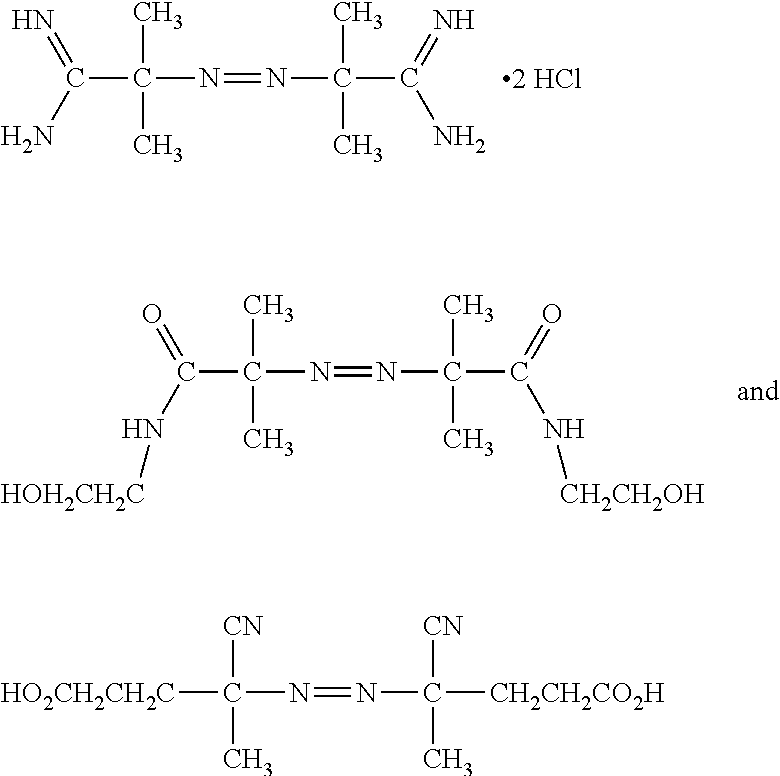
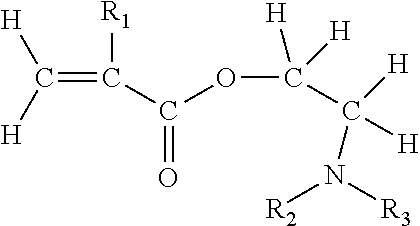
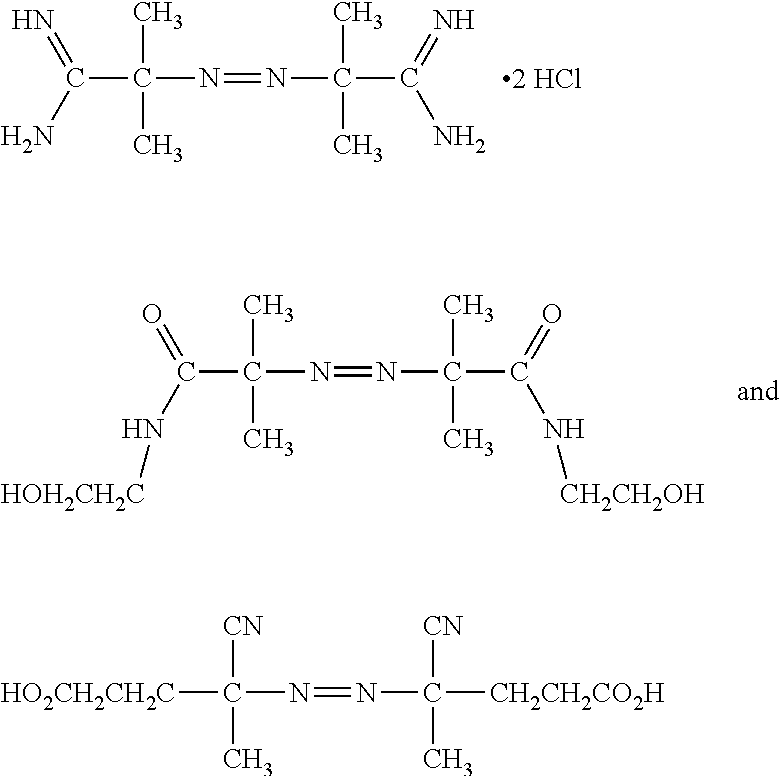
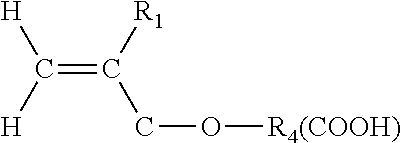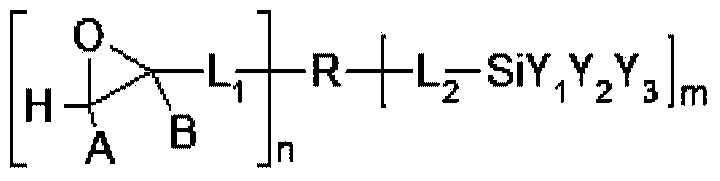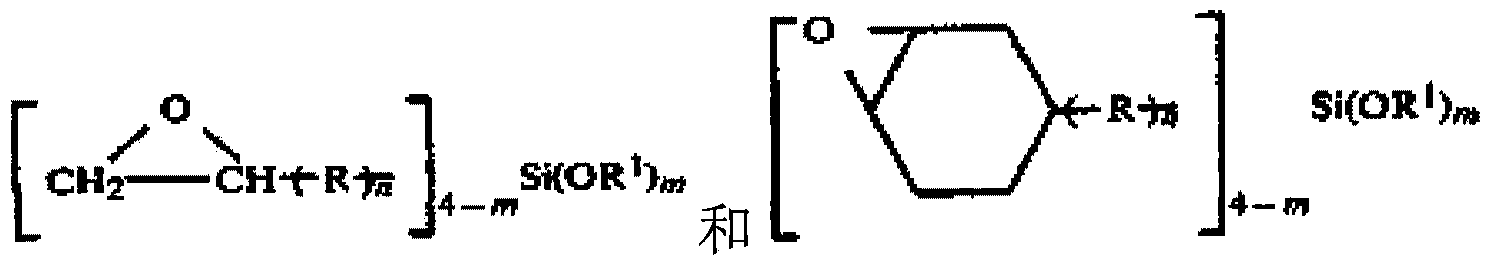Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
81results about How to "Enhanced release properties" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
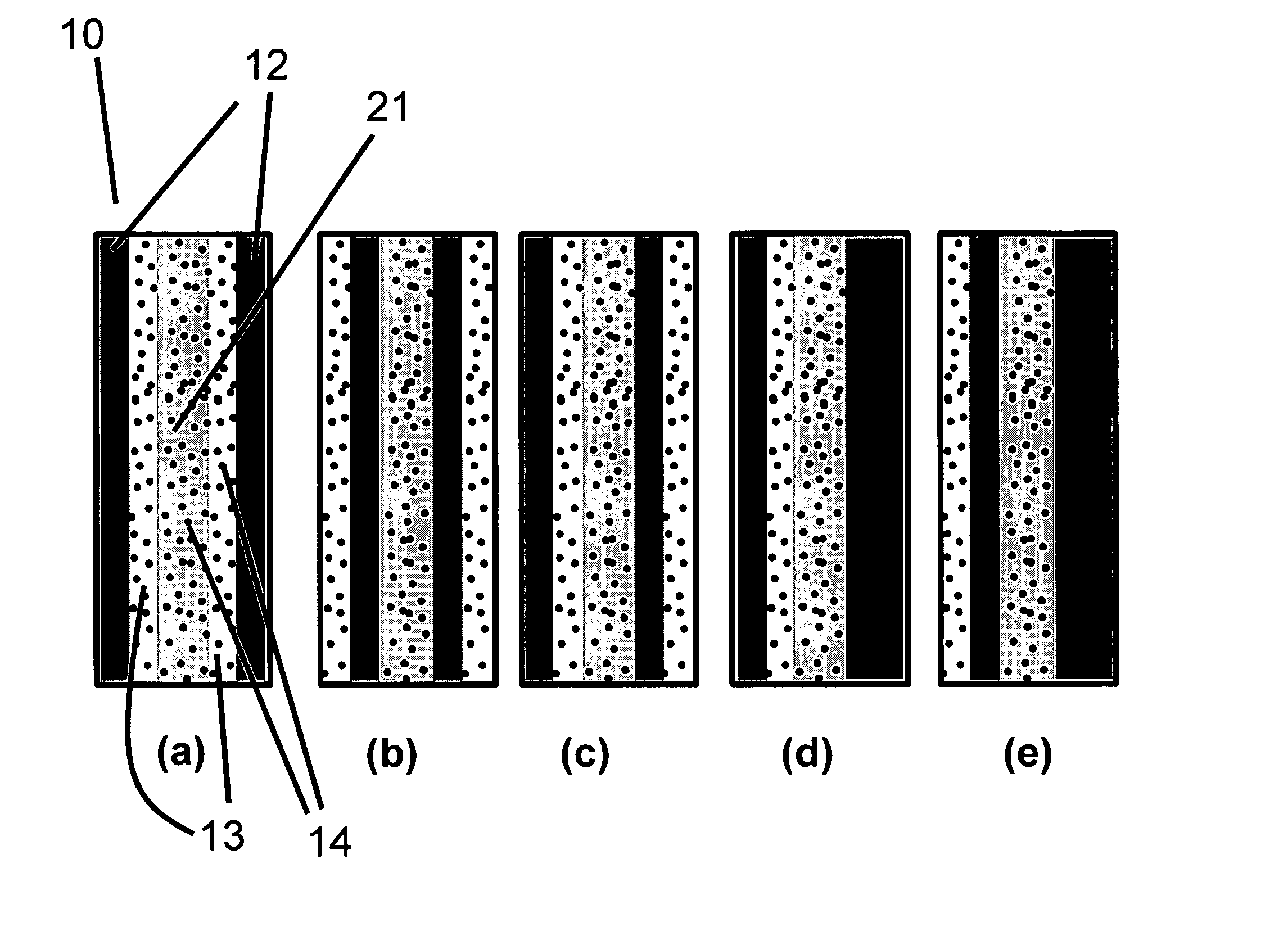
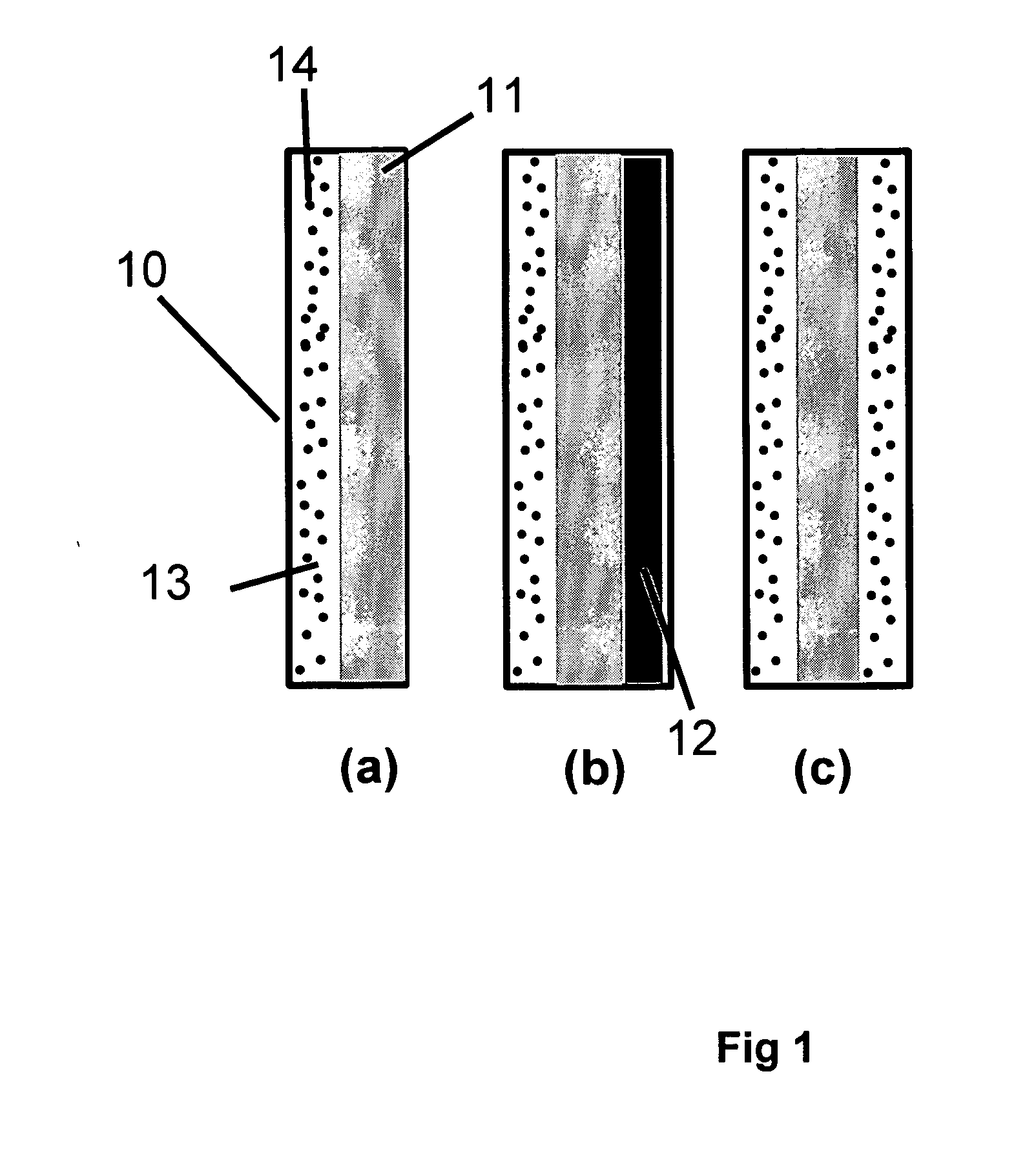
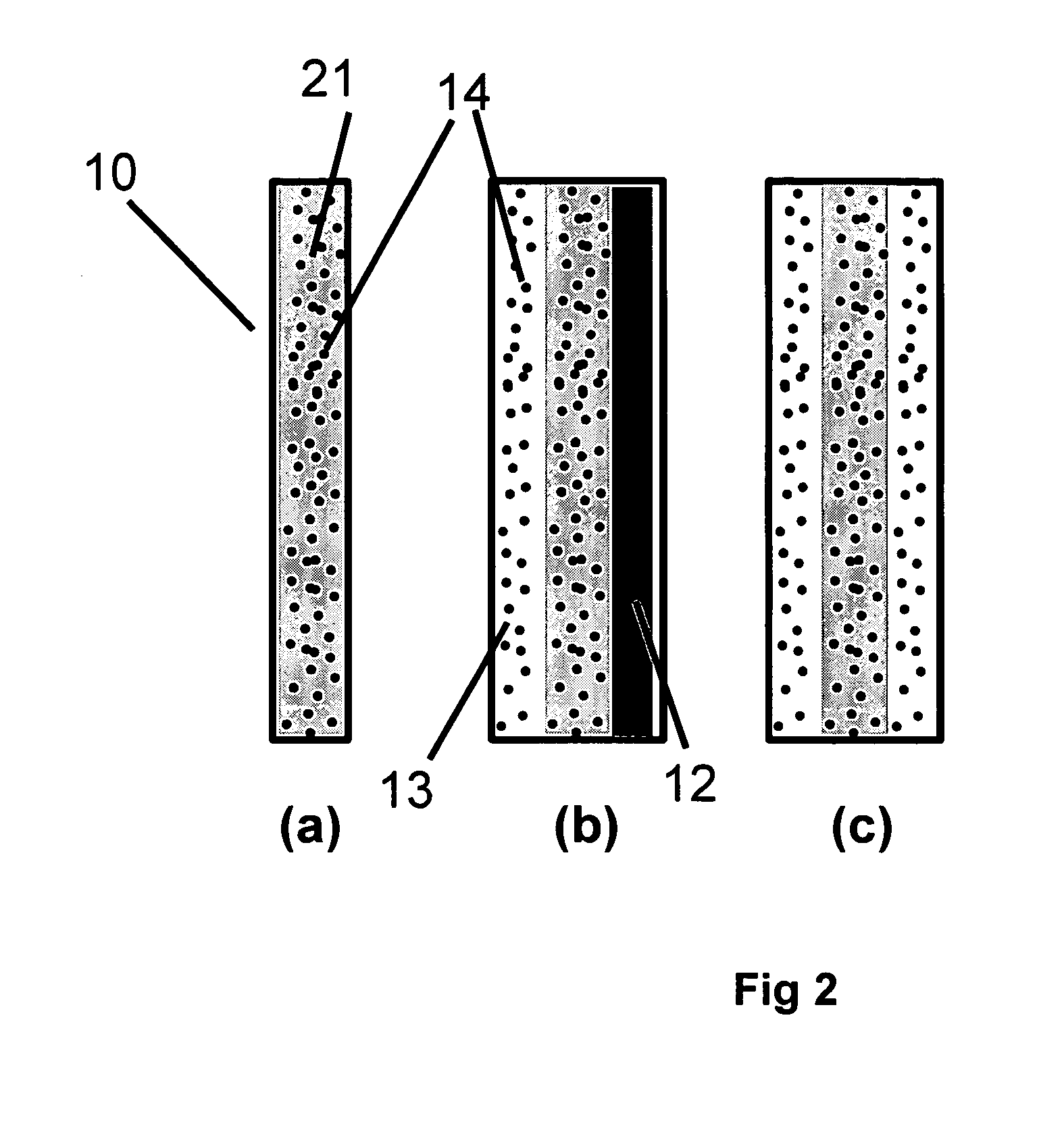
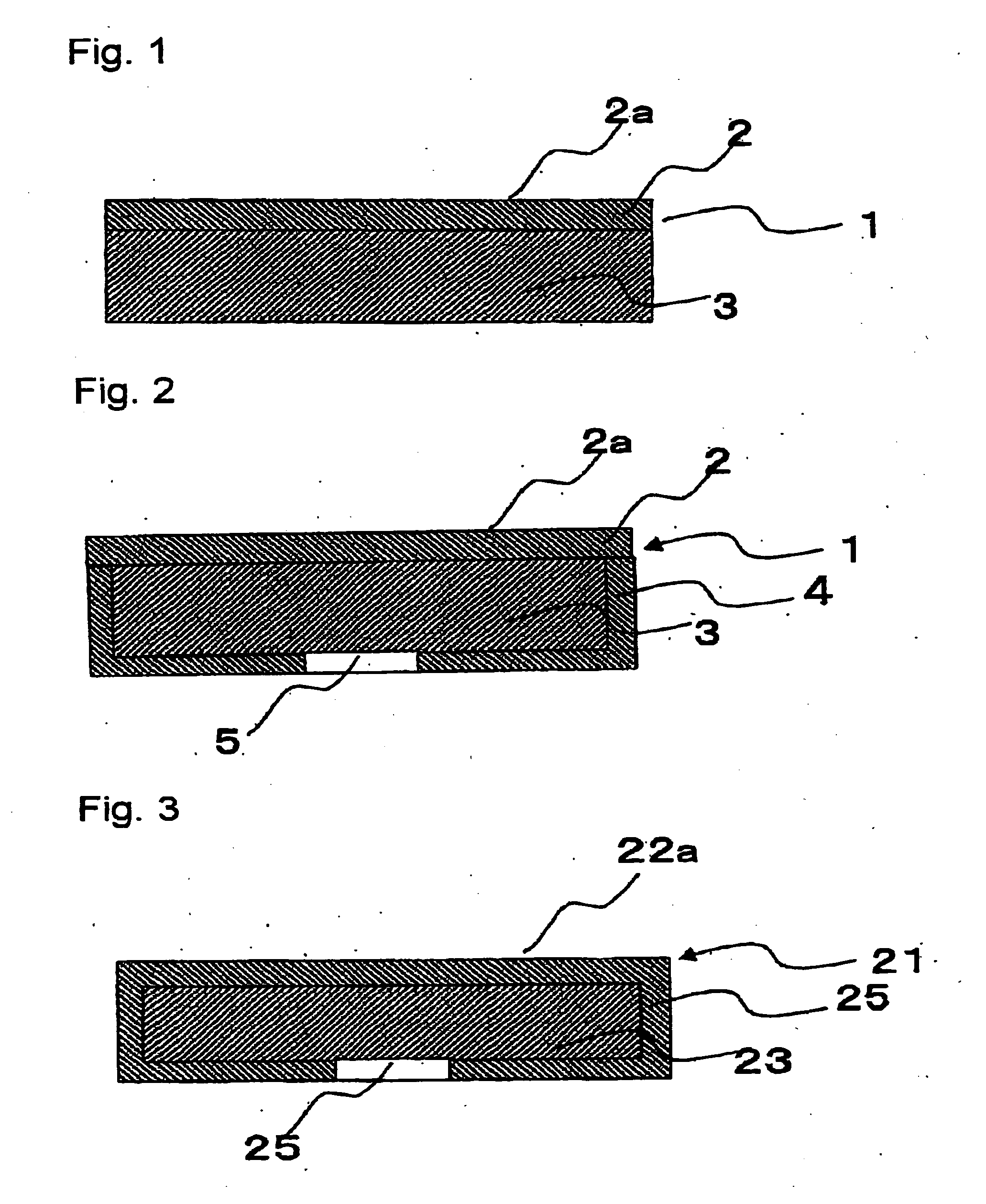
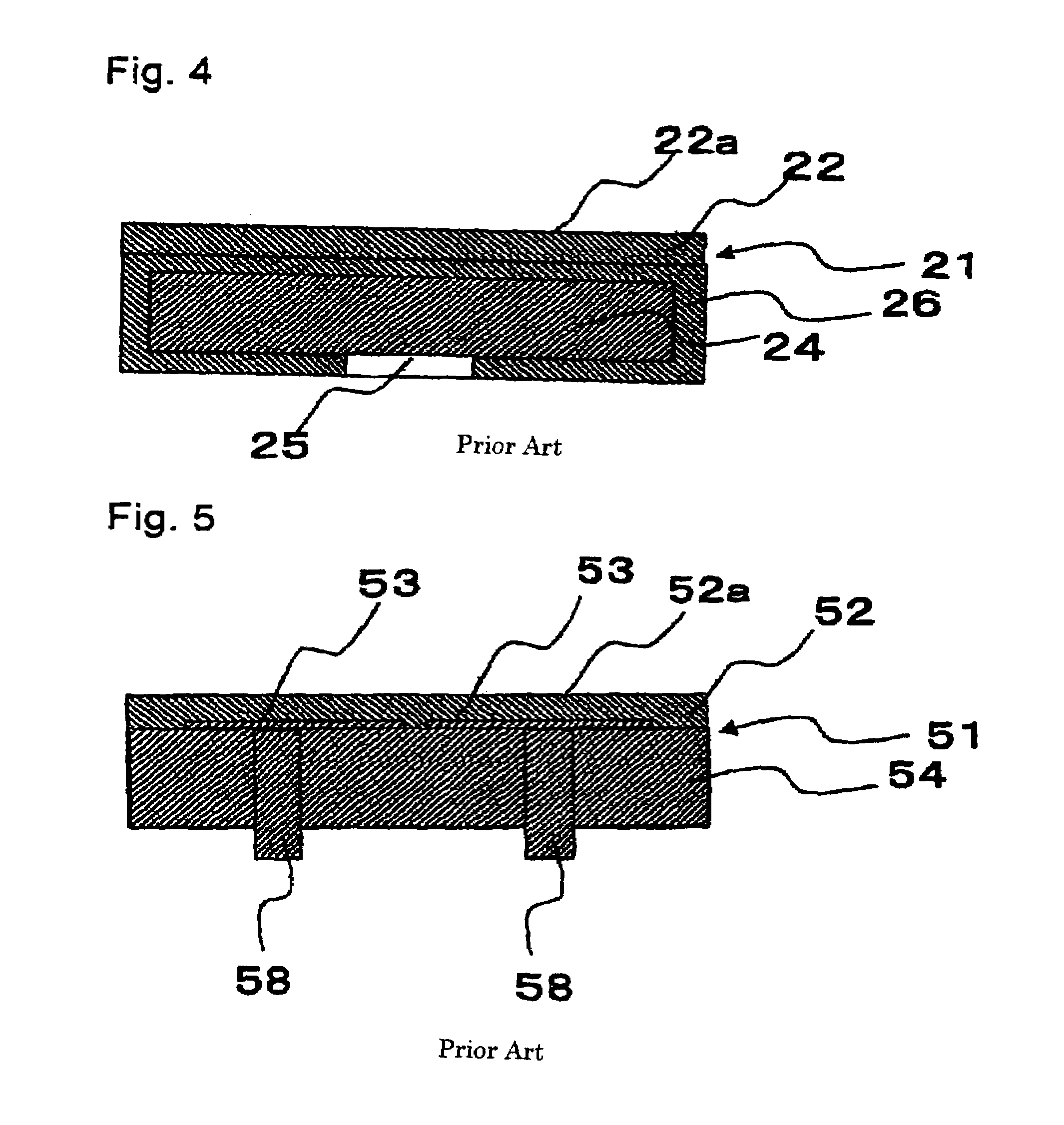
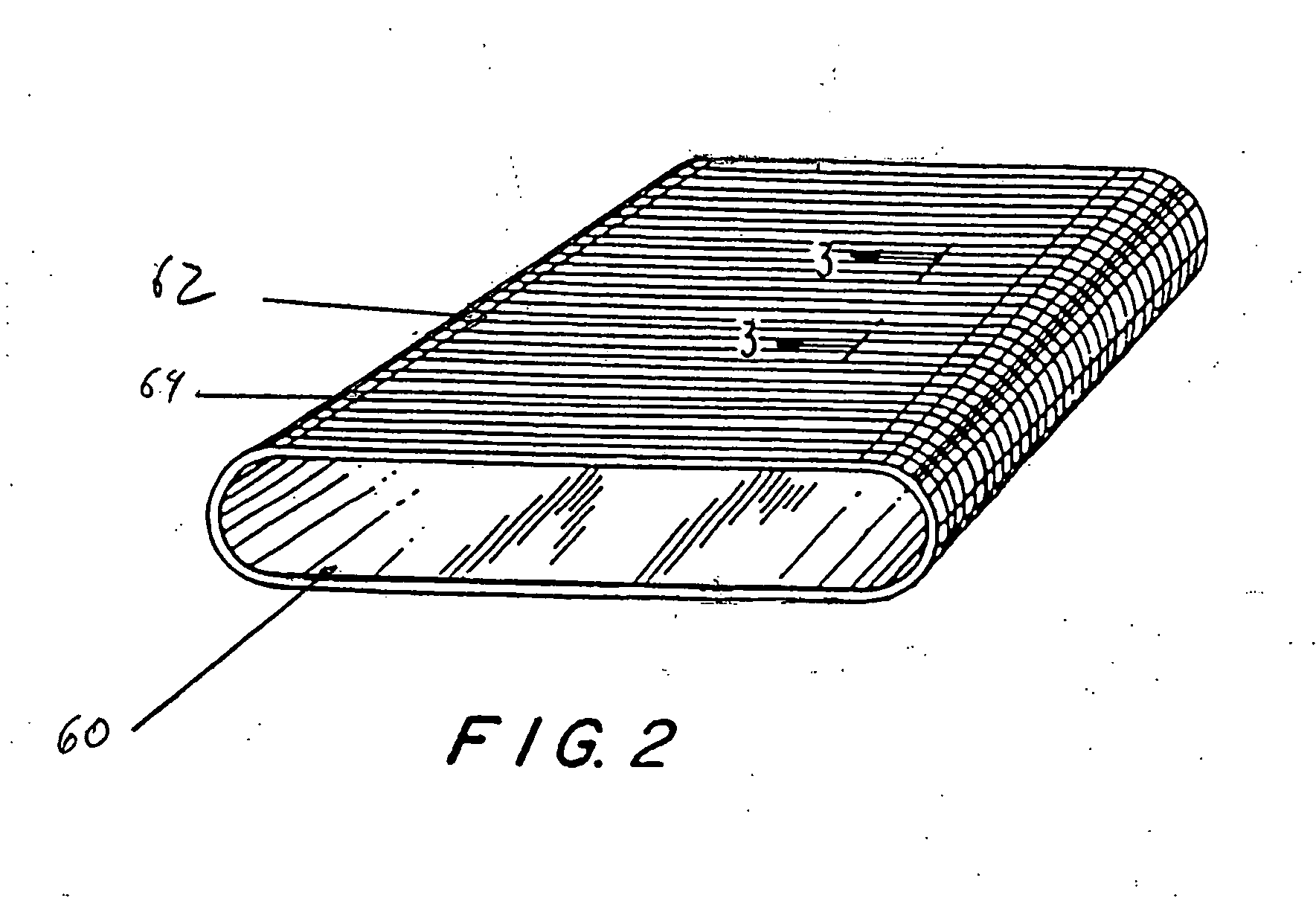
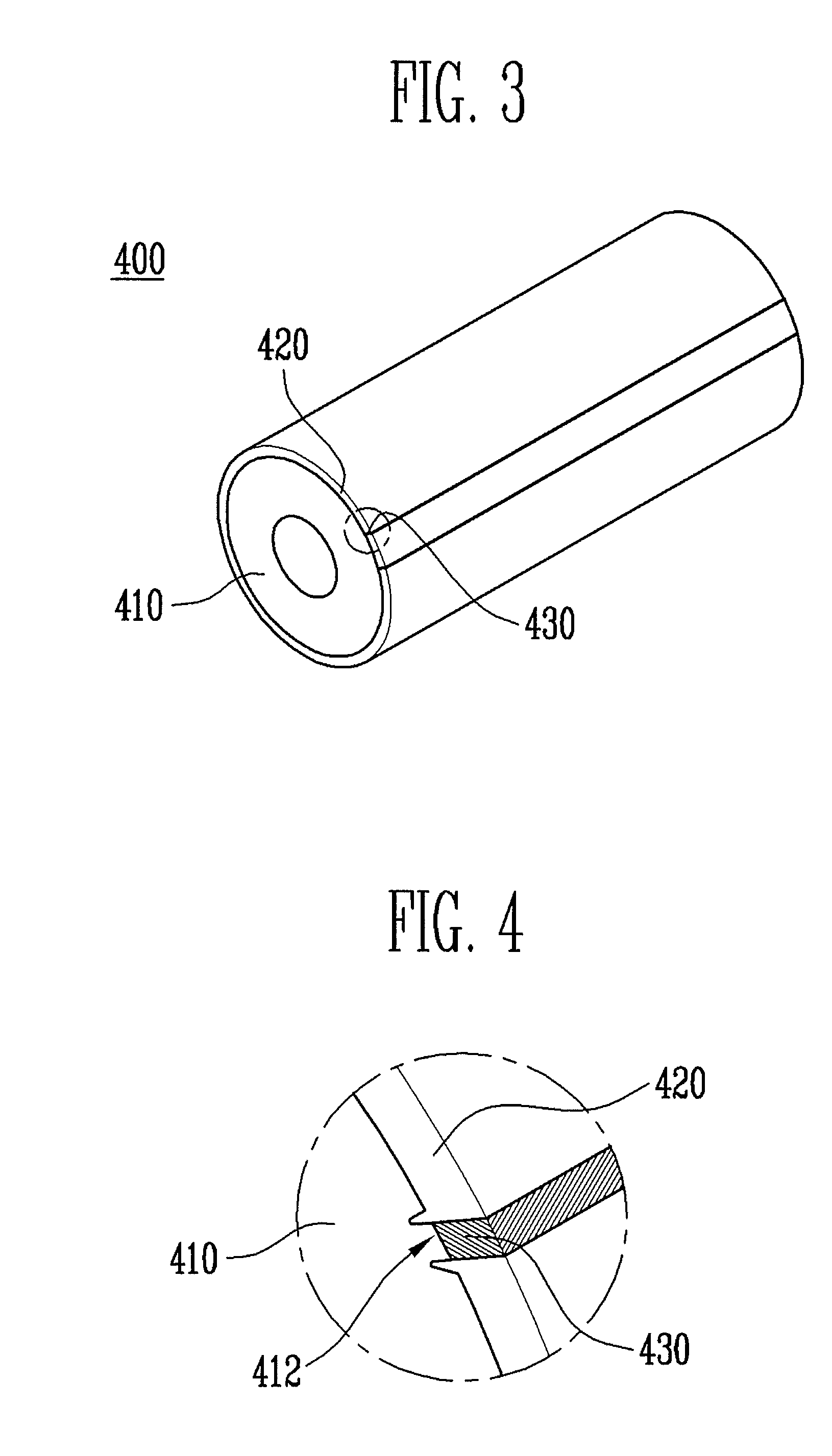
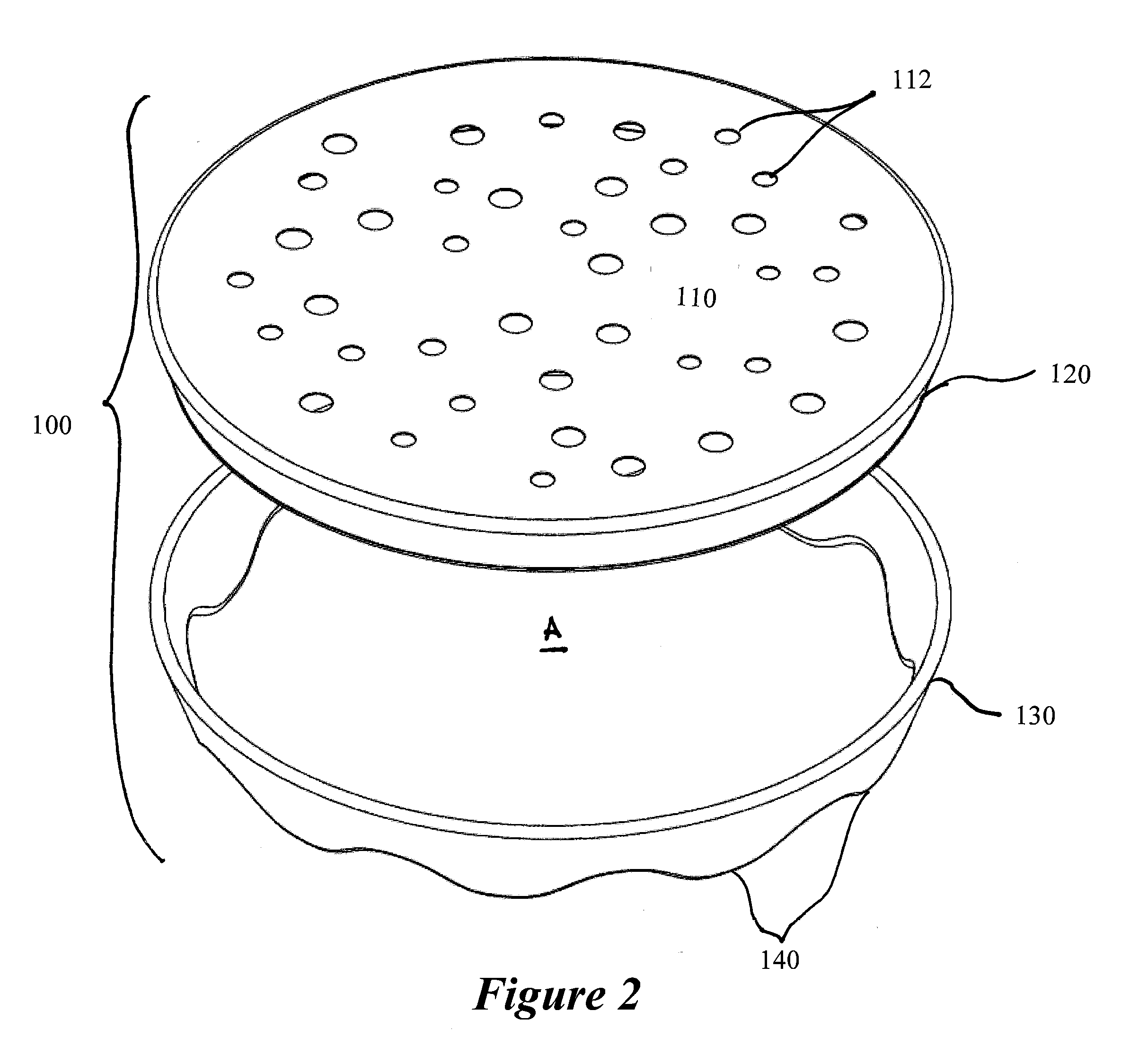
Solid polymer electrolyte and process for making same
ActiveUS20070072036A1Enhanced release propertiesIon-exchanger regenerationFinal product manufactureFiberIon exchange
A solid polymer electrolyte membrane having a first surface and a second surface opposite the first surface, where the solid polymer electrolyte membrane has a failure force greater than about 115 grams and comprises a composite membrane consisting essentially of (a) at least one expanded PTFE membrane having a porous microstructure of polymeric fibrils, and (b) at least one ion exchange material impregnated throughout the porous microstructure of the expanded PTFE membrane so as to render an interior volume of the expanded PTFE membrane substantially occlusive; (c) at least one substantially occlusive, electronically insulating first composite layer interposed between the expanded PTFE membrane and the first surface, the first composite layer comprising a plurality of first carbon particles supporting a catalyst comprising platinum and an ion exchange material, wherein a plurality of the first carbon particles has a particle size less than about 75 nm, or less than about 50 nm, or less than about 25 nm.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
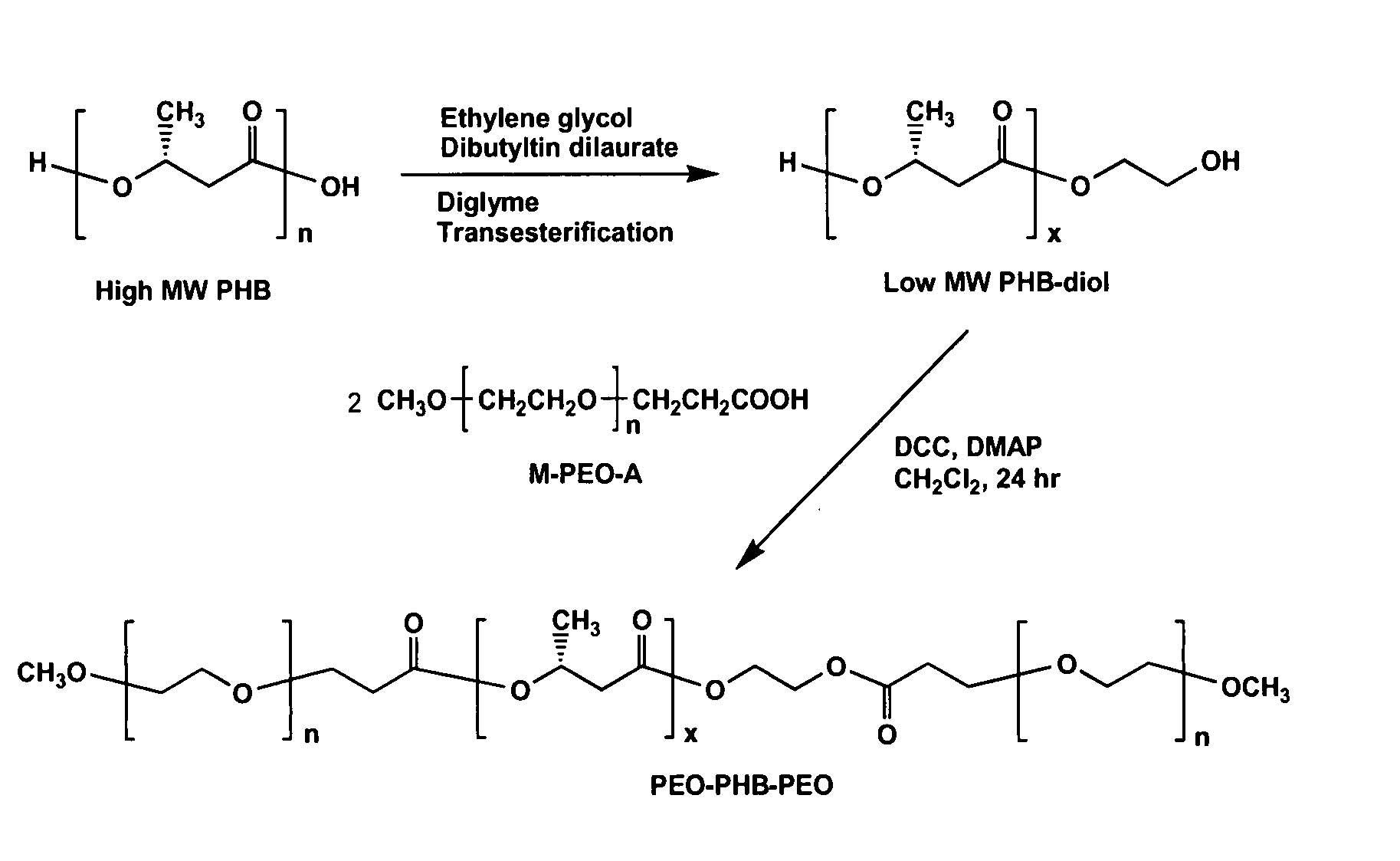
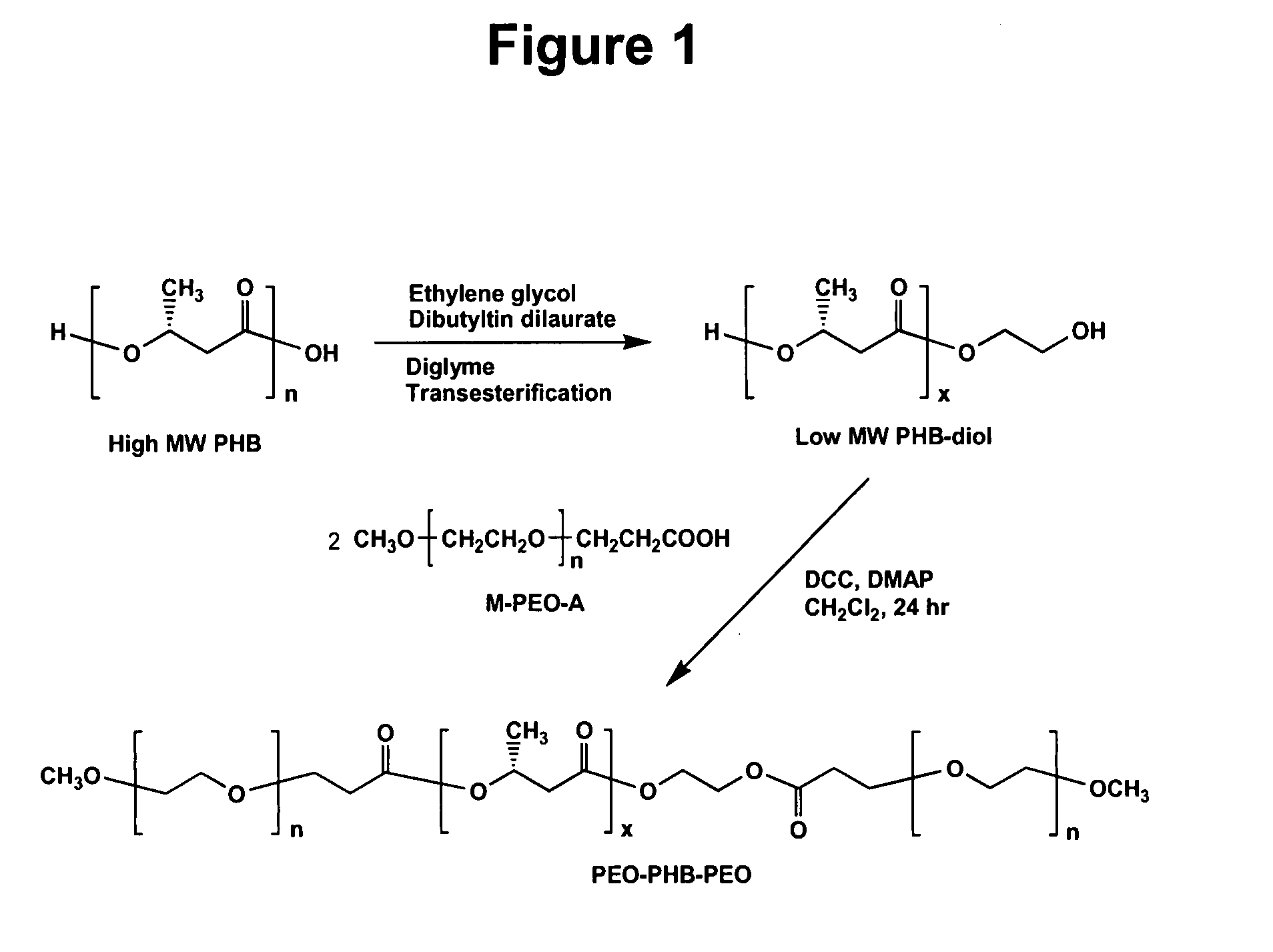
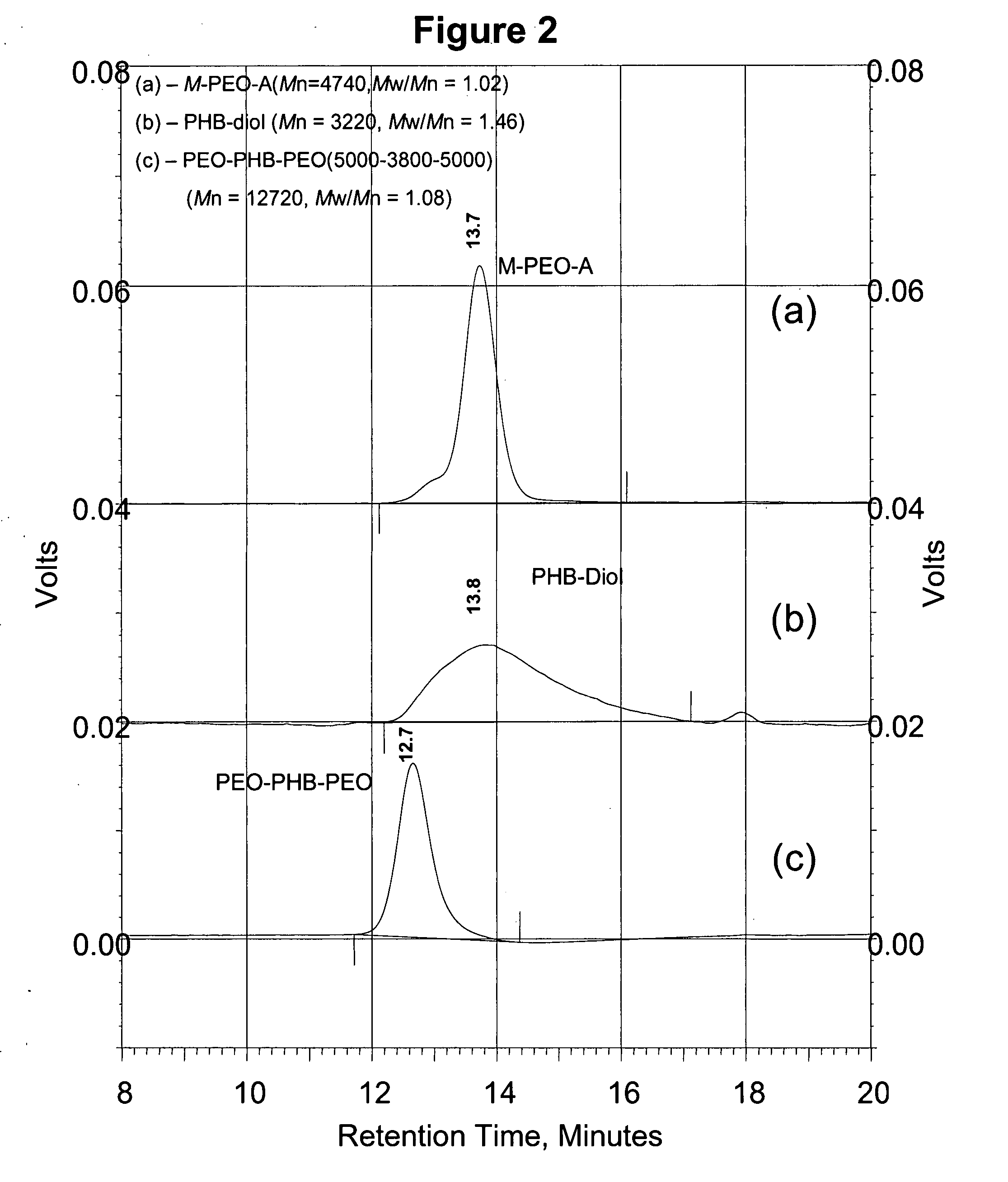
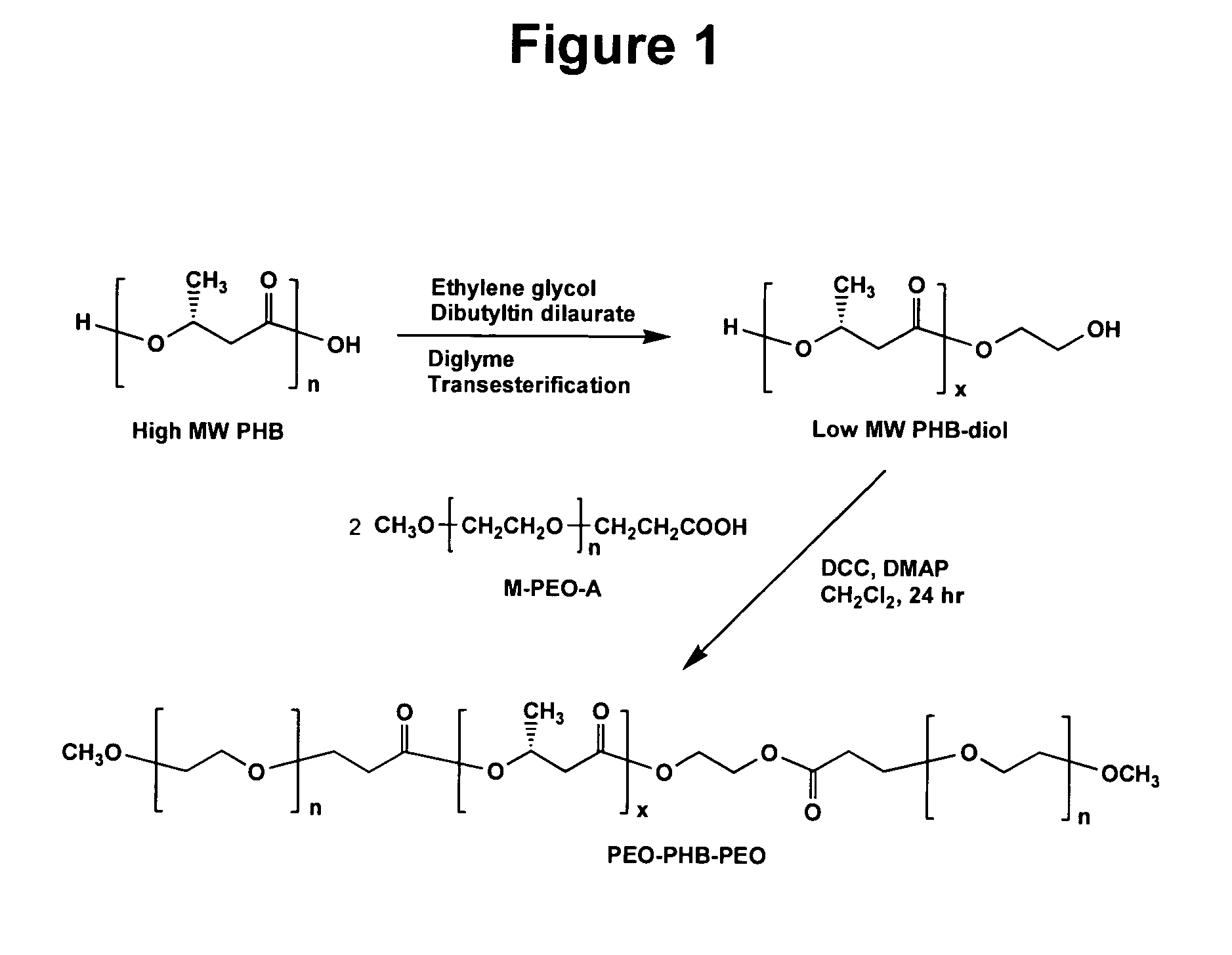
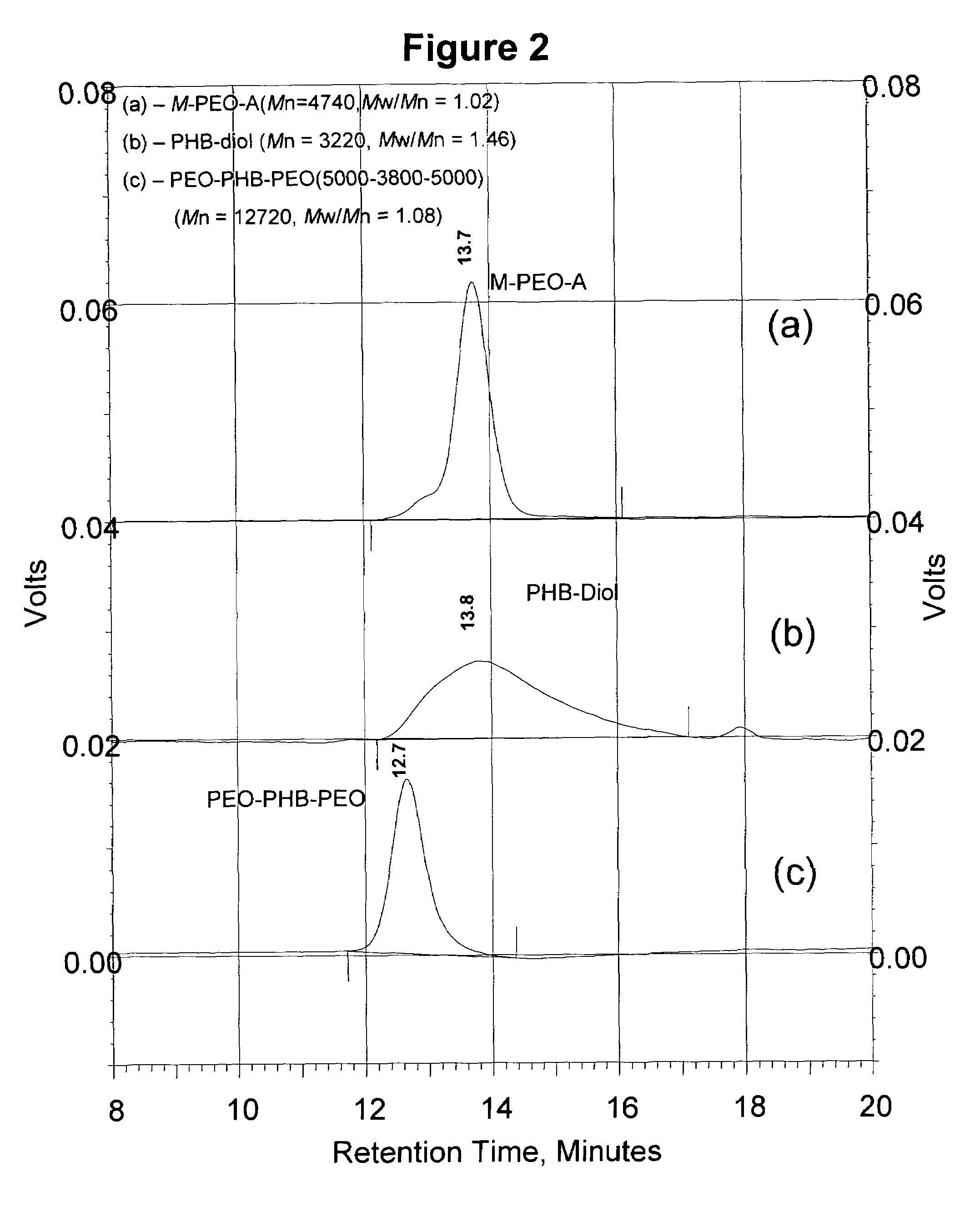
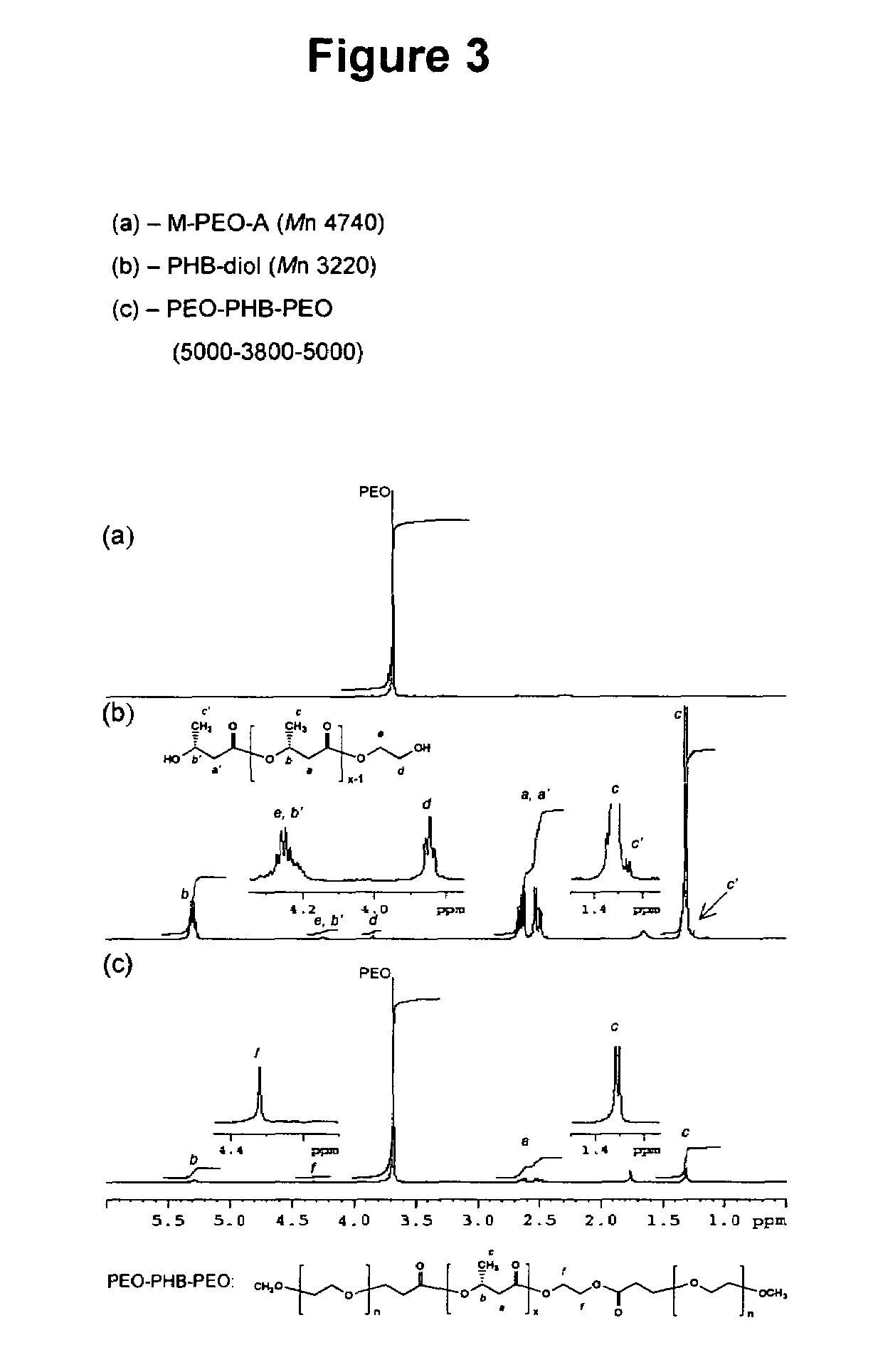
Biodegradable triblock copolymers, synthesis methods therefore, and hydrogels and biomaterials made there from
InactiveUS20080057128A1Interesting propertyVivo degradation ratePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsPolymer scienceSynthesis methods
A drug delivery system that includes micelles formed from an amphiphilic copolymer that includes an A polymer block comprising a poly(alkylene oxide) and a B polymer block comprising a poly(hydroxyalkanoate), and a therapeutically effective amount of at least one therapeutic agent intimately contained within the micelles. In one preferred embodiment of the invention, the A polymer block is poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) and the B polymer block is poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate] (PHB), and the copolymer is the triblock ABA copolymer PEO-PHB-PEO. A method of synthesizing the amphiphilic triblock copolymer is also provided.
Owner:OMEROS CORP
Method for controlling distribution of fluid components on a body
ActiveUS20070141271A1Suitable adhesionForming accuratelyAntibacterial agentsNanoinformaticsSuperimpositionEngineering
The present invention provides a method of controlling the distribution of a fluid on a body that features compensating for varying distribution of constituent components of a composition that moved over a surface of a substrate. To that end, the method includes generating a sequence of patterns of liquid upon a substrate, each of which includes a plurality of spaced-apart liquid regions, with voids being defined between adjacent liquid regions. A second of the patterns of liquid of the sequence is arranged so that the liquid regions associated therewith are in superimposition with the voids of a first of the patterns of liquid of the sequence.
Owner:MOLECULAR IMPRINTS
Crosslinked polysaccharide gel compositions for medical and cosmetic applications
InactiveUS20130136780A1Enhanced release propertiesGood sustained releasePowder deliveryCosmetic preparationsDiseasePolysaccharide
Methods of producing a biocompatible polysaccharide gel composition having sustained release properties are disclosed. Also disclosed is a biocompatible polysaccharide gel composition having sustained release properties, a method of treating a disease or condition using the present biocompatible polysaccharide gel composition, and a method of controlling rate of release of at least one target solute from the biocompatible polysaccharide gel composition. Pharmaceutical compositions which include the present biocompatible polysaccharide gel composition also are disclosed.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
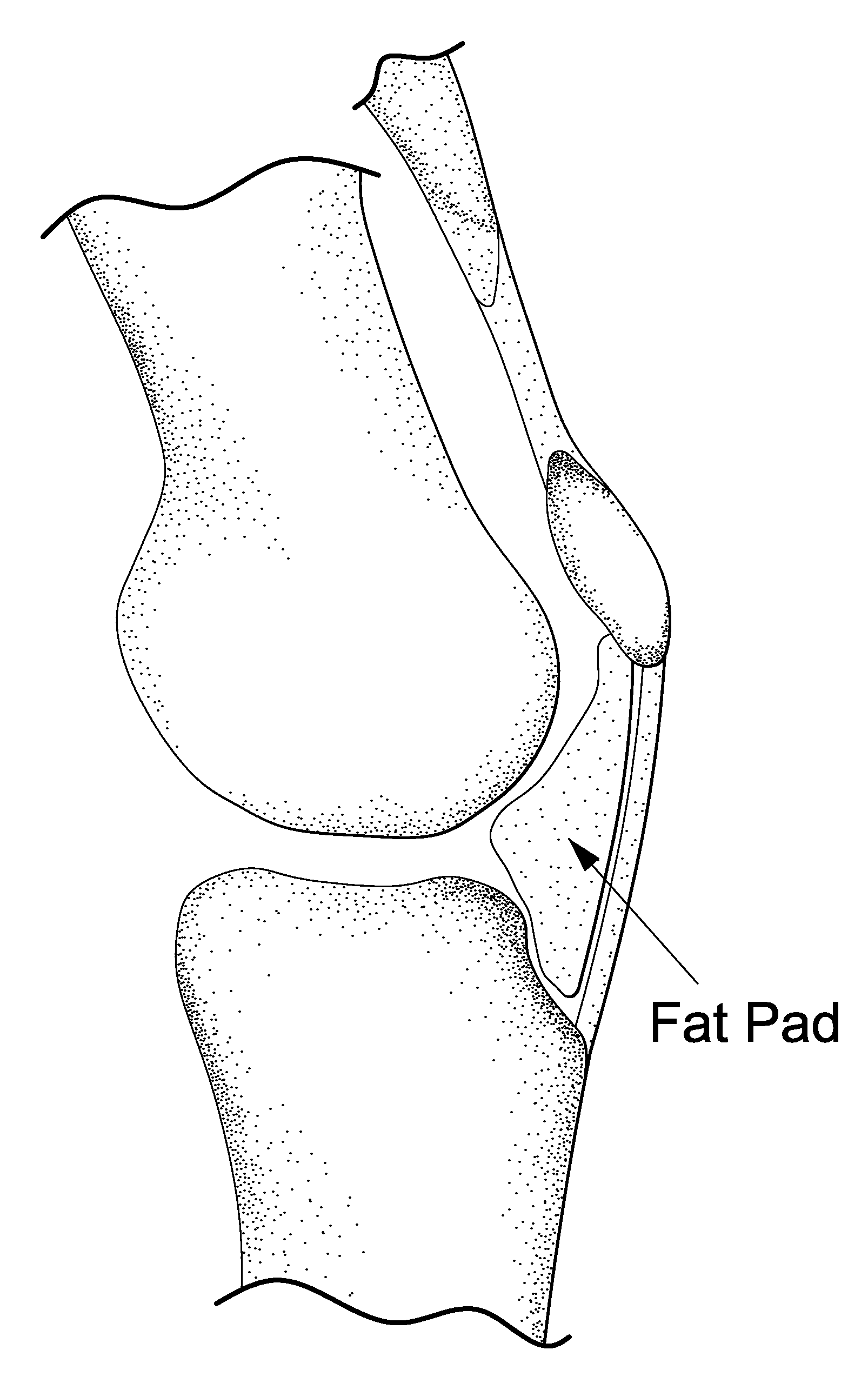
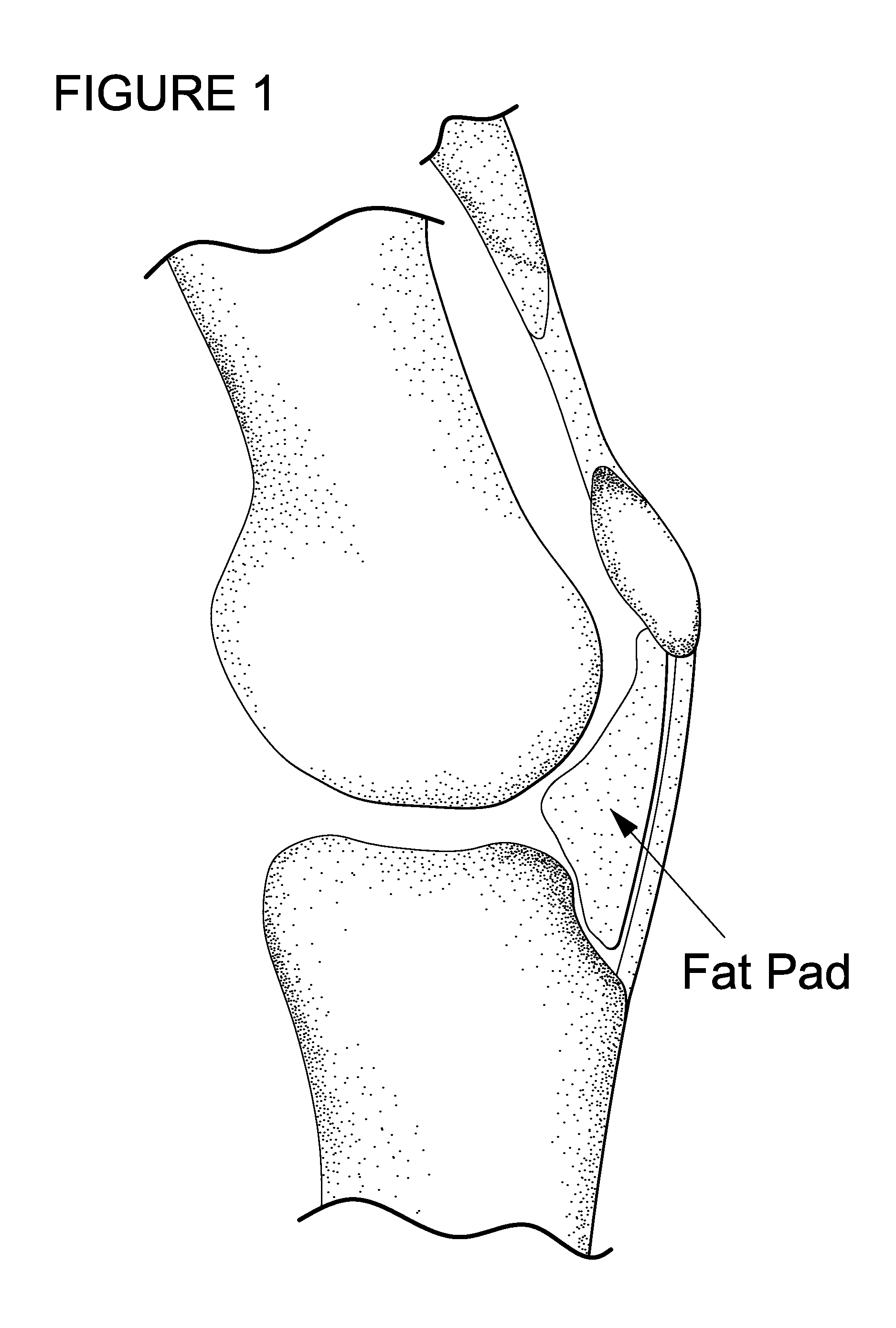
Method for improving cartilage repair and/or preventing cartilage degeneration in a joint
InactiveUS20100215731A1Convenient treatmentRelieve painPowder deliveryBiocideRepair tissueActive agent
The invention is in the field of methods for medical treatment. It provides an improved method for repairing damaged cartilage and / or preventing cartilage degeneration in tissue, in particular in a joint by administering a pharmaceutically active agent directly into the fat pad of a joint. The pharmaceutically active agent is preferably selected from the group consisting of agents that stimulate chondrogenic differentiation and / or cartilage matrix synthesis; agents that inhibit osteogenesis and / or hypertrophy, anti-inflammatory agents, agents that inhibit apoptosis of chondrocytes, agents that inhibit senescence of chondrocytes and agents that enhance lubrication of a joint.
Owner:ACADEMIC HOSPITAL MAASTRICHT +1
Electrostatic chuck
InactiveUS20050024809A1Enhanced release propertiesExcellent characteristic of releasing wafer WSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingContactsCeramicPrincipal plane
The electrostatic chuck includes: a conductive base formed of metal or both metal and ceramics, serving as a chucking electrode; and an insulating film formed on one principal plane of the conductive base, the top face of the insulating film serving as a placing surface for placing a wafer; wherein the insulating film is formed of a uniform amorphous ceramics of an oxide and has a thickness in a range of 10 to 100 μm, thereby preventing cracking and insulation breakdown in the insulating film and improving characteristics of releasing the wafer.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Electrostatic chuck
InactiveUS7312974B2Enhanced release propertiesExcellent characteristic of releasing wafer WSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrostatic holding devicesCeramicMaterials science
The electrostatic chuck includes: a conductive base formed of metal or both metal and ceramics, serving as a chucking electrode; and an insulating film formed on one principal plane of the conductive base, the top face of the insulating film serving as a placing surface for placing a wafer; wherein the insulating film is formed of a uniform amorphous ceramics of an oxide and has a thickness in a range of 10 to 100 μm, thereby preventing cracking and insulation breakdown in the insulating film and improving characteristics of releasing the wafer.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Biodegradable triblock copolymers, synthesis methods therefore, and hydrogels and biomaterials made there from
A drug delivery system that includes a hydrogel formed from cyclodextrin and an amphiphilic copolymer that includes an A polymer block comprising a poly(alkylene oxide) and a B polymer block comprising a poly(hydroxyalkanoate), and a therapeutically effective amount of at least one therapeutic agent intimately contained within the hydrogel. In one preferred embodiment of the invention, the A polymer block is poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) and the B polymer block is poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate] (PHB), and the copolymer is the triblock ABA copolymer PEO-PHB-PEO. A method of synthesizing the amphiphilic triblock copolymer is also provided.
Owner:OMEROS CORP +1
Belt fuser for a color electrophotographic printer
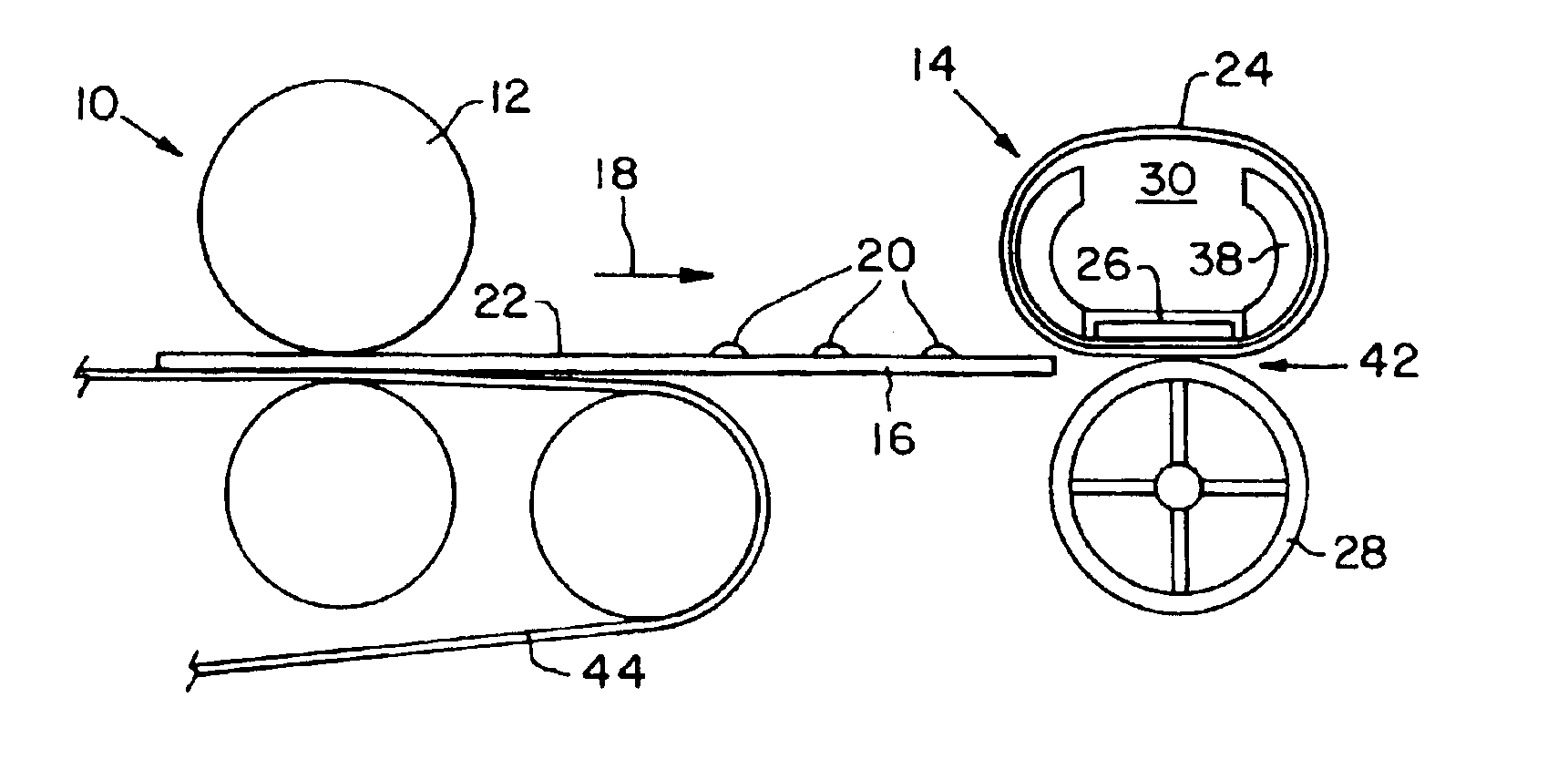
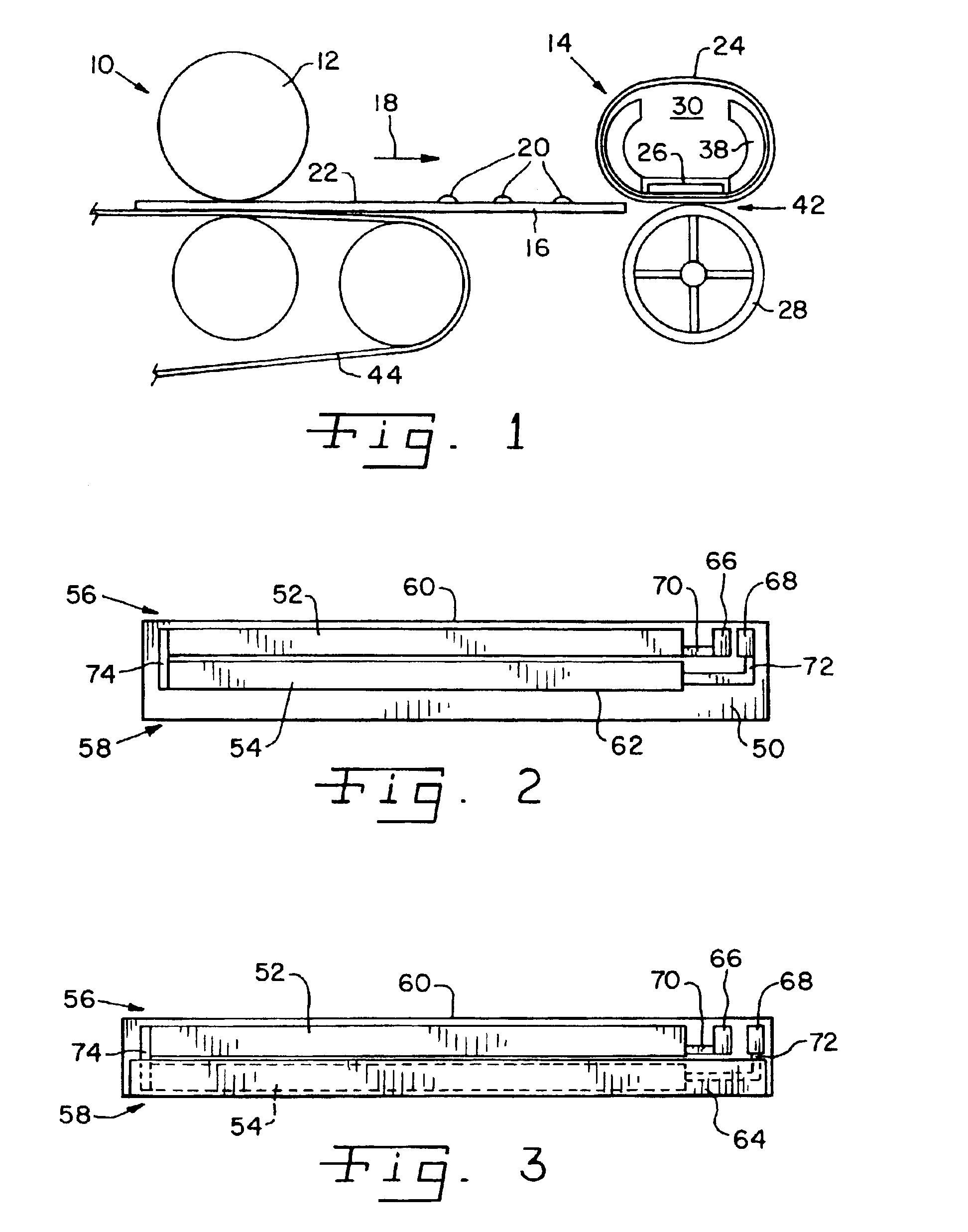
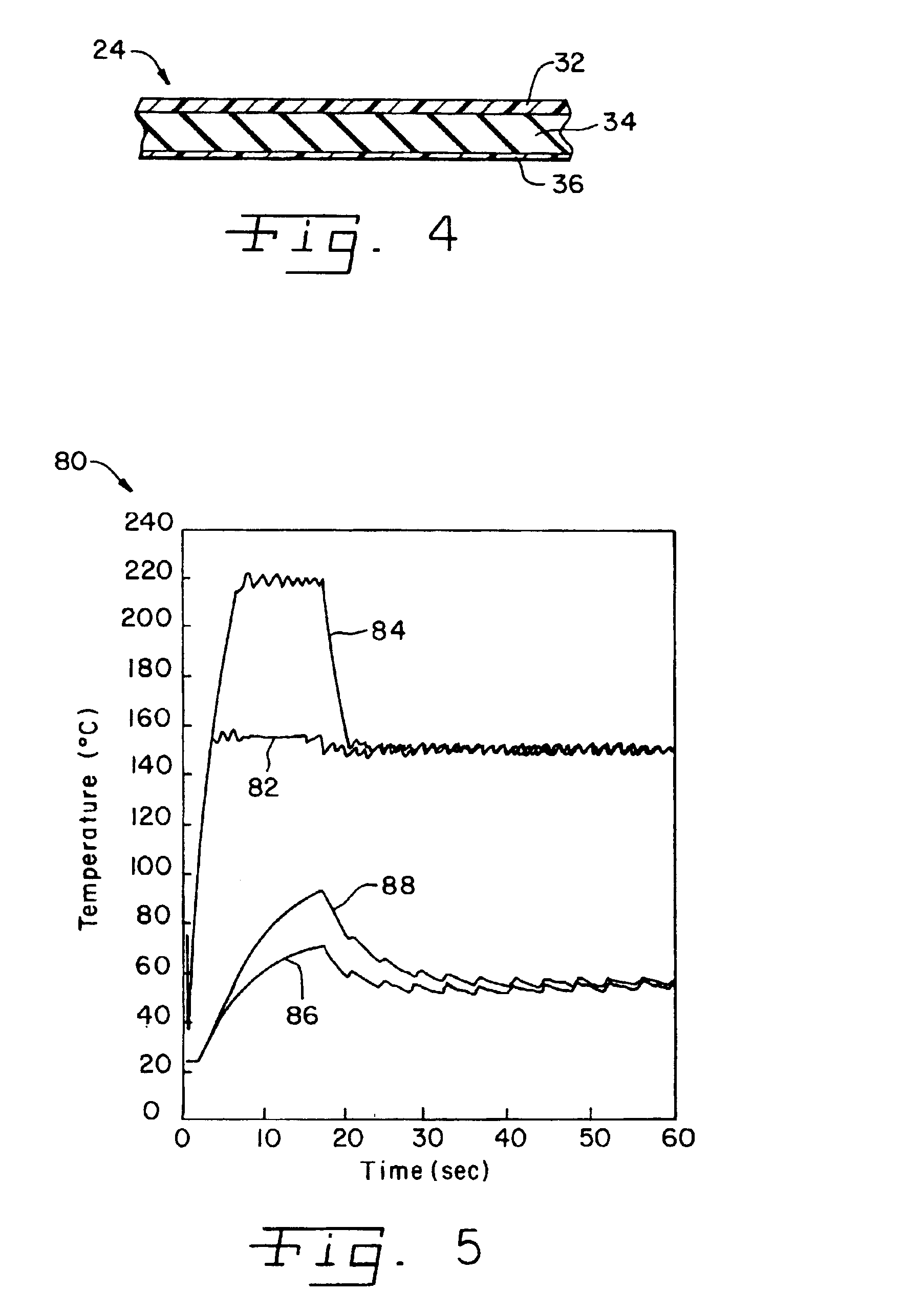
InactiveUS6879803B2Improve fusion qualityReduced toner offsetOhmic-resistance heatingElectrographic process apparatusPrint mediaInner loop
A fuser for fusing an image to print media in a color electrophotographic printer. The fuser includes an endless idling belt defining an inner loop, and a ceramic heater positioned in contact with the belt, within the inner loop. A pressure roller defines a nip with the belt. The belt includes a compliant layer for conforming to variations in toner pile height. The heater is configured to provide a cooler nip exit and a hotter nip entrance.
Owner:LEXMARK INT INC
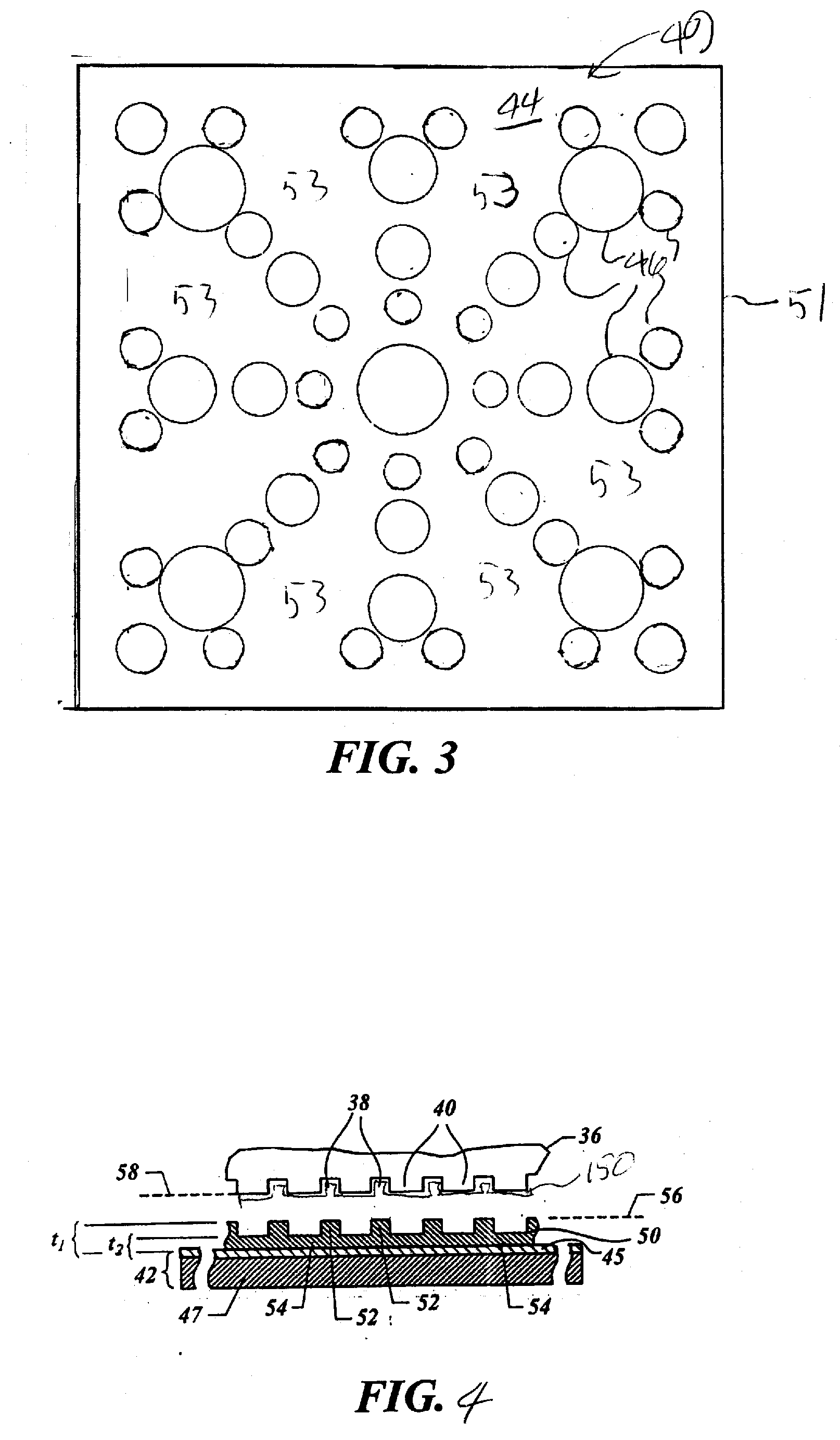
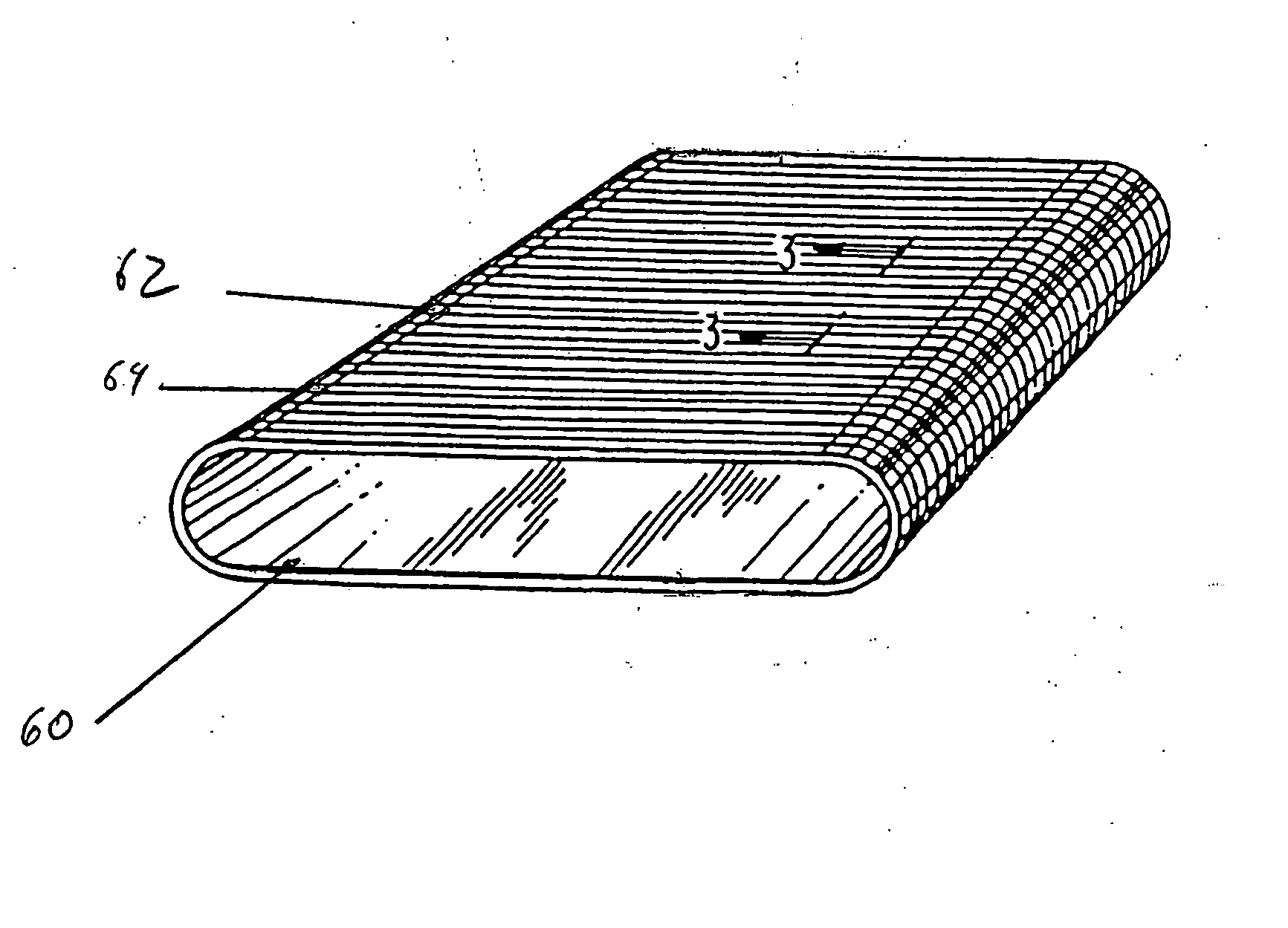
Solid Polymer Electrolyte and Process for Making Same
A solid polymer electrolyte membrane having a first surface and a second surface opposite the first surface, where the solid polymer electrolyte membrane has a failure force greater than about 115 grams and comprises a composite membrane consisting essentially of (a) at least one expanded PTFE membrane having a porous microstructure of polymeric fibrils, and (b) at least one ion exchange material impregnated throughout the porous microstructure of the expanded PTFE membrane so as to render an interior volume of the expanded PTFE membrane substantially occlusive; (c) at least one substantially occlusive, electronically insulating first composite layer interposed between the expanded PTFE membrane and the first surface, the first composite layer comprising a plurality of first carbon particles supporting a catalyst comprising platinum and an ion exchange material, wherein a plurality of the first carbon particles has a particle size less than about 75 nm, or less than about 50 nm, or less than about 25 nm.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Intermediate transfer member, method for producing the same and image forming method
ActiveUS20070065607A1High quality imagingIncreased durabilityV-beltsRopes and cables for vehicles/pulleyImage formationRecording media
An intermediate transfer member for use in an image forming apparatus in which a toner image is formed on a photoreceptor, firstly transferred from the photoreceptor to the intermediate transfer member, and further secondly transferred from the intermediate transfer member to a recording medium, the intermediate transfer member, includes an intermediate transfer belt containing a volatile substance in a range of from 10 to 10,000 ppm as an average concentration of an entire intermediate transfer belt thereof.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA BUSINESS TECH INC
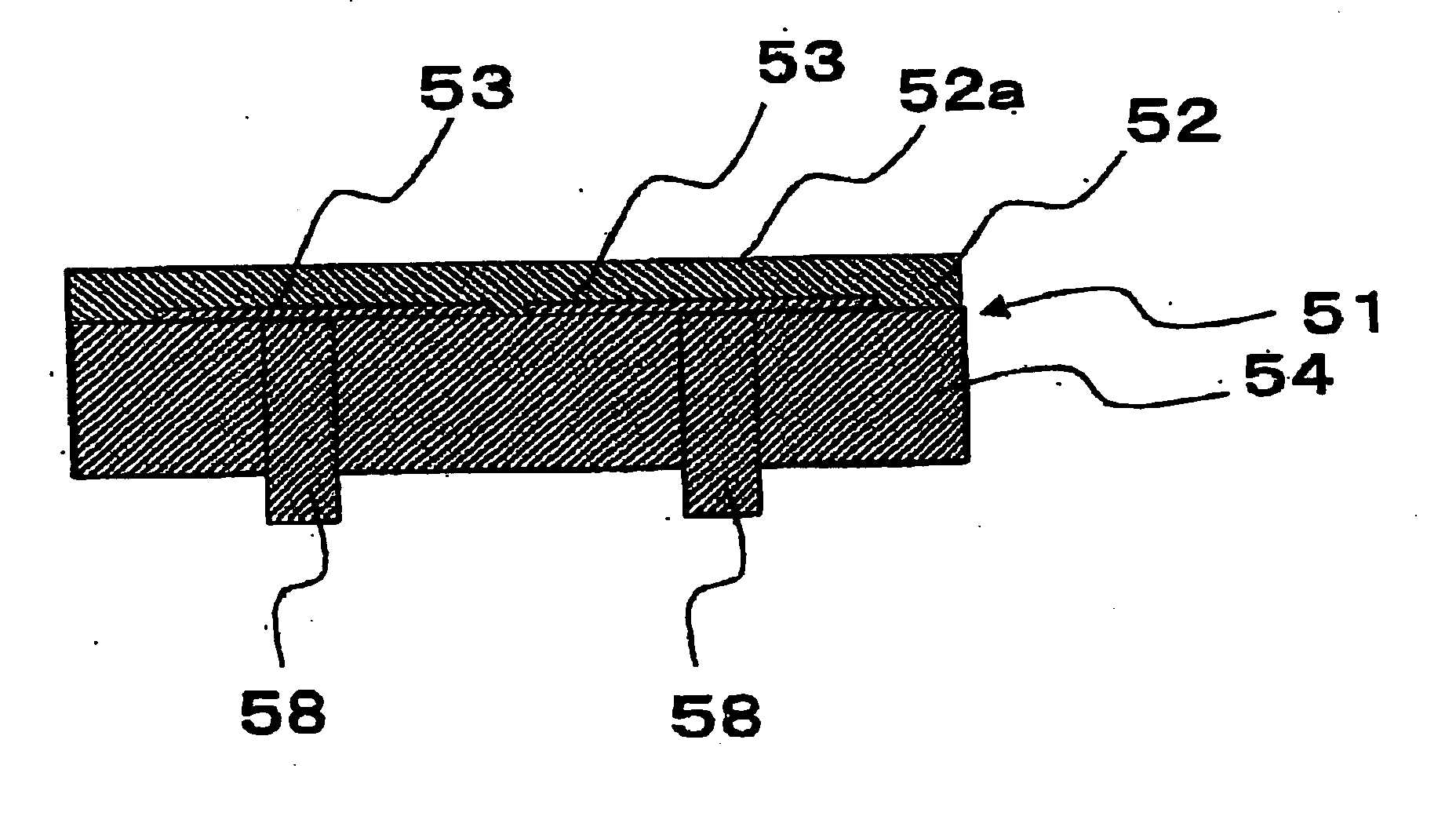
Grooved single facer belt
InactiveUS20050112332A1Improve release characteristicSufficient frictional characteristicMechanical working/deformationPaper/cardboard articlesYarnEngineering
The present invention relates to a single facer corrugator belt having a base structure. The base structure includes an inside and an outside surface and a machine or running direction and a cross machine direction. The base structure is formed by machine direction yarns and cross machine direction yarns and has grooves formed in a surface of the base structure. Alternatively, the corrugator belt may include includes holes formed in a surface of the base structure.
Owner:ALBANY INT CORP
Preparation method of micro-emulsive nonferrous metal mold releasing agent
ActiveCN103386461AImproved particle size rangeEnhanced release propertiesFoundry mouldsFoundry coresOil and greasePhase conversion
The invention discloses a micro-emulsive nonferrous metal mold releasing agent as well as a preparation method thereof. The formula of raw materials comprises the following components in parts by weight: 35-42 parts of emulsifying agents, 10-20 parts of modified plant oil and fat, 5-10 parts of auxiliaries and 29-50 parts of deionized water. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: 1) selecting raw materials; 2) preparing emulsifying agents according to proportion, stirring and heating, thereby obtaining a substance A; 3) heating the modified plant oil and fat; 4) adding the substance A into the modified plant oil and fat in step 3), thereby preparing a substance B through a phase conversion emulsifying method; 4) adding deionized water at 80 DEG C-90 DEG C by multiple times, and stirring at high speed, thereby obtaining a substance C; and 5) preparing the auxiliaries into a solution, adding the solution into the substance C at room temperature, stirring, and filtering, thereby obtaining the micro-emulsive nonferrous metal mold releasing agent. According to the micro-emulsive nonferrous metal mold releasing agent disclosed by the invention, synthetic polyethylene wax is taken as a membrane forming substance so as to obtain the nano particle size mold releasing agent, is beneficial to mold filling by metal liquid and reducing of the mold releasing force, and the defects that the domestic mold releasing agent is poor in mold releasing effect, pollutes a container, can block a spraying pipeline easily and the like are overcome.
Owner:哈威光电科技(苏州)有限公司
Nanoparticle-modified fluoropolymer coatings
InactiveUS20110287251A1Improve release characteristicEnhanced release characteristicLayered productsSpecial tyresColloidal silicaPolymer chemistry
A fluoropolymer coating that includes nanoparticles for providing the coating with improved release characteristics together with improved abrasion resistance. In one embodiment, the nanoparticles are silica particles that may be incorporated into the coating by adding colloidal silica to the liquid coating formulation that is applied to a substrate, typically over a primer, and then cured. After the coating is cured, the coating demonstrates enhanced release characteristics together with improved abrasion resistance. It has been unexpectedly observed that a combination of desired release characteristics and improved abrasion resistance is found when the average particle size of the nanoparticles is between 30 and 120 nm, with the abrasion resistance generally increasing with increasing particle size.
Owner:WHITFORD
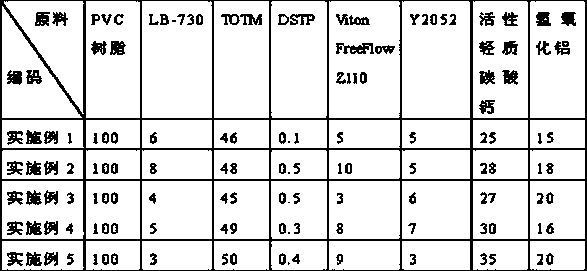
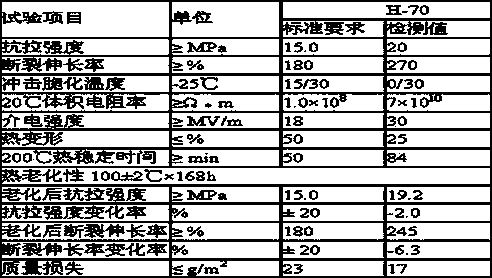
Easily peeled PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) cable sheath material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103665627AGood physical and mechanical propertiesMeet environmental protection requirementsPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsPolymer sciencePolyvinyl chloride
The invention belongs to the field of cable materials, and in particular relates to an easily peeled PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) cable sheath material which is mainly prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 100 parts of PVC resin, 3-8 parts of anti-impact modifying agent, 45-50 parts of plasticizing agent, 0.1-0.5 part of antioxidant, 3-10 parts of fluorine lubricant, 3-7 parts of thermal stabilizing agent, 25-35 parts of filling agent and 15-20 parts of flame retardant. The easily peeled PVC cable sheath material provided by the invention is excellent in mechanical physical property, and meanwhile a product meets the environment-friendly requirements; due to addition of the fluorine lubricant, a cable sheath layer has good release properties with an insulating layer, and when being recycled, the insulating layer and the sheath layer can be easily separated.
Owner:苏州德亮材料科技有限公司
Controlled release dual walled microcapsules
ActiveUS20160108339A1Enhanced release propertiesGood physical propertiesCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsMethacrylatePolymer science
A method of forming dual melamine / acrylic walled microcapsules having improved physical properties and release control as well as the microcapsules formed by the process wherein the capsule wall is formed by the use of select (meth)acrylate monomers and / or oligomers and / or select self-condensing melamine resins.
Owner:ENCAPSYS LLC
Controlled release dual walled microcapsules
ActiveUS9714396B2Enhanced release propertiesGood physical propertiesCosmetic preparationsOrganic detergent compounding agentsMethacrylatePolymer science
Owner:ENCAPSYS LLC
Pneumatic tire
InactiveUS20060016537A1Favorable mold release characteristicShorten the progressTyre tread bands/patternsNon-skid devicesMeanderEngineering
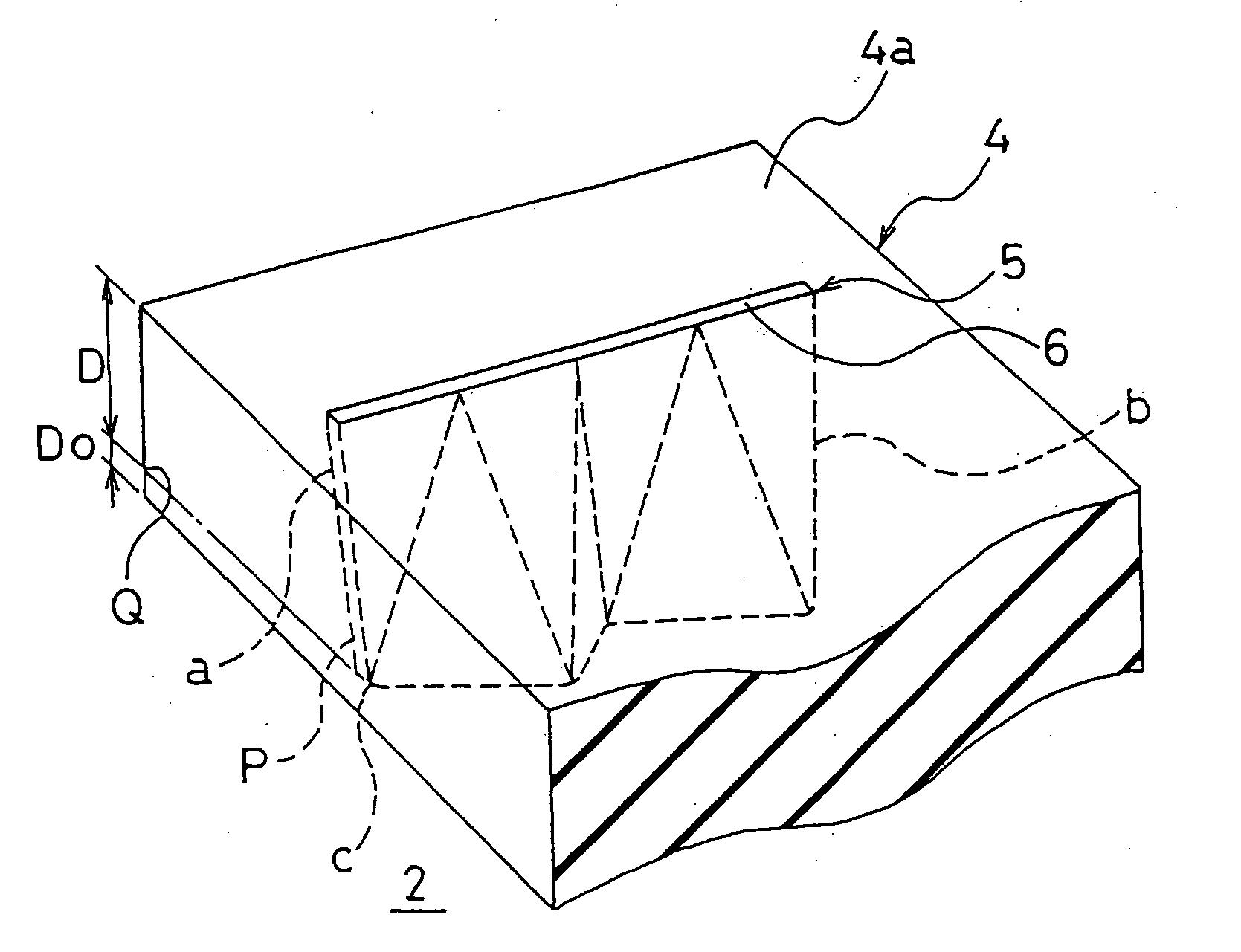
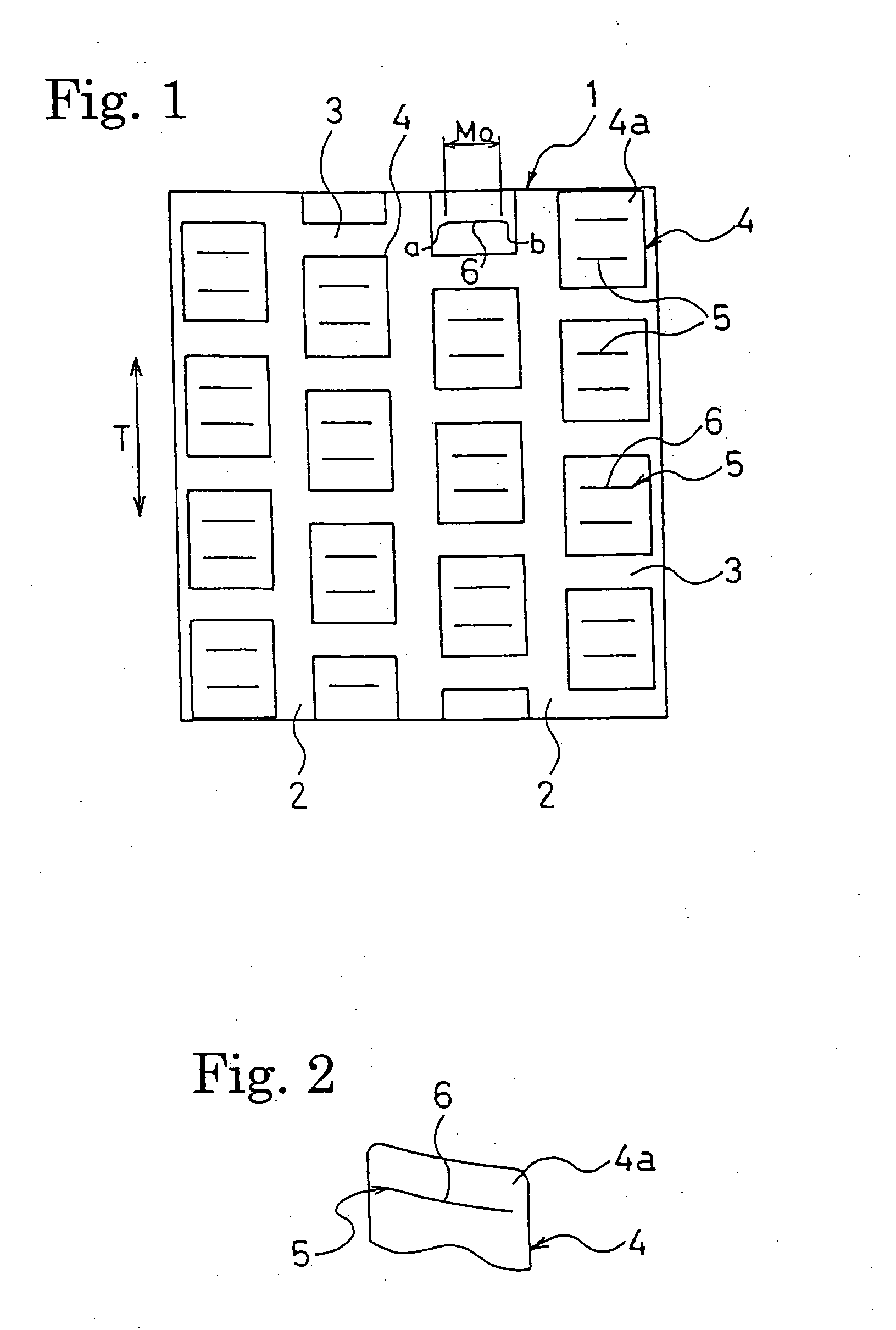
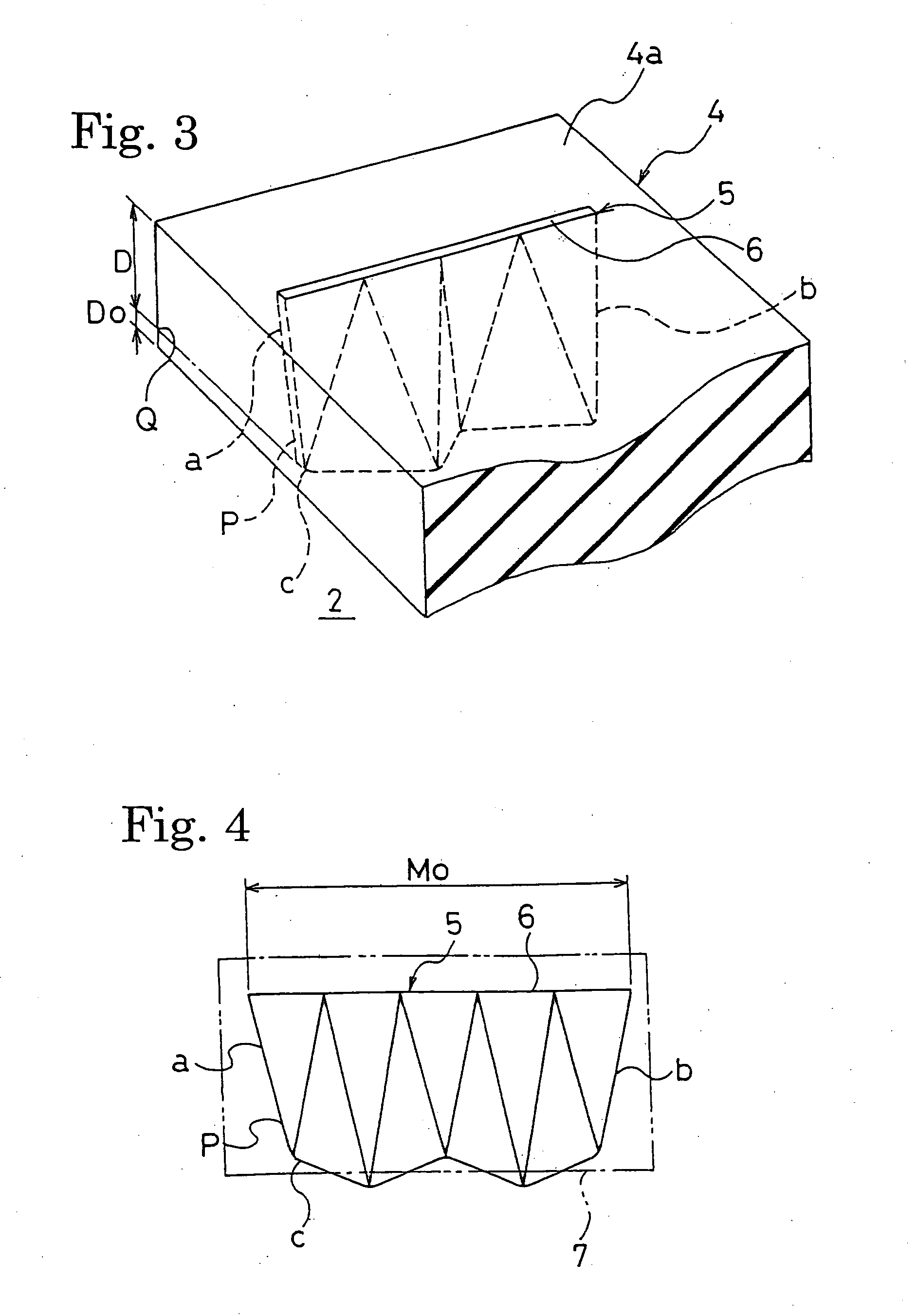
A pneumatic tire including sipes that have at least one ends positioned within blocks. The sipes are arranged such that each of the sipes meanders from the one end to the other end thereof to form a meandrous shape, and as the depth of the sipes increases, the meander width of the sipes gradually increases from their openings to at least the 80%-worn position of the blocks. The sipes each have a sipe length L, which is defined as a center line length between an intersection of a center line passing the center of the meander width of the meandrous shape with a first straight line and an intersection of the center line with a second straight line, the first straight line being orthogonally drawn to the center line from the one end of the sipe and the second straight line being orthogonally drawn to the center line from the other end of the sipe at the same depth position of the sipe, the sipe length L gradually decreasing as the sipe depth increases. The ratio L80 / M0 of the sipe length L80 at the 80% worn position to the opening length M0 of the sipes is in the range of 0.8 to 0.95, and the ratio M80 / M0 of the actual length M0 of the sipes at the 80% worn position to the opening length M0 is in the range of 1.0 to 1.15.
Owner:YOKOHAMA RUBBER CO LTD
System and method for electropolishing or electroplating conveyor belts
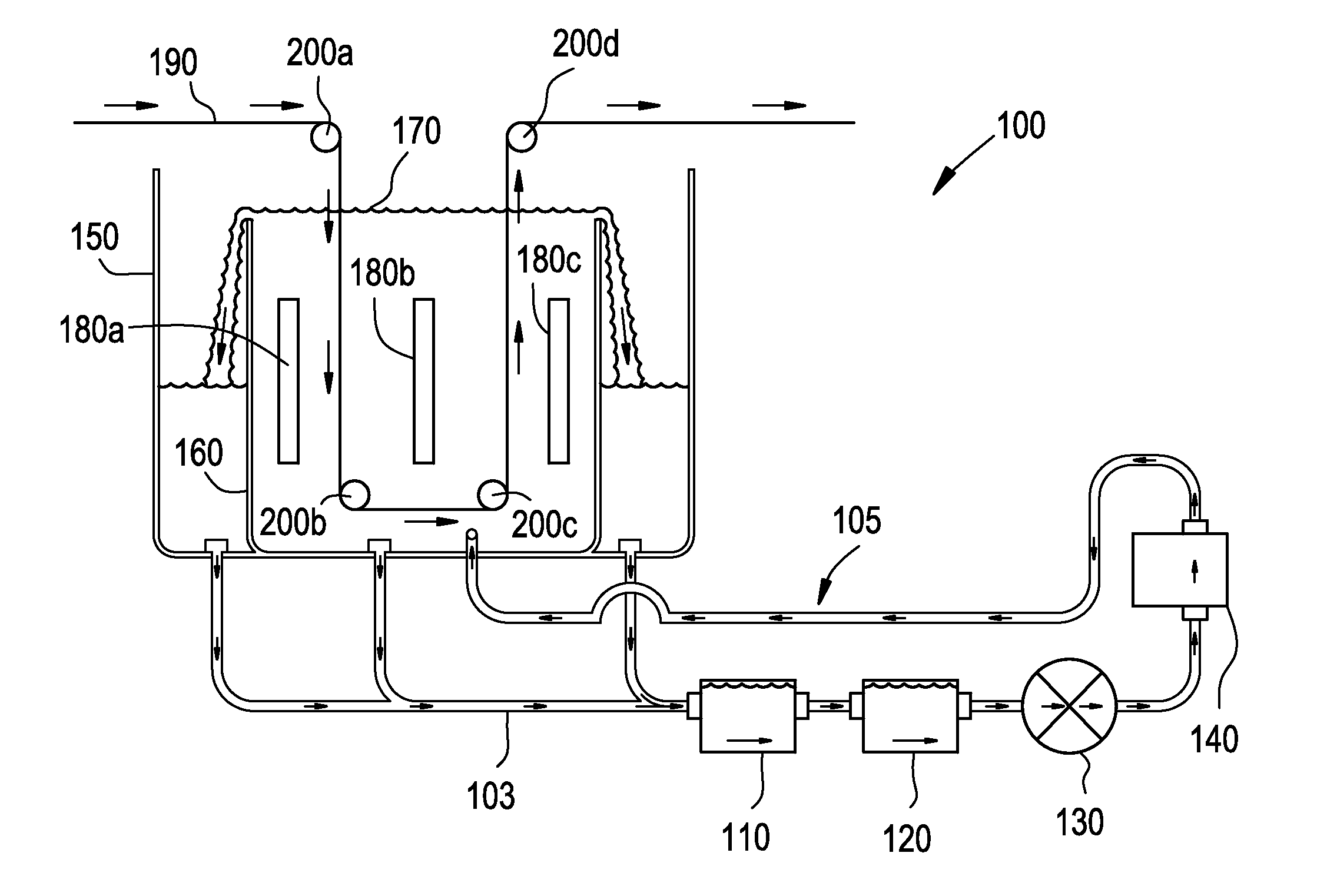
ActiveUS20130168256A1Improve sanitationImproves product release characteristicElectrolysis componentsElectrochemical machining apparatusInterior spacePower flow
An electropolishing or electroplating system and method for metal conveyor belts is described. In some embodiments, the system has a metal conveyor belt held in constant tension; a tank for holding an electrolytic fluid, the tank having an interior space suitable to contain the fluid, a metal plate and the metal conveyor belt; and an electrical current supply. In an electropolishing application, the current passes from the metal conveyor belt, through the fluid and into the metal plate. In an electroplating application, the current passes from the metal plate, through the fluid and into the metal conveyor belt.
Owner:ASHWORTH BROS
Roller type stamper
InactiveUS20100203183A1Strong adhesion to metalEnhanced release propertiesDough-sheeters/rolling-machines/rolling-pinsConfectioneryEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:SAMSUNG MOBILE DISPLAY CO LTD
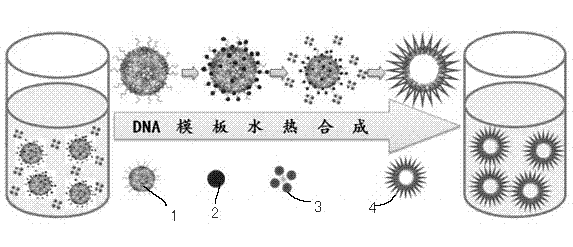
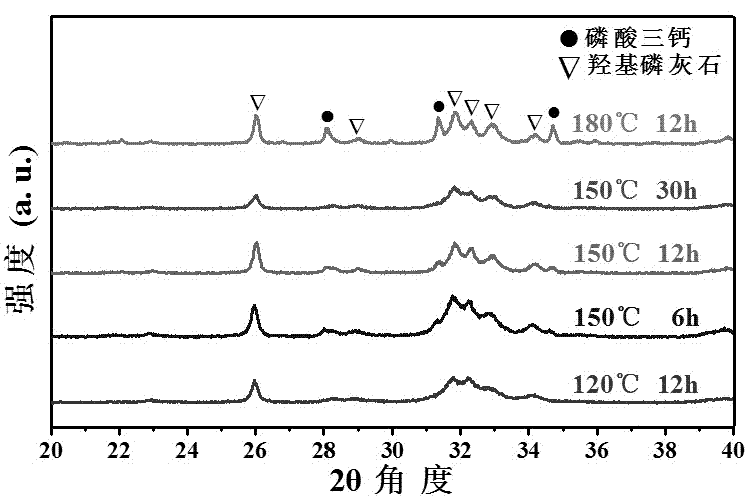
Hydroxyapatite hollow microsphere and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102807202AEnhanced drug loading capacityEffective adjustment diameterMaterial nanotechnologyPhosphorus compoundsMicrospherePhosphate
The invention relates to a hydroxyapatite hollow microsphere and a preparation method thereof. The hydroxyapatite hollow microsphere is prepared by using water-soluble calcium salt and phosphate as raw materials, water as a solvent and DNA as a template agent through hydrothermal reaction. The diameter of the hydroxyapatite hollow microsphere and the size of the cavity can be effectively adjusted by changing the adding amount of the DNA.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods and apparatus for forming shaped edible pieces
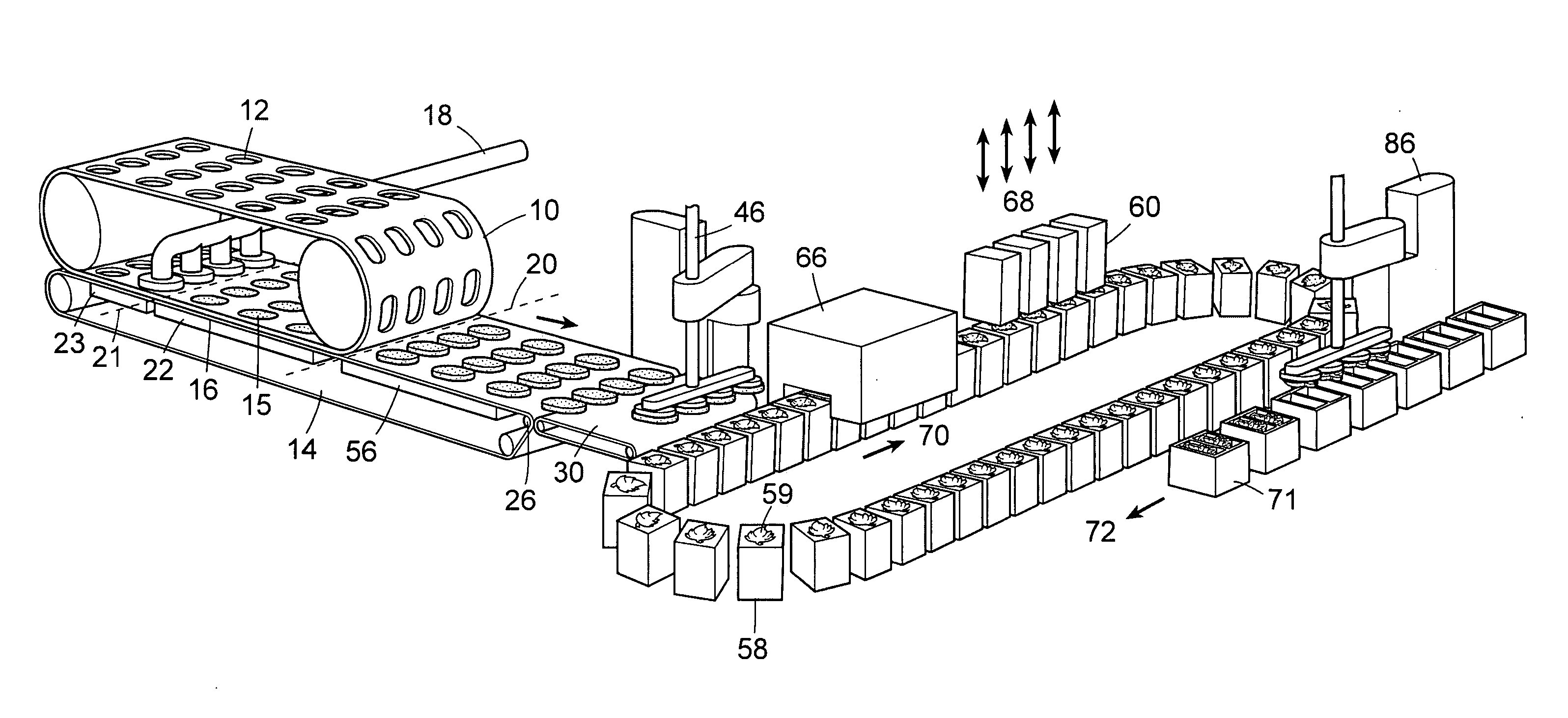
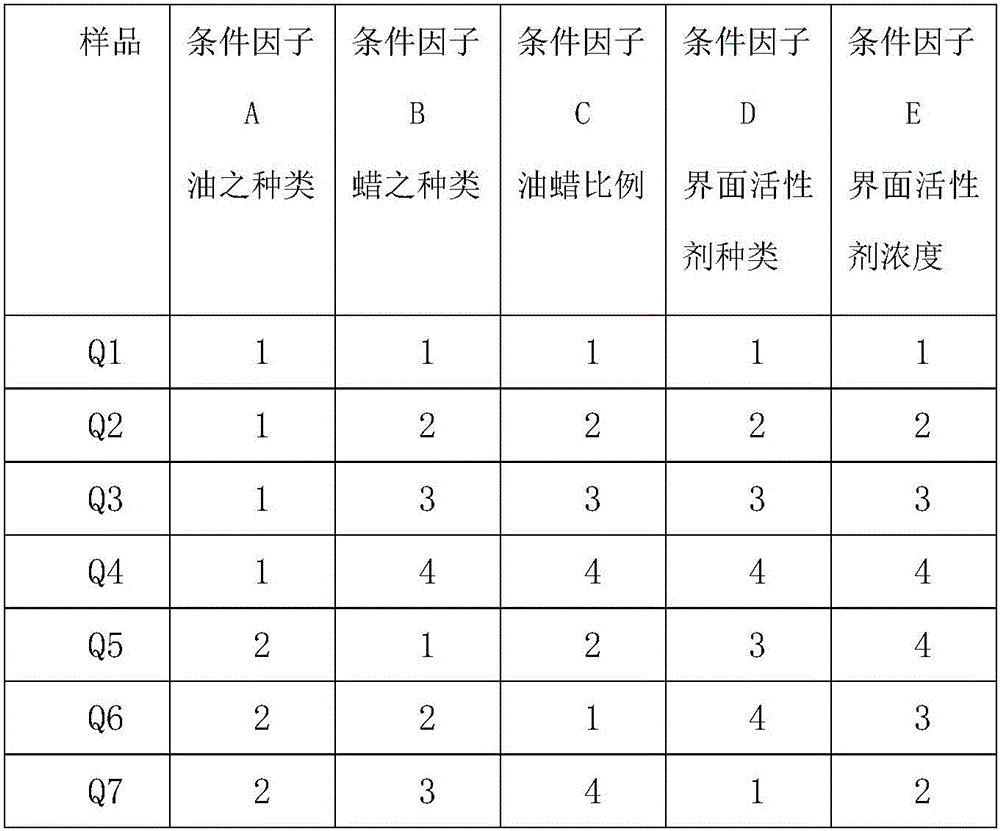
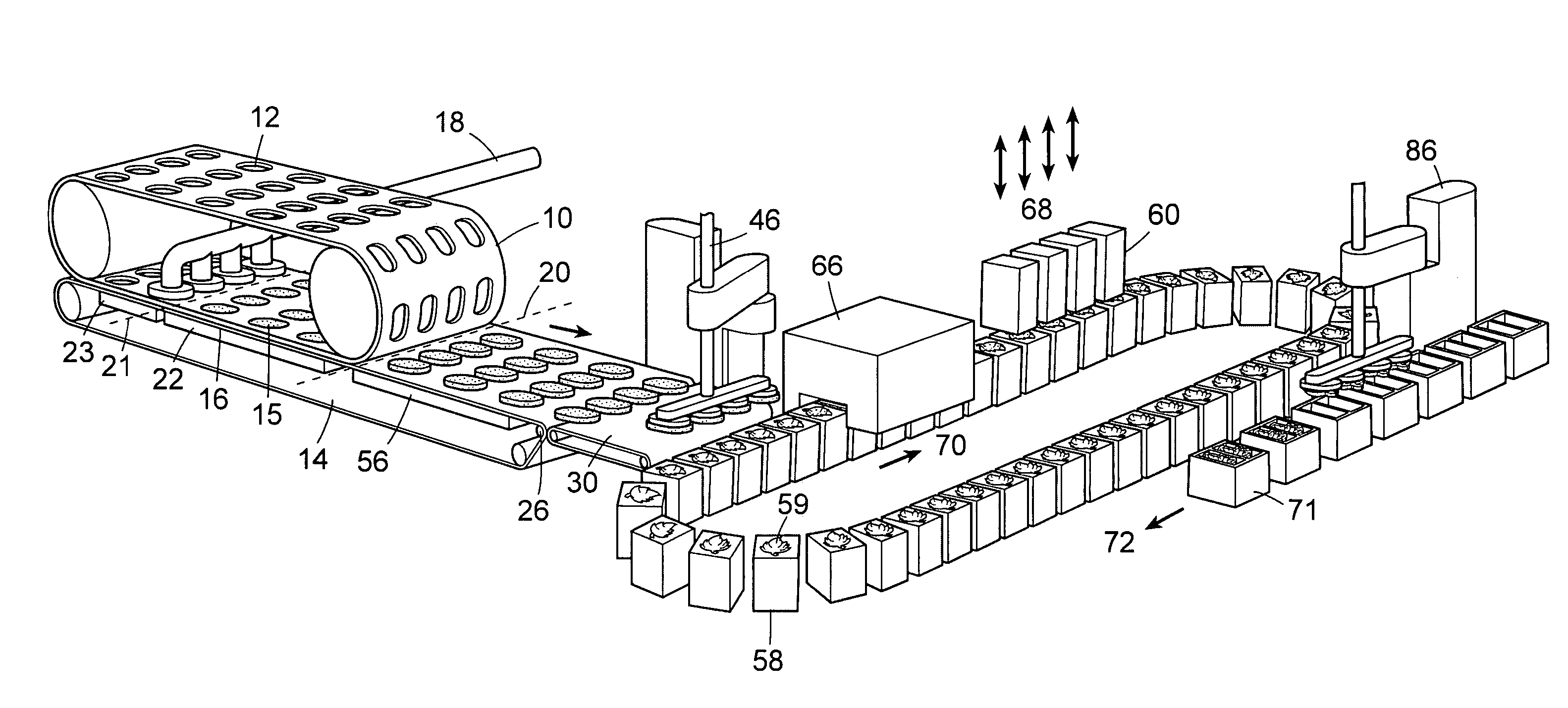
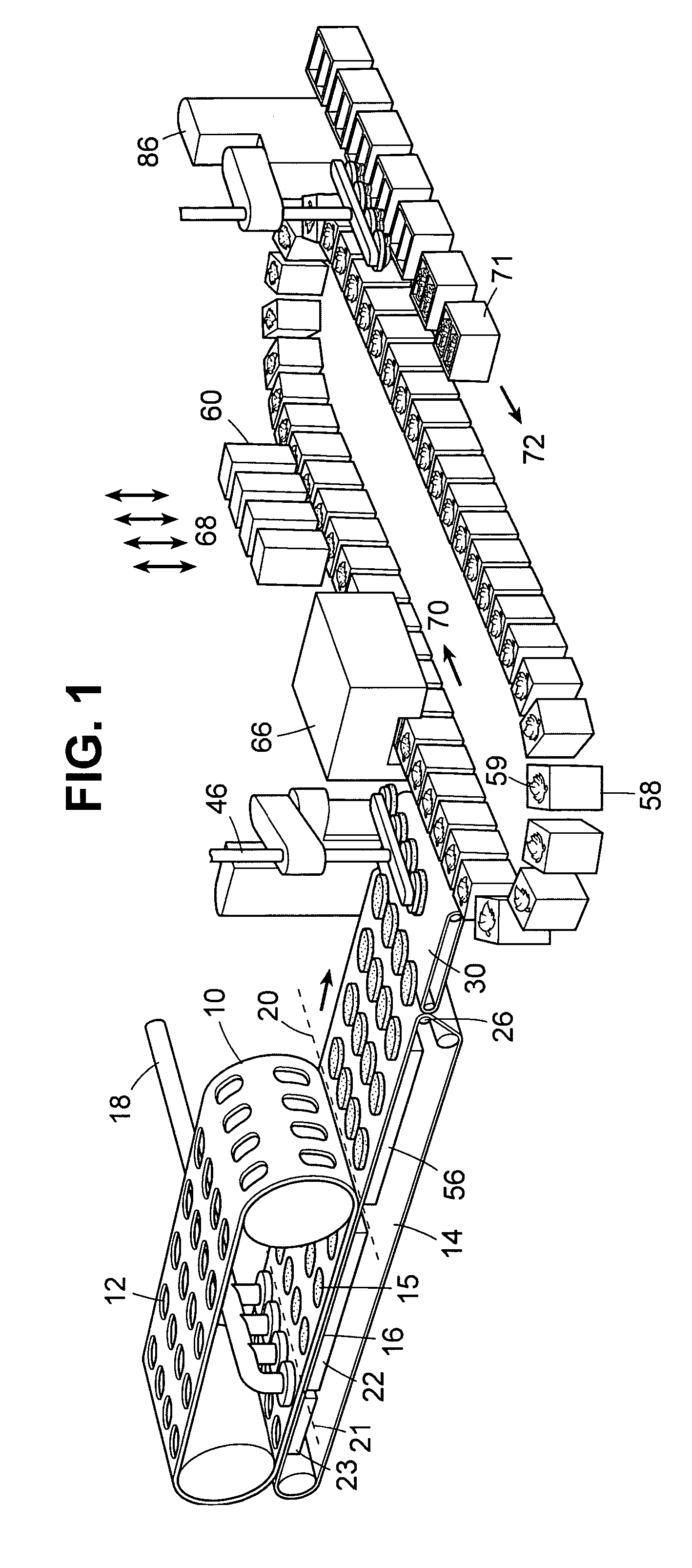
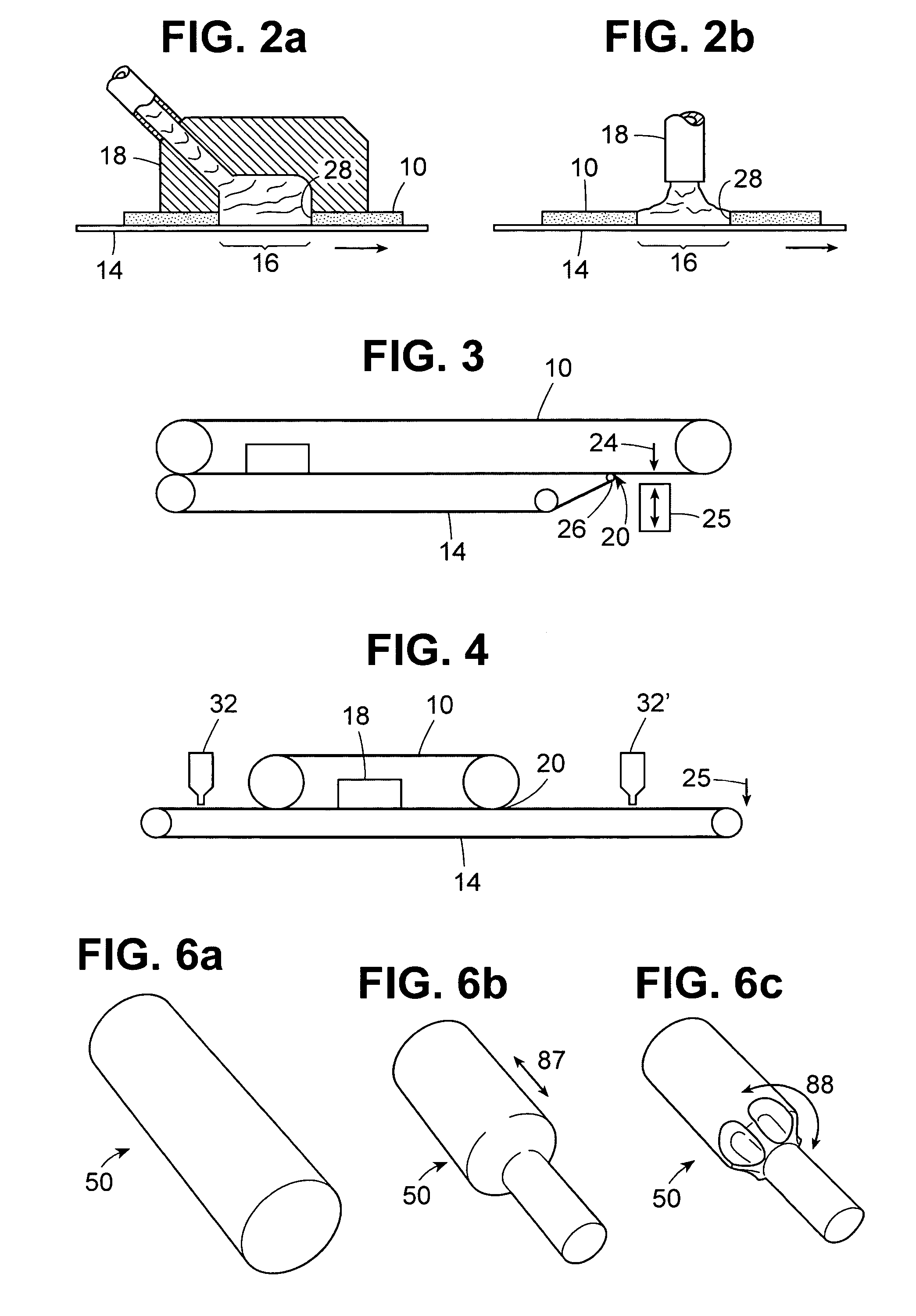
ActiveUS20060210672A1Enhanced release propertiesConfectionerySweetmeatsThree dimensional shapeReady to use
A method for forming thin edible pieces uses two continuous belts that cooperate to form a fill cavity. An edible mass, such as chocolate, is flowed into the fill cavity where it forms an edible blank which is transported on a belt path with the two belts moving in tandem. After the edible blank is released from the first or second continuous belt, a three-dimensional shape may be imparted to the edible blank at a forming station using one or more stamping dies or a forming drum. Using the techniques and apparatus described herein, novel edible products, and particularly novel chocolate products, can be made having shape characteristics that cannot be obtained using known molding or forming techniques.
Owner:MARS INC
Microwavable cooking implements and methods for crisping food items using the same
A cooking implement comprising a resilient cooking surface made of silicone and maintained at tension, the cooking surface comprising a plurality of holes and a support device having a curved periphery disposed about the periphery of the cooking surface to stretch and maintain the cooking surface at tension. The support device is configured to support the cooking surface at a distance above a ground surface.
Owner:MASTRAD
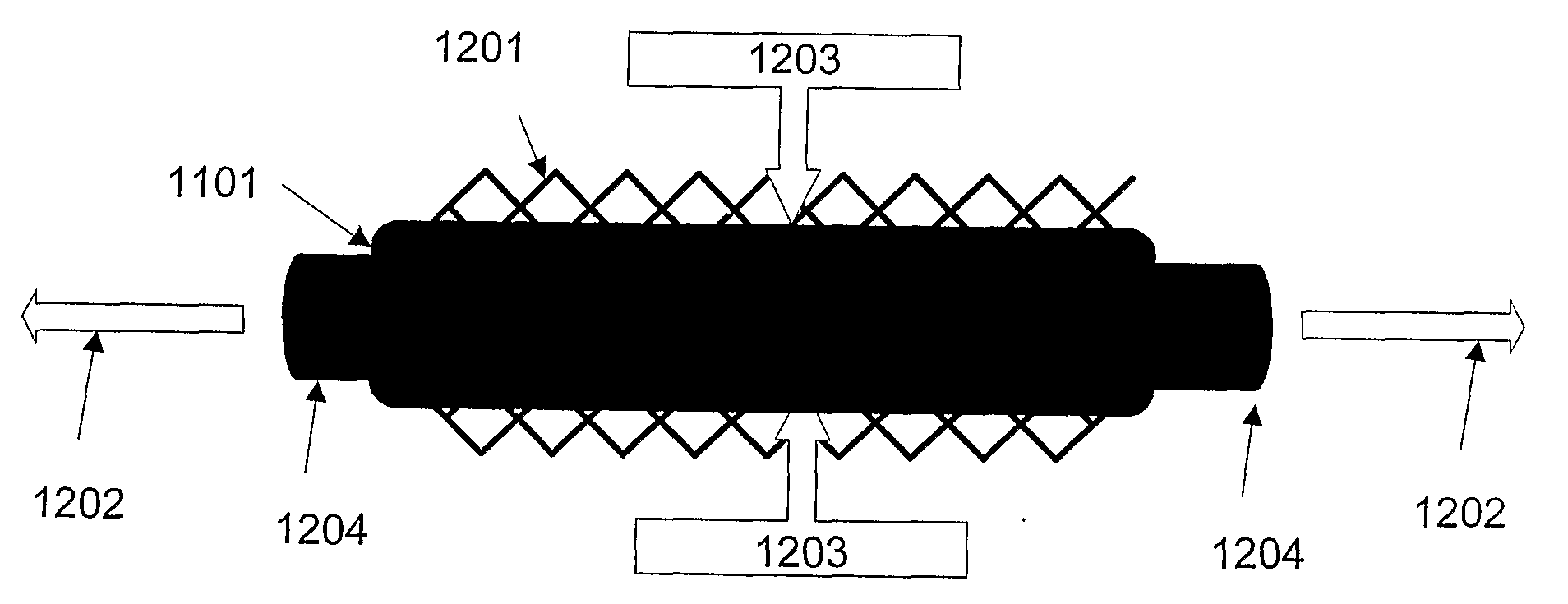
Stent manufacturing methods
A novel method of manufacturing stents by use of molds (1101) made of a biocompatible, flexible material, preferably silicone. Some embodiments use silicone polymers; a two-dimensional, waffle mold; injection molds whereby the core of the injection mold is silicone polymer. In some embodiments, the stent polymer or particles of stent polymers are injected into the mold, around a cylinder of silicone, to form a three-dimensional stent. In some embodiments, particles of silicone polymer are mechanically forced into the negative spaces and then fused together to form the finished product. In other embodiments, metal stents or metal molds are used to manufacture a reverse mold. The reverse mold (901) is then used to create positive silicone molds. The silicone molds can subsequently be used by any means to make polymer stents, lending themselves to automation.
Owner:ARTERIAL REMODELING TECH SA
Hyaluronic acid modified hectorite amide nanoparticle and preparation and application of hyaluronic acid modified hectorite amide nanoparticle
InactiveCN104644560AEnhanced release propertiesImprove targetingPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsCancer cellNanoparticle
The invention relates to a hyaluronic acid-modified amide hectorite nanoparticle and a preparation and an application of the hyaluronic acid modified hectorite amide nanoparticle. The hyaluronic acid modified hectorite amide nanoparticle is (3-amino propyl) ethoxydimethylsilane modified hectorite; and the mass fraction of the hyaluronic acid in the nanoparticle is 17.17%-19.09%. The preparation method comprises the following steps: modifying a hectorite surface with (3-amino propyl) ethoxydimethylsilane on to obtain hectorite amide; and through covalent action of amino and carboxyl, grafting the hectorite amide surface with hyaluronic acid, thus obtaining the hyaluronic acid modified hectorite amide nanoparticle. The stability and the biocompatibility of the nanoparticle are improved; meanwhile, the hyaluronic acid-modified hectorite amide nanoparticle has specific targeting action on cancer cells with high expression for a CD44 receptor, and can be applied to targeted delivery of anti-cancer drugs; and the hyaluronic acid-modified hectorite amide nanoparticle is simple in preparation method, mild in reaction condition and easy to operate, and has an industrial implementation prospect.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Nano-scale solid-state lipid drug delivery system and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106236596AHigh embedding rateHigh drug loadingCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsEmbedding rateDark spot
The present invention provides a nano-scale solid-state lipid drug delivery system, wherein a liquid lipid and a solid lipid are mixed as a raw material to prepare the 4-n-butylresorcinol embedded drug delivery system, and specifically the drug delivery system is the oil-in-grease and oil-in-water (O / F / W) composite nanometer lipid drug delivery system, and has characteristics of high embedding rate, high drug loading, high stability, low toxicity and good drug release. The invention further provides applications of the drug delivery system in formulas for cosmetic preparation, wherein the nano-scale solid-state lipid drug delivery system further has effects of skin whitening, dark spot removing, and freckles and melanin production inhibiting.
Owner:上海格兰化妆品有限公司
Cannabinoid chewing gum with high intensity sweeteners
ActiveUS11406593B2Facilitated releaseQuick releaseHydroxy compound active ingredientsPill deliveryNatural resinPolymer science
The present invention relates to a chewing gum for mucosal delivery of cannabinoids, the chewing gum includes water-soluble chewing gum ingredients and water-insoluble gum base, wherein the gum base has one or more natural resins in an amount of 10-40% by weight of the gum base, one or more elastomers in an amount of 3-30% by weight of the gum base, and one or more elastomer plasticizers in an amount of 8-50% by weight of the gum base, and wherein the chewing gum includes one or more high intensity sweeteners in an amount of 0.01 to 1% by weight of the chewing gum, and wherein the chewing gum has one or more cannabinoids.
Owner:NORDICCAN AS
Methods and apparatus for forming shaped edible pieces
ActiveUS7820218B2Enhanced release propertiesConfectionerySweetmeatsShell moldingThree dimensional shape
A method for forming thin edible pieces uses two continuous belts that cooperate to form a fill cavity. An edible mass, such as chocolate, is flowed into the fill cavity where it forms an edible blank which is transported on a belt path with the two belts moving in tandem. After the edible blank is released from the first or second continuous belt, a three-dimensional shape may be imparted to the edible blank at a forming station using one or more stamping dies or a forming drum. Using the techniques and apparatus described herein, novel edible products, and particularly novel chocolate products, can be made having shape characteristics that cannot be obtained using known molding or forming techniques.
Owner:MARS INC
Hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticle loaded with rotenone and preparation method thereof
PendingCN113475512AHarm controlReduce selection pressureBiocideAnimal repellantsNanoparticleSolvent evaporation
The invention relates to a hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticle loaded with rotenone and a preparation method thereof. The nanoparticle comprises an effective component and a nano-carrier, wherein the effective component is rotenone; and the rotenone accounts for 10.0% of the total weight of the nanoparticle, with the balance being the nano-carrier. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, a self-template synthesis method is adopted, and on the basis of synthesizing a solid mesoporous silica nanoparticle (HMSNs), water is used as an etching agent to prepare the hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticle (HMSNs). Researches show that the particle size of the prepared HMSNs is about 250 nm, and the specific surface area of the prepared HMSNs reaches 999.4 m<2> / g; and biogenic pesticide rotenone (Rot) is loaded into pores of the HMSNs through a solvent evaporation method, and the prepared rotenone-loaded nanoparticle (Rot-coated HMSNs) is uniform in particle size, has a drug loading rate of 46.7%, has good release characteristics and shows good prevention and treatment effects on imported cabbageworm larvae.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Hardcoat compositions
InactiveCN103890045AEnhanced release propertiesFree from scratchesOriginals for photomechanical treatmentCoatingsSilane compoundsPhotochemistry
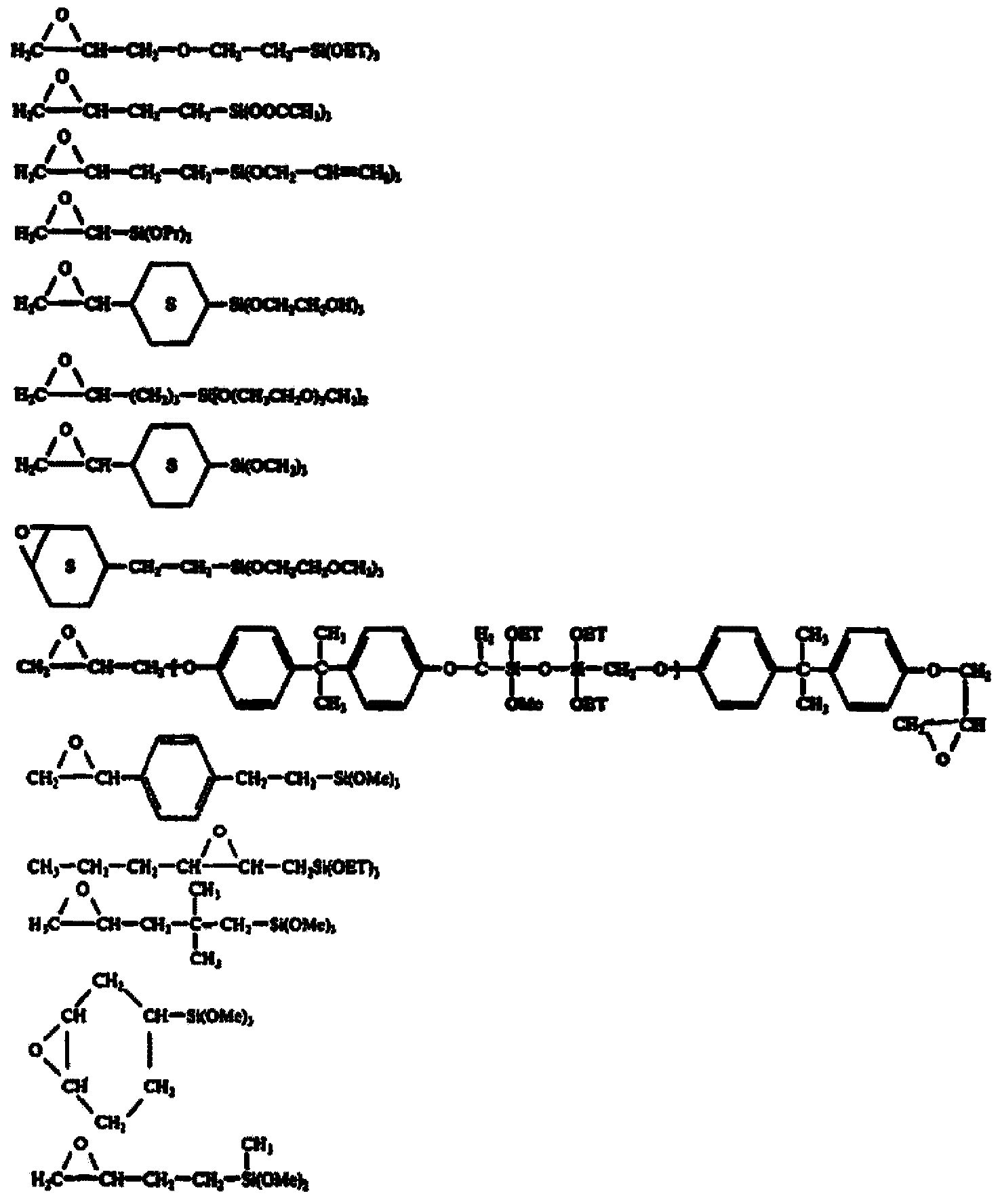
A hardcoat composition comprises (a) an epoxy silane compound, (b) a reactive silicone additive and (c) photo-acid generator. The reactive silicone additive has one of the following general structures:formula (I) or X-SiR1R2-(O-SiR1R2)n-X (Formula 2) wherein: R1, R2, and R3 are independently a C1-C6 alkyl group or aromatic group with or without substitution; X is a curable group selected from -OH, -OR, -OC(0)R, -OSiY^Y3, -CHzCHrL-SiYVY3, and -C(O)(R)3, wherein: L is a divalent linkage group; Y1, Y2, and Y3 are independently selected from a C1-C6 alkyl group, and a curable group selected from -OH, -OC(O)R, and -OR, with the proviso that at least one of Y1, Y2, and Y3 is a curable group; R is a C1-C4 alkyl group; and n is at least 2 and m is at least 1, provided that the weight average molecular weight (Mw) of the reactive silicone additive is no more than 4200.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com