Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
112 results about "Perpendicular magnetic field" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
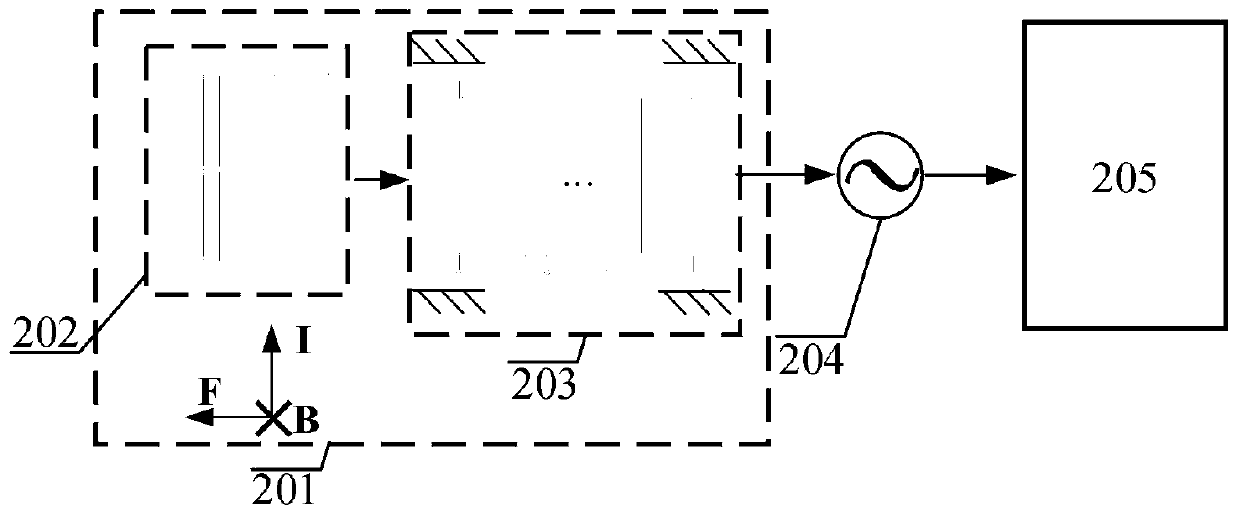
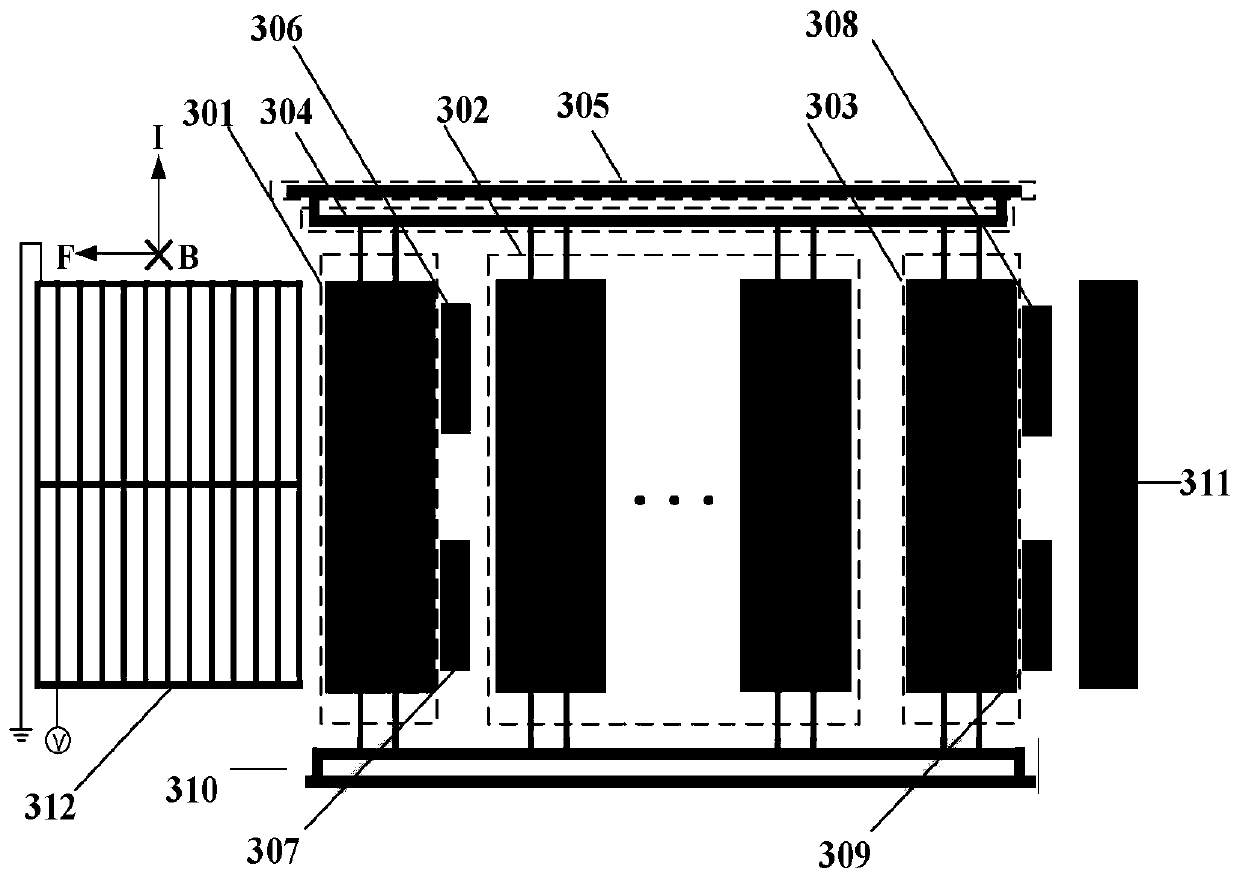
A magnetic field is perpendicular to the plane of a single-turn circular coil.
Magnetic sensor
ActiveUS20120200292A1Simple configurationLow costNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsMagnetizationPerpendicular magnetic field
A magnetic sensor includes magnetoresistive elements and a soft magnetic body. The magnetoresistive elements have multi layers including a magnetic layer and a nonmagnetic layer on a substrate, and exert a magnetoresistance effect. The soft magnetic body is electrically disconnected with the magnetoresistive elements, and converts a vertical magnetic field component from the outside into a magnetic field component in a horizontal direction so as to provide the magnetoresistive elements with the horizontally converted magnetic field component. The magnetoresistive elements have a pinned magnetic layer having a fixed magnetization direction and a free magnetic layer having a variable magnetization direction. The free magnetic layer is stacked on the pinned magnetic layer with a nonmagnetic layer interposed between the free magnetic layer and the pinned magnetic layer. The magnetization directions of the pinned magnetic layers of the magnetoresistive elements are the same direction. The magnetoresistive elements form a bridge circuit.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Device for hybrid plasma processing
InactiveUS6899054B1Add deviceElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas passingPerpendicular magnetic field
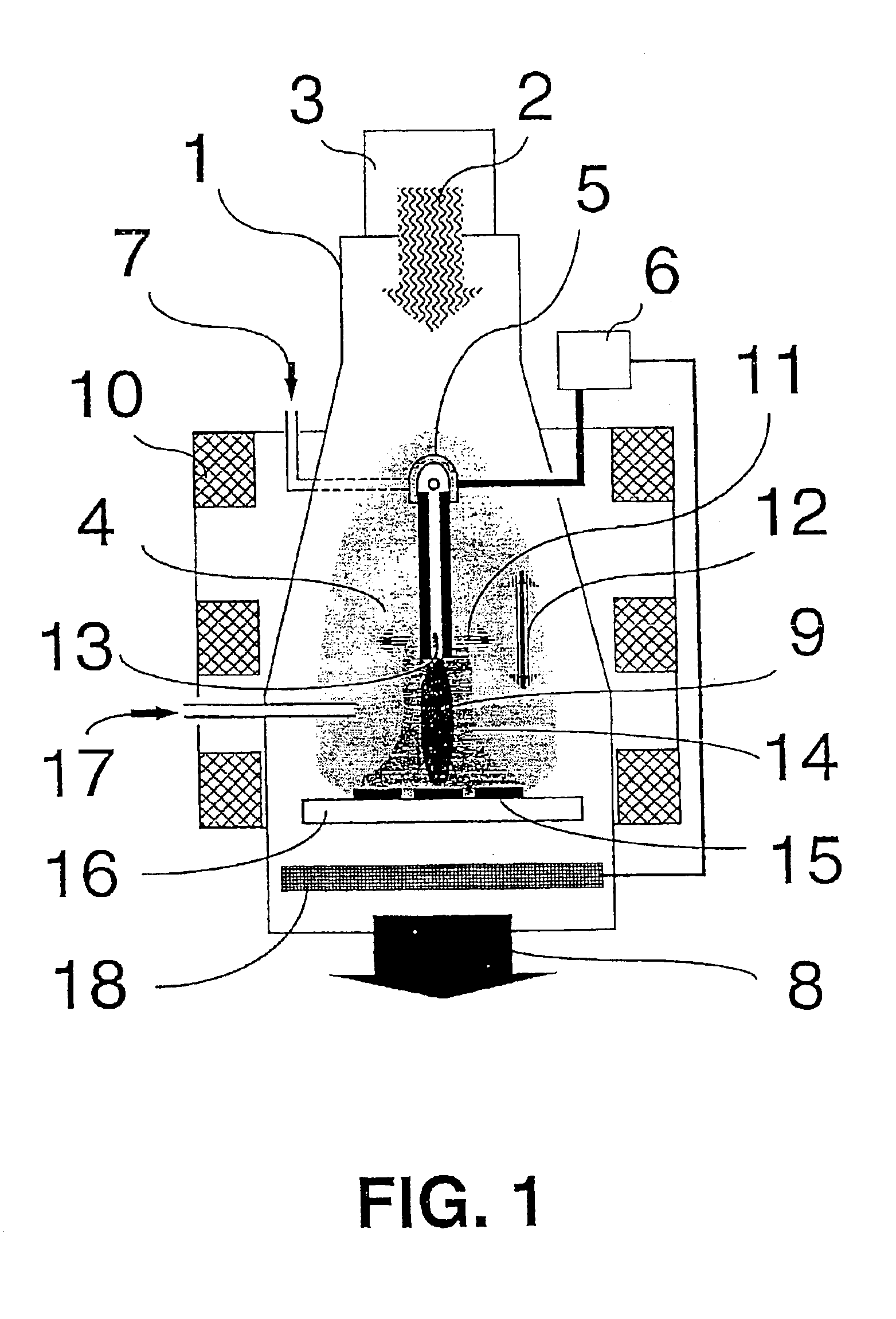
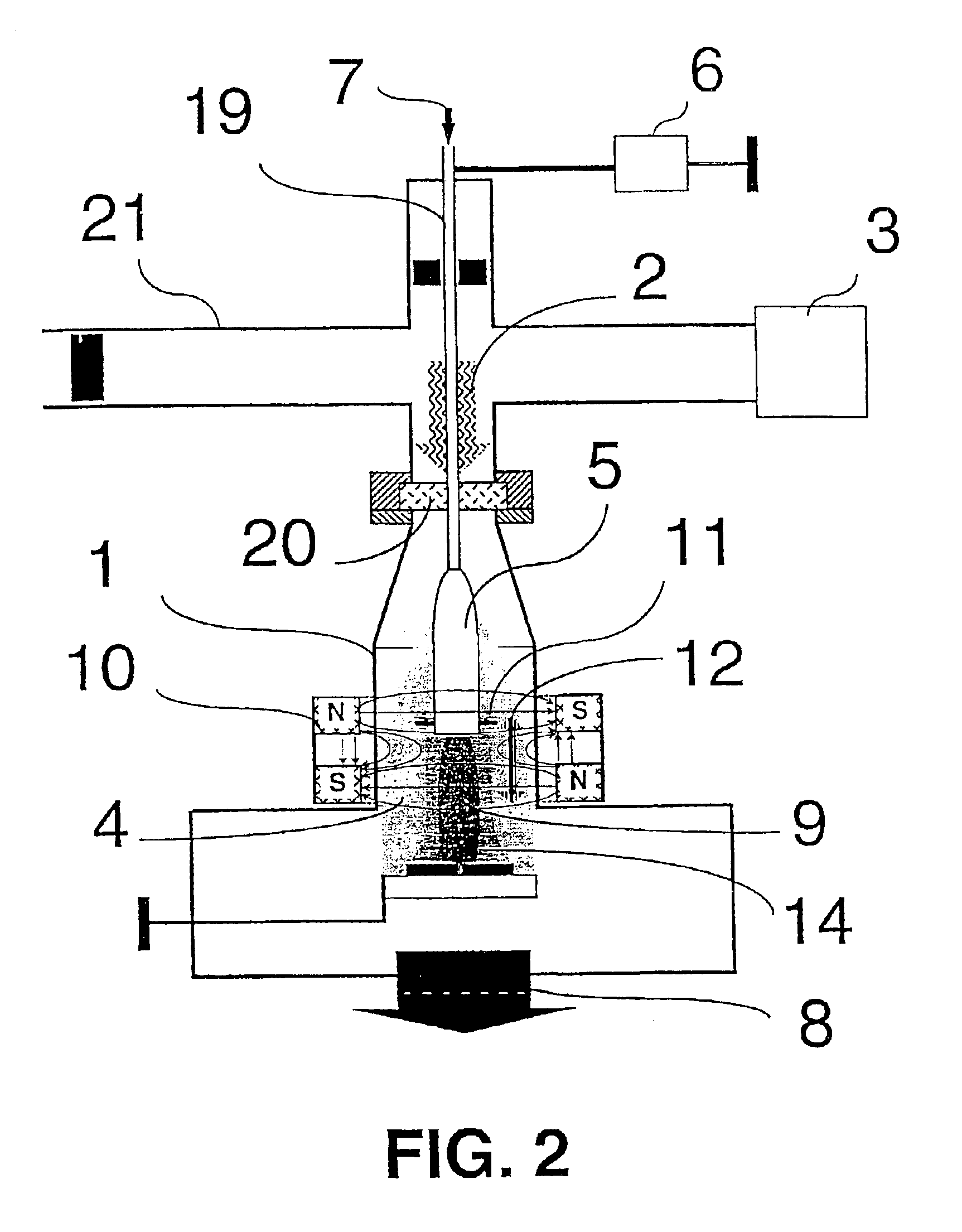
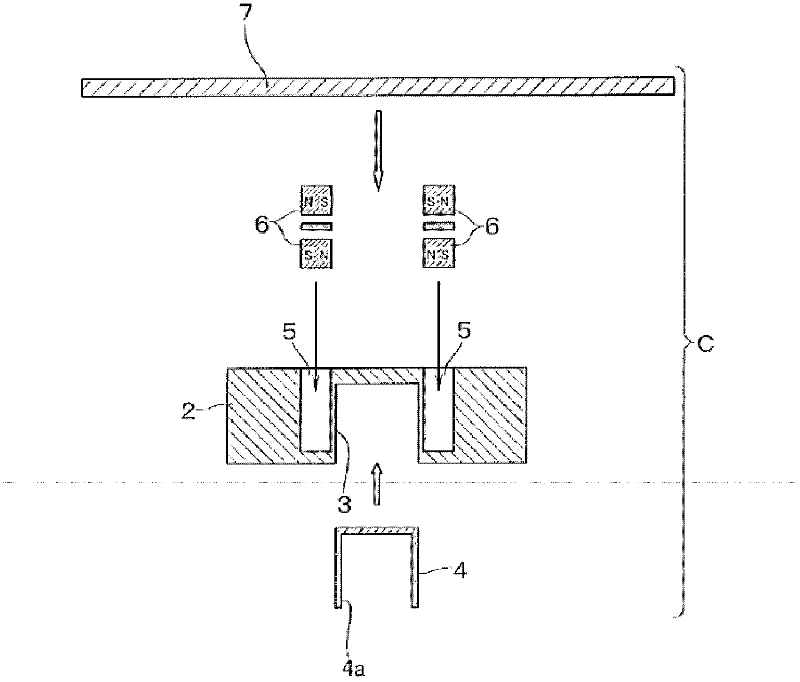
A device for hybrid plasma processing, particularly for deposition of thin films and for plasma treatment of samples, in a plasma reactor with pumping system characterized in that at least one feeder of microwave power (2) is installed in the plasma reactor (1) and connected to a microwave generator (3) for generation of a microwave plasma (4) in contact with at least one hollow cathode (5) in the plasma reactor, where the hollow cathode is powered from a cathode power generator (6). At least one inlet for a processing gas (7) is installed behind the hollow cathode and the gas is admitted into the plasma reactor through the hollow cathode where a hollow cathode plasma (9) is generated. A magnetic element (10) is used for generation of a perpendicular magnetic field (11) and / or a longitudinal magnetic field (12) at an outlet (13) from the hollow cathode.
Owner:BARDOS LADISLAV +1
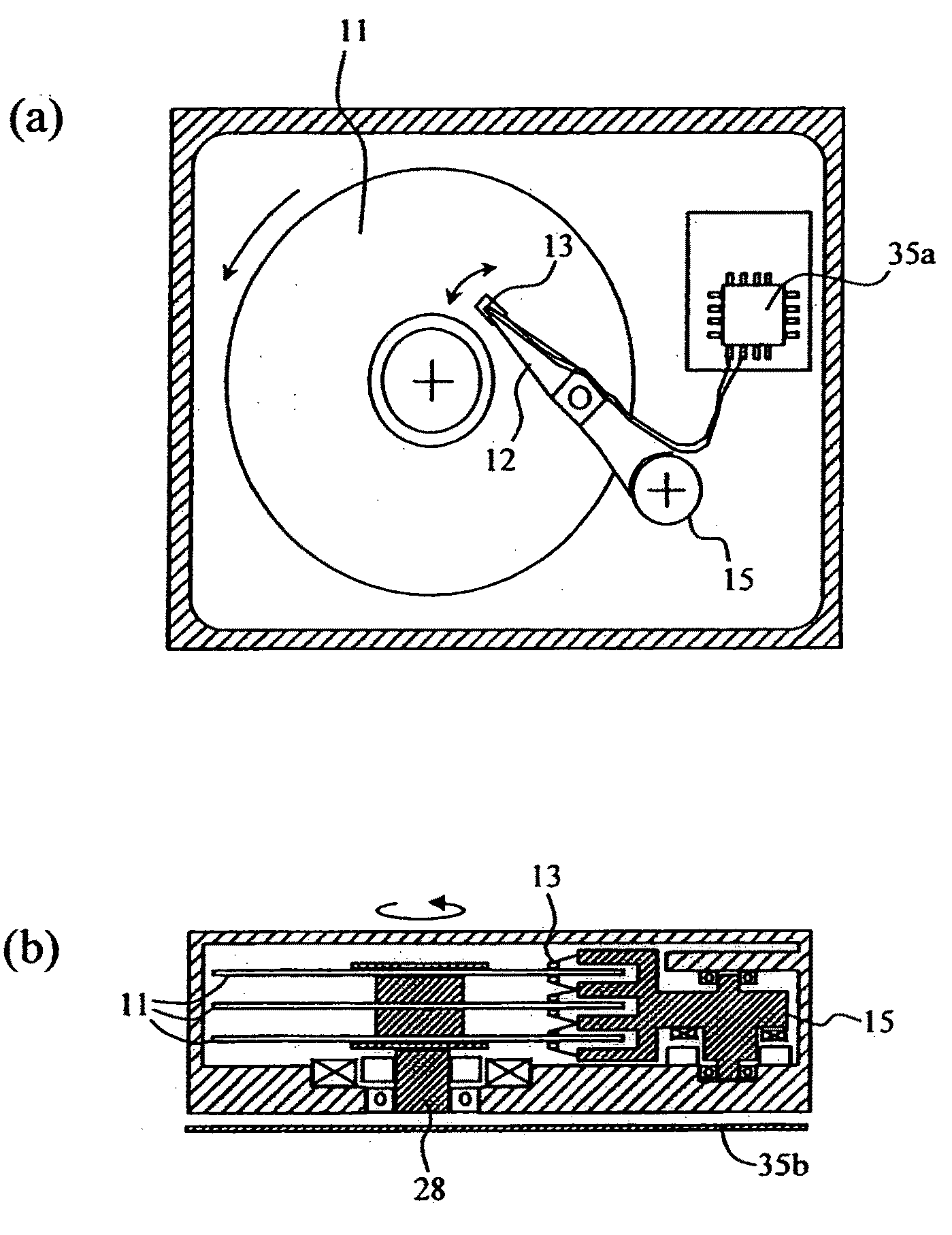
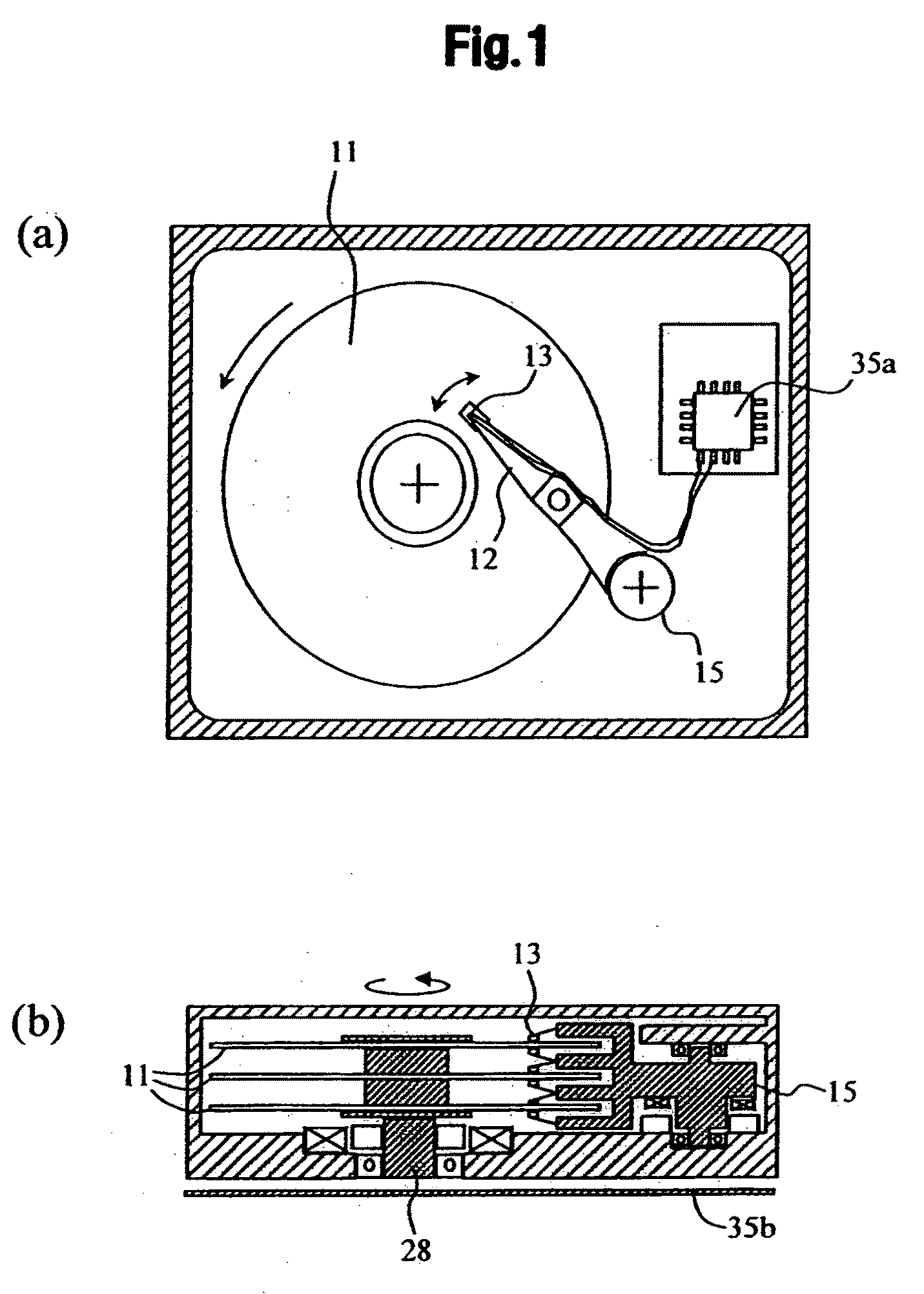
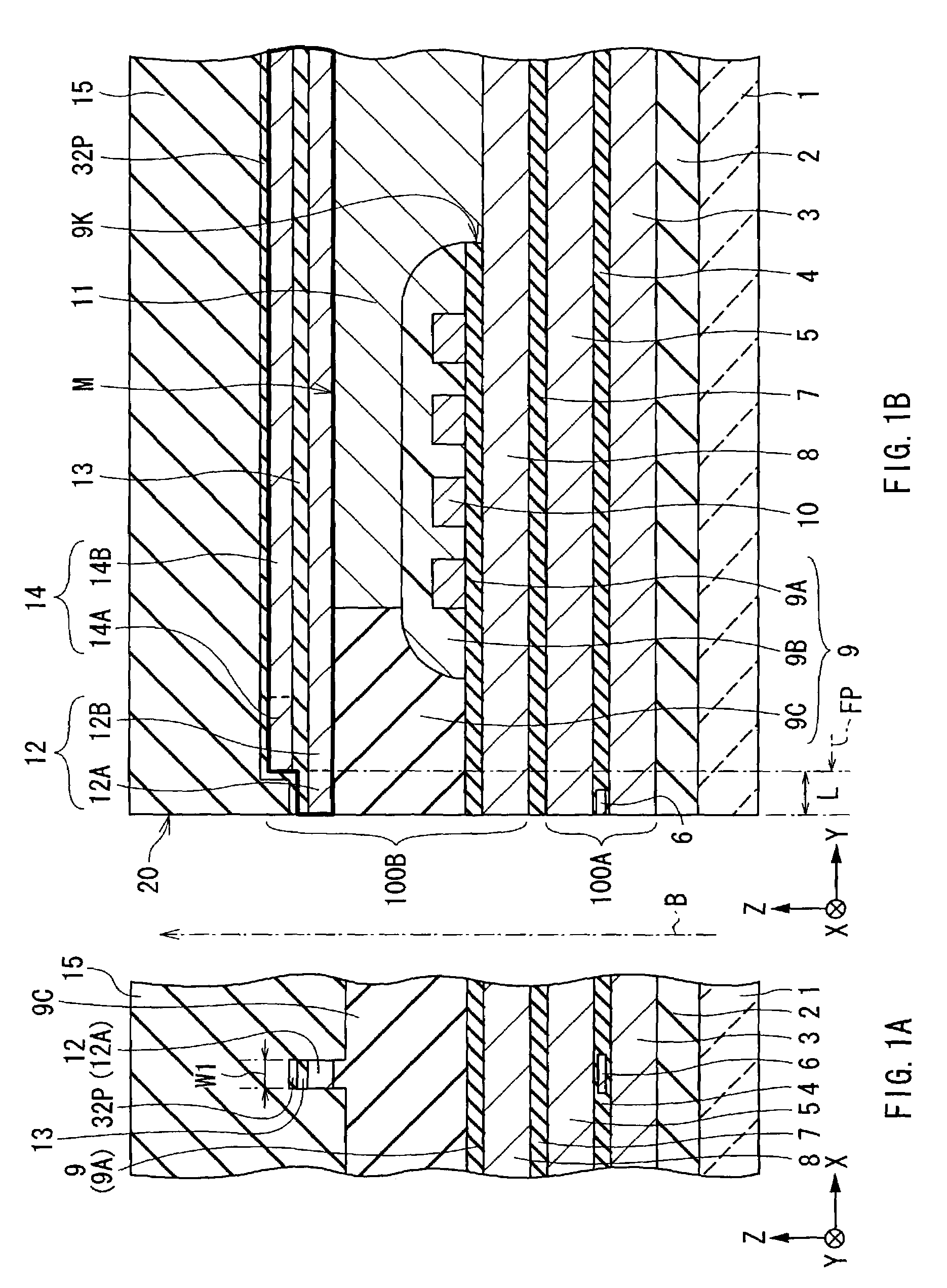
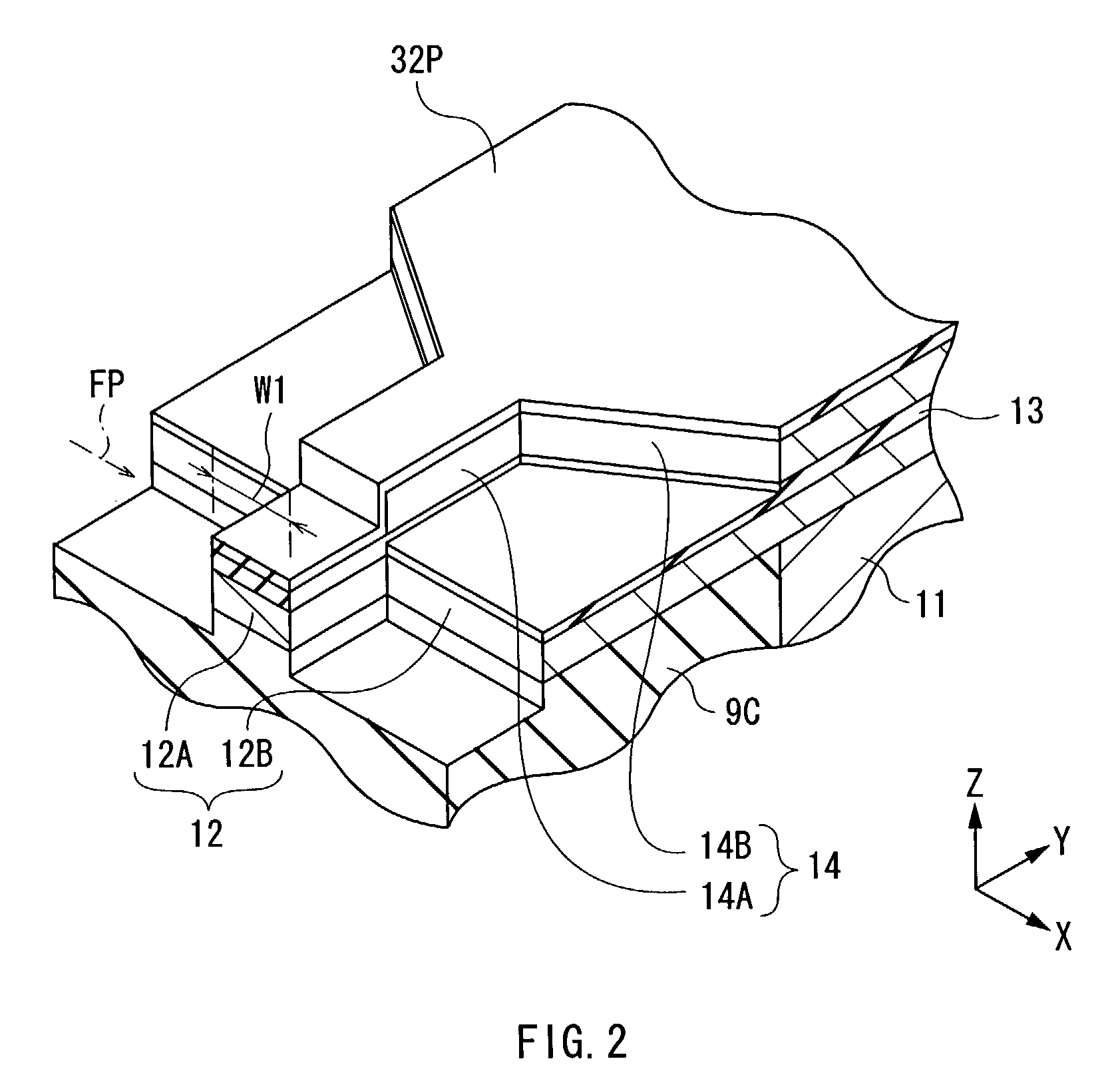
Thin film magnetic head and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS6952325B2Improve recording effectEasy to manufactureManufacture head surfaceHeads using thin filmsMagnetic polesPerpendicular magnetic field
Provided is a thin film magnetic head capable of ensuring the strength of a perpendicular magnetic field and improving recording performance. A bottom pole portion layer and a top pole portion layer constituting a part of a main magnetic pole are formed so that a cross sectional area of a complex including front end portions of the bottom pole portion layer and the top pole portion layer is smaller than a cross sectional area of a complex including rear end portions thereof, and a width of a top edge in an exposed surface is larger than a width of a bottom edge, and is equal to or larger than a width of the exposed surface in a middle position between the top edge and the bottom edge. In recording, magnetic fluxes flowing in a main magnetic pole are focused toward an air bearing surface, and are concentrated on the front end portion of the top pole portion layer which is a main emitting portion of the magnetic fluxes, so sufficient magnetic fluxes can be supplied to the air bearing surface.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Coil System Comprising Eccentrically Coiled Magnetic Substance
InactiveUS20090066466A1Loop antennas with ferromagnetic coreElectromagnets without armaturesPerpendicular magnetic fieldEngineering
The present invention provides a coil system comprising an eccentrically coiled magnetic substance capable of exciting vertical magnetic field components in its center portion and preventing sensitivity of the coil system deteriorating in its center. In the coil system comprising a magnetic substance 6 and a coil 2, no coil is wound around a center portion of the magnetic substance 6, but a coil is wound around one end portion of the magnetic substance. When the coil system is mounted on a metal surface, it can excites vertical magnetic field components to the metal surface without deteriorating sensitivity in the center of a tag or sensor arranged above the coil system.
Owner:SMART CO LTD
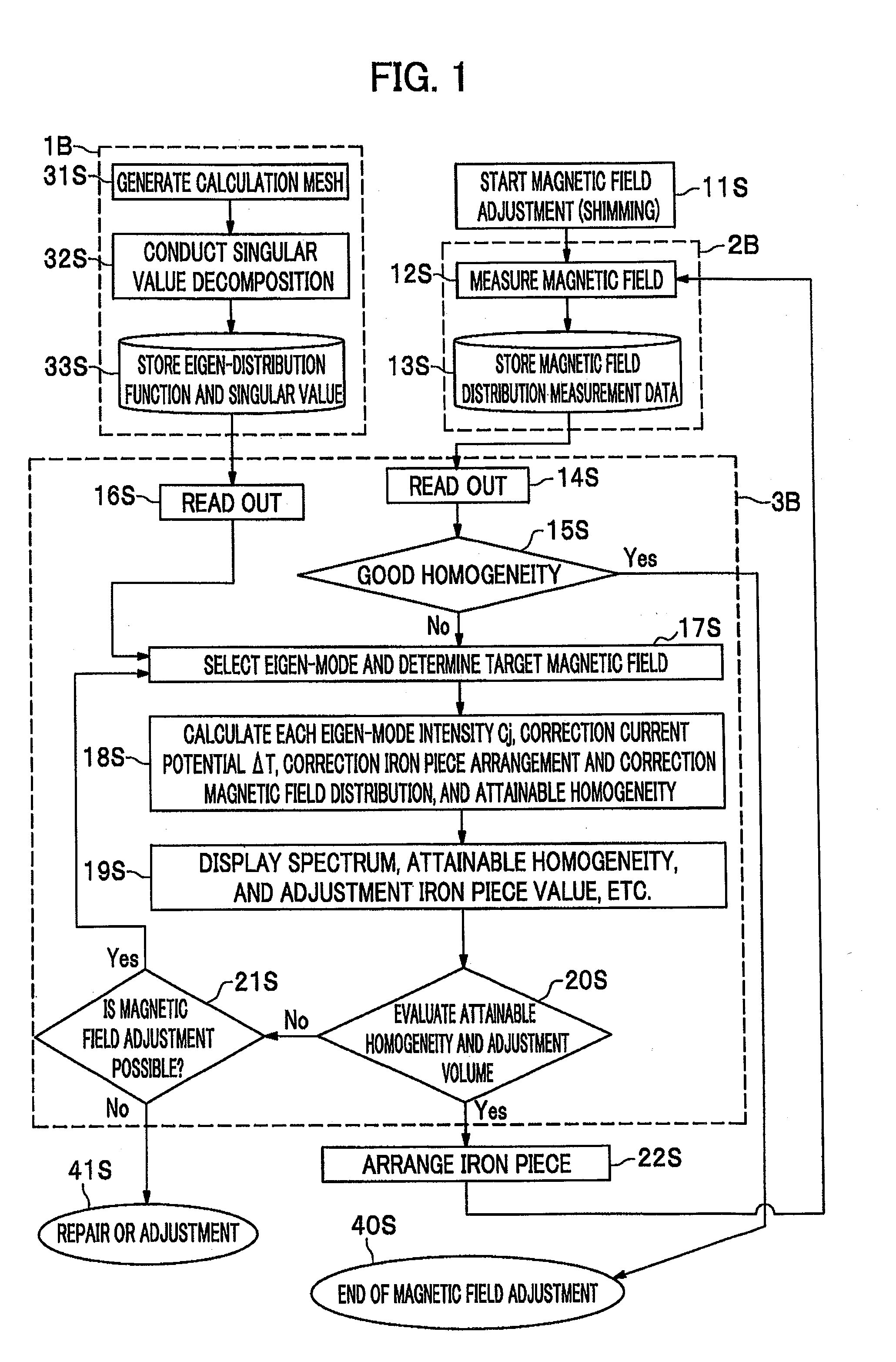
Magnetic field adjustment method for MRI device
InactiveUS20120268119A1Low costImprove accuracyElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRPerpendicular magnetic fieldMagnet device
An eigen-mode to be corrected is selected in accordance with an attainable magnetic field accuracy (homogeneity) and appropriateness of arranged volume of the iron pieces. Because the adjustment can be made with the attainable magnetic field accuracy (homogeneity) being grasped, an erroneous adjustment can be grasped, and the adjustment is automatically done during repeated adjustment. When the magnetic field adjustment is carried out with support by the method of the present invention according to the first and second embodiments or an apparatus including this method therein, the magnetic field adjustment can be surely completed. As a result, the apparatus with a high accuracy can be provided. In addition, there is an advantageous effect of earlier detection of a poor magnet by checking the attainable homogeneity. They are applicable to magnet devices for the horizontal magnetic field type, being an open type MRI, and vertical magnetic field type MRI.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
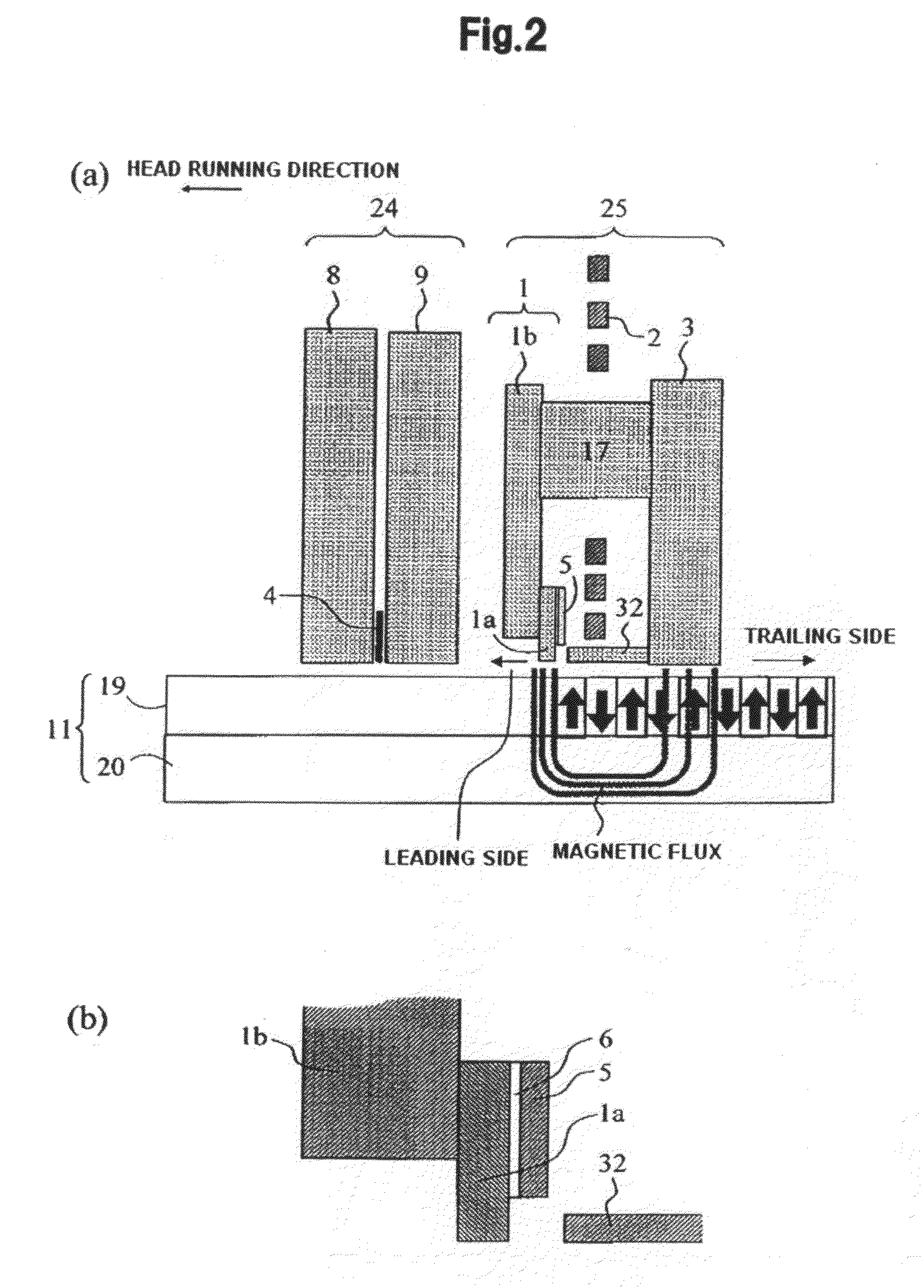
Magnetic head for perpendicular magnetic recording and method of manufacturing same
ActiveUS20070211377A1Protrusion suppressionSuppress the wide-range adjacent track eraseRecord information storageHeads for perpendicular magnetisationsCouplingPerpendicular magnetic field
A pole layer has an end face located in a medium facing surface, allows a magnetic flux corresponding to a magnetic field generated by a coil to pass therethrough, and generates a write magnetic field for writing data on a recording medium by means of a perpendicular magnetic recording system. A shield incorporates: a first layer having an end face located in a region of the medium facing surface forward of the end face of the pole layer along the direction of travel of the recording medium; a second layer disposed in a region sandwiching the pole layer with the first layer; a first coupling portion coupling the first layer to the second layer without touching the pole layer; and a second coupling portion coupling the pole layer to the second layer and located farther from the medium facing surface than the first coupling portion.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Perpendicular stt-mram having logical magnetic shielding
InactiveUS20140327096A1Low coercivityGrowth inhibitionGalvano-magnetic material selectionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBit lineDielectric
A perpendicular STT-MRAM comprises apparatus and a method of manufacturing a plurality of magnetoresistive memory element having local magnetic shielding. As an external perpendicular magnetic field exists, the permeable dielectric layers, the permeable bit line and the permeable bottom electrode are surrounding and have capability to absorb and channel most magnetic flux surrounding the MTJ element instead of penetrate through the MTJ element. Thus, magnetization of a recording layer can be less affected by the stray field during either writing or reading, standby operation.
Owner:GUO YIMIN
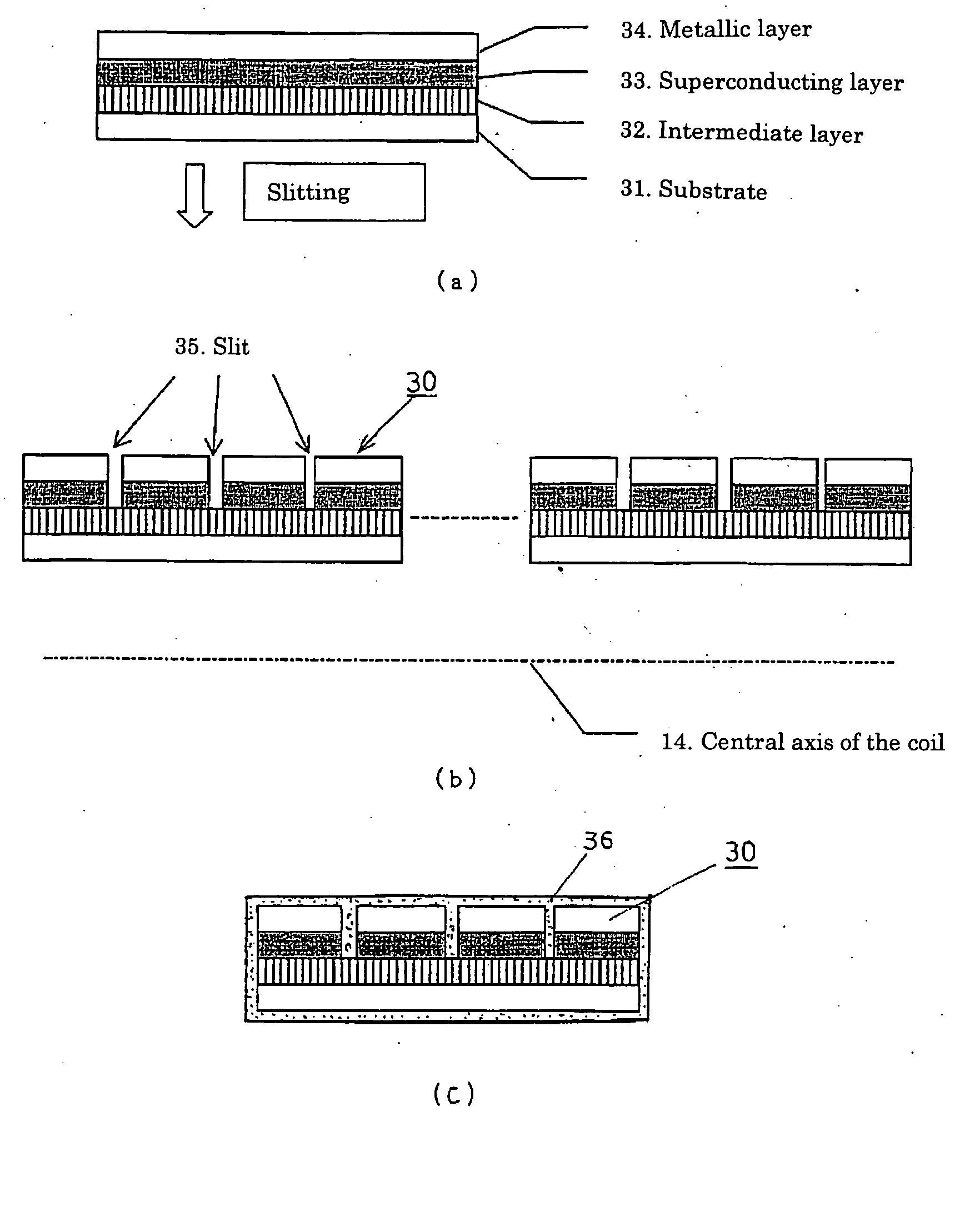
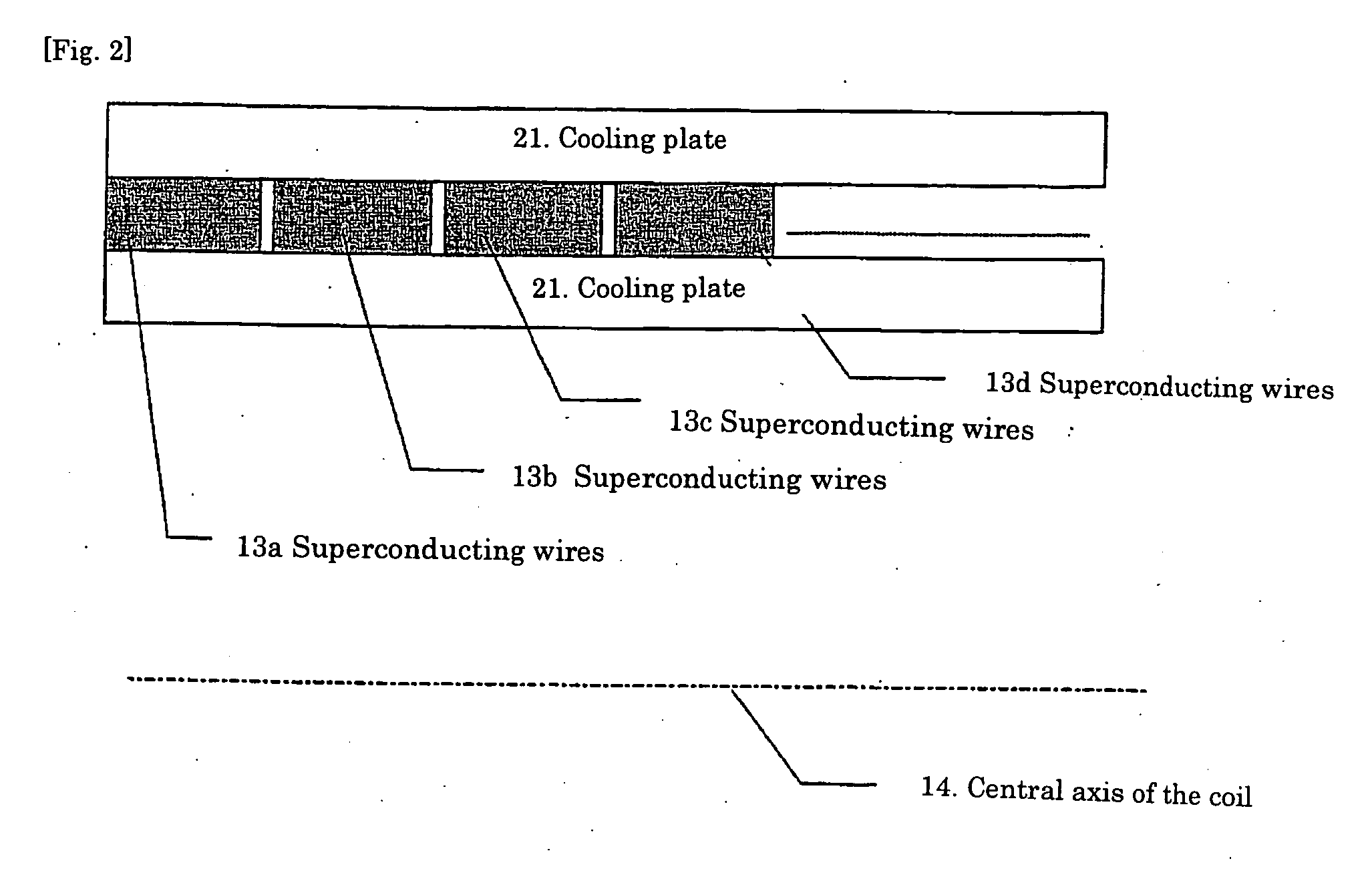
Superconducting wire and superconducting coil employing it
ActiveUS20060077025A1Improve thermal stabilityReduce operating costsSuperconductors/hyperconductorsTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsElectrical conductorBand shape
Tape-shaped superconducting wires are made by forming a superconducting film on the substrate. At least the superconducting film is slit, electrically separated into a plurality of superconducting film parts each having a rectangular cross section and arranged in parallel to form parallel conductors. This provides superconducting wires capable of containing AC loss. A superconducting coil is made by winding the superconducting wires described above, wherein the provision of a coil structure containing at least partially a part wherein the perpendicular interlinkage magnetic flux acting among various conductor elements of the parallel conductors by the distribution of the magnetic field generated by the superconducting coils cancel mutually enables a simple structure without transposition to cancel mutually the interlinkage magnetic flux by the perpendicular magnetic field against wires, to contain circulating current within the wires by the perpendicular magnetic field and to make shunt current uniform. This provides a low-loss superconducting coil.
Owner:KISU TAKANOBU +4
Amr-type integrated magnetoresistive sensor for detecting magnetic fields perpendicular to the chip
ActiveUS20160202329A1Low efficiencyHigh concentration effectLine/current collector detailsSingle device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsMagnetization
An AMR-type integrated magnetoresistive sensor sensitive to perpendicular magnetic fields is formed on a body of semiconductor material covered by an insulating region. The insulating region houses a set / reset coil and a magnetoresistor arranged on the set / reset coil. The magnetoresistor is formed by a magnetoresistive strip of an elongated shape parallel to the preferential magnetization direction. A concentrator of ferromagnetic material is arranged on top of the insulating region as the last element of the sensor and is formed by a plurality of distinct ferromagnetic regions aligned parallel to the preferential magnetization direction.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Electromechanical Latching Relay and Method of Operating Same
A latching relay employing a movable cantilever with a first permanent magnet and a nearby second magnet is disclosed. The permanent magnet affixed to the cantilever is permanently magnetized along its long (horizontal) axis. The cantilever has a first end associated to the first pole (e.g., north pole) of the first magnet, and a second end associated to the second pole (e.g., south pole) of the first magnet. When the first end of the cantilever approaches the second magnet, the first pole of the first magnet induces a local opposite pole (e.g., south pole) in the second magnet and causes the first end of the cantilever to be attracted to the local opposite pole of the second magnet, closing an electrical conduction path (closed state). An open state on the first end of cantilever 10 can be maintained either by the second pole of first magnet being attracted to a local opposite pole in the second magnet or by a mechanical restoring force of flexure spring which supports the cantilever. A third electromagnet (e.g., a coil or solenoid), when energized, provides a third perpendicular magnetic field about the first magnet and produces a torque on the associated cantilever to force the cantilever to switch between closed and open states. A few alternate embodiments of the relay are also disclosed which include a case where the latching feature is disabled, and another case where an external magnet is used to switch the cantilever.
Owner:SHEN JUN +1
Perpendicular magnetic recording head including heating element
ActiveUS20080030905A1Decrease riseAvoid thermal expansionRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsPerpendicular magnetic fieldComputer science
A perpendicular magnetic recording head includes a read part disposed on a substrate to read magnetic recording information from a recording medium by a magnetoresistance effect; a write part disposed above the read part to record magnetic information on the recording medium by applying a perpendicular magnetic field, and including a write coil; a heating element disposed between the write coil and the read part; and a heat-dissipating layer disposed between the write coil and the heating element. The heating element generates heat when supplied with current so that the read part is thermally expanded to protrude toward the recording medium. The heat-dissipating layer has a heat dissipation effect.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Perpendicular magnetic recording head
InactiveUS20090154021A1High recording field strengthStable supplyConstruction of head windingsRecord information storagePerpendicular magnetic fieldEngineering
Embodiments of the present invention provide a magnetic head that can stably supply a perpendicular magnetic field component while generating high recording field strength from a main pole. According to one embodiment, a magnetic body is deposited in a trailing side of a pole tip of a main pole via a nonmagnetic layer, so that a second flare section is magnetically coupled with each sidewall.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Magnetic resonance inspecting apparatus
Provided is a vertical magnetic type MRI apparatus, which can image an arbitrary section of a wide range such as the whole body of a specimen at a high speed in a high sensitivity of even a deep portion of the specimen while suppressing the increase in a channel number. A receiving coil unit (500) is constituted to comprise a bed coil unit (600) having its longitudinal direction aligned with the body axis direction of an inspection object (103), and an upper coil unit (700) mounted removably on the bed coil unit (600). This bed coil unit (600) includes a placing face (601) for placing the inspection object (103), and a plurality of lower sub-coils arranged below the placing face (601). The upper coil unit (700) includes a plurality of upper sub-coils connected with the lower sub-coils. The upper sub-coils are arranged separately on an inner support (20-1) having a flexibility for covering the placing face (601) and an outer support (20-2) having a flexibility for covering the outer side of the inner support (20-1). The upper sub-coils and the lower sub-coils are connected by attaching the upper coil unit (700) to the bed coil unit (600), so that a plurality of kinds of sub-coils can be formed.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Magnetic sensor
ActiveUS9530957B2Simple configurationLow costNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsMagnetic reluctanceMagnetization
A magnetic sensor includes magnetoresistive elements and a soft magnetic body. The magnetoresistive elements have multi layers including a magnetic layer and a nonmagnetic layer on a substrate, and exert a magnetoresistance effect. The soft magnetic body is electrically disconnected with the magnetoresistive elements, and converts a vertical magnetic field component from the outside into a magnetic field component in a horizontal direction so as to provide the magnetoresistive elements with the horizontally converted magnetic field component. The magnetoresistive elements have a pinned magnetic layer having a fixed magnetization direction and a free magnetic layer having a variable magnetization direction. The free magnetic layer is stacked on the pinned magnetic layer with a nonmagnetic layer interposed between the free magnetic layer and the pinned magnetic layer. The magnetization directions of the pinned magnetic layers of the magnetoresistive elements are the same direction. The magnetoresistive elements form a bridge circuit.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
All-optical magnetic recording system using circularly polarized light and bit-patterned media
A perpendicular magnetic recording system uses bit-patterned media (BPM) and circularly polarized light to switch the magnetization of the discrete magnetic bits by the inverse Faraday effect. Circularly polarized light generates an external rotating electric field in a plane orthogonal to the light propagation direction, which induces a magnetic field parallel to the light propagation direction in a magnetic material exposed to the electric field. The BPM is a generally planar substrate with discrete spaced-apart metal or metal alloy magnetic islands that are magnetizable in a perpendicular direction and are separated by nonmagnetic spaces of non-metallic material on the substrate. A near-field metal transducer is patterned into at least three tips, with the tips surrounding and defining a transducer active region. The circularly polarized light is incident on the tips, which produce a strong in-plane rotating electric field. A magnetic island exposed to the rotating electric field will experience an induced perpendicular magnetic field that switches the magnetization of the magnetic island.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Perpendicular magnetic recording head, method of manufacturing the same, and magnetic recording apparatus
ActiveUS20060098338A1Minimize the possibilityNot easily erasedRecord information storageHeads for perpendicular magnetisationsPerpendicular magnetic fieldMagnetic flux
A perpendicular magnetic recording head capable of minimizing the possibility of erasing recorded information without intention at the time of recording information is provided. A pole layer has a structure in which a main pole layer disposed on a leading side and an auxiliary pole layer disposed on a trailing side are laminated. Even if a part of a magnetic flux contained in the auxiliary pole layer is directly emitted from an air bearing surface to outside not via the main pole layer, as the magnetic flux is contained in the magnetic layer, the magnetic flux is not easily emitted from the air bearing surface to the outside directly. Therefore, an unnecessary perpendicular magnetic field is not easily generated by the magnetic flux. Thereby, a recording medium is not easily magnetized again by the unnecessary magnetic field, so information recorded on the recording medium is not easily erased without intention.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Method and equipment for oil-water separation
InactiveCN1796296AFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesWater cleaningPerpendicular magnetic fieldOil water
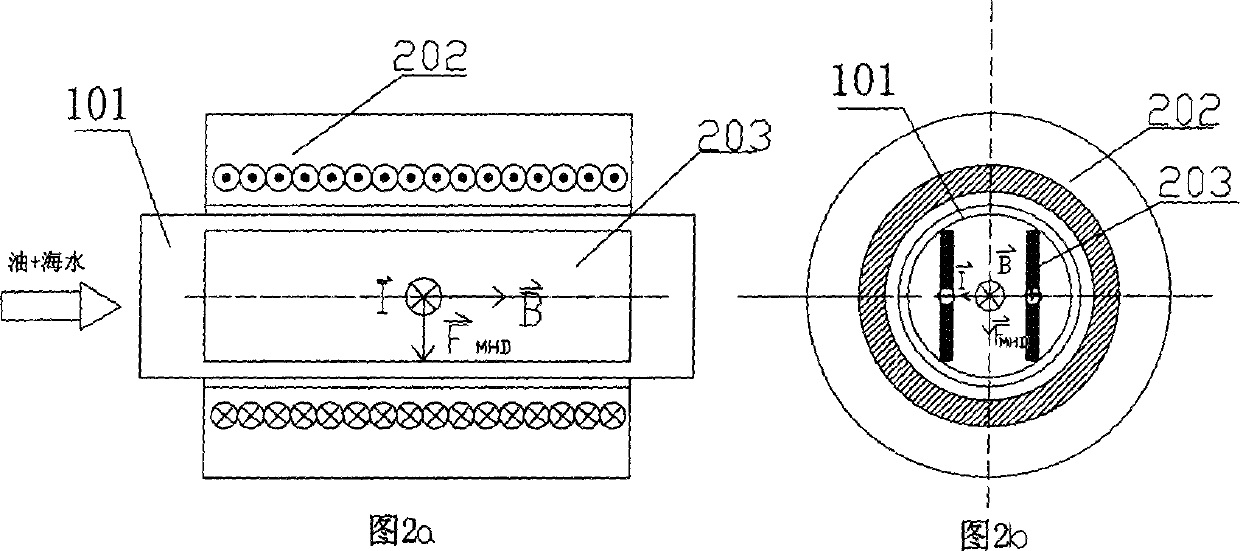
This is a new method and equipment for oil-water separation. This invention is based on the fundamental principle that the magnetic force which the electrified seawater suffers from the perpendicular magnetic field is FMHD=Ií‡B. According to this principle, each of the electrified seawater micelles in the oil-seawater mixture is extruded downwards as a result of the downward magnetic force after they enter into the interaction region between the electric and magnetic fields in the electromagnetic fluid separation passage. The buoyancy of the oil droplet in the seawater is of the same magnitude but in opposite directions, so the oil droplets float upward and assemble in the upper layer of the seawater. Consequently the oil and water are separated into two layers and depart from each other at the vent of the separation passage. There are two constitutional modes for the equipment that applies this invention: (1) solenoid superconductive magnet, tubular electromagnetic fluid separation passage and built-in passage tube parallel electrode pair; (2) saddle-polar superconductive magnet, tubular electromagnetic fluid separation passage and built-in passage tube annular electrode pair. Under the effect of magnetic force in the designed working condition of this invention, the rising velocity of oil-water separation can be accelerated by 1~2 order-of-magnitude in contrast to the result of the specific gravity difference between oil and water.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Perpendicular magnetic recording head including heating element
ActiveUS7898767B2Decrease riseAvoid thermal expansionRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsPower flowPerpendicular magnetic field
A perpendicular magnetic recording head includes a read part disposed on a substrate to read magnetic recording information from a recording medium by a magnetoresistance effect; a write part disposed above the read part to record magnetic information on the recording medium by applying a perpendicular magnetic field, and including a write coil; a heating element disposed between the write coil and the read part; and a heat-dissipating layer disposed between the write coil and the heating element. The heating element generates heat when supplied with current so that the read part is thermally expanded to protrude toward the recording medium. The heat-dissipating layer has a heat dissipation effect.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Magnetic field adjustment method for MRI device
InactiveCN102665542AMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringSingular value decompositionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
Owner:HITACHI LTD
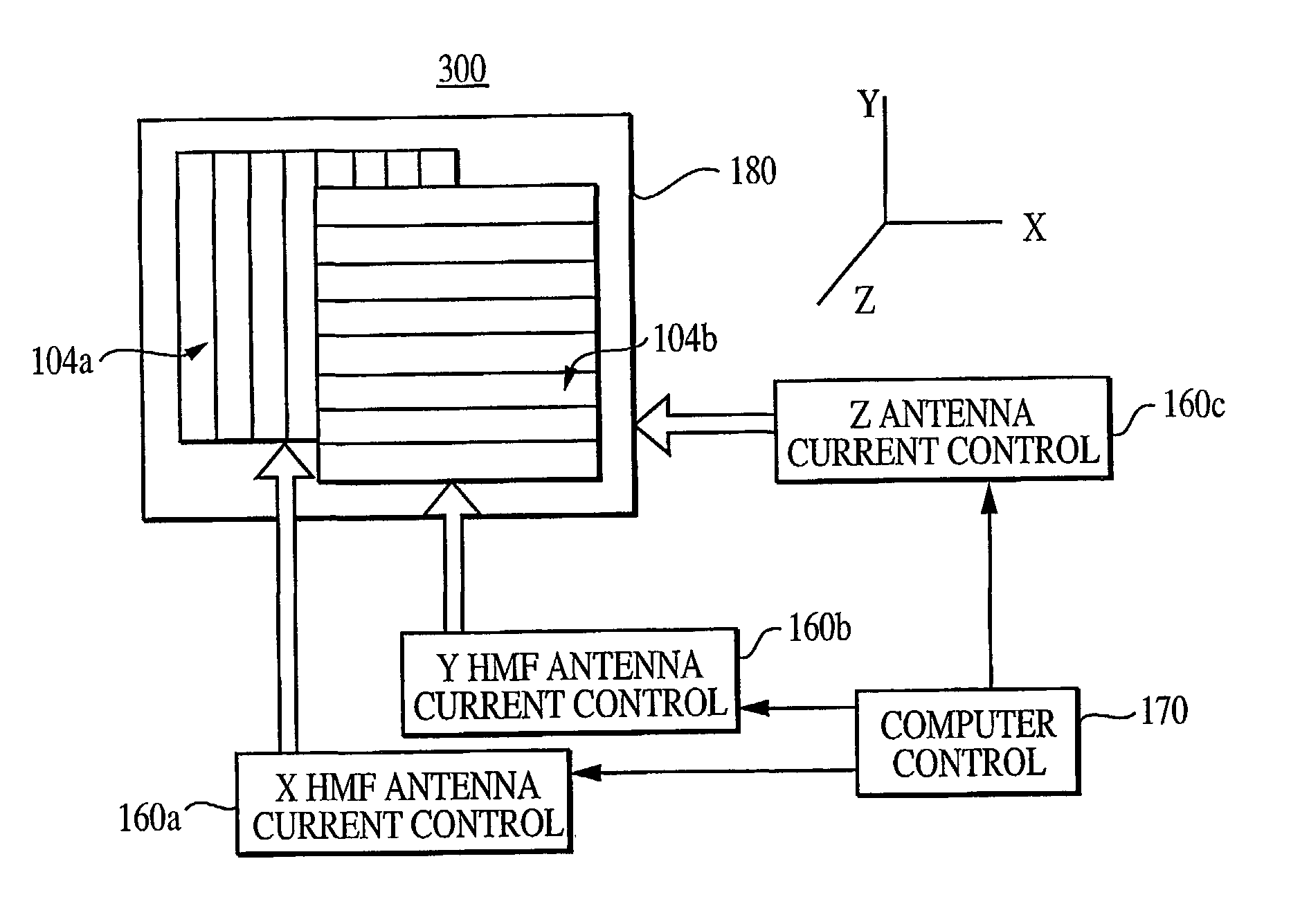
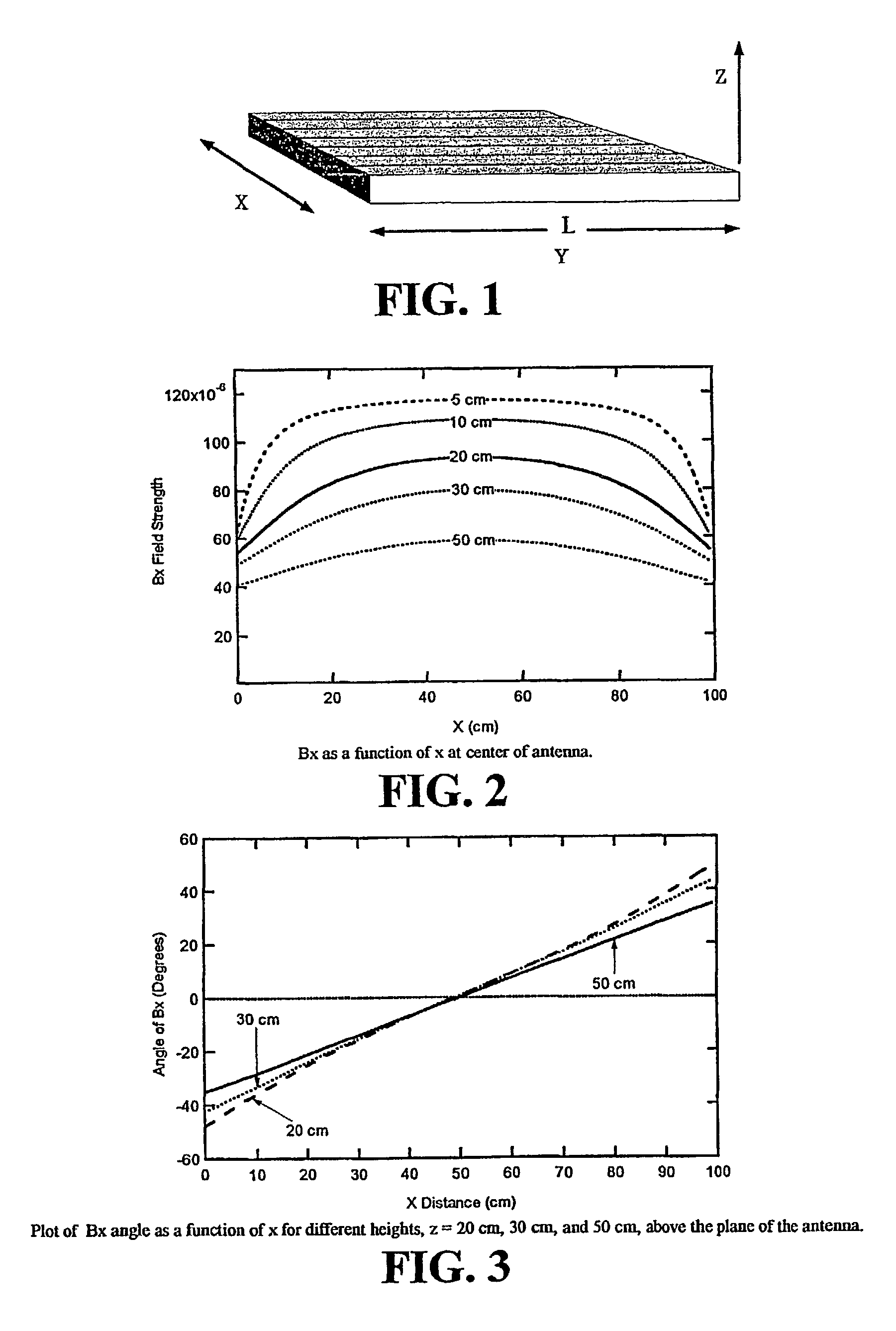
Steerable three-dimensional magnetic field sensor system for detection and classification of metal targets
InactiveUS7030759B2Uniform magnetic fieldBurglar alarm by hand-portable articles removalBurglar alarm electric actuationPolarizability tensorPerpendicular magnetic field
A steerable electromagnetic induction (EMI) sensor system for measuring the magnetic polarizability tensor of a metal target. Instead of creating a vertical magnetic field from a horizontal loop transmitter configuration used by most prior art EMI metal detectors, the transmitter geometry of the sensor system's antenna is designed especially for creating multiple horizontal and vertical magnetic fields and for steering the same in all directions. The horizontal magnetic field (HMF) antenna has the potential advantage of a relatively uniform magnetic field over a large volume. A second potential advantage of the HMF antenna is that compared to a conventional loop antenna, the magnetic field intensity falls off slowly with distance from the plane of the antenna. Combining two HMF sensor systems creates a steerable two-dimensional magnetic field sensor. Combining the steerable HMF sensor with a vertical magnetic field antenna forms a three-dimensional steerable magnetic field sensor system.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Thin film magnetic head, method of manufacturing the same and magnetic recording apparatus
InactiveUS6984333B2Improve recording effectImprove accuracyElectrical transducersDecorative surface effectsMagnetic field gradientPerpendicular magnetic field
Owner:TDK CORPARATION +1
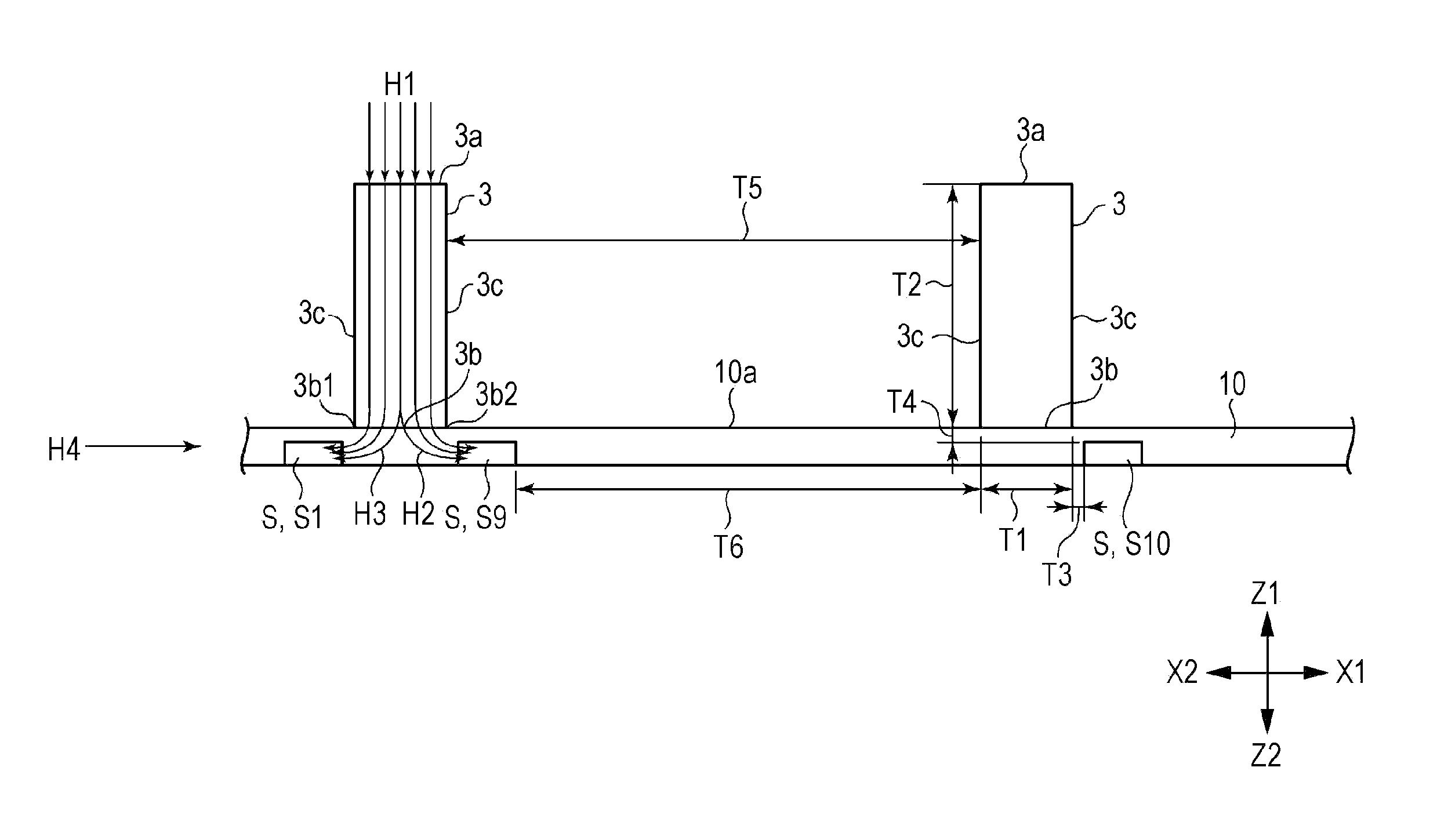
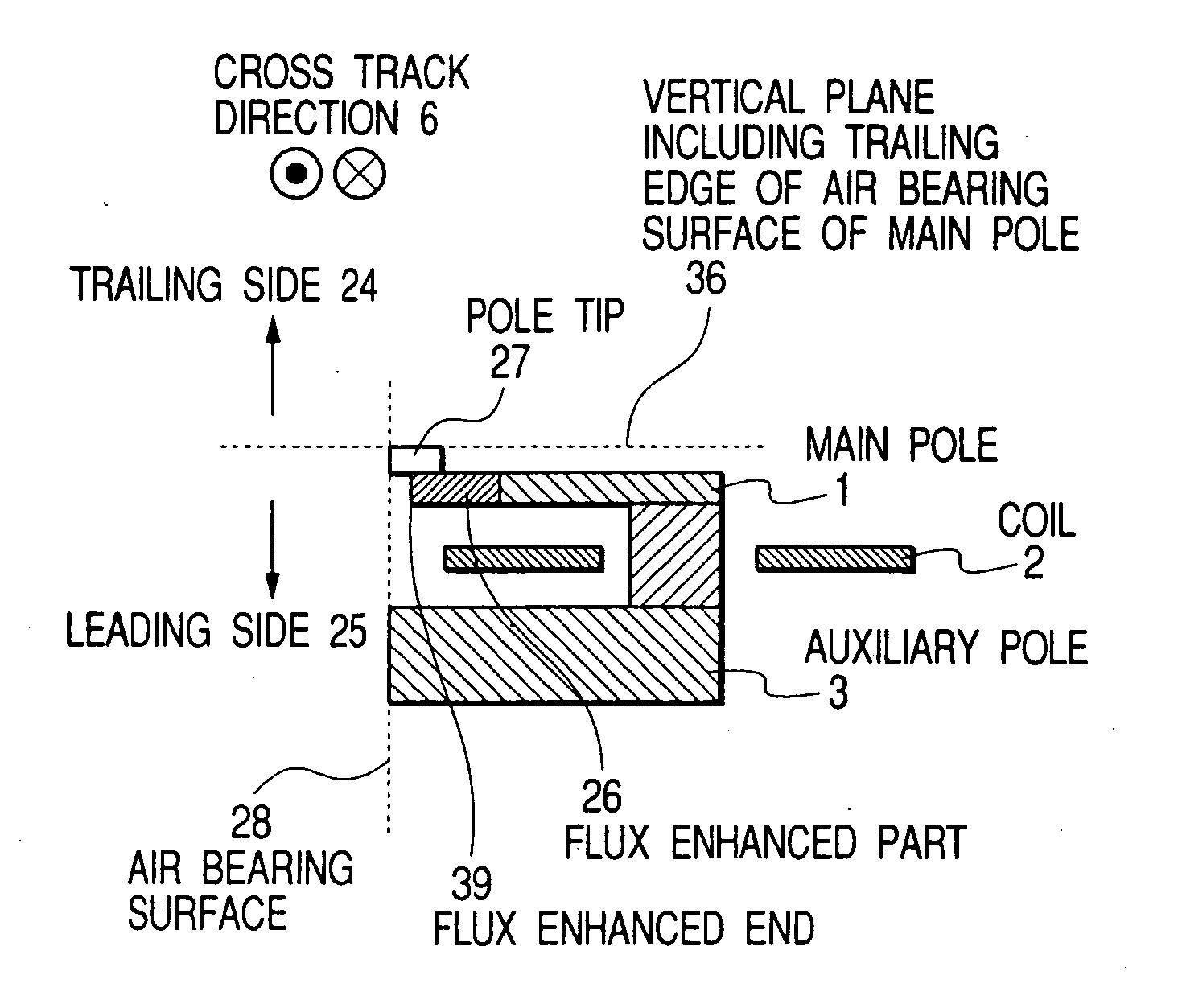
High gradient-field recording head for perpendicular magnetic recording and fabrication method therefore
InactiveUS20050157424A1Deterioration of magnetic field gradientReduce magnetic field gradientManufacture head surfaceElectrical transducersResistPerpendicular magnetic field
A thin film magnetic head for perpendicular recording of a single-pole type has a flux enhanced part and a flux enhanced end arranged on a leading side of the main pole parallel with the cross track direction. The side surface of the main pole intersecting the cross track direction is arranged on the track center side perpendicular to the track width. The field gradient of a perpendicular magnetic field on the trailing side of the main pole and near both ends of the track is made steep to realize a higher areal recording density. The head is fabricated by forming a first resist pattern on an inorganic insulating layer. A slope is formed on the inorganic insulating layer with the resist pattern as a mask. A second resist pattern is then formed on the inorganic insulating layer to form a magnetic layer on the inorganic insulating layer.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH JAPAN LTD
Weak magnetic field measurement device and method based on modal localization effect
InactiveCN110542869ANot affected by residual stressEliminate distractionsMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsCapacitanceDc current
The invention discloses a high-sensitivity magnetic field measurement method and device and belongs to the field of an electronic measurement instrument. The device comprises a magnetic field measurement chip and a test signal processing method. The chip comprises at least two weakly coupled resonators, a driving electrode, a detection electrode and an outer gate-type structure. The AC current isapplied to the weakly coupled resonators through a driving electrode, and when the chip is placed in a vertical magnetic field, the resonators are subjected to changed Lorentz force to generate simpleharmonic vibration; when the external magnetic field changes, a vibration state of the resonators changes accordingly, moreover, the DC current is applied to the gate-type structure, the gate-type structure is subjected to Lorentz force in the horizontal direction, and the electrostatic negative stiffness between the gate-type structure and the weakly coupled resonators is changed, so energy distribution of a weakly coupled resonator system is severely unbalanced. Two sets of detection electrodes are designed on two sides of an output resonator, single-resonator amplitude difference detectionis achieved, feed-through capacitance interference is eliminated, and high-sensitivity measurement of the weak magnetic field intensity can be achieved by measuring resonator amplitude difference. The device is advantaged in that real-time measurement of the weak magnetic field can be realized, the anti-interference capability is high, and use significance is high.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Perpendicular STT-MRAM having logical magnetic shielding
InactiveUS9024399B2Growth inhibitionLow coercivityMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionBit lineDielectric
A perpendicular STT-MRAM comprises apparatus and a method of manufacturing a plurality of magnetoresistive memory element having local magnetic shielding. As an external perpendicular magnetic field exists, the permeable dielectric layers, the permeable bit line and the permeable bottom electrode are surrounding and have capability to absorb and channel most magnetic flux surrounding the MTJ element instead of penetrate through the MTJ element. Thus, magnetization of a recording layer can be less affected by the stray field during either writing or reading, standby operation.
Owner:GUO YIMIN
Magnetofluid deformable mirror device
InactiveCN103235410AIncrease mirror distortionIncreased ability to correct aberrationsOptical elementsPerpendicular magnetic fieldDeformable mirror
The invention discloses a magnetofluid deformable mirror device. Ferromagnetic fluid is contained in a container, liquid reflecting film material is poured on the ferromagnetic fluid, a metal-like liquid reflecting film forms and floats on the surface of the ferromagnetic fluid, and a basic mirror system of a magnetofluid deformable mirror is formed. A miniature electromagnetic coil assembly is disposed below the container and is connected to a current drive circuit through a wire, and a mirror deformation drive system of the magnetofluid deformable mirror is formed and the ferromagnetic fluid is kept below basic electromagnetic field. A Helmholtz electromagnetic coil is disposed outside the container and applies additional electromagnetic field, perpendicular to lines of magnetic force of the basic electromagnetic field, to the ferromagnetic fluid, and the additional electromagnetic field is evenly superposed to the basic electromagnetic field. The invention further discloses a production method of the magnetofluid deformable mirror device. The great and high-uniformity perpendicular magnetic field is superposed so as to allow the magnetofluid deformable mirror to respond to linearization under the condition of same control input current, and mirror response deformation amplitude is increased evidently.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Magnetic field shielding device of high-temperature superconducting coil
InactiveCN101752050AReduce the vertical magnetic field componentGuaranteed critical currentMagnetic/electric field screeningSuperconducting magnets/coilsCarrying capacitySuperconducting electric machine
The invention relates to a magnetic field shielding device of a high-temperature superconducting coil, which solves the problem that the current carrying capacity of a high-temperature superconducting coil used as an armature winding in a high-temperature superconducting motor is limited by an additional vertical magnetic field. The magnetic field shielding device comprises a cryostat, a vacuum container, a first magnetic conduction sheet and a second magnetic conduction sheet, wherein the high-temperature superconducting coil is fixed in the cryostat; the cryostat is fixed in the vacuum container; liquid nitrogen is introduced into the cryostat; the first magnetic conduction sheet and the second magnetic conduction sheet are respectively fixed above and below the axial direction of the high-temperature superconducting coil; and the width of the first magnetic conduction sheet and the width of the second magnetic conduction sheet are 1.1-1.5 times of the thickness of the high-temperature superconducting coil. The device of the invention can enable the original vertical magnetic field of the surface of the high-temperature superconducting coil to be reduced by more than 50%, and is used for shielding the vertical magnetic field of the surface of the coil.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Spin current magnetization rotational element, magnetoresistance effect element, magnetic memory, and high-frequency magnetic element
ActiveUS20190074123A1Galvano-magnetic material selectionGalvano-magnetic device detailsSpin orbit torquePerpendicular magnetic field
Provided is a spin current magnetization rotational element including: a spin-orbit torque wiring that extends in a first direction and is configured to generate a spin current; a first ferromagnetic layer that is laminated in a second direction intersecting the spin-orbit torque wiring and is configured for magnetization direction to be changed; and a first perpendicular magnetic field applying layer that is disposed to be separated from the spin-orbit torque wiring and the first ferromagnetic layer, the first perpendicular magnetic field applying layer being configured to apply an assistant magnetic field assisting a magnetization rotation of the first ferromagnetic layer.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Thin film magnetic head and magnetic recording apparatus
InactiveUS20060221499A1Gradient of increasedHigh strengthRecord information storageHeads for perpendicular magnetisationsMagnetic polesPerpendicular magnetic field
The present invention provides a thin film magnetic head realizing the gradient and the strength of a perpendicular magnetic field increased as much as possible. A main magnetic pole layer is made recede from a write shield layer. As compared with the case where the magnetic pole layer is not receded from the write shield layer, an overlap range in which the main magnetic pole layer and the write shield layer are overlapped one another is smaller. Accordingly, the amount of magnetic flux emitted from the main magnetic pole layer toward a recording medium relatively increases, and the amount of magnetic flux leaked from the main magnetic pole layer to the write shield layer relatively decreases.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Sputtering device and sputtering method
InactiveCN102245798AElectric discharge tubesVacuum evaporation coatingInterior spacePerpendicular magnetic field
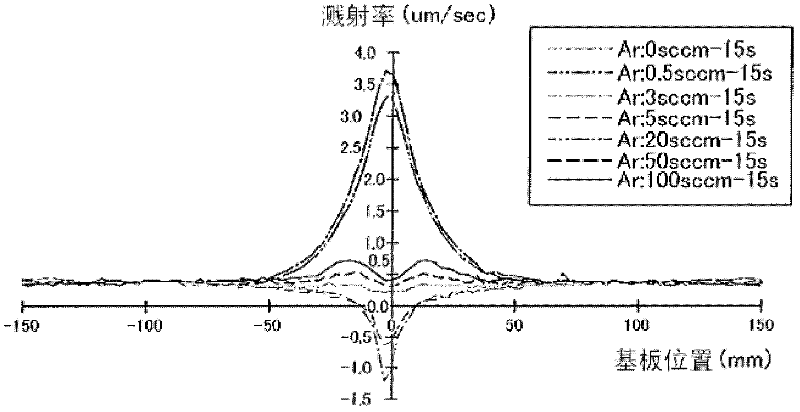
Disclosed is a sputtering device capable of forming a film having good coverage with respect to each fine hole with a high aspect ratio formed the surface of a substrate. This device is equipped with: a vacuum chamber (1) in which a substrate (W) is disposed; a cathode unit (C), which is disposed in the vacuum chamber facing the substrate, and which has a holder (2) on one face of which at least one concave part (3) is formed, with a target material (4) having a closed-bottom cylindrical shape being mounted from the bottom side thereof, and to which is attached a magnetic field generation means (6) that generates a magnetic field in the interior space of the target material; an anode shield (8) to which a positive potential is applied; a gas introduction means (12) which introduces a sputter gas into the vacuum chamber; a power supply which supplies power to the cathode unit; a vertical magnetic field generation means comprised of a power supply and a coil (15) which is provided on the wall surface of the vacuum chamber around the reference axis connecting the cathode unit and the substrate; and a control means (16) which controls the on / off of the introduction of the sputter gas from the gas introduction means.
Owner:ULVAC INC
Hall element
ActiveUS20160209480A1Reduction in chip sideLow costMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesRotational axisRotary switch
Provided is a Hall element integrated on a single substrate capable of cancelling offset voltage with a spinning switch configured to switch spinning current and capable of simultaneously detecting a horizontal direction magnetic field and a vertical direction magnetic field. The Hall element has a four-fold rotational axis and includes: a P-type semiconductor substrate layer (100) formed of P-type silicon; a vertical magnetic field detection N-type doped region (110) formed on the P-type semiconductor substrate layer; and eight horizontal magnetic field detection N-type doped regions (120, 121) formed so as to surround the vertical magnetic field detection N-type doped region.
Owner:ABLIC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com