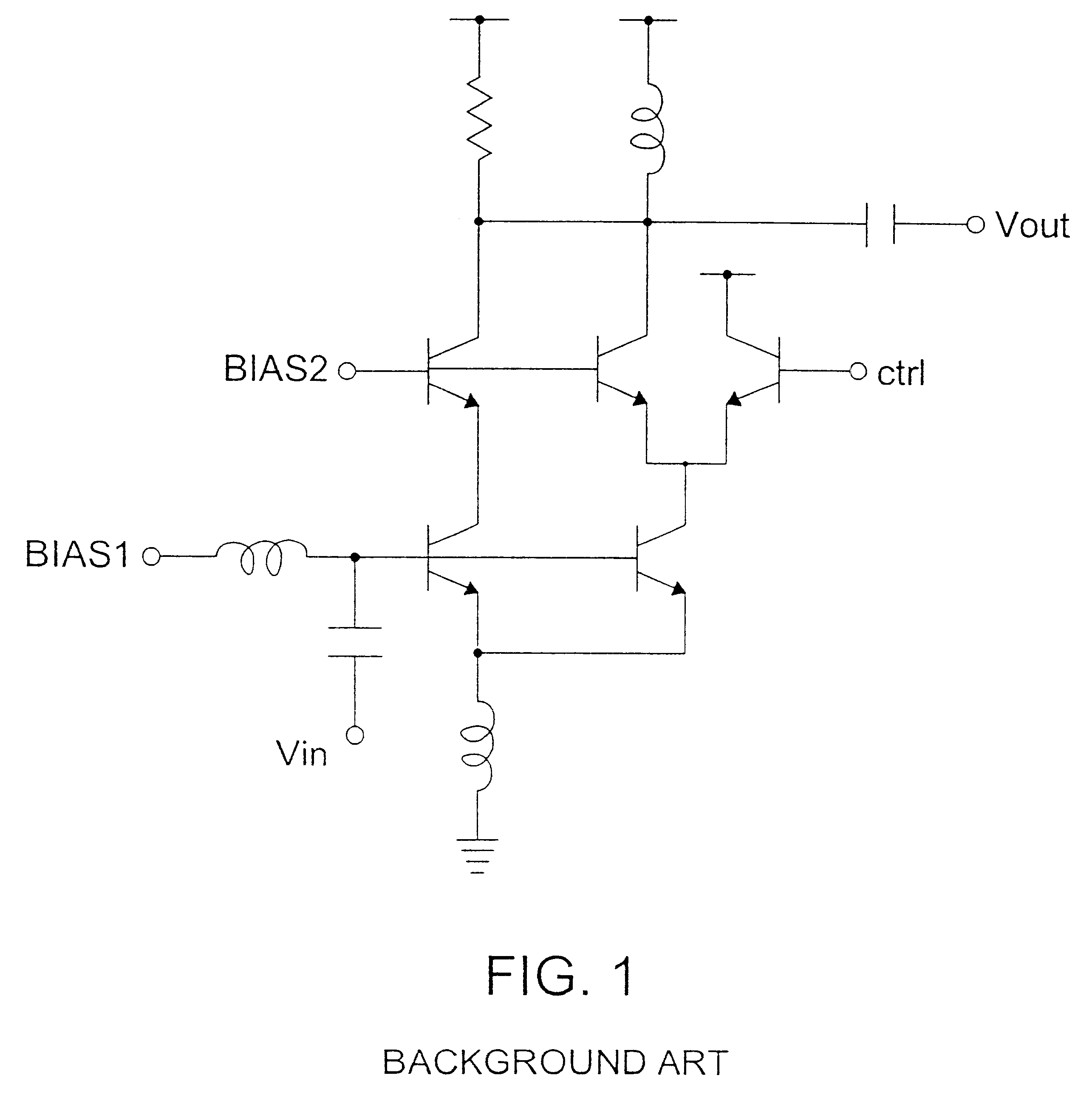
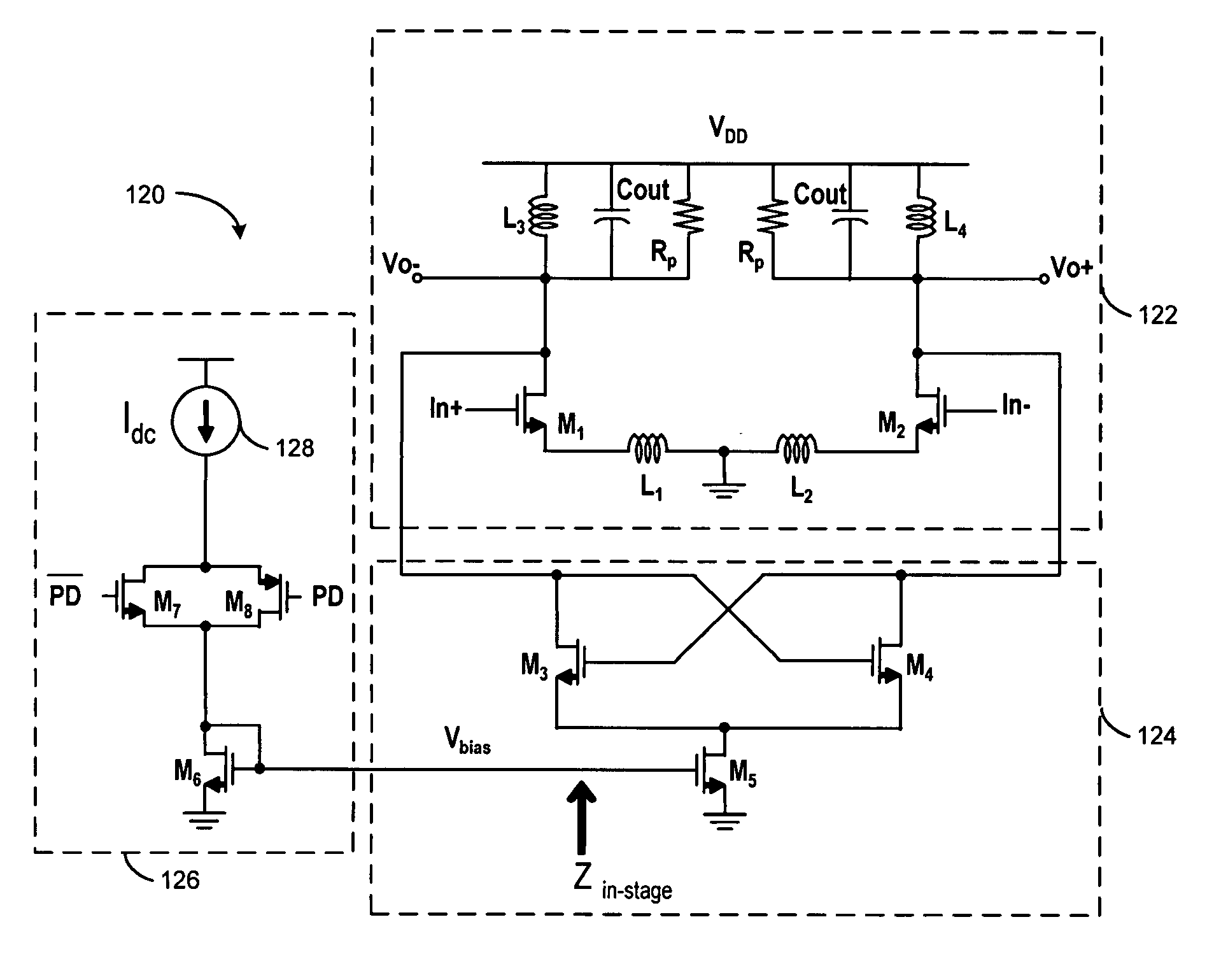
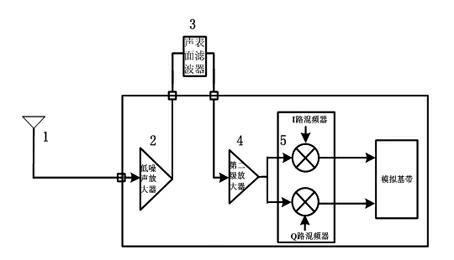
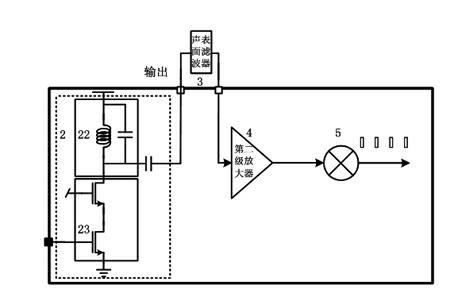
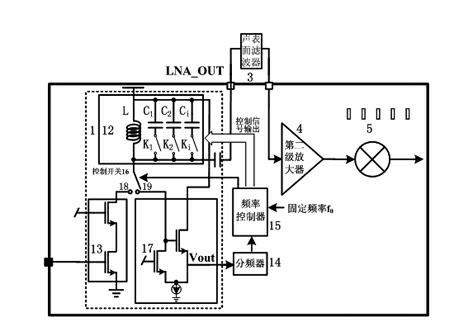
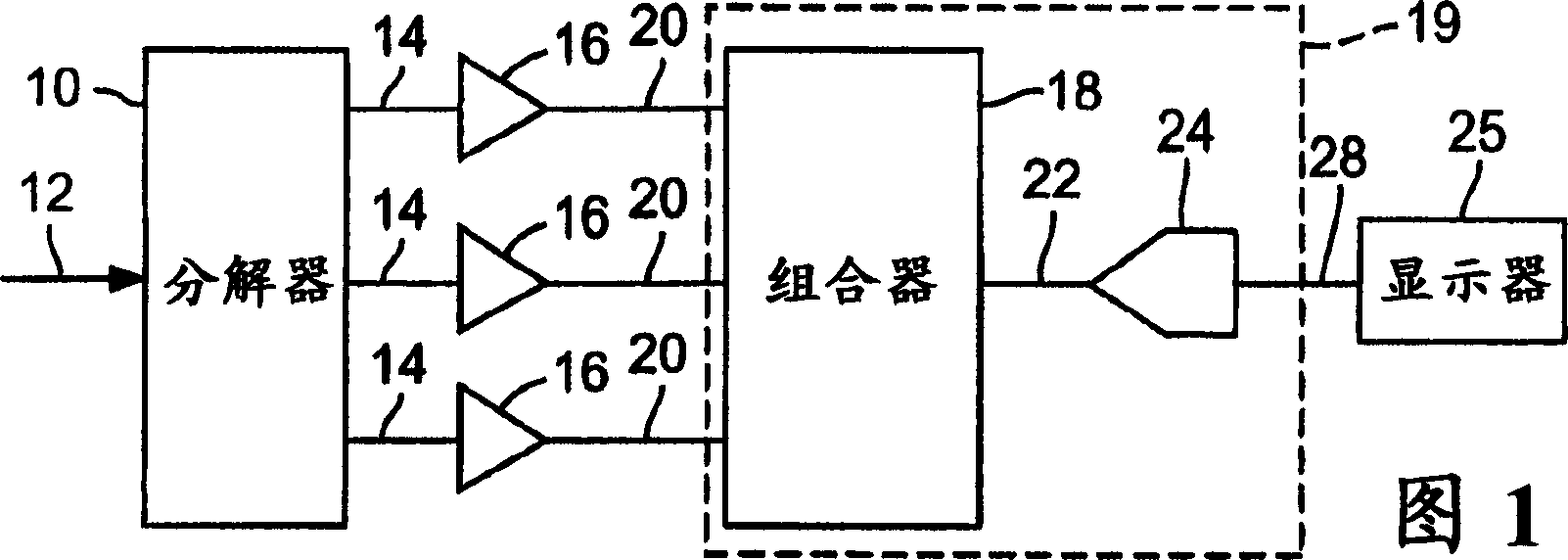
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
61 results about "Tuned amplifier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A tuned amplifier is an electronic amplifier which includes bandpass filtering components within the amplifier circuitry. They are widely used in a variety of wireless applications.
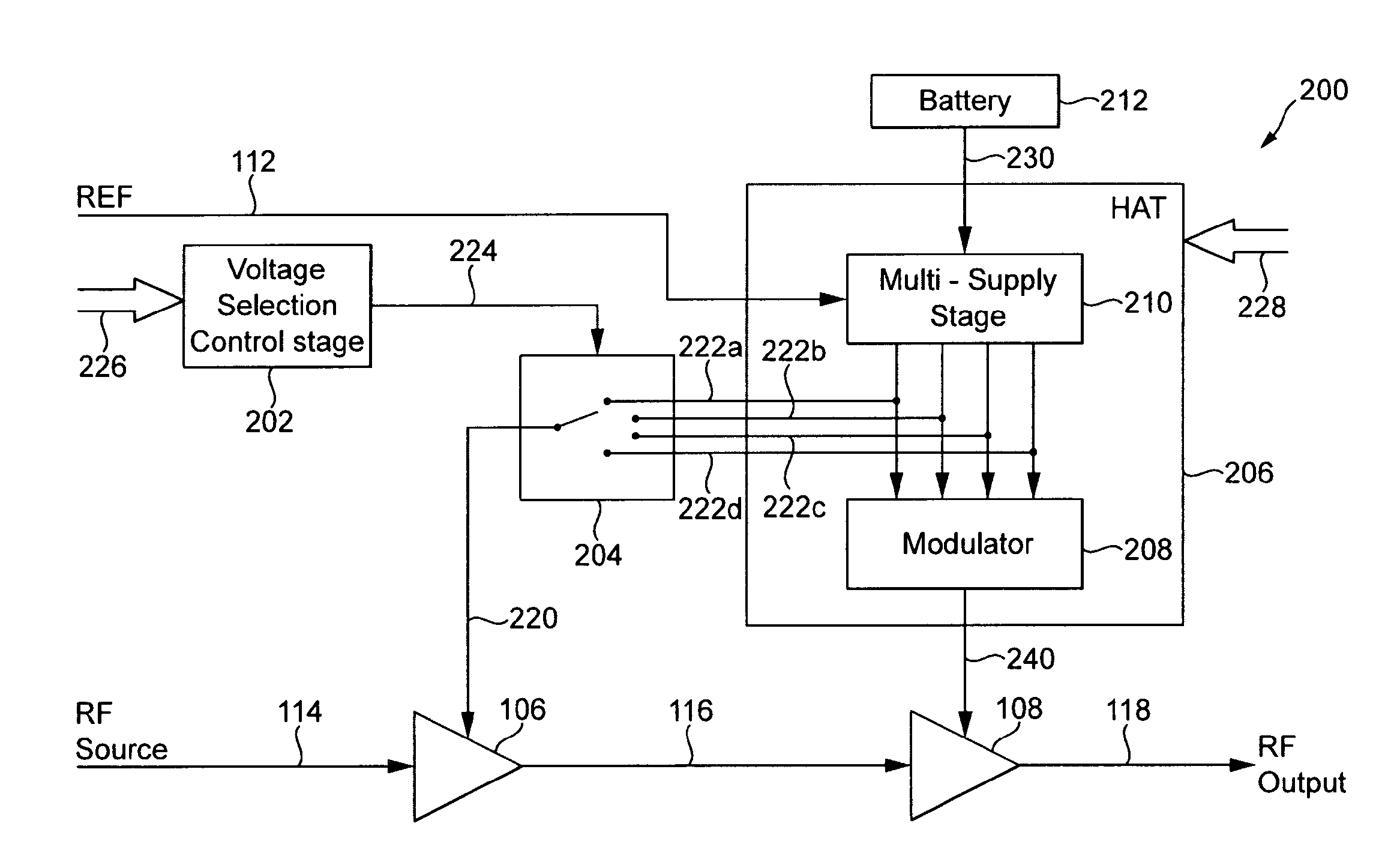
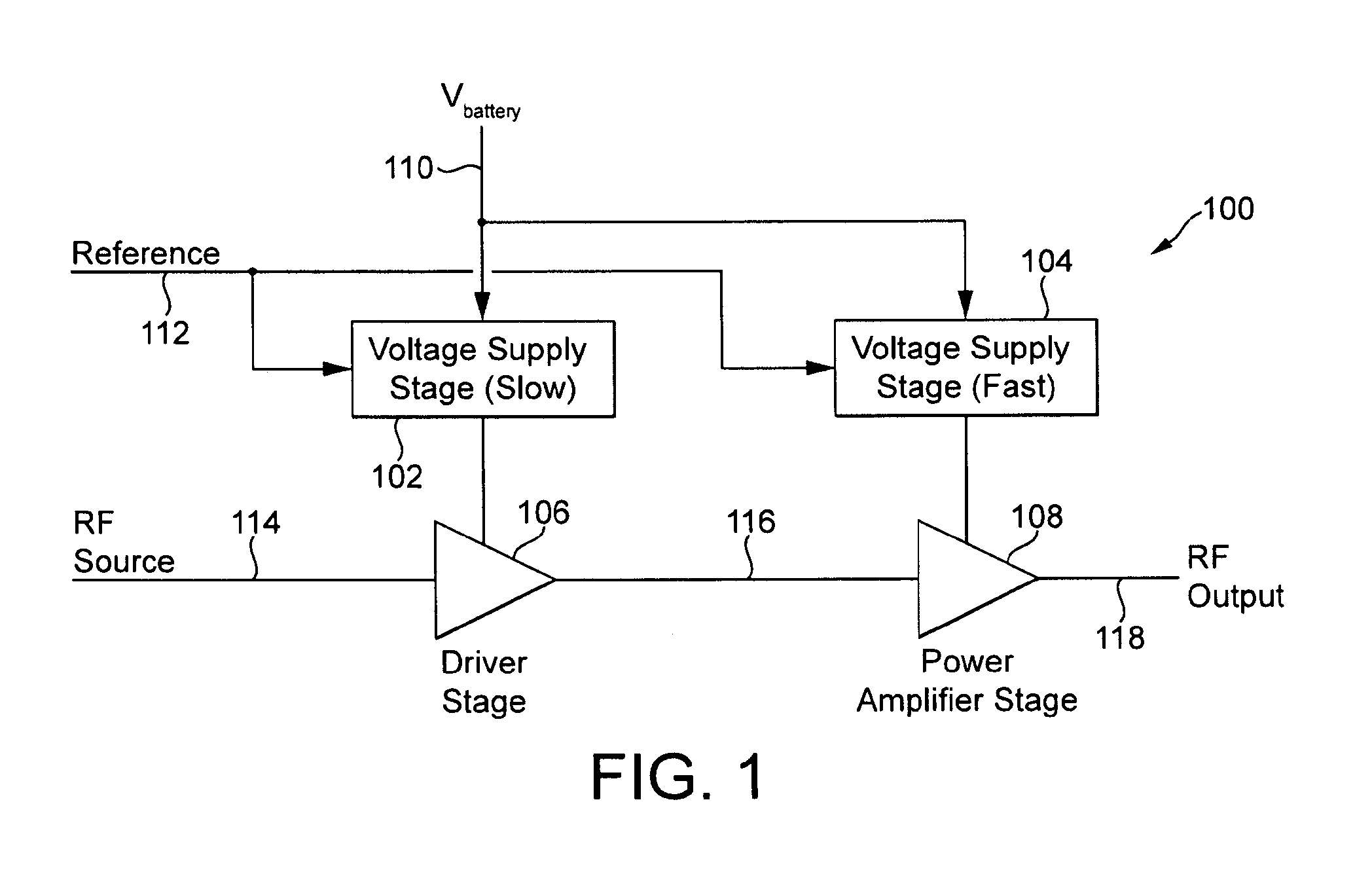
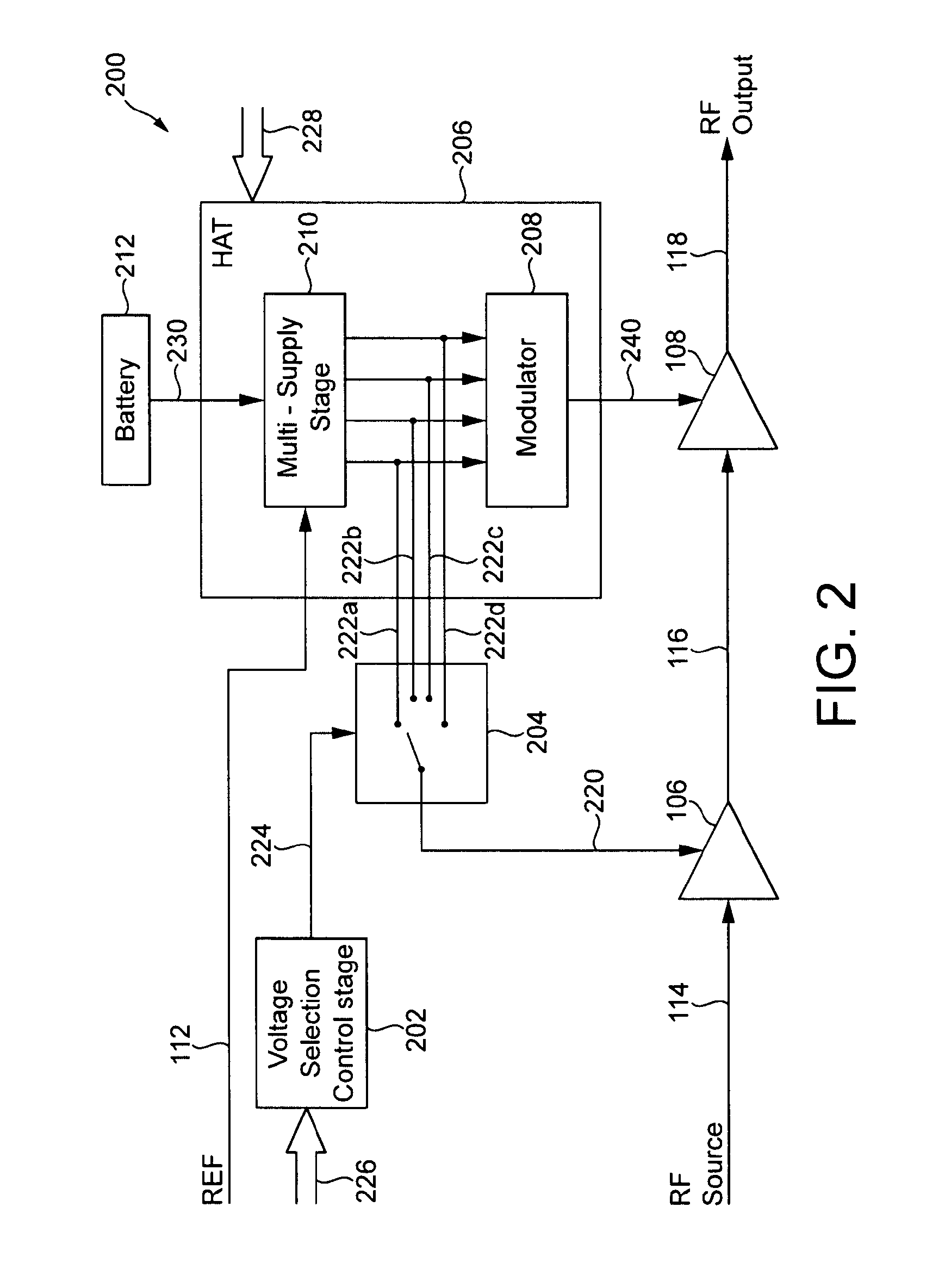
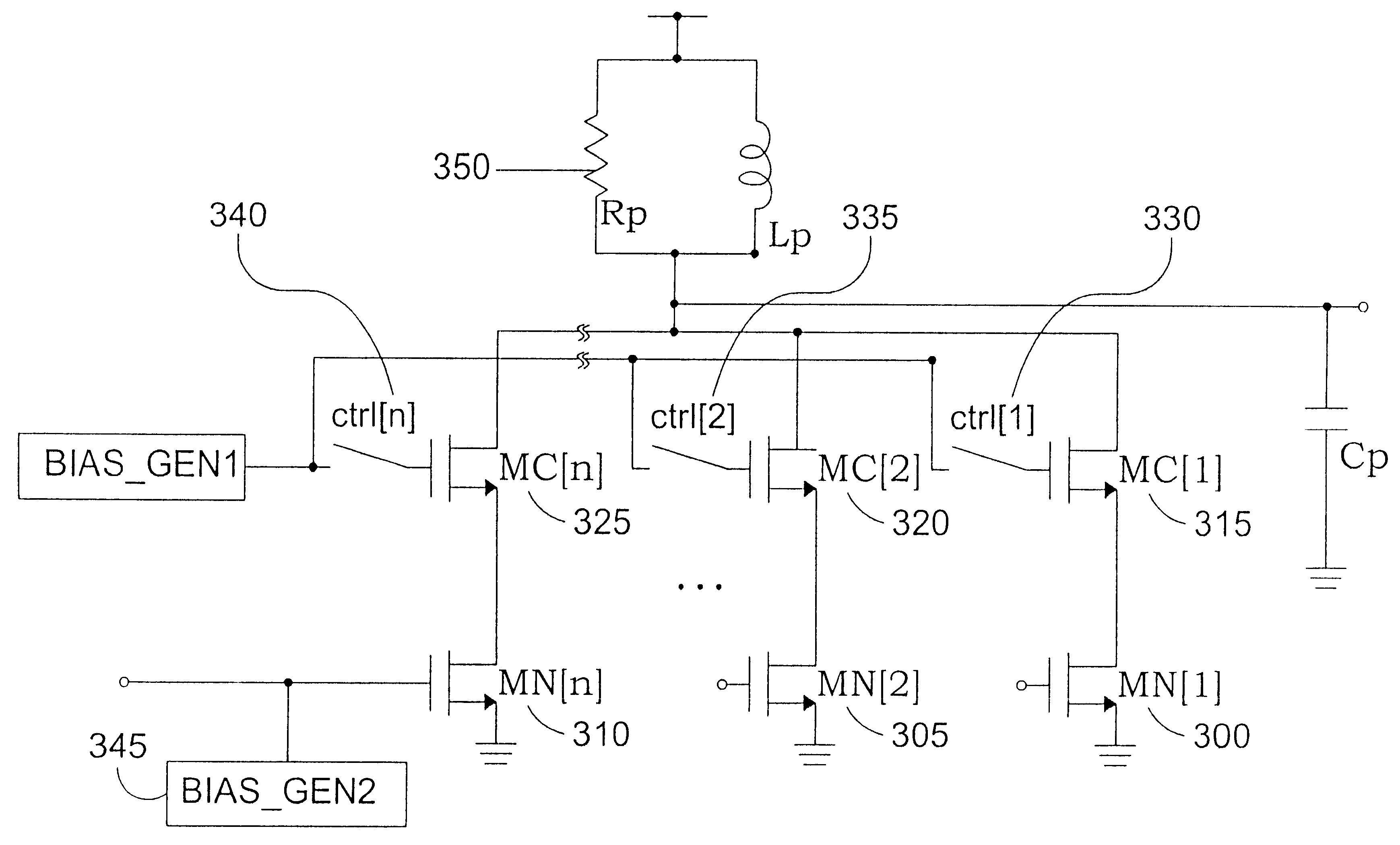
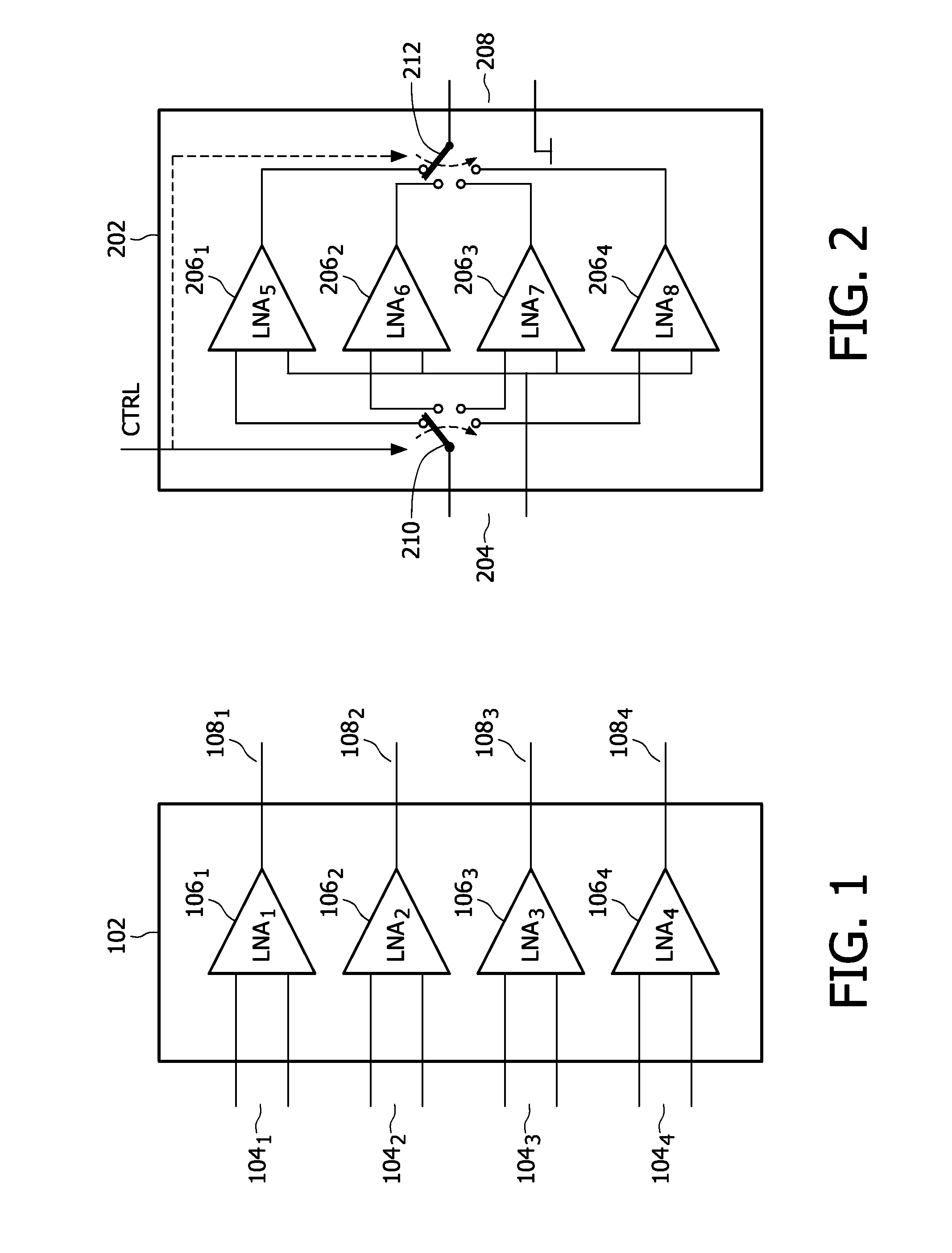
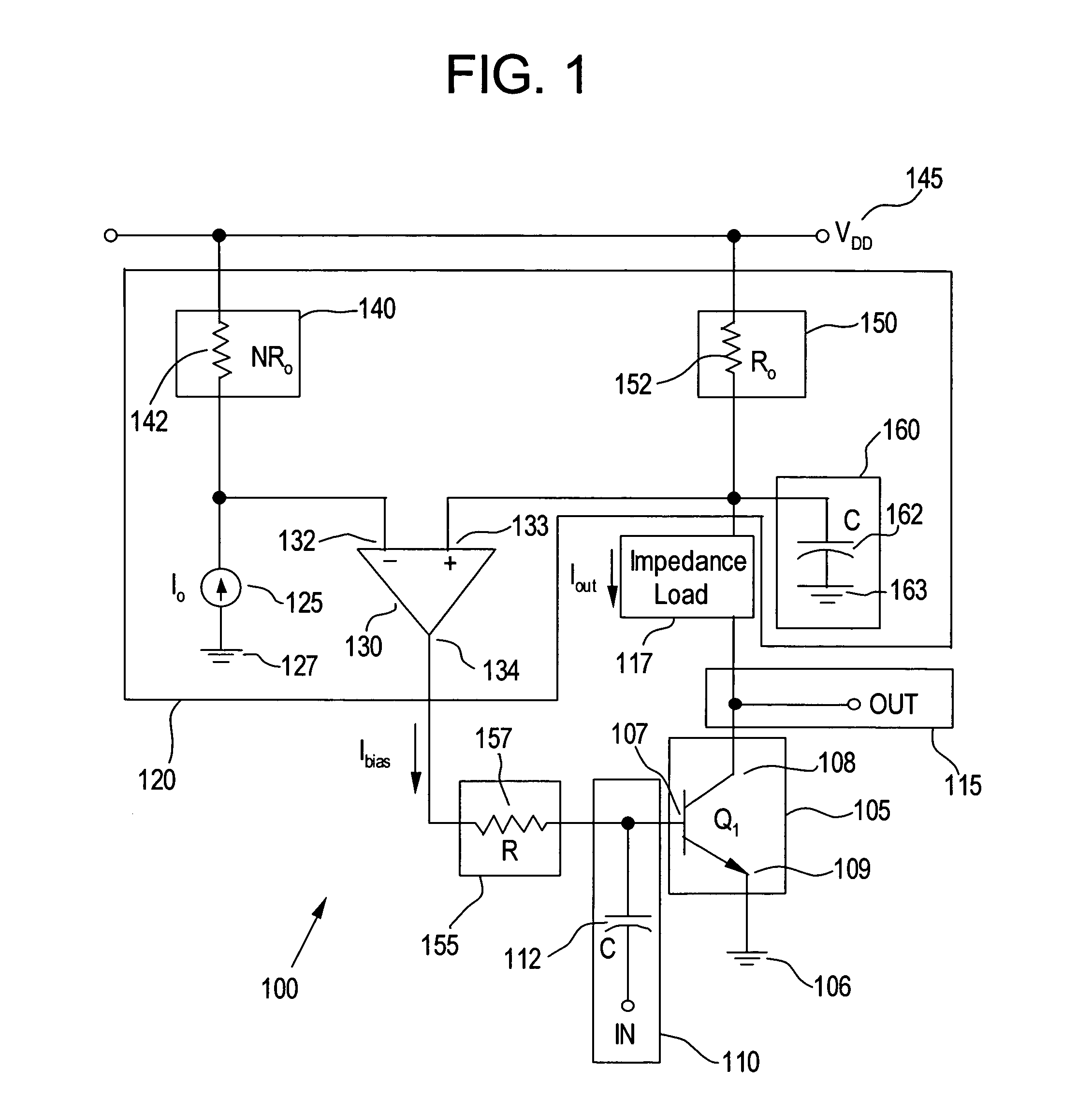
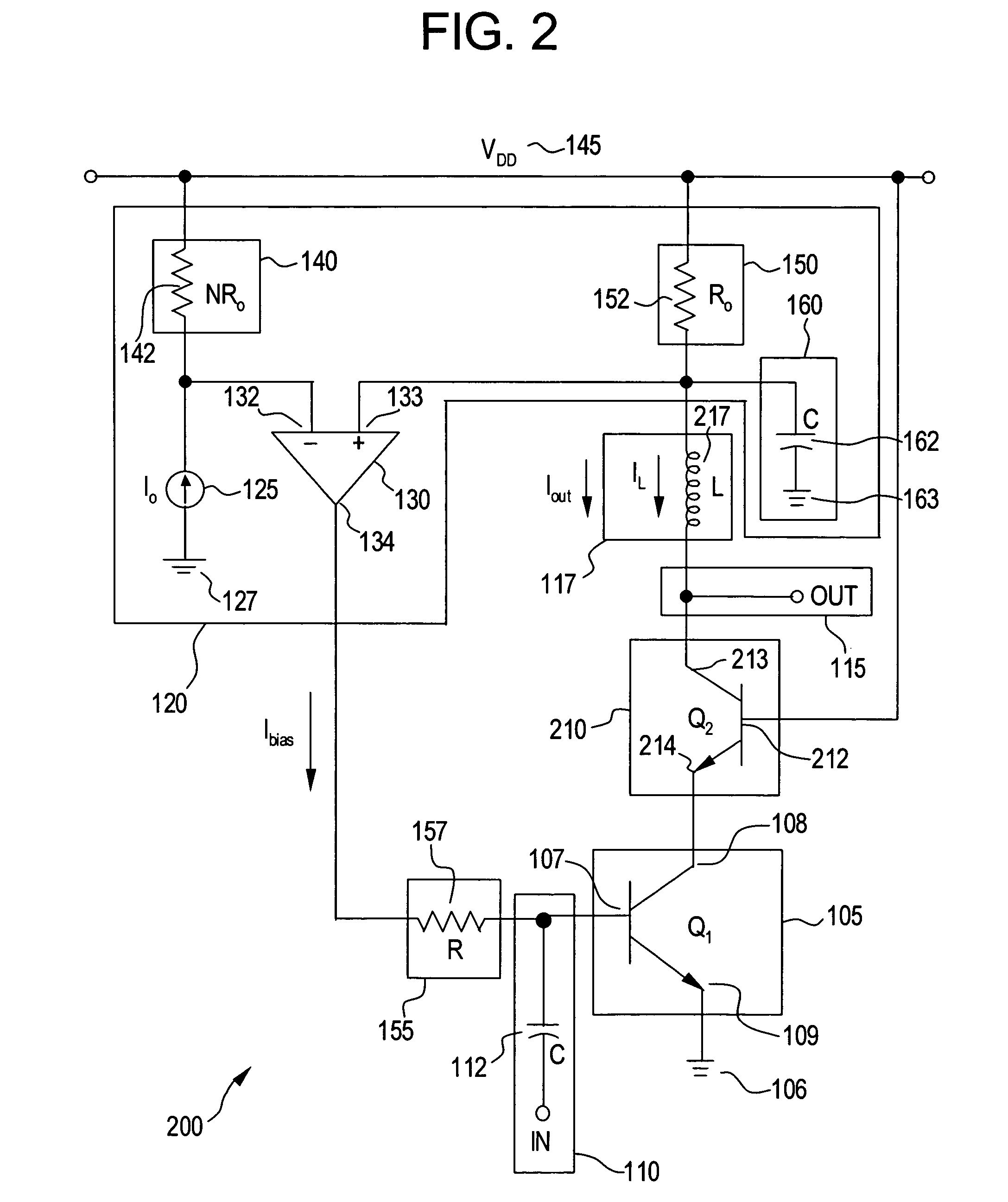
Power supply arrangement for multi-stage amplifier
There is disclosed a multi-stage amplifier comprising: a first amplifier stage; a second amplifier stage; a first voltage supply stage arranged to provide a supply voltage to the first amplifier in dependence on an average power of a signal to be amplified; and a second voltage supply stage arranged to provide a supply voltage to the second amplifier in dependence on an instantaneous power of a signal to be amplified.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
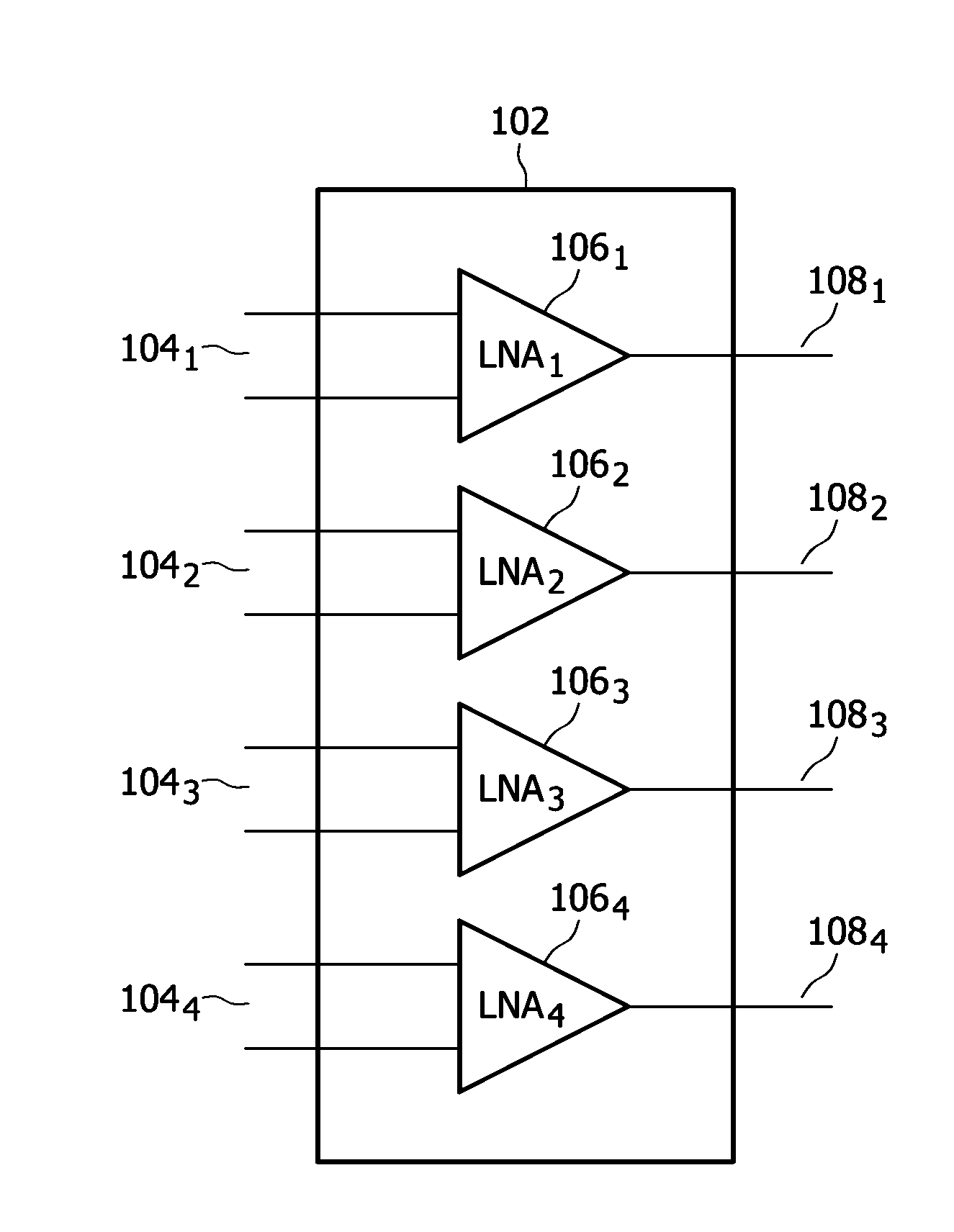
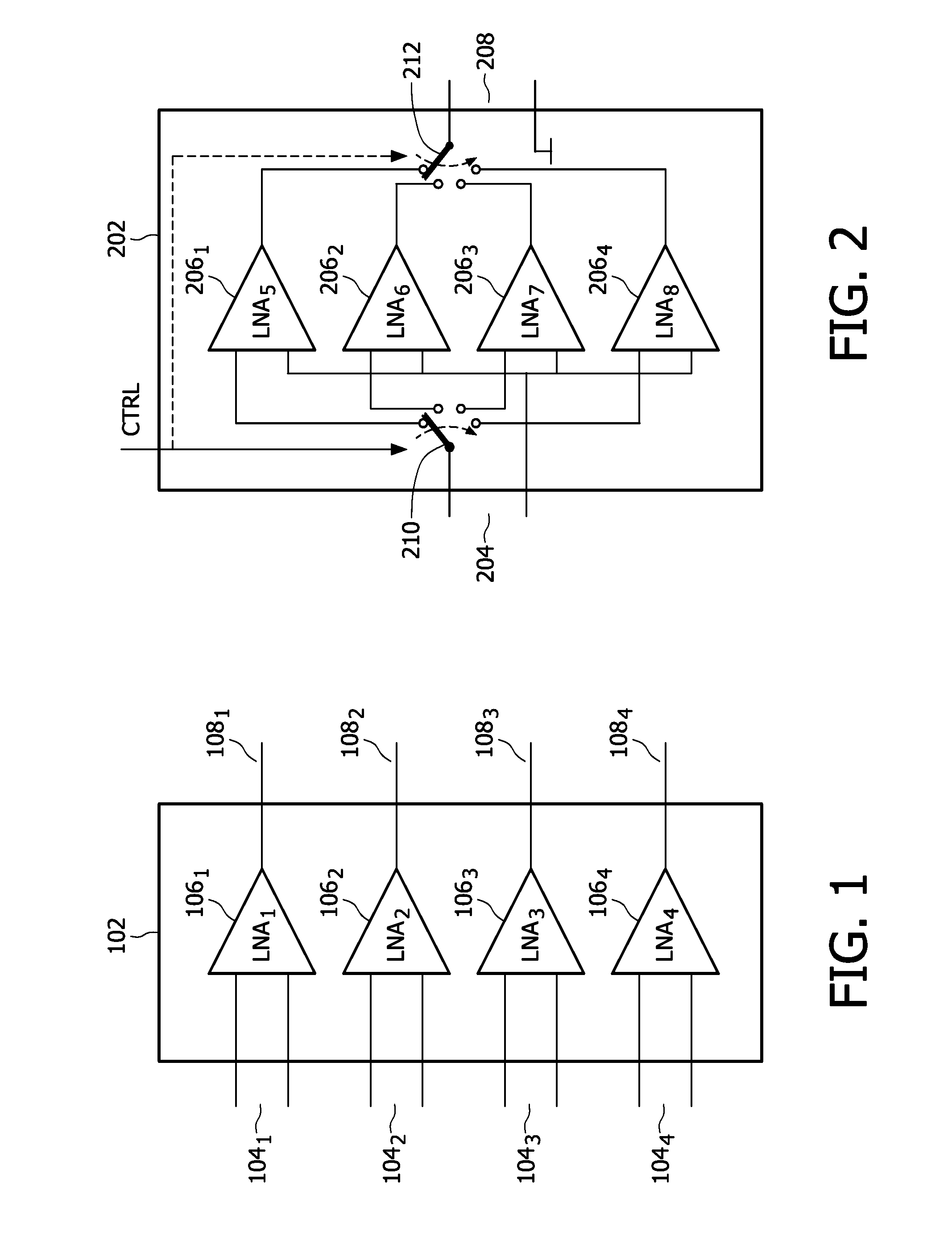
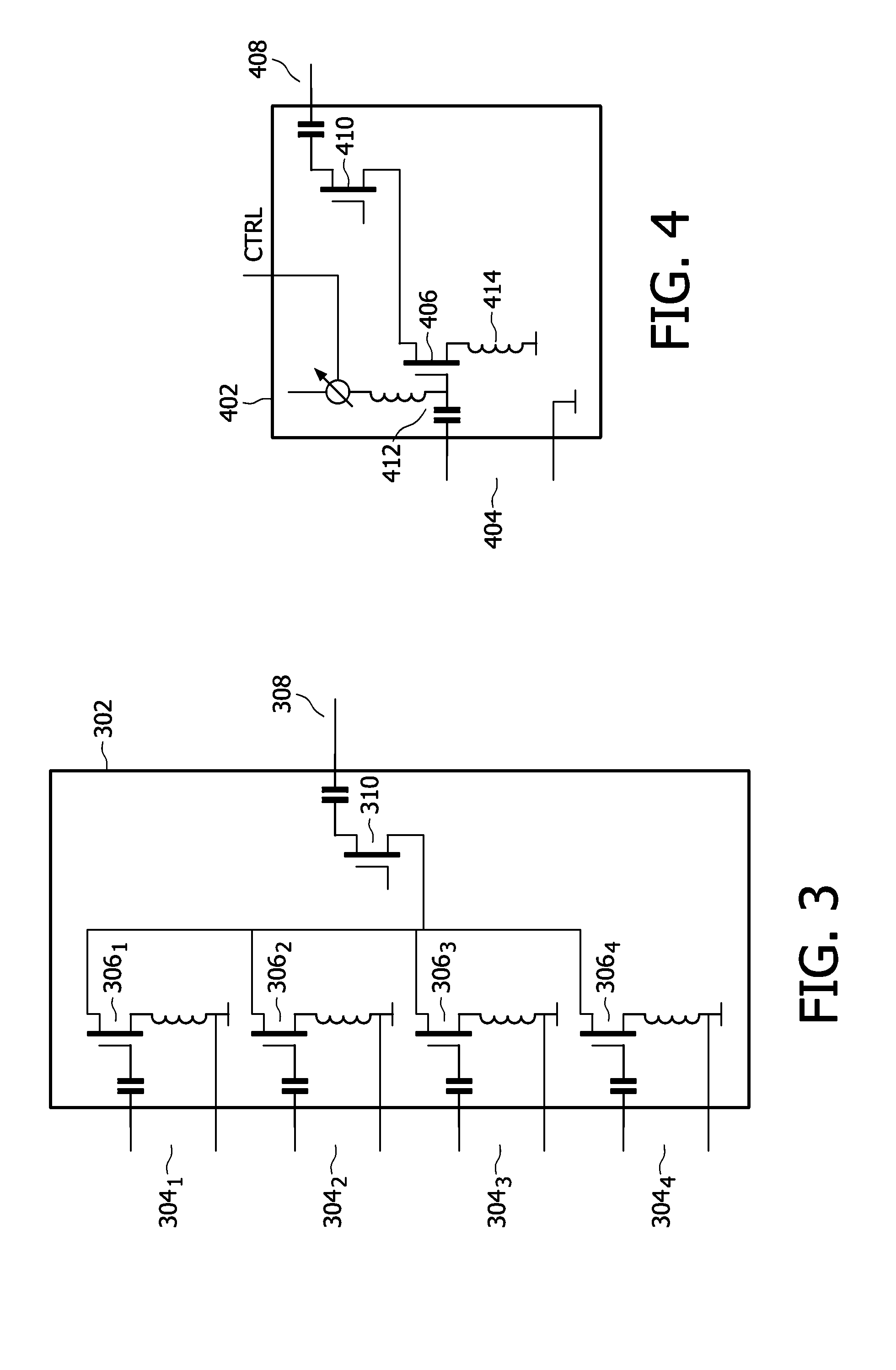
Variable gain low-noise amplifier for a wireless terminal
InactiveUS6657498B2Reduces and avoids clippingNot to wasteGain controlGated amplifiersTuned amplifierEngineering
A variable gain, low noise amplifier is described, which is suitable as the input amplifier for a wireless terminal, or as the pre-amplifier stage of a wireless terminal transmitter. The amplifier may achieve variable gain by deploying a network of transistors in a parallel array, each independently selectable by a PMOS switch, and providing the variable resistance for the resonant circuit. Power dissipation can also be mitigated by using a network of driving transistors, each independently selectable by a PMOS switch. The resonant frequency of the amplifier may be made tunable by providing a selection of optional pull-up capacitors.
Owner:GCT SEMICONDUCTOR INC
Integrated Wideband RF Tracking Filter for RF Front End with Parallel Band Switched Tuned Amplifiers
InactiveUS20090251618A1Uniform gainMultiple-port networksTelevision system detailsRF front endTuned amplifier
A wideband RF tracking filter having a set of parallel tuned resonator amplifier stages with a de-Q resistor for each subband is disclosed. The resonant amplifier contains programmable tuned LC tank impedance and an array of parallel voltage to current converters (V2I) for each subband. The de-Q resistor together with the array of V2I converters provides a flat gain over each subband and each of the other subbands covering different frequencies.
Owner:NXP BV
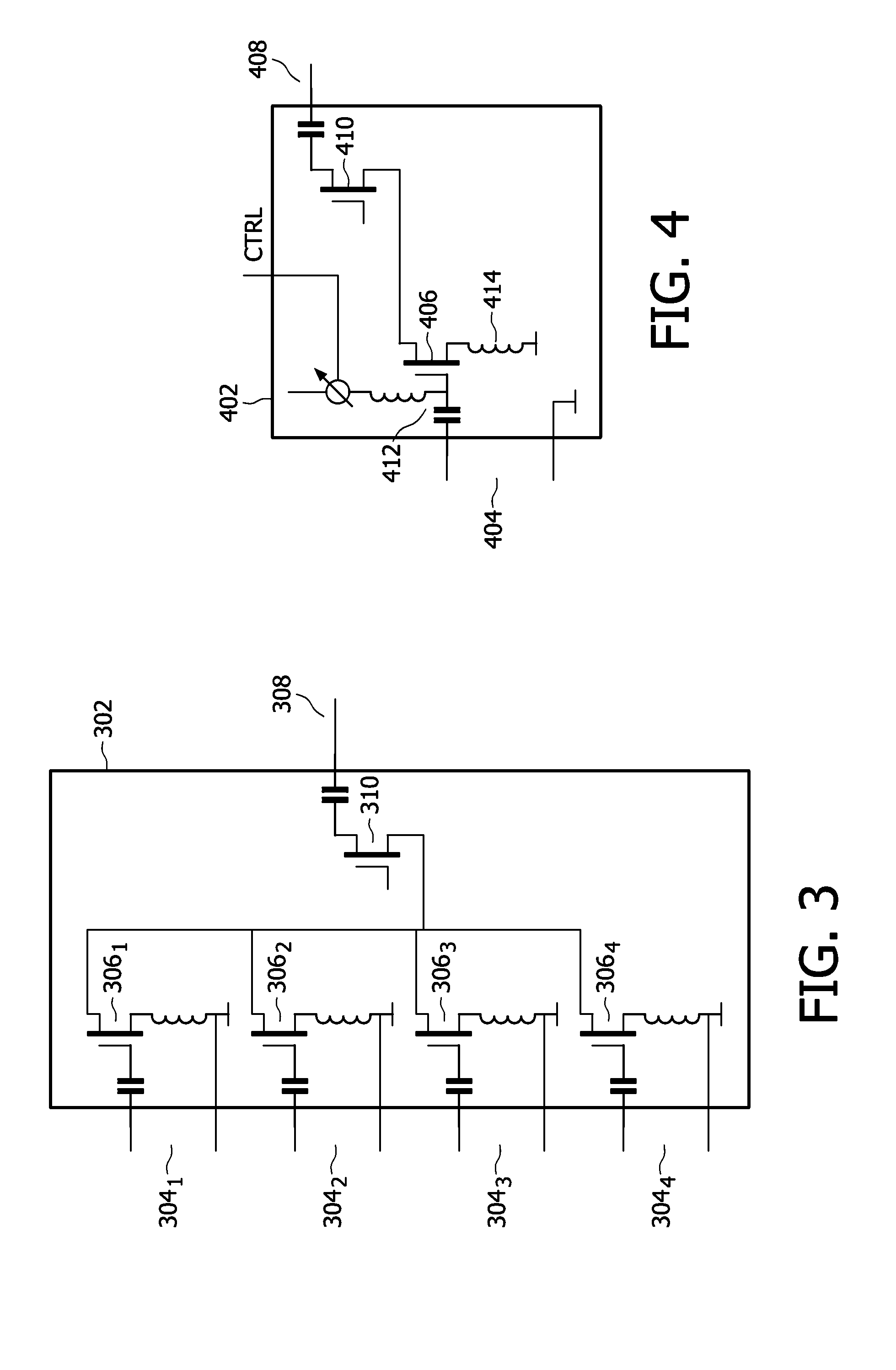
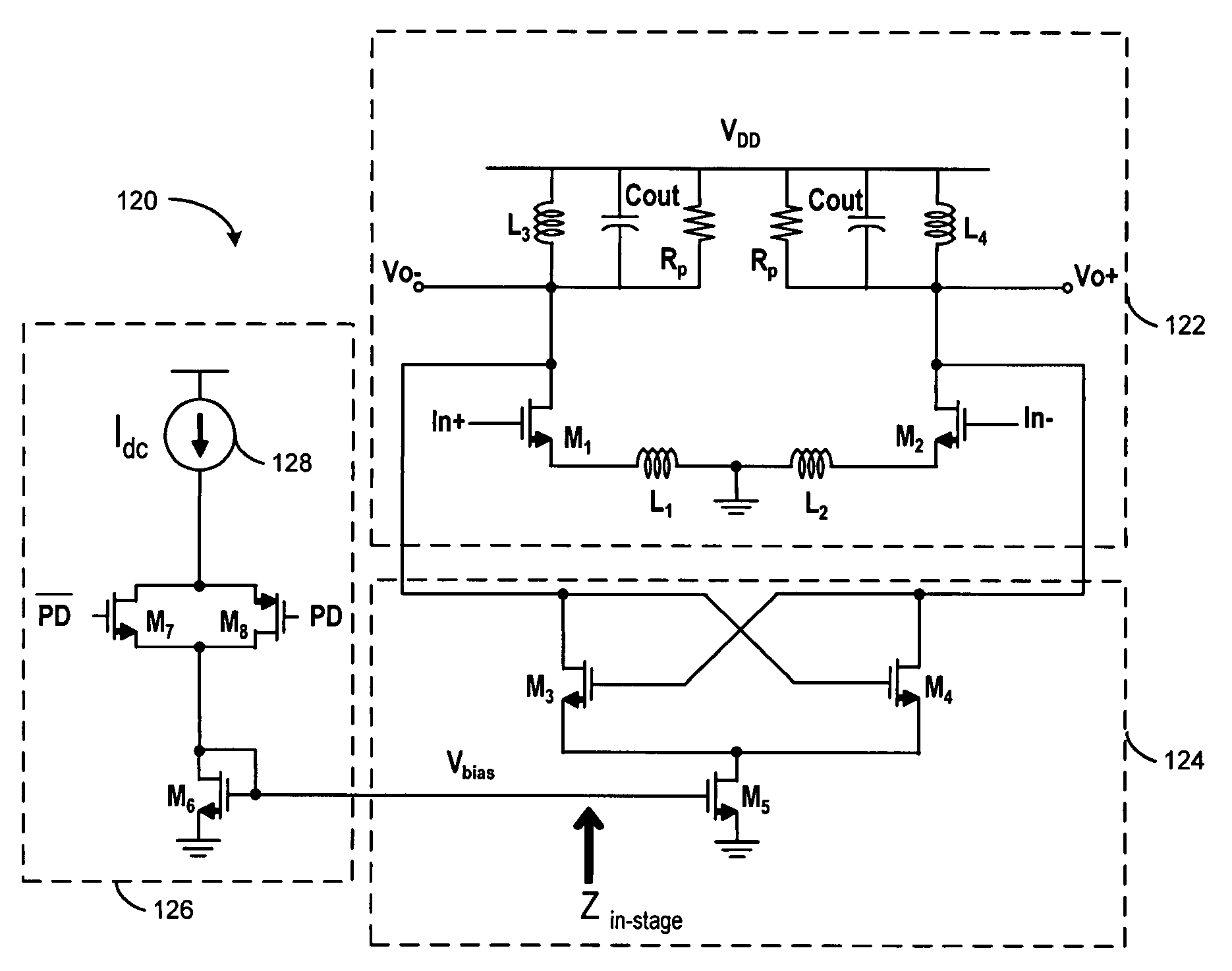
Gain boosting for tuned differential LC circuits
InactiveUS20060145762A1Generate efficientlyAnalog signal digital controlDifferential amplifiersAudio power amplifierTuned amplifier
A gain boost circuit and methodology are described for providing improved gain boosting with tuned amplifier circuits, such as differential low noise amplifier circuits having output resonant tank circuits. By selectively controlling the current source for a negative transconductance stage coupled between the differential amplifier output and the output resonant tank circuits, the amplifier gain may be adjusted to compensate for temperature variations. In addition, the amplifier gain boost may be selectively added, removed or even incrementally adjusted by using a current source control circuit in the negative transconductance stage to adjust the negative transconductance value generated by the negative transconductance stage.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Integrated-circuit low-noise amplifier
InactiveUS20100164498A1Increase the number ofUnwanted noise enhancementHigh frequency amplifiersAmplifier combinationsAudio power amplifierTuned amplifier
It is proposed herein to improve the specifications of a low-noise amplifier (LNA) by integrating it in a chip. In order to cover a range of operating frequencies using a single chip, the integrated-circuit amplifier proposed herein comprises an input port configured to receive a magnetic resonance (MR) signal from a radio-frequency (RF) coil, one or more LNAs configured to amplify the received MR signal, and an output port configured to output the amplified MR signal from the one or more LNAs. The operating frequency of the RF coil depends on the field strength, The matching circuit, if present, needs to be tuned to operate at the operating frequency of the RF coil, and depends on the component values in the loop, thus on loop size. In contrast, the proposed integrated-circuit amplifier is capable of directly connecting to RF coils with different loop sizes, without the need for a matching circuit.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Radio-frequency ultra-wideband low-noise amplifier based on inductance compensation
InactiveCN102497167AImprove transconductanceHigh gainAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceHigh frequency amplifiersUltra-widebandTuned amplifier
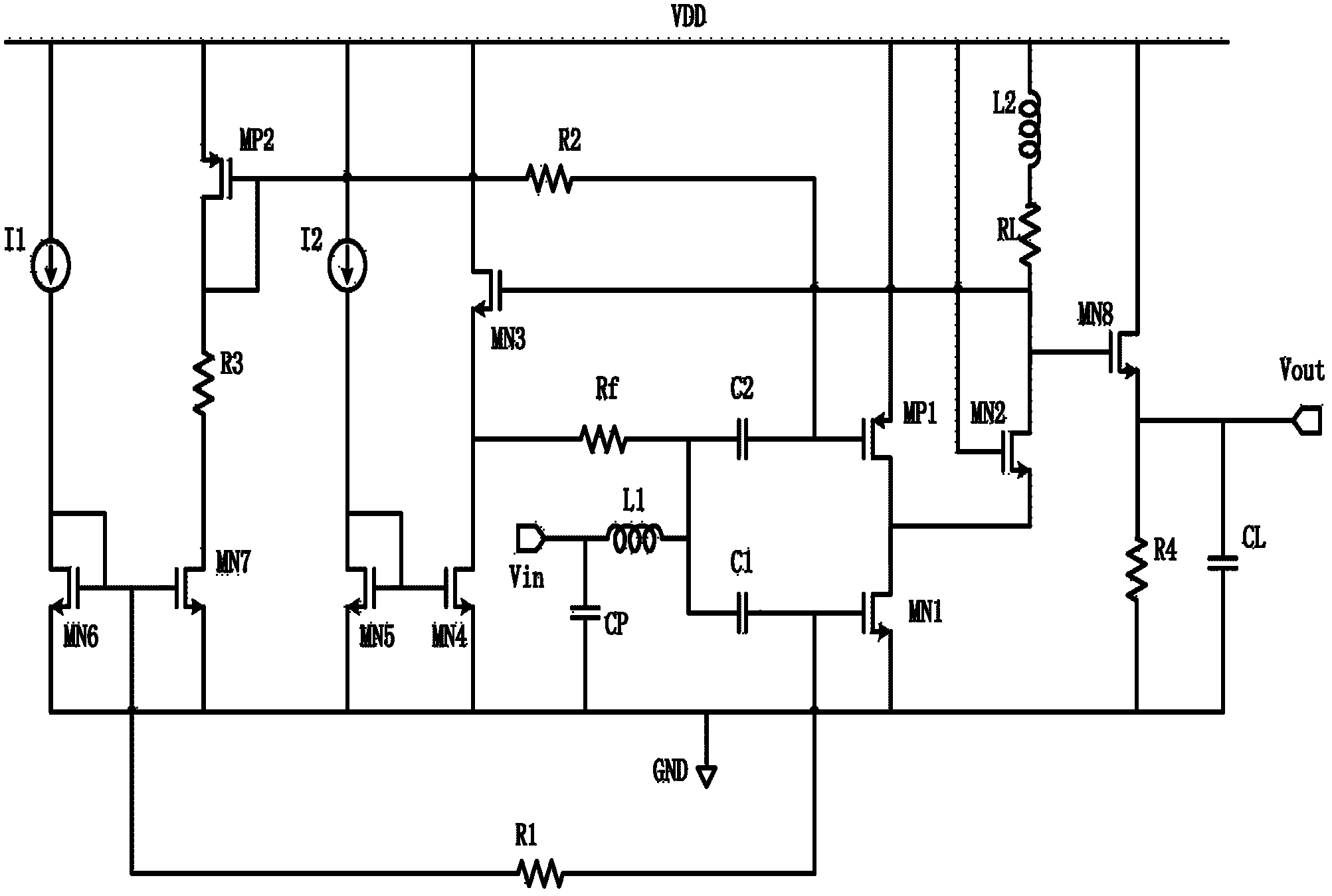
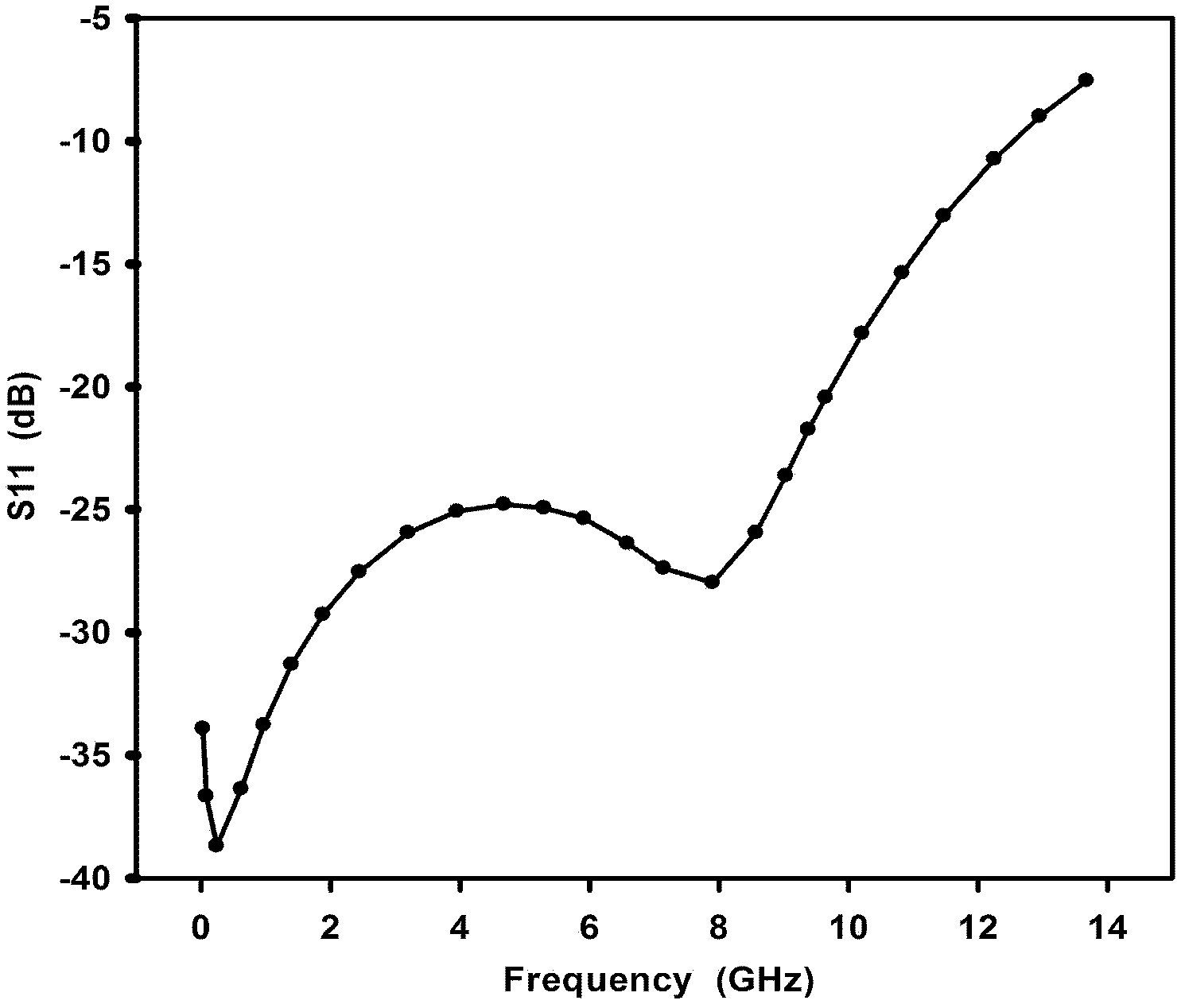
The invention discloses a radio-frequency ultra-wideband low-noise amplifier based on inductance compensation, relating to a radio-frequency integrated circuit technology. The radio-frequency ultra-wideband low-noise amplifier mainly consists of an input amplification-stage circuit, a feedback-stage circuit, a matching-stage circuit, a load-stage circuit, a bias-stage circuit and an output buffering-stage circuit jointly. According to the radio-frequency ultra-wideband low-noise amplifier, both the input matching stage and the load stage are subjected to inductance compensation, and the sensitivity of the low-noise amplifier on the technology is reduced by adopting a current multiplexing technology with independent bias, so that the performance is more stable, the ultra-wideband is also realized, and the working frequency range is 0.1-12GHz; meanwhile, the radio-frequency ultra-wideband low-noise amplifier gets favorable indexes, such as noise, linearity, gain, power consumption and the like and is suitable for an ultra-wideband multi-standard wireless communication receiving system.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
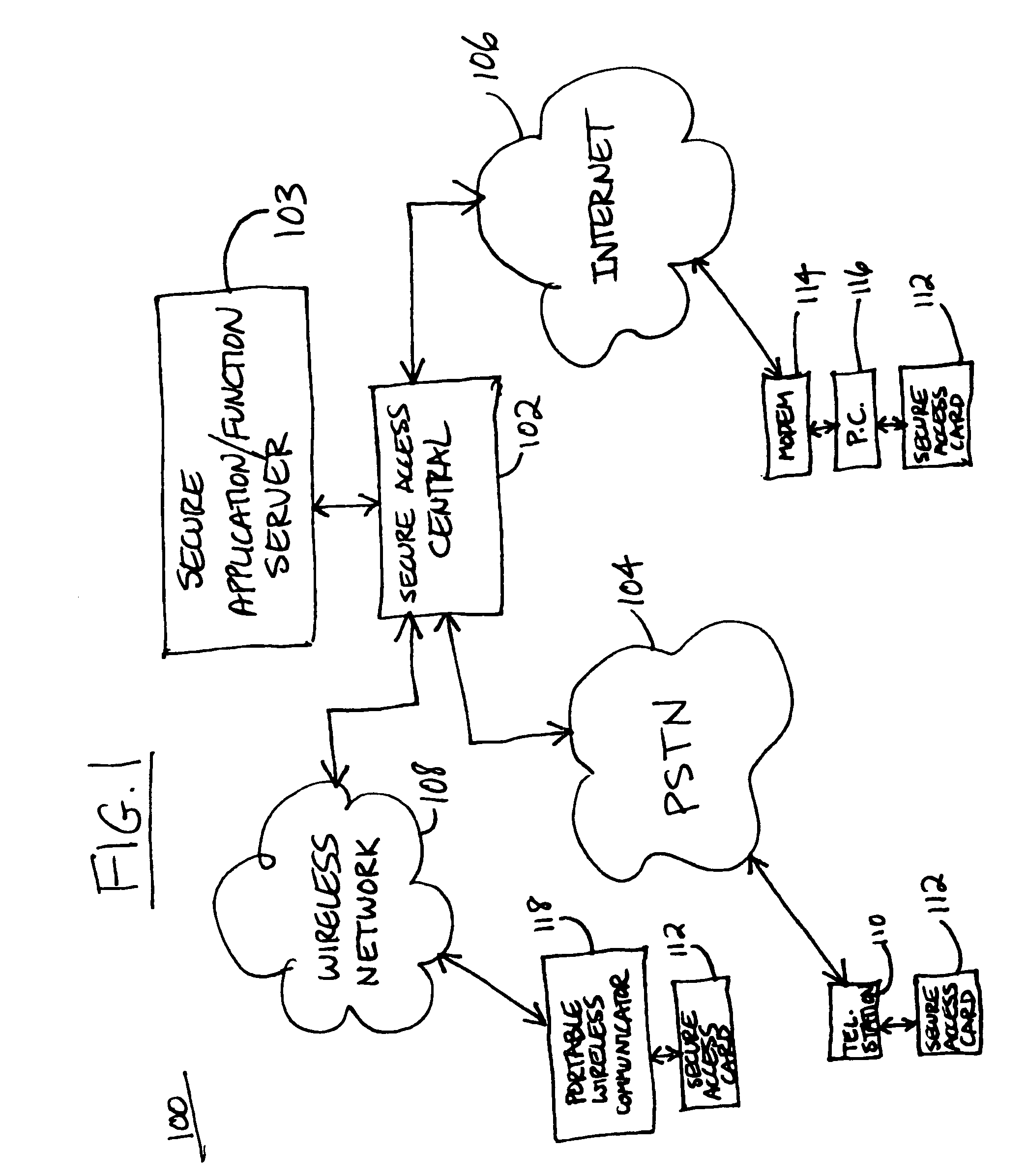
Universal intelligent card for secure access to system functions
InactiveUS7013393B1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwareAudio power amplifier
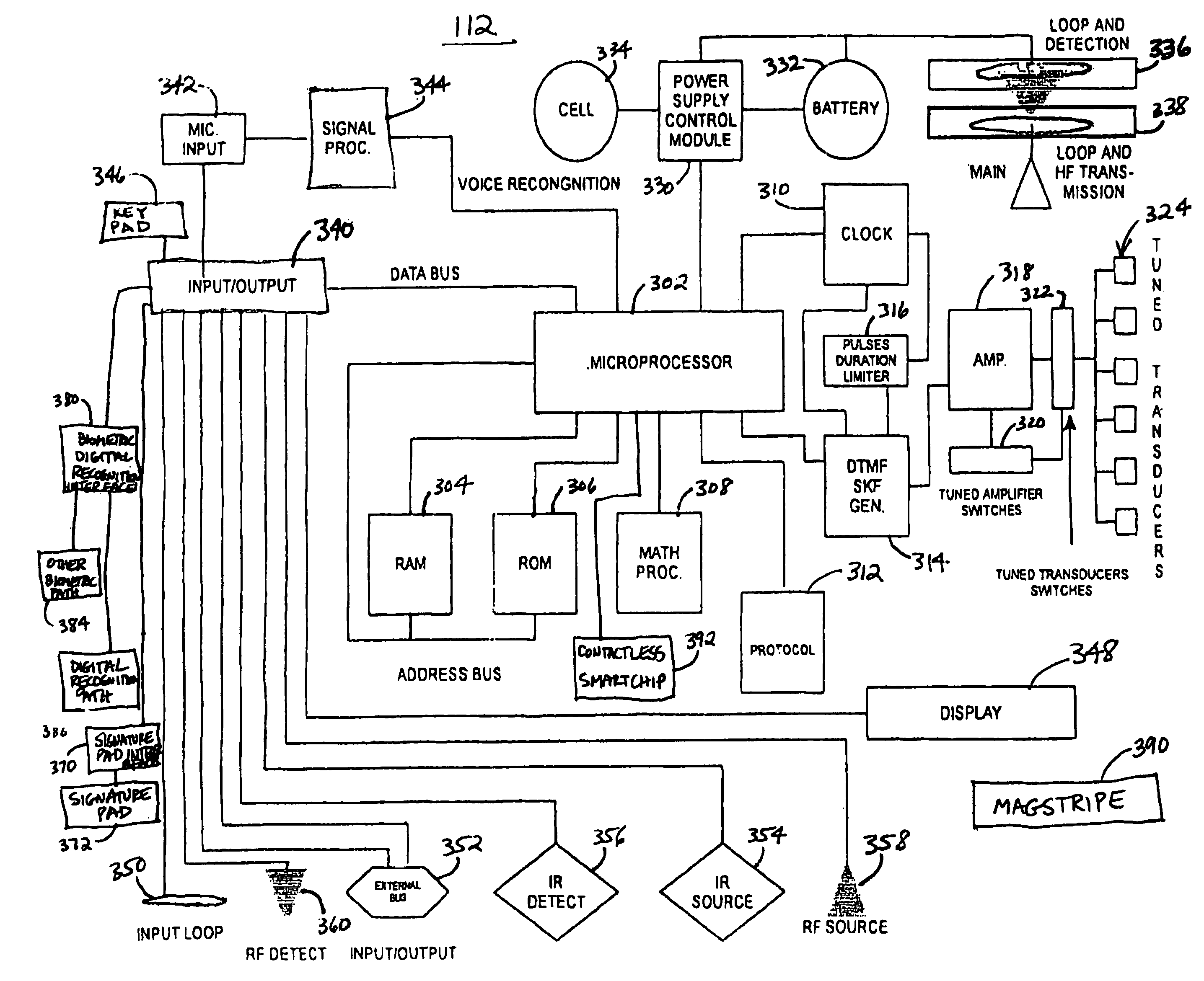
A method and apparatus for secure access to secured system functions utilizing a universal access card. The card includes a bank of tuned amplifier circuits and tuned audio transducers to maximize audio output power from the card, such as for telephone communications. The card includes a variety of other interfaces for the user to communicate with a secure access central system. The card includes a keypad, signature input pad, voice audio input, and fingerprint input, to capture data from a user to determine whether the user is an authorized user. The user utilizes the card to conduct a secure access authorization process with the central. After the card and user are authenticated, the user can access certain functions of a system.
Owner:INTEGRATED INTELLIGENCE INC +2
Wideband low noise amplifier
InactiveCN101252341AImprove Noise PerformanceReduce designAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceTransmissionOperating pointTuned amplifier
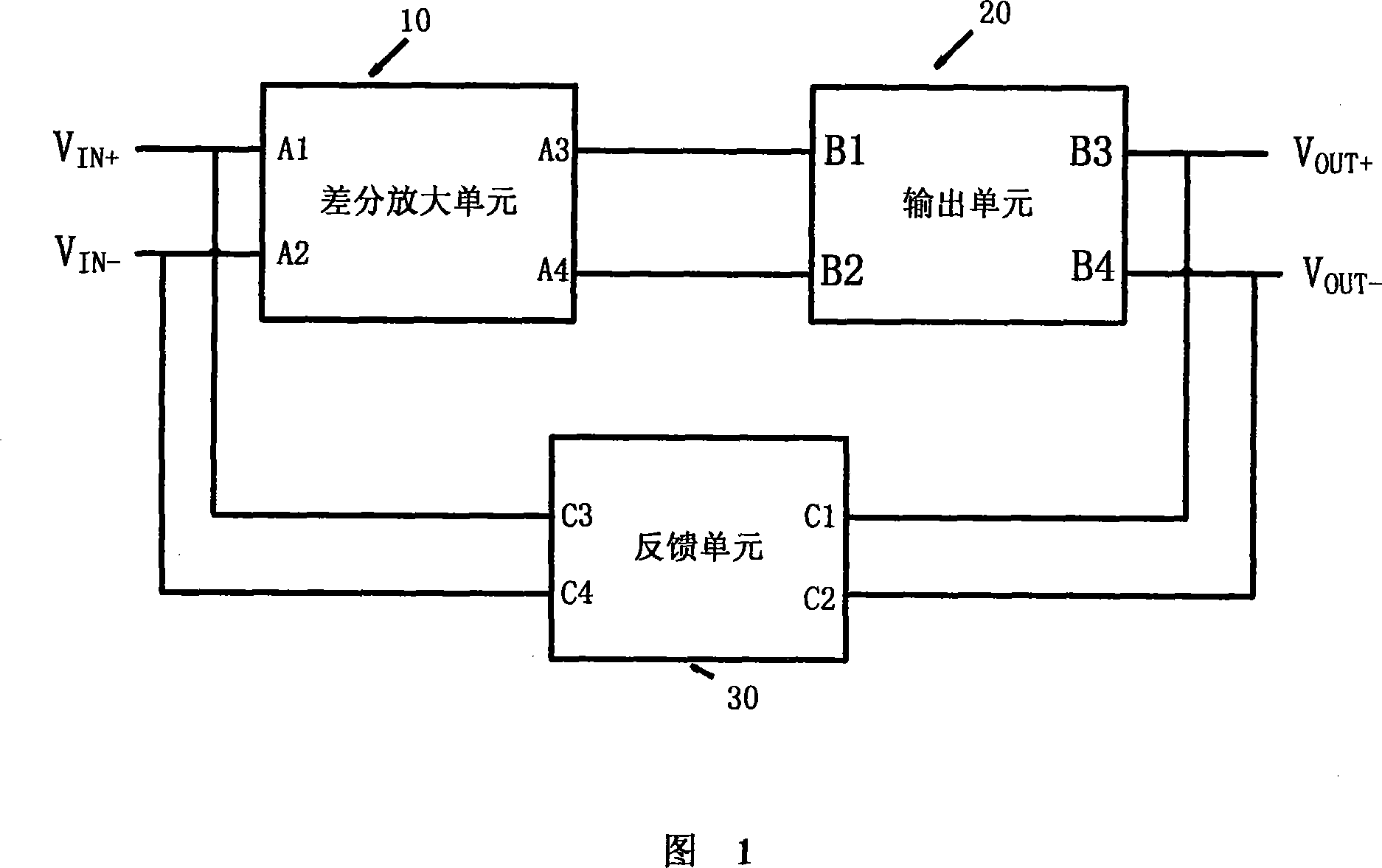
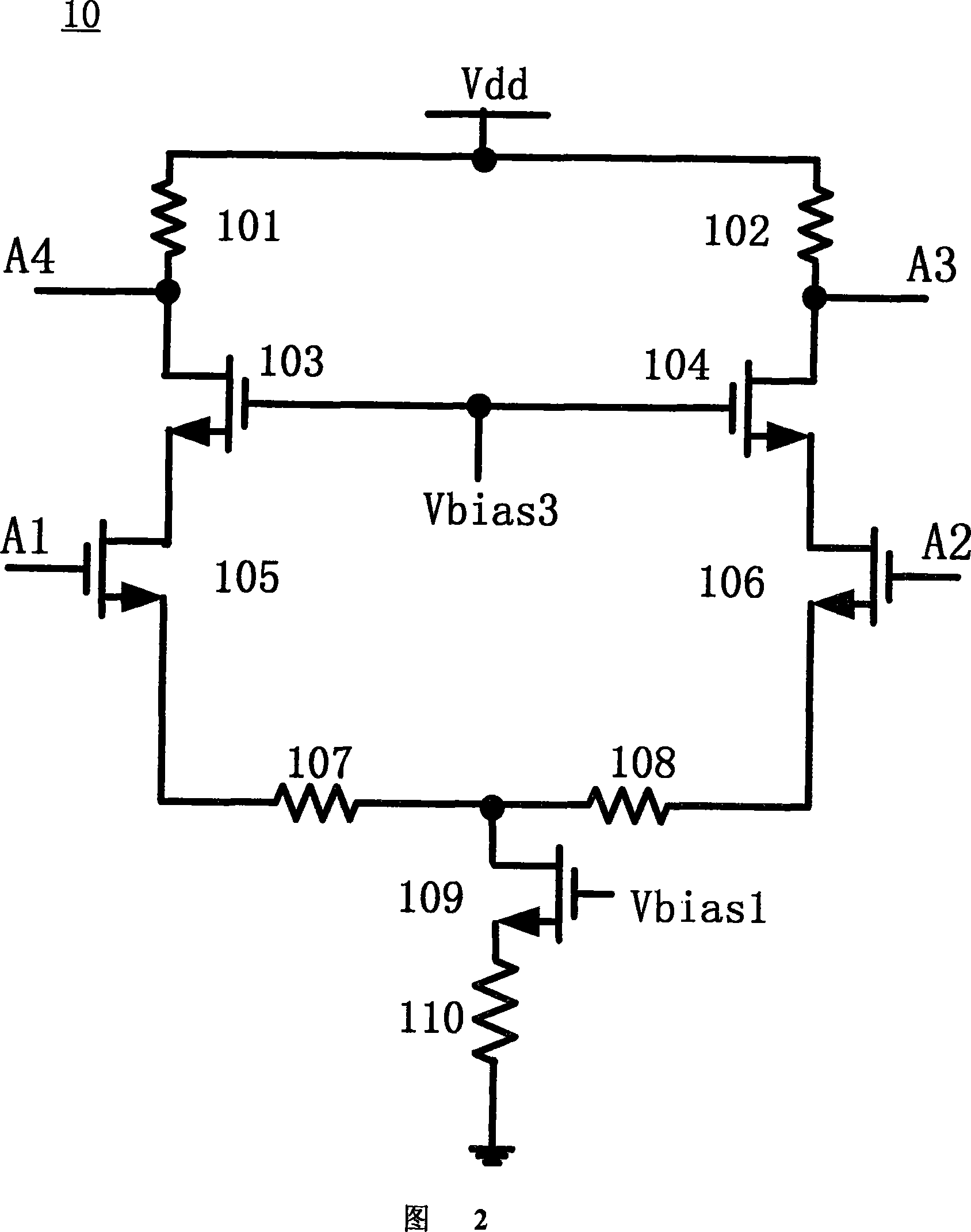
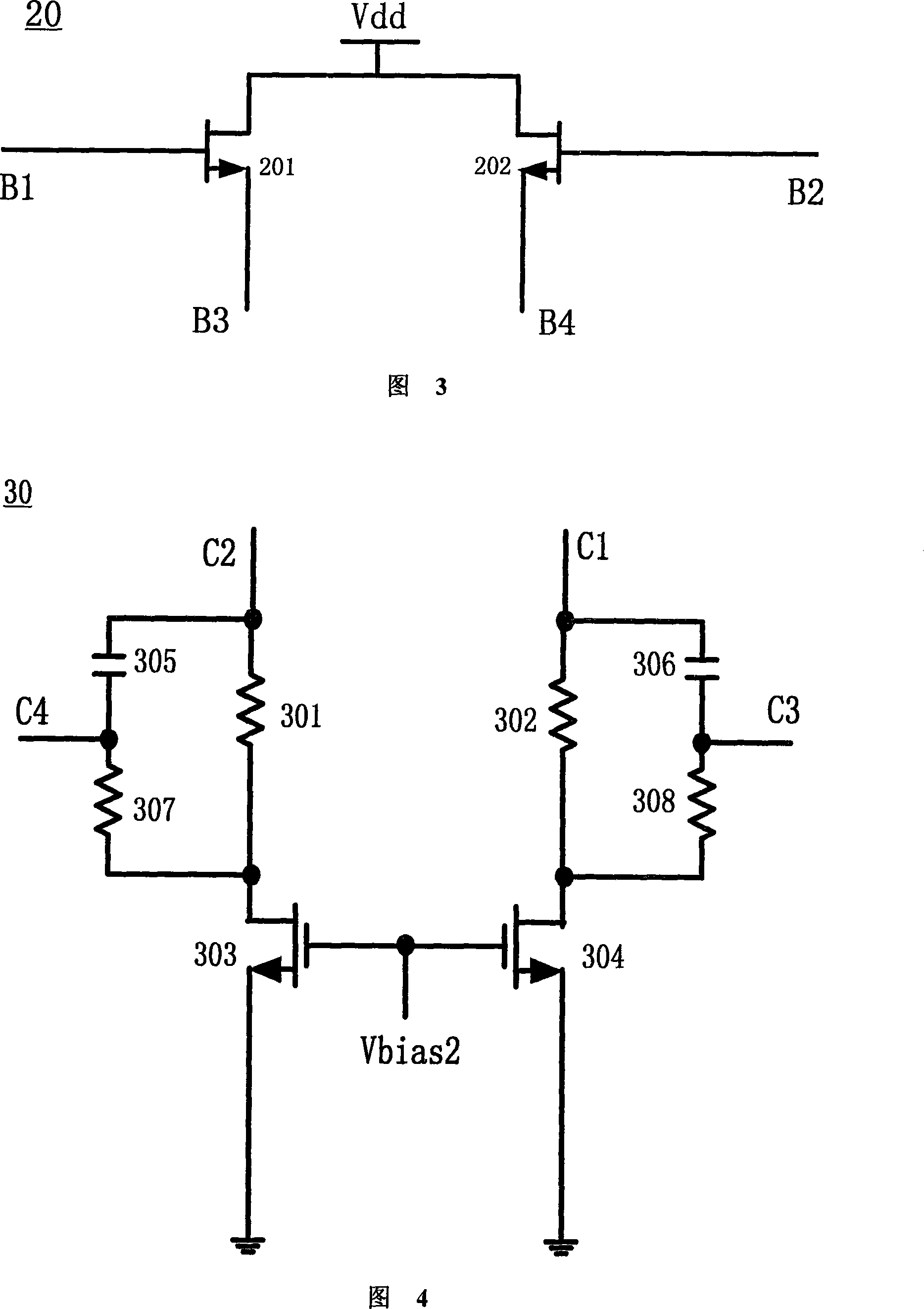
Disclosed is a broadband low-noise amplifier which is a low noise amplifier used to amplify broadband radio frequency signals and a broadband input matching design method. The low noise amplifier comprises a differential amplifier unit(10), an output unit(20), a feedback unit(30). The amplifier adopts a differential structure and employs a parallel-parallel negative feedback structure to realize input impedance matching within the broadband so as to optimize the noise performance of the circuit, and meanwhile, the feedback circuit provides DC offset to an input transistor, thus combining the functions of feeding back the alternating current and providing DC offset, making a DC operating point more stable.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV +1
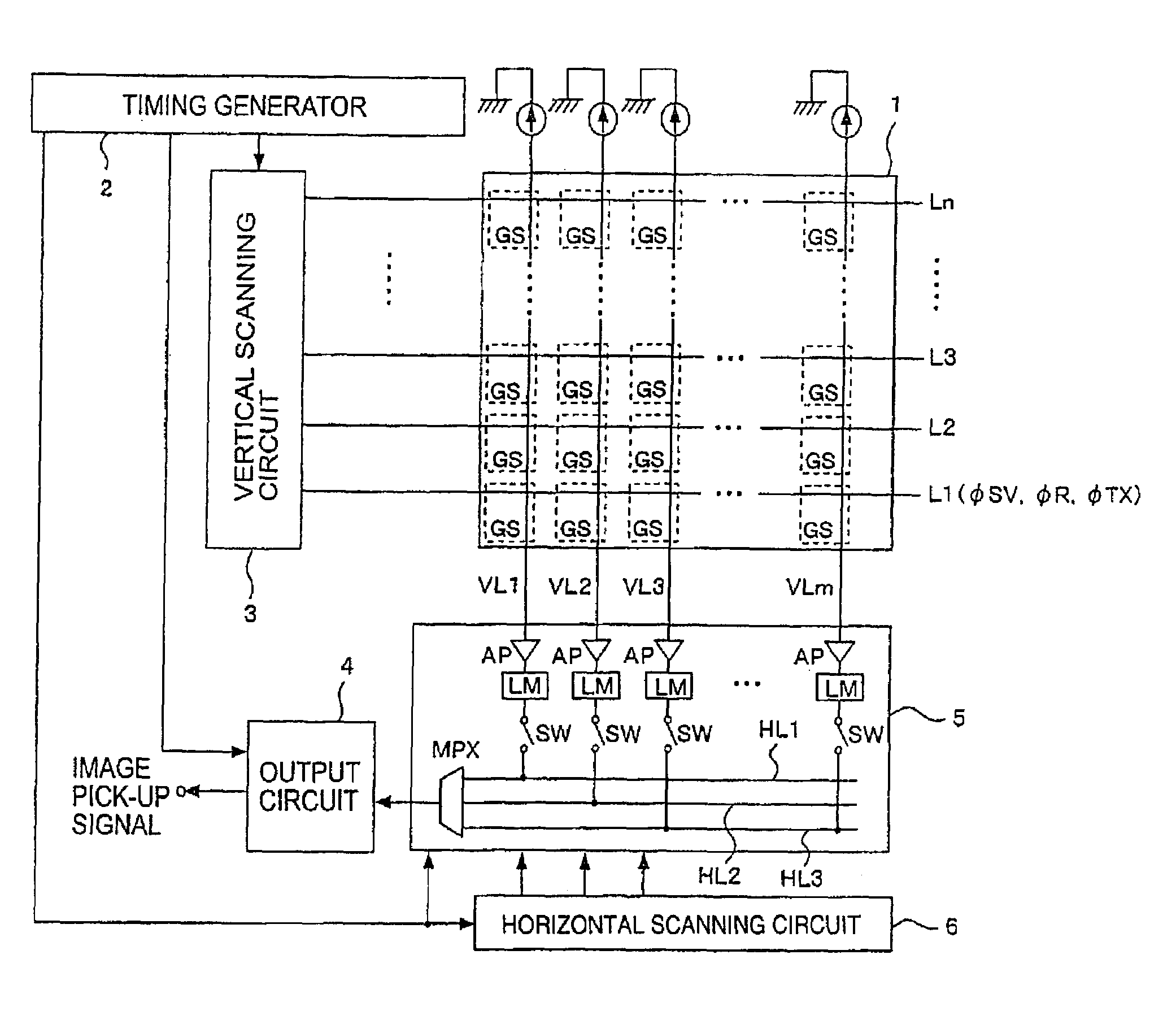
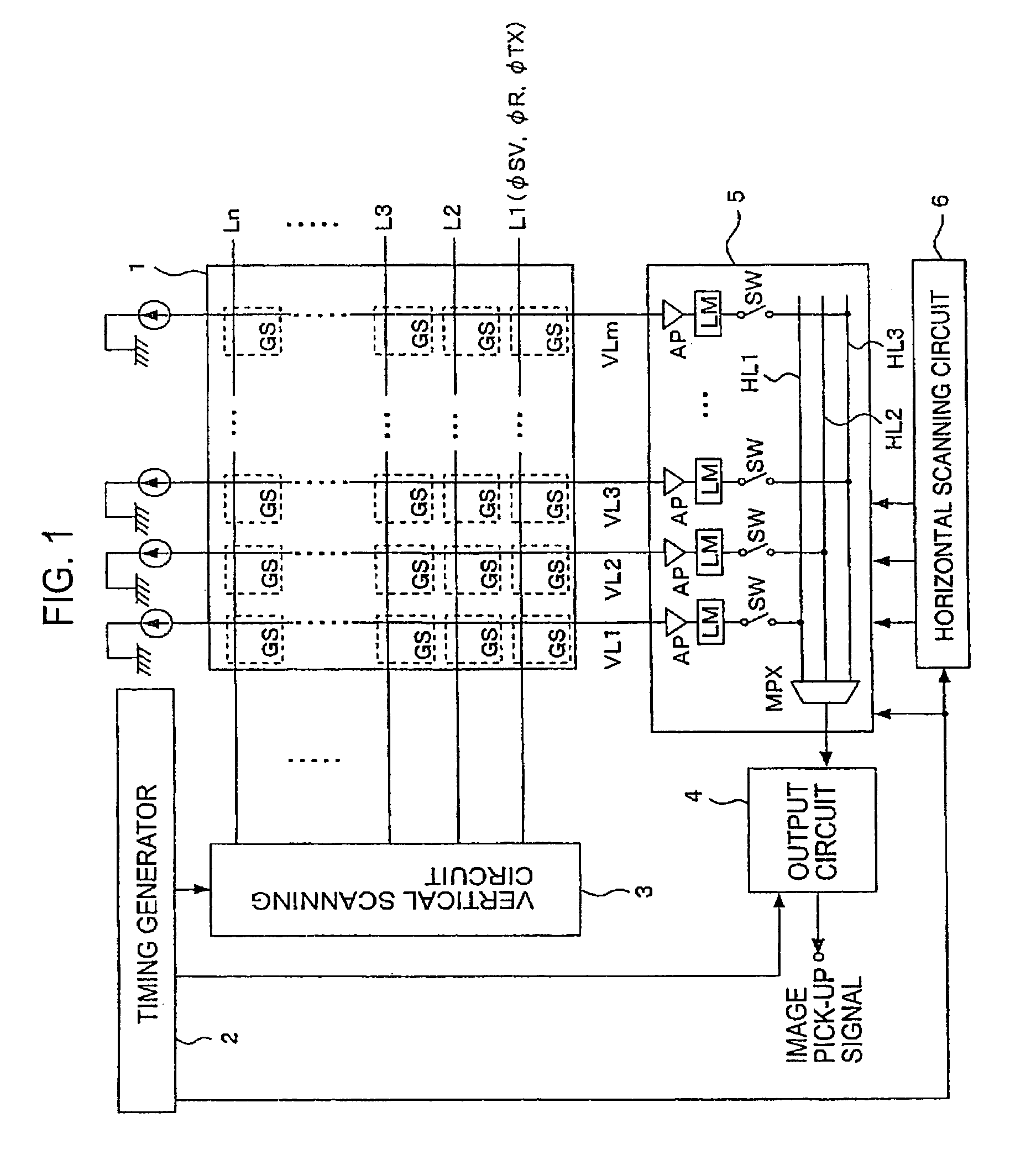
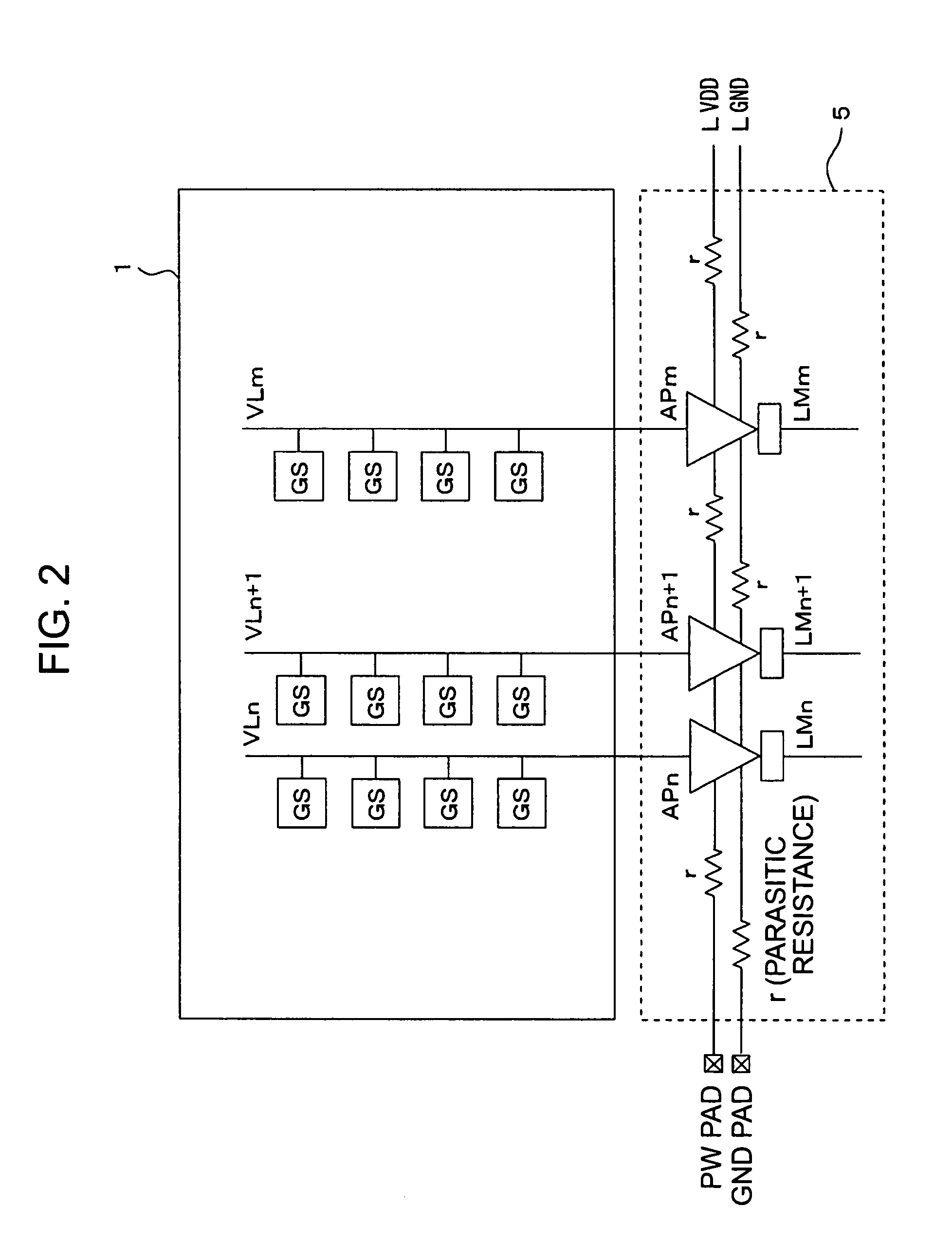
Solid-state image-pickup device with column-line amplifiers and limiters
ActiveUS7141775B2Reduce current consumptionInhibit outputTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsAudio power amplifierTuned amplifier
The levels of the power supply and the ground are kept constant against a parasitic resistance by keeping the constant current of an amplifier irrespective of the size of a pixel signal and the gain of the amplifier in this case in an image signal reading circuit system having the amplifier arranged to each column. The amplifier has a limiter at an output terminal thereof which limits an output voltage of the amplifier to a range for keeping the constant consumption-current.
Owner:SONY CORP
Magnetic resonance integrated-circuit low-noise amplifier
InactiveUS8324900B2Increase the number ofSmall sizeHigh frequency amplifiersAmplifier combinationsAudio power amplifierTuned amplifier
It is proposed herein to improve the specifications of a low-noise amplifier (LNA) by integrating it in a chip. In order to cover a range of operating frequencies using a single chip, the integrated-circuit amplifier proposed herein comprises an input port configured to receive a magnetic resonance (MR) signal from a radio-frequency (RF) coil, one or more LNAs configured to amplify the received MR signal, and an output port configured to output the amplified MR signal from the one or more LNAs. The operating frequency of the RF coil depends on the field strength. The matching circuit, if present, needs to be tuned to operate at the operating frequency of the RF coil, and depends on the component values in the loop, thus on loop size. In contrast, the proposed integrated-circuit amplifier is capable of directly connecting to RF coils with different loop sizes, without the need for a matching circuit.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Gain boosting for tuned differential LC circuits
ActiveUS20070200628A1Generate efficientlyAnalog signal digital controlDifferential amplifiersAudio power amplifierTuned amplifier
A gain boost circuit and methodology are described for providing improved gain boosting with tuned amplifier circuits, such as differential low noise amplifier circuits having output resonant tank circuits. By selectively controlling the current source for a negative transconductance stage coupled between the differential amplifier output and the output resonant tank circuits, the amplifier gain may be adjusted to compensate for temperature variations. In addition, the amplifier gain boost may be selectively added, removed or even incrementally adjusted by using a current source control circuit in the negative transconductance stage to adjust the negative transconductance value generated by the negative transconductance stage.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Low-noise amplifier and a front-end system with same
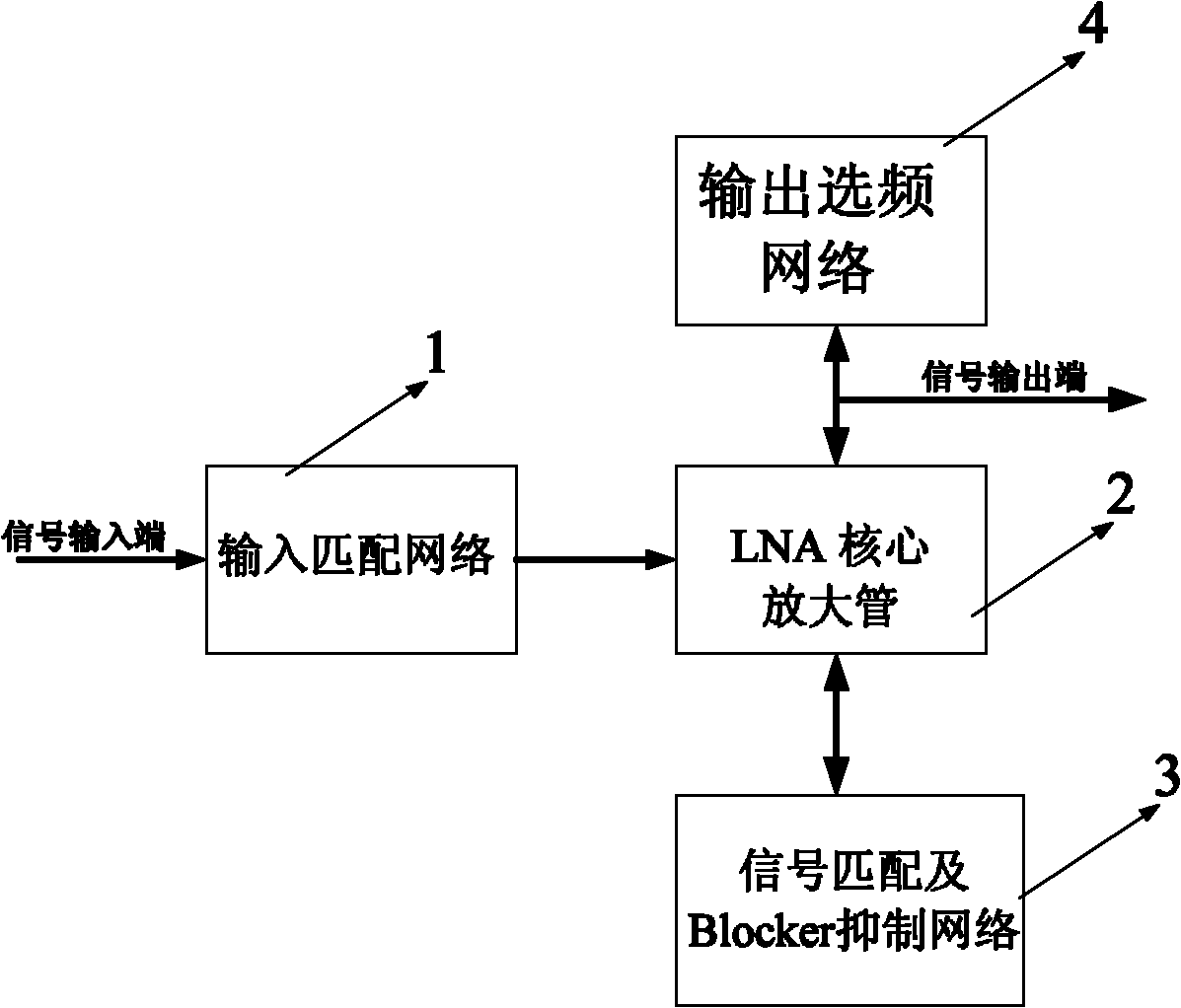
ActiveCN102611394AReduce areaReduce power consumptionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceTransmissionTD-SCDMAAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses a low-noise amplifier and a TD-SCDMA (time division-synchronous code division multiple access) radio-frequency front-end system with the same. Antenna receiving comprises a useful signal and a signal interfering signals. Firstly, matching processing is carried out on the useful signal through an input matching network and a blocker interference suppression network, and blocker interference is realized, so as to present high-impedance suppression; and then amplification processing is carried out on the signal through a core amplification tube of the low-noise amplifier; and finally frequency selection is carried out on the useful signal through outputting an LC frequency selection network, so as to output a non-interference signal; the blocker suppression network is designed in the low-noise amplifier, so as to displace an SAW (surface acoustic wave) filter outside a chip, and the blocker suppression network is combined with the input matching network; the received interference signals are filtered out from the LNA (low-noise amplifier), thus realizing the purposes that the interference signals are filtered out, simultaneously the area of the chip is reduced, the system power consumption is lowered, and the system performance is improved.
Owner:LEADCORE TECH
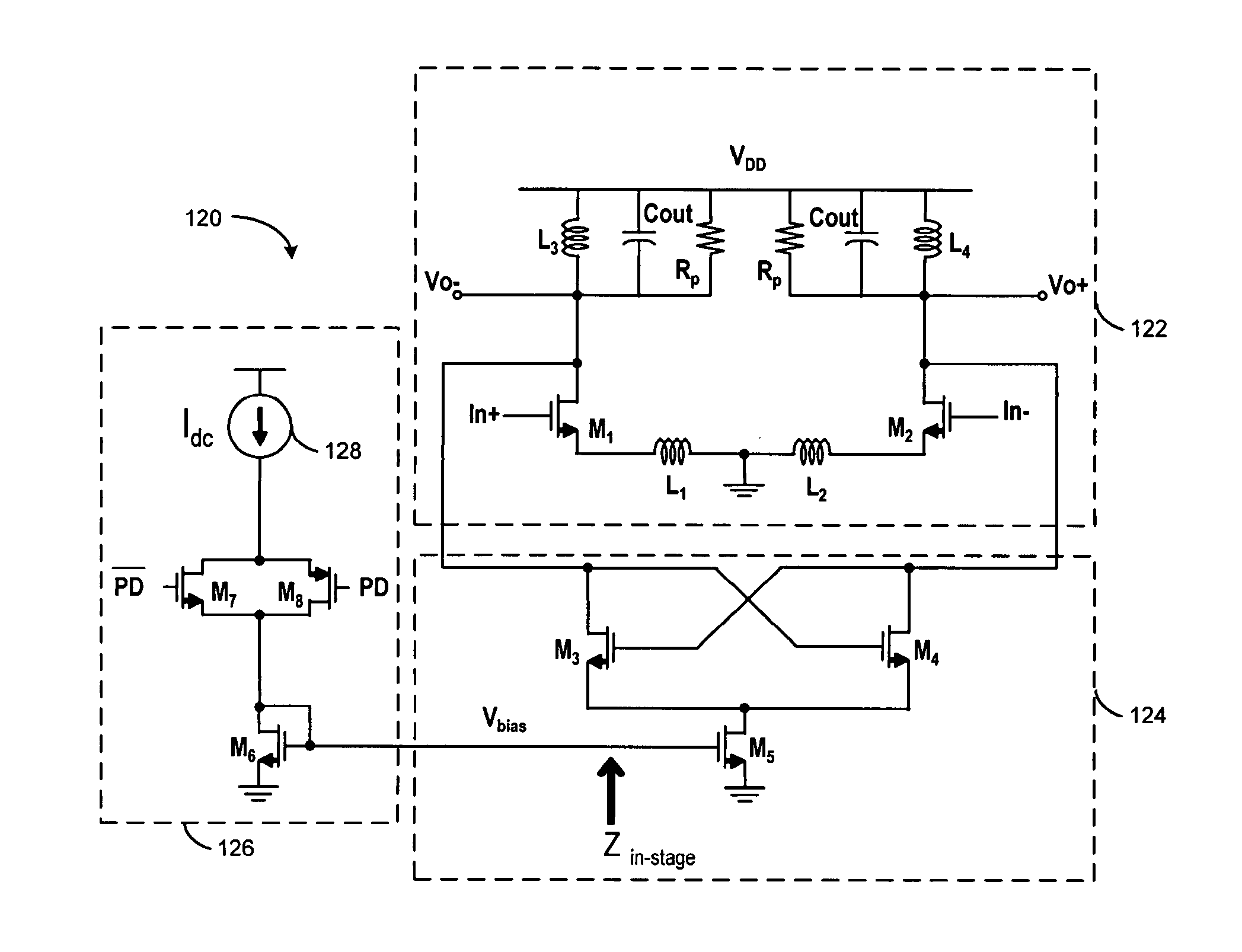
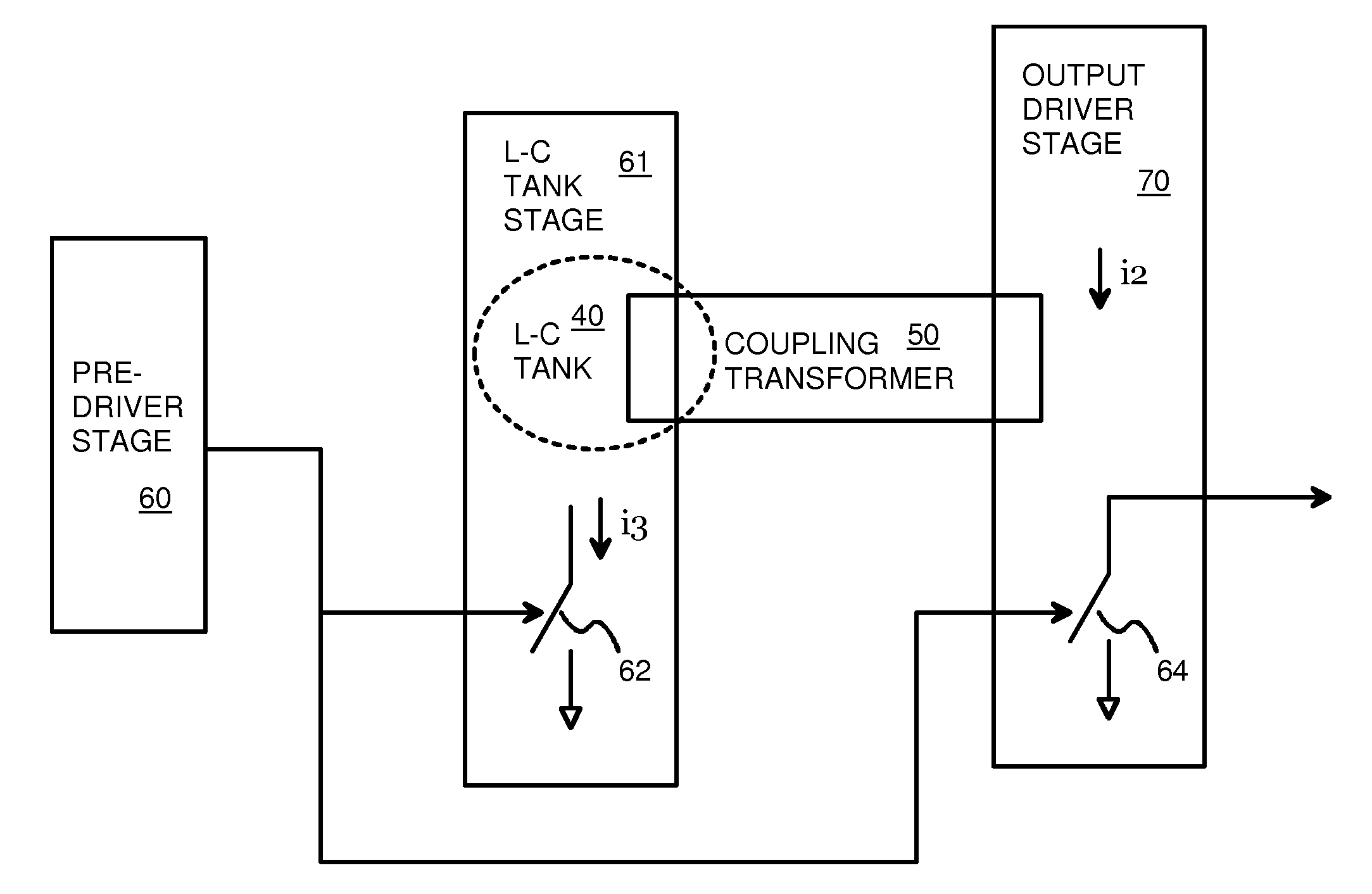
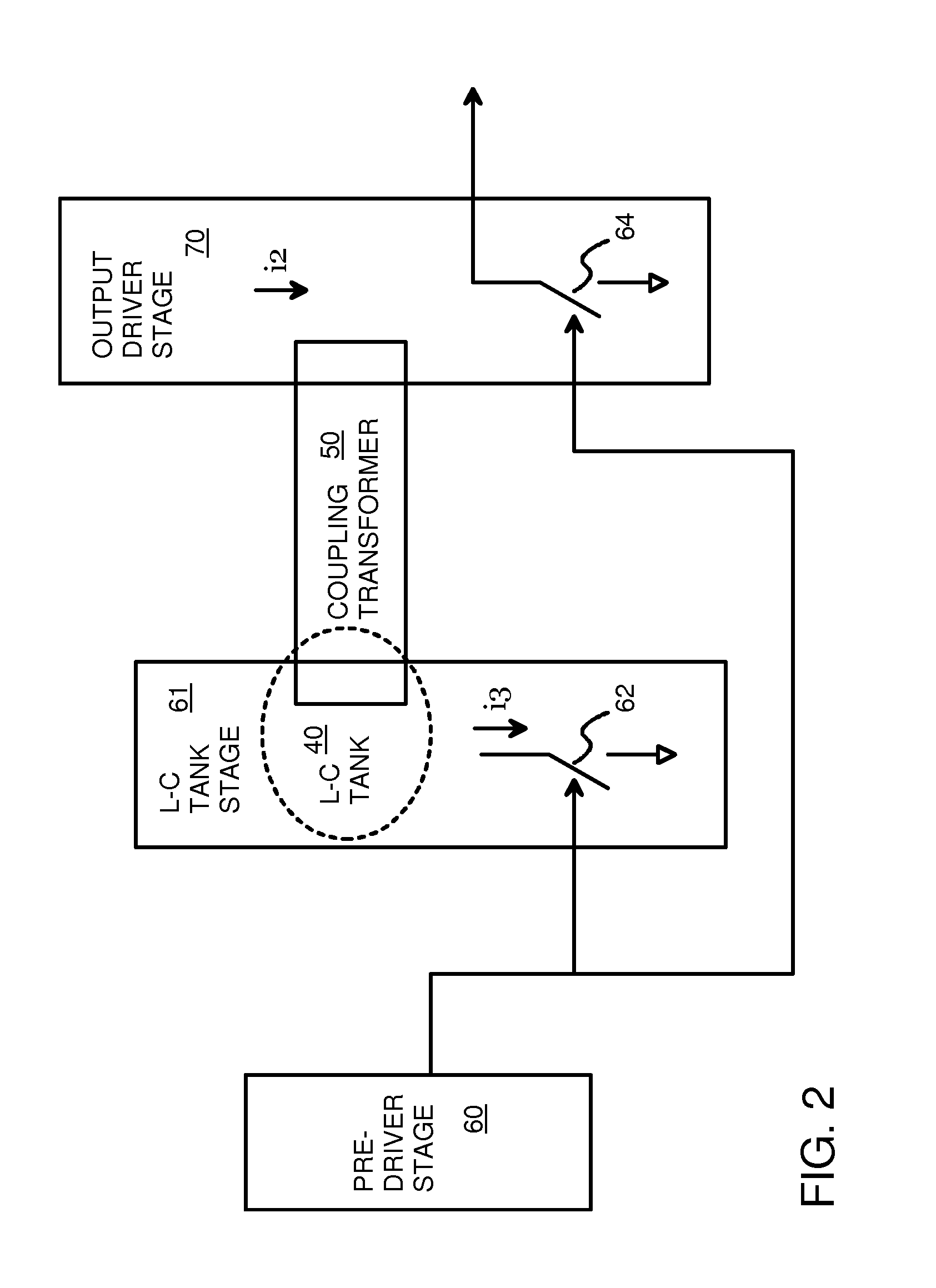
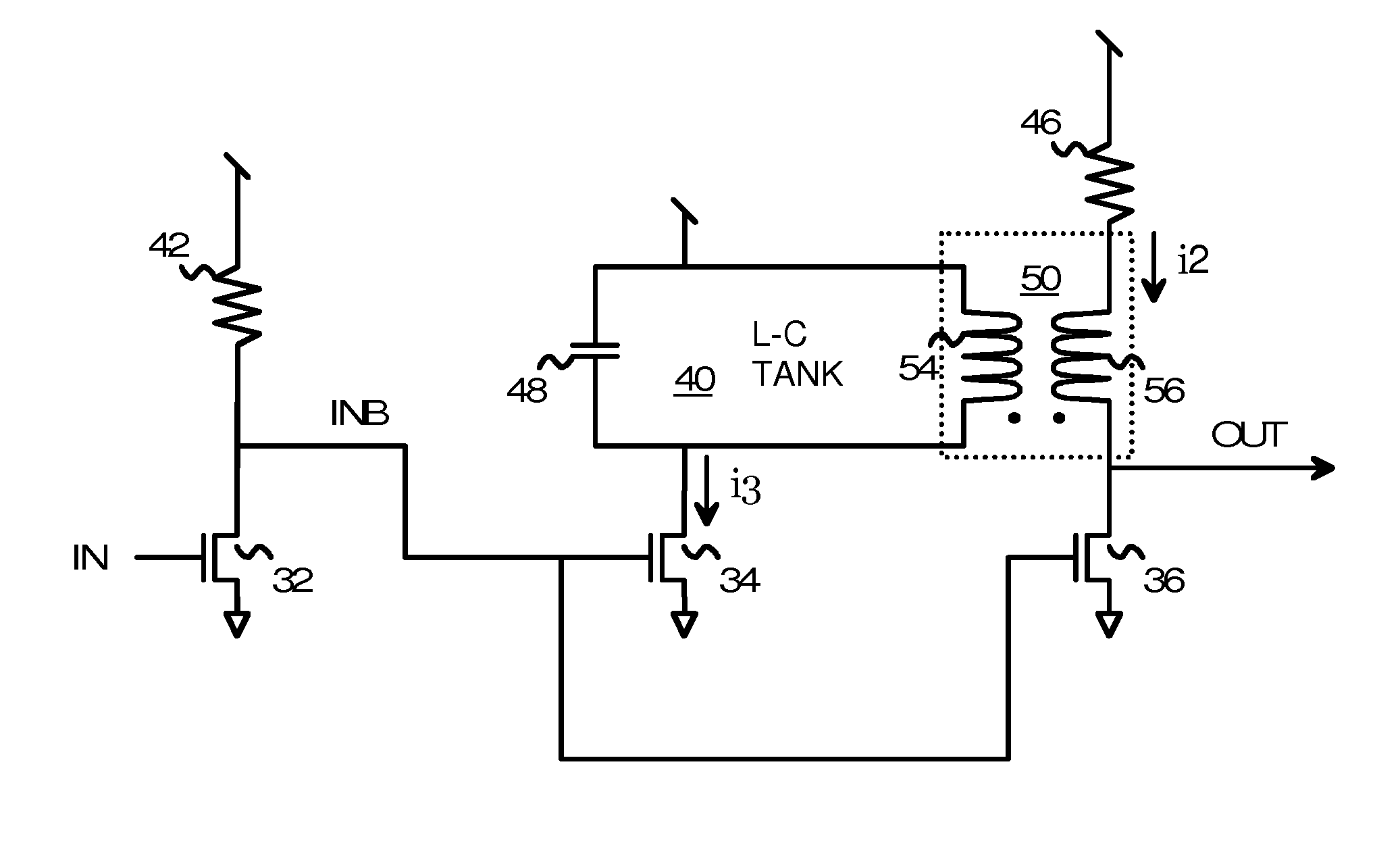
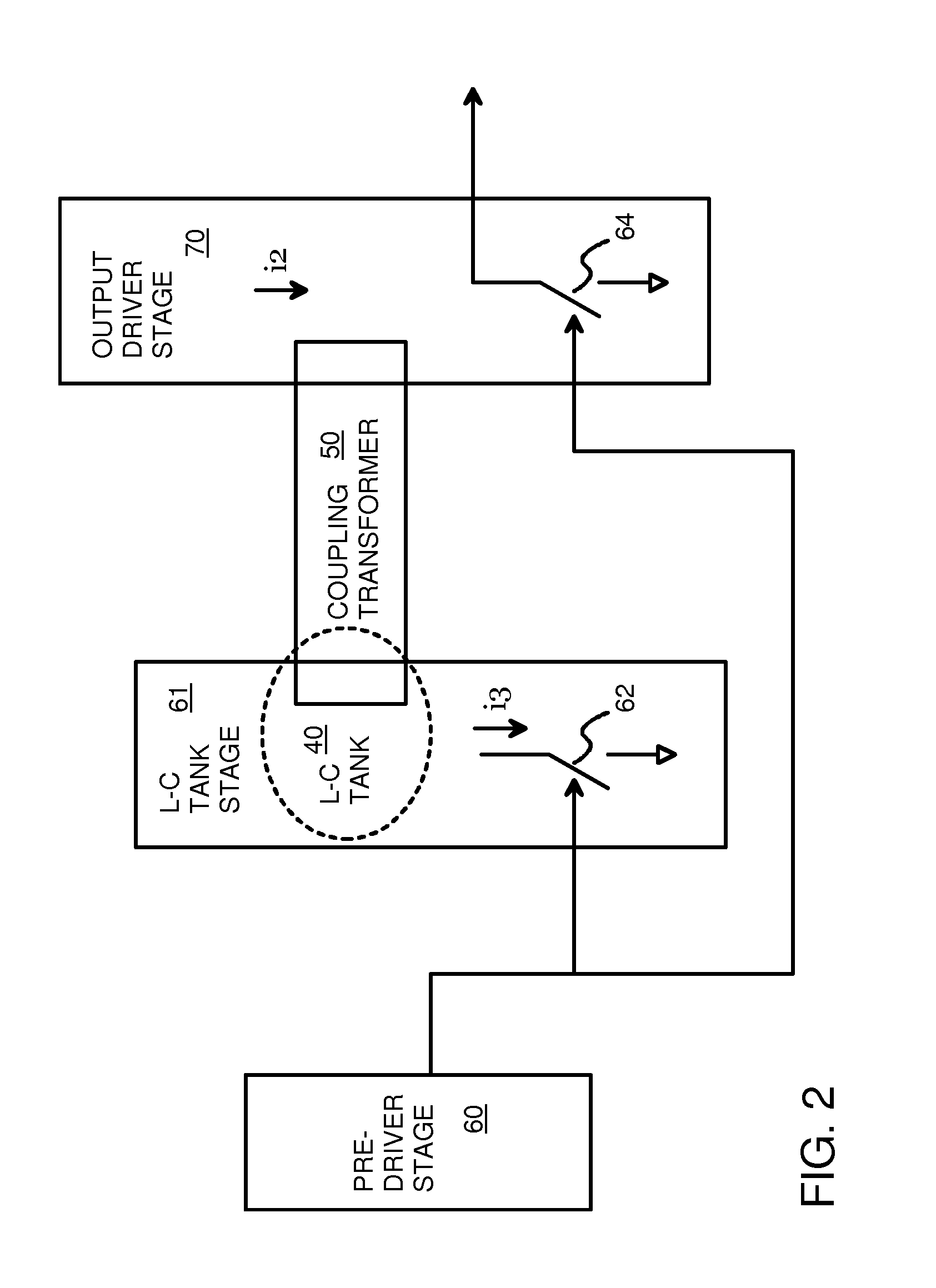
Re-Driver with Pre-Emphasis Injected Through a Transformer and Tuned by an L-C Tank
InactiveUS20120242377A1Amplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesElectric pulse generatorDriver circuitAudio power amplifier
A re-driver circuit has pre-driver, intermediate, and output stages. Pre-emphasis on the output is generated by the intermediate stage and injected into an output stage. The intermediate stage is a frequency-tuned amplifier that has an inductive-capacitive L-C tank circuit that is tuned to a desired frequency of the output. The intermediate stage does not directly drive the output stage. Instead, an on-chip coupling transformer couples the L-C tank circuit to the output stage. The coupling transformer has a first inductor that is part of the L-C tank circuit in the intermediate stage, and a second inductor that is part of the output stage. Mutual inductance between the first inductor and the second inductor inductively couple a pre-emphasis voltage onto the output. The magnitude of the pre-emphasis can be changed by adjusting current in the intermediate stage.
Owner:DIODES INC
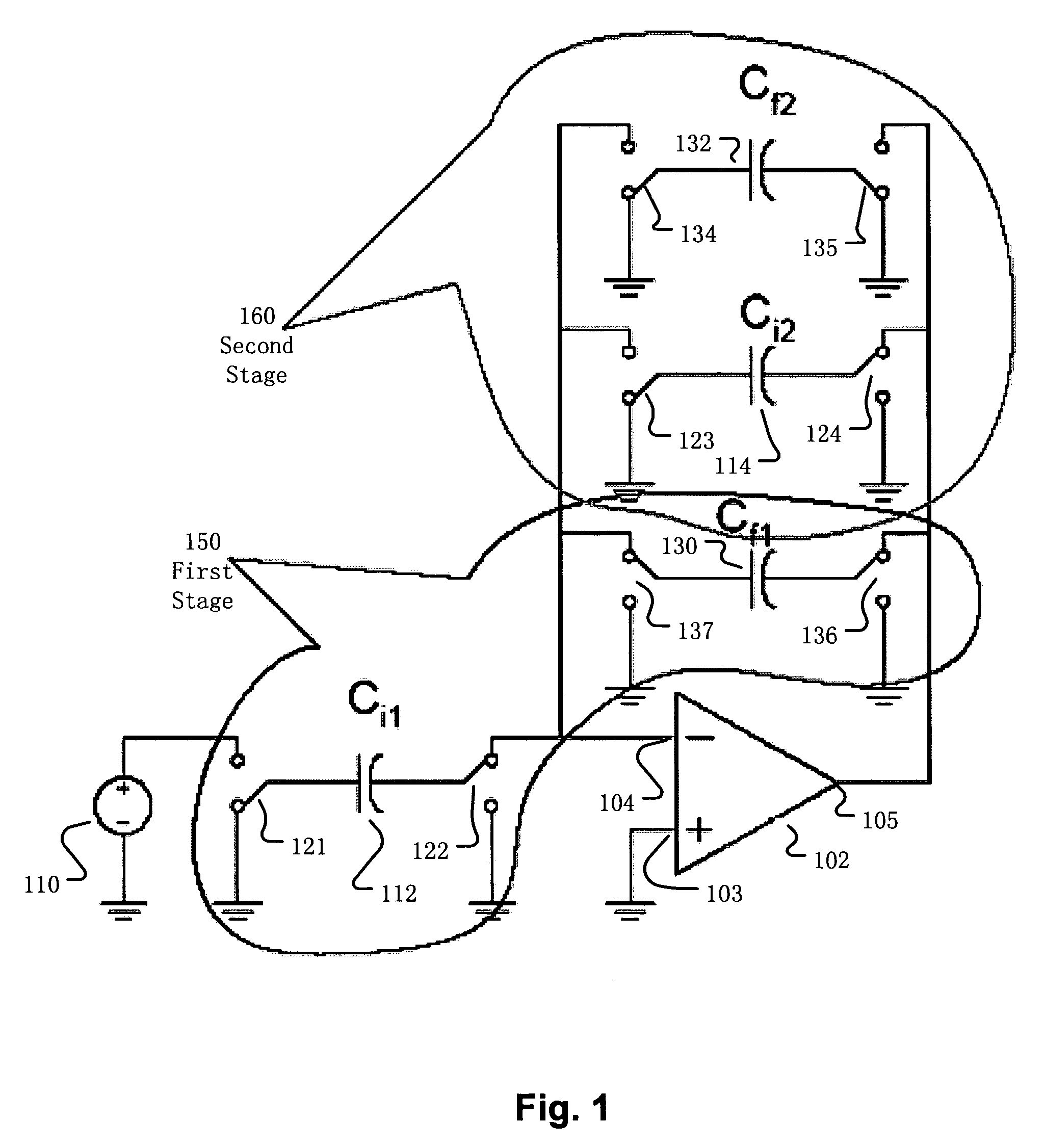
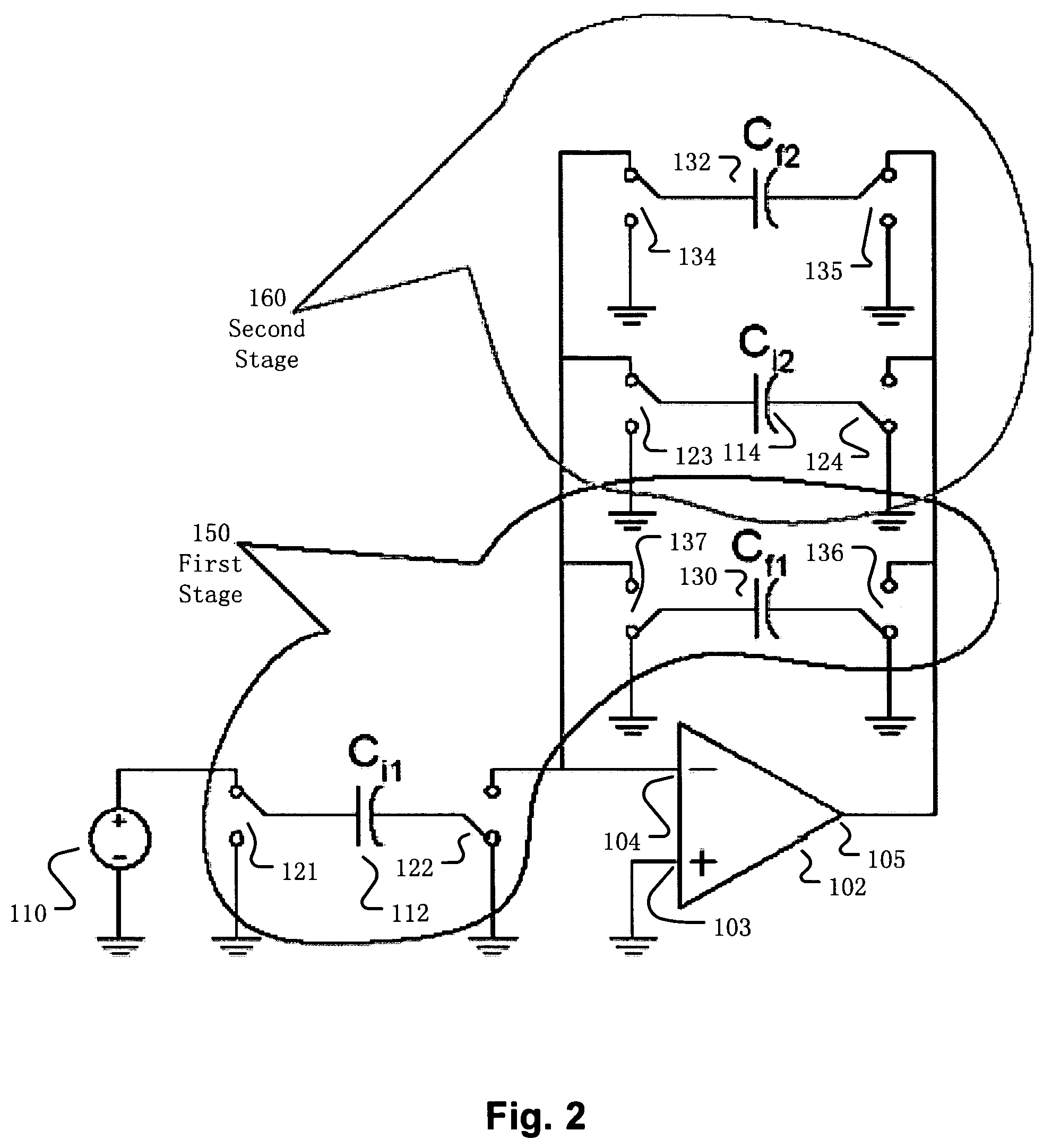
Multi-stage amplifier with switching circuitry
InactiveUS7199654B1Reducing parasitic chargeAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAmplifiers using switched capacitorsAudio power amplifierTuned amplifier
Disclosed are a multi-stage amplifier circuit, a method of operating a multi-stage amplifier circuit, and a device with the multi-stage amplifier circuit. The amplifier circuit technology includes an operational amplifier shared among multiple stages and switching circuitry. The various switching circuitry switches among elements to provide different input signals and different feedback to the shared operational amplifier at the different stages of operation of the amplifier circuit. The various switching circuitry also stores and discharges charge at one or more operational amplifier inputs.
Owner:RE SECURED NETWORKS LLC
Gain boosting for tuned differential LC circuits
InactiveUS7202740B2Generate efficientlyAnalog signal digital controlDifferential amplifiersAudio power amplifierTuned amplifier
A gain boost circuit and methodology are described for providing improved gain boosting with tuned amplifier circuits, such as differential low noise amplifier circuits having output resonant tank circuits. By selectively controlling the current source for a negative transconductance stage coupled between the differential amplifier output and the output resonant tank circuits, the amplifier gain may be adjusted to compensate for temperature variations. In addition, the amplifier gain boost may be selectively added, removed or even incrementally adjusted by using a current source control circuit in the negative transconductance stage to adjust the negative transconductance value generated by the negative transconductance stage.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Self-biased ultra wideband low-power-consumption low-noise amplifier (LNA)
ActiveCN104779919AReduce Design ComplexityConstrained total power dissipationAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceGain controlUltra-widebandTuned amplifier
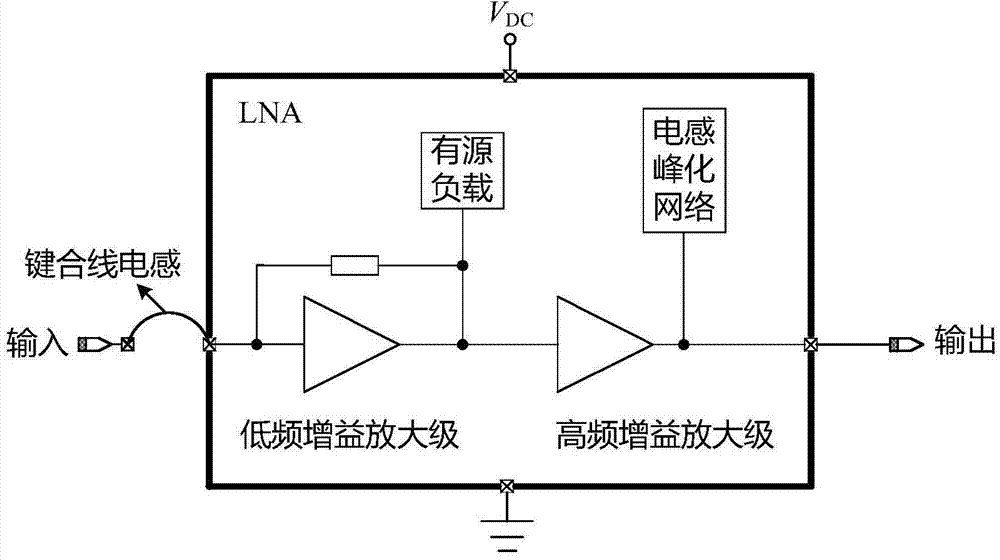
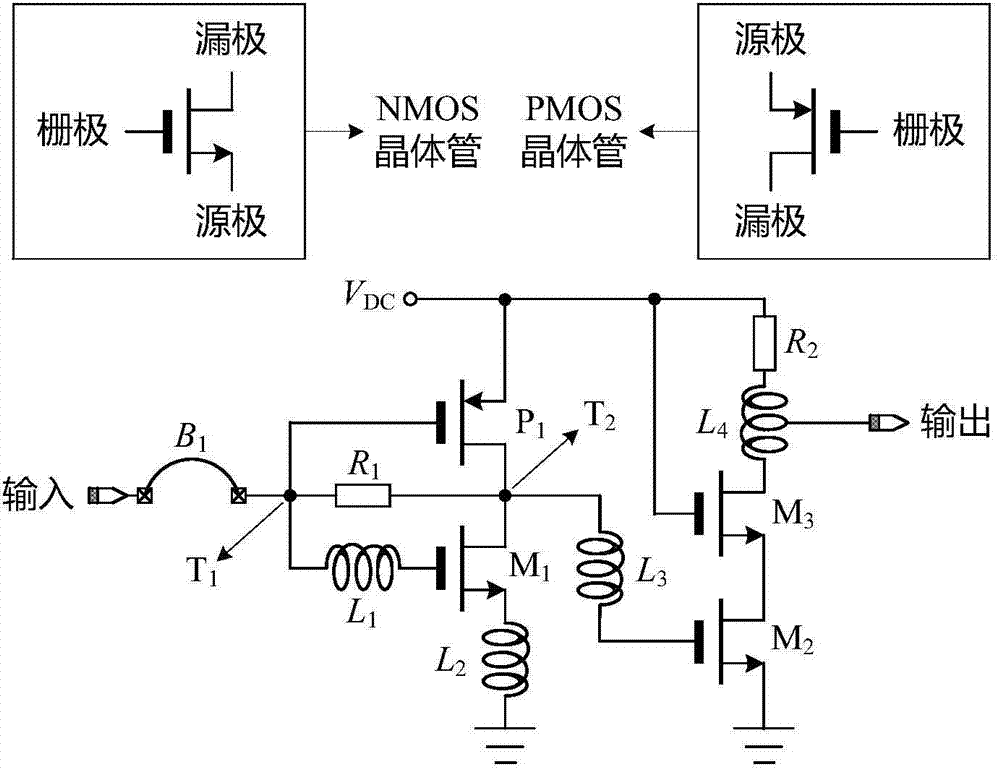
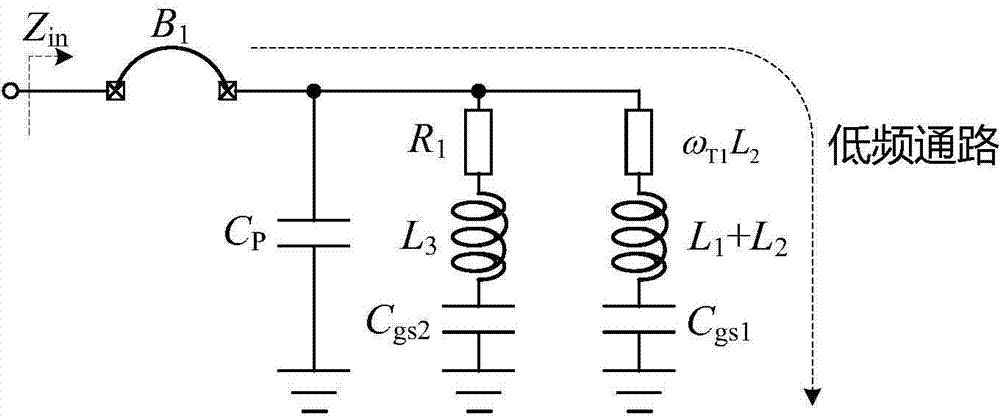
The invention provides a self-biased ultra wideband low-power-consumption low-noise amplifier (LNA) and belongs to the field of radio frequency integrated circuits. The LNA only contains a low-frequency amplifier stage and a high-frequency amplifier stage. At the low-frequency amplifier stage of the LNA, an active load is combined with the resistive negative feedback technology to provide bias for a circuit at the same stage and a circuit at a backward stage, self-bias of the overall LNA circuit is achieved, the circuit design is simplified, and circuit power consumption is restrained. According to the structural features of the circuit, and high-frequency matching and noise performance of the circuit are optimized by fully utilizing parasitic inductance of bonding wires. At the high-frequency amplifier stage, the working frequency range of the LNA is expanded through the inductance peaking technology. The LNA can stably work within the frequency range of 0.2-6 GHz, and gain of 16+ / -1.3 dB, the noise coefficient smaller than 2-8 dB and good input matching are maintained. The self-biased ultra wideband low-power-consumption LNA can be applied to receiver front-end chips applied to digital broadcasting, wireless local area networks, ultrashort wave radars and other devices.
Owner:NO 54 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP
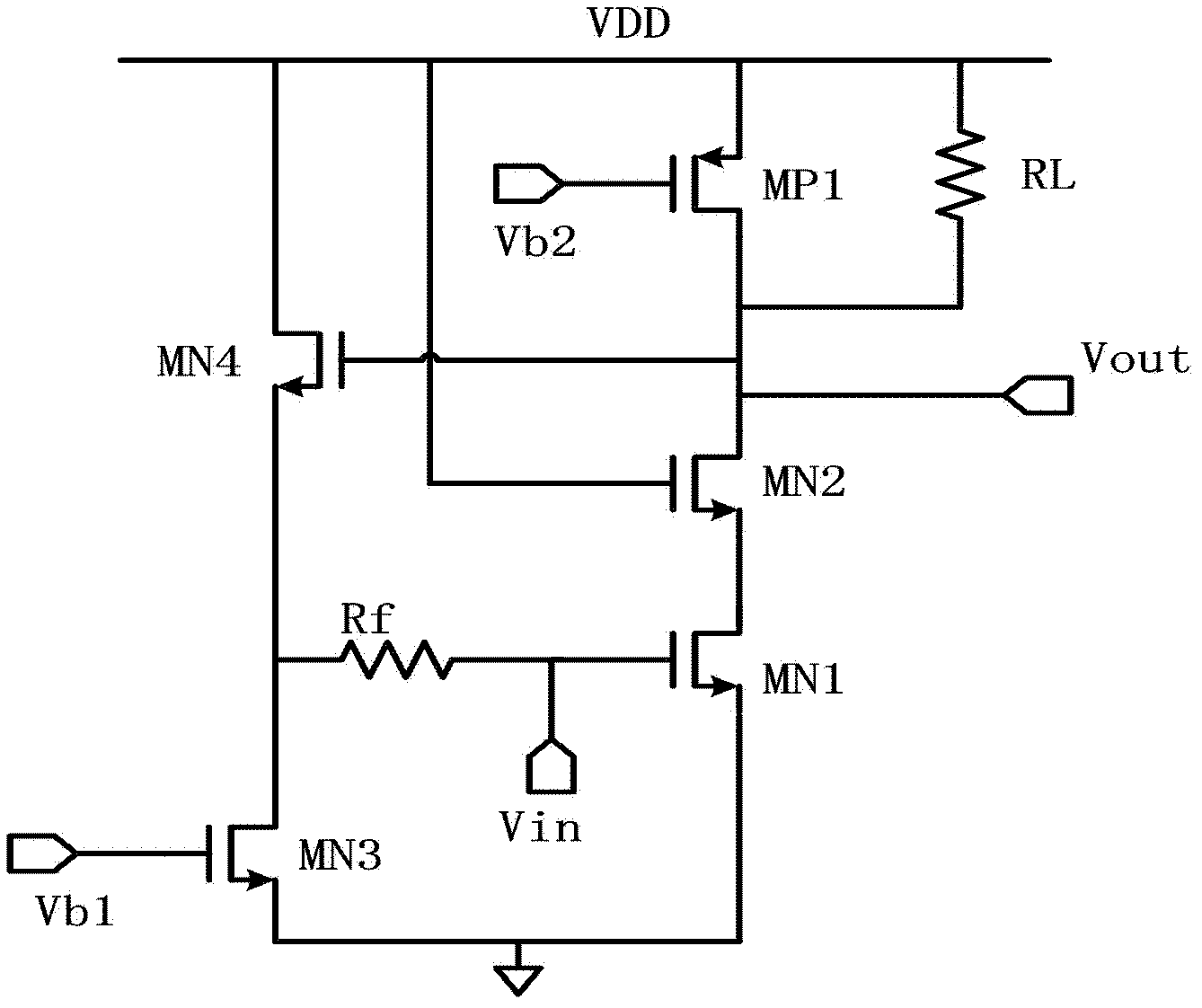
Active bias circuit for low-noise amplifiers
InactiveUS7113043B1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceGain controlLow noiseAudio power amplifier
A low-noise amplifier includes a first amplification device. The first amplification device includes a control terminal, a first terminal, and a second terminal. The low-noise amplifier also includes a feedback circuit in communication with the control terminal and the first terminal. The feedback circuit compares a voltage, corresponding to an output current associated with the first terminal, with a predetermined reference voltage to generate a bias signal applied to the control terminal for biasing the low-noise amplifier.
Owner:MARVELL INT LTD
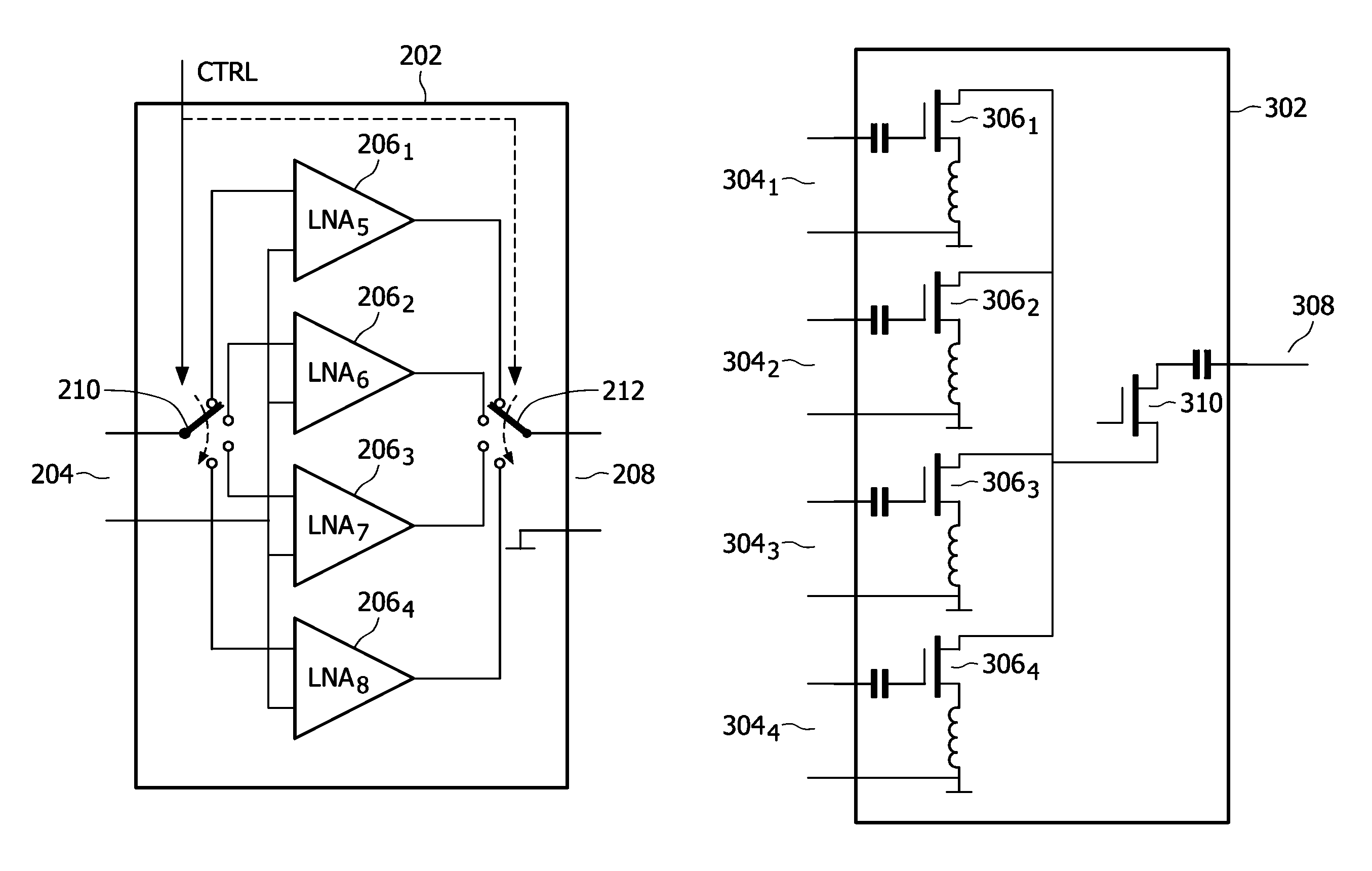
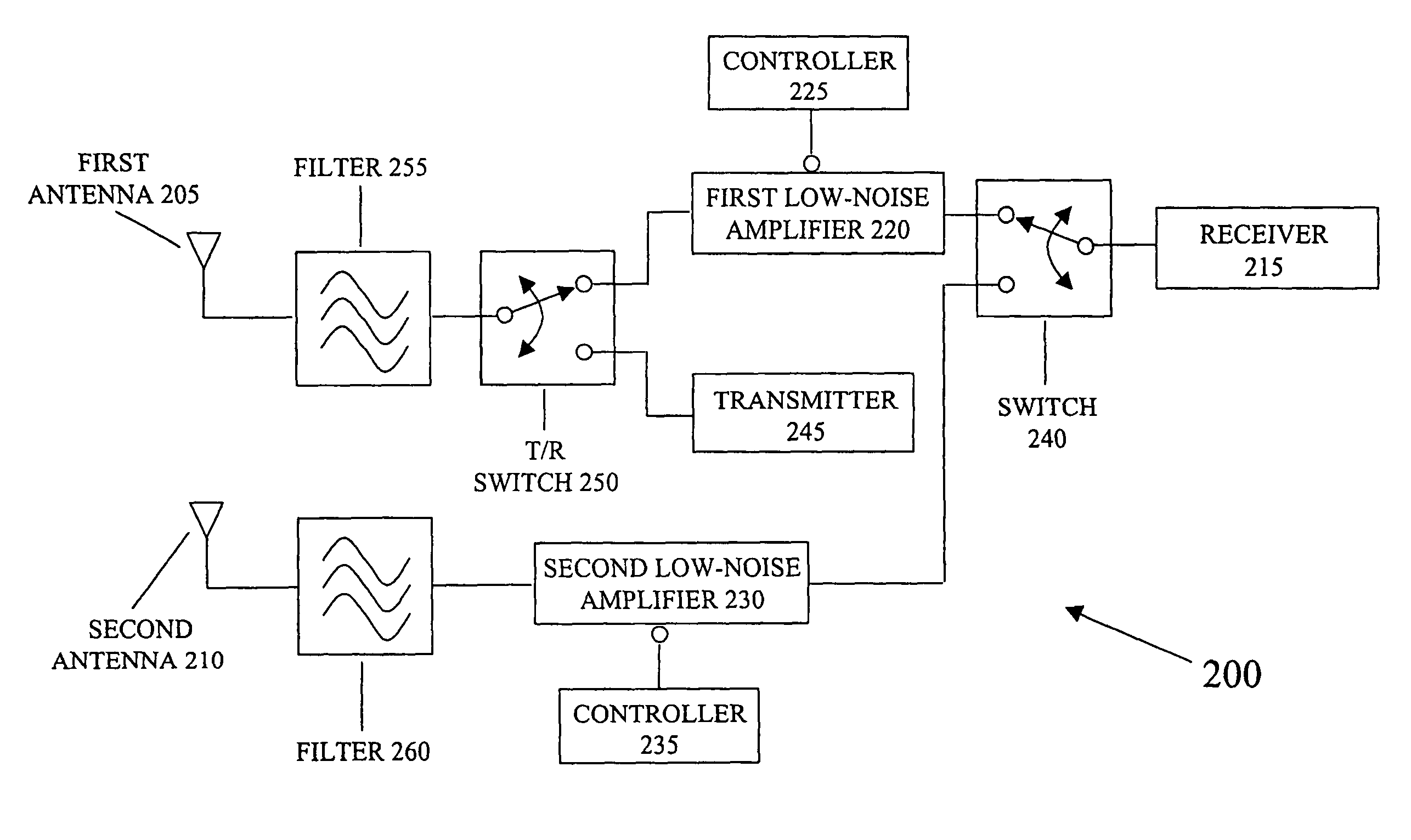
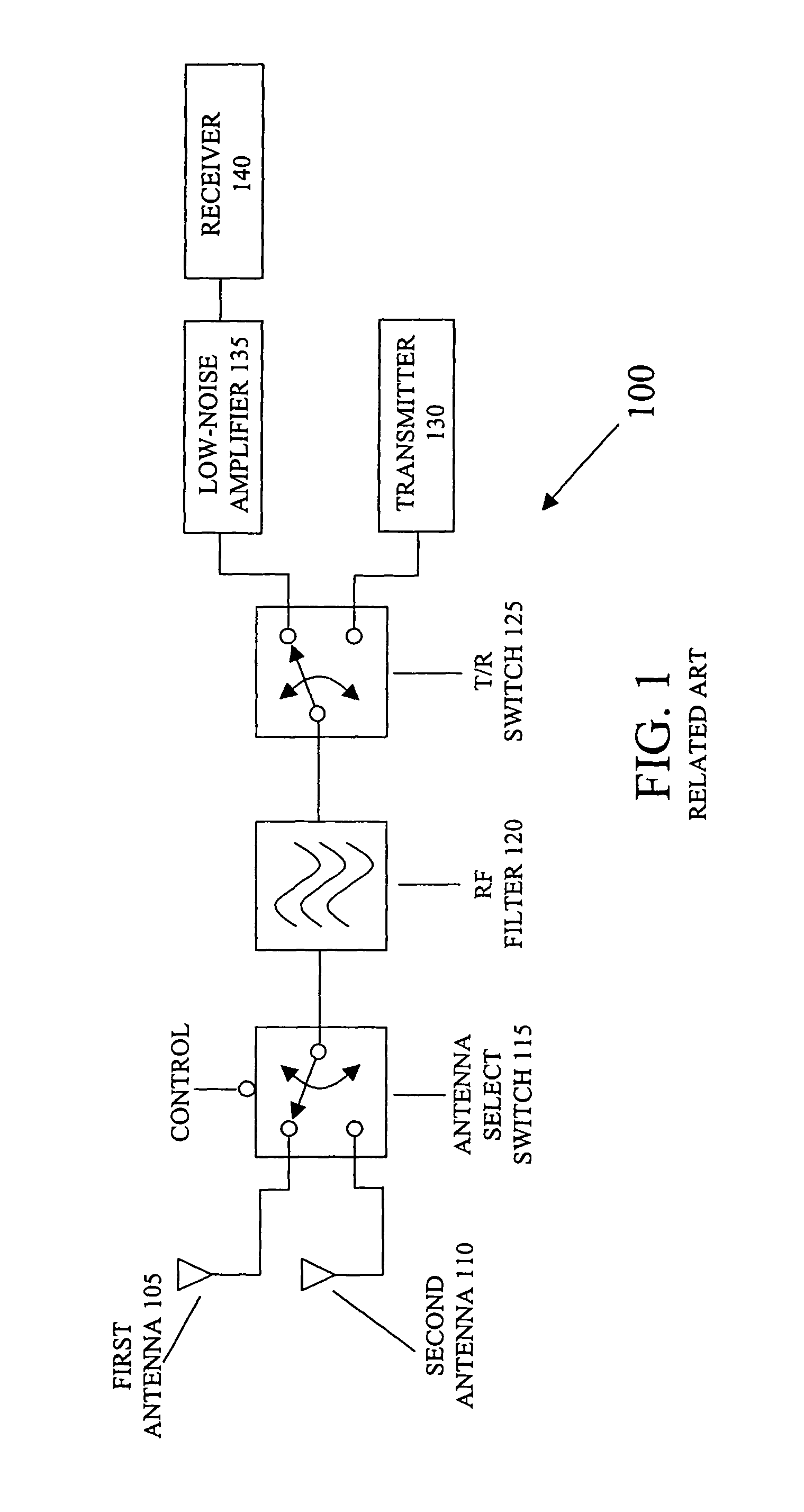
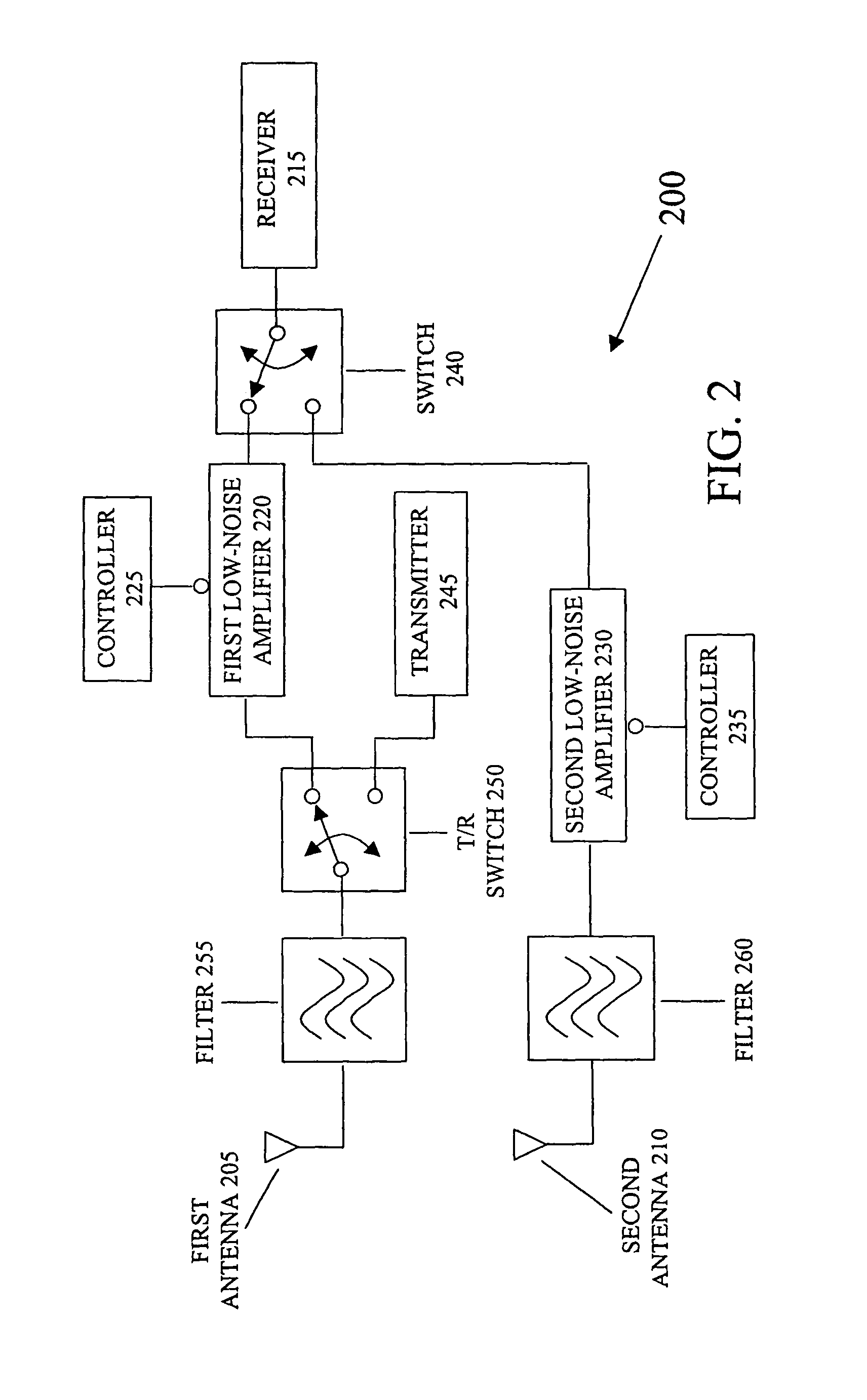
Transceiver system including dual low-noise amplifiers
A system for communicating information signals includes a receiver in selective communication with a first antenna and a second antenna. The receiver is configured to selectively receive information signals via the first or second antenna. The system includes a first low-noise amplifier in communication with the first antenna and in selective communication with the receiver. The first low-noise amplifier is configured to amplify a first information signal received by the first antenna to generate a first amplified signal. The system includes a second low-noise amplifier in communication with the second antenna and in selective communication with the receiver. At least the first and second low-noise amplifiers are formed on a monolithic substrate. The second low-noise amplifier is configured to amplify a second information signal received by the second antenna to generate a second amplified signal. Either the first or second amplified signal is selectively applied to the receiver.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
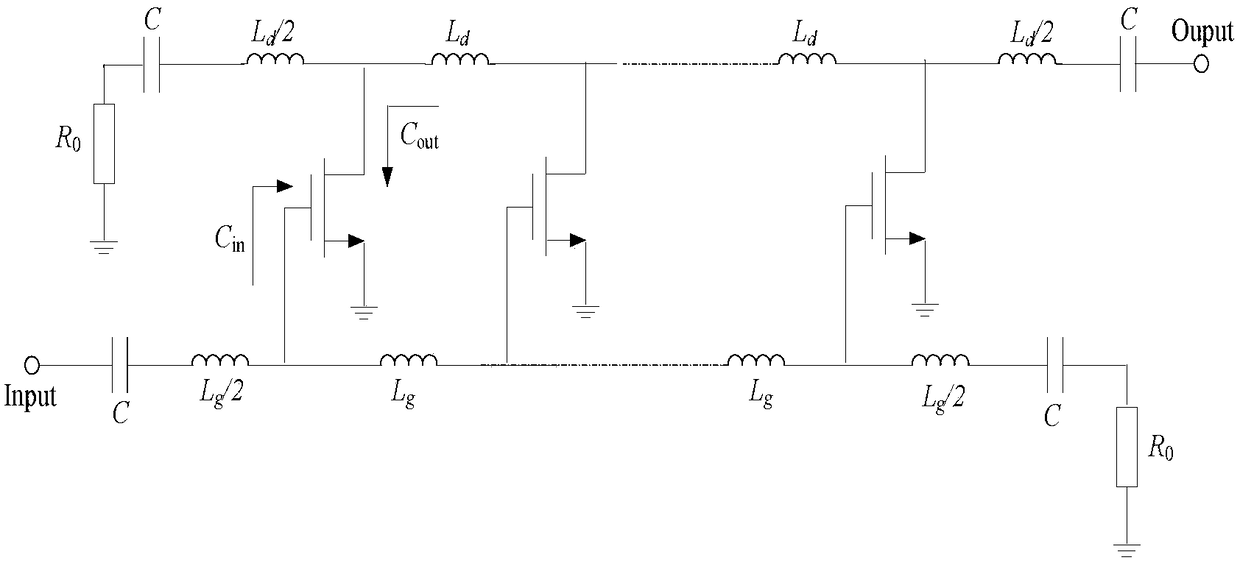
Cascaded distributed low-noise amplifier
ActiveCN108336978ALower noise figureExcellent radio frequency indexAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceGain controlArtificial transmission lineAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses a cascaded distributed low-noise amplifier. The cascaded distributed low-noise amplifier comprises a first stage amplifier, a second stage amplifier, and a third stage amplifier; each of the amplifiers is composed of a gain and an on-chip inductor, and the structures of the gain units of the amplifiers are completely same; the on-chip inductor and the input impedance of each gain unit form an input artificial transmission line, and the on-chip inductor and the output impedance of each gain unit form an output artificial transmission line. And the gain units of the amplifiers adopt the structure in single-end input to differential output. The low-noise amplifier disclosed by the invention is simple in structure, low in input echo loss, small in in-band fluctuation, high in gain, and low in noise coefficient; the limitation on the gain bandwidth product in the traditional amplifier can be overcome, the large flat gain can be obtained in wide frequency band, and the good noise performance is realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM +1
Re-driver with pre-emphasis injected through a transformer and tuned by an L-C tank
InactiveUS8362813B2Amplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesElectric pulse generatorDriver circuitAudio power amplifier
A re-driver circuit has pre-driver, intermediate, and output stages. Pre-emphasis on the output is generated by the intermediate stage and injected into an output stage. The intermediate stage is a frequency-tuned amplifier that has an inductive-capacitive L-C tank circuit that is tuned to a desired frequency of the output. The intermediate stage does not directly drive the output stage. Instead, an on-chip coupling transformer couples the L-C tank circuit to the output stage. The coupling transformer has a first inductor that is part of the L-C tank circuit in the intermediate stage, and a second inductor that is part of the output stage. Mutual inductance between the first inductor and the second inductor inductively couple a pre-emphasis voltage onto the output. The magnitude of the pre-emphasis can be changed by adjusting current in the intermediate stage.
Owner:DIODES INC
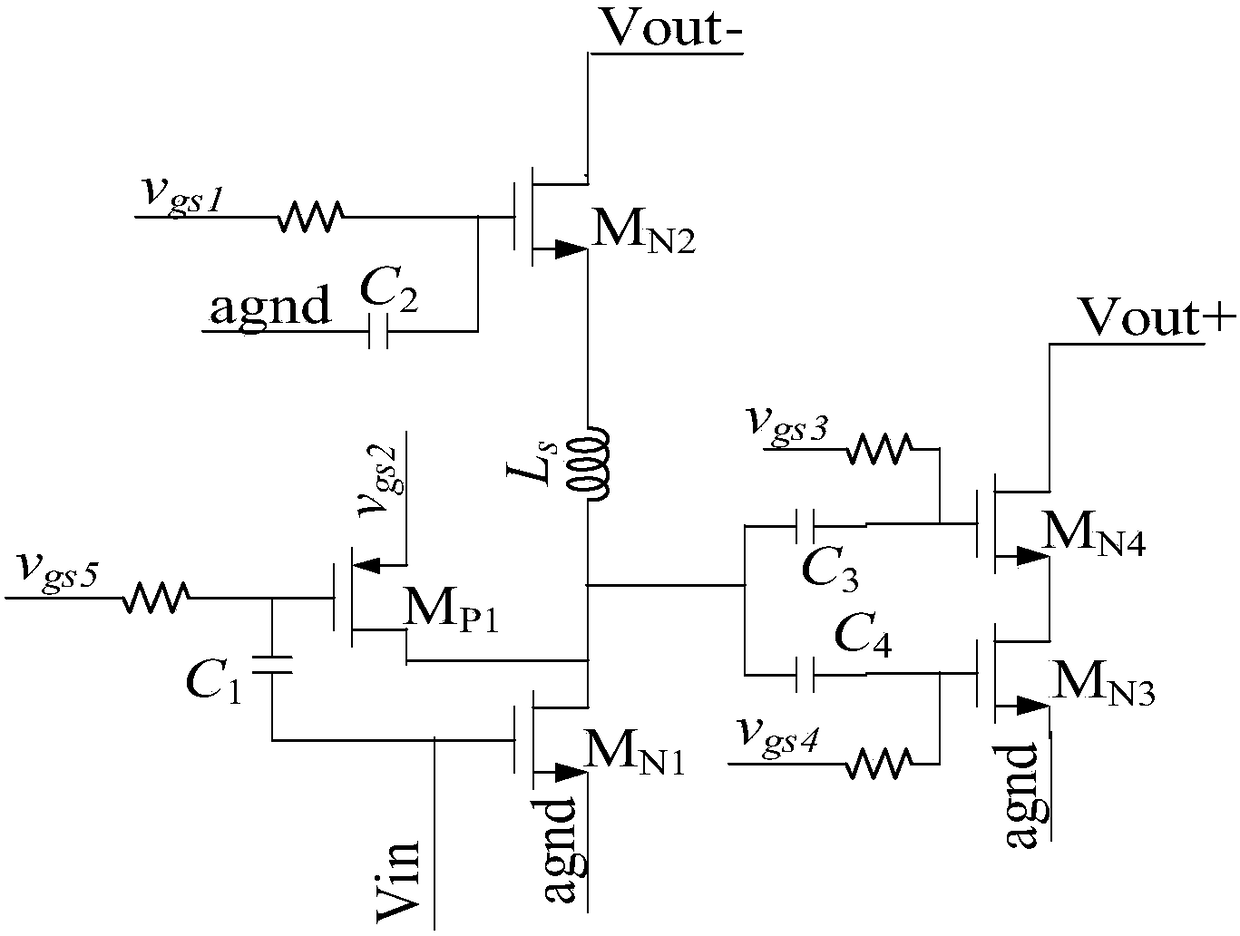
Differential complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) multimode low-noise amplifier with on-chip active Balun
InactiveCN102332877AReduce demandStable jobAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceTuned amplifierEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of radio frequency integration circuits and particularly relates to a differential complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) multimode low-noise amplifier with an on-chip active Balun. In the differential CMOS multimode low-noise amplifier, a first-level amplifier consists of a matching level, an amplifying level, a feedback level and a load level; a second-level amplifier consists of the active on-chip Balun; the matching level forms a matching network by using a bonding wire inductor, a parasitic capacitor, a grid inductor and circuit input impedance; in the amplifying level, a common-source NMOS tube and a PMOS tube are used as input ends, and a common-gate NMOS tube is used as a current follower; an NMOS tube between the grid of an input NMOS tube and the drain of the NMOS tube of the current follower and a resistor form a voltage-current type negative feedback access; and the active Balun of a third-level amplifier realizes single-to-dual function of the Balun by using a common source and a source follower respectively. The differential CMOS multimode low-noise amplifier has a simple structure, low power consumption and large bandwidth coverage range, occupies a small area of a chip and improves the practicability of a circuit. The low-noise amplifier can be applied to front ends of multimode receivers with frequencies of 0.5 to 10.6GHz.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Controlled-gain wideband feedback low noise amplifier
InactiveUS8102214B2Increases the entire low-noise amplification gainNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsHigh frequency amplifiersAudio power amplifierTuned amplifier
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Multi-mode radio frequency front-end circuit and control method therefor
ActiveCN109150227AReduce transmission power consumptionAvoid saturationTransmissionLow noiseAudio power amplifier
The invention proposes a multi-mode radio frequency front-end circuit, and the circuit comprises a power amplifier and a low-noise amplifier, which are coupled to an antenna. The power amplifier is atleast formed by the combination of a first amplifier stage and a second amplifier stage. The output of the first amplifier stage is coupled to the output end of the low-noise amplifier through a first switch to form a first additional loop. The output end of the low-noise amplifier is also connected with the input end through a second switch to form a second additional loop. A mode switching control circuit is used for controlling the on / off states of the first and second switches, and also controlling the first amplifier stage, the second amplifier stage and the low-noise amplifier to be inthe working state or forbidden state, thereby enabling the radio frequency front-end circuit to be in a required working mode. According to the above circuit structure, the circuit design is simplified, and the improved radio frequency front-end circuit to have the high-efficiency advantage of a low-power output mode of the power amplifier and a low noise coefficient of the low-noise amplifier ina low-gain mode.
Owner:安徽矽磊电子科技有限公司
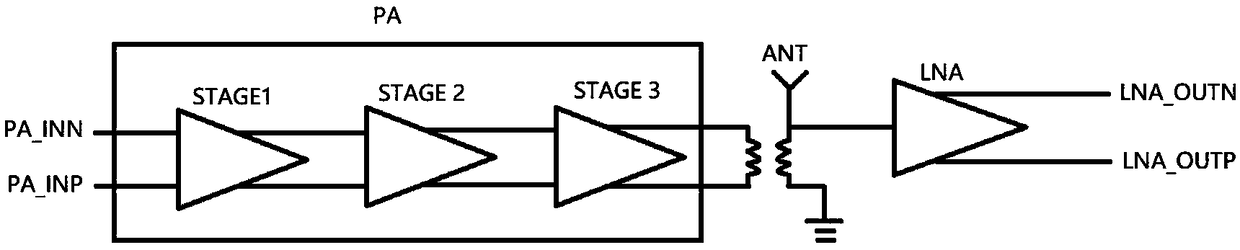
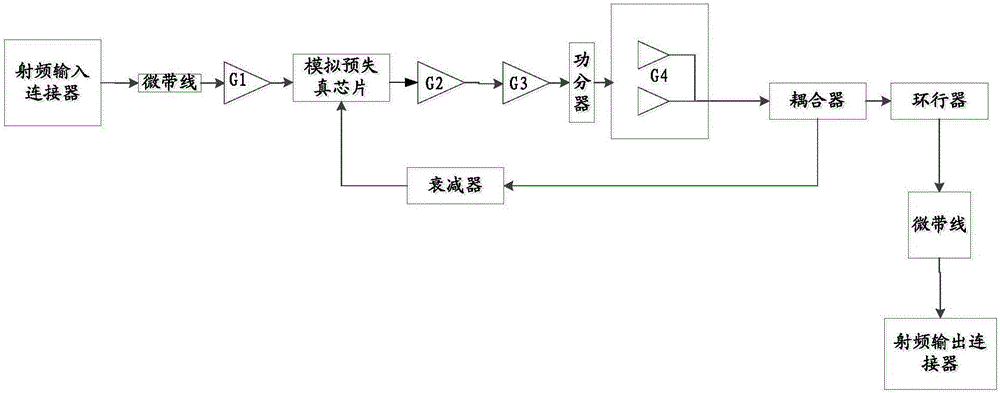
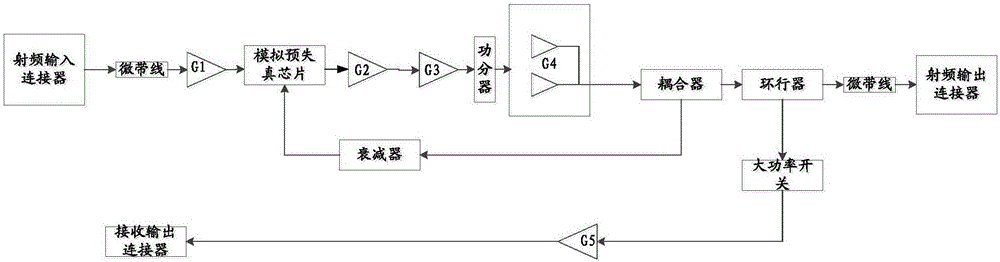
Power amplifier
InactiveCN106788484AImprove efficiencySolution volumeAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionHigh frequency amplifiersTuned amplifierEngineering
The invention provides a power amplifier. The power amplifier comprises a transmitting circuit and a receiving circuit; the transmitting circuit includes a radio-frequency input connector, a first stage amplifier, a pre-distortion circuit, a second stage amplifier, a third stage amplifier, a fourth stage amplifier, a coupler, a circulator and a radio-frequency output connector which are connected in sequence; the pre-distortion circuit includes an analog pre-distortion chip and is used for performing analog pre-distortion processing on communication data; a Doherty amplifier is adopted by the fourth stage amplifier; and the fourth stage amplifier outputs to the coupler by employing a quarter-wave synthetic wire, and is used for amplifying power of a communication signal. According to the power amplifier provided by the invention, the analog pre-distortion chip is adopted, so the requirement on adjacent channel suppression is met; a Doherty circuit structure is adopted by the fourth stage amplifier, so the requirement on efficiency is met, and the requirement on system miniaturization is met; and therefore, the problems of relatively large volume and relatively low efficiency of the existing power amplifier can be solved.
Owner:AUCTUS TECH CO LTD
Low-noise amplifier used in navigation system receiver and having automatic calibration function
InactiveCN102185567ASimple structureReduce noiseAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influencePower amplifiersResonant cavityMultiplexing
The invention provides a low-noise amplifier used in a navigation system receiver and having an automatic calibration function. The low-noise amplifier comprises an LC resonant cavity, a cascode tube, a negative resistance tube, a frequency divider, a frequency controller and a control switch; the LC resonant cavity and the negative resistance tube form a voltage control oscillator; and the LC resonant cavity works in a multiplexing and interacting way due to switching of the control switch, so the LC resonant cavity is used as a load of the low-noise amplifier or a part of the voltage control oscillator. By the method for multiplexing the LC resonant cavity, the design requirements of the voltage control oscillator and the low-noise amplifier can be met at the same time; the frequency is calibrated automatically; moreover, the low-noise amplifier is low in noise, high in gain and reliability, stable in parameters and simple in circuit structure.
Owner:上海迦美信芯通讯技术有限公司
Multi-band amplifier for test and measurement instruments
InactiveCN1854741AElectrical measurement instrument detailsElectrical testingMulti bandAudio power amplifier
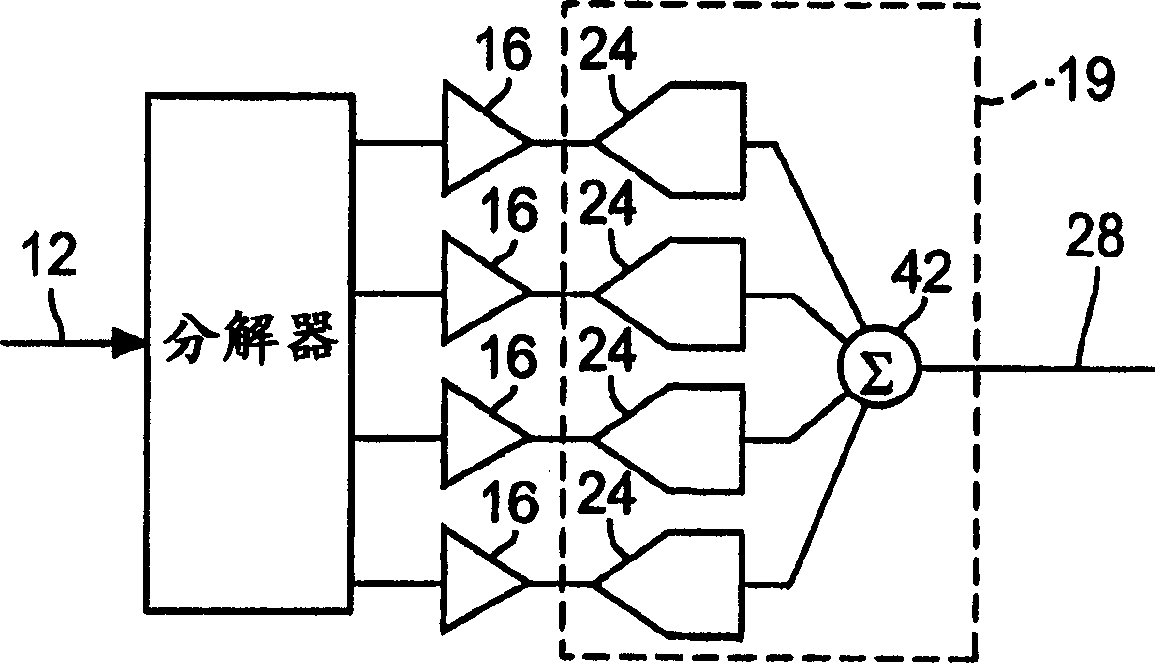
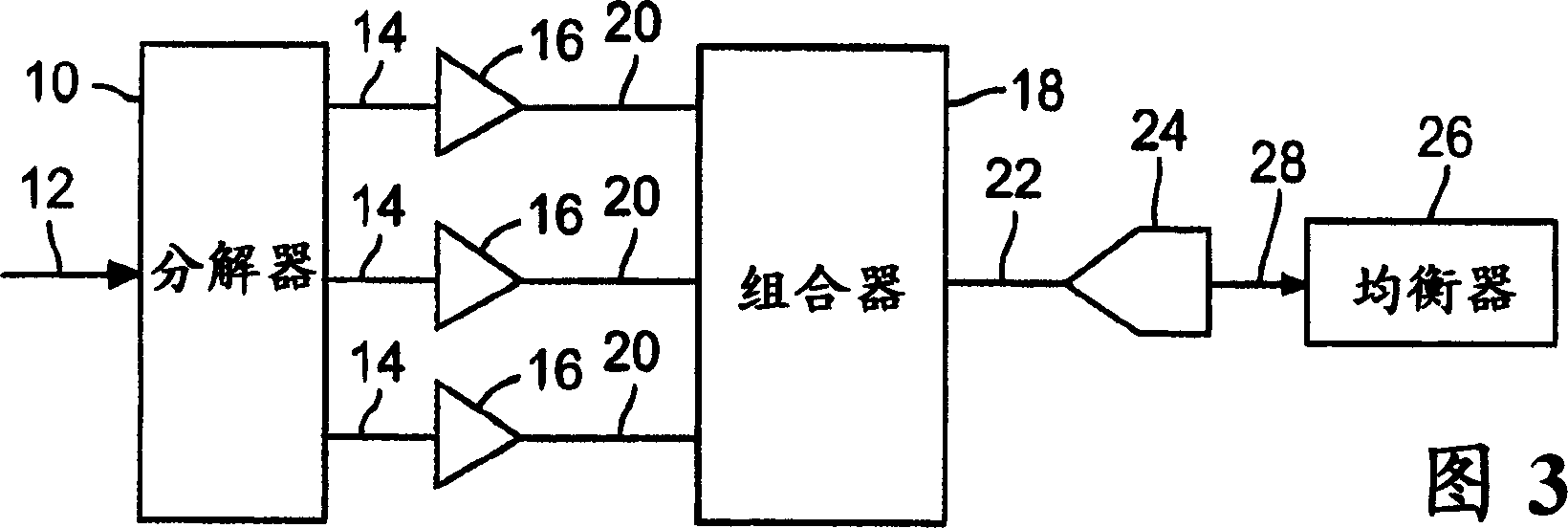
A multiband amplifier for a test and measurement instrument includes a splitter to split an input signal into split signals, amplifiers, and means for combining and digitizing the amplified signals into a digitized signal. Each amplifier is configured to amplify an associated split signal over an amplifier passband. The amplifier passband of at least one amplifier is different from the amplifier passband of another amplifier.
Owner:TEKTRONIX INC
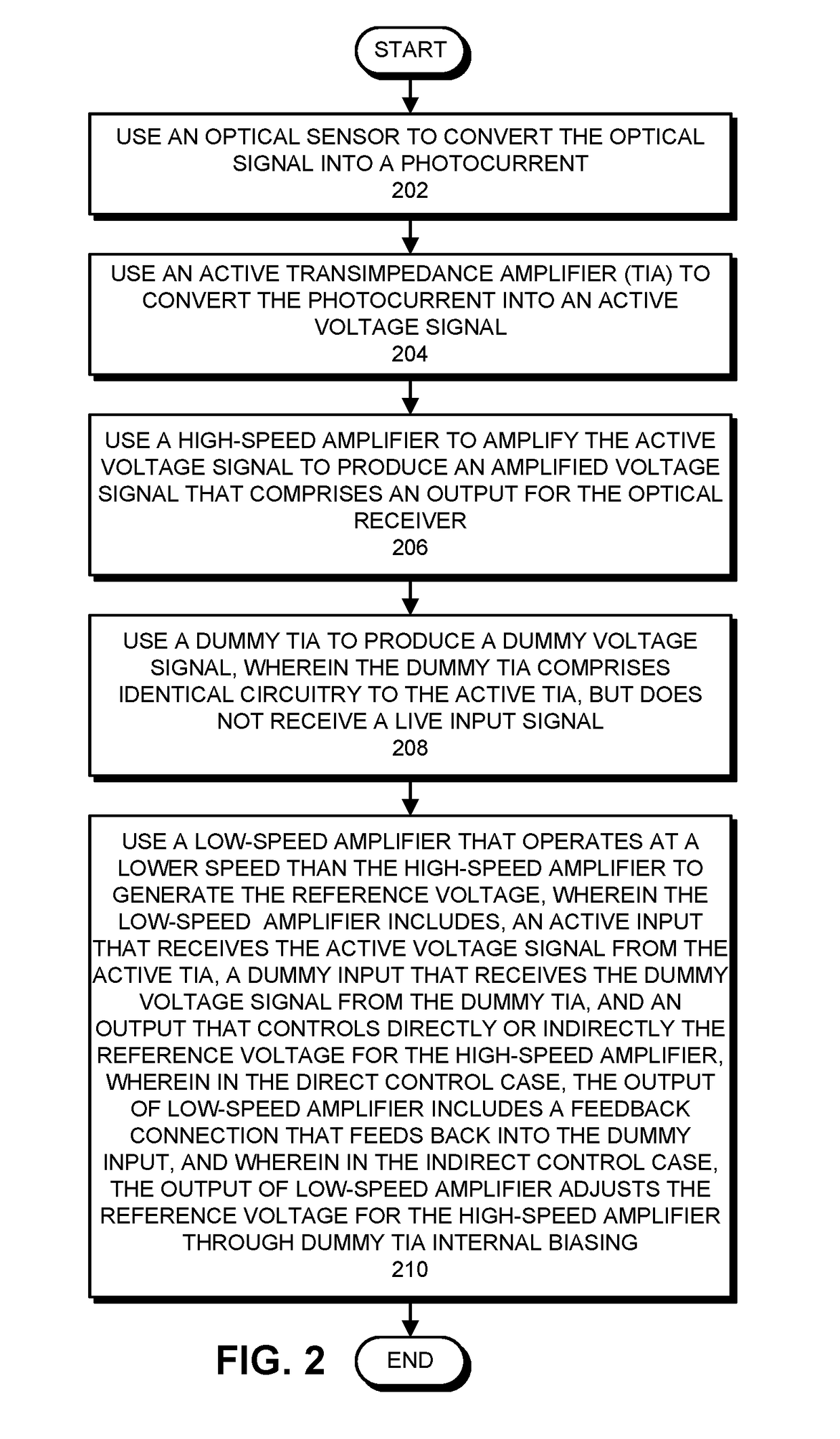
Extracting an embedded DC signal to provide a reference voltage for an optical receiver
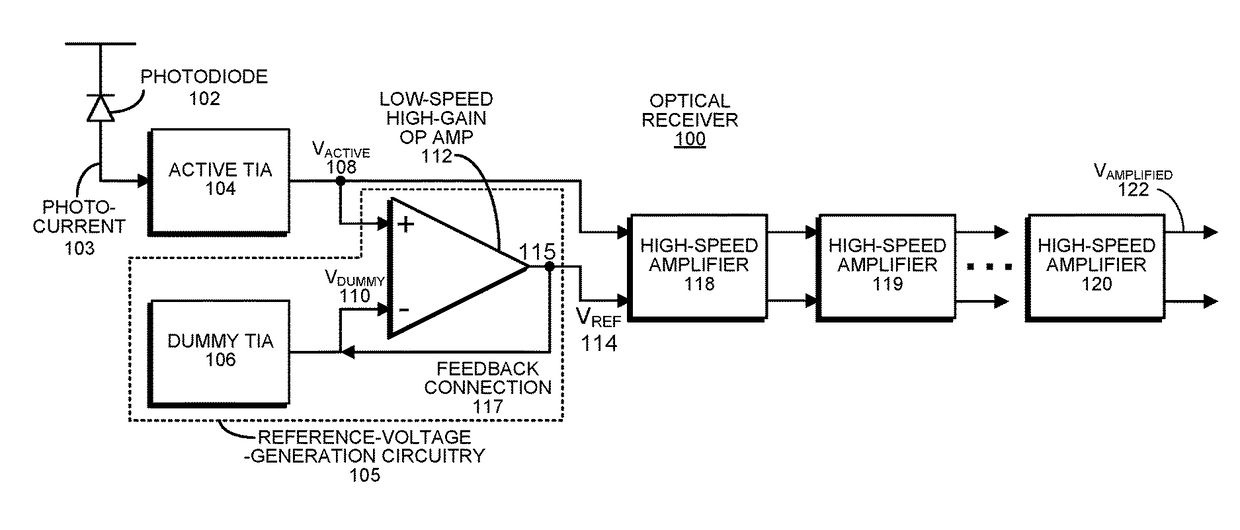
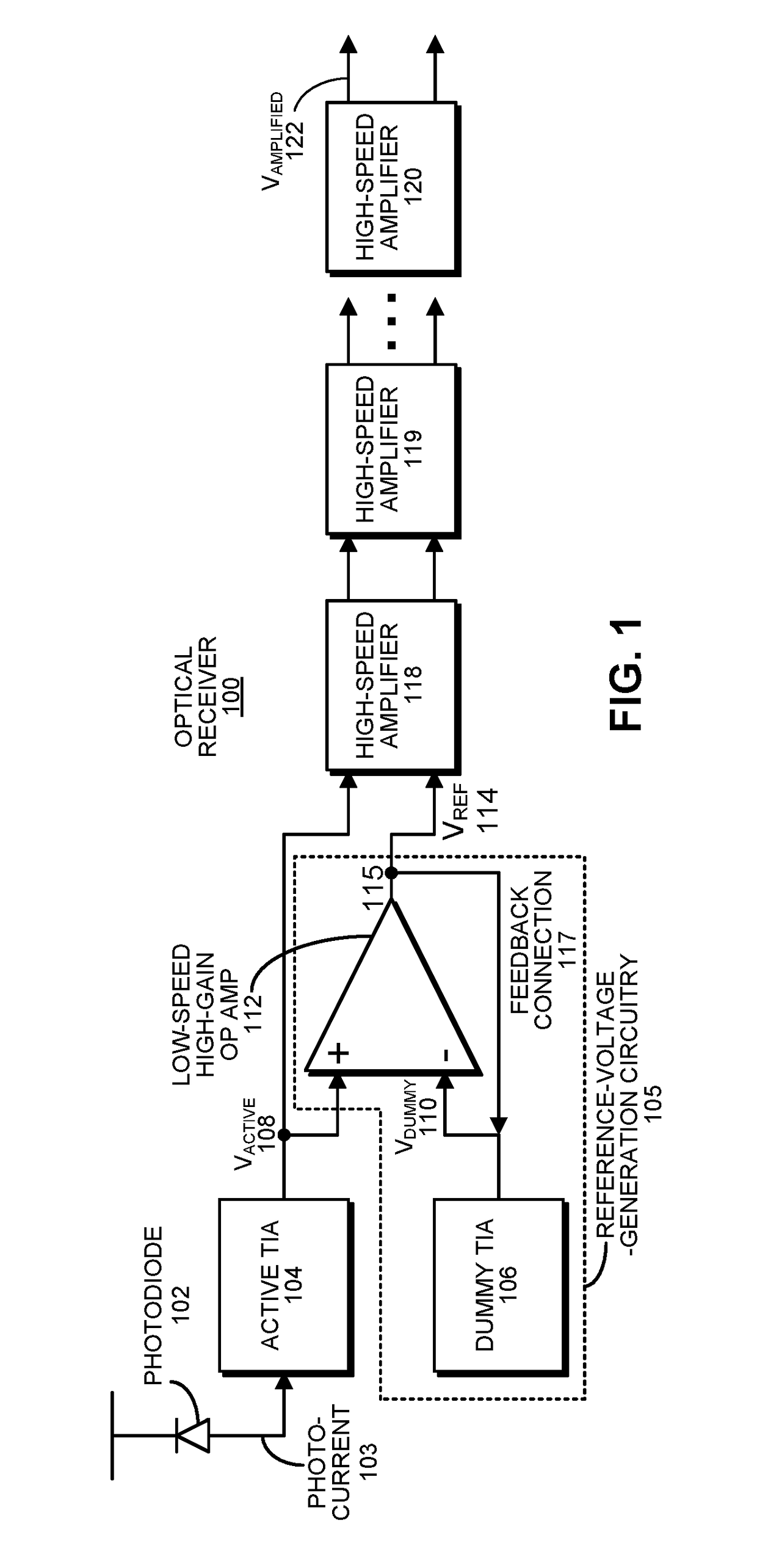
An optical receiver includes: an active transimpedance amplifier (TIA) that converts a photocurrent from a photosensor into an active voltage signal; a high-speed amplifier that amplifies the active voltage signal to produce an amplified voltage signal that comprises an output for the optical receiver; and a reference-voltage-generation circuit that generates a reference voltage for the high-speed amplifier. This reference-voltage-generation circuit includes a dummy TIA that is identical to the active TIA, but does not receive a live input signal, and produces a dummy voltage signal. It also includes a low-speed amplifier which includes: an active input that receives the active voltage signal from the active TIA output; a dummy input that receives the dummy voltage signal from the dummy TIA output; and an output that controls directly or indirectly the reference voltage for the high-speed amplifier. In the direct control case, the output of low-speed amplifier includes a feedback connection that feeds back into the dummy input. In the indirect control case, the output of low-speed amplifier adjusts the reference voltage for the high-speed amplifier through dummy TIA internal biasing.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
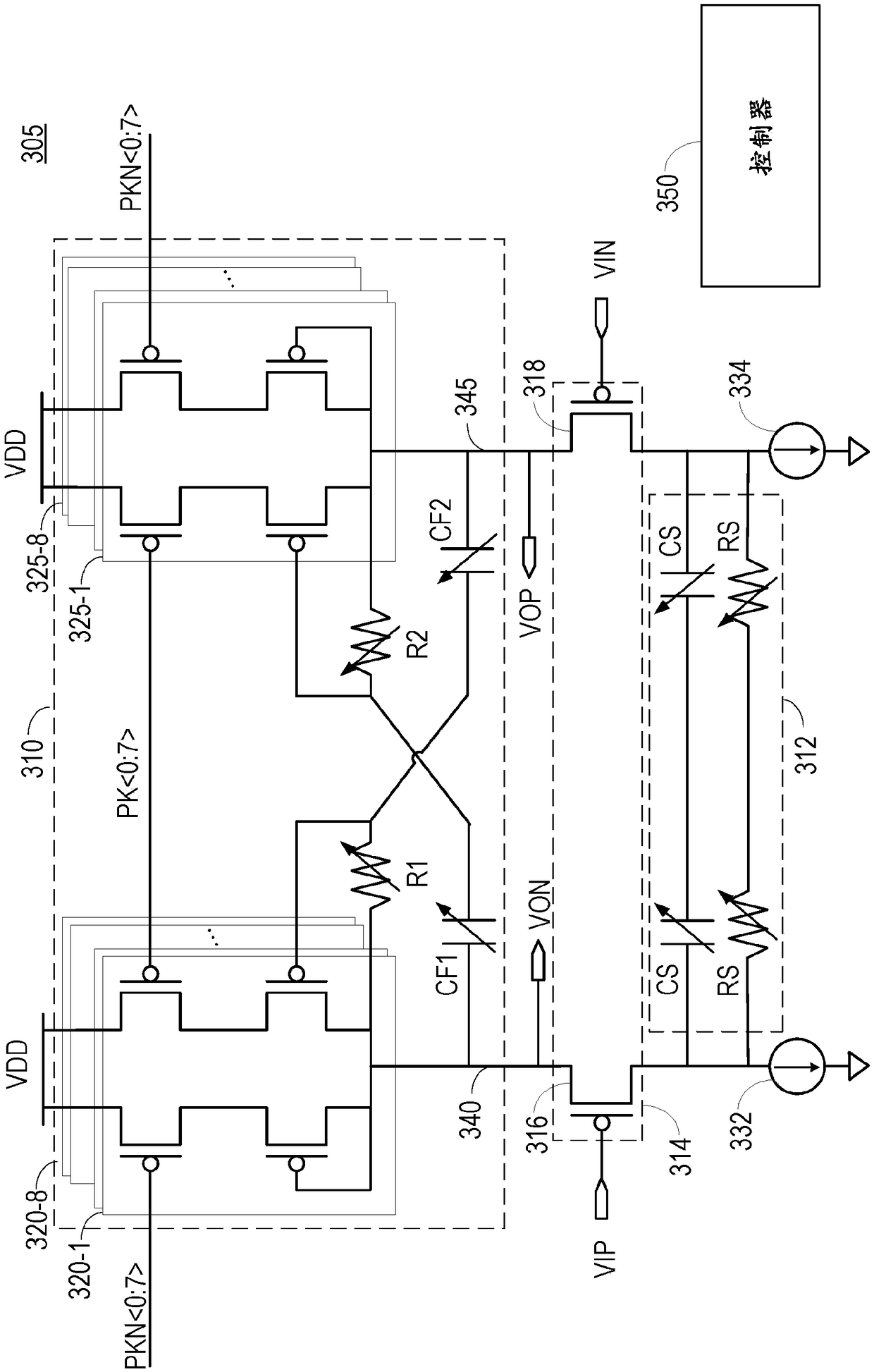
Amplifier with boosted peaking
In one implementation, an amplifier (305) comprises a load circuit (310) comprising a plurality of inductor cells, and a drive circuit (314) configured to receive an input signal, and to drive the load circuit (310) based on the input signal to generate an amplified signal. The amplifier (305) also comprises a controller (350) configured to tune a peaking gain of the amplifier (305) by adjusting anumber of the inductor cells that are enabled.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
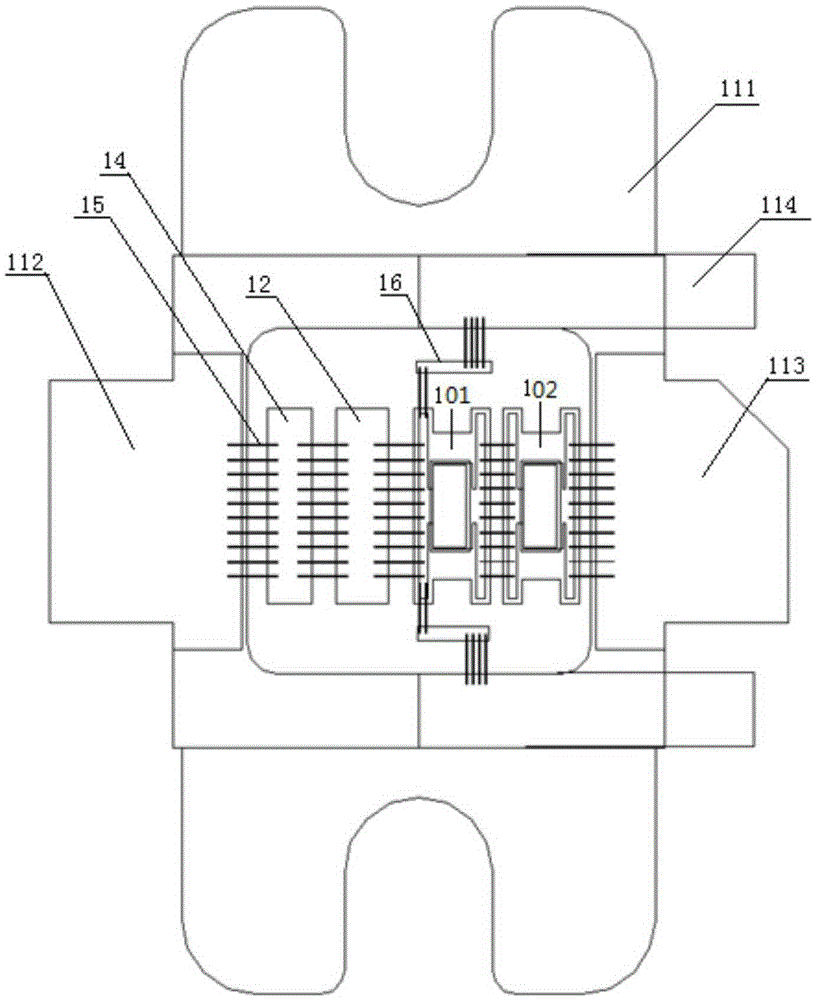
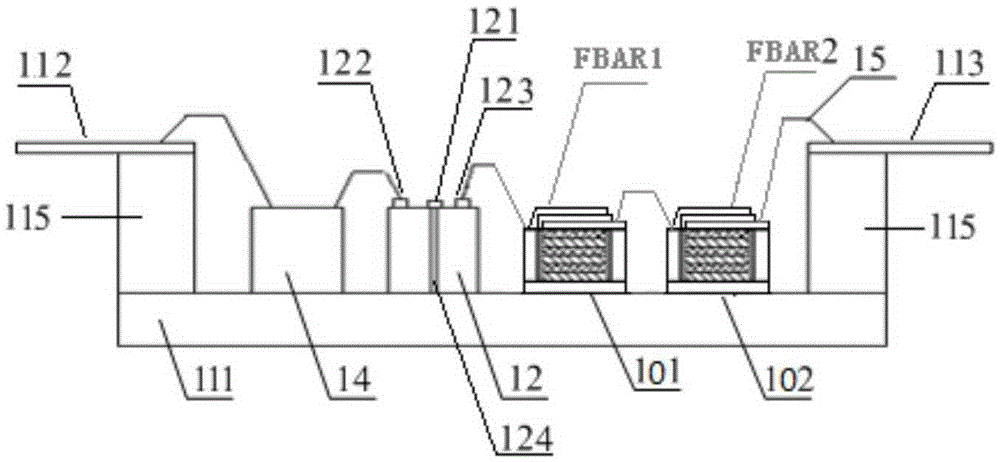
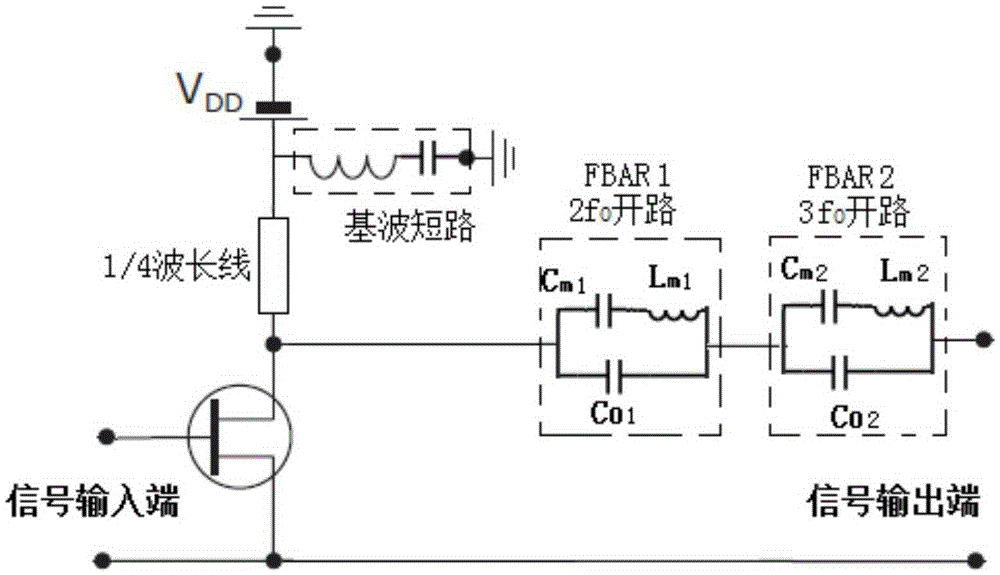
Film bulk acoustic resonator harmonic tuned amplifier module
ActiveCN106253873AImprove efficiencyImprove linearityAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionImpedence networksThin-film bulk acoustic resonatorAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses a film bulk acoustic resonator harmonic tuned amplifier module which comprises a signal input end and a signal output end, a transistor arranged between the signal input end and the signal output end and comprising a transistor input end, a transistor output end and a transistor grounding end, a first film bulk acoustic resonator group array electrically connected in series between the transistor output end and the signal output end, and / or a second film bulk acoustic resonator group array electrically connected in series between the transistor input end and the signal input end. The film bulk acoustic resonator group arrays are used for transistor high-harmonic circuit opening. Each film bulk acoustic resonator group array includes at least one film bulk acoustic resonator group. Each film bulk acoustic resonator includes a first electrode, a second electrode, and a dielectric film layer arranged between the two electrodes. The film bulk acoustic resonators tune the harmonic of the amplifier module in order to increase the efficiency of an amplifier based on the amplifier module and improve the linearity.
Owner:DYNAX SEMICON
Low-power consumption high-gain low-noise amplifier and operation method thereof
ActiveCN106374843ASmall currentReduce gainAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplififers with field-effect devicesAudio power amplifierTuned amplifier
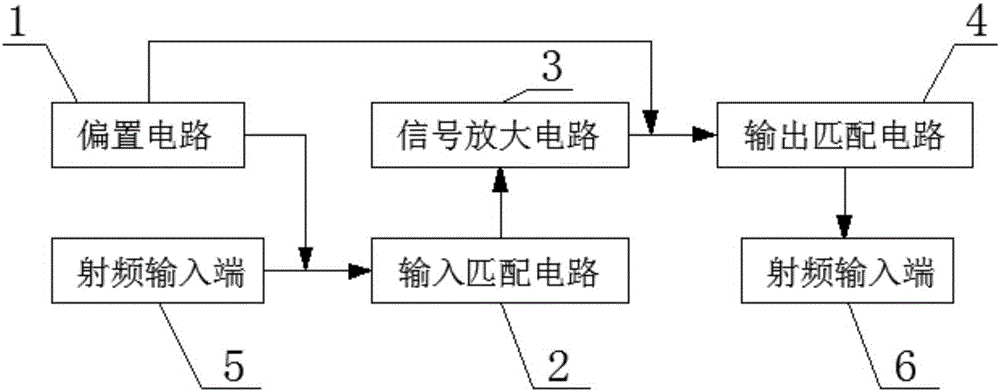
The invention relates to a low-power consumption high-gain low-noise amplifier and an operation method thereof. The amplifier comprises a biasing circuit, an input matching circuit, a signal amplification circuit and an output matching circuit. The input matching circuit inputs radio frequency signals and performs primary impedance matching on the radio frequency signals; the signal amplification circuit performs signal amplification on the radio frequency signals having undergone impedance matching; the output matching circuit performs secondary impedance matching on the amplified signals and outputs the radio frequency signals having undergone the secondary impedance matching; and the biasing circuit provides a bias voltage for the input matching circuit and performs gain on the amplified signals. Compared with the prior art, the low-power consumption high-gain low-noise amplifier saves a current of the biasing circuit, and the circuit gain can be increased under the conditions that power consumption of the circuit is not increased.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com