Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
66 results about "Resonance frequency shift" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
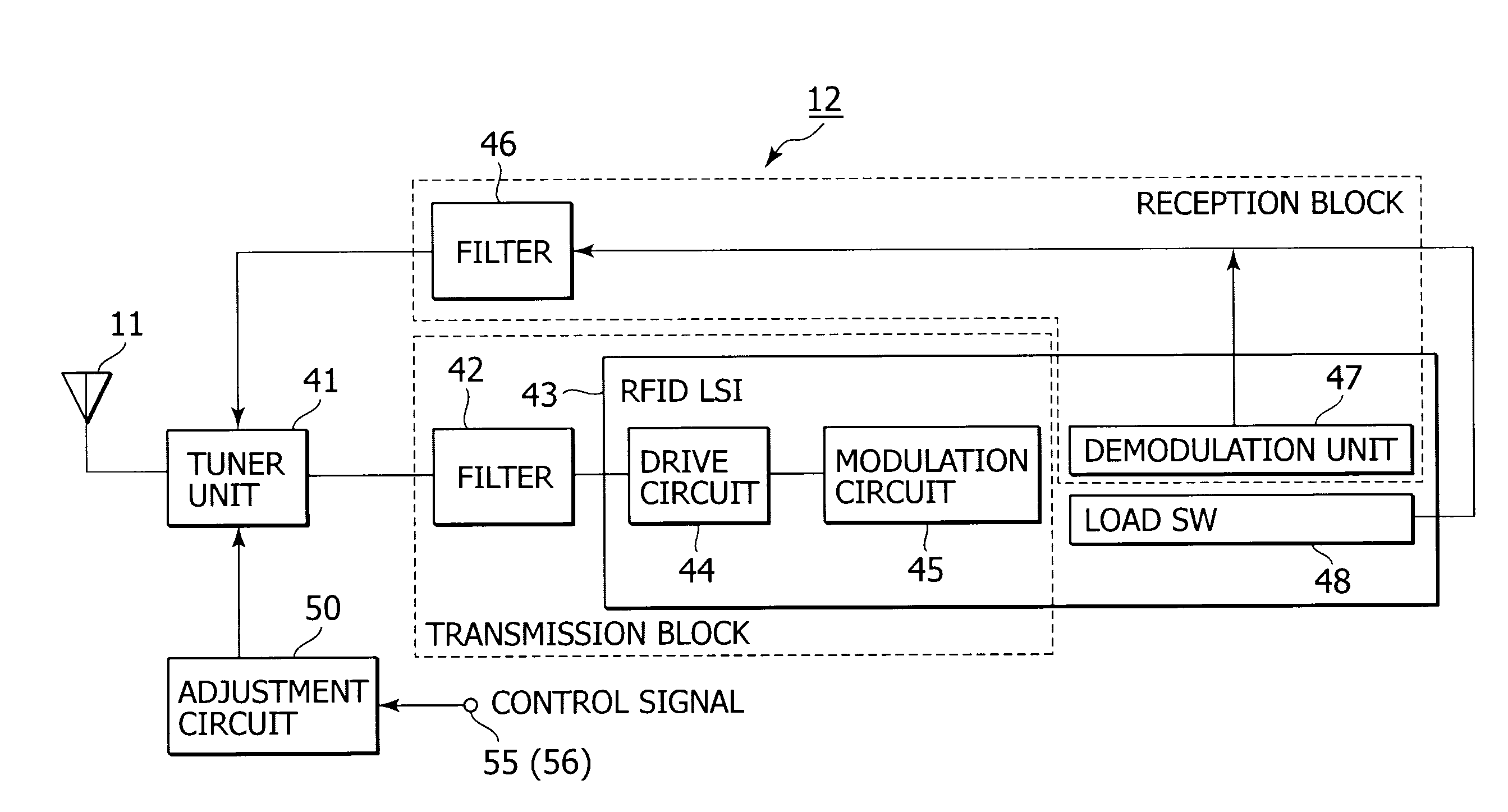
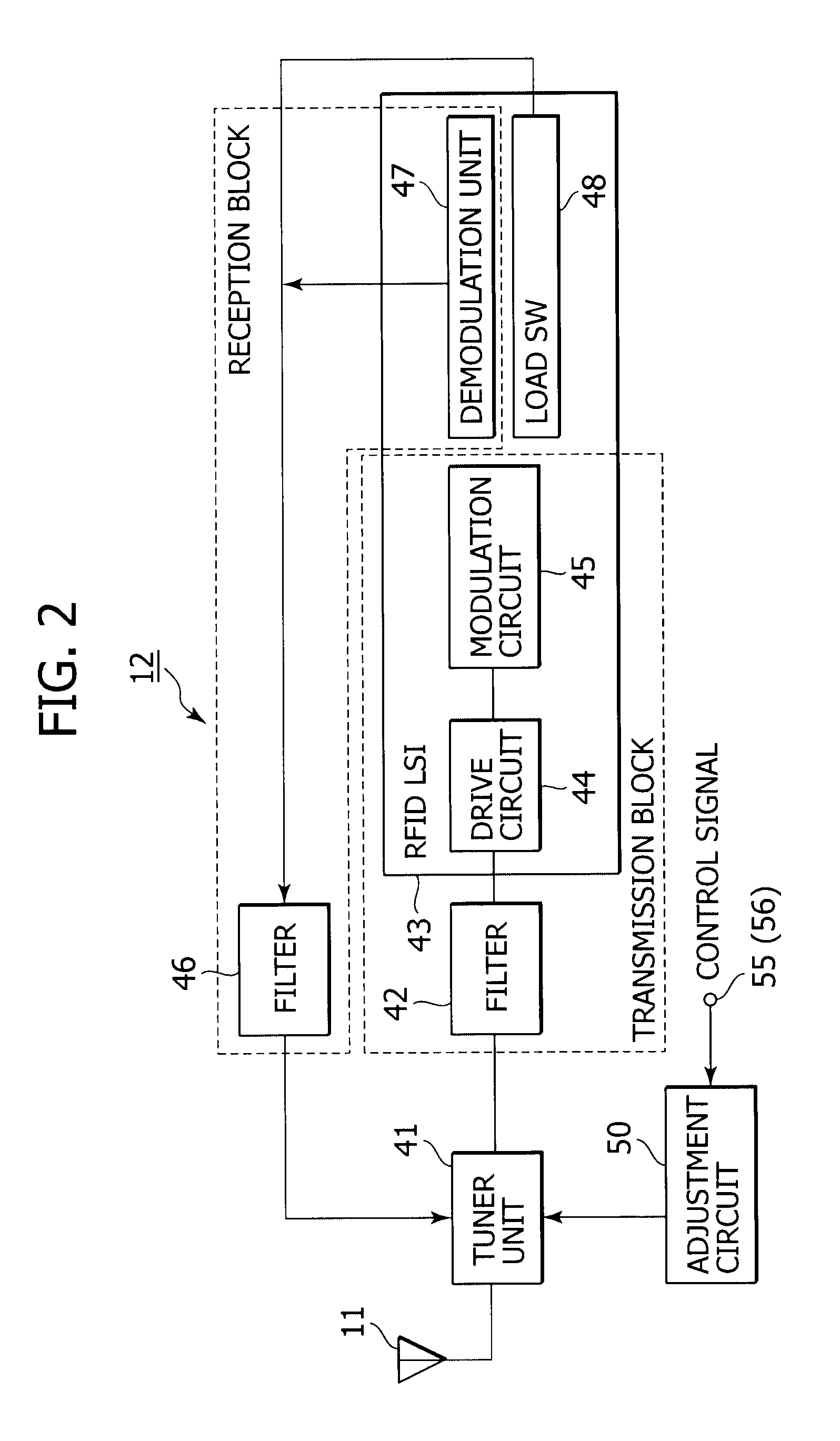
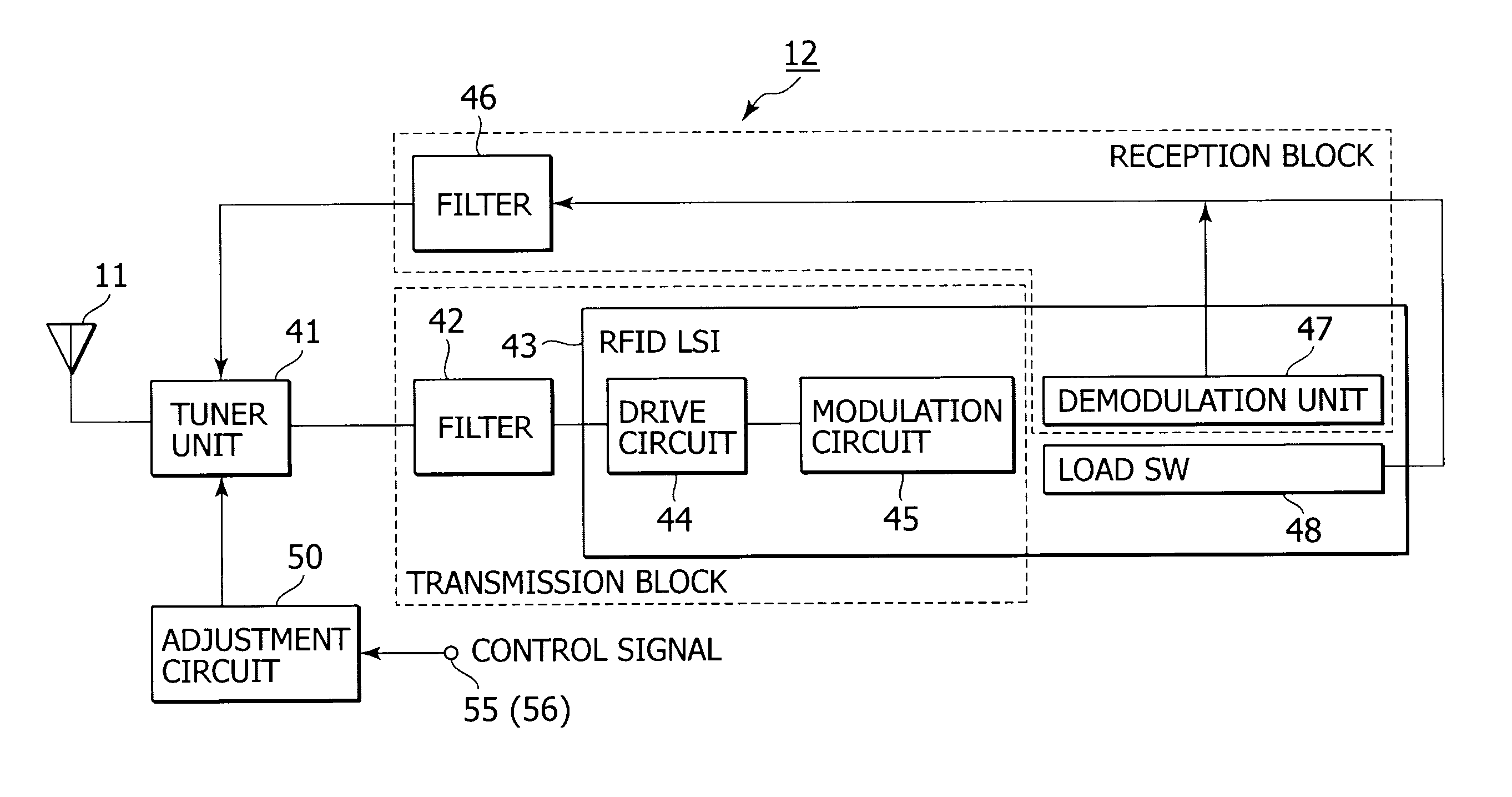
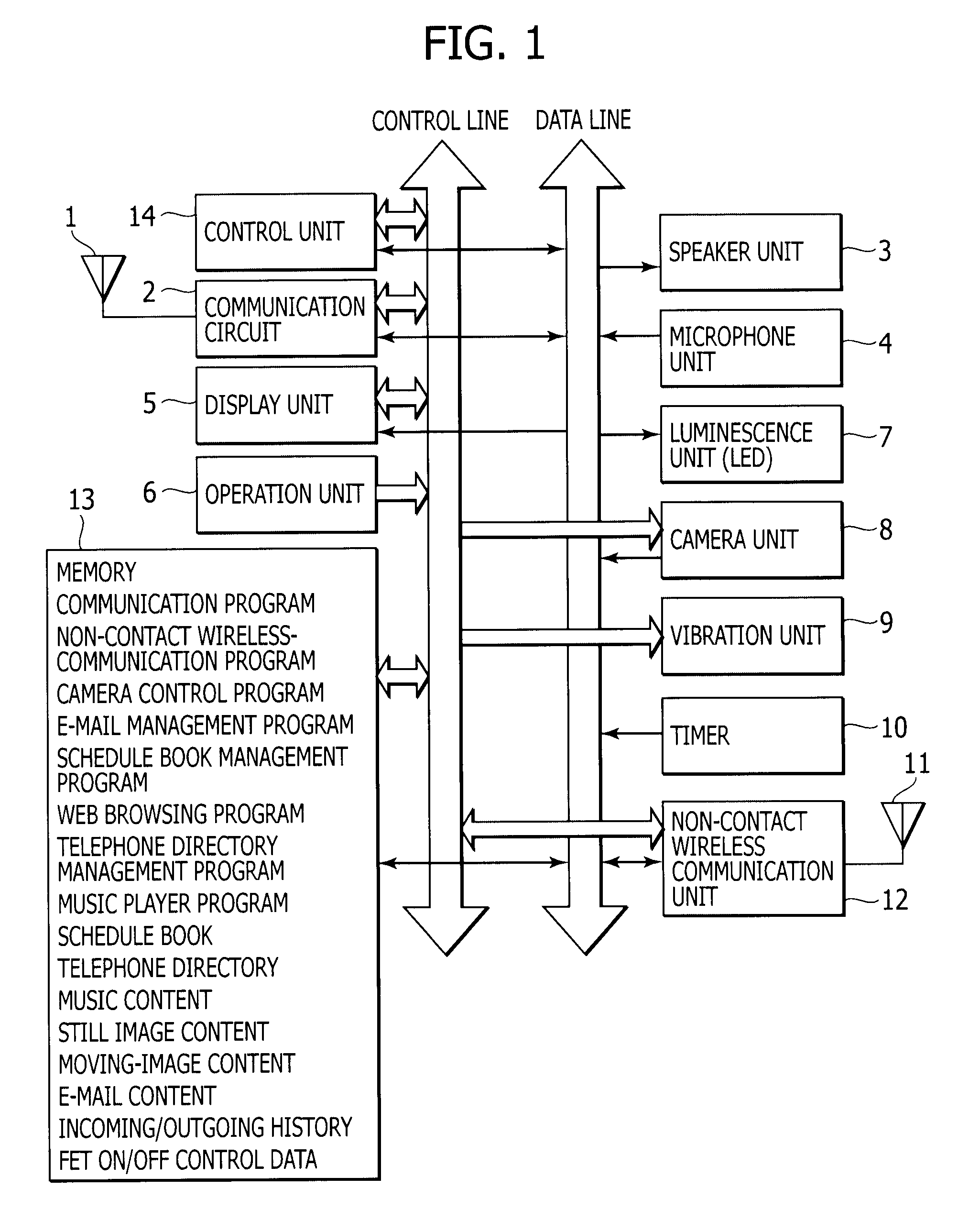
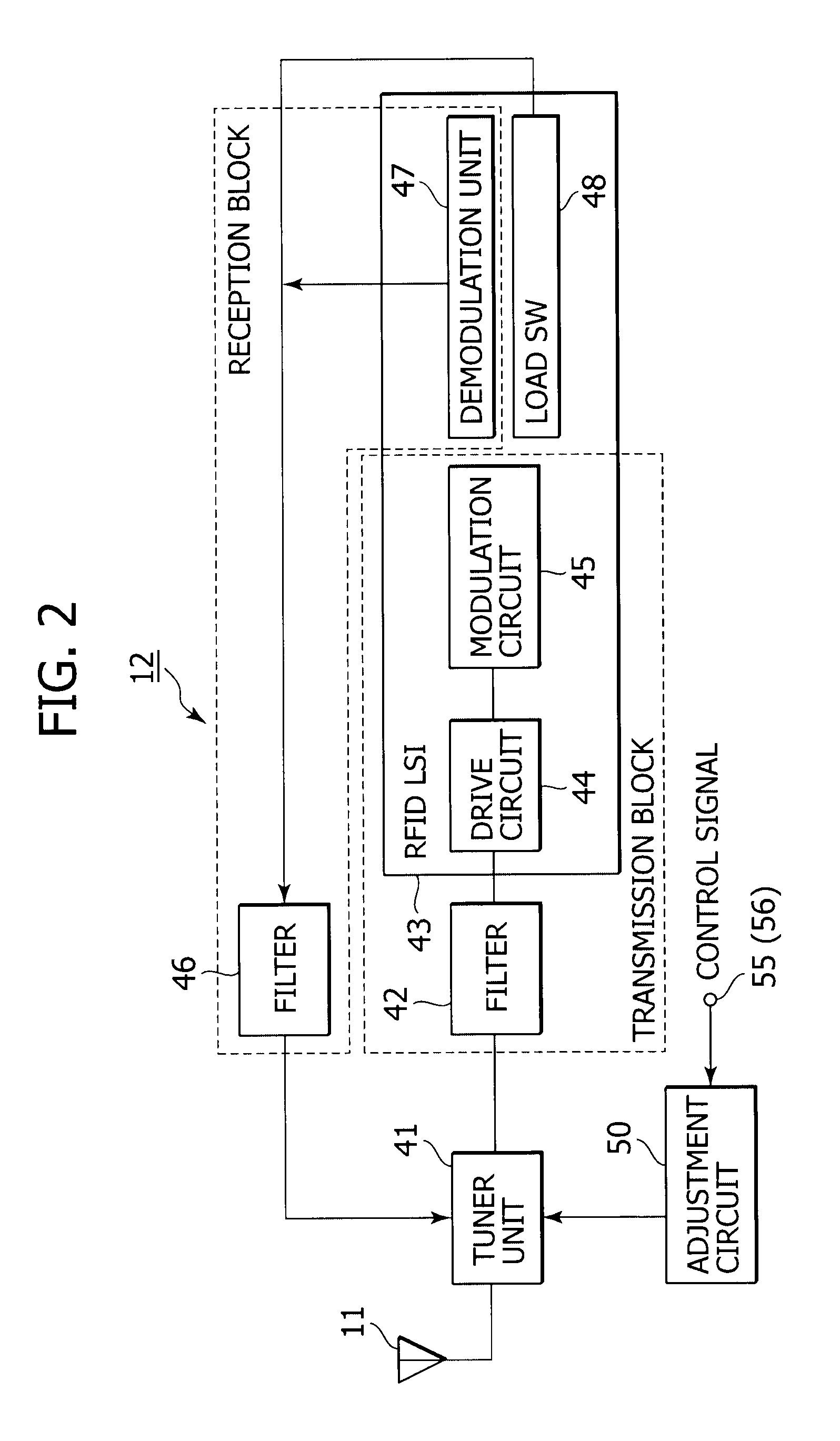
Non-contact wireless communication apparatus, method of adjusting resonance frequency of non-contact wireless communication antenna, and mobile terminal apparatus
ActiveUS20090146892A1Range of resonance frequency can be extendedEasy to adjustBatteries circuit arrangementsElectromagnetic wave systemCapacitanceTerminal equipment
A non-contact wireless communication apparatus and a mobile terminal apparatus are provided. The non-contact wireless communication apparatus includes a non-contact wireless communication antenna, a resonance capacitor, connected in parallel with the non-contact wireless communication antenna, for obtaining a predetermined resonance frequency with the non-contact wireless communication antenna, a resonance frequency adjustment unit for changing a resonance capacitance of the resonance capacitor to adjust the resonance frequency, a capacitance change amount control unit for controlling a change in resonance capacitance of the resonance capacitor in the resonance frequency adjustment unit, a resonance frequency shift unit for shifting the resonance frequency of the non-contact wireless communication antenna, and on / off control unit for performing on / off control of the resonance frequency shift unit in accordance with the amount of change in resonance capacitance of the resonance capacitor by the capacitance variation control unit.
Owner:SONY CORP
Non-contact wireless communication apparatus, method of adjusting resonance frequency of non-contact wireless communication antenna, and mobile terminal apparatus
ActiveUS8260200B2Avoid areaEasy to manufactureBatteries circuit arrangementsSubstation equipmentCapacitanceTerminal equipment
A non-contact wireless communication apparatus and a mobile terminal apparatus are provided. The non-contact wireless communication apparatus includes a non-contact wireless communication antenna, a resonance capacitor, connected in parallel with the non-contact wireless communication antenna, for obtaining a predetermined resonance frequency with the non-contact wireless communication antenna, a resonance frequency adjustment unit for changing a resonance capacitance of the resonance capacitor to adjust the resonance frequency, a capacitance change amount control unit for controlling a change in resonance capacitance of the resonance capacitor in the resonance frequency adjustment unit, a resonance frequency shift unit for shifting the resonance frequency of the non-contact wireless communication antenna, and on / off control unit for performing on / off control of the resonance frequency shift unit in accordance with the amount of change in resonance capacitance of the resonance capacitor by the capacitance variation control unit.
Owner:SONY CORP
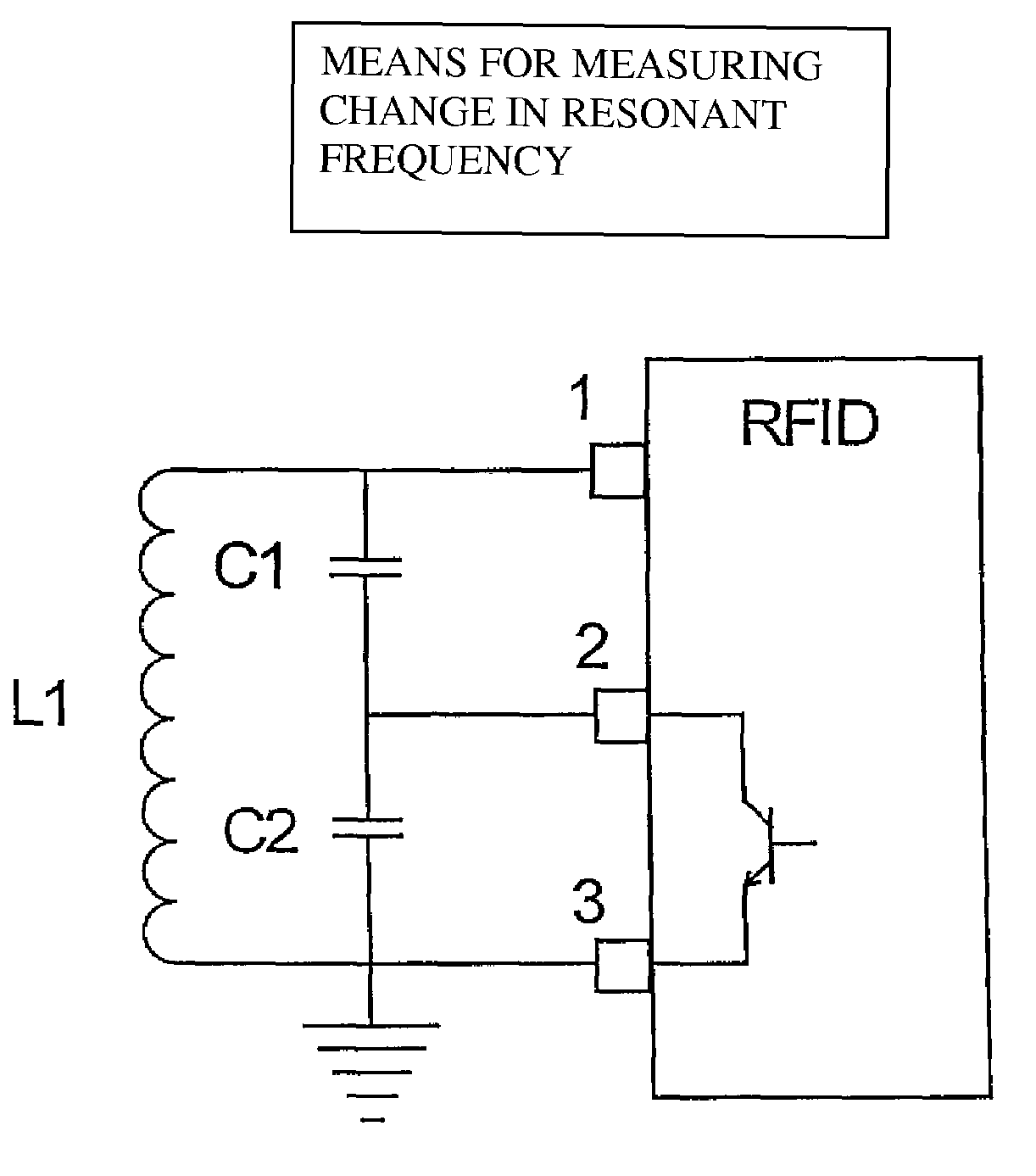
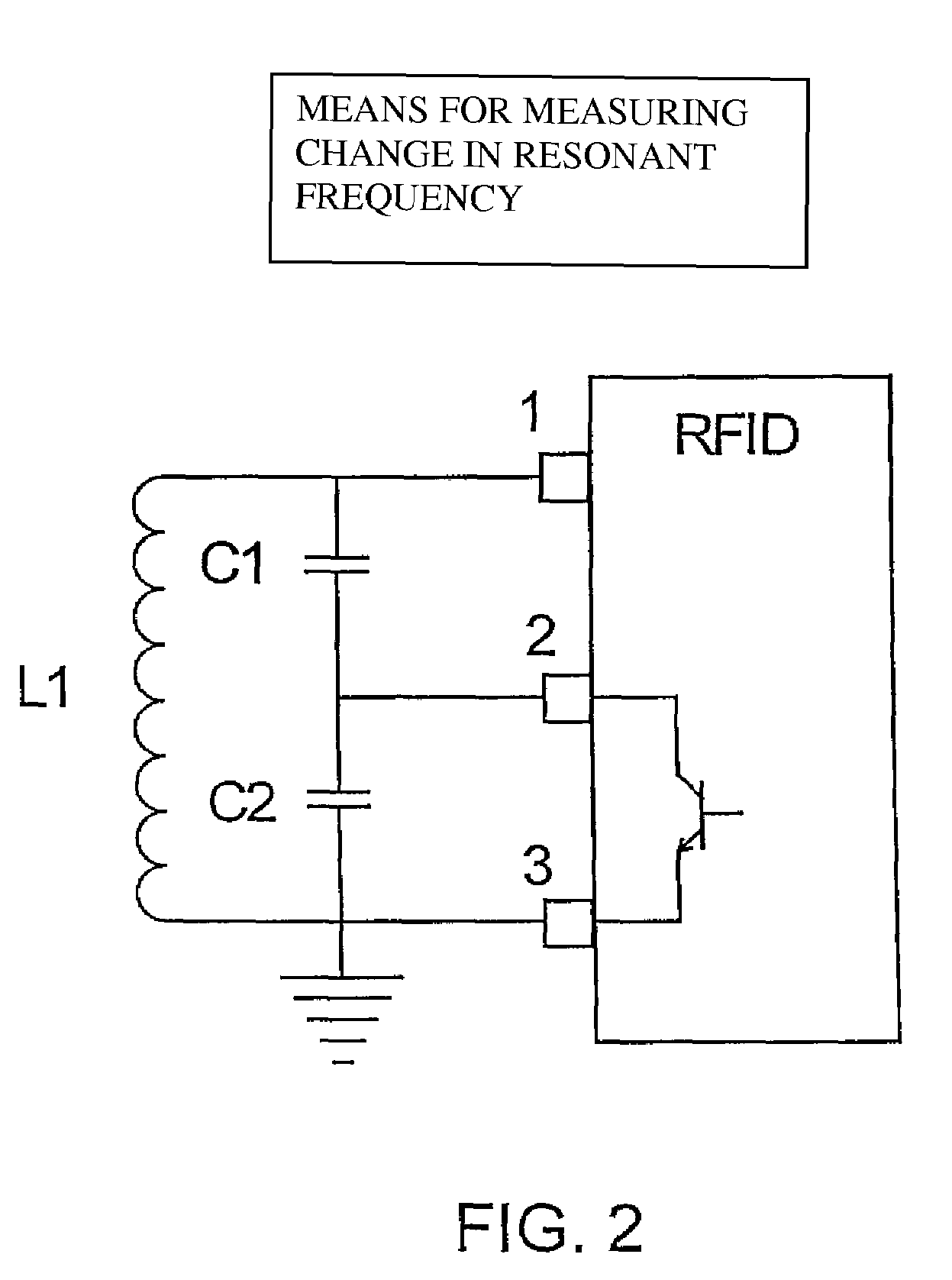
Sensor for monitoring environmental parameters in concrete
InactiveUS7551058B1Extended service lifeLow infrastructure costMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDigital computer detailsCapacitanceCapacitor
The invention provides a sensor for monitoring an environmental parameter in concrete comprising an enclosure for embedding in concrete; a detecting means connected to the enclosure for detecting at least one environmental parameter in concrete, the detecting means comprising at least one capacitive element for measuring capacitive change; an active material connected to the enclosure, the active material being liable to respond to the environmental parameter and the active material being operably connected to the capacitive element; a RFID chip mounted within the enclosure, the RFID chip being operably connected to the detecting means; and an antenna operably connected to the RFID chip, the antenna being operably connected to the detecting means, and the antenna being part of an L-R-C circuit whose resonance frequency shifts within an assigned frequency band. The invention also provides a MEMS-based capacitor that responds to an environmental parameter in concrete.
Owner:ADVANCED DESIGN CONSULTING USA
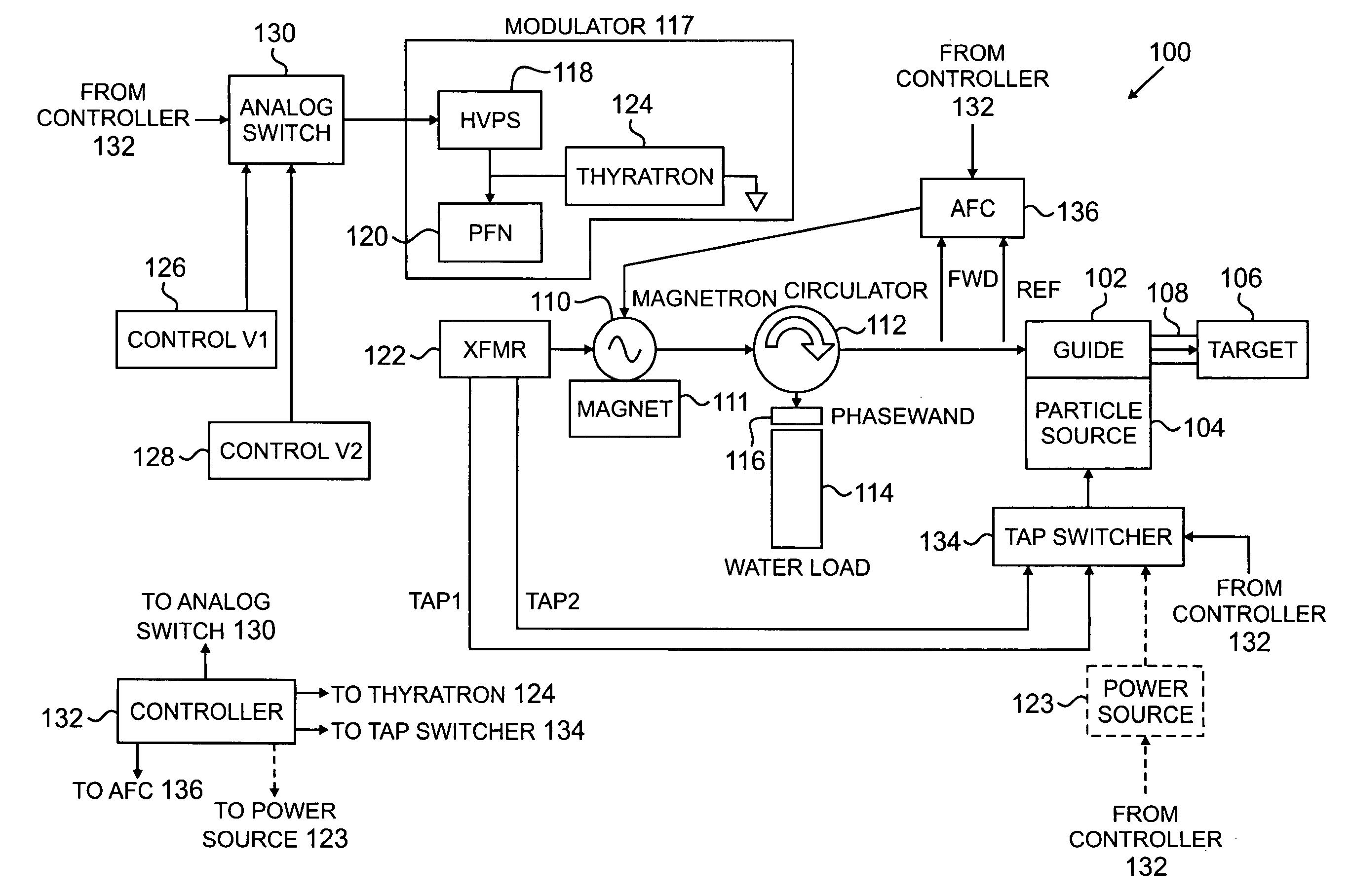
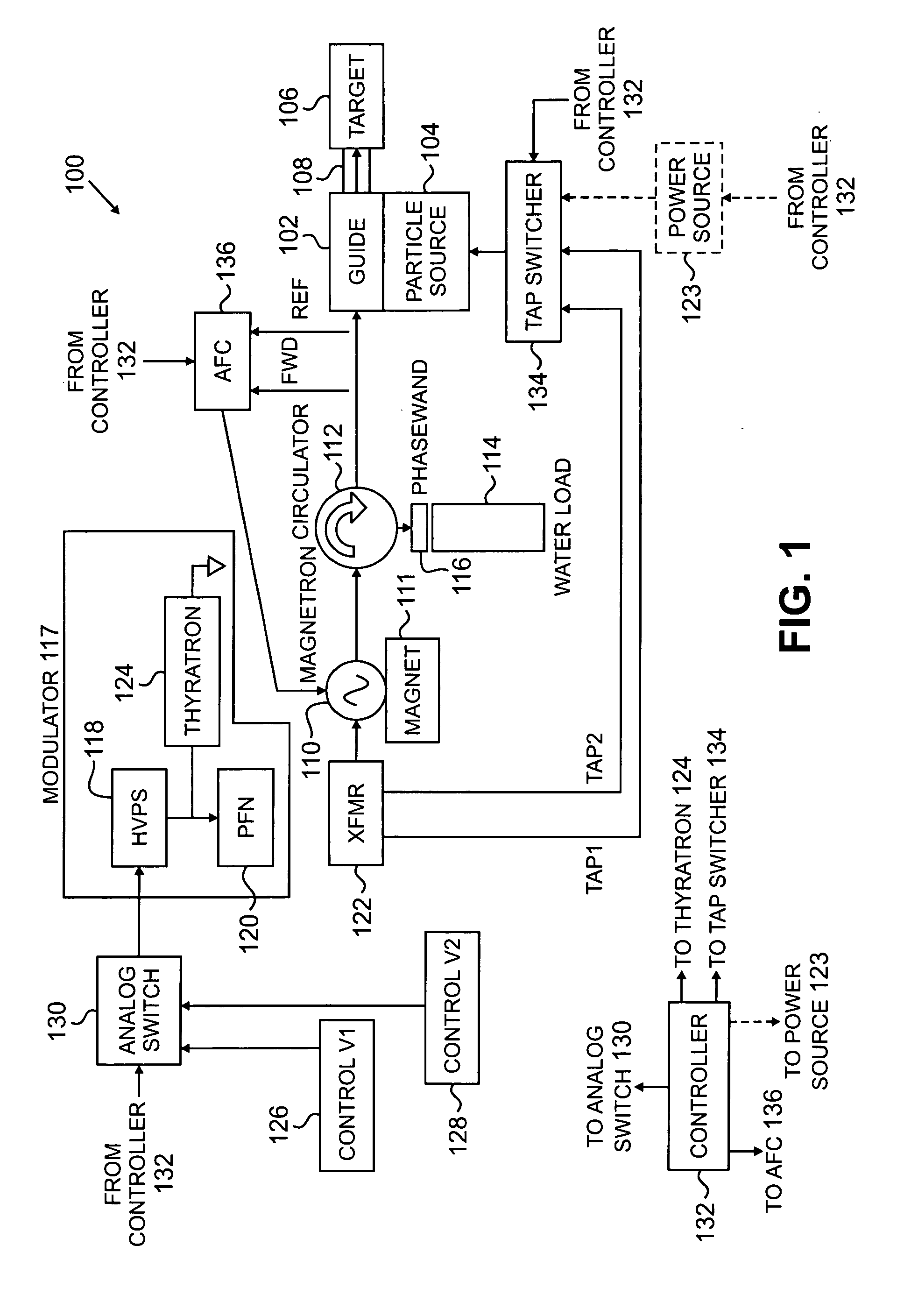
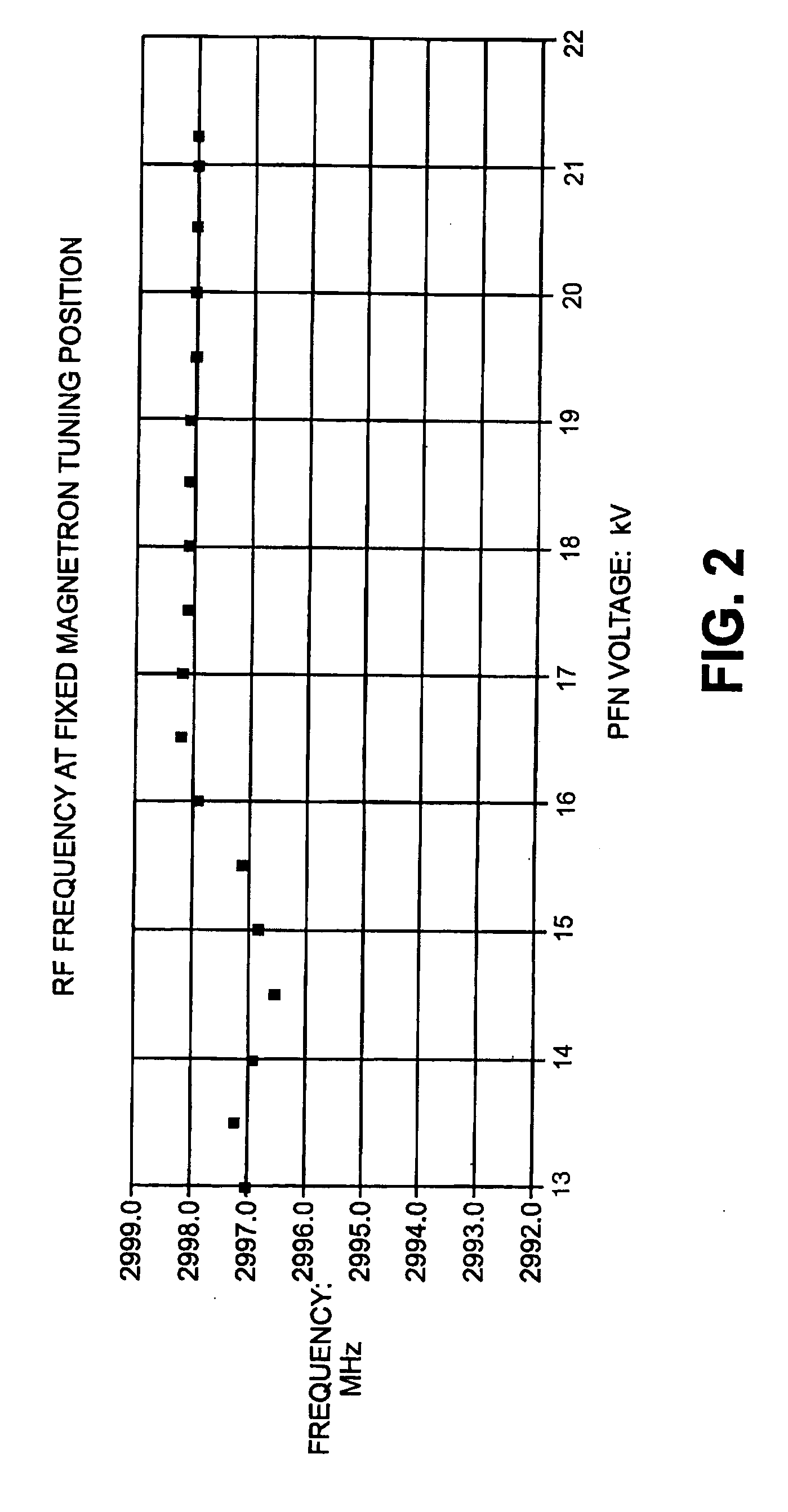
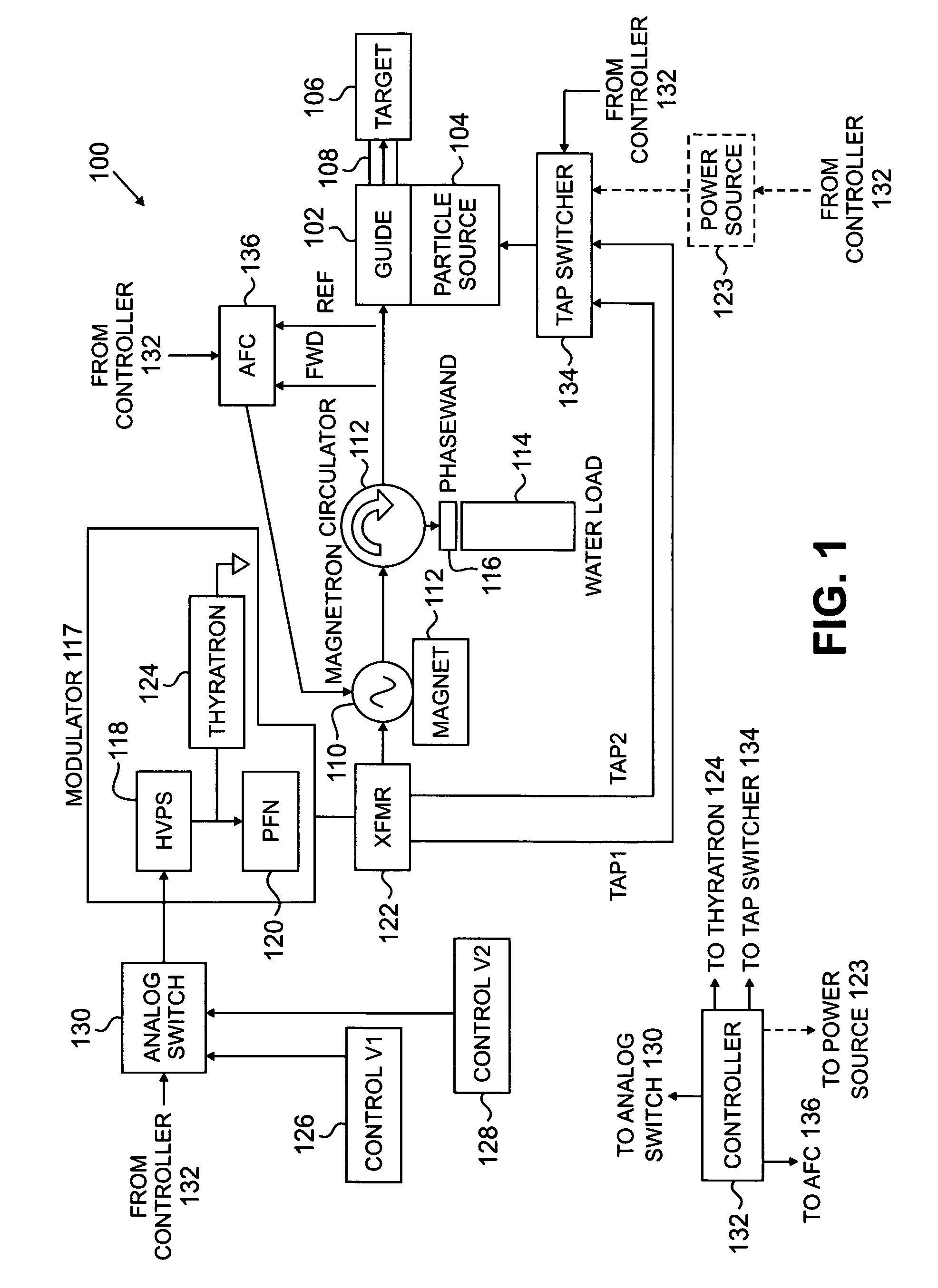
Interlaced multi-energy radiation sources
ActiveUS20100038563A1Improved frequency controlEasy to controlPhotometryTransit-time tubesKlystronElectricity
Multi-energy radiation sources comprising charged particle accelerators driven by power generators providing different RF powers to the accelerator, capable of interlaced operation, are disclosed. Automatic frequency control techniques are provided to match the frequency of RF power provided to the accelerator with the accelerator resonance frequency. In one example where the power generator is a mechanically tunable magnetron, an automatic frequency controller is provided to match the frequency of RF power pulses at one power to the accelerator resonance frequency when those RF power pulses are provided, and the magnetron is operated such that frequency shift in the magnetron at the other power at least partially matches the resonance frequency shift in the accelerator when those RF power pulses are provided. In other examples, when the power generator is a klystron or electrically tunable magnetron, separate automatic frequency controllers are provided for each RF power pulse. Methods and systems are disclosed.
Owner:VAREX IMAGING CORP
Piezoelectric cantilever sensors
ActiveUS7458265B2Less lengthVibration measurement in solidsWeighing by removing componentViscous liquidAnalyte
A piezoelectric cantilever with a non-piezoelectric, or piezoelectric tip useful as mass and viscosity sensors. The change in the cantilever mass can be accurately quantified by monitoring a resonance frequency shift of the cantilever. For bio-detection, antibodies or other specific receptors of target antigens may be immobilized on the cantilever surface, preferably on the non-piezoelectric tip. For chemical detection, high surface-area selective absorbent materials are coated on the cantilever tip. Binding of the target antigens or analytes to the cantilever surface increases the cantilever mass. Detection of target antigens or analytes is achieved by monitoring the cantilever's resonance frequency and determining the resonance frequency shift that is due to the mass of the adsorbed target antigens on the cantilever surface. The use of a piezoelectric unimorph cantilever allows both electrical actuation and electrical sensing. Incorporating a non-piezoelectric tip (14) enhances the sensitivity of the sensor. In addition, the piezoelectric cantilever can withstand damping in highly viscous liquids and can be used as a viscosity sensor in wide viscosity range.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Local magnetic resonance image quality by optimizing imaging frequency
InactiveUS20050165295A1Improve image qualityReduce image qualityDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsImaging qualityRadio frequency
In a method and magnetic resonance (MR) imaging apparatus for reducing artifacts due to resonance frequency offsets in a diagnostic MR image, a number of MR scout images of a portion of a subject containing a region of interest (ROI) are generated respectively using different radio frequency (RF) excitation frequencies. Each of the MR scout images has an identifiable image quality in the ROI. The MR scout images are analyzed as to the image quality in the ROI to identify one of the MR scout images having the best image quality in the ROI. An MR diagnostic image is then generated of the portion of the subject containing the ROI, using the RF excitation frequency that was used to generate the MR scout image having the best image quality in the ROI.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
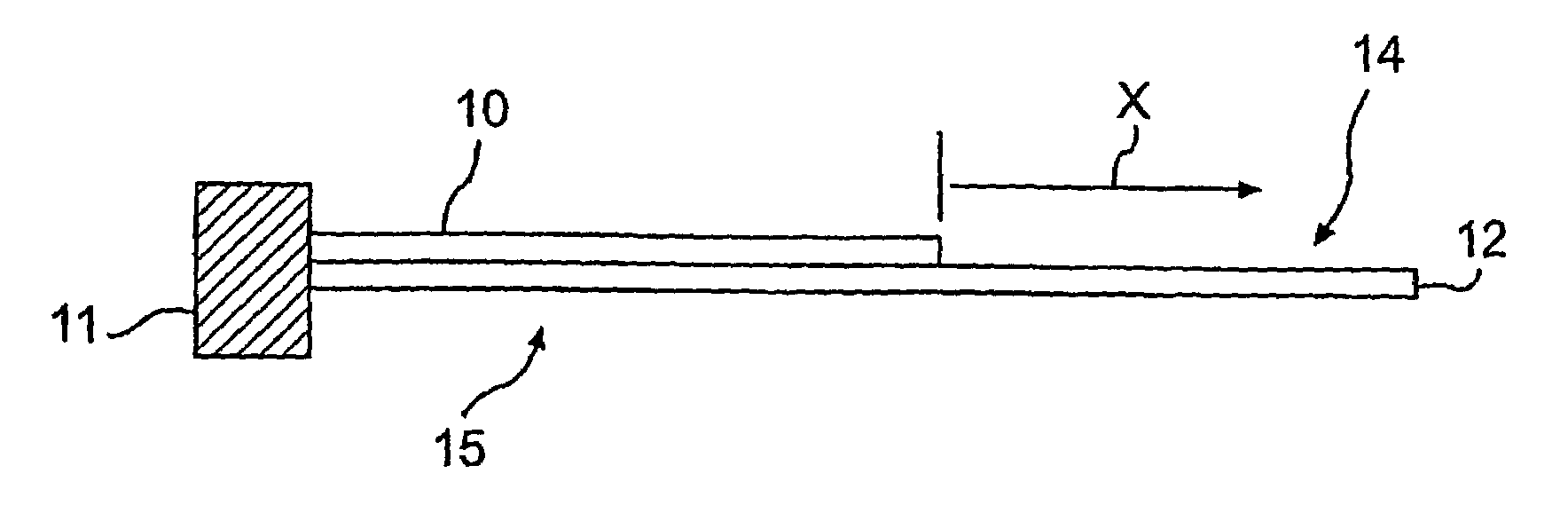
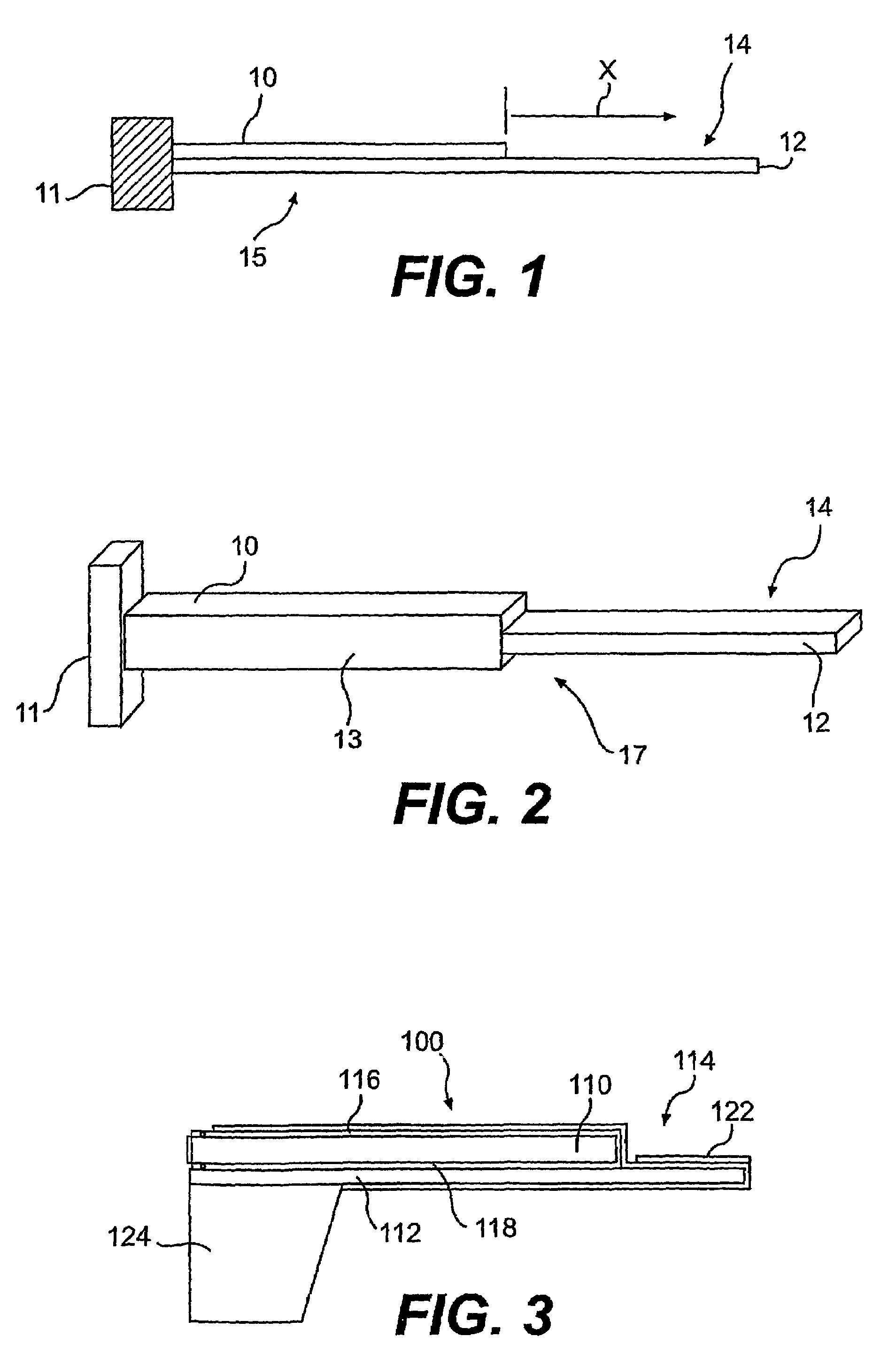
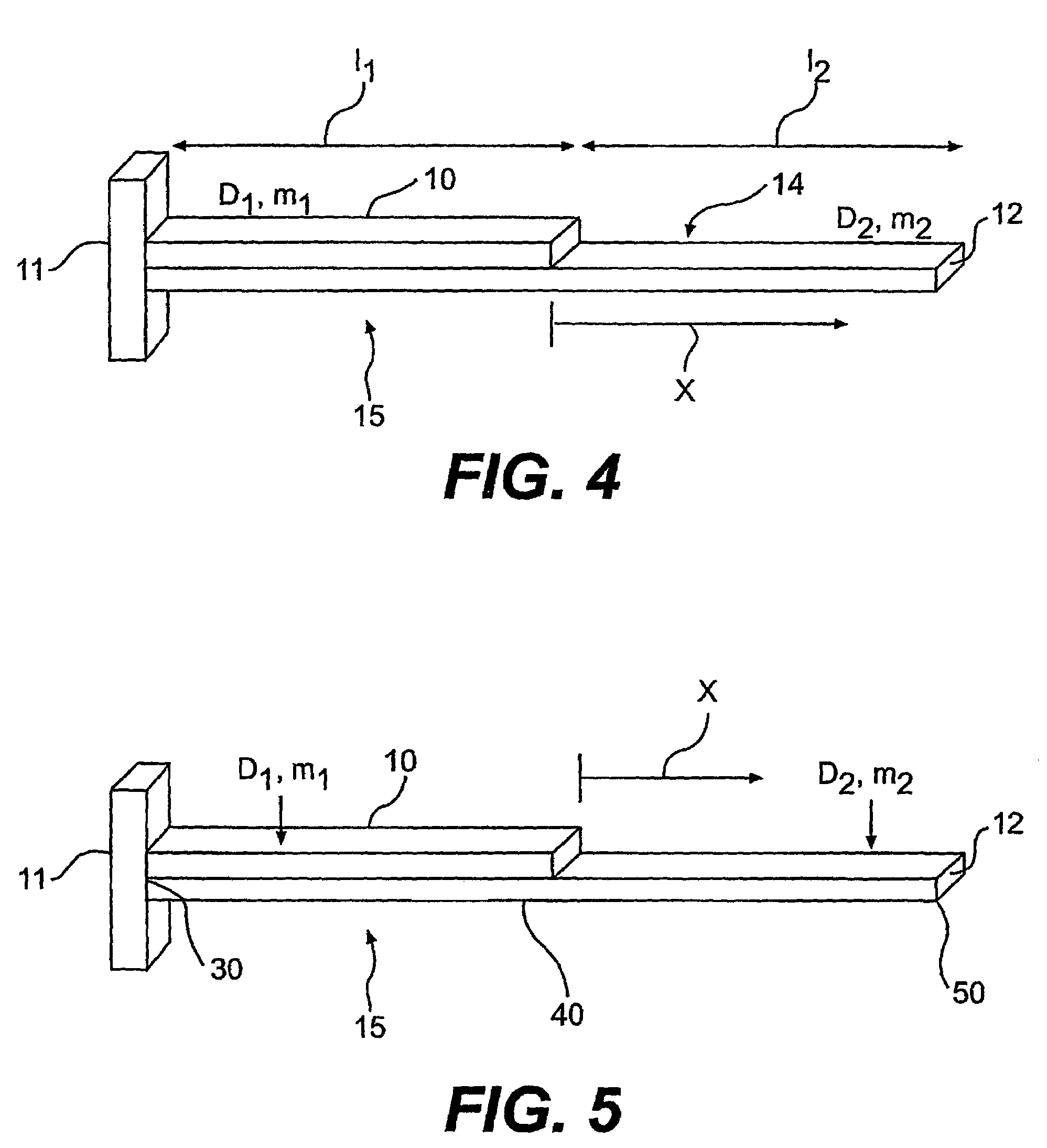
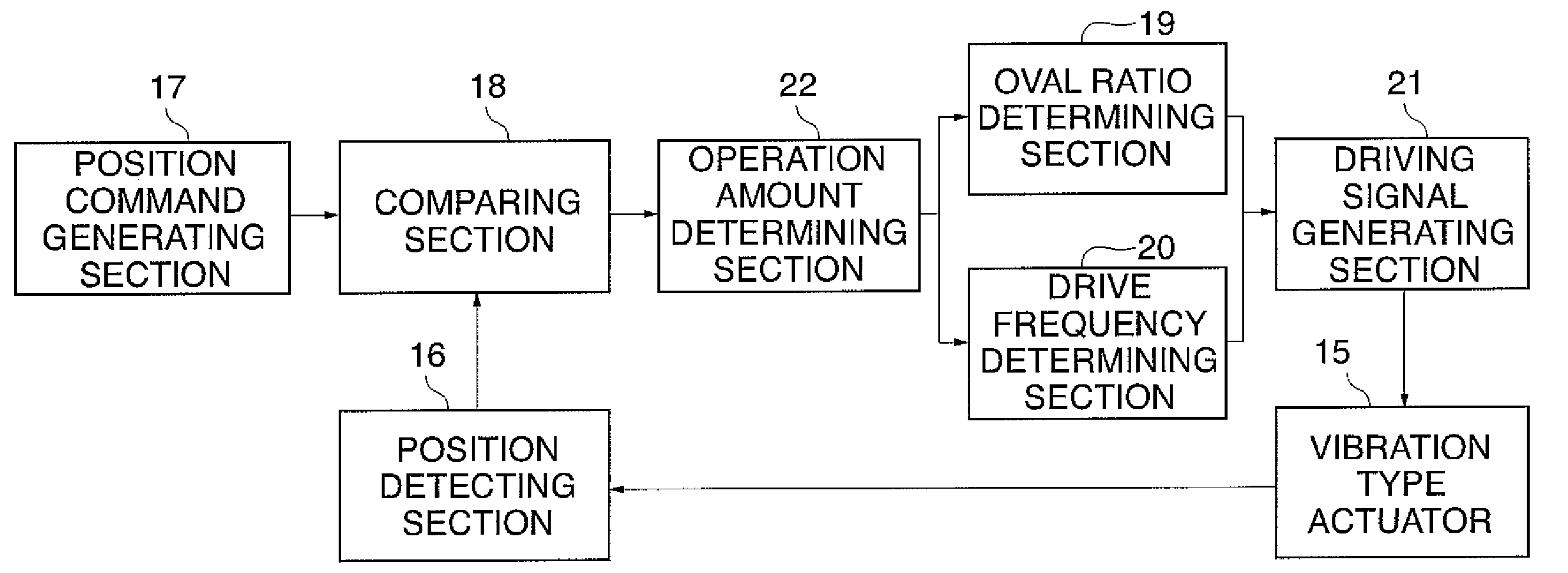
Control apparatus and control method for vibration wave driven apparatus
ActiveUS20090066187A1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesPhase differenceActuator
A vibration wave driven apparatus capable of preventing a resonance frequency of a vibrator from being shifted to a frequency side higher than a fixed drive frequency of the vibrator during the execution of phase difference control or voltage control. Driving signals are supplied from a control apparatus to a vibration-type actuator having a piezoelectric element that functions as an electromechanical energy conversion element. To control the drive of the vibration-type actuator, either a phase difference between the driving signals or a voltage of the driving signals is changed. When either the phase difference or the driving signal voltage is changed, the frequency of the driving signals is set to a predetermined frequency higher than the frequency for use when neither the phase difference nor the driving signal voltage is changed.
Owner:CANON KK
Electrostatic ultrasonic transducer drive control method, electrostatic ultrasonic transducer, ultrasonic speaker using the same, audio signal reproduction method, ultra-directional acoustic system, and display device
InactiveUS20070154036A1High strengthImprove energy conversion efficiencyMicrophonesSignal processingSonificationUltrasonic sensor
A Push-Pull-type electrostatic ultrasonic transducer includes a first electrode having a through hole, a second electrode having a through hole making a pair with the through hole of the first electrode, and a vibration film held between a pair of electrodes composed of the first and the second electrodes and having a conductive layer to which a direct-current bias voltage is applied, and holds the pair of electrodes and the vibration film. Assuming that λ is the wavelength of the carrier wave having a frequency shifted as a predetermined amount of frequency from the resonance frequency, which is the mechanical resonance frequency of the vibration film, the thickness t of each of the pair of electrodes is set to (λ / 4)·n or roughly (λ / 4)·n (where, λ is the wavelength of the ultrasonic wave, n is a positive odd number), and an alternating-current signal, which is a modulated wave obtained by modulating the carrier wave in the ultrasonic frequency band with a signal wave in an audible frequency band, is applied between the pair of electrodes.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
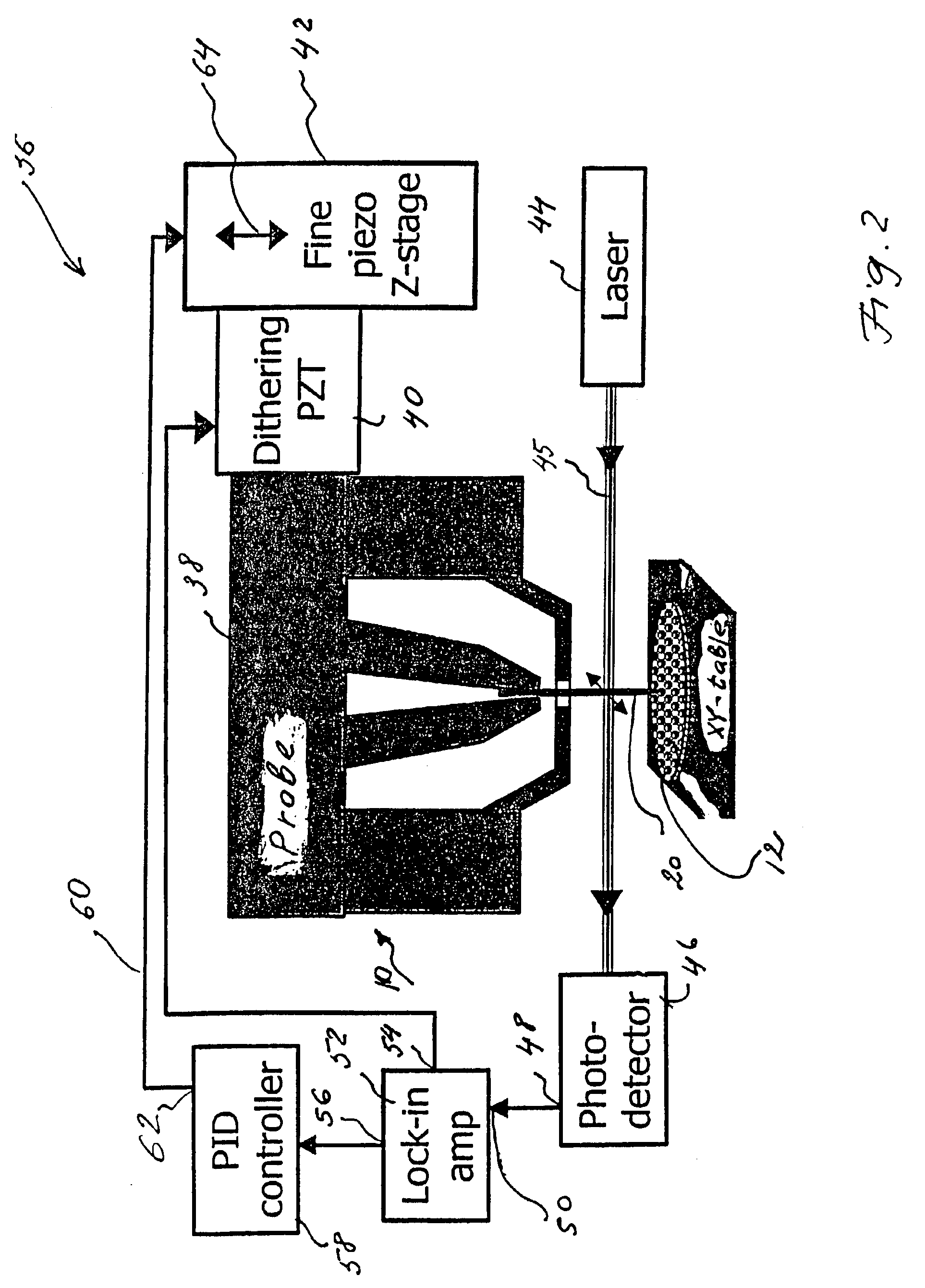
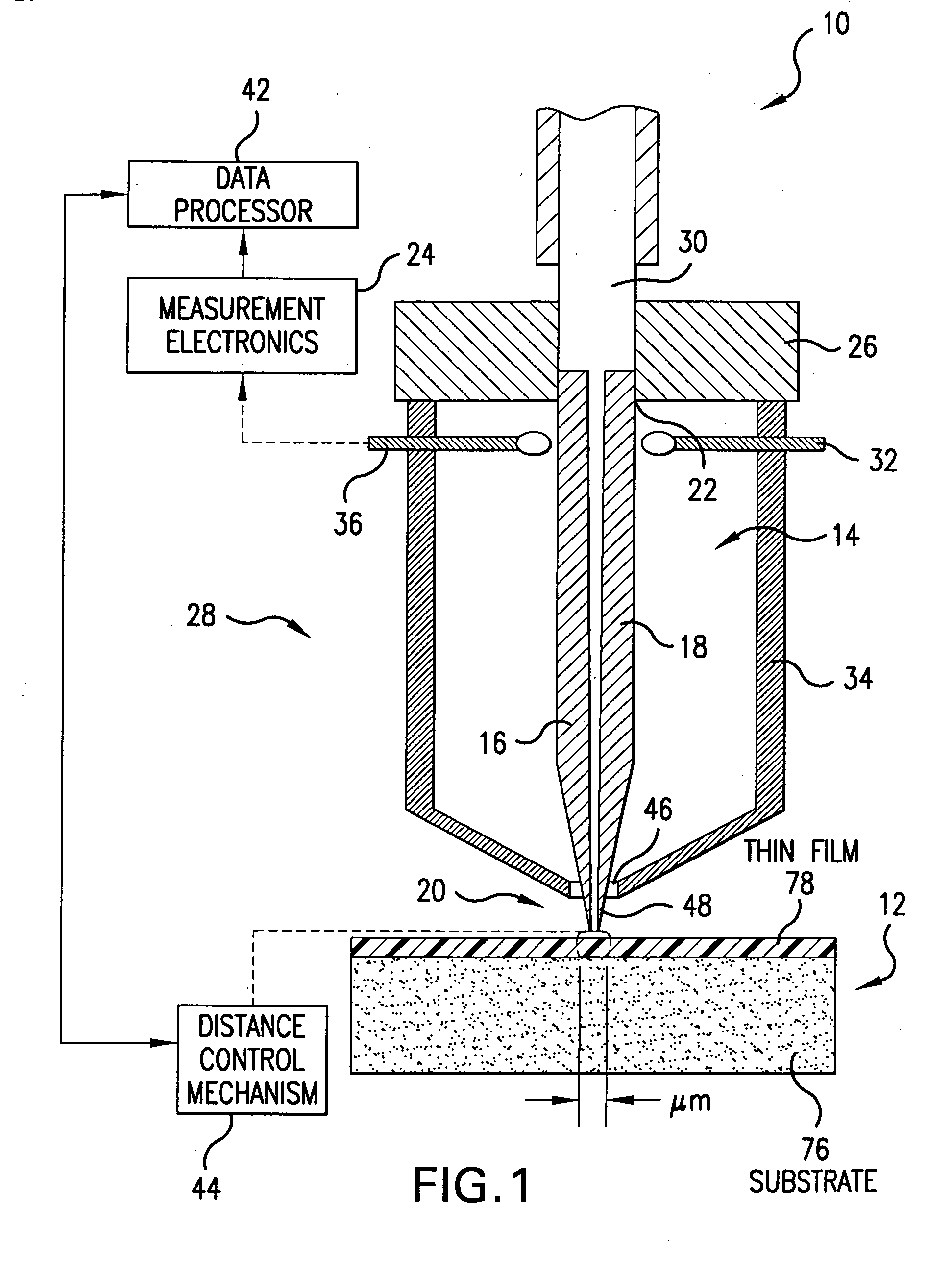
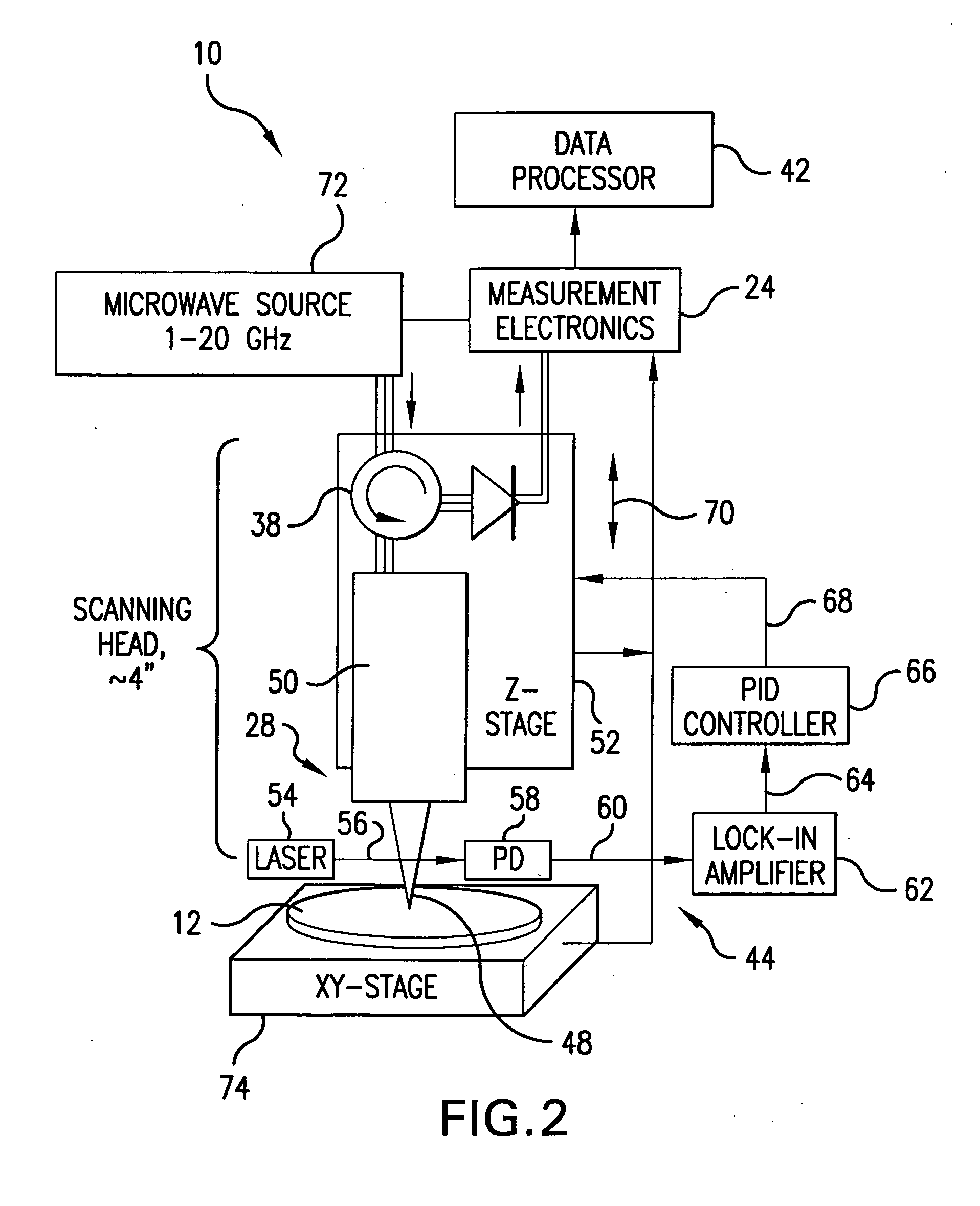
System and method for quantitative measurements of a material's complex permittivity with use of near-field microwave probes
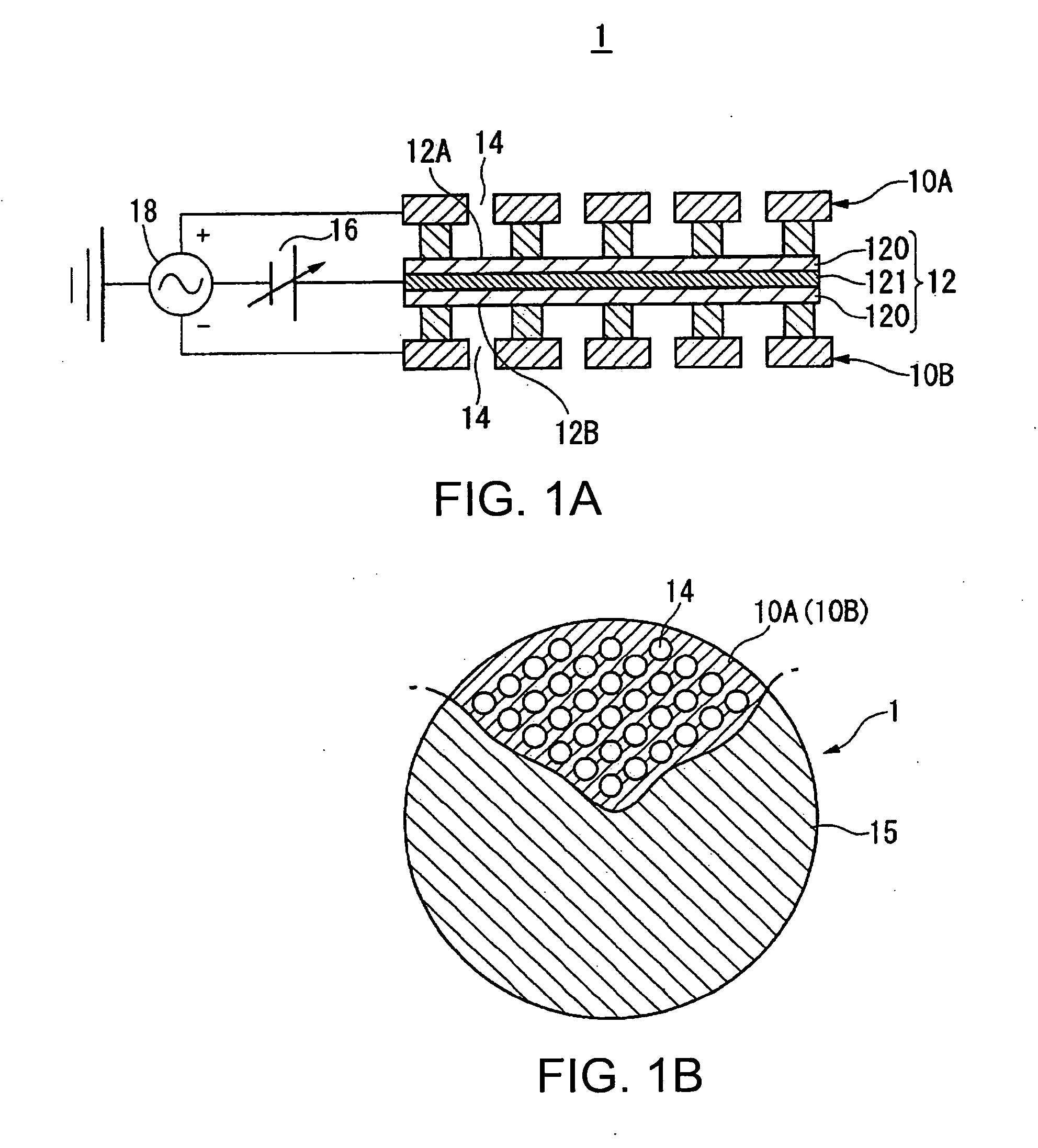
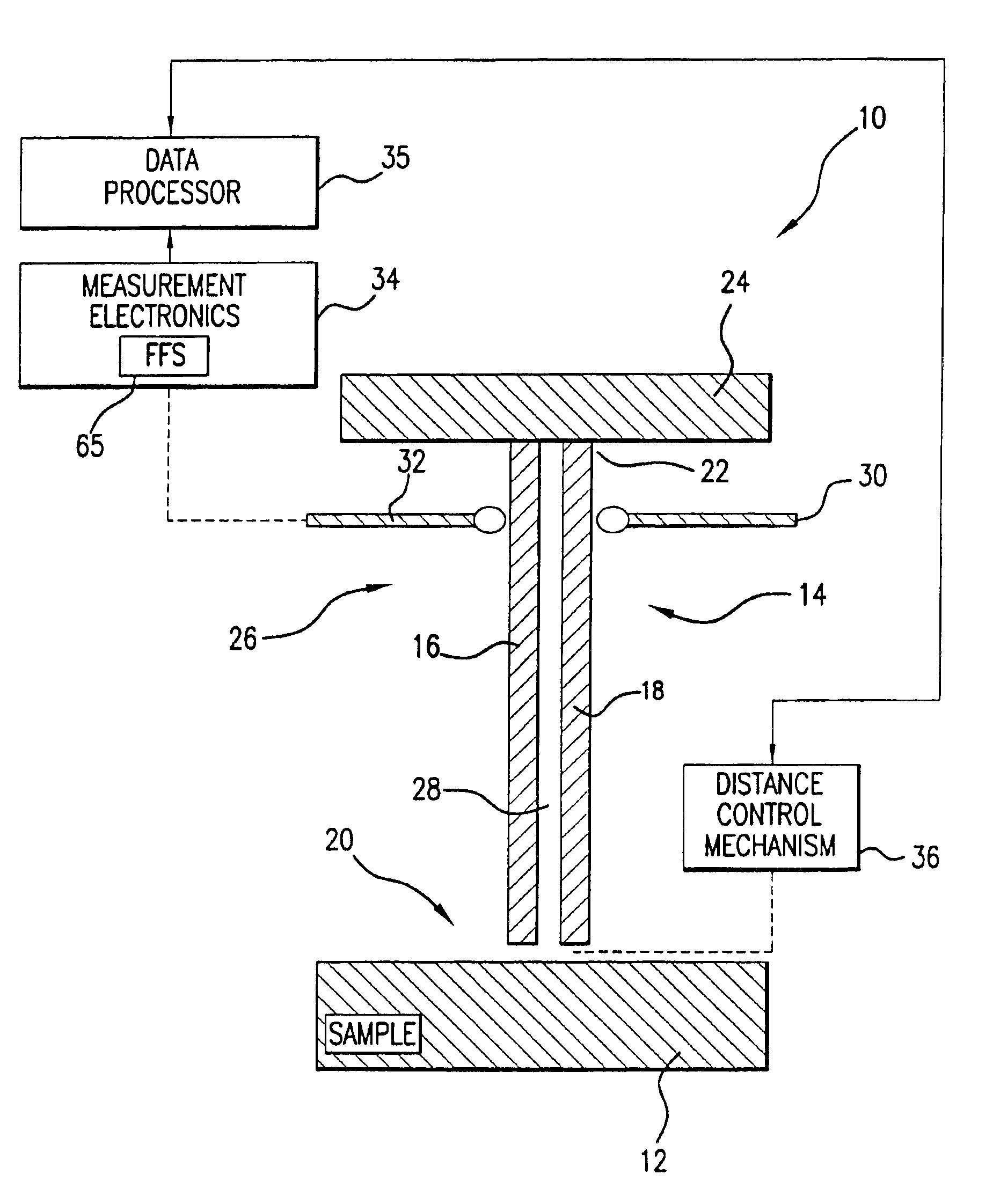
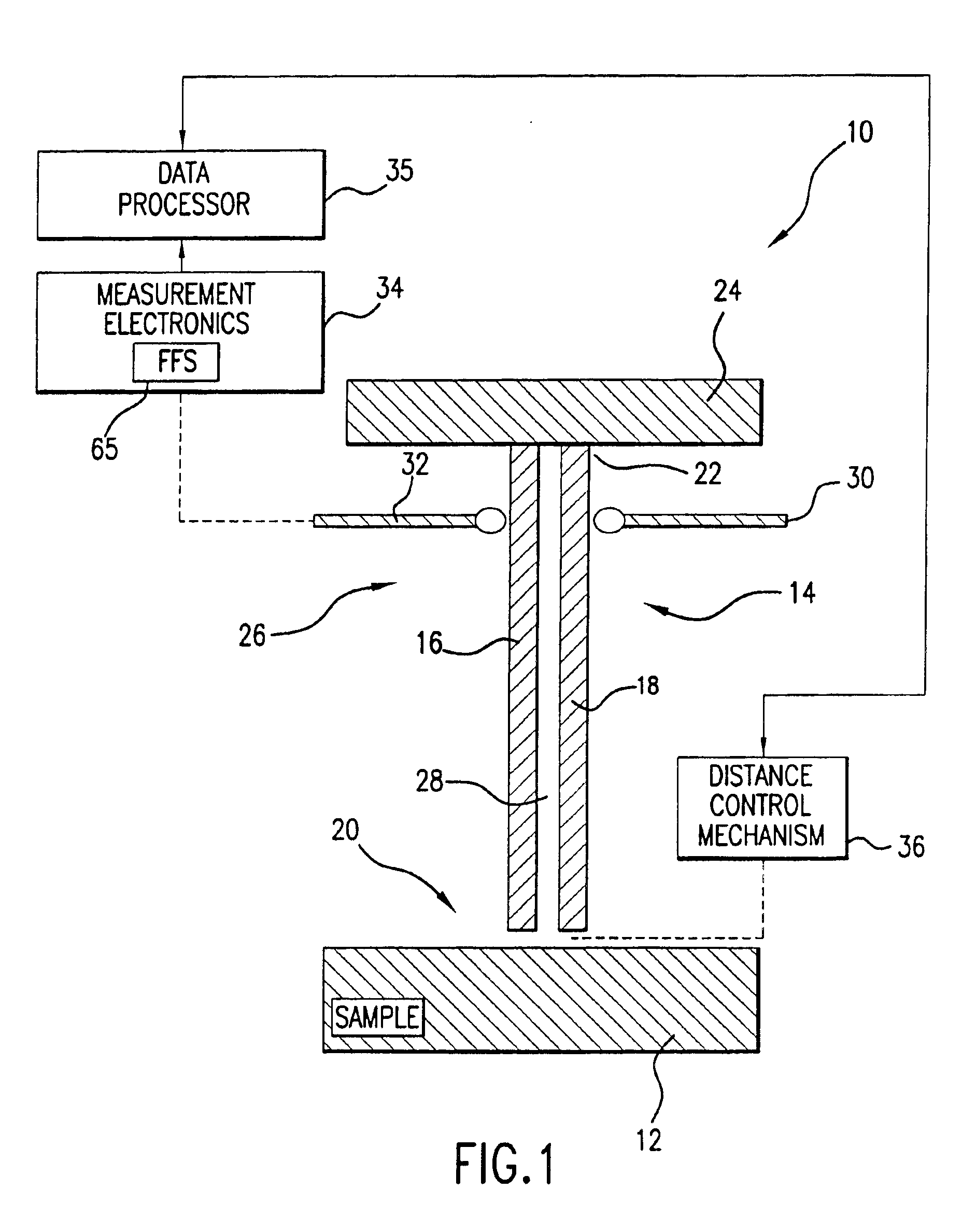
InactiveUS6856140B2High precision measurementEasily controlled for modificationResistance/reactance/impedenceMaterial analysis using microwave meansFigure of meritFrequency shift
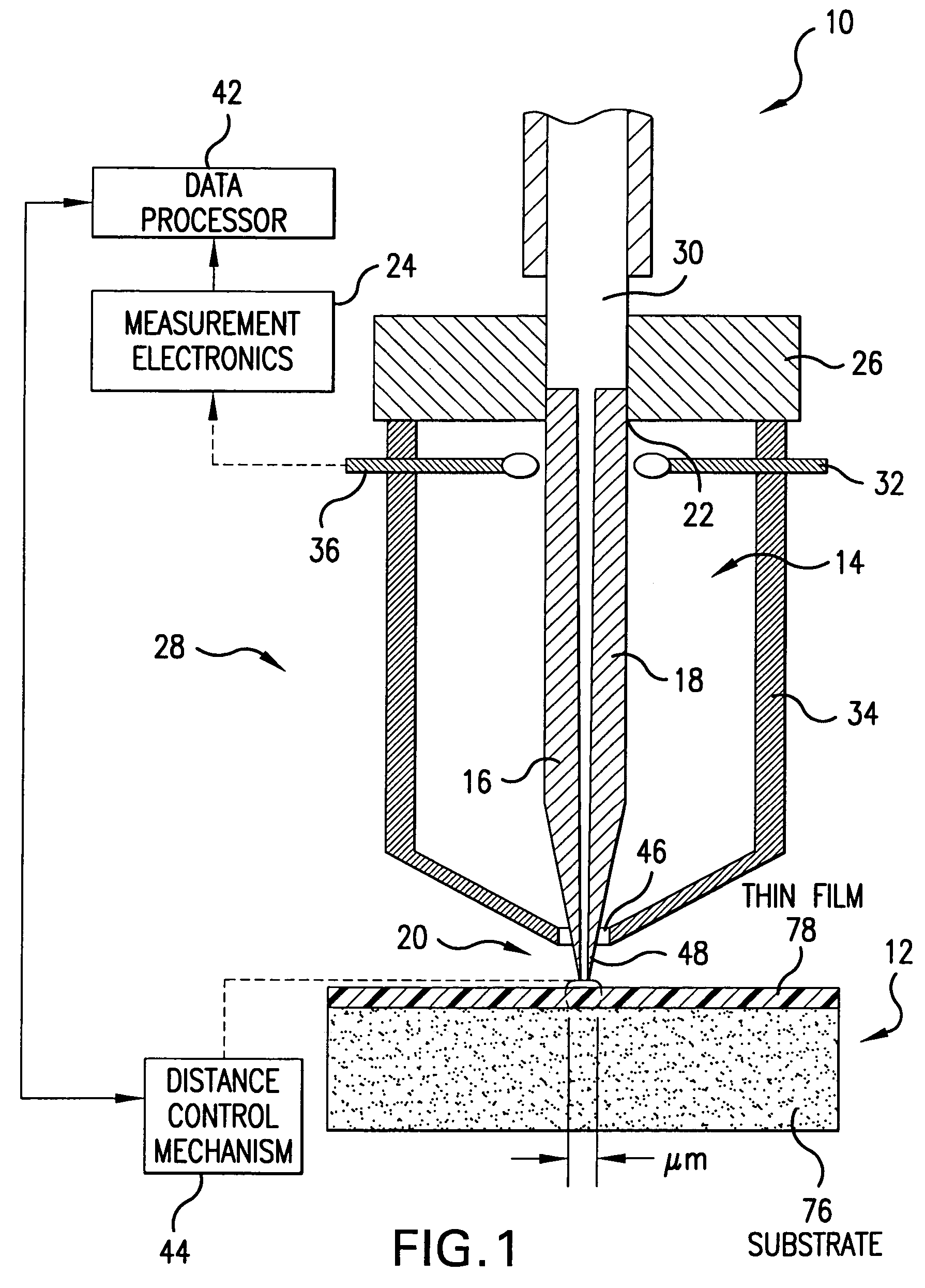
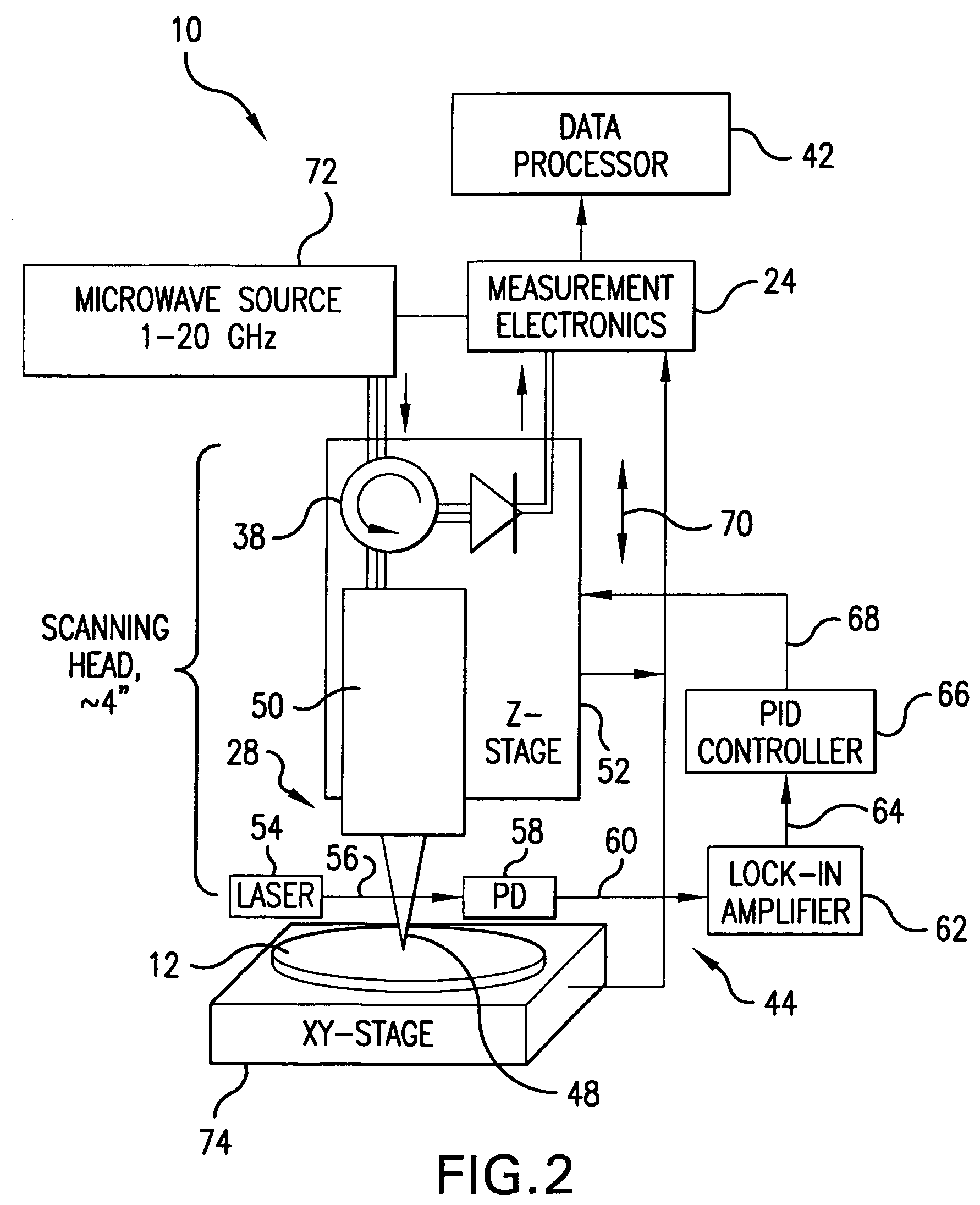
A method for measuring a material's complex permittivity is provided where a near-field microwave probe is positioned a predetermined distance from a first and a second standard sample for measuring a relative resonant frequency shift of the near-field microwave probe for standard samples. Based on measurements, calibration coefficients are calculated. A relative resonant frequency shift of the near-field microwave probe for a sample under study is measured by fast frequency sweep technique while the distance between the tip of the probe and the sample under the study is maintained nominally at the distance between the tip of the probe and each standard sample during a calibration procedure by a shear-force based distance control mechanism. Also, the change in the quality factor of the probe for unloaded and loaded resonator is measured. The dielectric constant of the sample under study is calculated using the resonant frequency shift and the change in the quality factor of the near-field microwave probe for the sample under study and the calibration coefficients obtained during the calibration procedure.
Owner:SEMICON PHYSICS LAB
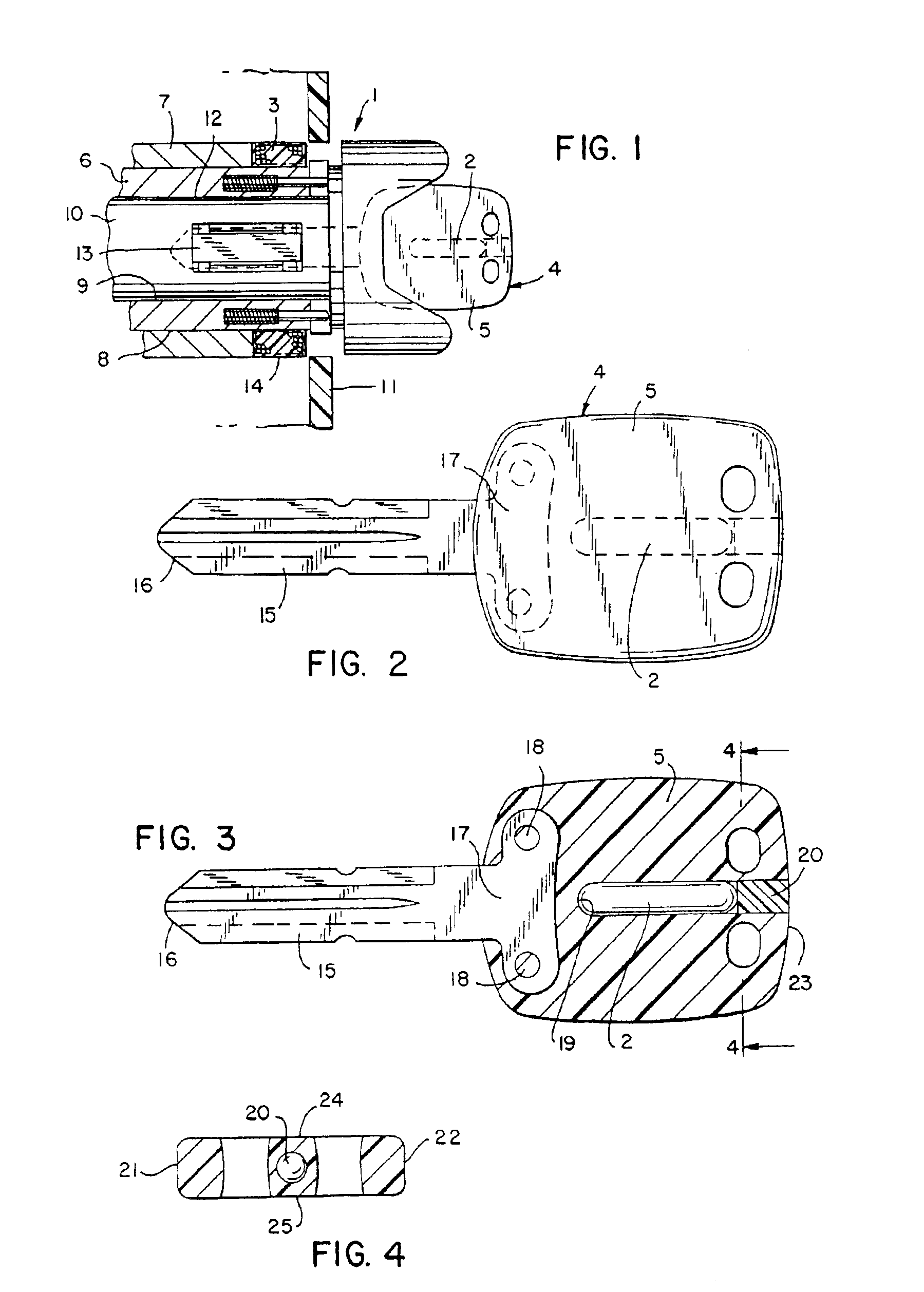
Key assembly for vehicle ignition locks
InactiveUS6948344B2Minimize impactLower potentialNon-mechanical controlsKeysElectricityMetallic materials
A method of decreasing resonant frequency shifting of an electrical circuit mounted on a vehicle key includes providing a frame in an opening in the head portion of a vehicle key and locating the transponder in the frame. The frame comprises substantially rigid non-metallic material, and the frame includes a support structure for supporting the transponder while decreasing forces produced on the transponder by thermal expansion and contraction of the head portion of the key, thereby decreasing shift in the resonance of the electrical circuit of the transponder. The frame, the transponder and the head portion of the key are overmolded providing an outer covering that encloses and protects the transponder.
Owner:STRATTEC SECURITY
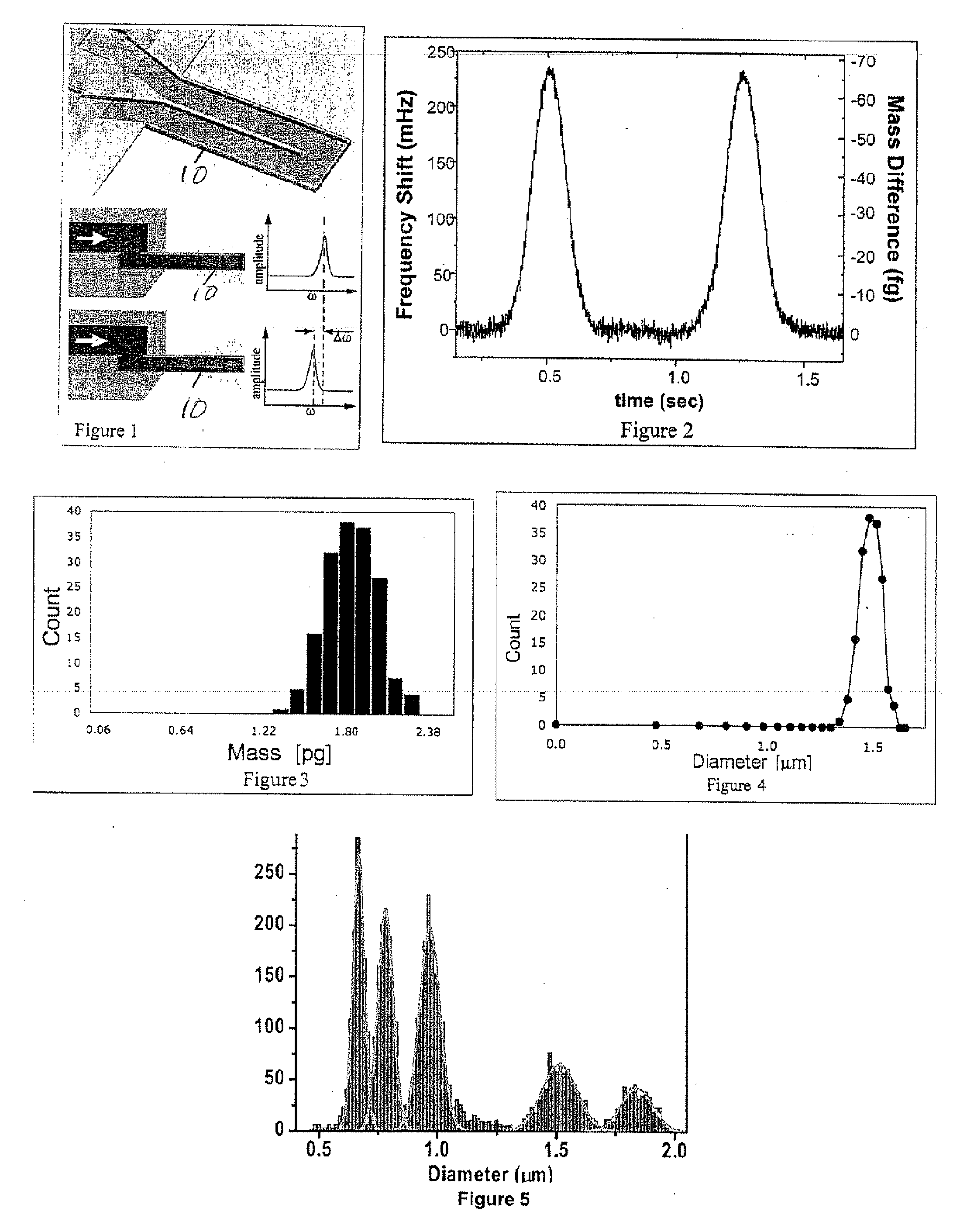
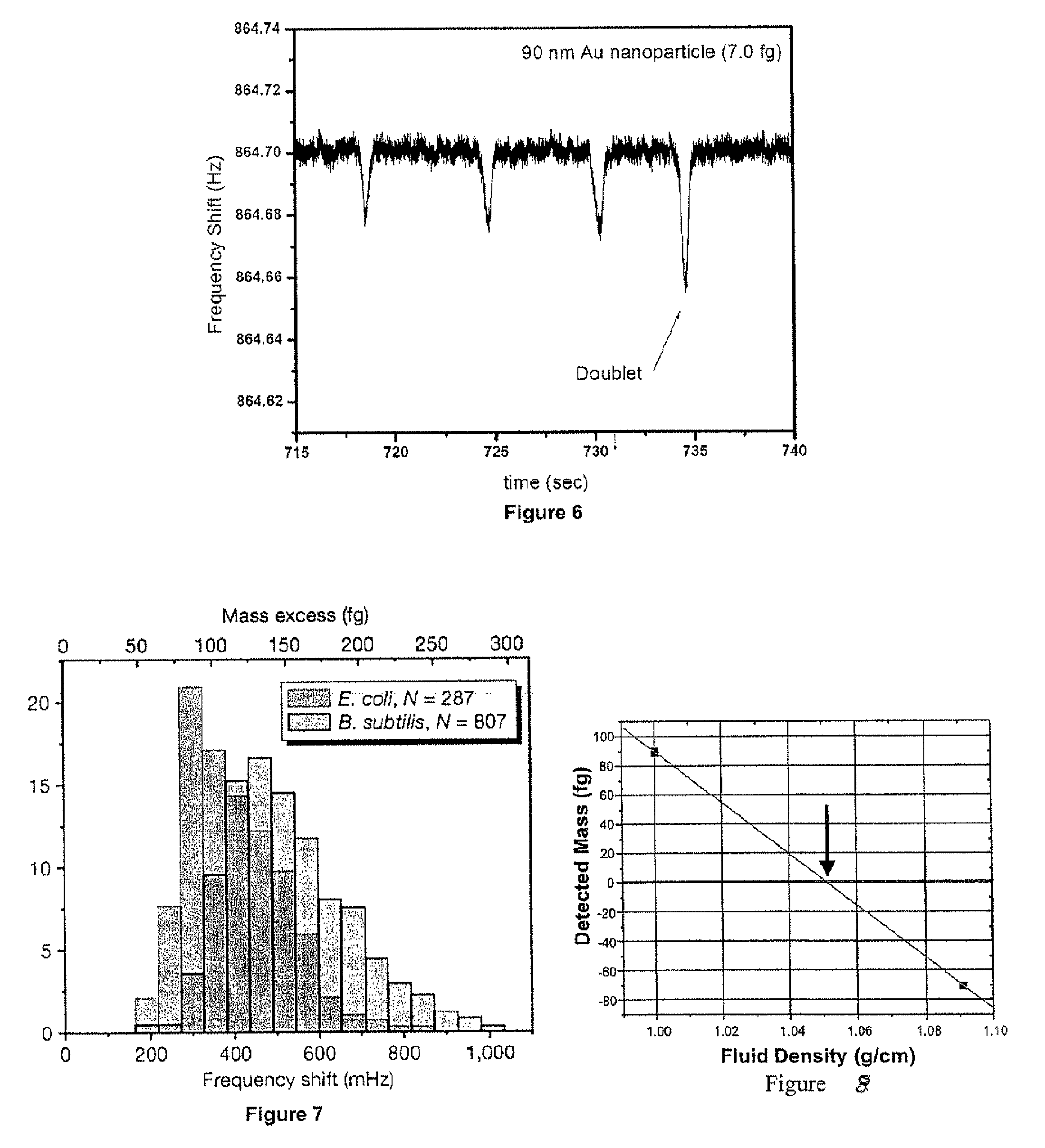
Method And Apparatus For Measuring Particle Characteristics through Mass Detection
ActiveUS20090044608A1Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesIndividual particle analysisParticle propertiesParticle density
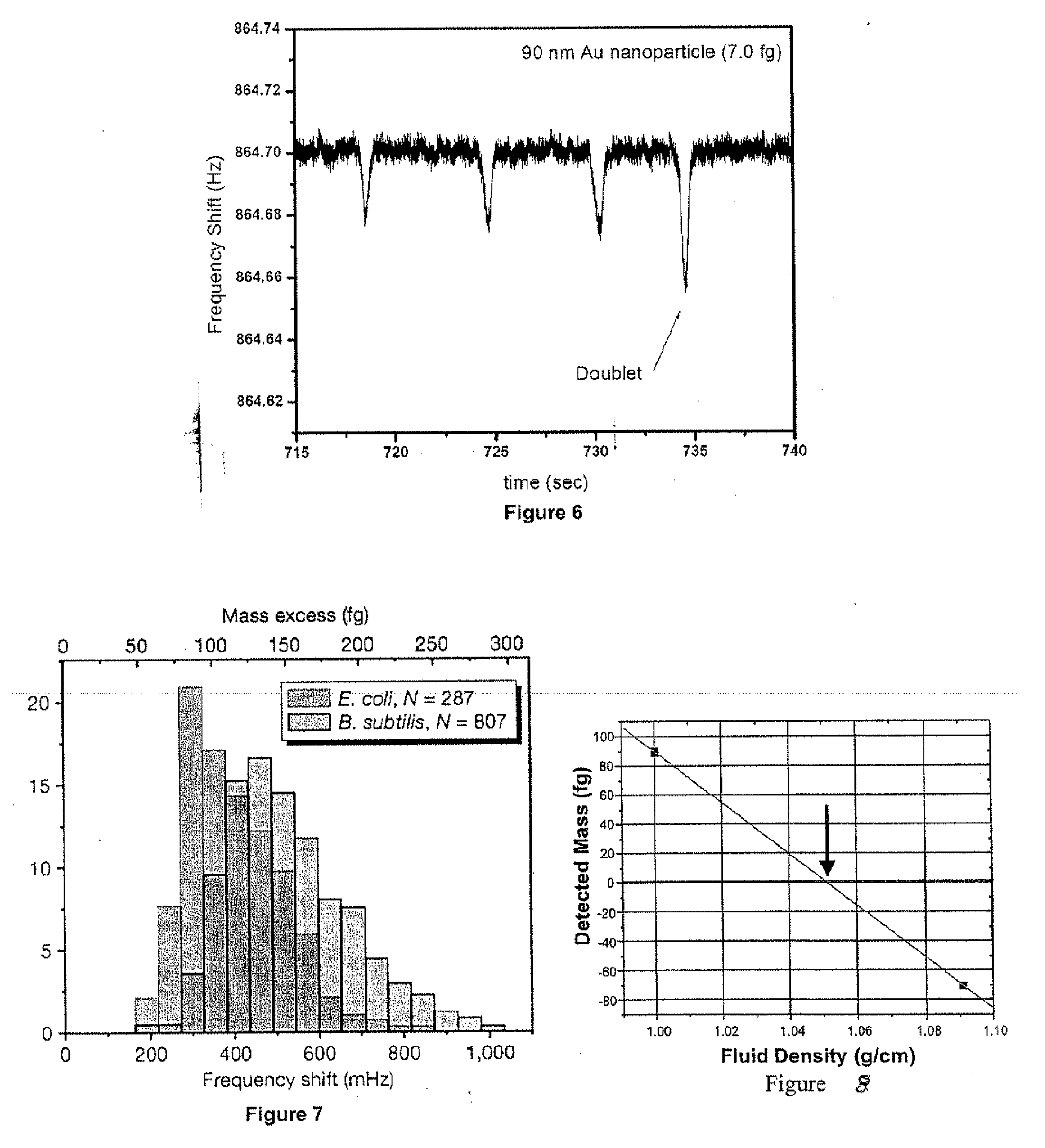
Method for measuring a target particle property. A suspended microchannel resonator is calibrated to determine the relationship between a detected mass and a resonance frequency shift of the resonator. The target particle is suspended in a fluid and introduced into the resonator, and the resonator frequency shift due to the particle is measured. Target particle mass is calculated from the resonator frequency shift, the target particle density, and the fluid density. A target particle property such as size or volume is determined from the calculated target particle mass.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
Method and system for measurement of dielectric constant of thin films using a near field microwave probe
InactiveUS7285963B2Highly accurate determination of dielectric constantSimplicity and precisenessMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationResistance/reactance/impedenceDielectricElectricity
A measurement technique based on a microwave near-field scanning probe is developed for non-contact measurement of dielectric constant of low-k films. The technique is non-destructive, non-invasive and can be used on both porous and non-porous dielectrics. The technique is based on measurement of resonant frequency shift of the near-field microwave resonator for a plurality of calibration samples vs. distance between the probe tip and the sample to construct a calibration curve. Probe resonance frequency shift measured for the sample under study vs. tip-sample separation is fitted into the calibration curve to extract the dielectric constant of the sample under study. The calibration permits obtaining a linear calibration curve in order to simplify the extraction of the dielectric constant of the sample under study.
Owner:SEMICON PHYSICS LAB
Method and apparatus for measuring grammage
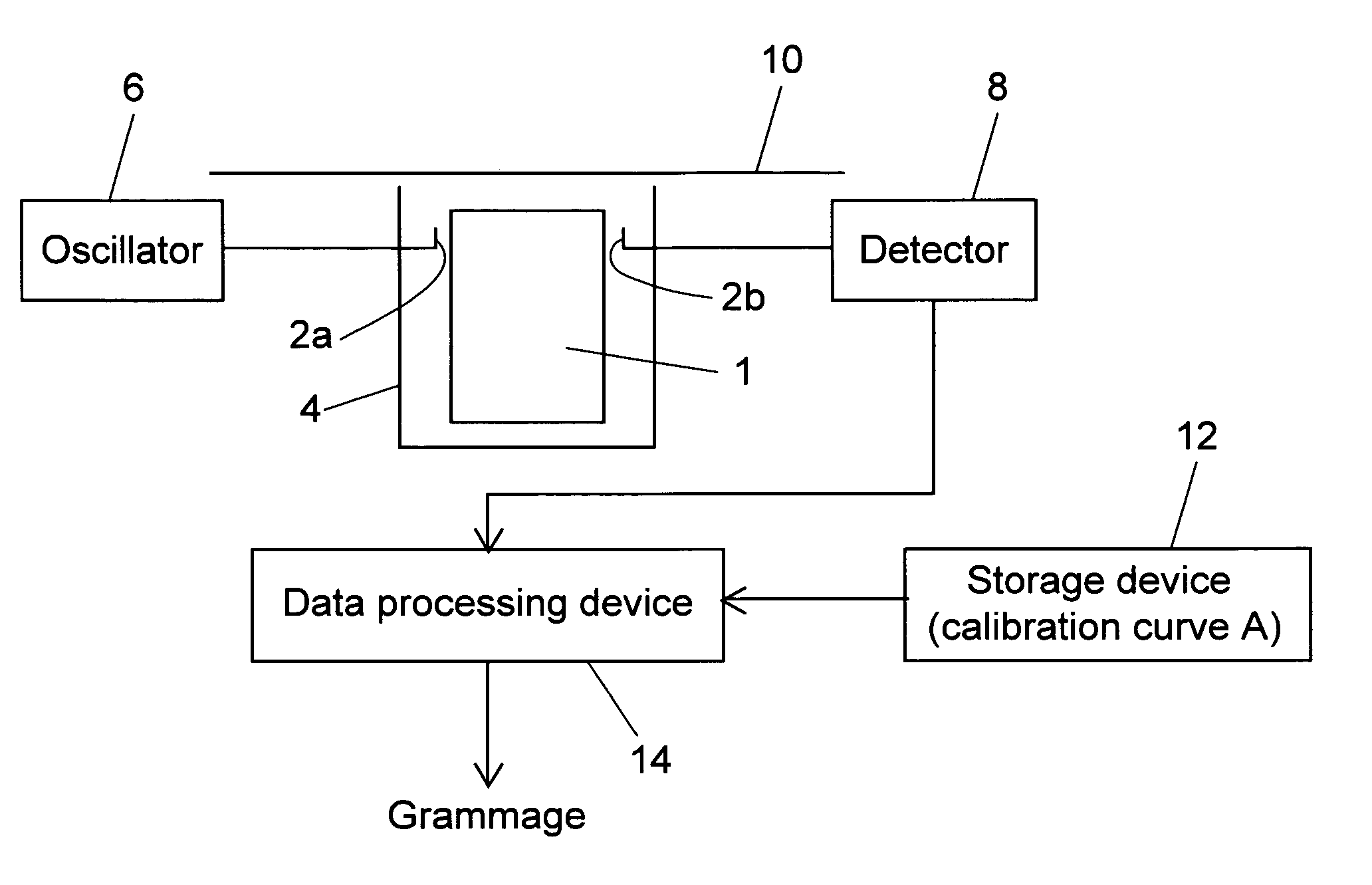
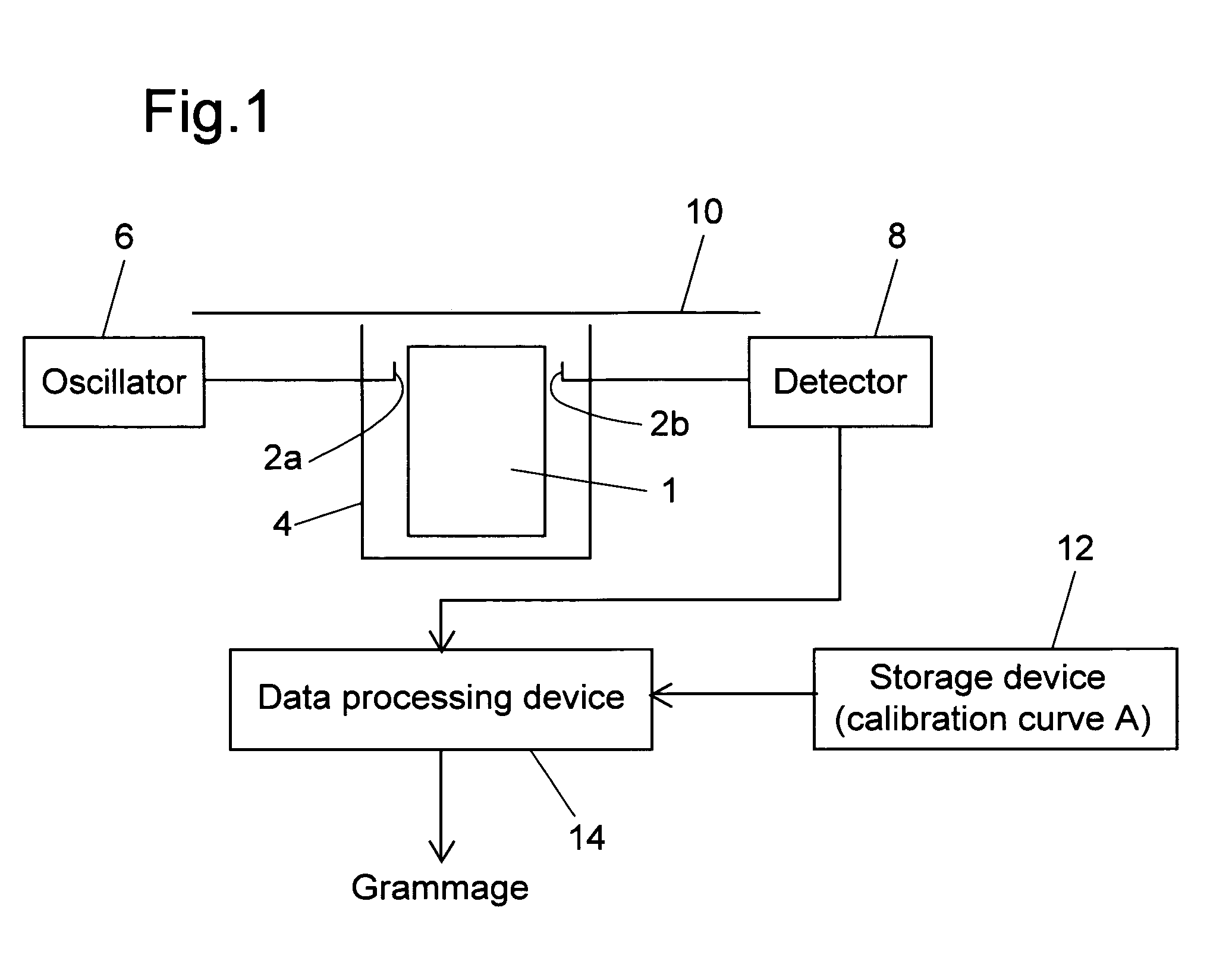
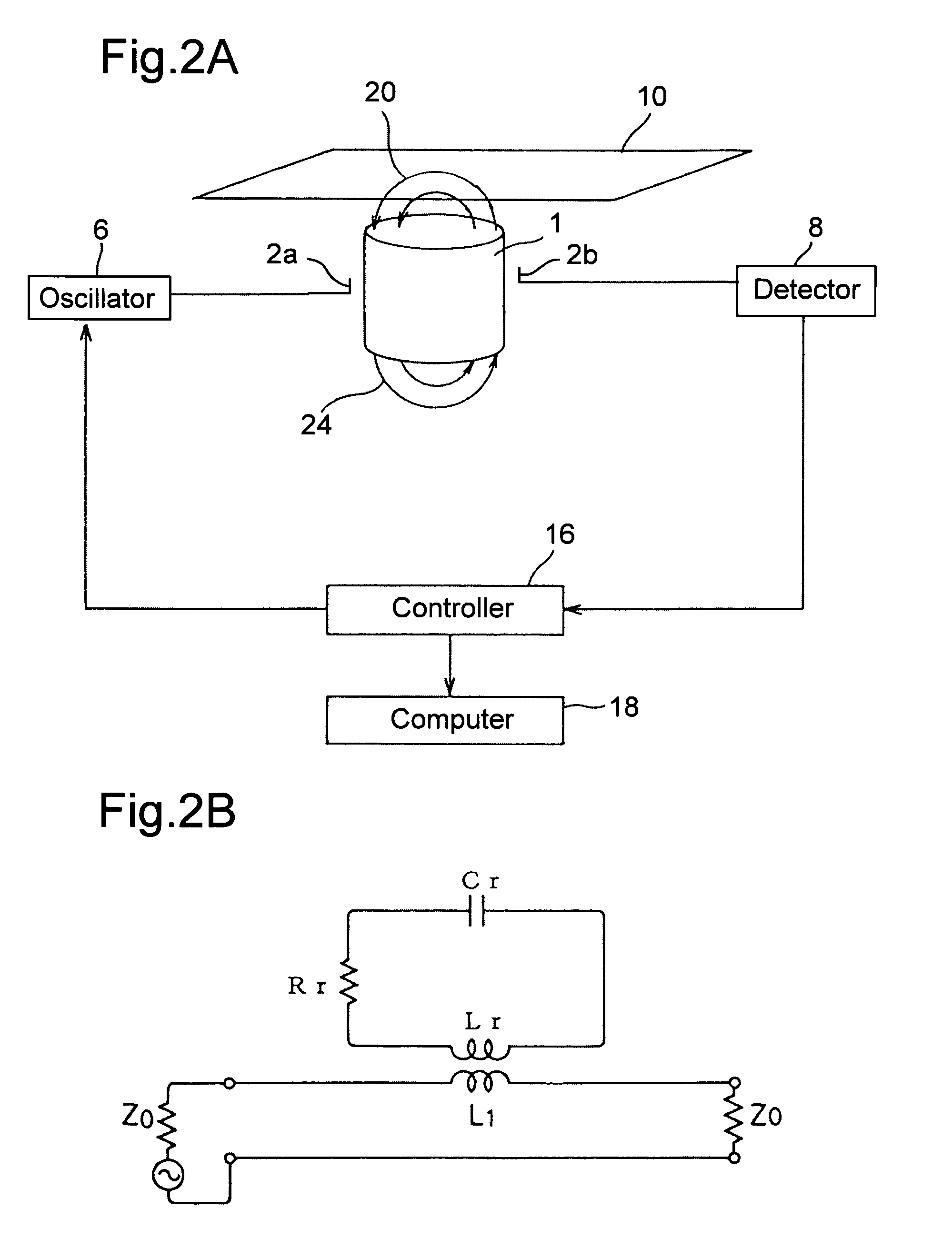
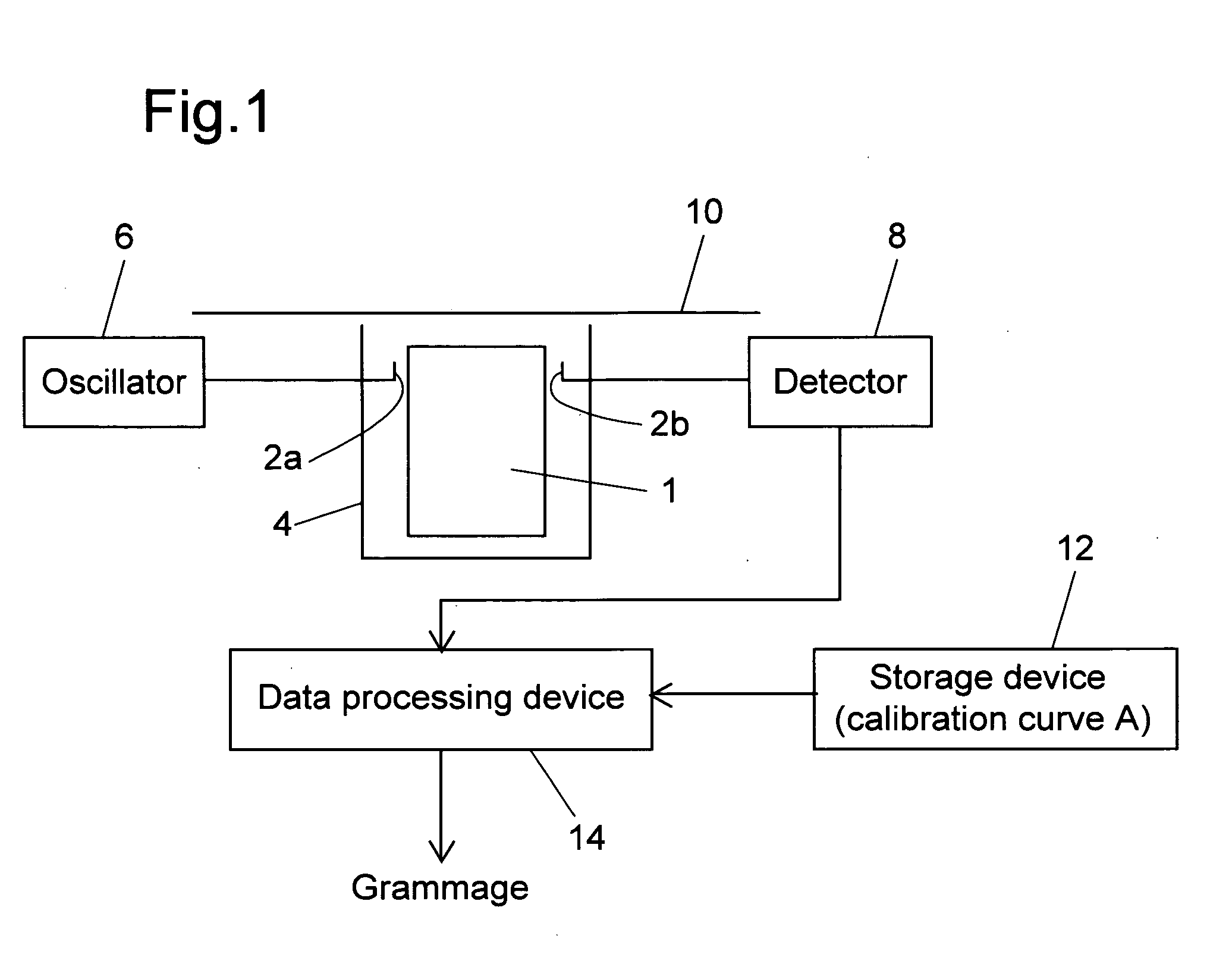
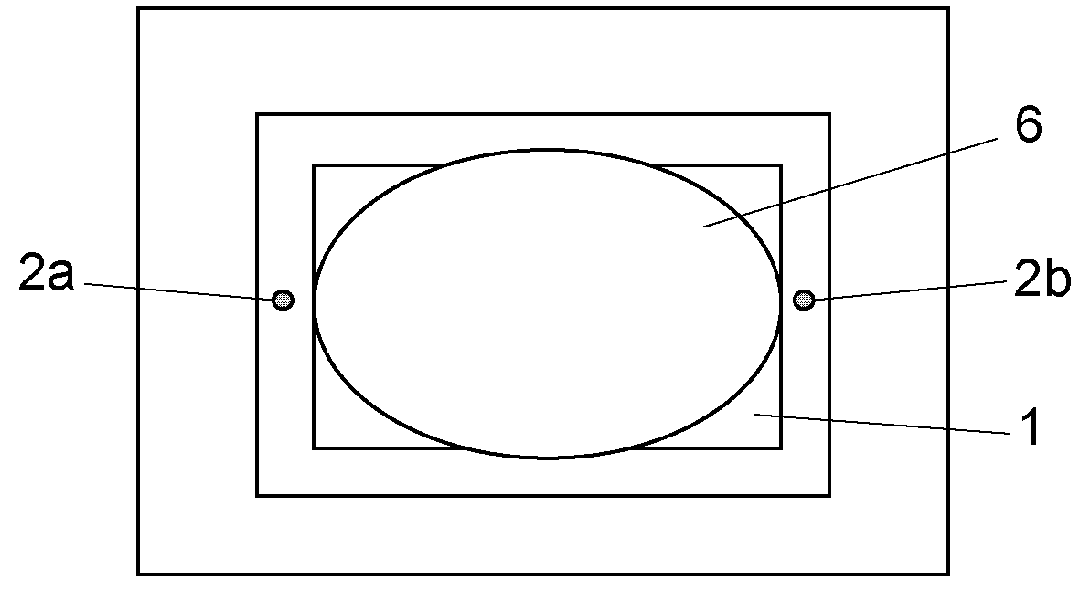
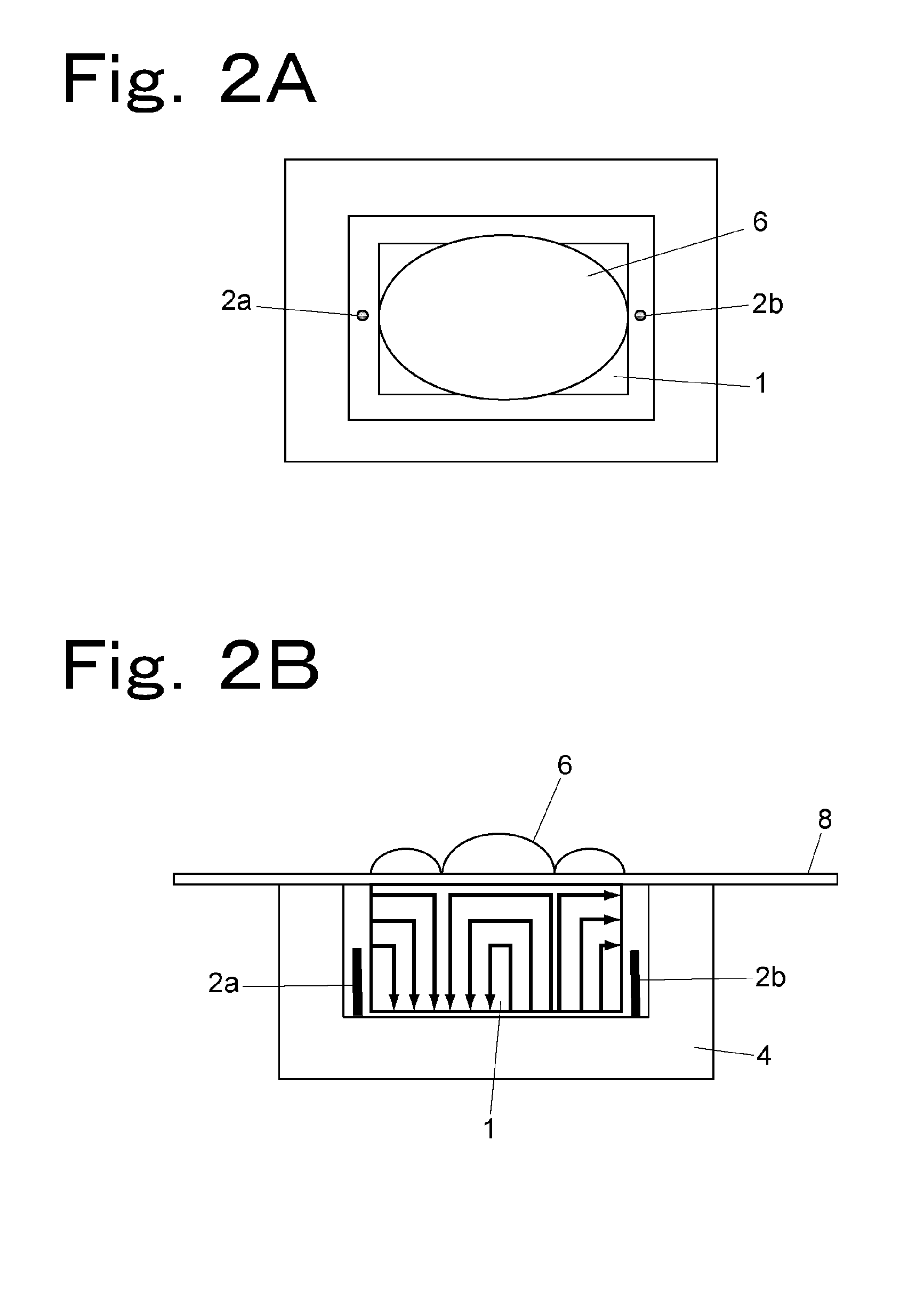
InactiveUS7423435B2Easy to handleMeasure securityResistance/reactance/impedenceMoisture content investigation using microwavesMicrowaveSample Measure
A grammage measuring apparatus including a dielectric resonator which is arranged only at one side surface of a sample; a shielding container with which the dielectric resonator is substantially covered except for a sample measuring surface; a microwave excitation device which causes the dielectric resonator to generate an electric field vector; a detection device which detects transmission energy or reflection energy by the dielectric resonator; a storage device in which a calibration curve indicating a resonance frequency shift amount for a grammage is stored; and a data processing device which calculates the grammage of a measuring sample from the calibration curve and measurement result of the resonance frequency shift amount of the measuring sample.
Owner:OJI PAPER CO LTD
Method and system for measurement of dielectric constant of thin films using a near field microwave probe
InactiveUS20050230619A1Highly accurate determination of dielectric constantSimplicity and precisenessMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationResistance/reactance/impedenceDielectricNon invasive
A measurement technique based on a microwave near-field scanning probe is developed for non-contact measurement of dielectric constant of low-k films. The technique is non-destructive, non-invasive and can be used on both porous and non-porous dielectrics. The technique is based on measurement of resonant frequency shift of the near-field microwave resonator for a plurality of calibration samples vs. distance between the probe tip and the sample to construct a calibration curve. Probe resonance frequency shift measured for the sample under study vs. tip-sample separation is fitted into the calibration curve to extract the dielectric constant of the sample under study. The calibration permits obtaining a linear calibration curve in order to simplify the extraction of the dielectric constant of the sample under study.
Owner:SEMICON PHYSICS LAB
Interlaced multi-energy radiation sources
Multi-energy radiation sources comprising charged particle accelerators driven by power generators providing different RF powers to the accelerator, capable of interlaced operation, are disclosed. Automatic frequency control techniques are provided to match the frequency of RF power provided to the accelerator with the accelerator resonance frequency. In one example where the power generator is a mechanically tunable magnetron, an automatic frequency controller is provided to match the frequency of RF power pulses at one power to the accelerator resonance frequency when those RF power pulses are provided, and the magnetron is operated such that frequency shift in the magnetron at the other power at least partially matches the resonance frequency shift in the accelerator when those RF power pulses are provided. In other examples, when the power generator is a klystron or electrically tunable magnetron, separate automatic frequency controllers are provided for each RF power pulse. Methods and systems are disclosed.
Owner:VAREX IMAGING CORP
Method and apparatus for measuring particle characteristics through mass detection
ActiveUS8087284B2Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesIndividual particle analysisParticle propertiesParticle density
Method for measuring a target particle property. A suspended microchannel resonator is calibrated to determine the relationship between a detected mass and a resonance frequency shift of the resonator. The target particle is suspended in a fluid and introduced into the resonator, and the resonator frequency shift due to the particle is measured. Target particle mass is calculated from the resonator frequency shift, the target particle density, and the fluid density. A target particle property such as size or volume is determined from the calculated target particle mass.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
Electrostatic ultrasonic transducer drive control method, electrostatic ultrasonic transducer, ultrasonic speaker using the same, audio signal reproduction method, ultra-directional acoustic system, and display device
InactiveUS7907740B2High strengthImprove energy conversion efficiencyMicrophonesSignal processingUltrasonic sensorSonification
A Push-Pull-type electrostatic ultrasonic transducer includes a first electrode having a through hole, a second electrode having a through hole making a pair with the through hole of the first electrode, and a vibration film held between a pair of electrodes composed of the first and the second electrodes and having a conductive layer to which a direct-current bias voltage is applied, and holds the pair of electrodes and the vibration film. Assuming that λ is the wavelength of the carrier wave having a frequency shifted as a predetermined amount of frequency from the resonance frequency, which is the mechanical resonance frequency of the vibration film, the thickness t of each of the pair of electrodes is set to (λ / 4)·n or roughly (λ / 4)·n (where, λ is the wavelength of the ultrasonic wave, n is a positive odd number), and an alternating-current signal, which is a modulated wave obtained by modulating the carrier wave in the ultrasonic frequency band with a signal wave in an audible frequency band, is applied between the pair of electrodes.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method for detecting shock-absorption and noise-reduction performance of car damping material
ActiveCN104267104AEliminate the disadvantages of being separated from the actual car bodyReflect actual usageAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPerformance indexEngineering
The invention discloses a method for detecting shock-absorption and noise-reduction performance of a car damping material. The method comprises detection on two aspects, i.e. the detection of a damping material on the aspect of the feeling of passengers for the vibration noise in the process of simulating the real driving process, and the detection of the damping material on the aspect of reducing the vibration of the overall structure of a car body and the bias of resonant frequency. By adopting a novel method for detecting the shock-absorption and noise-reduction performance of the damping material which is reasonably combined with the car body of a specific car, the shock-absorption performance index of the damping material applied to the car can be simply and intuitively expressed, the complicated modeling work can be omitted, the detection work is relatively simplified, the result is intuitive and dependable, and the application prospect is remarkable.
Owner:LIUZHOU XINGTA IND & TRADE
Terahertz non-bianisotropic metamaterial unmarked sensor, and preparation method and use thereof
ActiveCN108827903AHigh theoretical sensitivityHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by optical meansCancer cellTitanium metal
The invention relates to a terahertz non-bianisotropic metamaterial unmarked sensor, and a preparation method and a use thereof, and belongs to the biotechnical field. The unmarked sensor comprises aflexible substrate polyimide, a metal layer is arranged on the flexible substrate polyimide, the metal layer comprises a lower titanium metal layer having a thickness of 20 nm and an upper gold metallayer having a thickness of 200 nm, the titanium metal layer is arranged on the flexible substrate polyimide, and the metal layer is a metal resonance ring with two openings. The asymmetric metal resonance ring with two openings is designed to realize electromagnetic induction of a transparent formant, the surface of a metamaterial is inoculated with cells through cell culture, the resonance frequency shift of a device is detected in a back transmission manner, and the theoretic sensitivity reaches up to 455 GHz / RIU, so the concentration of cancer cells can be rapidly preliminarily detected inan unmarked manner, and the apoptosis trend of oral cancer cells HSC3 under different anticancer drug action times is obtained.
Owner:ZAOZHUANG UNIV
Control apparatus and control method for vibration wave driven apparatus
ActiveUS7755251B2Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive devicesPhase differenceMechanical energy
A vibration wave driven apparatus capable of preventing a resonance frequency of a vibrator from being shifted to a frequency side higher than a fixed drive frequency of the vibrator during the execution of phase difference control or voltage control. Driving signals are supplied from a control apparatus to a vibration-type actuator having a piezoelectric element that functions as an electro-mechanical energy conversion element. To control the drive of the vibration-type actuator, either a phase difference between the driving signals or a voltage of the driving signals is changed. When either the phase difference or the driving signal voltage is changed, the frequency of the driving signals is set to a predetermined frequency higher than the frequency for use when neither the phase difference nor the driving signal voltage is changed.
Owner:CANON KK
Method and apparatus for measuring grammage
InactiveUS20060288782A1Measure securityEasy to handleVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSample MeasureMeasurement device
A grammage measuring apparatus includes a dielectric resonator which is arranged only at one surface side of a sample; a shielding container with which the dielectric resonator is substantially covered except for a sample measuring surface; a microwave excitation device which causes the dielectric resonator to generate an electric field vector; a detection device which detects transmission energy or reflection energy by the dielectric resonator; a storage device in which a calibration curve indicating a resonance frequency shift amount for a grammage is stored; and a data processing device which calculates the grammage of a measuring sample from the calibration curve and measurement result of the resonance frequency shift amount of the measuring sample.
Owner:OJI PAPER CO LTD
Perturbation approach to resonance shift of whispering gallery modes in a dielectric microsphere as a probe of a surrounding medium
InactiveUS20040238744A1Radiation pyrometryPhase-affecting property measurementsDielectricWhispering gallery
A first-order perturbation theory similar to the one widely used in quantum mechanics is developed for transverse-electric and transverse-magnetic photonic resonance modes in a dielectric microsphere. General formulas for the resonance frequency shifts in response to a small change in the exterior refractive index and its radial profile are derived. The formulas are applied to two sensor applications of the microsphere to probe the medium in which the sphere is immersed: a refractive index detector; and a refractive index profile sensor.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INST OF NEW YORK
Detection and/or Characterisation of Oligomers
InactiveUS20100087011A1High selectivityHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesDisease diagnosisCapacitanceAnalyte
Disclosed is a method of detecting the presence of an oligomer analyte in a liquid sample, the method comprising the steps of: (a) contacting a sample comprising the oligomer or aggregate with an oscillating sensor surface, which surface may optionally be coated with a receptor that binds directly or indirectly to at least one component of the oligomer or aggregate, so as to cause direct or indirect binding of the oligomer or aggregate to the surface; (b) using a detection circuit to measure or calculate at least two of the following parameters: series resonance frequency (f0), and hence the series resonance frequency shift (ΔF); motional resistance (RM), and hence the motional resistance shift ΔR; motional inductance (LM); motional capacitance (CM); parallel capacitance (C0); frequency half-band half-width (Γ); Q-factor (=f / (2Γ); dissipative factor (1 / Q); impedance or admittance phase (φ) and hence phase shift (Δφ); and impedance or admittance amplitude (Z, or Y) and hence amplitude change (ΔZ, or ΔY); (c) and analysing the calculated values to derive data which vary according to the presence and / or amount of oligomer in the sample; (d) and, optionally, repeating the measurements continuously or intermittently to derive data which vary according to the presence and / or amount of oligomer or aggregate in the sample to be calculated as a function of elapsed time.
Owner:INVERNESS SWITZERLAND GMBH
Concrete beam prestress value and prestress loss monitoring method
InactiveCN104198095AAccurately assess bearing capacityForce measurement using piezo-resistive materialsElectricityPrestressed concrete beam
The invention relates to a concrete beam prestress value and prestress loss monitoring method. The method includes extracting resonant frequency and root-mean-square deviation from piezoelectric admittance signals of piezoelectric ceramic of the prestress concrete beam to recognize prestress value of a prestress concrete beam and extracting resonant frequency deviation indexes and root-mean-square deviation indexes to recognize prestress loss of the prestress concrete beam. The method provides a new way for real-time monitoring of the prestress value and the prestress loss of the prestress concrete. Compared with the prior art, the method can achieve quick monitoring, can obtain the prestress value and the prestress loss quickly of the prestress concrete beam not provided with a sensor for measuring the prestress value, and can accurately evaluate the loading force of the prestress concrete beam in the normal use state.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
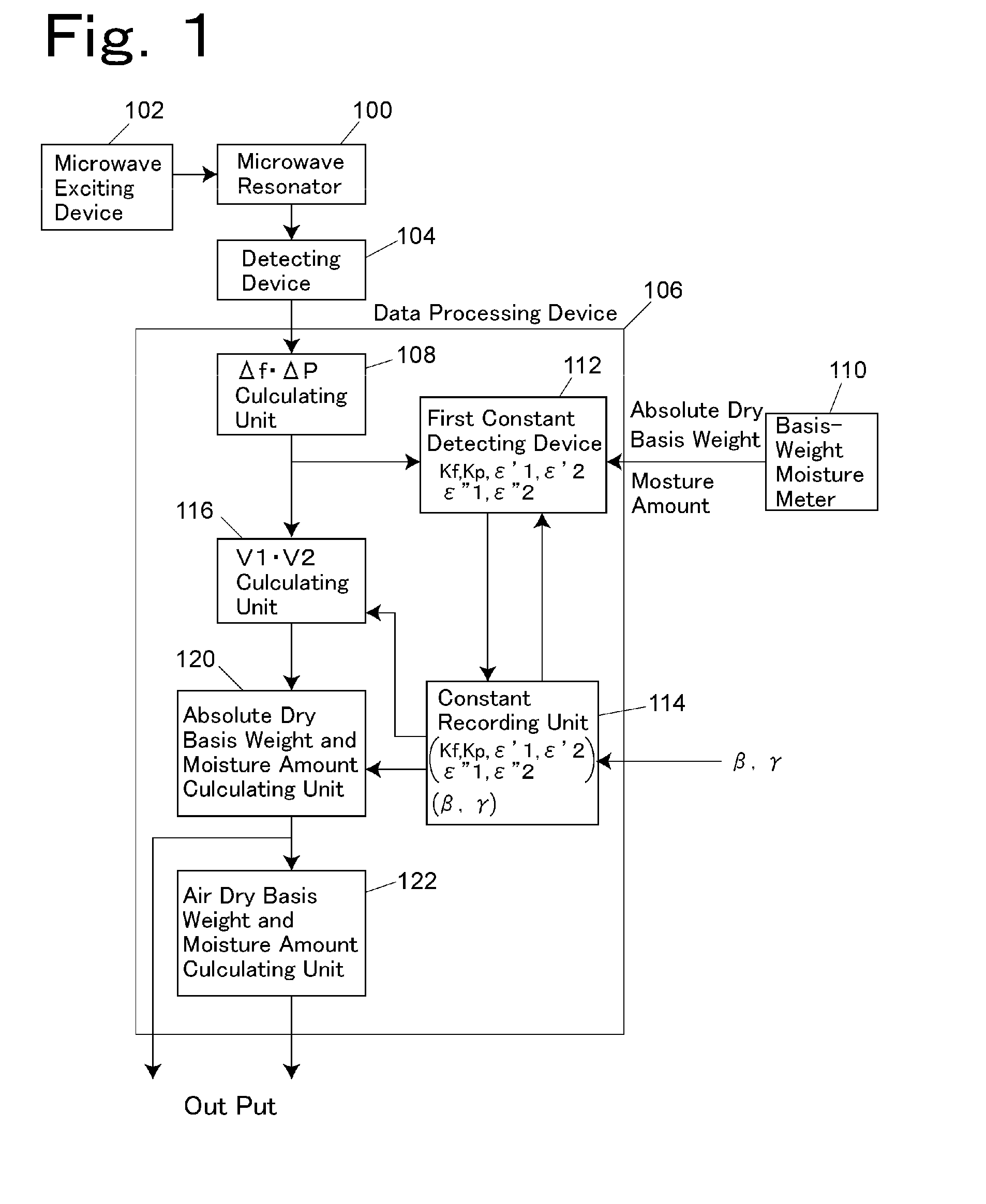
Method and device for measuring basis weight and moisture content amount
ActiveUS20130025350A1Measure securitySatisfy safety performance requirementsMaterial moisture contentMoisture content investigation using microwavesPeak valueMoisture
A resonance frequency shift amount Δf and a peak level change amount ΔP are measured using a microwave resonator, V1 and V2 are obtained based on V1=(Δf·∈″2 / Kf−ΔP·∈′2 / Kp) / (∈′1·∈″2−∈″1·∈′2), and V2=(Δf·∈″1 / Kf−ΔP·∈′1 / Kp) / (∈″1·∈′2−∈′1·∈″2), and an absolute dry basis weight and a moisture amount are obtained based on absolute dry basis weight=β·V1, and moisture amount=γ·V2. For the constants Kf, Kp, c′1, ∈′2, ∈″1 and ∈″2, the constants ∈′1, ∈′2, ∈″1 and ∈″2 are determined so that the variance values of Kf and Kp are smaller than a predetermined value.
Owner:OJI HLDG CORP
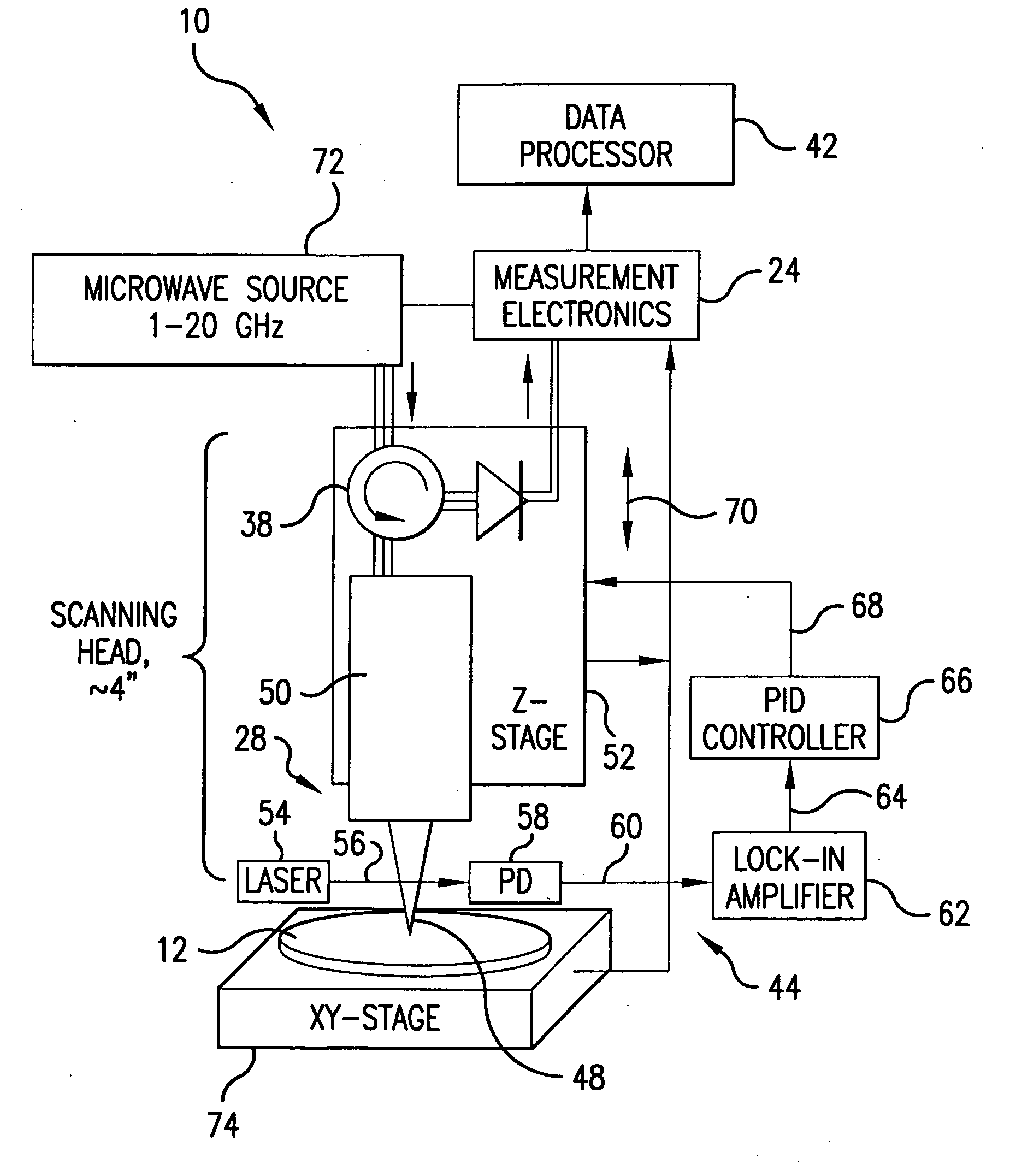
Atomic force microscope
ActiveUS20100024082A1Quick checkPulse automatic controlPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesAtomic force microscopyPhase shifted
There is provided an atomic force microscope (AFM) with increase the speed and sensitivity of detection of the resonant frequency shift in a cantilever. An AFM (1) extracts a reference signal and a phase shift signal from a detection signal from a displacement sensor of the cantilever. The reference signal is restrained from a phase change in accordance with the resonant frequency shift. The phase shift signal has a phase shifted in accordance with the resonant frequency shift. The AFM (1) determines the phase difference of the phase shift signal from the reference signal, as the resonant frequency shift. The AFM (1) may detect the phase difference between a plus-minus inversion point on the reference signal and a corresponding plus-minus inversion point on the phase shift signal. The AFM (1) may adjust phase before phase detection. The phase adjustment may move the detection point for the resonant frequency shift defined on the oscillation waveforms to the plus-minus inversion point. The detection point is set at a position where the cantilever and a sample are closest to each other on the oscillation waveform.
Owner:KANAZAWA UNIV
Resonance-enhanced dielectric sensing of chemical and biological species
InactiveUS20050032233A1Degree of selectivity enhancedHigh sensitivityMaterial thermal conductivityMaterial analysis using microwave meansDielectricElectricity
A dielectric sensing method and apparatus are provided for detection and classification of chemical and biological materials. Resonance patterns of a sample within a resonator are detected for identifying a shift in resonance frequency and a change of line width before and after introduction of the sample. The identified shift in resonance frequency and change of line width are used for determining a complex dielectric constant of the sample for the material detection and classification. A degree of selectivity at any excitation frequency is enabled for the dielectric sensing method from the manner in which the complex dielectric constant of a material affects the resonance pattern of the resonator with respect to shift in resonance frequency and the change in line width. By selecting the excitation frequencies to generally correspond to one of the resonance frequencies of the sample material under test, the degree of selectivity and the sensitivity of detection are enhanced.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Information processing apparatus and control method
InactiveUS20110128222A1Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsInformation processingComputer module
According to one embodiment, a switch circuit switches a resonance frequency band of an antenna in a display unit between first and second resonance frequency bands. The second resonance frequency band is overlapped with a part of the first resonance frequency band and is higher than the first resonance frequency band. A wireless communication module wirelessly transmits and receives signals using a transmission frequency band and a reception frequency band which are included in the first resonance frequency band. A screen image orientation control module changes an orientation of a screen image displayed on the display unit. A resonance frequency shift module shifts the resonance frequency band of the antenna from the first resonance frequency band to the second frequency band by controlling the switch circuit when the orientation of the screen image is an orientation in which the antenna is positioned on a downward side of the screen image.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Resonance-frequency shifting method and system for wireless charging of automobiles
ActiveCN104283293BRealize constant current and voltage limiting controlStable negative feedbackBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerWireless controlAutomotive battery
The invention provides a method and system for achieving vehicle wireless charging through resonance-frequency shift. By the adoption of the method and system, wireless high-power vehicle charging with the power ranging from about 5 kW to about 150 kW is achieved, and constant-current voltage-limited charging management is completed. The system comprises a non-vehicle-end variable frequency emitting device and a power receiving device installed on an electric vehicle. According to the method and system for achieving vehicle wireless charging through resonance-frequency shift, frequency-shifted electric energy is emitted from a power emitting disk through two resonance circuits in a wireless mode, the electric energy is received by a power receiving disk, after rectification, a battery pack of the electric vehicle is charged, the requirement of the charging instruction of a battery management system BMS is met, in other words, the output power of the power emitting end and the output power of the power receiving end are controlled in a frequency shifted mode, and then constant-current voltage-limited charging is achieved. By the adoption of the mode that NFC and Bluetooth communication are combined, the electric vehicle can accurately establish the unique wireless communication channel link with a charging pile or a charger of the parking stall of the electric vehicle, the electric vehicles in a parking lot are in communication with the charging piles or the chargers in the parking lot in a one-to-one mode, link interference is avoided, and a stable negative feedback wireless control circuit is provided.
Owner:SHENZHEN TTK TECH
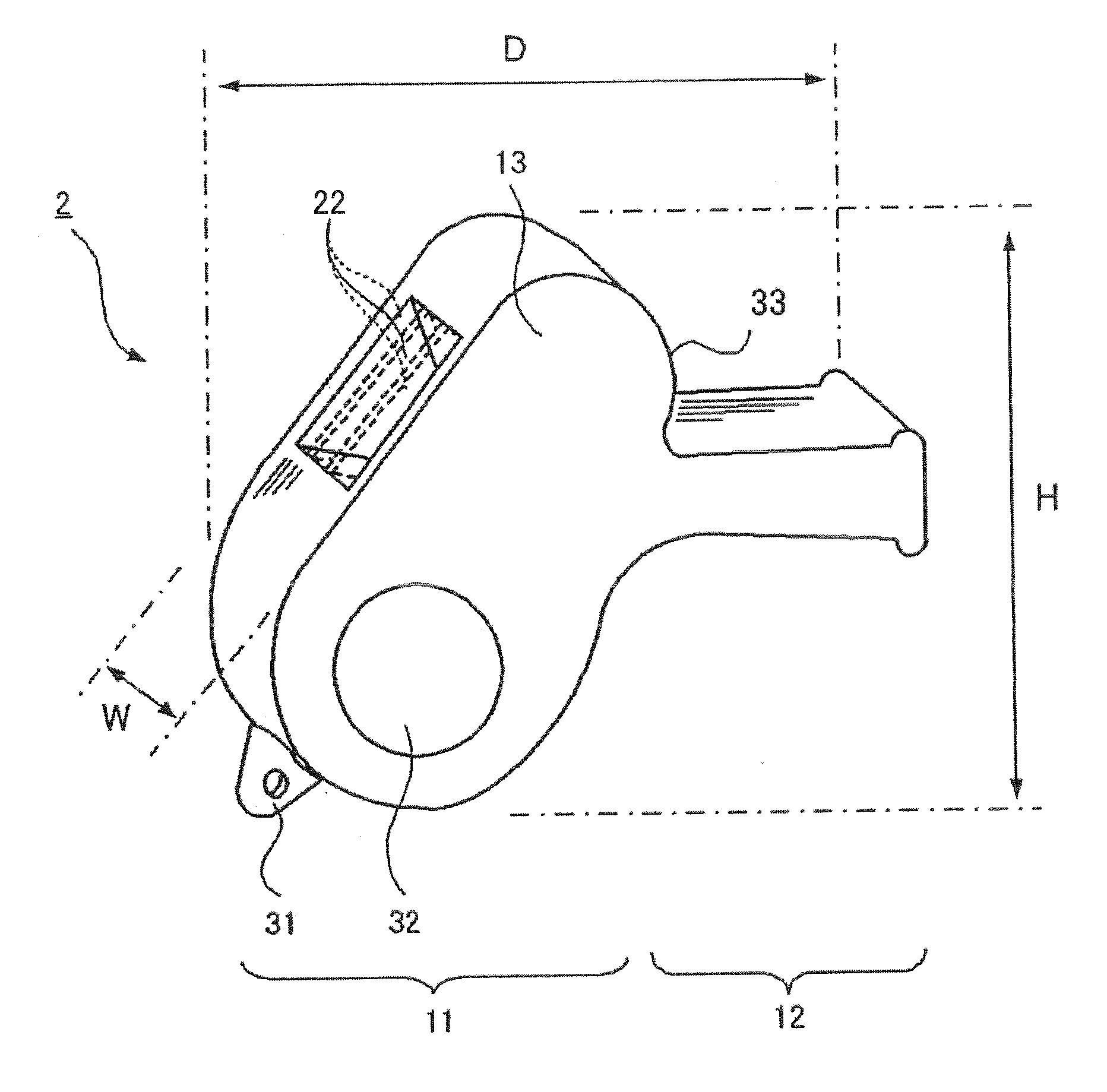
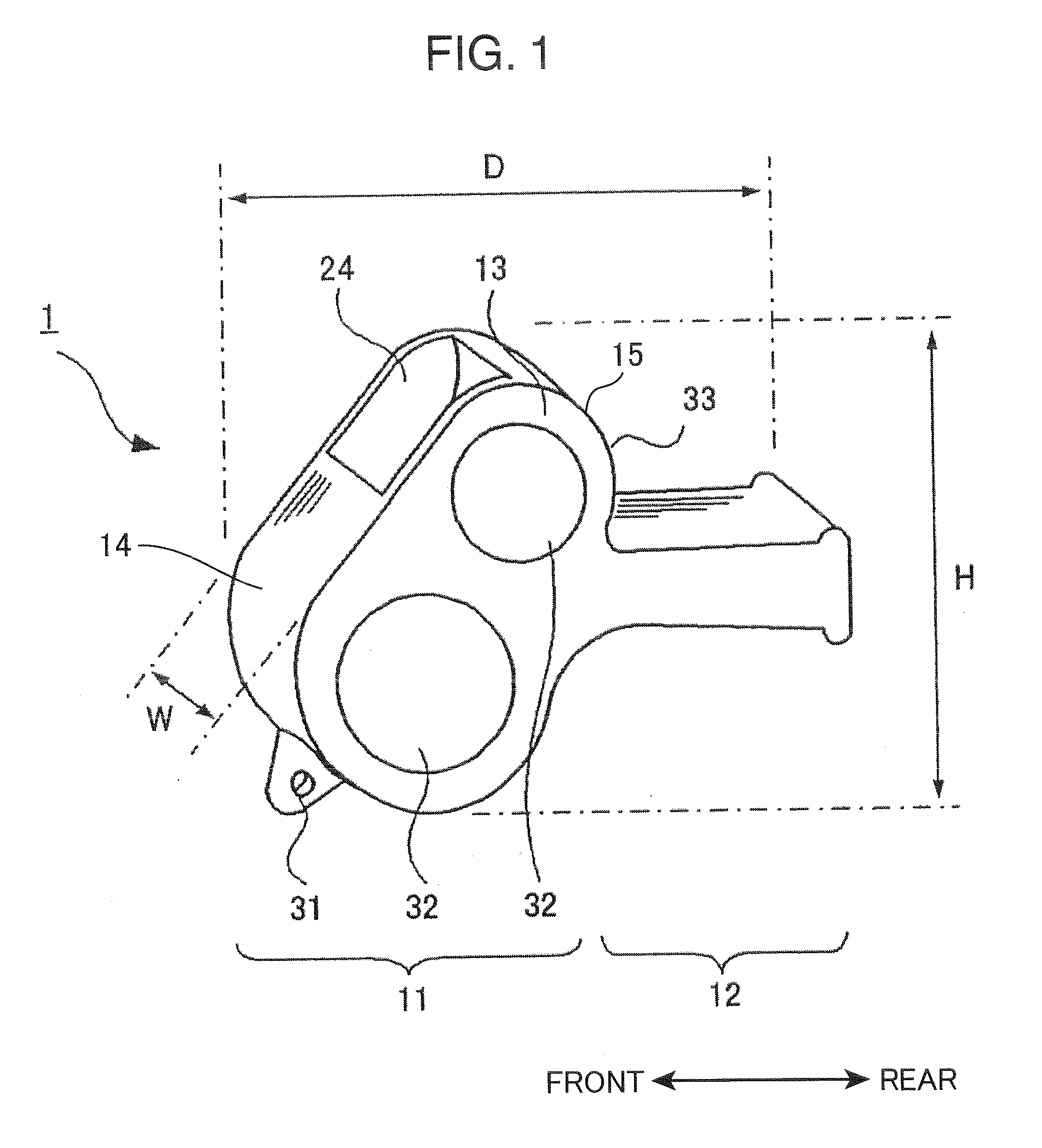
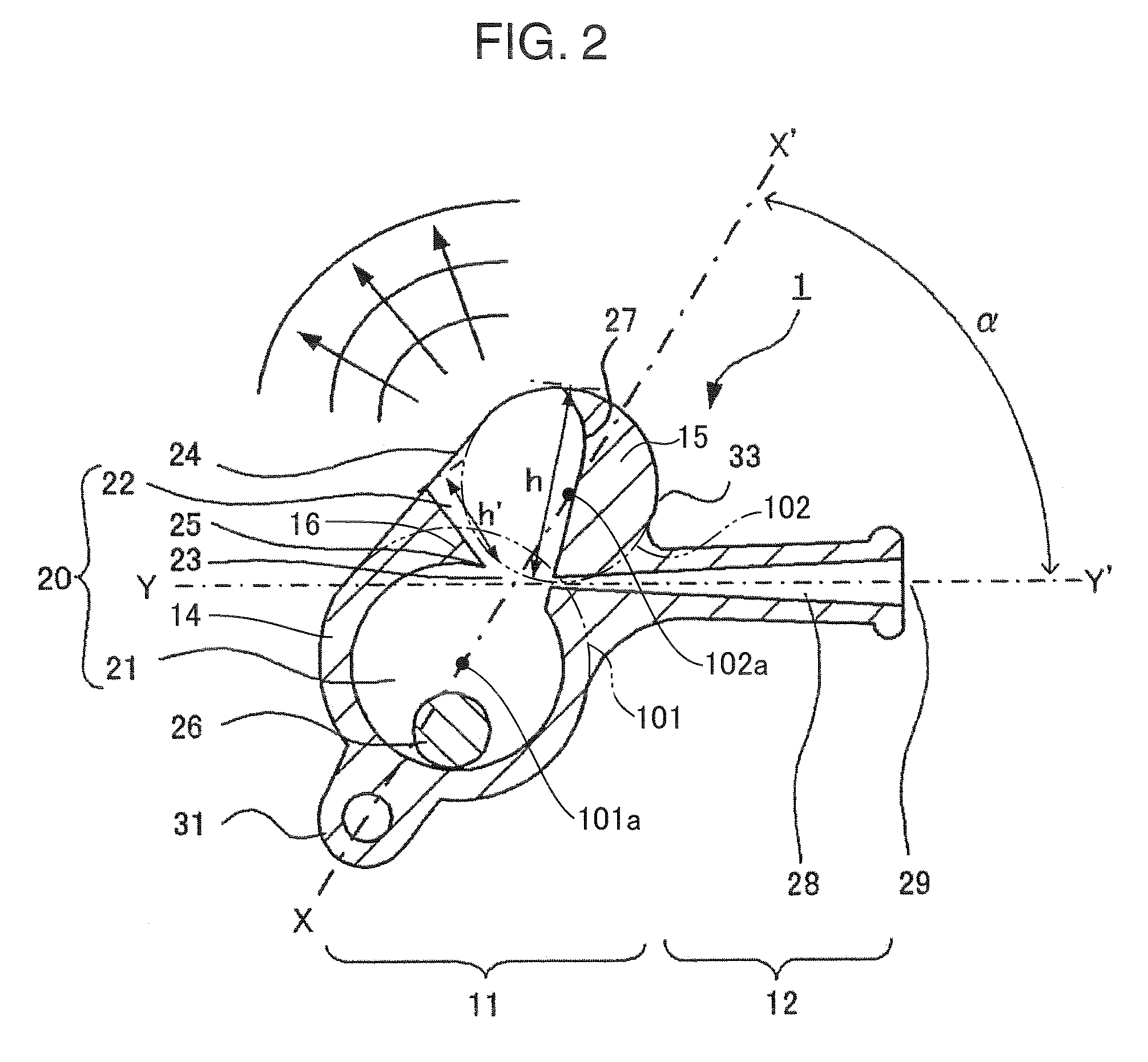
Whistle
InactiveUS20090272310A1Long wavelengthAvoid excessive frequencyMusical toysWhistlesEngineeringResonance frequency shift
An object of the present invention is to provide a whistle which has a resonance frequency shifted to the low-frequency side and a pleasant tone while retaining a compact size and light weight. In order to attain this object, a whistle comprises a mouthpiece portion, inside which an air passageway is formed and in which an air opening is opened, and a body portion, in which a connected resonance chamber that is connected to the air passageway is formed; the connected resonance chamber comprises a first resonance chamber, a second resonance chamber in which a sound-emitting opening is opened, and an orifice connecting the first resonance chamber and the second resonance chamber.
Owner:SHISHIDO HIDEOMI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com