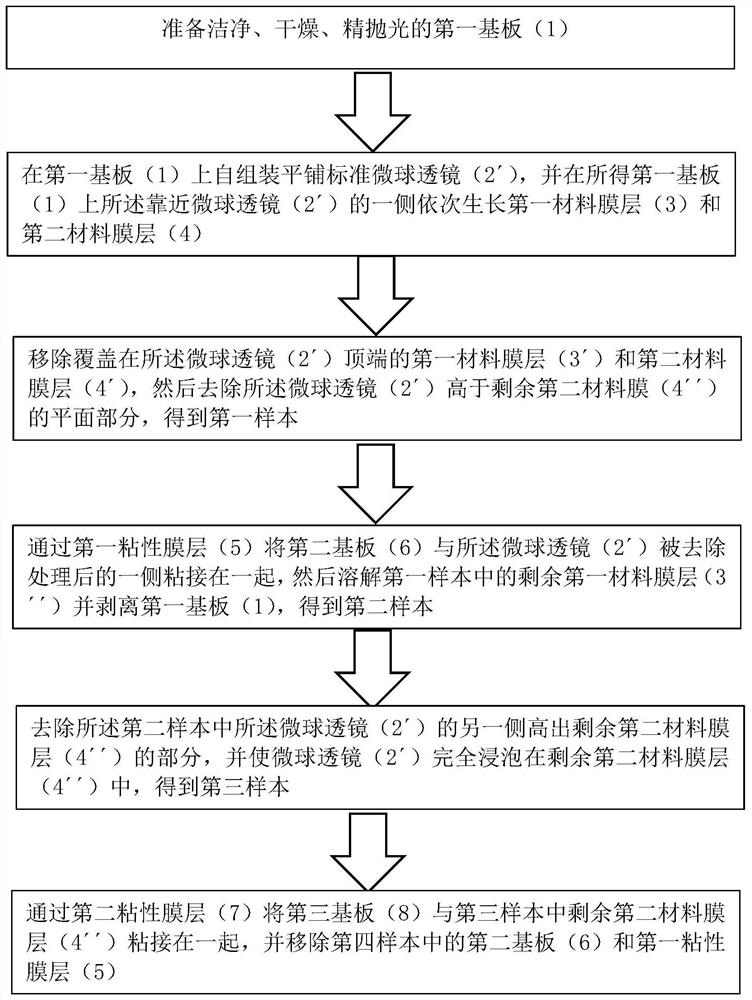
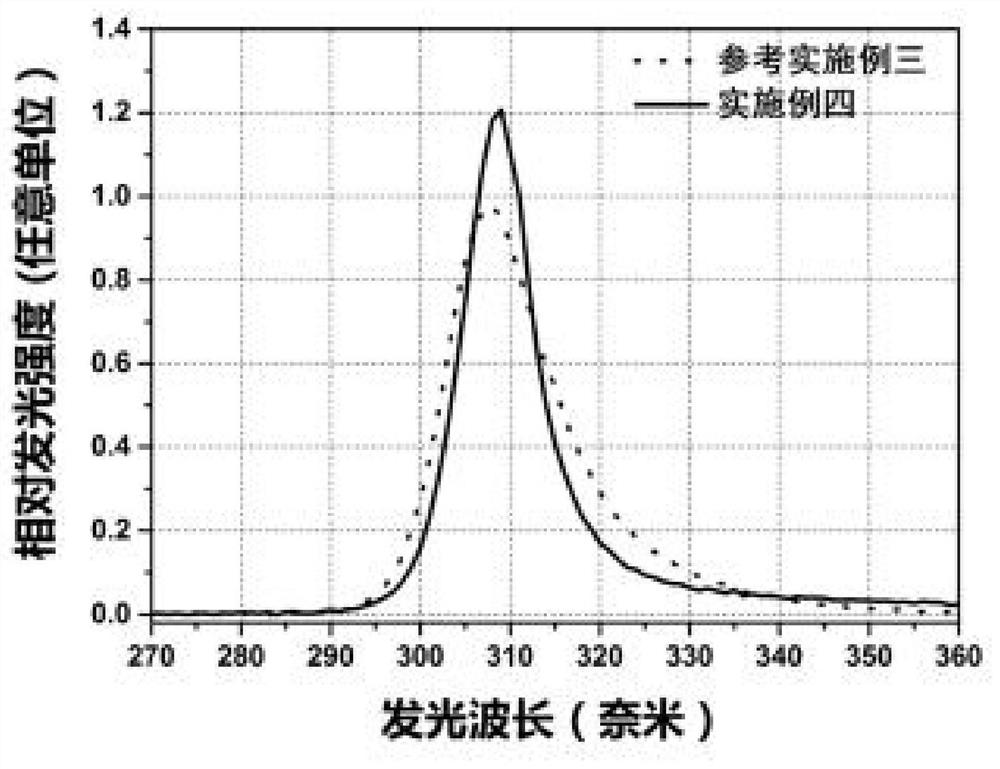
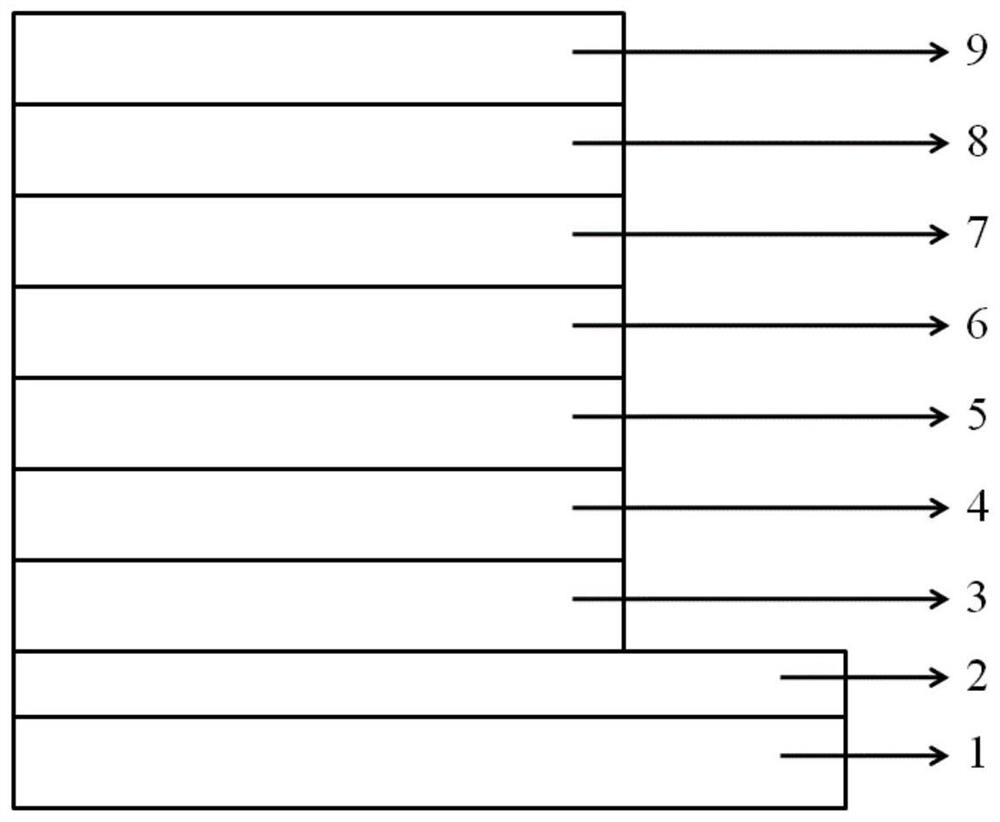
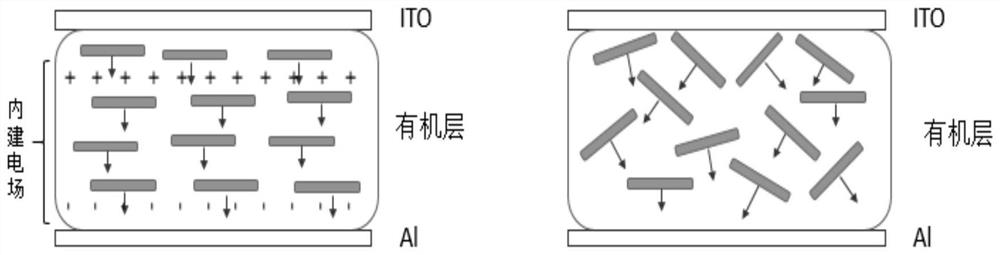
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
50results about How to "Reduce FWHM" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
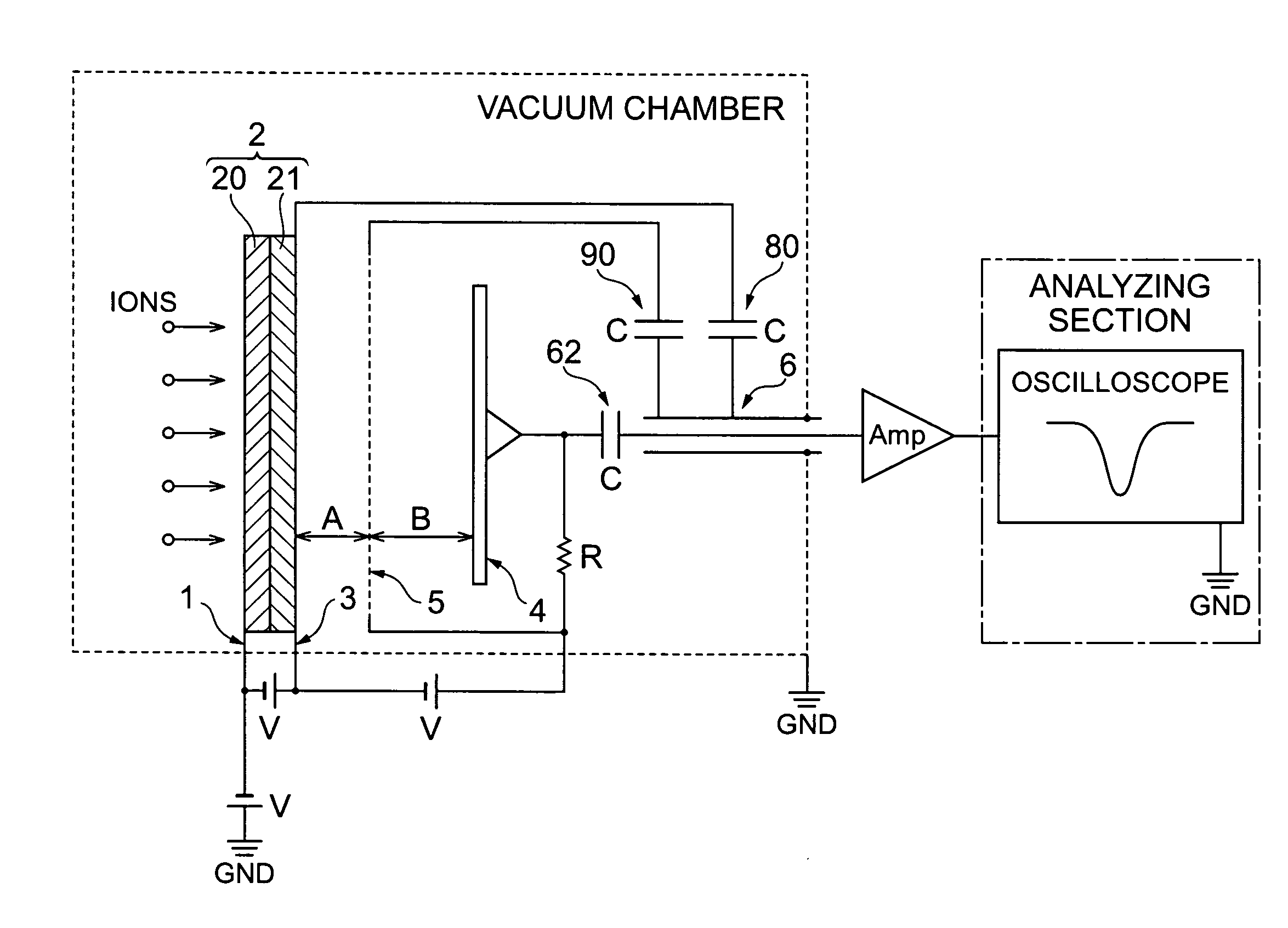
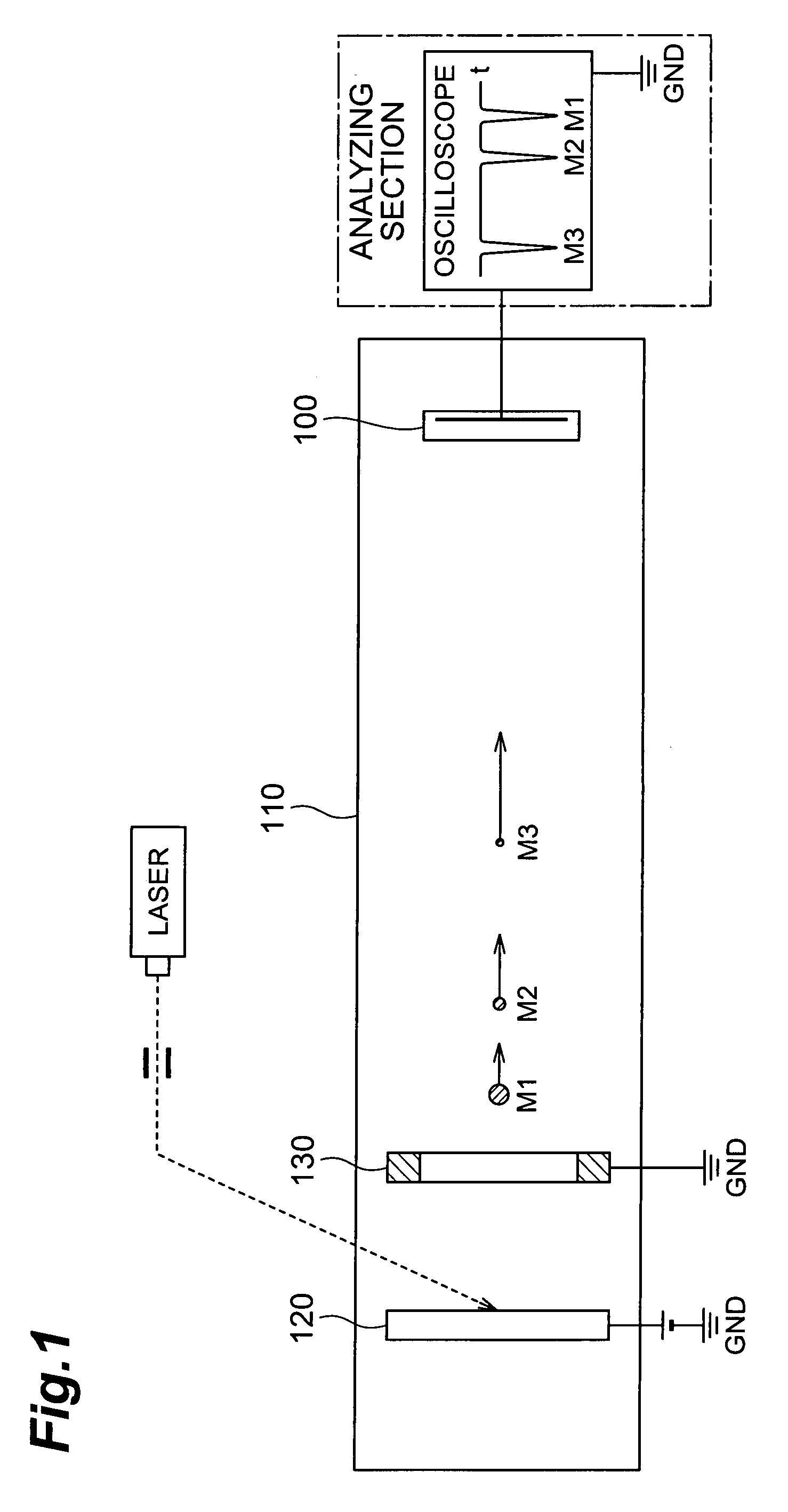
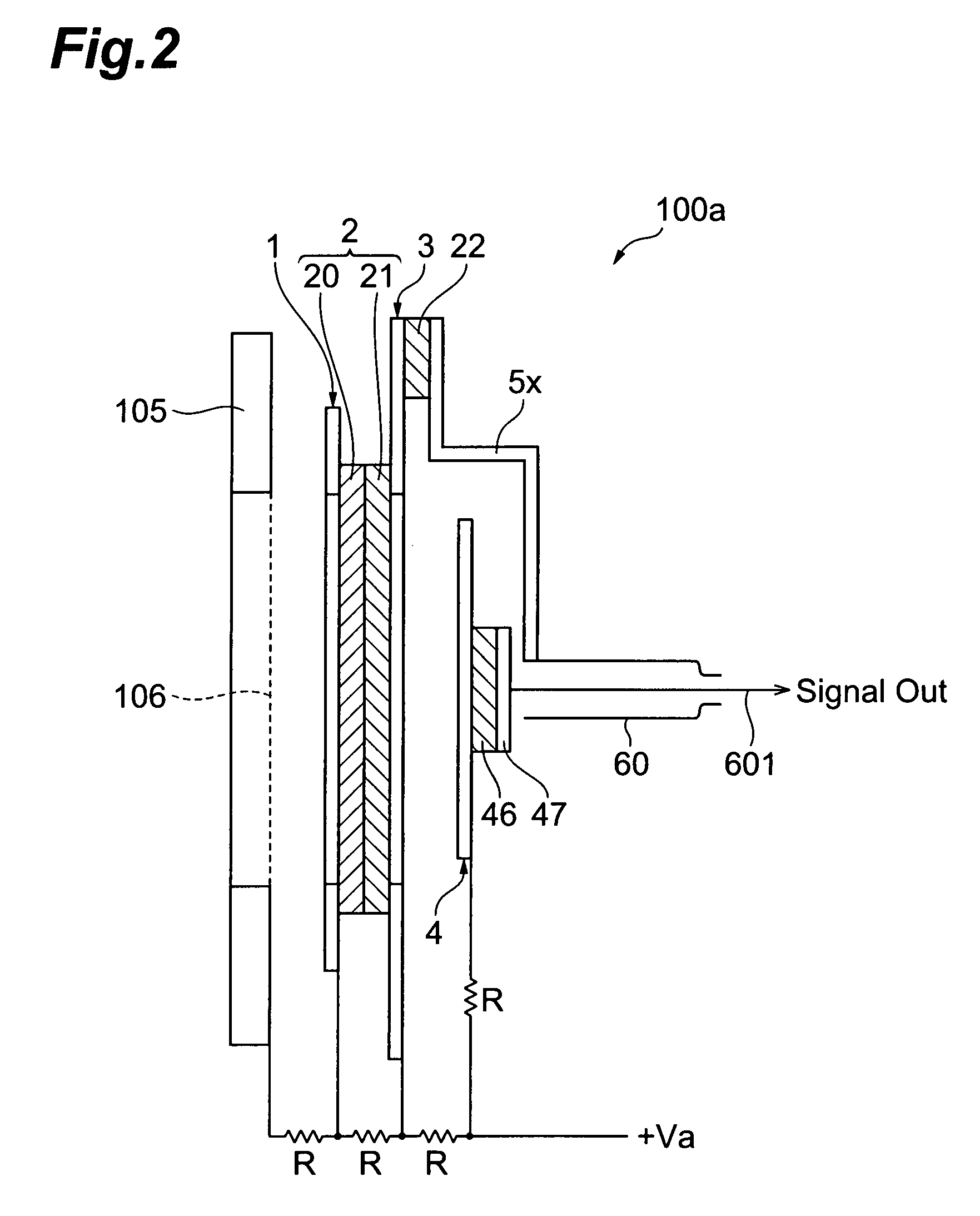
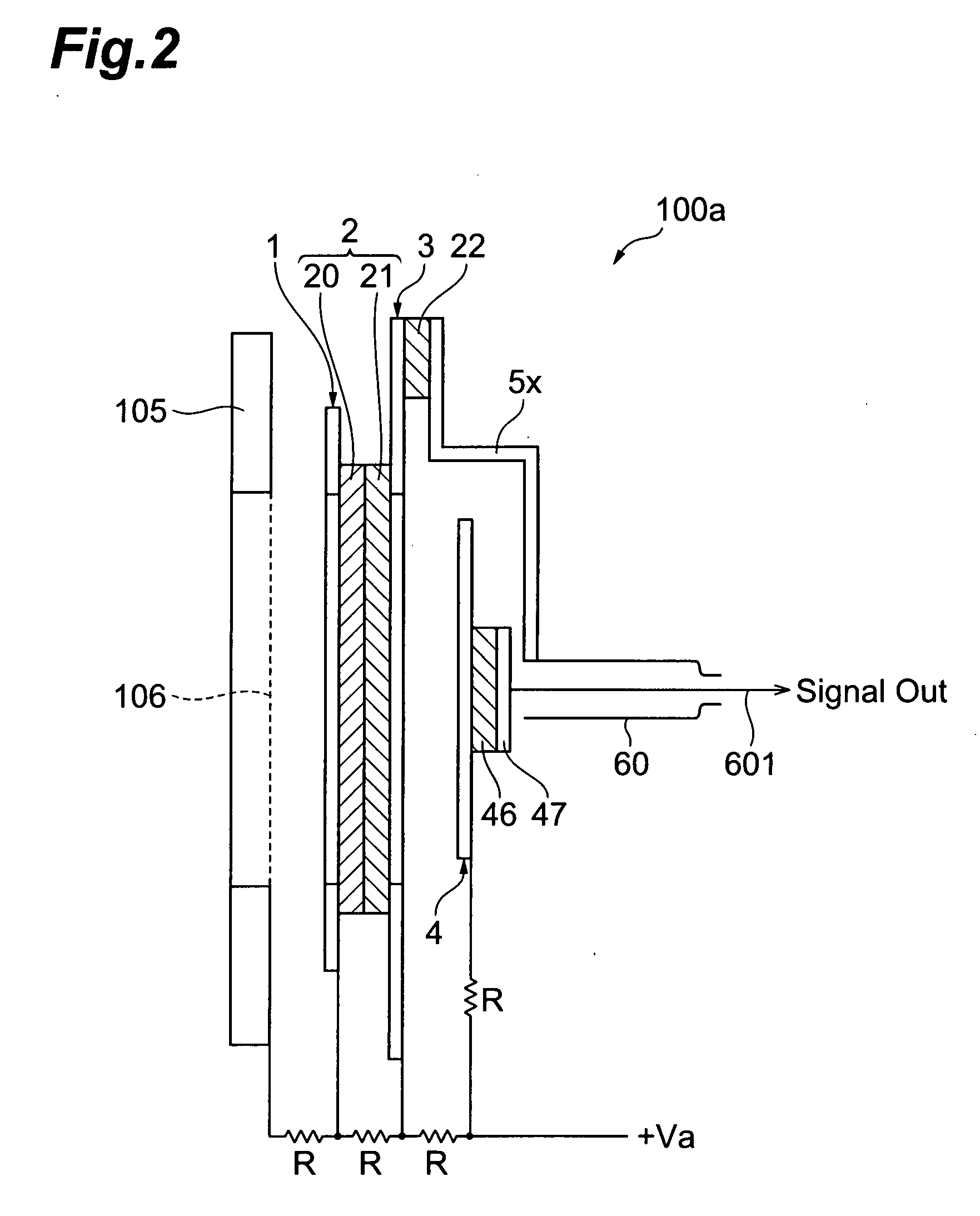
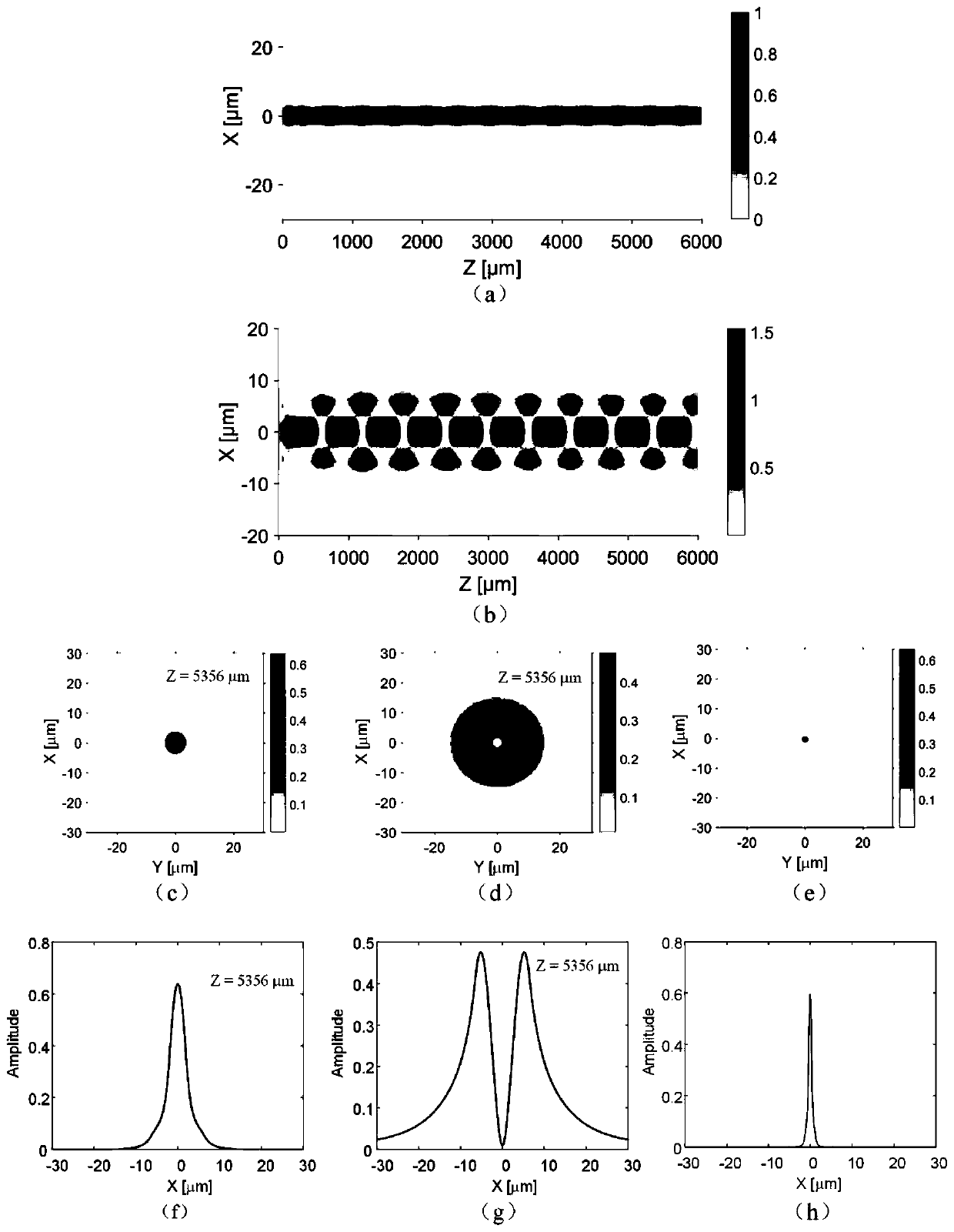
MCP unit, MCP detector and time of flight mass spectrometer
ActiveUS7564043B2Reduce widthShortened fall timeThermometer detailsSpectrometer detectorsTime-of-flight mass spectrometryTime response
The present invention relates to an MCP unit or the like having a structure intended to achieve a desired time response characteristic, without depending on a limitation imposed by a channel diameter of MCP. The MCP unit comprises the MCP for releasing secondary electrons internally multiplied in response to incidence of charged particles, an anode arranged in a position where the secondary electrons reach, and an acceleration electrode arranged between the MCP and the anode. In particular, the acceleration electrode includes a plurality of openings which permit passing of the secondary electrons migrating from the MCP toward the anode. Further, the acceleration electrode is arranged such that the shortest distance B between the acceleration electrode and the anode is longer than the shortest distance A between the MCP and the acceleration electrode. Thus, an FWHM of a detected peak appearing in response to the incidence of the charged particles is remarkably shortened.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
MCP unit, MCP detector and time of flight mass spectrometer
ActiveUS20080290267A1Reduce widthShortened fall timeThermometer detailsSpectrometer detectorsTime responseTime-of-flight mass spectrometry
The present invention relates to an MCP unit or the like having a structure intended to achieve a desired time response characteristic, without depending on a limitation imposed by a channel diameter of MCP. The MCP unit comprises the MCP for releasing secondary electrons internally multiplied in response to incidence of charged particles, an anode arranged in a position where the secondary electrons reach, and an acceleration electrode arranged between the MCP and the anode. In particular, the acceleration electrode includes a plurality of openings which permit passing of the secondary electrons migrating from the MCP toward the anode. Further, the acceleration electrode is arranged such that the shortest distance B between the acceleration electrode and the anode is longer than the shortest distance A between the MCP and the acceleration electrode. Thus, an FWHM of a detected peak appearing in response to the incidence of the charged particles is remarkably shortened.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Coherent maser radiation cold atomic clock
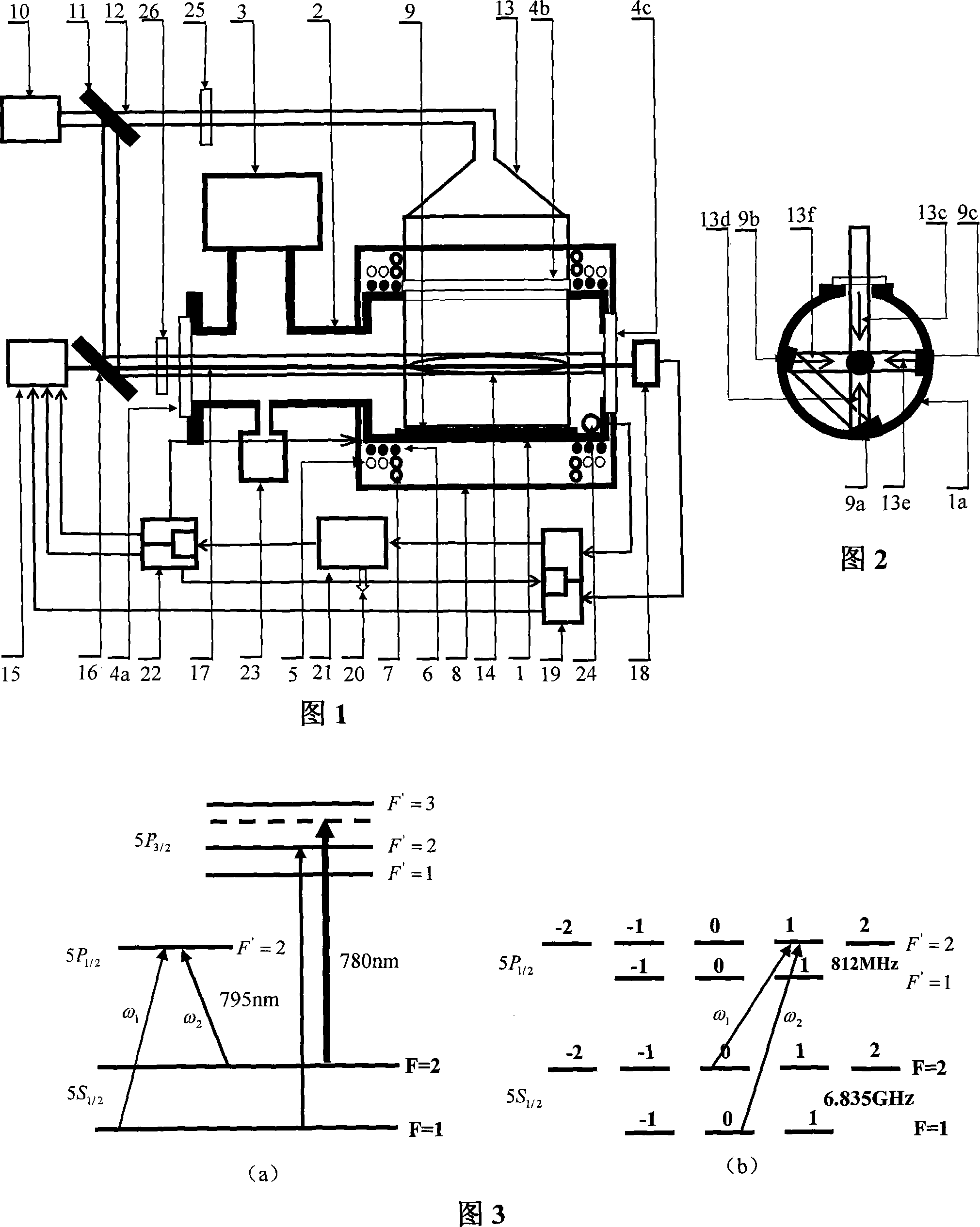
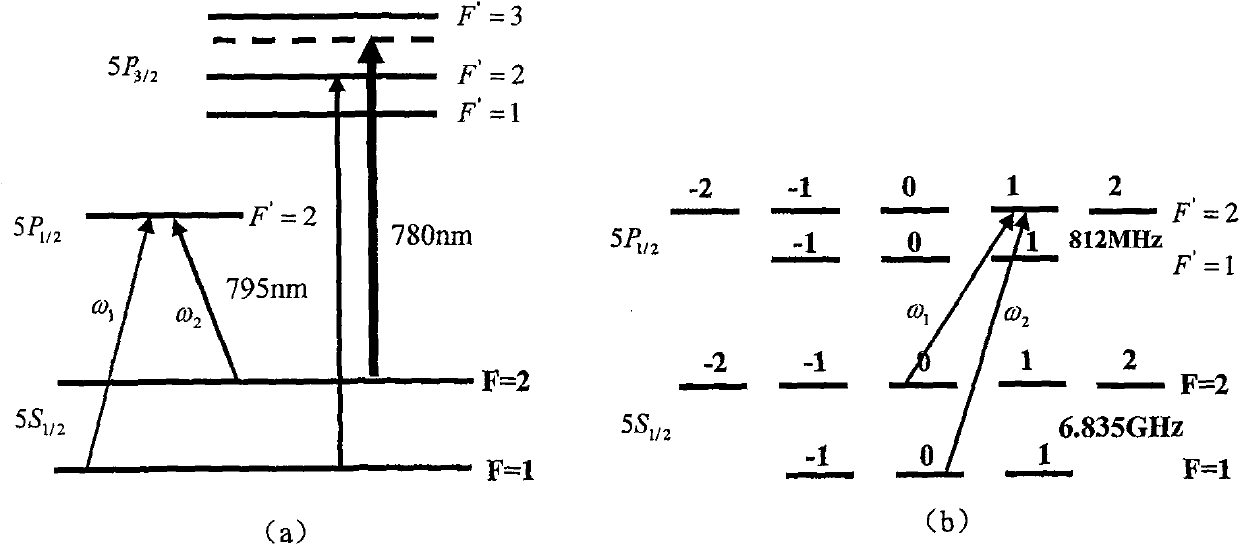
InactiveCN101145025AReduce FWHMExtended transit timeApparatus using atomic clocksPulse automatic controlMaserHelmholtz coil
The present invention discloses a coherent microwave-radiation cold atomic clock; and an ion pump is connected with a vacuum catheter which is connected with a microwave cavity; a light window is fixed in the microwave cavity by quartz glass and three reflective mirrors; a pair of anti-Helmholtz coils and a pair of Helmholtz coils are fixed on the microwave cavity; a pair of rectangular coils are fixed on the microwave cavity; a magnetic shielding system is connected with a vacuum system; semiconductor laser provides captive light and beams of pump-back light; a semiconductor laser on the vertical cavity surface provides a plurality of beams of captive light; a voltage-controlled crystal oscillator is connected with a frequency synthesizers connected with a signal receiver and processor; the semiconductor laser on the vertical cavity surface is connected with the microwave cavity; a photoelectric detector and a microwave-power receiver are connected with the signal receiver and processor connected with the voltage-controlled crystal oscillator as well as the semiconductor laser on the vertical cavity surface. The present invention is characterized in that the structure is compact and the size is small, and has good stability, high accuracy as well as good applicability.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Electroluminescent device based on exciplex system and matched with boron-containing organic compound
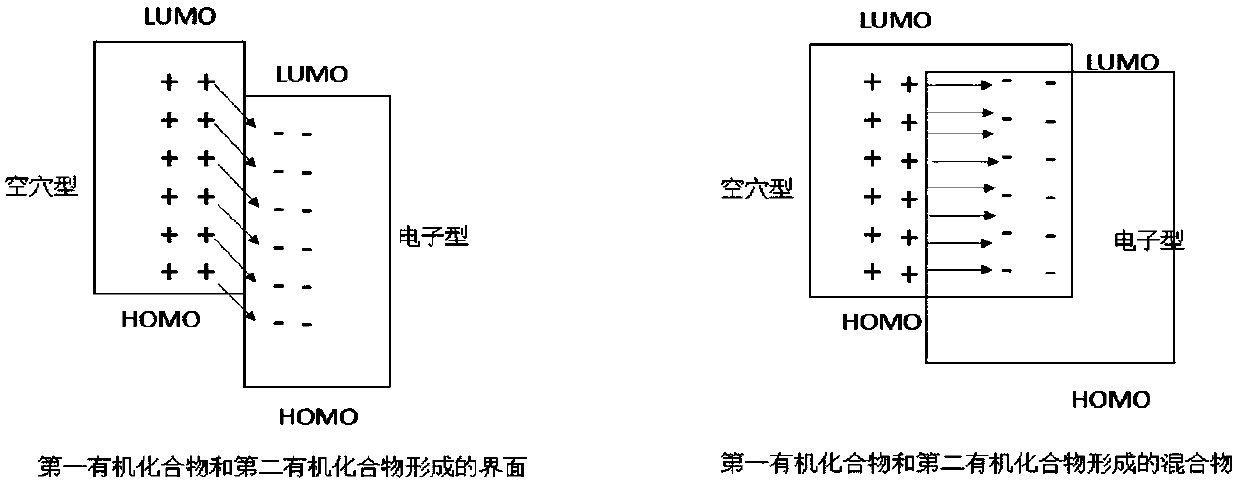
ActiveCN110492009AImprove stabilityReduce concentrationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSimple Organic CompoundsOrganic light emitting device
The invention relates to an electroluminescent device based on an exciplex system and matched with a boron-containing organic compound, wherein a subject material contains a first organic compound anda second organic compound, the difference between the HOMO energy level of the first organic compound and the HOMO energy level of the second organic compound is 0.2 eV or more, and the difference between between the LUMO energy level of the first organic compound and the LUMO energy level of the second organic compound is 0.2 eV or more. A mixture or an interface formed by the first organic compound and the second organic compound generates an exciplex under the excitation of the light or an electric field, the singlet energy level of the exciplex is higher than that of an object material, and the triplet energy level of the exciplex is higher than that of the object material. The first organic compound and the second organic compound have different carrier transport characteristics, andthe object material is the boron-containing organic compound. An organic light-emitting device prepared by the method has the characteristics of high efficiency and long service life.
Owner:JIANGSU SUNERA TECH CO LTD
Birefringent phase control super-surface unit and broadband polarization and phase control array and device
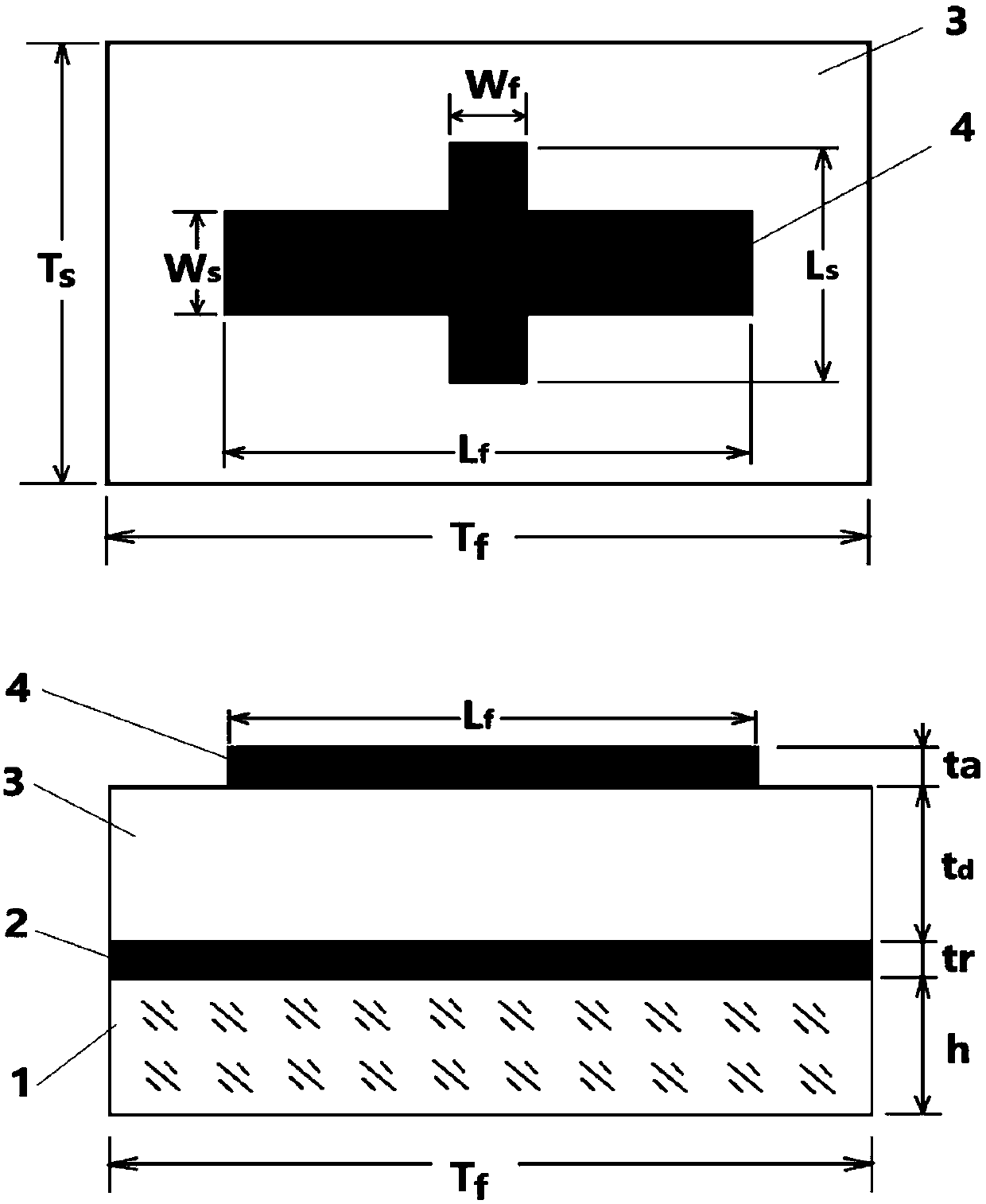
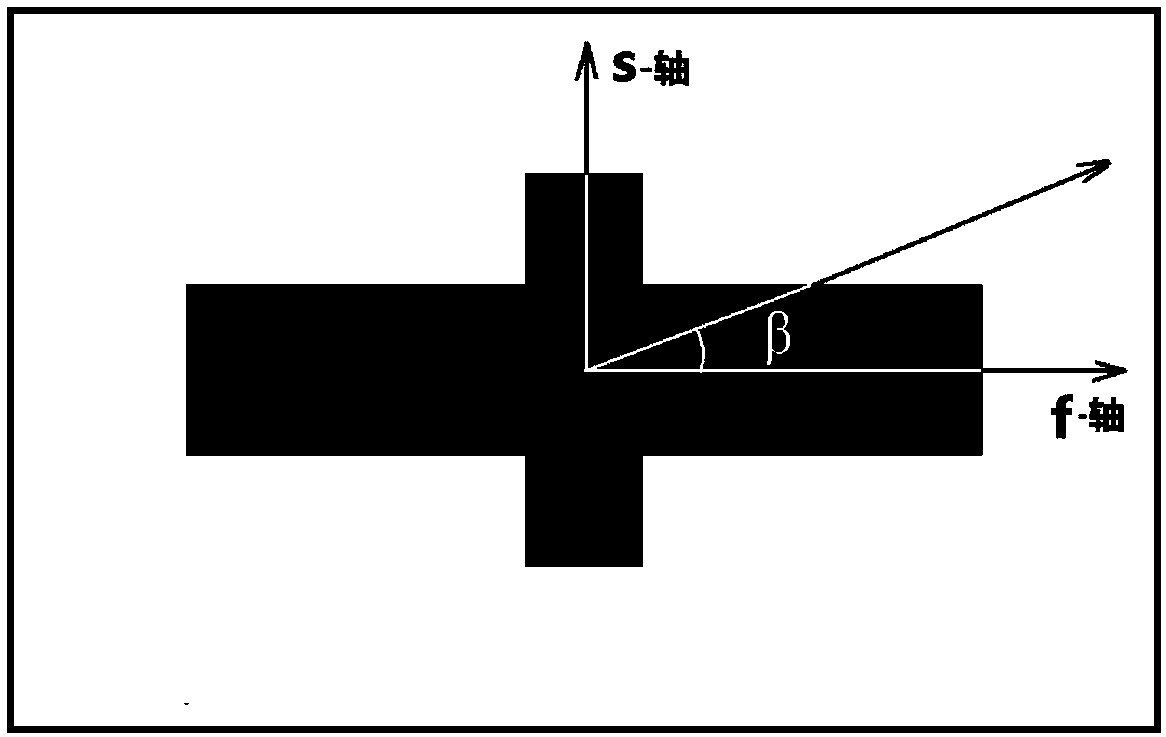
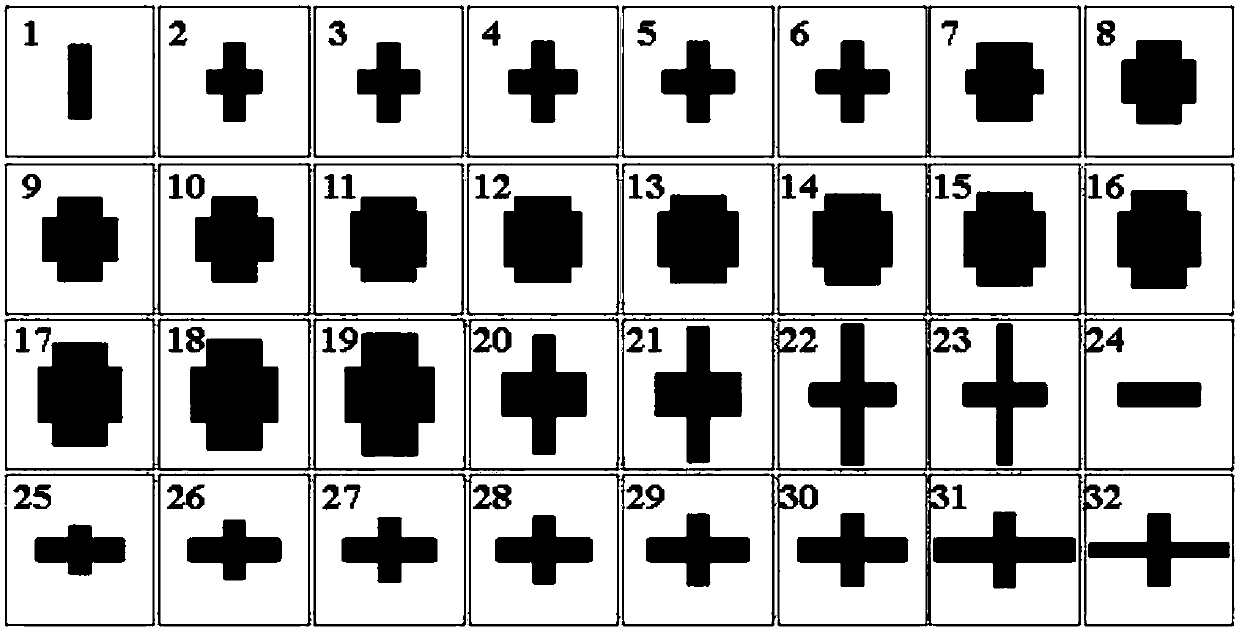
The invention discloses a broadband polarization and phase control array based on a birefringent super-surface structure. The broadband polarization and phase control array comprises a substrate, a metal reflection film, a medium layer, a cross sub-wavelength optical antenna unit, a birefringent phase control super-surface structure unit and a birefringent phase control super-surface structure array. According to a reasonable design, the birefringent phase control super-surface structure unit has a birefringent effect and a phase control function, and under incident conditions of circularly polarized light, the reflected light further has polarization control and phase control functions of space sub-wavelength resolution; and with respect to the circularly polarized incident light, the birefringent phase control super-surface structure units are arranged to form a birefringent phase control super-surface structure array according to the needed space polarization and phase distributionin order to obtain a special optical field with any polarization and phase distribution. Moreover, the birefringent phase control super-surface structure unit and the birefringent phase control super-surface structure array have wide operating wavelength ranges.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method for growing RFeO3 photomagnetic function crystal by secondary melting method
InactiveCN102011188AQuality improvementImprove the finishPolycrystalline material growthBy zone-melting liquidsCzochralski methodPhysical chemistry
The invention relates to the field of research on growth of RFeO3 photomagnetic function crystal, an optical floating zone secondary melting method is a brand new and efficient growth method for the materials at present. In the method, high-purity ferric oxide and rare earth oxide are used as raw materials to prepare a material bar through processes of milling, sintering, isostatic pressing and the like according to chemical proportion, and then, the material bar is placed in an optical floating zone furnace to grow in air atmosphere. A surface of a single crystal prepared by the method has ideal surface finish, density and uniformity, a characteristic peak of the single crystal is obviously increased, and FWHM is obviously reduced, so that crystallization quality of the crystal is greatly improved, a pure-phase integral RFeO3 crystal can be obtained more easily; simultaneously, the method has high efficiency and can appropriately adjust growth speed in a rang of 1-9mm / h according to different application goals, that is unachievable to traditional methods, such as a pulling method, a hydrothermal method, a descending method and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
All-fiber STED super-resolution microscopic illumination device
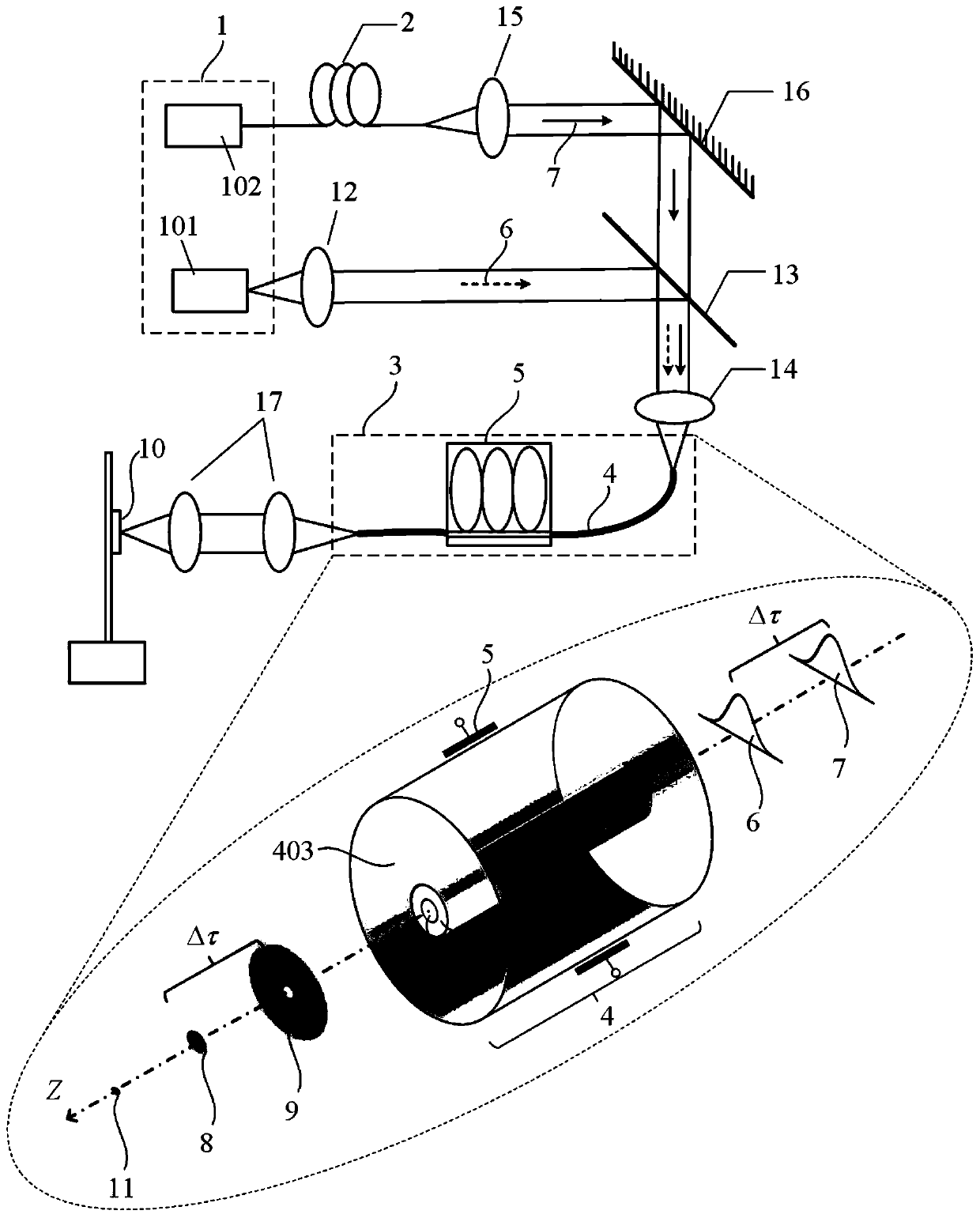
The invention provides an all-fiber STED super-resolution microscopic illumination device. The device mainly consists of a laser 1, a delay unit 2 and a beam generator 3, wherein the beam generator 3mainly consists of a double-clad fiber 4 and a polarization controller 5; the beam generator 3 can convert short-wave laser light 6 and long-wave laser light 7 emitted by the laser 1 into Gauss-shapedexcitation light 8 and hollow annular loss light 9, respectively; and since the light spot centers of the generated light are completely coincided and the light is irradiated on a fluorescent sample10 in sequence after the delay of the delay unit 2, stimulated emission depletion (STED) is generated, fluorescent light 11 with extremely small light spot is stimulated, and the final resolution is not limited by the diffraction of light, thereby breaking the diffraction limit and realizing all-fiber STED super-resolution microscopic illumination. The device has the advantages of highly integrating light beam generators and enabling equipment to be more flexible and stable.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Spectrum selective photoelectric detector and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102651421AHigh spectral selectivityPlay the role of "filter"Semiconductor devicesPhotovoltaic detectorsIndium
The invention provides a spectrum selective photoelectric detector and a preparation method thereof, which comprises a substrate, and a plasmon structure layer and a tin indium oxide layer which are sequentially arranged on the substrate, the plasmon structure layer comprises a plurality of medium structure units, each medium structure unit comprises a strip type main absorbing window and one pair or multiple pairs of strip type absorbing adjustment windows, and the strip type absorbing adjustment windows are positioned on one side or two sides of the strip type main absorbing window. The invention also provides a preparation method for the spectrum selective photoelectric detector, which comprises the following steps that: 1) the substrate is provided; 2) the plasmon structure layer is grown on the substrate and is graphed to form the medium structure unit; and 3) the tin indium oxide layer is grown on the plasmon structure layer.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Double face high-temperature superconducting film multi-layer structures and method for producing the same
InactiveCN101162626AImprove textureGood lattice matchingSuperconductors/hyperconductorsLayered productsHigh temperature superconductingSingle crystal
The invention discloses a double-sided high temperature super-conductive film multiple-layer structure and the preparation method. The double-sided high temperature super-conductive film multiple-layer structure comprises a non-monomorph oxide uropatagia of low cost, both sides of the non-monomorph oxide uropatagia of low cost are provided with a metal film layer, an oxide film layer of biaxial texture and a super-conductive film layer. At first, the metal film with a good surface is arranged on the non-monomorph oxide uropatagia of low cost and then the ion beam ancillary deposition technology is adopted to prepare the oxide film material of biaxial texture on the metal film, saving the expensive oxide monomorph material as the material of the uropatagia of large area of double-sided high temperature super-conductive film but choosing the Si monomorph of low cost and the like. The double-sided high temperature super-conductive film that is prepared is of low cost.
Owner:GENERAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR NONFERROUS METALS BEIJNG
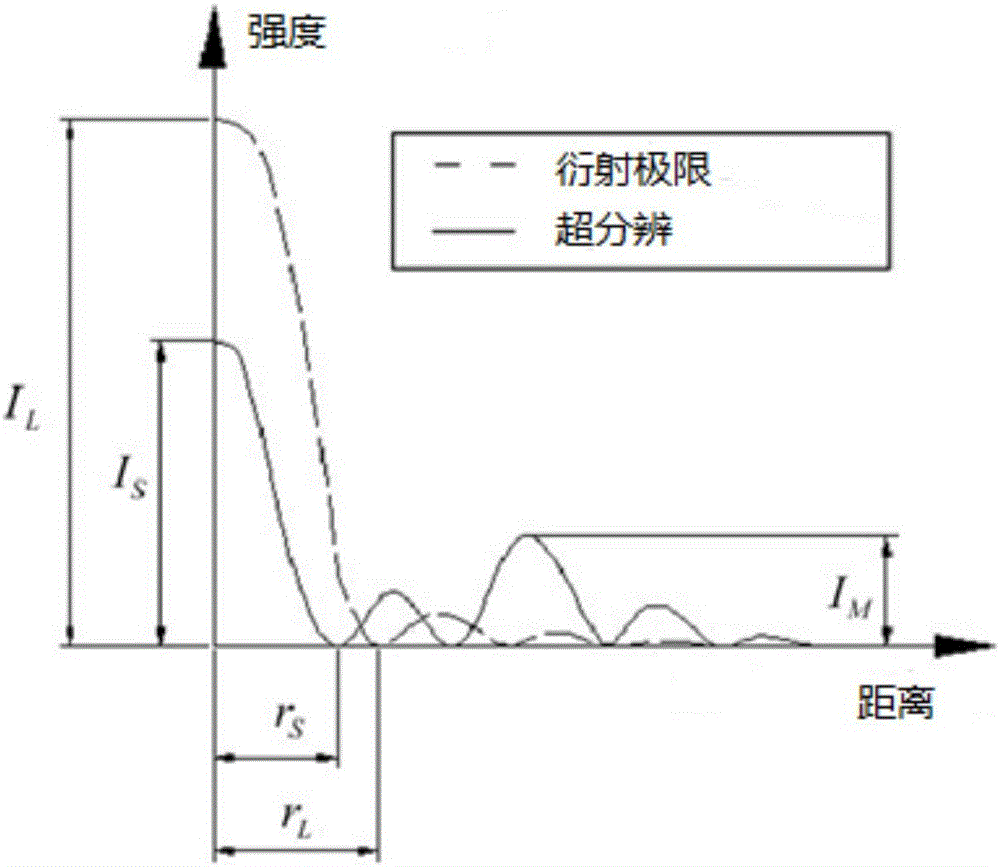
Super-resolution confocal ophthalmoscope based on optical pupil filter and dark field technique
The invention discloses a super-resolution confocal ophthalmoscope based on an optical pupil filter and a dark field technique. The super-resolution confocal ophthalmoscope is capable of accurately acquiring super-resolution dark field images of retinas of living human eyes in real time, and comprises a beacon light source, an imaging light source, an optical pupil filter, a two-dimensional scanning galvanometer, a Hartmann sensor, a deformable mirror, an optical filter and a photoelectric detection system. The beacon light source is used for correcting human eye aberrations; the imaging light source is used for acquiring human eye images. The operating method comprises the following steps: characterizing resolution according to Rayleigh criterion by using full width at half maximum, adding a two-zone type phase optical pupil filter at an illumination end, wherein the pinhole is equal to Airy disk size; allowing the pinhole to be equal to 1.5 times that of Airy disk size when the filter(s) is / are arranged at the imaging end or two ends, so that the diffraction limit condition can be realized when the transverse full width at half maximum is less than the pinhole of a general microscope equal to the Airy disk size, and the super-resolution image can be acquired at a super-resolution ratio. On the basis, the pinhole equal to the Airy disk size is translated by an Airy disk distance, the pinhole equal to 1.5 times that of the Airy disk size is subjected to central blocking or linear blocking, so that dark field imaging can be realized.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Backlight unit and display device comprising same
ActiveUS10168461B2Reduce FWHMWide color gamutMechanical apparatusLight guides with fluorescent dopantsPhosphorDisplay device
A backlight unit including a light source formed to provide primary light; a quantum dot phosphor excited by the primary light provided from the light source to emit secondary light having a wavelength different from a wavelength of the primary light and disposed to be spaced apart from the light source; an optical agent absorbing light having a specific wavelength from the primary light provided by the light source and the secondary light emitted from the quantum dot phosphor; and a matrix configured to support the quantum dot phosphor and the optical agent. Further, the quantum dot phosphor and the optical agent are randomly mixed in the matrix; and the quantum dot phosphor, the optical agent, and the matrix form a composite.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
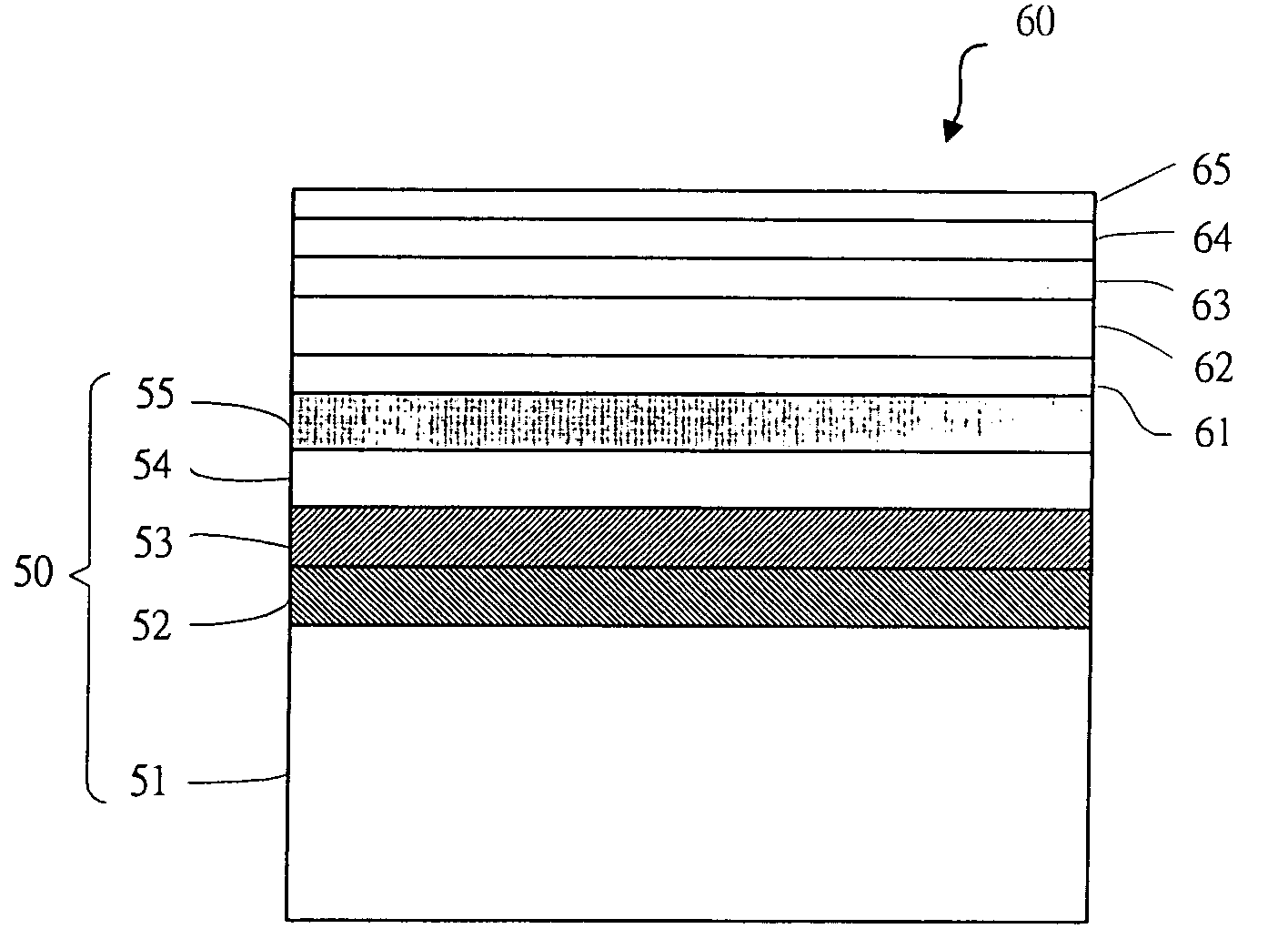
Method for fabricating a compound semiconductor epitaxial wafer
InactiveUS20060011129A1Low occurrenceEliminate stressPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesDislocationCompound (substance)
The present invention discloses a compound semiconductor epitaxial wafer and its fabrication method. The method comprises the steps of the followings: depositing a first buffer layer of silicon on a silicon substrate; depositing a compound semiconductor second buffer layer on the first buffer layer; growing a compound semiconductor first epitaxy layer on the second buffer layer; reducing the threading dislocation density by a thermal treatment, which is caused by the discrepancy in the lattice constants or in the thermal expansion coefficients of the silicon substrate and the compound semiconductor epitaxy layers; growing a compound semiconductor second epitaxy layer on the first epitaxy layer; and, applying a thermal treatment again. Accordingly, a compound semiconductor epitaxy layer with excellent crystal quality is obtained.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
An all-fiber sted super-resolution micro-illumination device
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Display devices with different light sources
ActiveUS20210028383A1Wide viewing angleReduce manufacturing costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhosphorDisplay device
Embodiments of a display device are described. A display device includes first and second sub-pixels. The first sub-pixel includes a first light source having a quantum dot (QD) film, a blocking layer disposed on the QD film, and a first portion of an organic phosphor film disposed on the blocking layer and a first substrate configured to support the first light source. The blocking layer is configured to prevent emission of light from the first portion of the organic phosphor film and the QD film is configured to emit a primary emission peak wavelength in a red, green, cyan, yellow, or magenta wavelength region of an electromagnetic (EM) spectrum. The second sub-pixel includes a second light source and a second substrate configured to support the second light source. The second light source has a second portion of the organic phosphor film disposed adjacent to the QD film. The second portion of the organic phosphor film is configured to emit a primary emission peak wavelength in a blue, violet, or ultraviolet wavelength region of an EM spectrum.
Owner:SHOEI CHEM IND CO LTD
LED package, backlight unit and liquid crystal display device
ActiveUS10573792B2Increase brightnessReduce FWHMNon-linear opticsSemiconductor devicesLiquid-crystal displayOrganic solvent
Disclosed is a light emitting diode package that includes: a frame having a light emitting diode (LED) thereon; and a glass cell over the LED, the glass cell including a quantum dot dispersed in one of a resin and an organic solvent.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
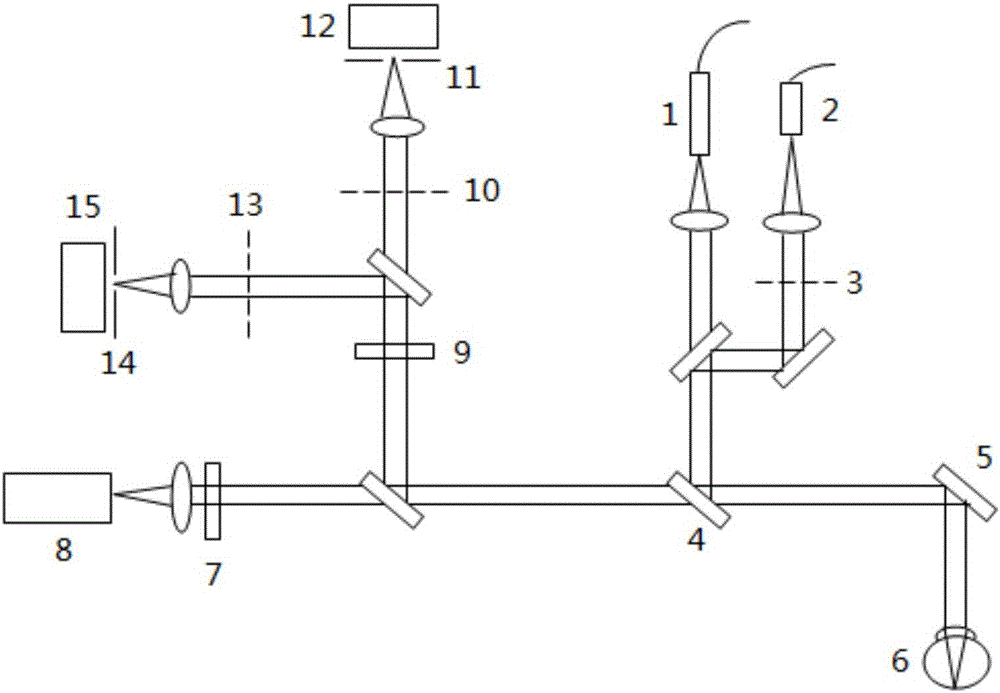
Dual-wavelength dual-confocal laser microscopic measurement device and measurement method
InactiveCN113189102AReduce FWHMImprove horizontal resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansBeam splitterErbium lasers
The invention discloses a dual-wavelength dual-confocal laser microscopic measurement device and a measurement method, relates to the technical field of optical precision detection, and aims to improve the axial resolution capability and the transverse resolution capability of a laser confocal system at the same time. According to the method, the dual-wavelength dual-confocal laser microscopic measurement device comprises lasers, an incident light path, a reflection light path and a detection device, a first laser I and a first laser II respectively emit laser beams with different wavelengths, and the laser beams are converged to a sample through a beam splitter, a collimator, a polarizing beam splitter, a quarter-wave slide and an objective lens; and the reflected light is reflected by the polarizing beam splitter after passing through the objective lens and the quarter-wave slide, is divided into two paths by the semi-reflecting and semi-transmitting mirror, and then enters the detector I and the detector II respectively for detection. According to the method, the detector I and the detector II are respectively arranged at positions conjugated with the focus of the objective lens, and the output obtained by multiplying the normalized axial response curves of the double detectors is used as the output of the confocal system, so the confocal system is suitable for optical high-resolution measurement.
Owner:LASER FUSION RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Light emitting diode and driving method thereof, light source device and electronic equipment
ActiveCN111599899AImprove shade color purityAbsorb moreStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesHigh energyColored light
The invention provides a light emitting diode and a driving method thereof, a light source device and electronic equipment, and relates to the technical field of semiconductors. The light emitting diode comprises a substrate, a reflective light emitting layer, a first electrode, a second electrode, a first insulating layer, a saturable absorber layer, a third electrode, a fourth electrode and a reflective composite layer, wherein the reflective light emitting layer disposed on the substrate; the first electrode, the second electrode and the first insulating layer are separately arranged on thereflective light emitting layer; the saturable absorber layer disposed on the first insulating layer; the third electrode, the fourth electrode and the reflective composite layer are separately arranged on the saturable absorber layer, and the reflectivity of the reflective light emitting layer is greater than that of the reflective composite layer; and orthographic projections of the saturable absorber layer, the third electrode, the fourth electrode and the reflective composite layer on the reflective light emitting layer are not overlapped with the first electrode and the second electroderespectively. According to the invention, after the light emitted by the reflective light emitting layer passes through the saturable absorber layer, the light with low energy is absorbed more, and the light with high energy is absorbed less, so that the full width at half maximum of the spectrum of the light emitting diode is reduced, and the color purity of the colored light of the light emitting diode is improved.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
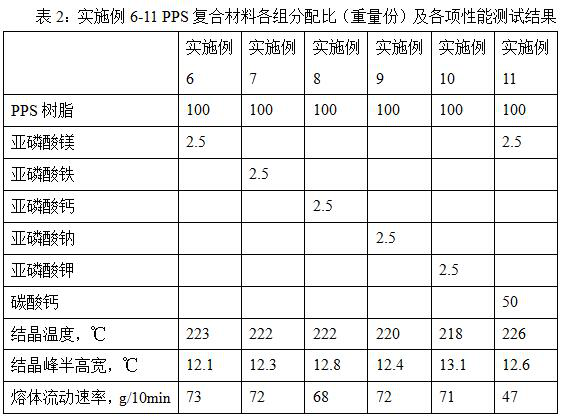
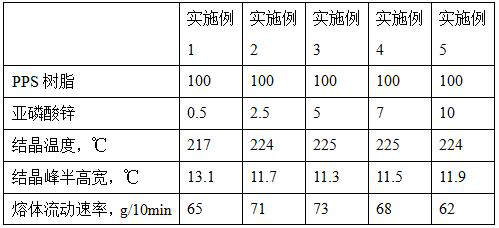
PPS composite material, and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a PPS composite material which comprises the following components in parts by weight: 100 parts of PPS resin, and 0.1-10 parts of a phosphorous acid metal salt. By adding the phosphorous acid metal salt, the crystallization rate of the PPS composite material can be increased. The PPS composite material has the advantage of rapid crystallization, and the melt flow rate of the PPS composite material can be increased.
Owner:KINGFA SCI & TECH CO LTD
Coherent maser radiation cold atomic clock
InactiveCN100589049CReduce FWHMExtended transit timeApparatus using atomic clocksPulse automatic controlMaserHelmholtz coil
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Composite micro-nano structure array on high light-transmission substrate and method and application thereof
ActiveCN101544348BSimple structureEasy to integrateCoupling light guidesFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicro nanoFluorescence
The invention relates to a composite micro-nano structure array on a high light-transmission substrate and a method and application of the same. The invention is characterized in that micro-nano structure arrays of light guide materials on the high light-transmission substrate are taken as supporting structures of fluorescent conjugated polymers for detection. The method comprises: firstly, preparing the micro-nano structure arrays and secondary structure arrays of the light guide materials on the high light-transmission material substrate such as quartz and the like; and secondly, coating the fluorescent conjugated polymers which are sensitive to specified analyte on the surface of the nano structure substrate to form the composite micro-nano structure array which is used for detecting an object. The invention takes the micro-nano structure arrays of different light guide materials as adhesive substrates of the fluorescent conjugated polymers and utilizes the advantages of micro-nanostructures such as large specific surface area, evanescent wave effect, micro resonant cavity action and the like to improve the sensitivity of detection and the signal intensity, prolong the servicelife and improve the reutilization property. The composite micro-nano structure array on the high light-transmission substrate can be applied to the detection of the specificity and high sensitivity of solid, liquid and gas molecules.
Owner:浙江同创海诚科技有限公司
Full wave-transparent zone plate
ActiveCN108646330AIncrease light intensityImprove efficiencyDiffraction gratingsFull waveRefractive index
The embodiment of the invention discloses a full wave-transparent zone plate. The full wave-transparent zone plate includes a concentric ring structure, wherein the concentric ring structure includesa first ring body and a second ring body which are alternately arranged, and the radius rk of the kth ring of the concentric ring structure satisfies the formula (as shown in the description), whereinf is the focal length of the full wave-transparent zone plate, and lambda is the wavelength of the incoming wave, and k is a positive integer; and the first ring body and the second ring body have the same height and satisfy the formula (as shown in the description), wherein n1 is the refractive index of the second ring body, and a is a positive odd number. The full wave-transparent zone plate can focus the parallel incoming wave, and can improve the light intensity of the focused light spot and the focusing efficiency.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Honeycomb-type collimator for X-ray pencil beam scanning intensity modulation radiation therapy
The invention relates to a honeycomb-type collimator for X-ray pencil beam scanning intensity modulation radiation therapy. The honeycomb-type collimator consists of all-blank collimator units and full-gear collimator units, wherein the all-blank collimator units can make X-rays pass through the all-blank collimator units, the transmissivity of the full-gear collimator units is not greater than 3%so that the X-rays cannot pass through the full-gear collimator units, four side end faces of each all-blank collimator unit are designed into trapezoid end faces traced to the target center (point)of an X-ray source so as to form four-faced focusing. The all-blank collimator units and the full-gear collimator units are arranged in the way similar to a bidimensional checkerboard to form a honeycomb-type collimator set. According to each all-blank collimator unit in the honeycomb-type collimator set, each X-ray pencil beam entering the all-blank units can be further collimated, so that the full width at half maximum of each beam is reduced to 3-8 mm.
Owner:胡逸民
FABRICATION METHOD OF InP BASED QUANTUM DOT BY USING AMINOPHOSPHINE TYPE P PRECURSOR AND CORE SIZE-SORTING PROCEDURE
ActiveUS20200362241A1High quantum yieldReduce FWHMNanoopticsLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingPhysical chemistryQuantum dot
A method for fabricating quantum dots according to the present disclosure includes (a) synthesizing InP cores based on an aminophosphine type phosphorus (P) precursor, (b) size-sorting the InP cores, and (c) forming at least two shells on the size-sorted InP cores. In this instance, the size-sorting includes precipitating the InP cores with an addition of a dispersive solvent and a nondispersive solvent to the InP cores and separating the InP cores using a centrifugal separator, wherein the InP cores are separated in a descending order by size by performing iteration with a gradual increase in an amount of the nondispersive solvent.
Owner:HONGIK UNIV IND ACAD COOP FOUND
Sensing chip
InactiveCN106338496AImprove detection limitReduce FWHMMaterial analysis by optical meansNano structuringDielectric layer
The invention discloses a sensing chip. The sensing chip comprises a substrate, and a plurality of nano structures; the nano structures are arranged on the substrate periodically; each of the nano structures comprises a bottom metal layer arranged on the substrate, a middle dielectric layer arranged on the bottom metal layer, and a top metal layer arranged on the middle dielectric layer; and the area of each bottom metal layer is larger than that of a corresponding top metal layer.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
A multivalued phase-binary amplitude hyperdiffractive hollow ring focusing device
The invention provides a multi-value phase-binary amplitude super-diffraction hollow ring focusing device comprising a base, medium circle structure units and metal circle structure units. The medium circle structure regulated and controlled by multi-value phase and the metal circle structure regulated and controlled by binary amplitude are adopted. The phase of emergent light is determined by the thickness of the medium circle structure. The amplitude of emergent light is determined by the thickness of the metal circle structure. Multi-value phase regulation and control and binary amplitude regulation and control can be realized by changing the thickness of the medium circles and the metal circles. A space plane concentric circle array is formed by utilizing the medium circle and metal circle structure units so that focusing device transmission function amplitude phase space distribution required by far-field super-diffraction angular polarization hollow ring focusing is realized, the far-field super-diffraction angular polarization hollow ring focusing function breaking through the diffraction limit is realized, the far-field super-diffraction angular polarization hollow ring focusing performance is enhanced, far-field super-diffraction focusing spots are reduced, focusing efficiency is enhanced, sidelobe is suppressed and the range of field of view is enlarged.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
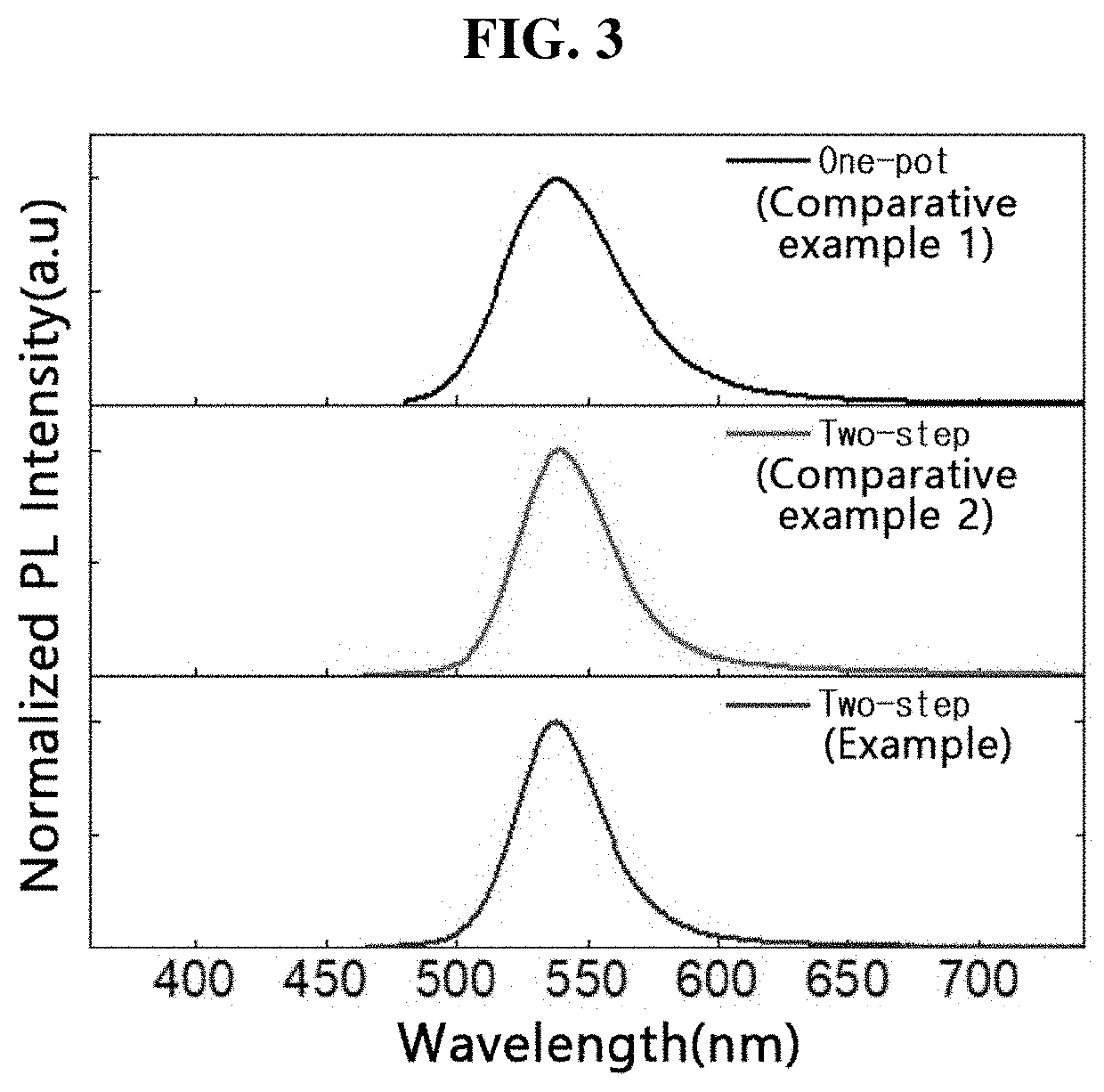
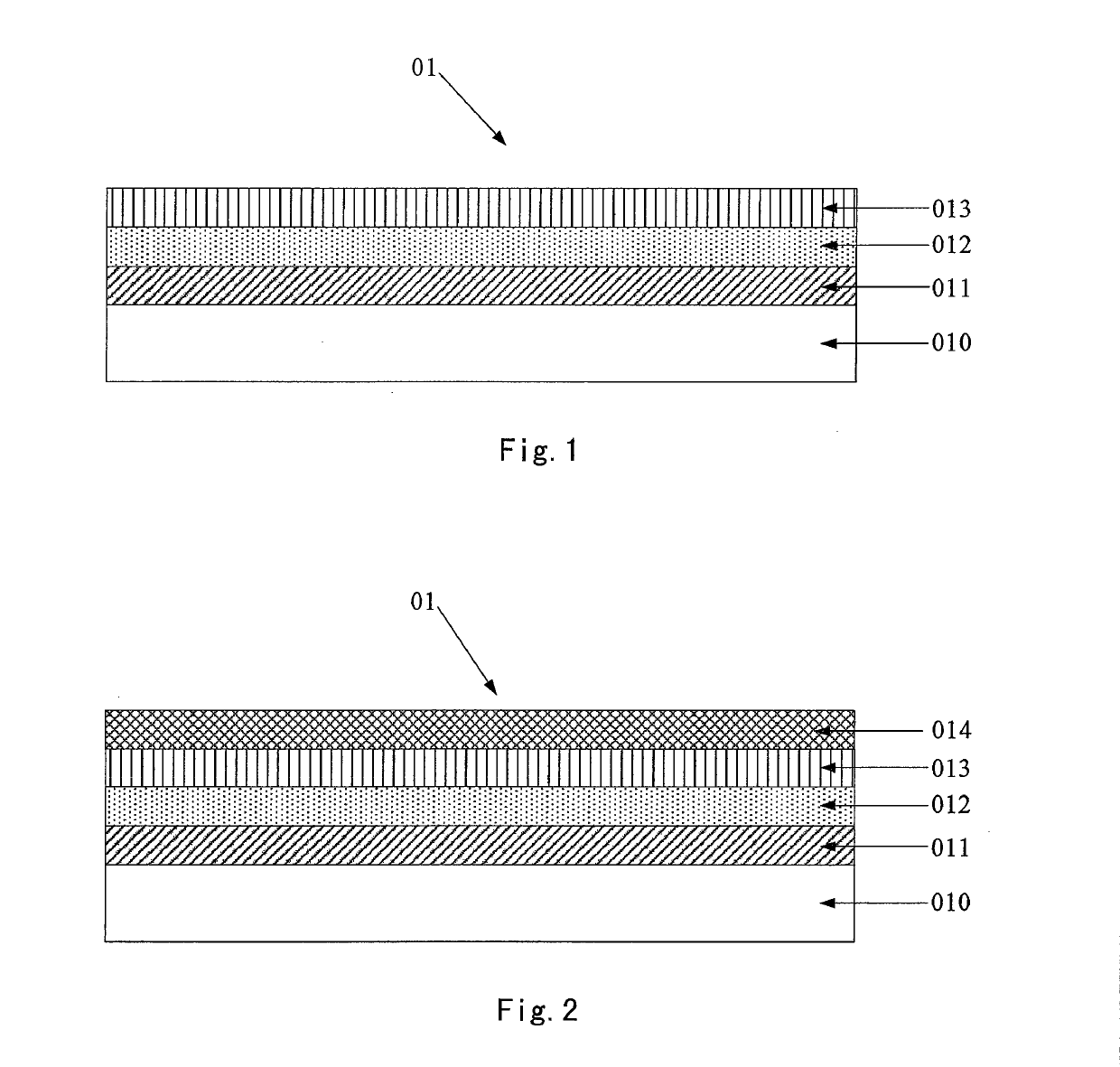
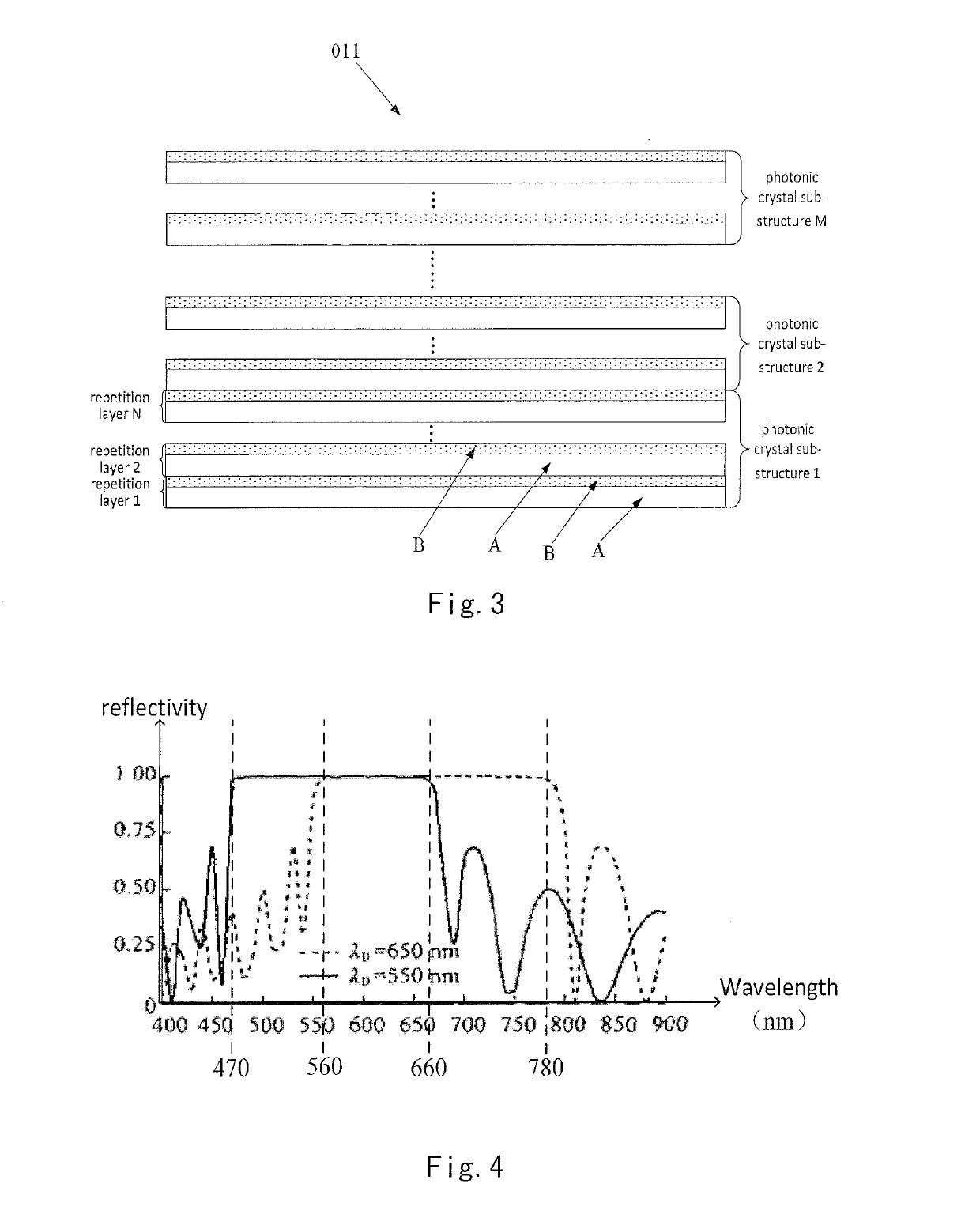
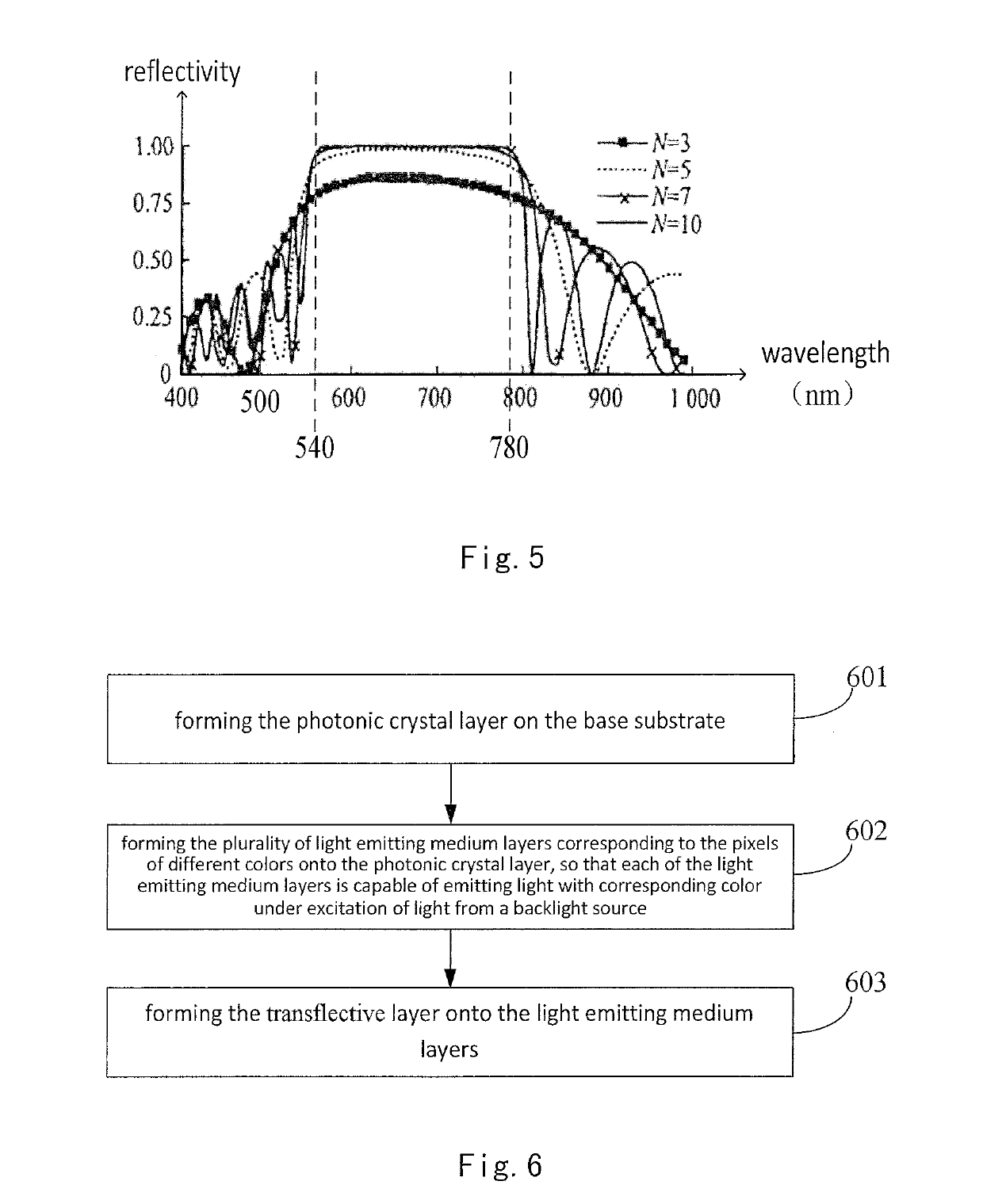
Color filter substrate, producing method thereof and display apparatus
ActiveUS10267964B2Lower capability requirementsIncrease power consumptionNon-linear opticsOptical elementsPhotonic crystalReflective layer
The present disclosure provides a color filter substrate, a method for producing the same and a display apparatus. The color filter substrate includes a base substrate; a photonic crystal layer located on the base substrate; a plurality of light emitting medium layers corresponding to pixels of different colors located on the photonic crystal layer, wherein the light emitting medium layer is capable of emitting light of corresponding color under excitation of light from a backlight source; a transflective layer located on the light emitting medium layers; wherein the photonic crystal layer is used to reflect the light emitted from the light emitting medium layers to the transflective layer, so that the light is oscillated and interferes between the photonic crystal layer and the transflective layer and finally exits from the transflective layer.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
A kind of hemispherical microlens and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a hemispherical microlens and a preparation method thereof. The lens includes at least one lens body (2), and the lens body (2) is: a standard microsphere lens (2') passing through a ball The surface of the center, and part of the spherical surface is cut in parallel on both sides of the surface passing through the center of the sphere. The preparation method is to cut off part of the spherical surface in parallel on both sides of the standard microsphere lens, and then soak it in the second material film layer (4). When the incident light parallel to the optical axis is incident on the partially cut spherical surface of the hemispherical microlens When , the light passing through the cut spherical surface will not participate in the formation of the spot, which is beneficial to improve the half-width of the spot; the light passing through the uncut spherical surface is farther away from the optical axis, forming a focal spot with a longer working distance, It can be applied in far-field parallel imaging / lithography to improve the efficiency of pattern parallel imaging / lithography with feature sizes close to or greater than 300nm.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Structure of deep ultraviolet light emitting diode and preparation method thereof
PendingCN113594314AReduce FWHMImprove luminous efficiencySemiconductor devicesFinal product manufactureMultiple quantumElectron blocking layer
The invention discloses a deep ultraviolet light-emitting diode structure and a preparation method thereof, and aims to improve the electroluminescent spectral characteristics of the current deep ultraviolet light-emitting diode, especially reduce the full width at half maximum of the spectrum, improve the purity of light and improve the luminous efficiency of the light. Therefore, the effectiveness of application to sterilization and phototherapy is promoted. The light-emitting diode at least comprises a substrate, an AlN layer located on the surface of one side of the substrate, an N-type AlaGa1-aN ohmic contact layer located on the surface of the AlN layer, an AlbGa1-bN / AlN / AlcGa1-cN interface planarization multi-layer structure located on the surface of the N-type AlaGa1-aN ohmic contact layer, an AlxGa1-xN first quantum barrier layer located on the surface of the AlbGa1-bN / AlN / AlcGa1-cN interface planarization multi-layer structure, an AlyGa1-yN / AlxGa1-xN multi-quantum well active layer located on the surface of the AlxGa1-xN first quantum barrier layer, an AlzGa1-zN final quantum barrier layer located on the surface of the AlyGa1-yN / AlxGa1-xN multi-quantum well active layer, a P-type AldGa1-dN electron barrier layer located on the surface of the AlzGa1-zN final quantum barrier layer, and a P-type AleGa1-eN ohmic contact layer located on the surface of the P-type AldGa1-dN electron barrier layer.
Owner:江西力特康光学有限公司
An electroluminescent device based on an exciplex system with a boron-containing organic compound
ActiveCN110492009BImprove stabilityReduce concentrationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSimple Organic CompoundsHost material
The invention relates to an electroluminescent device based on an exciplex system with a boron-containing organic compound, wherein the host material includes a first organic compound and a second organic compound, the HOMO energy level of the first organic compound and the energy level of the second organic compound The HOMO energy level difference is 0.2 eV or more, and the LUMO energy level difference of the first organic compound and the LUMO energy level of the second organic compound is 0.2 eV or more. The mixture or interface formed by the two generates exciplexes under the excitation of light or electric field. The singlet energy level of the exciplex is higher than that of the guest material, and the triplet energy level is higher than that of the guest material; and the first organic compound and the second organic compound have different carriers Transport characteristics; the guest material is an organic compound containing boron atoms. The organic electroluminescent device prepared by this method has the characteristics of high efficiency and long life.
Owner:JIANGSU SUNERA TECH CO LTD
Method for synthesizing a semiconducting nanosized material
PendingUS20220259495A1Low FWHMHigh quantum yieldNanoopticsPhosphorus compoundsSemiconductorNanomaterials
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com