Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
420 results about "Gain correction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
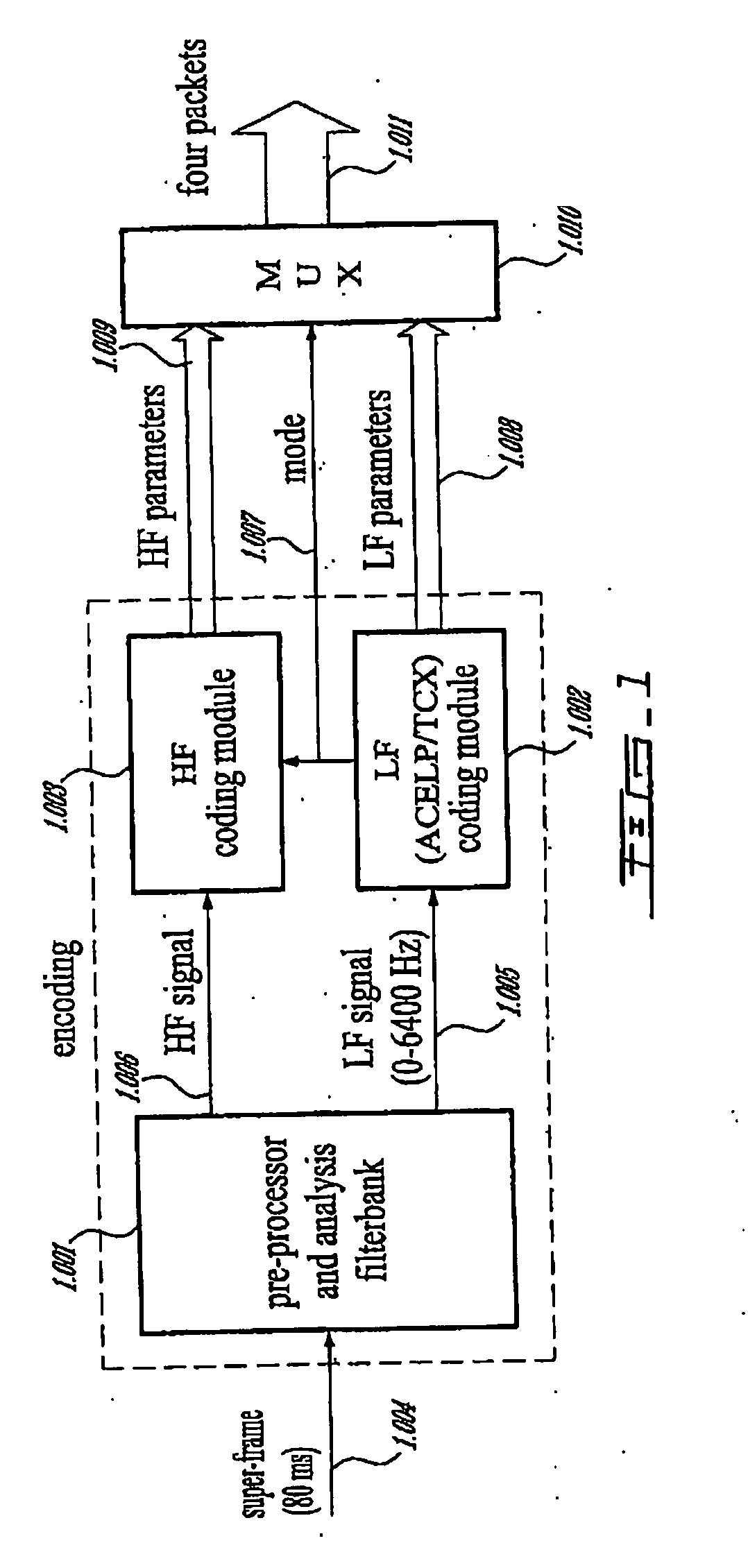
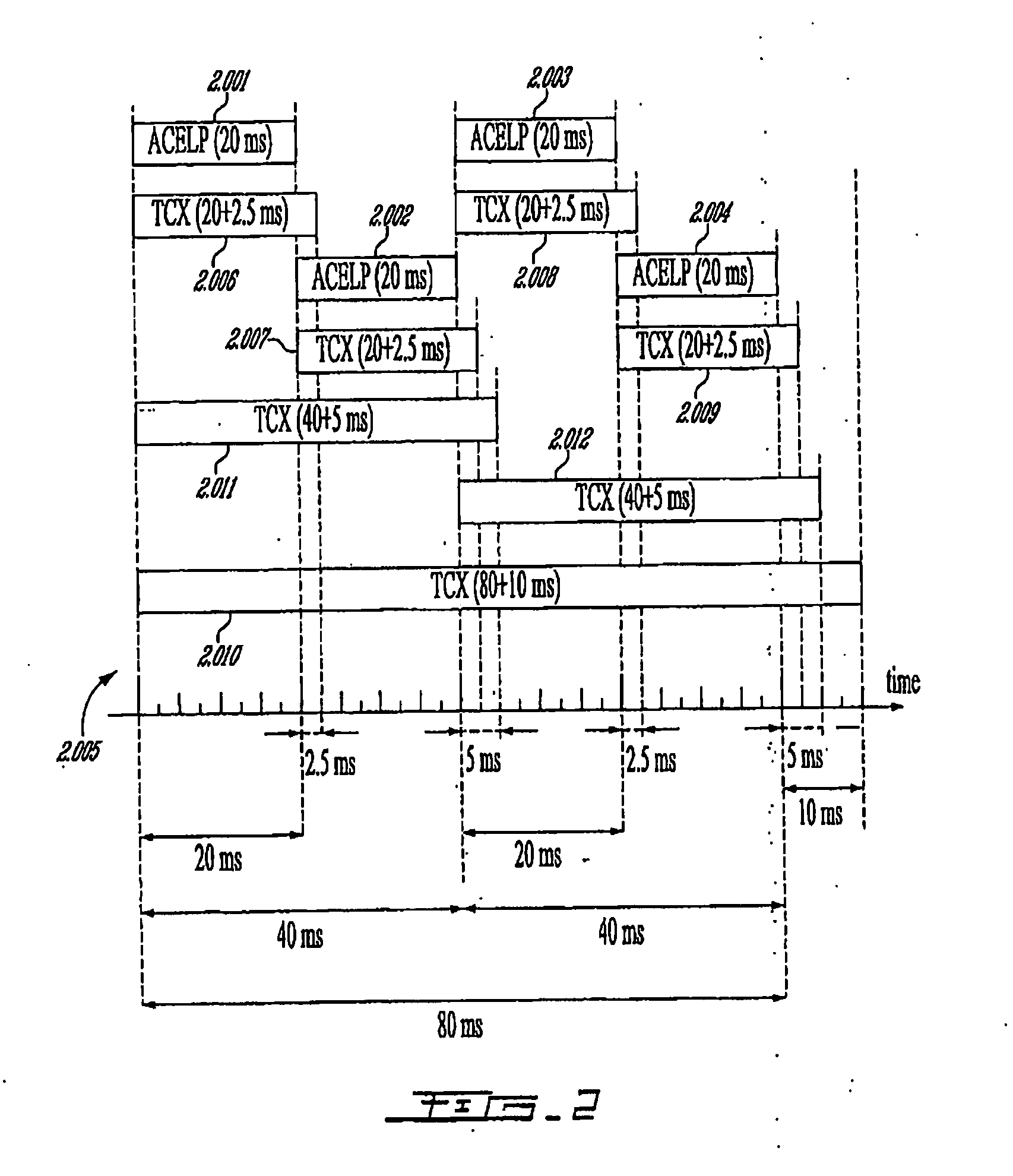
Methods and Devices for Low-Frequency Emphasis During Audio Compression Based on Acelp/Tcx
ActiveUS20070282603A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionBandwidth extensionFrequency spectrum
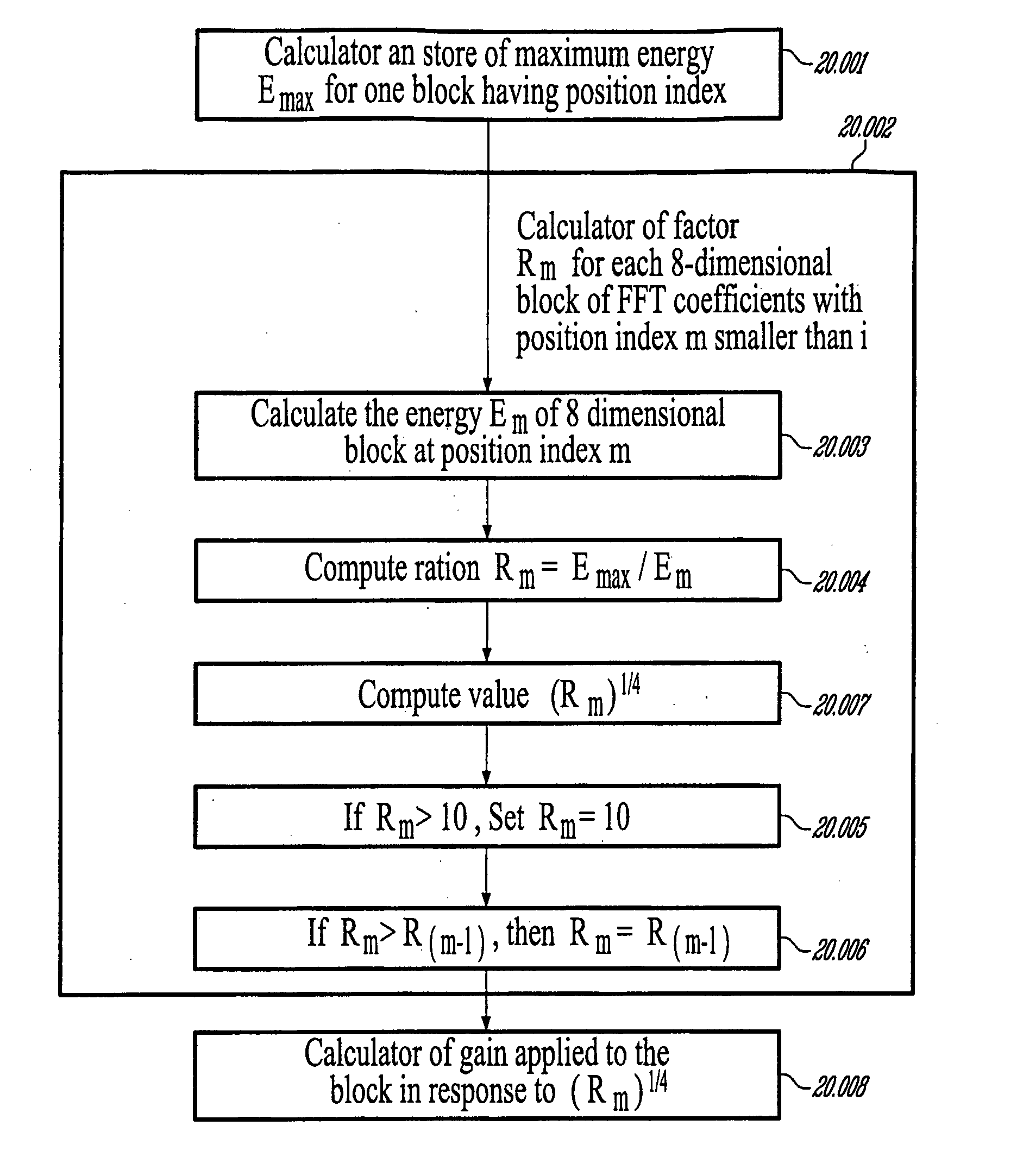
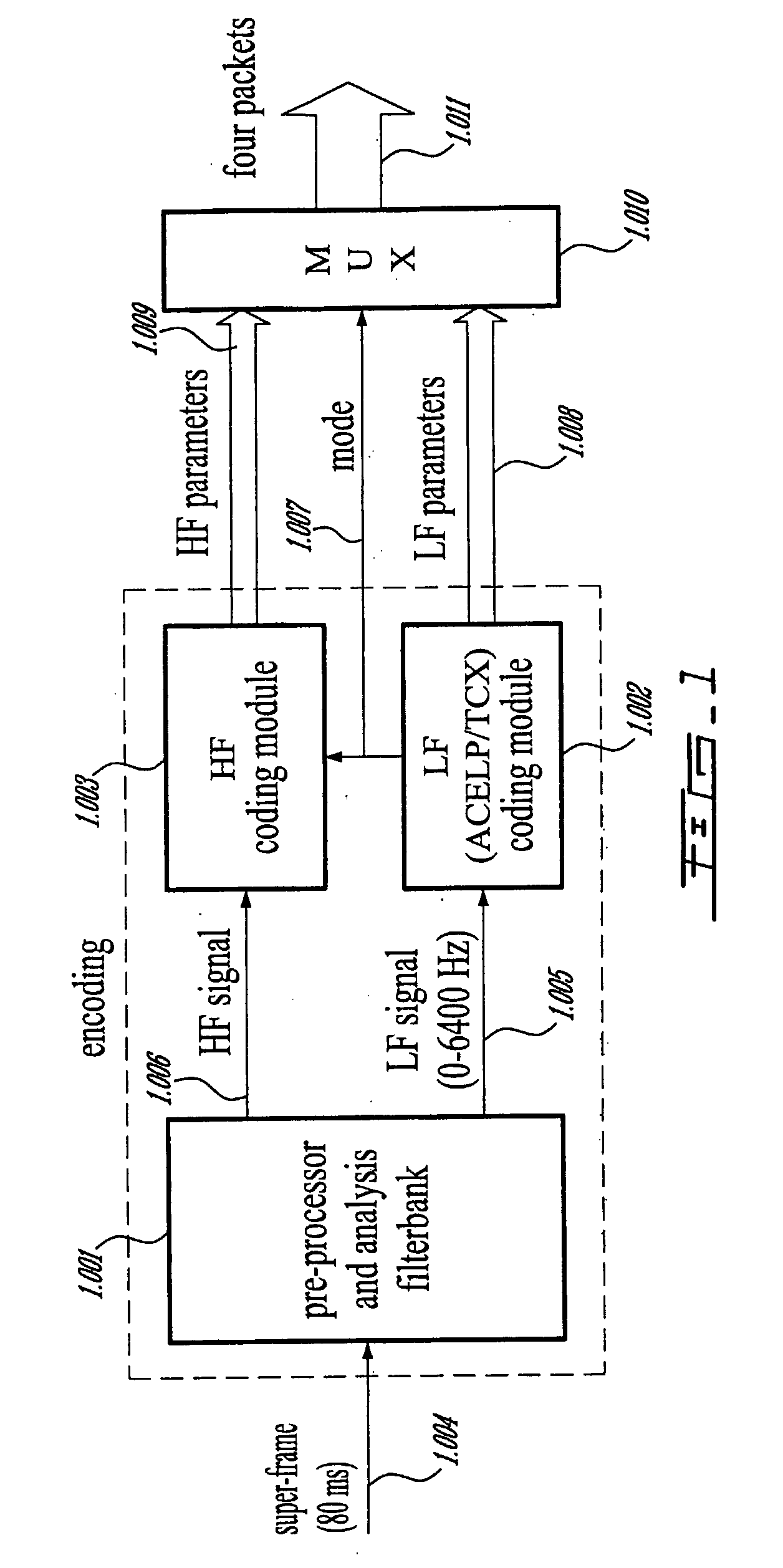
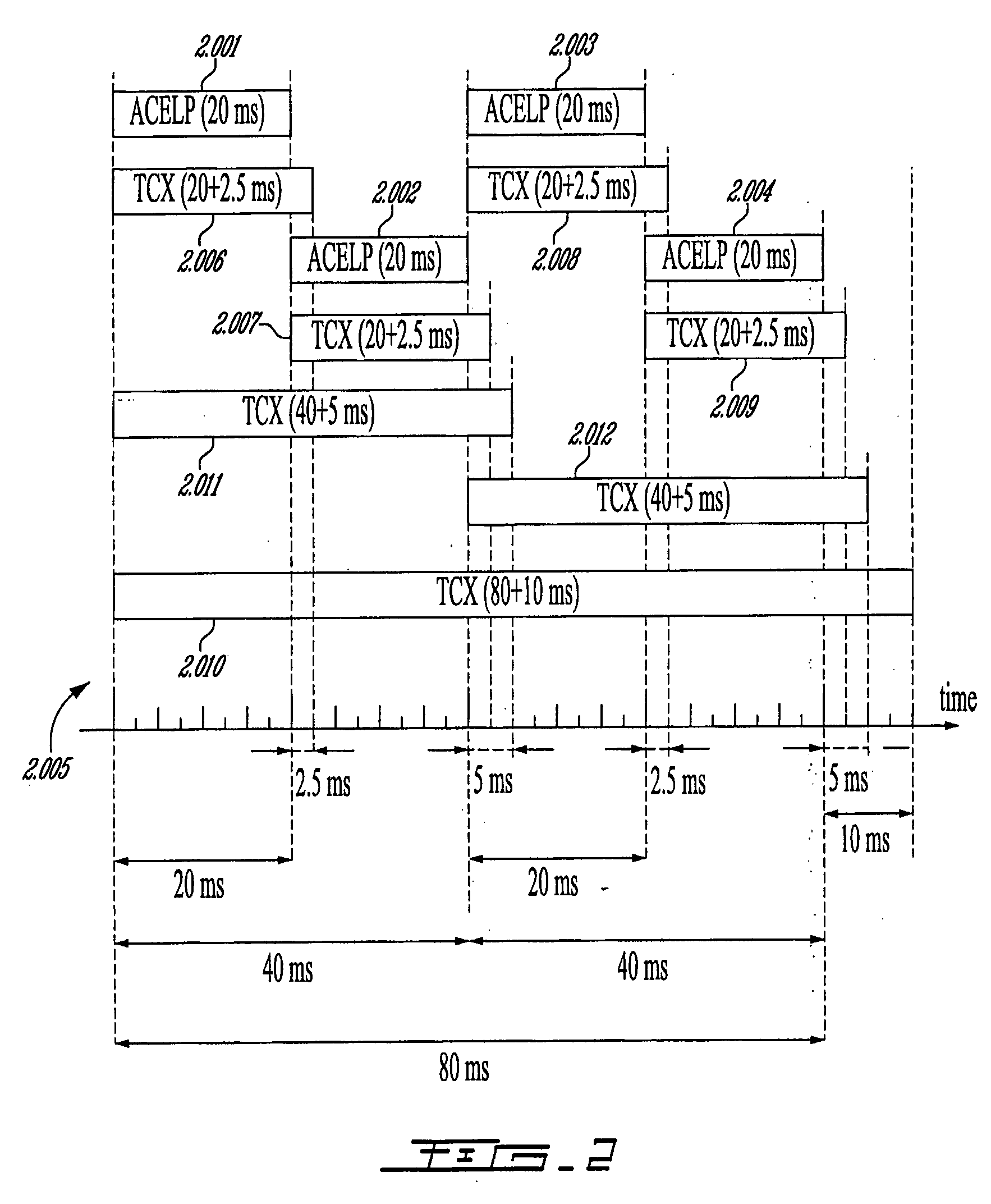
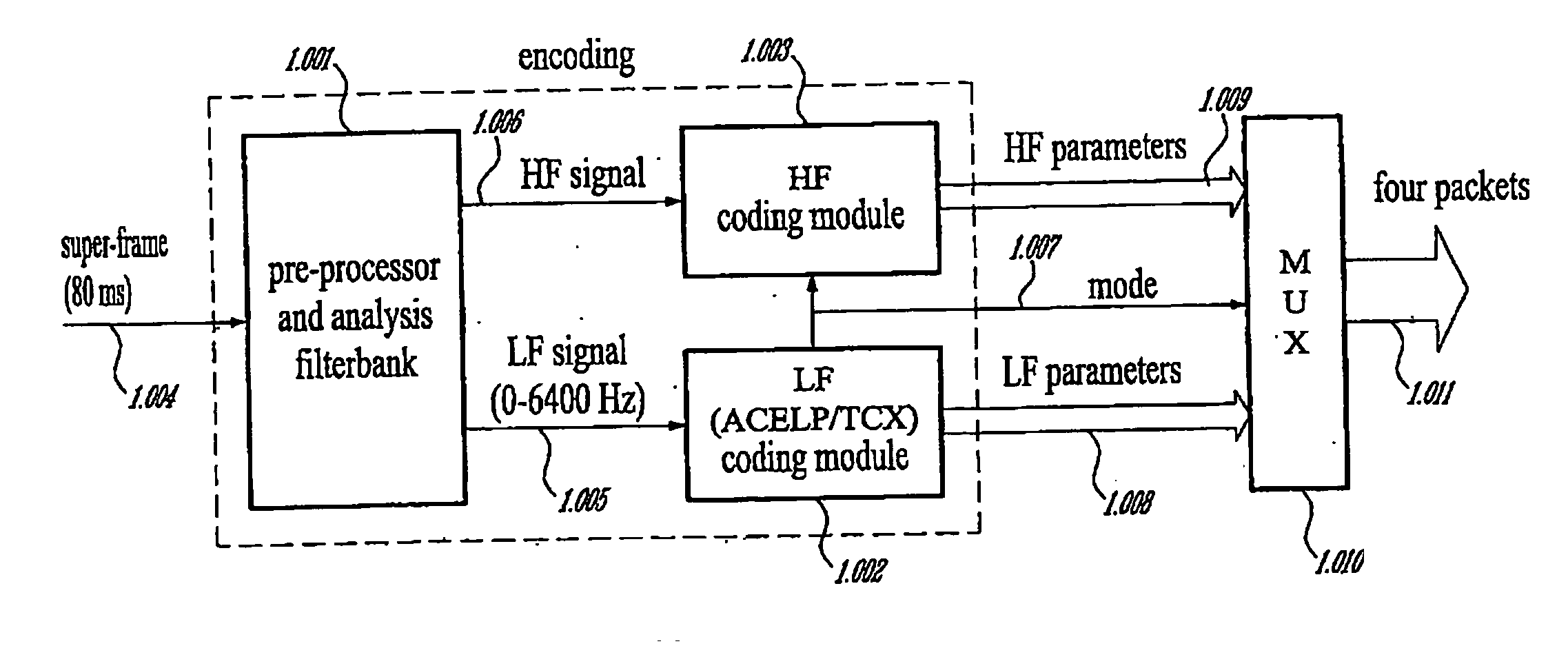
A first aspect of the present invention relates to a method for low-frequency emphasizing the spectrum of a sound signal transformed in a frequency domain and comprising transform coefficients grouped in a number of blocks, in which a maximum energy for one block is calculated and a position index of the block with maximum energy is determined, a factor is calculated for each block having a position index smaller than the position index of the block with maximum energy the calculated maximum energy and the energy of the block, and, for each block, a gain determining from the factor is applied to the transform coefficients of the block. Another aspect of the invention is concerned with an HF coding method for coding, through a bandwidth extension scheme, an HF signal obtained from separation of a full-bandwidth sound signal into the HF signal and a LF signal, in which an estimation of the an HF gain is calculated from LPC coefficients, the energy of the HF signal is calculated, the LF signal is processed to produce a synthesized version of the HF signal, the energy of the synthesized version of the HF signal is calculated, a ratio between the energy of the HF signal and the energy of the synthesized version of the HF signal is calculated and expressing as an HF gain, and a difference between the estimation of the HF gain and the HF gain is calculated to obtain a gain correction. A third aspect of the invention is concerned with a method for producing from a decoded target signal an overlap-add target signal in a current frame coded according to a first coding mode. According to this method, the decoded target signal of the current frame is windowed and a left portion of the window is skipped. A zero-input response of a weighting filter of the previous frame coded according to a second coding mode is calculated and windowed so that the zero-input response has an amplitude monotonically decreasing to zero after a predetermined time period. Finally, the calculated zero-input response is added to the decoded target signal to reconstruct the overlap-add target signal.
Owner:VOICEAGE CORP
Methods and devices for low-frequency emphasis during audio compression based on ACELP/TCX
A first aspect of the present invention relates to a method for low-frequency emphasizing the spectrum of a sound signal transformed in a frequency domain and comprising transform coefficients grouped in a number of blocks, in which a maximum energy for one block is calculated and a position index of the block with maximum energy is determined, a factor is calculated for each block having a position index smaller than the position index of the block with maximum energy the calculated maximum energy and the energy of the block, and, for each block, a gain determining from the factor is applied to the transform coefficients of the block. Another aspect of the invention is concerned with an HF coding method for coding, through a bandwidth extension scheme, an HF signal obtained from separation of a full-bandwidth sound signal into the HF signal and a LF signal, in which an estimation of the an HF gain is calculated from LPC coefficients, the energy of the HF signal is calculated, the LF signal is processed to produce a synthesized version of the HF signal, the energy of the synthesized version of the HF signal is calculated, a ratio between the energy of the HF signal and the energy of the synthesized version of the HF signal is calculated and expressing as an HF gain, and a difference between the estimation of the HF gain and the HF gain is calculated to obtain a gain correction. A third aspect of the invention is concerned with a method for producing from a decoded target signal an overlap-add target signal in a current frame coded according to a first coding mode. According to this method, the decoded target signal of the current frame is windowed and a left portion of the window is skipped. A zero-input response of a weighting filter of the previous frame coded according to a second coding mode is calculated and windowed so that the zero-input response has an amplitude monotonically decreasing to zero after a predetermined time period. Finally, the calculated zero-input response is added to the decoded target signal to reconstruct the overlap-add target signal.
Owner:VOICEAGE CORP
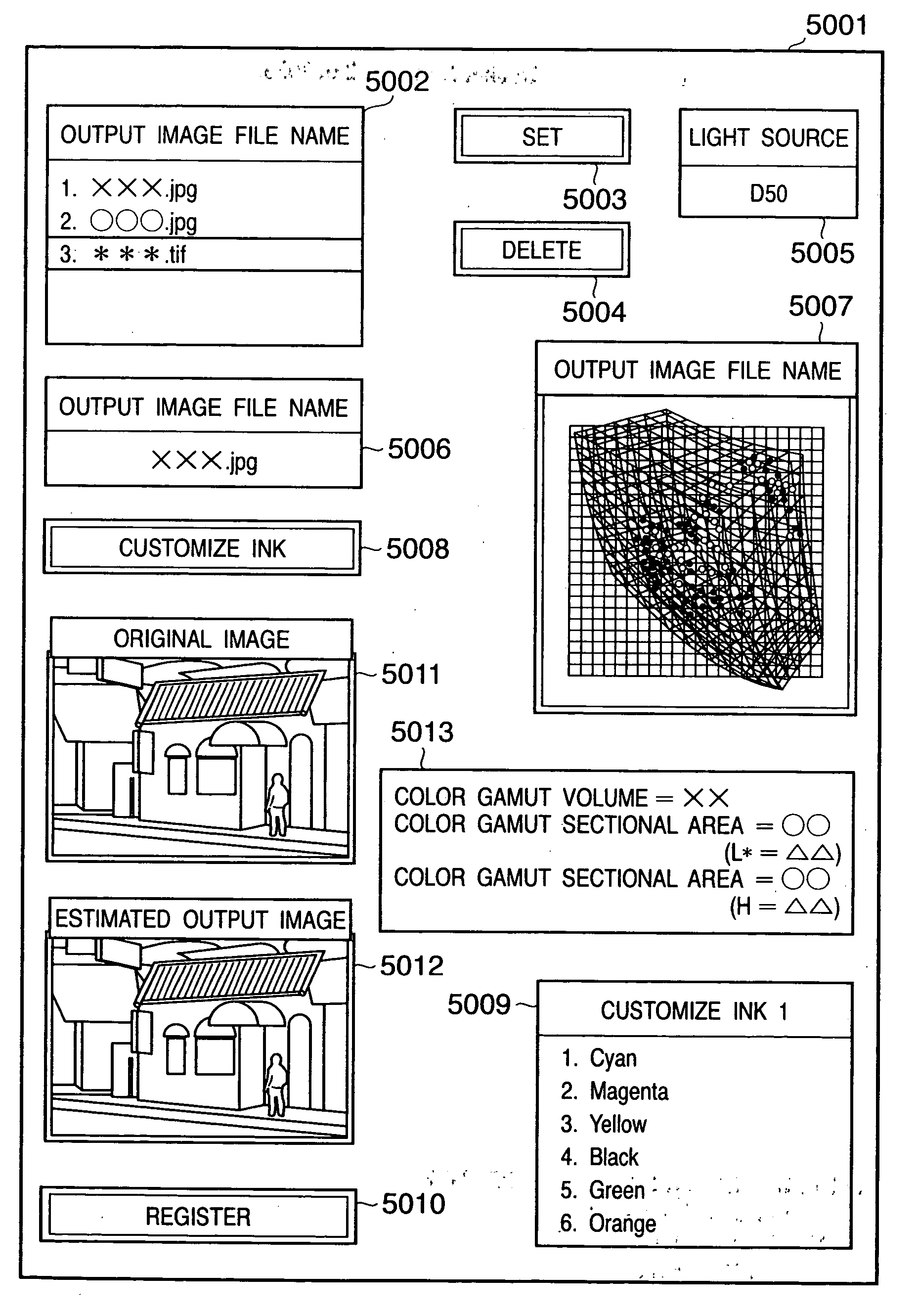
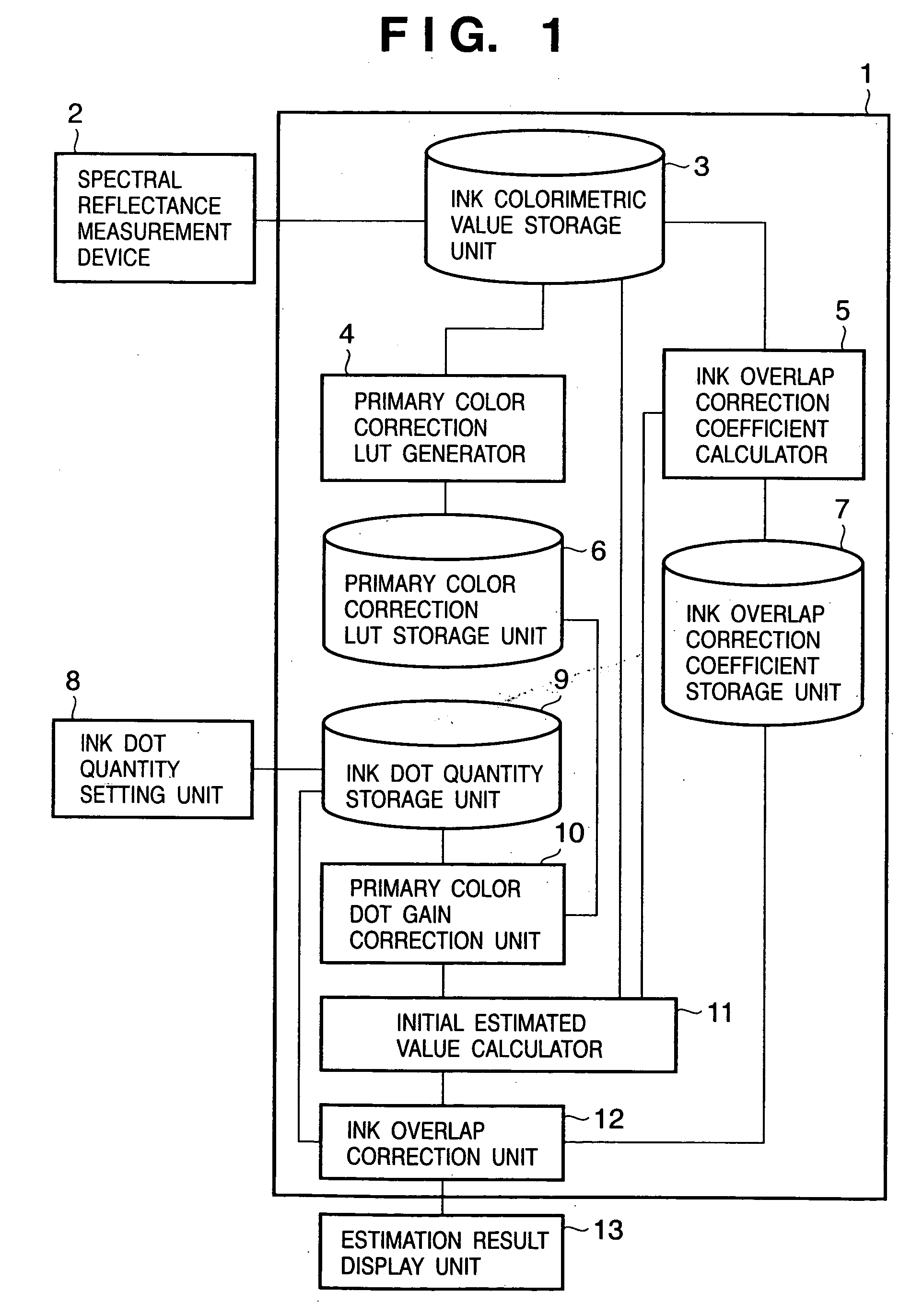
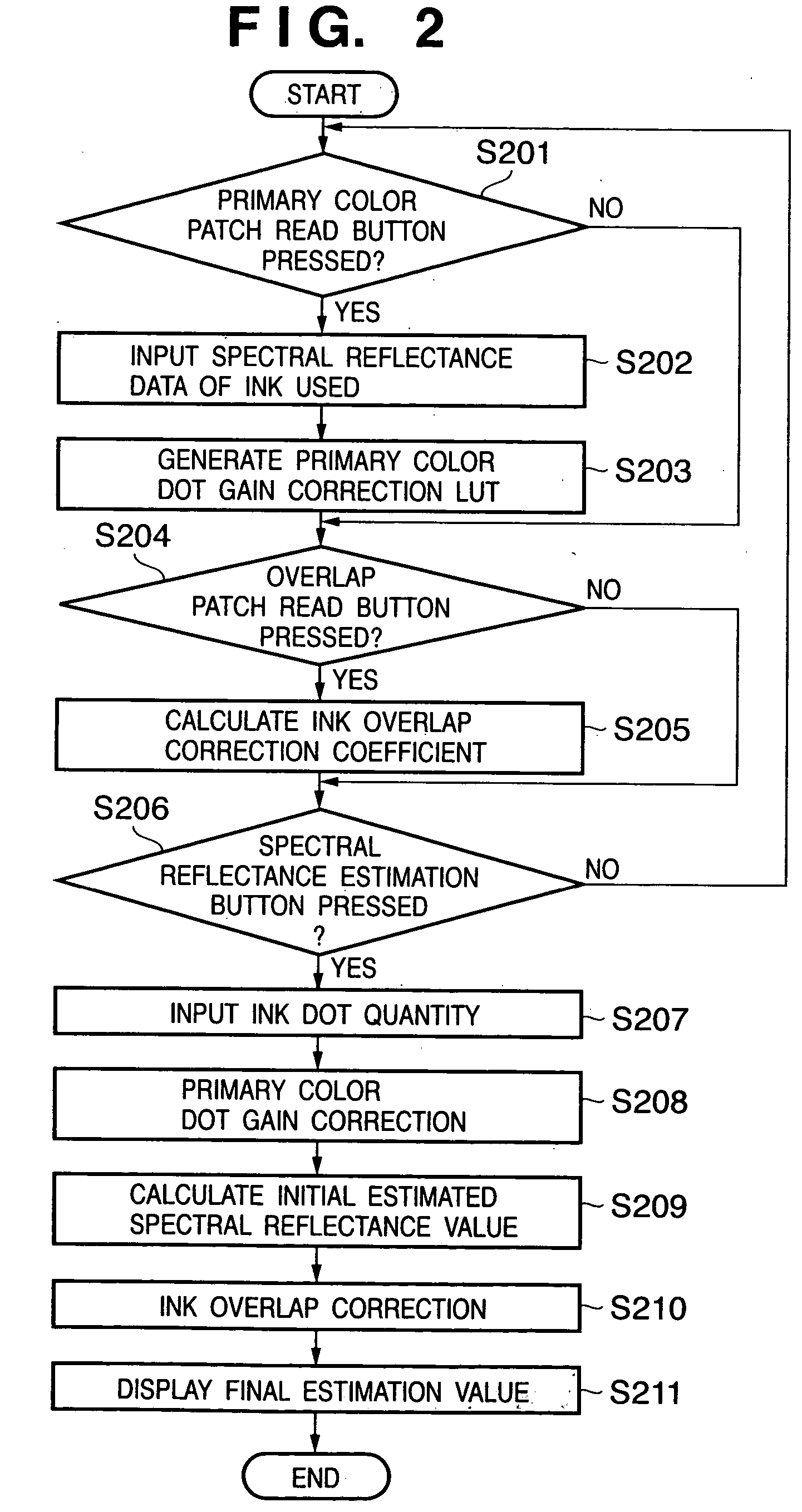
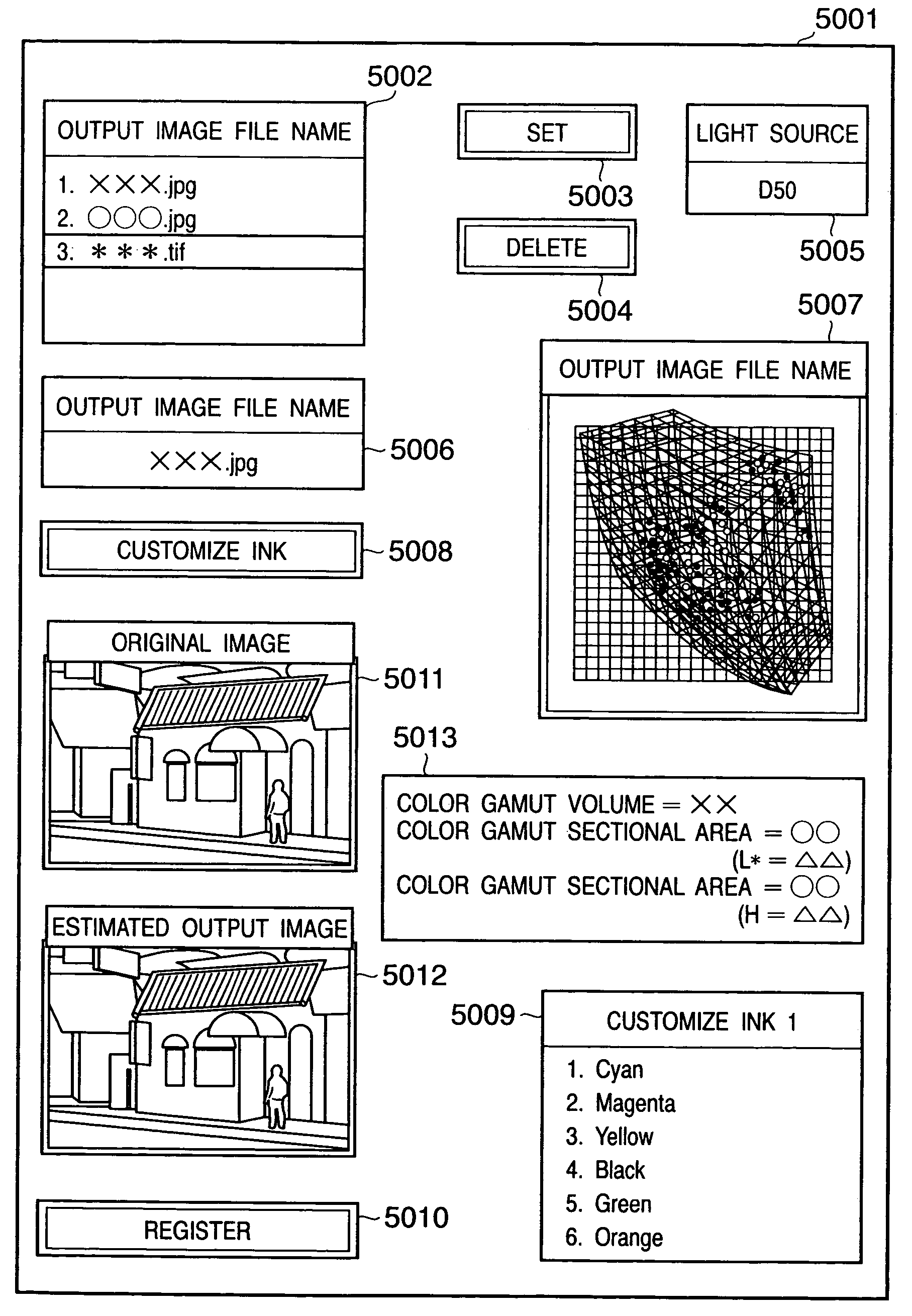
Reproduction color prediction apparatus and method
InactiveUS20050083346A1Improve accuracyAvoid difficult choicesDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsPattern recognitionDot gain
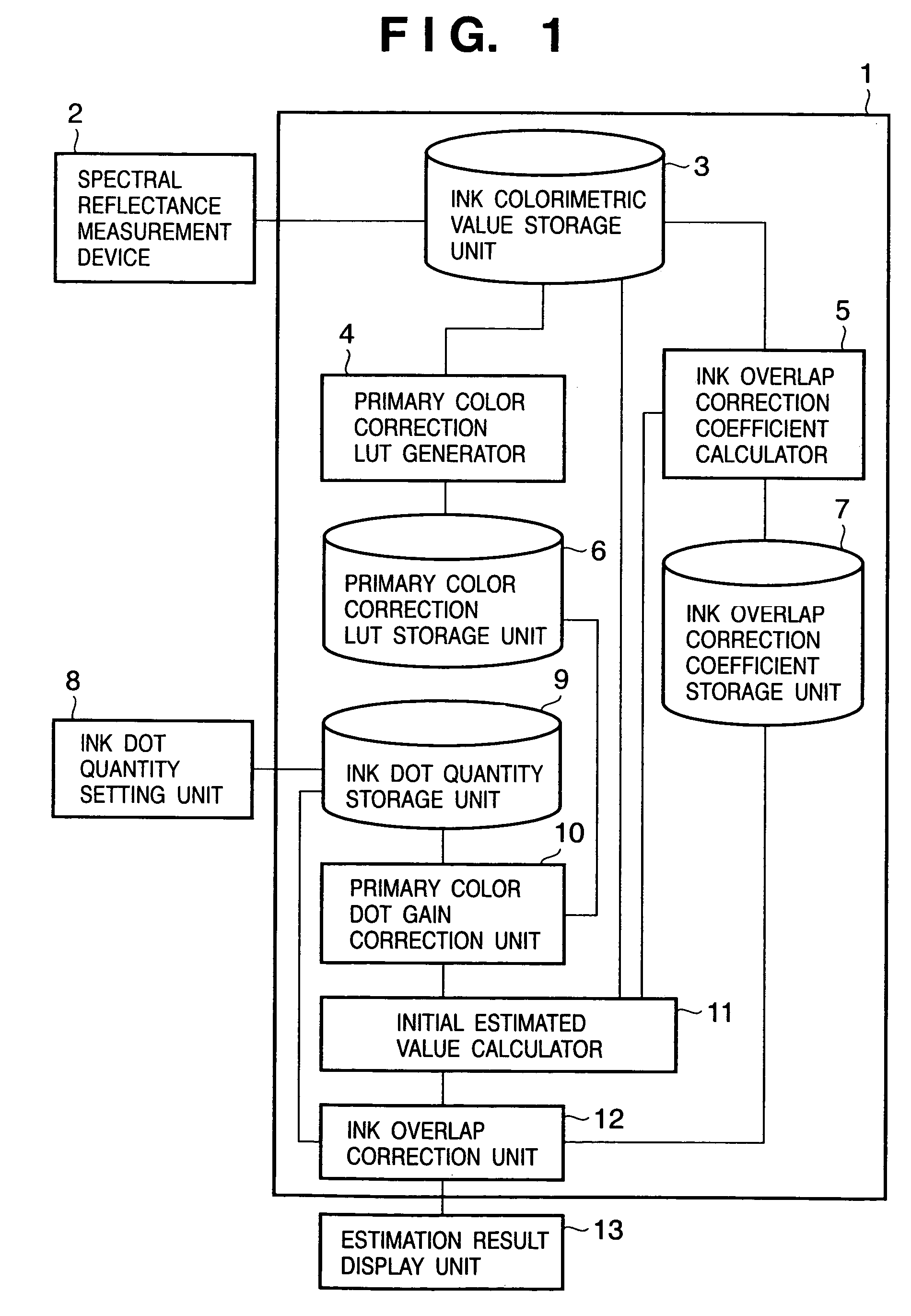
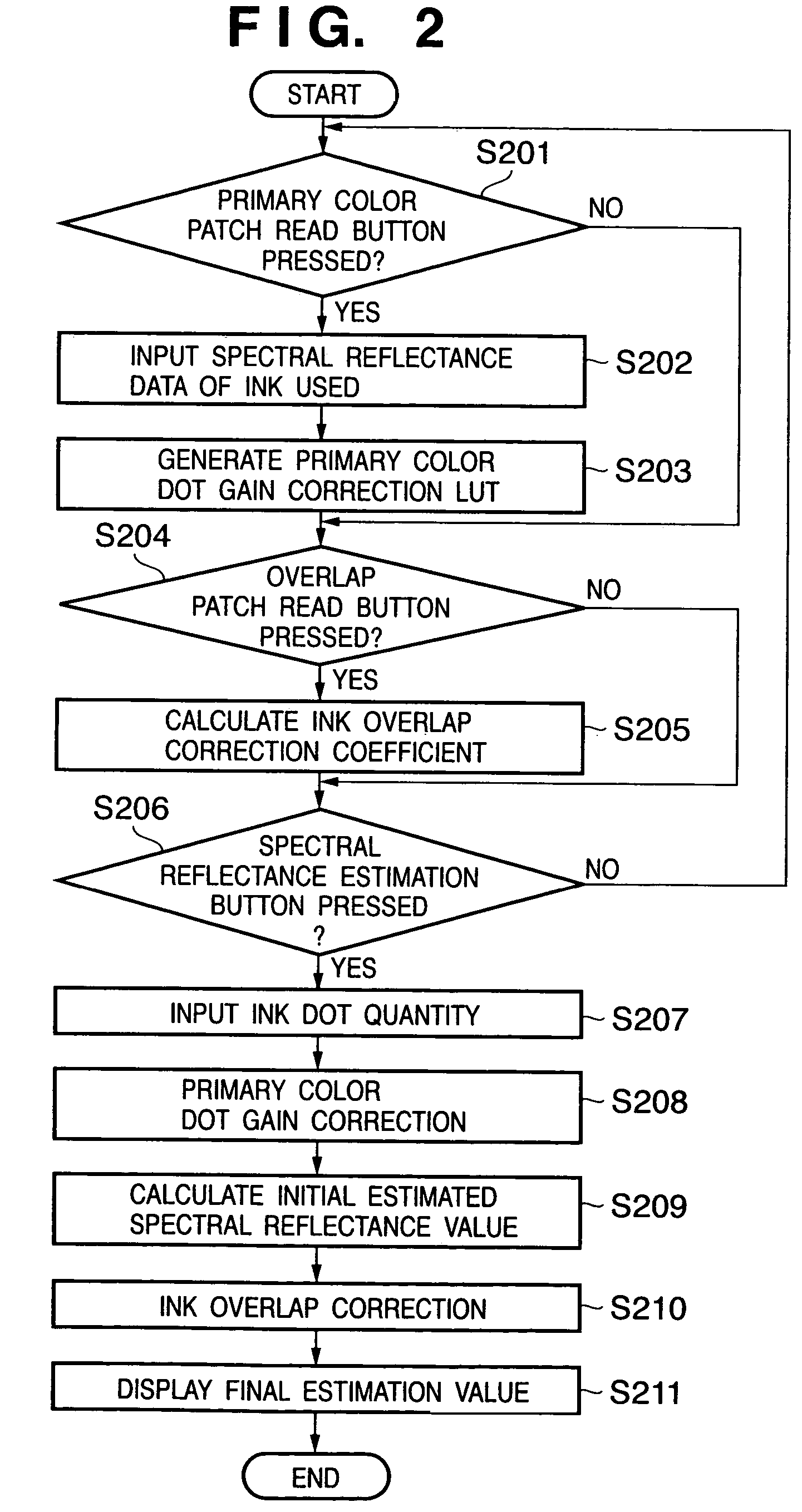
A primary color dot gain correction unit corrects the spectral reflectance of each of a plurality of color agents on the basis of the dot quantity set for each color agent. An initial estimated value calculator estimates a mixed color by the KM theory using spectral reflectance data corrected by the primary color dot gain correction unit. An ink overlap correction coefficient storage unit stores correction coefficients, which are determined on the basis of errors between the actually measured values of spectral reflectance data of color patches obtained using the plurality of color agents, and estimated values estimated by the initial estimated value calculator based on the dot quantities of the respective color agents on the color patches. An ink overlap correction unit obtains the prediction result of a reproduction color by correcting the spectral reflectance data of the mixed color calculated by the initial estimated value calculator on the basis of the correction coefficients stored in the ink overlap correction coefficient storage unit.
Owner:CANON KK
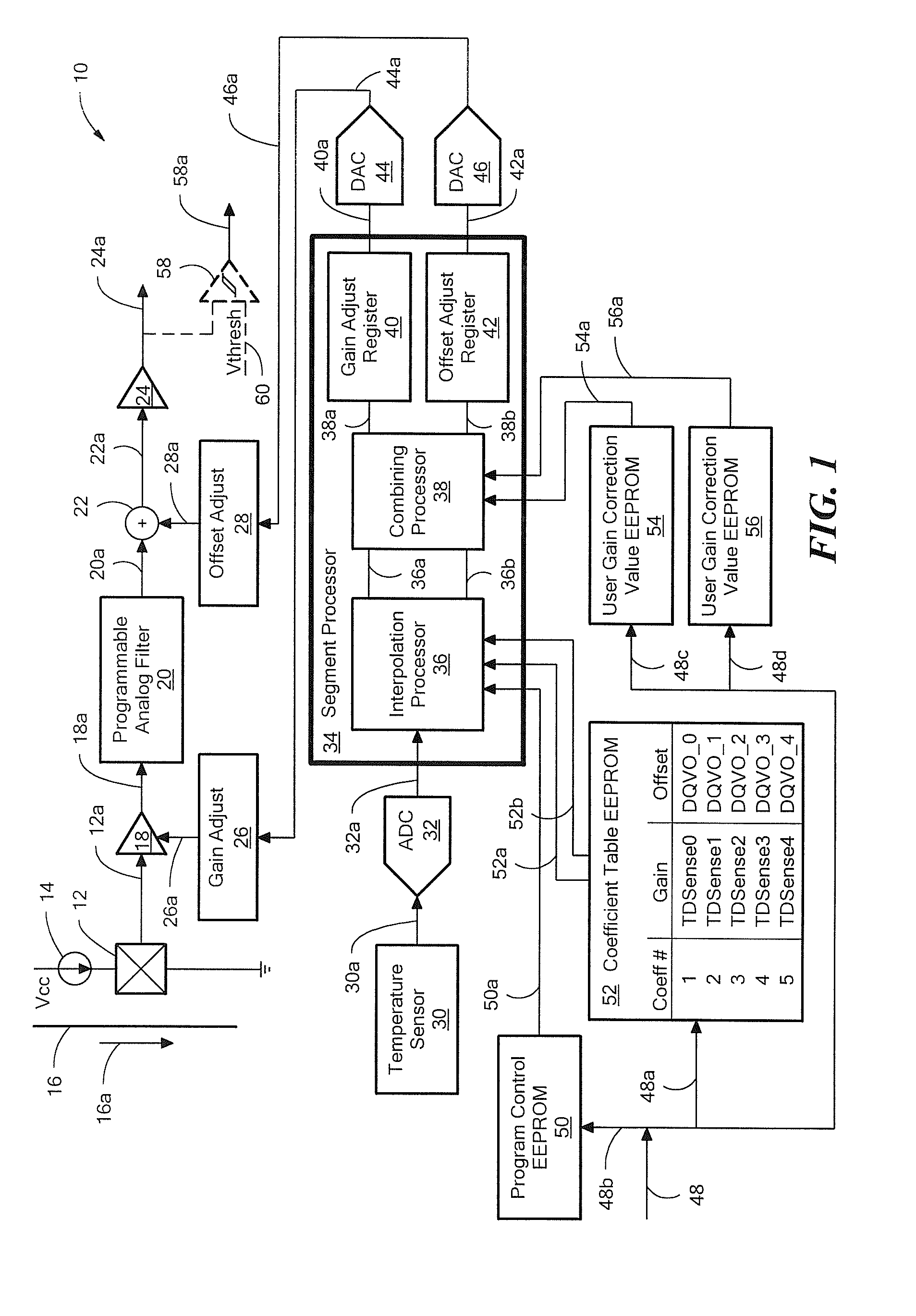
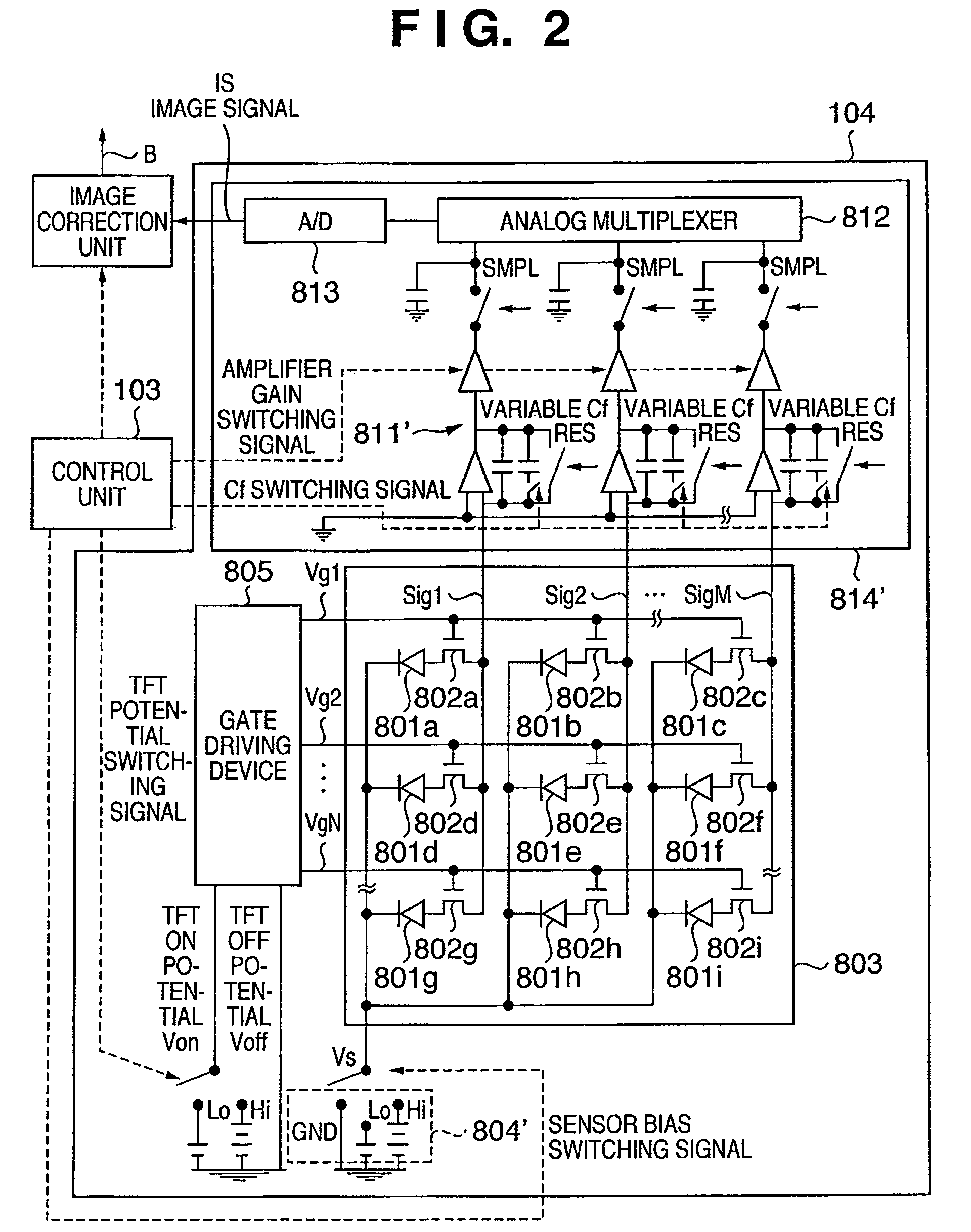
Radiation imaging apparatus, radiation imaging system, and correction method
ActiveUS20070131843A1Accurate signalEliminate the effects ofTelevision system detailsPhotometry using reference valueRadiation imagingRadiography
The invention intends to be able to adequately perform a gain correction. Hence, at the time of radiographing an object, a gain correction of the object image is performed based on a gain correction image (XRc1) derived by performing a light reset. On the other hand, at the time of radiographing an object, when a light reset is not performed, a gain correction of the object image is performed based on a gain correction image (XRc2) derived without performing the light reset.
Owner:CANON KK
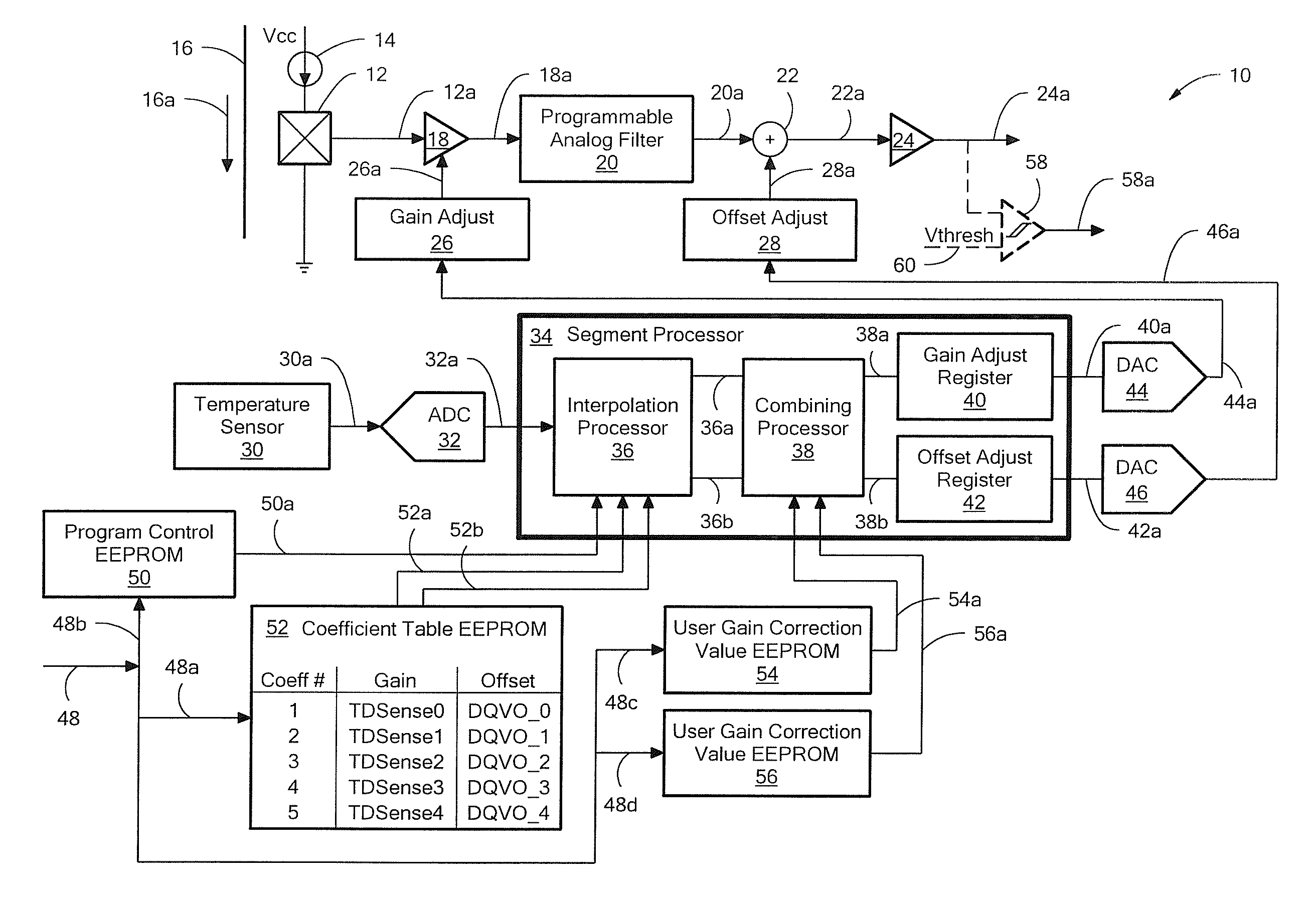
Magnetic Field Sensor and Method Used in a Magnetic Field Sensor that Adjusts a Sensitivity and/or an Offset Over Temperature
ActiveUS20120086442A1Fast response timeAchieves offset accuracyElectrical measurementsMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsAnalog signalCondensed matter physics
A magnetic field sensor and a method associated with the magnetic field sensor provide gain correction coefficients and / or offset correction coefficients stored in the magnetic field sensor in digital form. The gain correction coefficients and / or offset correction coefficients can be used to generate analog control signals to control a sensitivity and / or an offset of an analog signal path through the magnetic field sensor.
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
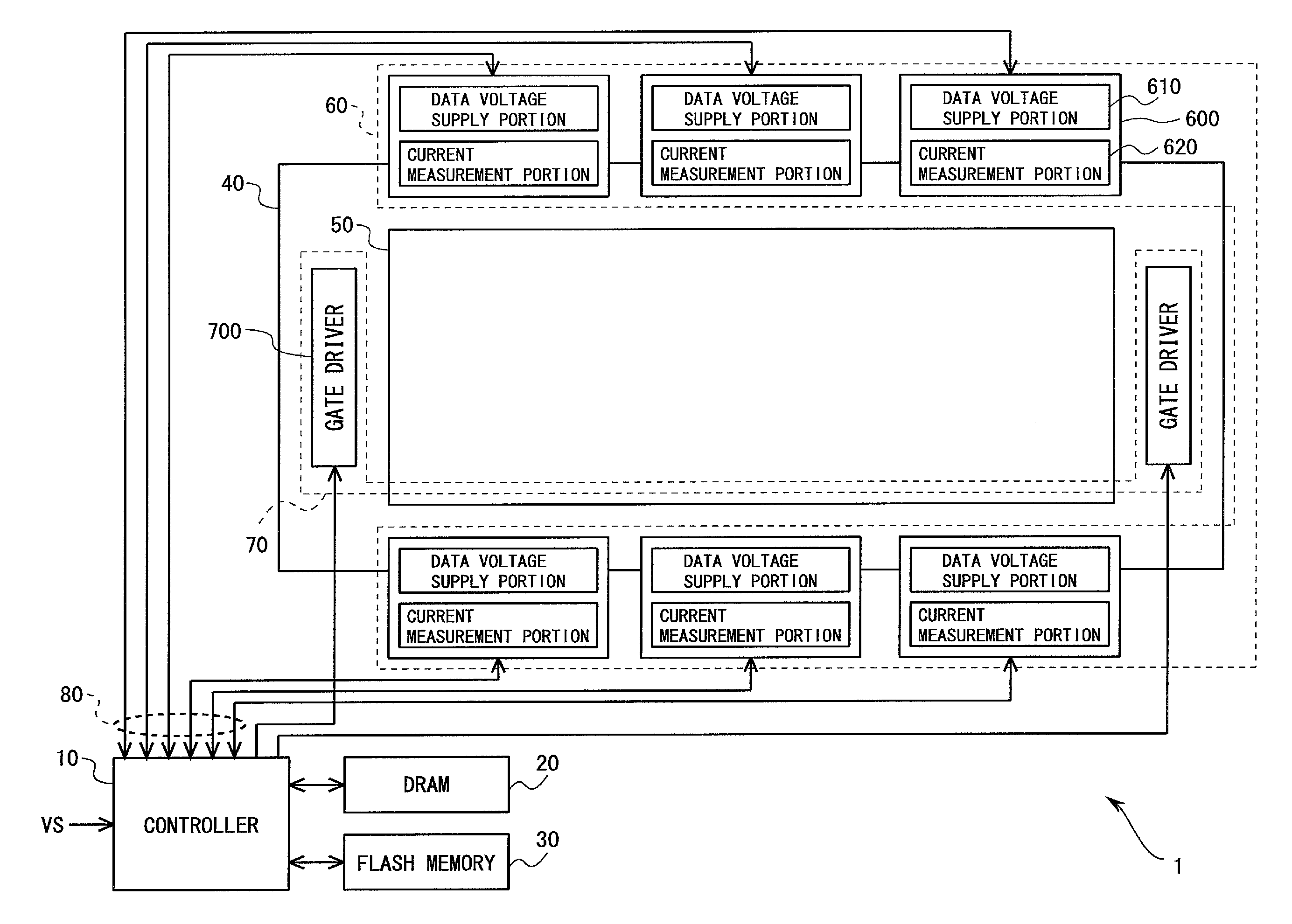
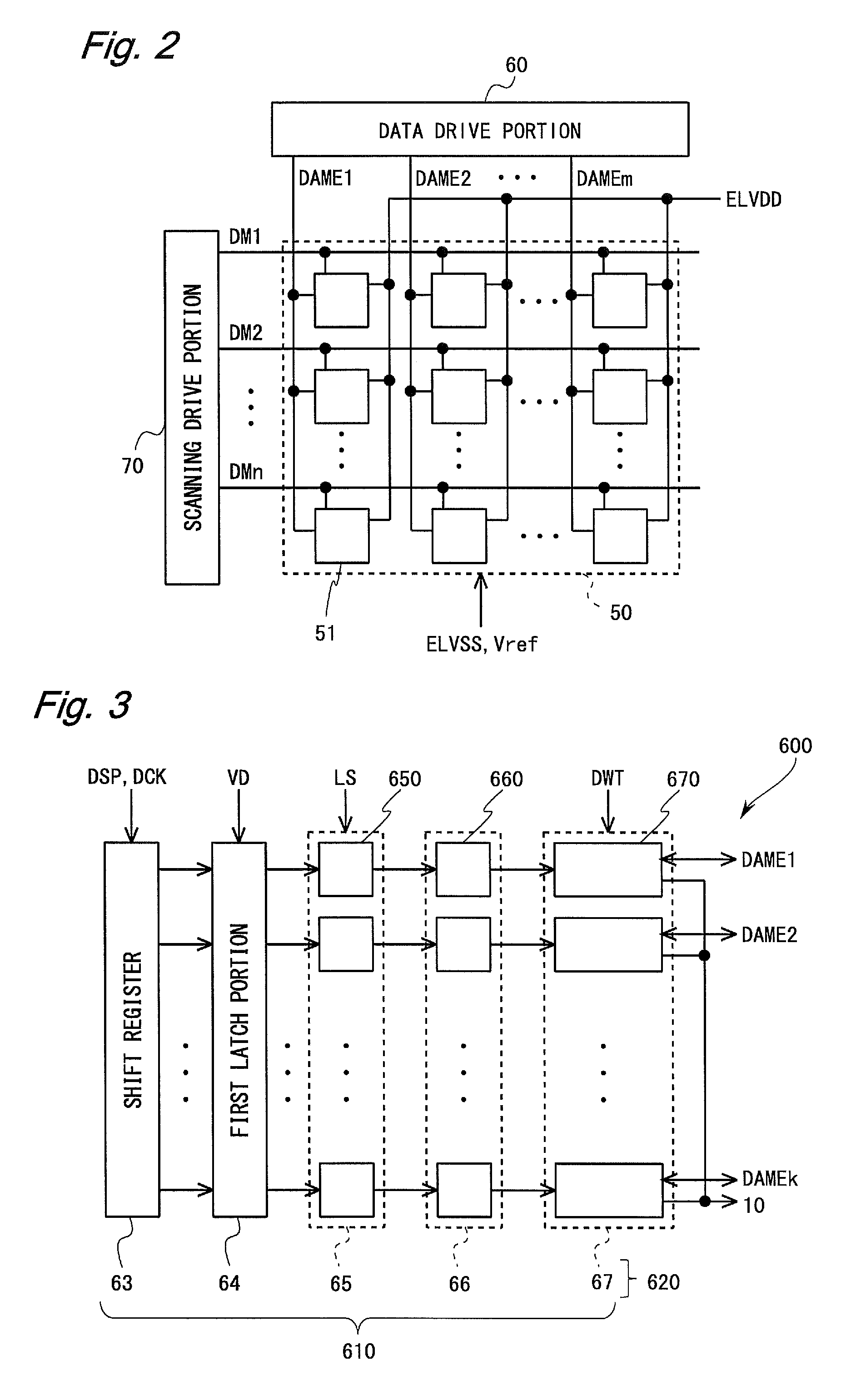
Display device and method for driving the same
ActiveUS20150213757A1Large control voltageImprove performanceCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingData controlDisplay device
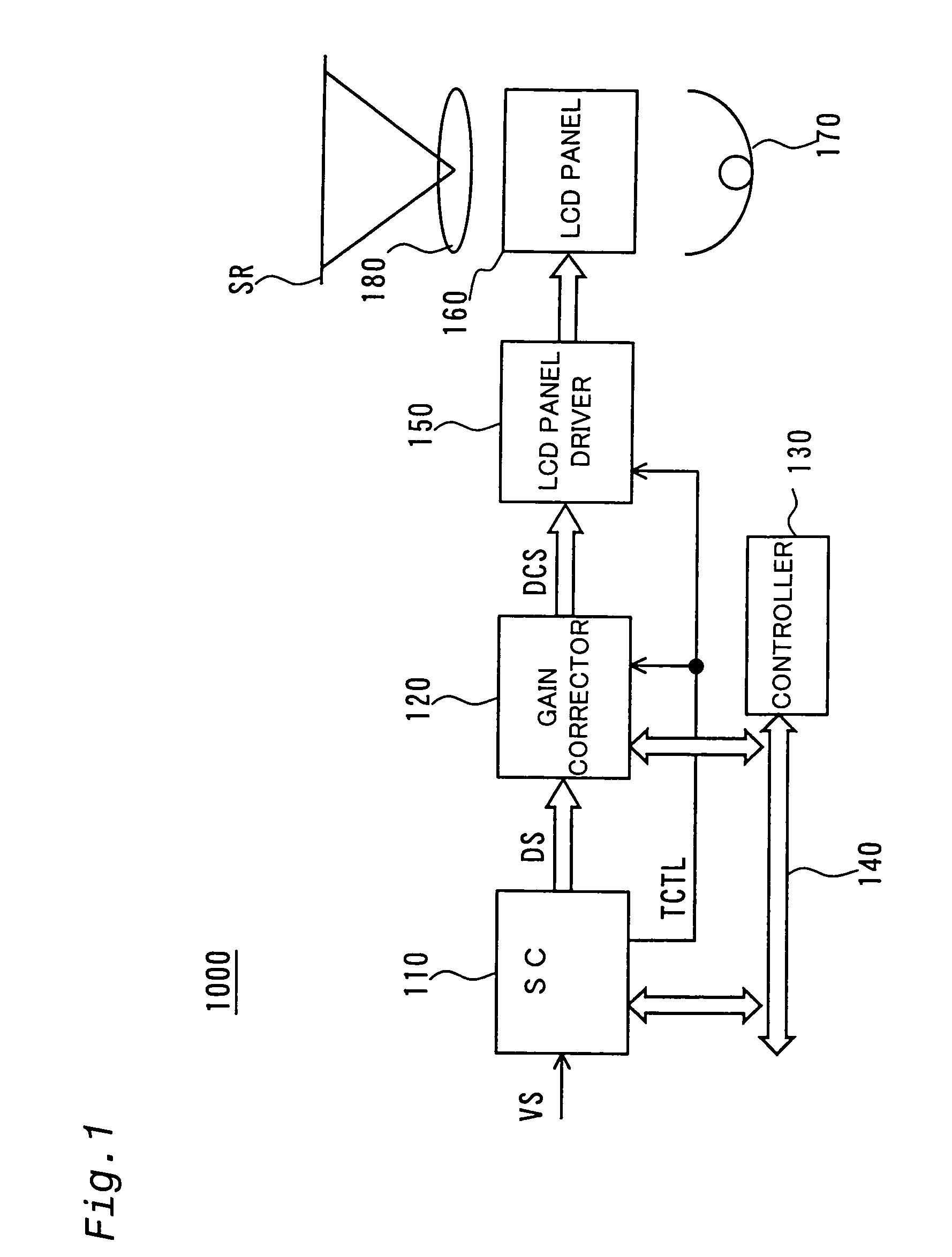
An organic EL display device includes a controller, a data driver, and a DRAM which provides a gain correction memory and a threshold voltage correction memory. The data driver sends, to the controller, first and second measurement data Im corresponding to the first and second measuring data voltages Vm, respectively. The controller compares ideal characteristic data IO(P) with the first and second measurement data Im, and updates threshold voltage correction data Vt and gain correction data B2R based on the comparison results. The controller corrects video data Vm based on the threshold voltage correction data Vt and the gain correction data B2R. Thereby, both threshold voltage compensation and gain compensation of a drive transistor are performed with respect to each pixel circuit, while display is performed.
Owner:SHARP KK
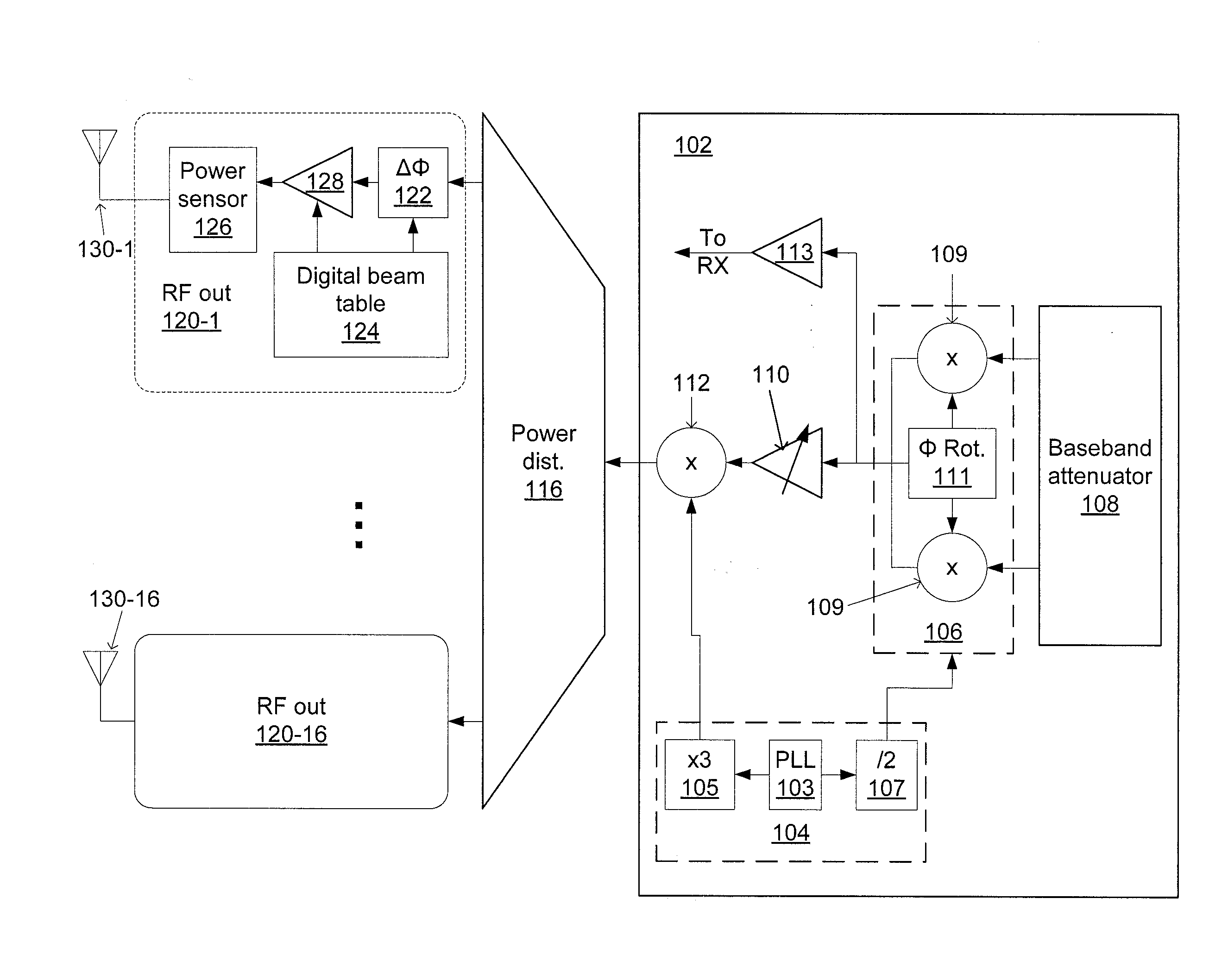
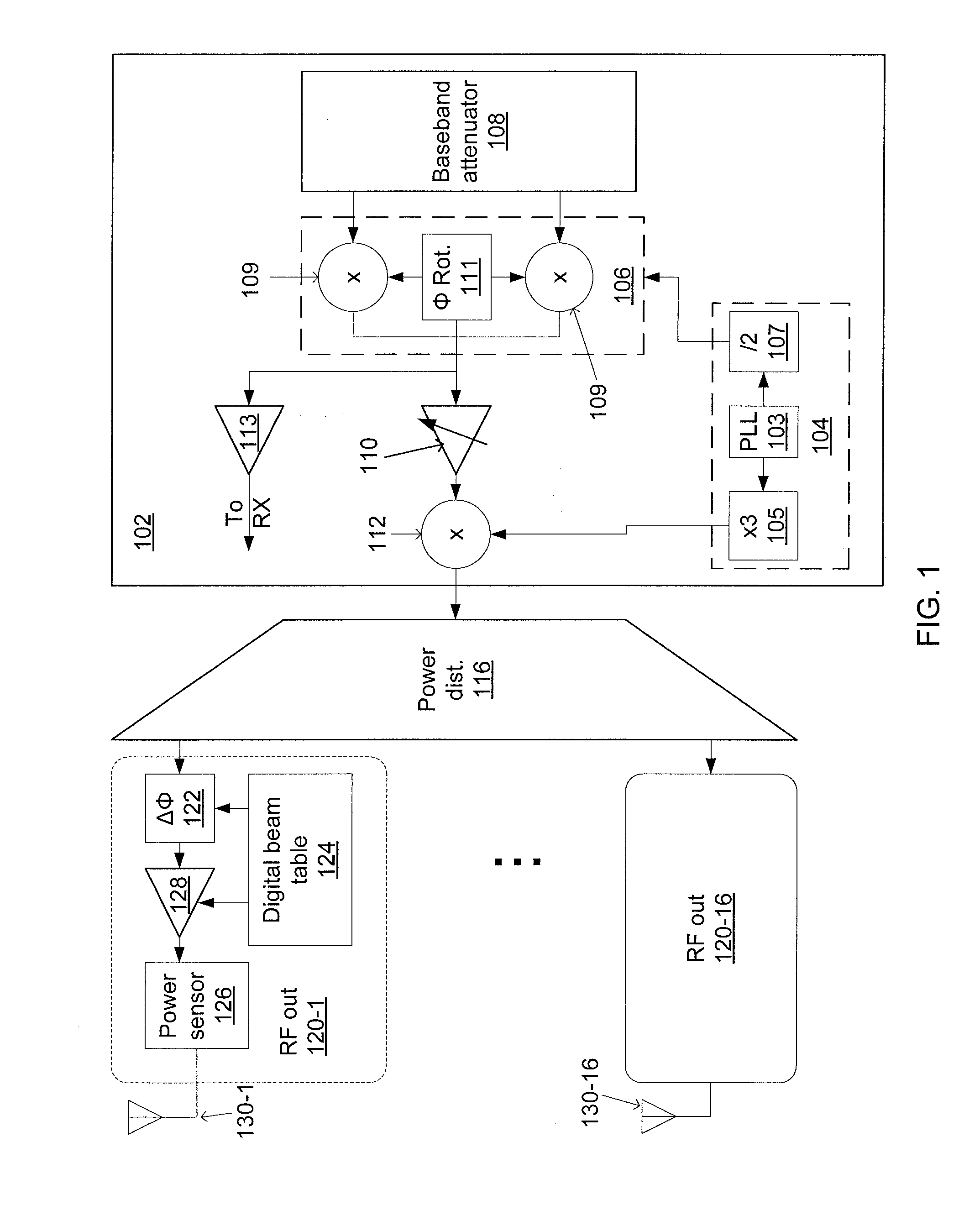
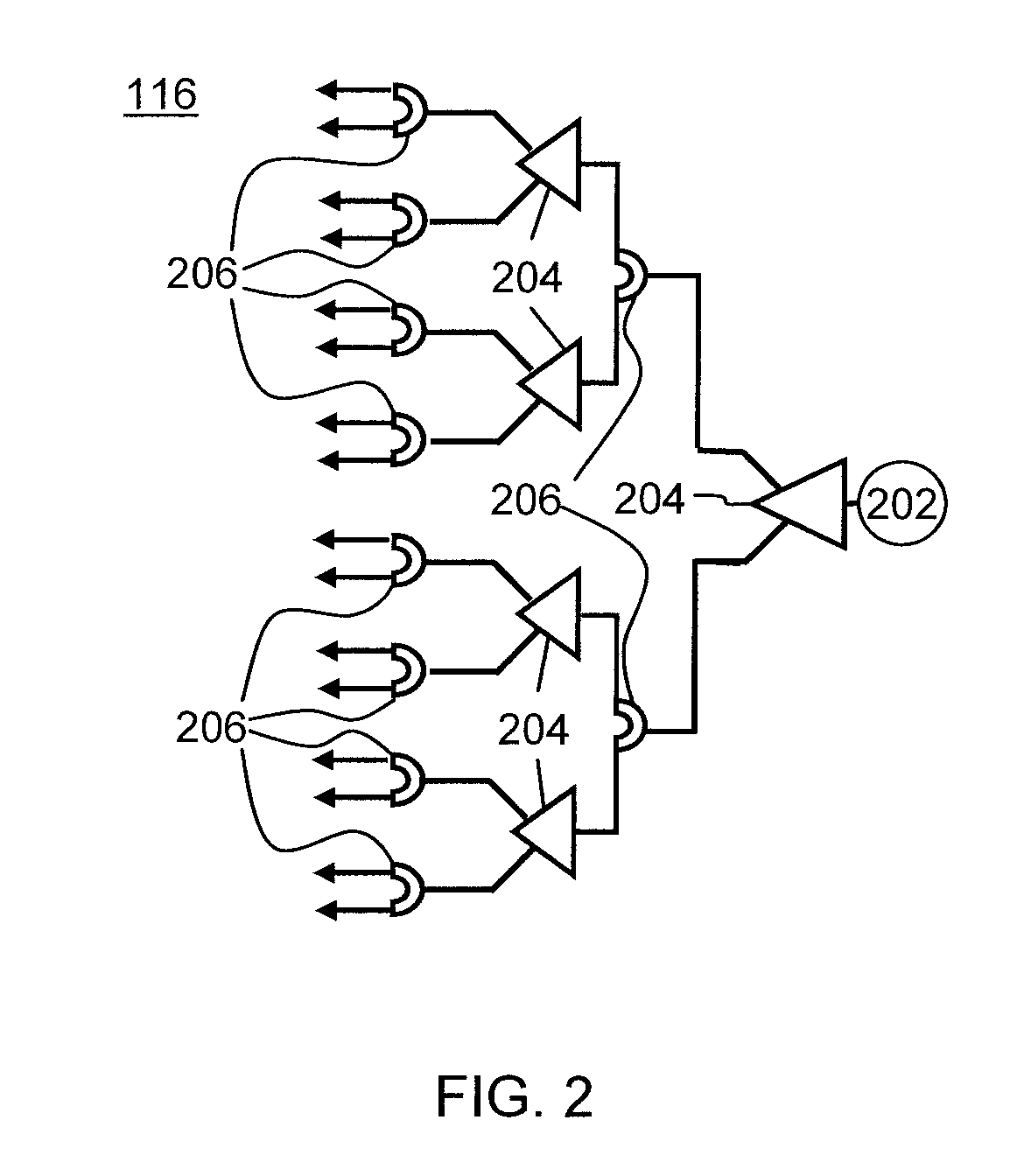
Phased-array transceiver for millimeter-wave frequencies
ActiveUS20110063169A1Wide power consumptionWide signal dynamic rangeAntennasTransceiverMillimetre wave
A phased-array transmitter and receiver that may be effectively implemented on a silicon substrate. The transmitter distributes to front-ends, and the receiver combines signals from front-ends, using a power distribution / combination tree that employs both passive and active elements. By monitoring the power inputs and outputs, a digital control is able to rapidly provide phase and gain correction information to the front-ends. Such a transmitter / receiver includes a plurality of radio frequency (RF) front-ends and a power splitting / combining network that includes active and passive components configured to distribute signals to / from the front-ends.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
Image processing circuit and method for processing image
ActiveUS6965416B2Reduce contrastIncrease the compression ratioImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImaging processingStill camera
The present invention relates to an image processing circuit and an image processing method, and is applied to, for example, a video camera, an electronic still camera and the like, for compressing the dynamic range at a high compression rate with evading the lowering of an impression concerning the contrast and the unnatural edge emphasis. The present invention smoothes an input image X while preserving the edge to obtain a gain correction coefficient, and corrects the pixel value x(i, j) of the input image X with the gain correction coefficient.
Owner:SONY CORP
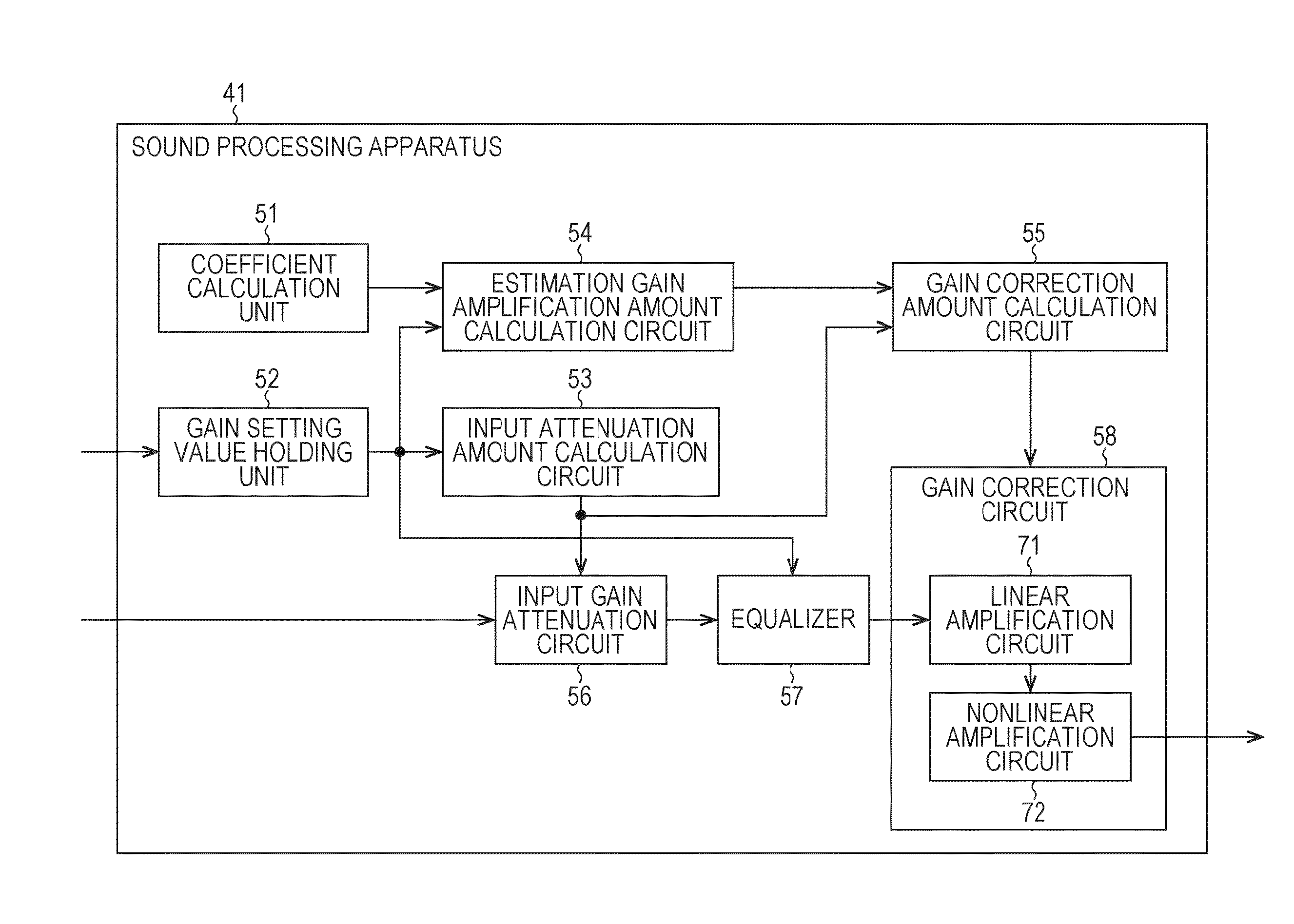
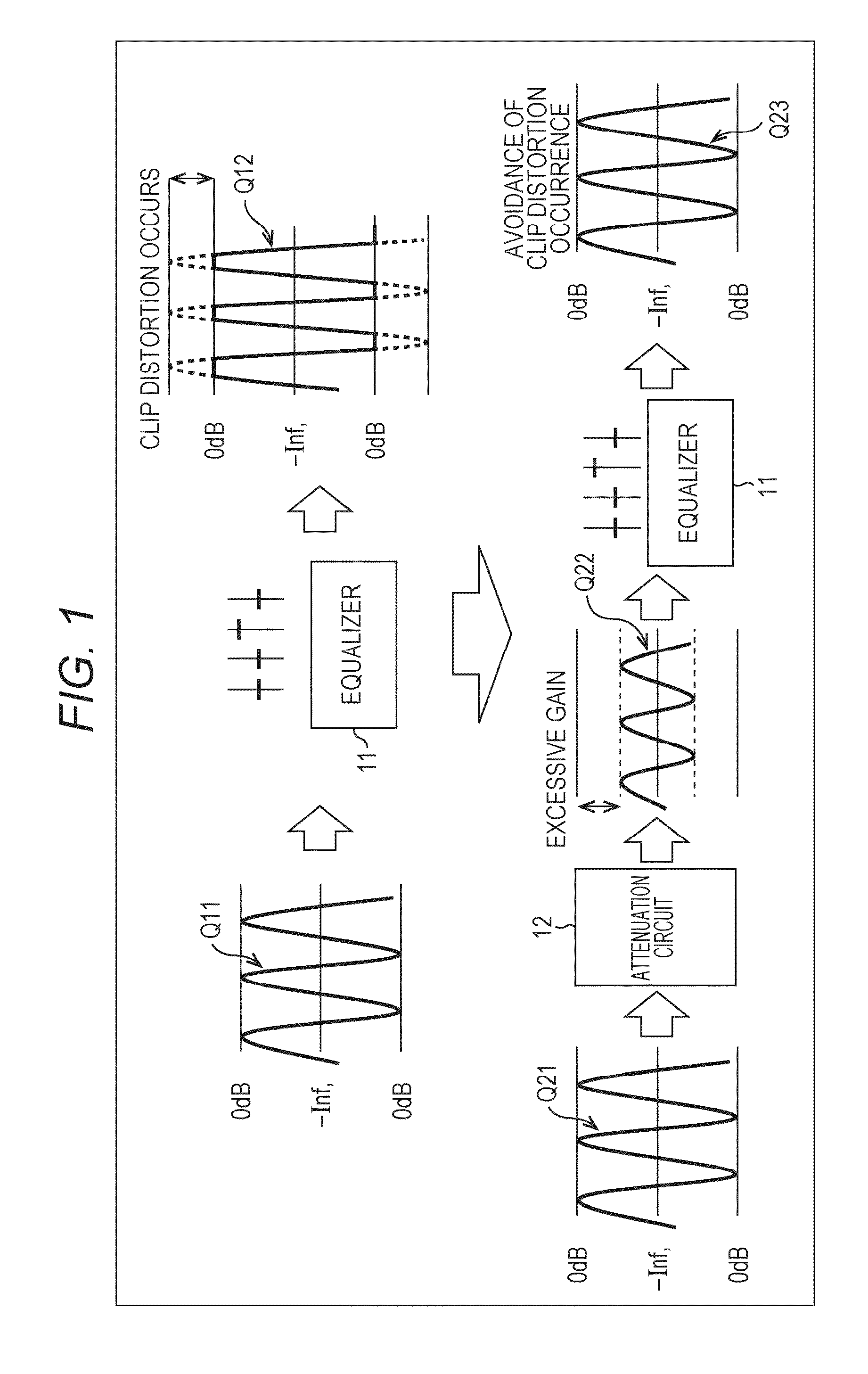
Sound processing apparatus, method, and program
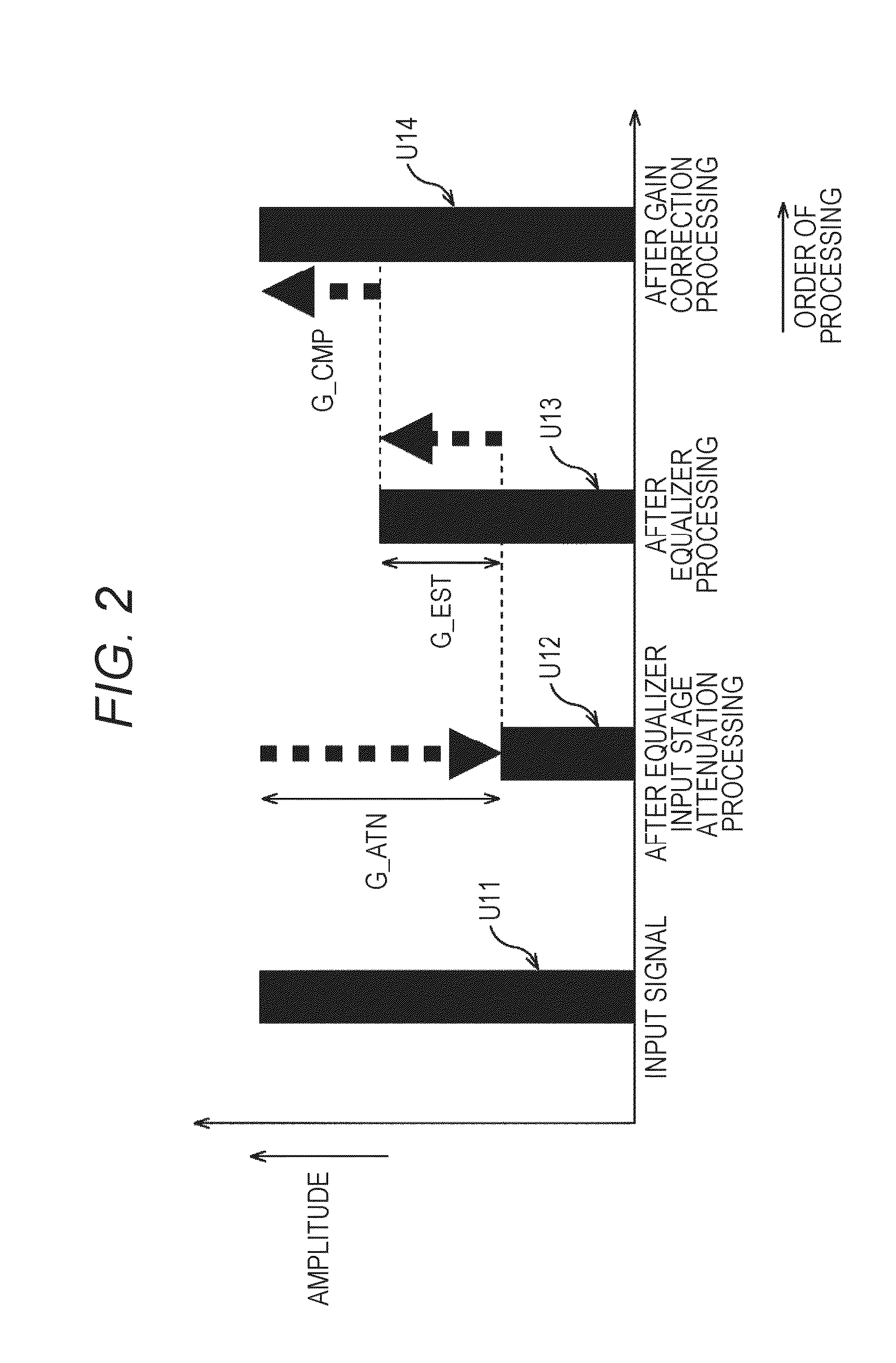
ActiveUS9294062B2Reduce quality degradationQuality improvementAnalog signal digital controlAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlUltrasound attenuationWeight coefficient
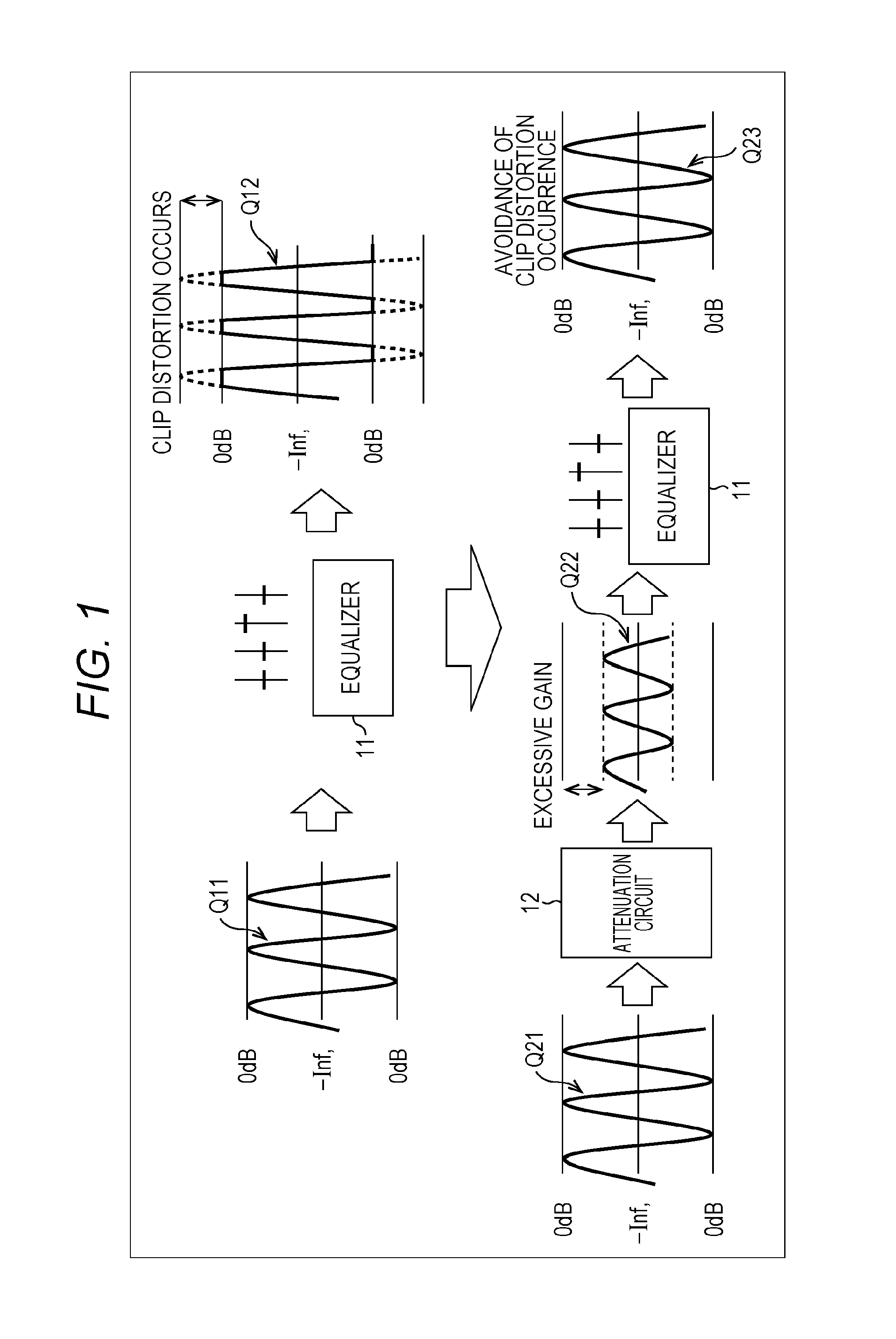
The present technique relates to a sound processing apparatus, a method, and a program capable of alleviating degradation of the quality of sound in a case where the gain of a sound signal is amplified.When equalizer processing for adjusting the gain of each frequency band of an input signal on the basis of a gain setting value is performed, an input signal is attenuated by an input attenuation amount derived from the gain setting value, and the equalizer processing is performed on the input signal attenuated. The amount of amplification of the gain of the input signal in the equalizer processing is estimated on the basis of the gain setting value and a weight coefficient of each frequency band derived from a generally-available music signal prepared in advance, and a difference of the estimation value and the input attenuation amount is calculated as a gain correction amount. Further, nonlinear amplification processing is performed on the input signal so as to actually amplify the input signal, which has been subjected to the equalizer processing, by a gain correction amount, and an output signal is obtained. The present technique can be applied to a sound processing apparatus.
Owner:SONY CORP
Apparatus and method for improving dynamic range in a receiver
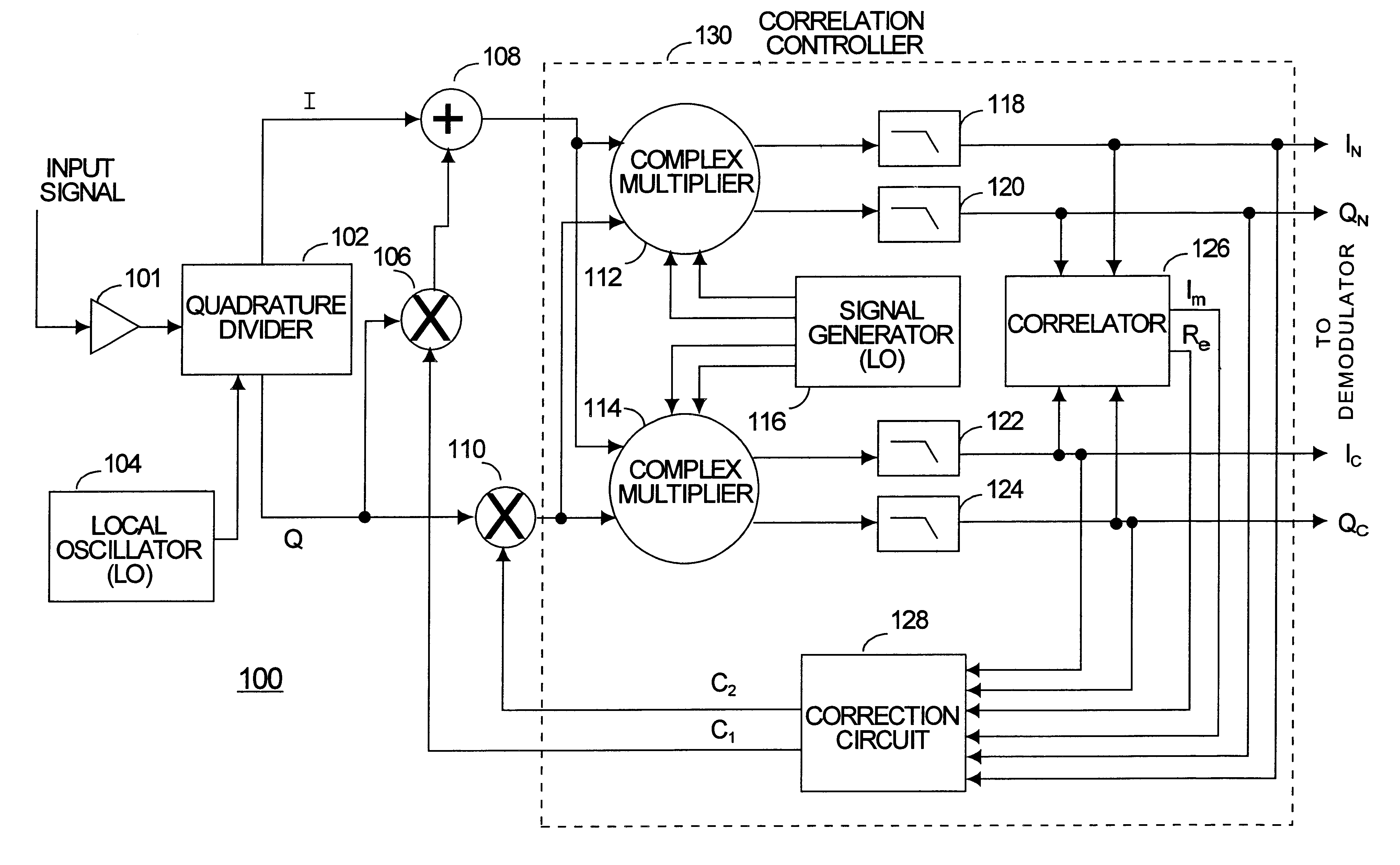
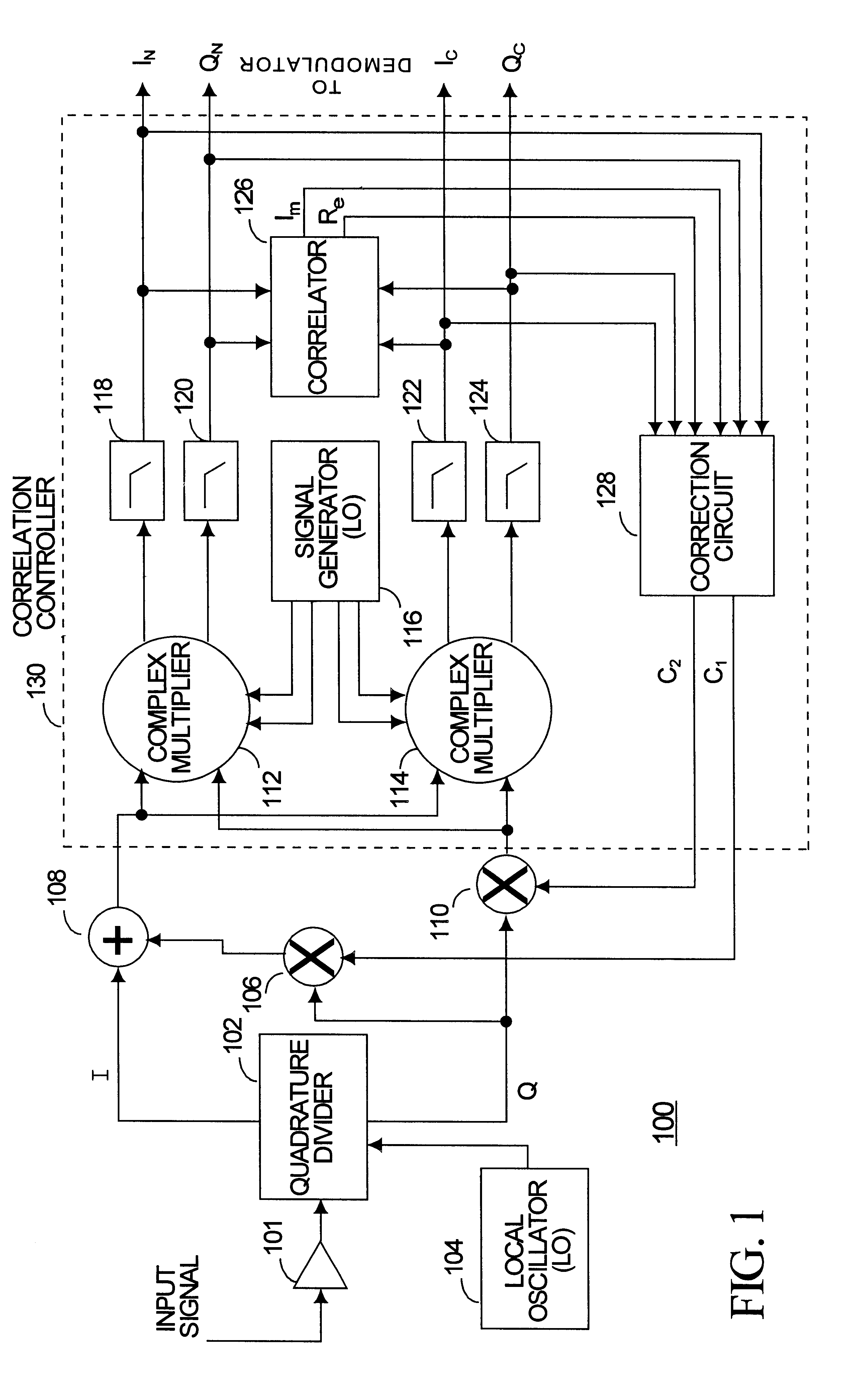
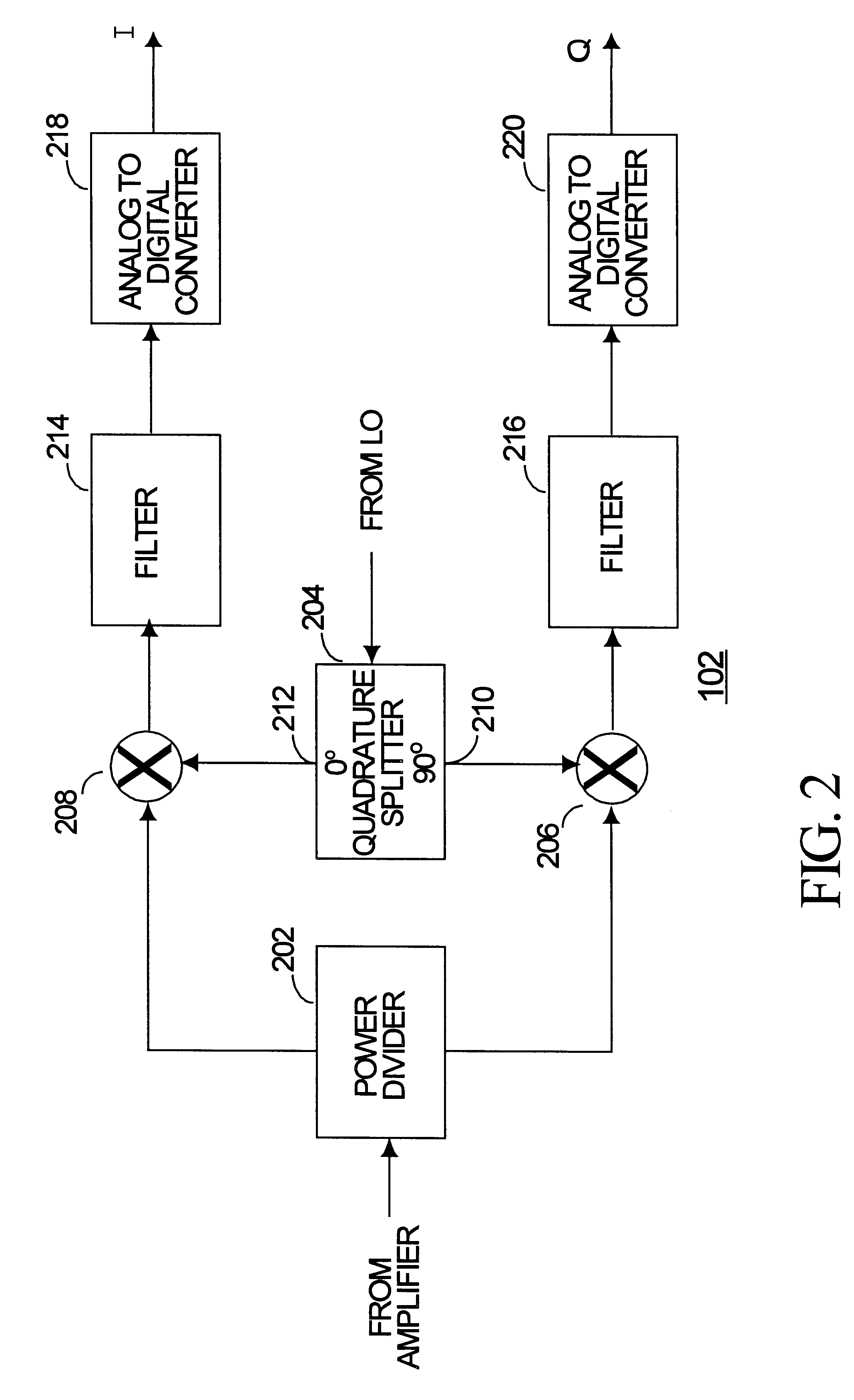
InactiveUS6289048B1Multiple-port networksWave based measurement systemsPhase correctionIntermediate frequency
Phase errors and gain errors are reduced in a receiver to increase the dynamic range of the receiver. An input signal is shifted to an intermediate frequency (IF) and divided into a first channel and a second channel. The first and second channels are multiplied by a complex intermediate frequency signal having a frequency equal to the negative of the IF and by the complex conjugate of the intermediate frequency signal to produce a complex normal signal and a complex conjugate signal. A gain correction factor and a phase correction factor are adjusted based on a correlation signal produced by multiplying the complex normal signal by the complex correlation signal.
Owner:CUBIC COMM
Display uniformity calibration system and method for a staring forward looking infrared sensor
InactiveUS20030183756A1Eliminate needHysteresis effectTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesHysteresisEngineering
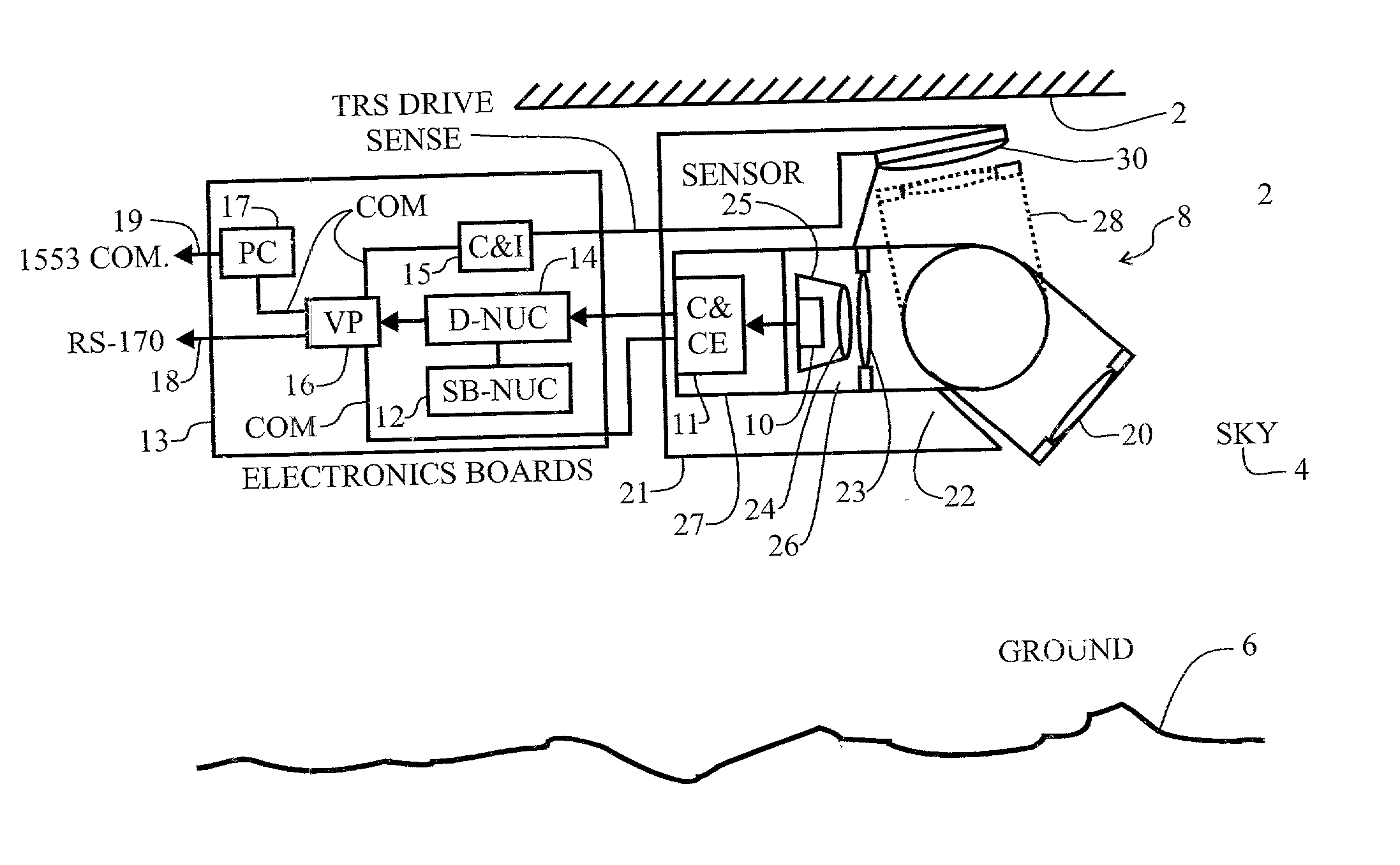
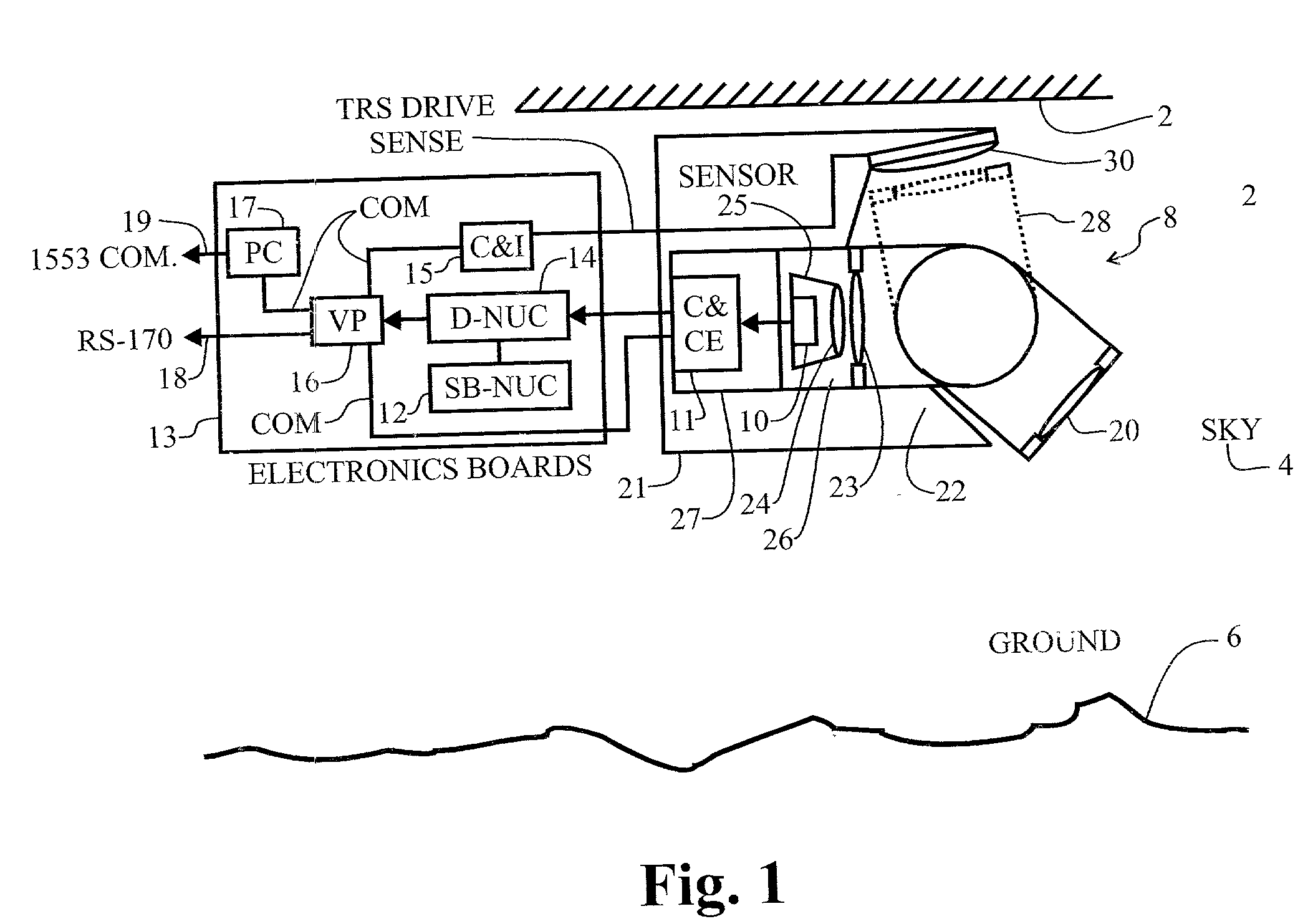
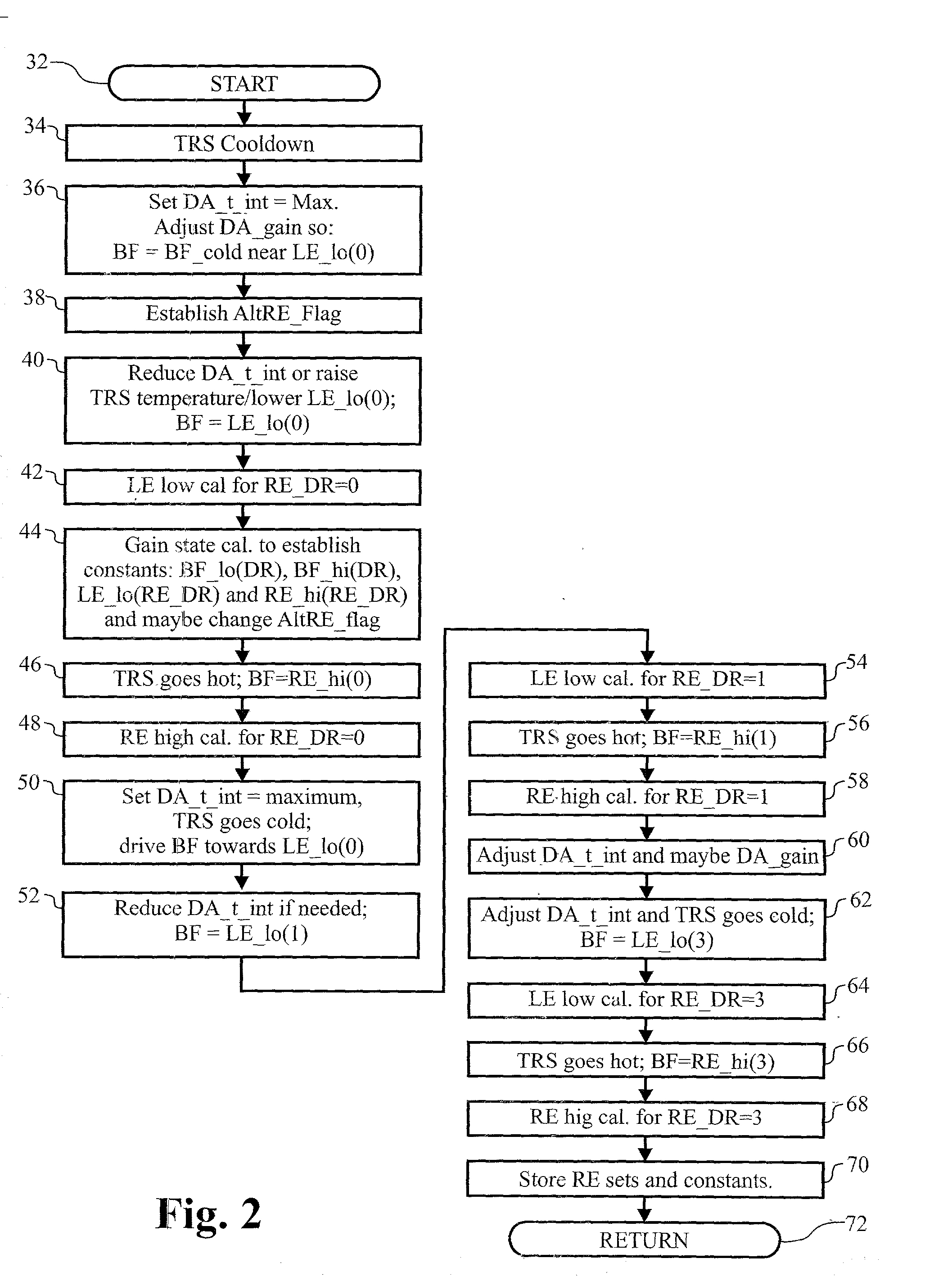
A method and system for maintaining uniformity in a FLIR display. During a one-time initialization procedure, a plurality of dynamic ranges are defined by covering a specific range of bucket fill levels when in a certain gain. To cover all dynamic ranges possible, a plurality of pairs of responsivity equalization (RE) calibrations (each pair producing a RE set of pixel gain corrections) are also accomplished in the same one time initialization period. A plurality of corresponding level equalization (LE) calibrations (each using the appropriate calibrated RE set and producing a LE set of pixel level corrections) for each anticipated dynamic range are made at every power-up initialization. Each of the calibrations is done with respect to a thermal reference source to produce a uniform scene at the desired bucket fill level. An algorithm is employed which forces the two bucket fill points defined during the responsivity calibration to span as far as possible the dynamic range and forces the level equalization bucket fill point to fall within the two bucket fill points of the responsivity calibration. Then, during an operational time period, the scene and optics temperatures are monitored, and if the average bucket fill value exceeds the bucket fill range of the present dynamic range, the presently selected dynamic range is changed to a second dynamic range (gain is changed along with the RE set and LE set). The dynamic ranges are designed to overlap so that a hysteresis effect is achieved. The pre-calibrations and automatic dynamic range switching prevent saturation and create the best uniformity (lowest fix pattern noise) possible while allowing for continuous operation of the FLIR system, thus eliminating the interruption caused by the prior art touch-up calibration procedure.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
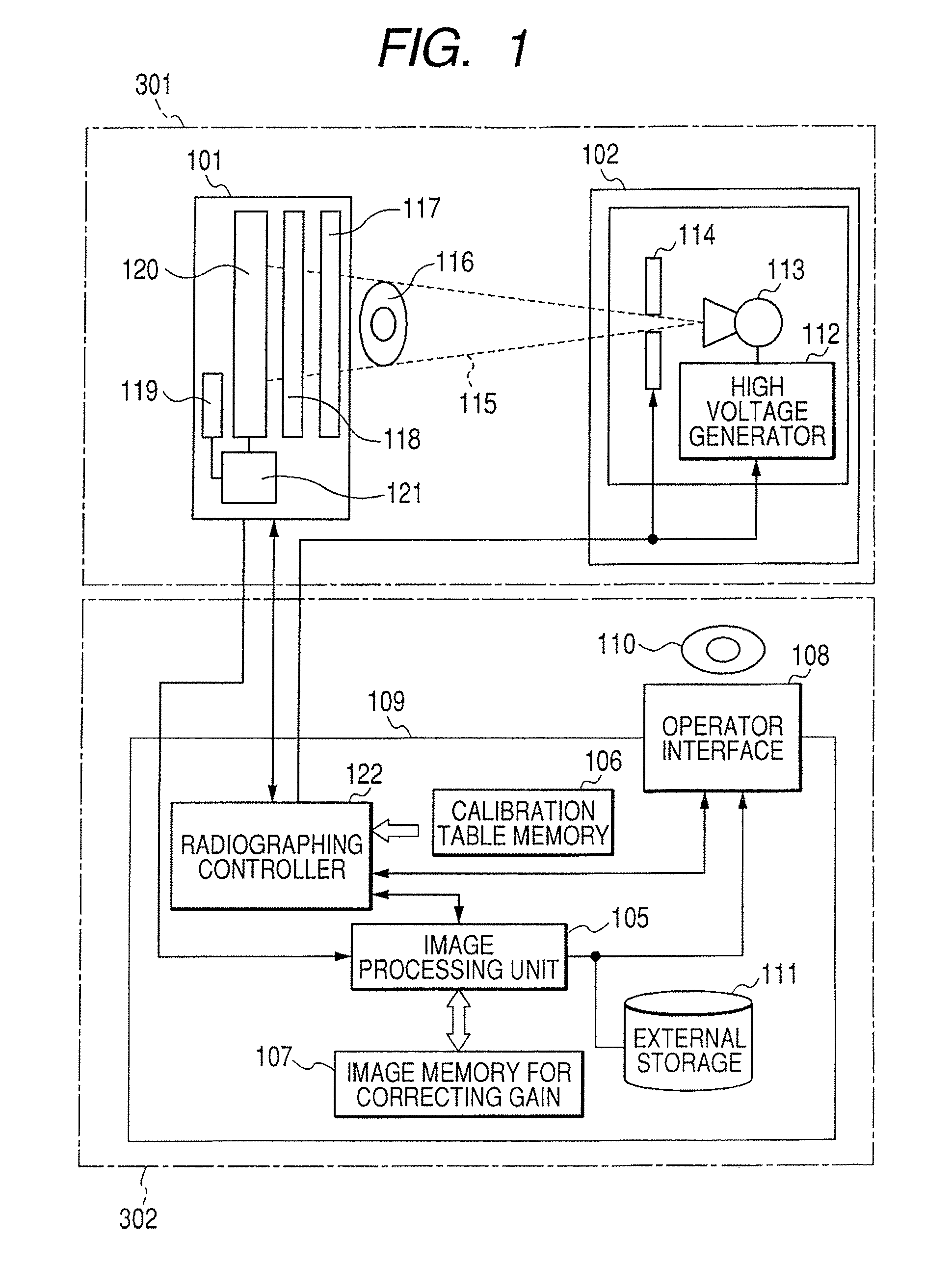
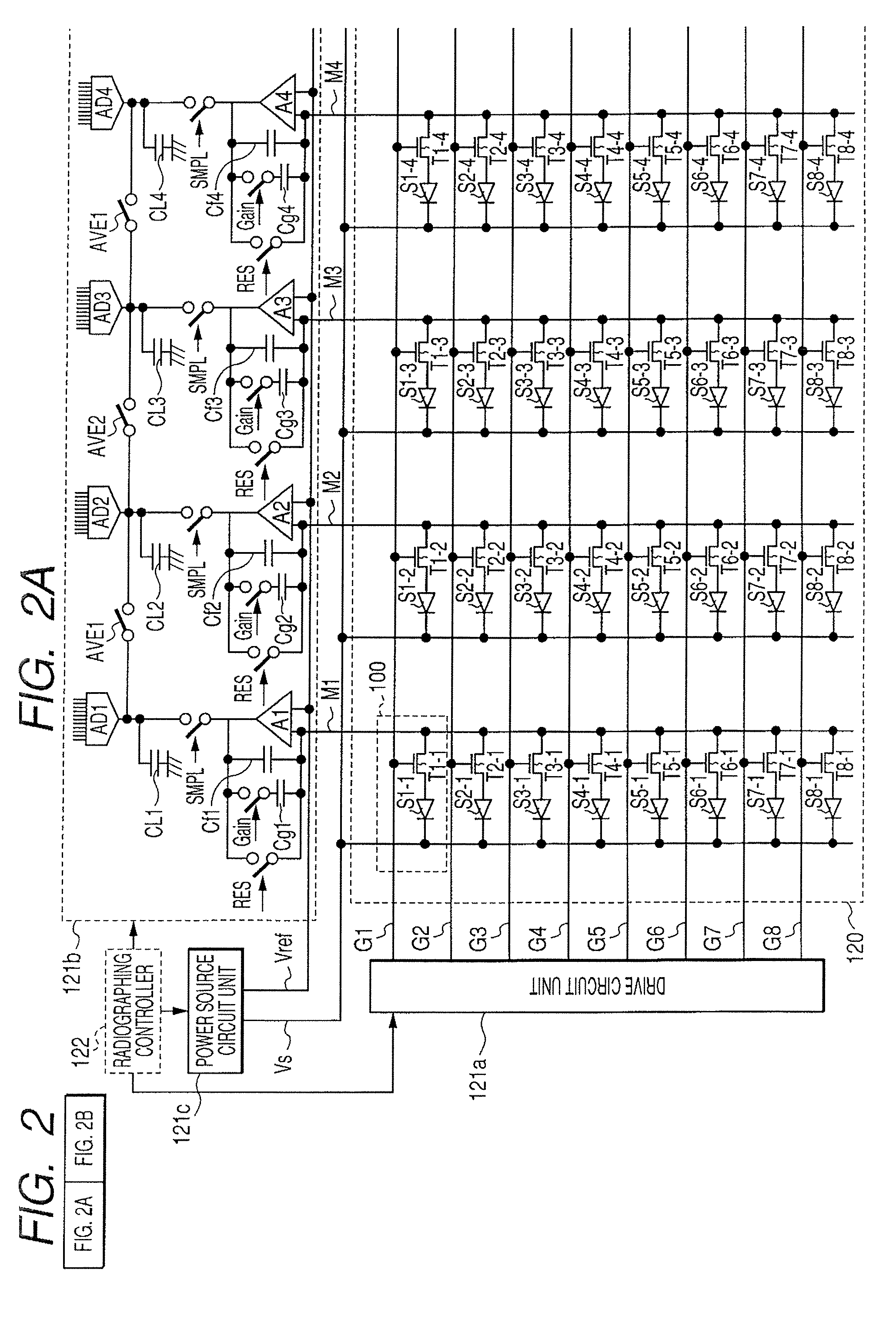
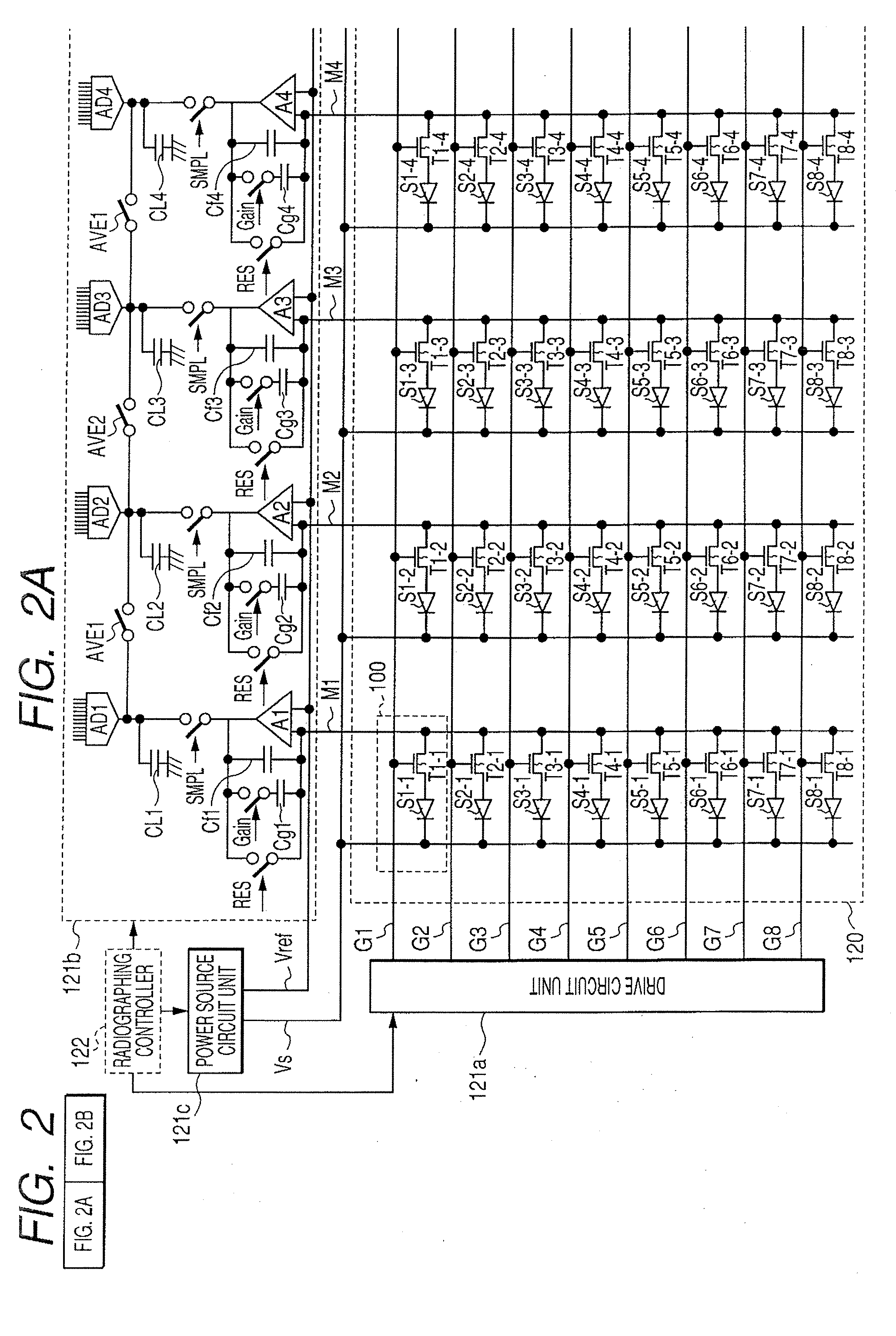
Radiation imaging system and driving method thereof
InactiveUS7476027B2Little noiseImprove signal-to-noise ratioX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationImaging processingRadiation imaging
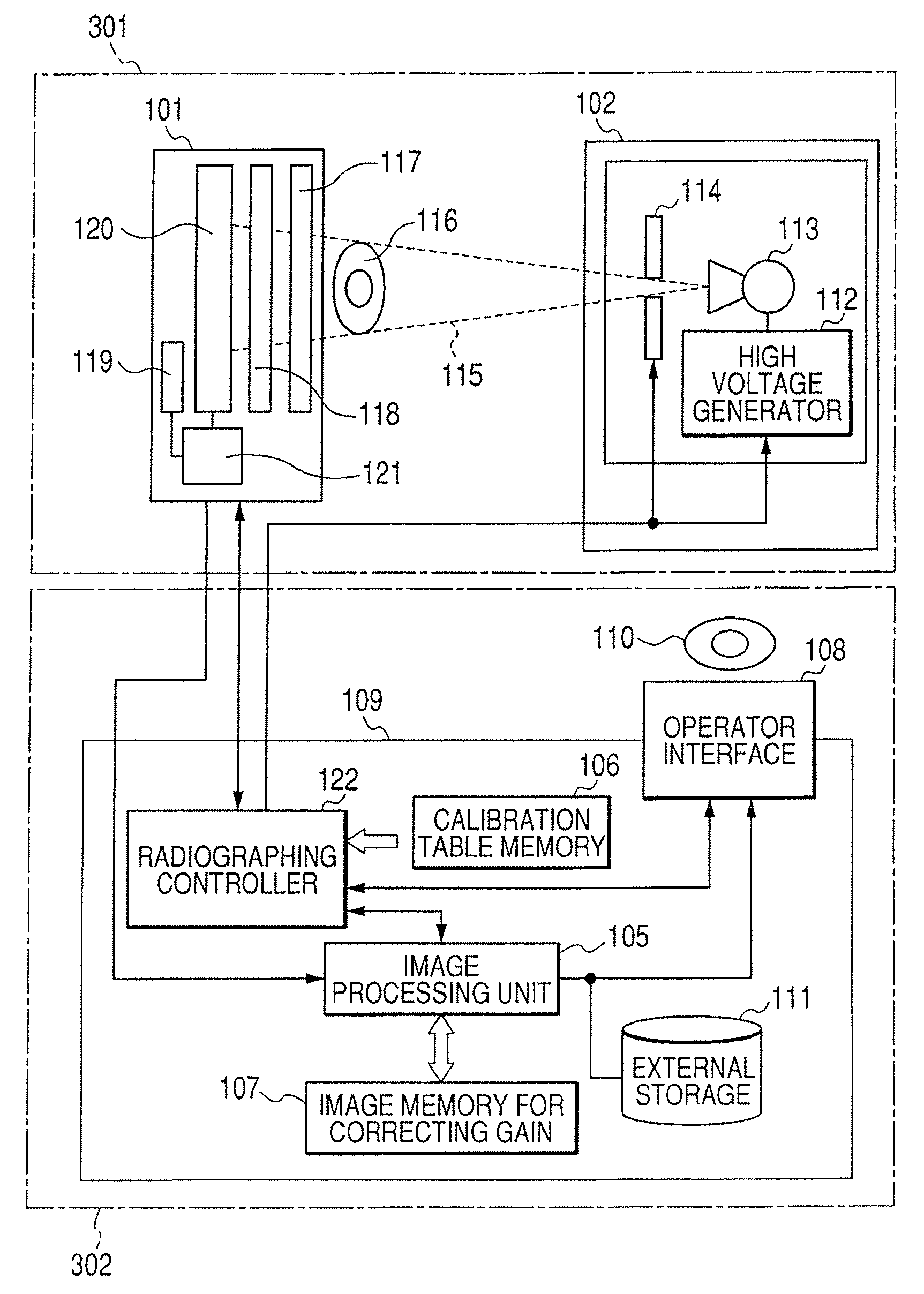
When a gain correction is performed for the radiographed object image, the acquisition of the object image having a high grade quality and no artifact is realized. For that purpose, an image storing unit is provided for storing an image for correction radiographed based on conditions set with the table in a state in which no object exists to each operation modes of the plurality of operation modes; and an image processing unit is provided for performing a gain correction processing of the radiographed object image and performs the gain correction processing of the radiographed object image obtained based on the conditions set in the table of the operation mode selected by the selecting unit in a state in which the object exists using a corresponding image for correction extracted from the image storage unit based on the operation mode selected by the selecting unit.
Owner:CANON KK
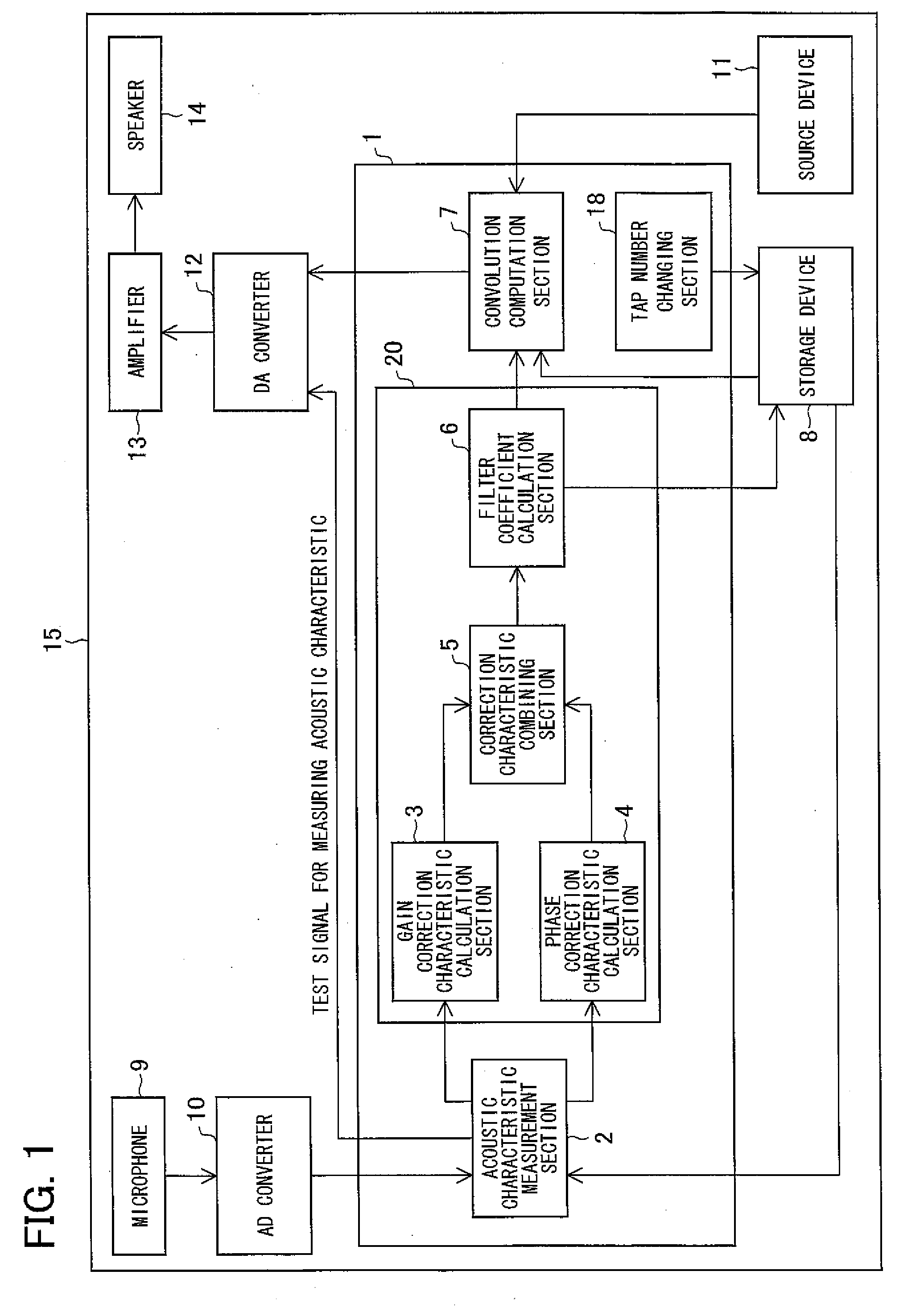
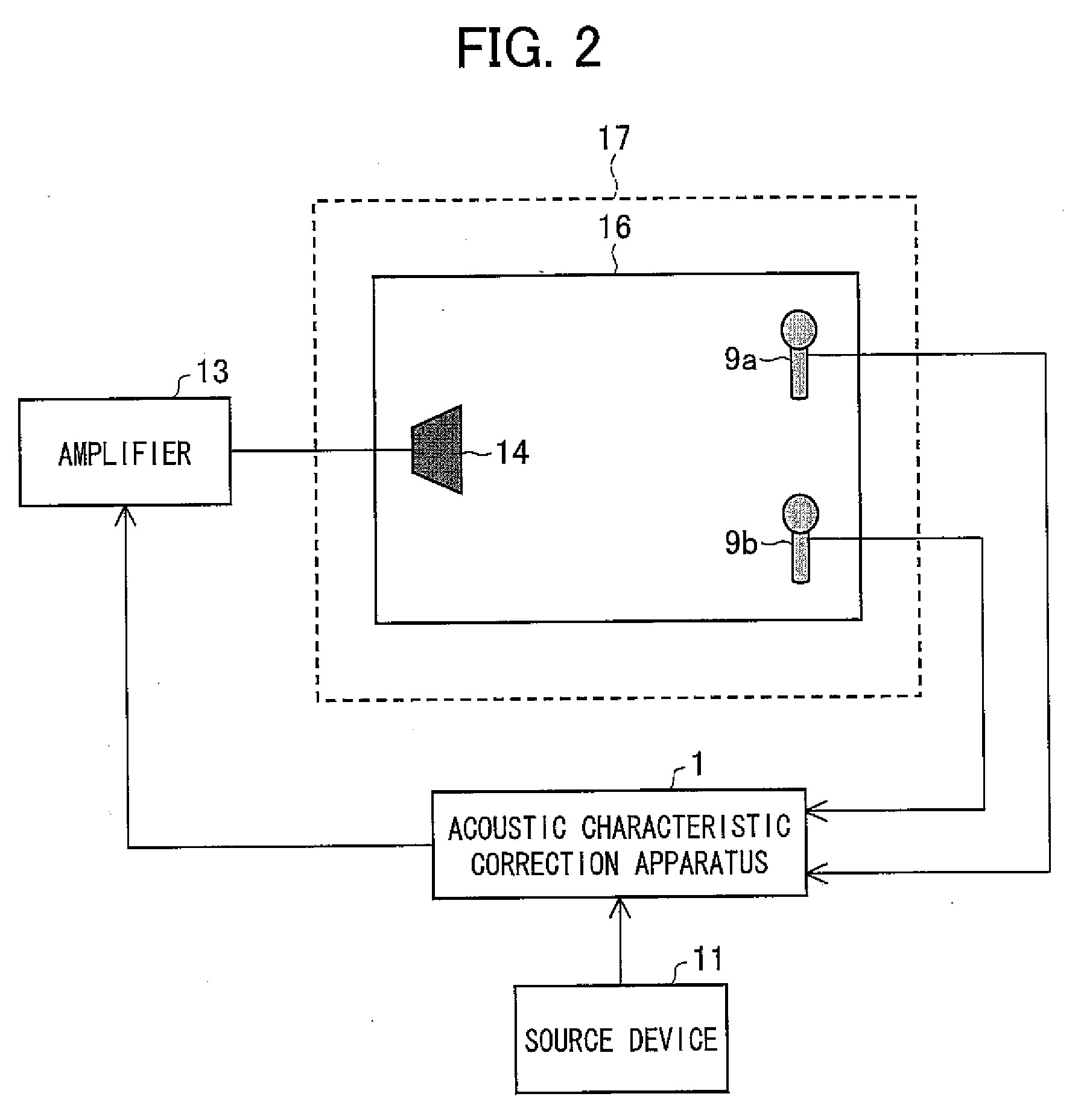
Filter coefficient calculation device, filter coefficient calculation method, control program, computer-readable storage medium, and audio signal processing apparatus
InactiveUS20080192957A1Makes it possibleReduce the amplitudeAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlFrequency response correctionPhase correctionPeak value
In a filter coefficient calculation device according to the present invention, a gain correction characteristic calculation section calculates impulse responses corresponding to a linear-phase filter having an inverse characteristic of a gain characteristic of a reproduction system, and calculates, as a gain correction characteristic, a frequency characteristic of continuous-time impulse responses that include a peak value, the continuous-time impulse responses being impulse responses, clipped from the calculated impulse responses, whose number is identical to the preset number of filter taps. Moreover, a phase correction characteristic calculation section calculates a phase correction characteristic by normalizing, from an inverse characteristic of a frequency characteristic of the reproduction system, a gain characteristic of the inverse characteristic, and a filter coefficient calculation section calculates, as filter coefficients of the reproduction characteristic correction filter, filter coefficients of a filter having a synthetic correction characteristic obtained by combining the gain correction characteristic with the phase correction characteristic. This makes it possible to correct acoustic characteristics with high accuracy even in cases where the number of taps is limited.
Owner:SHARP KK
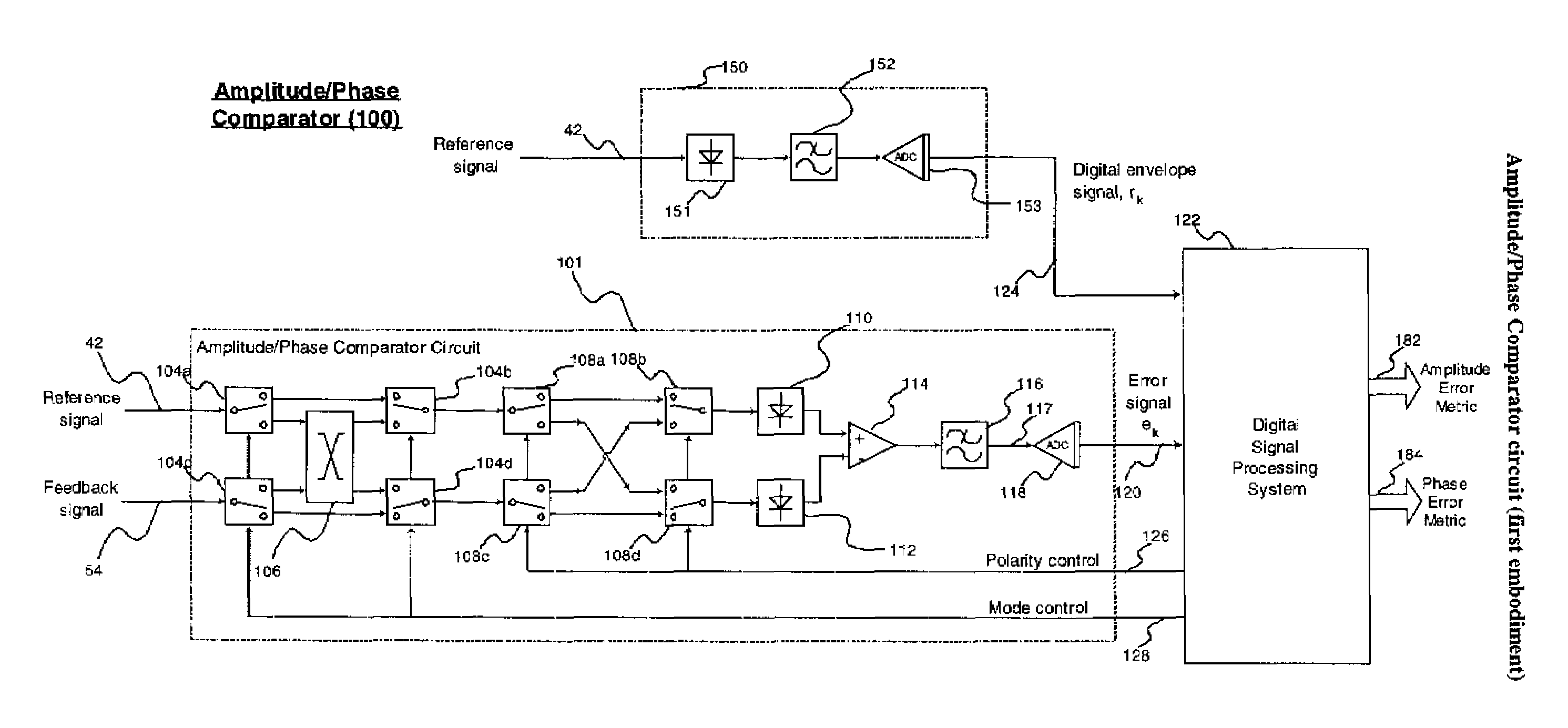
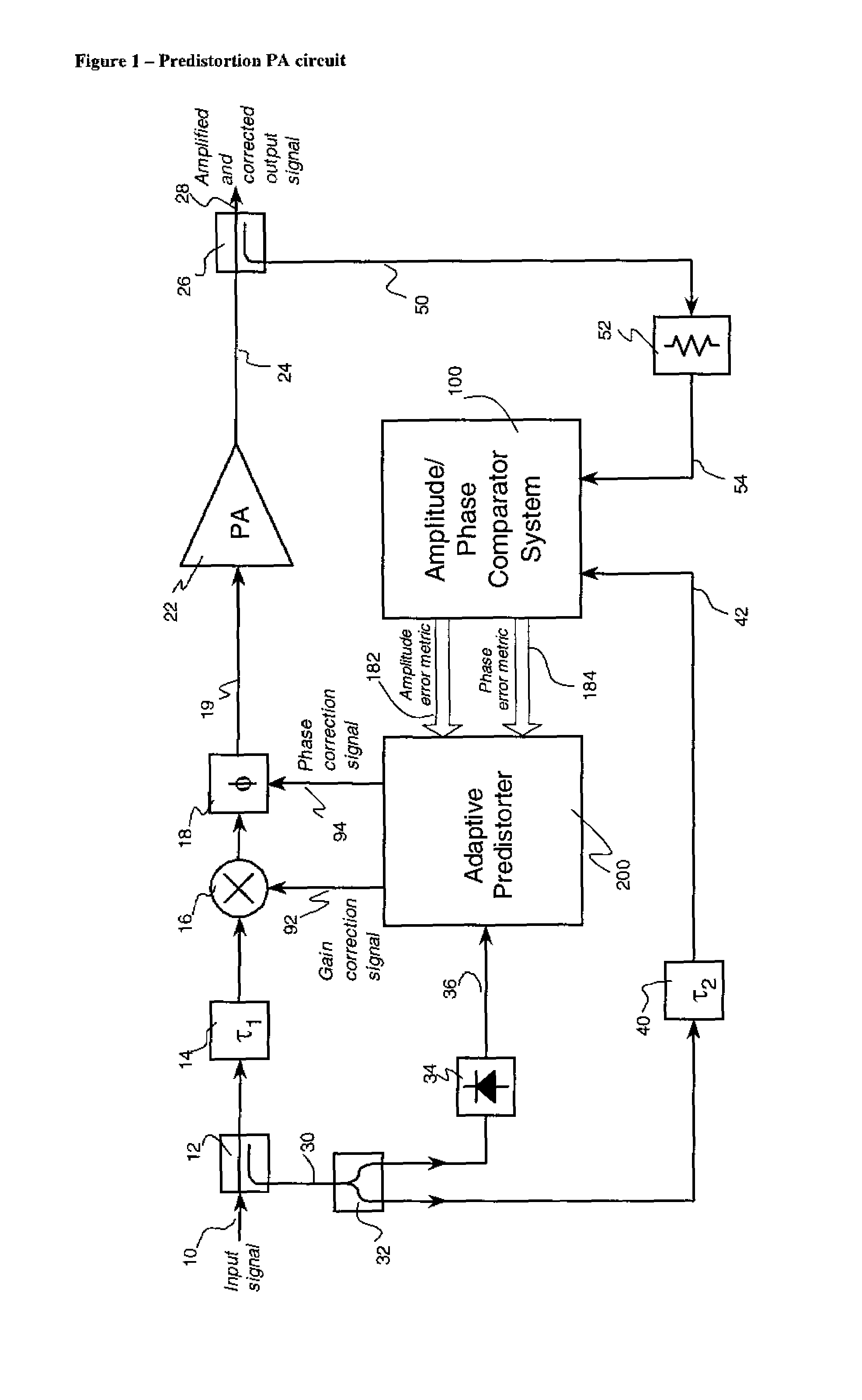
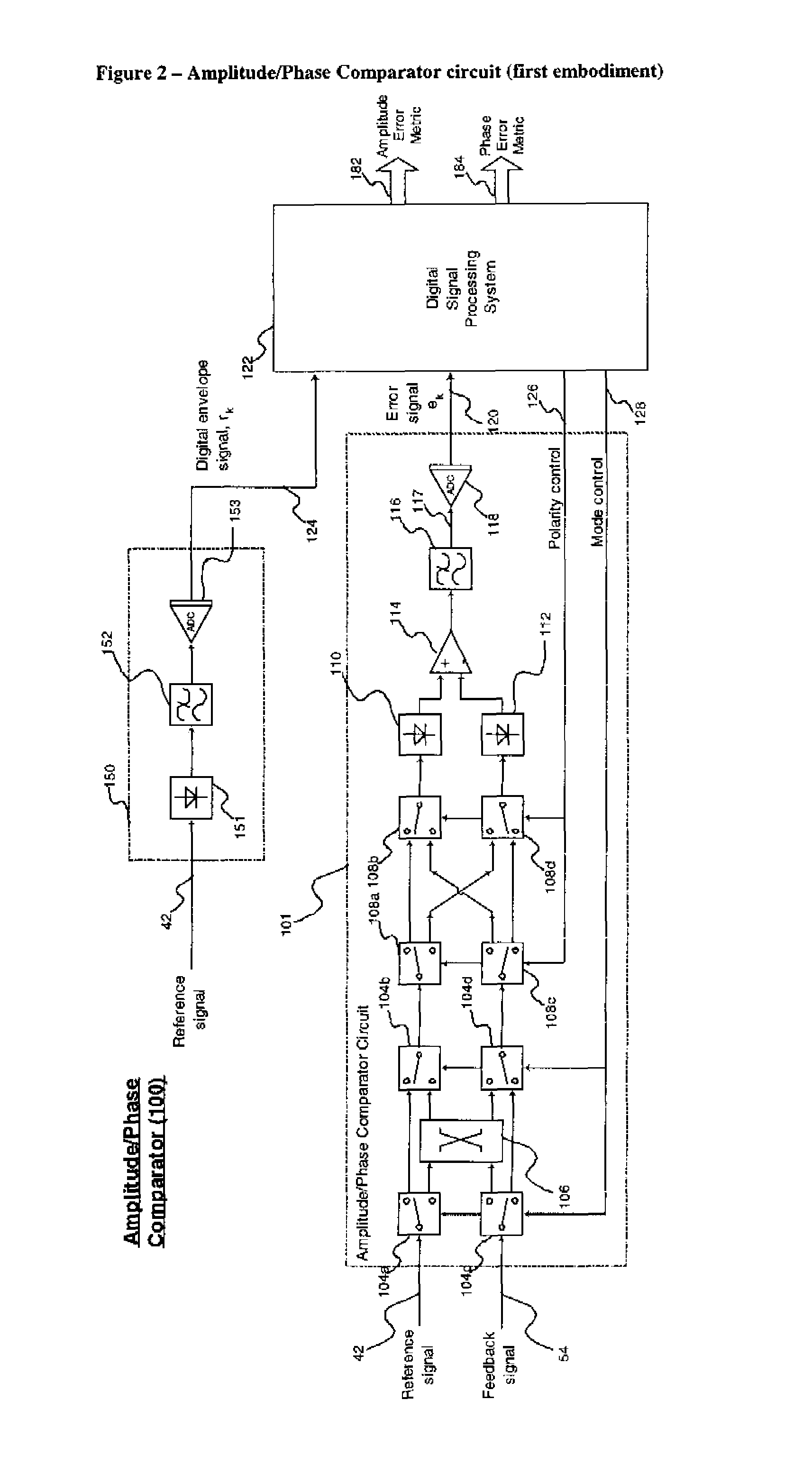
Amplitude and phase comparator for microwave power amplifier
InactiveUS7362818B1Detection errorWide signal bandwidth capabilityModulated-carrier systemsSecret communicationPhase correctionAudio power amplifier
A predistortion power amplifier architecture has a power amplifier which receives an input via an amplitude modulator and a phase modulator. A sample of the output of the amplifier and a sample of the input to the amplifier are applied to an adaptive pre-distorter subsystem. The adaptive pre-distorter generates a gain correction signal which is applied to the amplitude modulator and a phase correction signal which is applied to the phase modulator. This serves to predistort the input signal to the power amplifier to compensate for non-linearities in the power amplifier. A switching arrangement alternately couples a sample of the input and output of the amplifier to a first and a second envelope detector. The outputs of the envelope detectors are applied to a difference amplifier. The switching arrangement has a chopping action on the signals which helps to offset imbalances in the characteristics of the two envelope detectors.
Owner:APPLE INC
Magnetic field sensor and method used in a magnetic field sensor that adjusts a sensitivity and/or an offset over temperature
ActiveUS8350563B2Fast response timeAchieve accuracyElectrical measurementsMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsAnalog signalCondensed matter physics
A magnetic field sensor and a method associated with the magnetic field sensor provide gain correction coefficients and / or offset correction coefficients stored in the magnetic field sensor in digital form. The gain correction coefficients and / or offset correction coefficients can be used to generate analog control signals to control a sensitivity and / or an offset of an analog signal path through the magnetic field sensor.
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
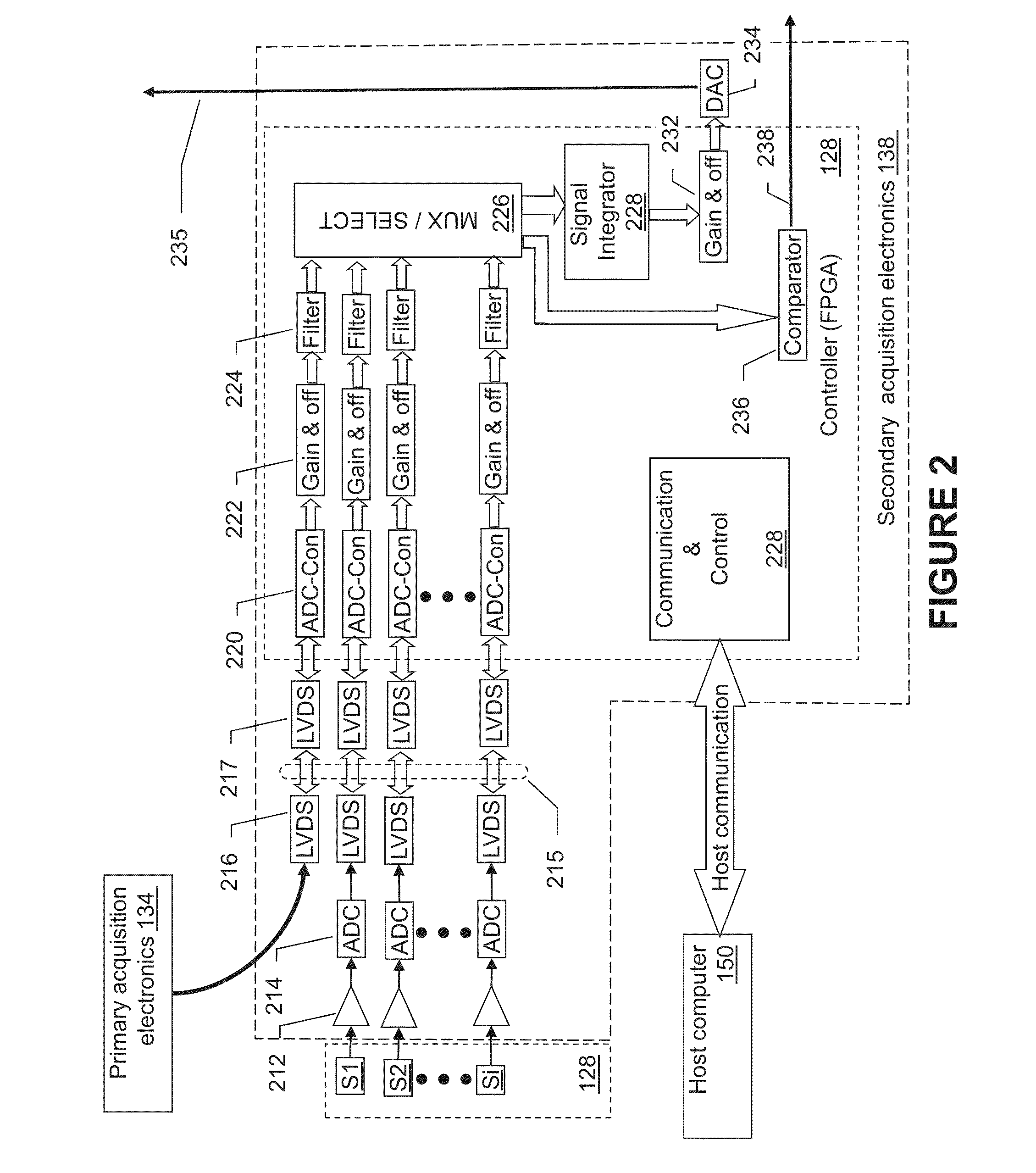
X-ray radiation detector with automatic exposure control
ActiveUS20130126742A1Material analysis by optical meansPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsCMOSSignal correction
An apparatus and method for radiation detection is herein described. The apparatus consists of two radiation-detection arrays: A primary radiation-detection array, based on scintillator-CMOS design, and a secondary radiation-detection array, mounted on the back of said primary array. A method of controlling the detection operation is described, where output of the secondary array is exploited for controlling the acquisition-start and acquisition-stop of the primary array. Further, the apparatus is equipped with fast memory for storage of correction tables, and with a processor for fast computation of the correction. A method of calibration is also describes with tables for: offset correction, gain correction, and for defect-pixel correction. These tables are evaluated by the fast processor and stored on the fast memory. A method of real-time evaluation of the signal corrections is described, which depends on the acquisition-start and acquisition-stop timings and which results a clean, artifact-free image.
Owner:CMT - MEDICAL TECHNOLGIES
Radiation imaging system and driving method thereof
InactiveUS20070291904A1Fast frame rateIncrease the number ofX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationImaging processingRadiation imaging
When a gain correction is performed for the radiographed object image, the acquisition of the object image having a high grade quality and no artifact is realized. For that purpose, an image storing unit is provided for storing an image for correction radiographed based on conditions set with the table in a state in which no object exists to each operation modes of the plurality of operation modes; and an image processing unit is provided for performing a gain correction processing of the radiographed object image and performs the gain correction processing of the radiographed object image obtained based on the conditions set in the table of the operation mode selected by the selecting unit in a state in which the object exists using a corresponding image for correction extracted from the image storage unit based on the operation mode selected by the selecting unit.
Owner:CANON KK
Reproduction color prediction apparatus and method
InactiveUS7433102B2Avoid difficult choicesExact reproductionDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsDot gainErrors and residuals
A primary color dot gain correction unit corrects the spectral reflectance of each of a plurality of color agents on the basis of the dot quantity set for each color agent. An initial estimated value calculator estimates a mixed color by the KM theory using spectral reflectance data corrected by the primary color dot gain correction unit. An ink overlap correction coefficient storage unit stores correction coefficients, which are determined on the basis of errors between the actually measured values of spectral reflectance data of color patches obtained using the plurality of color agents, and estimated values estimated by the initial estimated value calculator based on the dot quantities of the respective color agents on the color patches. An ink overlap correction unit obtains the prediction result of a reproduction color by correcting the spectral reflectance data of the mixed color calculated by the initial estimated value calculator on the basis of the correction coefficients stored in the ink overlap correction coefficient storage unit.
Owner:CANON KK
Control apparatus and method for optical amplifier, optical amplifier, optical transmission apparatus, individual band gain equalizer, wavelength multiplexing transmission apparatus, optical amplifier and wavelength multiplexing transmission system using the same equalizer
ActiveUS20060203329A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationMultiplexingSignal light
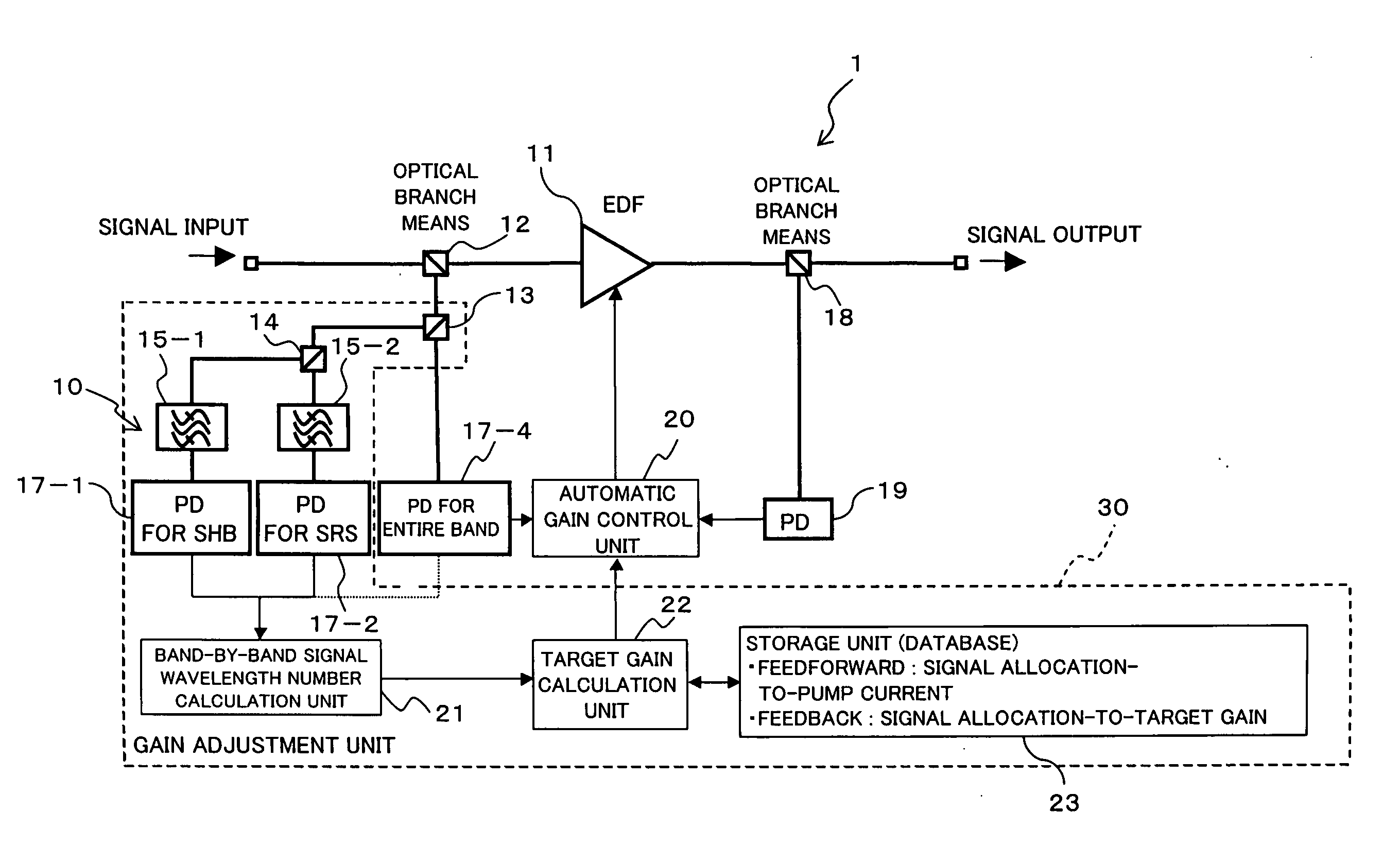
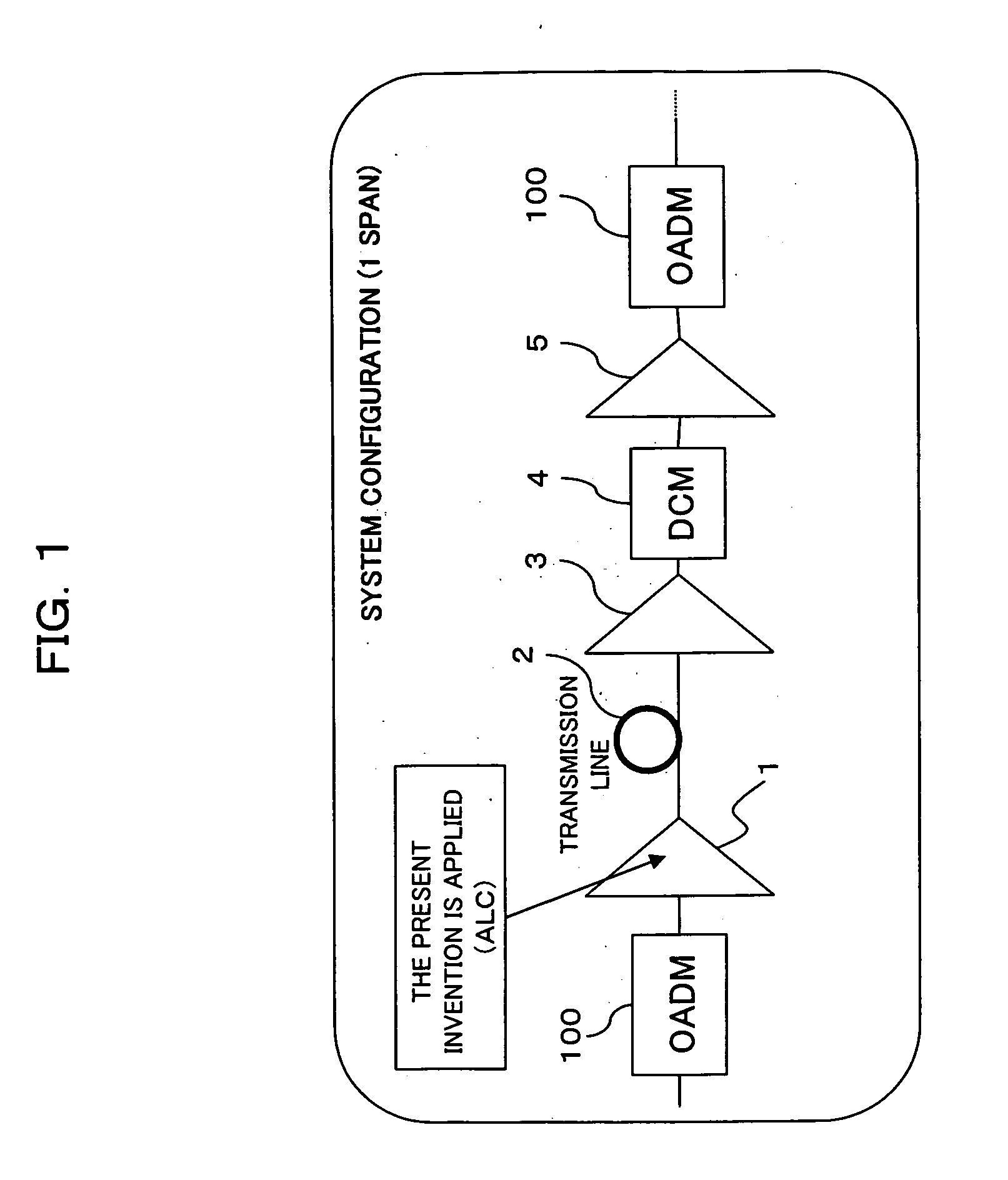
A control apparatus comprises a light monitoring unit for dividing a signal wavelength band into at least a band in which output light power of an optical amplifier tends to decrease at an decrease in the number of signal wavelengths and a band including a gain deviation band, and for monitoring inputted light power for the individual divided bands, a calculation unit for obtaining the number of signal wavelengths in the individual divided bands based on a monitor result, and a target gain correction unit for correcting a target gain based on a result of the calculation. This suppresses a transient variation of signal light level due to SHB or SRS at a high speed with a simple configuration without deteriorating noise characteristic, thus enabling optical amplifiers to be further disposed in a multi-stage fashion, which can lengthen the transmission distance of a transmission system including an optical add / drop unit.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method and apparatus to determine impedance variations in a skin/electrode interface
InactiveUS20110251817A1Testing/calibration apparatusSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsElectrode impedanceImpedance variation
The present invention relates to a system for measuring the impedance of a skin / electrode interface and selectively modifying the system gain of the monitoring circuit to compensate for errors introduced by variations in the skin / electrode impedance. More particularly, a simplified, low-cost method for measuring and compensating for skin / electrode impedance variations is provided. The skin / electrode impedance measuring circuit and determines a system gain correction factor which may be applied to the measured signal using a software algorithm, thereby eliminating the need to change the circuit topology with a programmable gain amplifier or programmable resistor network.
Owner:REPRODIVE RES TECH
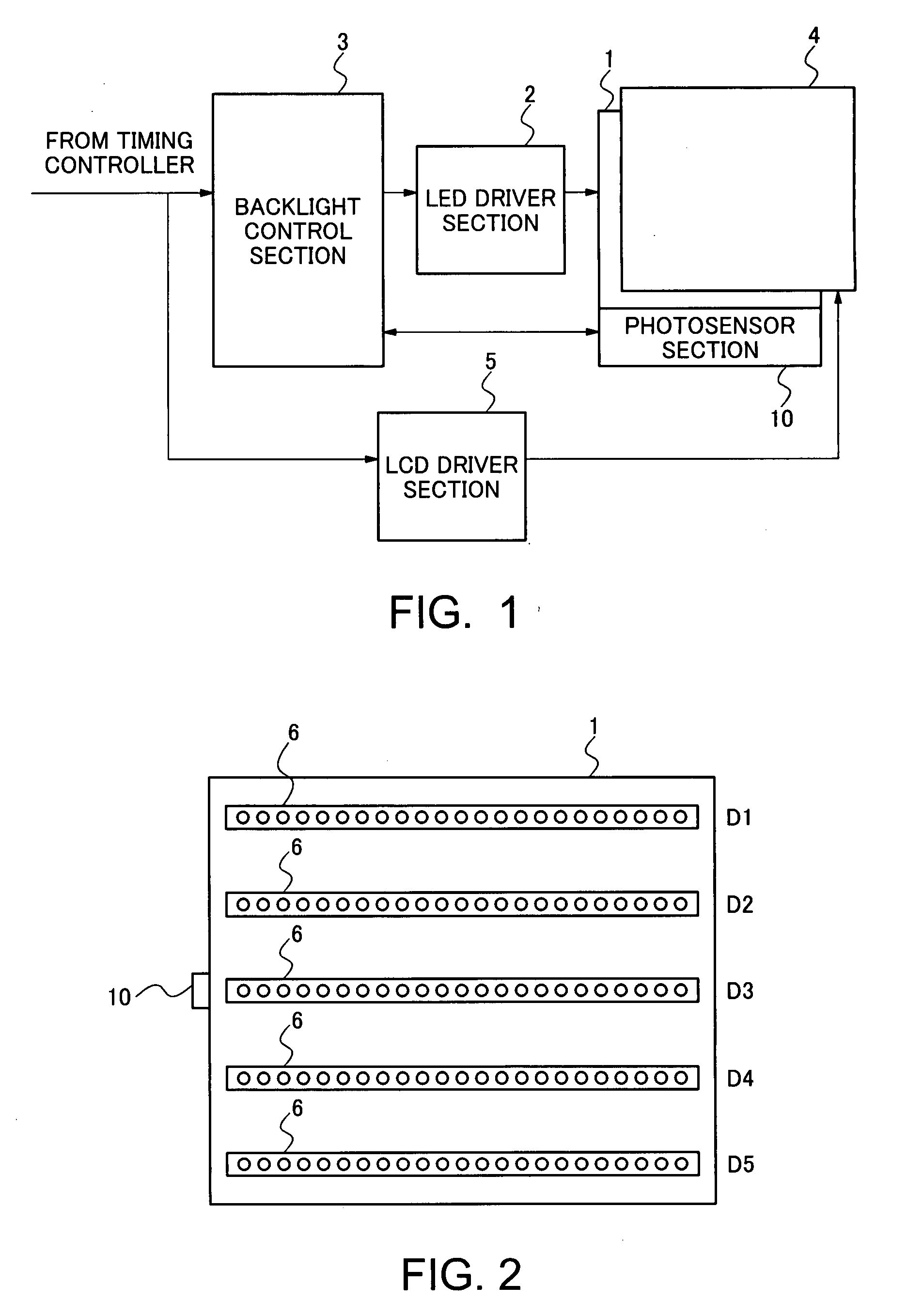
Backlight system, liquid crystal display including the same, and method of adjusting backlight
InactiveUS20070242459A1Good white balanceSmall color deviationStatic indicating devicesElectric circuit arrangementsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
A photosensor section is disposed in a vicinity of the center of a shorter side of an LED panel including plural arrays of LED units in each of which plural LEDs are arranged. A gain of the photosensor section is adjusted on the basis of gain correction information set in advance according to the position of each LED unit. Thereby, the calibration of the photosensor section is performed. While the photosensor section, which has been adjusted in this manner, sequentially detects the amounts of light from the LED units, a backlight unit emits backlight toward a liquid crystal display panel.
Owner:NEC LCD TECH CORP
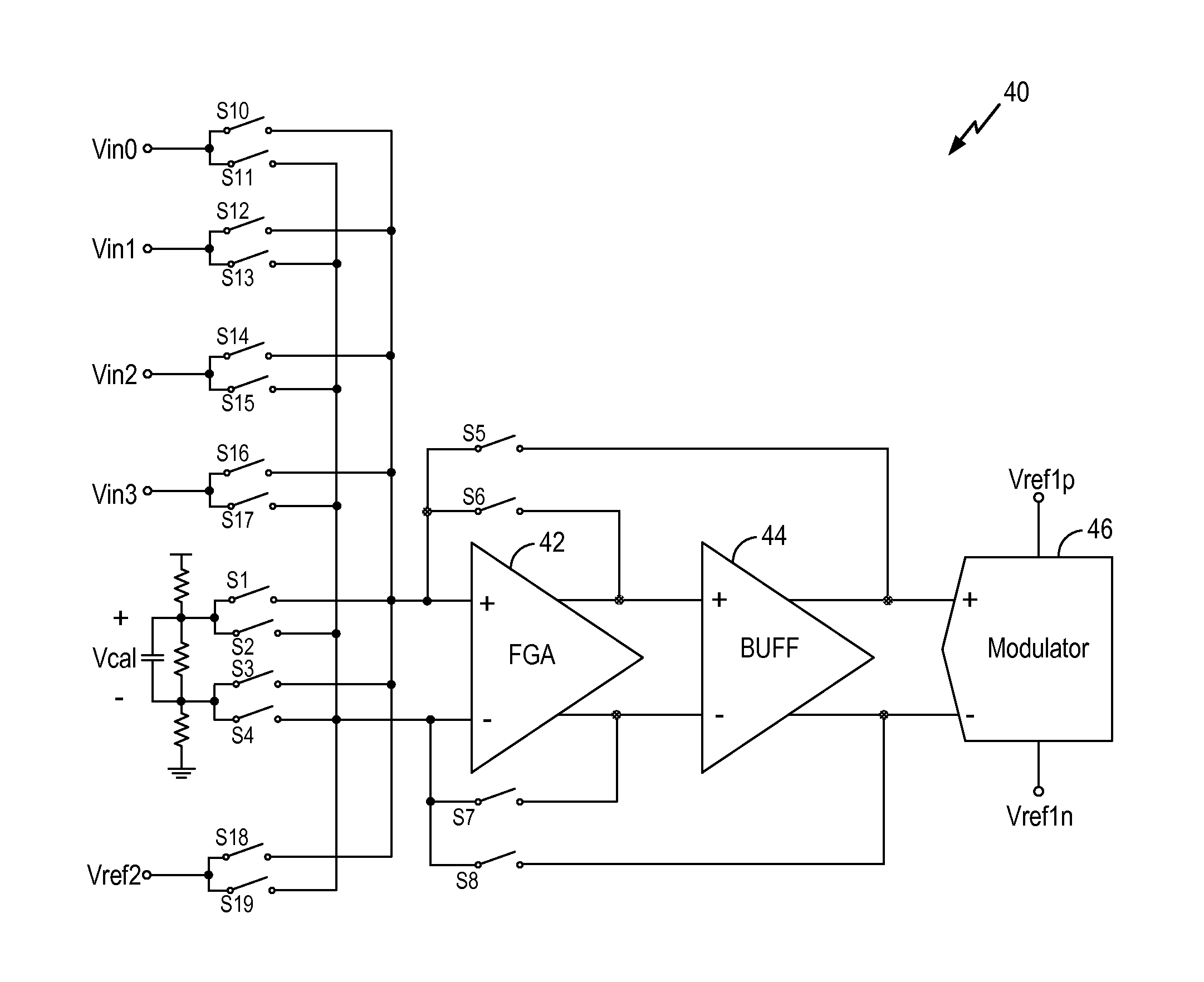
Signal conditioning system with adjustable gain and offset mismatches
ActiveUS6900750B1Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionSignal conditioningEngineering
A signal conditioning system includes first and second converters coupled to a random clock which provides a random sampling rate. Corresponding offset sensor coupled with the first and second converters sense and adjust an offset signal difference. A gain sensor is coupled with the first and second converters to sense a gain difference between the first and second converters and a gain corrector is coupled with the gain sensor to adjust the gain difference.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
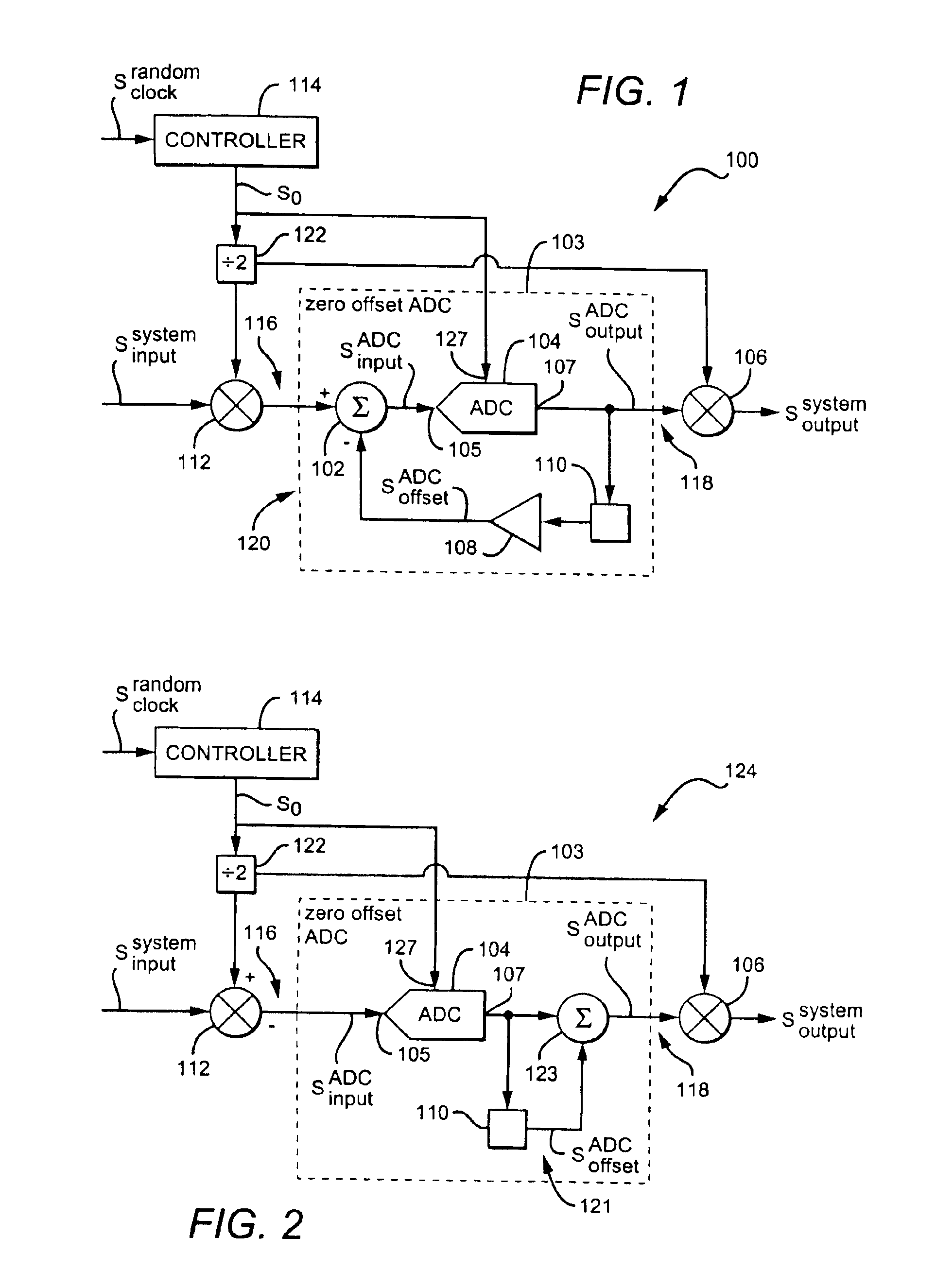
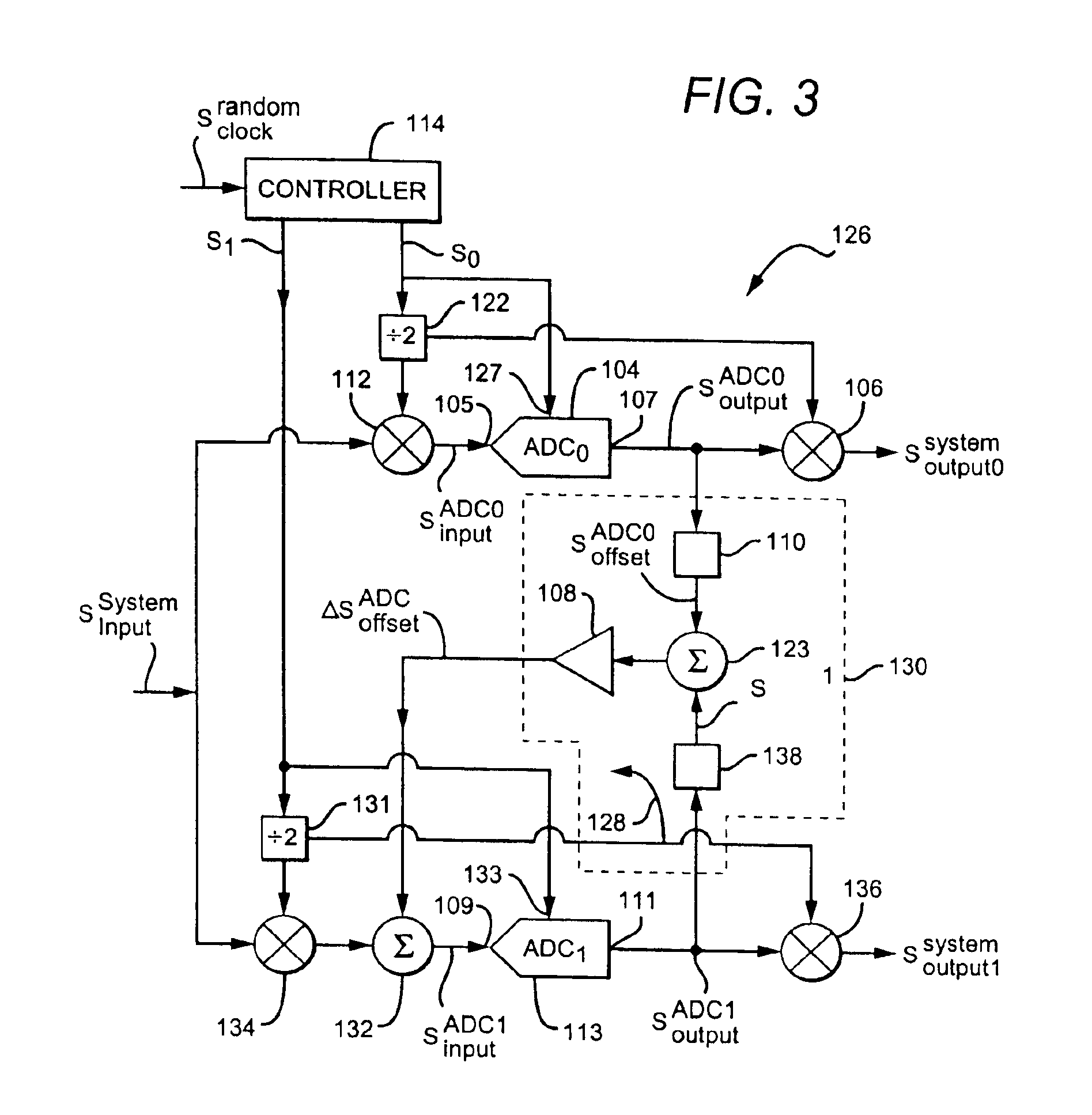
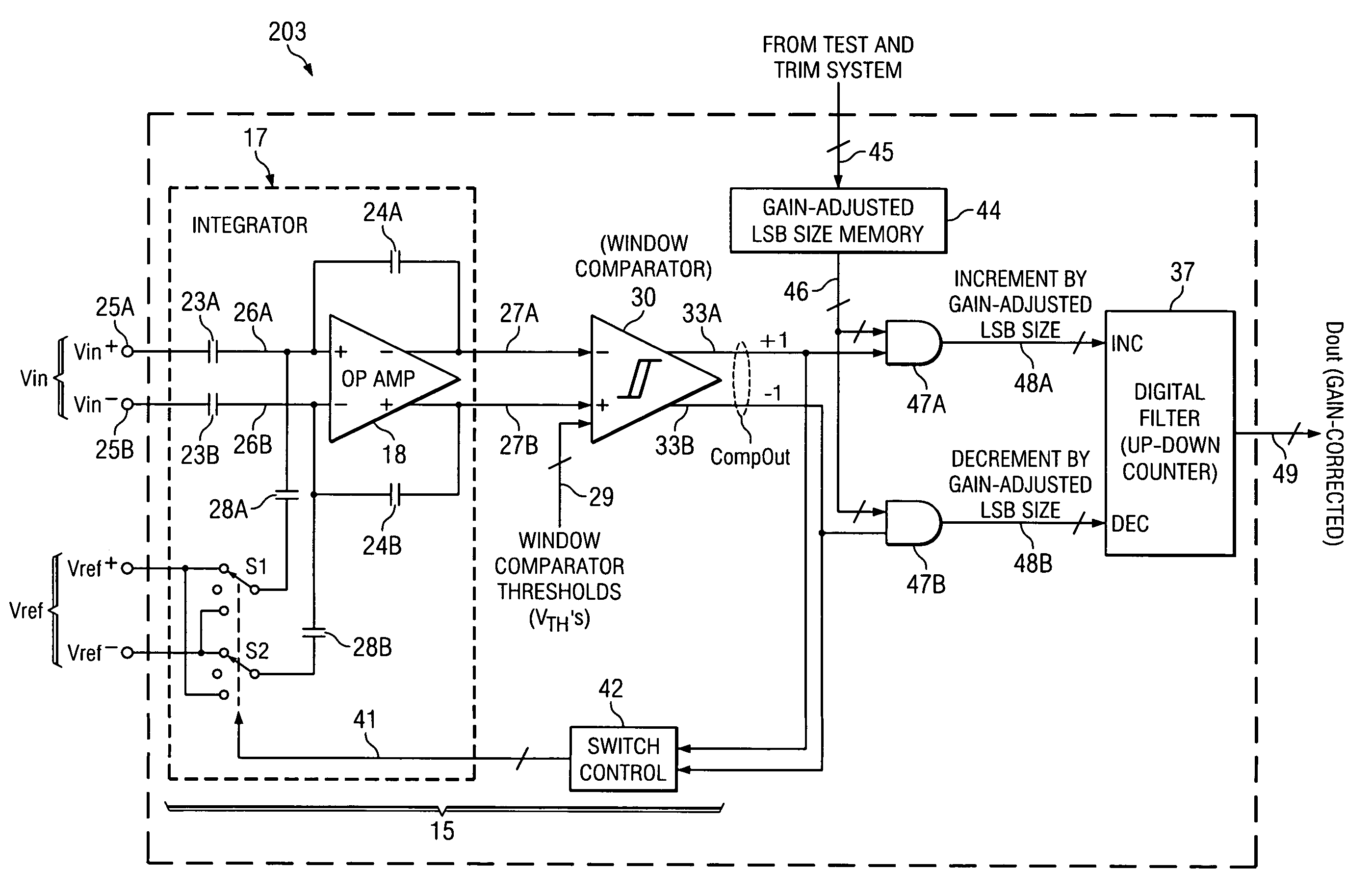
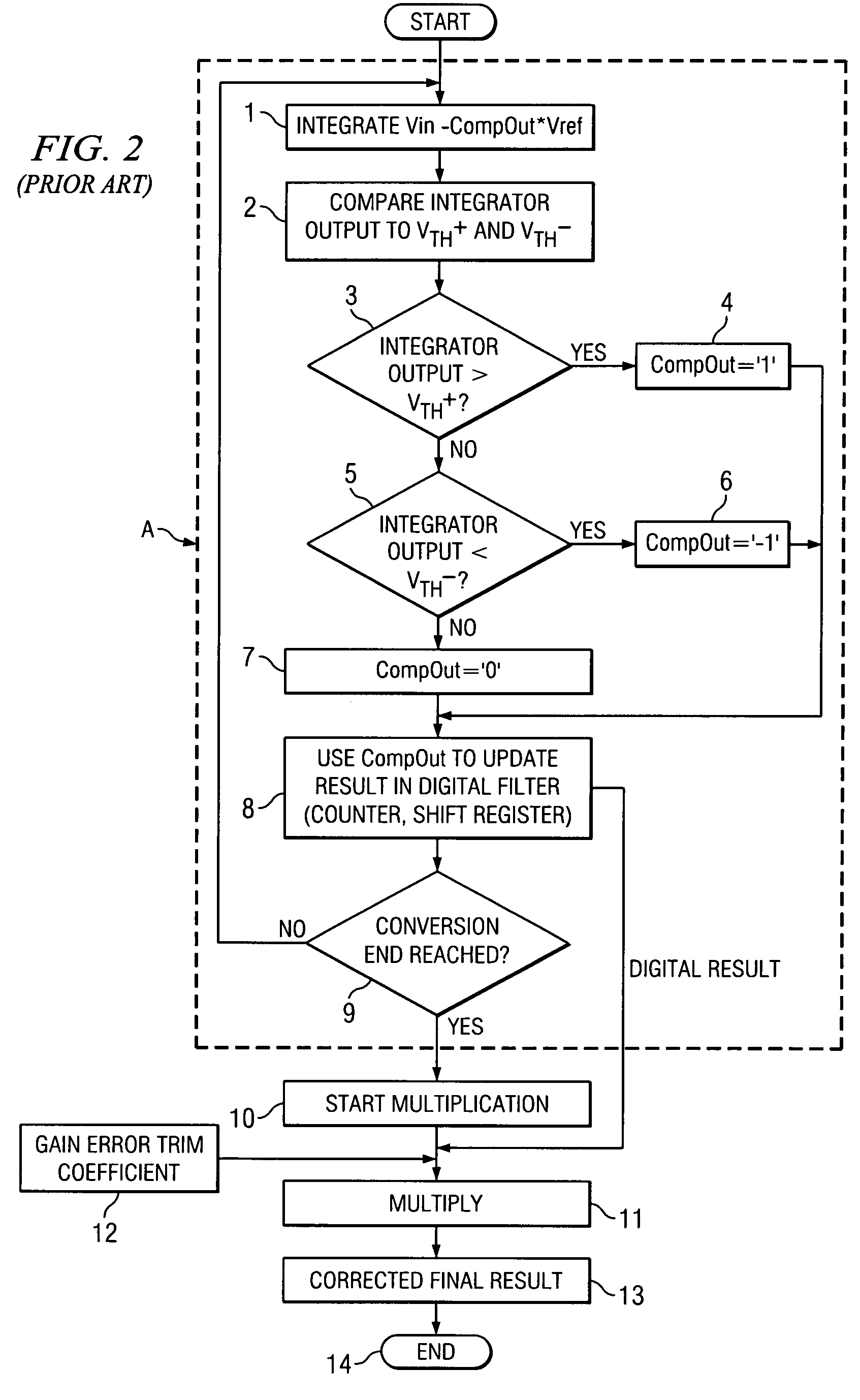
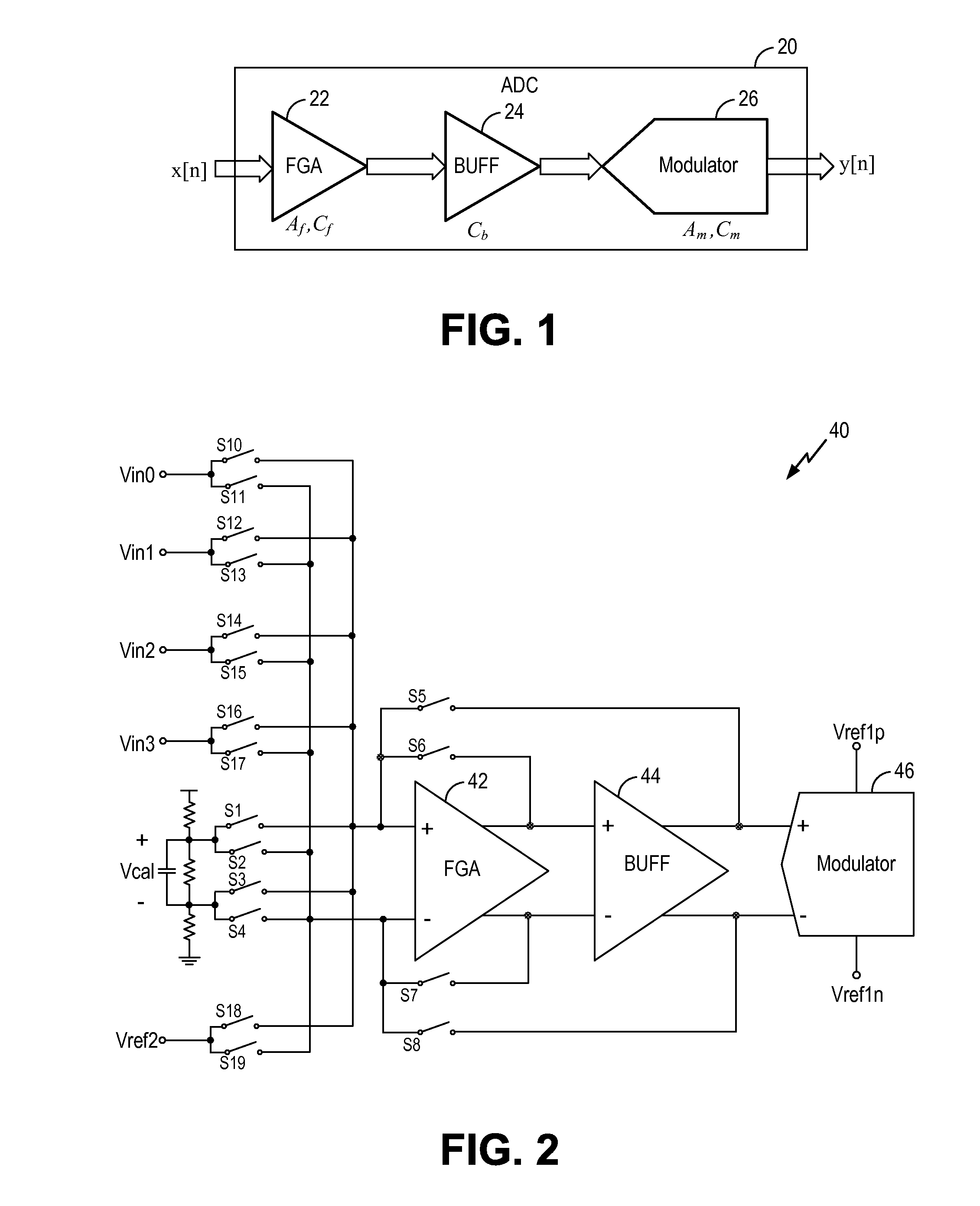
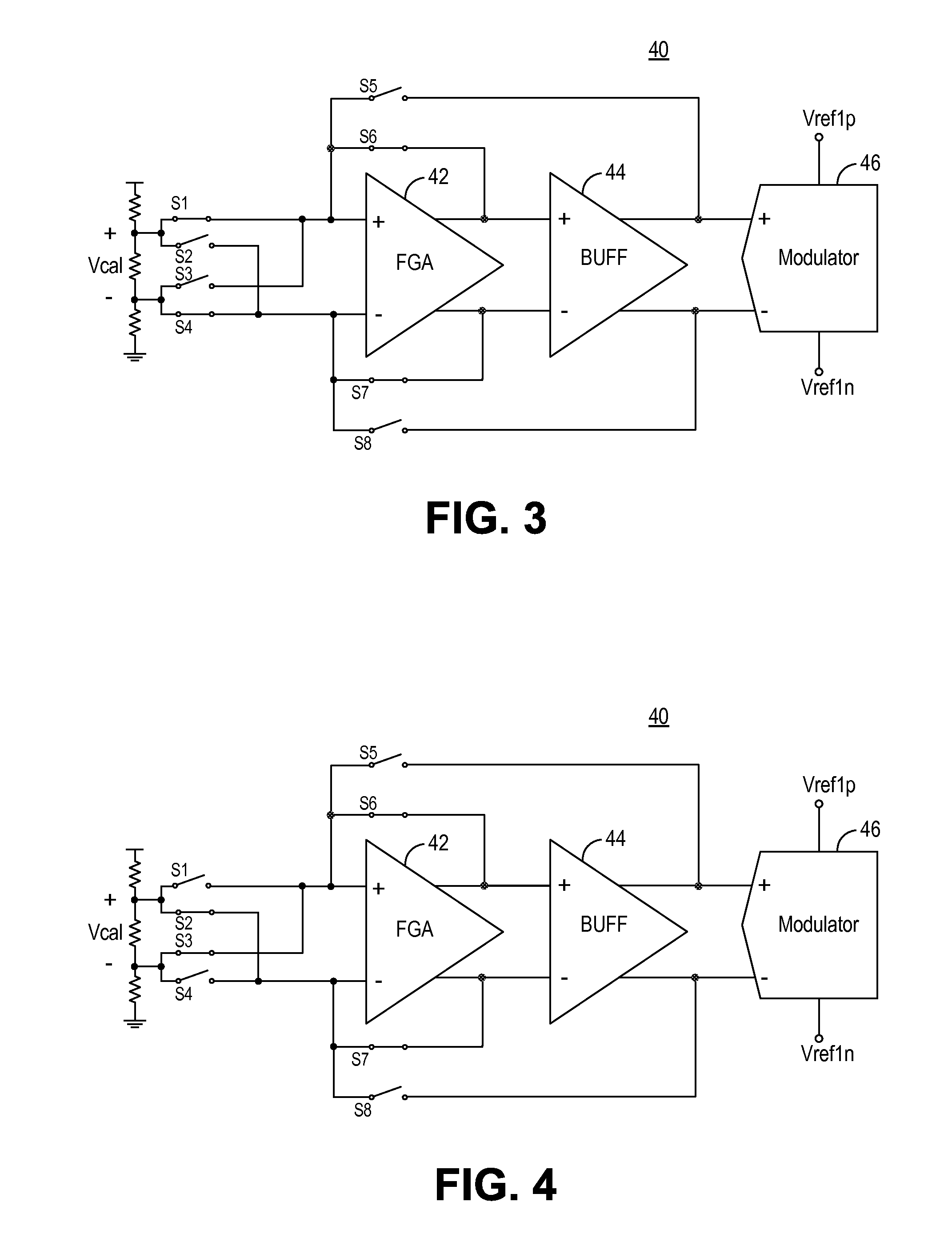
Circuit and method for gain error correction in ADC
ActiveUS7495589B1Extension of timeReduce the amount of solutionElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionIntegratorDigital filter
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Imaging apparatus, imaging system, imaging method, and computer program
A correction process is performed using different gain correction signals (GSA, GSB) in accordance with radiographic modes (moving image radiographic mode / still image radiographic mode) set in an X-ray imaging apparatus, respectively. This makes it possible to acquire an image with decreased correction errors even when the X-ray imaging apparatus is configured using an imaging unit having different gain characteristics in the still image radiographic mode and moving image radiographic mode.
Owner:CANON KK
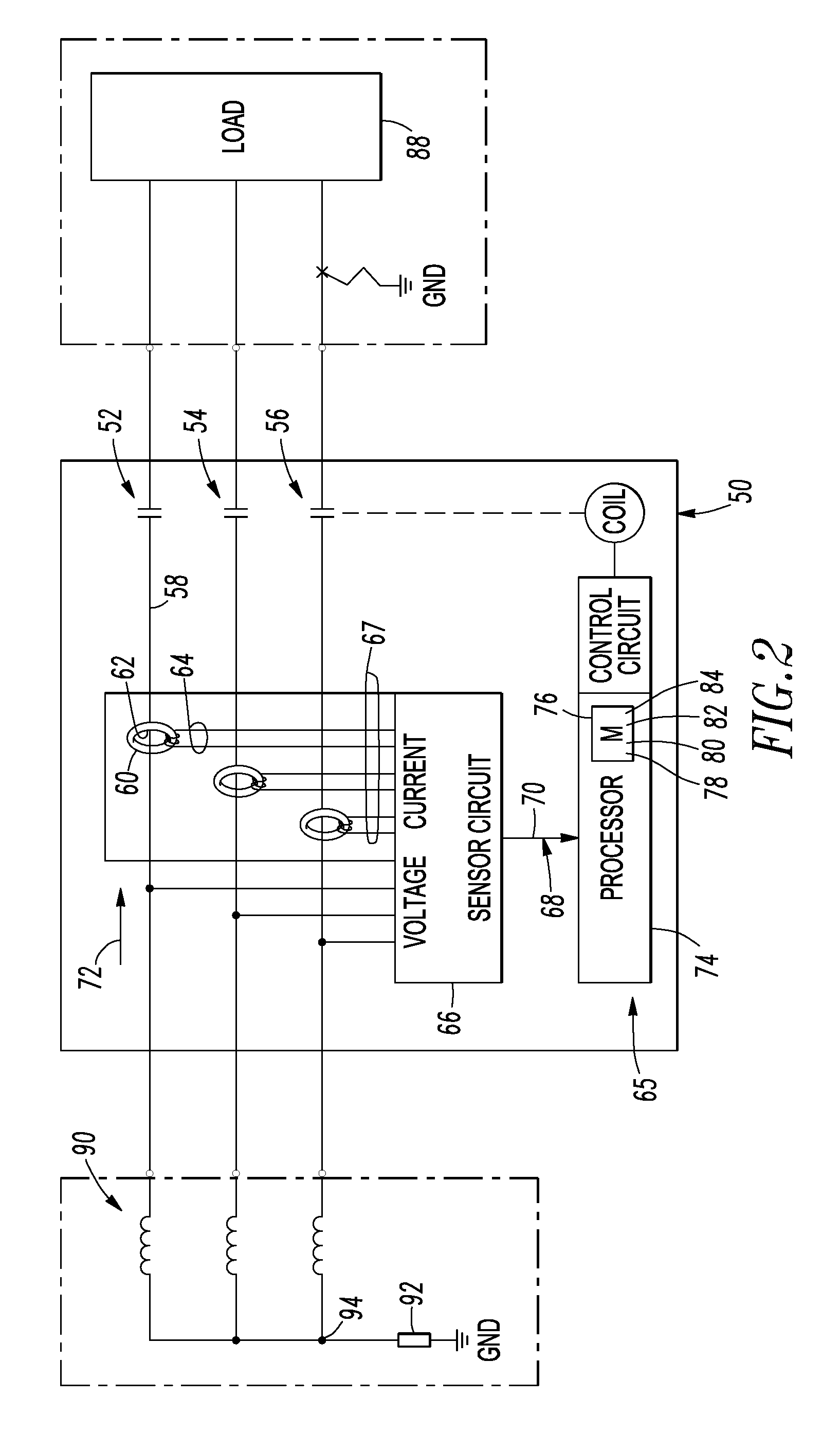
Electrical switching apparatus including a plurality of rogowski coils and method of calibrating the same
ActiveUS20110050154A1Improve system accuracySensitive high resistance ground fault detectionParameter calibration/settingMotor/generator/converter stoppersElectricityElectrical conductor
An electrical switching apparatus includes a plurality of poles each having a Rogowski coil and a conductor passing through an opening thereof, and a processor circuit including a sensor circuit including a plurality of inputs each electrically interconnected with an output of the Rogowski coil of a corresponding pole. The sensor circuit further includes a number of outputs having values each corresponding to current flowing through the conductor, a memory including for each corresponding pole an offset value and a gain correction factor for the sensor circuit, and a gain correction factor for the Rogowski coil, a number of routines, and a processor cooperating with the sensor circuit and the routines to provide for each pole a corrected current value as a function of a corresponding one of the values, the sensor circuit offset value and gain correction factor, and the Rogowski coil gain correction factor.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LIMITED
Background calibration method for fixed gain amplifiers
ActiveUS8330631B2Electric signal transmission systemsGated amplifiersAudio power amplifierDigital down converter
A method for calibrating a fixed gain amplifier configured as a front-end amplification stage of an analog-to-digital converter including sampling a calibration voltage with normal and inversed polarity and with the fixed gain amplifier bypassed and with the fixed gain amplifier connected. An actual gain value of the fixed gain amplifier is computed from offset corrected digital output codes generated from converting the calibration voltage. A gain correction value for the fixed gain amplifier can then be computed based on the ratio of the actual gain to the ideal gain. In another embodiment, a method for calibrating an analog-to-digital converter including a fixed gain amplifier, an input buffer and a modulator generates an offset correction value using normal and polarity inversed input samples. The offset correct value provides correction for at least offset errors in the fixed gain amplifier, the input buffer and the modulator.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Sound processing apparatus, method, and program
ActiveUS20140205111A1Reduce quality degradationQuality improvementAnalog signal digital controlAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlUltrasound attenuationSignal on
The present technique relates to a sound processing apparatus, a method, and a program capable of alleviating degradation of the quality of sound in a case where the gain of a sound signal is amplified.When equalizer processing for adjusting the gain of each frequency band of an input signal on the basis of a gain setting value is performed, an input signal is attenuated by an input attenuation amount derived from the gain setting value, and the equalizer processing is performed on the input signal attenuated. The amount of amplification of the gain of the input signal in the equalizer processing is estimated on the basis of the gain setting value and a weight coefficient of each frequency band derived from a generally-available music signal prepared in advance, and a difference of the estimation value and the input attenuation amount is calculated as a gain correction amount. Further, nonlinear amplification processing is performed on the input signal so as to actually amplify the input signal, which has been subjected to the equalizer processing, by a gain correction amount, and an output signal is obtained. The present technique can be applied to a sound processing apparatus.
Owner:SONY CORP
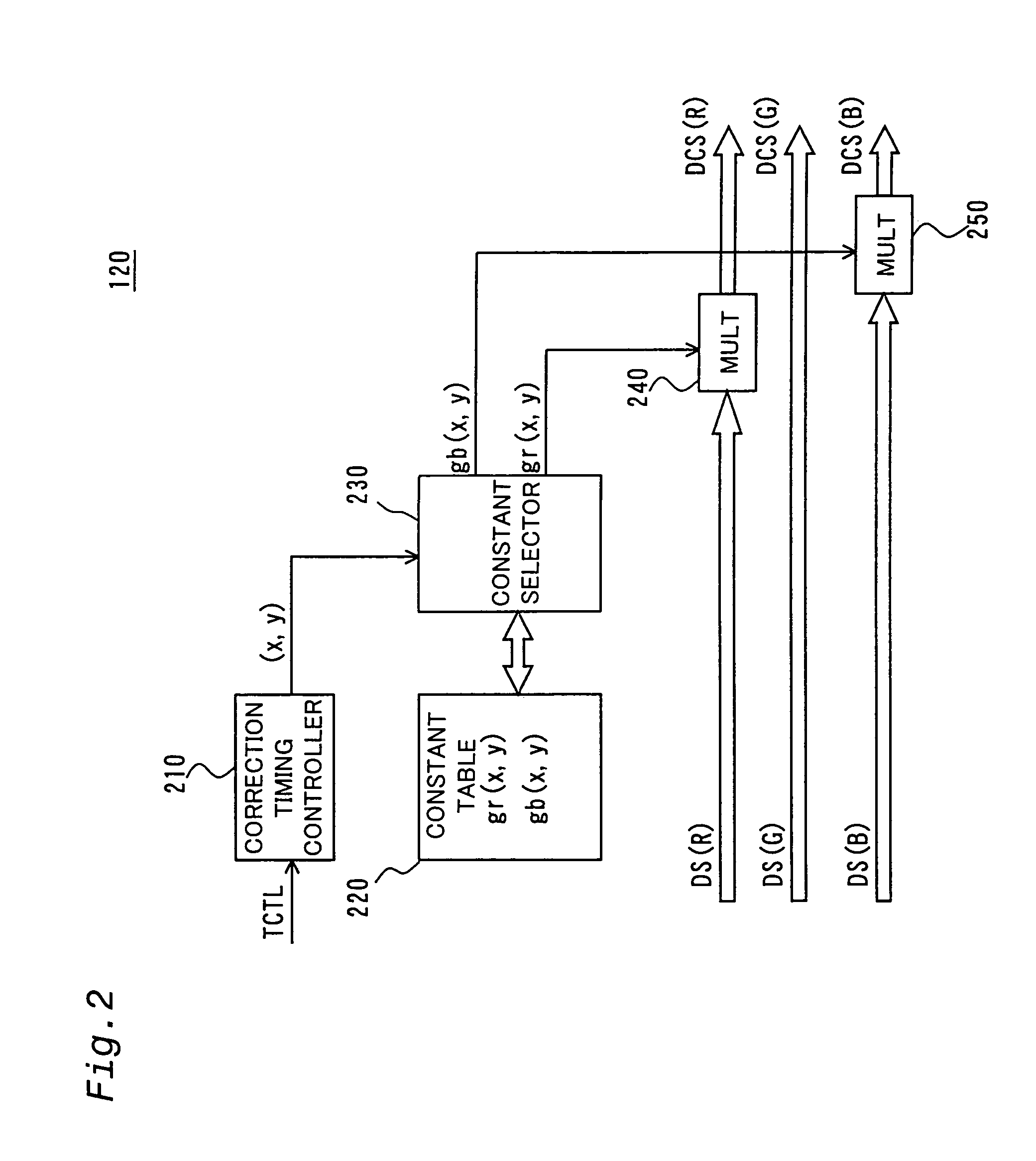
Color correction in image display
InactiveUS7050074B1Suppress color unevennessReduce the differenceBrightness and chrominance signal processing circuitsCathode-ray tube indicatorsDisplay deviceColor correction
The image display apparatus comprises: an image processor for outputting image data including plural color component data; a gain corrector for correcting levels of the image data output by the image processor; and an image display device having a plurality of pixels from each of whose pixels light for forming an image exits in accordance with the corrected image data corrected by the gain corrector. The gain corrector corrects the level of at least one of the plural color component data applied to the pixels in accordance with the positions of the pixels such that, when image data representing an image of a prescribed uniform color are output from the image processor, difference in chromaticity of light exiting from the pixels is reduced among the pixels without making luminance of the light exiting from the pixels of the image display device the same at all pixels.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method and system for multiphase current sensing
ActiveUS20090189553A1Less powerLess expensiveMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersPhase currentsSecondary stage
A multiphase current sensing method wherein the sum of the phase currents is zero including: sensing a.c. and / or d.c. currents in first and second phases; sensing a.c. current in a predetermined a.c. frequency range in a third phase; and combining the current sensed in the first and third phases and the second and third phases and determining a gain correction factor to be applied to the currents sensed in the first and second phases.
Owner:GE HYBRID TECH
Auto-gain correction and common mode voltage cancellation in a precision amplifier
ActiveUS7696817B1Amplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesAudio power amplifierEngineering
Auto-gain correction in a precision amplifier provides continuous calibration of the gain of the two differential input stages relative to each other and thus significantly minimizes the effects of device mismatch and temperature. Auto-gain correction together with auto-zero minimizes the effects of common mode input voltage on the amplifier and eliminates the need for trim associated with the matching of the two differential input stages. Improved gain matching enhances the accuracy of the auto-zero, which further improves the accuracy of auto-gain correction, resulting in a synergy with both operating together. The implementation of the auto-zero using an input pair of series capacitors in conjunction with a common input reference and a feedback pair of series capacitors in conjunction with a common feedback reference provides for decoupling the common mode voltage of the input differential pair or feedback differential pair. Various features may be used in sub-combinations as desired.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com