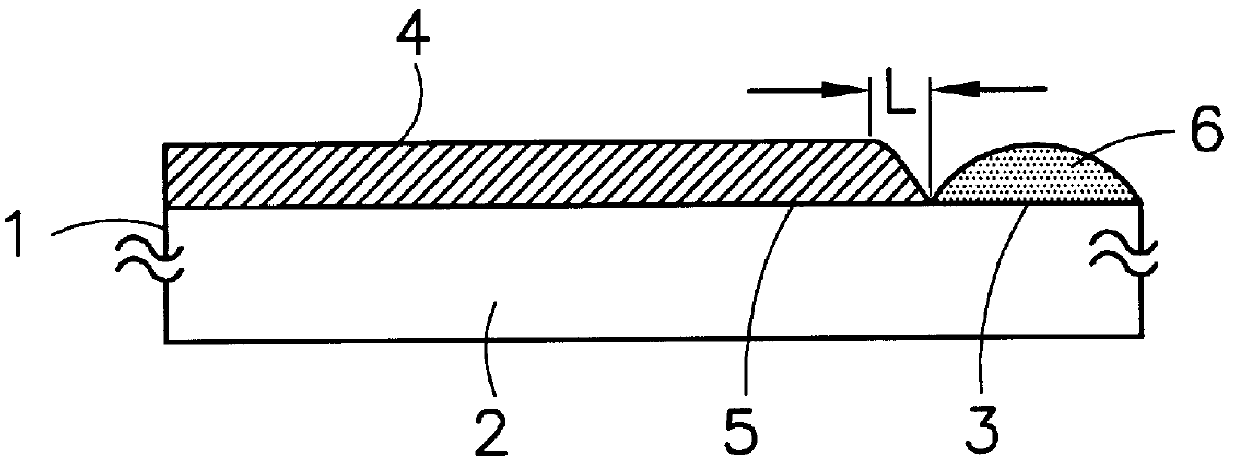
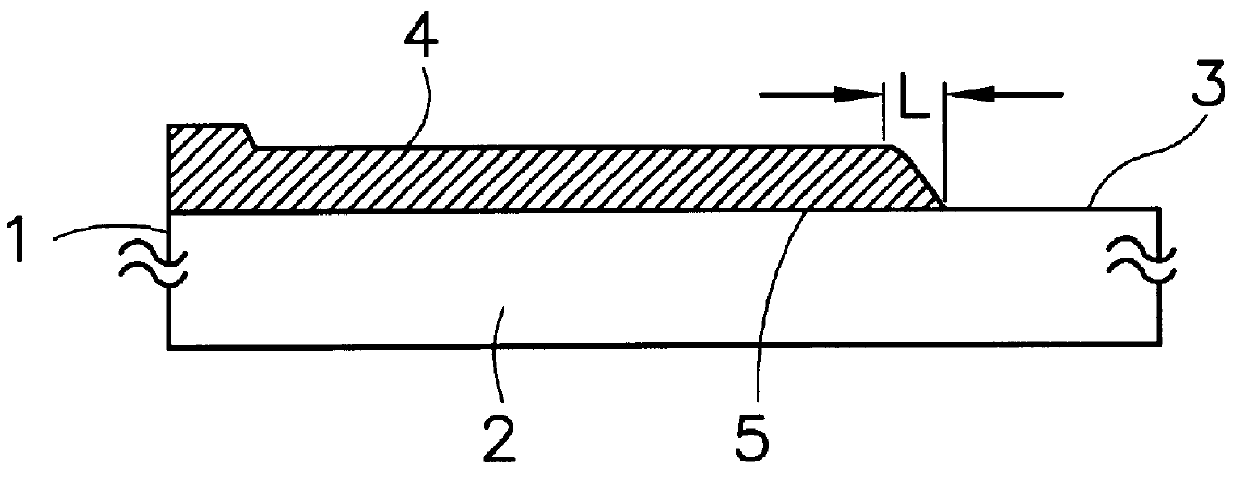
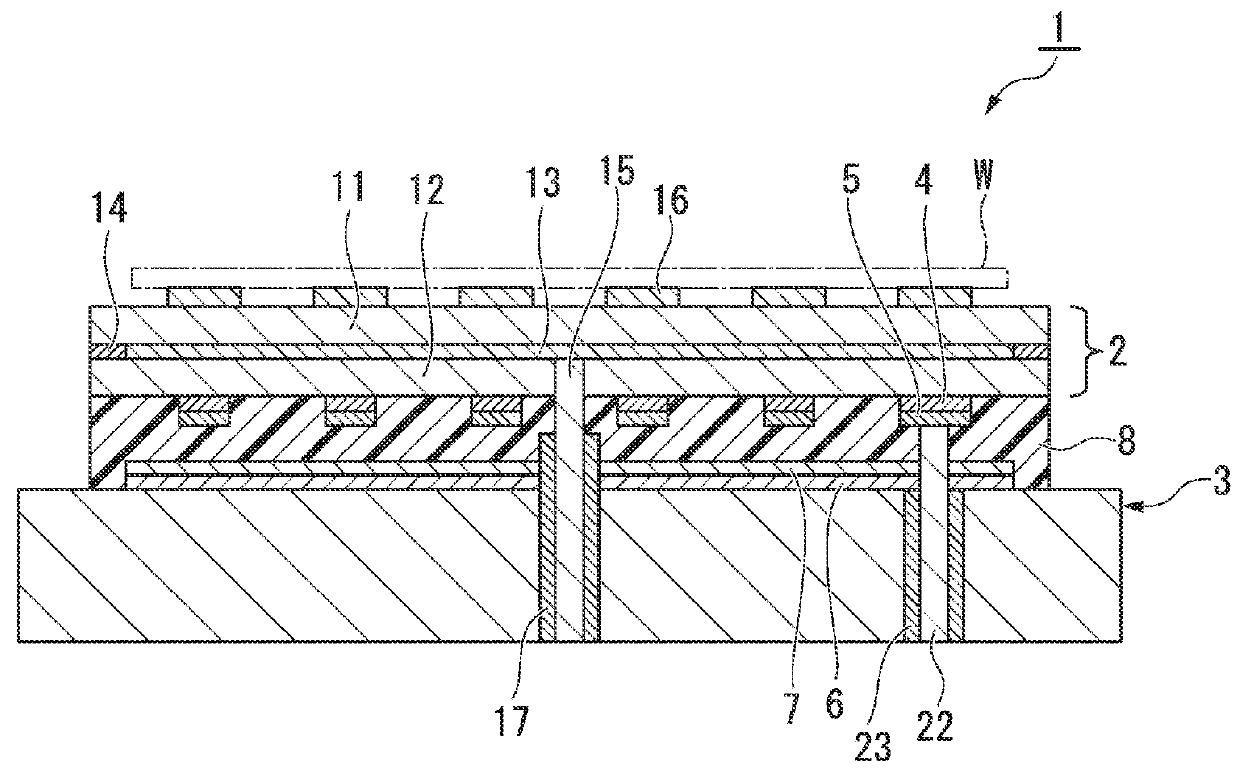
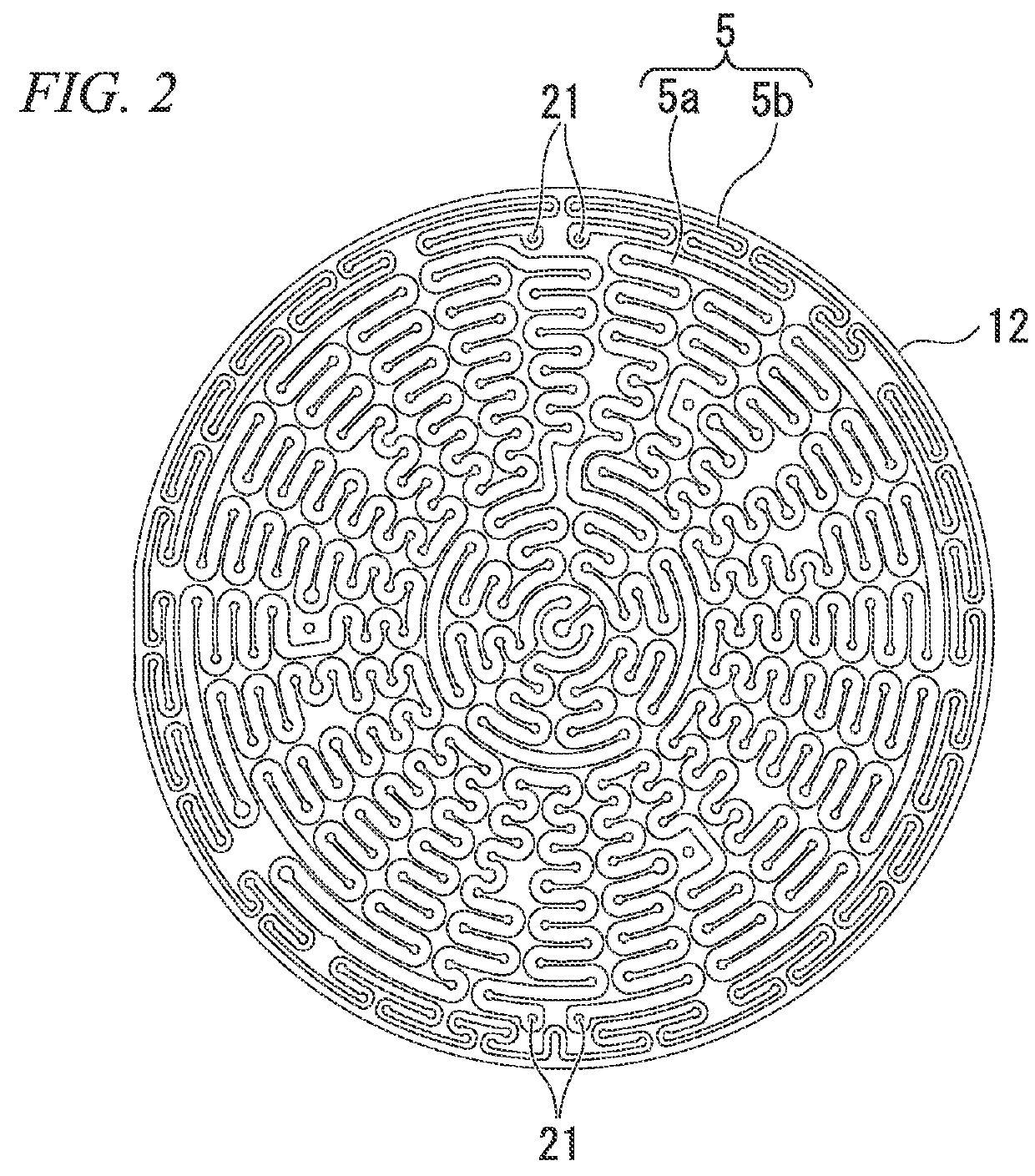
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
139results about How to "Avoid insulation breakdown" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
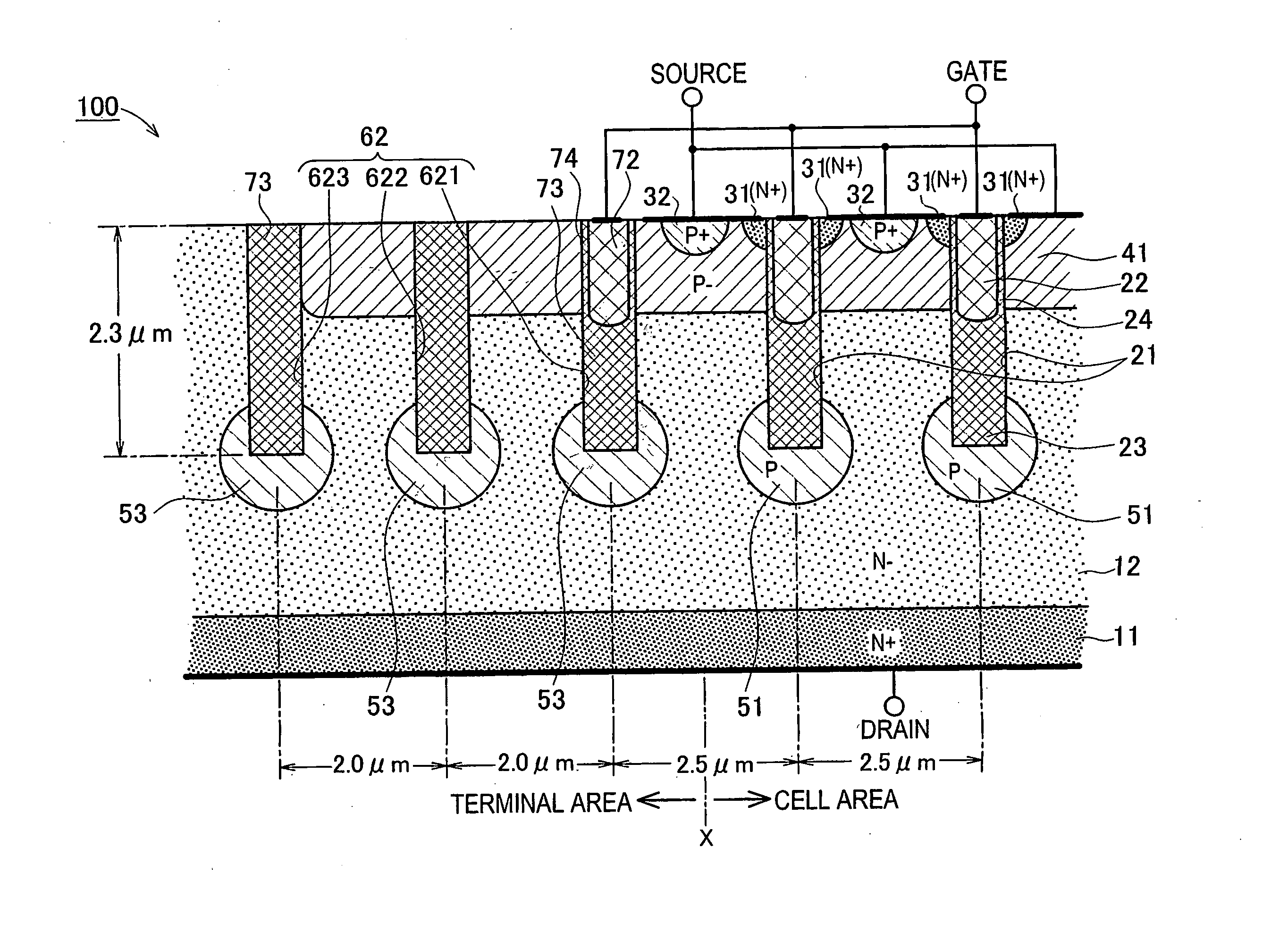
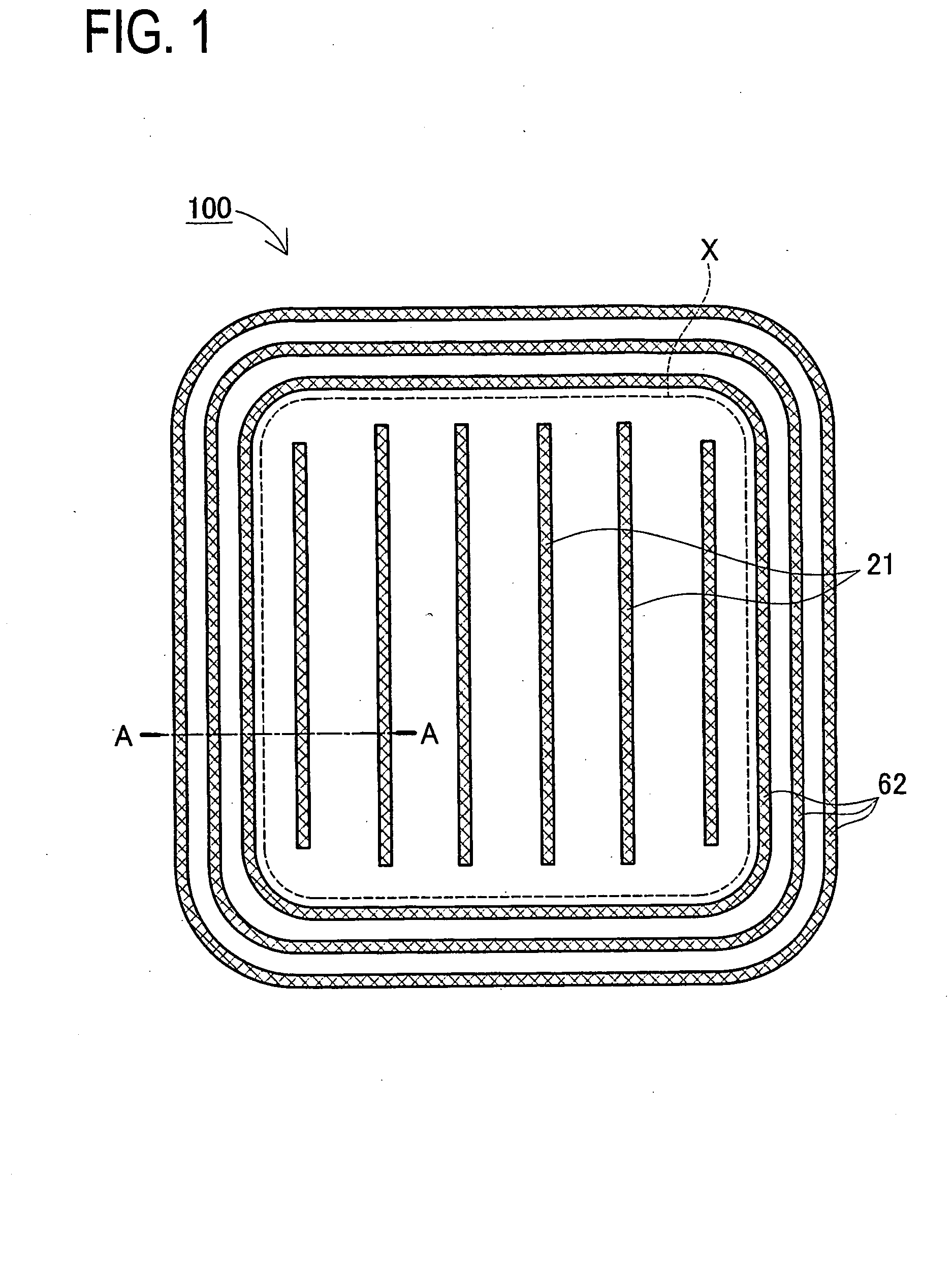
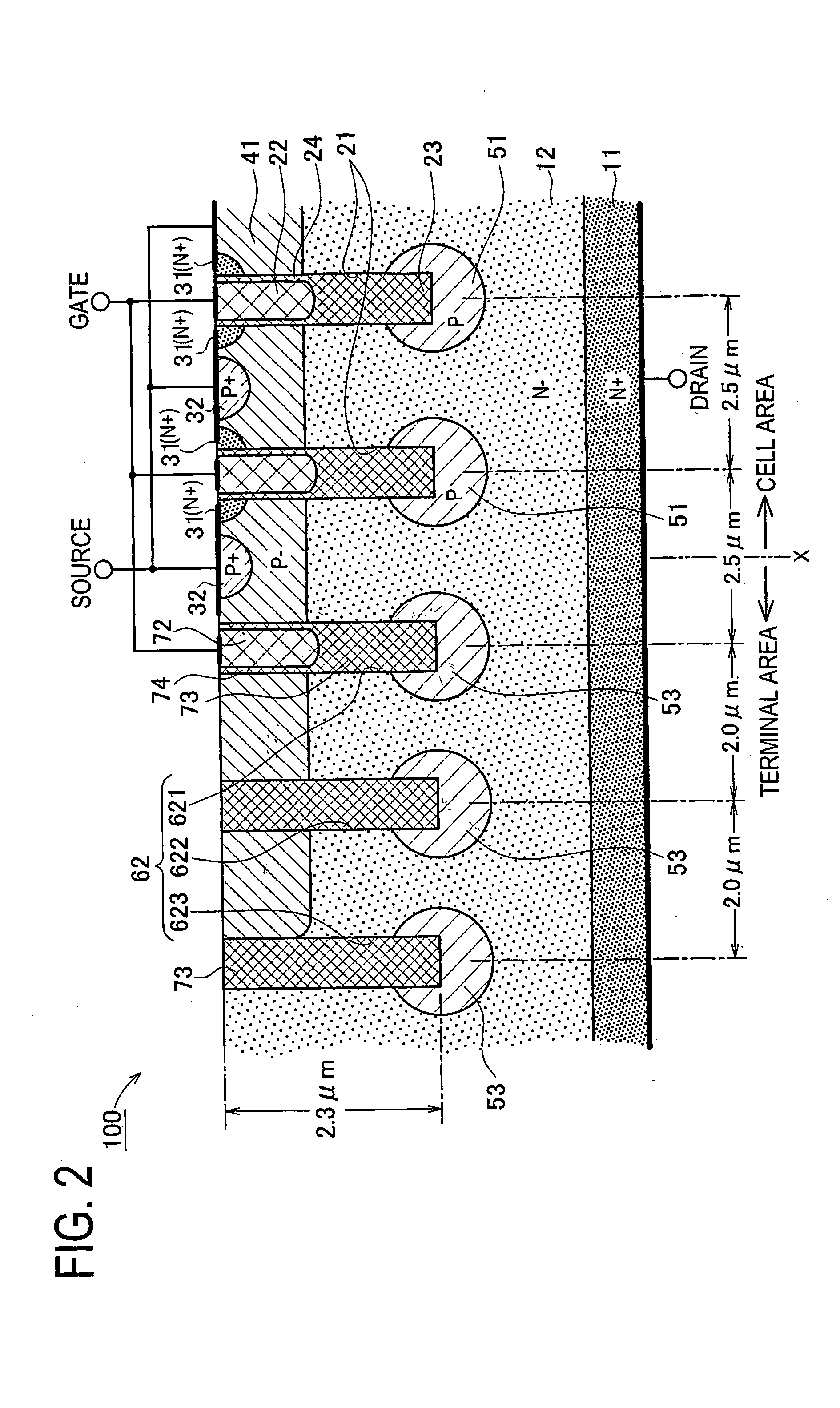
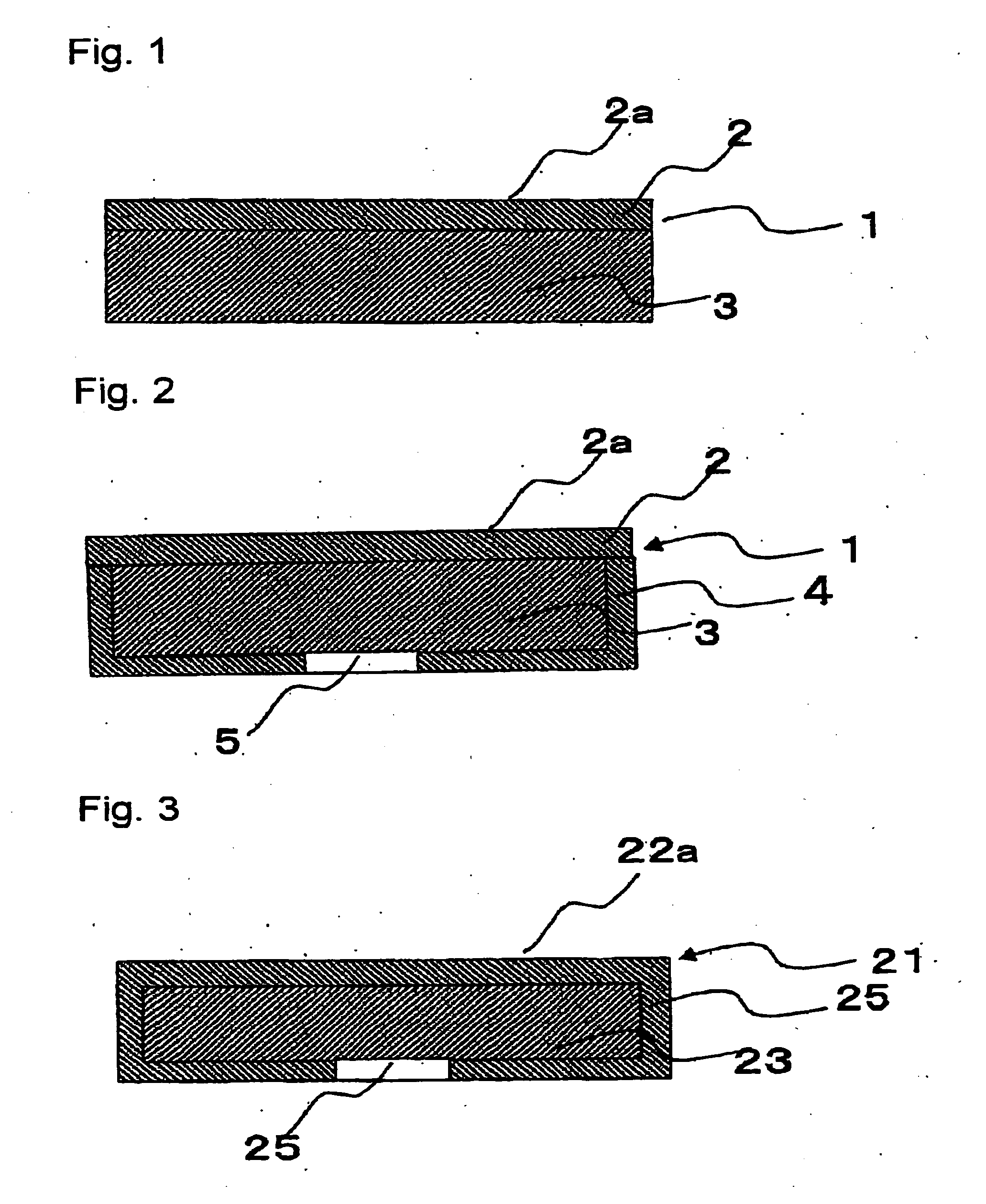
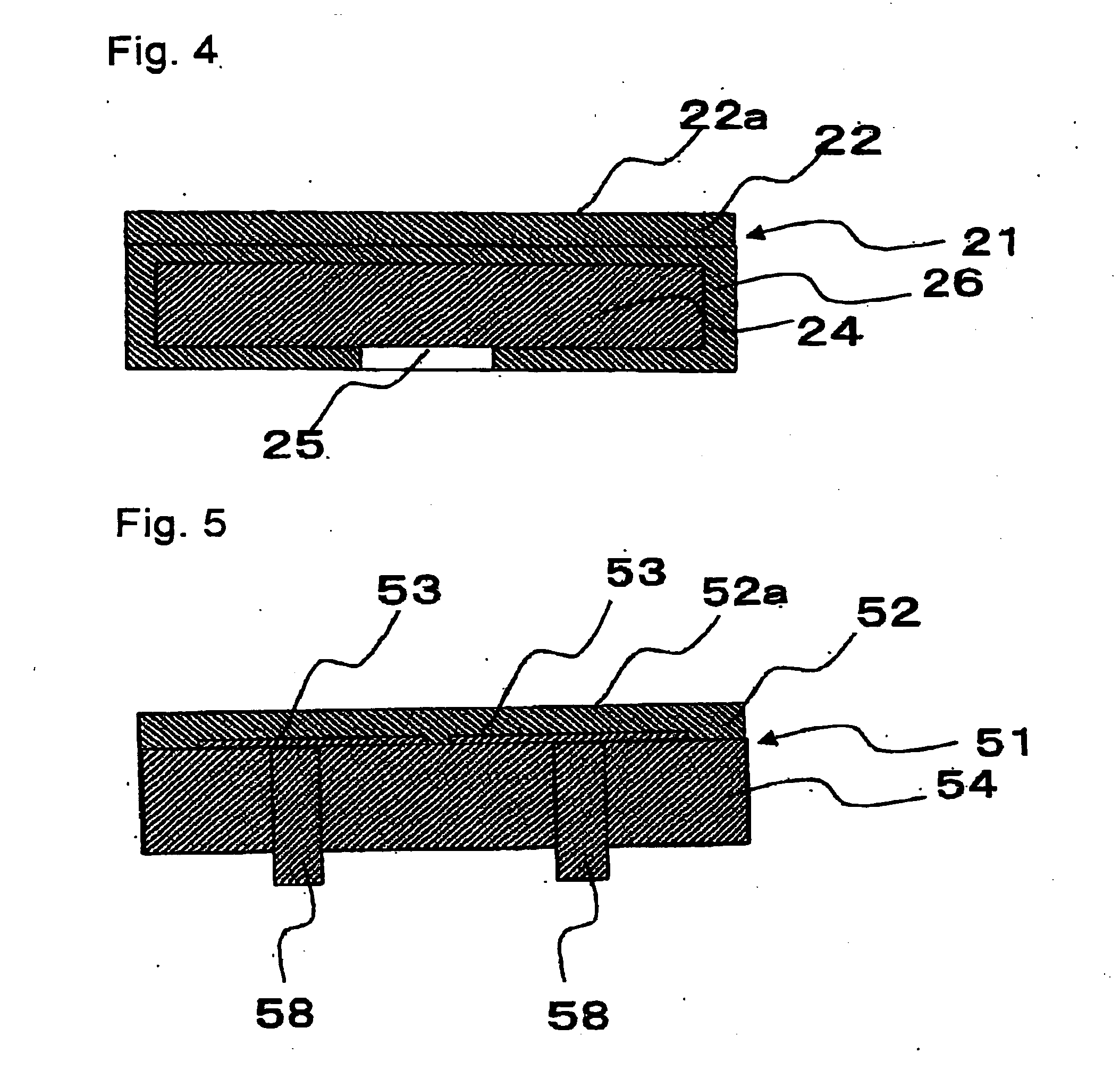
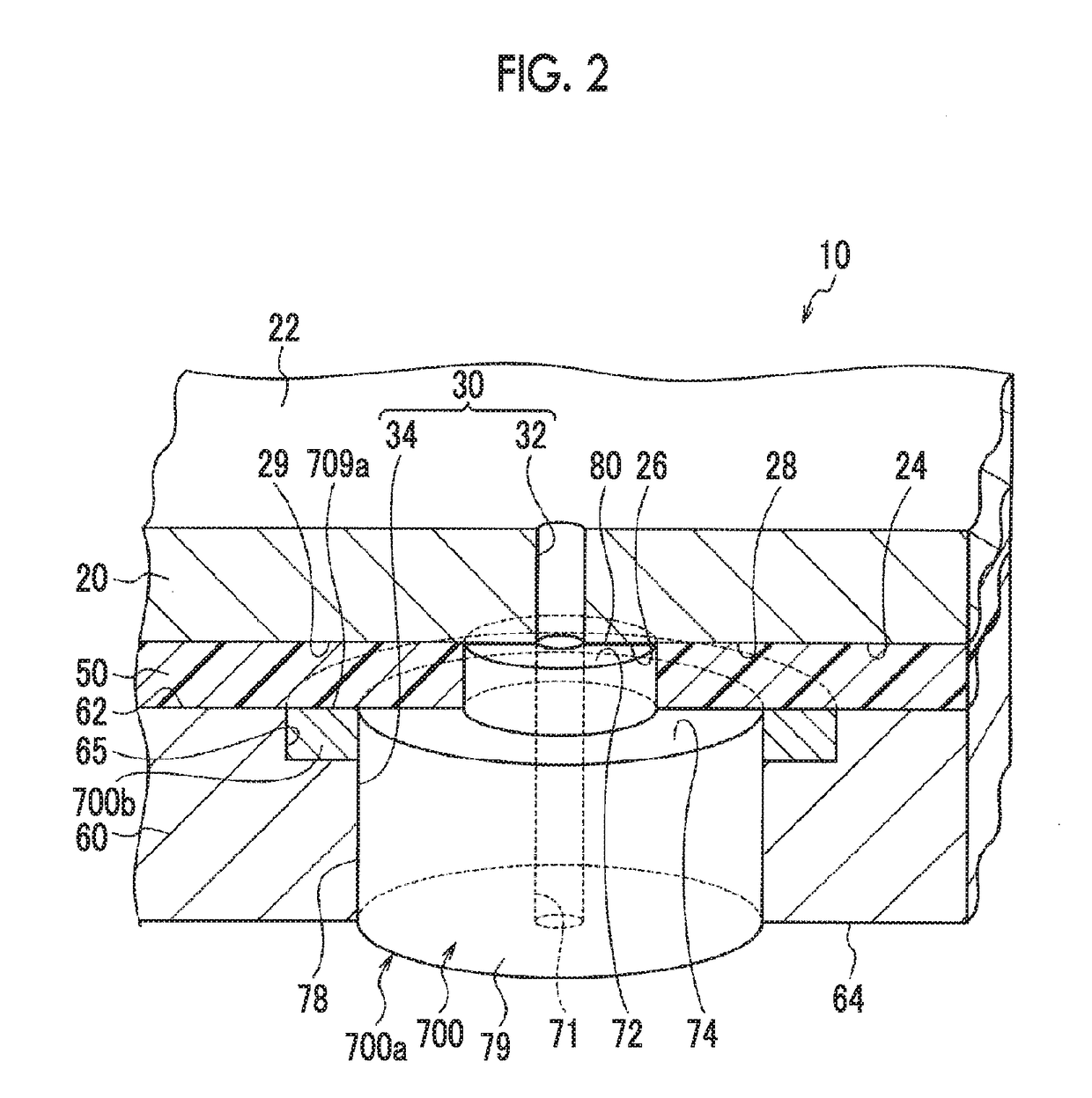
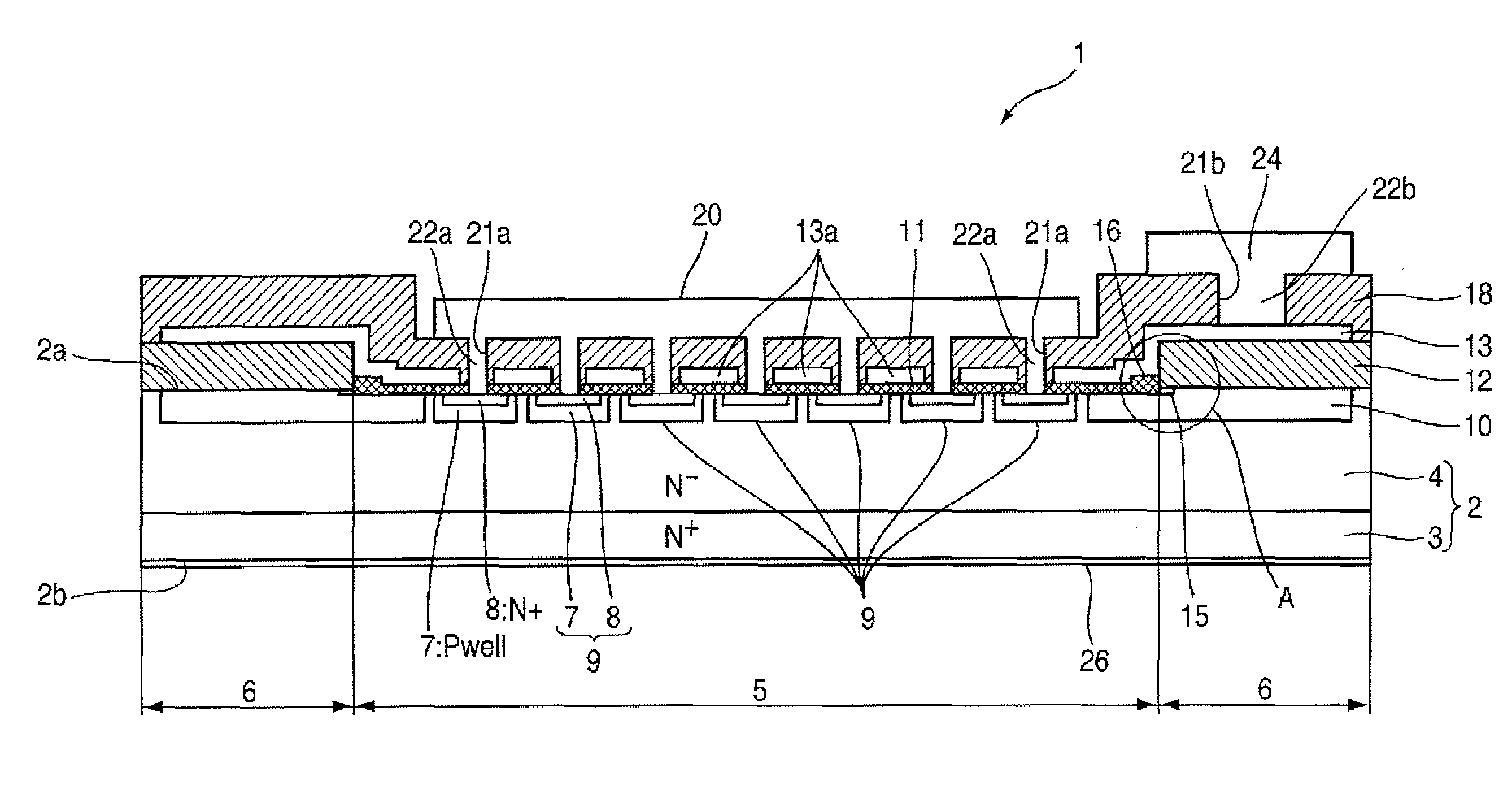
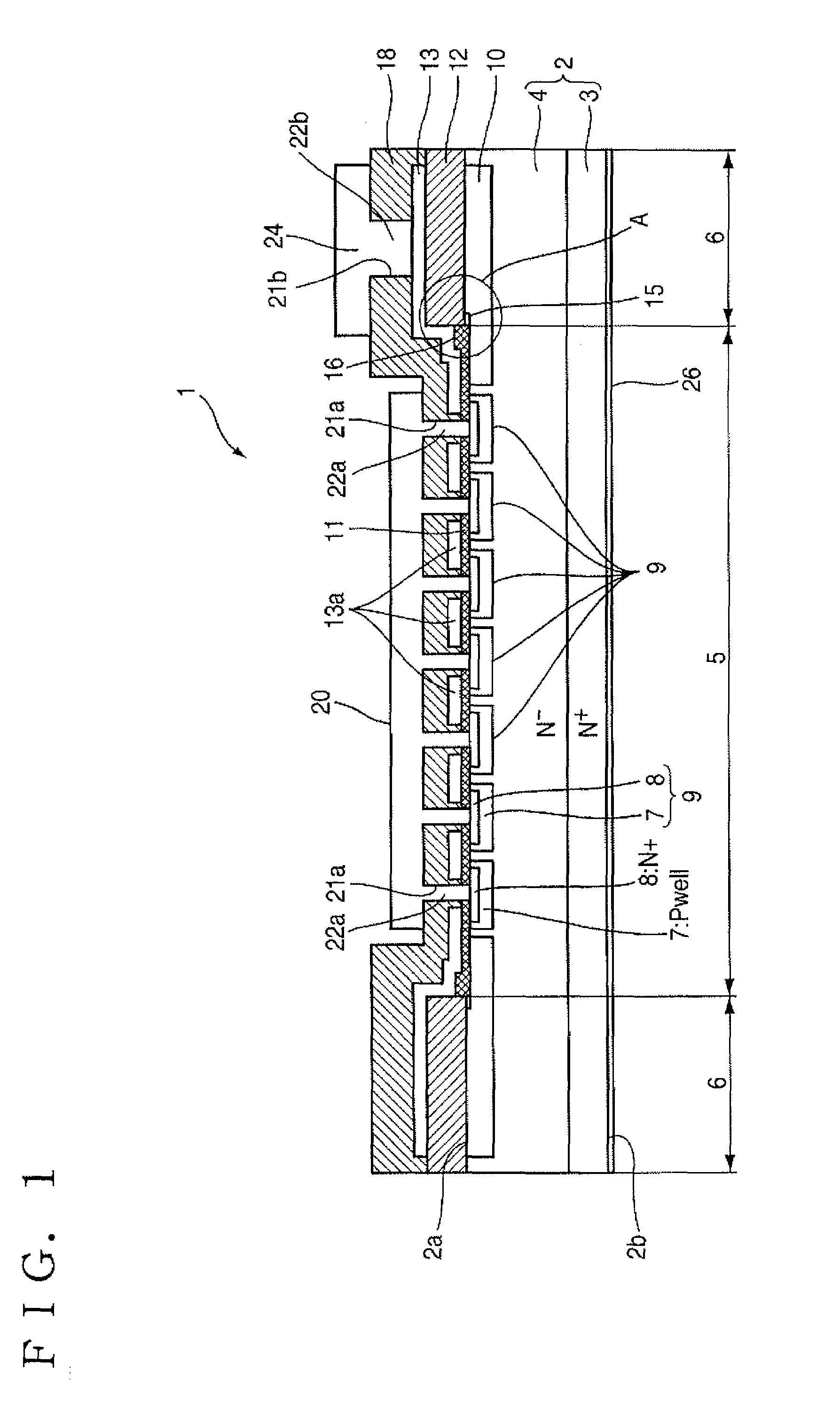
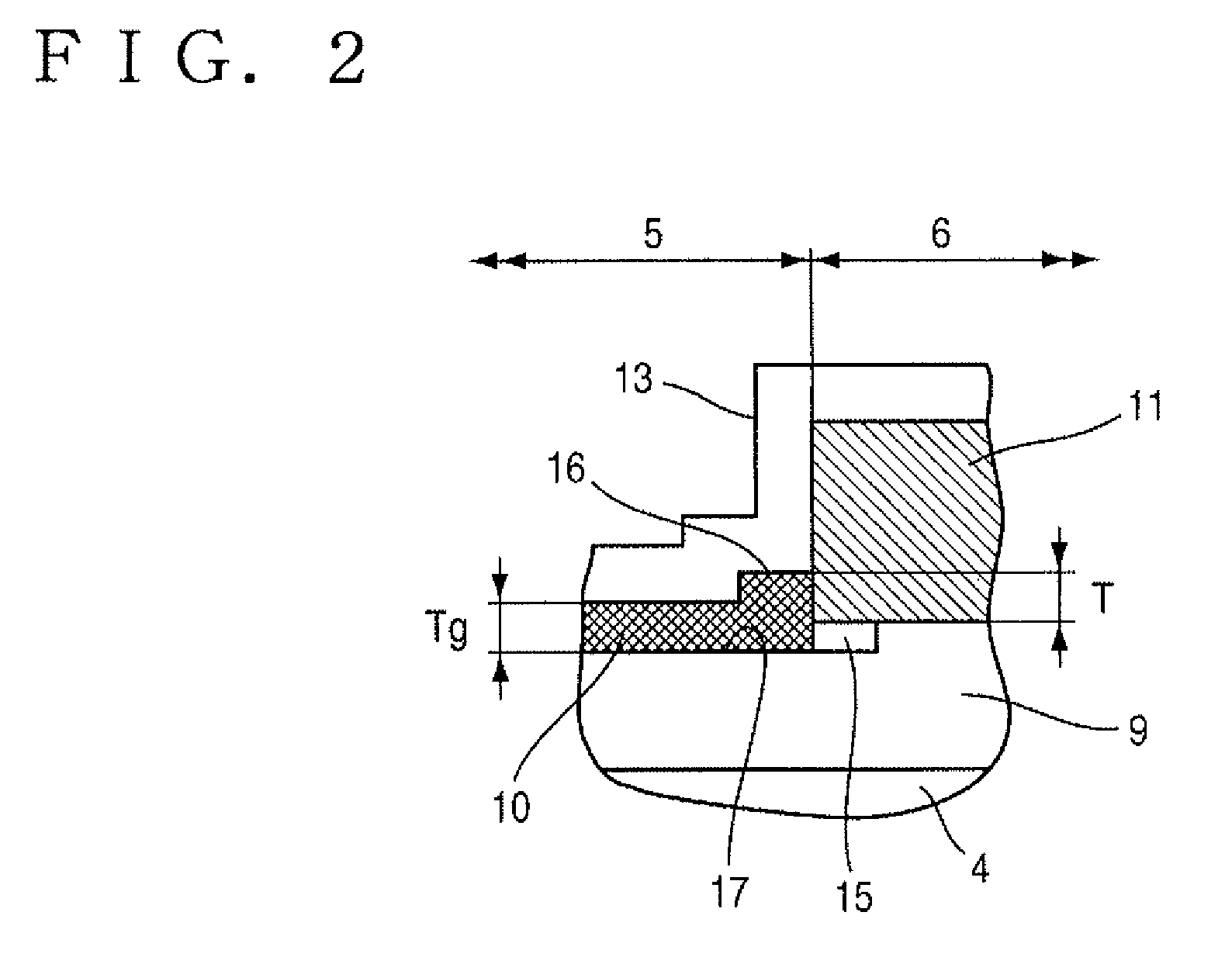
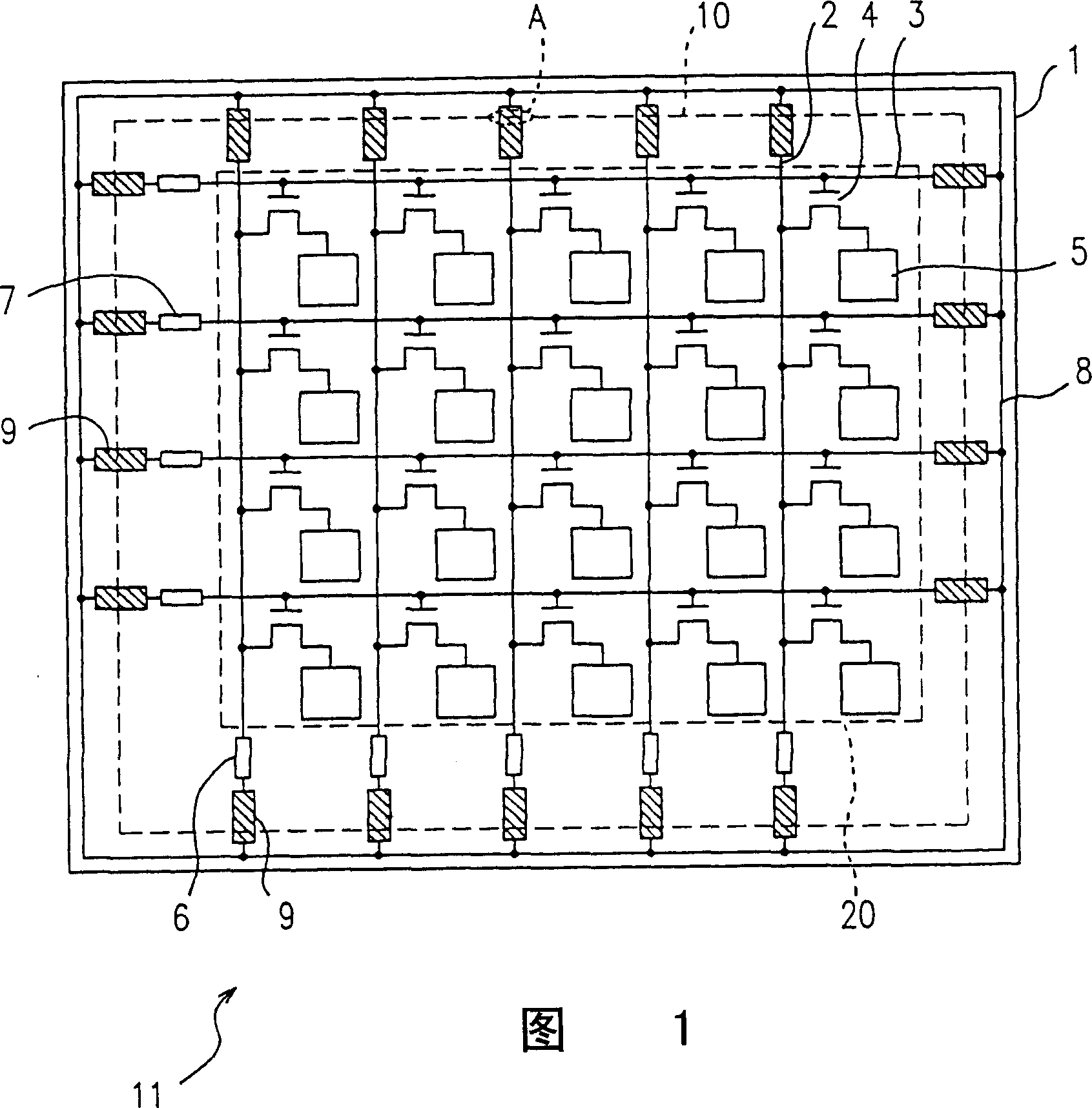
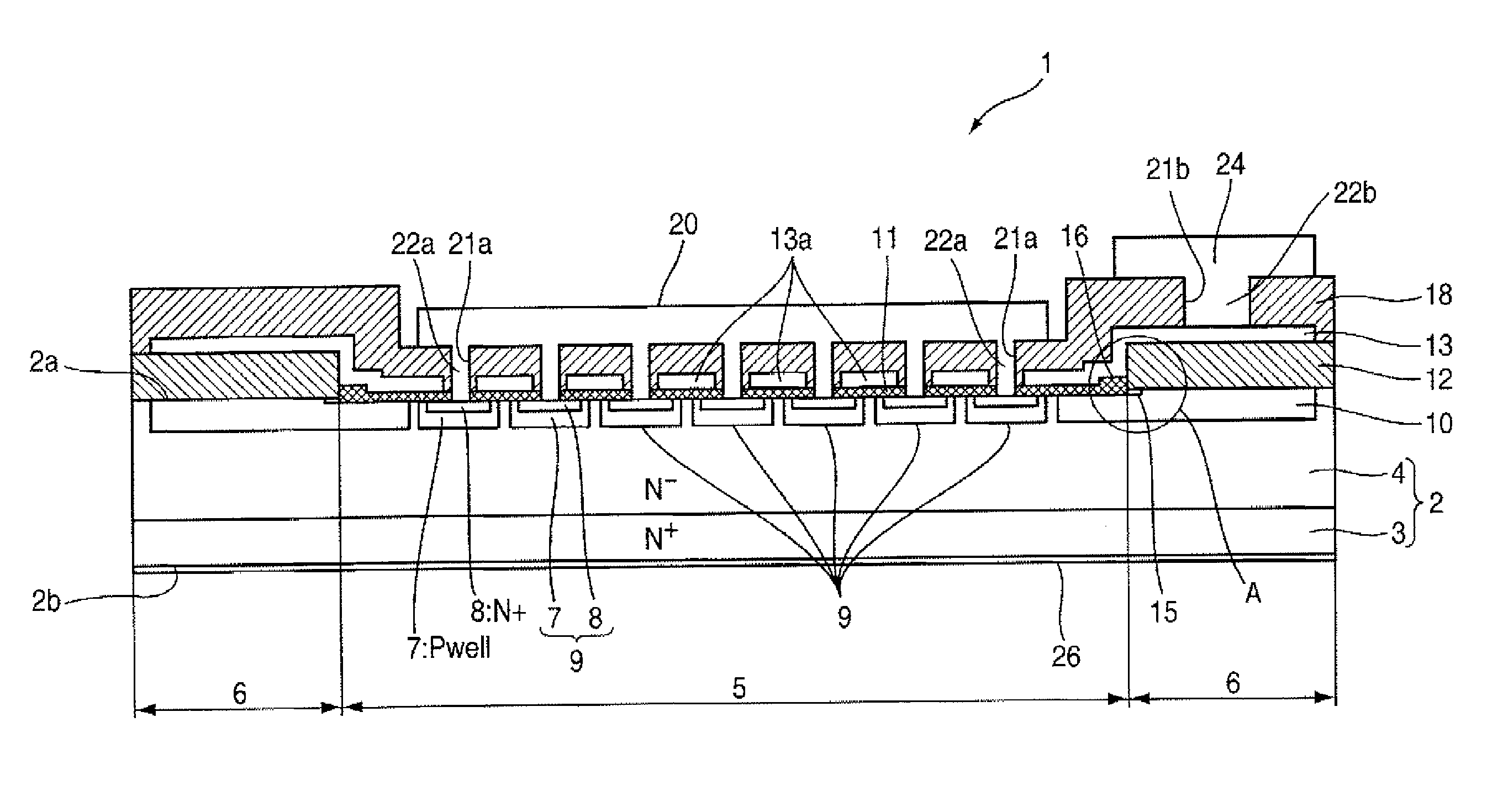
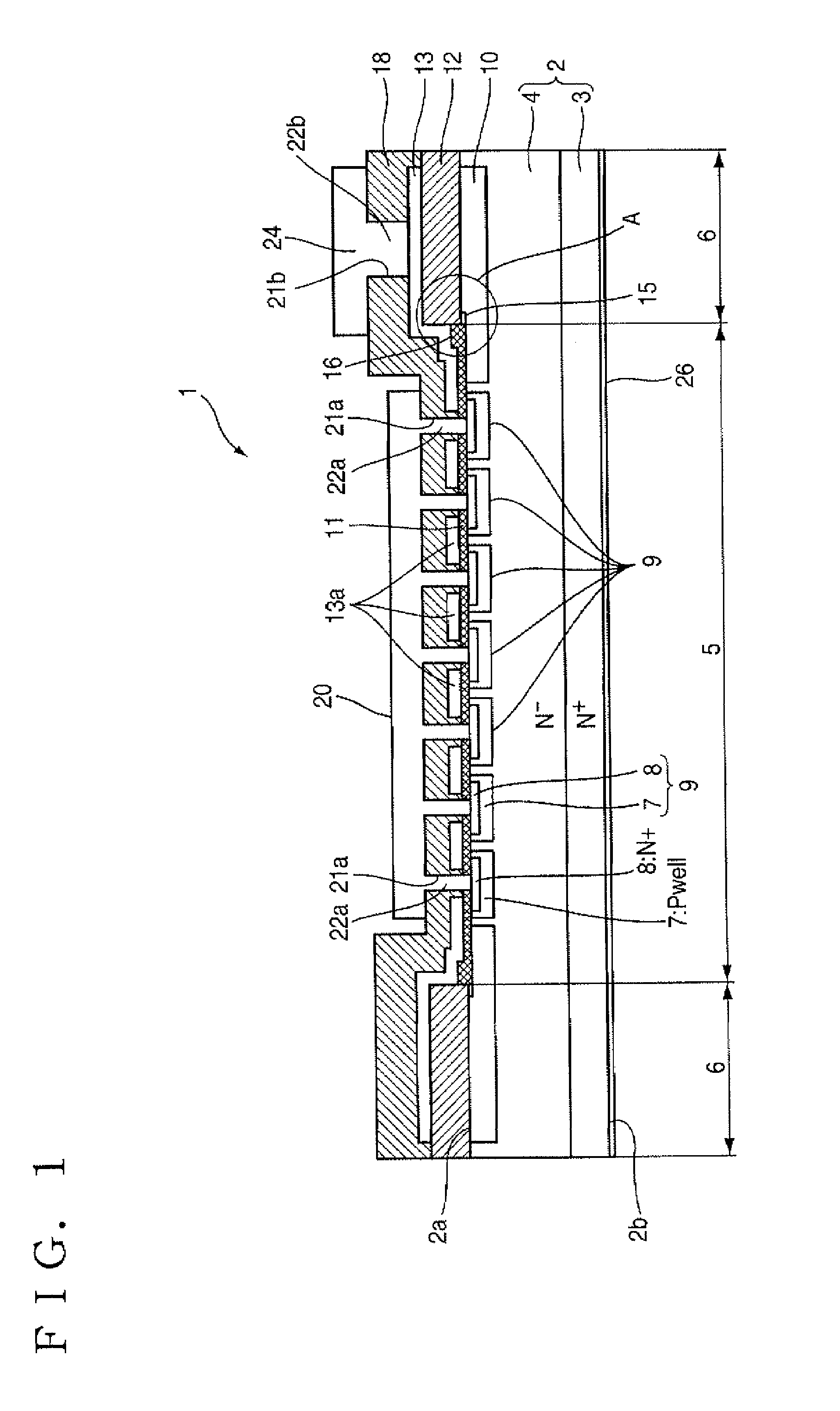
Insulated Gate Semiconductor Device and Method for Producing the Same
ActiveUS20080087951A1Firmly connectedImprove breakdown voltageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
The invention has an object to provide an insulation gate type semiconductor device and a method for producing the same in which high breakdown voltage and compactness are achieved. The semiconductor device has a gate trench and a P floating region formed in the cell area and has a terminal trench and a P floating region formed in the terminal area. In addition, a terminal trench of three terminal trenches has a structure similar to that of the gate trench, and the other terminal trenches have a structure in which an insulation substance such as oxide silicon is filled. Also, the P floating region 51 is an area formed by implanting impurities from the bottom surface of the gate trench, and the P floating region is an area formed by implanting impurities from the bottom surface of the terminal trench.
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
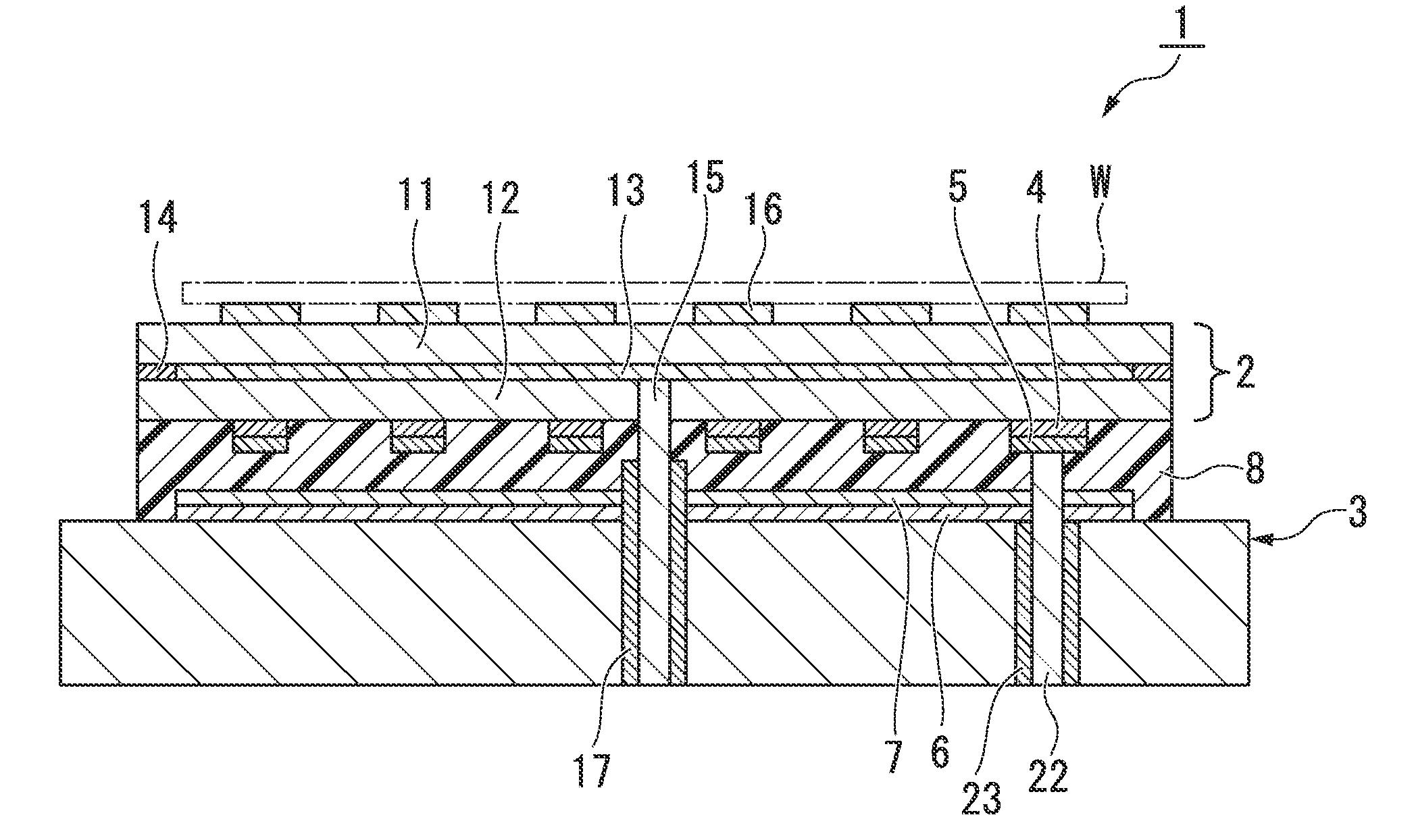
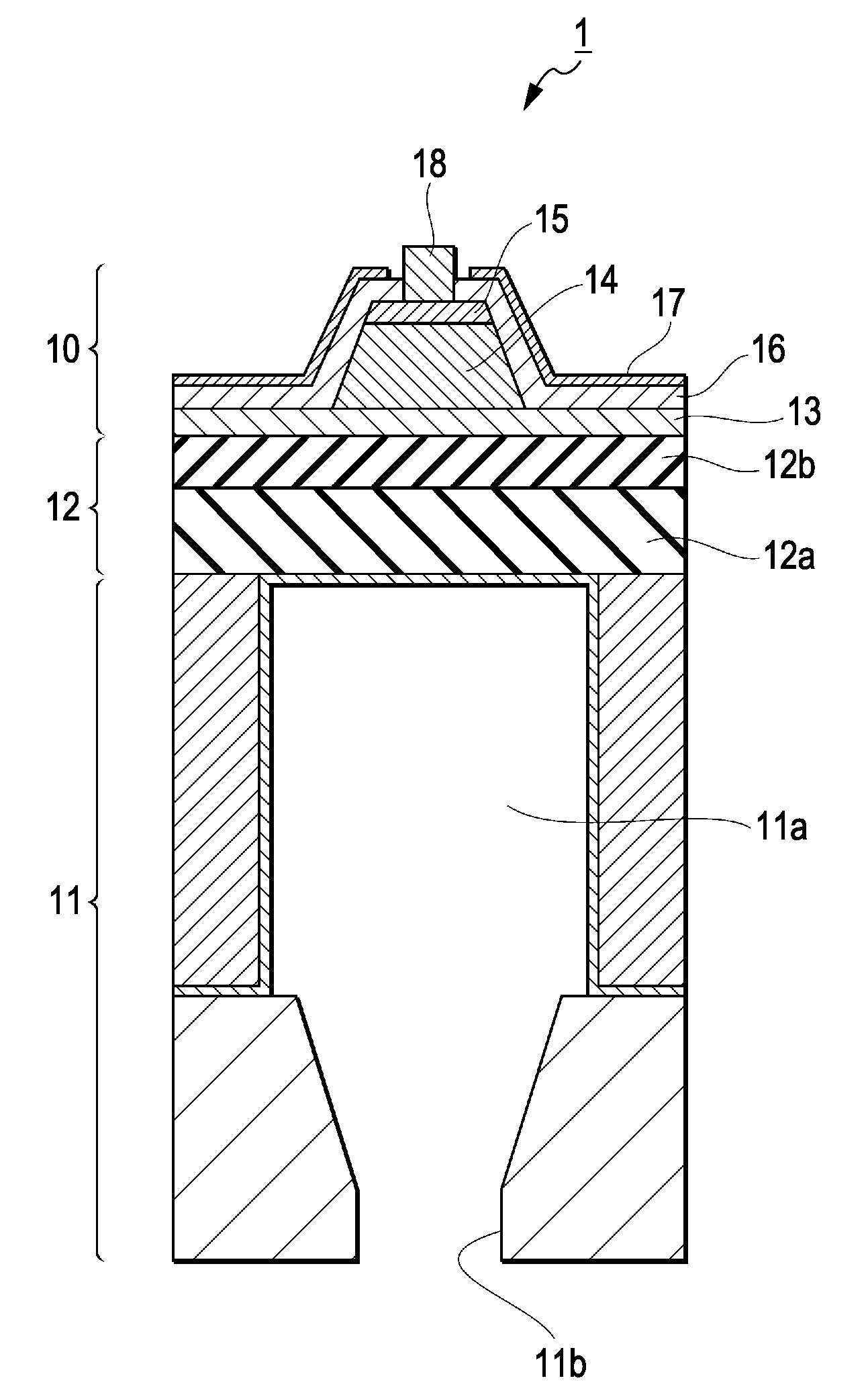
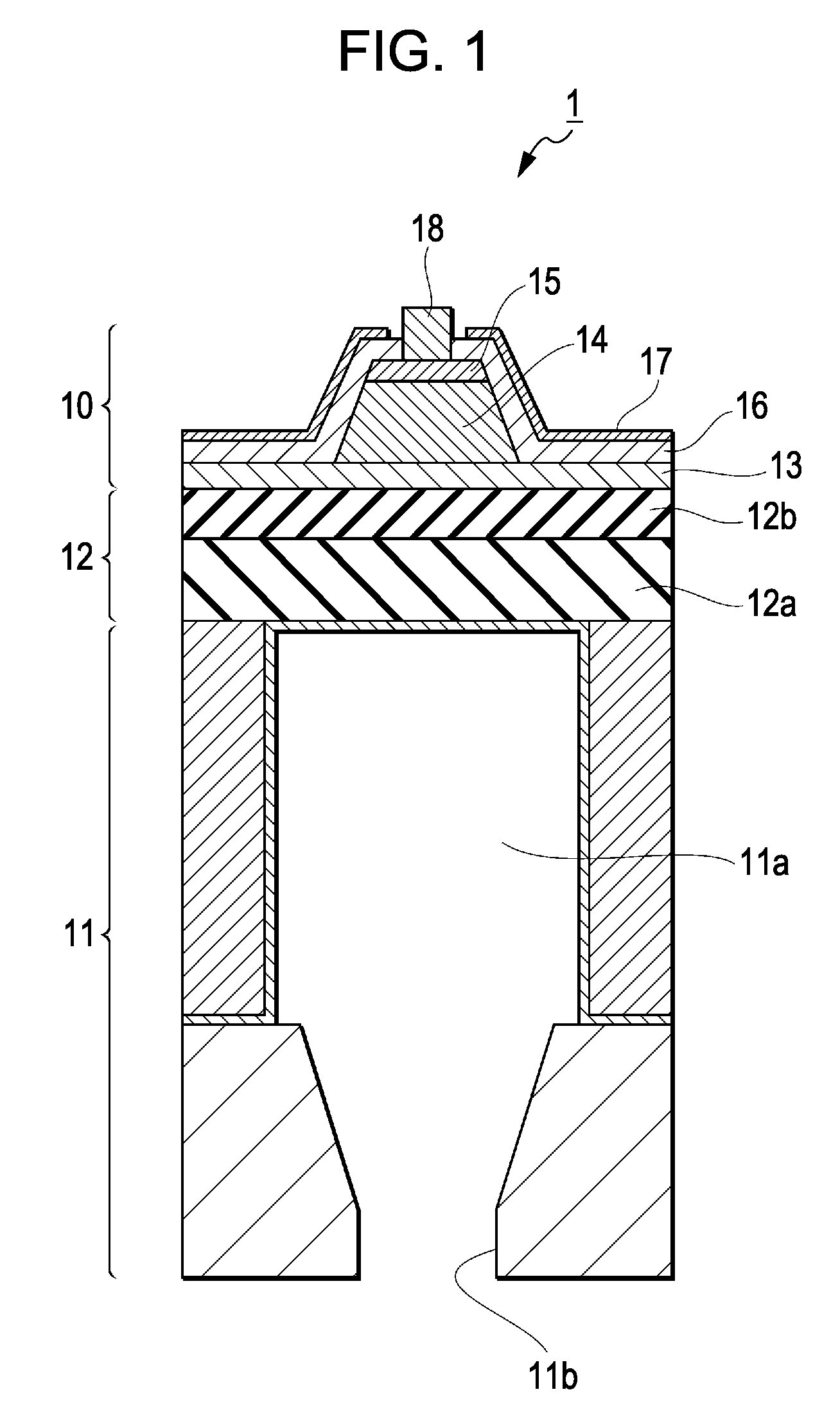
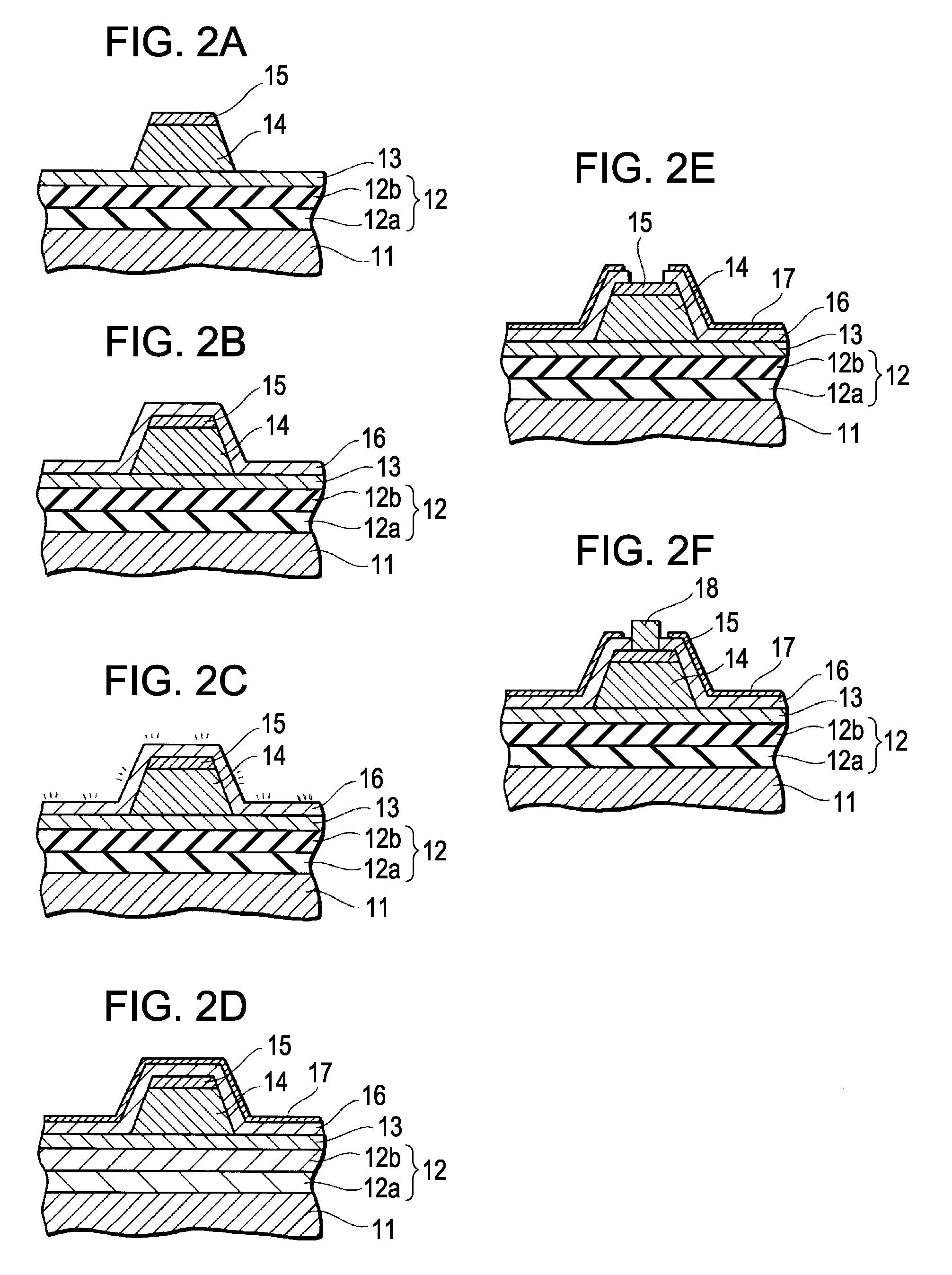
Electrostatic chuck apparatus
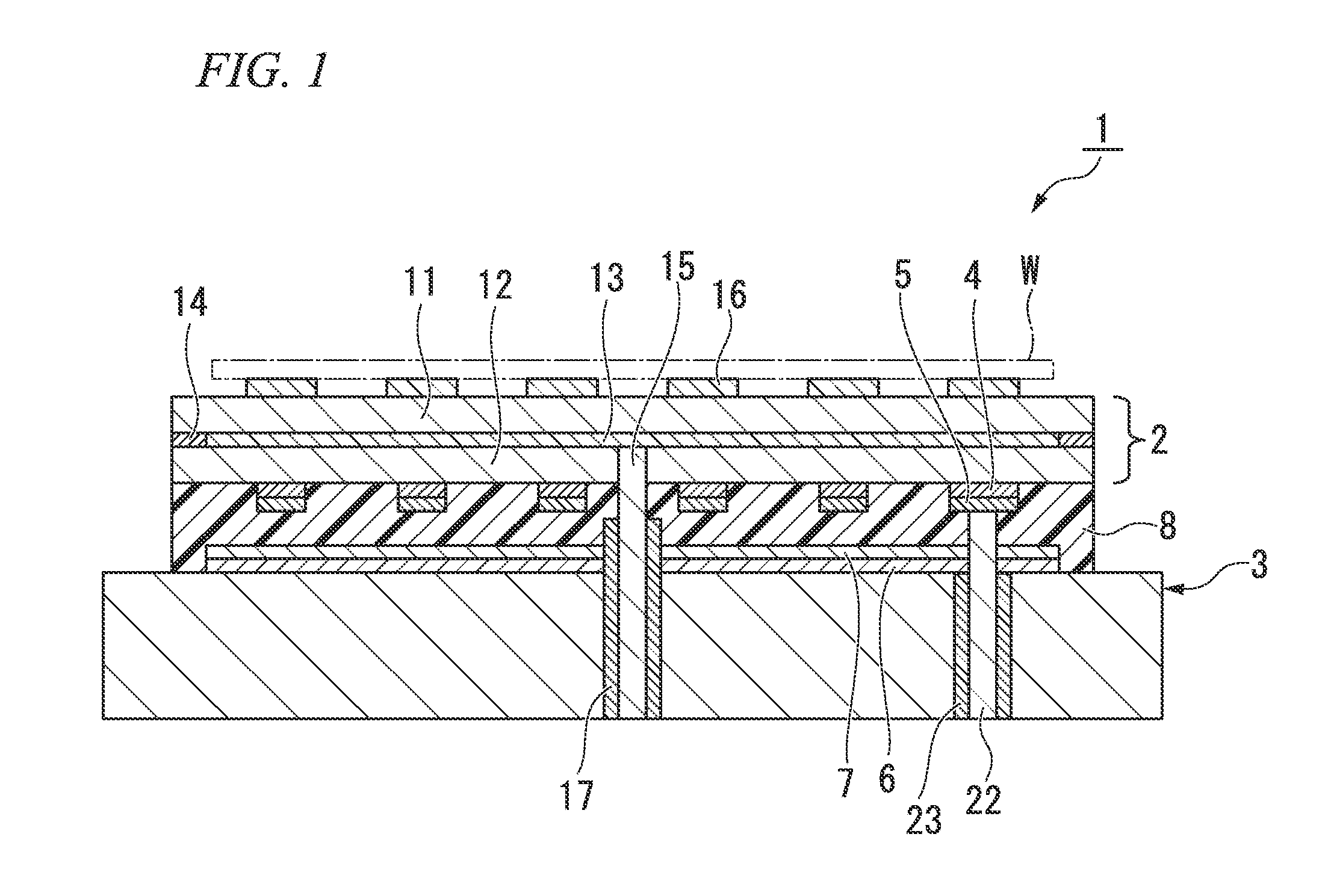
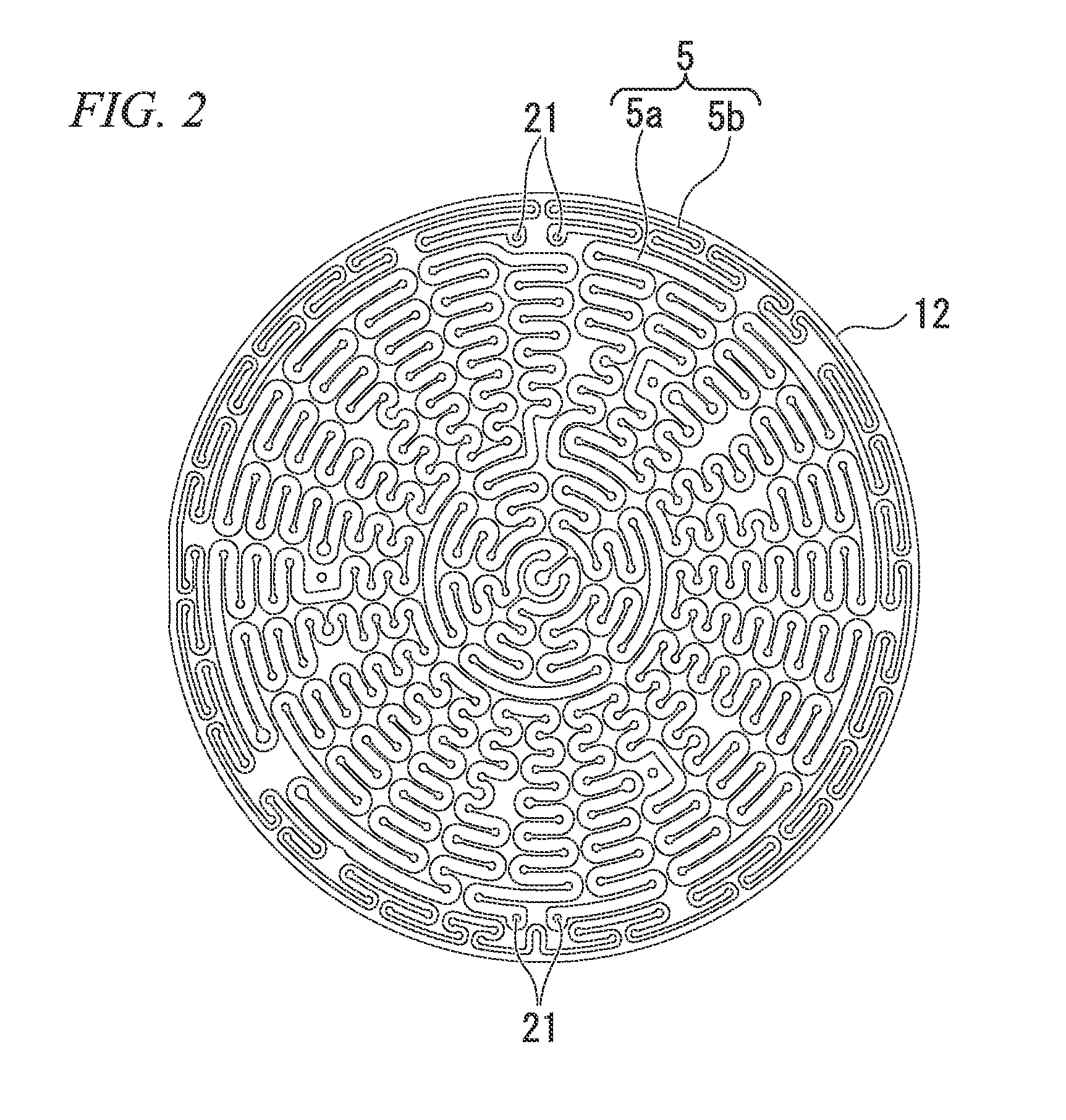
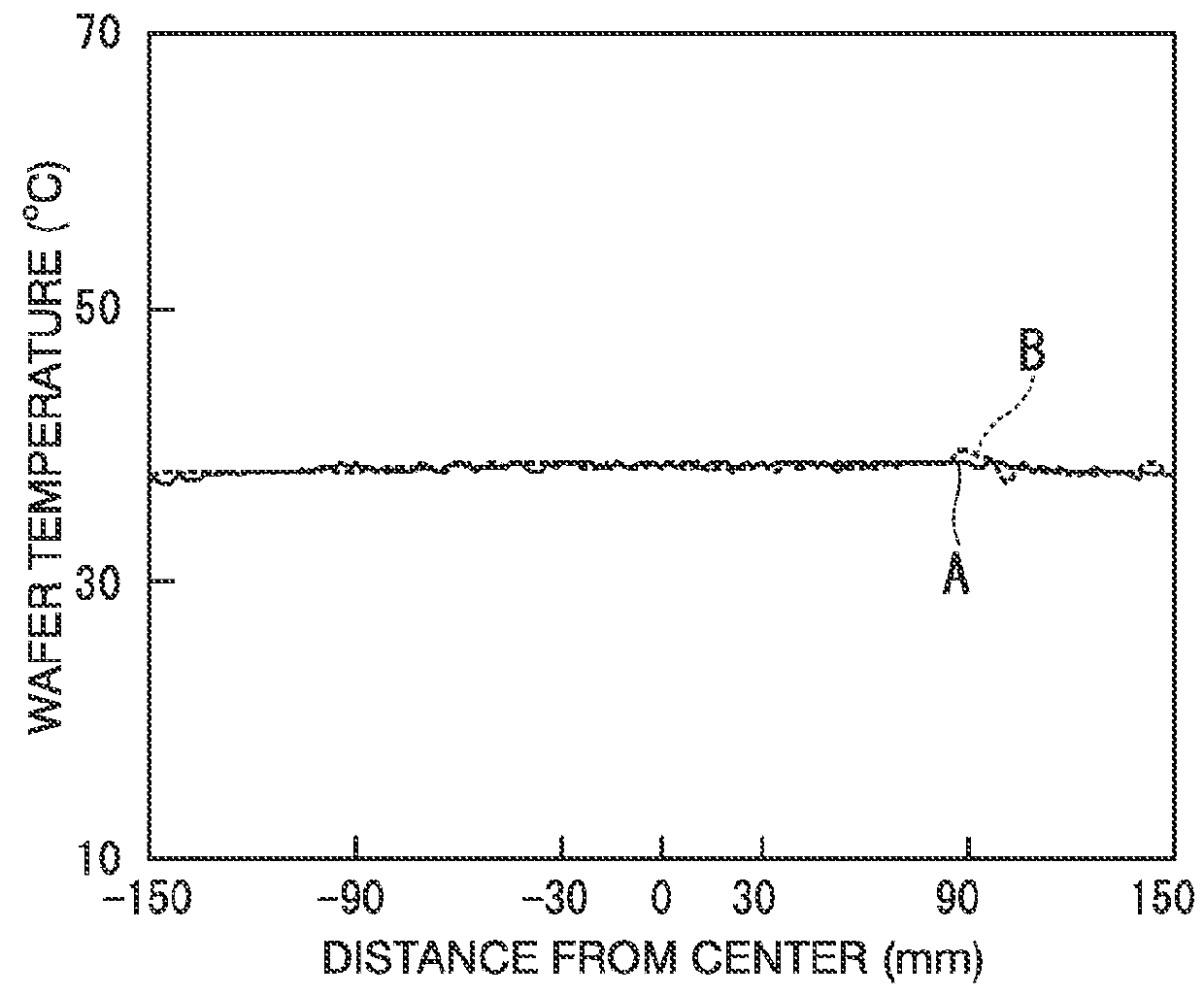
ActiveUS20120299253A1Voltage endurance can be enhancedAvoid insulation breakdownSleeve/socket jointsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
The present invention provides an electrostatic chuck apparatus including:an electrostatic chuck section having one main surface that is a mounting surface on which a plate specimen is mounted, and being equipped with an electrostatic adsorbing internal electrode; and a temperature adjusting base section that adjusts the electrostatic chuck section to a desired temperature, wherein a heating member is bonded to a main surface of the electrostatic chuck section, which is opposite to the mounting surface, via an adhesive material, the whole or a part of the main surface of the temperature adjusting base section, which is on the side of the electrostatic chuck section, is covered with a sheet-like or film-like insulating material, and the electrostatic chuck section bonded with the heating member and the temperature adjusting base section covered with the sheet-like or the film-like insulating material are bonded and integrated via an insulating organic adhesive layer formed by curing a liquid adhesive.
Owner:SUMITOMO OSAKA CEMENT CO LTD
Semiconductor device
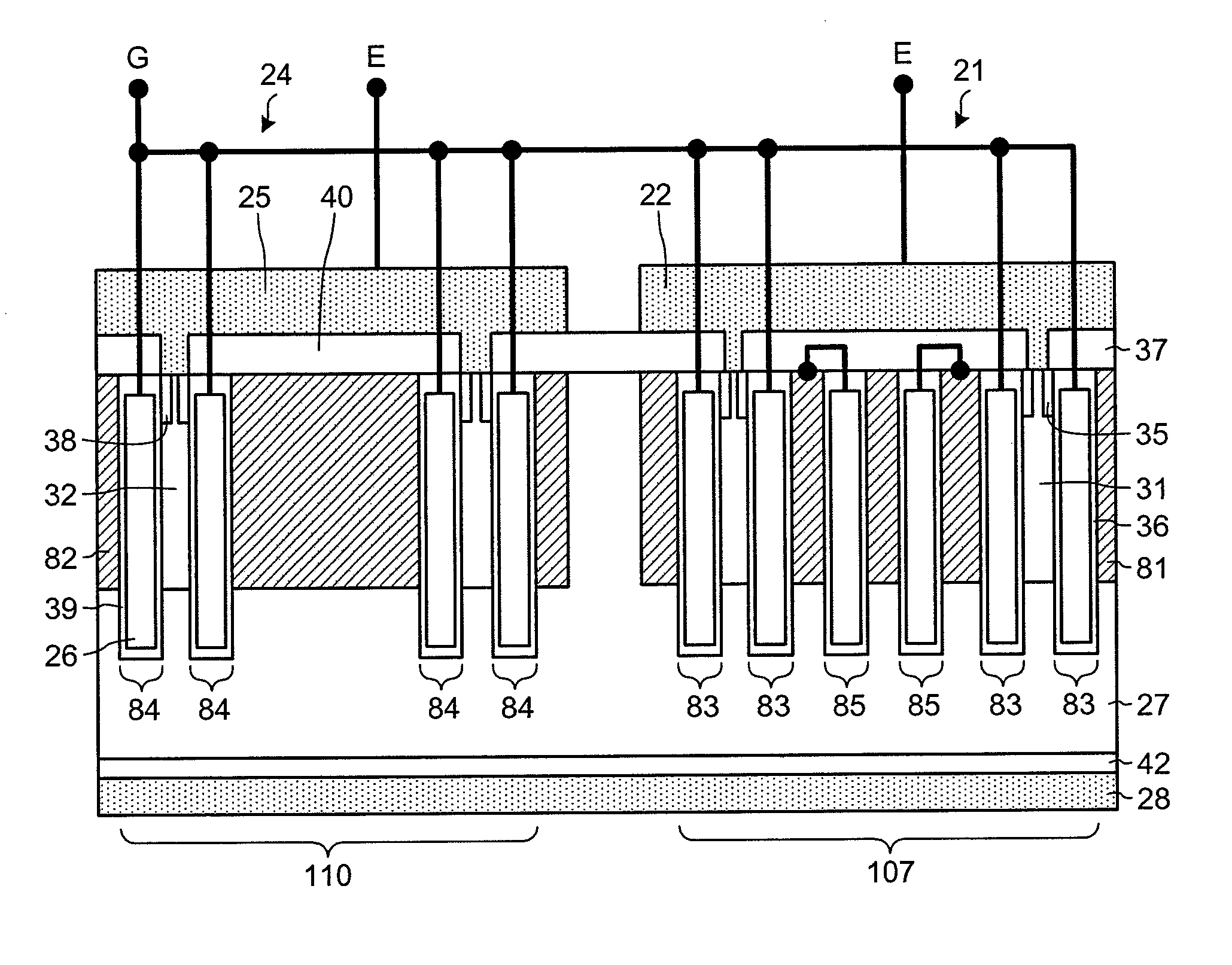
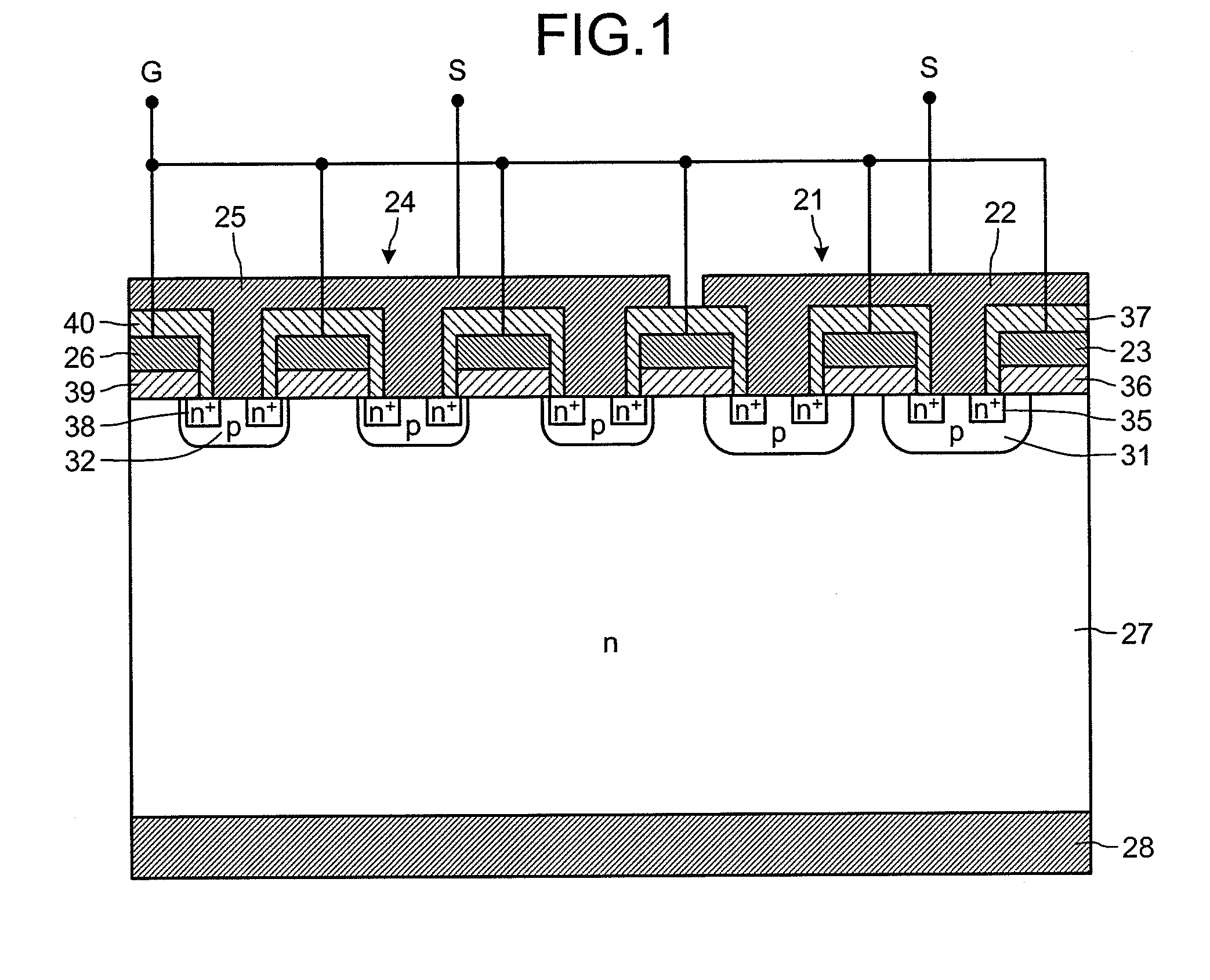
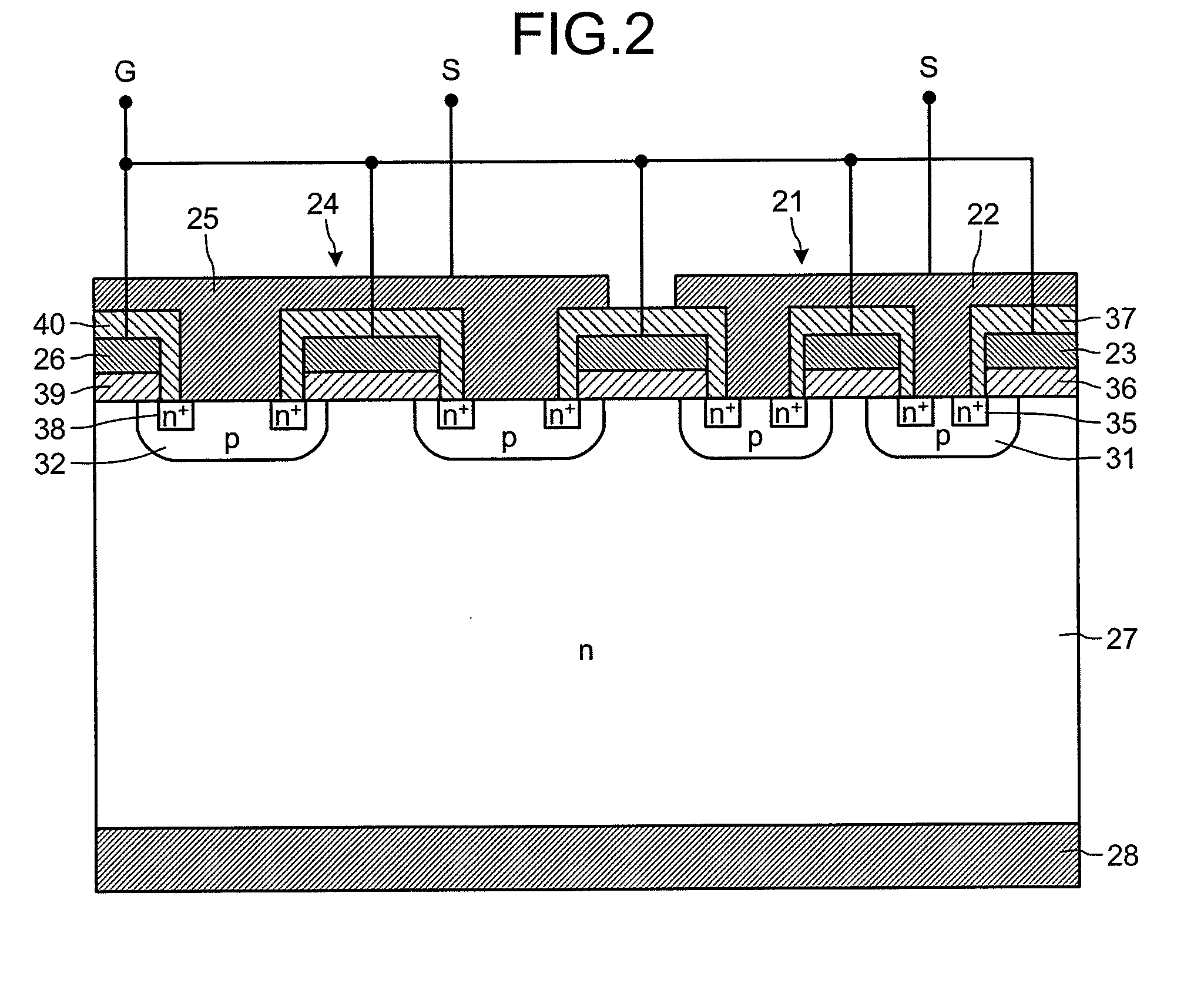
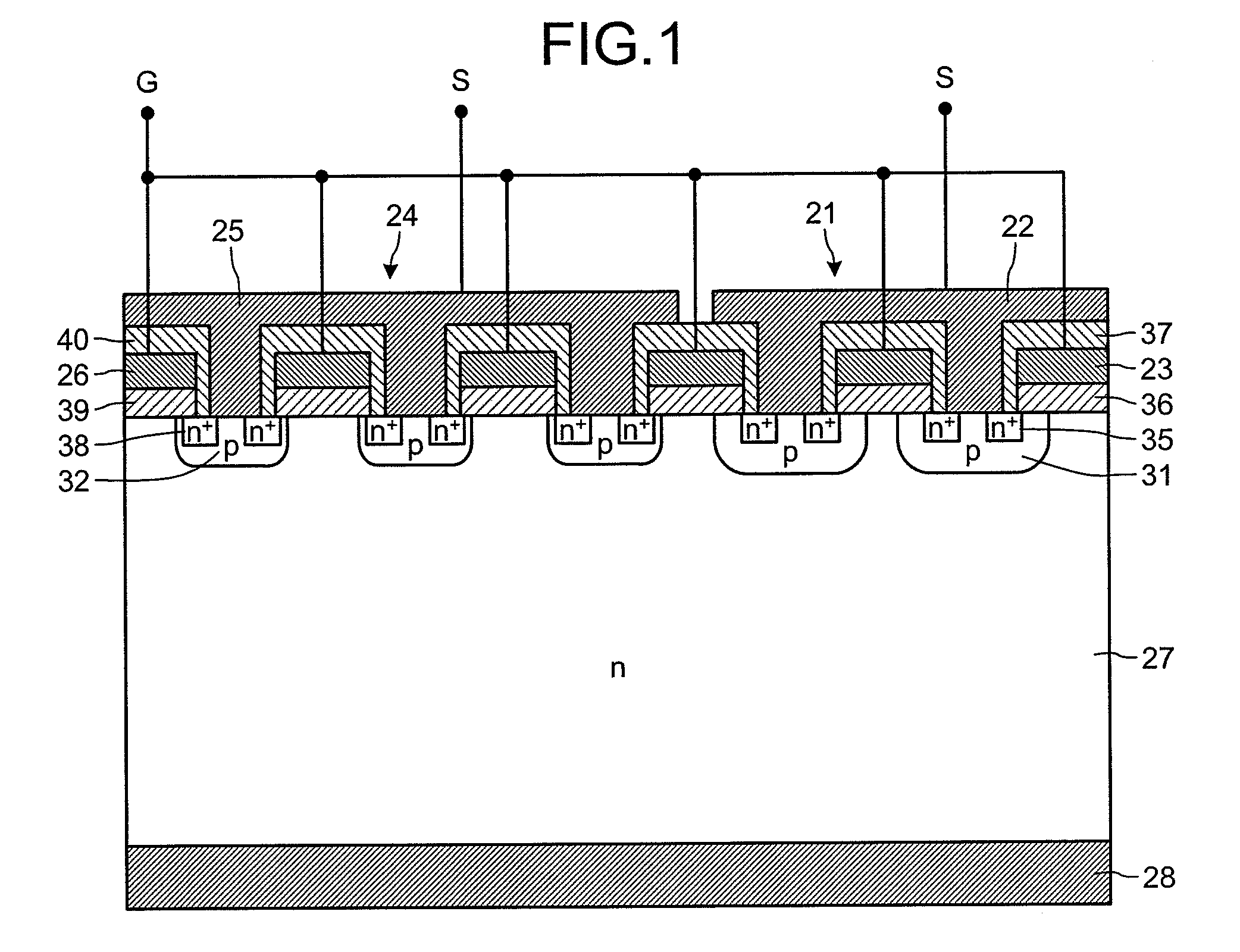
ActiveUS20110012195A1Avoid insulation breakdownTransistorSolid-state devicesDielectricElectric field
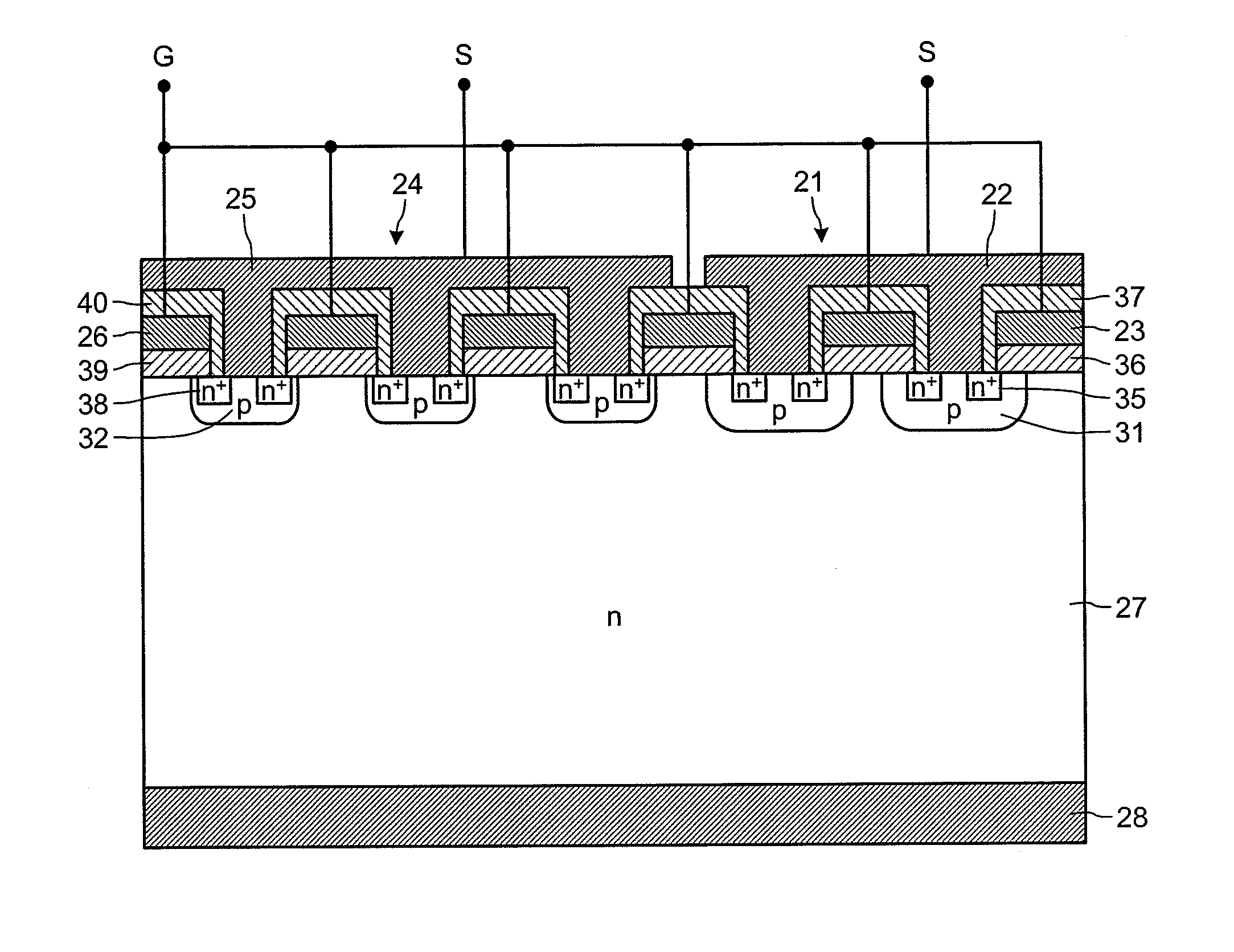
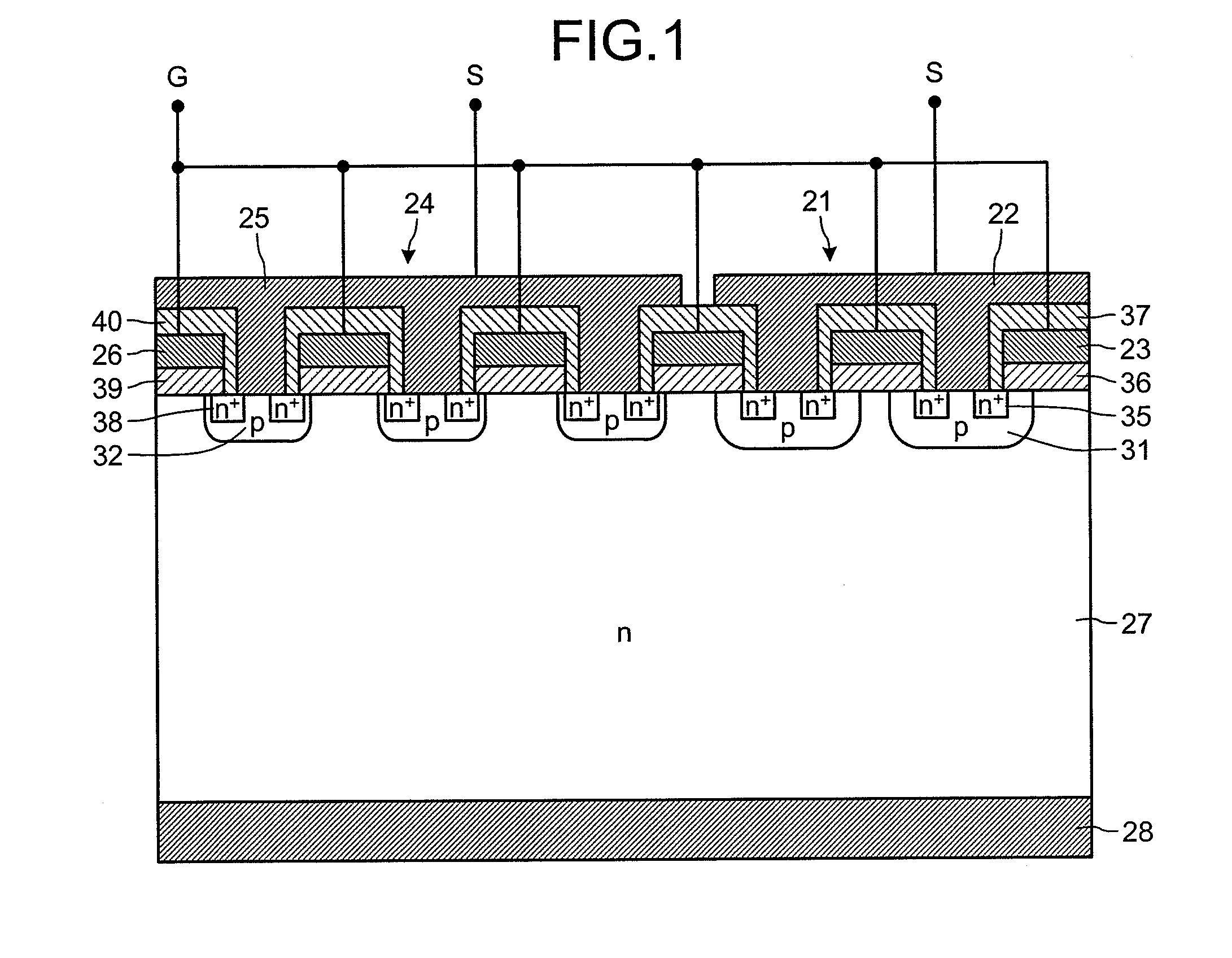
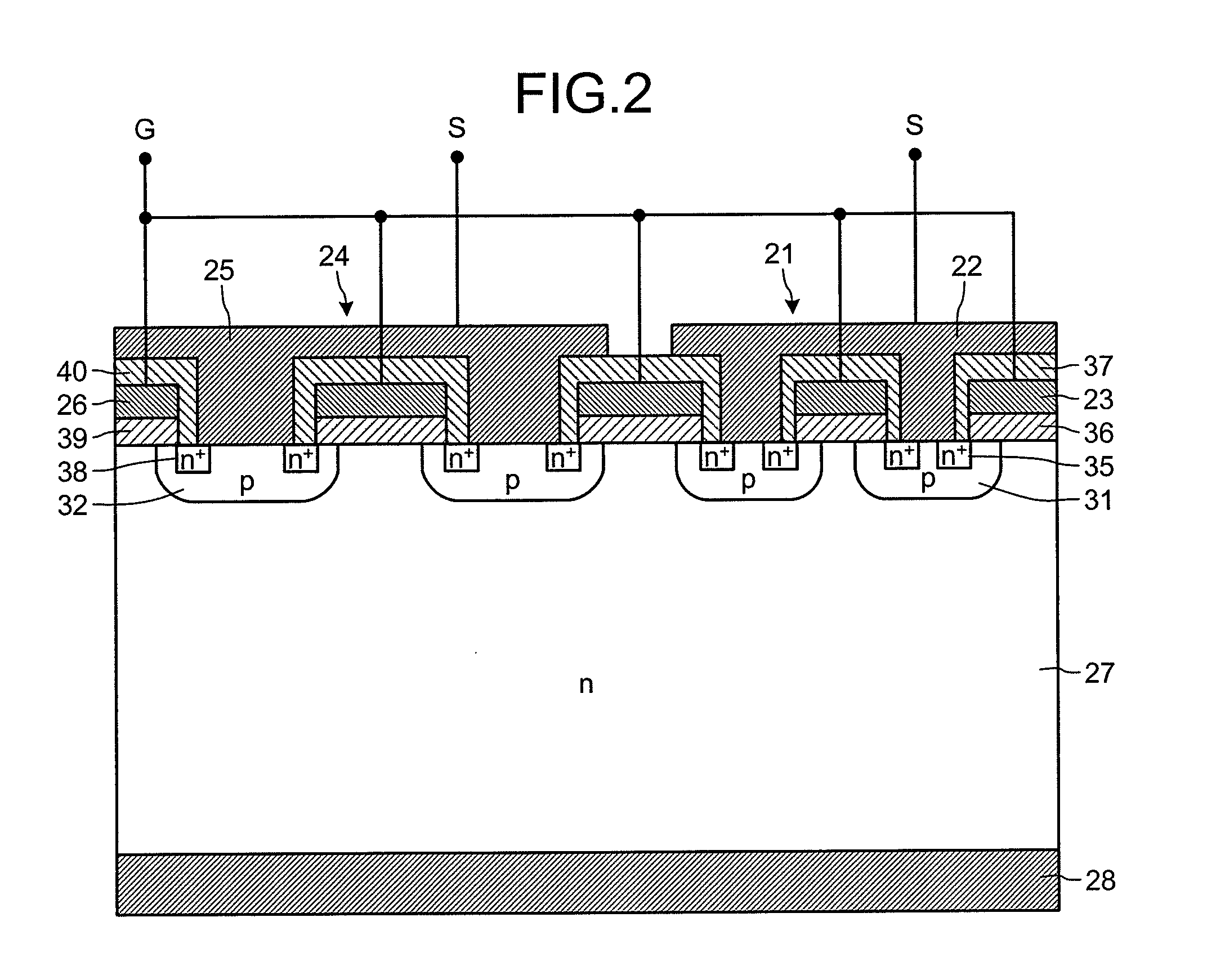
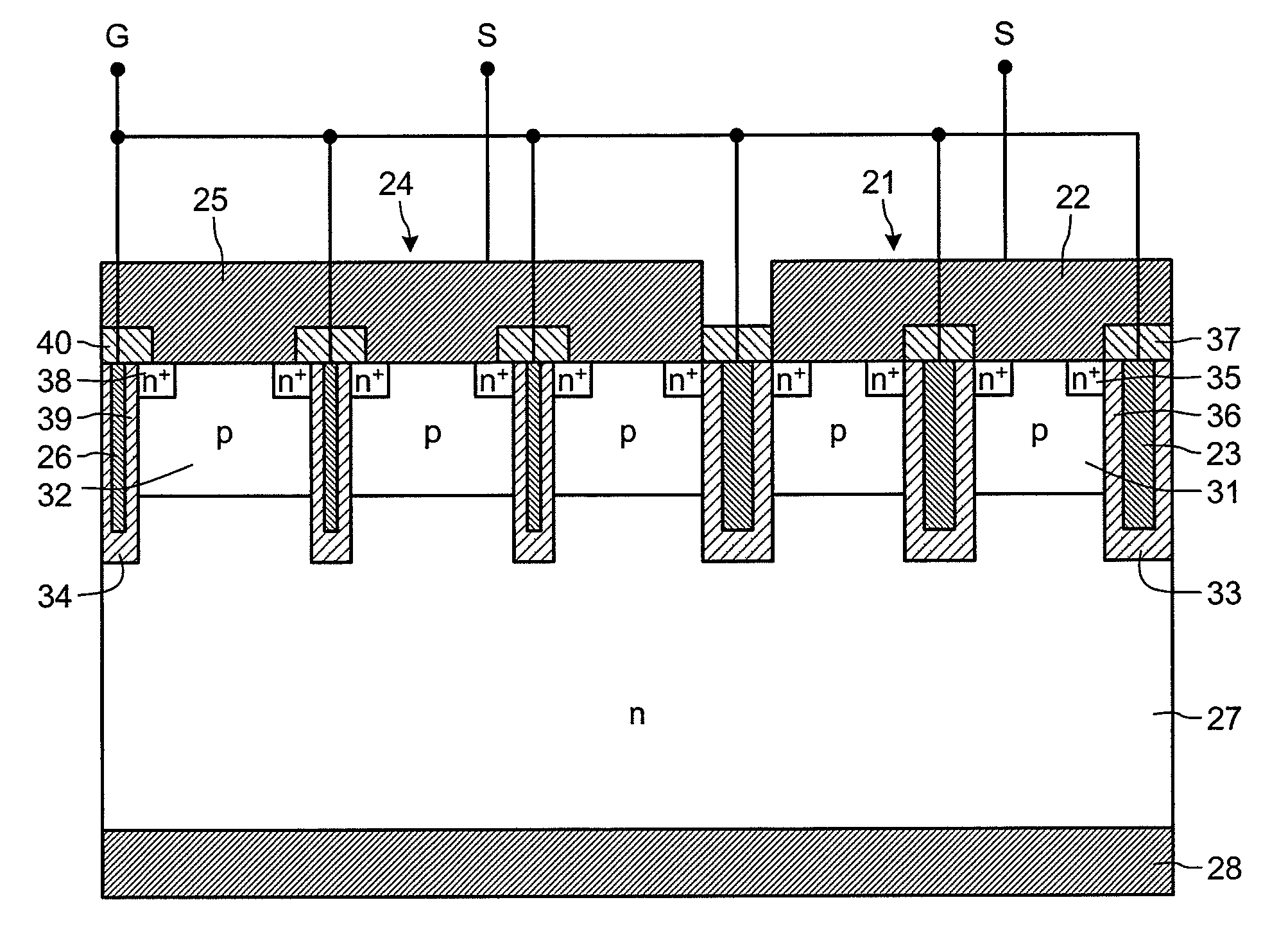
Between a source electrode (25) of a main device (24) and a current sensing electrode (22) of a current detection device (21), a resistor for detecting current is connected. Dielectric withstand voltage of gate insulator (36) is larger than a product of the resistor and maximal current flowing through the current detection device (21) with reverse bias. A diffusion length of a p-body region (32) of the main device (24) is shorter than that of a p-body (31) of the current detection device (21). A curvature radius at an end portion of the p-body region (32) of the main device (24) is smaller than that of the p-body (31) of the current detection device (21). As a result, at the inverse bias, electric field at the end portion of the p-body region (32) of the main device (24) becomes stronger than that of the p-body region (31) of the current detection device (21). Consequently, avalanche breakdown tends to occur earlier in the main device 24 than the current detection device (21).
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
Method for Growing III-V Epitaxial Layers and Semiconductor Structure
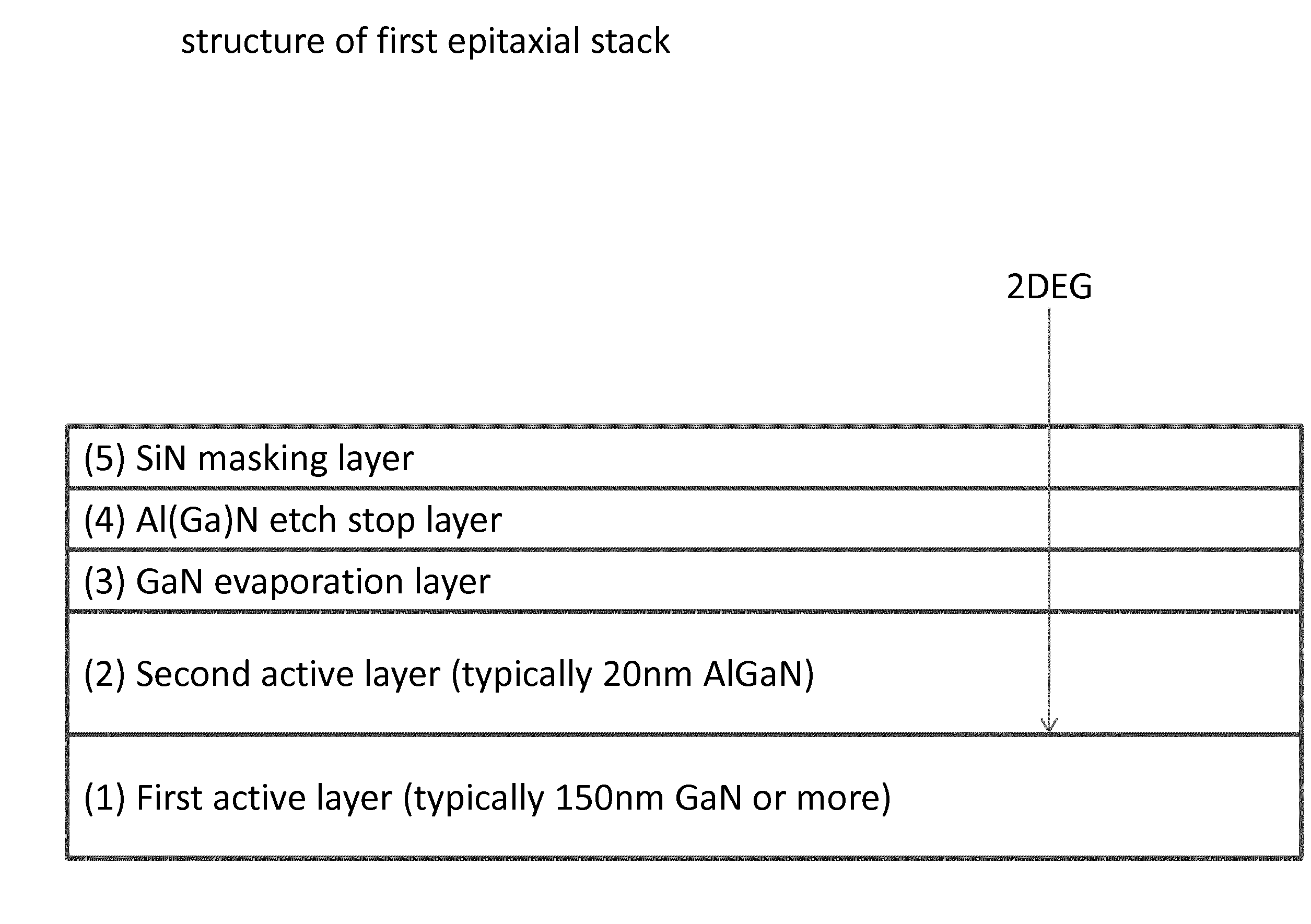
ActiveUS20140159119A1Without jeopardizing functionality and advantageGood ohmic contactSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor structurePower switching
Disclosed are methods of growing III-V epitaxial layers on a substrate, a semiconductor structure comprising a substrate, a device comprising such a semiconductor structure, and an electronic circuit. Group III-nitride devices, such as, for example, high-electron-mobility transistors, may include a two-dimensional electron gas (2DEG) between two active layers. For example, the 2DEG may be between a GaN layer and a AlGaN layer. These transistors may work in depletion-mode operation, which means the channel has to be depleted to turn the transistor off. For certain applications, such as, for example, power switching or integrated logic, negative polarity gate supply is undesired. Transistors may then work in enhancement mode (E-mode).
Owner:EPIGAN NV
Electrostatic chuck
InactiveUS20050024809A1Enhanced release propertiesExcellent characteristic of releasing wafer WSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingContactsCeramicPrincipal plane
The electrostatic chuck includes: a conductive base formed of metal or both metal and ceramics, serving as a chucking electrode; and an insulating film formed on one principal plane of the conductive base, the top face of the insulating film serving as a placing surface for placing a wafer; wherein the insulating film is formed of a uniform amorphous ceramics of an oxide and has a thickness in a range of 10 to 100 μm, thereby preventing cracking and insulation breakdown in the insulating film and improving characteristics of releasing the wafer.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
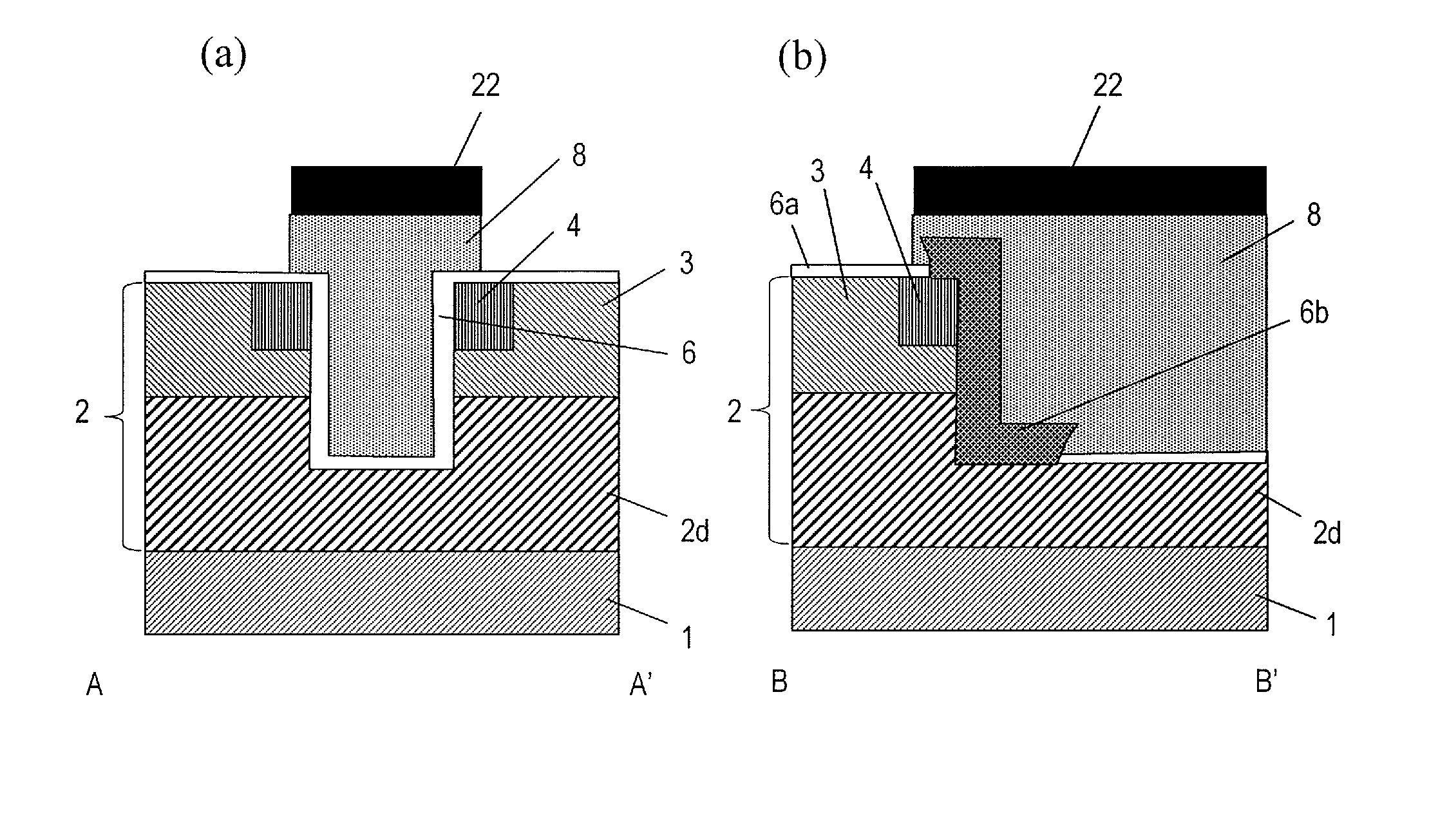
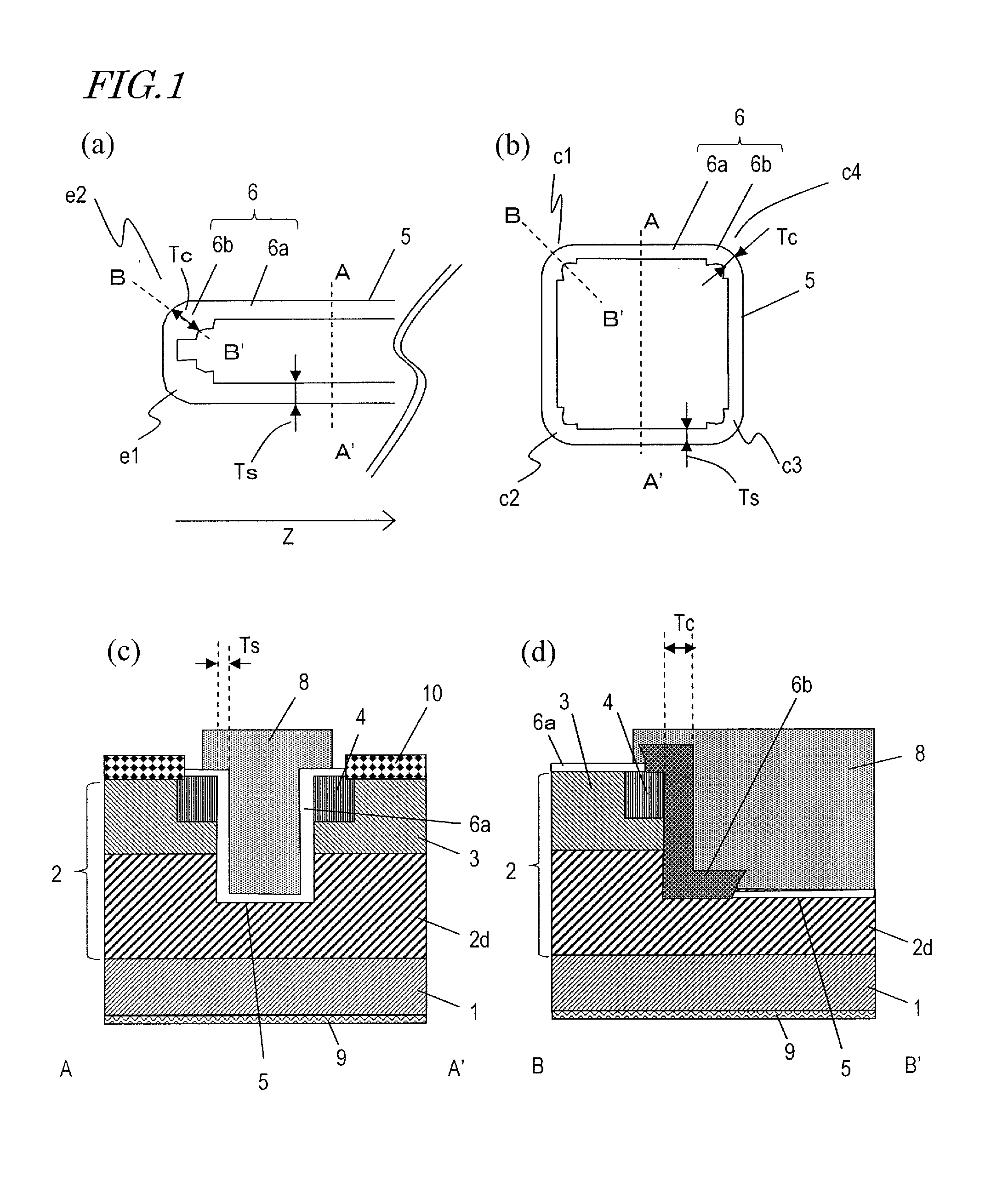
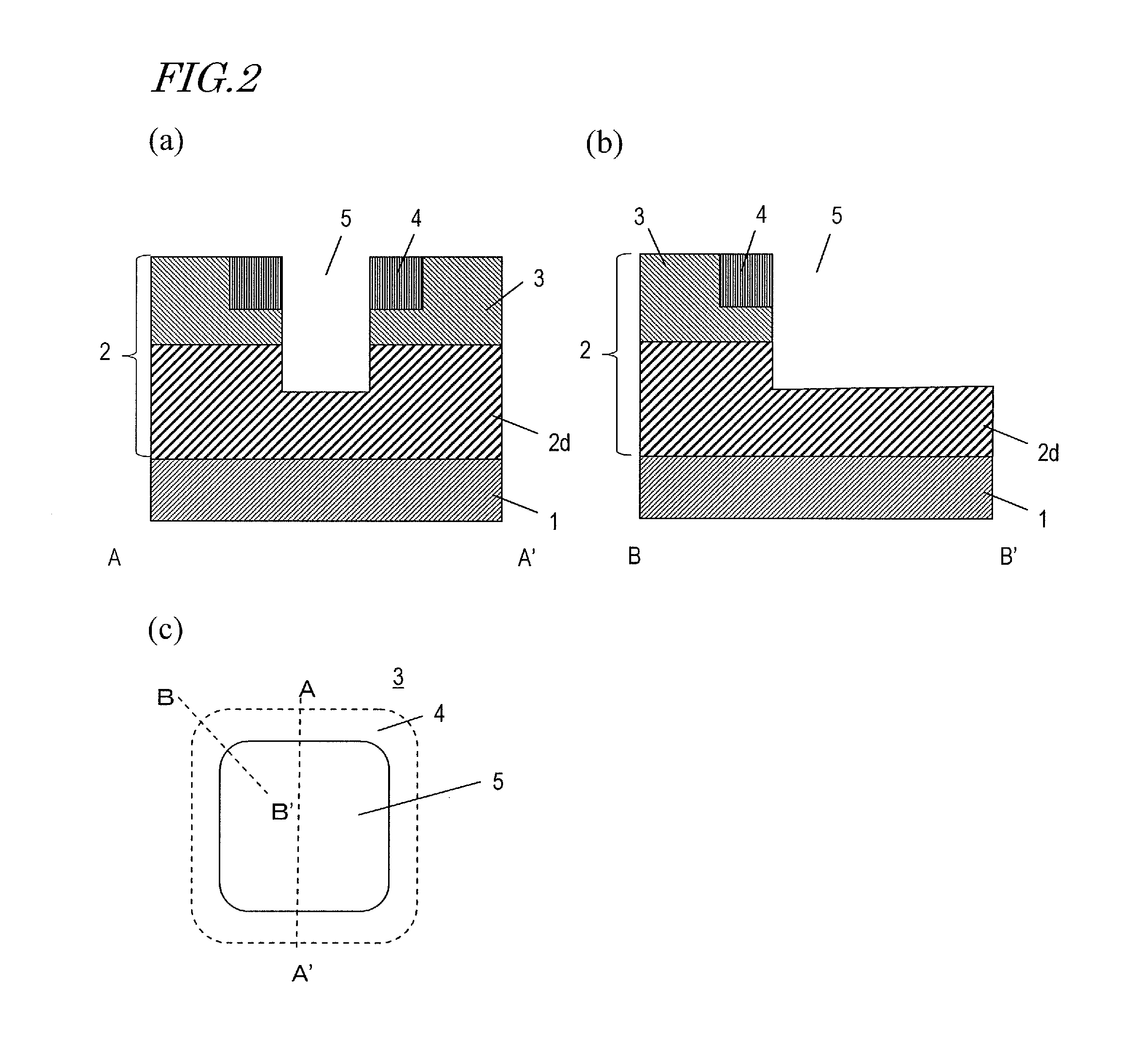
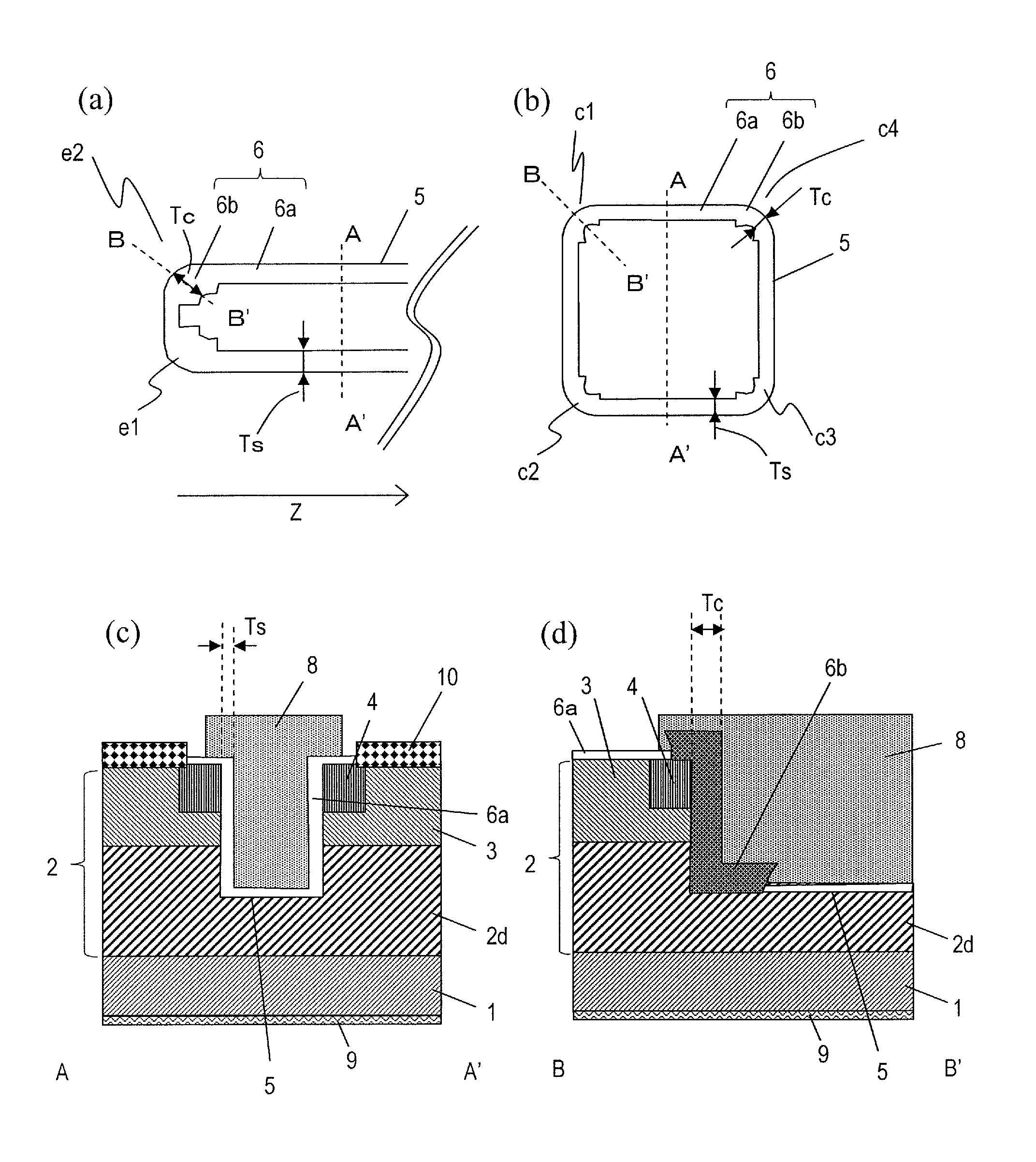
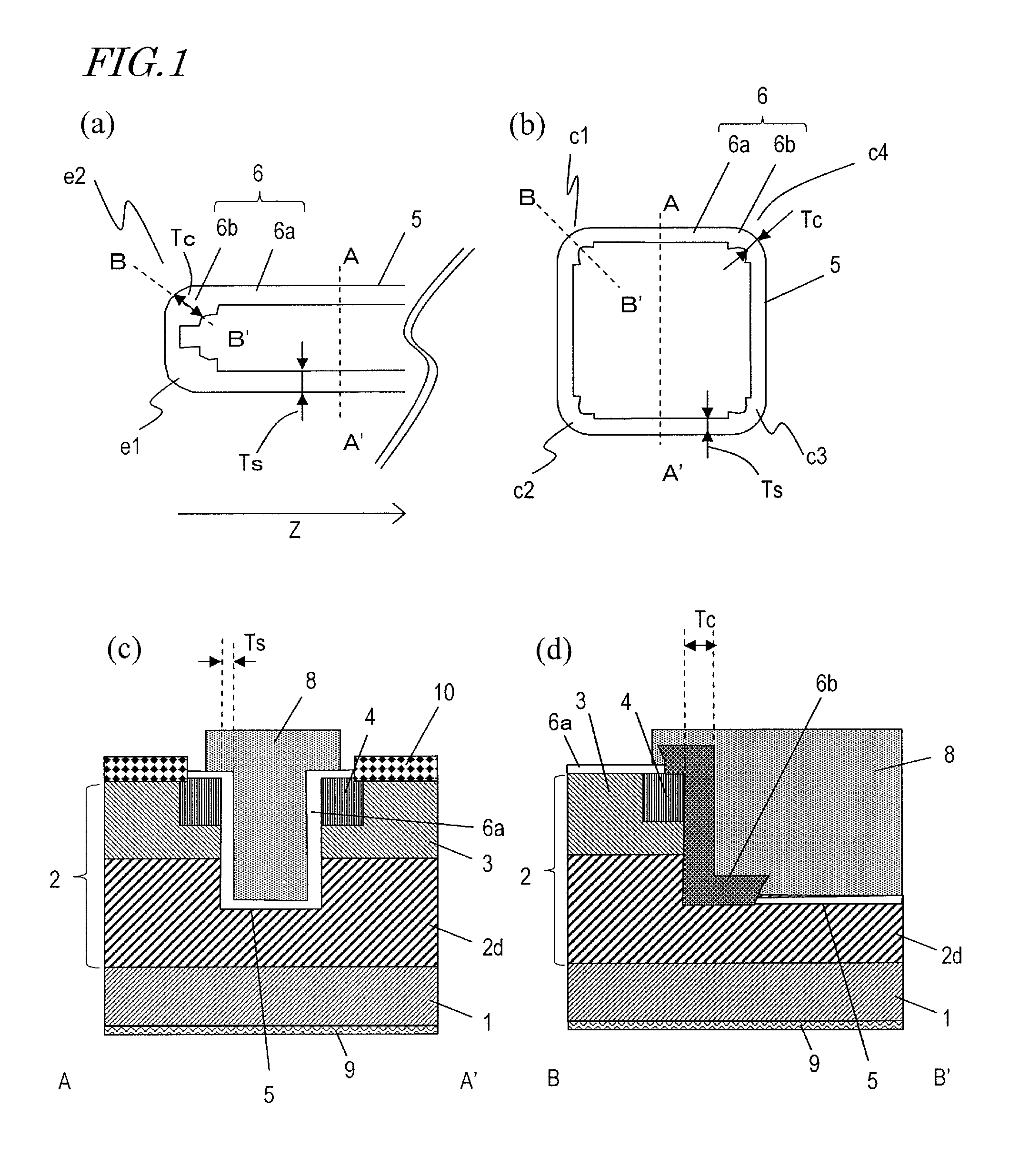
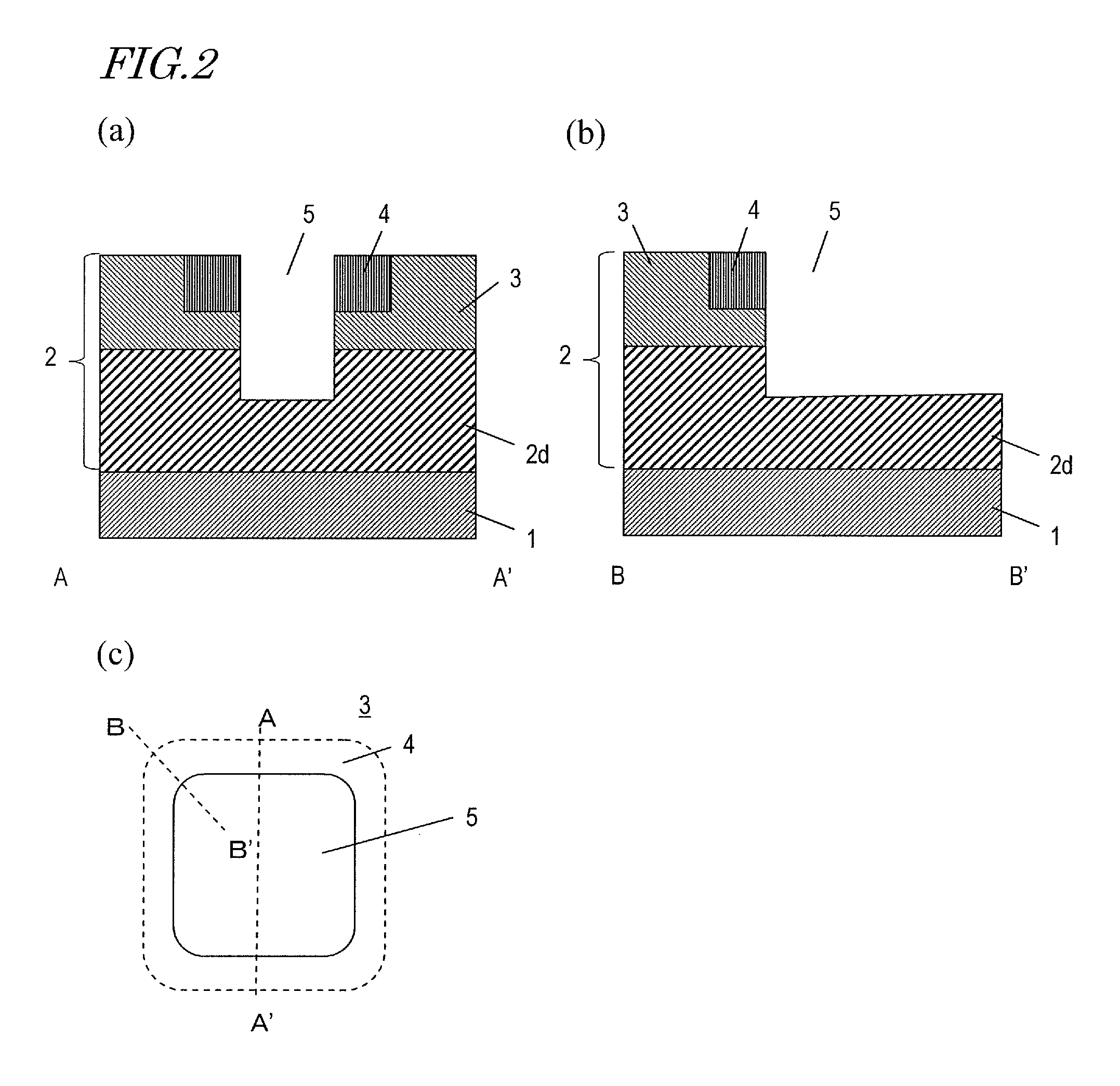
Semiconductor device and method for producing same
InactiveUS20130306982A1Reduce intensityAvoid insulation breakdownTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialEngineering
A semiconductor device according to an embodiment of the present invention includes: a semiconductor layer 2 of a wide band gap semiconductor arranged on a principal surface of a substrate 1; a trench 5 arranged in the semiconductor layer and including a bottom surface, a plurality of main side surfaces, and a plurality of corner side surfaces each connecting together two adjacent main side surfaces; a gate insulating film 6 arranged on the bottom surface, the main side surfaces and the corner side surfaces of the trench 5; and a gate electrode 8 arranged in the trench, wherein the semiconductor layer includes a drift region 2d of a first conductivity type, and a body region 3 of a second conductivity type arranged on the drift region; the trench runs through the body region 3 and has the bottom surface inside the drift region; the corner side surfaces of the trench do not have a depressed portion; the gate insulating film 6 is thicker on the corner side surfaces of the trench than on the main side surfaces of the trench; and a portion of the gate insulating film 6 that is located on the corner side surfaces is a first insulating layer 6b, and a portion of the gate insulating film 6 that is located on the main side surfaces is a second insulating layer 6a.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
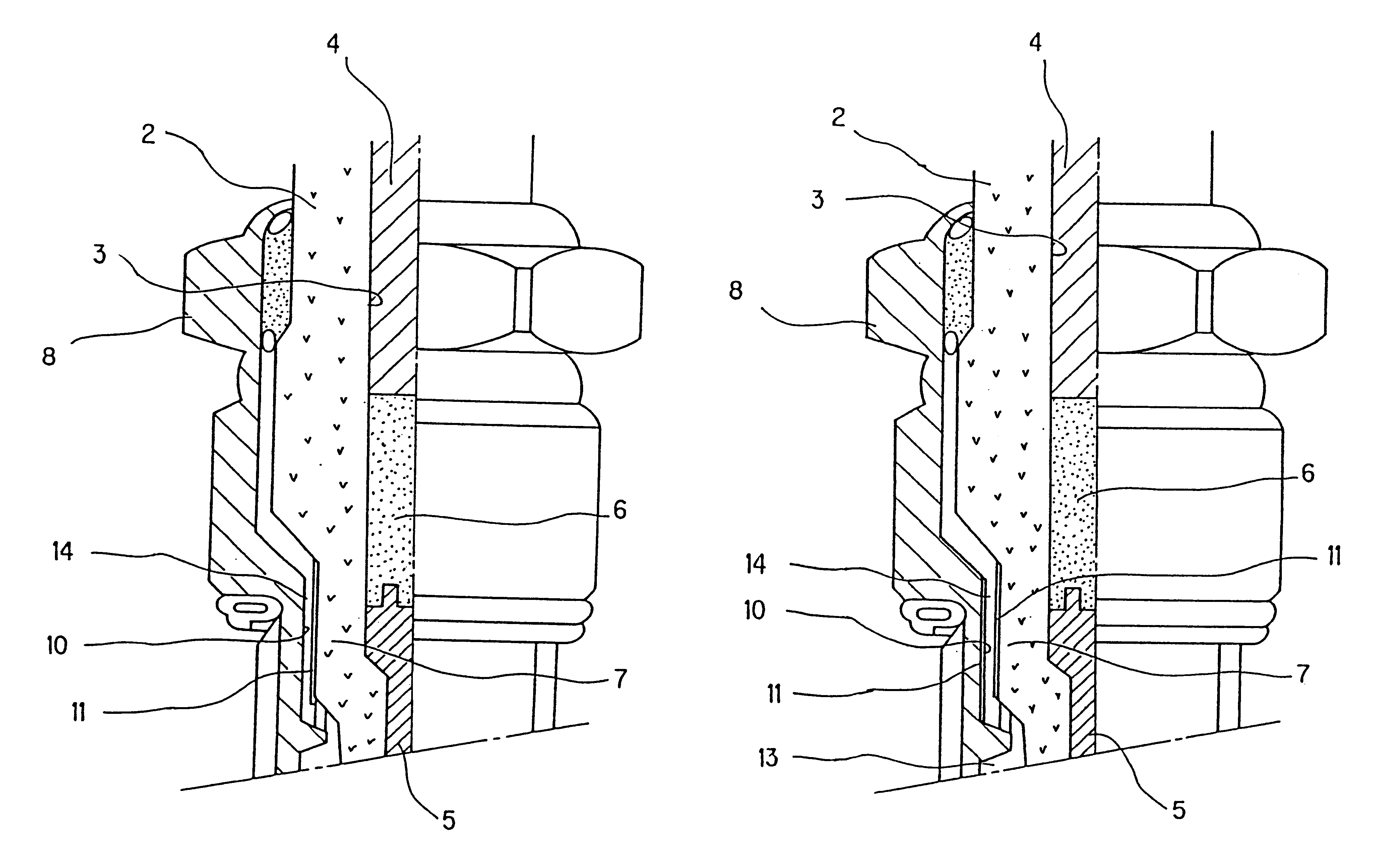
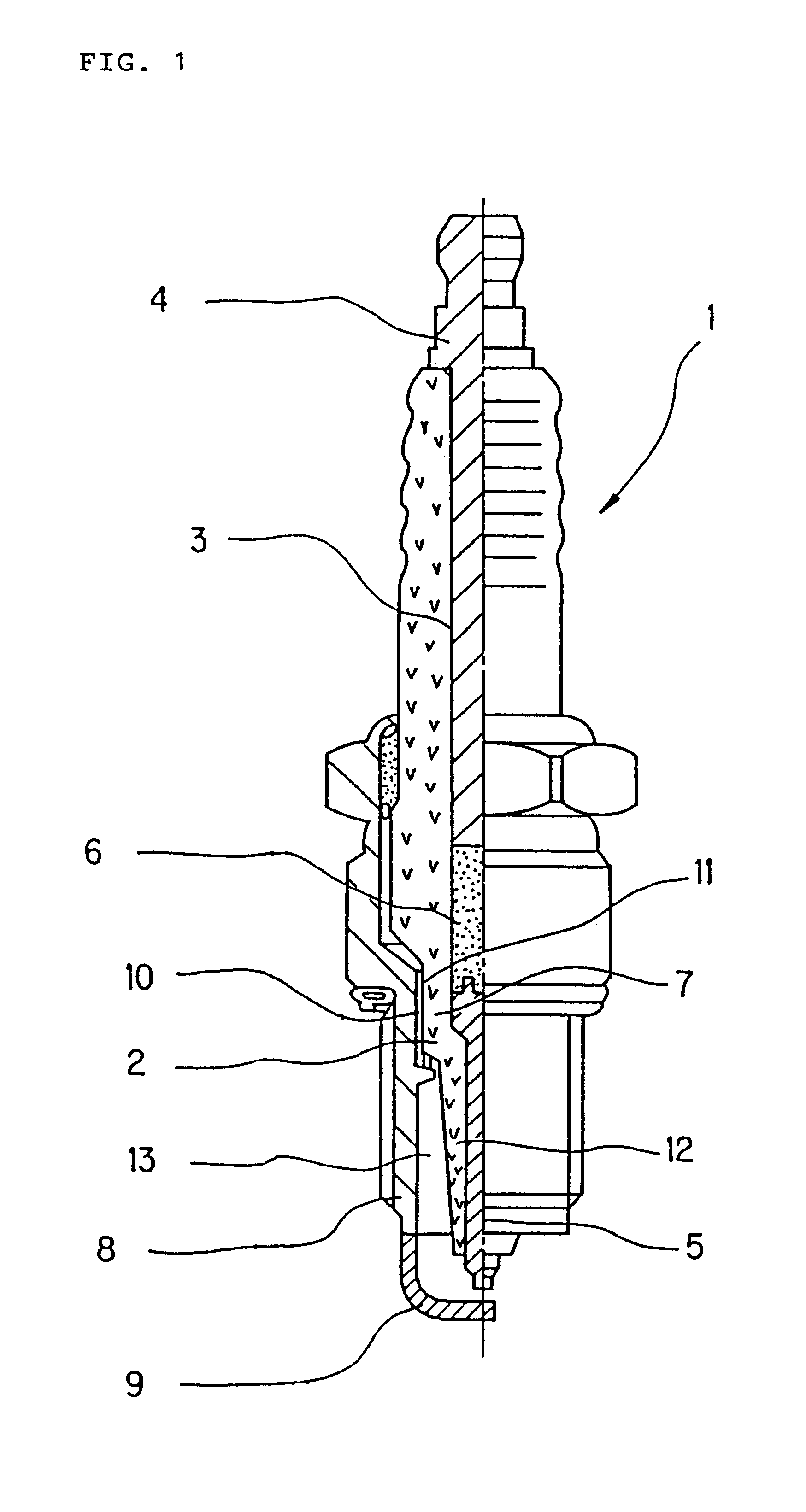
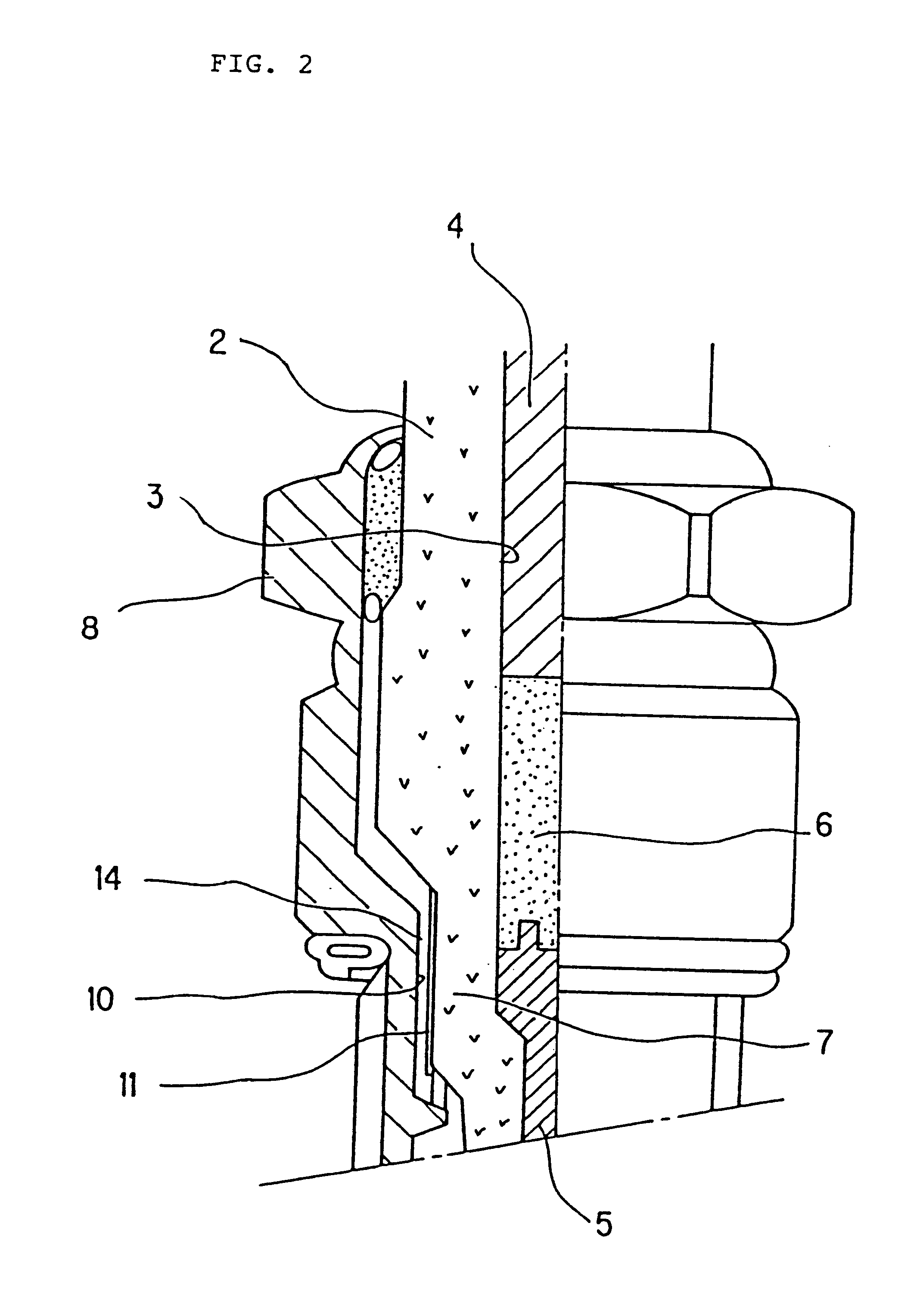
Spark plug having an oil film on an intermediate portion of the insulator or intermediate portion of the metallic shell
InactiveUS6858975B1Avoid insulation breakdownEasy to changeSpark gapsFuel injection apparatusElectric fieldEngineering
In a spark plug for an internal combustion engine oil is applied onto at least either the surface of an intermediate body portion of an insulator or the surface of an intermediate hole portion of a metallic shell, thereby forming an oil film. Since the oil film has a dielectric constant falling between those of the insulator and an ambient air layer, a great change in dielectric constant between the insulator and the ambient air layer is eased. Also, since the oil film is of liquid, the oil film smoothes a dent or protrusion or a fine defect such as crack present on the surface of the intermediate body portion of the insulator. Thus, electric field concentration is suppressed, thereby preventing dielectric breakdown caused by such a dent, protrusion or fine defect.
Owner:NGK SPARK PLUG CO LTD
Boiling-resistant epoxy adhesive as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102329584AStrong adhesionEasy to useNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesOther chemical processesPolyolAlcohol
The invention relates to a boiling-resistant epoxy adhesive as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The boiling-resistant epoxy adhesive consists of a component A and a component B; epoxy resin, toughener and coupling agent are mixed, and are stirred and heated, activated inorganic filler and activated inorganic flame retardant are added, polyhydric alcohol or polyhydric phenol is then added, and thereby the component A is prepared; anhydride and catalyst are mixed and heated, activated inorganic filler and activated inorganic flame retardant are then added, and after depressurization for defoaming, the component B is prepared; when in use, the component A and the component B are uniformly mixed according to the proportion by weight of 1 to 3:1, and thereby the boiling-resistant epoxy adhesive is prepared. Compared with the prior art, the boiling-resistant epoxy adhesive has high adhesive force for electronic elements, is convenient to use, and has excellent high-temperature-resistant property, high strength and good weather fastness and impregnating property, the surface properties of solidified product is excellent, and the post-solidification phenomenon caused by cracking is prevented.
Owner:上海海鹰粘接科技有限公司
Electrostatic chuck
InactiveUS7312974B2Enhanced release propertiesExcellent characteristic of releasing wafer WSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrostatic holding devicesCeramicMaterials science
The electrostatic chuck includes: a conductive base formed of metal or both metal and ceramics, serving as a chucking electrode; and an insulating film formed on one principal plane of the conductive base, the top face of the insulating film serving as a placing surface for placing a wafer; wherein the insulating film is formed of a uniform amorphous ceramics of an oxide and has a thickness in a range of 10 to 100 μm, thereby preventing cracking and insulation breakdown in the insulating film and improving characteristics of releasing the wafer.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Metallized film, a production method thereof, and a capacitor using it
InactiveUS6018454AAvoid insulation breakdownFew defectFixed capacitor electrodesFixed capacitor dielectricPolymer scienceThin membrane
A metallized film including a polymer film, a metal layer having a surface resistance of about 1 OMEGA / sq. to about 15 OMEGA / sq. deposited on a portion of the polymer film, the polymer film having another portion defined as a margin having a surface resistance of about 1x1010 OMEGA / sq. or more, which portion is free of deposited metal; and an about 0.02 to about 1 mm wide boundary zone of deposited metal formed between the deposited metal layer and the margin which substantially continuously decreases in thickness from the deposited metal layer to the margin.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Electrostatic chuck apparatus
ActiveUS9343346B2High voltageAvoid insulation breakdownSleeve/socket jointsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringAdhesive materials
Owner:SUMITOMO OSAKA CEMENT CO LTD
Electric precipitator and electrode thereof
ActiveUS8349052B2Avoid insulation breakdownInhibition electric field strengthWave amplification devicesExternal electric electrostatic seperatorElectricityLow voltage
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Substrate for a display panel, a display panel having the substrate, a production process of the substrate, and a production process of the display panel
ActiveUS20100000765A1Electrical discharge be preventNo increase in costSolid-state devicesConductive pattern formationEngineeringElectrical conductor
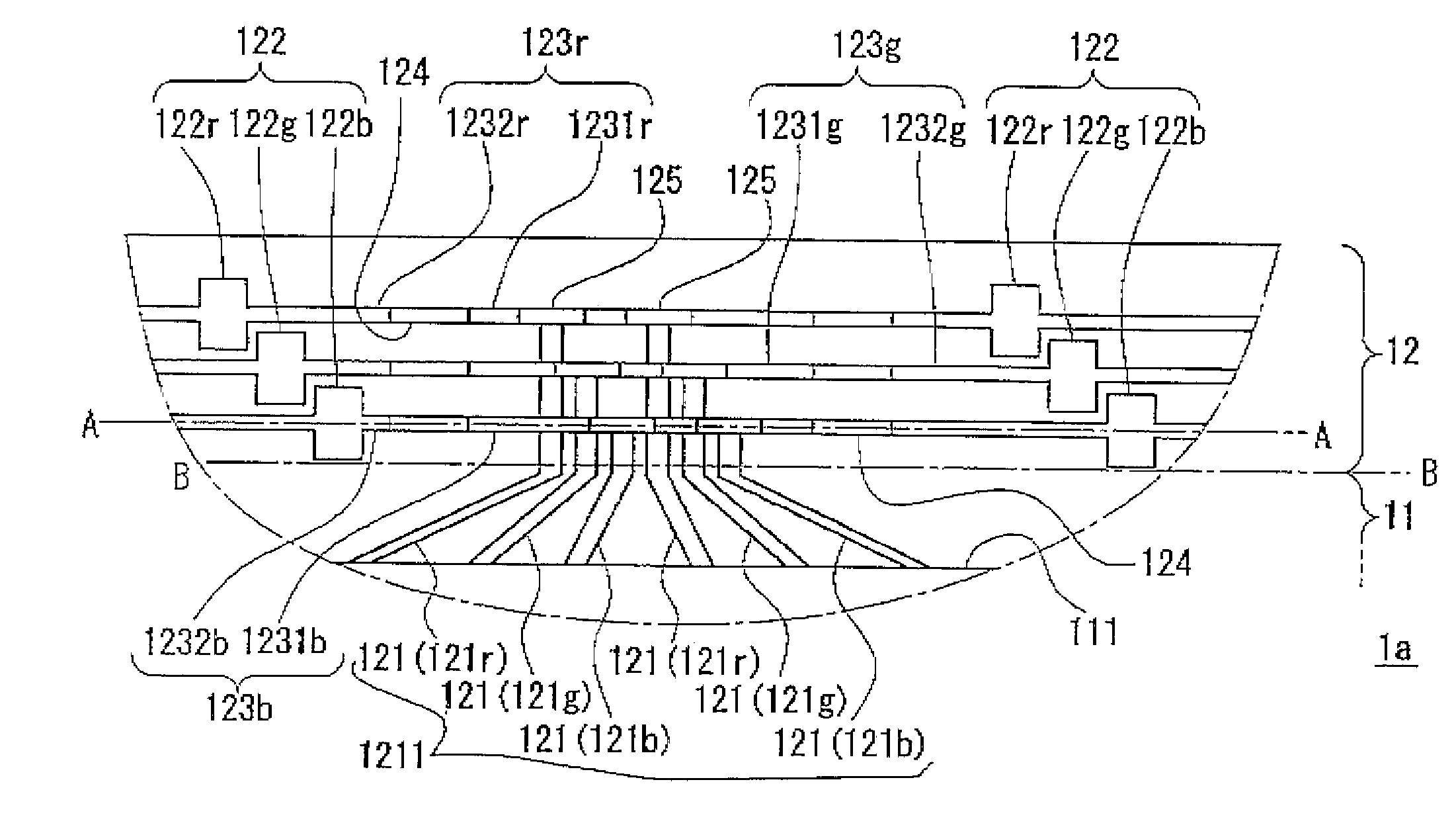
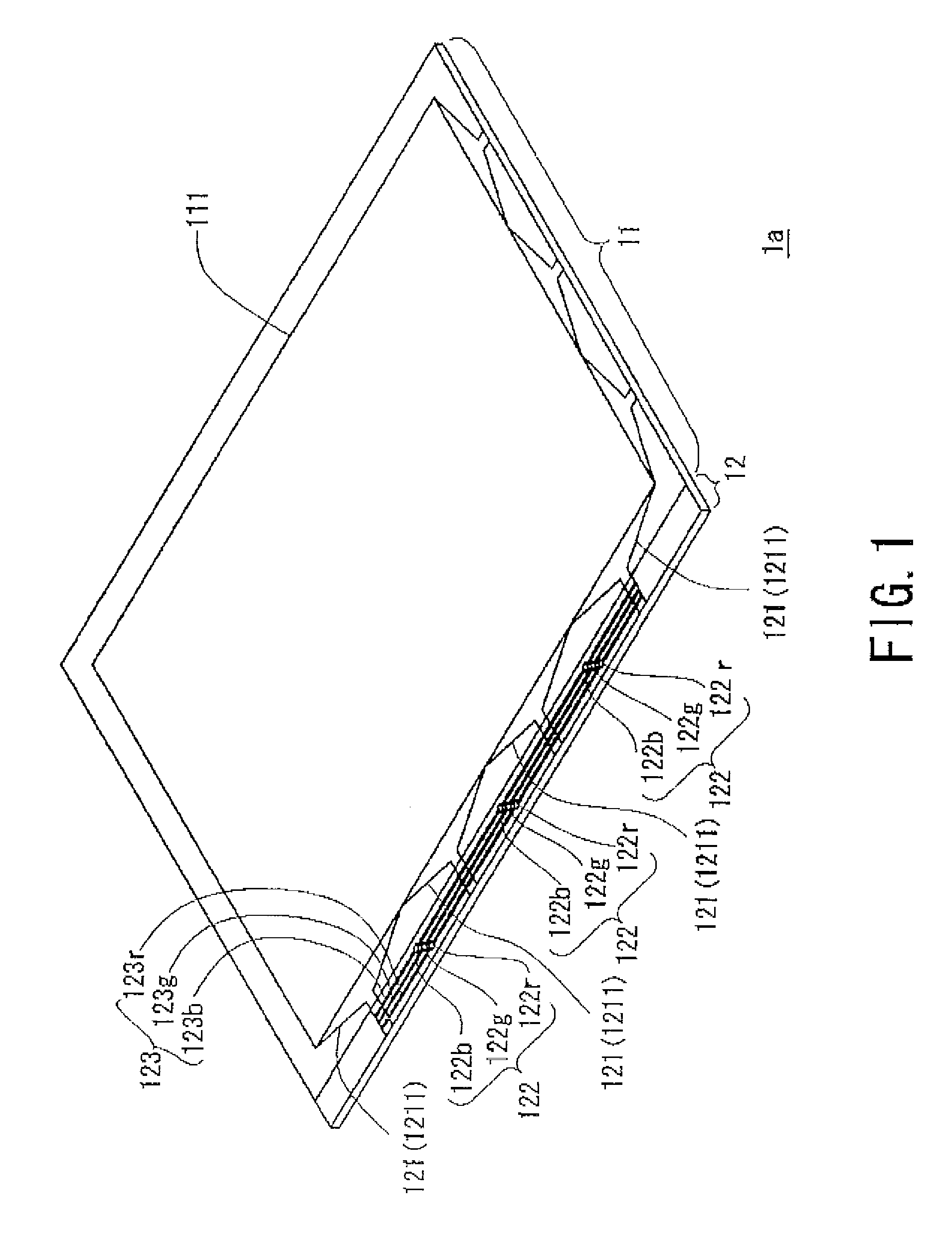
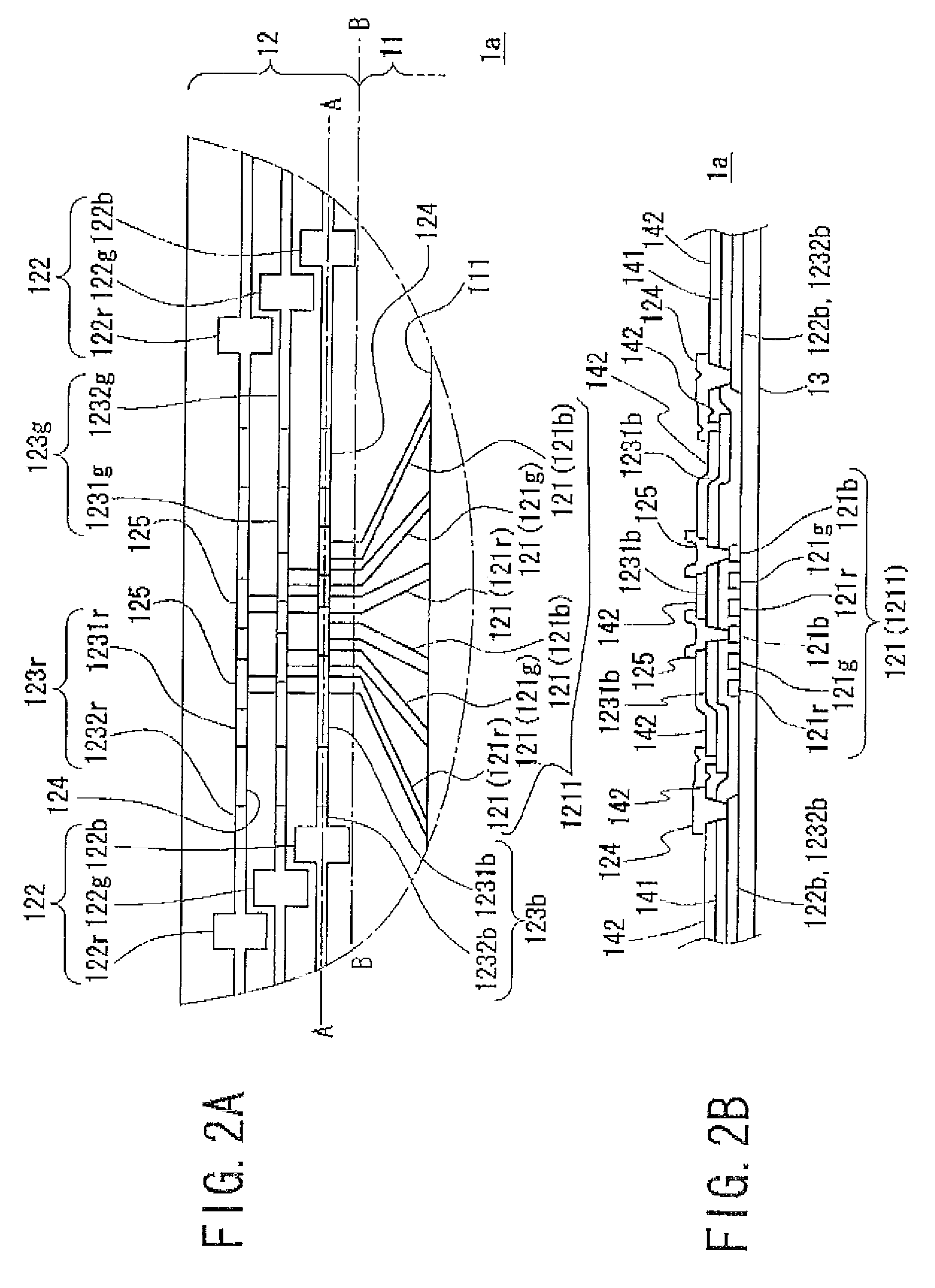
A substrate for a display panel in which insulation breakdown of an insulating film can be prevented, a display panel having the substrate, a production process of the substrate and a production process of the display panel.The substrate includes an inspection line 123 for transferring a signal for inspection which includes a first section 1231 including a portion overlapping with and / or intersecting an input line 121 drawn from a data signal line in a display region 111 between which an insulating film 141 is sandwiched and a second section 1232 which includes a portion other than the portion overlapping with and / or intersecting the input line 121 which are formed to be electrically independent from each other and are arranged to be electrically connected by a conductor 128, wherein a difference between areas of the first section 1231 and the input line 121 is reduced.
Owner:SHARP KK
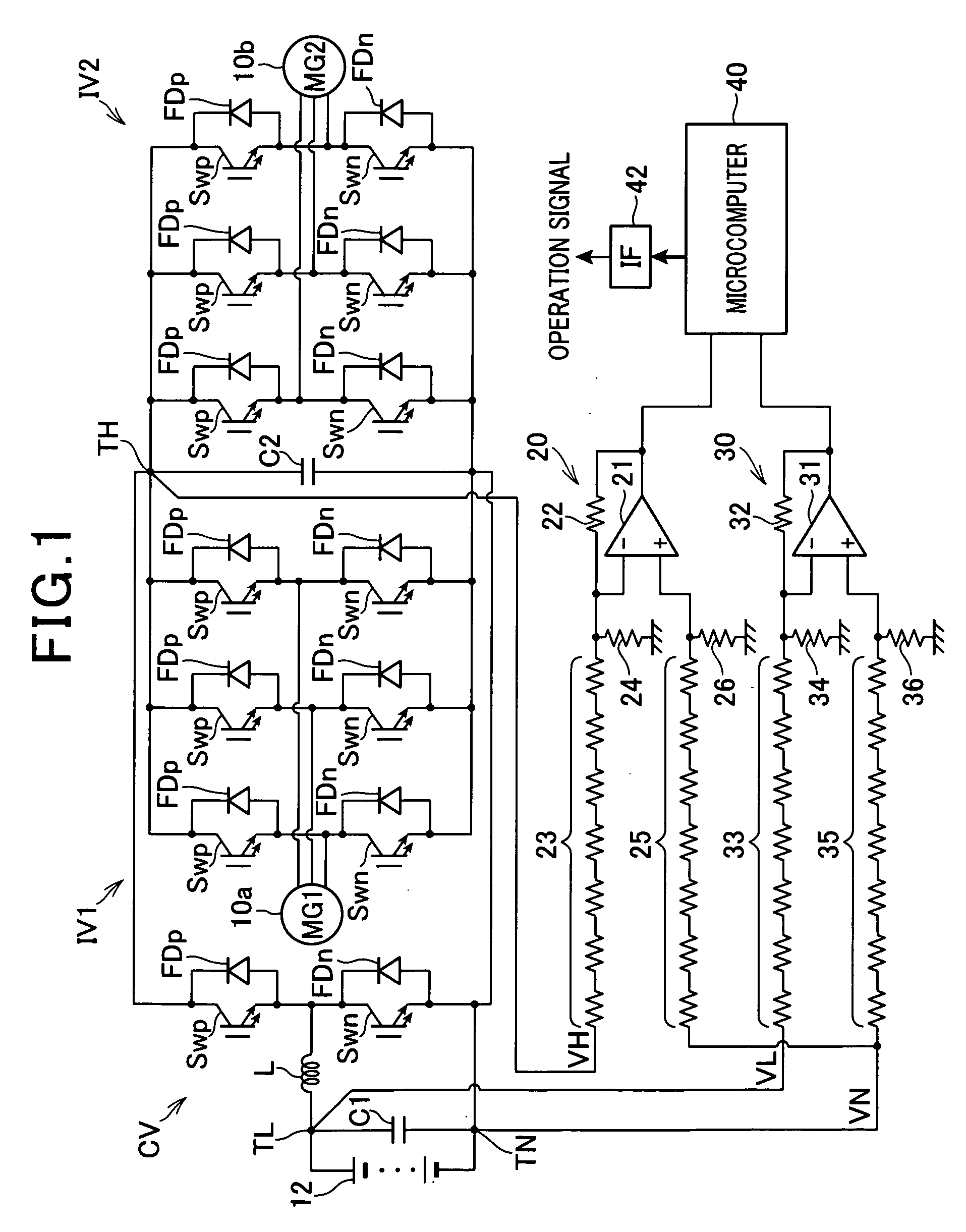
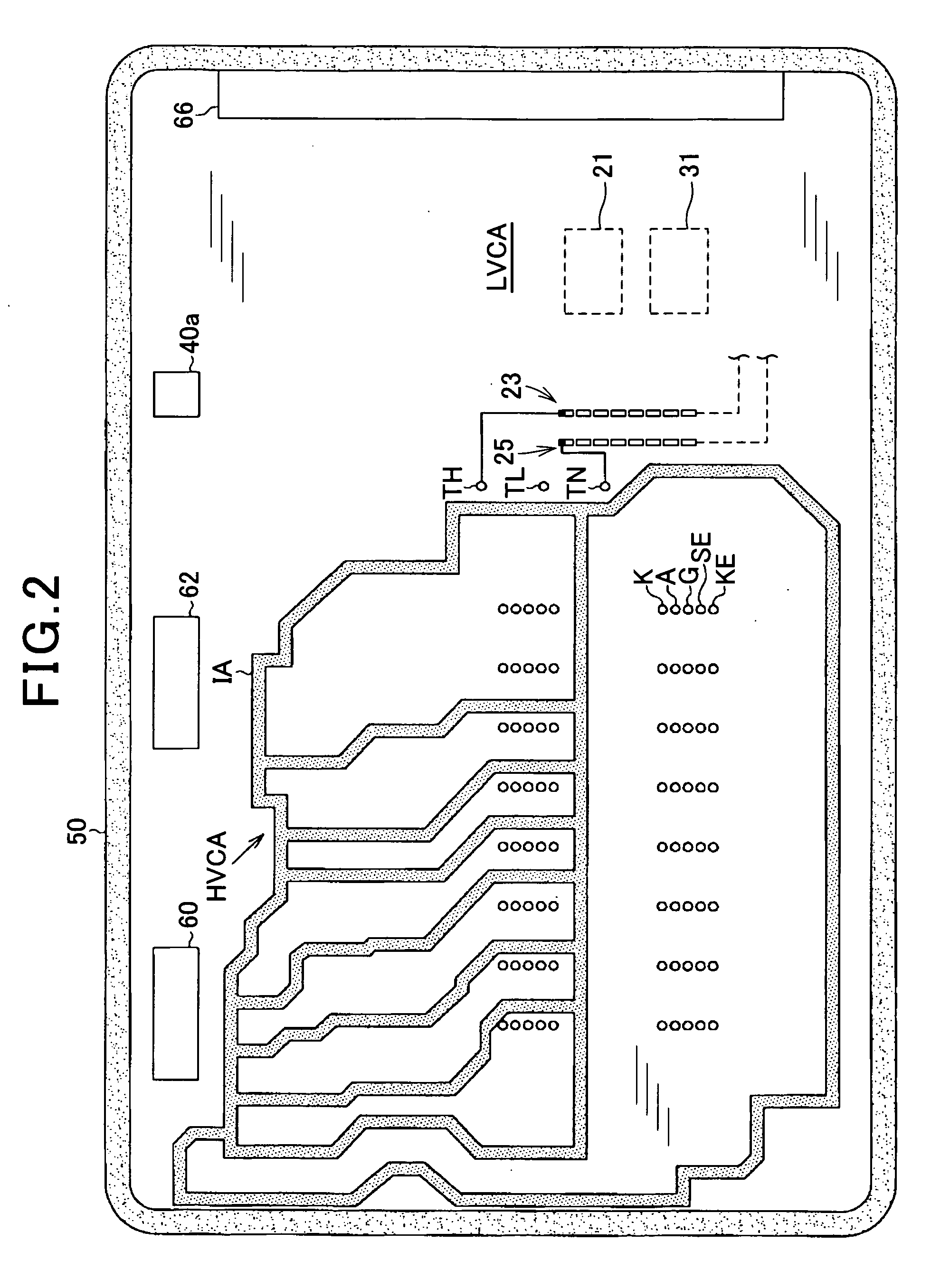
Power conversion apparatus provided with substrate having insulating area
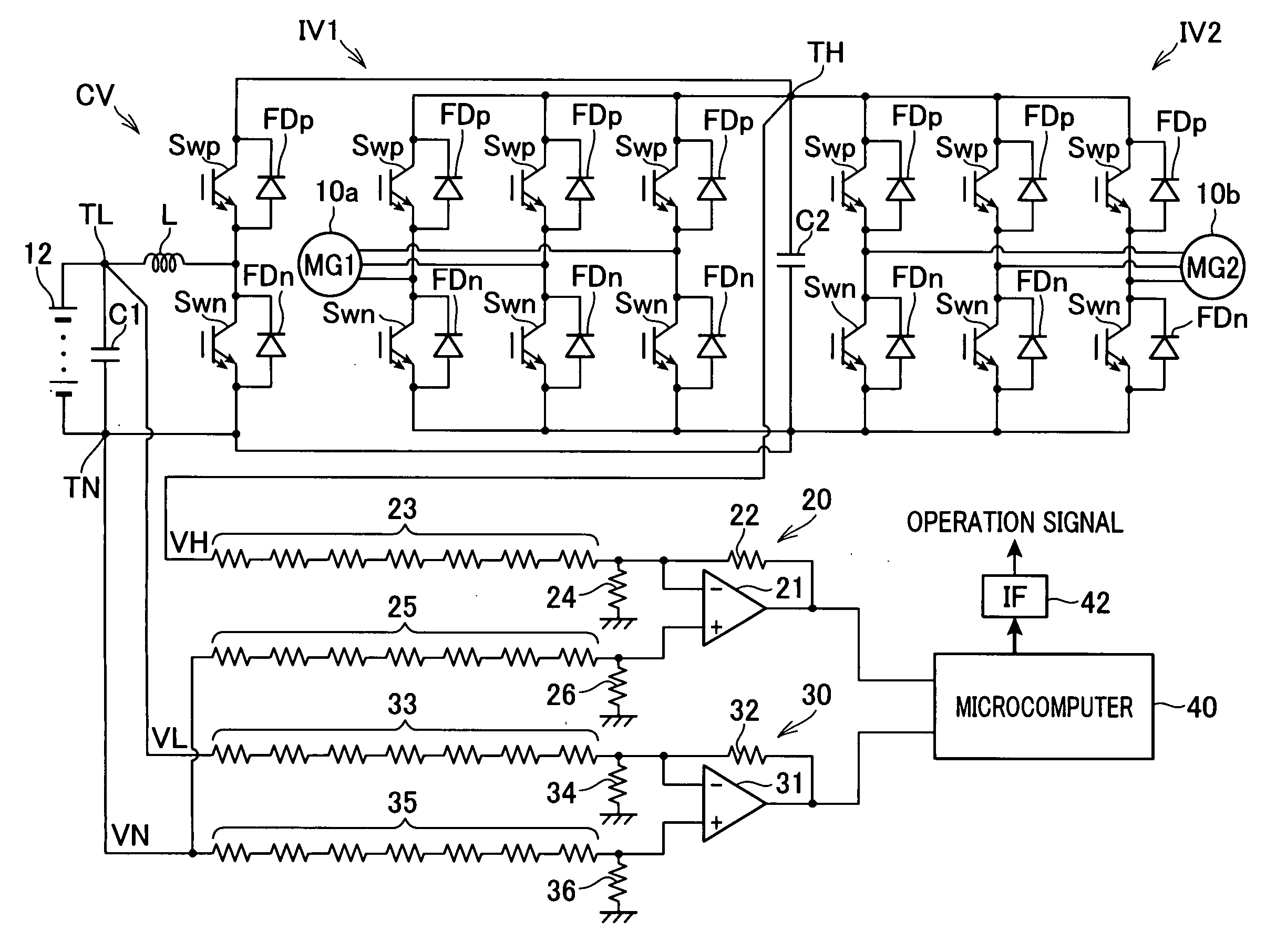
ActiveUS20120286717A1Avoid insulation breakdownReduce areaSynchronous motors startersAC motor controlLow voltage circuitsVoltage range
A power conversion apparatus includes: a high-voltage circuit; a low-voltage circuit operating with an operating voltage lower than that of the high-voltage circuit; and a substrate. The substrate includes an edge section, portions corresponding to the low-voltage circuit and the high-voltage circuit formed thereon and a voltage conversion circuit converting a voltage range of the high-voltage to be capable of operating by the low-voltage circuit. The substrate is provided with an insulating area in a periphery of the high-voltage circuit, and the voltage conversion circuit being provided with an insulating area in a periphery thereof. The insulating area provided in the periphery of the voltage conversion circuit shares an area with at least either of the insulating area provided in the periphery of the high-voltage circuit and the edge section of the substrate.
Owner:DENSO CORP
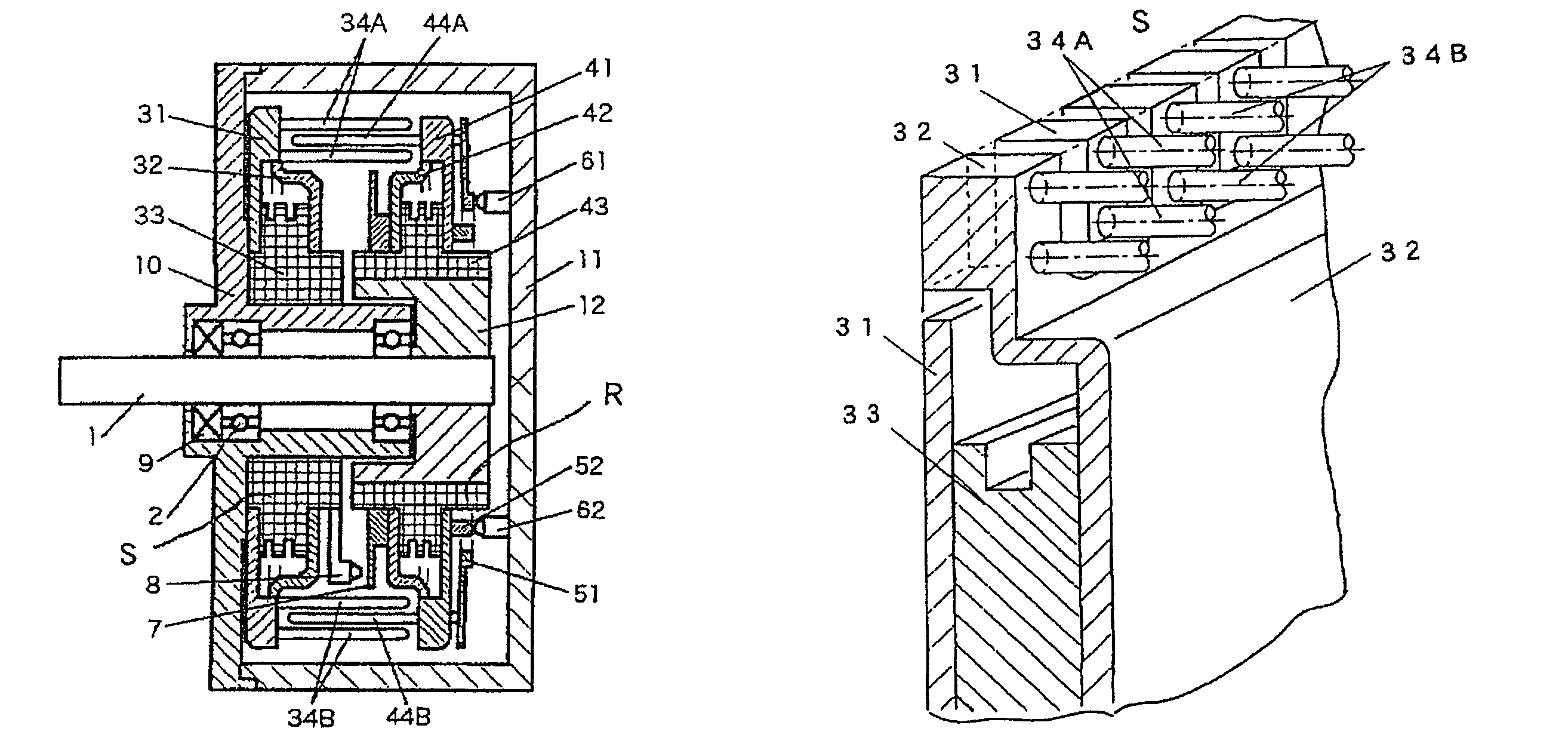
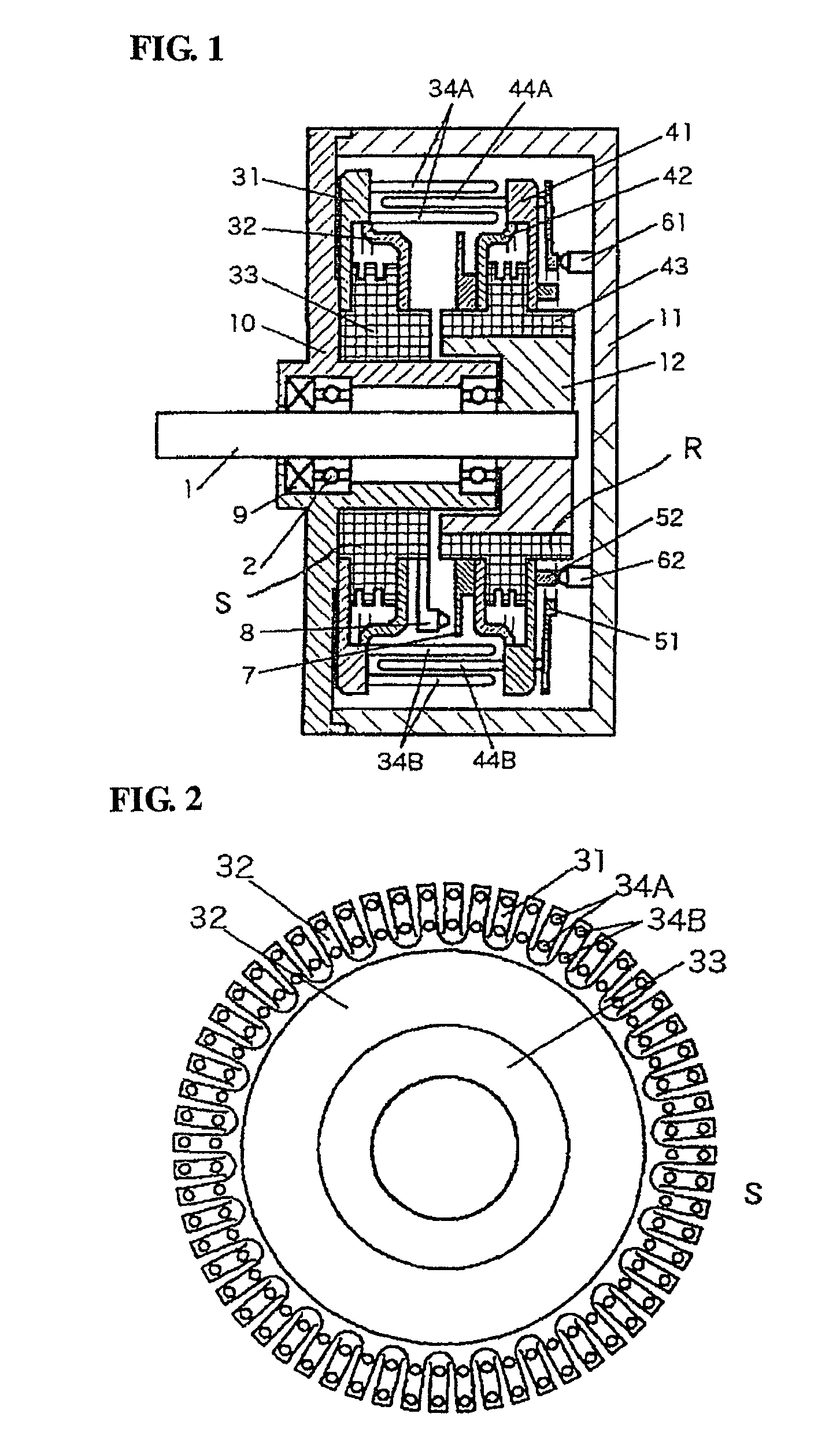
Electrostatic motor
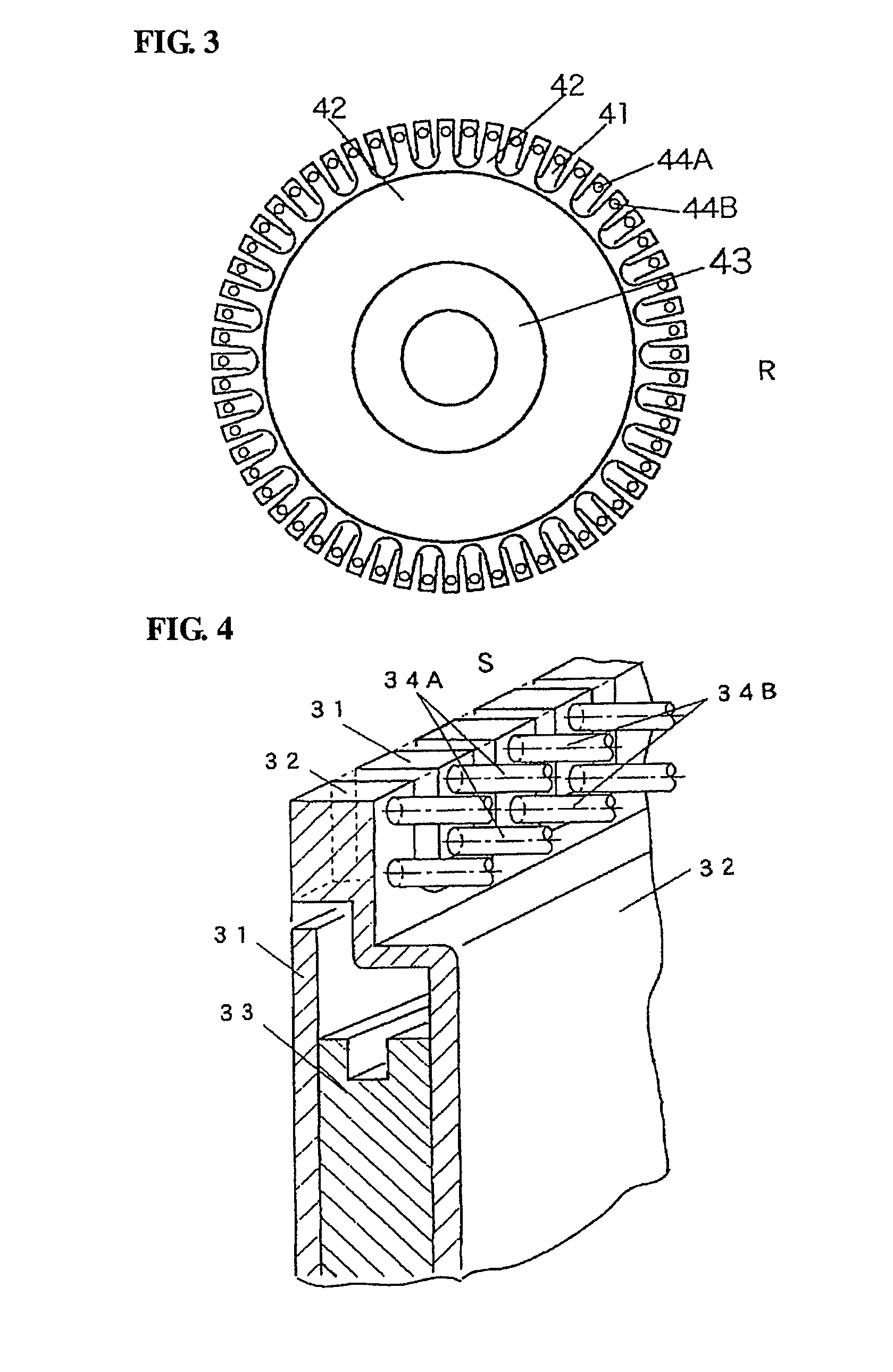
ActiveUS8278797B2Sufficient driving forceIncrease productionElectrostatic motorsElectrostatic motorEngineering
An electrostatic motor has a disc-shaped stator and a disc-shaped rotor are opposed to each other in a vacuum container. In the stator, first electrodes and second electrodes, which are attached to electrode supports, and which are electrically insulated from each other by an insulator, are arranged alternately in the circumferential direction. In the rotor, first electrodes and second electrodes, which are attached to electrode supports, and which are electrically insulated from each other by an insulator, are arranged alternately in the circumferential direction. The first electrodes and the second electrodes on the side of the stator are arranged at a spacing of two or more rows at a predetermined distance from the center of a rotating shaft. The first electrodes and the second electrodes on the side of the rotor are arranged at a predetermined distance from the center of the rotating shaft and at an intermediate position between the rows of the first electrodes and the second electrodes on the side of the stator. As a result, the electrostatic motor can establish a high electric field in the vacuum so that it can rotationally drive with a sufficient driving force.
Owner:SHINSEI CO LTD
Electrode piece for electrostatic chuck, electrostatic chuck device and its adsorptiong method
ActiveCN1581460AAvoid insulation breakdownSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPositioning apparatusDielectricPotential difference
Provided is an electrostatic chuck device which is high in holding force of an insulating material and durability to the dielectric breakdown, an electrodeposition sheet for it, and a method for using the electrostatic chuck device. In the electrostatic chuck device, an electrode sheet 10 is composed of an insulating layer 1 made of an insulating material, first / second electrode layers 2, 3 provided on both faces of the insulating layer for generating the potential difference via the insulating layer, and insulating thin films 4, 5 for covering the surfaces of the two electrode layers. The electrode sheet 10 is pasted on a base 7 so that the second electrode layer is located at the base side. The first electrode of the electrostatic chuck device is grounded. A voltage is applied to the second electrode. A body to be adsorbed is adsorbed on the insulating thin film 4.
Owner:TOMOEGAWA PAPER CO LTD
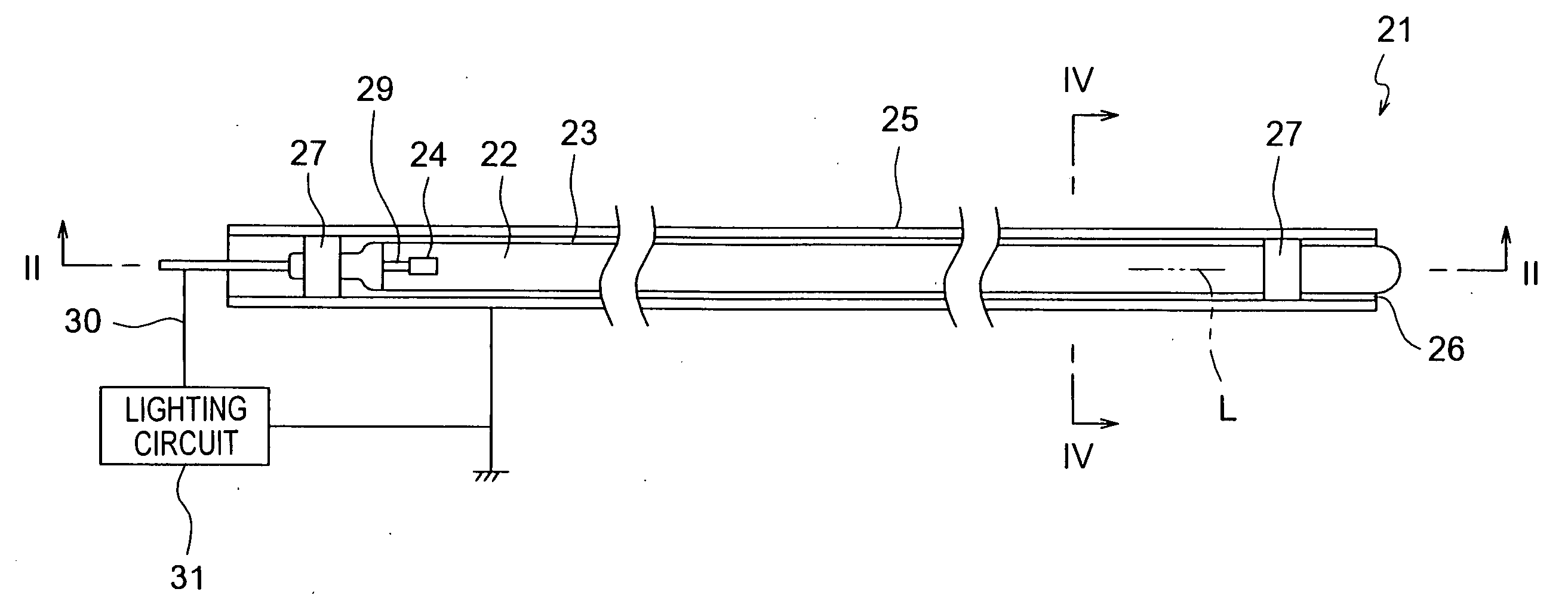
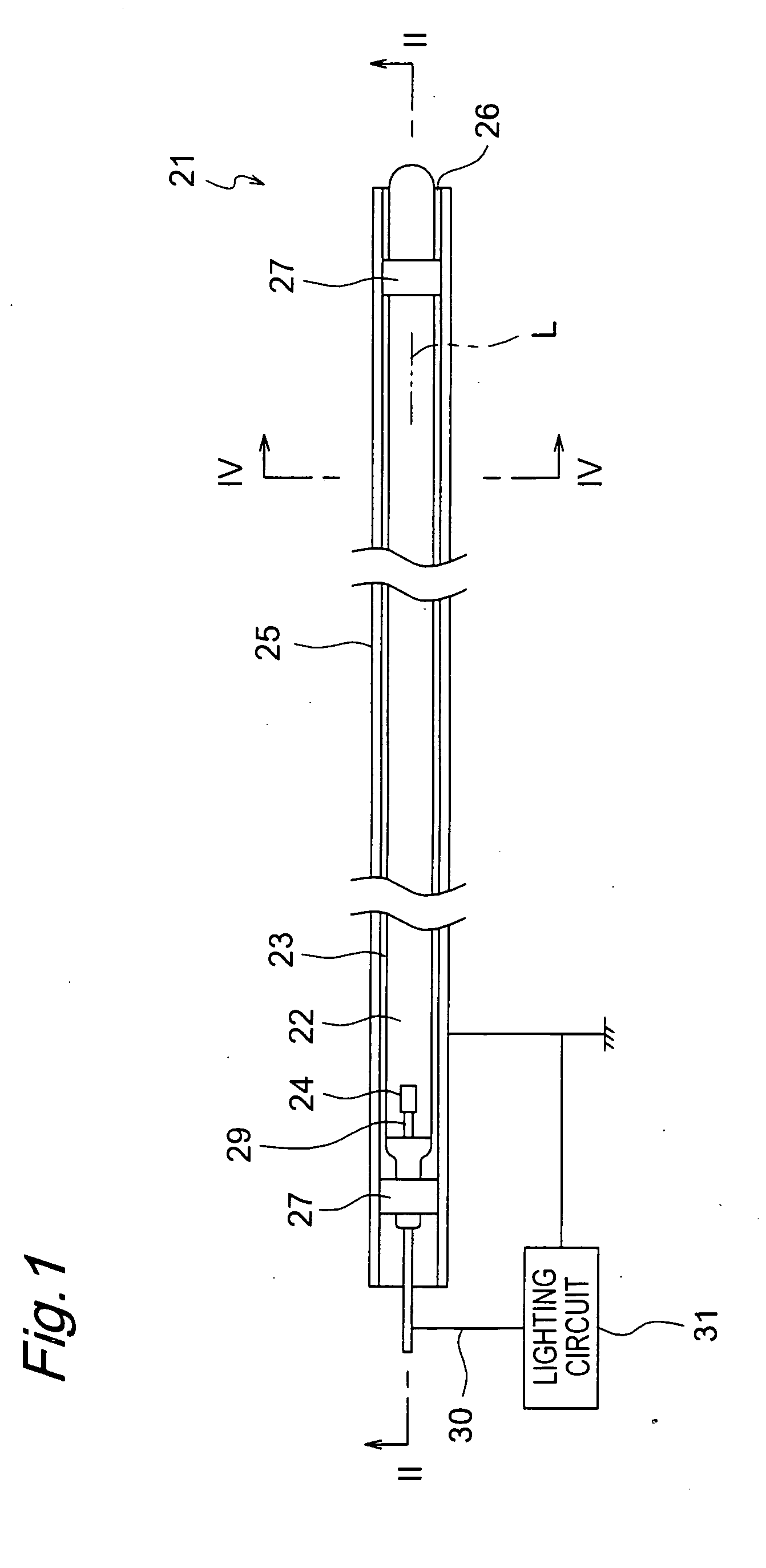
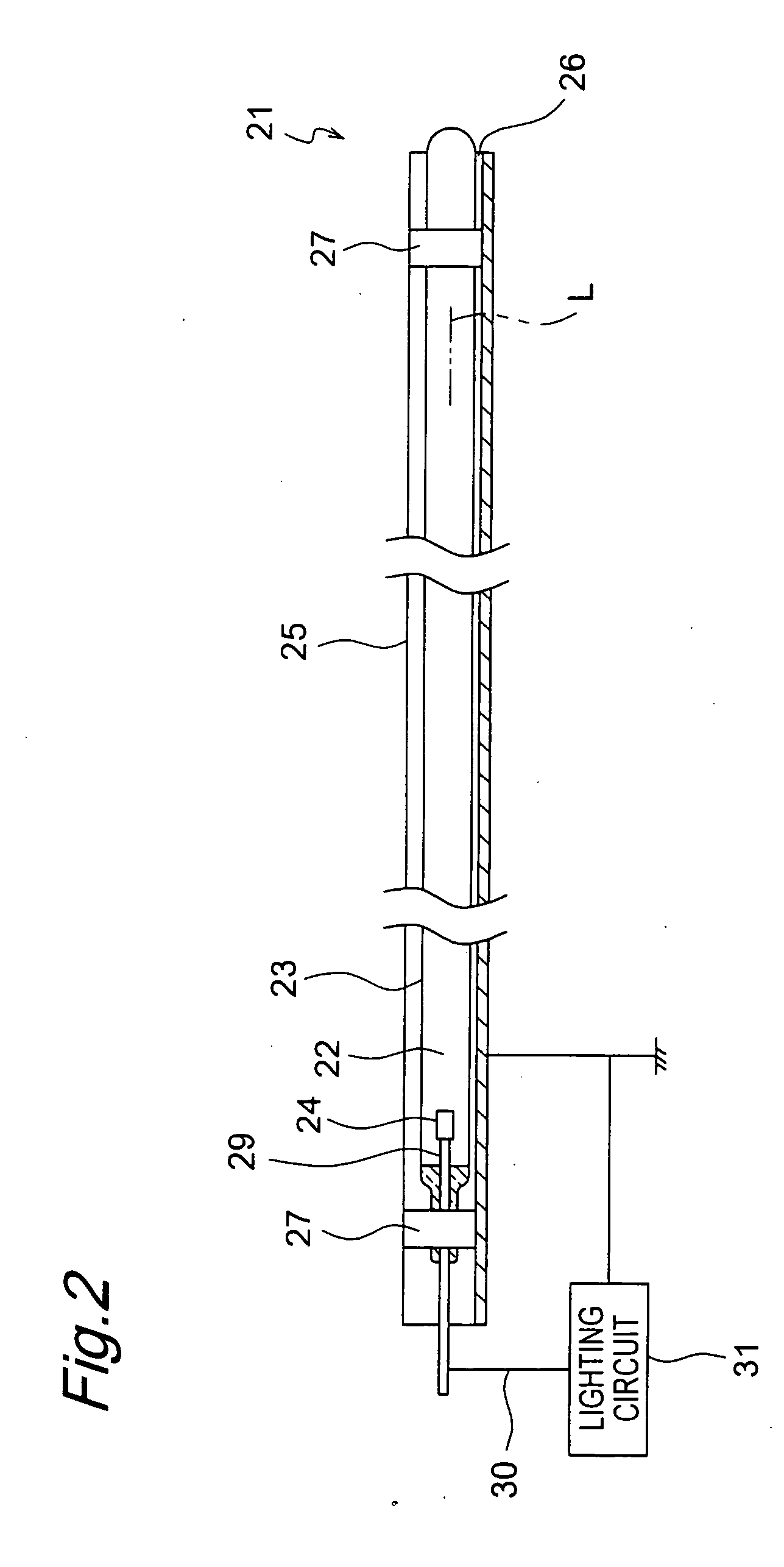
Light source device, lighting device and liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20060139934A1Luminous properties are stableImprove reliabilityMechanical apparatusElongate light sourcesLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
The light source device has a bulb, a discharge medium containing rare gas sealed inside the bulb, an internal electrode disposed inside the bulb, and an external electrode disposed outside the bulb. A holder member holds the external electrode so that the external electrode is opposed to the bulb with a predetermined distance of a space therebetween.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
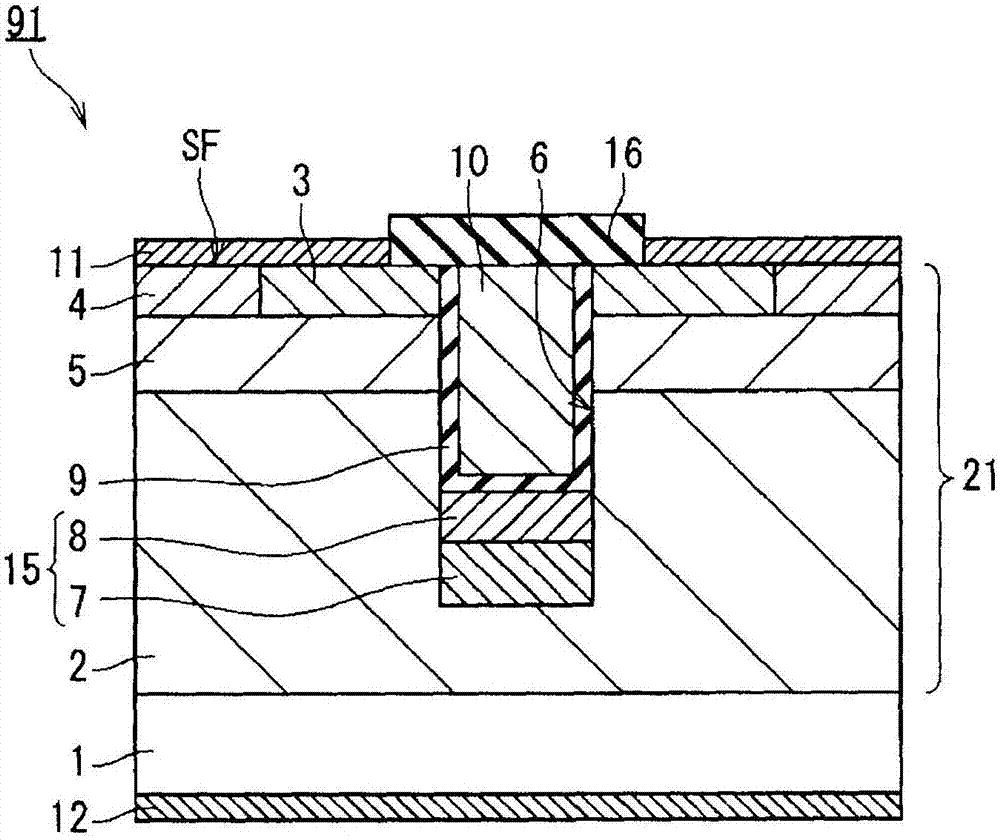
Silicon carbide semiconductor device and method for manufacturing same
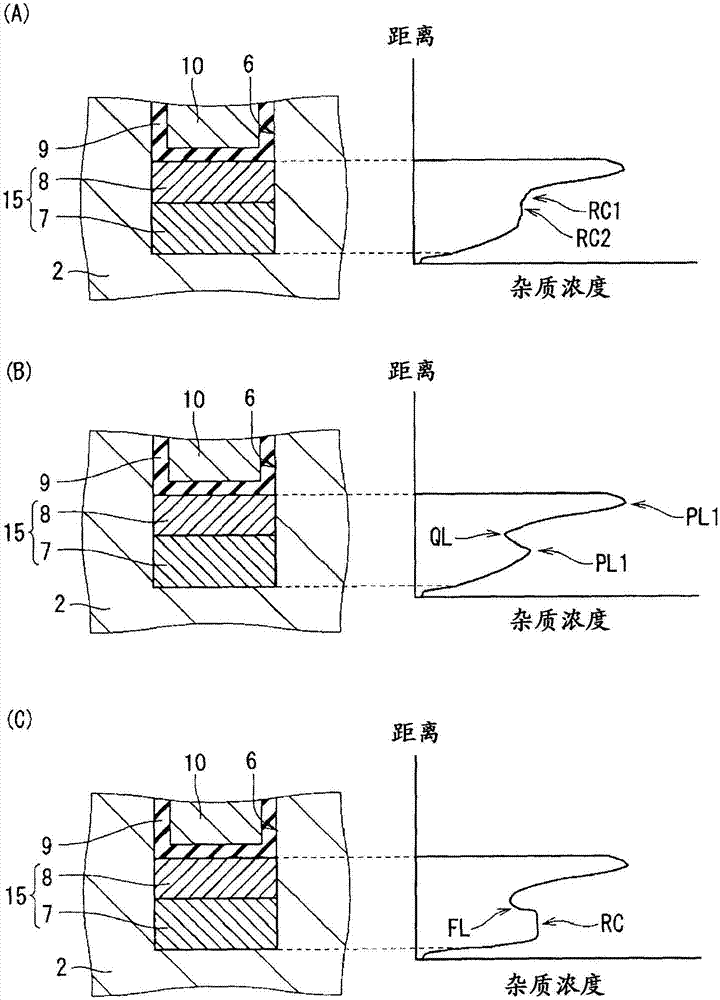
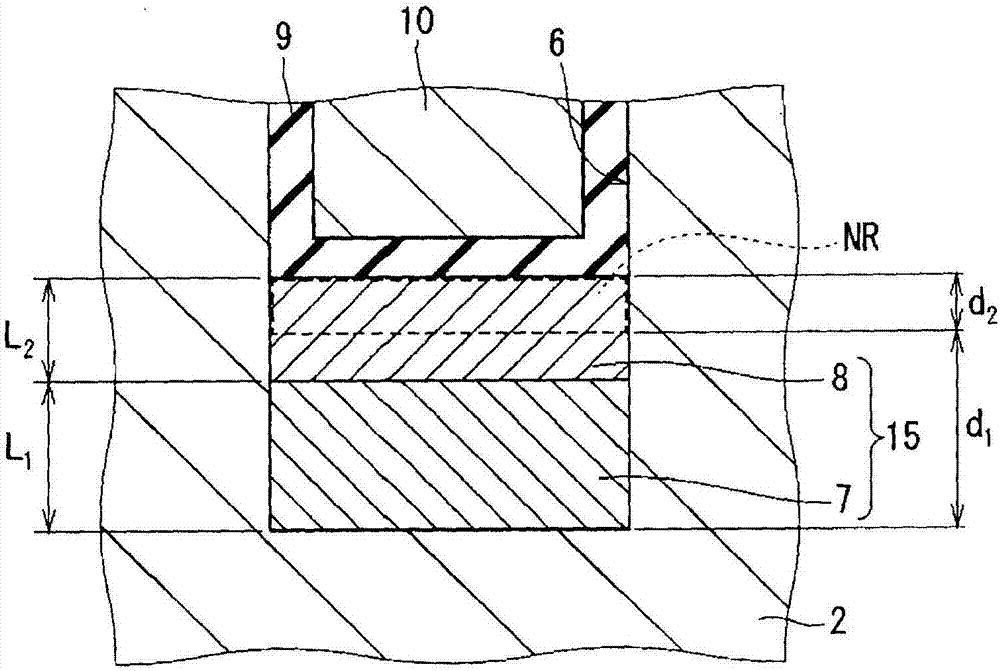
ActiveCN107431091AAvoid insulation breakdownImprove breakdown voltageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDevice materialElectrical connection
The invention provides a silicon carbide semiconductor device and a method for manufacturing the same. According to the invention, a first-conductivity-type drift layer (2) comprises silicon carbide. A second-conductivity-type body region (5) is provided on the drift layer (2). A first-conductivity-type source region (3) is provided on the body region (5). A source electrode (11) is connected to the source region (3). A gate insulating film (9) is provided on the side surfaces and the bottom surface of a trench (6) that passes through the body region (5) and the source region (3). A gate electrode (10) is provided inside the trench (6) with the gate insulating film (9) interposed therebetween. A second-conductivity-type trench-bottom-surface protective layer (15) is provided below the bottom surface of the trench (6) within the drift layer (2), and is electrically connected to the source electrode (11). The trench-bottom-surface protective layer (15) has: a high-density protective layer (8); and a first low-density protective layer (7) provided below the high-density protective layer (8) and having a lower impurity density than the high-density protective layer (8).
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Electrostatic chuck device, and semiconductor manufacturing device
ActiveUS20180025933A1Prevent penetrationLimited coefficientSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPositioning apparatusEngineeringMechanical engineering
An electrostatic chuck part of an electrostatic chuck device has an electrostatic chuck part inner peripheral surface surrounding an opening of a chuck part through-hole, and an electrostatic chuck part outer peripheral surface surrounding the electrostatic chuck part inner peripheral surface. An insulator has an insulator main body in which an insulator through-hole having an opening on the electrostatic chuck part side is formed, an insulator inner end face, and an insulator outer end face which faces the electrostatic chuck part outer peripheral surface. The insulator inner end face and the electrostatic chuck part inner peripheral surface are in contact with each other, or an adhesion layer or a plasma-resistant adhesive layer extends in a gap between the insulator inner end face and the electrostatic chuck part inner peripheral surface. The plasma-resistant adhesive layer is formed between the electrostatic chuck part outer peripheral surface and the insulator outer end face.
Owner:SUMITOMO OSAKA CEMENT CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method for producing same
InactiveUS8748977B2Reduce intensityAvoid insulation breakdownTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower semiconductor deviceEngineering
A semiconductor device according to an embodiment of the present invention includes: a semiconductor layer 2 of a wide band gap semiconductor arranged on a principal surface of a substrate 1; a trench 5 arranged in the semiconductor layer and including a bottom surface, a plurality of main side surfaces, and a plurality of corner side surfaces each connecting together two adjacent main side surfaces; a gate insulating film 6 arranged on the bottom surface, the main side surfaces and the corner side surfaces of the trench 5; and a gate electrode 8 arranged in the trench, wherein the semiconductor layer includes a drift region 2d of a first conductivity type, and a body region 3 of a second conductivity type arranged on the drift region; the trench runs through the body region 3 and has the bottom surface inside the drift region; the corner side surfaces of the trench do not have a depressed portion; the gate insulating film 6 is thicker on the corner side surfaces of the trench than on the main side surfaces of the trench; and a portion of the gate insulating film 6 that is located on the corner side surfaces is a first insulating layer 6b, and a portion of the gate insulating film 6 that is located on the main side surfaces is a second insulating layer 6a.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Silicon Carbide Semiconductor Device and Manufacturing Method Thereof
ActiveUS20080224149A1Avoid insulation breakdownImprove insulation withstand-voltage and breakdown lifetimeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHigh concentrationSide lying
The present invention provides a silicon carbide semiconductor device comprising a semiconductor substrate comprising silicon carbide, which contains a first conductivity type impurity diffused therein in a high concentration, a semiconductor layer formed over the semiconductor substrate and containing the first conductivity type impurity diffused therein in a low concentration, a plurality of well regions formed on a front surface side of a cell forming area set to the semiconductor layer and in which a second conductivity type impurity corresponding to a type opposite to the first conductivity type impurity is diffused, source layers formed on the front surface side lying within the well regions and each containing the first conductivity type impurity diffused therein in a high concentration, an outer peripheral insulating film thick in thickness, which is formed over the semiconductor layer in an outer peripheral area that surrounds the cell forming area, a gate oxide film formed over the front surface of the semiconductor layer in the cell forming area, and a gate electrode layer formed so as to extend from above the gate oxide film to above the outer peripheral insulating film, wherein each of steplike portions adjacent to the outer peripheral insulating film and thicker than the gate oxide film in thickness is provided at an edge portion of the gate oxide film.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Display panel
InactiveCN1495473AAvoid insulation breakdownTransistorStatic indicating devicesHigh resistanceEngineering
A display panel of the present invention includes: a first substrate and a second substrate opposing each other with a display medium interposed therebetween; a plurality of signal lines and a plurality of scanning lines provided on the first substrate to cross each other and be insulated from each other; and a plurality of pixel electrodes each provided in a vicinity of an intersection between one of the plurality of signal lines and one of the plurality of scanning lines so as to be connected to the one of the plurality of signal lines and the one of the plurality of scanning lines via a switching element, while the plurality of pixel electrodes define a display region of the display panel. At least one of each of the plurality of signal lines and each of the plurality of scanning lines has a high resistance portion proximate an end thereof outside the display region. The high resistance portion is interposed at least partially between the first substrate and the second substrate.
Owner:SHARP KK
Silicon carbide semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS7679132B2Avoid insulation breakdownImprove insulation withstand-voltage and breakdown lifetimeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSide lyingGate oxide
A silicon carbide semiconductor device includes a semiconductor substrate containing silicon carbide, a semiconductor layer formed over the semiconductor substrate, and a plurality of well regions formed on a front surface side of a cell forming area set to the semiconductor layer. The device further includes source layers formed on the front surface side lying within the well regions, an outer peripheral insulating film thick in thickness, which is formed over the semiconductor layer in an outer peripheral area surrounding the cell forming area, a gate oxide film formed over the front surface of the semiconductor layer in the cell forming area, and a gate electrode layer formed so as to extend from above the gate oxide film to above the outer peripheral insulating film.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Piezoelectric element, liquid ejecting head, and liquid ejecting apparatus
ActiveUS20100265301A1Reduce in quantityAvoid insulation breakdownPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device detailsLiquid jetEngineering
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Piezoelectric element, liquid ejecting head, and liquid ejecting apparatus
ActiveUS8322830B2Reduce in quantityAvoid insulation breakdownPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device detailsPrintingEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
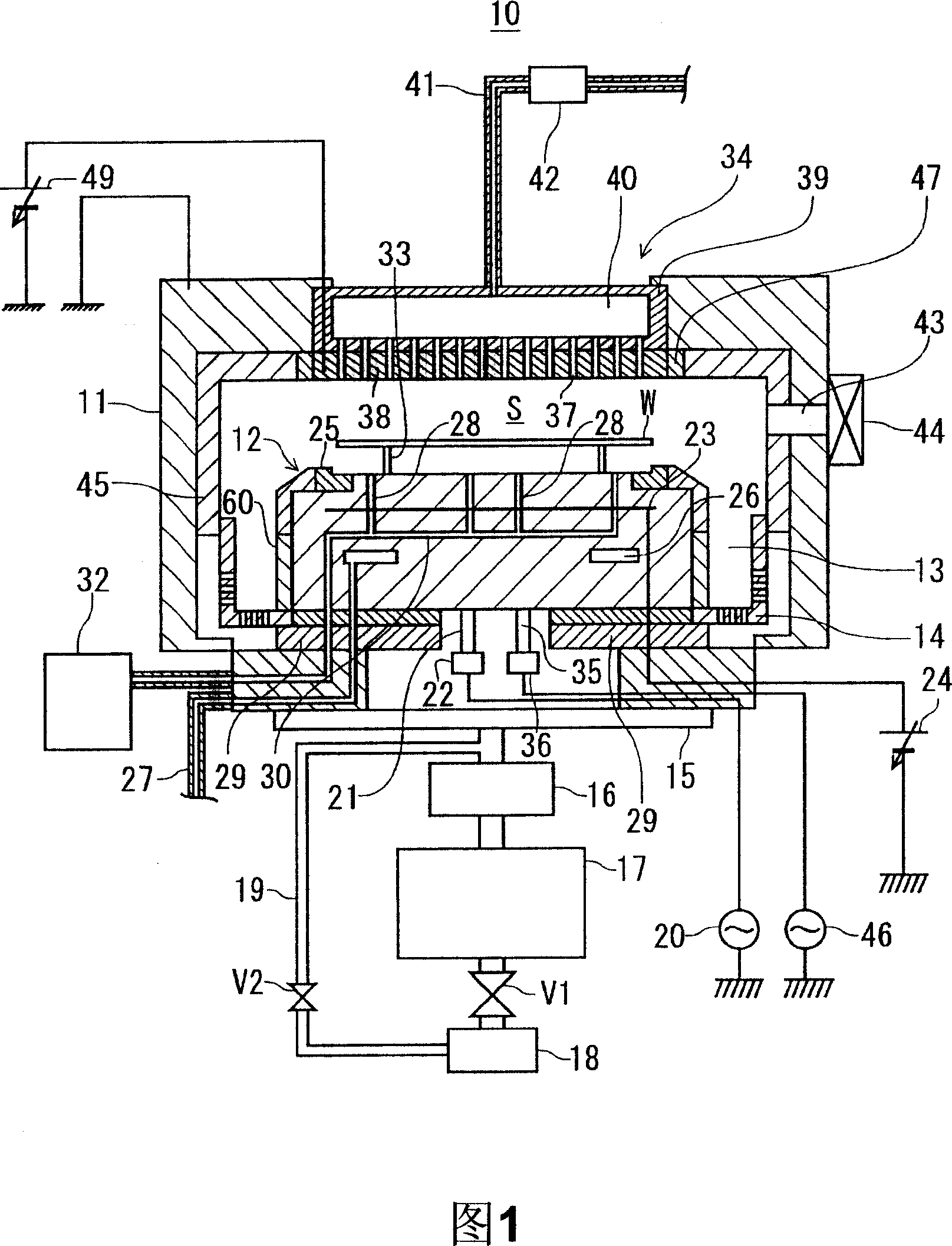
Cleaning method for substrate processing chamber, storage medium, and substrate processing chamber
ActiveCN101022693AAvoid generatingAvoid it happening againElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh frequency powerCleaning methods
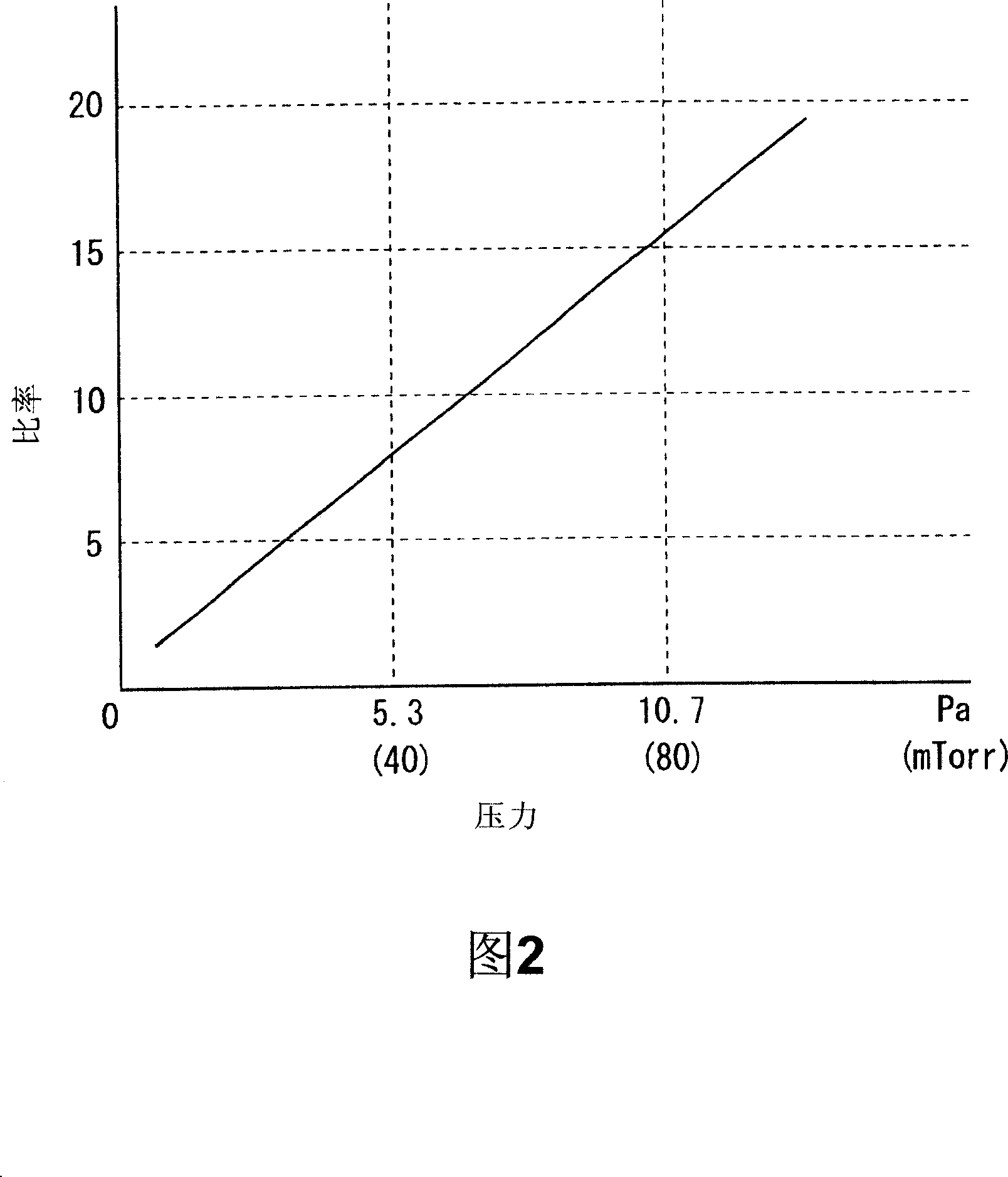
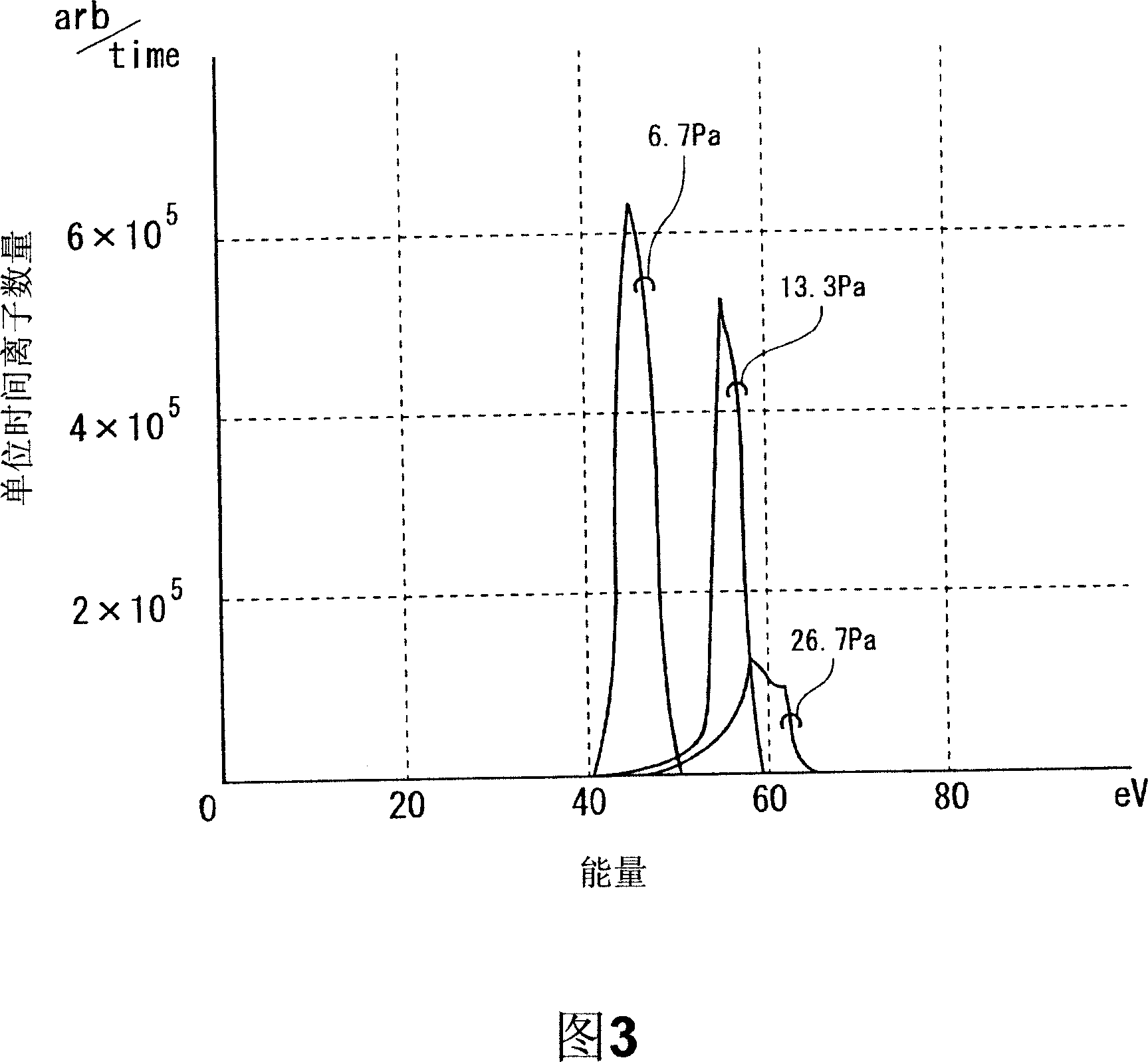
The invention provides a method for cleaning a baseplate processing chamber, which can prevent oxidation film from forming on the surface of a part in the baseplate processing chamber. In a plasma processing device (10) with reaction products adhering to the surface of an upper plate electrode (38), after a wafer (W) is moved out of the baseplate processing chamber (11), oxygen is led into the processing space (S) of the baseplate processing chamber, and the pressure of the processing space (S) is set to be 26.7Pa to 80.0Pa. The potential difference of the surface of the plate electrode and the space is set to be 0eV; and high frequency power of 40MHz is set to be below 500W. High frequency power of 40MHz is used for generation of plasma for dry-cleaning. Carbon tetrafluoride gas is further led into the processing space (S), and high frequency power of 40MHz and 2MHz is used for generating plasma for removal of oxide.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Semiconductor device
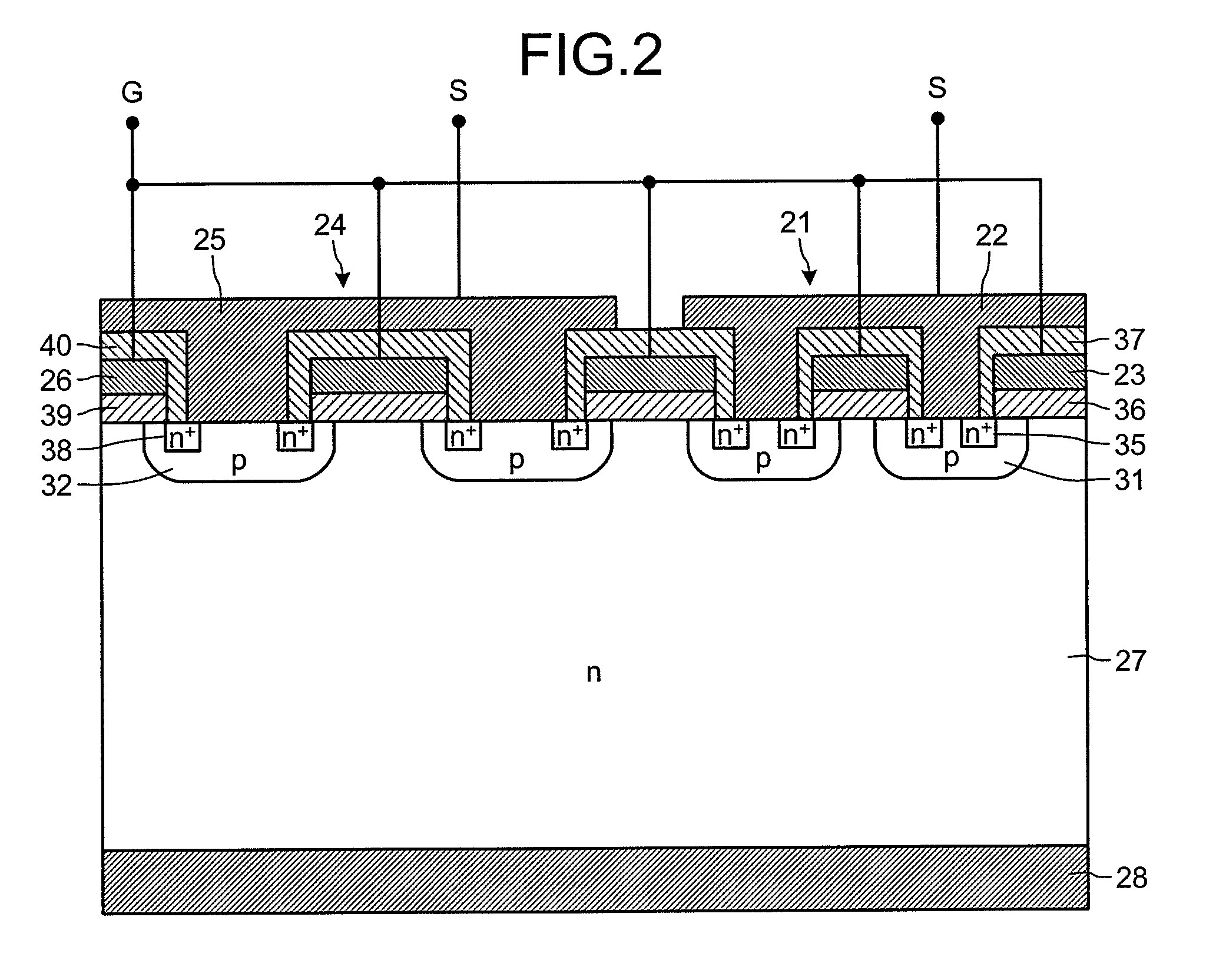
ActiveUS20160372460A1Avoid insulation breakdownTransistorSolid-state devicesDielectricElectric field
Between a source electrode (25) of a main device (24) and a current sensing electrode (22) of a current detection device (21), a resistor for detecting current is connected. Dielectric withstand voltage of gate insulator (36) is larger than a product of the resistor and maximal current flowing through the current detection device (21) with reverse bias. A diffusion length of a p-body region (32) of the main device (24) is shorter than that of a p-body (31) of the current detection device (21). A curvature radius at an end portion of the p-body region (32) of the main device (24) is smaller than that of the p-body (31) of the current detection device (21). As a result, at the inverse bias, electric field at the end portion of the p-body region (32) of the main device (24) becomes stronger than that of the p-body region (31) of the current detection device (21). Consequently, avalanche breakdown tends to occur earlier in the main device 24 than the current detection device (21).
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
Gas laser oscillator
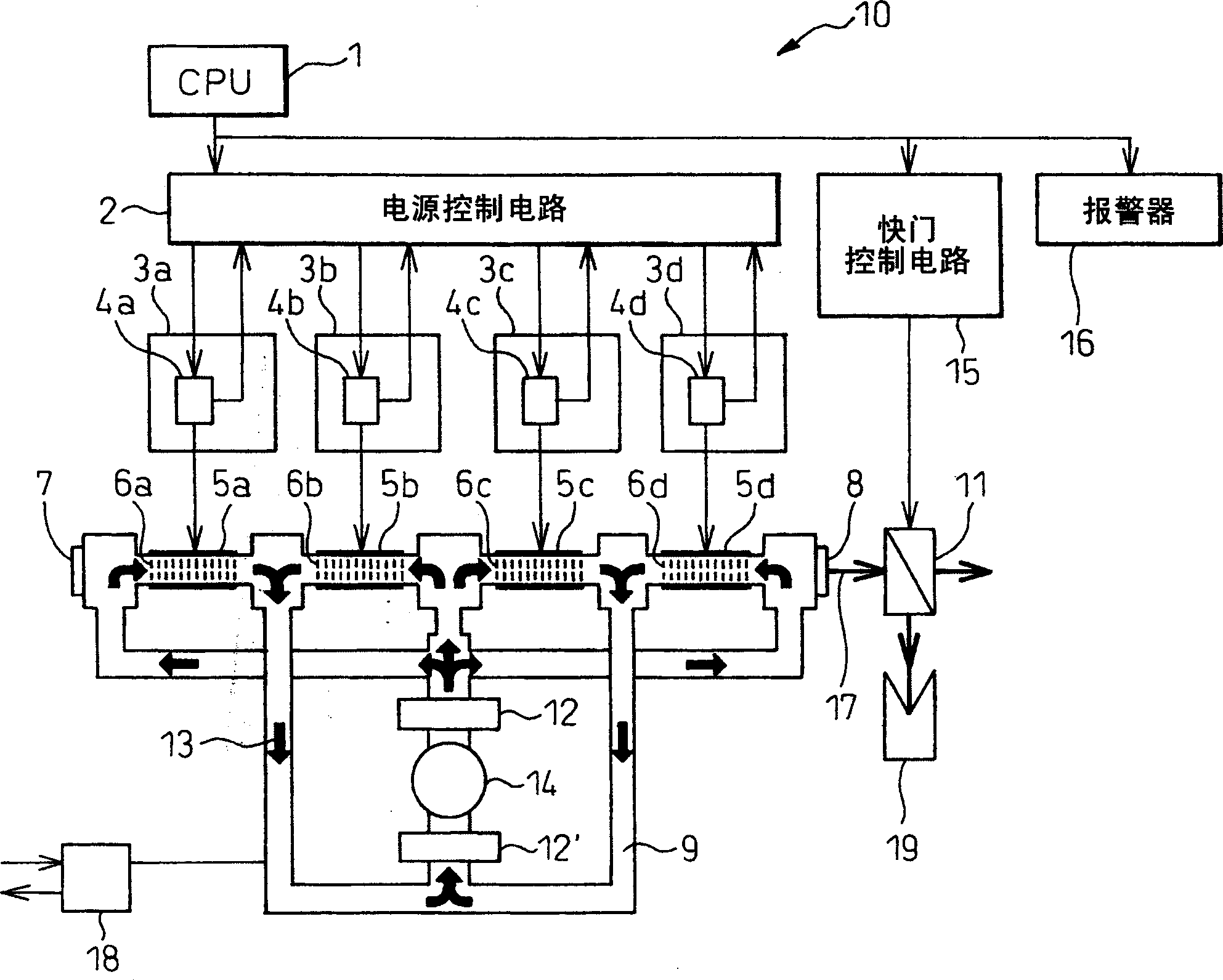
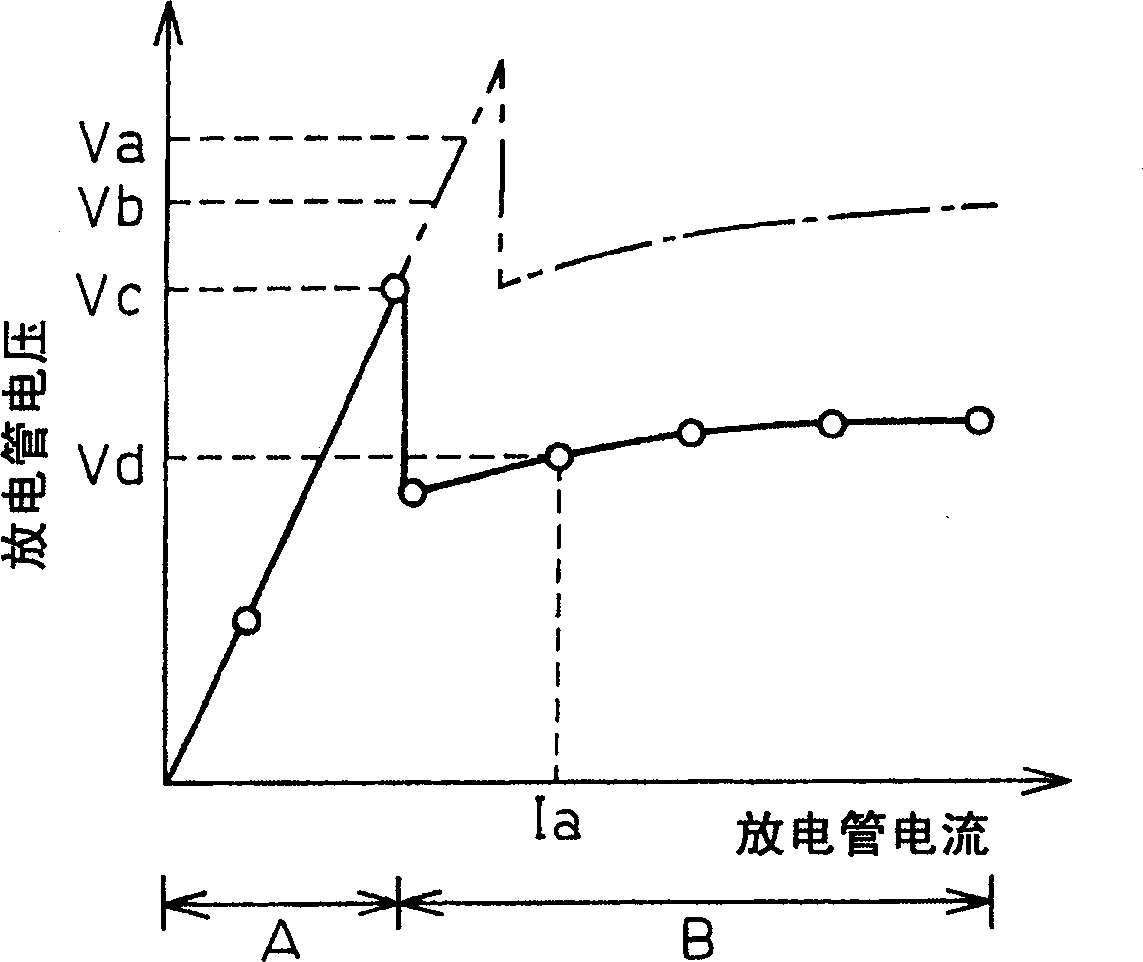
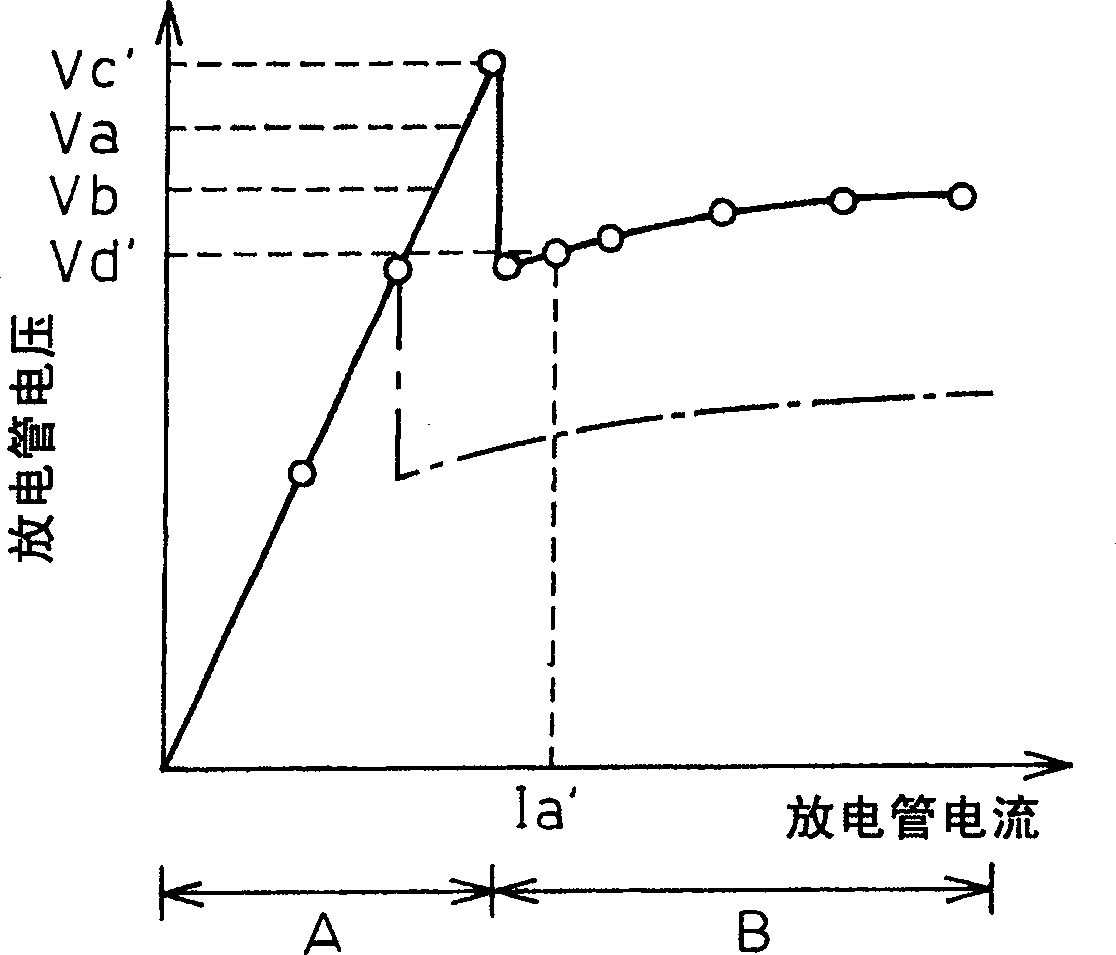
A gas laser oscillator (10) provided with voltage detecting means (4a to 4d) for detecting the voltage of each of a plurality of discharge tube segments (6a to 6d) of a discharge tube before start of discharge and a discharge tube segment start judging means (1) for judging if each of the plurality of discharge tube segments (6a to 6d) has started based on the voltage of the discharge tube segments (6a to 6d) detected by the voltage detecting means (4a to 4d), wherein the discharge tube segment start judging means (1) allows all of the plurality of discharge tube segments (6a to 6d) to start only when the voltages of all of the discharge tube segments (6a to 6d) of the plurality of discharge tube segments are smaller than a predetermined voltage (Vb) is provided. Due to this, it is possible to judge an abnormality in the laser gas before the start of discharge without any work on the part of the operator and thereby prevent the discharge tube from being damaged.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Electrostatic motor
ActiveUS20100164322A1Sufficient driving forceIncrease productionElectrostatic motorsElectrostatic motorElectrostatic voltmeter
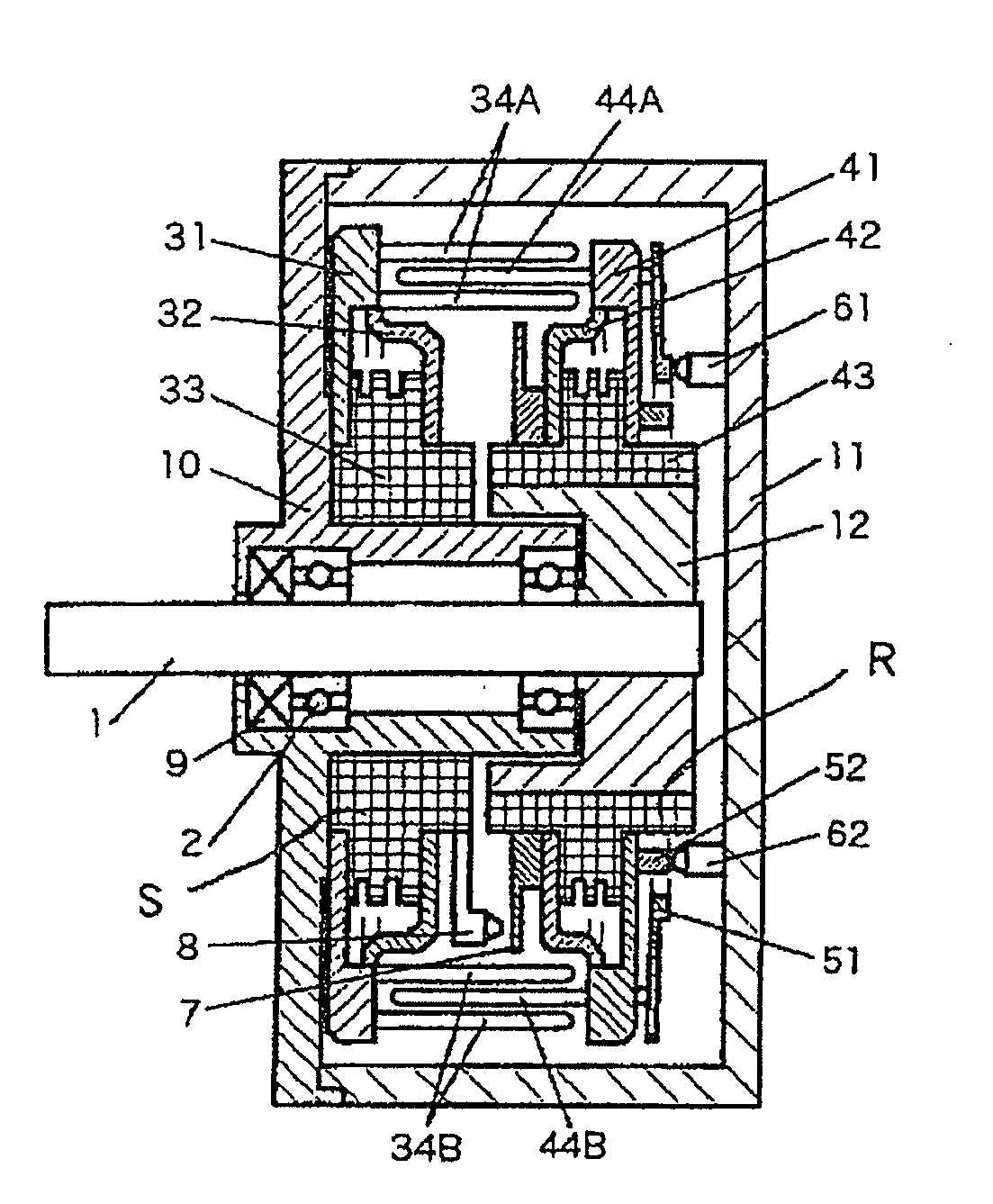
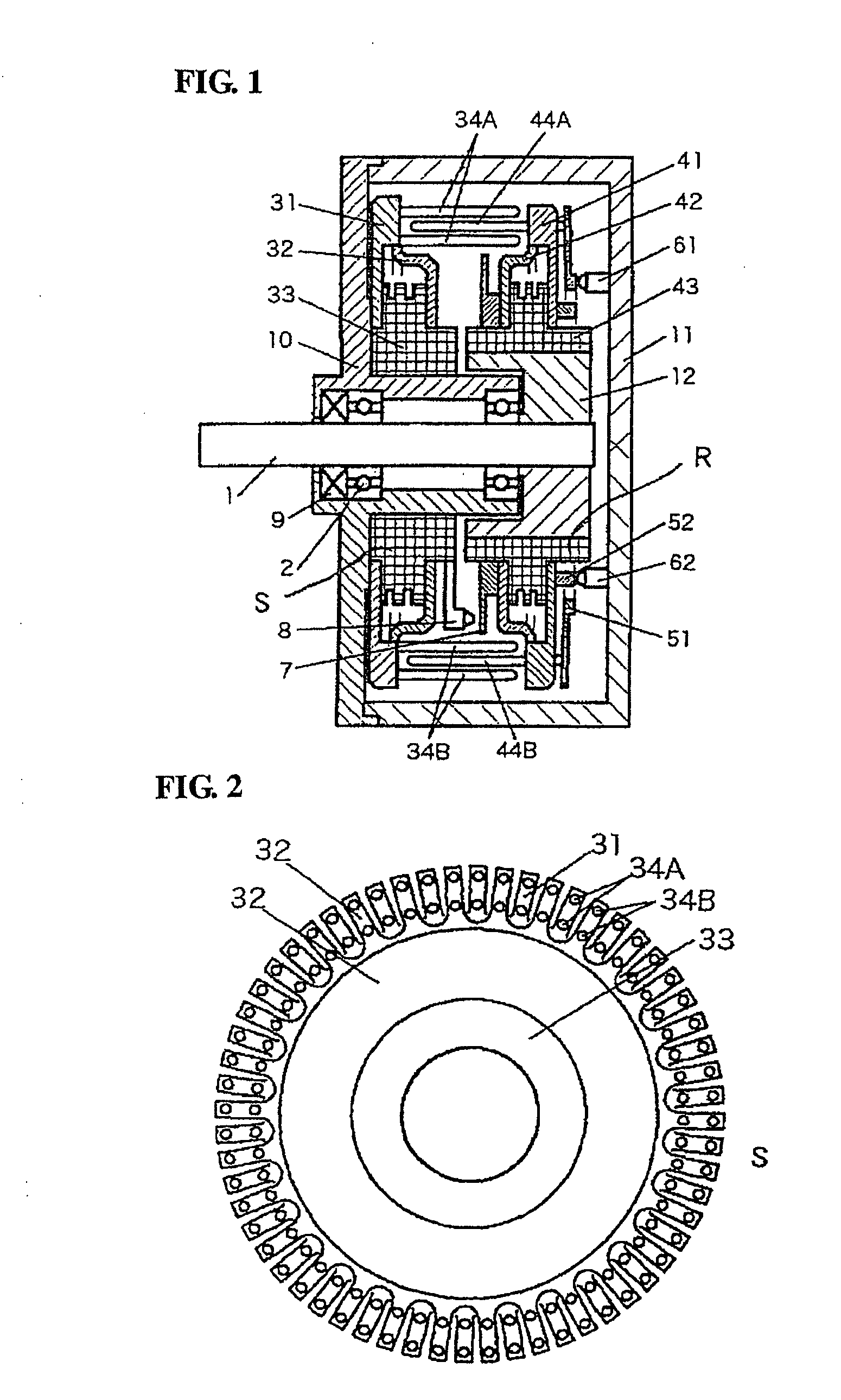
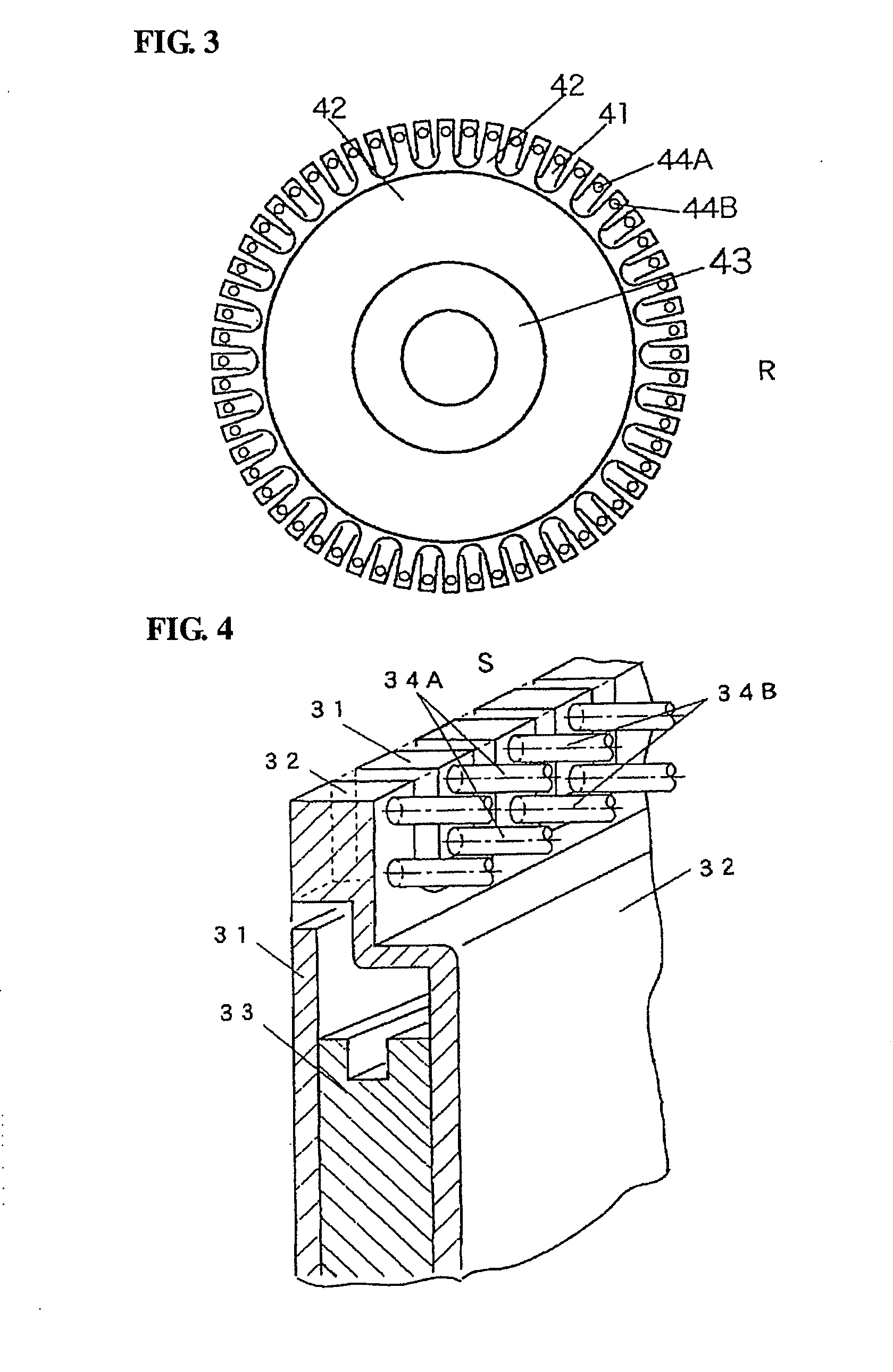
Provided is an electrostatic motor, in which a disc-shaped stator (S) and a disc-shaped rotor (R) are opposed to each other in a vacuum container (11). In the stator (S), first electrodes (34A) and second electrodes (34B), which are attached to electrode supports (31, 32), respectively, and which are electrically insulated from each other by an insulator (33), are arranged alternately in the circumferential direction. In the rotor (R), first electrodes (44A) and second electrodes (44B), which are attached to electrode supports (41, 42), respectively, and which are electrically insulated from each other by an insulator (43), are arranged alternately in the circumferential direction. The first electrodes (34A) and the second electrodes (34B) on the side of the stator (S) are arranged at a spacing of two or more rows at a predetermined distance from the center of a rotating shaft (1). The first electrodes (44A) and the second electrodes (44B) on the side of the rotor (R) are arranged at a predetermined distance from the center of the rotating shaft (1) and at an intermediate position between the rows of the first electrodes (34A) and the second electrodes (34B) on the side of the stator (S). As a result, the electrostatic motor can establish a high electric field in the vacuum so that it can rotationally drive with a sufficient driving force.
Owner:SHINSEI CO LTD
Semiconductor device
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com