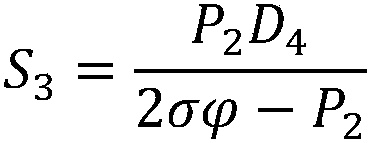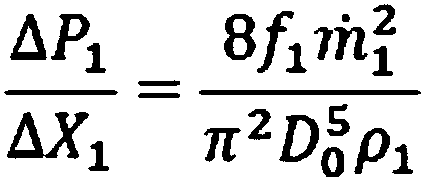Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
98results about How to "Reduce leakage power" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
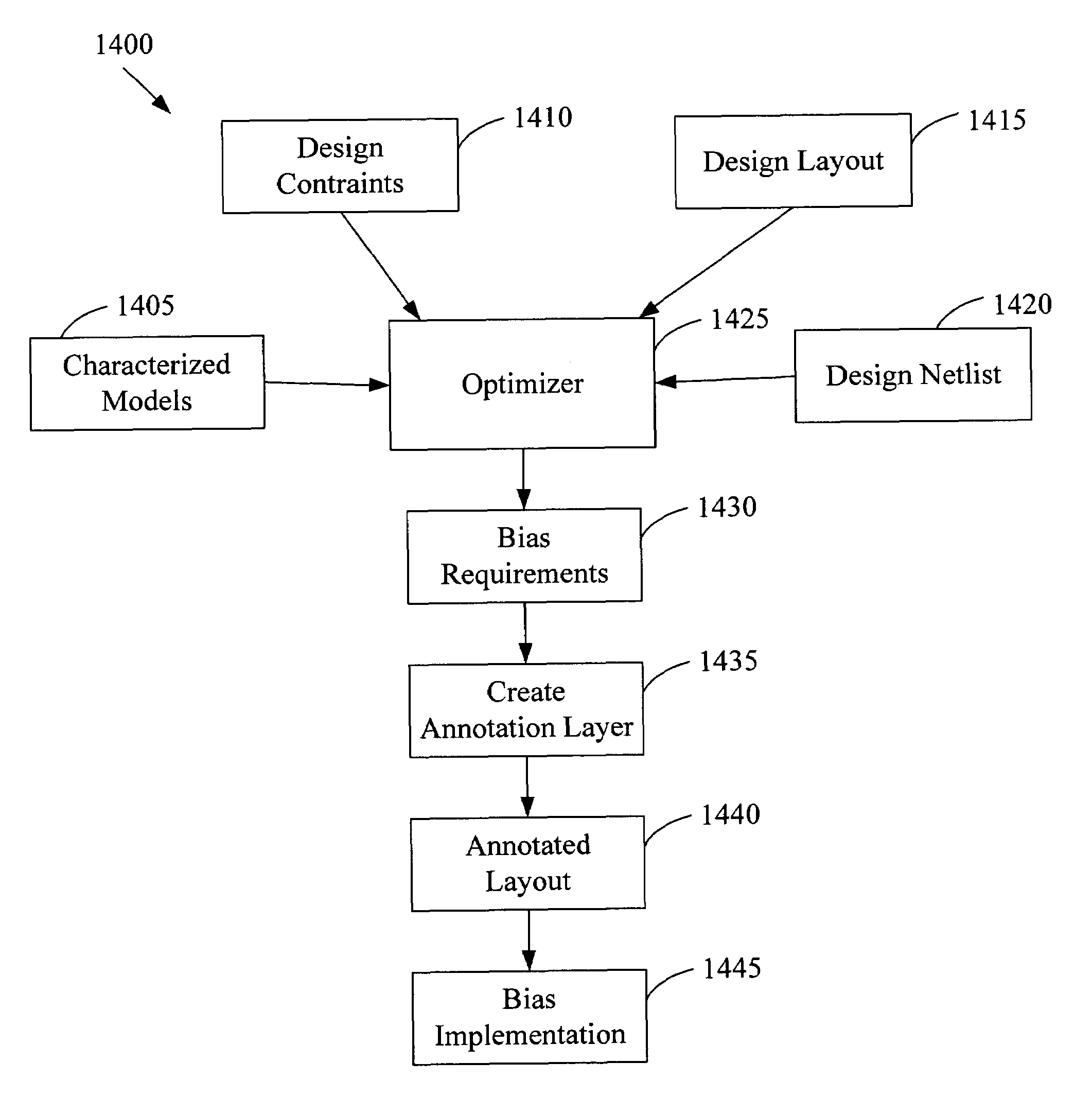
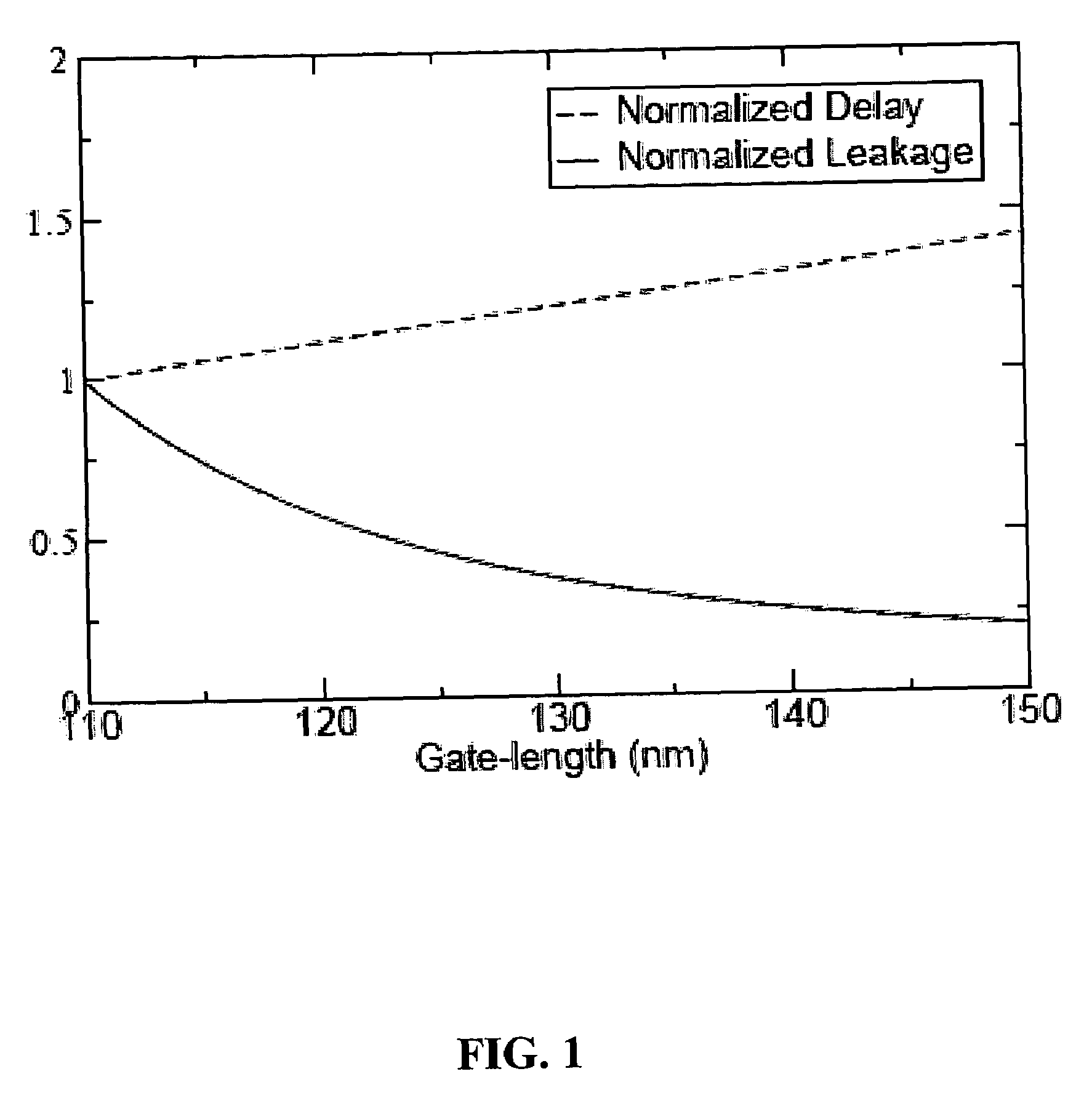
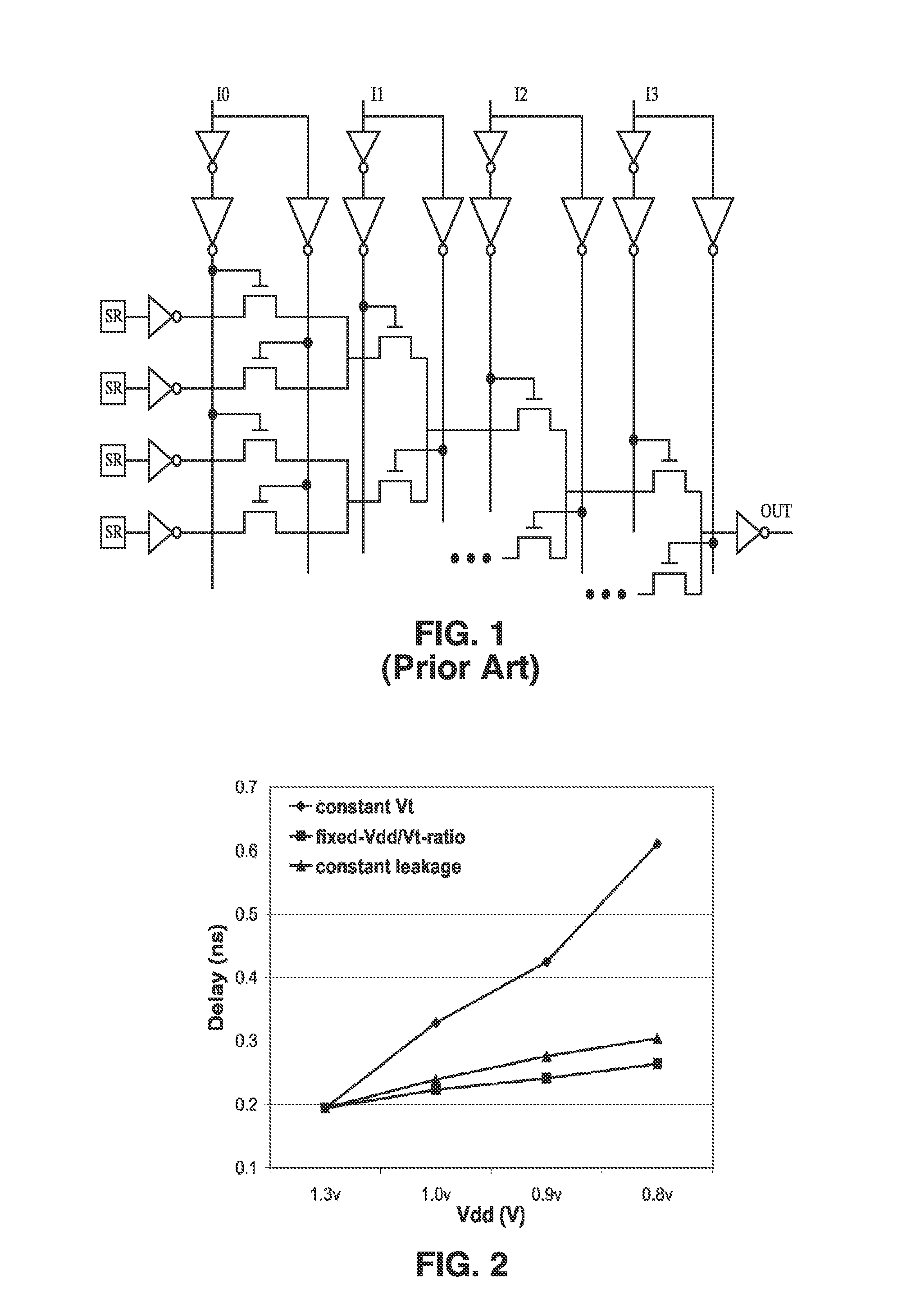
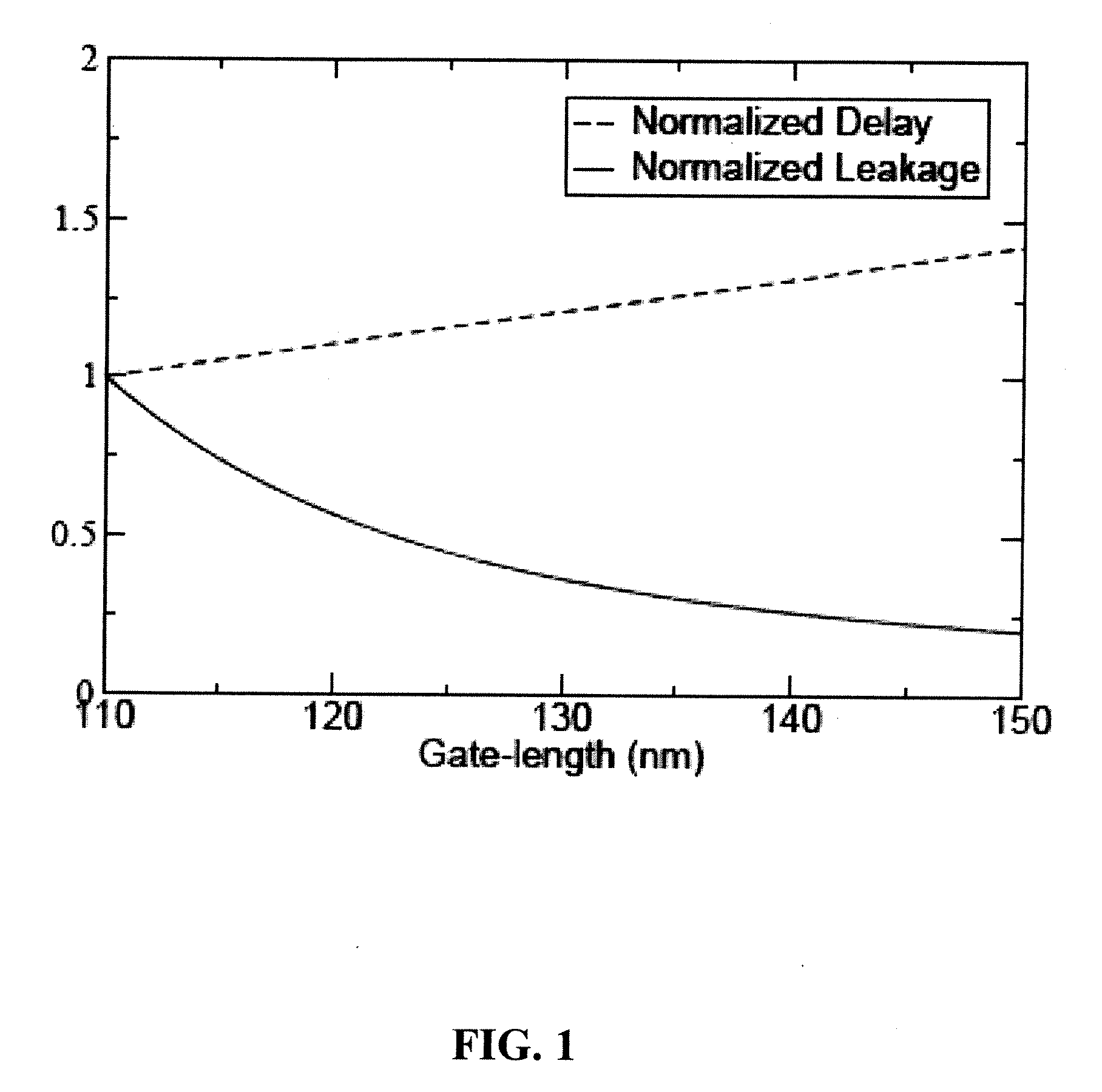
Gate-length biasing for digital circuit optimization
InactiveUS7441211B1Reduce impactImpairing time delay performance only linearlySolid-state devicesCAD circuit designEngineeringDigital electronics
Methods and apparatus for a gate-length biasing methodology for optimizing integrated digital circuits are described. The gate-length biasing methodology replaces a nominal gate-length of a transistor with a biased gate-length, where the biased gate-length includes a bias length that is small compared to the nominal gate-length. In an exemplary embodiment, the bias length is less than 10% of the nominal gate-length.
Owner:RPX CORP
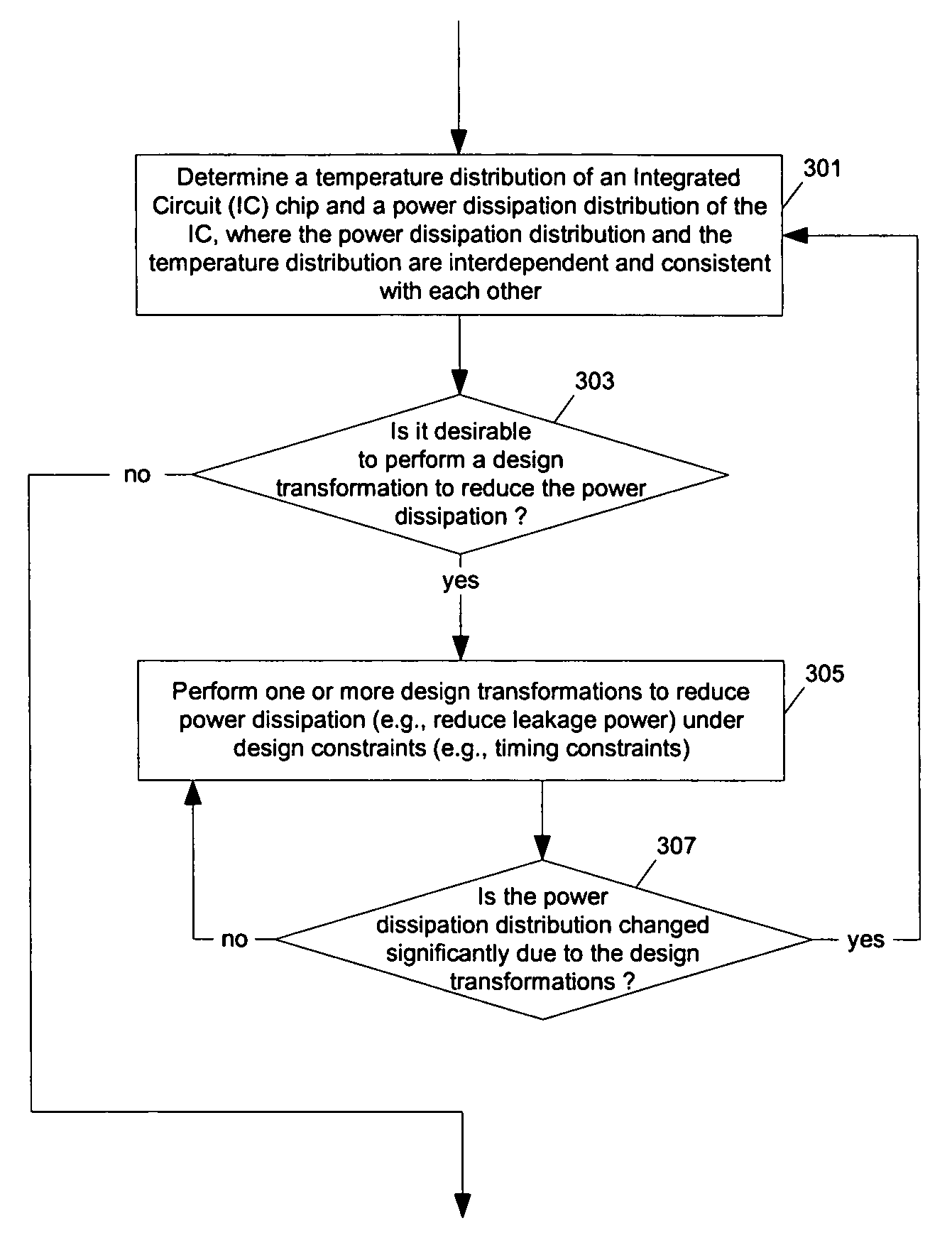
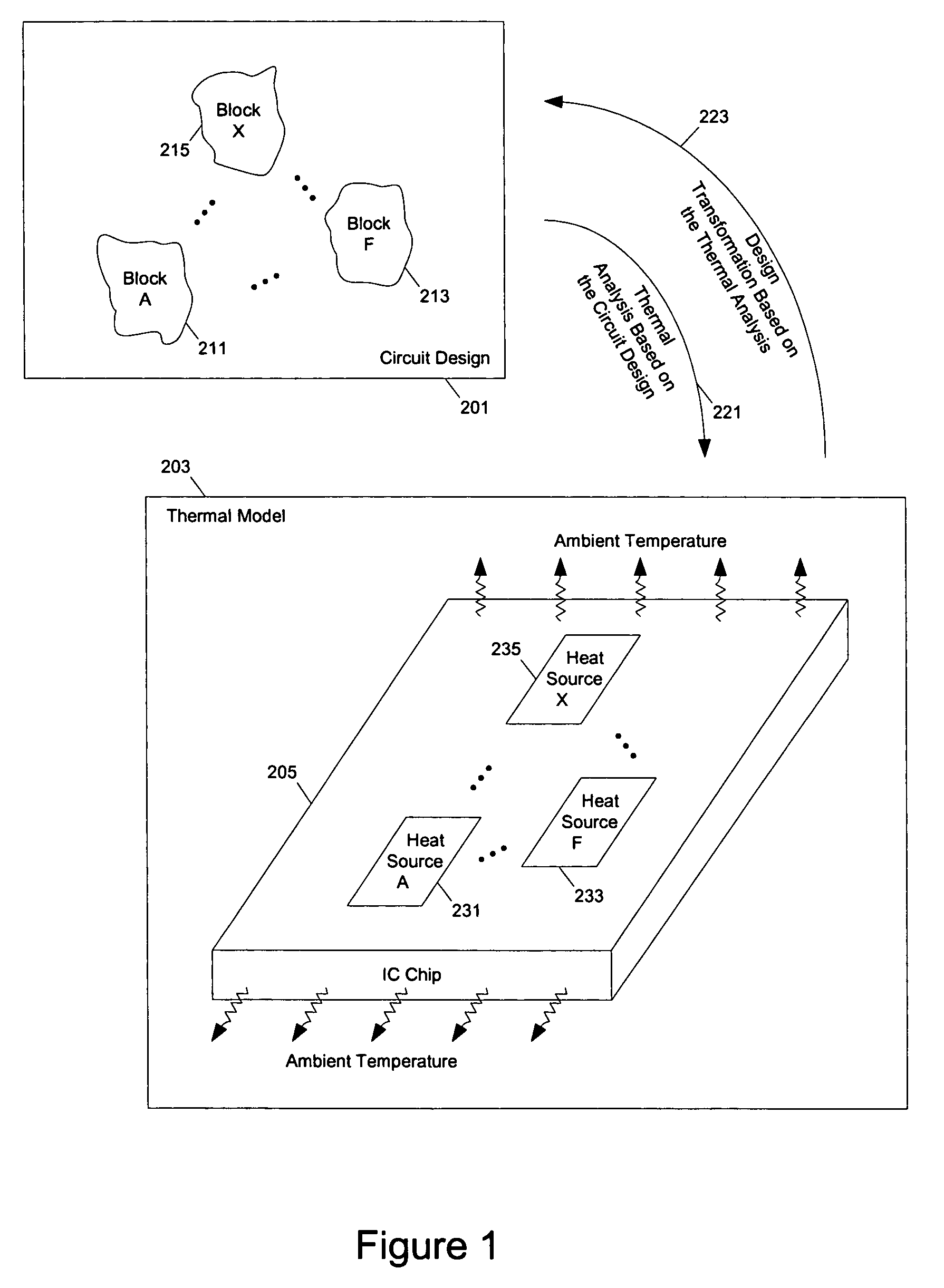
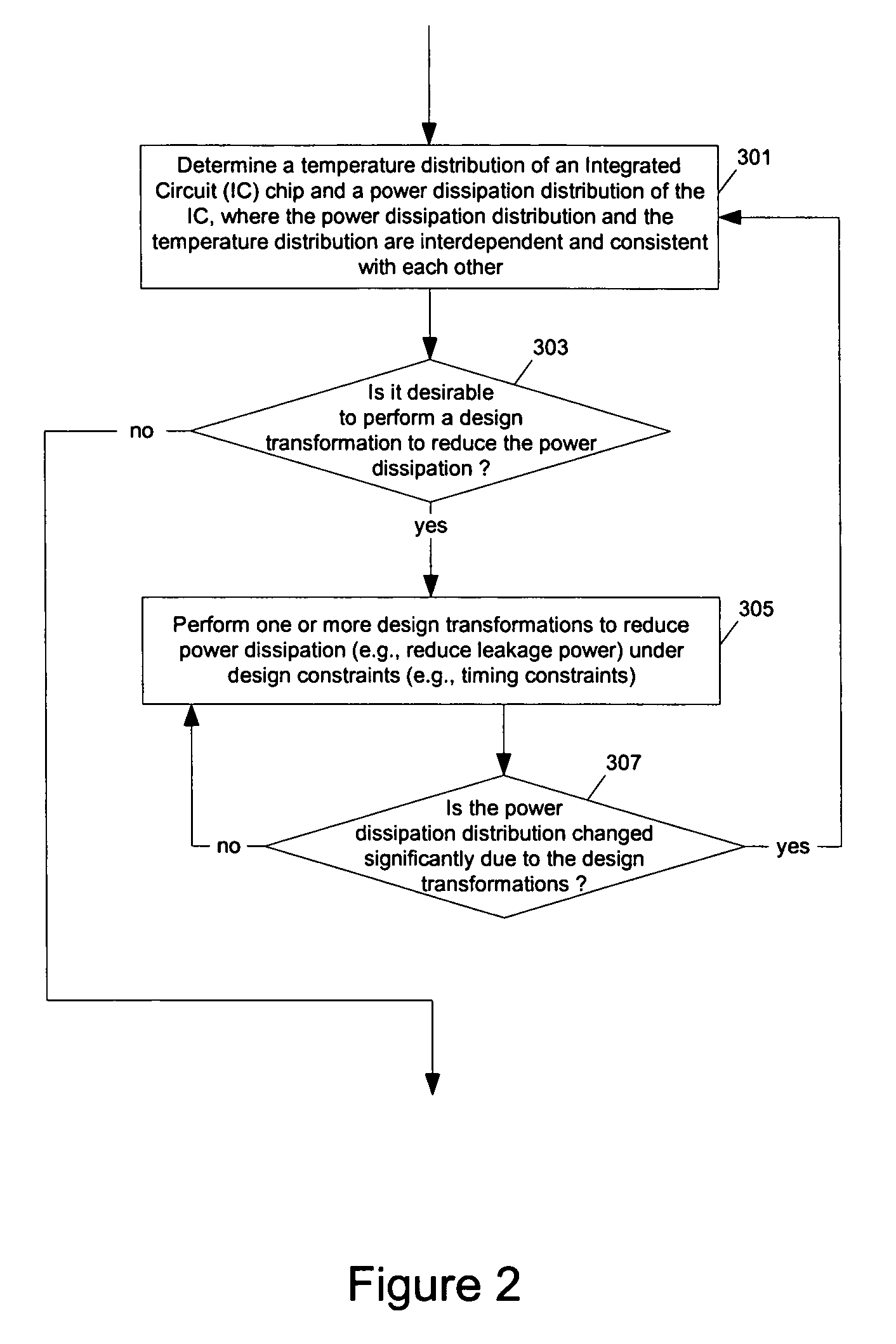
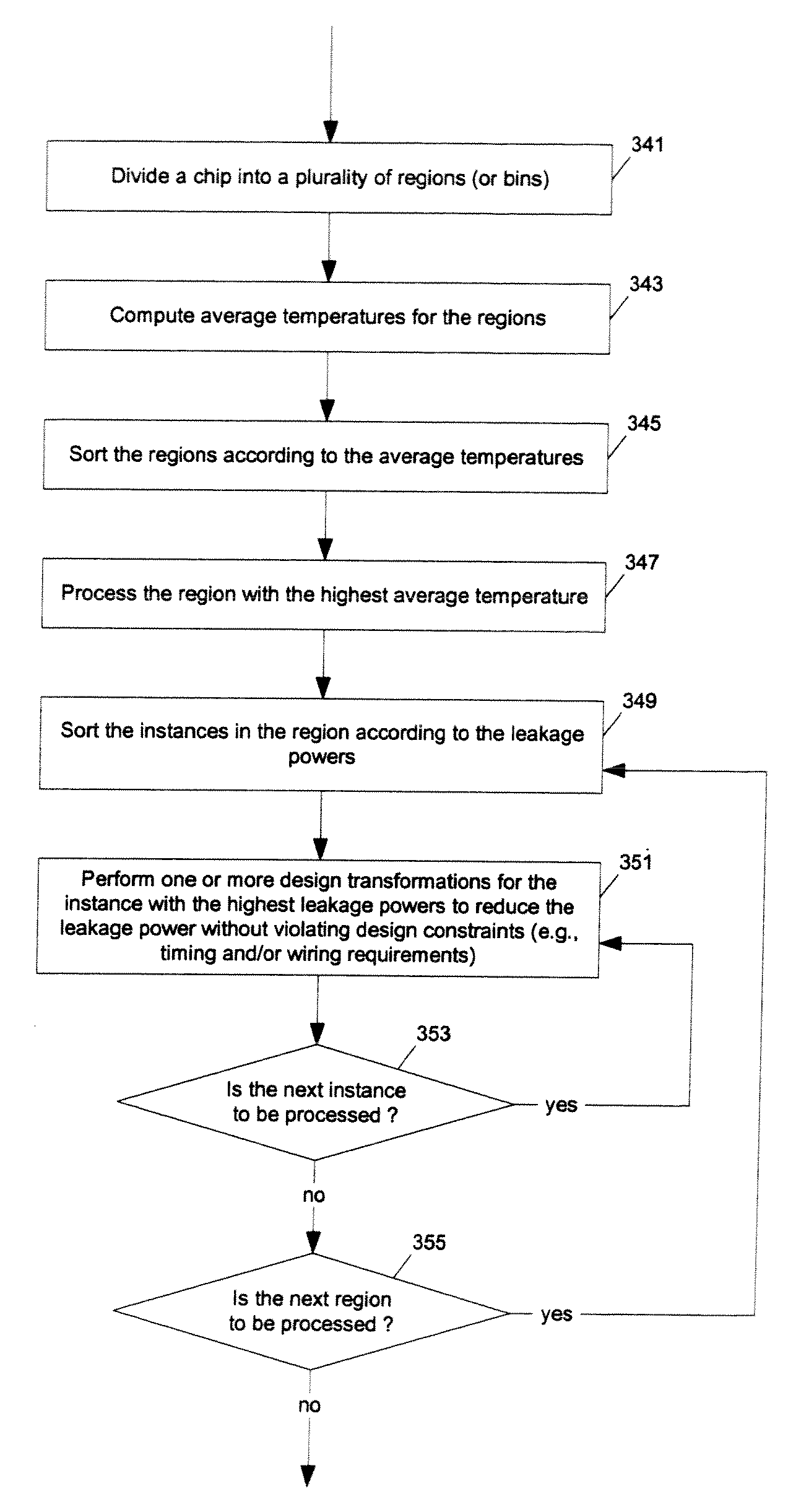
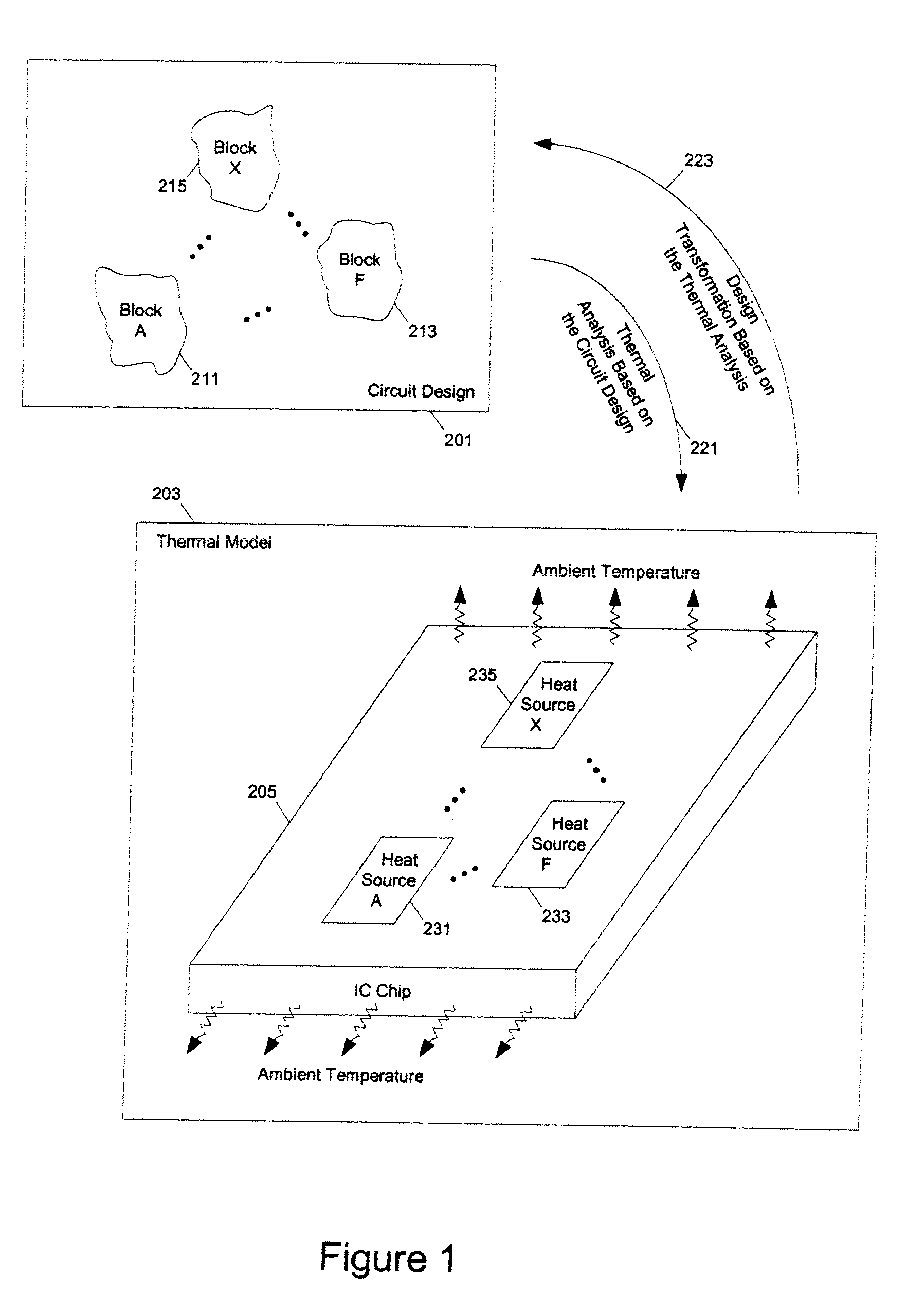
Methods and apparatuses for thermal analysis based circuit design
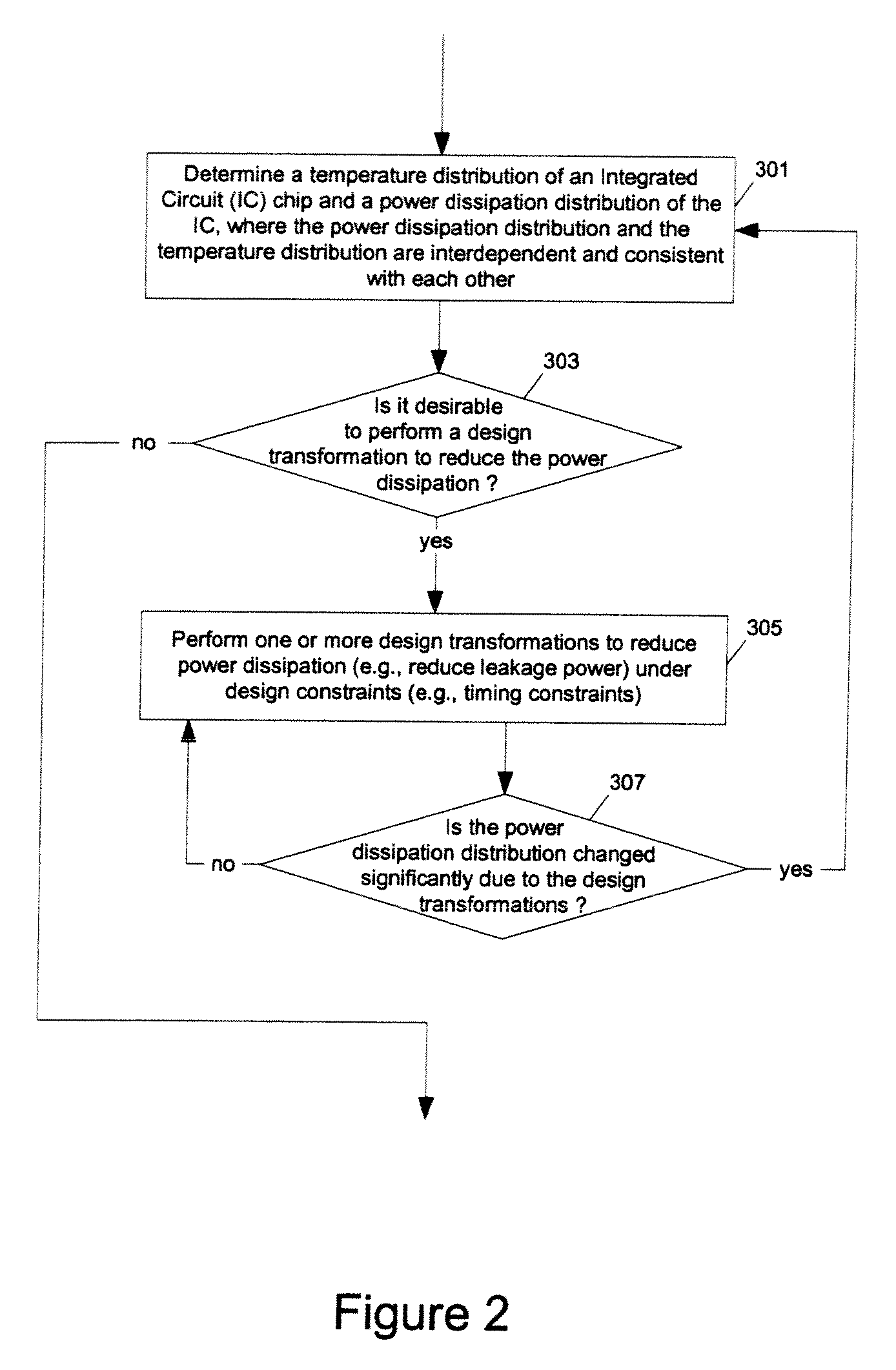
ActiveUS7366997B1Reduce power consumptionExtension of timeSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationSpecial data processing applicationsPower usageTransition time
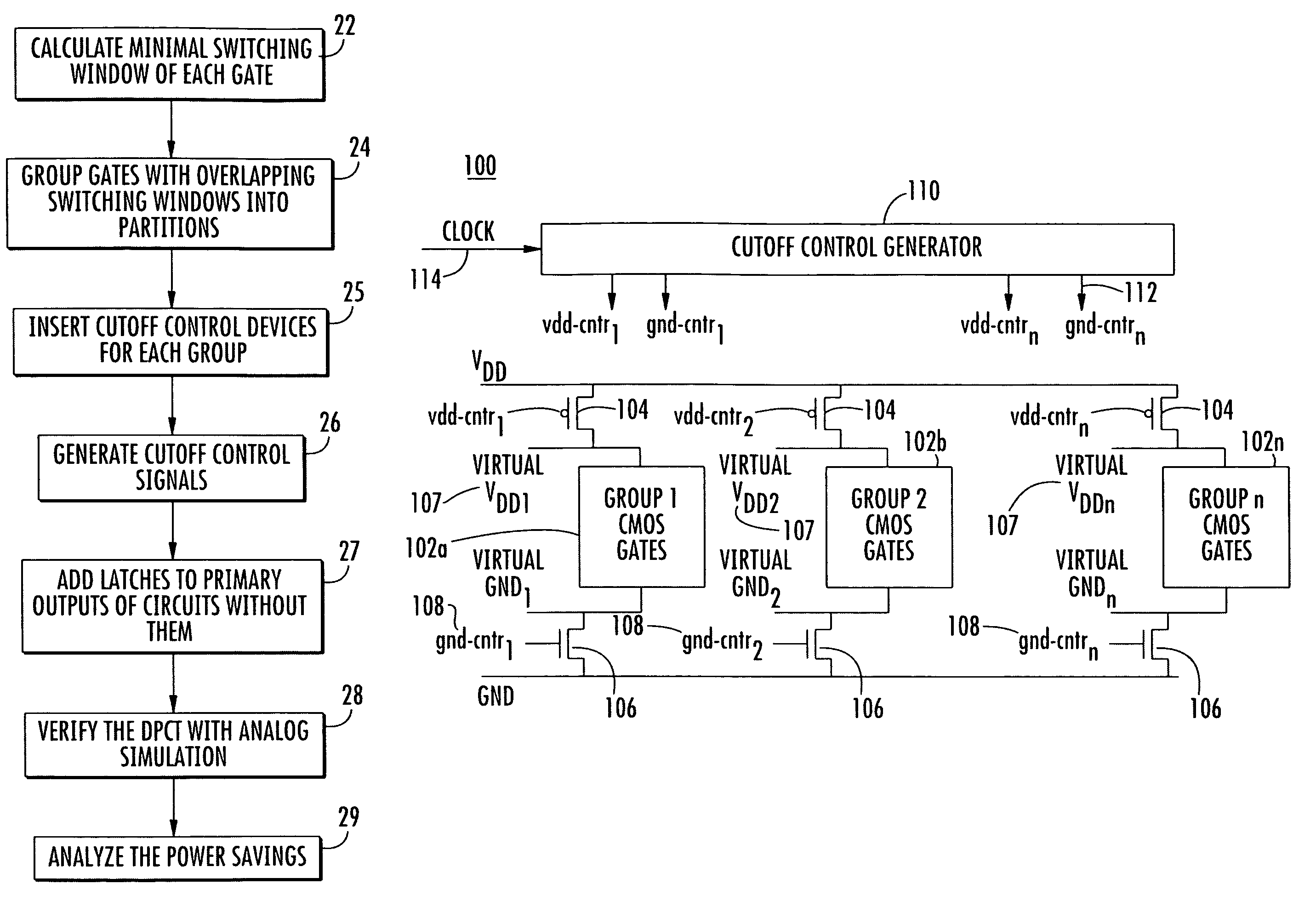
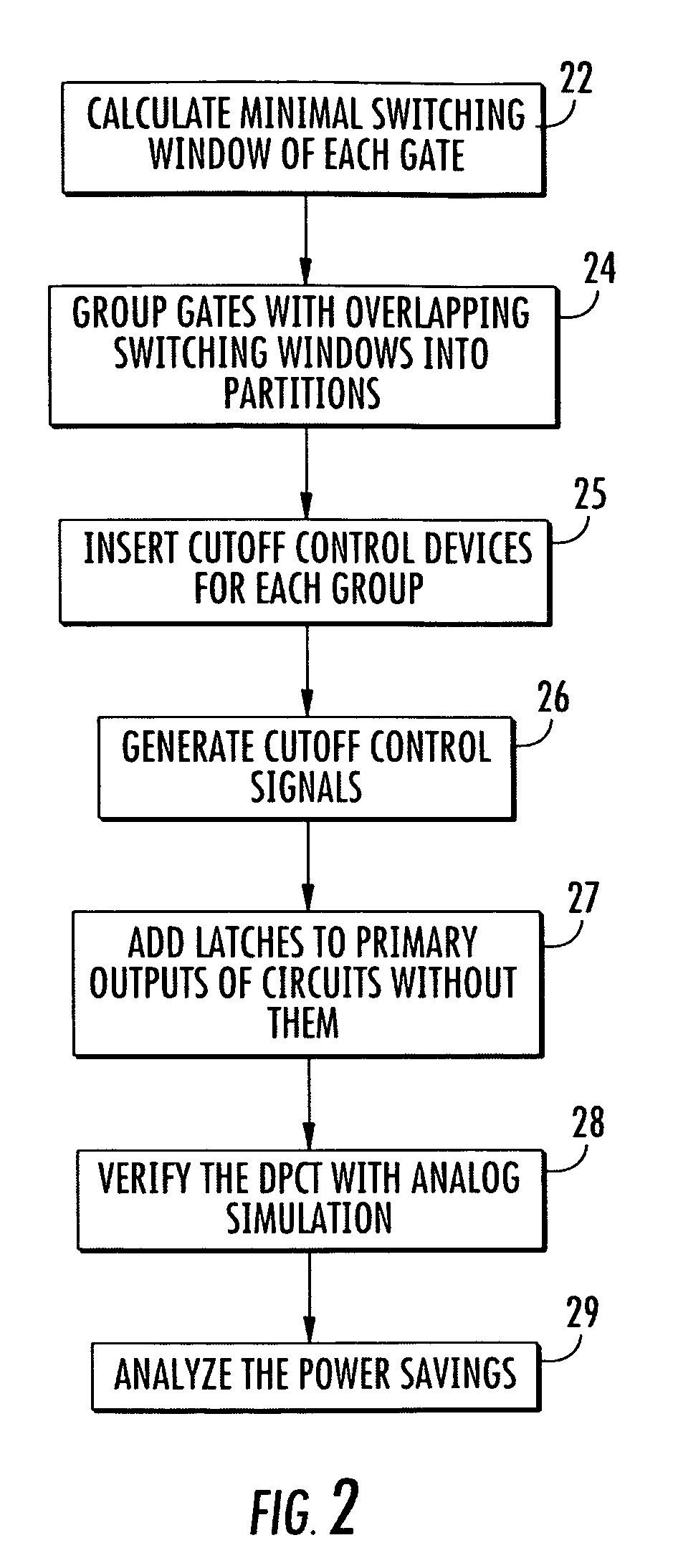
Methods and apparatuses for circuit design to reduce power usage, such as reducing temperature dependent power usage, and / or to improve timing, such as reducing temperature dependent delay or transition time. At least one embodiment of the present invention reduces the power dissipation and improves the timing of an integrated circuit to optimize the design. A thermal analysis is used to determine the temperature dependent power dissipation of a circuit and the temperature distribution of the circuit resulting from dissipating the heat created by the temperature dependent power dissipation. Then, the components of the design are selectively transformed to reduce the power dissipation and to improve timing based on the temperature solution. The transformation may include placement changes and netlist changes, such as the change of transistor threshold voltages for cells or for blocks of the circuit chip.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Methods and apparatuses for thermal analysis based circuit design
ActiveUS20080168406A1Reduce power consumptionExtension of timeSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringPower usage
Methods and apparatuses for circuit design to reduce power usage, such as reducing temperature dependent power usage, and / or to improve timing, such as reducing temperature dependent delay or transition time. At least one embodiment of the present invention reduces the power dissipation and improves the timing of an integrated circuit to optimize the design. A thermal analysis is used to determine the temperature dependent power dissipation of a circuit and the temperature distribution of the circuit resulting from dissipating the heat created by the temperature dependent power dissipation. Then, the components of the design are selectively transformed to reduce the power dissipation and to improve timing based on the temperature solution. The transformation may include placement changes and netlist changes, such as the change of transistor threshold voltages for cells or for blocks of the circuit chip.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
High-power amplifier apparatus for TDD wireless communication system
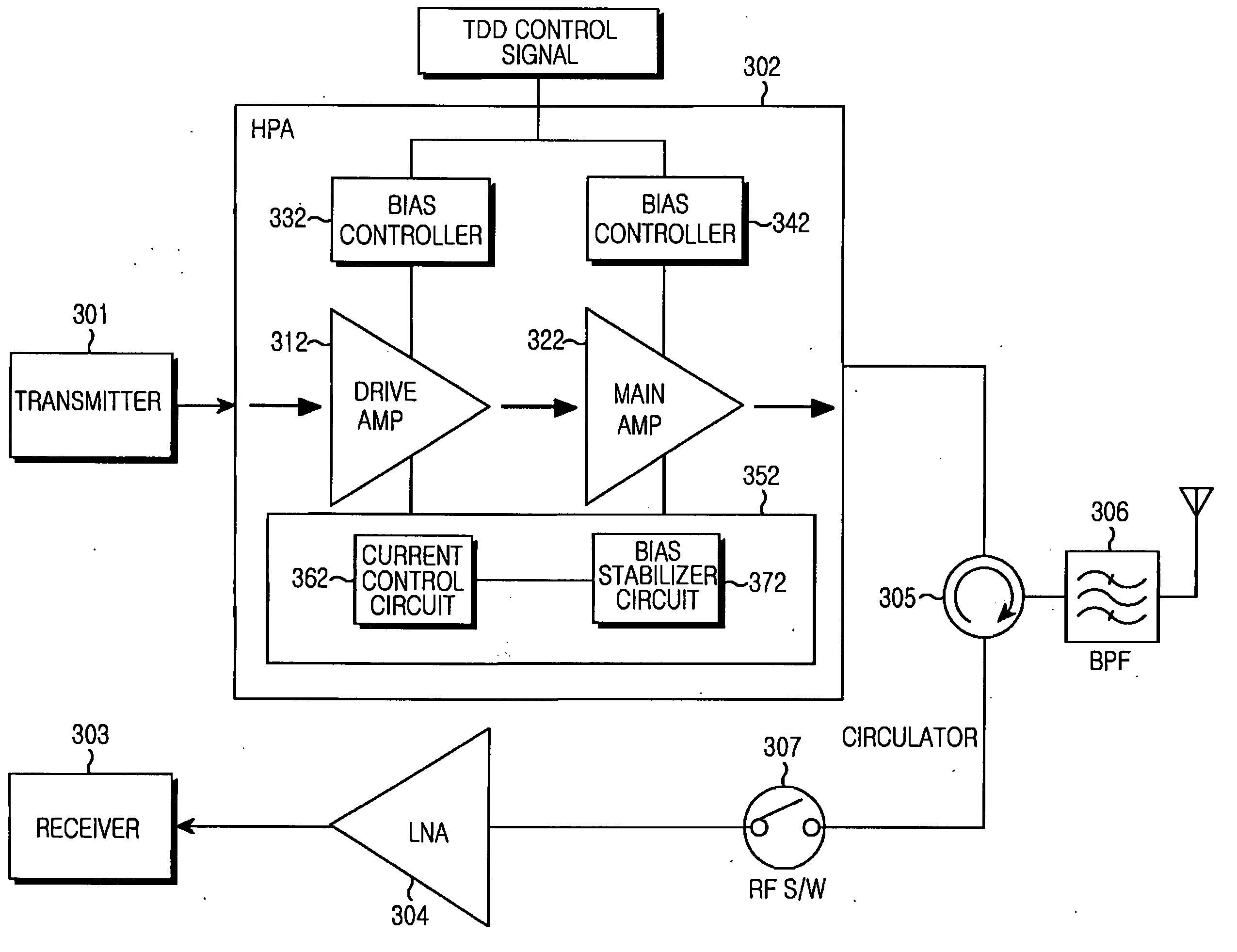
ActiveUS20070111686A1Avoid powerReduce leakage powerResonant long antennasHigh frequency amplifiersCommunications systemAudio power amplifier
Provided is an HPA apparatus for a TDD wireless communication system. In the HPA apparatus, a power amplifier amplifies the power of an input signal. A gate bias controller turns on / off a gate bias of the power amplifier in accordance with a TDD control signal. A constellation error optimizer circuit removes a current fluctuation and a power noise, which occur when the gate bias controller turns on / off the power amplifier in a TX mode, to stabilize a drain bias thereof.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Data processing system
ActiveUS20110271126A1Easy to adaptData processing processEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementData processing systemPower domains
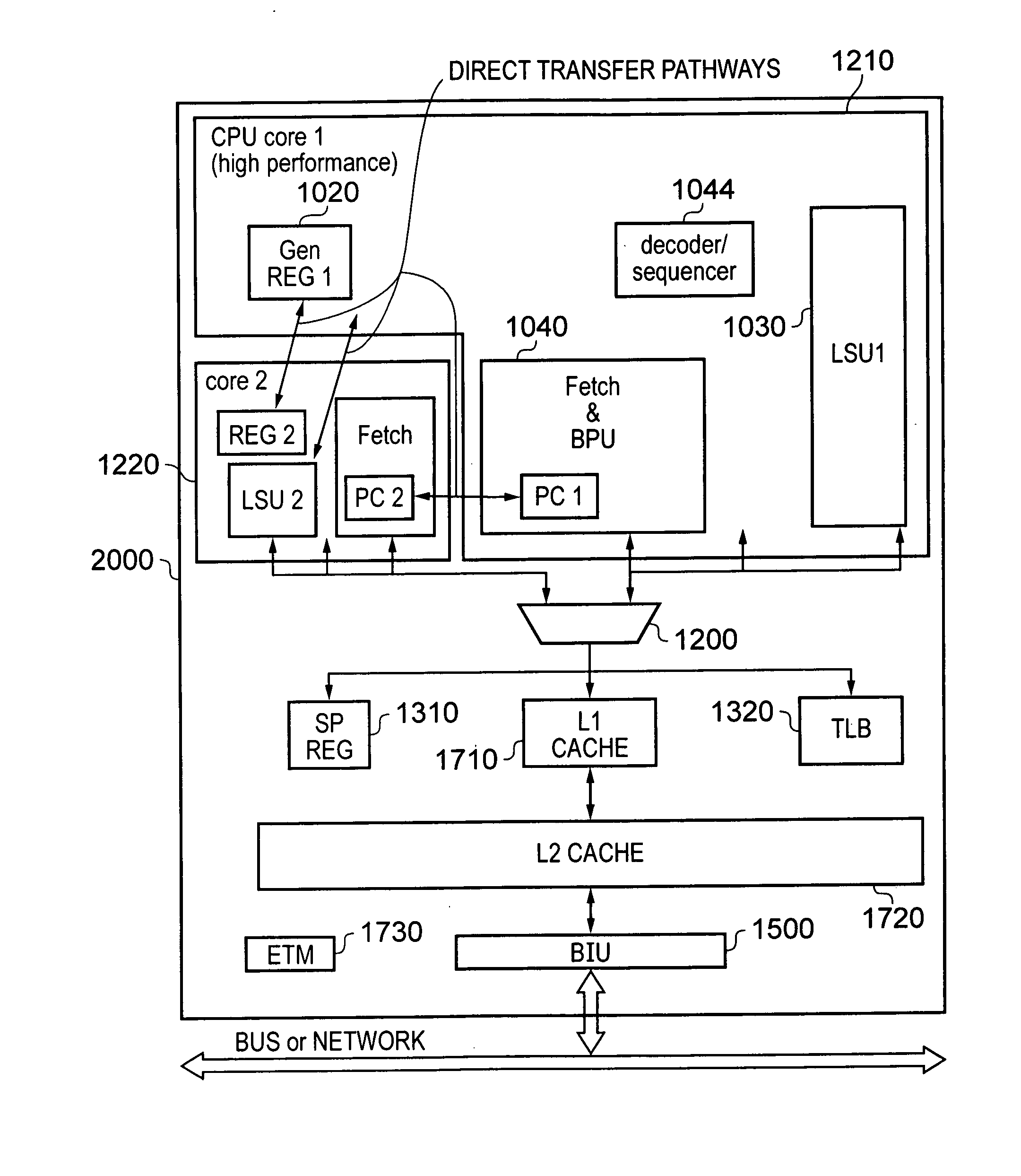
A data processing apparatus is provided comprising first processing circuitry, second processing circuitry and shared processing circuitry. The first processing circuitry and second processing circuitry are configured to operate in different first and second power domains respectively and the shared processing circuitry is configured to operate in a shared power domain. The data processing apparatus forms a uni-processing environment for executing a single instruction stream in which either the first processing circuitry and the shared processing circuitry operate together to execute the instruction stream or the second processing circuitry and the shared processing circuitry operate together to execute the single instruction stream. Execution flow transfer circuitry is provided for transferring at least one bit of processing-state restoration information between the two hybrid processing units.
Owner:ARM LTD
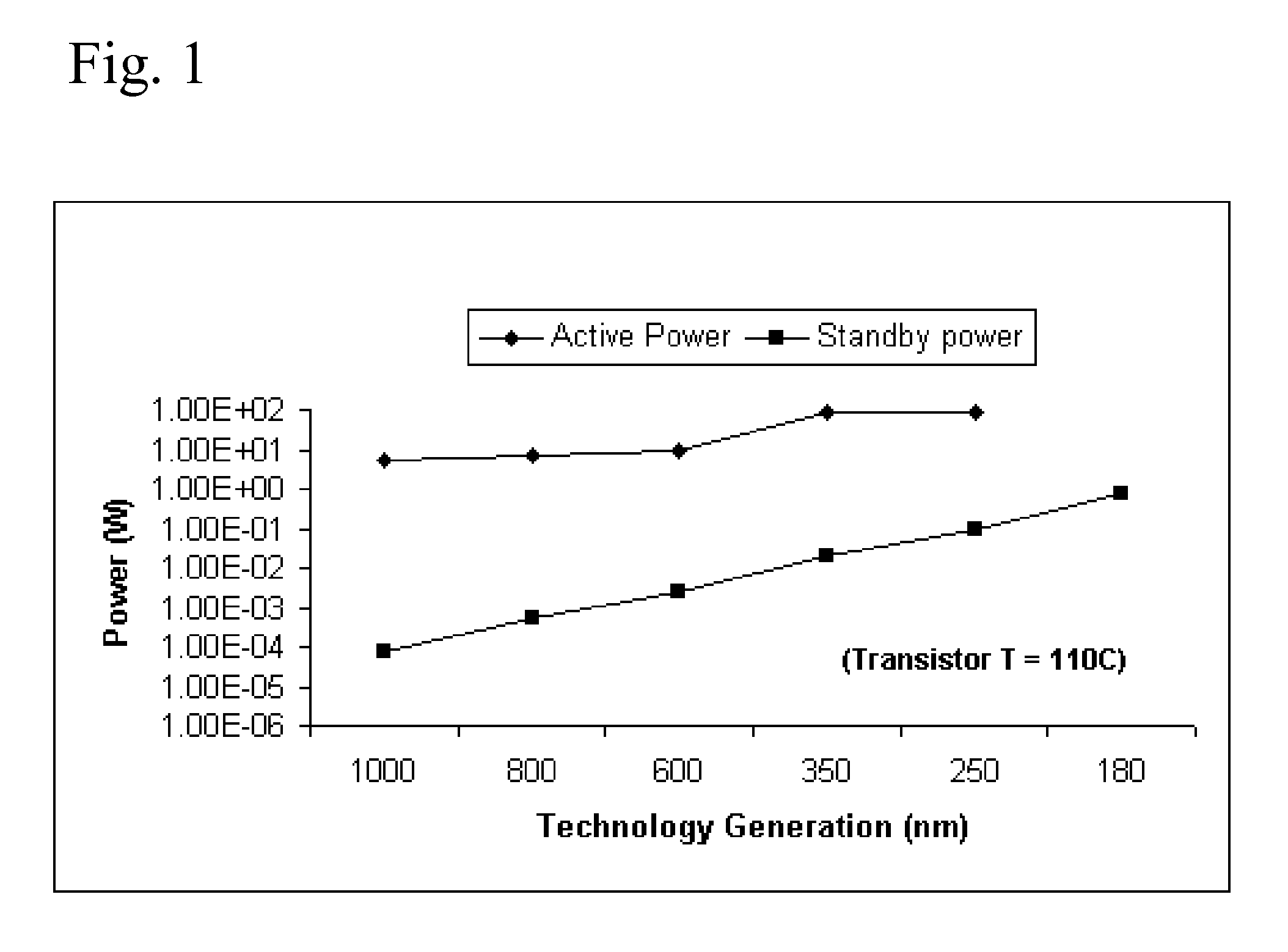
Method for determining and using leakage current sensitivities to optimize the design of an integrated circuit
InactiveUS20050044515A1Reduce leakage powerImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCAD circuit designPower marginIntegrated circuit
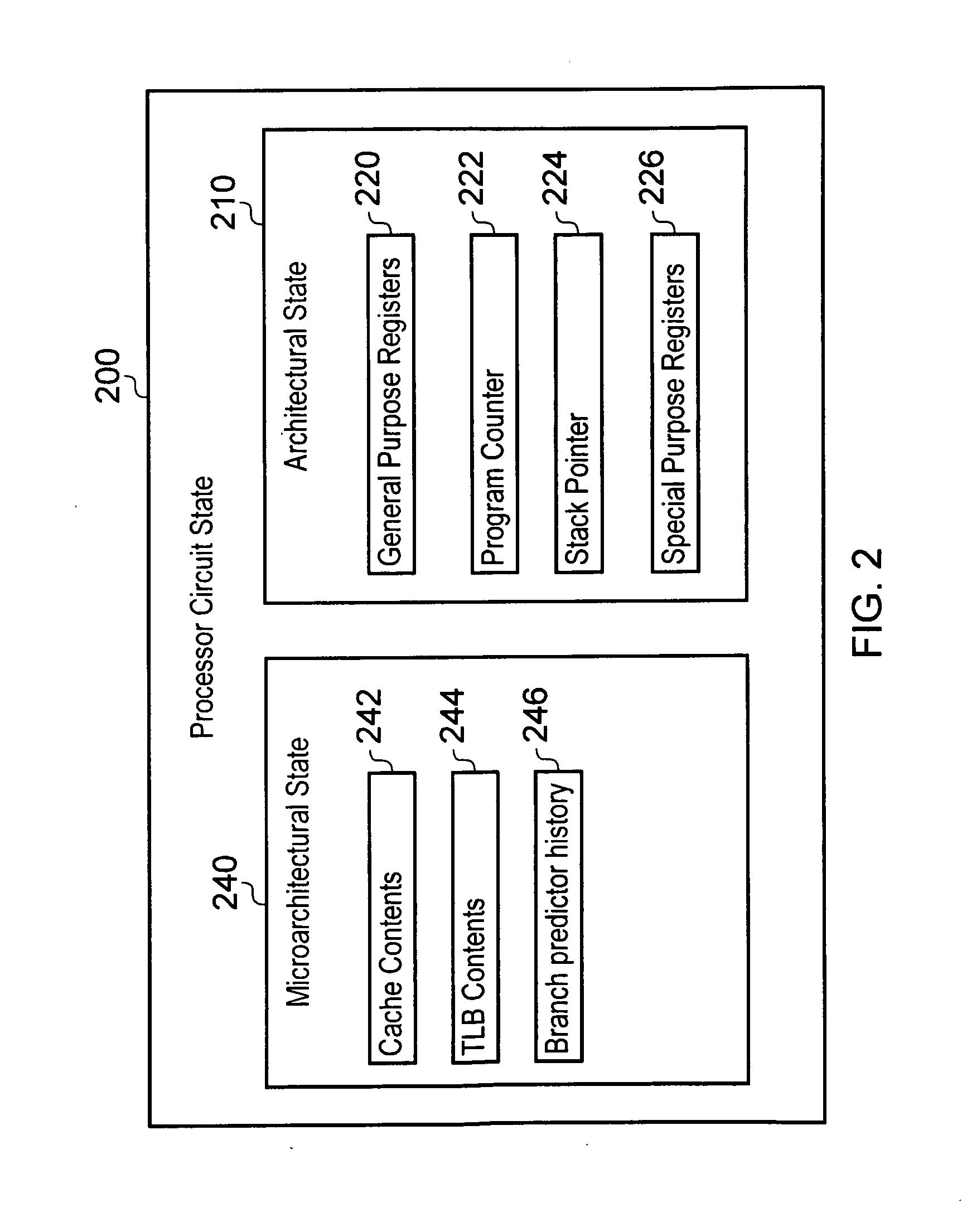
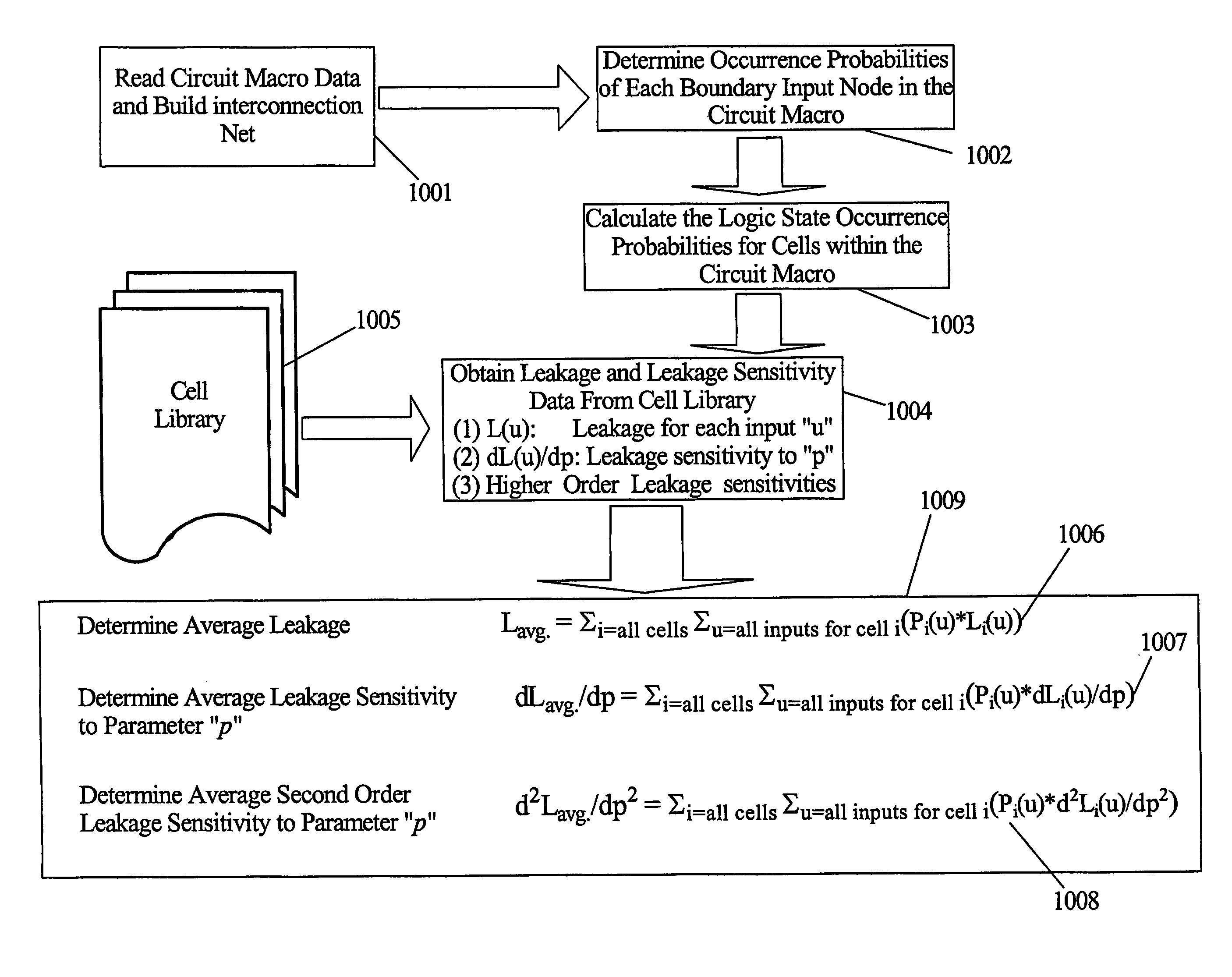
An integrated circuit design has circuit macros made up of device cells. The cells are characterized by determining the leakage current dependency on various process, environmental and voltage parameters. When circuit macros are designed their leakage power is calculated using this data and multi-dimensional models for power and temperature distribution. Circuit macros are identified as timing-critical and timing-noncritical macros. Statistical methods are used to determine the average leakage sensitivities for the specific circuit macros designed. The designer uses the sensitivity data to determine how to redesign selected circuit macros to reduce leakage power. Reducing leakage power in these selected circuits may be used to reduce overall IC power or the improved power margins may be used in timing-critical circuits to increase performance while keeping power dissipation unchanged.
Owner:IBM CORP
Low-power FPGA circuits and methods
InactiveUS7714610B2Increase profitEasy to controlSolid-state devicesCAD circuit designEngineeringLevel converter
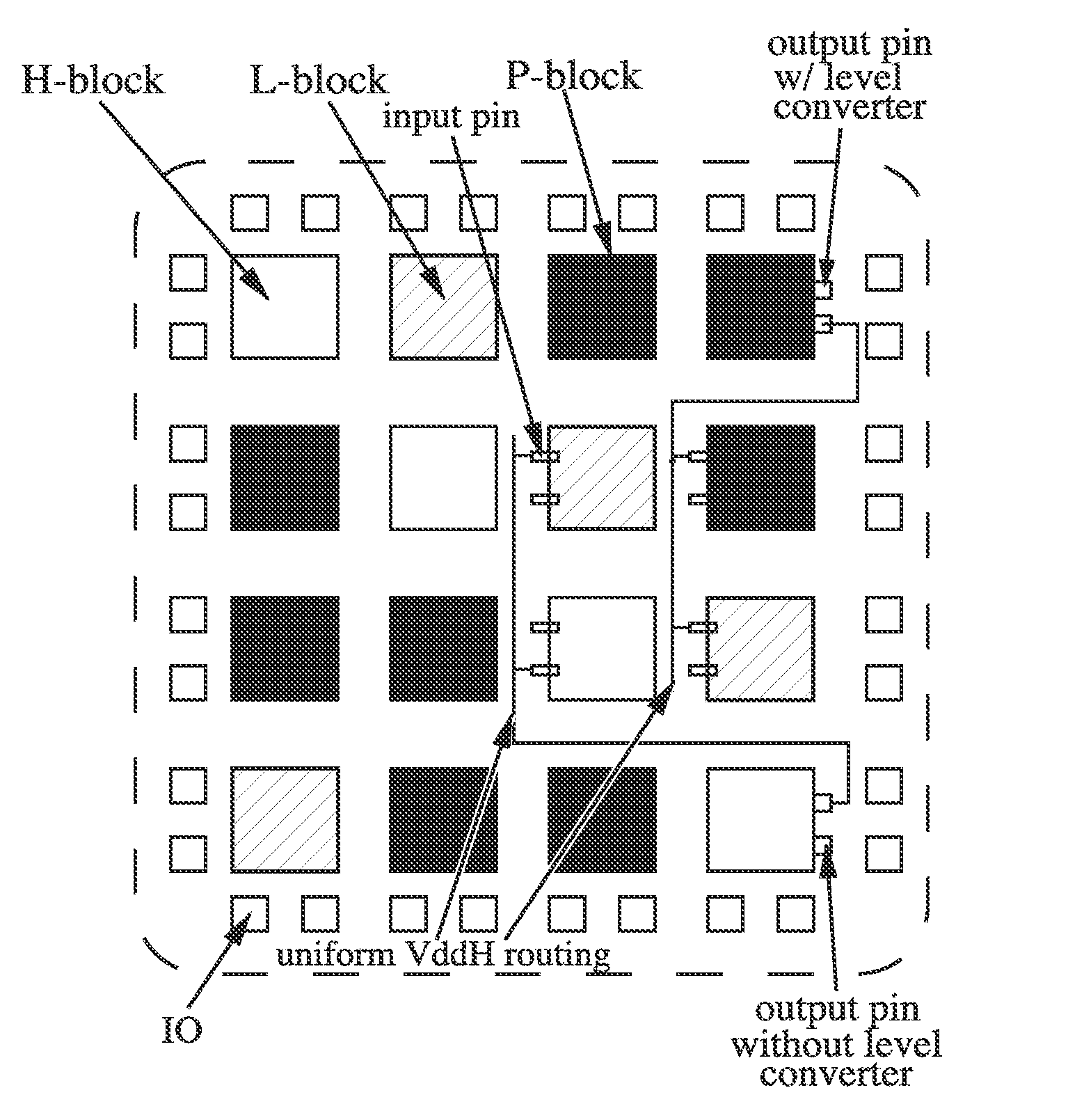
Field Programmable Logic Arrays (FPGAs) are described which utilize multiple power supply voltages to reduce both dynamic power and leakage power without sacrificing speed or substantially increasing device area. Power reduction mechanisms are described for numerous portions of the FPGA, including logic blocks, routing circuits, connection blocks, switch blocks, configuration memory cells, and so forth. Embodiments describe circuits and methods for implementing multiple supplies as sources of Vdd, multiple voltage thresholding Vt, signal level translators, and power gating of circuitry to deactivate portions of the circuit which are inactive. The supply voltage levels can be fixed, or programmable. Methods are described for performing circuit CAD in the routing and assignment process on FPGAs, in particular for optimizing FPGA use having the power reduction circuits taught. Routing methods describe utilizing slack timing, power sensitivity, trace-based simulations, and other techniques to optimize circuit utilization on a multi Vdd FPGA.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
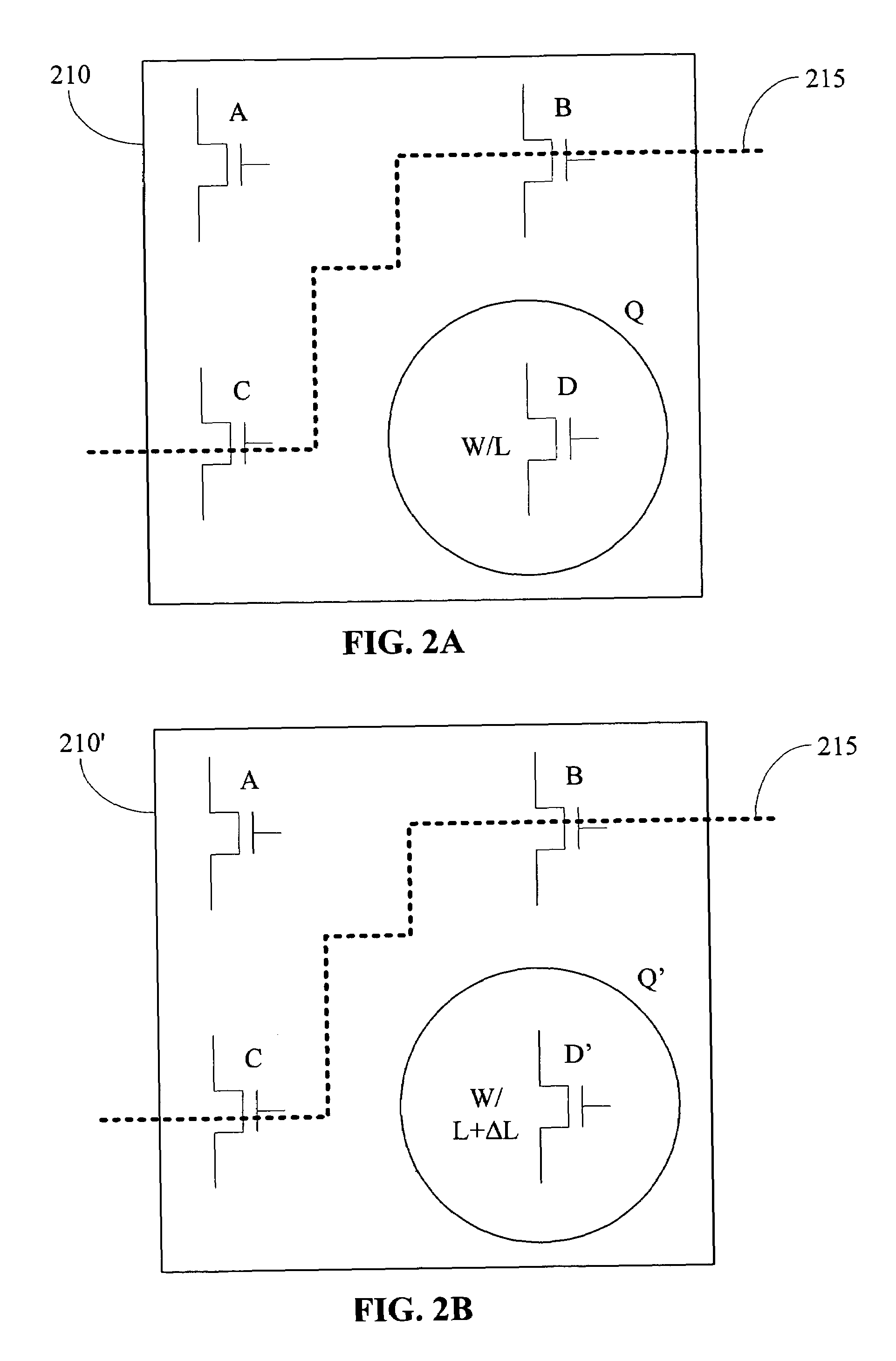
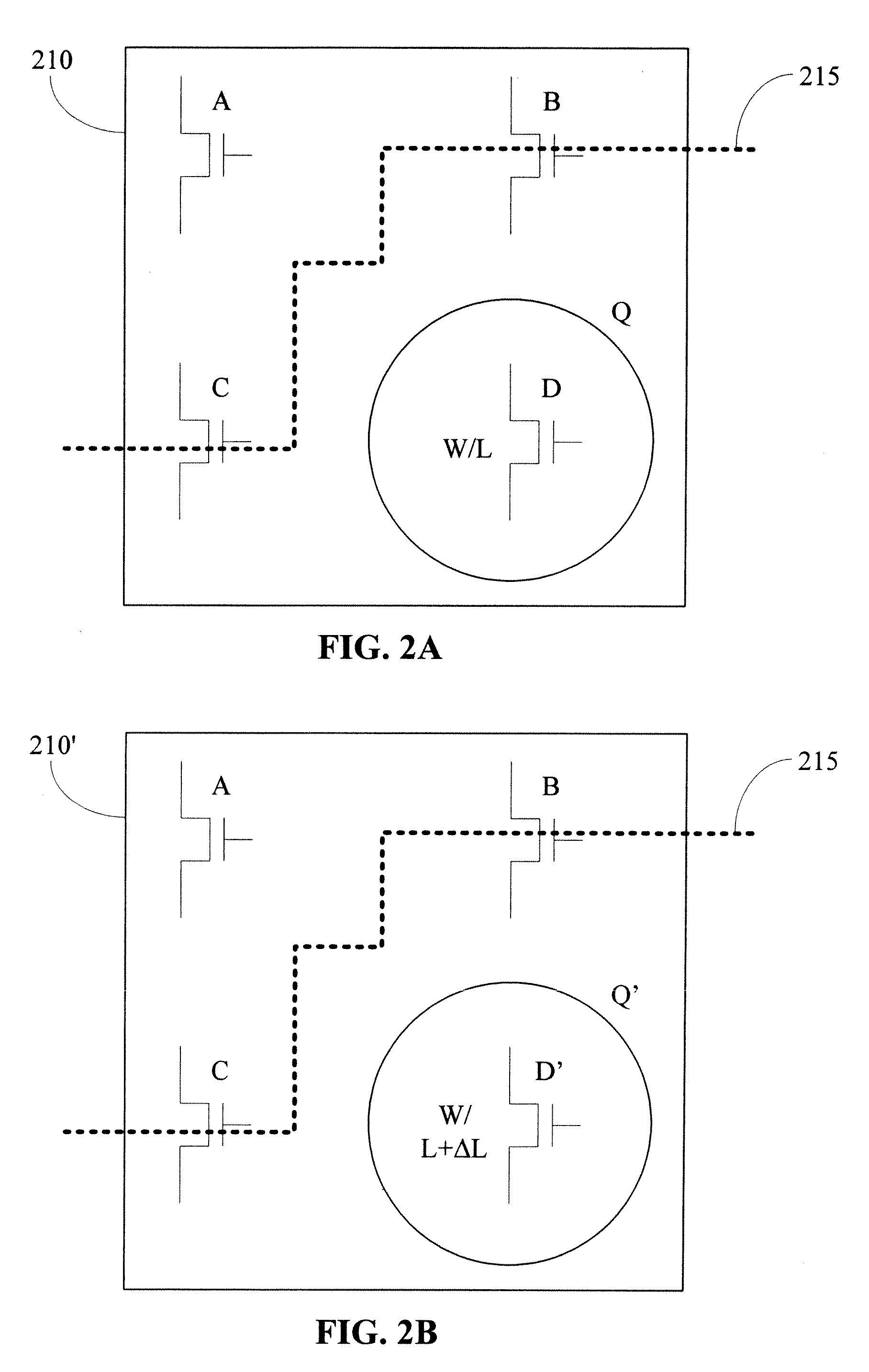
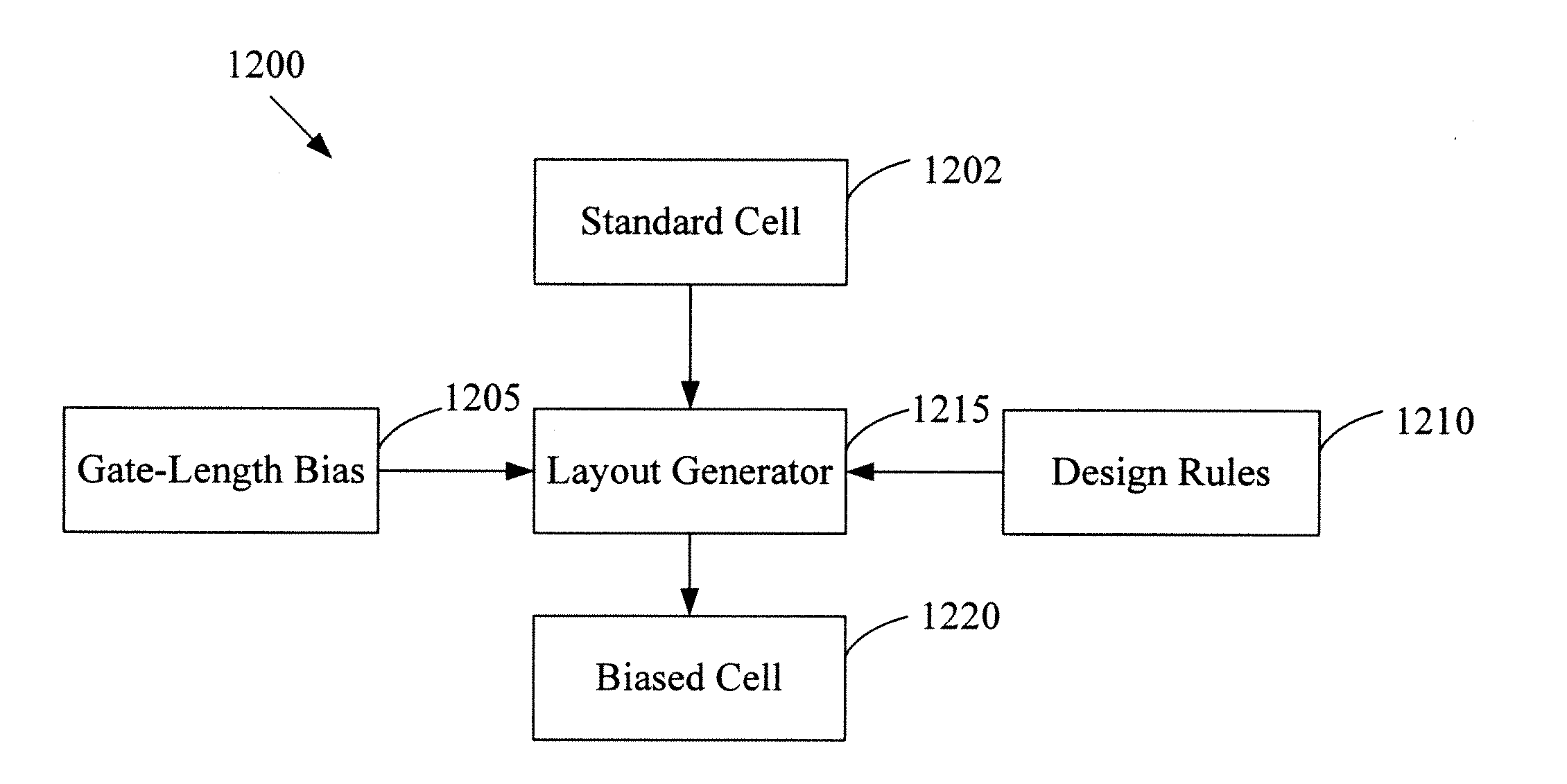
Standard cells having transistors annotated for gate-length biasing
InactiveUS20100169847A1Reduce impactImpairing time delay performance only linearlyCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsSemiconductor chipAnnotation
A standard cell library is disclosed. The standard cell library contains cells wherein at least one transistor in at least one cell is annotated for gate length biasing. Gate length biasing includes the modification of the gate length, so as to change the speed or power consumption of the modified gate length. The standard cell library is one used in the manufacturing of semiconductor devices (e.g., that result as semiconductor chips), by way of fabricating features defined on one or more layouts of geometric shapes. The annotations serve to identify which ones of the transistor gate features are to be modified before using the geometric shapes for manufacturing the semiconductor device.
Owner:RPX CORP
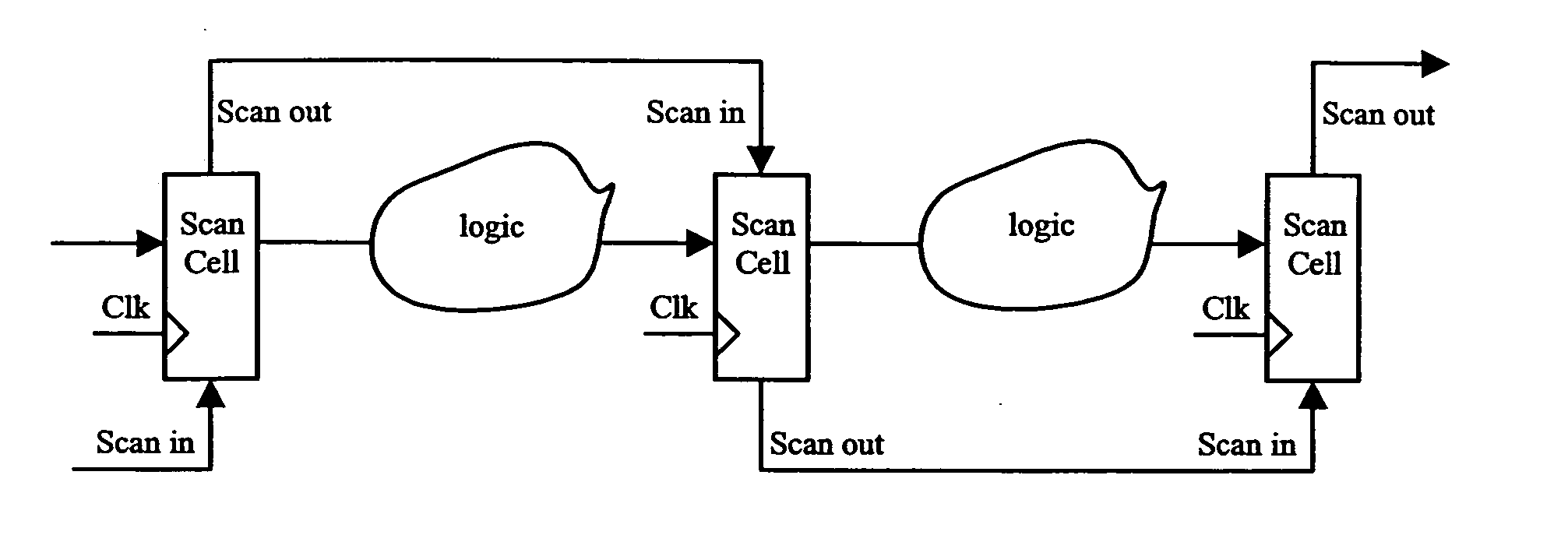
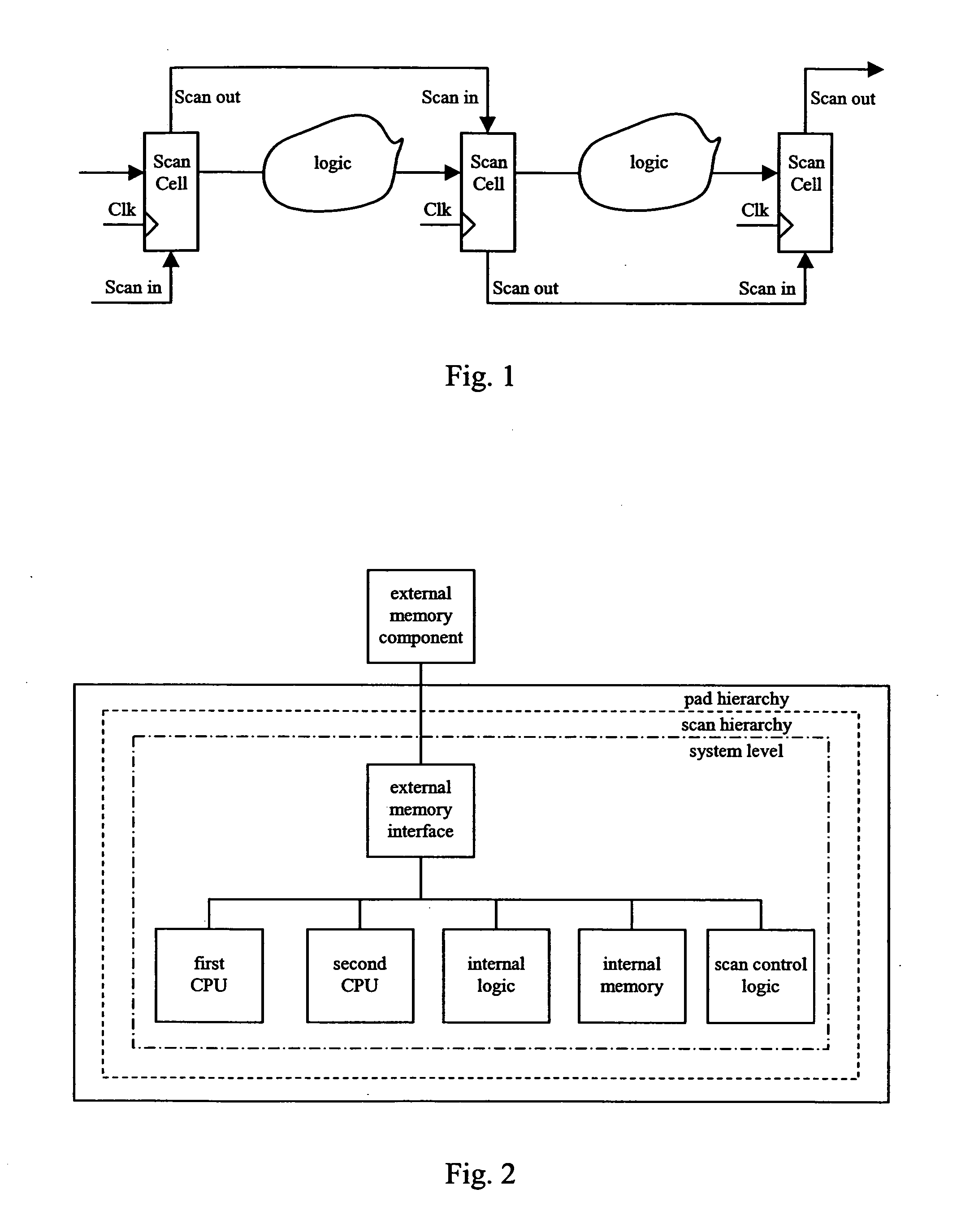
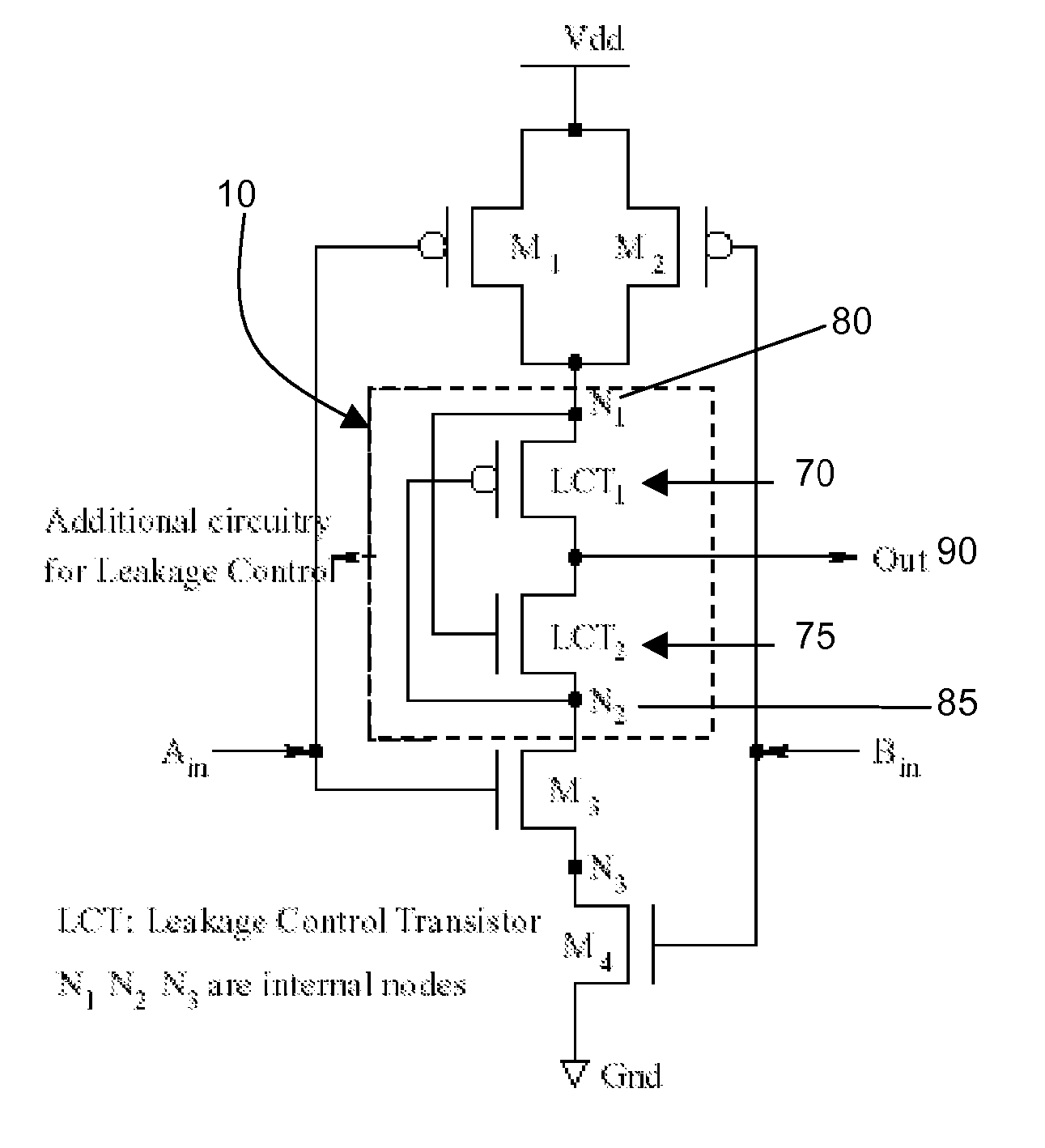
Integrated circuit with leakage control and method for leakage control
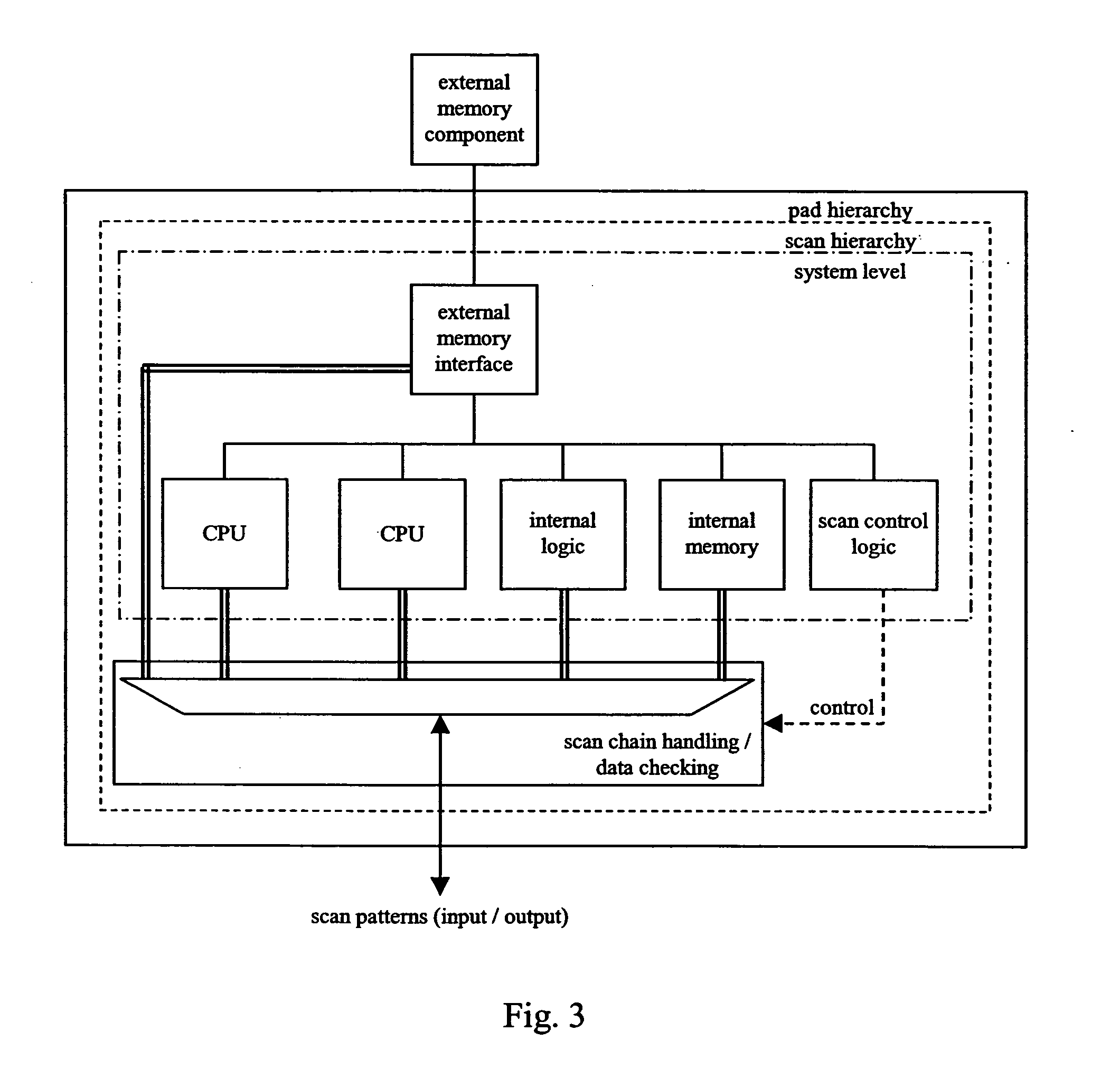
InactiveUS20050149799A1Improved leakage power controlReduce leakage powerPower reduction by control/clock signalDigital circuit testingPower modeState variable
The present invention relates to integrated circuit with reduced leakage power and in particular to a methodology for retaining an operational state of at least a part of the integrated circuit while the part is in standby / low power mode. In detail, the inventive methodology is based on the use of scan chains being implemented in the integrated circuit for production testing purposes. Via the scan chains circuit-internal state-variable memory element content is read out and / or written in such that the operational state of for instance a specific part (power domain) of the integrated circuit may be captured on the basis of the circuit internal contents, retained in an adequately provided data storage and afterwards scanned into the specific part of the integrated circuit to restore the operational state thereof.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Method and system for reshaping a transistor gate in an integrated circuit to achieve a target objective
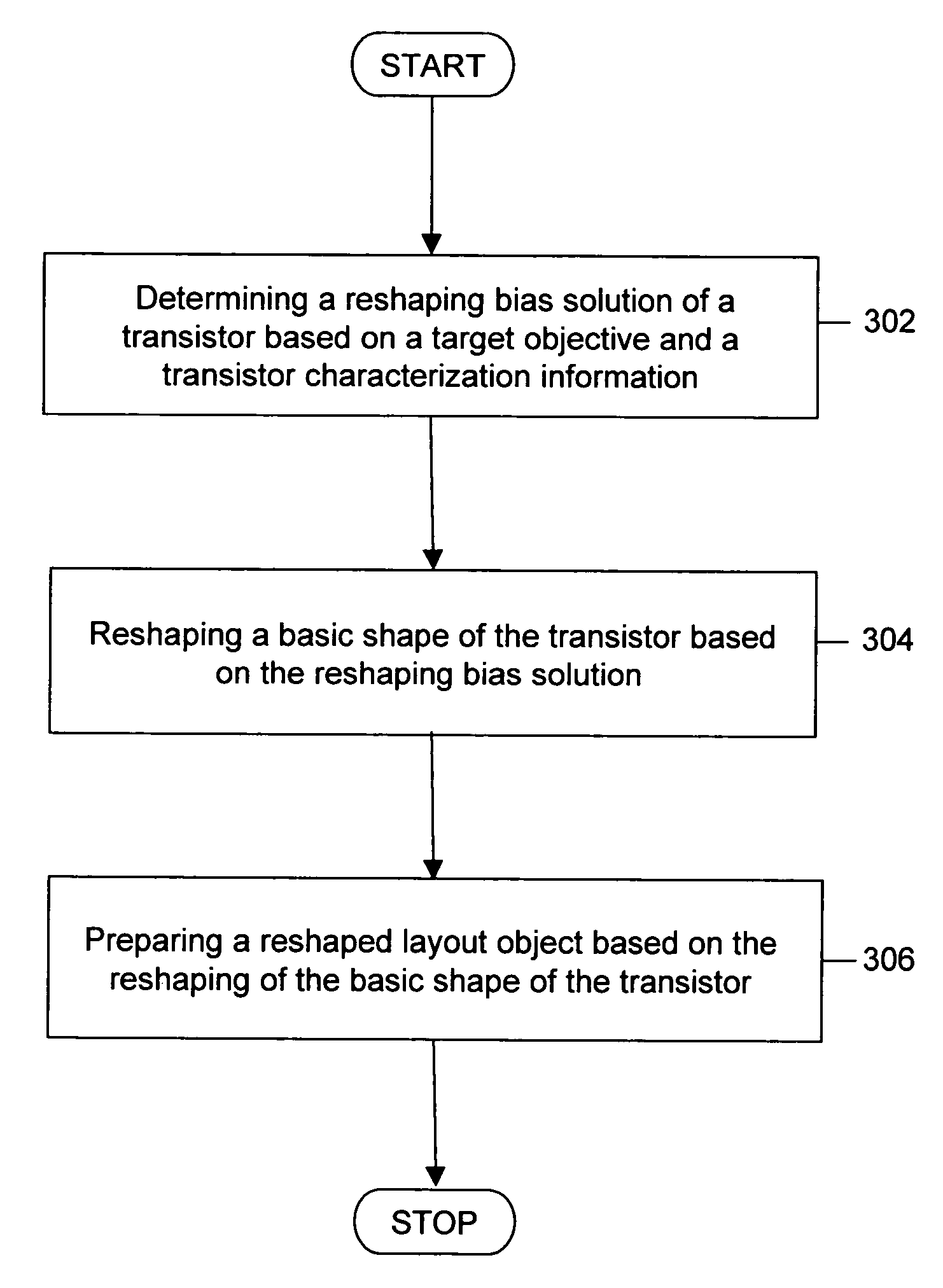
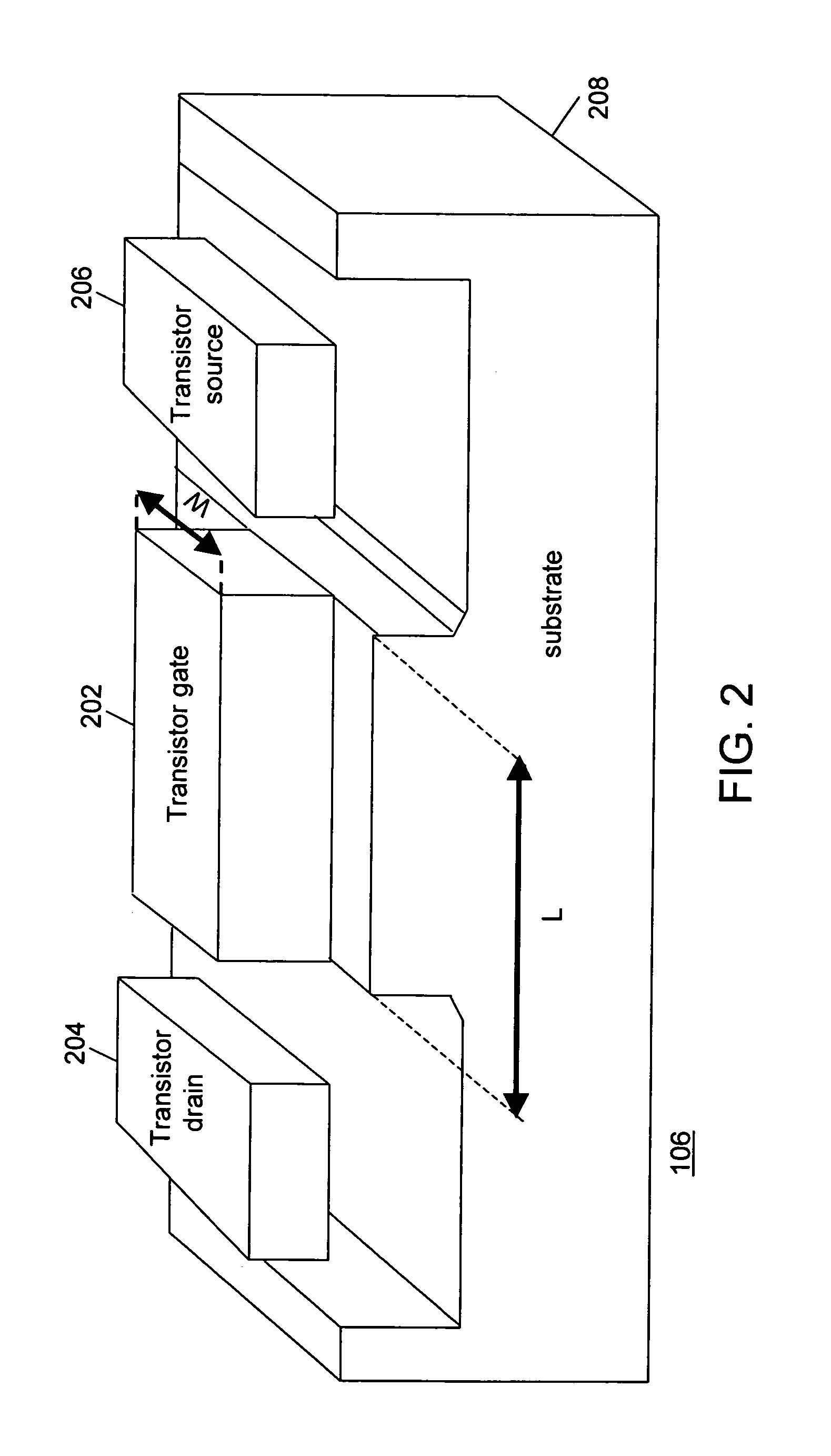
InactiveUS7730432B1Reduce leakage powerCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationIntegrated circuit layoutEngineering
The present invention provides a method and system for designing an integrated circuit (IC). The IC comprises a plurality of cells, and each of the cells comprises a plurality of transistors. The method achieves a target objective of a transistor, of a cell, or of part of or the entire IC. The method of designing the IC includes reshaping a basic shape of the transistor. The method includes determining a reshaping bias solution of the transistor. The method further includes modifying the basic shape of the transistor channel, based on the reshaping bias solution, and preparing a reshaped layout design.
Owner:RPX CORP
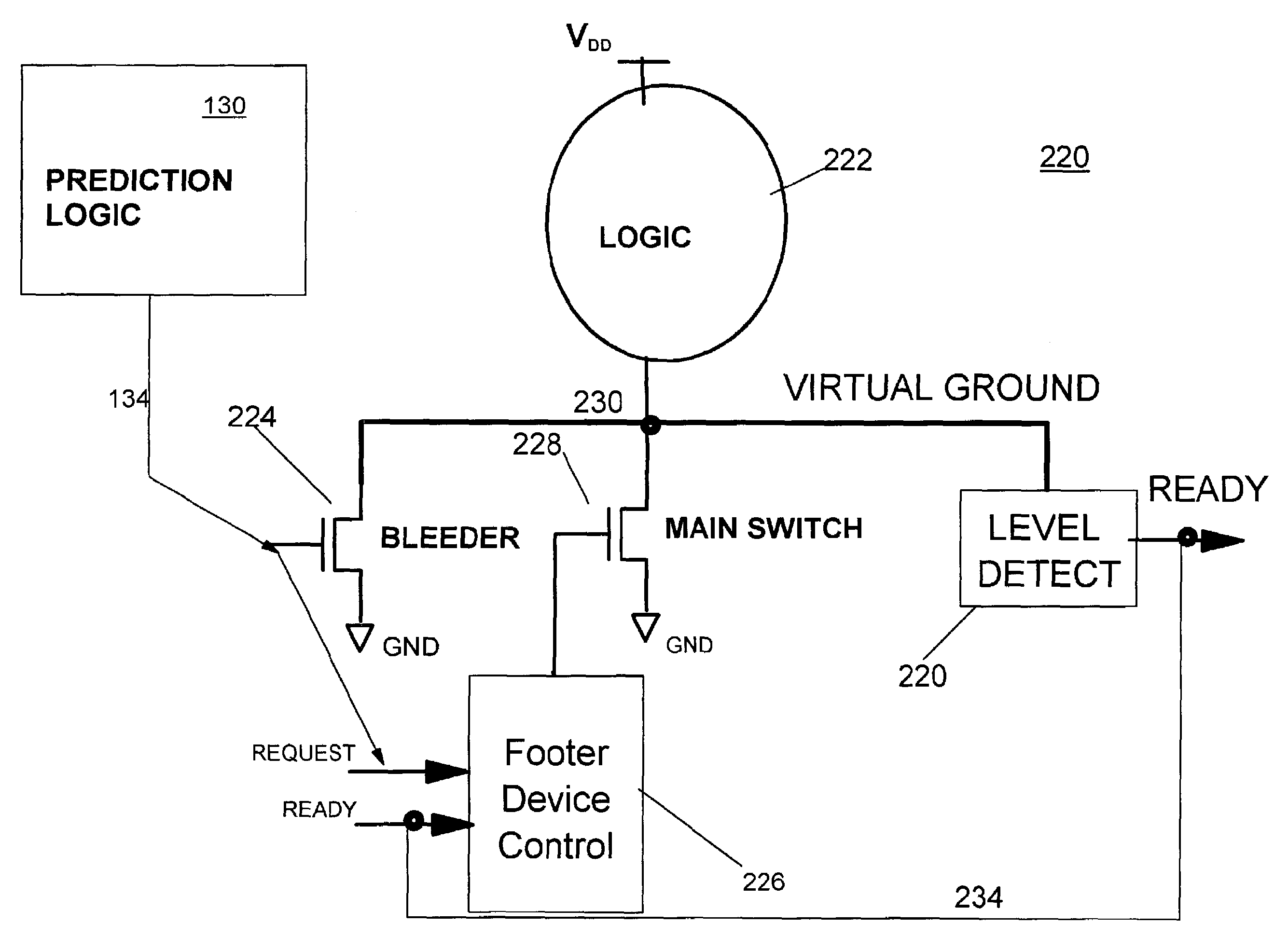
Processor with low overhead predictive supply voltage gating for leakage power reduction
ActiveUS7134028B2Decreasing processor power consumptionNo performance lossEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementTurn on timeLeakage power
An integrated circuit (IC) including unit power control, leakage reduction circuit for controllably reducing leakage power with reduced LdI / dt noise in the IC and, an activity prediction unit invoking active / dormant states in IC units. The prediction unit determines turn on and turn off times for each IC unit. The prediction unit controls a supply voltage select circuit selectively passing a supply voltage to a separate supply line at the predicted turn on time and selectively blocking the supply voltage at the predicted turn off time.
Owner:IBM CORP
High-performance low leakage power consumption master-slave type D flip-flop
InactiveCN103199823ASimple structureLow transistor countElectric pulse generatorLow leakageEngineering
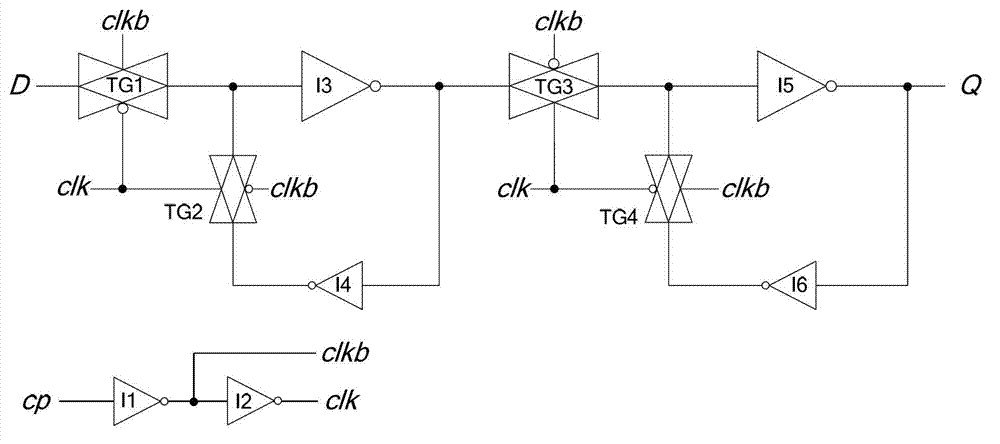
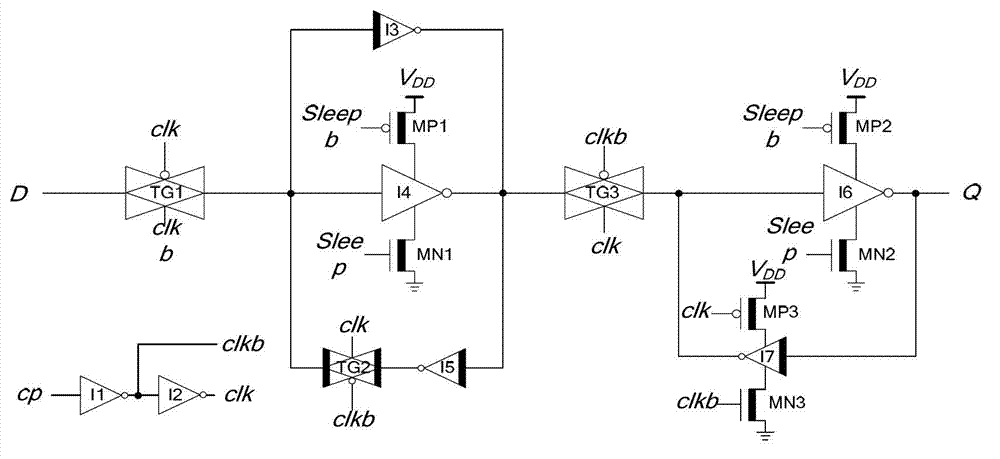
The invention discloses a high-performance low leakage power consumption master-slave type D flip-flop. The high-performance low leakage power consumption master-slave type D flip-flop is characterized by comprising a clock signal inverter circuit, a master latch circuit, a slave latch circuit, an N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (NMOS) pipe power control switch, a P-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor (PMOS) pipe power control switch and a maintaining inverter. The clock signal inverter circuit is connected with the master latch circuit, the clock signal inverter circuit is connected with the slave latch circuit, the master latch circuit is connected with the slave latch circuit, the slave latch circuit is connected with the maintaining inverter, the maintaining inverter is connected with the PMOS pipe power control switch, the clock signal inverter circuit, the master latch circuit and the slave latch circuit are all connected with the NMOS pipe power control switch, and the maintaining inverter is connected with the PMOS pipe power control switch. The high-performance low leakage power consumption master-slave type D flip-flop has the advantages of being simple in circuit structure, small in the number of transistors, simple in timing sequence switching of a normal working state and a sleep mode, good in working performance, low in dynamic power consumption and leakage power consumption, and suitable for being used as a standard cell of a digital circuit to be applicable to the design of a low power consumption integrated circuit in deep submicron complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor transistor (CMOS) process.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
State Retention using a variable retention voltage
ActiveUS20100269004A1Rapid switchBuildError preventionTransmission systemsVariable retentionZero error
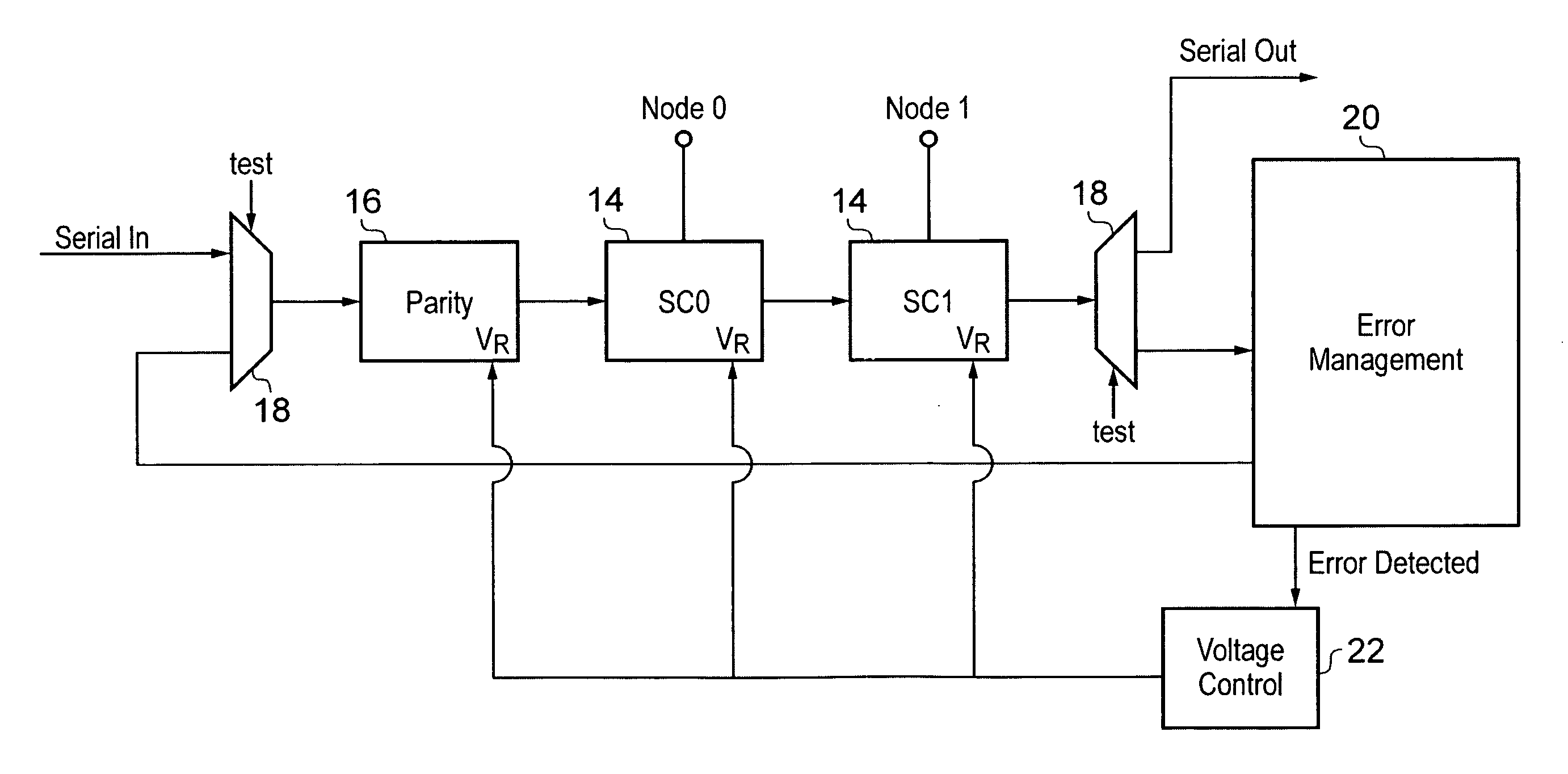
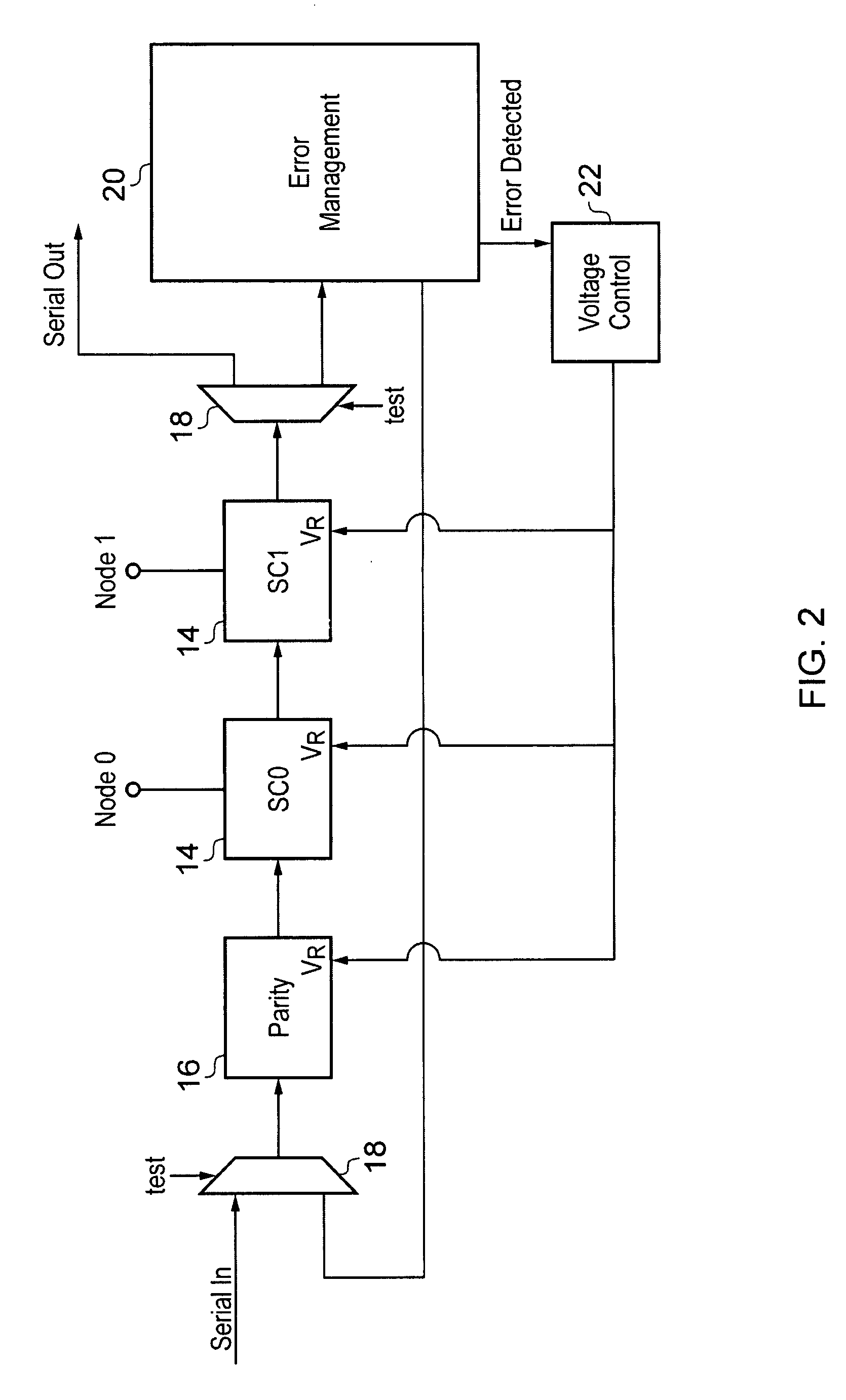
A data processing apparatus is provided with state retention circuits 14 into which state values are saved from nodes within the data processing circuitry when entering a sleep mode from an active mode. Error management circuitry 20 is coupled to the state retention circuits and detects errors in the retention of the state values. If errors are detected then an error recover response is triggered. A voltage controller 22 coupled to the error management circuitry serves to vary a supply voltage VR to the state retention circuits during the sleep mode so as to maintain a finite non-zero error rate in the retention of the state values by the state retention circuits.
Owner:ARM LTD
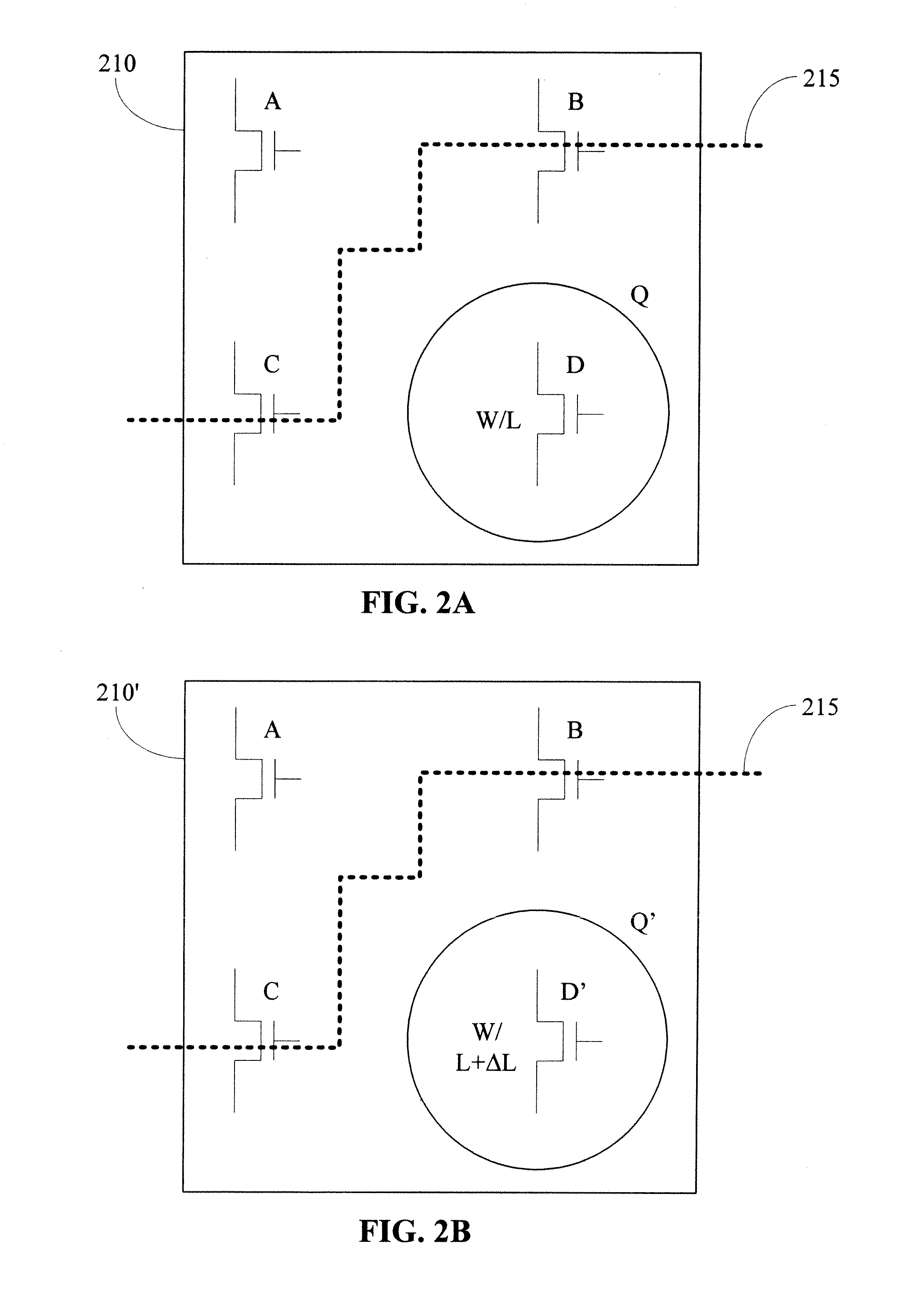
Methods for gate-length biasing using annotation data
InactiveUS20100169846A1Reduce impactImpairing time delay performance only linearlySolid-state devicesCAD circuit designEngineeringIntegrated circuit
Methods for generating a biased layout for making an integrated circuit are disclosed. One such method includes obtaining a nominal layout defined by one or more cells, where each cell has one or more transistor gate features with a nominal gate length. Then, obtaining an annotated layout. The annotated layout contains information describing gate-length biasing of one or more of the transistor gate features in one or more cells of the nominal layout. A biased layout is produced by modifying the nominal layout using the information from the annotated layout. The biasing modifies a gate length of those transistor gate features identified by the information of the annotated layout.
Owner:RPX CORP
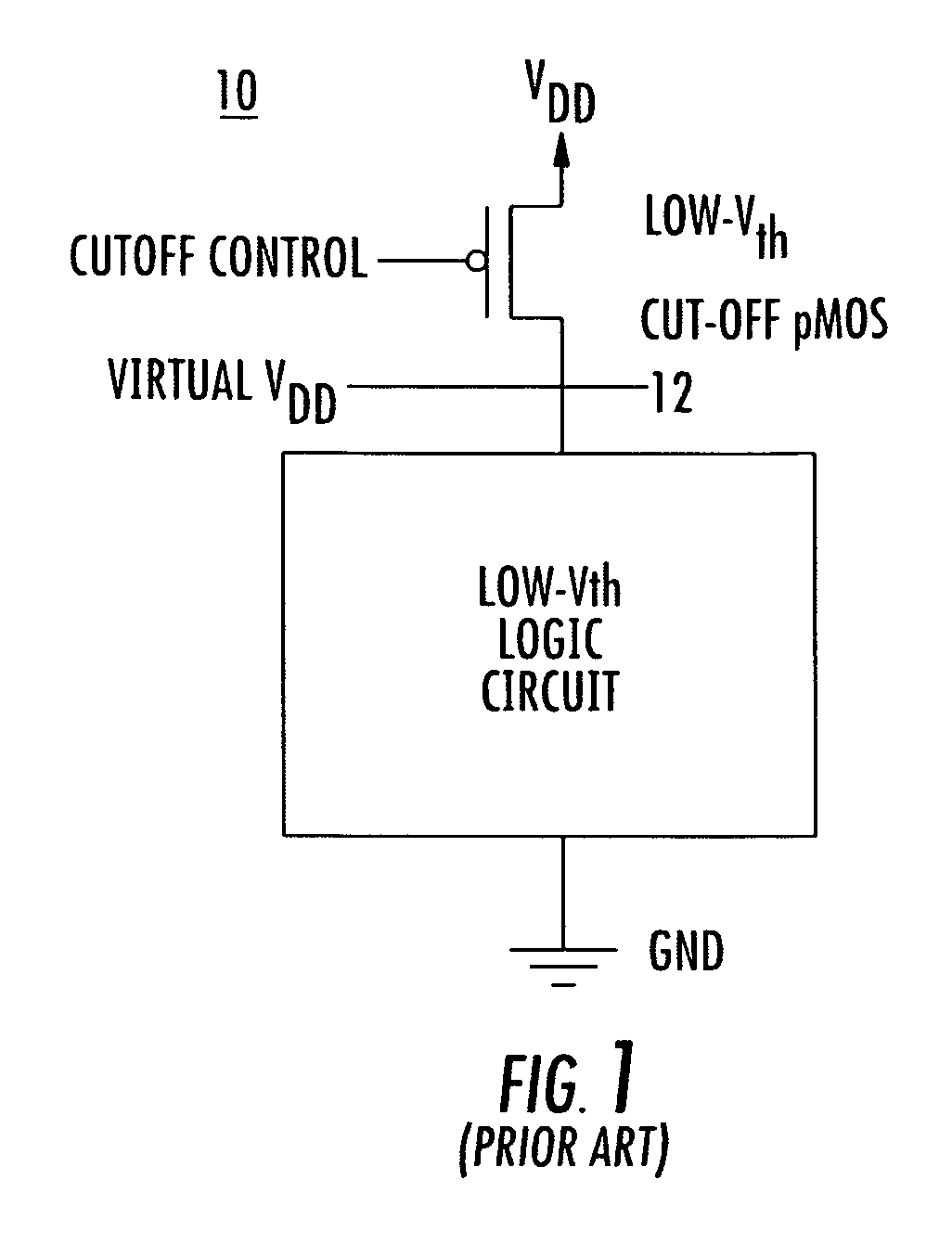
A Method and Apparatus for Reducing Leakage in Integrated Circuits
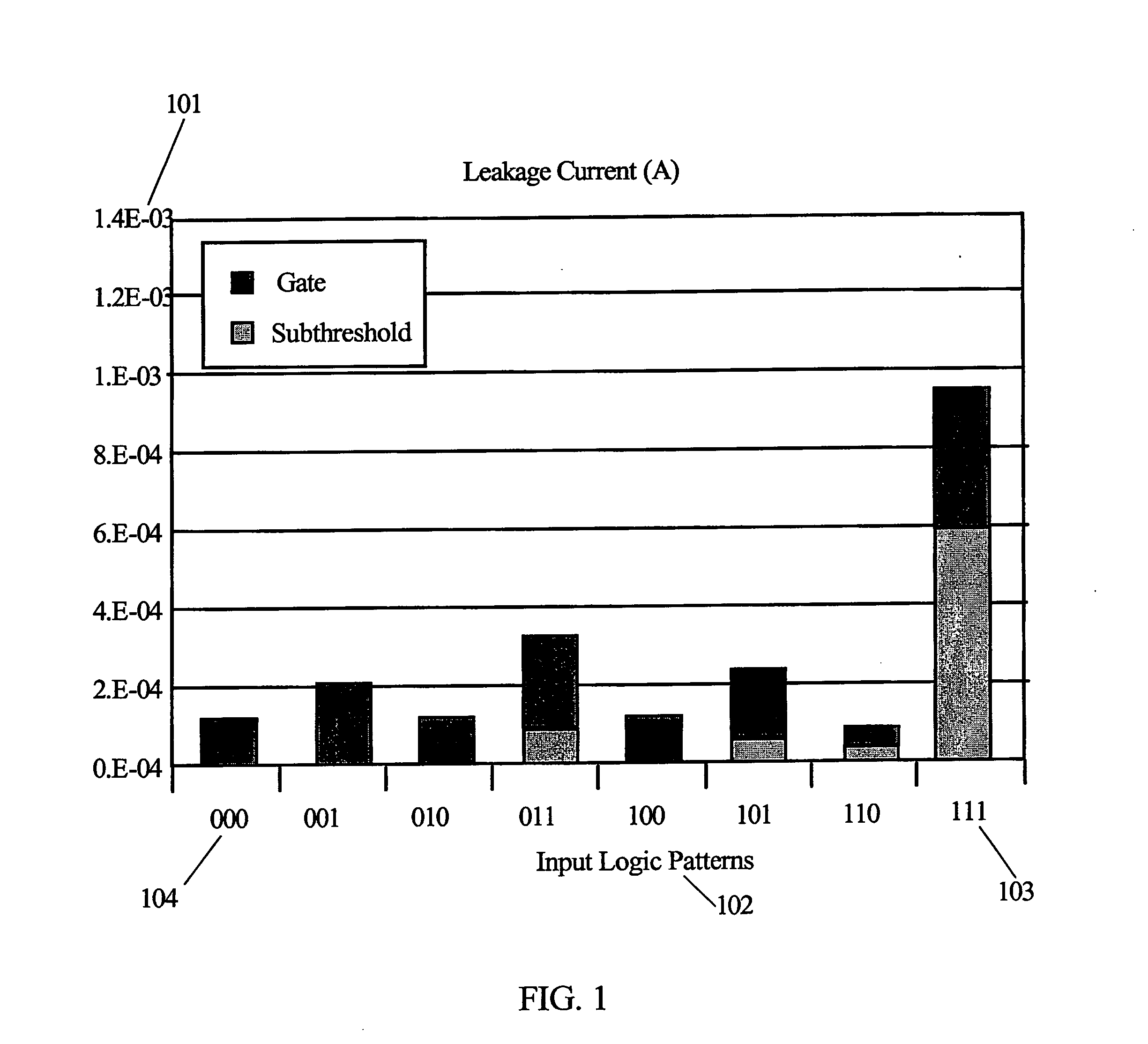
ActiveUS20070007996A1Not add additional fabrication complexityMinimal impactPower reduction in field effect transistorsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionCMOSTransistor sizing
An efficient design methodology in accordance with the present invention is described for reducing the leakage power in CMOS circuits. The method and apparatus in accordance with the present invention yields better leakage reduction as the threshold voltage decreases and hence aids in further reduction of supply voltage and minimization of transistor sizes. Unlike other leakage control techniques, the technique of the present invention does not need any control circuitry to monitor the states of the circuit. Hence, avoiding the sacrifice of obtained leakage power reduction in the form of dynamic power consumed by the additional circuitry to control the overall circuit states.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Communication semiconductor integrated circuit device and wireless communication system
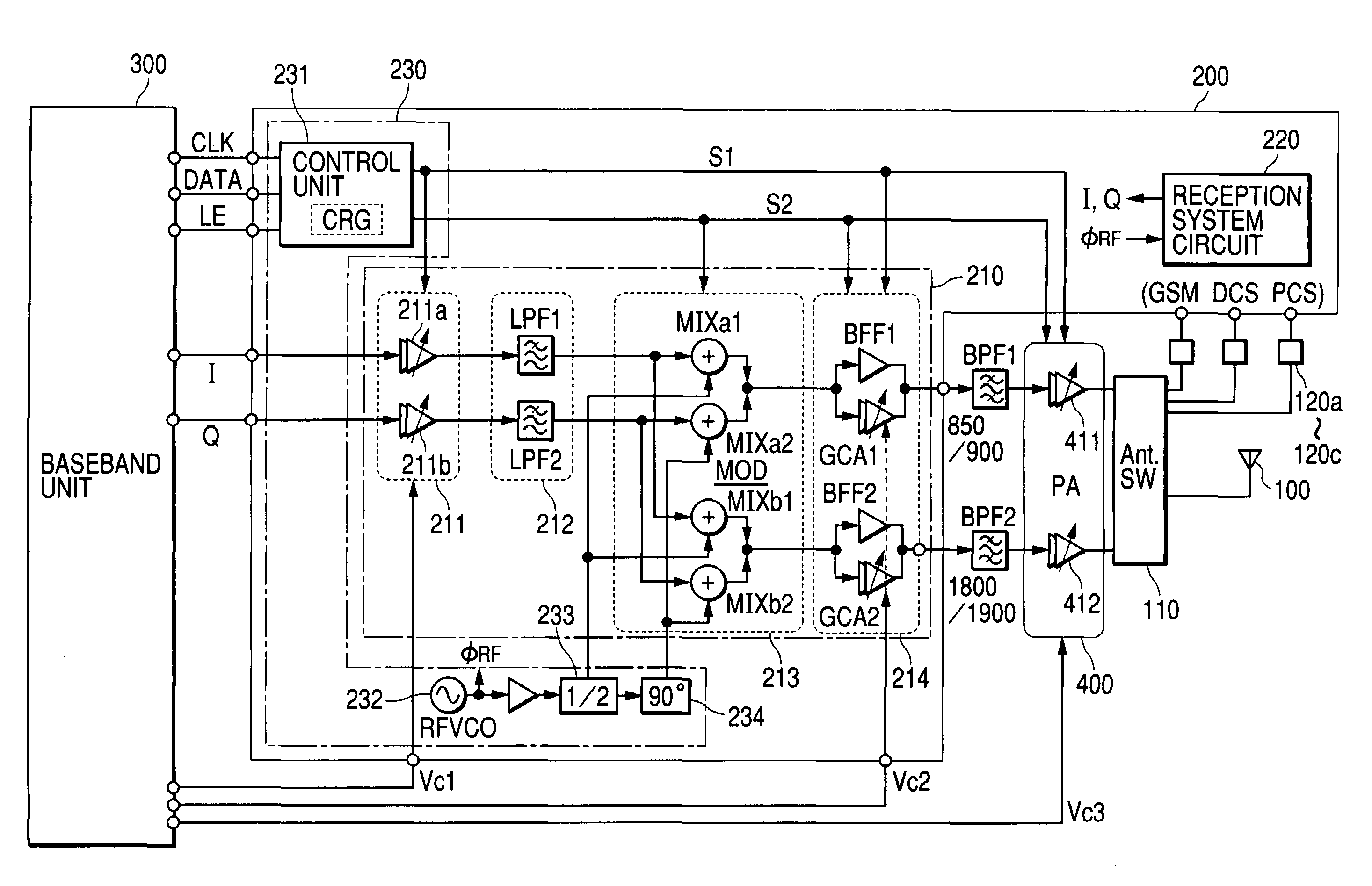
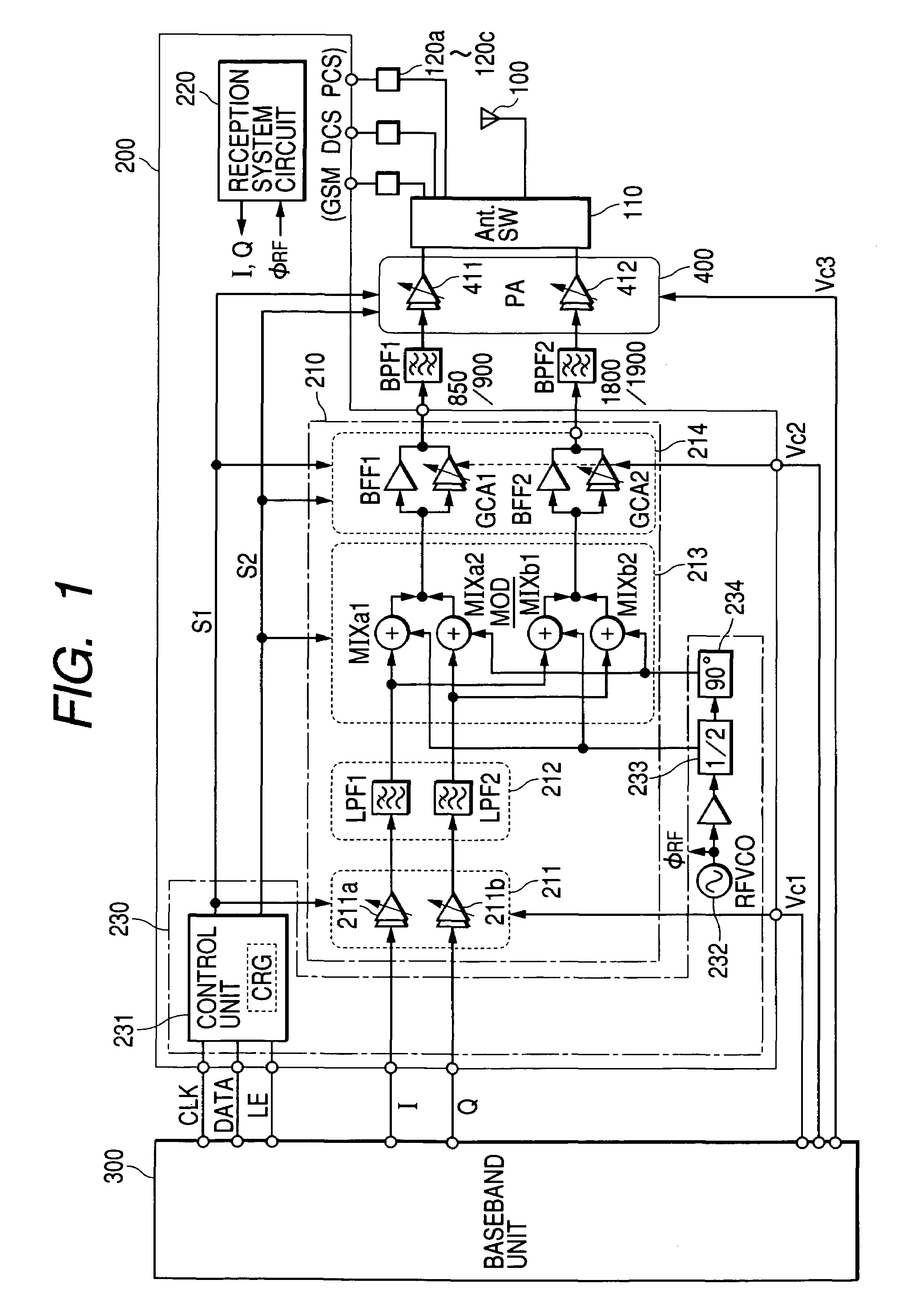
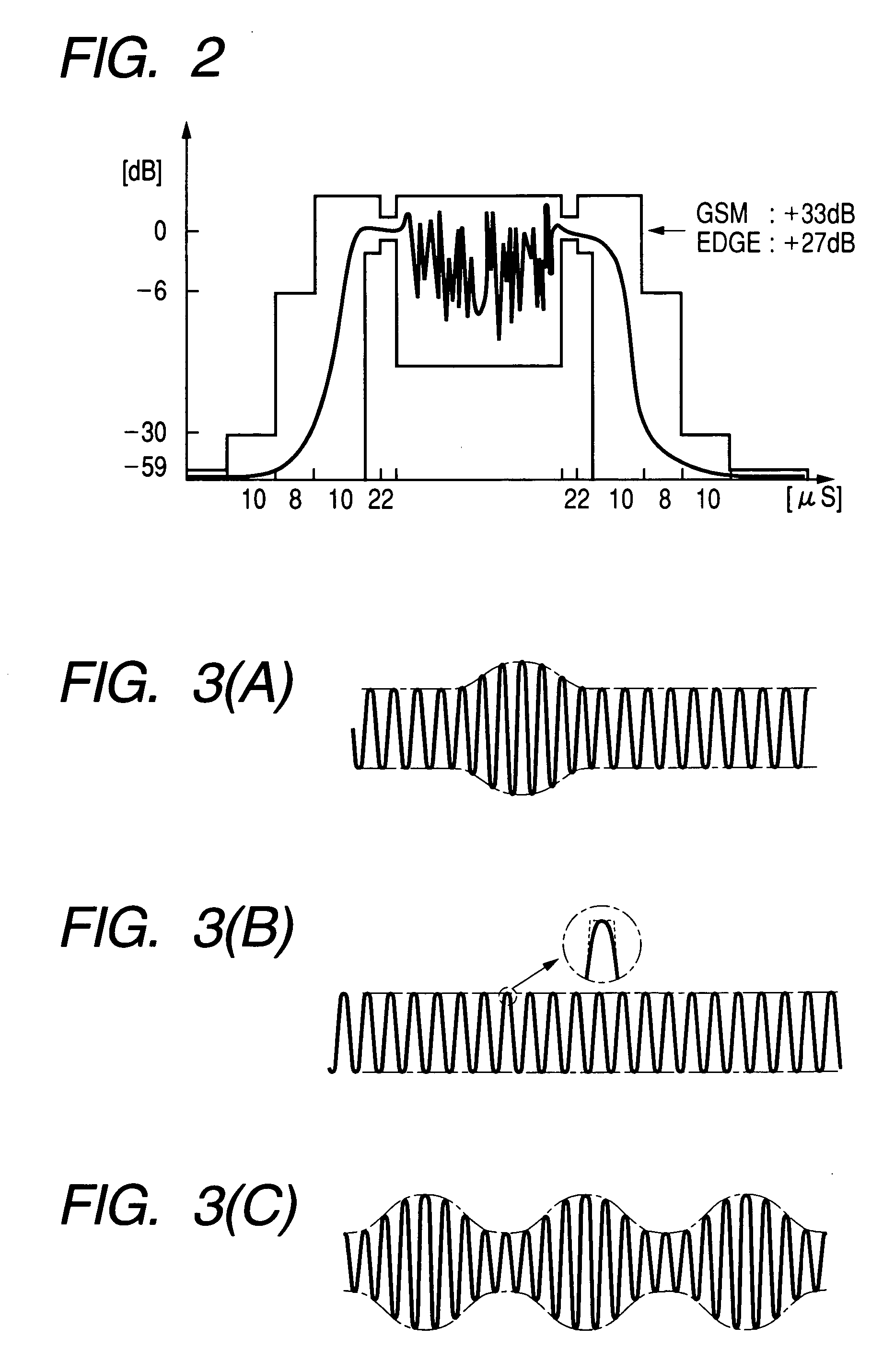
InactiveUS7239855B2Reduce chip sizeAccuracy of transmission being degradedResonant long antennasCode division multiplexCommunications systemLow-pass filter
A communication semiconductor integrated circuit device is capable of transmission in two or more different modulation modes and outputting transmission signals with less distortion. The communication semiconductor integrated circuit device comprises a gain variable amplification circuit which amplifies I-signals and Q-signals; and a mixer circuit which synthesizes the amplified I-signals and Q-signals and local oscillation signals to carry out modulation and frequency conversion. The communication semiconductor integrated circuit device is capable of transmission in two or more different modulation methods, for example, in GSM mode and EDGE mode. A low-pass filter of second or higher order is placed between the gain variable amplification circuit and the mixer circuit.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Protective circuit, battery charger, and power storage device
ActiveUS20130257354A1Reduce power consumptionTotal current dropElectric powerCharging/discharging current/voltage regulationElectricityPower controller
A low-power protective circuit includes a detection unit that intermittently detects a voltage across a secondary battery; a battery management unit that includes a buffer memory device and a processor and determines, based on a value of the voltage, whether the secondary battery needs to be charged; a switch circuit that establishes or breaks electrical continuity between a host system and the secondary battery; a switch control unit that turns on or off the switch circuit in accordance with the judgment made by the battery management unit; a switch that controls supply of power supply voltage from the secondary battery to the battery management unit; and a power controller that intermittently stops supply of the power supply voltage to the battery management unit by turning off the switch.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Adaptive data-retention-voltage regulating system for SRAM
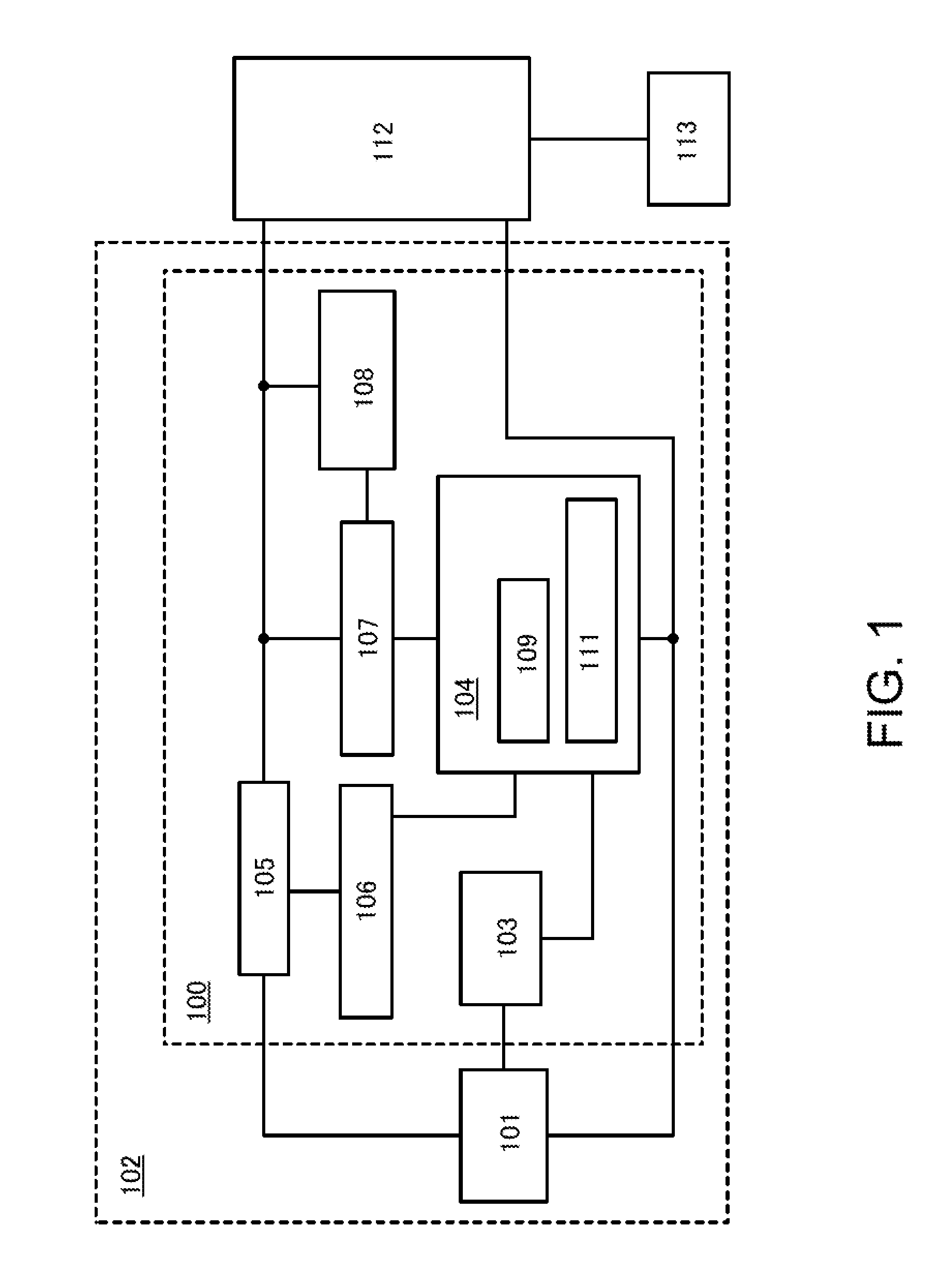
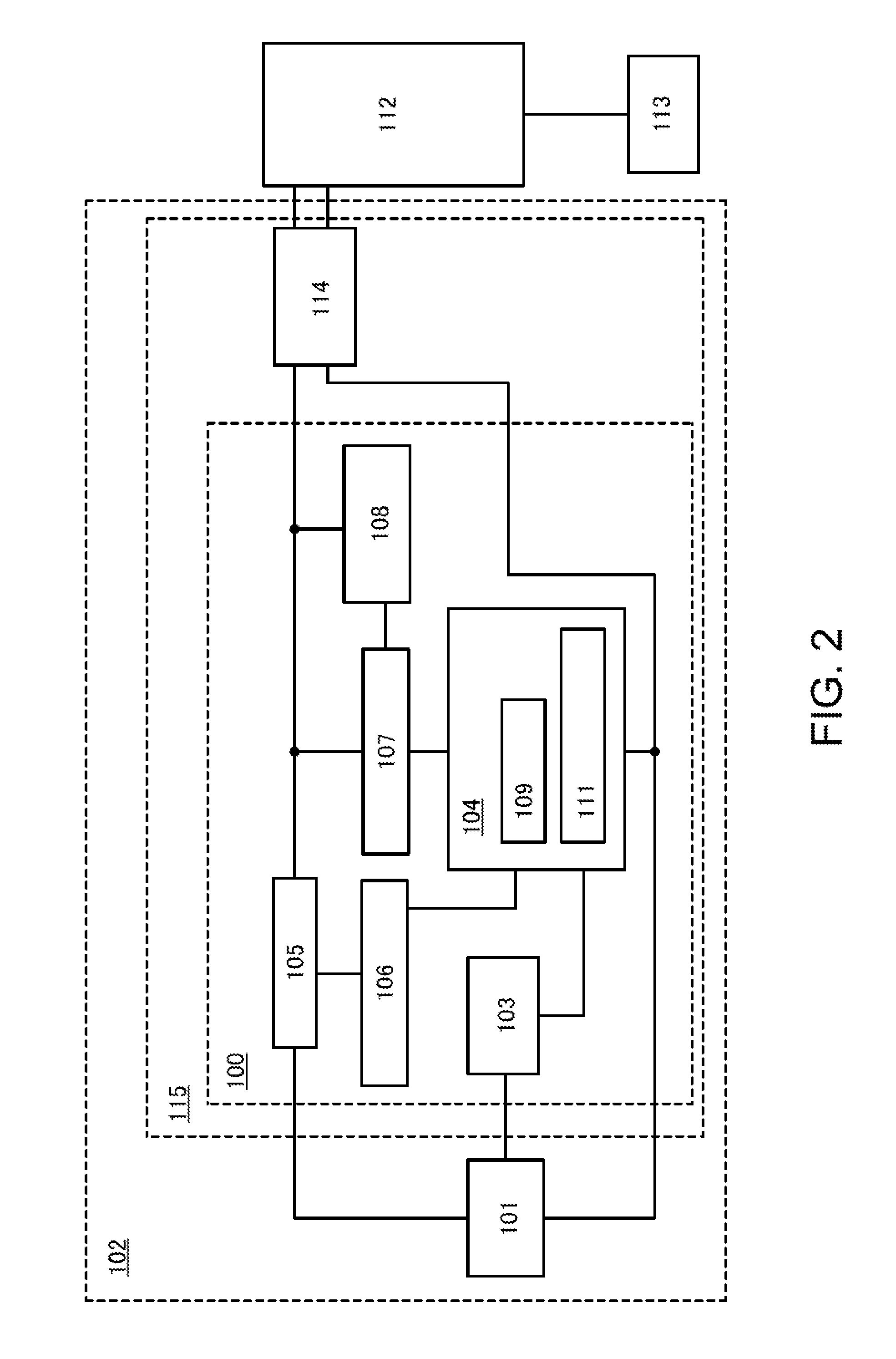
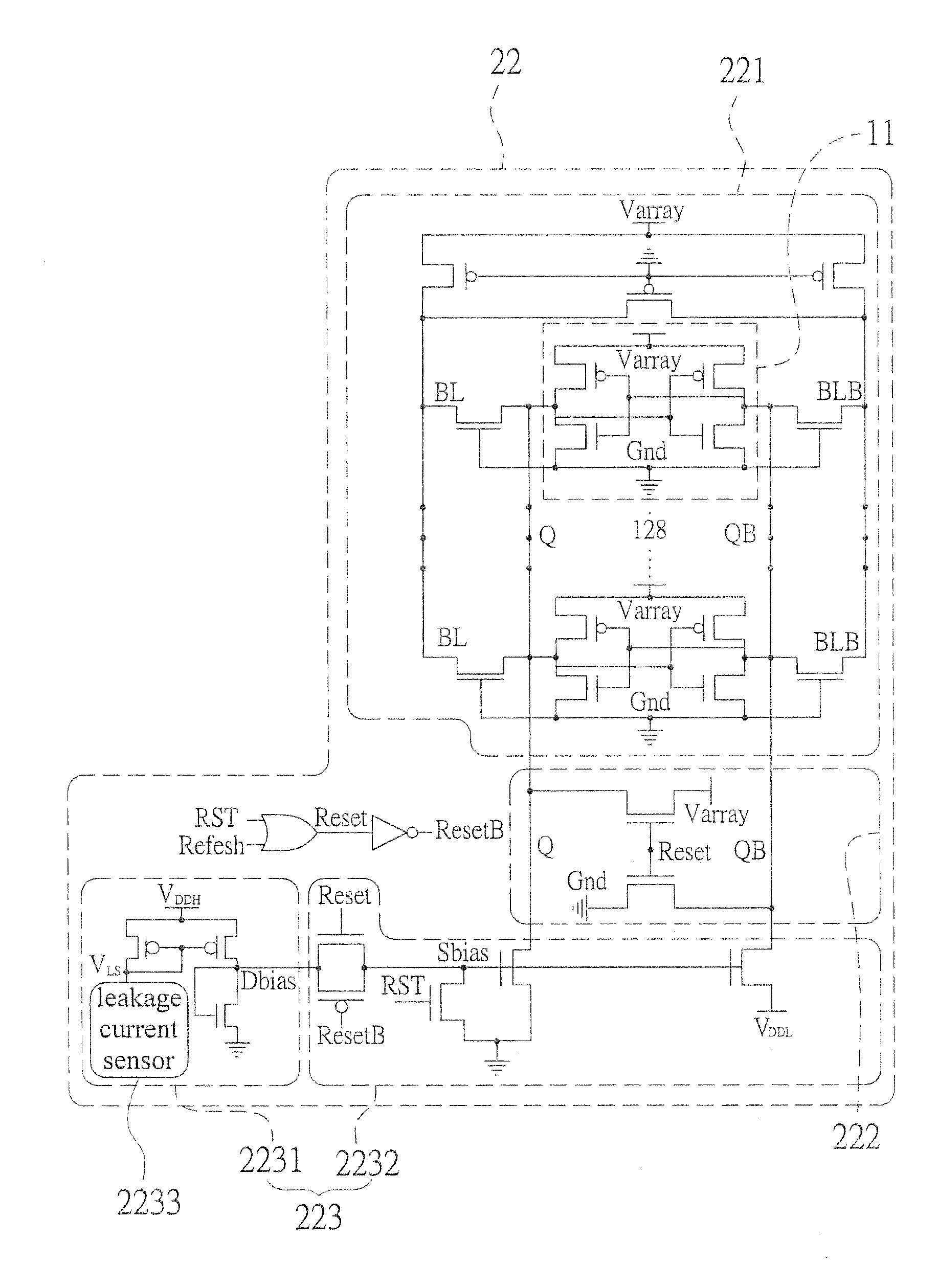
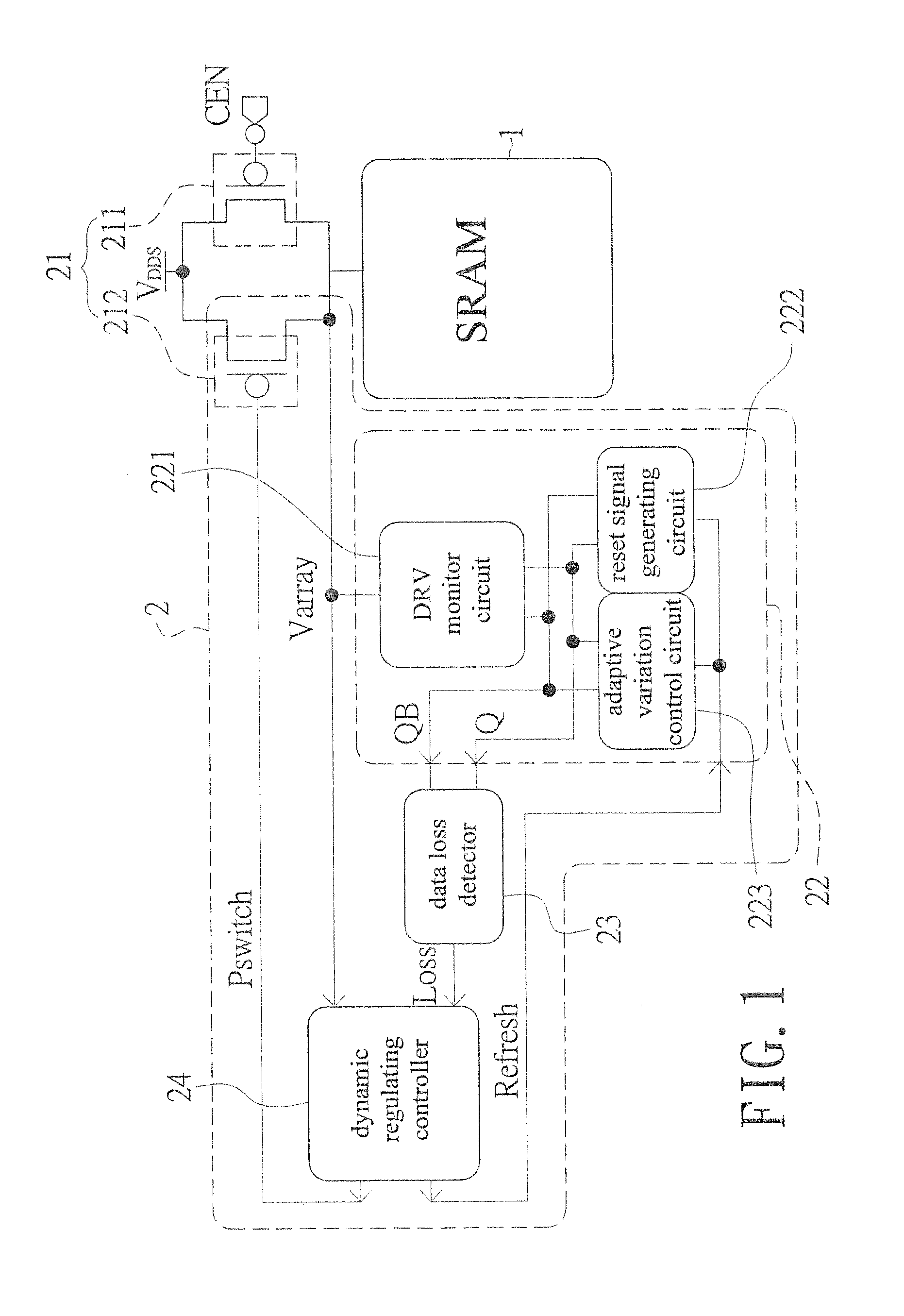
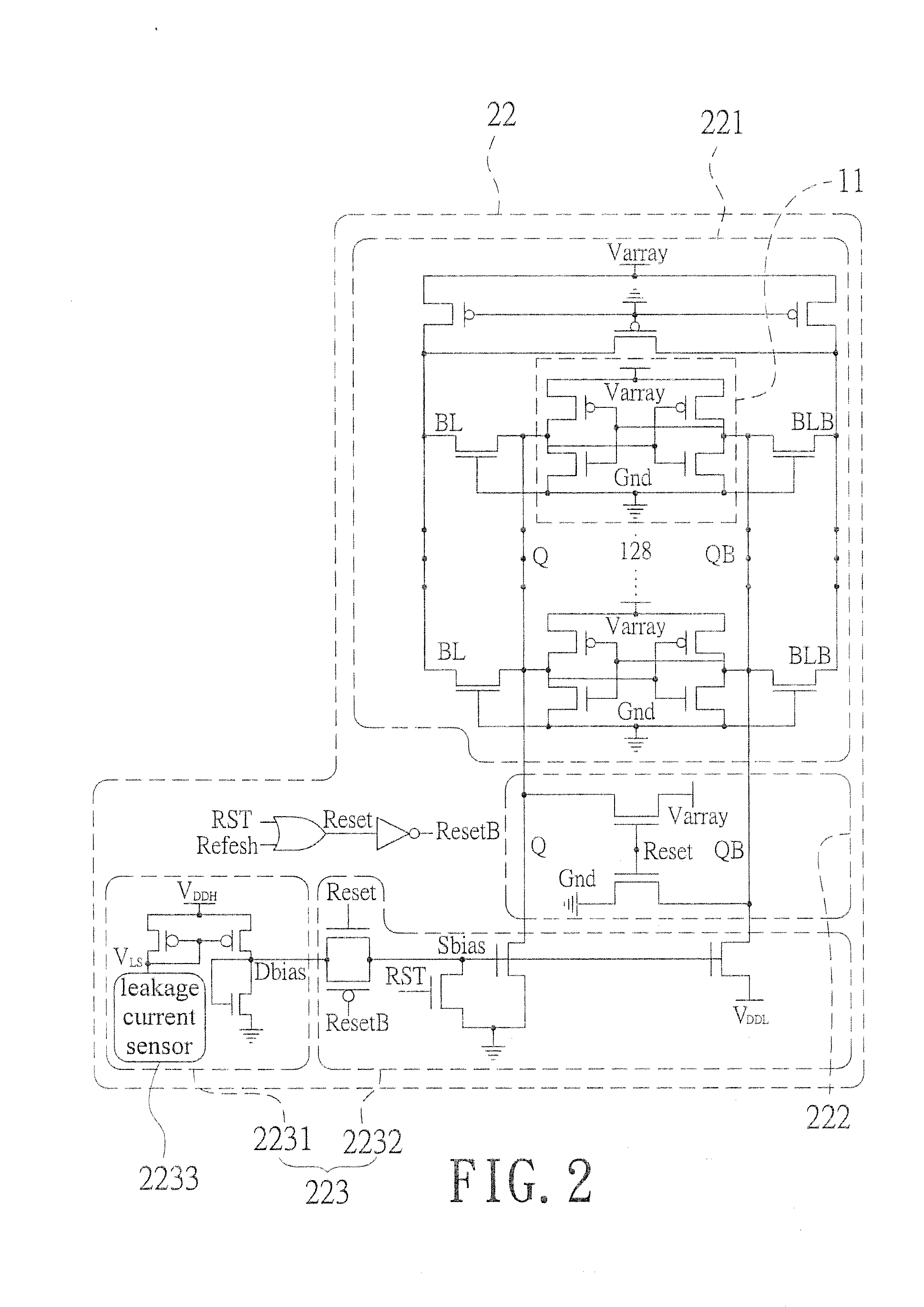
InactiveUS20150092477A1Reduce leakage powerReduce power supply voltageDigital storagePower supply for data processingData retention voltageStatic random-access memory
An adaptive data-retention-voltage regulating system for static random-access memory (SRAMs) is revealed. The system includes a power supply unit, a data-retention-voltage (DRV) monitor cell for monitoring static noise margin (SNM) of SRAM, a data loss detector for generating a data loss signal, and a dynamic regulating controller that receives the data loss signal for generating a refresh signal and a switch signal. The DVR monitor cell consists of a DRV monitor circuit mounted with a plurality of memory cells, a reset signal generating circuit for resetting the DRV monitor circuit, and an adaptive variation control circuit that generates noise bias according to leakage current to adjust reaction speed of the DRV monitor circuit correspondingly.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
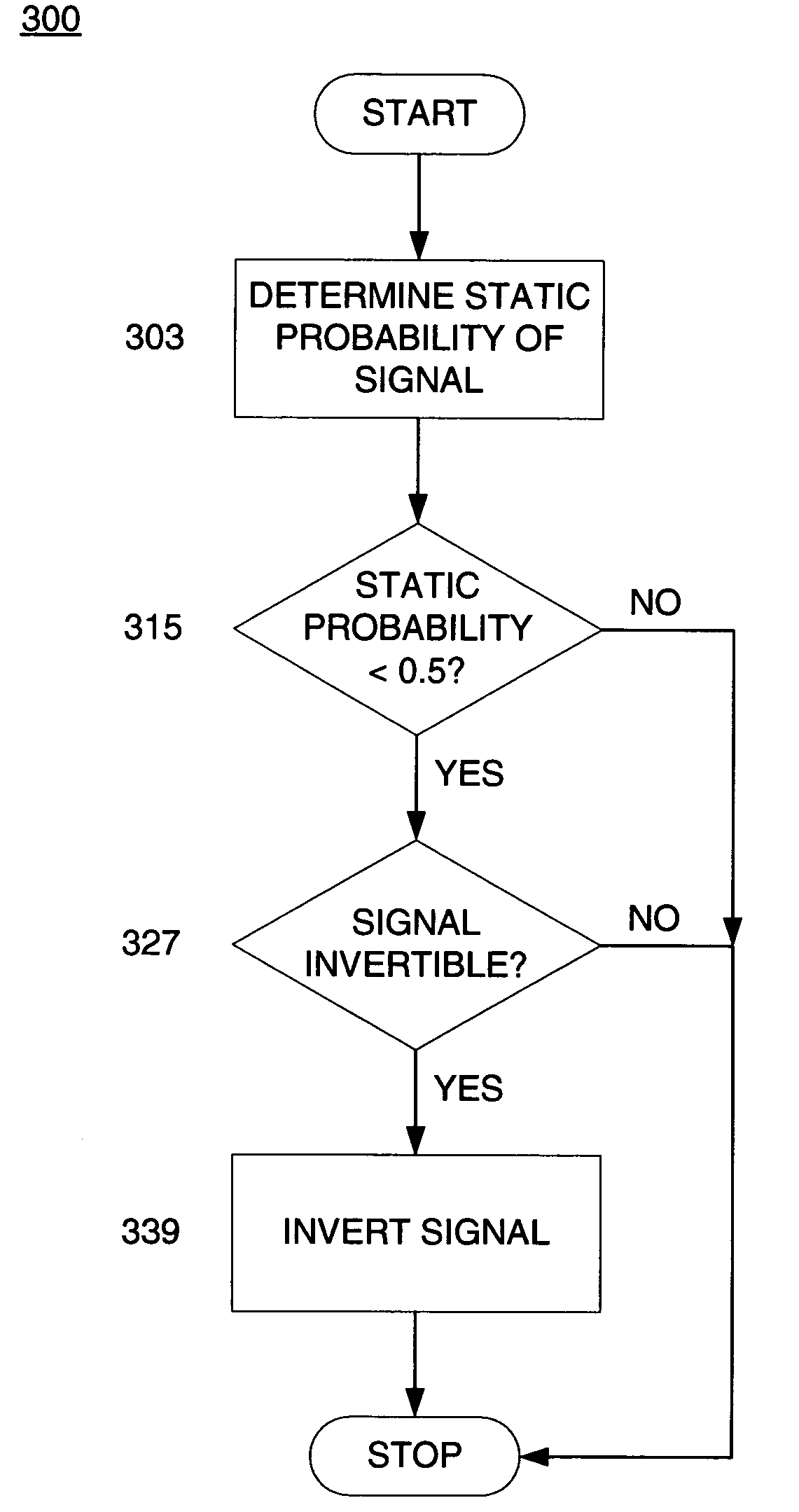
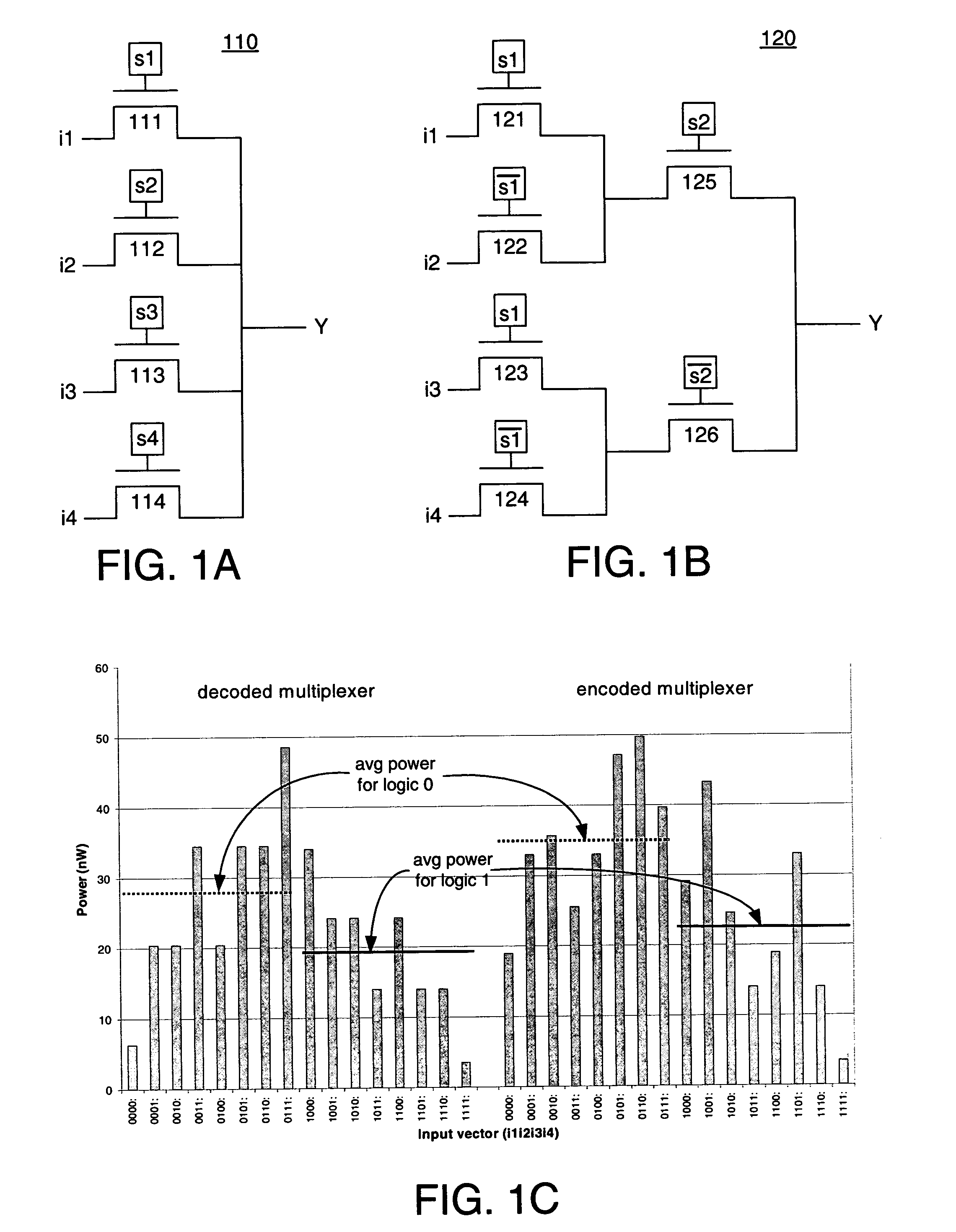
Leakage power optimization for integrated circuits
ActiveUS6993737B1Reduce leakage powerArea penaltyCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationProgrammable logic deviceDigital signal
A method for reducing leakage power in a system comprises determining the static probability for a signal in the system. If the static probability of the signal is in a high power range, then the signal is modified such that the static probability of the modified signal is in a low power range, and such that functionality of the system is not affected. In some embodiments, where the signal is a digital signal, modifying the signal comprises inverting the signal. In some embodiments, where the system comprises a programmable logic device, modifying the signal has no area or performance penalty.
Owner:XILINX INC
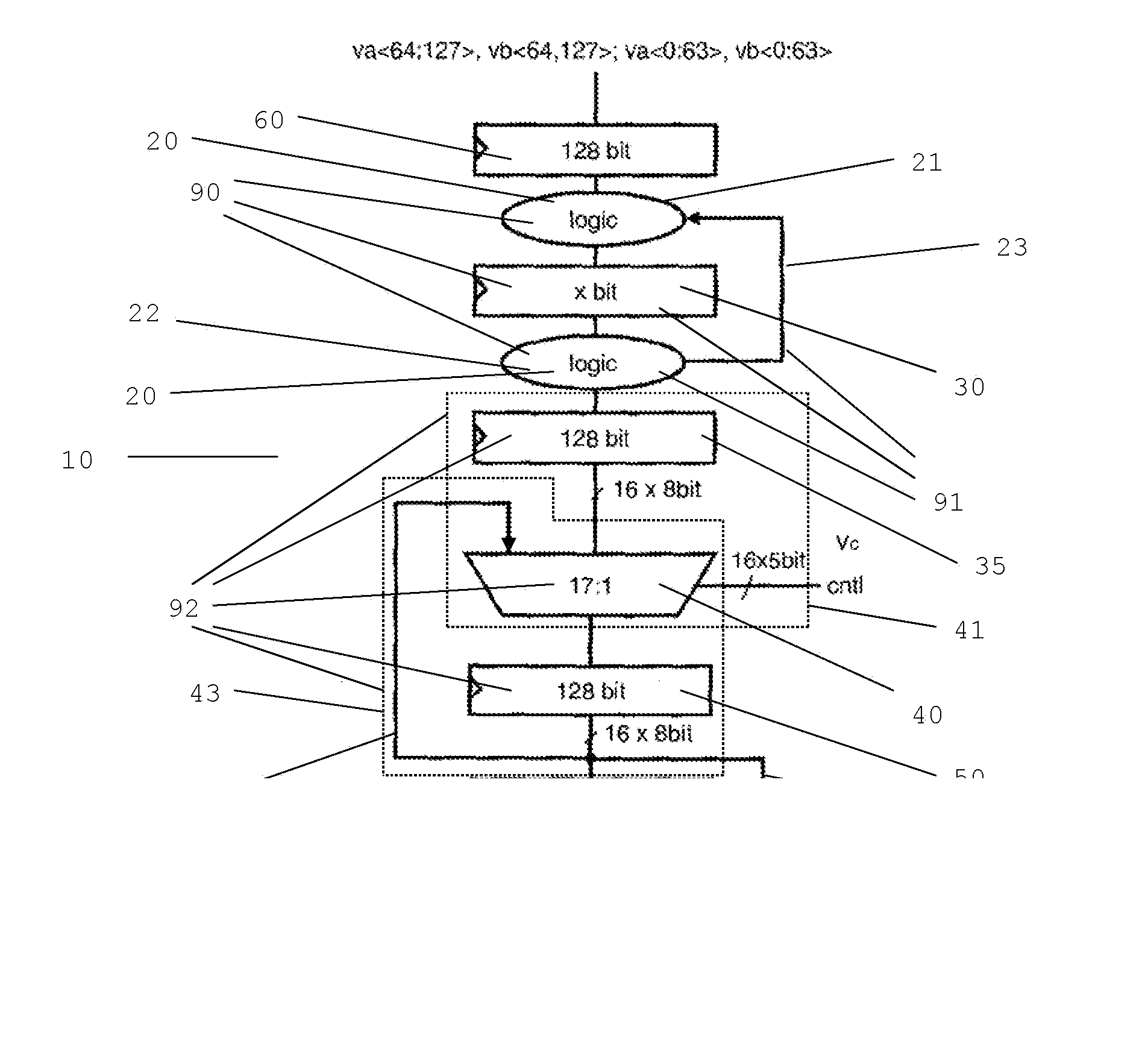
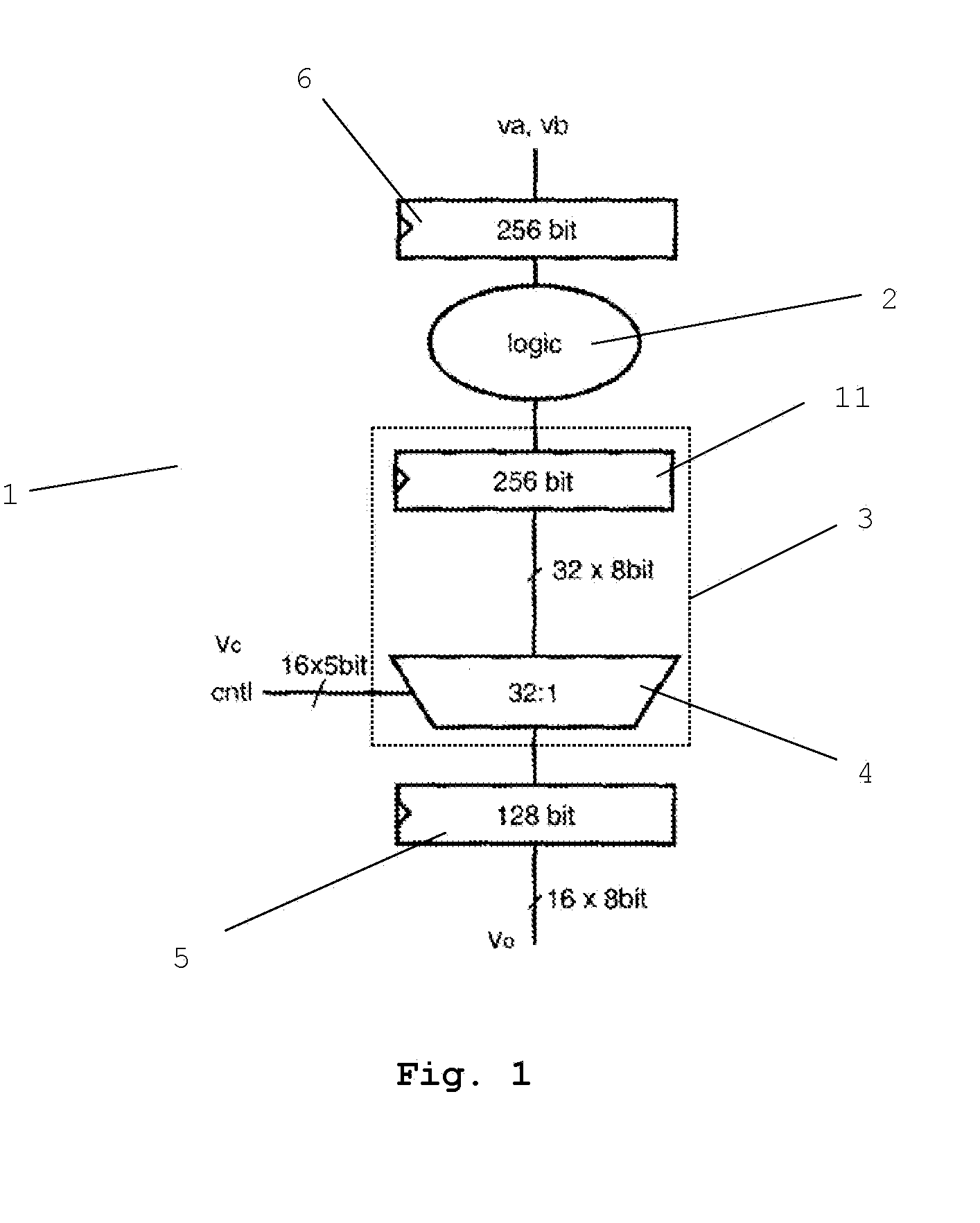
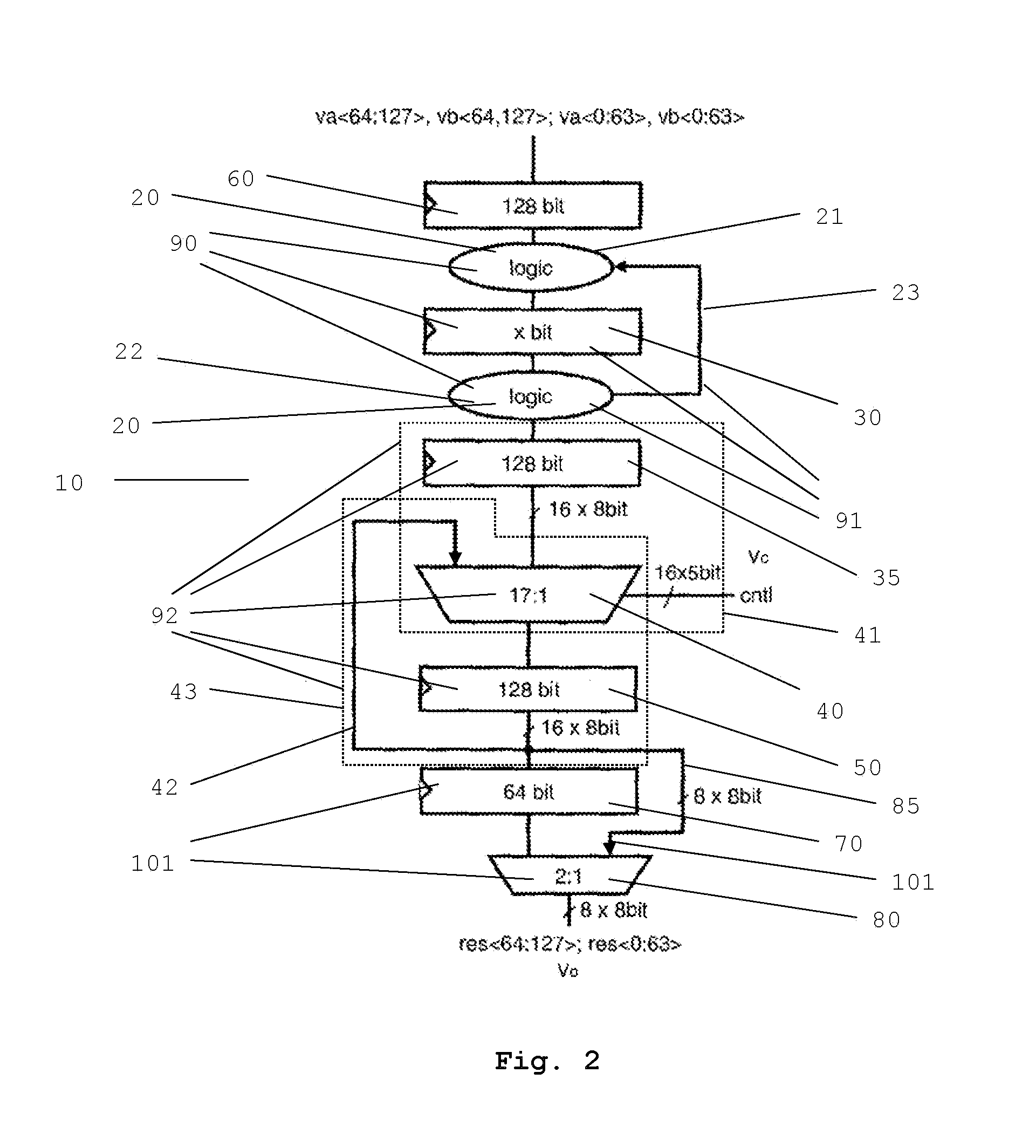
Permute Unit and Method to Operate a Permute Unit
InactiveUS20080130871A1Low costReduce complexityEnergy efficient ICTDigital data processing detailsCrossbar switchEngineering
Owner:IBM CORP
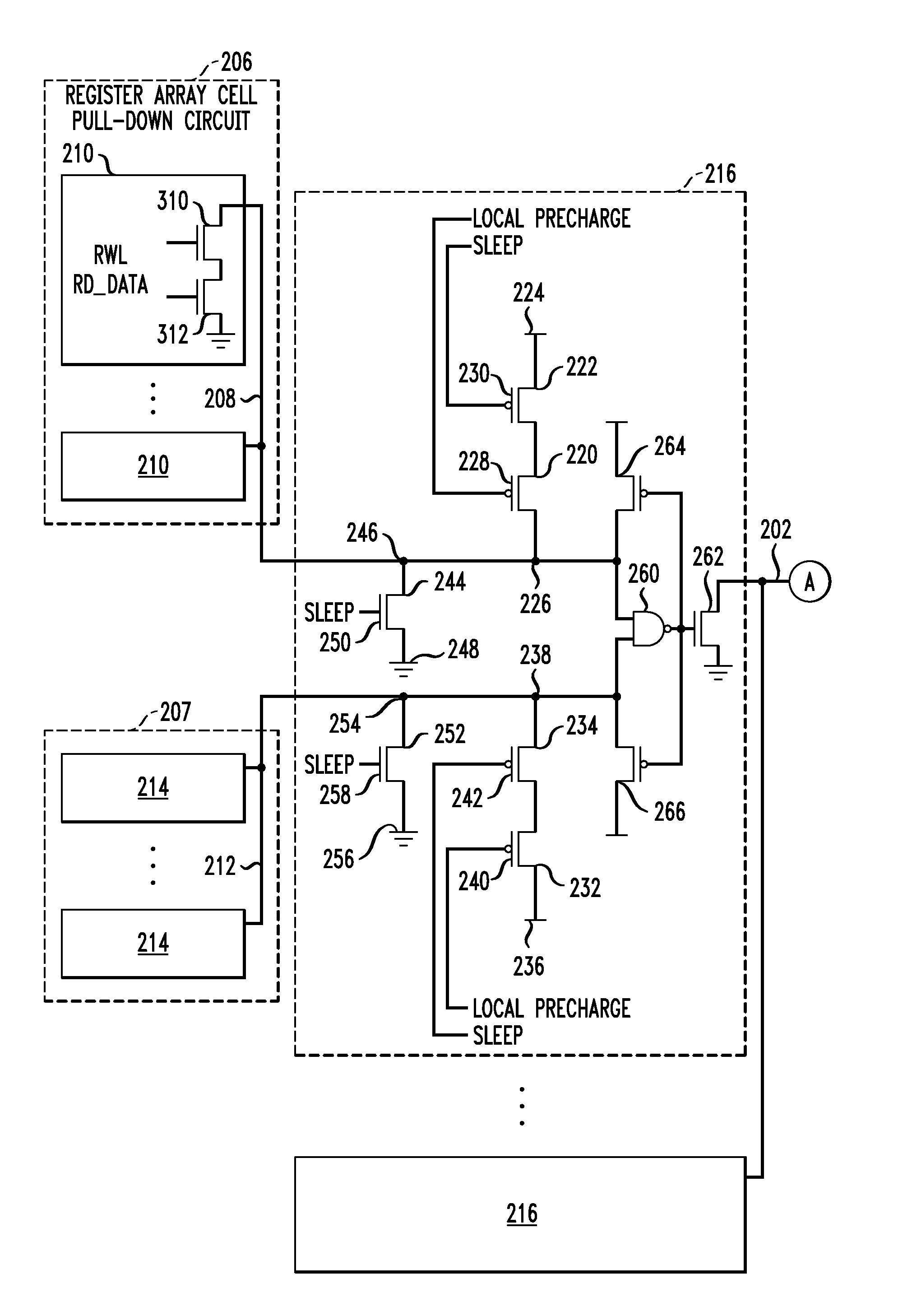
Memory circuits with reduced leakage power and design structures for same
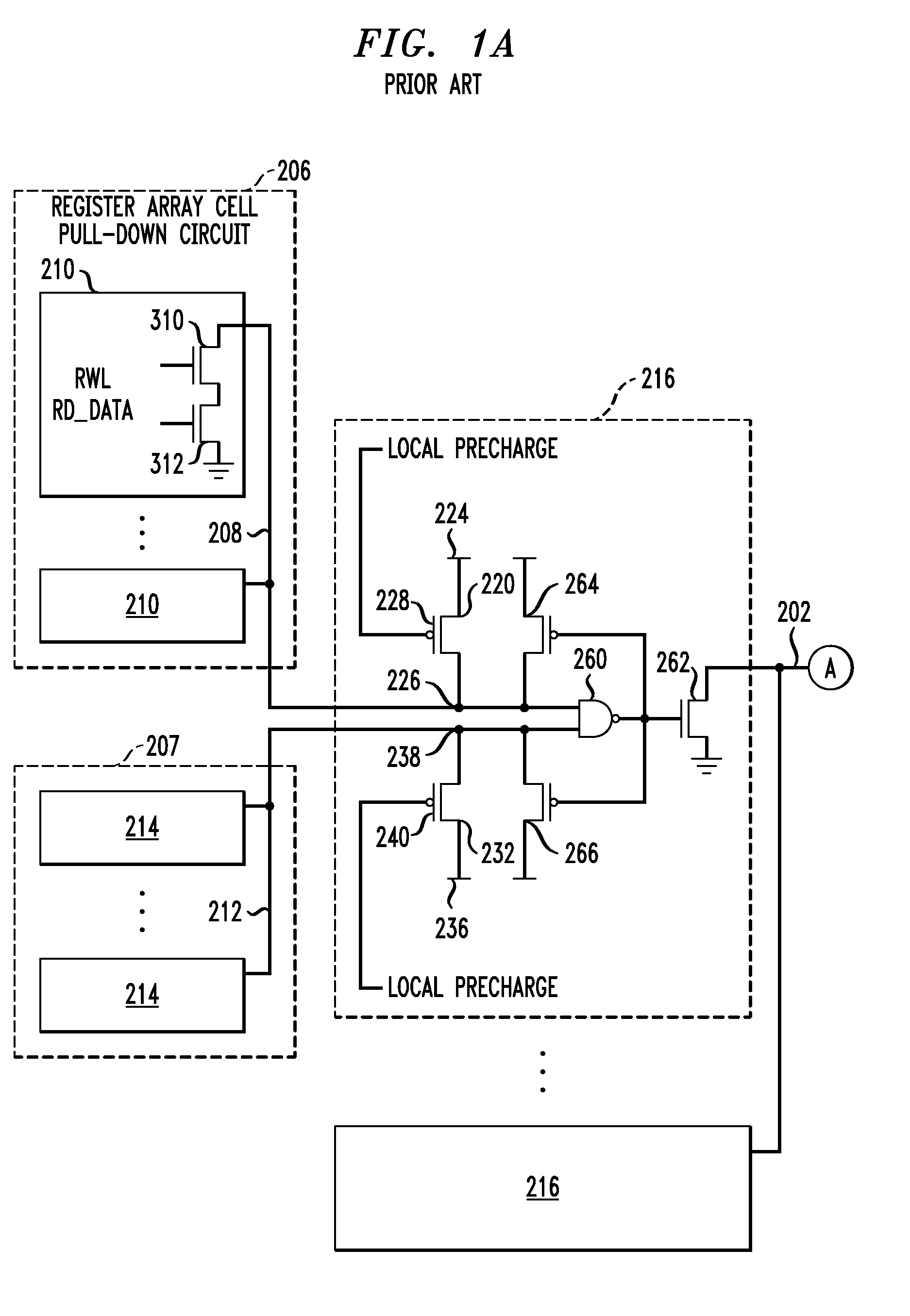
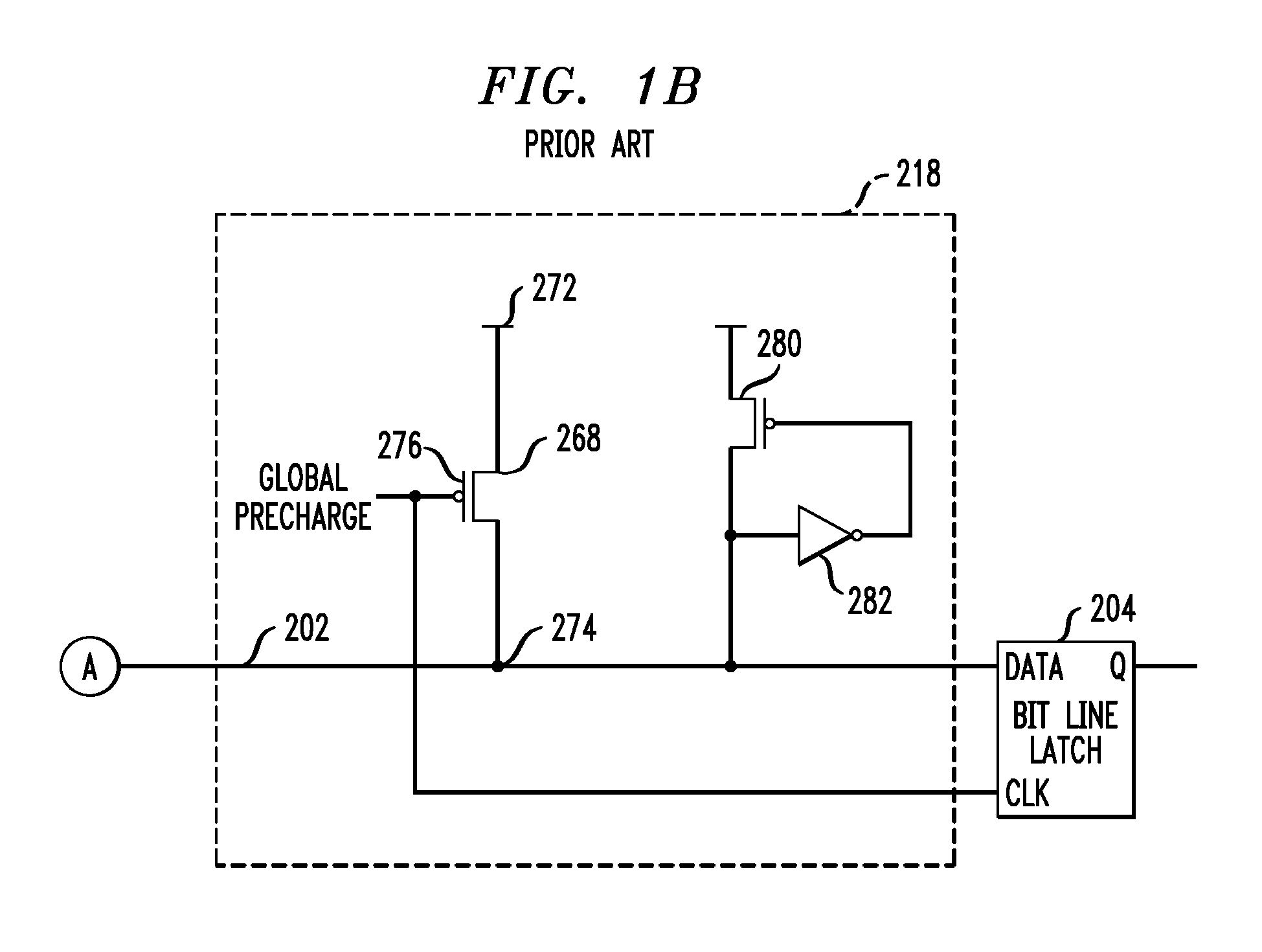
A memory circuit includes a global read bit line, a global read bit line latch, and a plurality of sub-arrays, each of which includes first and second local read bit lines, first and second local write bit lines, and first and second pluralities of memory cells interconnected, respectively, with the first and second local read bit lines and the first and second local write bit lines. The local read bit lines are decoupled from the local write bit lines. A local multiplexing block is interconnected with the first and second local read bit lines and is configured to ground the first and second local read bit lines upon assertion of a SLEEP signal, and to selectively interconnect the local read bit lines to the global read bit line. A global multiplexing block is interconnected with the global read bit line and is configured to maintain the global read bit line in a substantially discharged state upon assertion of the SLEEP signal and to interconnect the global read bit line to the global read bit line latch. Also included are design structures for circuits of the kind described.
Owner:TWITTER INC
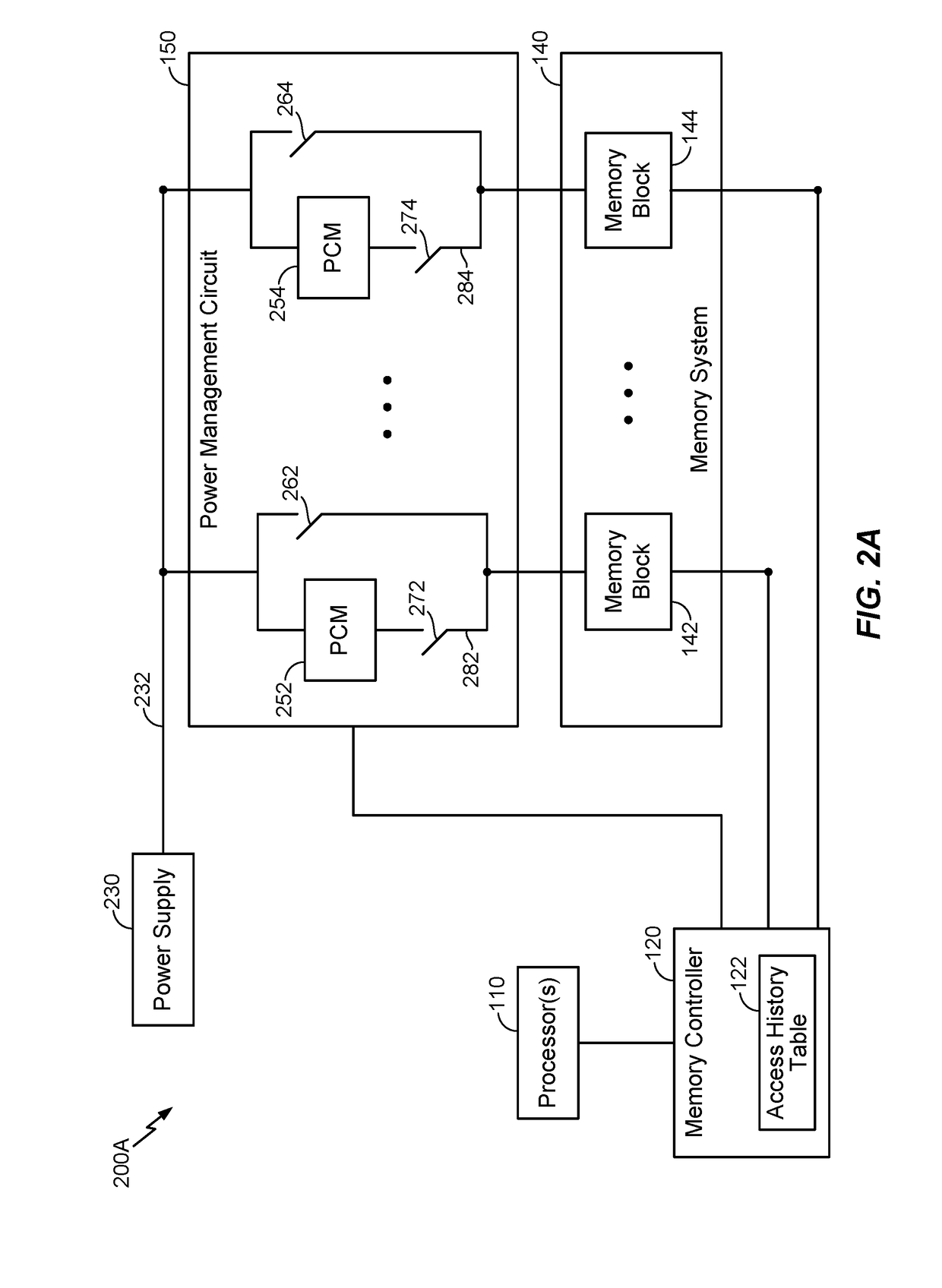
Ultra-low-power design memory power reduction scheme
ActiveUS20180067539A1Reduce leakage powerIncreased power consumptionDigital storagePower supply for data processingEngineeringLeakage power
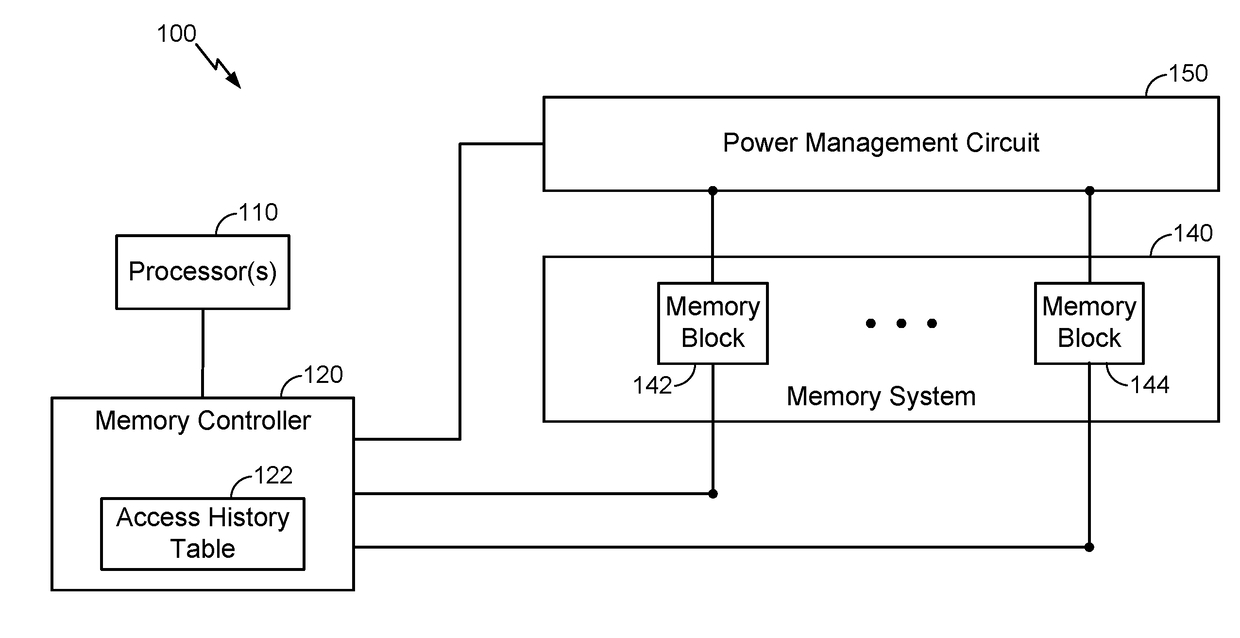
The disclosure generally relates to a memory power reduction scheme that can flexibly transition memory blocks among different power states to reduce power consumption (especially with respect to leakage power) in a manner that balances tradeoffs between reduced power consumption and performance impacts. For example, according to various aspects, individual memory blocks may be associated with an access-dependent age, whereby memory blocks that are not accessed may be periodically aged. As such, in response to the age associated with a memory block crossing an appropriate threshold, the memory block may be transitioned to a power state that generally consumes less leakage power and has a larger performance penalty. Furthermore, one or more performance-related criteria may be defined with certain memory blocks to prevent and / or automatically trigger a transition to another power state.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
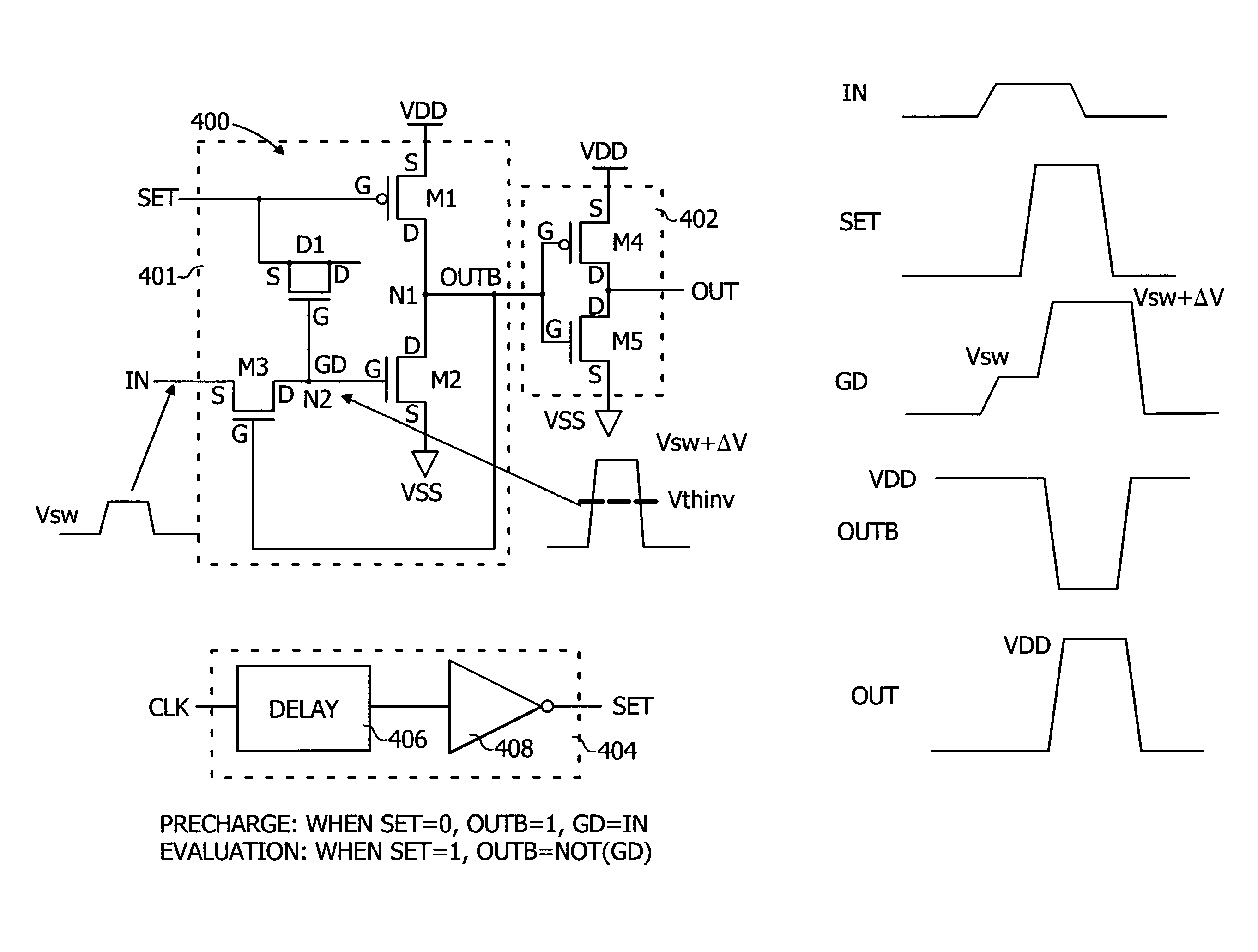
Low-swing signaling scheme for data communication
ActiveUS8410816B1High sensitivityReduce receiver leakage powerLogic circuit coupling/interface arrangementsCapacitanceTelecommunications
A low-swing receiver includes a sense amplifier including a first transistor having a source connected with a first voltage supply and a gate for receiving a control signal, and a second transistor having a source connected with a second voltage supply, a drain connected to a drain of the first transistor, and a gate coupled to a second control signal via a capacitive element. A switching circuit is operative to selectively couple an input signal supplied to the sense amplifier with the gate of the second transistor as a function of a signal generated at an output of the sense amplifier. The sense amplifier is operative in a first mode to store charge in the capacitive element, and is operative in a second mode to impart a voltage on the gate of the second transistor which is indicative of the charge stored in the capacitive element.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
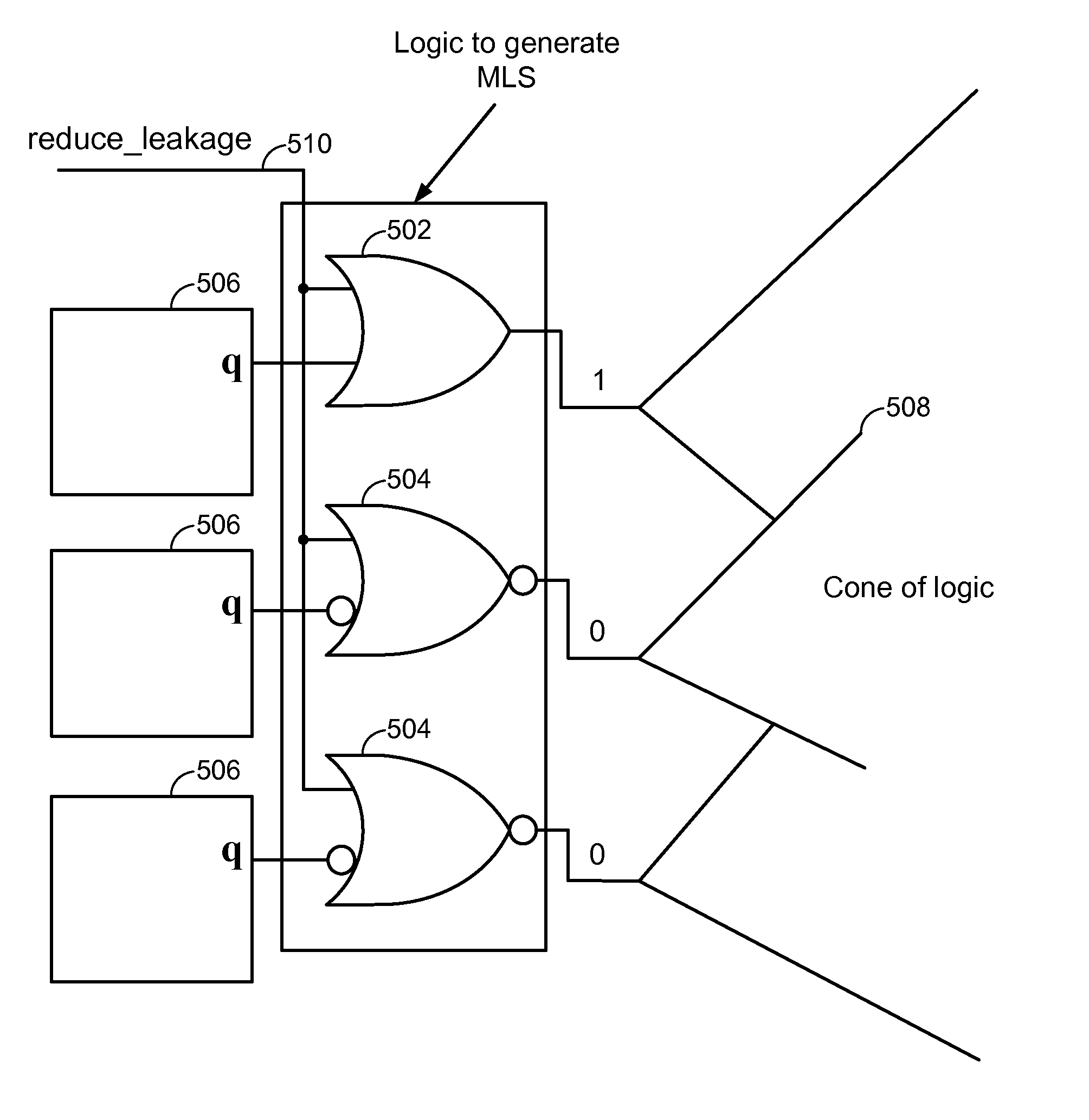
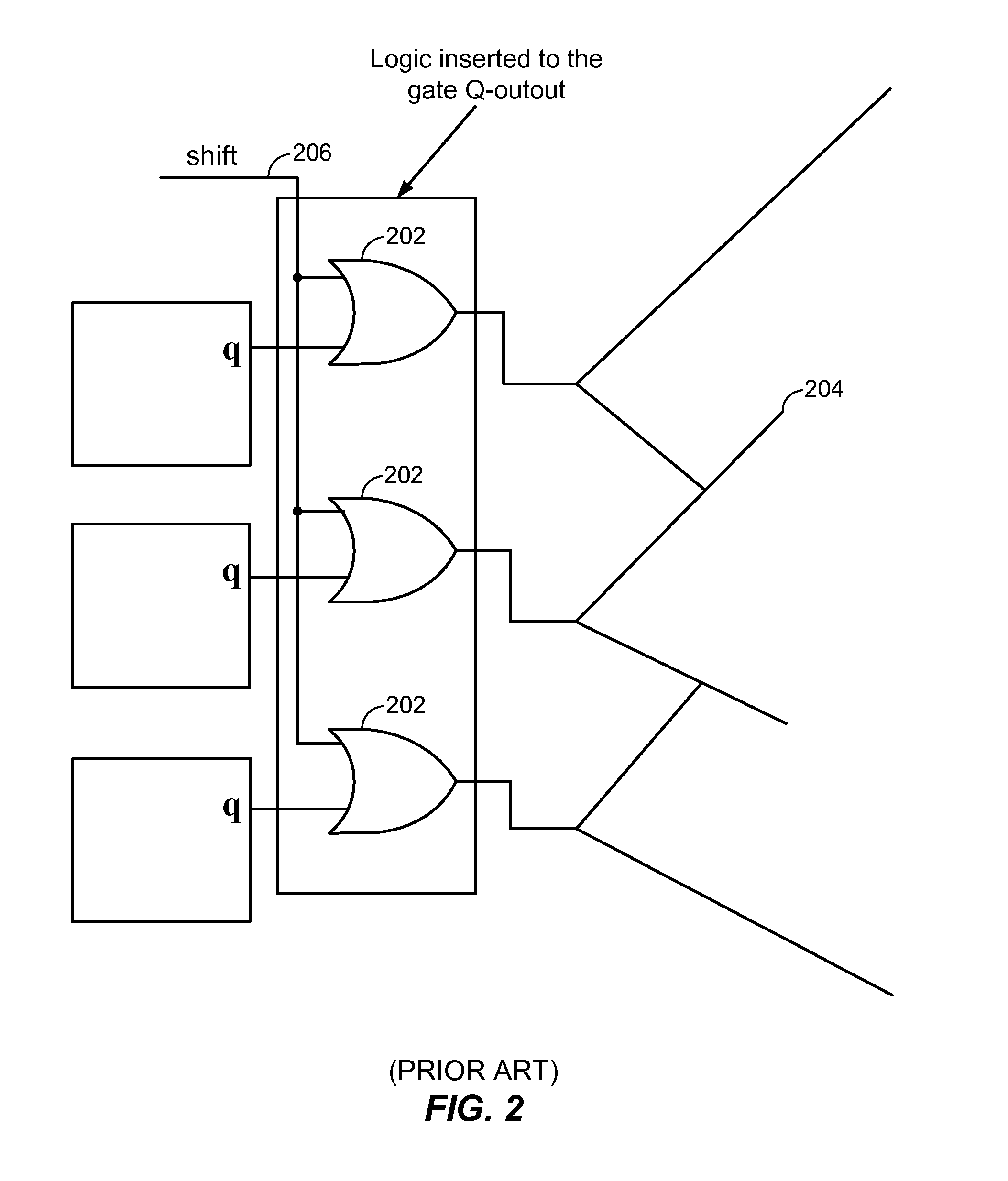
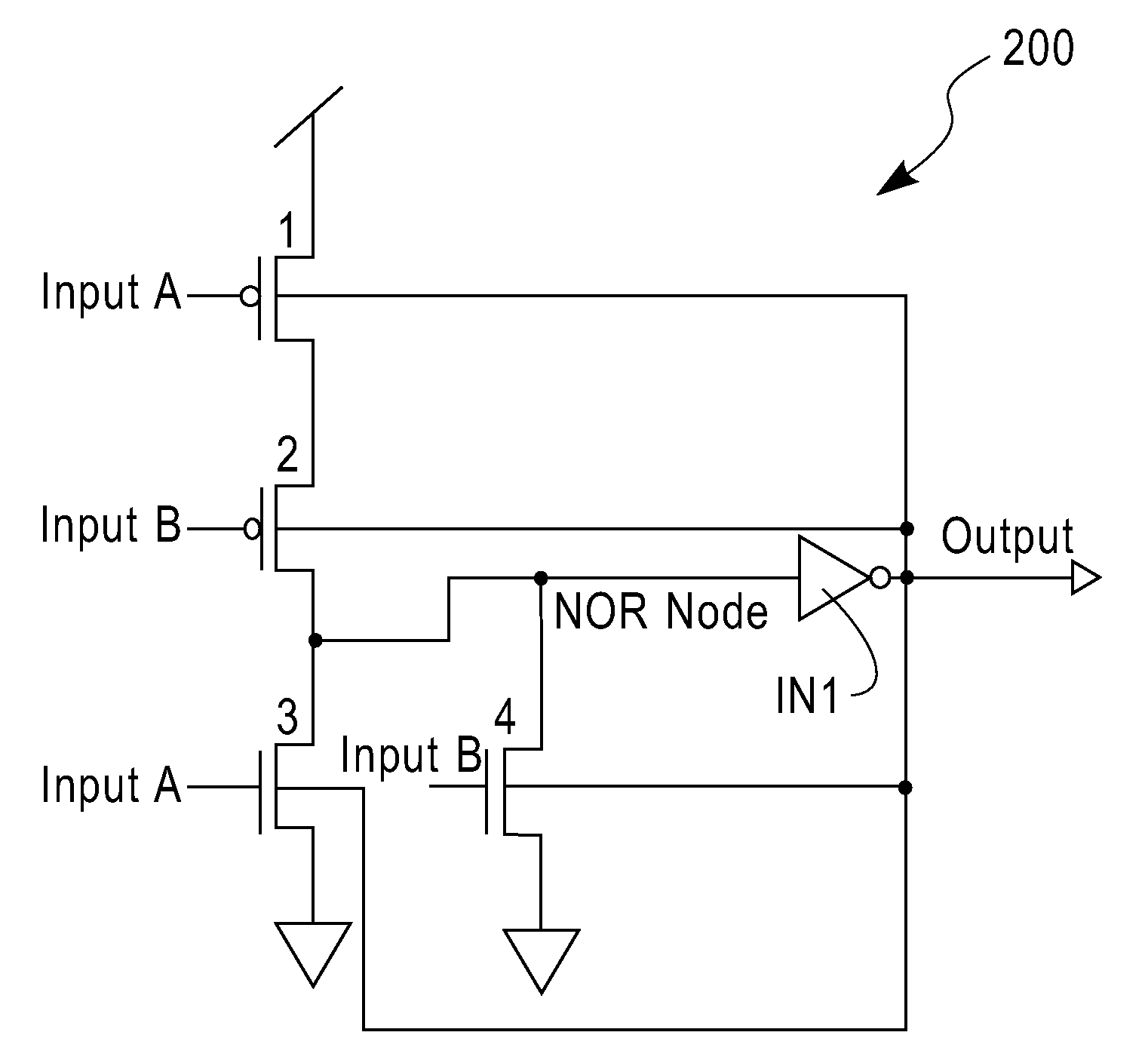
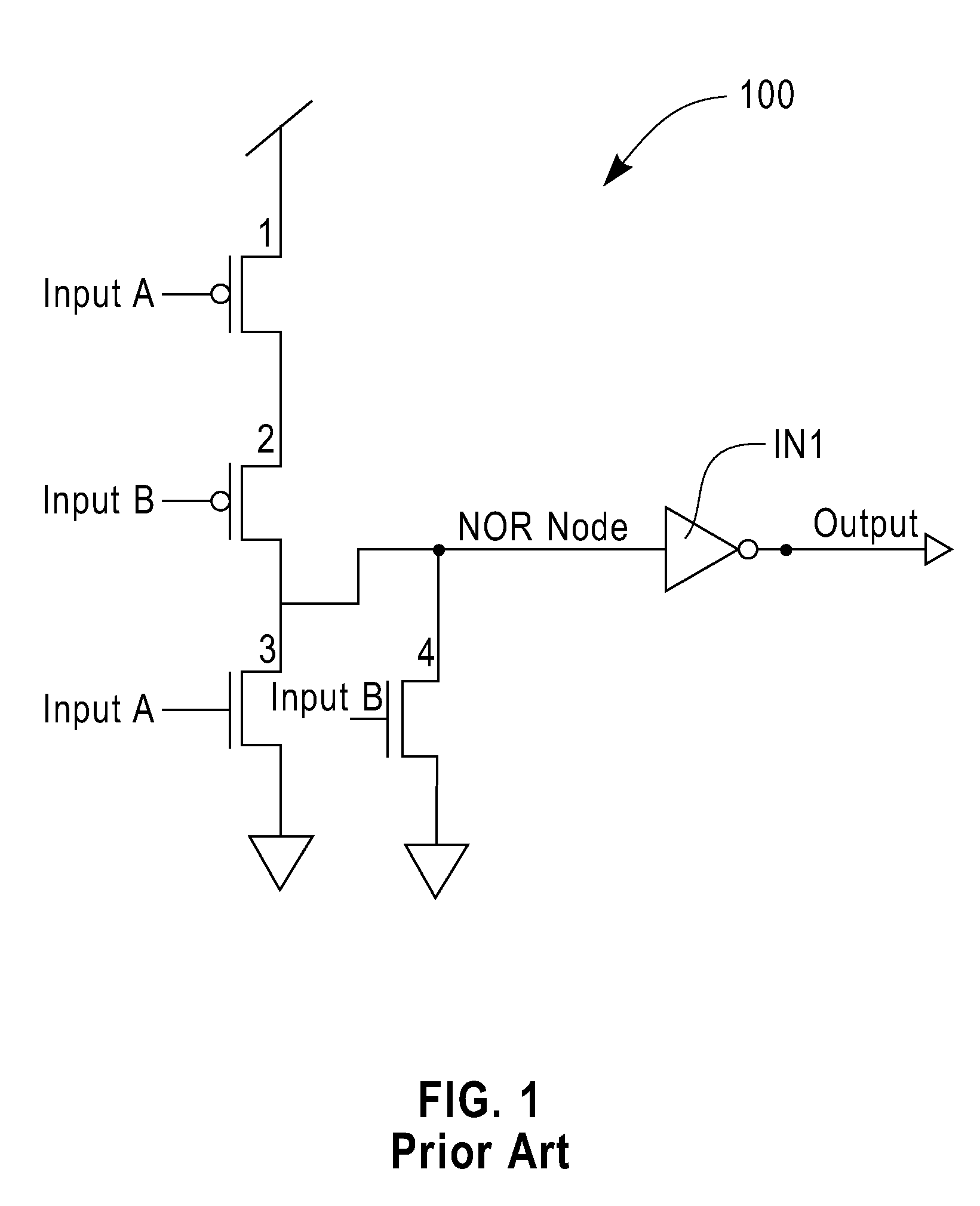
Integrated Circuit Leakage Power Reduction using Enhanced Gated-Q Scan Techniques
ActiveUS20120068734A1Reduce leakage powerMajority/minority circuitsPower consumption reductionLow leakageIntegrated circuit
Specific logic gates for q-gating are selected by determining the minimum leakage state for a circuit design and then selecting logic gates that hold the circuit design in its lowest leakage state. Depending on the input desired to implement the minimum leakage state, the gate may be selected as a NOR or OR gate. Q-gating that is implemented with gates chosen to implement the minimum leakage state may be enabled during selected operating modes. The minimum leakage state of a circuit can be determined with an automatic test pattern generation (ATPG) tool.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
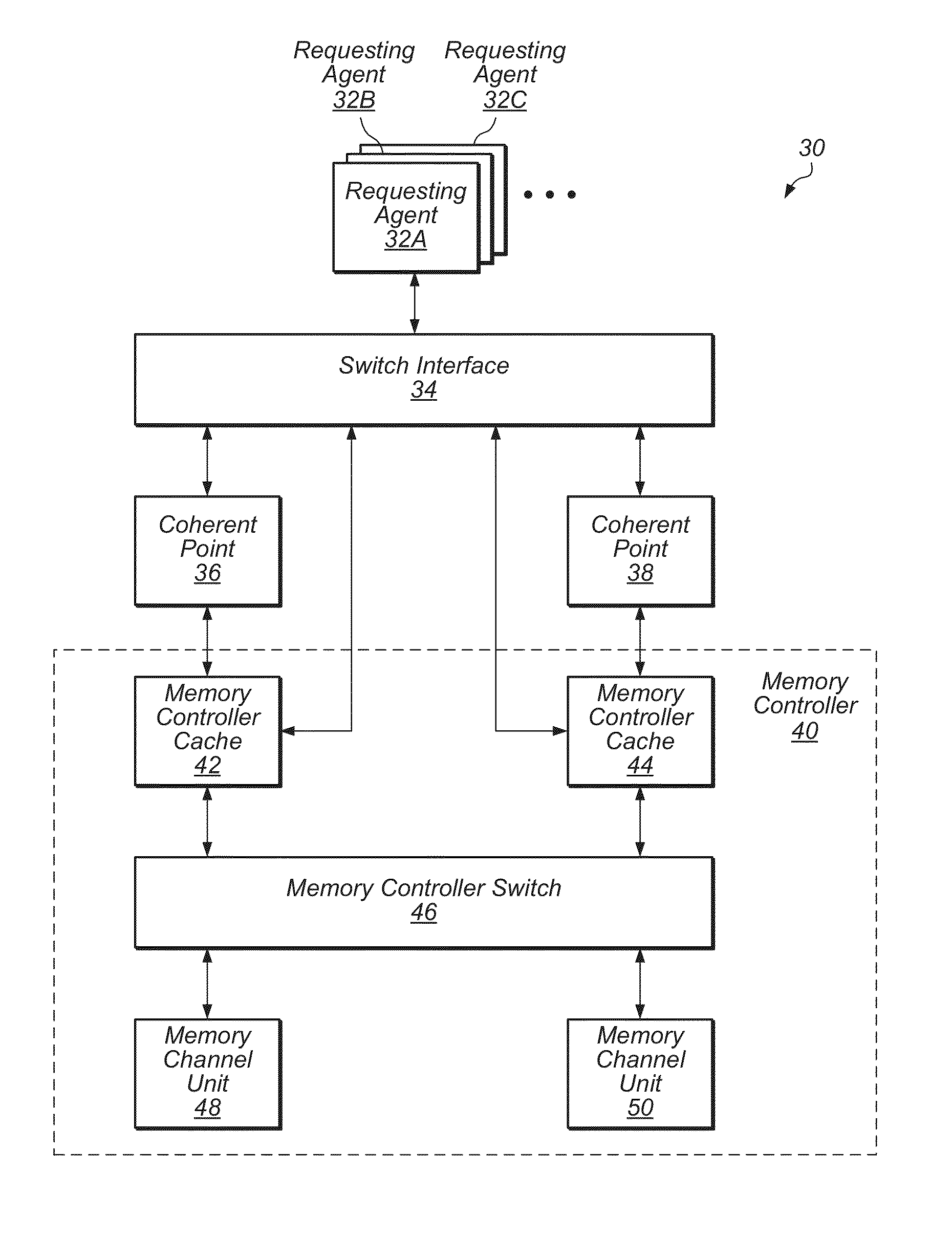
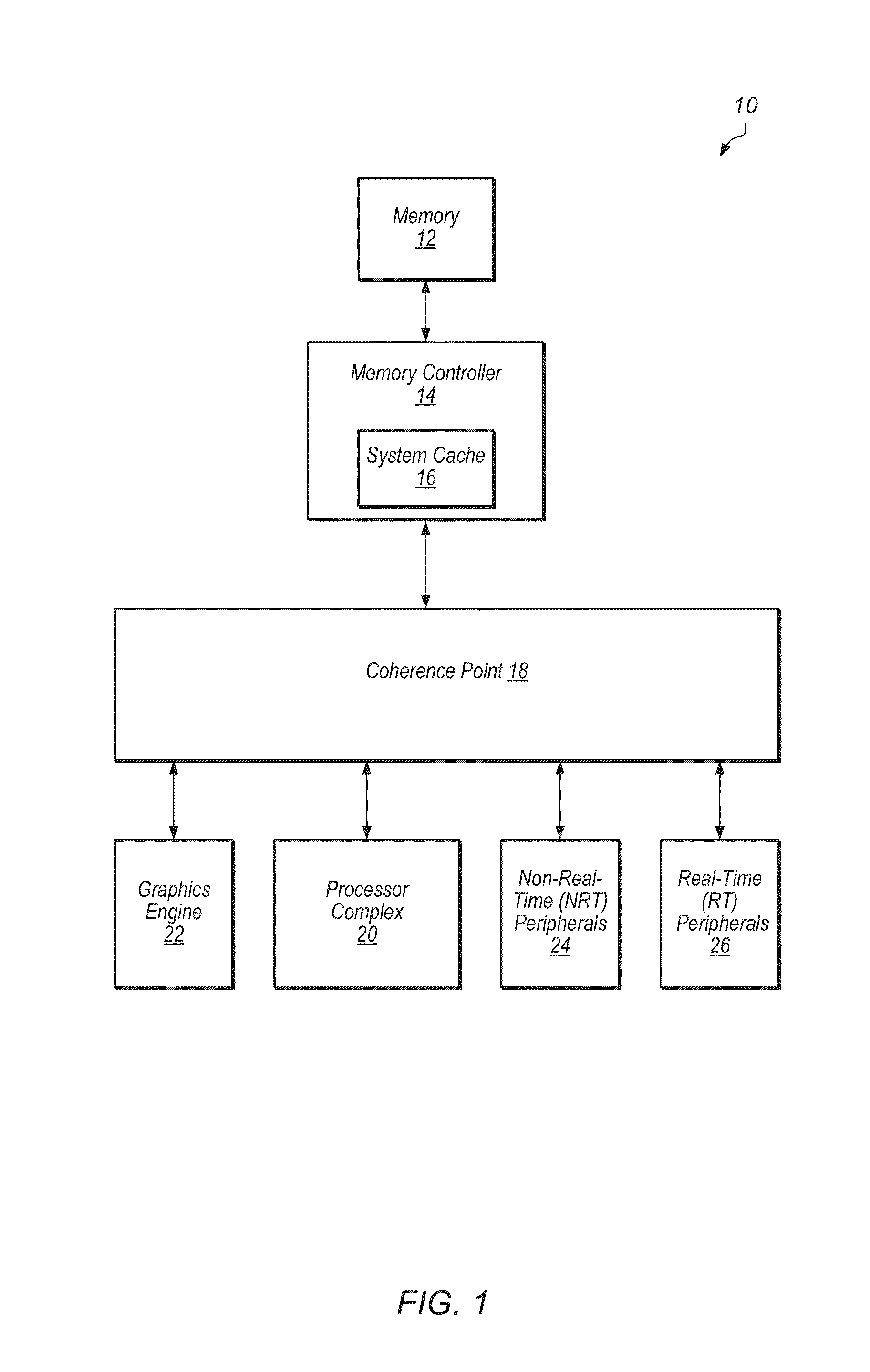
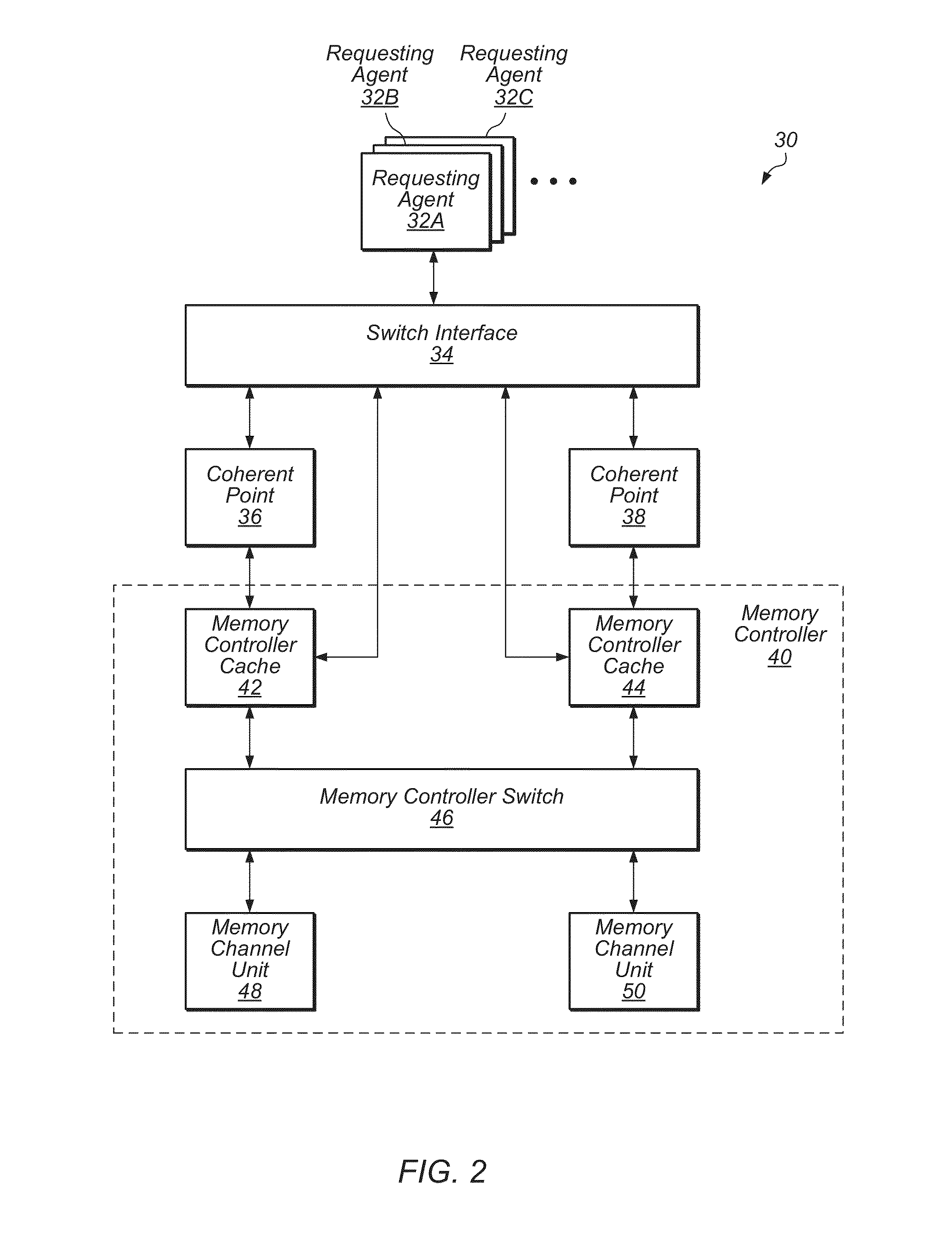
System cache with fine grain power management
ActiveUS20140095777A1Reduce leakage powerReduce in quantityDigital data processing detailsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSufficient timeMemory controller
Methods and apparatuses for reducing leakage power in a system cache within a memory controller. The system cache is divided into multiple small sections, and each section is supplied with power from a separately controllable power supply. When a section is not being accessed, the voltage supplied to the section is reduced to a voltage sufficient for retention of data but not for access. Incoming requests are grouped together based on which section of the system cache they target. When enough requests that target a given section have accumulated, the voltage supplied to the given section is increased to a voltage sufficient for access. Then, once the given section has enough time to ramp-up and stabilize at the higher voltage, the waiting requests may access the given section in a burst of operations.
Owner:APPLE INC
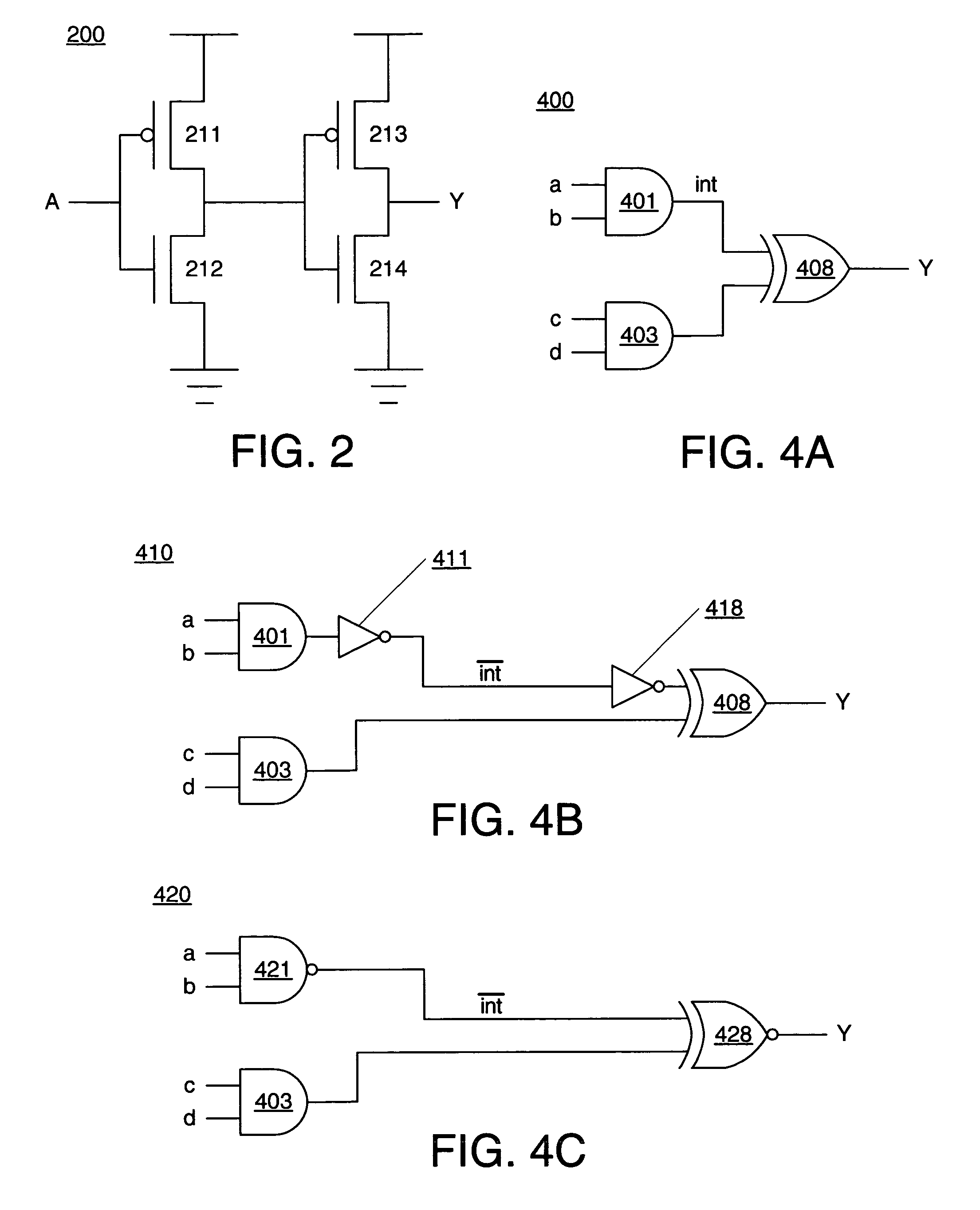
CMOS back-gated keeper technique
InactiveUS20090224803A1Reduce leakage currentImprove noise immunityPower consumption reductionLogic circuits characterised by logic functionMOSFETCMOS
A novel methodology for the construction and operation of logical circuits and gates that make use of and contact to a fourth terminal (substrates / bodies) of MOSFET devices is described in detail. The novel construction and operation provides for maintaining such body-contacted MOSFET devices at a lower threshold voltage (VTh) when actively on (to increase overdrive and performance), and at a higher relative threshold voltage when off (to reduce leakage power). Because the threshold potential of a gate moves inversely to its body potential, it follows then that in general, the body of a given device must be tied to the inverse of the device's drain voltage to achieve such a desirable threshold potential modulation effect for improved device, circuit, gate and logical family operation.
Owner:IBM CORP
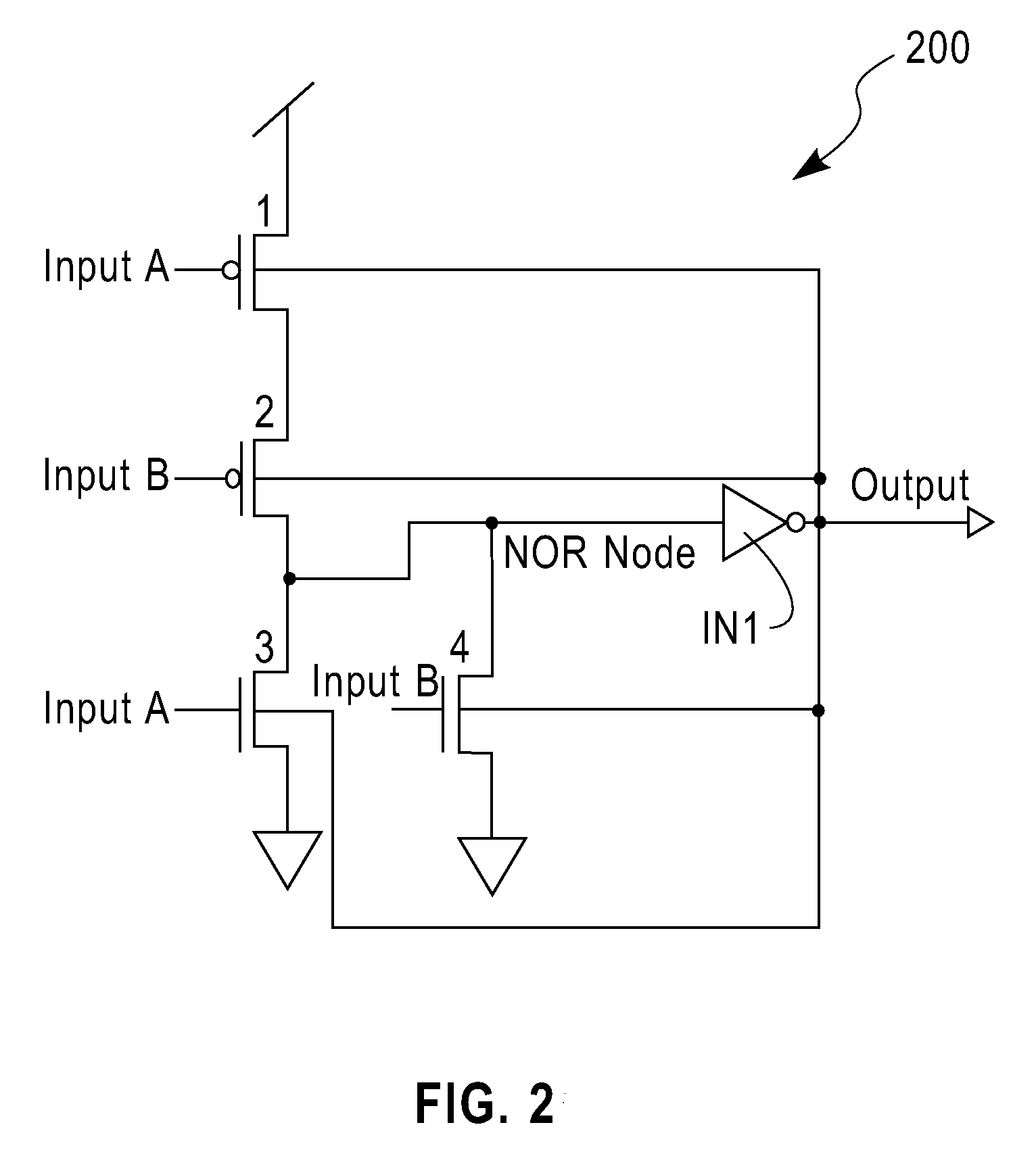
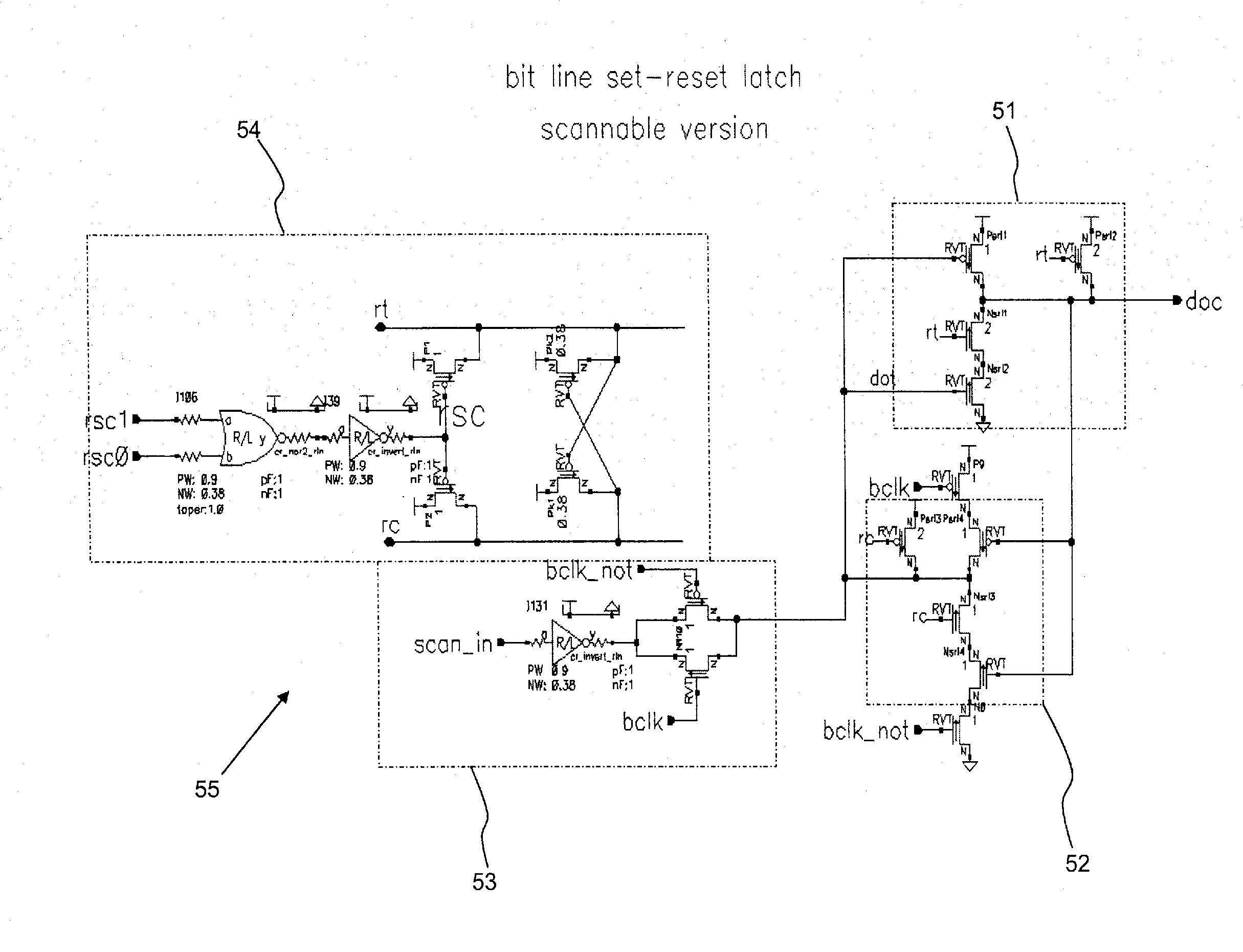
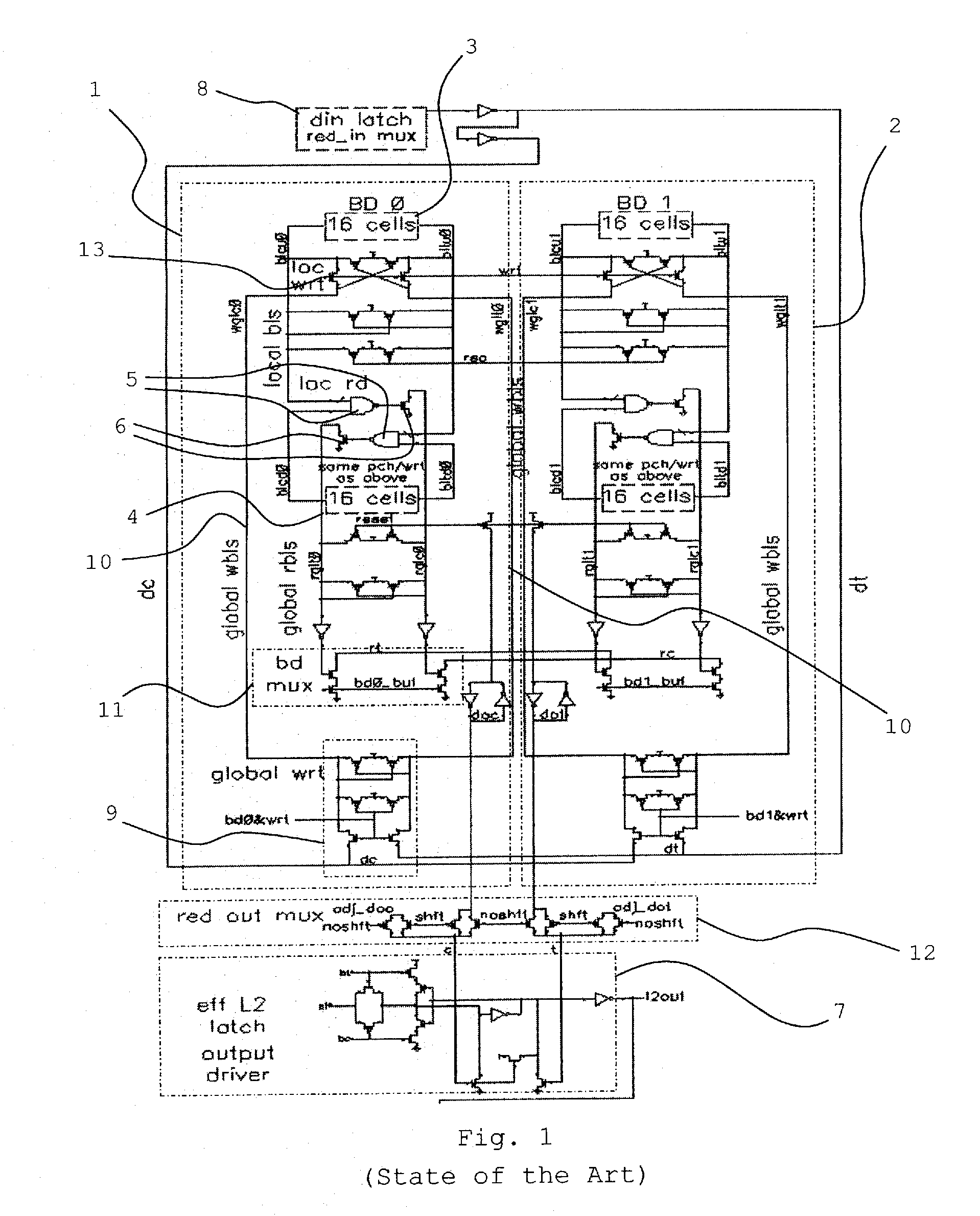
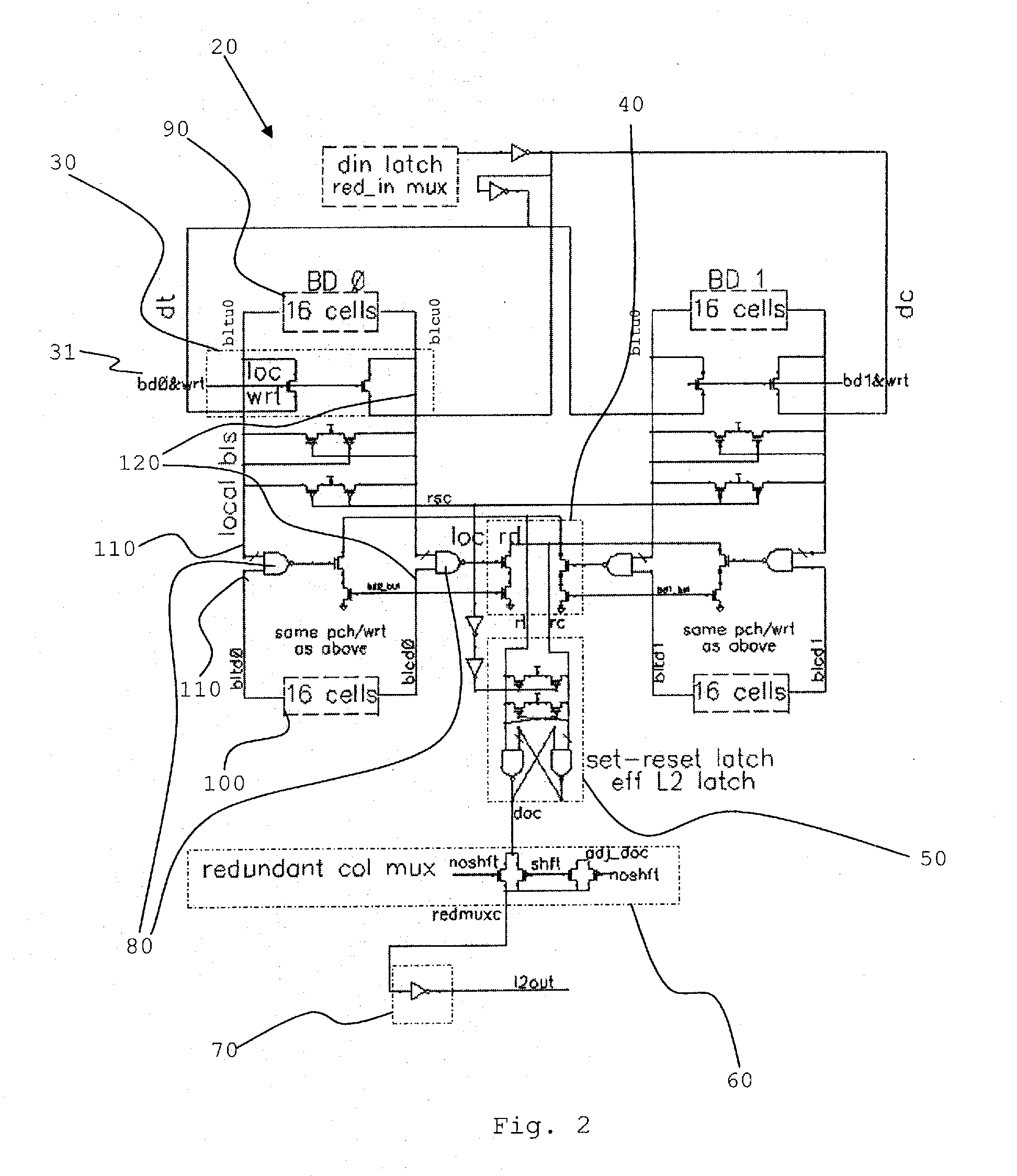
Method and structure for domino read bit line and set reset latch
A domino read bit line structure (20) integral to an SRAM array (1, 2) with thirty-two word lines or less to access SRAM cells divided into two groups (3, 4, 90, 100) is described. The bit line structure (20) includes a dynamic bit decode multiplexer (11, 40) and two NAND circuits (5, 80) used to combine the two groups (3, 4, 90, 100), wherein in order to reduce power consumption the two NANDS (80) drive the dynamic bit decode multiplexer (40) directly, such that true and complement dynamic outputs (rt, rc) drive a set-reset latch (50) to convert the dynamic outputs (rt, rc) to a single static signal (doc), wherein the output of the set-reset latch (50) is already static so that the set-reset latch (50) acts as an effective array output latch (7).
Owner:IBM CORP
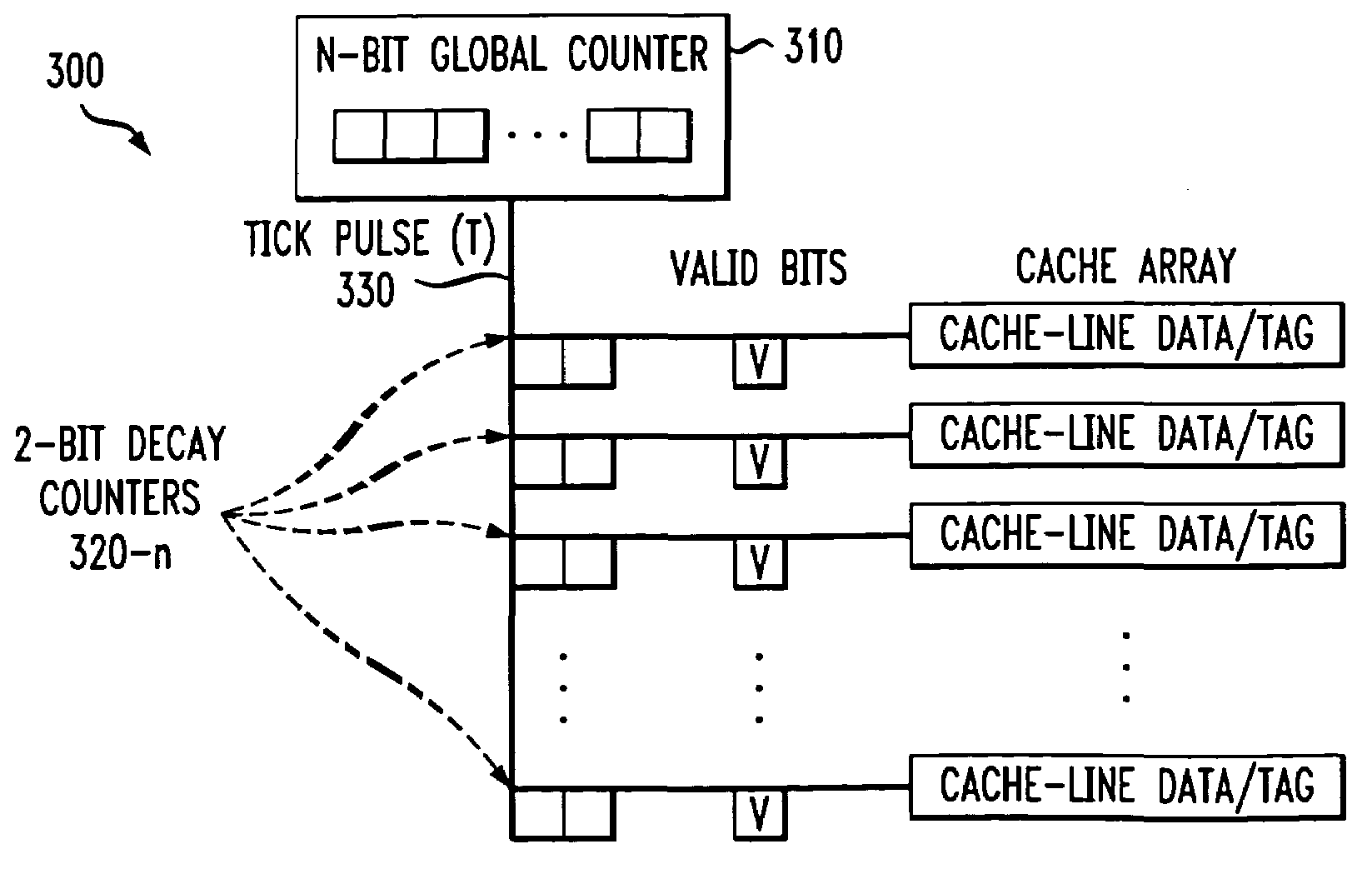
Method and apparatus for reducing leakage power in a cache memory by using a timer control signal that removes power to associated cache lines
InactiveUS6983388B2Reduce leakage powerReduce power consumptionVolume/mass flow measurementMemory adressing/allocation/relocationElectricityMemory hierarchy
A method and apparatus are disclosed for reducing leakage power in a cache memory. A cache decay technique is employed for both data and instruction caches that removes power from cache lines that have not been accessed for a predefined time interval, referred to as the decay interval. The cache-line granularity of the present invention permits a significant reduction in leakage power while at the same time preserving much of the performance of the cache. The decay interval is maintained using a timer that is reset each time the corresponding cache line is accessed. The decay interval may be fixed or variable. Once the decay interval timer exceeds a specified decay interval, power to the cache line is removed. Once power to the cache line is removed, the contents of the data and tag fields are allowed to decay and the valid bit associated with the cache line is reset. When a cache line is later accessed after being powered down by the present invention, a cache miss is incurred while the cache line is again powered up and the data is obtained from the next level of the memory hierarchy.
Owner:BROADCOM INT PTE LTD
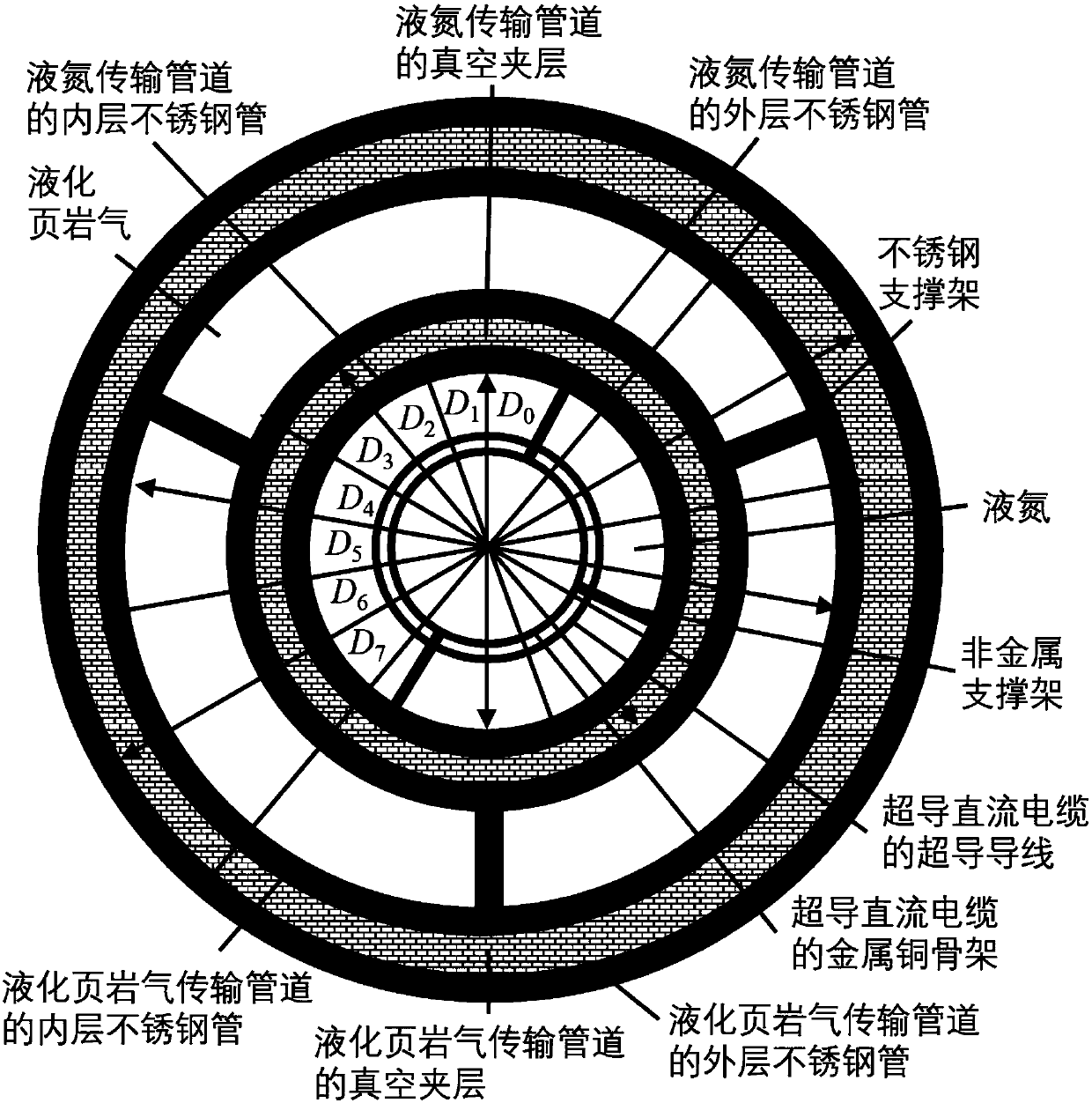
Design method for combined energy pipeline of liquefied shale gas, liquid nitrogen and superconducting cable
ActiveCN107631105AReduce development costsLow running costPipe supportsThermal insulationEnergy transferEngineering
The invention discloses a design method for a combined energy pipeline of liquefied shale gas, liquid nitrogen and a superconducting cable. According to the method, three operation limiting conditions, namely the maximum allowable pressure drop, the maximum allowable temperature rise and the maximum allowable vacuum degree change rate, inside the combined energy transferring pipeline are met, so that the problem that the vacuum maintenance time is excessively short due to unreasonable design of a vacuum or heat insulation structure or potential safety hazards are generated due to excessively-severe heat leakage of the pipeline is avoided. Meanwhile, a liquid nitrogen transferring pipeline is directly arranged in a liquefied shale gas transferring pipeline, development cost of the whole combined energy pipeline is lowered, and the heat leakage power of the liquefied shale gas transferring pipeline is lowered; and furthermore, operating cost of a low-temperature refrigerator arranged outside the combined energy pipeline is saved.
Owner:SICHUAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com