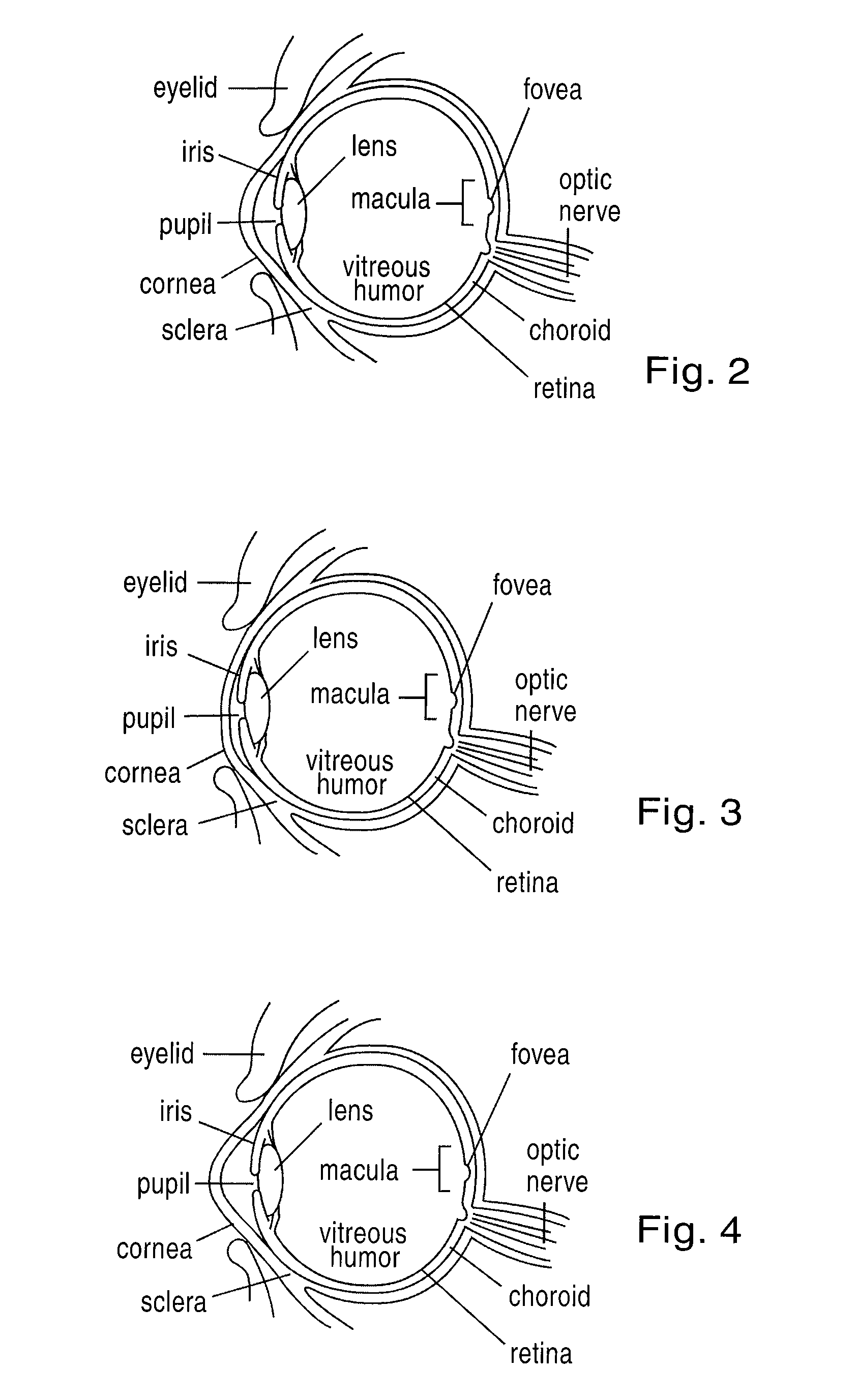
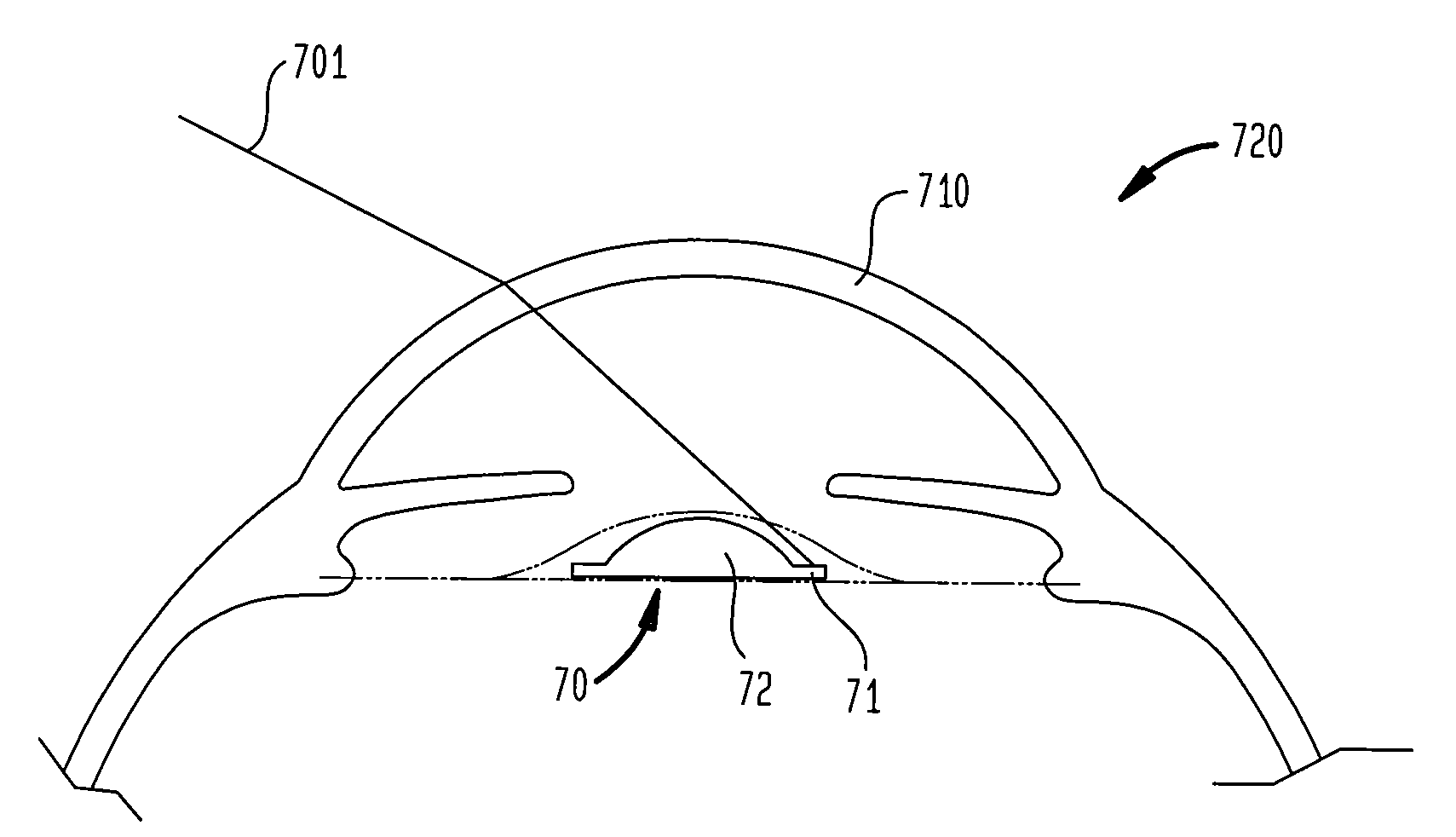
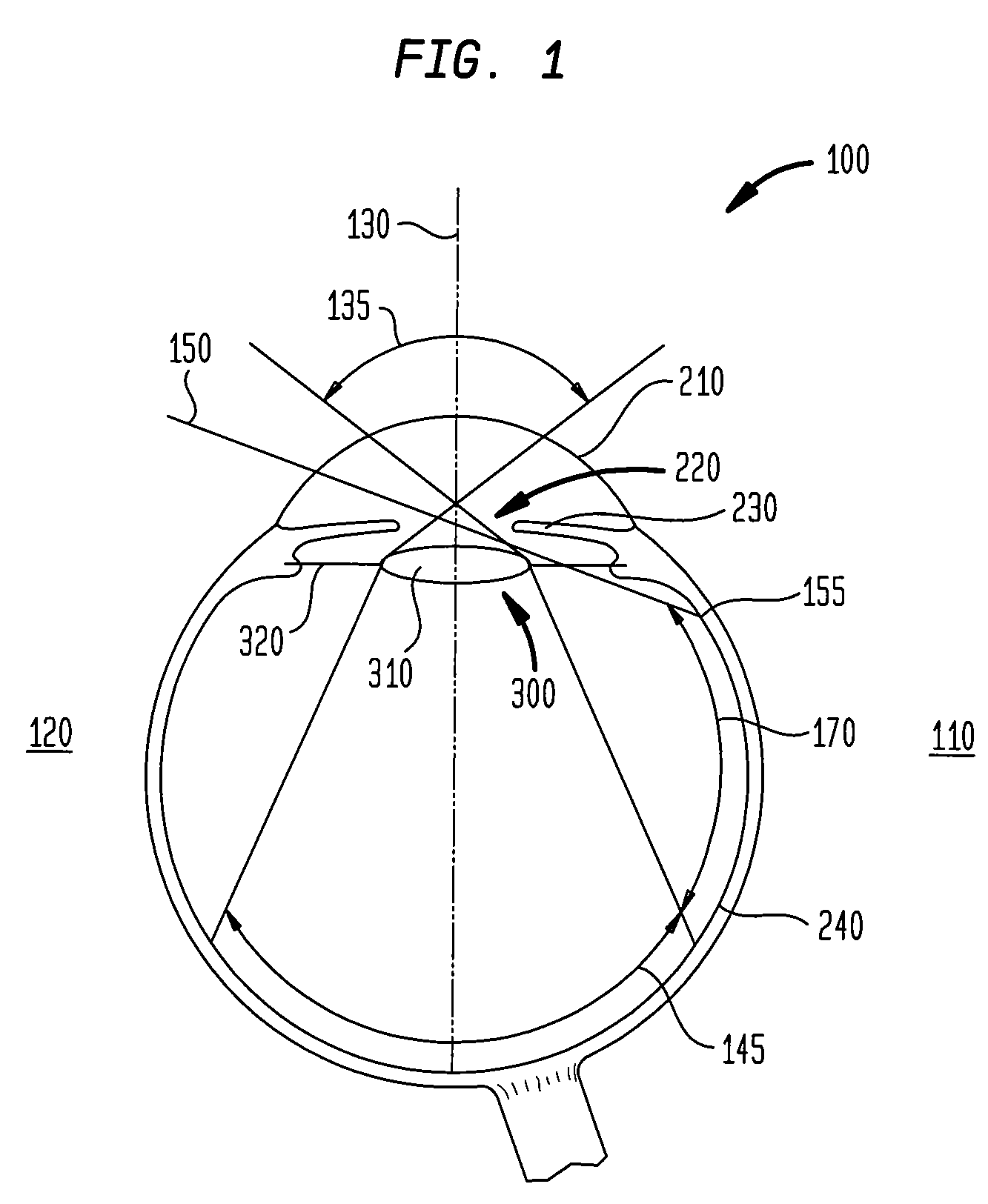
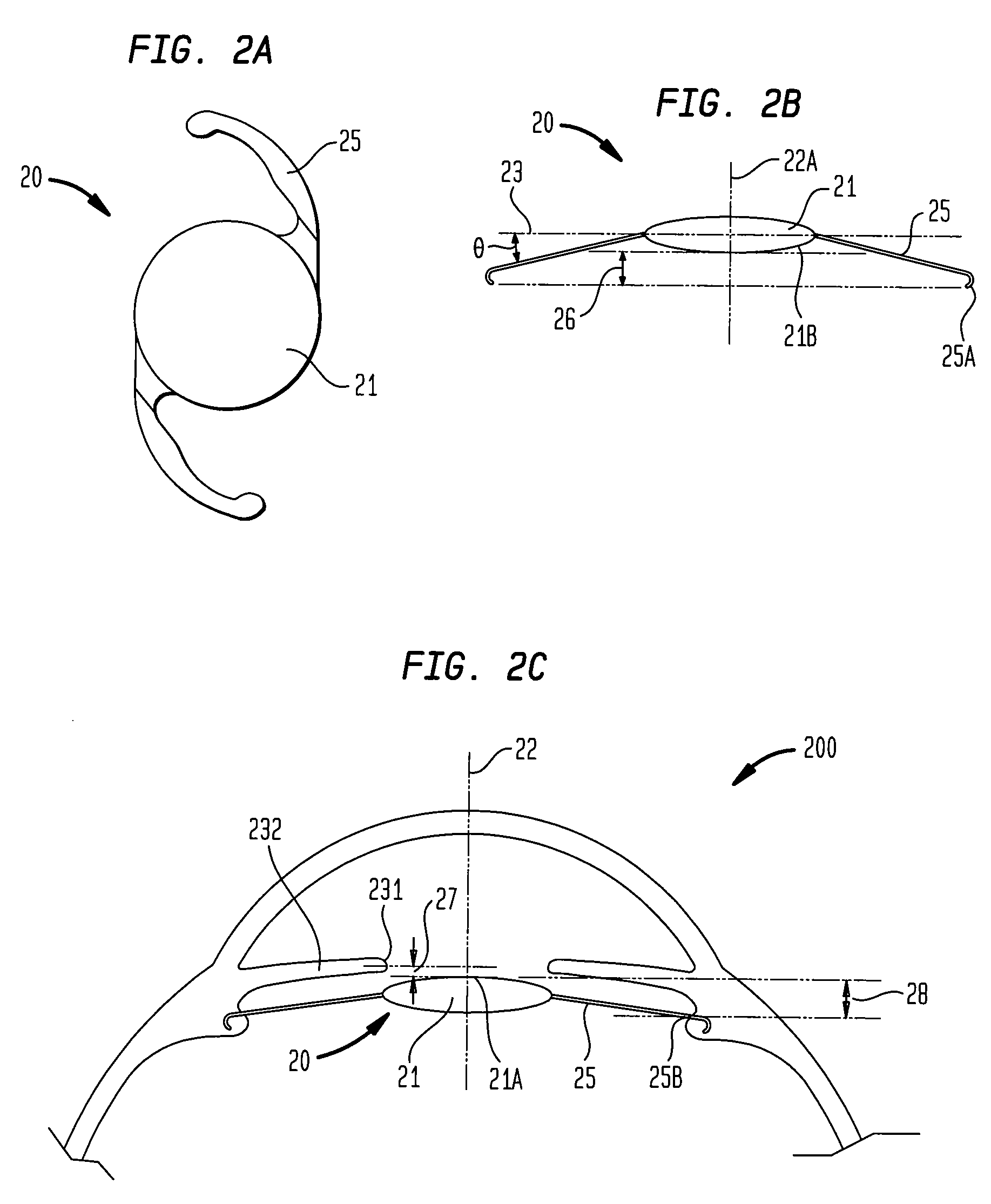
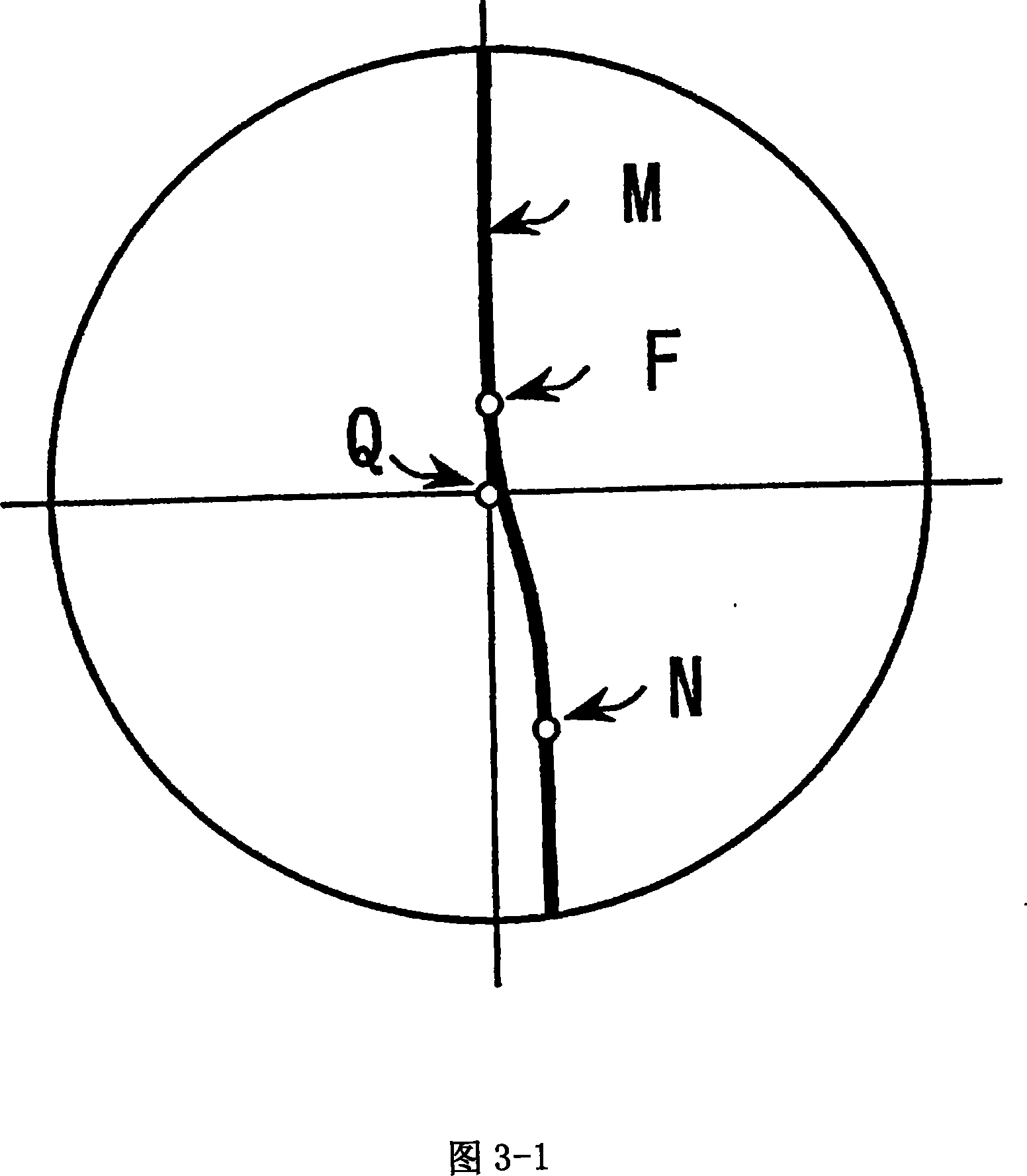Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
75 results about "Visual Disorders" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Visual Disorders. Visual problems are common among those with MS and are often a first sign of the disease. Optic neuritis is often the first symptom of MS. This occurs when inflammation and demyelination are present along the optic nerve (the nerve that connects the brain to the eye).
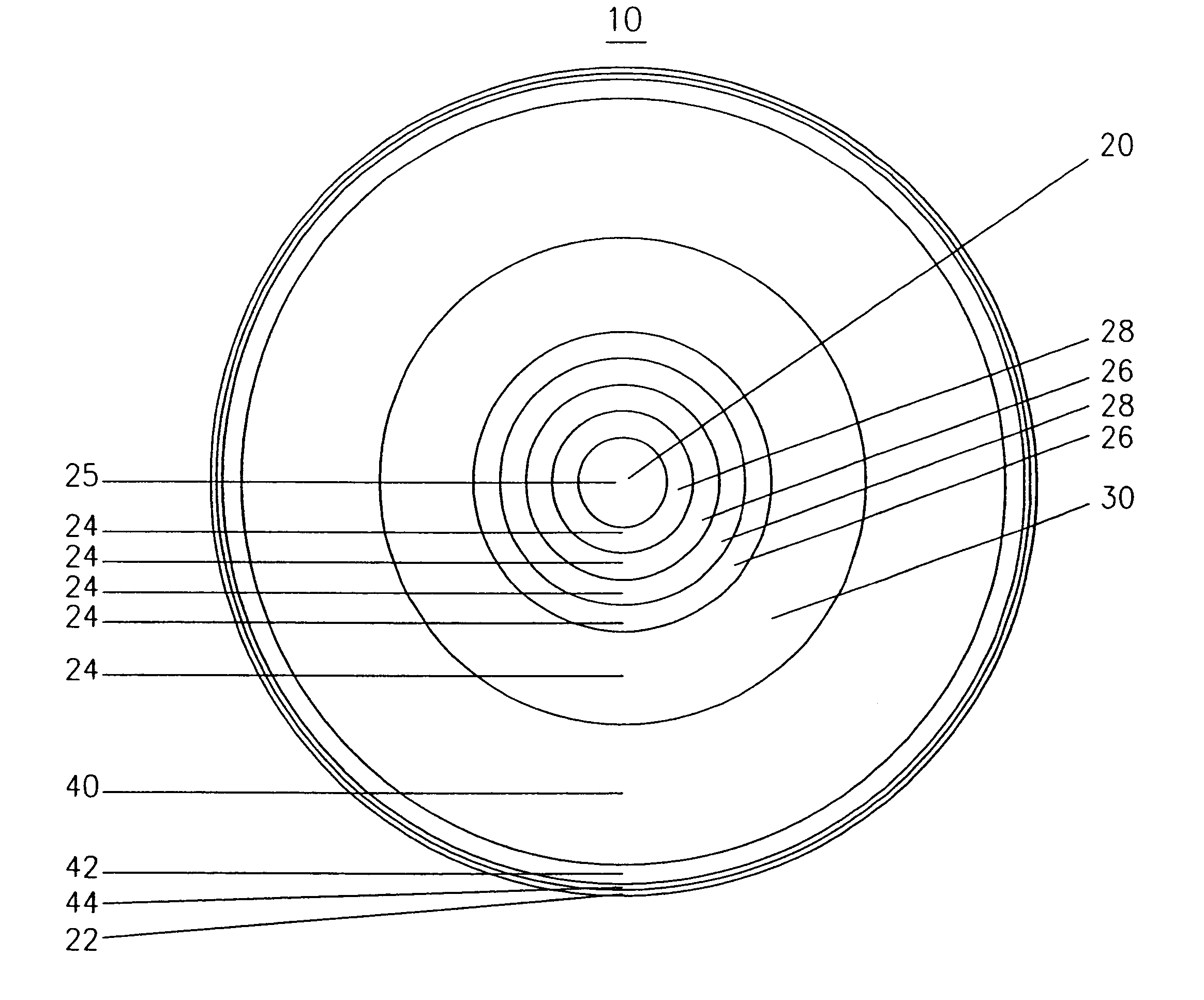
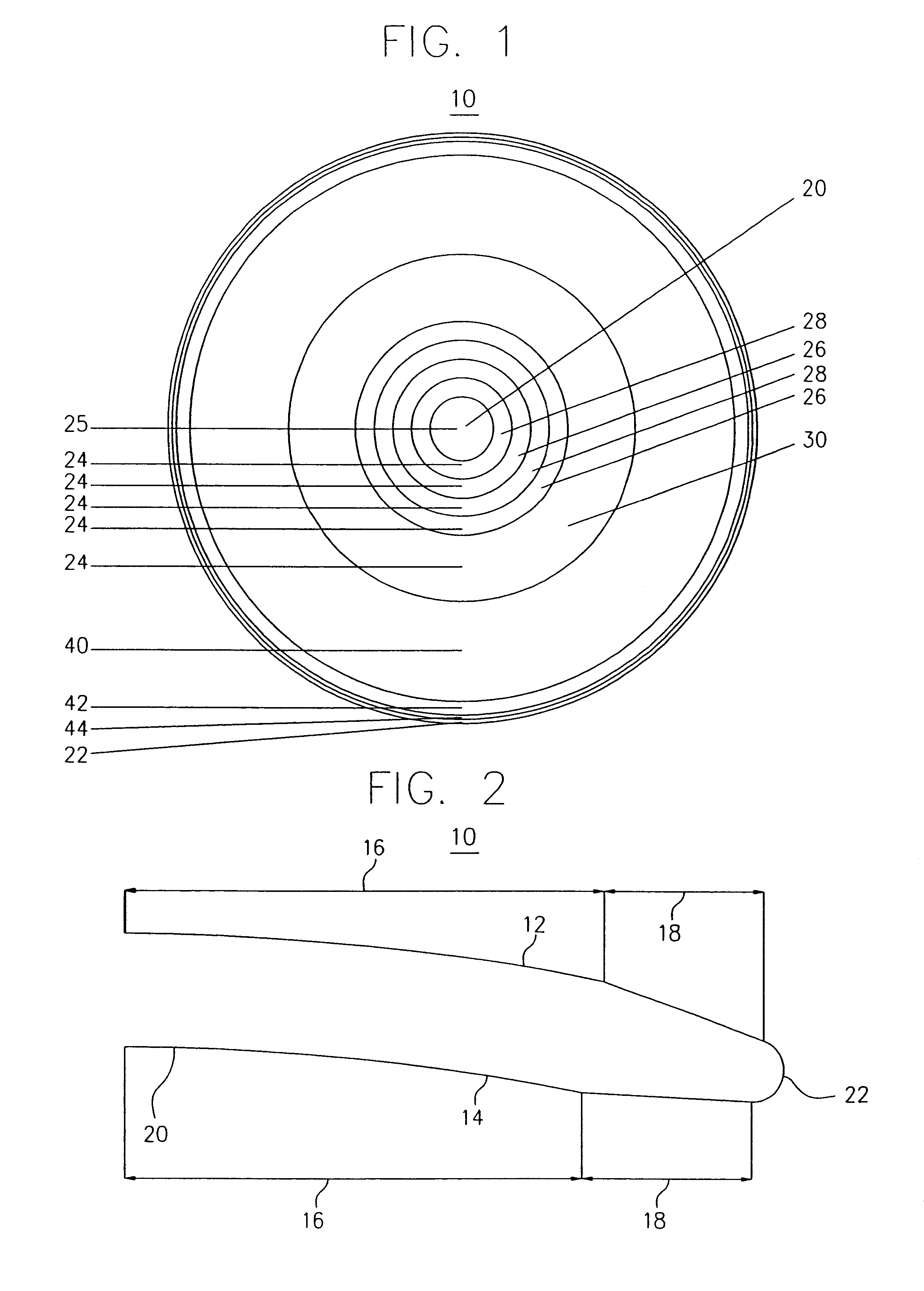
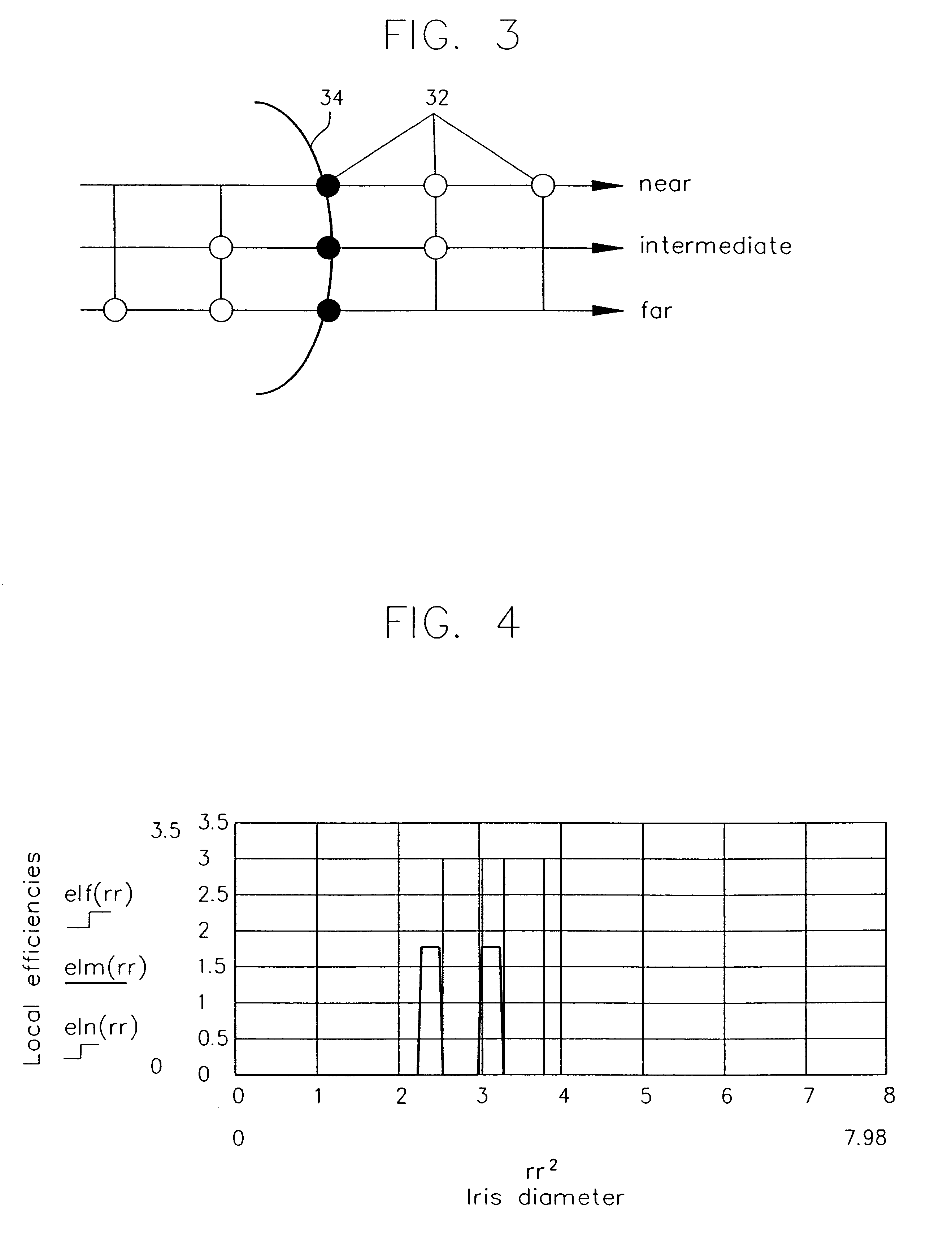
Simultaneous multifocal contact lens and method of utilizing same for treating visual disorders
A simultaneous multifocal contact lens for correcting vision acuity of an individual is disclosed. The contact lens comprises a central region radially surrounded by at least one far vision focal region and at least one near vision focal region, wherein a near vision additional correction of the at least one near vision focal region is overcorrected by at least 10% with respect to the near vision additional correction prescribed for the
Owner:HOLO OR
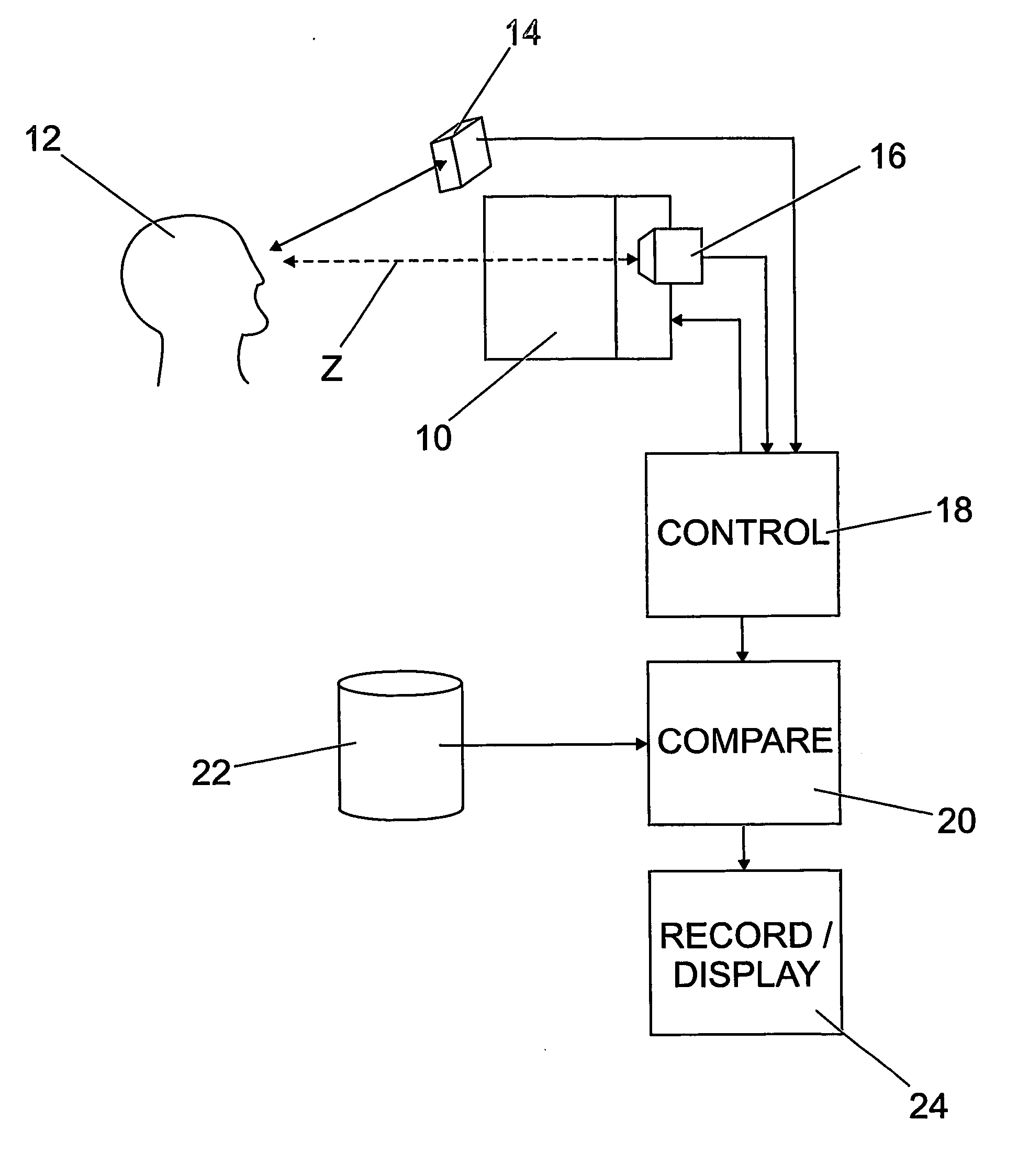
Method and apparatus for the diagnosis of glaucoma and other visual disorders
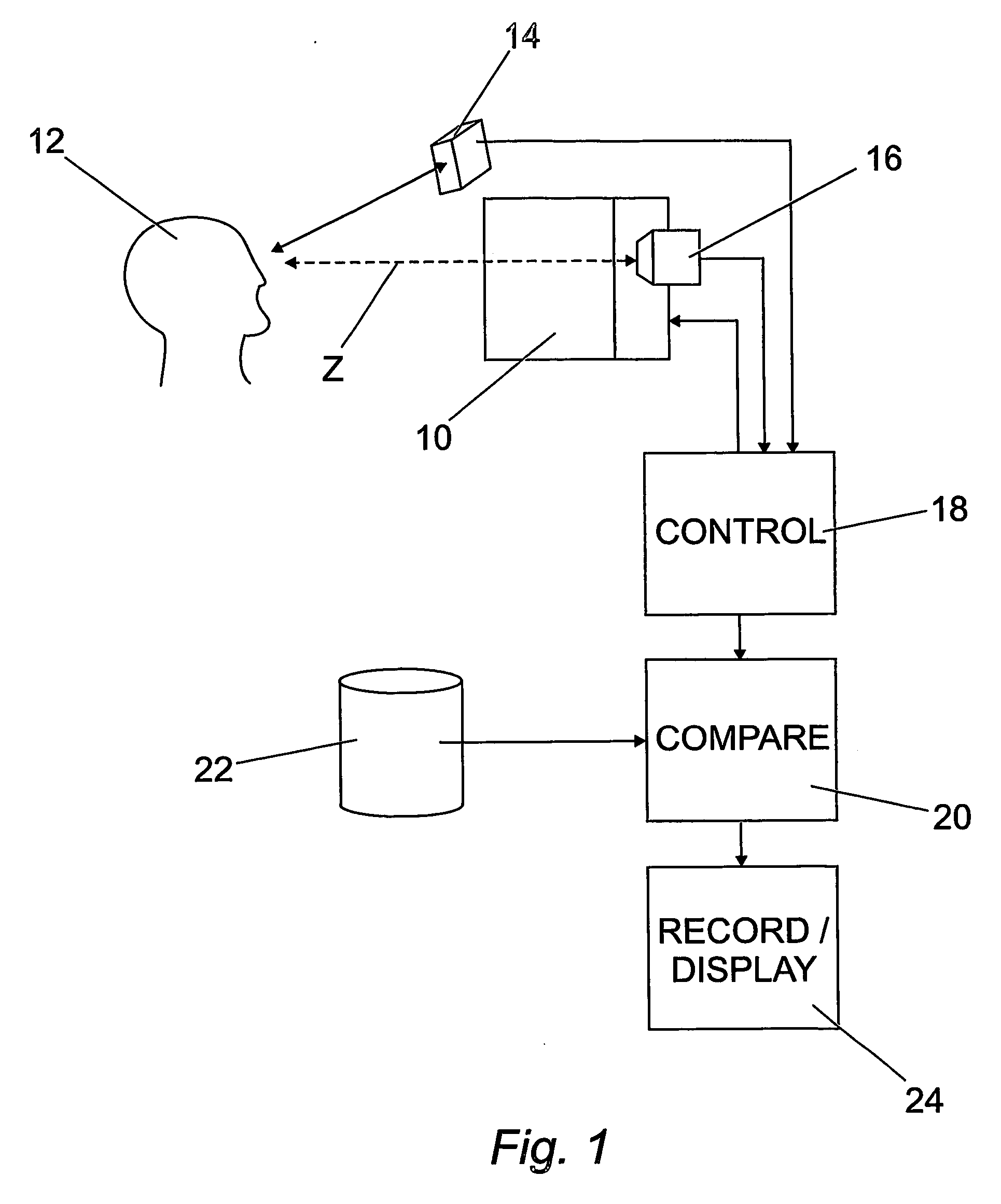
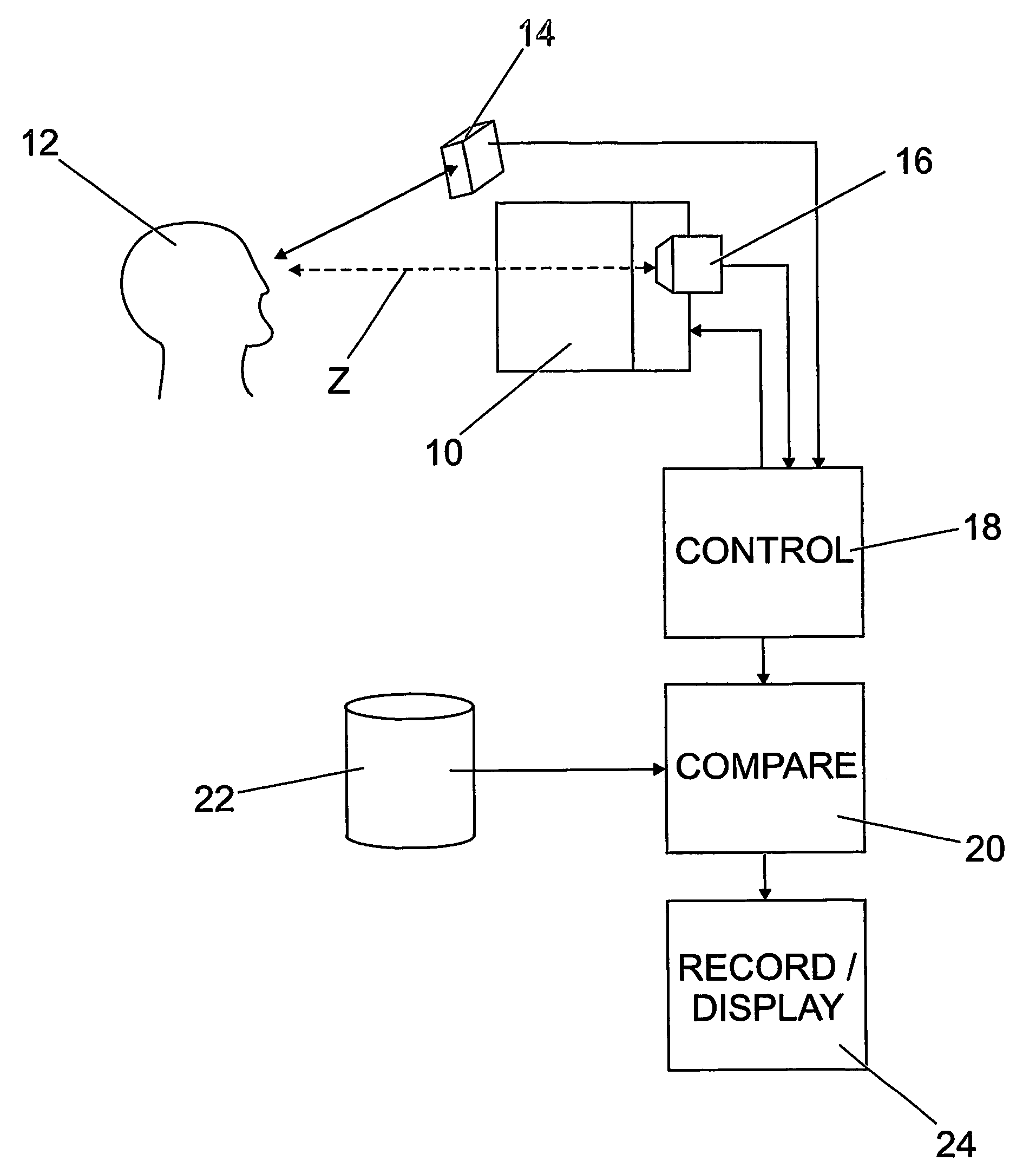
A subject (12) observes an image on a display (10). A control (18) produces a fixation image at a selected position in the display, followed by a stimulus spaced from the fixation image. An eye position sensor (14) detects a saccade movement towards the stimulus. The stimulus is then replaced with a fixation image and the cycle repeated. The time taken to saccade plus the intensity of the stimulus are used to produce a retinal map of field of vision, or to assess other characteristics of the subject.
Owner:MCGRATH JOHN ANDREW MURRAY +1
Head wearing type vision auxiliary system for patients with vision disorder
ActiveCN104306102AImprove scalabilityVisual aids and enhancementsEye treatmentImaging processingVisual Disorders
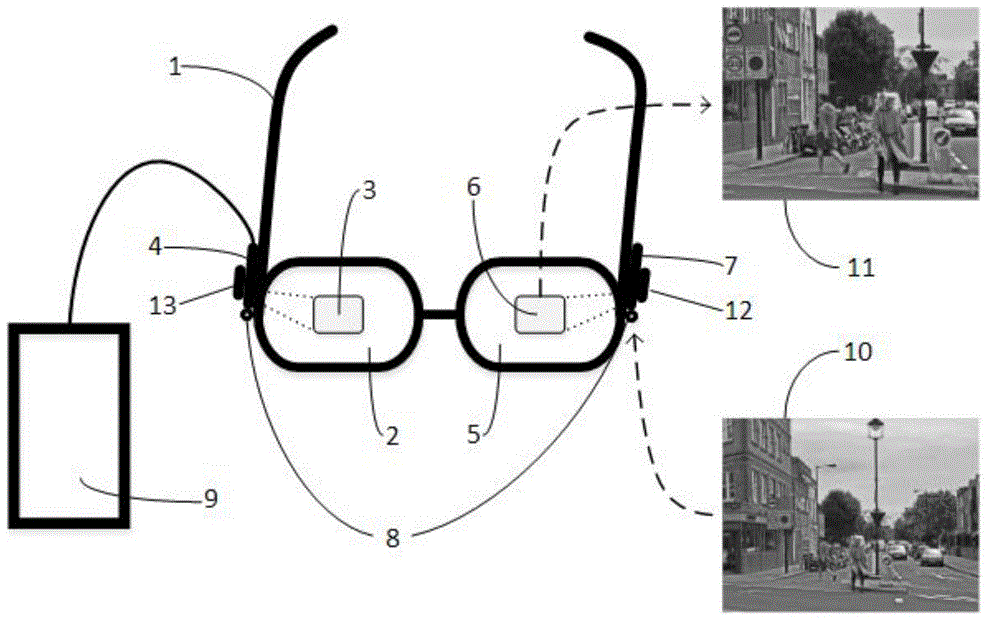
The invention provides a head wearing type vision auxiliary system for patients with vision disorder. The head wearing type vision auxiliary system comprises a head wearing type glasses bracket which is used for installing and connecting each part of the system and facilitating a user to wear, a left eye display panel and a right eye display panel which are used for respectively displaying left and right eye images, two-path image collection equipment which is used for collecting the images according to the visual angle of human eyes, various sensors which are used for detecting the external environment and glasses states; a data processing center which is used for overall control of the system, image collection, processing and projection display, reception and processing of data of the sensors and implementation of related image processing algorithms, a matched image processing program which is designed for the patients with vision disorder and used for enhancing the vision of the patients, and a training and rehabilitation program which is designed for treating different vision diseases. The system provided by the invention can be used for collecting reality scenes in real time, and processing the collected images, the images are displayed in a method which is more accepted by the patients with vision disorder and the aim of vision assisting is fulfilled.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
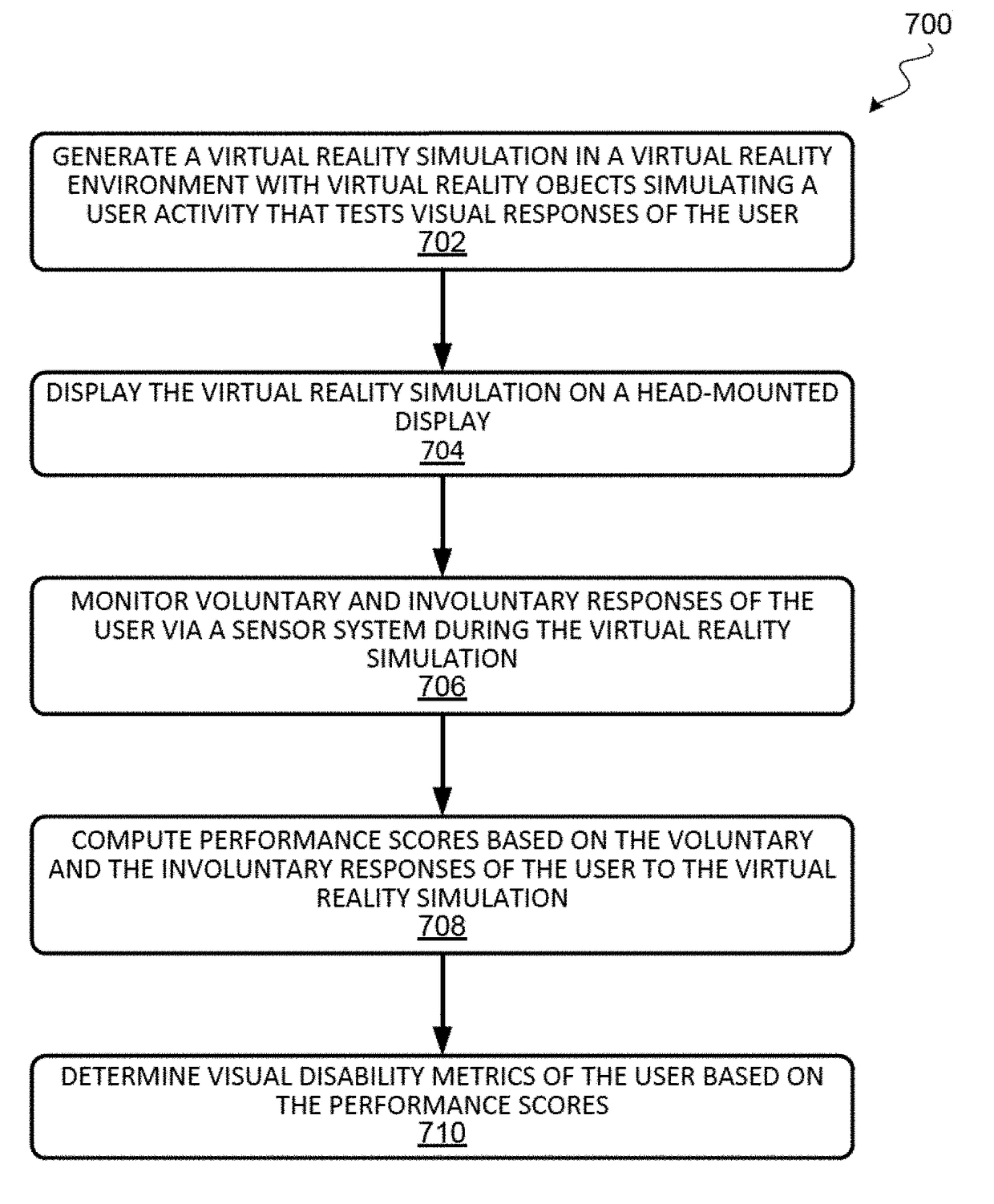
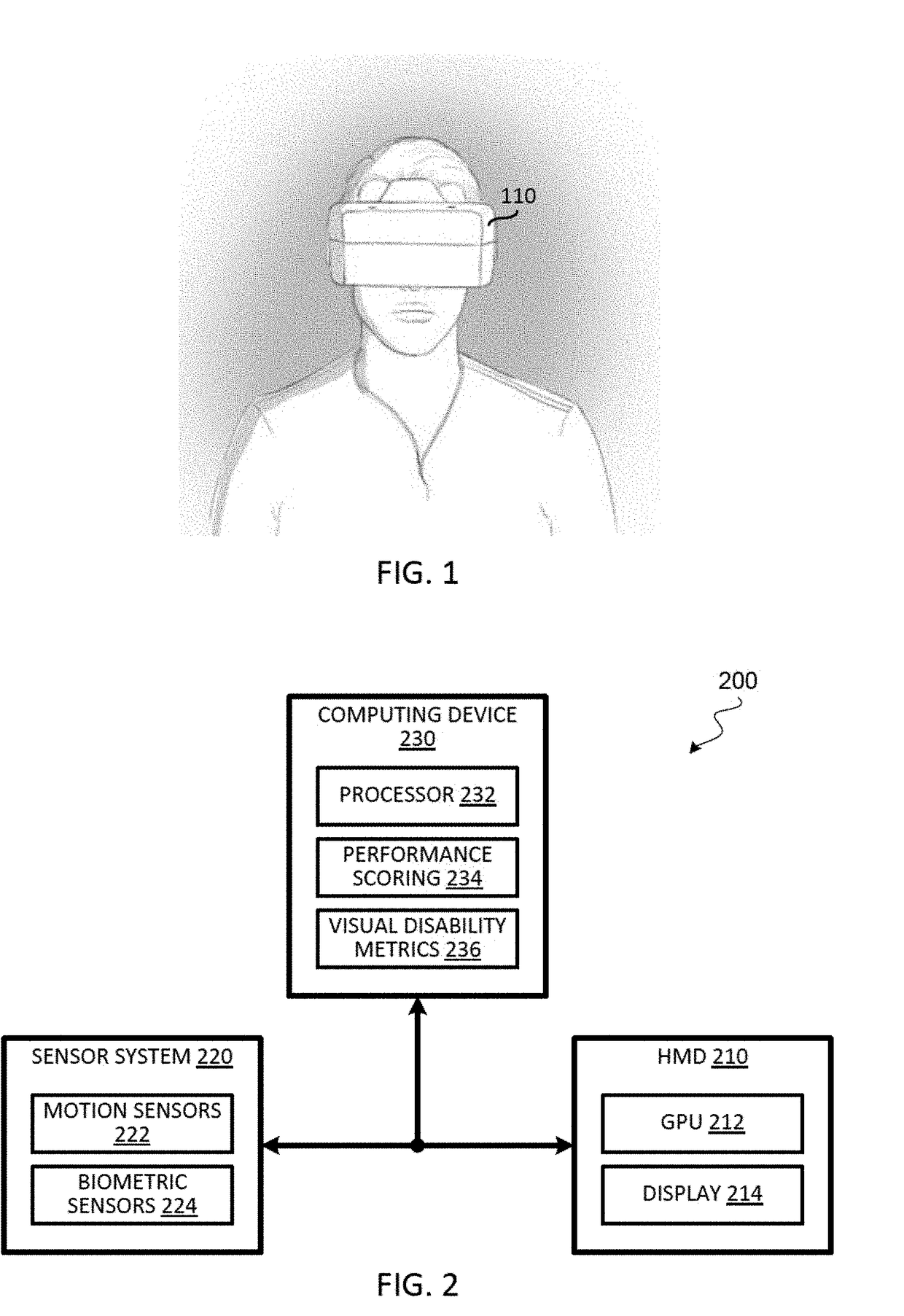
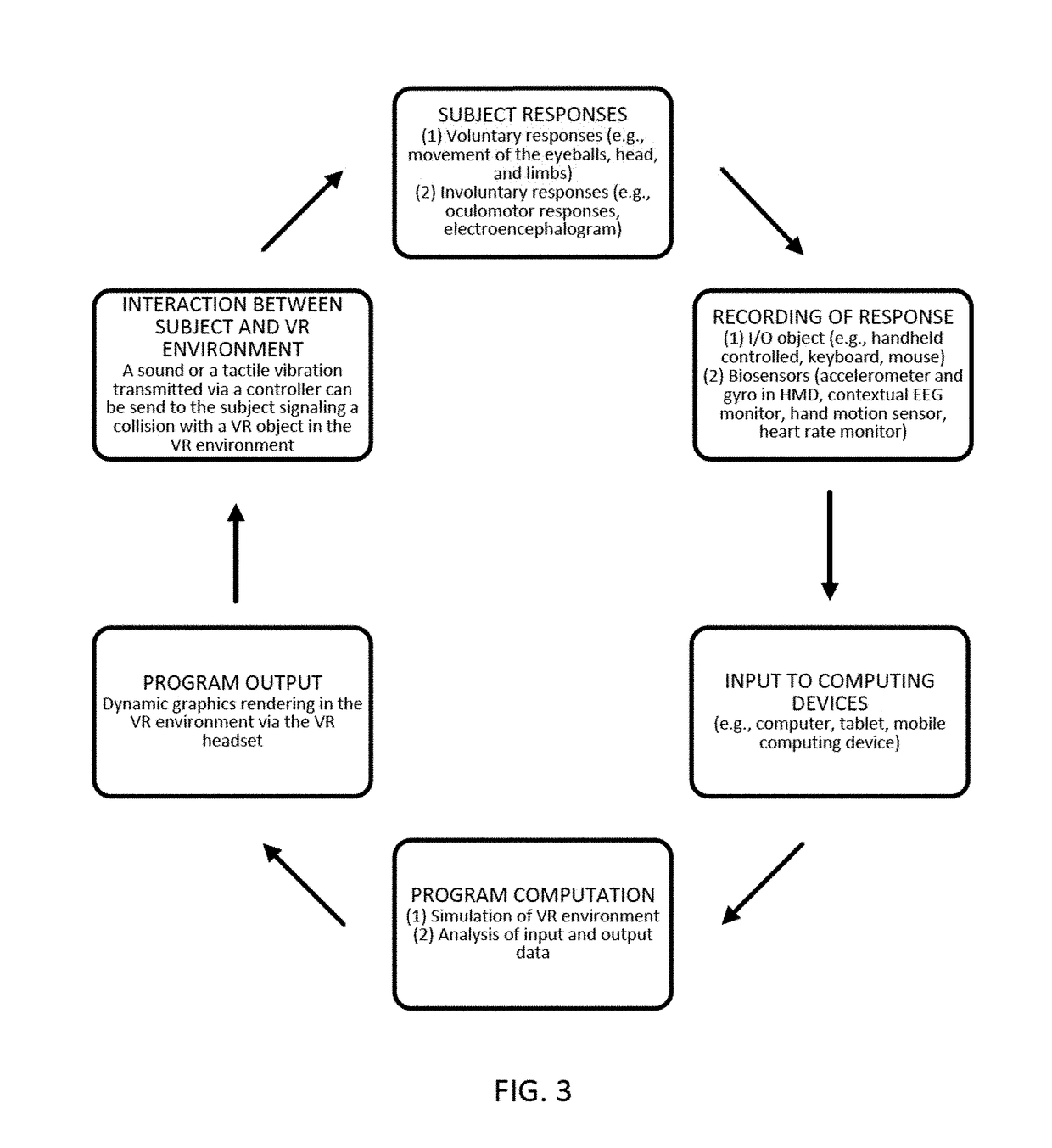
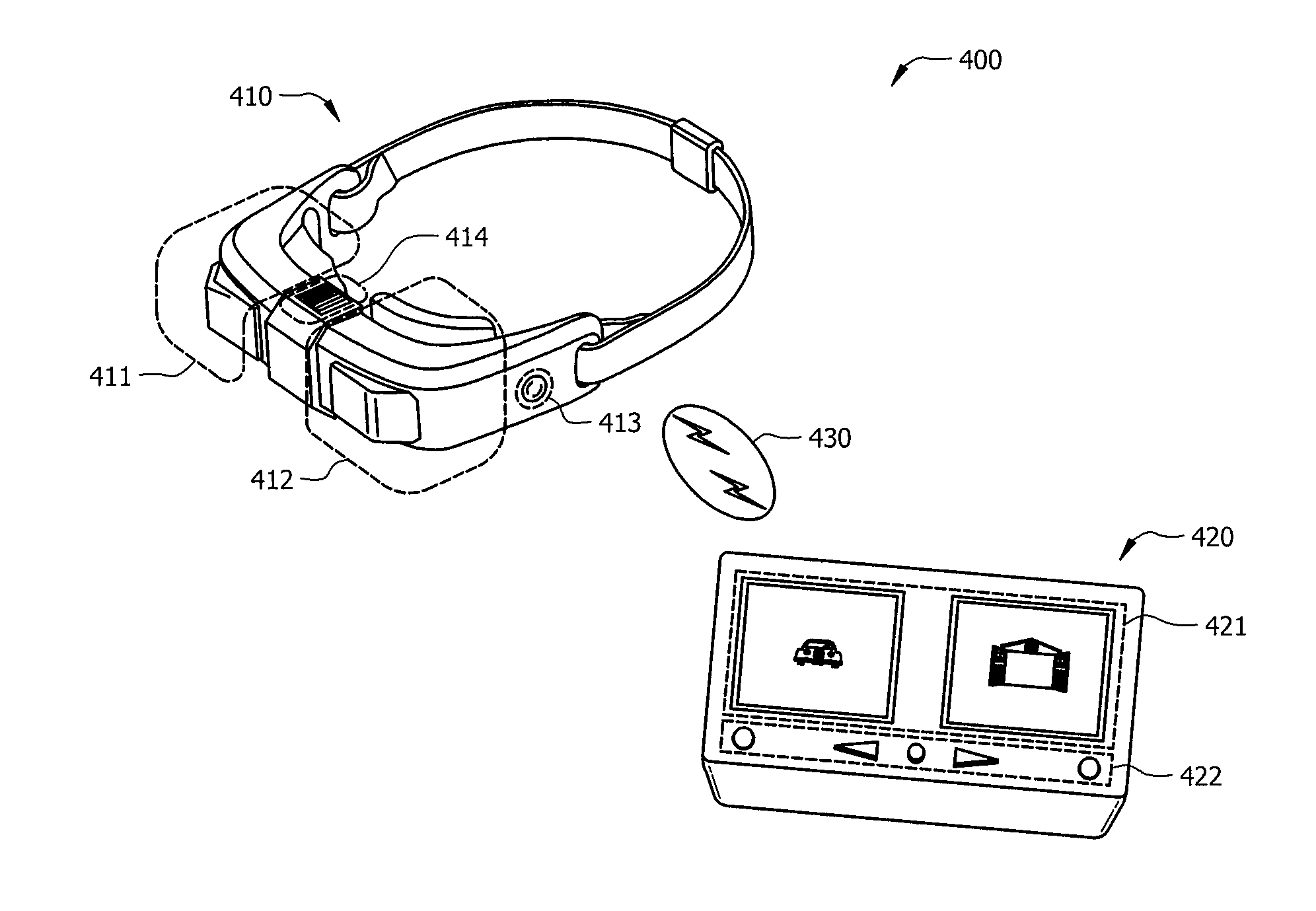
Visual disability detection system using virtual reality
ActiveUS20170273552A1Better clinical managementEasy to understandPhoroptersImage data processingVisual functionImpaired visual acuity
Techniques for a visual disability detection system that employs virtual reality to assess visual performance of a patient based on activities of daily living are described. The virtual reality platform can integrate the testing of different components of visual function based on activities of daily living to provide a direct and clinically relevant measure of the impact of any visual disability on a patient's daily life. By simulating daily tasks for evaluation of visual disability, clinicians can better understand from a patient's perspective how visual impairment affects their daily tasks and quality of life.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
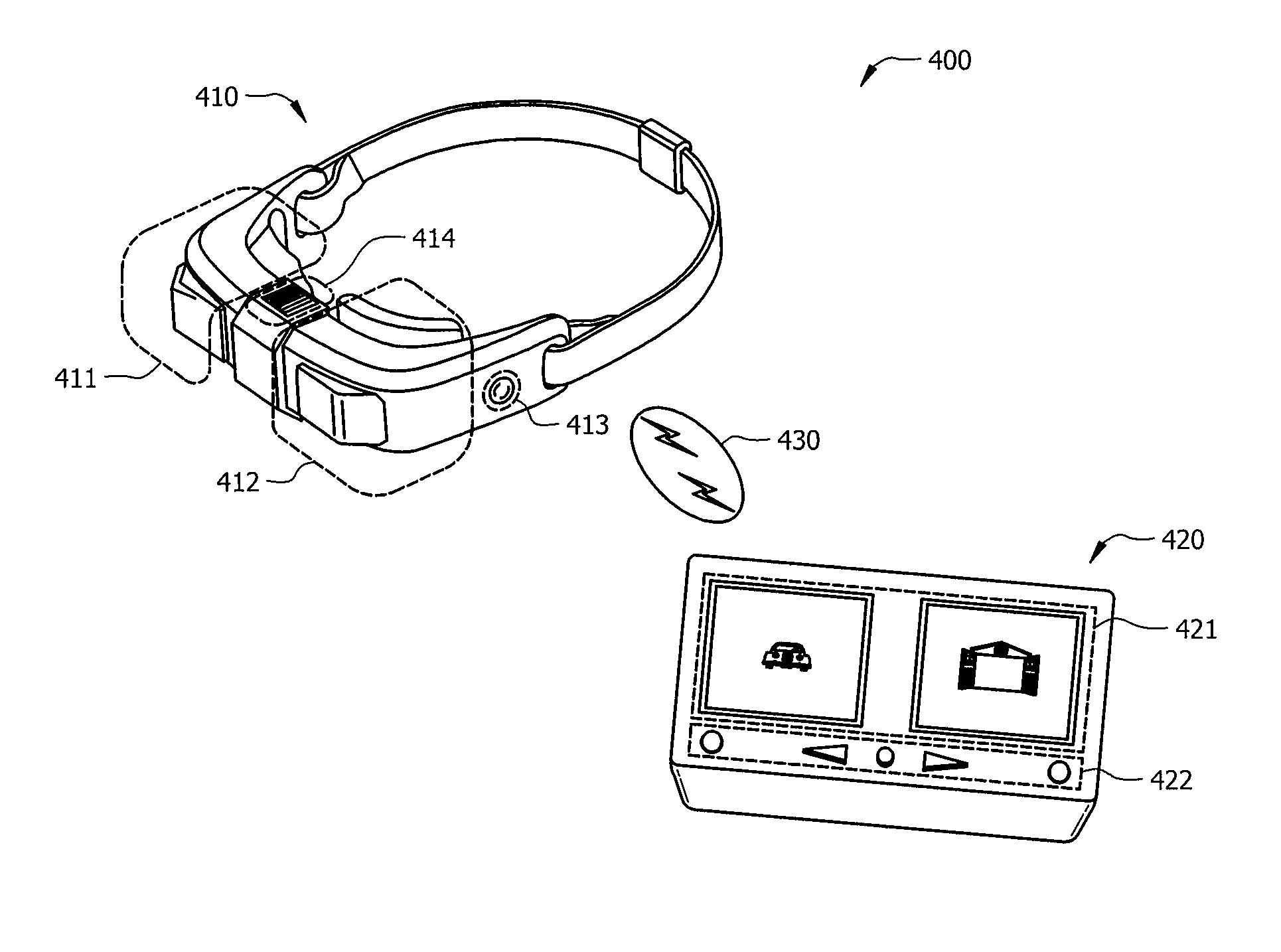
Systems and Methods for Binocular Vision Diagnosis and Treatment
ActiveUS20120069296A1Minimization requirementsReduce manufacturing costEye exercisersEye diagnosticsDisplay deviceVisual perception
A device for at least one of diagnosis and treatment of binocular vision disorders is disclosed. The device comprises a portable, wearable viewing apparatus that includes a left eye electronic display and a right eye electronic display, a dual data channel input, wherein each data channel corresponds to a respective one of the left eye and right eye electronic displays, a left eye adjustable optic structure adjusting a view of the left eye electronic display, and a right eye adjustable optic structure adjusting a view of the right eye electronic display. The device also includes a controller in communication with the dual data channel input that renders a first image at the left eye electronic display and a second image at the right eye electronic display simultaneously, in which the first and second images are different, and a memory in communication with the controller configured to store at least one of a diagnosis image pattern and a treatment image pattern for said binocular vision disorders for display by the viewing apparatus.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
Low intensity light therapy for treatment of retinal, macular, and visual pathway disorders
Owner:LOREAL SA
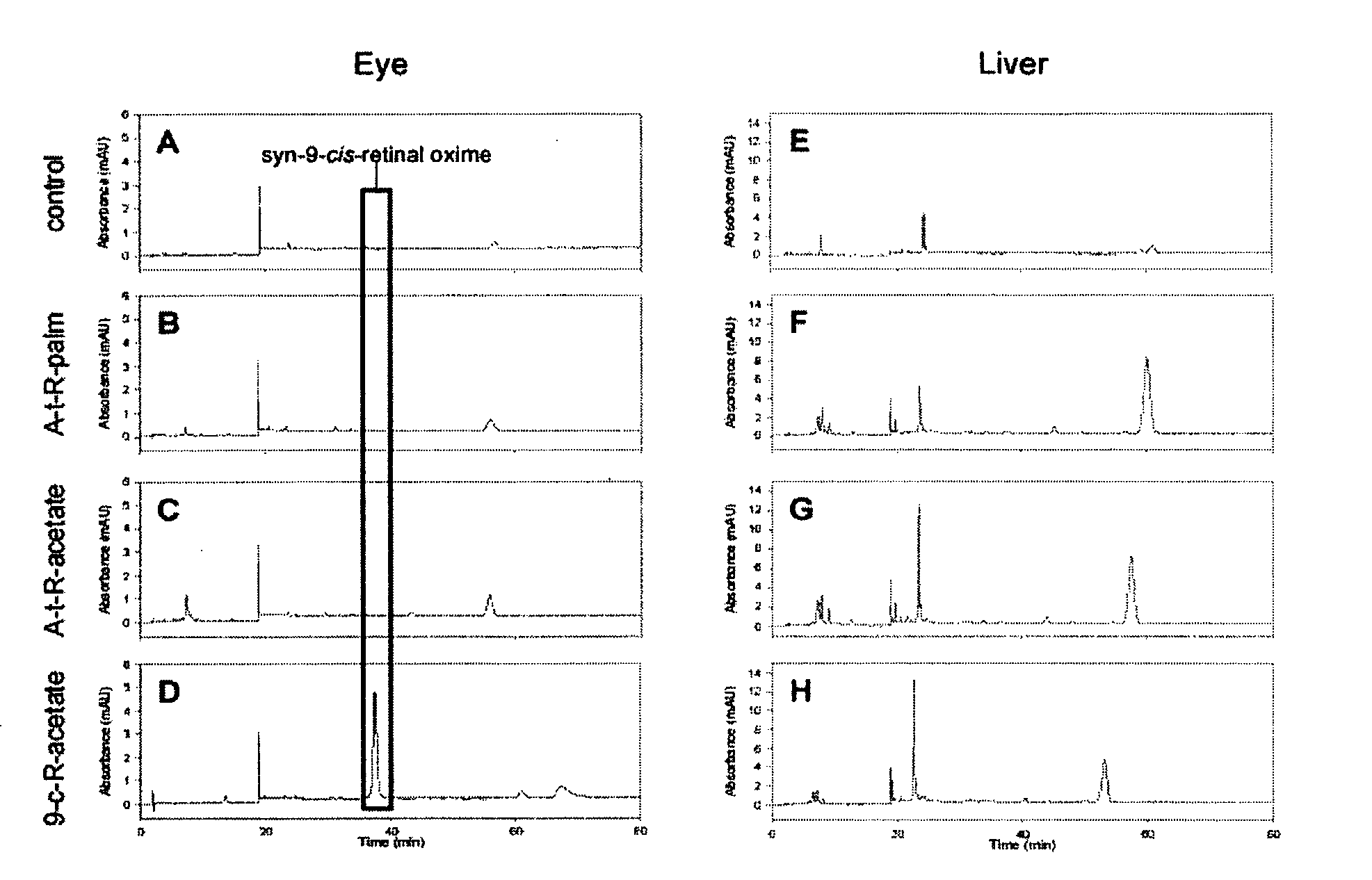
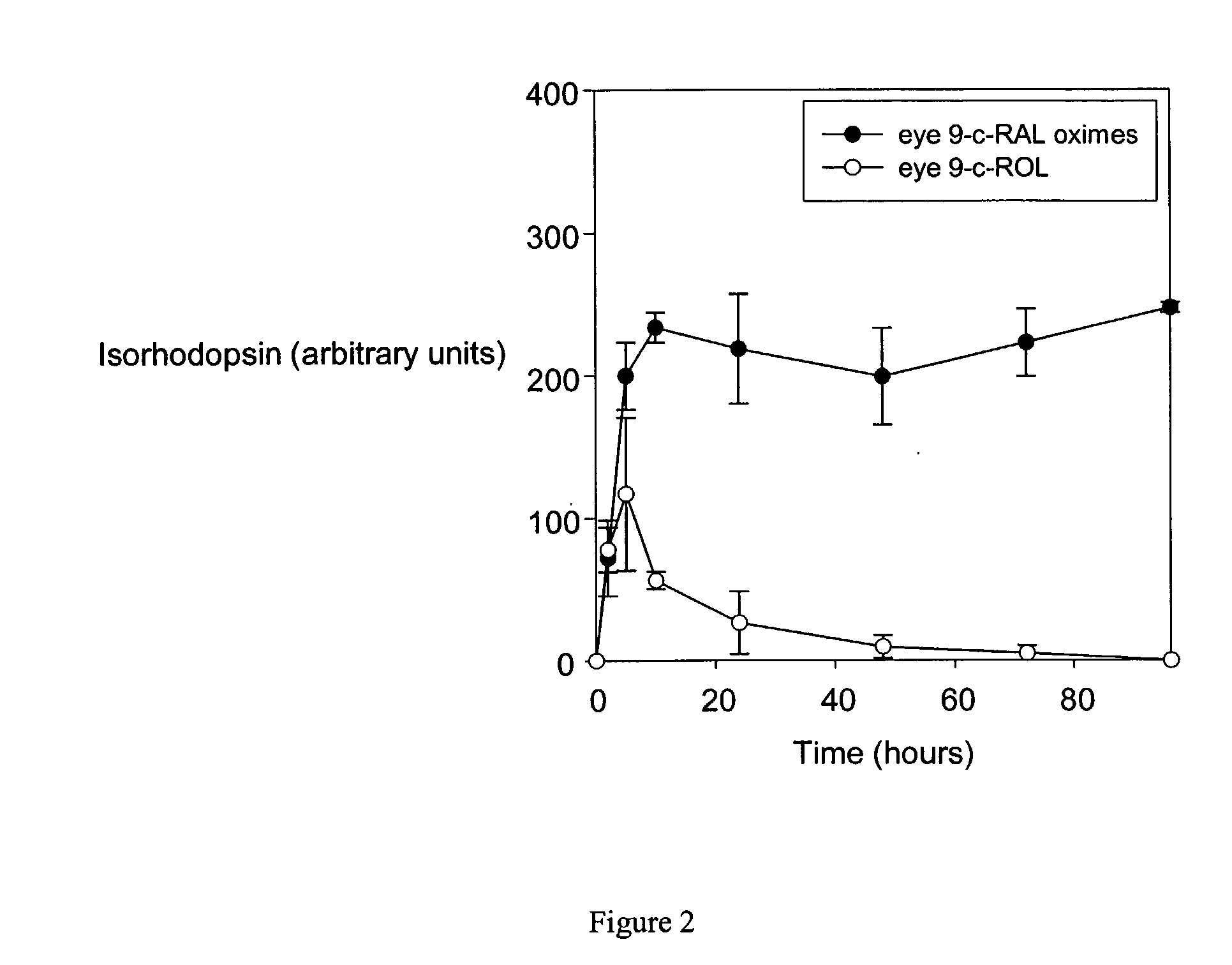
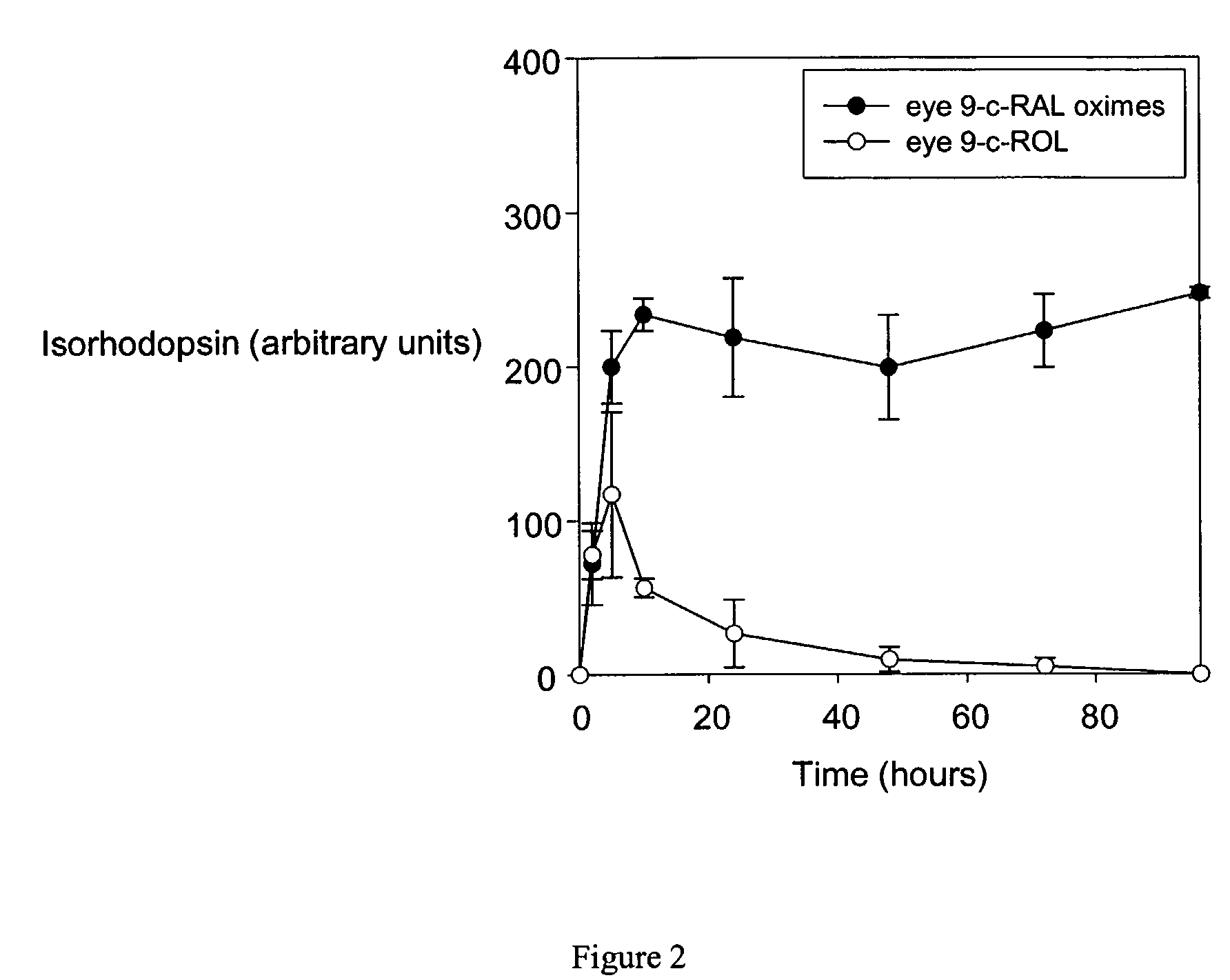
Retinal Derivatives and Methods for the Use Thereof for the Treatment of Visual Disorders
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
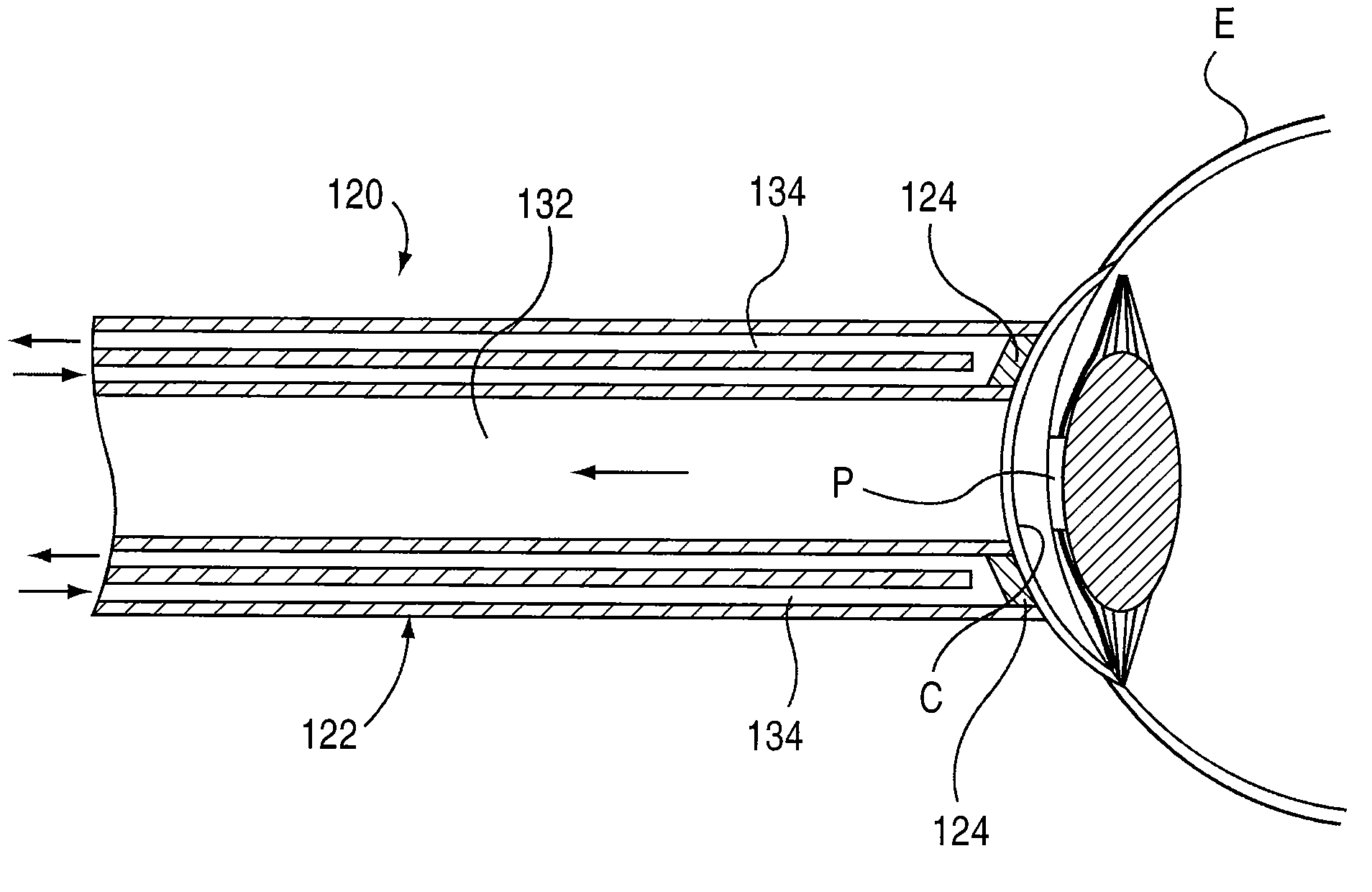
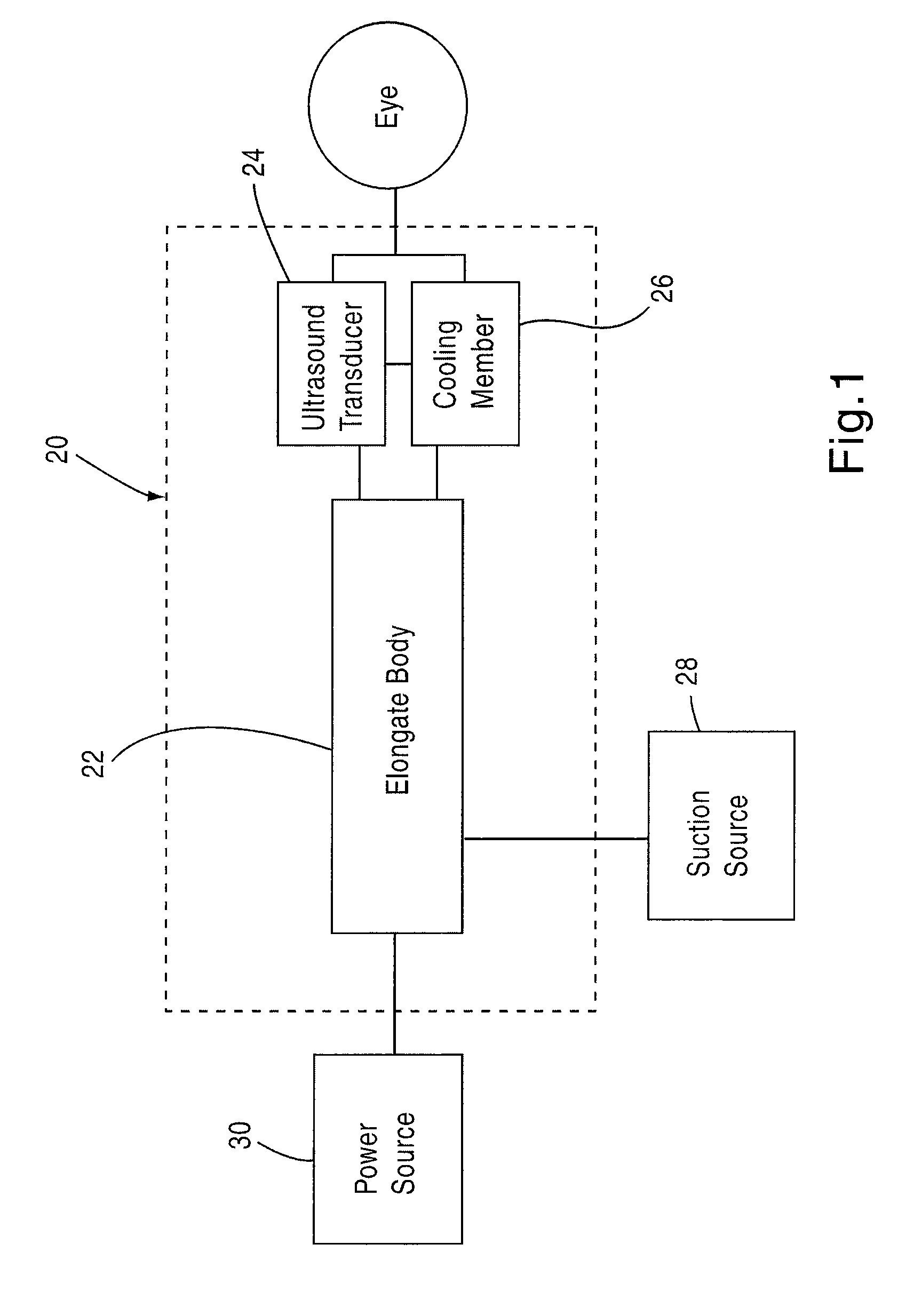
Apparatus and method for treating visual disorders
In one embodiment, an apparatus includes an elongate body having a proximal end and a distal end and an ultrasound transducer coupled to the distal end of the elongate body. A cooling member is coupled to the ultrasound transducer. The cooling member and / or the ultrasound transducer is configured to directly contact an outer surface of an eye such that ultrasound energy can be applied to a targeted portion of the eye. A method includes disposing a medical device such that a distal end of the medical device is in contact with an outer surface of an eye. The medical device includes an elongate body and an ultrasound transducer coupled to a distal end of the elongate body. Ultrasound energy is applied to a targeted portion of the eye while the medical device is disposed in contact with the outer surface of the eye to reshape the cornea of the eye.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Retinal derivatives and methods for the use thereof for the treatment of visual disorders
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Ocular implant to correct dysphotopsia, glare, halos and dark shadow type phenomena
InactiveUS20080269883A1Reduce complicationsReduce the overall diameterIntraocular lensOphthalmologyVisual Disorders
Methods and devices for inhibiting the dark shadow effect, known as dysphotopsia, perceived by some subjects having implanted intraocular lenses (IOLs) are presented. In one aspect, an IOL can include an optic and one or more fixation members for facilitating placement of the IOL. The fixation member can be adapted to position the optic sufficiently close to the iris to inhibit dysphotopsia. As some examples, a fixation member can position an optic to within some distance of the tip of the iris, or the fixation member can be adapted to contact a portion of an eye posterior to an optic's posterior surface; or the fixation member can have an end that is posterior to a posterior surface of the optic. Various techniques for achieving these improvements among others are discussed, both in terms of the structures of improved IOLs, and methods for alleviating dysphotopsia.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Retinal derivatives and methods for the use thereof for the treatment of visual disorders
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Dyslexia glasses that remove the problems associated with visual dyslexia
Owner:HAYES JOHN ATLEY
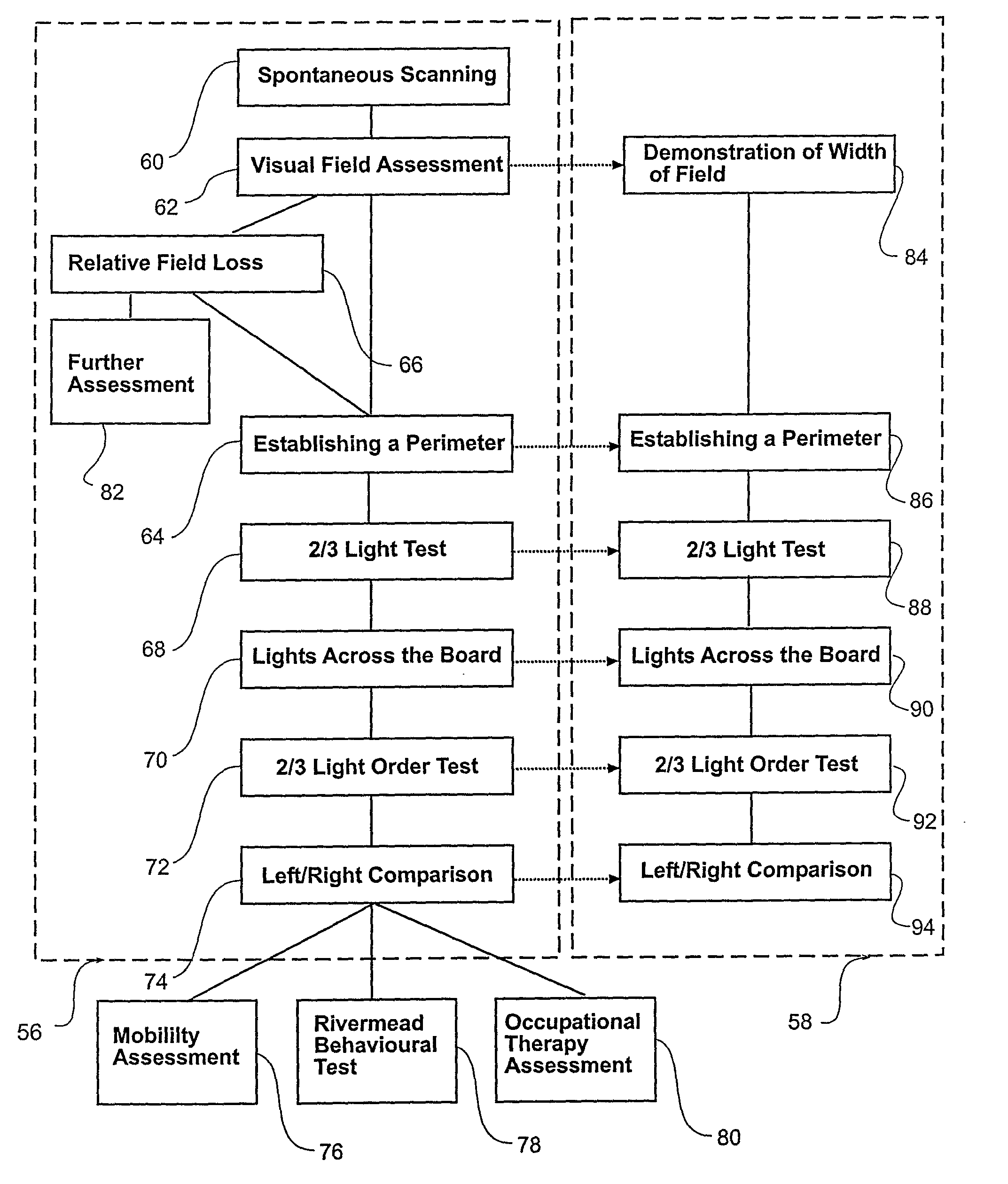
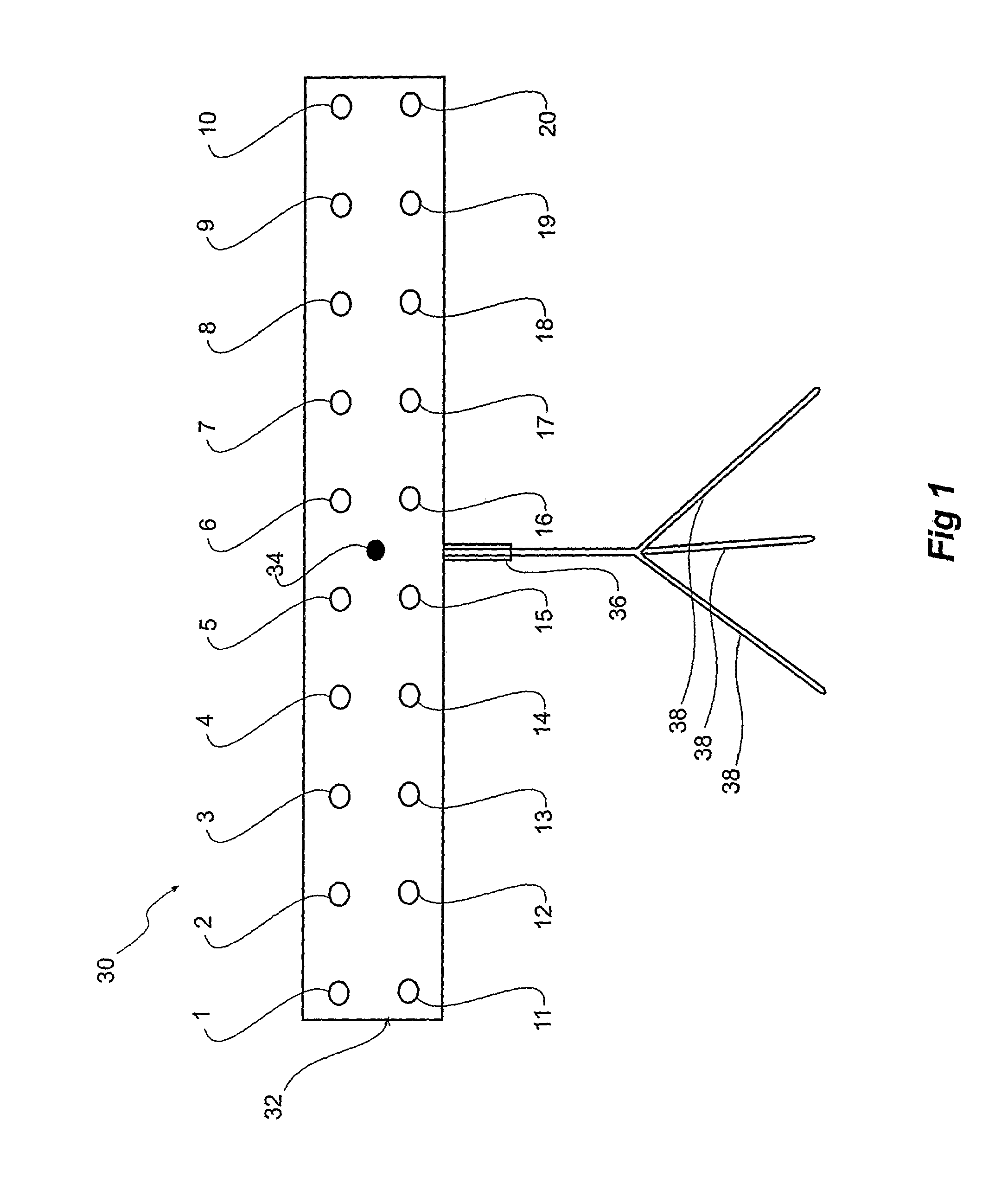
Apparatus and method for assessment and rehabilitation after acquired brain injury
ActiveUS8857984B2High degreeReduce the amount requiredEye diagnosticsSensorsImpaired visual acuityInjury brain
The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for the assessment and rehabilitation of vision impairment. In particular, the invention is concerned with an apparatus displaying visual stimuli and the method of using this device for the purpose of assessment and rehabilitation of individuals with acquired brain injury and visual impairment resulting therefrom. The apparatus comprises a display means with a plurality of visual stimuli switched on and off in predetermined sequences. The sequences are adapted to be used to assess and rehabilitate a person's visual impairment.
Owner:LIDDLE GREGORY WILLIAM +1
Comparison correlation visual analysis method aimed at two kinds of hierarchical data, and application
ActiveCN105224656AView efficientlyAvoid visual clutterOther databases browsing/visualisationSpecial data processing applicationsEeg dataVisual Disorders
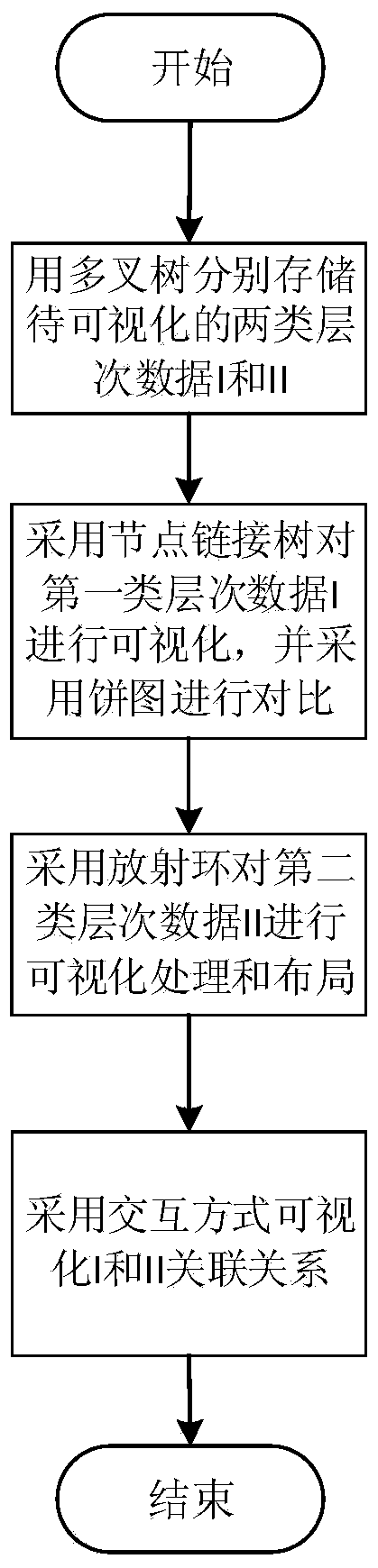
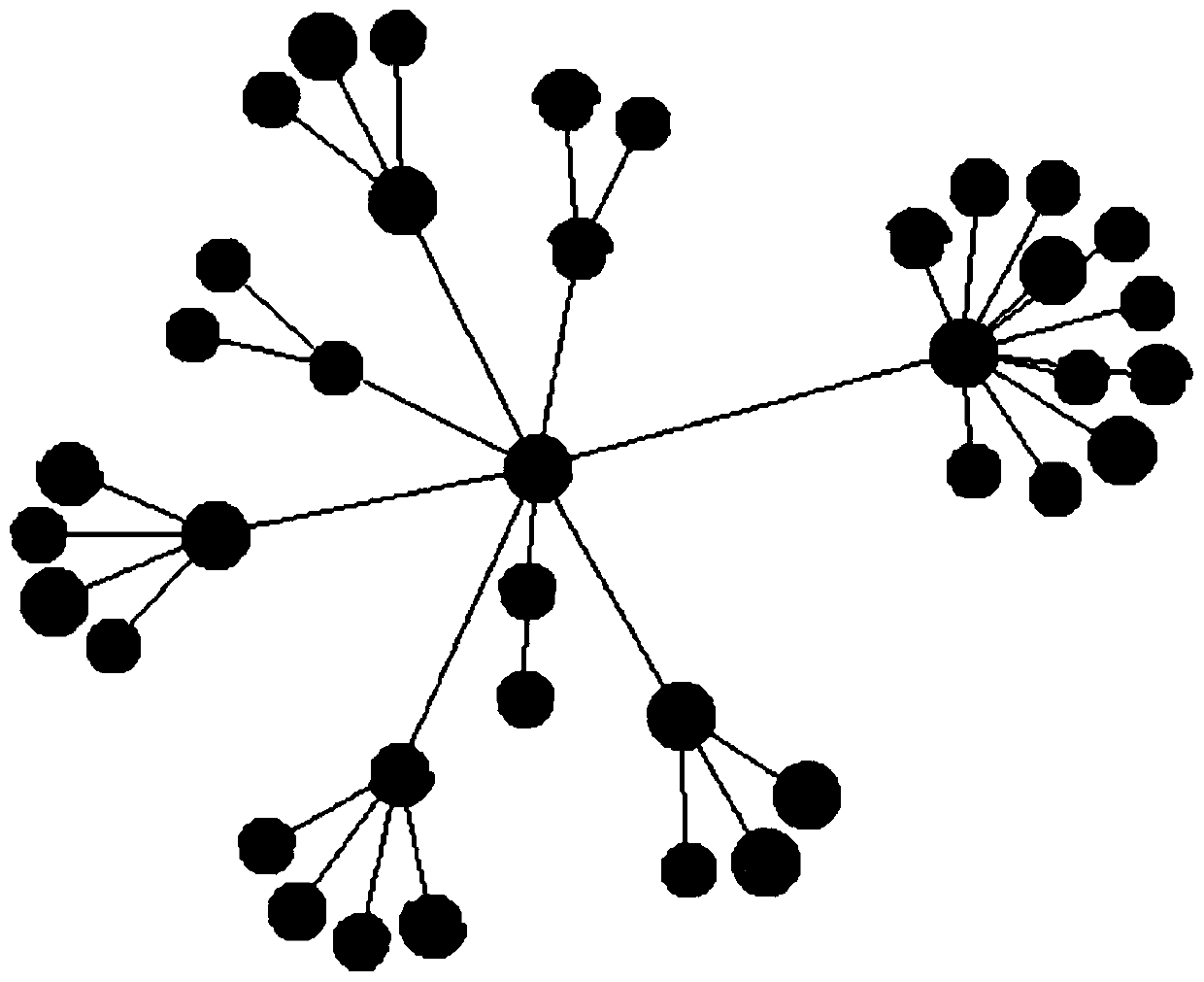
The invention discloses a comparison correlation visual analysis method (comparison relevance tree) aimed at two kinds of hierarchical data, and application. The method comprises: respectively using a node-link tree based on force orientation and a space filling tree based on radiation rings to represent two kinds of hierarchical data, nodes in the node-link tree representing as a pie chart, space filling of the radiation rings being distinguished by colors; and through an interactive method, showing comparison and correlation of different hierarchical data of the two kinds of data. The visual method can show hierarchical relations and association of two different kinds of hierarchical data at the same time, and can directly compare correlation information and other data of the same kind of hierarchical data, and is intuitive and effective, and visual disorder is prevented. The method helps users to efficiently check associations among data, so as to perform further data analysis.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
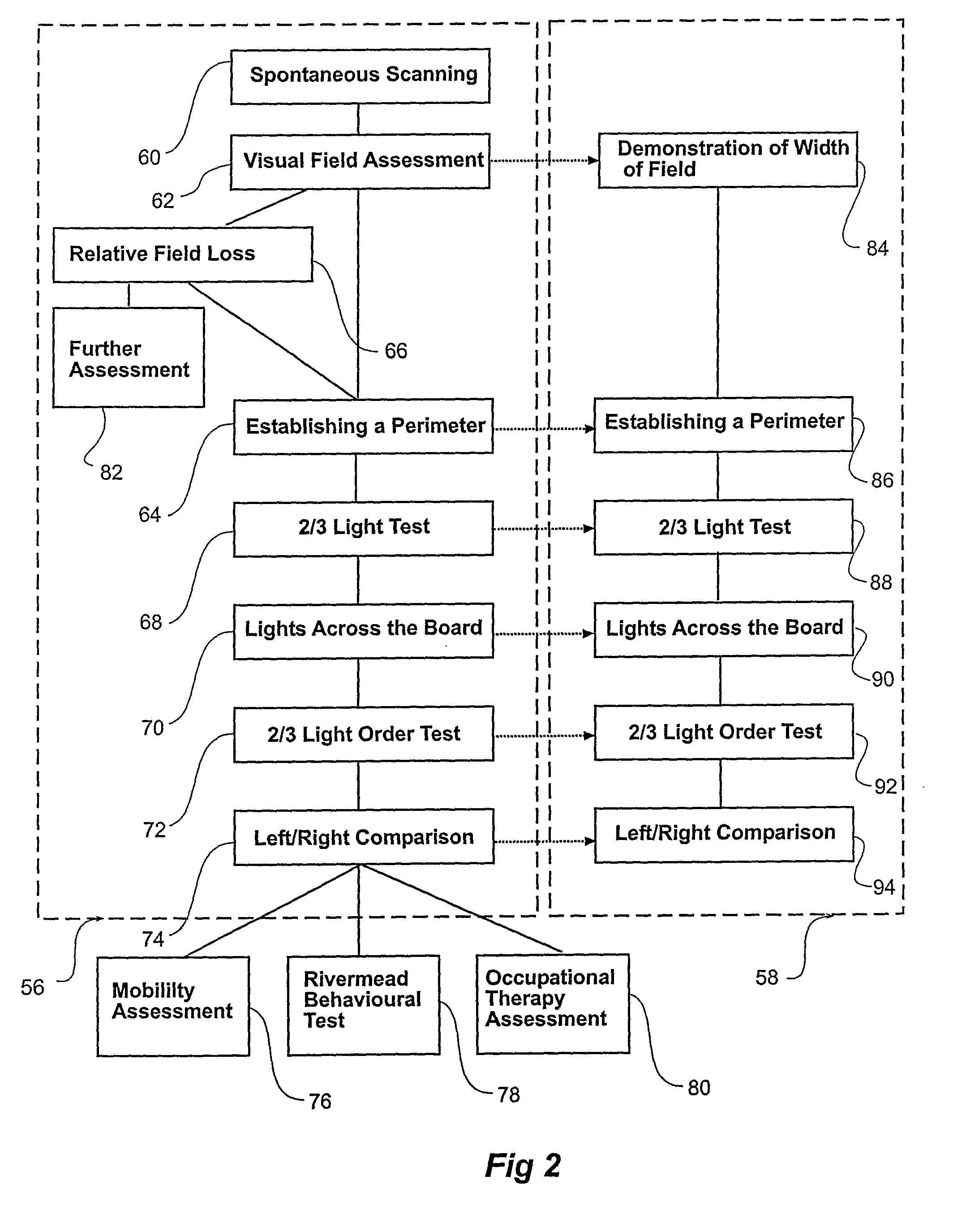
Method and apparatus for the diagnosis of glaucoma and other visual disorders
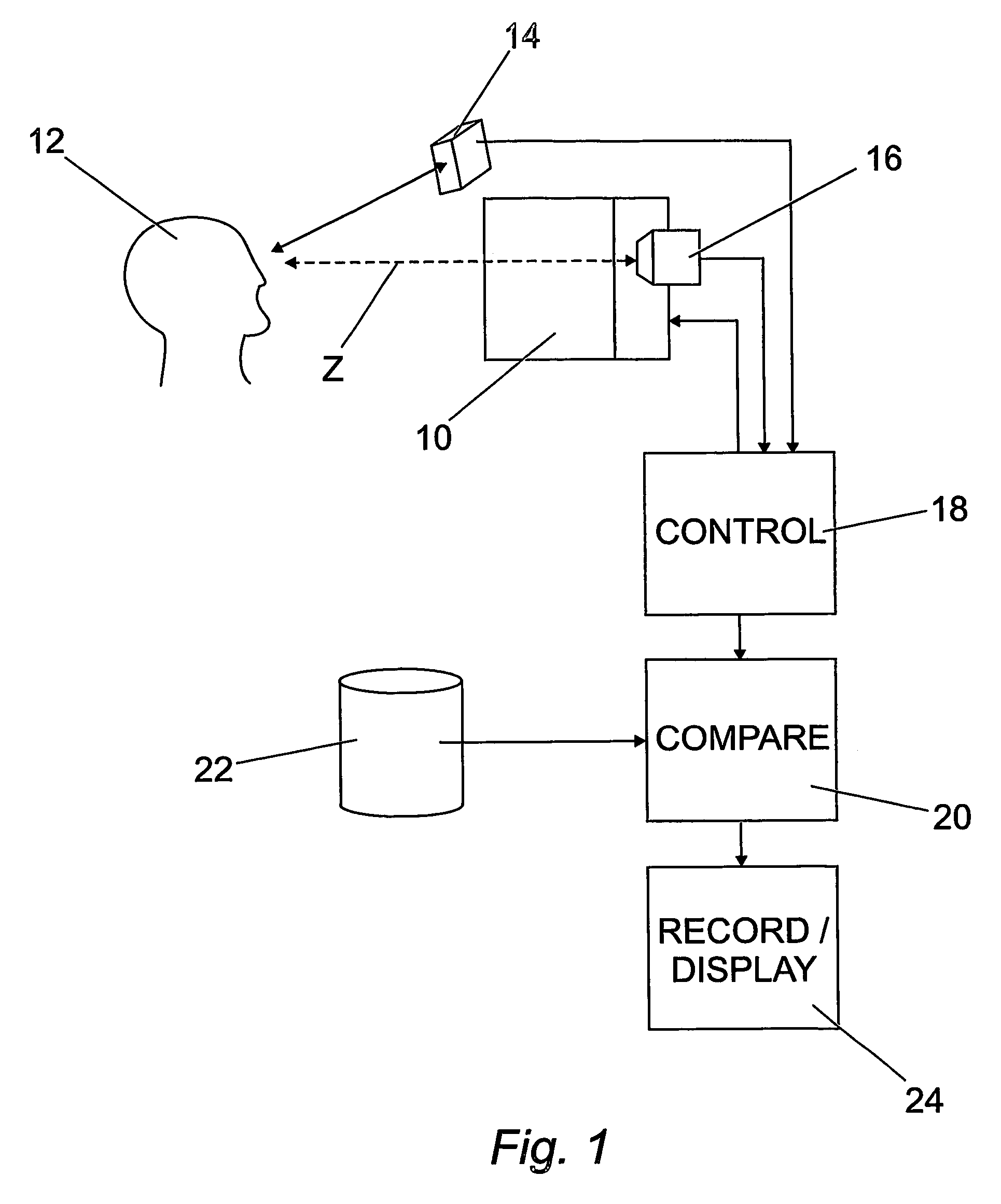
A subject (12) observes an image on a display (10). A control (18) produces a fixation image at a selected position in the display, followed by a stimulus spaced from the fixation image. An eye position sensor (14) detects a saccade movement towards the stimulus. The stimulus is then replaced with a fixation image and the cycle repeated. The time taken to saccade plus the intensity of the stimulus are used to produce a retinal map of field of vision, or to assess other characteristics of the subject.
Owner:MCGRATH JOHN ANDREW MURRAY +1
Intra-regional vehicle driving status information sharing informing platform system
ActiveCN103116998AReduce driving safety hazardsSolve the collision problemAnti-collision systemsInformation processingVisual Disorders
An intra-regional vehicle driving status information sharing informing platform system comprises at least two mobile stations which are arranged on different vehicles within the region and with a driving status information sharing function. Each of the mobile stations comprises an information-sending module used for sending self-driving-status information, an information-receiving module used for receiving driving status information of other vehicles within the region, an information-processing module used for expressing and processing vehicle driving status information and a terminal display used for displaying a processing result of the information-processing module, wherein the information-sending module, the information-receiving module and the terminal display are respectively connected with the information-processing module. According to the intra-regional vehicle driving status information sharing informing platform system, transmission modes such as electromagnetic wave are used, vehicle driving status information transmission and sharing are conducted among the mobile stations, visual disorder of drivers within the region can be overcome and driving status information of other vehicles out of sight can be acquired, and thus the problem that vehicle collision is prone to occurring at the corner or at the crossroads and the potential safety hazard of out of sight when overtaking is conducted are effectively resolved.
Owner:安徽哥伦布智能科技有限公司
Method and system for assessing visual disorder
A method of diagnosis is disclosed. The method comprises using a display device for presenting a motion perception test to a subject and determining a subject response to the motion perception test. The response can be used for assessing presence or absence of demyelination and / or remyelination.
Owner:HADASIT MEDICAL RES SERVICES & DEVMENT
Systems and methods for binocular vision diagnosis and treatment
ActiveUS8328354B2Minimization requirementsReduce manufacturing costEye exercisersEye diagnosticsVisual DisordersDisplay device
A device for at least one of diagnosis and treatment of binocular vision disorders is disclosed. The device comprises a portable, wearable viewing apparatus that includes a left eye electronic display and a right eye electronic display, a dual data channel input, wherein each data channel corresponds to a respective one of the left eye and right eye electronic displays, a left eye adjustable optic structure adjusting a view of the left eye electronic display, and a right eye adjustable optic structure adjusting a view of the right eye electronic display. The device also includes a controller in communication with the dual data channel input that renders a first image at the left eye electronic display and a second image at the right eye electronic display simultaneously, in which the first and second images are different, and a memory in communication with the controller configured to store at least one of a diagnosis image pattern and a treatment image pattern for said binocular vision disorders for display by the viewing apparatus.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
Method of designing both-plane aspherical progressive refractive power lens group and both-plane aspherical progressive refractive power lens group
ActiveCN101203796AWide field of visionIncreased efficiency in batch manufacturingSpectales/gogglesOptical partsFar-sightednessVisual Disorders
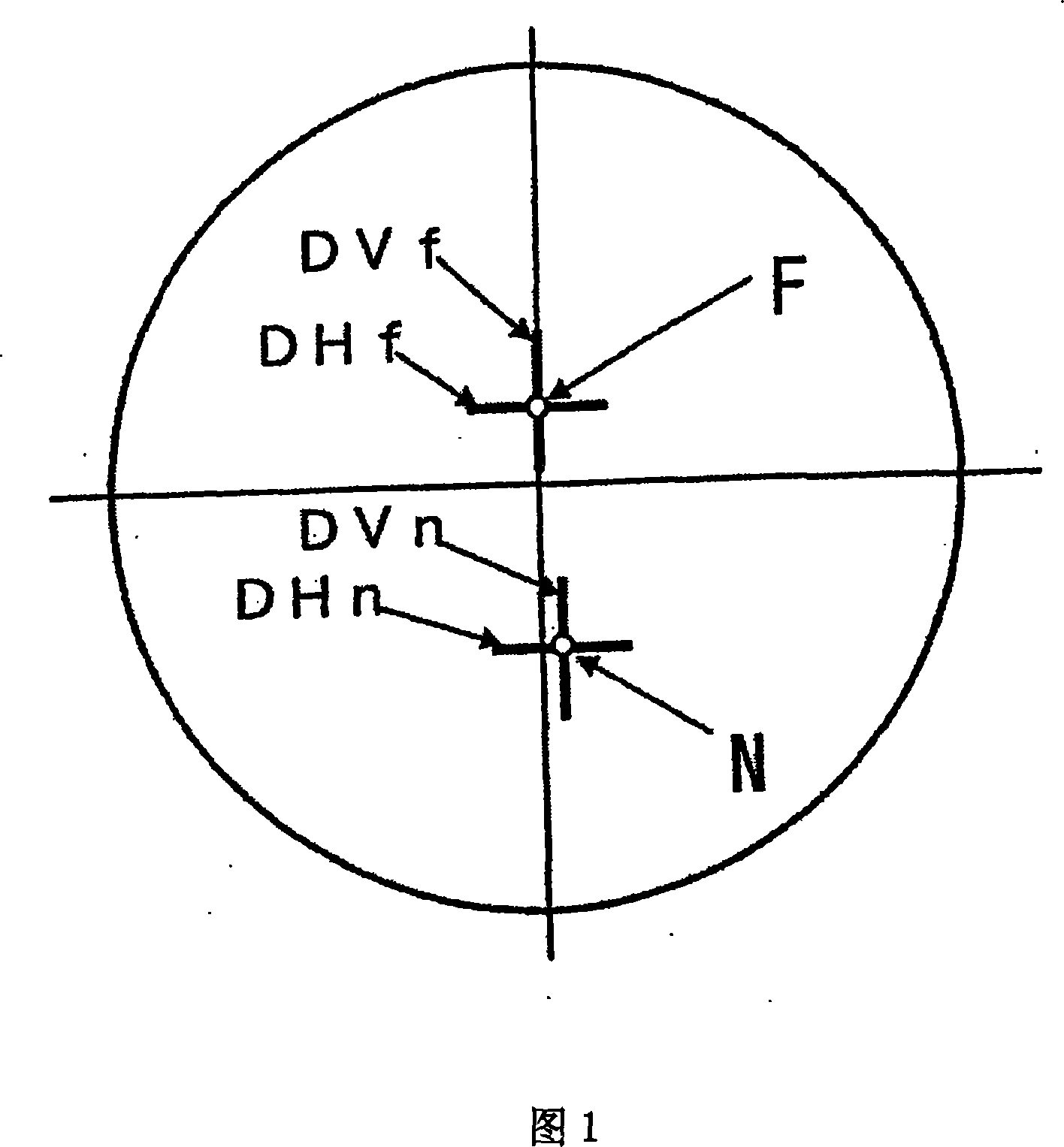
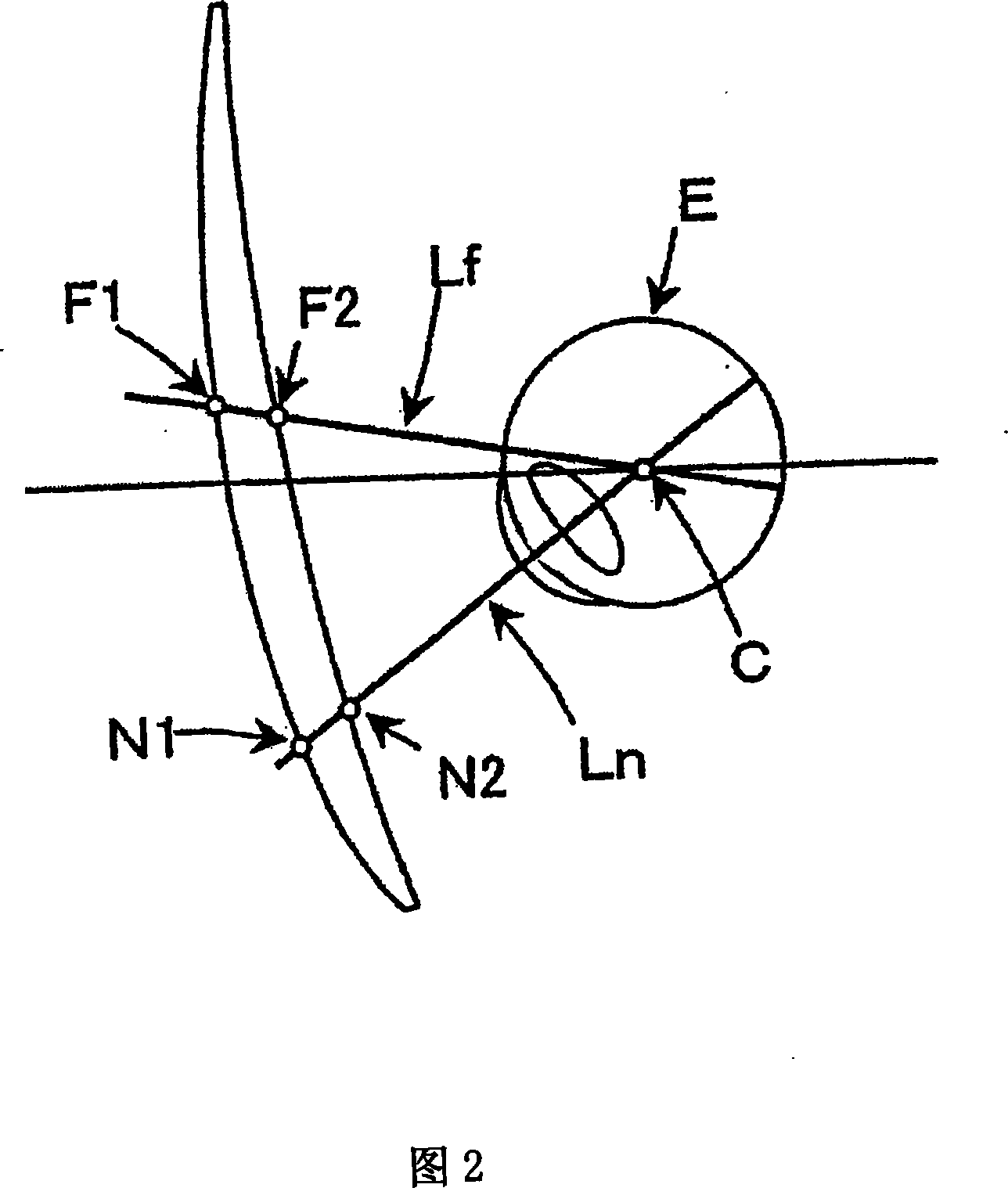
A double aspheric progressive refractive index lens group capable of reducing processing costs. In the double aspheric progressive index lens, the relationship: DHf+DHn<DVf+DVn and DHn<DVn or further the relationship: DVn−DVf>ADD / 2 and DHn−DHf<ADD / 2 is satisfied. DHf and DVf are respectively designated as the surface refractive index in the horizontal direction and the surface refractive index in the vertical direction at the farsighted power measurement position F1 on the first refraction surface as the object-side surface; DHn and DVn are respectively designated as The surface refractive index in the horizontal direction and the surface refractive index in the vertical direction at the myopia power measurement position N1 on the first refraction surface. The surface glare components at F1 and N1 of the first refractive surface are eliminated by the second refractive surface, the first and second refractive surfaces being combined to provide far vision power (Df) and add power (ADD) based on prescribed values. Therein, the same first refractive surface is used for at least two or more different addition degrees.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Method for optimizing diurnal lighting of exit section of long tunnel of express way
InactiveCN103218484AResearch results are reliableEliminate dark adaptation problemsAerodynamics improvementSpecial data processing applicationsIlluminanceVisual Disorders
The invention discloses a method for optimizing diurnal lighting of an exit section of a long tunnel of an express way. The method comprises the steps of collecting data of tunnel lighting parameters, visual adaptation time and driver pupil area, establishing a driver pupil area and illuminance model, an illuminance and tunnel depth model and a driver visual adaption model, making a three-dimensional curved surface among the driver pupil area, the visual adaptation time and the corresponding environmental illuminance by utilizing software, establishing a function model according to parameters obtained through the curved surface and finally obtaining the relationship among the tunnel exit distance, the vehicle speed and the tunnel optimized illuminance according to calculation. By using the method, not only can the problem of dark adaptation caused by illuminance difference when a vehicle is driven in a nighttime tunnel environment be eliminated and traffic accidents evoked by visual disorder be reduced, but also electric energy consumption of tunnel lighting facilities can be greatly decreased at the same time.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Handset with function of reading aloud, and implementation method
InactiveCN1960532AIncrease reading functionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTelephone set constructionsText recognitionVisual Disorders
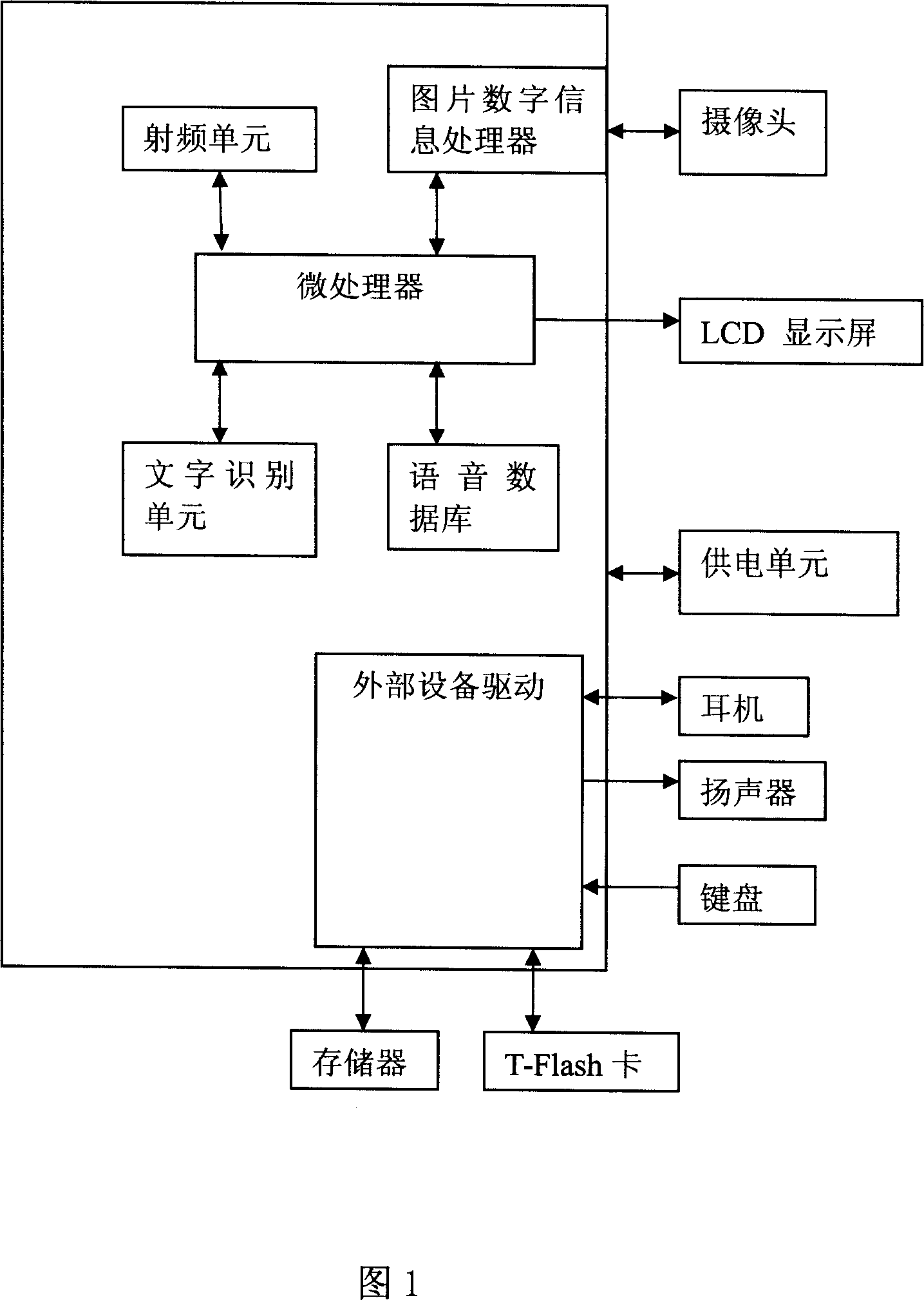
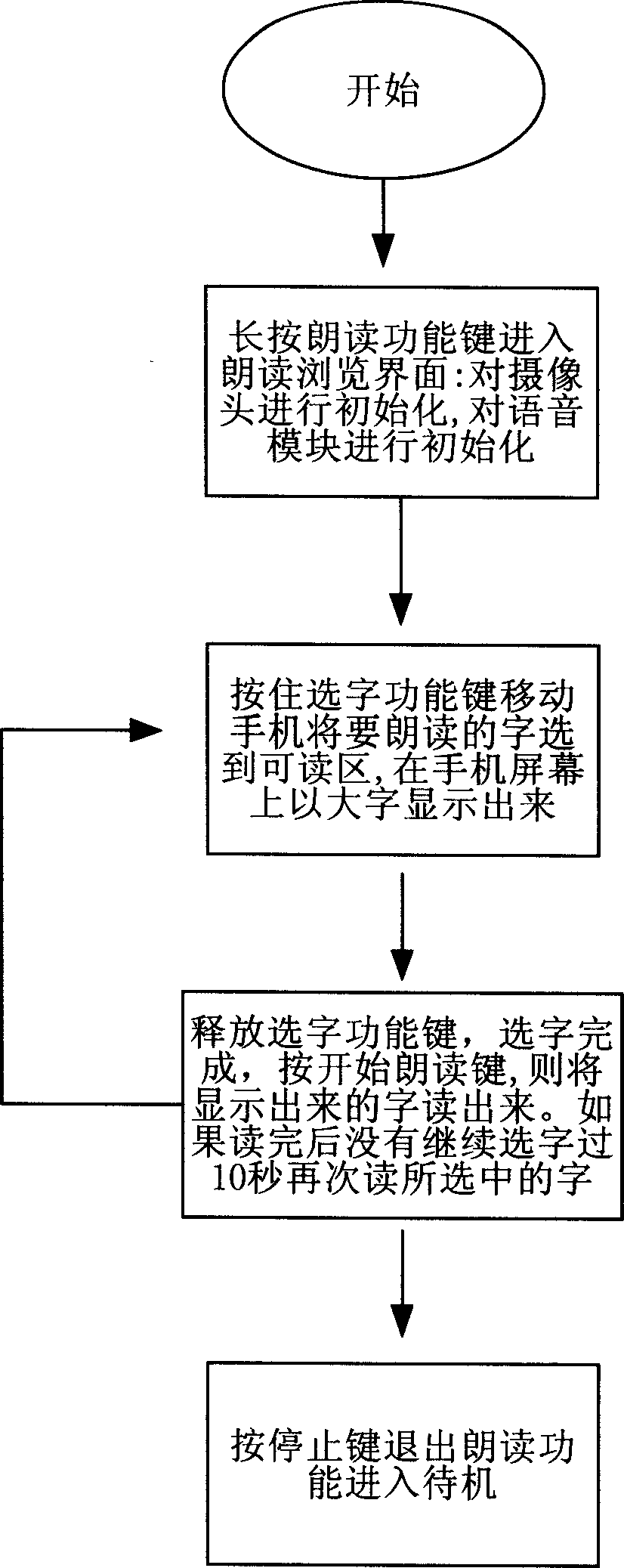
The mobile phone thereof comprises: pick-up head; MPU; and audio output device; and a character recognition unit for receiving the image captured from pick-up head, recognizing the characters image, converting the word information into voice information saved in voice database, and transmitting the voice information to the player to play. The invention can be used by the peoples with visual disorder.
Owner:QINGDAO HISENSE MOBILE COMM TECH CO LTD
Sound indicating device for man of visual disorder
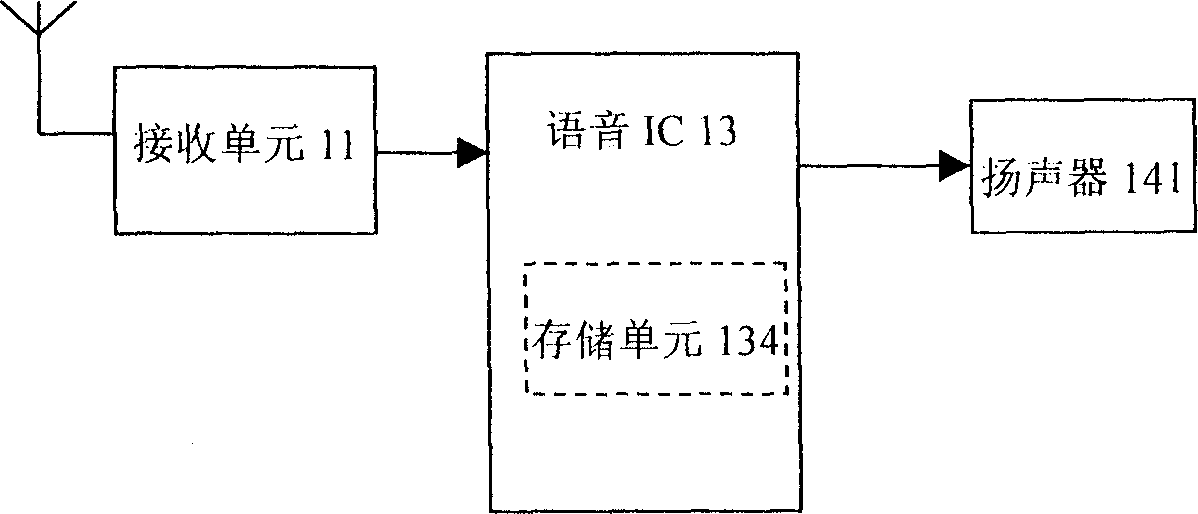
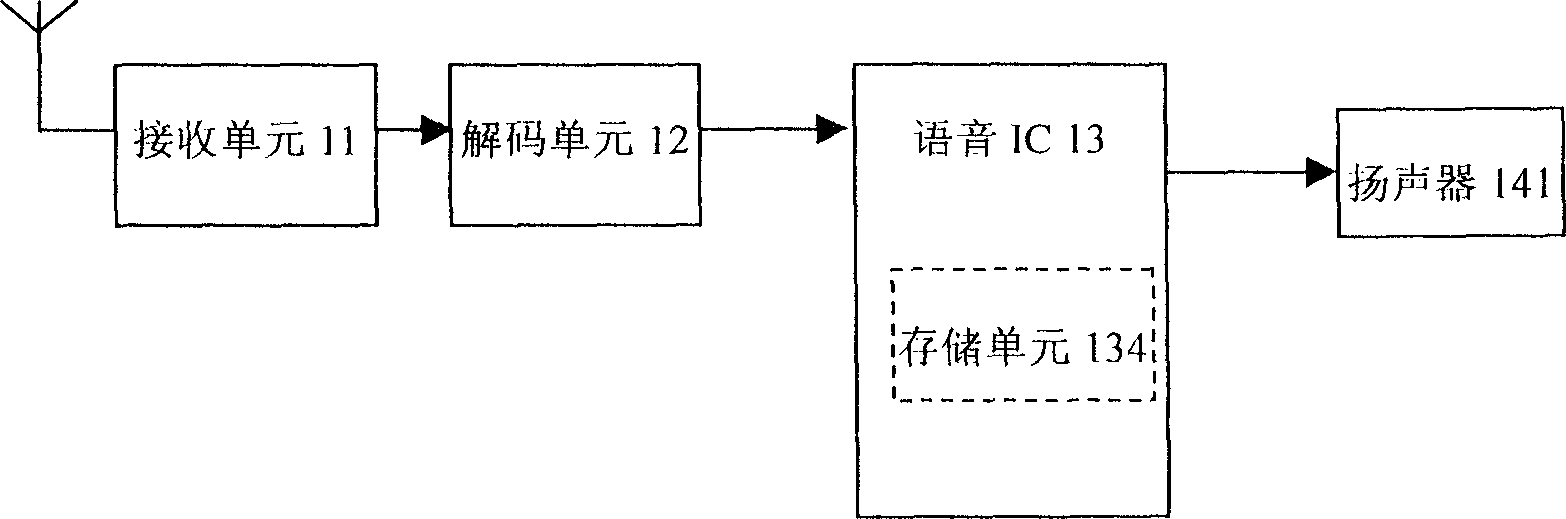
InactiveCN1828687AEasy accessMeet needsControl with pedestrian guidance indicatorEye treatmentElectricityVisually impaired
The related device (1) comprises a voice output unit (14) with prestored voice content, a control and process unit (131) to control the output unit for outputting or not according to signal, a signal decoding unit (12) to reduce the emission signal into the digital signal, and a signal receive unit (11). This invention can reduce the environmental effect, and introduces convenience for the visually impaired staff in strange environment.
Owner:陈安平
Method and apparatus for performing vision screening
InactiveUS7287857B2Easy to storeFacilitates ease of transport and storageEye diagnosticsMeasurement deviceImpaired visual acuity
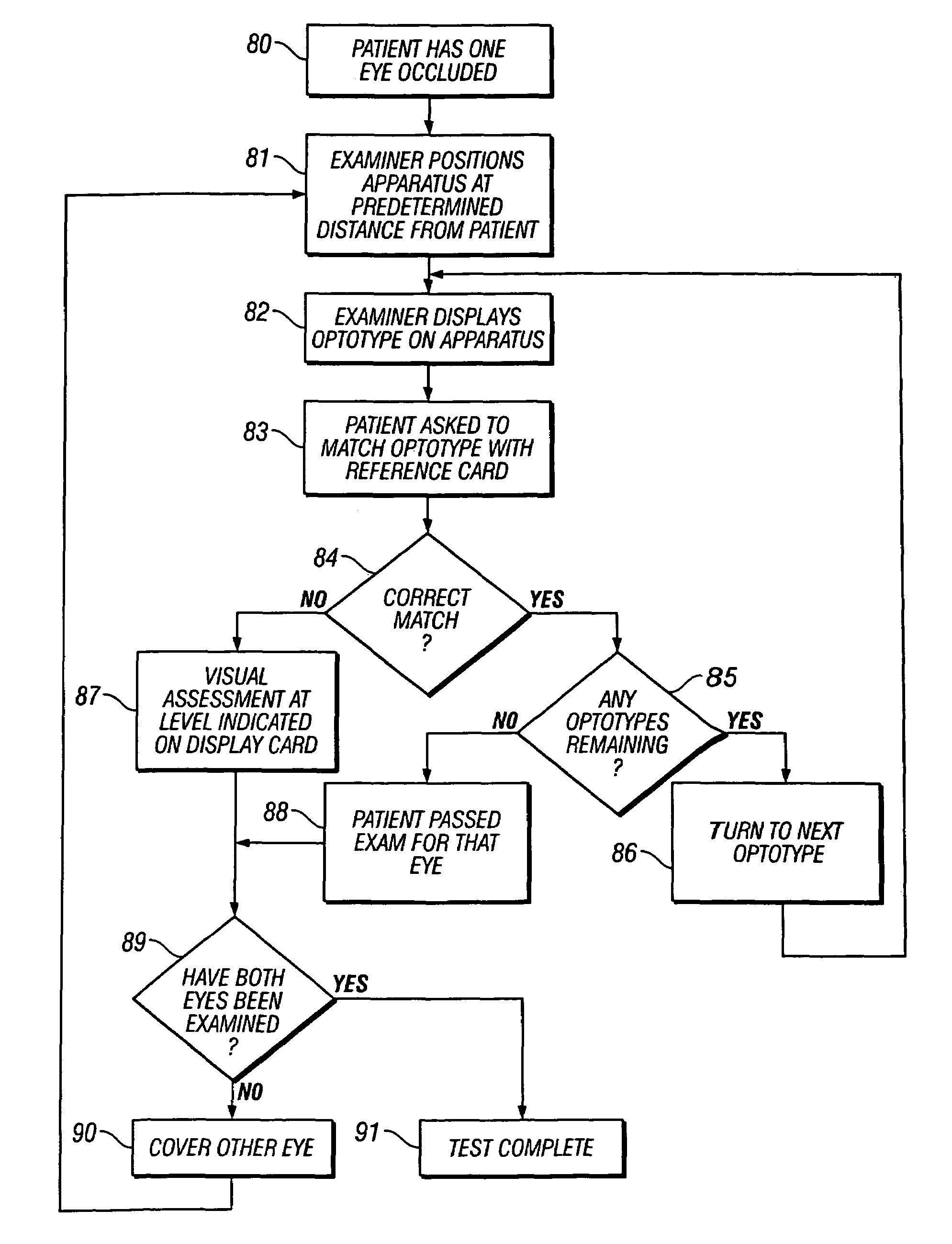
The present invention relates to a vision screening system and a method for using the system to easily perform screenings for vision disorders, including amblyopia in children using only one examiner. The system includes a lightweight, portable apparatus having a surface upon which a series of images are imprinted, projected, or digitally altered. The size, shape, appearance, arrangement, and quantity of the images are chosen to allow an examiner to rapidly screen the examinee for a visual disorder such as amblyopia. The apparatus also includes a measurement tool, integrated with the apparatus, which enables the examiner maintain the surface of the device at a predetermined distance from the examinee's eyes. To screen a child's vision, the apparatus is positioned at a predetermined distance from the examinee's eyes using the systems built-in measuring distance device. With one eye covered at a time with adhesive patches provided as part of the vision screening system, the examinee is asked to either identify an image displayed on the apparatus, or point to a matching image on a card provided as part of the system, that is located at a close distance to the examinee. Based upon the examinee's collective responses, the examiner can determine whether the examinee is affected by a visual disorder such as amblyopia. The entire system (the optotypes target apparatus with built-in measuring device, matching optotypes card, adhesive eye occluders, and instructions) are all provided in a self-contained, small, lightweight box or package for ease of transport and storage.
Owner:GLASER VISION
Nutritional health product of pollen and Chinese wolfberry and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101744283APrevent visual fatiguePreserve the flavorFood preparationAdjuvantVisual Disorders
The invention relates to a nutritional health product of pollen and Chinese wolfberry and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of nutritional health foods. The nutritional health product of the pollen and Chinese wolfberry comprises the following components in percent by weight: 5-40% of pollen extract, 10-40% of Chinese wolfberry extract, 10-35% of chrysanthemum extract and 5-70% of adjuvant. The nutritional health product of the pollen and Chinese wolfberry of the invention is suitable for all classes of people who frequently contact TV, computers, mobile telephones, microwave ovens and electromagnetic ovens for relieving and improving various insalubrious symptoms of radiation hazard, visual disorder and overstrain of nerves, malnutrition, fatigue and the like caused by surfing on the internet in a net bar for a long time. The invention has the advantages of convenient carrying and taking, good taste, easy absorption, sweet and sour taste, high bioavailability and the like, and an effervescent preparation can quickly and automatically dissolve.
Owner:苏明寿 +1
Voice playing method for mobile phone
InactiveCN101193367AConvenient voice promptConvenient lifeSubstation speech amplifiersSpecial service for subscribersVisual DisordersLoudspeaker
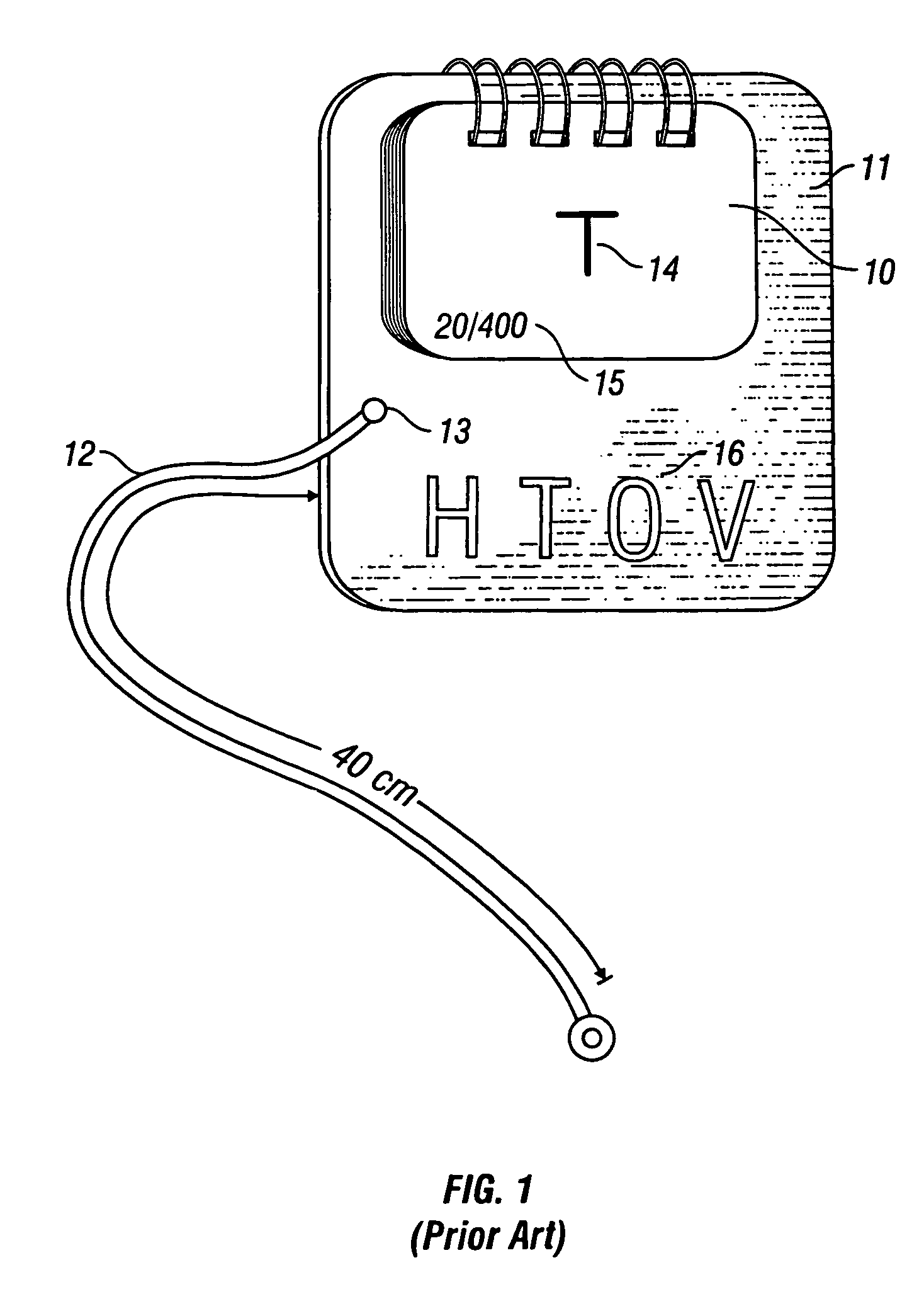
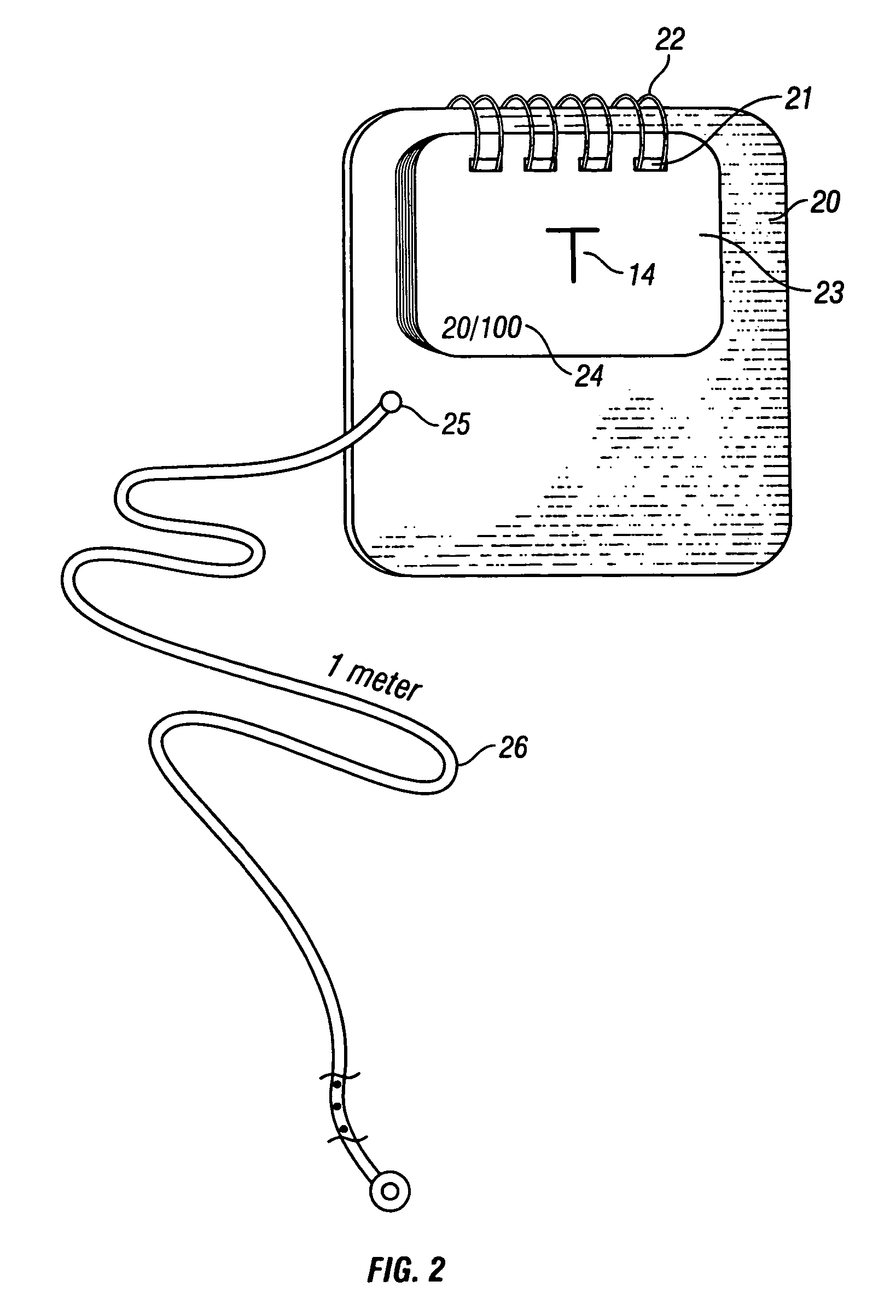
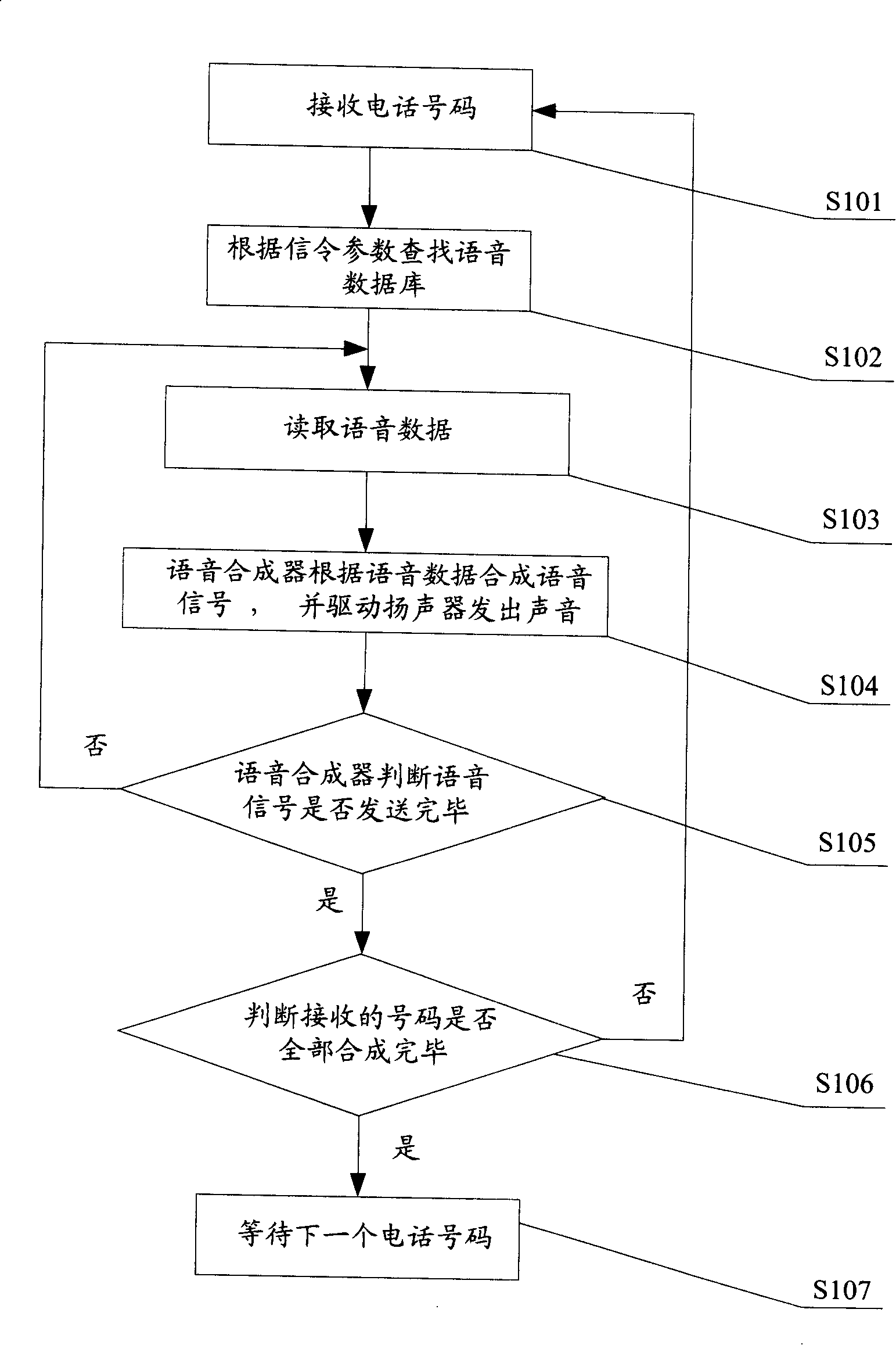
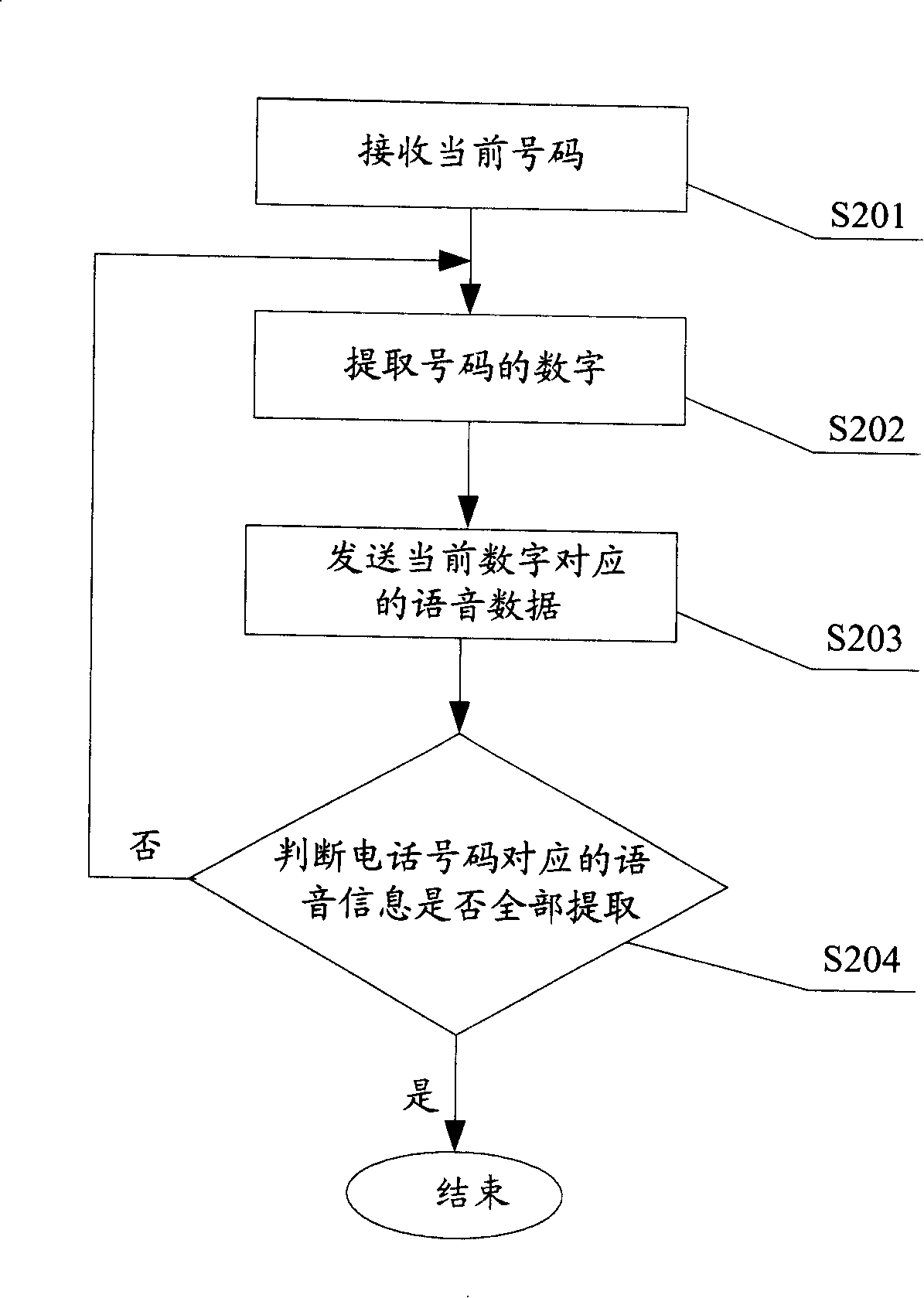
The invention discloses a voice broadcast method for mobile phone, which comprises the following steps that: the position of a phone number in the database of a voice system is searched for; the voice data to which the phone number corresponds is read and sent; the voice system synthesizes the received voice data into a voice signal and sends the voice signal; a loudspeaker receives and broadcasts the voice signal. The invention realizes that the user is informed of the incoming call or input phone number in the mode of voice, thus ensuring that the user can conveniently hear the corresponding voice prompt and greatly delivering convenience particularly for the life of users having a visual disorder.
Owner:ZTE CORP
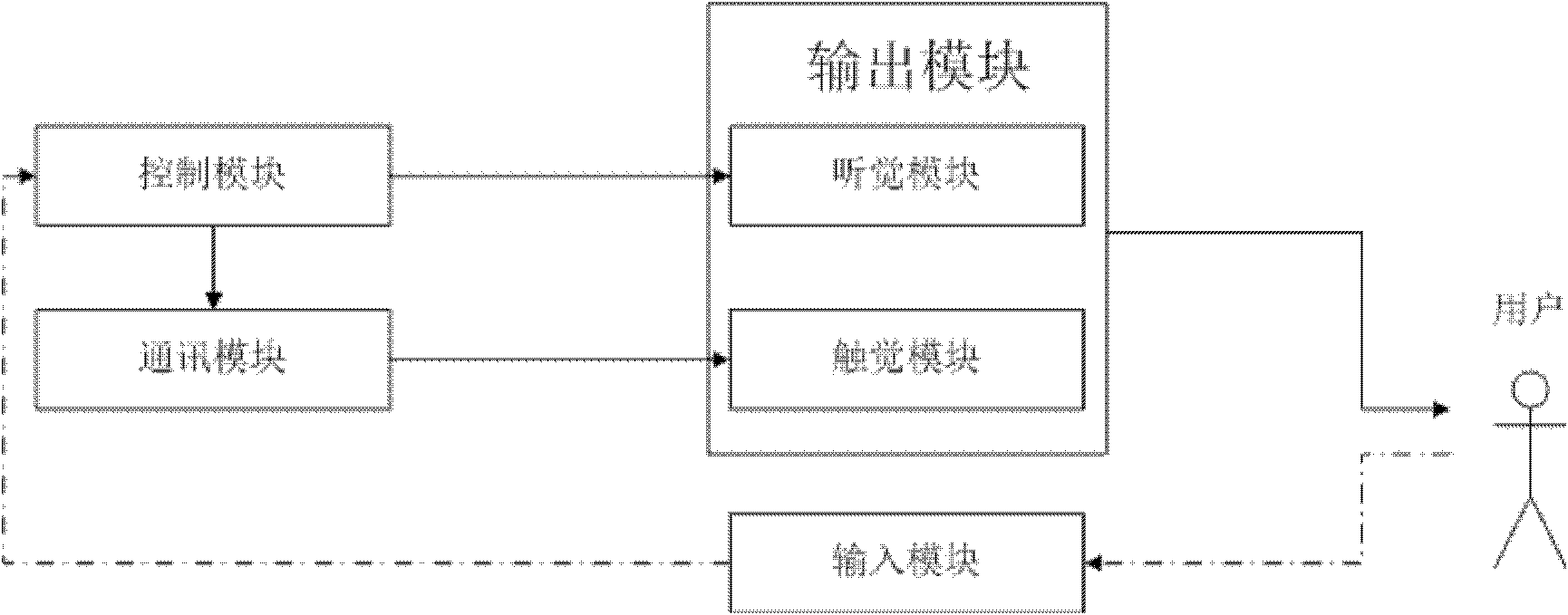
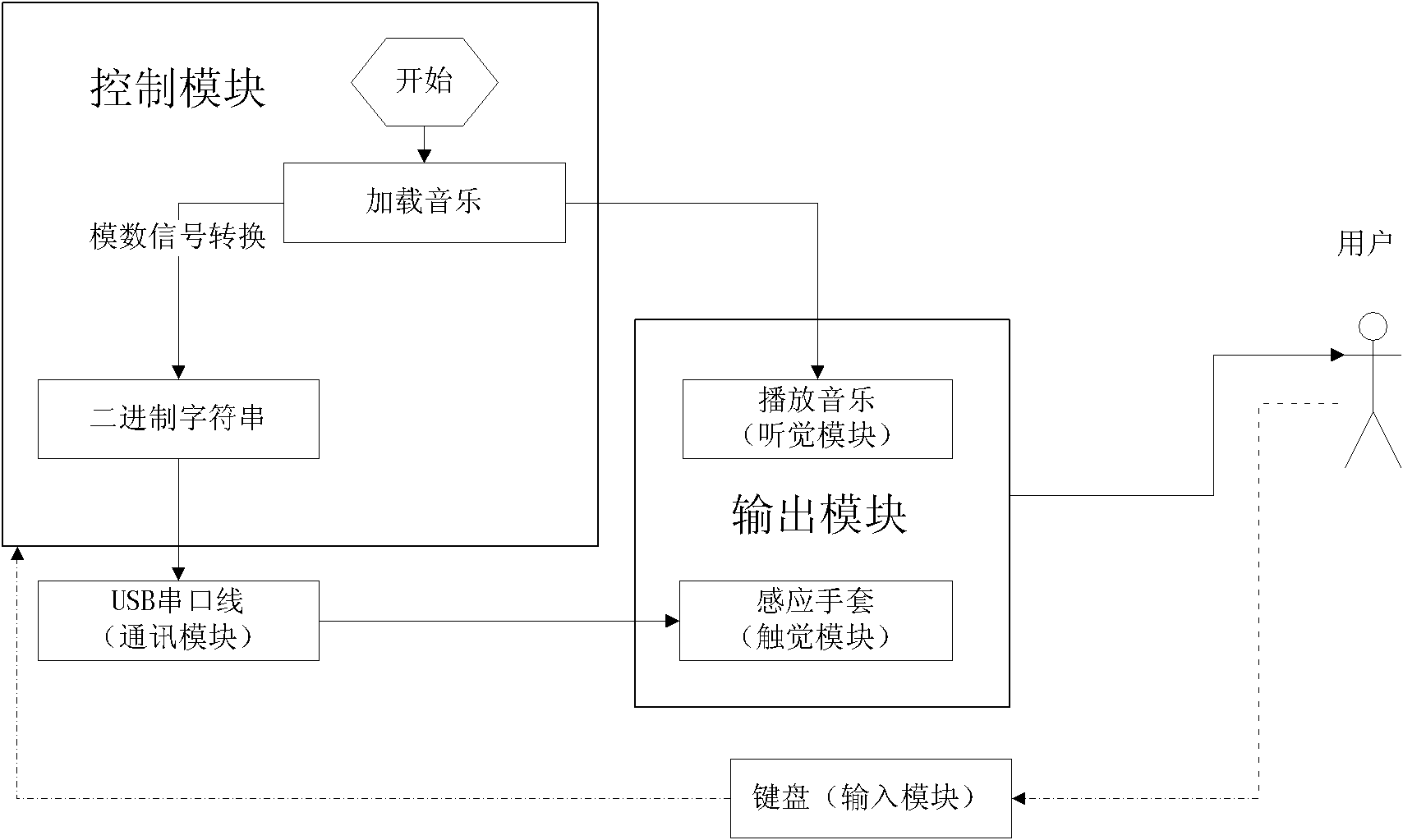
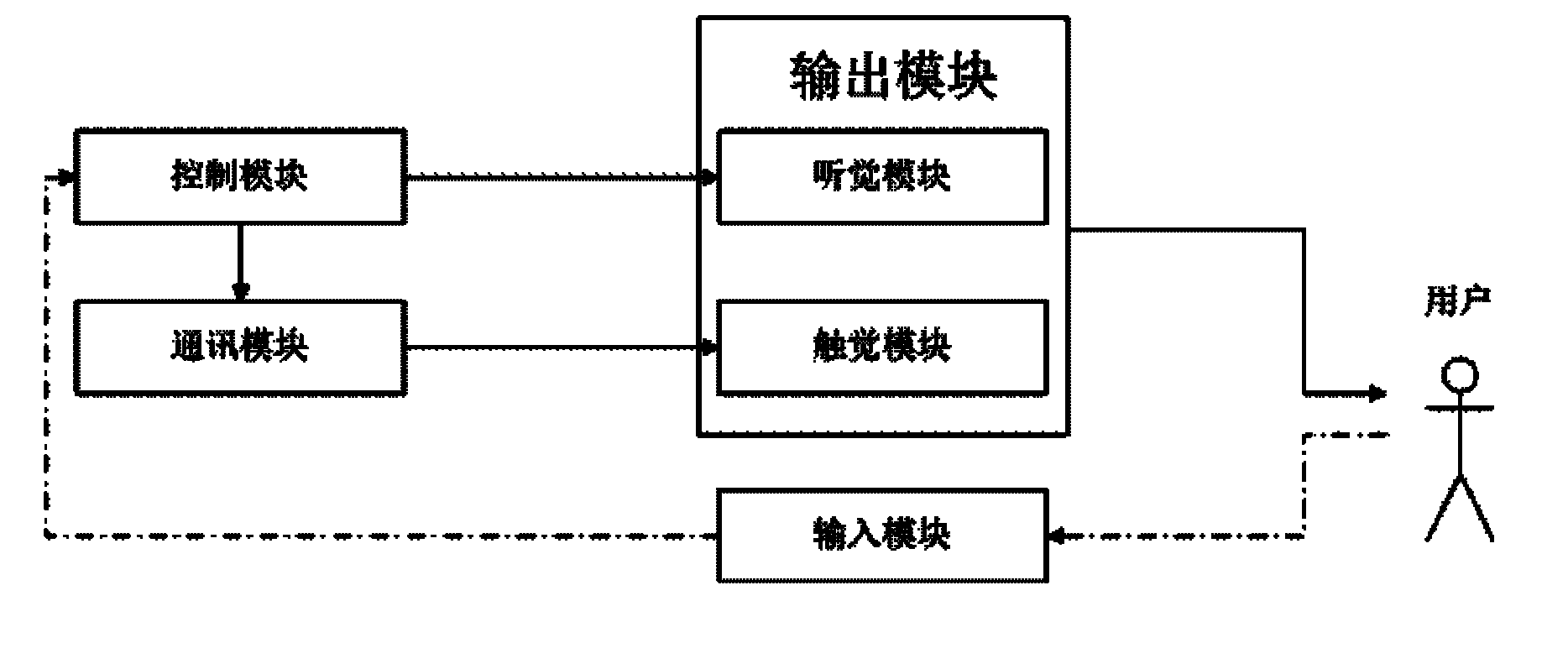
Interactive music entertainment equipment based on touch sensation
The invention relates to interactive music entertainment equipment based on touch sensation, which comprises a control module, an input module, a hearing module and a touch sensation module, wherein the control module is used for providing music generating notes according to user selection and converting the music generating notes into digital signals, the control module internally comprises an evaluating unit for analyzing and evaluating user input; the input module is used for configuring games by a user when the games start and completing game actions through pressing keys by the user during the games; the hearing module is used for receiving the signals of the control module, playing music selected by the user and assisting the user to complete the games by music rhythms and warning tones; the control module is in signal connection with the touch sensation module through a communication module; and the touch sensation module is used for receiving the digital signals of the control module and providing touch sensation warning information for the user in a vibration mode. The invention has the advantage of providing the touch sensation warning information to ensure that patients with visual disorder or people wanting to obtain vision rest can also enjoy music games.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
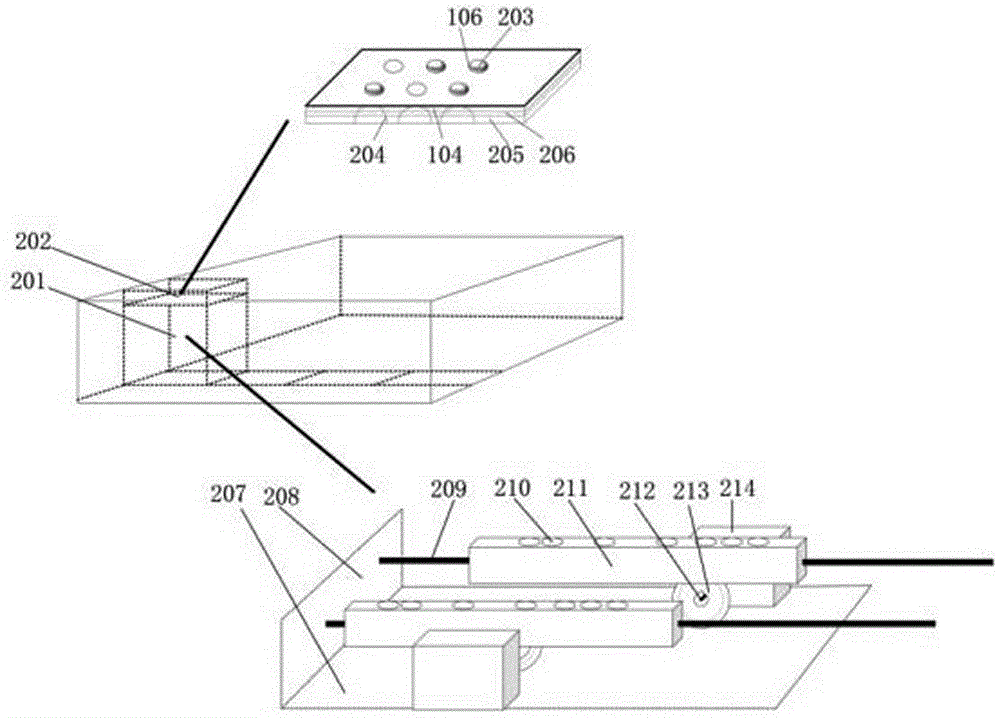
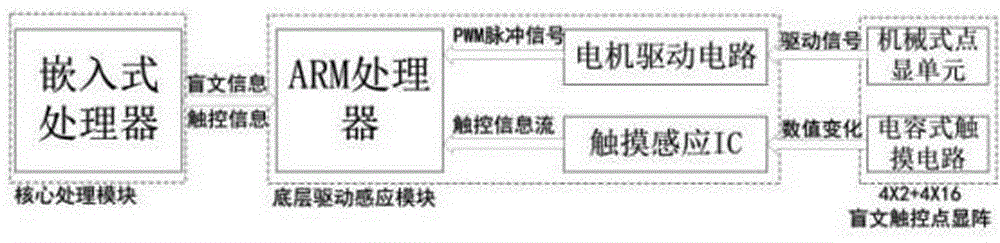
Dot matrix type braille dot display touch control screen
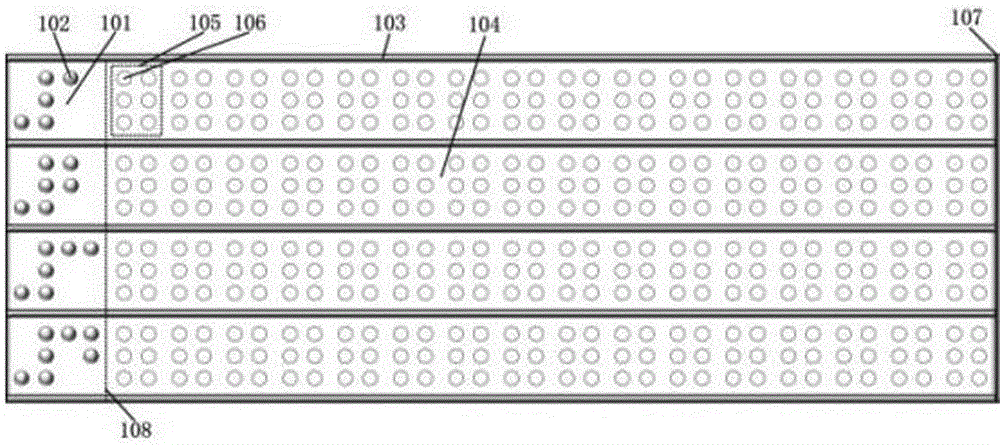
InactiveCN106775123AIncrease refresh rateHigh speedInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingDot matrixVisual Disorders
The invention relates to a dot matrix type braille dot display touch control screen and aims to provide a low-cost and practical integrated braille input / output solution for people with visual disorder. The dot matrix type braille dot display touch control screen comprises 4*16 dot display touch control units, 4*2 fixed braille touch control units, a bottom drive sensing module and a core processing module, wherein each dot display touch control unit comprises six contacts arranged in three rows and two lines, and the whole unit comprises a surface film, a surface material layer, a touch circuit layer, six beads, a slide rod, a guide rail of the slide rod, a motor, a connecting rod and a gear from top to bottom, the six beads are respectively located into six through holes, and the slide rod is provided with a specially-designed circular groove; the four fixed braille touch control units are arranged in a line on the left of the touch control screen, and each fixed braille touch control unit comprises two squares of fixed braille salient dots and comprises a surface film, the fixed braille salient dots, a surface material layer, a touch circuit layer and a bottom mechanical part from top to bottom; a lateral bar and multiple rows of guide bars are arranged on the top surface of the touch control screen.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
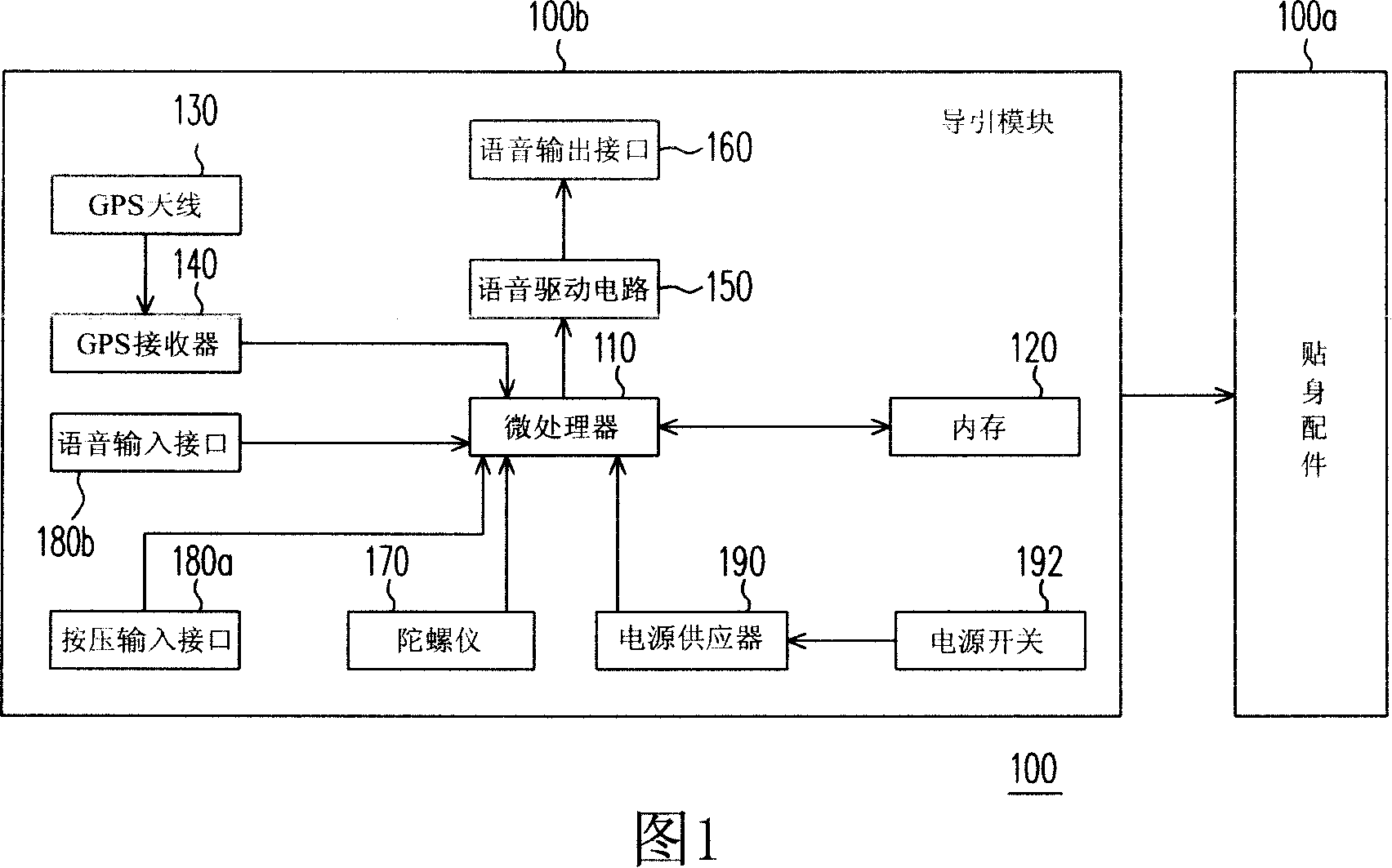
Voice guiding means used for visual handicap
InactiveCN101153800AEasy to wearIncrease autonomy of activitiesInstruments for road network navigationBeacon systems using radio wavesVisual DisordersGlobal Positioning System
A voice guiding device for visual disorder comprises a microprocessor, a memory, a global positioning system antenna, a global positioning system module, a voice driving circuit and a voice output interface, wherein, the microprocessor is used for judging a received signal and exports the signal after processing, the memory is coupled to the microprocessor and used for storing a map database and a voice database relative to the map database, the global positioning system antenna is used for receiving a positioning signal emitted from a satellite system, while the global positioning system module is coupled to the global positioning system antenna and used for receiving the positioning signal emitted from the global positioning system antenna and transmitted the signal to the microprocessor after processing, the voice driving circuit is coupled to the microprocessor and used for receiving the signal from the microprocessor and exported the signal after processing, the voice output interface is coupled to the voice driving circuit and used for receiving the signal from the voice driving circuit, and voice information is exported.
Owner:MITAC COMP (SHUN DE) LTD +1
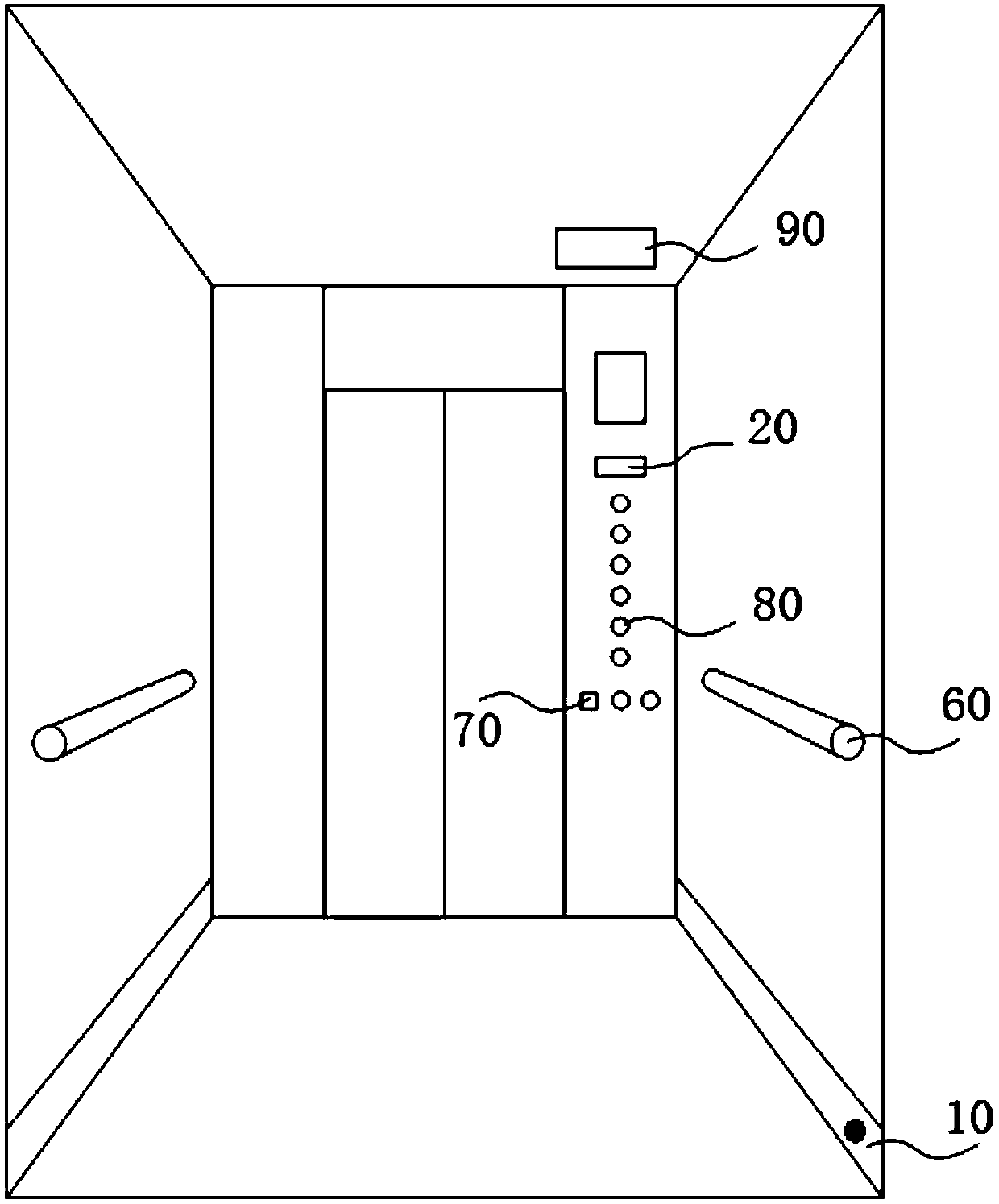
Elevator destination floor registering device
InactiveCN110342359AImprove the convenience of taking the elevatorImprove the elevator experienceElevatorsWheelchairVisual Disorders
The invention discloses an elevator destination floor registering device. The elevator destination floor registering device comprises an infrared sensor, a voice recognition device 20 and a loudspeaker, wherein infrared light emitted by the infrared sensor is parallel to the left wall or the right wall or the rear wall in a lift car, the distance between the infrared light emitted by the infraredsensor and the car wall is smaller than 5 cm, and the distance between the infrared light and a lift car bottom plate is smaller than 10 cm; the infrared sensor outputs an infrared trigger signal to the voice recognition device if the infrared light emitted by the infrared sensor is blocked, and the voice recognition device can perform voice recognition; and if the voice recognition device receives the infrared trigger signal, the voice recognition device is activated, and the loudspeaker is controlled to perform voice output of destination floor inquiry information. According to the elevatordestination floor registering device, the elevator taking convenience of special passengers such as passengers with the two hands filled with objects, passengers who sit on wheelchairs or passengers with visual disorders is facilitated, and meanwhile the elevator using experience of ordinary passengers is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI MITSUBISHI ELEVATOR CO LTD
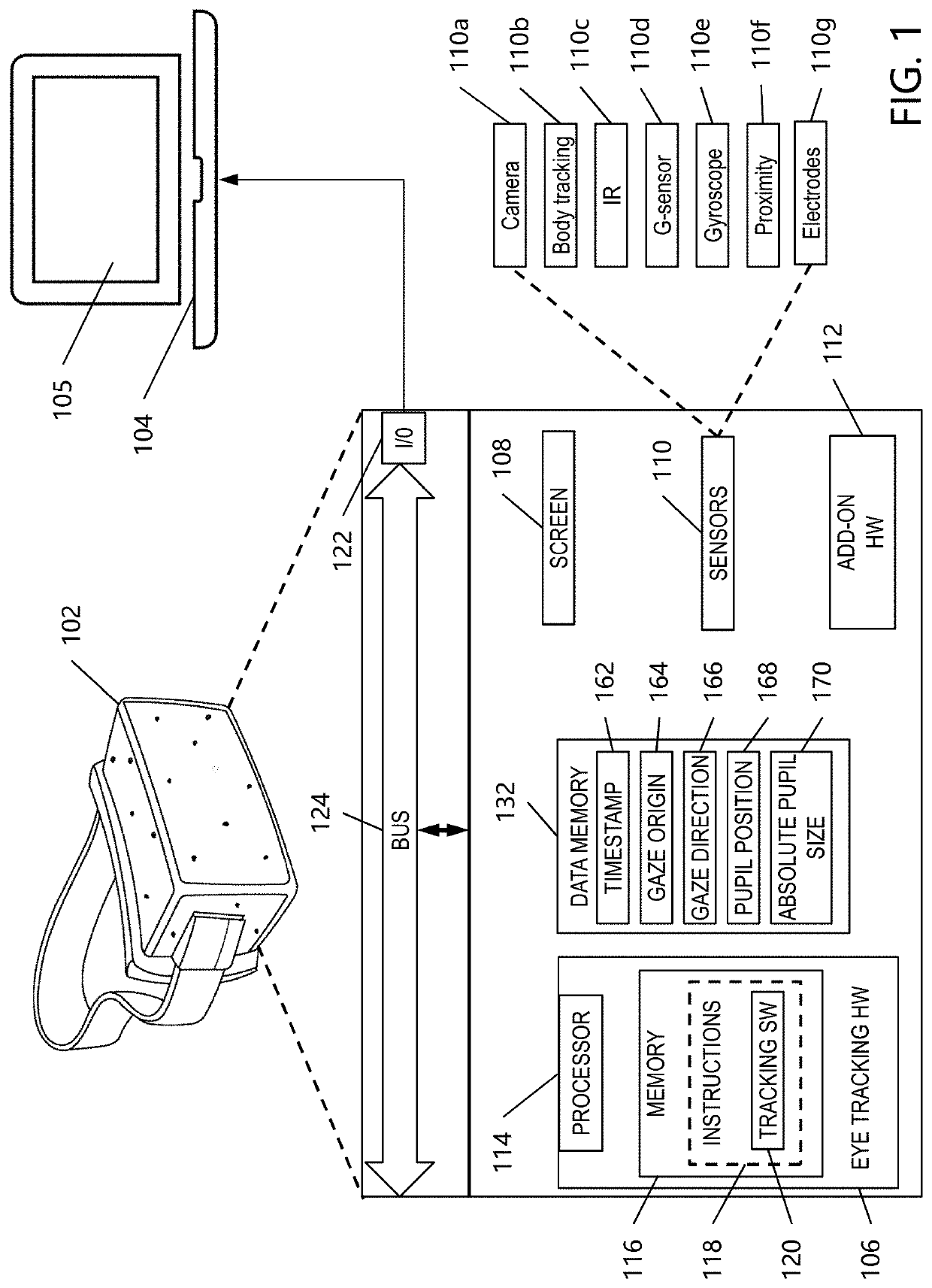
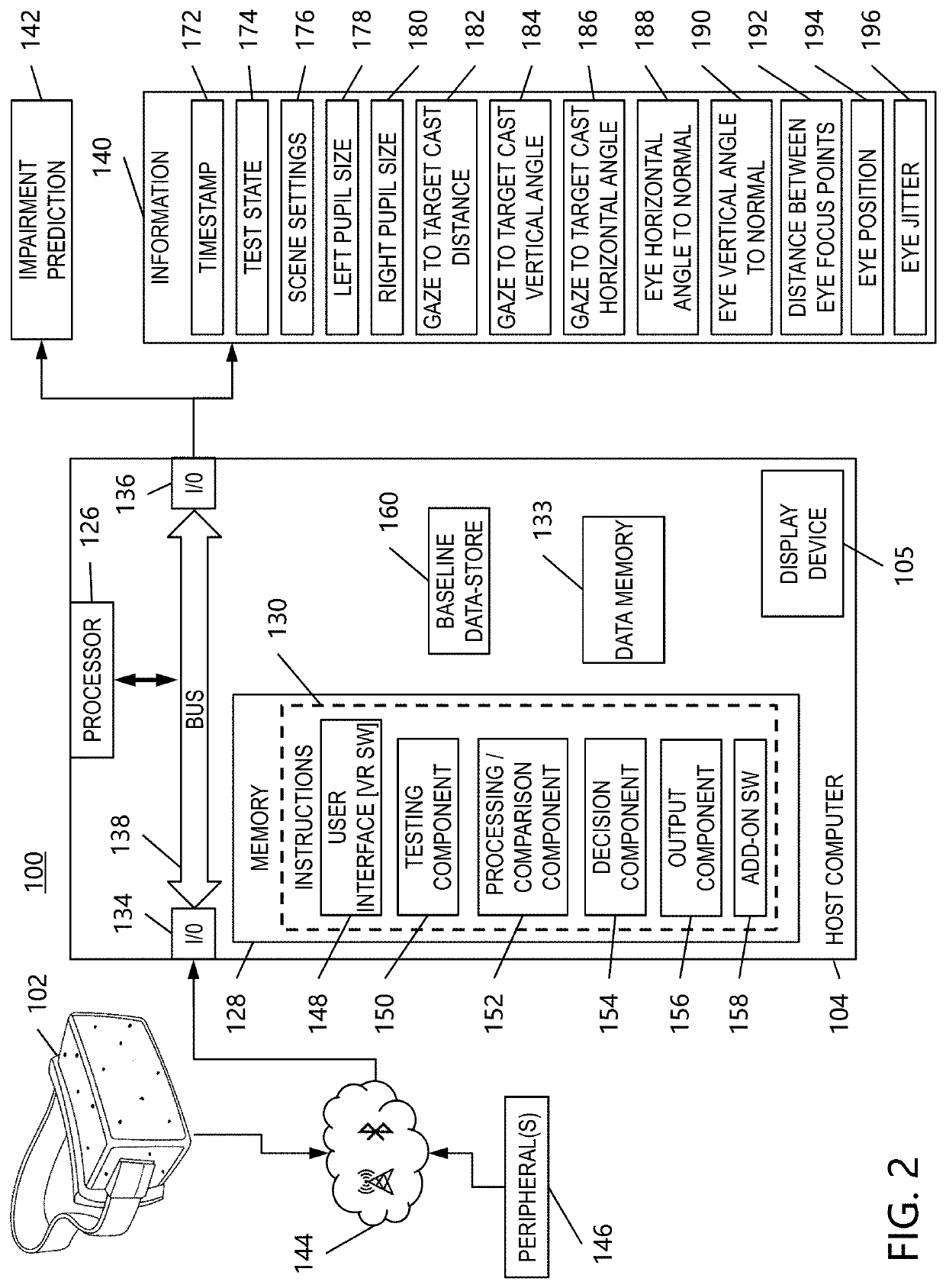
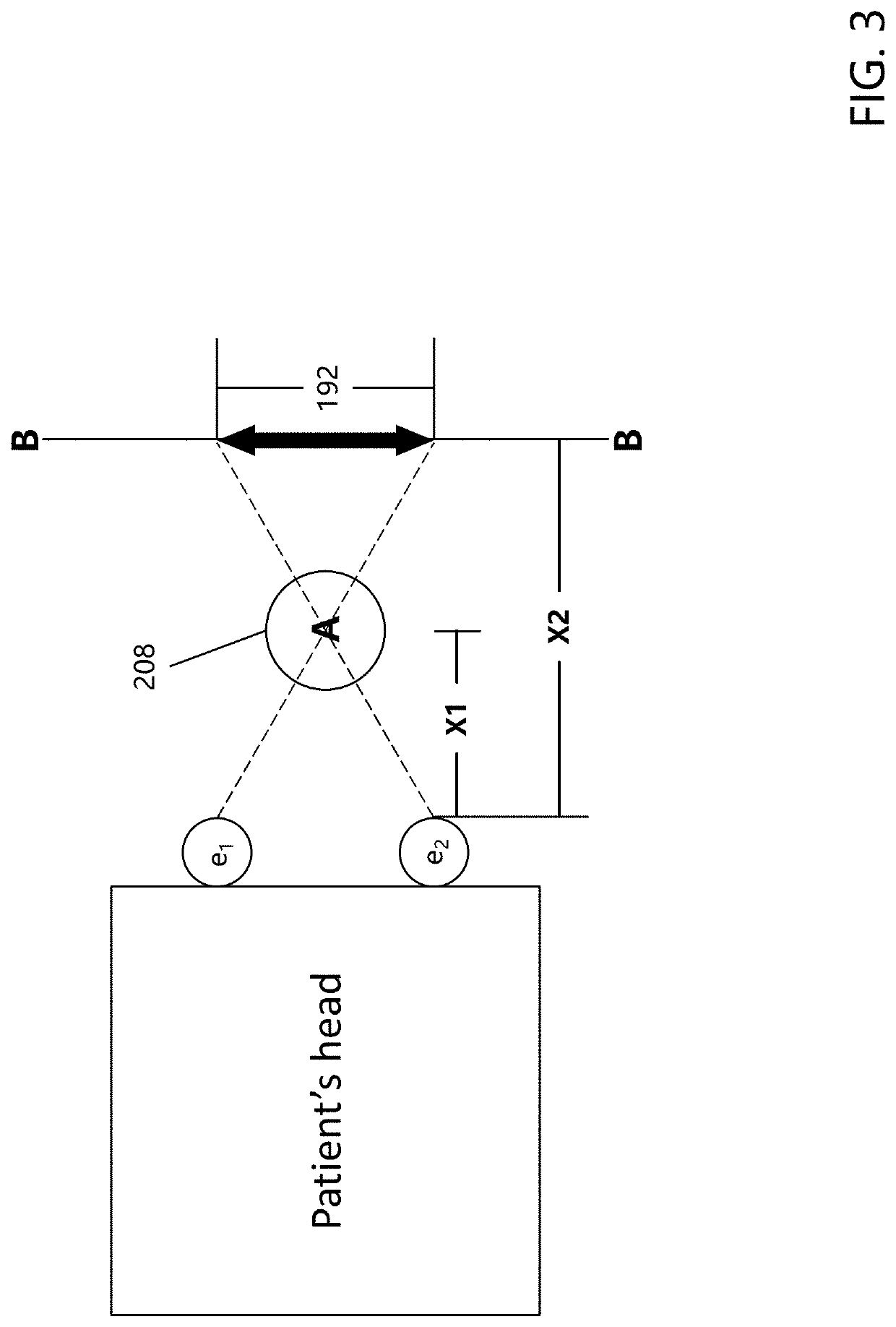
Medical condition sensor
InactiveUS20200121195A1Accurate measurementIncrease sampling rateInput/output for user-computer interactionElectroencephalographyVisual symptomsPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The present disclosure relates generally to a system and method for detecting or indicating a state of visual impairment of a patient due to a medical condition, and more particularly to a method, system and application or software program configured to create a virtual-reality (“VR”) environment that implements visual symptom tests, and which utilizes eye tracking technology to detect or indicate visual symptoms and associated medical conditions.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com