Cascaded distributed low-noise amplifier
A technology of low-noise amplifiers and amplifiers, applied in amplifiers, radio frequency amplifiers, amplifier types, etc., can solve problems such as the inability to effectively increase the gain-bandwidth product of amplifiers, and achieve the effects of simple structure, excellent radio frequency indicators, and low input return loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0018] Embodiments of the present invention will be described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
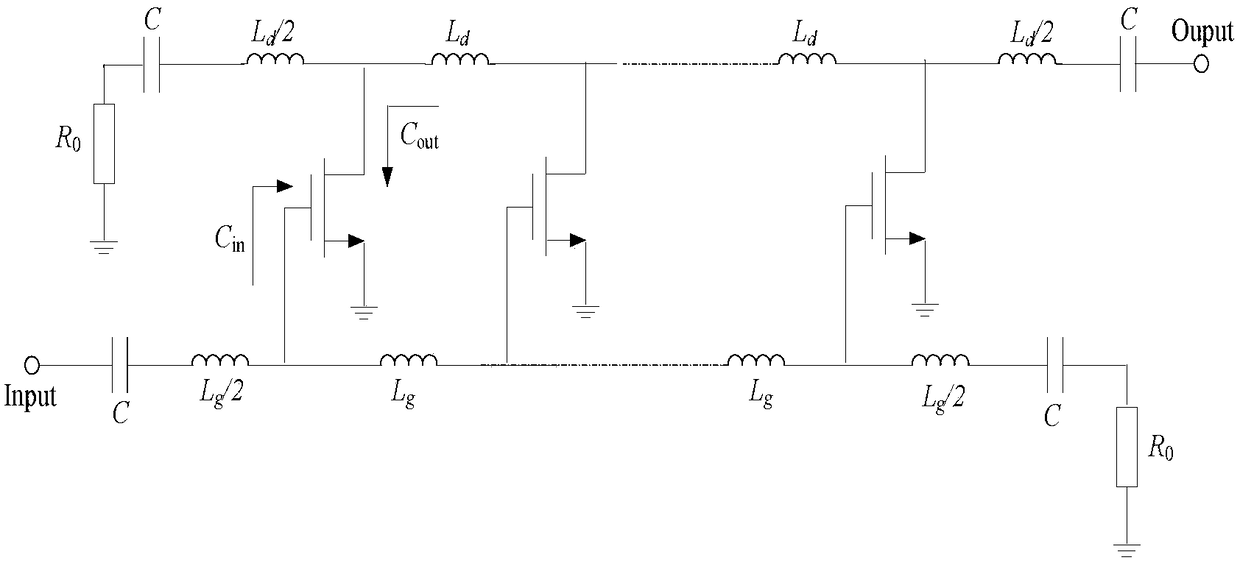
[0019] The basic principle of the traditional distributed low noise amplifier is to form an artificial transmission line with the parasitic capacitance of the transistor and the inductance element, so as to overcome the gain roll-off caused by the parasitic capacitance. The circuit schematic diagram is as follows figure 1 Shown, where vdd is the supply voltage, vgs is the DC bias voltage, the on-chip inductor Lg and the input impedance of the gain unit constitute the input artificial transmission line, and the on-chip inductor Ld and the output impedance of the gain unit constitute the output artificial transmission line. Obviously, the input / output artificial transmission lines are all low-pass filter structures.
[0020] According to the principle analysis of the distributed low noise amplifier, the input and output terminals of the distributed low noise ampl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com