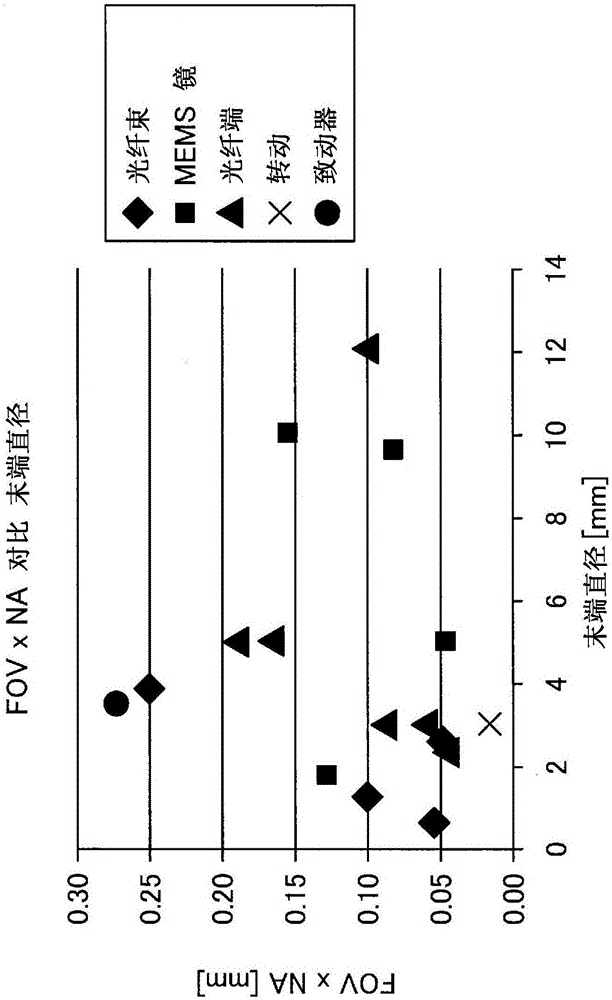
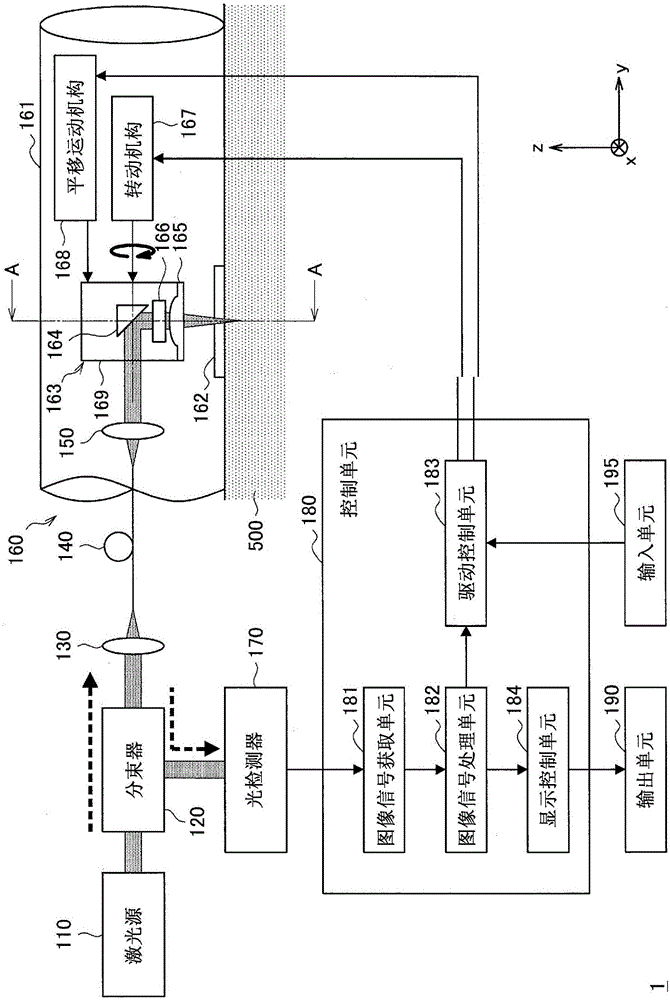
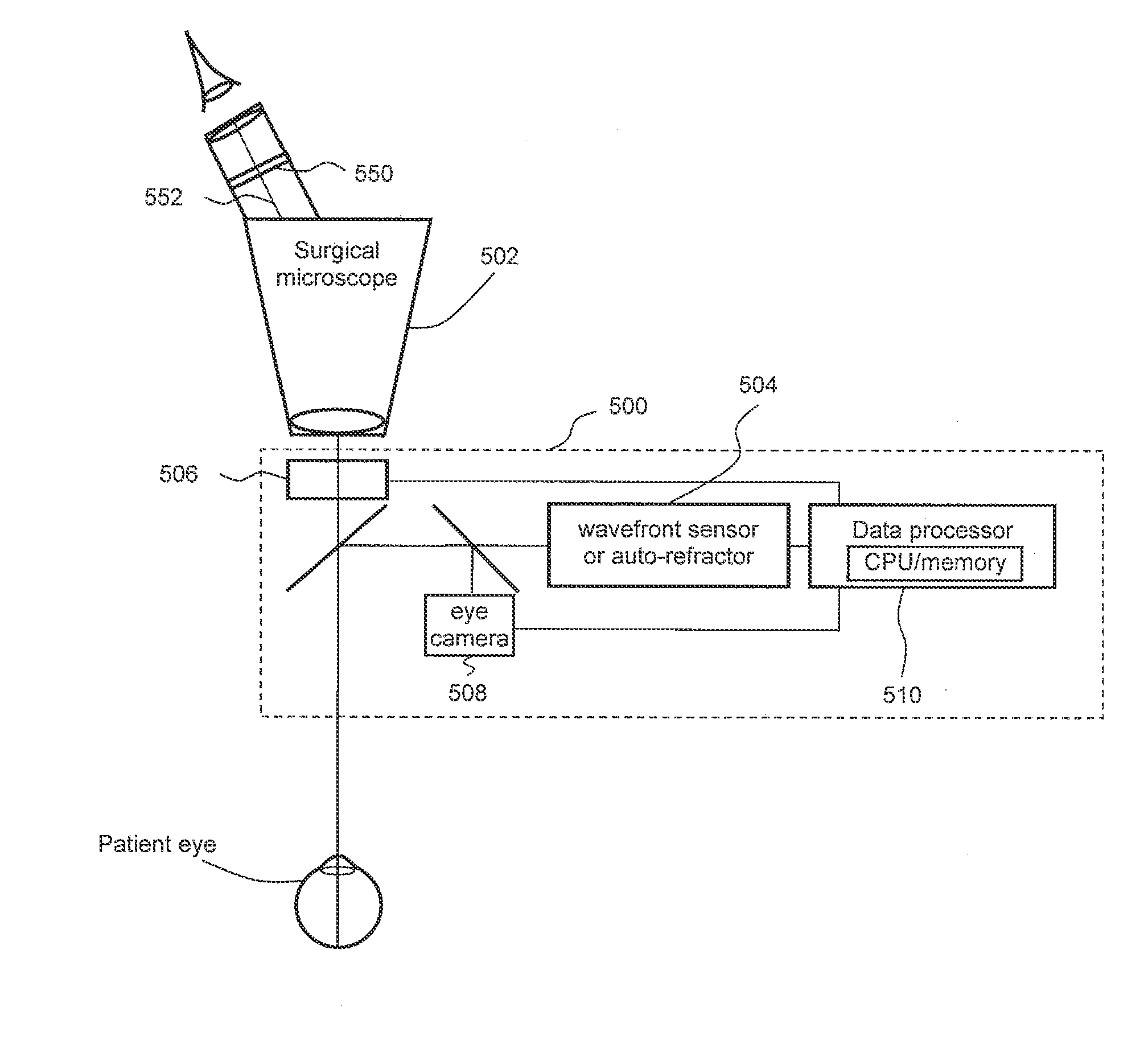
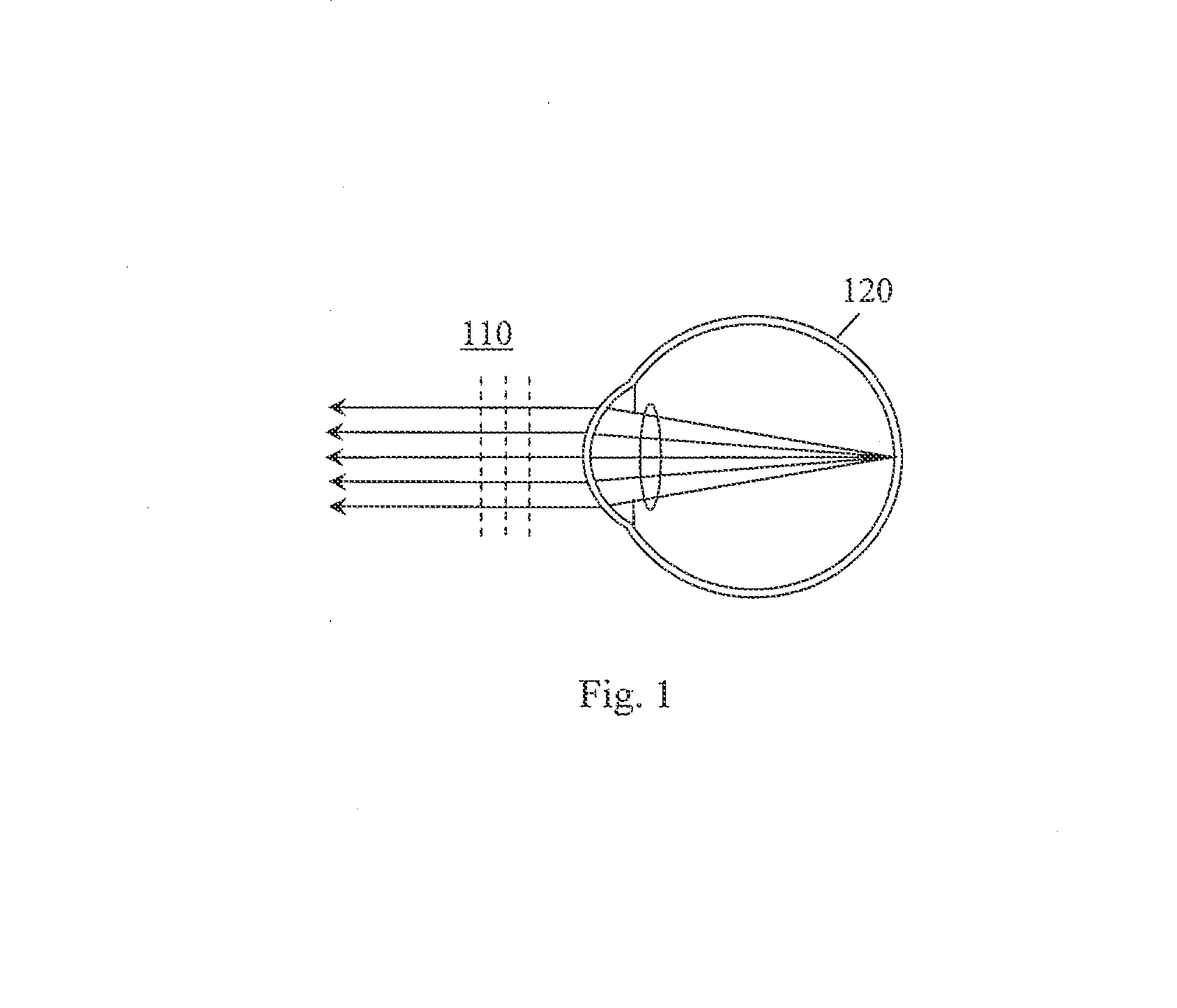
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
102 results about "Astigmatism correction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
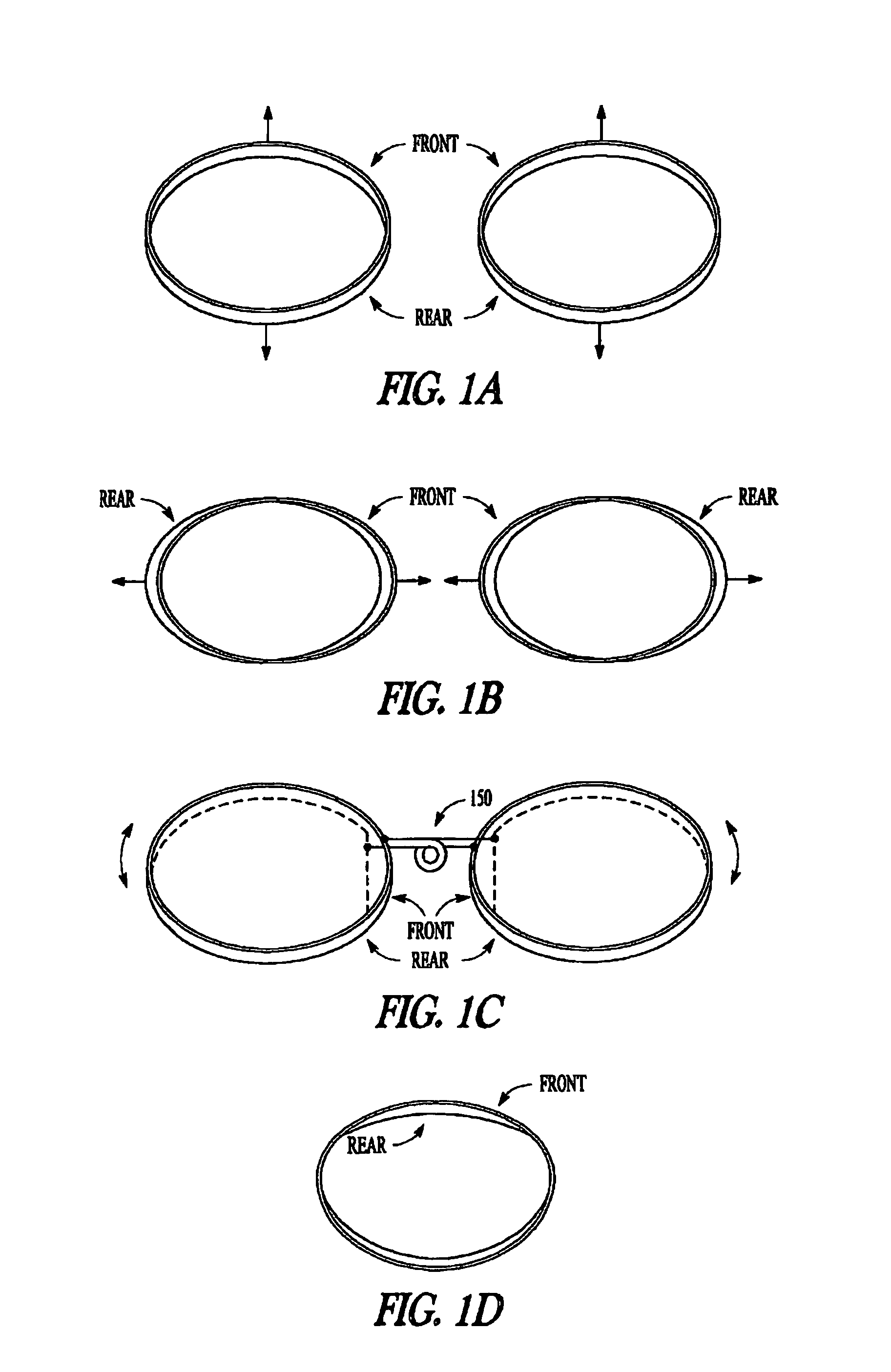
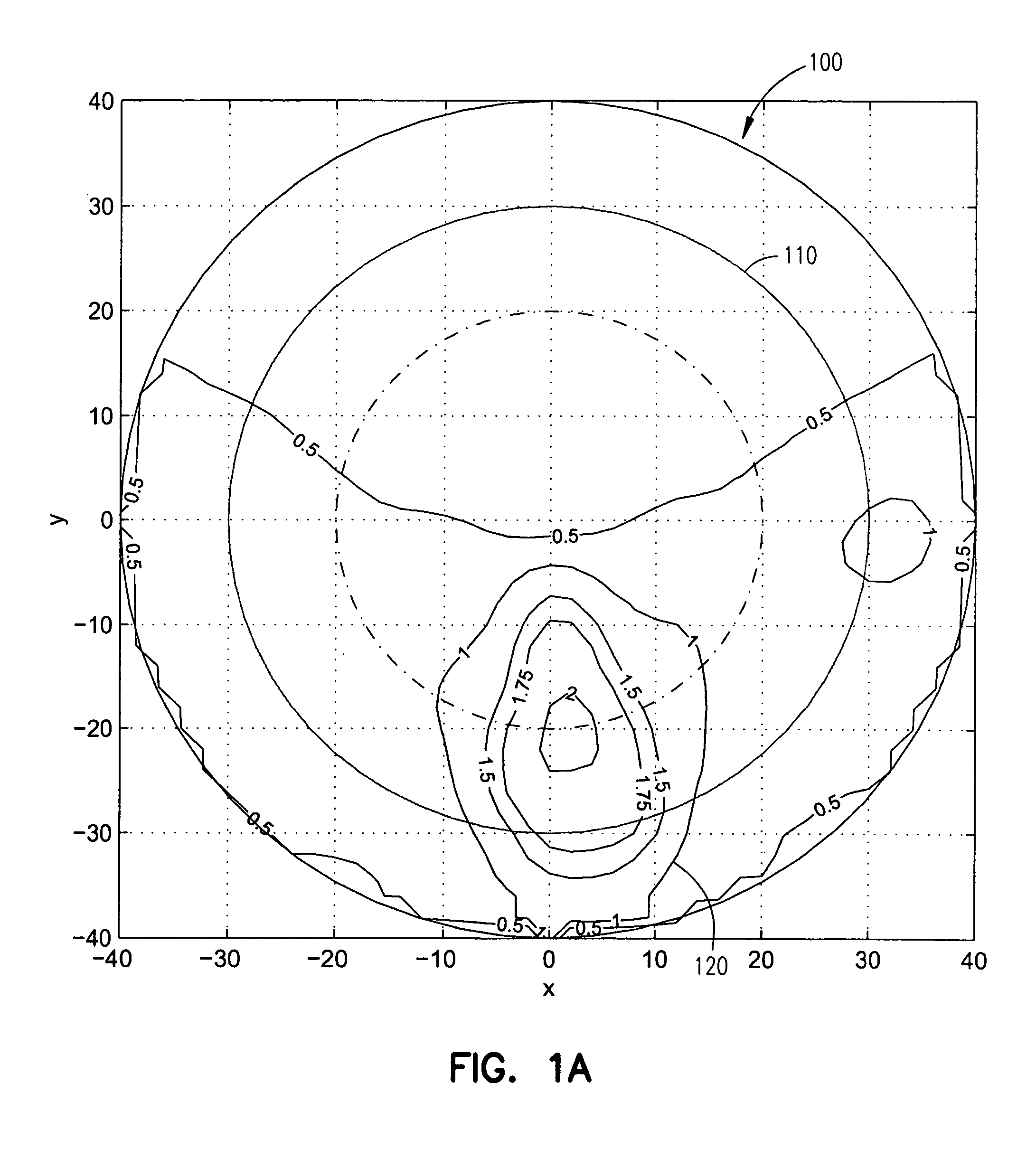
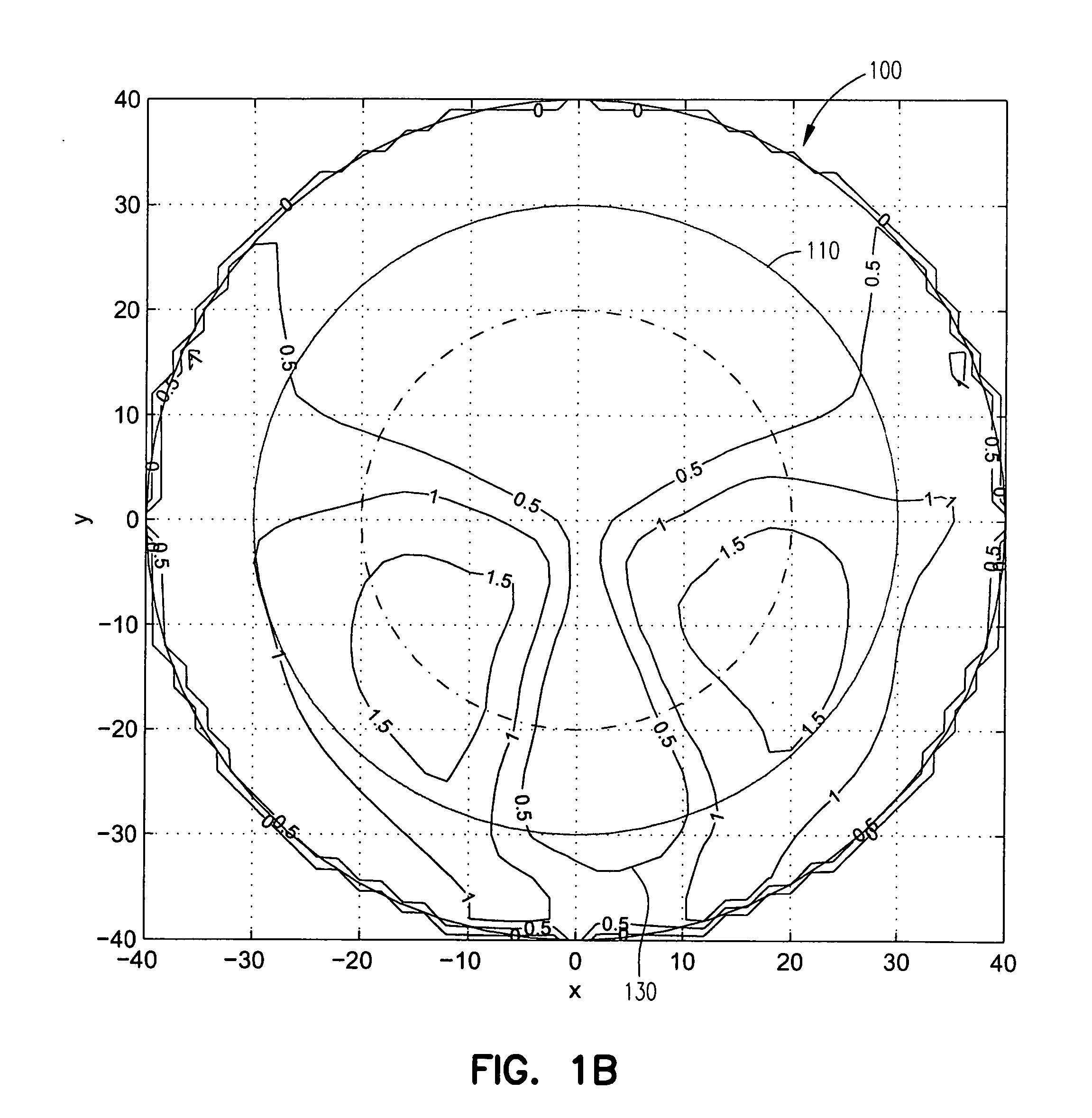
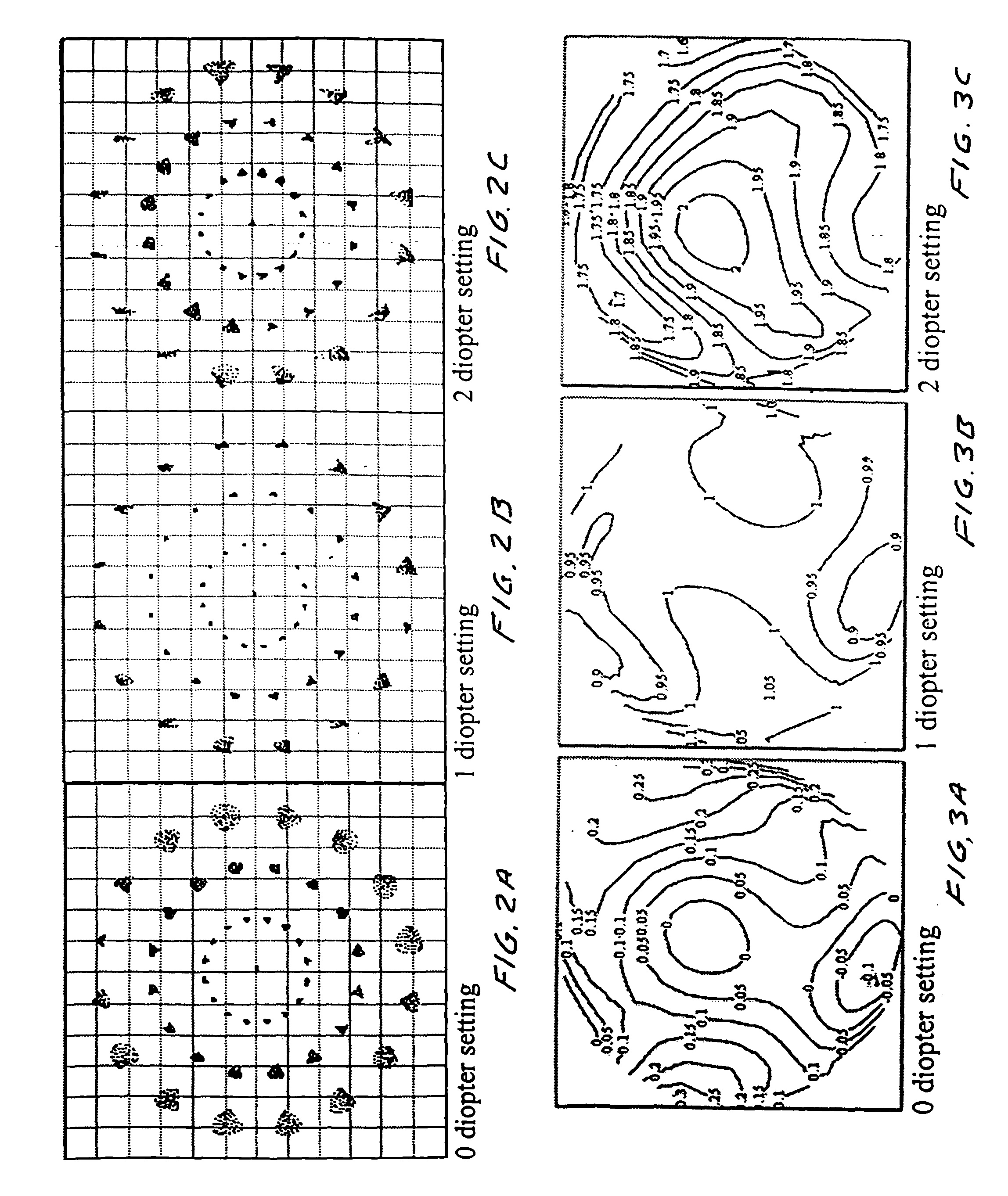
Astigmatism Correction Options. The first number (-2.50) is the sphere power (in diopters) for the correction of myopia in the flatter (less nearsighted) principal meridian of the eye. The second number (-1.00) is the cylinder power for the additional myopia correction required for the more curved principal meridian.
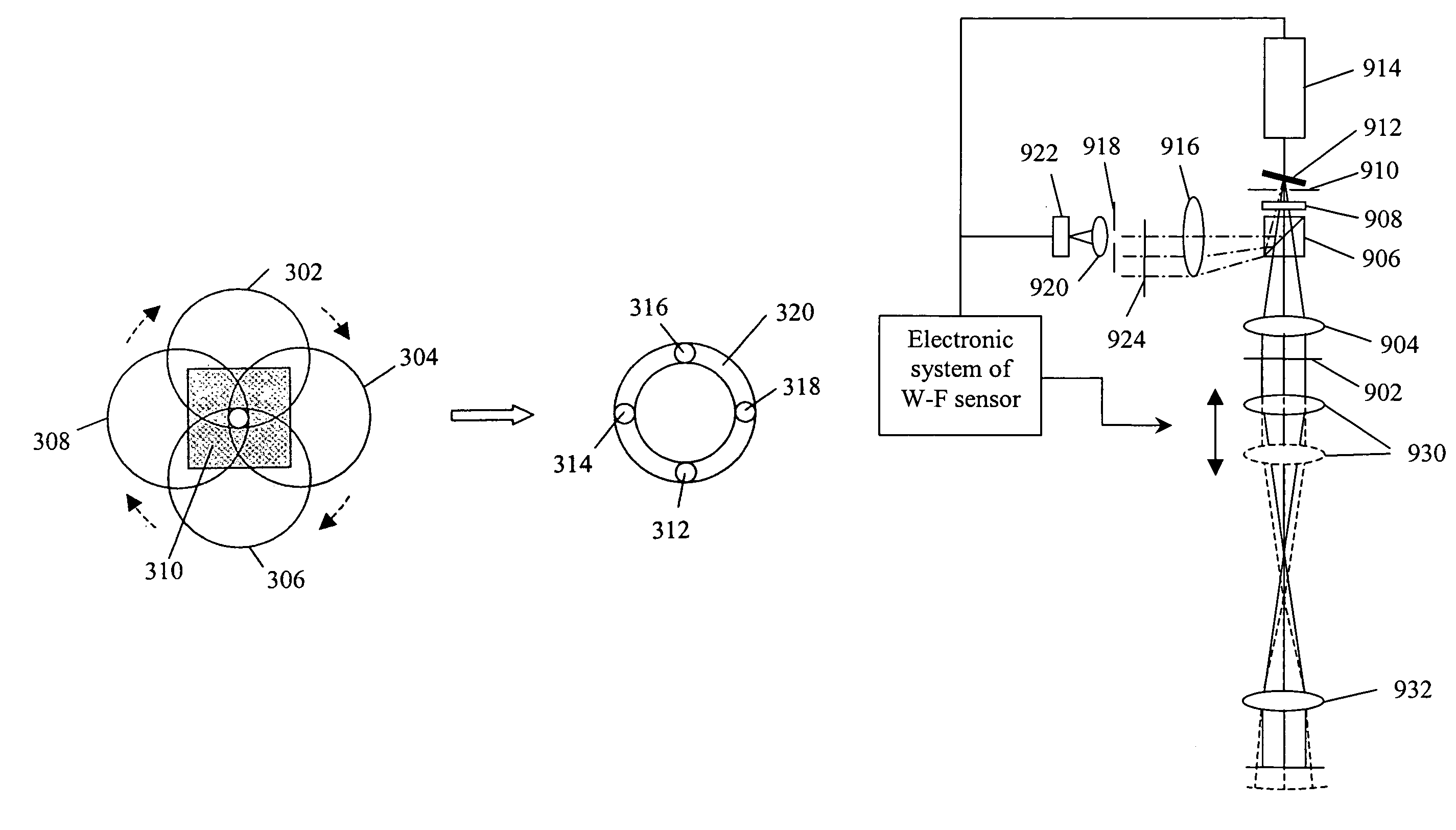
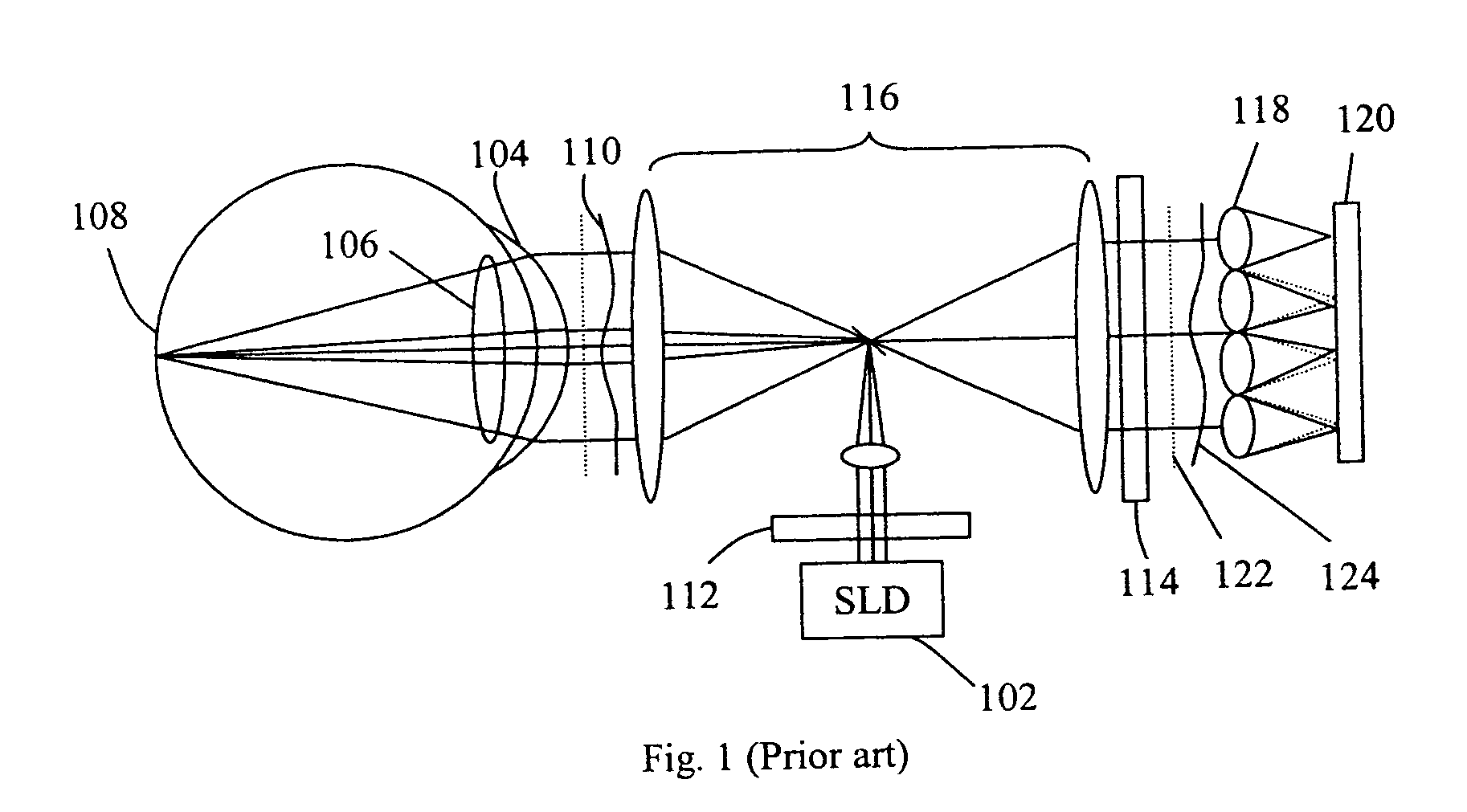
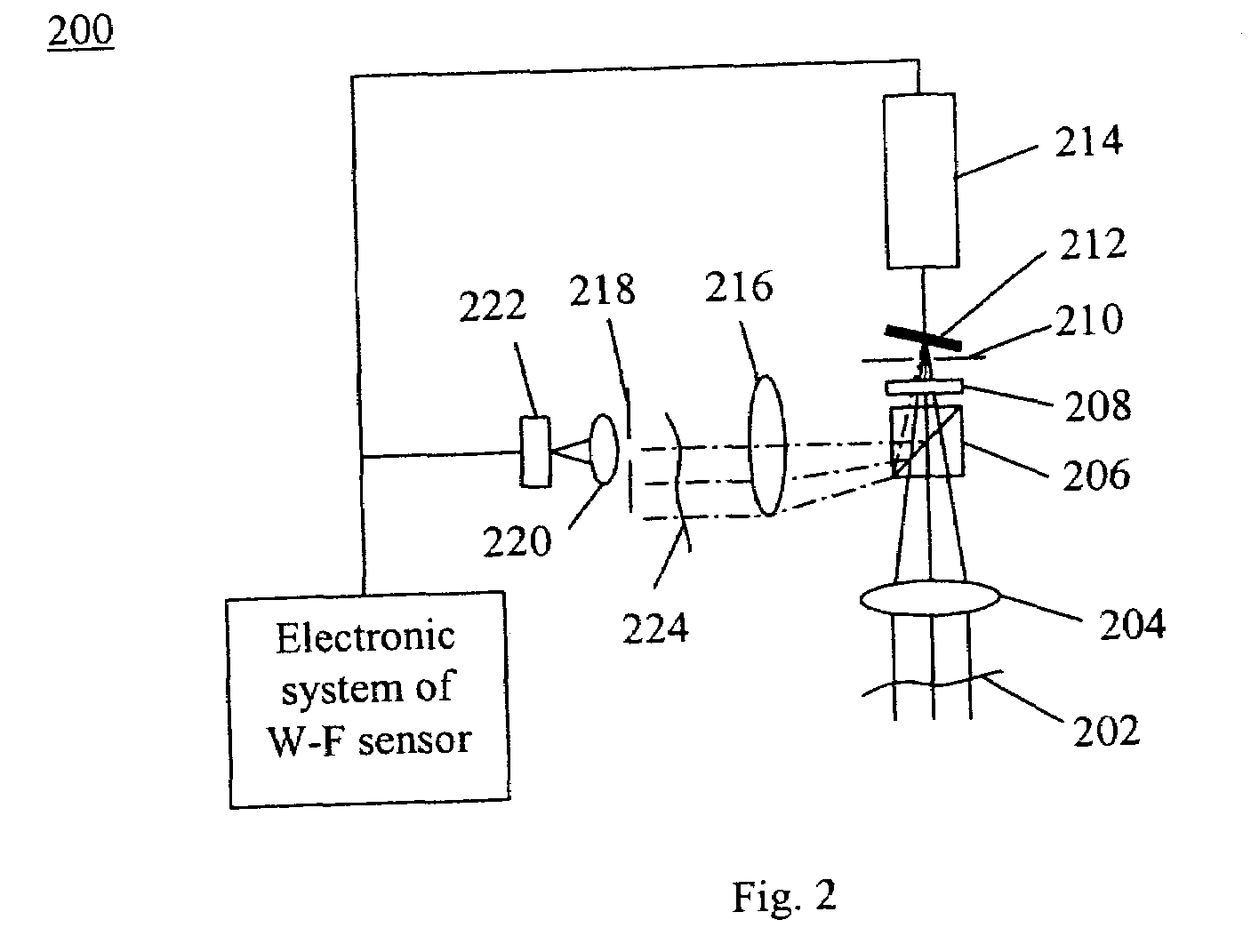
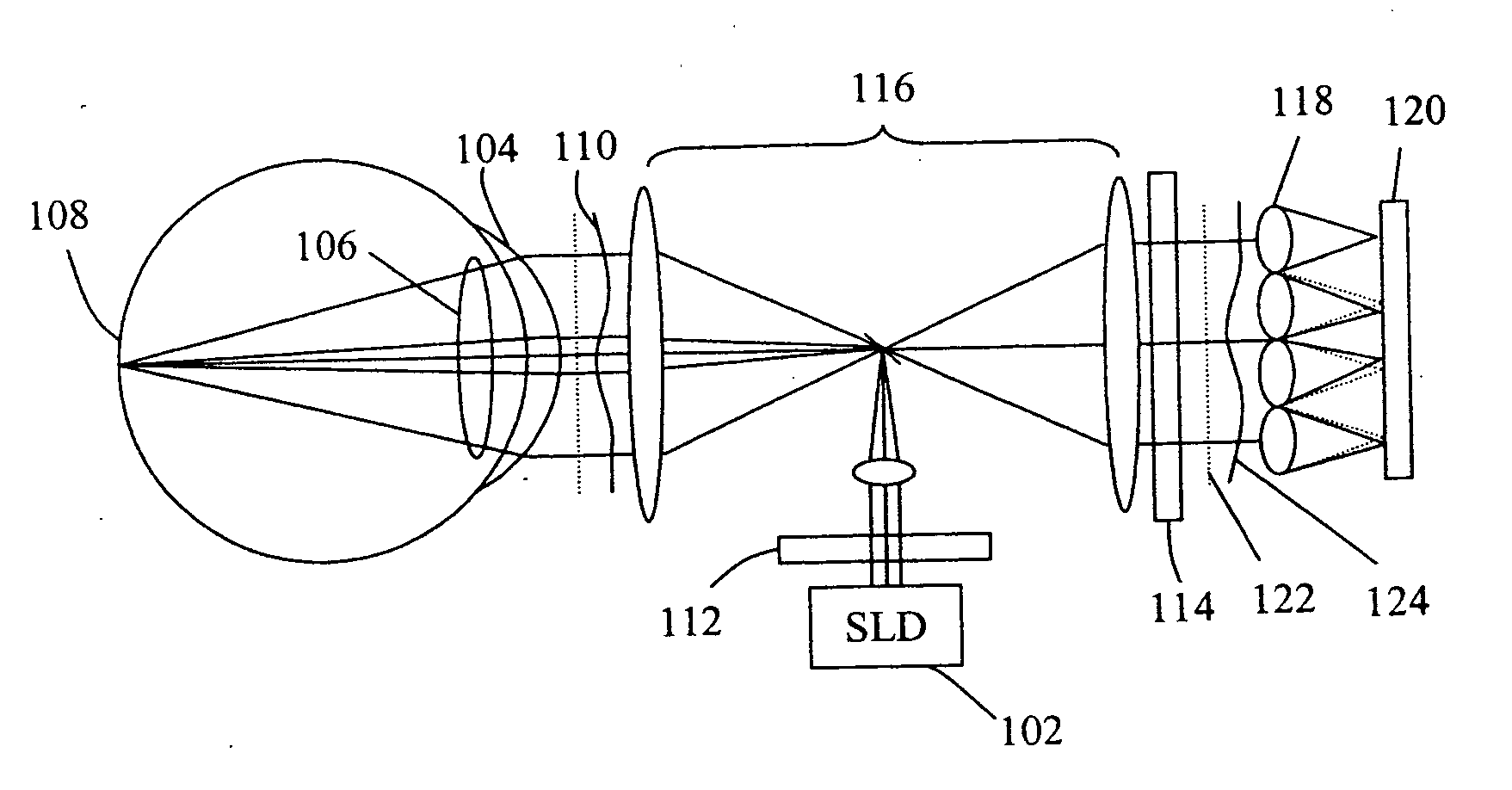
Sequential wavefront sensor
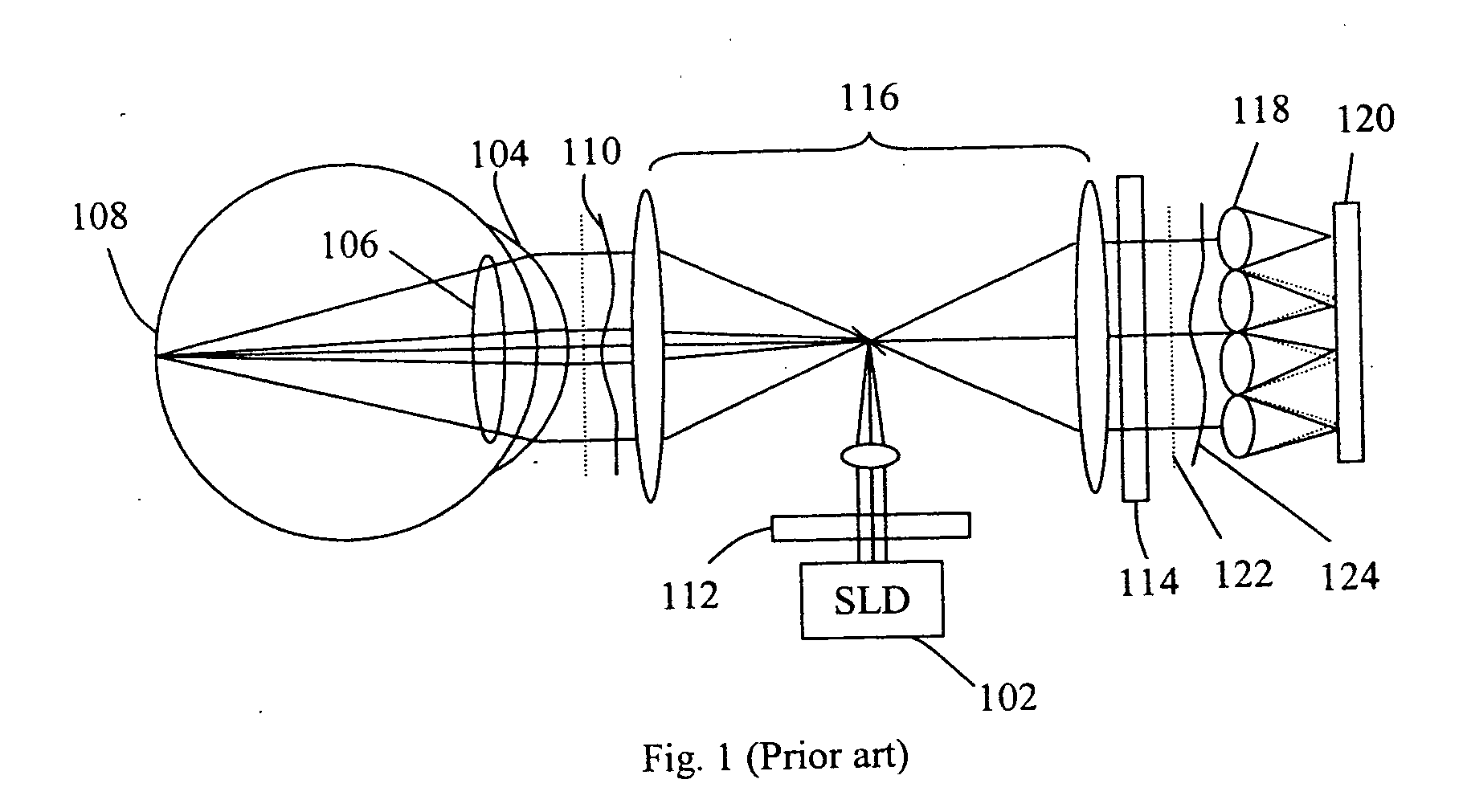
A sequential wavefront sensor comprises a light beam scanning module, a sub-wavefront focusing lens, a detector with more than one photosensitive area and a processor for calculating the sequentially obtained centroids of a number focused light spots from the sub-wavefronts to determine the aberration of the input wavefront. A sequential wavefront sensing method comprises the steps of; sequentially projecting a number of sub-wavefronts onto a sub-wavefront focusing lens and a detector with more than one photosensitive areas, calculating the centroid of the focused light spot from each sub-wavefront, and processing the centroid information to determine the aberration of the wavefront. In particular, a method for auto-focusing and / or auto-astigmatism-correction comprises the steps of sequentially projecting a number of sub-wavefronts around an annular ring of a wavefront to a sub-wavefront focusing lens and a detector, calculating the centroid of focused light spot from each sub-wavefront to figure out the centroid trace and hence the defocus and / or astigmatism, adjusting the focus and / or astigmatism of the optical imaging system before the wavefront sensor so that the measured defocus and / or astigmatism is minimized.
Owner:CLARITY MEDICAL SYST
Sequential wavefront sensor
A sequential wavefront sensor comprises a light beam scanning module, a sub-wavefront focusing lens, a detector with more than one photosensitive area and a processor for calculating the sequentially obtained centroids of a number focused light spots from the sub-wavefronts to determine the aberration of the input wavefront. A sequential wavefront sensing method comprises the steps of; sequentially projecting a number of sub-wavefronts onto a sub-wavefront focusing lens and a detector with more than one photosensitive areas, calculating the centroid of the focused light spot from each sub-wavefront, and processing the centroid information to determine the aberration of the wavefront. In particular, a method for auto-focusing and / or auto-astigmatism-correction comprises the steps of sequentially projecting a number of sub-wavefronts around an annular ring of a wavefront to a sub-wavefront focusing lens and a detector, calculating the centroid of focused light spot from each sub-wavefront to figure out the centroid trace and hence the defocus and / or astigmatism, adjusting the focus and / or astigmatism of the optical imaging system before the wavefront sensor so that the measured defocus and / or astigmatism is minimized.
Owner:CLARITY MEDICAL SYST
Laser scanning observation device and laser scanning method
InactiveUS20160299170A1High precision observationAccurate observationEndoscopesMicroscopesLaser scanningLaser light
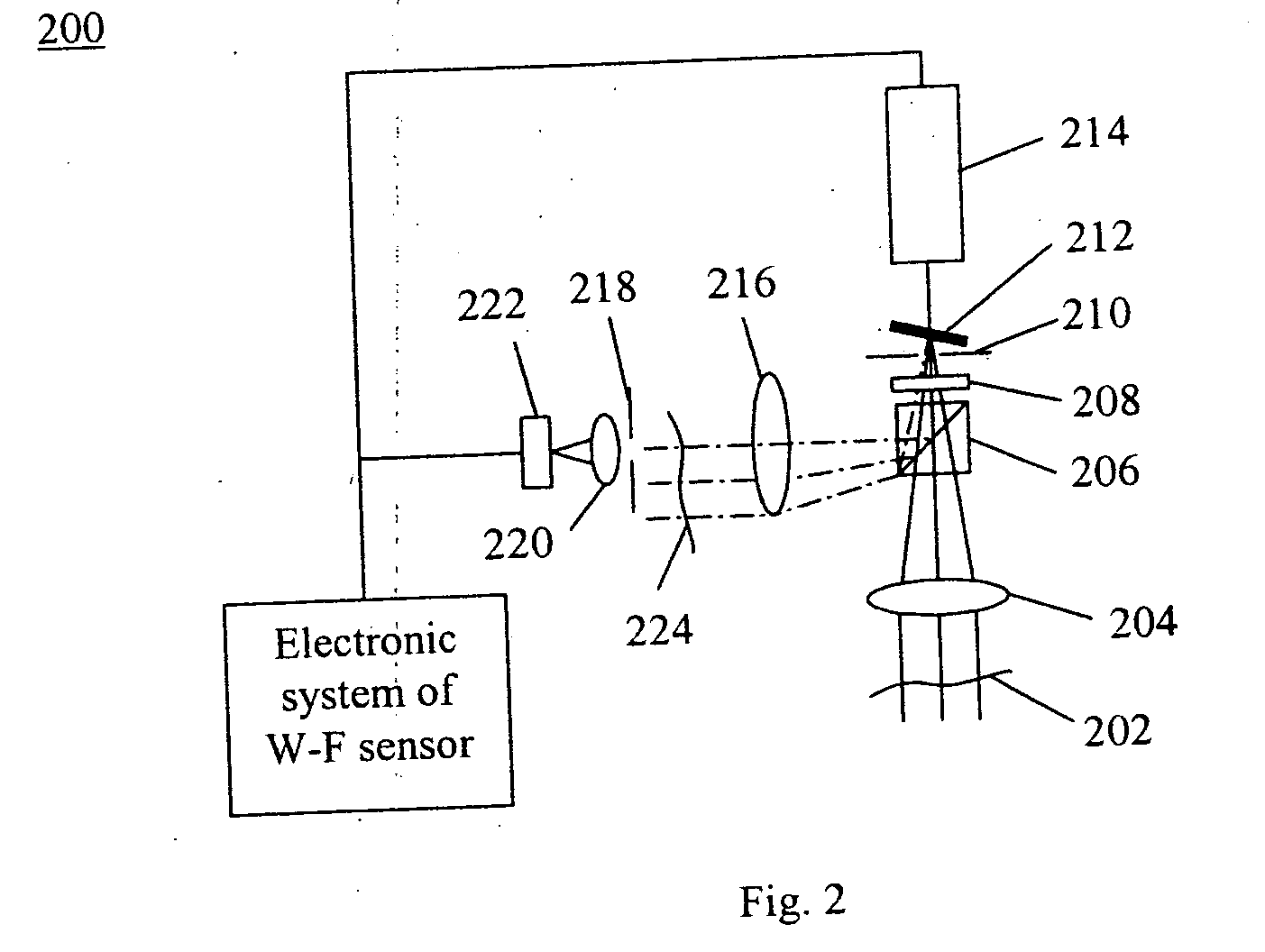
Provided is a laser scanning observation device including: a window unit provided in a partial area of a casing and configured to be in contact with or close to an observation target; an objective lens configured to collect laser light on the observation target through the window unit; an optical path changing element configured to change a direction of travel of the laser light guided within the casing toward the window unit; an astigmatism correction element provided in a front stage of the window unit and configured to correct astigmatism occurring upon the collection of the laser light on the observation target; and a rotation mechanism configured to allow at least the optical path changing element to rotate about a rotation axis perpendicular to a direction of incidence of the laser light on the window unit to scan the observation target with the laser light.
Owner:SONY CORP
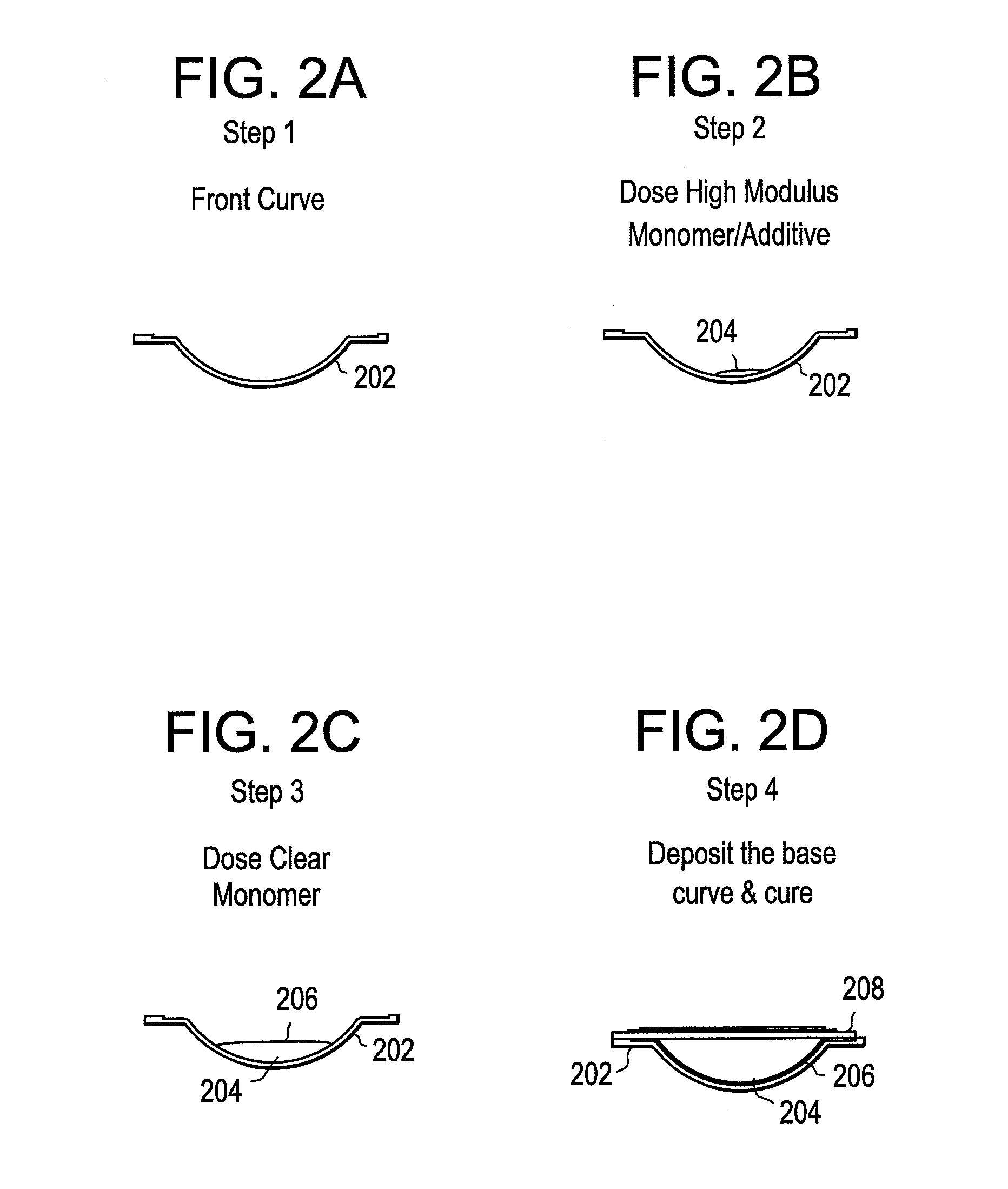
Increased stiffness center optic in soft contact lenses for astigmatism correction
InactiveUS20130258276A1Increase stiffnessHigh modulusOptical articlesOptical partsRefractive errorStigmatism
A molded contact lens comprising a stiffer optic zone relative to the peripheral zone of the contact lens provides an optical element for correcting astigmatism without the need for or substantially minimizing the need for the correction of rotational misalignment. The higher elastic modulus optic zone vaults over the cornea thereby allowing a tear lens to form. The tear lens follows or assumes the shape of the back surface of the contact lens. The combination of the tear lens and the optical zone provide an optical element for correction of refractive error.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Low inventory method of making eyeglasses
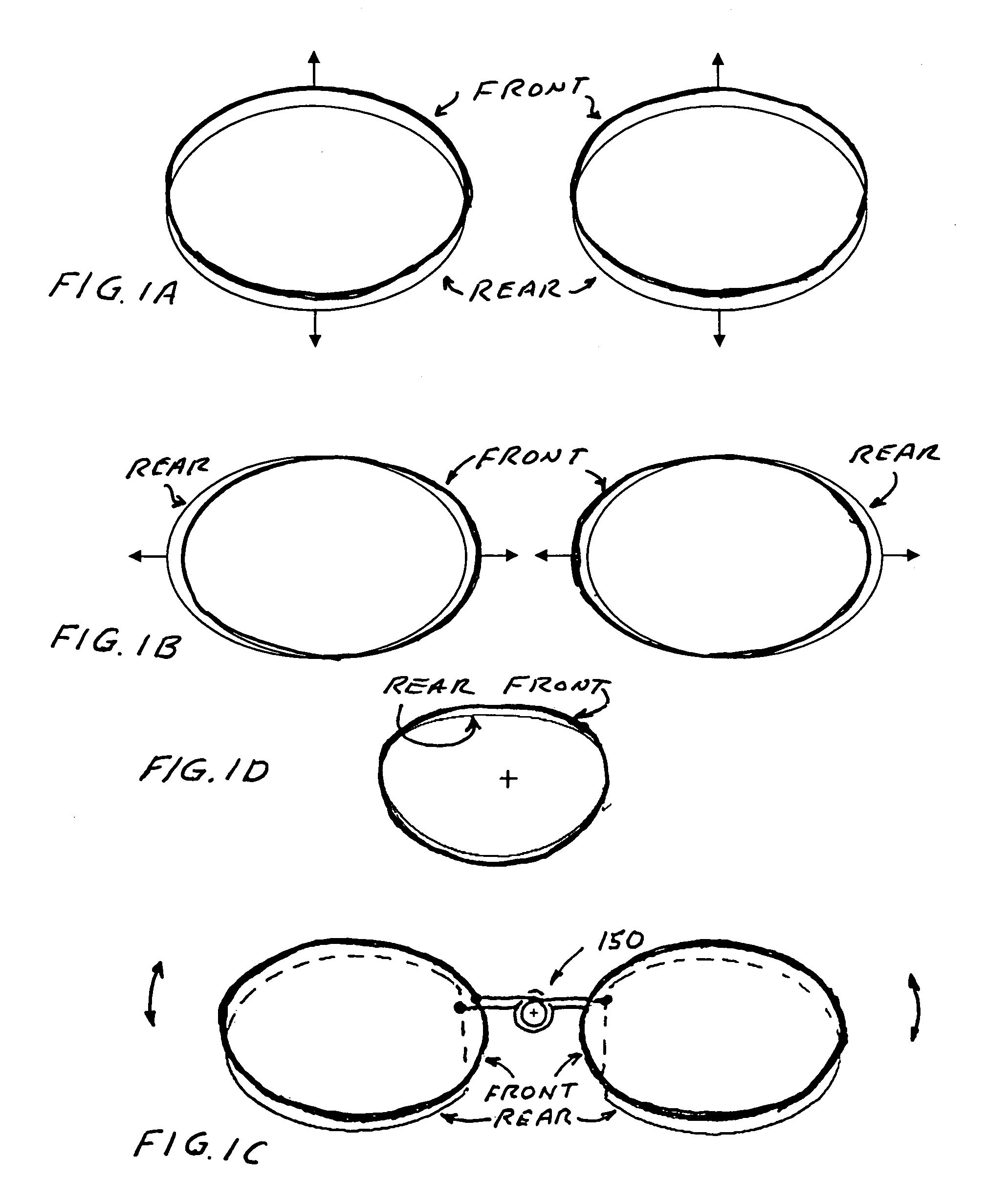
A low inventory method of making eyeglasses. Two lens elements having special complementary surfaces are provided. These lens elements can be positioned relative to each other to provide wide ranges of focus correction and astigmatism correction. Various preferred embodiments of the invention are described. In one embodiment the required inventory is only identical sets of two complementary lenses for providing correction for almost all needed eye correction for a typical population. In this embodiment, the lens units are first adjusted relative to each other to provide a desired focusing power. Astigmatism may be corrected by a small adjustment in a second direction perpendicular to the first direction followed by a rotation of the two lenses about the axis of the two lenses. When the adjustments have been made the two lenses are fixed with respect to each other and installed in eyeglass frames. Cutting to the shape of the eyeglass frames can occur either before or after the fixing.
Owner:QUEXTA
Laser scanning observation device and laser scanning method
Provided is a laser scanning observation device which comprises: a window portion which is provided in one area of a housing and comes into contact with or close to an object to be observed; an objective lens that converges laser light to the object to be observed through the window portion; a light path changing element which changes the direction of travel of the laser light that has been guided inside the housing toward the window portion; an astigmatism correction element which is provided at a front stage of the window portion and corrects astigmatism that occurs when the laser light is converged to the object to be observed, and a rotation mechanism which rotates at least the light path changing element in a vertical rotation axis with respect to an incidence direction of the laser light into the window portion such that the laser light scans the object to be observed. The astigmatism correction element corrects the astigmatism in a correction amount that corresponds to change in the astigmatism that occurs along with the change in the observation depth which is the depth of a converging position of the laser light in the object to be observed.
Owner:SONY CORP
Electronic eye marking/registration
InactiveUS20140125949A1Improve astigmatism correction/neutralization outcomePromote resultsRefractometersSkiascopesRefractive errorKeratorefractive surgery
One embodiment is a method for finding, calculating and electronically marking a reference axis for astigmatism correction / neutralization of a patient eye during a refractive surgery.The reference axis for astigmatism correction / neutralization can be determined intra-operatively based on one or more eye property measurements together with simultaneous recording a live eye image. The determined reference axis of astigmatism correction / neutralization can be updated and registered with one or more land mark(s) of the recorded eye image(s); and overlaid onto a live image of the eye. Another embodiment is a method of calculating and displaying in real time compensated refractive errors of the eye under operation with refractive components due to temporary surgically induced factors removed and refractive components due to surgeon-induced factors added.
Owner:CLARITY MEDICAL SYST
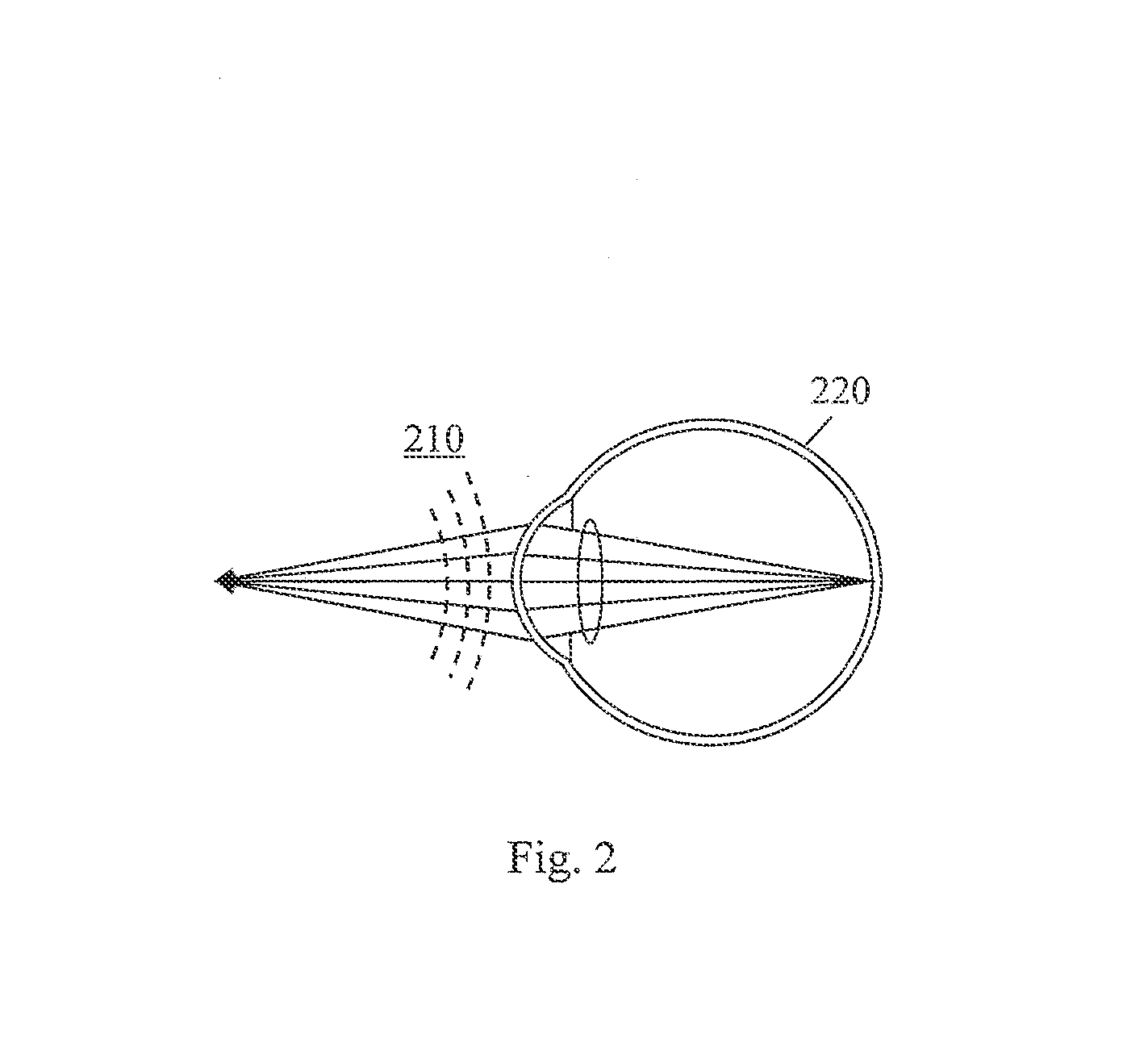
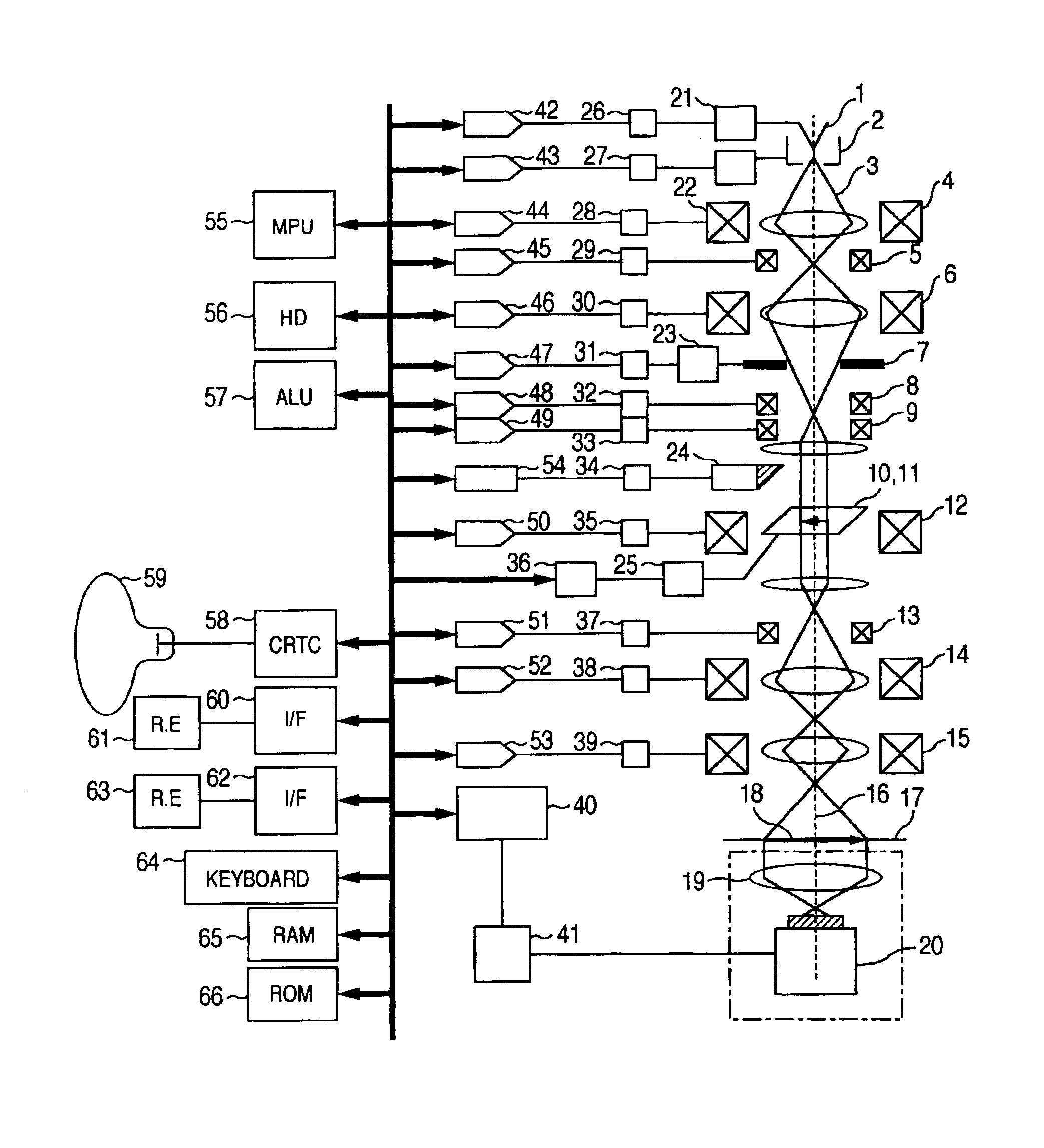
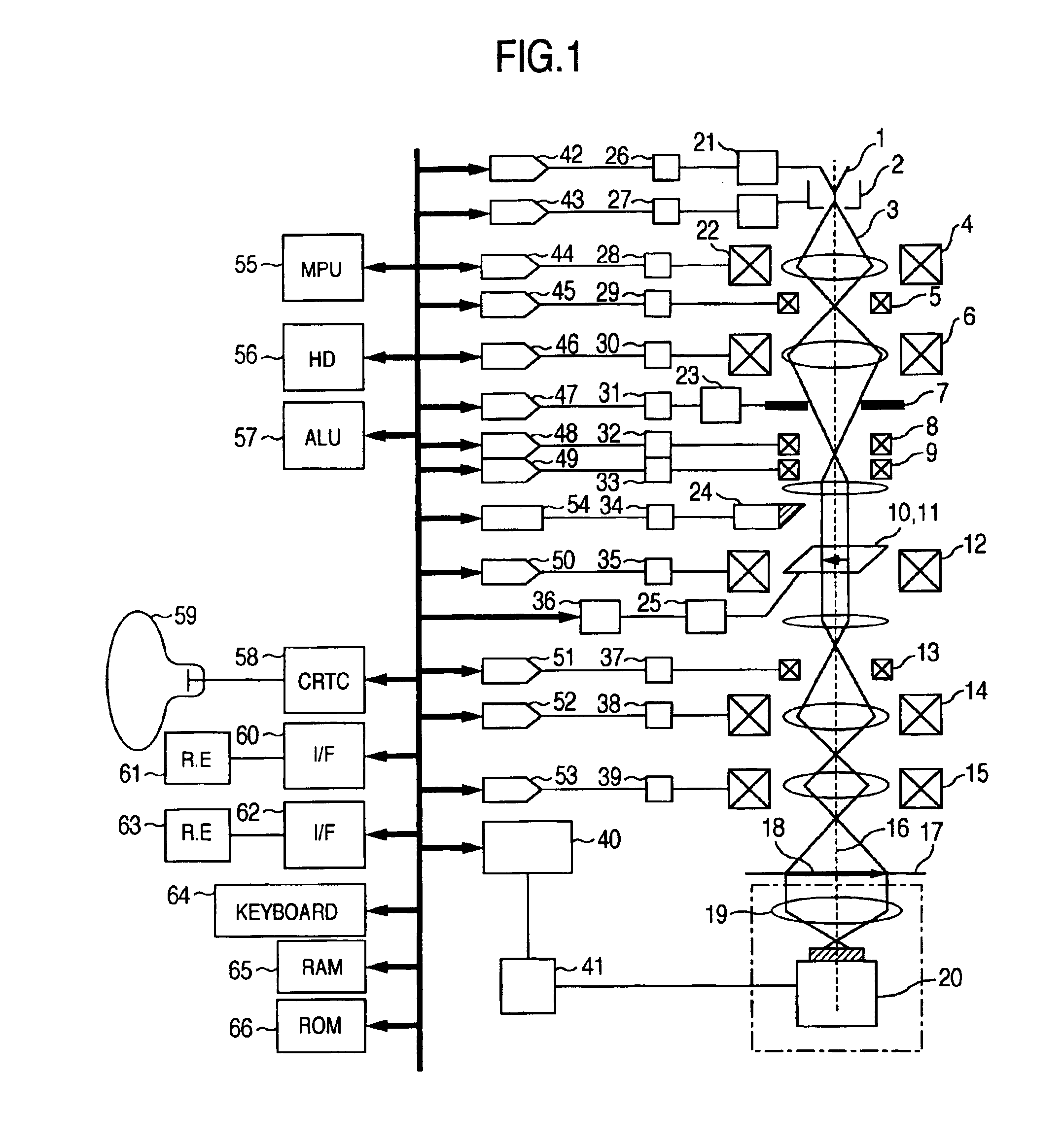
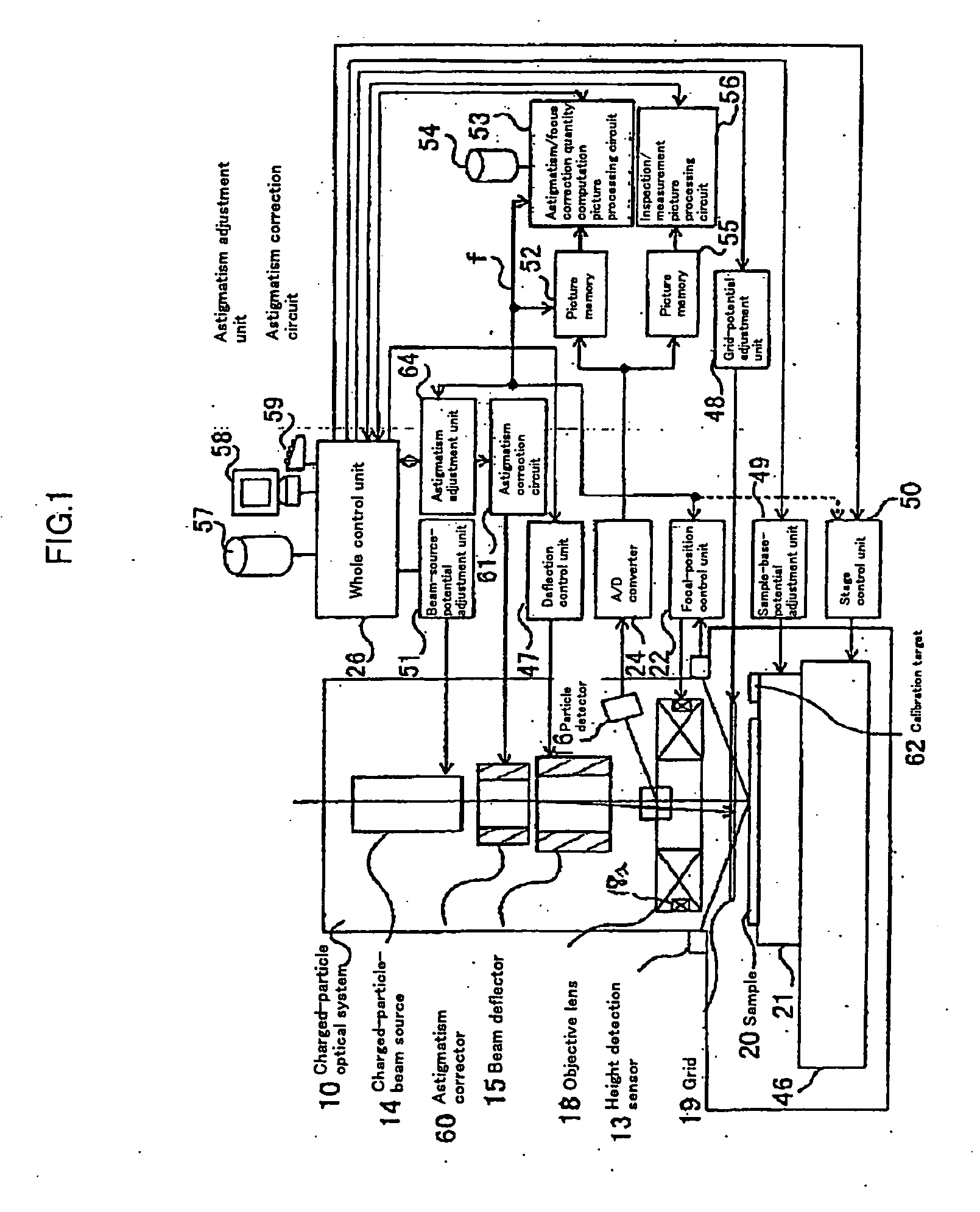
Charged particle beam adjusting method and charged particle beam apparatus
InactiveUS20050236570A1Improve accuracyImprove processing speedMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesAutomatic controlAstigmatism correction
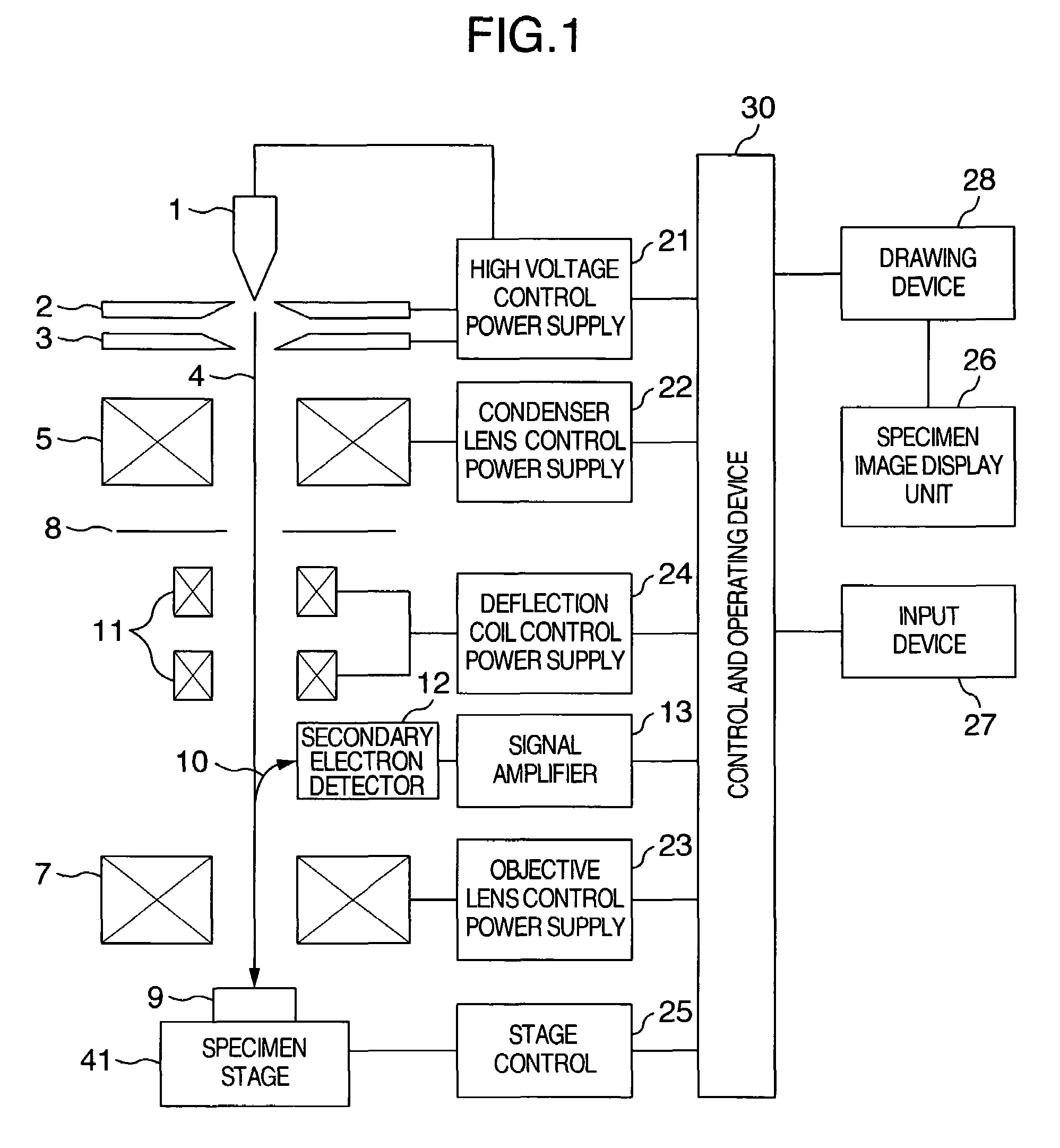
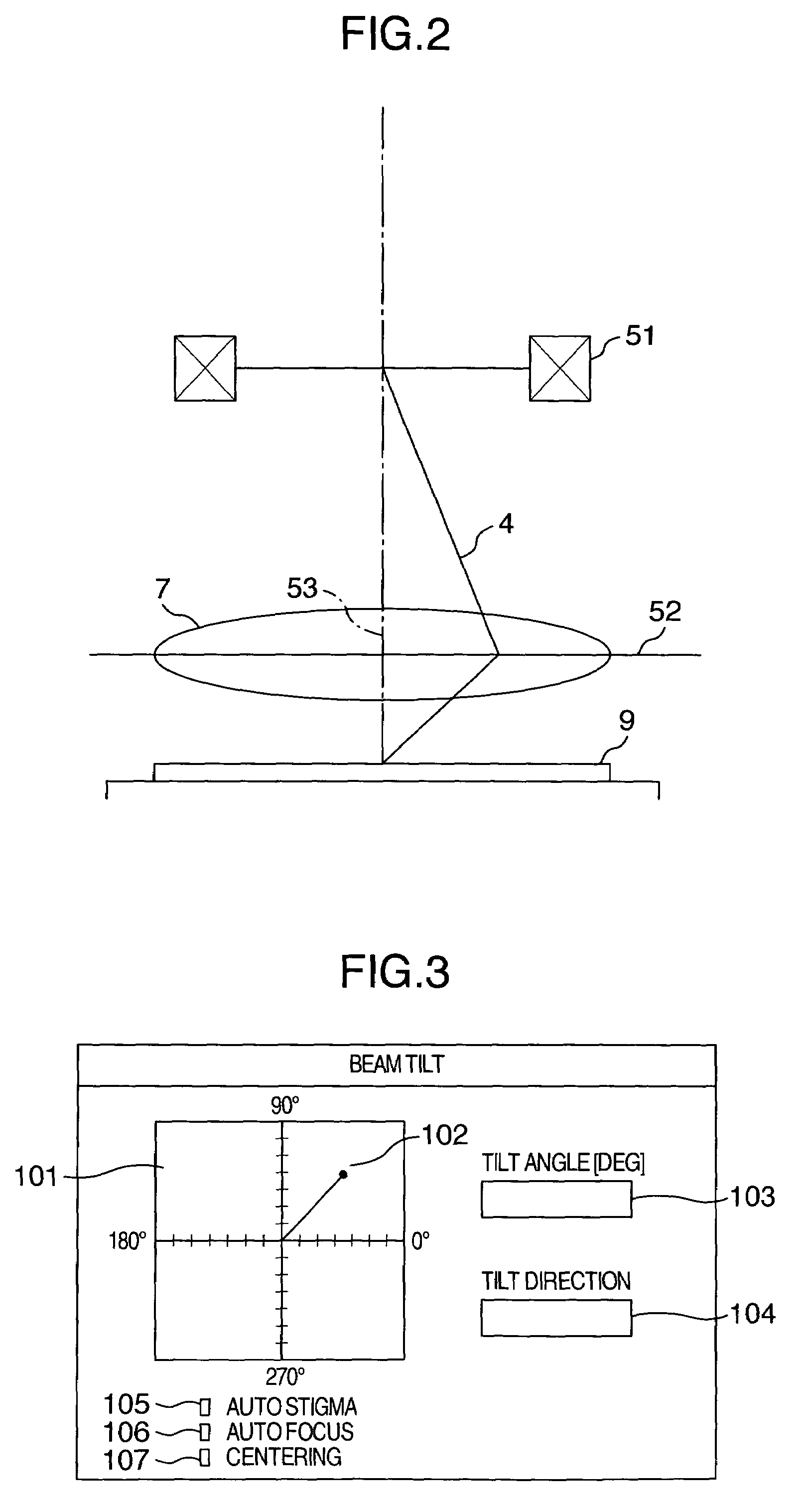
In an apparatus for obtaining an image by irradiating a charged particle beam on a specimen, a condition of the beam conditioned differently from vertical incidence as in the case of the beam being tilted is required to be adjusted. To this end, the apparatus has a controller for automatically controlling a stigmator, an objective lens and a deflector such that astigmatism is corrected, focus is adjusted and view filed shift is corrected. The controller has a selector for inhibiting at least one of the astigmatism correction, focus adjustment and FOV shift correction from being executed.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
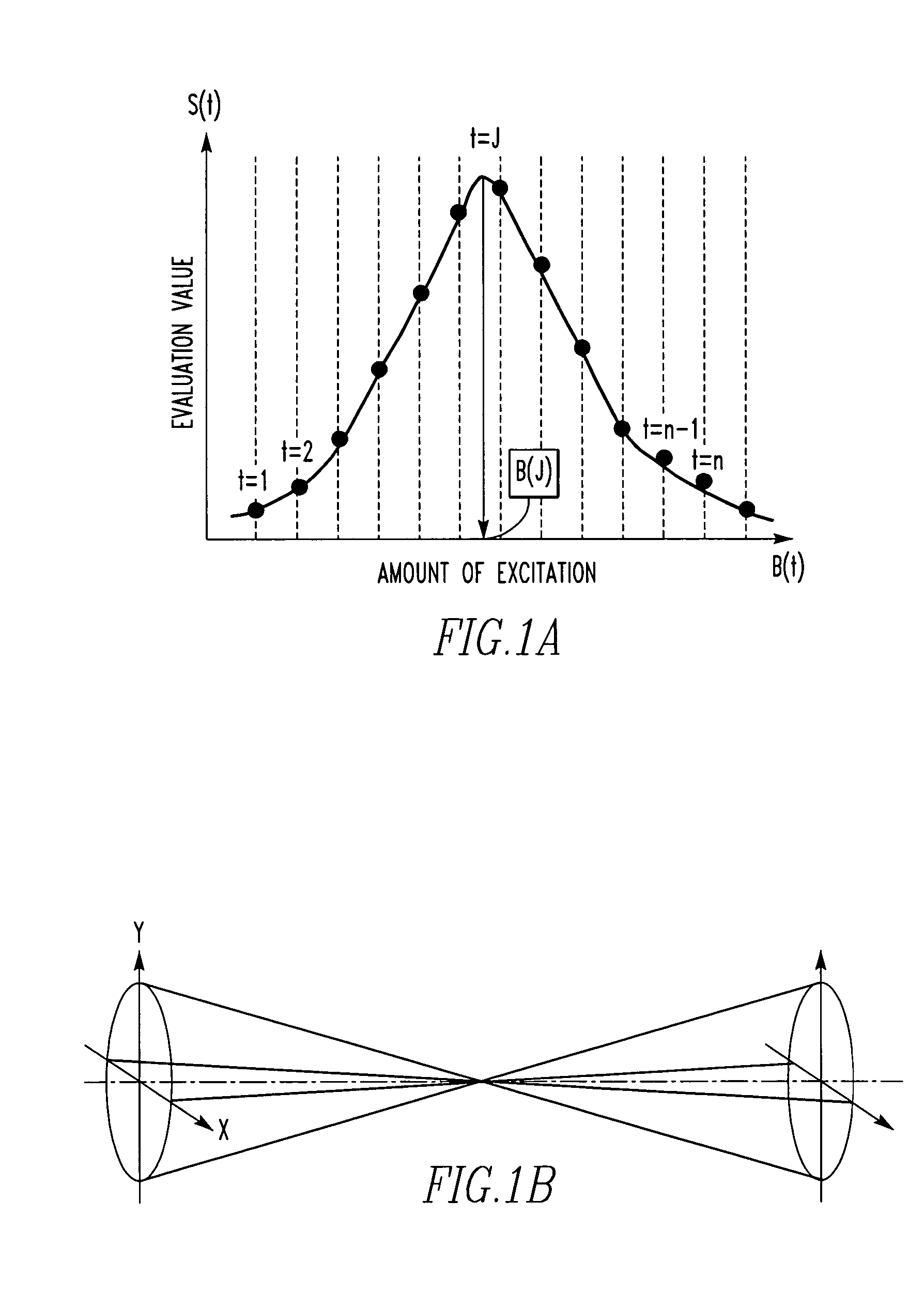
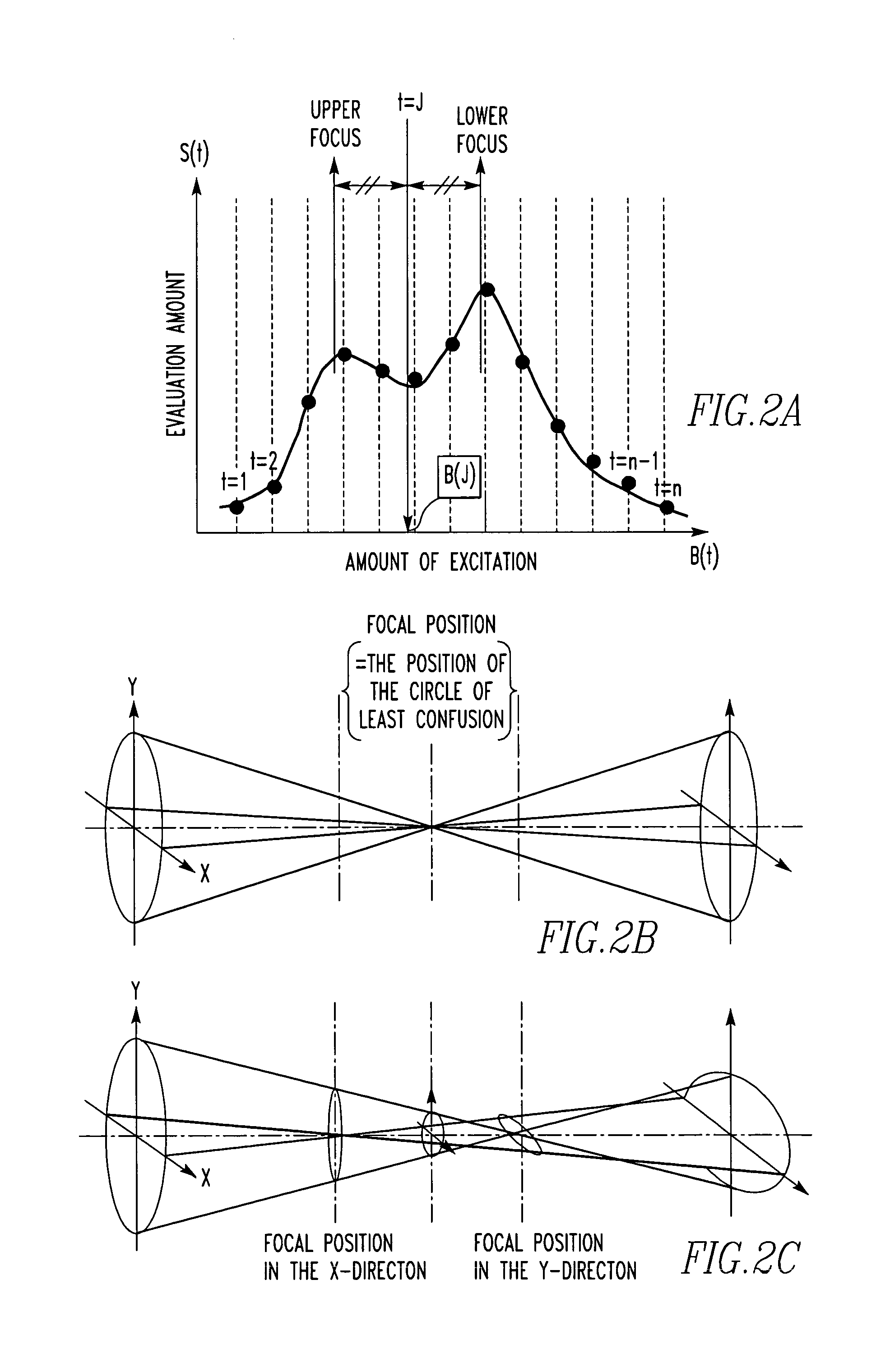
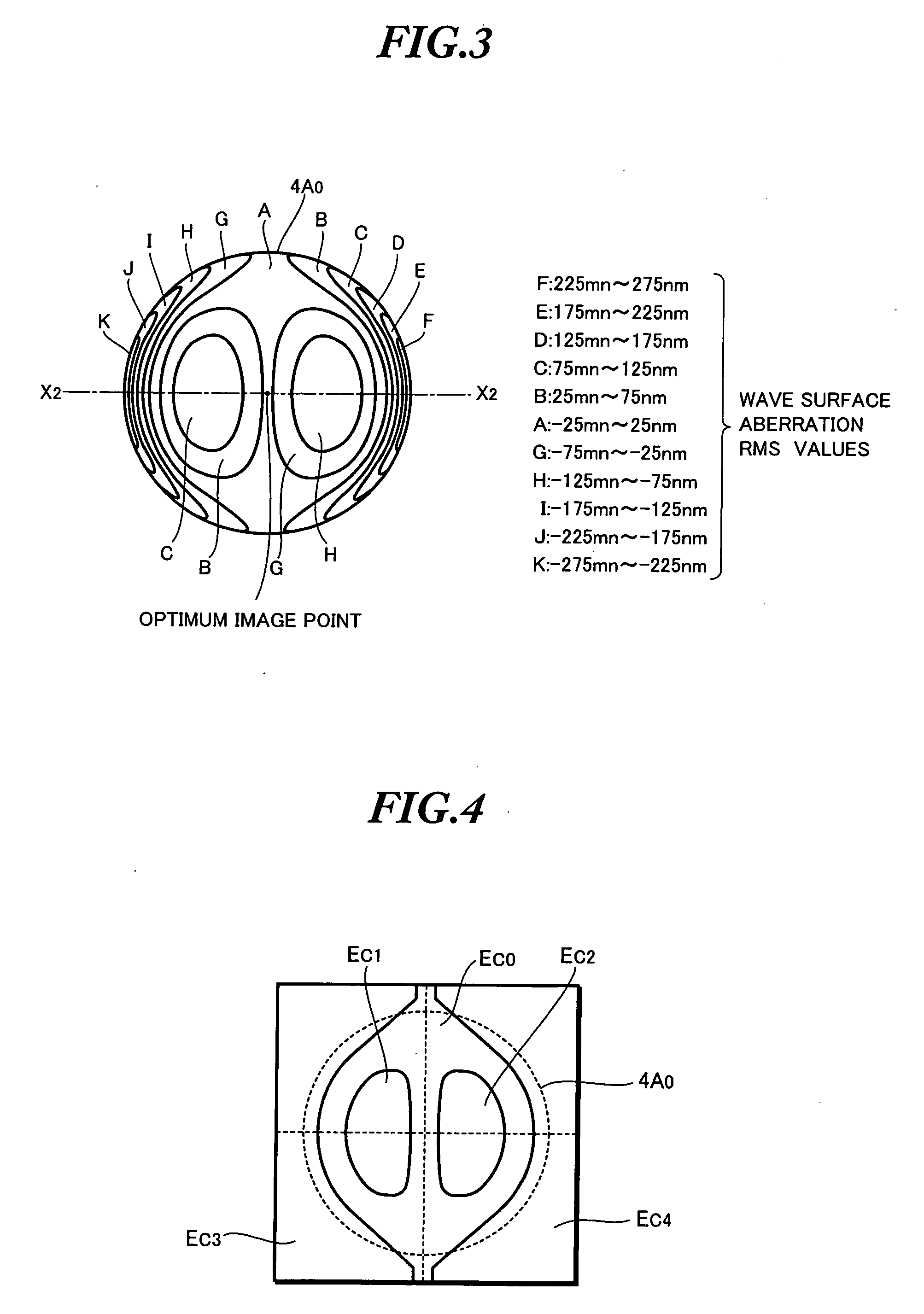
Automatic methods for focus and astigmatism corrections in charged-particle beam instrument
InactiveUS20050035290A1Thermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationNoise reductionAstigmatism correction
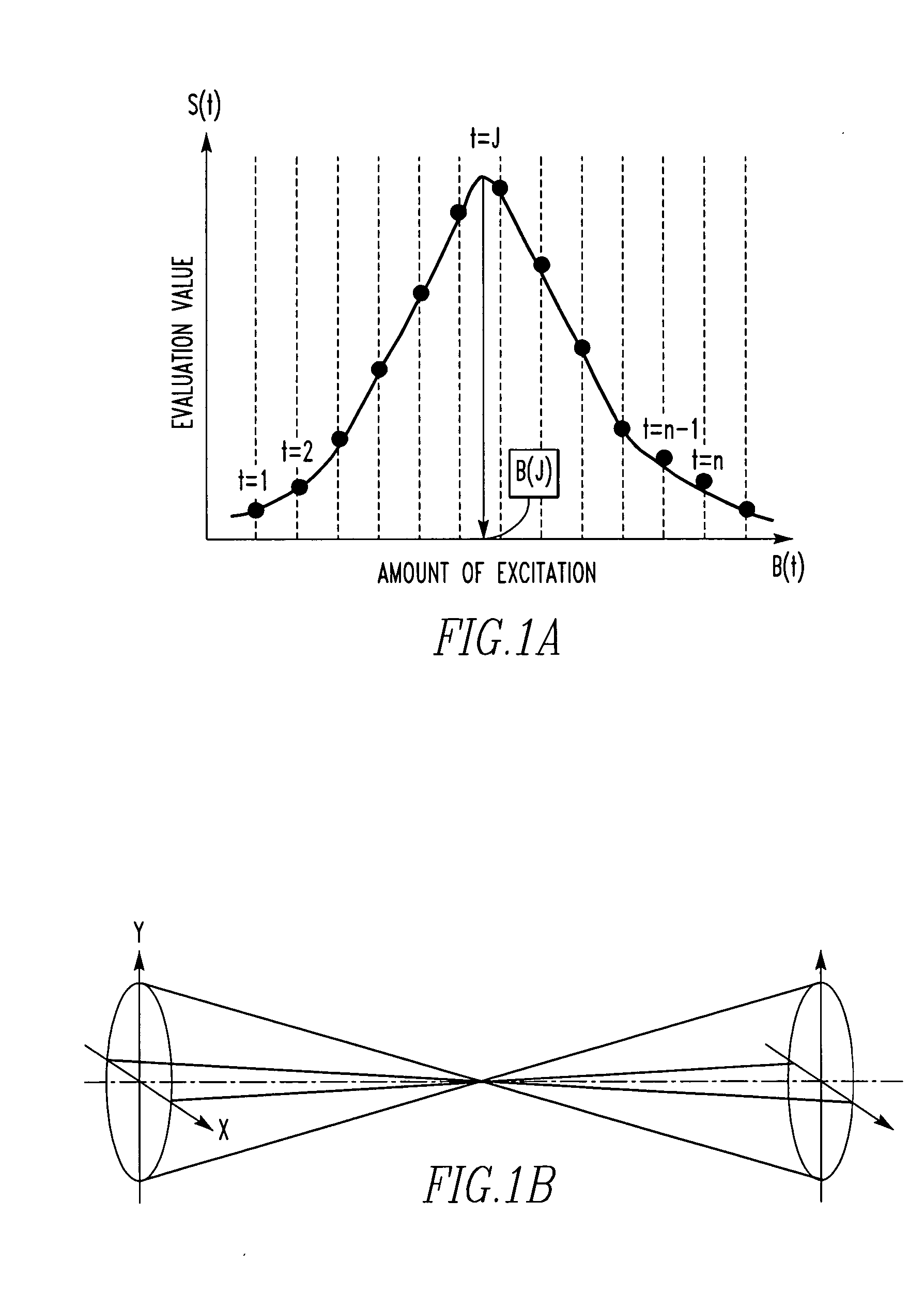
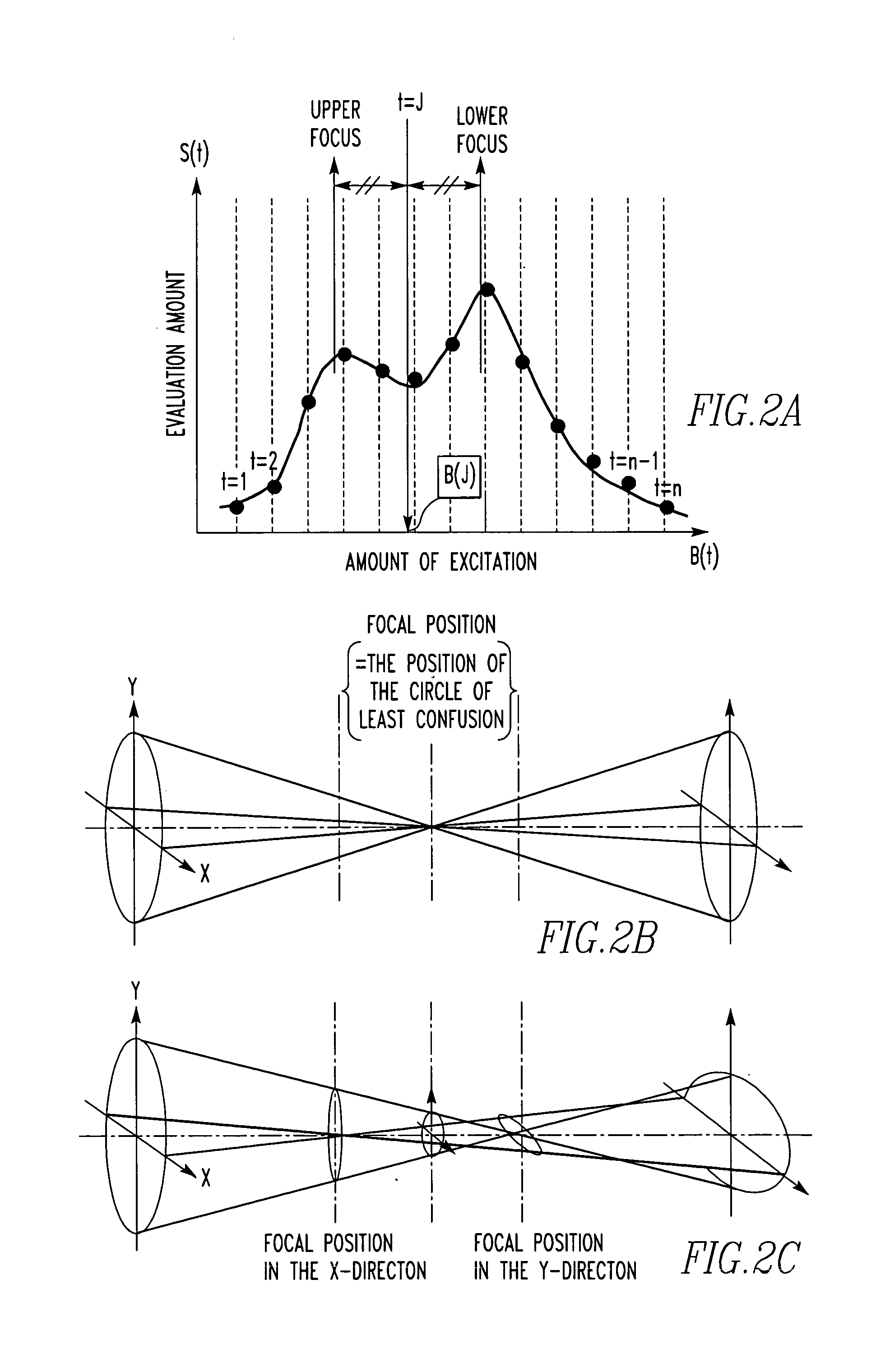
Automatic methods for focus and astigmatism corrections in a charged-particle beam instrument find an amount of excitation of the objective lens that provides the position of a circle of least confusion and can perform accurate automatic corrections of focus and astigmatism. The edge components of the original image along the X- and Y-directions are extracted separately, using respective filters. Noise reduction and normalization of numerical values are performed for each of the resulting two sets of data. Two-dimensional matrices of numerical values indicating the edge components in the X- and Y-directions, respectively, are found independently. The sums of the elements of the matrices are taken as focus evaluation values of the original image in the X- and Y-directions, respectively.
Owner:JEOL LTD
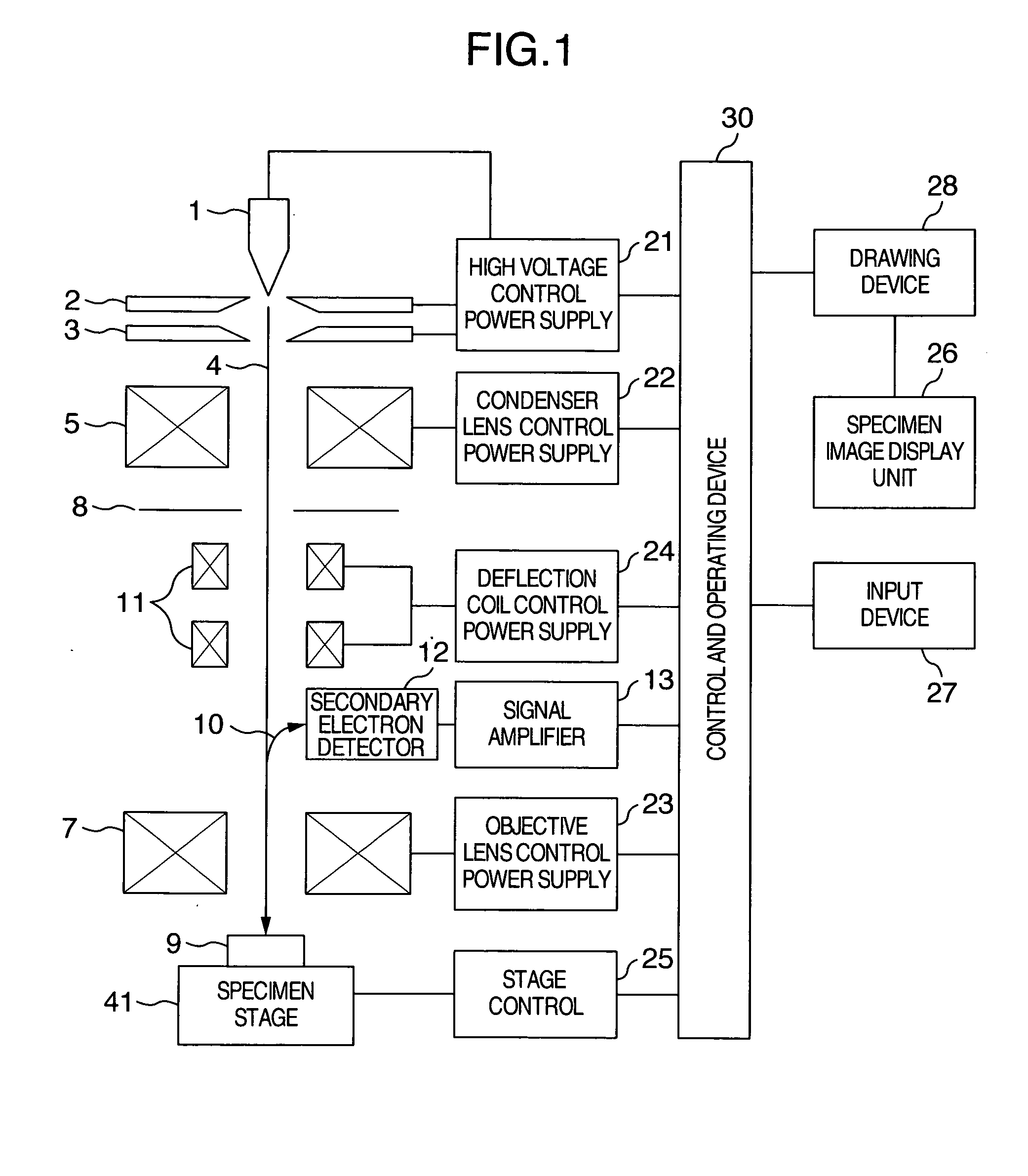
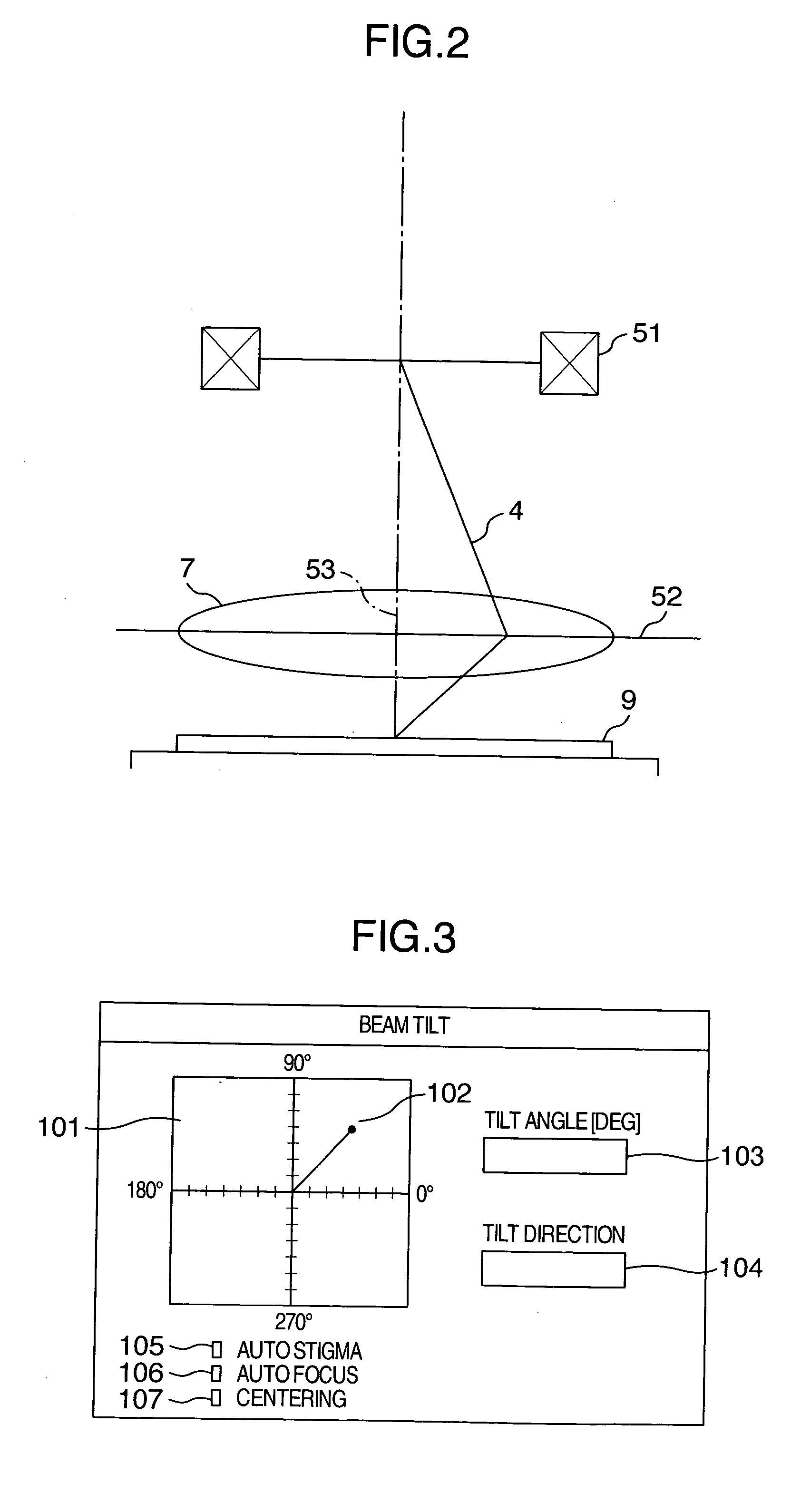
Electron microscope
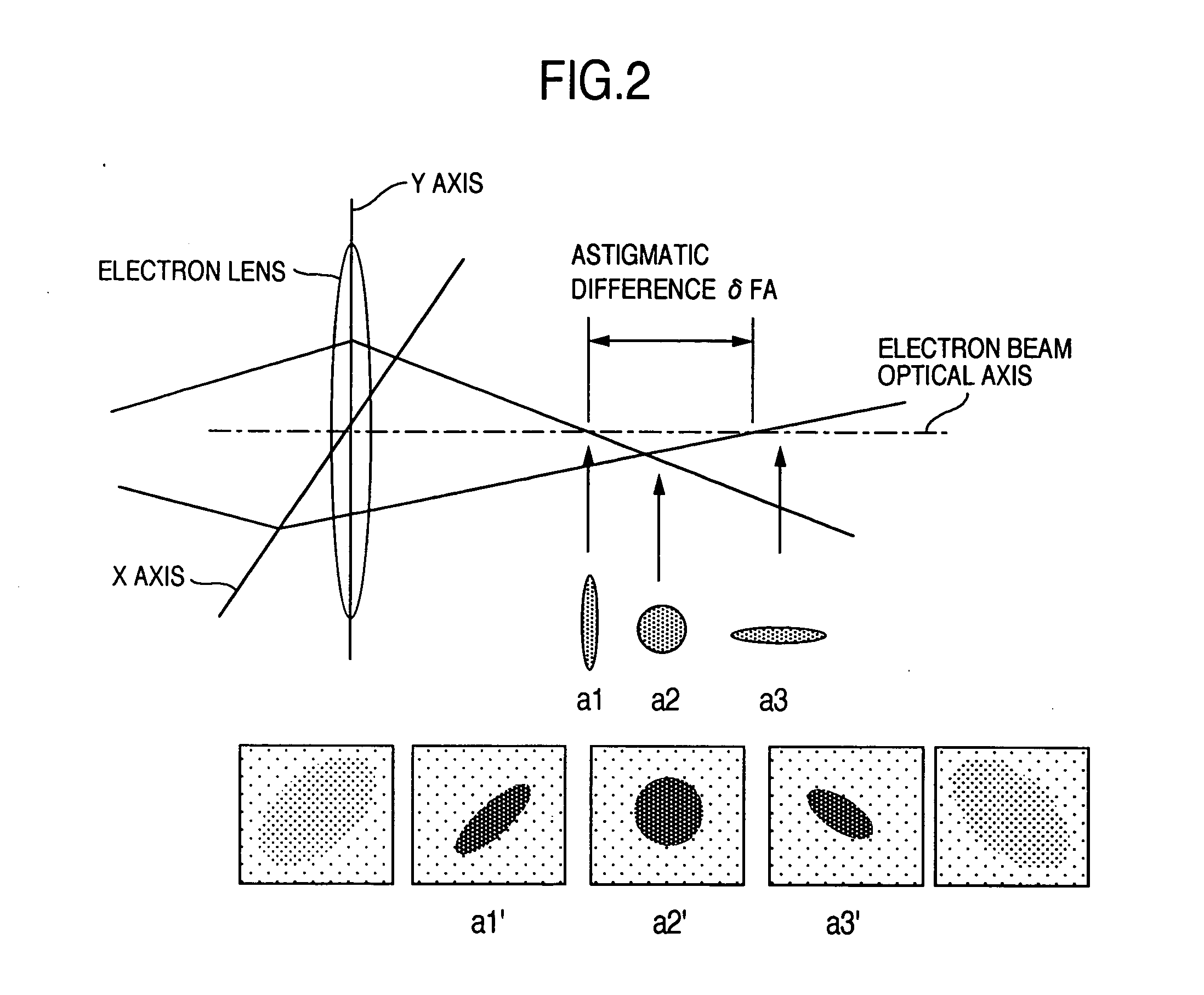
ActiveUS20050072920A1Good reproducibilityEasy to operateElectric discharge tubesUsing optical meansArithmetic logic unitExcitation current
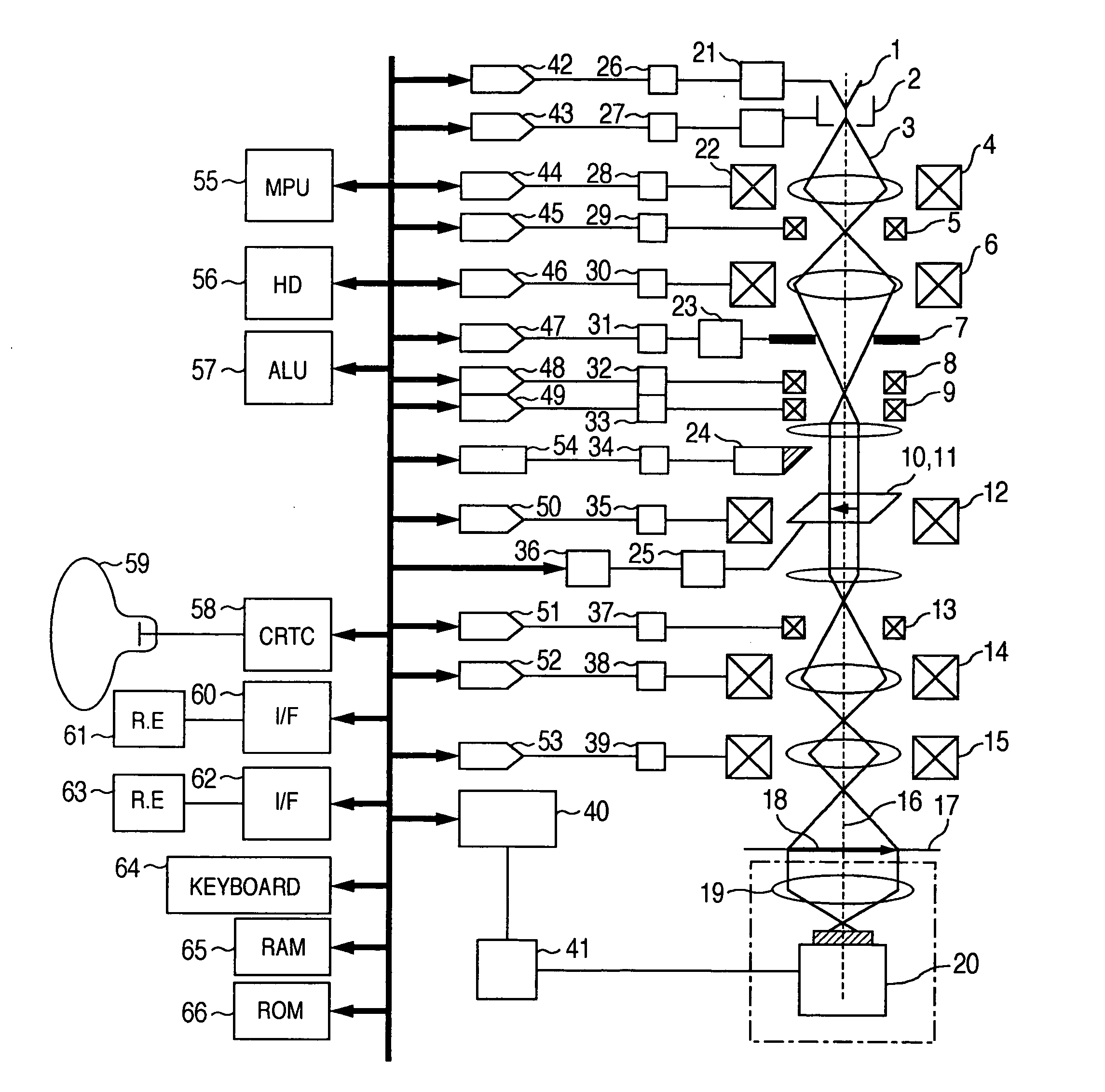
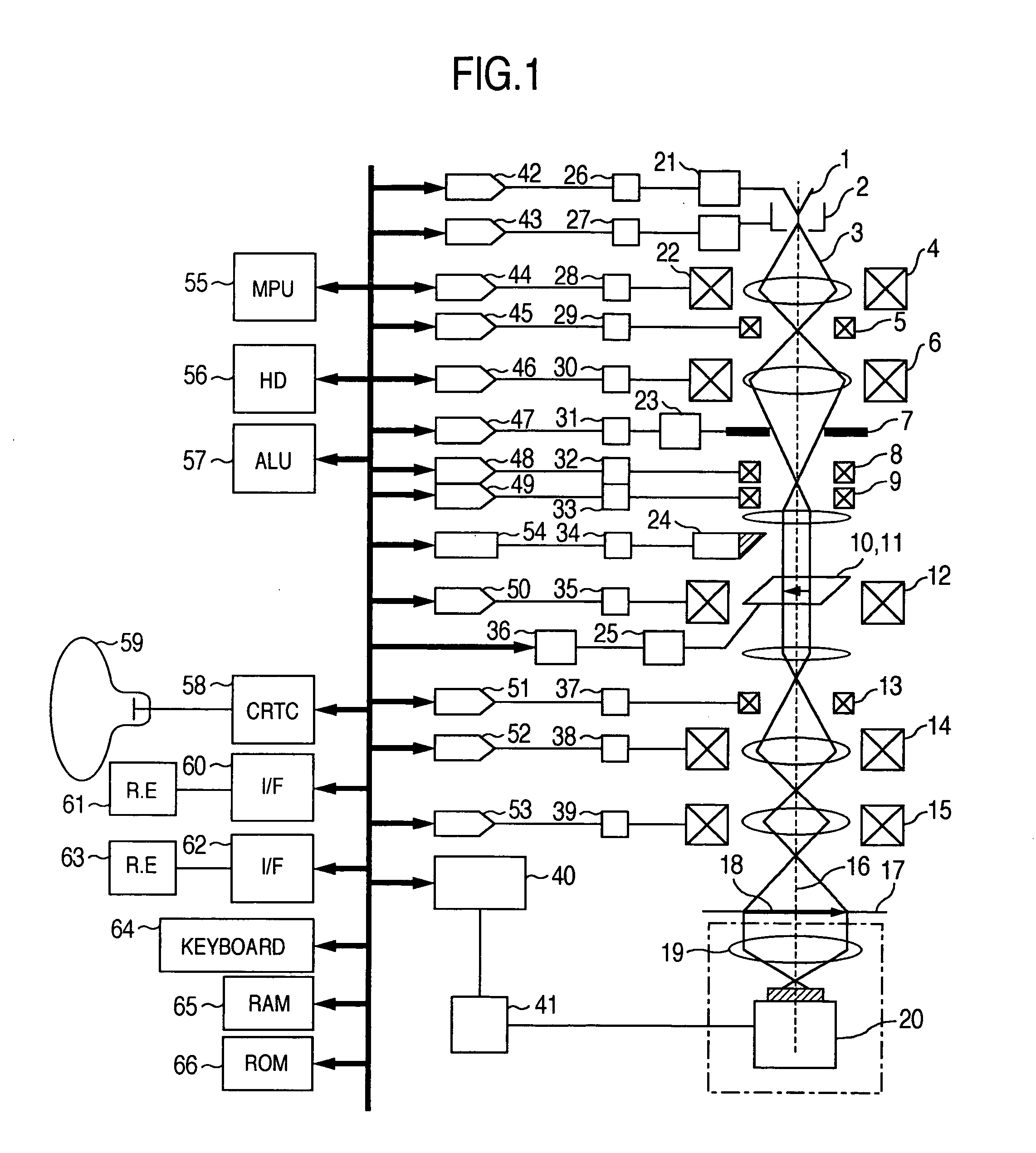
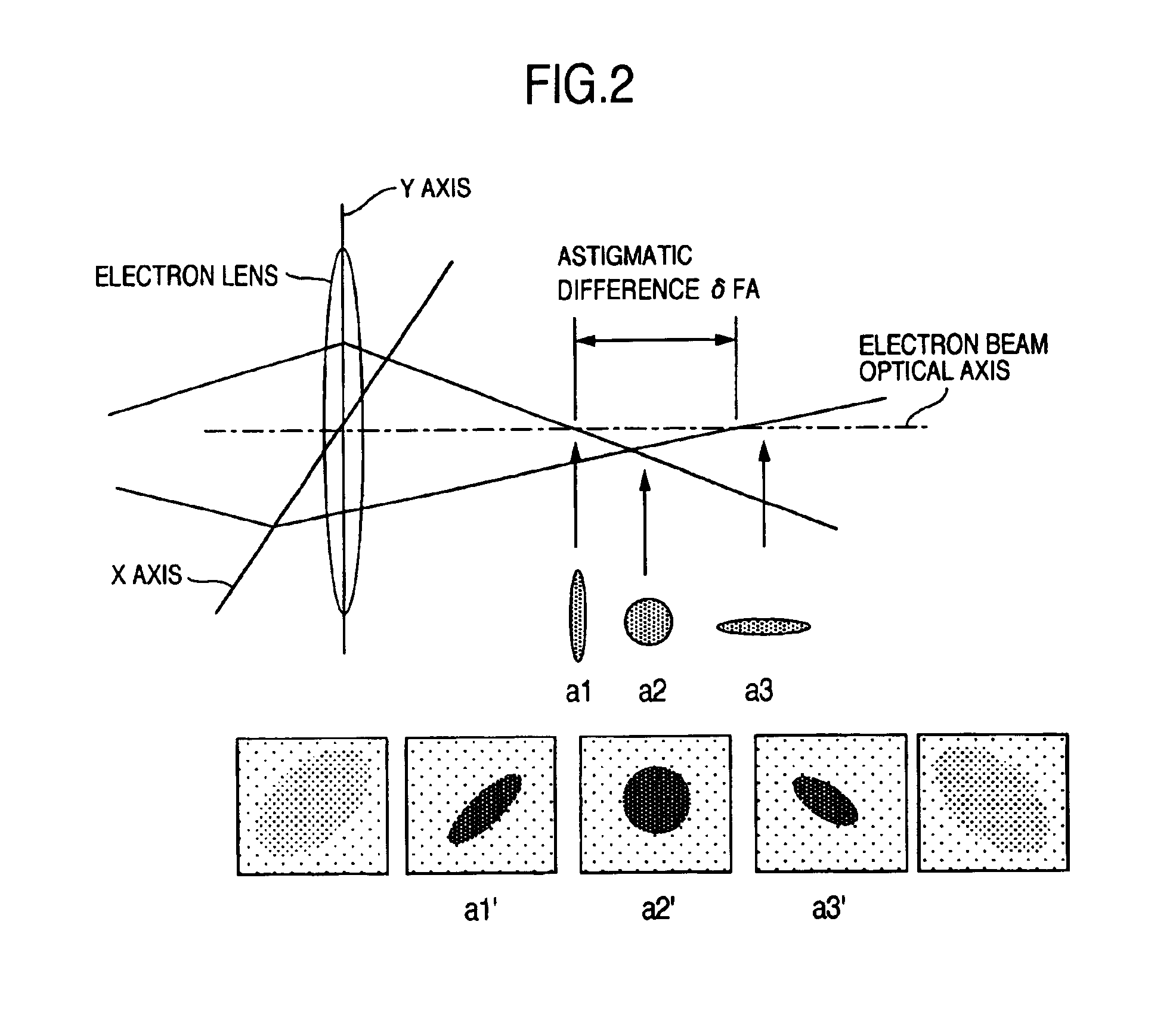
In an electron microscope, focus correction is carried out automatically, an astigmatic difference amount is displayed and astigmatism correction is executed quantitatively. Enlarged specimen images obtained by irradiating an electron beam on a specimen while changing excitation currents of an objective lens and of a stigmator coil are picked up by a capturing unit comprised of an optical lens and a capturing device and image sharpness coefficients are calculated by means of an arithmetic logic unit. A suitable astigmatism correction direction is chosen on the basis of an angular component value of the obtained image sharpness coefficients and then, a correction excitation current is supplied to a stigmator coil to correct astigmatism and a correction excitation current is supplied to an objective lens coil to perform focus correction.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
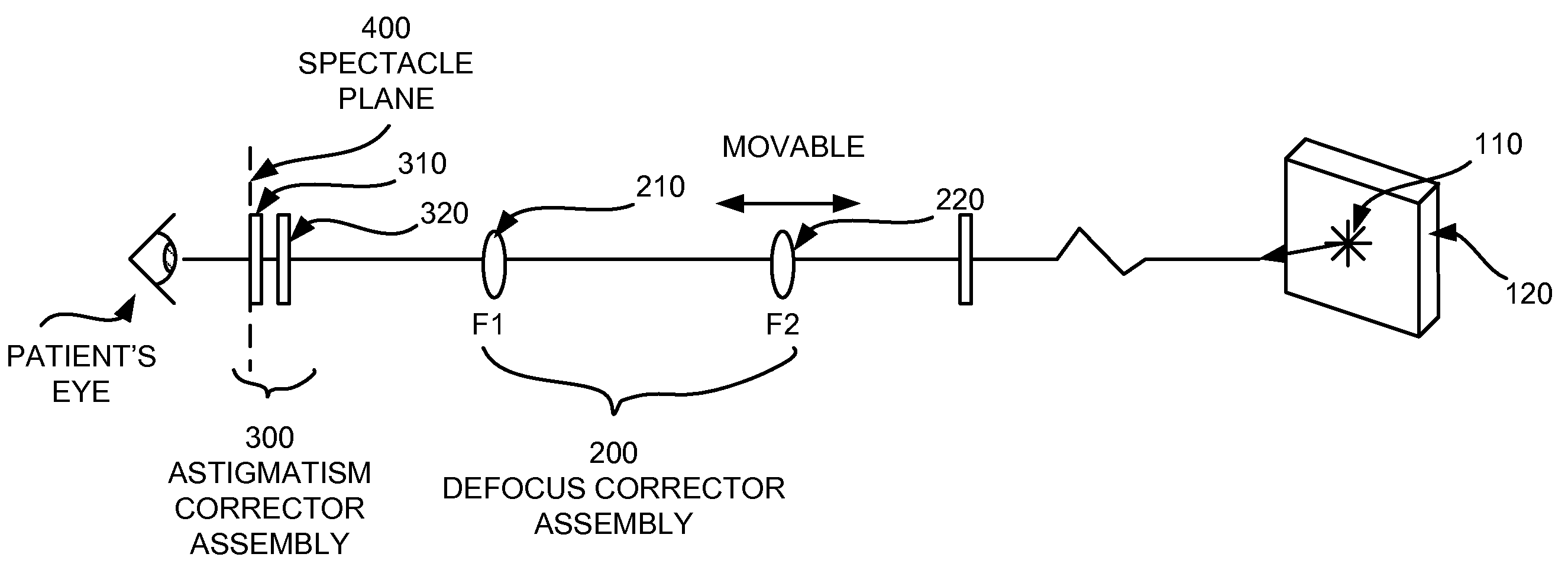
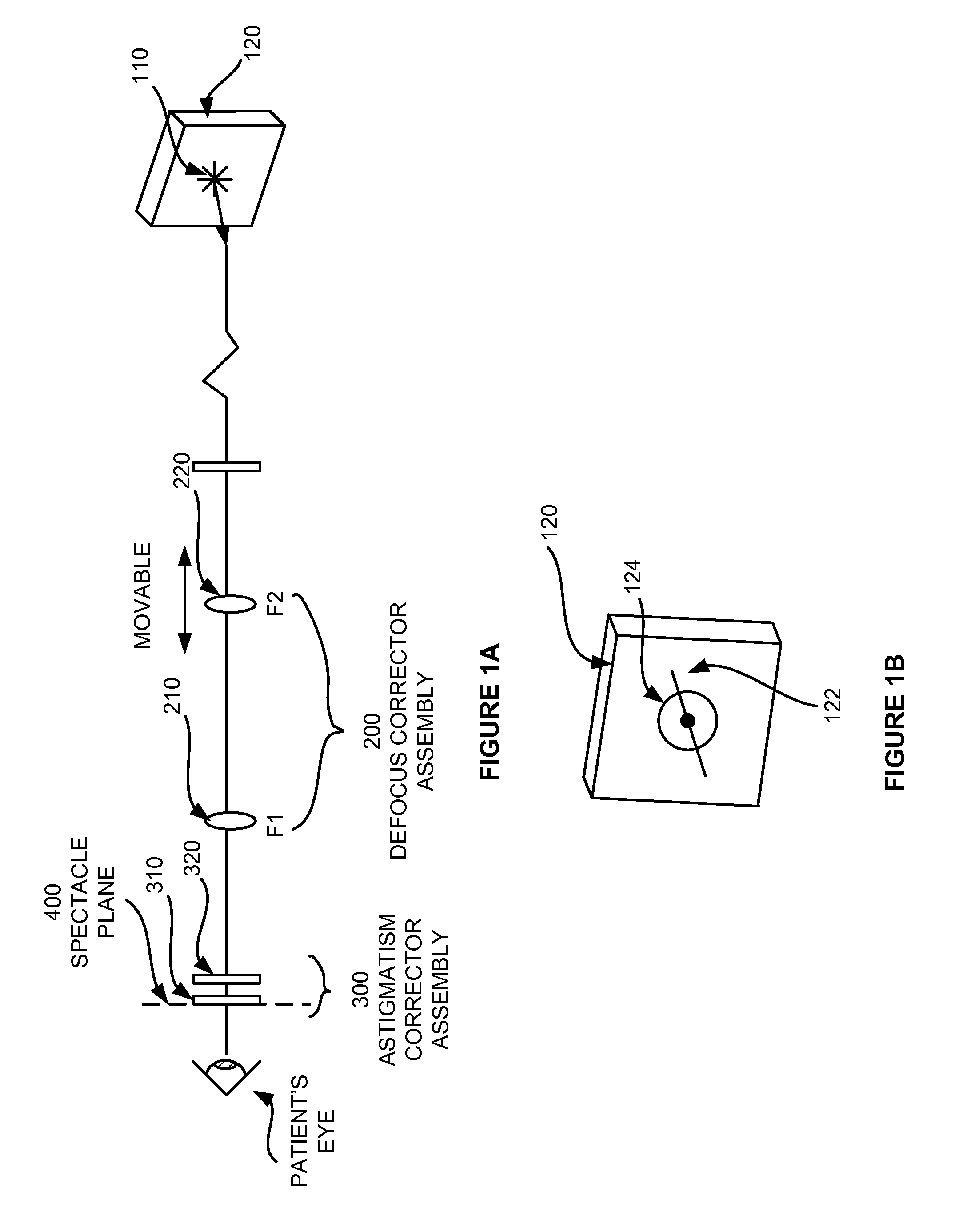
Subjective refraction method and device for correcting low and higher order aberrations
A subjective refraction technique uses a plane wave light source including substantially a point as a viewing target. The refraction method provide for a number of distinct identifiable end points. By finding such end points the process leads to an aberration-corrected vision. A defocus corrector assembly (DCA) includes a lens that is moveable along an optical axis between a patient's eye and the point light source for adjusting defocus power until the patient indicates that the blurry image has become a relatively focused line image. An astigmatism corrector assembly (ACA) which is capable of continuously variable in its amplitude is provided including a pair of astigmatism plates for adjusting astigmatism power and axis angle. The ACA is adjusted until the patient indicates that the line image has become a substantially round image. A reference marker provides displayed items including a sweep line overlapping at the point source and having an orientation which is adjustable. The patient may subjectively control the sweep angle of the sweep line and indicate that the sweep line is aligned with the sharp line image of the point source, thereby providing axis angle data of astigmatism errors of the patient's eye.
Owner:LAI SHUI T
Low inventory method of making eyeglasses
A low inventory method of making eyeglasses. Two lens elements having special complementary surfaces are provided. These lens elements can be positioned relative to each other to provide wide ranges of focus correction and astigmatism correction. Various preferred embodiments of the invention are described. In one embodiment the required inventory is only identical sets of two complementary lenses for providing correction for almost all needed eye correction for a typical population. In this embodiment, the lens units are first adjusted relative to each other to provide a desired focusing power. Astigmatism may be corrected by a small adjustment in a second direction perpendicular to the first direction followed by a rotation of the two lenses about the axis of the two lenses. When the adjustments have been made the two lenses are fixed with respect to each other and installed in eyeglass frames. Cutting to the shape of the eyeglass frames can occur either before or after the fixing.
Owner:QUEXTA
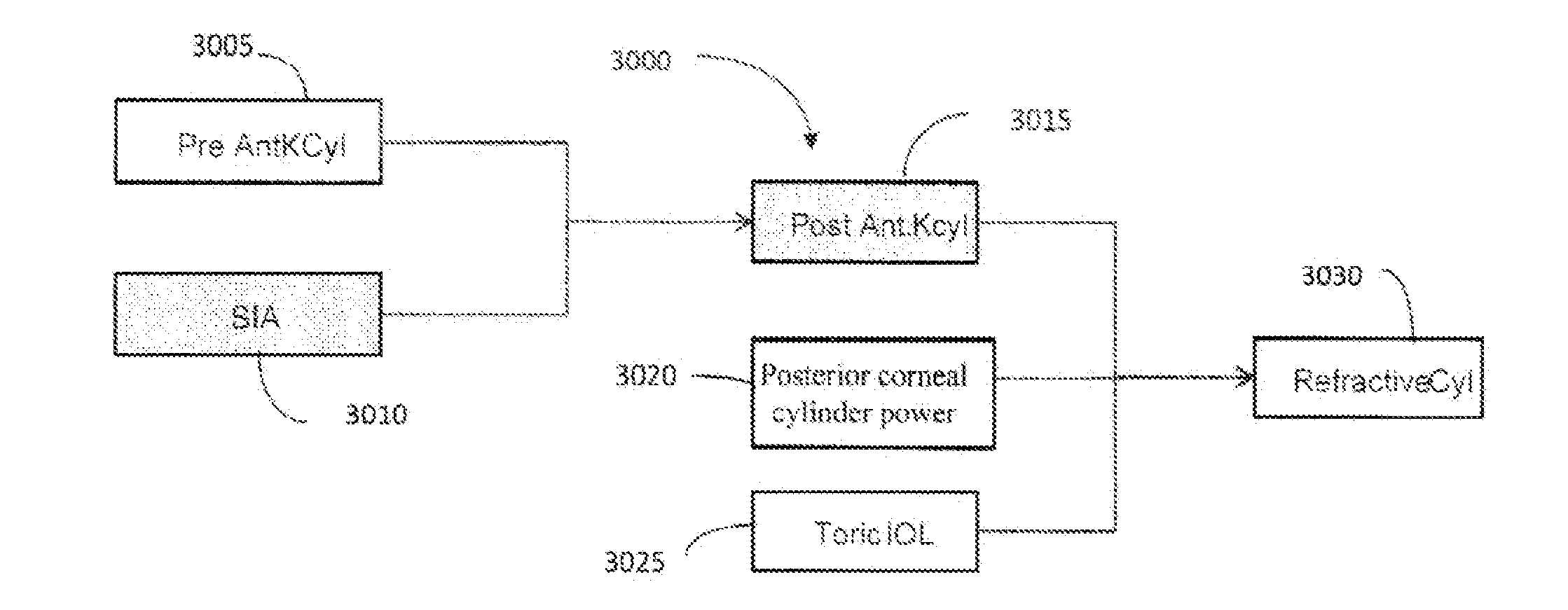
Systems and methods for providing astigmatism correction
ActiveUS20150062529A1Promote resultsImprove selection accuracyEye diagnosticsAnterior corneaAstigmatism correction
A method of selecting a toric lens by taking into consideration the magnitude and orientation of the posterior cornea and / or the location of the incision axis is described. The magnitude and orientation of the posterior cornea can be calculated as a function of the measured pre-operative orientation of the steep meridian of the anterior cornea.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
Spectrometer using cylindrical lens for astigmatism correction
InactiveCN101634591AHigh measurement sensitivityReduce volumeSpectrum investigationGratingLight beam
The invention relates to a spectrometer using a cylindrical lens for astigmatism correction. The spectrometer comprises an incidence slit, a cylindrical surface lens, a concave surface alignment reflector, a plane grating, a concave focusing mirror and a line array CCD detector, wherein incidence lights pass through the incidence slit and the cylindrical surface lens in sequence, and then are irradiated on the concave surface alignment reflector; light beams of the concave surface alignment reflector are parallelly irradiated on the plane grating; and the light beams split by the plane grating are irradiated on the focusing mirror and focused on the linear array CCD detector. The spectrometer uses the cylindrical surface lens for focusing and correcting spectrometer astigmatism and increases the measuring sensitivity of the spectrometer in the situation of non obvious increased cost compared with the light path adopted at the present. The spectrometer is characterized by small volume and low cost.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Multifocal optical device design
InactiveUS20050254007A1Reduce computing timeDesign optimisation/simulationEye diagnosticsTriangulationEngineering
Multifocal optical device designs receive input parameters to specify a desired power distribution function, a power deviation weight function, and an astigmatism weight function over the design field. A fourth-order partial differential variational equation is linearized by defining the optical surface in terms of perturbations from a base surface such as a sphere or a toric. The solution may be expressed as piecewise quadratic splines superposed over a triangulation of the field. Evaluation of the surface may use a set of tensor-product splines. An astigmatic base surface permits both multiple magnifying powers and a prescribed astigmatism correction in a single optical surface.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Low inventory method of making eyeglasses
Owner:QUEXTA
Multifocal optical device design
InactiveUS20050052615A1Reduces computation time for accurate powersDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsTriangulationEngineering
Multifocal optical device designs receive input parameters to specify a desired power distribution function, a power deviation weight function, and an astigmatism weight function over the design field. A fourth-order partial differential variational equation is linearized by defining the optical surface in terms of perturbations from a base surface such as a sphere or a toric. The solution may be expressed as piecewise quadratic splines superposed over a triangulation of the field. Evaluation of the surface may use a set of tensor-product splines. An astigmatic base surface permits both multiple magnifying powers and a prescribed astigmatism correction in a single optical surface.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Increased stiffness center optic in soft contact lenses for astigmatism correction
ActiveUS10209534B2Increase loadHigh modulusSpectales/gogglesOptical articlesRefractive errorStigmatism
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Toric small aperture intraocular lens with extended depth of focus
ActiveUS20180338826A1Address bad outcomesSimple treatmentIntraocular lensStigmatismAstigmatism correction
An intraocular lens is provided that includes a refractive element and a mask. The refractive element has a first power in a first meridian and a second power greater than the first power in a second meridian. A magnitude of the first and second powers and a location of the first and second meridians are configured to correct astigmatism in a human eye. The mask is configured to block a substantial portion of light from passing through an annular region thereof and to permit a substantial portion of light to pass through a central aperture thereof to enhance an astigmatism correction rotational misplacement range and depth of focus.
Owner:ACUFOCUS
Electron microscope
ActiveUS7126120B2Reduce contrastPrecise positioningElectric discharge tubesUsing optical meansArithmetic logic unitExcitation current
In an electron microscope, focus correction is carried out automatically, an astigmatic difference amount is displayed and astigmatism correction is executed quantitatively. Enlarged specimen images obtained by irradiating an electron beam on a specimen while changing excitation currents of an objective lens and of a stigmator coil are picked up by a capturing unit comprised of an optical lens and a capturing device and image sharpness coefficients are calculated by means of an arithmetic logic unit. A suitable astigmatism correction direction is chosen on the basis of an angular component value of the obtained image sharpness coefficients and then, a correction excitation current is supplied to a stigmator coil to correct astigmatism and a correction excitation current is supplied to an objective lens coil to perform focus correction.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Charged particle beam adjusting method and charged particle beam apparatus
InactiveUS7705300B2Improve accuracyProcessing speedMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesAutomatic controlAstigmatism correction
In an apparatus for obtaining an image by irradiating a charged particle beam on a specimen, a condition of the beam conditioned differently from vertical incidence as in the case of the beam being tilted is required to be adjusted. To this end, the apparatus has a controller for automatically controlling a stigmator, an objective lens and a deflector such that astigmatism is corrected, focus is adjusted and view filed shift is corrected. The controller has a selector for inhibiting at least one of the astigmatism correction, focus adjustment and FOV shift correction from being executed.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Electron microscope and method for controlling focus position thereof
InactiveUS6984823B2Realize automatic adjustmentThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationImage transferFourier transform on finite groups
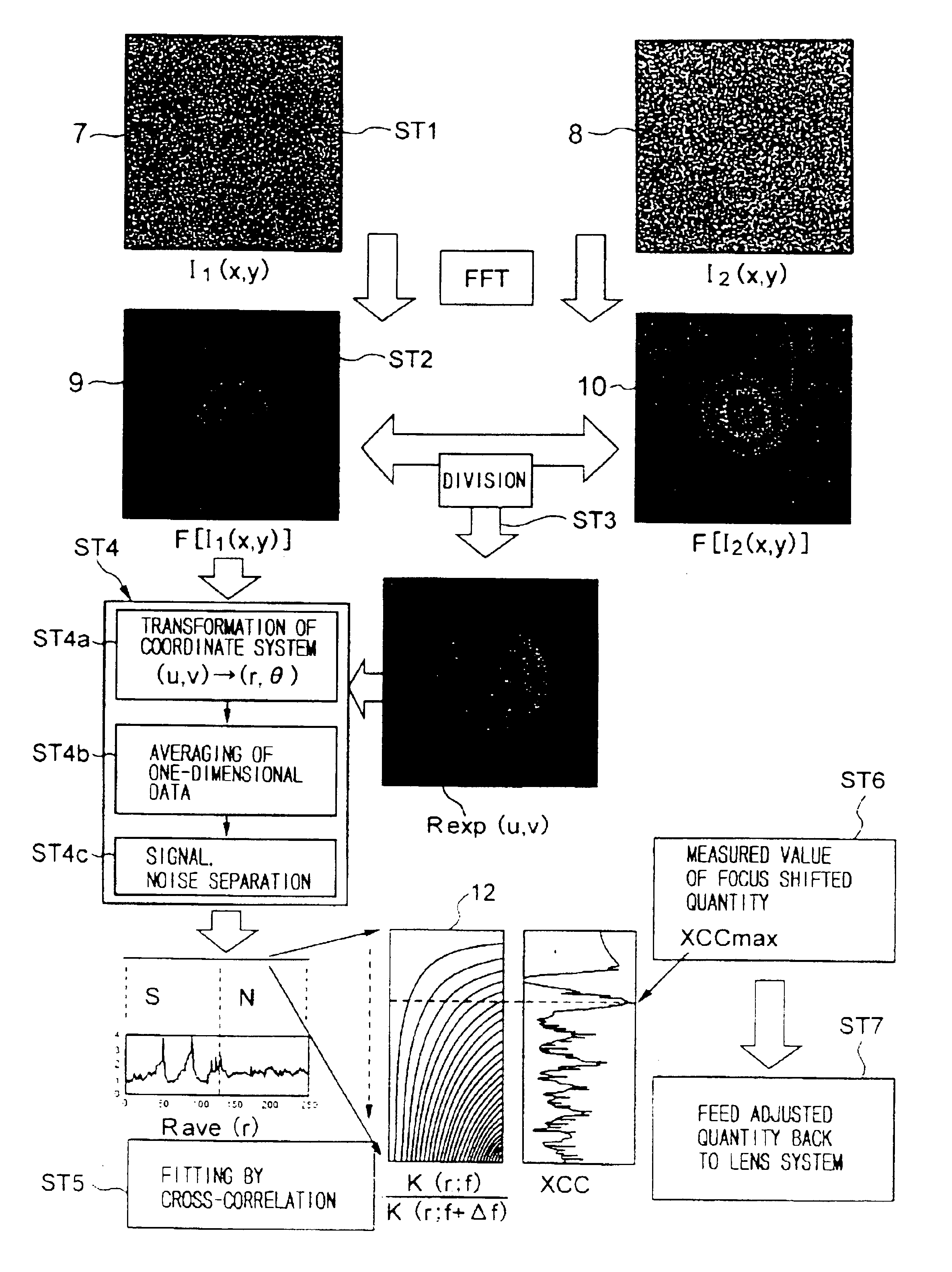
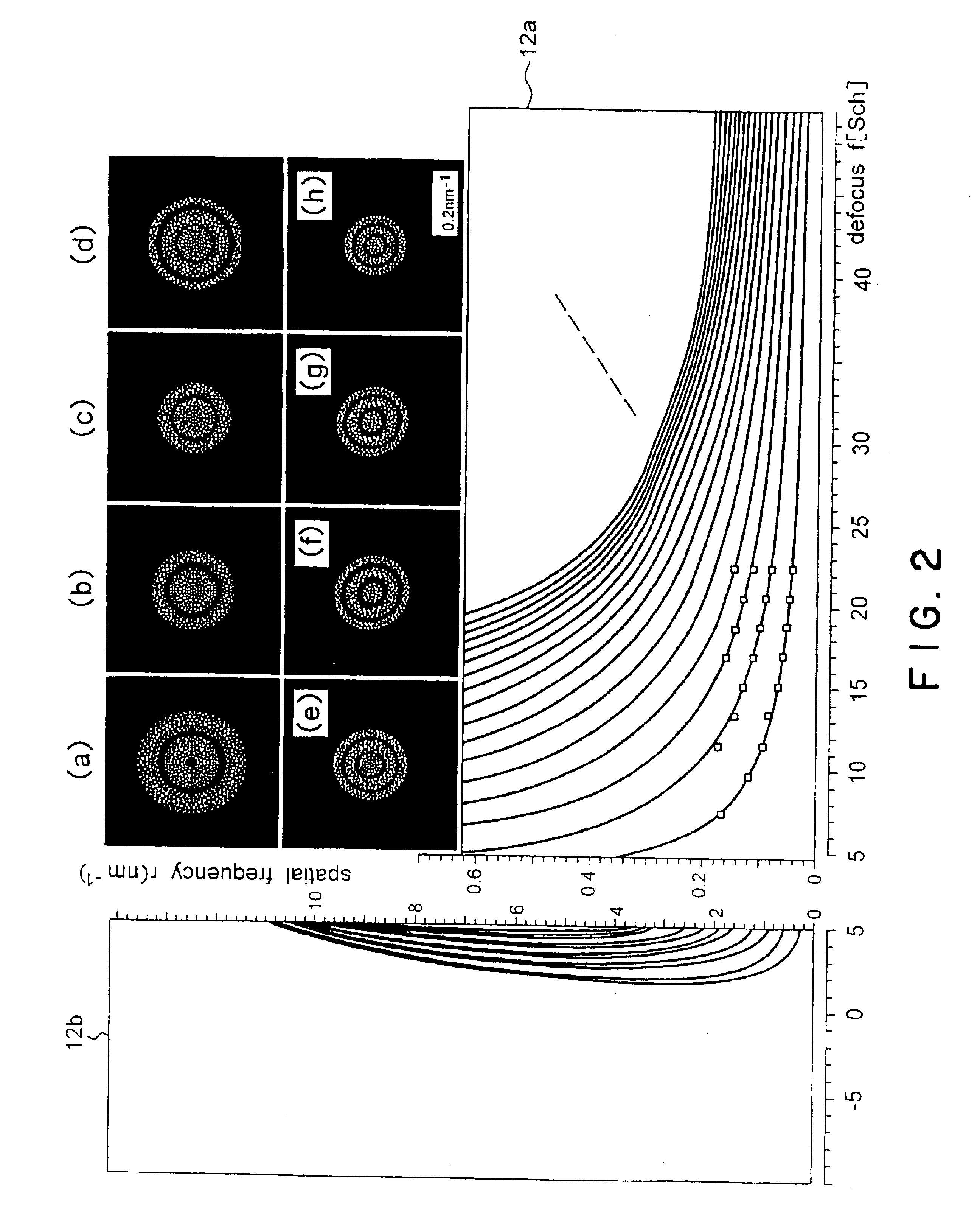
There are provided an electron microscope capable of carrying out focusing and astigmatism correction without depending on characteristics of a sample, and a method for controlling its focus position.The electron microscope according to the present invention comprises: an electron optical system (2); a focus control part (3); an image detecting part (4); a first operating part (11) for mutually dividing first and second transformed images (9) and (10), which are obtained by carrying out the fast Fourier transform of first and second images (7) and (8) detected at two focus positions of a first focus position (f1) and a second focus position (f2) shifted from the first focus position by a known focus shifted quantity Δf, to obtain a measured divided quantity Rexp; divided quantity data (12) previously prepared and stored as a function of focus positions and spatial frequencies as a set of theoretical divided quantities, the theoretical divided quantities being obtained by substituting the two focus positions shifted by the focus shifted quantity Δf for an image transfer function (r,f) to obtain first and second transfer function values K(r;f) and (r;f+Δf) to mutually divide the first and second transfer function values K(r;f1) and (r;f+Δf) on a spatial frequency plane; and a second operating part (13) for making a reference to the divided quantity data (12) to derive a theoretical divided quantity K(r;f0) correlating to the measured divided quantity Rexp, and for deriving a focus position f0 corresponding to the derived theoretical divided quantity K(r;f0) / K(r;f0+Δf) as a first focus position f1.
Owner:RIKEN
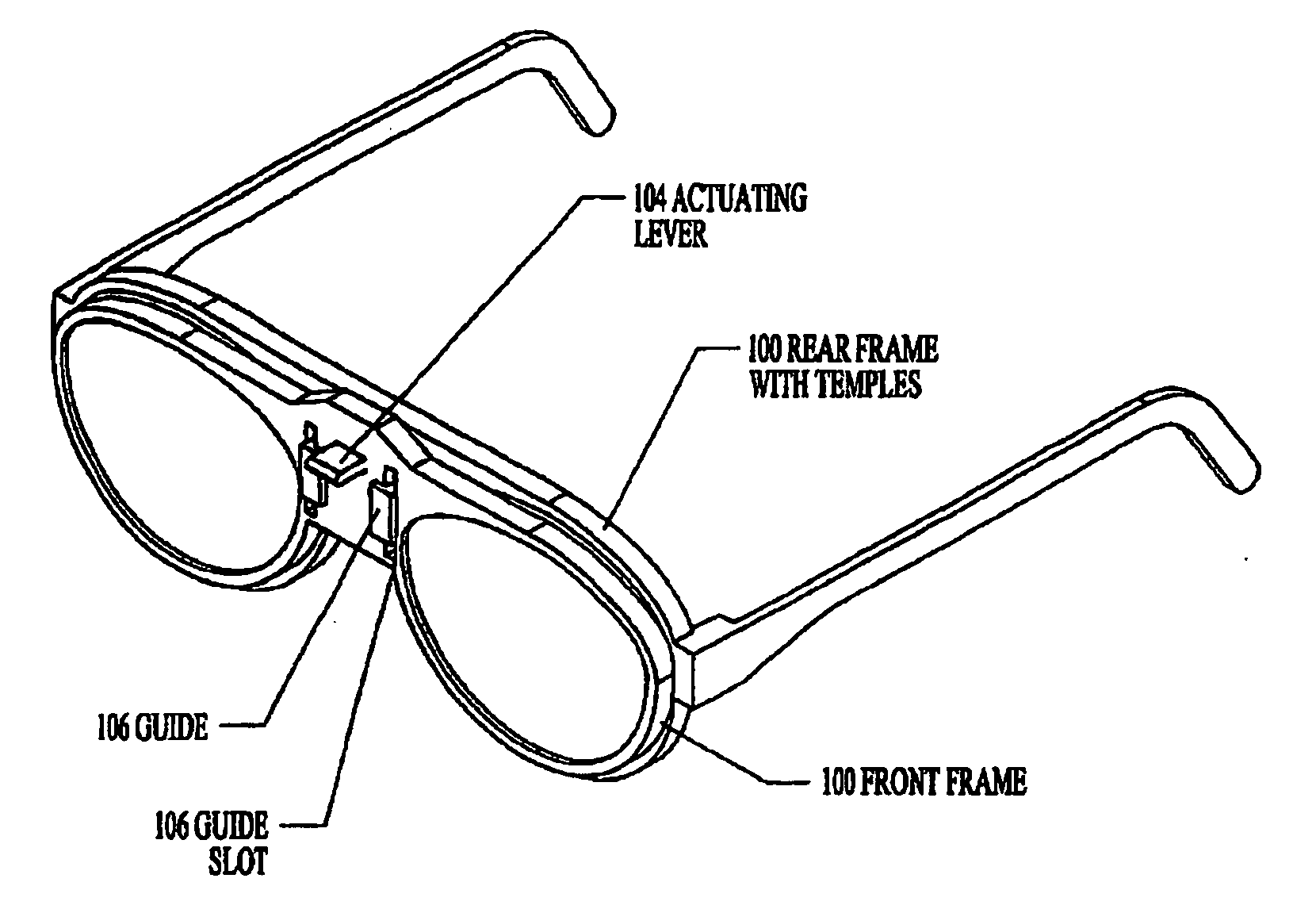
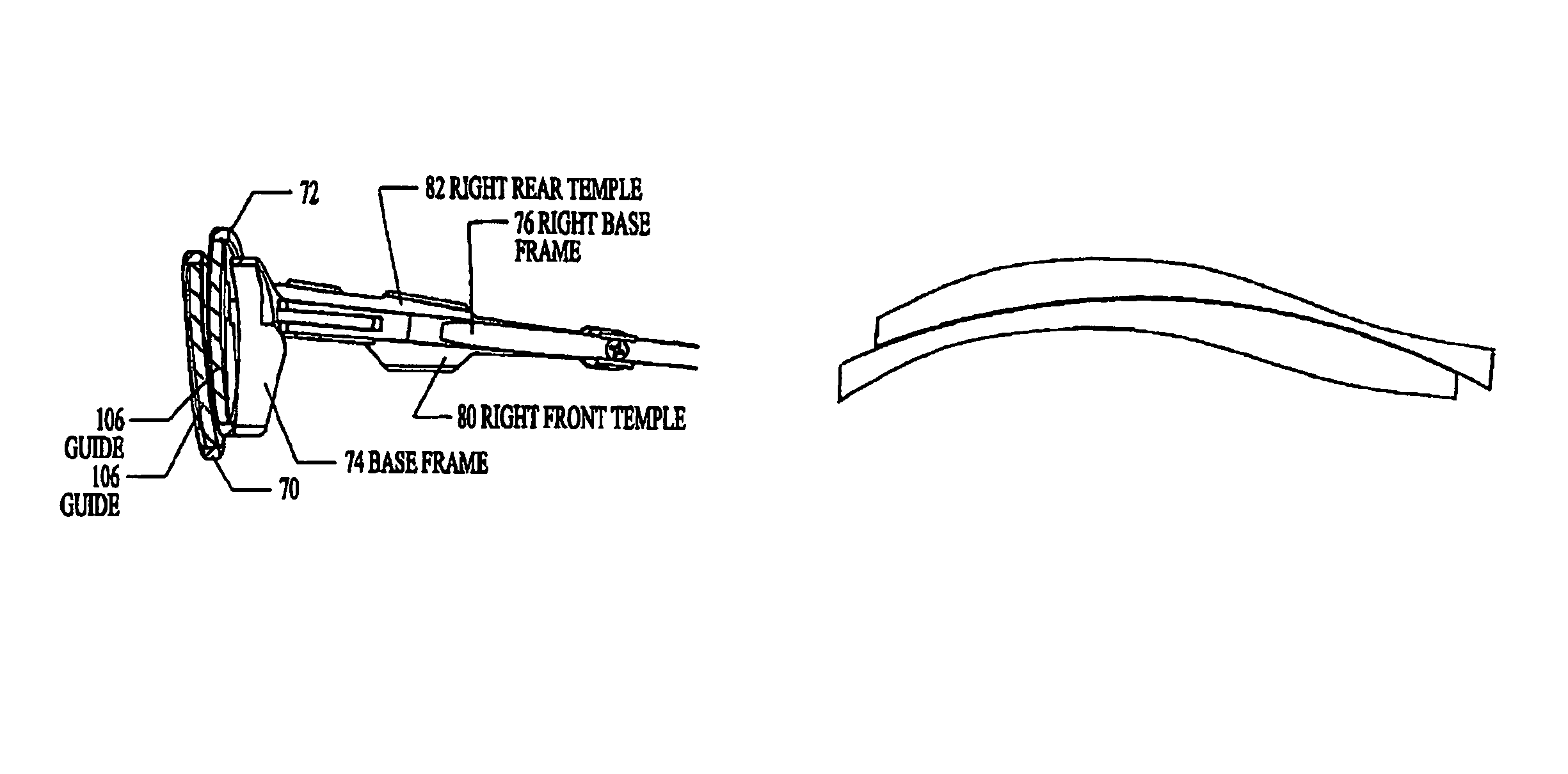
Wide field spherical lenses and protective eyewear
InactiveCN1471651ASmall distortionExcellent edge visual characteristicsCoatingsOptical partsLow distortionSpherical shaped
The present invention relates to novel ophthalmic lens elements (402, 404) and eyewear (400) having wide field of view, low distortion, improved astigmatism correction where required and enhanced eye protection properties. Series of lens elements have steeply curved spherical reference surfaces. The edged lenses of the series have approximately consistent aperture size, shape and hollow depth across a range of common prescriptions. Novel sunglasses, laser protection eyewear, and lens edgings, coatings, and frames are included in the invention.
Owner:卡尔蔡司光学股份有限公司
Ophthalmologic operation microscope
ActiveUS20060098274A1Satisfactory visual fieldEye surgerySurgeryAxis–angle representationEngineering
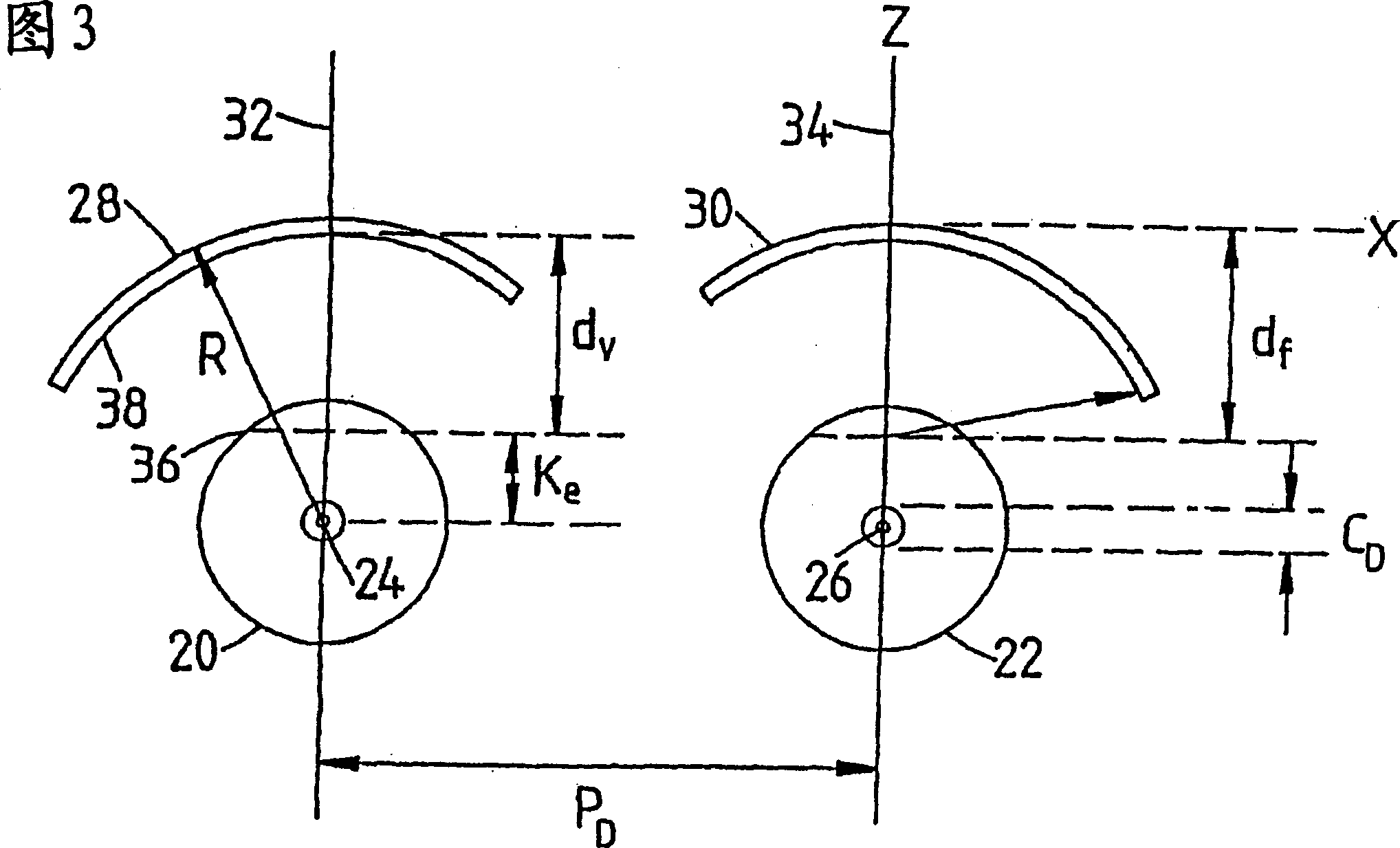
Disclosed is an observation apparatus capable of eliminating in a suitable manner astigmatism and chromatic aberration generated in an observed image. The apex angle θ of a contact prism is input by operating an apex angle setting knob of a control panel, and the attachment angle thereof is input by operating an attachment angle setting knob. Based on the observation magnification recognized and the input apex angle θ, a control device determines the astigmatism correction amount for a left observation optical system and determines the astigmatism correction amount for the right observation optical system. Further, based on the input attachment angle, the axial angles of the astigmatisms of the left observation optical system and the right observation optical system are determined. Next, variable cross cylinder lens rotation drive devices are respectively controlled to rotate the respective cylinder lenses of the left and right observation optical systems to achieve the axial angle and correction amount as determined.
Owner:KK TOPCON
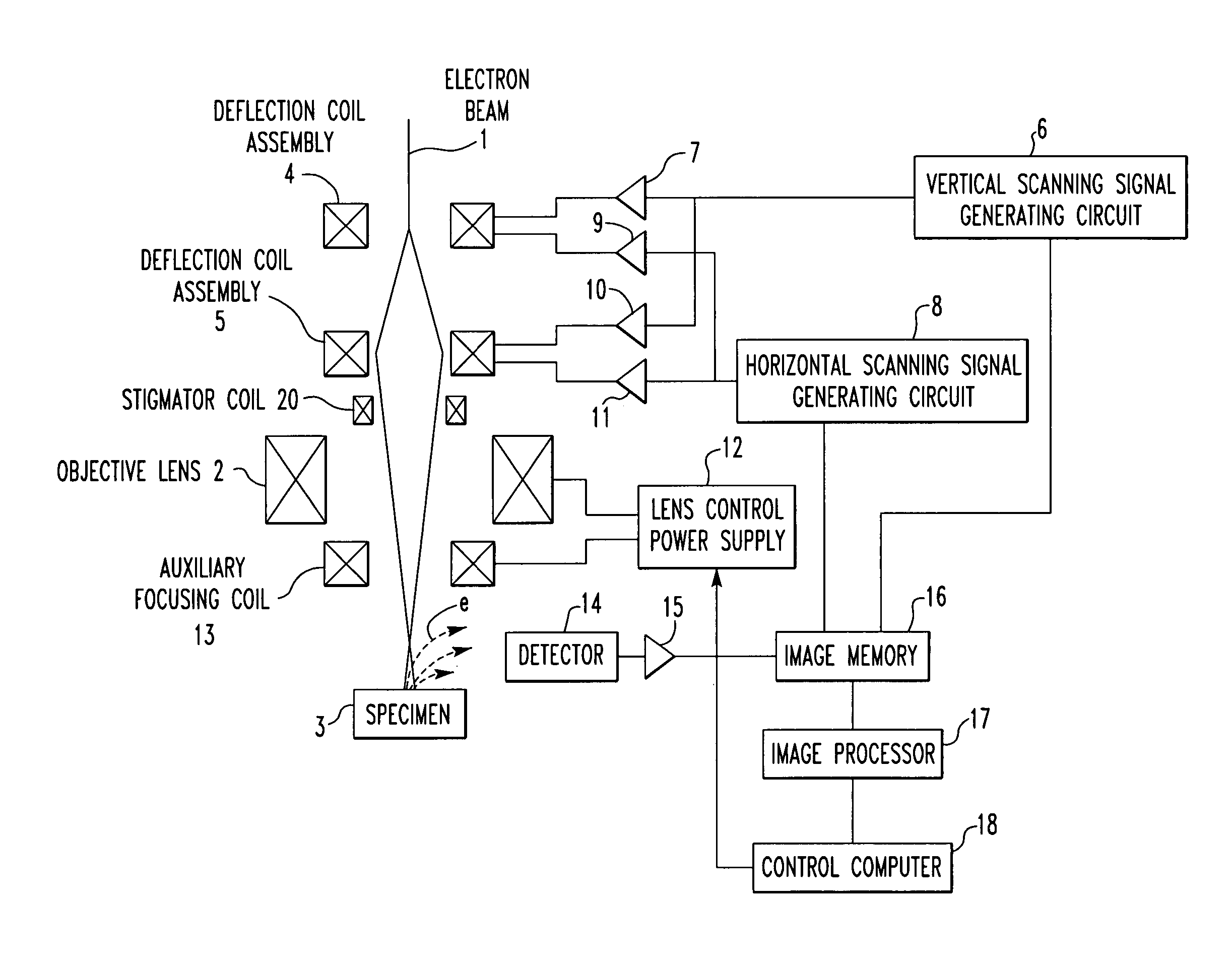
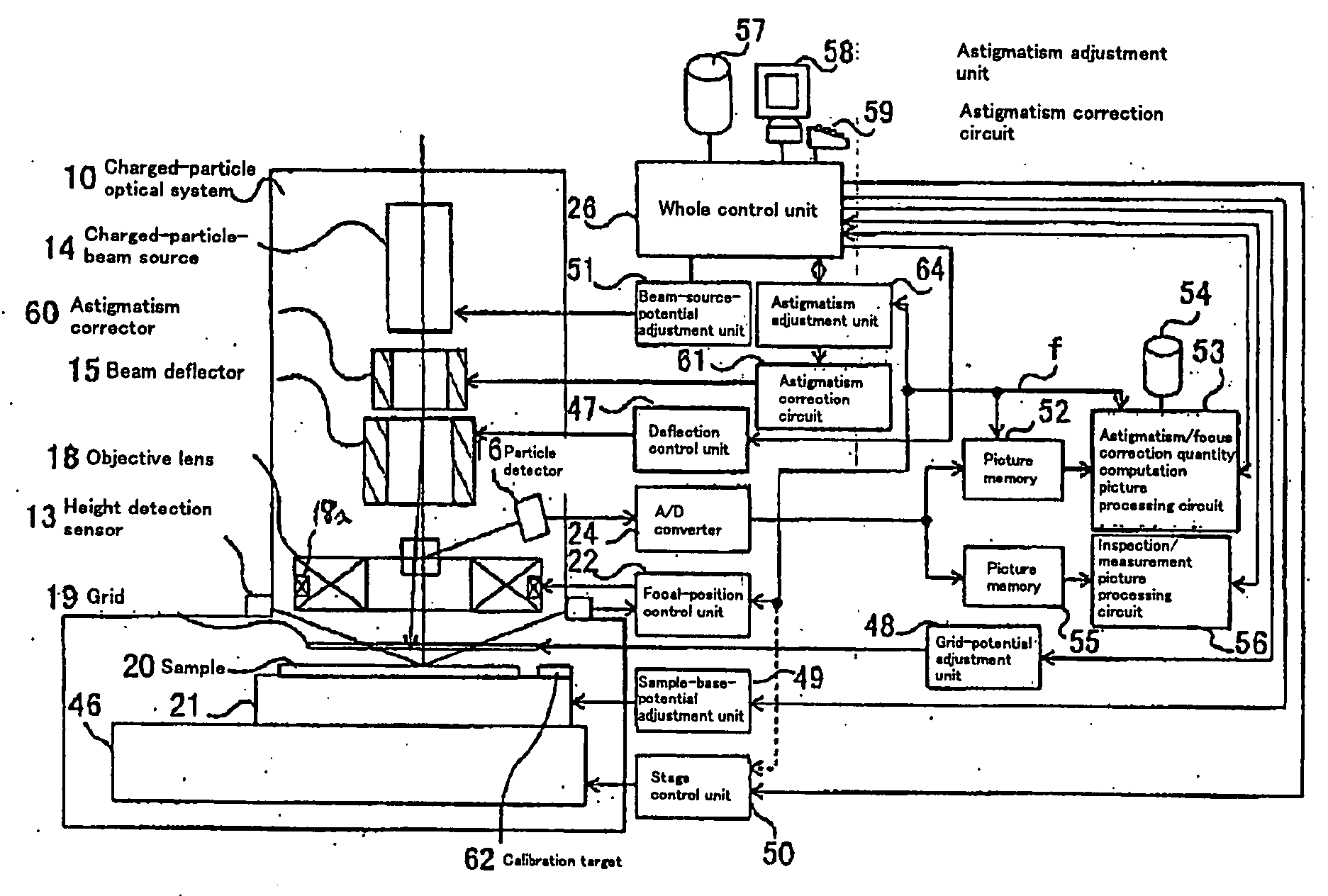
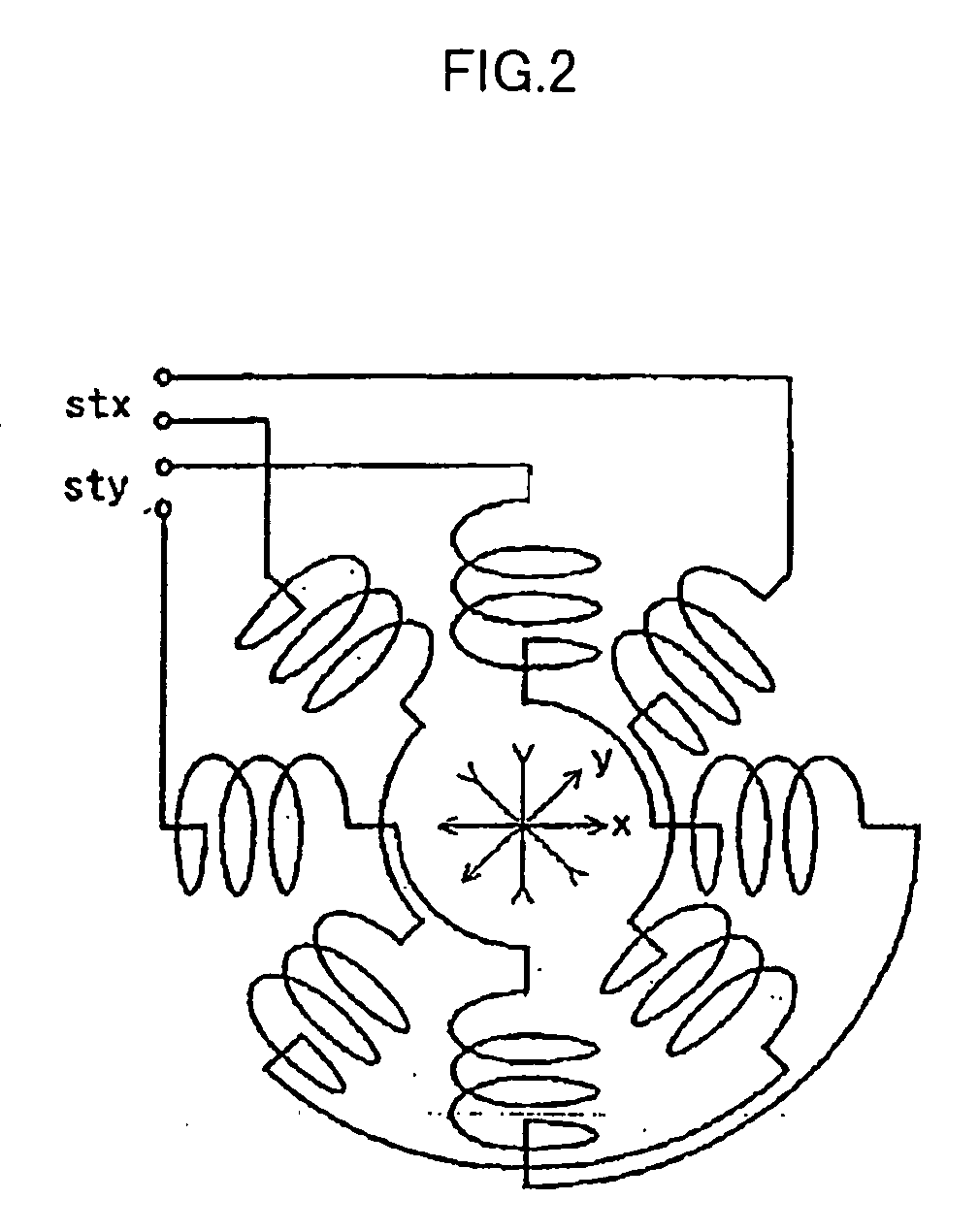
Charged particle beam apparatus and automatic astigmatism adjustment method
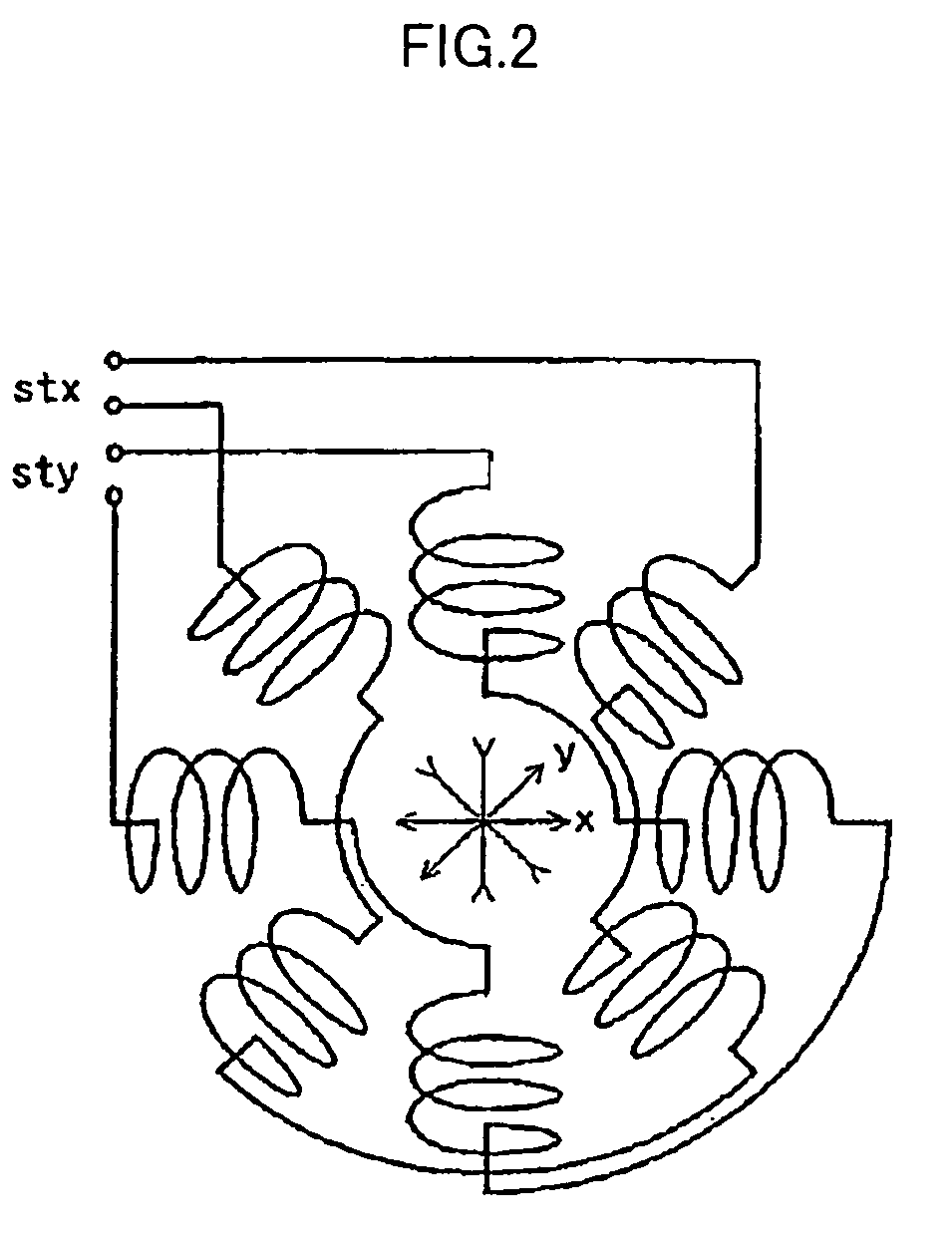
InactiveUS7030394B2Minimize damageHigh precisionThermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersParticle beamAstigmatism correction
According to the invention, techniques for automatically adjusting for astigmatism in a charged particle beam apparatus. Embodiments according to the present invention can provide a charged particle beam apparatus and an automatic astigmatism adjustment methods capable of automatically correcting astigmatism and a focal point in a relatively short period of time by finding a plurality of astigmatism correction quantities and a focal point correction quantity in a single operation from a relatively small number of 2 dimensional images. Specific embodiments can perform such automatic focusing while minimizing damages inflicted on subject samples. Embodiments include, among others, a charged particle optical system for carrying out an inspection, a measurement and a fabrication with a relatively high degree of accuracy by using a charged particle beam.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Automatic methods for focus and astigmatism corrections in charged-particle beam instrument
InactiveUS7026614B2Thermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationConfusionStigmatism
Automatic methods for focus and astigmatism corrections in a charged-particle beam instrument find an amount of excitation of the objective lens that provides the position of a circle of least confusion and can perform accurate automatic corrections of focus and astigmatism. The edge components of the original image along the X- and Y-directions are extracted separately, using respective filters. Noise reduction and normalization of numerical values are performed for each of the resulting two sets of data. Two-dimensional matrices of numerical values indicating the edge components in the X- and Y-directions, respectively, are found independently. The sums of the elements of the matrices are taken as focus evaluation values of the original image in the X- and Y-directions, respectively.
Owner:JEOL LTD
Aberration Correction Device, Aberration Correction Method And Optical Pickup
InactiveUS20080055713A1Improve aberrationEasy to controlOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageOptical pickupDevice form
The present invention is to provide an improved aberration correction device formed by inserting an electro-optic panel such as a liquid crystal panel in an image-formation optical system to correct aberrations in the image-formation optical system, characterized in that such a correction device is capable of correcting three or more kinds of aberrations using only one electro-optic panel. Divided areas concerning coma aberration correction and divided areas concerning astigmatism correction are formed in one of the transparent electrodes of the electro-optic panel, while the rest of divided areas concerning coma aberration correction and divided areas concerning spherical aberration correction are formed in the other of the transparent electrodes. In this way, it is possible to form divided areas divided into electrode patterns suitable for correcting various aberrations, simplify as much as possible the electrode structure of the transparent electrodes consisting of the divided areas, thereby simplifying a control of voltages to be applied to the divided areas.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Charged particle beam apparatus and automatic astigmatism adjustment method
InactiveUS20050092930A1Minimizing damage inflictedHigh precisionThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAstigmatism correctionMolecular physics
According to the invention, techniques for automatically adjusting for astigmatism in a charged particle beam apparatus. Embodiments according to the present invention can provide a charged particle beam apparatus and an automatic astigmatism adjustment methods capable of automatically correcting astigmatism and a focal point in a relatively short period of time by finding a plurality of astigmatism correction quantities and a focal point correction quantity in a single operation from a relatively small number of 2 dimensional images. Specific embodiments can perform such automatic focusing while minimizing damages inflicted on subject samples. Embodiments include, among others, a charged particle optical system for carrying out an inspection, a measurement and a fabrication with a relatively high degree of accuracy by using a charged particle beam.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Progressive multifocal lens and method of designing the same
Owner:HOYA LENS MFG PHILIPPINES
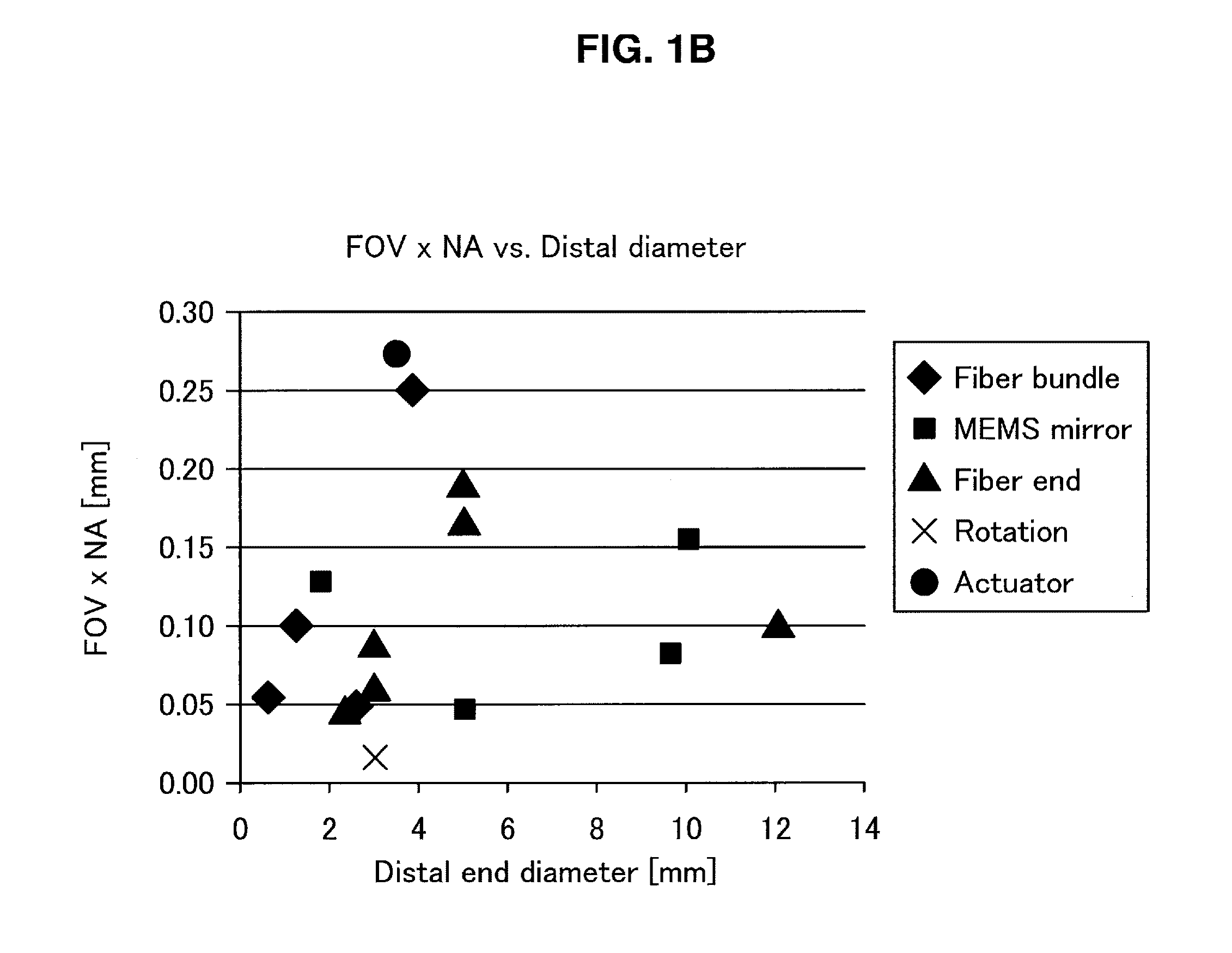
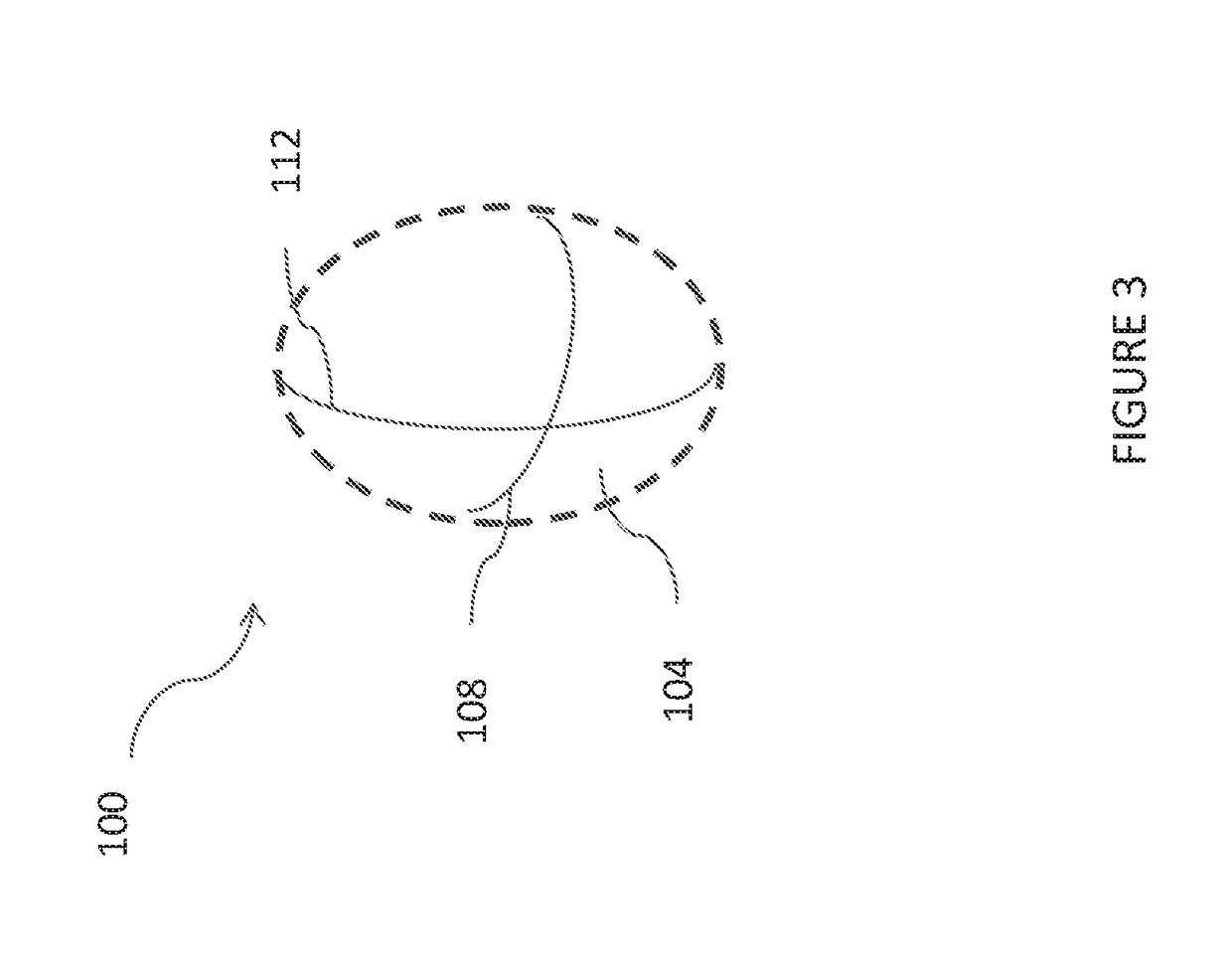
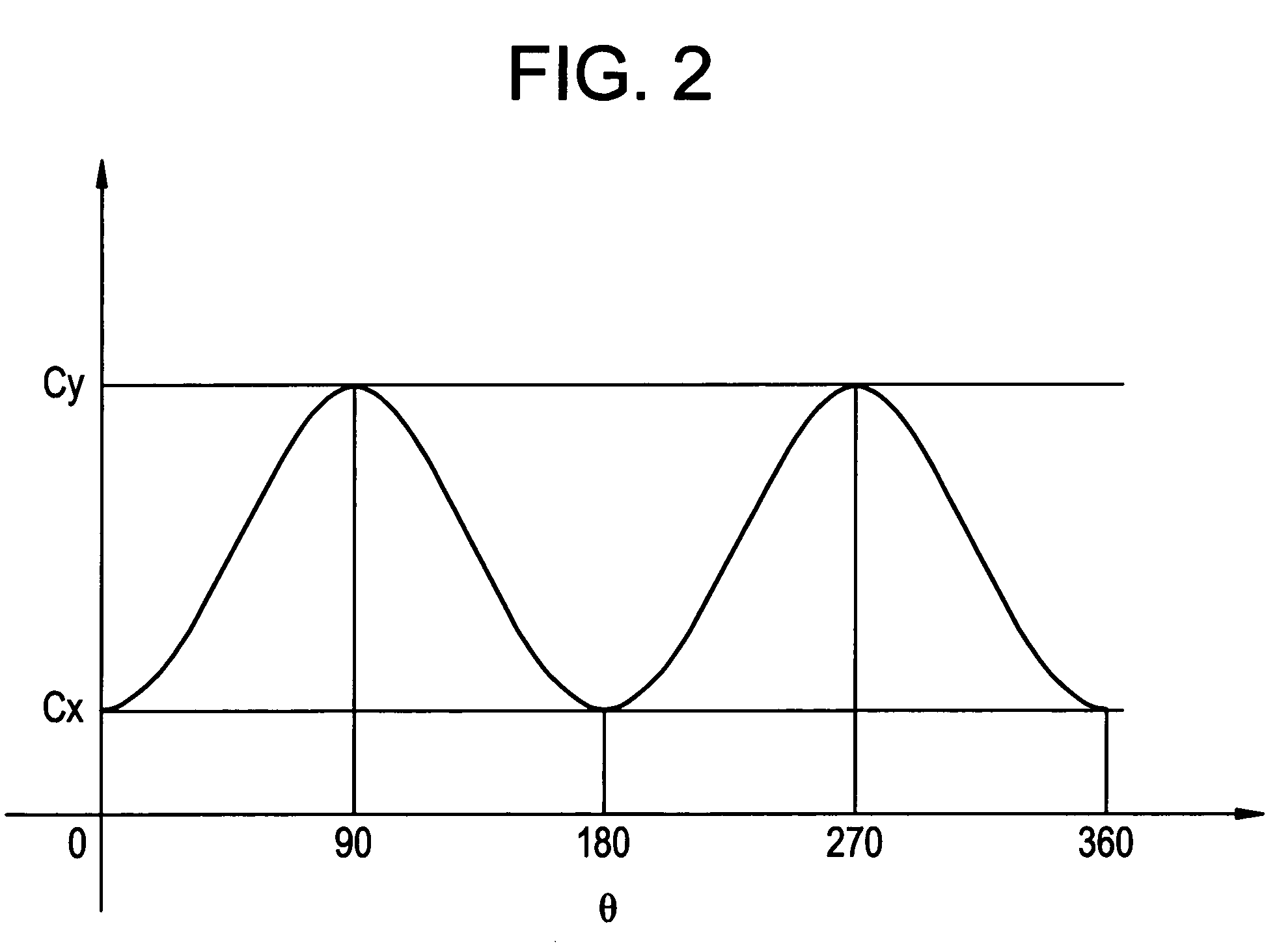
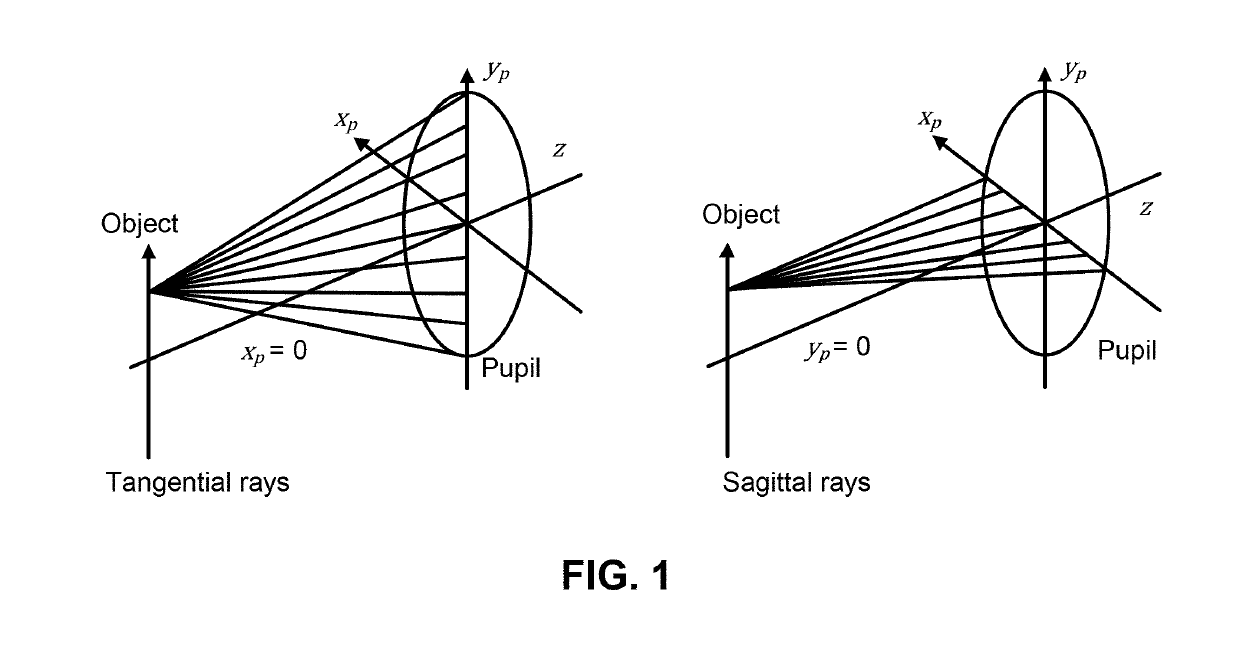
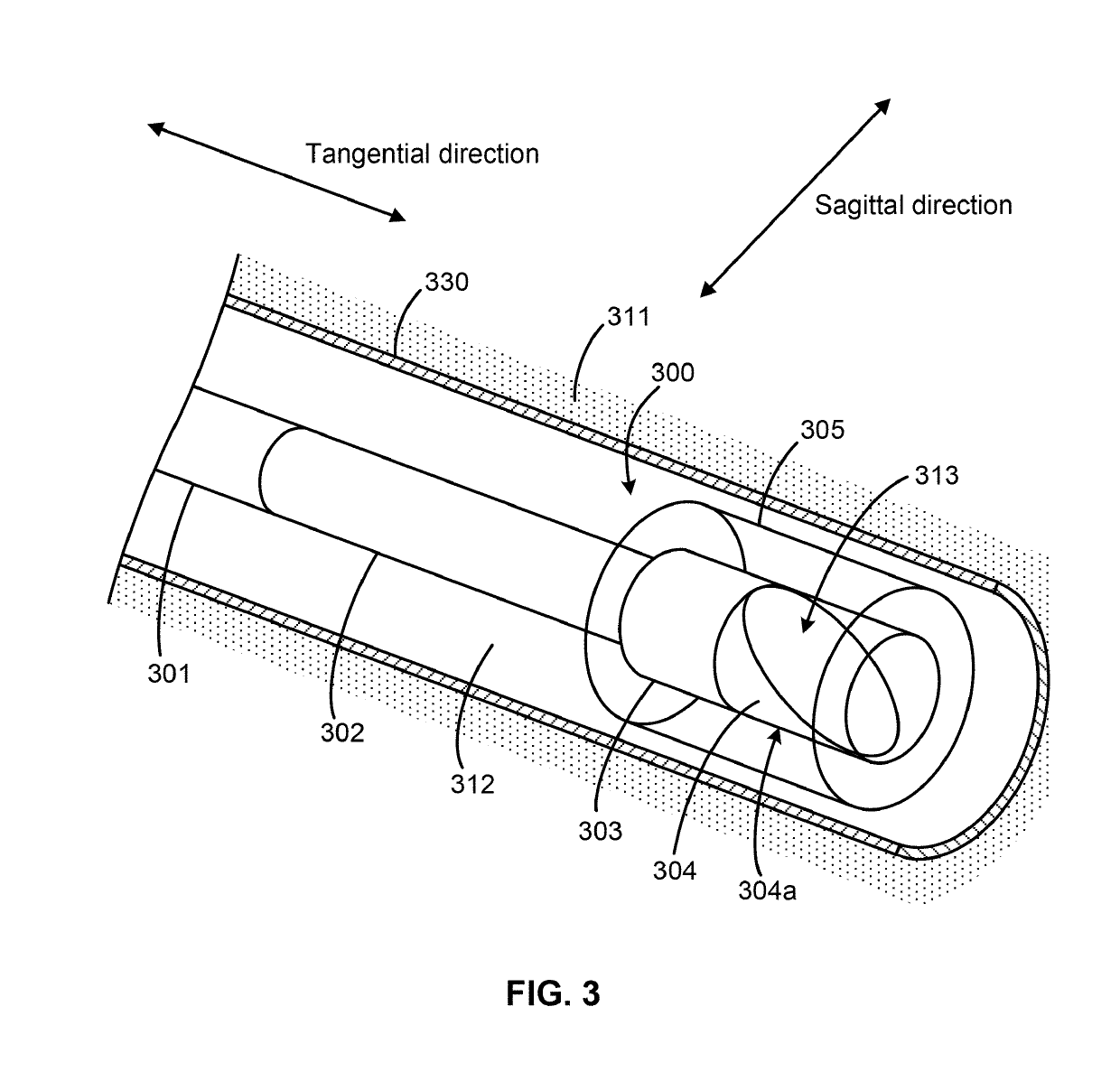
Optical probes with correction components for astigmatism correction
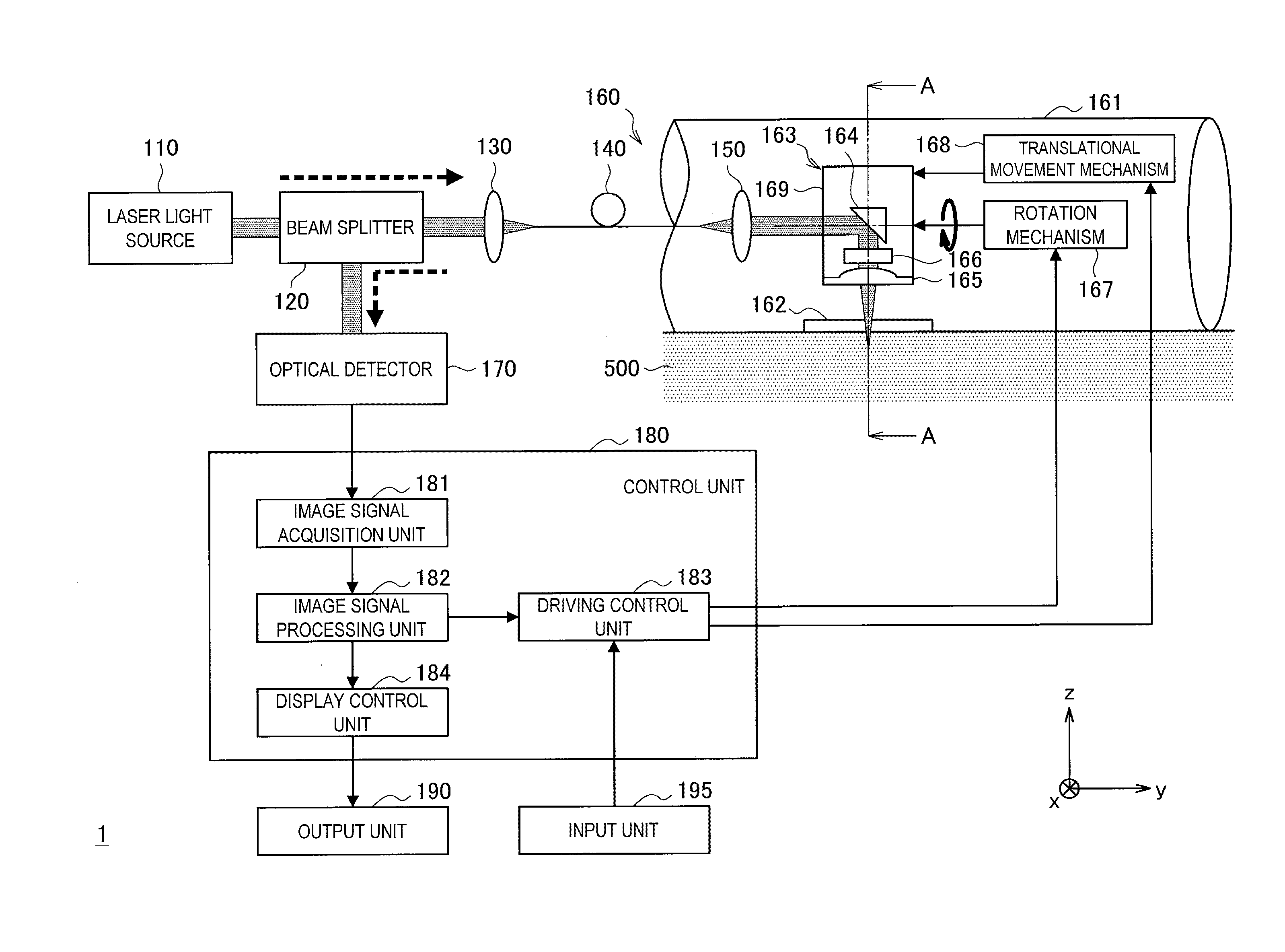
An optical probe comprises a light-guiding component, an optical component, a light-reflecting component that is configured to receive light from the optical component and direct the light along a path, and a correction component. The correction component lies in the path, the correction component has an optical power, and the correction component has a center of curvature that substantially coincides with an optical axis of the optical component.
Owner:CANON USA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com