Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
482results about "Analog signal digital control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
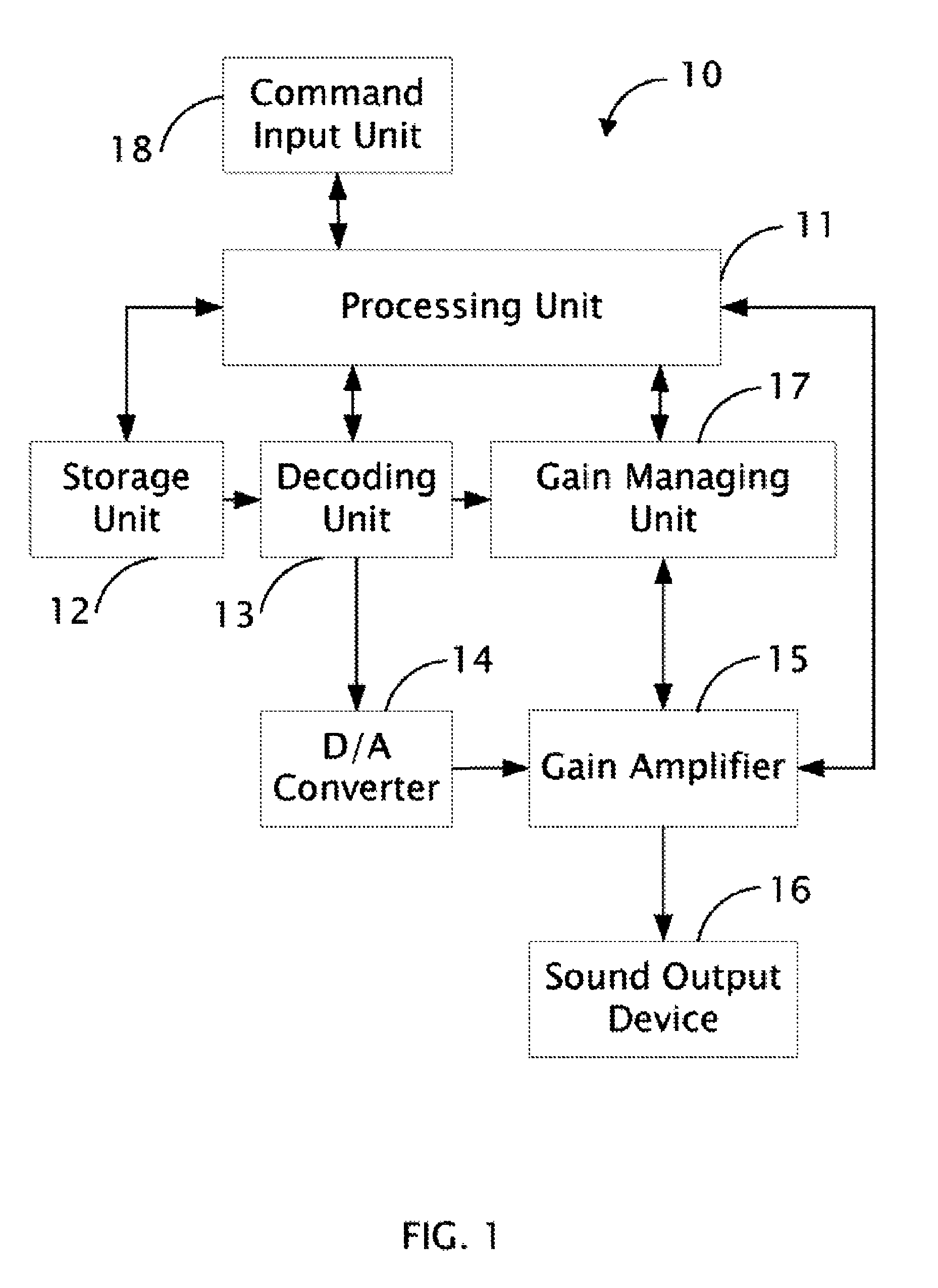
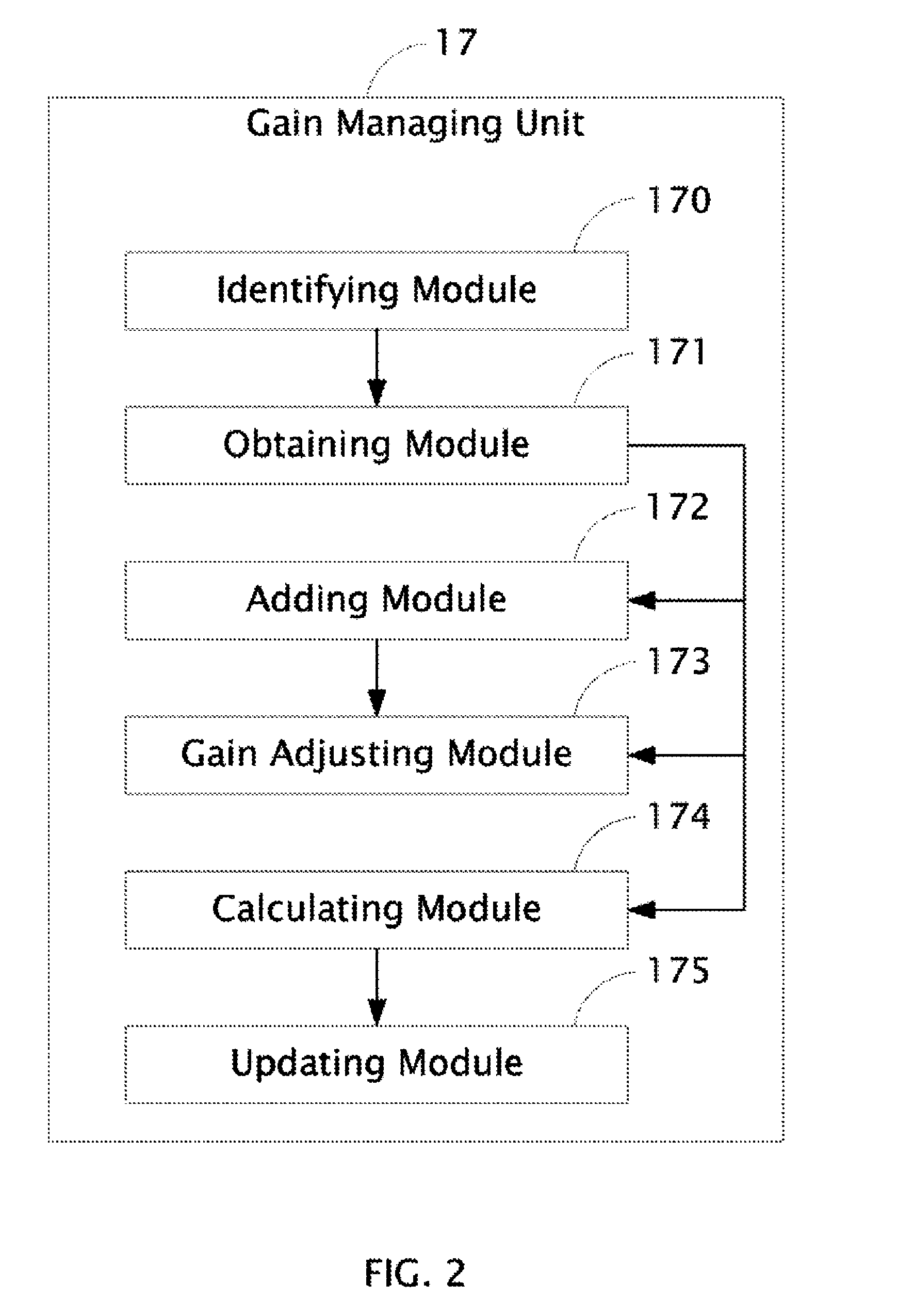
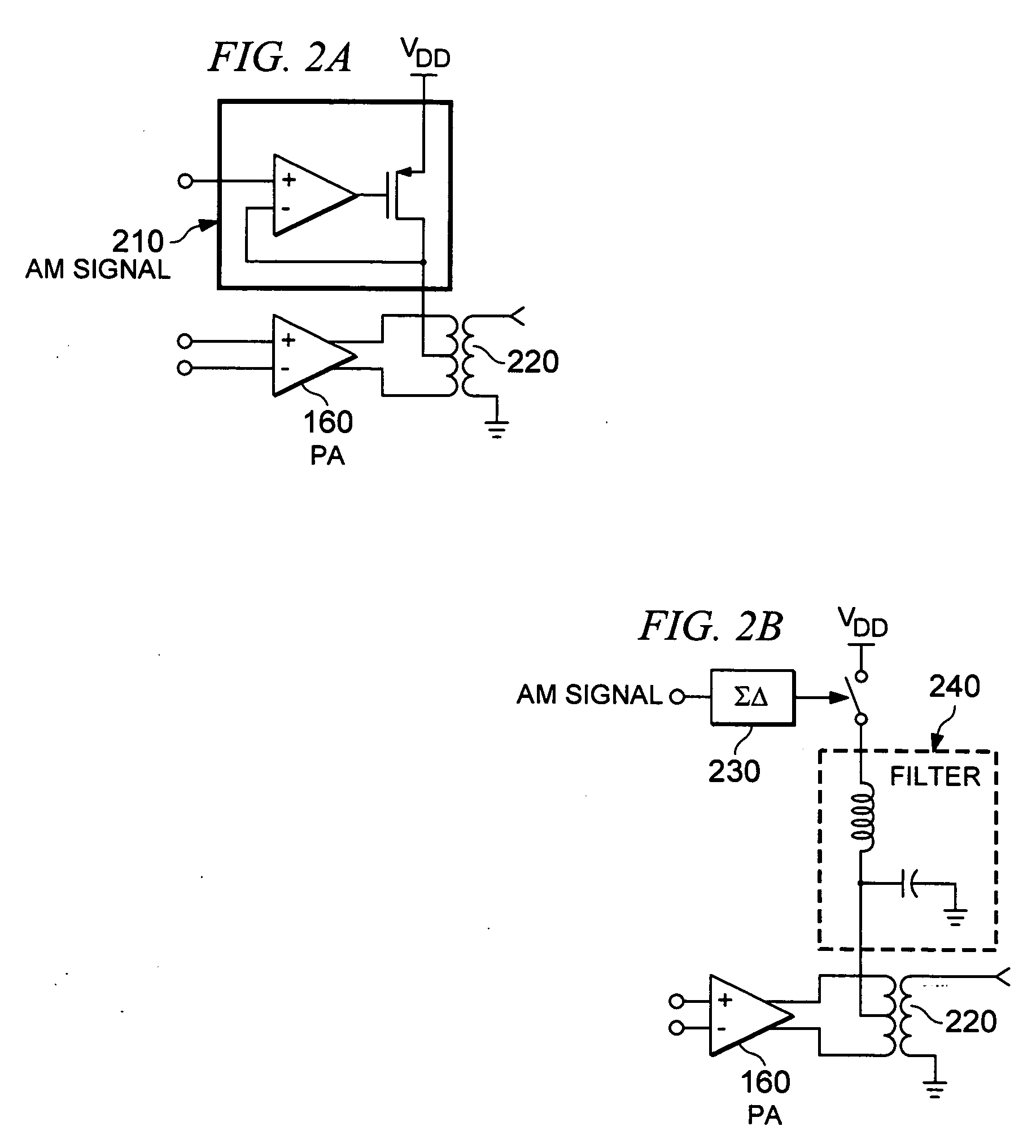
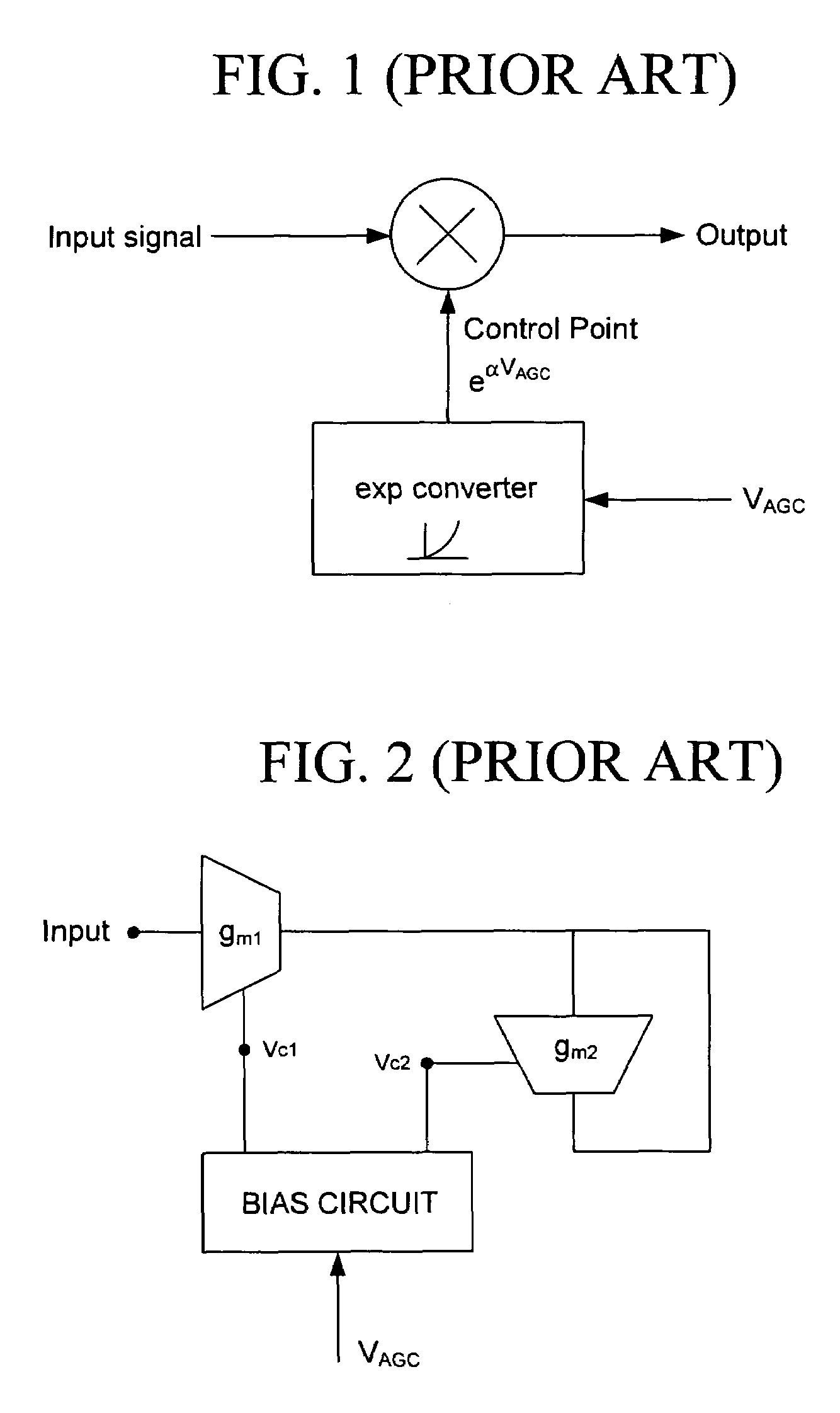
Audio processing system with function of automatic gain control and method thereof
ActiveUS8019094B2Analog signal digital controlSpecial data processing applicationsAudio power amplifierAutomatic control
The present invention relates to an audio processing system with function of automatic gain control and method thereof. The method includes steps of: receiving a playing command to play an audio file; reading a genre type of the audio file from a tag of the audio file; reading a genre gain value of the genre type from a gain setting table stored in a storage unit; decoding the audio file and generating digital audio signals; converting the digital audio signals to analog audio signals; and signaling a gain amplifier to amplify the analog audio signals by the genre gain value, thereby sounds corresponding to the analog audio signals amplified is proper to a listener's hearing.
Owner:HANNSTAR DISPLAY CORPORATION
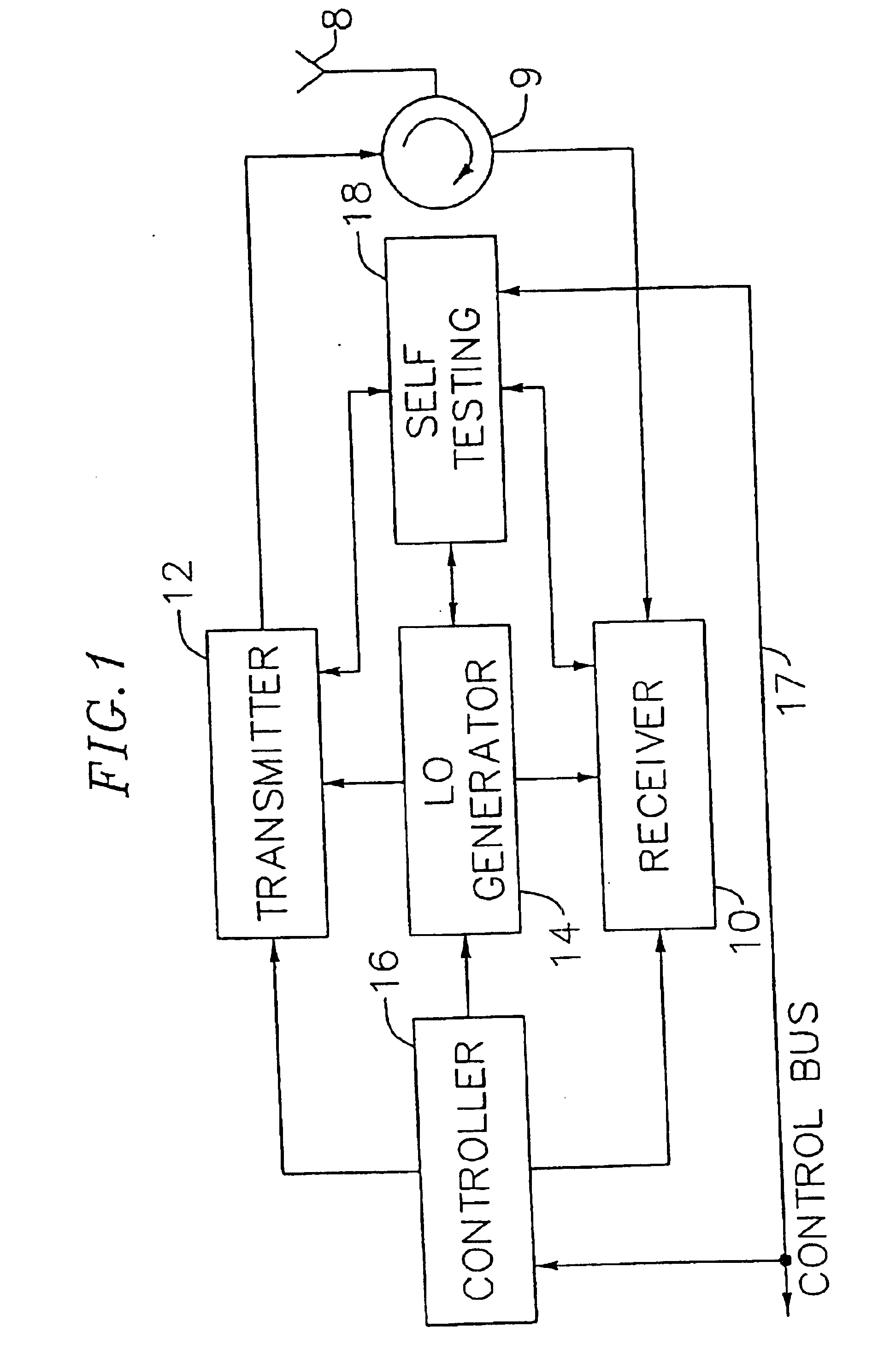
Adaptive radio transceiver with floating MOSFET capacitors
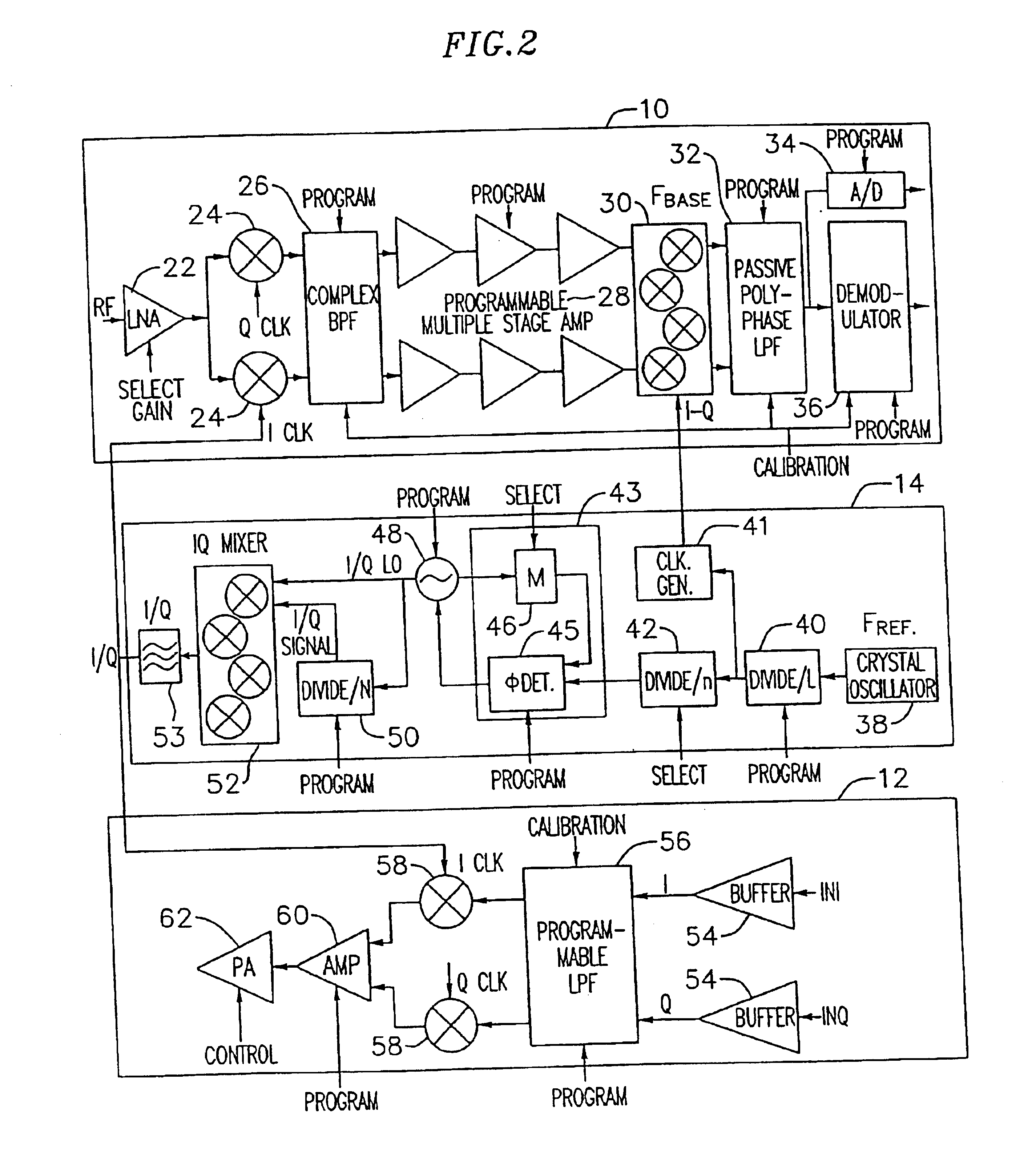
An exemplary embodiment of the present invention described and shown in the specification and drawings is a transceiver with a receiver, a transmitter, a local oscillator (LO) generator, a controller, and a self-testing unit. All of these components can be packaged for integration into a single IC including components such as filters and inductors. The controller for adaptive programming and calibration of the receiver, transmitter and LO generator. The self-testing unit generates is used to determine the gain, frequency characteristics, selectivity, noise floor, and distortion behavior of the receiver, transmitter and LO generator. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
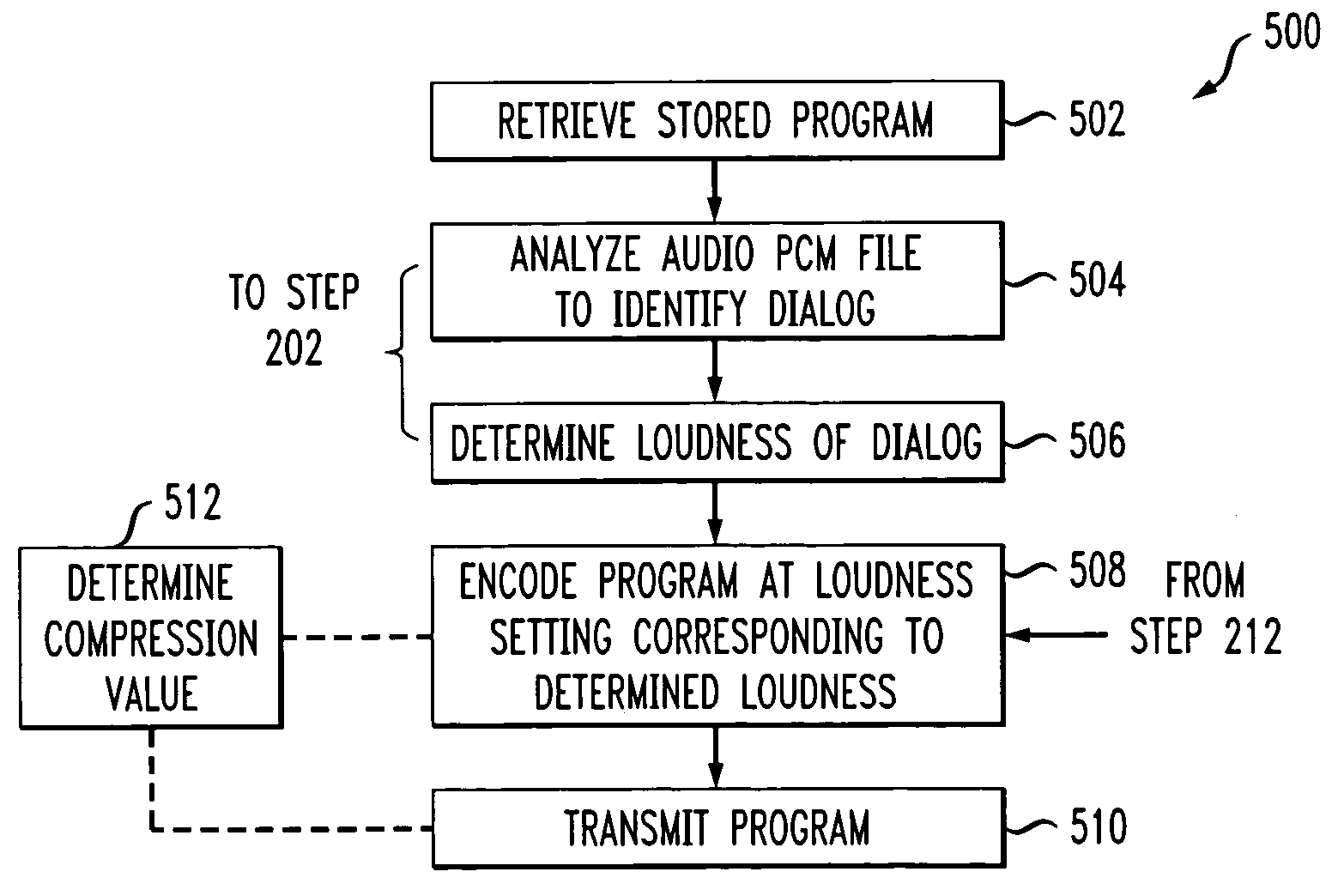
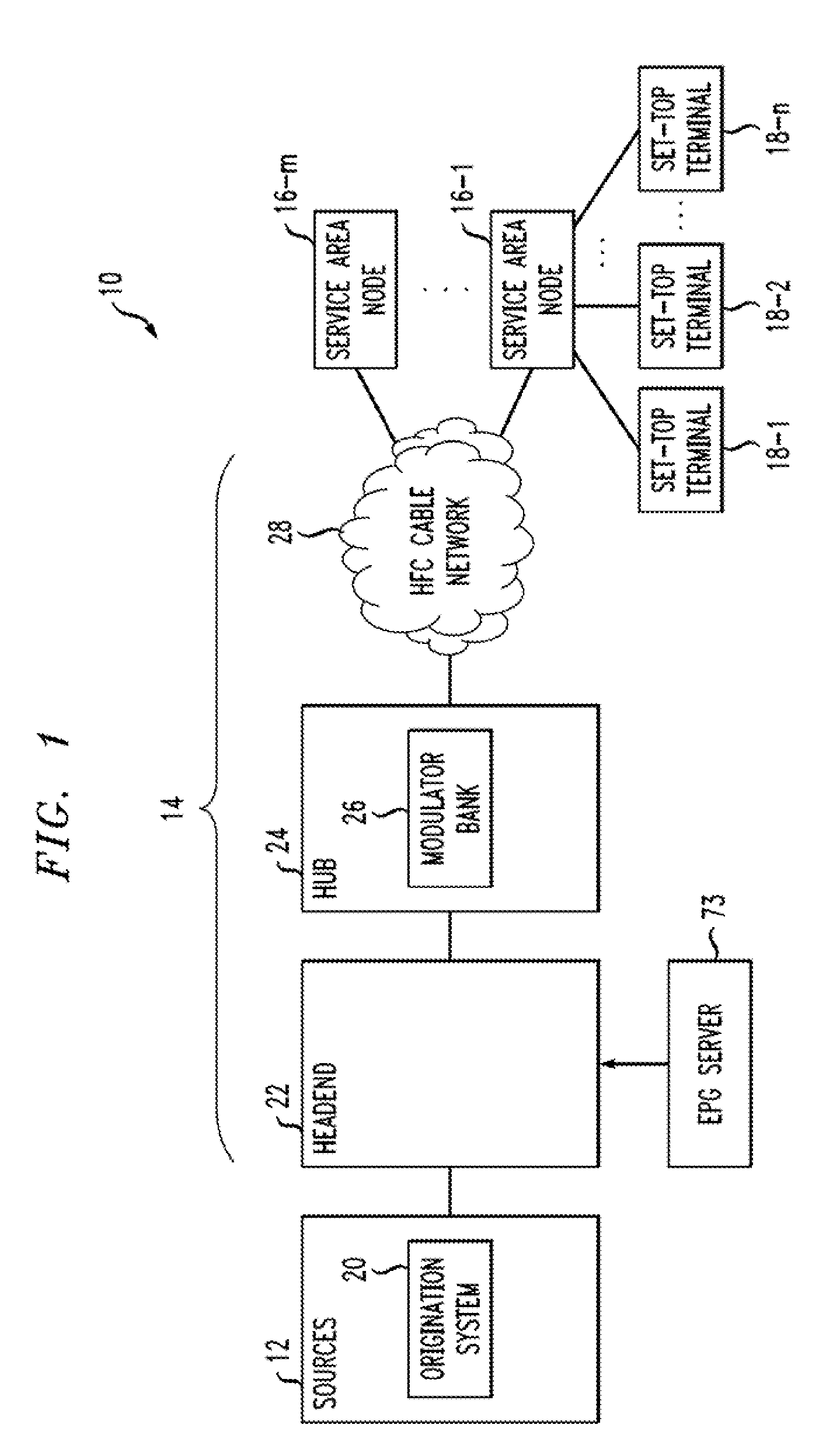
Methods and systems for determining audio loudness levels in programming
An example of a method of correcting an audio level of a stored program asset comprises retrieving a stored program asset having audio encoded at a first loudness setting. Dialog of the audio of the asset is identified, a loudness of the dialog is determined and the determined loudness is compared to the first loudness setting. The asset is re-encoded at a second loudness setting corresponding to the determined loudness, if the first loudness setting and the second loudness are different by more than a predetermined amount. The determined loudness is preferably a DIALNORM of the dialog. The asset may be stored with the re-encoded loudness setting. The method may be applied to programs as they are being received from a source, as well. Aspects of the method may also be applied to programs to be provided by a source. Systems are also disclosed.
Owner:TIME WARNER CABLE ENTERPRISES LLC
DAC based switching power amplifier
InactiveUS7509102B2Simultaneous amplitude and angle modulationResonant long antennasAudio power amplifierControl signal
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Staggered AGC with digitally controlled VGA
ActiveUS20050058228A1Reduce gain requirementsSimple designDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionLine balance variation compensationVariable-gain amplifierA d converter
The invention relates to the field of wireless communications, more particularly to a method of and device for automatic gain control (AGC) incorporating digitally controlled variable gain amplifiers (VGAs). The invention provides an AGC circuit comprising an I / Q baseband strip comprising multiple AGC stages wherein each of the AGC stages comprises: respective I and Q VGAs; a detector for detecting respective I and Q output signals received from the respective I and Q VGAs; an analogue to digital converter (ADC) for converting the detected I and Q output signals; and a digital engine for adjusting the respective I and Q VGAs for differences between the detected I and Q output signals and a reference signal. The use of staggered AGCs incorporating respective I and Q VGAs means that the total dynamic range is split between n-stages, thereby allowing for reduced gain requirements in the VGAs. Additionally, the use of digital control for setting the VGA gains means that analogue variations and I / Q gain imbalances are reduced. Additionally, the use of multiple update rates or magnitudes in the VGA control improves the dynamic settling time.
Owner:ZARBANA DIGITAL FUND
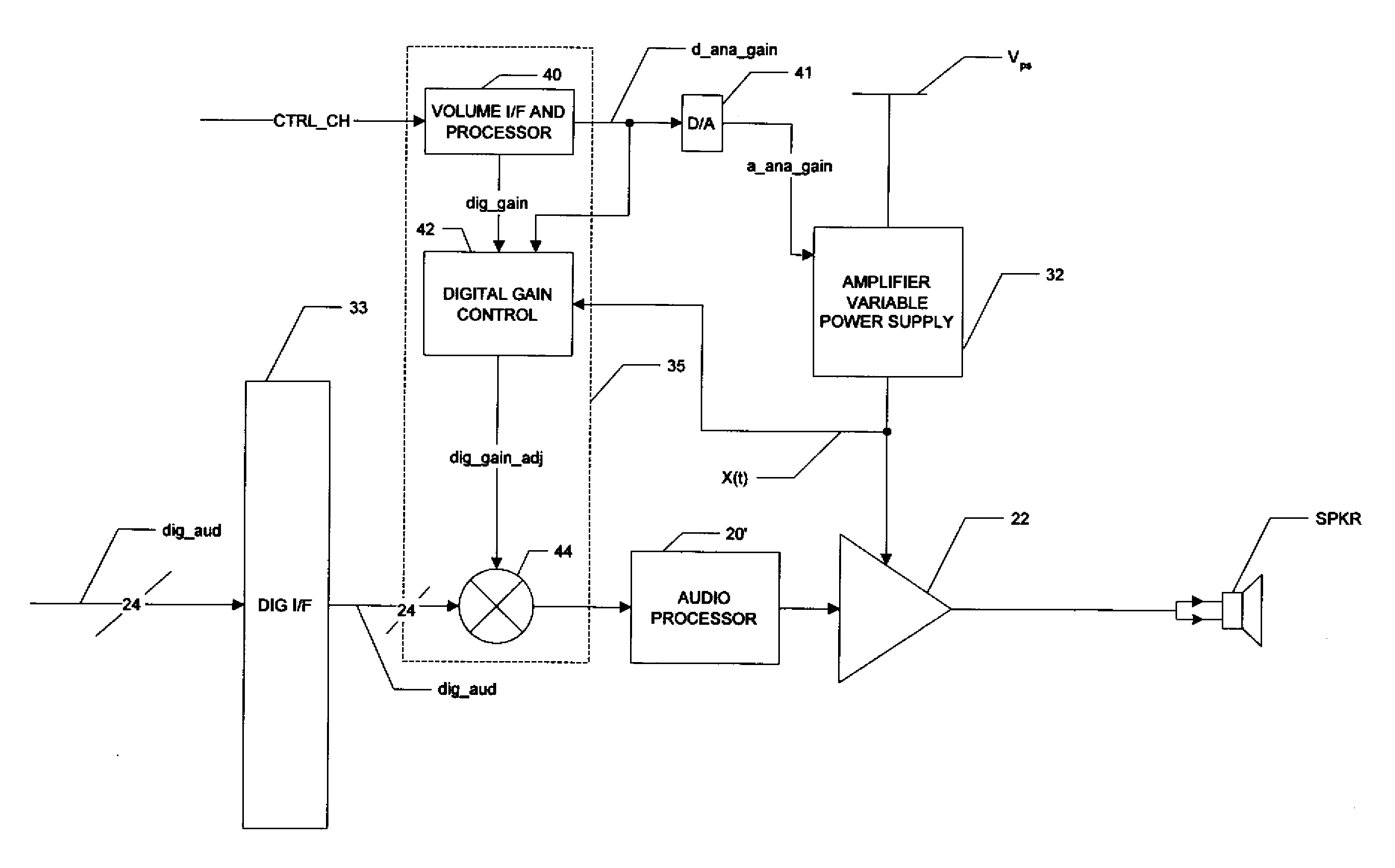
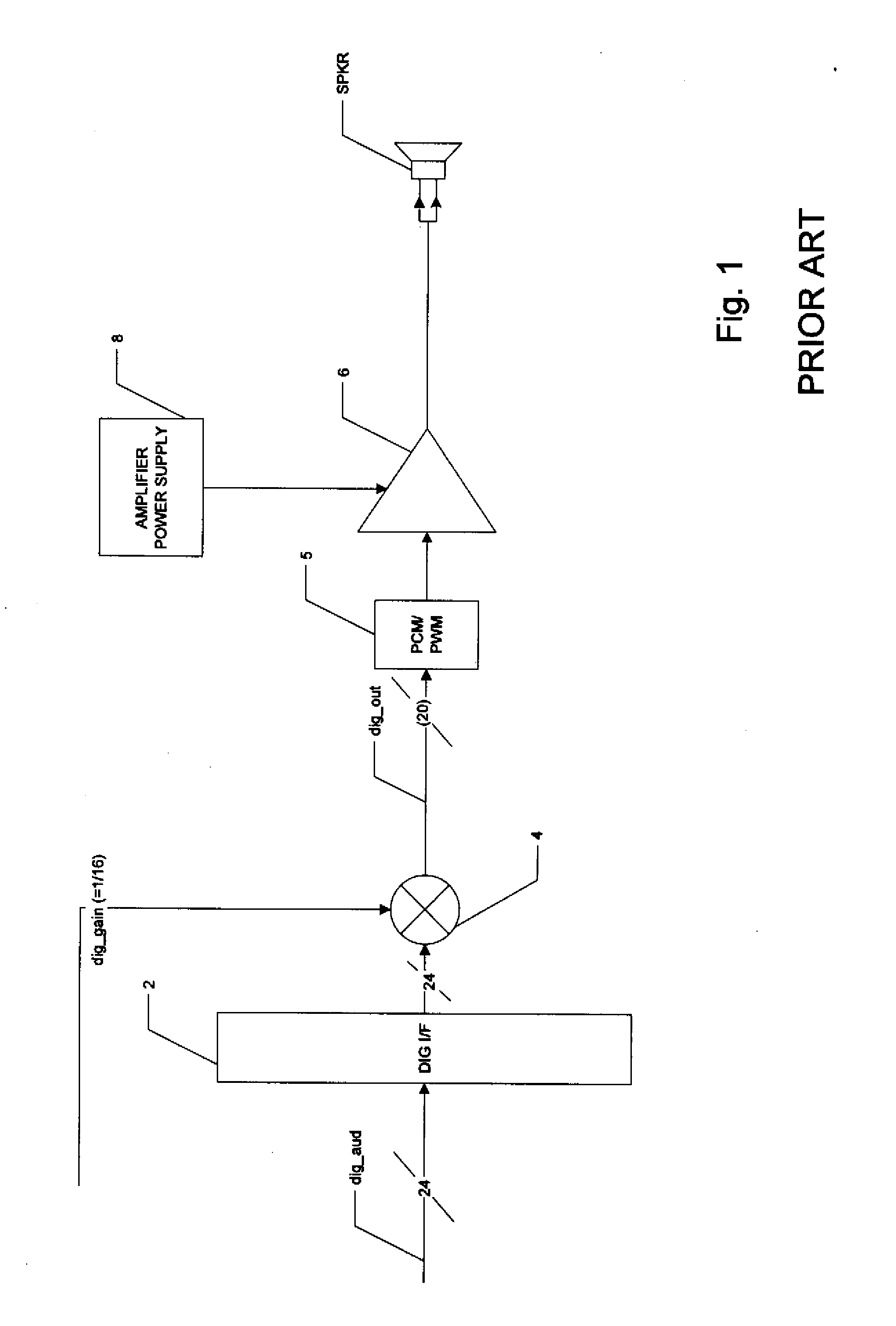
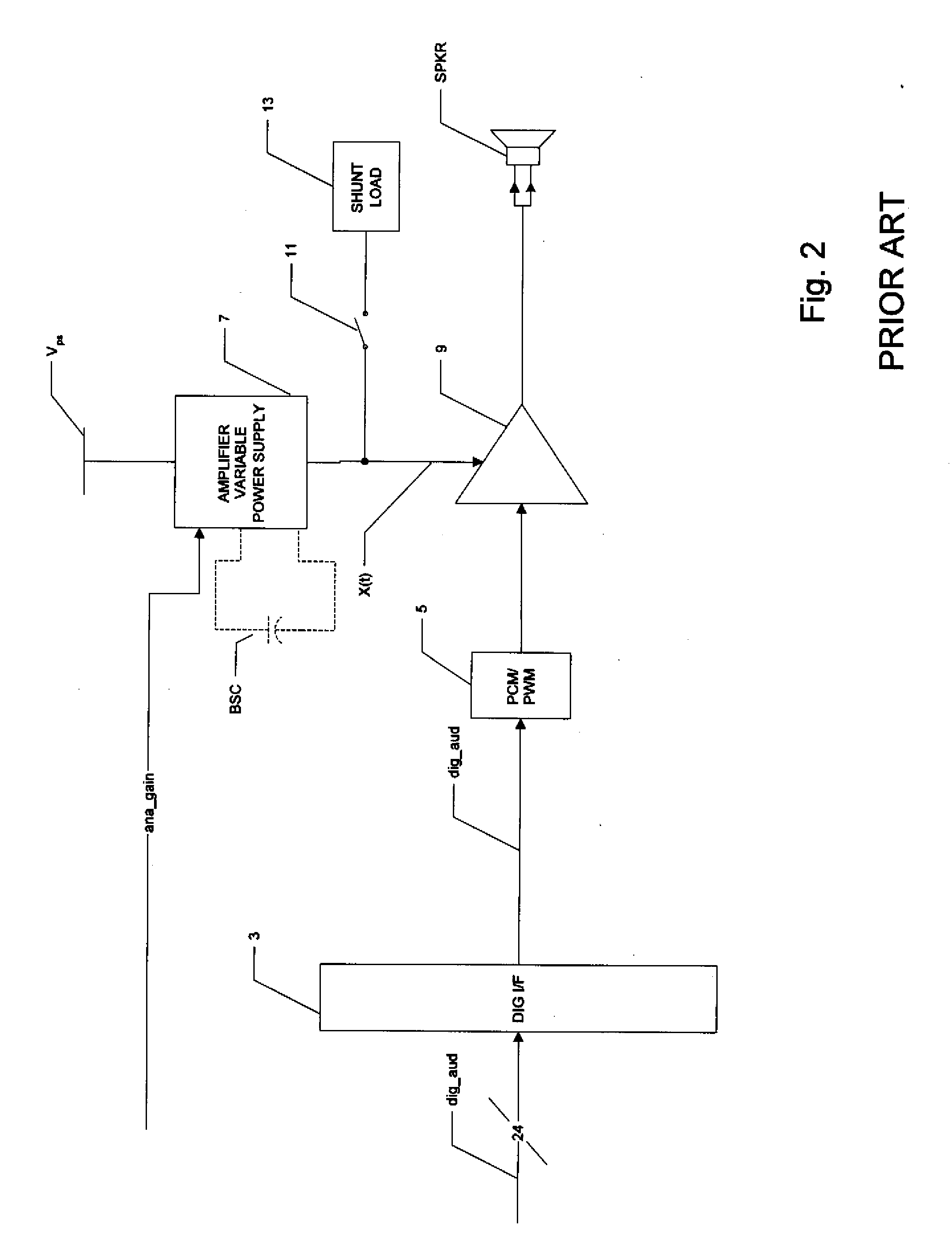
Digital Compensation of Analog Volume Control Gain in a Digital Audio Amplifier
ActiveUS20080123873A1Maintain fidelityEasy to implementSupply voltage varying controlAnalog signal digital controlAudio power amplifierControl signal
A digital audio system including a combination of analog and digital volume control is disclosed. A variable power supply voltage biases a power amplifier for each channel, and applies a bias voltage corresponding to an analog volume control signal. In one disclosed embodiment, digital gain control circuitry compares the bias voltage with the level expected for the analog volume control signal; if the bias voltage has not dropped in response to a reduction in the analog volume control signal, the digital gain control circuitry reduces the digital gain of the input digital audio signal, until the bias voltage responds to the reduced volume. In another disclosed embodiment, modeling or characterization of the audio system is used to derive a digital gain control signal based on the desired volume signal and the amplitude of the digital audio signal itself. In another disclosed embodiment, a slew rate limiter slows the rate of change of the control signal applied to the variable power supply, in which case the slowed control signal is used in the comparison or calculations of the reduced digital gain.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
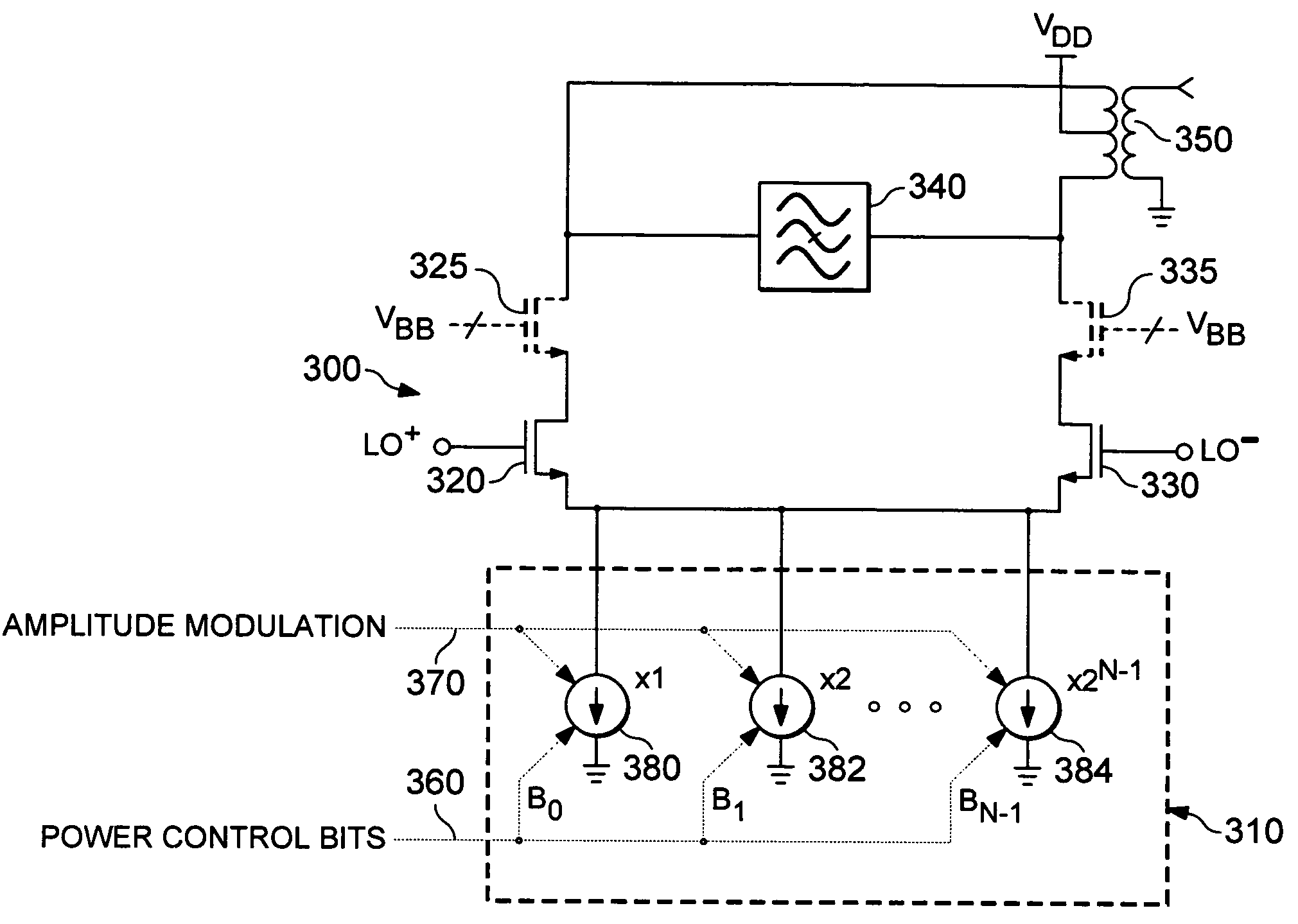
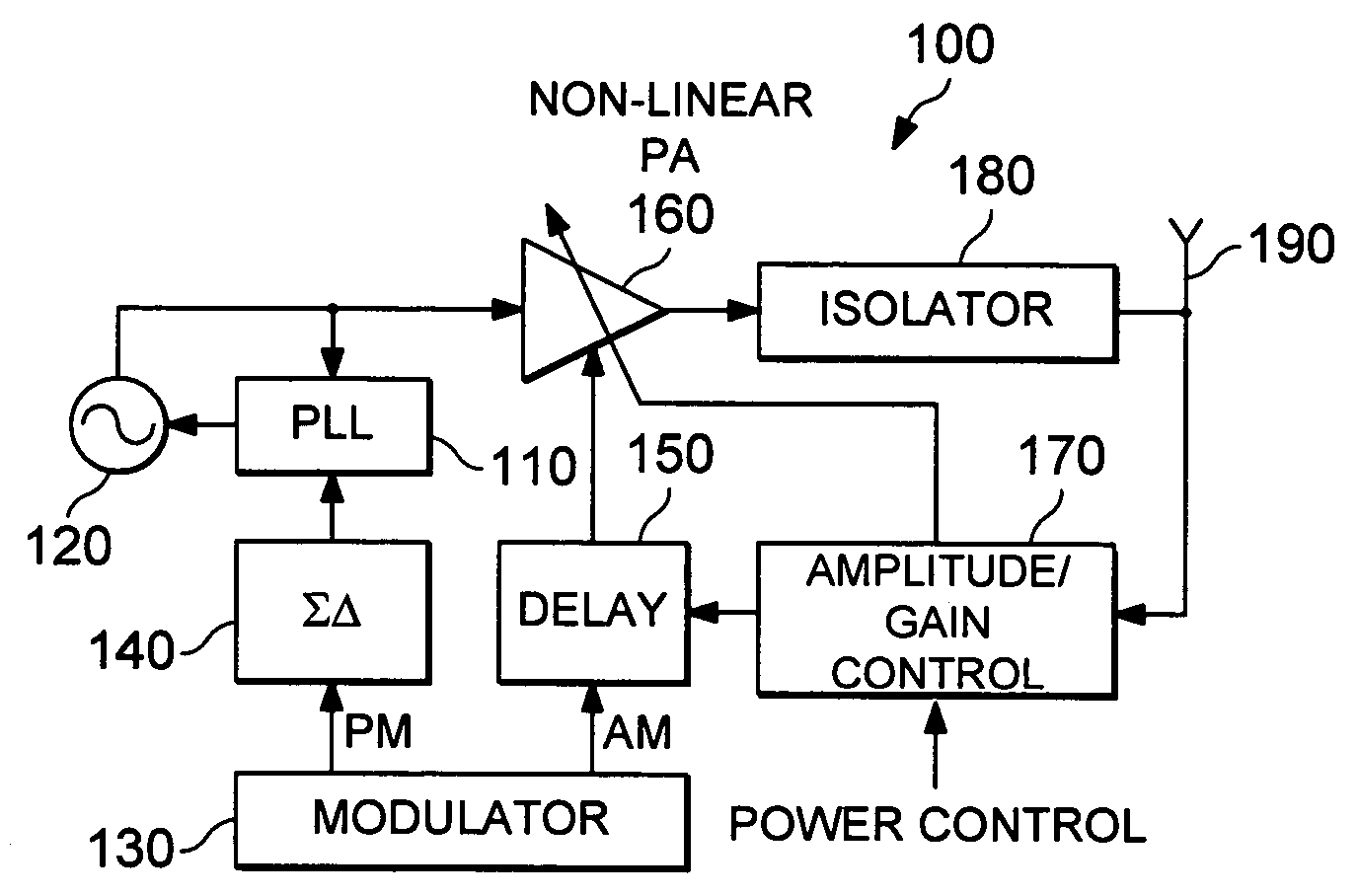
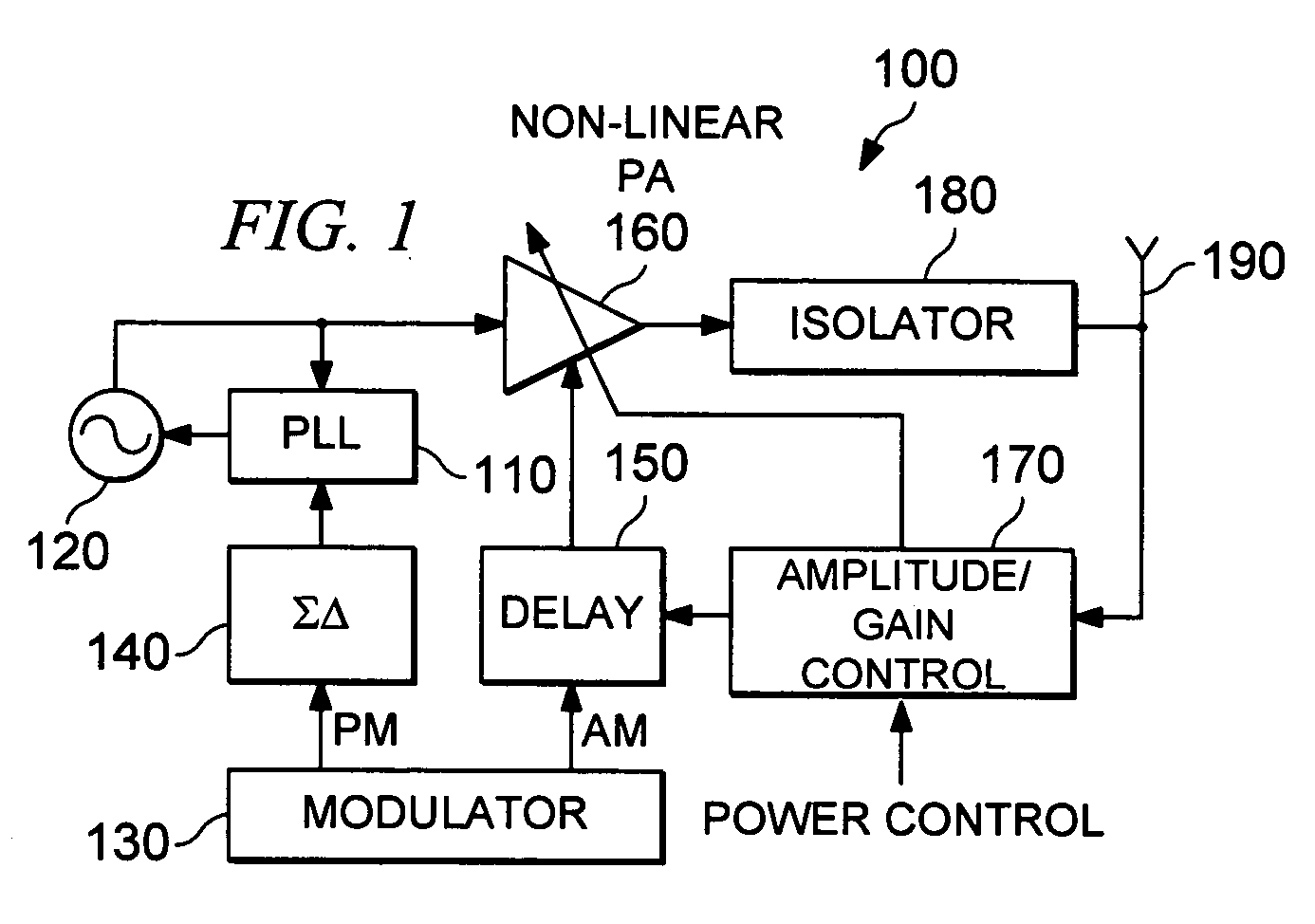
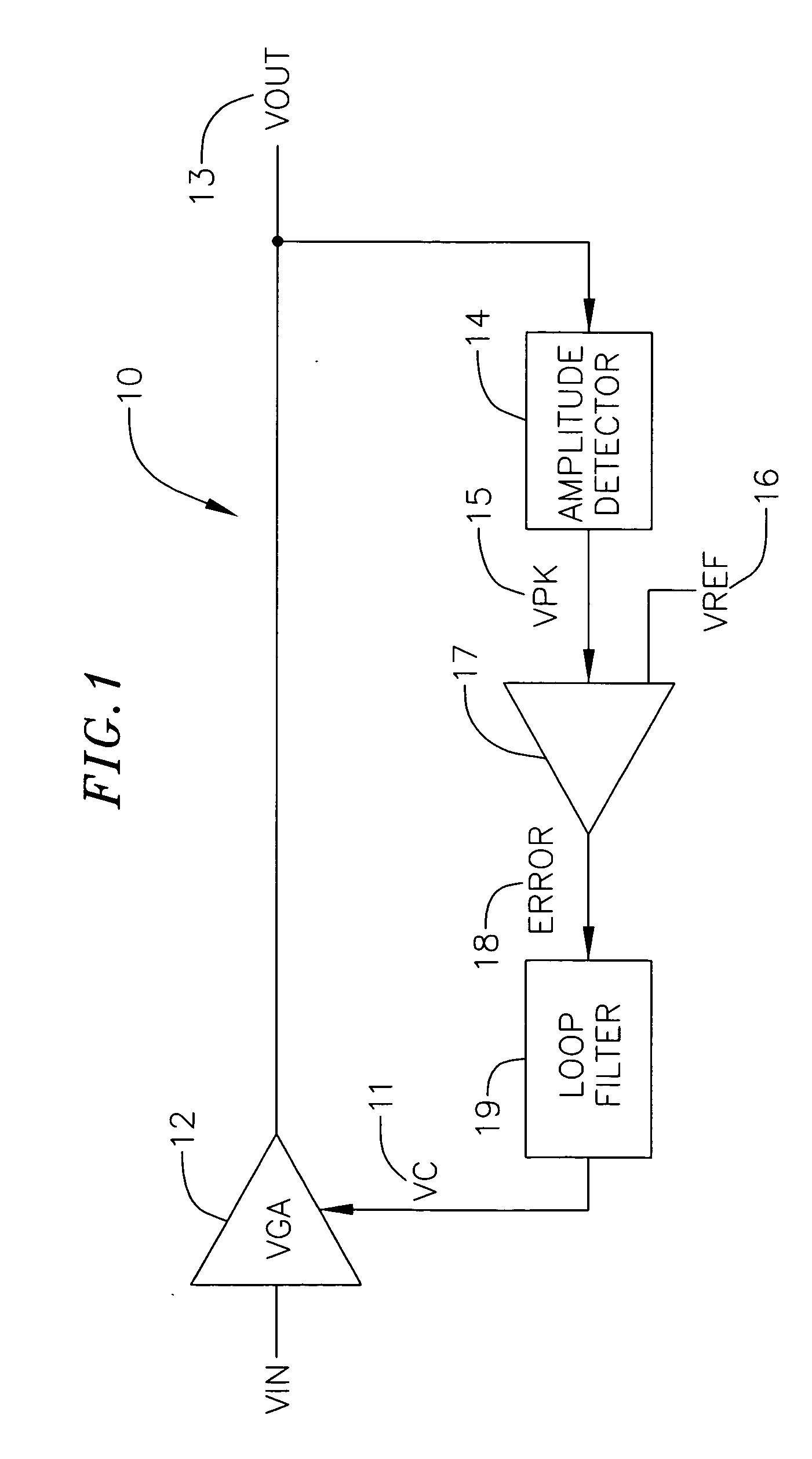
Power control feedback loop for adjusting a magnitude of an output signal
InactiveUS7558539B2Resonant long antennasAnalog signal digital controlAudio power amplifierEngineering
A circuit for adjusting a magnitude of a transmit signal includes a transmitter (105), providing a transmit signal (107). It also includes a transmitter amplifier (109), receiving the transmit signal (107) and a power control adjustment signal (121), and responsive thereto, providing an amplified transmit signal (111). The circuit also includes a detector (123), for detecting an amplitude of the amplified transmit signal (111). Also included is an error component (137) for determining the difference between the amplitude and a reference level (129). Further provided is a digital signal generator (155), receiving the difference (145), and responsive thereto, generating (157) a reference signal (125) and the power control adjustment signal (117, 121), where the reference level (129) is responsive to the reference signal (125).
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
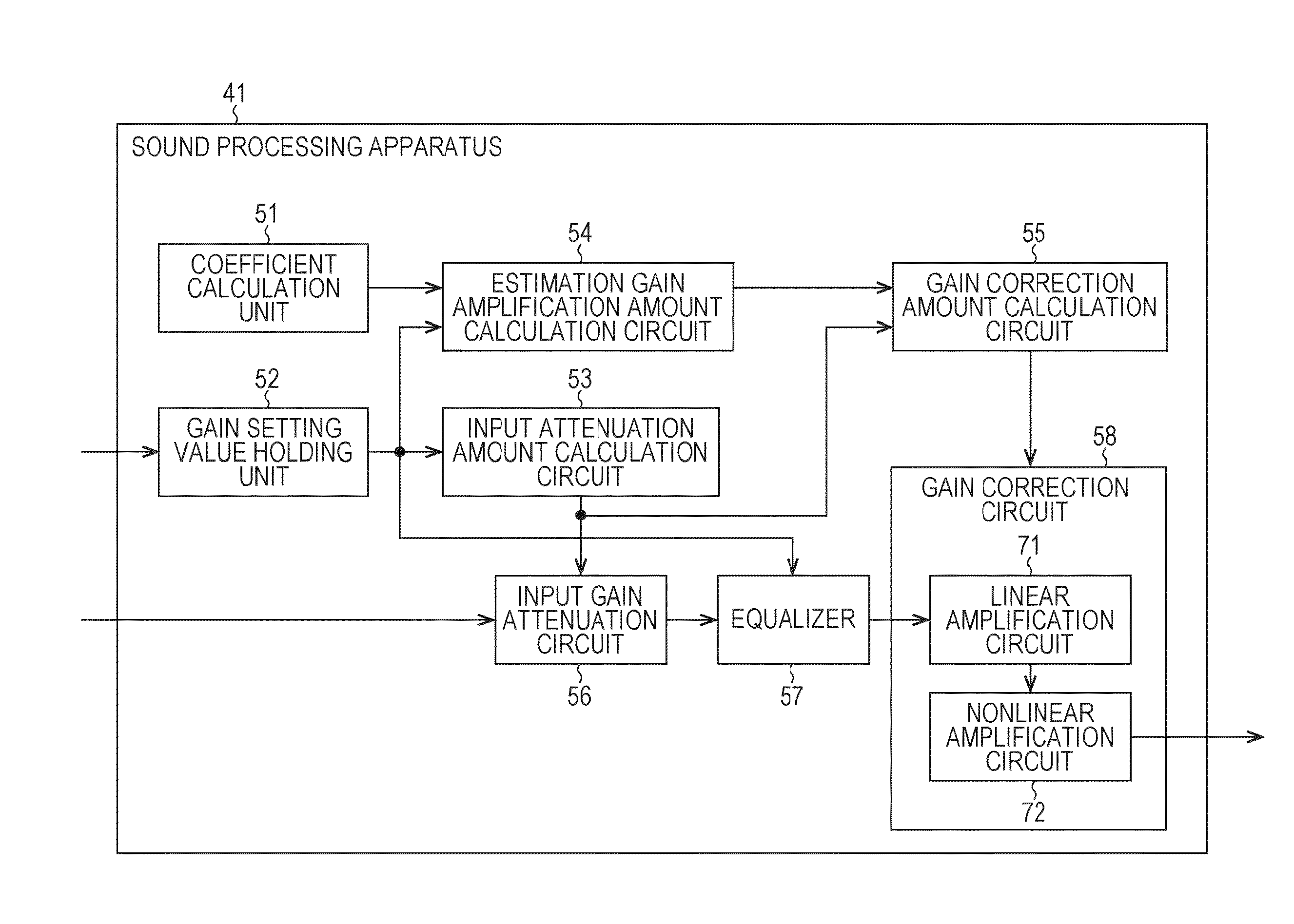
Sound processing apparatus, method, and program
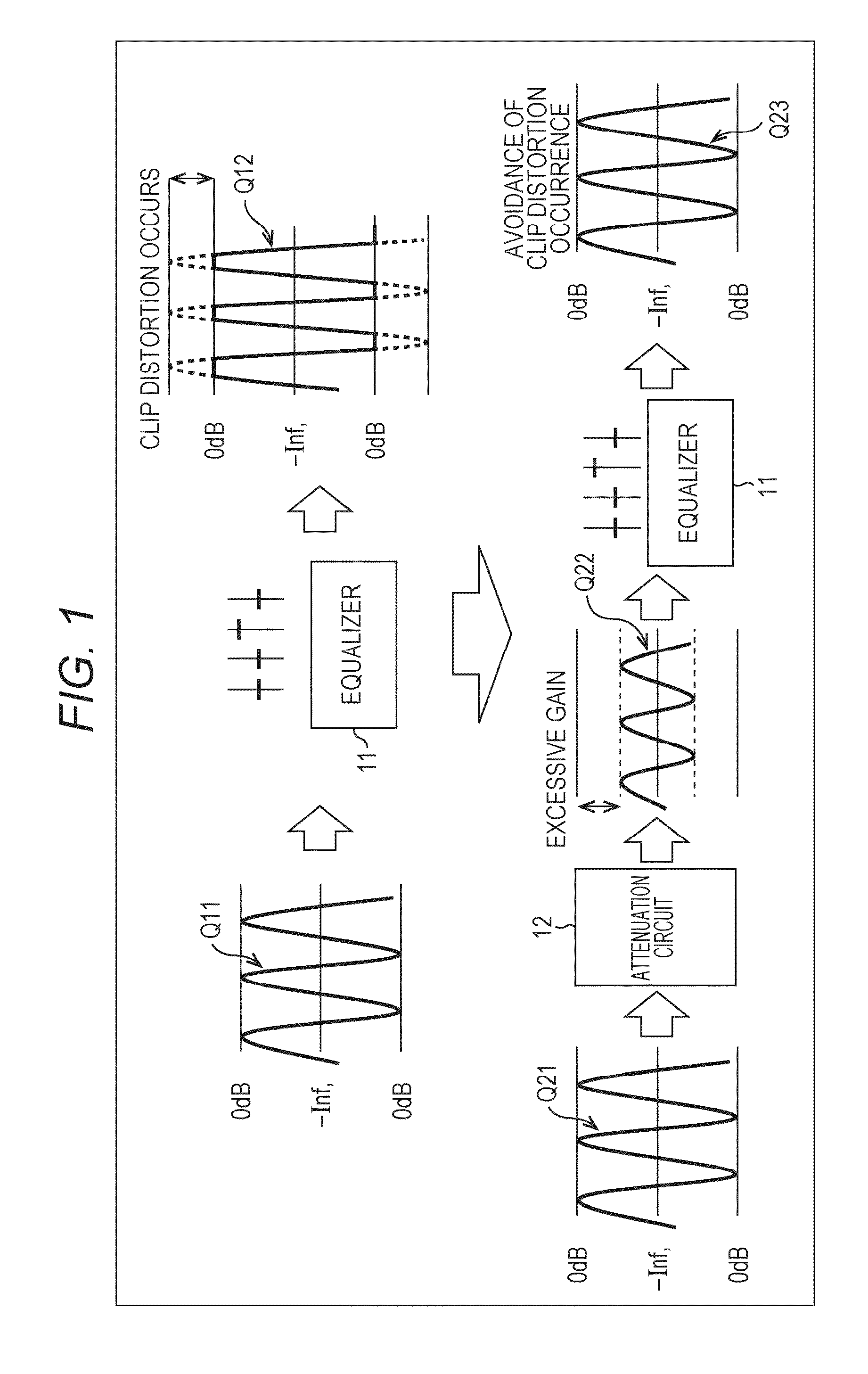
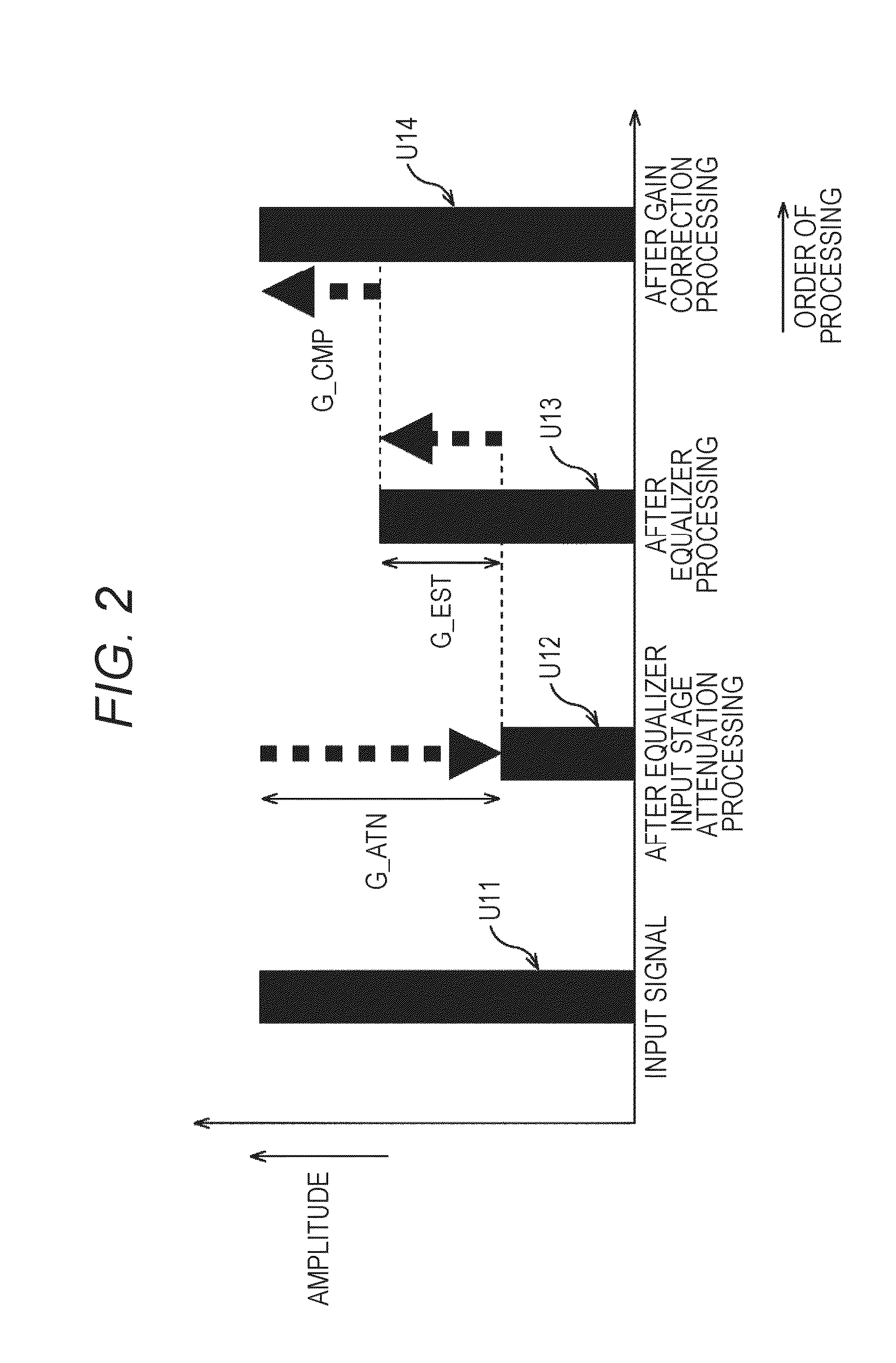
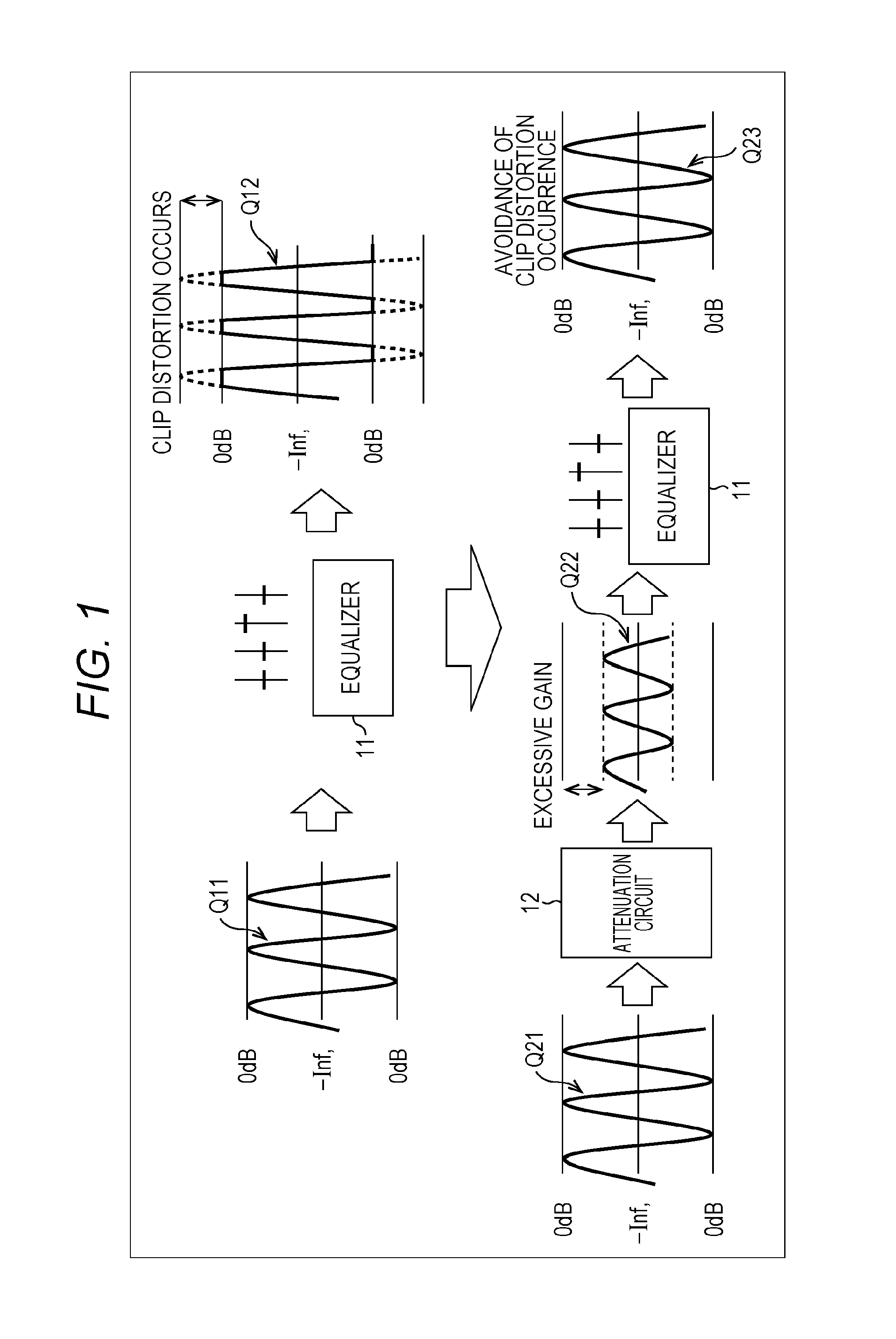
ActiveUS9294062B2Reduce quality degradationQuality improvementAnalog signal digital controlAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlUltrasound attenuationWeight coefficient
The present technique relates to a sound processing apparatus, a method, and a program capable of alleviating degradation of the quality of sound in a case where the gain of a sound signal is amplified.When equalizer processing for adjusting the gain of each frequency band of an input signal on the basis of a gain setting value is performed, an input signal is attenuated by an input attenuation amount derived from the gain setting value, and the equalizer processing is performed on the input signal attenuated. The amount of amplification of the gain of the input signal in the equalizer processing is estimated on the basis of the gain setting value and a weight coefficient of each frequency band derived from a generally-available music signal prepared in advance, and a difference of the estimation value and the input attenuation amount is calculated as a gain correction amount. Further, nonlinear amplification processing is performed on the input signal so as to actually amplify the input signal, which has been subjected to the equalizer processing, by a gain correction amount, and an output signal is obtained. The present technique can be applied to a sound processing apparatus.
Owner:SONY CORP
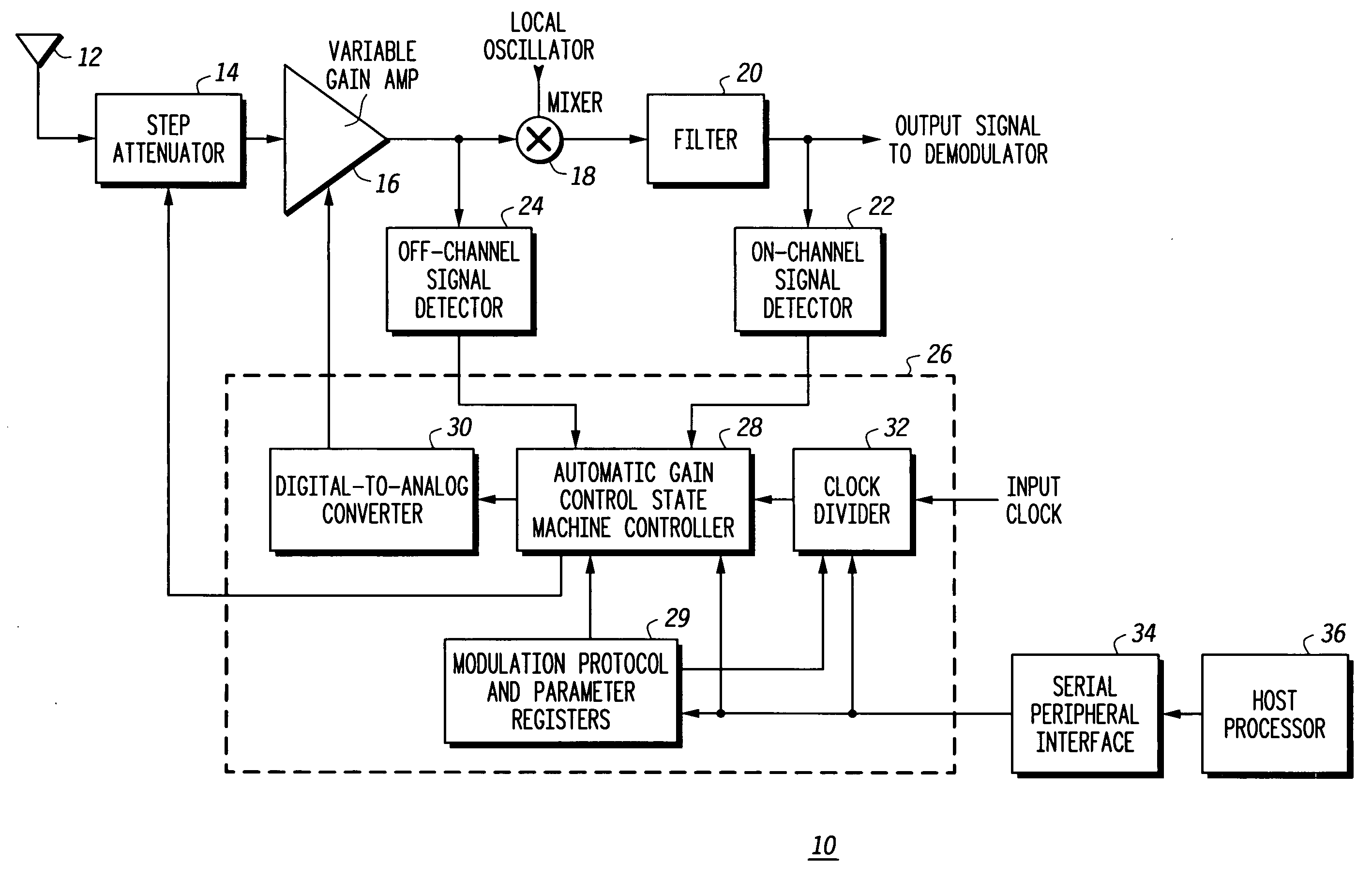
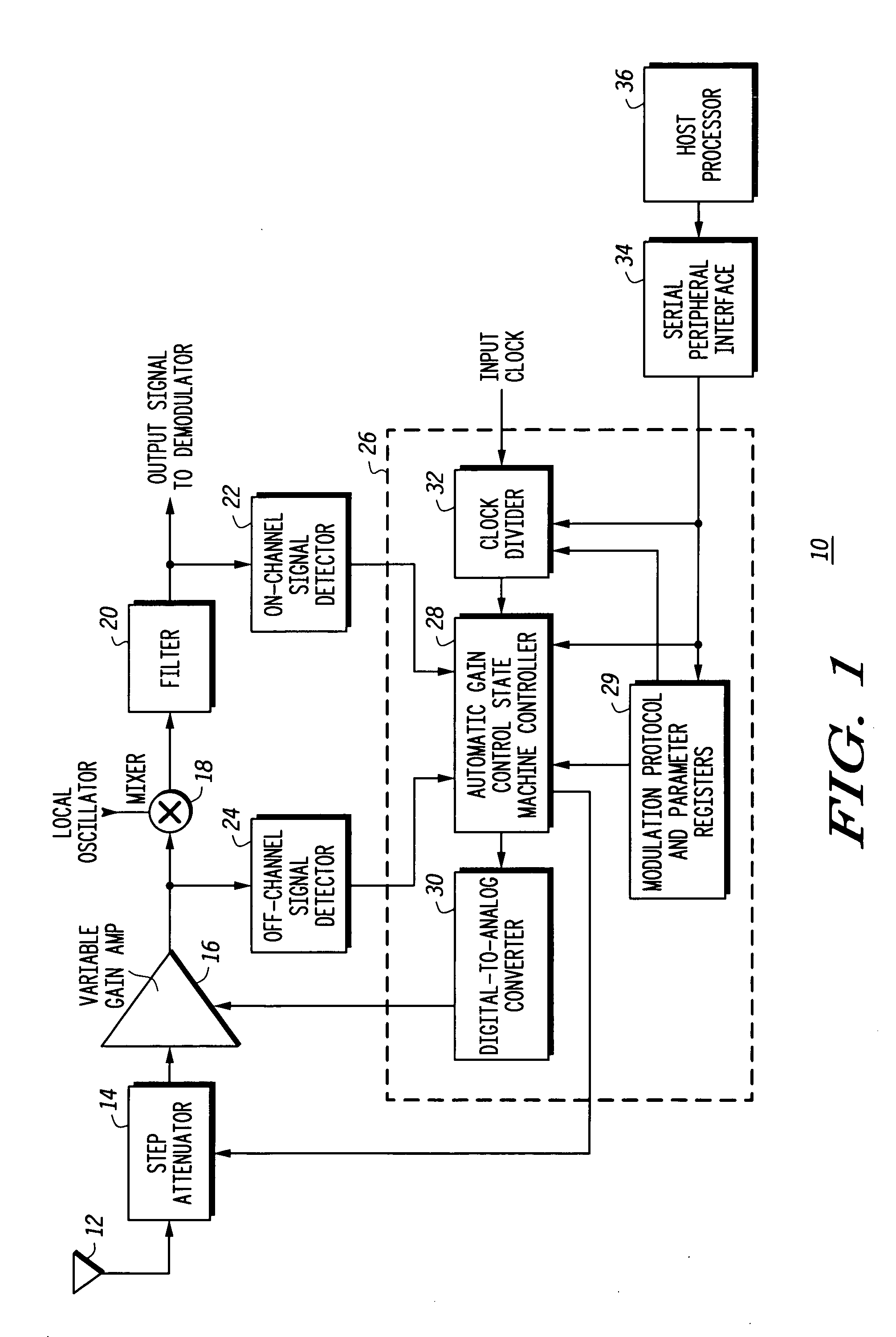
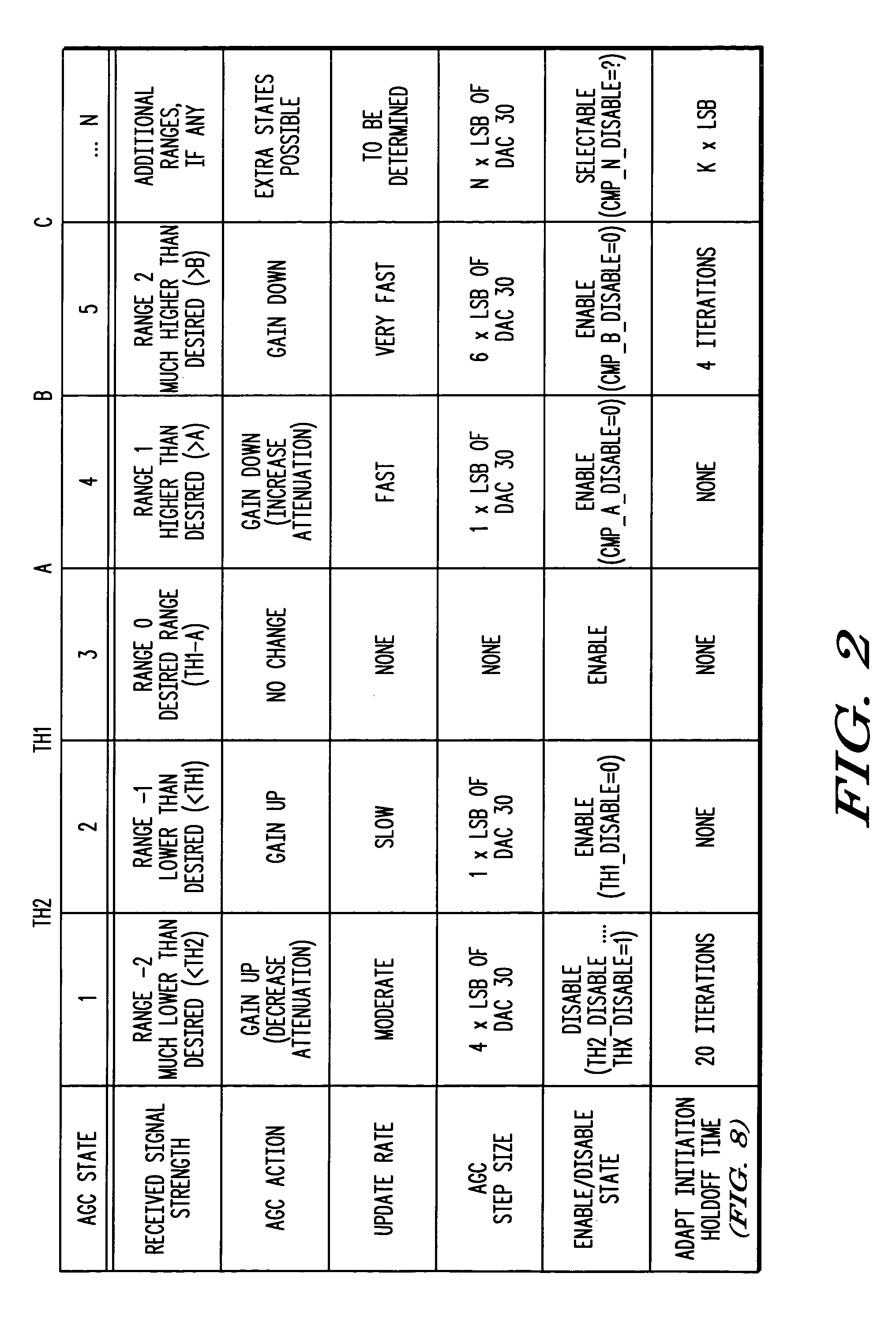
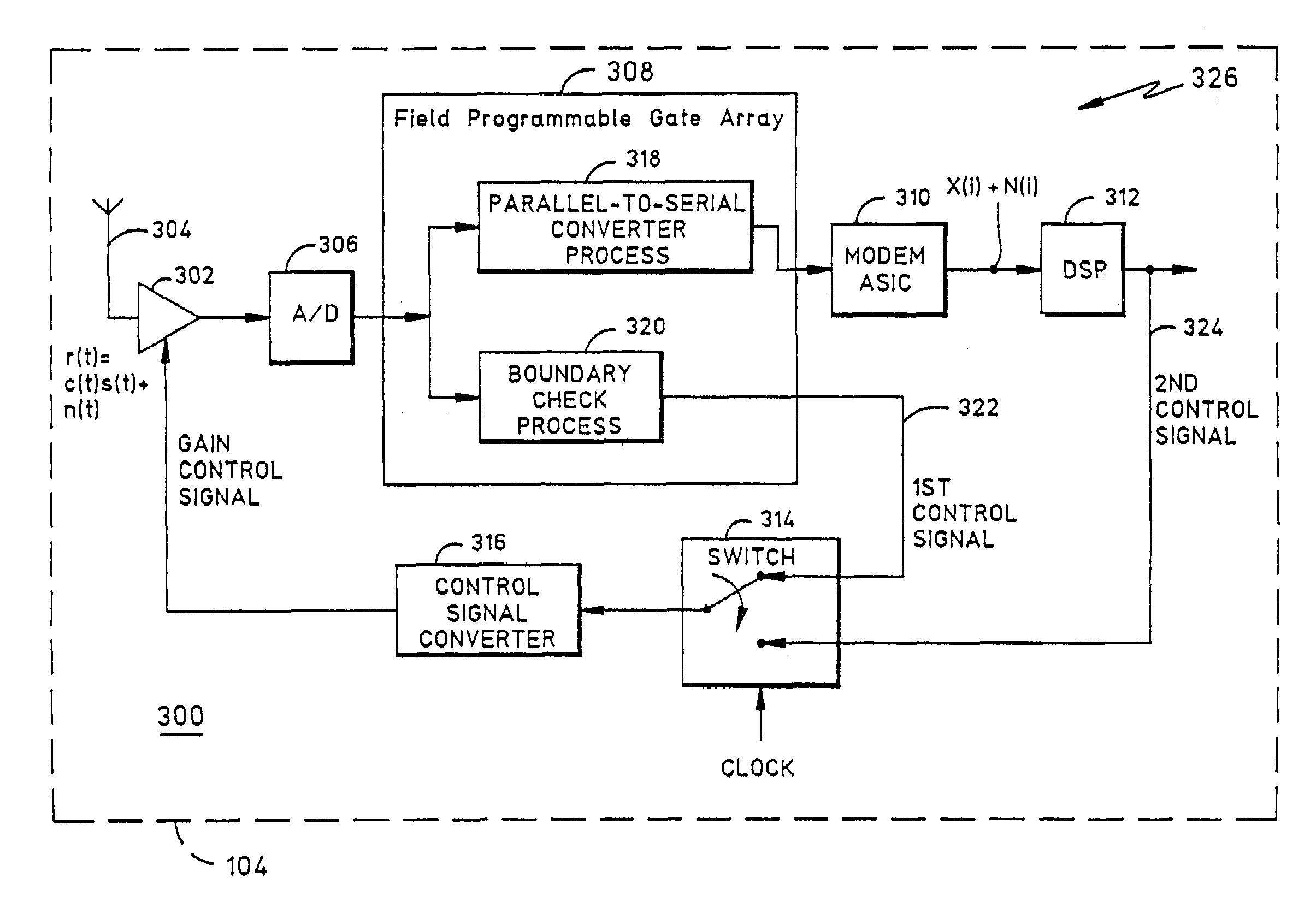
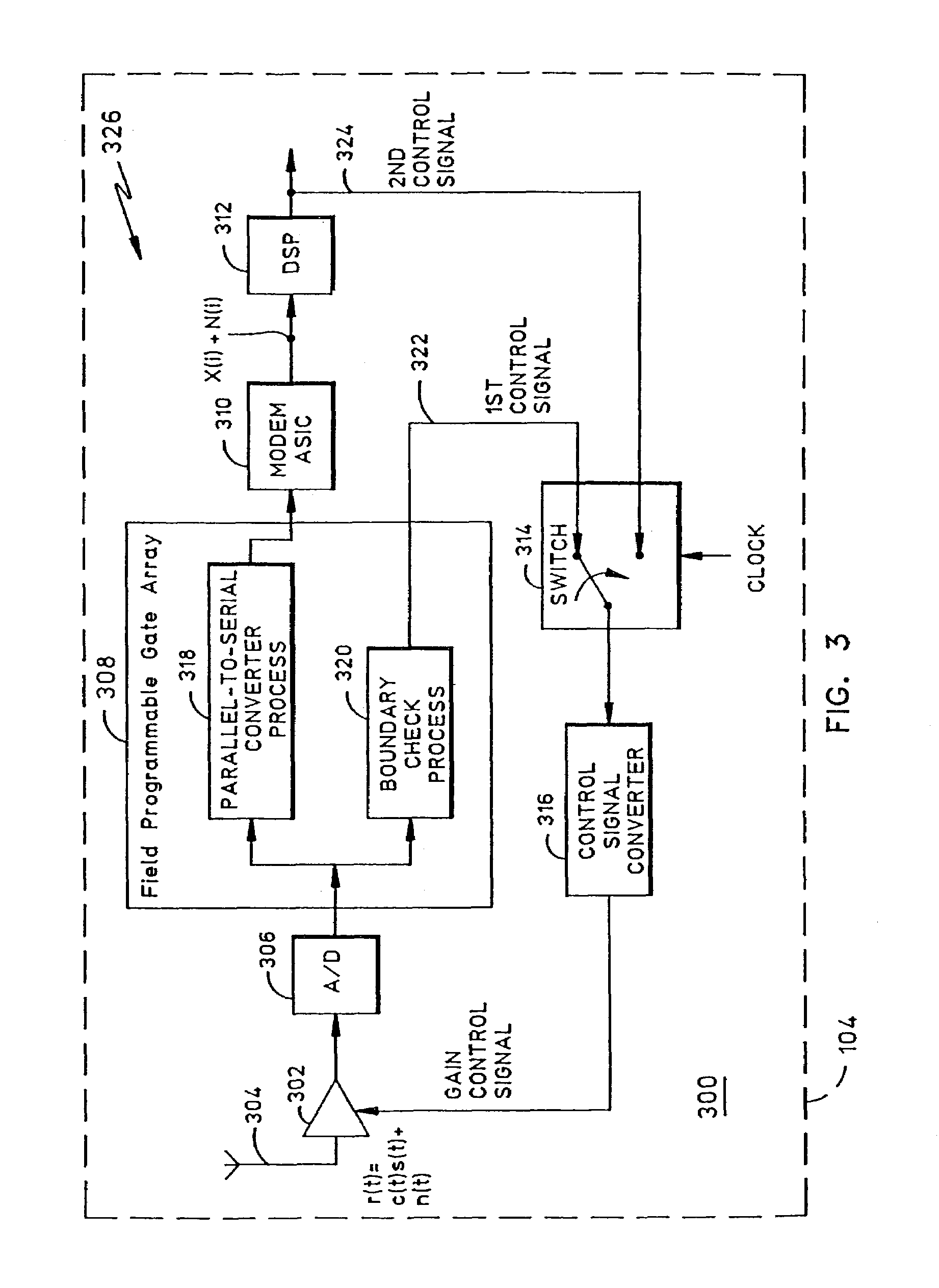
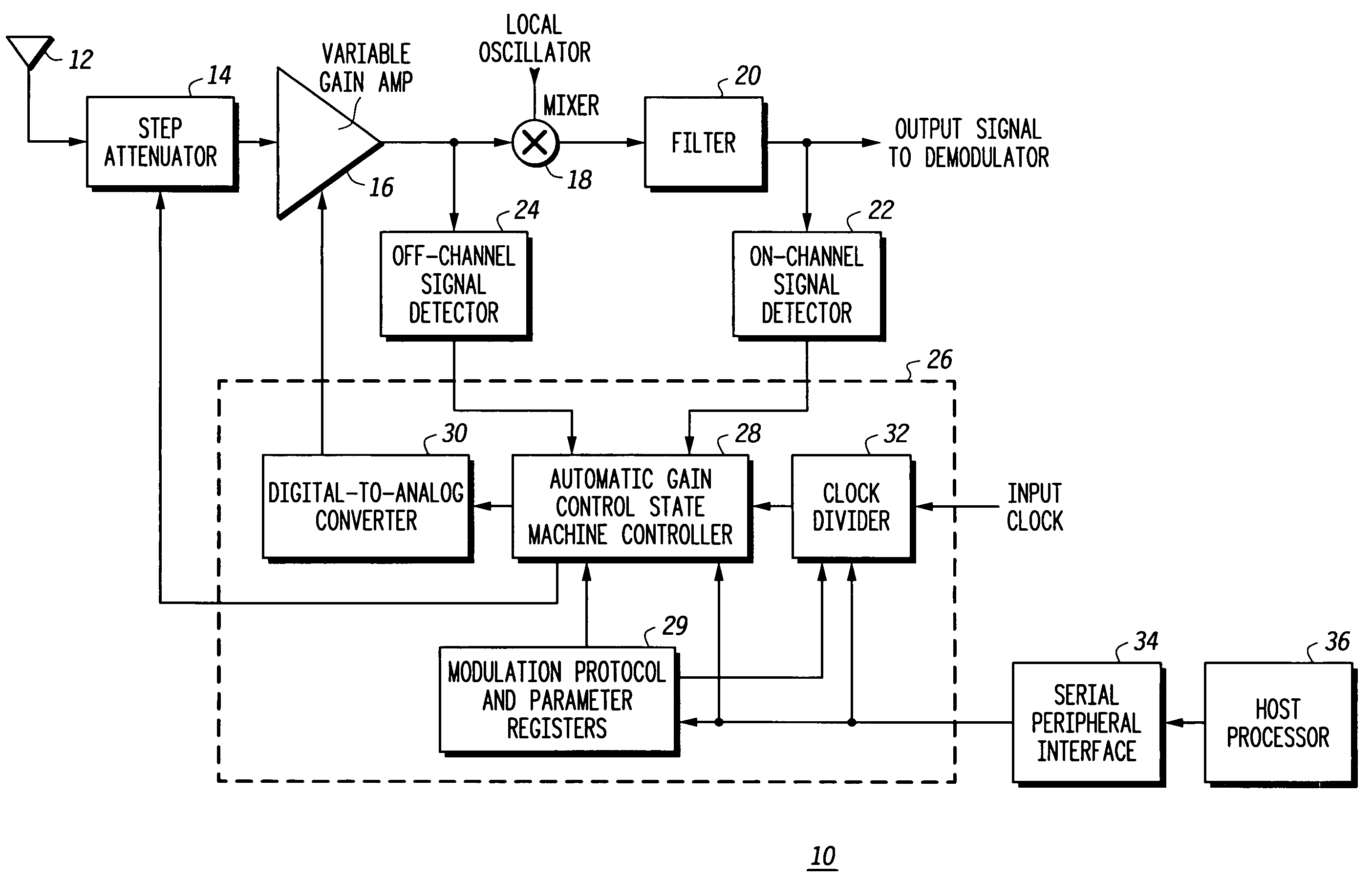
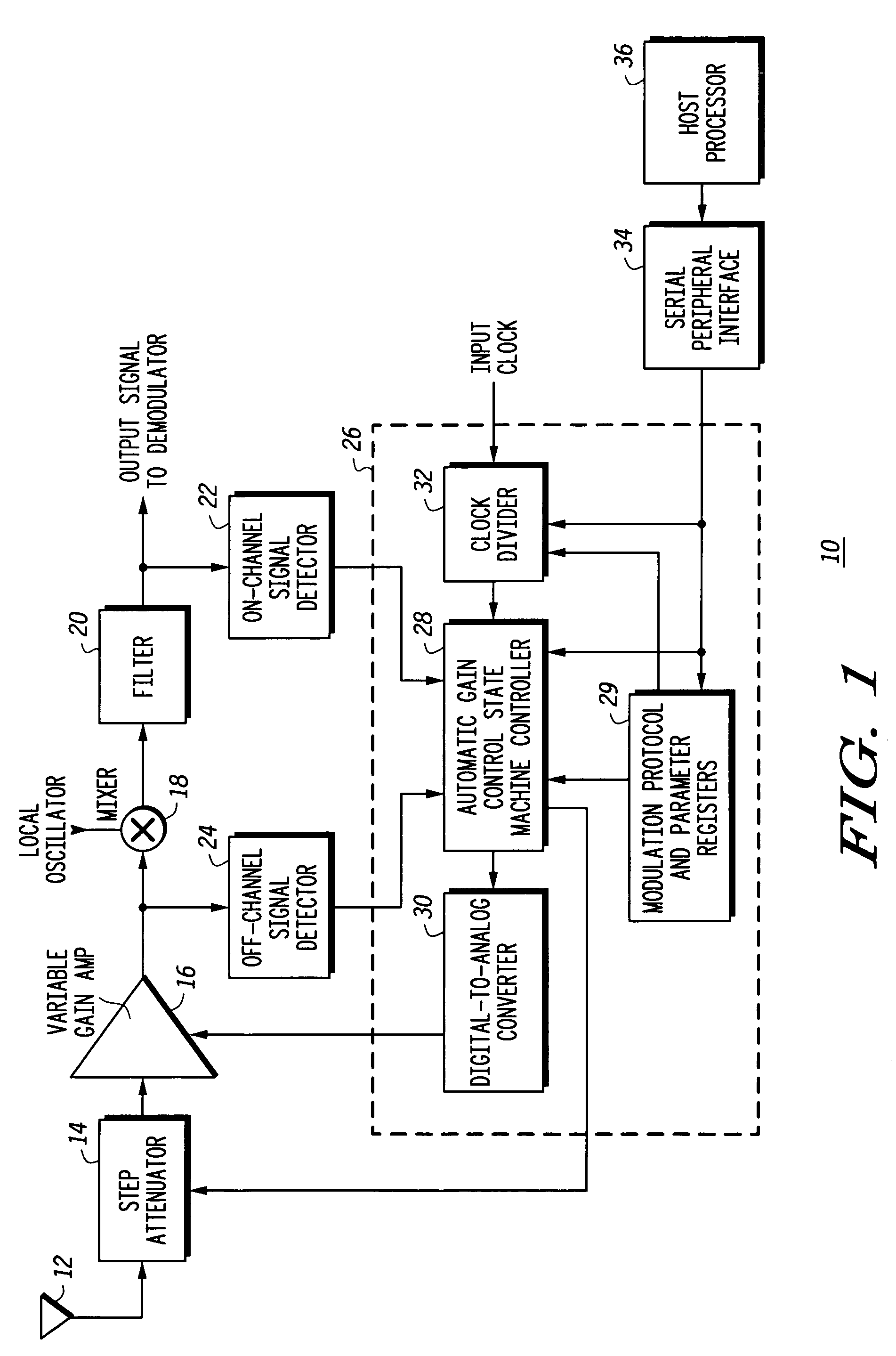
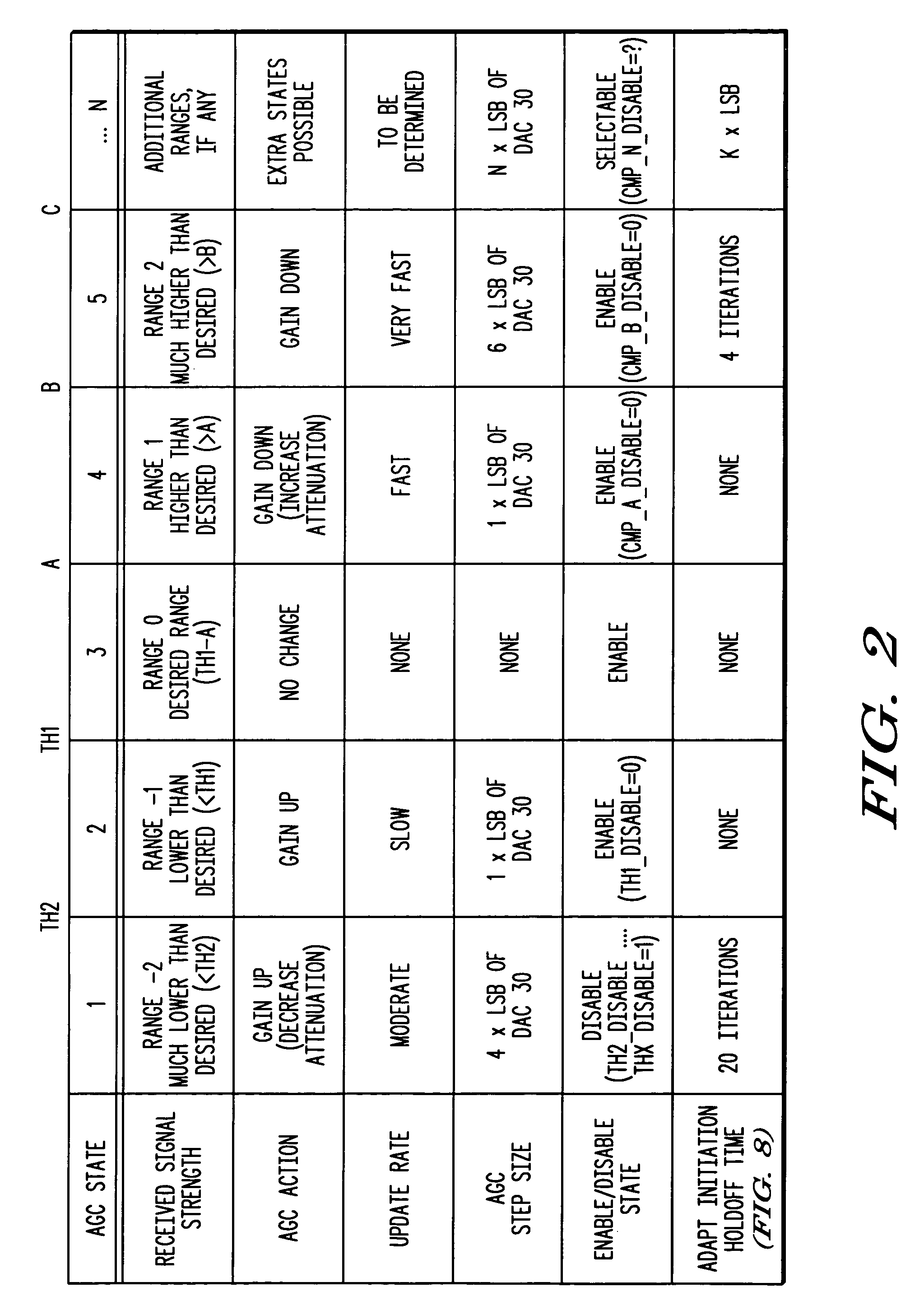
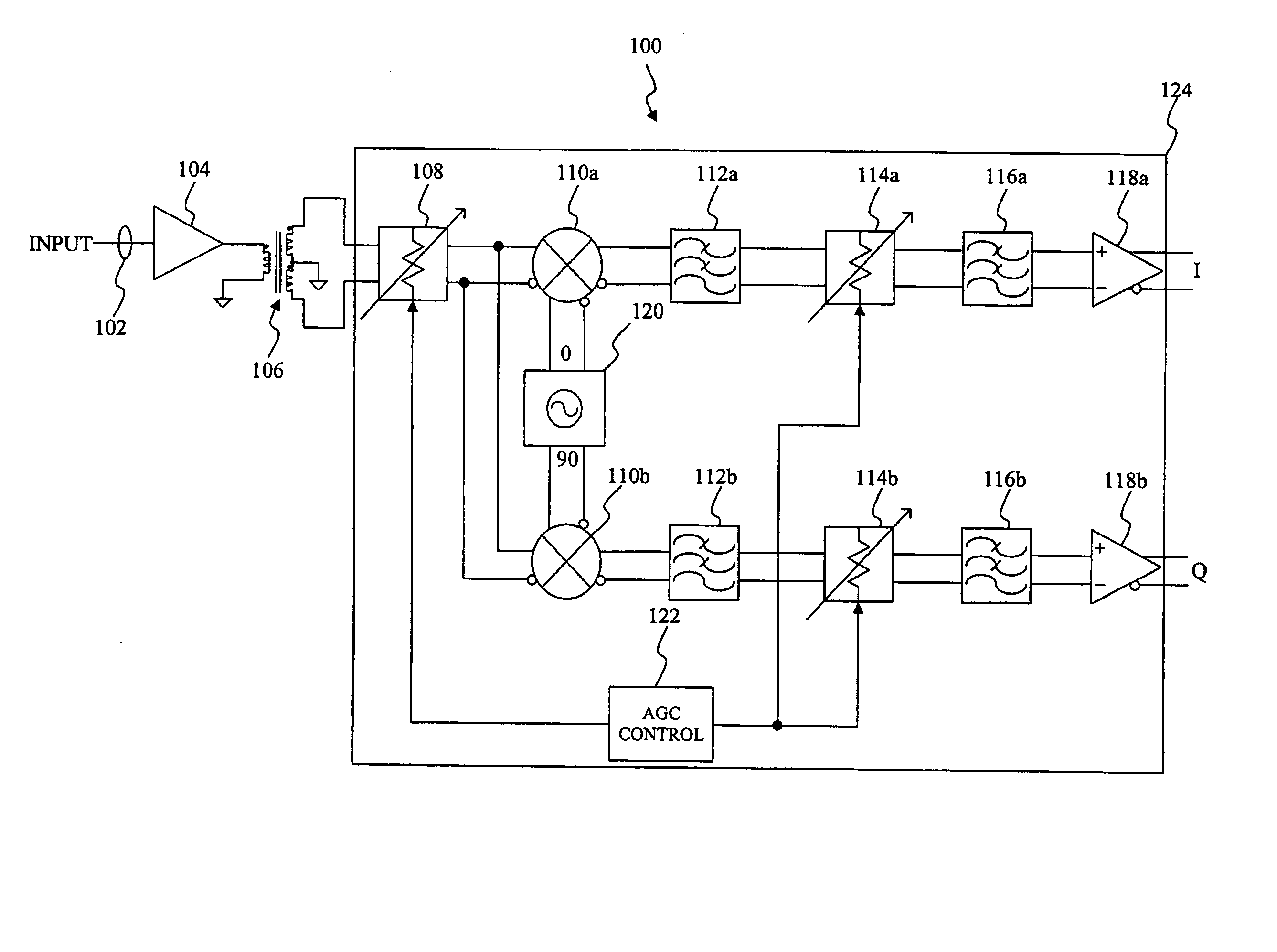
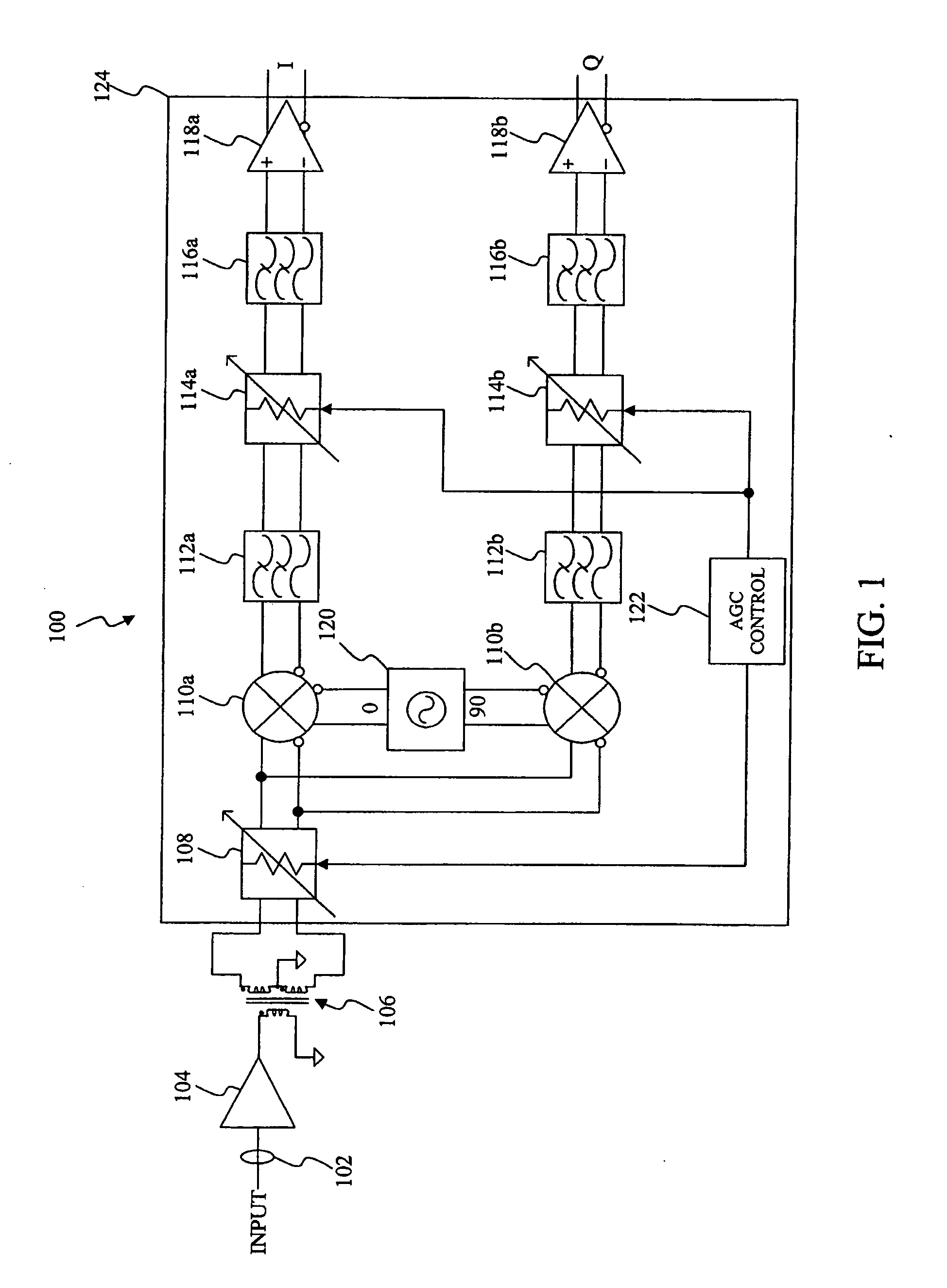
Receiver with automatic gain control that operates with multiple protocols and method thereof
ActiveUS20050047533A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsAnalog signal digital controlAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
An automatic gain control (AGC) method and circuit (10) within a receiver uses a digital state machine (26) to implement the AGC function. independent from interaction with a host processor (36) and for multiple modulation protocols without duplicating circuitry. Modulation protocol and parameters for any of various gain responses are stored in a register (29). Multiple states, each corresponding to a predetermined range of RF input signal strength, are stored in the register. Each state contains parameters that determine a gain control signal for controlling a variable gain amplifier (16). The states are independent and may be selectively disabled to create asymmetric responses. Within any state, an adaptable number of iterations may be set to implement a different update rate or step size after a predetermined number of closed loop gain change iterations has not resulted in a transition to a state that represents a desired output gain.
Owner:APPLE INC
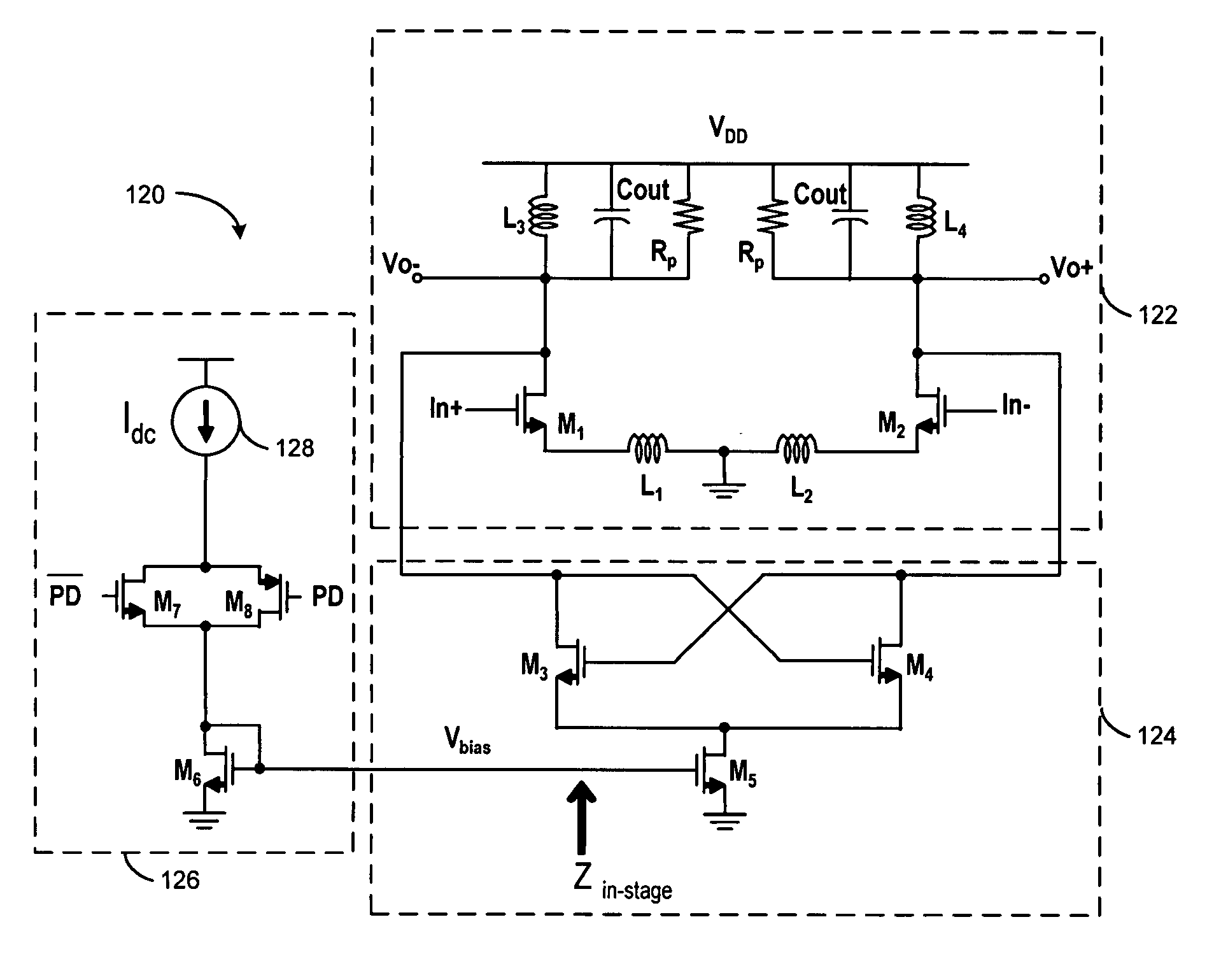
Gain boosting for tuned differential LC circuits
InactiveUS20060145762A1Generate efficientlyAnalog signal digital controlDifferential amplifiersAudio power amplifierTuned amplifier
A gain boost circuit and methodology are described for providing improved gain boosting with tuned amplifier circuits, such as differential low noise amplifier circuits having output resonant tank circuits. By selectively controlling the current source for a negative transconductance stage coupled between the differential amplifier output and the output resonant tank circuits, the amplifier gain may be adjusted to compensate for temperature variations. In addition, the amplifier gain boost may be selectively added, removed or even incrementally adjusted by using a current source control circuit in the negative transconductance stage to adjust the negative transconductance value generated by the negative transconductance stage.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
System for processing audio data
InactiveUS20100046765A1Increase valueReduce processing workloadSpeech analysisAnalog signal digital controlSpeech recognitionMulti channel
A device (110) for processing audio data (106) for a multi channel audio playback system (100), comprises an identification unit (115), an extraction unit (120), and an averaging unit (125). The identification unit identifies segments of the audio data (106) related to a selected one of the channels (101 to 103) and belonging to a reference audio class. The extraction unit (120) extracts an audio property of the identified segments. The averaging unit (125) estimates an average value over a predetermined time period of the audio property of the channel (101) based on the extracted audio property of the identified segments.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
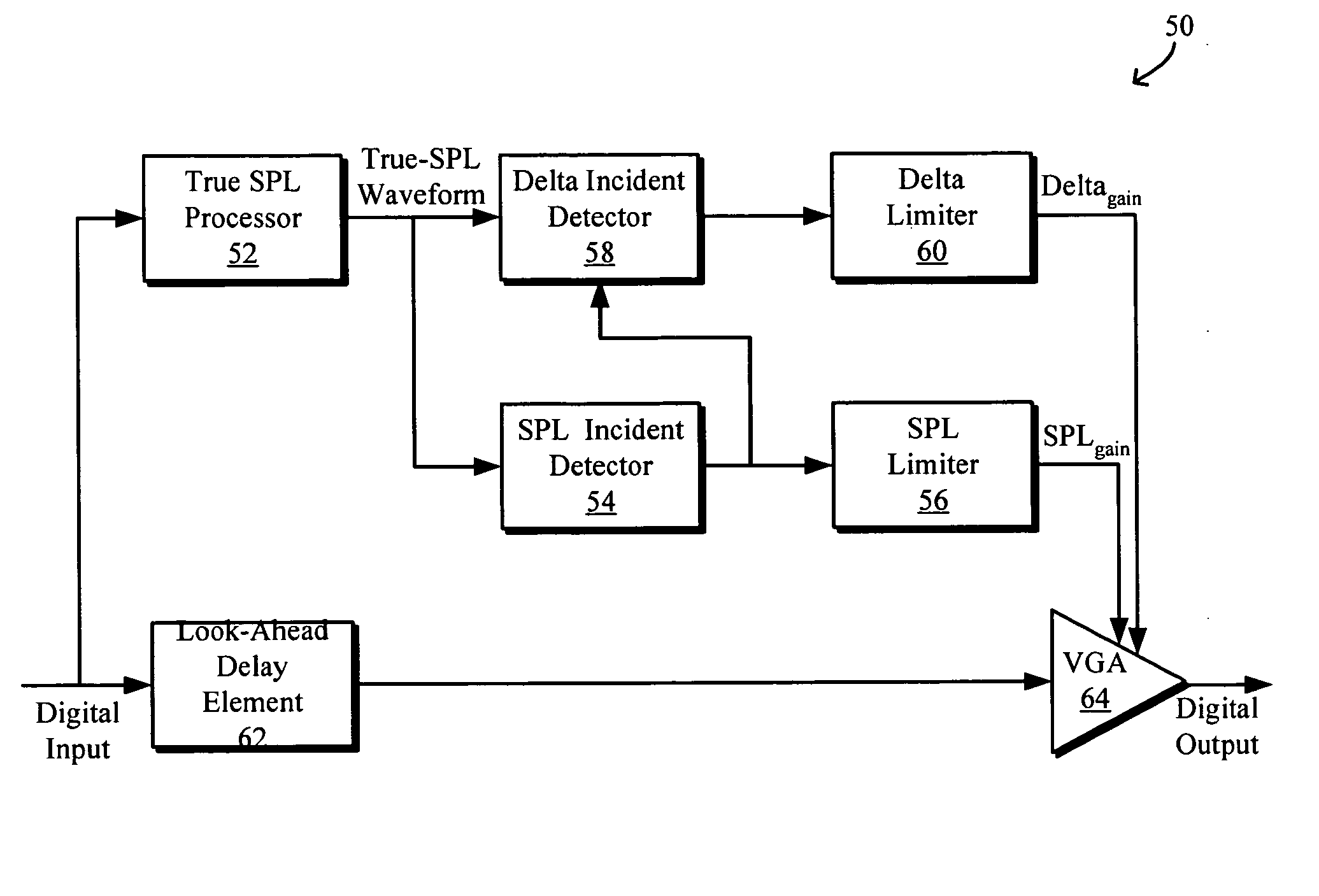
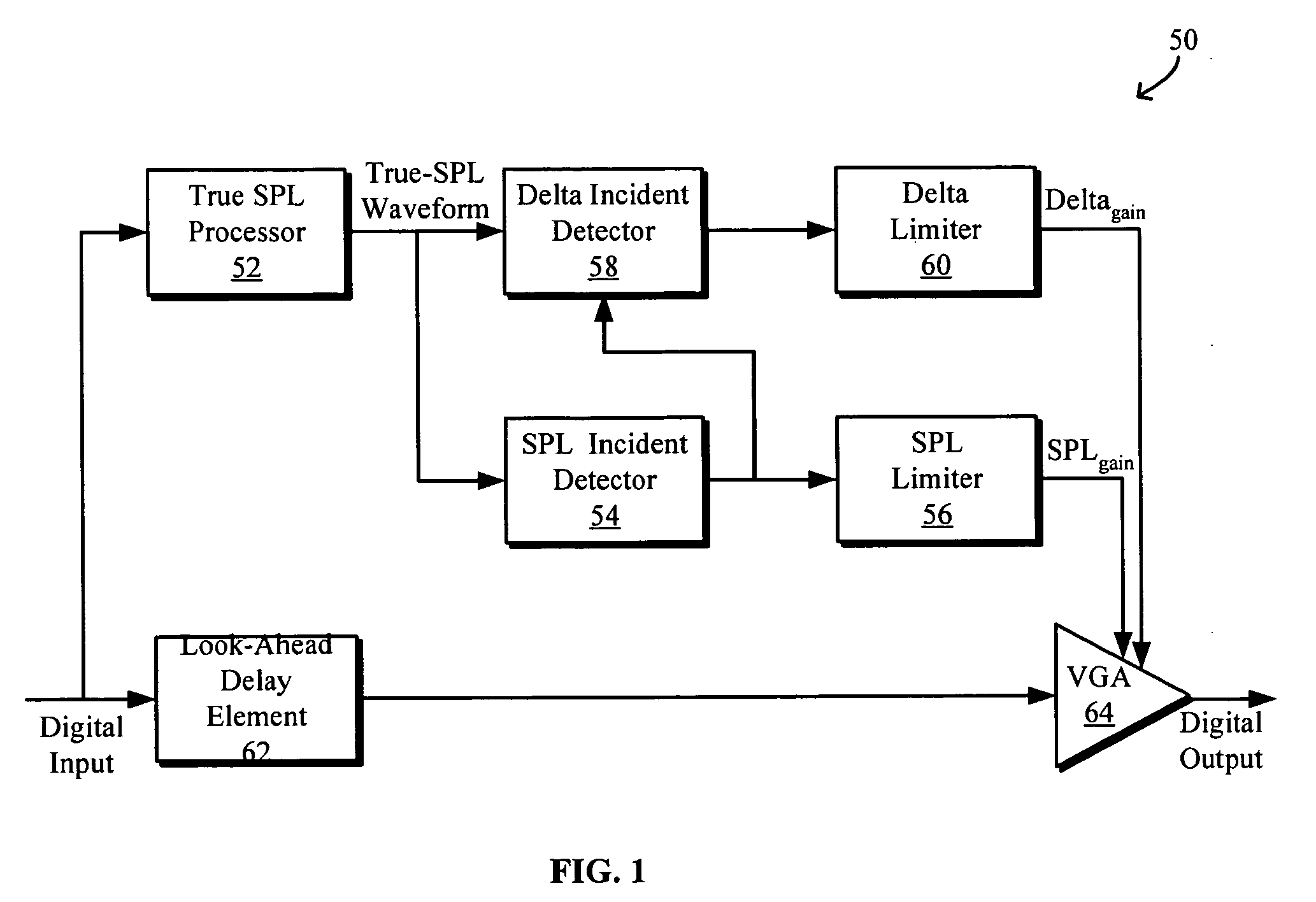
Sound pressure level limiter with anti-startle feature
ActiveUS20060147049A1Volume compression/expansion in digital/coded amplifiersAnalog signal digital controlAudio power amplifierTransducer
Sound pressure level limiter with anti-startle feature for audio systems are disclosed. The anti-startle feature may be implemented with a delta incident detector for detecting delta acoustic incidents that exceed a predetermined acoustic startle boundary, a delta limiter for determining an anti-startle gain, and an amplifier to apply the anti-startle gain to the input signal. The delta incident detector may detect delta incidents based on an estimated true SPL delivered by a transducer to a predetermined datum point. The estimated true SPL may be determined by based on a measured receiving frequency response of the transducer. An SPL limiter may also determine an SPL gain in response to detecting an SPL acoustic incident that exceeds a predetermined SPL threshold, and an amplifier may apply the SPL gain to the input signal to reduce it below the threshold.
Owner:PLANTRONICS
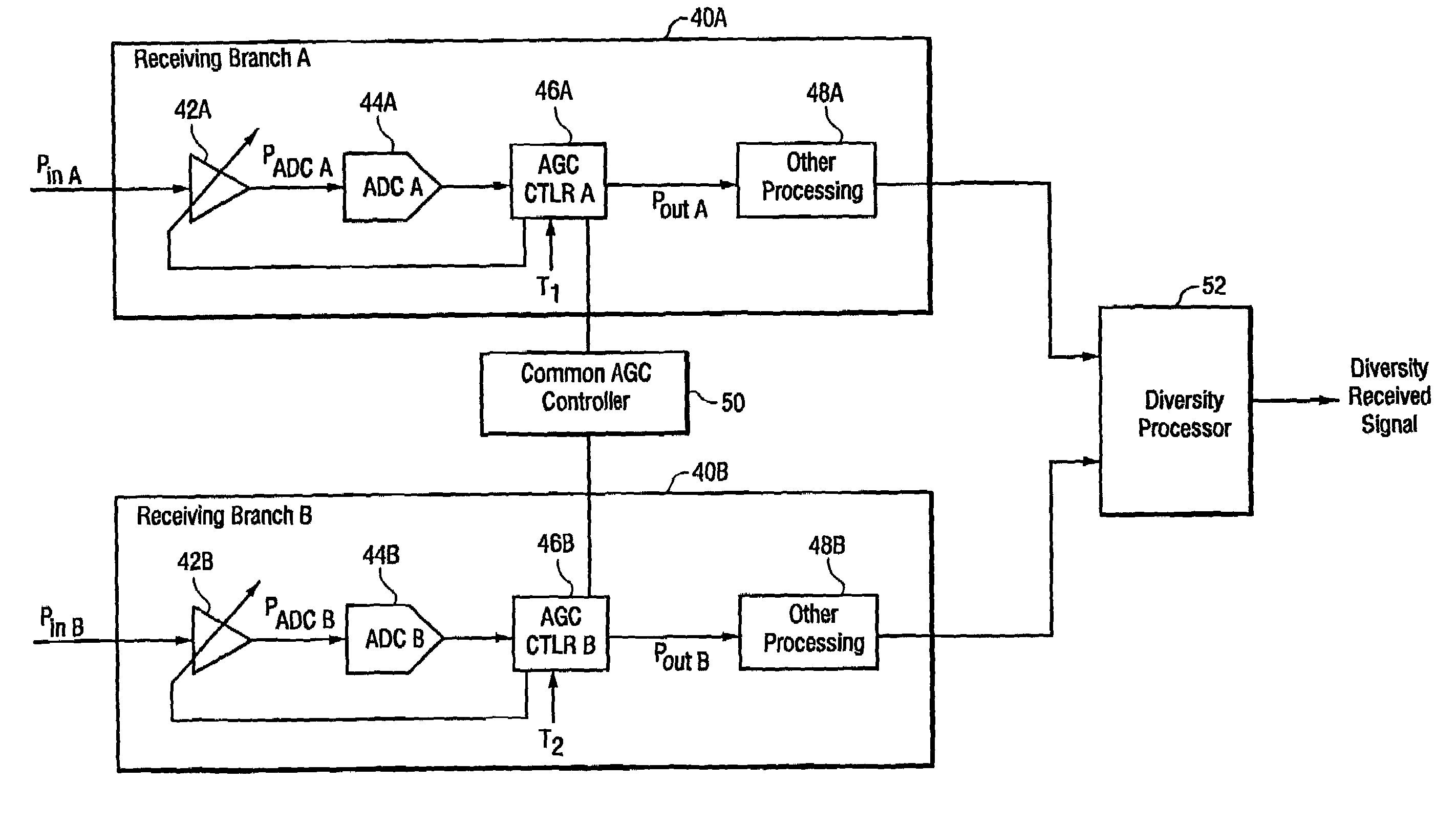
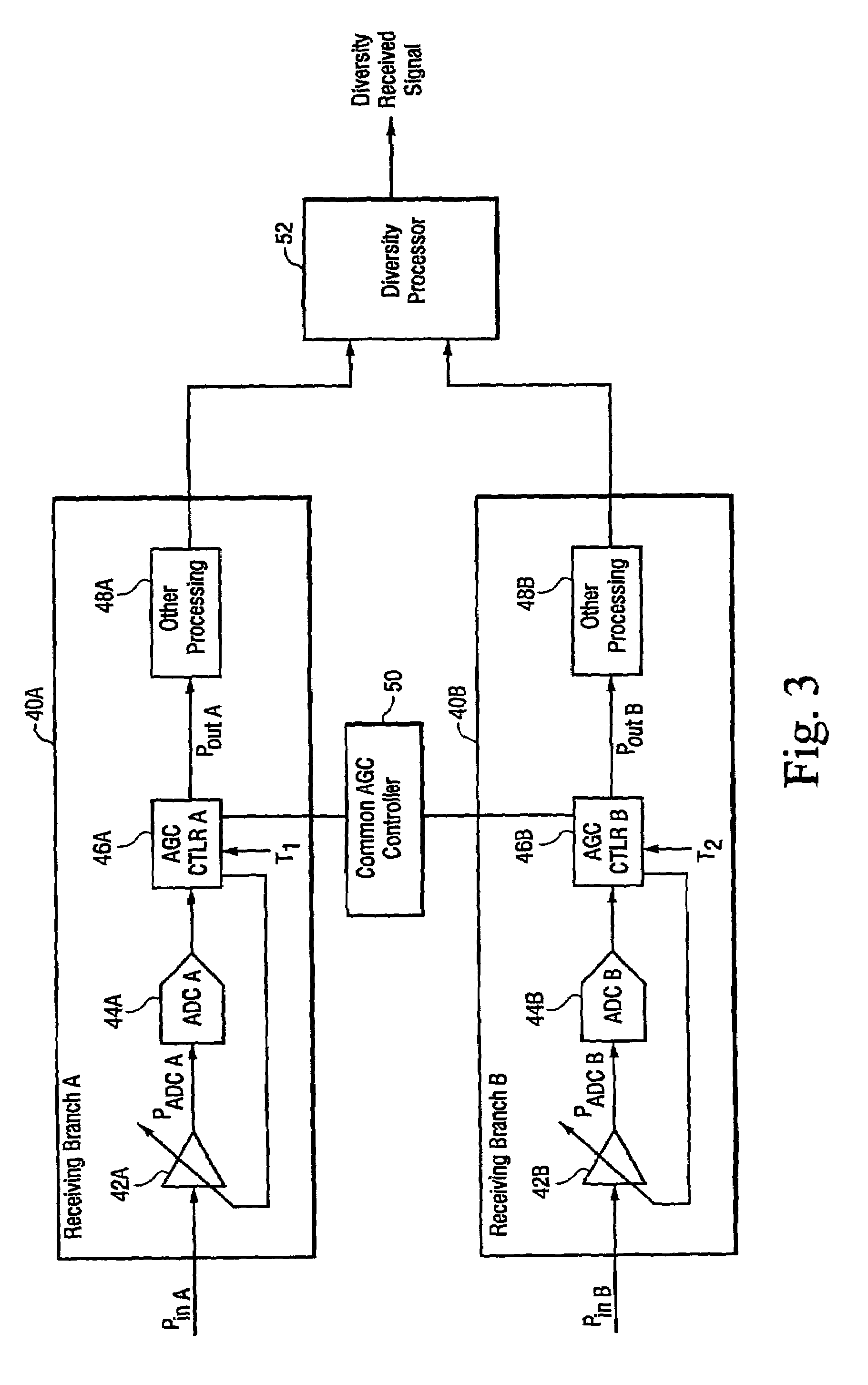
Method and apparatus for reducing the effect of AGC switching transients
InactiveUS6963733B2Balance sensitivity/accuracyIncrease signal levelSpatial transmit diversityAnalog signal digital controlDiversity schemeAutomatic gain control
The present invention reduces automatic gain control (AGC) transients using first and second AGC processing branches to receive a signal. A gain is selectively adjusted (if desired) in the one of the AGC processing branches during a first time period. However, a gain is not adjusted in the other AGC processing branch during that first time period. The signals generated by the first and second AGC processing branches are then diversity processed to generate a received signal. The diversity processing effectively reduces the effect of any AGC transient.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Automatic gain control methods and apparatus suitable for use in OFDM receivers
InactiveUS7065165B2Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsAnalog signal digital controlAudio power amplifierMultiple frequency
Automatic gain control (AGC) methods and apparatus suitable for use in orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) receivers are described. One AGC method includes the steps of repeatedly performing a first AGC process which adjusts amplifier gain based on determining that a signal level of multiple time sample values is outside a limit set by a first predefined threshold; and repeatedly performing a second AGC process which adjusts the amplifier gain based on determining that a signal level of multiple frequency sample values associated with a plurality of pilot tones is outside a limit set by a second predefined threshold. Preferably, the first AGC process is performed repeatedly at a first rate and the second AGC process is performed repeatedly at a second rate that is less than the first rate.
Owner:AT&T MOBILITY II LLC
Receiver with automatic gain control that operates with multiple protocols and method thereof
ActiveUS7227916B2Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsAnalog signal digital controlAutomatic Generation ControlAutomatic control
An automatic gain control (AGC) method and circuit (10) within a receiver uses a digital state machine (26) to implement the AGC function. independent from interaction with a host processor (36) and for multiple modulation protocols without duplicating circuitry. Modulation protocol and parameters for any of various gain responses are stored in a register (29). Multiple states, each corresponding to a predetermined range of RF input signal strength, are stored in the register. Each state contains parameters that determine a gain control signal for controlling a variable gain amplifier (16). The states are independent and may be selectively disabled to create asymmetric responses. Within any state, an adaptable number of iterations may be set to implement a different update rate or step size after a predetermined number of closed loop gain change iterations has not resulted in a transition to a state that represents a desired output gain.
Owner:APPLE INC
DAC based switching power amplifier
InactiveUS20070275676A1Simultaneous amplitude and angle modulationResonant long antennasAudio power amplifierControl signal
A power amplifier for use in a transmitter includes a first transistor having an input, a first node and a second node, a second transistor having an input, a first node and a second node and a digital to analog conversion module. The input of the first transistor is operably coupled to receive a first input, while the input of the second transistor is operably coupled to receive a second input. The second nodes of the first and second transistors provide an output of the power amplifier. The digital to analog conversion module is operably coupled to control current through the first and second transistors based on at least one of a power control signal and an amplitude modulation control signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
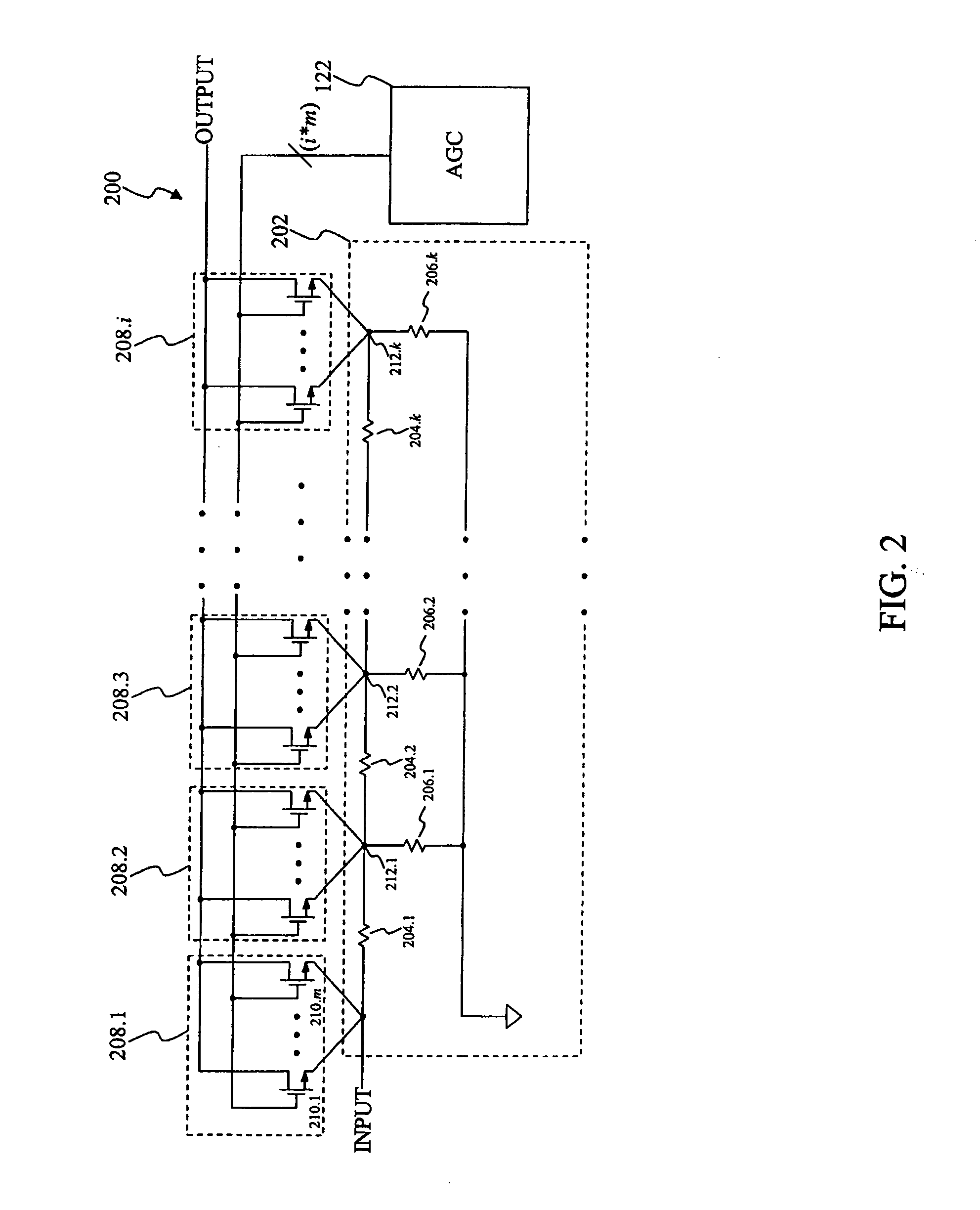
Programmable attenuator using digitally controlled CMOS switches
A programmable attenuator includes a resistor ladder having a plurality of taps to provide a coarse gain control. Coupled to each tap is a plurality of switches. Control logic activates or deactivates individual switches in the plurality of switches to provide a fine gain control. More specifically, a set of activated switches provides fine gain control by determining an overall attenuation level interpolated between an adjacent pair of taps.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Methods and systems for determining audio loudness levels in programming
An example of a method of correcting an audio level of a stored program asset comprises retrieving a stored program asset having audio encoded at a first loudness setting. Dialog of the audio of the asset is identified, a loudness of the dialog is determined and the determined loudness is compared to the first loudness setting. The asset is re-encoded at a second loudness setting corresponding to the determined loudness, if the first loudness setting and the second loudness are different by more than a predetermined amount. The determined loudness is preferably a DIALNORM of the dialog. The asset may be stored with the re-encoded loudness setting. The method may be applied to programs as they are being received from a source, as well. Aspects of the method may also be applied to programs to be provided by a source. Systems are also disclosed.
Owner:TIME WARNER CABLE ENTERPRISES LLC
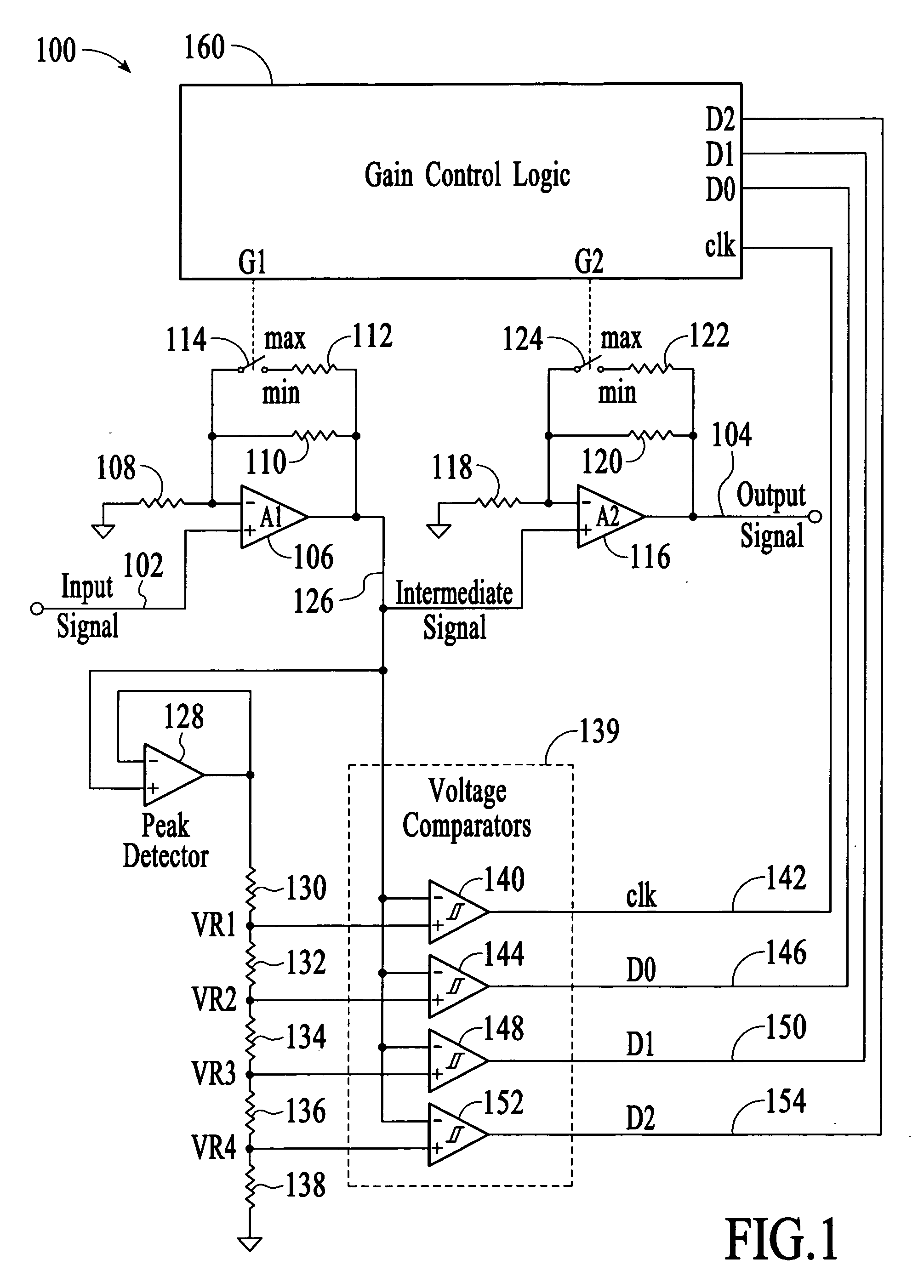
Fast-settling digital automatic gain control
InactiveUS20070139118A1Analog signal digital controlDifferential amplifiersAudio power amplifierEngineering
A fast-settling digital automatic gain control circuit comprises first and second gain-controllable amplifiers in series. Each amplifier can be digitally switched between minimum and maximum gains by control logic that receives inputs from a multi-level voltage comparator. A peak detector connected to the output of the first gain-controlled amplifier is used to set the overall operating ranges for several threshold detectors. Four reference voltages are generated from the peak detector. The highest reference voltage is used to clock and reset the gain control logic with a hysteresis comparator to the instantaneous input signal from the first gain-controlled amplifier. The three other lower reference voltages are used to provide three-bits of digital input data to the gain control logic. Two digital controls are output, a min / max gain bit for the first gain-controlled amplifier, and a similar min / max gain bit for the second gain-controlled amplifier.
Owner:LITE ON TECH CORP
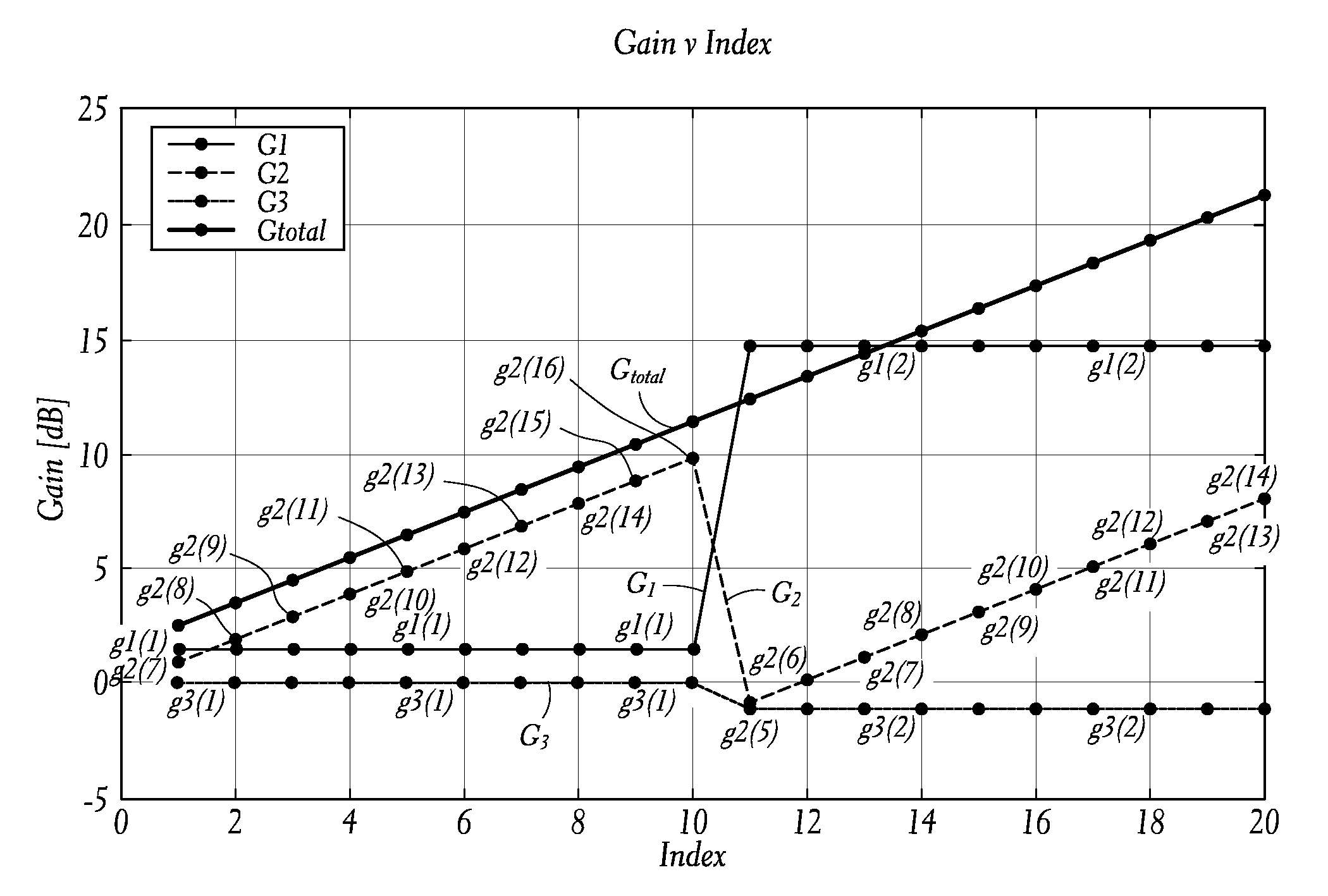
Transceiver gain calibration
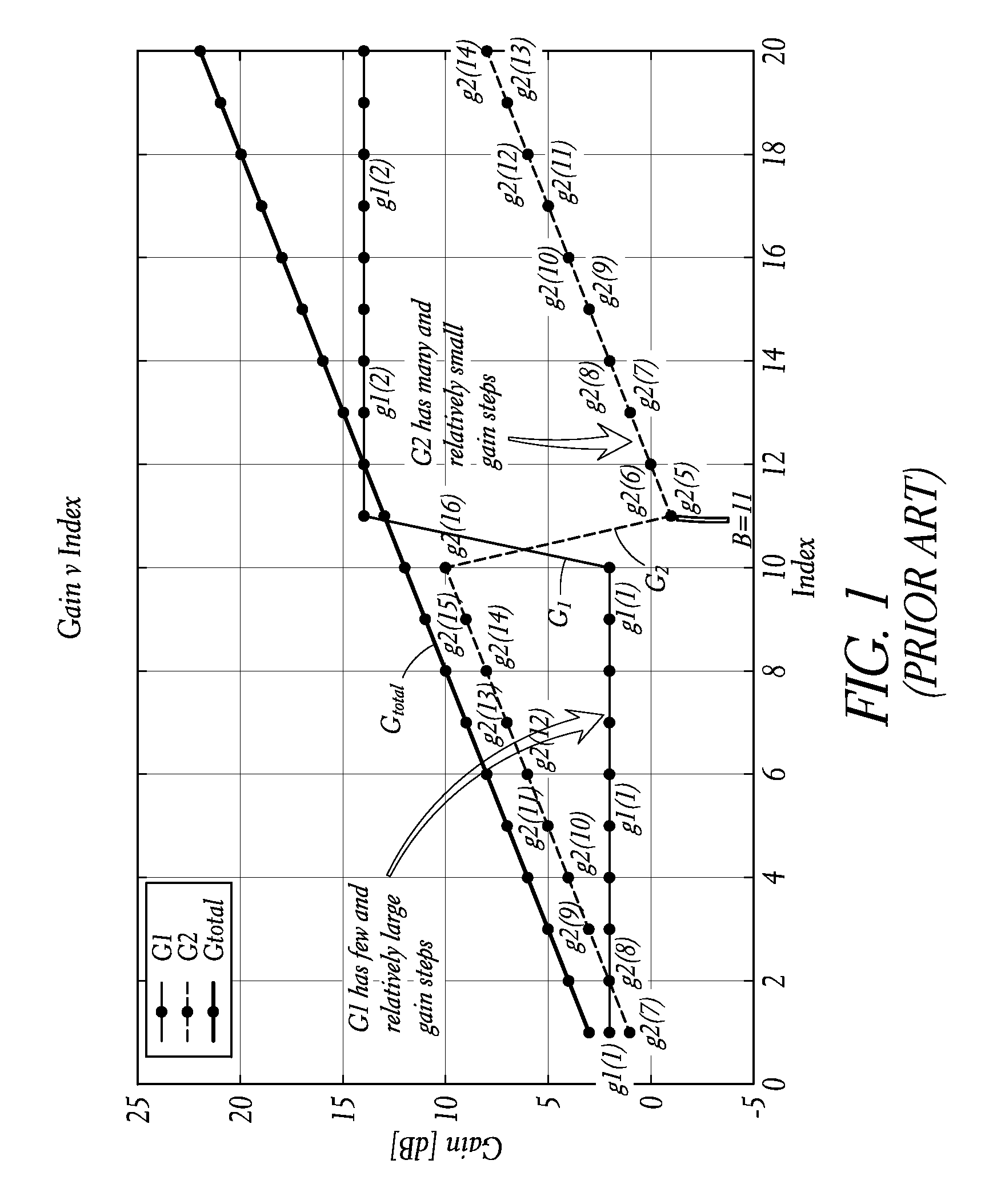
Transceivers with multiple gain stages that include open loop and closed loop amplifiers are subject to differential non-linearity (DNL) errors in their total gain versus gain index curve due to the gain step variability of the open loop amplifiers. The initial and time varying DNL can be reduced by a control loop that uses the relative gain step precision of the closed loop amplifiers and of passive attenuators to establish a control loop to reduce the DNL of the total gain.
Owner:MAXLINEAR ASIA SINGAPORE PTE LTD
Sound processing apparatus, method, and program
ActiveUS20140205111A1Reduce quality degradationQuality improvementAnalog signal digital controlAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlUltrasound attenuationSignal on
The present technique relates to a sound processing apparatus, a method, and a program capable of alleviating degradation of the quality of sound in a case where the gain of a sound signal is amplified.When equalizer processing for adjusting the gain of each frequency band of an input signal on the basis of a gain setting value is performed, an input signal is attenuated by an input attenuation amount derived from the gain setting value, and the equalizer processing is performed on the input signal attenuated. The amount of amplification of the gain of the input signal in the equalizer processing is estimated on the basis of the gain setting value and a weight coefficient of each frequency band derived from a generally-available music signal prepared in advance, and a difference of the estimation value and the input attenuation amount is calculated as a gain correction amount. Further, nonlinear amplification processing is performed on the input signal so as to actually amplify the input signal, which has been subjected to the equalizer processing, by a gain correction amount, and an output signal is obtained. The present technique can be applied to a sound processing apparatus.
Owner:SONY CORP
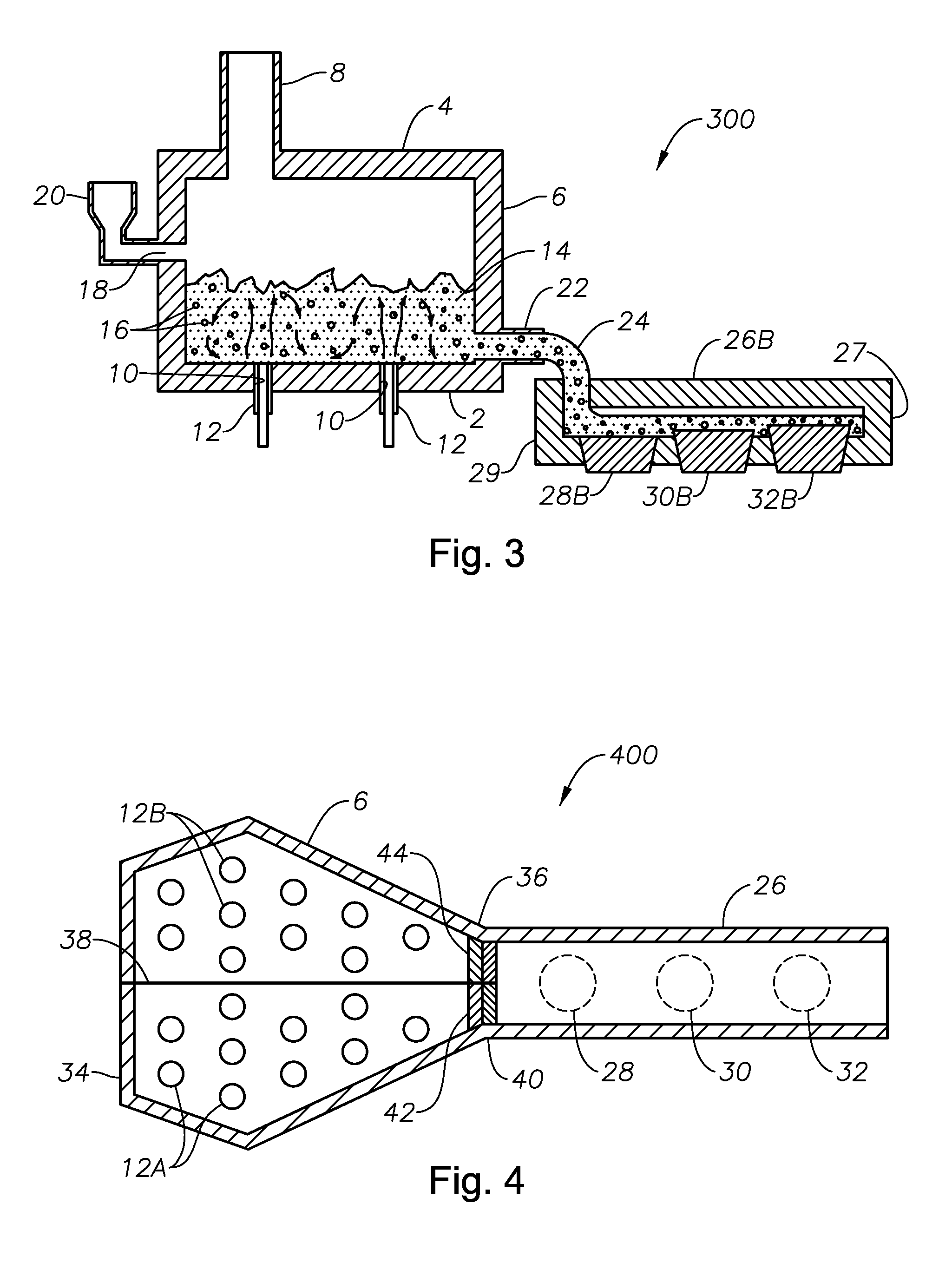
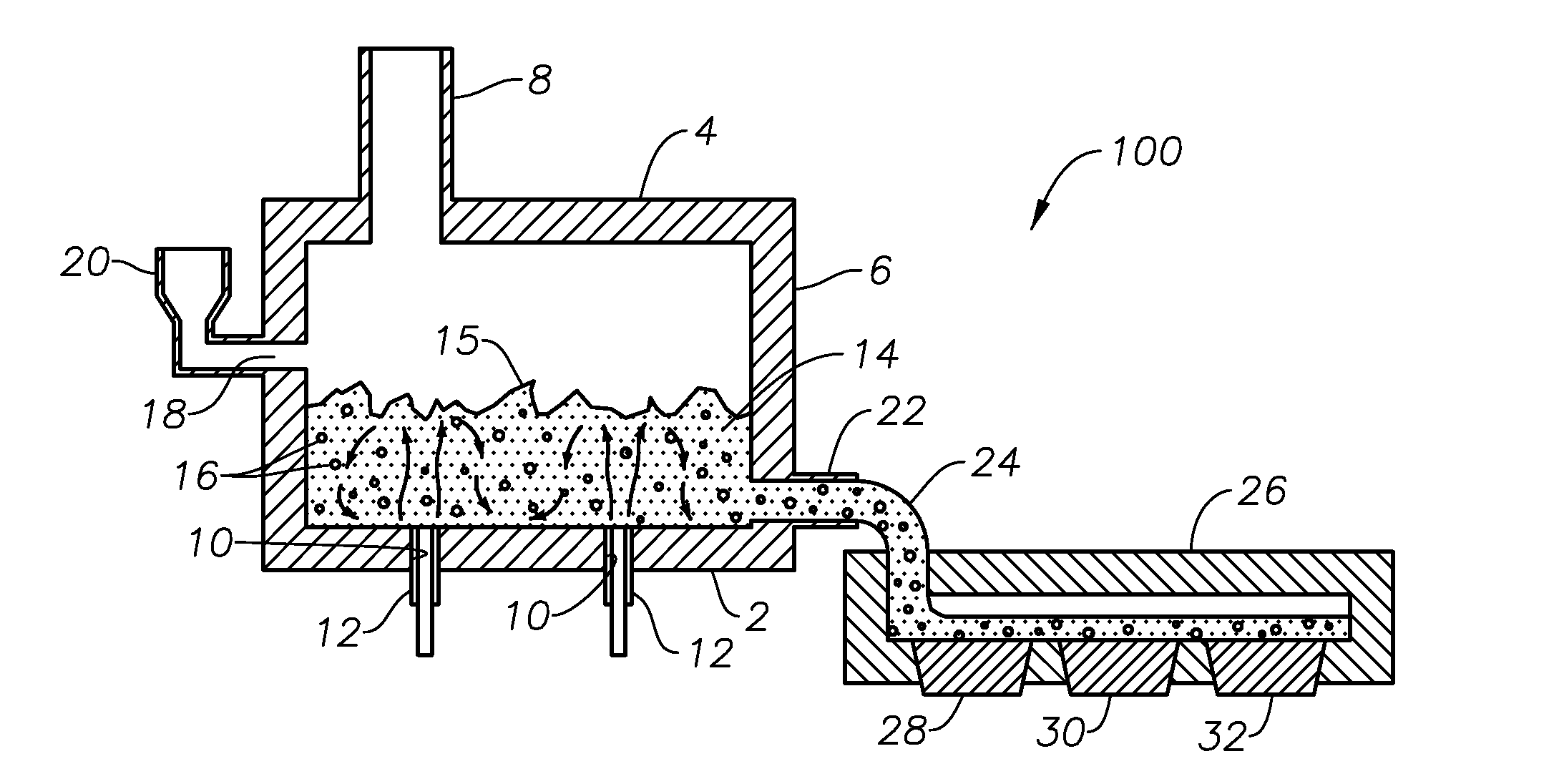
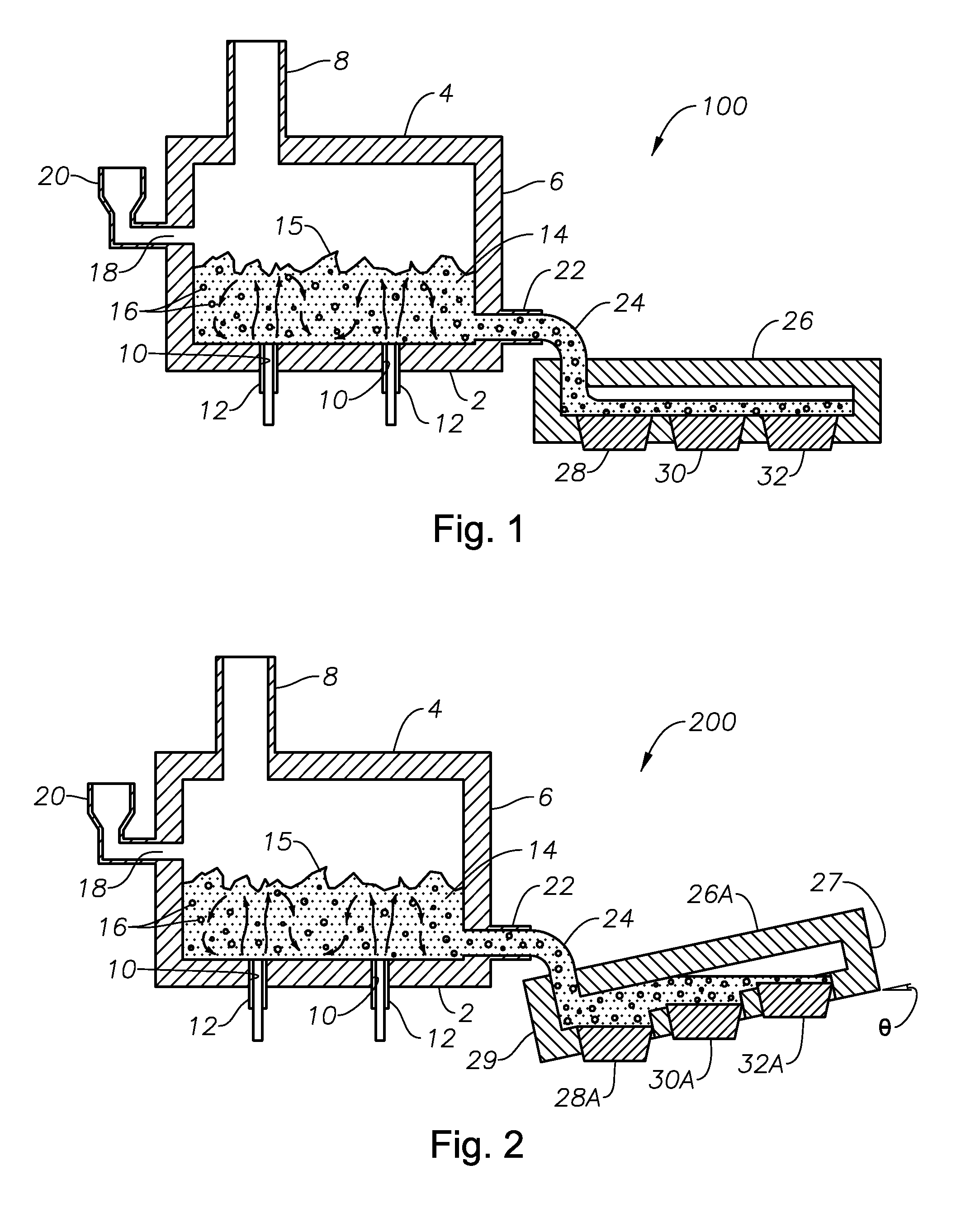
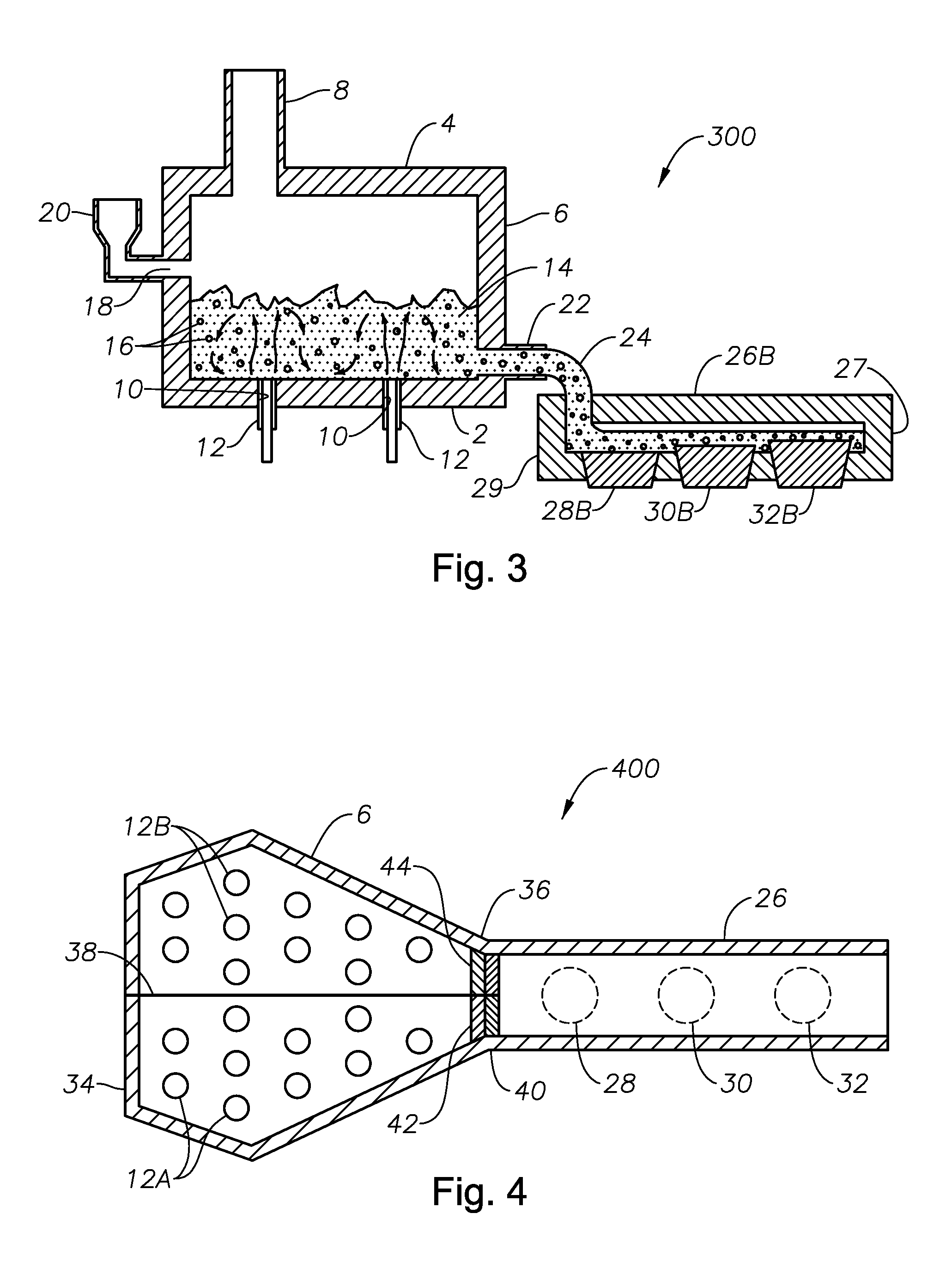
Process of using a submerged combustion melter to produce hollow glass fiber or solid glass fiber having entrained bubbles, and burners and systems to make such fibers
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Automatic gain control using multi-comparators
InactiveUS20060261895A1Amplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesAnalog signal digital controlStep responseEngineering
A method and apparatus for an automatic gain control (AGC) loop that utilizes multiple comparators to provide constant bandwidth tracking and step response, as well as fine granularity for decision directed convergence. In one embodiment, an odd number of comparators is used with square-law scaling at the output to achieve constant bandwidth step response for a wide range of input amplitude changes.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Process of using a submerged combustion melter to produce hollow glass fiber or solid glass fiber having entrained bubbles, and burners and systems to make such fibers
Processes and systems for producing glass fibers having regions devoid of glass using submerged combustion melters, including feeding a vitrifiable feed material into a feed inlet of a melting zone of a melter vessel, and heating the vitrifiable material with at least one burner directing combustion products of an oxidant and a first fuel into the melting zone under a level of the molten material in the zone. One or more of the burners is configured to impart heat and turbulence to the molten material, producing a turbulent molten material comprising a plurality of bubbles suspended in the molten material, the bubbles comprising at least some of the combustion products, and optionally other gas species introduced by the burners. The molten material and bubbles are drawn through a bushing fluidly connected to a forehearth to produce a glass fiber comprising a plurality of interior regions substantially devoid of glass.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
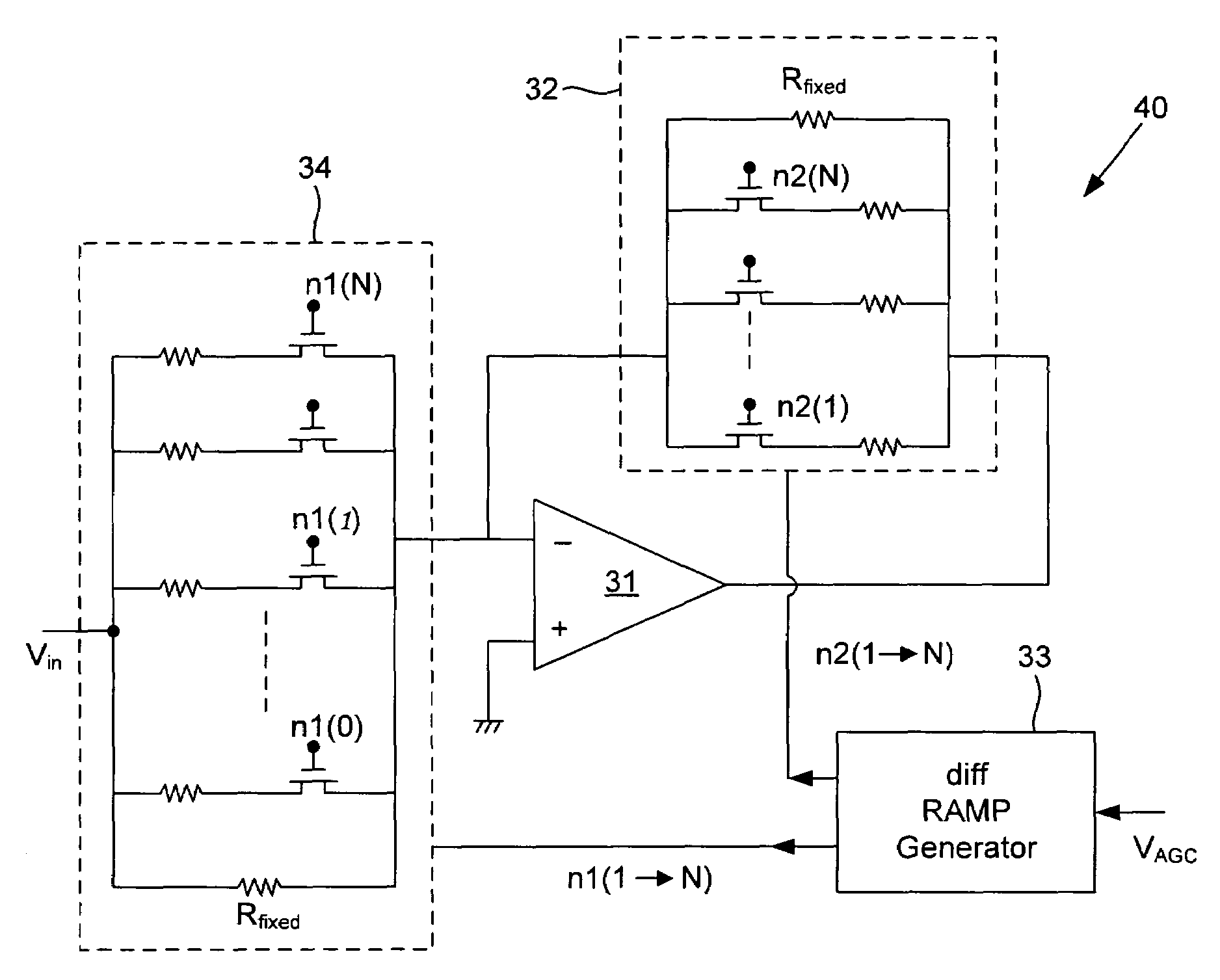
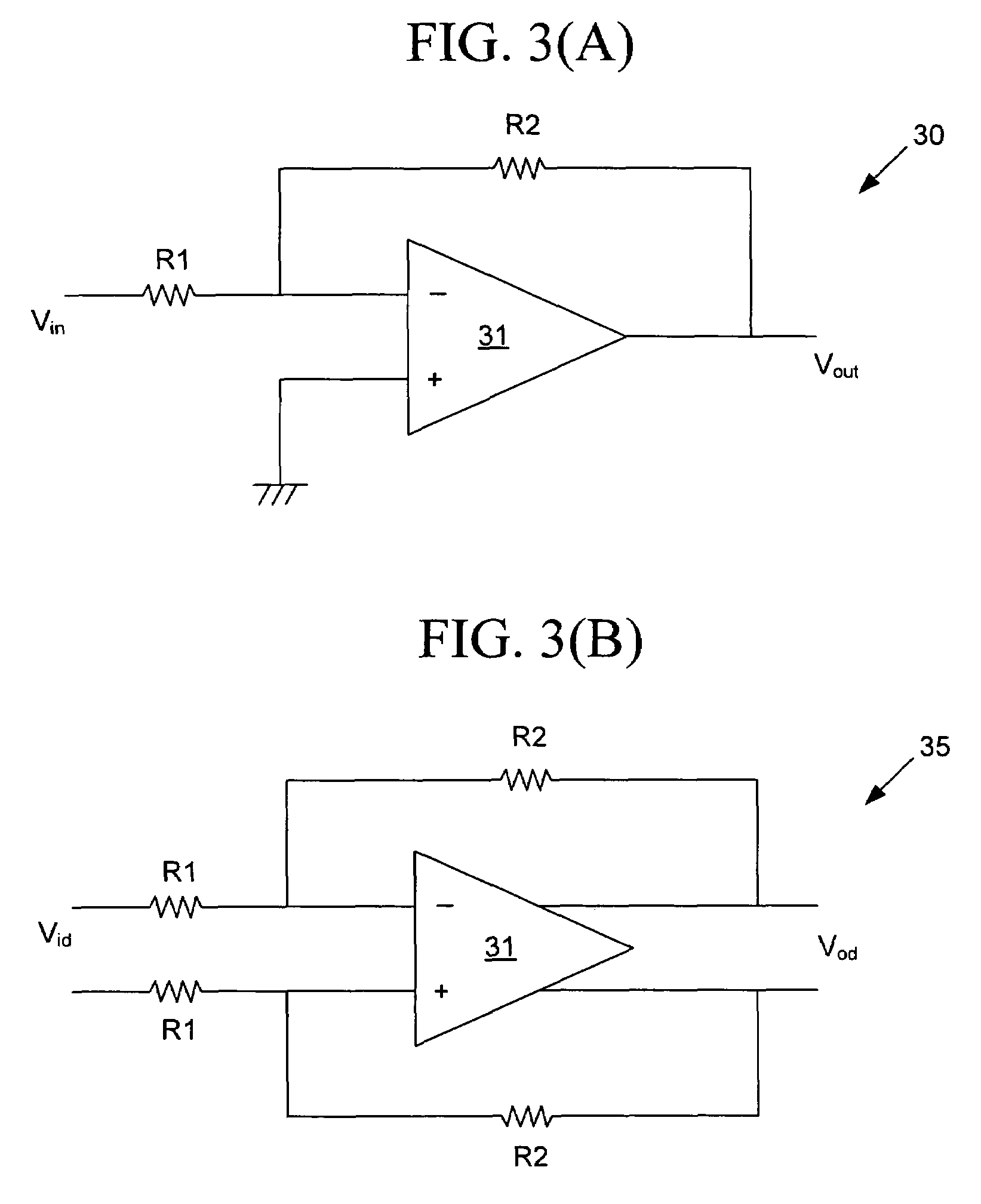
dB-linear analog variable gain amplifier (VGA) realization system and method
ActiveUS7352238B2Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsVolume compression/expansion having semiconductor devicesAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
A dB-linear variable gain amplifier, a method for creation, and a system includes an amplifier; a pair of resistor arrays operatively connected to the amplifier, wherein each resistor array comprises MOS transistor resistive switches; a differential ramp-generator circuit operatively connected to the pair of resistor arrays; and voltage control lines generated by the differential ramp-generator circuit, wherein the voltage control lines are operatively connected to each of the MOS transistor resistive switches in the pair of resistor arrays. The number of the voltage control lines that are operatively connected to the each of the MOS transistor resistive switches is equal to the number of resistors in a particular resistor array. The differential ramp-generator circuit is preferably operable to take an automatic gain control voltage and generate a series of differential ramp voltages and apply the series of differential ramp voltages to one of the MOS transistor resistive switches.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
Multi-channel programmable gain amplifier controlled with a serial interface
InactiveUS6847904B2Simple interfaceAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesAnalog signal digital controlMultiplexerProgrammable-gain amplifier
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Methods and systems for determining audio loudness levels in programming
ActiveUS20090046873A1Volume compression/expansion in digital/coded amplifiersAnalog signal digital controlLoudnessAudio frequency
An example of a method of correcting an audio level of a stored program asset comprises retrieving a stored program asset having audio encoded at a first loudness setting. Dialog of the audio of the asset is identified, a loudness of the dialog is determined and the determined loudness is compared to the first loudness setting. The asset is re-encoded at a second loudness setting corresponding to the determined loudness, if the first loudness setting and the second loudness are different by more than a predetermined amount. The determined loudness is preferably a DIALNORM of the dialog. The asset may be stored with the re-encoded loudness setting. The method may be applied to programs as they are being received from a source, as well. Aspects of the method may also be applied to programs to be provided by a source. Systems are also disclosed.
Owner:TIME WARNER CABLE ENTERPRISES LLC
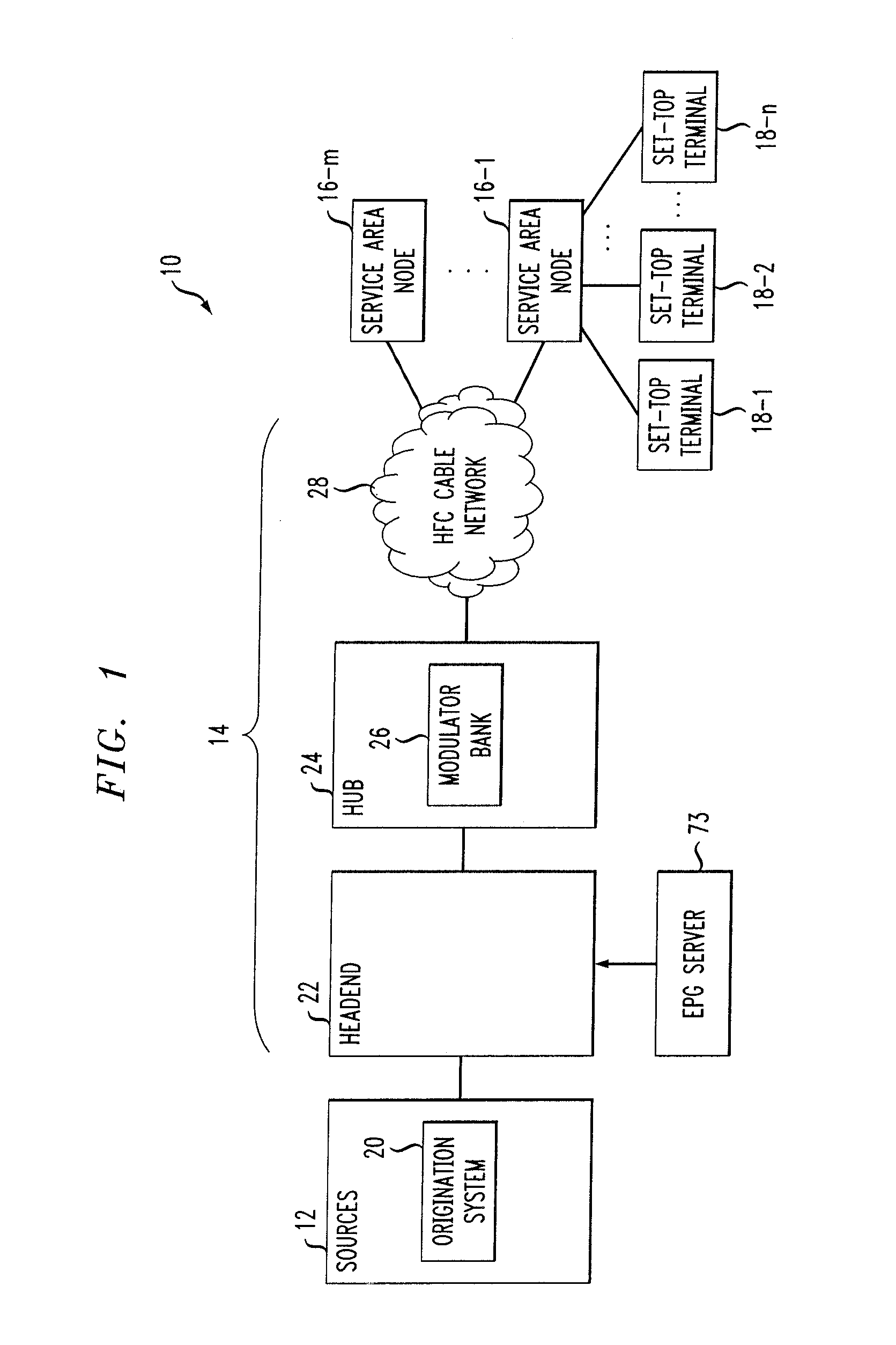
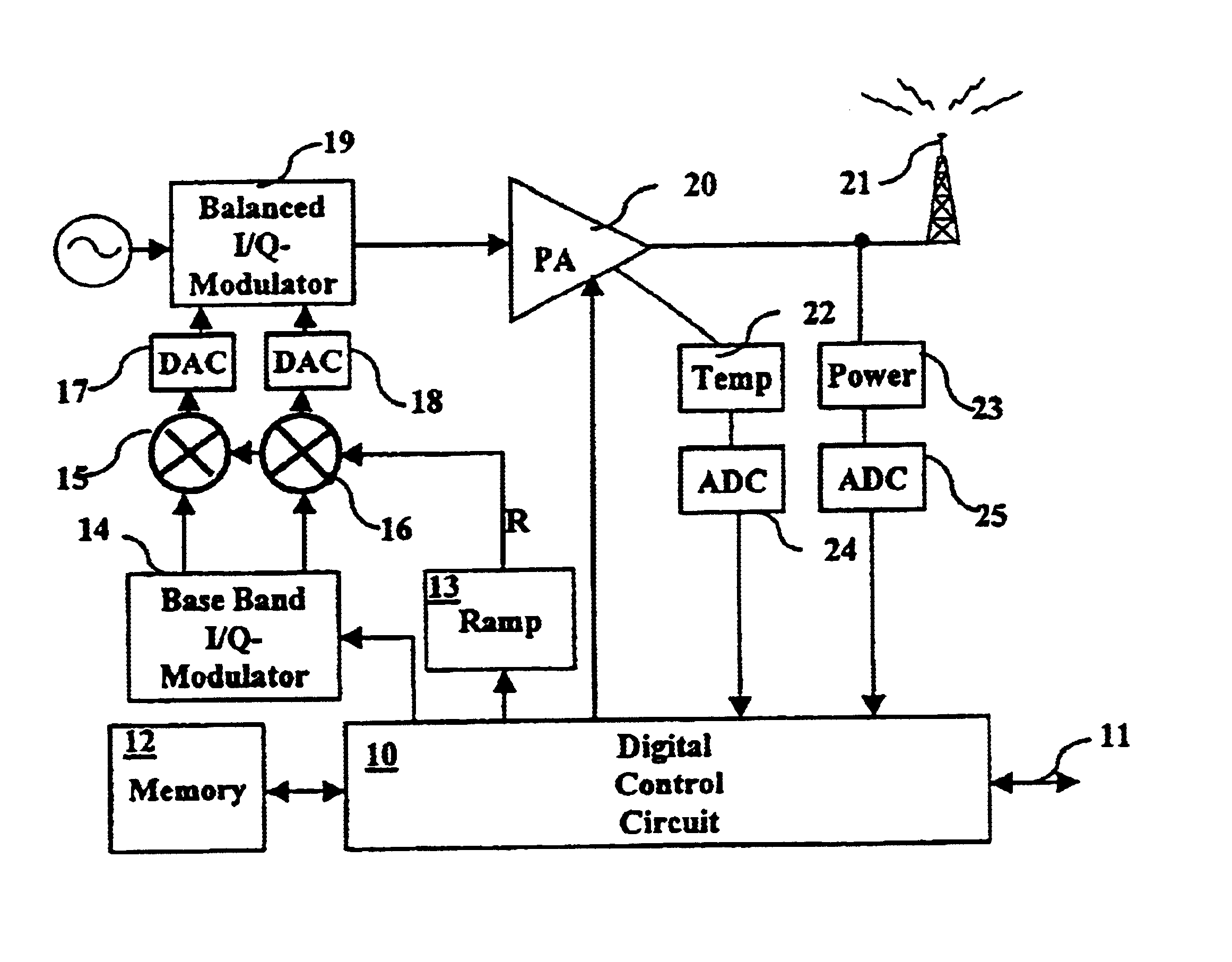
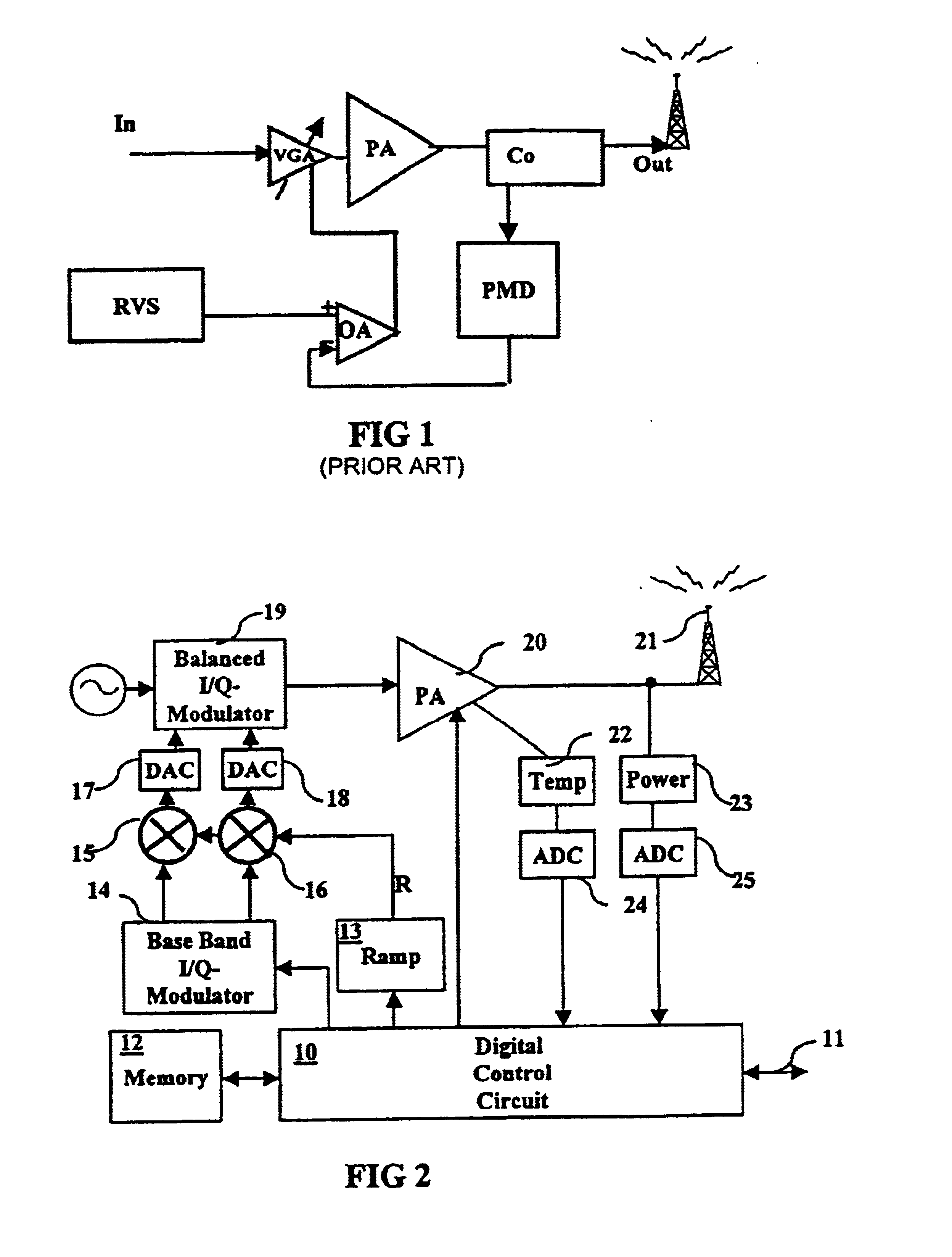
Power characteristic of a radio transmitter
The present invention relates to radio transmission of bursts in for example a TDMA cellular radio system. The burst starts with a ramping up period, ends with a corresponding ramping down ramping down period and with the pay-load information therebetween. The ramp form is created in a ramp generator (13) which gives a multiplication value to multiply the digital information to be transmitted in multipliers (15, 16). The multiplied values are converted into analogue form and amplified before being transferred to the antenna (21). Output power and temperature of the transmitting equipment are measured (22, 23) and used to update the output power levels during the next burst.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Apparatus and method for automatically switching volume control mode
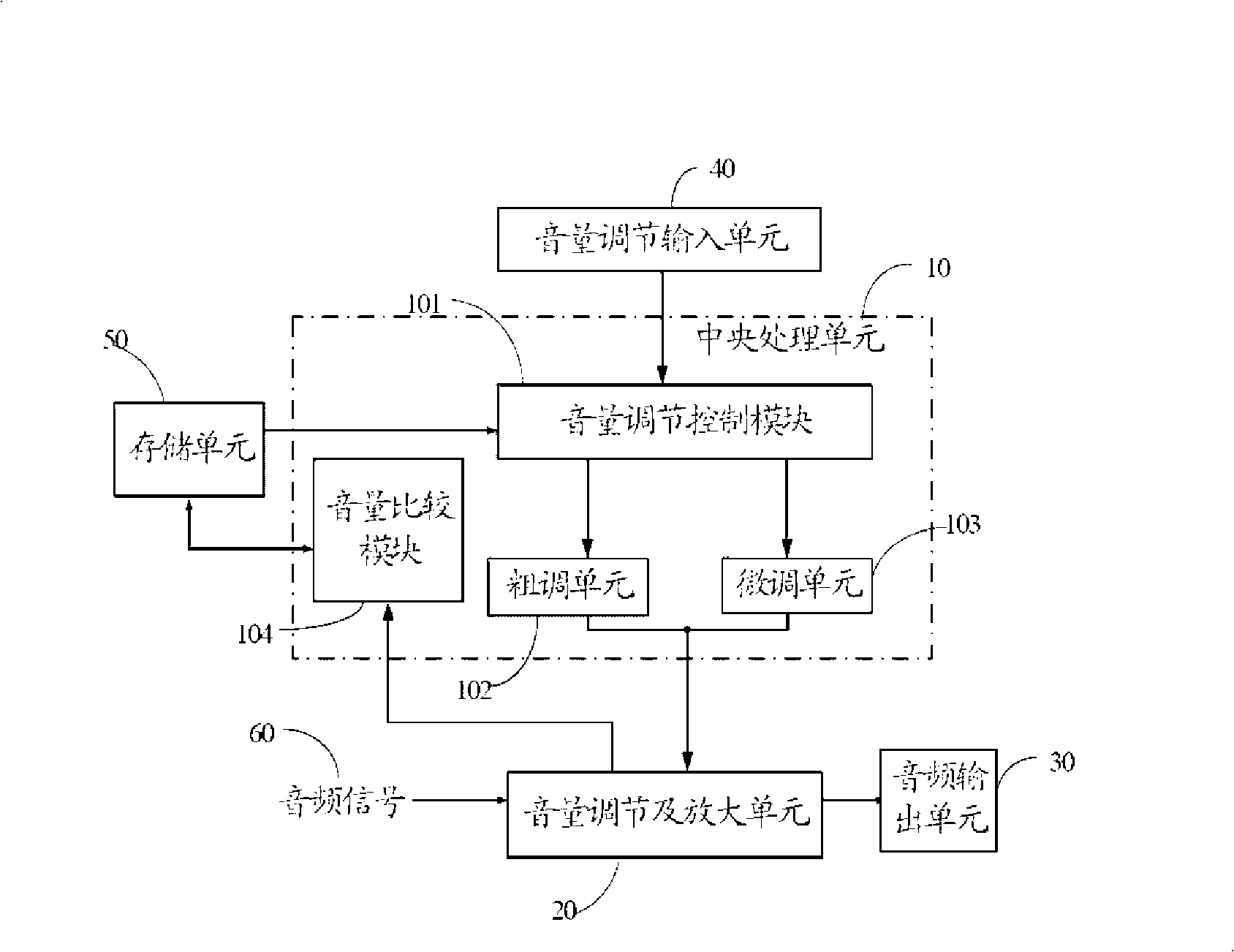
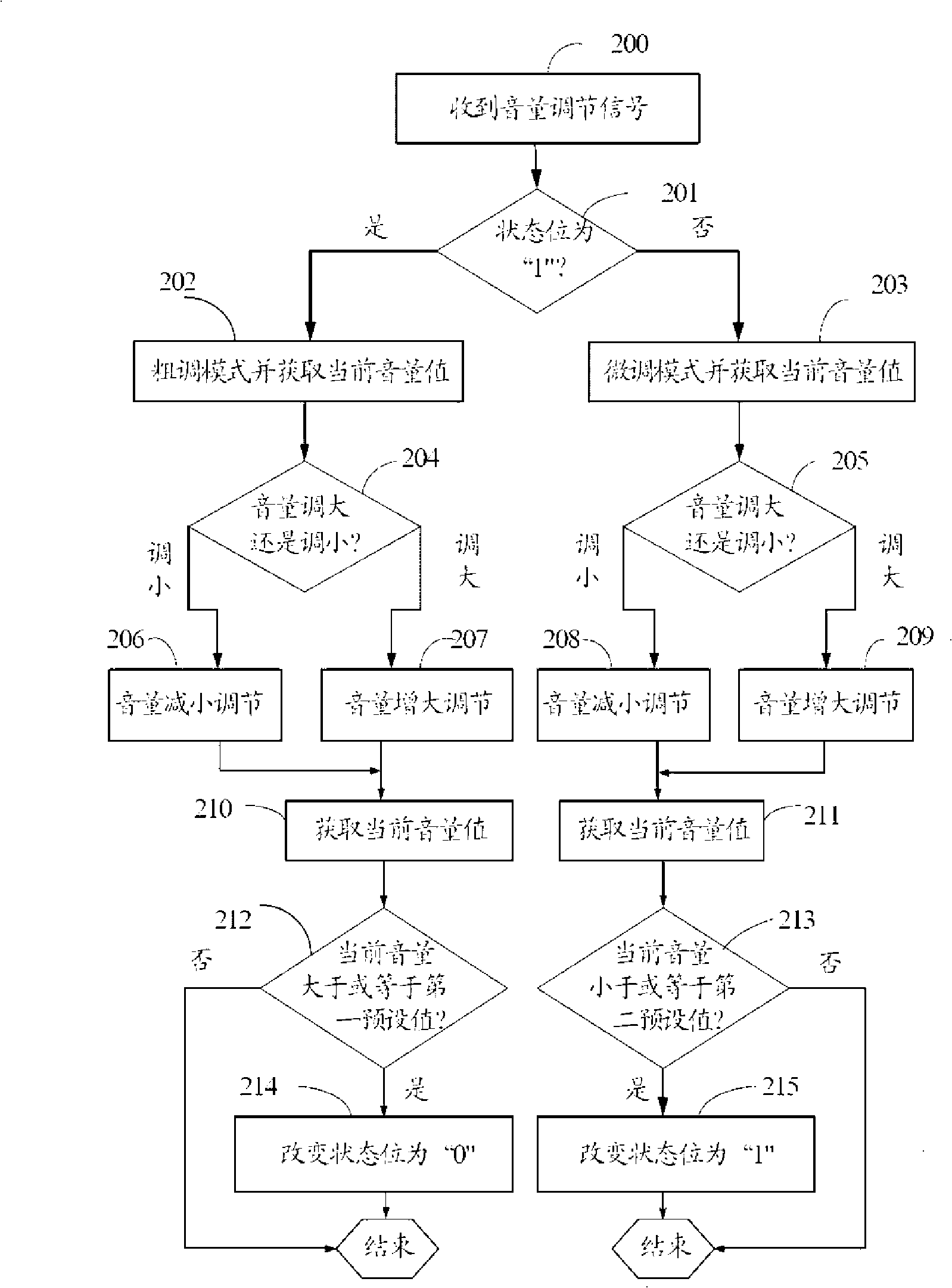
InactiveCN101350604AEmbody humanizationManually-operated gain controlAnalog signal digital controlComputer scienceControl mode
The present invention relates to a method of automatically switching volume control mode, which can be used for automatically switching the volume into the fine-tuning mode when the volume is regulated to have a high value through rough adjustment. The method comprises the following steps: a first preset value and a second preset value are stored in the system; wherein, the first preset value is larger than the second preset value; the control mode is first judged when the volume control signals occur; the rough adjustment is adopted in the mode of rough adjustment; when the volume is higher than or equal to the first preset value in the process of rough adjustment, the volume is automatically switched into the fine-tuning mode. The method also comprises the following steps: the volume is processed by fine tuning in the fine-tuning mode; when the volume is lower than or equal to the second preset value in the fine-tuning process, the volume is automatically switched into the mode of rough adjustment. Therefore, the volume adjustment is automatically switched into the fine-tuning mode after the volume is regulated to have a higher volume value through rough adjustment, which prevents the damage to ears caused by the sudden increase of the volume; simultaneously, the volume can be finely tuned within a certain range; thus the method reflects the humanity.
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
Noise masking communications apparatus
InactiveUS7349547B1Minimises levelRatio of amplitudeInterconnection arrangementsAnalog signal digital controlEngineeringHeadphones
A communications headset with a movable microphone boom that extends to different distances from the mouth, where the movement of the boom operates electrical, mechanical or acoustic means to adjust the transmit and / or receive sensitivity of the headset.
Owner:PLANTRONICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com