Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
32 results about "Transition density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
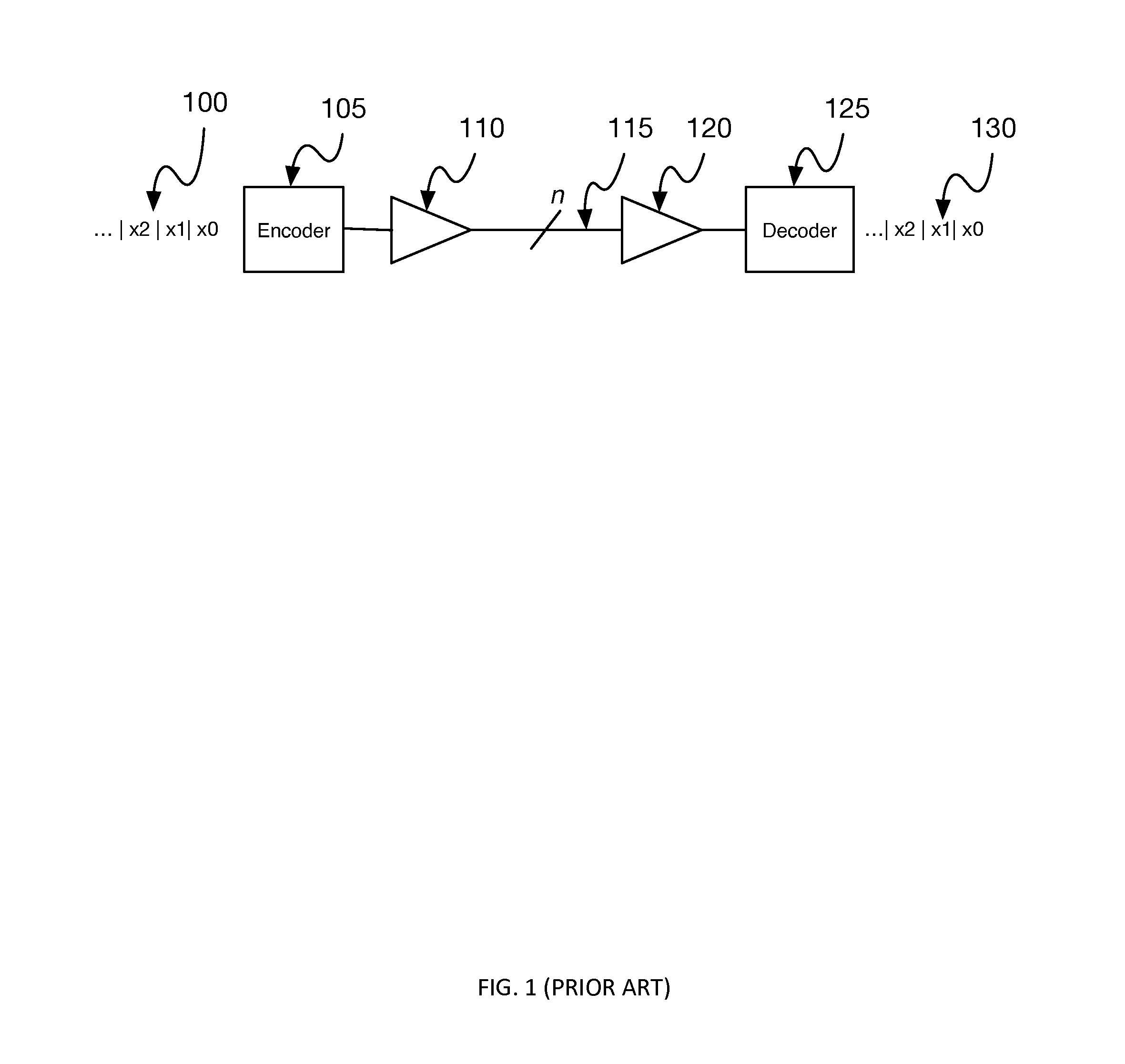
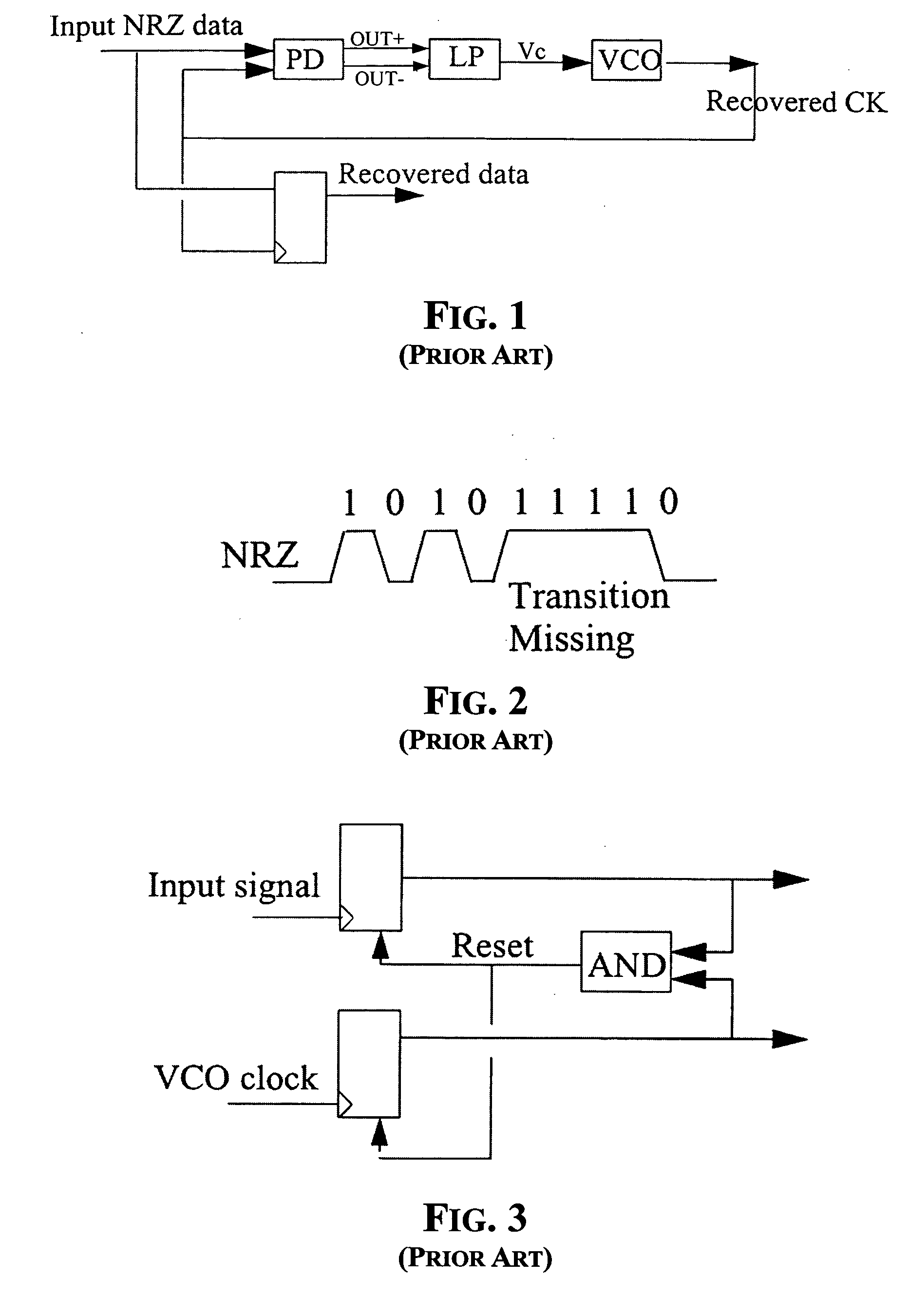
DEFINITION OF “TRANSITION DENSITY”. Transition Density is the ratio of transitions (or edges) to the number of unit intervals in a serial data stream. For many serial communications test signals, this ratio approaches 0.5, or half as many transitions as bit intervals.
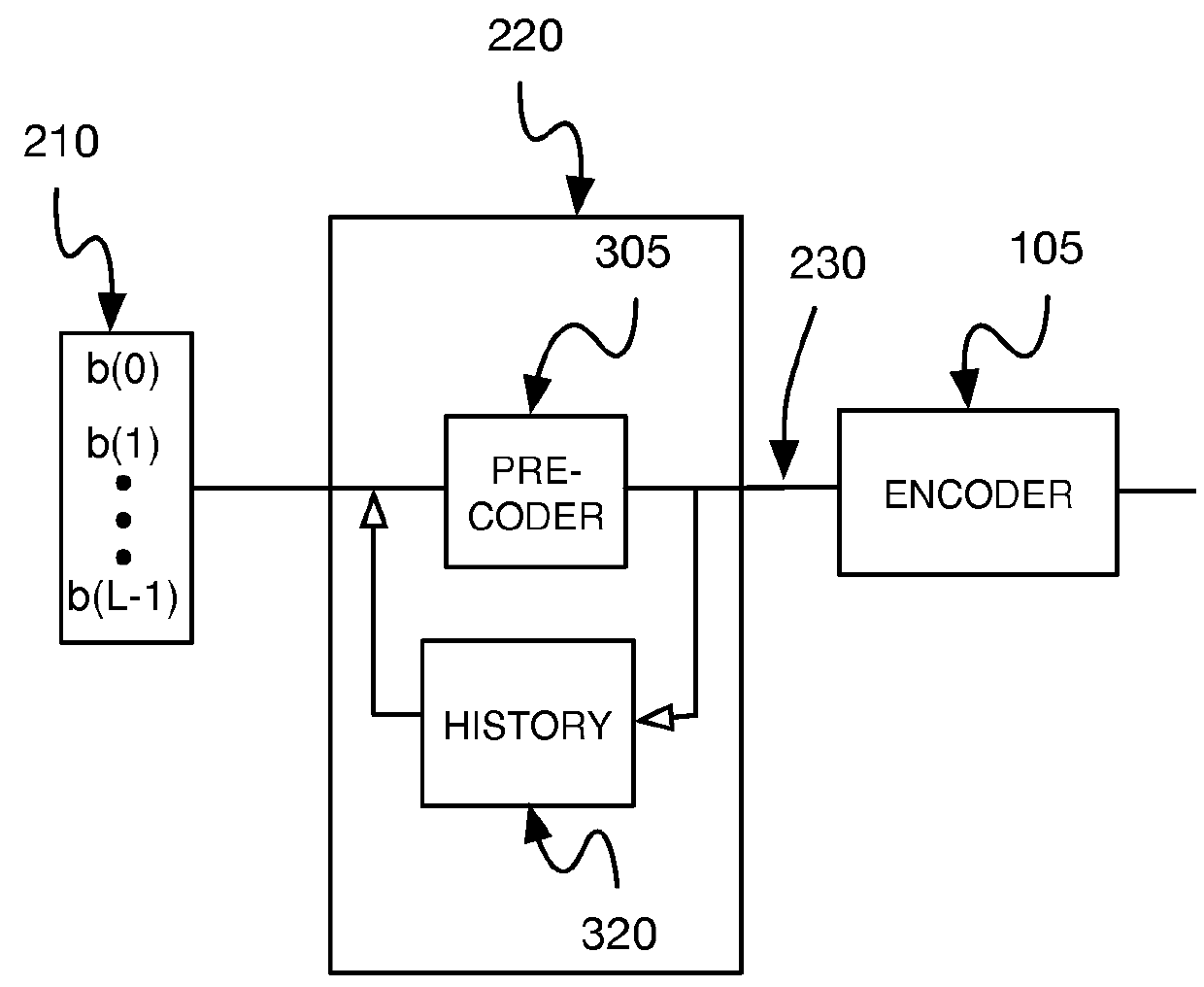
Clock-Embedded Vector Signaling Codes
ActiveUS20150249559A1Line-faulsts/interference reductionTransmitter/receiver shaping networksTransition densityData element
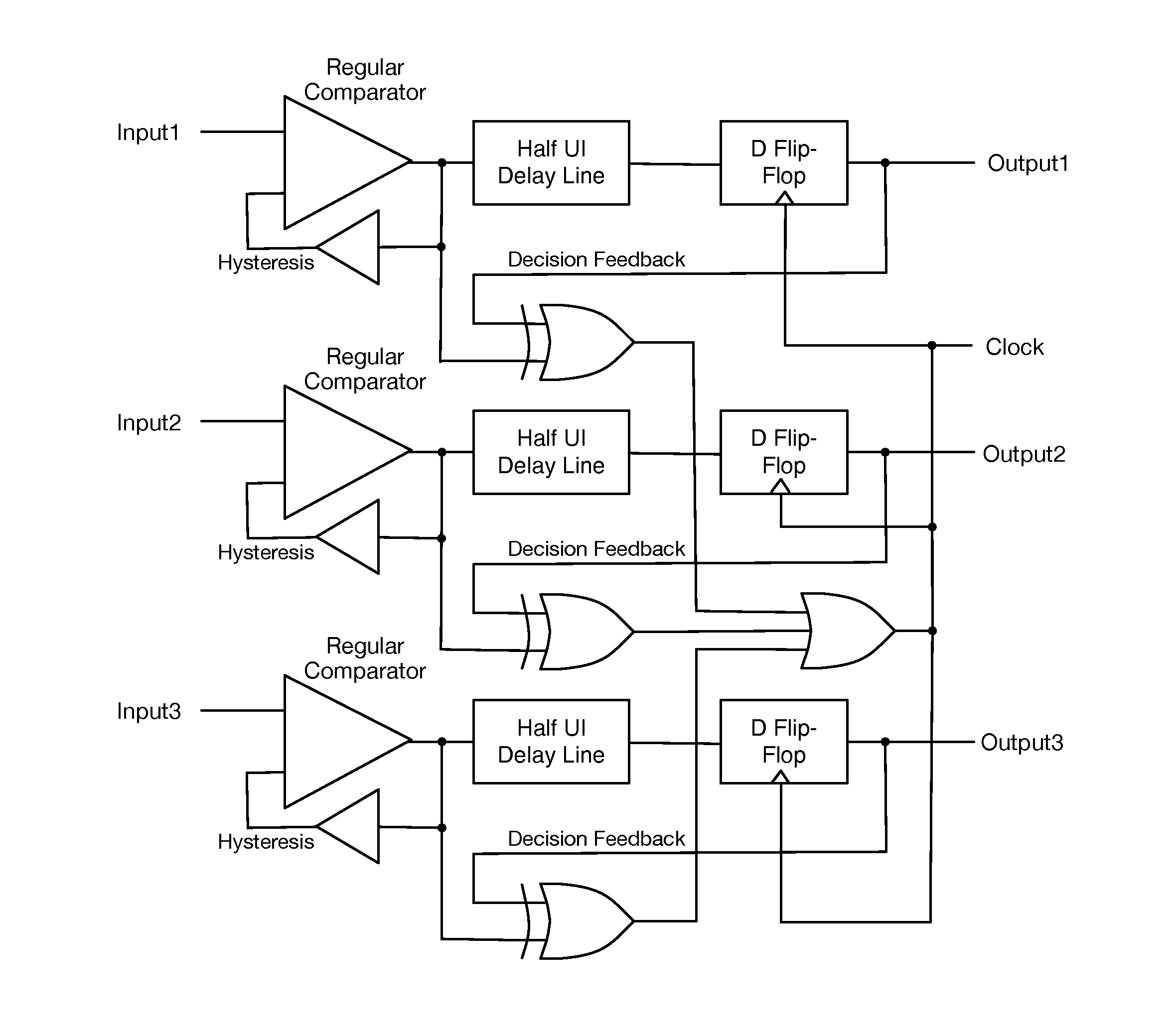
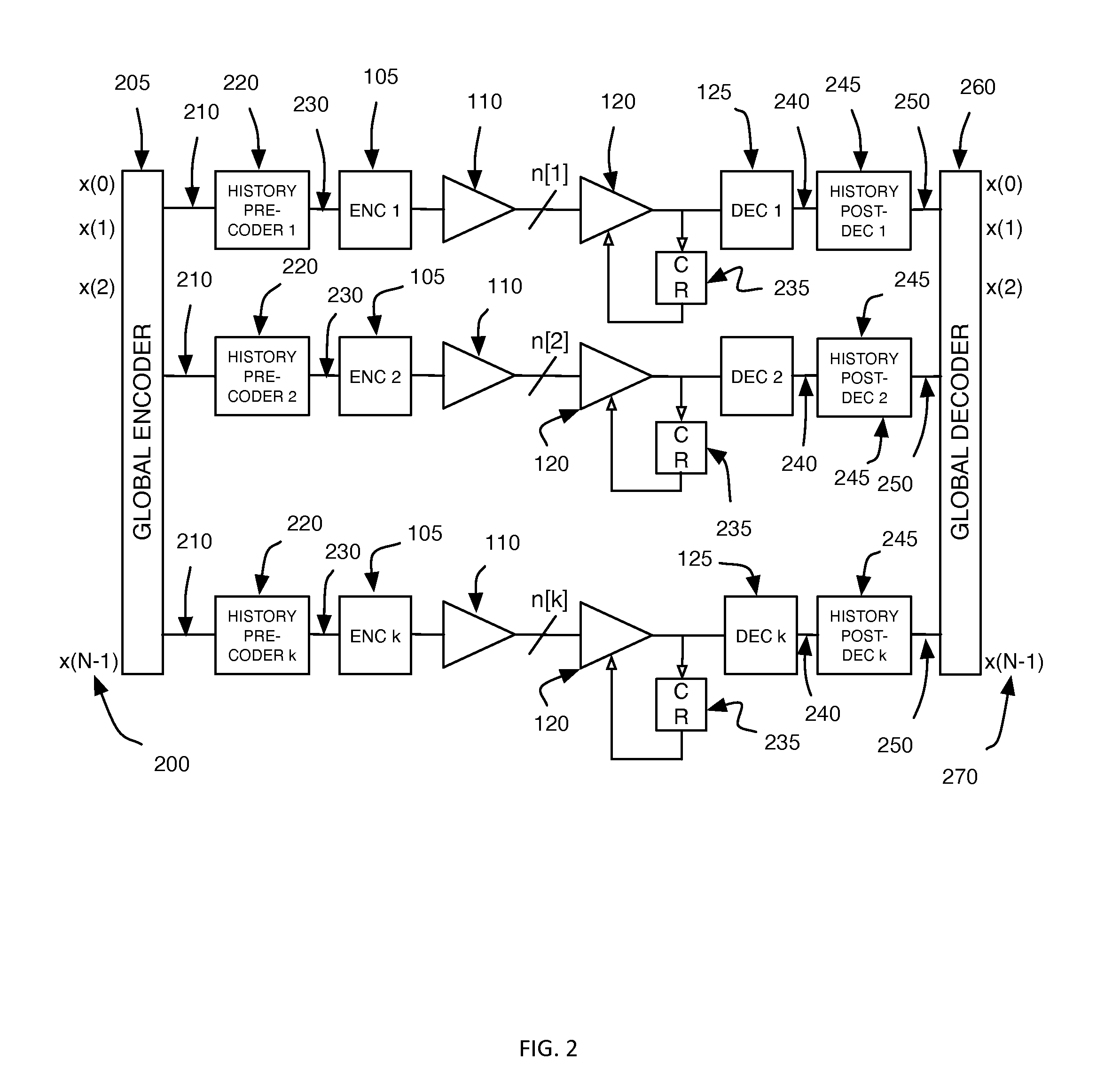
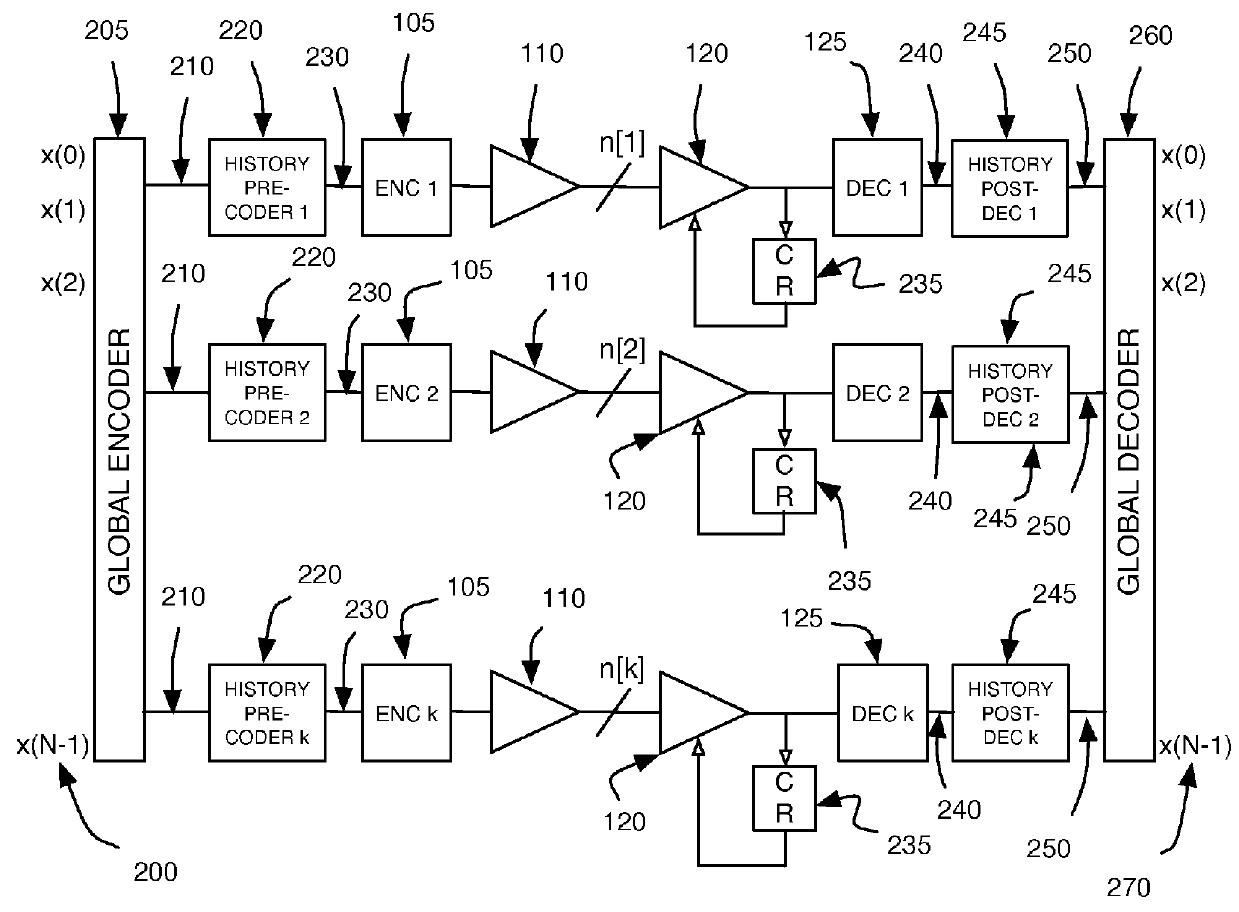
Vector signaling codes providing guaranteed numbers of transitions per unit transmission interval are described, along with methods and systems for their generation and use. The described architecture may include multiple communications sub-systems, each having its own communications wire group or sub-channel, clock-embedded signaling code, pre- and post-processing stages to guarantee the desired code transition density, and global encoding and decoding stages to first distribute data elements among the sub-systems, and then to reconstitute the received data from its received sub-system elements.
Owner:KANDOU LABS
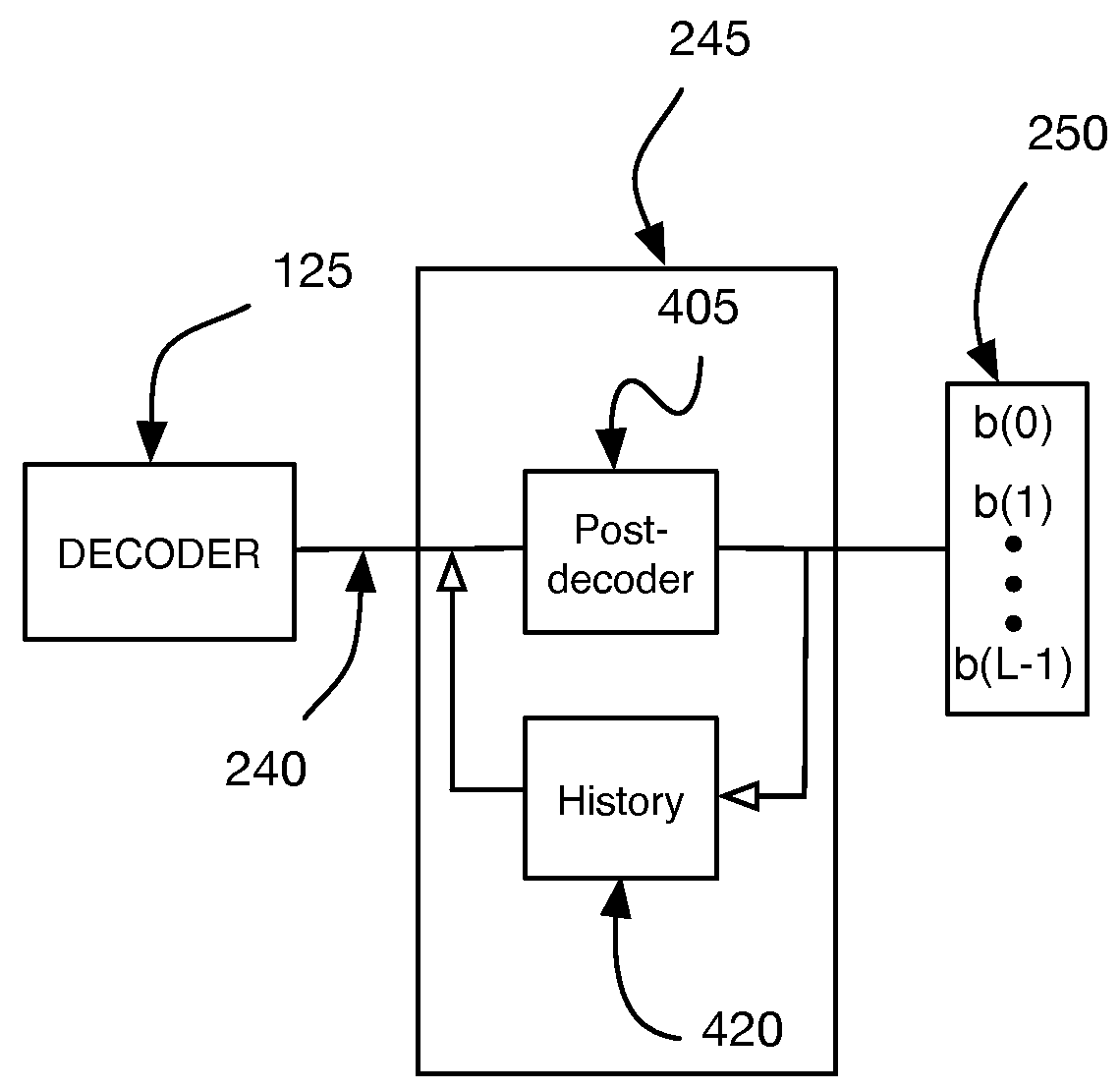
Clock-embedded vector signaling codes
ActiveUS9363114B2Line-faulsts/interference reductionTransmitter/receiver shaping networksTransition densityData element
Vector signaling codes providing guaranteed numbers of transitions per unit transmission interval are described, along with methods and systems for their generation and use. The described architecture may include multiple communications sub-systems, each having its own communications wire group or sub-channel, clock-embedded signaling code, pre- and post-processing stages to guarantee the desired code transition density, and global encoding and decoding stages to first distribute data elements among the sub-systems, and then to reconstitute the received data from its received sub-system elements.
Owner:KANDOU LABS
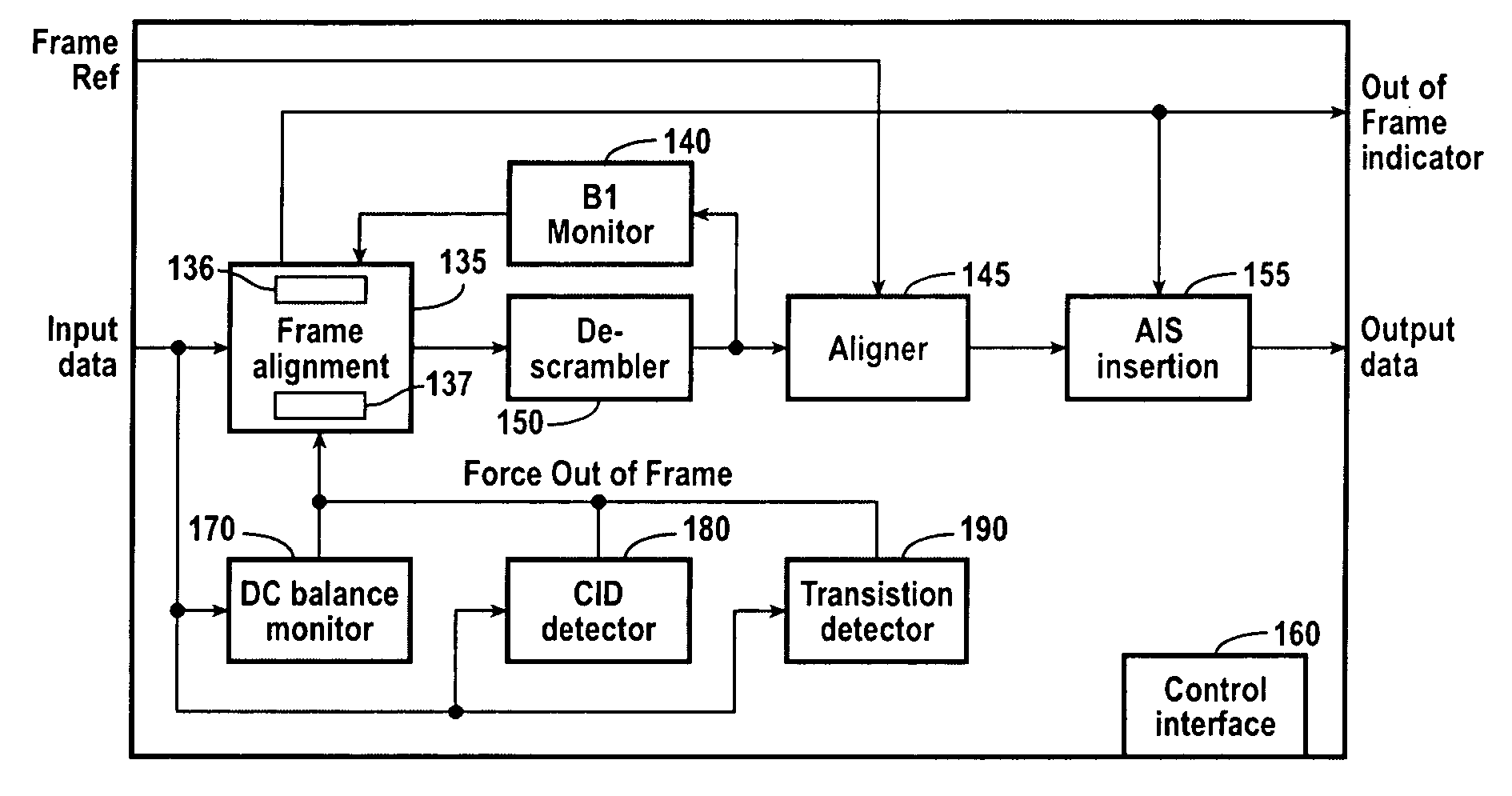
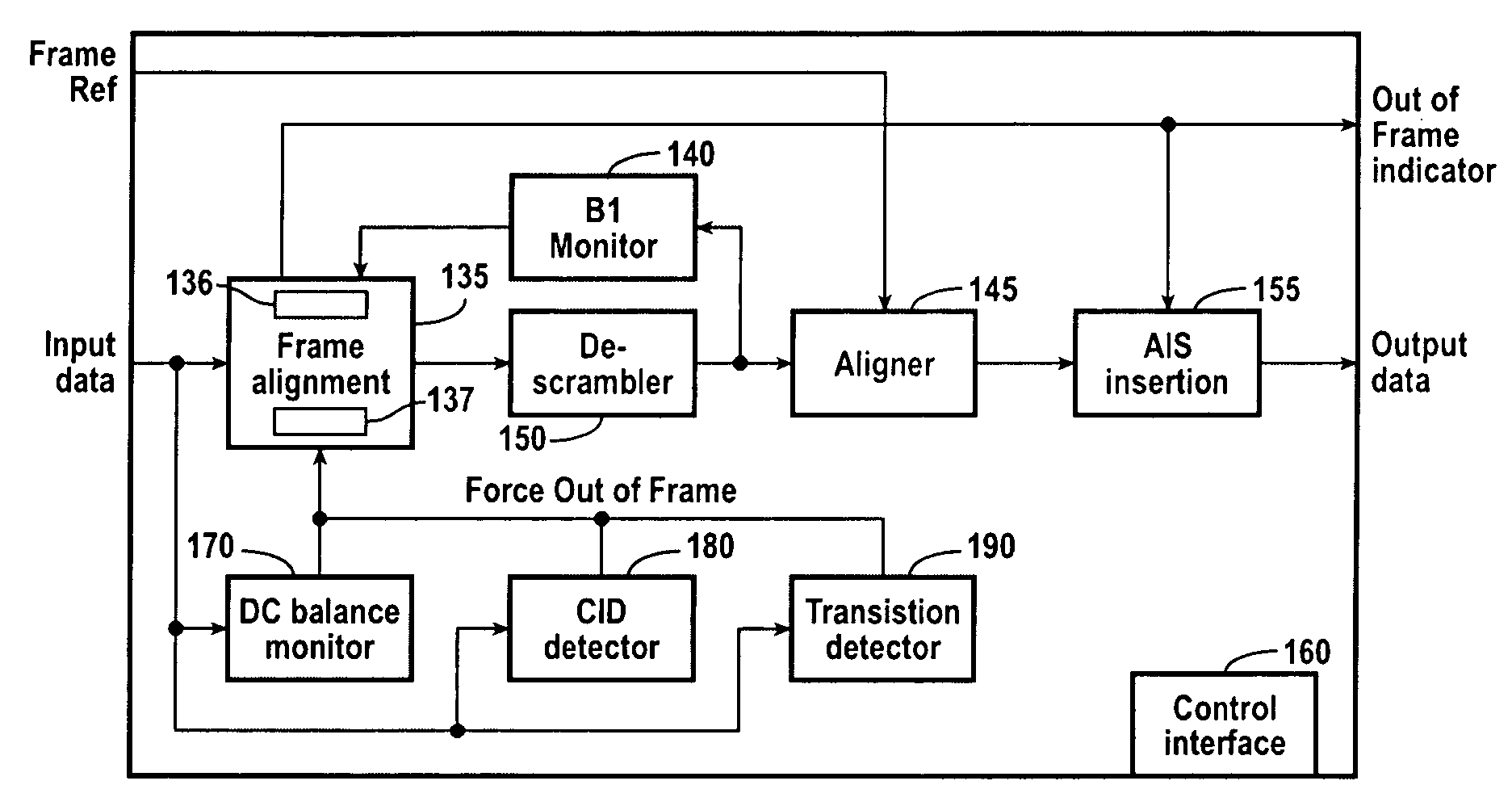
Serial data validity monitor
InactiveUS20050025195A1Avoid dataReduce the possibilityError preventionTime-division multiplexTransition densityData stream
A data detection system includes, in part, a CID detector, a DC balance monitor and a transition density detector. The CID detector is configured to detect whether the received data stream includes a CID exceeding a predetermined threshold count. The DC balance monitor is configured to detect DC imbalances in the incoming data and that may be indicative of errors in the data. The transition density detector is configured to detect whether a minimum transition density exists during a given time period. If a violation is detected by any one of these three detectors, an out-of-frame signal is asserted. The incoming data stream may be a scrambled SONET or SDH data stream.
Owner:PMC-SIERRA
Method and apparatus for estimating random jitter (RJ) and deterministic jitter (DJ) from bit error rate (BER)
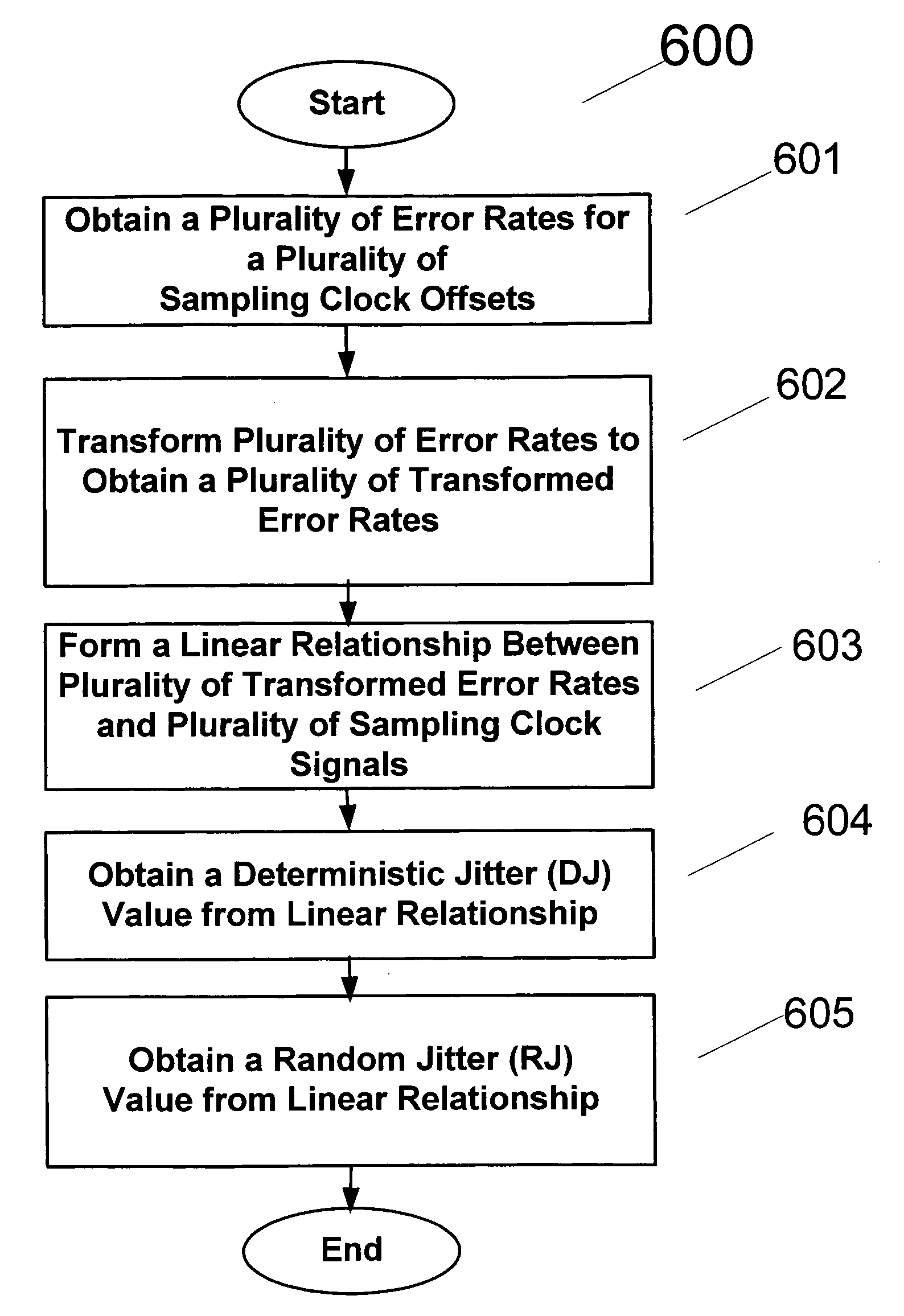
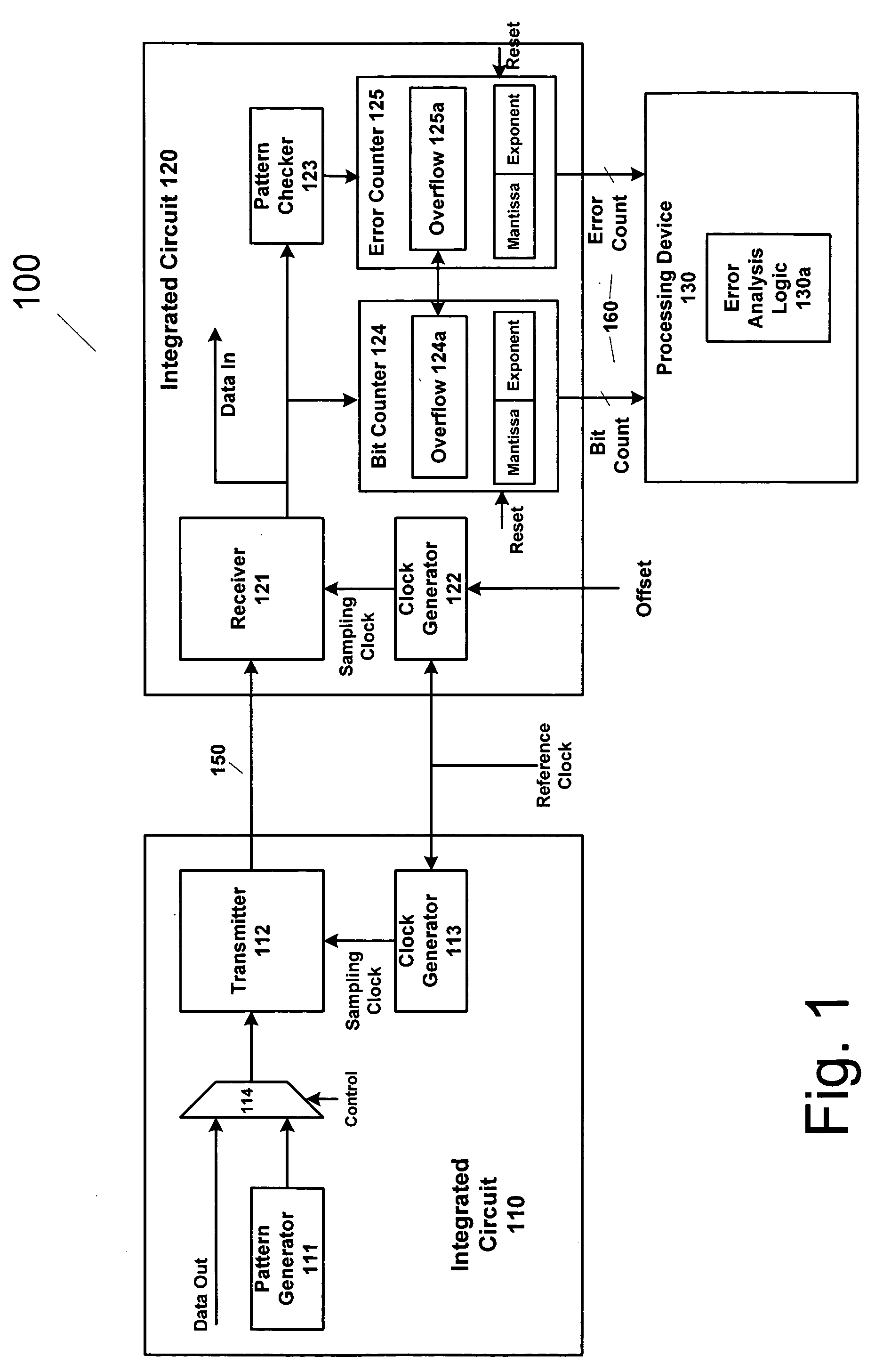
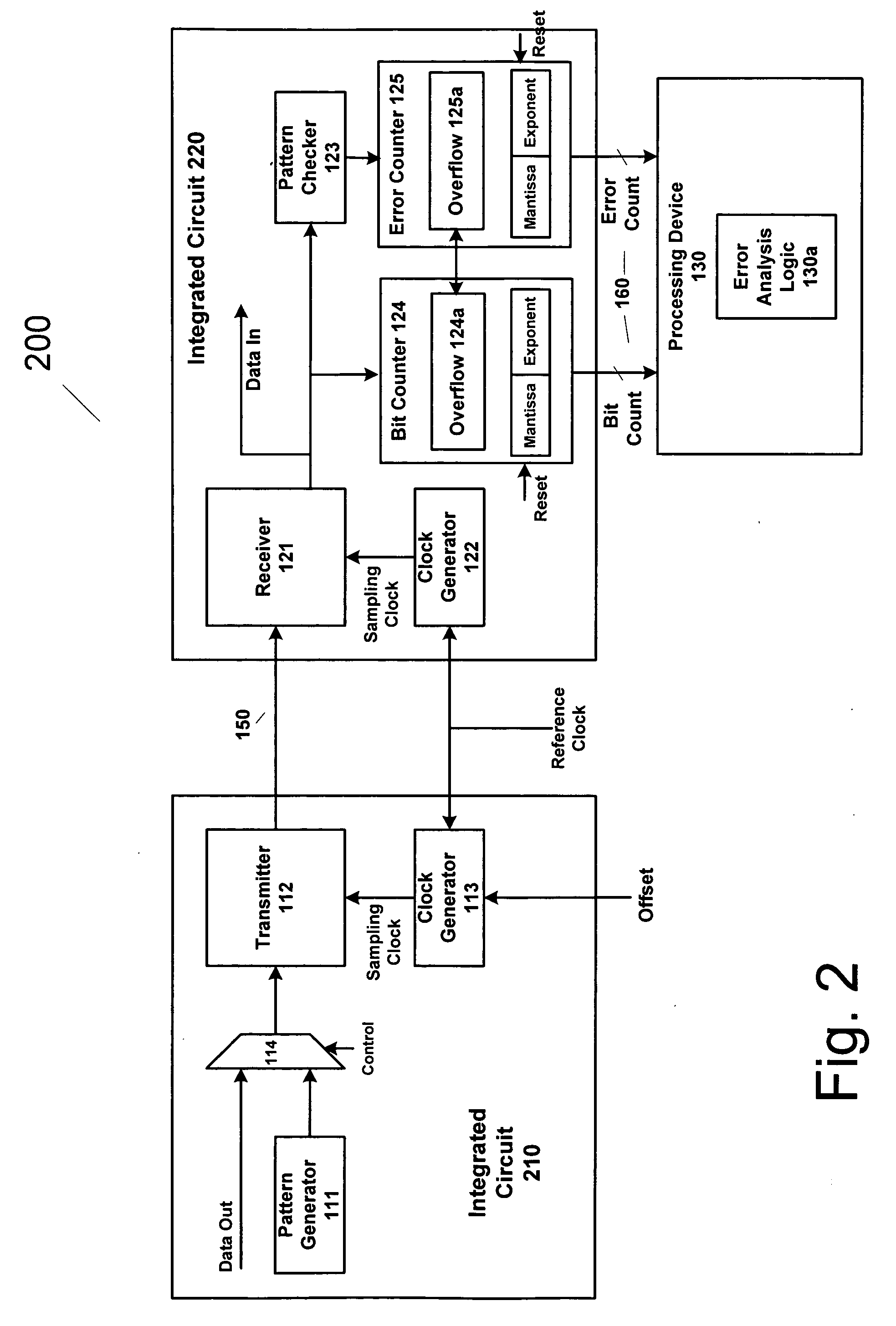
An apparatus and method provides prediction of BER for an interface between ICs, such as a processor and a memory device, without using special test equipment. A known data pattern or PRBS is transmitted to a receiver, which compares the received data values with expected data values to determine if a bit error has occurred in an embodiment of the present invention. A center of data eye and the edge of the data eye are sampled (over sampled) in order to determine if a bit error has occurred in an alternate embodiment of the present invention. A first counter is used to count the total number of bits sampled and the second counter is used to count the number of errors that occurred in the total number of bits sampled. In an embodiment of the present invention, the first and second counters are logarithmic counters that include overflow protection. The counter values are output to a processing device to perform the BER calculation in an embodiment of the present invention. A plurality of BER values is then obtained for corresponding offsets. A subset of the plurality of BER values corresponding to the plurality of offsets is selected. An inverse of the standard normal cumulative distribution (NormSlnv) function for respective BER values is calculated. Two linear fits on the transformed BER values and offsets are performed to obtain the x-intercepts that correspond to a DJ component and the slopes corresponding to a RJ component. The DJ and RJ components are used with the Fibre Channel jitter model equation to predict BER as a function of transition density and offset value.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
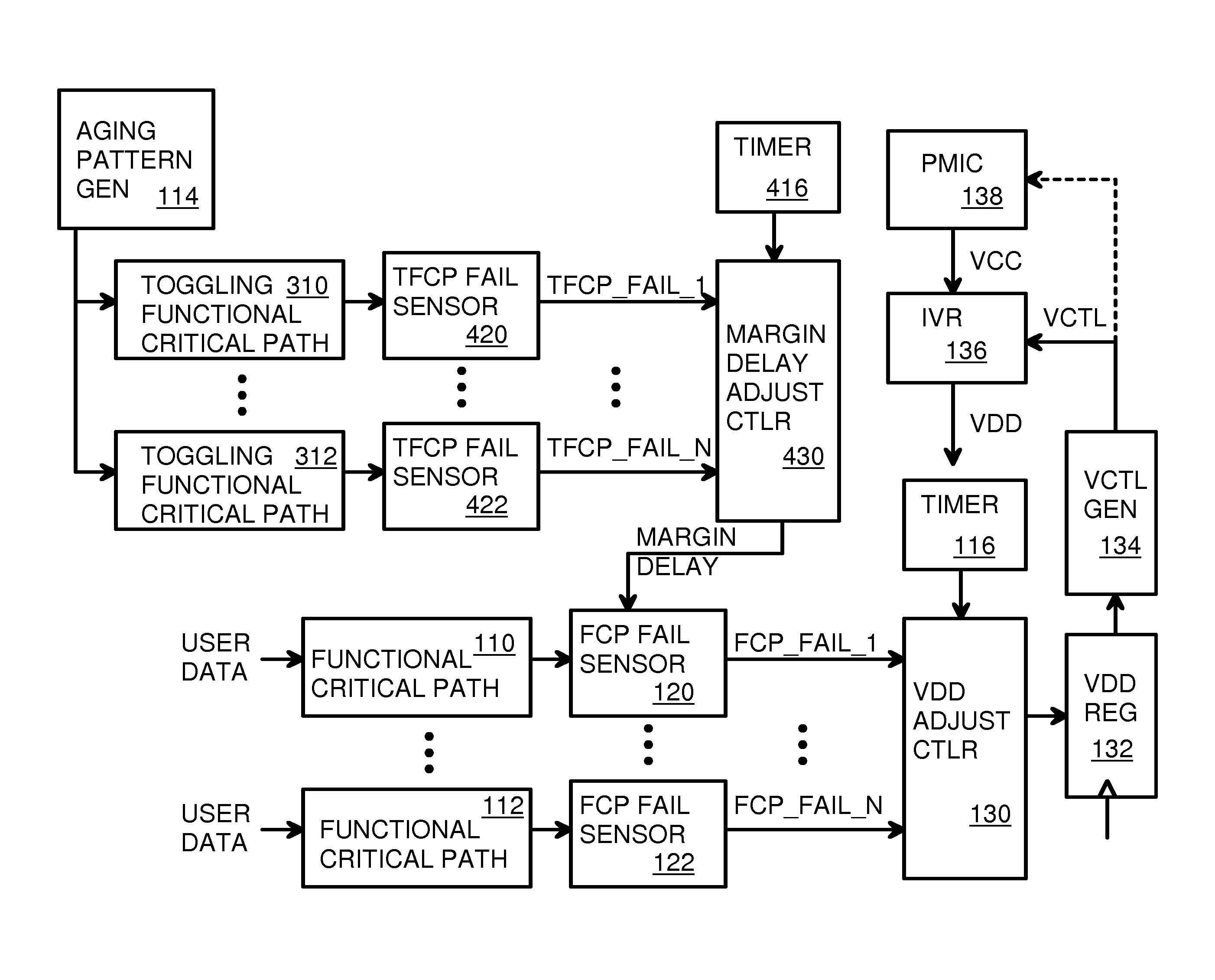
Circuitry and method for timing speculation via toggling functional critical paths
InactiveUS9564883B1Power consumption reductionSingle output arrangementsTransition densityExclusive or
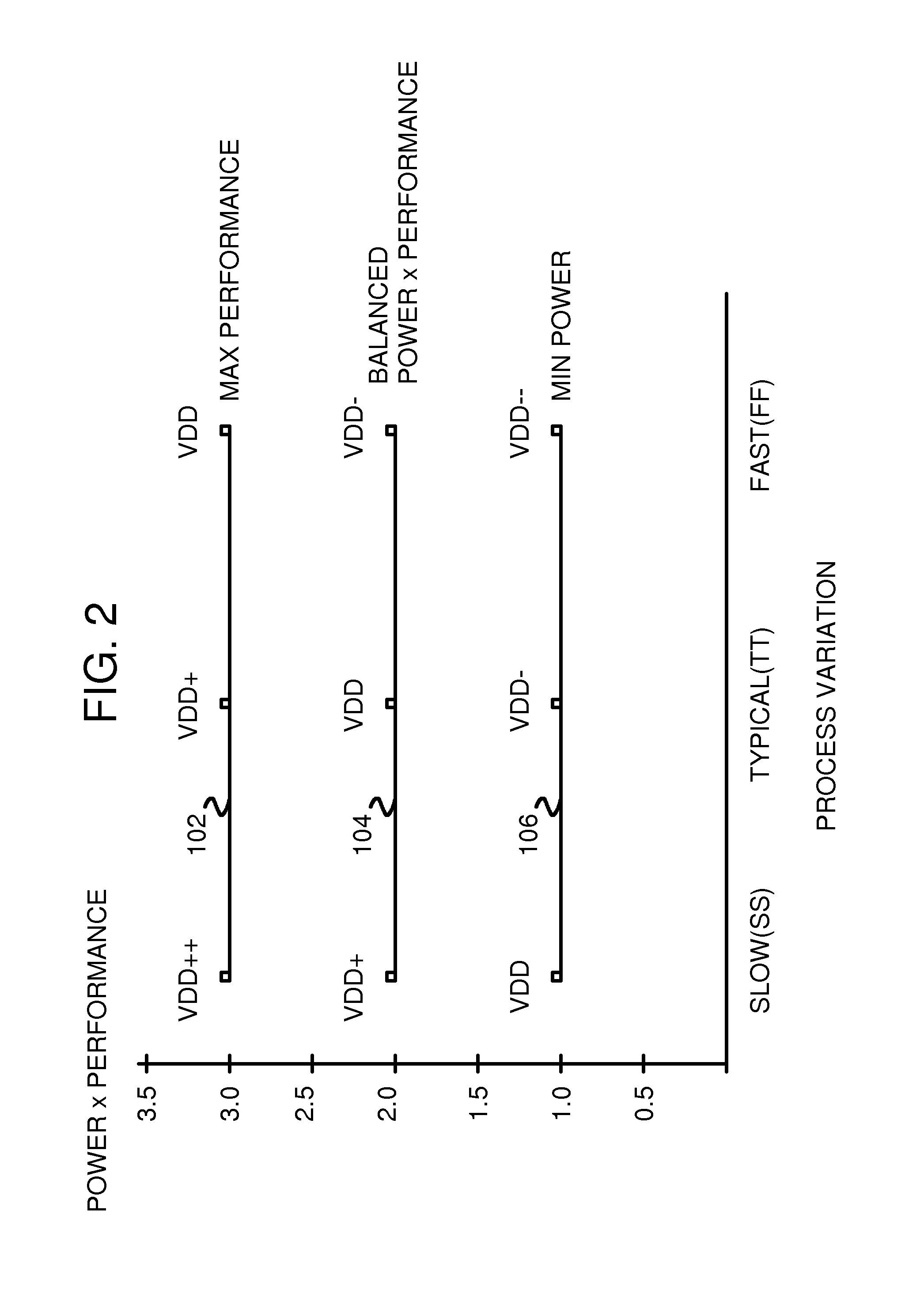
Toggling functional critical path timing sensors measure delays in toggling functional critical paths that are replicas of actual critical paths or representations of worst-case delay paths. A Toggle flip-flop or Linear-Feedback-Shift Register (LFSR) drives high-transition-density test patterns to the toggling functional critical paths. When a toggling functional critical path's delay fails to meet set-up timing requirement to a next register, the toggling functional critical path timing sensors signal a controller to increase VDD. When no failures occur over a period of time, the controller decreases VDD. A margin delay buffer adds a delay to the toggling functional critical path before being clocked into an early capture flip-flop. A reference register receives the test pattern without the delay of the toggling functional critical path, and an exclusive-OR (XOR) gate compares outputs of reference and early capture flip-flops to generate timing failure signals to the controller.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
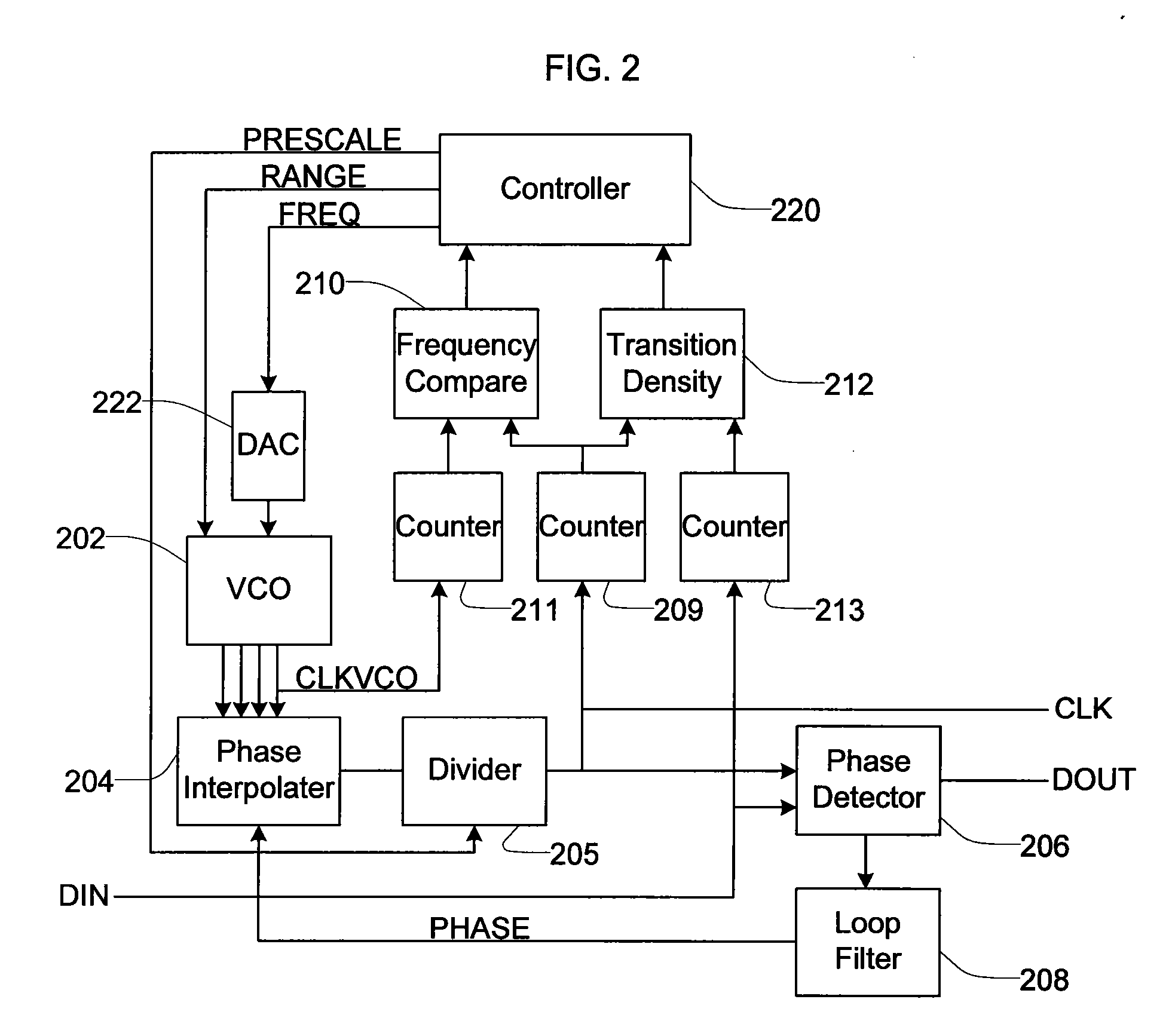
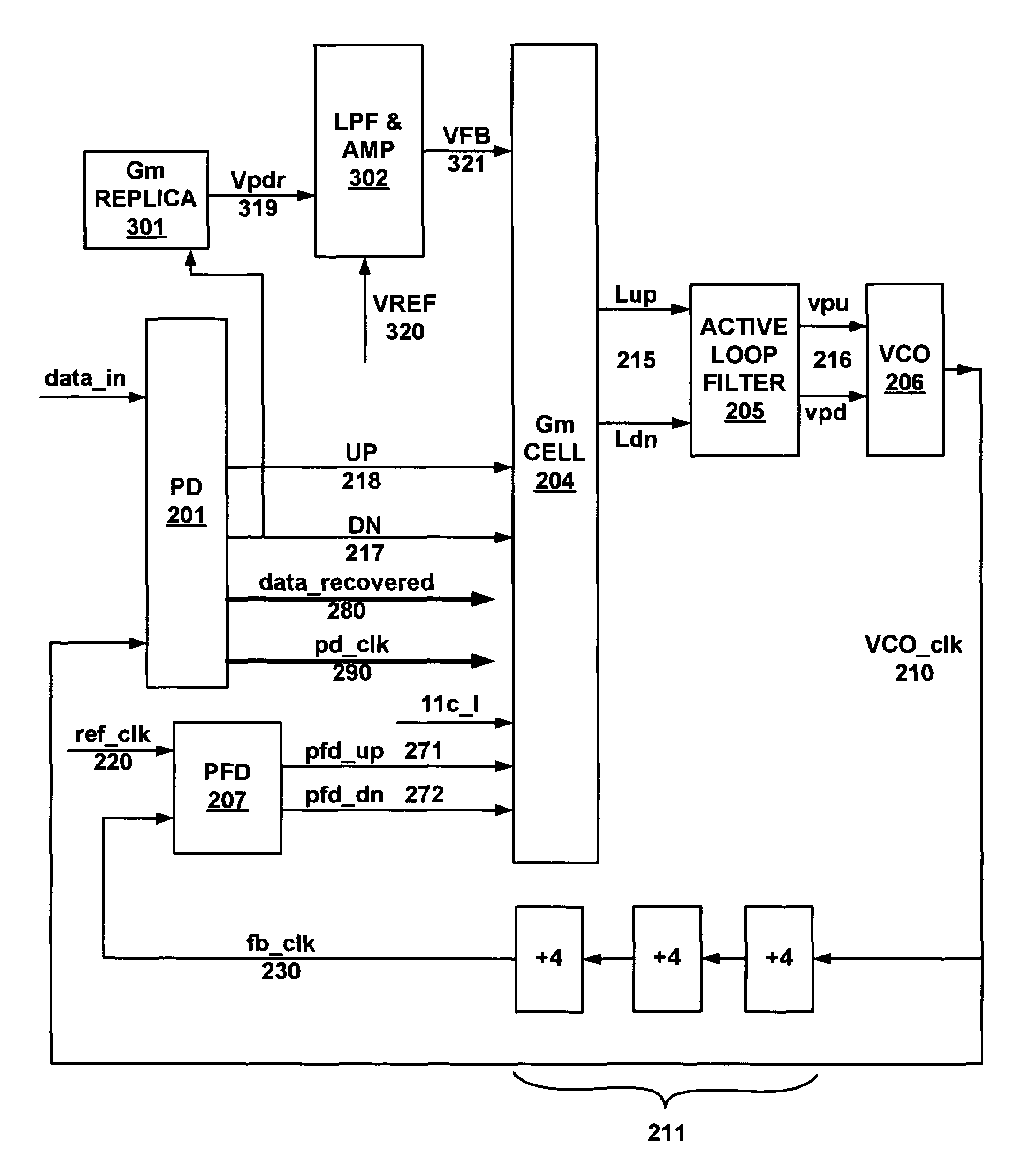
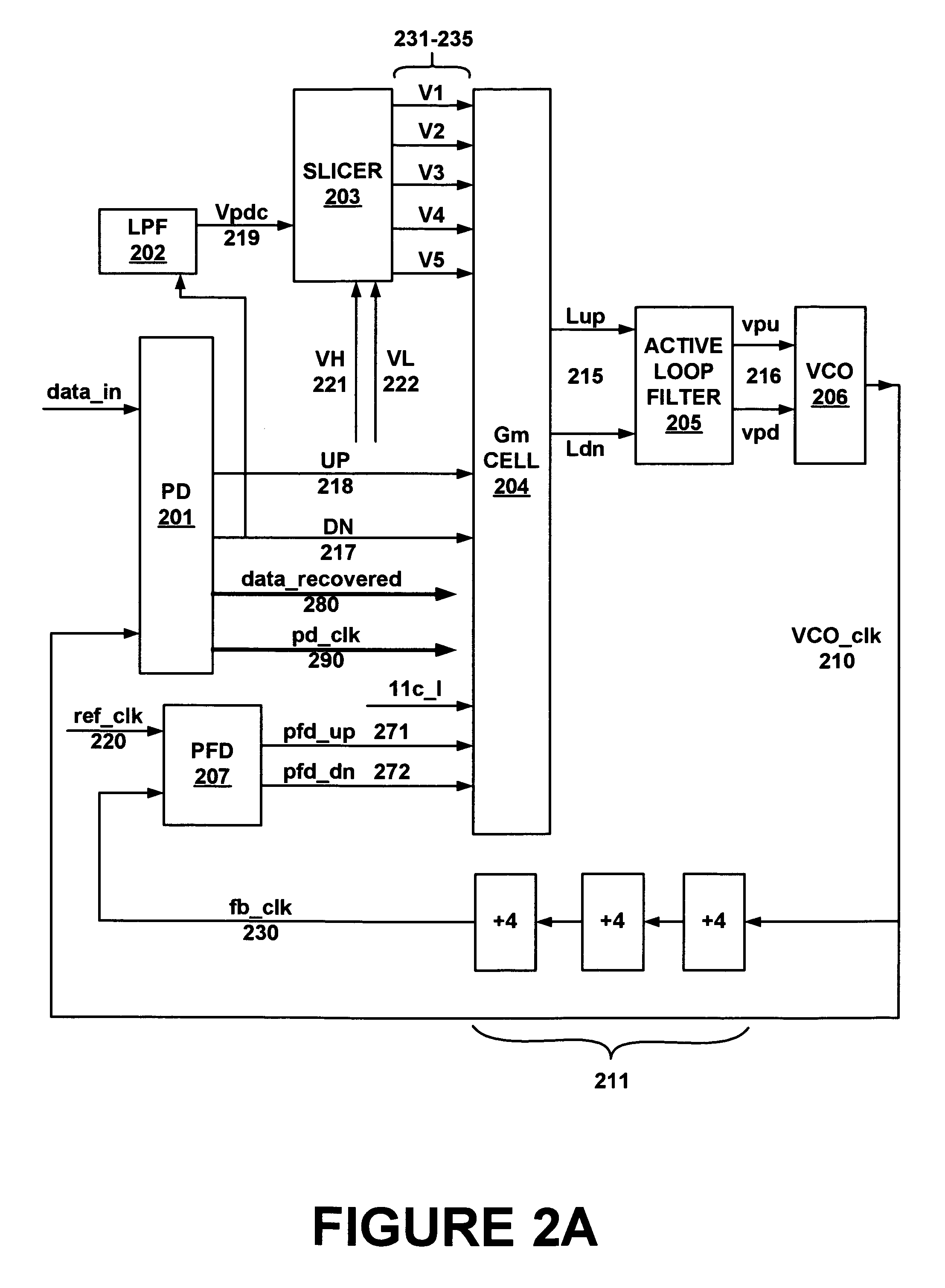
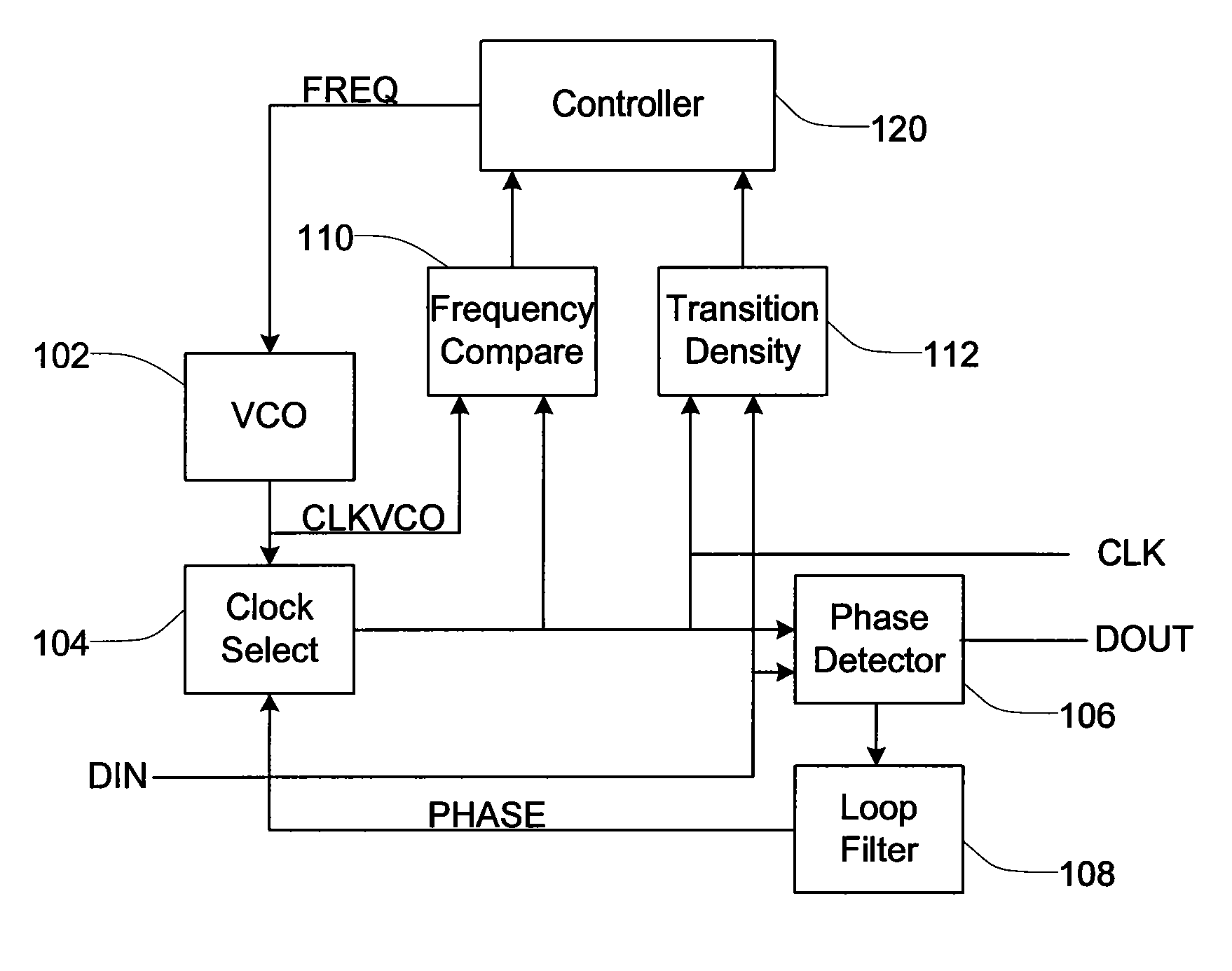
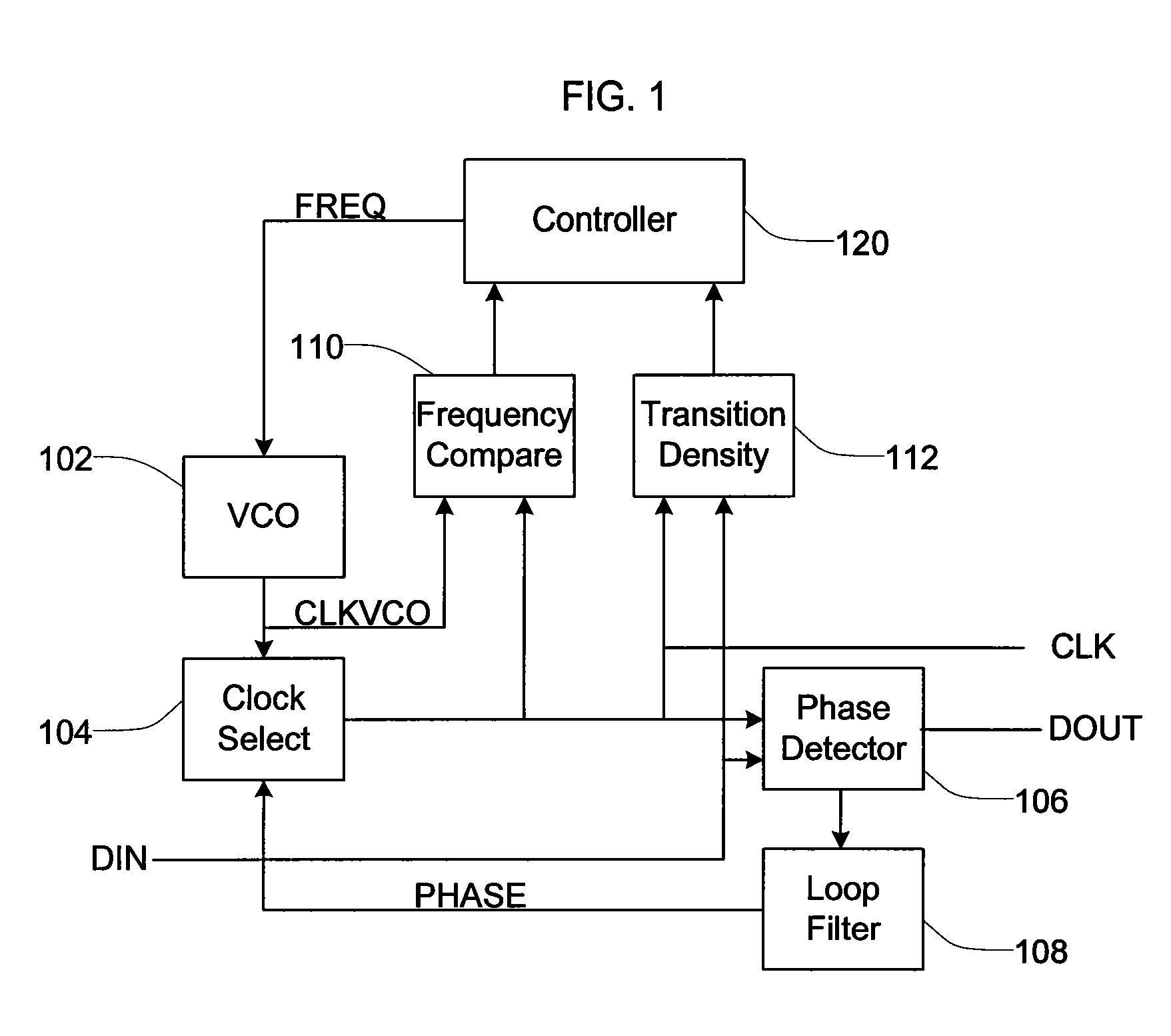
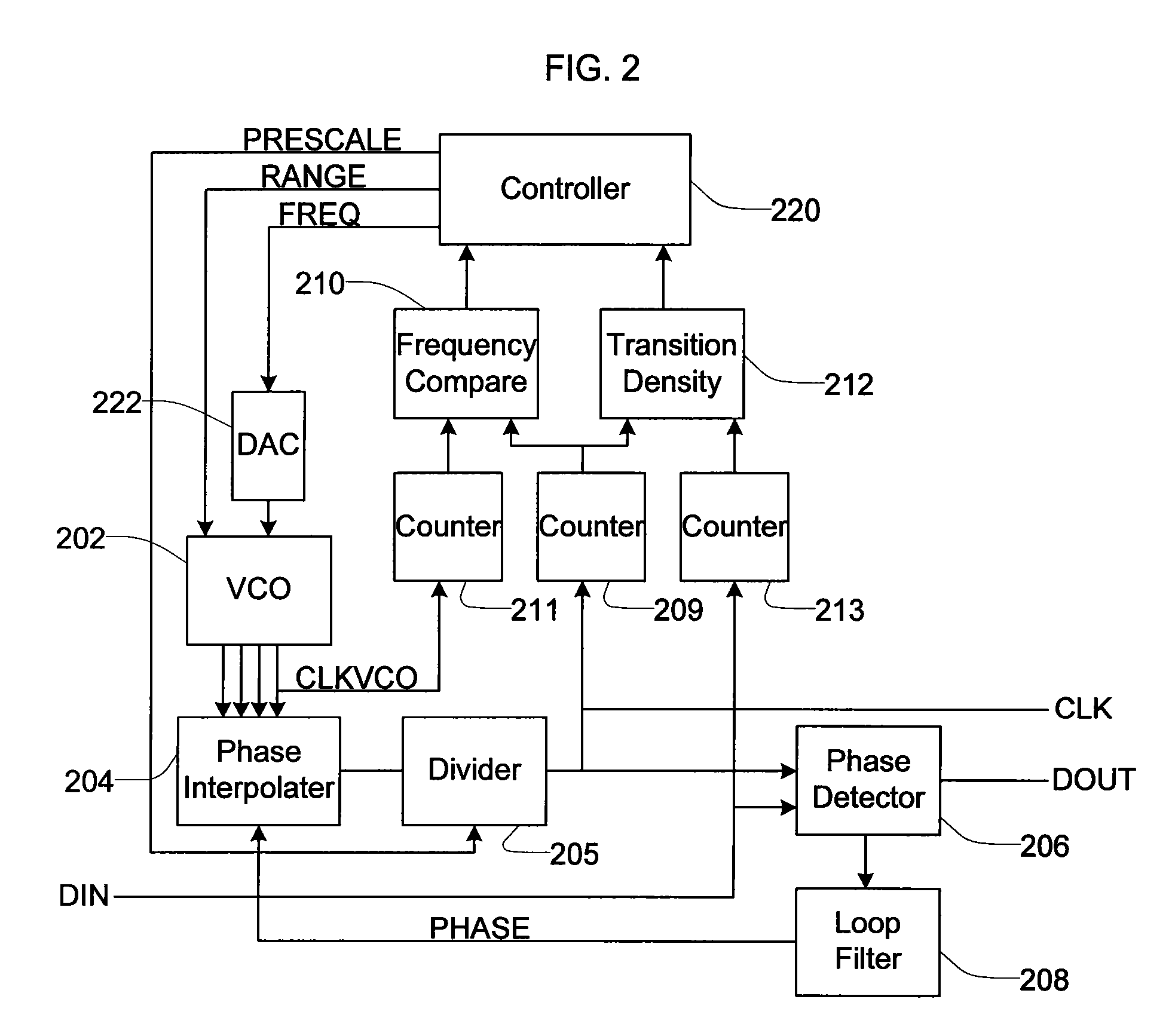
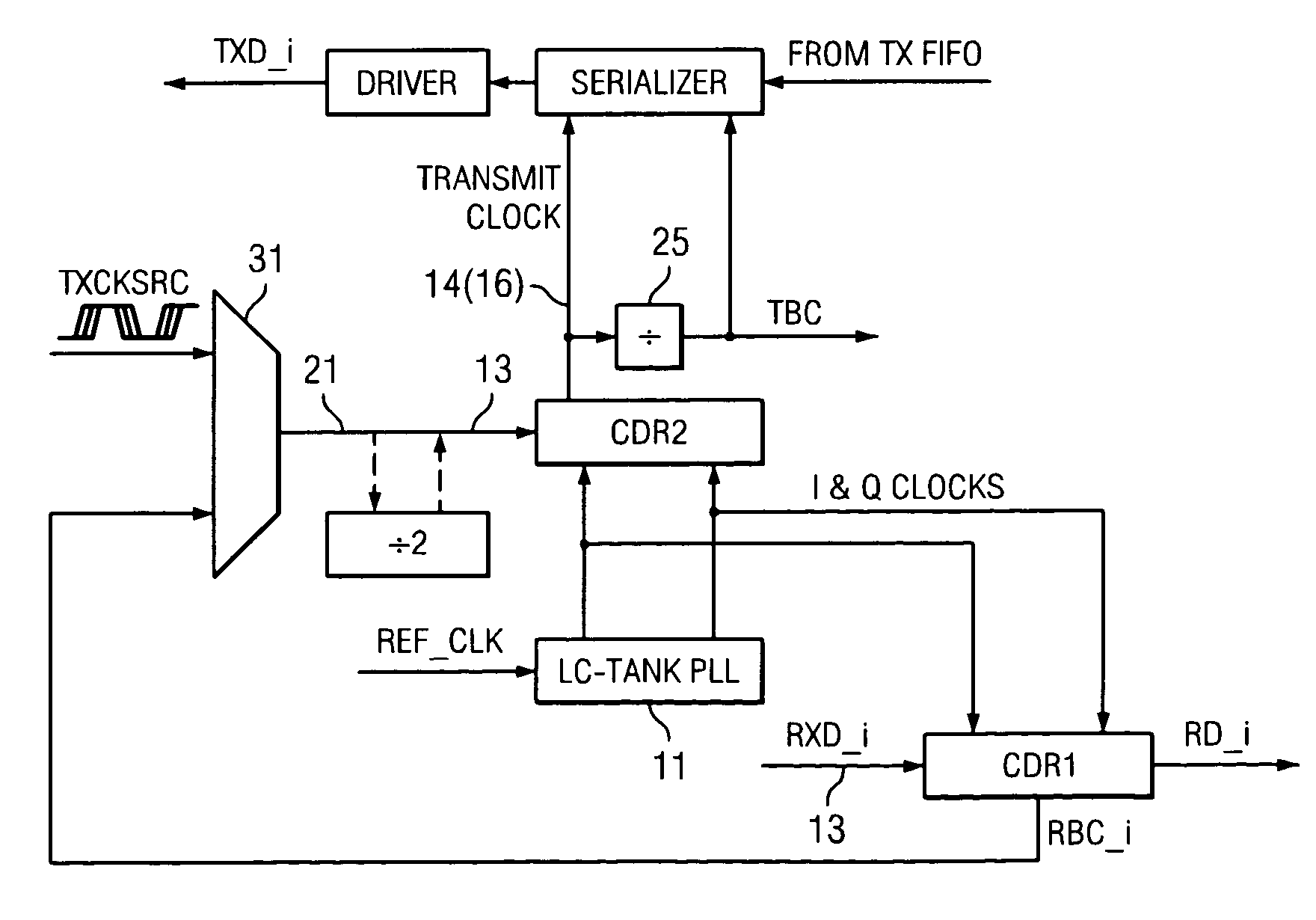
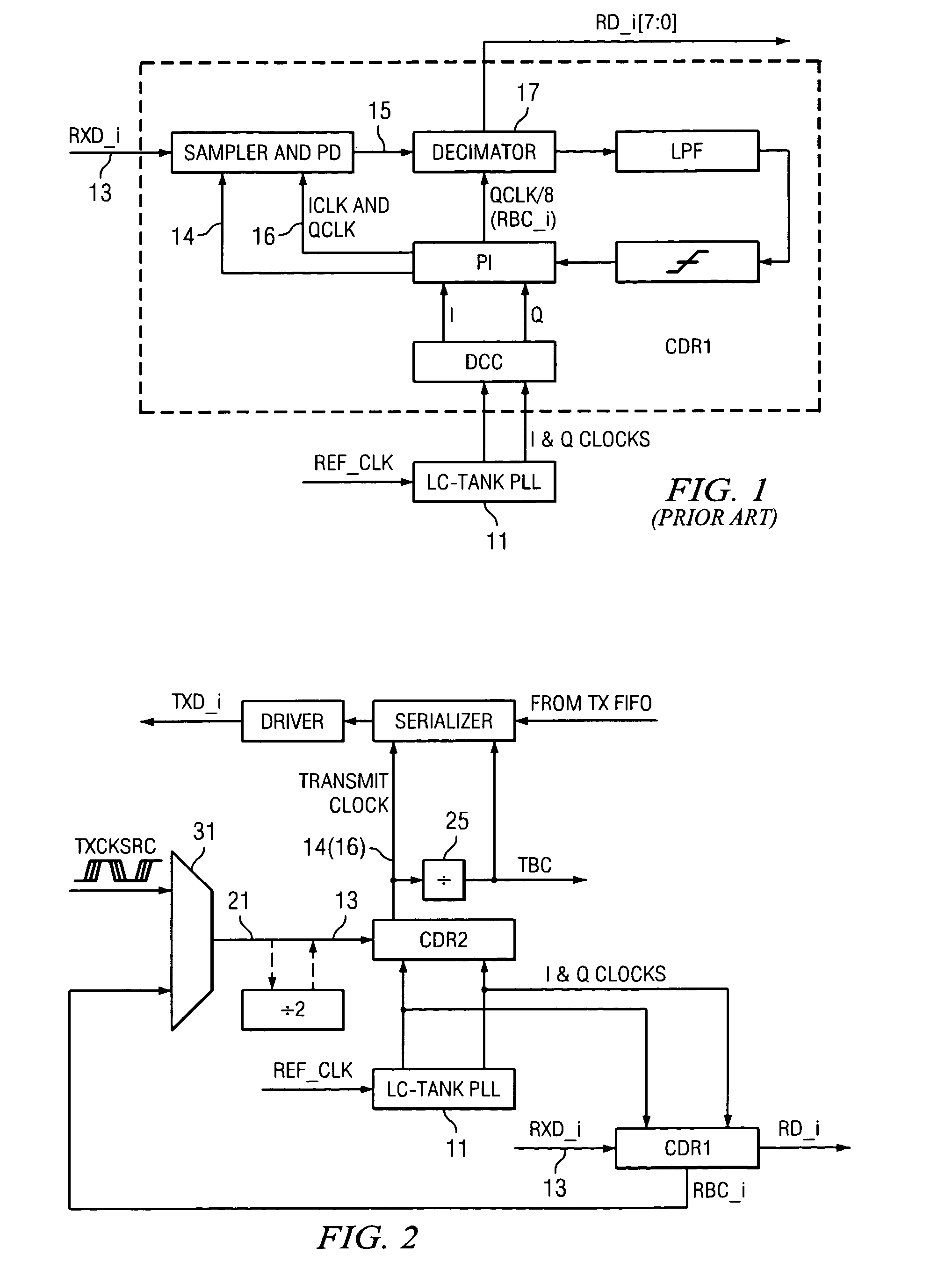
Frequency and phase acquisition of a clock and data recovery circuit without an external reference clock
ActiveUS20110169535A1Fully comprehendedAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsTransition densityData stream
A clock and data recovery device receives a serial data stream and produces recovered clock and data signals. The clock and data recovery device operates over a range of frequencies and without use an external reference clock. A first loop supplies a first clock signal to a second loop. The second loop modifies the first clock signal to produce the recovered clock signal and uses the recover clock signal to produce the recovered data signal. The first loop changes the frequency of the first clock signal based on frequency comparison and data transition density metrics.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
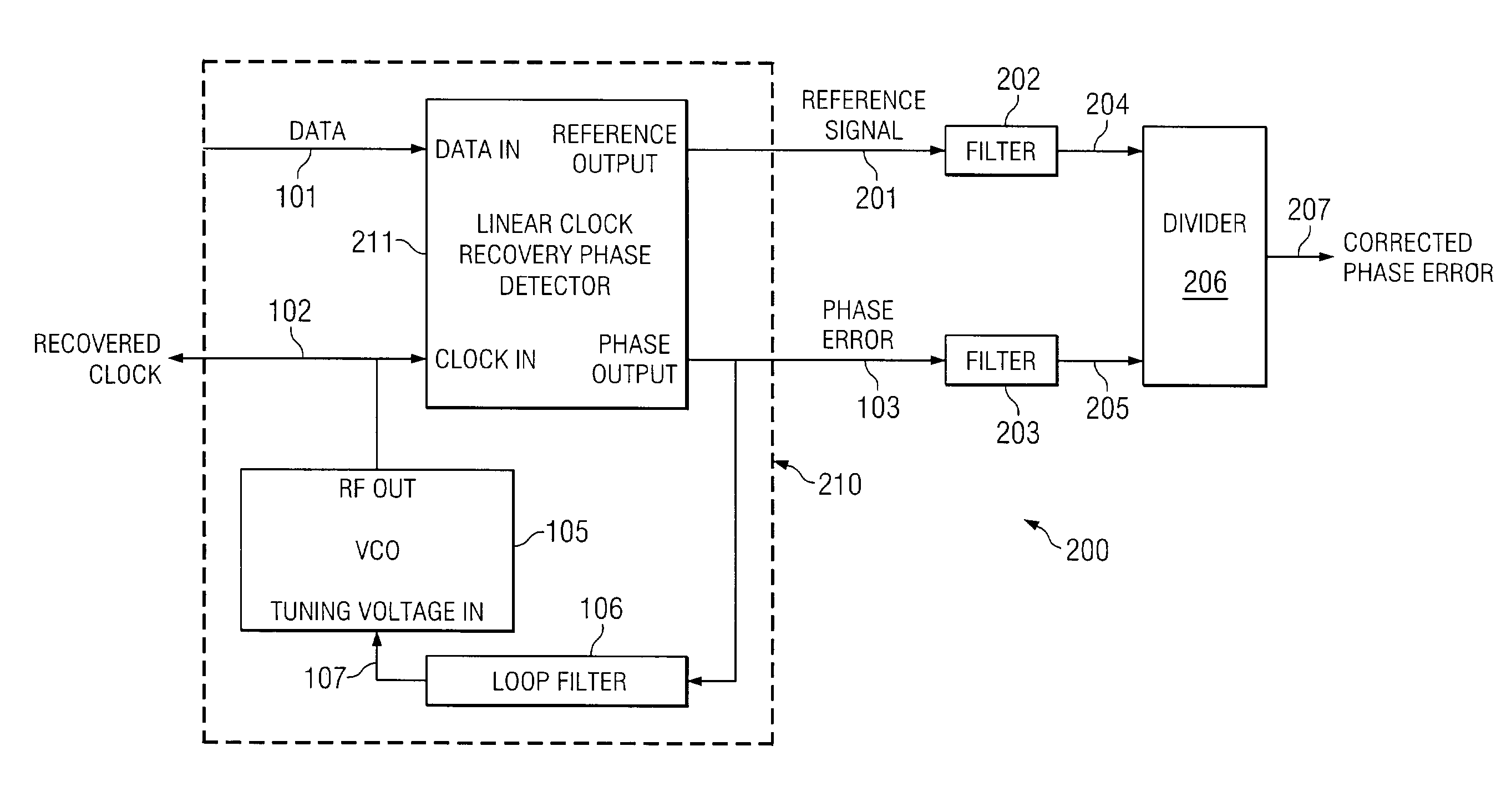
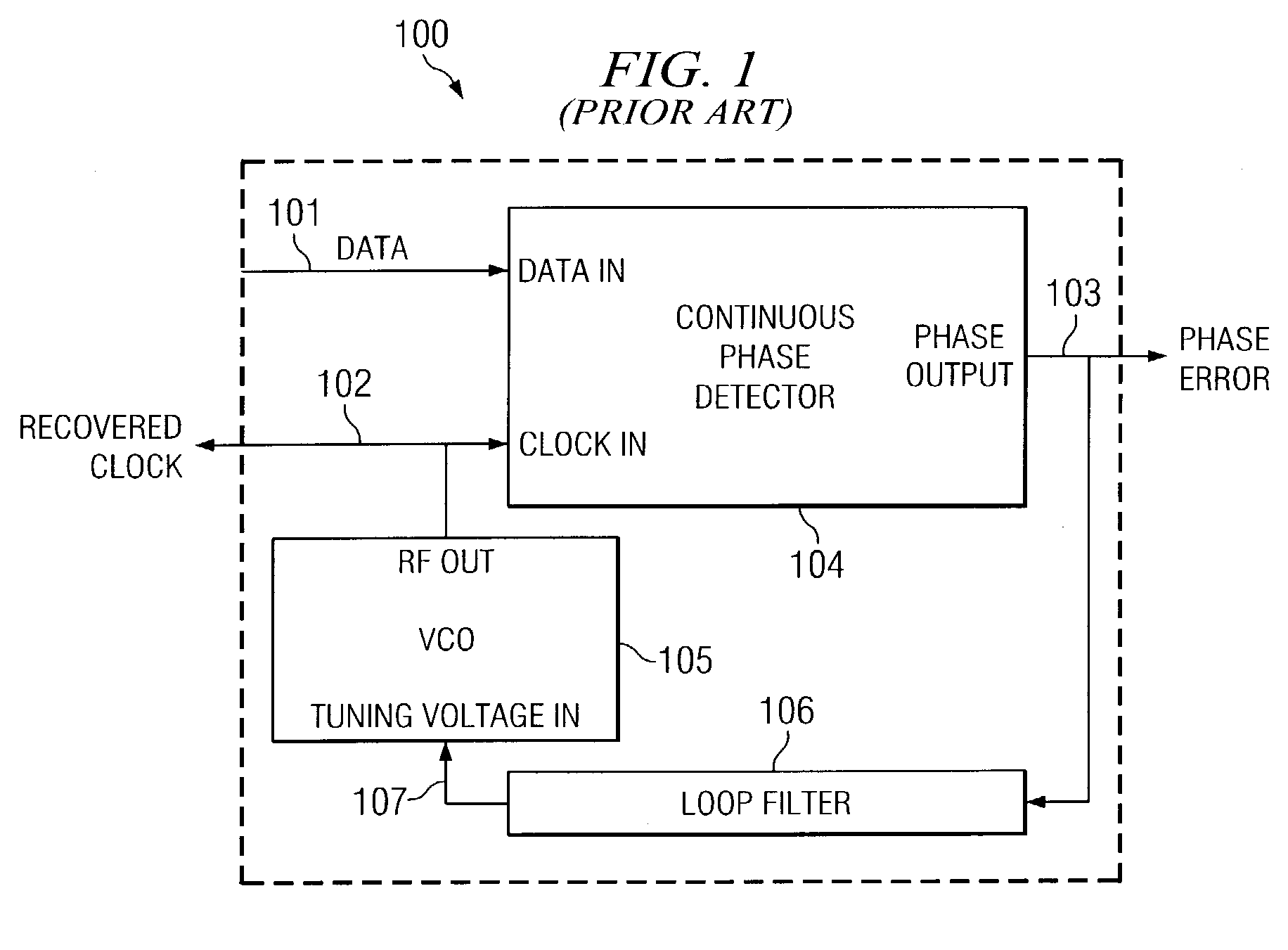
Systems and methods for correcting gain error due to transition density variation in clock recovery systems
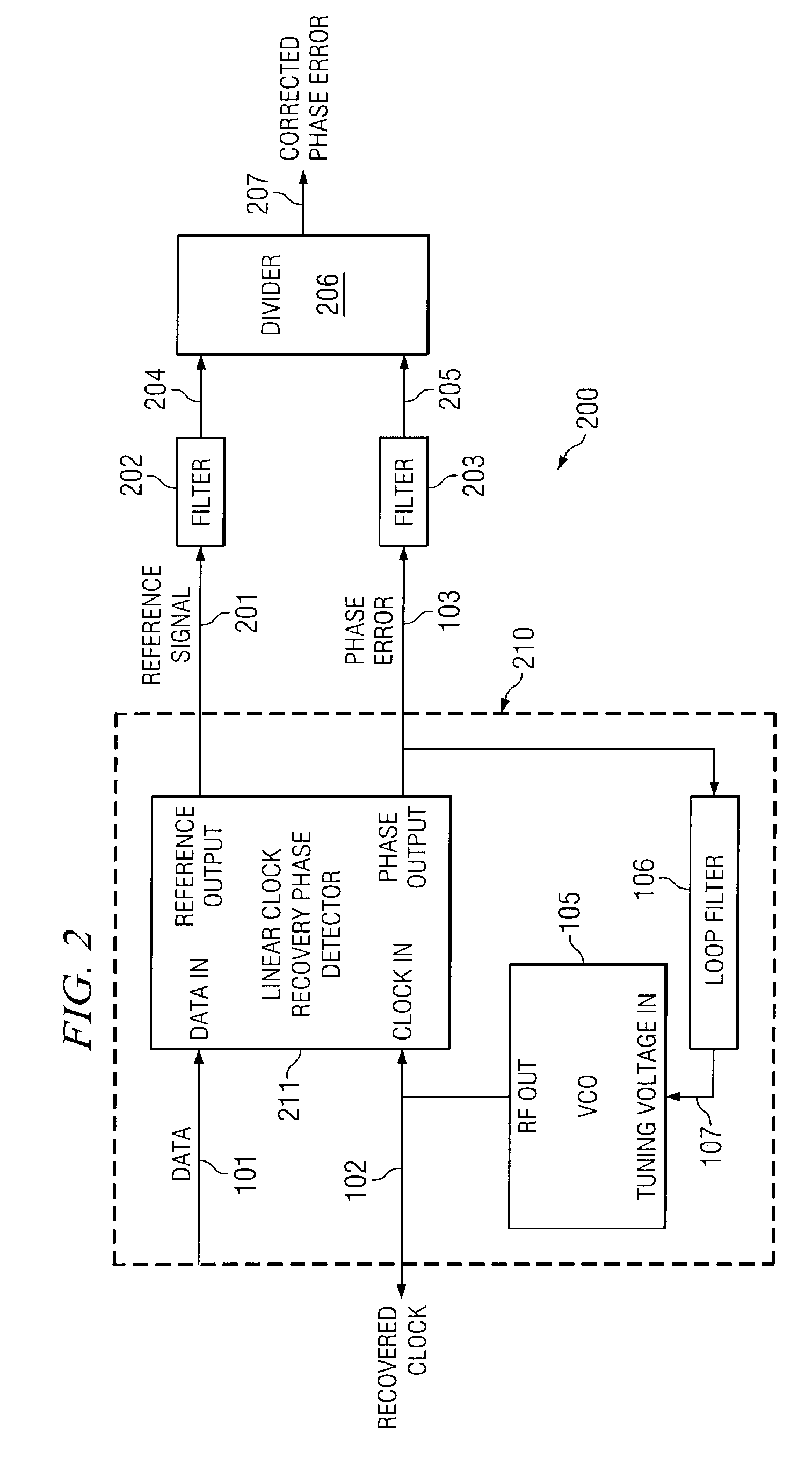
InactiveUS7173995B2Pulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionPhase detectorTransition density
In one embodiment, the present invention is directed to a system for processing a data stream. The system comprises: a voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) that generates a VCO signal in response to a tuning signal; a phase detector that generates an error signal that is indicative of a phase difference between a data signal and the VCO signal; a first filter that filters a reference signal that is indicative of an occurrence of a data transition; a second filter that filters the error signal, wherein the first filter and second filter are low-pass filters that possess a bandwidth that approximately equals one half of the reciprocal of: a unit interval multiplied by a maximum run length; and a divider circuit that divides the filtered error signal by the filtered reference signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
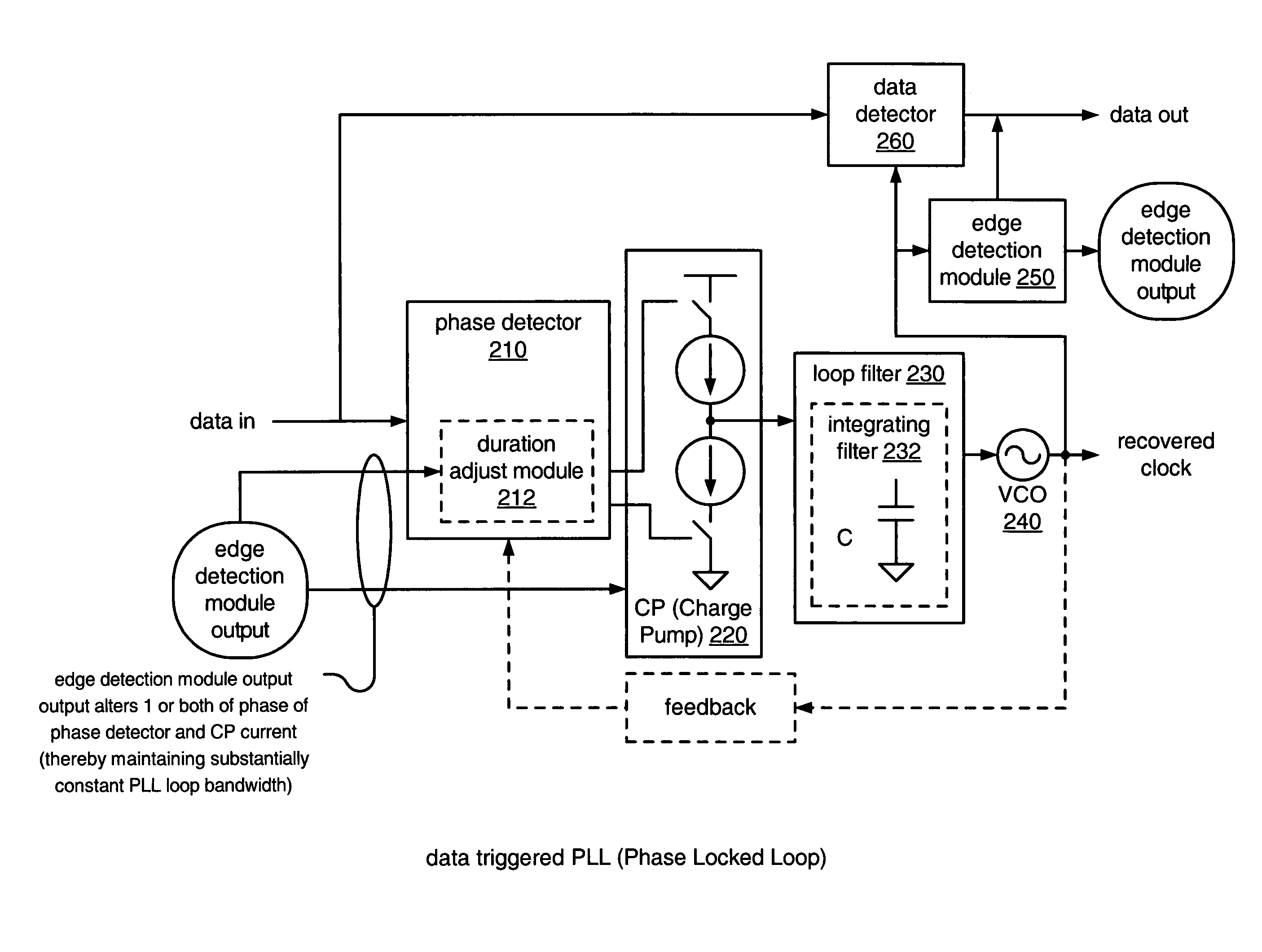
Adaptive transition density data triggered PLL (phase locked loop)
Adaptive transition density data triggered PLL (Phase Locked Loop). A novel solution is presented within a data triggered PLL whereby the missing data edge transitions may be detected and used to modify a phase difference between a data signal and a feedback signal and / or a current of a CP (Charge Pump) thereby maintaining a substantially constant loop bandwidth of the PLL for varying data edge transition rates. In one embodiment, an estimation of a substantially linear shift in PLL phase relative to the data phase is employed in the absence of data edge transitions. Alternatively, other means of implementing the shifts may be employed (e.g., non-linear) as desired in particular applications. This solution provides for a data triggered PLL that is practically impervious to variations in data edge transition density.
Owner:XILINX INC
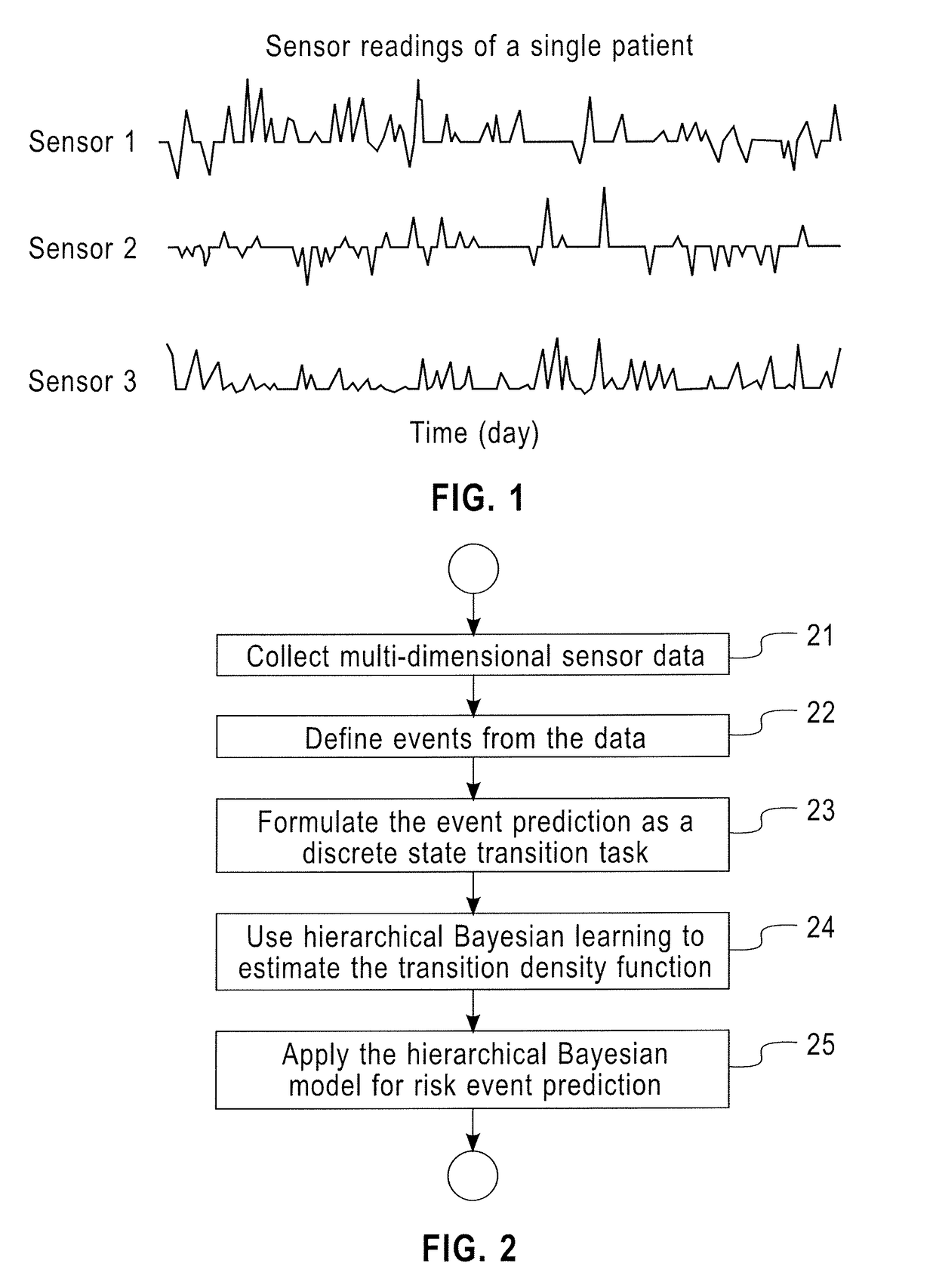
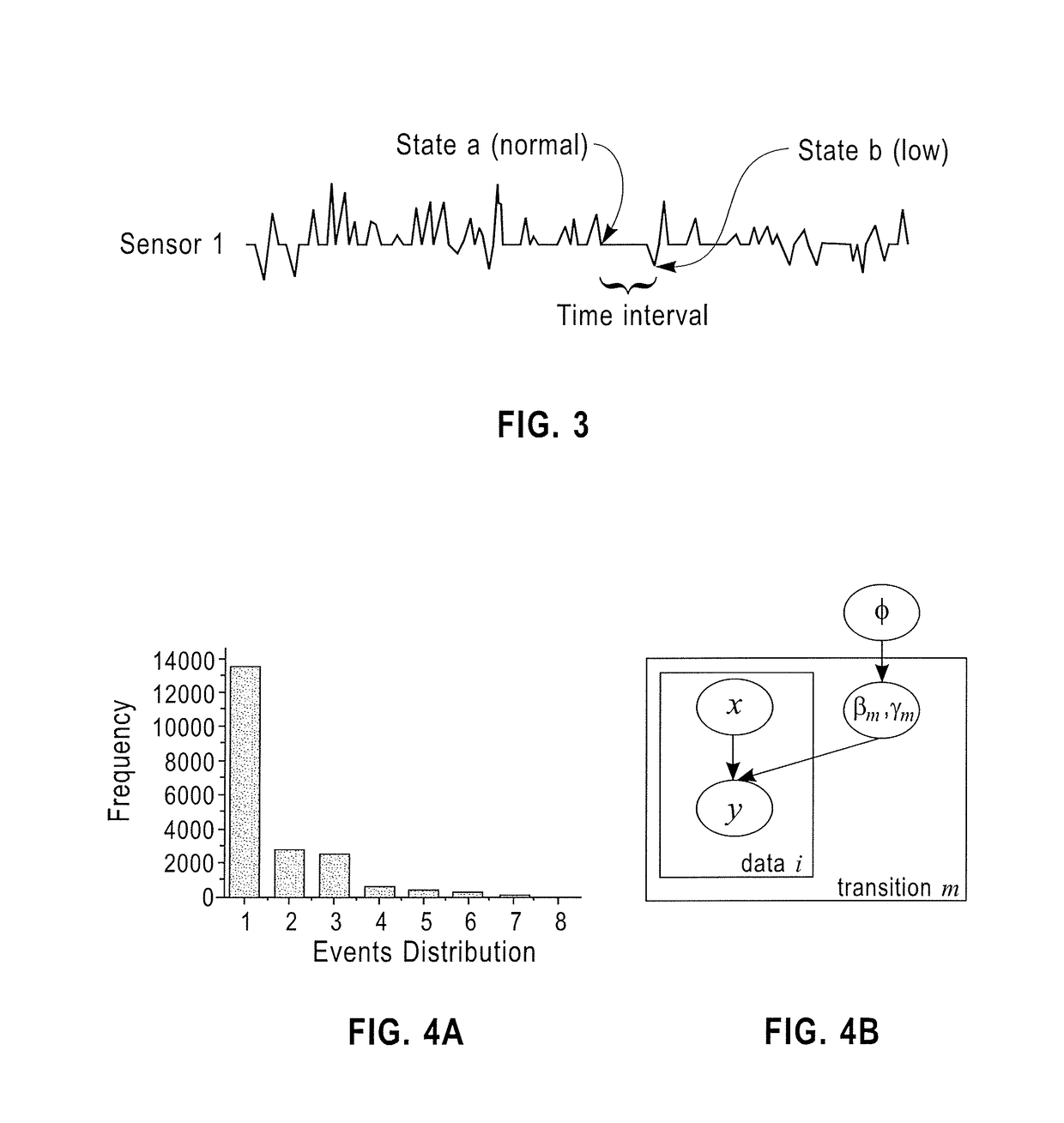
Time-varying risk profiling from health sensor data
A method and system for time varying risk profiling from sensor data includes receiving data time series from a plurality of sensors associated with a single patient, identifying events from the data, wherein an event is a transition between two states in the data of a sensor, formulating event prediction as a discrete state transition task using Markov jump processes to handle irregular sampling rates, estimating a transition density function for time varying continuous event probability using a hierarchical Bayesian model, and predicting risk events for the single patient by applying the hierarchical Bayesian model.
Owner:IBM CORP
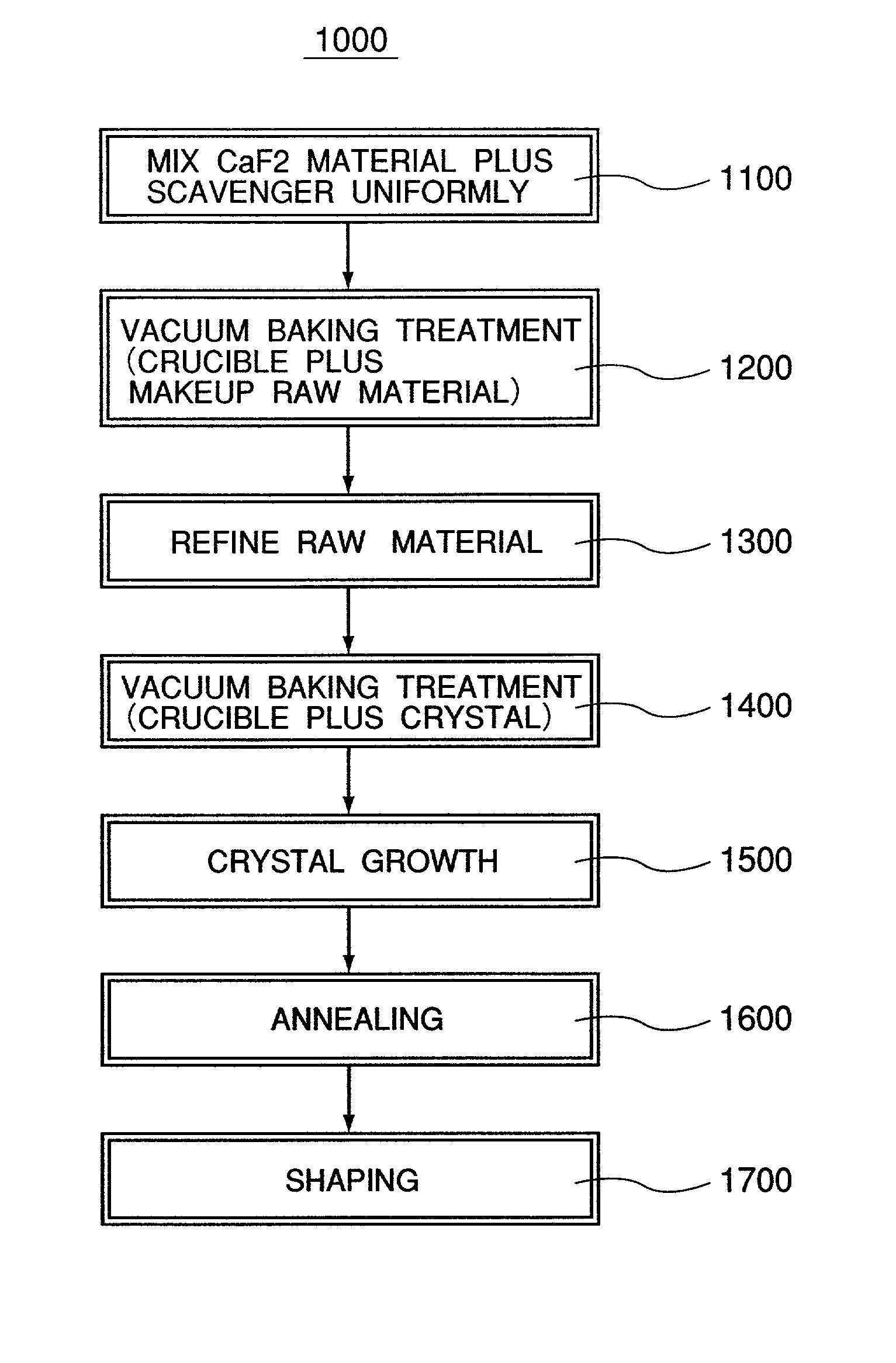
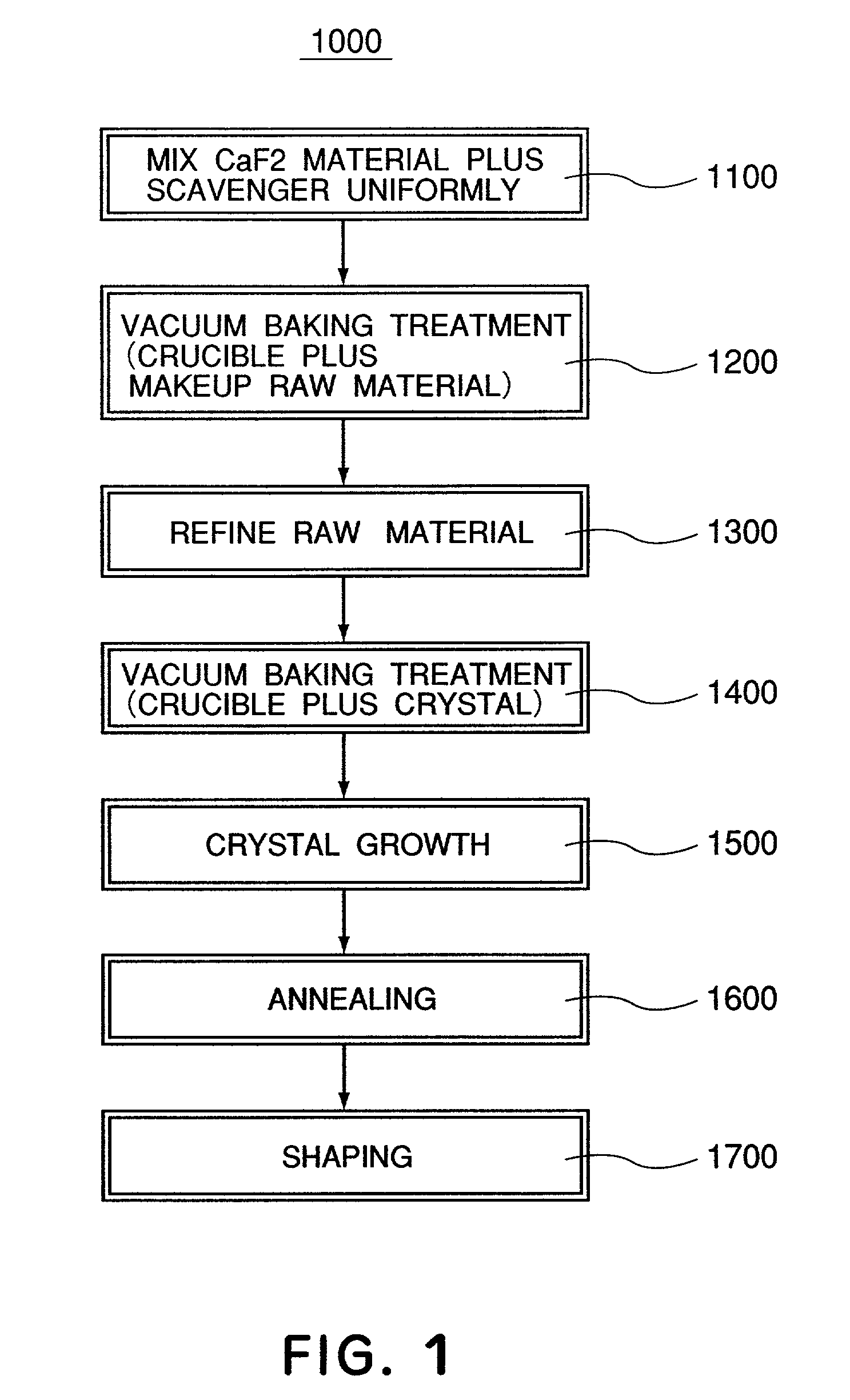
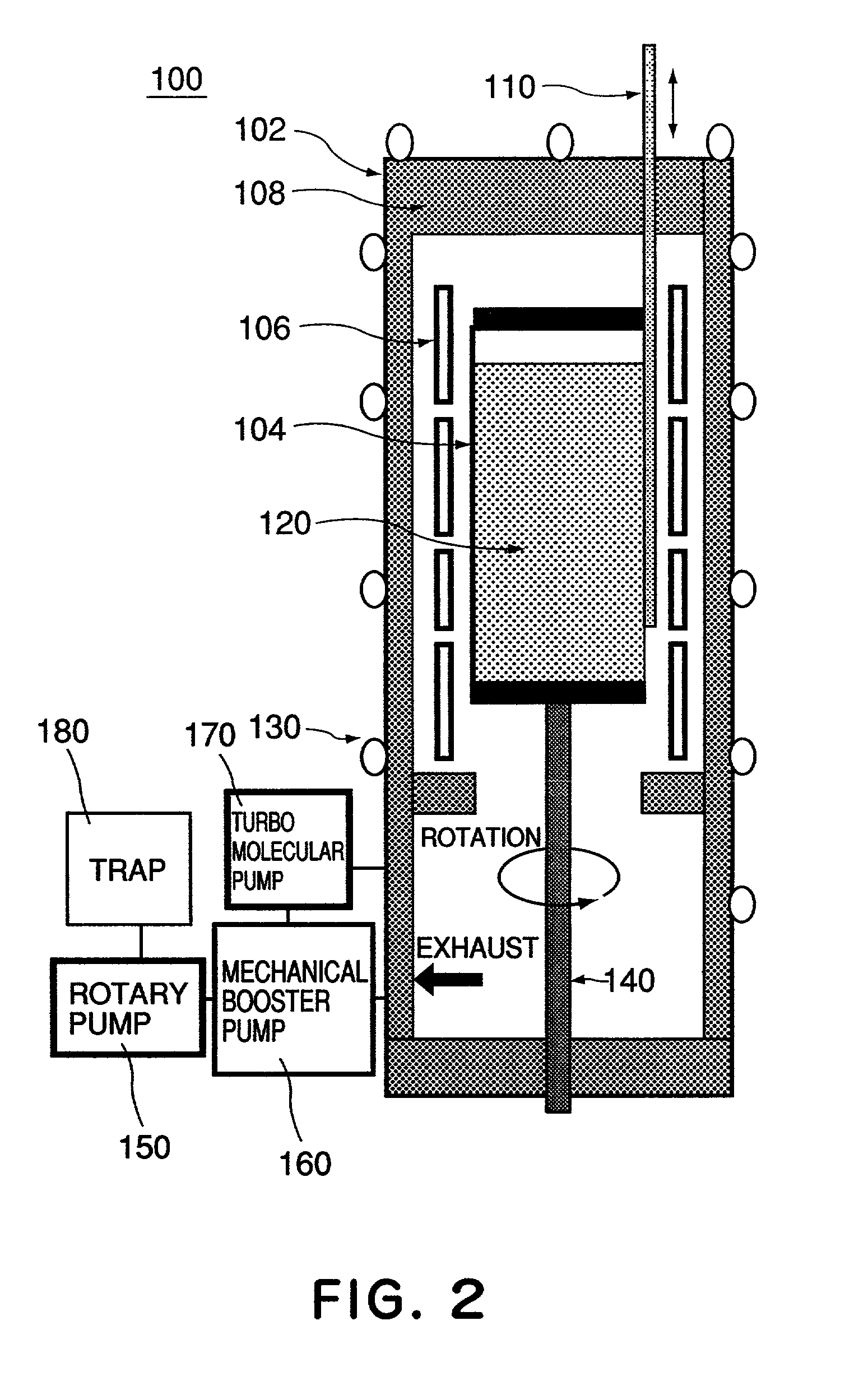
Calcium fluoride crystal and method and apparatus for using the same
InactiveUS6989060B2Decrease of refractive index homogeneityLess residueMagnesium fluoridesPolycrystalline material growthTransition densityCrystal growth
A calcium fluoride crystal produced in accordance with a method for producing calcium fluoride crystal on the basis of refining a raw material of calcium fluoride and causing crystal growth of the refined calcium fluoride, the method including a process of raising a purity of the calcium fluoride to complement the refining, wherein a transition density in crystal is not greater than 1×105 / cm2, and that dispersion of transition density inside an effective portion in crystal is in a range of ±5×104 / cm2. Also disclosed is an optical element to be manufactured by use of such CaF2 crystal.
Owner:CANON KK
Circuitry and method for measuring negative bias temperature instability (NBTI) and hot carrier injection (HCI) aging effects using edge sensitive sampling
InactiveUS9564884B1Electrical testingSingle output arrangementsTransition densityCritical path method
Toggling functional critical path timing sensors measure delays in toggling functional critical paths that continuously receive patterns from an aging pattern generator. Wear is accelerated. A margin delay adjustment controller sweeps margin delays until failures occur to measure delays. The margin delay is then adjusted in functional critical path timing sensors that add the margin delay to functional critical paths that carry user data or chip controls during normal operation. When the path delays fail to meet requirements, the functional critical path timing sensors signal a controller to increase VDD. When no failures occur over a period of time, the controller decreases VDD. Wear on the toggling functional critical paths is accelerated using both toggle and low-transition-density patterns. Circuit aging is compensated for by increasing margin delays to timing sensors.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Clock data recovery method and circuit for network communication
InactiveUS7158601B1Efficiently and reliably recoveredReliable and accurate and low data receptionPulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionTransition densityData signal
Owner:RPX CORP
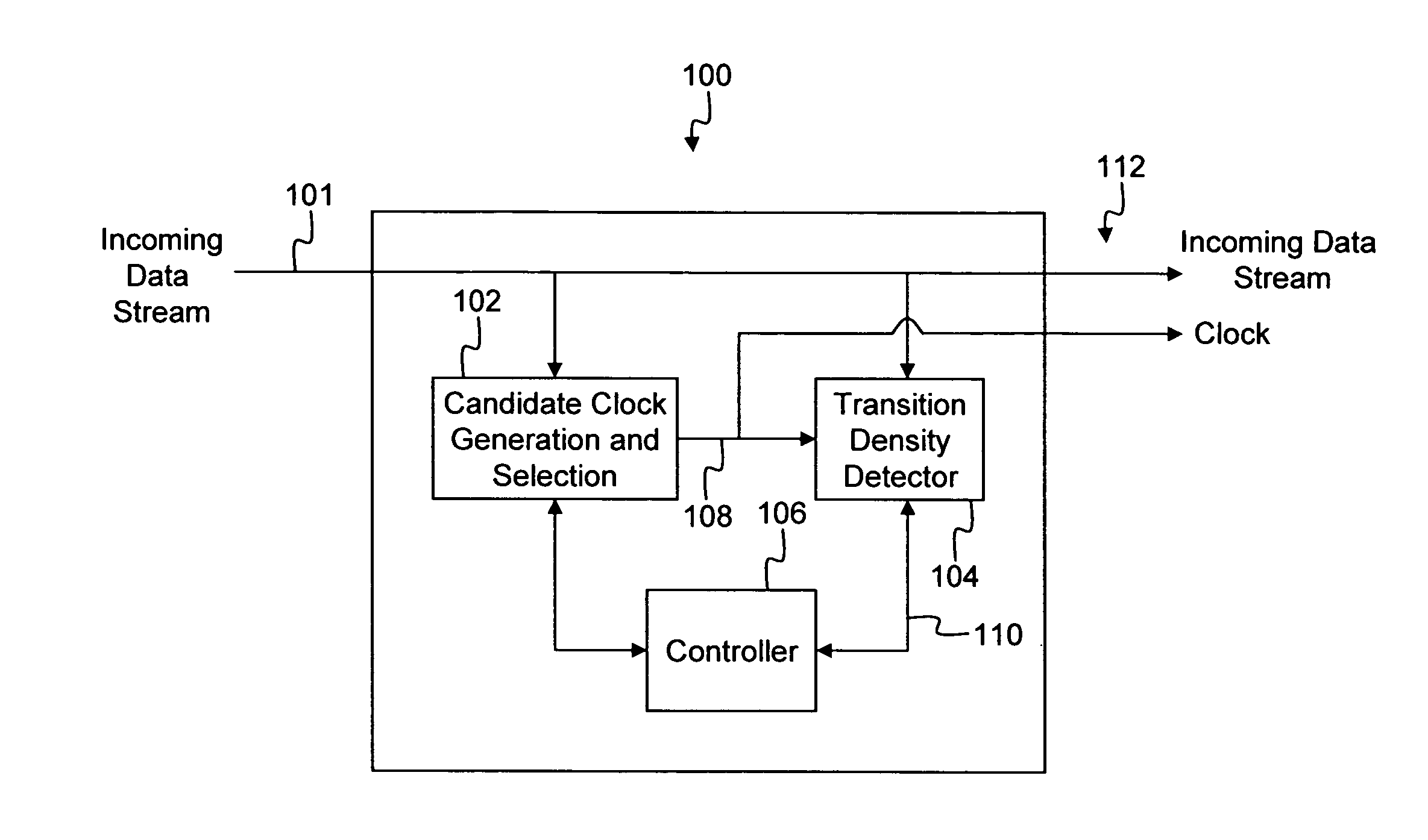
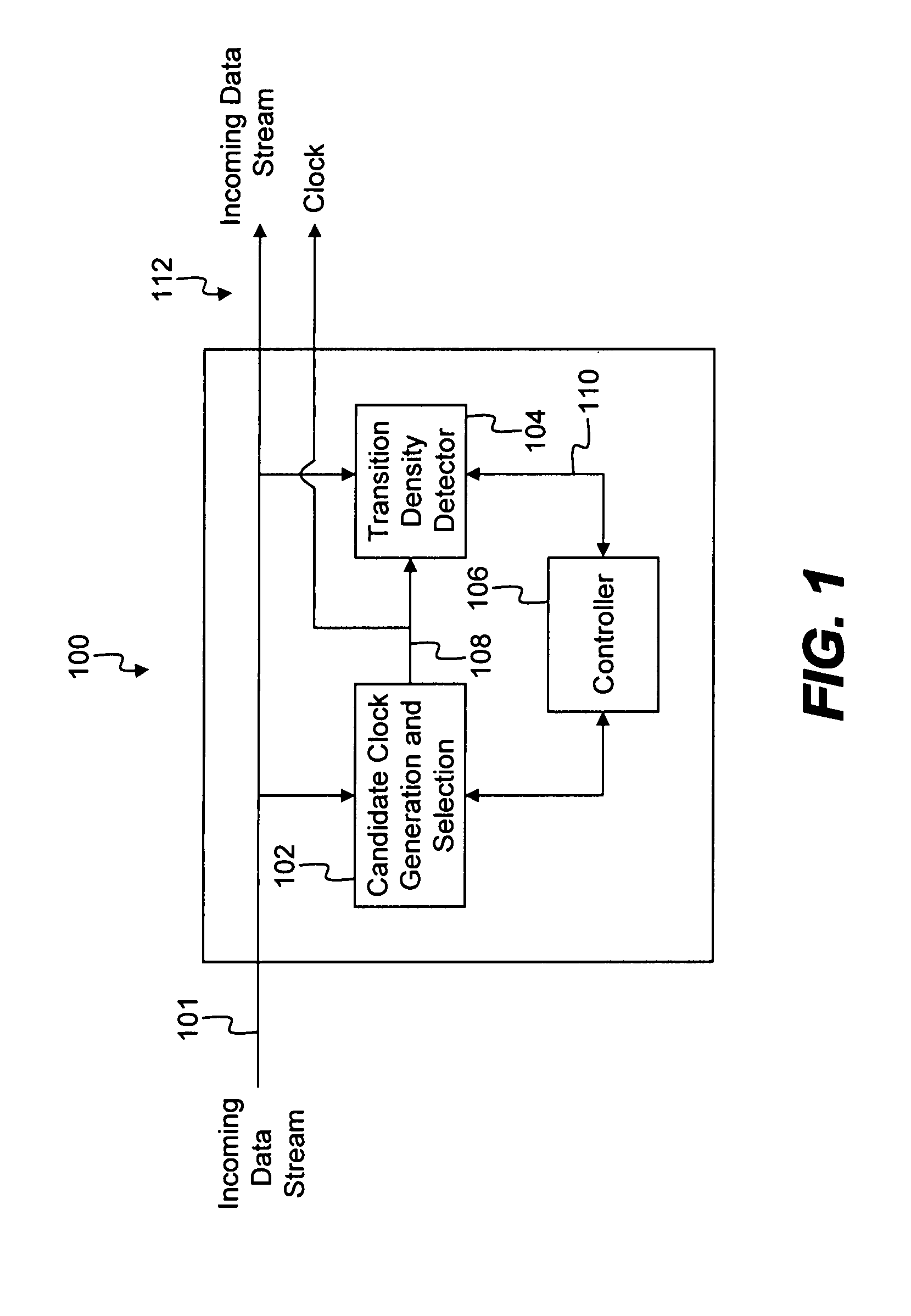
System for clock and data recovery
ActiveUS7251296B2Improve accuracyWithout errorPulse automatic controlData rate detection arrangementsTransition densityDetector circuits
A clock and data recovery (CDR) system that generates one or more clock signals from a received data stream and determines an optimal clock signal to associate with the incoming data stream. The system includes a candidate clock generation circuit that operates to receive the incoming data stream and generate candidate clock signals. A transition density detector circuit determines a transition density parameter associated with each of the candidate clock signals. A controller operates to determine the optimal clock signal based on the transition density parameters.
Owner:CIENA
Frequency and phase acquisition of a clock and data recovery circuit without an external reference clock
ActiveUS8284888B2Fully comprehendedAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsTransition densityData stream
A clock and data recovery device receives a serial data stream and produces recovered clock and data signals. The clock and data recovery device operates over a range of frequencies and without use an external reference clock. A first loop supplies a first clock signal to a second loop. The second loop modifies the first clock signal to produce the recovered clock signal and uses the recover clock signal to produce the recovered data signal. The first loop changes the frequency of the first clock signal based on frequency comparison and data transition density metrics.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
Out-of-channel received signal strength indication (RSSI) for RF front end
ActiveUS7979041B1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsAnalog signal digital controlTransition densityRF front end
The signal strength of an out-of-channel interferer is estimated by measuring the transition density of the sign of the down-converted signal. RF interferers at a higher or lower frequency than the desired RF signal appear as high frequency content in the down-converted signal, thus increasing the likelihood of zero-crossings.
Owner:MAXLINEAR ASIA SINGAPORE PTE LTD
Serial data validity monitor
InactiveUS7543193B2Avoid dataReduce the possibilityError preventionError detection/correctionTransition densityData stream
A data detection system includes, in part, a CID detector, a DC balance monitor and a transition density detector. The CID detector is configured to detect whether the received data stream includes a CID exceeding a predetermined threshold count. The DC balance monitor is configured to detect DC imbalances in the incoming data and that may be indicative of errors in the data. The transition density detector is configured to detect whether a minimum transition density exists during a given time period. If a violation is detected by any one of these three detectors, an out-of-frame signal is asserted. The incoming data stream may be a scrambled SONET or SDH data stream.
Owner:PMC-SIERRA
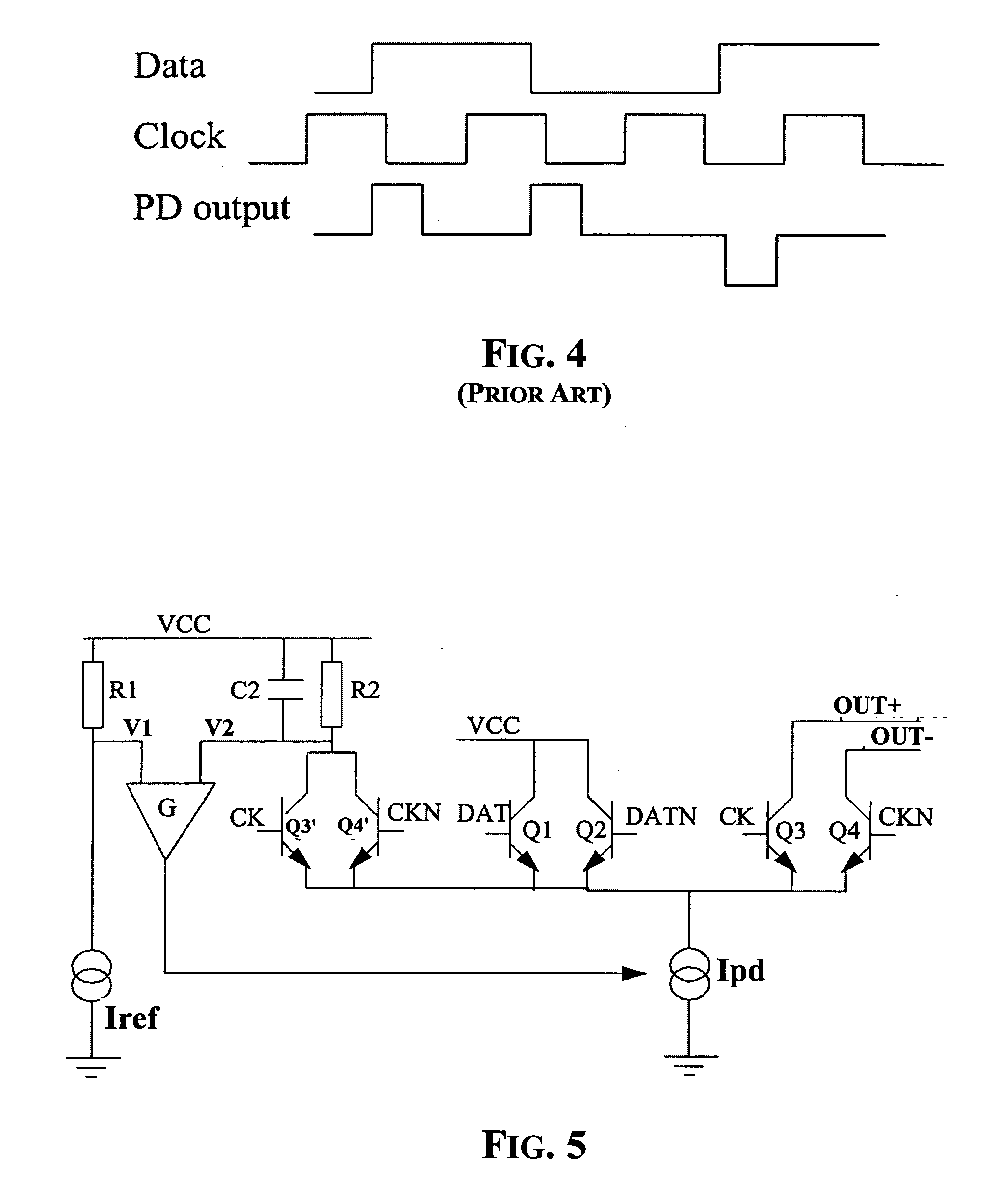
Method and circuit for sensing the transition density of a signal and variable gain phase detecting method and device
InactiveUS20050111589A1Improve performancePulse automatic controlFrequency-modulated carrier systemsTransition densityPhase detector
A linear phase detector has a variable gain that is regulated as a function of the monitored transition density of the input signal. The transition density is sensed by a circuit that generates a signal corresponding to a time averaged common mode component of the differential signal output by an output stage of the phase detector.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
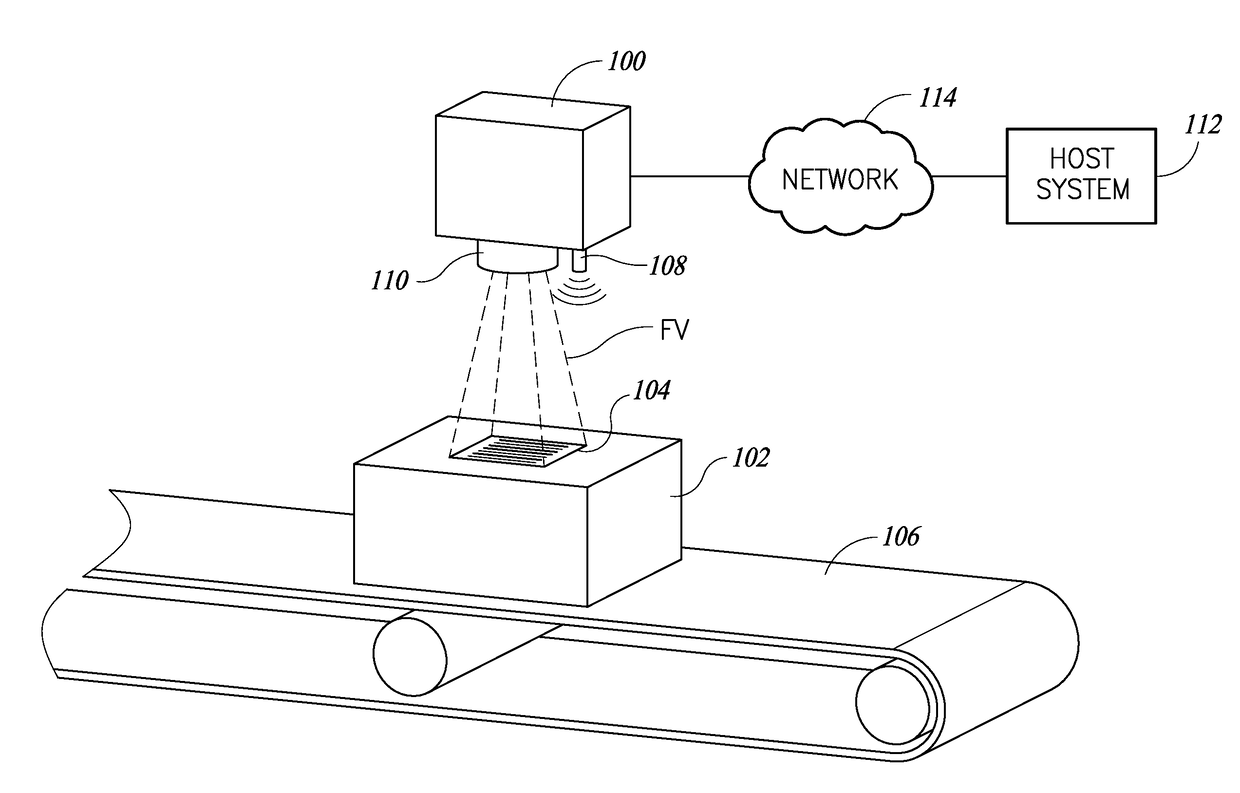
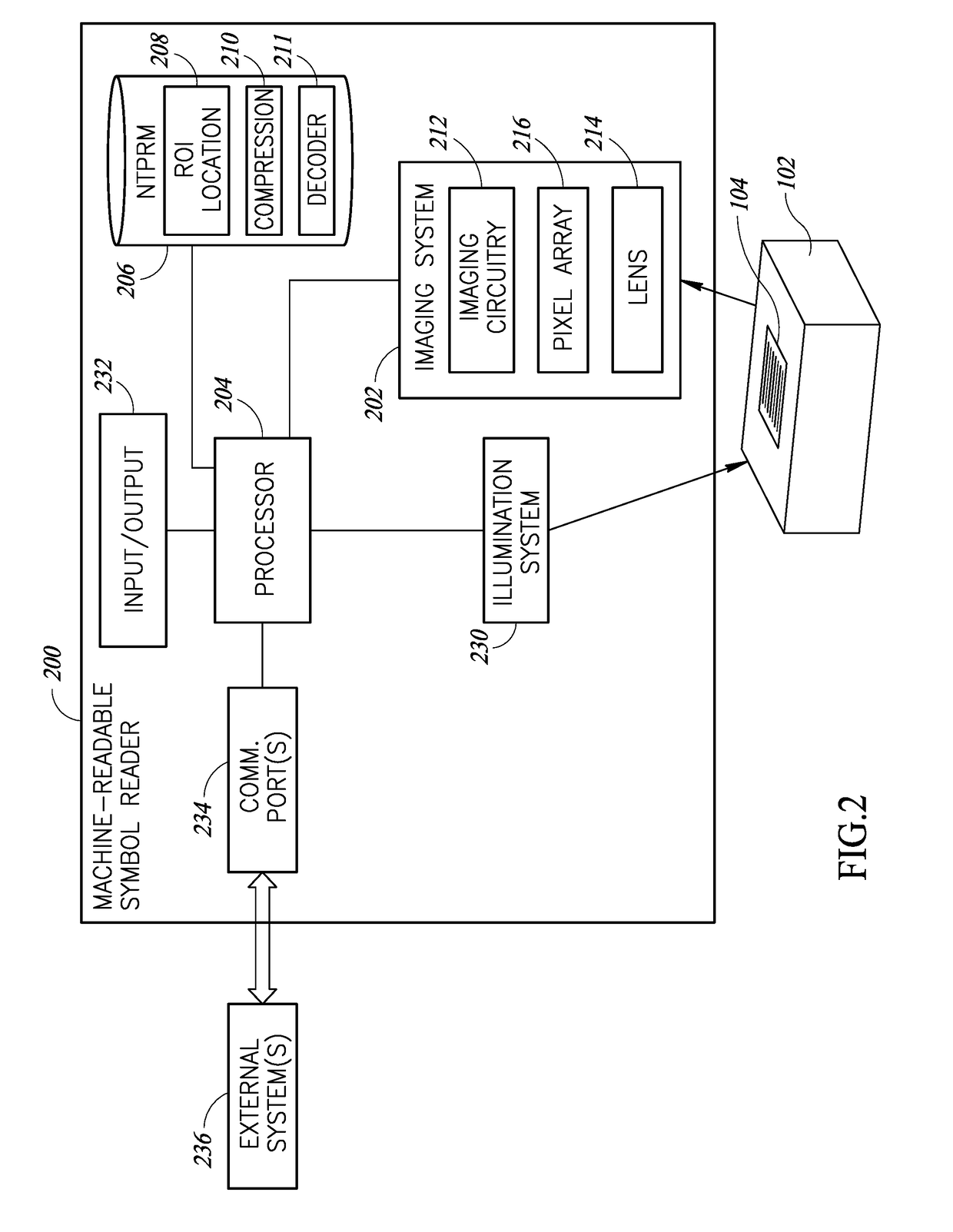
Region of interest location and selective image compression
ActiveUS9785817B2Character and pattern recognitionRecord carriers used with machinesTransition densityImage resolution
Systems and methods of operation for an image processor system to process images to locate two-dimensional regions which are likely to contain machine-readable symbol data or text. Such regions of interest (ROIs) may be preserved at full resolution, while the contents of non-ROIs are averaged into a single pixel value. Transition densities in an image may be converted into a numeric value. Such transition densities may be indicative of the presence of data of interest, such as textual data and / or machine-readable symbol data. The pixels values for the pixels in the ROIs may be sent to a decoder unchanged (i.e., full resolution), which absolves the decoder from having to perform any ROI location computations. Modified or altered images may be compressed to much smaller size files while maintaining lossless ROIs, which allows for transmission of such images to processor-based devices over a data communications channel in real time.
Owner:DATALOGIC USA INC
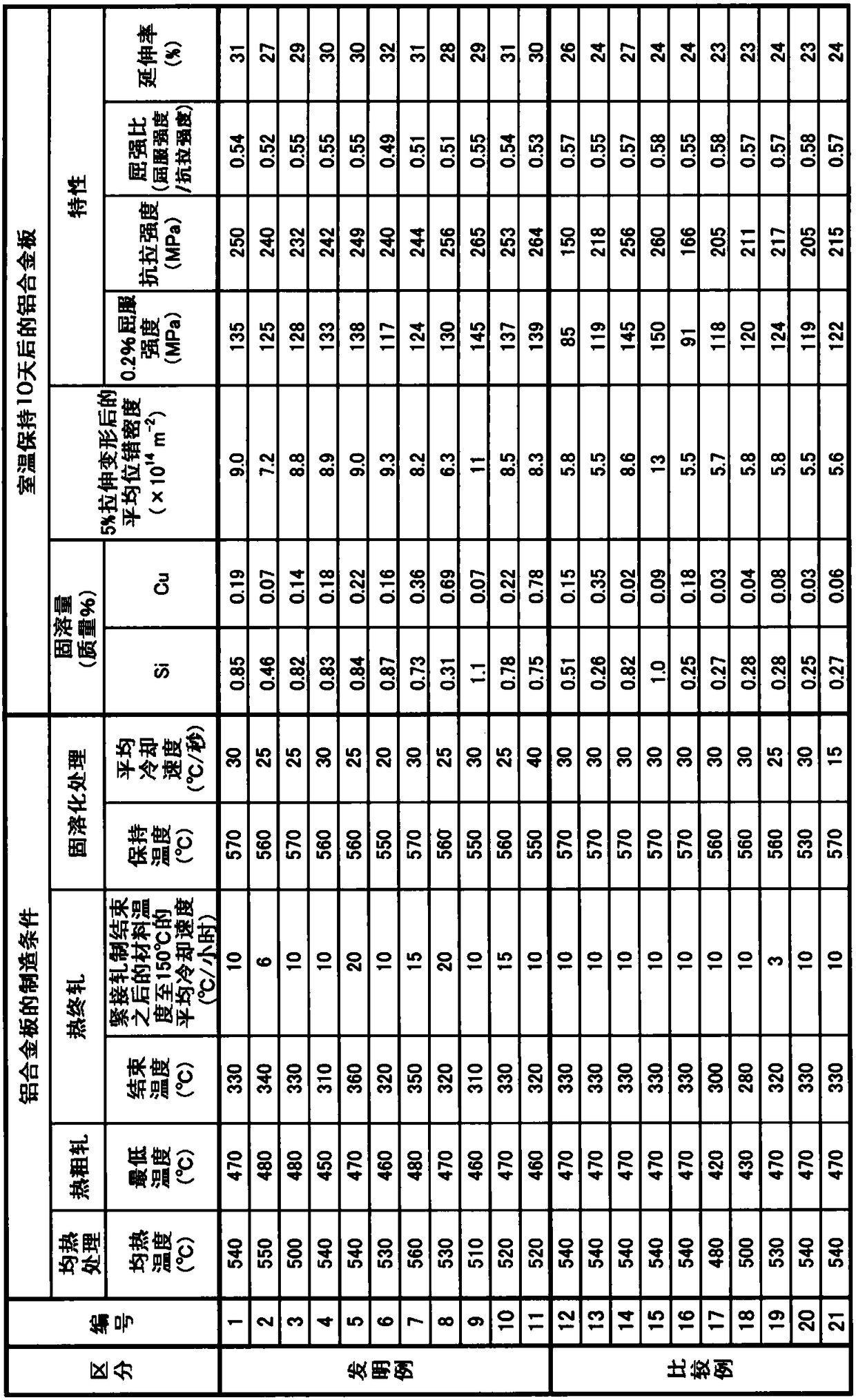
Aluminum alloy sheet having high mold-ability
InactiveCN108866393ASuppresses the localization of dislocationsUniform dislocation propagationTransition densityAlloy
The invention aims to provide a 6000 series aluminum alloy sheet having high mold-ability capable of being manufactured as for an automotive panel material without largely changing a conventional composition or manufacturing condition. High work hardening property is achieved by increasing a solid solution Si amount and a solid solution Cu amount of an Al-Mg-Si-based aluminum alloy sheet at good balance, suppressing localization of transition introduced into a material by tensile deformation during press molding to an automotive panel material with transition density in a specific range when tensile deformation in low strain region to the sheet, increasing transition uniformly from low strain range to high strain range and suppressing non-uniform deformation in molding to the automotive panel material.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
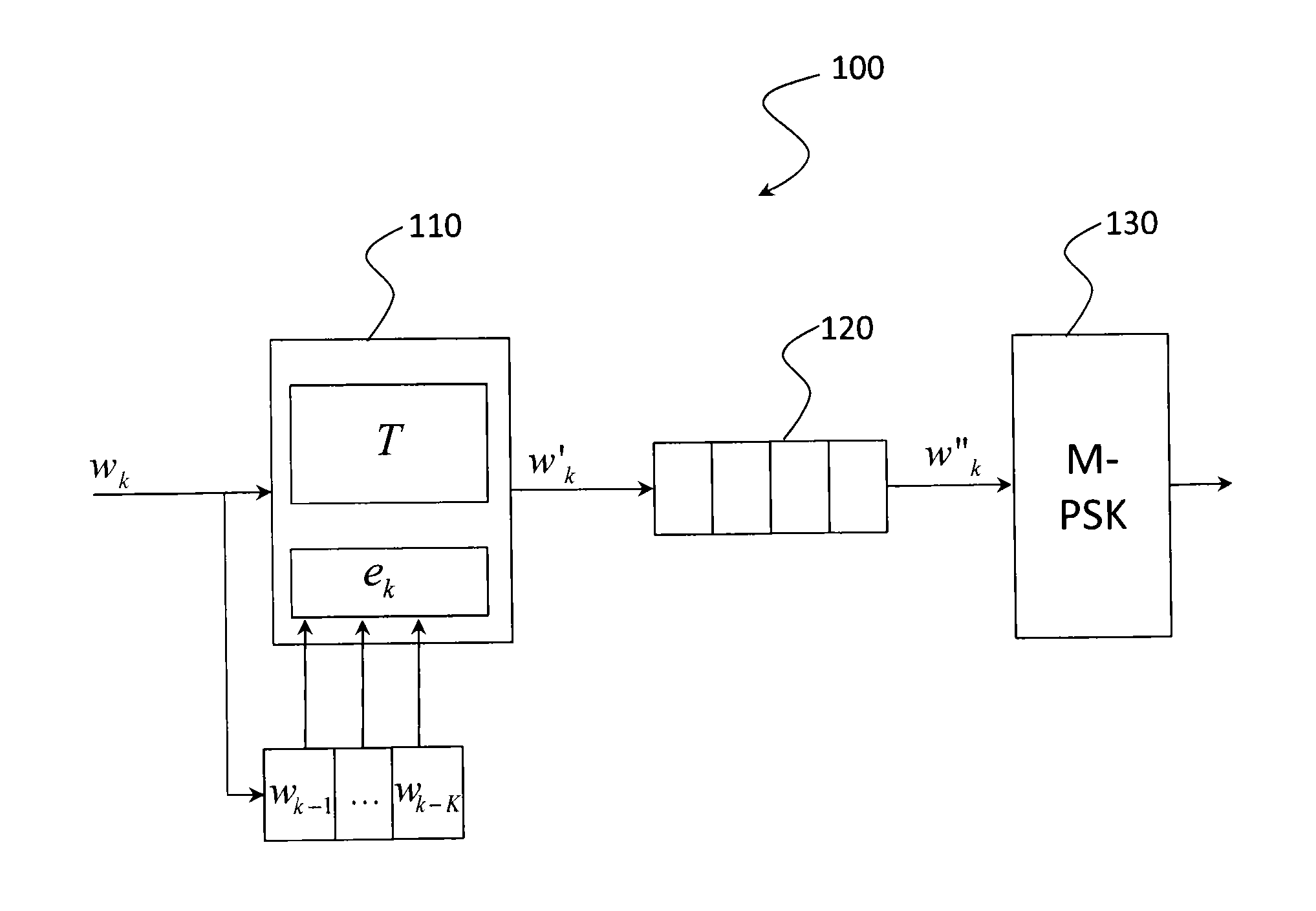
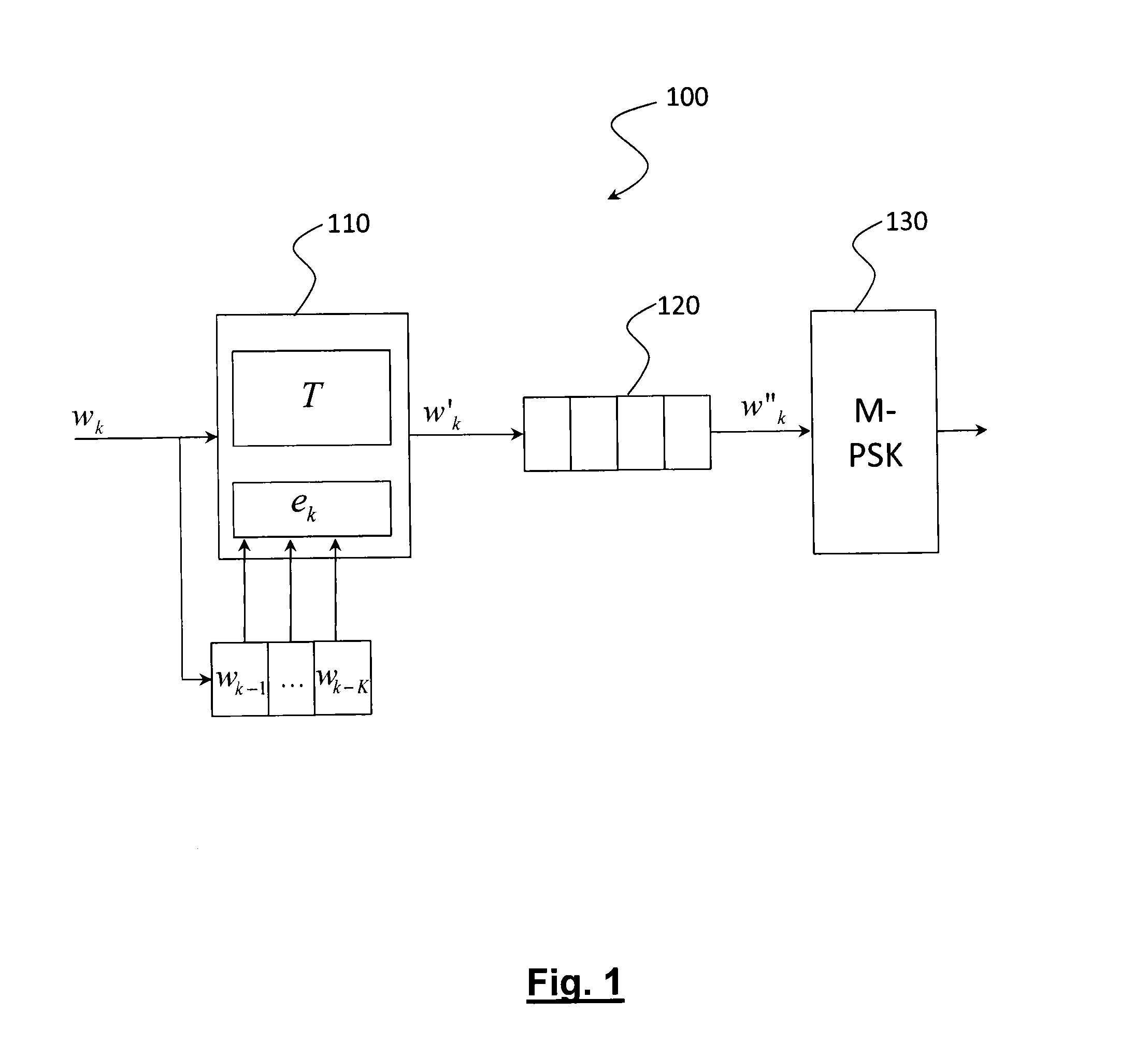
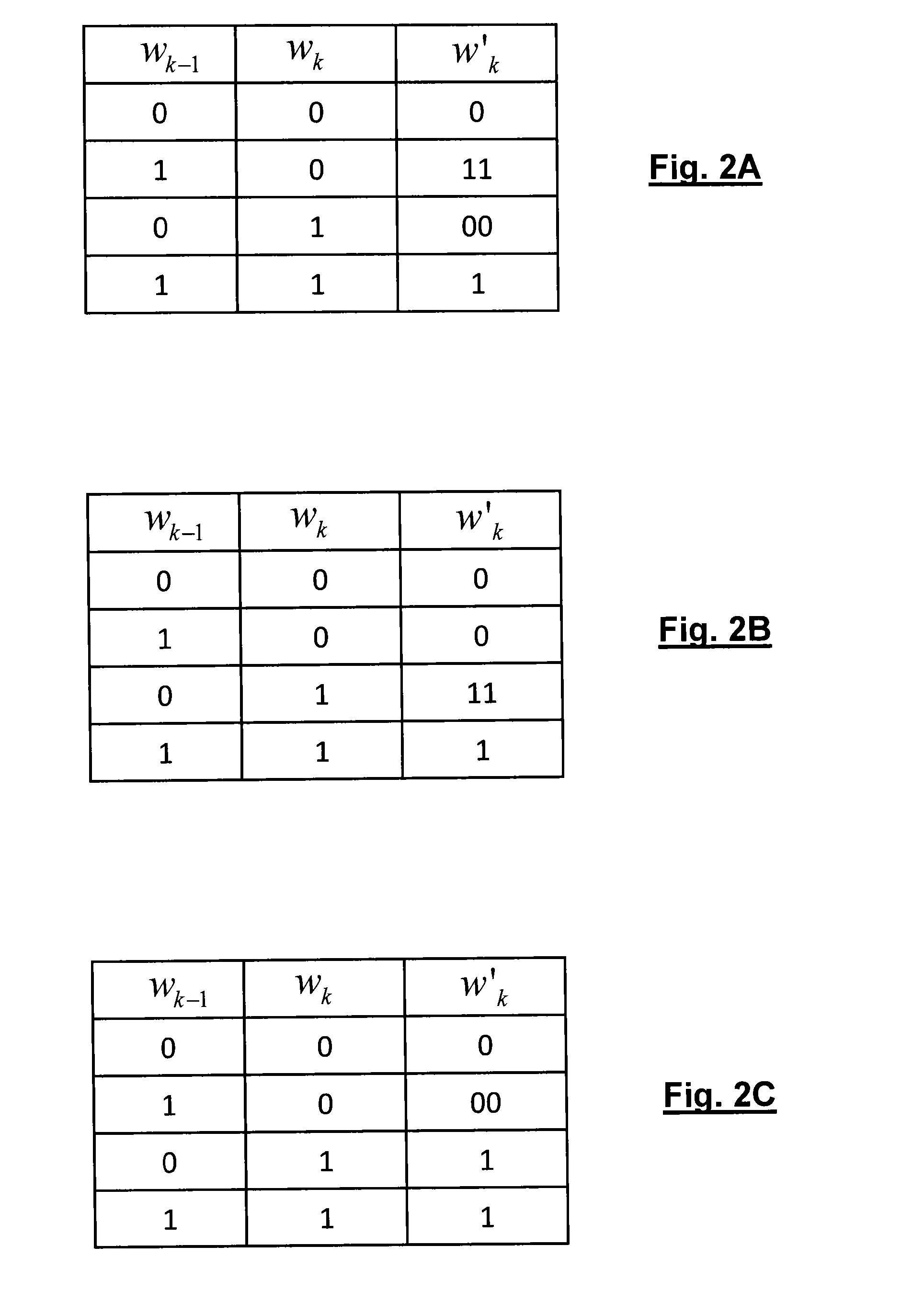
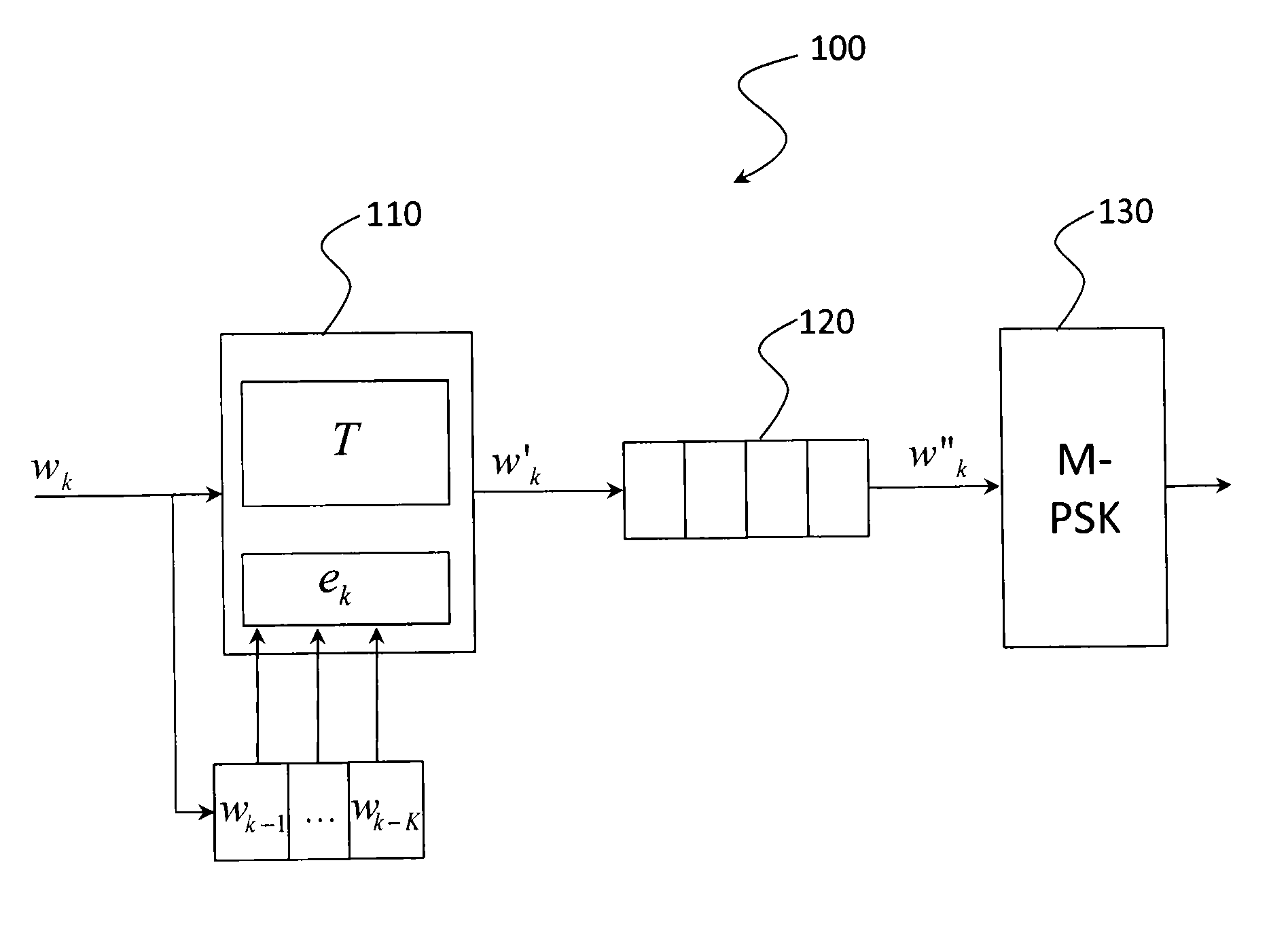
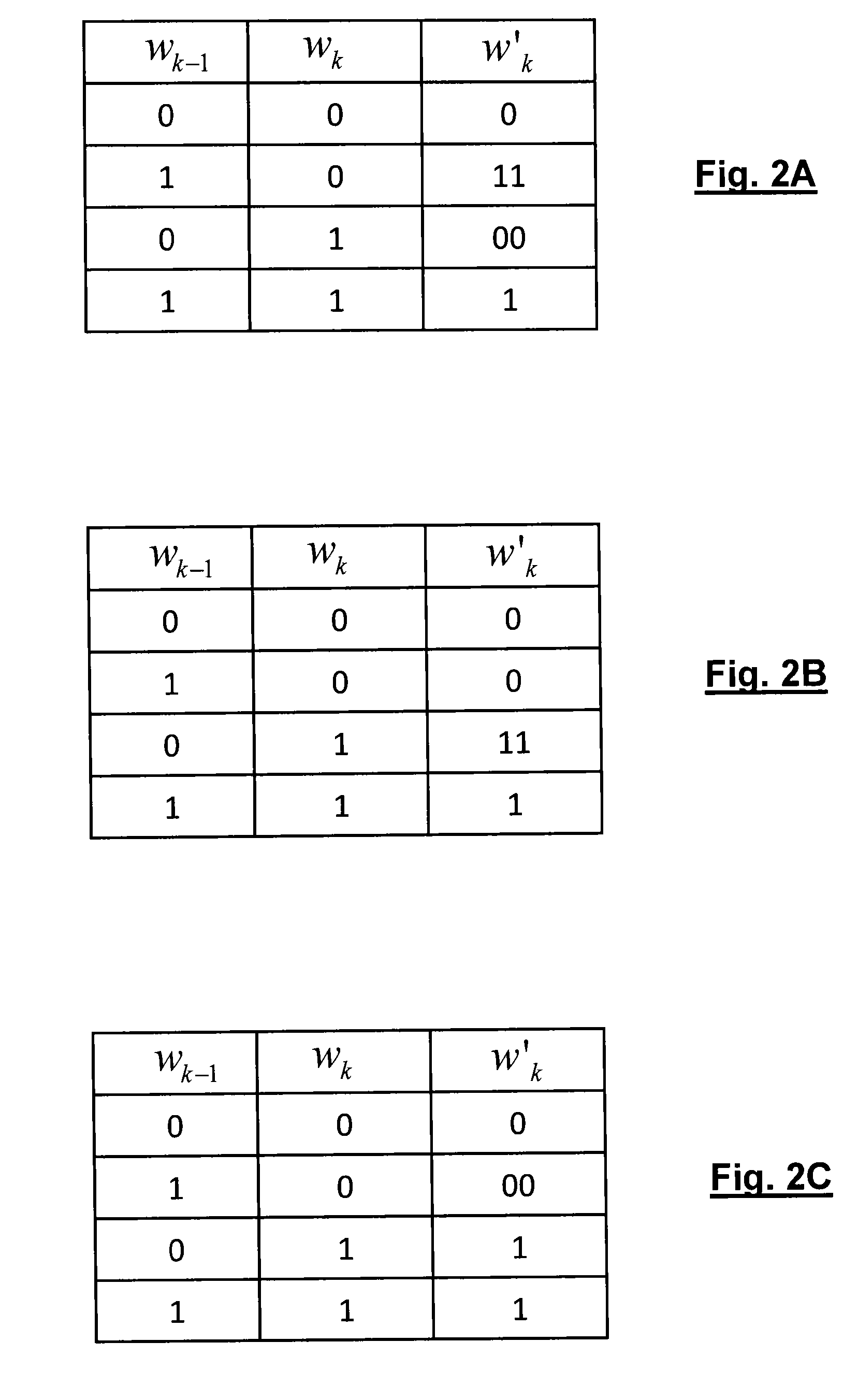
Method and device for digital modulation with low transition density
The present invention relates to a digital modulation method and a corresponding modulator. The modulator comprises a transcoder (110) followed by a FIFO register (120) and a 2-PSK modulator (130). The transcoder codes a binary word of fixed size into a code word of variable size using a transcoding table. The transcoding table codes at least one first binary word, leading to a first number of phase transitions at the output of the modulator, into a second word of size greater than that of the first word, leading to, at the output of the modulator, a second number of phase transitions less than the first number of phase transitions.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Phase detetor and phase detecting method
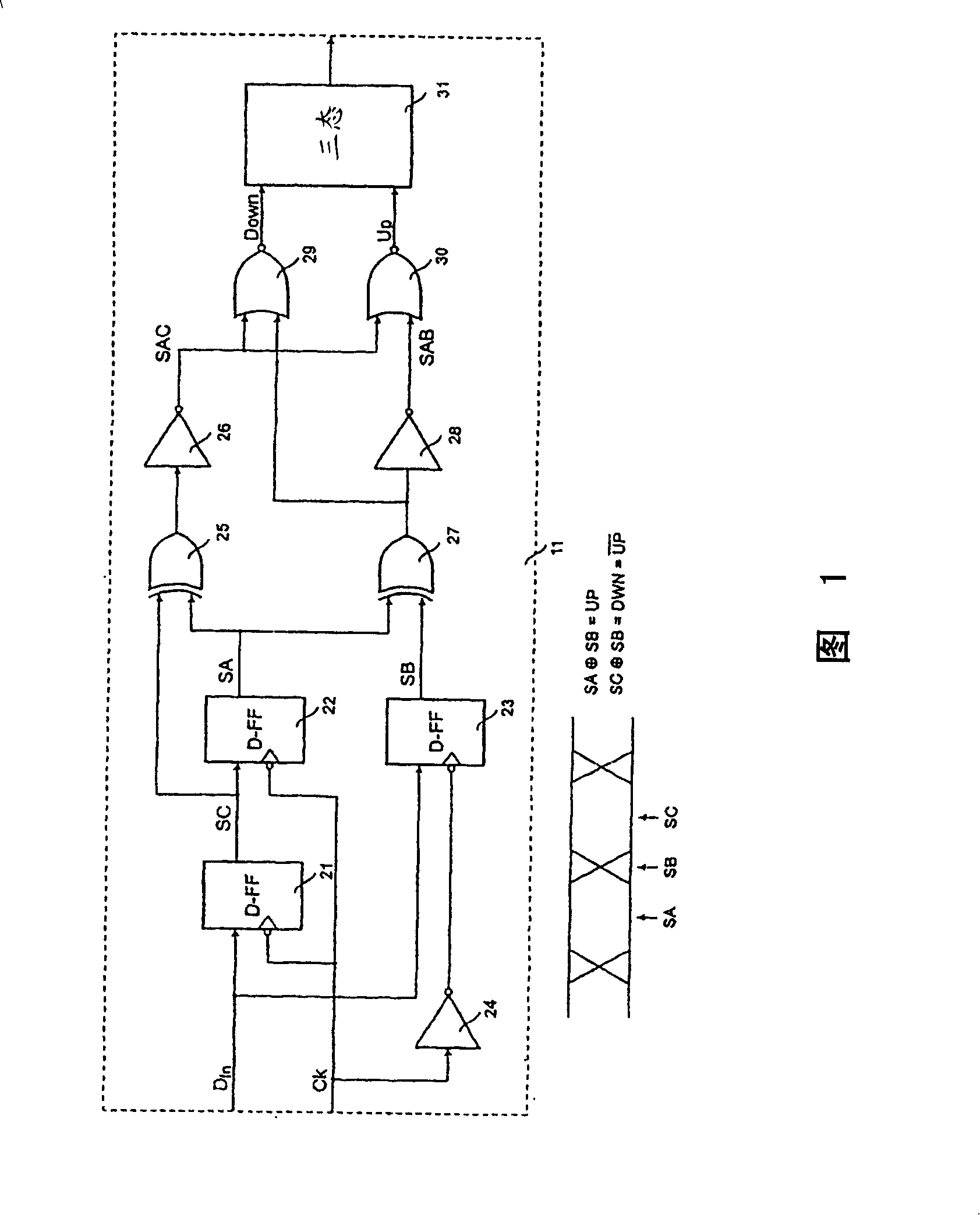
InactiveCN100403652CConversion Density ConstantExclusive-OR circuitsPulse automatic controlPhase detectorTransition density
The present invention relates to a phase detector and utilisation of the phase detector for synchronisation of a digital signal with a clock signal. It is an object of the present invention to provide a phase detector with improved characteristics including jitter tolerance and jitter transfer. It is another object of the invention to provide a phase detector that generates an output signal that, when used as a control signal in a phase or frequency locked loop, keeps the gain of the control loop substantially invariant to the transition density of the phase detector input signals. According to the invention, these aspects are fulfilled by provision of a phase detector for detection of a phase difference between a first signal and a second signal. The phase detector comprises a first logic circuit for detection of a data transition of the first signal and a second logic circuit that generates a logic output signal of a first logic value upon detection of a data transition of the first signal if a transition of the second signal occurs before the transition of the first signal and of a second logic value if the transition of the second signal occurs after the transition of the first signal.
Owner:GIGA APS
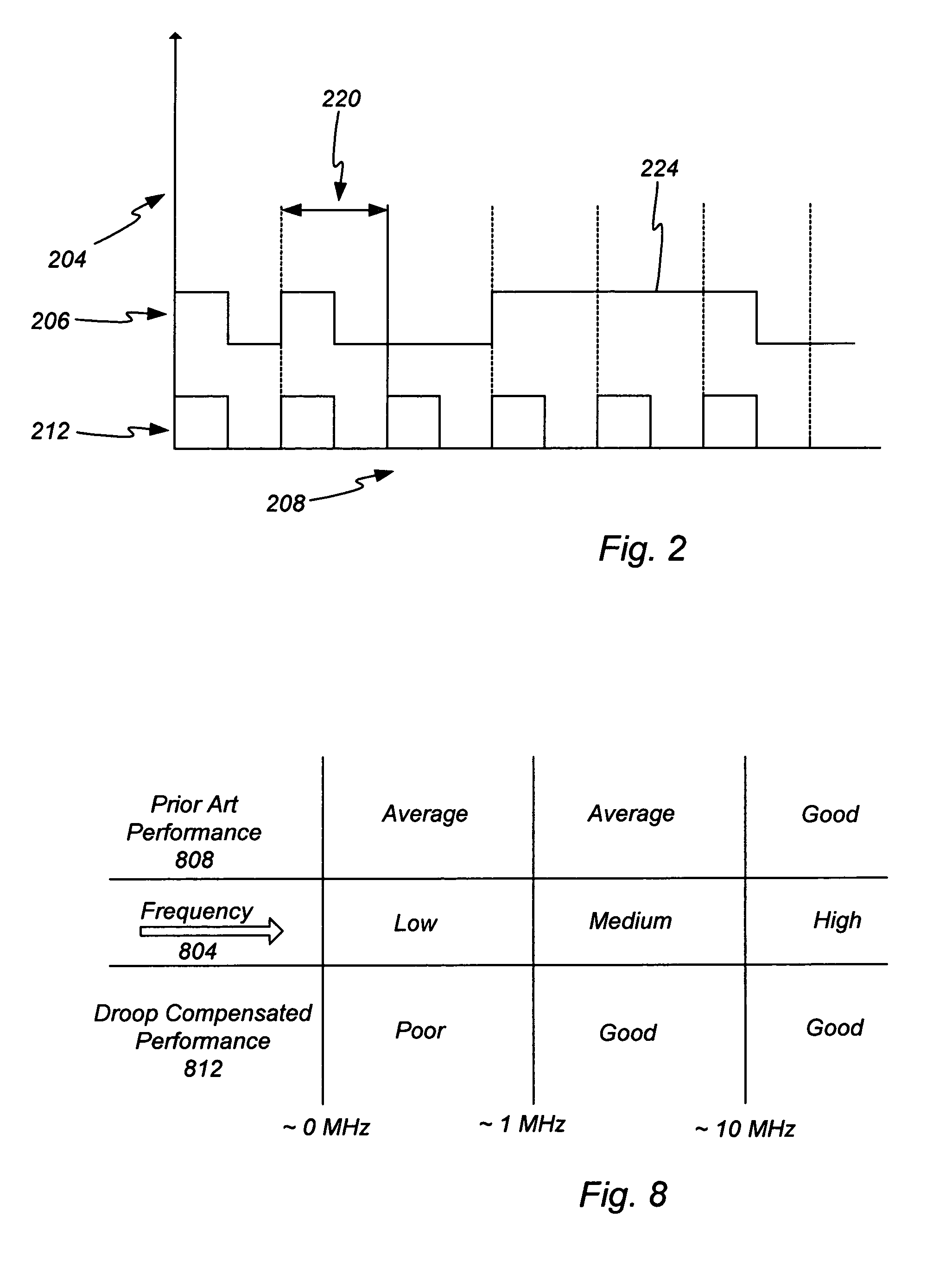
Method and apparatus for reducing transmitter AC-coupling droop
InactiveUS8049537B2High energyElectric pulse generatorOscillations generatorsTransformerCurrent driver
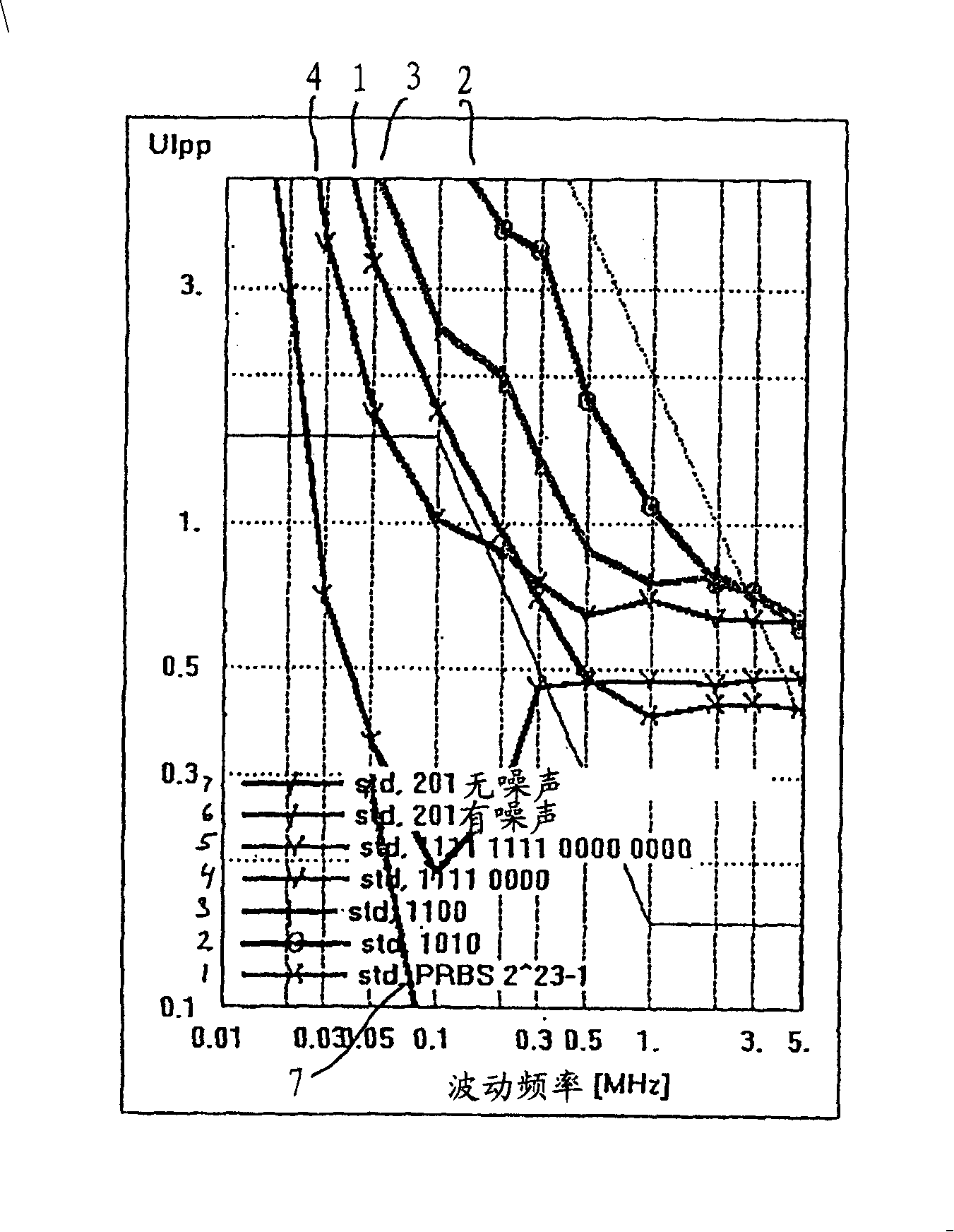
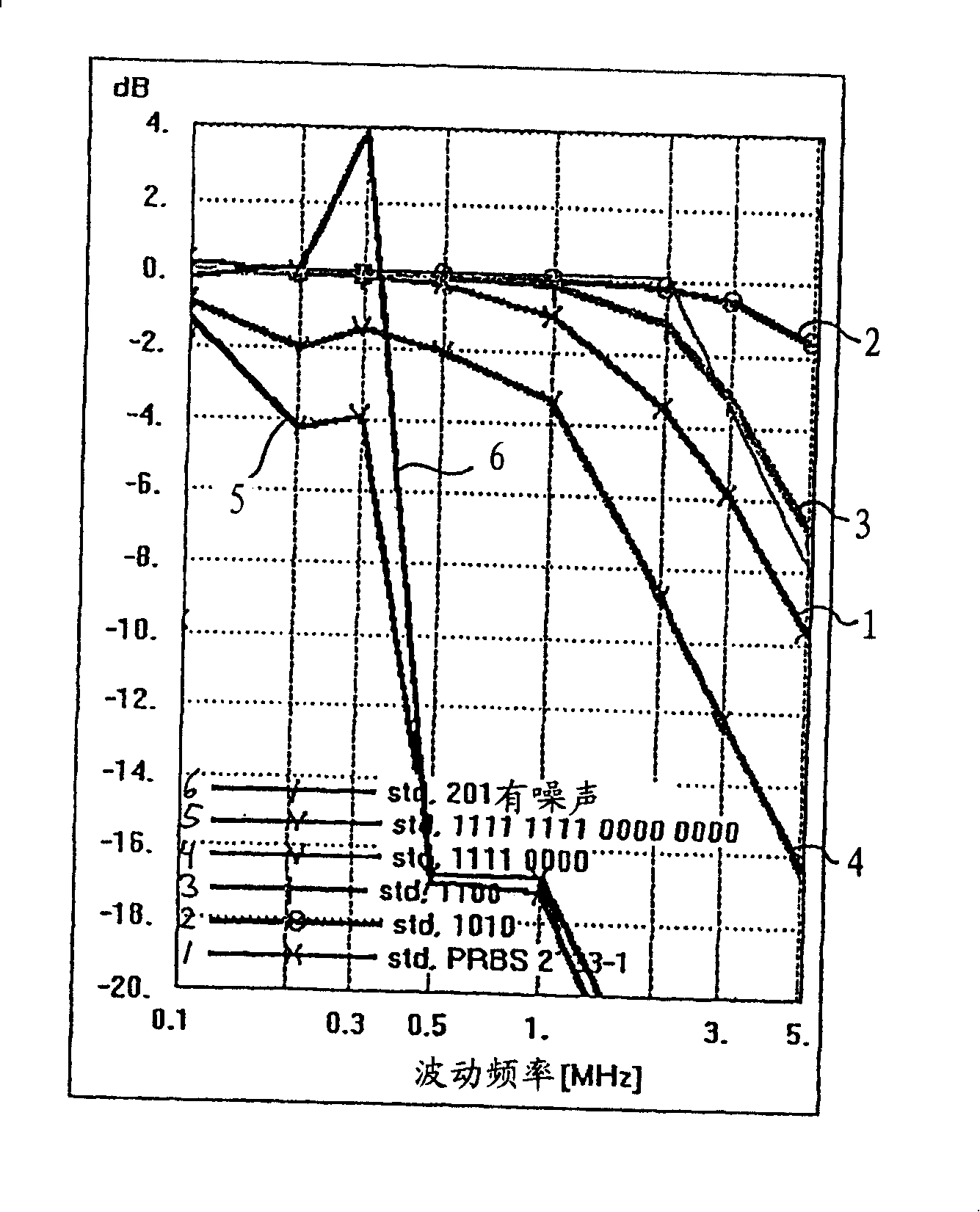
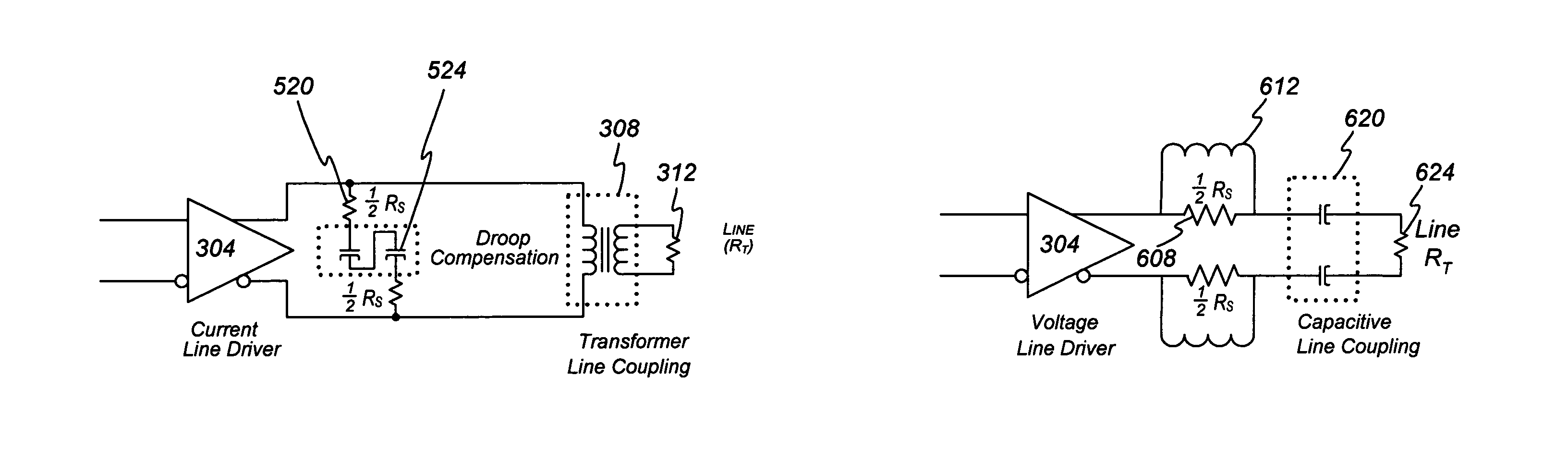
As part of a transmitter and receiver system a droop compensator is provided between the channel isolation device and the driver system to compensate for reduced transition densities. The droop compensator is configured to improve power transfer to the channel in response to reductions in transition density without affecting power transfer during periods of high transition density. The droop compensator creates an impedance mismatch between the matching circuit and driver in relation to the line impedance. The droop compensator may comprise passive elements, such as capacitors, inductors, or resistor, or active elements including transistors or power control modules. The droop compensator may be configured to operate with transformer line couplers or capacitor line couplers, and either current drivers or voltage drivers.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
CDR-based clock synthesis
A clock signal can be synthesized by performing a clock and data recovery (CDR) operation on a potentially noisy clock source signal which has a known transition density. The CDR operation produces a desired clock signal in response to the clock source signal. In order to reduce crosstalk between plesiochronous receive and transmit clock domains of a serial data transceiver, a single common PLL is used both to recover the receive clock from the received data and to synthesize the transmit clock from a potentially noisy transmit clock source signal.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG +1
Method and device for digital modulation with low transition density
The present invention relates to a digital modulation method and a corresponding modulator. The modulator comprises a transcoder (110) followed by a FIFO register (120) and a 2-PSK modulator (130). The transcoder codes a binary word of fixed size into a code word of variable size using a transcoding table. The transcoding table codes at least one first binary word, leading to a first number of phase transitions at the output of the modulator, into a second word of size greater than that of the first word, leading to, at the output of the modulator, a second number of phase transitions less than the first number of phase transitions.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
CDR-based clock synthesis
A clock signal can be synthesized by performing a clock and data recovery (CDR) operation on a potentially noisy clock source signal which has a known transition density. The CDR operation produces a desired clock signal in response to the clock source signal. In order to reduce crosstalk between plesiochronous receive and transmit clock domains of a serial data transceiver, a single common PLL is used both to recover the receive clock from the received data and to synthesize the transmit clock from a potentially noisy transmit clock source signal.
Owner:MAXLINEAR INC +1
Region of interest location and selective image compression
ActiveUS20180018491A1Character and pattern recognitionSensing by electromagnetic radiationTransition densityImage resolution
Owner:DATALOGIC USA INC
Method and apparatus for maintaining data density for derived clocking
Some embodiments of the invention implement point-to-point memory channels that virtually eliminate the need for mandatory synchronization cycles for a derived clocking architecture by tracking the number of data transitions on inbound and outbound data lanes to make sure the minimum number of transitions occur. Other embodiments of the invention perform data inversions to increase the likelihood of meeting the minimum data transition density. Still other embodiments are described in the claims.
Owner:INTEL CORP
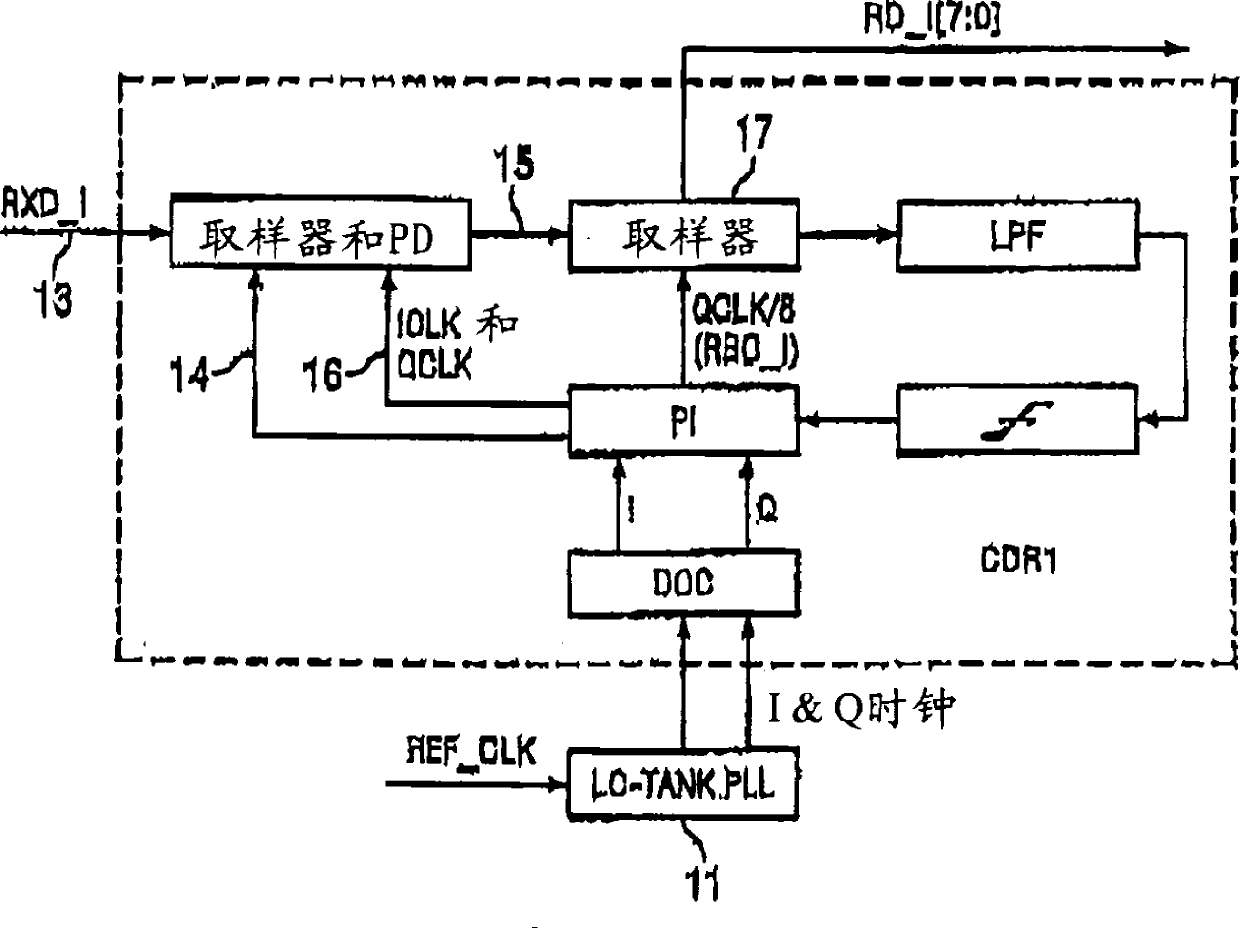
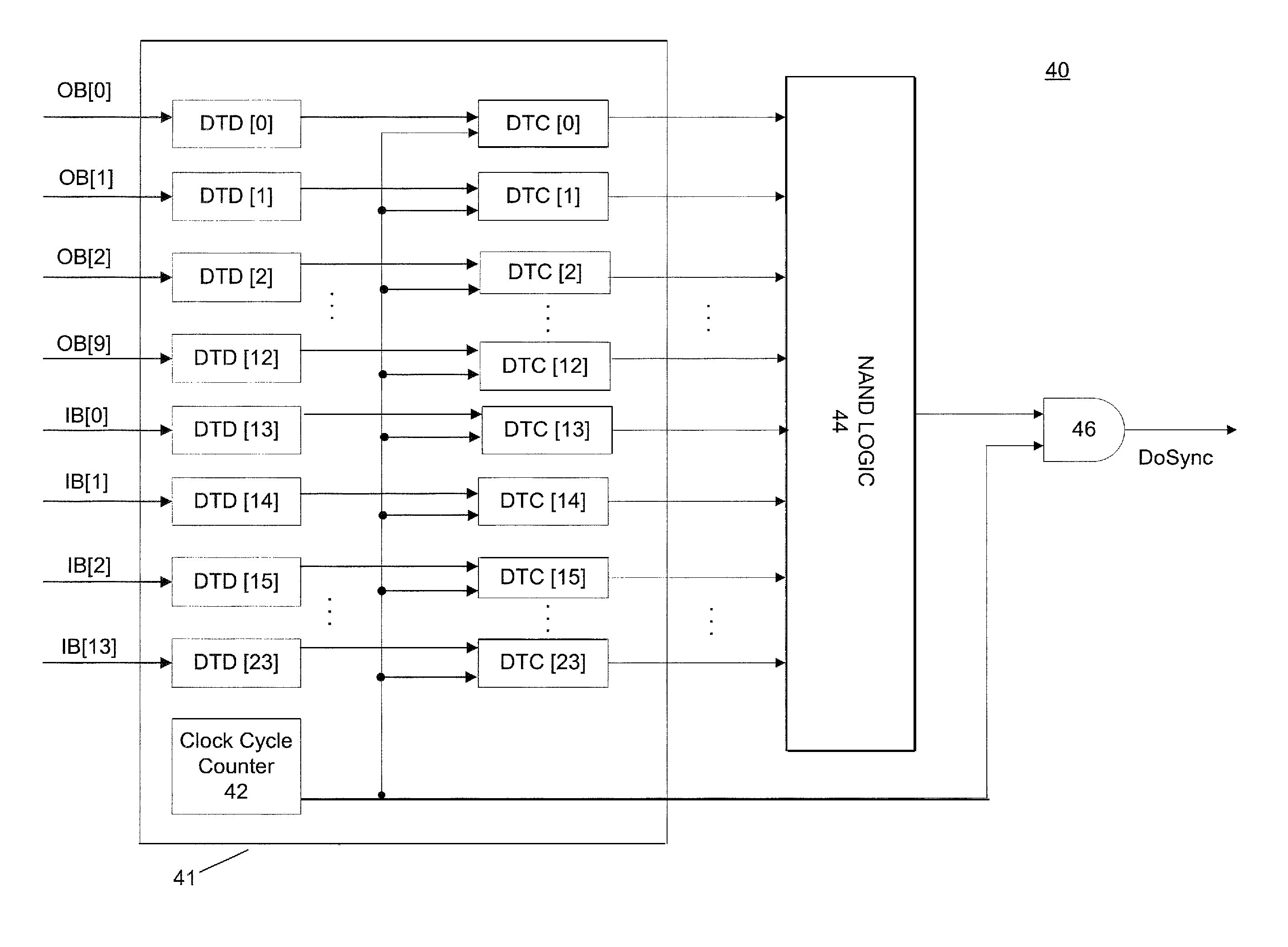
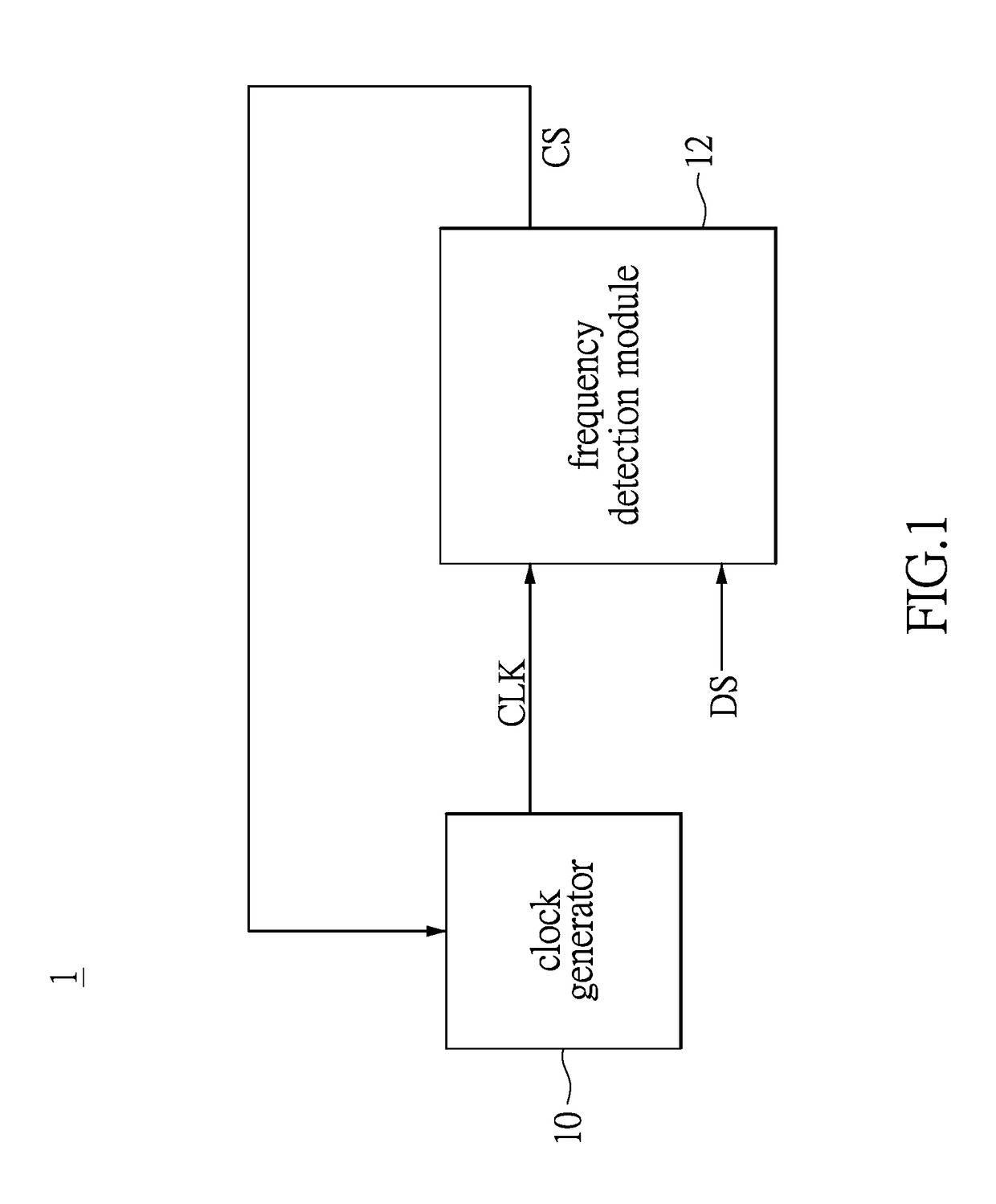
Clock and data recovery circuit and frequency detection method thereof
ActiveUS9686105B2Increase and decrease frequencyAccurate detectionAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionSynchronising arrangementTransition densityControl signal
The present disclosure provides a crystal-less clock and data recovery (CDR) circuit and a frequency detection method thereof. The CDR circuit includes a clock generator and a frequency detection module. The clock generator is operable to generate a clock signal. The frequency detection module coupled to the clock generator is configured for outputting a control signal to the clock generator to increase or decrease the frequency of the clock signal according to a data signal received and a transition density.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
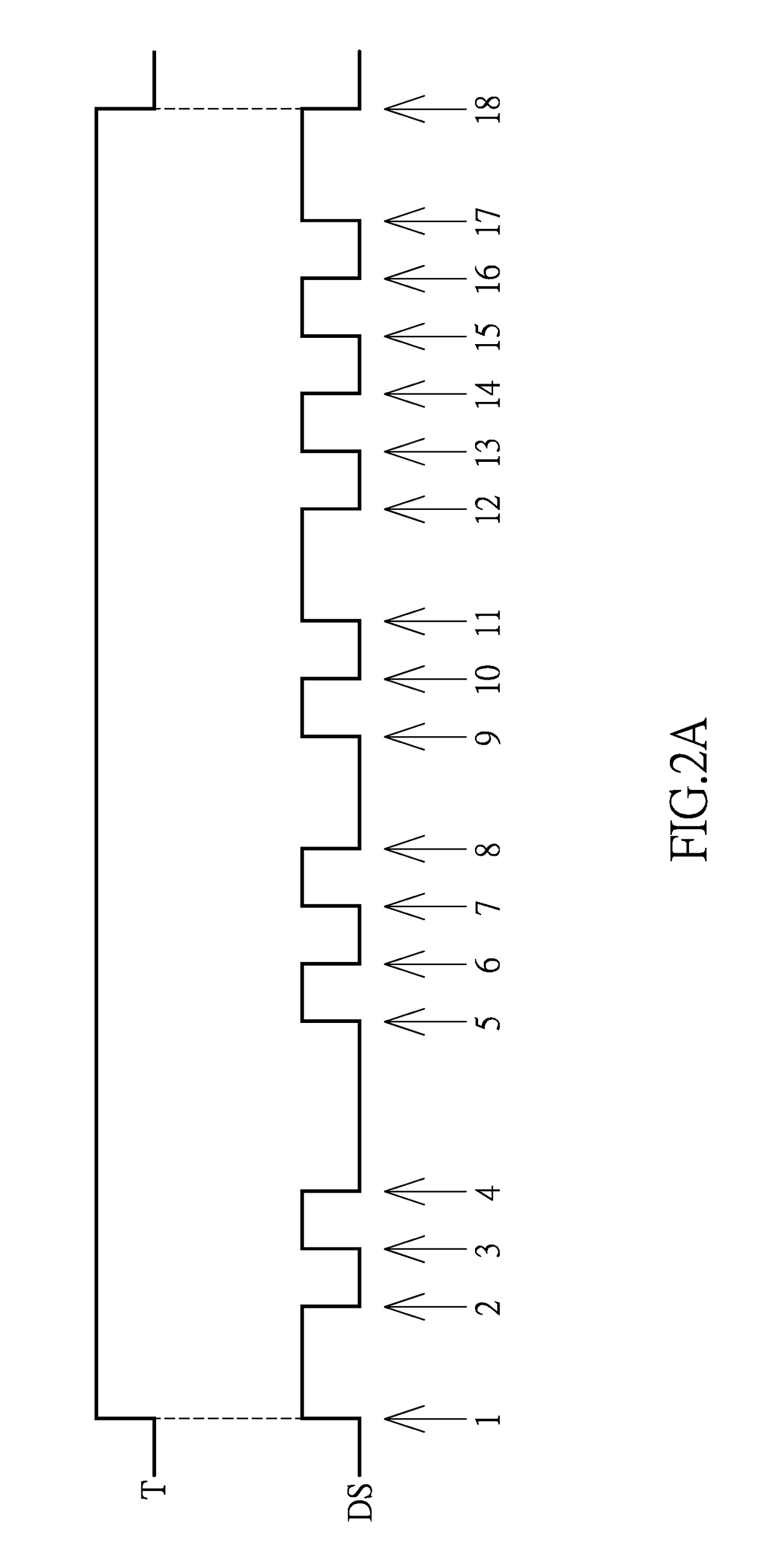
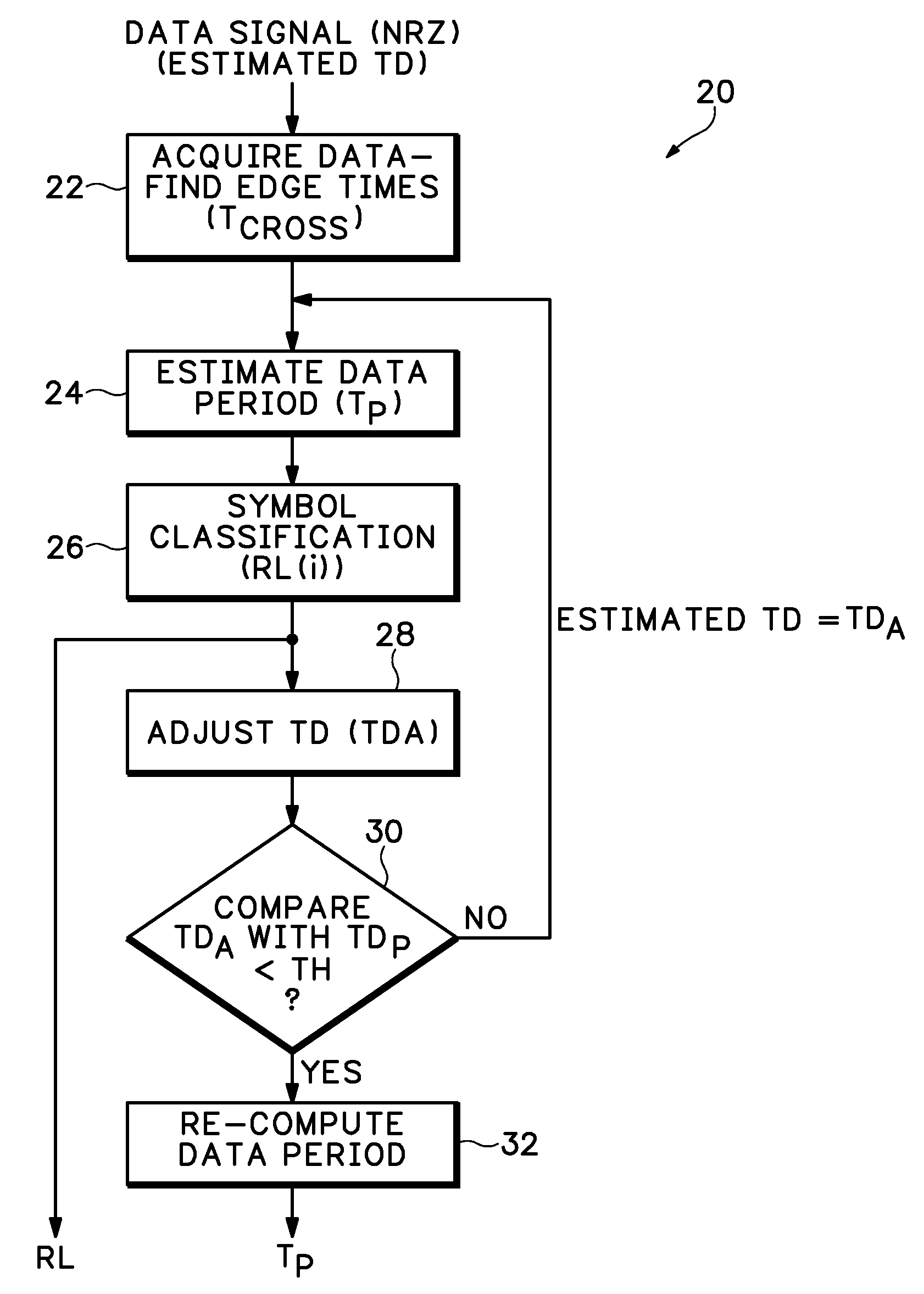
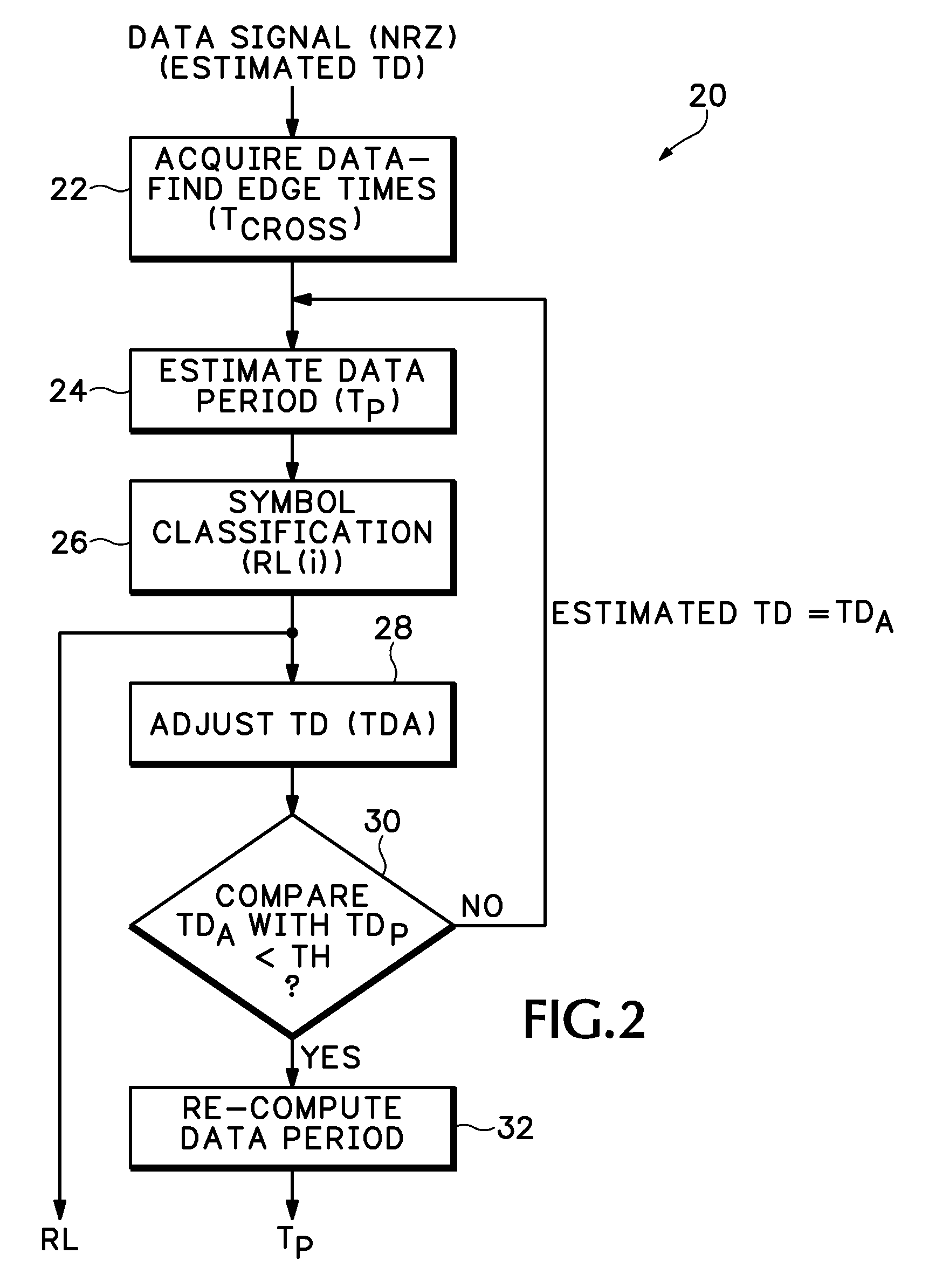
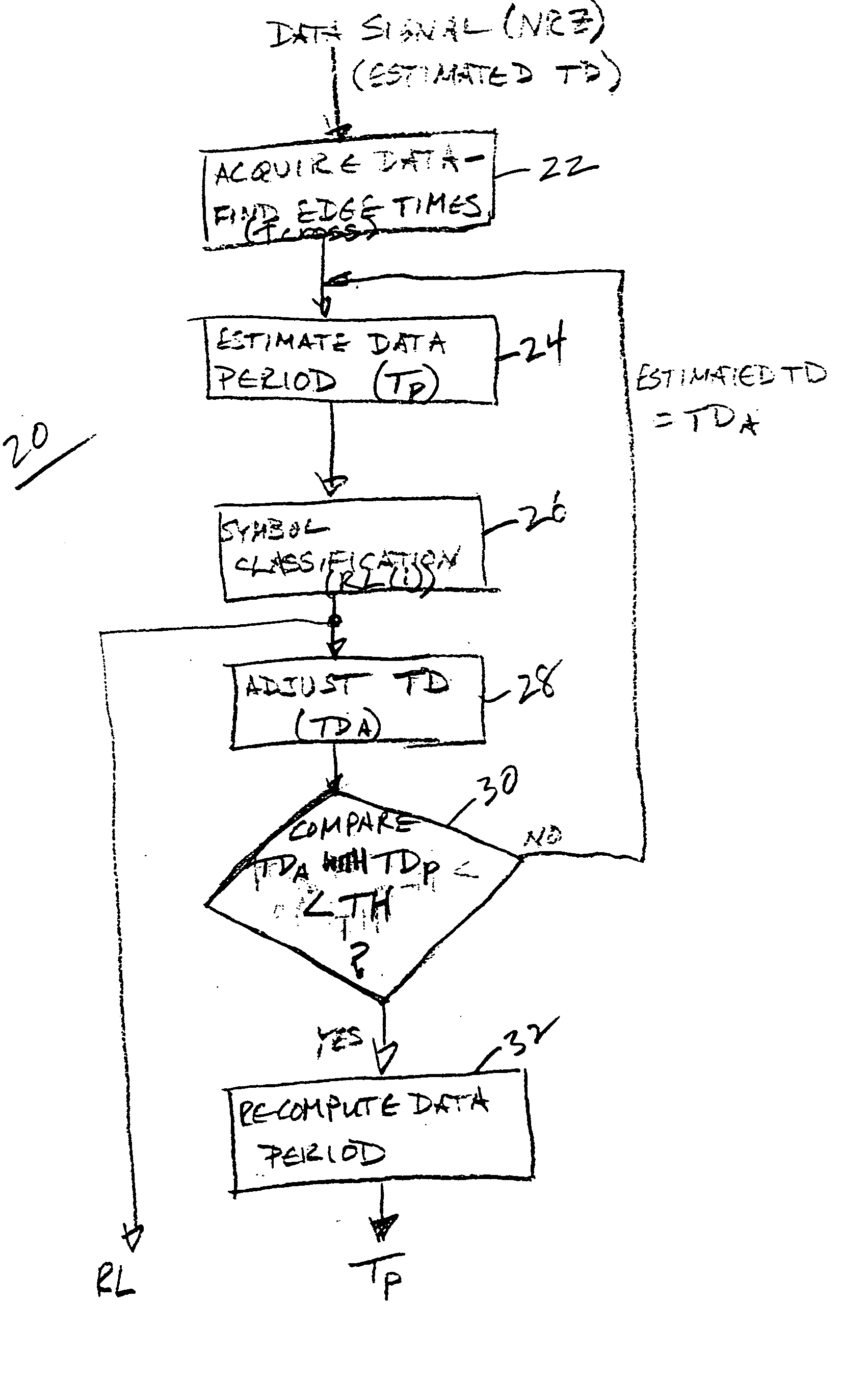
Transition-density based time measurement method
ActiveUS7376524B2Error preventionNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementTransition densityAlgorithm
Owner:TEKTRONIX INC
Transition-density based time measurement method
ActiveUS20050234668A1Noise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementError preventionTransition densityAlgorithm
A transition-density based data timing measurement method uses an estimated transition density (TD) value for an acquired data signal together with edge crossing times to estimate a data period for the acquired data signal. The estimated data period is used for symbol classification to determine a number of bits between adjacent edge crossings, which results are used to adjust the TD value. The adjusted TD value is then used to re-compute the data period.
Owner:TEKTRONIX INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com