Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
964 results about "Dross" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
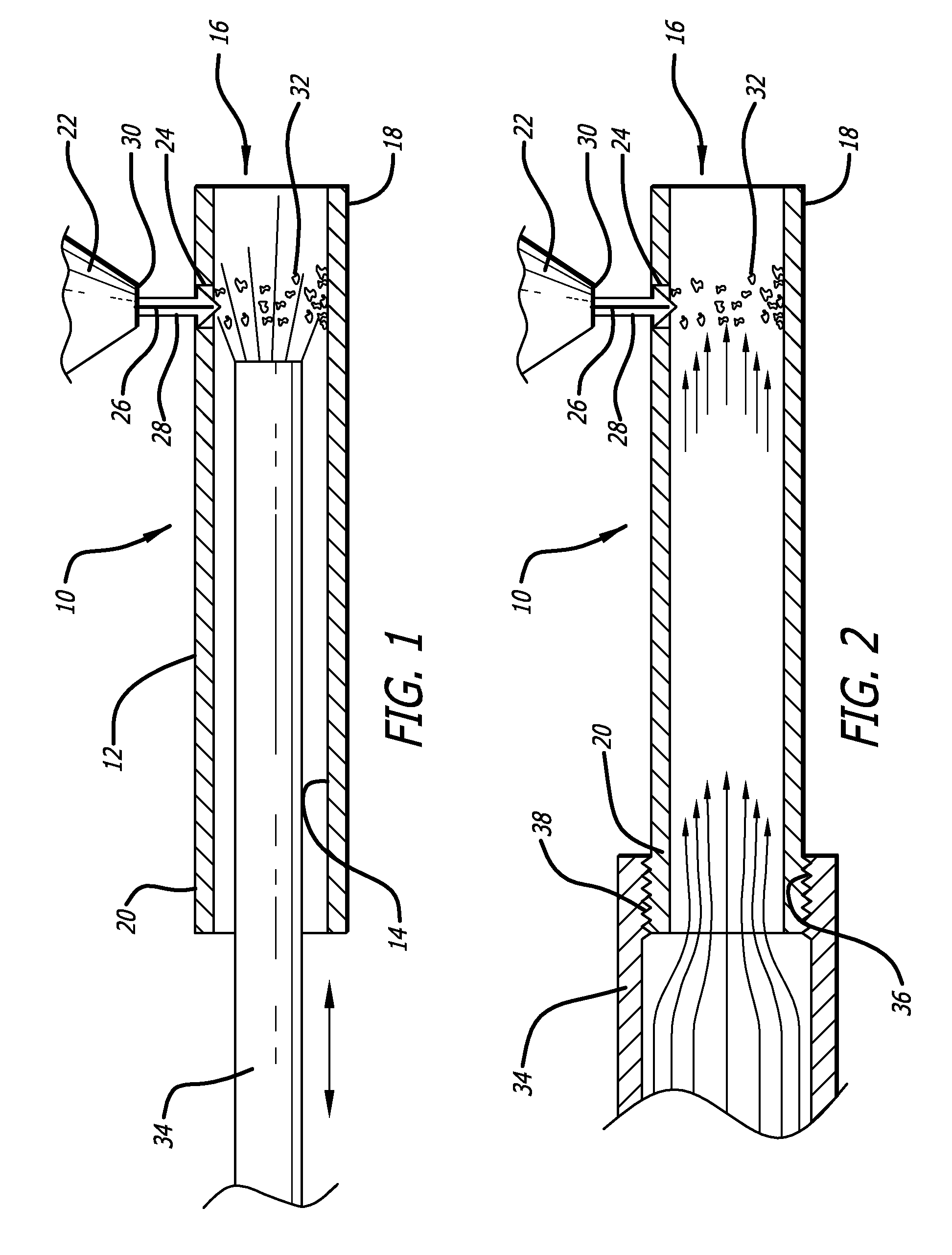
Dross is a mass of solid impurities floating on a molten metal or dispersed in the metal, such as in wrought iron. It forms on the surface of low-melting-point metals such as tin, lead, zinc or aluminium or alloys by oxidation of the metal. For higher melting point metals such as steel, oxidized impurities melt and float making them easy to pour off.
Oily sludge recycling and innocent comprehensive treatment process
InactiveCN102039301APromote resource utilizationEliminate secondary pollutionSolid waste disposalTreatment with plural serial refining stagesSlagOil sludge
The invention provides an oily sludge recycling and innocent comprehensive treatment process, which comprises the following four steps of: 1, pretreating oily sludge: adding water into the oil sludge, heating and stirring to form fluidized sludge, and separating in a stainless steel screen; 2, conditioning the oily sludge, adding a demulsifier and a flocculant into the separated fluidized sludge for conditioning the oily sludge; 3, performing centrifugal separation on three phases of the oily sludge: introducing separated oil into an oil-water separation system for recovering crude oil, conveying separated water to the oily sludge pretreatment step for recycling, drying the separated residual oily sludge, and solid impurities and floating slag which are separated in the oily sludge pretreatment, and introducing the dried substances into a rotary kiln incinerator; and 4, performing mixed combustion on the residual oily sludge and biomass, performing high temperature incineration treatment after the residual oily sludge, the separated solid impurities and floating slag, and the biomass are mixed in a rotary kiln to remove the secondary pollution of the oily sludge, and recovering afterheat from high temperature flue gas.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Galvanizing bath apparatus
InactiveUS8475594B2Reduce buildSpeed up the conversion processHot-dipping/immersion processesPretreated surfacesHigh concentrationDross
A continuous galvanizing line uses a coating pot containing a molten zinc bath having bottom dross and further comprises a pump. The pump agitates the bottom dross so the bottom dross interacts with aluminum and converts to top dross, which can be removed without needing to stop the galvanizing line. A reaction vessel may also be used to provide a higher concentration of aluminum to react with the bottom dross.
Owner:PYROTECK INC
Method of processing rock with laser and apparatus for the same
ActiveUS20100001179A1Improvement factorEasy to implementLaser using scattering effectsDisloding machinesPhysicsDross
An object is to provide a method capable of boring a borehole even when quartz glass or silicon dioxide is deposited as molten dross by laser irradiation. A laser irradiation position of a workpiece is irradiated with a laser having wavelength of 1.2 μm or longer and a high factor of absorption into liquid, for example, a CO2 laser, from a laser oscillator through liquid. By high pressure generated in an advancing microbubble flow occurring in the liquid, molten dross is scattered. Thus, the processing, such as boring, of the rock is performed.
Owner:JAPAN DRILLING CO LTD +2
Water-preserving nutrient soil for indoor flowers
The invention discloses a water-preserving nutrient soil for indoor flowers, which comprises pond sludge, chaff ash, bean curd dross, Attapulgite clay, alta-mud, quartz sand, potassium permanganate, ferrous sulfate, copper sulfate, sulphur, 45% content of azophoska composite fertilizer and high water absorbent resin.
Owner:蒋文兰
Harmless and comprehensive utilization method of secondary aluminum dross
InactiveCN107555447ARealize harmless treatmentTo achieve the purpose of "zero emission" utilizationChloride preparationFluoride preparationSlurryLiquid solid
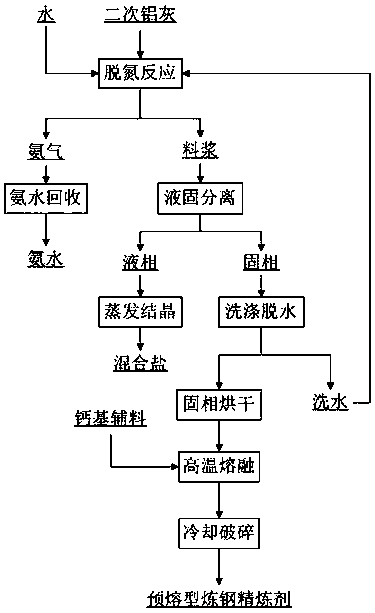
The invention provides a harmless and comprehensive utilization method of secondary aluminum dross and relates to a harmless and comprehensive utilization method of secondary aluminum dross produced in an aluminum dross treating process. The harmless and comprehensive utilization method is characterized in that slurry is prepared from the secondary aluminum dross produced in the aluminum dross treating process and water, a stirring deamination reaction is performed, and ammonia gas formed through the reaction is condensed or absorbed by water; slurry after the reaction is subjected to liquid-solid separation, separated liquid phase is subjected to evaporative crystallization, and a chlorate and fluoride salt mixture is obtained; separated solid phase is used for producing a calcium aluminate material. With adoption of the method, the aluminum dross can be treated harmlessly, useful components in the aluminum dross are recovered efficiently, the harmless secondary aluminum dross can replace high-alumina bauxite for preparing a calcium aluminate product, production cost is reduced greatly, zero-release utilization of the aluminum dross is realized, the process is simple, the operation is convenient, the cost is low, environmental protection is realized, and the method has wide applicability.
Owner:GUIZHOU BRANCH CHINA ALUMINUM IND
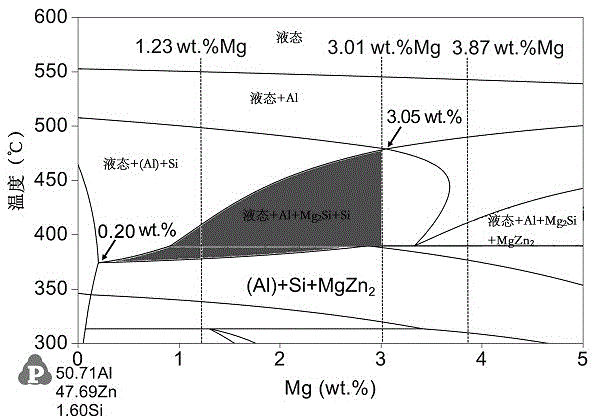
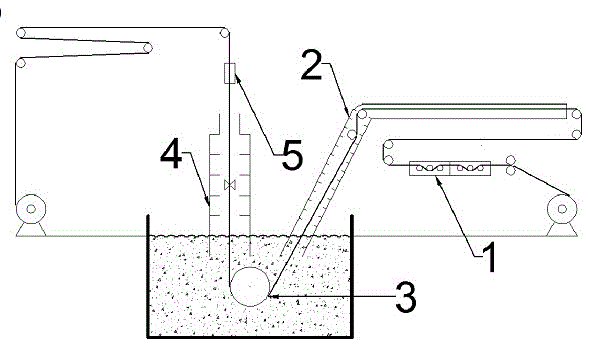
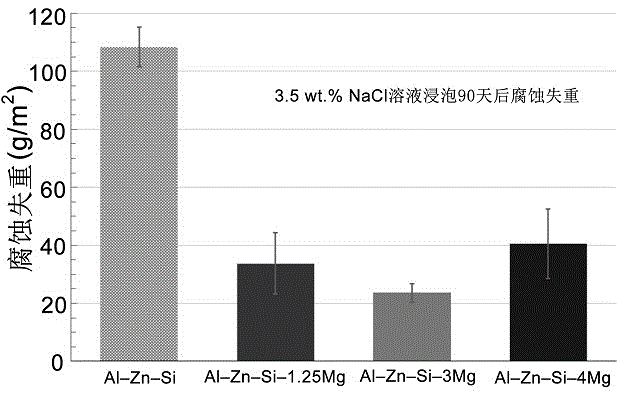
Method for plating surface of steel with Al-Zn-Mg-Si alloy plating layer in continuous hot-dipping manner
The invention relates to a method for plating the surface of steel with an Al-Zn-Mg-Si alloy plating layer in a continuous hot-dipping manner and a manufacturing process of the Al-Zn-Mg-Si alloy plating layer. The Al-Zn-Mg-Si alloy plating layer manufactured through the process comprises, by weight percentage, 48% to 55% of Al, 40% to 50% of Zn, 1% to 4% of Mg and 1% to 3% of Si. The manufacturing process of the Al-Zn-Mg-Si alloy plating layer includes the steps of firstly, surface cleaning treatment, secondly, reducing and annealing, thirdly, hot-dipping plating in plating liquid at the temperature from 550 DEG C to 700 DEG C, fourthly, the annealing process for 0.1 s to 5 s at the temperature from 400 DEG C to 700 DEG C and air cutter leveling and fifthly, cooling. The manufactured alloy plating layer contains Al-rich dendritic crystal phases, Zn-rich interdendritic phases, Mg2Si phases and a small amount of MgZn2 phases. The preferable alloy components can guarantee the even plating liquid components, floating residues are few, and the quality of the plating layer manufactured through the continuous hot-dipping process is uniform and stable. The content of the Mg2Si phases on the surface of the plating layer can be increased through the annealing process performed after dipping plating is performed, and the corrosion resistance of the plating layer is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Dual gas laser cutting of medical devices
ActiveUS20100230391A1Reduce in quantityPrevent oxidationStentsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesSlagOptoelectronics
A system prevents oxidation of a laser cut workpiece by utilizing a laser source that utilizes laser source with an inert gas, such as argon or helium, rather than air or oxygen, to create the slots or kerfs which form the pattern cut into the workpiece. The system introduces oxygen gas through the workpiece as it is being laser cut to oxidize any slag or dross created during the laser cutting process. Oxygen or a mixture of oxygen with other gases cools the slag and the workpiece while at the same time oxidizing the slag to either completely burn or partial burn the slag before it strikes an exposed surface of the tubular member.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
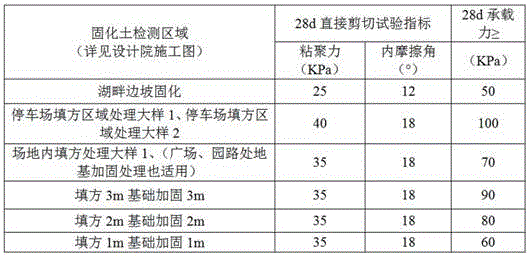
Silt solidification soil construction technology
The invention discloses a silt solidification soil construction technology which comprises the steps of surface cleaning drainage, silt sampling, detection analysis, excavation stacking, stirring and mixing, filling and grinding and stabilized soil maintenance. Through solidification soil in-situ solidification, silt and a curing agent are stirred and mixed to form silt solidification soil, and the curing agent is prepared through expanded graphite, activated carbon, cement, quick lime, gypsum, lignocelluloses, coal ash, granulated blast-furnace slag powder, coal gangue, caustic dross, hydroxypropyl methyl celluloses, furfural residues, medical stone and smectite clay. By means of the silt solidification soil construction technology, original flowing high-water-content low-strength high-compressibility silt is converted into high-compressive-strength excellent-entire-board-performance, good-durability and environment-friendly solidification soil, and the requirement of shallow ground earthwork materials for roads, storage yards, ports, reclamation projects, afforesting and the like can be met.
Owner:福建港湾岩土工程集团有限公司
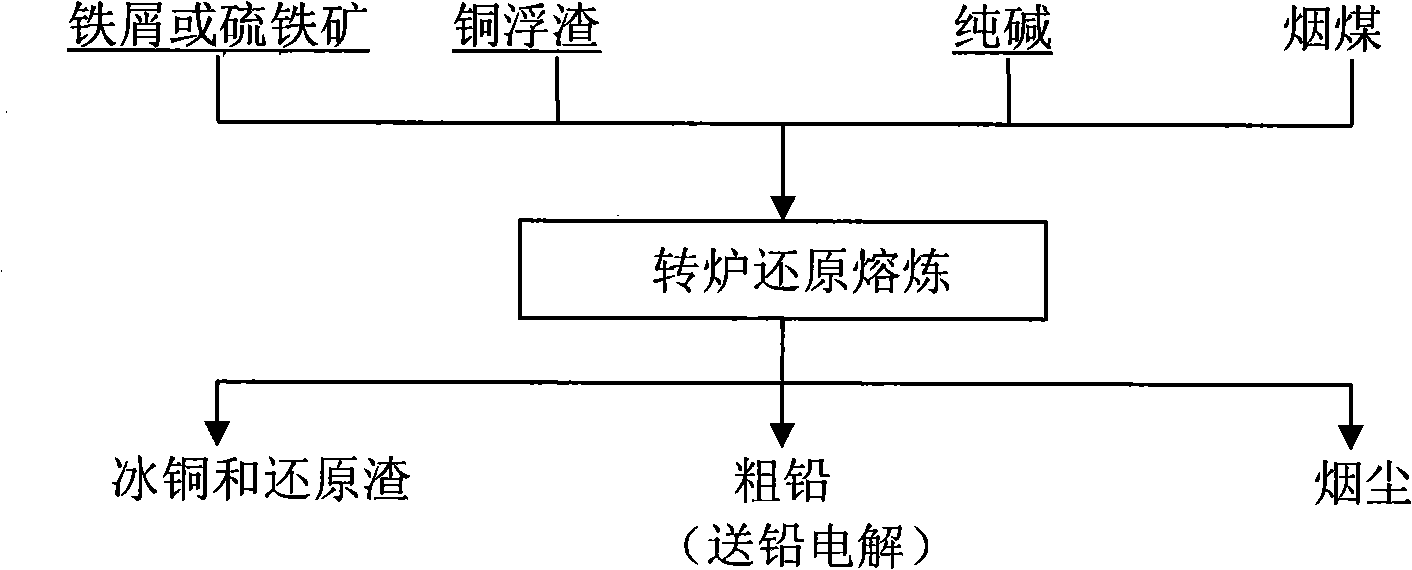
Method for treating copper scum using converter
The invention relates to a method for processing copper dross slag by using a converter, which belongs to the technical field of thermometallurgy. Copper dross slag, calcined soda, scrap iron or sulfurous iron ore and soft coal are proportioned in proportion and then are added into a converter for retailoring. The temperature is controlled within the range of from 700 DEG C to 800 DEG C, the smelting lasts for 1.5 hours to 2 hours, so that lead in the metal form in the copper dross slag is separated from copper; then the temperature is increased to the slag overtemperature of 1100 DEG C to 1250 DEG C, the smelting lasts for 2.5 hours to 3 hours, so that lead compound is deoxygenated to produce metal lead, and the copper becomes copper matte to realize the separation of copper and the lead. The dross slag on the copper matte and the wet lead are fished out to obtain the copper matte and the wet lead. Because the operation process of the invention is carried out in the converter, the separation of copper and lead is more complete. The method can solve the problems of high energy consumption, heavy environmental pollution, low metal recovery ratio, high production cost and the like in the prior copper dross slag processing.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Continuous casting method of large-length hollow ductile cast iron sections and method for arcing hollow ductile cast iron sections after local continuous heating
InactiveCN101638748ASolve technical problems that are difficult to produceCorrosion resistancePhysical fieldVolumetric Mass Density
The invention relates to a continuous casting method of large-length hollow ductile cast iron sections and a method for arcing the hollow ductile cast iron sections after local continuous heating. Thesection comprises the following components by weight percent: 3.4-3.6% of C, 2.8-3.2% of Si, 0.40-0.60% of Mn, S less than or equal to 0.1%, P less than or equal to 0.1% and the balance Fe. Molten iron is subjected to shaping and continuous casting under multiple physical fields to become the hollow sections. The molten iron in heat preserving furnaces is separated from dross, sand and gas in twoways, thus completely solving the defects of dross inclusion, sand inclusion and pores; liquid column cores in a crystallizer carry out continual feeding on condensing tube shells, thus eliminating the possibility of shrinkage porosity inside the tube walls, obtaining highly dense cast structure of (ferritic matrix+spherical graphite) and eliminating crack initiation origins in thermoplastic deformation to be carried out later. The intense cooling speed in the crystallizer enables the volumes of eutectic cells to be only 1 / 15-1 / 25 of the volumes of traditional sand mould casts. The density ofthe graphite balls reaches around 500 / mm<2>. In plastic deformation, the micro slip orientation is increased and the ductility is enhanced, therefore, the hollow cast iron sections can be arced by medium frequency induction heating and bending.
Owner:SHAN XI TONGXIN LIANZHU PIPE IND
Tin-lead welding strip for solar photovoltaic assembly and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102254978AImprove adhesionImprove conductivityFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationMicrometerDross
The invention discloses a tin-lead welding strip for a solar photovoltaic assembly, which comprises a copper strip base material, wherein a compact tin-lead alloy layer with a thickness of 3-20 micrometers covers the surface of the copper strip base material. A manufacturing method of the tin-lead welding strip for the solar photovoltaic assembly comprises the step of: covering the compact tin-lead alloy layer on the copper strip base material by adopting an electroplating method, wherein the thickness of the tin-lead alloy layer is 3-20 micrometers. Because the electroplating method is adopted, a cladding material has a crystal lattice characteristic and capacities of enhancing adhesive force of the welding strip and improving the conductivity of the photovoltaic welding strip. The welding strip has a volume resistivity of 0.0185-0.021omega mm<2> / m which is lower than that of the welding strip manufactured through thermal tin immersion and a melting point of 183-190 DEG C lower than that of a lead-free welding strip, and has no abnormal phenomena such as tin knobs, tin dross, copper cuttings, discoloration and the like. A process capability index (CPK) value is effectively increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI WELNEW MICRO ELECTRONICS
Method for manufacturing refined high cleanliness Al-Ti-B alloy
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing a refined high cleanliness Al-Ti-B alloy, comprising the following steps of: (1) melting an aluminum ingot, and adding potassium fluotitanate and potassium fluoborate for alloying; (2) pouring a reaction by-product floating on the surface of aluminum liquid, and neutralizing with alumina powder; (3) raising the temperature of the aluminum liquid, and scattering an alumina powder layer; (4) introducing argon or nitrogen with a pipe so that a residue solution coated in the aluminum liquid floats and is neutralized; (5) measuring the hydrogen content after the solution is treated by utilizing a small bubble rotation and degassing refining technology; (6) scattering a special high temperature anti-oxidation covering agent layer in the hot state of more than 800 DEG C; (7) raising the temperature of the aluminum liquid, introducing the aluminum liquid to a filtering box body filled with an alumina ceramic filter, and carrying out online filtering treatment on the alloy aluminum liquid; and (8) finally, reducing the temperature of the aluminum liquid, discarding scruff scum, and molding by casting to produce Al-Ti-B filaments. The method can effectively separate fluoride salt and other impurities in the Al-Ti-B alloy liquid so that the impurities in an Al-Ti-B alloy refining agent are reduced, and the cleanliness is greatly improved.
Owner:HUNAN JINLIANXING SPECIAL MATERIALS CO LTD
Full-automatic tin-soldering machine and tin-soldering method thereof
InactiveCN102357700AIncrease productivityImprove securityMetal working apparatusSoldering auxillary devicesFixed frameEngineering
The invention discloses a full-automatic tin-soldering machine. The full-automatic tin-soldering machine comprises a jig, a fixing frame, a vertical power device, a transverse power device, a soldering flux container, a soldering furnace and a tin dross scraping device, wherein the jig is used for containing an element to be tin-soldered; the fixing frame is used for mounting the jig; the vertical power device drives the fixing frame to move in the vertical direction; the transverse power device drives the fixing frame to move in the transverse direction; the soldering flux container contains a soldering flux and is used for binding the soldering flux on the element to be tin-soldered which is moved in place by the jig; the soldering furnace contains tin liquor and is used for tin-soldering the element to be tin-soldered which is moved in place by the jig and is bound with the soldering flux; and the tin dross scraping device is used for scraping tin dross on the surface of the tin liquor in the soldering furnace. The machine can automatically finish tin-soldering by only placing the element to be tin-soldered on the jig; compared with the traditional manual operation, the tin-soldering processes for more elements can be finished within shorter time, thus, the full-automatic tin-soldering machine has high production efficiency, can effectively lower the production cost, and has higher safety; and in addition, due to the adoption of automatic operation, the accuracy is higher, and the quality of products can be guaranteed.
Owner:中山市三礼电子有限公司
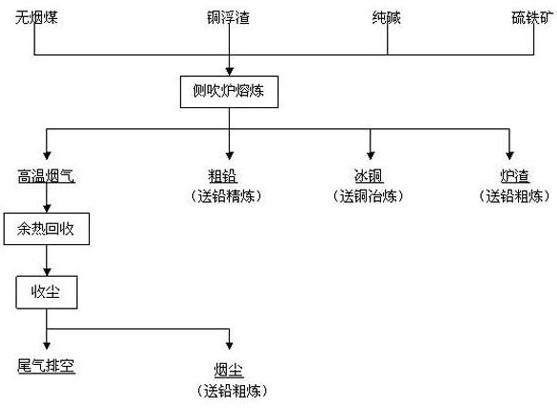
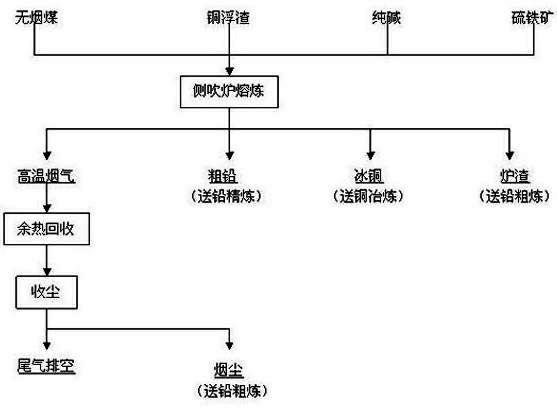
Method for producing lead bullion by means of copper dross side-blown smelting
The invention belongs to the technical field of metallurgy, and relates to a method for producing lead bullion by means of copper dross side-blown smelting. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) burdening copper dross, sodium carbonate and pyrite according to the proportion of 100:(8-10):(6-8), evenly feeding for 1-2 hours, wherein the feeding temperature is 600-800 DEG C, and evenly blowing anthracite by high-pressure wind; 2) smelting for 1-2 hours at the temperature of 600-800 DEG C after feeding, rising the temperature to 1100-1200 DEG C and smelting for 2-3 hours, and smelting the metallic lead and the chemical combination-state lead in the copper dross into the lead bullion; and 3) stopping blowing the anthracite, separating for 0.5-1 hour in a cleaning way, discharging the lead bullion and the copper matte in a siphon way, opening a slag hole to discharge the slag, and carrying out waste heat recovery and dust collection on the high-temperature smoke to be discharged to the air after the high-temperature smoke reaches the standard. The method takes the anthracite as the fuel or the reducing agent, and the other methods use the coke, the diesel oil or the electric energy, so that the method is more economical and suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:YUNNAN CHIHONG ZINC & GERMANIUM
Processing method for recycling aluminum dross
ActiveCN101913634ANo pollutionReduce pollutionAlkaline-earth metal aluminates/aluminium-oxide/aluminium-hydroxide preparationSocial benefitsPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a processing method for recycling aluminum dross, which comprises the following steps: adding crushed limestone and catalyst to aluminum dross, thoroughly homogenizing and mixing the three materials, carrying out catalyzed calcination on the thoroughly homogenized and mixed materials in a calcination reaction furnace, and directly grinding the calcined products or grinding the calcined products after cooling, thus obtaining the calcium aluminate powder product. The processing method has a simple operational process, and can not cause new environmental pollution, thereby according with the policy for industry development. The invention recycles the aluminum dross, simultaneously reduces environmental pollution caused by the aluminum dross, improves the environmental management on surrounding areas, and also provides a reasonable and effective way to recycle waste aluminum dross. Thus, the invention has obvious economic benefits and social benefits.
Owner:HENAN KETAI WATER PURIFYING MATERIALS
Method for processing silicon powder to obtain silicon crystals
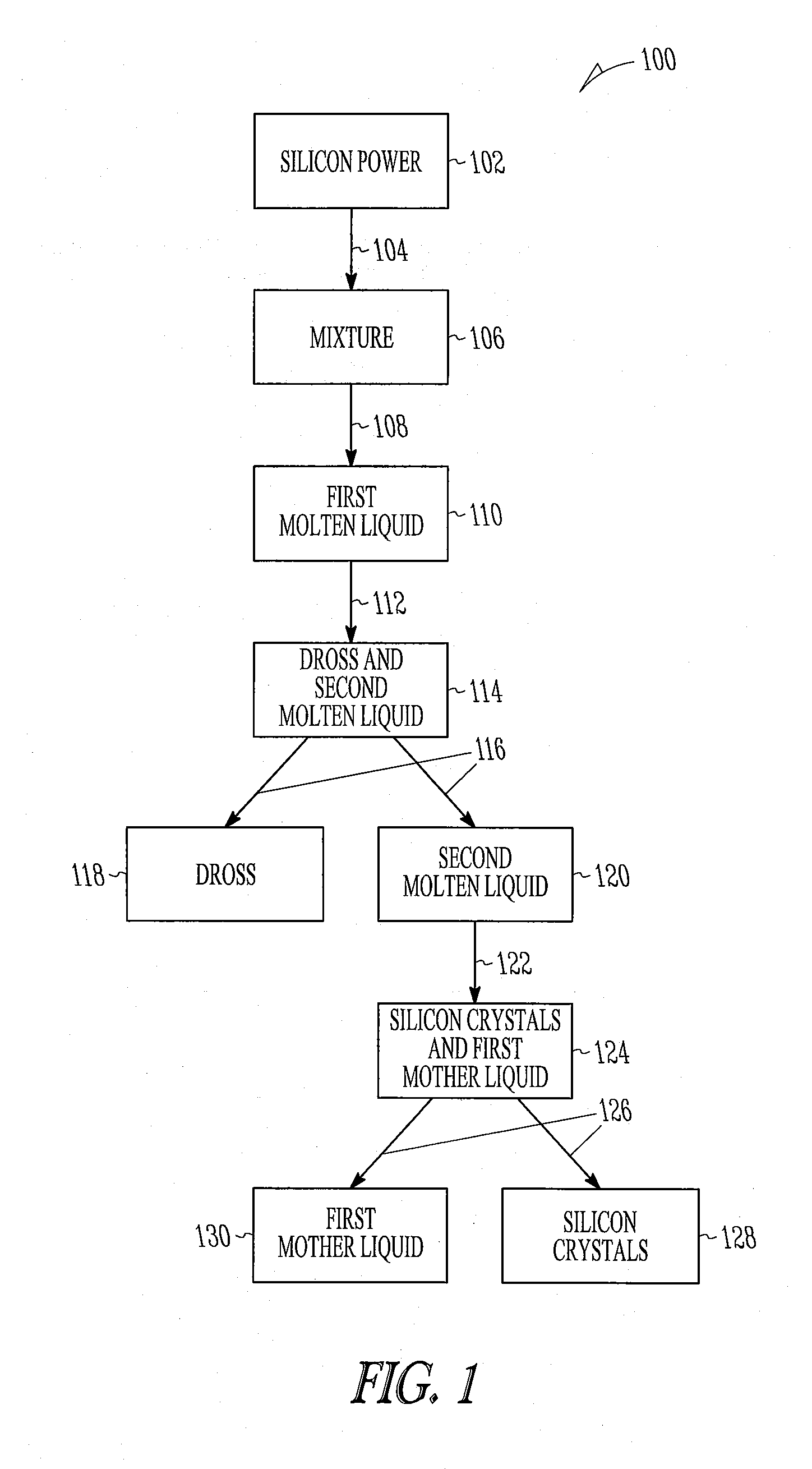
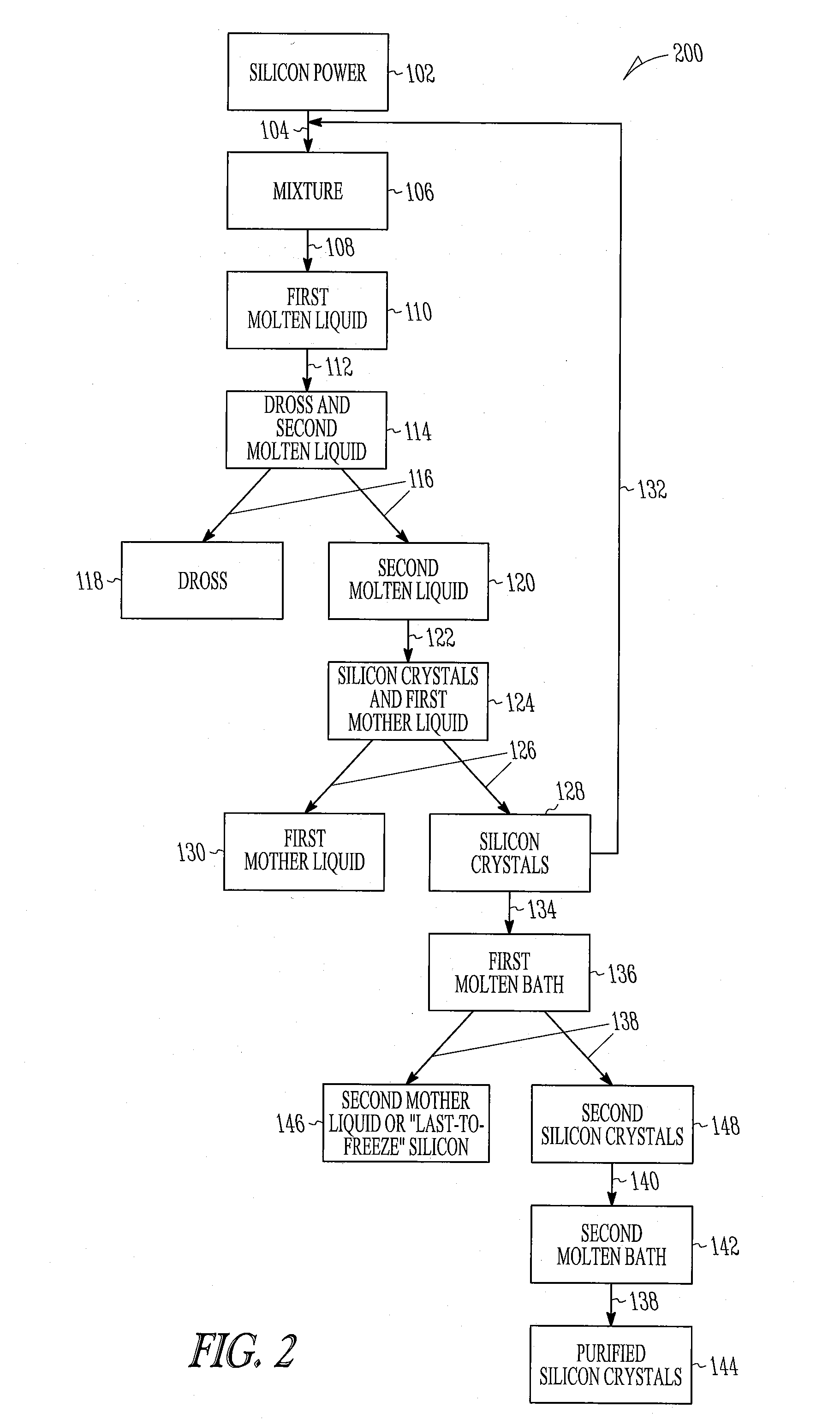
Embodiments of the present invention relate to a process for obtaining silicon crystals from silicon. The method includes contacting silicon powder with a solvent metal to provide a mixture containing silicon, melting the silicon under submersion to provide a first molten liquid, contacting the first molten liquid with a first gas to provide dross and a second molten liquid, separating the dross and the second molten liquid, cooling the second molten liquid to form first silicon crystals and a first mother liquid and separating the first silicon crystals and the first mother liquid.
Owner:HIGHLAND MATERIALS INC
Method for reclaiming electrolyte in carbon dross of aluminium electrolysis
A method for retrieving electrolyte form aluminum electrolysis carbon residue, characterized in that the aluminum electrolysis carbon residue is mixed with calcium fluoride serving as disperser with a weight of 1 to 10 wt. % of the carbon residue, and coal serving as combustion catalyst with a weight of 1 to 10 wt. % of the carbon residue, and then is roasted for 1 to 3 hours under a temperature of 650 to 850 degree C.. The method has the advantages of low process cost, high retrieving rate of electrolyte, easy implementation. The retrieved electrolyte has little impurity, and can be directly and completely returned to the electrolysis cell for use without negative effect to the quality of the electrolyte and aluminum melt.
Owner:GUIZHOU BRANCH CHINA ALUMINUM IND
Ultrahigh strength 6000 series aluminium alloy and preparation method thereof
Ultrahigh strength 6000 series aluminium alloy and a preparation method thereof belong to the technical field of metallurgy. The ultrahigh strength 6000 series aluminium alloy comprises the following components by weight: 0.9-1.4% of Si, 1.4-1.8% of Mg, 0.9-1.3% of Cu, 0.05-0.25% of Cr, 0.05-0.25% of Zr, 0.3-0.7% of Fe, no more than 0.04% of Ti, the balance of Al and impurities, has tensile strength of 500-520 MPa, yield strength of 465-503 MPa and elongation percentage no less than 10%. The preparation method is as below: (1) preparing raw materials; (2) melting and uniformly stirring the raw materials and heating to 745-755 DEG C; (3) carrying out degassing treatment, allowing standing and removing scum; (4) carrying out semi continuous casting to obtain ingot casting; (5) carrying out homogenization treatment; (6) insulating at 400-500 DEG C for 1-2 h, and then carrying out hot extrusion deformation, mold stripping and on-line water passing to obtain a extruded bar; and (7) carrying out solid solution treatment, water quenching and artificial aging treatment in order, carrying out air cooling to room temperature to obtain an ultrahigh strength 6000 series aluminium alloy bar. According to the invention, trace elements of Zr, Cr and a proper amount of Fe are added to the aluminium alloy to gain excellent strength and toughness performance, maintain the characteristics of easy formability, good welding performance and corrosion resistance; and the ultrahigh strength 6000 series aluminium alloy is suitable for production of high-strength lightweight structural members with complex sections.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
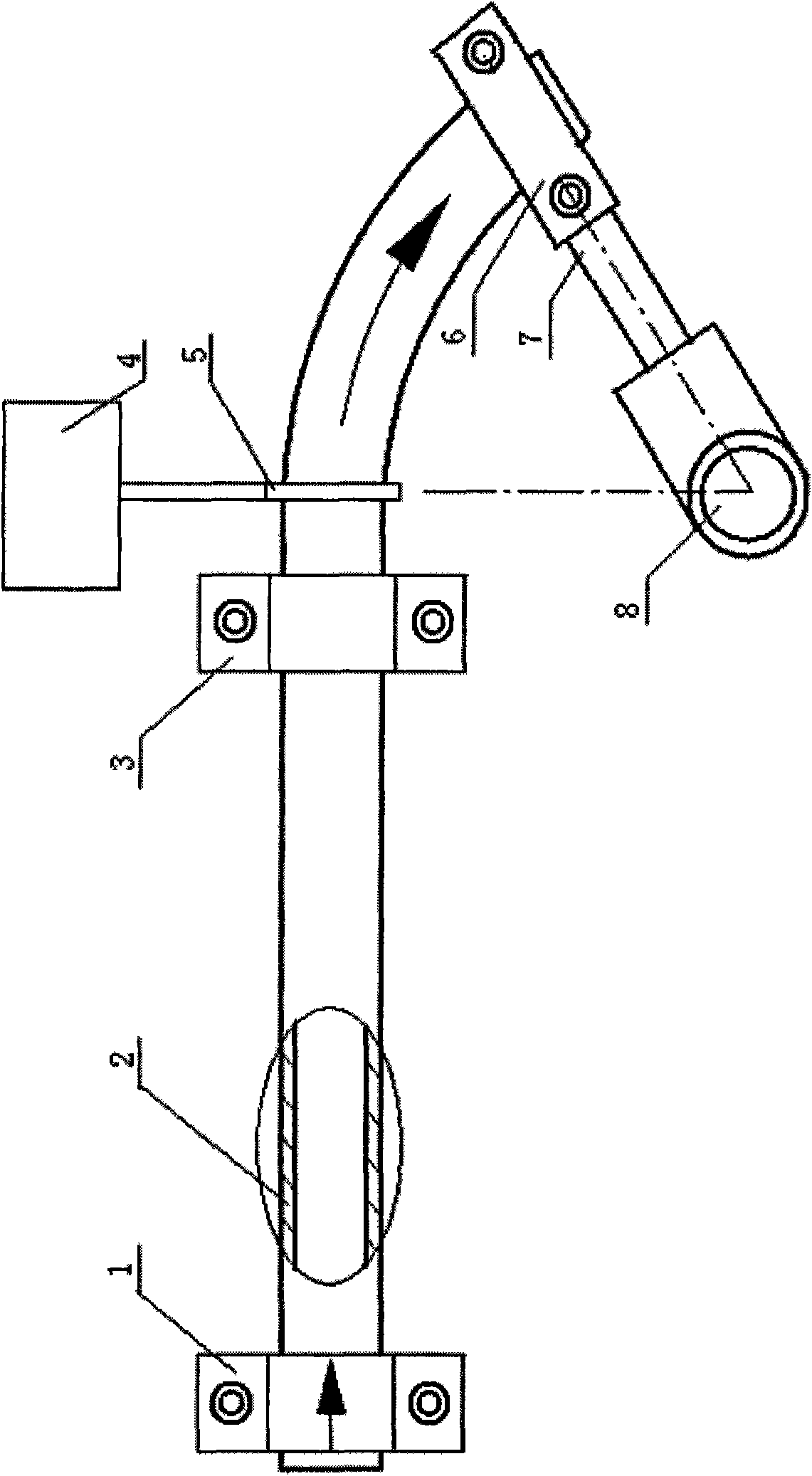
Device for removing zinc dross in galvanized wire zinc pot
InactiveCN101787506AReduce labor intensityEliminate hidden dangers of insecurityHot-dipping/immersion processesWaste productCantilever
The invention relates to a device for removing zinc dross in a galvanized wire zinc pot. The device aims at solving the following disadvantages caused due to that the zinc dross in the zinc pot is removed manually at present: as the zinc pot is full of zinc solution, the zinc solution can spill out; the zinc solution can volatilize toxic dust and the temperature is high; therefore, the labor intensity is high, the zinc solution is harmful to human bodies, and potential safety hazards can be incurred. The technical measures of the device are as follows: the device for removing the zinc dross in the galvanized wire zinc pot comprises a supporting post, a guide screw rod connected with the supporting post, a lifting motor, a cantilever structure, a dross scooping mechanism, a PLC controller and a dross pushing mechanism. The device eliminates the potential safety hazards in production, greatly lowers the labor intensity of operating personnel, improves the product quality, lowers the rejection rate and reduces the production cost.
Owner:WUHAN IRON & STEEL (GROUP) CORP
Method for hot-dip galvanizing
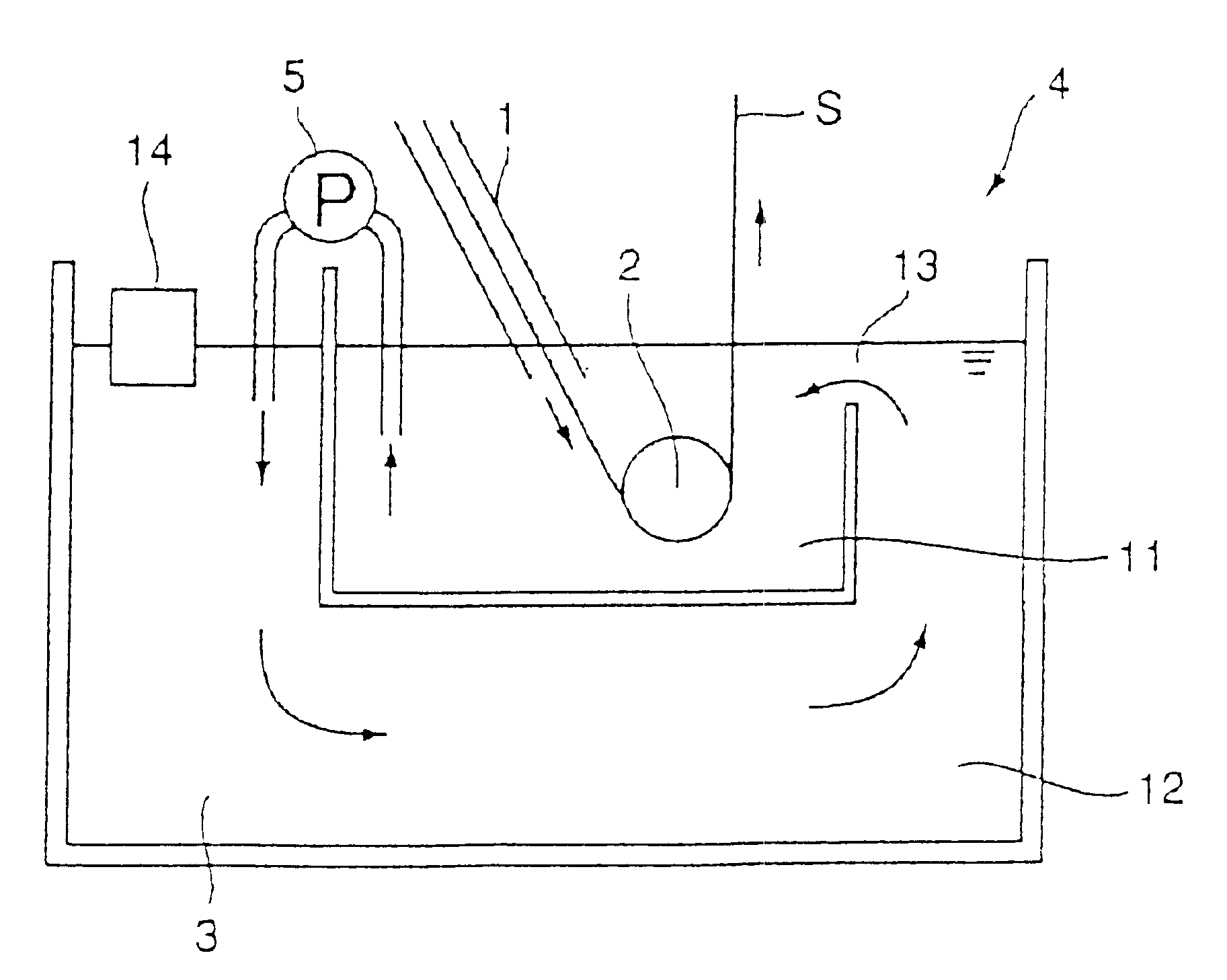
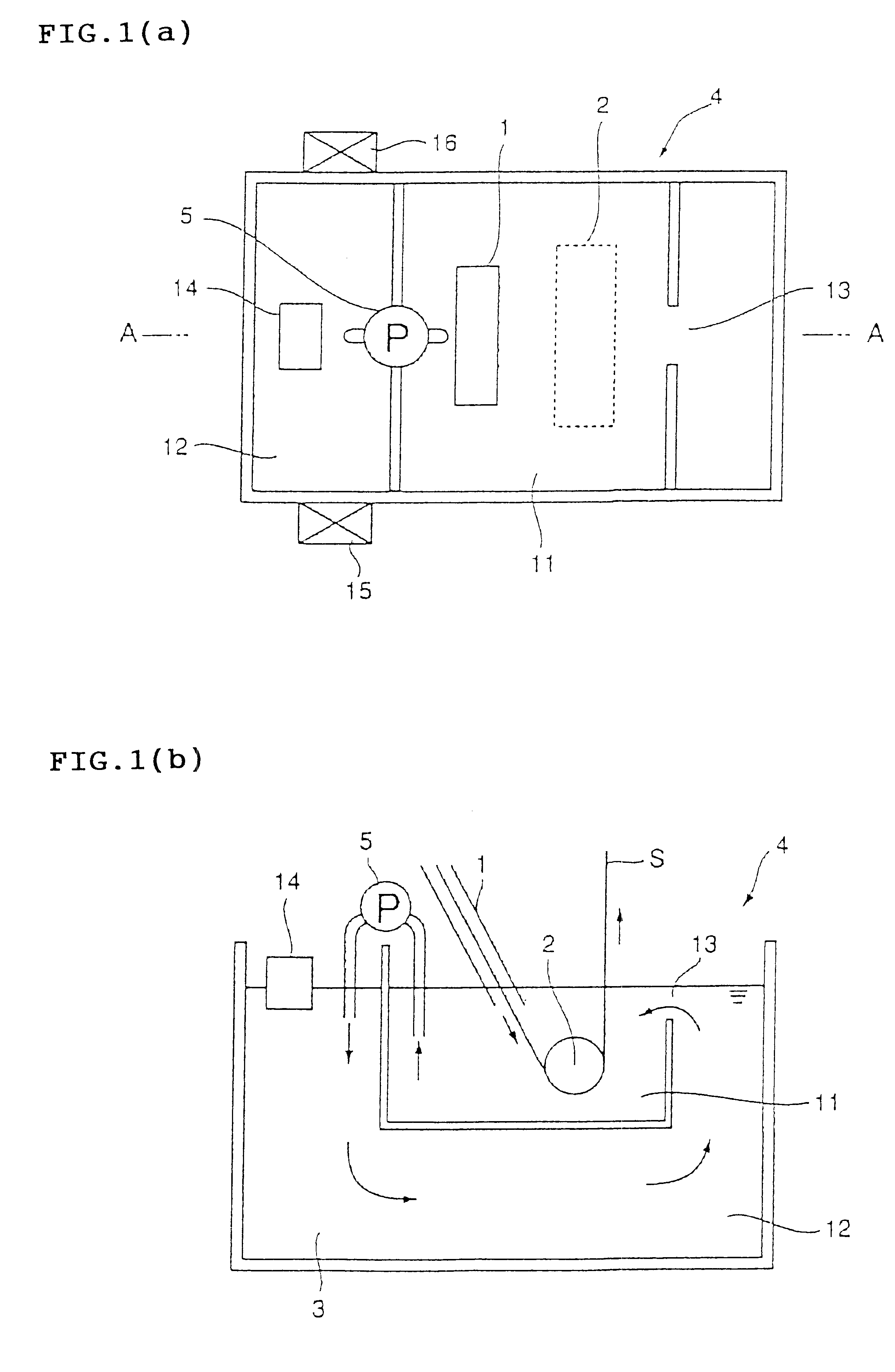
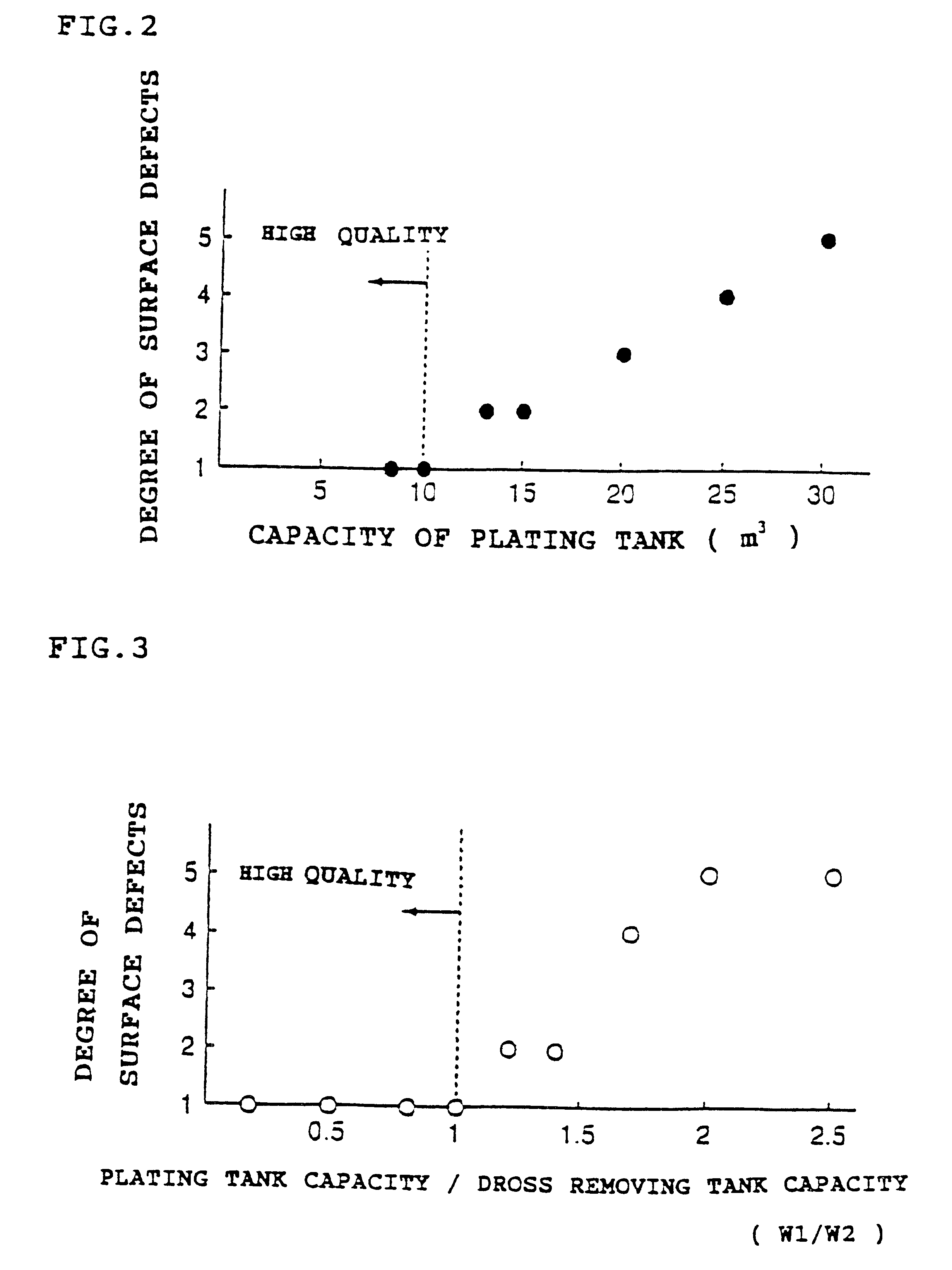
The method for hot dip galvanizing comprises the steps of: dividing a plating vessel holding a molten metal into a plating tank and a dross removing tank; conducting hot dip galvanizing to a steel strip by immersing thereof in the molten metal bath; then transferring the molten metal bath from the plating tank to the dross removing tank; removing a dross from the molten metal bath in the dross removing tank; and recycling the molten metal bath from the dross removing tank to the plating tank through an opening located on the plating tank. The apparatus for galvanizing comprises a plating tank, a dross removing tank, a means to transfer the molten metal bath from the plating tank to the dross removing tank, and an opening located on the plating tank to recycle the molten metal bath from the dross removing tank to the plating tank.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP +1
Method for comprehensively reclaiming arsenic caustic dross and sulfur dioxide flue gas in antimony pyrometallurgical smelting
ActiveCN101899574AEmission complianceSimple processDispersed particle separationProcess efficiency improvementSulfite saltEmission standard
The invention discloses a method for comprehensively reclaiming arsenic caustic dross and sulfur dioxide flue gas in antimony pyrometallurgical smelting. The method comprises the following steps: arsenic containing caustic dross in the antimony smelting process is leached; waste gas sulfur dioxide in the antimony-containing alkaline solution is absorbed; vulcanizer is used for dearsenizing; ferric sulfate is used for further dearsenizing; and purification, concentration and drying are performed; and the like. Therefore, the hard treated arsenic caustic dross and low content sulfur dioxide of the waste gas, which are generated in the antimony smelting process, can be treated completely, wherein the antimony reclaiming rate reaches 99 percent, arsenic removal rate is over 90 percent, sulfur dioxide removal rate is over 95 percent through absorption, so that the gas reaches emission standard, and alkali is transformed into sodium sulfite. The method has the advantages of simple technical process, small equipment investment, remarkable economic benefit and environmental benefit, completely solves the arsenic caustic dross and waste gas sulfur dioxide in the antimony smelting process, and cleans the antimony smelting process. Water solution in the whole process is circulated in a closed loop without wastewater discharge, and the waste gas is qualified to be exhausted to air, so the method is a clean and environment-friendly process.
Owner:锡矿山闪星锑业有限责任公司
Circulating tin plating process and device
The invention relates to the technical field of tin plating of copper wires, in particular to a circulating tin plating process and device. The circulating tin plating process comprises the following steps of: setting speed and stabilizing speed and tension in a tension buffer area; annealing in a high-temperature annealing area at high temperature; initially cooling in an annealing and cooling area; pre-plating tin in an inlet tin heating area; finally plating tin in an outlet tin heating area; scraping residual tin by using a tin plating mold for sizing; protecting reducing gas to deoxidize liquid tin and protecting a wire rod from being oxidized; cooling a hot plated tin wire with water; scraping water on the tin-plated wire with rubber; scraping water and possible tin beads by using a mold; drying residual water by using a drier; cooling the tin-plated wire to room temperature by using a cooling wind scoop; and rolling into a finished product, and the like. By adopting the circulating tin plating process, the product quality of the tin-plated wire is ensured, use of a soldering flux causing pollution can be avoided, noble rare earth metals are avoided or reduced, a large amount of electric energy is saved, waste of tin dross is reduced, operation is simplified and concealed danger of quality is reduced.
Owner:周开勇
Method for in-situ preparation of TiBO2 reinforced magnesium-based composite material
The invention relates to a method of in-situ preparing TiB2 granule strengthening Mg-based composite material in the composite material technical field. The steps are that: powder of K2TiF6, KBF4 and Na3AlF6 are mixed uniformly and then put into a kiln for drying, thus obtaining waterless powder. Aluminum ingot is melted in a resistance furnace with heat preservation and uniformity; the waterless powder after dried is added to the melting Al melt liquid by batch and then is stirred with a graphite disc, and scum on the surface of the melt liquid is removed after stirred and stewed, thus obtaining TiB2-Al intermediate alloy; magnesium alloy is smelted with the protection of SF6 and CO2 mixing gas, and flame retardant element beryllium is added; the TiB2-Al intermediate alloy is added into the magnesium alloy melting solution slowly, stirred, stewed and cast. The technology of the invention is comparatively simple, has low cost, and the density of TiB2 / Mg composite material is between 1.8-2.0g / cm<3> and tensile strength thereof is increased by more than 60 percent than base alloy.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
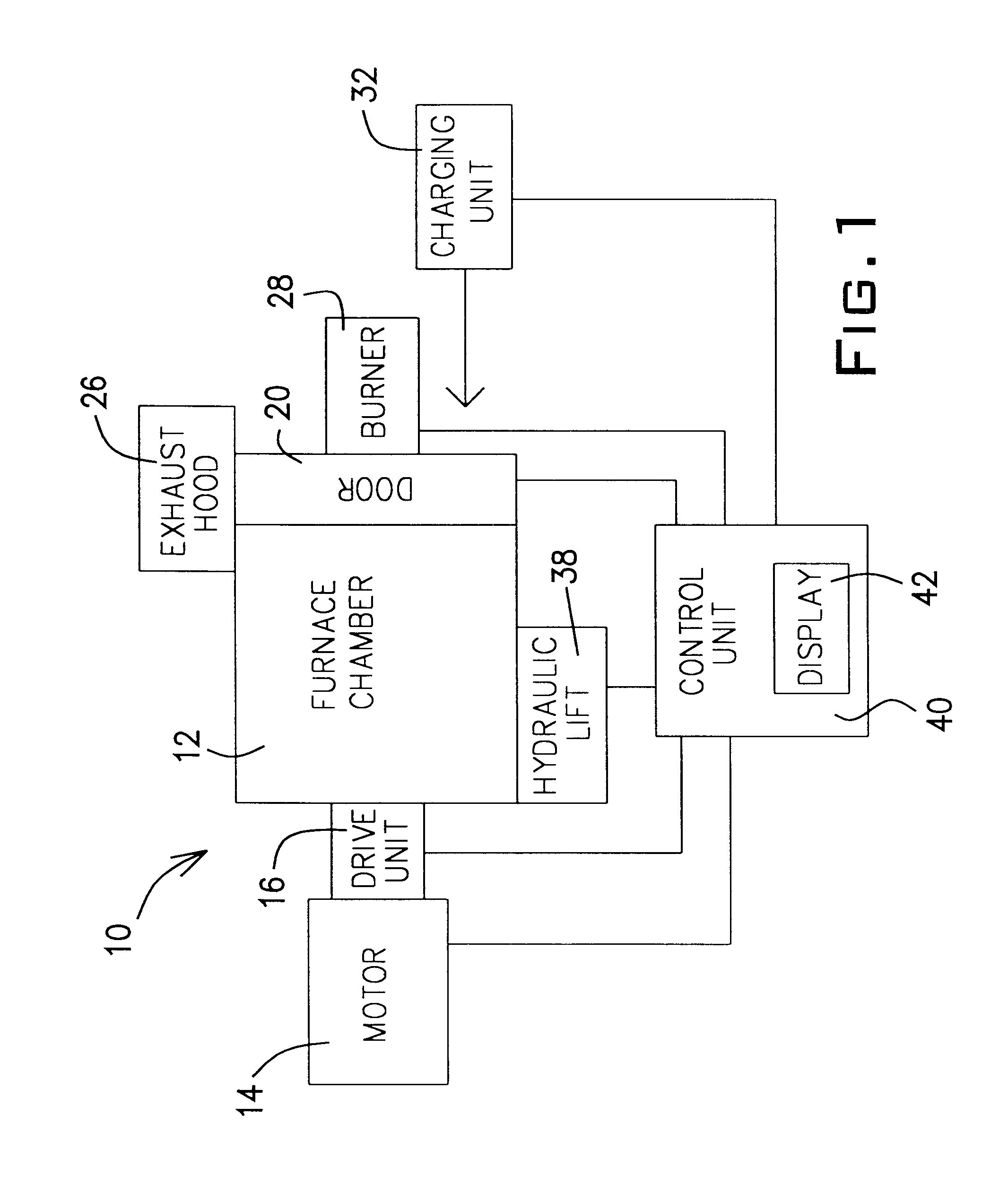
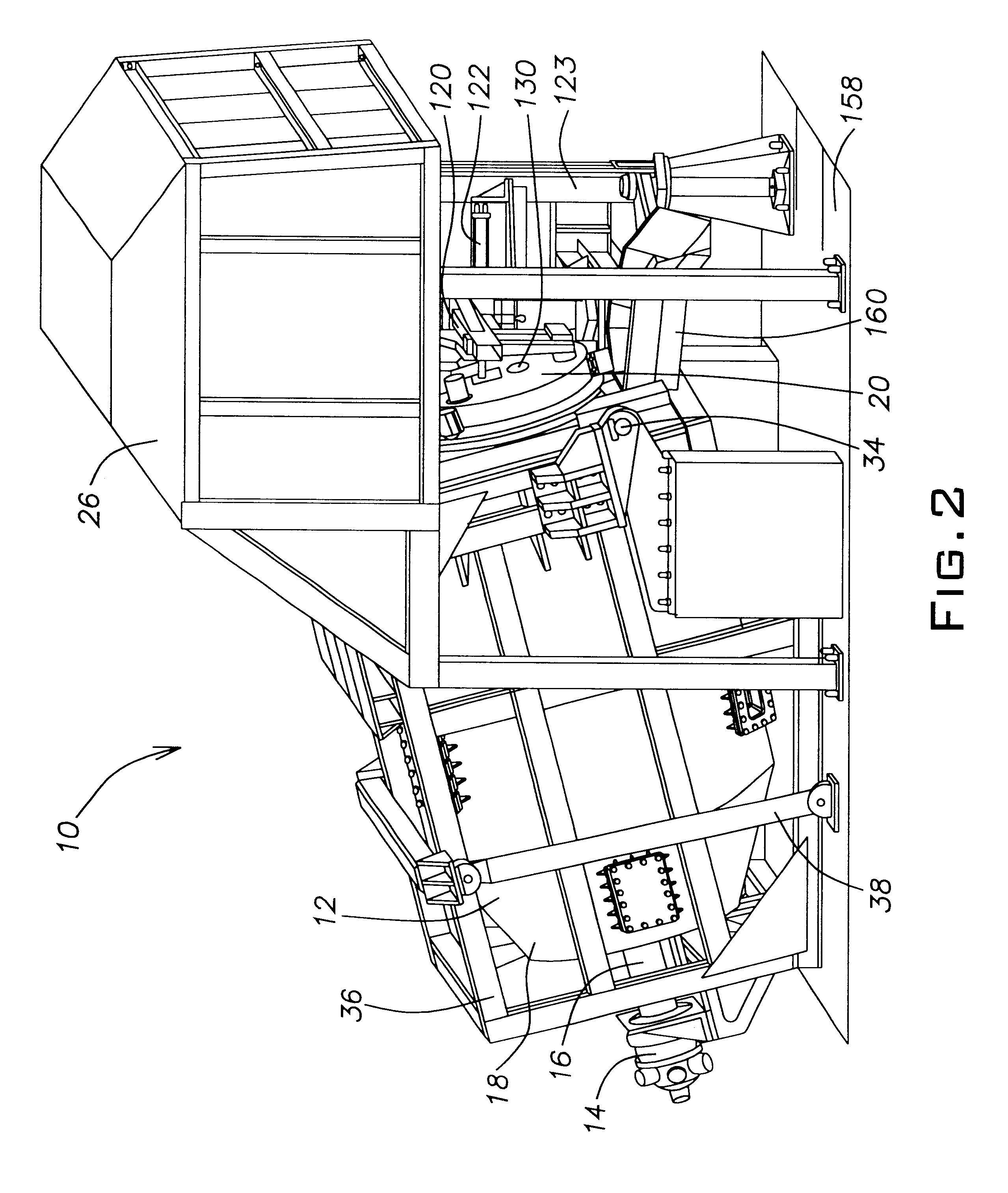
Tilting rotary furnace system for recovery of non-ferrous metals from scrap or dross and method of operation
InactiveUS6395221B1Reduces free airReduce the amount requiredRotary drum furnacesHeat treatment process controlRotary furnaceDross
A furnace system for recovering a non-ferrous metal from a charge of material containing the metal. The furnace system having a furnace chamber having walls defining a refractory chamber, the refractory chamber receiving the charge of material and the metal contained in the charge of material being heated into a flowable mode in the refractory chamber. The furnace system having at least one paddle radially projecting from an interior surface of the furnace chamber toward a longitudinal axis of the furnace chamber. Other features of the invention include a door having a closed position adjacent an inlet passage to the furnace chamber, the door having rollers and a suspension. Other features of the invention include a motor and a control unit which monitors torque to rotate the furnace chamber as an indication of viscosity of the charge of material. Methods of operating a furnace system for recovering non-ferrous metal from a charge of material containing the metal are also discussed.
Owner:ALTEK LLC
Production method for high-purity copper and low-oxygen bright copper rod
The invention relates to a high pure copper and a production method of low-oxidizing bright copper rod, comprising the steps of: performing melting and slag-skimming, poling and crystallisation by cooling to the waste copper crap to obtain the high pure copper; heating the copper to 1080-1120 DEG C to obtain the copper liquid, wherein the infusible high melting point impurities are eliminated by slag-skimming, after that, adding arenaceous quartz and silicon dioxide into the copper liquid and blowing excessive oxygen to convert the metals which are livelier than the copper into the scruff to remove, then pressurizing and blowing the oxygen to the copper liquid so that lead sub-oxide deposited at the bottom of furnace to sufficiently react with the arenaceous quartz to generate the scruff for removing the lead, guaranteeing the purity of the copper is larger than 99.5% and the lead content is less than 2ppm; the production method of low-oxidizing bright copper rod mainly comprises the steps of: taking purple copper crap as the raw material, directly placing the high pure copper liquid through the melting and slag-skimming, poling and crystallisation by cooling orderly into the continuous-casting and continuous-rolling apparatus to cast, the yield of low-oxidizing bright copper rod is larger than 98%, reaching the green environmental standard required by Europe Union ROHS, the production method has low production cost.
Owner:江苏万宝铜业集团有限公司
Method for recovering germanium from zinc dross
ActiveCN101760653ANo pollution in the processSolve the technical problems of recyclingProcess efficiency improvementIndiumEvaporation
Then invention relates to a method for recovering germanium from zinc dross, belonging to the technical field of non-ferrous metallurgy. After the secondary extracted zinc is leached by adopting the wet method, and the leached dross can be pre-treated, the germanium can be converted into the germanic from the low-valence in metal or germanium monoxide. Namely, hydrogen peroxide is used for oxidizing germanium, lead, indium, arsenic and other elements in the hydrochloric acid medium, so that the elements can be oxidized from low valence to high valence; the lead, indium, arsenic, gallium and the like react into solution, the low-valence germanium wrapped by the elements can be exposed and oxidized to be the germanic by the hydrogen peroxide under the acid condition into hydrochloric acid solution, and the germanic can escape in a form of germanium tetrachloride by evaporation, so as to realize the separation with other purities; and then, the separated germanium tetrachloride is purified and hydrolyzed, so as to prepare germanium dioxide. In the zinc dross with the germanic being more than 2.0%, the recovery rate of the germanic can reach more than 98%; in the zinc dross with the germanic being more than 1.0-2.0%, the recovery rate of the germanic can reach more than 95%; and in the zinc dross with the germanic being 0.1-1.0%, the recovery rate of the germanic can reach more than 90%.
Owner:YUNNAN WUXIN IND
Recycled high-performance concrete and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104446175AConvenience to workIncreased durabilitySolid waste managementRoad engineeringToughening
The invention relates to recycled high-performance concrete and a preparation method thereof. The recycled high-performance concrete is prepared from recycled coarse aggregates, made from crushed construction waste, as a raw main raw material, and added with natural sand, cement, coal ash, aluminum dross, an admixture, graphene and water in a stirring manner. According to the preparation method, a micropore of a cement-based composite material is filled with a nanometer material, namely graphene, so that the effects of reinforcing, toughening, and reducing the shrinkage are achieved. The aluminum dross produced in the electrolytic aluminum production process is adopted as the admixture; and aluminite powder in the aluminum dross expands in water, so as to play a shrinkage-compensating role. The concrete is small in shrinkage besides good working performance, durability and relatively high strength, and can be widely applied to road engineering, structure engineering and the like.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
High-protein microbiological feed and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102960539ASolve pollutionRaw materials are easy to getAnimal feeding stuffMagnesium saltPhosphate
The invention provides a high-protein microbiological feed and a preparation method of the high-protein microbiological feed. Dross is one of products produced in the process of floating and clarifying the mixed juice during sugar preparing by the sugarcane, and is rich in various organic non-sugar components; the dross is always considered as impurities and mixed in the mud juice by a sugar plant, and finally becomes lime sludge to cause waste. The preparation method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of taking the dross in the crane sugar plant as the raw material, and taking a non-protein nitrogen source, phosphate and magnesium salt and the like as the auxiliary materials; mixing the raw material and the auxiliary materials; sterilizing; adding beneficial zymocyte preparation; and fermenting at the aerobic condition so as to obtain the high-protein microbiological feed. By adopting the preparation method provided by the invention, the problems that a large quantity of dross is in the crane sugar plant and is adhered and hardly processed, and the loss of the sugar is serious can be solved well; and the current situation that the protein feed resources are in a shortage can be relieved. According to the preparation method, the cost is low, the period is short, the production technology is simple, the limitation from the field and equipment is less, and the quality and the yield of the high-protein microbiological feed are high, and the preparation method plays an important role in popularization and application of the mixed juice floating and clarifying technology in sugar plants.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION CENT FOR ANALYSIS & TEST RES +1
Silt solidification method
ActiveCN103253899AAchieve recyclingHigh chemical activitySludge treatmentSolid waste managementSuperplasticizerDross
The invention discloses a silt solidification method, which comprises the following steps: weighting raw materials in parts by weight: 100 parts of marine silt, 5-20 parts of caustic dross, 0-5 parts of mineral powder, 5-30 parts of a solidifying agent, wherein the solidifying agent comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 10-50 parts of fly ash, 20-80 parts of mineral waste residues and 2-10 parts of a catalyst, the catalyst is selected from a naphthalene-based superplasticizer, an early-strength slushing agent and an antifreezing agent and the like, and the marine silt is obtained by capturing and stockpiling; adding the raw materials into a mixer in part by weight to mix uniformly, thereby obtaining a mixture; and carrying out transportation, compaction, maintenance and detection on the mixture. The method disclosed by the invention can be applied to the filed stirring and solidification of dredger fills, cement injection piles and the like of roadbases, cement stabilization layers, soft-soil foundation reinforced working underlayers and loading layers in municipal, transportation, water conservancy and port engineering. The method disclosed by the invention can save the construction period and save the cost, is rapid in solidification effect and good in effect, and can achieve an effect of environmental protection and economy and reaches the sustainable development of renewable energy sources.
Owner:连云港港口工程设计研究院有限公司
Method for manufacturing cast magnesium alloy
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing cast magnesium alloy, omprising the steps: 1, batching: calculating the percentage of elements including Gd, Y, Zr, and Mg as balance; calculating the weight and the respective batching weight of elements; 2: smelting: adding in sequence Mg, Mg-Gd, Mg-Y and Mg-Zr with Gd, Y and Zr as intermediate alloy; feeding in SF6 / CO2 protective gas for refining; dredging up dregs at the bottom of a crucible, then reheating the crucible to 780-800 DEG C, standing the crucible for 30 minutes under heat preservation, and cooling the crucible to 730-740 DEG C along with furnace and subsequently removing scum on the surface; 3: pouring: preheating a mould, adjusting the temperature of magnesium alloy melt and pouring; 4: heat treatment, including: solution treatment and aging treatment. Solving the problems of high cost, low elongation percentage, inadequate heat resistance of the manufactured material, environmental pollution and the like, the method obtains the effect of high strength, good heat resistance, small tendency of incompactness, segregation and crack of the manufactured material.
Owner:SHANGHAI SPACE PRECISION MACHINERY RES INST +1
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com