Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
991 results about "Eye position" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
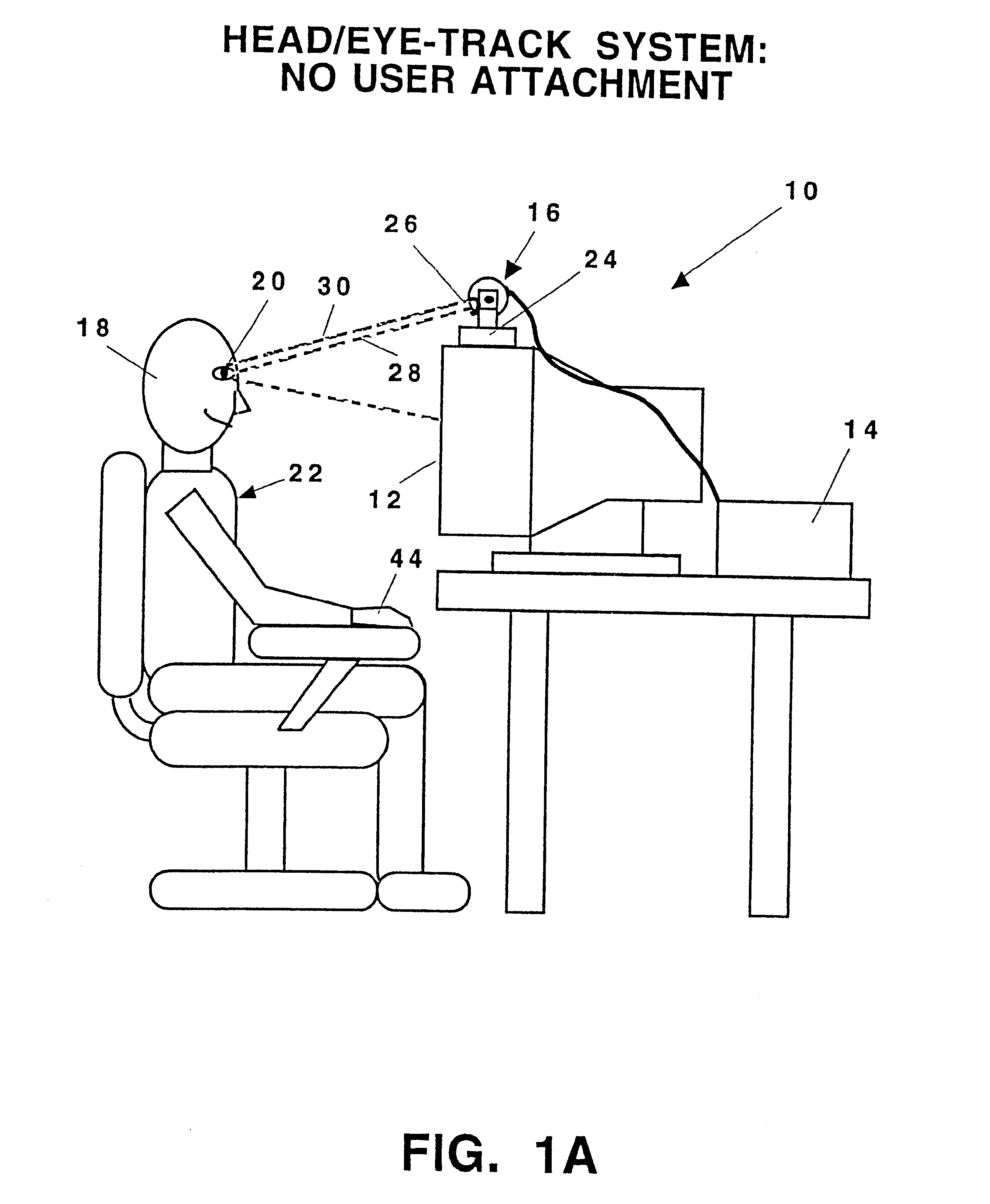
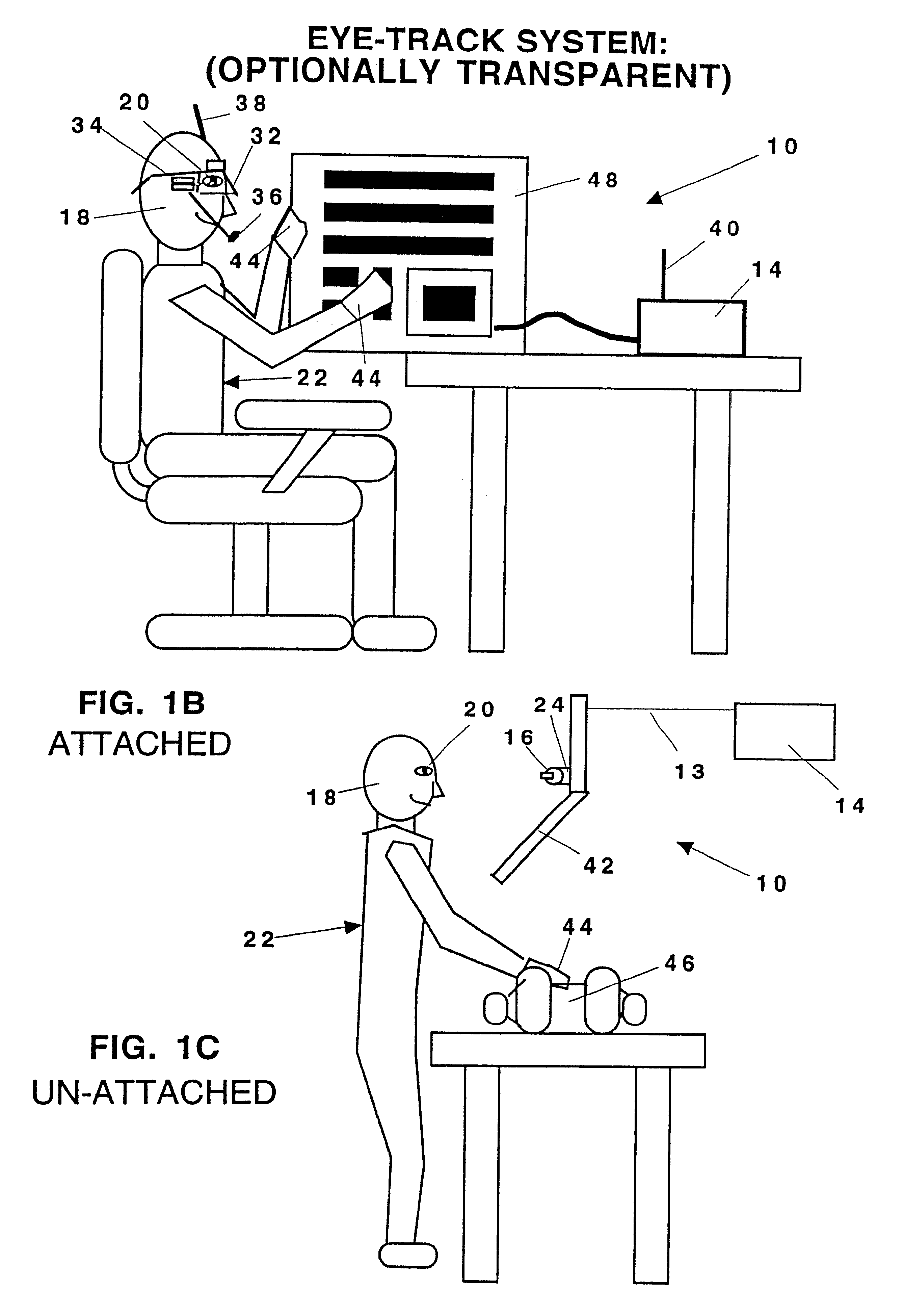
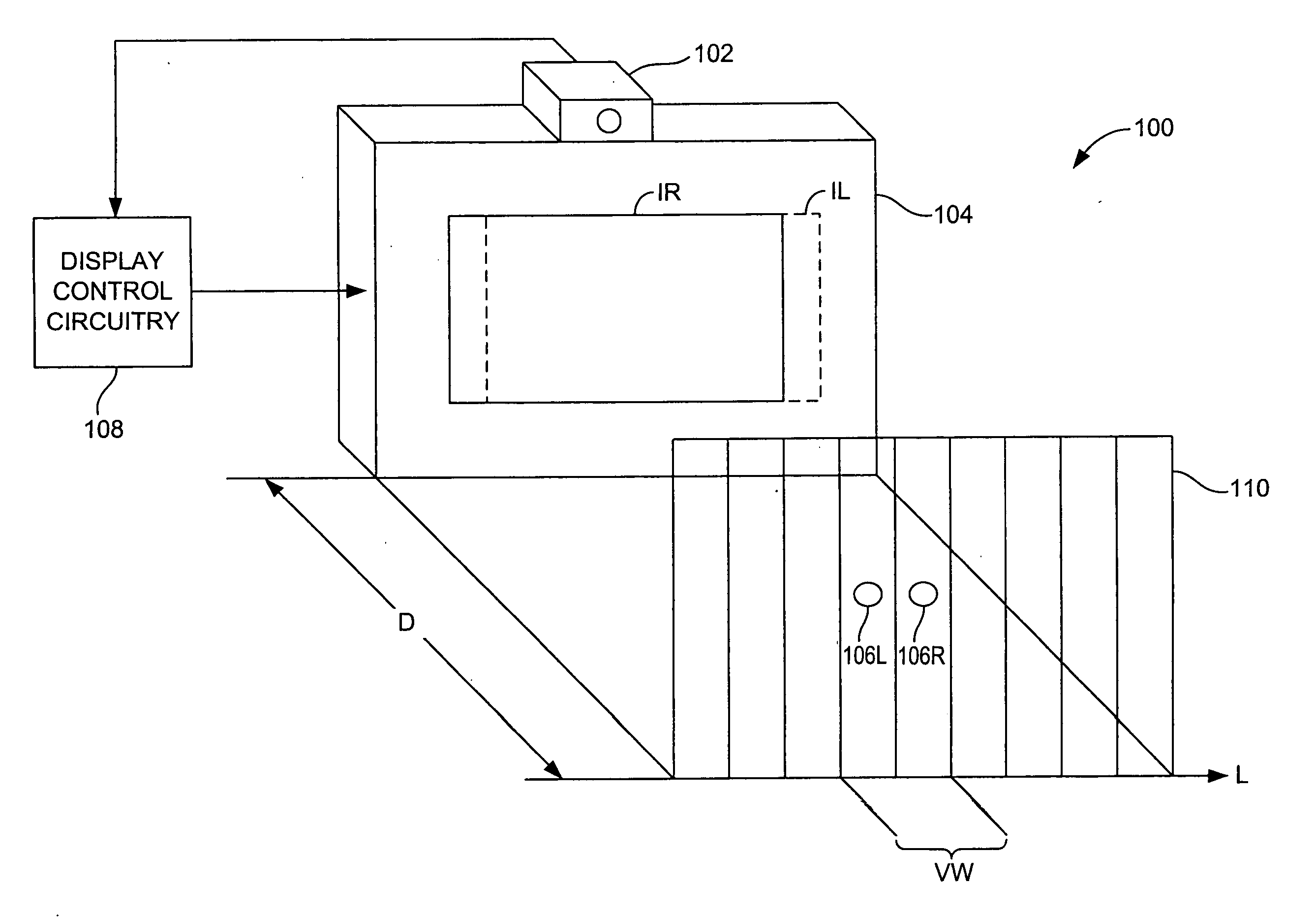
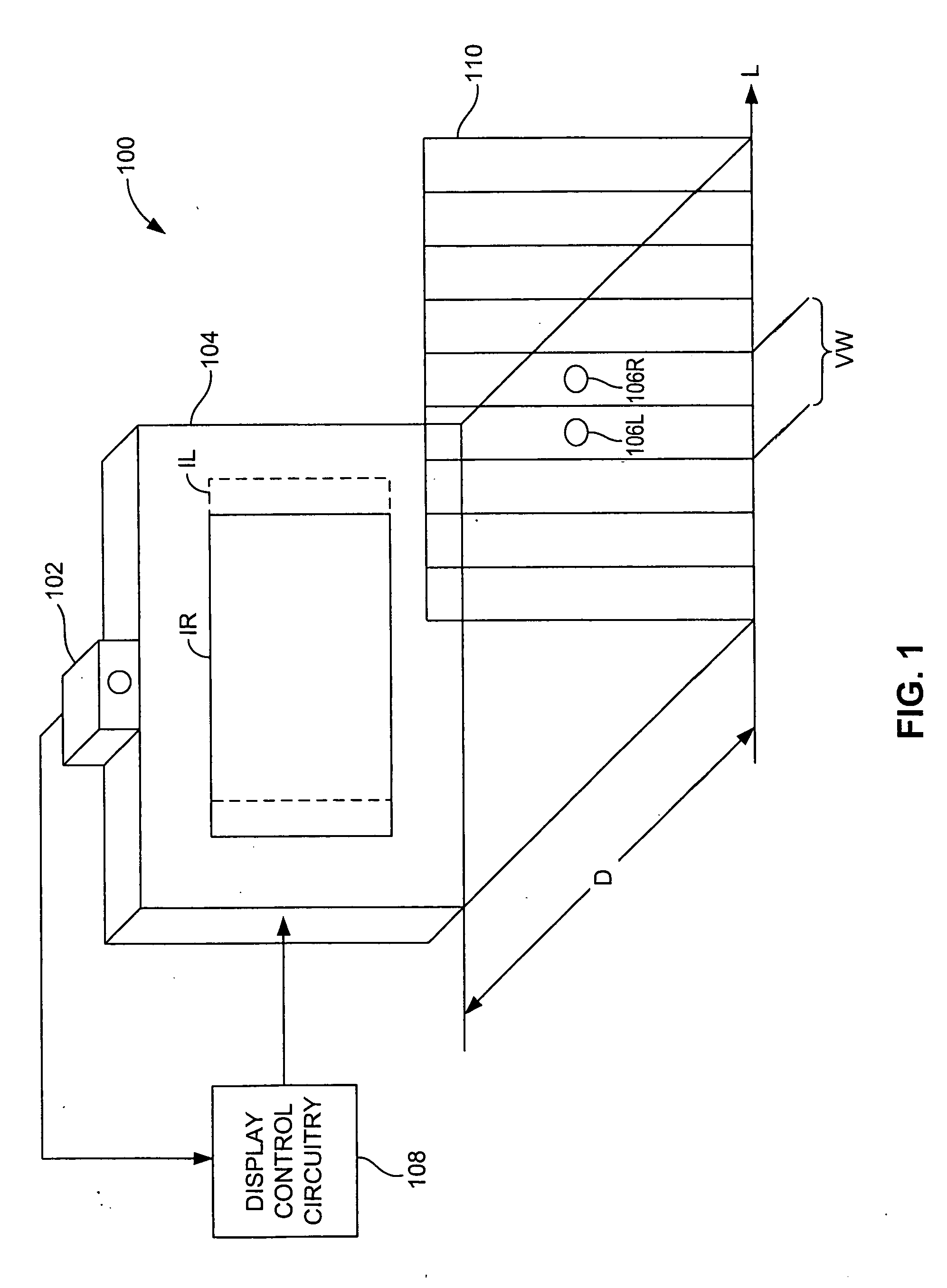
In the design of human-machine user interfaces (HMIs or UIs), the Design Eye Position (DEP) is the position from which the user is intended to view the workstation for an optimal view of the visual interface. The Design Eye Position represents the ideal but notional location of the operator's view and is usually expressed as a monocular point midway between the pupils of the average user.
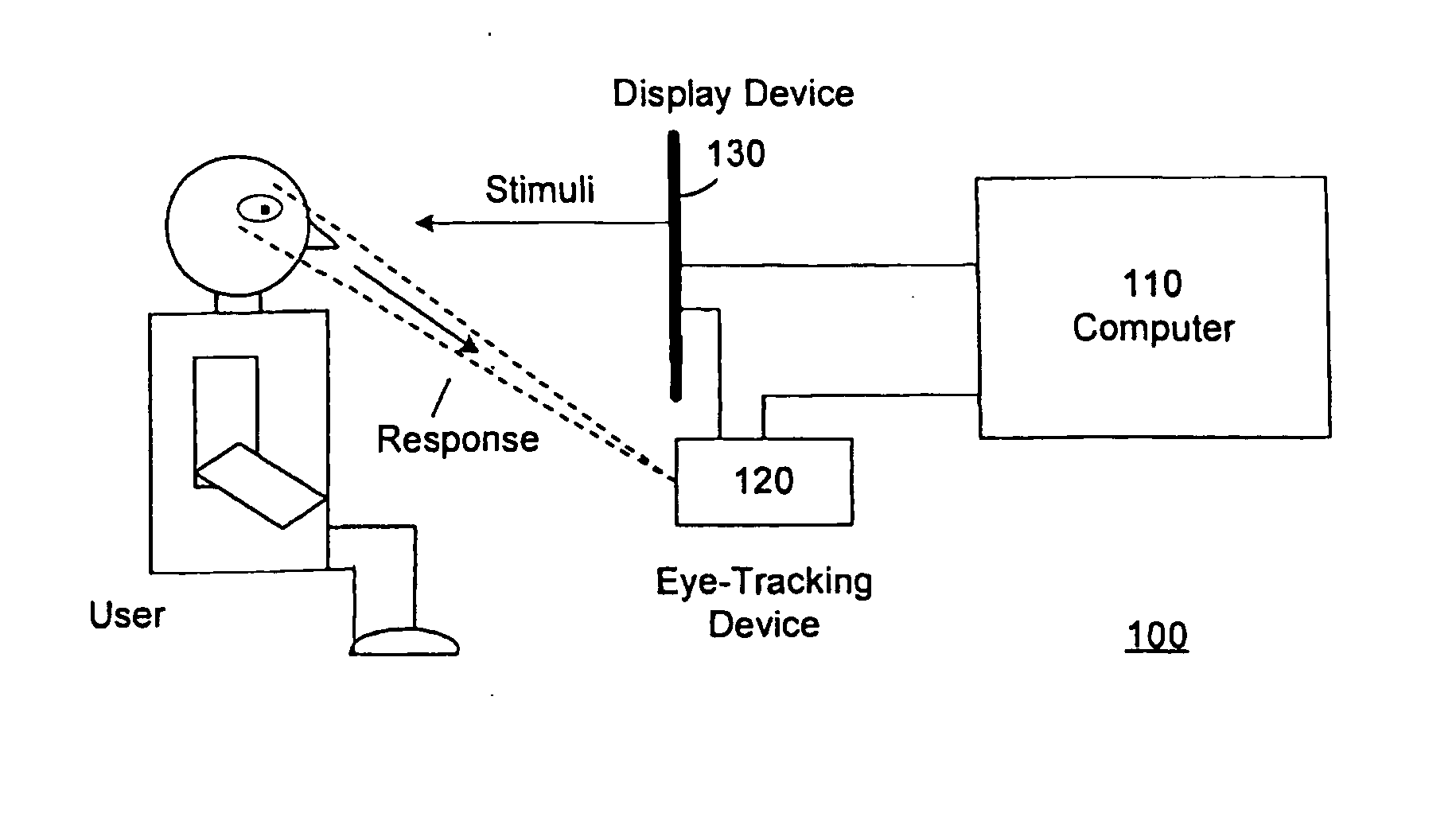
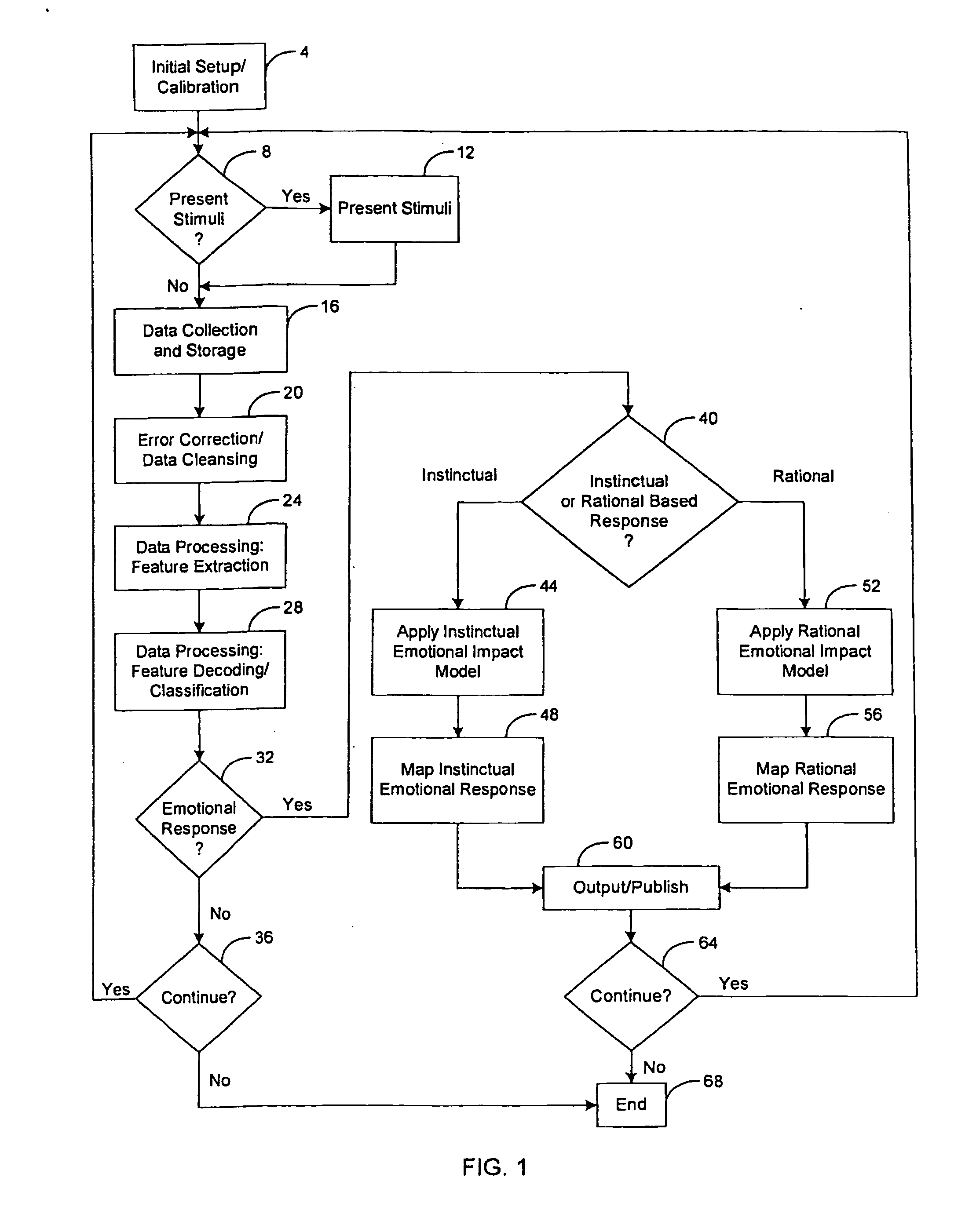
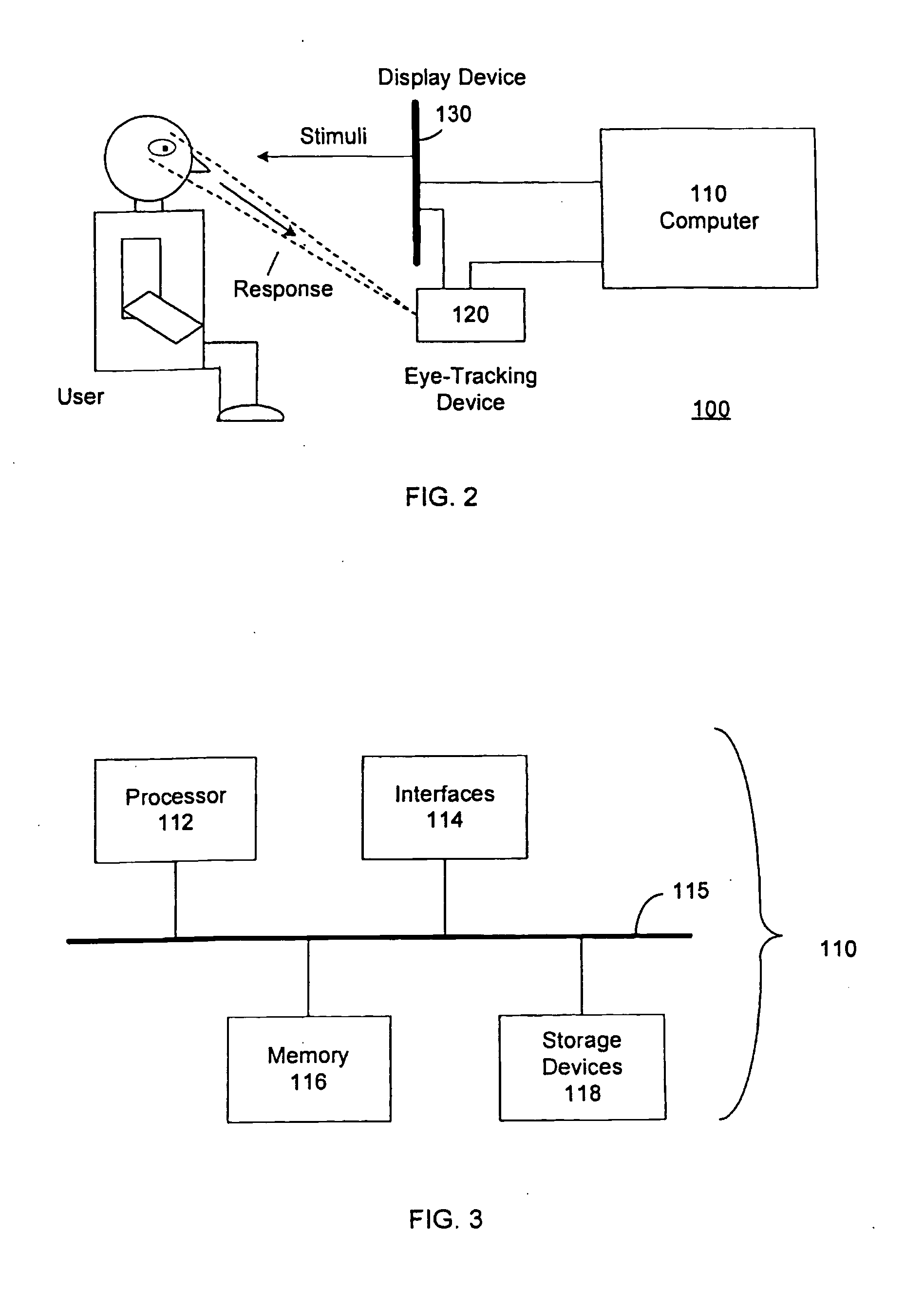
System and method for determining human emotion by analyzing eye properties
InactiveUS20070066916A1Cancel noiseEasy to explainLocal control/monitoringComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionPupilComputer science
The invention relates to a system and method for determining human emotion by analyzing a combination of eye properties of a user including, for example, pupil size, blink properties, eye position (or gaze) properties, or other properties. The system and method may be configured to measure the emotional impact of various stimuli presented to users by analyzing, among other data, the eye properties of the users while perceiving the stimuli. Measured eye properties may be used to distinguish between positive emotional responses (e.g., pleasant or “like”), neutral emotional responses, and negative emotional responses (e.g., unpleasant or “dislike”), as well as to determine the intensity of emotional responses.
Owner:IMOTIONS EMOTION TECH
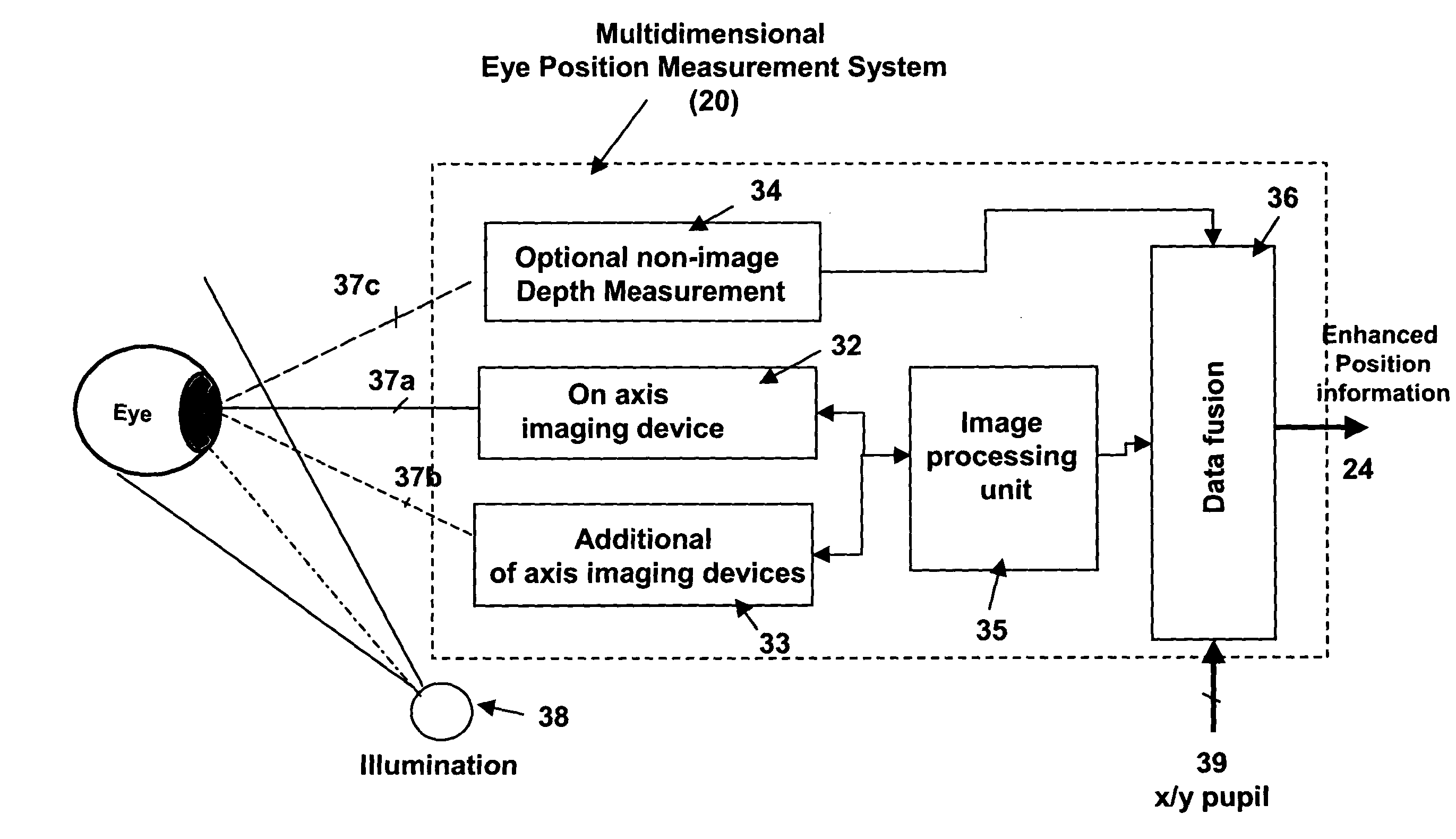
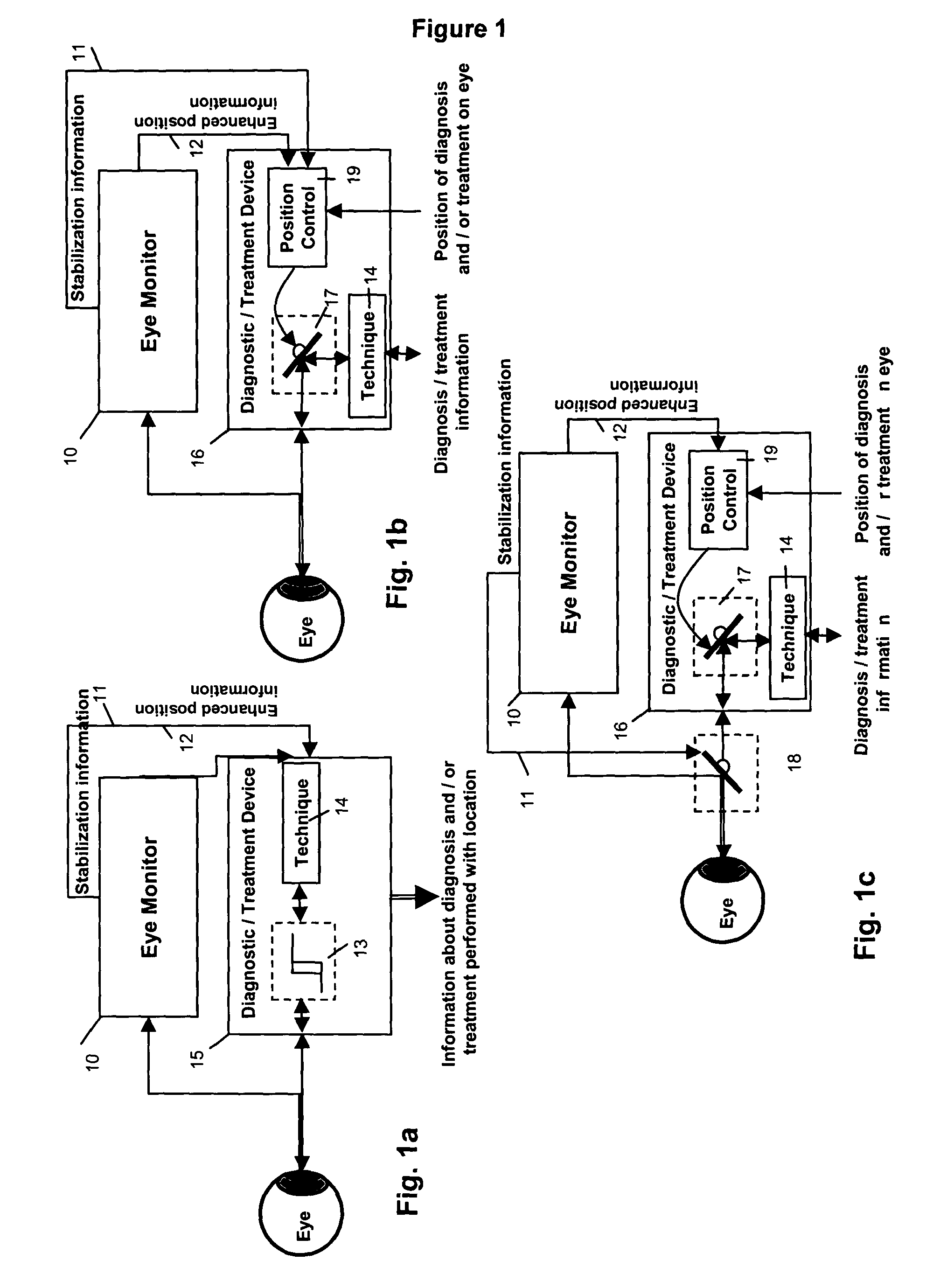
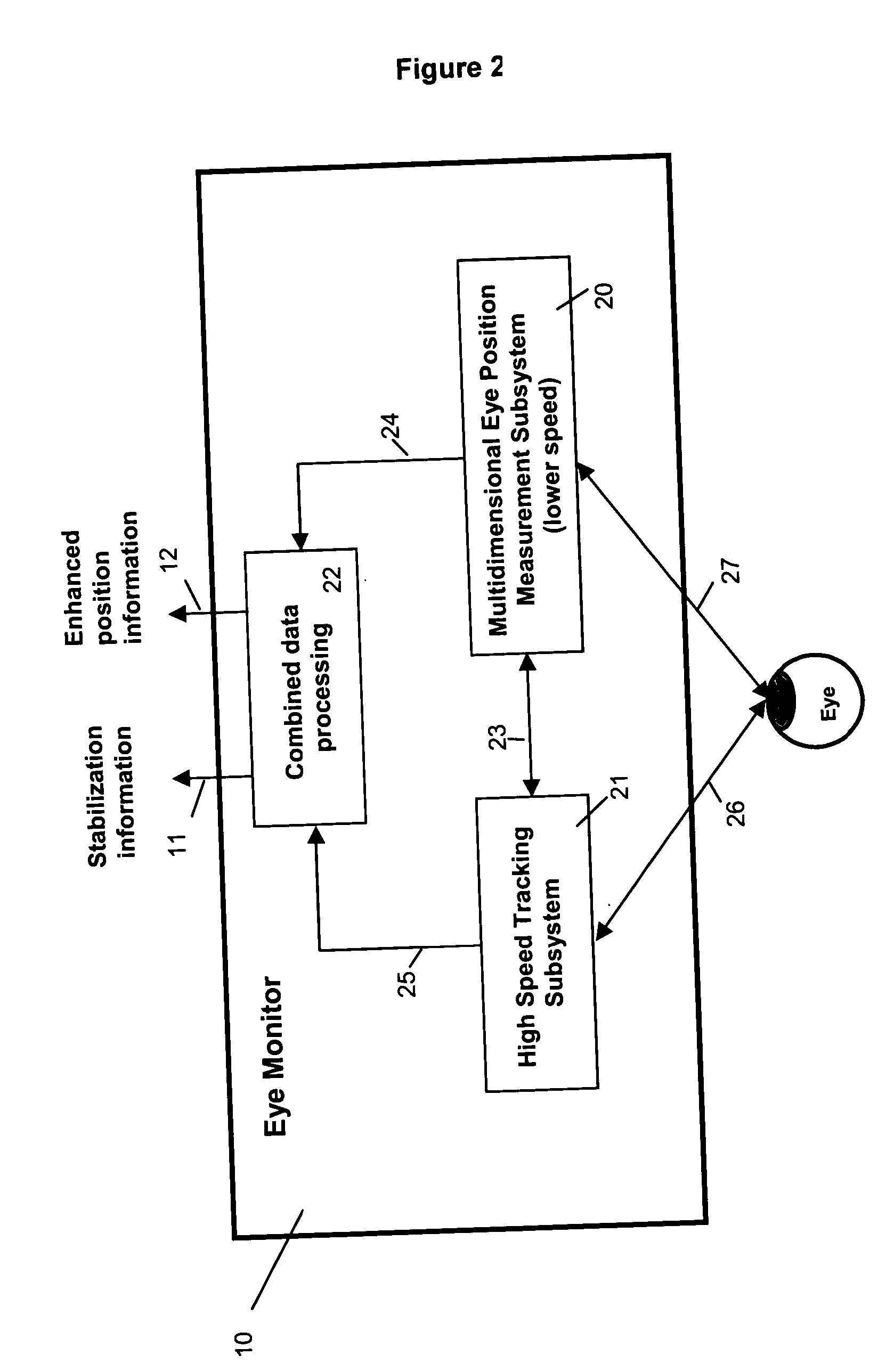
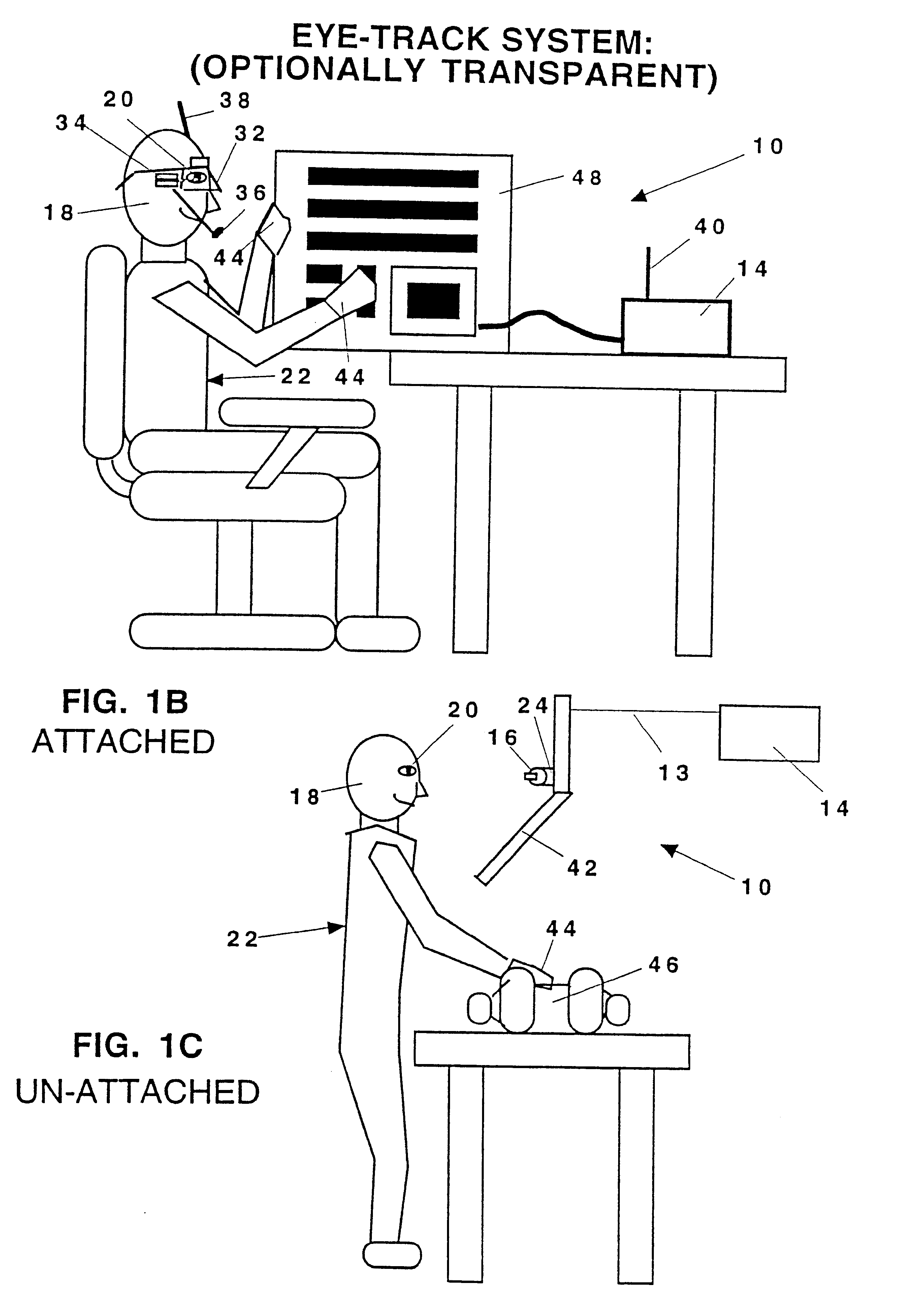
Multidimensional eye tracking and position measurement system for diagnosis and treatment of the eye
ActiveUS20050024586A1Improve spatial resolutionLess field of viewLaser surgeryCharacter and pattern recognitionMeasurement deviceSaccadic movements
The present invention relates to improved ophthalmic diagnostic measurement or treatment methods or devices, that make use of a combination of a high speed eye tracking device, measuring fast translation or saccadic motion of the eye, and an eye position measurement device, determining multiple dimensions of eye position or other components of eye, relative to an ophthalmic diagnostic or treatment instrument.
Owner:SENSOMOTORIC INSTR FUR INNOVATIVE SENSORIK MBH D B A SENSOMOTORIC INSTR
Facial image processing system
InactiveUS7043056B2Image analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingPostural orientation
A method of determining an eye gaze direction of an observer is disclosed comprising the steps of: (a) capturing at least one image of the observer and determining a head pose angle of the observer; (b) utilizing the head pose angle to locate an expected eye position of the observer, and (c) analyzing the expected eye position to locate at least one eye of the observer and observing the location of the eye to determine the gaze direction.
Owner:NXP BV +1
System and methods for controlling automatic scrolling of information on a display or screen
InactiveUS6351273B1Input/output for user-computer interactionSpeech analysisAutomatic controlDisplay device
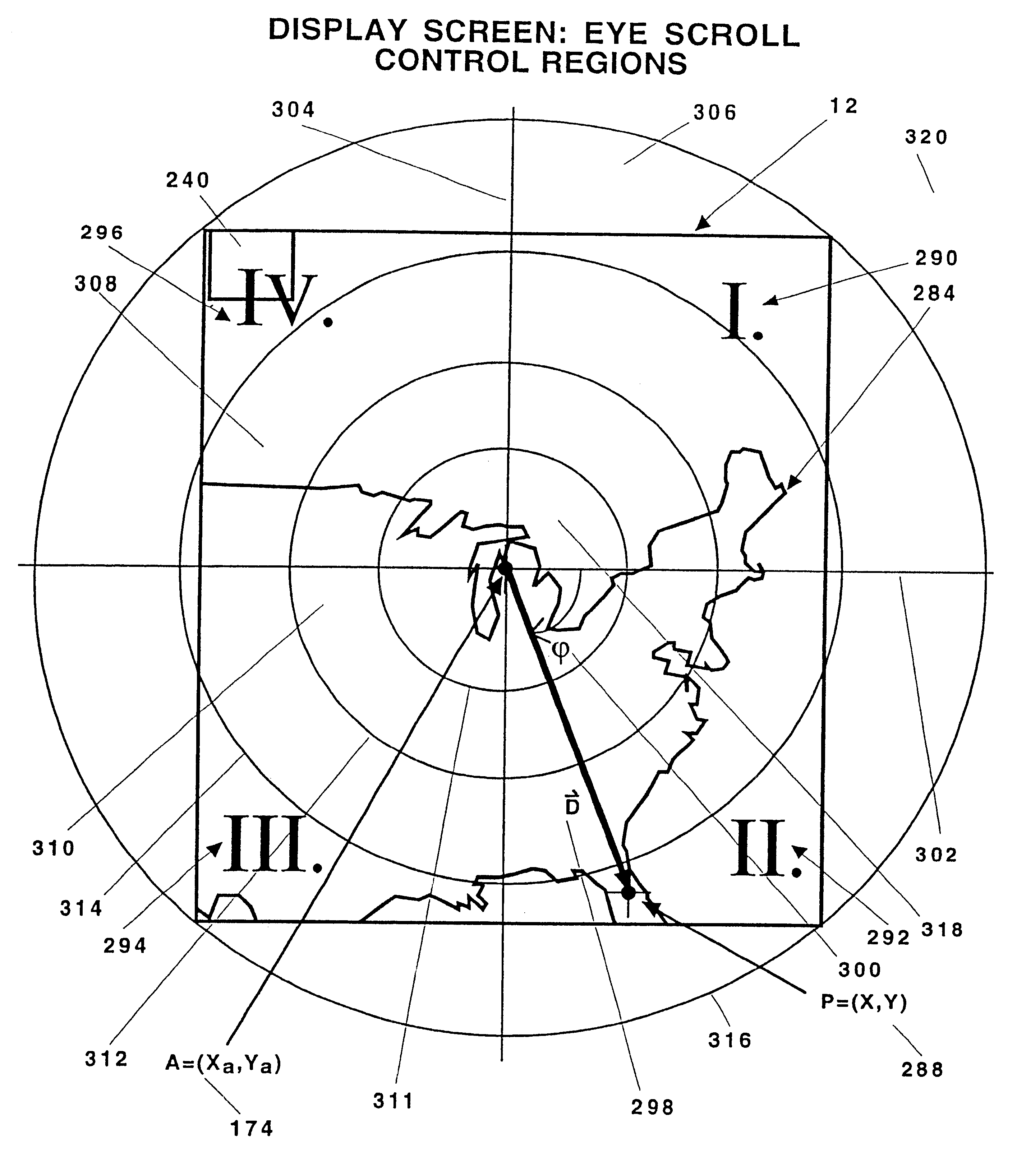
A system for controlling the automatic scrolling of information on a computer display. The system includes a computer display, a computer gimbaled sensor for tracking the position of the user's head and user's eye, and a scroll activating interface algorithm using a neural network to find screen gaze coordinates implemented by the computer. A scrolling function is performed based upon the screen gaze coordinates of the user's eye relative t activation area(s) on the display. The gimbaled sensor system contains a platform mounted at the top of the display. The gimbaled sensor system tracks the user's head and eye allowing the user to be free from attachments while the gimbaled sensor system is tracking, still allowing the user to freely move his head. A method of controlling automatic scrolling of information on a display includes the steps of finding a screen gaze coordinate on the display of the user determining whether the screen gaze coordinate is within at least one activated control region, and activating scrolling to provide a desired display of information when the gaze direction is within at least one activated control region. In one embodiment, the control regions are defined as upper control region, lower region, right region and left region for controlling the scrolling respectively in downward, upward, leftward and rightward directions. In another embodiment, control regions are defined by concentric rings for maintaining the stationary position of the information or controlling the scrolling of the information towards the center of the display or screen.
Owner:LEMELSON JEROME H +1
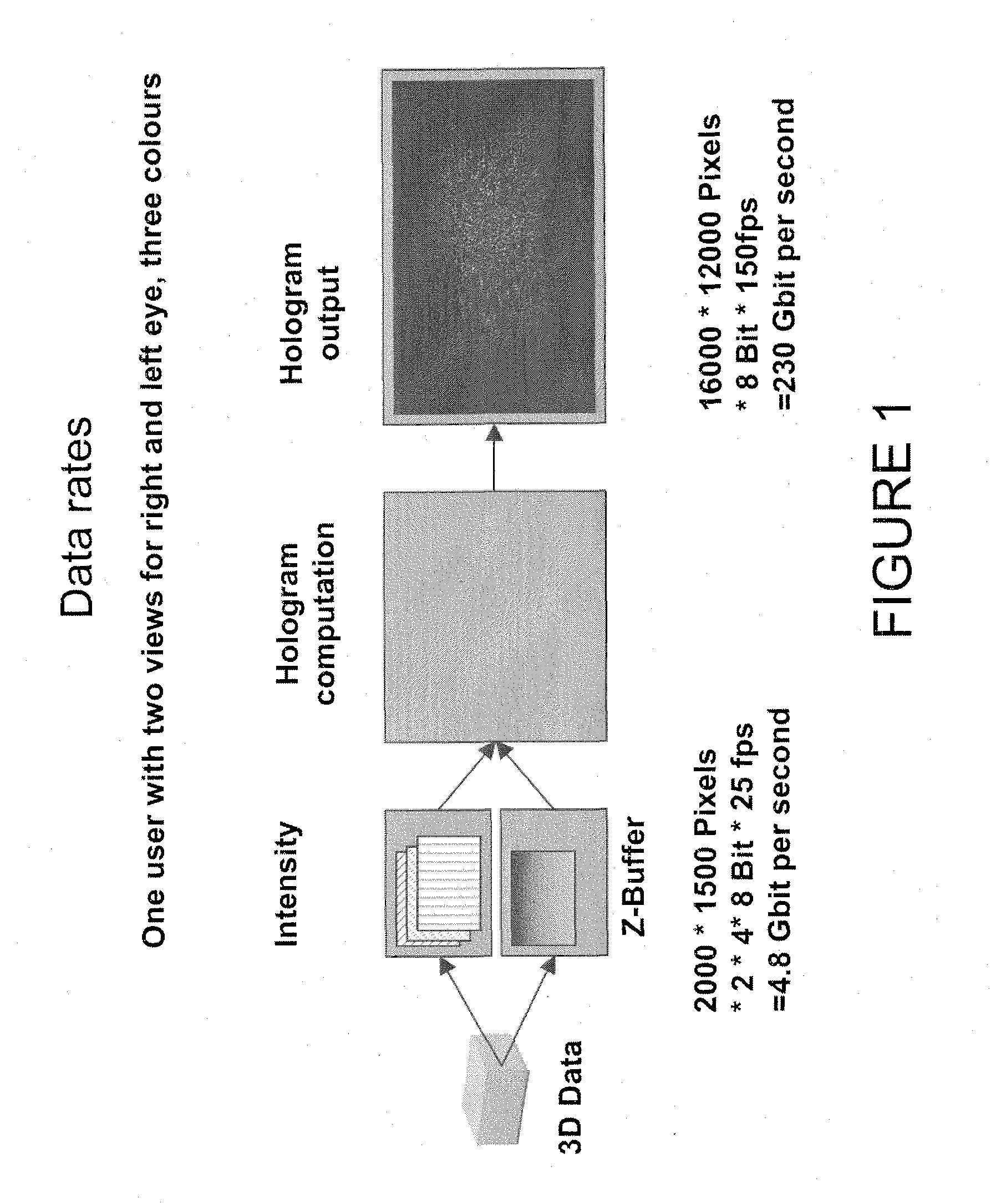
Method of computing a hologram
ActiveUS20060139711A1Reduce calculationQuality improvementHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesHolographic optical componentsWavefrontComputer science
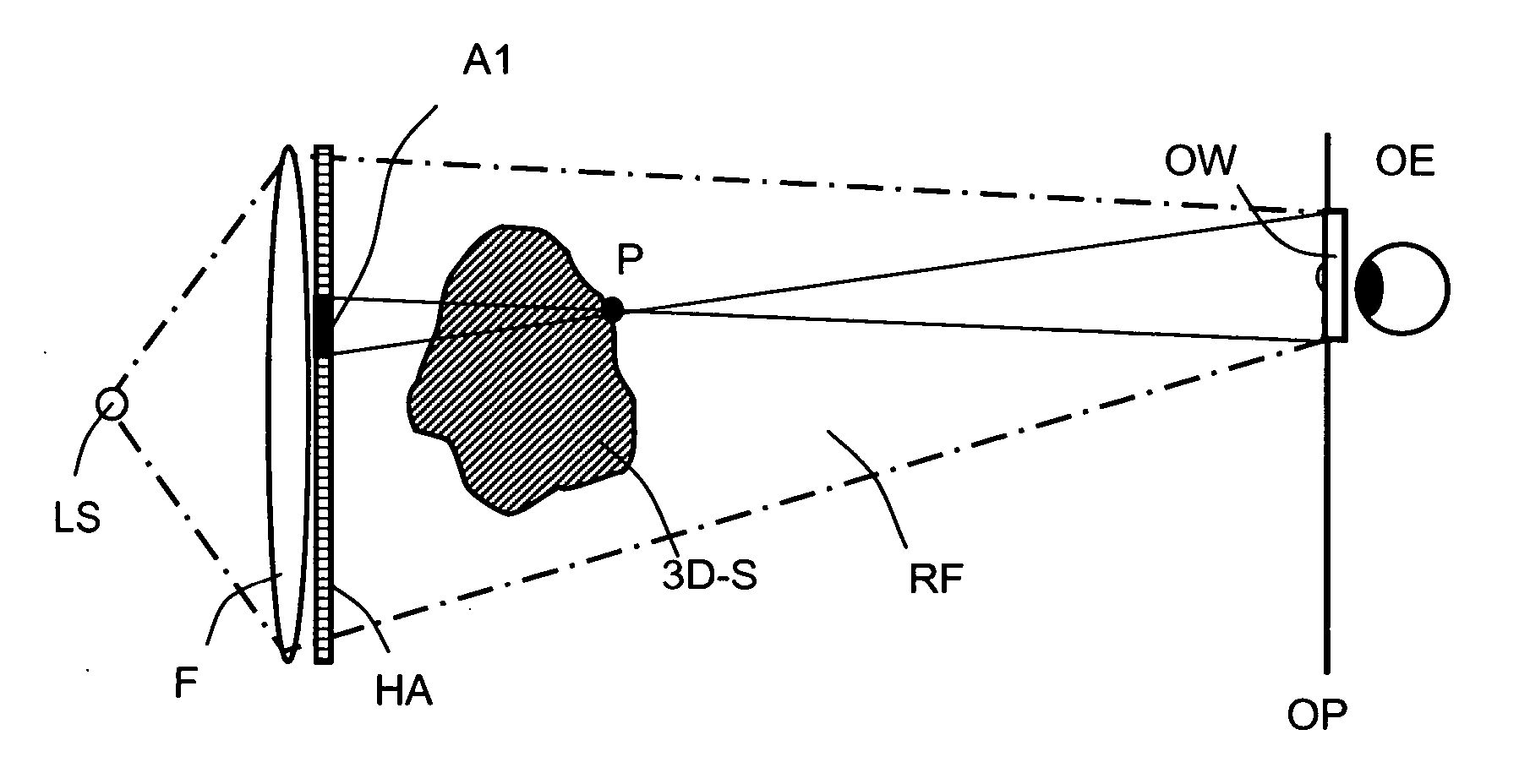
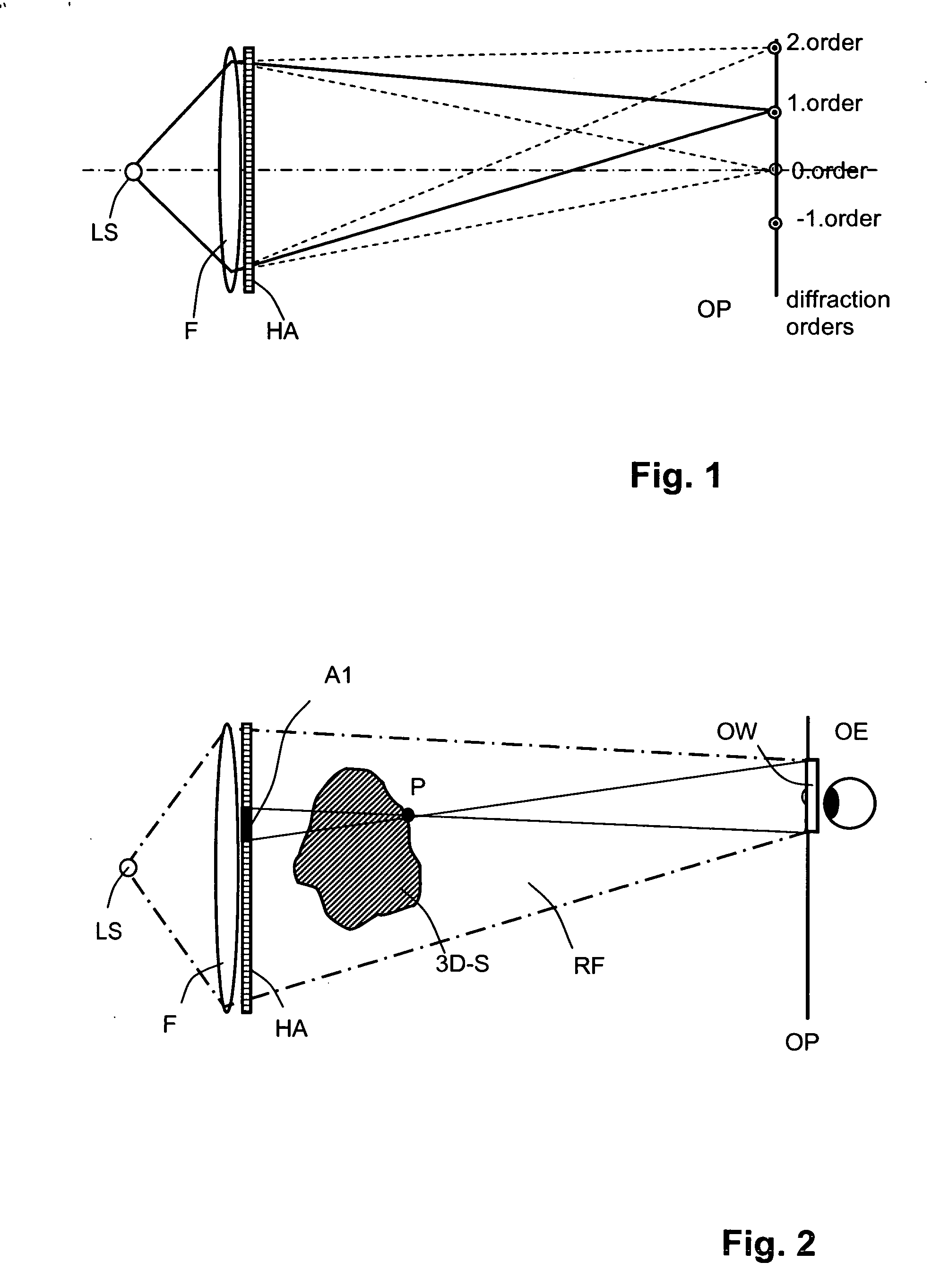
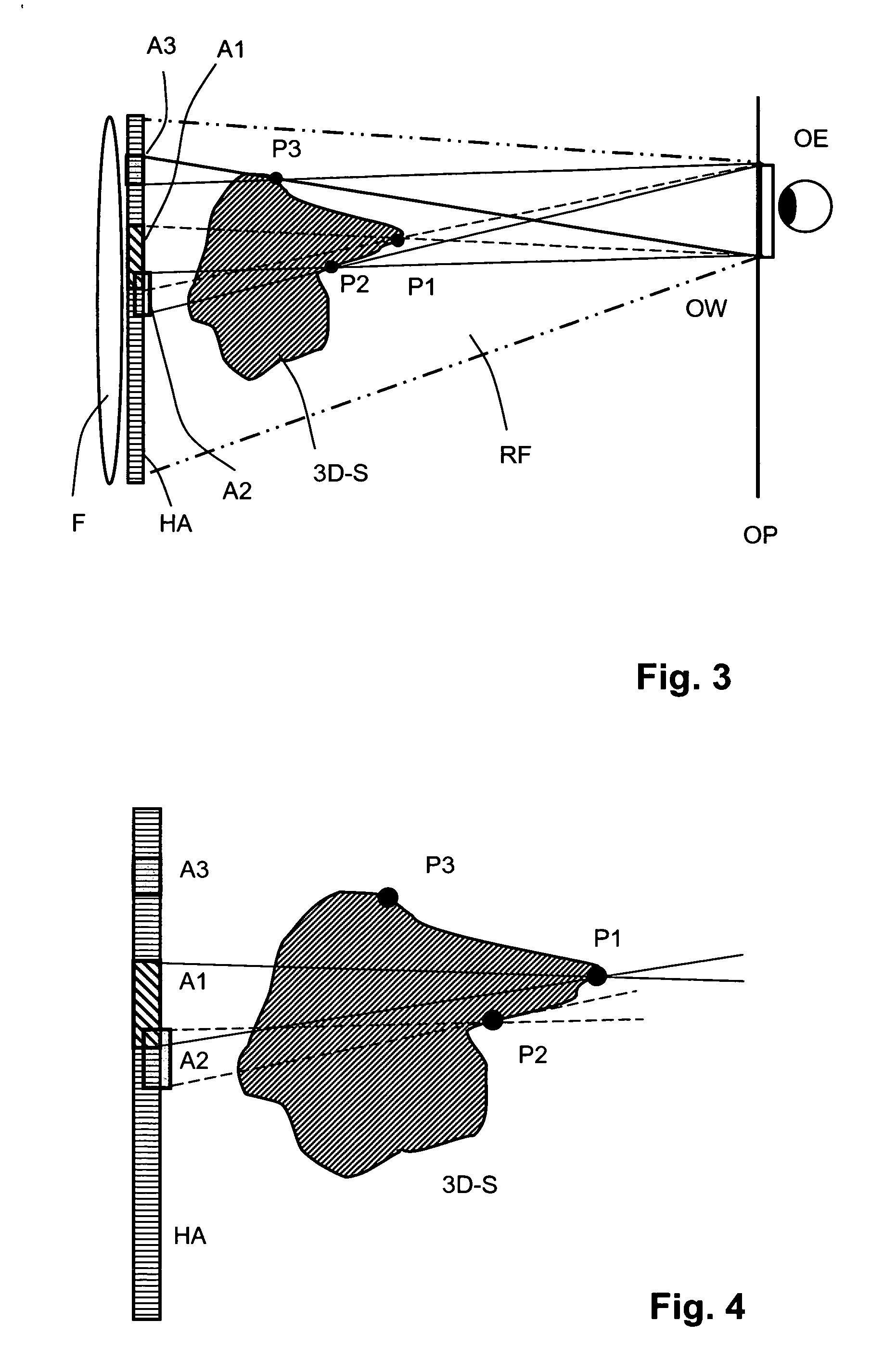
A method of computing a hologram by determining the wavefronts at the approximate observer eye position that would be generated by a real version of an object to be reconstructed. In normal computer generated holograms, one determines the wavefronts needed to reconstruct an object; this is not done directly in the present invention. Instead, one determines the wavefronts at an observer window that would be generated by a real object located at the same position of the reconstructed object. One can then back-transforms these wavefronts to the hologram to determine how the hologram needs to be encoded to generate these wavefronts. A suitably encoded hologram can then generate a reconstruction of the three-dimensional scene that can be observed by placing one's eyes at the plane of the observer window and looking through the observer window.
Owner:SEEREAL TECHNOLOGIES
Augmented reality glasses for medical applications and corresponding augmented reality system
Owner:BADIALI GIOVANNI +3
Eye detection system and method for control of a three-dimensional display
An autostereoscopic display system includes an autostereoscopic display subsystem operable to display stereoscopic images and to adjust characteristics of the displayed images responsive to detected viewer eye position parameters. An eye detection subsystem detects through differential-angle illumination the eye position of a viewer positioned in front of the display subsystem and generates corresponding viewer eye position parameters. The eye detection subsystem applies the detected viewer eye position parameters the display subsystem to adjust the characteristics of the displayed images.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Augmented reality display system and method for vehicle
ActiveUS20120154441A1Intuitive informationRoad vehicles traffic controlAcquiring/recognising eyesDriver/operatorView camera
A system includes a head front display device, an eye position tracking camera to track movement of a driver's irises, a front view camera to take a picture of a front view of the driver, a head front display device controller to implement at least one of an angle change, forward movement, backward movement, upward movement, downward movement, leftward movement, and rightward movement of the head front display device, an image adjuster to adjust an object displayed on the head front display device in association with an object of an actual view seen through the front window of the vehicle based on positions of the driver's irises obtained through the eye position tracking camera and an image of the front view obtained by the front view camera, and a display unit controlled by the image adjuster and configured to display information on the head front display device.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method and system for input detection using structured light projection
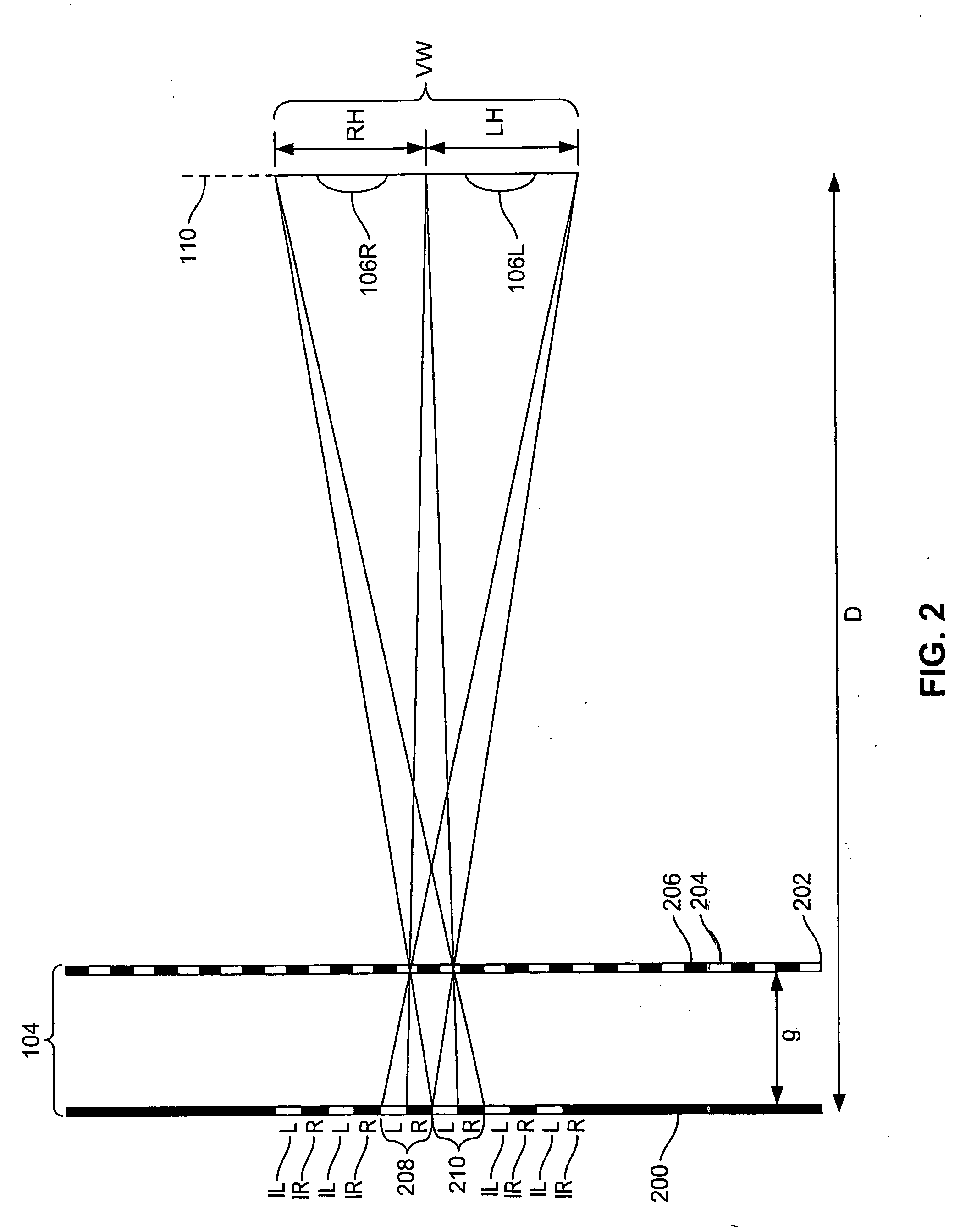
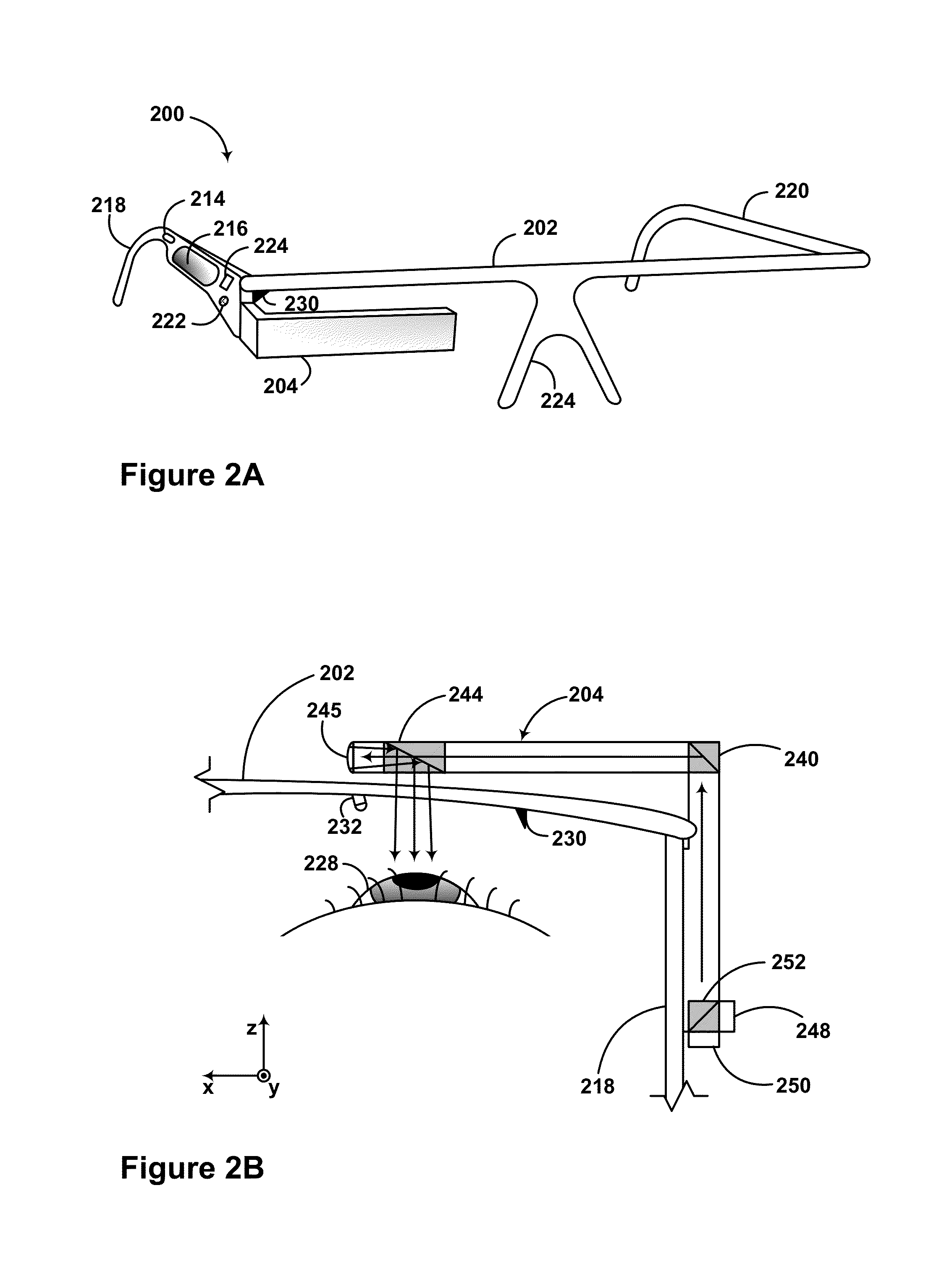
Exemplary methods and systems help provide for tracking an eye. An exemplary method may involve: causing the projection of a pattern onto an eye, wherein the pattern comprises at least one line, and receiving data regarding deformation of the at least one line of the pattern. The method further includes correlating the data to iris, sclera, and pupil orientation to determine a position of the eye, and causing an item on a display to move in correlation with the eye position.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Multi-user autostereoscopic display with position tracking
InactiveUS20070188667A1Low costLittle laborOptical rangefindersMicroscopesDisplay deviceImaging equipment
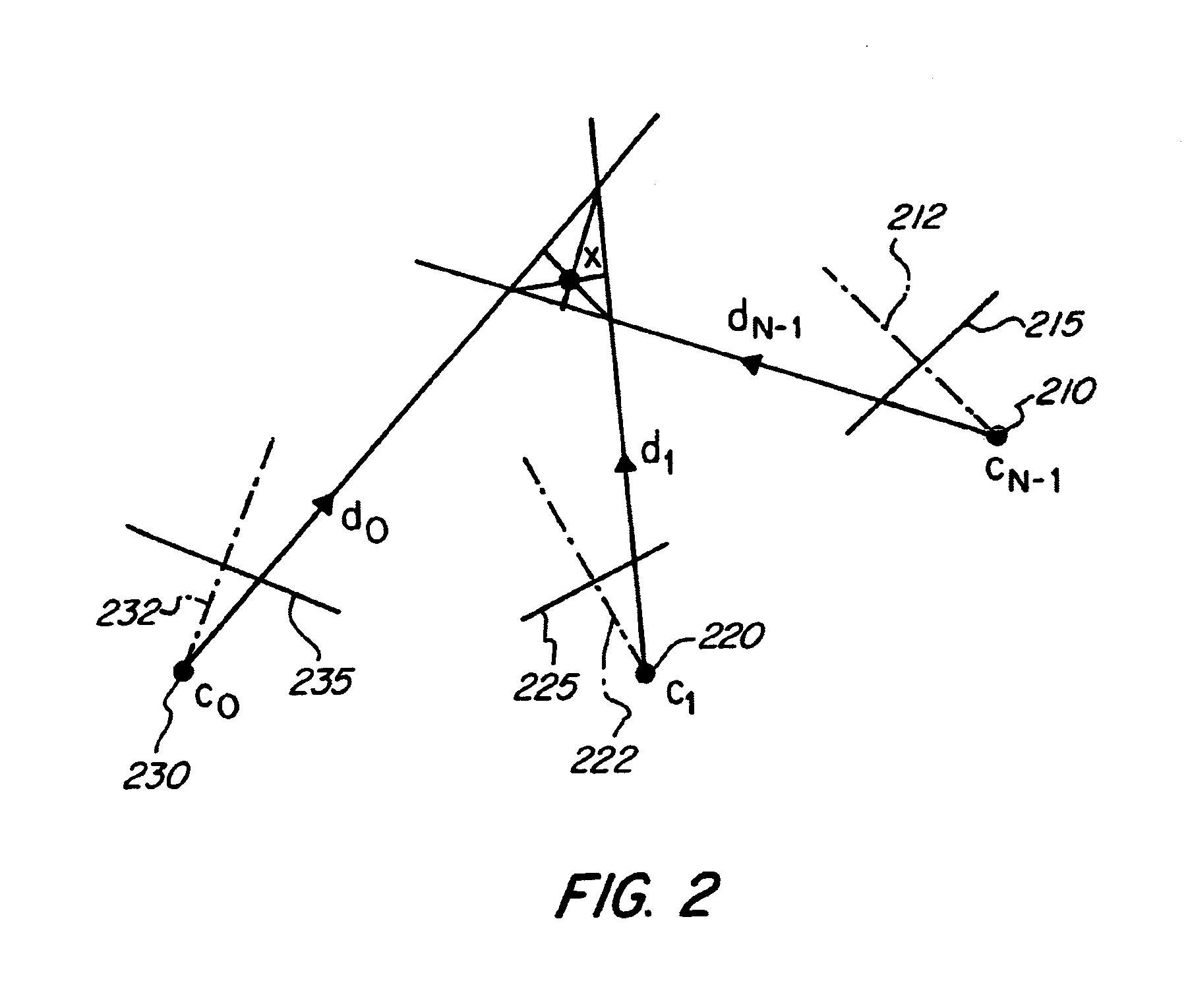
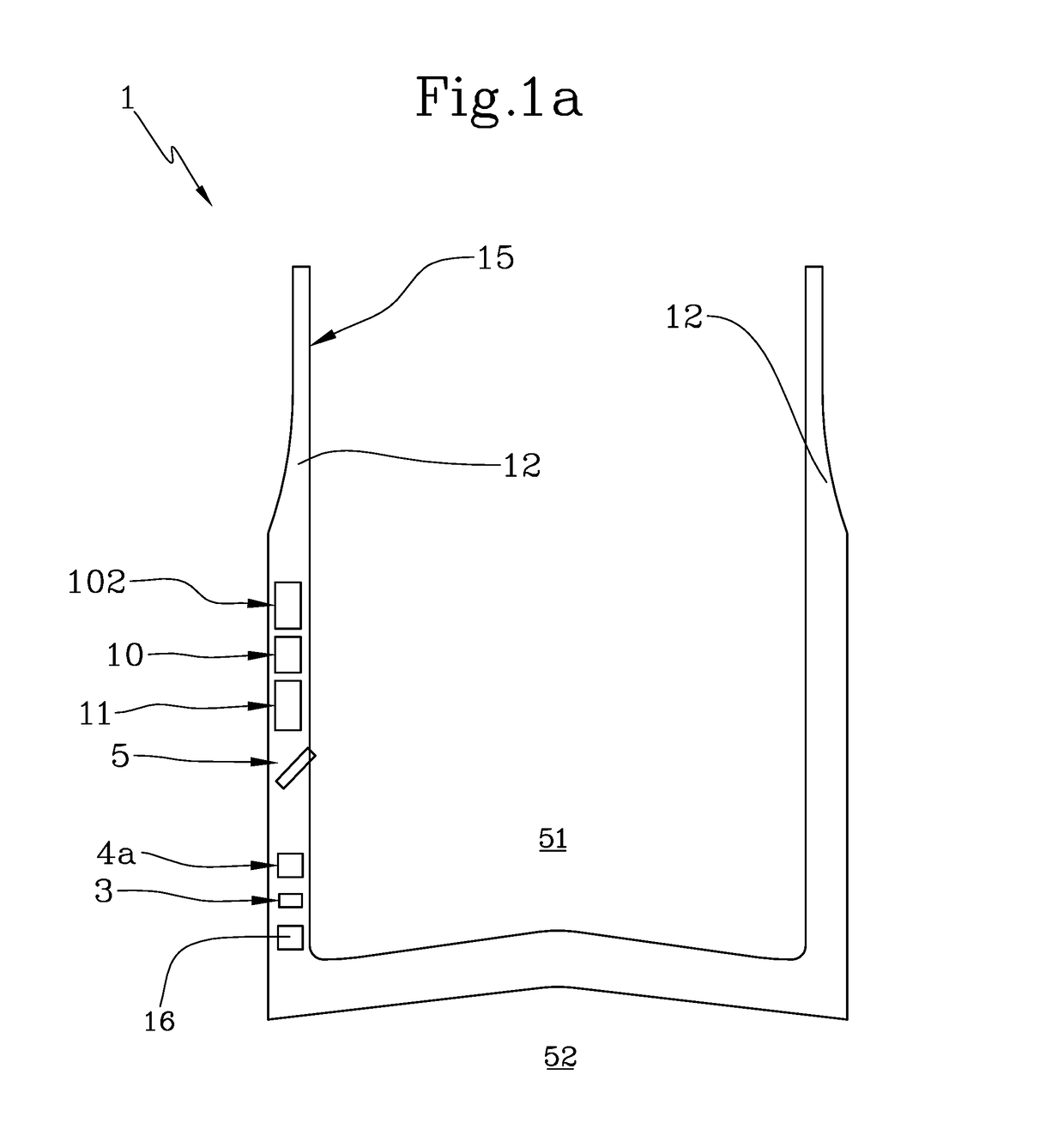
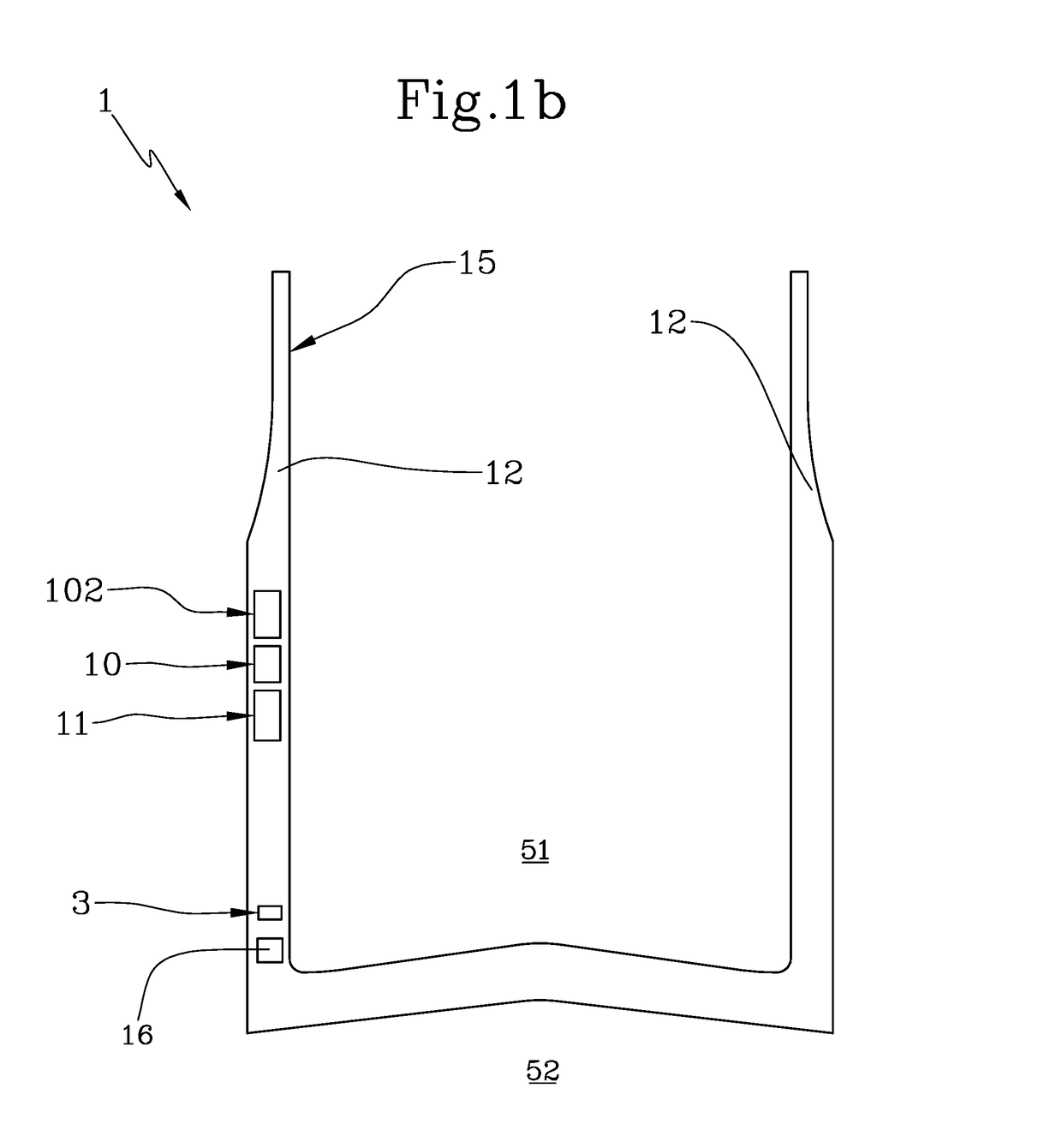
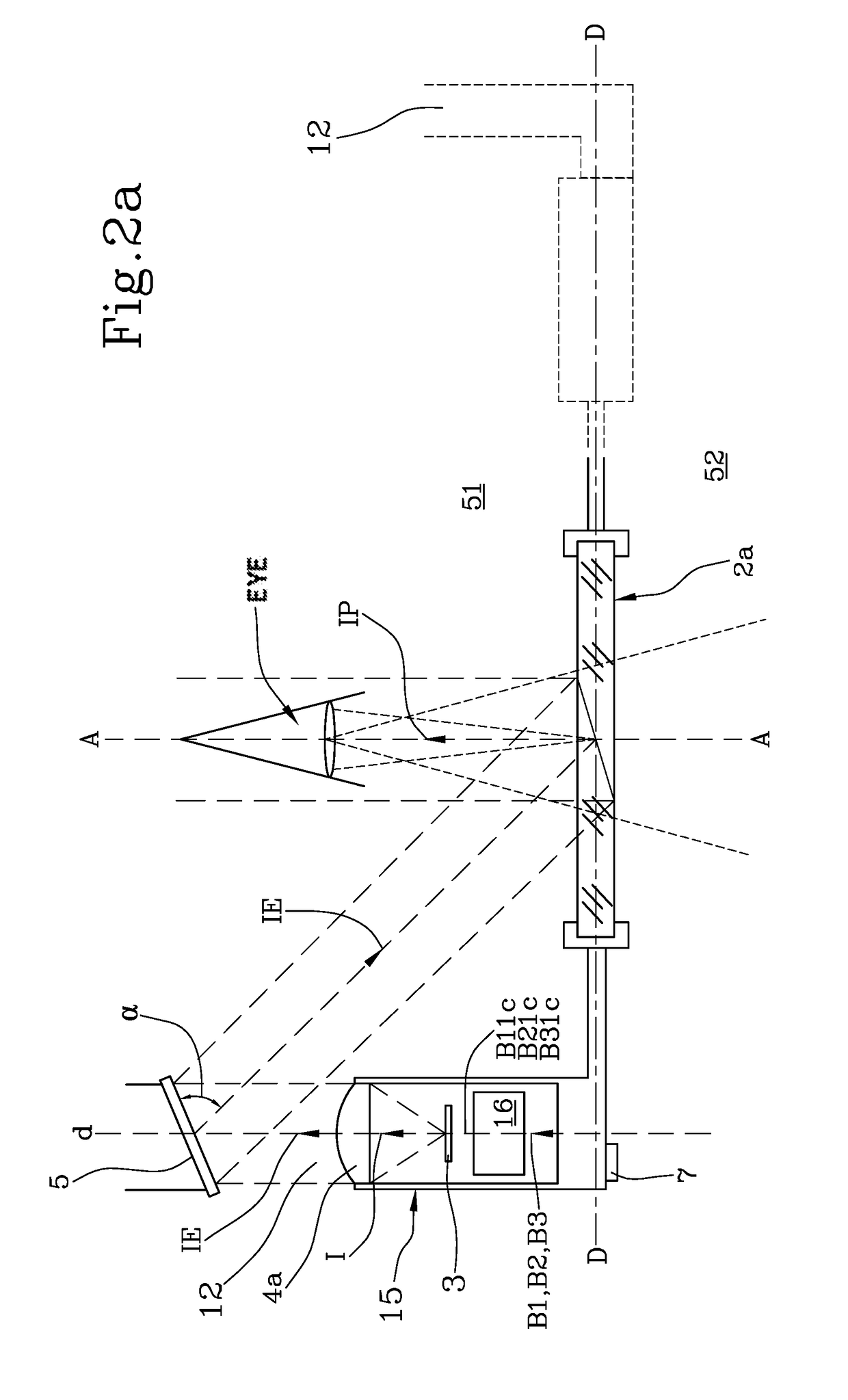
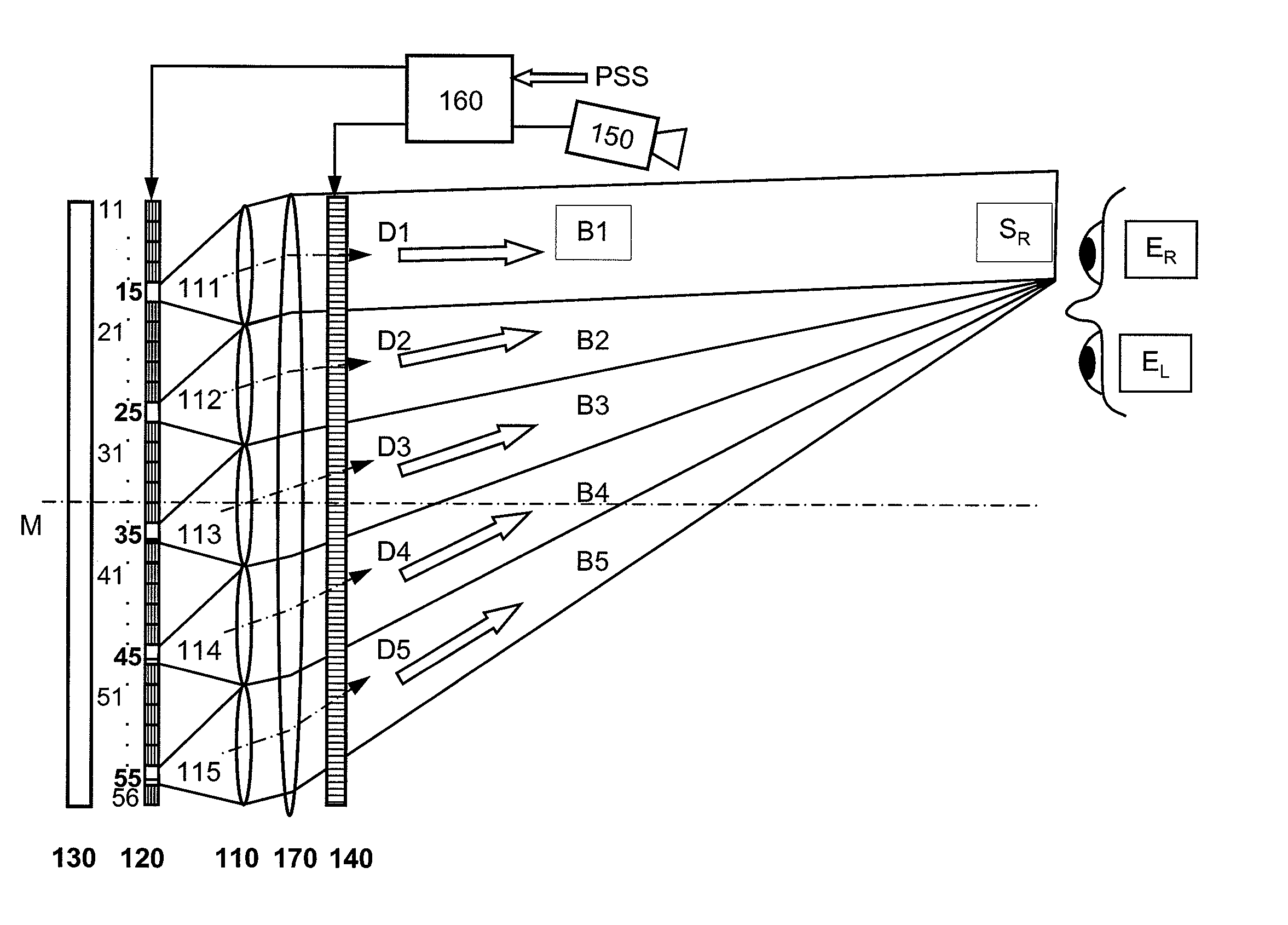
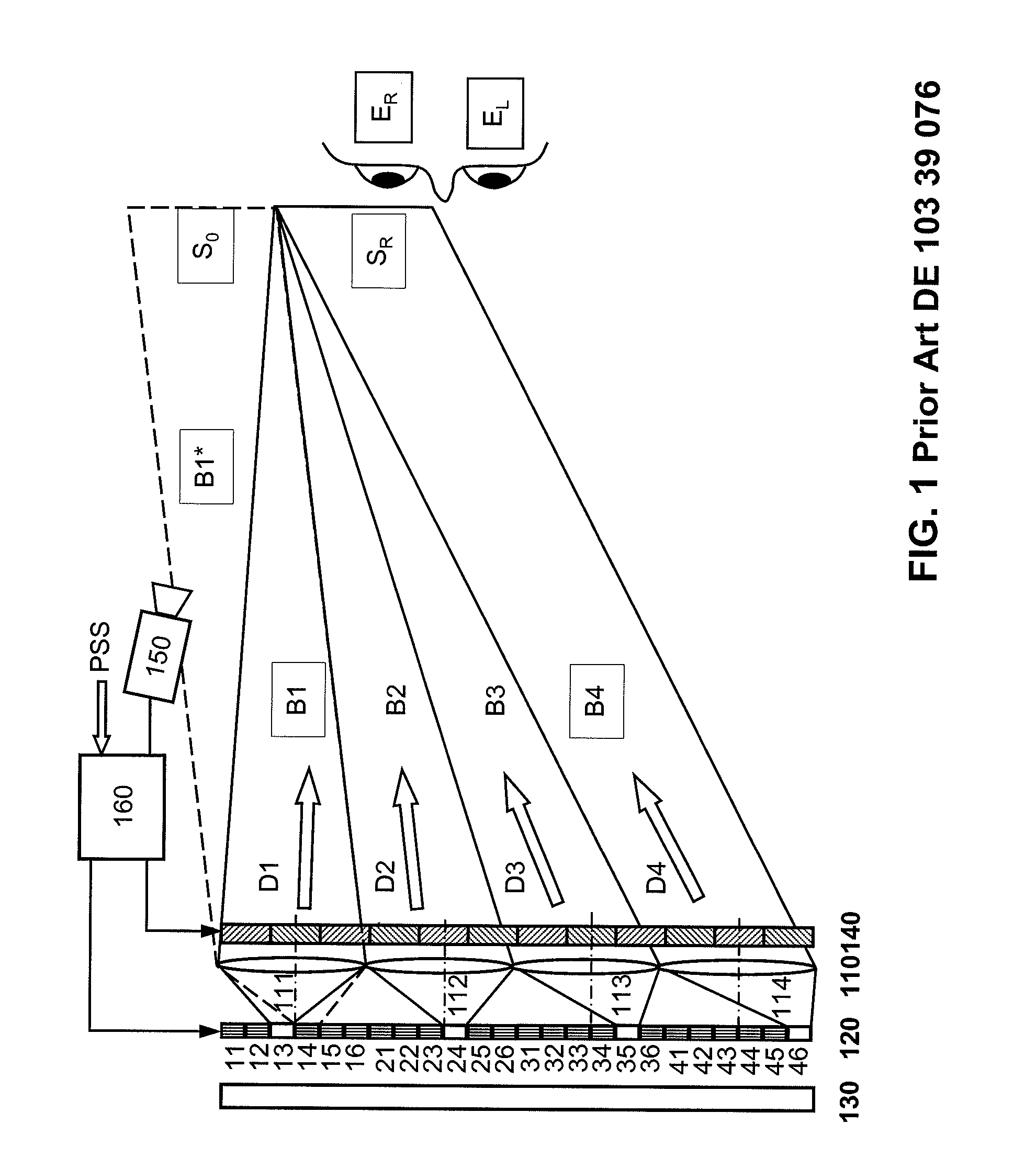
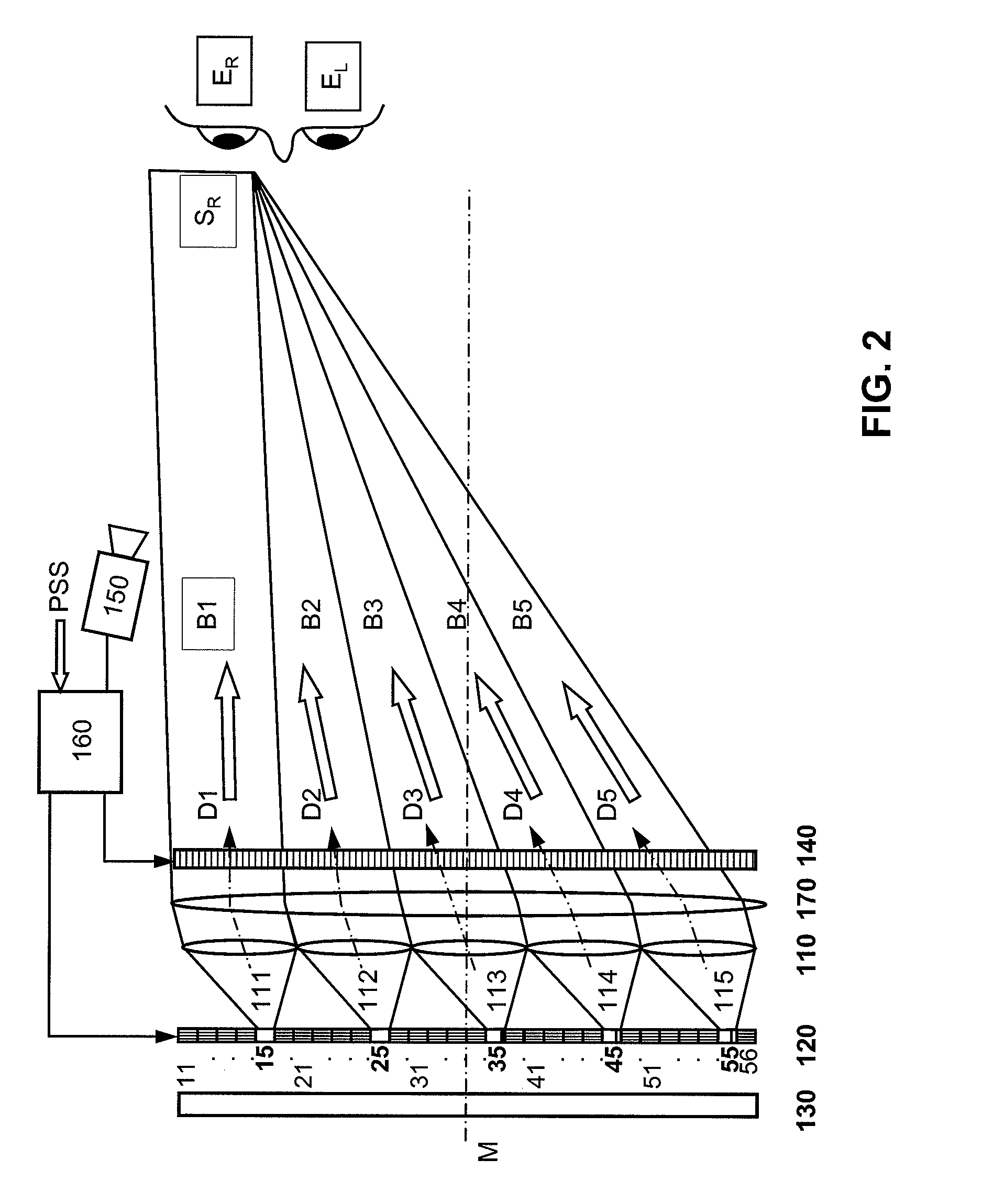
An autostereoscopic multi-user display comprising a sweet-spot unit which is directionally controlled by a tracking and image control device (160), wherein an illumination matrix (120) is provided with separately activatable illuminating elements (11 . . . 56), in addition to an imaging device used to alternatingly image active illuminating elements, for making expanded sweet spots (SRI / SR2) visible to various eye positions (EL1 / ERI, EL2 / ER2) of viewers observing alternating images or a stereoscopic image sequence on a transmissive image matrix (140) with the aid of directed beams (B1R . . . B5L). According to the invention, the imaging device comprises an imaging matrix (110) provided with a plurality of lens elements (111 115) whose focal length is small in order to image the active illuminating elements in an enlarged manner onto the sweet spots (SRI / SR2), and a field lens (171), which follows the imaging matrix (110), in order to keep the distances of the activated illuminating elements between adjacent beams (B1, B2,B4, B5) as constant as possible and in order to assist selection of the directions (D1. . . D5) with the illumination matrix (120) for the beams.
Owner:SEEREAL TECHNOLOGIES
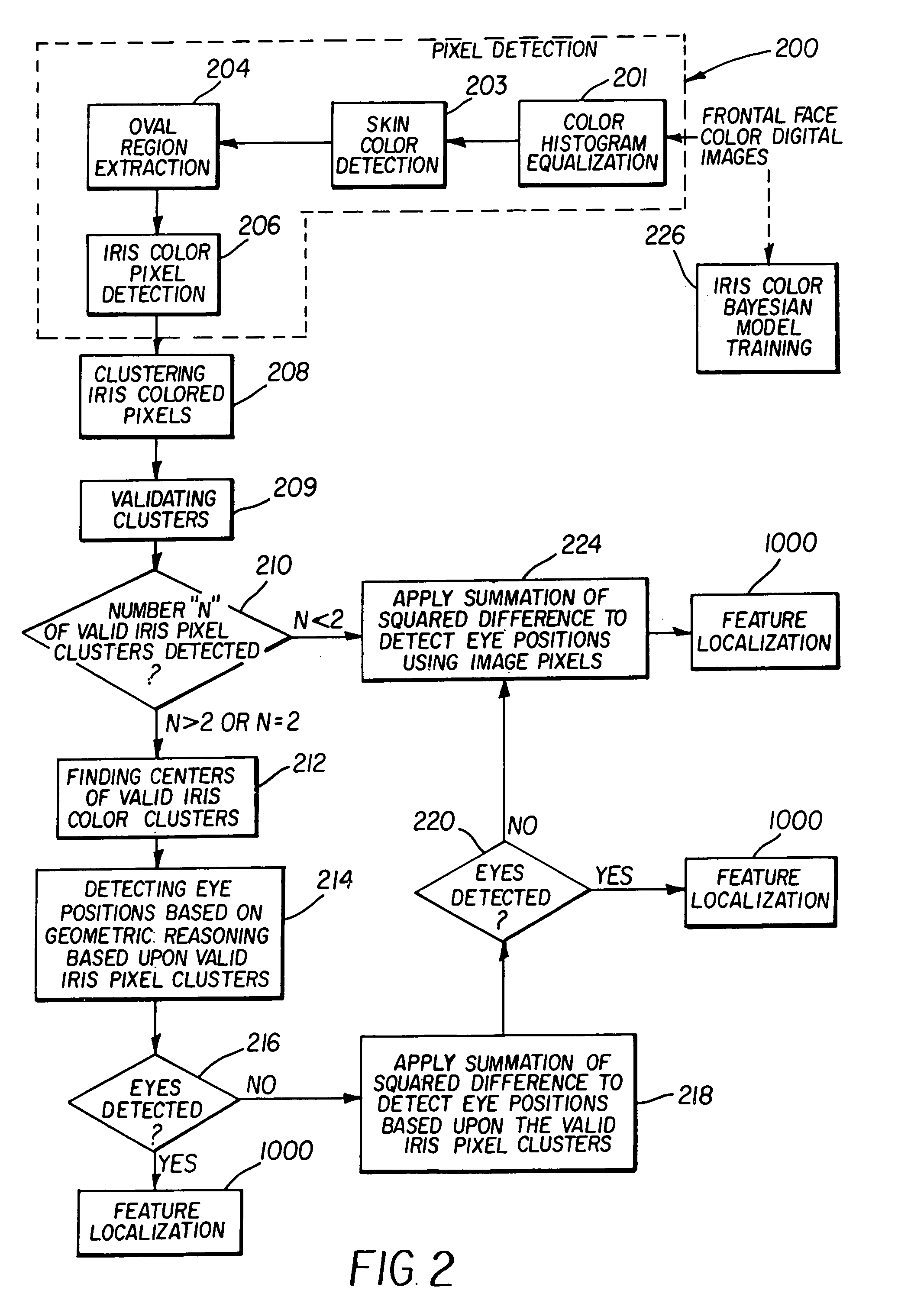
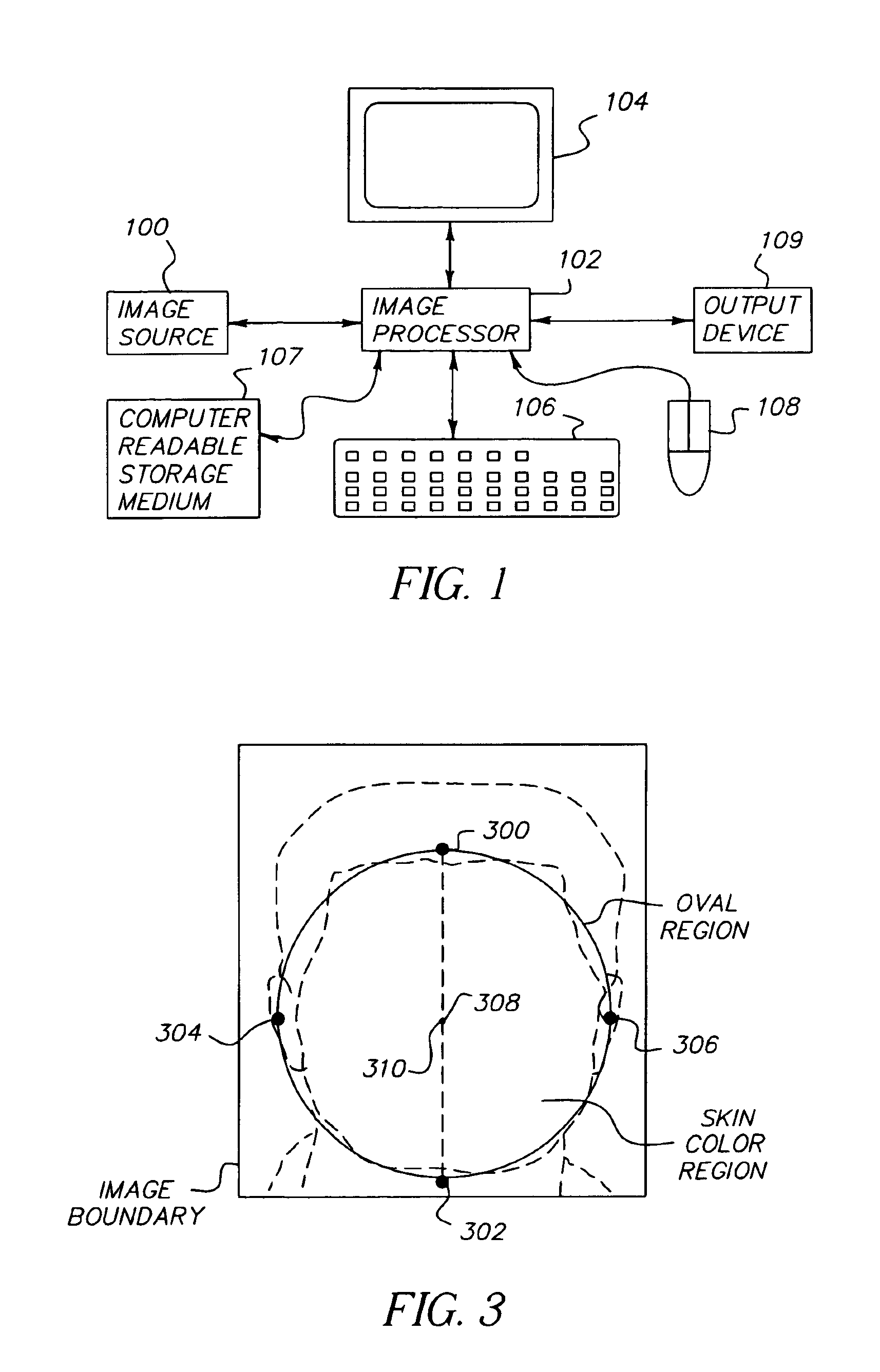
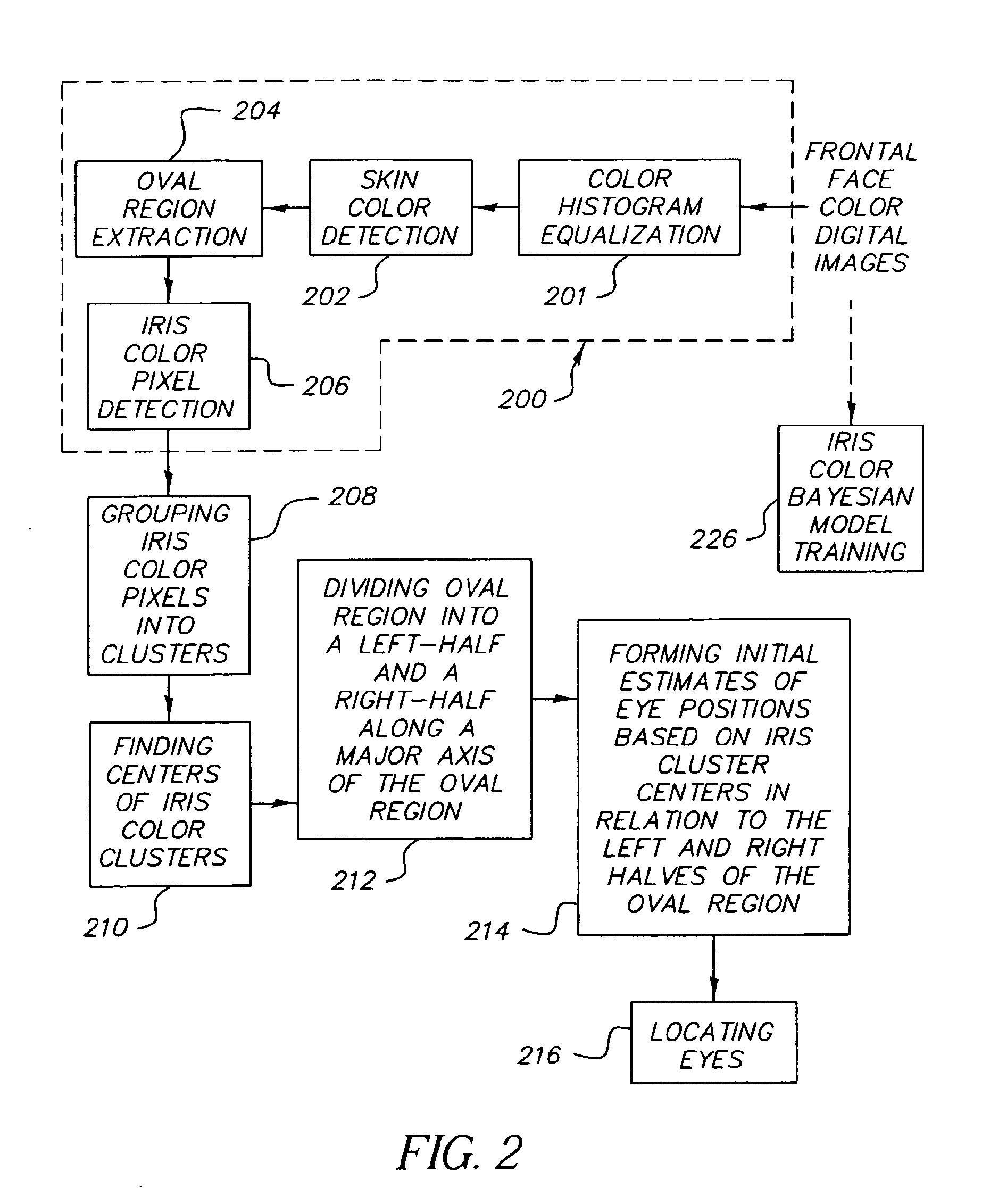
Method and computer program product for locating facial features
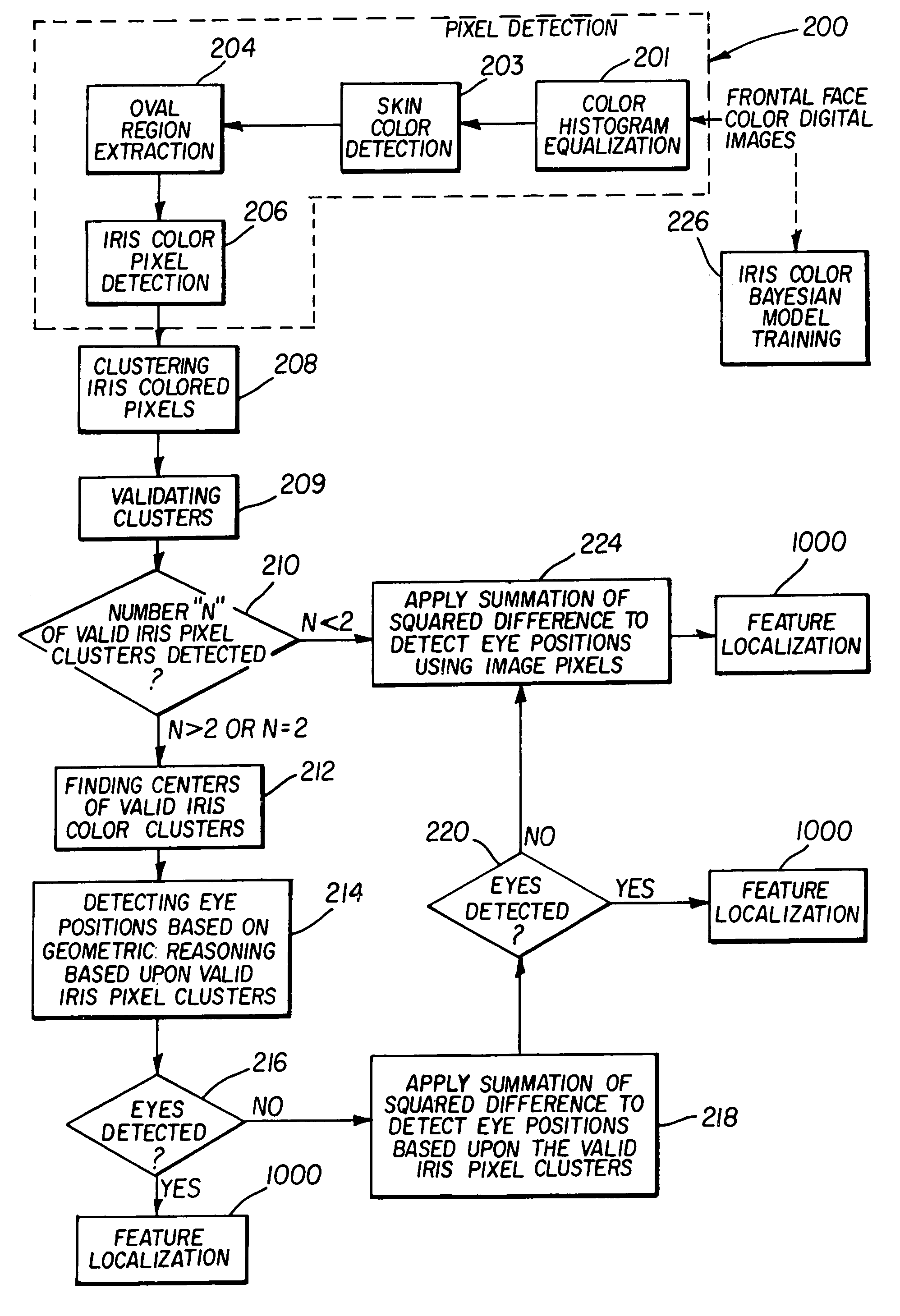
A digital image processing method detects facial features in a digital image. This method includes the steps of detecting iris pixels in the image, clustering the iris pixels, and selecting at least one of the following schemes to identify eye positions: applying geometric reasoning to detect eye positions using the iris pixel clusters; applying a summation of squared difference method using the iris pixel clusters to detect eye positions; and applying a summation of squared difference method to detect eye positions from the pixels in the image. The method applied to identify eye positions is selected on the basis of the number of iris pixel clusters, and the facial features are located using the identified eye positions.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
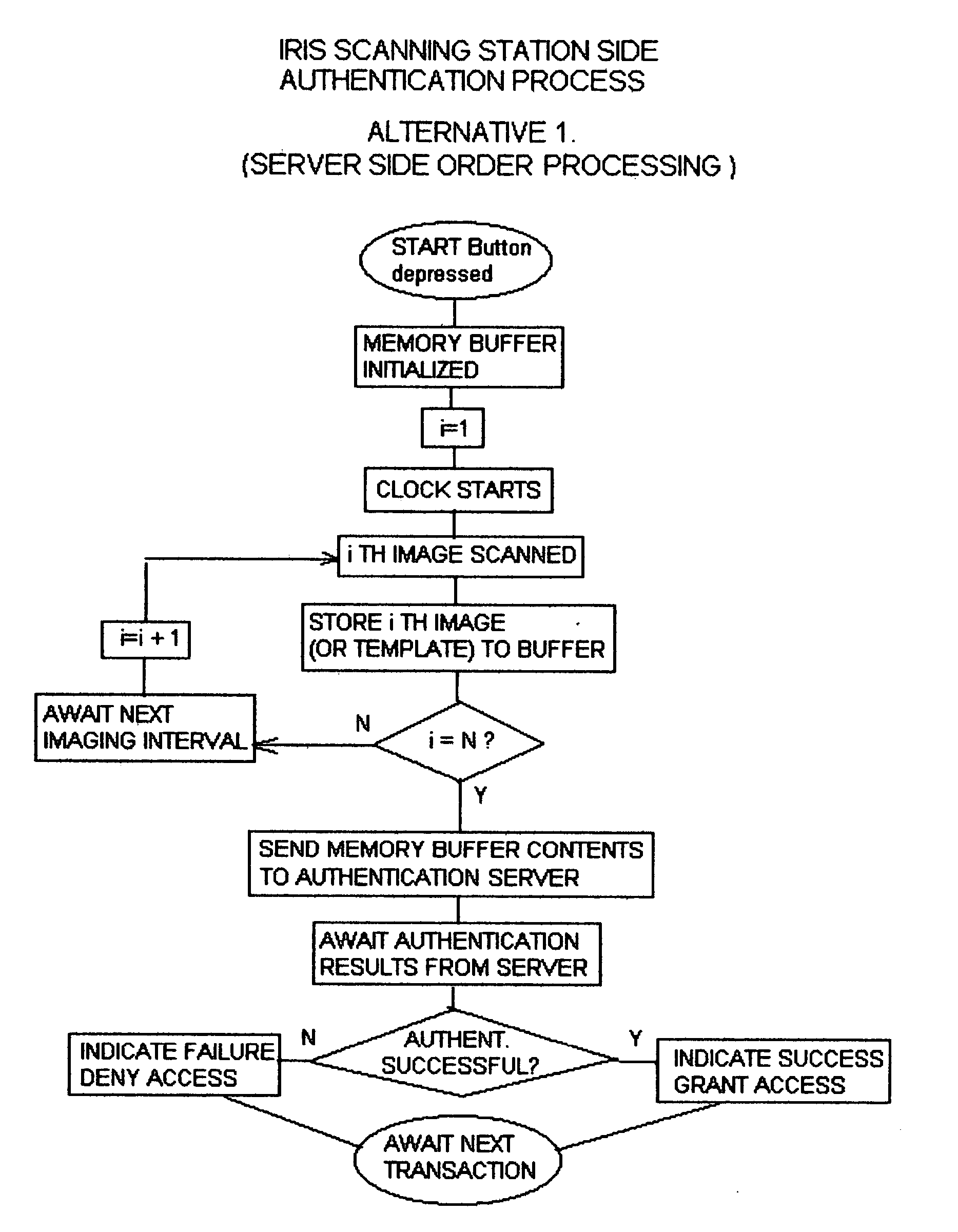
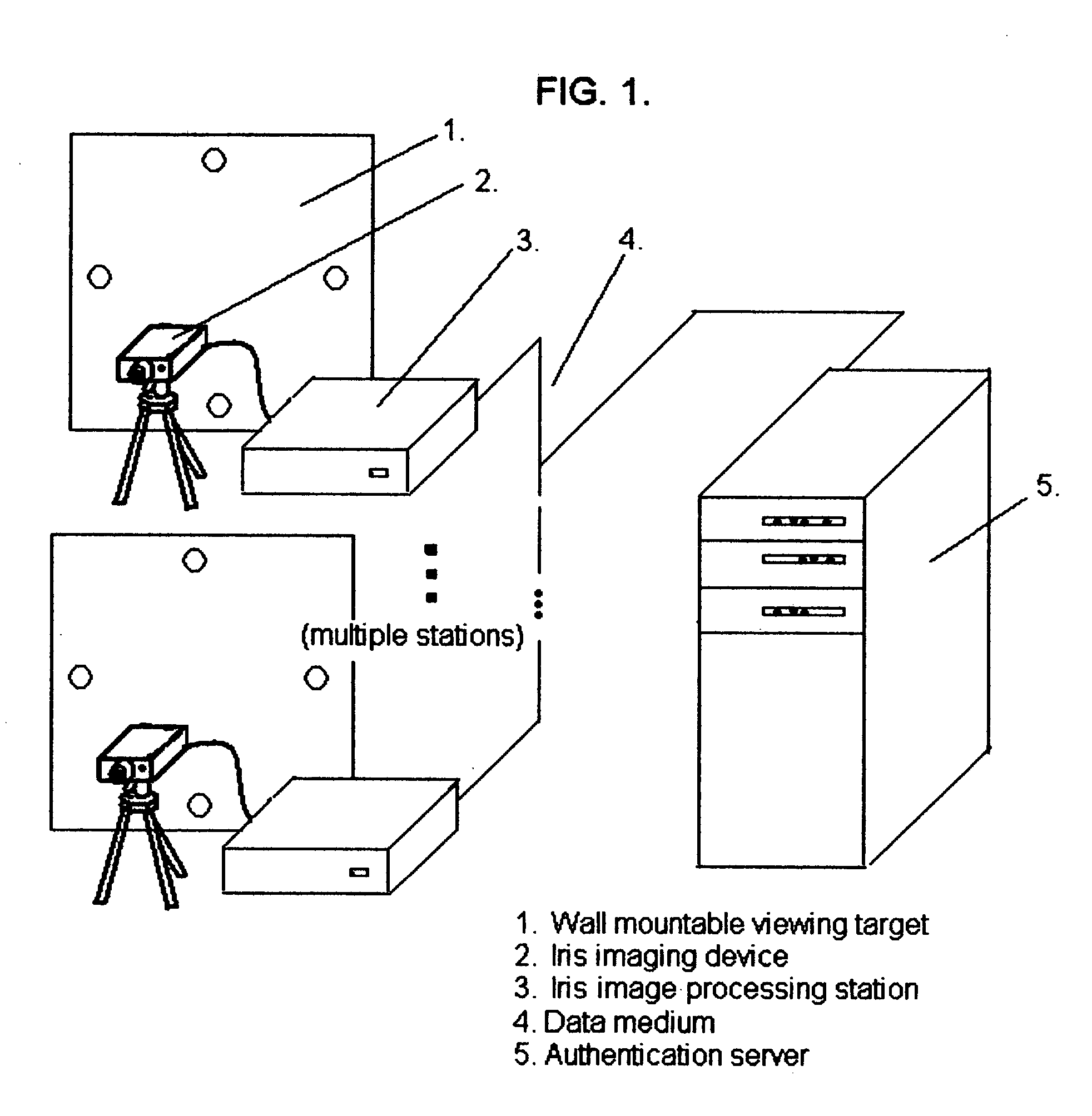
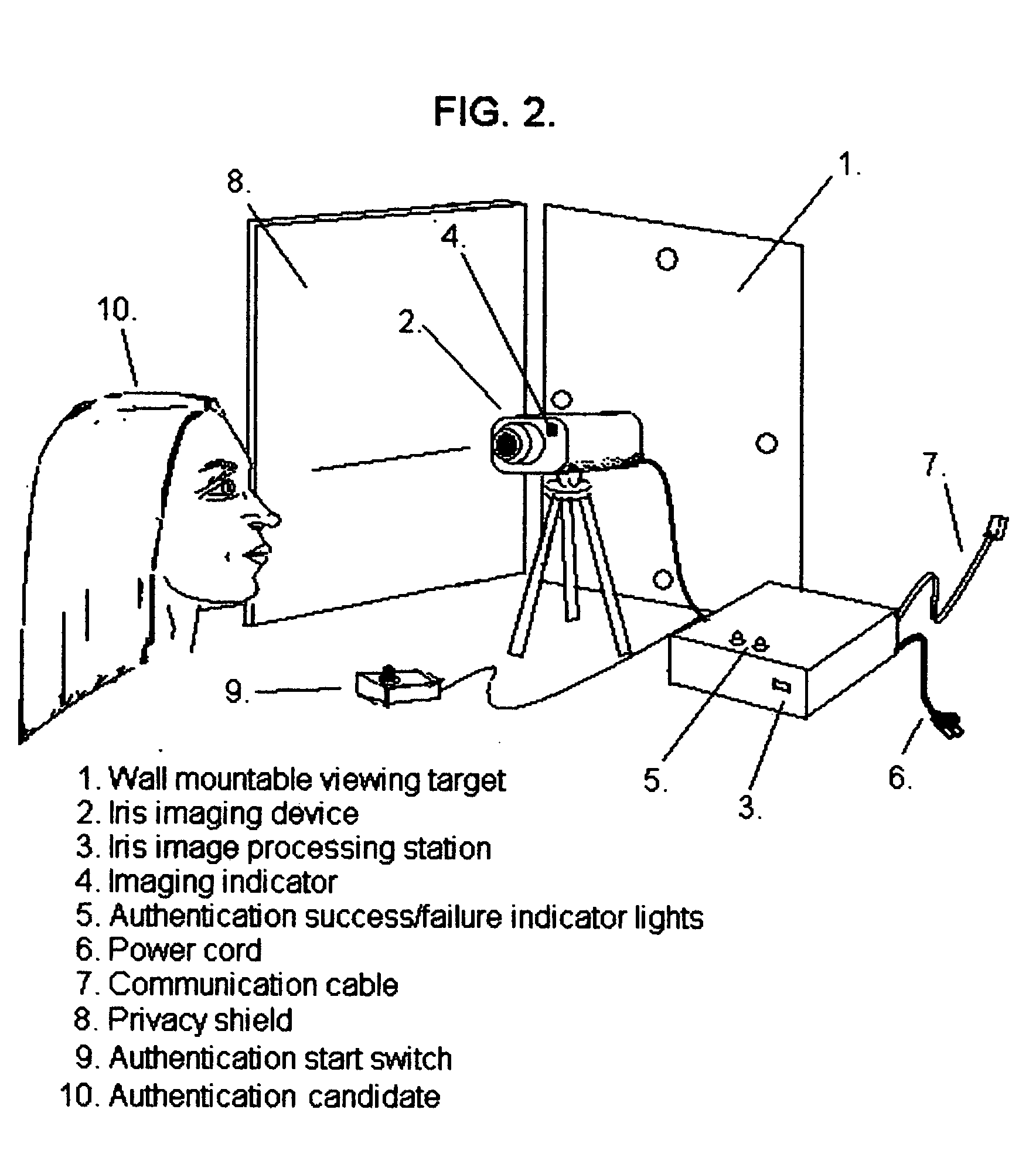
Technique using eye position and state of closure for increasing the effectiveness of iris recognition authentication systems
InactiveUS20050129286A1Increase in sizeSupport repeatabilitySpoof detectionEye stateInternet privacy
The invention, which is an embodiment of what the inventor calls, “Active Behavior Enhanced Iris Recognition Authentication”, employs a sequential iris imaging process where the authenticating party directs his or her gaze in specific directions, or closes their eyes for each image, so that an “eye state order” can be used to improve authentication security. Authentication security is strengthened based upon the reduced likelihood that a potential intruder would 1.) know what the correct sequence of eye states (i.e. up, down, left, right, camera view and closed) were associated with the control authentication template; 2.) be able to successfully “hack” the authentication server in order to gain access to the iris image information and also the eye state order information which would be required in order to fully compromise the authentication system. The technique embodied by the invention represents an overlay of a known, ordered sequence, over the iris recognition authentication process itself.
Owner:HEKIMIAN CHRISTOPHER DAVID
Method and report assessing consumer reaction to a stimulus by matching eye position with facial coding
InactiveUS7930199B1Digital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionFacial expressionEye position
A method of reporting consumer reaction to a stimulus and resultant report generated by (i) recording facial expressions and eye positions of a human subject while exposed to a stimulus throughout a time period, (ii) coding recorded facial expressions to emotions, and (iii) reporting recorded eye positions and coded emotions, along with an identification of the stimulus.
Owner:SENSORY LOGIC
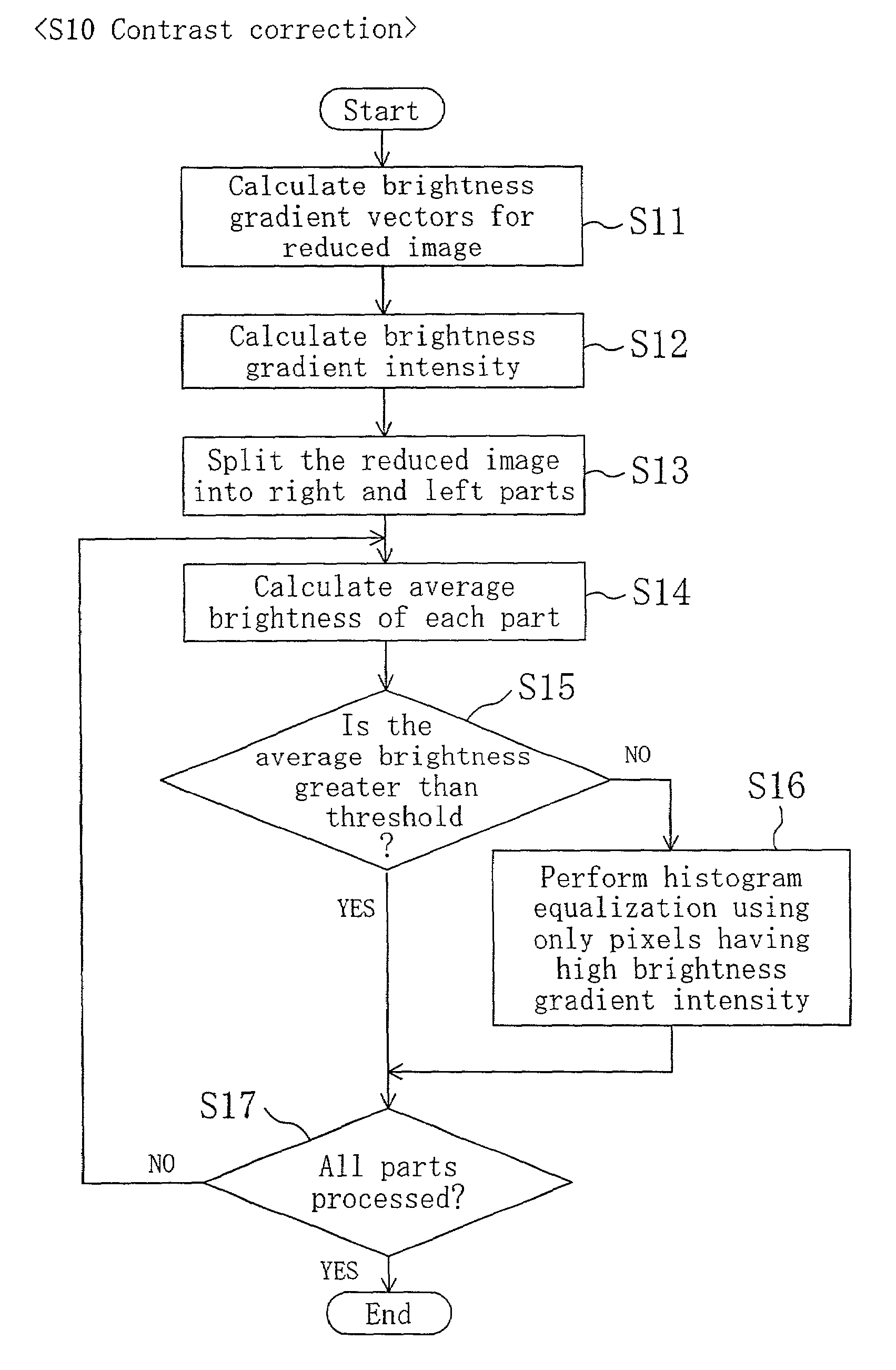
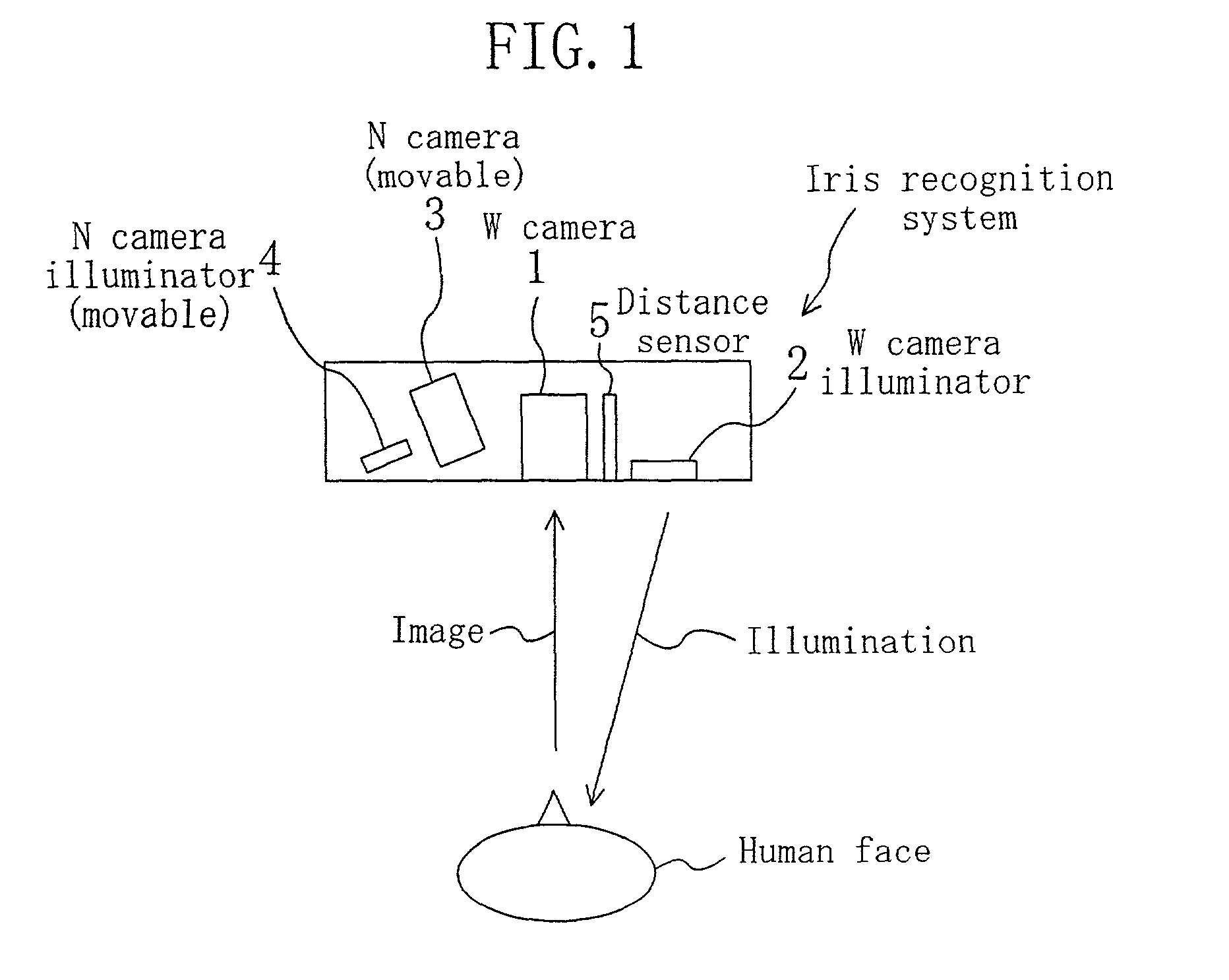
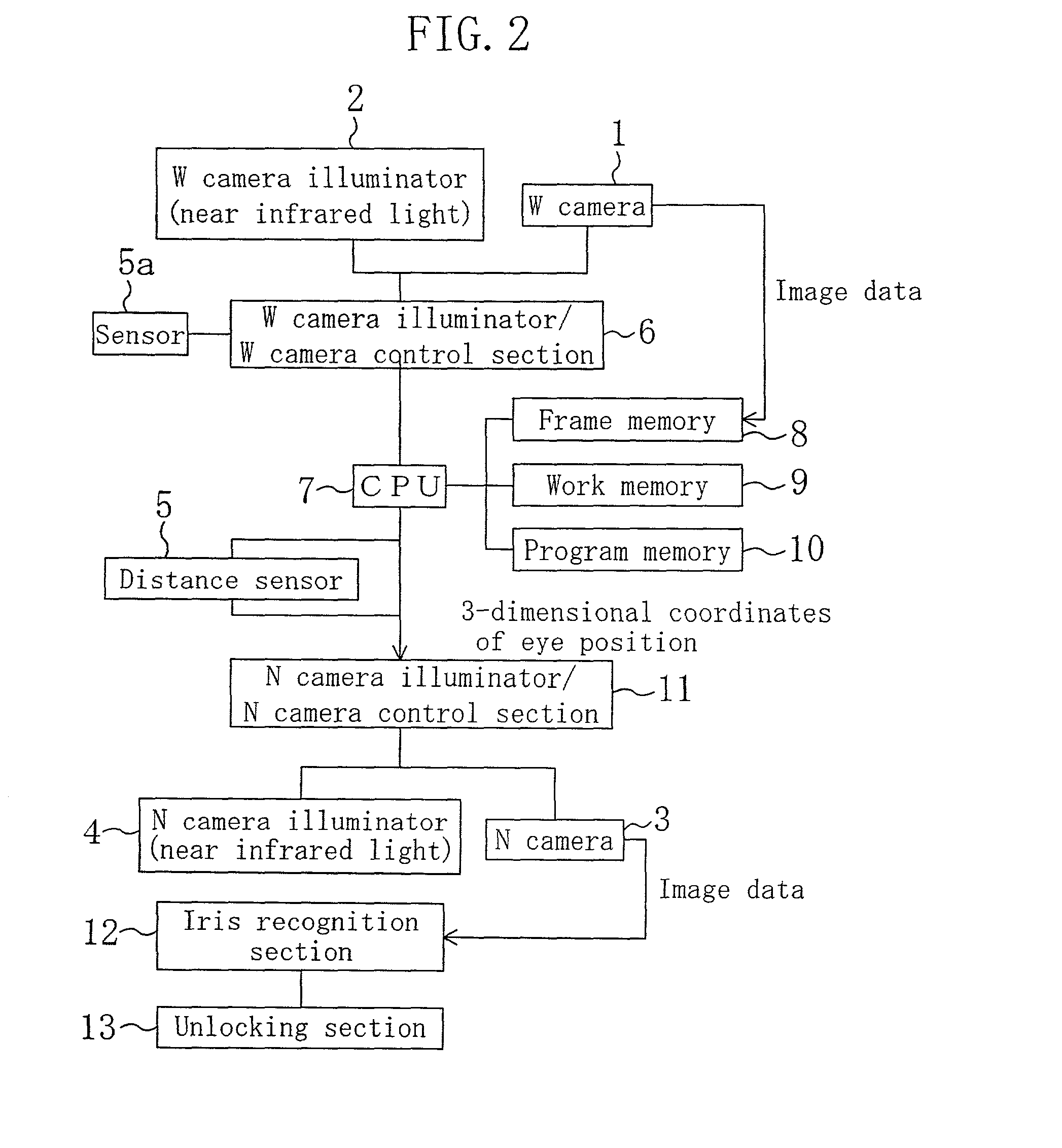
Eye position detection method and device
ActiveUS7130453B2Improve accuracyShort timeImage analysisPerson identificationPupilBrightness gradient
The position of an eye is detectable with high precision from a face image of a person taken under near infrared illumination or the like. After pre-processing, the face image is subjected to brightness correction to increase the contrast between the sclera portion and iris portion of the eye. Brightness gradient vectors are calculated for the brightness-corrected image, and matching is performed between a brightness gradient image generated using the calculated brightness gradient vectors and an eye template. Further, matching with a pupil template is performed to correct the eye center position. Final positions of both eyes are then determined.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
System and methods for controlling automatic scrolling of information on a display or screen
InactiveUS6603491B2Input/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsDisplay deviceBiological activation
A system for controlling the automatic scrolling of information on a computer display or screen is disclosed. The system includes a gimbaled sensor system for following the position of the user's head and user's eye, and scroll activating interface algorithm to find screen gaze coordinates implemented so the scrolling function is performed based upon the screen gaze coordinates of the user's eye relative to a certain activation area(s) on the display or screen. A method of controlling automatic scrolling of information on a display or screen by a user is also disclosed. The method generally includes the acts of finding a screen gaze coordinate on the display or screen of the user, determining whether the screen gaze coordinate is within at least one activated control region, and activating scrolling to provide a desired display of information when the gaze direction is within at least one activated control region.
Owner:LEMELSON JEROME H +1
Image adjustment derived from optical imaging measurement data
ActiveUS20080055543A1Minimize misalignmentEnhance the imageOthalmoscopesComputer scienceImaging data
A method and apparatus for imaging within the eye is provided whereby a component of eye position is detected using optical imaging data. Tracking eye position over time and correctly registering imaging data for scan locations or using eye position to detect decentration achieves improved imaging. In one embodiment, essentially perpendicular B-scans are imaged sequentially and the corneal arc within each B-scan is analyzed to determine the vertex of the eye. The eye vertex is tracked over pairs of perpendicular B-scans to determine eye motion. In another embodiment, the decentration in the Pachymetry map is removed by correcting for the misalignment of the center of the Pachymetry map and the actual location of the corneal vertex.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
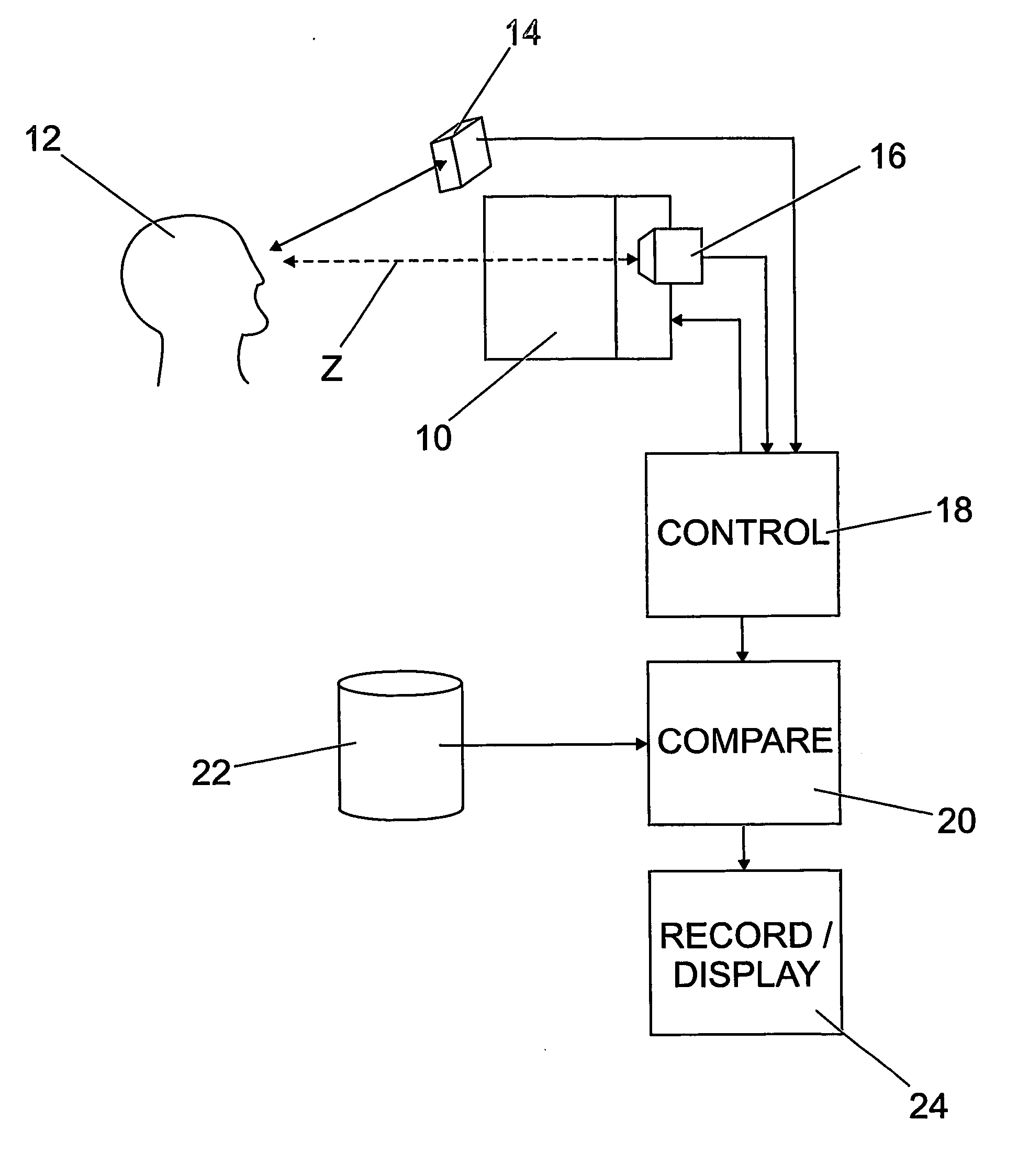
Method and apparatus for the diagnosis of glaucoma and other visual disorders
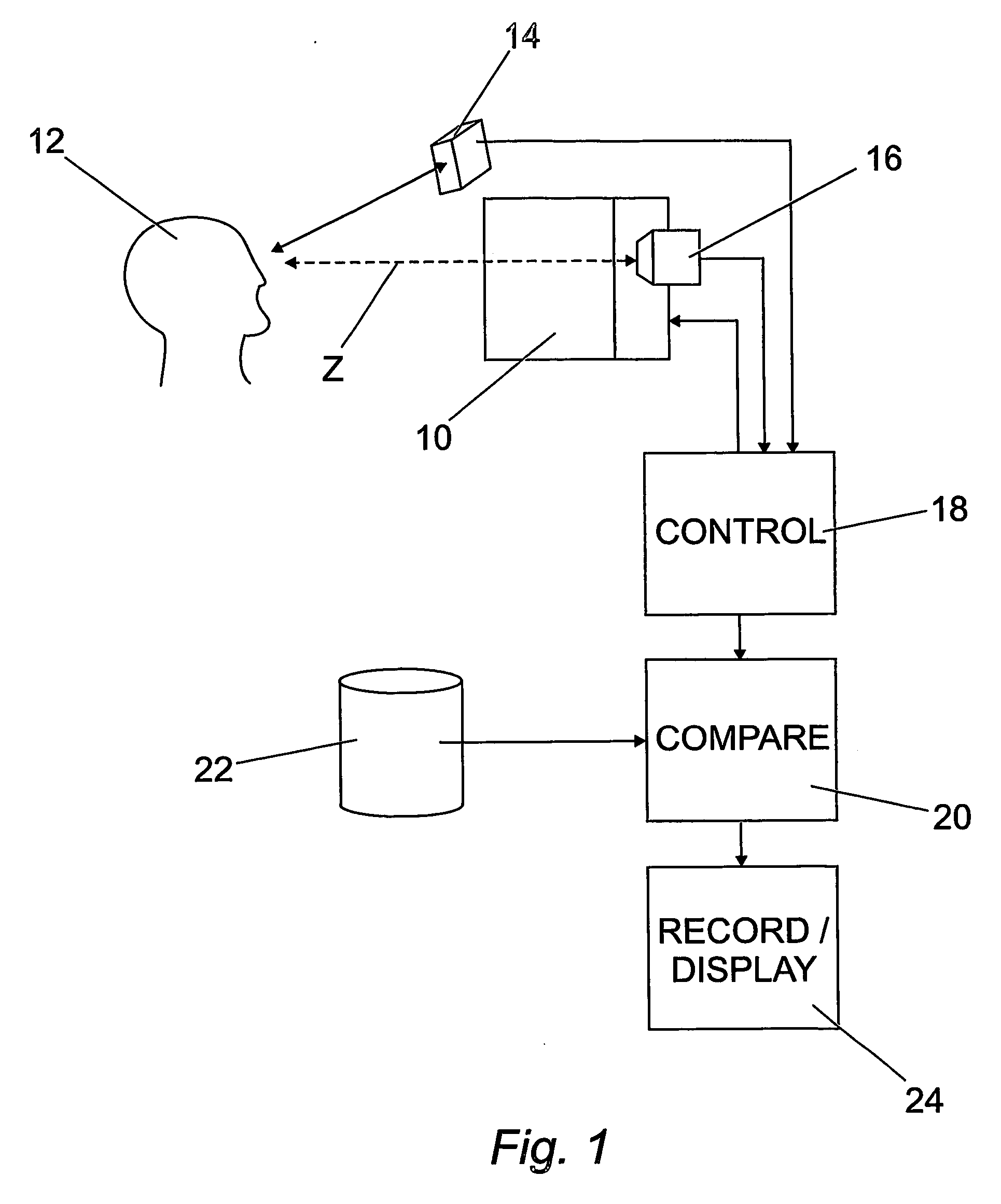
A subject (12) observes an image on a display (10). A control (18) produces a fixation image at a selected position in the display, followed by a stimulus spaced from the fixation image. An eye position sensor (14) detects a saccade movement towards the stimulus. The stimulus is then replaced with a fixation image and the cycle repeated. The time taken to saccade plus the intensity of the stimulus are used to produce a retinal map of field of vision, or to assess other characteristics of the subject.
Owner:MCGRATH JOHN ANDREW MURRAY +1
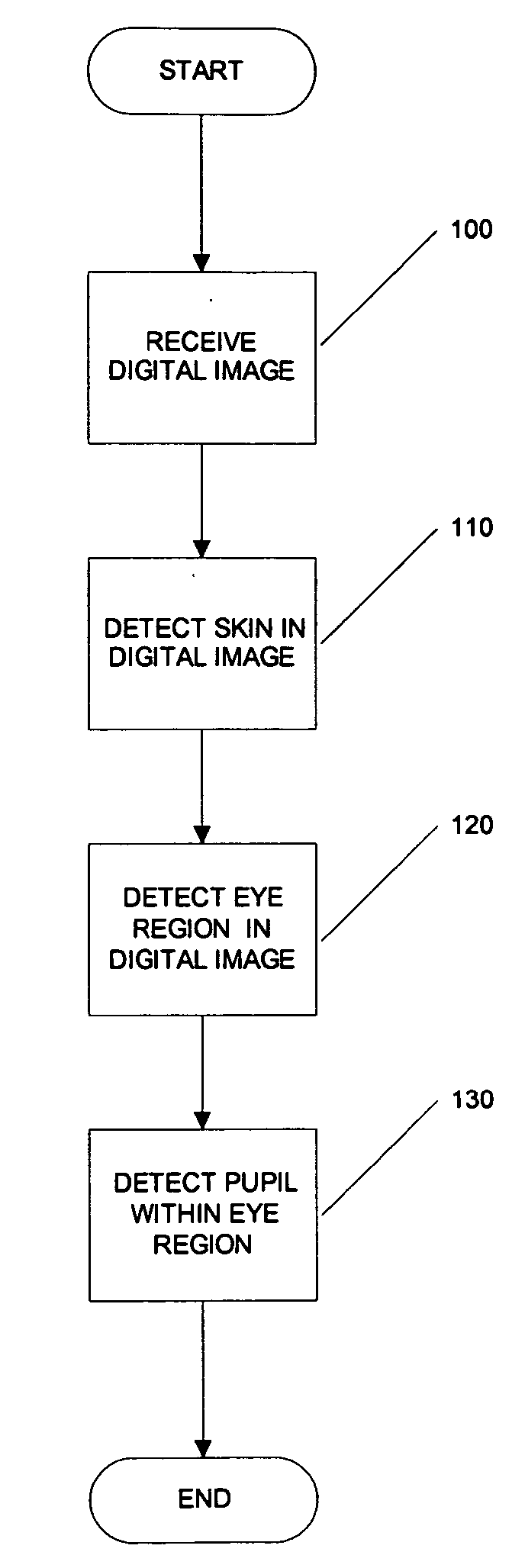
Systems and methods for detecting skin, eye region, and pupils
InactiveUS20050031173A1Improve security levelReduce chanceCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionJPEG
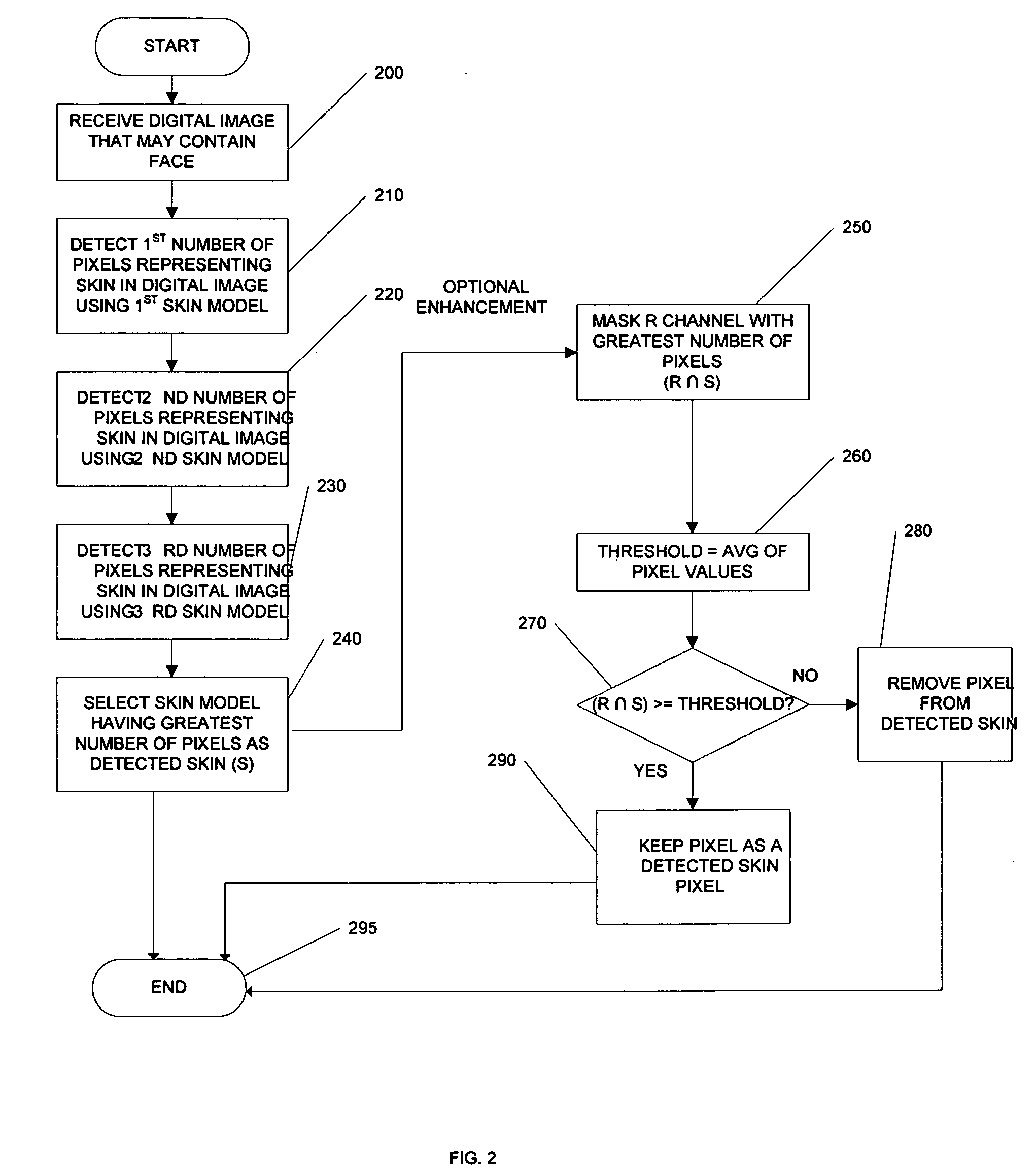
Systems, methods, and processes are provided for locating pupils in a portrait image for applications such as facial recognition, facial authentication, and manufacture of identification documents. One proposed method comprises three steps; skin detection, eye detection, and pupil detection. In the first step, the skin detection employs a plurality of Gaussian skin models. In the second step, coarse eye locations are found by using the amount of deviation in the R (red) channel with an image that has been cropped by skin detection. A small block centered at an obtained coarse location is then further processed in pupil detection. The step of pupil detection involves determining a Pupil Index that measures the characteristics of a pupil. Experiments tested on highly jpeg compressed images show that the algorithm of this embodiment successfully locates pupil images. It is believed that this novel technique for locating pupils in images can improve the accuracy of face recognition and / or face authentication.
Owner:L 1 SECURE CREDENTIALING
Digital eye camera
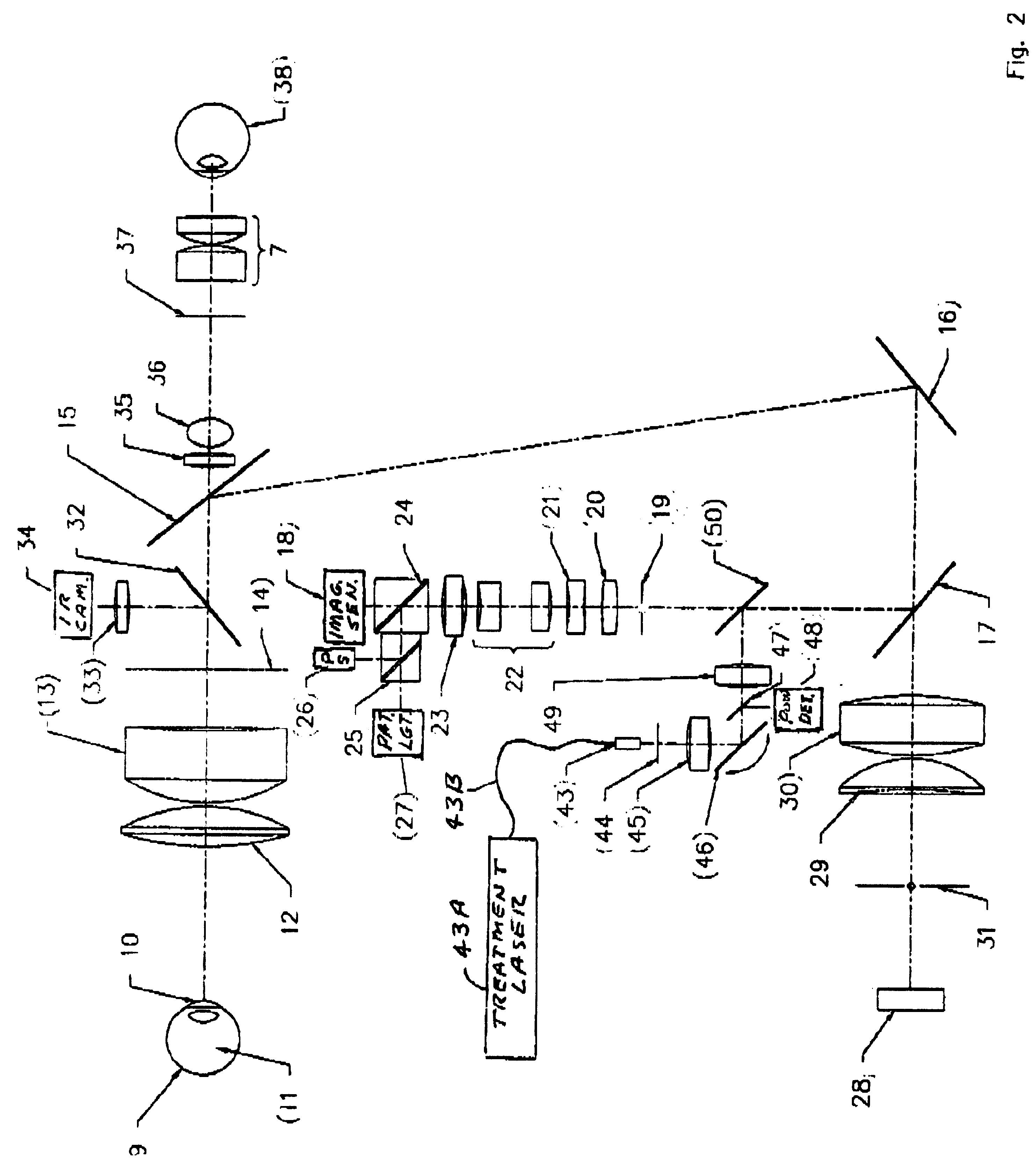
InactiveUS6361167B1High resolutionIncrease contrastLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsEyepieceRetina
A digital camera that combines the functions of the retinal camera and corneal camera into one, single, small, easy to use instrument. The single camera can acquire digital images of a retinal region of an eye, and digital images of a corneal region of the eye. The camera includes a first combination of optical elements for making said retinal digital images, and a second combination of optical elements for making said corneal digital images. A portion of these elements are shared elements including a first objective element of an objective lens combination, a digital image sensor and at least one eyepiece for viewing either the retina or the cornea. The retinal combination also includes a first changeable element of said objective lens system for focusing, in combination with said first objective element, portions or all of said retinal region at or approximately at a common image plane. The retinal combination also includes a retinal illuminating light source, an aperture within said frame and positioned within said first combination to form an effective retinal aperture located at or approximately at the lens of the eye defining an effective retinal aperture position, an infrared camera for determining eye position, and an aperture adjustment mechanism for adjusting the effective retinal aperture based on position signals from said infrared camera. The cornea combination of elements includes a second changeable element of said objective lens system for focusing, in combination with said first objective element, portions or all of said cornea region at or approximately at a common image plane.
Owner:CLARITY MEDICAL SYST
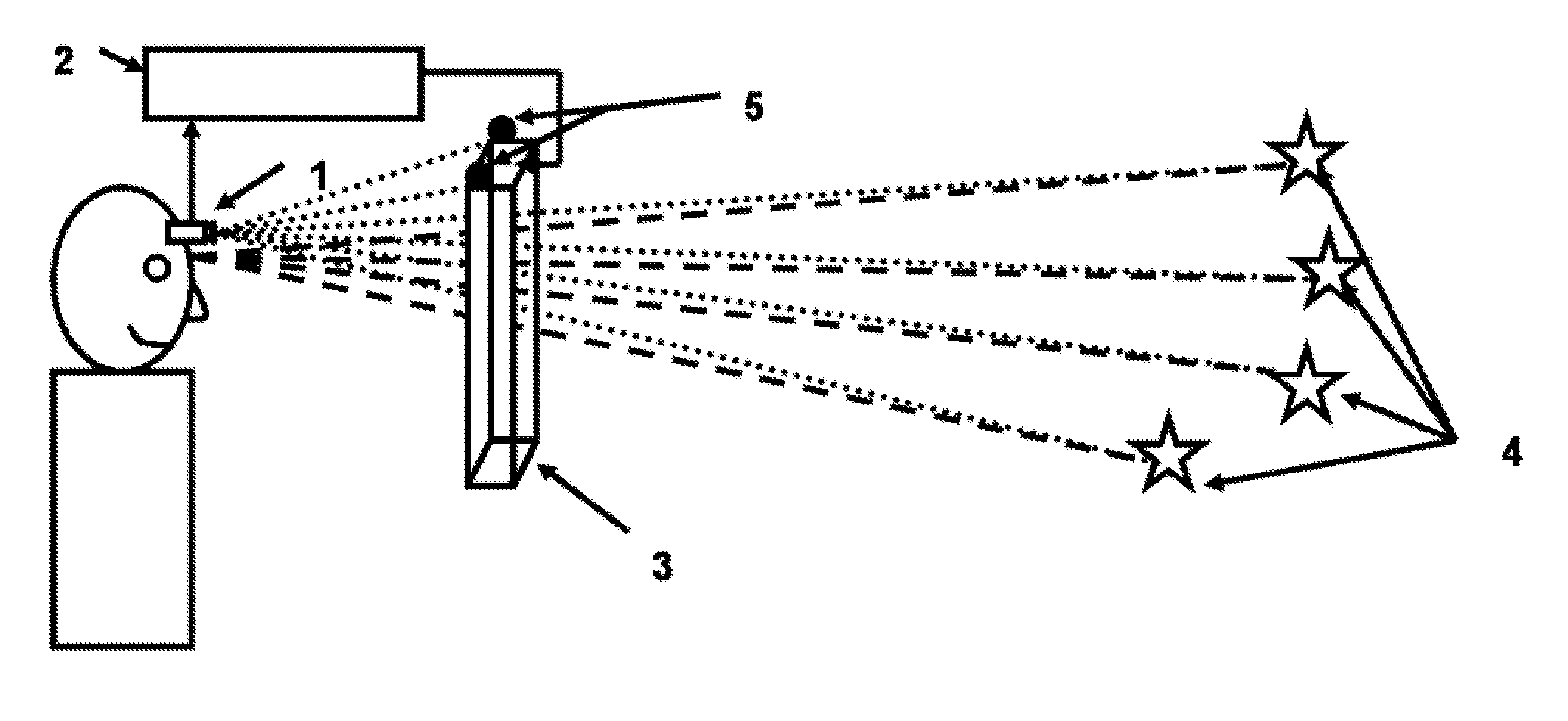
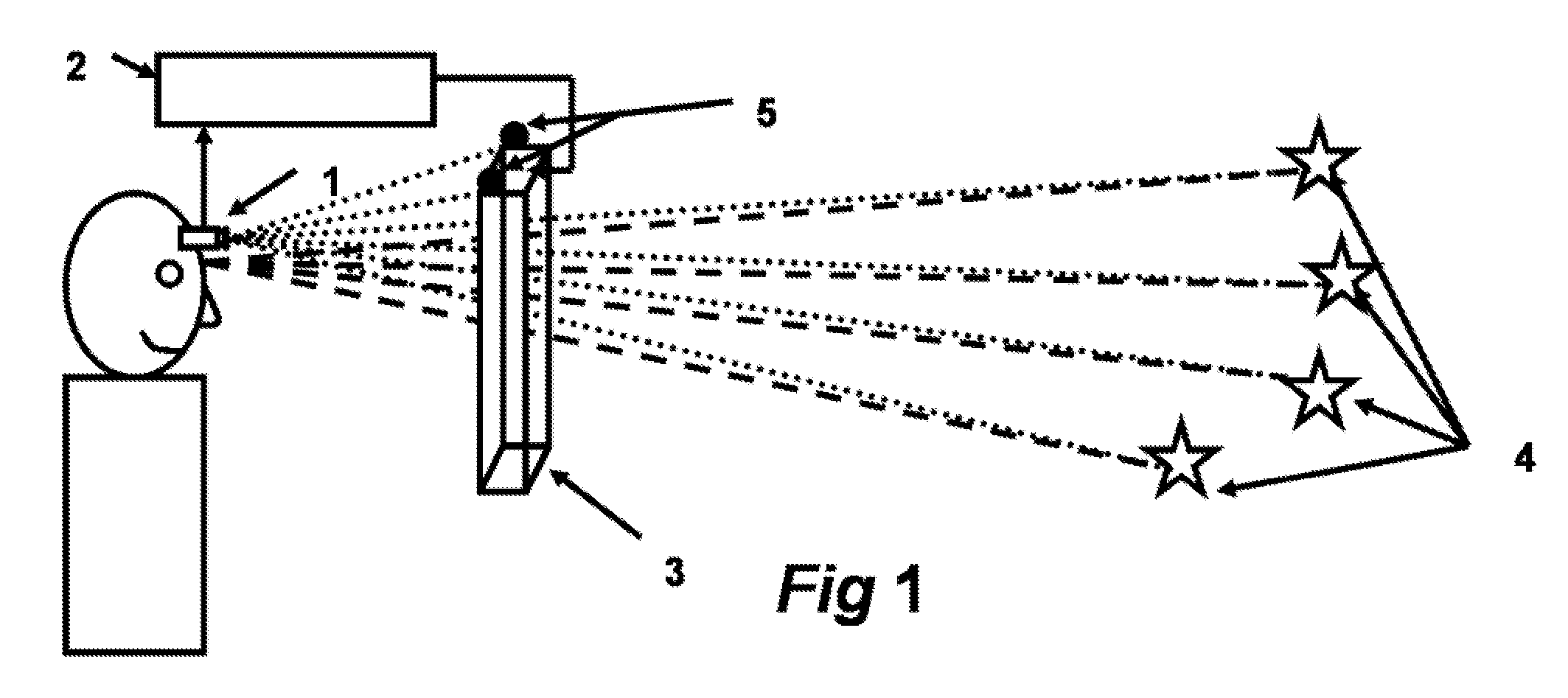
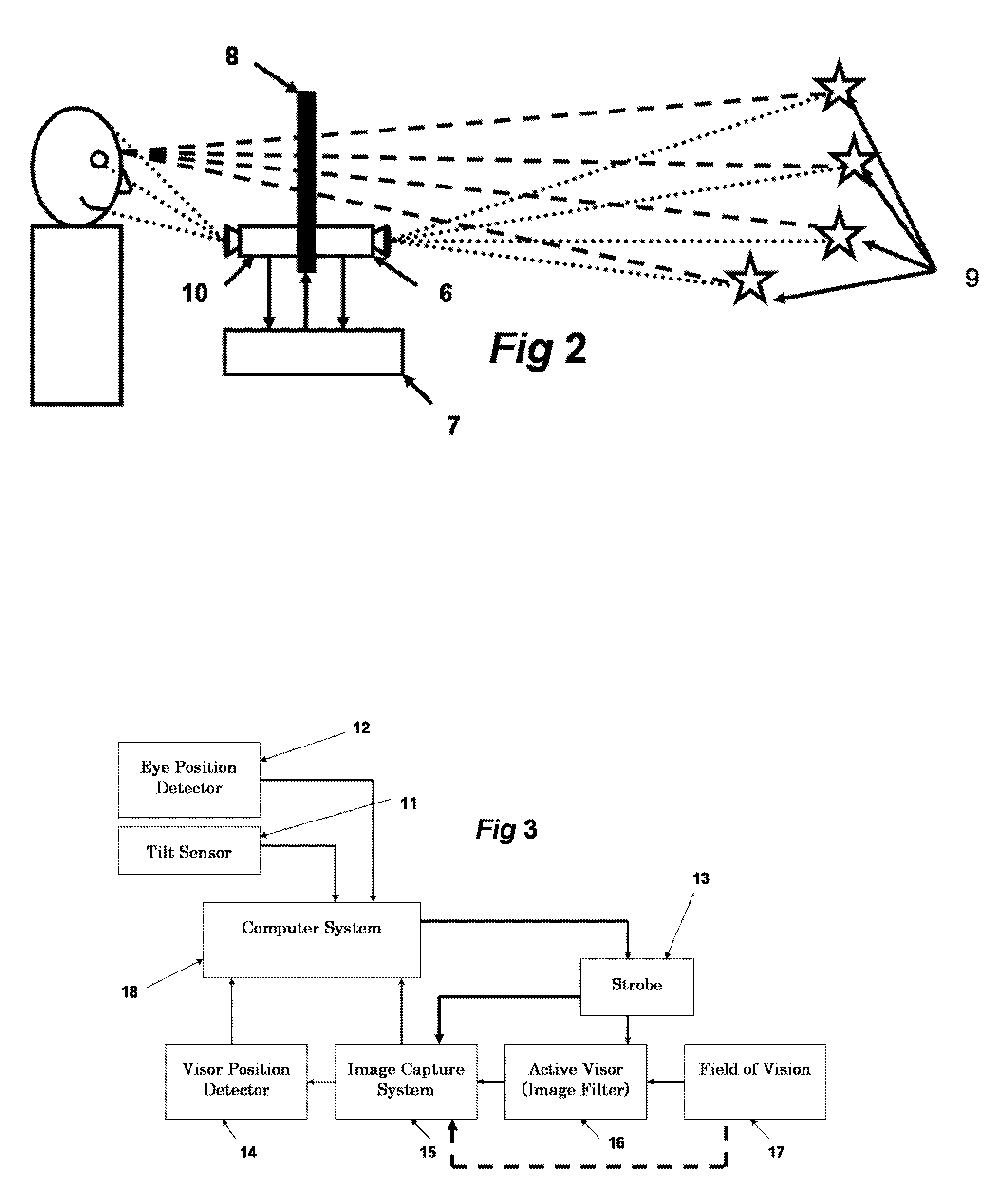
Active visor system for eliminating glare in field-of-vision from mobile and transient light sources and reflective surfaces
InactiveUS20060140502A1Reduce the amount requiredAntiglare equipmentCharacter and pattern recognitionVision processingMachine shop
A field-of-vision processing and filtering system for eliminating glare from mobile and transient light sources and reflective surfaces, using image recording, eye-position detection, and a active matrix screen functioning as a dynamically controllable visor, for modifying the field of vision appropriately. The system filters out high light intensity points from the field of vision, without seriously affecting the relevant parts of the field of vision. One embodiment of the system can be used by drivers for filtering glare from oncoming headlight at night, as well as during day time to block glare from the sun. Another embodiment of the system can be used for protection from glare of welding iron in a machine shop.
Owner:TSENG ALLAN S +1
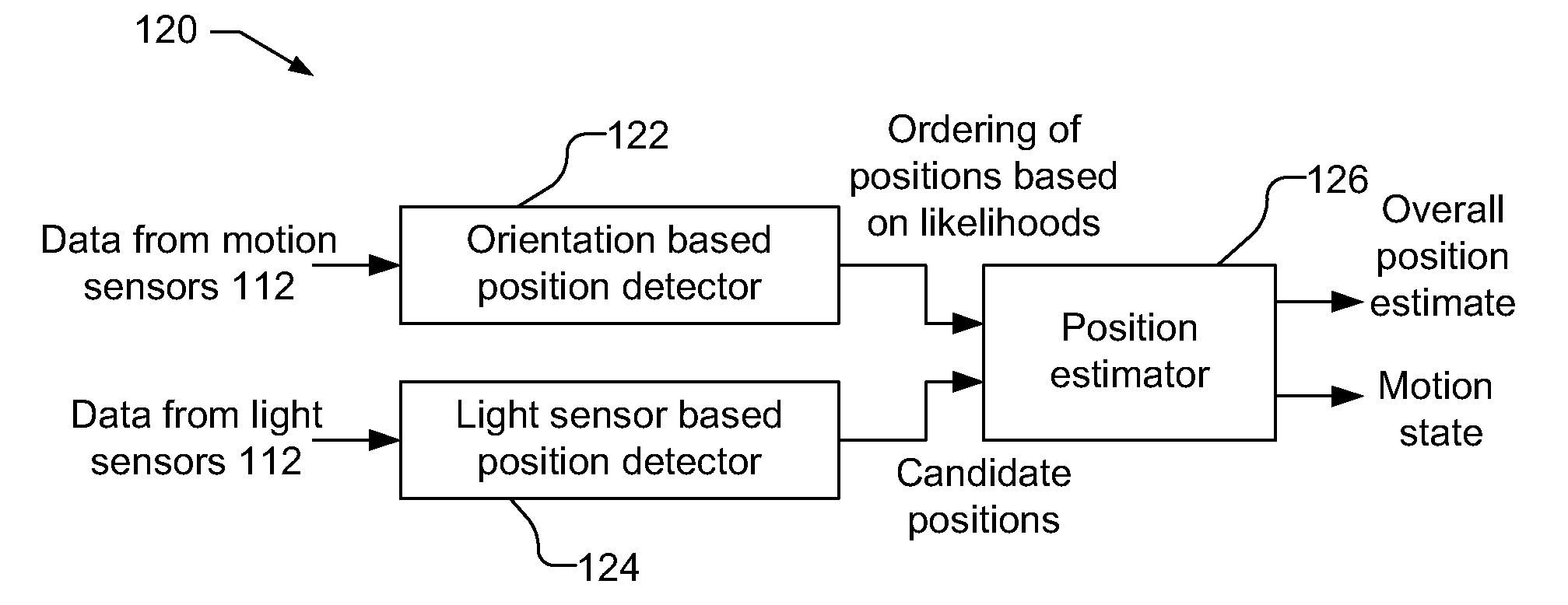
Device position estimates from motion and ambient light classifiers
ActiveUS20120265482A1Digital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsProximity sensorAccelerometer
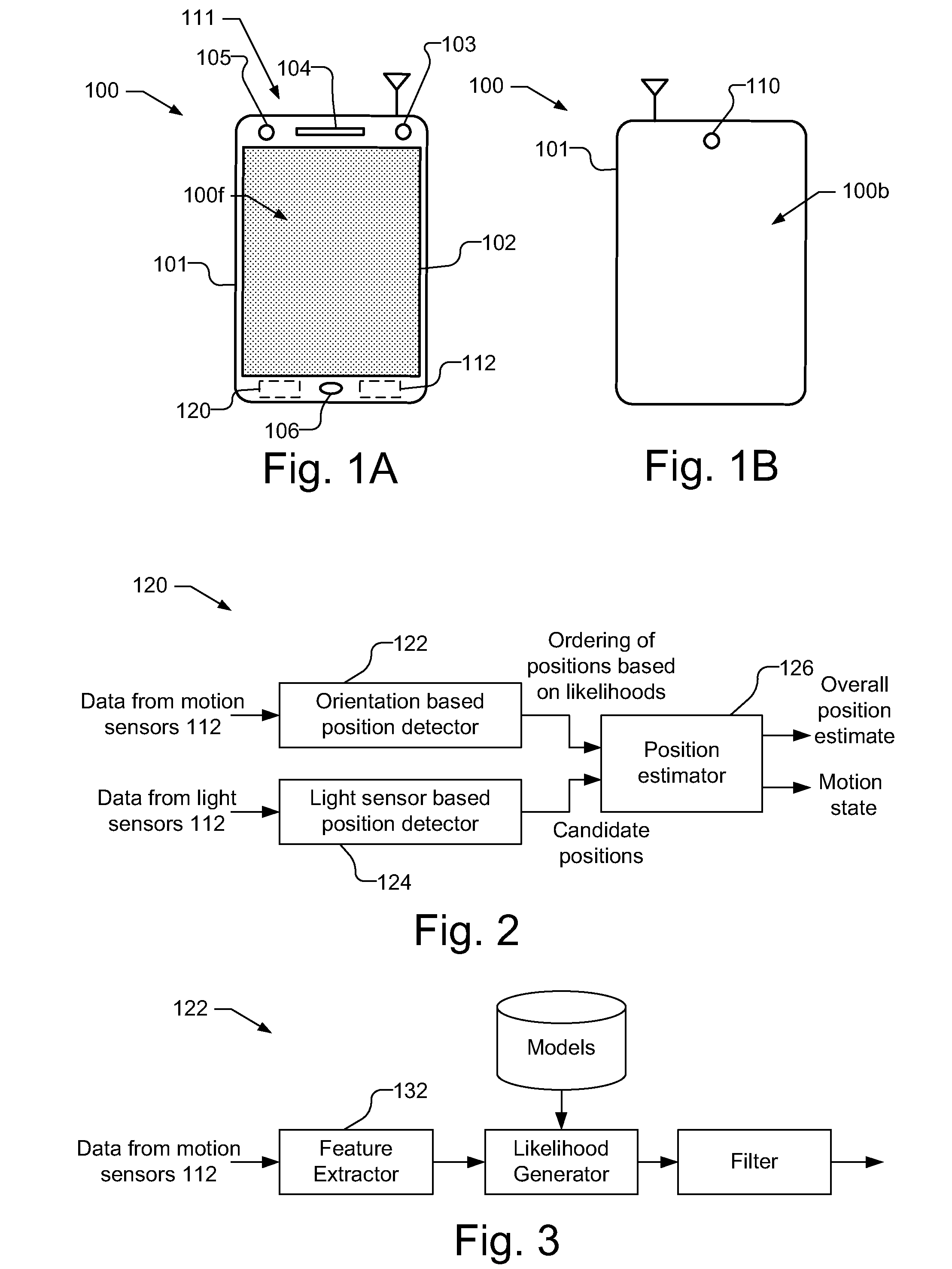
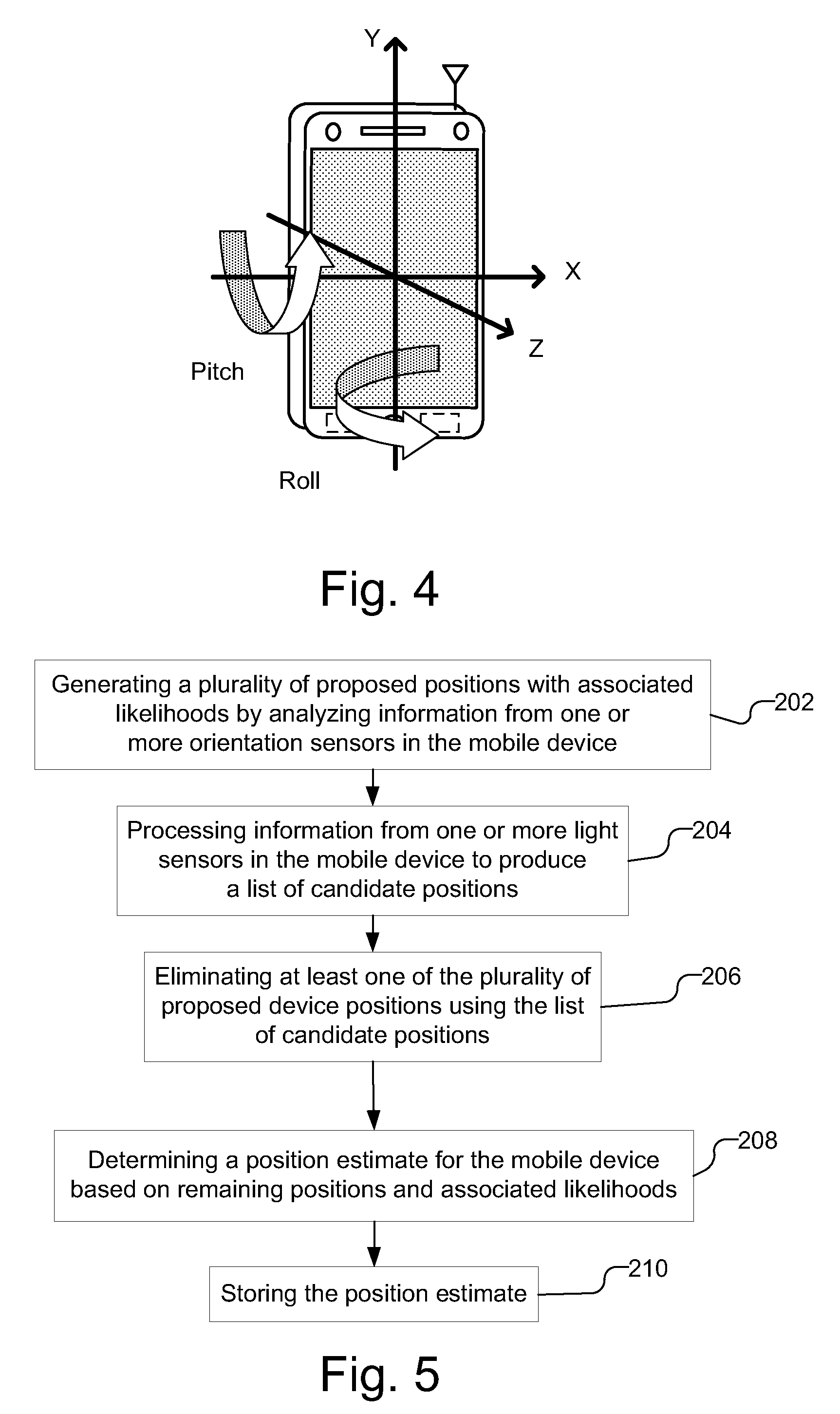
A position estimate for a mobile device is generated using data from motion sensors, such as accelerometers, magnetometers, and / or gyroscopes, and data from light sensors, such as an ambient light sensor, proximity sensor and / or camera intensity sensor. A plurality of proposed positions with associated likelihoods is generated by analyzing information from the motion sensors and a list of candidate positions is produced based on information from the light sensors. At least one of the plurality of proposed positions is eliminated using the list of candidate positions and a position estimate for the mobile device is determined based on the remaining proposed positions and associated likelihoods. The proposed positions may be generated by extracting features from the information from the motion sensors and using models to generate likelihoods for the proposed positions. The likelihoods may be filtered over time. Additionally, a confidence metric may be generated for the estimated position.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Stereoprojection system
InactiveUS20090102915A1Add depthReduces pushing border effectMirrorsProjectorsMonitoring systemProjection system
The invention relates to stereo projection systems for displaying stereopaired images on mirror-spherical or parabolic screens and for collectively watching a stereo effect without using stereo spectacles. Said invention makes it possible to continuously dynamically superimpose the projections of the left and right picture frames of a steropair with the user's left and right eyes, respectively. Such impositions are carried out simultaneously and independently for each viewer. The technical result is attainable by that the inventive stereo projection system comprises stereo projectors which are individually allocated to each viewer and in-series connected, a monitoring system for continuously and accurately determining the viewers' eye positions, a self correcting device, video-correcting devices, automatic drives for the mechanical self-correction of the stereo projectors and the system optical elements, units which are used for forming stereopair projected images in the stereo projector and which are coupled with the video-correcting device for the video-correction of the optimal parameters of the screen images. The inventive system makes it possible to carry out the self- and video-correction in an integral manner in such a way that the comfort of the stereo effect viewing is maximally satisfied.
Owner:ARSENICH SVYATOSLAV IVANOVICH
Methods and devices for orthovoltage ocular radiotherapy and treatment planning
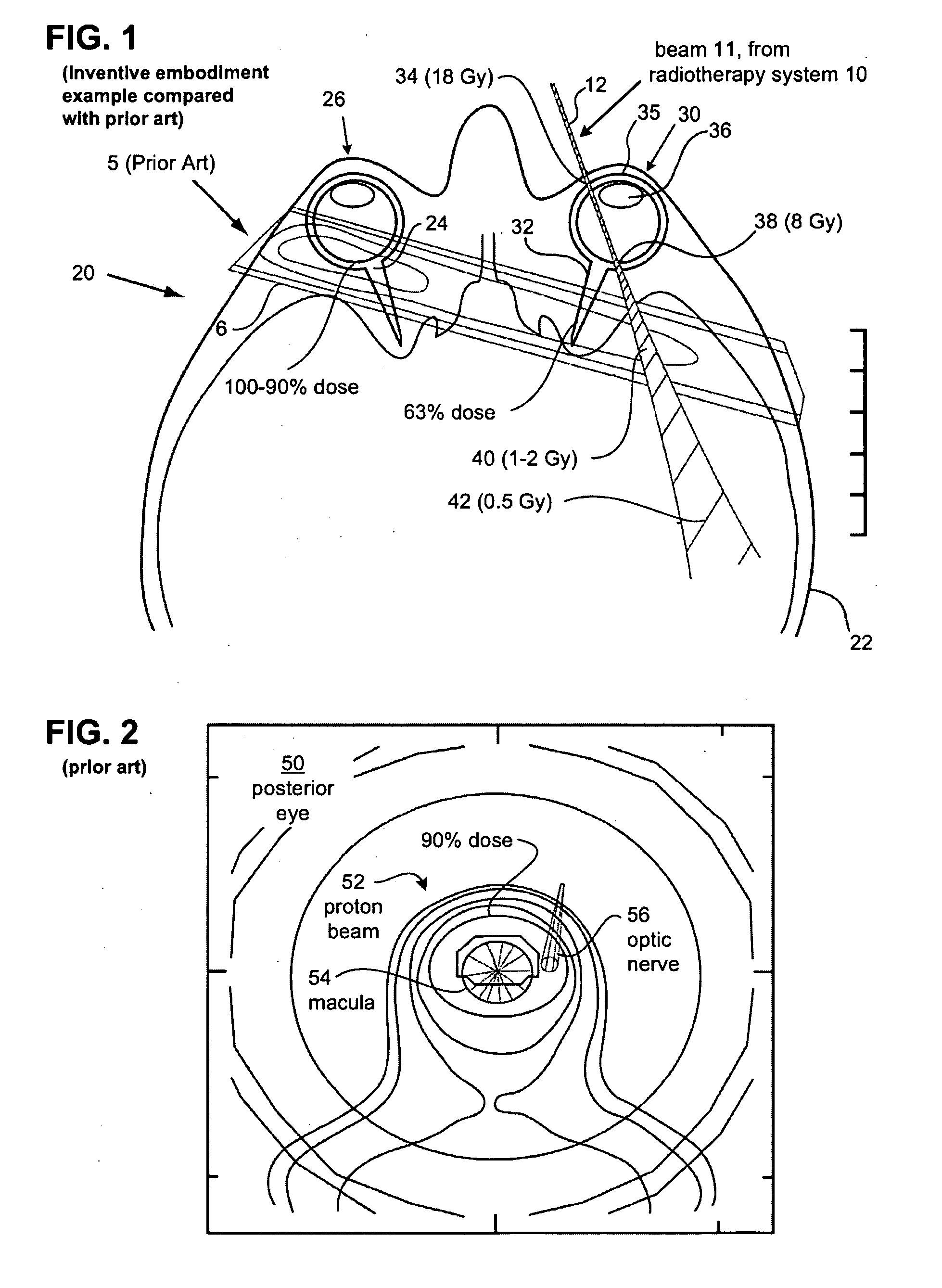
ActiveUS20090161826A1Reduce eye motionEfficient relationshipSurgical instrument detailsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyX-rayDose level
A method, code and system for planning the treatment a lesion on or adjacent to the retina of an eye of a patient are disclosed. There is first established at least two beam paths along which x-radiation is to be directed at the retinal lesion. Based on the known spectral and intensity characteristics of the beam, a total treatment time for irradiation along each beam paths is determined. From the coordinates of the optic nerve in the aligned eye position, there is determined the extent and duration of eye movement away from the aligned patient-eye position in a direction that moves the patient's optic nerve toward the irradiation beam that will be allowed during treatment, while still maintaining the radiation dose at the patient optic nerve below a predetermined dose level.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
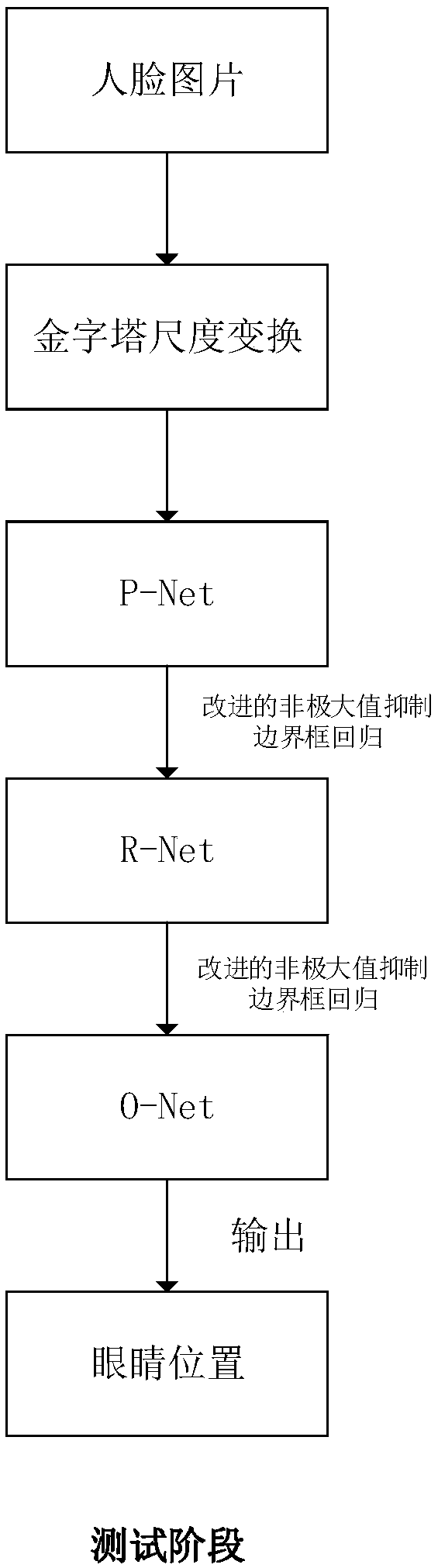
Multi-pose eye positioning algorithm based on cascaded convolutional neural network
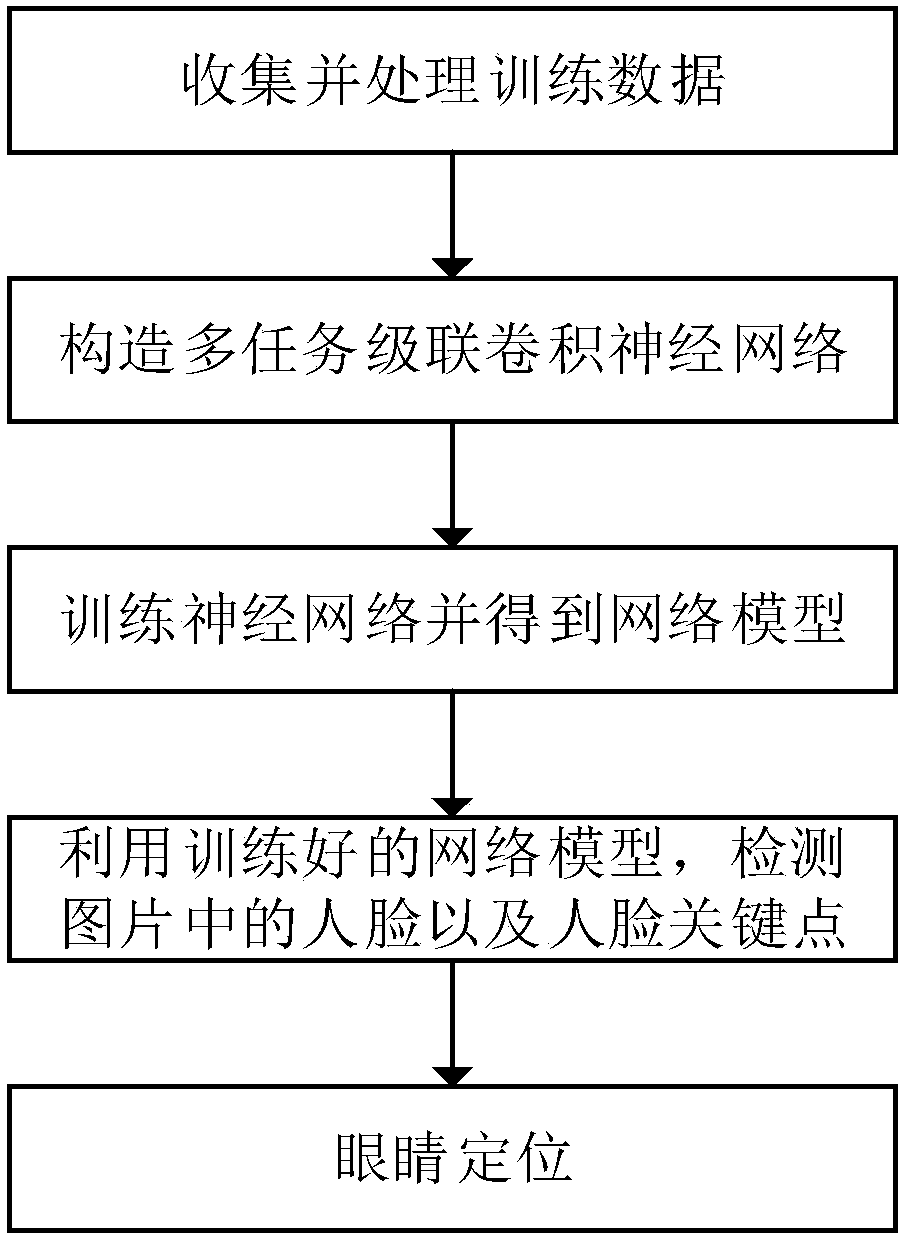
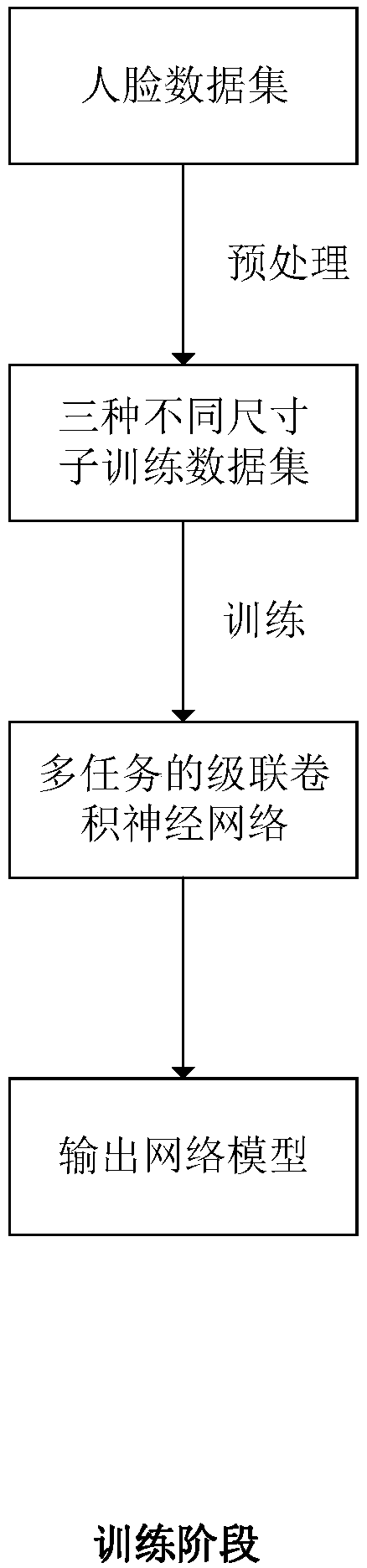
InactiveCN107748858AGood effectEfficient multi-pose face detectionCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsFace detectionNerve network
The invention discloses a multi-pose eye positioning algorithm based on the cascaded convolutional neural network, belongs to the machine learning and computer vision field and is suitable for intelligent systems such as face recognition, sight tracking and driver fatigue detection. The method comprises steps that face pictures marked with various types of information are collected to form a training data set; the multi-task cascaded convolutional neural network is constructed; the training data set is utilized to train the network to acquire a network model; and lastly, the network model is utilized to detect faces and face key points of the pictures, and the smallest rectangular box containing the eye key points is selected as the eye positioning result. The method is advantaged in thatthe multi-task cascading convolutional neural network is utilized to accomplish face detection and face key point detection, so the multi-pose eye positioning effect is obviously improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
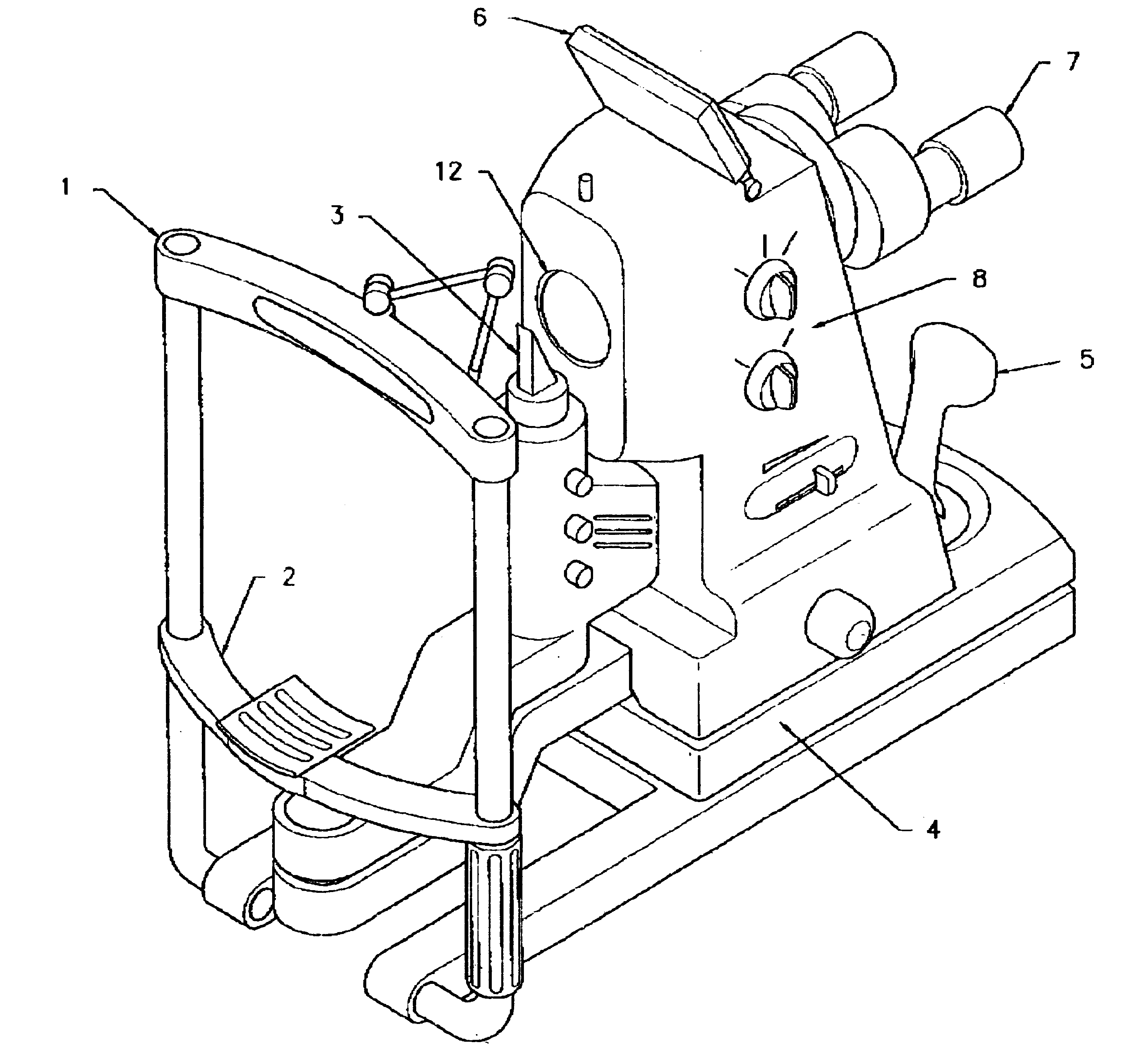
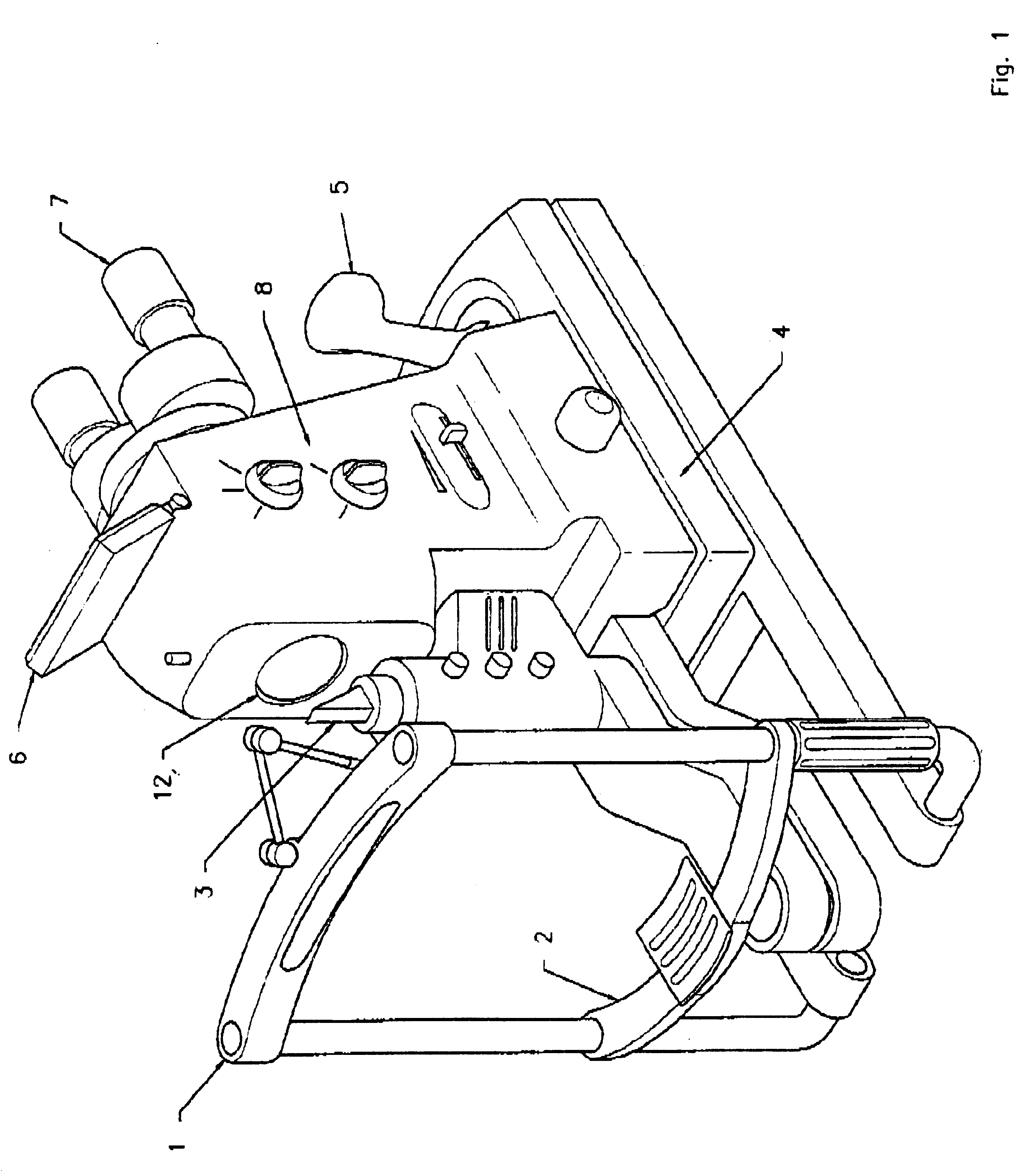
Mounting/adjusting mechanism for vision enhancement system
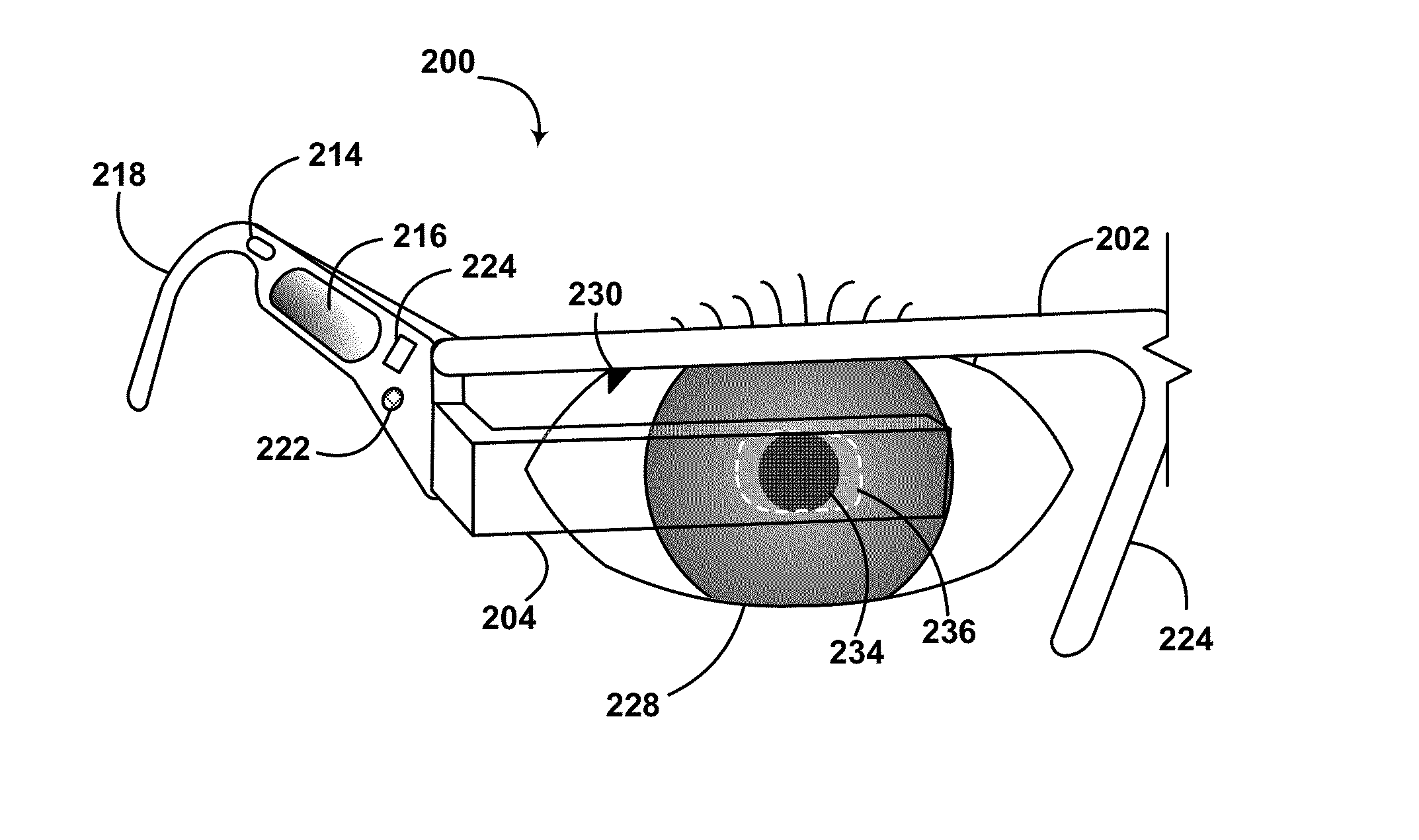
A mounting assembly for a vision enhancement device and associated vision enhancement display, the assembly comprising a display mounted to an arm positionable in front of the user's eye, a base member for receiving a cradle for the vision enhancement device and for attaching to a head-mounting platform, and one or more intermediate members for connecting the arm to the cradle. In one embodiment, the mounting system comprises one or more mechanisms for aligning the display optical axis with the vision enhancement device optical axis and with the user's line of sight, one or more mechanisms for orienting the vision enhancement device within multiple degrees of freedom without changing the alignment of the display optical axis with the device optical axis, and one or more mechanisms for toggling the display between an in-use position to at least one storage position, and, optionally, between right eye and left eye positions.
Owner:ELBIT SYSTEMS OF AMERICA LLC
Method for verifying users and updating database, and face verification system using the same
ActiveUS7187786B2Preventing recognition performanceAvoid performanceImage analysisDigital computer detailsPattern recognitionFace verification
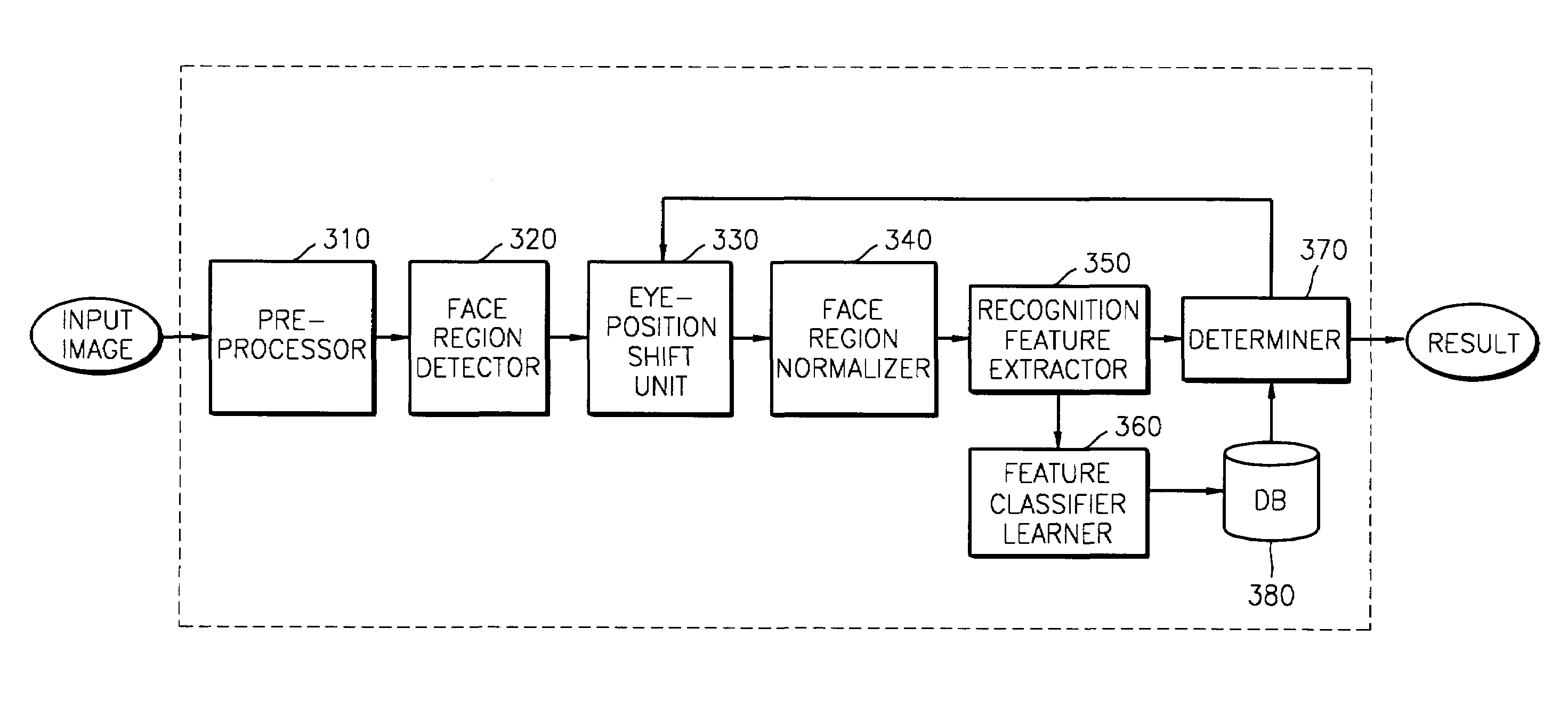
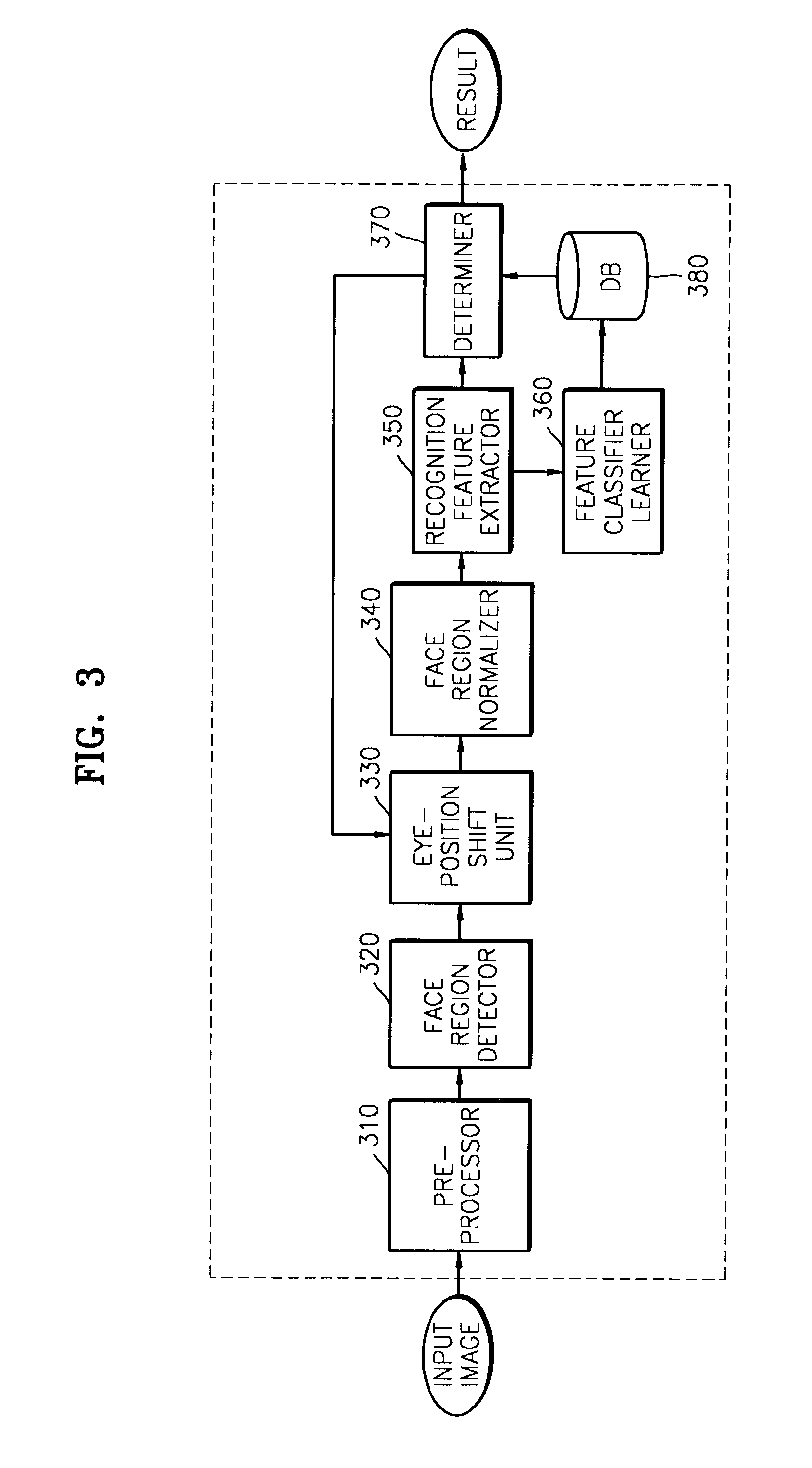
To reduce degradation of recognition performance due to eye detection errors during face verification and to overcome a problem in that sufficient data to design an optimum feature classifier cannot be obtained during face registration, a method includes shifting the positions of eyes detected during face registration in predetermined directions by a predetermined distance to generate pairs of new coordinate points of the eyes; normalizing a face image on the basis of each pair of new coordinate points of the eyes; using the results of normalization in teaching a feature classifier, thereby coping with eye detection errors. In addition, two threshold values are used to prevent a database from being updated with a face of an unregistered person and to update the database with a normal client's face image that has been used during the latest face verification.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
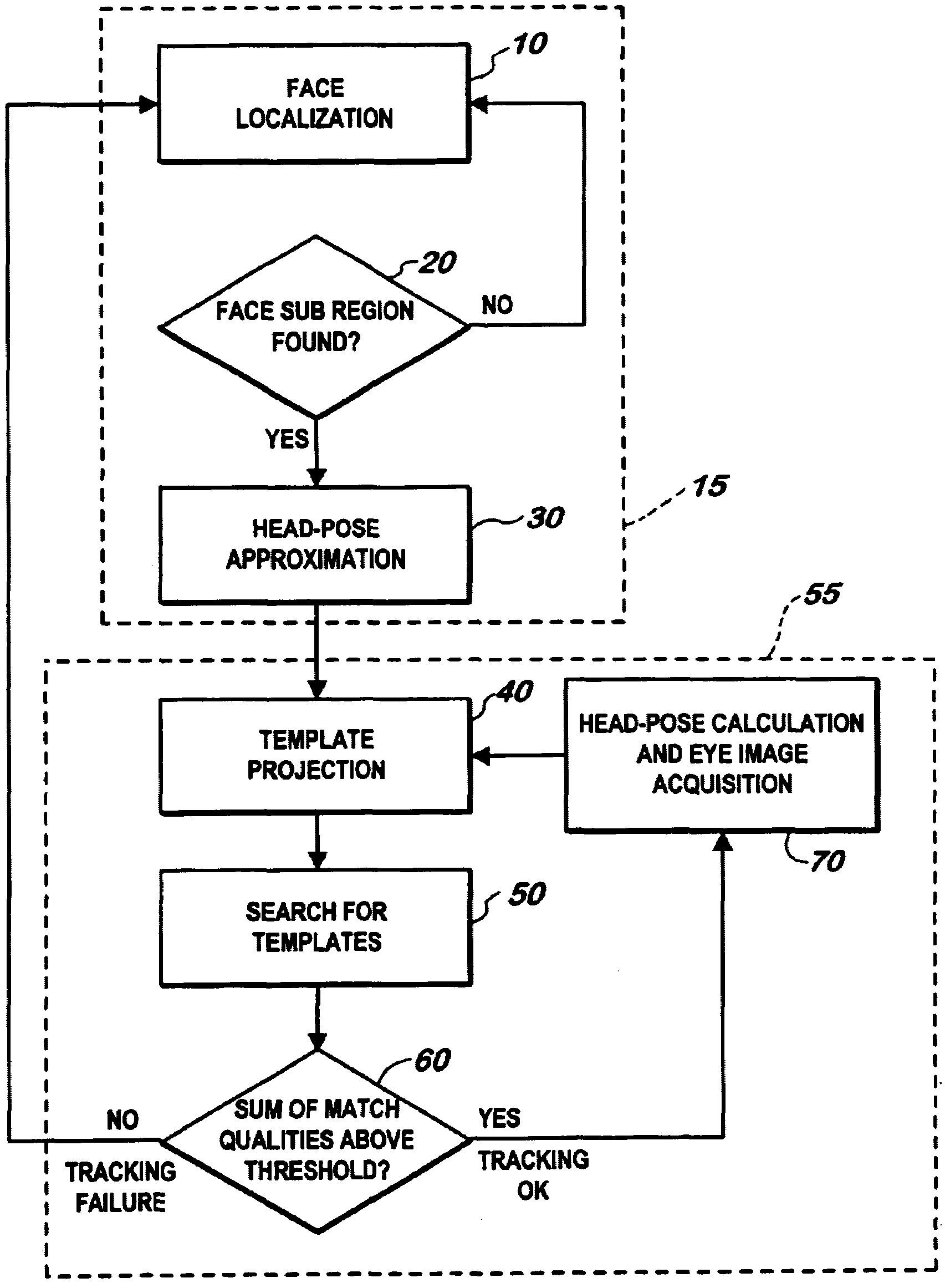
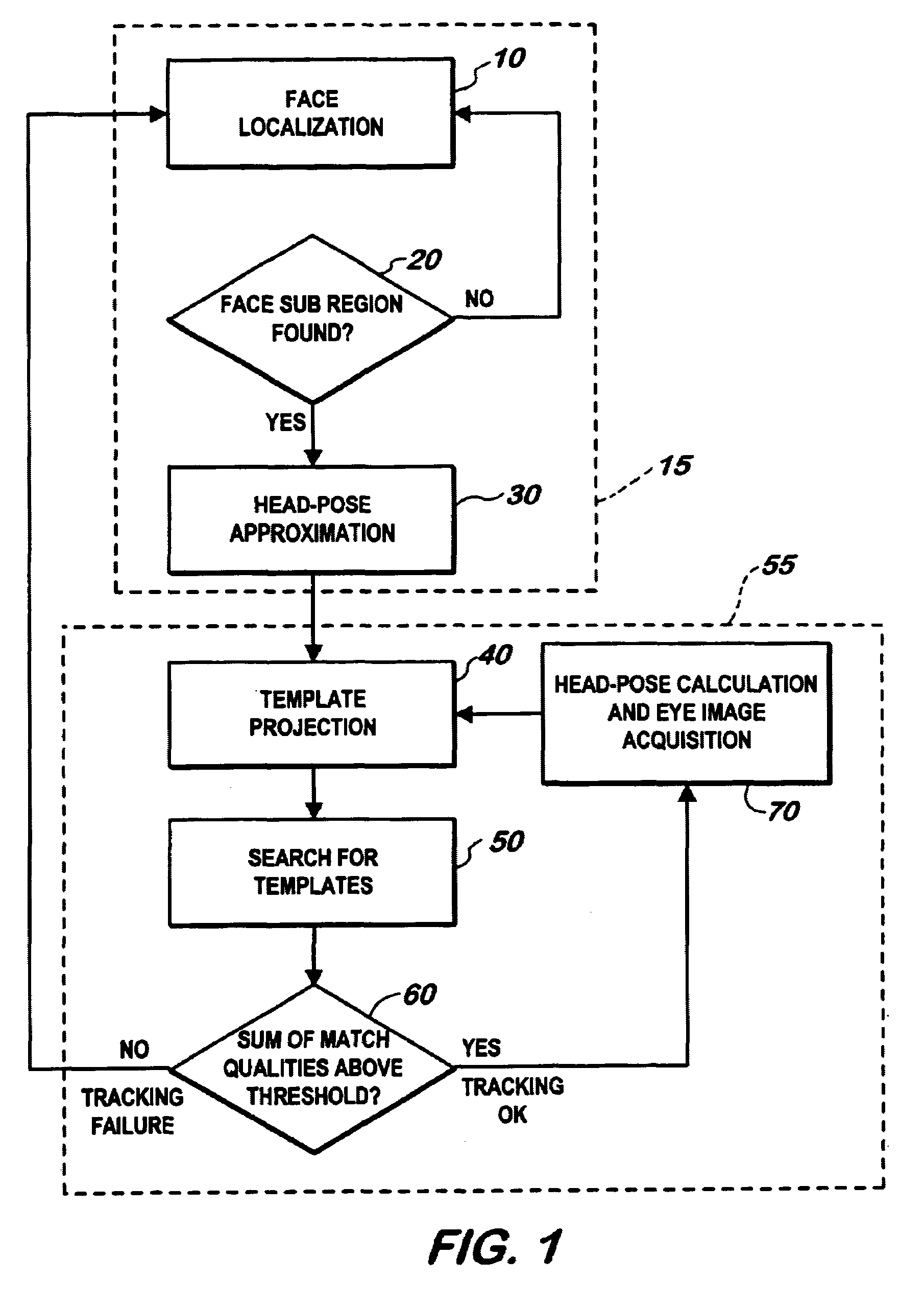
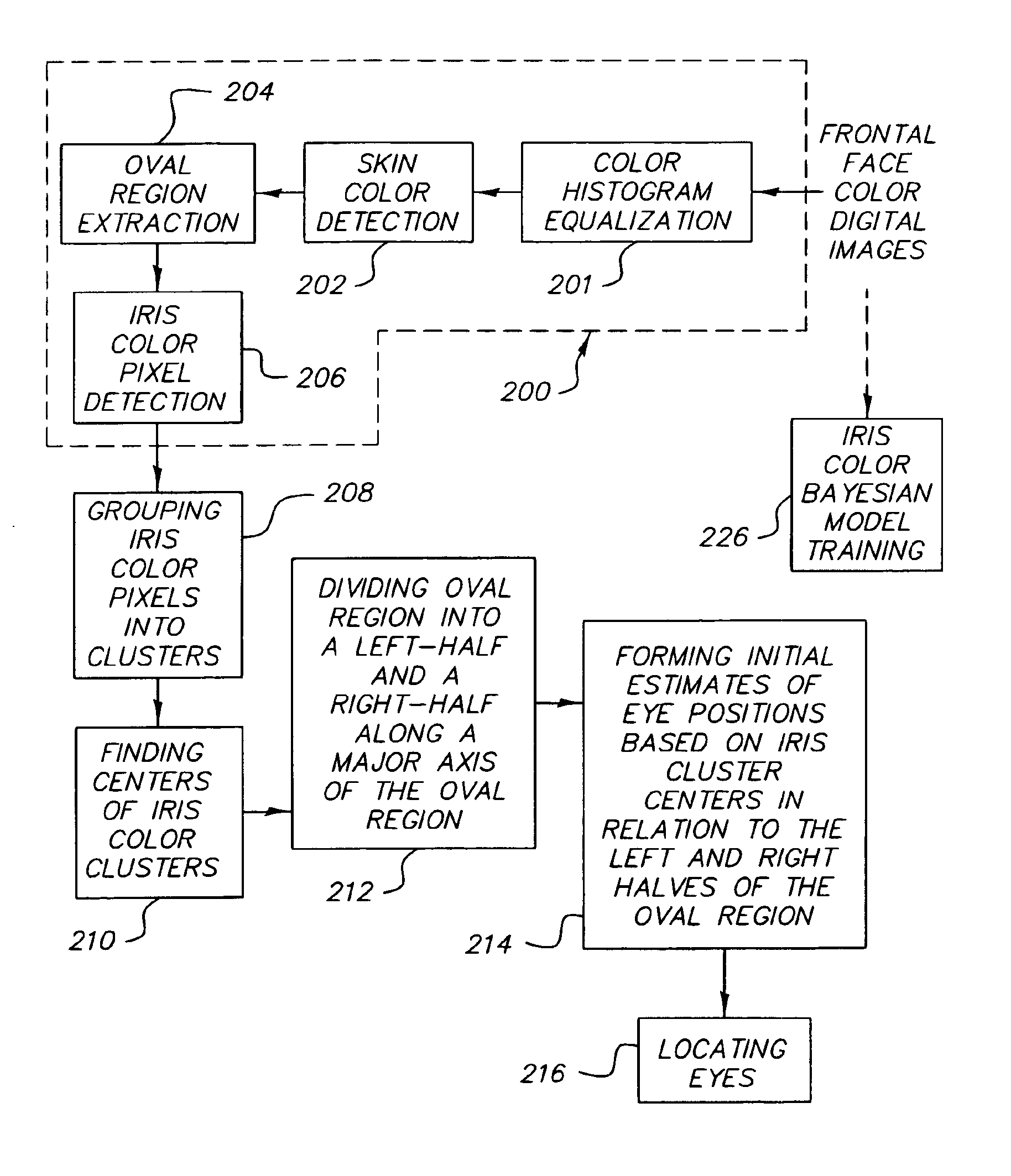
Method for automatically locating eyes in an image
InactiveUS6895103B2Reducing region of imageReduce calculationProgramme controlElectric signal transmission systemsPattern recognitionSkin color
A digital image processing method for locating human eyes in a digital image, includes the steps of detecting a skin colored region in the image; detecting human iris color pixels in the skin colored region; forming initial estimates of eye positions using the locations of the detected iris color pixels in the skin colored region; estimating the size of each eye based on the distance between the estimated initial eye positions; forming a first search window for one eye, the center of the window being the estimated initial position for the one eye and the size of the window being proportional to the estimated size of the one eye; and employing a template to locate an eye in the first search window.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
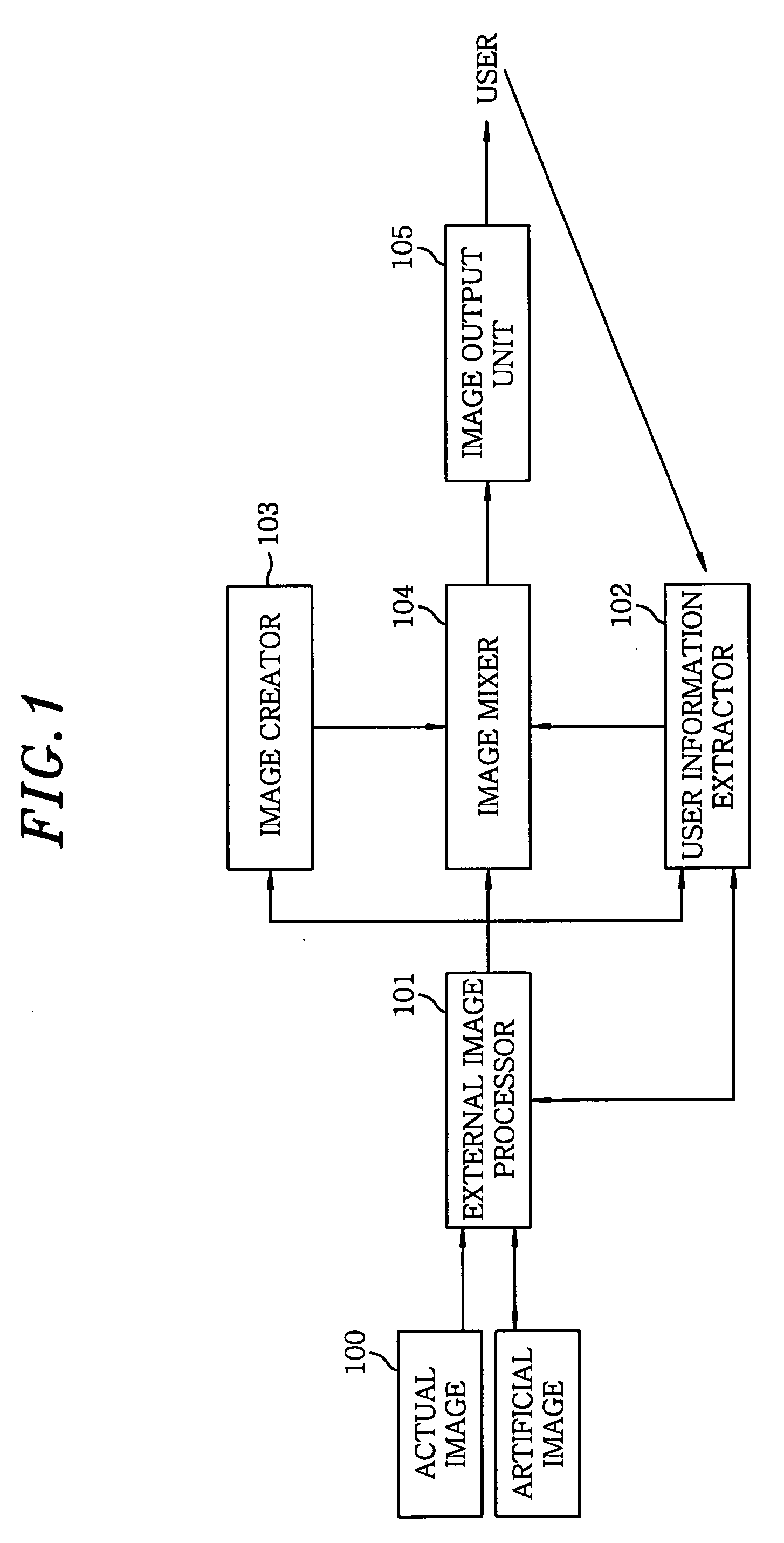
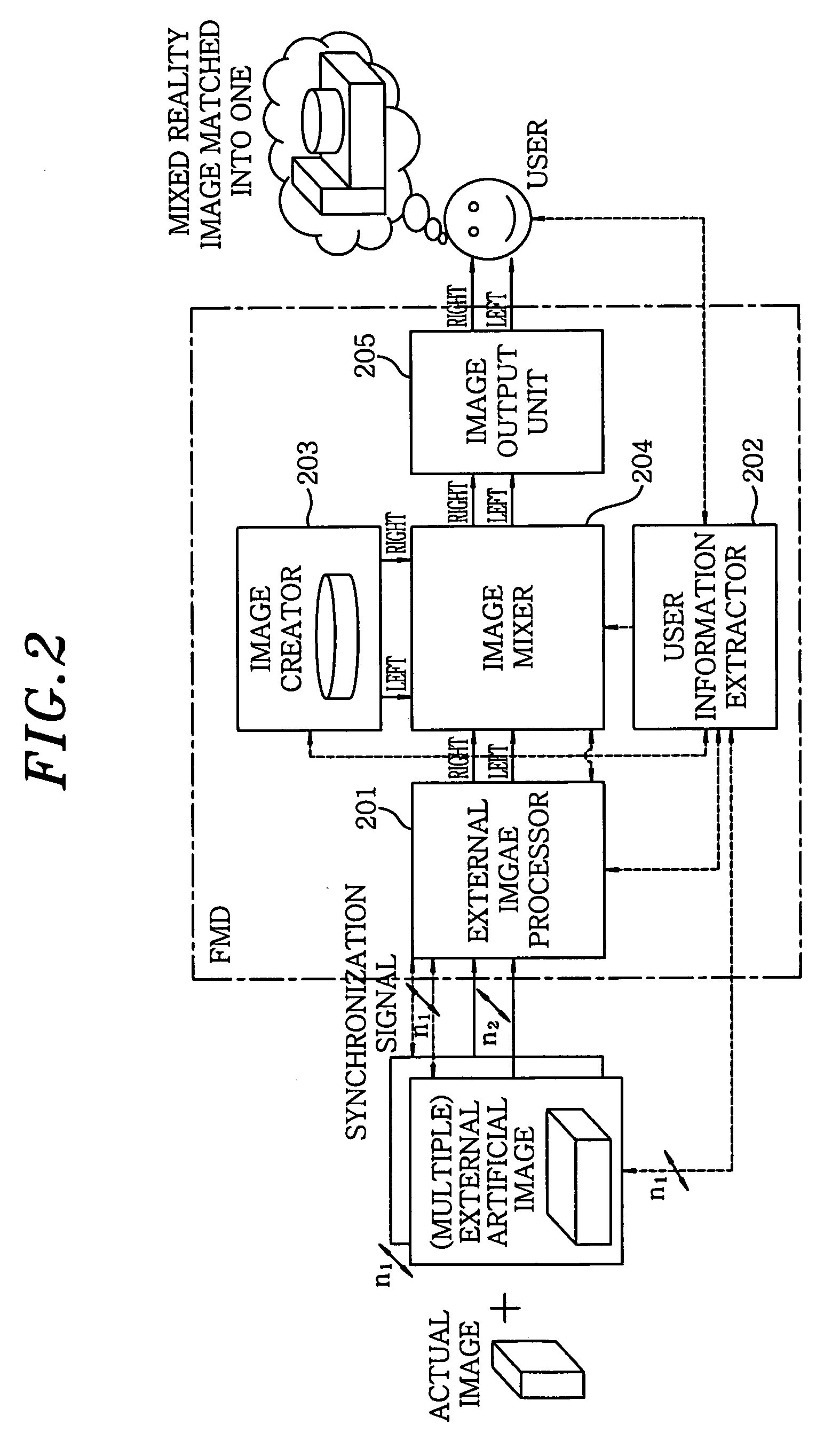
Face-mounted display apparatus for mixed reality environment
A display apparatus for a mixed reality environment includes an image processor for mixing an actual image of an object around a user and a artificial stereo images to produce multiple external image signals, a user information extractor for extracting the user's sight line information including the user's position his / her eye position, direction of a sight line and focal distance; an image creator for creating a stereo image signal based on the extracted user's sight line information; an image mixer for synchronously mixing the multiple external image signals and the stereo image signal; and an image output unit for outputting the mixed image signal to the user.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Rapid computation of local eye vectors in a fixed point lighting unit
InactiveUS6014144ADigital computer detailsElectric digital data processingFixation pointSpecular reflection
A rapid method for calculating a local eye vector in a fixed point lighting unit. For a given triangle primitive which is to be projected into a given viewport in screen space coordinates, the local eye vector corresponds to a given eye position and a first vertex of the given triangle primitive. (A different local eye vector is calculated for each vertex of the given triangle primitive). The method first comprises generating a view vector matrix which corresponds to the given eye position and corner coordinates of the given viewport, where the corner coordinates are expressed in screen space coordinates. The view vector matrix is usable to map screen space coordinates to an eye vector space which corresponds to the given viewport. The method next includes receiving a first set of coordinates (in screen space) which correspond to the first vertex. The first set of coordinates are then scaled to a numeric range which is representable by the fixed point lighting unit. Next, the first set of coordinates are transformed using the view vector matrix, which produces a non-normalized local eye vector within the eye vector space for the given viewport. The non-normalized local eye vector is normalized to form a normalized local eye vector. The normalized local eye vector is then usable to perform subsequent lighting computations such as computation of specular reflection values for infinite light sources, producing more realistic lighting effects than if an infinite eye vector were used. These more realistic lighting effects do not come at decreased performance, however, as the local eye vector may be calculated rapidly using this method.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
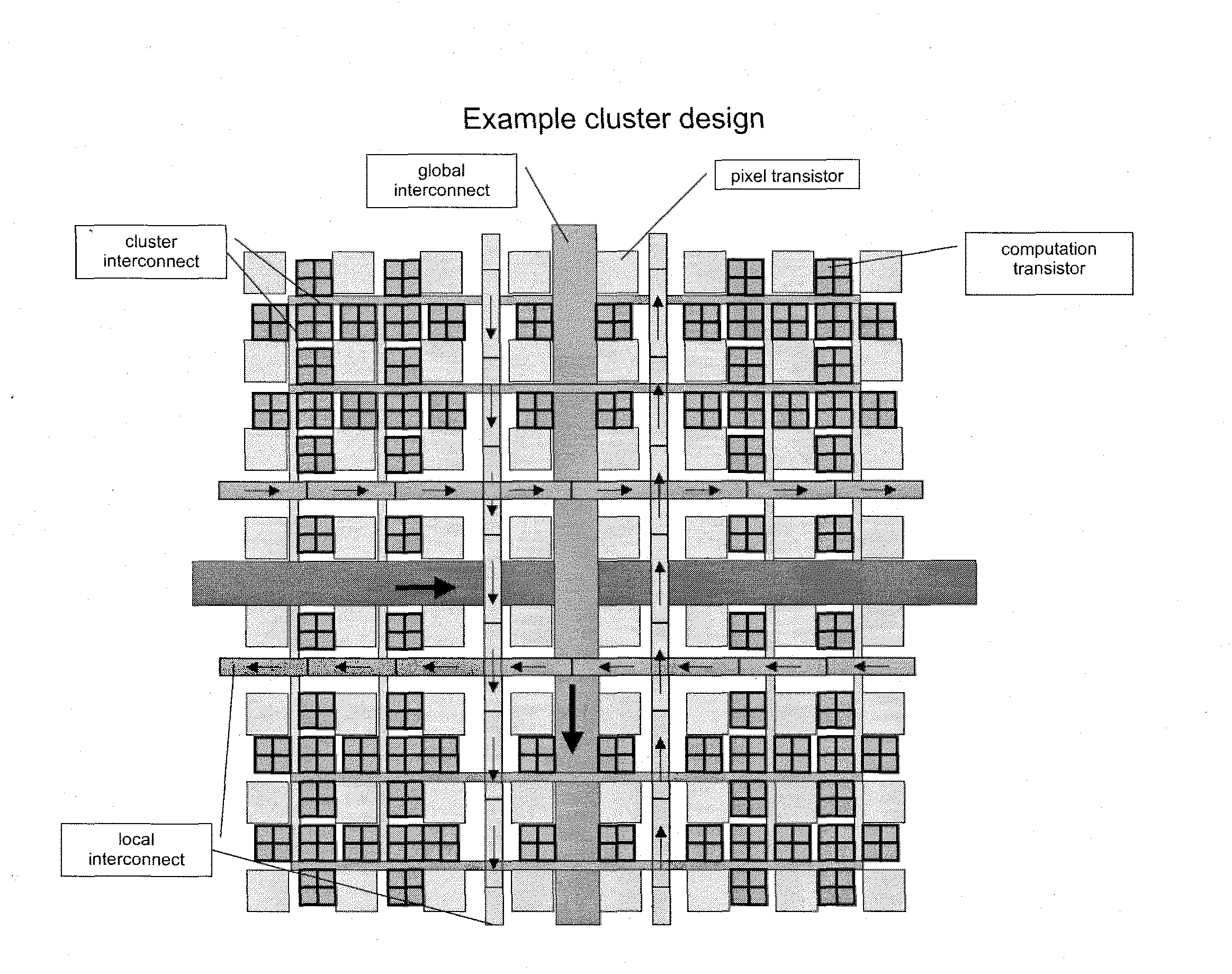
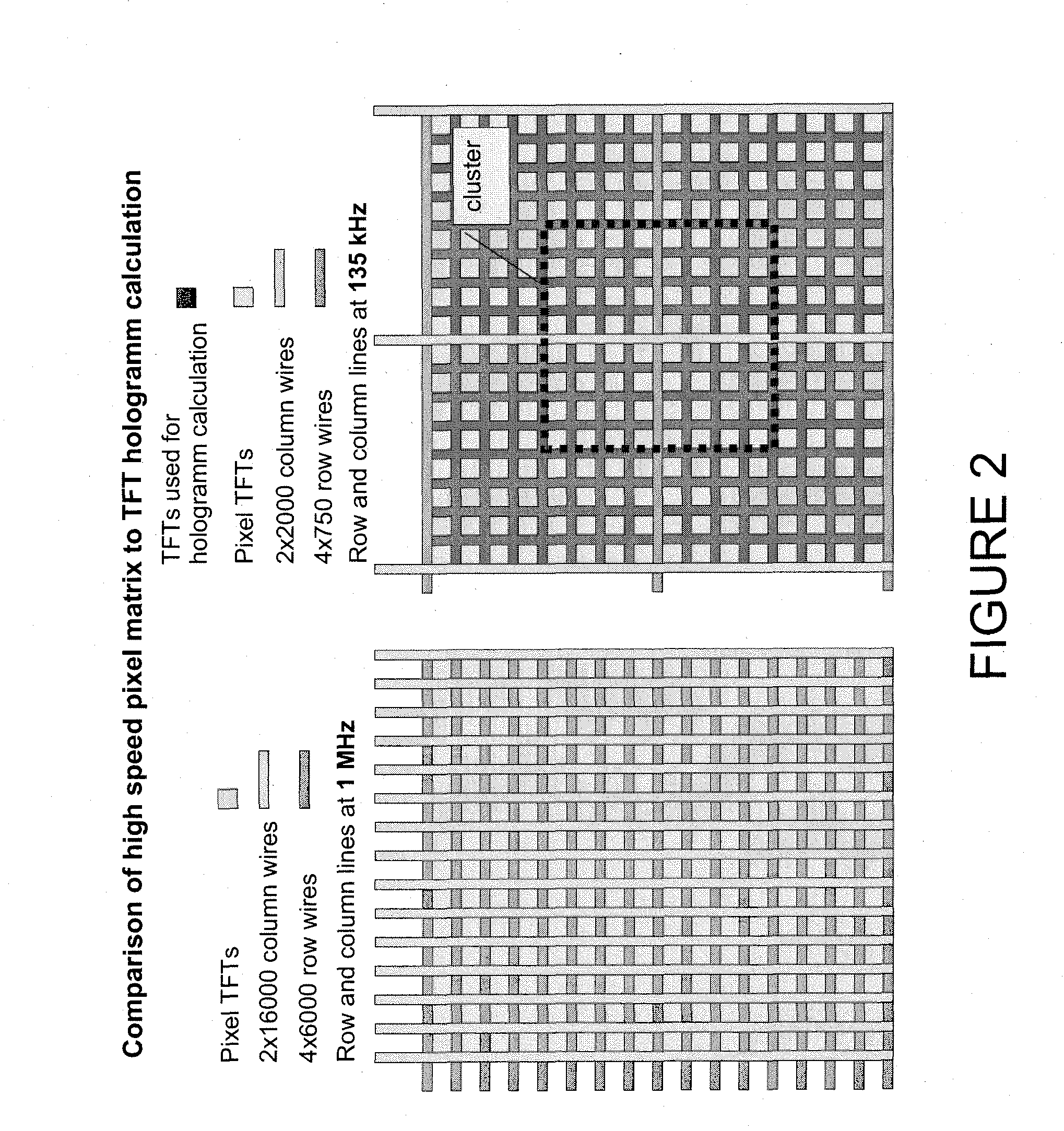
Holographic Display
ActiveUS20100157399A1Reduce optical effectsHolographic optical componentsDigital holography electronic componentSpatial light modulatorLight beam
Disclosed is a holographic display including a spatial light modulator, and including a position detection and tracking system, such that a viewer's eye positions are tracked, with variable beam deflection to the viewer's eye positions being performed using a microprism array which enables controllable deflection of optical beams.
Owner:SEEREAL TECHNOLOGIES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com