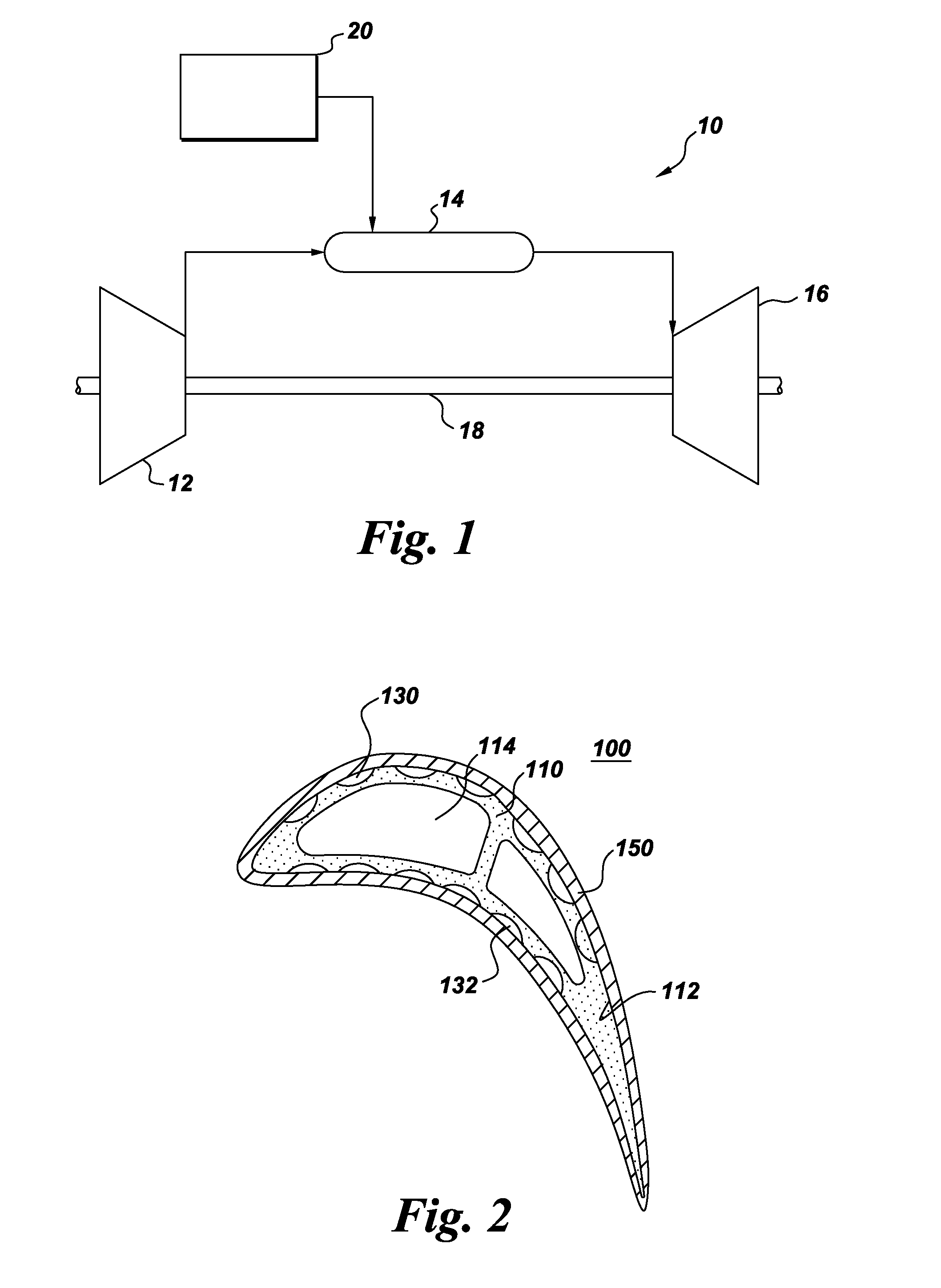
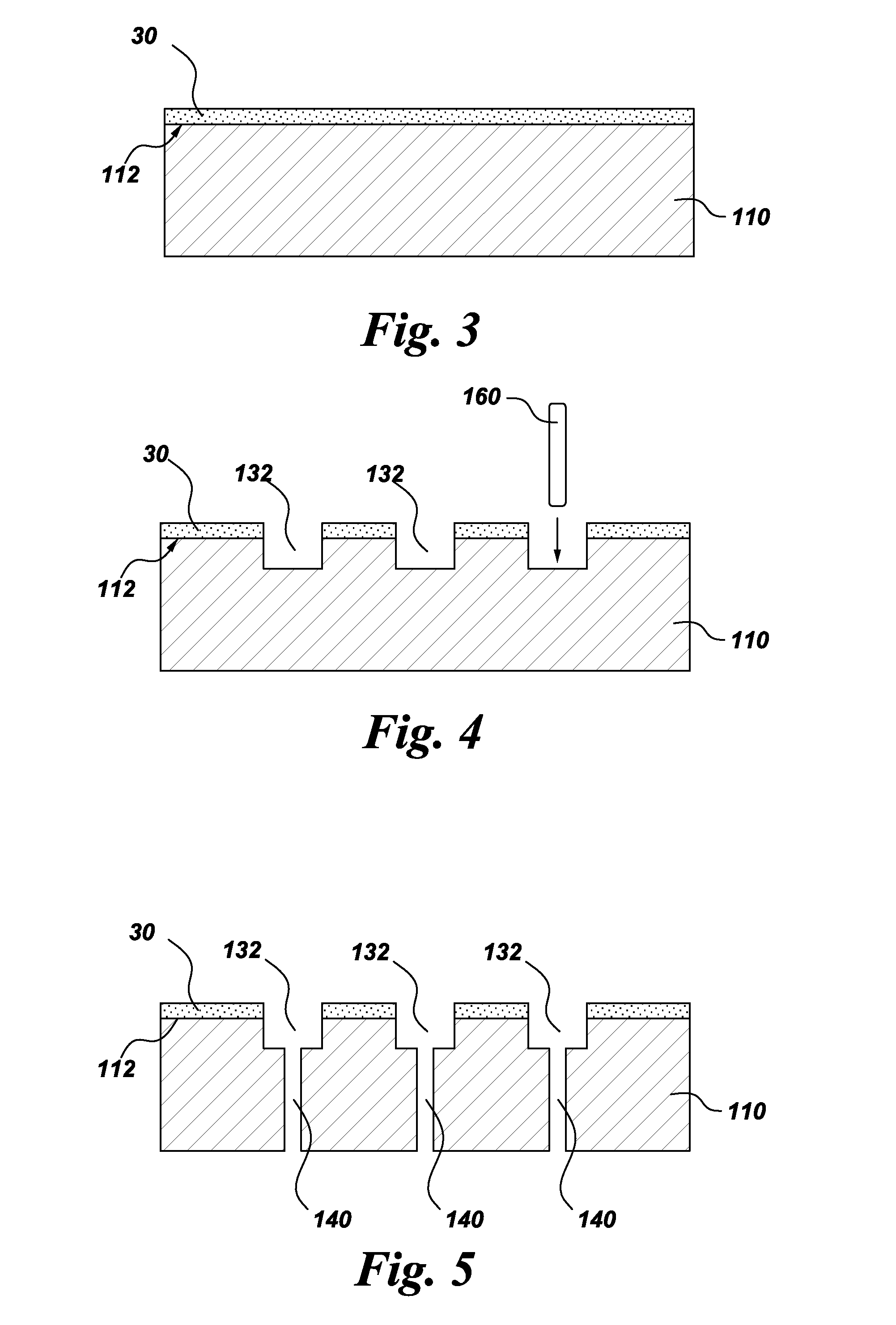
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
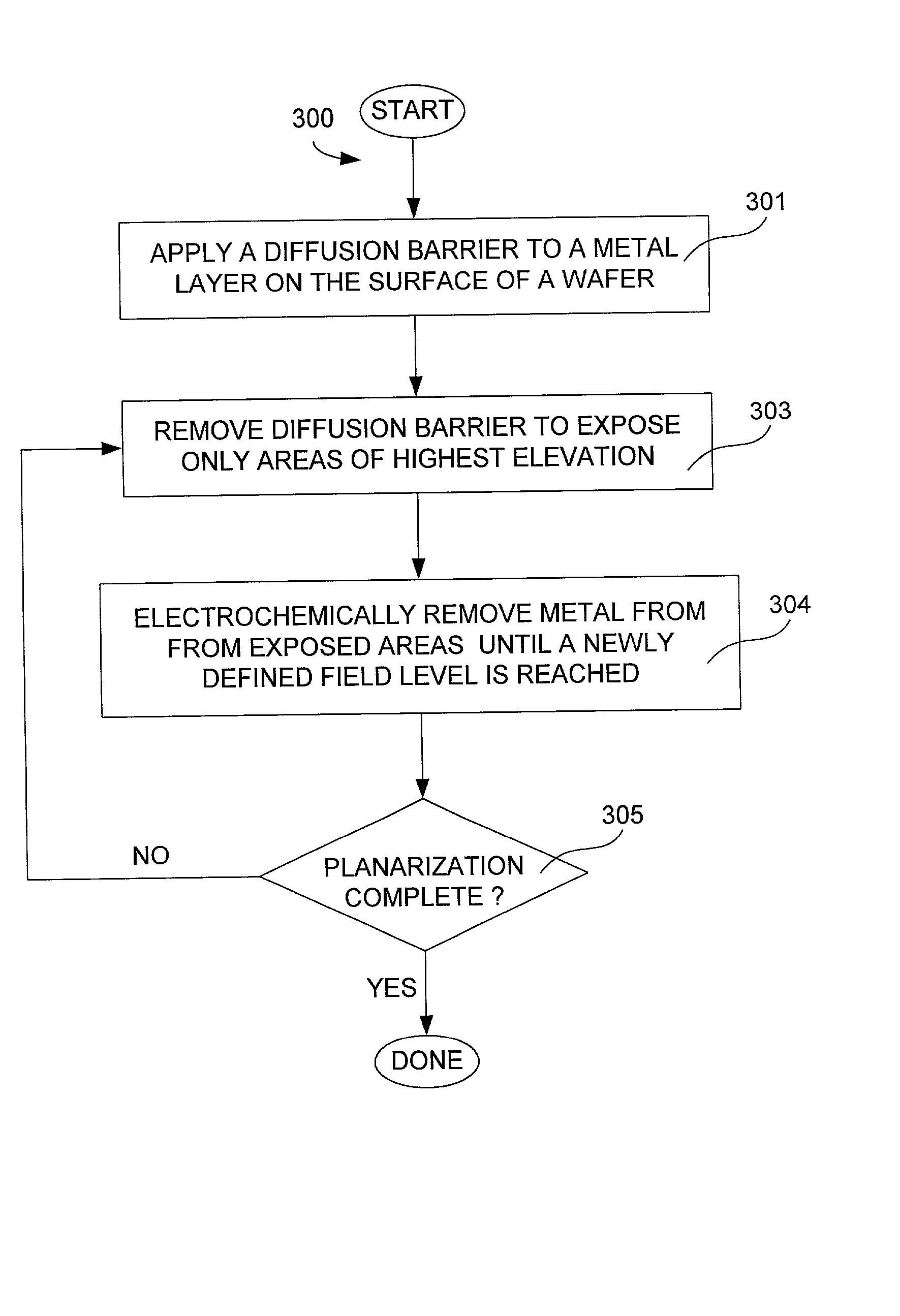
1382results about "Electrochemical machining apparatus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
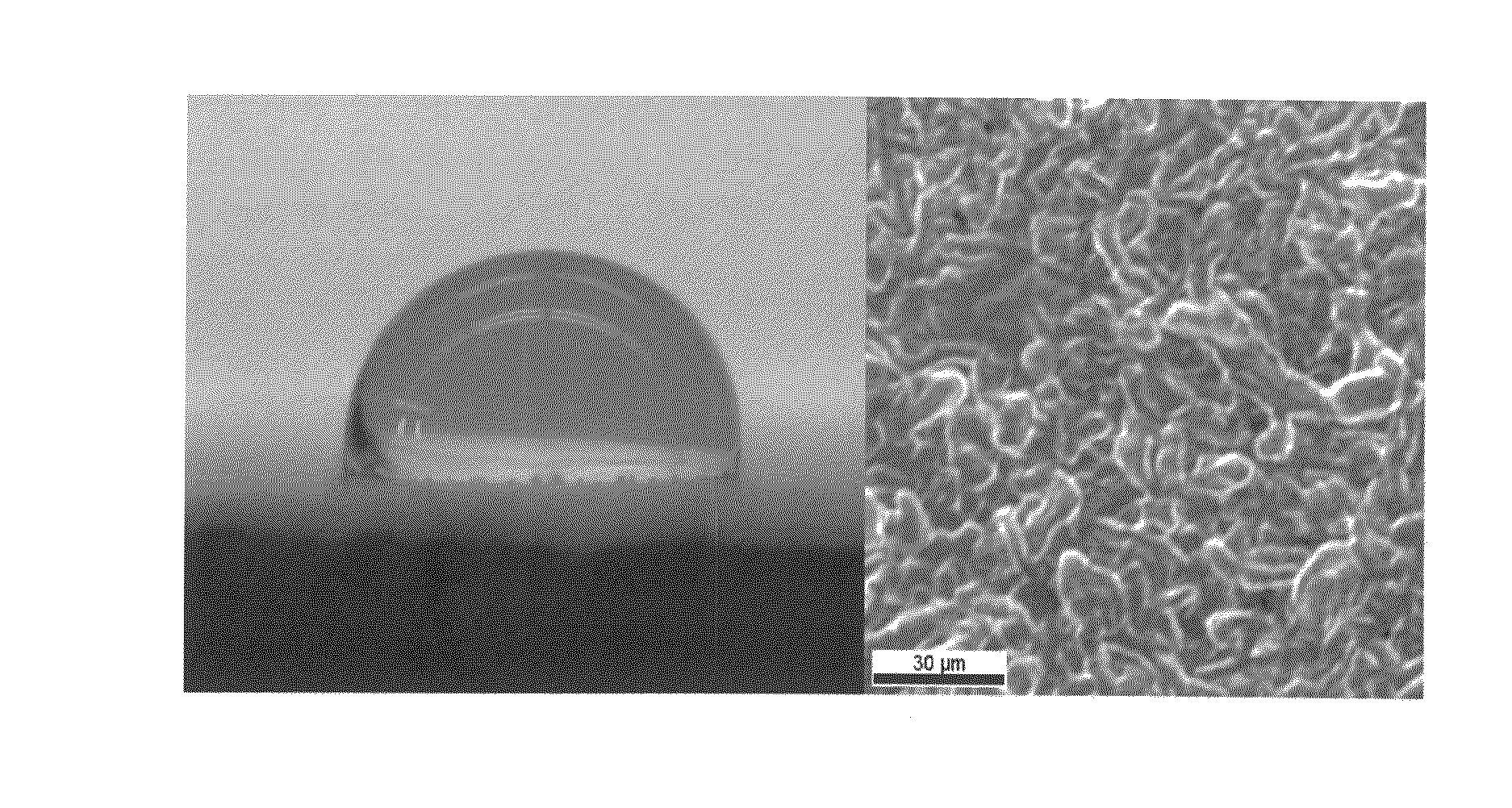
Hdp-cvd multistep gapfill process
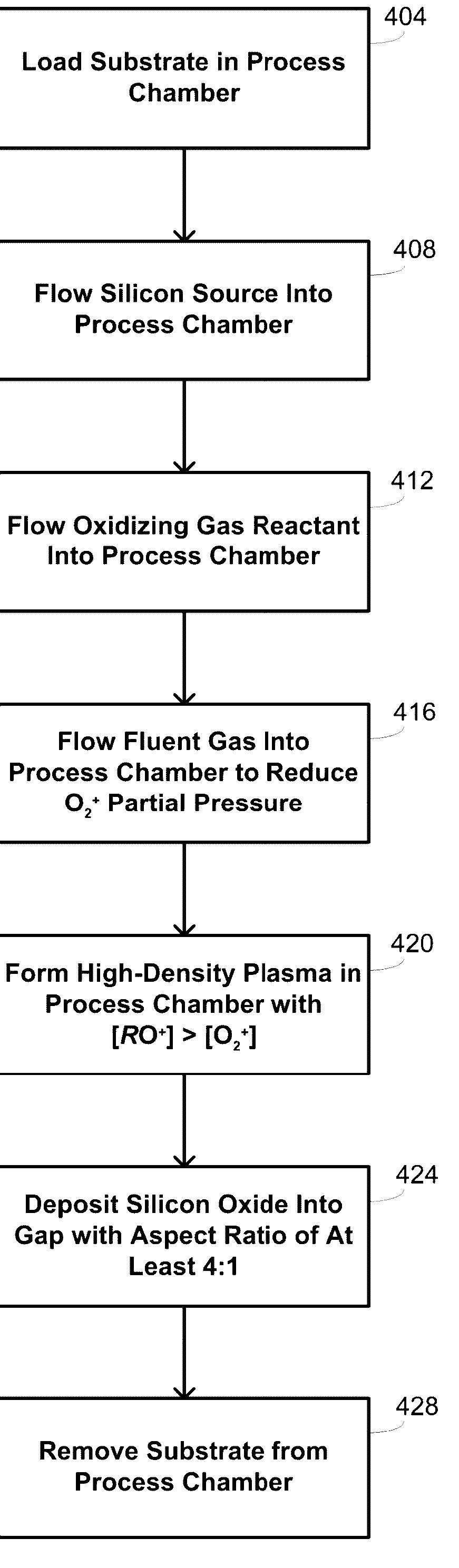
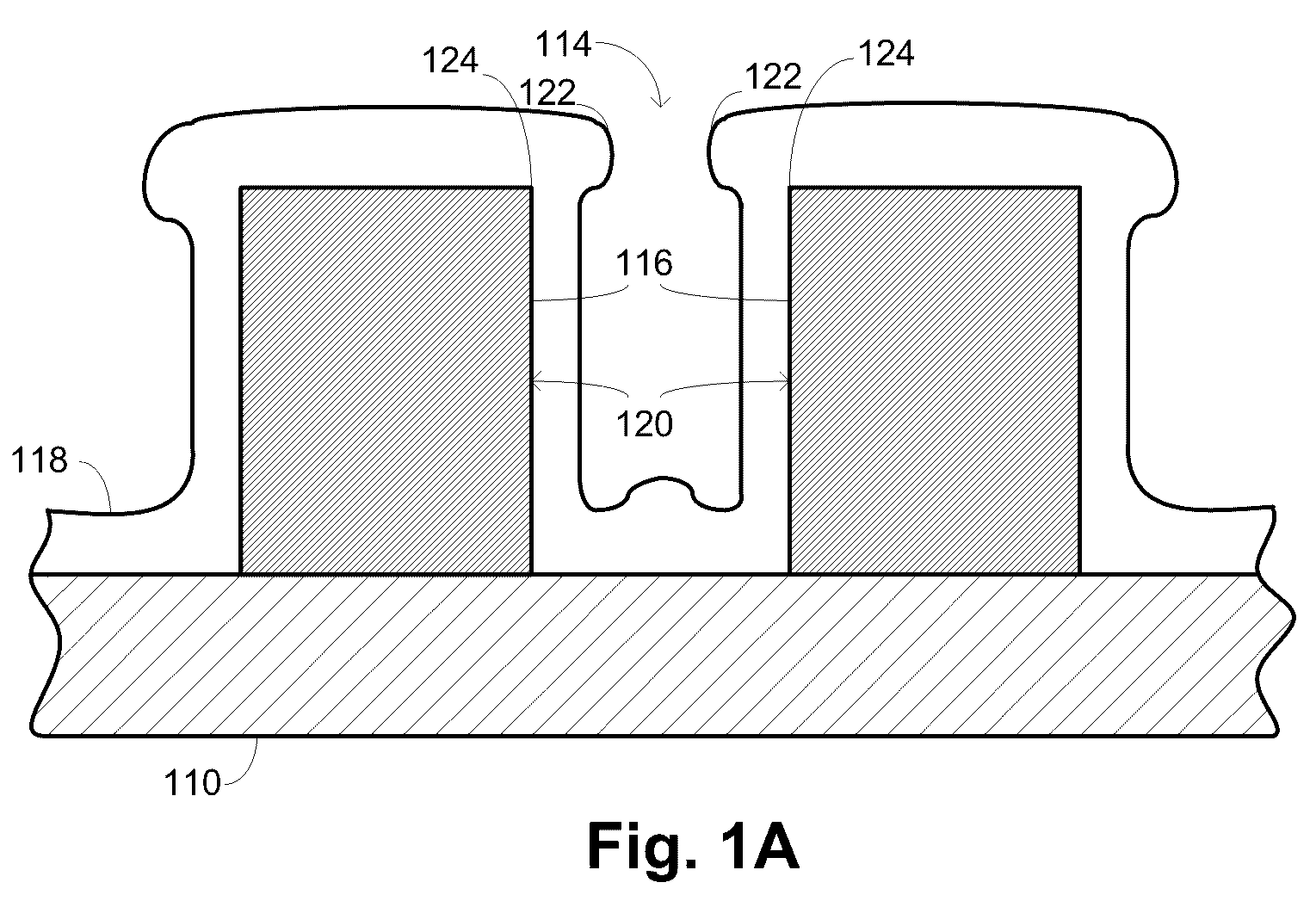
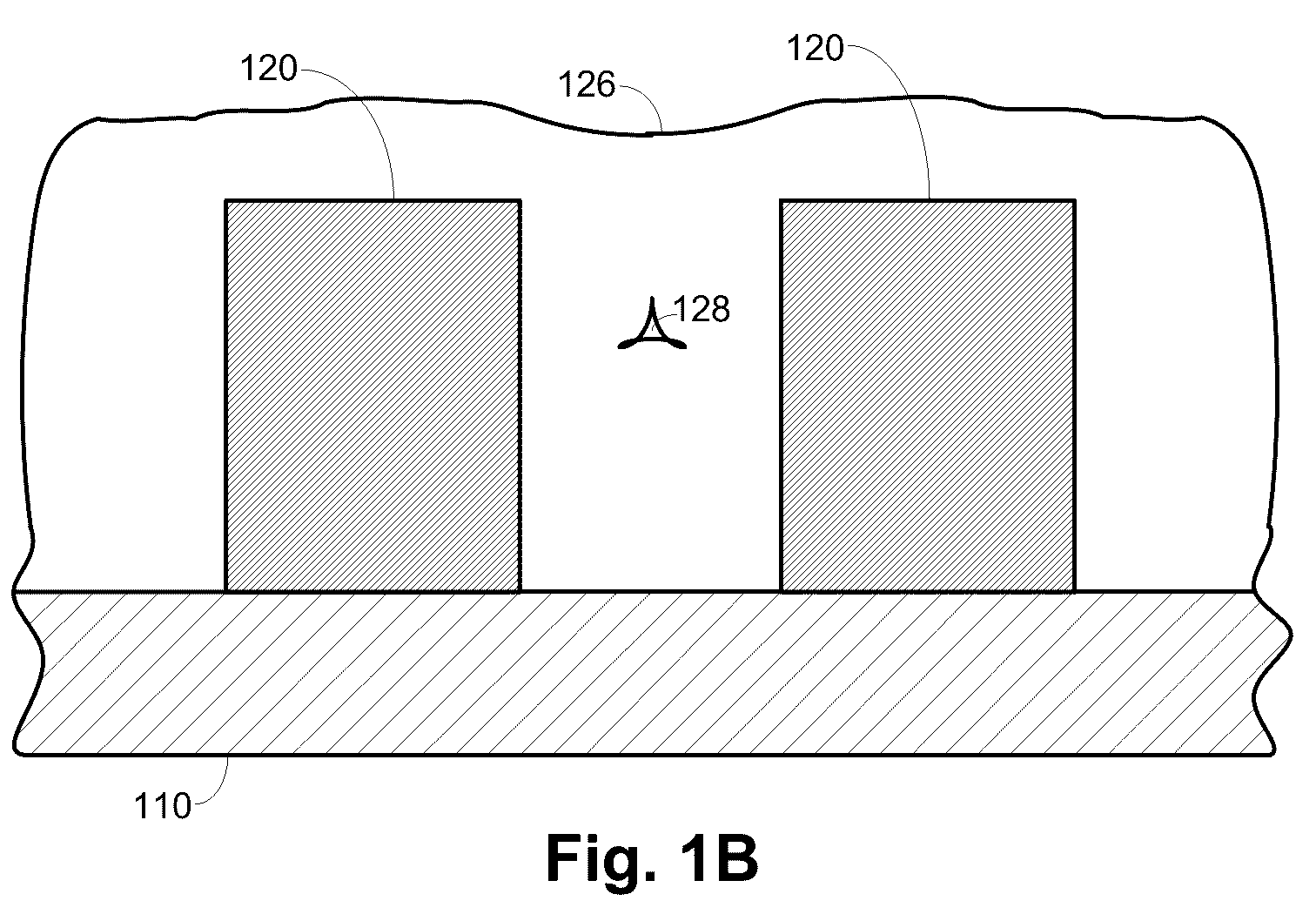
InactiveUS20040245091A1Reduce molecular weightReduced sputtering characteristicVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingProduct gasChemistry
Abstract of the Disclosure A gapfill process is provided using cycling of HDP-CVD deposition, etching, and deposition step. The fluent gas during the first deposition step includes an inert gas such as He, but includes H2 during the remainder deposition step. The higher average molecular weight of the fluent gas during the first deposition step provides some cusping over structures that define the gap to protect them during the etching step. The lower average molecular weight of the fluent gas during the remainder deposition step has reduced sputtering characteristics and is effective at filling the remainder of the gap.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
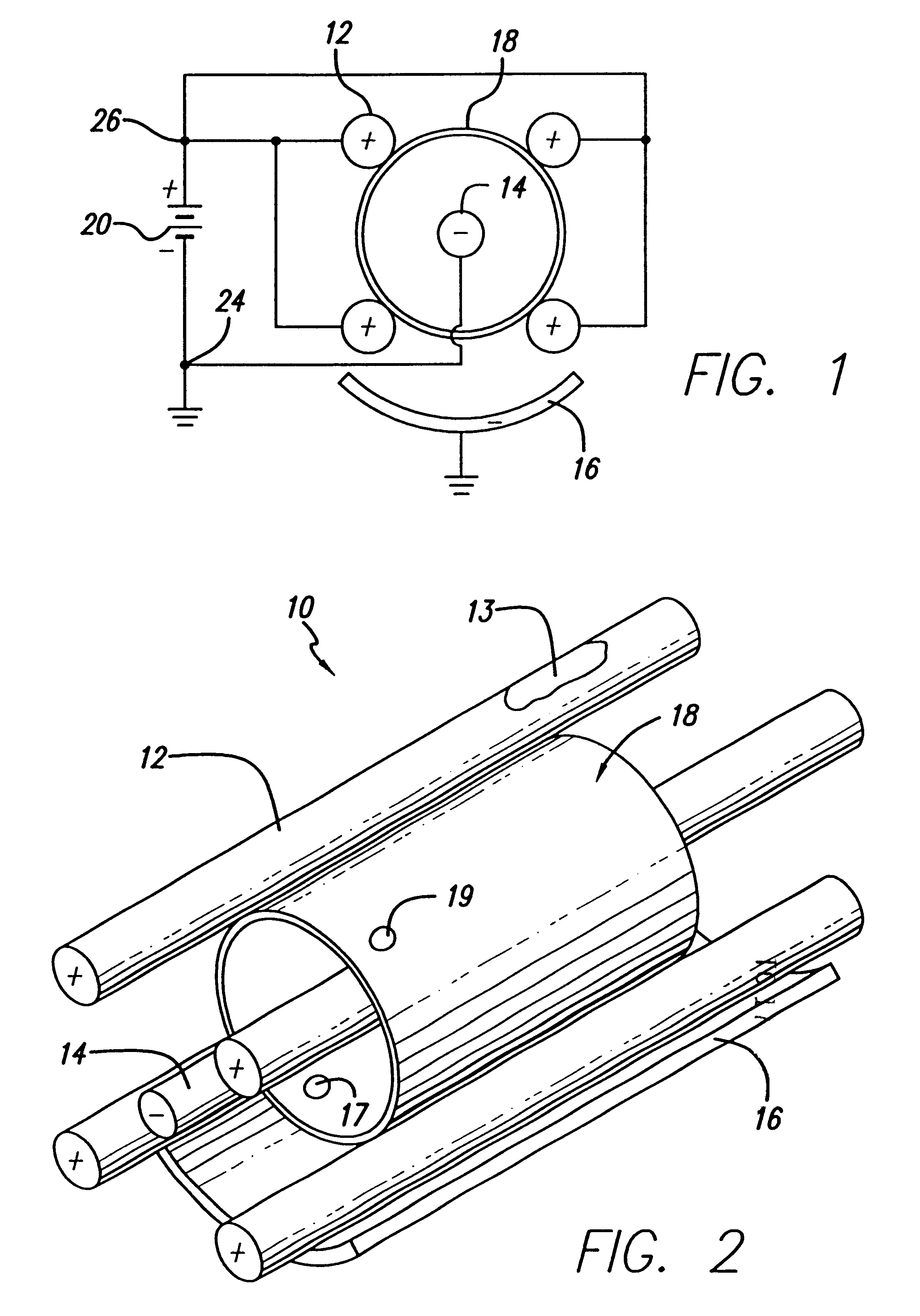
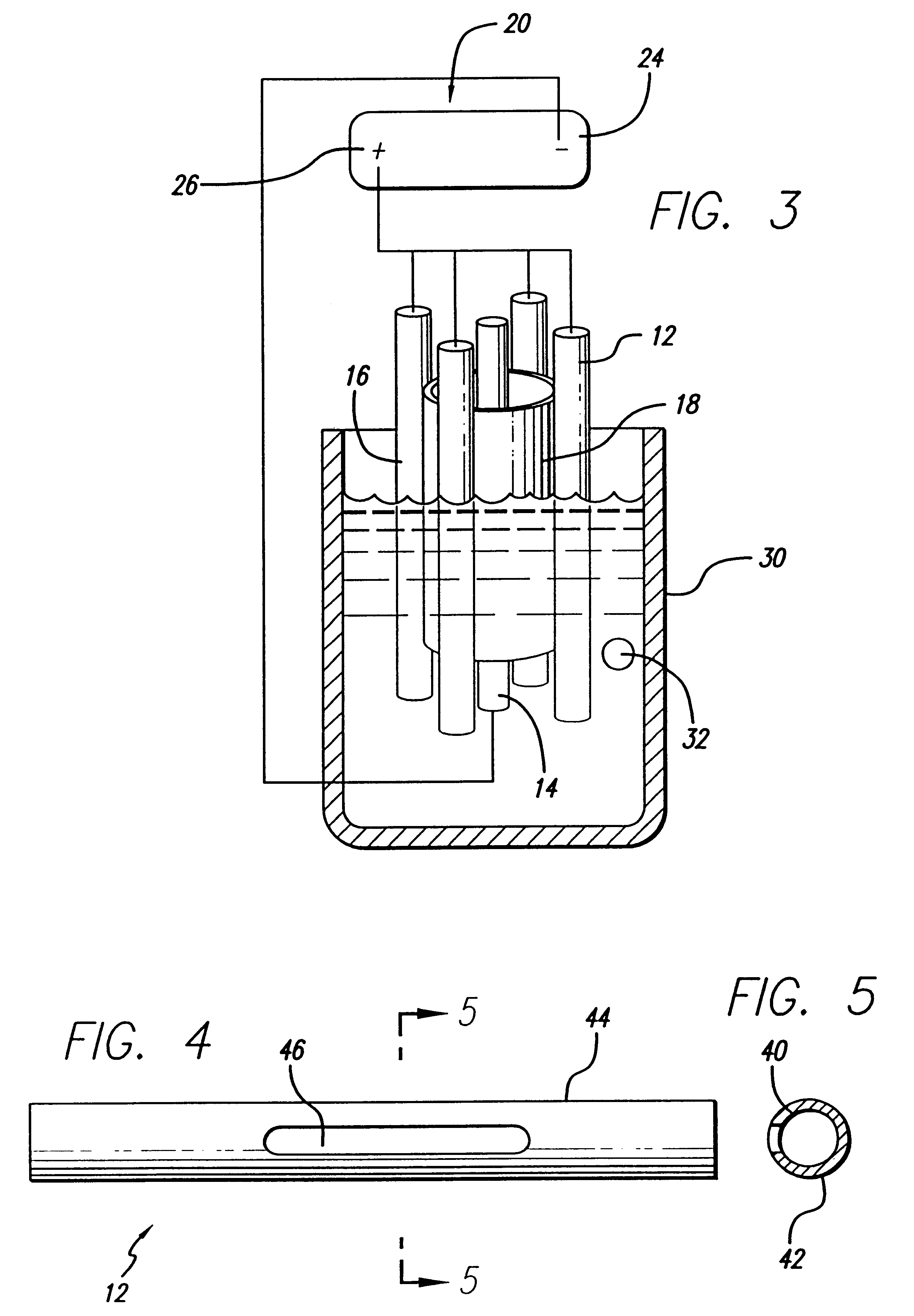
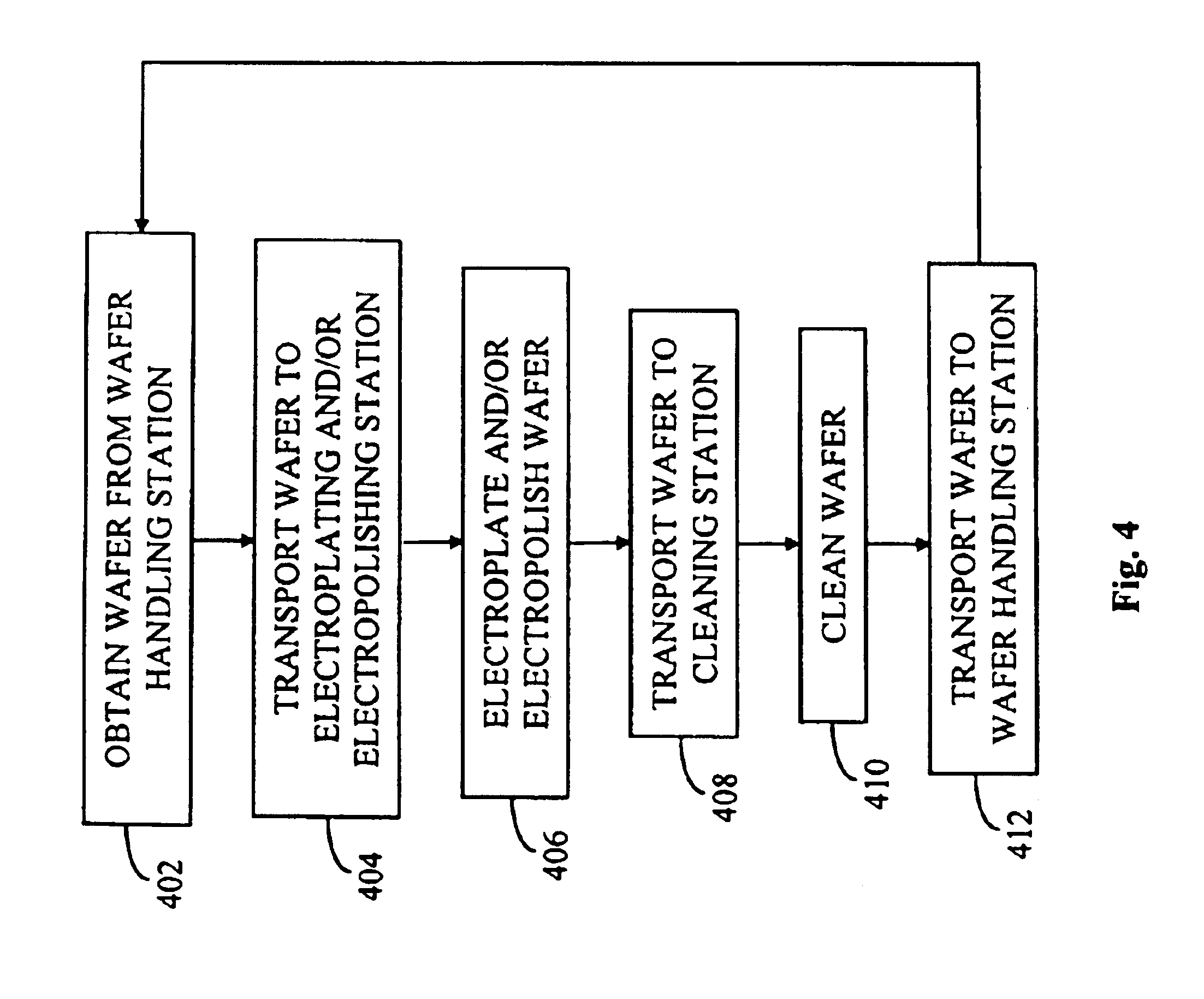
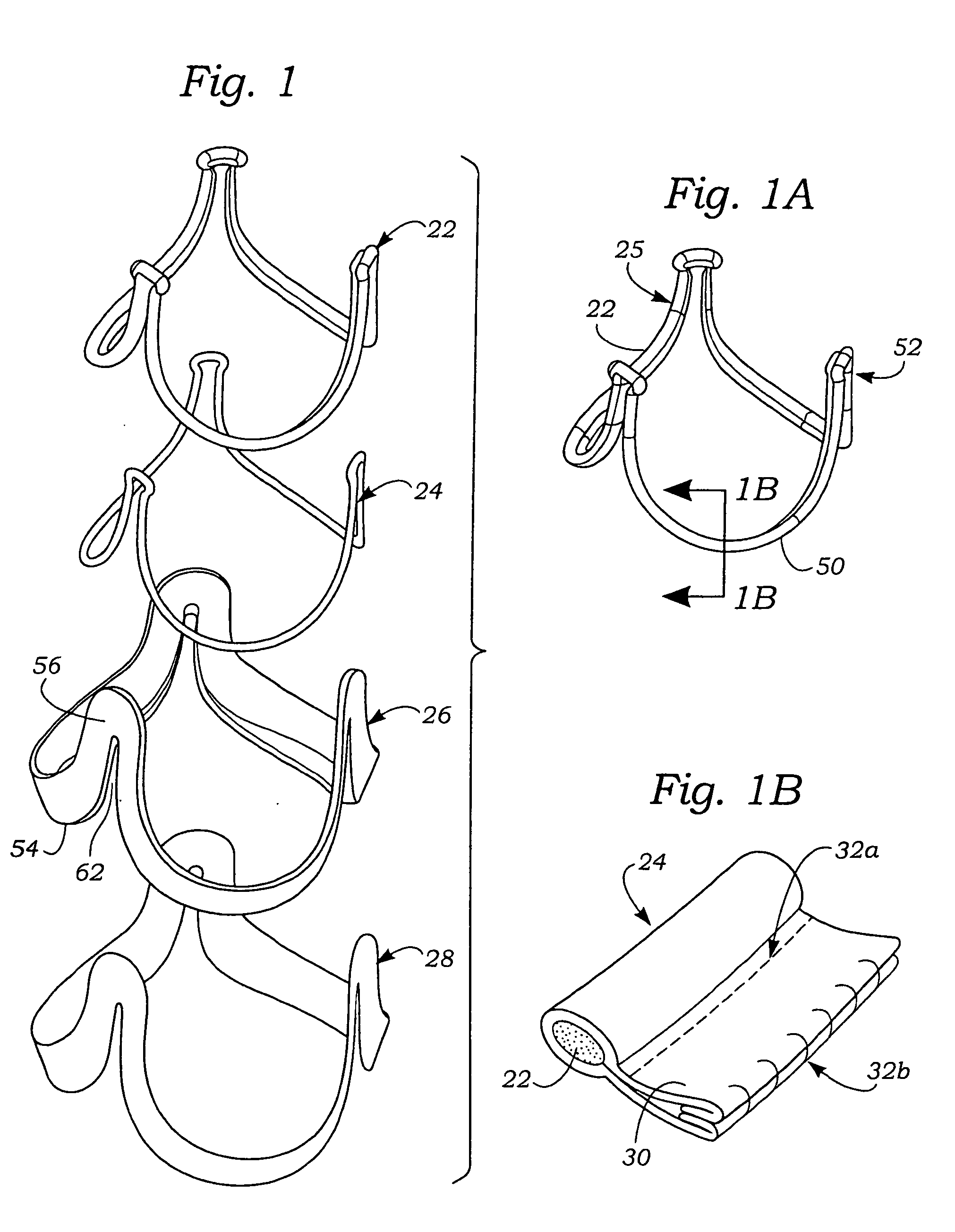
Electro-polishing fixture and electrolyte solution for polishing stents and method
An electro-polishing fixture for polishing stents which incorporates multiple anodes in contact with the stent and a center cathode disposed coaxially within the interior of the stent and a curved exterior cathode disposed about the perimeter of the stent. The invention further includes an electrolyte solution adapted for polishing stents composed of nickel-titanium alloy and a method of using the electrolyte in combination with the electro-polishing fixture.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
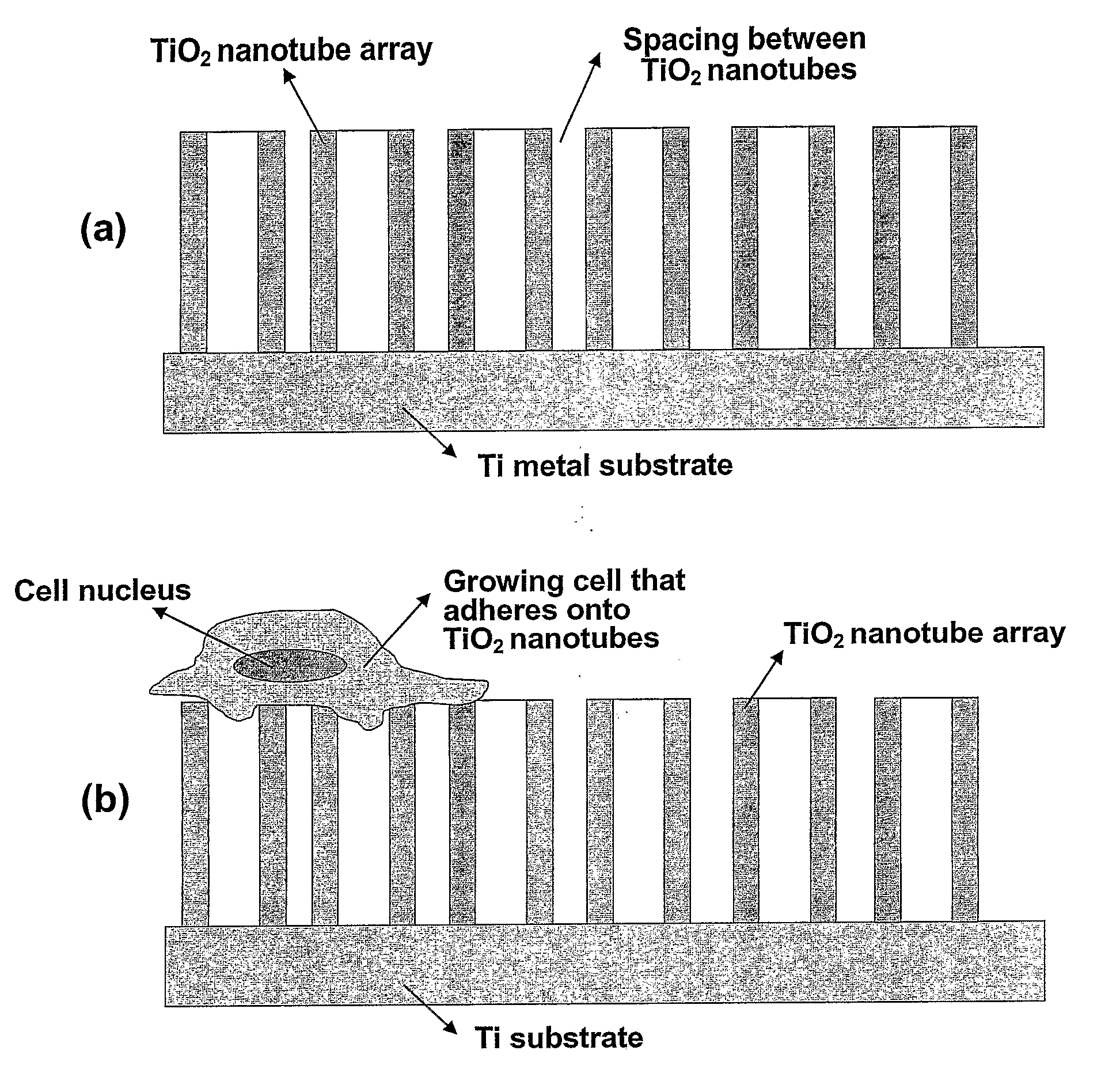
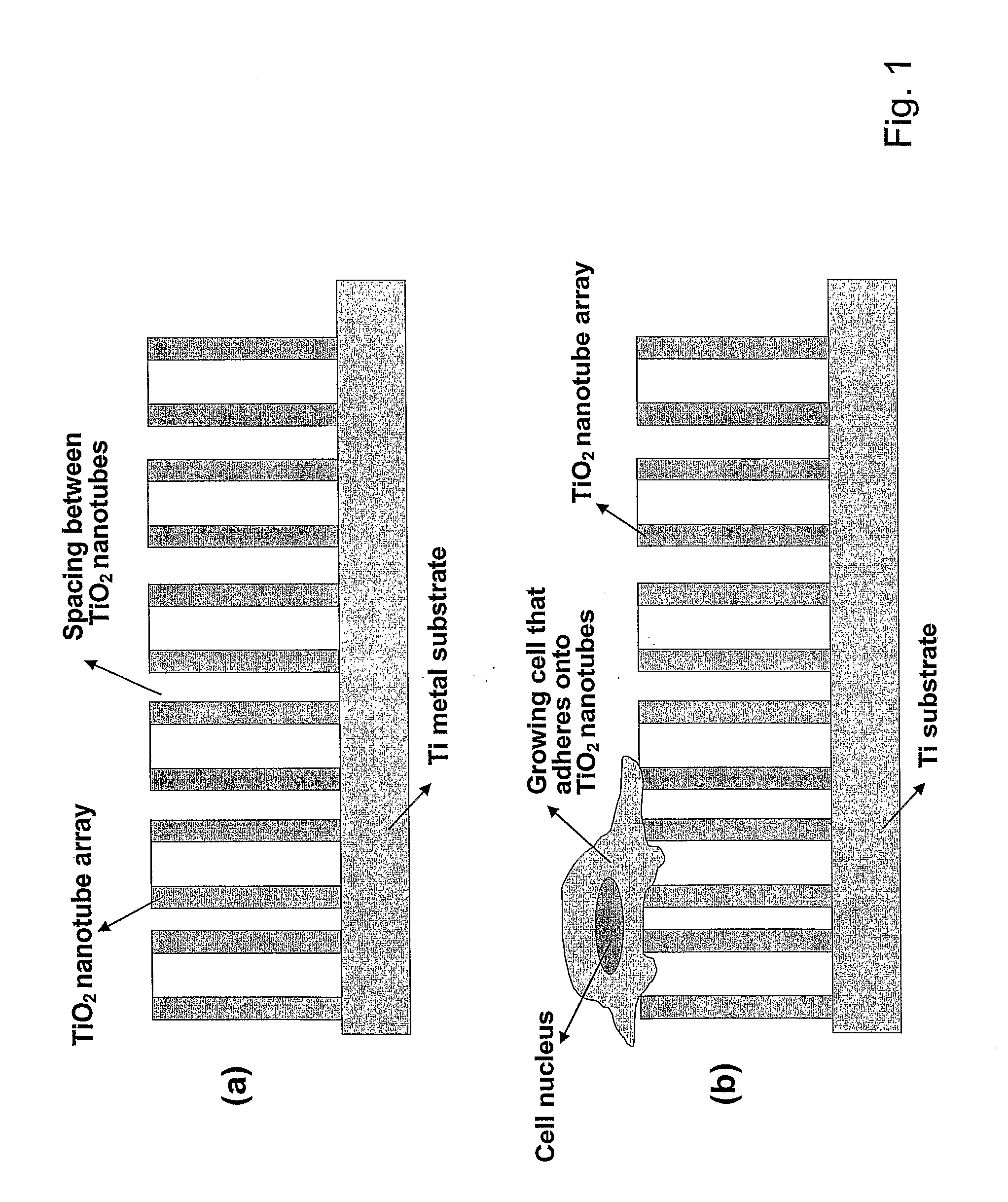
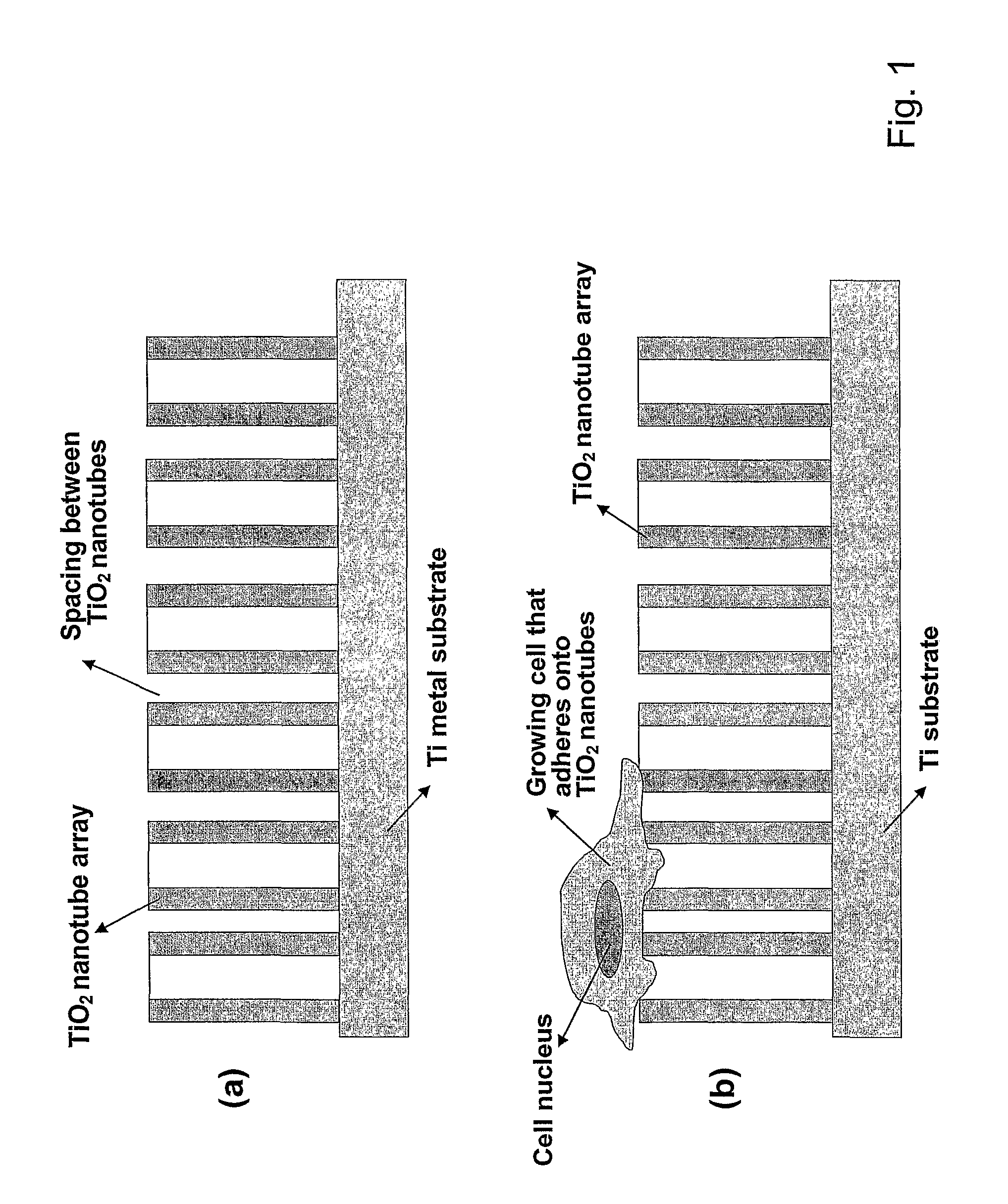
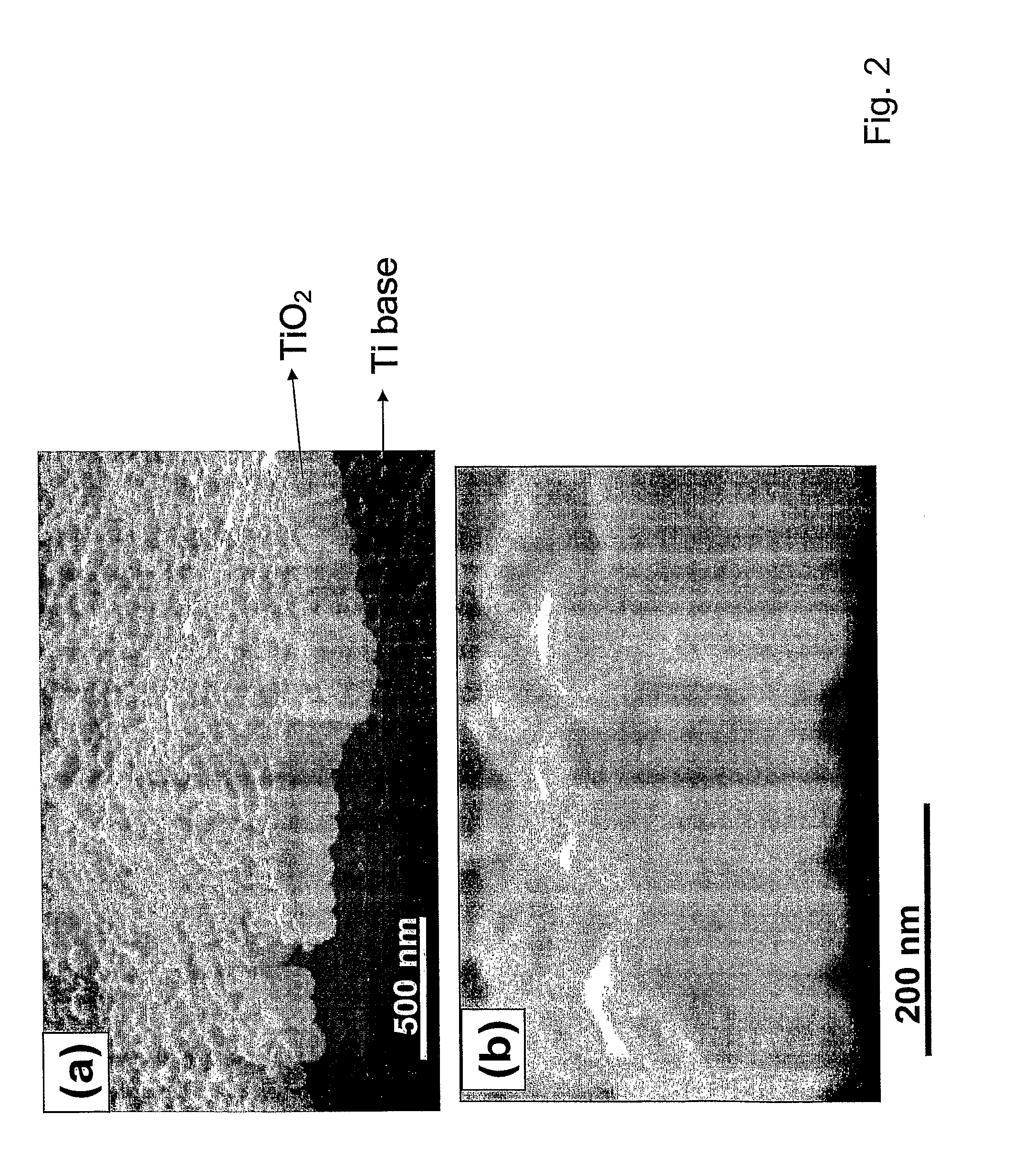
Compositions comprising nanostructures for cell, tissue and artificial organ growth, and methods for making and using same
ActiveUS20090220561A1Improve bone formationIncreased durabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrolysis componentsIn vivoNanostructure
The invention provides articles of manufacture comprising biocompatible nanostructures comprising nanotubes and nanopores for, e.g., organ, tissue and / or cell growth, e.g., for bone, kidney or liver growth, and uses thereof, e.g., for in vitro testing, in vivo implants, including their use in making and using artificial organs, and related therapeutics. The invention provides lock-in nanostructures comprising a plurality of nanopores or nanotubes, wherein the nanopore or nanotube entrance has a smaller diameter or size than the rest (the interior) of the nanopore or nanotube. The invention also provides dual structured biomaterial comprising micro- or macro-pores and nanopores. The invention provides biomaterials having a surface comprising a plurality of enlarged diameter nanopores and / or nanotubes.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
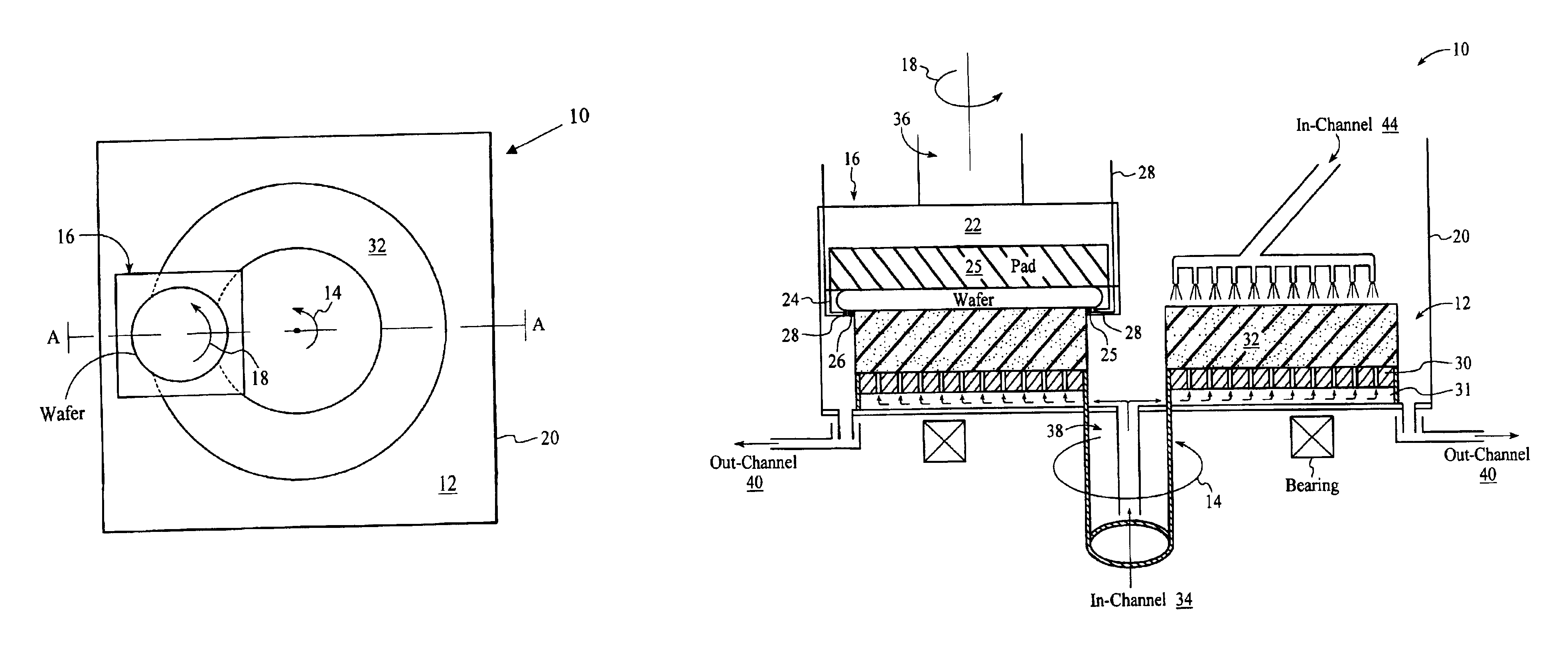
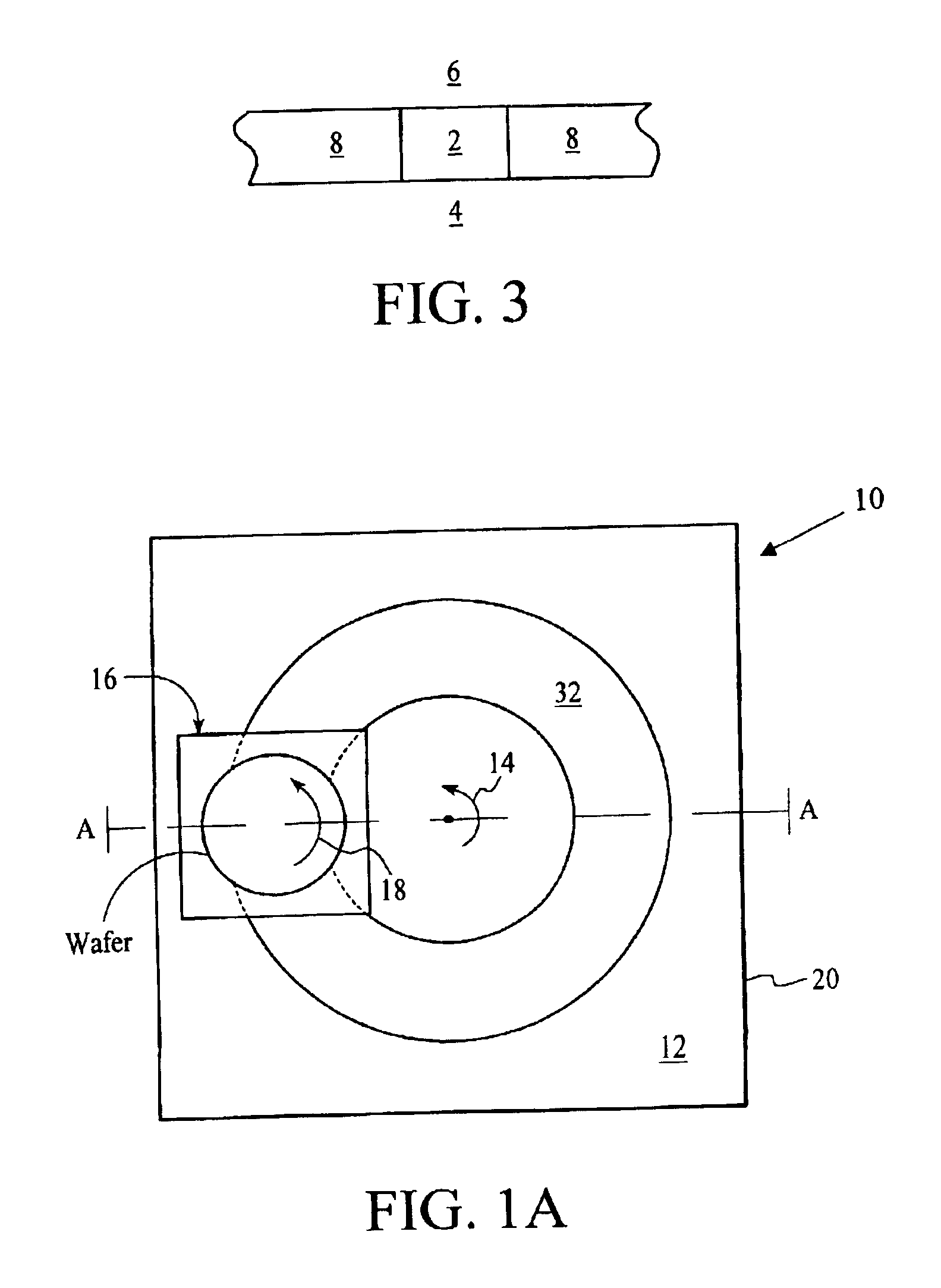
Planarization of substrates using electrochemical mechanical polishing
InactiveUS20020130049A1Electrolysis componentsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSubstrate surface
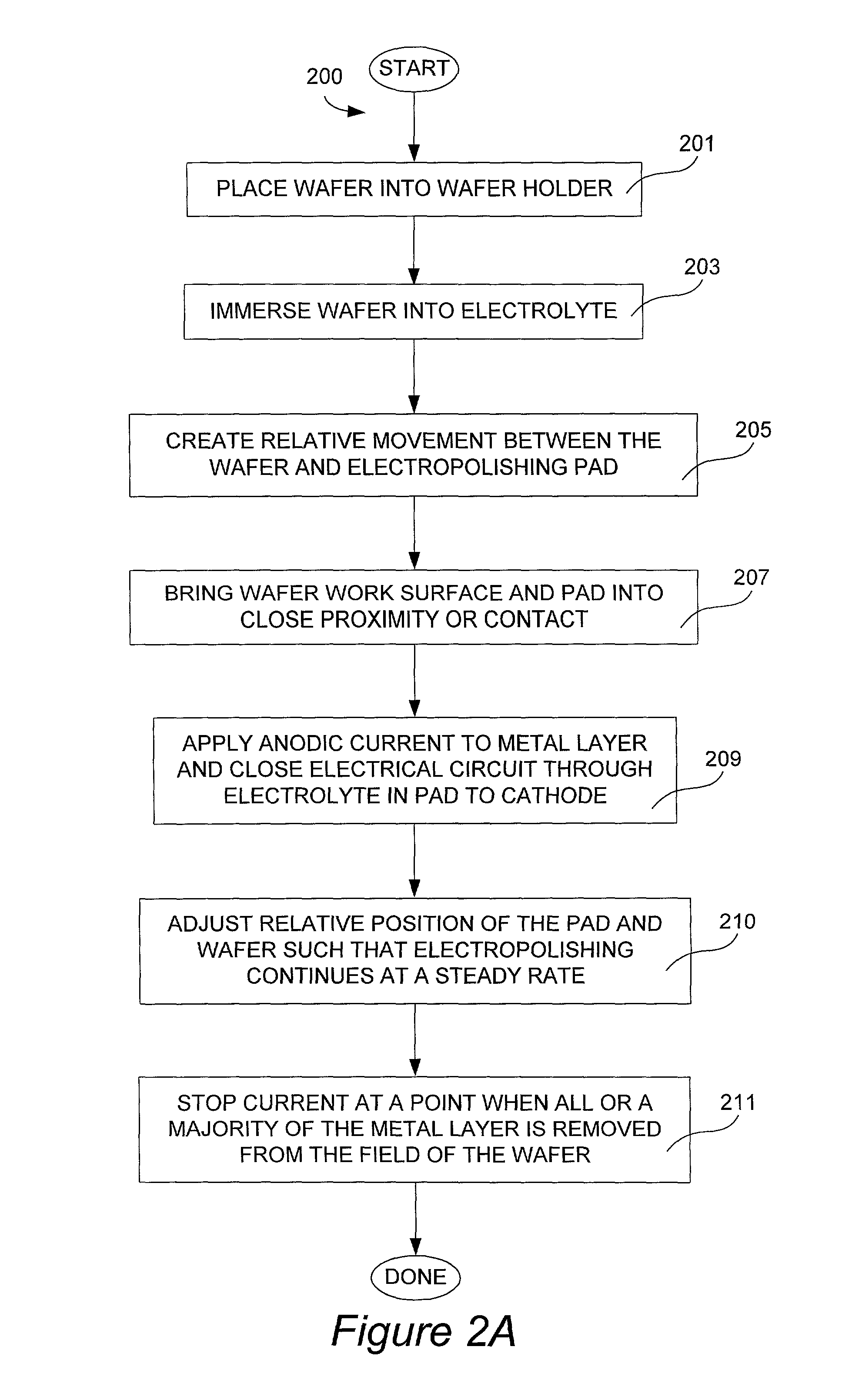
A method and apparatus are provided for planarizing a material layer on a substrate. In one aspect, a method is provided for processing a substrate including forming a passivation layer on a substrate surface, polishing the substrate in an electrolyte solution, applying an anodic bias to the substrate surface, and removing material from at least a portion of the substrate surface. In another aspect, an apparatus is provided which includes a partial enclosure, polishing article, a cathode, a power source, a substrate carrier movably disposed above the polishing article, and a computer based controller to position a substrate in an electrolyte solution to form a passivation layer on a substrate surface, to polish the substrate in the electrolyte solution with the polishing article, and to apply an anodic bias to the substrate surface or polishing article to remove material from at least a portion of the substrate surface.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
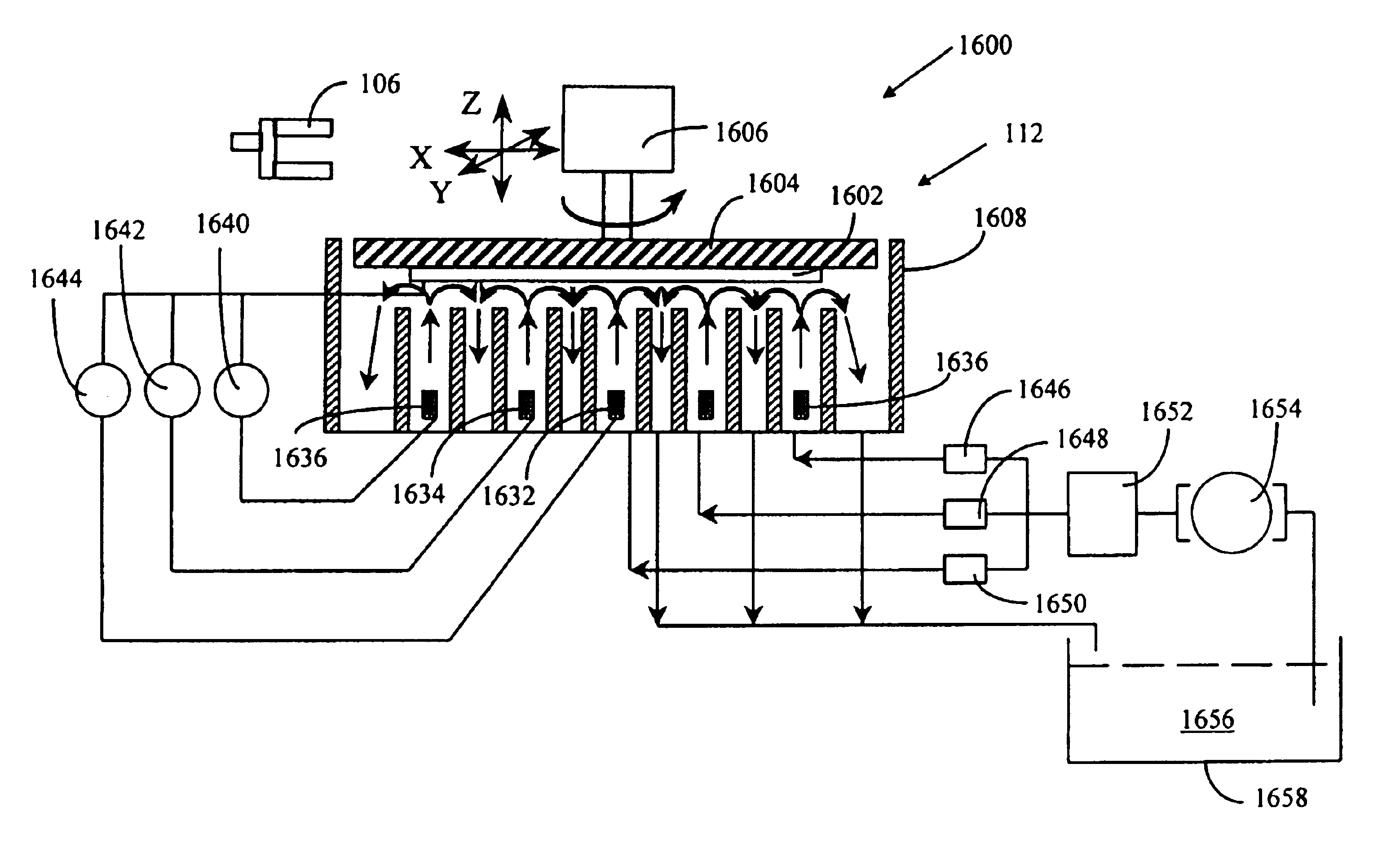
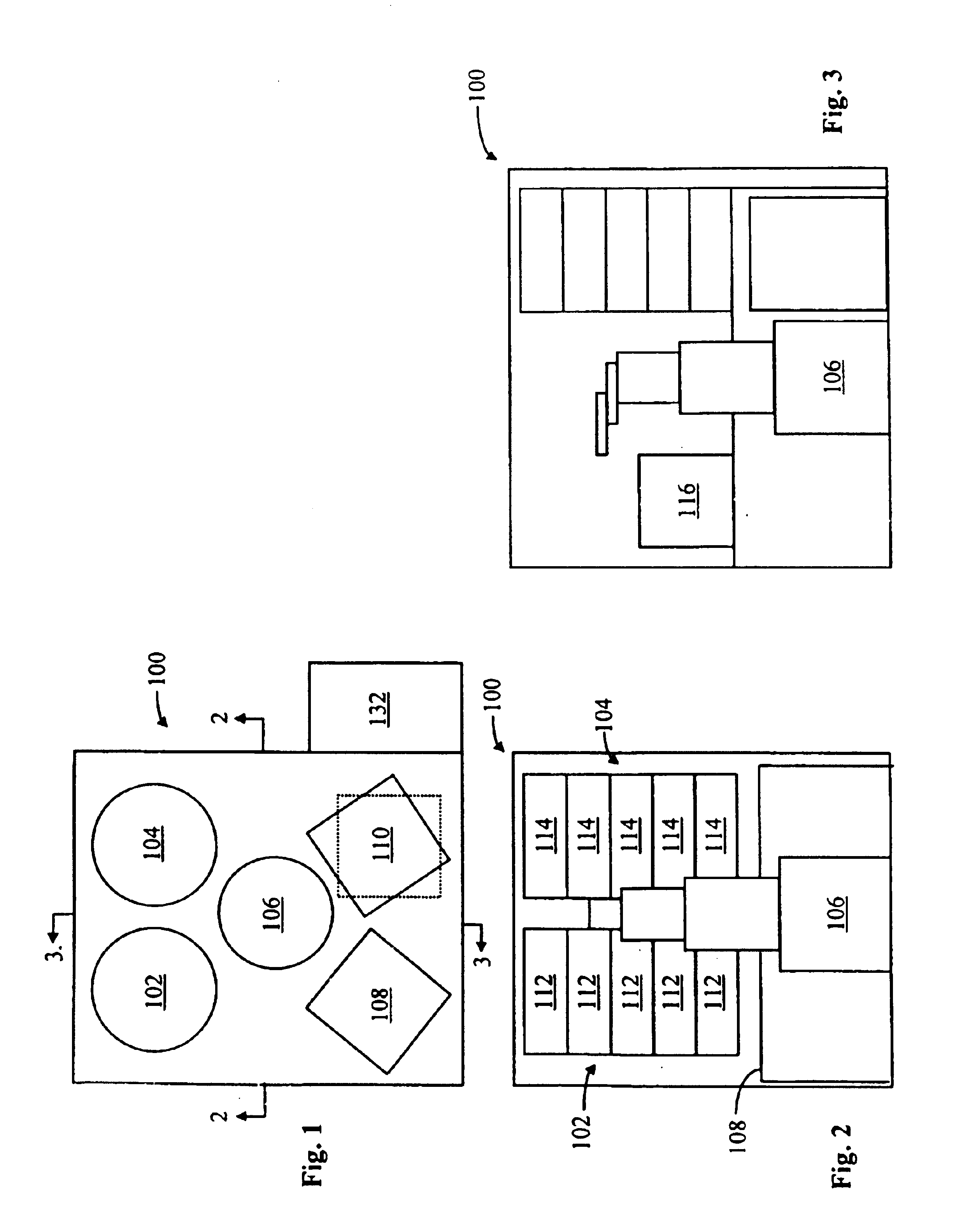
Methods and apparatus for holding and positioning semiconductor workpieces during electropolishing and/or electroplating of the workpieces
A wafer chuck assembly for holding a wafer during electroplating and / or electropolishing of the wafer includes a wafer chuck for receiving the wafer. The wafer chuck assembly also includes an actuator assembly for moving the wafer chuck between a first and a second position. When in the first position, the wafer chuck is opened. When in the second position, the wafer chuck is closed.
Owner:ACM RES
Method of manufacture of a heart valve support frame
InactiveUS20050150775A1Eliminate unevennessIncrease flexibilityElectrolysis componentsFrom normal temperature solutionsEngineeringReady to use
Methods for forming a support frame for flexible leaflet heart valves from a starting blank include converting a two-dimensional starting blank into the three-dimensional support frame. The material may be superelastic, such as NITINOL, and the method may include bending the 2-D blank into the 3-D form and shape setting it. A merely elastic material such as ELGILOY may be used and plastically deformed in stages, possibly accompanied by annealing, to obtain the 3-D shape. Alternatively, a tubular blank could be formed to define a non-tubular shape, typically conical. A method for calculating the precise 2-D blank shape is also disclosed. A mandrel assembly includes a mandrel and ring elements for pressing the blank against the external surface of the mandrel prior to shape setting.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
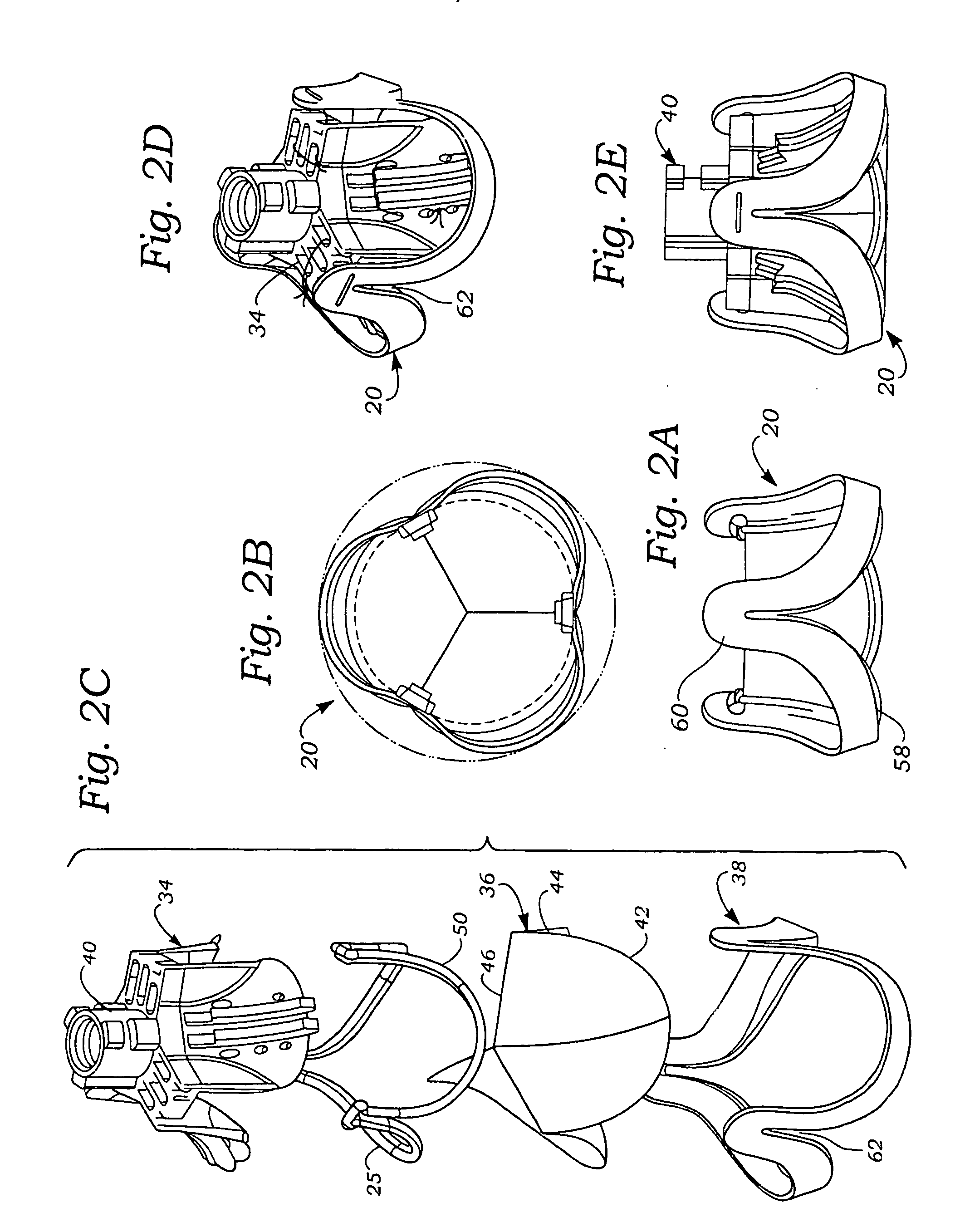
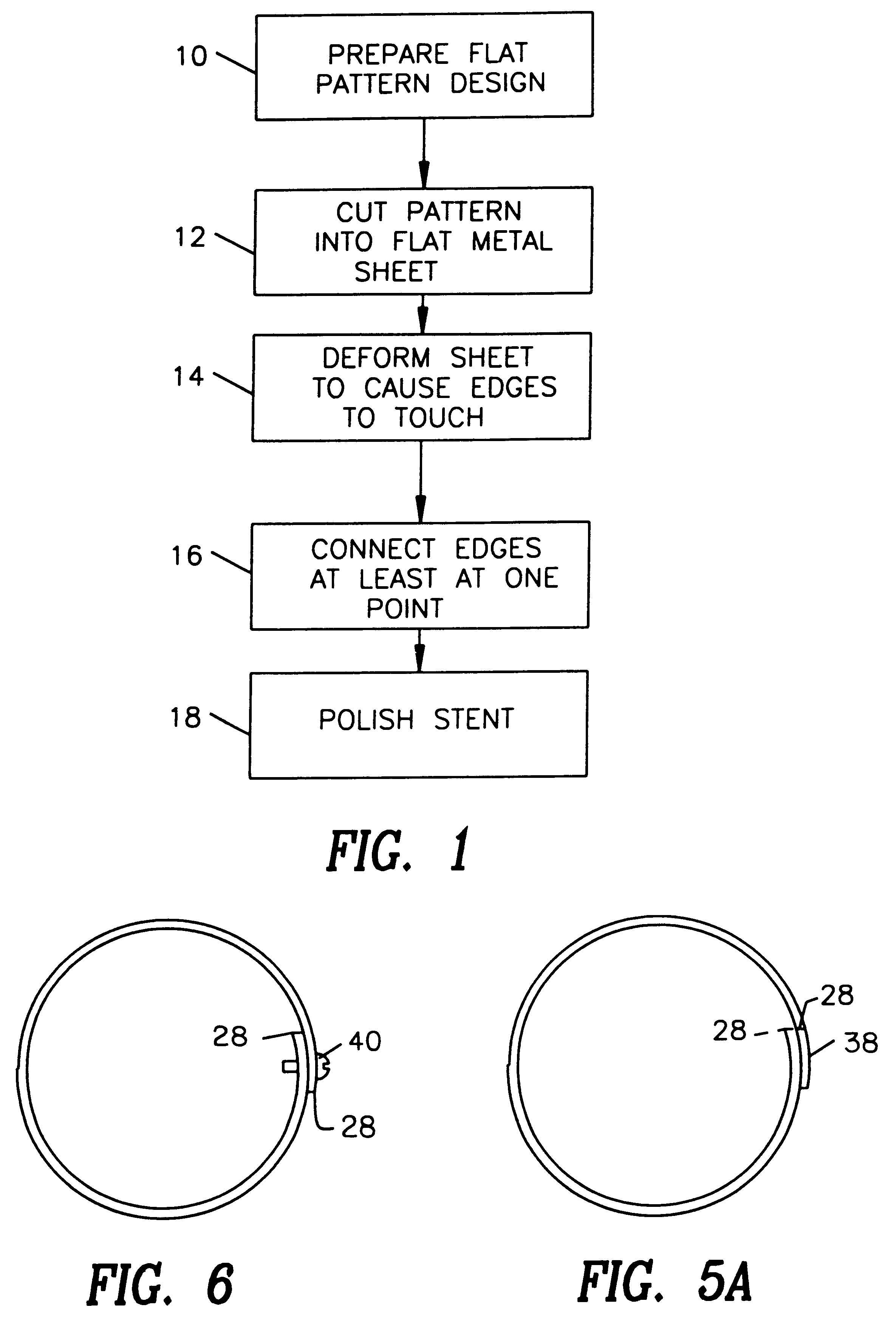
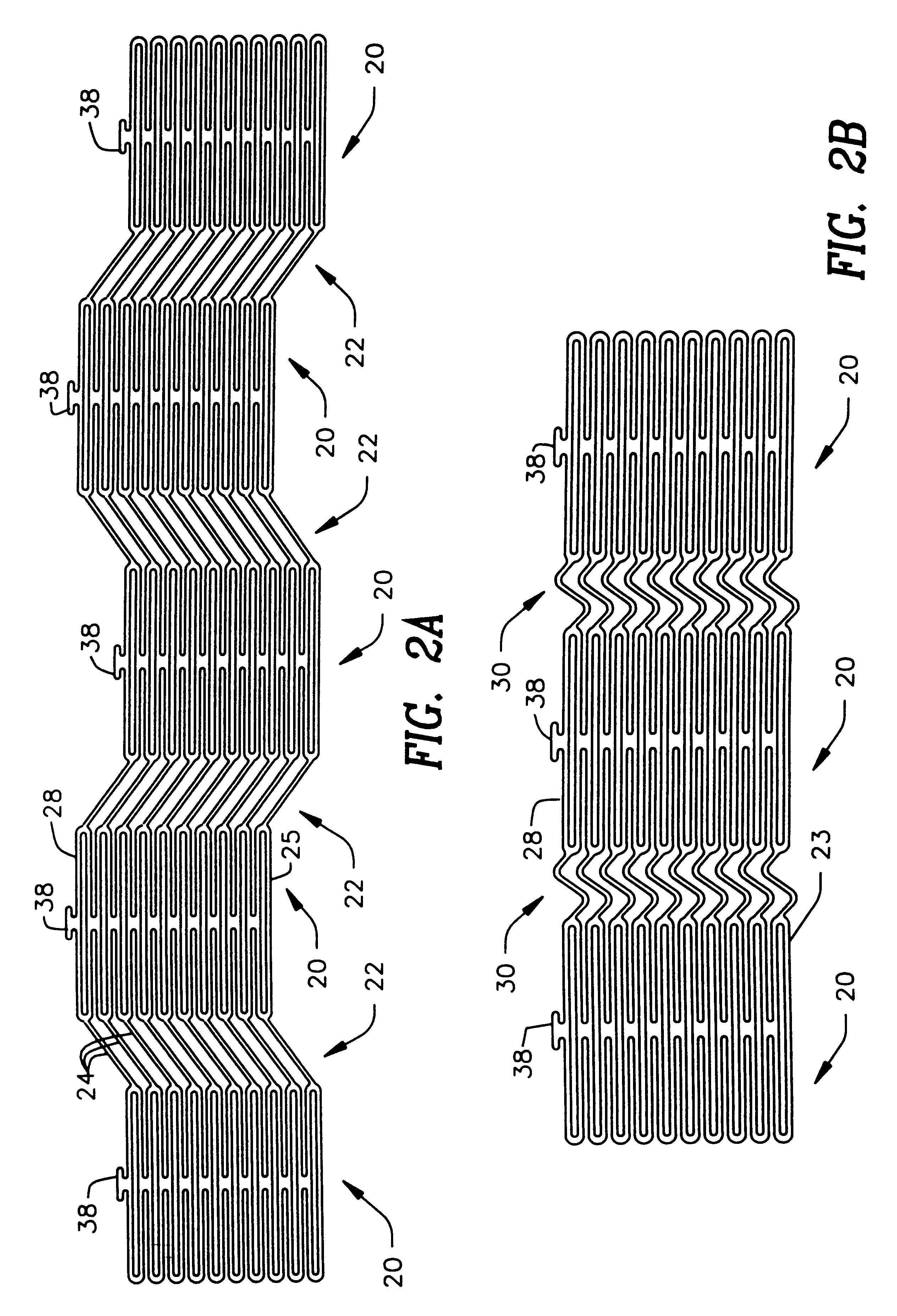
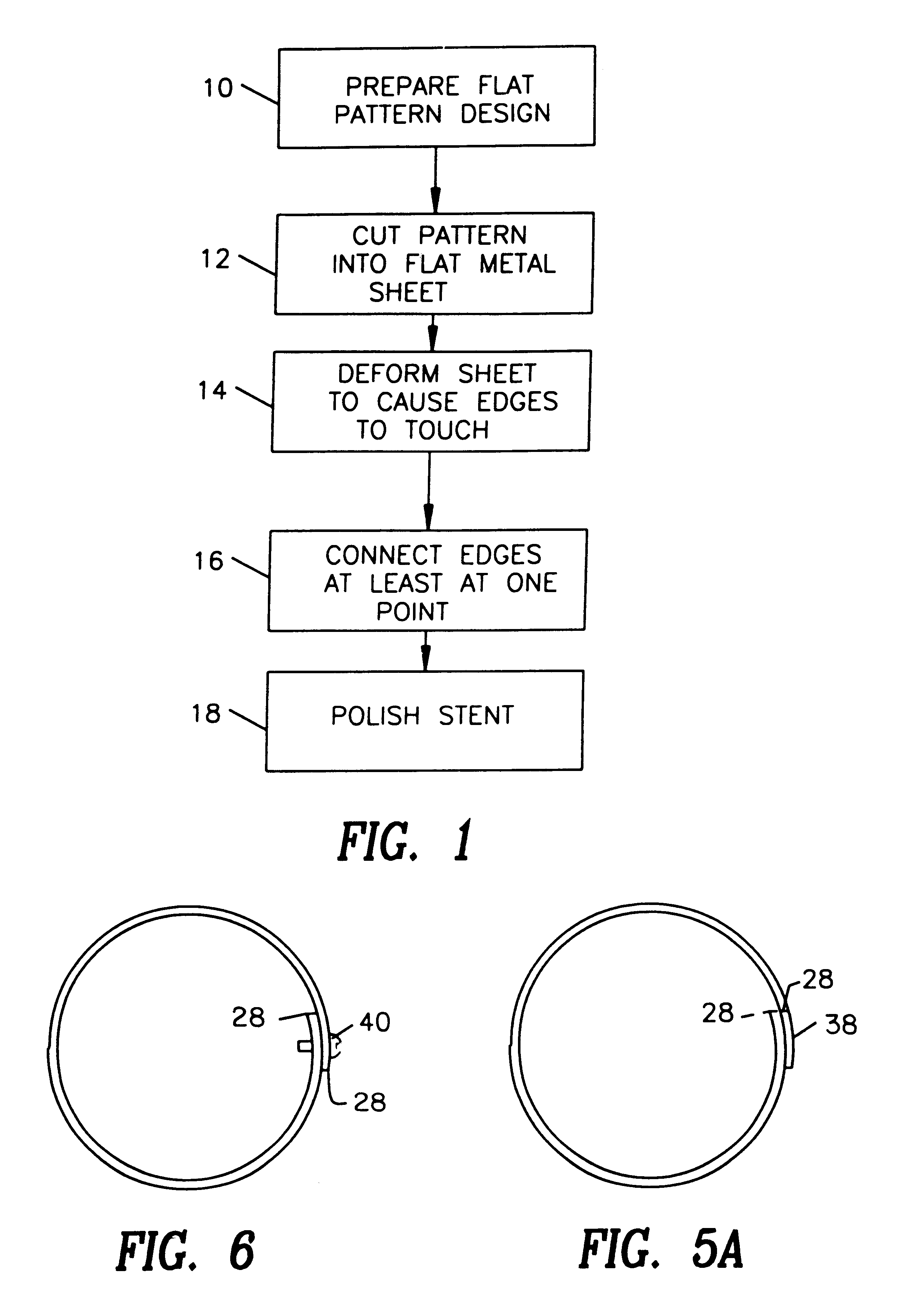
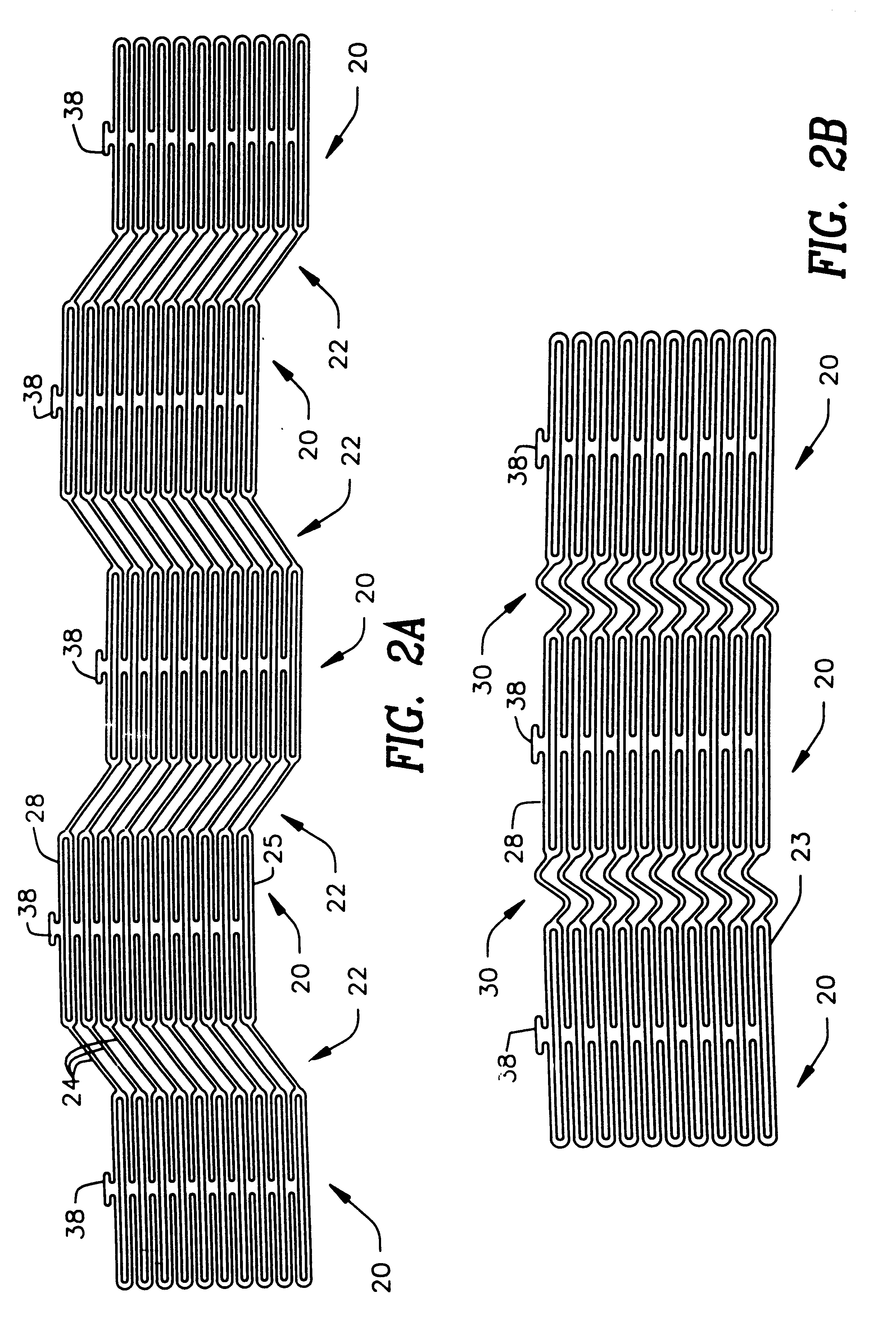
Stent
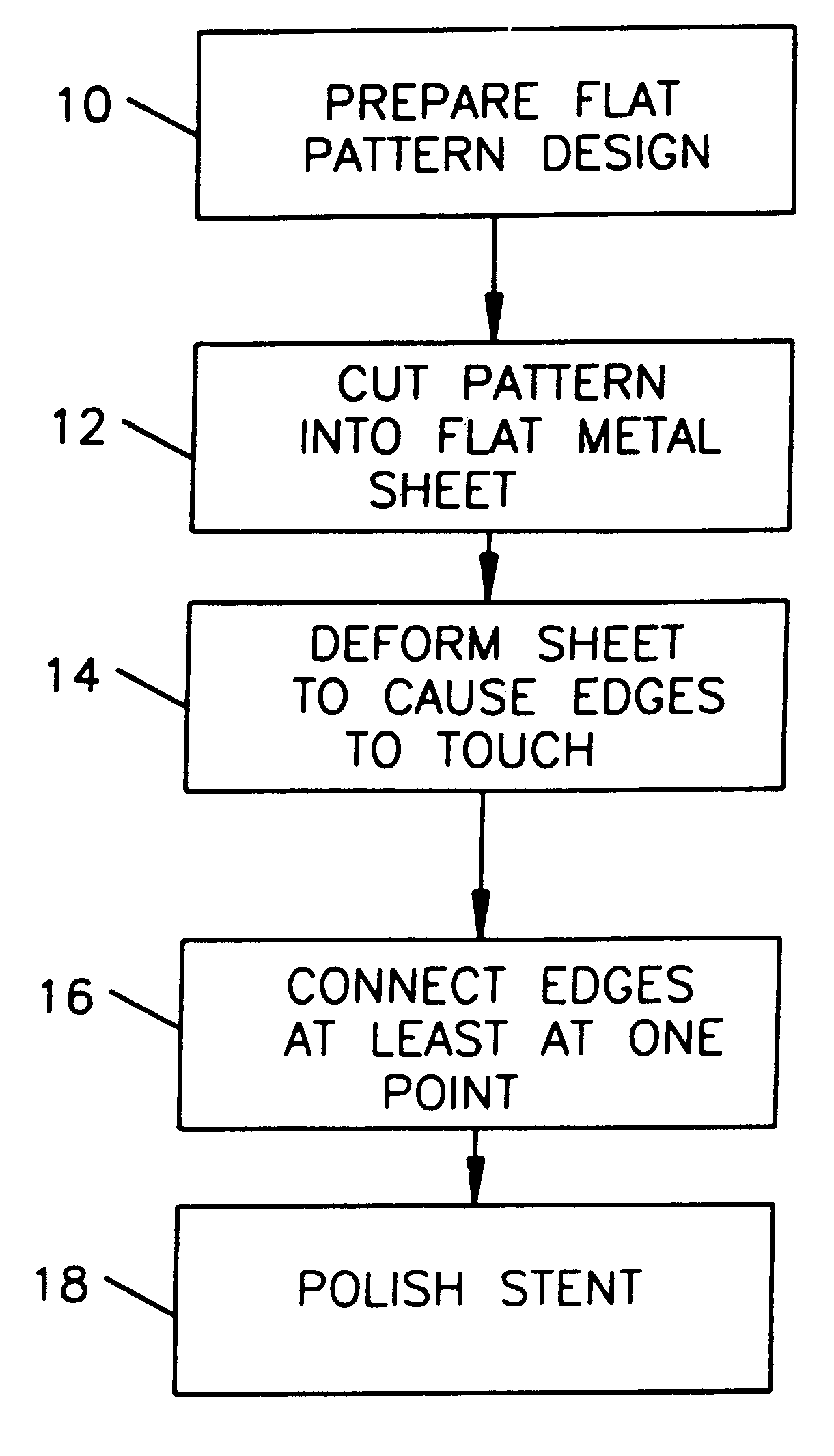
A stent and a method for fabricating the stent are disclosed. The stent has an originally flat pattern and connection points where the sides of the flat pattern are joined. The method includes the steps of a) cutting a stent pattern into a flat piece of metal thereby to produce a metal pattern, b) deforming the metal pattern so as to cause two opposing sides to meet, and c) joining the two opposing sides at least at one point. Substantially no portion of the stent projects into the lumen of the stent when the stent is expanded against the internal wall of a blood vessel.
Owner:MEDINOL LTD
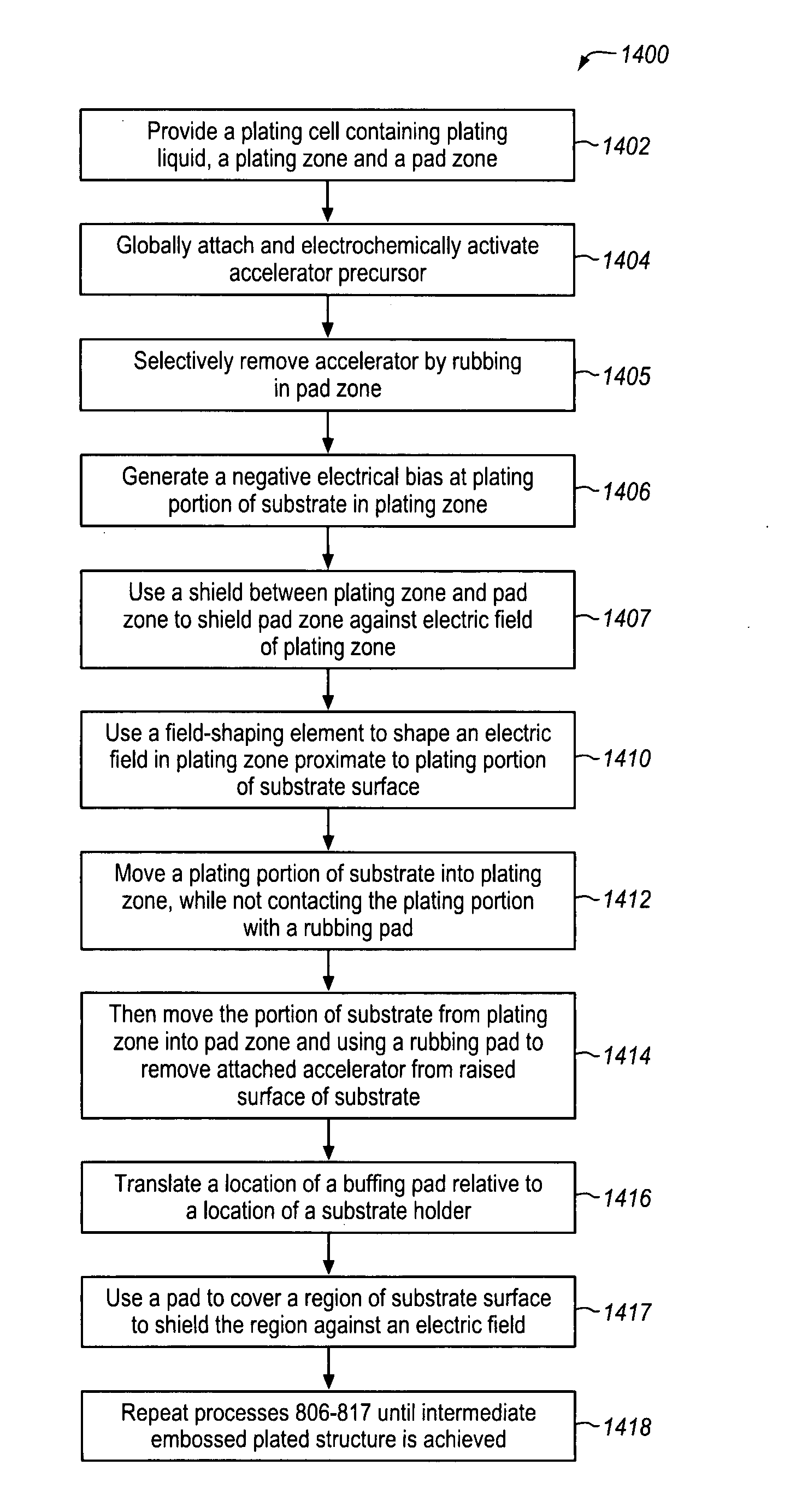
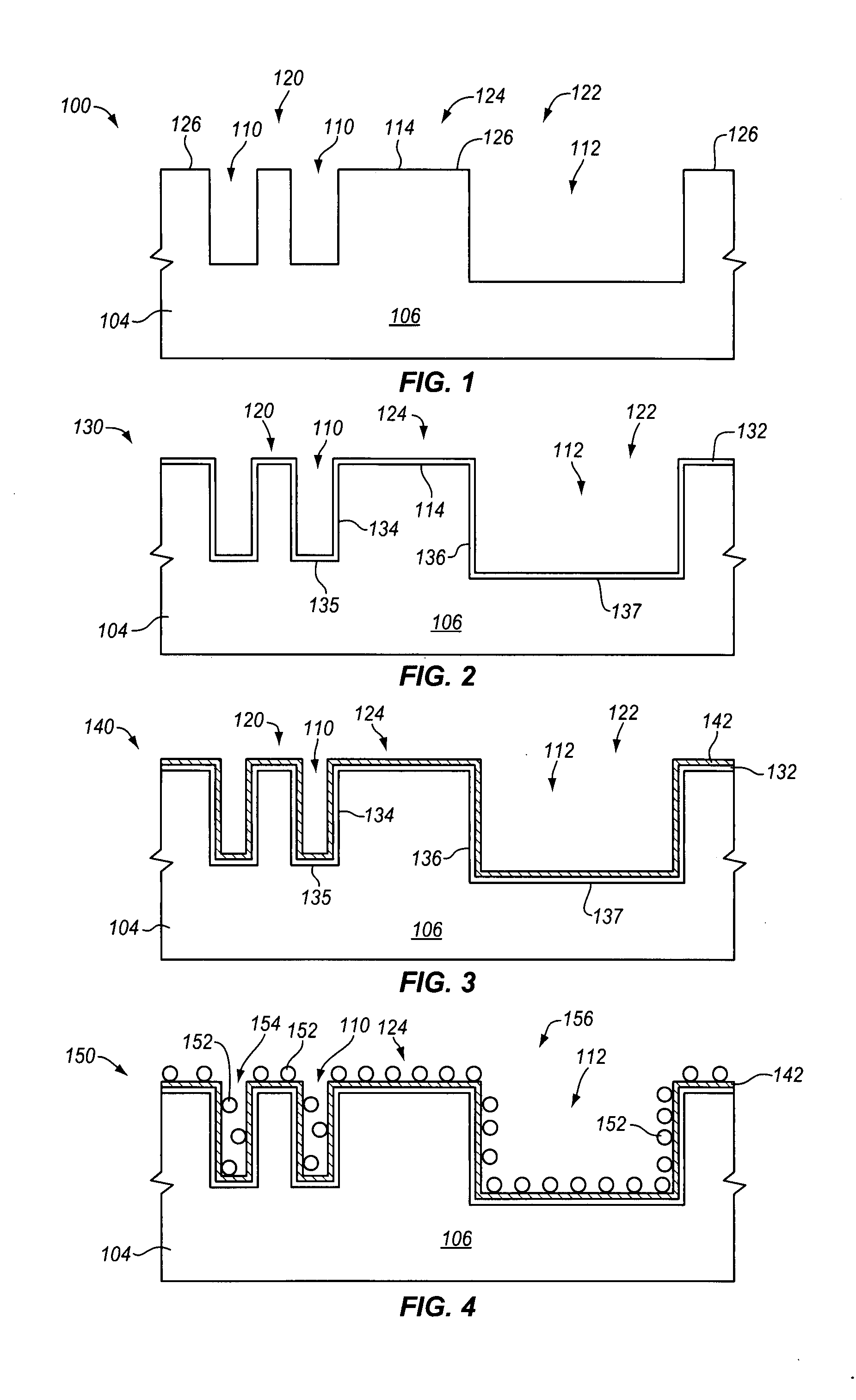
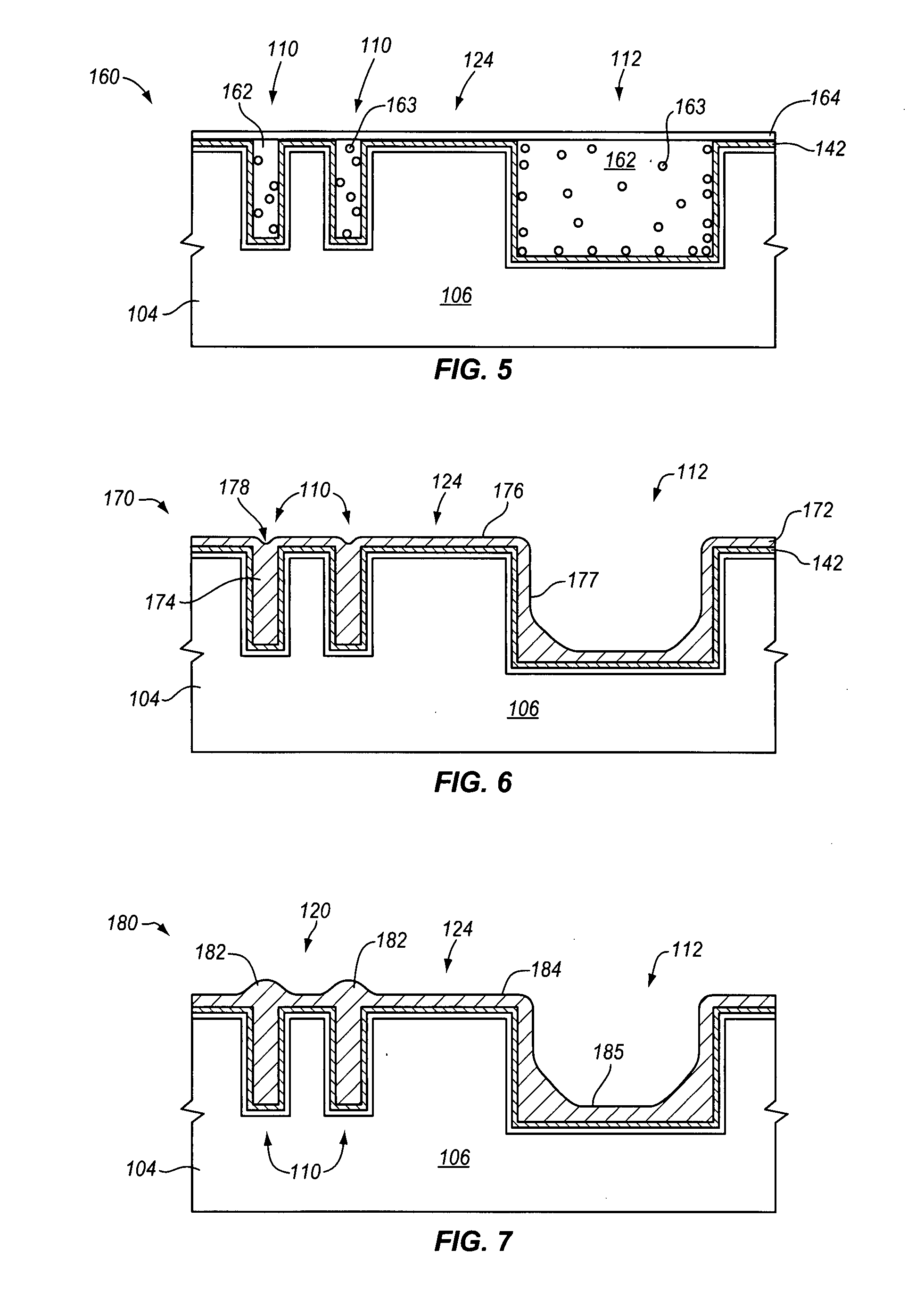
Topography reduction and control by selective accelerator removal
ActiveUS20090280649A1Improve throughputLow costCellsDecorative surface effectsMetal interconnectEtching
Plating accelerator is applied selectively to a substantially-unfilled wide (e.g., low-aspect-ratio feature cavity. Then, plating of metal is conducted to fill the wide feature cavity and to form an embossed structure in which the height of a wide-feature metal protrusion over the metal-filled wide-feature cavity is higher than the height of metal over field regions. Most of the overburden metal is removed using non-contact techniques, such as chemical wet etching. Metal above the wide feature cavity protects the metal-filled wide-feature interconnect against dishing, and improved planarization techniques avoid erosion of the metal interconnect and dielectric insulating layer. In some embodiments, plating of metal onto a substrate is conducted to fill narrow (e.g., high-aspect-ratio feature cavities) in the dielectric layer before selective application of plating accelerator and filling of the wide feature cavity.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Metallic articles with hydrophobic surfaces
ActiveUS20110287223A1Lower contact angleLarge scaleElectrolysis componentsPretreated surfacesMetal coatingMetallic materials
Articles containing fine-grained and / or amorphous metallic coatings / layers on at least part of their exposed surfaces are imprinted with surface structures to raise the contact angle for water in the imprinted areas at room temperature by equal to or greater than 10°, when compared to the flat and smooth metallic material surface of the same composition.
Owner:INTEGRAN TECH
High contrast transparent conductors and methods of forming the same
InactiveUS20090321113A1Material nanotechnologyElectrolysis componentsElectrical conductorNanostructure
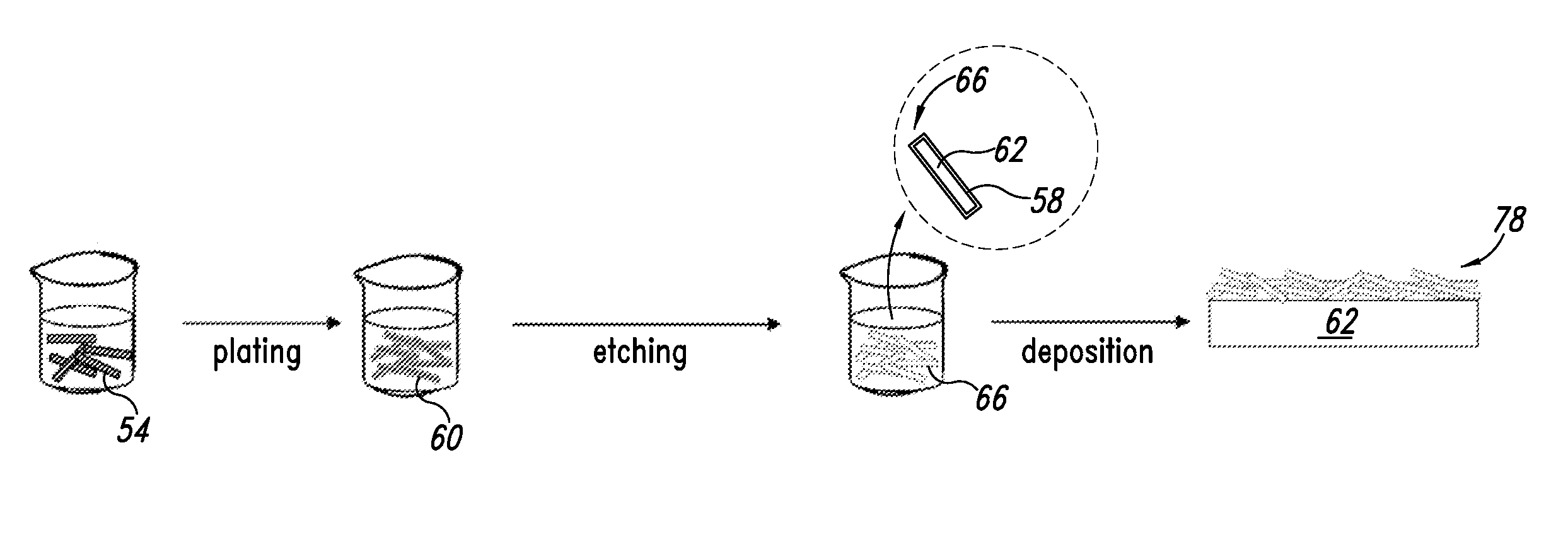
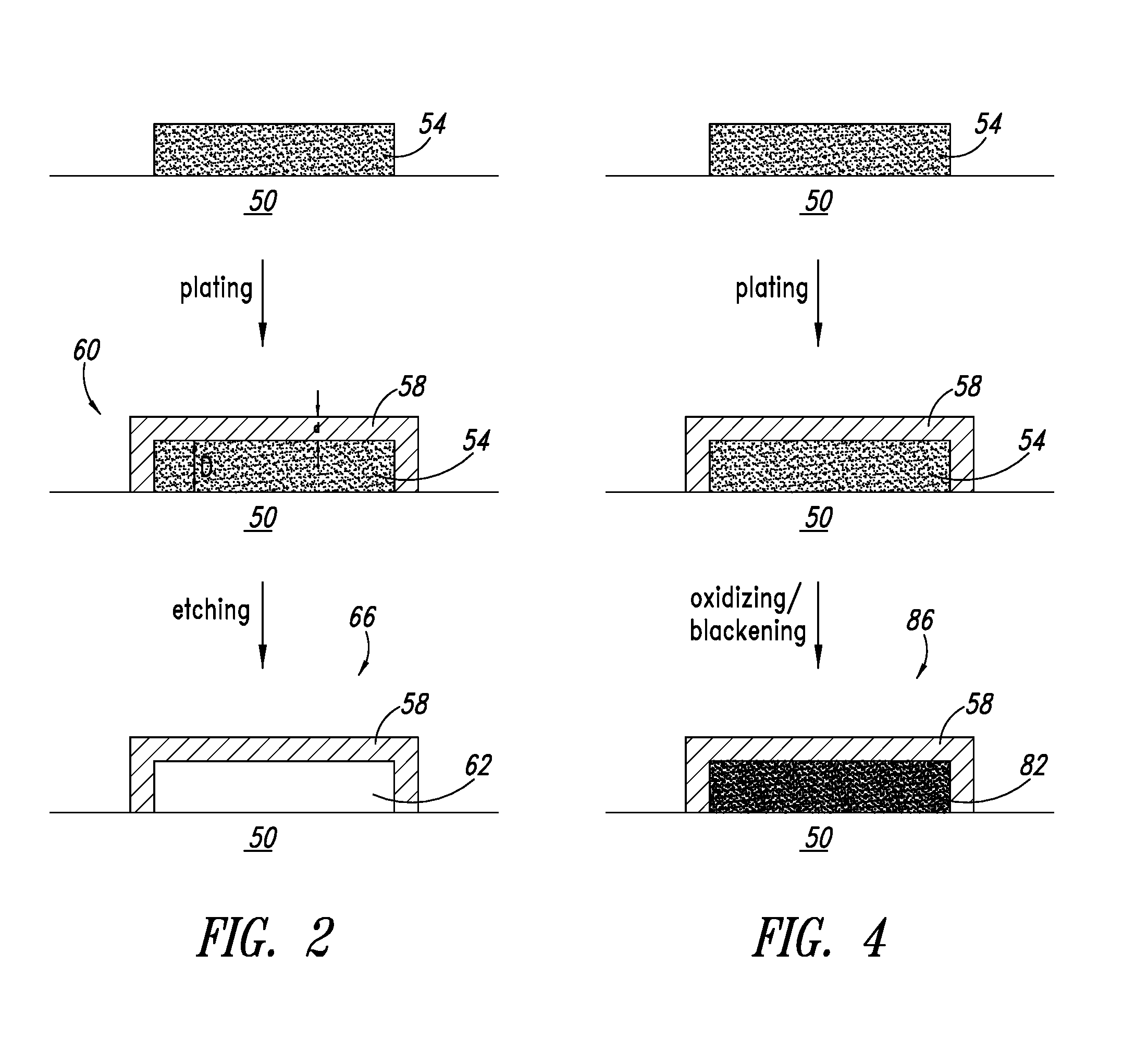
Methods of enhancing contrast ratio of conductive nanostructure-based transparent conductors are described. Contrast ratio is significantly improved by reduction of light scattering and reflectivity of the nanostructures through steps of plating the conductive nanostructures followed by etching or oxidizing the underlying conductive nanostructures.
Owner:CAM HLDG CORP +1
Stent fabrication method and apparatus
A method is provided for electropolishing a stent. A stent is mounted on a rack having electropolishing mounts. Each of the mounts has a base and an electrically conductive first member having a first end and a second end. The first end is connected to the base and the second end contacts the external surface of the stent. Each of the mounts also has a non-electrically conductive second member having a first end and a second end. The first end of the second member is attached to the base and the second end is placed in the bore of the stent. The second ends of the first and second members bias towards each other to secure the stent between them. The stent is immersed in an electropolishing bath and an electrical current is applied to the first member.
Owner:MEDINOL LTD
Method and apparatus for electro-chemical mechanical deposition
InactiveUS6902659B2Avoid accumulationReduce exposureElectrolysis componentsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringConductive materials
The present invention deposits a conductive material from an electrolyte solution to a predetermined area of a wafer. The steps that are used when making this application include applying the conductive material to the predetermined area of the wafer using an electrolyte solution disposed on a surface of the wafer, when the wafer is disposed between a cathode and an anode, and preventing accumulation of the conductive material to areas other than the predetermine area by mechanically polishing the other areas while the conductive material is being applied.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
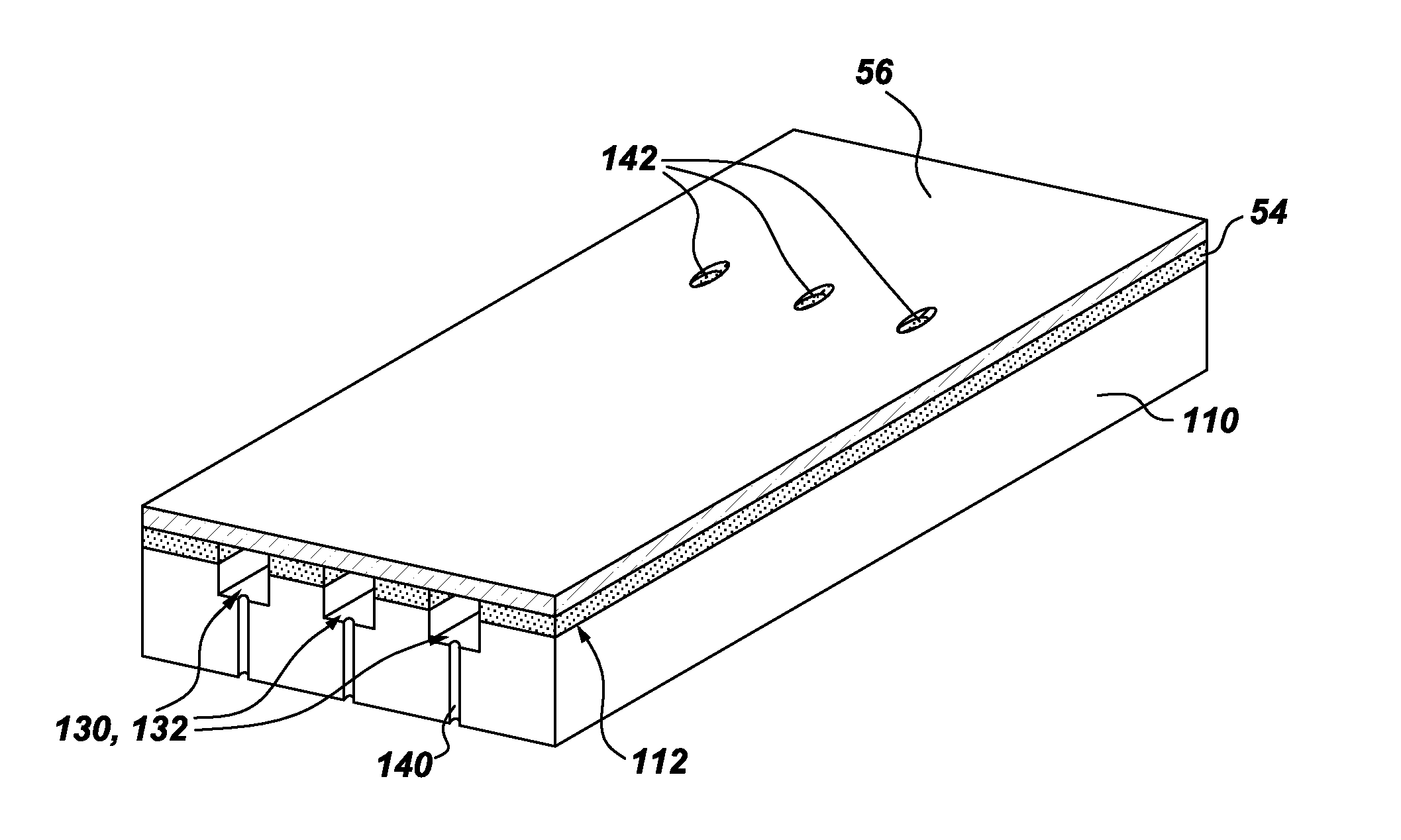
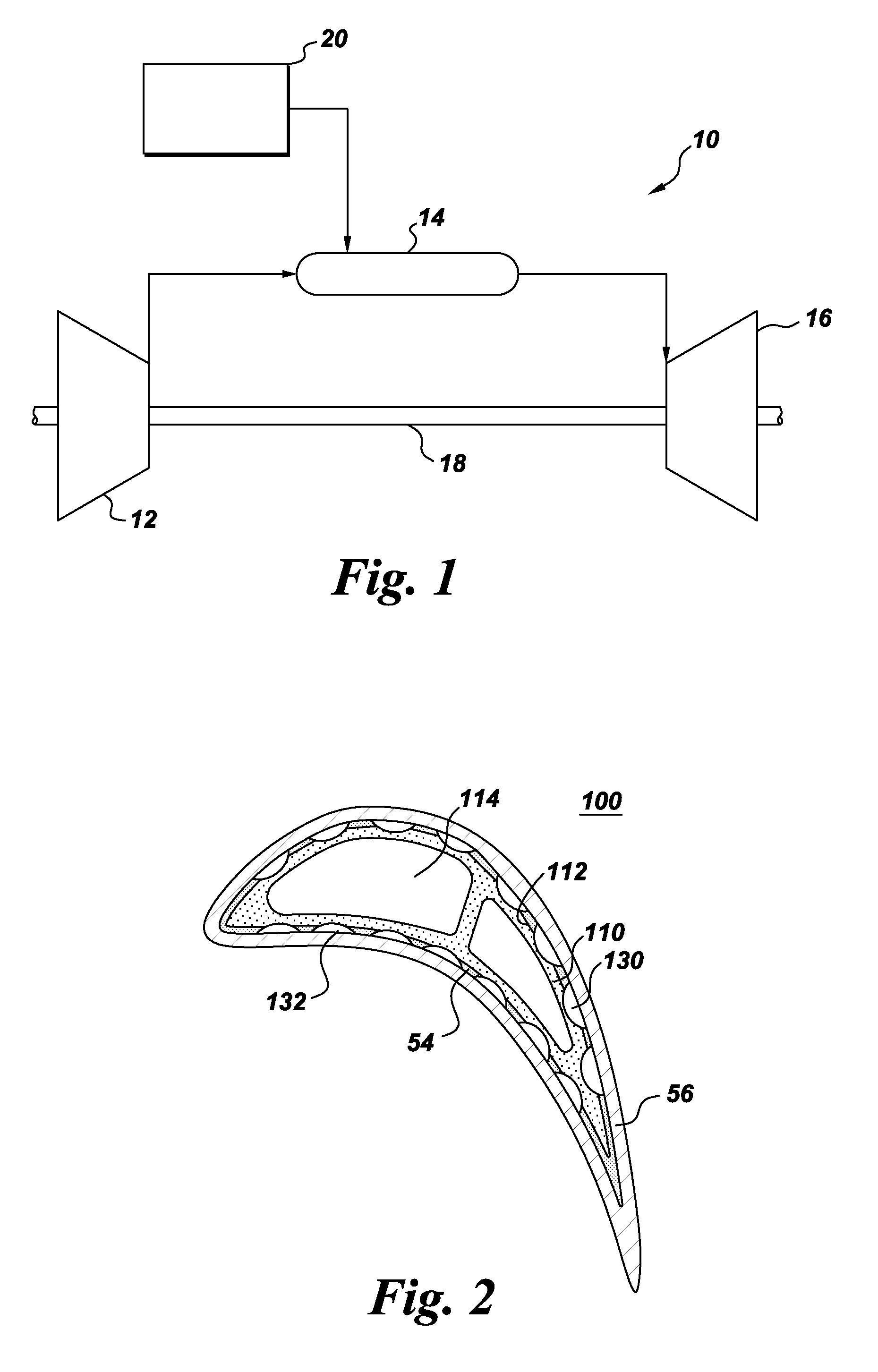
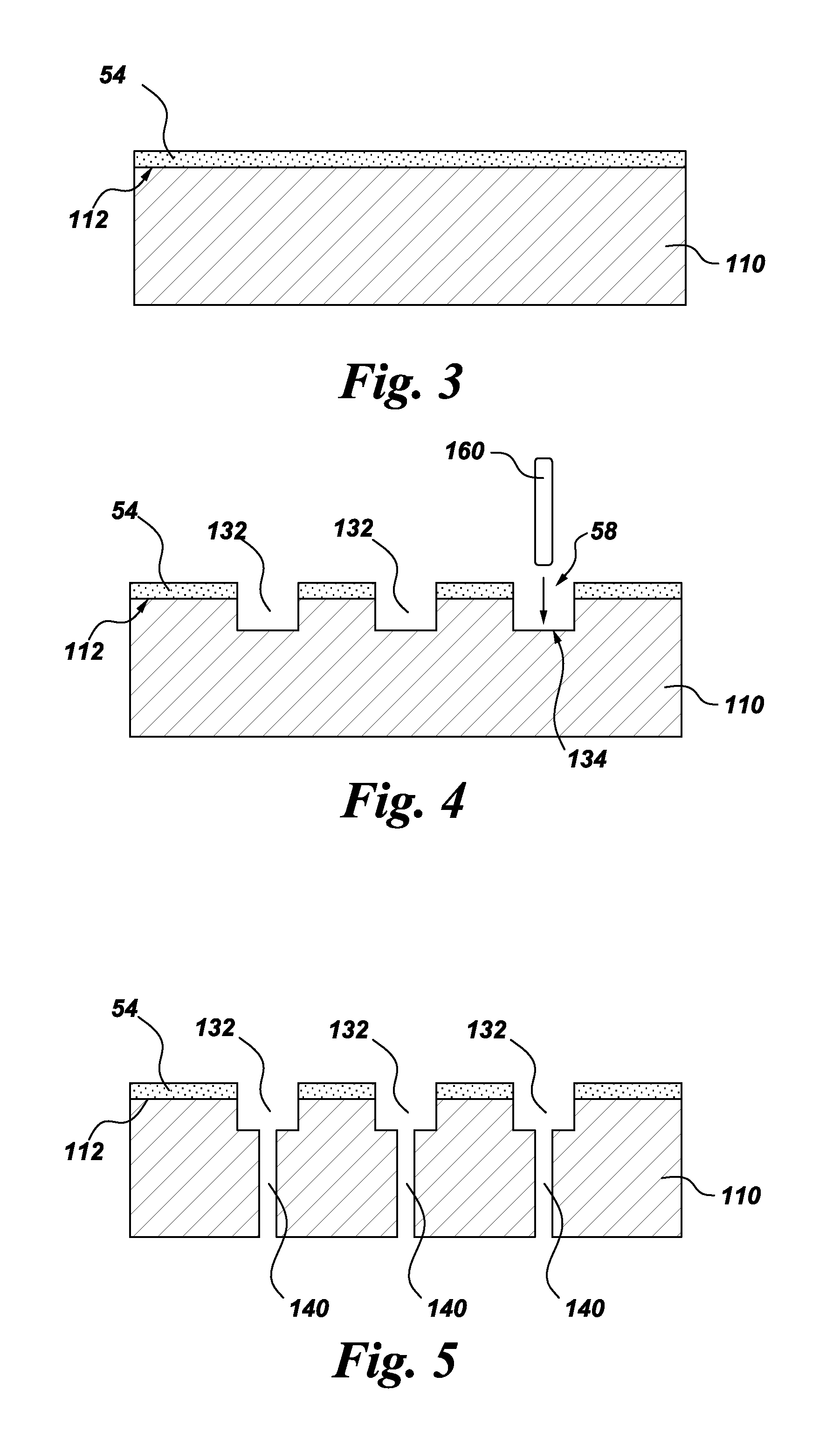
Method of fabricating a component using a two-layer structural coating
A method of fabricating a component is provided. The fabrication method includes depositing a first layer of a structural coating on an outer surface of a substrate. The substrate has at least one hollow interior space. The fabrication method further includes machining the substrate through the first layer of the structural coating, to define one or more openings in the first layer of the structural coating and to form respective one or more grooves in the outer surface of the substrate. Each groove has a respective base and extends at least partially along the surface of the substrate. The fabrication method further includes depositing a second layer of the structural coating over the first layer of the structural coating and over the groove(s), such that the groove(s) and the second layer of the structural coating together define one or more channels for cooling the component. A component is also disclosed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Progressive cavity pump/motor stator, and apparatus and method to manufacture same by electrochemical machining
ActiveUS7192260B2Improve heat transfer performanceReduce adverse effectsElectrolysis componentsEngine of intermeshing engagement typeElastomerElectricity
Electrochemical machining is used to generate the helical lobe profiles of the stator of a progressive cavity pump or motor. A thin, elastomeric liner, of uniform thickness is bonded either to the interior of the stator, or to the exterior of the rotor. Where the elastomeric liner is to be bonded to the interior of the stator, bonding is improved by electrically etching the interior of the stator during the electrochemical machining process to produce a roughened surface.
Owner:LEHR PRECISION
Method and composition for polishing a substrate
InactiveUS20060006074A1Removal rateRemoving conductiveElectrolysis componentsDecorative surface effectsOptoelectronicsConductive materials
Polishing compositions and methods for removing conductive materials from a substrate surface are provided. In one aspect, a method is provided for processing a substrate to remove conductive material disposed over narrow feature definitions formed in a substrate at a higher removal rate than conductive material disposed over wide feature definitions formed in a substrate by an electrochemical mechanical polishing technique, and then polishing the substrate by at least a chemical mechanical polishing technique.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Microneedle array chip, device and patch for transdermal drug delivery utilizing the same, and preparation method therof
InactiveUS20110237925A1Easy to punctureEasy to adjustElectrolysis componentsDecorative surface effectsAcute angleTherapeutic effect
The invention discloses a microneedle array chip comprising metal microneedles and a substrate, wherein the microneedle consists of a needle head with a tip at its top, a needle bar and a needle seat, and is fixed onto the substrate via the needle seat; and the needle bar of the metal microneedle, having a cylindrical or conical shape, is inclined toward the substrate at a preset angle, and the needle head has a conical shape, or the upper surface of the tip is an oval plane or oval ring plane parallel to the substrate or inclined toward it at a preset acute angle. The metal microneedles in the microneedle array chip of the invention have firm structures to avoid fracture, and have sharp tips to facilitate puncturing. The maximal puncturing depth of the microneedles is easy to adjust and control. The microneedles in the array have good uniformity, and are safe and reliable to use. The hollow microneedles, like conventional syringe needles, have lateral openings, and thus can effectively avoid the blockage of the infusion poles by skin, thereby facilitating rapid diffusion and absorption of drugs, and resulting in significant therapeutic effects.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method and apparatus for uniform electropolishing of damascene ic structures by selective agitation
InactiveUS20020074238A1Small apertureSufficiently porousElectrolysis componentsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectricityElectrolysis
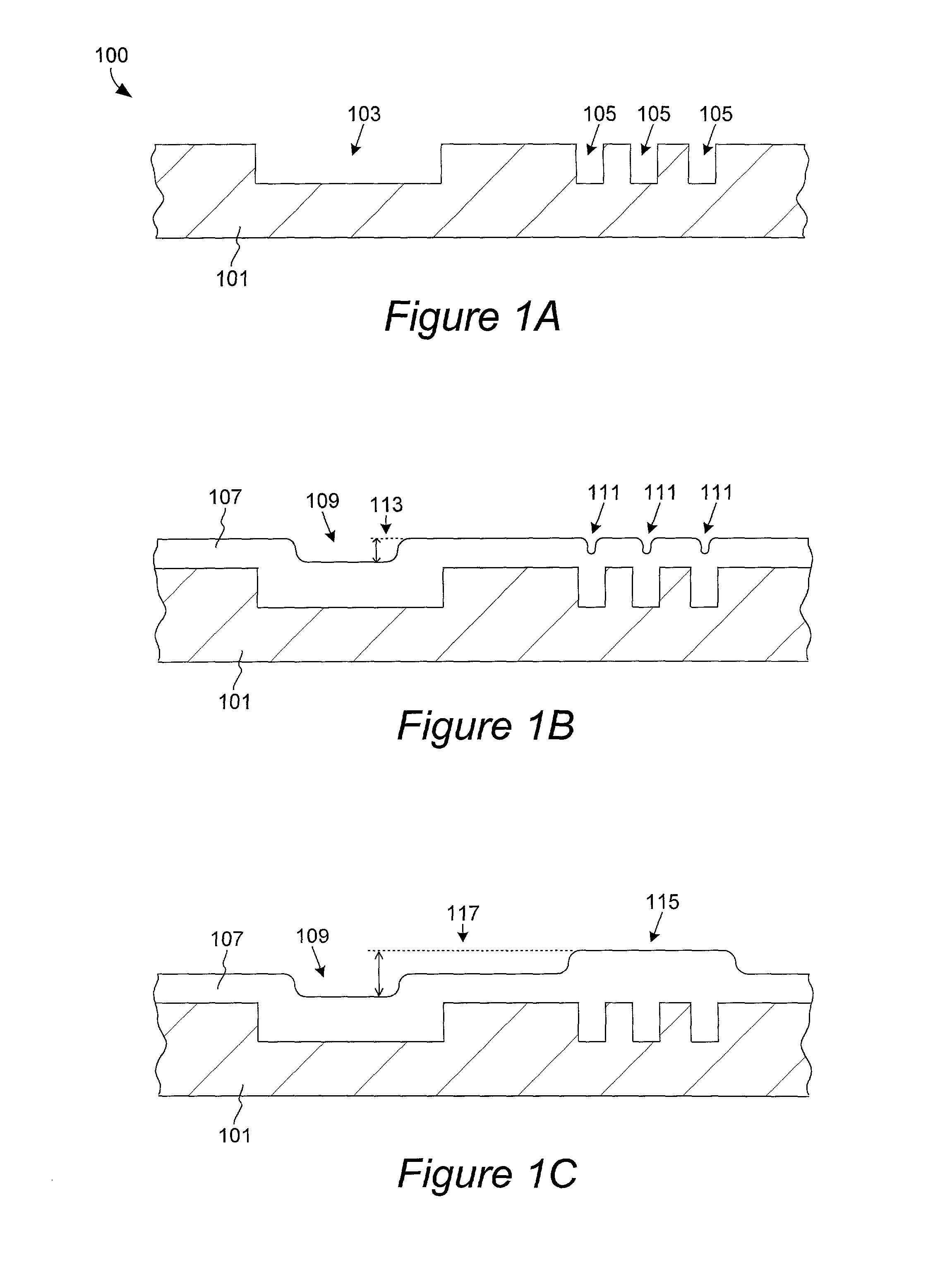
The present invention pertains to apparatus and methods for planarization of metal surfaces having both recessed and raised features, over a large range of feature sizes. The invention accomplishes this by increasing the fluid agitation in raised regions with respect to recessed regions. That is, the agitation of the electropolishing bath fluid is agitated or exchanged as a function of elevation on the metal film profile. The higher the elevation, the greater the movement or exchange rate of bath fluid. In preferred methods of the invention, this agitation is achieved through the use of a microporous electropolishing pad that moves over (either near or in contact with) the surface of the wafer during the electropolishing process. Thus, methods of the invention are electropolishing methods, which in some cases include mechanical polishing elements.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Method of fabricating a component using a fugitive coating
InactiveUS20120114868A1Molten spray coatingElectrolysis componentsInterior spaceBiomedical engineering
A method of fabricating a component is provided. The method includes depositing a fugitive coating on a surface of a substrate, where the substrate has at least one hollow interior space. The method further includes machining the substrate through the fugitive coating to form one or more grooves in the surface of the substrate. Each of the one or more grooves has a base and extends at least partially along the surface of the substrate. The method further includes forming one or more access holes through the base of a respective one of the one or more grooves to connect the respective groove in fluid communication with the respective hollow interior space. The method further includes filling the one or more grooves with a filler, removing the fugitive coating, disposing a coating over at least a portion of the surface of the substrate, and removing the filler from the one or more grooves, such that the one or more grooves and the coating together define a number of channels for cooling the component.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Compositions comprising nanostructures for cell, tissue and artificial organ growth, and methods for making and using same
ActiveUS8414908B2Increased durabilityHigh strengthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrolysis componentsArtificial organIn vivo
The invention provides articles of manufacture comprising biocompatible nanostructures comprising nanotubes and nanopores for, e.g., organ, tissue and / or cell growth, e.g., for bone, kidney or liver growth, and uses thereof, e.g., for in vitro testing, in vivo implants, including their use in making and using artificial organs, and related therapeutics. The invention provides lock-in nanostructures comprising a plurality of nanopores or nanotubes, wherein the nanopore or nanotube entrance has a smaller diameter or size than the rest (the interior) of the nanopore or nanotube. The invention also provides dual structured biomaterial comprising micro- or macro-pores and nanopores. The invention provides biomaterials having a surface comprising a plurality of enlarged diameter nanopores and / or nanotubes.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Reverse electroplating of barrier metal layer to improve electromigration performance in copper interconnect devices
InactiveUS6261963B1Electrolysis componentsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCopper interconnectOptoelectronics
A method is provided for forming a conductive interconnect, the method comprising forming a first dielectric layer above a structure layer, forming a first opening in the first dielectric layer, and forming a first conductive structure in the first opening. The method also comprises forming a second dielectric layer above the first dielectric layer and above the first conductive structure, forming a second opening in the second dielectric layer above at least a portion of the first conductive structure, the second opening having a side surface and a bottom surface, and forming at least one barrier metal layer in the second opening on the side surface and on the bottom surface. In addition, the method comprises removing a portion of the at least one barrier metal layer from the bottom surface, and forming a second conductive structure in the second opening, the second conductive structure contacting the at least the portion of the first conductive structure. The method further comprises forming the conductive interconnect by annealing the second conductive structure and the first conductive structure.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Method and Apparatus for a Porous Metal Electrospray Emitter
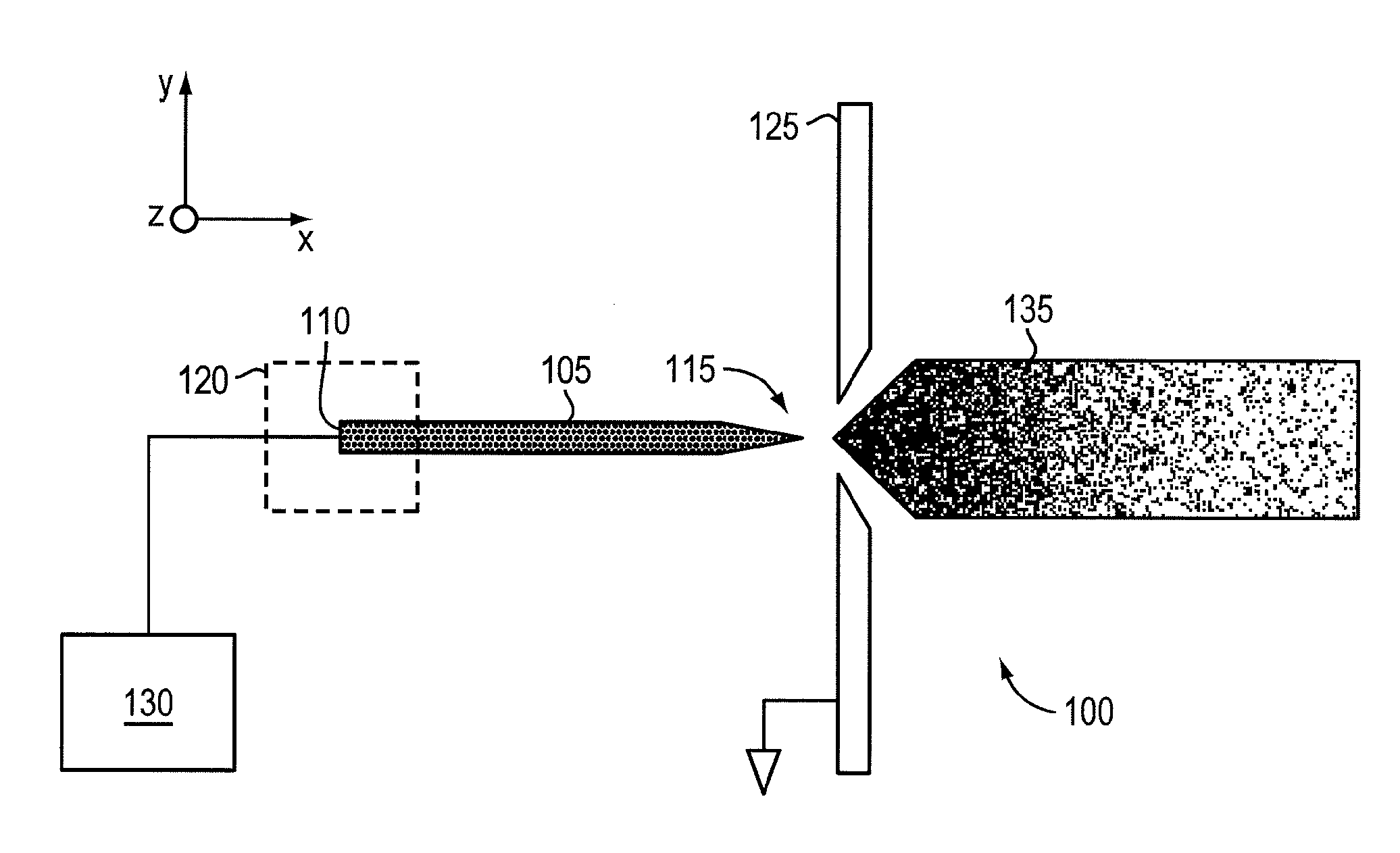
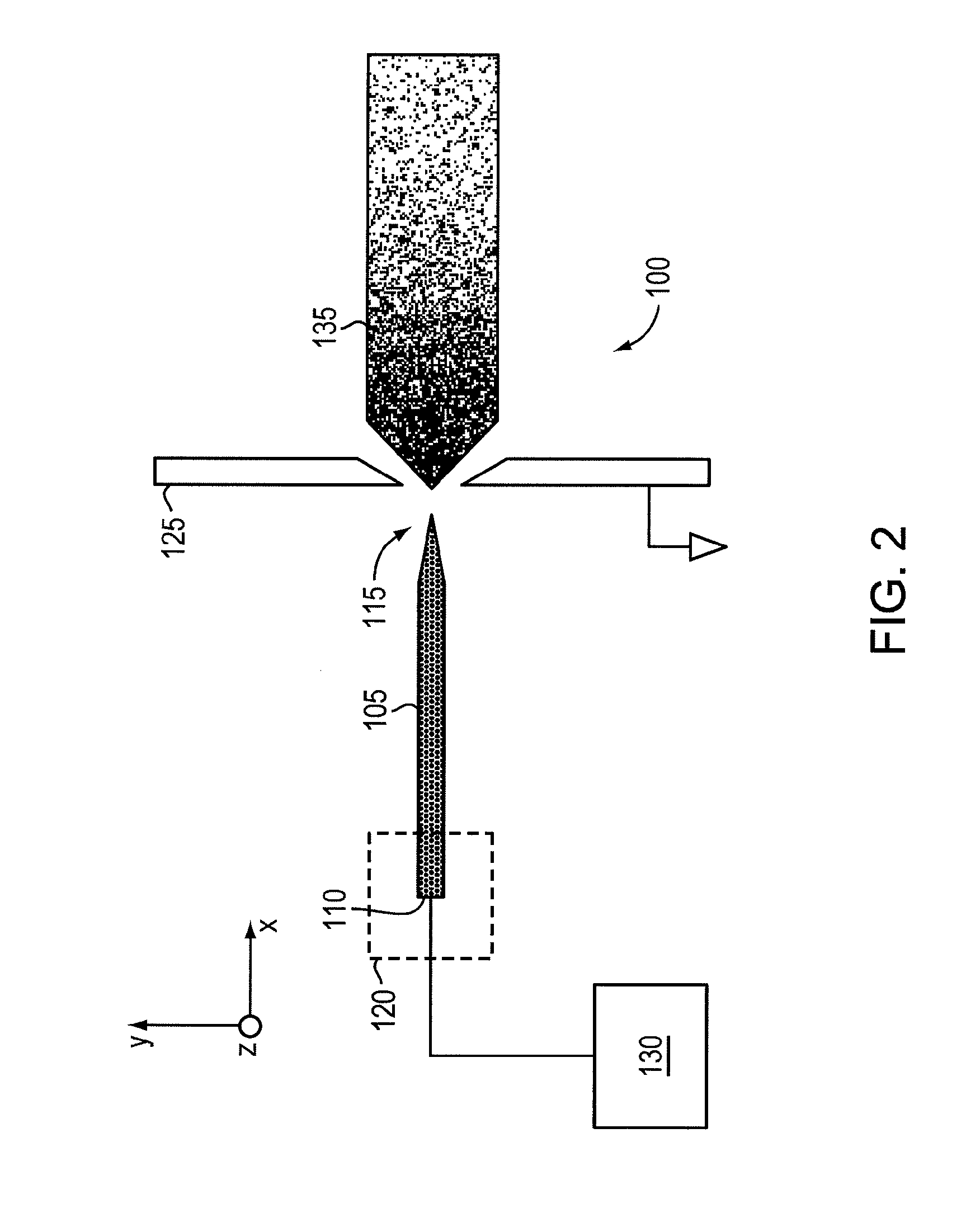
ActiveUS20110210265A1Increased capillary flow capacityReduce complexityElectrolysis componentsParticle separator tubesRoom temperatureMolten salt
An ionic liquid ion source can include a microfabricated body including a base and a tip. The microfabricated body can be formed of a porous metal compatible (e.g., does not react or result in electrochemical decaying or corrosion) with an ionic liquid or a room-temperature molten salt. The microfabricated body can have a pore size gradient that decreases from the base of the body to the tip of the body, so that the ionic liquid can be transported through capillarity from the base to the tip.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
System for electropolishing and electrochemical mechanical polishing
InactiveUS20050133379A1Overcome limitationsUniform removalCellsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPotential differenceEngineering
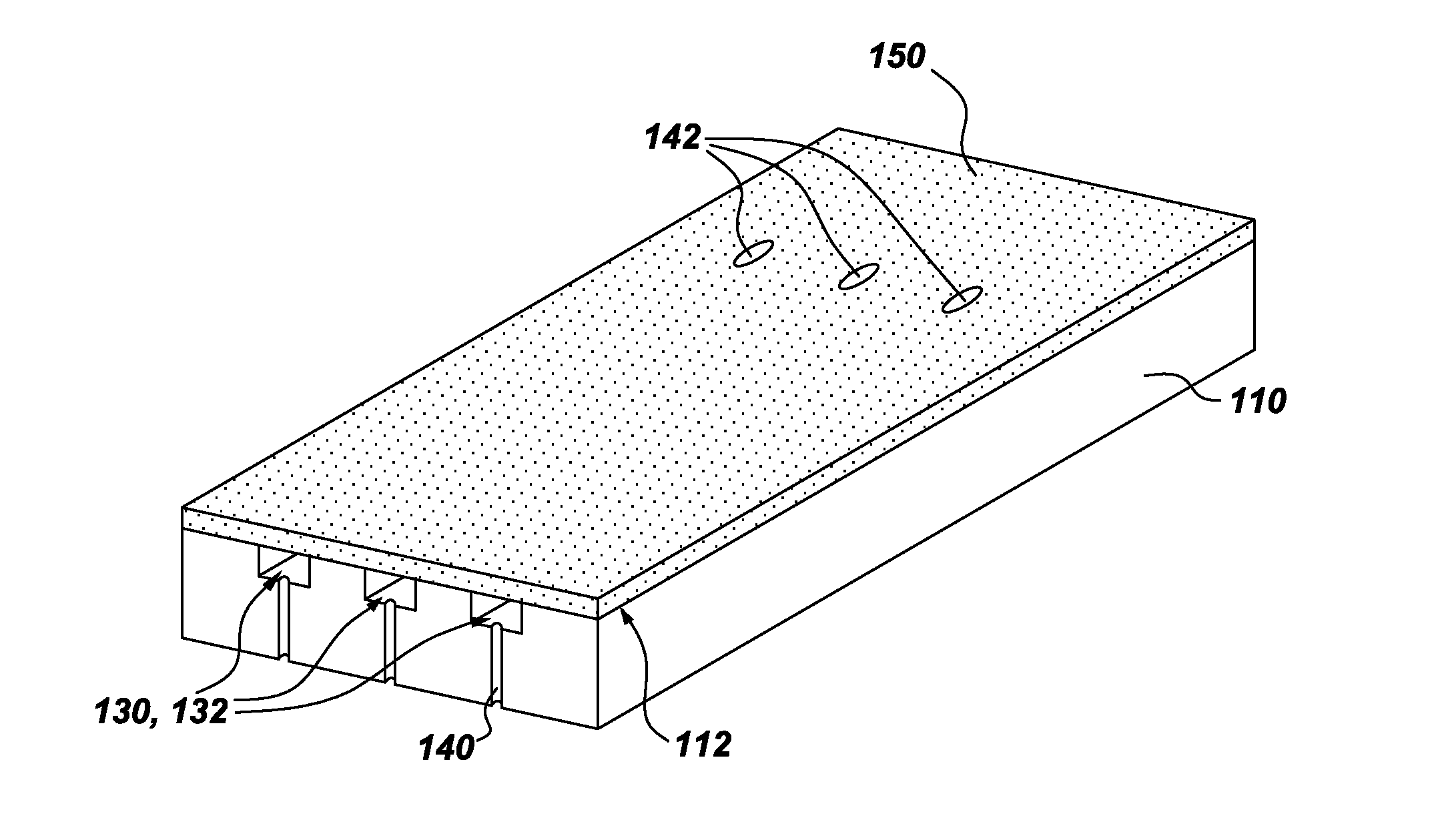
An apparatus for electropolishing a conductive layer on a wafer using a solution is disclosed. The apparatus comprises an electrode assembly immersed in the solution configured proximate to the conductive layer having a longitudinal dimension extending to at least a periphery of the wafer, the electrode assembly including an elongated contact electrode configured to receive a potential difference, an isolator adjacent the elongated contact electrode, and an elongated process electrode adjacent the isolator configured to receive the potential difference, a voltage supply is configured to supply the potential difference between the contact electrode and the process electrode to electropolish the conductive layer on the wafer.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Method of making silicon anode material for rechargeable cells
ActiveUS20120129049A1Excellent cast-abilityExcellent weld-abilityElectrolysis componentsElectrode manufacturing processesRechargeable cellSilicon
Owner:NEXEON LTD
Methods and systems for manufacturing components from articles formed by additive-manufacturing processes
ActiveUS20150144496A1High surface finishAchieve electrical continuityCellsTurbinesPower flowPotential difference
A method is provided for manufacturing a component. The method includes connecting a component comprising an internal passage and formed by an additive manufacturing process to a power supply, the component functioning as an anode, connecting a cathode to the power supply, the cathode being disposed in an electrolyte solution, the cathode being positioned externally to the internal passage of the component, contacting the internal passage of the component with the electrolyte solution, and using the power supply, applying a potential difference and current flow between the component and the cathode.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Method and apparatus for selectively removing coatings from substrates
InactiveUS6599416B2Maximize efficiency and selectivityReduce thicknessCellsPolycrystalline material growthElectrochemistryTurbine
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Removal of substances from metal and semi-metal compounds
InactiveUS6712952B1Polycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsMelting temperatureMetal
The present invention pertains to a method for removing a substance (X) from a solid metal or semi-metal compound (M<1>X) by electrolysis in a melt of M<2>Y, which comprises conducting the electrolysis under conditions such that reaction of X rather than M<2 >deposition occurs at a electrode surface, and that X dissolves in the electrolyte M<2>Y. The substance X is either removed from the surface (i.e., M<1>X) or by means of diffusion extracted from the case material. The temperature of the fused salt is chosen below the melting temperature of the metal M<1>. The potential is chosen below the decomposition potential of the electrolyte.
Owner:METALYSIS
Methods and apparatus for polishing a substrate
InactiveUS20050092620A1Electrolysis componentsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingConductive materialsRelative motion
Polishing compositions and methods for removing conductive material and barrier layer materials from a substrate surface are provided. Generally, variable amounts of abrasive particles are used for removing conductive material and barrier layer materials. In one aspect, a process is provided including providing an polishing composition between the first electrode and the substrate, wherein the polishing composition comprises a first concentration of abrasive particles, applying a bias between the first electrode and the second electrode, providing relative motion between the substrate and the polishing article, removing conductive layer material from the substrate, introducing abrasive particles to the polishing composition to form a second concentration of abrasive particles greater than a first concentration of abrasive particles, and removing barrier layer material from the substrate. The abrasive particles may be incrementally introduced or pulsed during a polishing process.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Electrolytic machining method for thin-wall machine case of aero-engine
ActiveCN104384643AFix stability issuesSolve the costElectrical-based machining electrodesElectrochemical machining apparatusConvex structureAviation
The invention provides an electrolytic machining method for a thin-wall machine case of an aero-engine, belonging to the technical field of electrolytic machining. The electrolytic machining method mainly aims at the machining of a surface concave-convex structure of a complicated thin-wall rotary body part in the aviation field, and is characterized in that a tool cathode is of a thin-wall strip-shaped structure or a rigid rotary body structure; window or lug boss structures with different shapes are distributed on the surface of the cathode. In a machining process, a workpiece anode automatically rotates and the tool cathode is fed to the anode in a peripheral movement process. In the whole machining process, electrodes do not need to be replaced, and the surface concave-convex structure of the thin-wall rotary body part is machined and molded once through rolling sleeve electrolytic action of a cathode window.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Controlled electrochemical polishing method
InactiveUS7998335B2Electrolysis componentsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOxidizing agentMaterials science
The invention relates to a method of polishing a substrate comprising at least one metal layer by applying an electrochemical potential between the substrate and at least one electrode in contact with a polishing composition comprising a reducing agent or an oxidizing agent.
Owner:CABOT MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Microfabricated microconcentrator for sensors and gas chromatography
InactiveUS7147695B2High sensitivityImprove signal-to-noise ratioElectrolysis componentsComponent separationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Gas phase
Devices for enhancing the sensitivity of a microsensor or any other micro device by providing on-line preconcentration. Microconcentrators that can be integrated with a sensor or a micromachined GC to enhance the signal to noise ratio can include a miniaturized sorbent trap fabricated on a microchip. The microconcentrator can be made on a silicon substrate so that a sensor can be integrated on the same chip. The microconcentrator is composed of at least one microchannel lined with a microheater for in-situ heating. Preconcentration may be achieved on a thin-film polymeric layer deposited above the heater in the microchannel. Rapid heating by the channel heater generates a “desorption pulse” to be injected into a detector or a sensor.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com