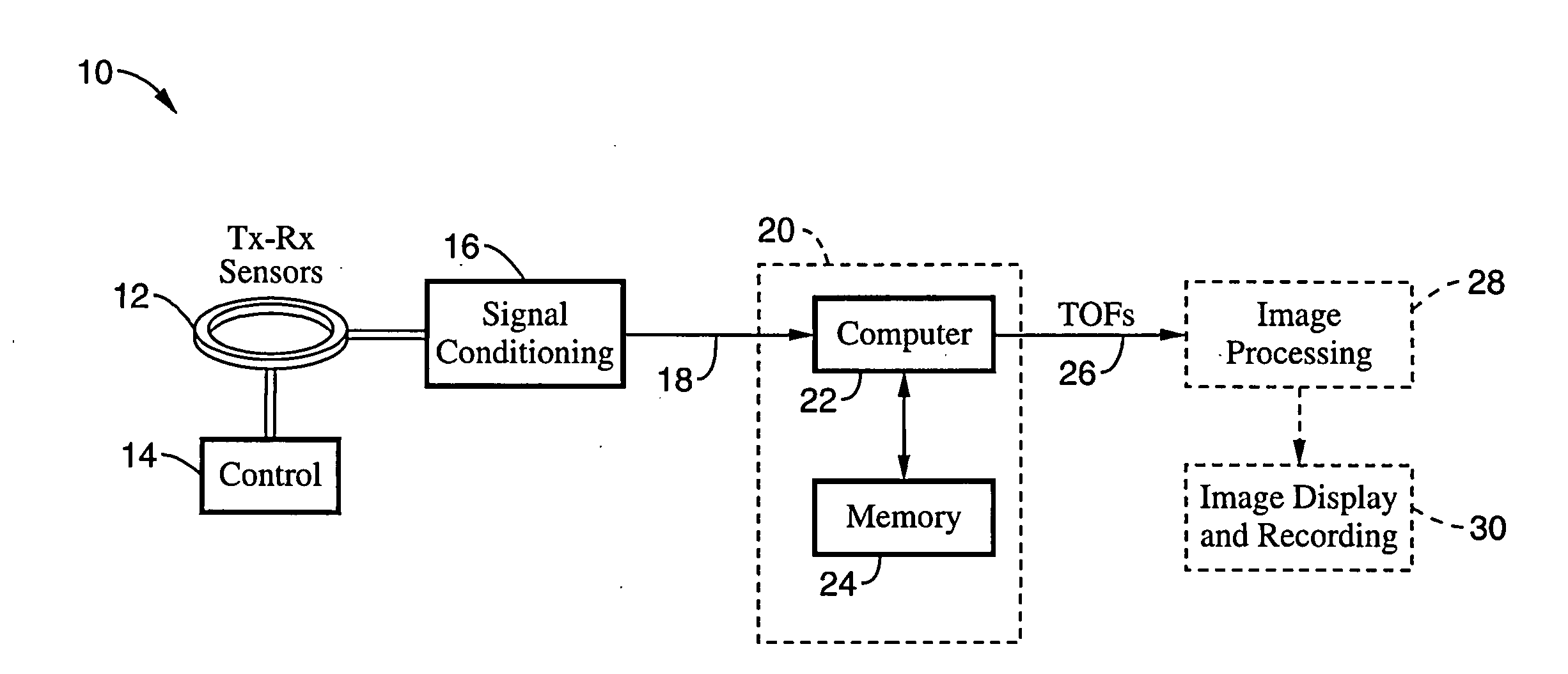
Ultrasonic transducer for ranging measurement with high directionality using parametric transmitting array in air and a method for manufacturing same
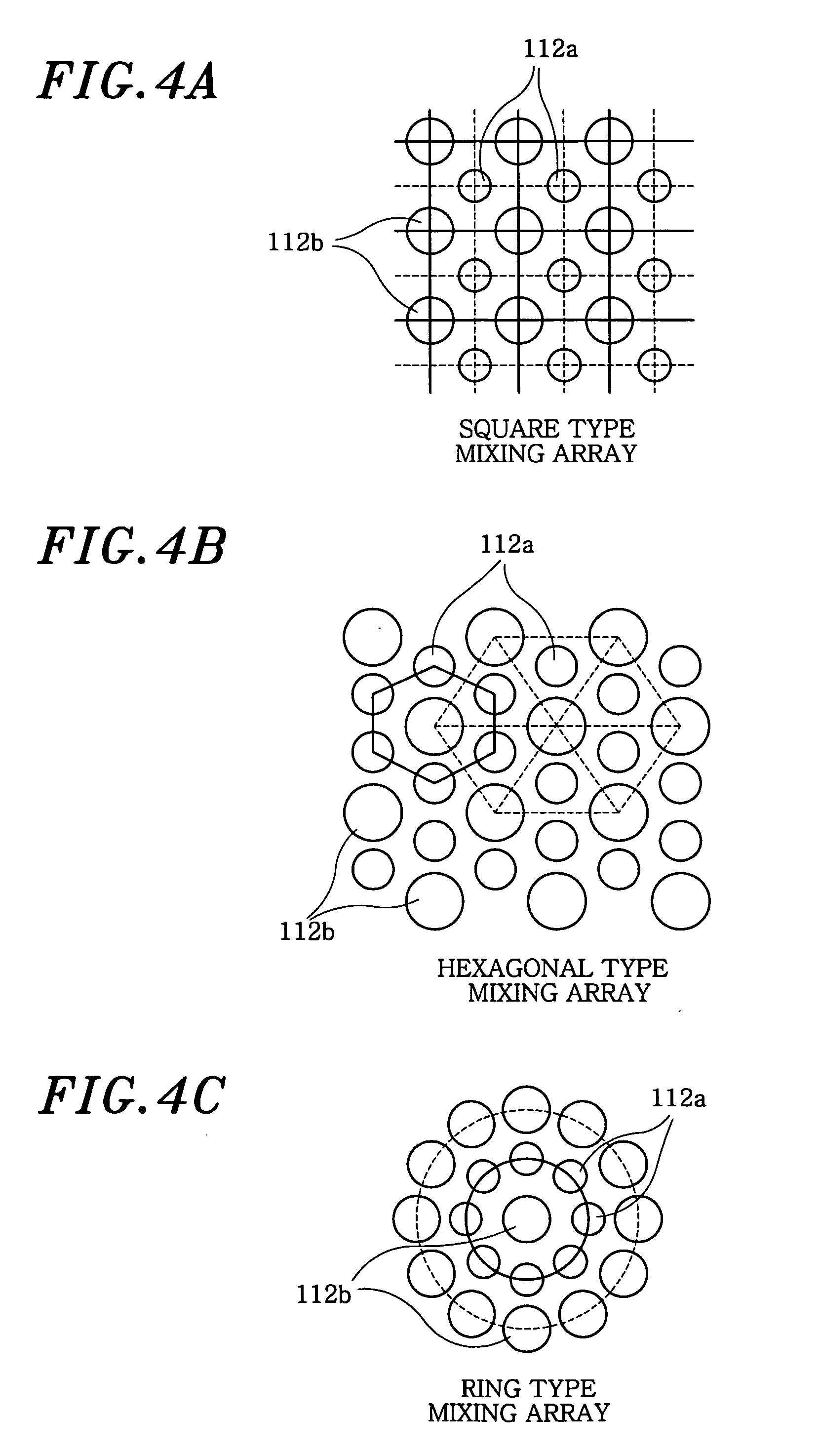
InactiveUS20080013405A1Improve directionalityMechanical vibrations separationAcoustic wave reradiationSonificationFrequency wave
A multiple resonances type ultrasonic transducer for a ranging measurement with high directionality using a parametric transmitting array in air, includes an ultrasonic actuator unit formed with a regularly mixing array of first unit actuators having a resonance frequency of f1 and second unit actuators having a resonance frequency of f2. The ultrasonic actuator unit generates a difference frequency wave (fd=f1−f2) with high directionality by forming a parametric transmitting array in air through generating two ultrasonic waves with high pressure in air. Further, the transducer includes an ultrasonic sensor unit formed with one or more unit sensors having a resonance frequency of the difference frequency (fd=f1−f2), for sensing a reflected ultrasonic pulse'signal from a target.
Owner:MOON WONKYU
Multi-modality system for imaging in dense compressive media and method of use thereof
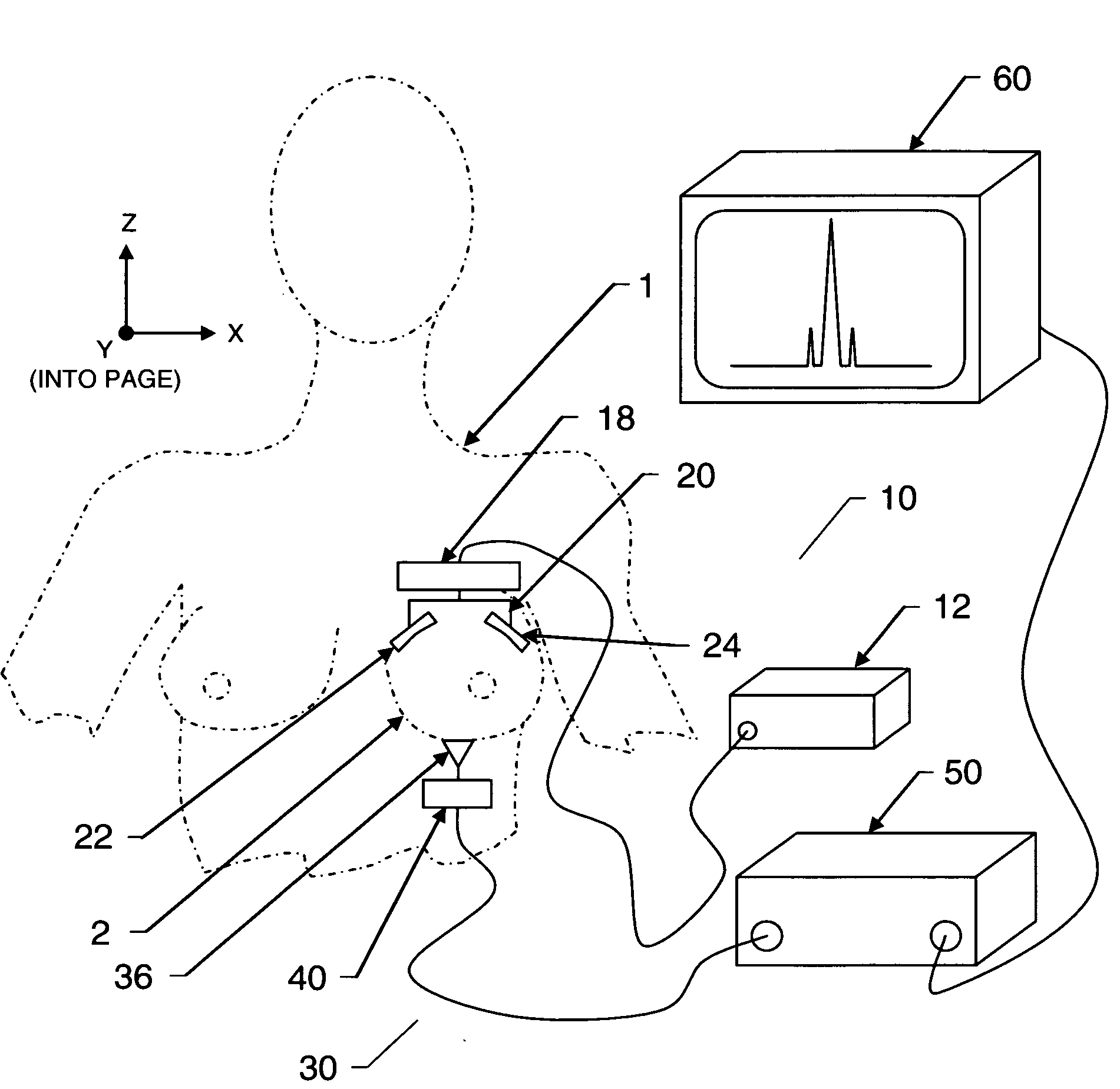
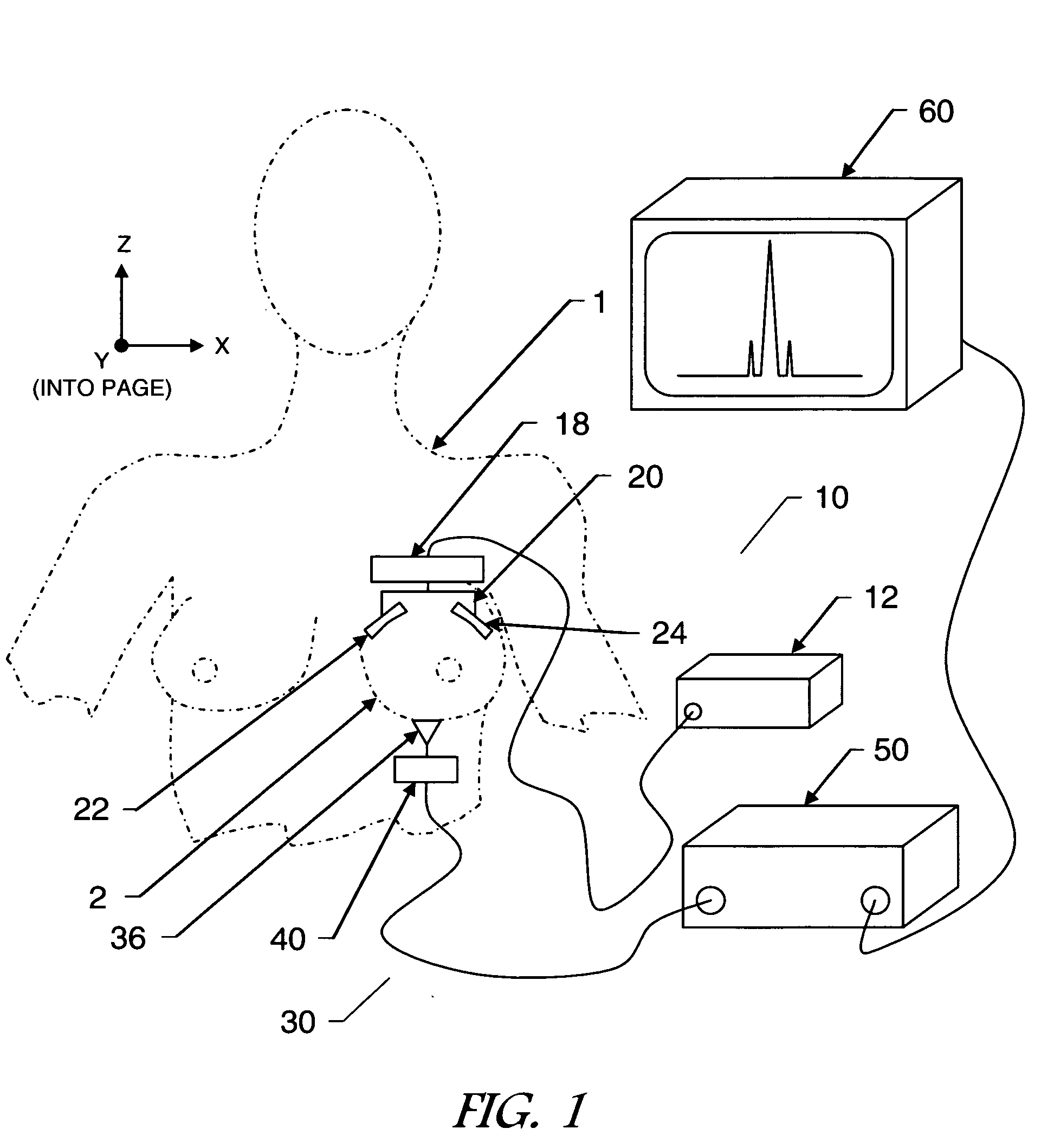
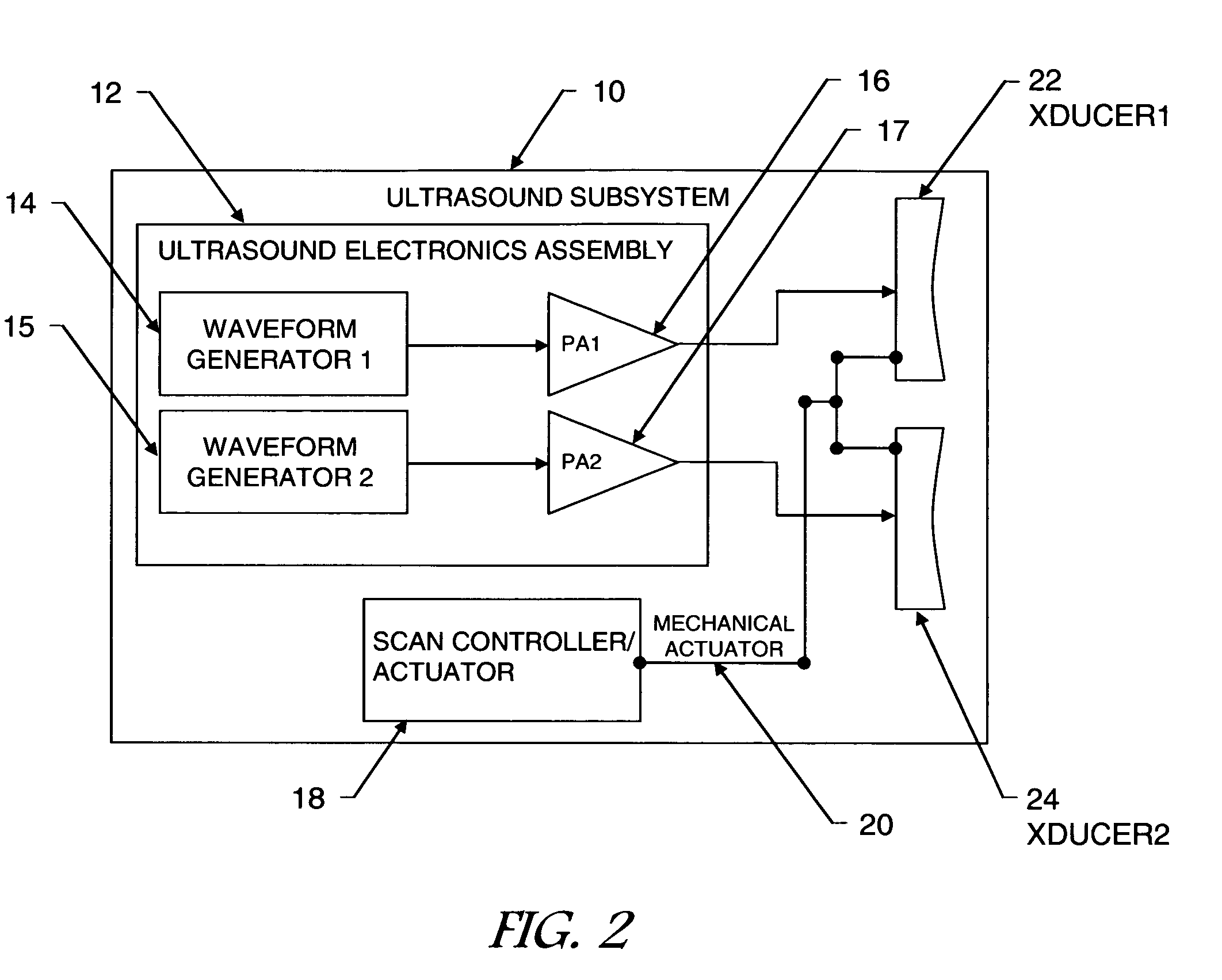
InactiveUS20090281422A1Improve permeabilityHigh resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostics using vibrationsFrequency waveMicrowave
A multi-modality system and method for performing detection, characterization and imaging of materials and objects in dense compressive media, such as in medical soft tissue applications, is disclosed. Medical tissue applications include but are not limited to the detection and diagnosis of breast tumors. Generally, an ultrasound subsystem is employed to excite a region in the dense compressive media and a microwave subsystem is employed to collect detection, characterization and imaging information from the excited region. In one preferred embodiment, multiple focused oscillating high-frequency ultrasound wave beams are transmitted into the media. The resultant low beat-frequency wave creates a force inducing motion in the materials and objects in the media. A radio-frequency microwave subsystem detects that motion and produces images based upon the Doppler effects of the excited materials and objects.
Owner:ULTRAWAVE LABS
Ultrasonic transducer for ranging measurement with high directionality using parametric transmitting array in air and a method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS7460439B2Mechanical vibrations separationAcoustic wave reradiationFrequency waveSonification
A multiple resonances type ultrasonic transducer for a ranging measurement with high directionality using a parametric transmitting array in air, includes an ultrasonic actuator unit formed with a regularly mixing array of first unit actuators having a resonance frequency of f1 and second unit actuators having a resonance frequency of f2. The ultrasonic actuator unit generates a difference frequency wave (fd=f1−f2) with high directionality by forming a parametric transmitting array in air through generating two ultrasonic waves with high pressure in air. Further, the transducer includes an ultrasonic sensor unit formed with one or more unit sensors having a resonance frequency of the difference frequency (fd=f1−f2), for sensing a reflected ultrasonic pulse signal from a target.
Owner:MOON WONKYU
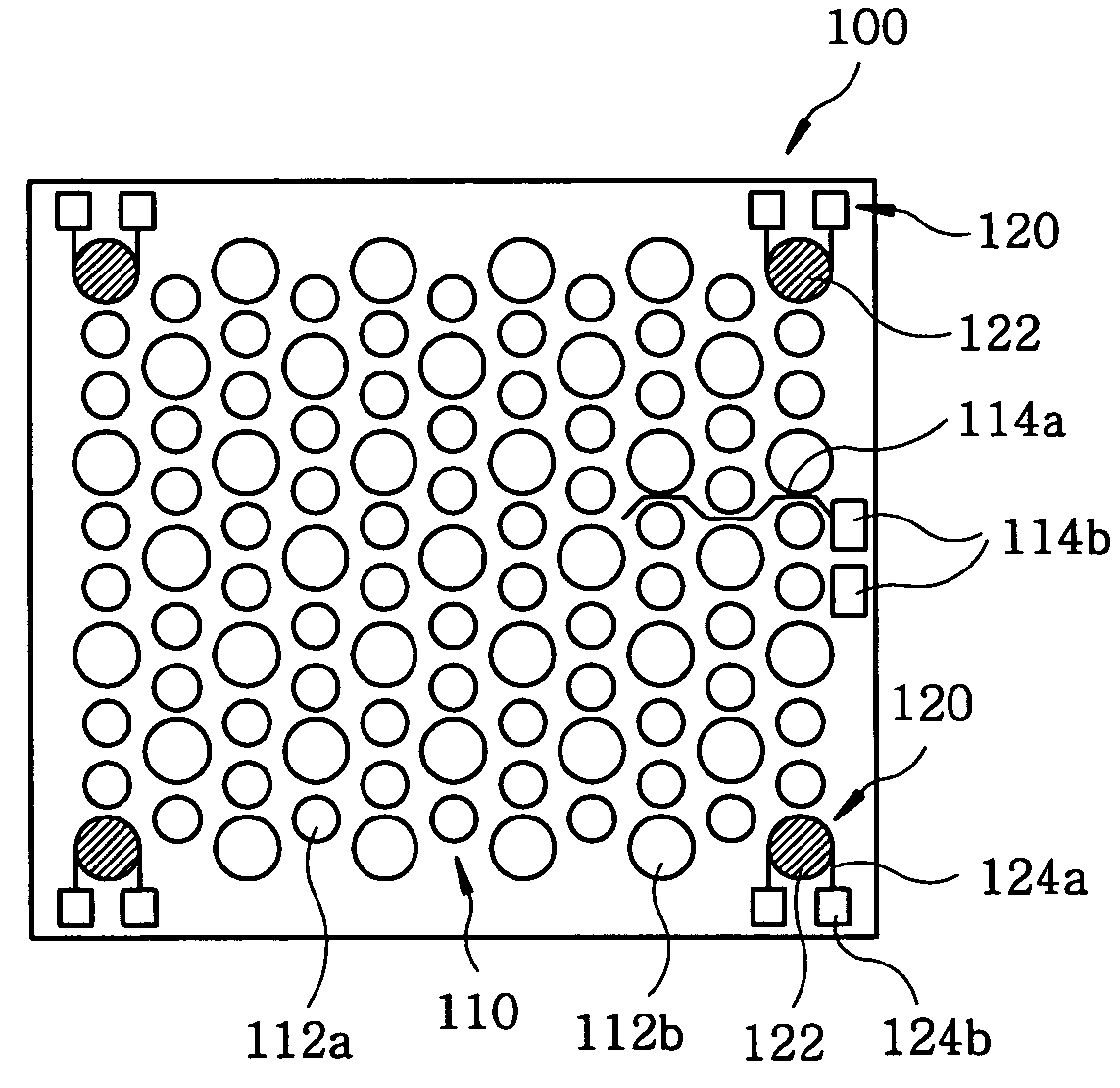
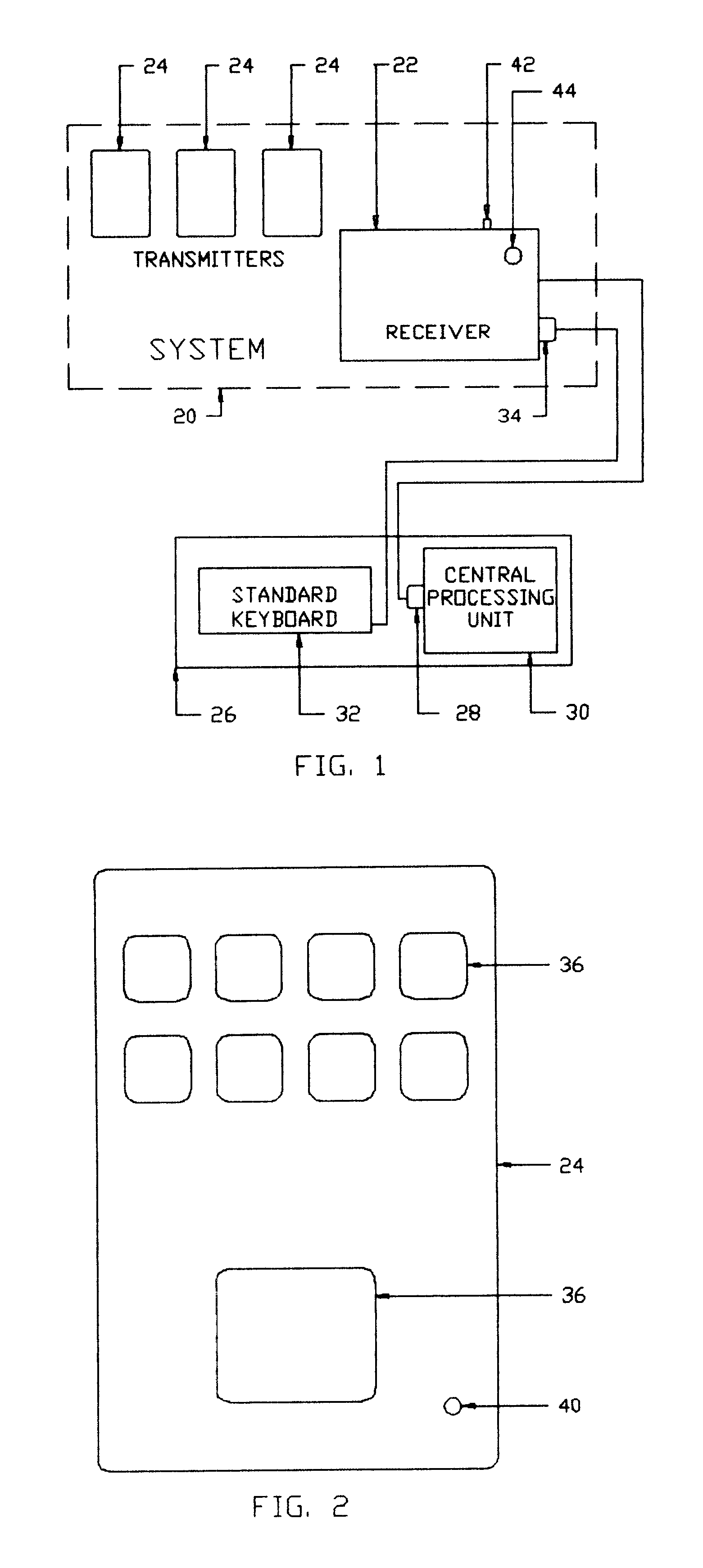
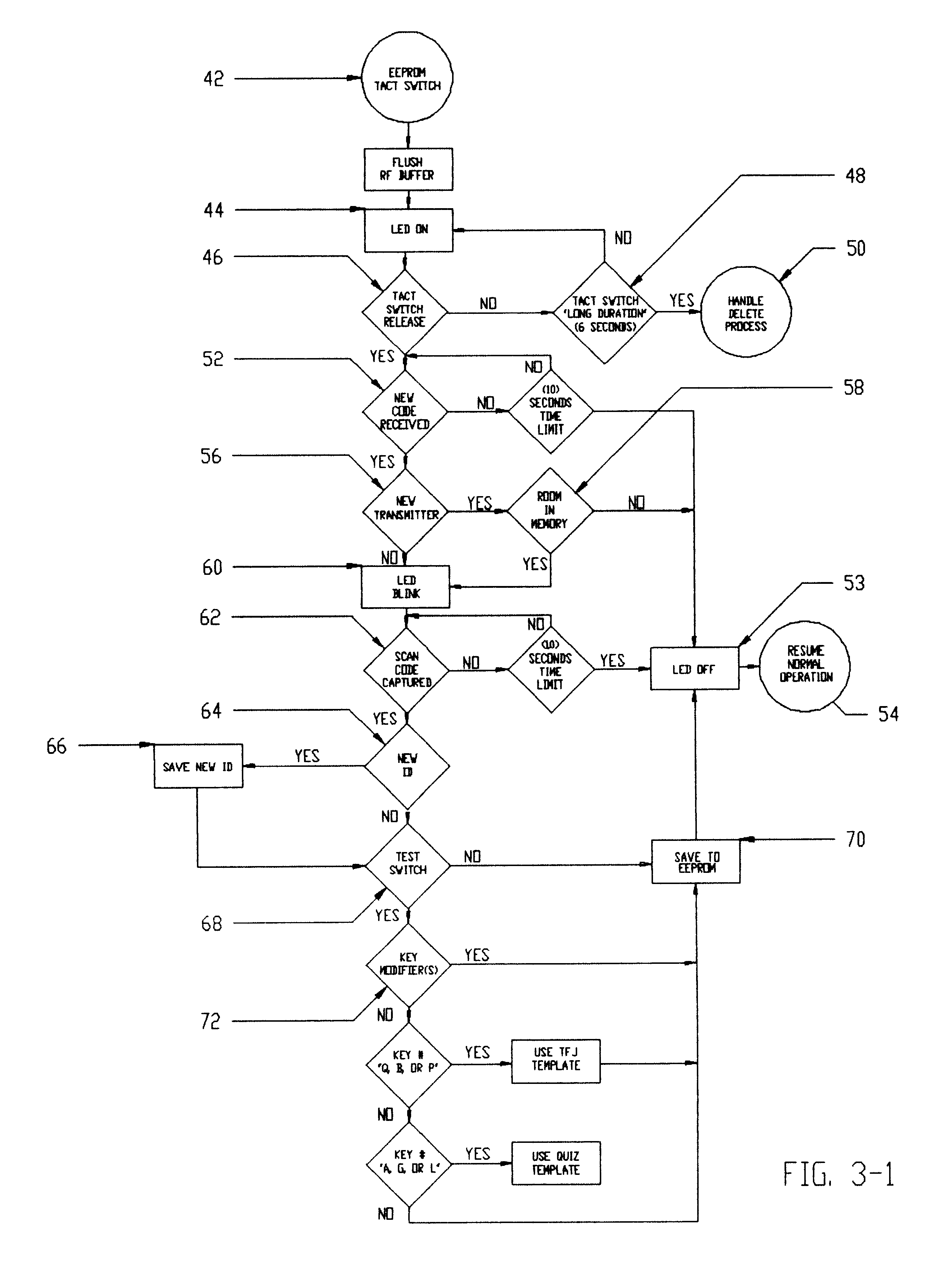
System for receiving ID-codes from at least one wireless transmitter having a plurality of transmitter buttons each of them being individually programmed
A wireless, remote, programmable keyboard input system for computers is provided. A single receiver is capable of simultaneous receipt of RF ID-Code transmissions from multiple remote transmitters, is plugged into the keyboard port of the central processing unit of a computer. The computer's standard keyboard is then plugged into the receiver and remains fully functional. The RF ID-Code of each button of each remote hand held transmitter is a unique fixed code. The receiver in this system is programmed by associating, in the receiver's memory, a unique transmitter button ID-Code with the scancode or modified scancode of a key or modified key from the standard keyboard of the computer. When the receiver, in the operation mode, recognizes that RF ID-Code from that transmitter button, it pulls the associated scancode or modified scancode from its memory and sends it off to the CPU of the computer. When several such previously programmed RF ID-Codes are sent to the receiver in succession, the receiver recognizes them in sequence and sends the corresponding scancodes or modified scancodes off to CPU in that same sequence. The invention can operate using either radio frequency or infrared frequency waves. A method of programming the system is also provided.
Owner:CURRENT WORKS
Seismic Acquisition And Filtering
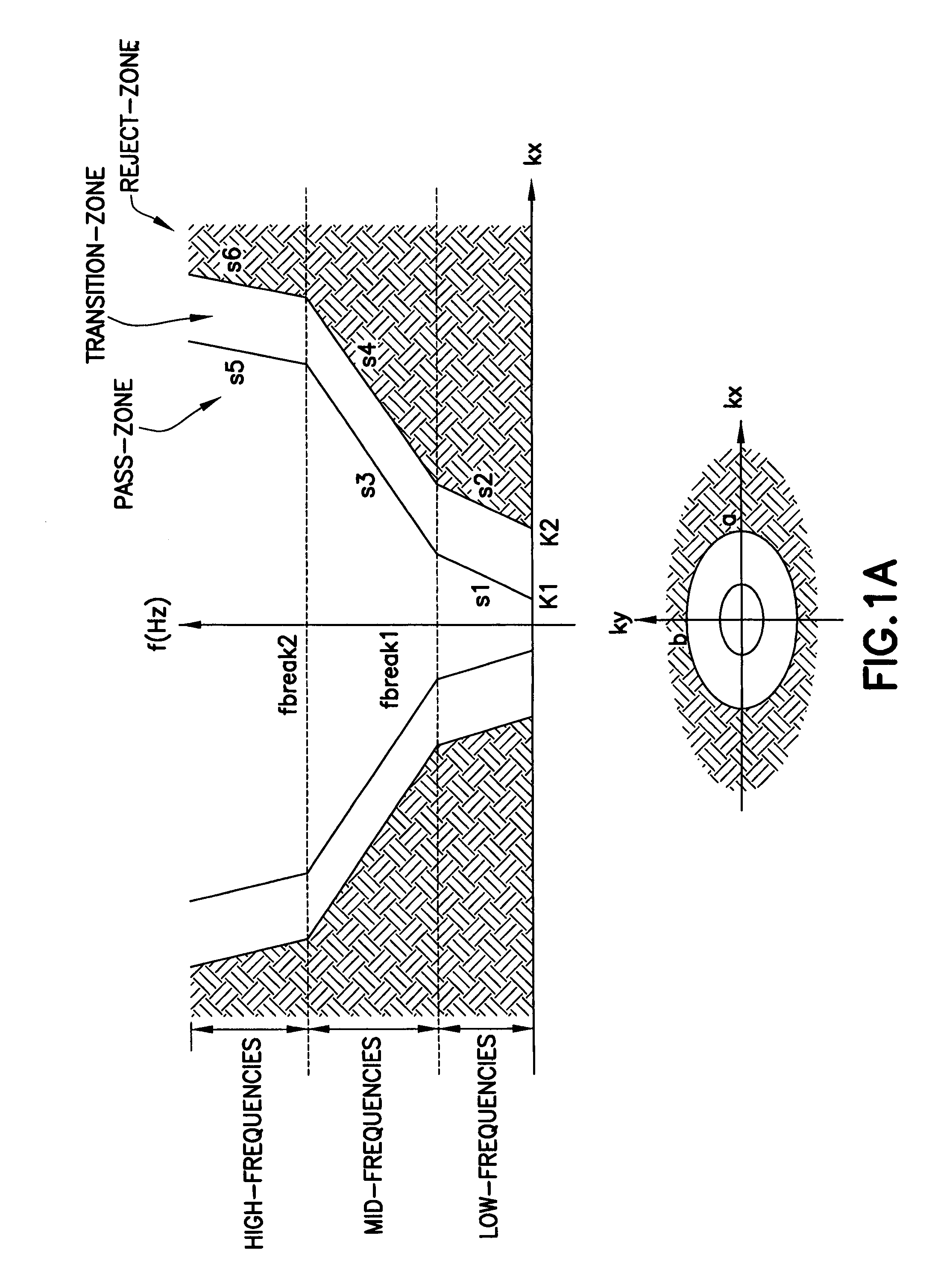
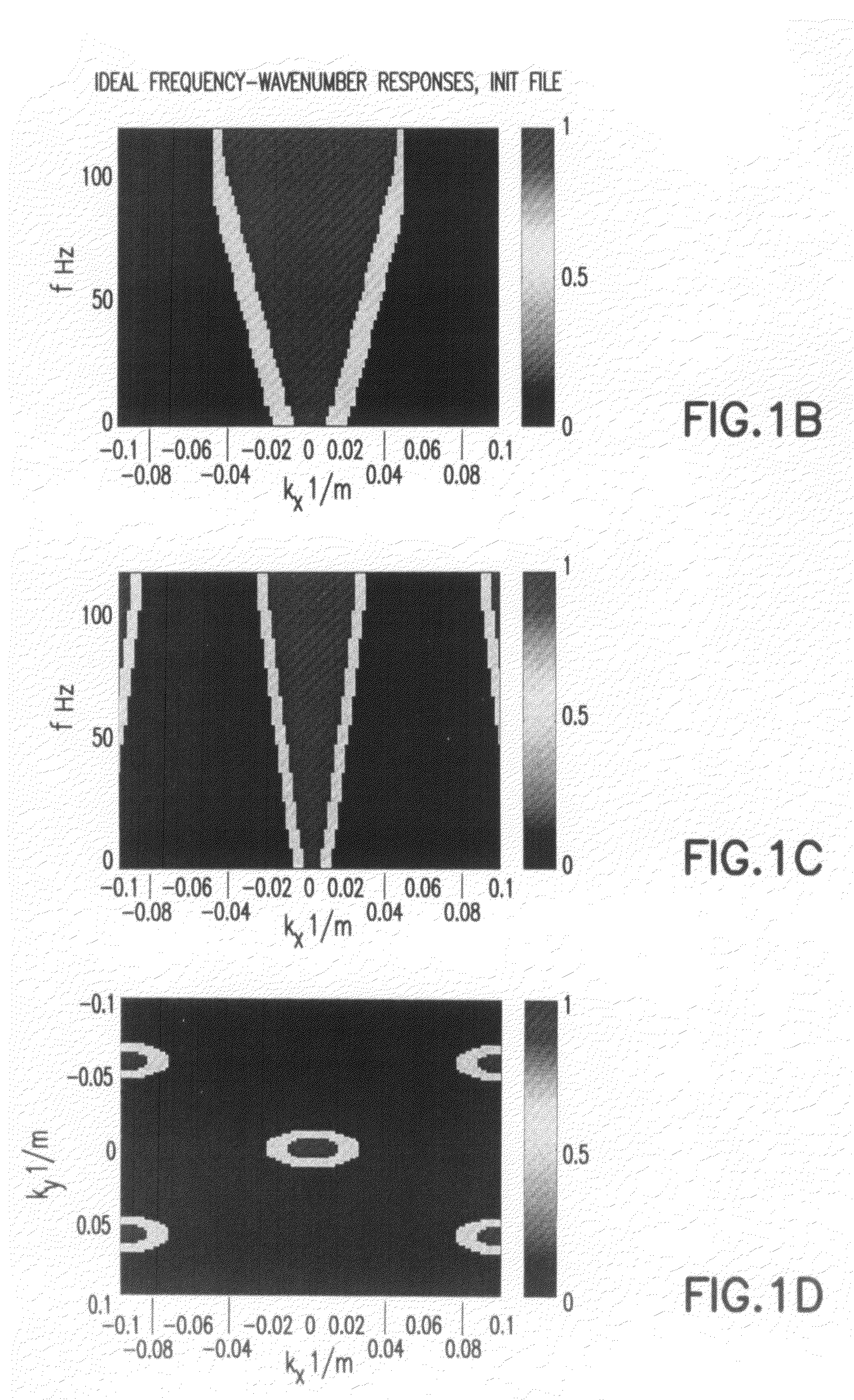
InactiveUS20080033655A1Promote resultsSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsFrequency waveSpacetime
An iterative process is described for obtaining a finite impulse filter to remove noise from seismic data through an iterative process with constraints on the filter applied in both, the original space-time and the transform frequency wave number at each iteration step.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
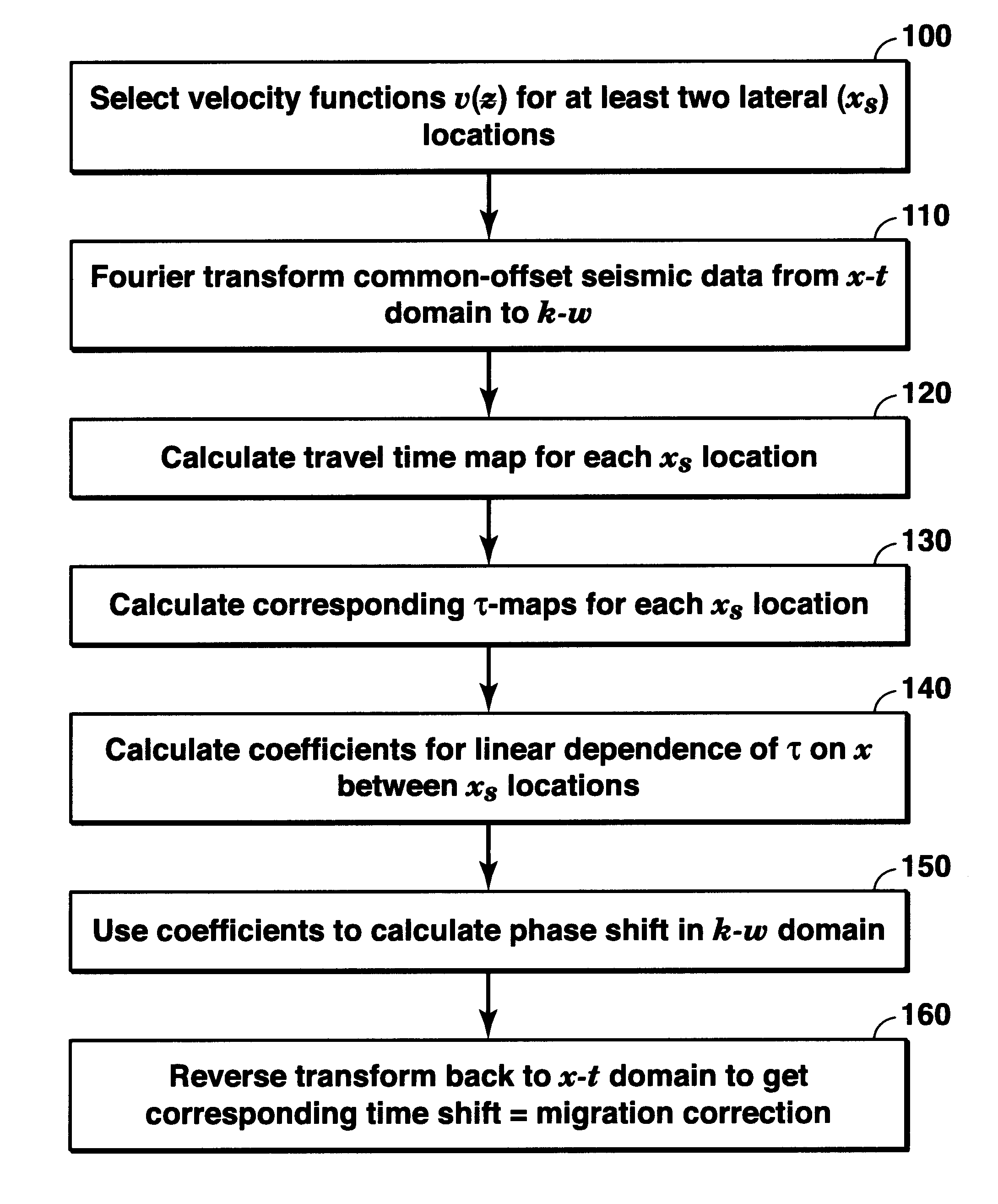
Method for compensating mild lateral velocity variations in pre-stack time migration in the frequency-wave number domain
InactiveUS6865489B2Seismic signal processingPermeability/surface area analysisFrequency wavePhase shifted
A method for performing pre-stack time migration of seismic data in a region where the subsurface seismic wave propagation velocity varies in both the vertical direction and a horizontal direction. The migration is performed in the wave number—frequency domain and involves using travel time maps to find a linear fitting of the migration phase shift for a given ray parameter and at a given vertical depth versus horizontal position. The slope and intercept parameters from the linear fit are used to adjust a known pre-stack time migration equation, with the accuracy of the linear approximation requiring mild horizontal velocity variation.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Electromagnetic induction interactive electronic white board and system thereof
InactiveCN101042625AImprove ease of useInput/output processes for data processingWhiteboardFrequency wave
This invention relates to one electromagnetic sense interacting electron board and system, which comprises input part, edge frame on input part, control circuit and computer connected interface or outside wireless radio frequency module, wherein, the control circuit comprises micro processor and control circuit; the input part comprises write layer and down sensor layer; the sense layer output is connected to control circuit; the sense layer comprises sense coils along X and Y axis directions with cross points insulated; the micro processor is set with time division operation program to generate different frequency wave electron pen and other operation; the system comprises electron board and more than different radio electromagnetic wave electron pen.
Owner:JULONG EDUCATIONAL TECH
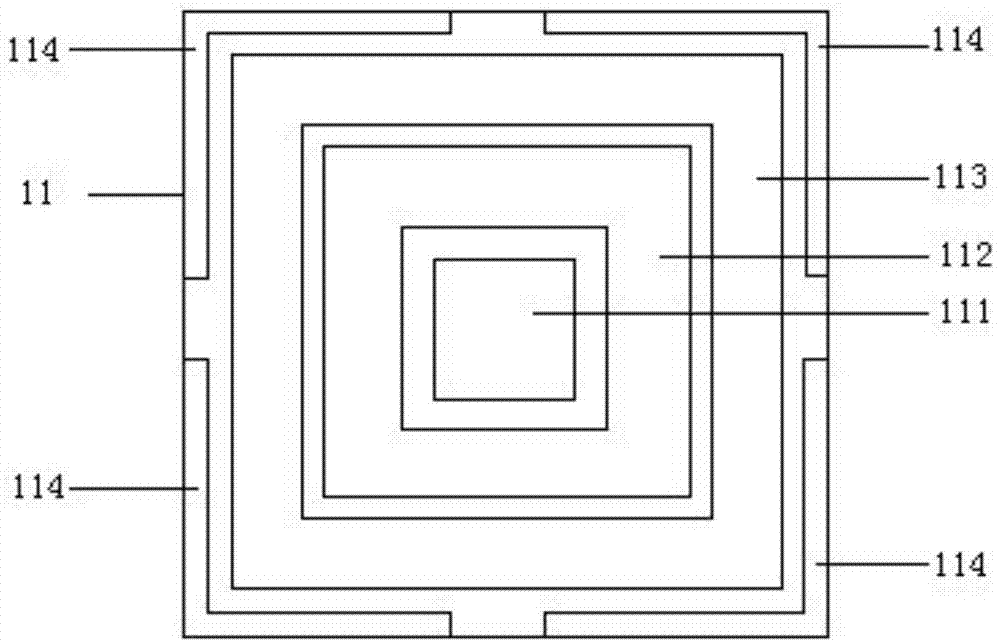
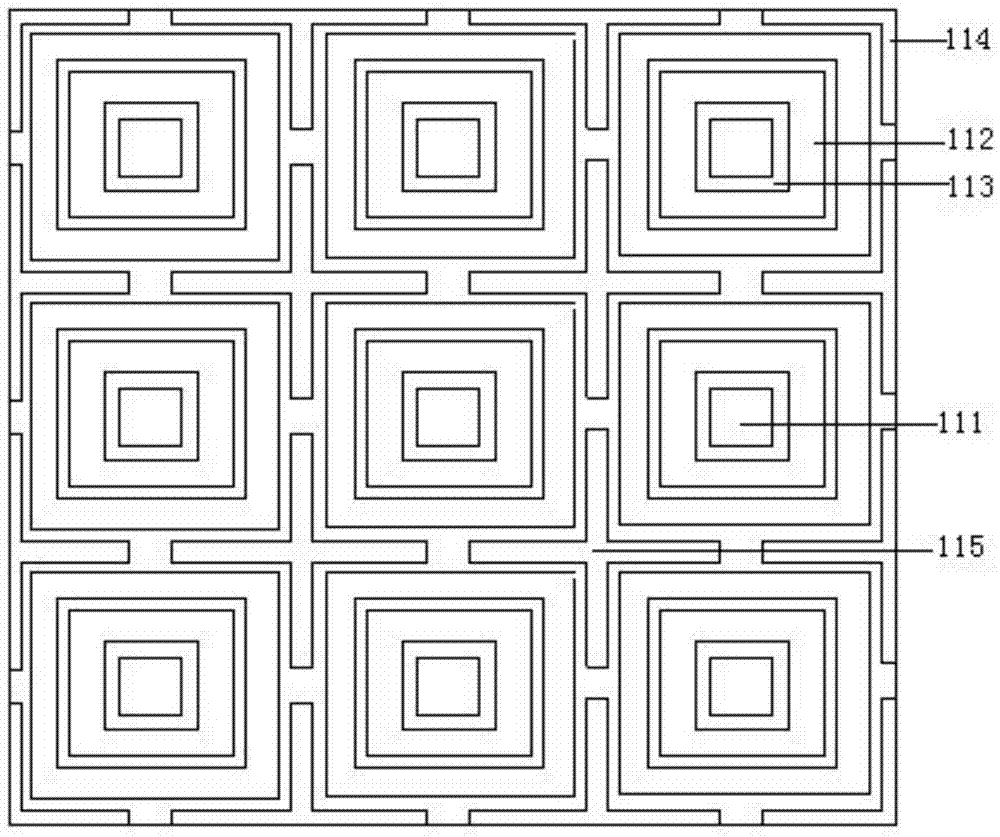
Ultrathin metallic resistance composite multi-frequency wave-absorbing material
ActiveCN103943967ASimple structureEasy to processAntennasElectrical resistance and conductanceFrequency wave
The invention relates to an ultrahigh metallic resistance composite multi-frequency wave-absorbing material and belongs to the technical field of wave-absorbing materials. The technical problems that in the prior art, a circuit simulation wave-absorbing structure is narrow in wave-absorbing bandwidth, single in wave-absorbing frequency band and large in relative thickness are solved. The wave-absorbing material comprises a frequency selecting surface, a medium layer and a metal bottom plate. The frequency selecting surface is composed of patch units arrayed periodically, and each patch unit comprises a square patch, a first square surrounding patch and a second square surrounding patch, wherein the square patch, the first square surrounding patch and the second square surround patch are sequentially arrayed from inside to outside according to the length of sides. The wave-absorbing material further comprises four L-shaped patches which are symmetrically arranged outside four right angles of the second square surrounding patch. The double-frequency or triple frequency wave-absorbing characteristic that the reflection coefficient, below -10dB, of the wave-absorbing material is adjusted within the 4 GHz-18 GHz range can be achieved, the reflection coefficient of about -20 dB can be achieved nearby a wave-absorbing harmonic peak, and therefore a higher wave-absorbing effect is achieved.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
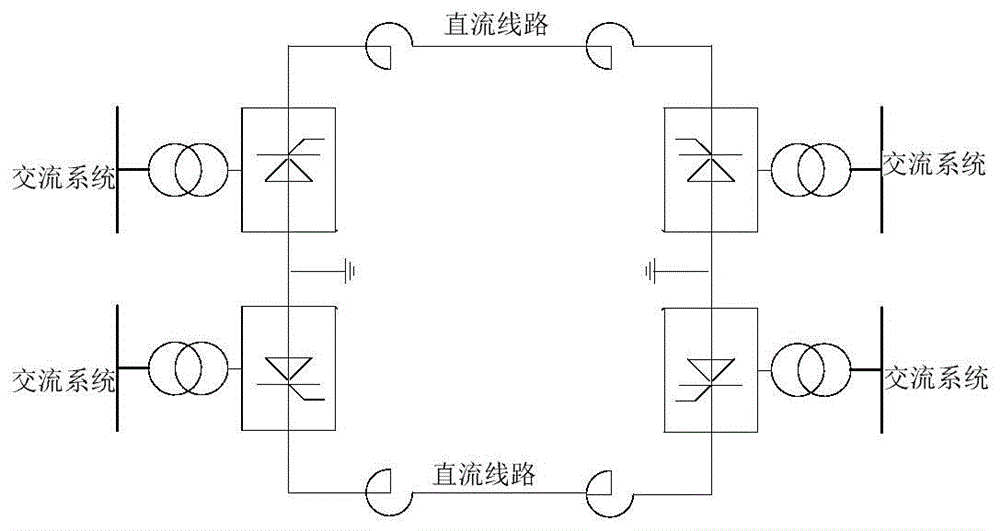
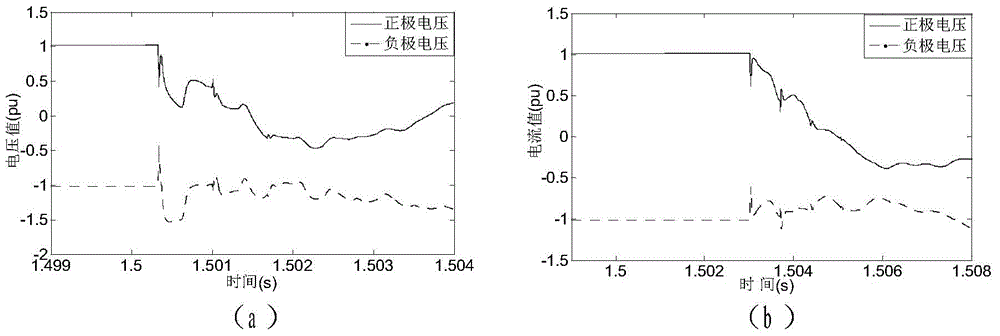
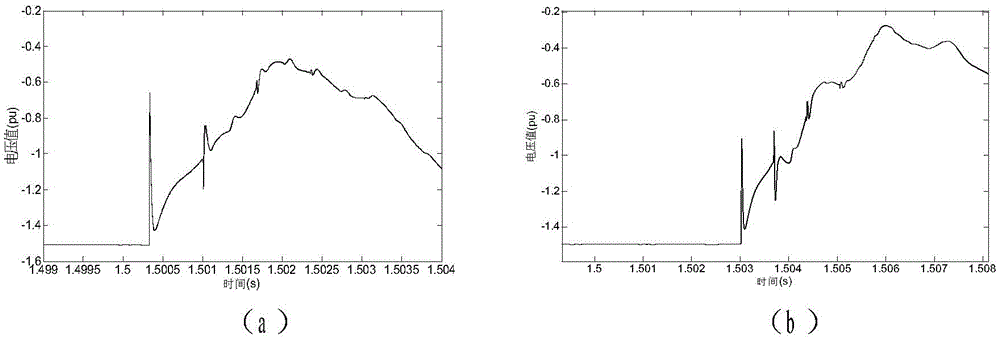
Method for measuring fault location of HVDC (High Voltage Direct Current) transmission line under consideration of measured wave velocity
ActiveCN104597376AResolve inconsistenciesImprove ranging accuracyFault locationFrequency waveClassical mechanics
The invention relates to a method for measuring fault location of a HVDC transmission line under consideration of measured wave velocity; the method is characterized by comprising the following steps: considering the variation characteristic of the wave velocity on the basis of the traditional dual-end location measuring method, and performing the calibration of a wave tip and the determination of the wave velocity in the same process; respectively acquiring the positive and negative data of the voltage of the HVDC transmission line by means of devices at two ends of the line; after the data is subjected to filtering processing and line-mode conversion, analyzing the obtained line-mode traveling wave, obtaining a time-frequency oscillogram of signals and determining the arrival time of the fault traveling wave to two ends of the line as well as a corresponding instantaneous frequency value; obtaining the corresponding line-mode wave velocity by using frequency-wave velocity curves; and finally, obtaining the fault distance by means of a dual-end distance measurement formula.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
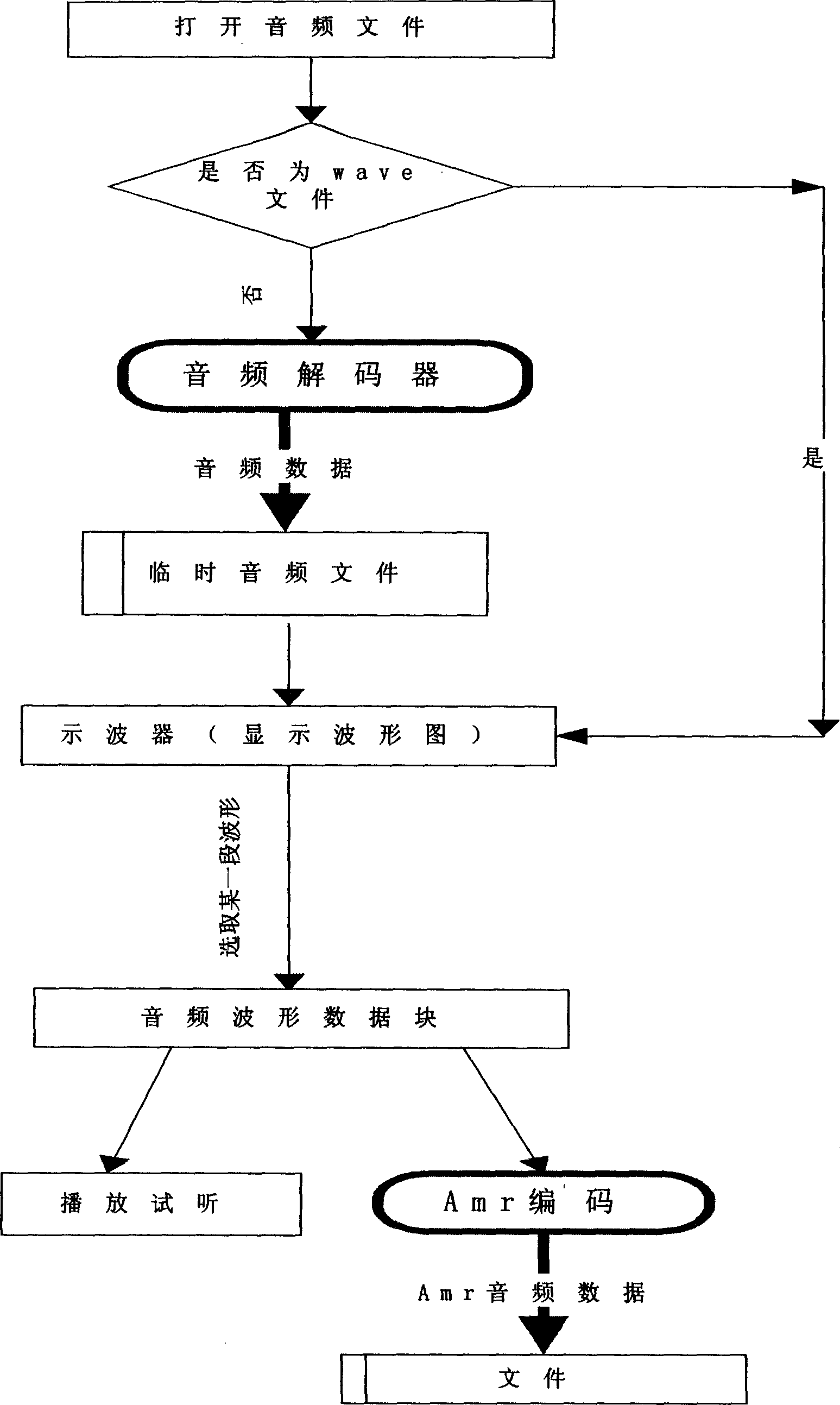
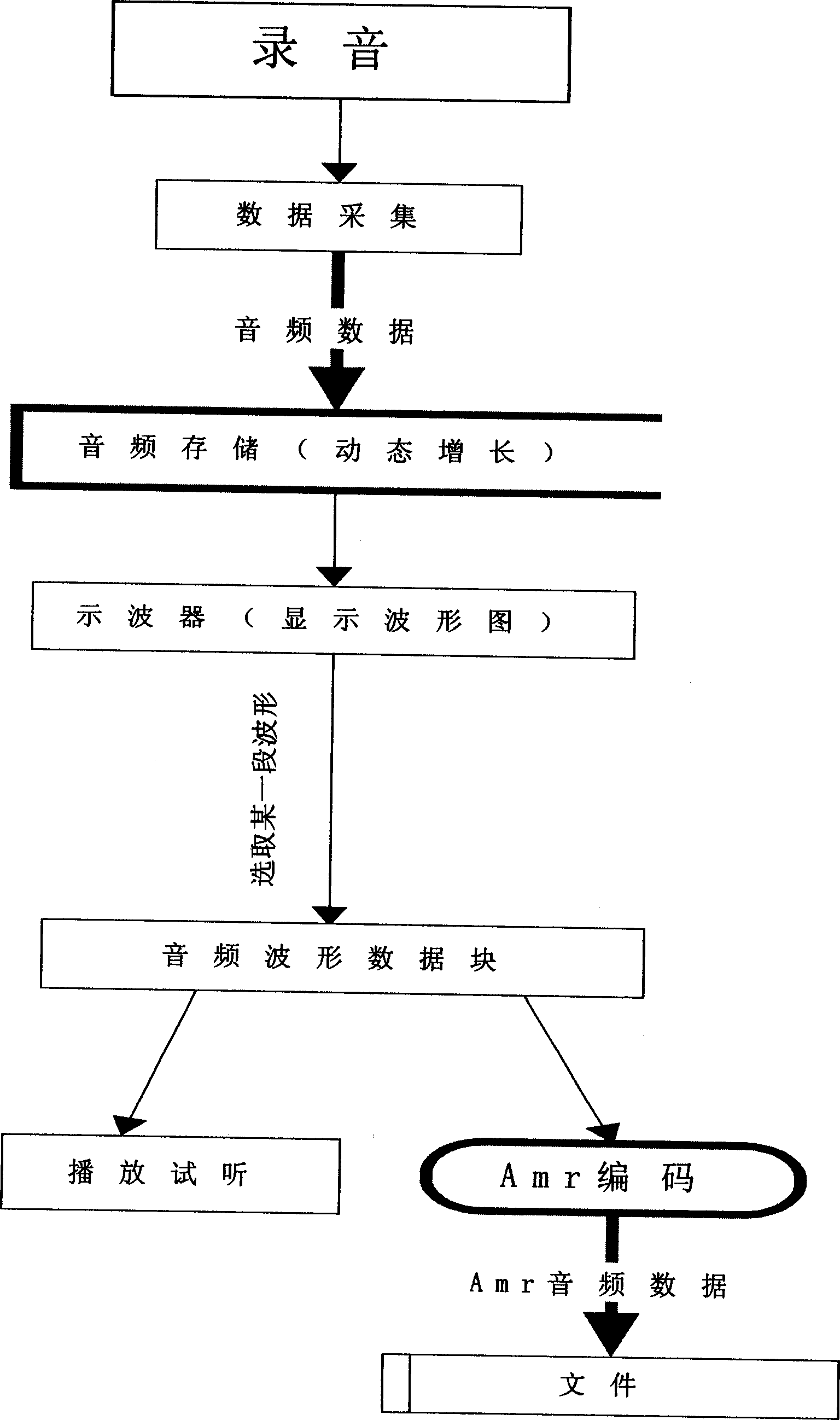
Audio-frequency editing and converting method by cutting audio-frequency wave form
InactiveCN1779777AImprove utilizationReduce information storageElectrophonic musical instrumentsSpeech recognitionData processing
A method for carrying out audio editing and converting by intercepting audio waveform includes using specific oscilloscope display boundary to display audio data and intercepting audio data according to required condition then converting obtained audio data to be required format for outputting.
Owner:万纳特科技(深圳)有限公司
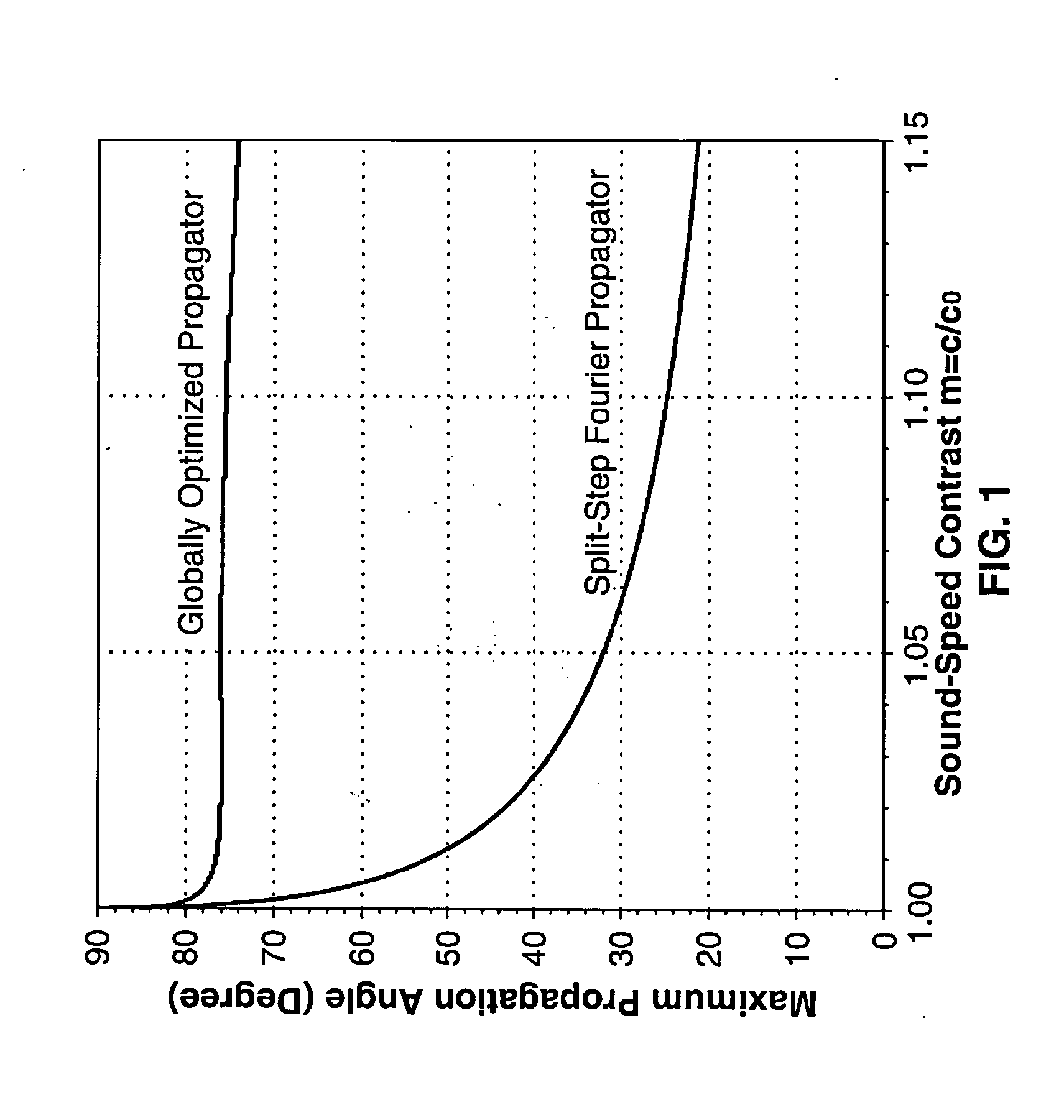
High-resolution wave-theory-based ultrasound reflection imaging using the split-step fourier and globally optimized fourier finite-difference methods
InactiveUS20130251222A1Quality improvementImprove resolutionVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesFrequency waveImaging quality
Methods for enhancing ultrasonic reflection imaging are taught utilizing a split-step Fourier propagator in which the reconstruction is based on recursive inward continuation of ultrasonic wavefields in the frequency-space and frequency-wave number domains. The inward continuation within each extrapolation interval consists of two steps. In the first step, a phase-shift term is applied to the data in the frequency-wave number domain for propagation in a reference medium. The second step consists of applying another phase-shift term to data in the frequency-space domain to approximately compensate for ultrasonic scattering effects of heterogeneities within the tissue being imaged (e.g., breast tissue). Results from various data input to the method indicate significant improvements are provided in both image quality and resolution.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Wavelength conversion laser
InactiveUS20100309438A1Improve wavelength conversion efficiencyReduce consistencyProjectorsActive medium shape and constructionSpectral widthFrequency wave
A wavelength conversion laser 100 is provided with a solid-state laser having a cavity, and a wavelength converting element 6 arranged within the cavity. The solid-state laser includes two or more types of laser crystals 4 and 5 and oscillates solid-state laser light of multiple wavelengths. The wavelength converting element 6 converts the solid-state laser light of multiple wavelengths into light of second harmonic waves and sum-frequency wave of multiple wavelengths and simultaneously generates the second harmonic waves and sum-frequency wave of multiple wavelengths. The wavelength conversion laser 100 outputs converted wavelength light having a broad spectral width and low coherency, thereby enabling it to carry out highly efficient and stable high-output oscillation.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method for suppressing controllable seismic-source harmonic-wave interference
InactiveCN102478671AAvoiding Shortcomings of Filtering MethodsSeismic signal processingTime domainFrequency wave
The invention discloses a method for suppressing harmonic-wave interference existed in an original seismic record of controllable land seismic source excitation acquisition. Method is characterized by: taking a related previous earthquake data to carry out short-time Fourier transform and transforming a time domain signal to a time-frequency domain; taking a time sampling sequence number and a frequency sampling sequence number in a related previous time-frequency domain signal as two coordinate axes of a rectangular coordinate, carrying out coordinate transformation so that a fundamental wave is parallel to a time axis; separating the harmonic wave interference from the signal, carrying out coordinate inverse transformation of the time-frequency domain and carrying out short-time Fourier inverse transform so as to acquire time domain data which can remove the harmonic wave interference; after all unrelated seismic data collected from a filed is processed, acquiring the related seismic data after the harmonic wave interference is suppressed. By using the method of the invention, disadvantages of a filtering method in a frequency wave number domain can be avoided. Through the controllable seismic source, the seismic data with high qualities can be collected.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
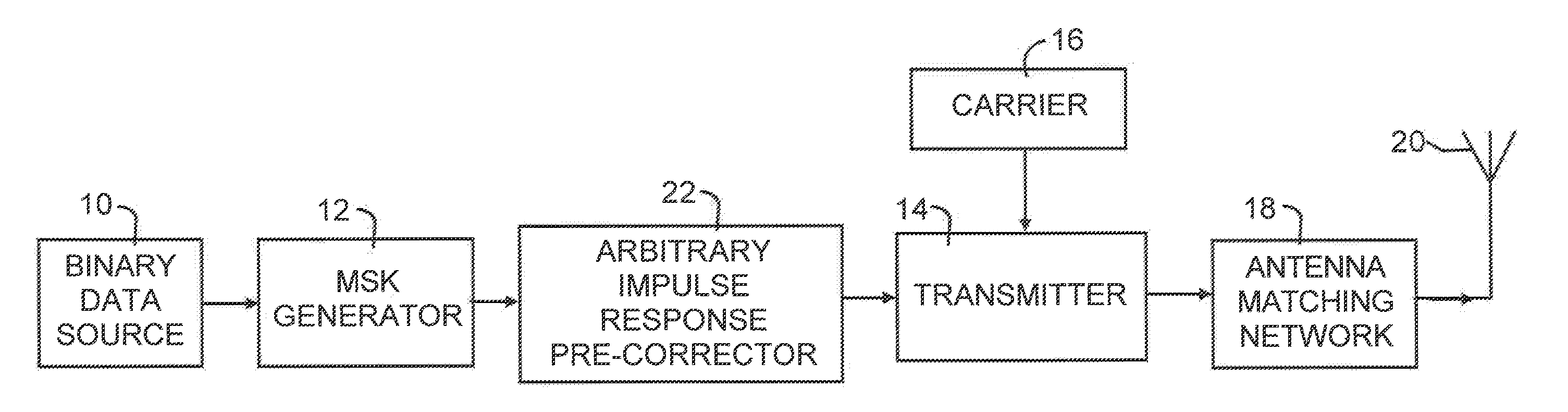
Radio transmitter system and method
ActiveUS20120300870A1Reduce voltage stressIncrease powerPower amplifiersFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationFrequency waveWave shape
A radio transmitter system responsive to a binary signal drives a narrow bandwidth VLF or LF antenna. A generator derives a first variable frequency wave frequency coded based on bit values of a binary signal. An arbitrary impulse response signal processor responsive to the first wave derives a first output signal having real and imaginary components representing the shape of a modulating wave having a variable amplitude envelope and the frequency of the coded values. A transmitter responsive to the processor output signal and a VLF or LF carrier supplies the antenna with another output signal including a modulation wave having a shape that is a substantial replica of the modulating wave shape. The processor causes the signal emitted by the antenna system to include modulation having a shape that is substantially the shape of the first wave.
Owner:CONTINENTAL ELECTRONICS CORP
Millimeter wave imaging method and system
InactiveCN104375145ADetection using electromagnetic wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency waveImaging processing
The invention relates to a millimeter wave imaging method and system. A first millimeter wave antenna array and a second millimeter wave antenna array transmit continuous frequency waves to an arc middle area and receive returned millimeter waves. The first millimeter wave antenna array and the second millimeter wave antenna array move in the vertical direction so as to transmit and receive the millimeter waves in the vertical direction of the arc middle area. An image processing module carries out image combination on the millimeter waves received by a first millimeter wave receiving and transmitting module and a second millimeter wave receiving and transmitting module so that a three-dimensional image of an objected to be imaged can be formed in the arc middle area. According to the millimeter wave imaging method and system, a detecting mode of combining translation scanning of vertical mechanical driving of switch antenna arrays and arc direction scanning is adopted, all-dimensional scanning of the human body can be effectively finished, and the safety inspection efficiency is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN & INVESTMENT HLDG GRP
Inversion method for stratigraphic quality factor
ActiveCN103376464AEliminate differencesImprove stabilitySeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingFrequency waveVertical seismic profile
The invention relates to an inversion method for a stratigraphic Q-factor by use of amplitude spectrum attributes of a downlink wave of vertical seismic profile data in geophysical exploration data processing technology. First, the F-K (frequency-wave number) method is used for wavefield separation of VSP raw data to obtain the downlink wave. Then a downlink wavelet and a monitor wavelet are selected for the Fourier transform to gain an amplitude spectrum, the amplitude spectrum are subjected to polynomial fitting to obtain an equivalent Q, and a formula between the equivalent Q and the stratigraphic Q is used for inversion of the stratigraphic Q. The inversion method for the stratigraphic quality factor has a strong random anti-interference capability and can eliminate the difference of an exciton wavelet. The algorithm is simple and workload can also be greatly reduced. The inversed stratigraphic Q value is good in stability and high in accuracy.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Metal plate defect location method based on laser Lamb wave frequency-wave number analysis
The invention discloses a metal plate defect location method based on laser Lamb wave frequency-wave number analysis and belongs to the field of laser ultrasonic non-destructive testing. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, excitation is performed by a laser excitation probe in a fixed position on a metal plate, a laser receiving probe scans defect lines to receive N groups of Lamb wave data, and a time-space wave field on a scanning path is obtained; secondly, signals under specific center frequency are extracted from the acquired N groups of Lamb wave data with a continuous wavelet transform method, and analyzability of a defect location result is guaranteed; finally, the extracted wave field signals are subjected to space-frequency-wave number imaging with short-space two-dimensional Fourier transform algorithm, and defect location is realized according to characteristics of a wave number spectrum on the scanning path. One completely non-contact type detection method is provided, and action rules between Lamb waves and defects in the wave number field are disclosed.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Heat cooking device
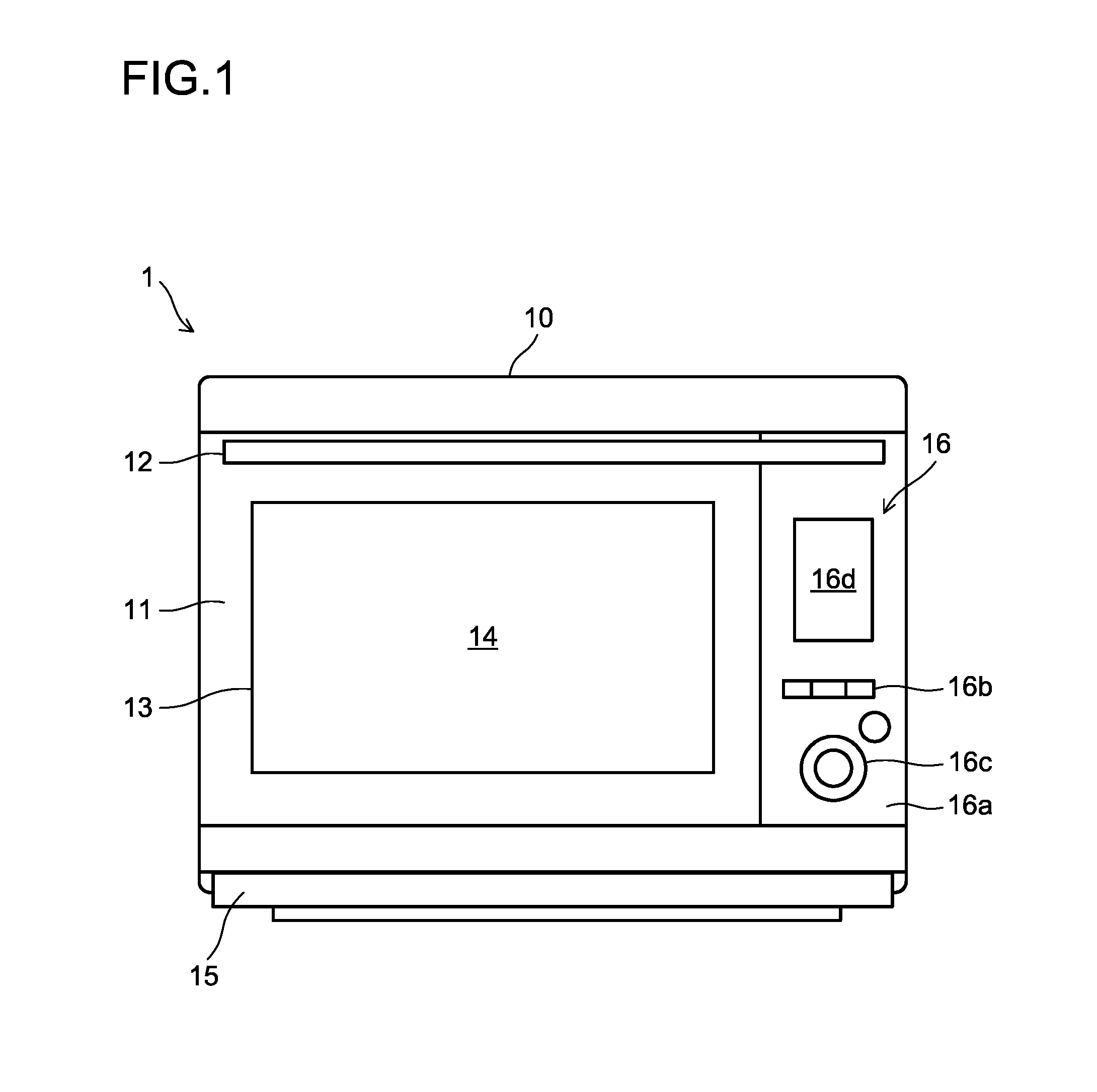
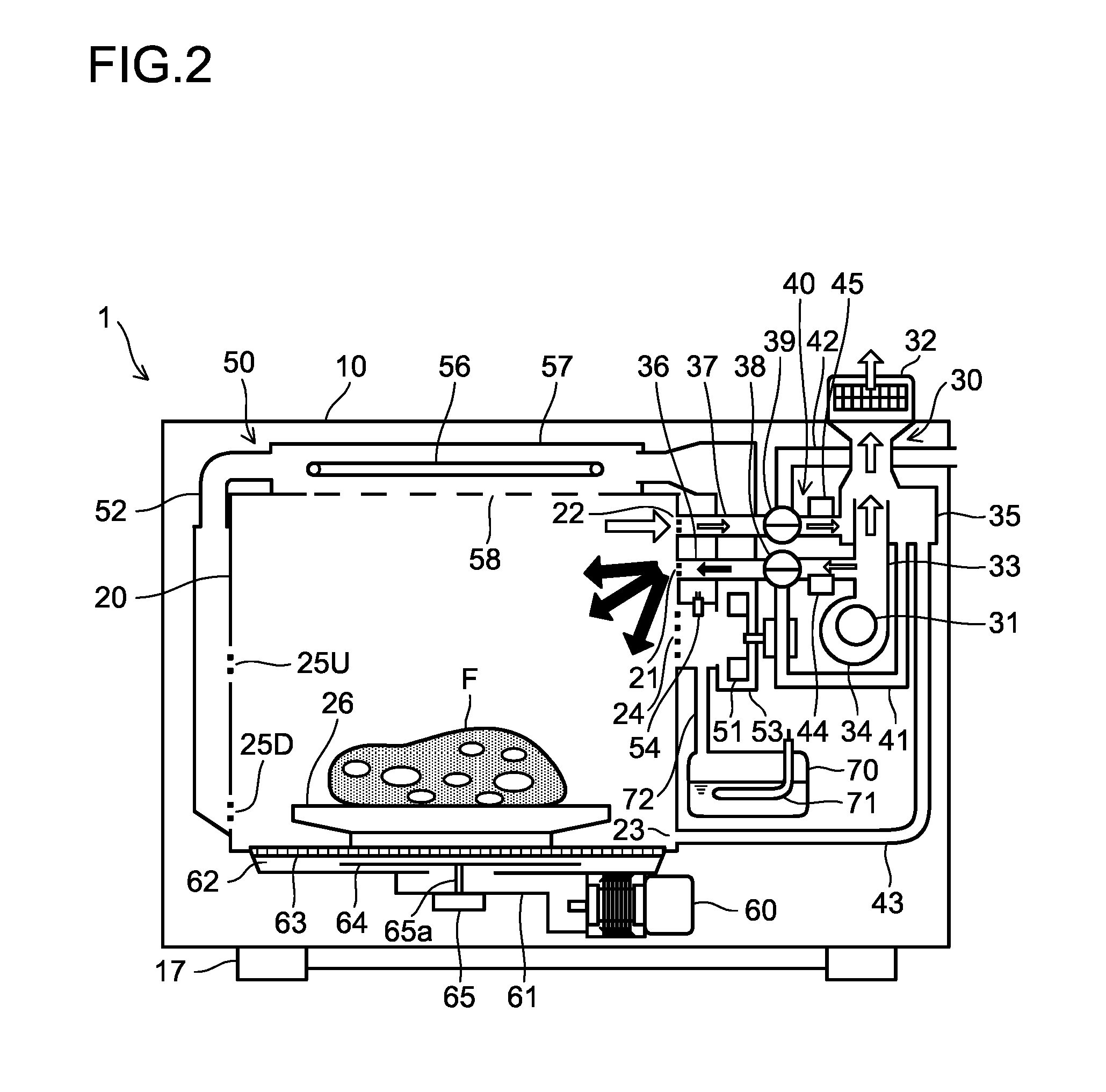
InactiveUS20130036918A1Domestic stoves or rangesLighting and heating apparatusAir emissionEngineering
Tableware (F) put inside a heating chamber (20) of the disclosed heat cooking device (1) is heated by means of high-frequency waves, steam, hot air, or a combination thereof. The heating chamber is provided with a circulating fan (51) and an air supply / emission fan (31). An air supply tube (36) to the heating chamber and an air emission tube (37) from the heating chamber are provided to a blowing duct (33) that links the air supply / emission fan and an emission port (32). An ion generator (44) is disposed at the air supply tube. A duct switching device (40) that selects whether to introduce positive / negative ions generated by the ion generator into the heating chamber or to release the ions to the outside of the heat cooking device is provided to the air supply tube and the air emission tube.
Owner:SHARP KK
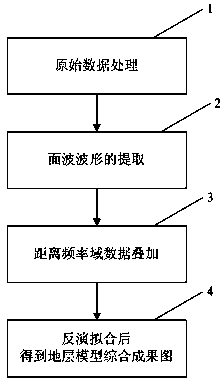
Method employing surface wave information in seismic records to investigate surface structure
The invention provides a method employing surface wave information in seismic records to investigate a surface structure. The method employing surface wave information in the seismic records to investigate the surface structure comprises steps that: step 1, original data is inputted, and original data processing is carried out; step 2, surface wave waveform extraction of the data processed in the step 1 is carried out in a frequency wave-number domain to acquire surface wave frequency dispersion data of base-order components; step 3, data stack of the surface wave frequency dispersion data acquired in the step 2 is carried out in a distance frequency domain to form a frequency dispersion file; and step 4, inversion fitting of the frequency dispersion file acquired in the distance frequency domain in the step 3 is carried out to acquire a stratum model integration accomplishment graph. The method employing surface wave information in the seismic records to investigate the surface structure settles a problem of strict requirements for a stratum speed and wave impedance existing in a traditional surface structure method and can acquire accurate shallow surface thickness and the speed data.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
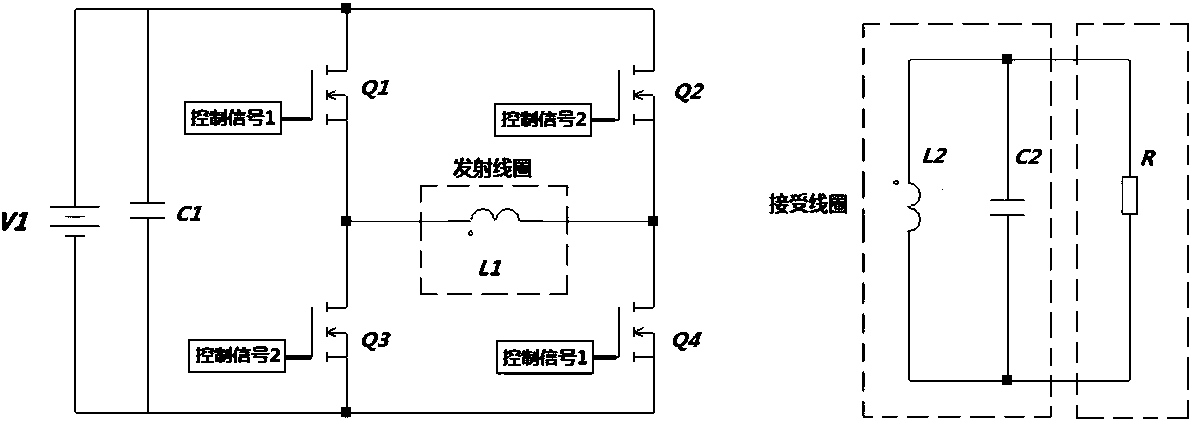
Magnetic coupling resonance wireless power supplying device using fundamental wave energy in high-frequency square wave
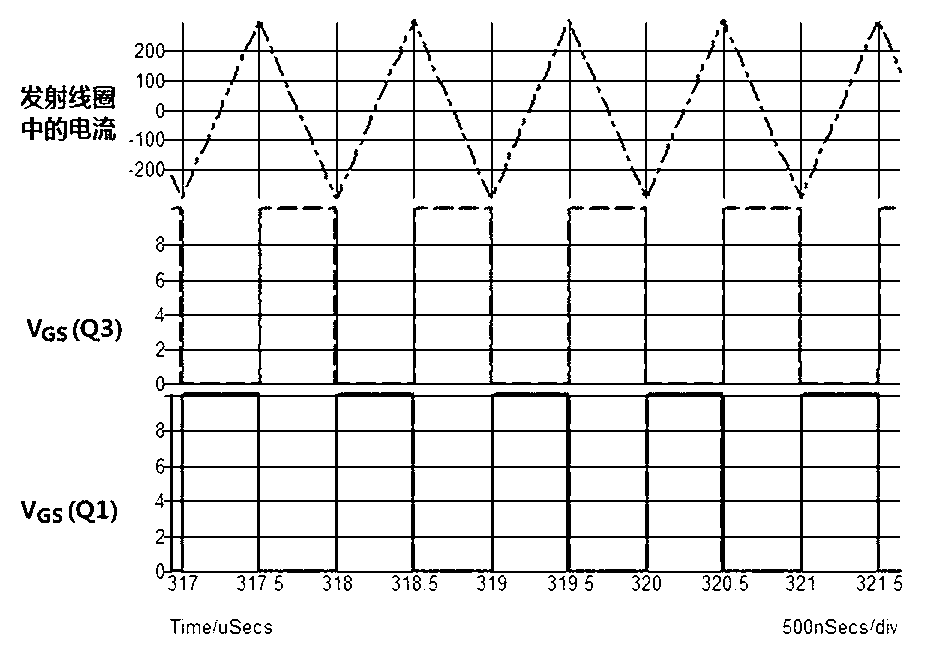
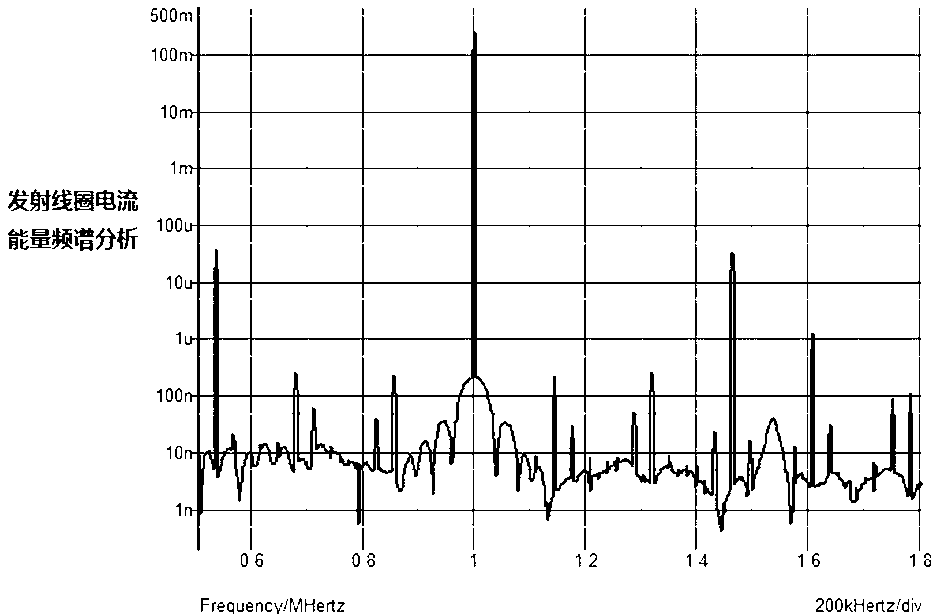
ActiveCN103259343ASimple structureEasy to implement ZVSElectromagnetic wave systemCircuit arrangementsFrequency waveDirect control
The invention discloses a magnetic coupling resonance wireless power supplying device using fundamental wave energy in a high-frequency square wave and belongs to wireless energy transmitting device. The magnetic coupling resonance wireless power supplying device comprises a control circuit, a drive circuit, an emitting circuit and a resonance receiving circuit. The emitting circuit comprises an input power supply and a non-resonance converter connected with the input power supply and comprising an emitting coil. The resonance receiving circuit comprises a receiving coil, a resonance capacitor and a load. The magnetic coupling resonance wireless power supplying device directly controls a square wave voltage frequency of the emitting coil in the non-resonance converter. When the square wave voltage frequency is identical with resonance frequency points of the receiving coil, the magnetic coupling resonance wireless power supplying is achieved. Two coils which share the same resonance point frequency are not needed for achieving resonance working and reliability of a wireless electric energy device is improved. ZVS switching in a total range is easy to achieve. EMI interference is low and an application prospect is wide.
Owner:ZONECHARGE (SHENZHEN) WIRELESS POWER TECH CO LTD
Catalytic simulation using radio frequency waves
InactiveUS6217712B1Facilitate chemical reactionsEliminate needAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceElectric/magnetic detectionPlatinumNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention relates to a method of using radio frequency waves to artificially create catalytic action in a catalyst-free chemical reaction within a substance. To mimic or imitate the catalyst, radio frequency waves are transmitted through the substance at a signal strength sufficient to electronically reproduce the effect of the physical presence of a selected catalyst. The radio frequency waves have a selected transmission frequency substantially equal to a catalyst signal frequency of the selected catalyst, defined as the signal frequency determined by nuclear magnetic resonance of the selected catalyst. It is commonplace to use nuclear magnetic resonance to identify elements within a substance and the signal frequencies of various elements (including catalysts) are listed in widely published tables. To date, the mechanism by which catalysts bring about chemical reactions has been unknown. The inventor has recognised that the physical presence of a catalyst brings about a chemical reaction due to the emission of low intensity radio frequency waves from the catalyst with the signal frequency that is emitted being the signal frequency of the catalyst that is commonly determined by nuclear magnetic resonance. Therefore, the invention can be used to eliminate the need for expensive metallic catalysts, such as platinum. The invention electronically reproduces the effect of the physical presence of a catalyst by transmission of a radio frequency wave with a signal frequency equal to that signal frequency emitted by the catalyst and as determined by nuclear magnetic resonance of the catalyst.
Owner:2141582 ONTARIO
Embedded composite meta-material absorber
InactiveCN105101769AAchieve strong absorptionThe overall thickness is thinMagnetic/electric field screeningFrequency waveUnit structure
The invention discloses an embedded composite meta-material absorber. The absorber is composed of periodical unit structures. Each unit structure is composed of a dielectric based superstructure, a patterned absorbing material and a metal backboard, wherein the dielectric based superstructure is composed of a metal pattern and a dielectric body, and the patterned absorbing material is a seamless fit with the dielectric based superstructure and embedded into the dielectric body under the metal patter to form an embedded structure, and the embedded structure is combined with the metal board in the vertical direction to form one unit structure. Due the embedded structure design, the problem that a present absorbing material is low in the low-frequency absorbing performance in an ultrathin state is solved, the high-frequency performance of the magnetic absorbing material is maintained to the largest degree, and brand new design ideals and methods are provided for ultrathin low-frequency ultra-wide-band absorbers, intelligent adjustable wave absorption, and ultrathin, ultralow-frequency wave absorption in future.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
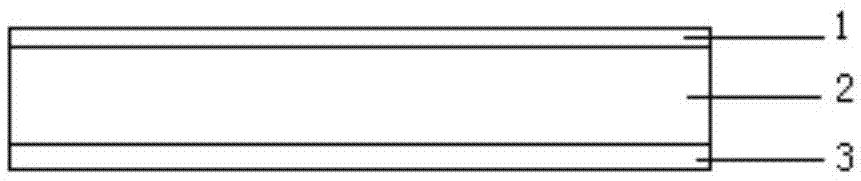
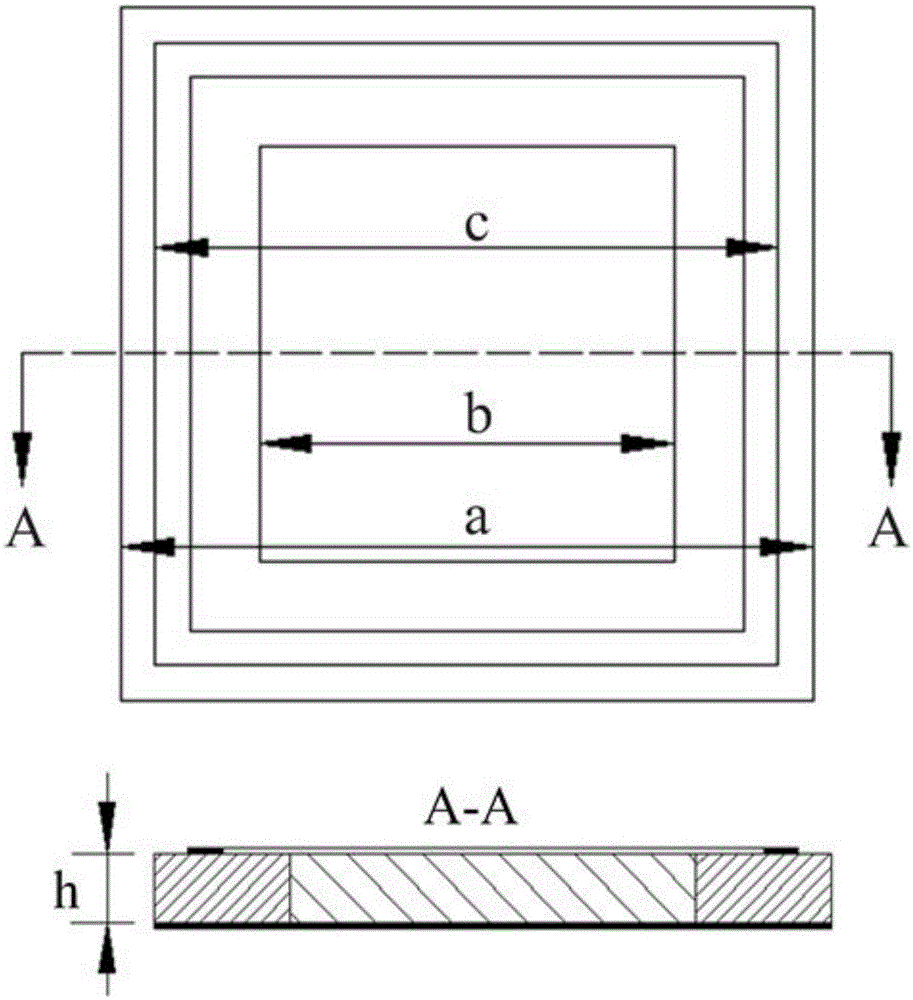
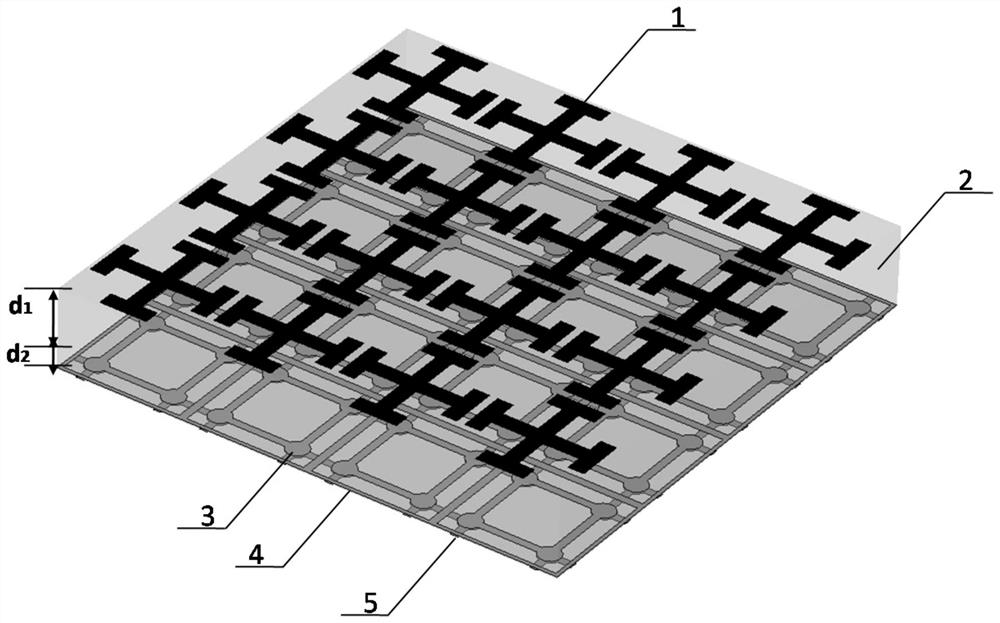
Absorption and transmission integrated frequency selective surface with high-frequency broadband wave absorption and low-frequency wave transmission functions
InactiveCN112821081AIncrease production capacityImprove absorbing performanceRadiating element housingsFrequency waveDielectric substrate
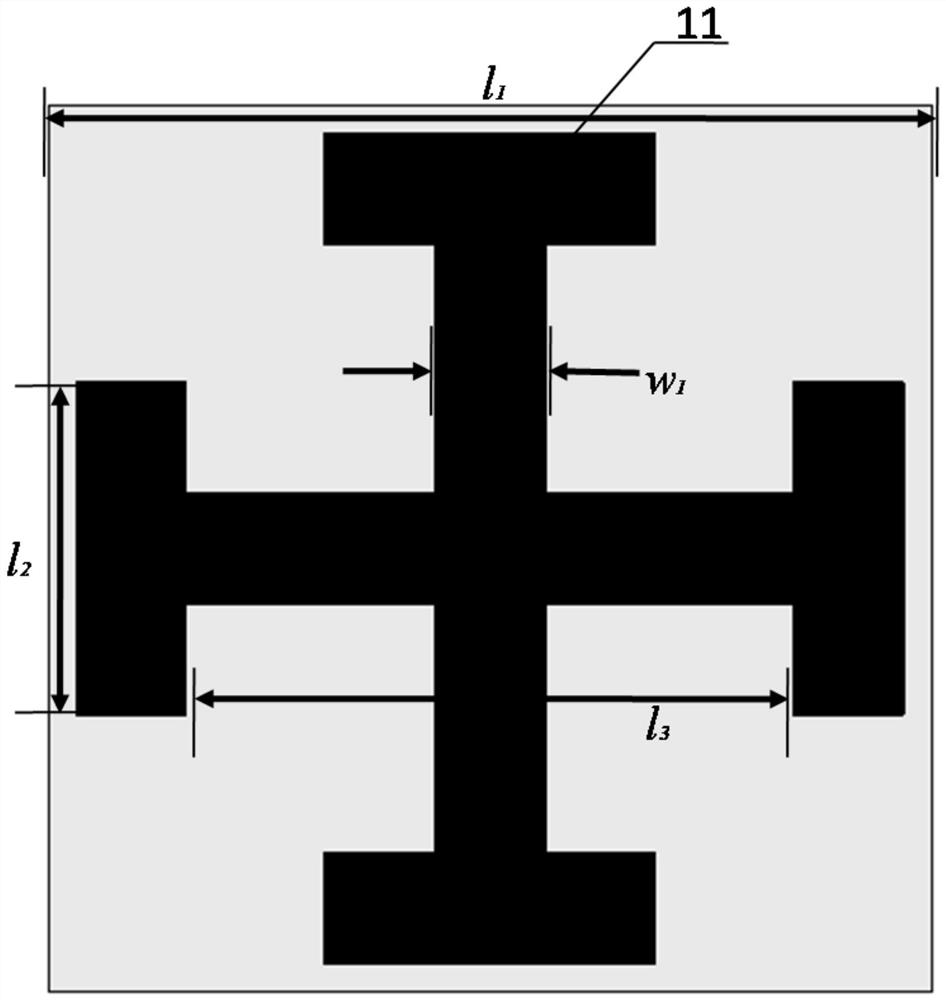
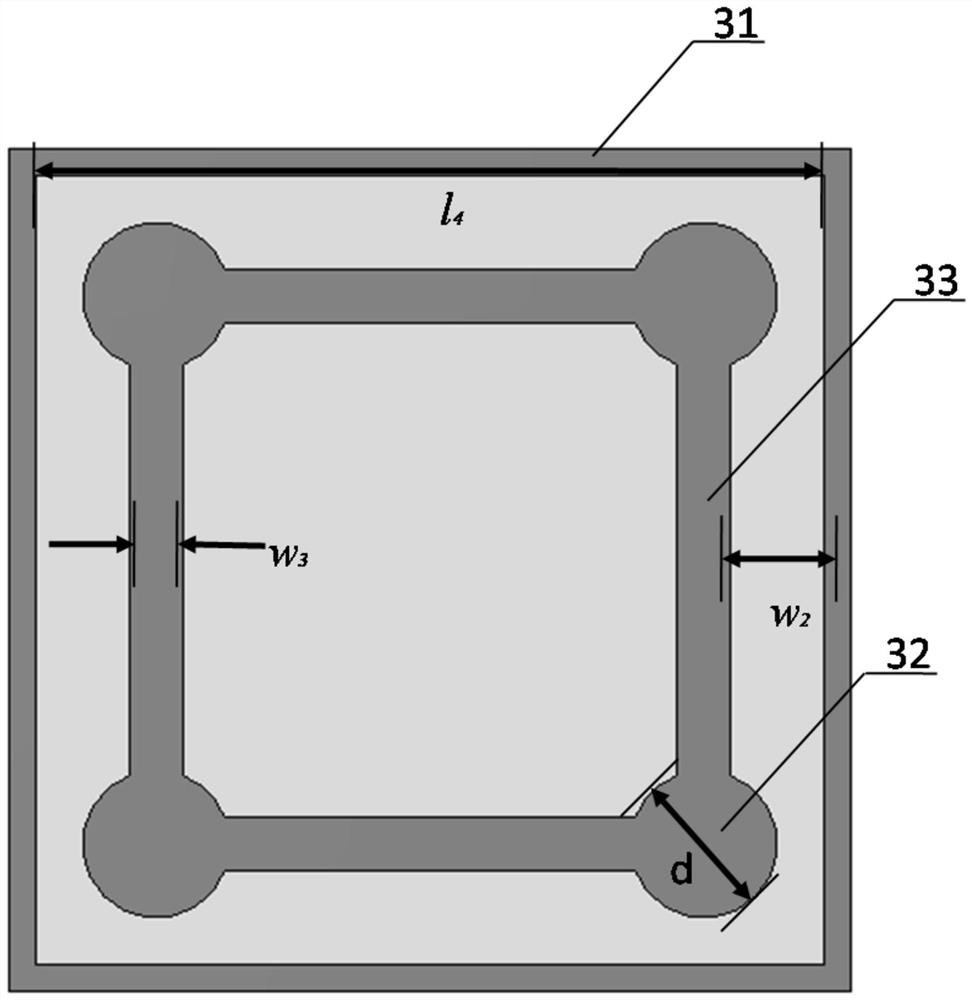
The invention discloses an absorption and transmission integrated frequency selective surface with high-frequency broadband wave absorption and low-frequency wave transmission functions; the surface comprises a top absorption layer, a middle resonance layer and a bottom resonance layer; a first dielectric substrate is arranged between the top absorption layer and the middle resonance layer, and a second dielectric substrate is arranged between the middle resonance layer and the bottom resonance layer. Each layer comprises a plurality of metal patch units, and each unit of the top absorption layer is composed of a resistive Jerusalem cross structure; each unit of the middle resonance layer is composed of square ring type metal strips, circular metal sheets and a square metal strip, the square metal strips are connected with the circular metal sheets through rotational symmetry, and the circular metal sheets are distributed in an axial symmetry mode; each unit of the bottom resonance layer is formed by combining circular metal sheets and square metal strips, and the circular metal sheets and the square metal strips are respectively distributed in an axial symmetry manner; the top absorption layer is connected with the first dielectric substrate; and the middle resonance layer, the second dielectric substrate and the bottom resonance layer are connected. The surface is excellent in wave-absorbing performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Seismic acquisition and filtering
InactiveUS7584057B2Promote resultsSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsFrequency waveSpacetime
An iterative process is described for obtaining a finite impulse filter to remove noise from seismic data through an iterative process with constraints on the filter applied in both, the original space-time and the transform frequency wave number at each iteration step.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Pressing method for true 3-d seismics data linear noise
The invention relates to a pressing method for using three-dimensional seismic data to process linear noise of the three-dimensional seismic data, belonging to the oil geophysical exploration field. The concrete steps are that: high density seismic data is collected and recorded; the data is divided into data groups with smallest data sets; rank ordering is carried out on all paths of each data group according to the shot-geophone distance and the azimuth, thus forming a three dimensional denoising smallest data set; the linear noise speed is analyzed according to the formed frequency wave-number spectrum (FK spectrum) or the original seismic data so as to eliminate the linear noise; pressing on the existing linear noise is repeated until the noise is eliminated. The pressing method is applicable to different seismic data collected by observation systems, in particular to non-cross banding and irregular bunchy orthogonality observation system, thus pressing the linear noise of the original data well.
Method for preparing core-shell type barium titanate/polyaniline composite wave-absorbing material
InactiveCN102775604AImprove the disadvantage of poor compatibilityGood claddingFrequency waveBarium titanate
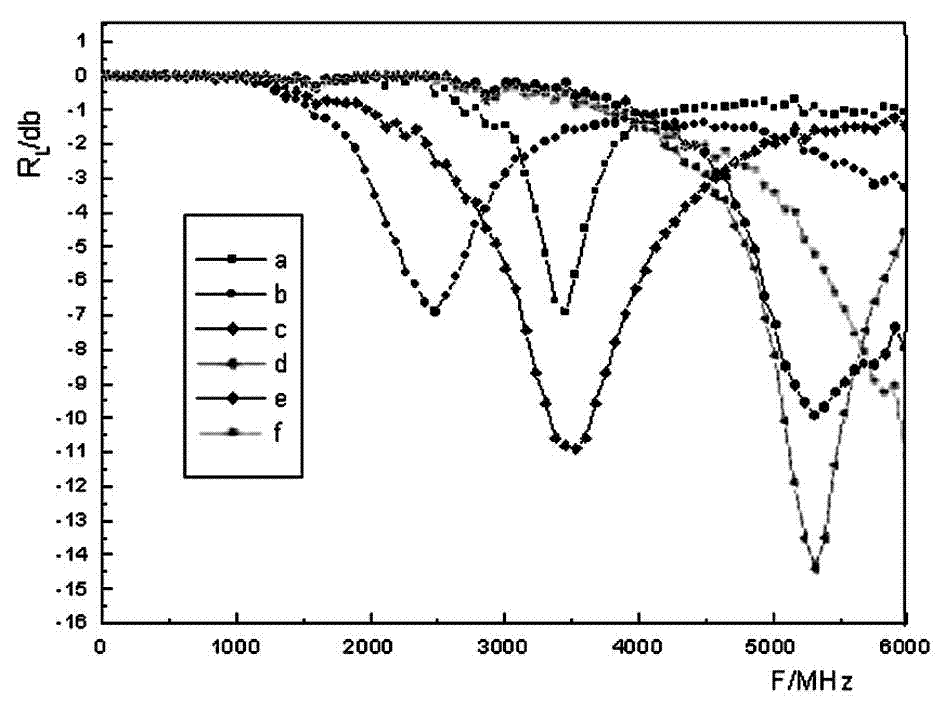
The invention discloses a method for preparing a core-shell type barium titanate / polyaniline composite wave-absorbing material. The method comprises the following steps of: adding an alcohol / water solution of a silane coupling agent into water dispersing agent of a nanometer barium titanate powder body; slowly dipping a hydrochloric acid solution of phenylamine; and finally dipping a hydrochloric acid solution of ammonium persulfate, and reacting to prepare the core-shell type barium titanate / polyaniline composite wave-absorbing material. Surface finishing on the nanometer barium titanate powder body is performed by using the silane coupling agent, so that polyaniline forms a good covering layer on the surface of barium titanate; and the prepared core-shell type barium titanate / polyaniline composite material has dielectric loss and magnetic loss; and because of specific magnetoelectric effect of the core-shell structure, the wide frequency wave-absorption performance of the material is obviously improved; the maximum reflectivity of the material is minus14.5dB in the range of 0-6GHz and is superior to minus 5dB and minus10dB; and the bandwidths are 1,200MHz and 750MHz respectively.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Determination Method for a Position Signal
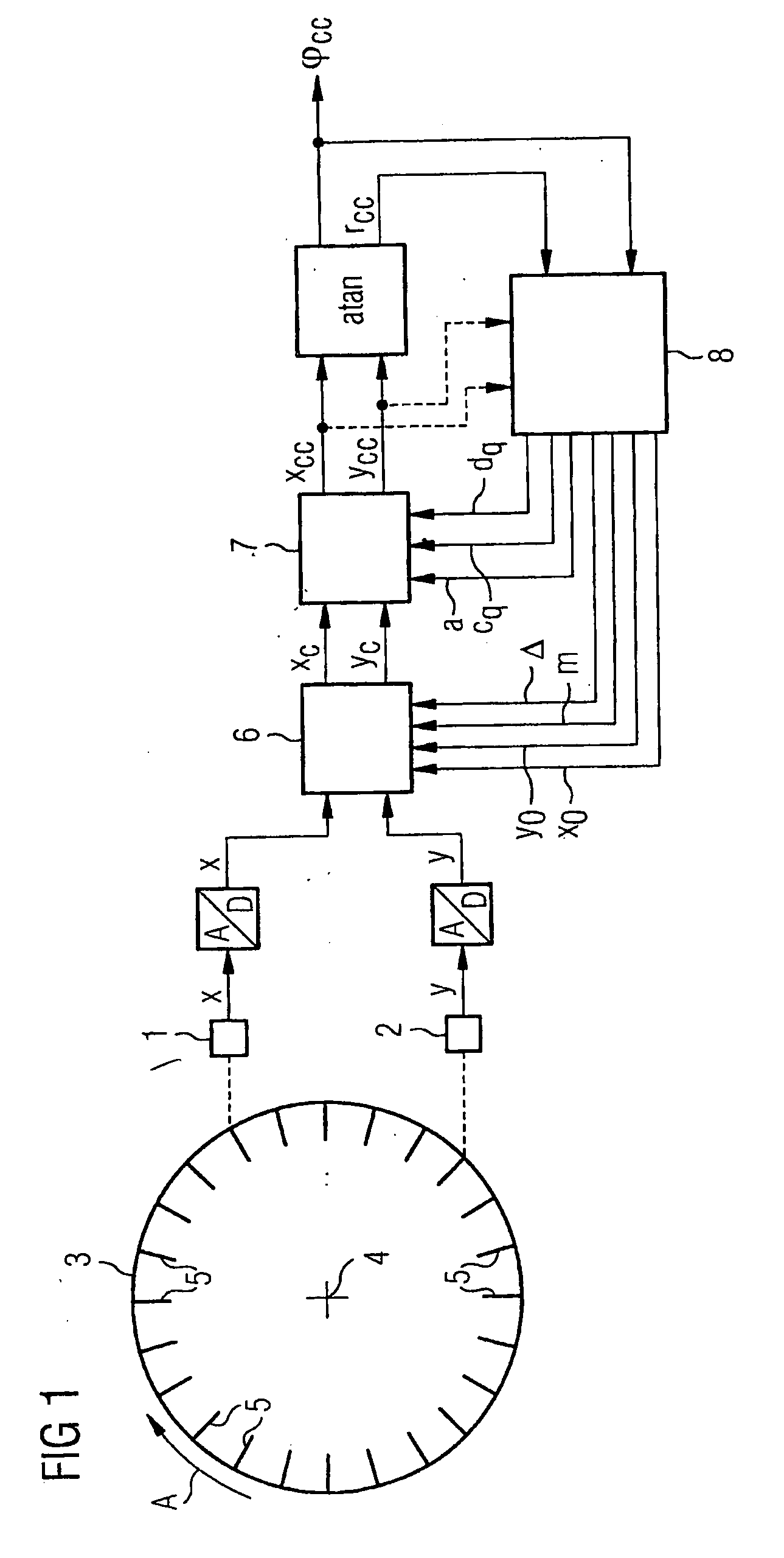
InactiveUS20070288187A1Easy to carryGuaranteed to workAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsPhase correctionRelative displacement
Two sensors scan a measuring scale, which can be displaced in relation to the sensors and comprises a plurality of equidistant measuring gradation, and deliver corresponding measuring signals. The measuring signals are periodic during a uniform relative displacement of the measuring scale, essentially sinusoidal and essentially phase-shifted by 90° in relation to one another. They have an essentially identical amplitude and a base frequency that corresponds to the relative displacement of the measuring scale. During a delivery period of measuring signals, the measuring scale carries out a relative displacement through one measuring gradation. Corrected signals are determined from the measuring signals using correction values. A signal of the position of the measuring scale in relation to the sensors is determined in turn using said correction signals. Fourier coefficients are determined in relation to the base frequency for the corrected signals or for at least one supplementary signal that is derived from the corrected signals, said coefficients being used in turn to update the correction values. Said correction values contain two shift correction values at least one amplitude correction value and at least one phase correction value for the measuring signals, or part of said values, in addition to at least one correction value for at least one higher frequency wave of the measuring signals.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Self-adaptive single-frequency narrow-band interference trapped wave filtering device and double-frequency filtering equipment
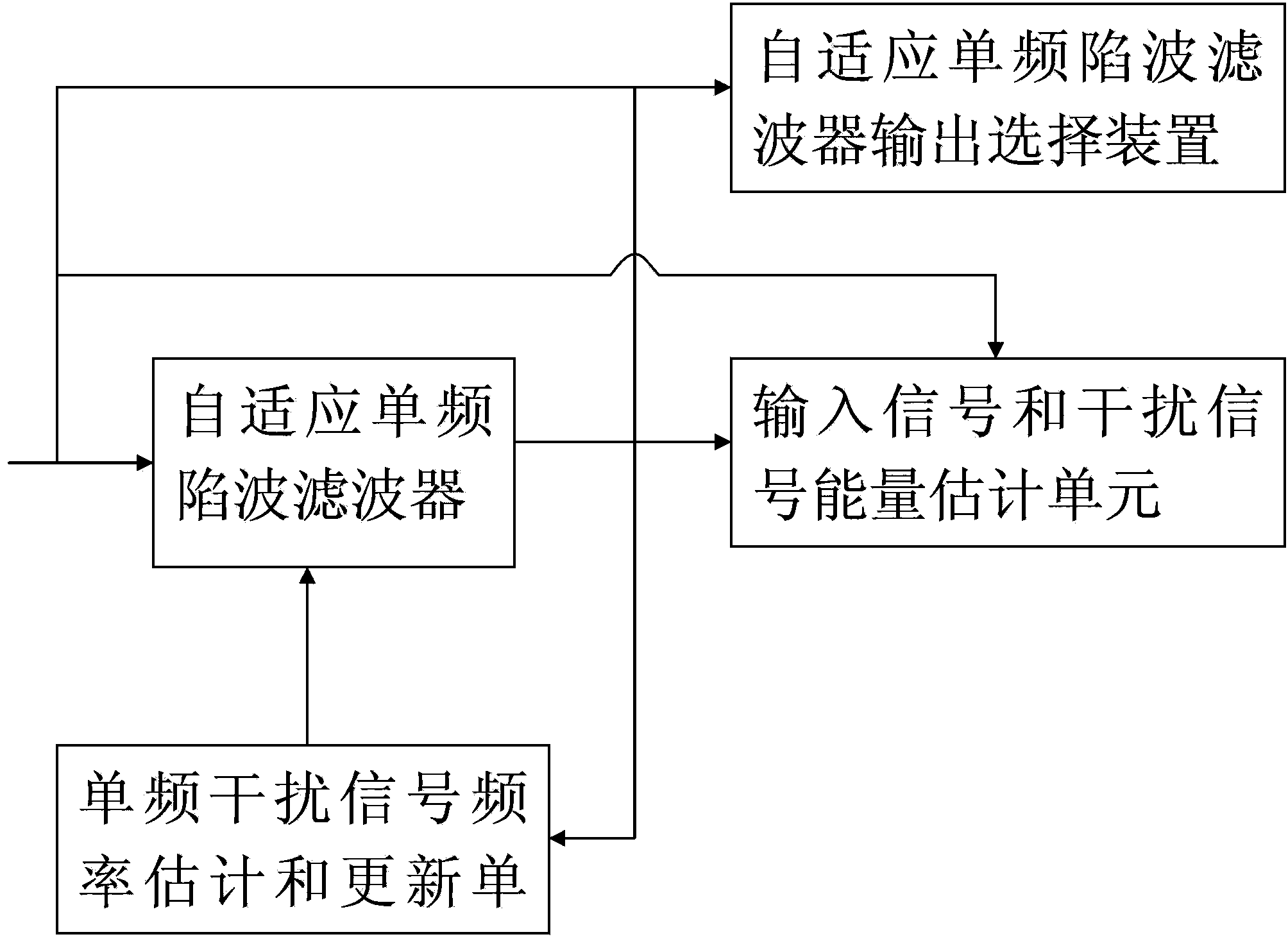
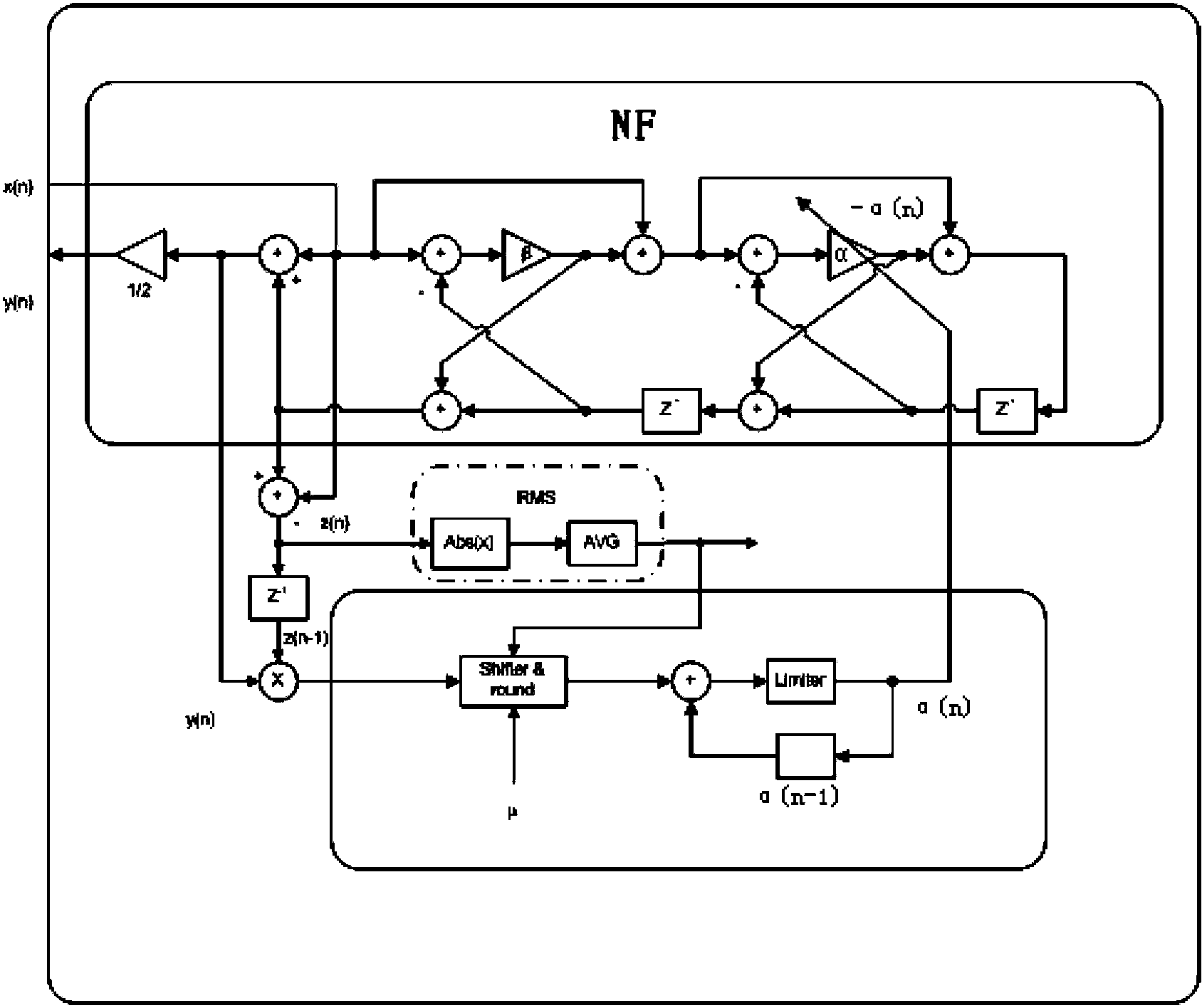
ActiveCN104144138AValuation deviation is smallGood notch effectDigital technique networkMulti-frequency code systemsHardware structureTrapping
The invention discloses a self-adaptive single-frequency narrow-band interference trapped wave filtering device and double-frequency filtering equipment. The self-adaptive single-frequency narrow-band interference trapped wave filtering device comprises a self-adaptive single-frequency trapped wave filter, a single-frequency interference signal frequency estimating and updating unit, an input signal and interference signal energy estimation unit and a self-adaptive single-frequency trapped wave filter output selection device. The double-frequency filtering equipment comprises two self-adaptive single-frequency narrow-band interference trapped wave filtering devices which are in cascade connection with each other and an auxiliary trapped wave filter. The self-adaptive single-frequency narrow-band interference trapped wave filtering device is expanded to a self-adaptive double-frequency wave trap and has a flexible hardware structure to achieve different functional combinations, that is, one or two single-frequency narrow-band interference signals are removed in a self-adaptive mode, so that the deviation of an estimated value of the narrow-band interference frequency is small, and the wave trapping effect is good.
Owner:HI TREND TECH SHANGHAI
System and method for suppression of seismic multiple reflection signals
ActiveUS8315124B2The result is accurate and effectiveSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsData modelingWave field
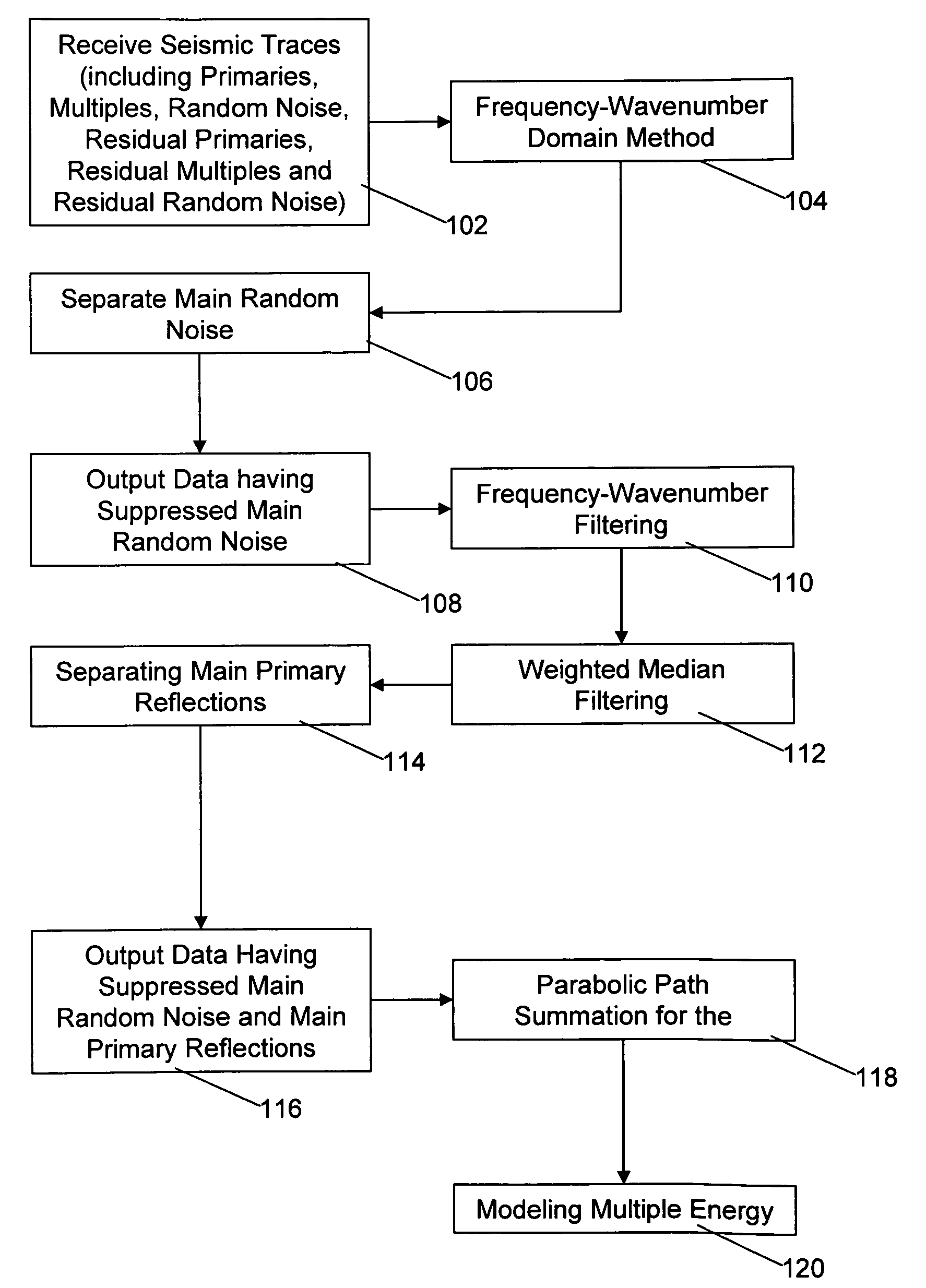
A method of modeling seismic wave-field data in order to suppress near-surface and sub-surface related multiple reflection signals is provided. The reflection signals include main primary reflection signals, main random noise signals, main multiple reflection signals, residual primary reflection signals, residual random noise signals, and residual multiple reflection signals. Main random noise signals are separated from the reflection signals using a frequency-wavenumber domain method to provide data having suppressed main random noise. Main primary reflection signals are separated from the data having suppressed main random noise using frequency-wavenumber filtering and weighted median filtering to provide data having suppressed main random noise and main primary reflections. Multiple reflection signals are modeled using parabolic path summation on the data having suppressed main random noise and main primary reflections.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Gas containing sandstone reservoir seismic responding value simulating method based on rock physical model
ActiveCN106125135AIntuitive and Accurate Seismic Response CharacterizationSeismic signal processingUltrasound attenuationFrequency wave
The invention provides a gas containing sandstone reservoir seismic responding value simulating method based on a rock physical model. Based on a spherical patchy saturation model, the physical and seismic dynamic characteristics of common gas containing sandstone can be well described, and a diffusivity-viscosity wave equation theory is used to introduce the attenuation and energy loss caused by the existence of fluids during the propagation process of earthquake waves. The frequency-wave number domain diffusivity-viscosity wave equation is utilized to carry out forward modeling to effectively represent the geophysical characteristics of a rock physical model; and by combining the diffusivity characteristics and viscosity characteristics introduced by the diffusivity-viscosity theory, the seismic corresponding characteristics of common gas containing sandstone can be represented more directly and precisely.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com