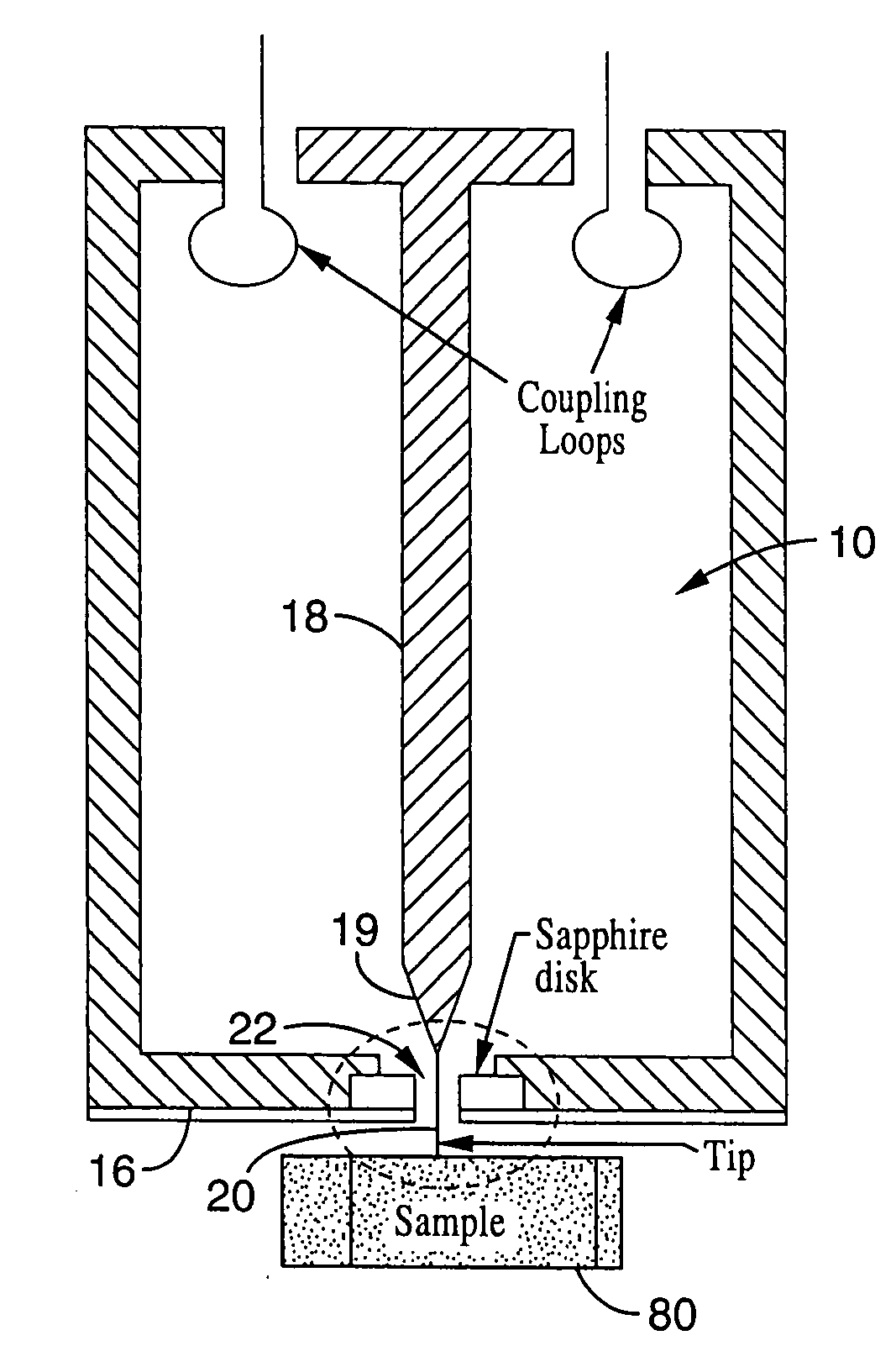
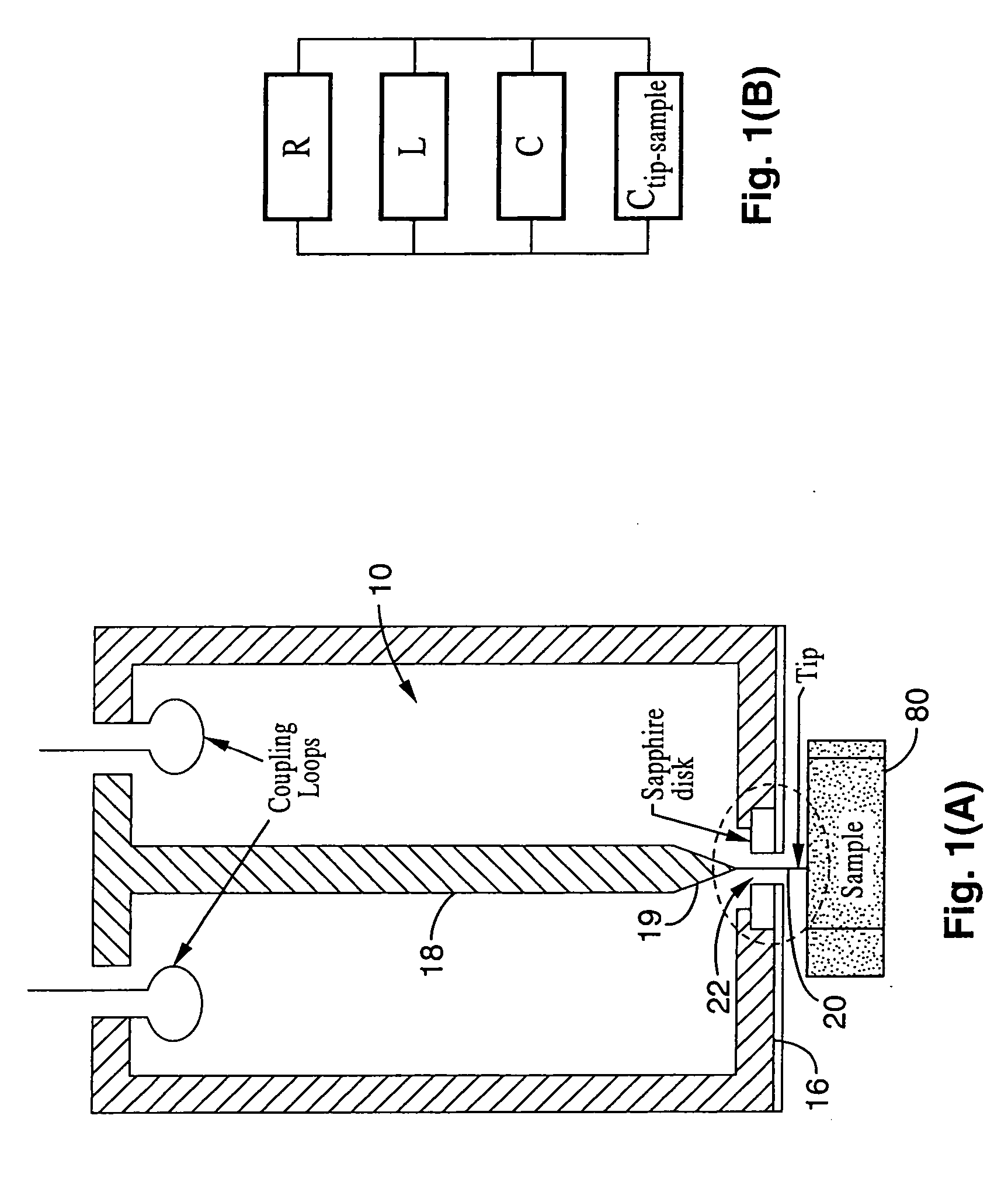
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
191 results about "Microwave probe" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The probe measures temperatures ranging from 85 to 199 degrees, depending on the type of microwave oven used. Some have a ``temperature hold`` feature that, along with the probe, maintains a set temperature for a given time.
Plasma lamp with bulb and lamp chamber
A dielectric waveguide integrated plasma lamp (DWIPL) with a body comprising at least one dielectric material having a dielectric constant greater than approximately 2, and having a shape and dimensions such that the body resonates in at least one resonant mode when microwave energy of an appropriate frequency is coupled into the body. A dielectric bulb within a lamp chamber in the body contains a fill which when receiving energy from the resonating body forms a light-emitting plasma. The bulb is transparent to visible light and infrared radiation emitted by the plasma. Radiative energy lost from the plasma is recycled by reflecting the radiation from thin-film, multi-layer coatings on bulb exterior surfaces and / or lamp chamber surfaces back into the bulb. The lamp further includes two- or three-microwave probe configurations minimizing power reflected from the body back to the microwave source when the source operates: (a) at a frequency such that the body resonates in a single mode; or (b) at one frequency such that the body resonates in a relatively higher mode before a plasma is formed, and at another frequency such that the body resonates in a relatively lower order mode after the plasma reaches steady state.
Owner:LUXIM CORP
Plasma lamp with dielectric waveguide integrated with transparent bulb
A dielectric waveguide integrated plasma lamp (DWIPL) with a body comprising at least one dielectric material having a dielectric constant greater than approximately 2, and having a shape and dimensions such that the body resonates in at least one resonant mode when microwave energy of an appropriate frequency is coupled into the body. A dielectric bulb within a lamp chamber in the body contains a fill which when receiving energy from the resonating body forms a light-emitting plasma. The bulb is transparent to visible light and infrared radiation emitted by the plasma. Radiative energy lost from the plasma is recycled by reflecting the radiation from thin-film, multi-layer coatings on bulb exterior surfaces and / or lamp chamber surfaces back into the bulb. The lamp further includes two- or three-microwave probe configurations minimizing power reflected from the body back to the microwave source when the source operates: (a) at a frequency such that the body resonates in a single mode; or (b) at one frequency such that the body resonates in a relatively higher mode before a plasma is formed, and at another frequency such that the body resonates in a relatively lower order mode after the plasma reaches steady state.
Owner:LUXIM CORP
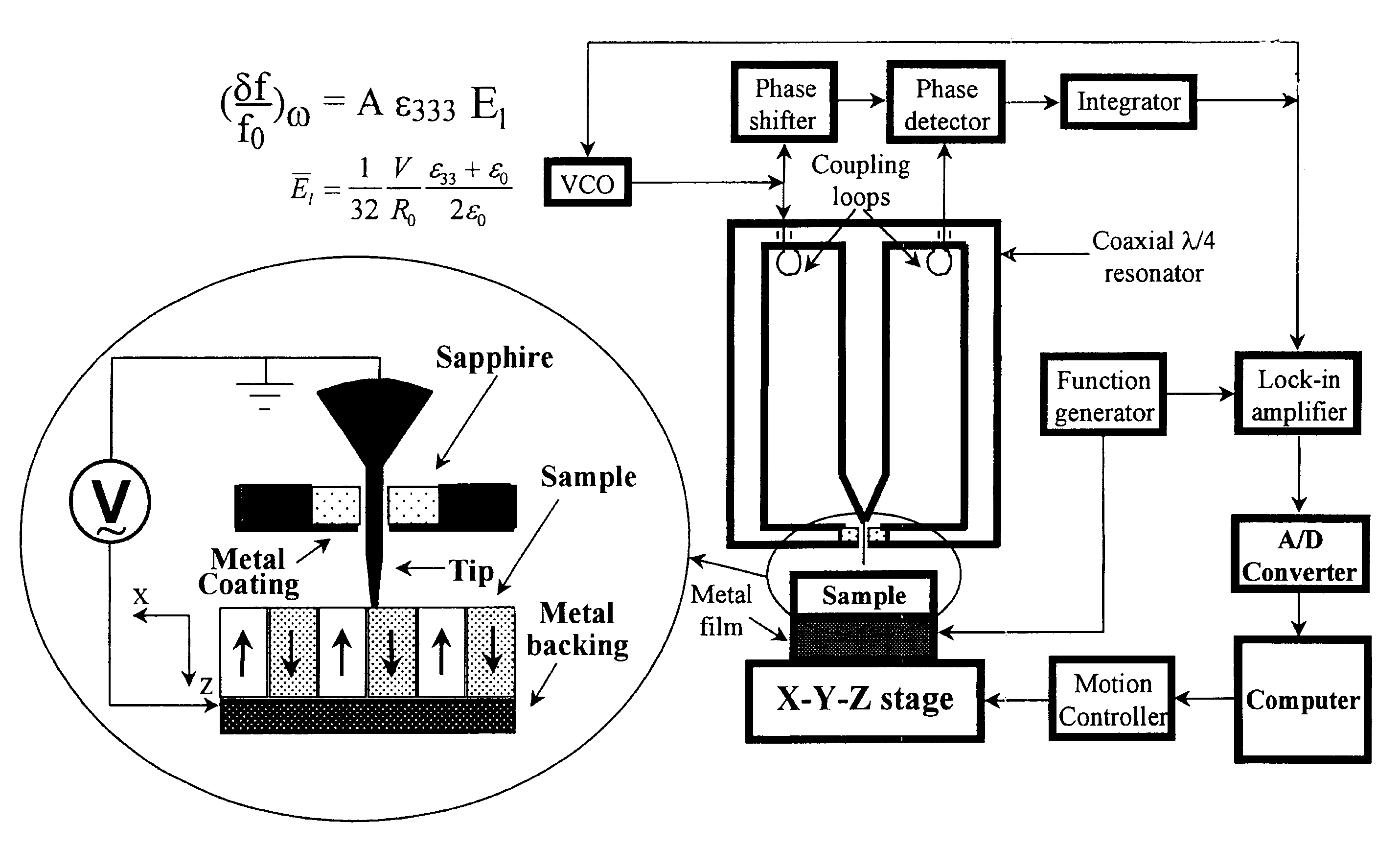
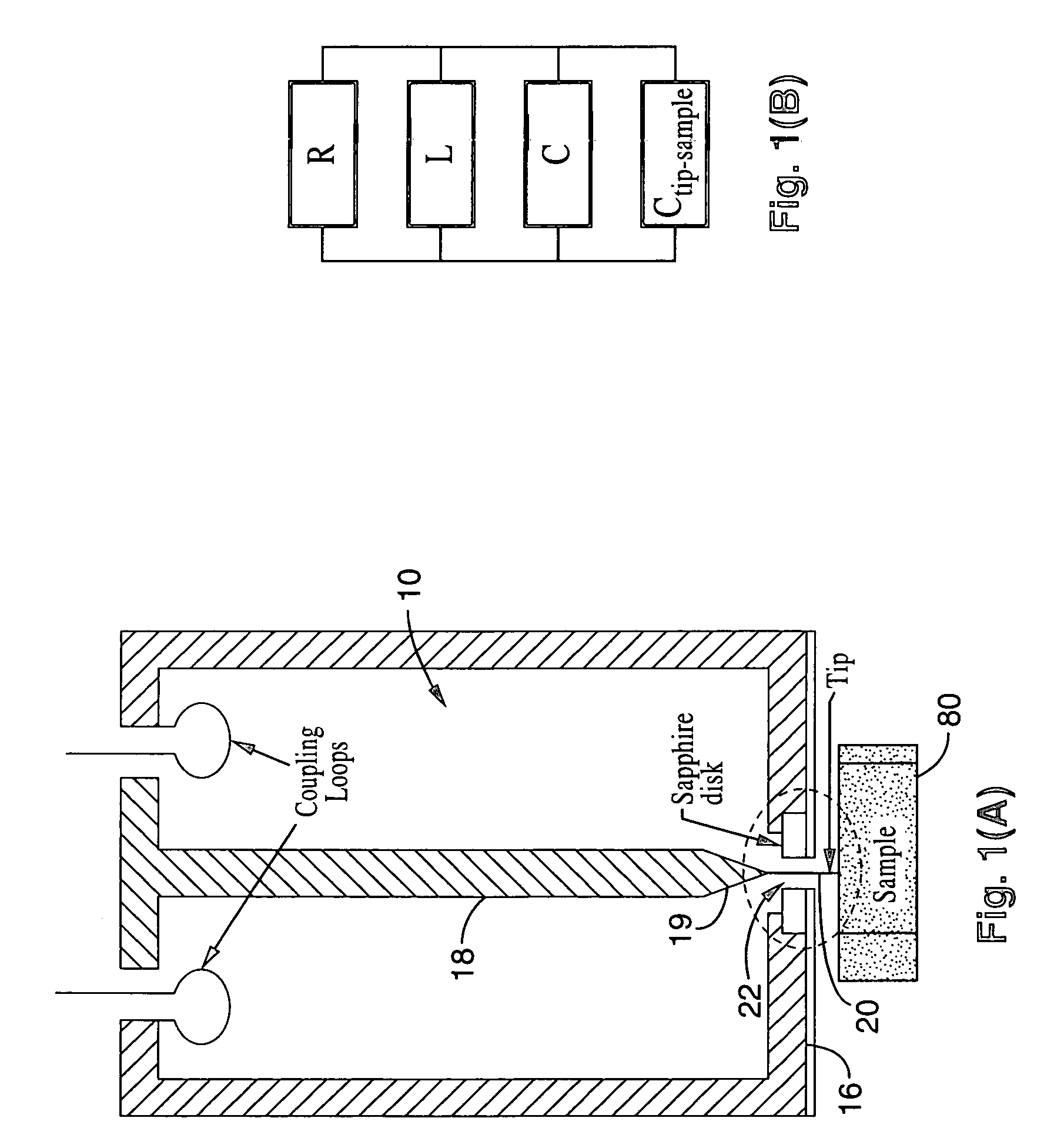
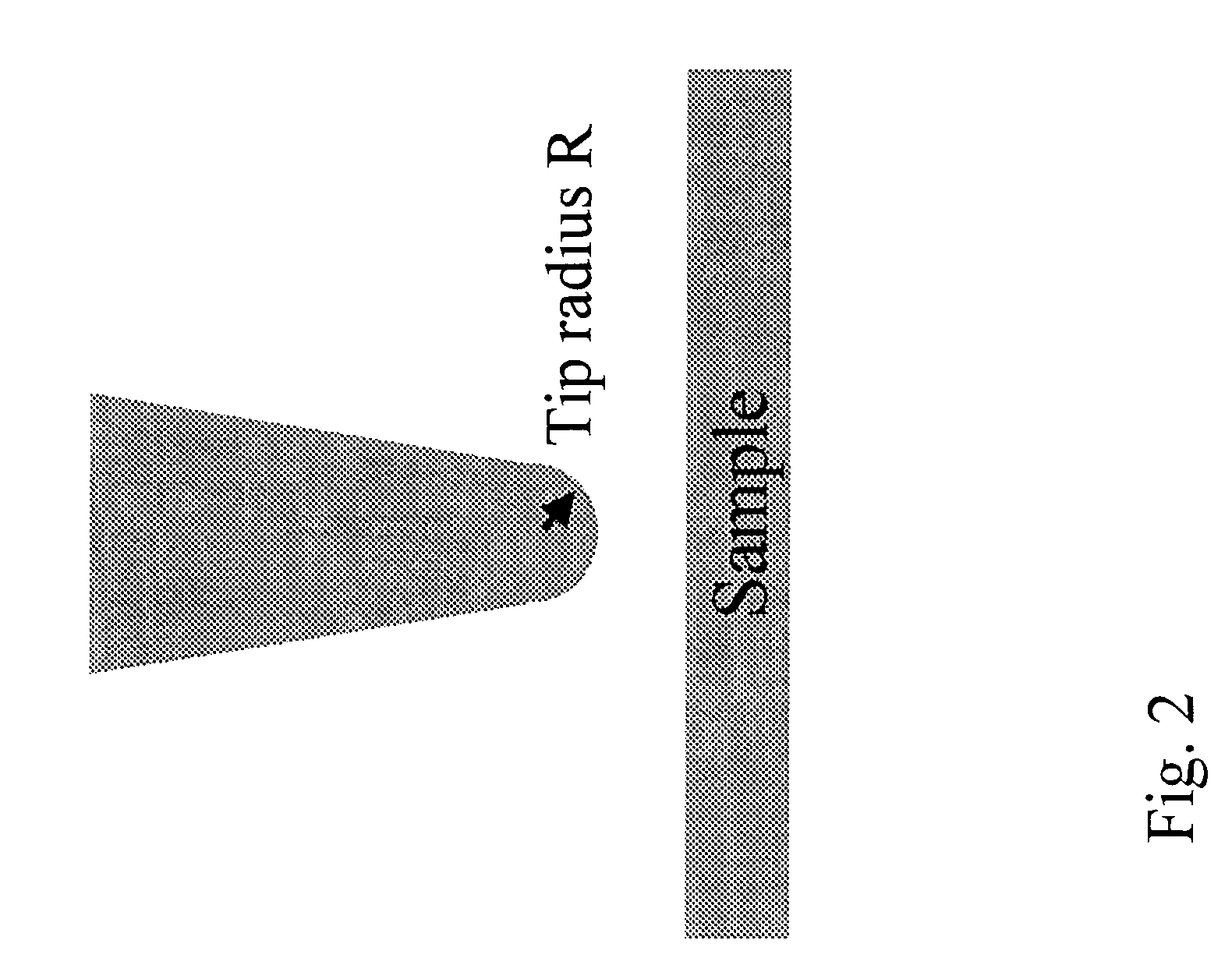
Evanescent microwave probe with enhanced resolution and sensitivity
InactiveUS20060125465A1High sensitivityImprove resolutionResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical testingActive feedbackImage resolution
Novel systems of an evanescent microwave probe (EWP) are disclosed, which enable measurements of physical properties of a sample with enhanced sensitivity and resolution, simultaneously. In one embodiment, new shielding features are added to the probe (which may be of either a sharpened tip or loop configuration) to reduce the effects of residual far field radiation, while maintaining the probe section that extends beyond the shielding aperture of the resonator. To further increase the sensitivity of the instrument, an automatic gain-controlled active feedback loop system may be added to the probe resonator to form a self-oscillator. This new active circuit feature significantly increases the effective Q of the resonator probe, enhancing the sensitivity of both the frequency and Q measurement.
Owner:INTEMATIX
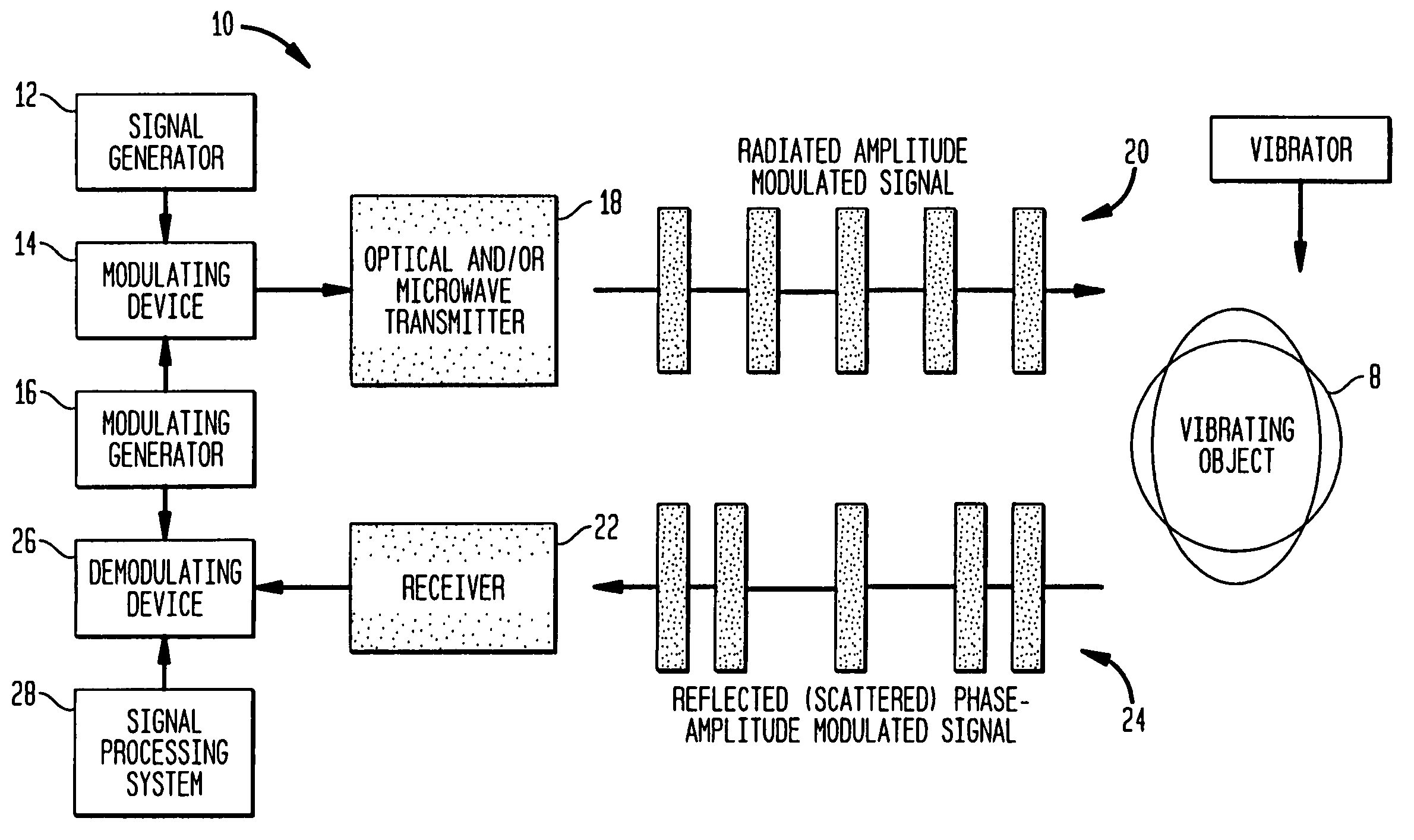
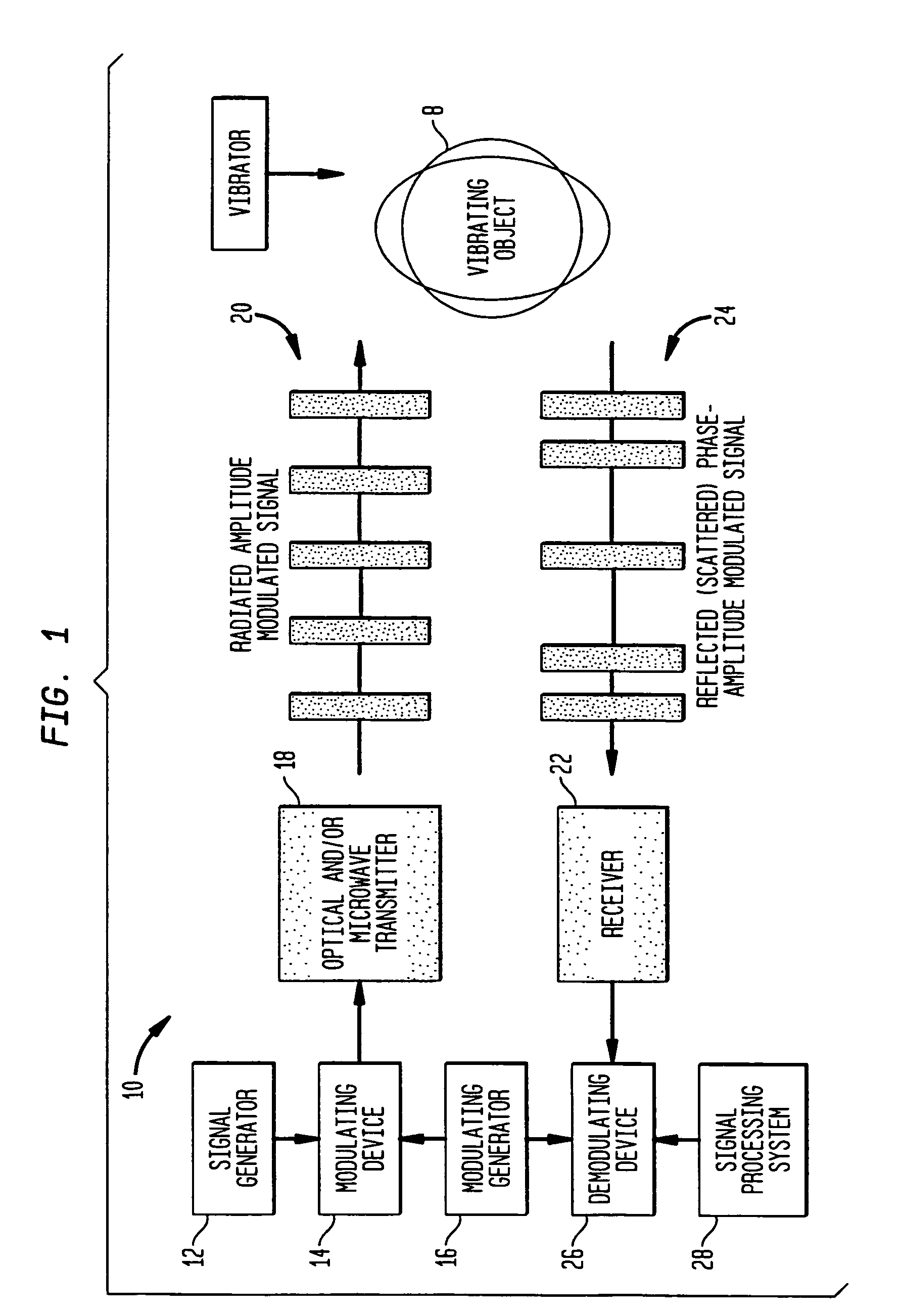
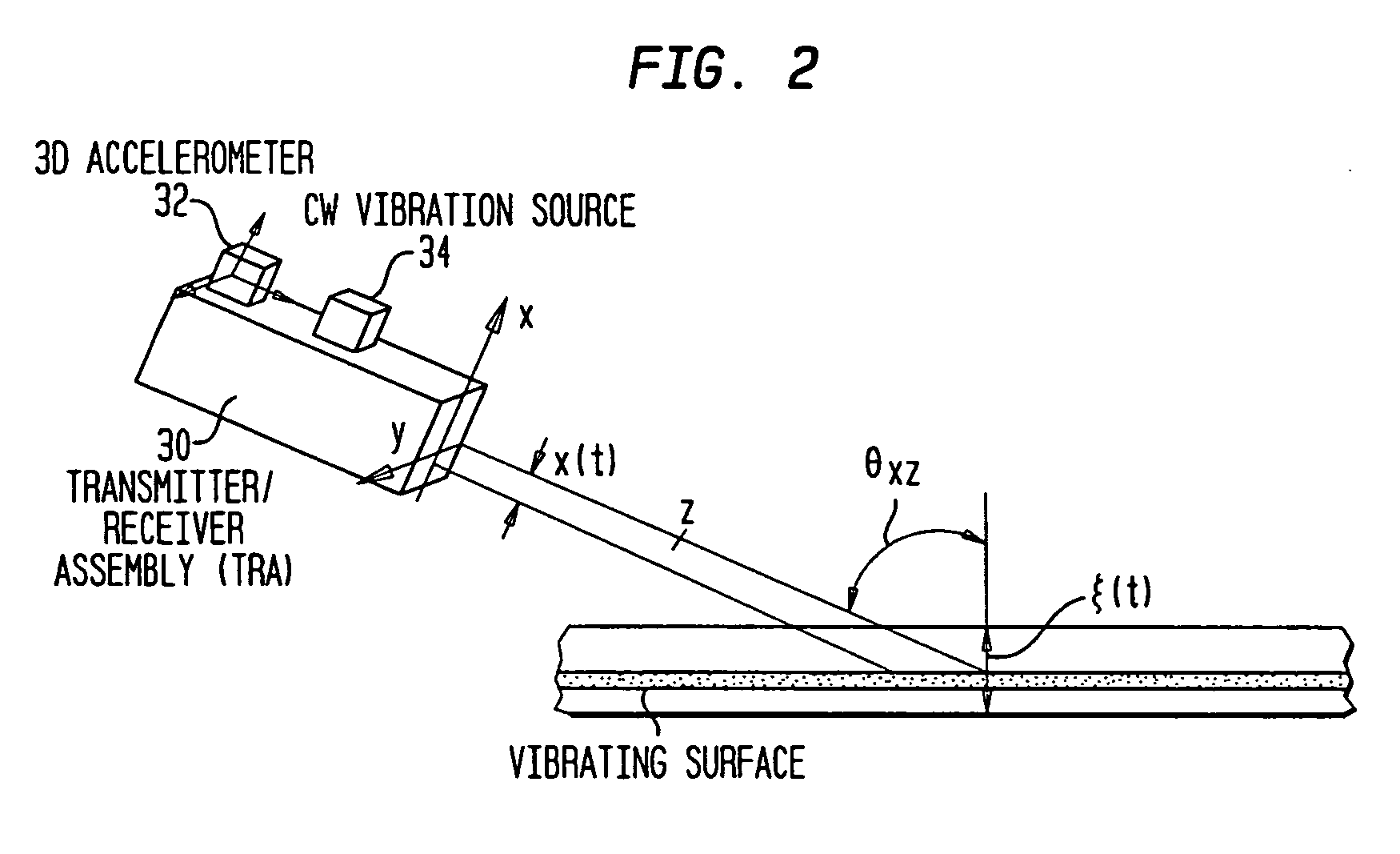
Method and apparatus for remote measurement of vibration and properties of objects
InactiveUS7073384B1Improve performanceUnwanted vibrationVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMicrowave frequency rangeVibration control
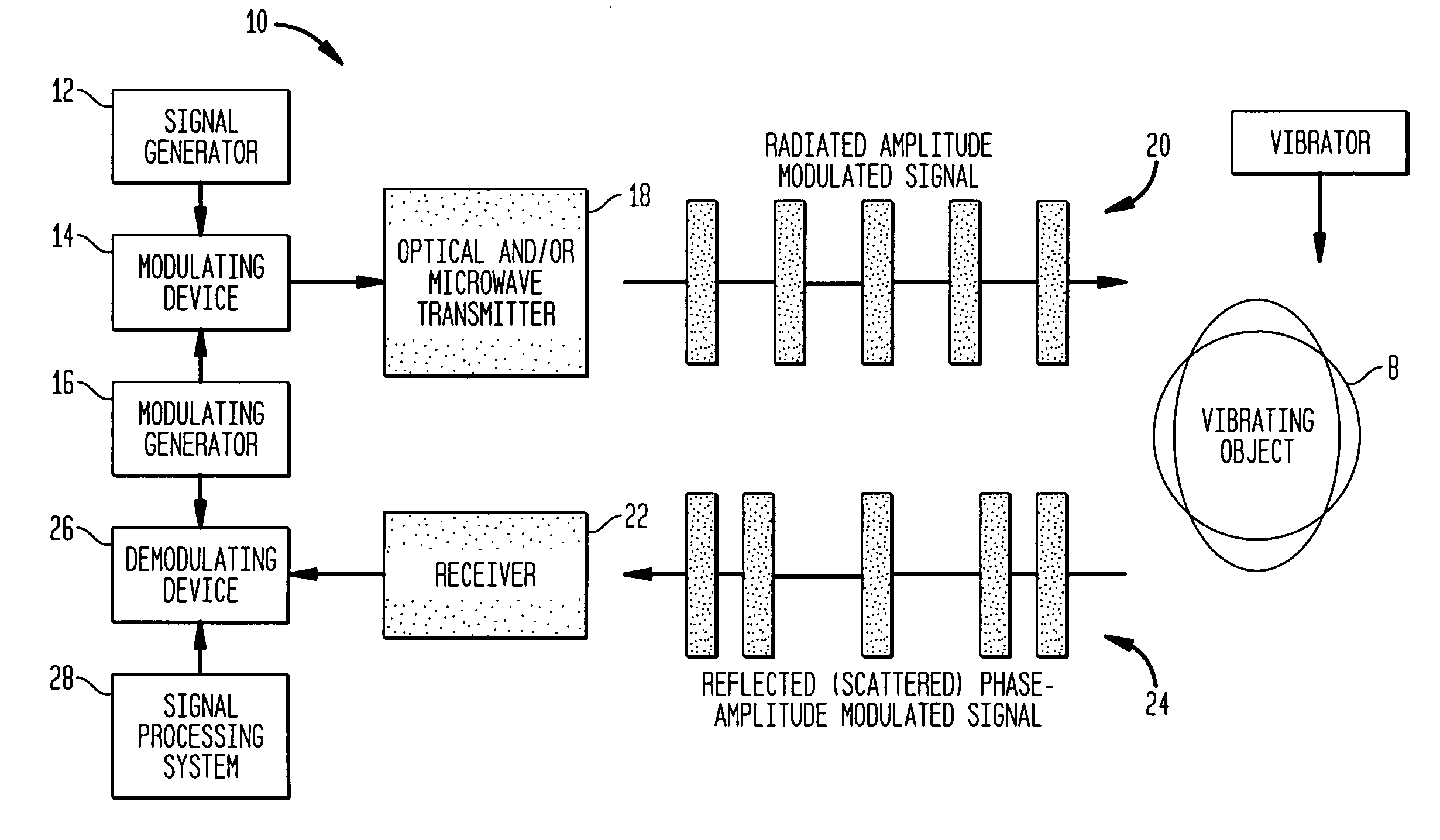
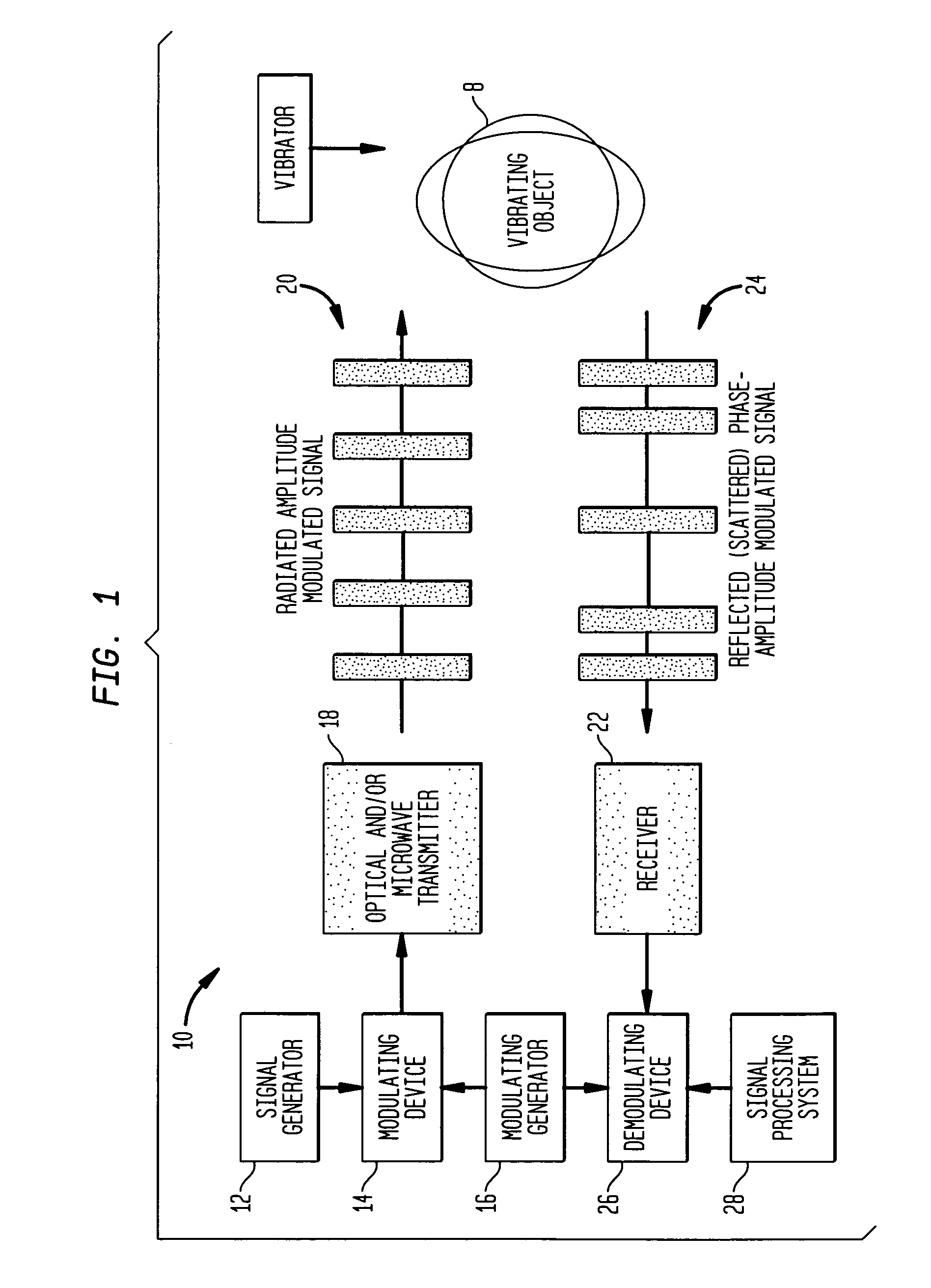
A method and apparatus (10) is provided which employs phase or amplitude modulated electromagnetic probing waves (20) (in optical or microwave frequency ranges or both) emitted toward a vibrating object (8). The optical and / or microwave probing signals (20) remotely irradiate an object (8) of interest. The object (8) reflects and / or scatters the probing wave (20) toward a receiver (22). The reflected / scattered modulated signal (24) is received with a remote sensor (receiver) (22). Vibration causes additional phase modulation to the probing wave (20). At the receiving end, the signal is demodulated to extract and analyze the vibration waveform (26,28). The present invention can be utilized for nondestructive testing, monitoring of technological processes, structural integrity, noise and vibration control, mine detection, etc.
Owner:STEVENS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
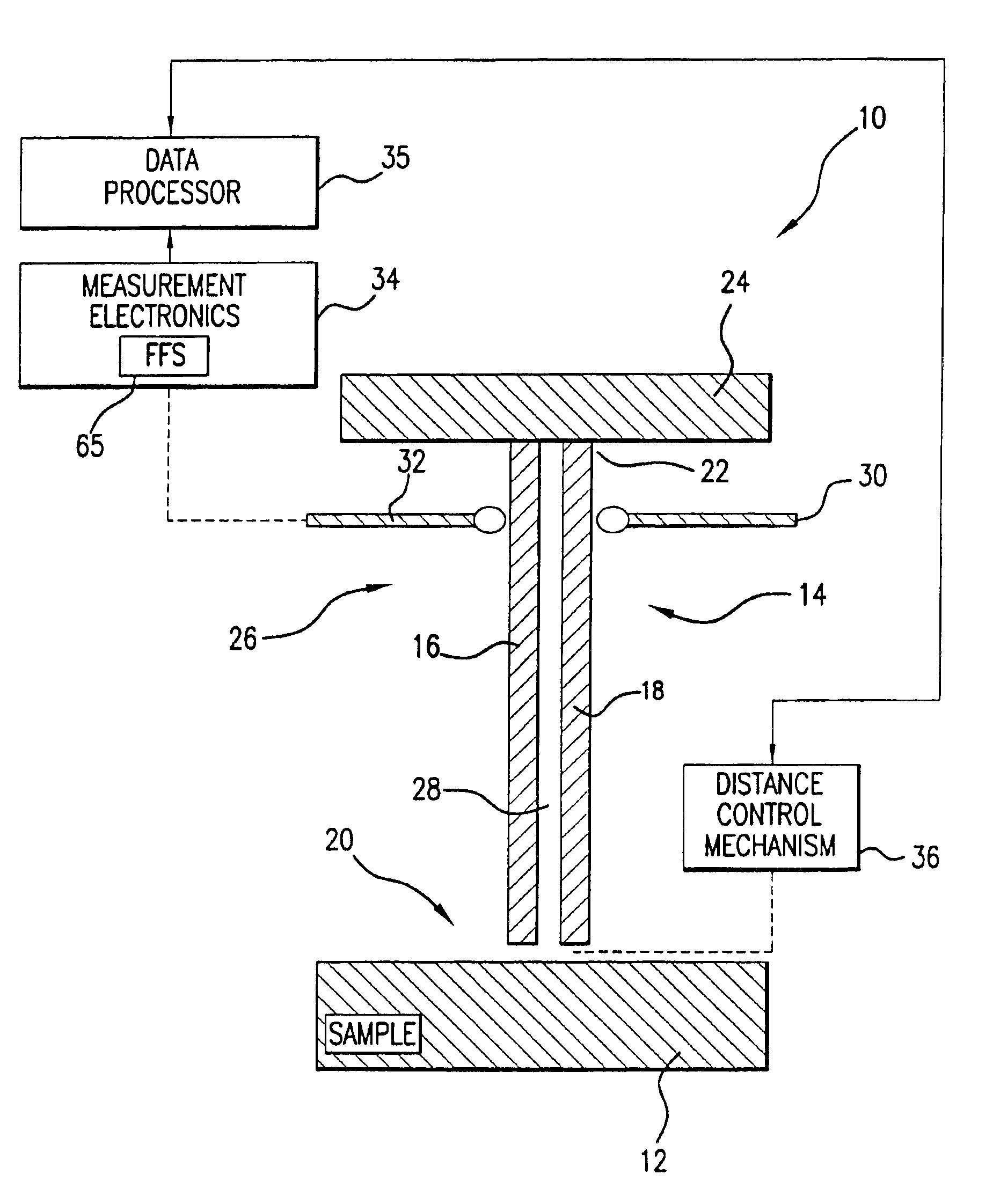
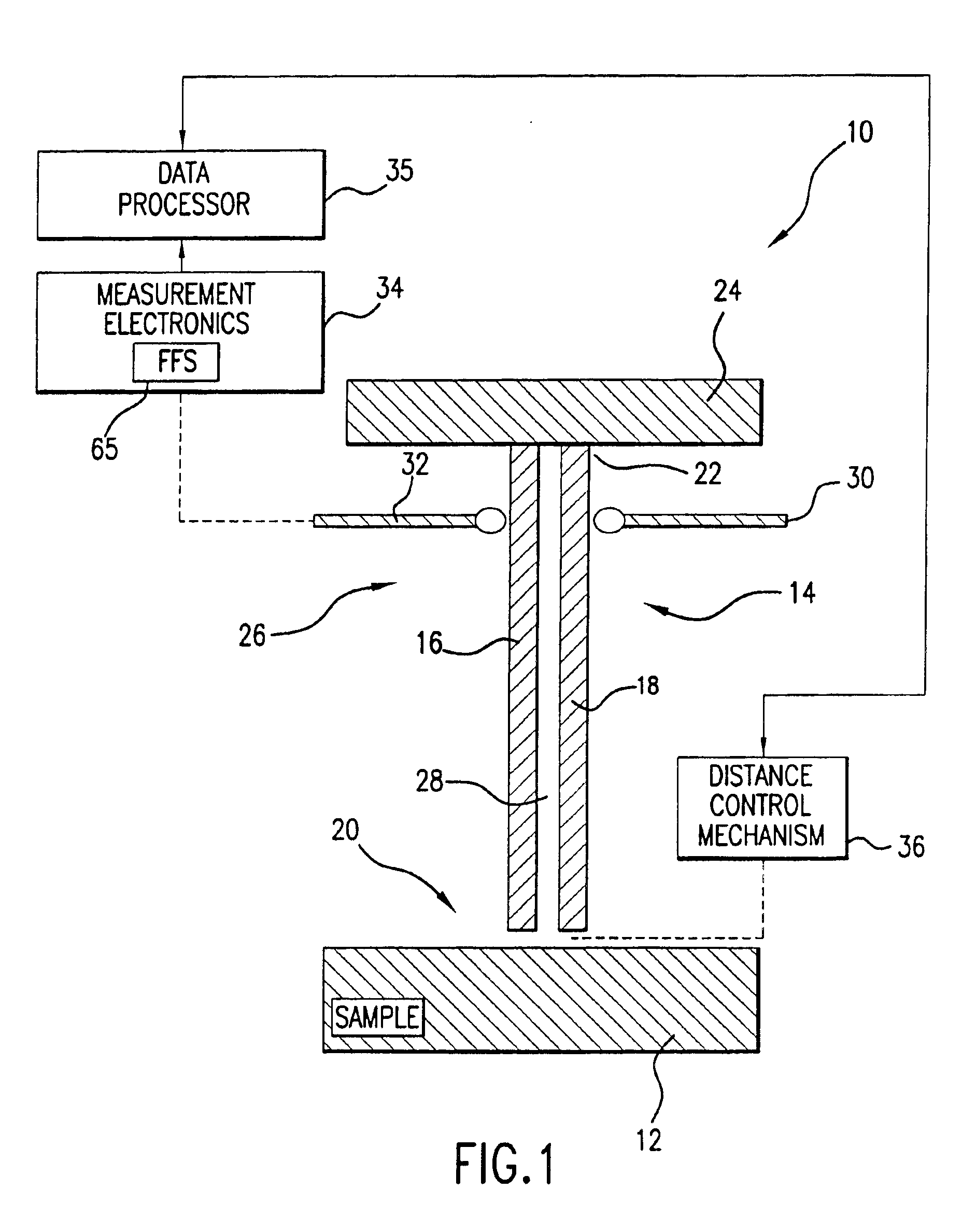
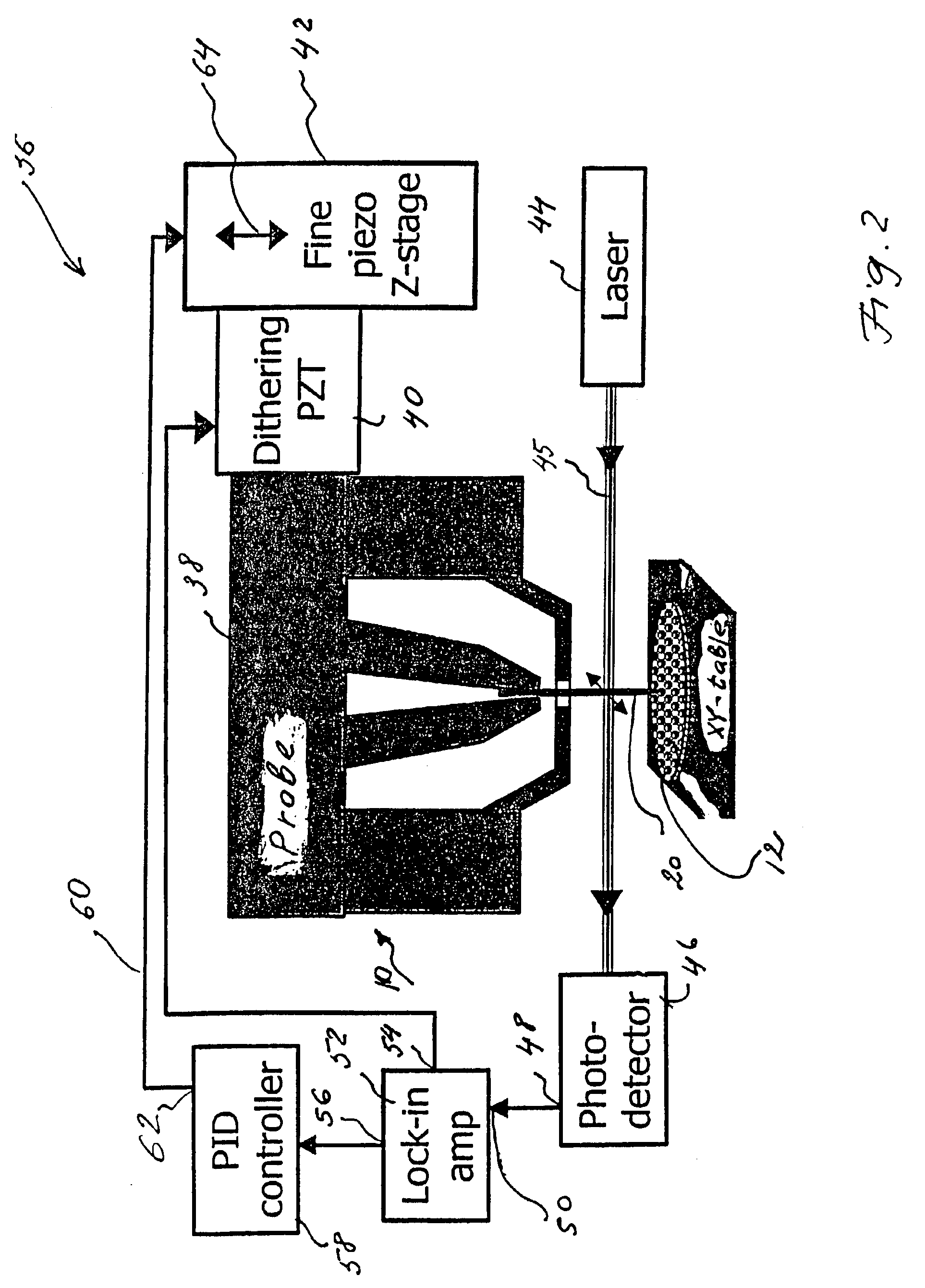
Analytical scanning evanescent microwave microscope and control stage
InactiveUS7550963B1Faster data acquisitionResistance/reactance/impedenceNanoopticsDielectricElectricity
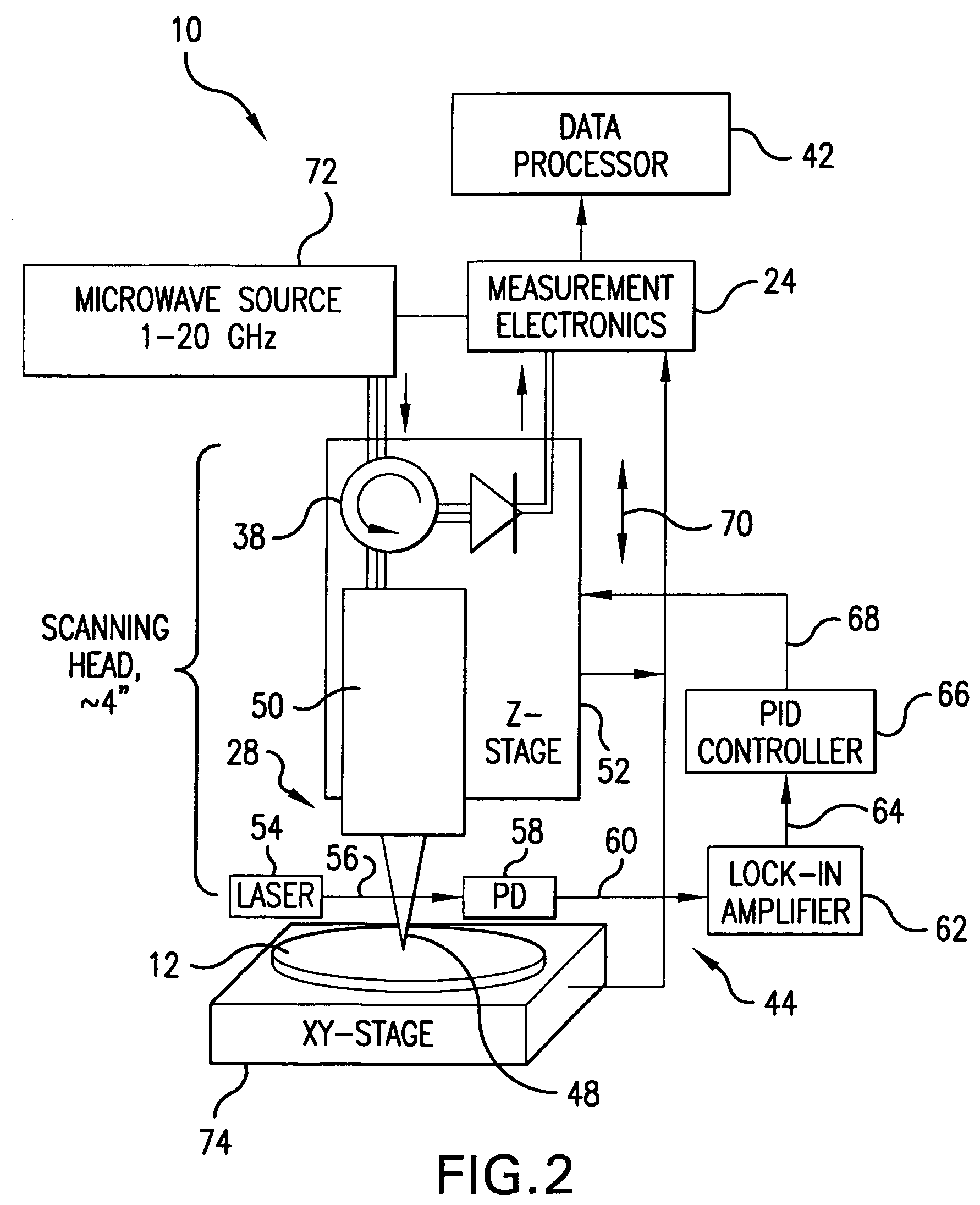
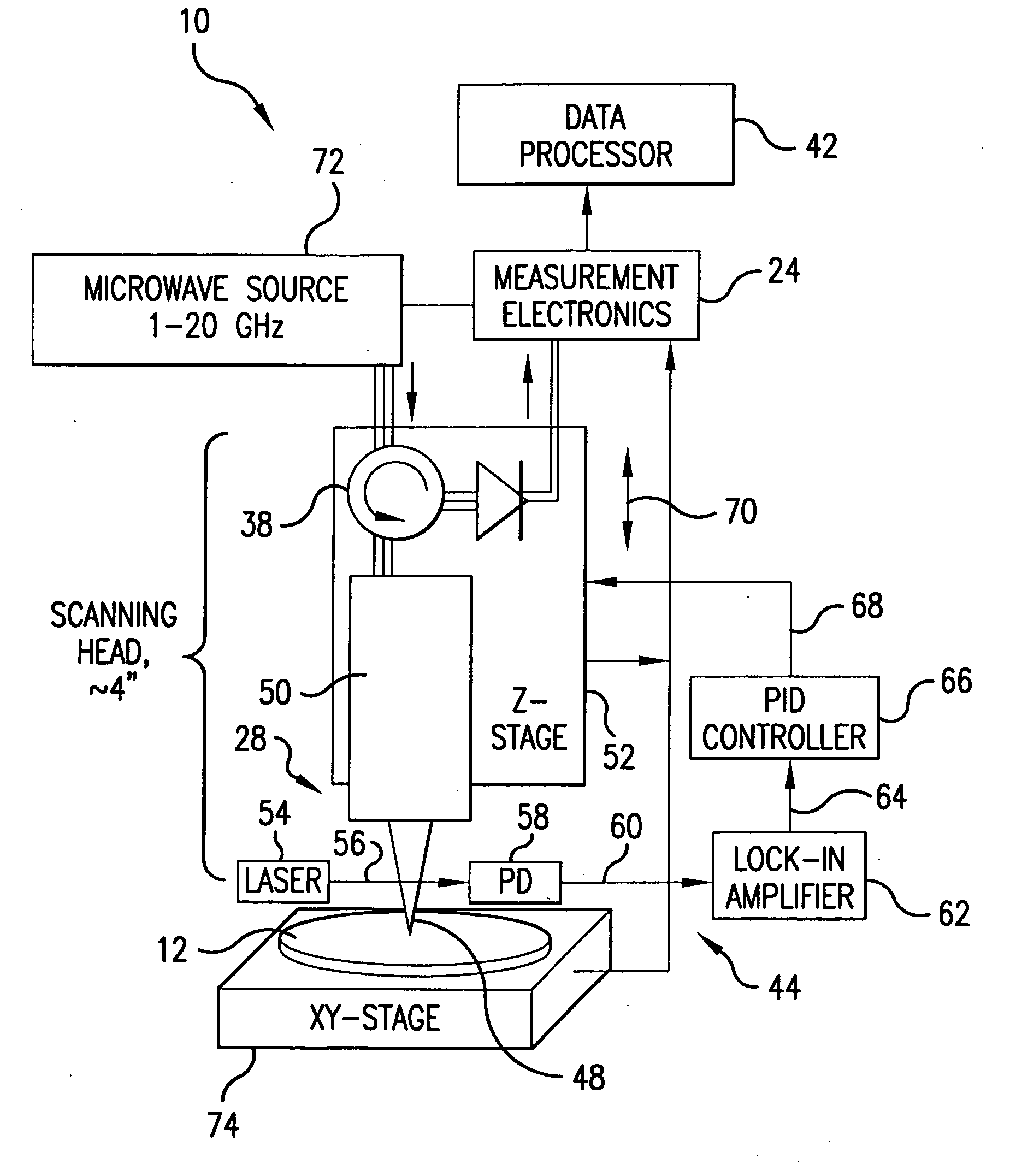
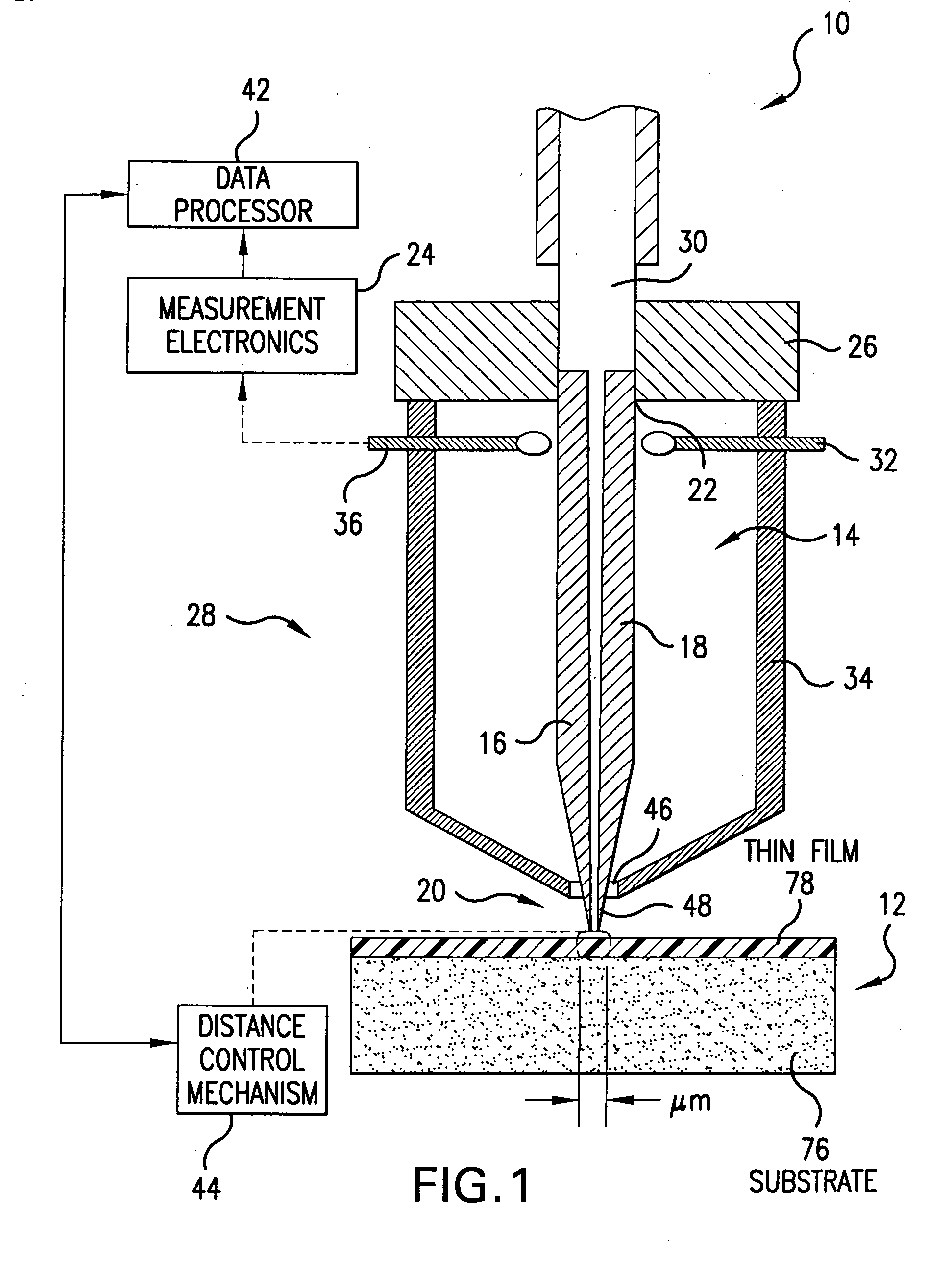
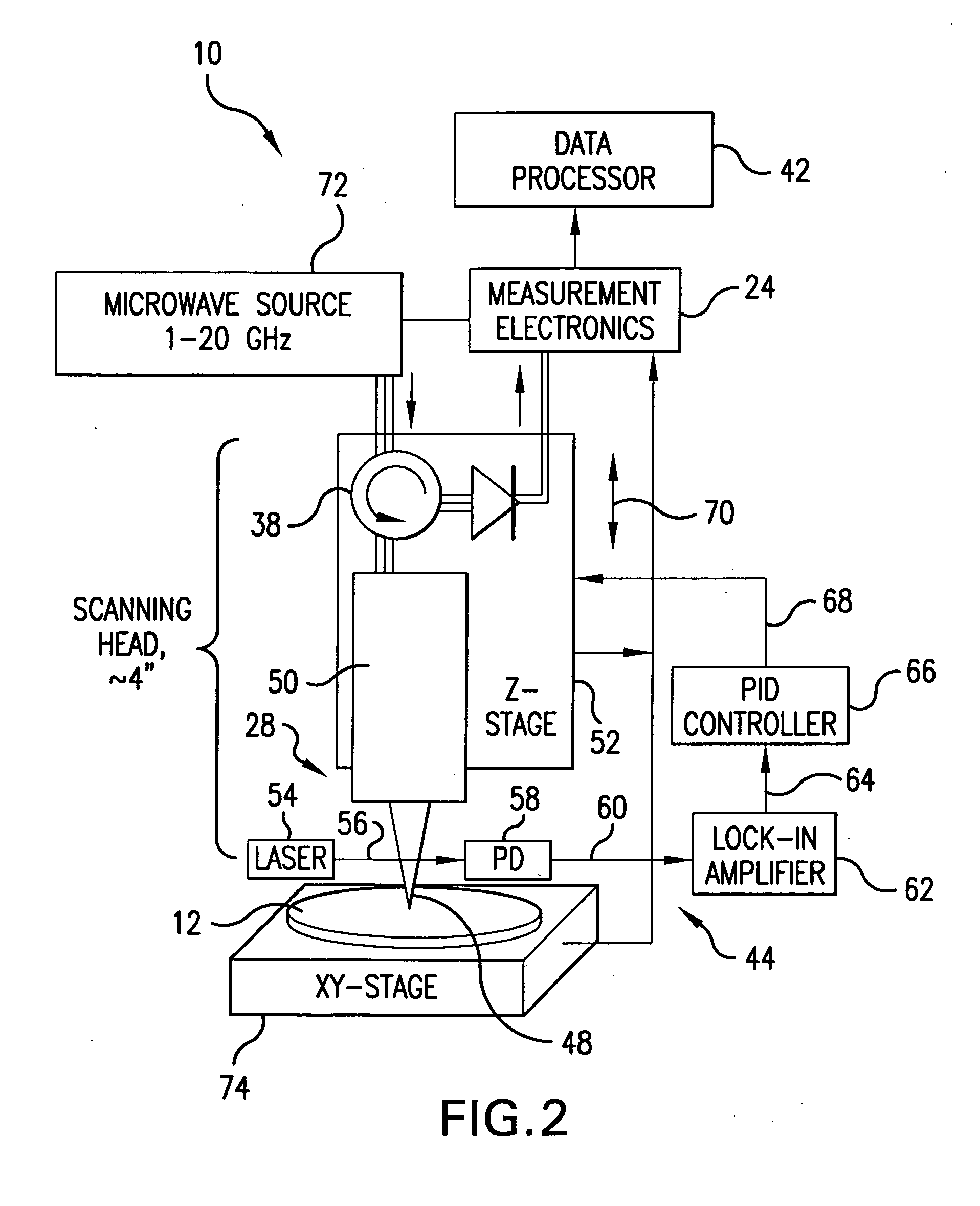
A scanning evanescent microwave microscope (SEMM) that uses near-field evanescent electromagnetic waves to probe sample properties is disclosed. The SEMM is capable of high resolution imaging and quantitative measurements of the electrical properties of the sample. The SEMM has the ability to map dielectric constant, loss tangent, conductivity, electrical impedance, and other electrical parameters of materials. Such properties are then used to provide distance control over a wide range, from to microns to nanometers, over dielectric and conductive samples for a scanned evanescent microwave probe, which enable quantitative non-contact and submicron spatial resolution topographic and electrical impedance profiling of dielectric, nonlinear dielectric and conductive materials. The invention also allows quantitative estimation of microwave impedance using signals obtained by the scanned evanescent microwave probe and quasistatic approximation modeling. The SEMM can be used to measure electrical properties of both dielectric and electrically conducting materials.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
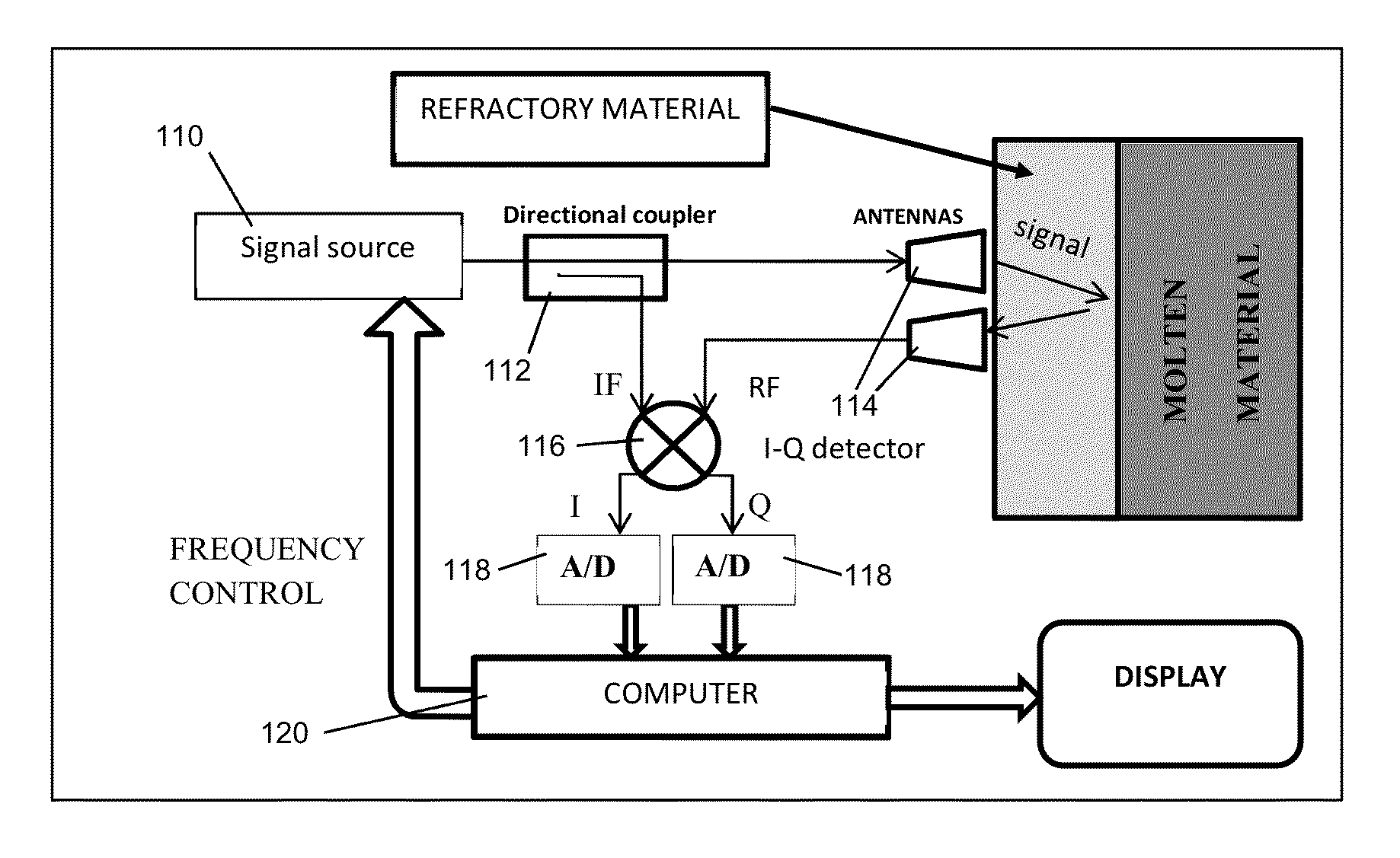
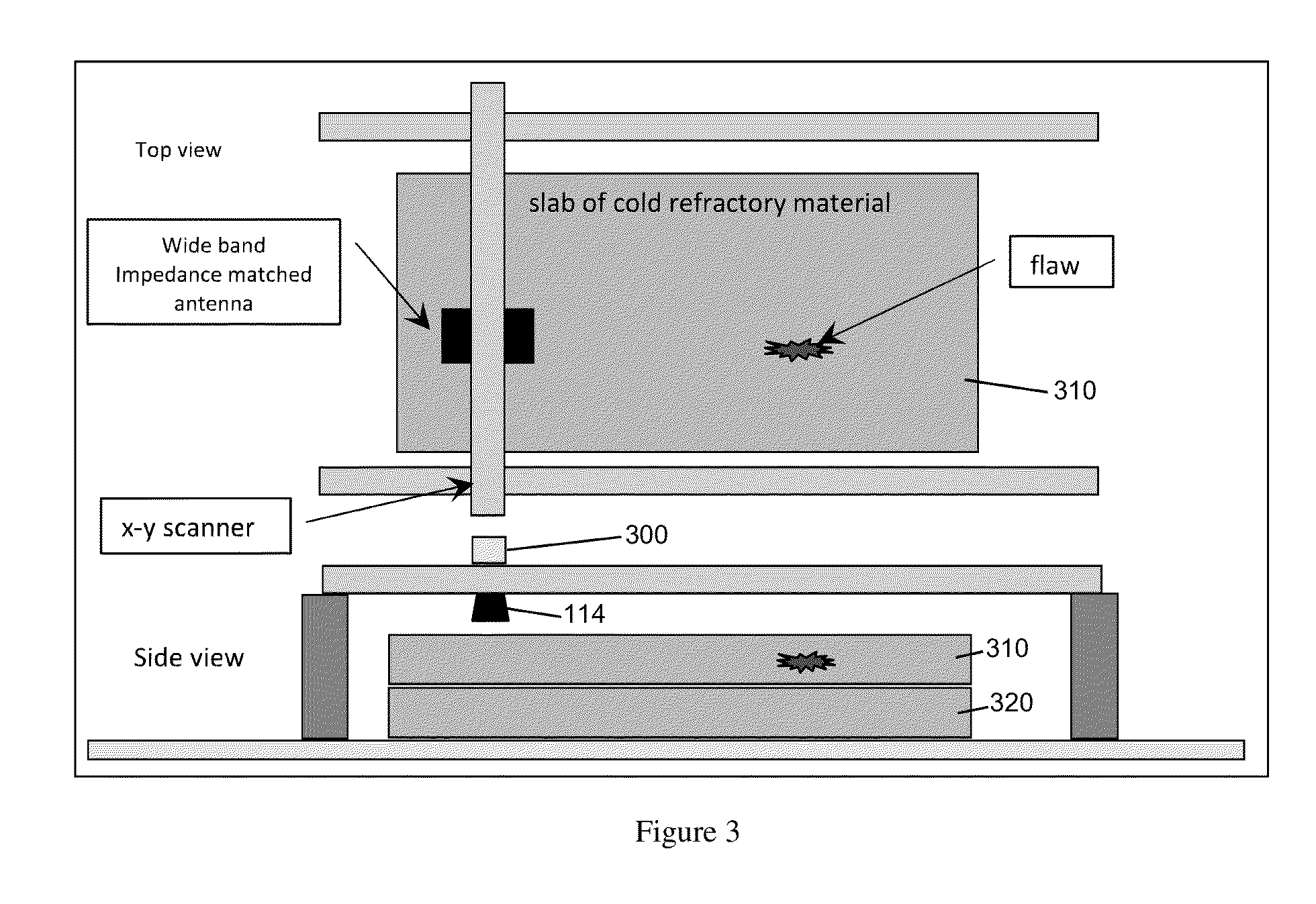
Microwave probe for furnace refractory material
ActiveUS20130144554A1Reduce lossesGood signal isolationFurnace componentsMaterial analysis by optical meansElectricityTime delays
Disclosed is a system and method to aid in these inspections that avoid the disadvantages of the prior art. The system and method are operative to take thickness measurements of, and thus evaluate the condition of, materials including but not limited to refractory materials, operating in frequency bands that result in less loss than previously known technologies, and utilizing a system configuration and signal processing techniques that isolate the reflected signal of interest from other spurious antenna reflections, particularly by creating (through the configuration of the antenna assembly) a time delay between such spurious reflections and the actual reflected signal of interest, thus enabling better isolation of the signal of interest. Still further, the antenna assembly is intrinsically matched to the material to be probed, such as by impedance matching the antenna to the particular material (through knowledge of the dielectric and magnetic properties of the material to be evaluated) to even further suppress spurious reflections.
Owner:PANERATECH
System and method for quantitative measurements of a material's complex permittivity with use of near-field microwave probes
InactiveUS6856140B2High precision measurementEasily controlled for modificationResistance/reactance/impedenceMaterial analysis using microwave meansFigure of meritFrequency shift
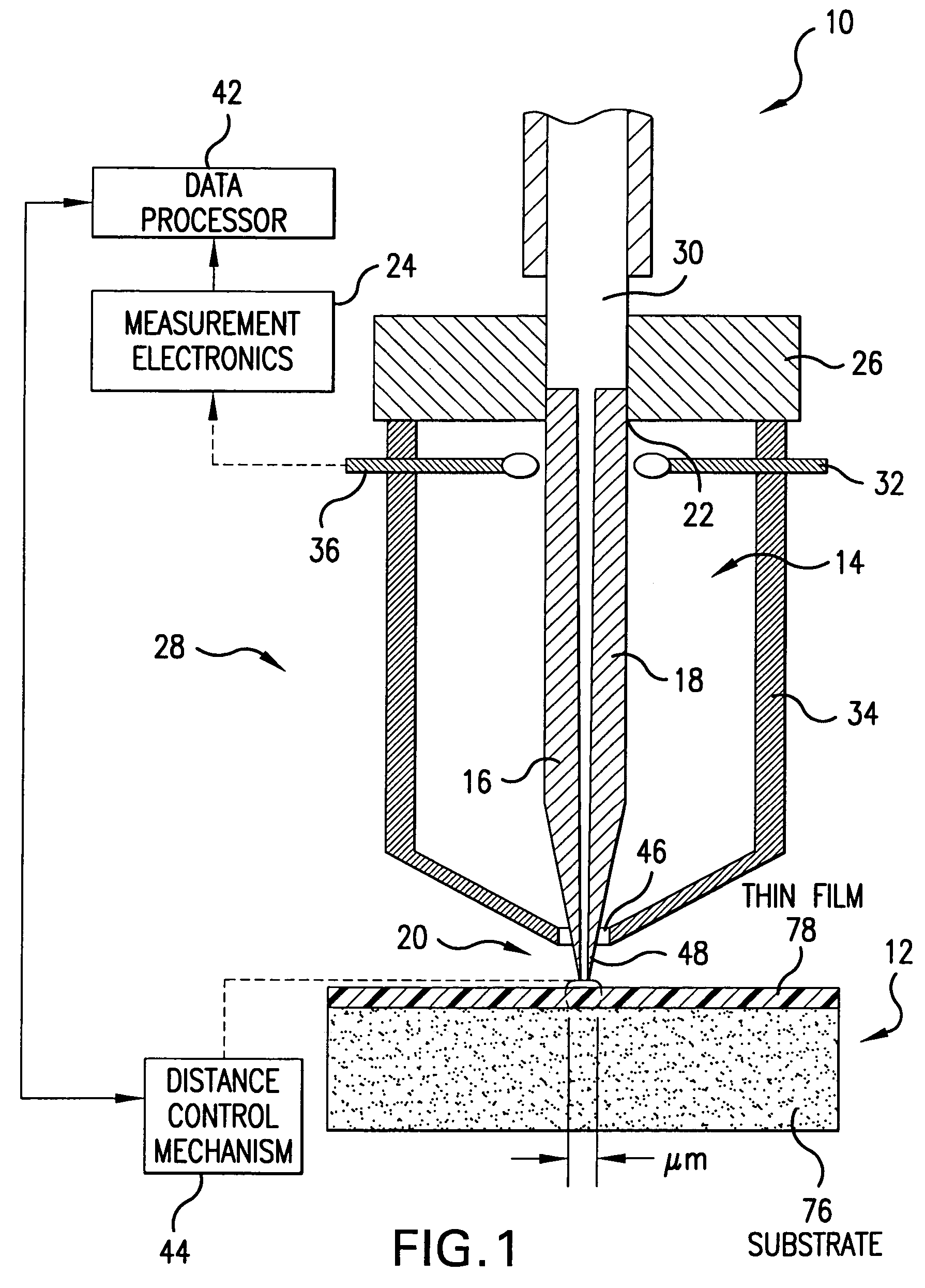
A method for measuring a material's complex permittivity is provided where a near-field microwave probe is positioned a predetermined distance from a first and a second standard sample for measuring a relative resonant frequency shift of the near-field microwave probe for standard samples. Based on measurements, calibration coefficients are calculated. A relative resonant frequency shift of the near-field microwave probe for a sample under study is measured by fast frequency sweep technique while the distance between the tip of the probe and the sample under the study is maintained nominally at the distance between the tip of the probe and each standard sample during a calibration procedure by a shear-force based distance control mechanism. Also, the change in the quality factor of the probe for unloaded and loaded resonator is measured. The dielectric constant of the sample under study is calculated using the resonant frequency shift and the change in the quality factor of the near-field microwave probe for the sample under study and the calibration coefficients obtained during the calibration procedure.
Owner:SEMICON PHYSICS LAB
Method and system for measurement of dielectric constant of thin films using a near field microwave probe
InactiveUS7285963B2Highly accurate determination of dielectric constantSimplicity and precisenessMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationResistance/reactance/impedenceDielectricElectricity
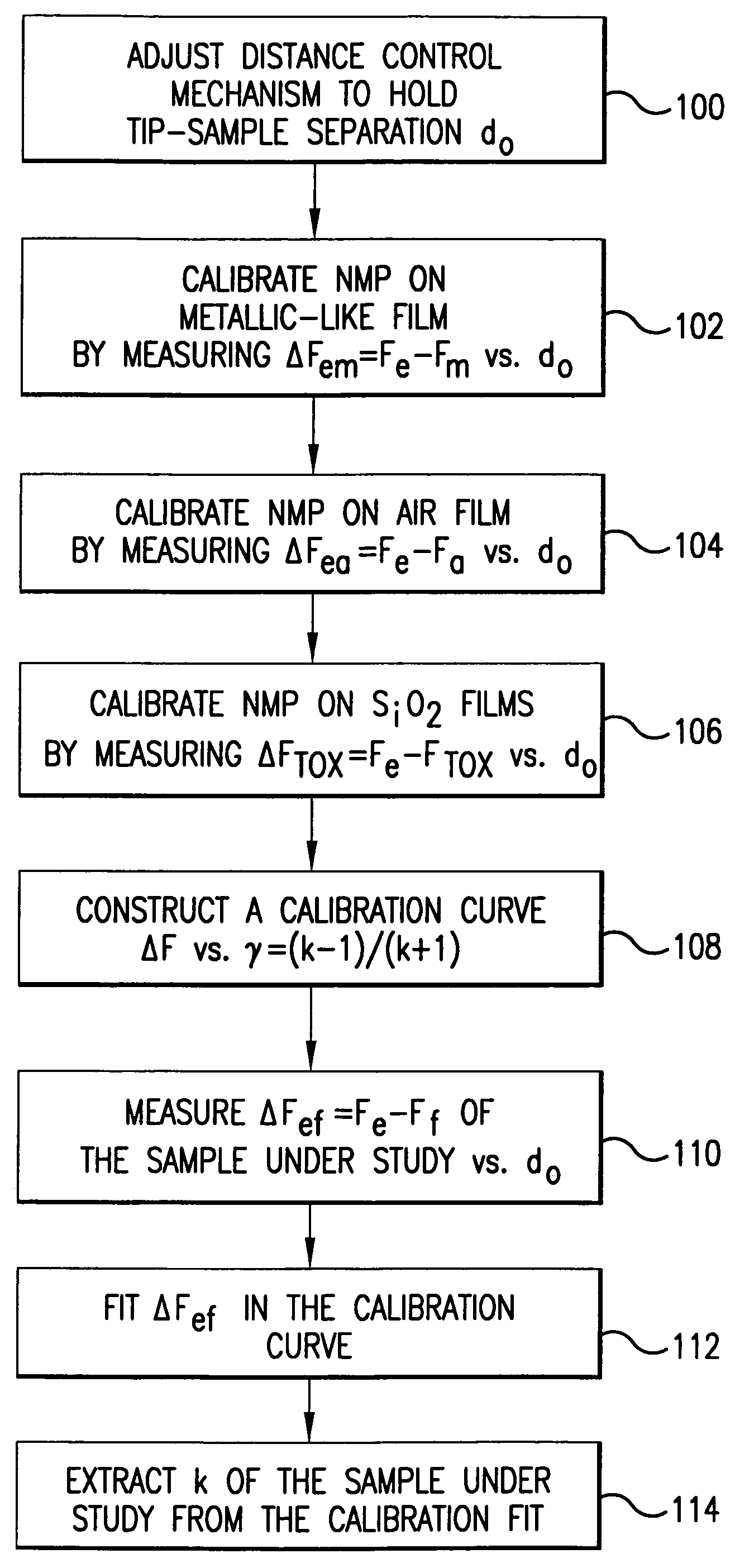
A measurement technique based on a microwave near-field scanning probe is developed for non-contact measurement of dielectric constant of low-k films. The technique is non-destructive, non-invasive and can be used on both porous and non-porous dielectrics. The technique is based on measurement of resonant frequency shift of the near-field microwave resonator for a plurality of calibration samples vs. distance between the probe tip and the sample to construct a calibration curve. Probe resonance frequency shift measured for the sample under study vs. tip-sample separation is fitted into the calibration curve to extract the dielectric constant of the sample under study. The calibration permits obtaining a linear calibration curve in order to simplify the extraction of the dielectric constant of the sample under study.
Owner:SEMICON PHYSICS LAB
Method and system for measurement of dielectric constant of thin films using a near field microwave probe
InactiveUS20050230619A1Highly accurate determination of dielectric constantSimplicity and precisenessMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationResistance/reactance/impedenceDielectricNon invasive
A measurement technique based on a microwave near-field scanning probe is developed for non-contact measurement of dielectric constant of low-k films. The technique is non-destructive, non-invasive and can be used on both porous and non-porous dielectrics. The technique is based on measurement of resonant frequency shift of the near-field microwave resonator for a plurality of calibration samples vs. distance between the probe tip and the sample to construct a calibration curve. Probe resonance frequency shift measured for the sample under study vs. tip-sample separation is fitted into the calibration curve to extract the dielectric constant of the sample under study. The calibration permits obtaining a linear calibration curve in order to simplify the extraction of the dielectric constant of the sample under study.
Owner:SEMICON PHYSICS LAB
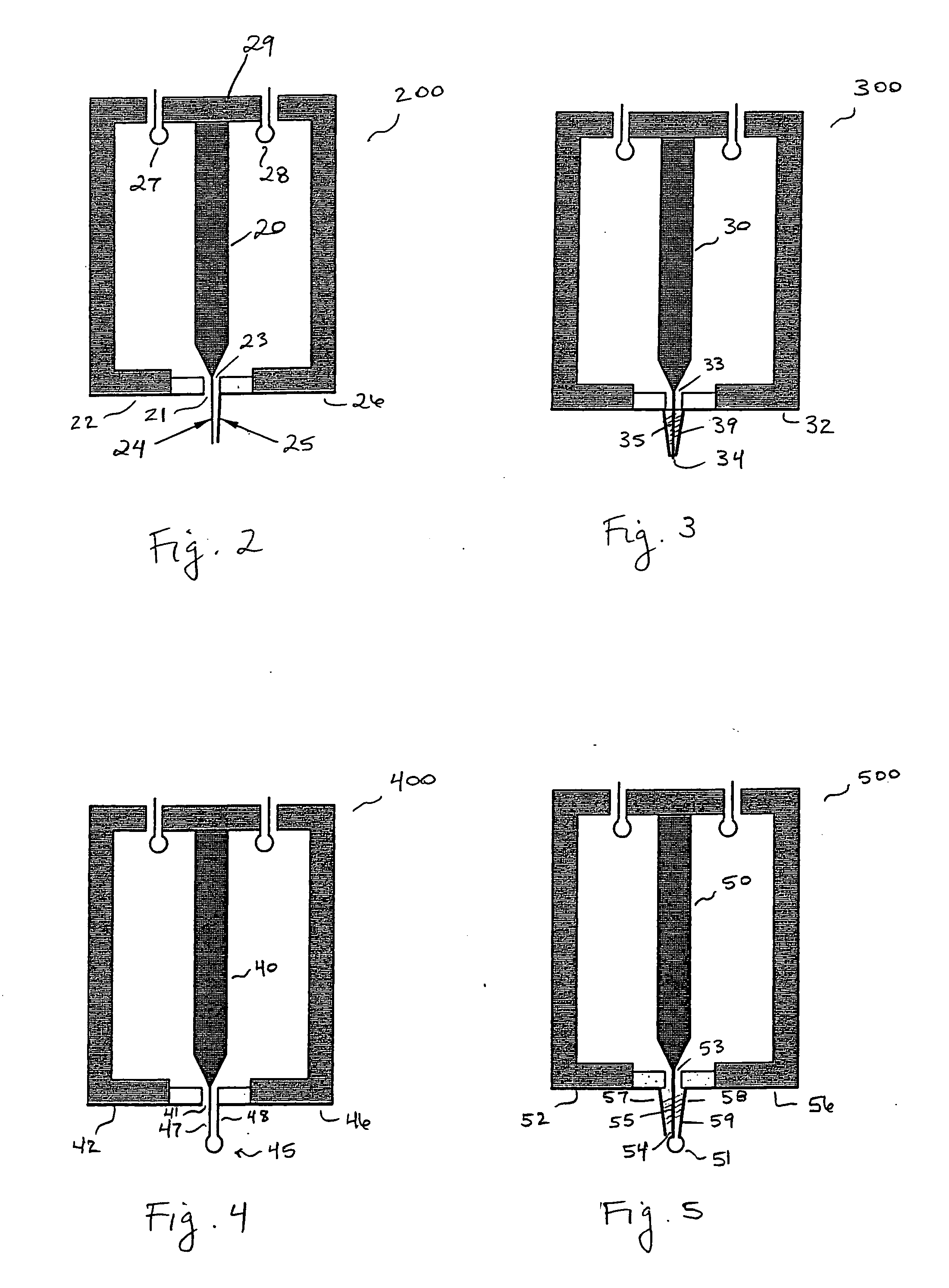
PAVR (Percutaneous Aortic Valve Replacement) operation conveying device with valve positioning function
InactiveCN105769387AIncrease success rateSimple structureHeart valvesCharacter and pattern recognitionPostoperative complicationPercutaneous aortic valve replacement
The invention discloses a PAVR (Percutaneous Aortic Valve Replacement) operation conveying device with a valve positioning function. The device comprises an active valve, a gripping device, a positioning rod, a regulating line, a hinge pin, an ultrasonic transducer, a microwave probe, a control device, a power supply device and a shell; the active valve is arranged at the tail end of the gripping device; the other end of the gripping device is connected with the positioning rod; the ultrasonic transducer is arranged at the right side of the shell; the tail end of the ultrasonic transducer is connected with the device shell by the hinge pin; the tail end of the ultrasonic transducer is connected with the regulating line; the control device is arranged at the outer end of the shell; the power supply device is connected with the control device. The PAVR operation conveying device with the valve positioning function has a simple structure and can take a good assisting effect on positioning on an implanted valve; intelligent control of the control device can improve a success rate of a PAVR operation, reduce operation difficulty, reduce postoperative complications, reduce operation pain and risks for patients, and reduce medical cost.
Owner:ZHUJIANG HOSPITAL SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
Device and method for restraining self-absorption effect of laser induced breakdown spectrometry by utilizing microwave-assisted stimulation
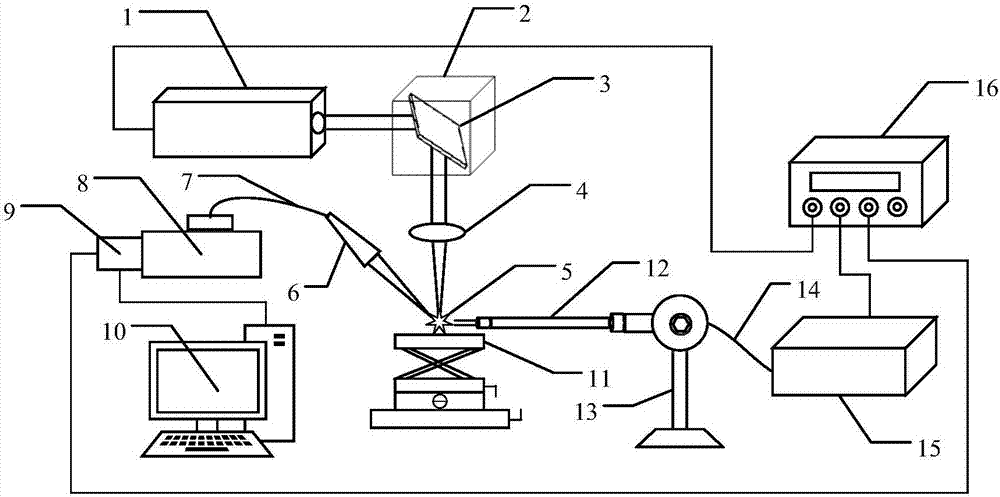
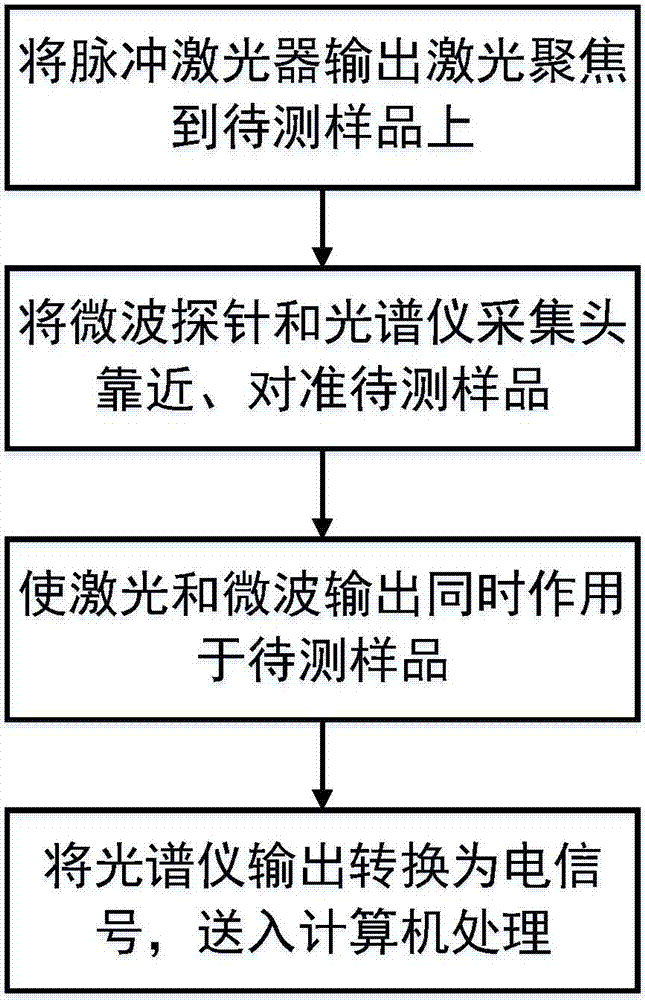
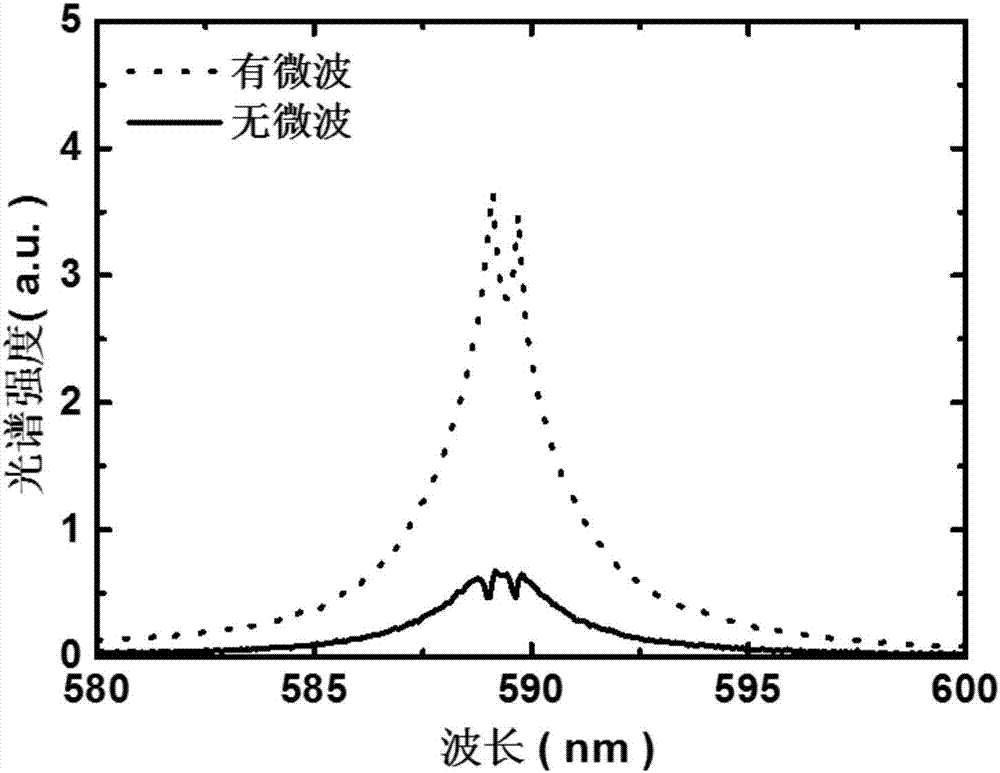
ActiveCN107014804AAvoid self-absorptionSelf-absorptionAnalysis by thermal excitationPhotovoltaic detectorsLaser-induced breakdown spectroscopy
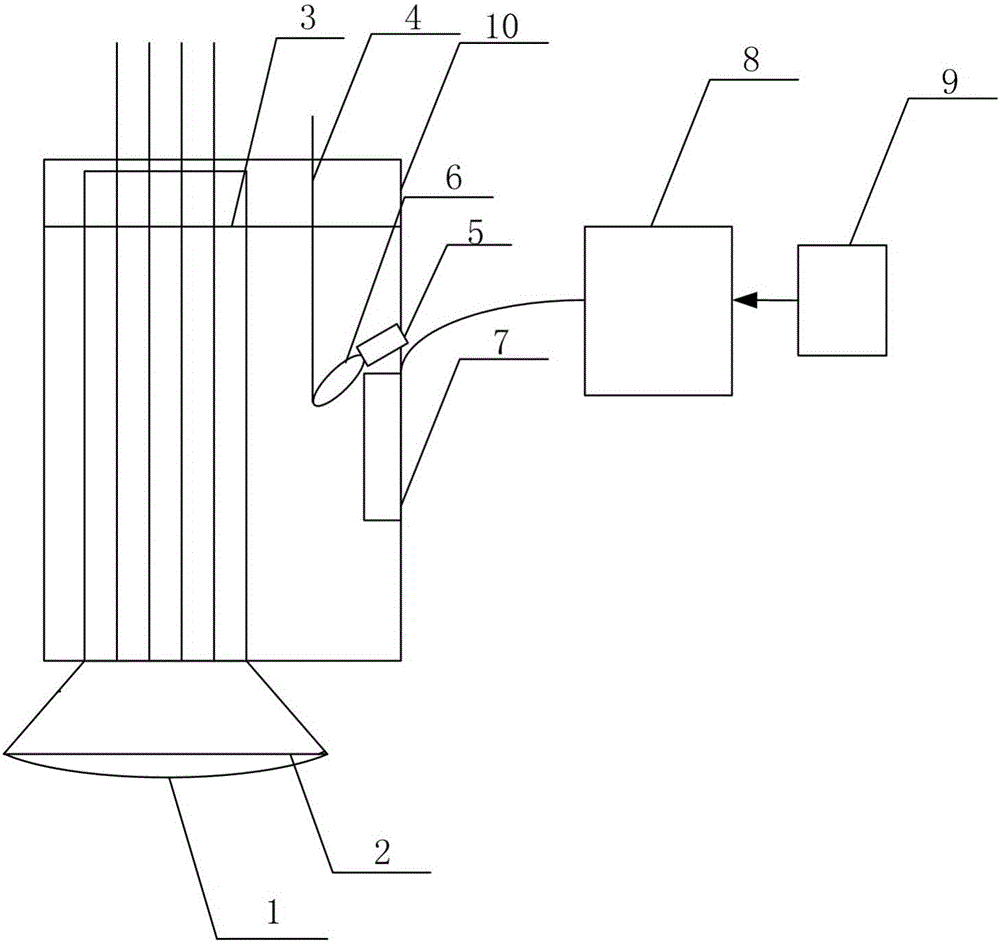
The invention discloses a device and a method for restraining a self-absorption effect of a laser induced breakdown spectrometry by utilizing microwave-assisted stimulation. The device comprises a pulse laser, a convergent lens, a spectrograph, a photoelectric detector, a computer, a three-dimensional displacement platform, a microwave probe and a microwave generator. The invention utilizes the excellent penetrability of the microwave-assisted stimulation to simultaneously stimulate the base particles of almost all the elements in plasma, avoid the self-absorption for central similar emission spectra, restrain and eliminate the self-absorption effect of the plasma from the source, so as to promote the accuracy and precision of laser induced breakdown spectrometry quantitative analysis. According to the invention, microwave is adopted for assisting the laser induced breakdown spectrometry, the microwave energy is radiated to laser plasma through a probe near field, no sealing chamber is required, a sample loading process is simple and the advantages of quick, in situ, real-time, multi-element and remote analysis of the laser induced breakdown spectrometry under atmospheric environment are remained.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method and apparatus for remote measurement of vibration and properties of objects
InactiveUS20060260407A1Improve performanceAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPhase-affecting property measurementsMicrowave frequency rangeVibration control
A method and apparatus is provided which employs phase or amplitude modulated electromagnetic probing waves (in optical or microwave frequency ranges or both) emitted toward a vibrating object. The optical and / or microwave probing signals remotely irradiate an object of interest. The object reflects and / or scatters the probing wave toward to a receiver. The reflected / scattered modulated signal is received with a remote sensor (receiver). Vibration causes additional phase modulation to the probing wave. At the receiving end, the signal is demodulated to extract and analyze the vibration waveform. The present invention can be utilized for nondestructive testing, monitoring of technological processes, structural integrity, noise and vibration control, mine detection, etc.
Owner:STEVENS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Automobile door opening anti-collision device
InactiveCN101927746APedestrian/occupant safety arrangementSignalling/lighting devicesMicrowave probePedestrian
The existing automobile is stopped, and passenger is easy to be collided by follow-up automobile or bicycle when opening door carelessly, thus causing personnel harm or automobile damage. The automobile door opening anti-collision device of the invention is that an infrared or microwave probe is arranged at the rail part of the automobile and the door lock of the automobile is controlled to be closed or opened by induction. When other vehicles or pedestrians follow up after the automobile, the probe firstly detected, the door lock is controlled to be closed, and the door can not be opened, thus collision with the follow-up vehicle or pedestrian can be avoided.
Owner:任立蓬
Loading device for rock sample force-thermal coupling under microwave radiation and test method of same
InactiveCN106769498AForce-thermal coupling implementationSimulate the realMaterial analysis using microwave meansMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesEngineeringWater loading
The invention relates to a loading device for rock sample force-thermal coupling under microwave radiation, wherein a sample pressure head is arranged in a press frame, the pressure head is connected with a computer through a hydraulic control mechanism, a pressure sensor is arranged on the hydraulic control mechanism, a displacement sensor is arranged on the sample pressure head, the pressure sensor and the displacement sensor are connected with the computer respectively; a microwave control cabinet is arranged at the external of the press frame, a magnetron is arranged in the microwave control cabinet, an output end of the magnetron is connected with a rectangular waveguide, the rectangular waveguide is in water-loading connection with a waveguide convertor through a circulator, an output end of the waveguide convertor is in coaxial-waveguide connection with a microwave probe; the rock sample clamped on the sample pressure head is provided with a drill hole, the microwave probe is inserted into the drill hole. The device provided by the invention has the advantages that direct measurement on the mechanical property of the rock sample in a microwave field can be realized, the force-thermal coupling of the rock sample under the microwave radiation is realized.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Dual-probe differential device for online measuring water content of microwave and measuring method
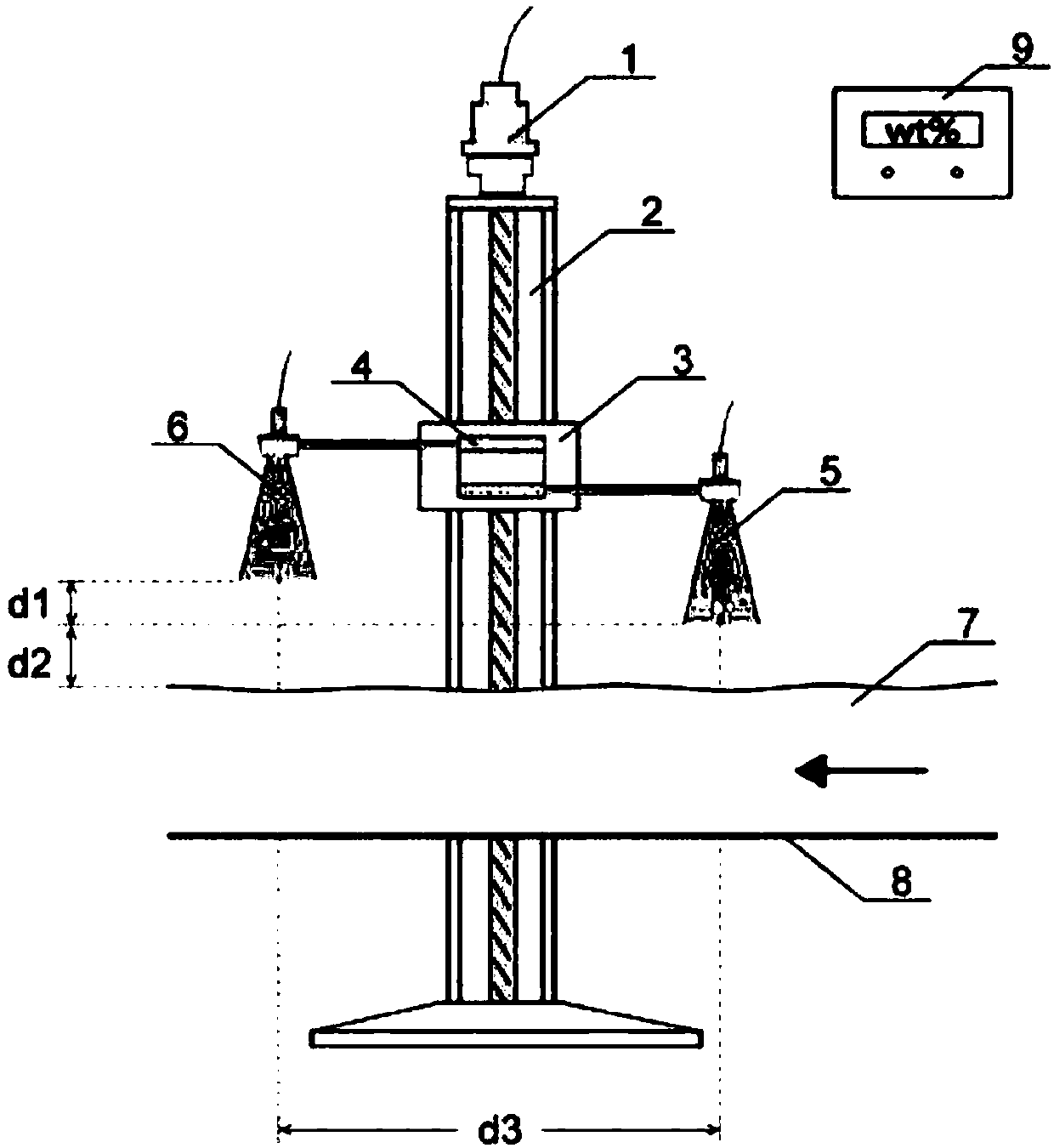
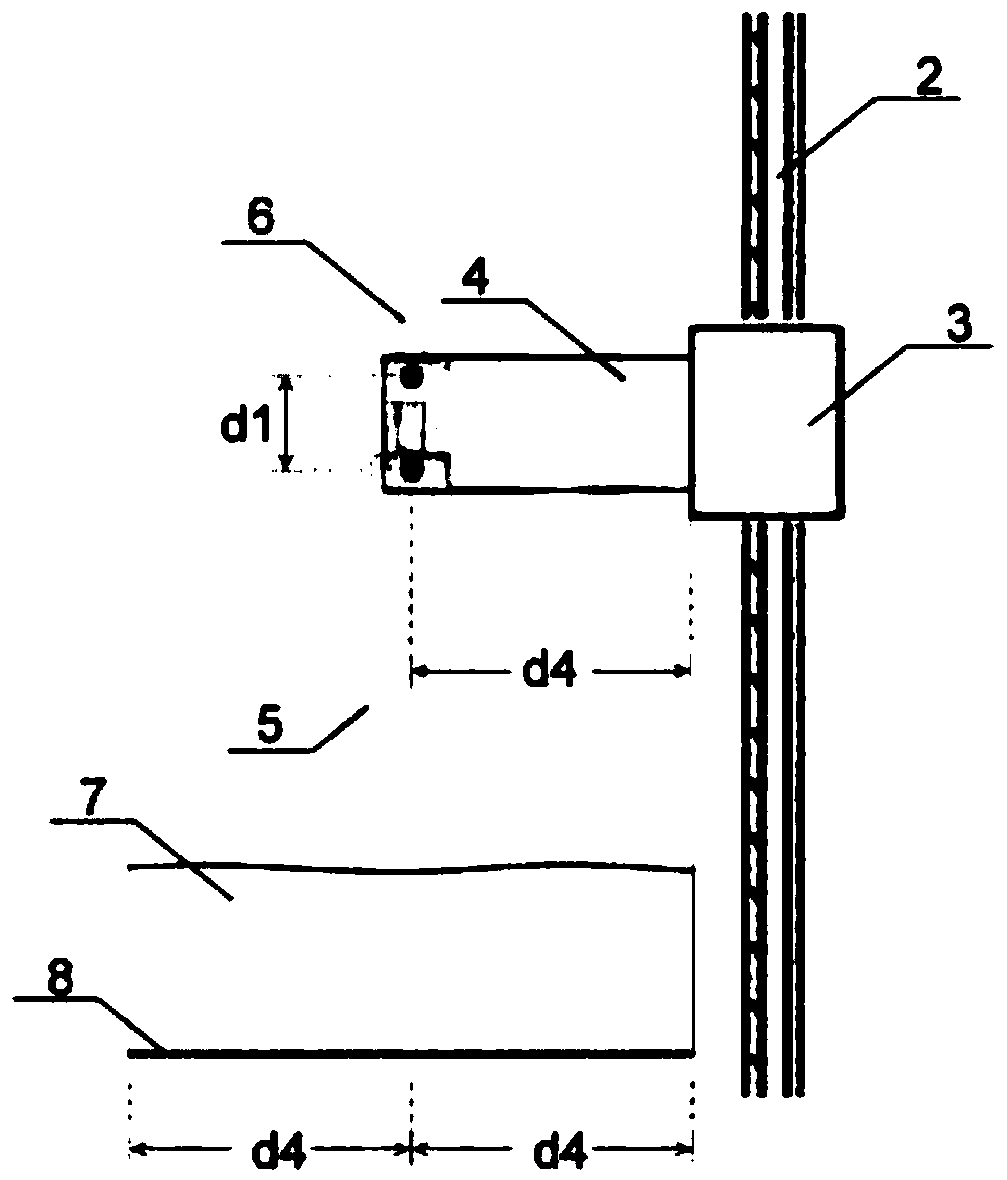
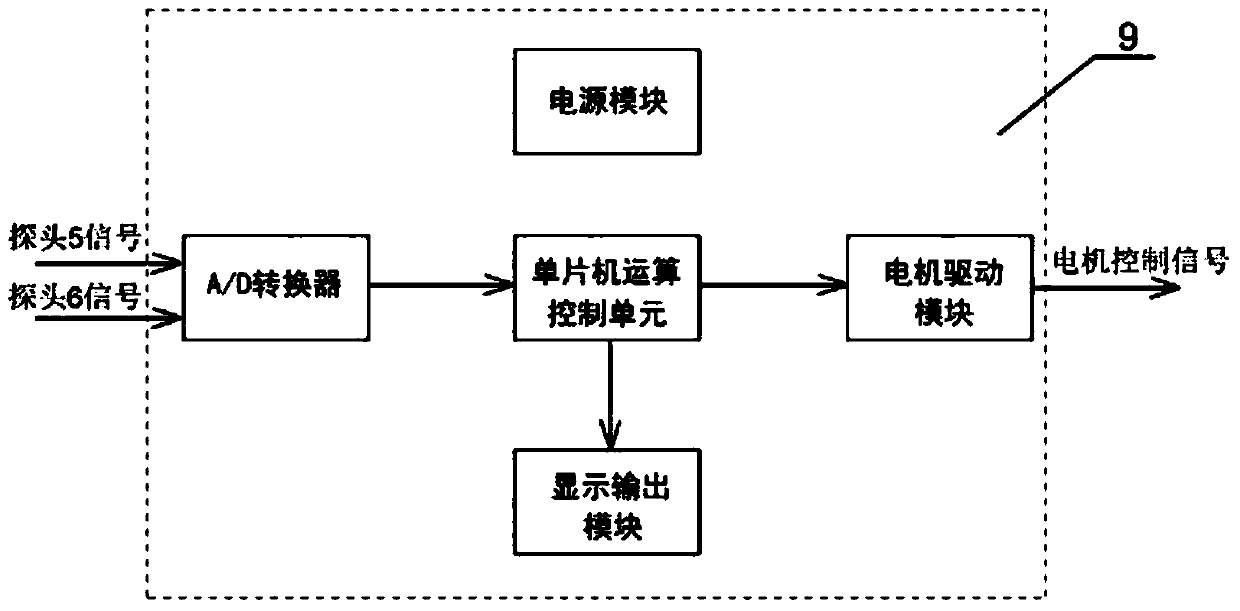
PendingCN108459032AImprove dynamic measurement accuracySimple structureMoisture content investigation using microwavesEngineeringWavelength
The invention belongs to the technical field of microwave application, and specifically relates to a dual-probe differential device for online measuring the water content of microwave and a measuringmethod. The device consists of microwave probe units, a probe fixed seat, a sliding platform a lead screw guide rail unit, a servo motor unit and a signal display control unit. The dual-microwave probes are mounted on the probe fixed seat in the material conveying direction, the vertical height difference is 1 / 4 of microwave length, the dual-microwave probes are integrally fixed on the sliding platform in the lead screw guide rail unit, the servo motor is connected with the lead screw guide rail unit to control the movement of the sliding platform, the signal display control unit is used for controlling the servo motor to rotate so that the dual-microwave probes are positioned at the positions of phase position extreme points respectively; dual-probe data are collected through synchronousdelay for carrying out differential inversion operation processing so as to obtain water information of a measured material. According to the dual-probe differential device, the measurement accuracy is improved, and rapid non-damage detection for water content of materials such as cereals, gravels and chemicals on a conveyor belt can be realized.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Electric-control broadband photon radio-frequency phase shifter based on silicon-based micro-ring resonant cavity
InactiveCN101799608AResonant cavity is smallReduce volumeWaveguide type devicesNon-linear opticsCarrier signalVoltage source
The invention relates to an electrical-control broadband photon radio-frequency phase shifter based on a silicon-based micro-ring resonant cavity, belonging to the technical field of optical field communication and comprising a carrier-suppression optical double-sideband generating system, a silicon-based micro-ring resonant cavity system, a voltage source and a measuring system, wherein the carrier-suppression optical double-sideband generating system comprises an adjustable laser, a radio-frequency signal generator, a Mach-Zehnder modulator and a optical amplifier; the silicon-based micro-ring resonant cavity system comprises the silicon-based micro-ring resonant cavity and a microwave probe, wherein the silicon-based micro-ring resonant cavity comprises two silicon-based micro-rings with equal electrodes and radii, and a direct waveguide; and the measuring system comprises an optical amplifier, an adjustable narrow-band filter, an optical detector and an oscilloscope. The invention has the advantages small volume, simple structure and easy integration of the used devices as well as large phase shifting range approximate to 4 pi, high reaction speed, simple operation and low cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Automatic spraying defoaming device for waste leachate treatment
InactiveCN101700930ASolve fouling and cloggingReduce processing costsTreatment using aerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentWaste treatmentPollution
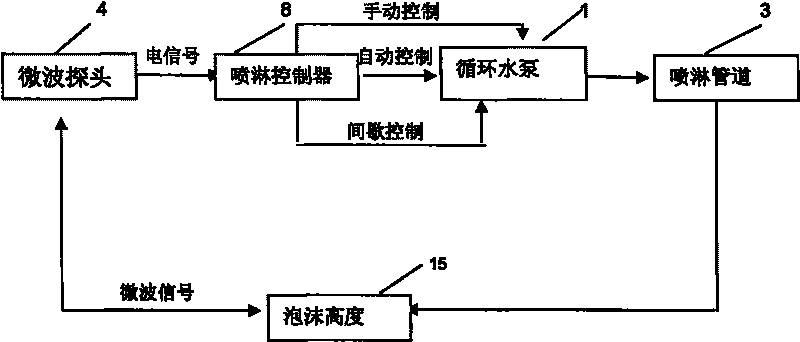
The invention relates to an automatic spraying defoaming device for waste leachate treatment, which comprises a biochemical reaction basin and an aeration device arranged in the biochemical reaction basin. A microwave probe for detecting foam height and a spraying hole tube are arranged above the water surface of the biochemical reaction basin; the microwave probe is connected with a spraying controller arranged outside the biochemical reaction basin; a control switch of the spraying controller is connected with a circulating water pump arranged under the water surface of the biochemical reaction basin; and the circulating water pump is connected with the spraying hole tube by a connecting tube to form a circulating device for waste water spraying and defoaming. The invention realizes the spraying and defoaming treatment in the aerobic phase of leachate biochemical treatment, solves dirt blockage during waste water spraying, avoids using a defoaming agent, thereby not only preventing secondary pollution, but also saving the cost of waste water treatment, wherein the automatic circulating defoaming treatment saves three fifths of defoaming cost, more than 90% electrical energy, and more than 95% waste water treatment cost, and can be popularized and applied to large-scale waste treatment sites.
Owner:NINGBO CITY YINZHOU DISTRICT LYUZHOU ENERGY UTILIZATION CO LTD +1
Method for reducing optical frequency shift of rubidium atomic frequency standard
InactiveCN102104382AReduce optical frequency shiftImprove linear functionPulse automatic controlResonanceFtir spectra
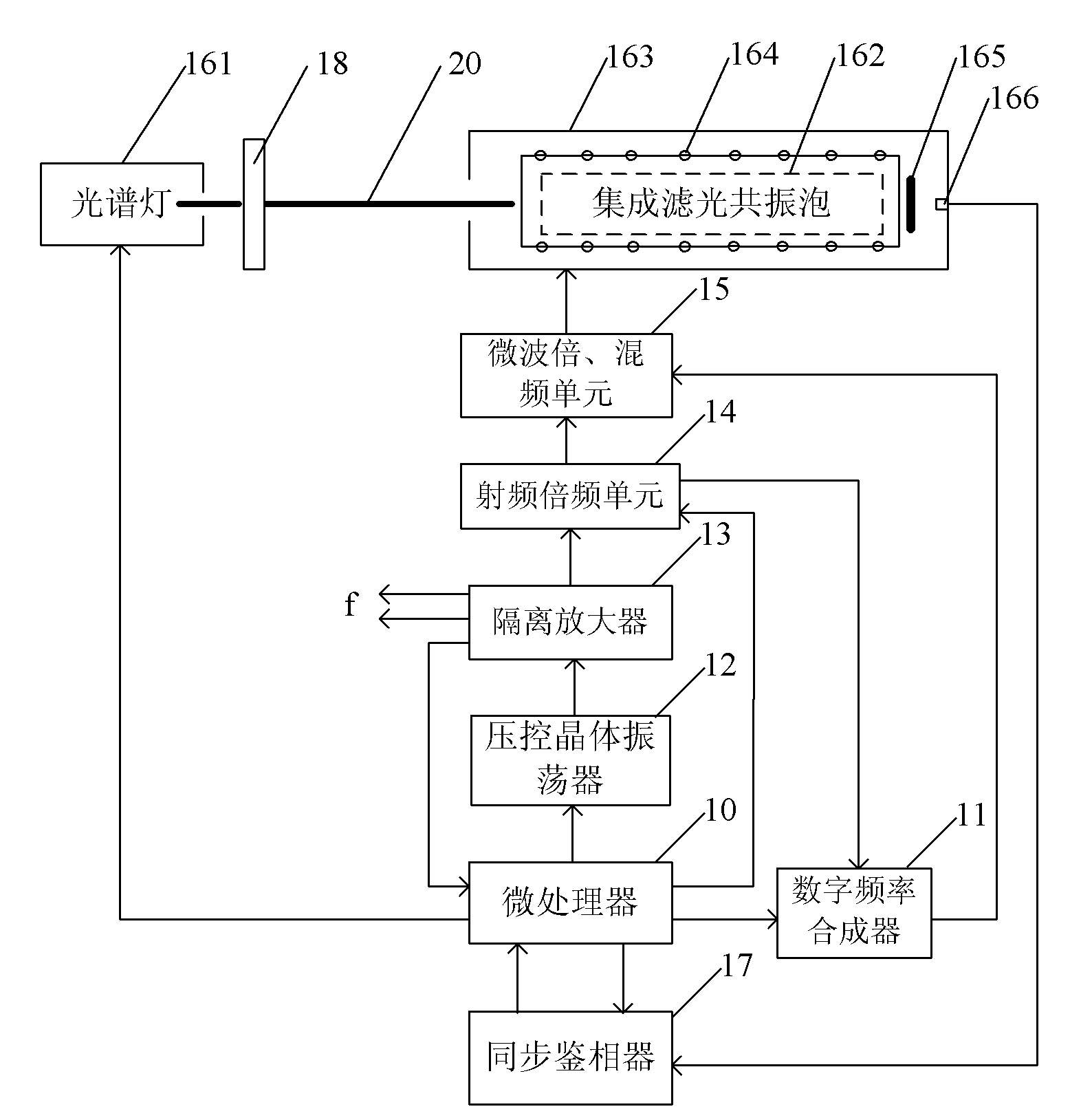
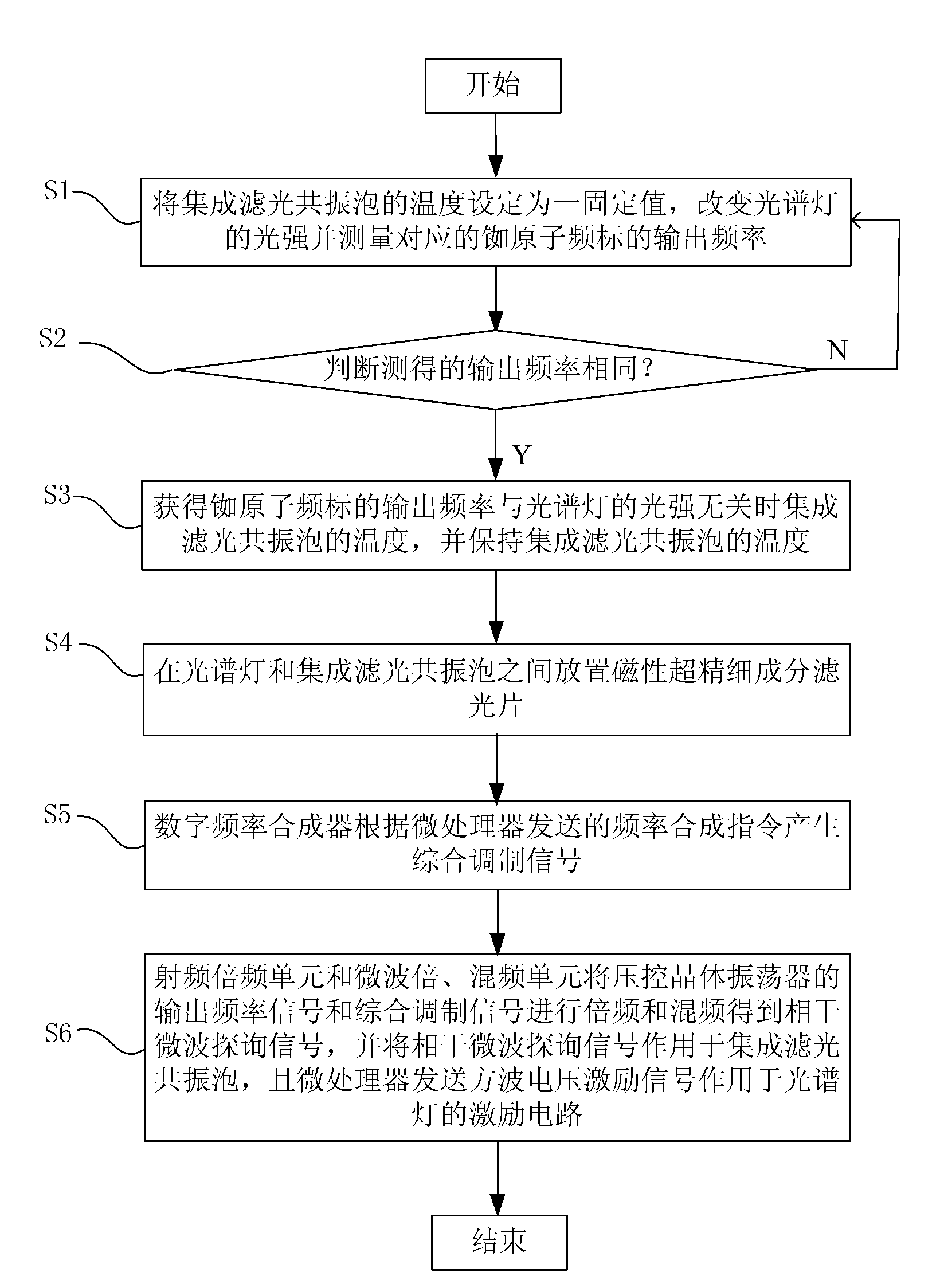
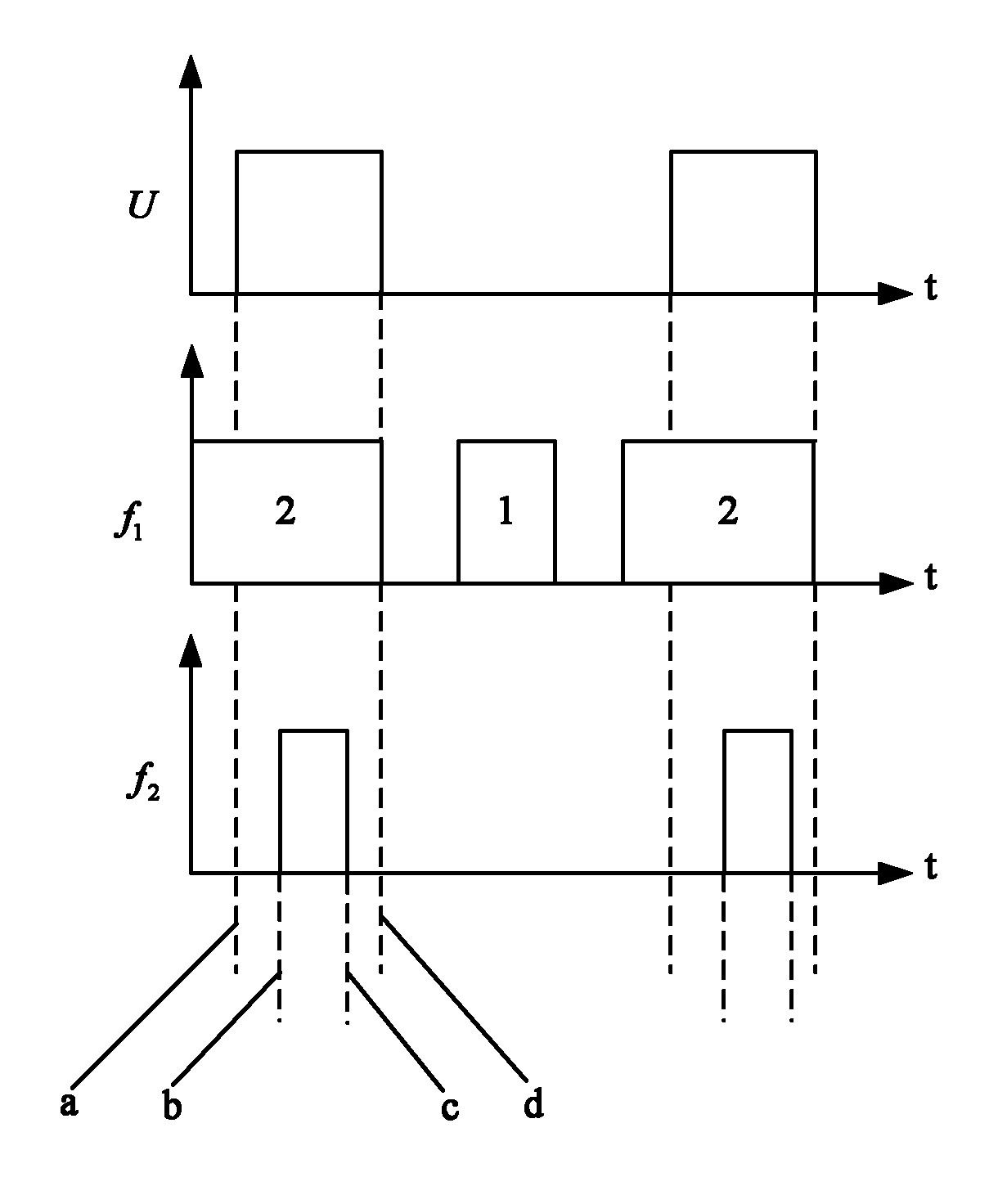
The invention discloses a method for reducing the optical frequency shift of a rubidium atomic frequency standard. The method comprises the following steps of: placing a filter between a spectrum lamp and an integrated filter resonance bubble; sending a coherent microwave probing signal to act on the integrated filter resonance bubble; and sending a voltage excitation signal to act on the spectrum lamp for controlling the working state of the spectrum lamp. The method can reduce the optical frequency shift of the rubidium atomic frequency standard so as to improve the accuracy of an output frequency of the rubidium atomic frequency standard.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
Standard sample wafer for microwave probe calibration
ActiveCN105068031AImprove accuracySolve the problem of inaccurate standard valuesElectrical measurementsUltrasound attenuationComputational physics
The invention provides a standard sample wafer for microwave probe calibration. The standard sample wafer comprises a balanced-bridge module having customized attenuation or standing wave values. The standard sample wafer eliminates resistivity sigma having larger uncertainty of measurement due to the adoption of a balanced-bridge structure, so that the design result can accord with the actual measurement result well; and the balanced-bridge structure also helps to eliminate standing-wave ratio error caused by L and W tolerance due to process zooming, thereby improving accuracy of the standard value of the standard sample wafer greatly, and solving the problem of inaccuracy of the standard value of the standard sample wafer in the prior art.
Owner:工业和信息化部电子工业标准化研究院
Method for testing ferromagnetic resonance linewidth in-plane distribution of magnetic material and system thereof
InactiveCN106872917AEnhanced microwave magnetic fieldEnhanced return signalMagnetic property measurementsMaterial analysis by using resonanceOptical testMaterials testing
The invention discloses a method for testing ferromagnetic resonance linewidth in-plane distribution of magnetic material and a system thereof, and relates to the technical field of magnetic material parameter testing. The disadvantages in the prior art that a microwave magnetic field formed by a microwave probe tip in magnetic material testing is weak can be overcome. The microwave magnetic field formed by the microwave probe tip in the magnetic material is enhanced and a vector network analyzer is enabled to acquire a stronger return signal so as to be used for testing the ferromagnetic resonance linewidth of a thinner magnetic film. The uniformity of the magnetic film can be further reflected by analyzing the difference of the ferromagnetic resonance linewidth of each area of the magnetic film sample so that the method has the advantages of being rapid and simple and convenient in comparison with the conventional optical test method.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
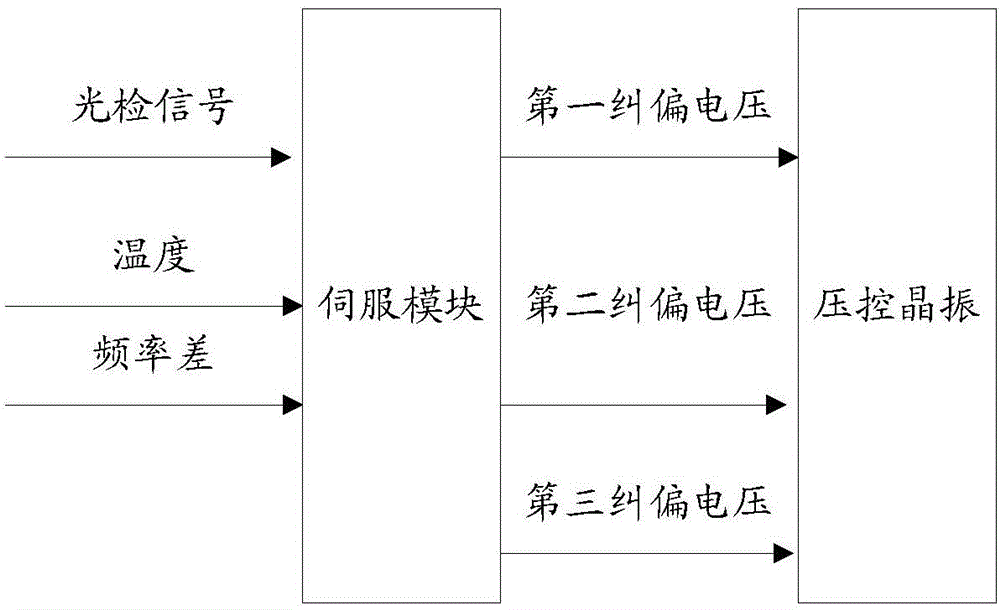
Control method for time standard equipment and time standard equipment
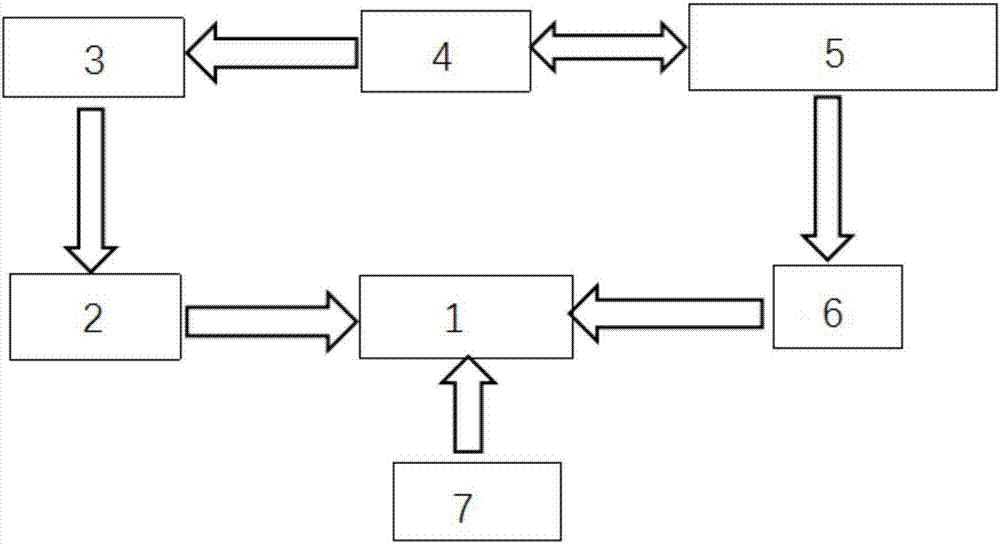
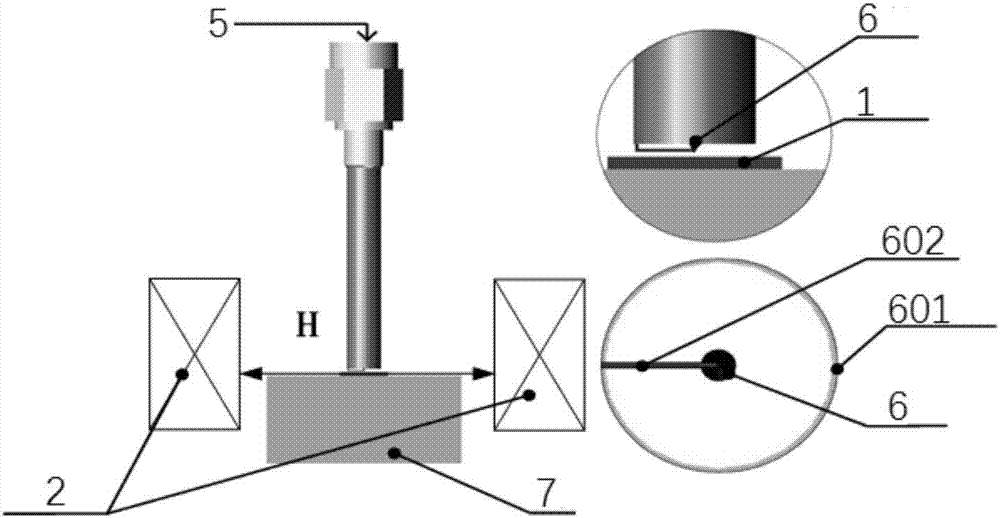
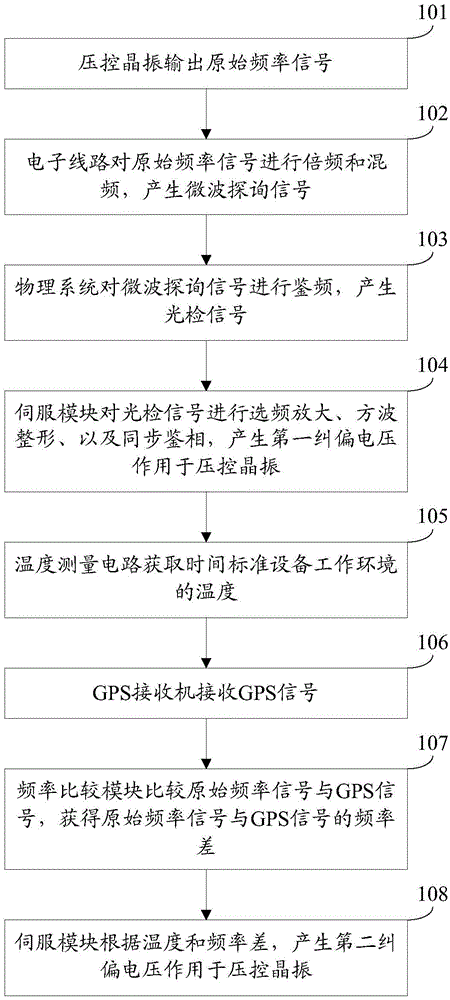
ActiveCN104485948AOutput frequency changePulse automatic controlRadio-controlled time-piecesPhysical systemEngineering
The invention discloses a control method for time standard equipment and the time standard equipment and belongs to the time standard technology field. The method comprises steps that, an original frequency signal is outputted by a voltage controlled crystal oscillator; frequency multiplication and frequency mixing of the original frequency signal are carried out by an electronic line to generate a microwave probing signal; frequency demodulation of the microwave probing signal is carried out by a physics system to generate a light detection signal; frequency selection amplification, square wave shaping and synchronization phase demodulation of the light detection signal are carried out by a servo module to generate a first error correcting voltage which acts on the voltage controlled crystal oscillator; the work environment temperature of the time standard equipment is acquired by a temperature measuring circuit; a GPS signal is received by a GPS receiver; the original frequency signal is contrasted with the GPS signal by a frequency contrasting module to acquire frequency difference of the original frequency signal and the GPS signal; a second error correcting voltage which is generated by the servo module according to the temperature and the frequency difference acts on the voltage controlled crystal oscillator. According to the control method, the output frequency of the voltage controlled crystal oscillator does not generate large-scope change caused by temperature change.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
Device and method for measuring phase spectrum of comb-shaped spectrum generator
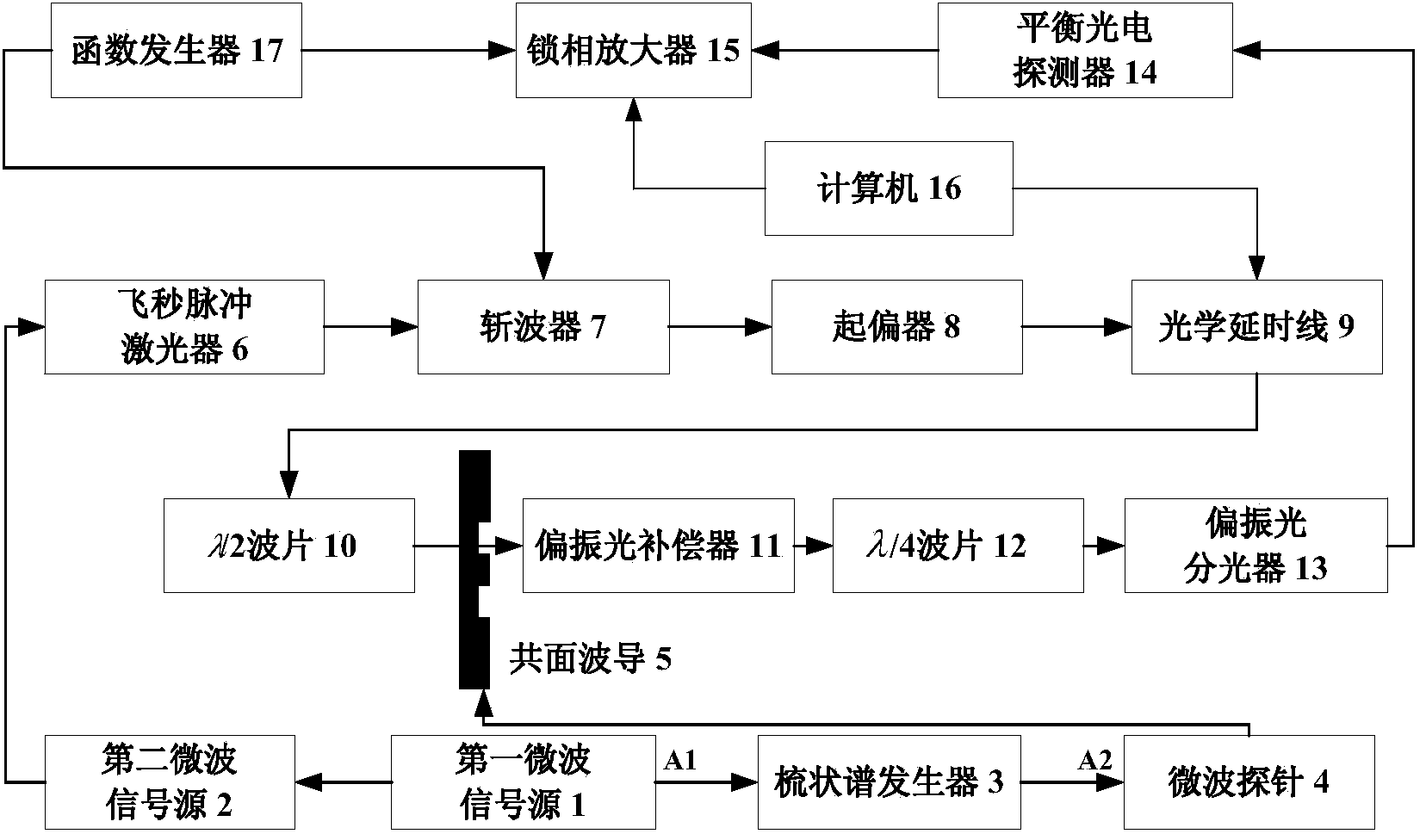
ActiveCN103529296ALess correction processingThe traceability chain is completeSpectral/fourier analysisVoltage-current phase angleCoplanar waveguideFemtosecond pulsed laser
The invention relates to a device for measuring a phase spectrum of a comb-shaped spectrum generator. The device comprises a reference signal output end for outputting a first microwave signal and a signal input end for inputting a comb-shaped spectrum signal synchronized with a femtosecond pulse laser beam, and further comprises a first microwave signal source, a second microwave signal source, a GSG microwave probe, a coplanar waveguide, a femtosecond pulse laser, a wave chopper, a polarizer, an optical delay line, a lambda / 2 wave plate, a polarized light compensator, a lambda / 4 wave plate, a polarized light separator, a balanced photoelectric detector, a lock-in amplifier, a control and calculation unit and a function generator. The device has the following advantages: the time-domain waveform of the comb-shaped spectrum generator can be accurately measured based on the photoelectric technology, so that the phase spectrum of the comb-shaped spectrum generator is obtained. The device can theoretically measure the comb-shaped spectrum generator with 110 GHz of band width, and has the advantages such as little correction processing and complete tracing chain compared with the traditional method for measuring the phase spectrum of the comb-shaped spectrum generator.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF RADIO METROLOGY & MEASUREMENT
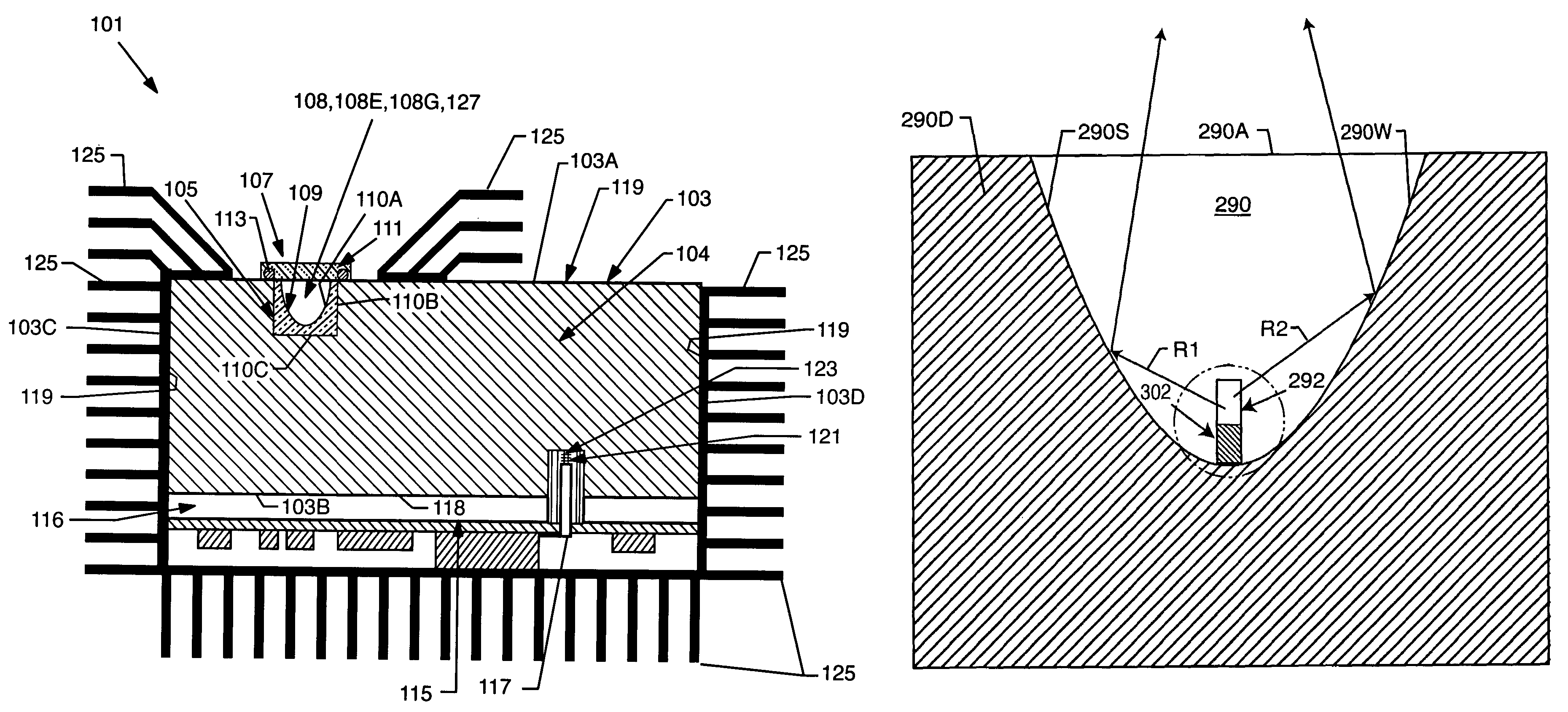
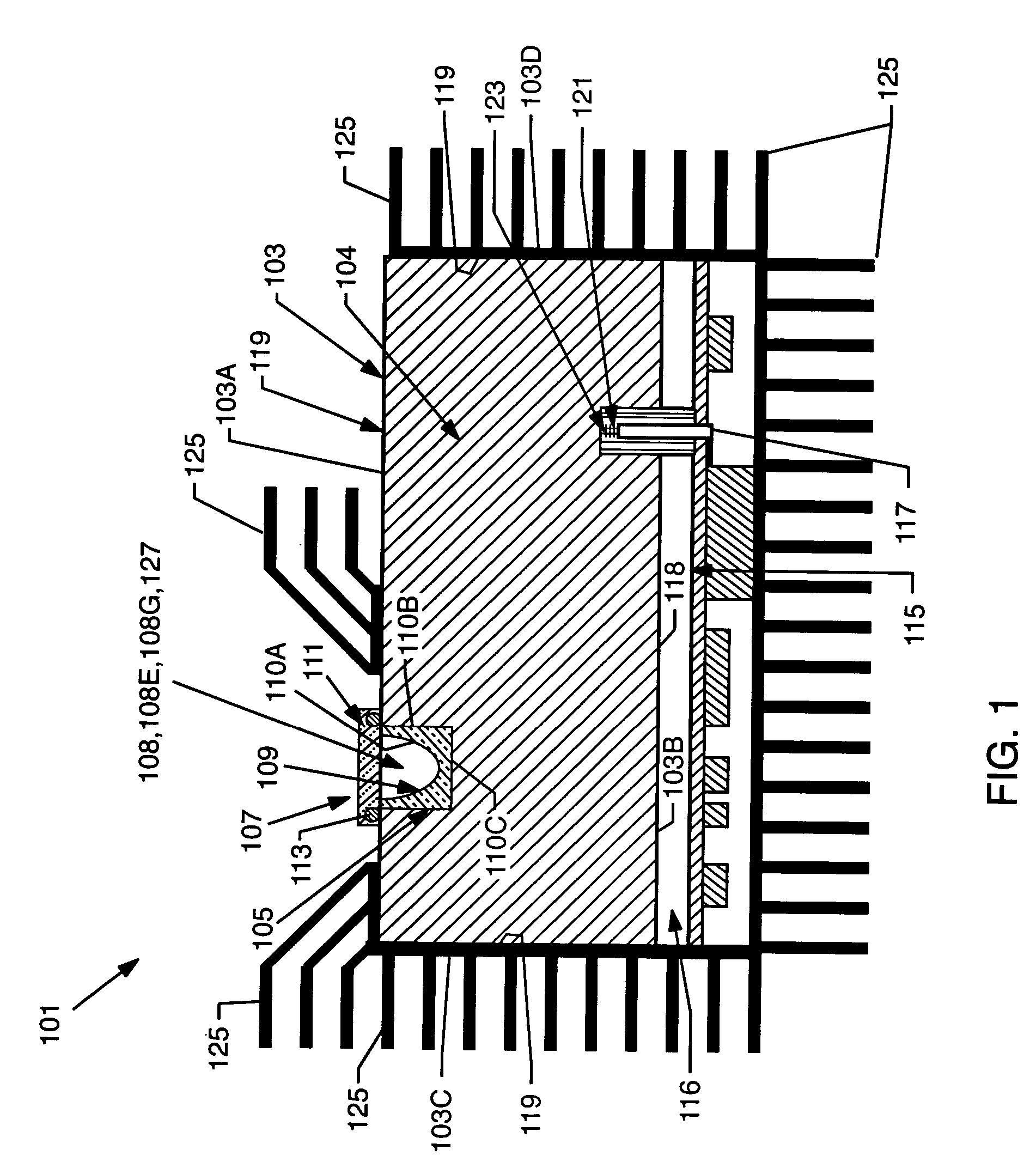
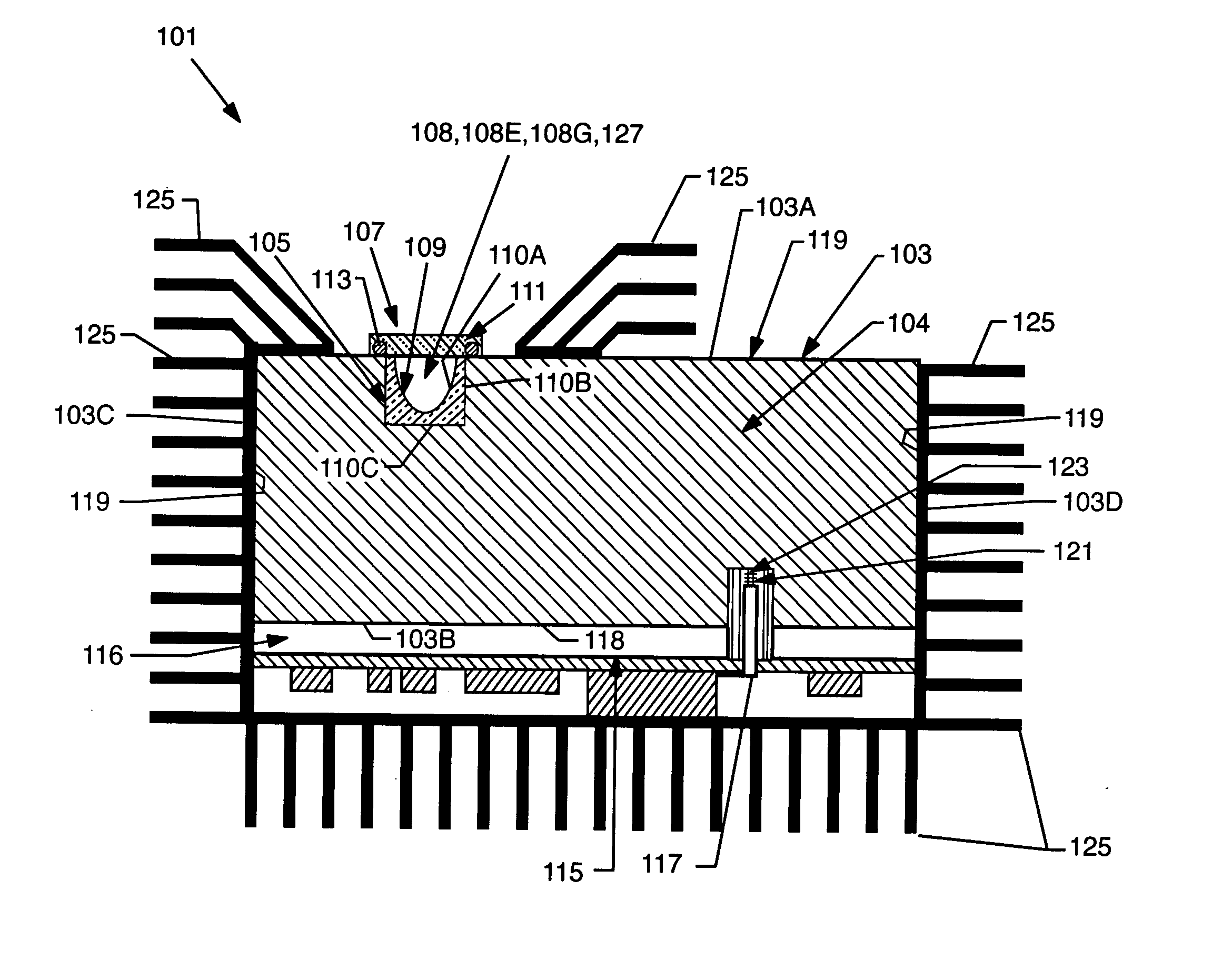
Method and structure for variable pitch microwave probe assembly
InactiveUS7161344B2Simplify the optimization processReduce inventory costsElectrical measurement instrument detailsElectrical testingCoplanar waveguideEngineering
A coplanar waveguide (CPW) probe includes at least one center probe element, each having a respective center probe contact point and at least one peripheral probe element, each having a respective peripheral contact point. The pitch between the at least one center contact point and the at least one peripheral contact point is adjustable.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Method and system for measurement of sidewall damage in etched dielectric structures using a near field microwave probe
InactiveUS20060087305A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementResistance/reactance/impedenceCapacitanceComputational physics
By using techniques for near field probes to measure dielectric values of blanket films, the measure of the sidewall damage of the patterned structure is calculated. The interaction between the near field probe and the etched structure is modeled to obtain the model total capacitance. The near field microwave probe is calibrated on a set of blanket films with different thicknesses, and the dielectric constant of the etched trench structure is calculated using the measured frequency shift and calibration parameters. The measured capacitance is further calculated for the etched trench structure using the dielectric constant and the total thickness of the etched trench structure. The effective dielectric constant of the structure under study is extracted where the model capacitance is equal to the measured capacitance. The measure of the sidewall damage is further calculated using the effective dielectric constant.
Owner:SEMICON PHYSICS LAB
Electric control impedance deploying chip based on radio frequency micro electro mechanical structure and microwave system
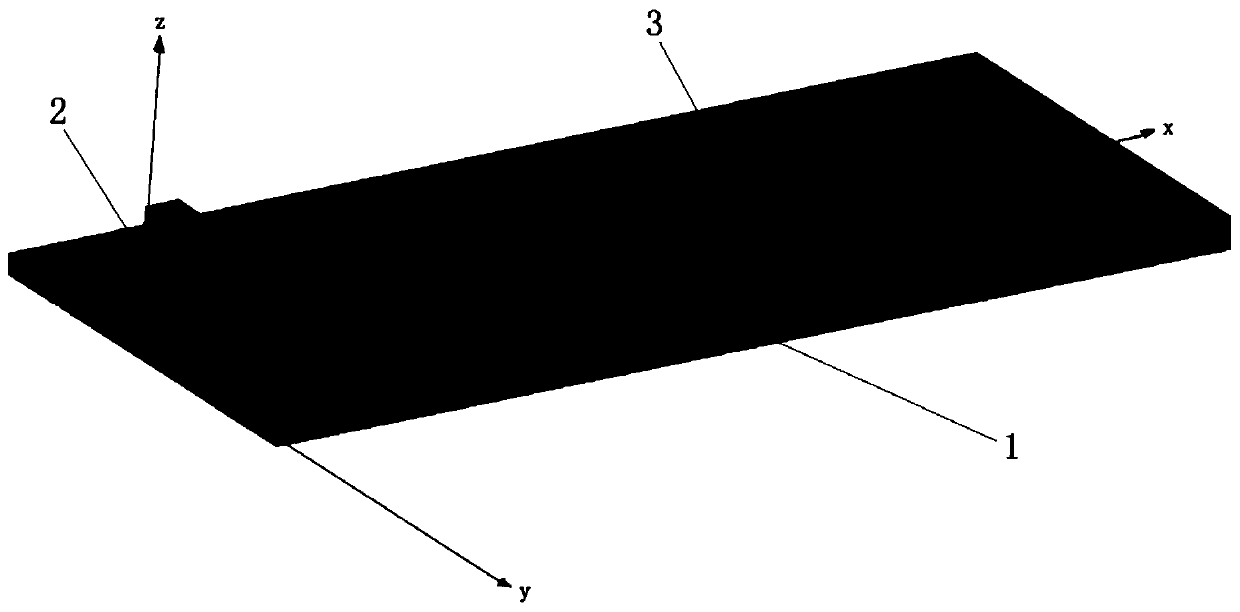
PendingCN110768643AEfficient deploymentEasy to integrateImpedence networksCoupling devicesMiniaturizationMicro motor
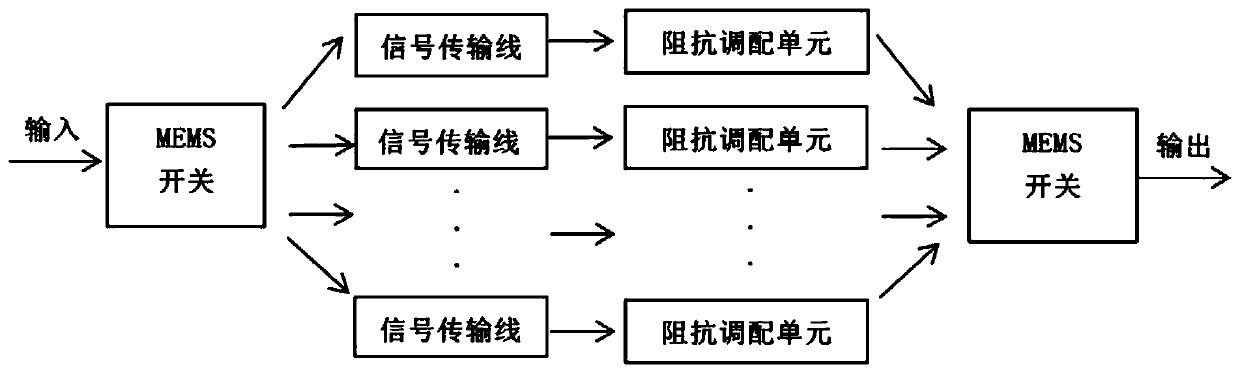
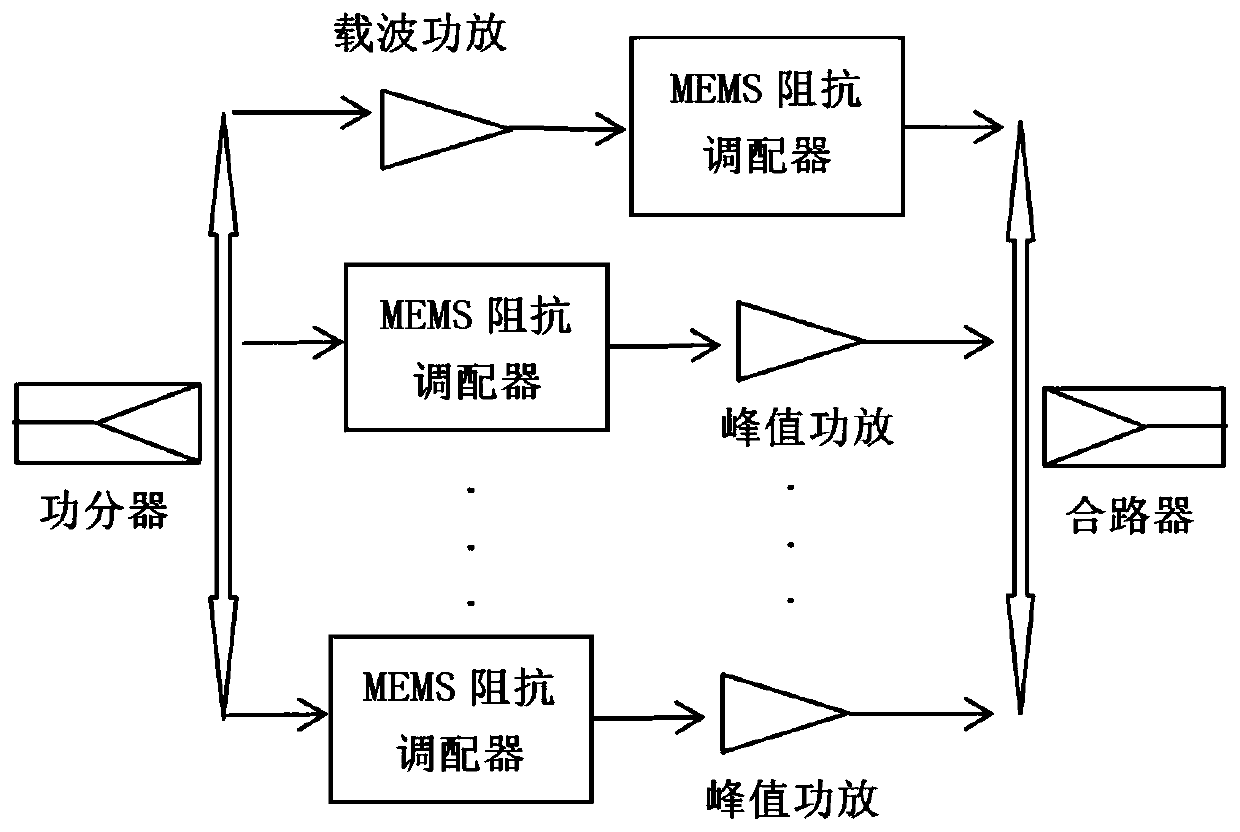
The invention discloses an electric control impedance deploying chip based on a radio frequency micro electro mechanical system (RF-MEMS) structure. The electric control impedance deploying chip comprises a chip substrate and an MEMS impedance deployer, and is characterized in that the MEMS impedance deployer is designed and manufactured on the chip substrate; the MEMS impedance tuner comprises amotor type impedance tuner or a switch type impedance tuner; the motor type impedance tuner comprises a micro electro mechanical device and a central conductor; the micro electro mechanical device comprises a micro motor with a radio frequency micro electro mechanical structure and a microwave probe; and the micro motor drives the microwave probe to move in the axial direction of the central conductor or in the vertical direction of the central conductor. The invention further provides an electronic control impedance deploying microwave system based on the radio frequency micro electro mechanical system structure. A typical application case comprises a power amplifier and a receiving and transmitting module. Due to the design, the integration and miniaturization of the microwave system with the impedance tuner structure are realized, and the working bandwidth and multi-channel adaptability of the MEMS impedance tuner system are improved, and the reliability of a working temperature zone is enhanced.
Owner:成都挚信电子技术有限责任公司
Pico-second superfast electrical property testing system for semiconductor device
ActiveCN106054054AIntegrity guaranteedIndividual semiconductor device testingEngineeringPulse sequence
The invention discloses a pico-second superfast electrical property testing system for a semiconductor device. The system is composed of a waveform processor, a broadband voltage amplifier, a broadband voltage bias device, a broadband pick-up three-way device, a first microwave probe and a second microwave probe. The system is characterized in that a pico-second pulse sequence waveform is applied to an electronic device, so that the electronic device is in an actual working environment like a CPU and thus electrical characteristics of the electronic device in the CPU at a practical switching speed of a 100-pS level are tested. The system is applied to electrical characteristic researches of a high-performance planar transistor using silicon, germanium or an III-V-group compound as a carrier subchannel and a fin type three-dimensional gate structure type or GAA structure type field effect transistor.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Analytical scanning evanescent microwave microscope and control stage
InactiveUS20060231756A1Faster data acquisitionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationNanoopticsDielectricHigh resolution imaging
A scanning evanescent microwave microscope (SEMM) that uses near-field evanescent electromagnetic waves to probe sample properties is disclosed. The SEMM is capable of high resolution imaging and quantitative measurements of the electrical properties of the sample. The SEMM has the ability to map dielectric constant, loss tangent, conductivity, electrical impedance, and other electrical parameters of materials. Such properties are then used to provide distance control over a wide range, from to microns to nanometers, over dielectric and conductive samples for a scanned evanescent microwave probe, which enable quantitative non-contact and submicron spatial resolution topographic and electrical impedance profiling of dielectric, nonlinear dielectric and conductive materials. The invention also allows quantitative estimation of microwave impedance using signals obtained by the scanned evanescent microwave probe and quasistatic approximation modeling. The SEMM can be used to measure electrical properties of both dielectric and electrically conducting materials.
Owner:INTEMATIX
Feeding Structure for Dual Slot Microwave Ablation Probe
ActiveUS20130267940A1Improves SAR iso-contourSurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingEngineeringTissue ablation
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Analytical scanning evanescent microwave microscope and control stage
InactiveUS20090302866A1Faster data acquisitionResistance/reactance/impedenceNanoopticsDielectricElectricity
A scanning evanescent microwave microscope (SEMM) that uses near-field evanescent electromagnetic waves to probe sample properties is disclosed. The SEMM is capable of high resolution imaging and quantitative measurements of the electrical properties of the sample. The SEMM has the ability to map dielectric constant, loss tangent, conductivity, electrical impedance, and other electrical parameters of materials. Such properties are then used to provide distance control over a wide range, from to microns to nanometers, over dielectric and conductive samples for a scanned evanescent microwave probe, which enable quantitative non-contact and submicron spatial resolution topographic and electrical impedance profiling of dielectric, nonlinear dielectric and conductive materials. The invention also allows quantitative estimation of microwave impedance using signals obtained by the scanned evanescent microwave probe and quasistatic approximation modeling. The SEMM can be used to measure electrical properties of both dielectric and electrically conducting materials.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Microwave scanning detection method of polyethylene pipeline electric smelting joint
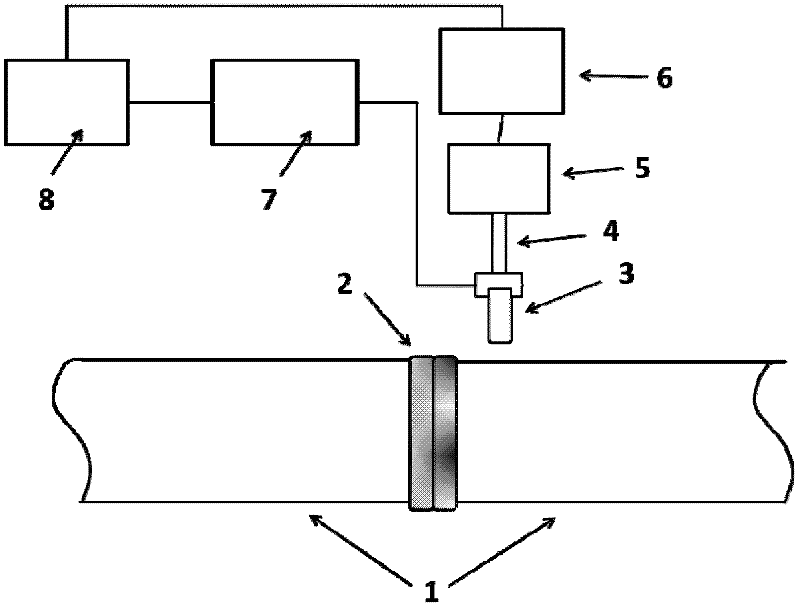
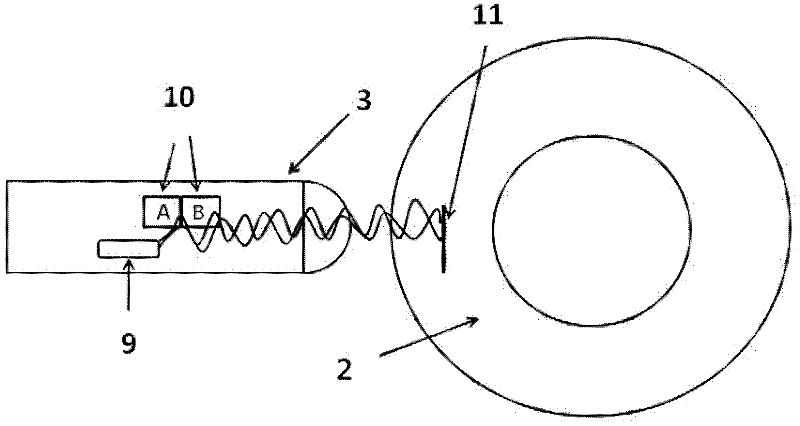
InactiveCN102401804AReliable detectionSolve pollutionFlaw detection using microwavesElectricityRelevant information
The invention relates to the field of detection of a pressure pipeline, in particular to a microwave scanning method of a polyethylene pipeline electric smelting joint, which comprises the steps of: detecting the polyethylene pipeline electric smelting joint by using a microwave scanning device, emitting microwaves to the joint to be detected by an emitter in a microwave probe, recording base line amplitudes by the microwaves through two receiving sensors, then penetrating through the surface of the joint to enter the inner part of the joint, when the travelling microwaves meet the defect, enabling the microwaves to generate reflection by the change of a dielectric constant; and generating interference by the reflected microwave signals and the emitted microwave signals, receiving by the receiving sensor and converting into a voltage signal, inputting to a computer after the voltage signal and scanning position information pass through a signal conversion system to obtain a scanning image, and obtaining relevant information of the defect in the electric smelting joint according to the scanning image. The detection method has the advantages of capability of detecting multiple types of defects, high detection sensitivity and precision, good reliability and the like, and can be especially used for effectively detecting process defects such as cold welding and the like, is convenient for operation, and has lower cost.
Owner:嘉兴市特种设备检验检测院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com