Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4207results about "Near-field systems using receivers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
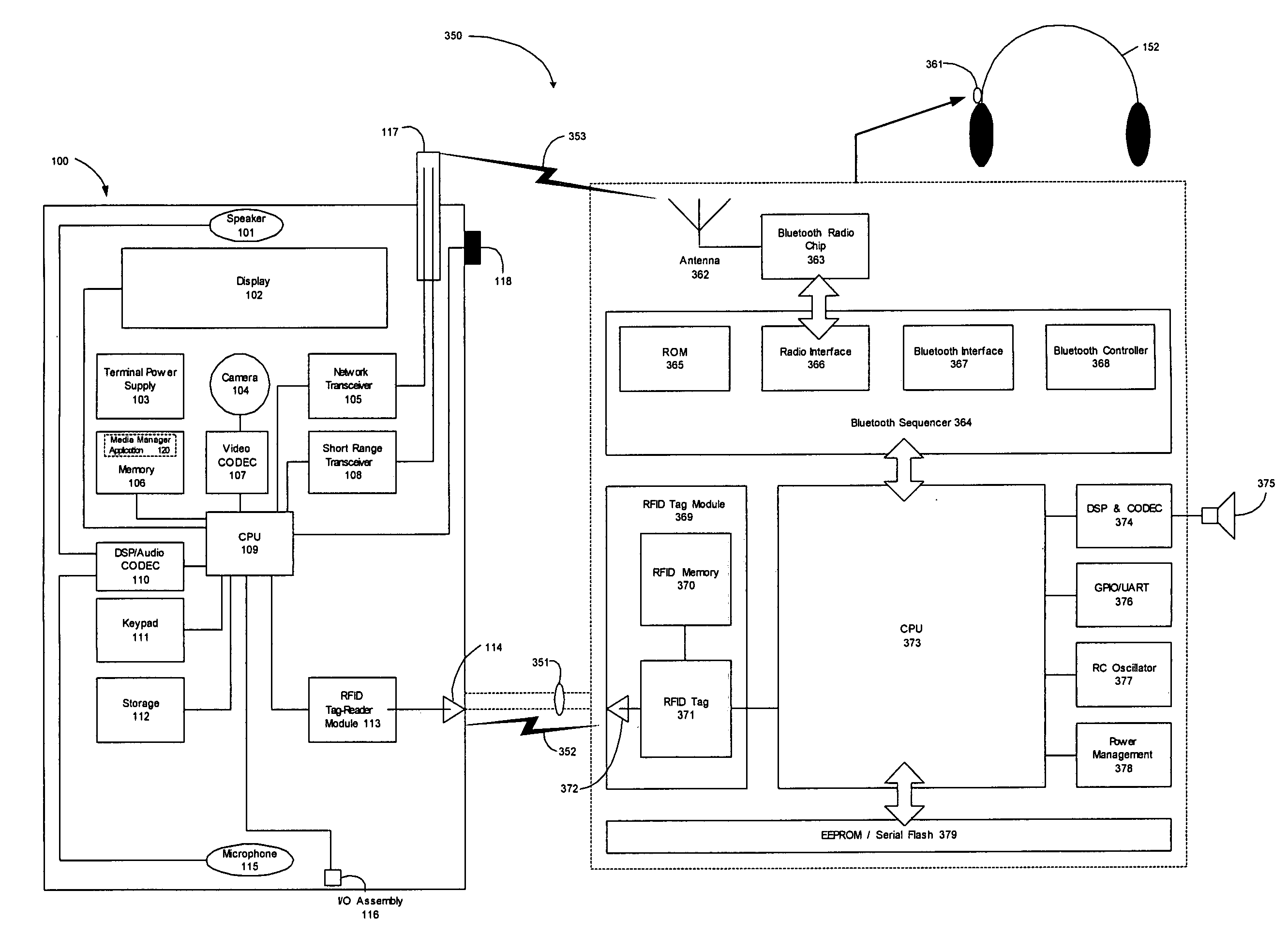
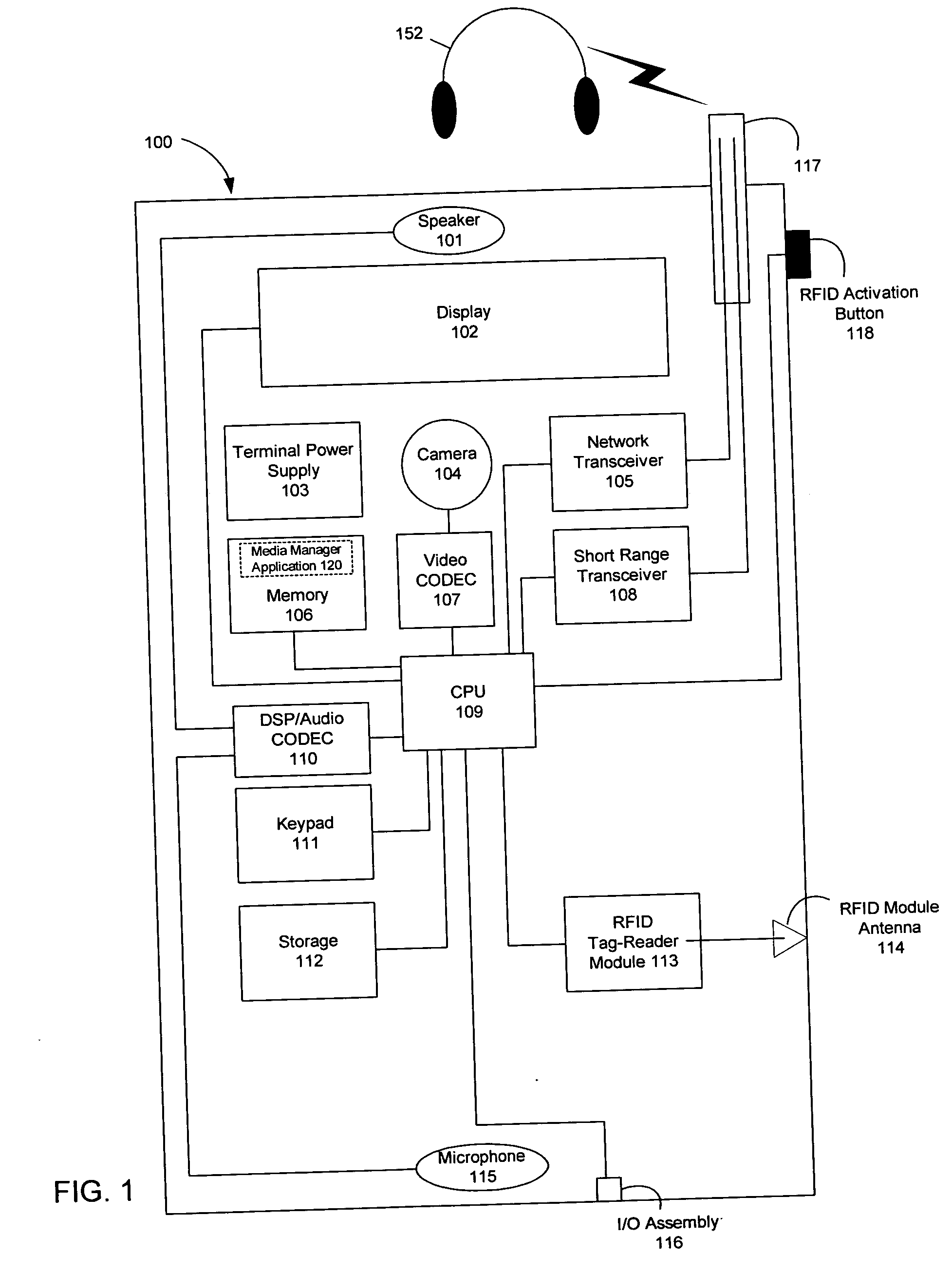
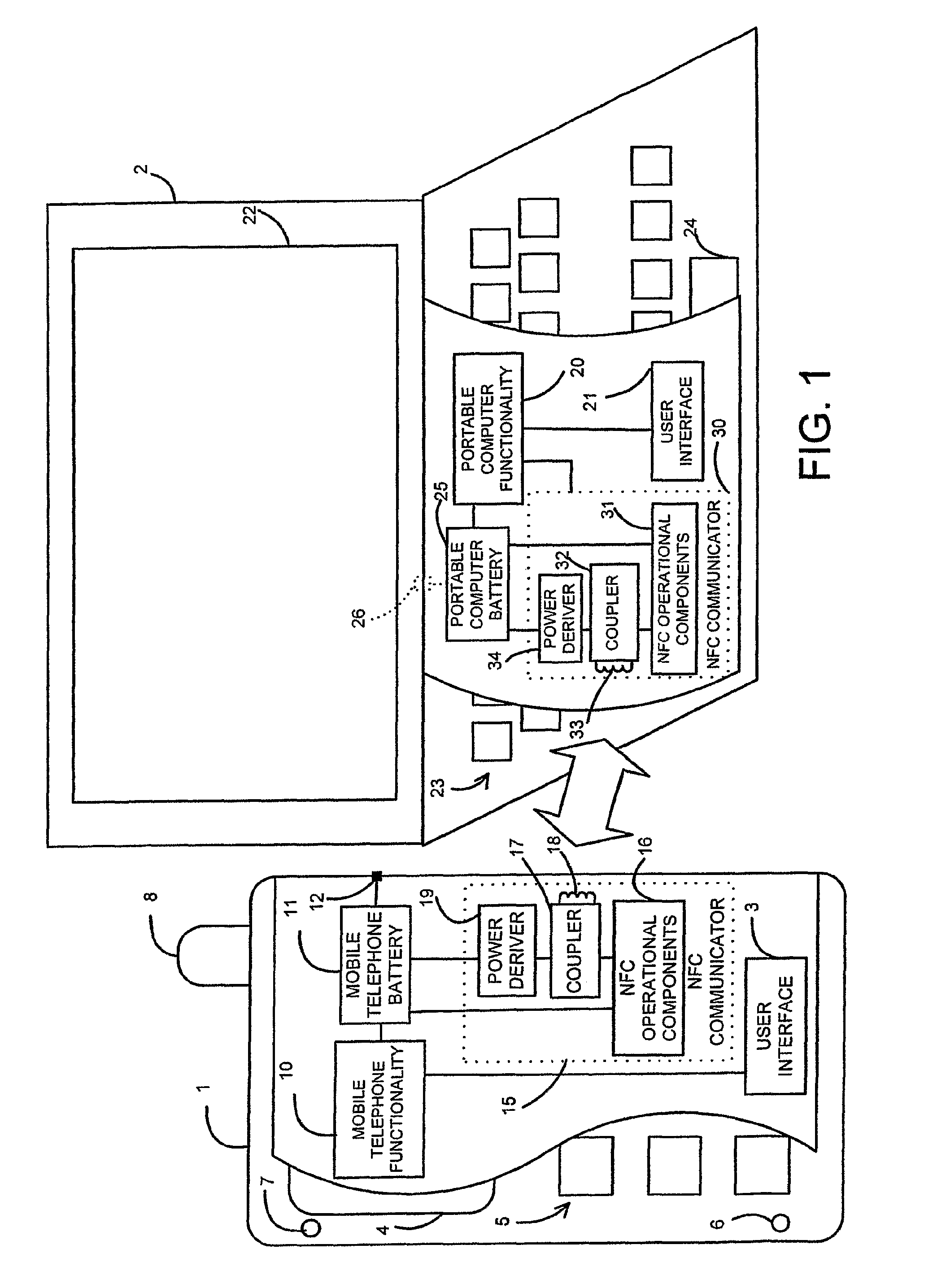
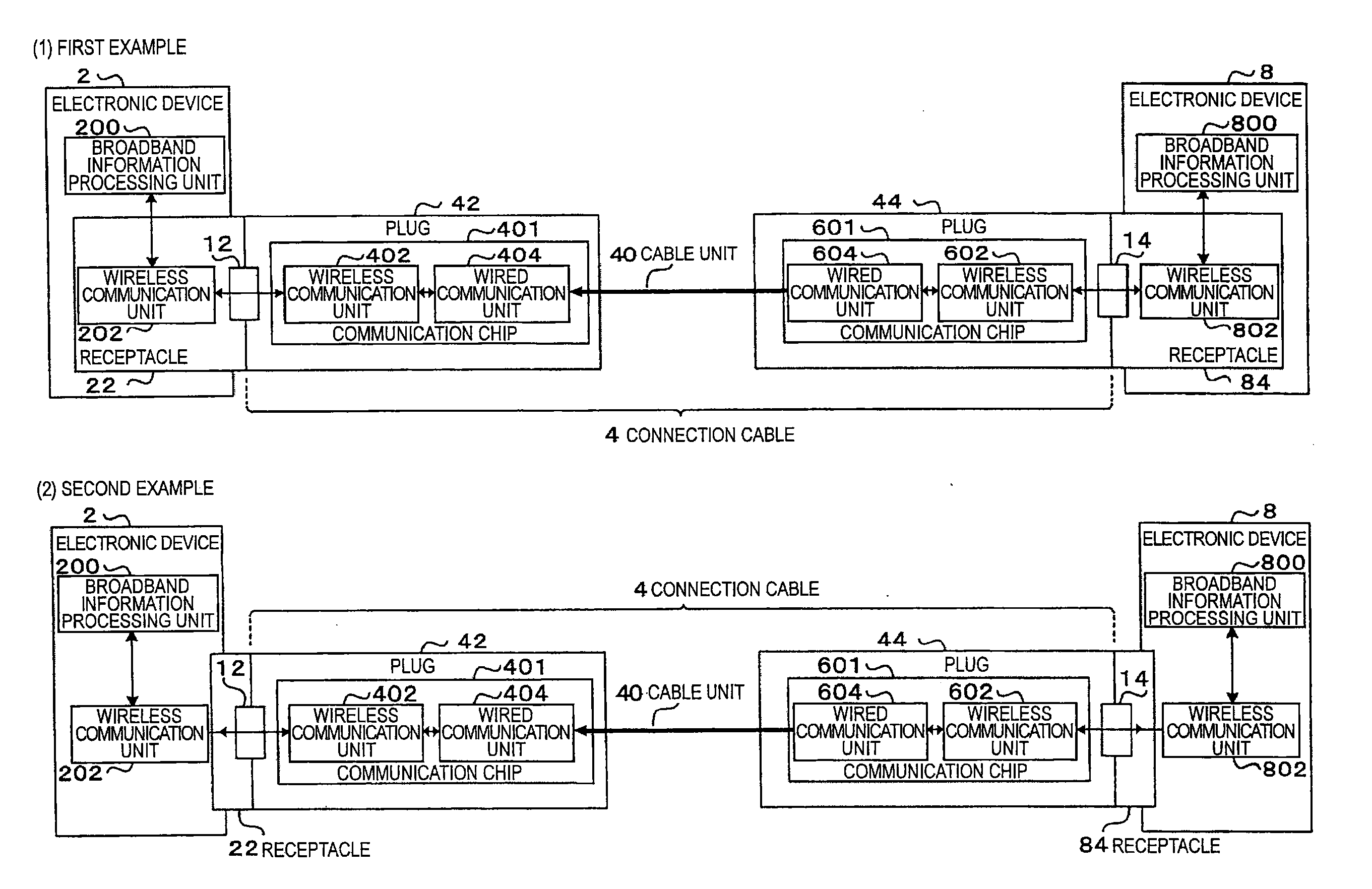
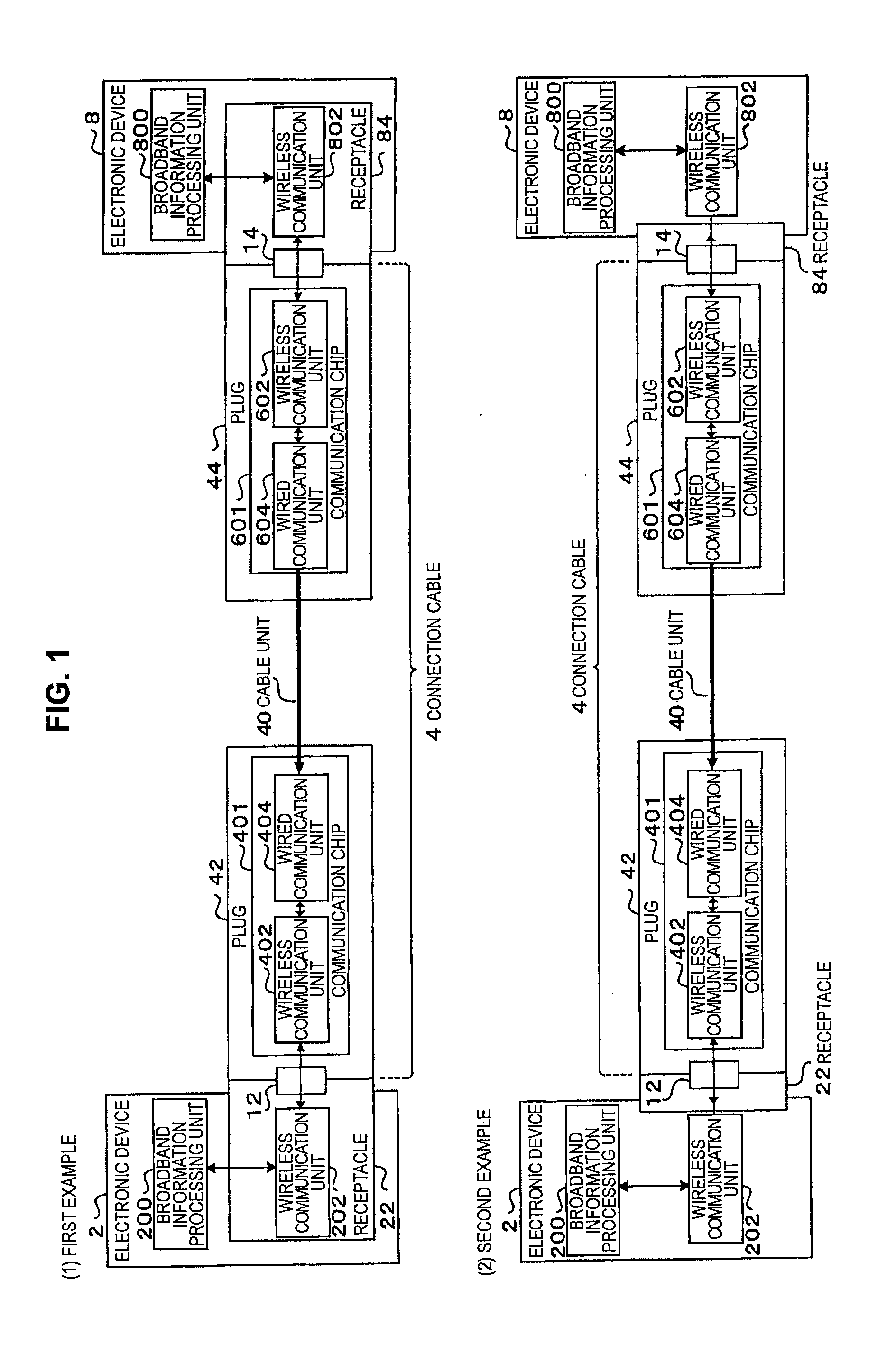
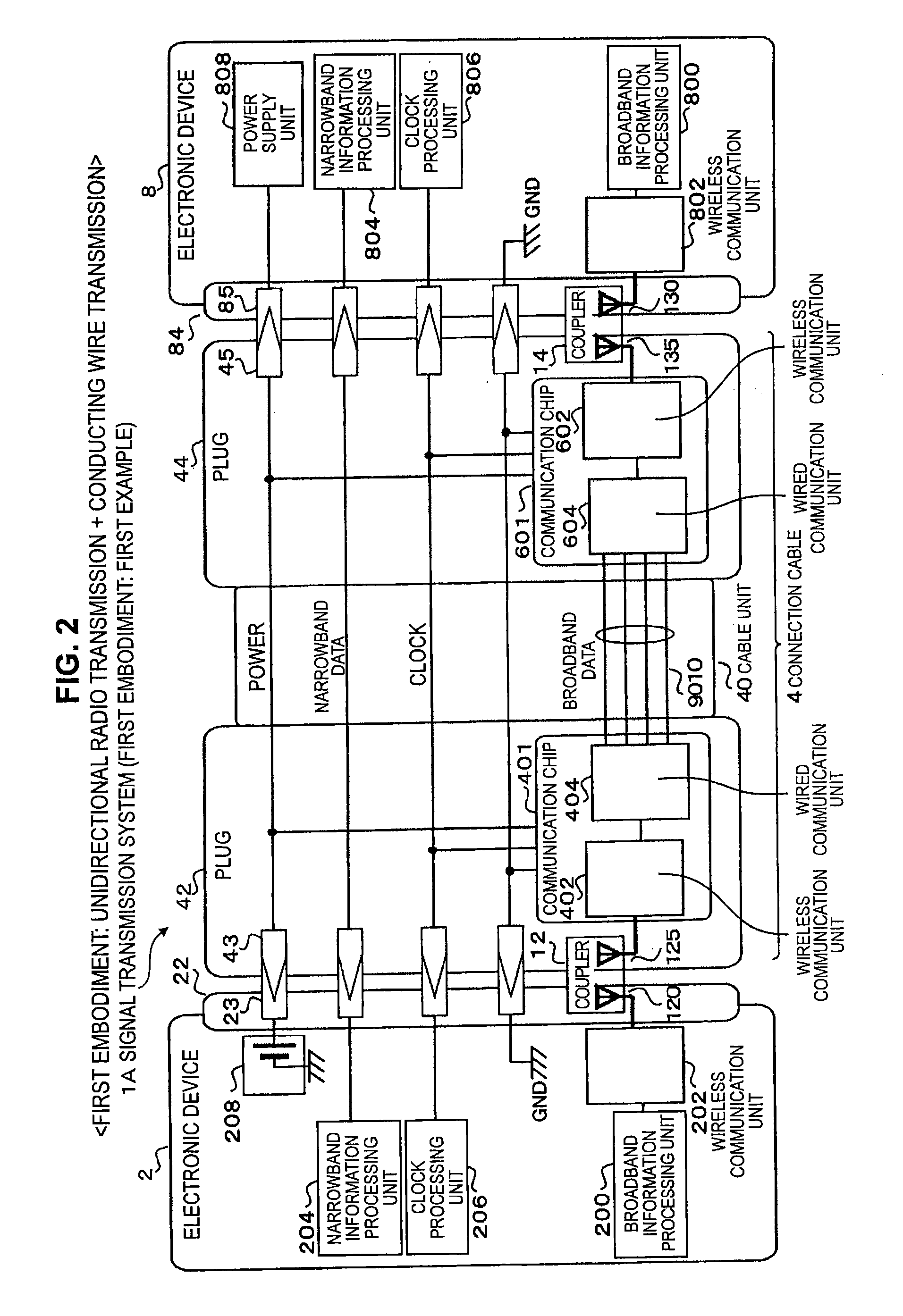
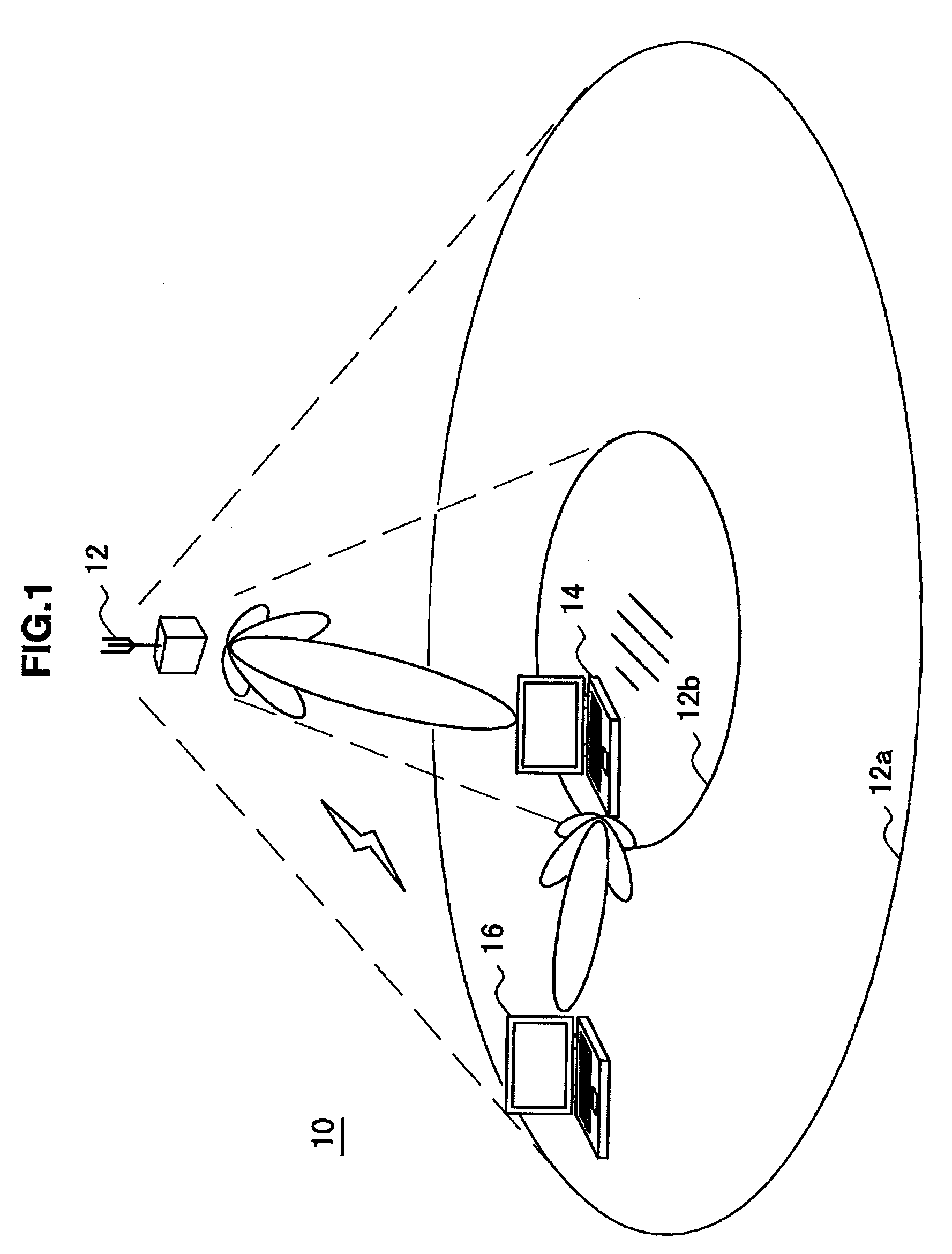
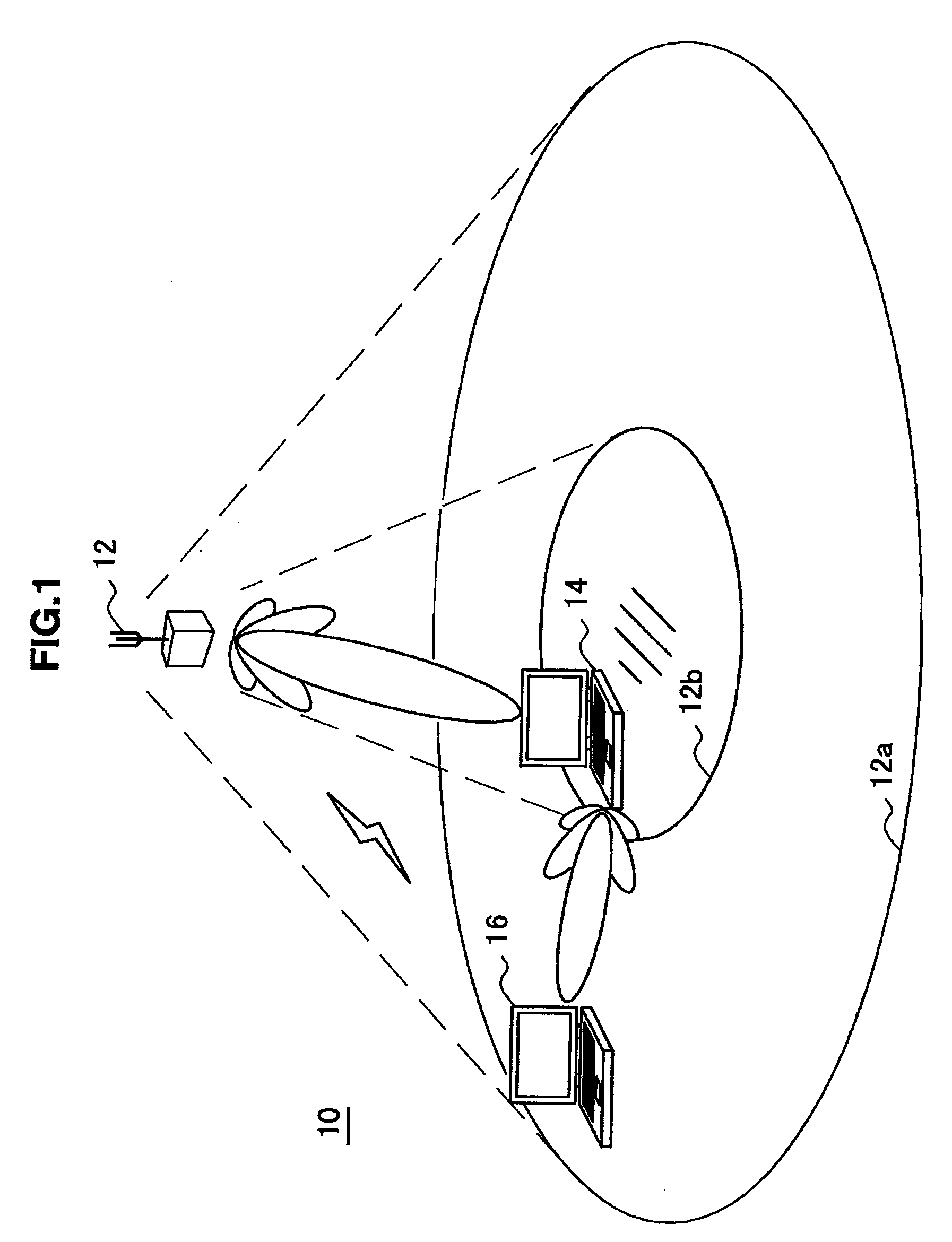
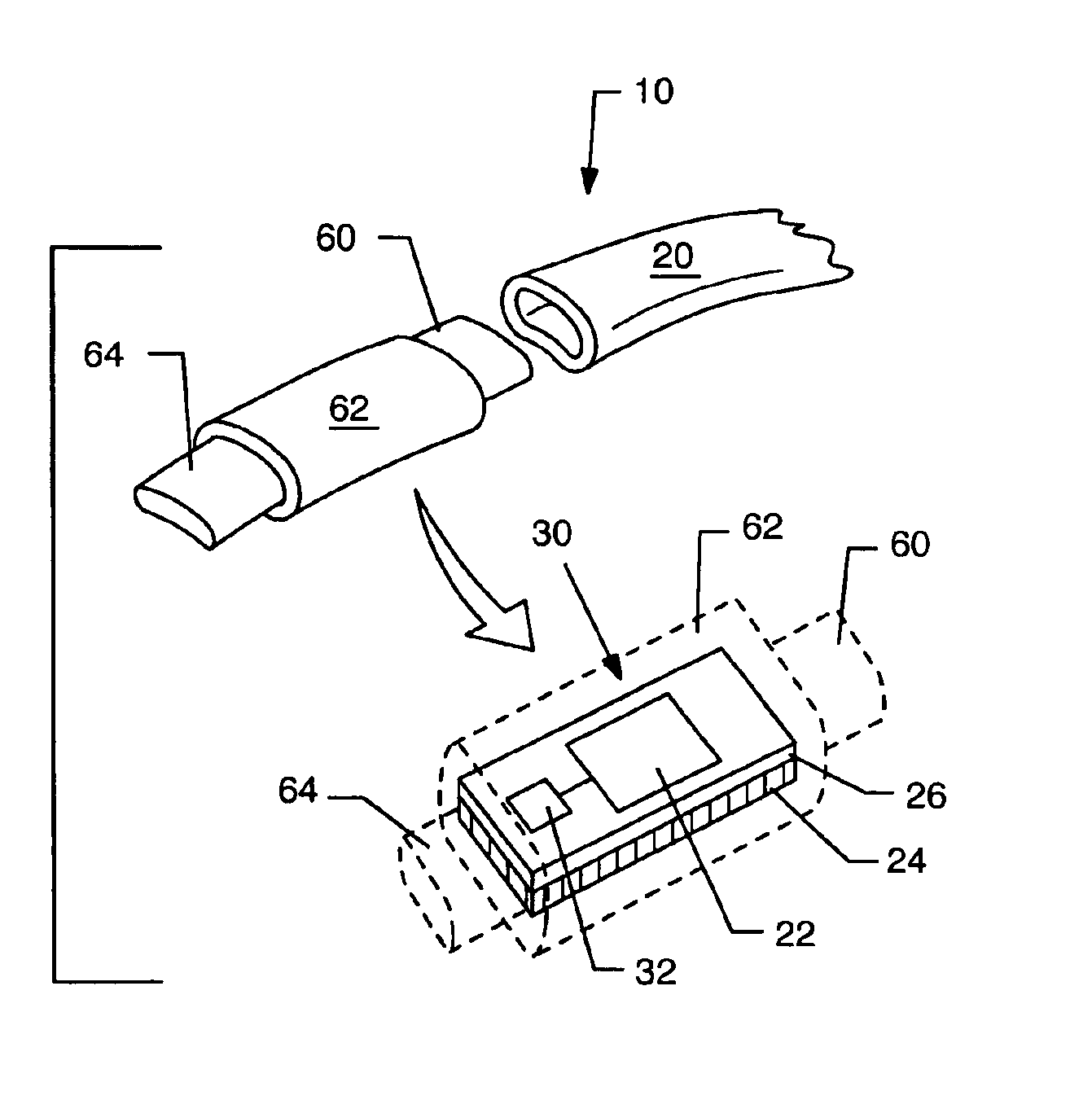
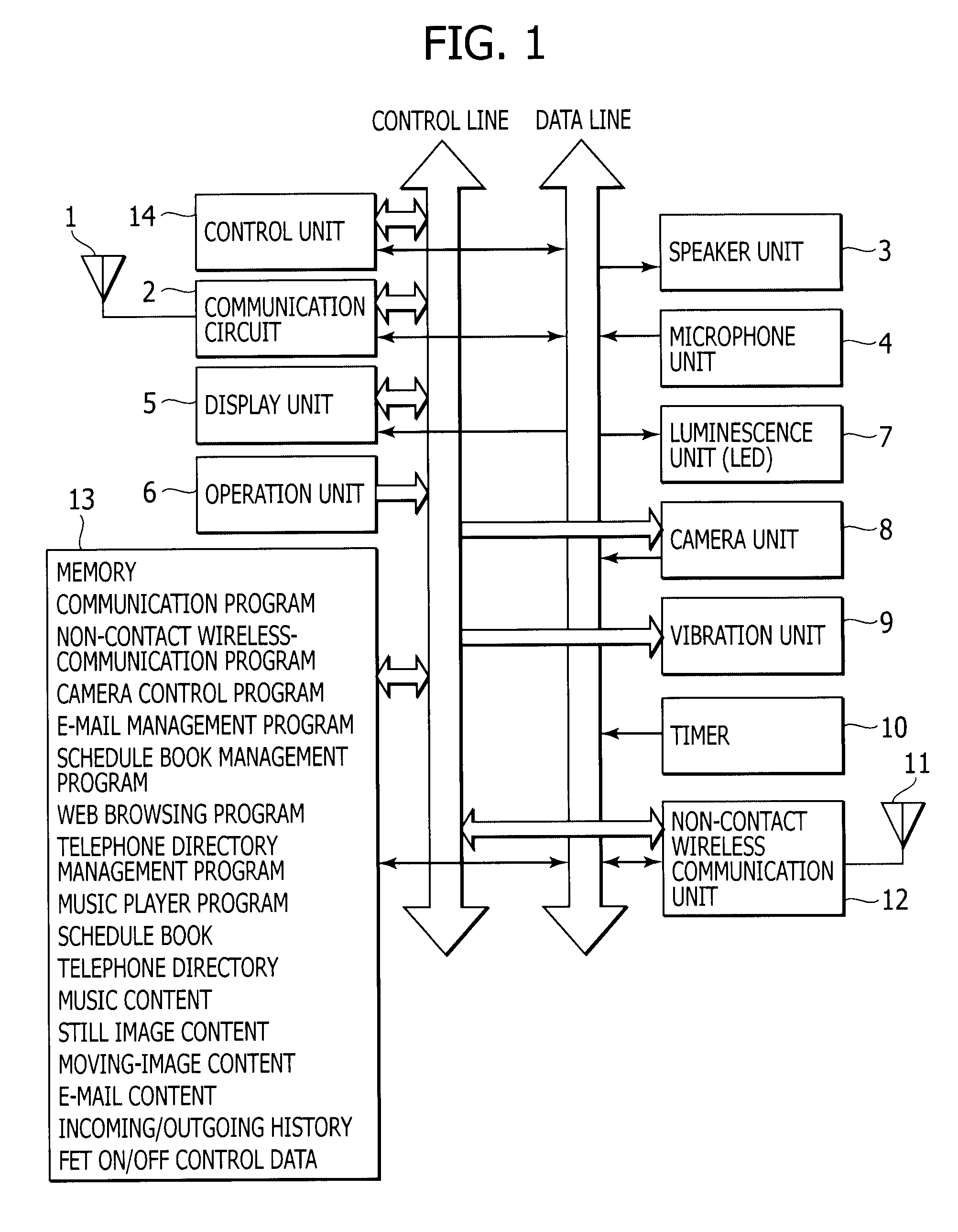
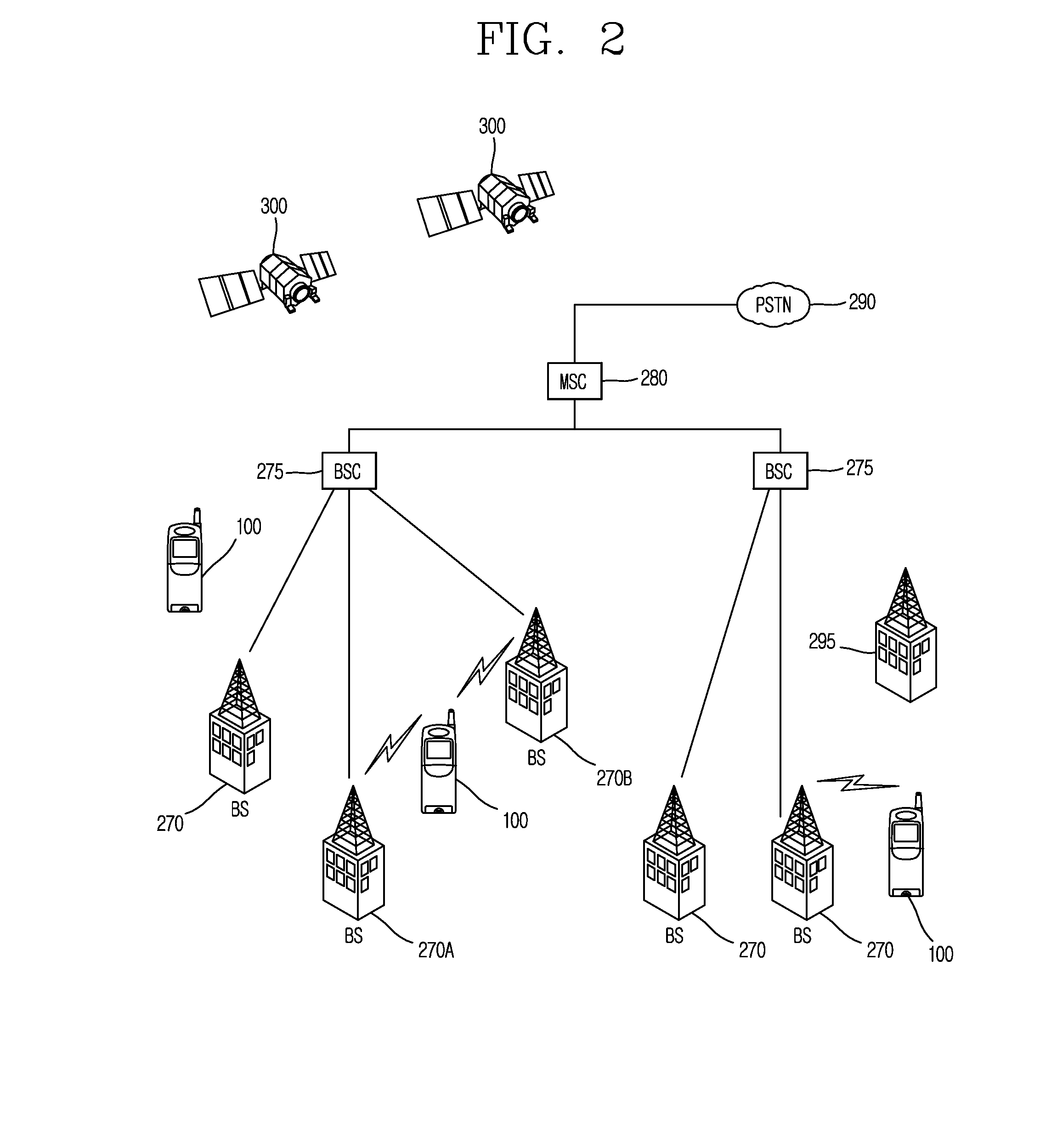
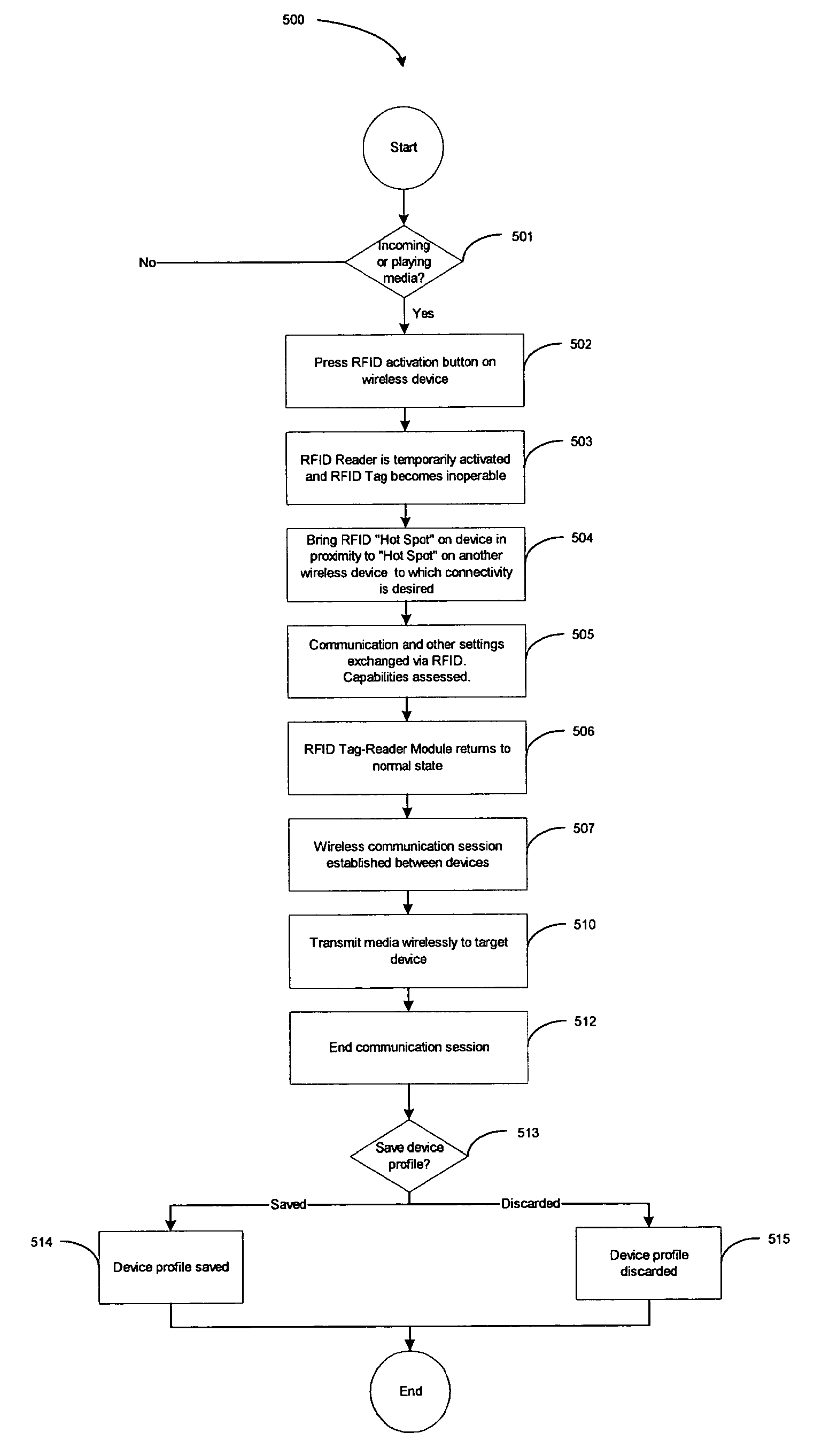
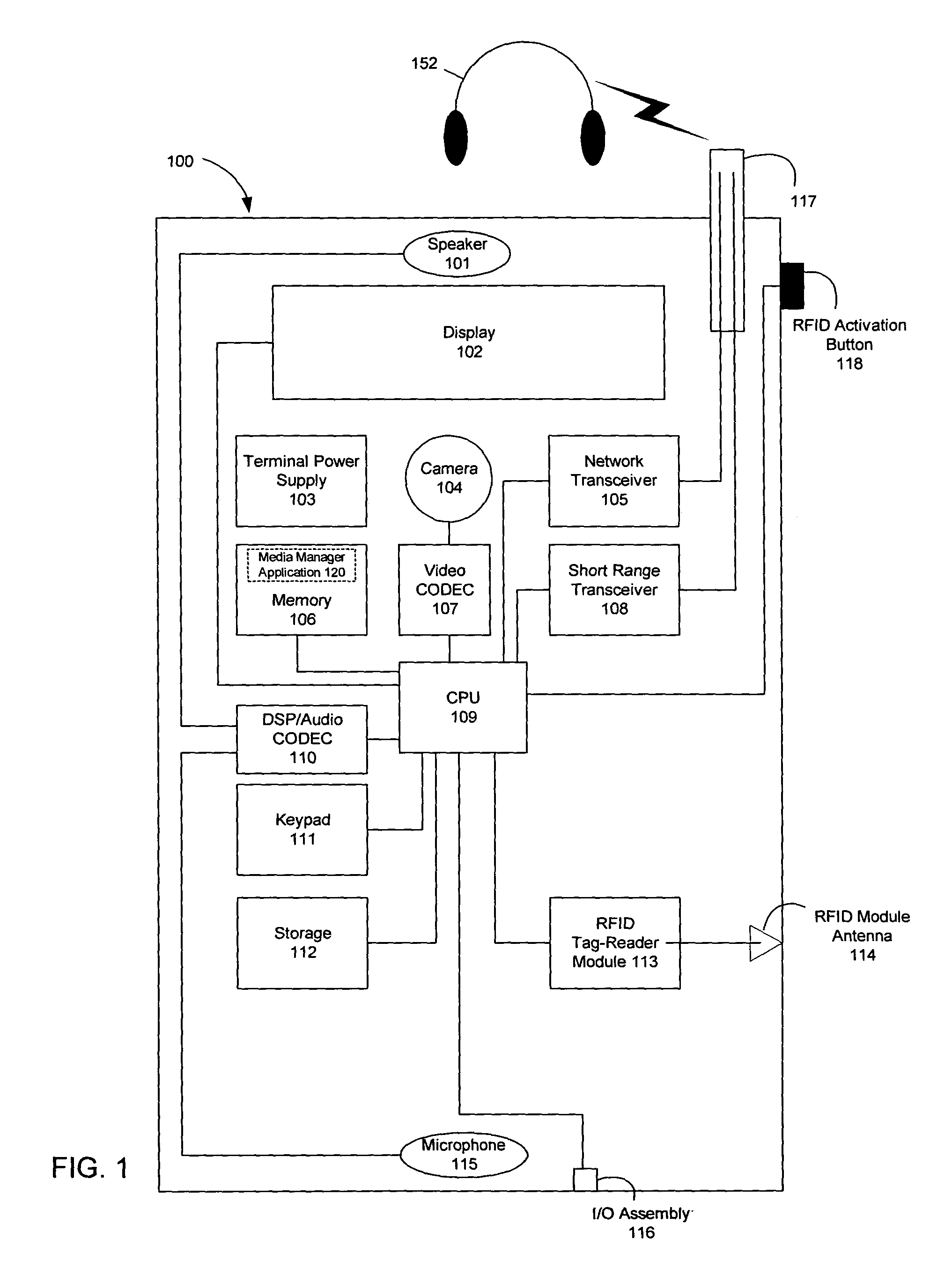
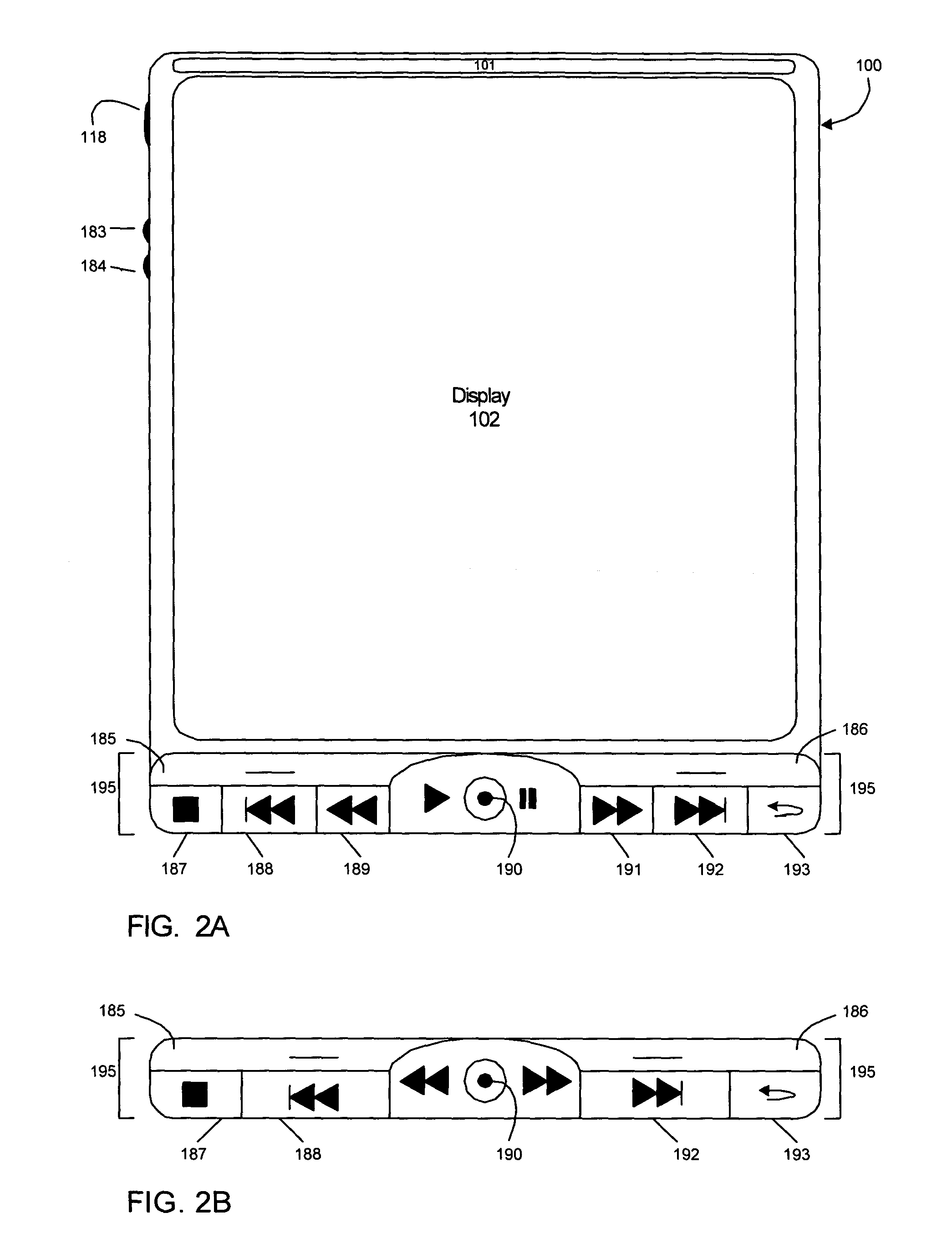
Wireless media system and player and method of operation
ActiveUS20060258289A1Easy to useMultimedia data browsing/visualisationPayment architectureUltra-widebandSecure communication
A wireless media player and a related system and methodology are disclosed. One aspect of the wireless media player system pertains to a virtual connector system, apparatus, and method for the automatic establishment of wireless connectivity with other electronic devices. In one embodiment, the media player device employs the use of integrated Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology to exchange communication settings, media capability, and other parameters with an external device that also has integrated RFID technology. The automatic exchange of settings and other information via a proximity-based RFID data exchange allows a media player to quickly establish a secure communication link with another device via a commonly supported wireless protocol such as Ultra Wideband (UWB) or Bluetooth. Another aspect of the media player system pertains to a method of using the captured media capability of the connecting device to customize certain menu options and software parameters in the media player.
Owner:SYNDEFENSE
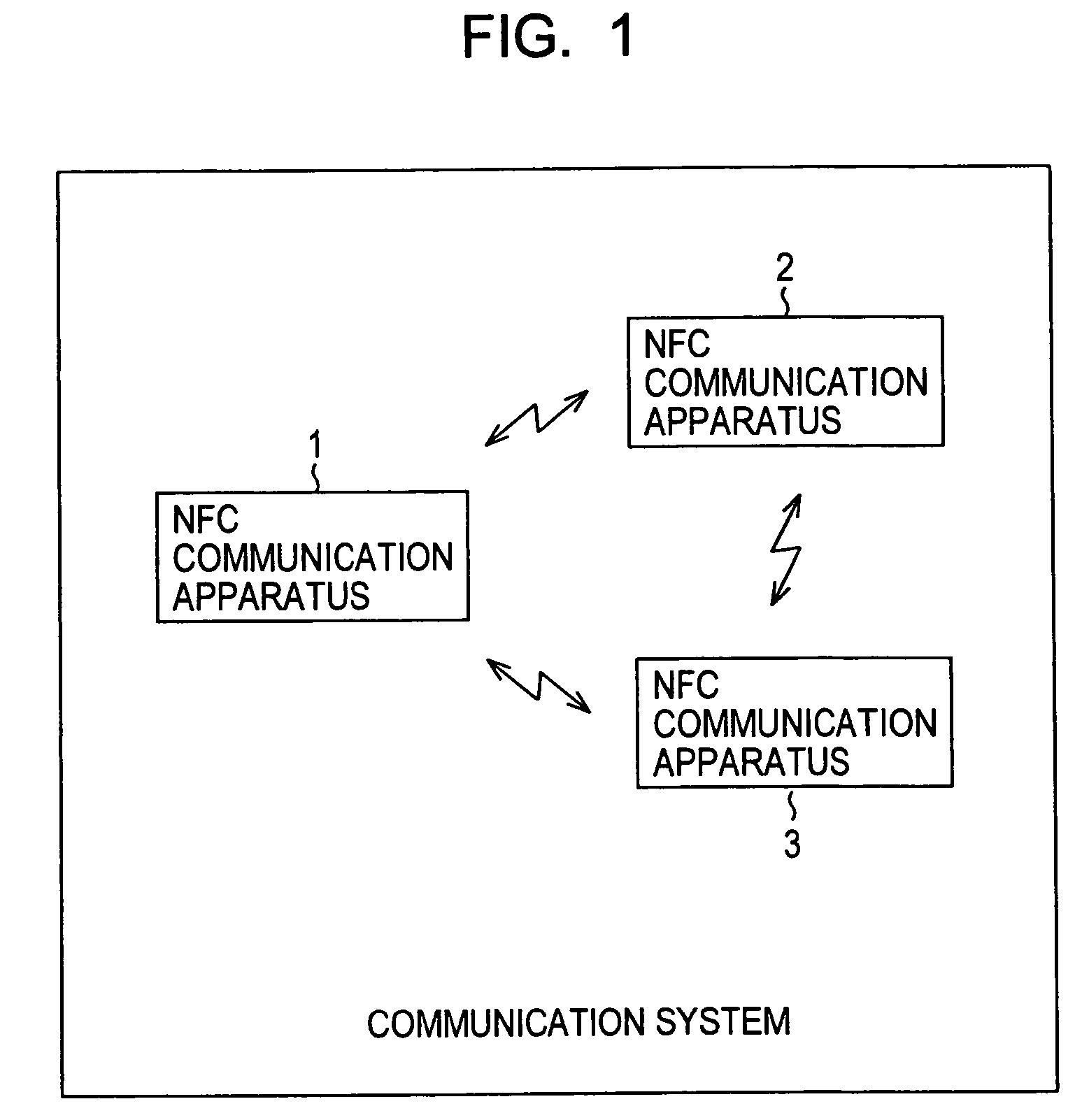
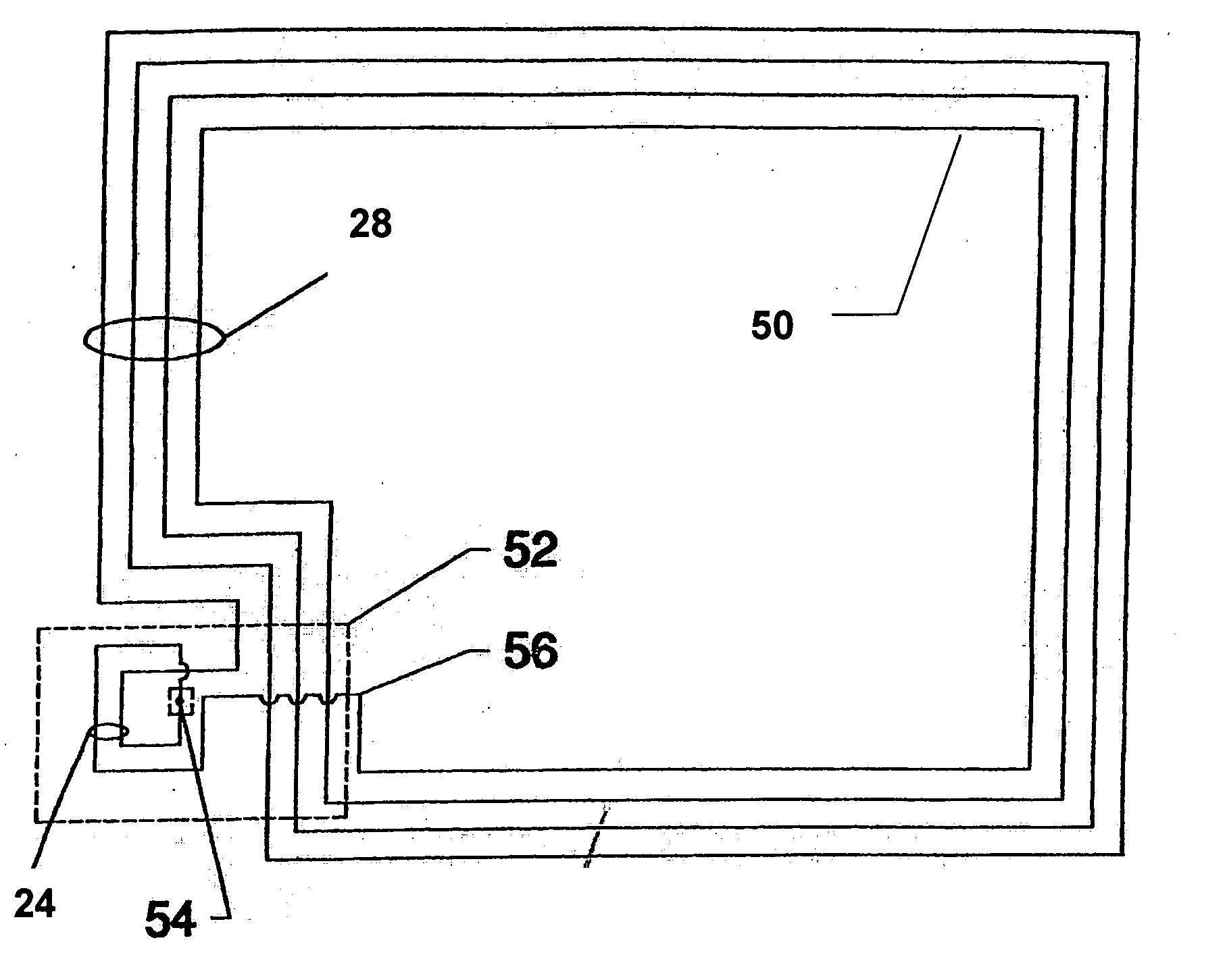
Communication System
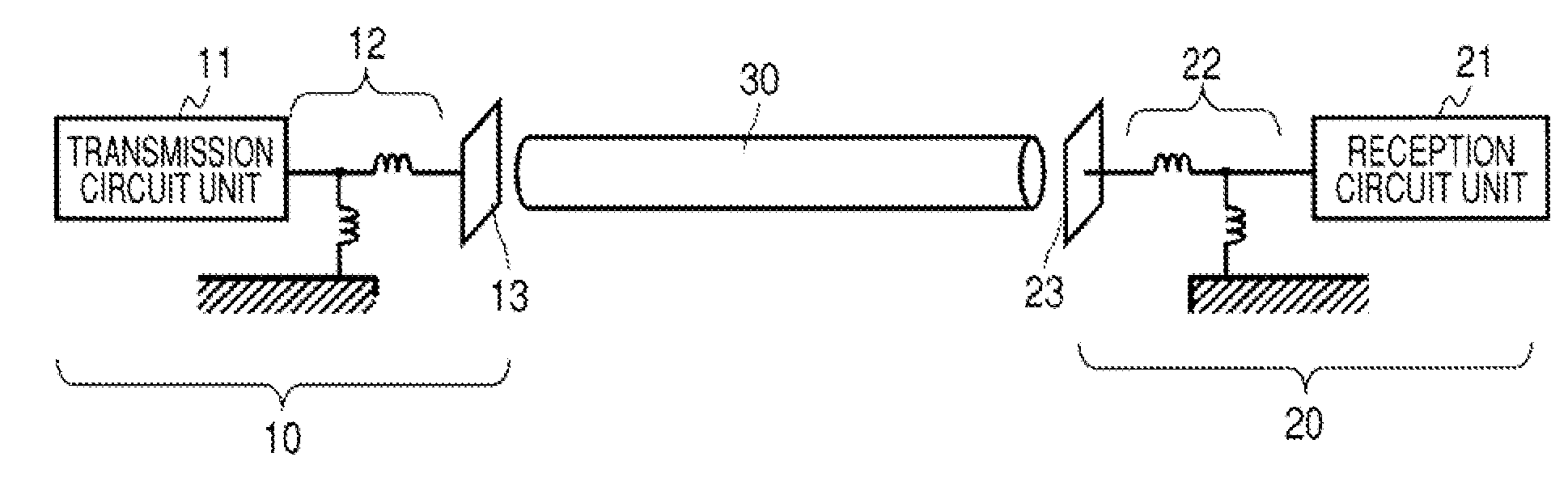
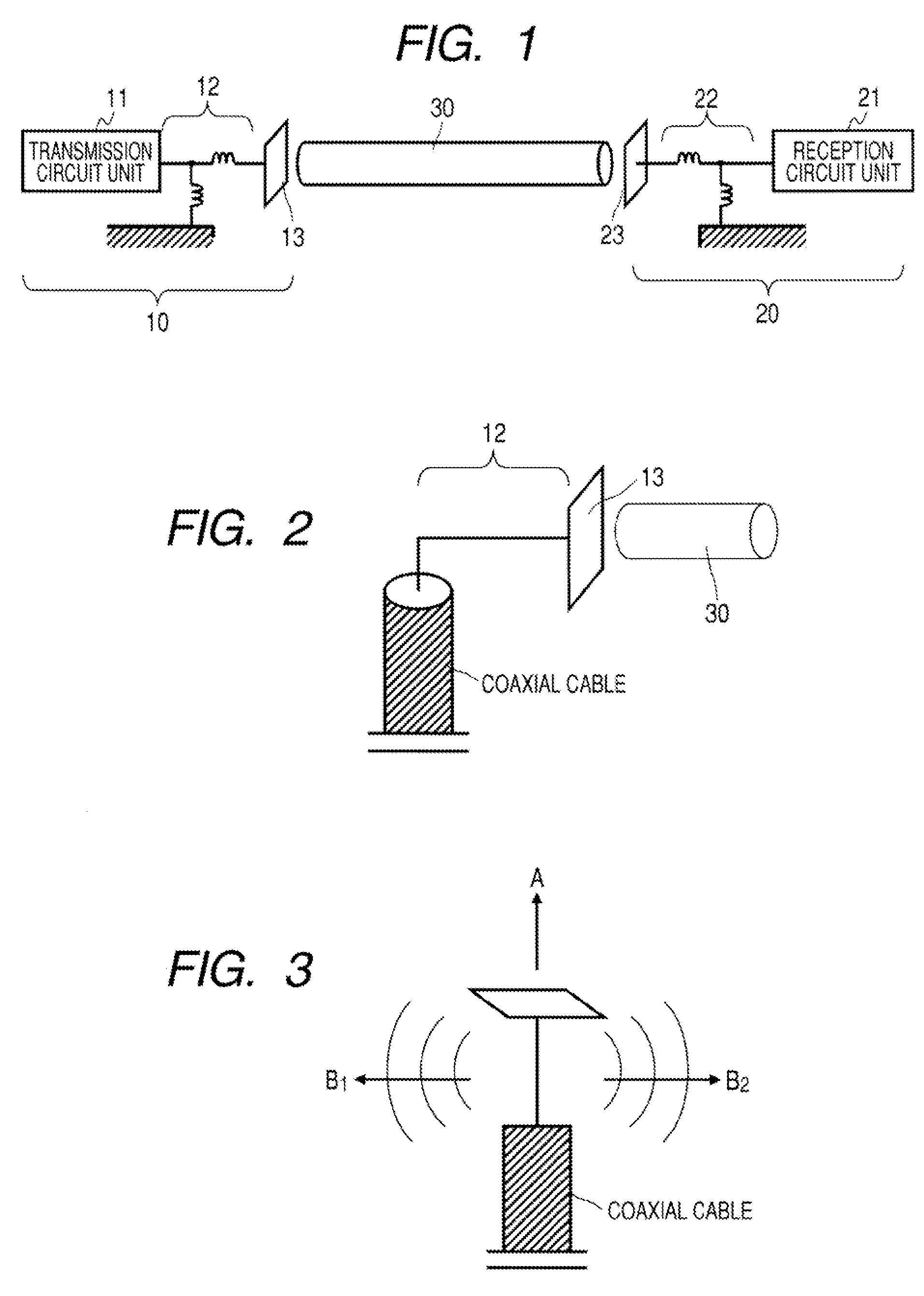
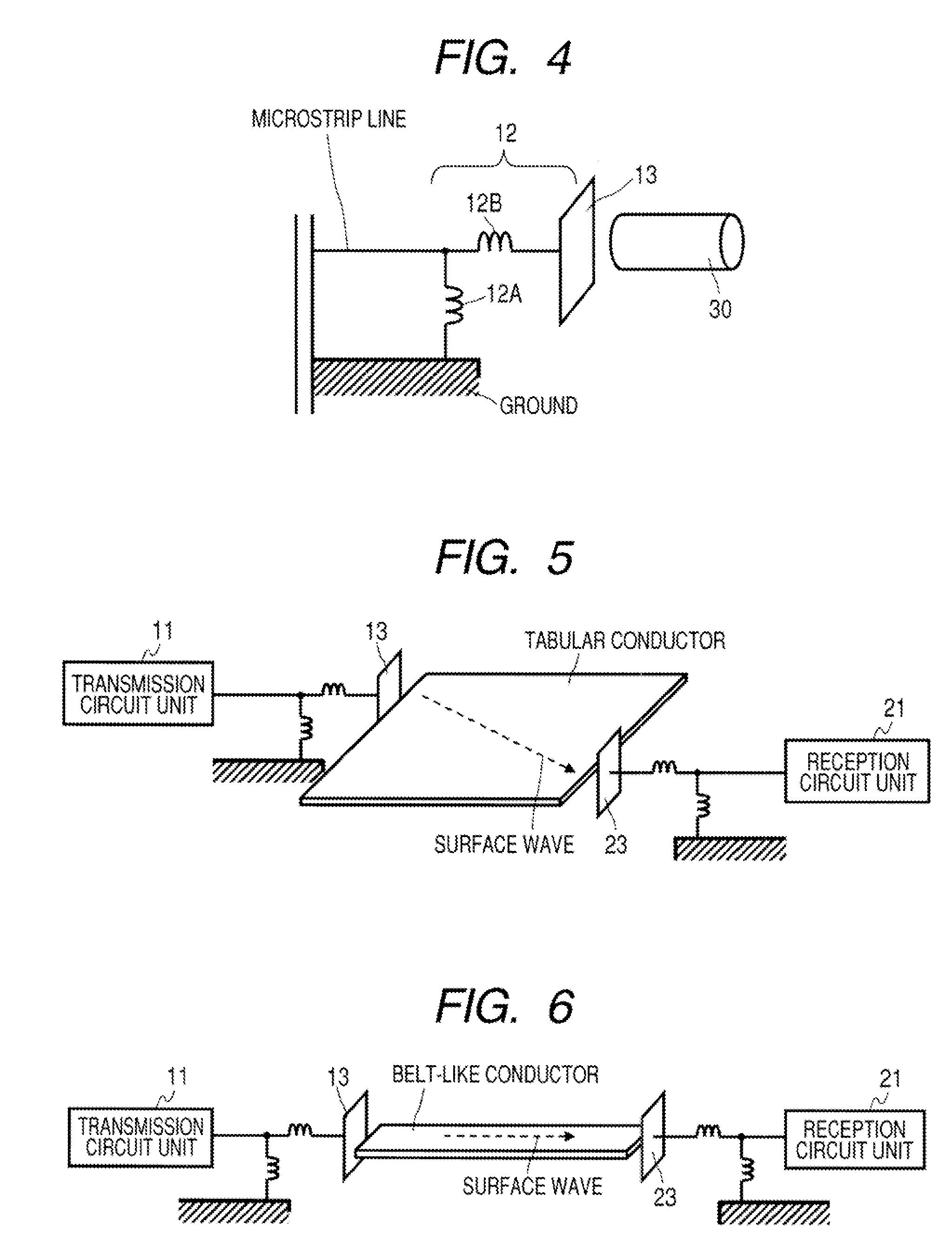
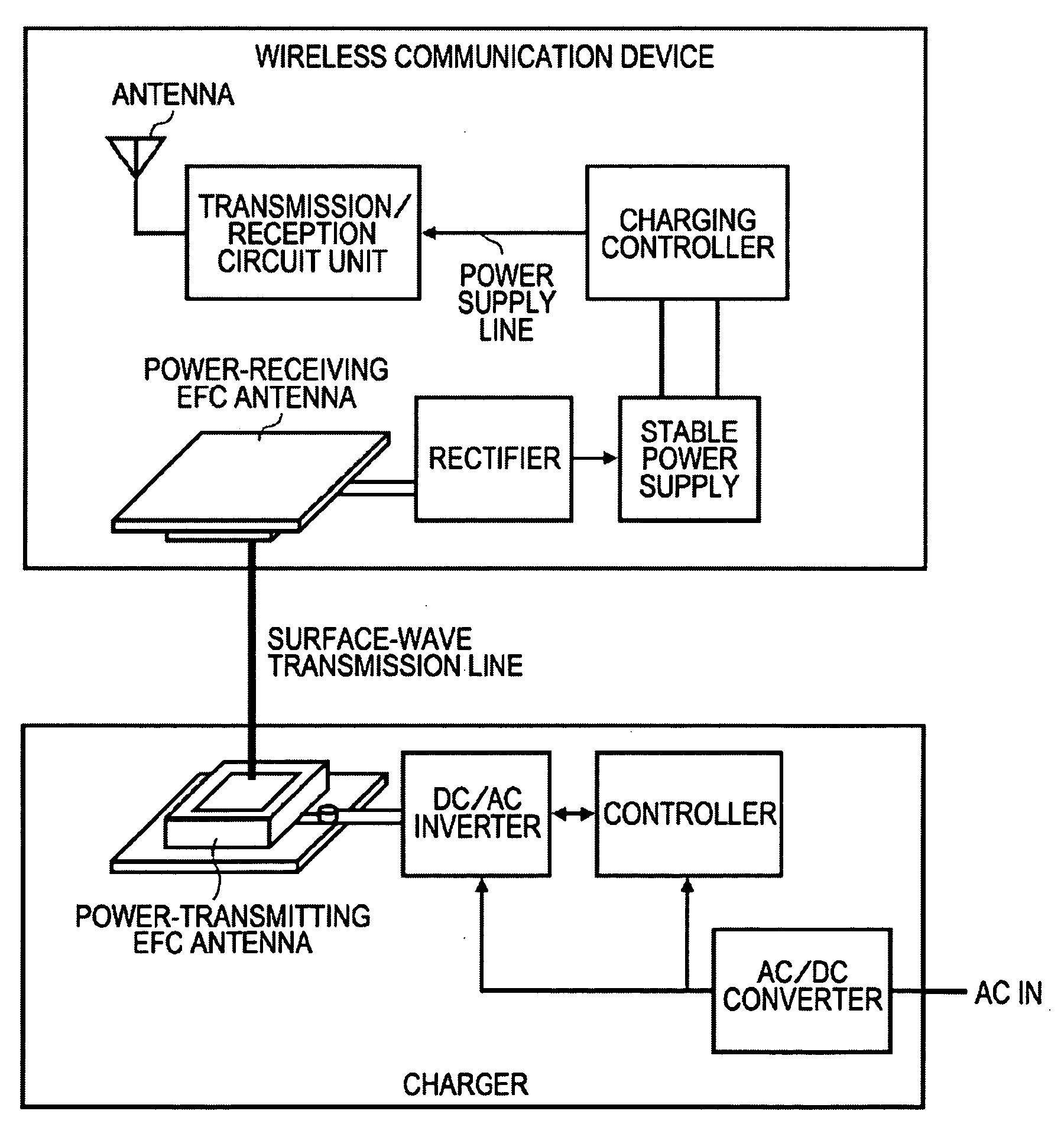
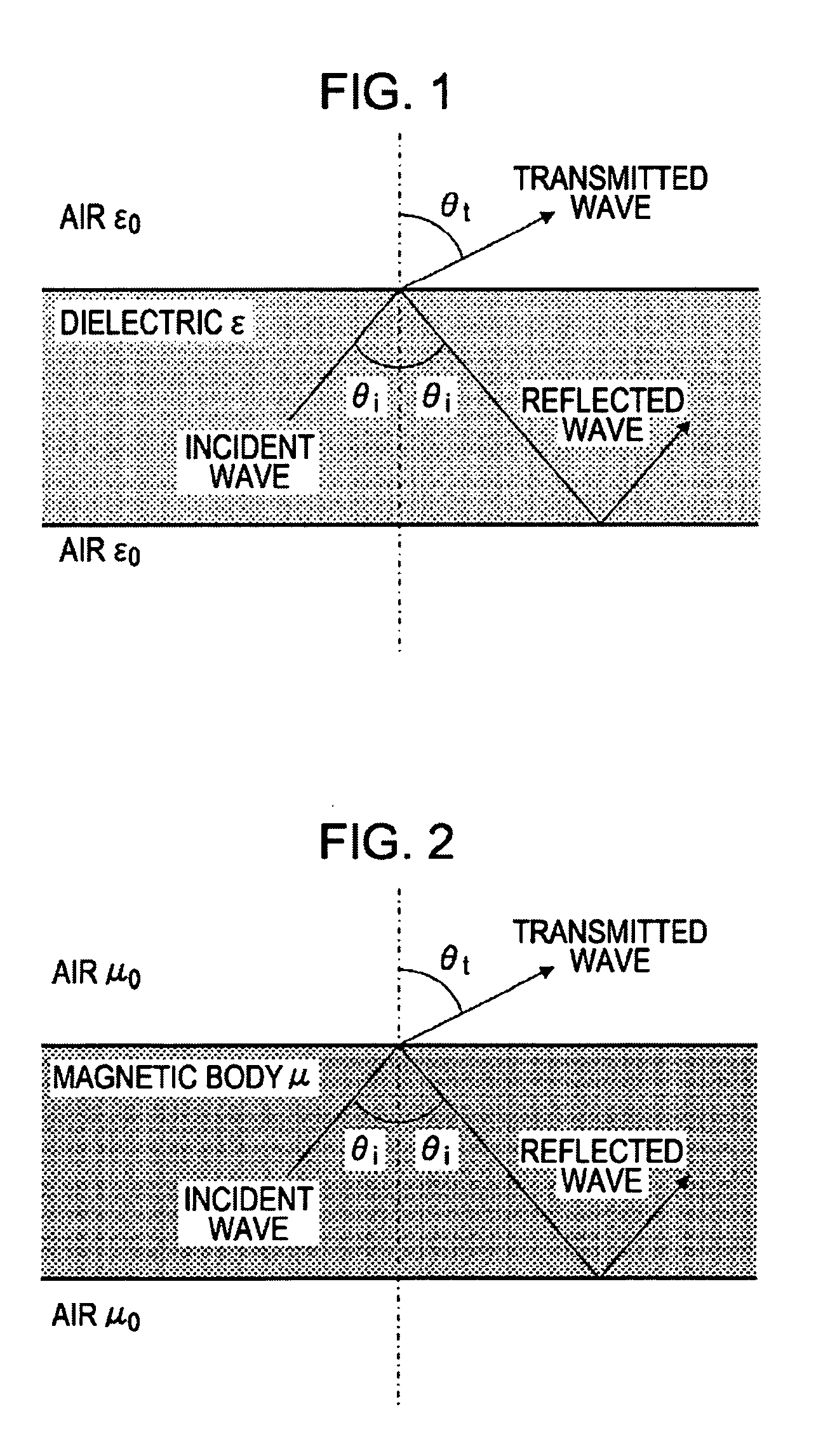
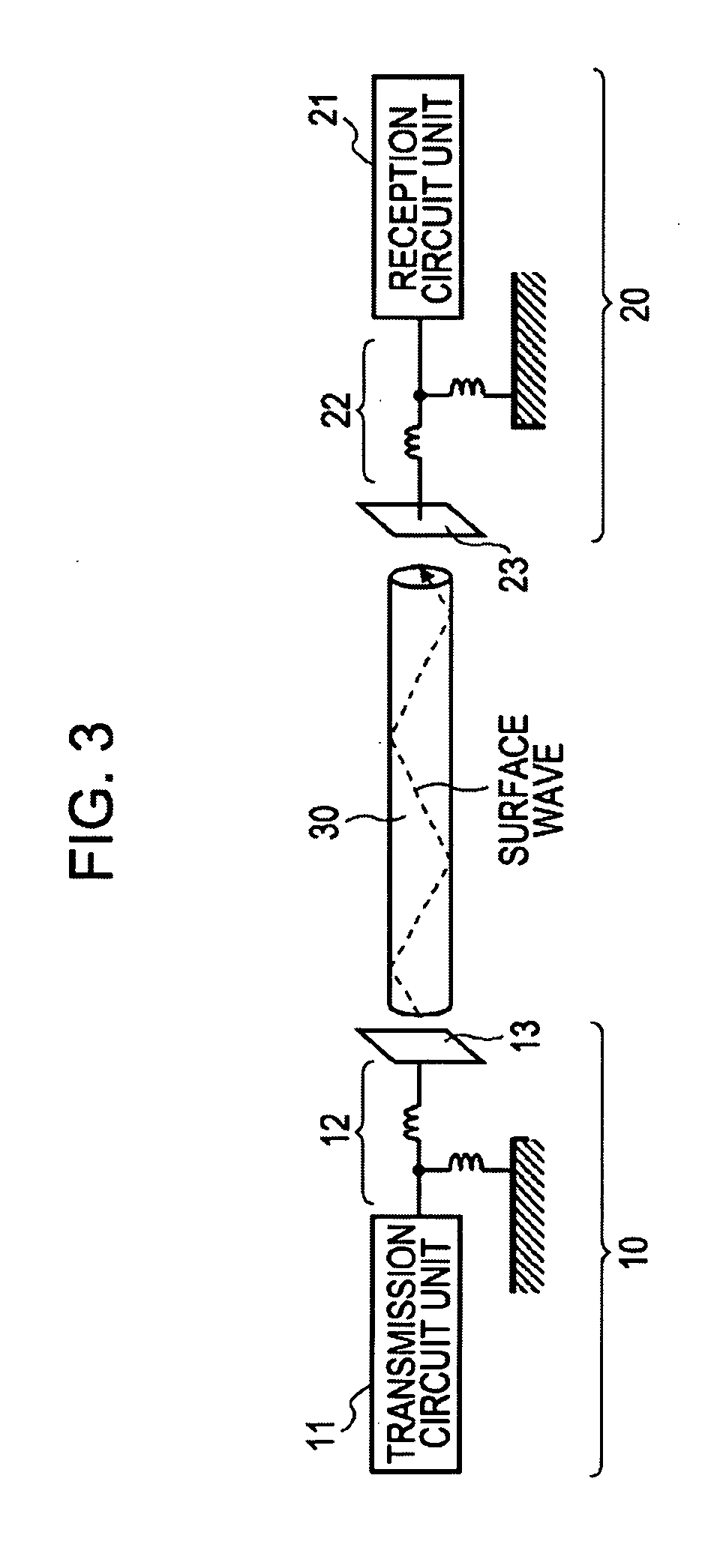
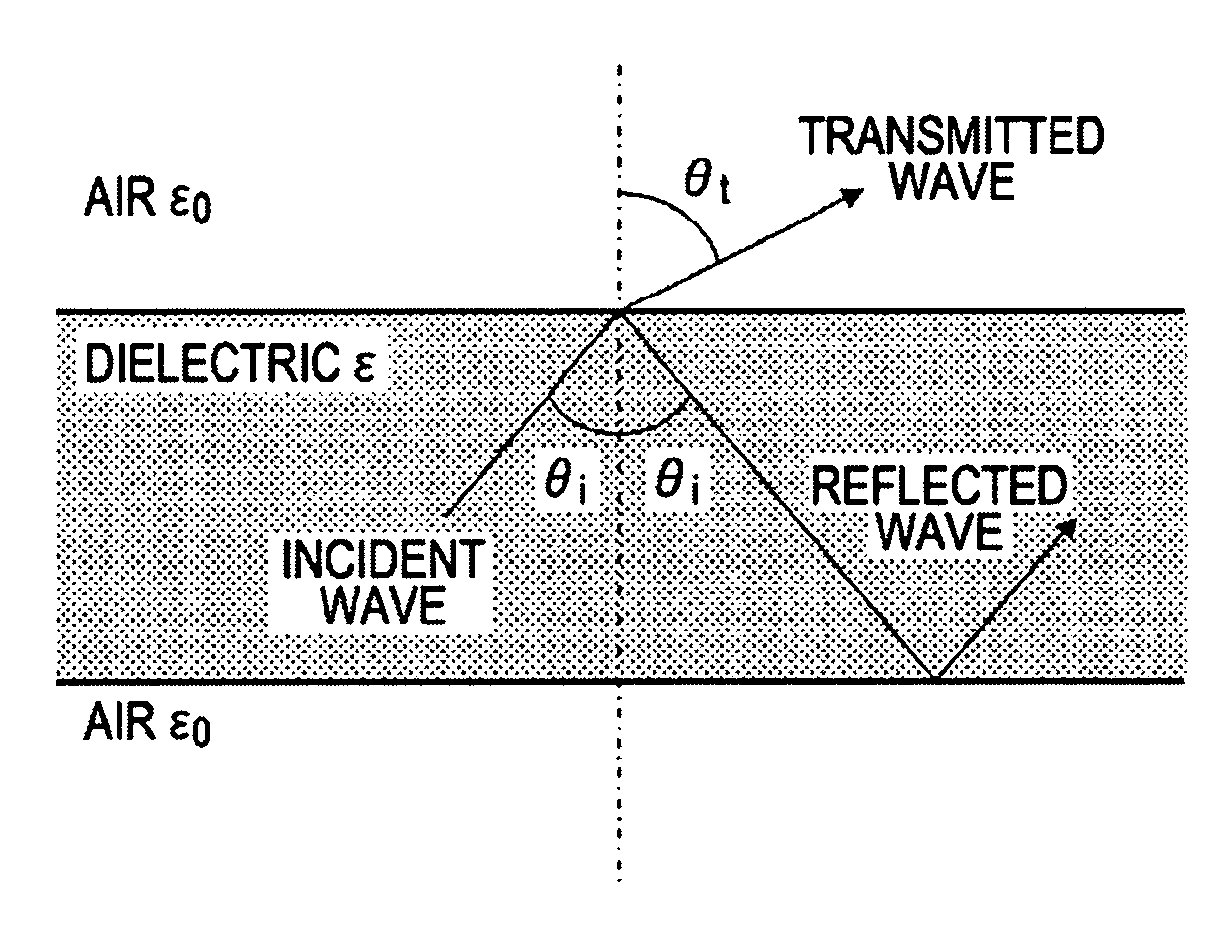
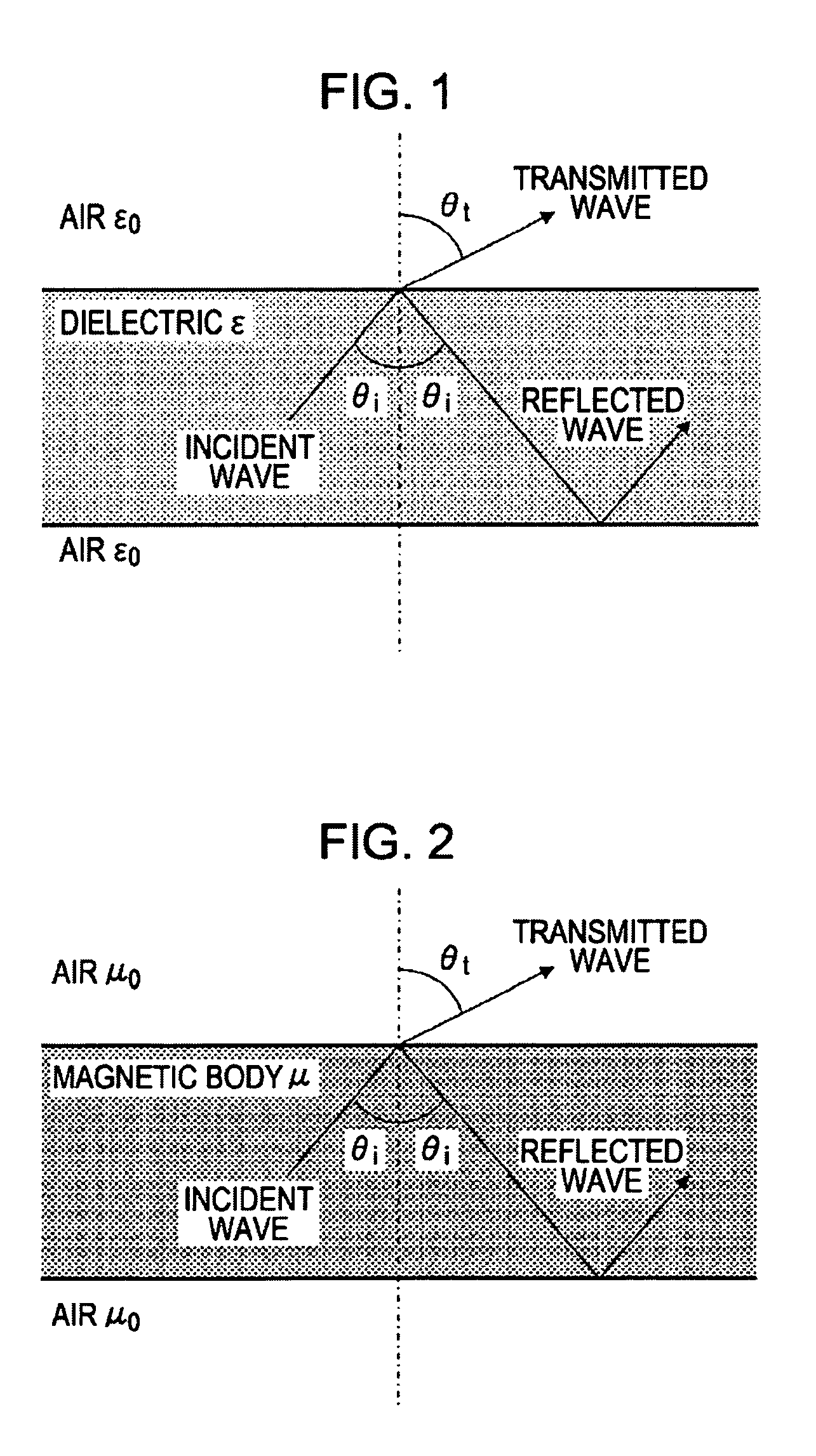
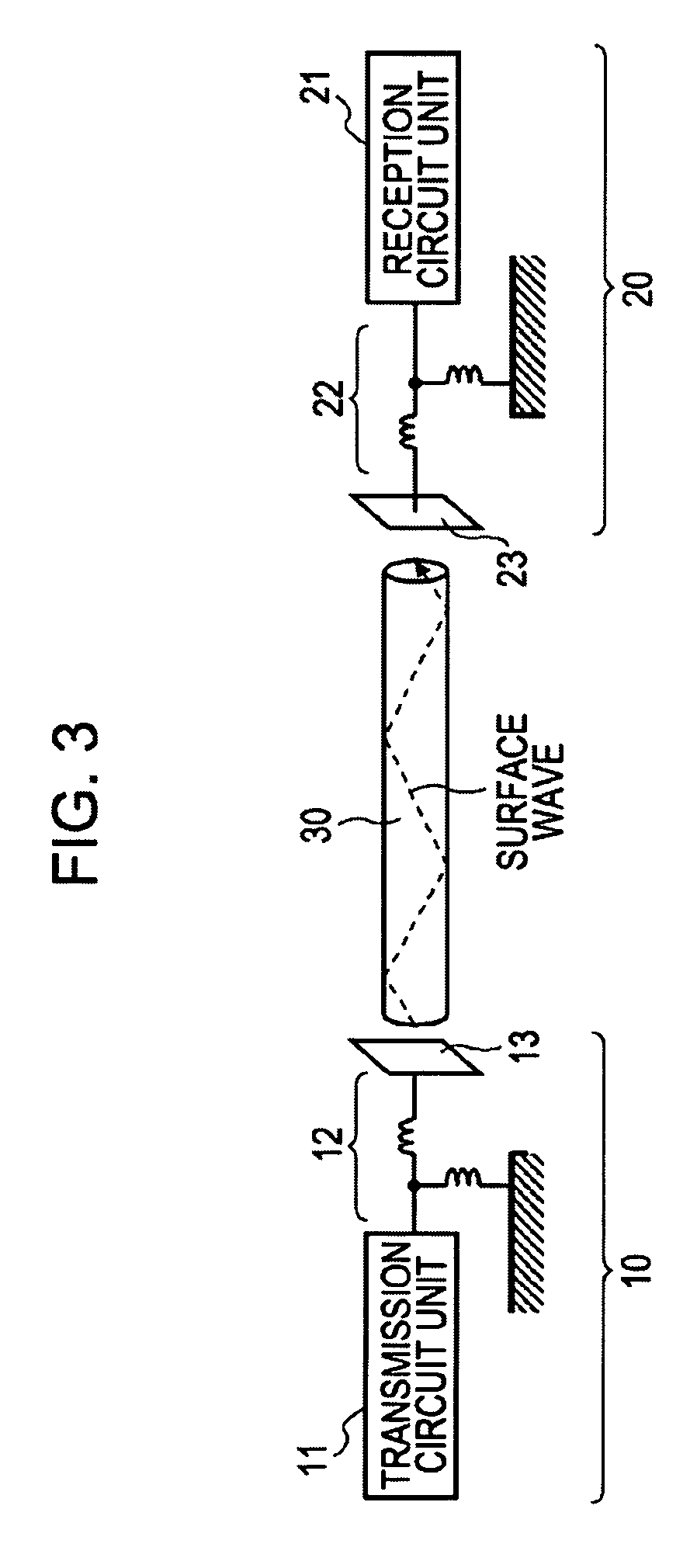
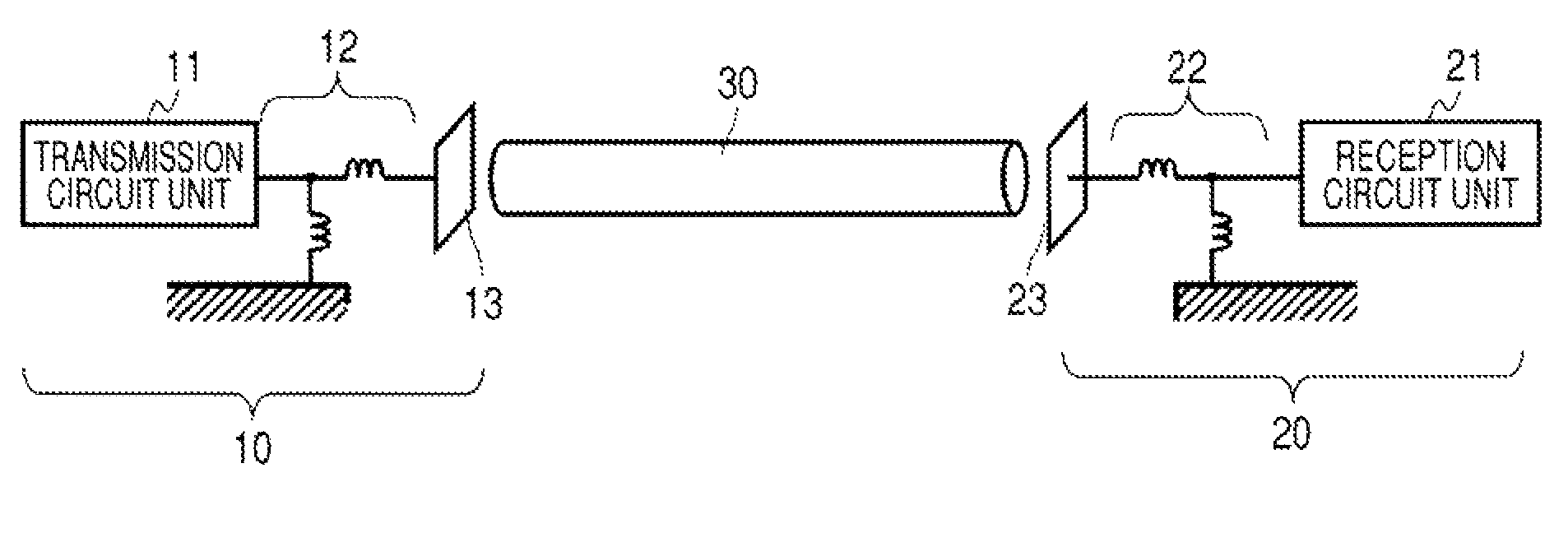
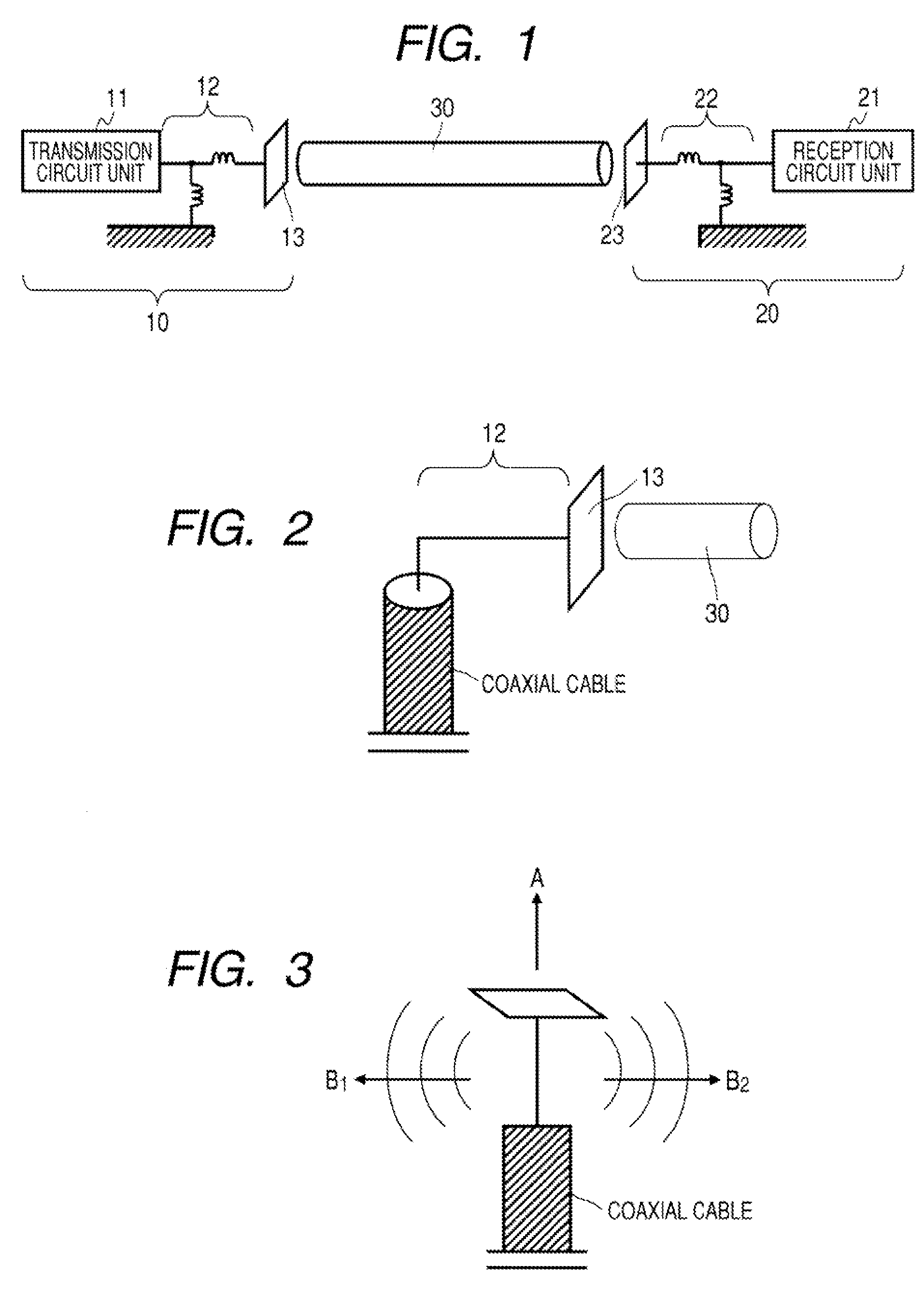
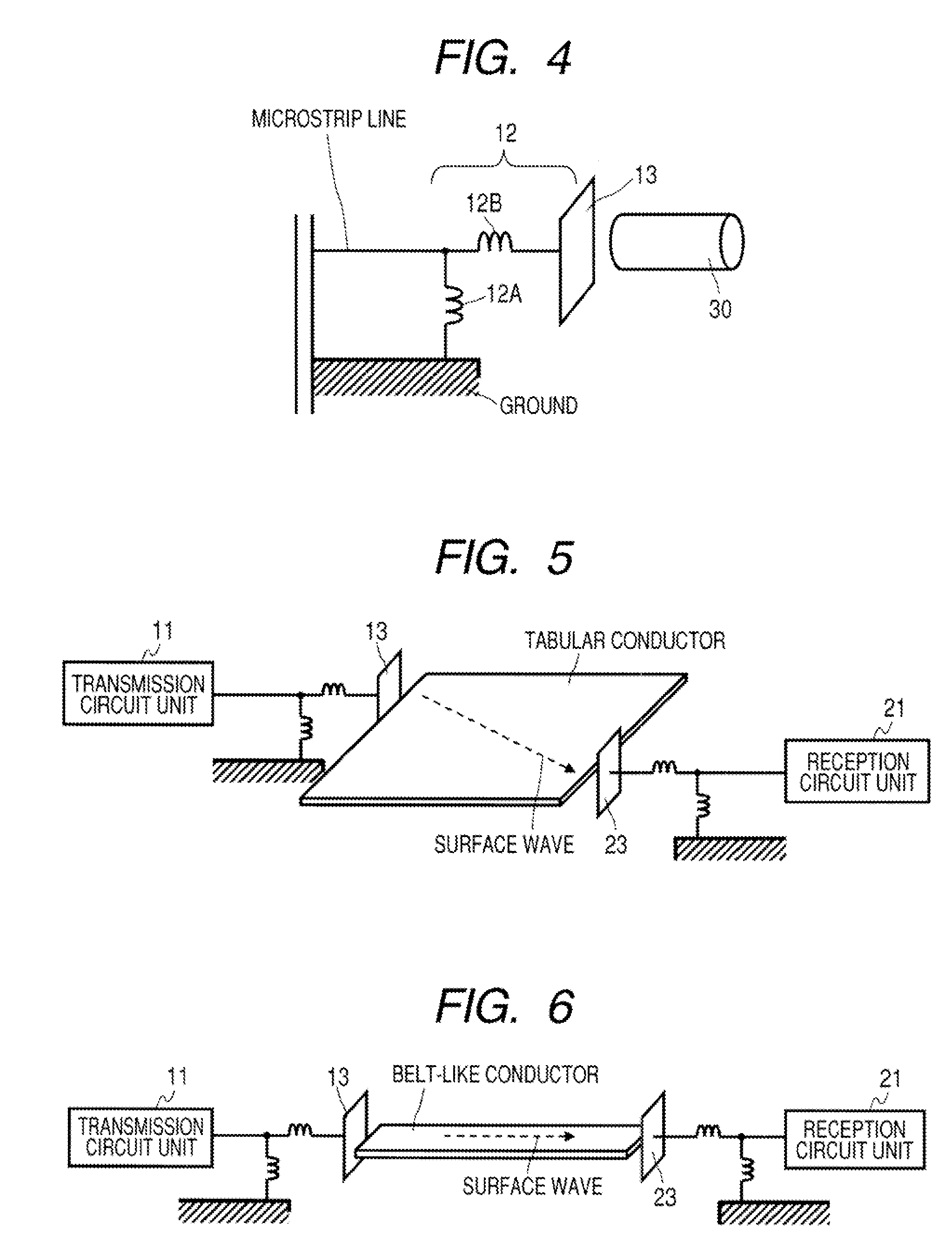
A communication system includes a transmitter including a transmission circuit unit that generates an RF signal for transmitting data and an electric-field-coupling antenna that transmits the RF signal as an electrostatic field, a receiver including an electric-field-coupling antenna and a reception circuit unit that subjects an RF signal received by the electric-field-coupling antenna to reception processing, and a surface-wave propagating means for providing a surface wave transmission line made of a conductor that propagates a surface wave radiated from the electric-field-coupling antenna of the transmitter along a surface of the surface wave transmission line.
Owner:SONY CORP
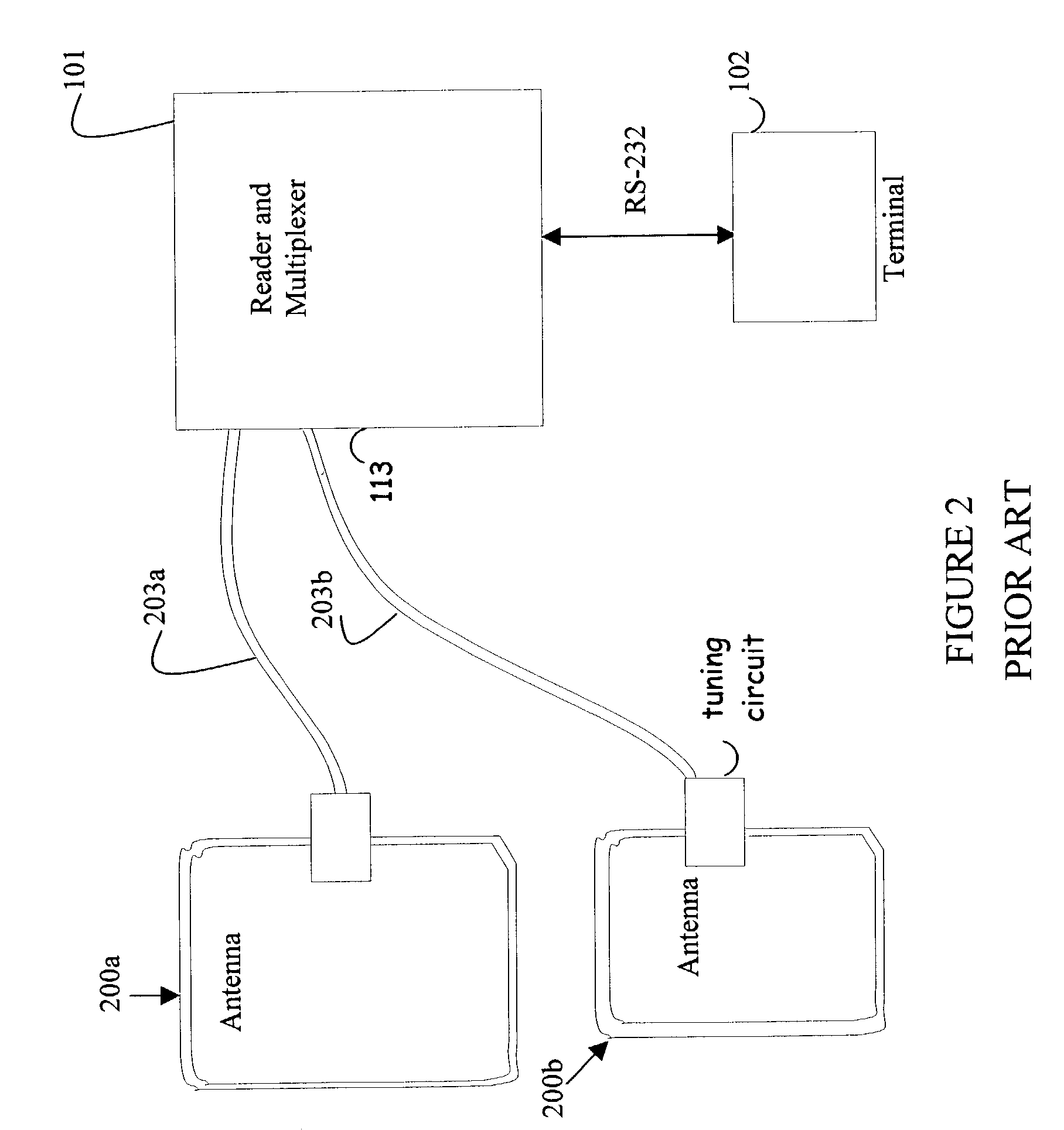
Intelligent station using multiple RF antennae and inventory control system and method incorporating same
ActiveUS7084769B2Boost RF signal strengthAntenna supports/mountingsCash registersControl systemEngineering
An inventory control system and method that tracks inventories of items with RFID tags, includes a reader unit and an intelligent station that tracks RFID tags to determine item information of items to be inventoried. The reader unit transmits and receives RF signals. The intelligent station includes a first RF antenna connected to the reader unit by a first transmission cable through a first switch, and one or more additional RF antennae connected to the reader unit by the same first transmission cable through additional switches. An inventory control processing unit receives item information from the intelligent stations to update inventory information regarding the items to be inventoried.
Owner:SENSORMATIC ELECTRONICS CORP
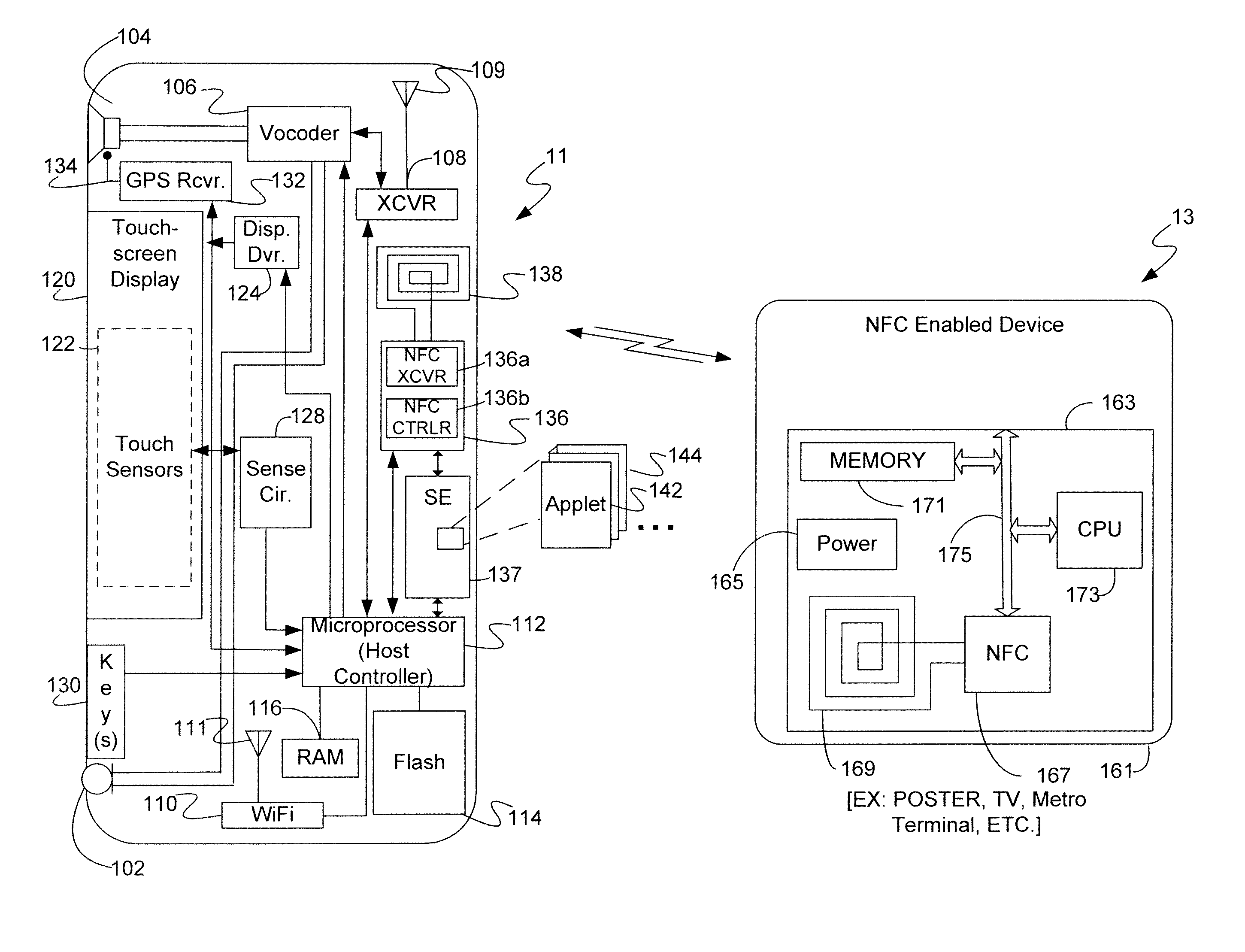
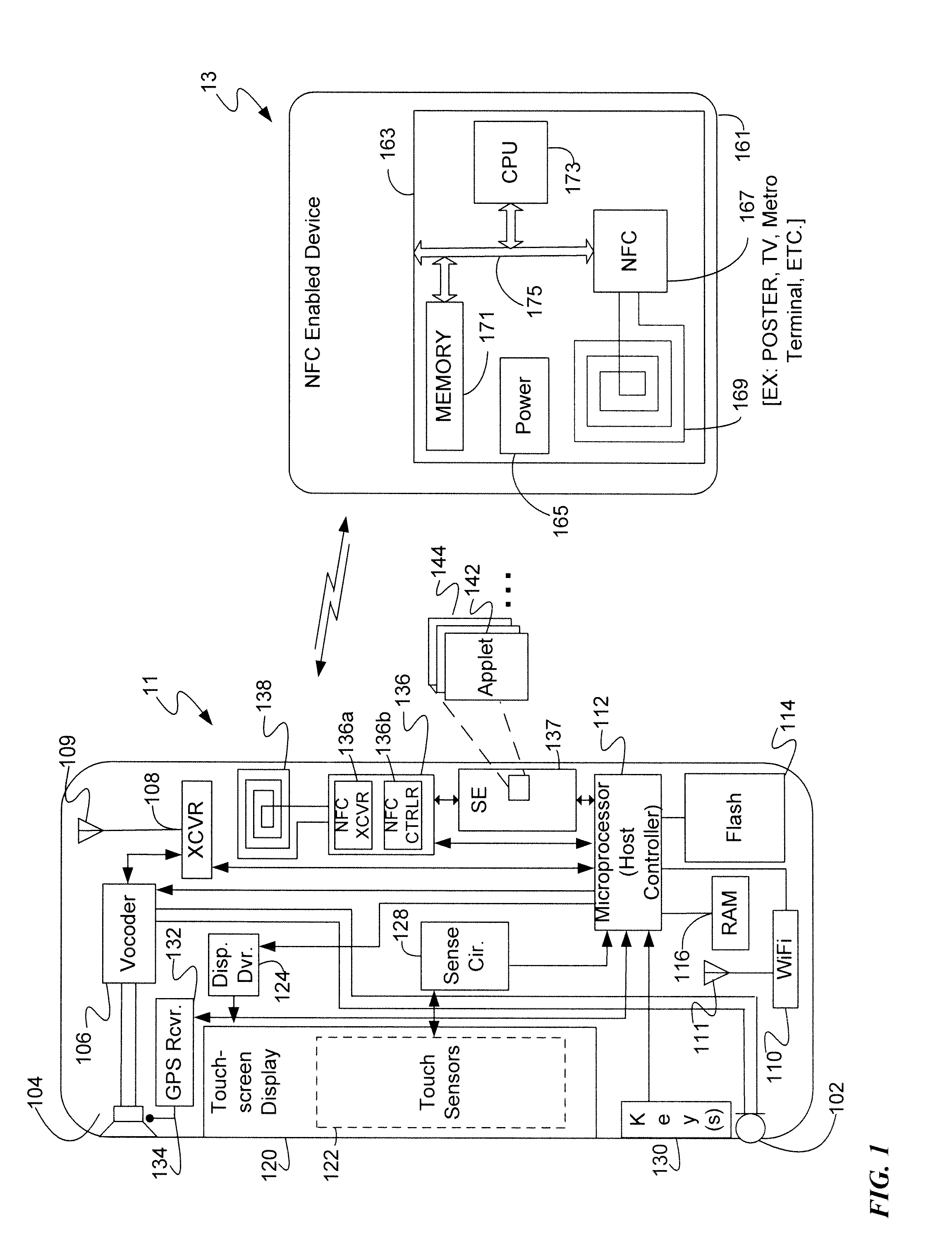
Secure NFC data authentication
ActiveUS20140256251A1Near-field systems using receiversPayment architectureTransceiverWireless transceiver
A mobile device includes a wireless transceiver, a host processor, a secure element (SE), and a near field communication (NFC) system having an NFC transceiver and an NFC controller implementing a contactless front end. The contactless front end routes a near field communication related to a payment transaction between the NFC system and the SE without going to or from the host processor. The contactless front end routes a near field communication not related to a payment transaction, but requiring a security function, between the NFC system and the SE without going to or from the host processor. The contactless front end routes a near field communication not related to a payment transaction, and not requiring a security function, between the NFC system and host processor without going to or from the SE.
Owner:CELLCO PARTNERSHIP INC
Communication System and Communication Apparatus
A communication system includes the following elements: a transmitter including a transmission circuit unit configured to generate an RF signal for transmitting data and an electric-field-coupling antenna configured to transmit the RF signal as an electrostatic field; a receiver including an electric-field-coupling antenna and a reception circuit unit configured to receive and process the RF signal received by the electric-field-coupling antenna; and a surface-wave propagation medium configured to provide a surface-wave transmission line to transmit a surface wave emanating from the electric-field-coupling antenna of the transmitter with low propagation loss.
Owner:SONY CORP
Communication system and communication apparatus
A communication system includes the following elements: a transmitter including a transmission circuit unit configured to generate an RF signal for transmitting data and an electric-field-coupling antenna configured to transmit the RF signal as an electrostatic field; a receiver including an electric-field-coupling antenna and a reception circuit unit configured to receive and process the RF signal received by the electric-field-coupling antenna; and a surface-wave propagation medium configured to provide a surface-wave transmission line to transmit a surface wave emanating from the electric-field-coupling antenna of the transmitter with low propagation loss.
Owner:SONY CORP
Communication system
Owner:SONY CORP
Near field RF communicators and near field communications enabled devices
ActiveUS8150321B2Near-field systems using receiversNear-field in transpondersEngineeringSignal generator
A near field RF communicator has: an antenna operable to generate an RF signal to enable inductive coupling via the magnetic field of the RF signal between the antenna and another near field RF communicator or RF transponder in near field range; and a signal generator operable to generate a multi-level digital sine wave drive signal to drive the antenna to generate the RF signal, wherein the signal generator comprises a selector operable to select one or more digital sequences to provide one or more digital signals from which the digital sine wave drive signal is generated.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Signal transmission system, connector apparatus, electronic device, and signal transmission method
ActiveUS20130109317A1Increase speedLarge capacityTwo pole connectionsPower distribution line transmissionElectromagnetic field couplingRadio signal
A signal transmission system including: a first connector apparatus, and a second connector apparatus that is coupled with the first connector apparatus. The first connector apparatus and the second connector apparatus are coupled together to form an electromagnetic field coupling unit, and a transmission object signal is converted into a radio signal, which is then transmitted through the electromagnetic field coupling unit, between the first connector apparatus and the second connector apparatus.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
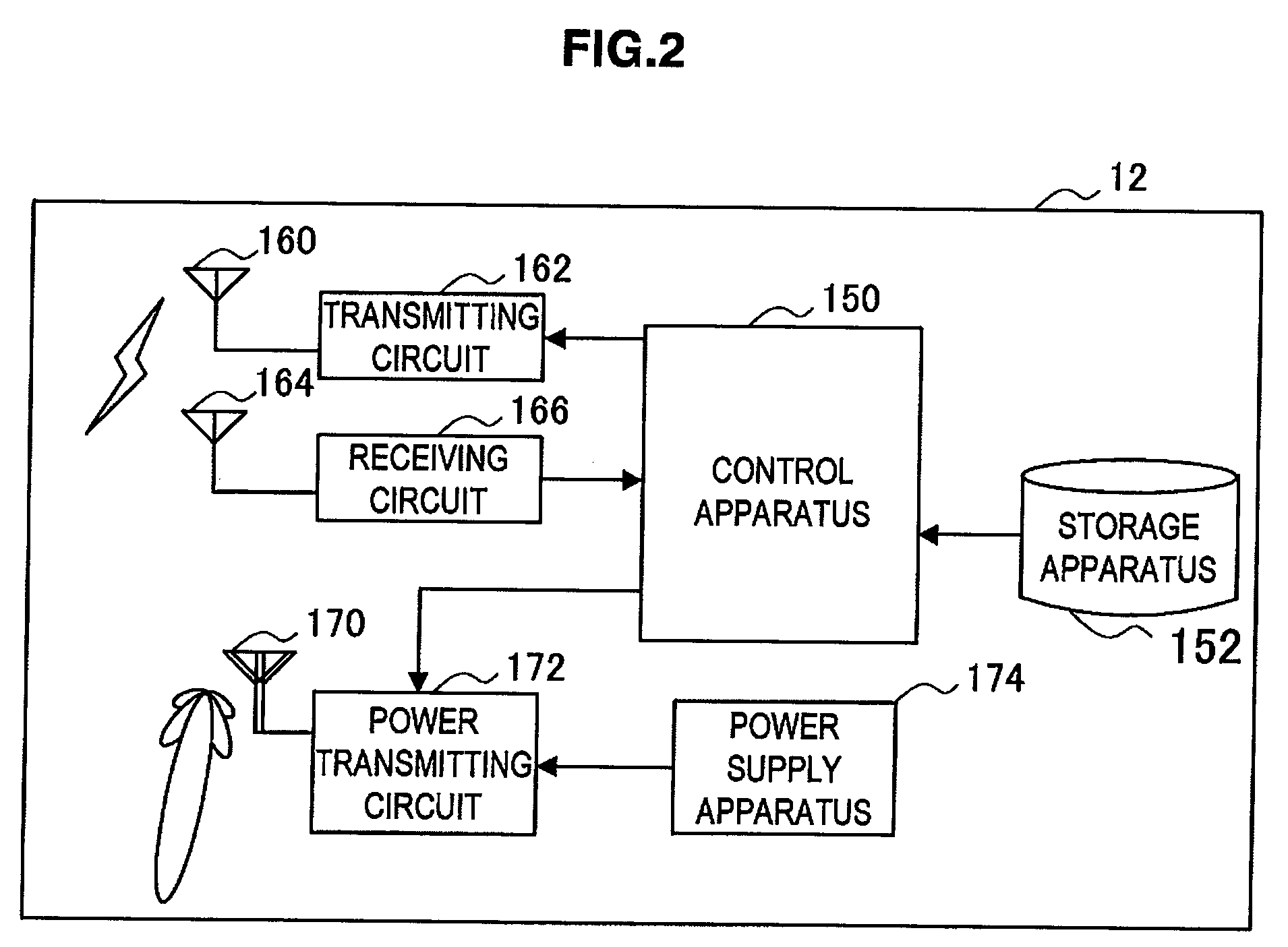
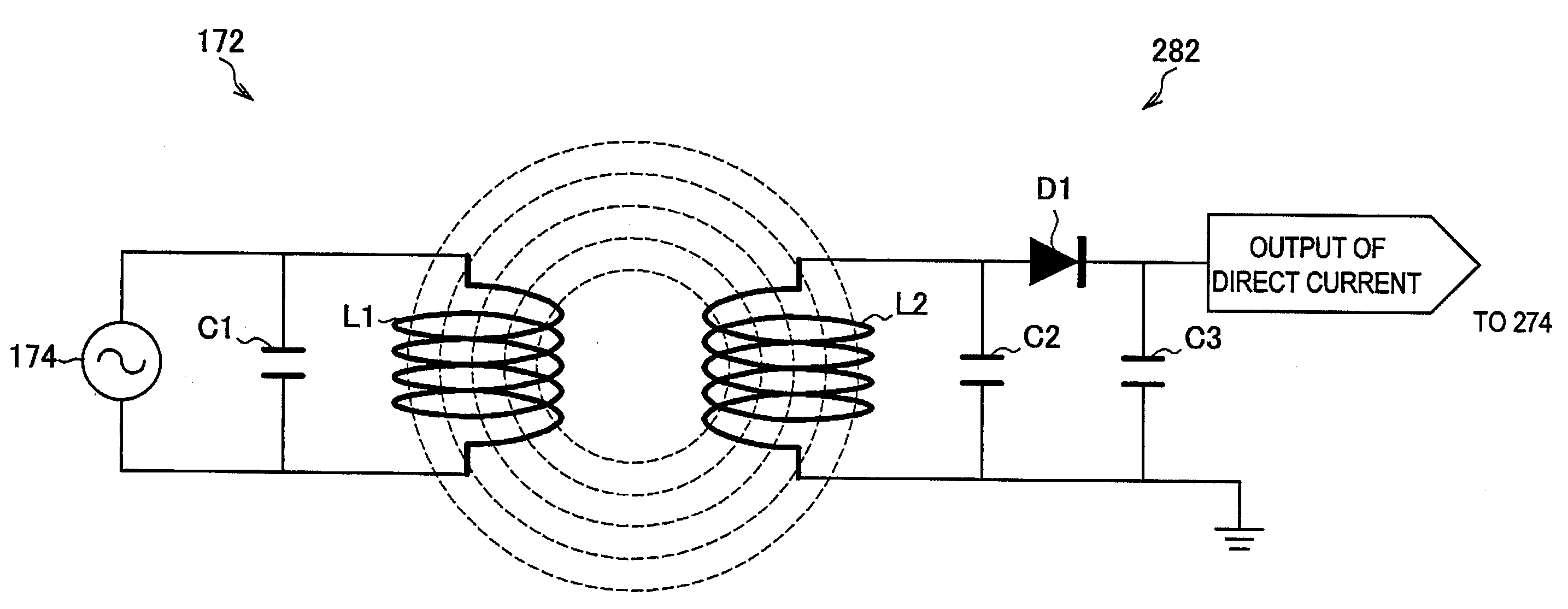
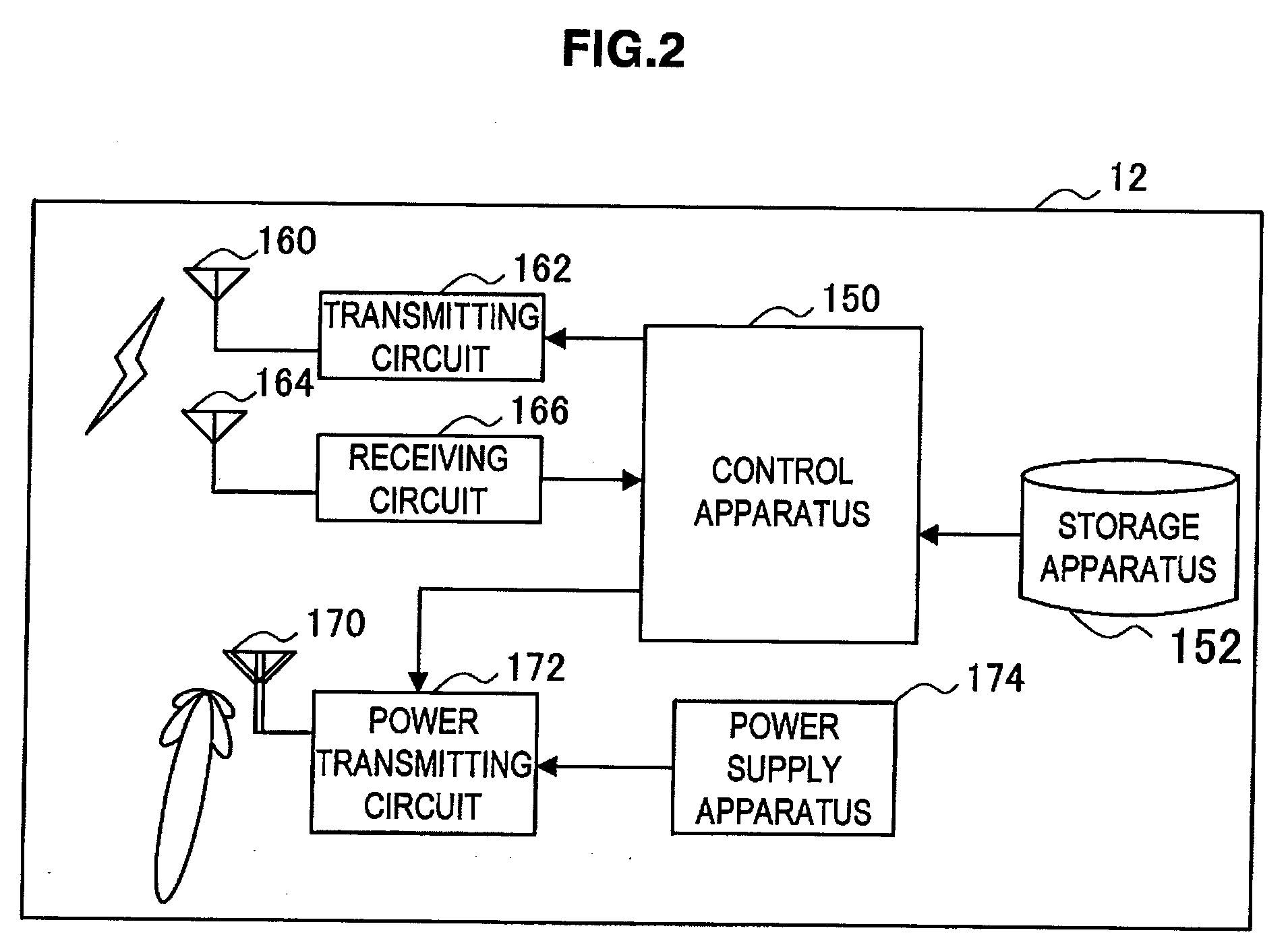
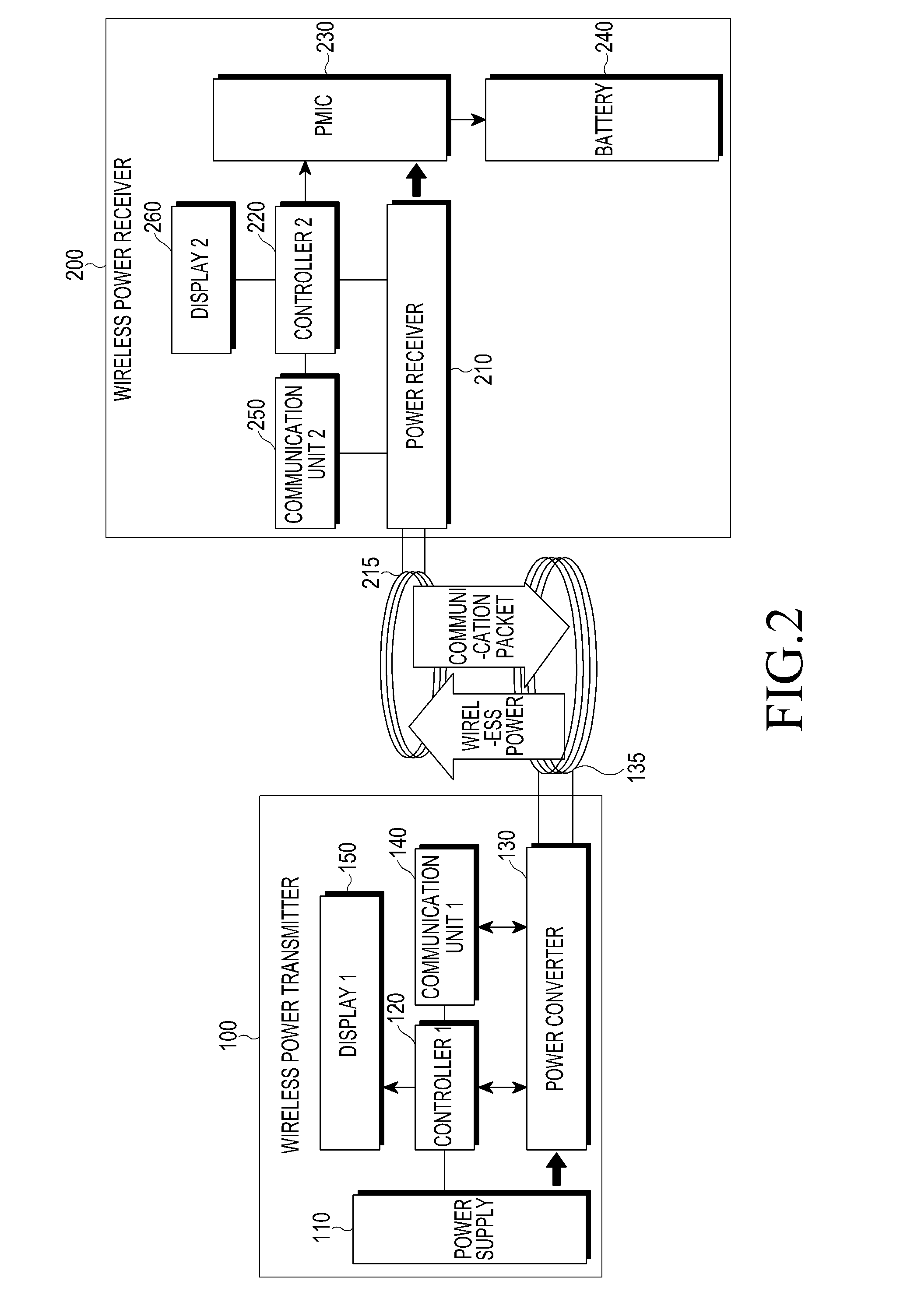
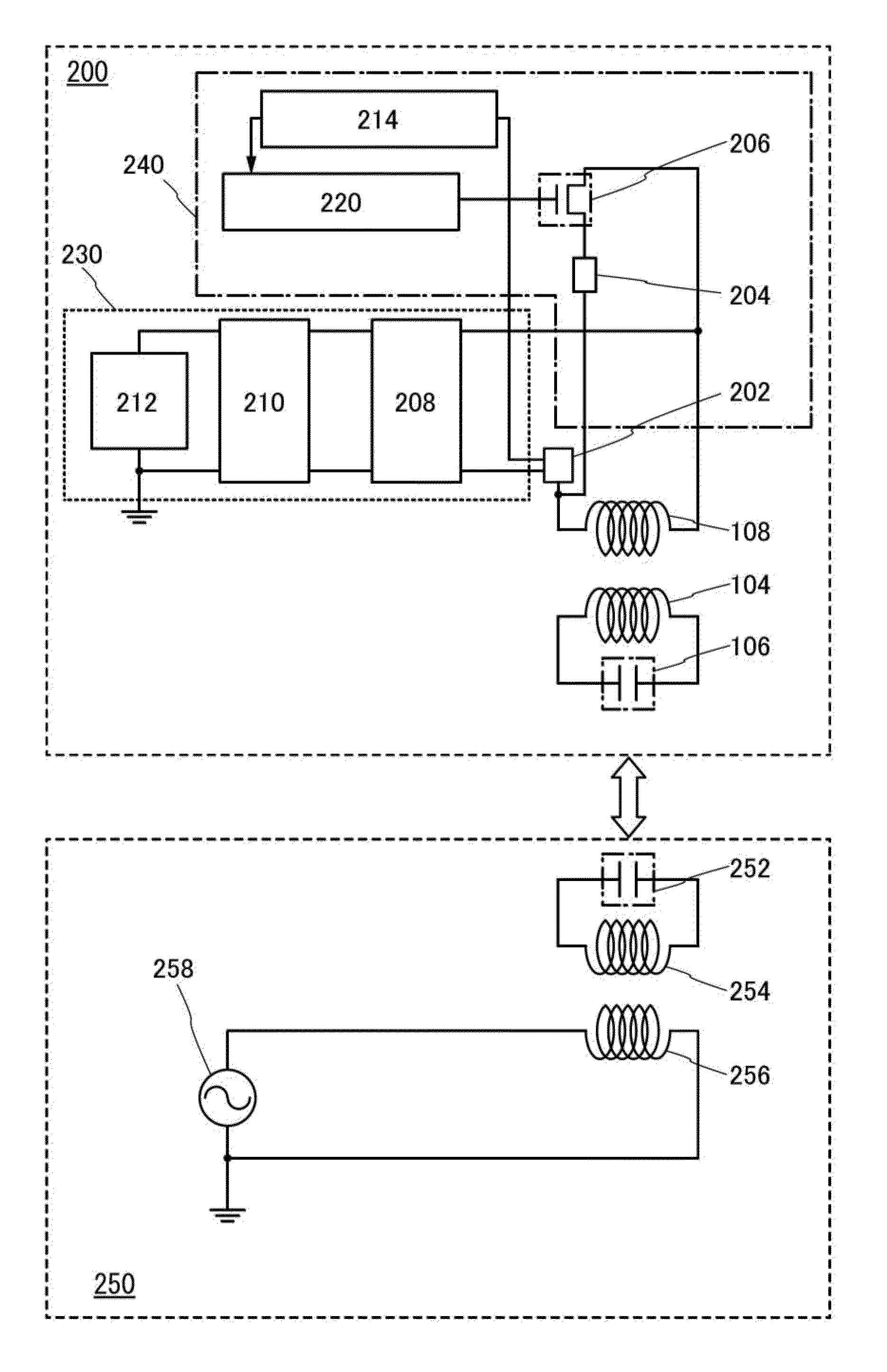
Wireless power and communication system
The present invention provides a wireless communication apparatus including: a communication processing unit that transmits and receives a radio signal; a wireless power transmitting unit that supplies power wirelessly to an apparatus located within a power supplyable range; a location data obtaining unit that obtains location data of a power receiver apparatus; and a control unit that controls a power supply to the power receiver apparatus based on the location data of the power receiver apparatus obtained by the location data obtaining unit.
Owner:SONY CORP
Wireless communication apparatus, power supply method, program, and wireless communication system
ActiveUS20090264069A1Improve power efficiencyBatteries circuit arrangementsReceivers monitoringElectricityCommunications system
The present invention provides a wireless communication apparatus including: a communication processing unit that transmits and receives a radio signal; a wireless power transmitting unit that supplies power wirelessly to an apparatus located within a power supplyable range; a location data obtaining unit that obtains location data of a power receiver apparatus; and a control unit that controls a power supply to the power receiver apparatus based on the location data of the power receiver apparatus obtained by the location data obtaining unit.
Owner:SONY CORP
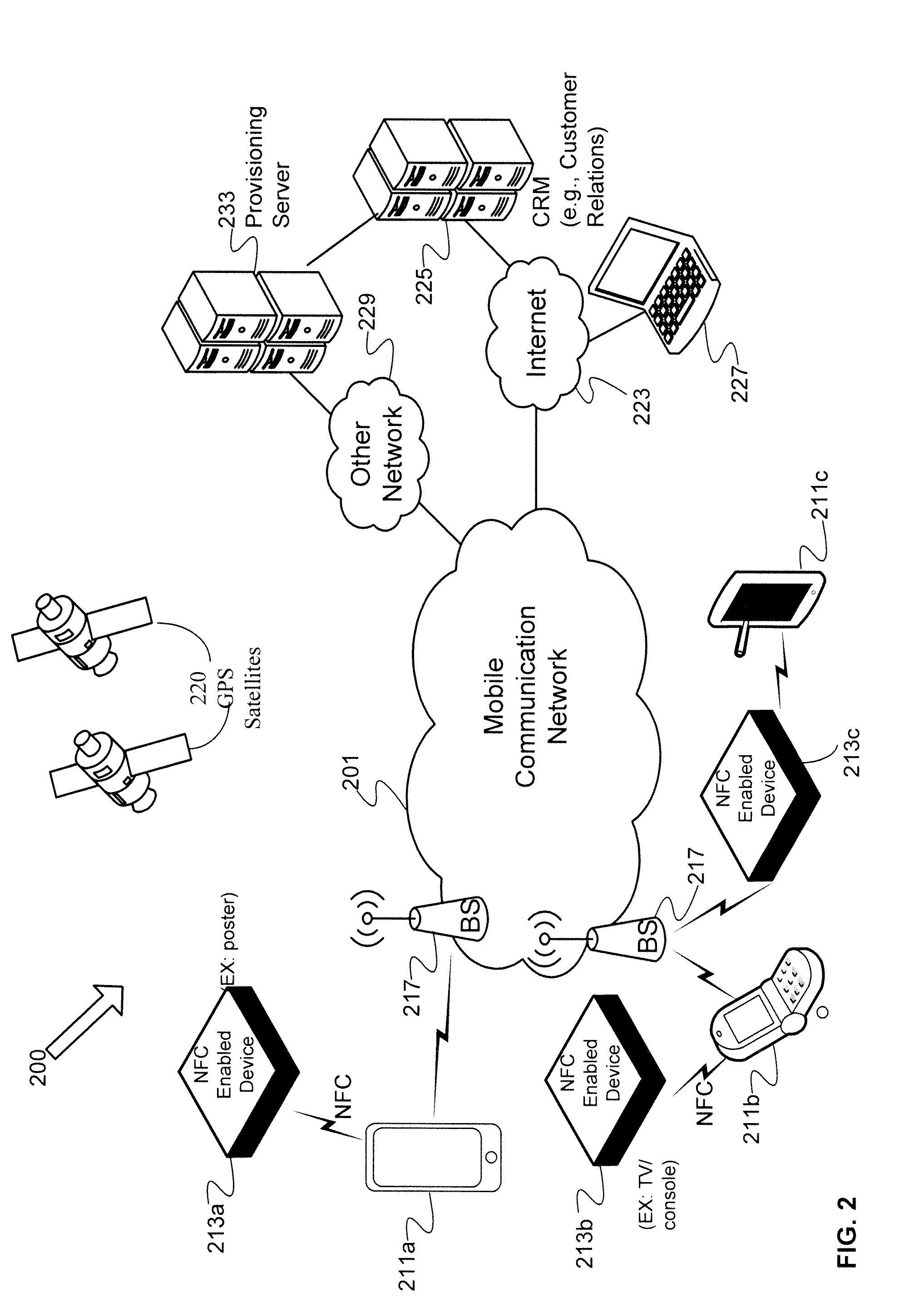
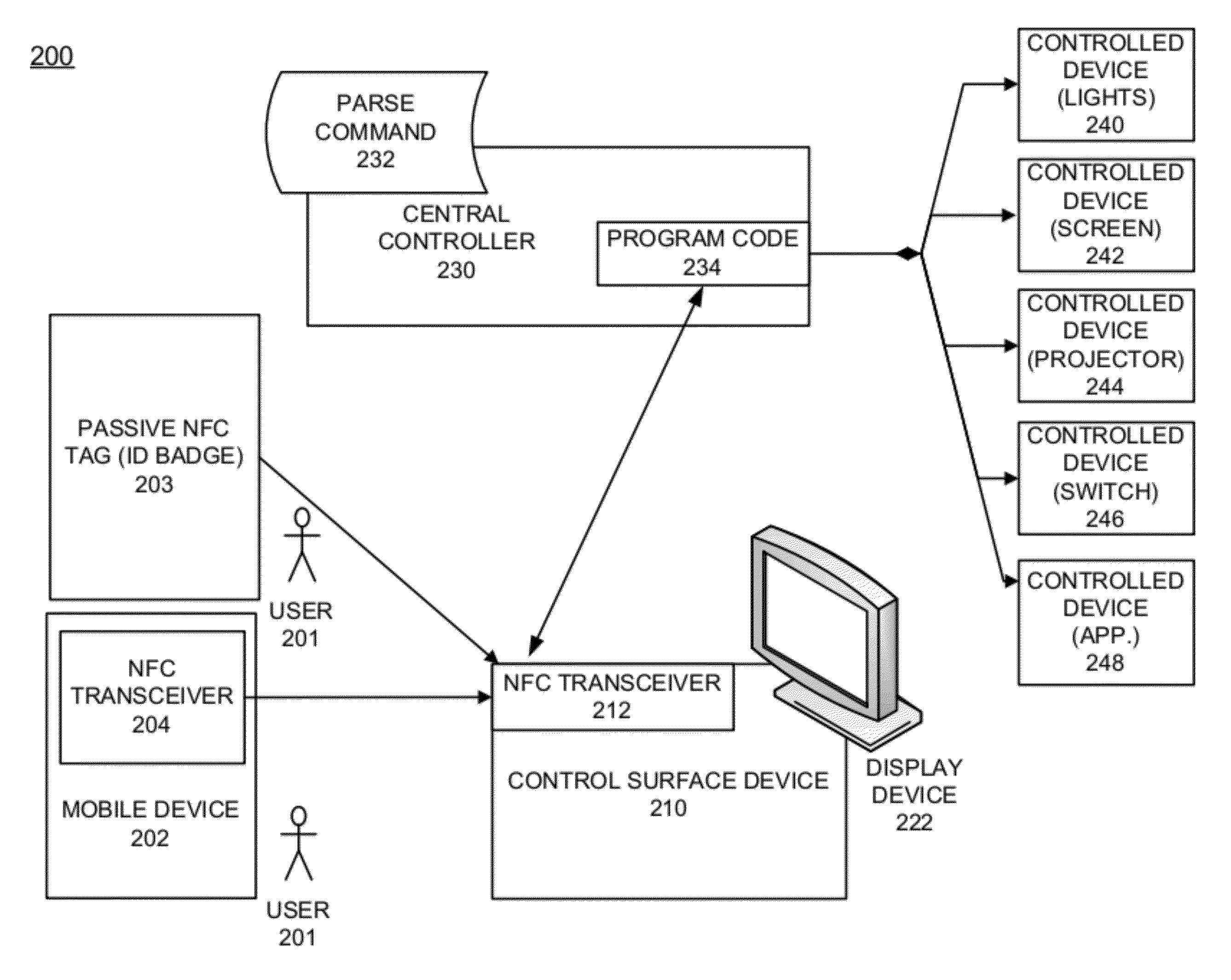
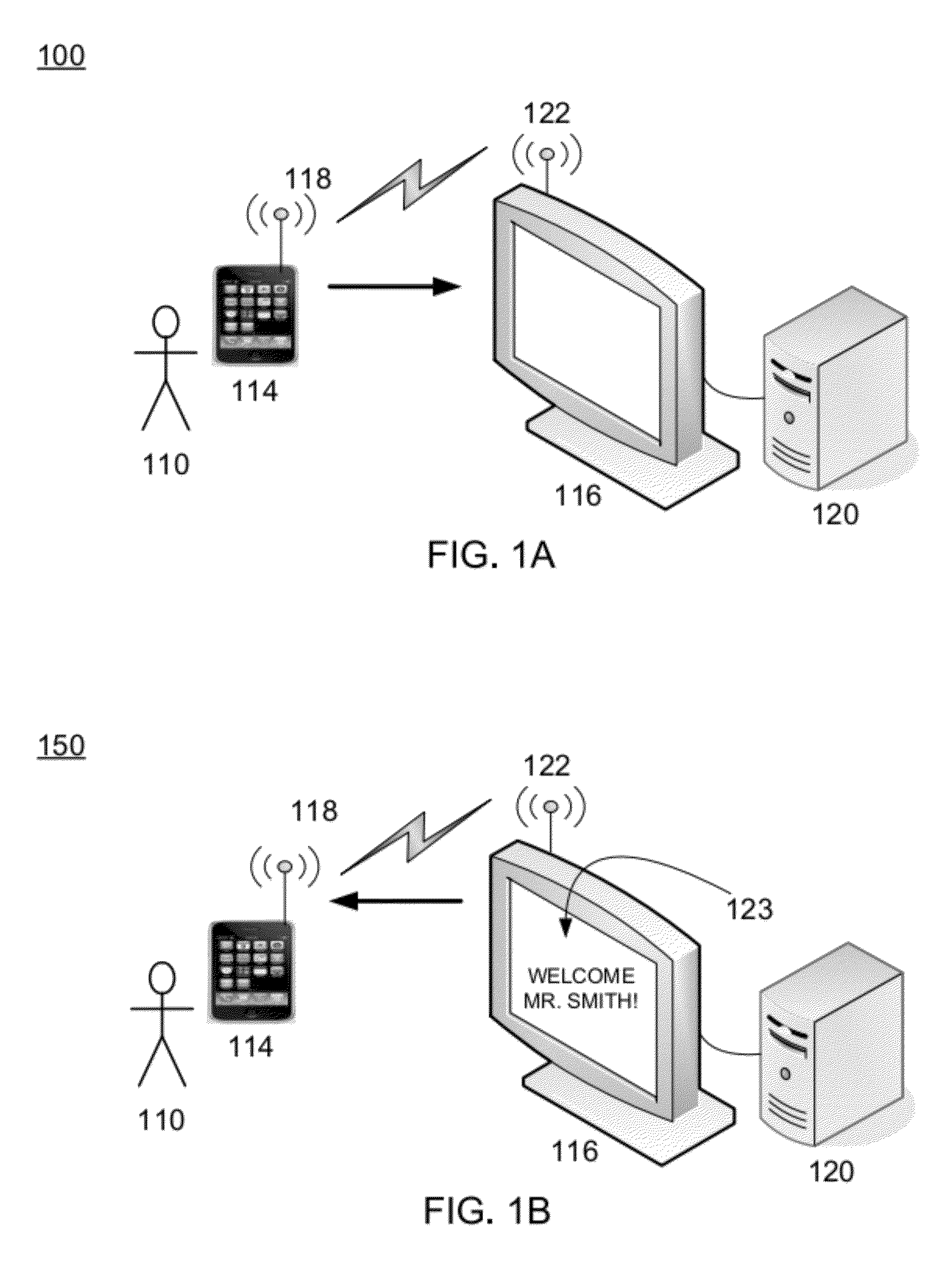
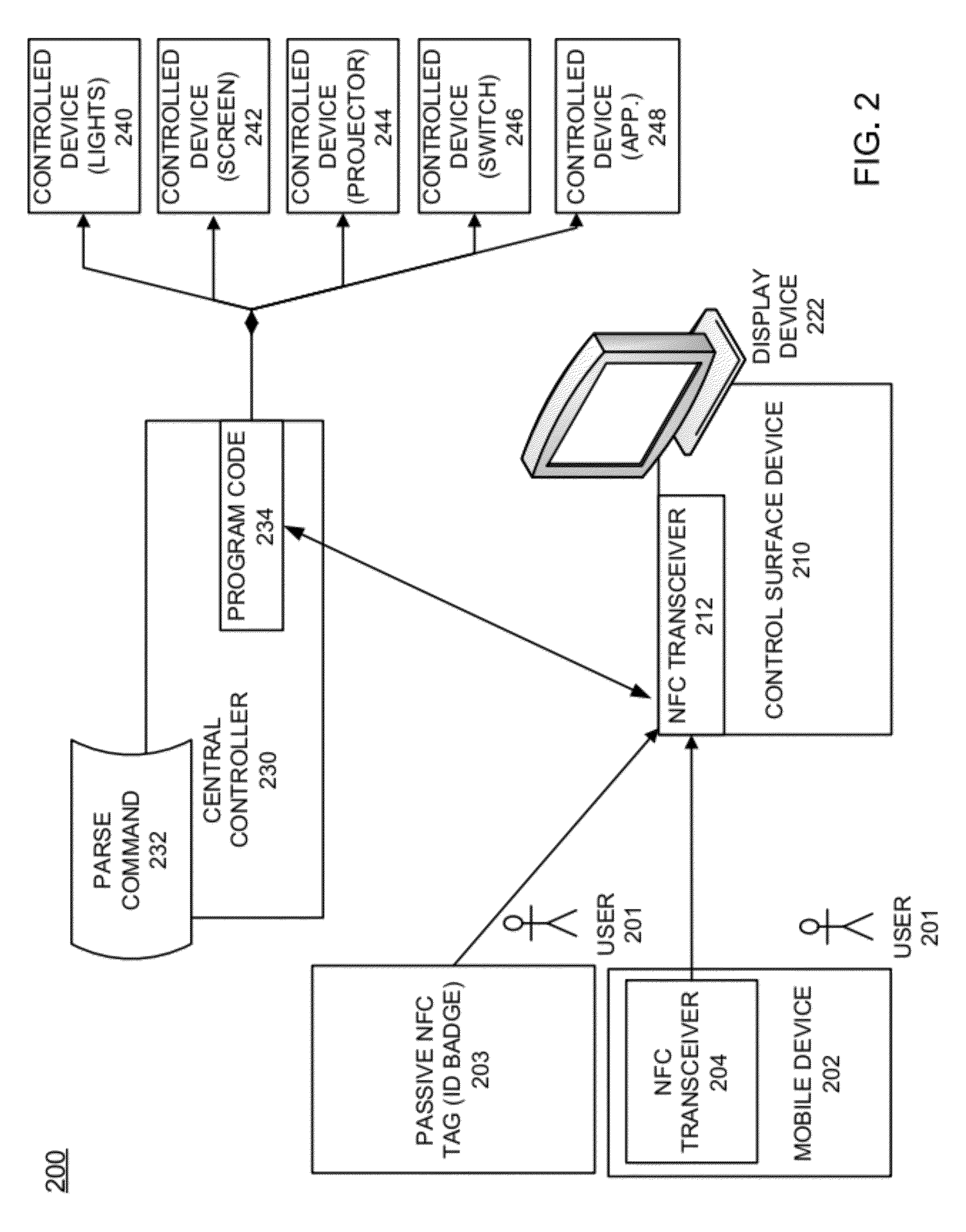
Processing near field communications between active/passive devices and a control system
Disclosed are example near field communication (NFC) devices and methods of operation configured to provide a user with easy access to operating a control system. One example method of operation may include accessing an application on a mobile device and identifying a user information parameter. The method may also provide generating a near field communication message that includes the user information parameter and transmitting the near field communication message to initiate a control procedure.
Owner:HARMAN PROFESSIONAL INC
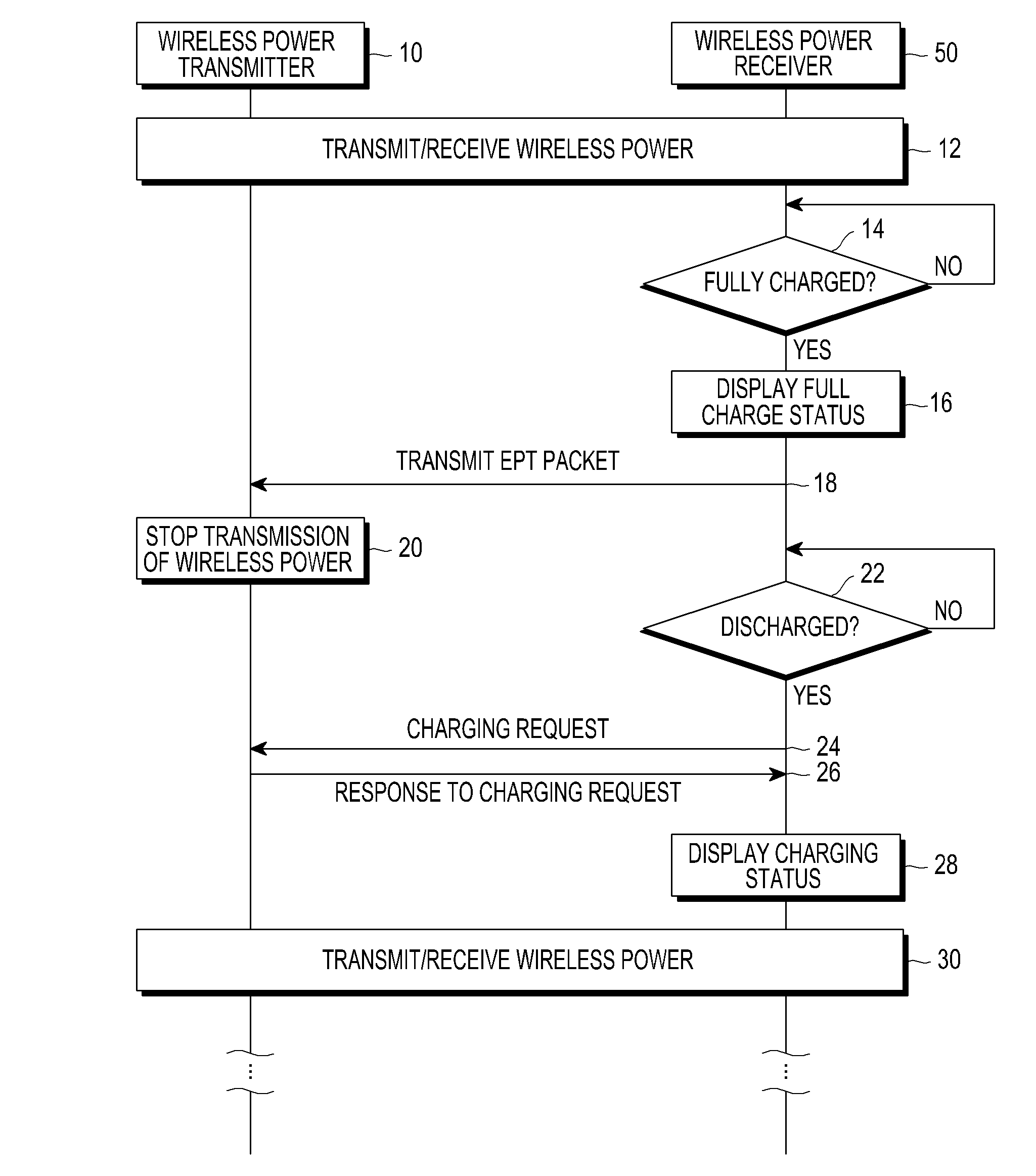
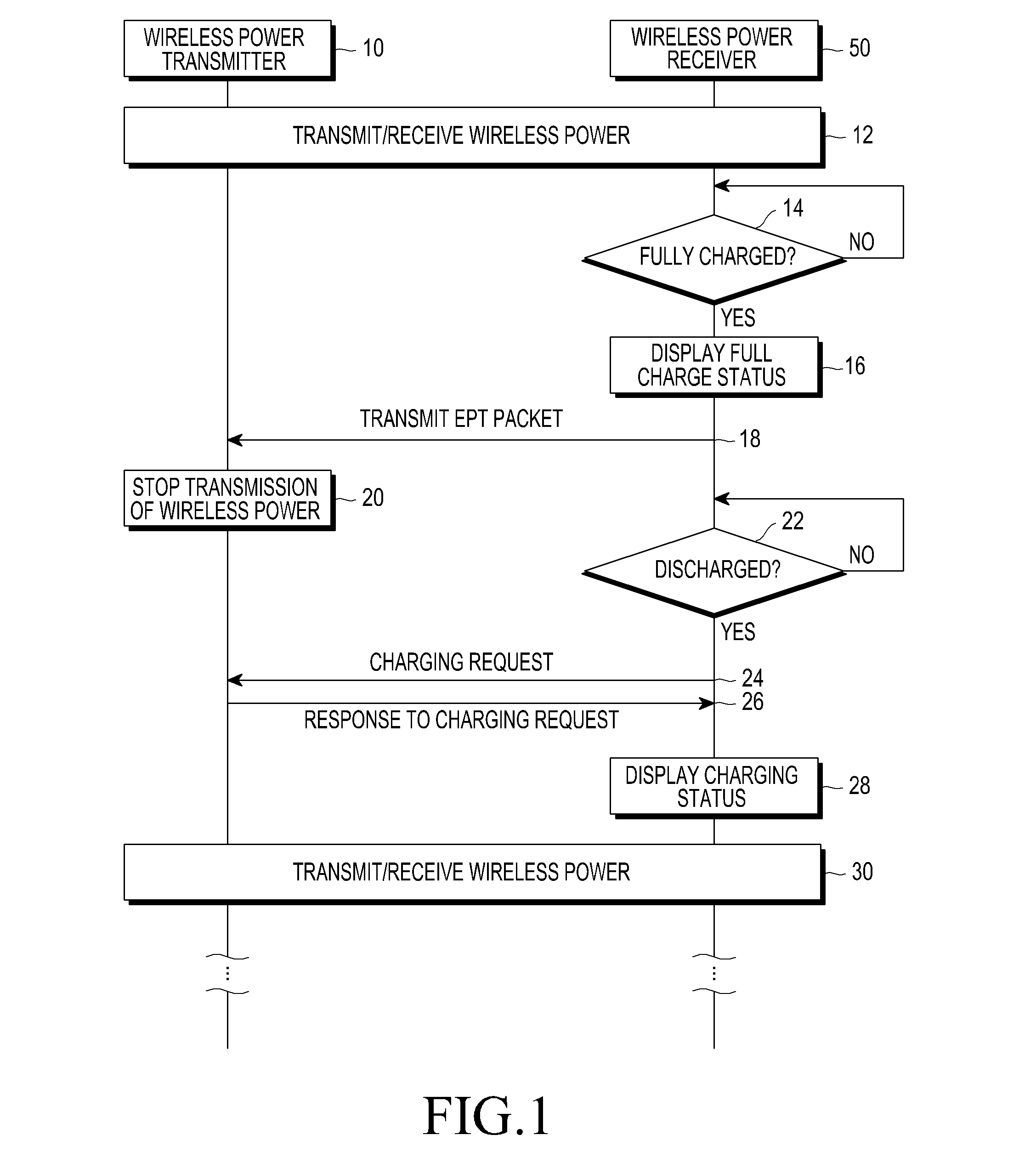
Wireless charging apparatus and method
ActiveUS20120293119A1Power transmissionReduced strengthEnergy efficient ICTCircuit monitoring/indicationCommunication unitEngineering
Methods and apparatus for wireless charging are provided. Transmission power transmitted from a wireless power transmitter is received at a power receiver of a wireless power receiver. A battery of the wireless power receiver is charged with the received transmission power. It is determined whether the battery is fully charged. A packet from a communication unit of the wireless power receiver is transmitted to the wireless power transmitter when the battery is fully charged. An auxiliary charge of the battery is performed by receiving strength-reduced transmission power from the wireless power transmitter.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Microstrip antenna for an identification appliance
InactiveUS6888502B2Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsEngineeringDegradation Problem
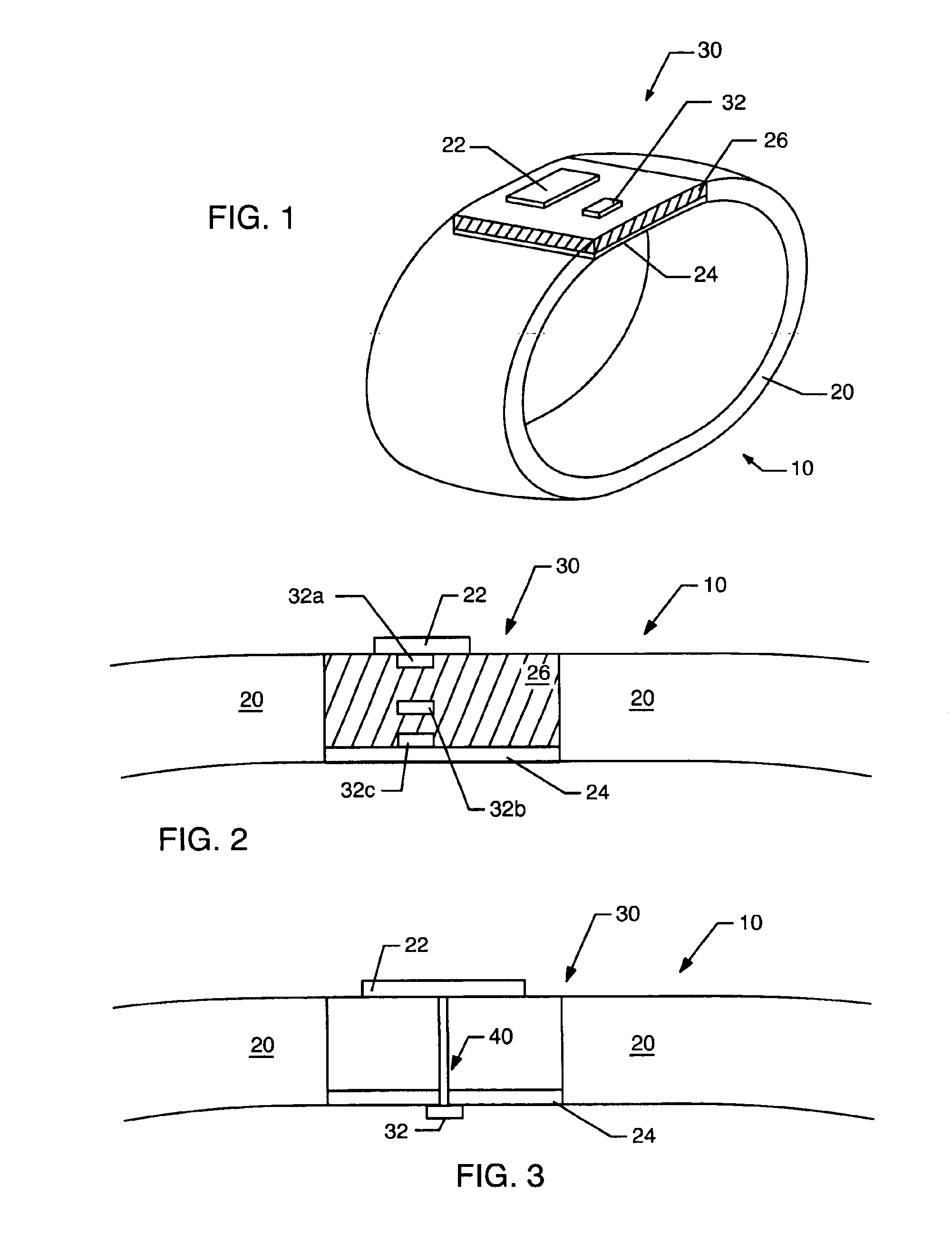
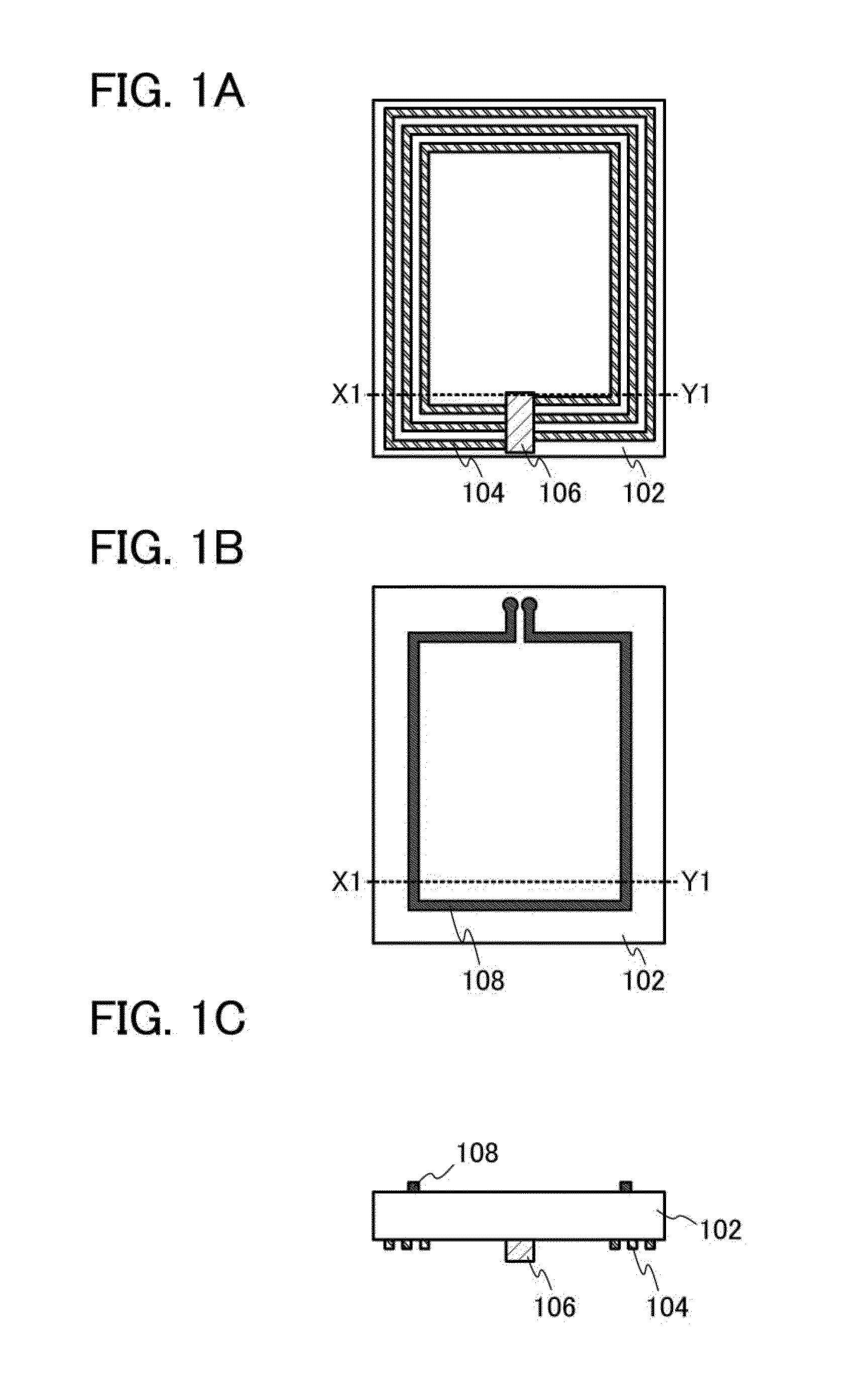
An identification appliance, such as a wristband, bracelet, patch, headband, necklace, card, sticker, or other wearable appliance, has an improved patch or microstrip antenna. The microstrip antenna comprises a conductive patch layer, a conductive ground layer and a dielectric layer in between the conductive layers. The microstrip antenna is mounted to or disposed in the identification appliance, where preferably the ground layer is closest to the user and the patch layer is furthest from the user. Electronic circuits may be located in the dielectric layer, on a surface of a conductive layer, or on another part of the identification appliance. Connecting holes through the dielectric layer may allow circuits to be connected to a conductive layer or layers. This improved antenna resolves detuning and communication degradation problems.
Owner:PRECISION DYNAMICS CORPORATION
Power-receiving device, wireless power-feeding system including power-receiving device, and wireless communication system including power-receiving device
InactiveUS20120228956A1Improve transmission efficiencyElectromagnetic wave systemTransformersCommunications systemResonance
When a portable electronic appliance is provided with two systems, a wireless power-feeding system and a wireless communication system, each system requires two power-receiving devices, a coil and an antenna, leading to a problem of increased electronic appliance size and cost. Wireless power feeding employs the resonance method and uses a resonance coil using the resonance method and a power-receiving coil that receives power from the resonance coil. At least one of the resonance coil and the power-receiving coil can also be used as an antenna for wireless communication. Thus, a power-receiving device that can be used for two systems, wireless power feeding and wireless communication, can be provided.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
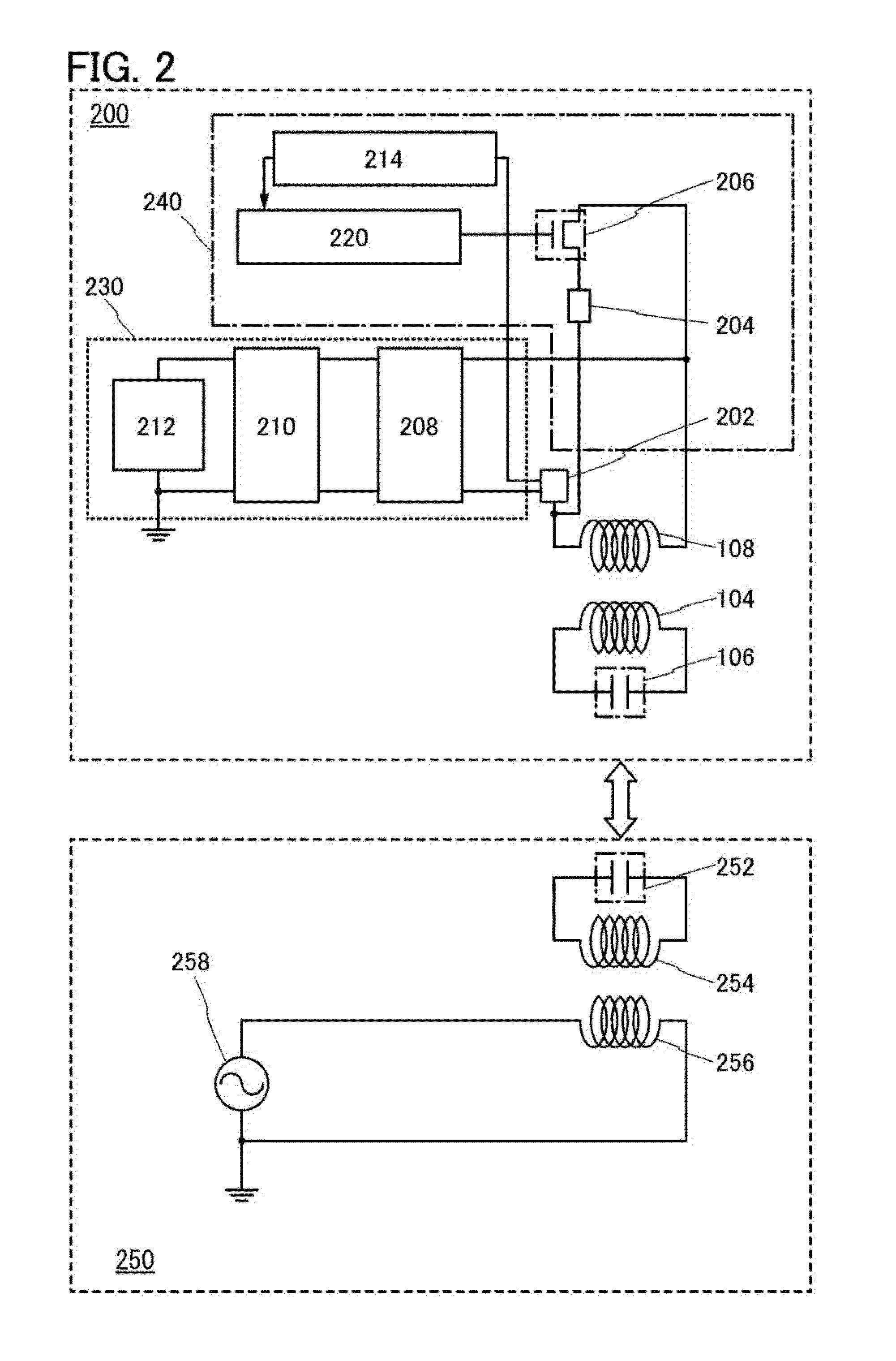
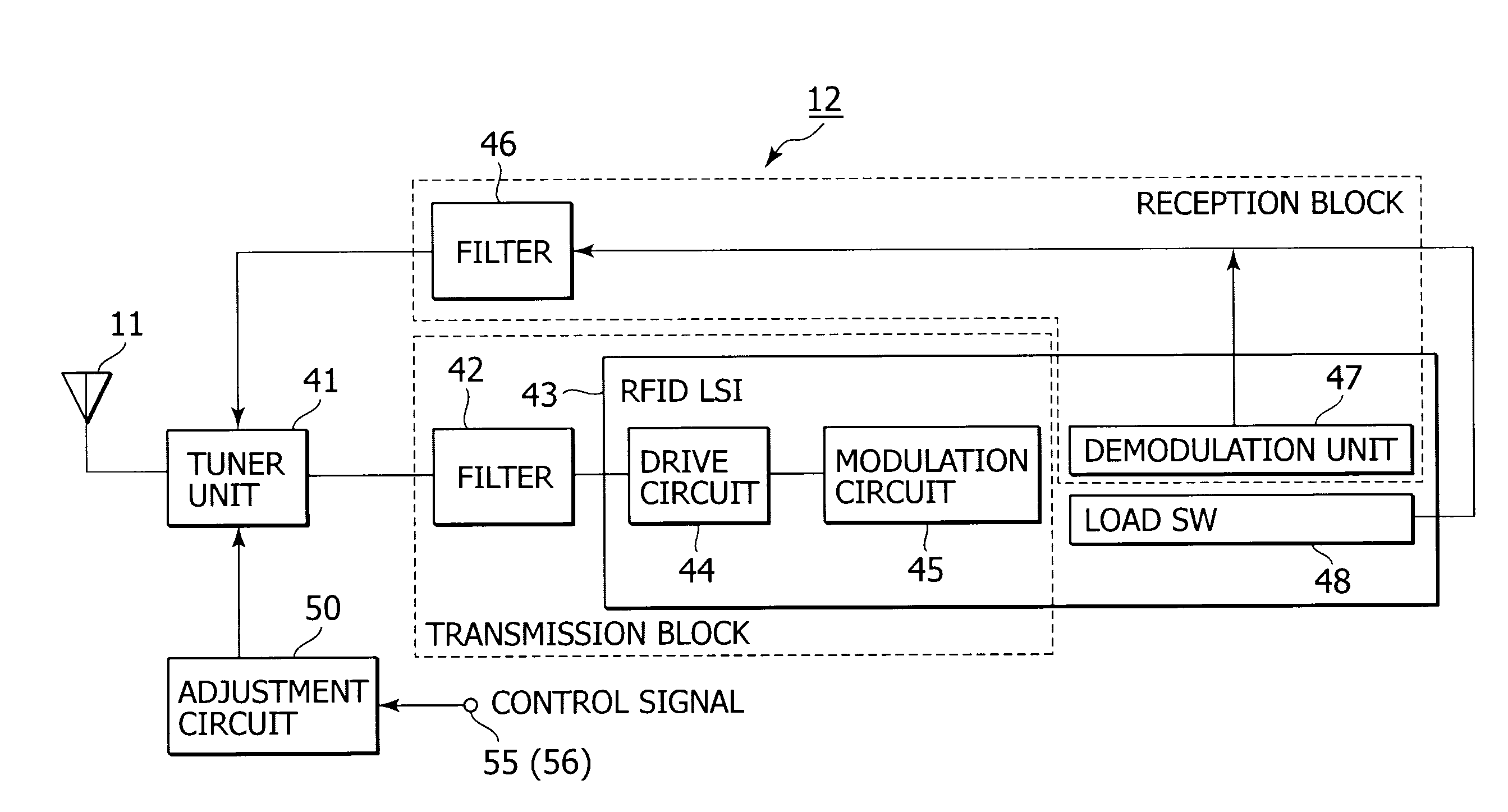
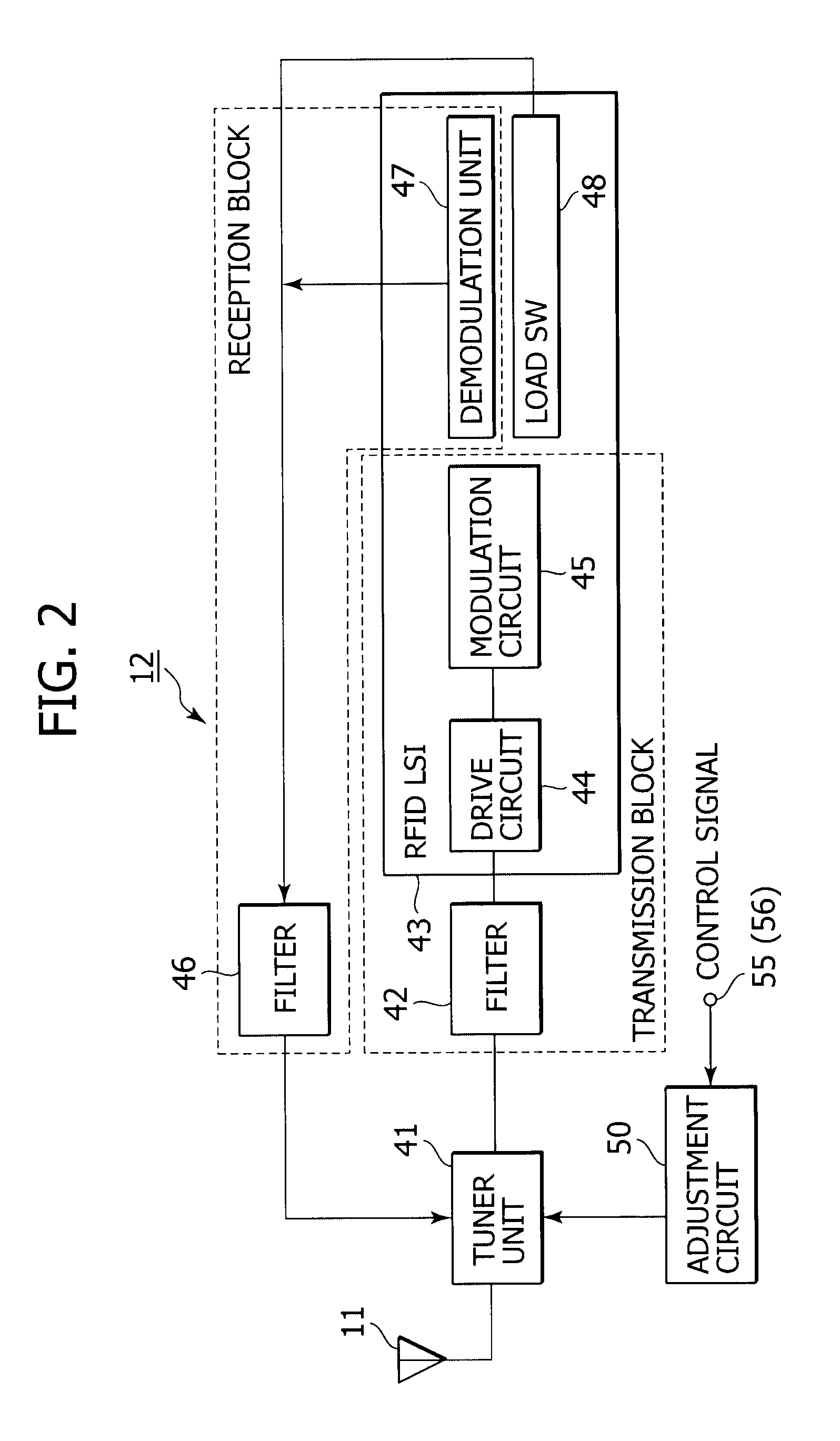
Non-contact wireless communication apparatus, method of adjusting resonance frequency of non-contact wireless communication antenna, and mobile terminal apparatus
ActiveUS20090146892A1Range of resonance frequency can be extendedEasy to adjustBatteries circuit arrangementsElectromagnetic wave systemCapacitanceTerminal equipment
A non-contact wireless communication apparatus and a mobile terminal apparatus are provided. The non-contact wireless communication apparatus includes a non-contact wireless communication antenna, a resonance capacitor, connected in parallel with the non-contact wireless communication antenna, for obtaining a predetermined resonance frequency with the non-contact wireless communication antenna, a resonance frequency adjustment unit for changing a resonance capacitance of the resonance capacitor to adjust the resonance frequency, a capacitance change amount control unit for controlling a change in resonance capacitance of the resonance capacitor in the resonance frequency adjustment unit, a resonance frequency shift unit for shifting the resonance frequency of the non-contact wireless communication antenna, and on / off control unit for performing on / off control of the resonance frequency shift unit in accordance with the amount of change in resonance capacitance of the resonance capacitor by the capacitance variation control unit.
Owner:SONY CORP
Information access system for accessing information in contactless information storage device, and method therefor
InactiveUS20070273486A1Reduce power consumptionAvoid collisionElectric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsInformation processingComputer hardware
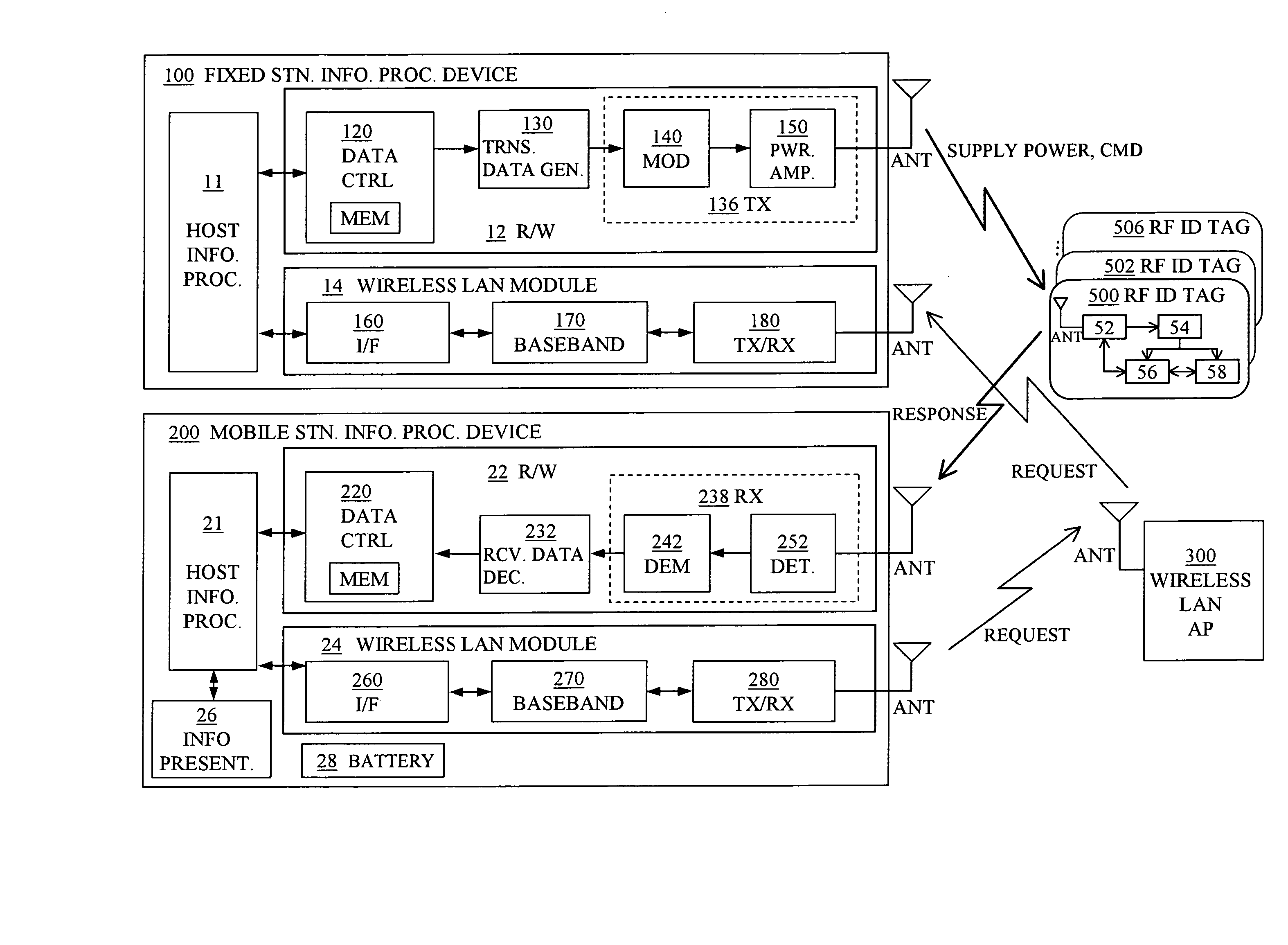
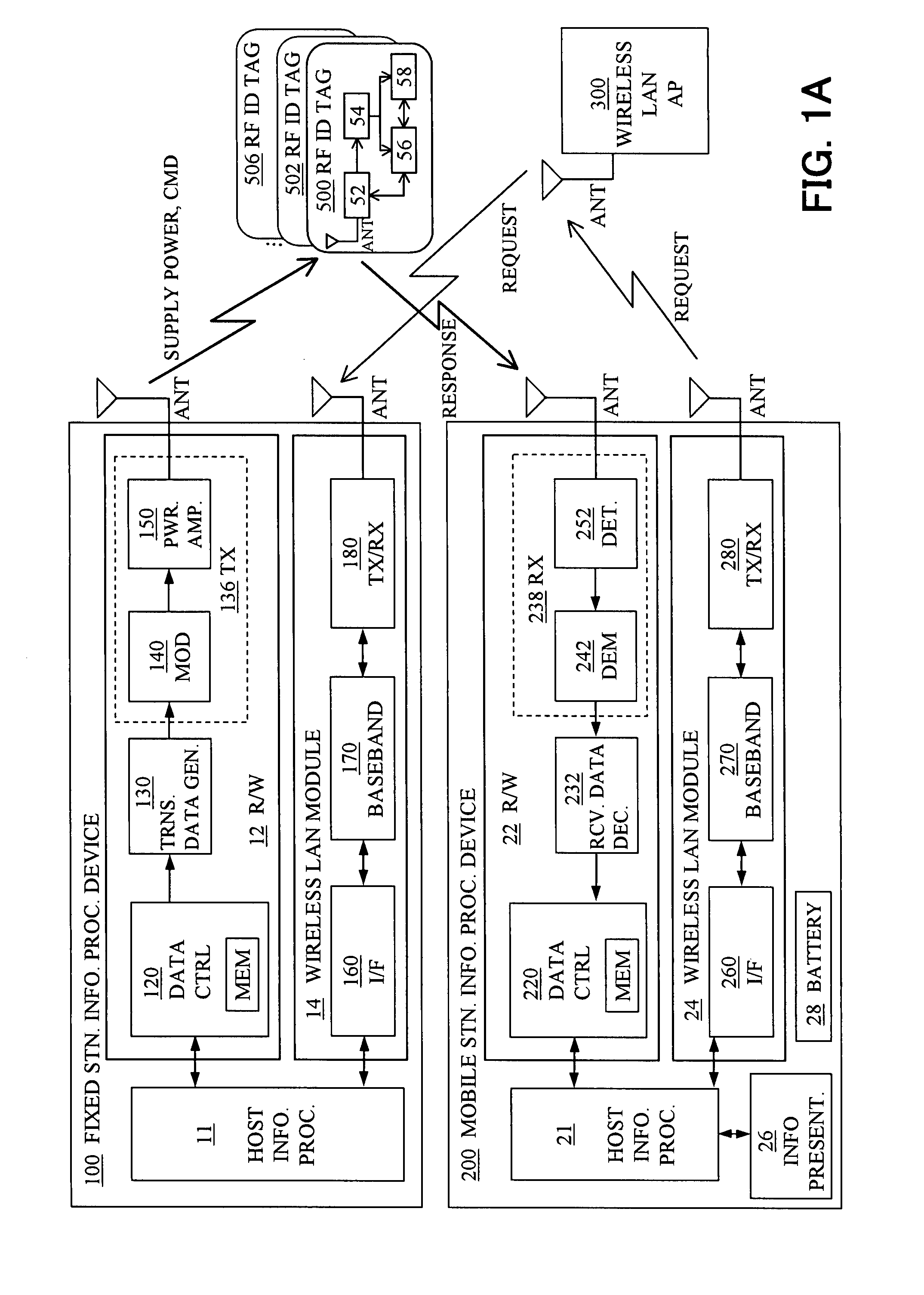
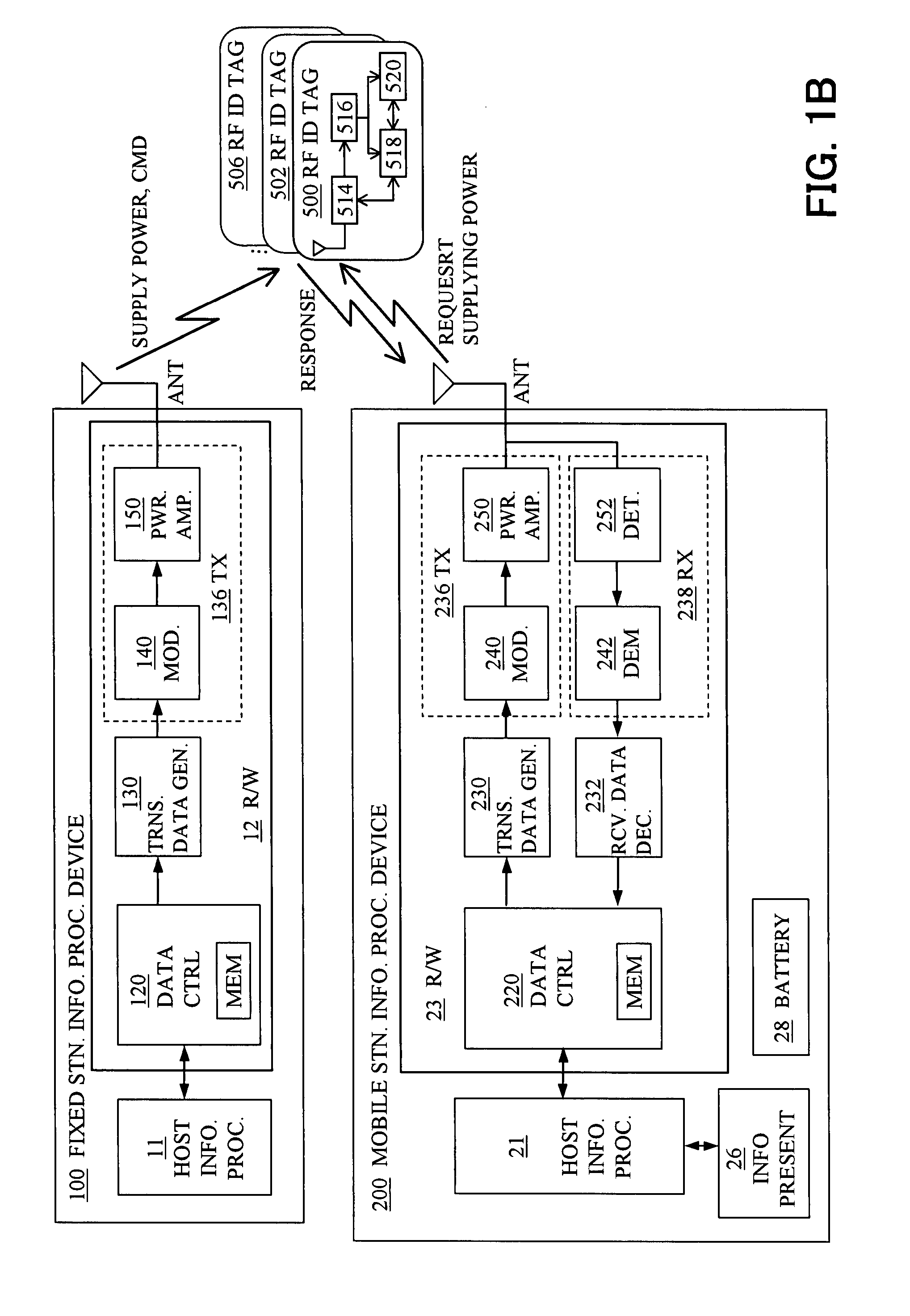
An information access system includes: a passive contactless information storage device (500) capable of transmitting and receiving signals; a fixed-station information processing device (100) having an information processing unit, and a wireless transmitter for transmitting, in a contactless manner, a command signal for requesting transmission of information stored in the information storage device and supplying power in a contactless manner to the information storage device; and a mobile-station information processing device (200) having an information processing unit, an information presenting unit, a battery, and a wireless receiver for receiving a response signal for response to the command signal, from the information storage device in a contactless manner. While the fixed-station device is supplying power to the information storage device in the contactless manner, the information storage device transmits, in response to the command signal, the response signal to the mobile-station device in the contactless manner.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
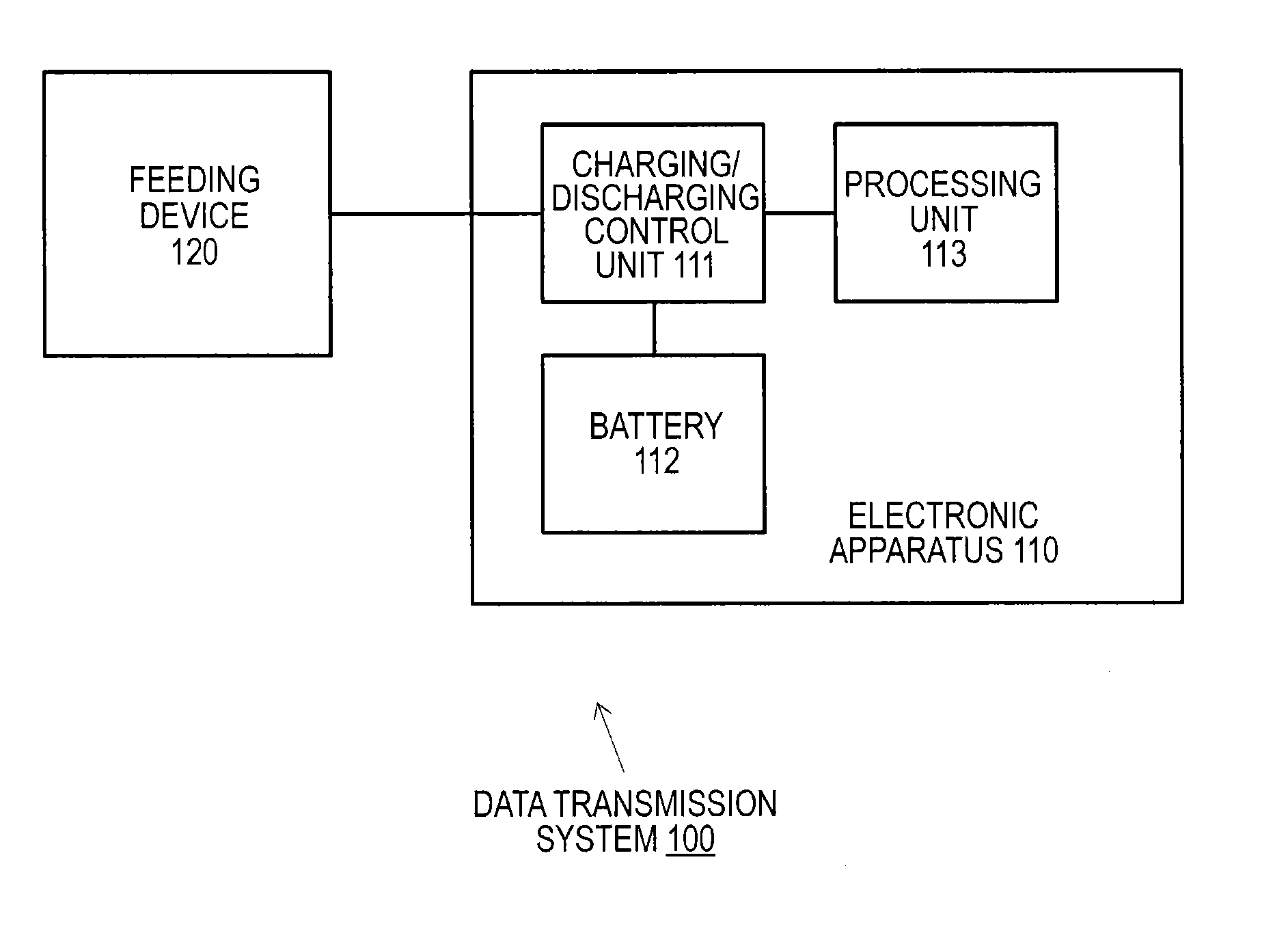
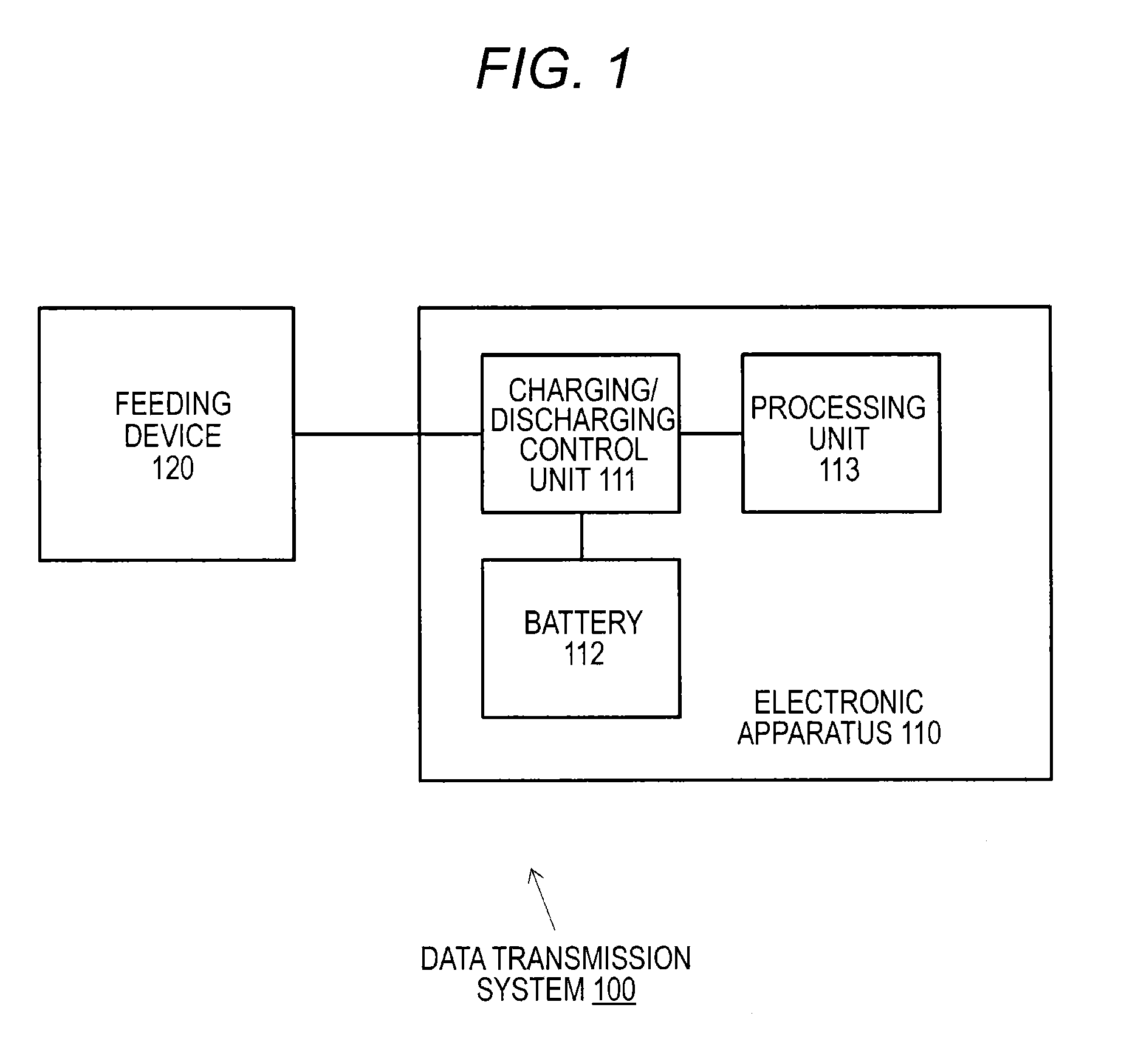
Electronic apparatus, charging control method, charging system, and data transmission system
ActiveUS20140245036A1Efficient chargingMaintain charging efficiencyCircuit monitoring/indicationNear-field systems using receiversElectrical batteryCharge control
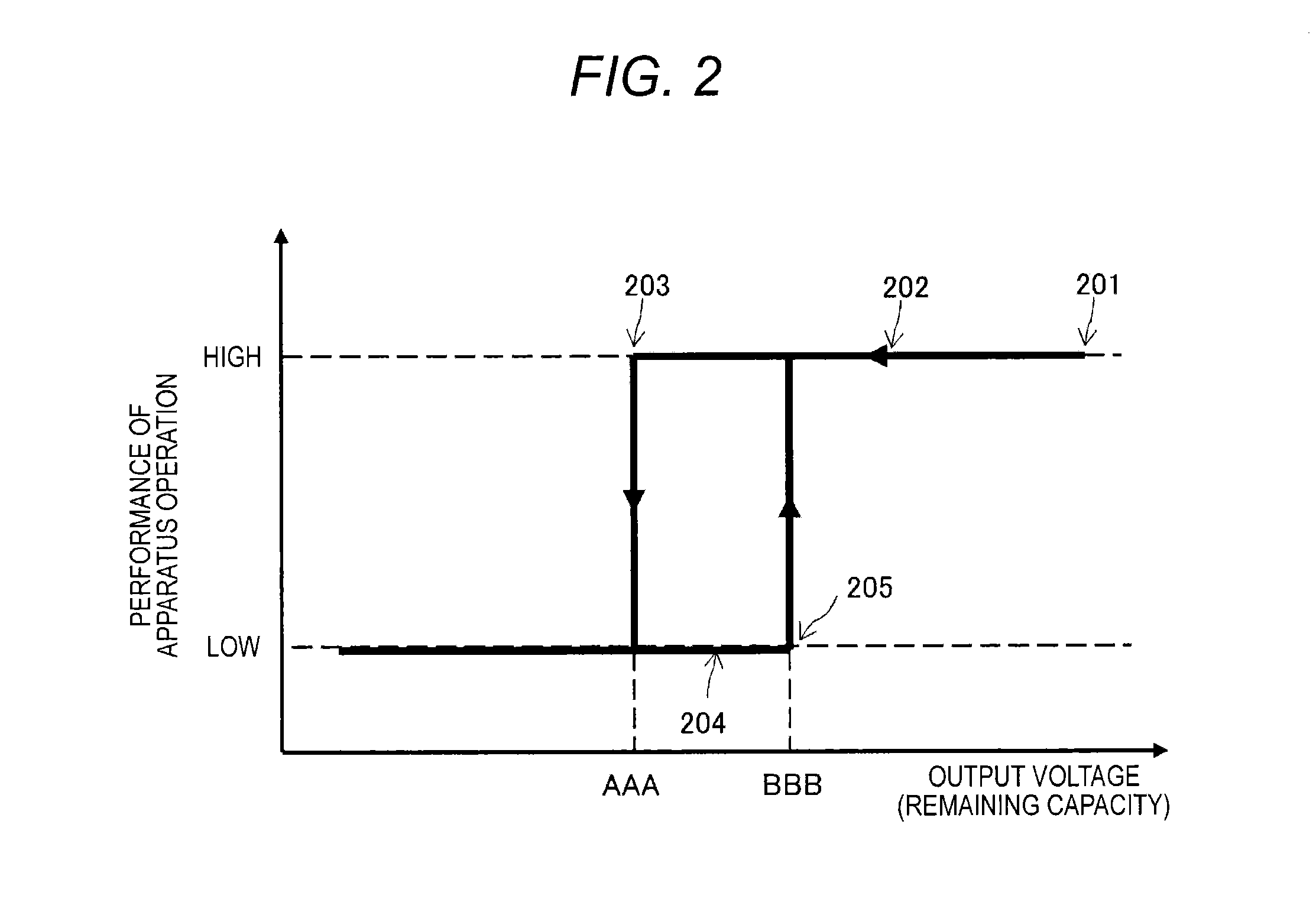
Even in a state in which the remaining capacity of a battery decreases, an apparatus operation is appropriately executed while charging efficiency of the battery is maintained.A processing unit 103 has a first operation mode in which an operation is enabled using only external power from a feeding device 120 and a second operation mode in which the operation is enabled by feeding from a battery 102 in addition to the external power from the feeding device 120. When the remaining capacity of the battery 102 is sufficient, the processing unit 103 executes an apparatus operation in the second operation mode. However, when the remaining capacity of the battery 102 decreases, the processing unit 103 changes an operation mode to the first operation mode and executes charging of the battery 102 while continuously executing the apparatus operation.
Owner:SONY CORP
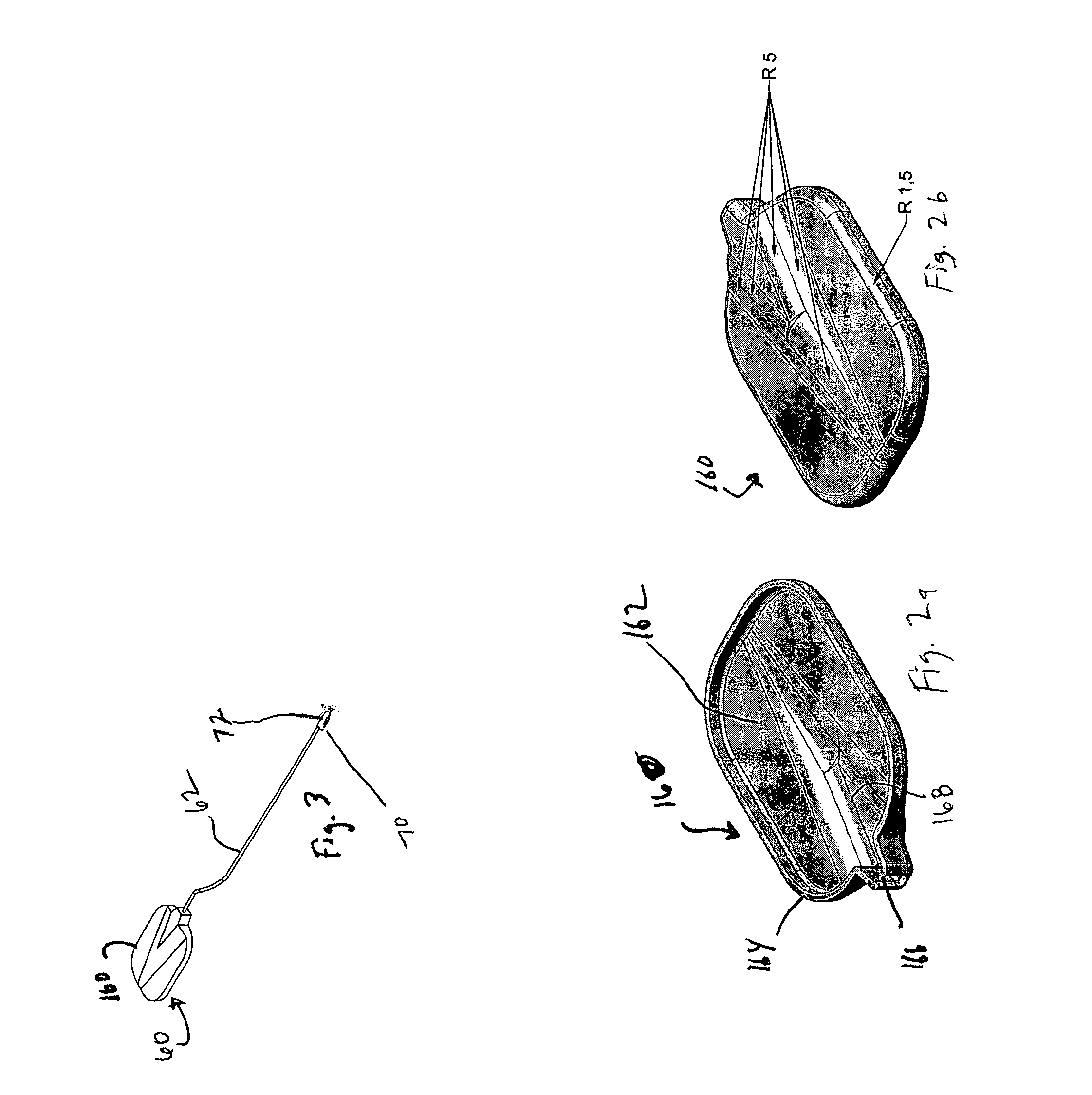
Tag assembly for radio frequency identification controlled heatable objects
ActiveUS7875836B2Improved operation/functionalityAdditional componentBoiling over preventionNear-field systems using receiversEngineeringRadio frequency
Components for use in a temperature controlled heatable object are provided in which a temperature sensor is connected to a transmitter such as a Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tag. The RFID tag is encased in a protective overmolding and connected to the temperature sensor via a mineral insulated cable. An end cap containing a potting material (such as silicone or ceramic) is placed over the temperature sensor and laser welded to a sheathing of the mineral insulated cable. A potting material for use in a heatable object is also provided comprising a silicone-based material that is modified by adding bauxite to increase thermal conductivity.
Owner:IMURA INT USA
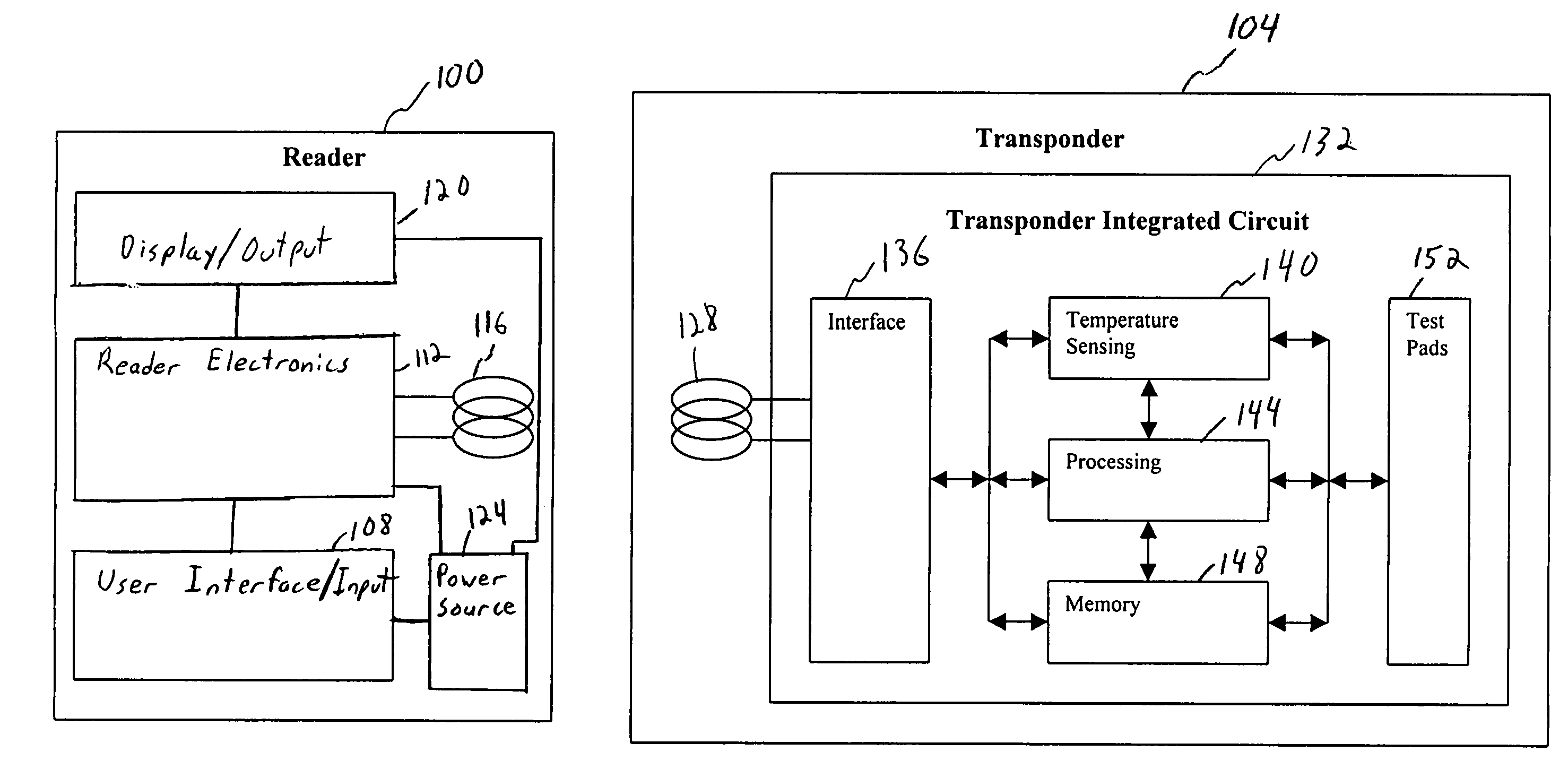
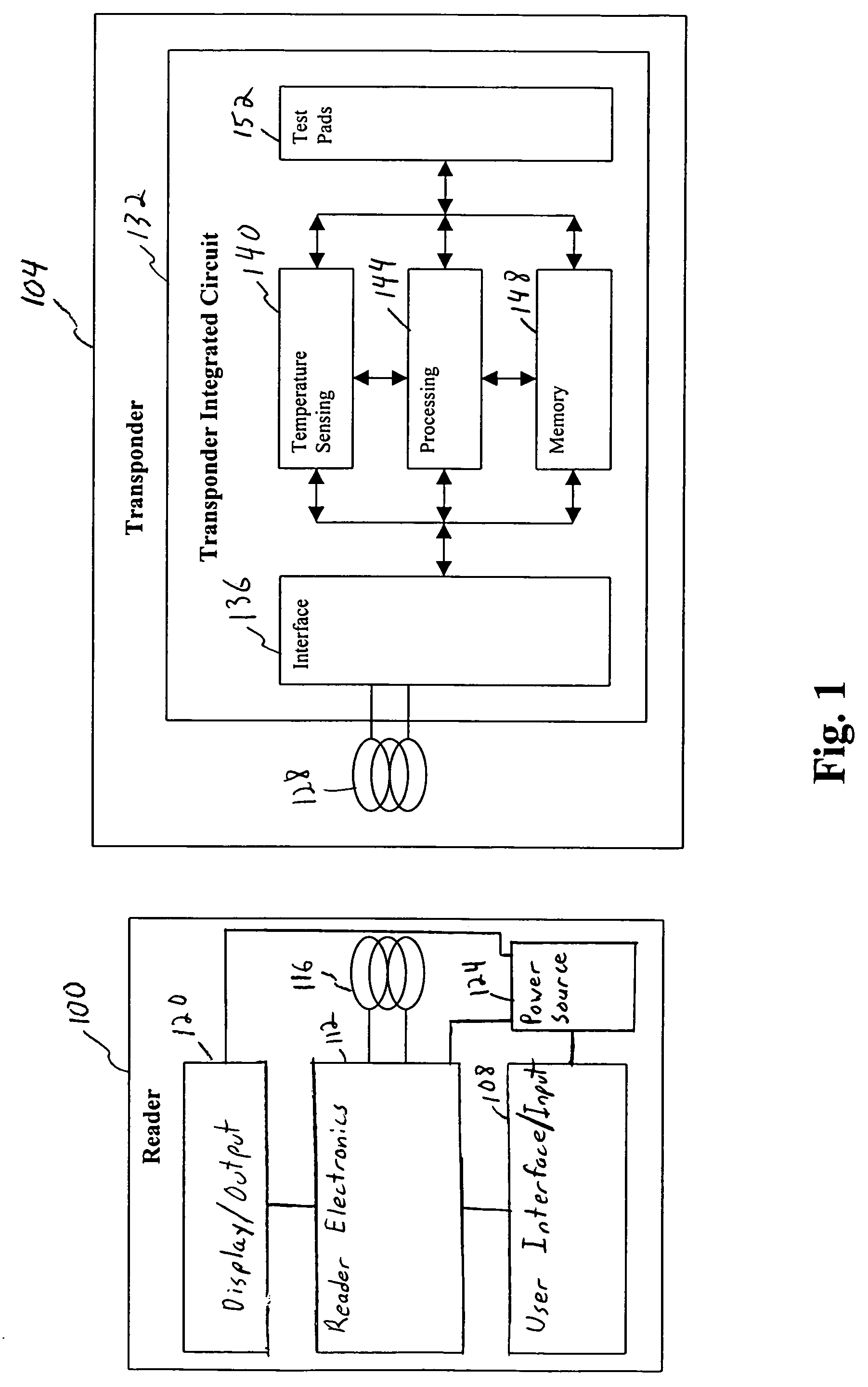
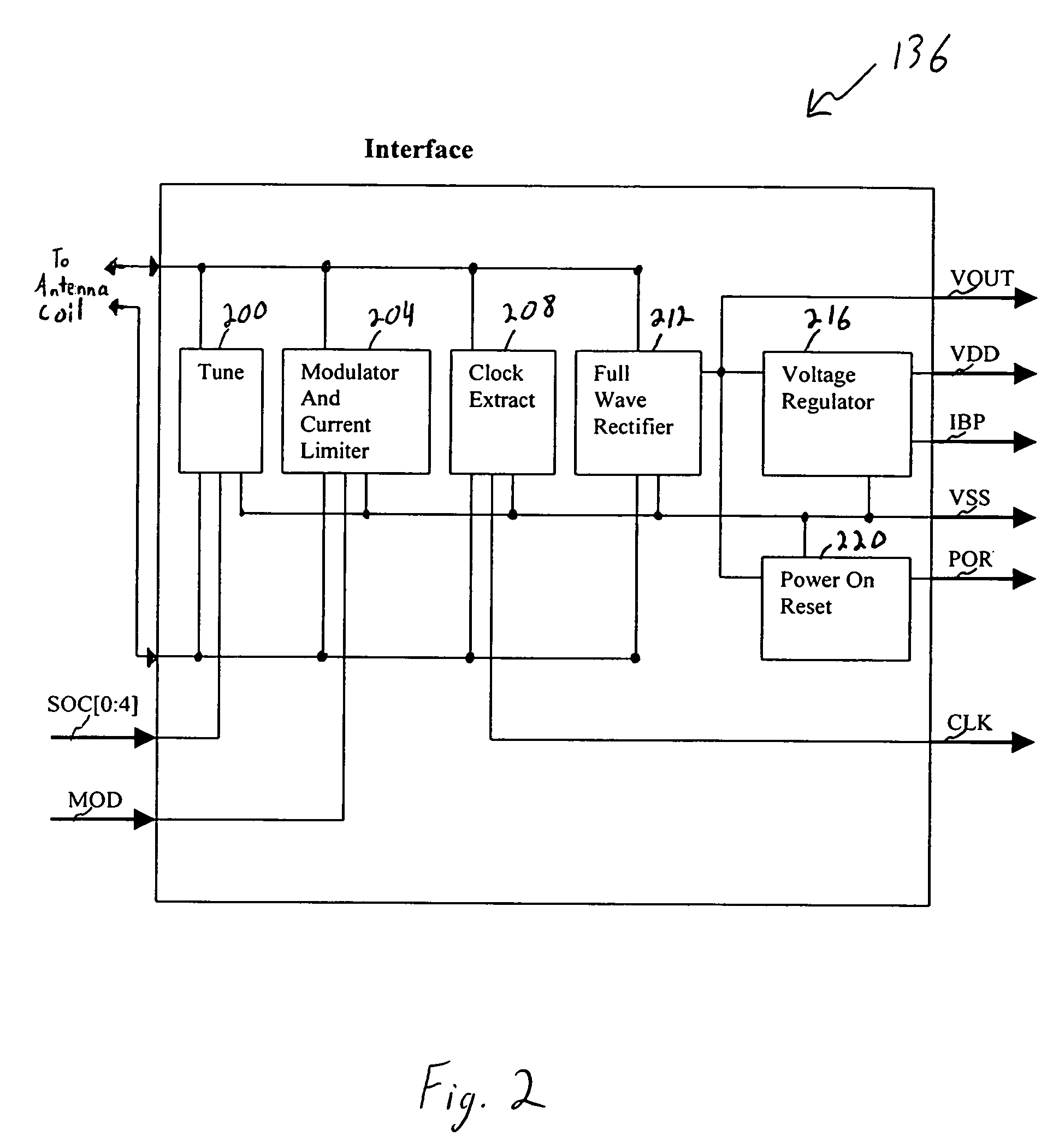
Method and apparatus for sensing and transmitting a body characteristic of a host
InactiveUS7015826B1Thermometer detailsElectric signal transmission systemsP–n junctionIntegrated circuit
A passive transponder including an integrated sensor is disclosed. The transponder receives an interrogation signal from a scanner, and is operable to transmit identification information and body characteristic information to a scanner. The scanner is operable to receive the identification and body characteristic information and display and / or store the information. The sensor is integrated into the transponder. If temperature is to be sensed, the transponder determines the temperature of the host using the temperature dependent characteristics of the P-N junction of the integrated circuit.
Owner:VERICHIP CORPORATION
Tightly-coupled near-field communication-link connector-replacement chips
ActiveUS20100159829A1Near-field systems using receiversRadio transmission for post communicationTelecommunications linkTransmitter antenna
Tightly-coupled near-field transmitter / receiver pairs are deployed such that the transmitter is disposed at a terminal portion of a first conduction path, the receiver is disposed at a terminal portion of a second conduction path, the transmitter and receiver are disposed in close proximity to each other, and the first conduction path and the second conduction path are discontiguous with respect to each other. In some embodiments of the present invention, close proximity refers to the transmitter antenna and the receiver antenna being spaced apart by a distance such that, at wavelengths of the transmitter carrier frequency, near-field coupling is obtained. In some embodiments, the transmitter and receiver are disposed on separate substrates that are moveable relative to each other. In alternative embodiments, the transmitter and receiver are disposed on the same substrate.
Owner:MOLEX INC
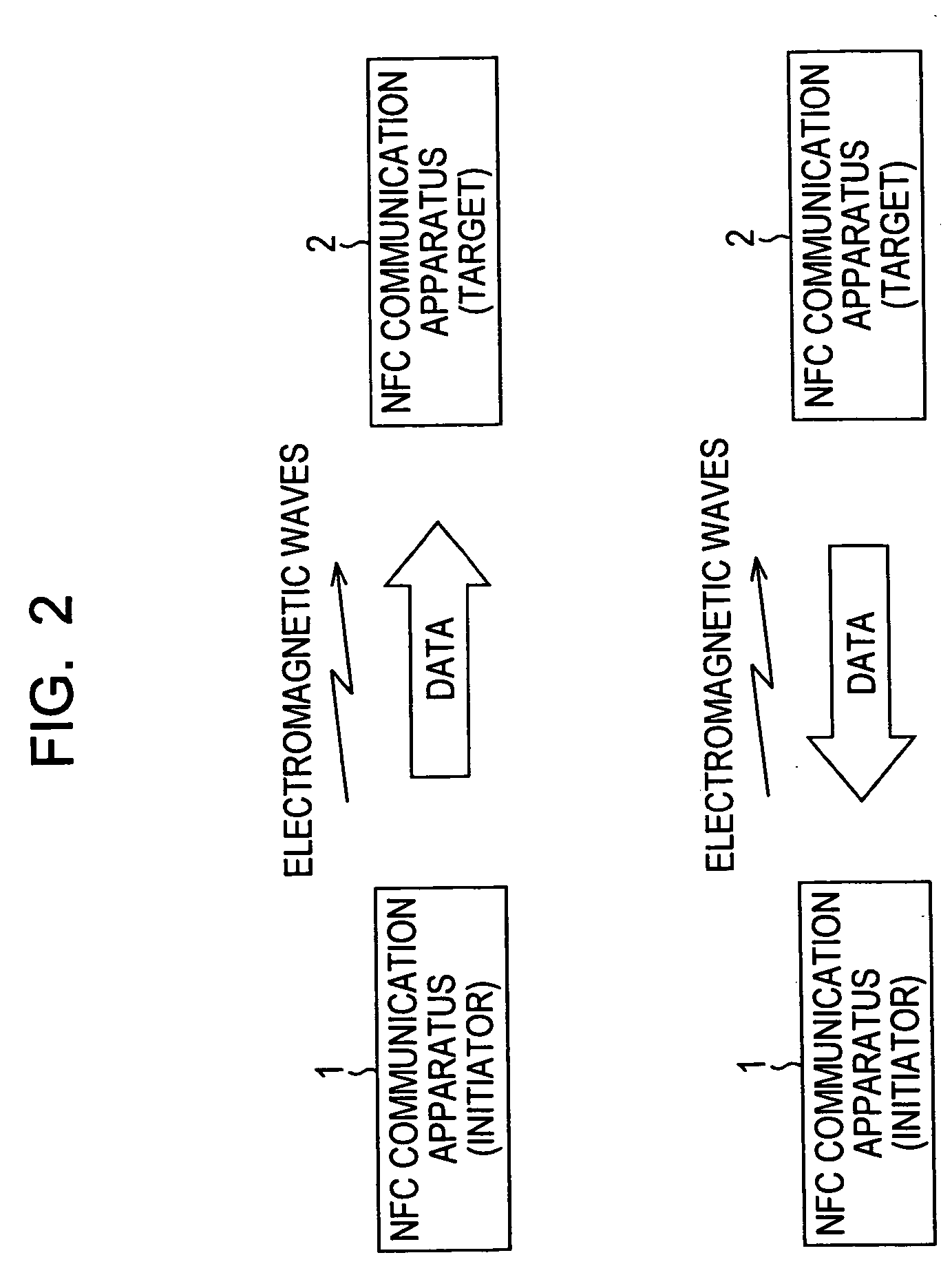
Communication system, communication method, and data processing apparatus
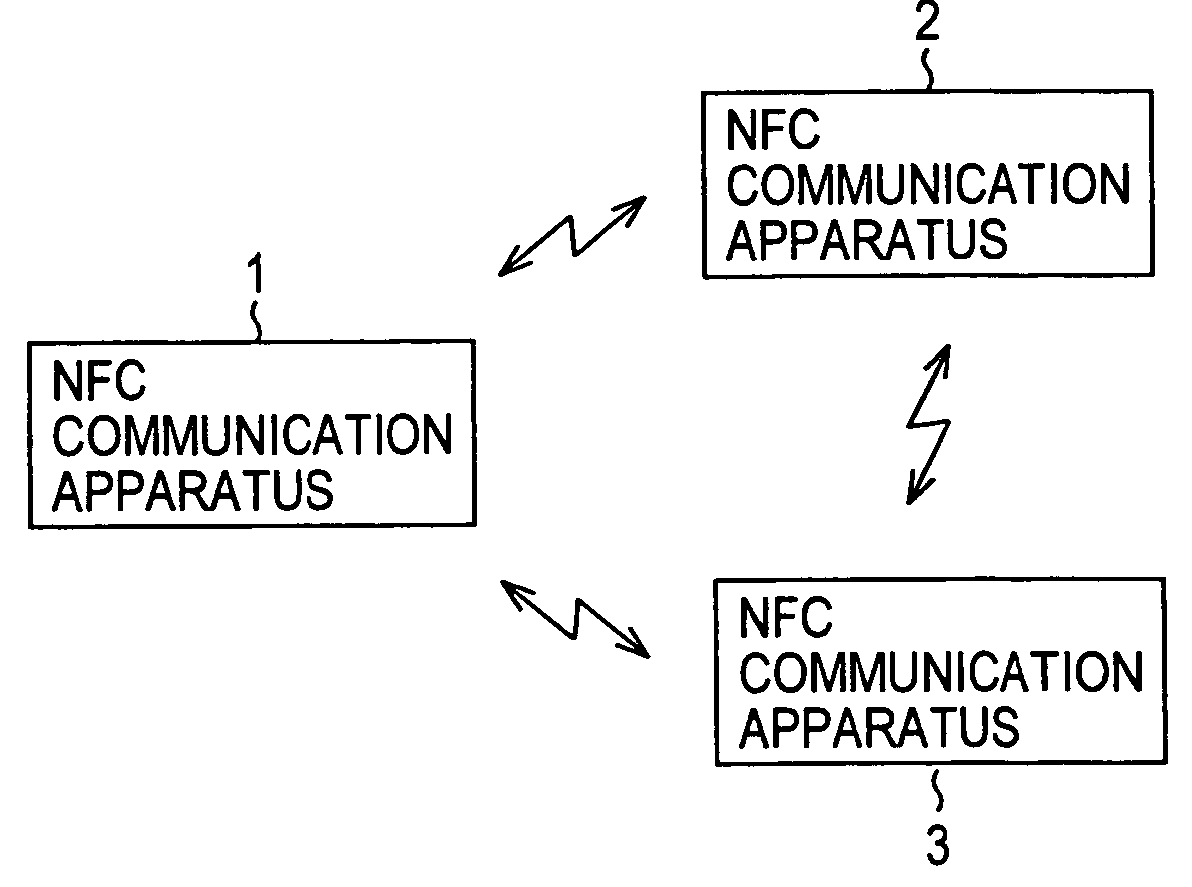
ActiveUS20050077356A1Co-operative working arrangementsNear-field for read/write/interrrogation/identification systemsCommunications systemData transmission
The present invention relates to a communication system and communication method which enable various types of near field communication, and a data processing apparatus. NFC communication apparatuses 1 to 3 have two features in that each can perform communication in two communication modes and that each can perform data transmission at a plurality of transfer rates. The two communication modes consist of a passive mode and an active mode. In the passive mode, between the NFC communication apparatuses 1 and 2, for example, the NFC communication apparatus 1 transmits data to the NFC communication apparatus 2 by modulating electromagnetic waves generated by itself, while the NFC communication apparatus 2 transmits data to the NFC communication apparatus 1 by performing load modulation on the electromagnetic waves generated by the NFC communication apparatus 1. Alternatively, in the active mode, either of the NFC communication apparatuses 1 and 2 transmits data by modulating electromagnetic waves generated by itself. The present invention can be applied to, for example, an IC card system, etc.
Owner:SONY CORP
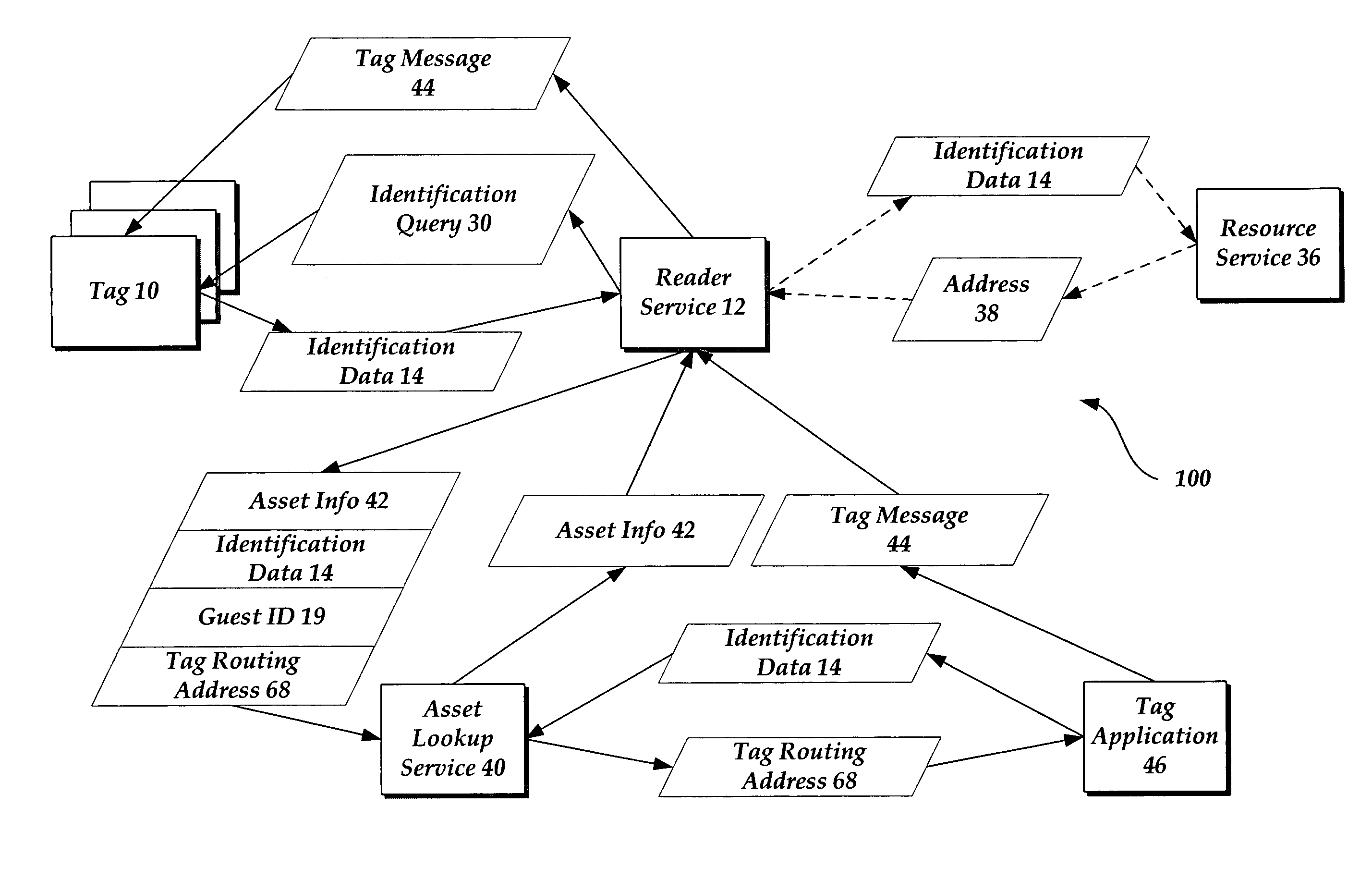
Method and system for communicating with identification tags
ActiveUS20050199716A1Electric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsNetworking protocolWorld Wide Web
A method, identification tag reader and computer program product for communication with an identification tag are disclosed. To communicate with the tag, identification data may be retrieved from an identification tag. A guest identification, compliant with at least a portion of a standard network protocol address, may be assigned to the identification tag. A message addressed to a tag routing address of the tag may be received, and a response to the message may be sent.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Transmitter and wireless system using the same
InactiveUS20080266060A1Improve abilitiesIncrease distanceElectric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsCommunications systemPeak value
When supplying a power from a base station to a terminal station on radio and a distance from a base station to a terminal station is long, it becomes impossible for the terminal station to rectify the power. The feature of the present invention is found in a wireless communication system in which the peak value and duty ratio of a transmission power are controlled simultaneously, keeping the transmission power of a base station below a fixed value, thereby allowing a voltage to be applied to a diode, which is a component of a rectifier circuit possessed by a terminal station, always in excess of a threshold voltage of the diode, and energy is exchanged between the base station and the terminal station below a limit power.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Self-adjusting RF assembly
InactiveUS20060066443A1Near-field in RFIDNear-field systems using receiversEngineeringElectromagnetic compatibility
A self adjusting RF assembly including an RF radiator is disclosed. The RF assembly includes at least one component that may be replaced by a user of the RF assembly. The RF assembly includes an identification element associated with the at least one component for representing at least one characteristic of the component. The RF assembly includes a monitoring element for monitoring the identification element at least during power up of the RF assembly. The RF assembly also includes an adjusting element for adjusting radiation from the RF radiator wherein the adjusting element is operably associated with the monitoring element to maintain radiation from the RF radiator below a preset limit. The preset limit is typically determined by local electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) regulations. A method for maintaining radiation from an RF assembly below a preset limit is also disclosed.
Owner:TAGSYS
Mobile terminal and method of performing NFC payment using the mobile terminal
Provided is a mobile terminal that has a function of changing a payment credit card at the time of near field communication (NFC) payment in a low battery state, and a method of performing the NFC payment using the mobile terminal. In the mobile terminal according to the present invention, unlike in a mobile terminal in the related art in which payment is simply performed with a default credit card, if the NFC payment is requested in the low battery state where the mobile terminal is powered off, a payment application based on a light operating system, which is executed on an embedded Linux, is displayed, and the NFC payment with a credit card selected from the payment application based on the corresponding light operating system is performed. Therefore, a credit card payment can be effectively performed in a low battery state as well.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Process for manufacture of novel, inexpensive radio frequency identification devices
InactiveUS20060071084A1Antenna supports/mountingsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical conductorTransformer coupling
A novel process for fabricating low cost RFID devices in which a pattern of metallic toner is printed on a substrate and the contacts on a silicon die are placed directly on contact points printed as part of the pattern of metallic toner; the whole device is then heated to both cure the metallic toner into metallic conductors and bond the silicon die to the metallic conductors. Alternatively, the silicon die can be physically attached to the substrate and the electrical pathway between the silicon die and the metallic conductors is established via a transformer coupling comprised of a coil winding on the silicon die and a pattern of coils printed as part of the metallic toner pattern. The pattern of coils can be comprised of individually printed coil loops printed on, and separated by, dielectric layers.
Owner:ELECTROX
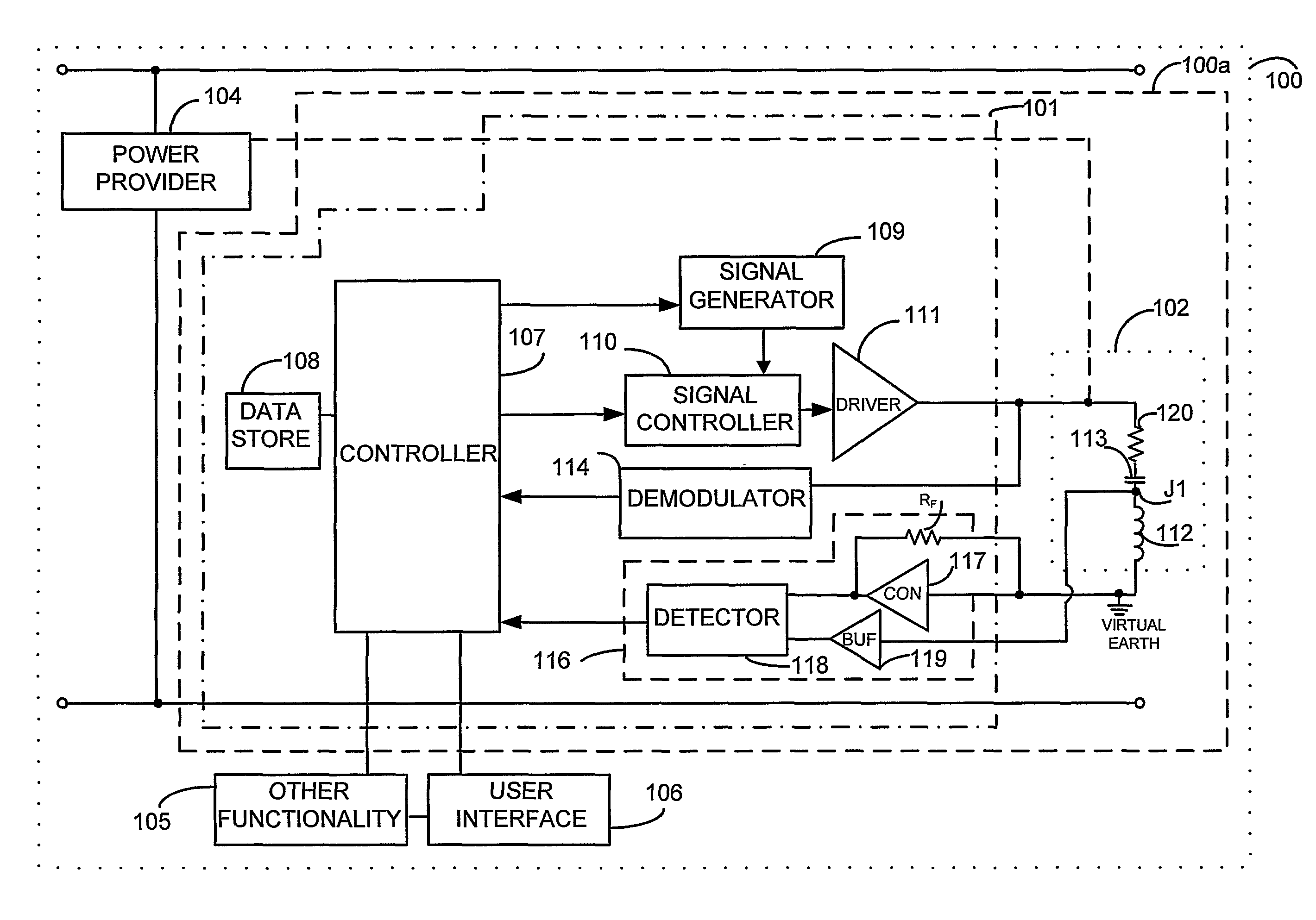
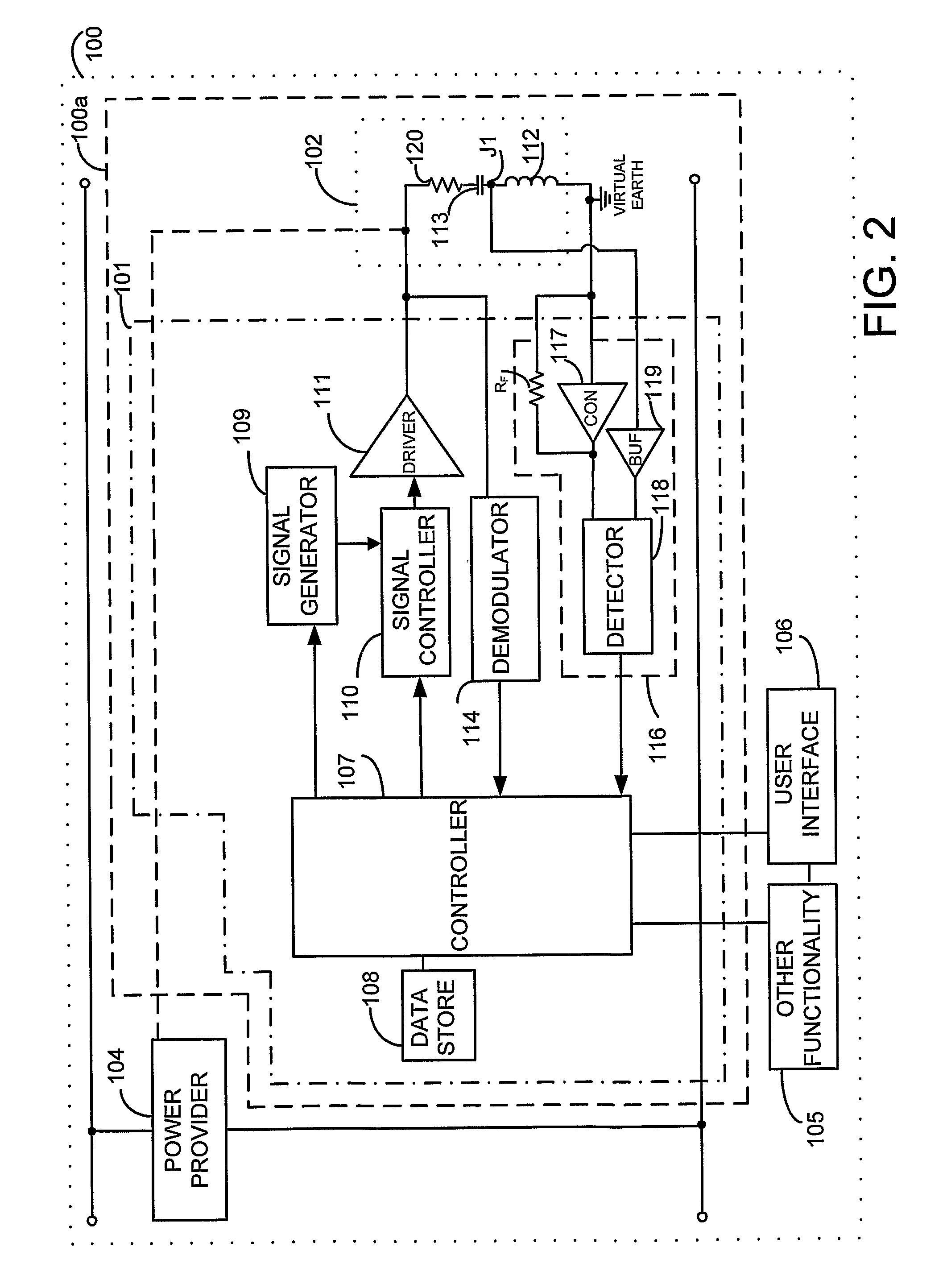
Near field RF communicators and near field RF communications enabled devices
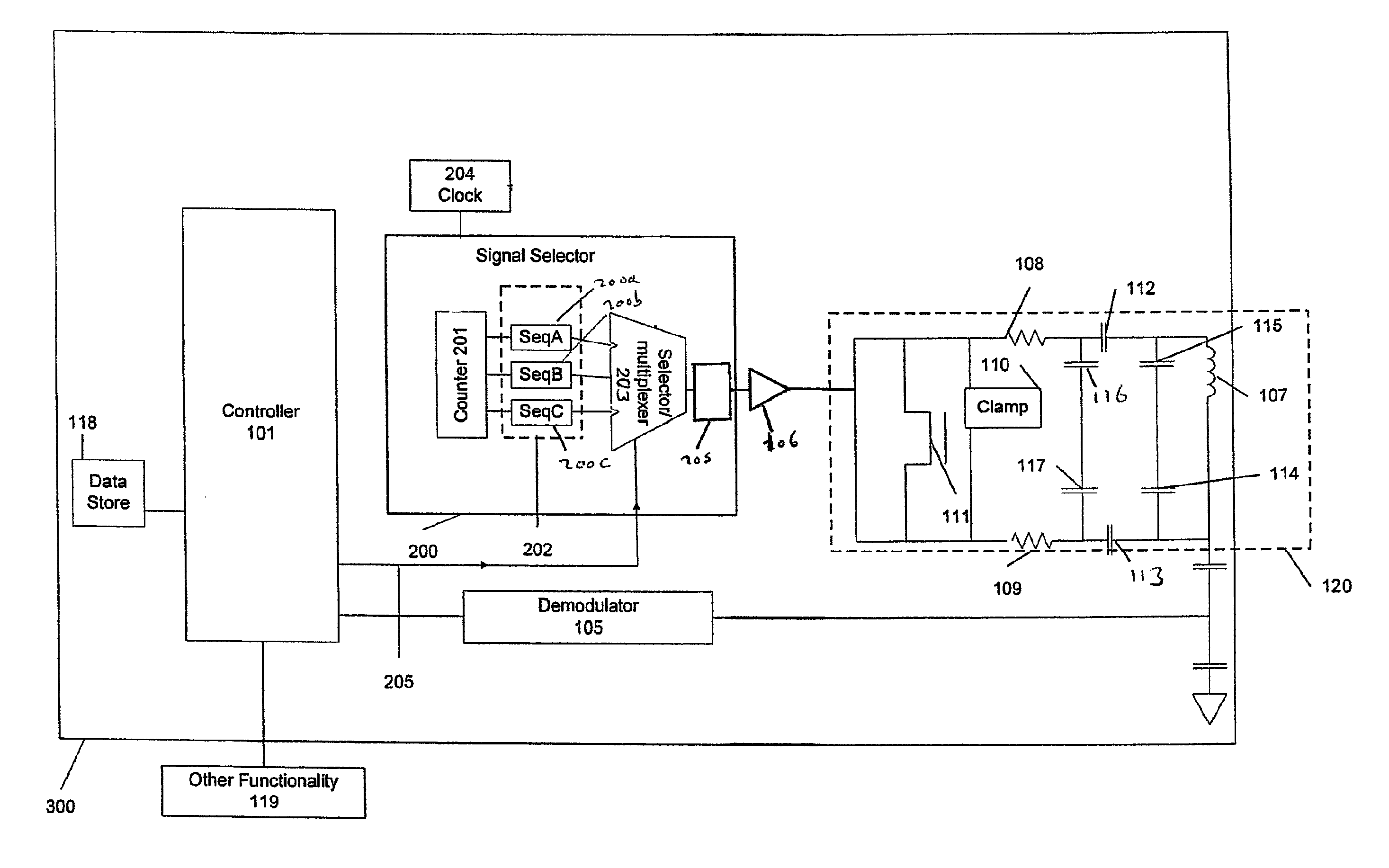
ActiveUS8140010B2Avoid powerAvoid timeTransformersNear-field systems using receiversPhase detectorCurrent voltage
A near field RF communicator (100) has an inductive coupler (102) and a first signal provider (109, 110, 111) to cause the inductive coupler to provide a first signal that when inductively coupled to the inductive coupler of another near field RF communicator in near field range is insufficient to cause initiation of communication with that other near field RF communicator. A sensor (116) senses a change in an impedance of the inductive coupler (102) due to inductive coupling of the first signal between the inductive couplers of the said near field RF communicator and a said other near field RF communicator in near field range. A controller (107) determines whether or not another near field RF communicator is in near field range on the basis of any change in impedance sensed by the sensor and, if another near field RF communicator is determined to be in near field range, causes a second signal to be inductively coupled to the other near field RF communicator to initiate communication between the two near field RF communicators. The sensor may use a phase detector (118) to enable a change in impedance to be sensed by detecting a change in a current-voltage phase relationship resulting from a change in impedance.
Owner:NXP USA INC
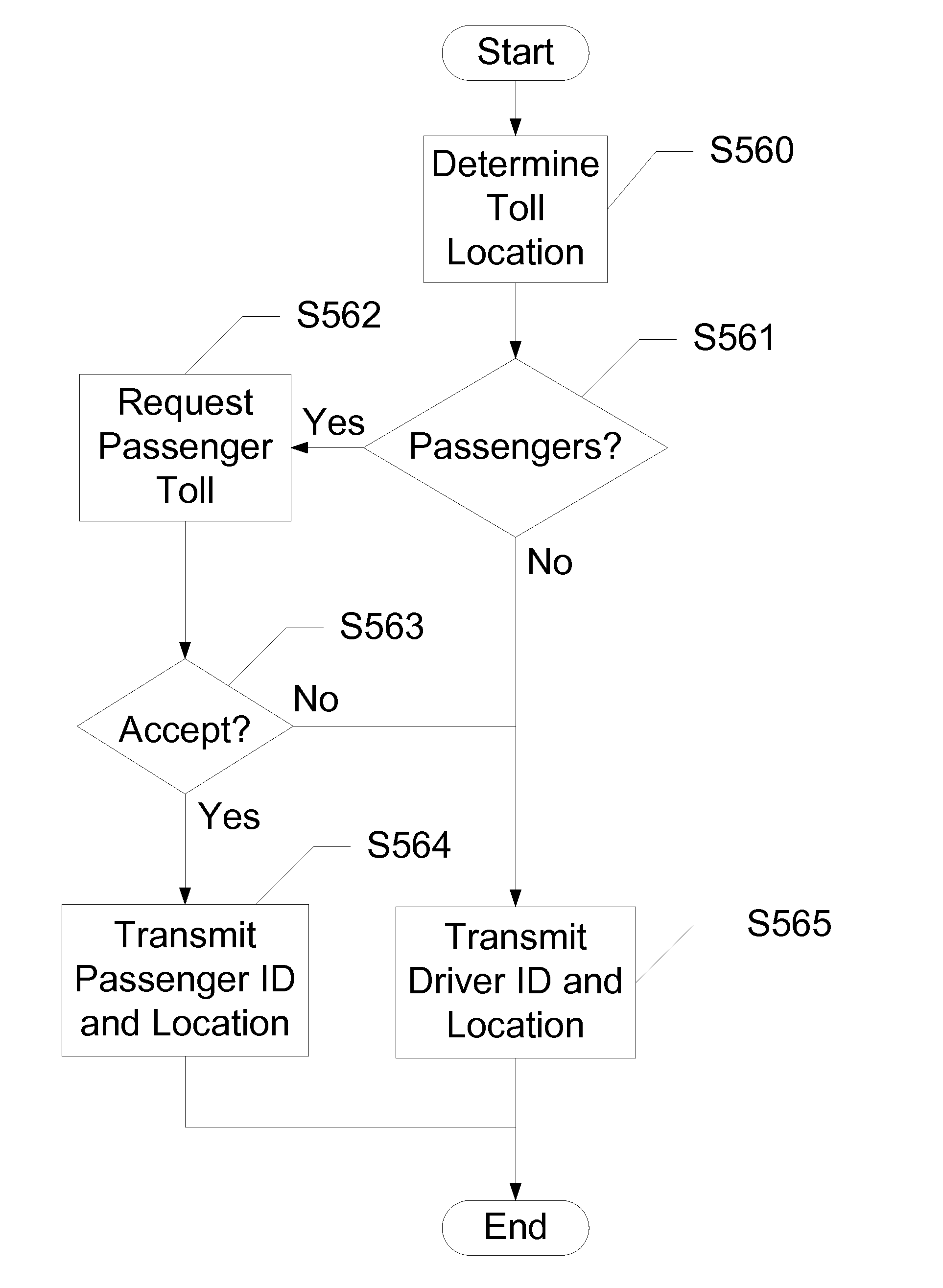
Devices, Systems and Methods for Identifying and/or Billing an Individual in a Vehicle
ActiveUS20110137773A1Electric signal transmission systemsTicket-issuing apparatusTransceiverCommunication device
Devices, systems, and methods are disclosed for identifying a driver versus a passenger within a smart vehicle. This involves a determination of the relative positions of the wireless communication devices within the smart vehicle using near-field communication (NFC) or GPS, AGPS, etc. The wireless communication device detected closest to the driver seat is assumed to be the device owned by the driver. Once identified, the driver can be billed for tolls and other road services, based on the location of the smart vehicle. For instance, as the smart vehicle approaches a toll, a notification can be sent to all of the wireless communication devices. A response from a particular wireless communication device will result in the corresponding user's account being billed for the toll. Further, the smart vehicle can communicate with near-field transceivers placed, for instance, alongside a High-Occupancy Vehicle (HOV) lane. A driver of the vehicle can be billed, fined, or ticketed based upon a determination of an absence of passengers in the smart vehicle.
Owner:LYFT INC
Wireless inter-device data processing configured through inter-device transmitted data
ActiveUS8244179B2Near-field for read/write/interrrogation/identification systemsBroadcast services for monitoring/identification/recognitionUltra-widebandComputer hardware
A wireless media player and a related system and methodology are disclosed. One aspect of the wireless media player system pertains to a virtual connector system, apparatus, and method for the automatic establishment of wireless connectivity with other electronic devices. In one embodiment, the media player device employs the use of integrated Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology to exchange communication settings, media capability, and other parameters with an external device that also has integrated RFID technology. The automatic exchange of settings and other information via a proximity-based RFID data exchange allows a media player to quickly establish a secure communication link with another device via a commonly supported wireless protocol such as Ultra Wideband (UWB) or Bluetooth. Another aspect of the media player system pertains to a method of using the captured media capability of the connecting device to customize certain menu options and software parameters in the media player.
Owner:SYNDEFENSE
Popular searches
Substation equipment Special data processing applications Short range communication service Subscription services Machine-to-machine/machine-type communication service Connection management Radio transmission Mobile application execution environments Home automation networks Input/output processes for data processing
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com