Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
536 results about "Harmonic rejection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
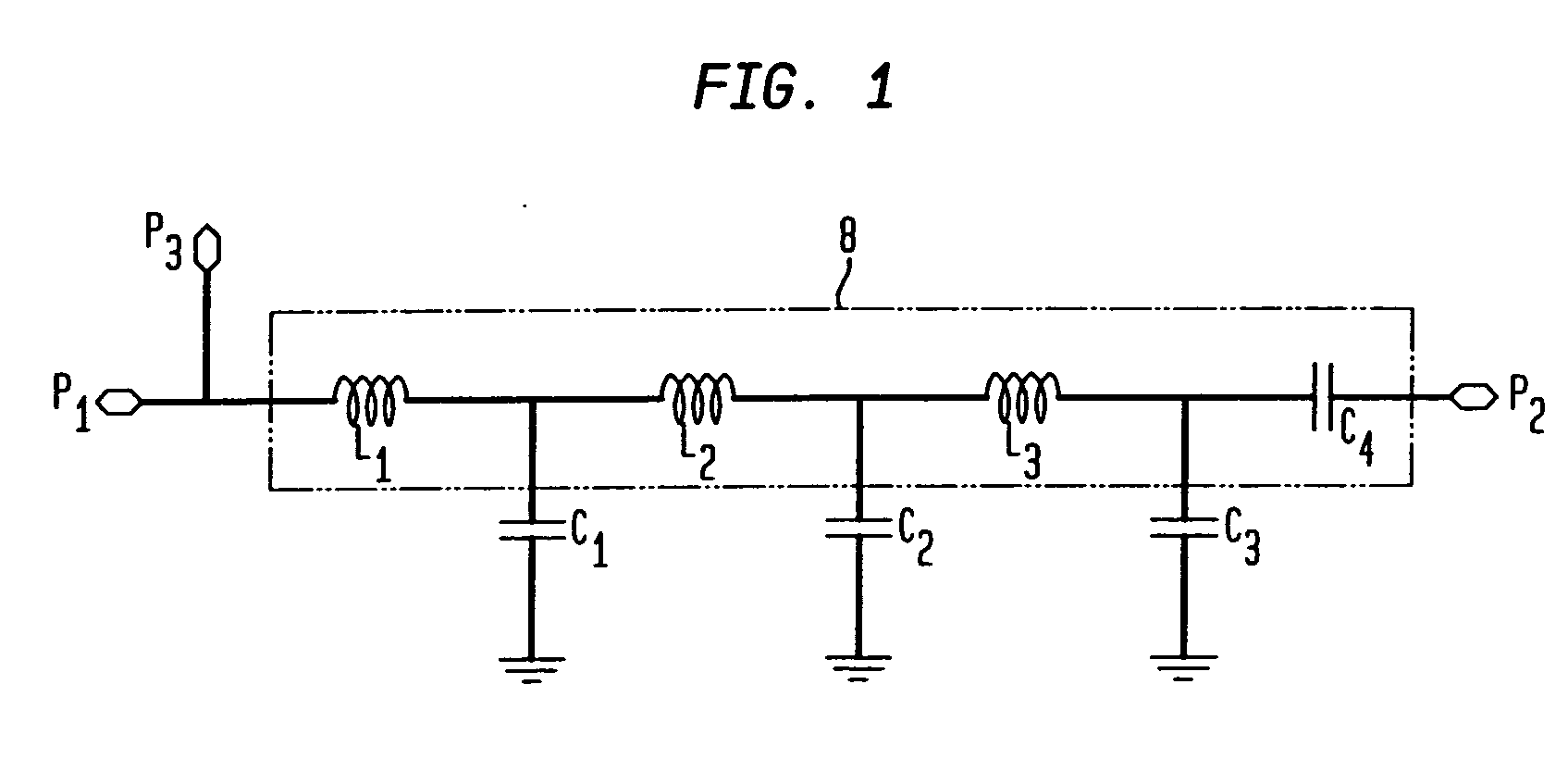
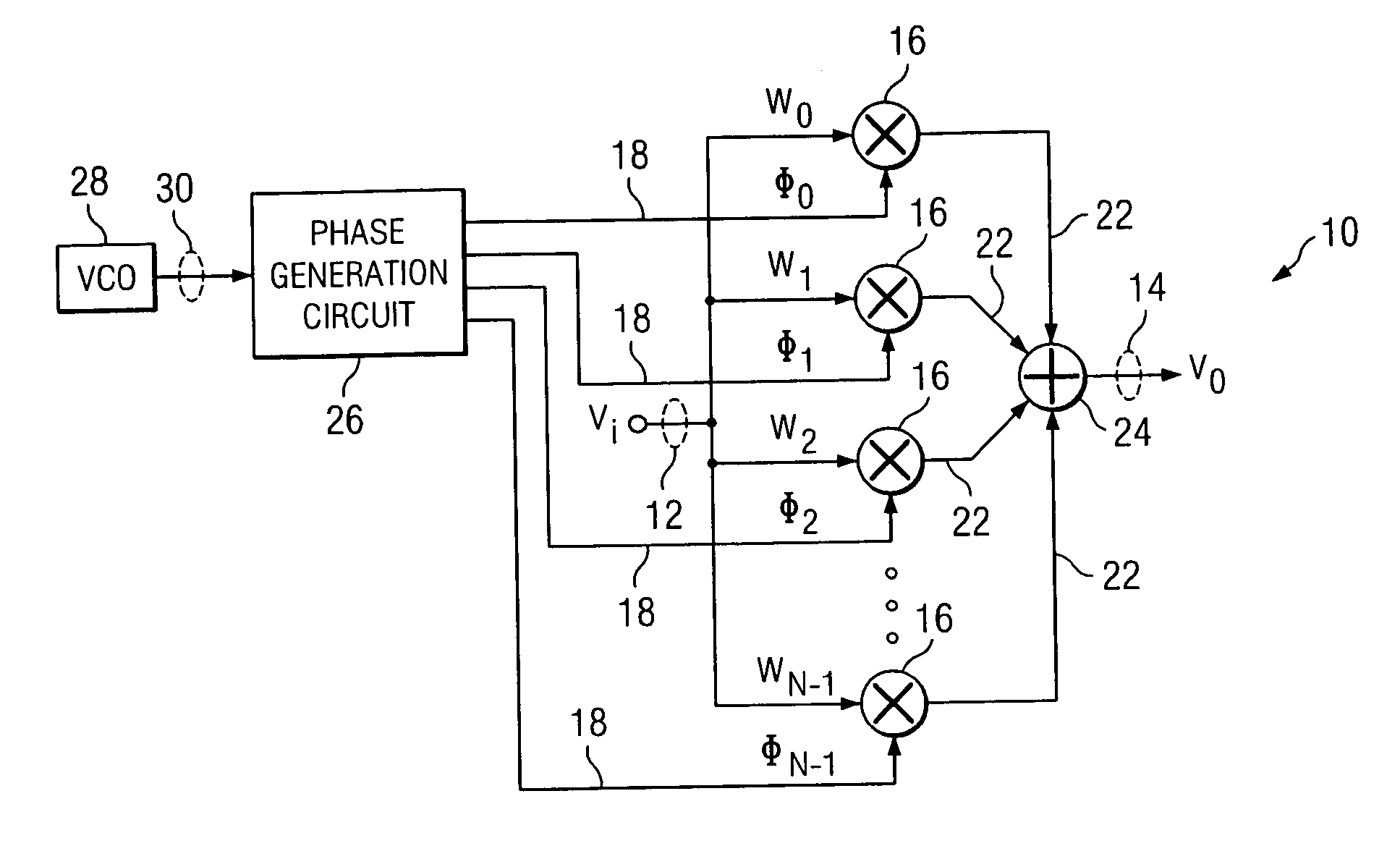
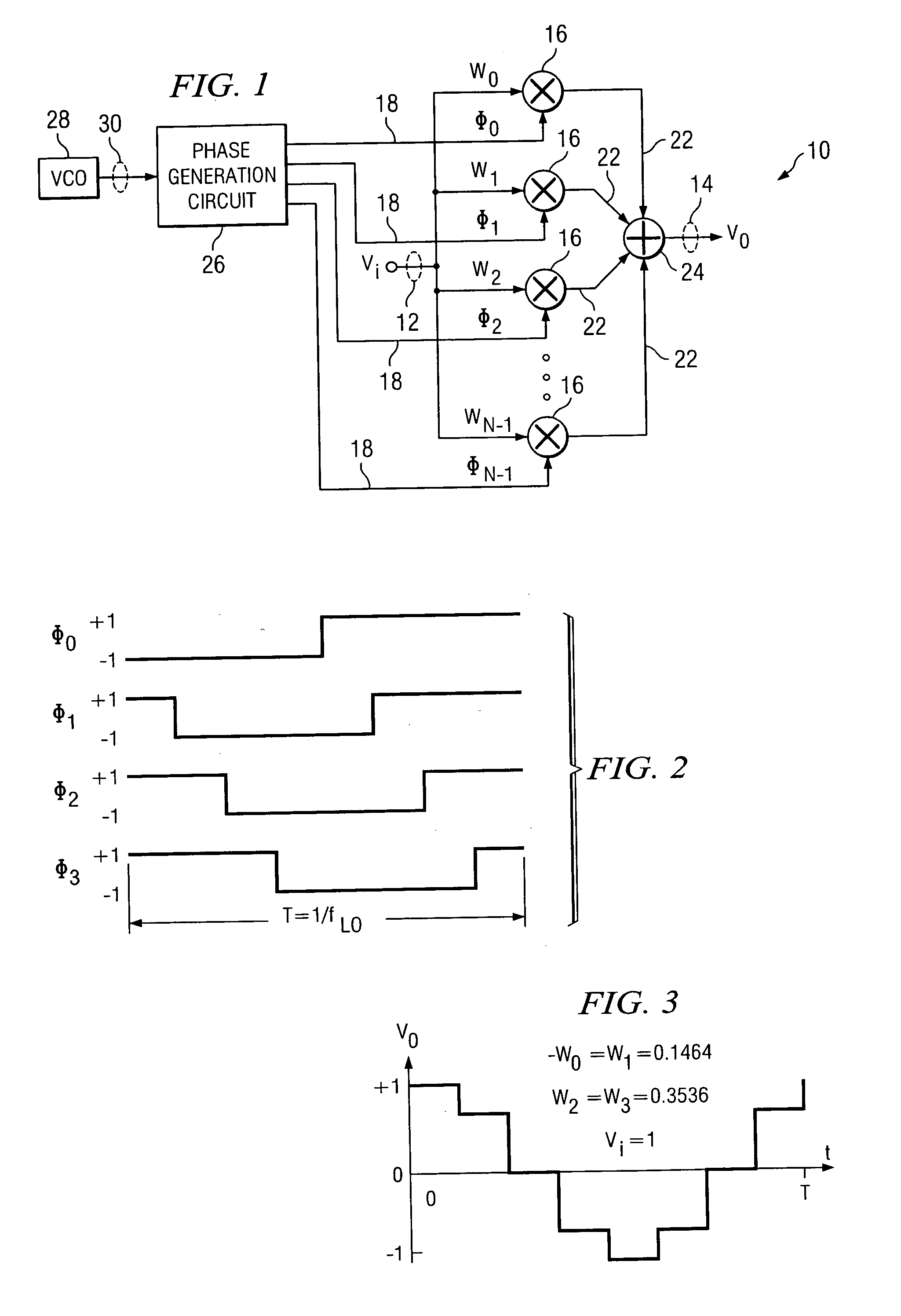
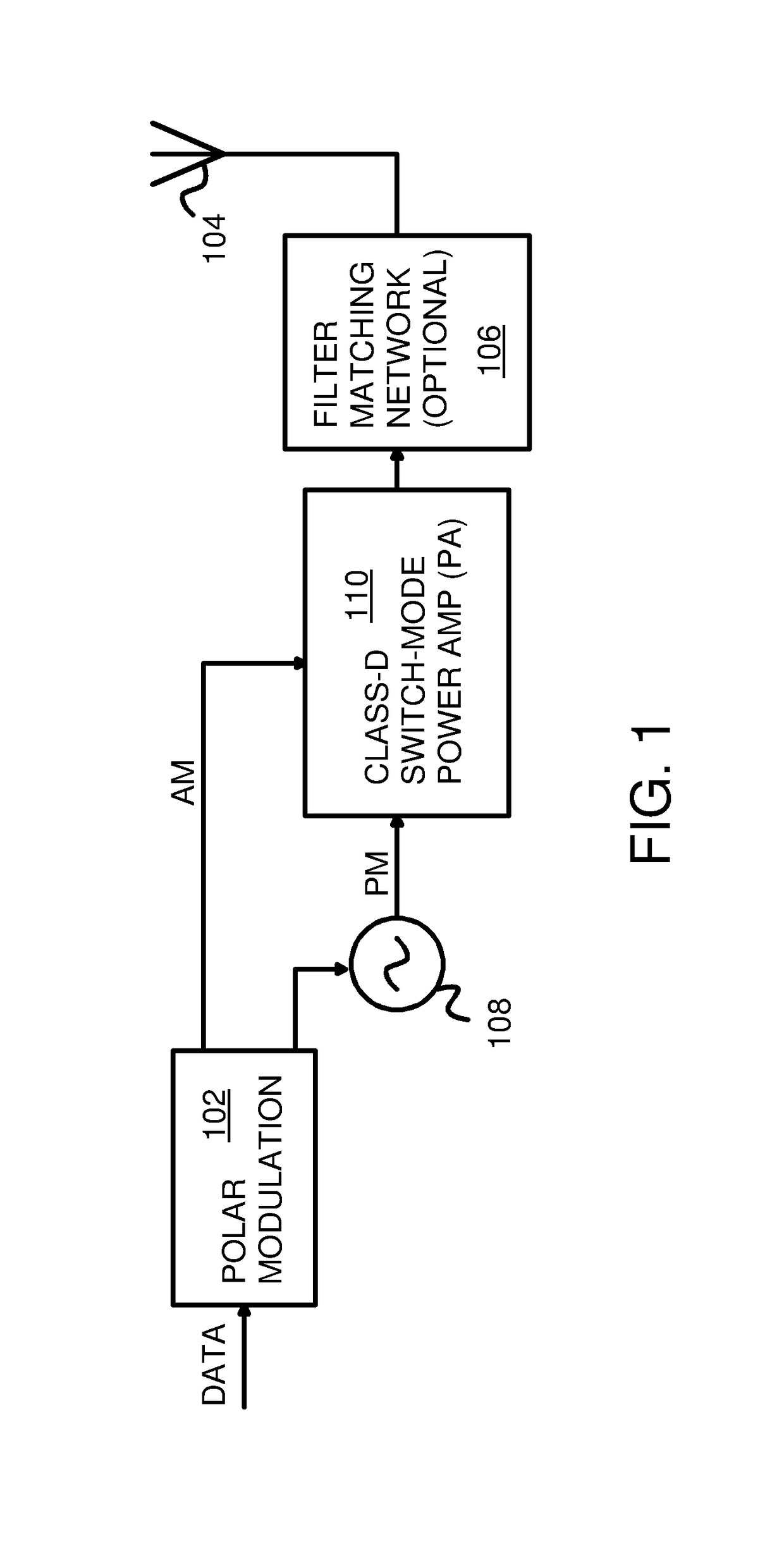
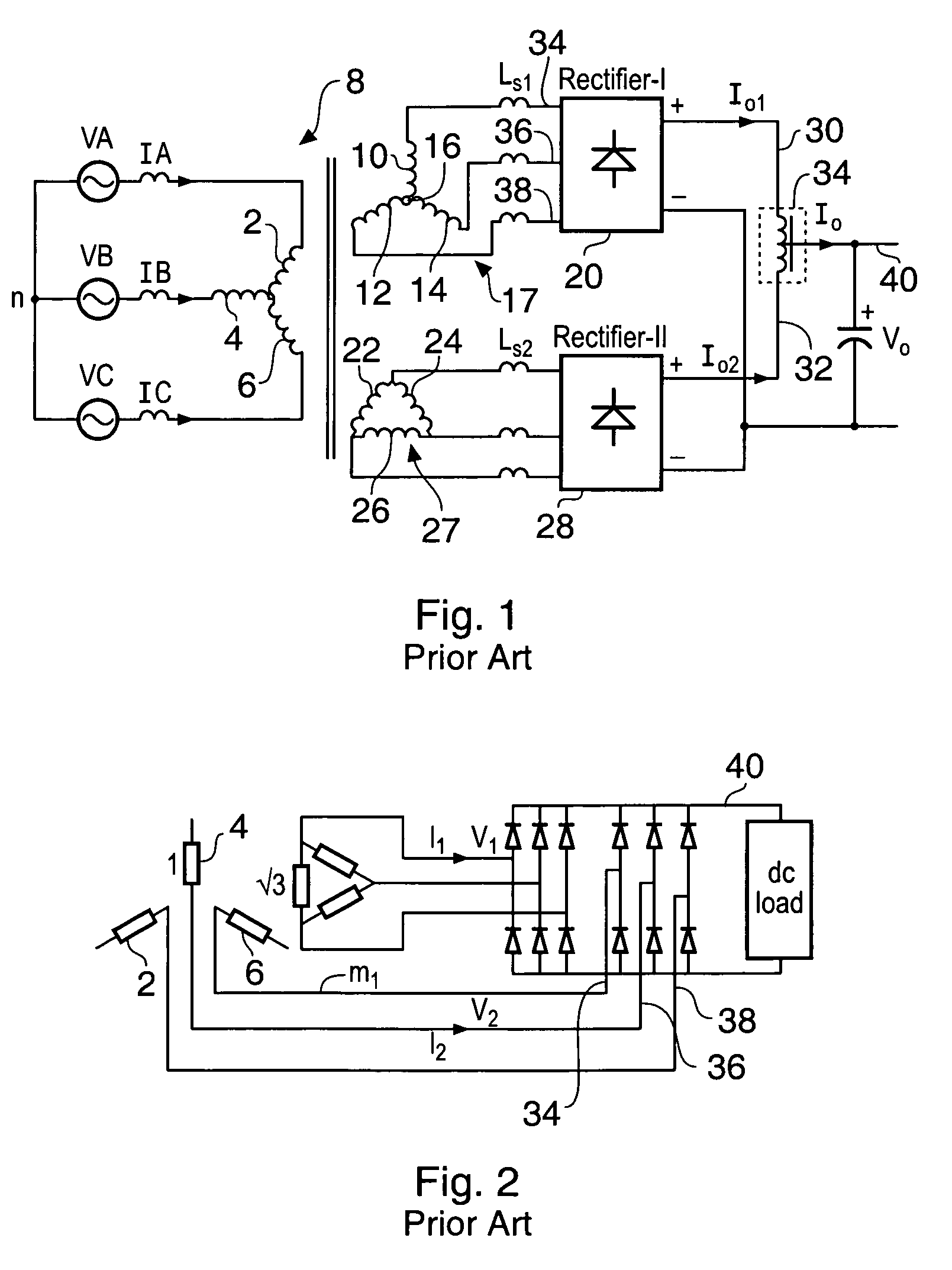
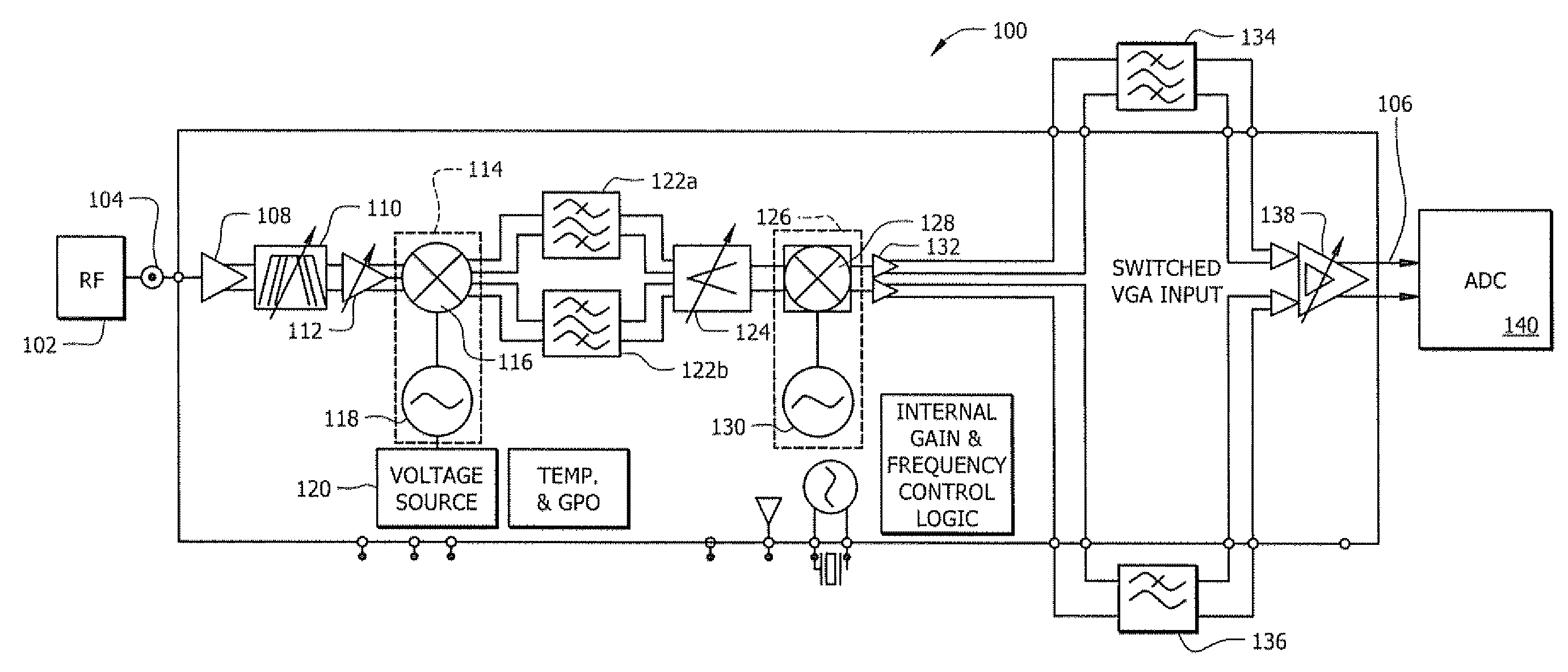
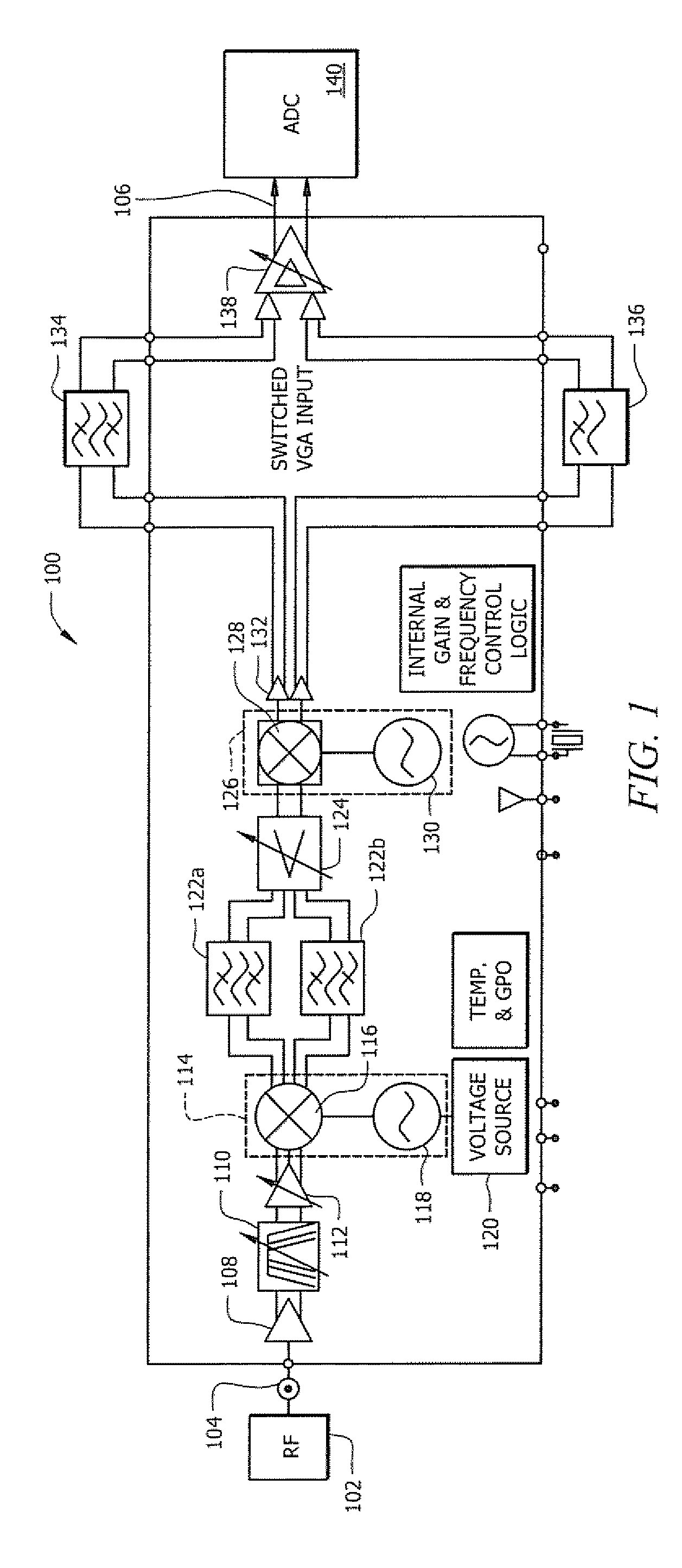
This dissertation presents novel Harmonic Rejection (HR) Mixer architectures to obtain a high level of harmonic rejection. This is achieved by reducing the sensitivity to mismatches in devices operating at high frequencies.
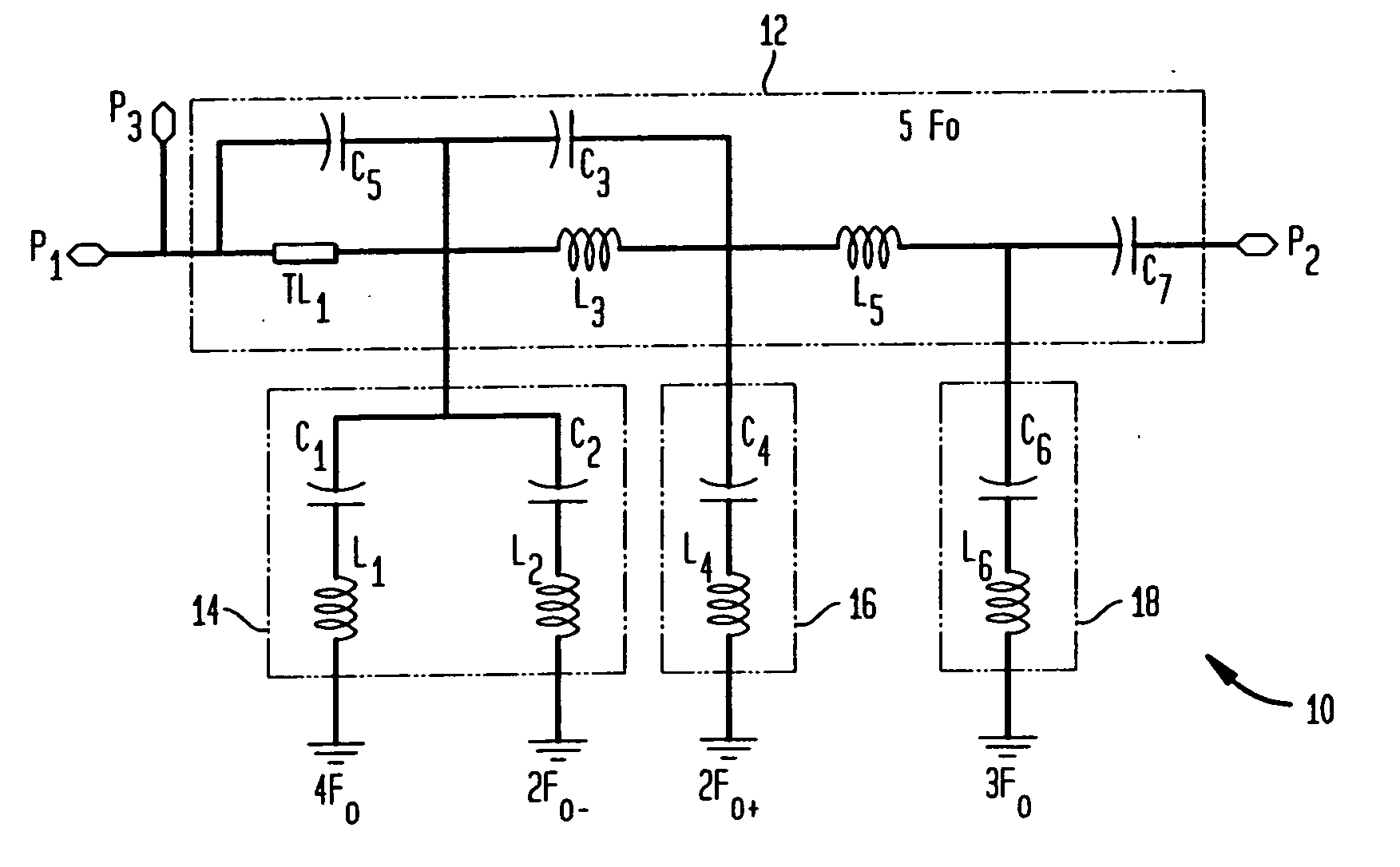
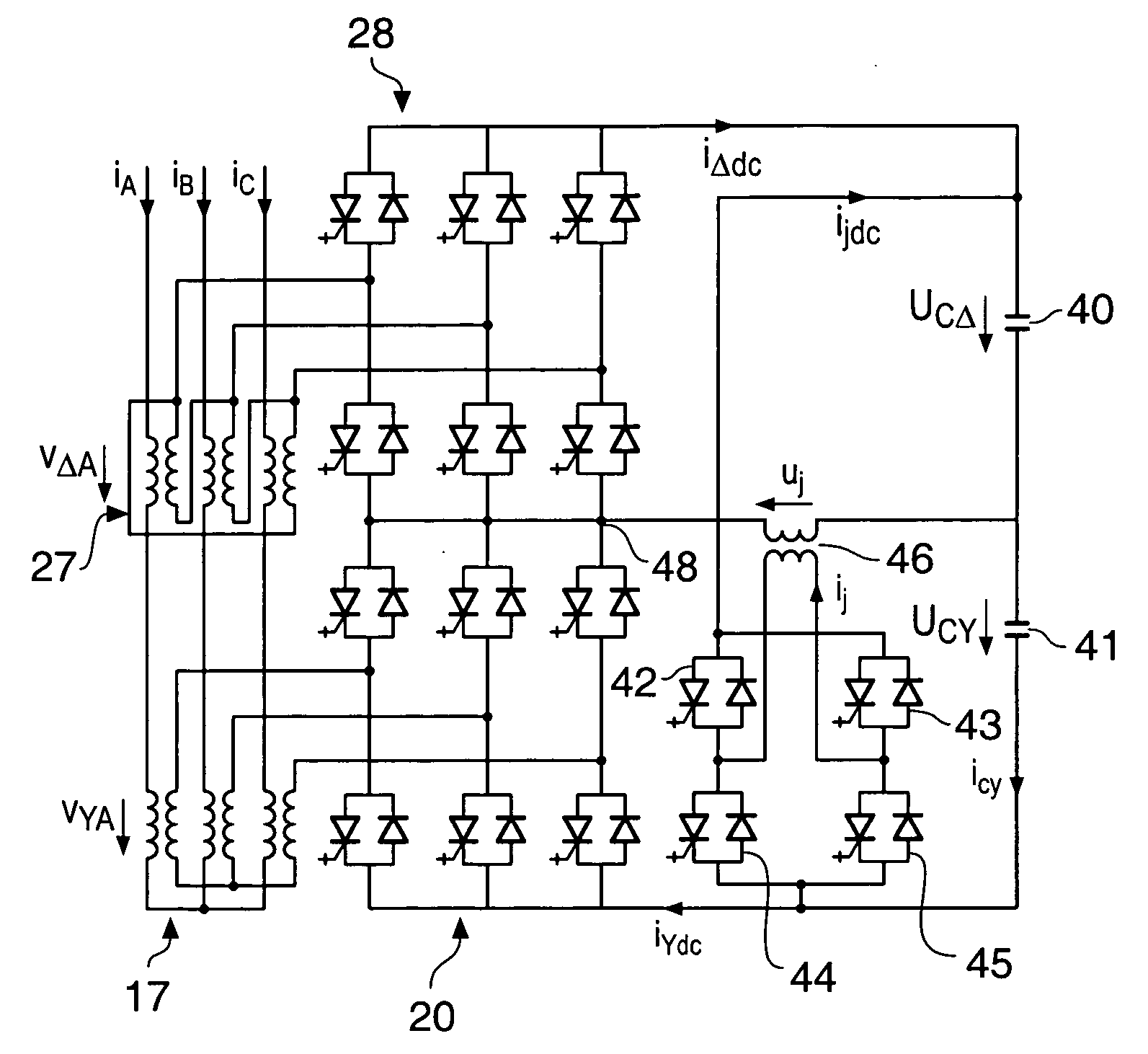
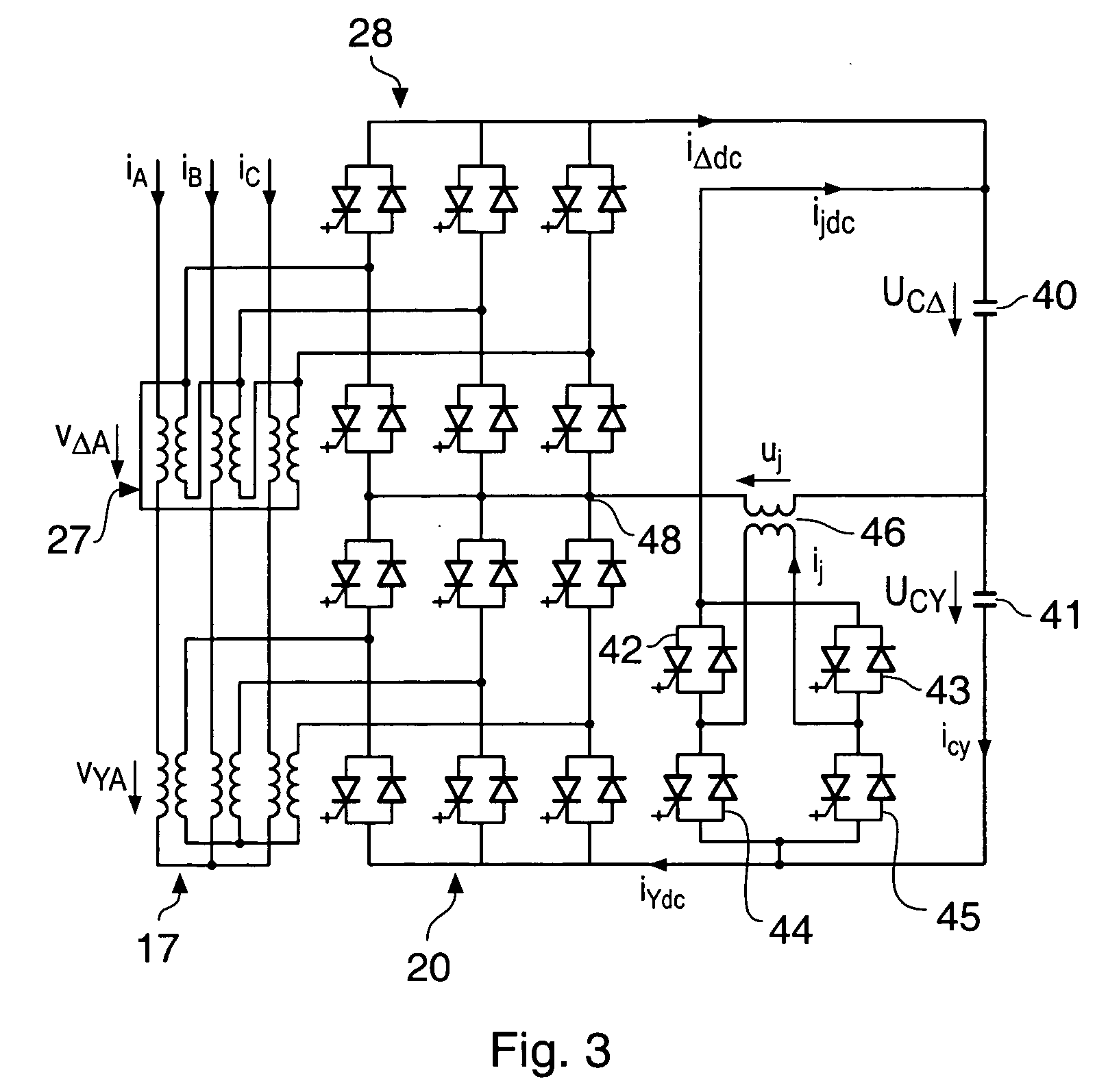
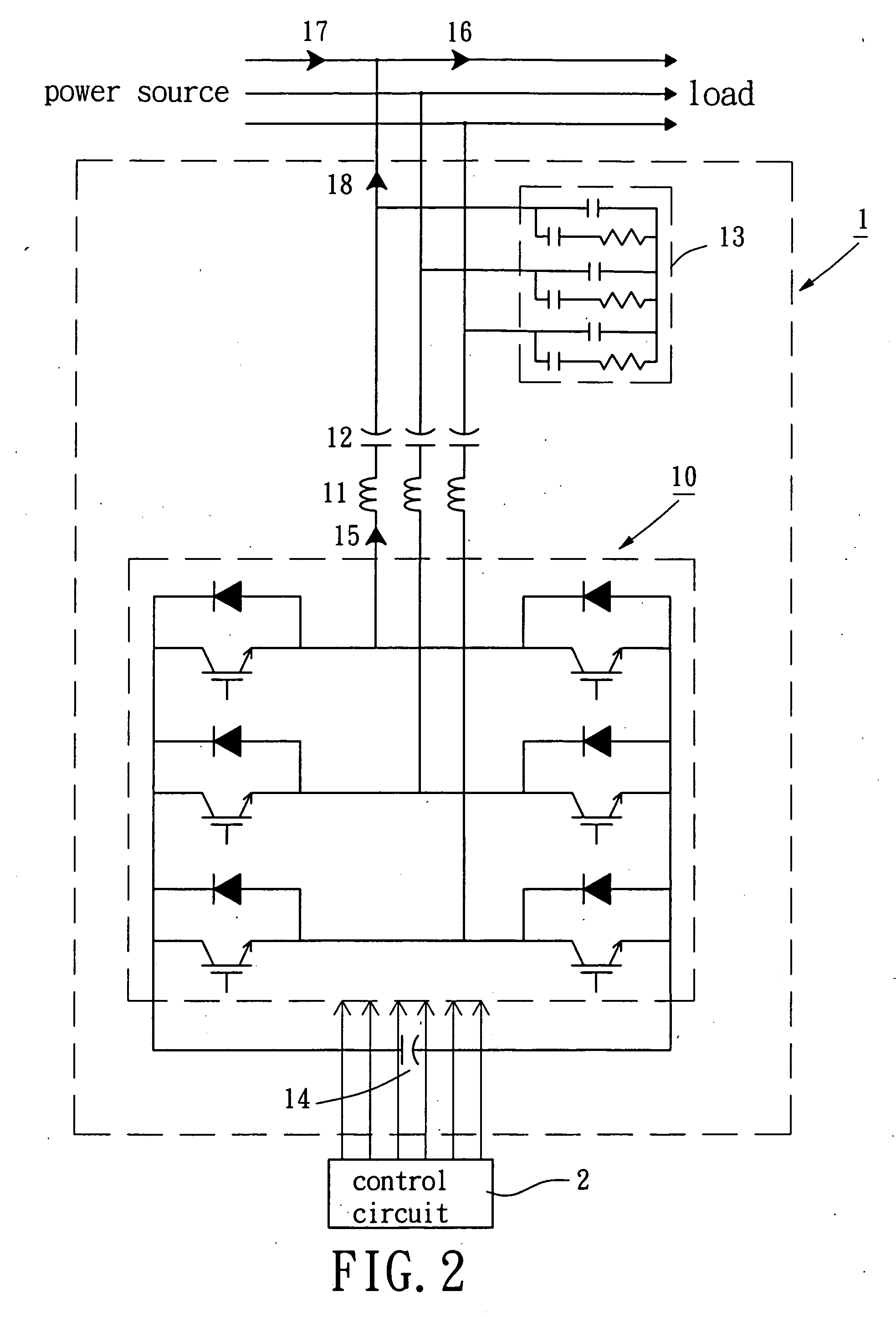
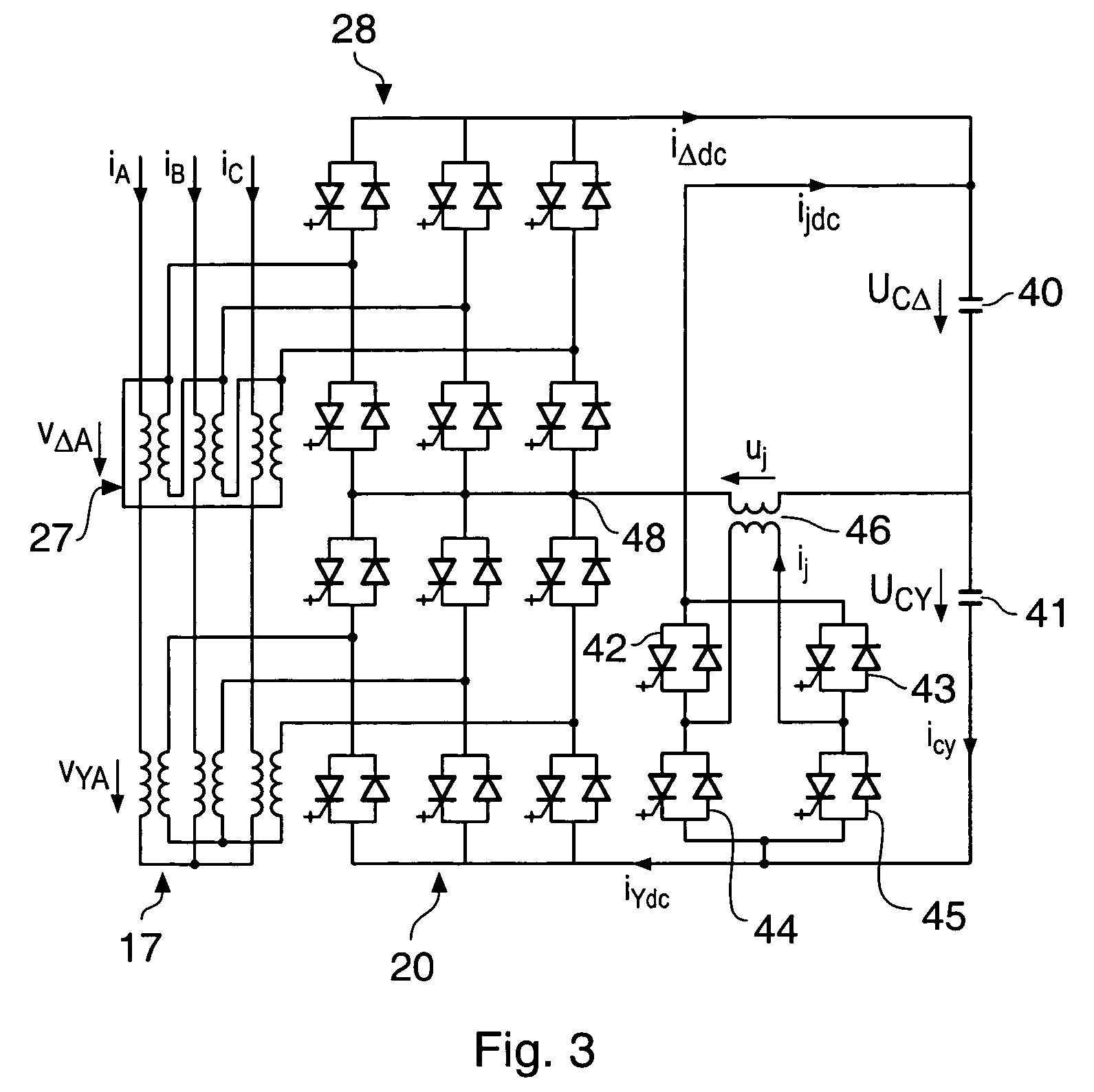
Combined matching and filter circuit
ActiveUS20050282503A1Good harmonic suppressionImprove abilitiesMultiple-port networksOne-port networksCapacitanceHarmonic
A combined matching and harmonic rejection circuit with increased harmonic rejection provided by a split resonance for one or more of the capacitive or inductive elements of the circuit. At a fundamental frequency, the circuit comprises an inductive series arm with capacitive shunt arms. The capacitance of a shunt arm may be provided by two or more parallel paths, each having a capacitor and an inductor in series so that, in addition to providing the effective capacitance necessary for impedance matching at the fundamental frequency, two separate harmonics represented by the series resonances of the parallel paths are rejected. In this manner, an extra null in the circuit's stop-band may be achieved using the same number of shunt elements necessary to achieve impedance matching at the fundamental frequency.
Owner:MACOM TECH SOLUTIONS HLDG INC
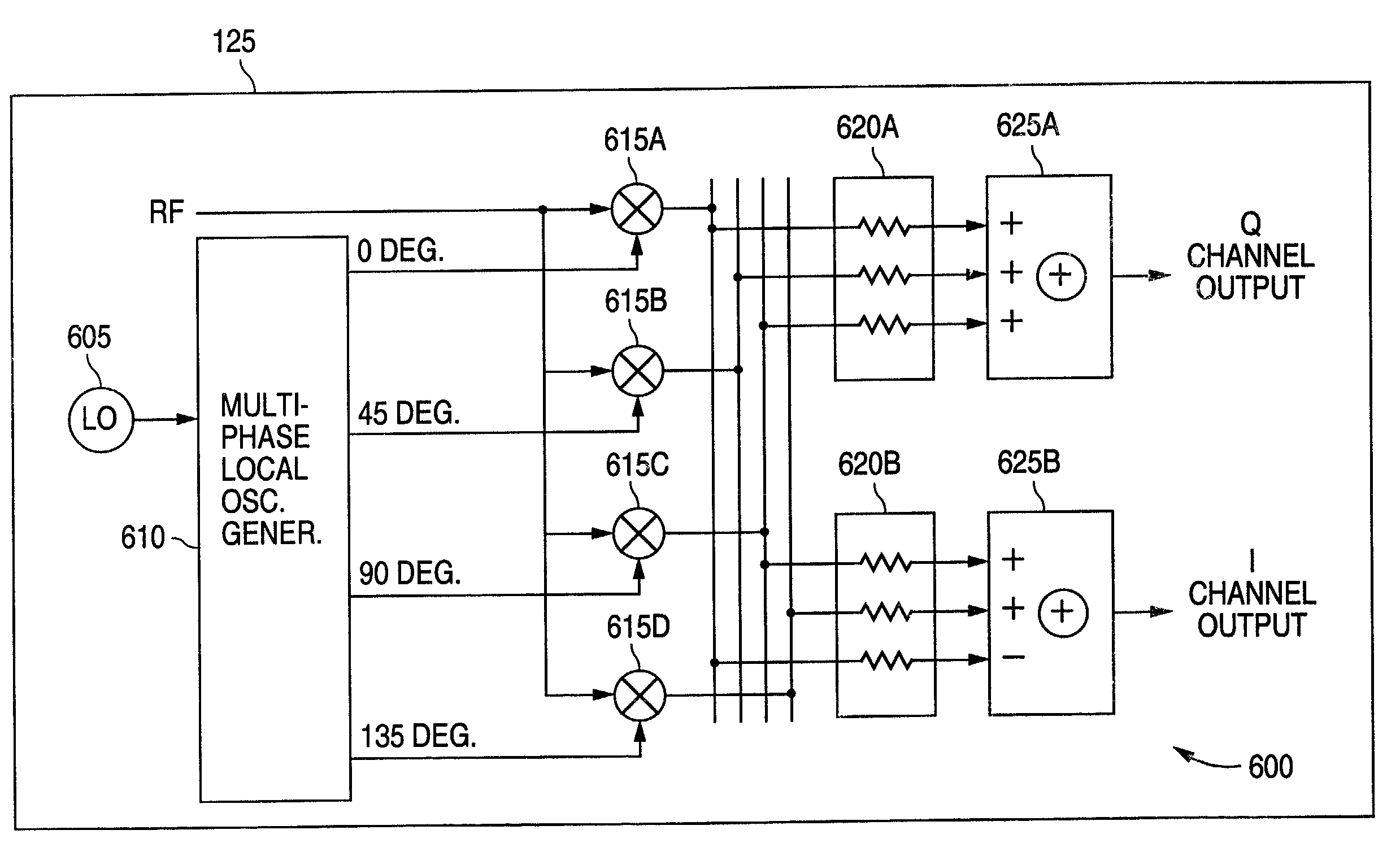
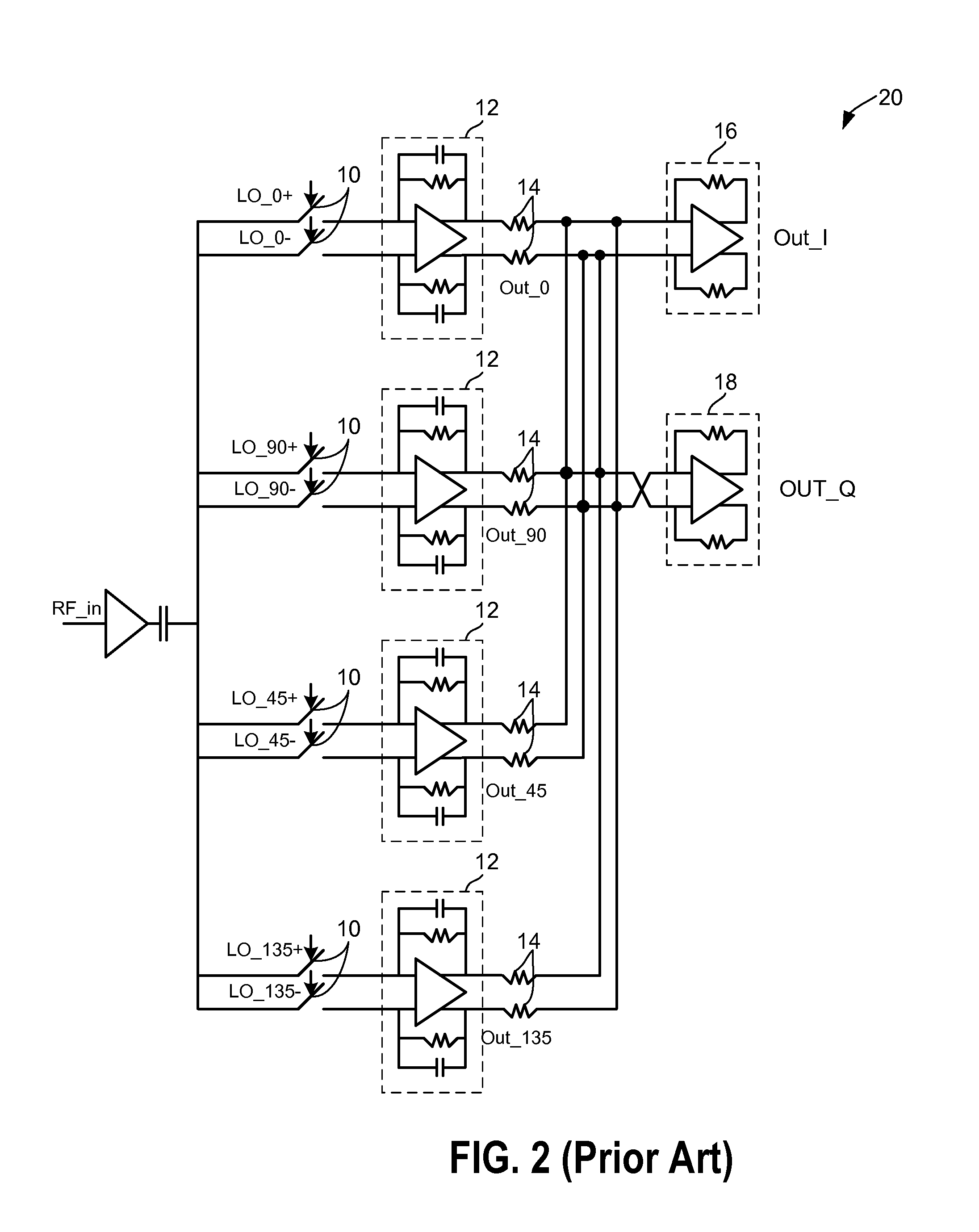
Harmonic rejection mixer and method of operation
InactiveUS7130604B1Suppress unwanted responseSuperb suppressionModulation transference by semiconductor devices with minimum 2 electrodesTransmissionPhase shiftedLocal oscillator signal
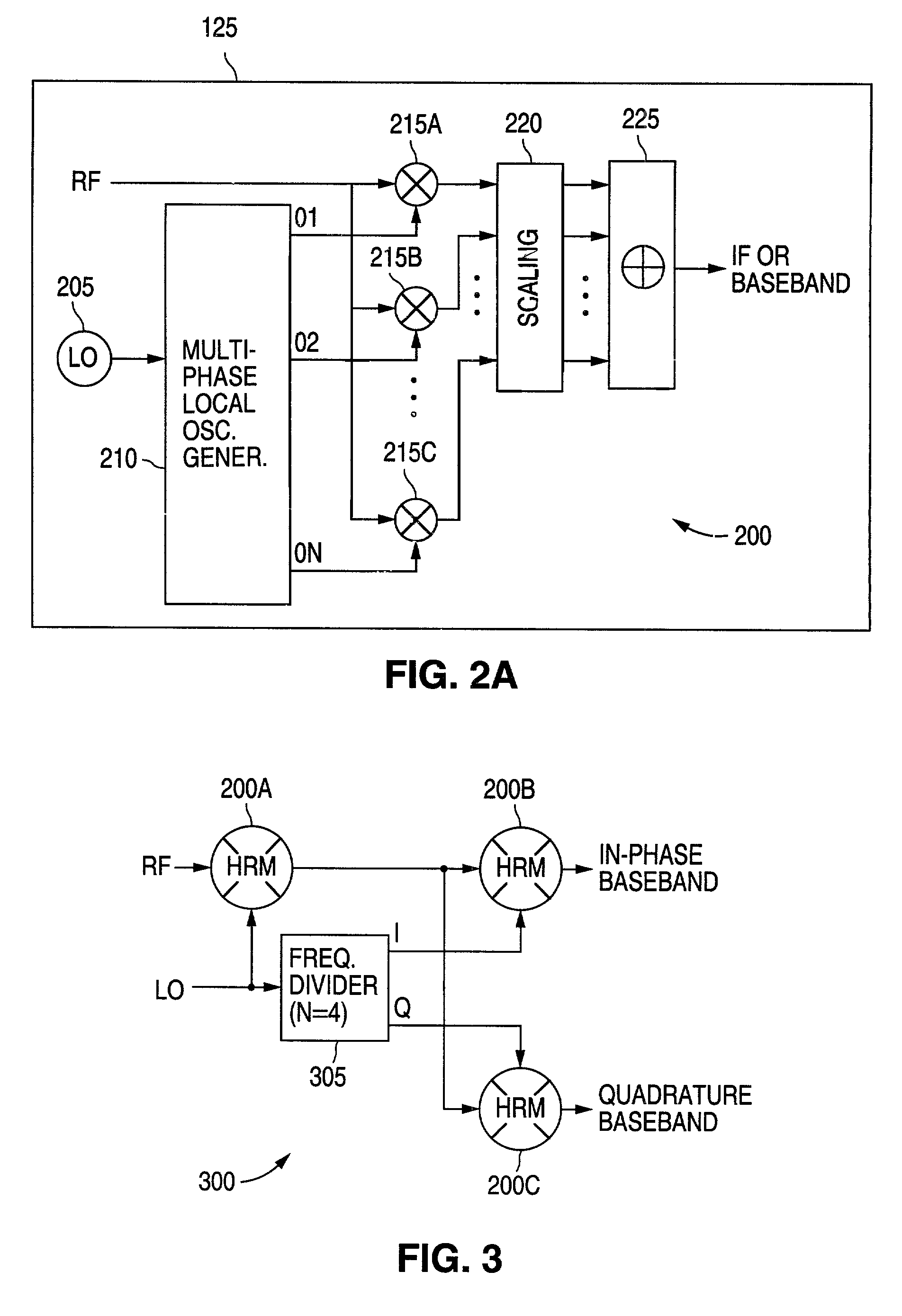
A radio frequency (RF) demodulation circuit comprising a harmonic rejection mixing stage capable of receiving and mixing an incoming radio frequency (RF) signal having a frequency RF and a reference local oscillator (LO) signal having a frequency LO and generating an output signal in which out-of-band harmonic signals are suppressed. The harmonic rejection mixing stage comprises 1) a multiphase local oscillator (LO) generator for receiving the reference LO signal and generating M phase-shifted local oscillator signals having frequencies LO and 2) M mixers, each of the M mixers receiving the incoming radio frequency signal and one of the M phase-shifted local oscillator signals. Each of the M mixers generates a subcomponent signal. The subcomponent signals are then scaled and combined to produce the output signal.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Single chip GSM/EDGE transceiver architecture with closed loop power control
InactiveUS7483678B2Resonant long antennasNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsClosed loopFrequency multiplier
Owner:INTEL CORP
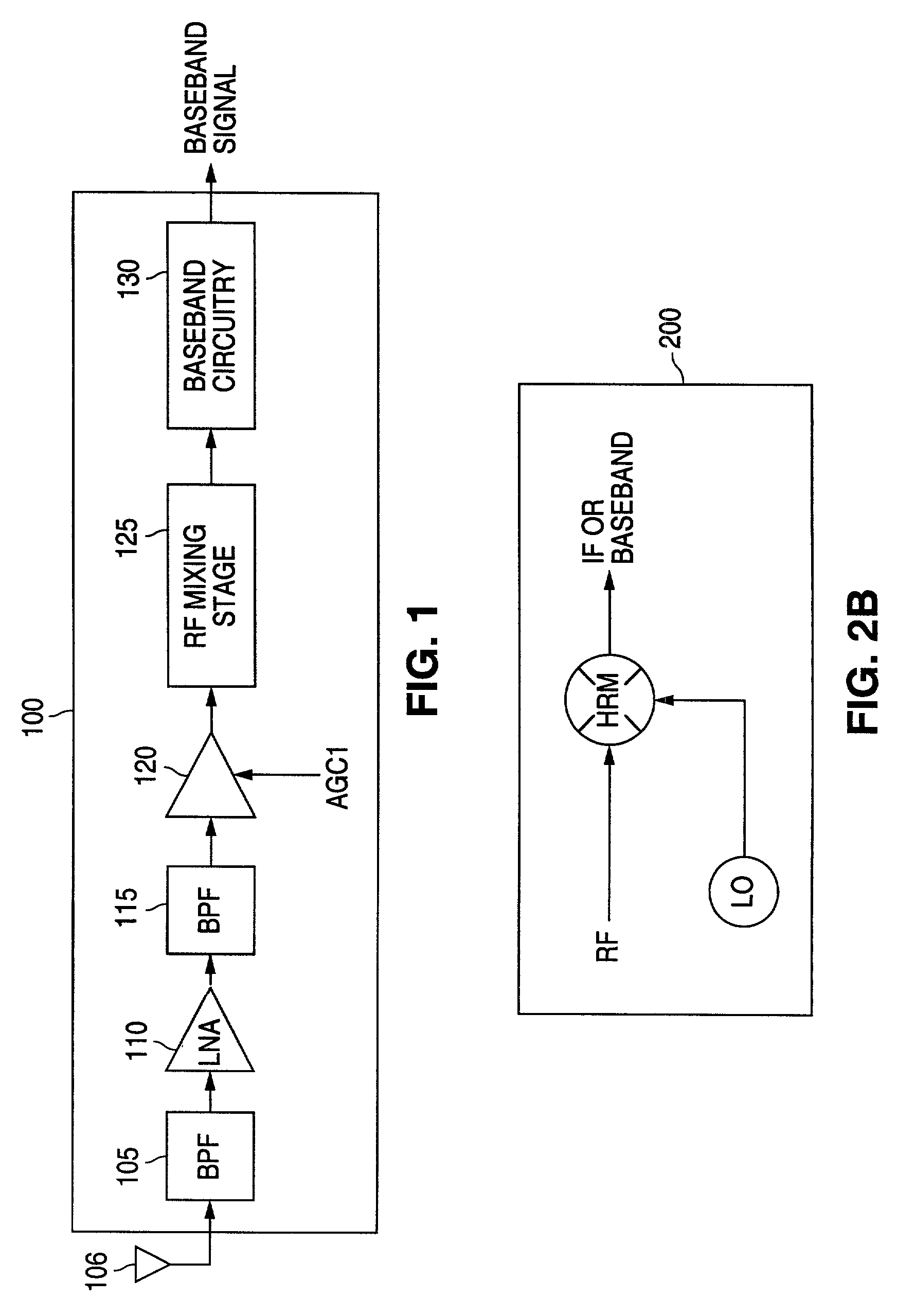
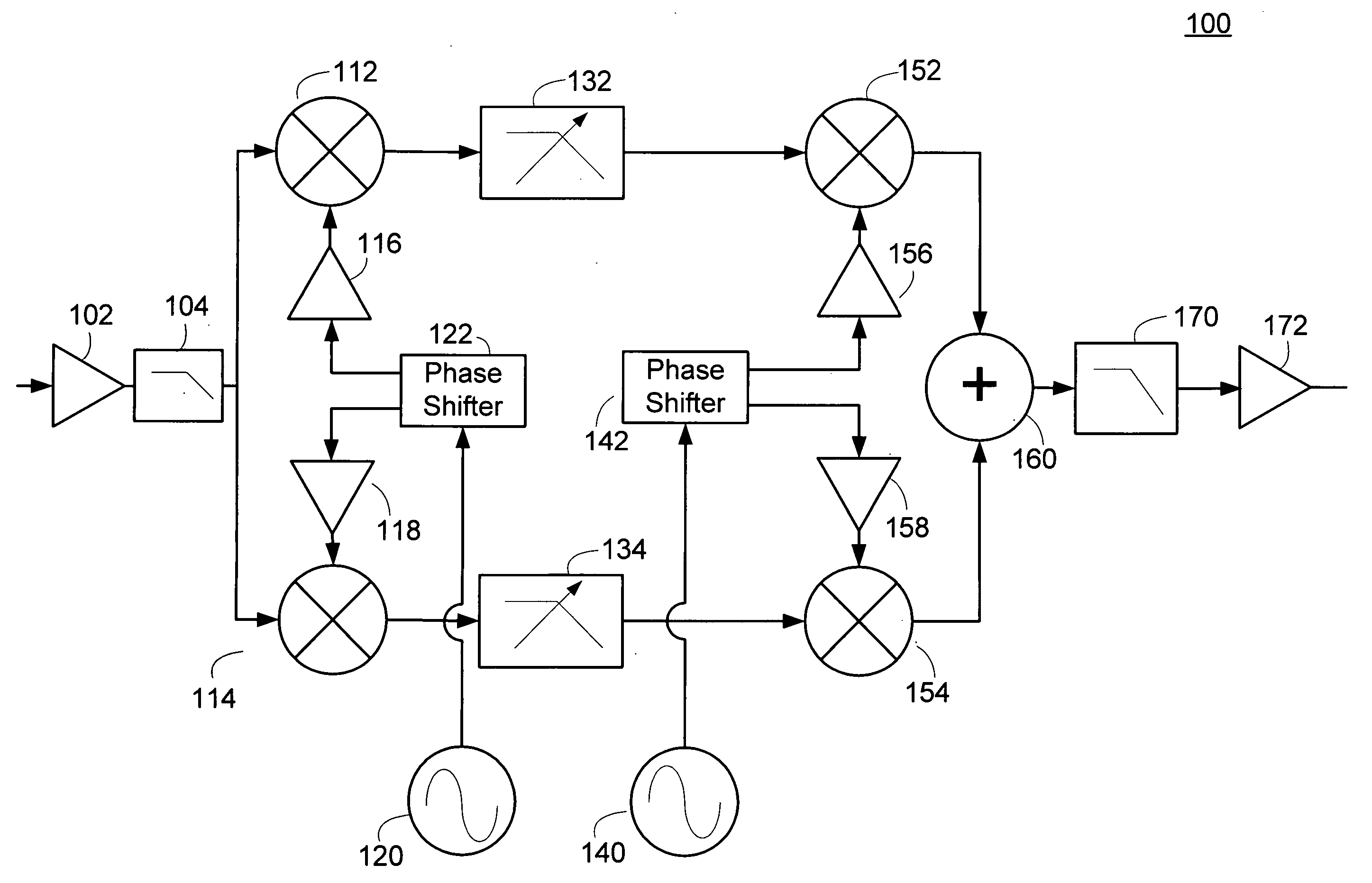
Harmonic reject receiver architecture and mixer
InactiveUS20060160518A1Reducing mixer responseReduced responseModulation transference balanced arrangementsMultiplex with amplitude-modulated carrierLocal oscillator signalFrequency mixer
Receiver architectures and methods of processing harmonic rich input signals employing harmonic suppression mixers are disclosed herein. The disclosed receivers, mixers, and methods enable a receiver to achieve the advantages of switching mixers while greatly reducing the mixer response to the undesired harmonics. A harmonic mixer can include a plurality of mixers coupled to an input signal. A plurality of phases of a local oscillator signal can be generated from a single local oscillator output. Each of the phases can be used to drive an input of one of the mixers. The mixer outputs can be combined to generate a frequency converted output that has harmonic rejection.
Owner:MAXLINEAR INC
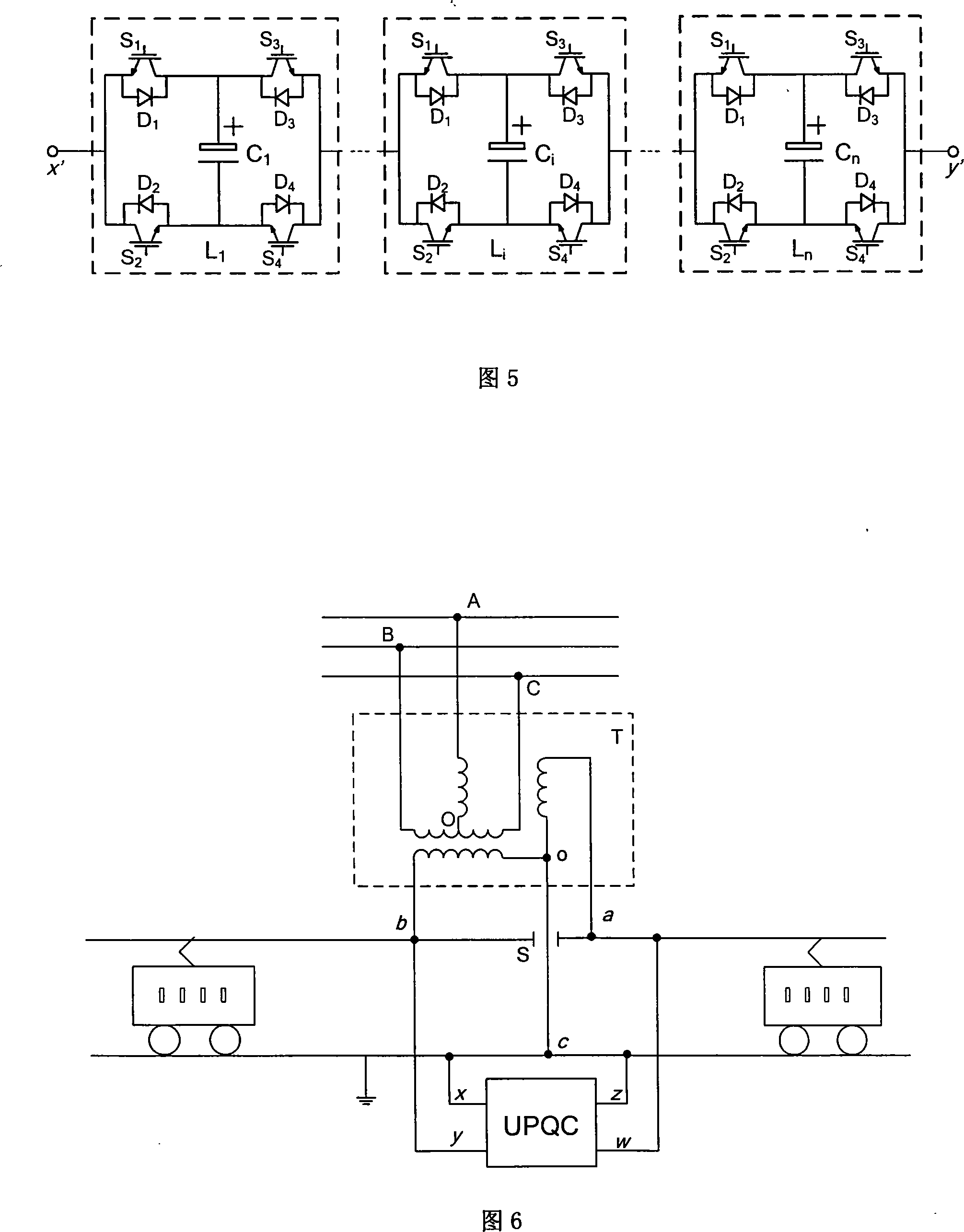
Single-phase integrated power quality controller for electric railway power supply
ActiveCN101170284AGuaranteed mutual equalityImprove capacity utilizationAc-dc conversion without reversalTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsCapacitanceSmall footprint
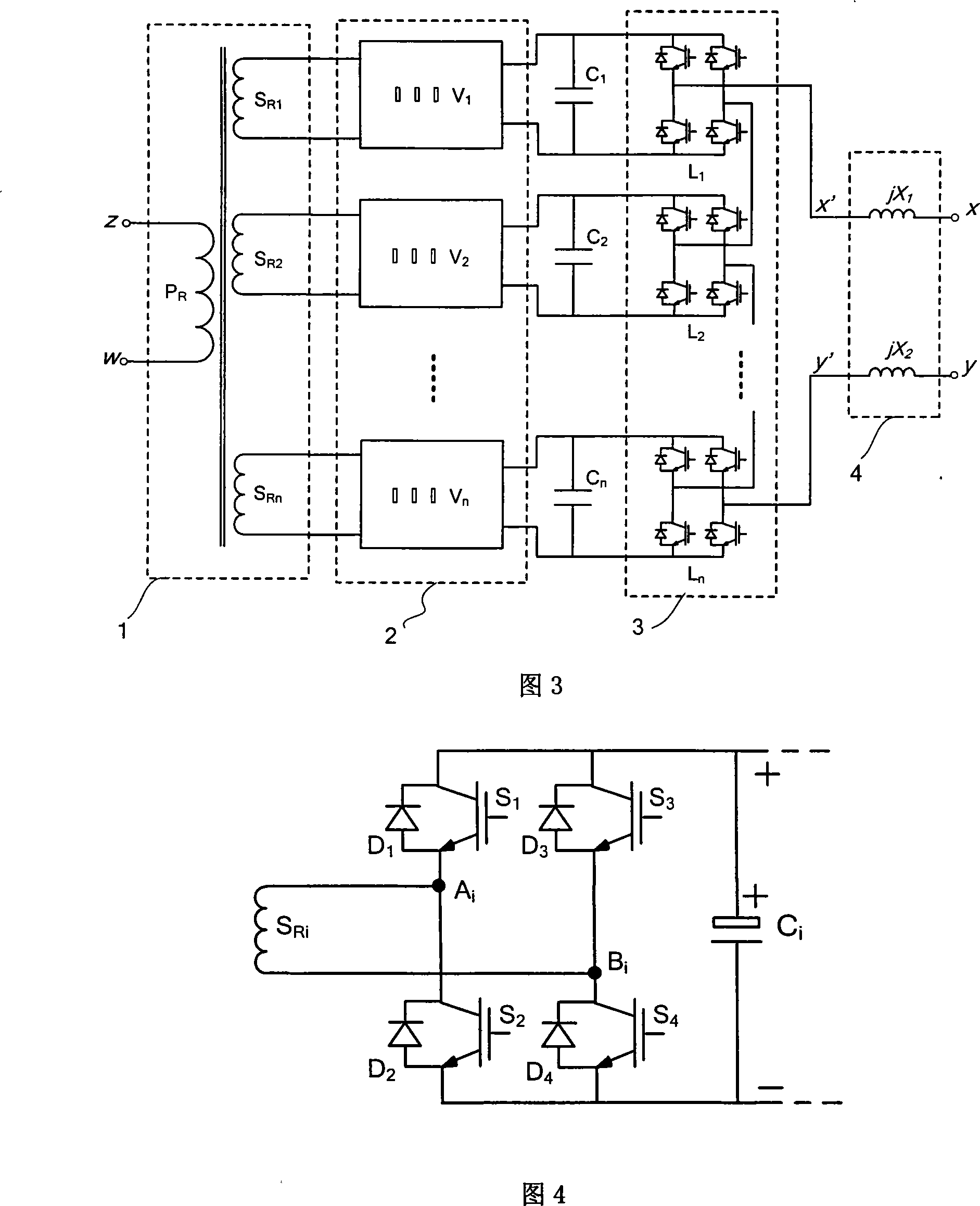
The invention relates to a single-phase universal electric energy quality controller for power supply for electrified railways, and belongs to the technical field of flexible AC power transmission and distribution; the invention comprises a single-phase multi-coil transformer composed of a primary coil and n secondary coils, so that the secondary coils of the transformer can be connected in parallel with n voltage sources of current transformers; n capacitors are connected with n voltage source current transformers, so as to form a single-phase chain-type H-bridge current transformer with n chains; the AC terminal of the H-bridge current transformer is directly connected with the traction grid through a reactor. The invention has the functions of active power control, reactive power compensation and harmonic compensation, so as to resolve three-phase voltage unbalance, voltage fluctuation, low power factor and harmonic pollution and so on that exist in ER traction transformer stations, effectively lower the capacity of traction transformers, increase ER transport capacity and transportation capability. Moreover, the invention is characterized in small occupied area, little loss and low cost, in order to gain perfect harmonic suppression characteristics and dynamic response features, and provide convenience in industrial production and improve device reliability.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
System and method for frequency translation with harmonic suppression using mixer stages
InactiveUS20050059376A1Disadvantages and reduced eliminatedTranslation reduced eliminatedTransmission noise suppressionAmplitude to angle modulation conversionHarmonicControl signal
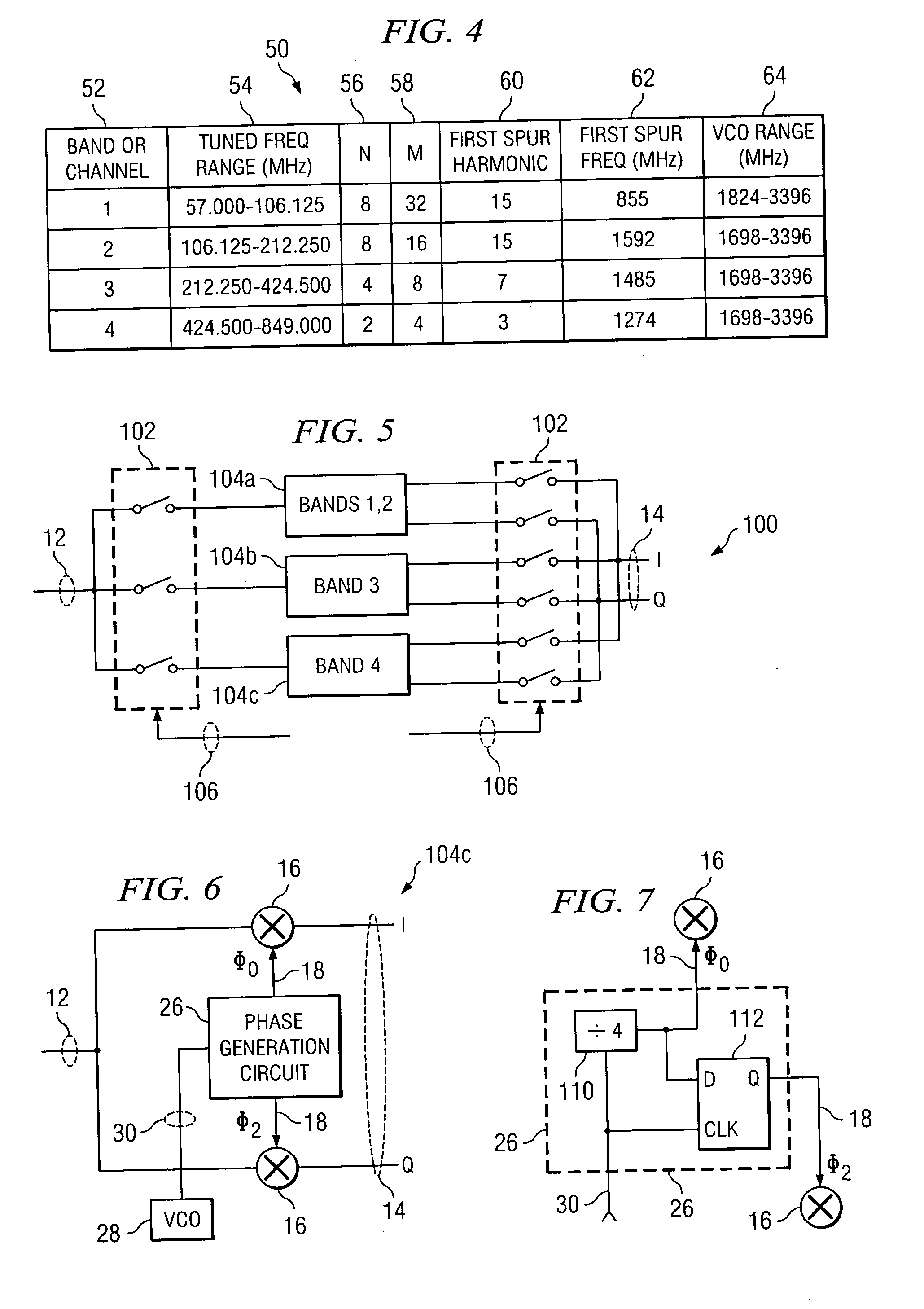
A circuit for frequency translating a radio frequency signal comprises a plurality of mixer stages, each stage associated with a particular range of frequencies of a radio frequency signal. The circuit further comprises a switching circuit that communicates the radio frequency signal to a selected one of the plurality of mixer stages in response to a control signal. The selected mixer stage comprises a phase generation circuit that generates a plurality of phase signals, and at least one mixer that combines the radio frequency signal with one of the plurality of phase signals to generate at least a portion of an intermediate frequency signal.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
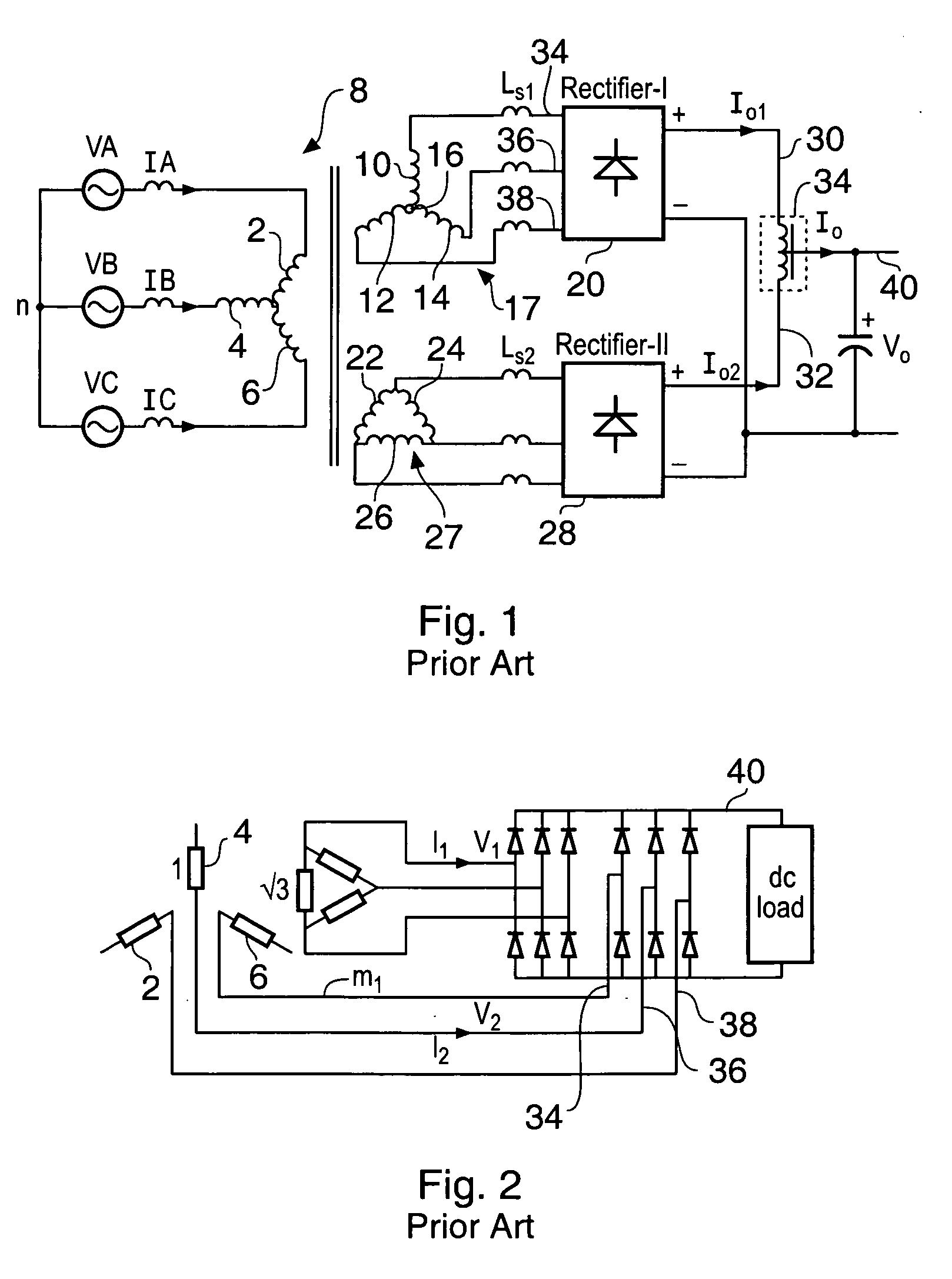
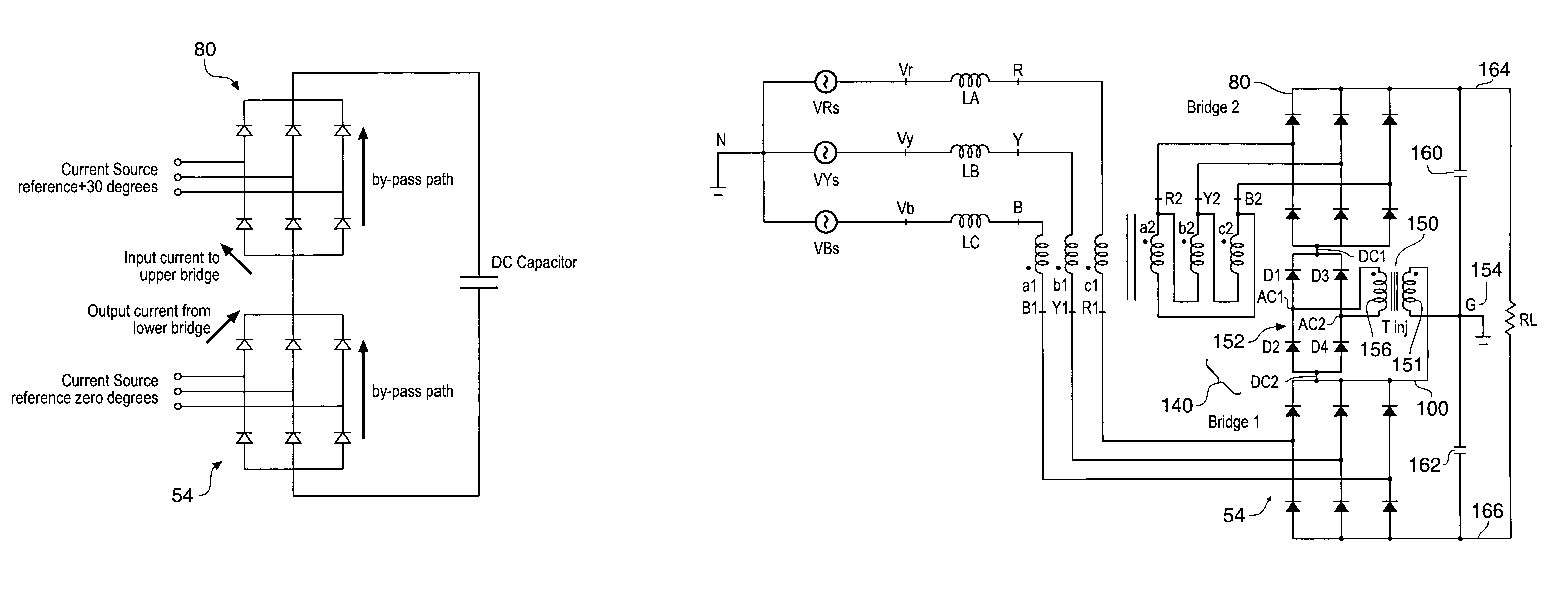
Multi-pulse converter circuits
ActiveUS20050146226A1Reduce Harmonic DistortionReduce harmonic interferenceDc network circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversion without reversalHarmonicEngineering
An AC to DC converter with harmonic suppression is provided. The harmonic suppression is provided by forcing an instantaneous current conflict between series connected rectifier bridges 54, 80, such that a voltage waveform at 6 times the AC supply frequency of the AC supply is automatically generated. This waveform is then injected via a injection circuit to give harmonic cancellation.
Owner:SAFRAN POWER UK
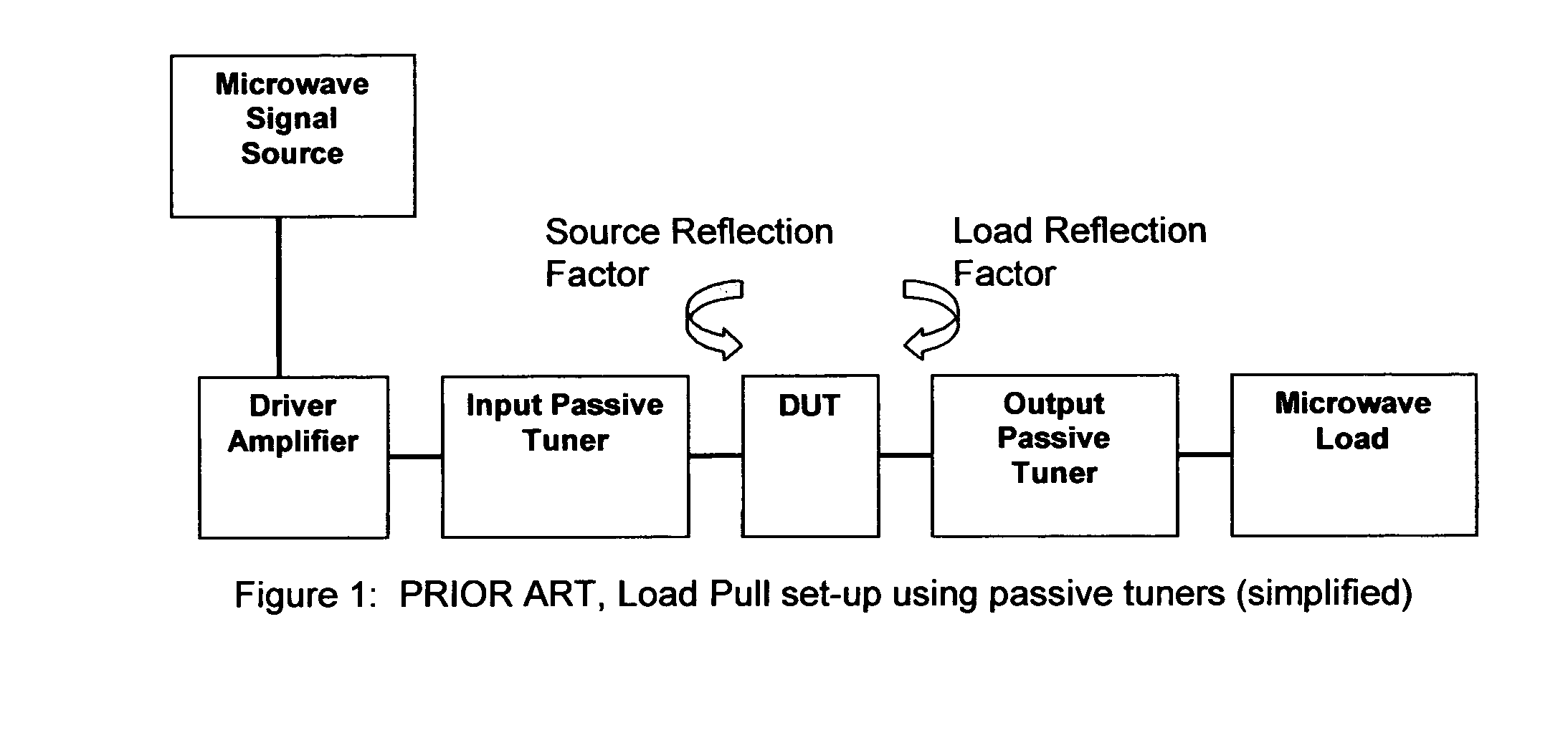
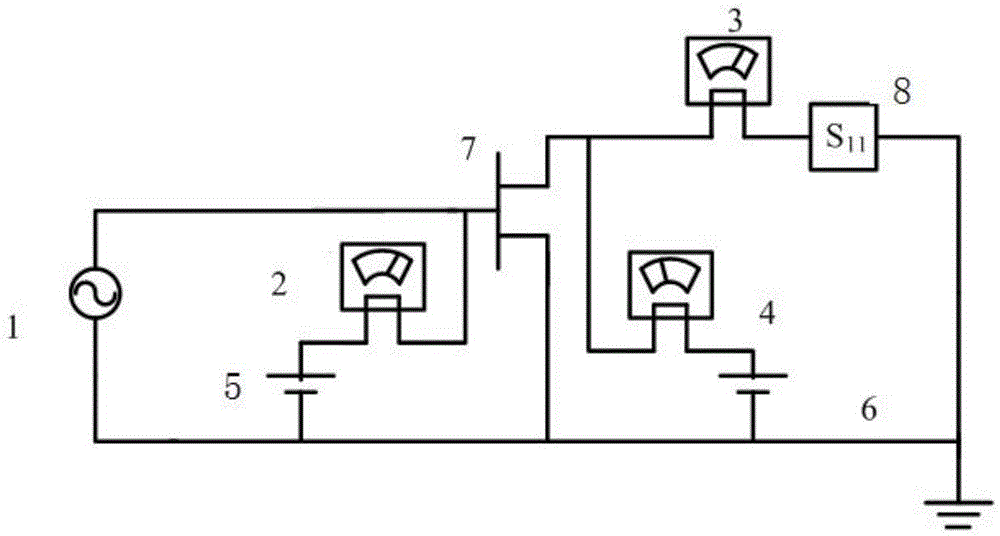
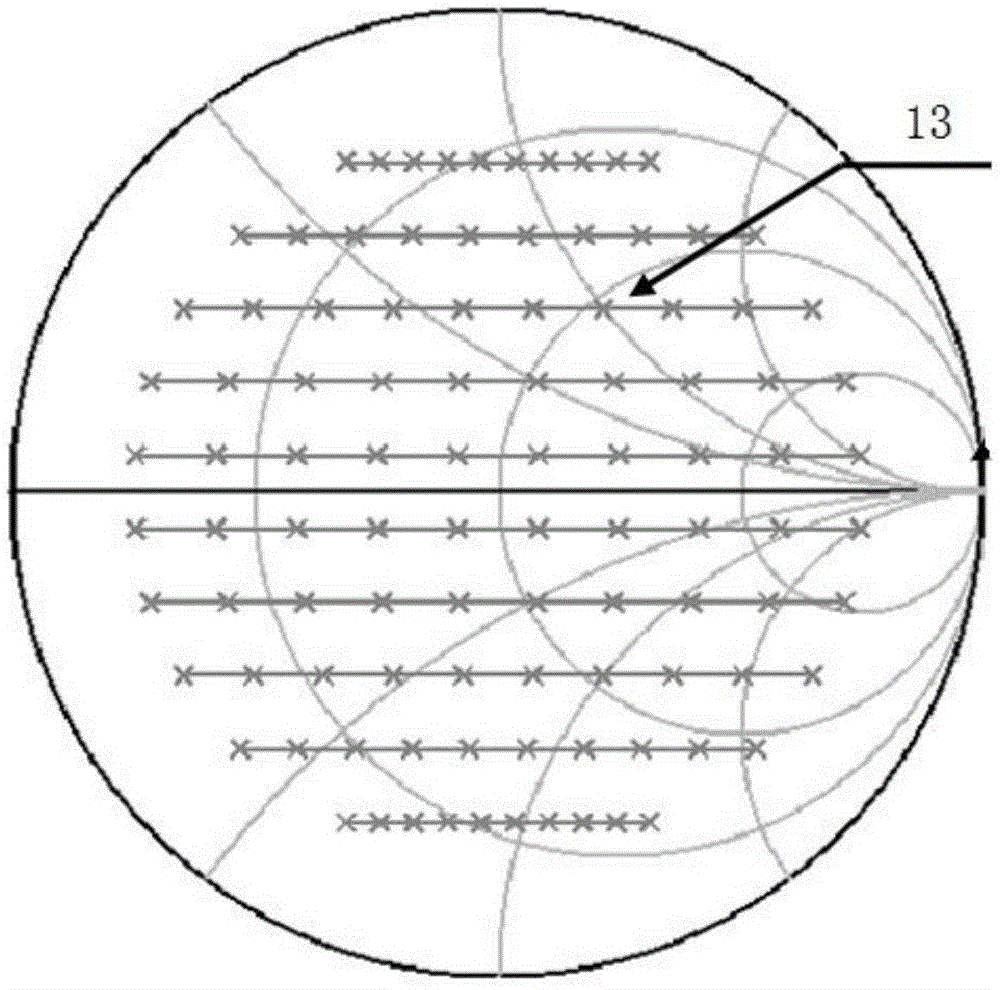
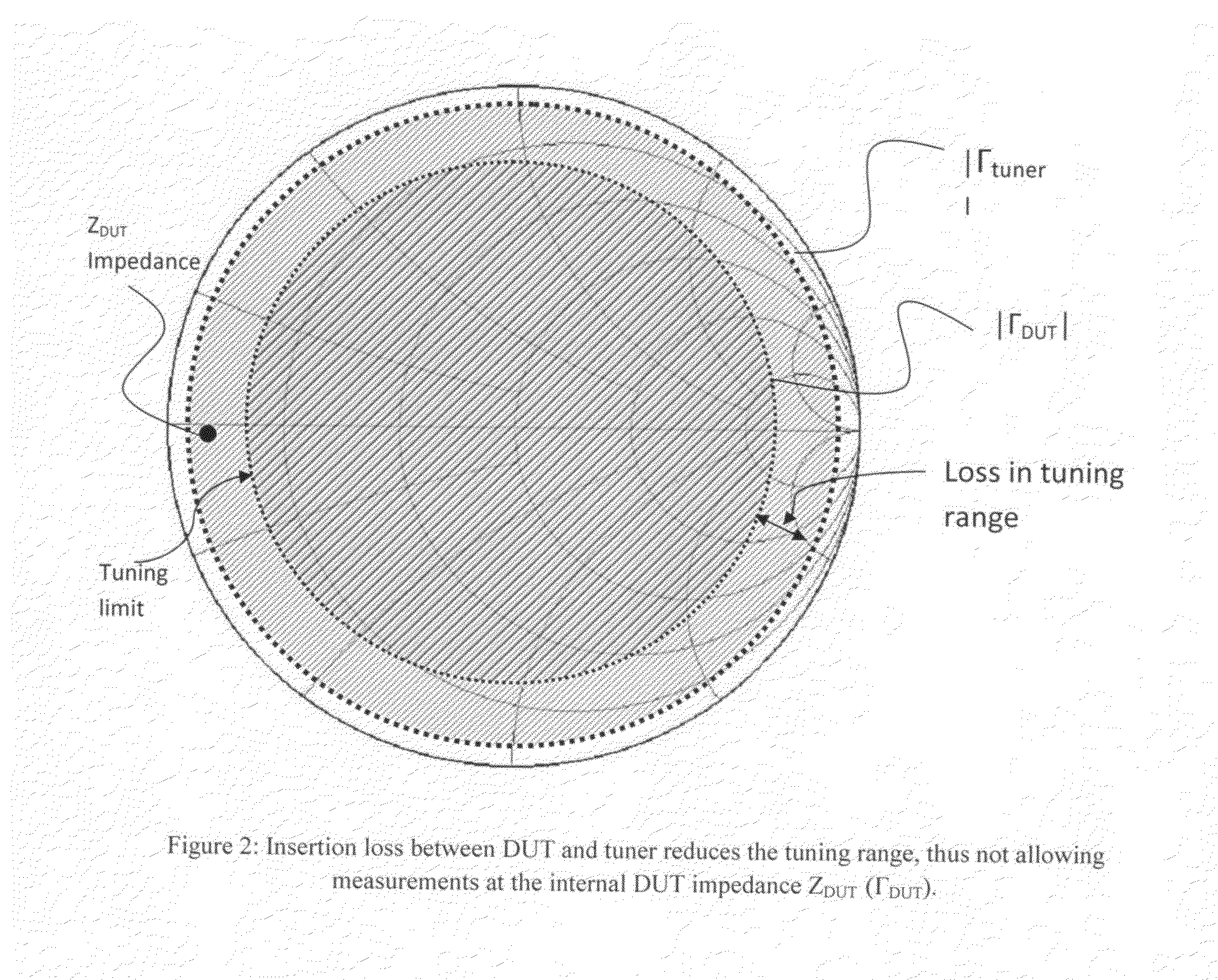
Frequency selective load pull tuner and method
ActiveUS7248866B1Easy to manufactureReadily available for frequency rangeResistance/reactance/impedenceRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsDiscriminatorMicrowave
An automatic, frequency selective microwave tuner, used for load pull transistor testing, is capable of generating independently controllable reflection factors, both in amplitude and phase, at several, harmonic or not, frequencies simultaneously. The tuner employs horizontally and vertically adjustable high Q resonant probes and replaces, when used in harmonic load pull set-ups, otherwise required combinations of wide-band tuners with harmonic rejection tuners or wide-band tuners and frequency discriminators (diplexers or triplexers).
Owner:TSIRONIS CHRISTOS
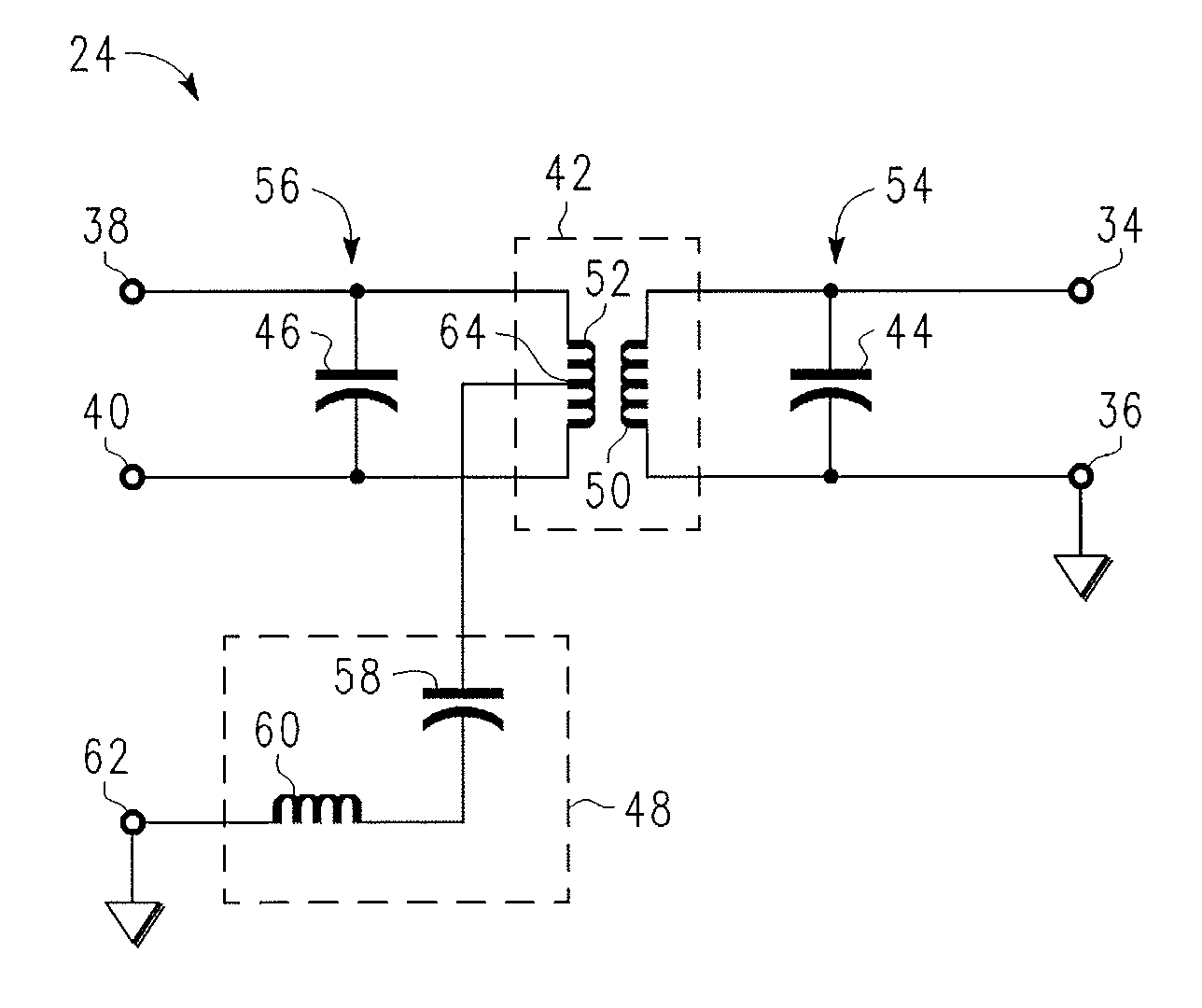
Balun transformer with improved harmonic suppression
ActiveUS20090195324A1Improve performanceImprove device performanceMultiple-port networksOne-port networksTransformerHarmonic
An electronic assembly includes a substrate (66), a balun transformer (42) formed on the substrate (66) and including a first winding (50) and a second winding (52), each having respective first and second ends, and a reaction circuit component (48) formed on the substrate (66) and electrically coupled to the second winding (52) between the first and second ends thereof. The balun transformer (42) and the reaction circuit component (48) jointly form a harmonically suppressed balun transformer having a fundamental frequency, and the reaction circuit component (48) is tuned such that the harmonically suppressed balun transformer resonates at a selected harmonic of the fundamental frequency.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Harmonic rejection load pull tuner
The present invention discloses a harmonic rejection load pull tuner. The tuner of the invention has a large-band tuner having an input and an output, and a transmission line having a longitudinal axis. The transmission line has an input connected to the output of a DUT and an output connected to the input of the large-band tuner. In parallel with the transmission line is at least one stub, the at least one stub having a length adapted to reflect out an nth order harmonic of a base frequency, where n is an integer greater than 1. The tuner of the present invention can be used to perform input or output characterisation (or both) of a DUT, by selectively reflecting out at least one harmonic frequency of the base frequency. Consequently, the characterisation of the DUT is improved, since the effects of the harmonics are considerably reduced. The present invention also concerns a method for performing input or output characterisation.
Owner:TSIRONIS CHRISTOS +1
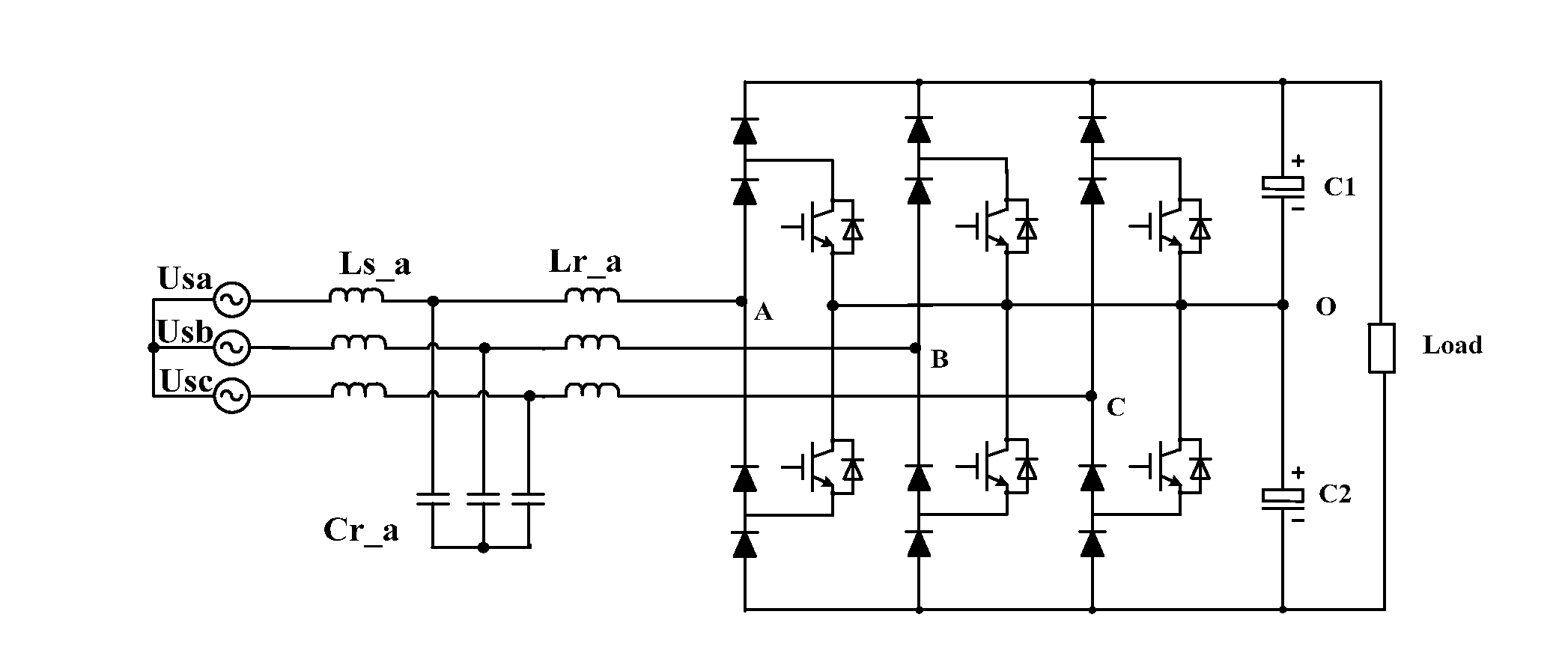
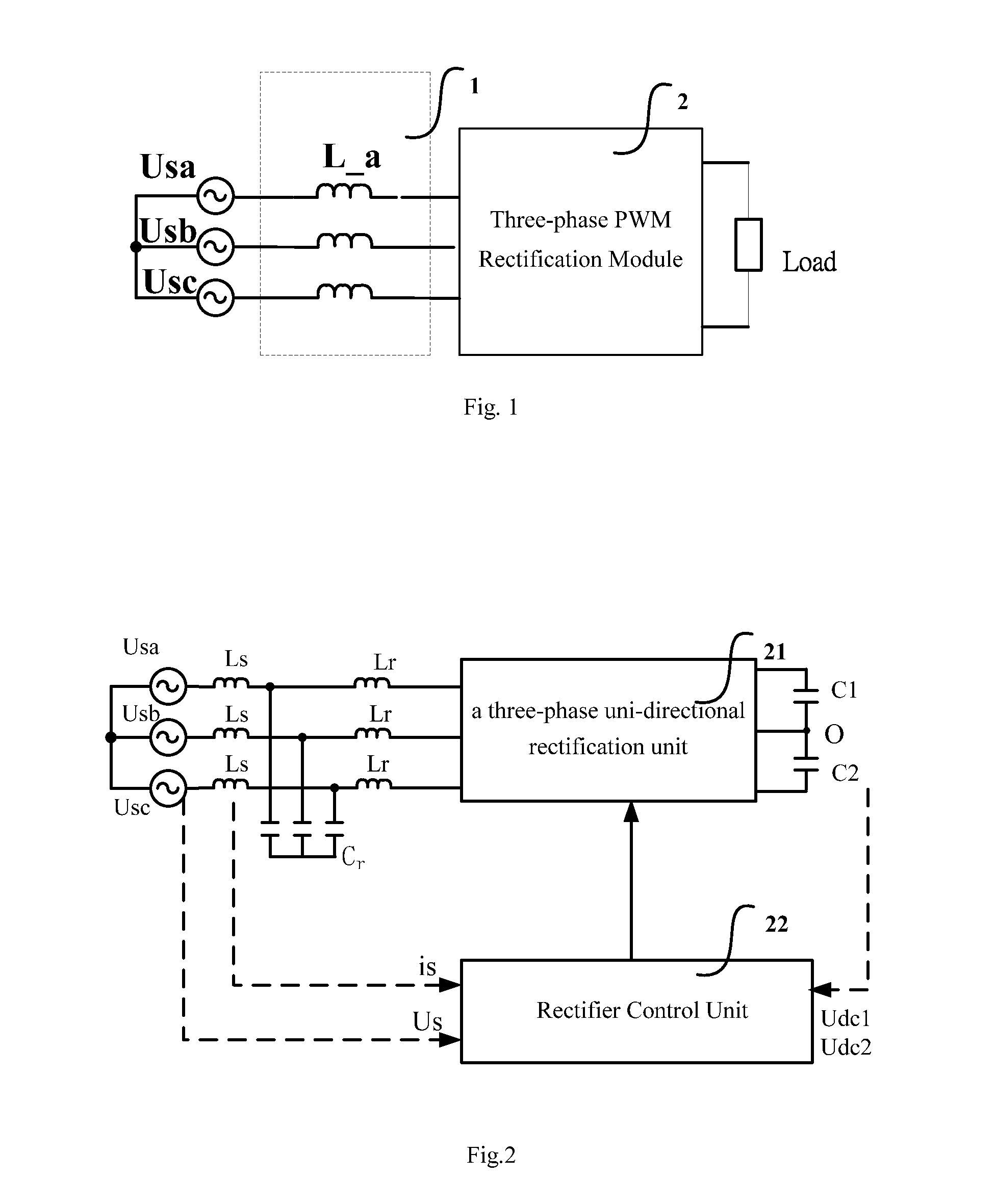
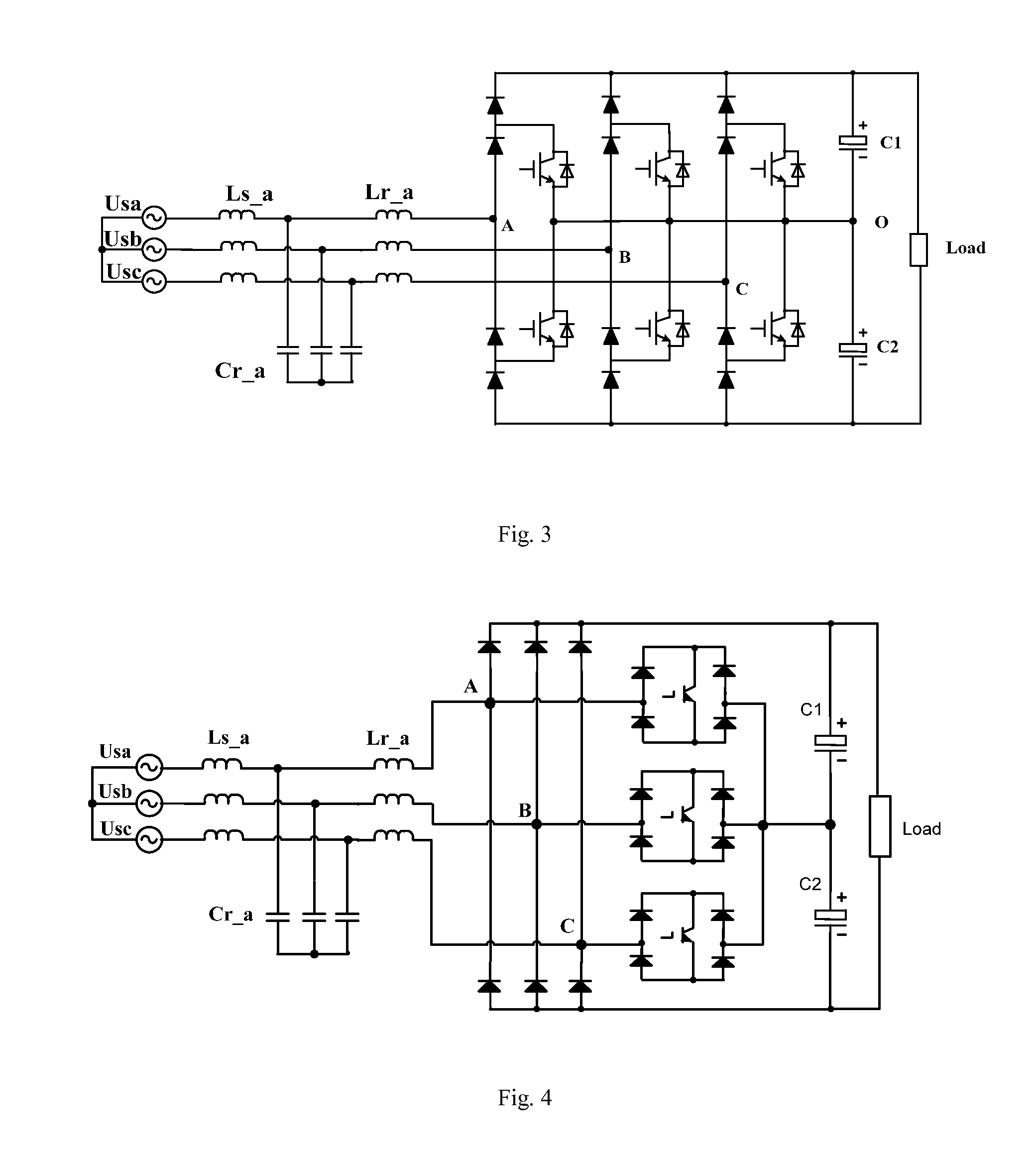
Three-phase rectification module, the system thereof and harmonic suppression method
ActiveUS20130083571A1Reduce Harmonic DistortionFewer switching devicesAC motor controlEfficient power electronics conversionPhase differencePower factor
A three-phase rectification module, the system thereof and harmonic suppression method are provided. The module includes a LCL filter unit, a three-phase uni-directional rectification unit coupled to the LCL filter unit, and a rectifier control unit for controlling power factor of three-phase AC power source and DC output voltage of the three-phase uni-directional rectification unit. A commutation diode is serially connected on the bridge-arm of each set of uni-directional rectification branch which is included in the three-phase uni-directional rectification unit, making it function as current uni-direction. Herein, the power factor of the three-phase AC power source is matched with the parameters of the LCL filter unit, such that the absolute value of the phase difference between AC input voltage and current of the three-phase uni-directional rectification unit is close or equal to a preset threshold.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Active type harmonic suppression apparatus
ActiveUS20060044850A1Active power filteringAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceHarmonicSwitching signal
An active type harmonic suppression apparatus, connected in parallel to a power feeder, supplies a compensation current for injecting into the power feeder such that a utility current of a power source is approached to a sinusoidal wave. The control circuit retrieves a load current, a utility current, an output current of the power converter, a power source voltage and a voltage of the dc power capacitor for calculating and sending a reference signal of compensation voltage to a pulse-width-modulation circuit which generates switching signals for the power converter. Furthermore, the harmonic suppression apparatus can provide a fixed or variable reactive power.
Owner:ABLEREX ELECTRONICS CO LTD
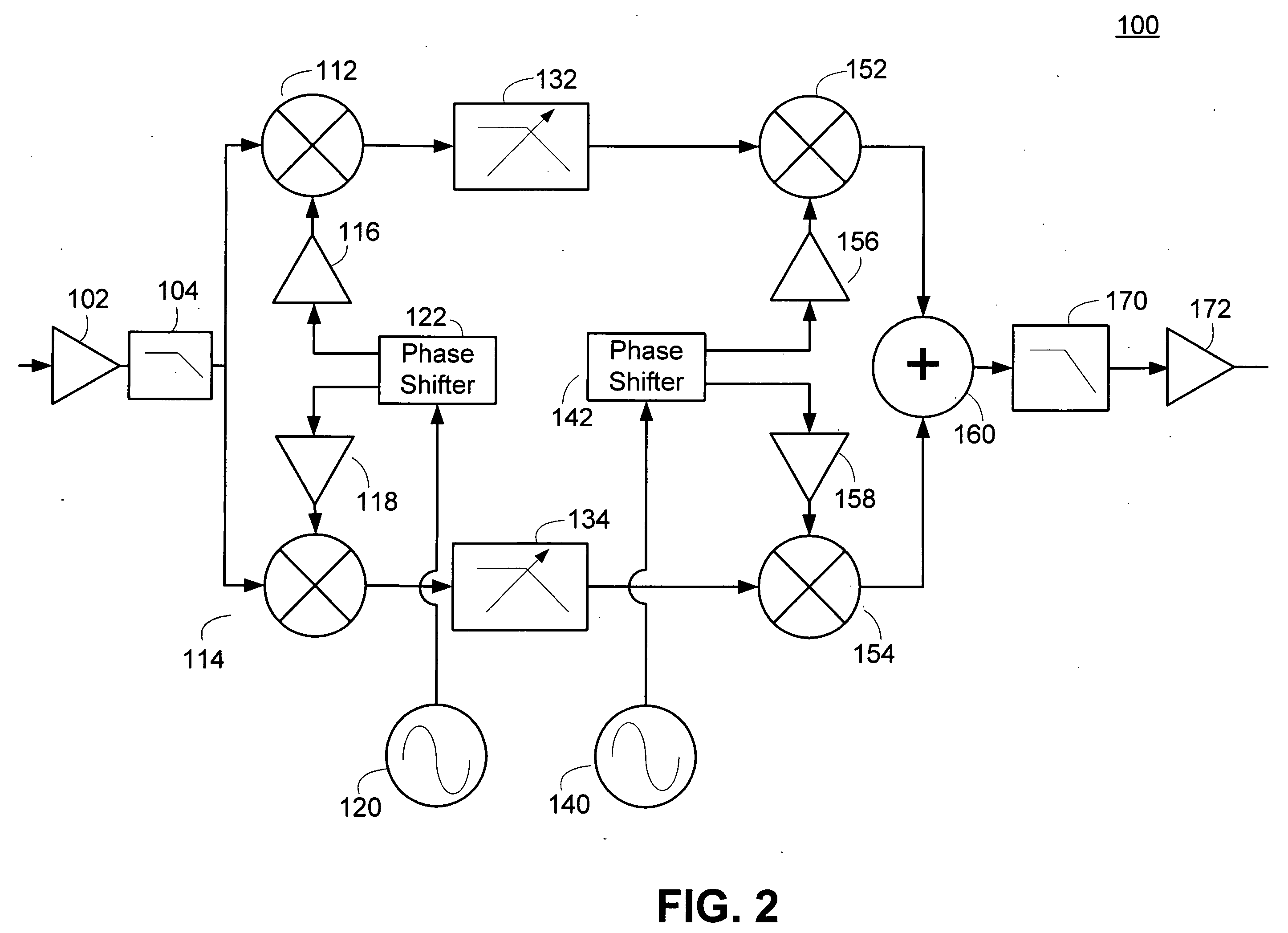
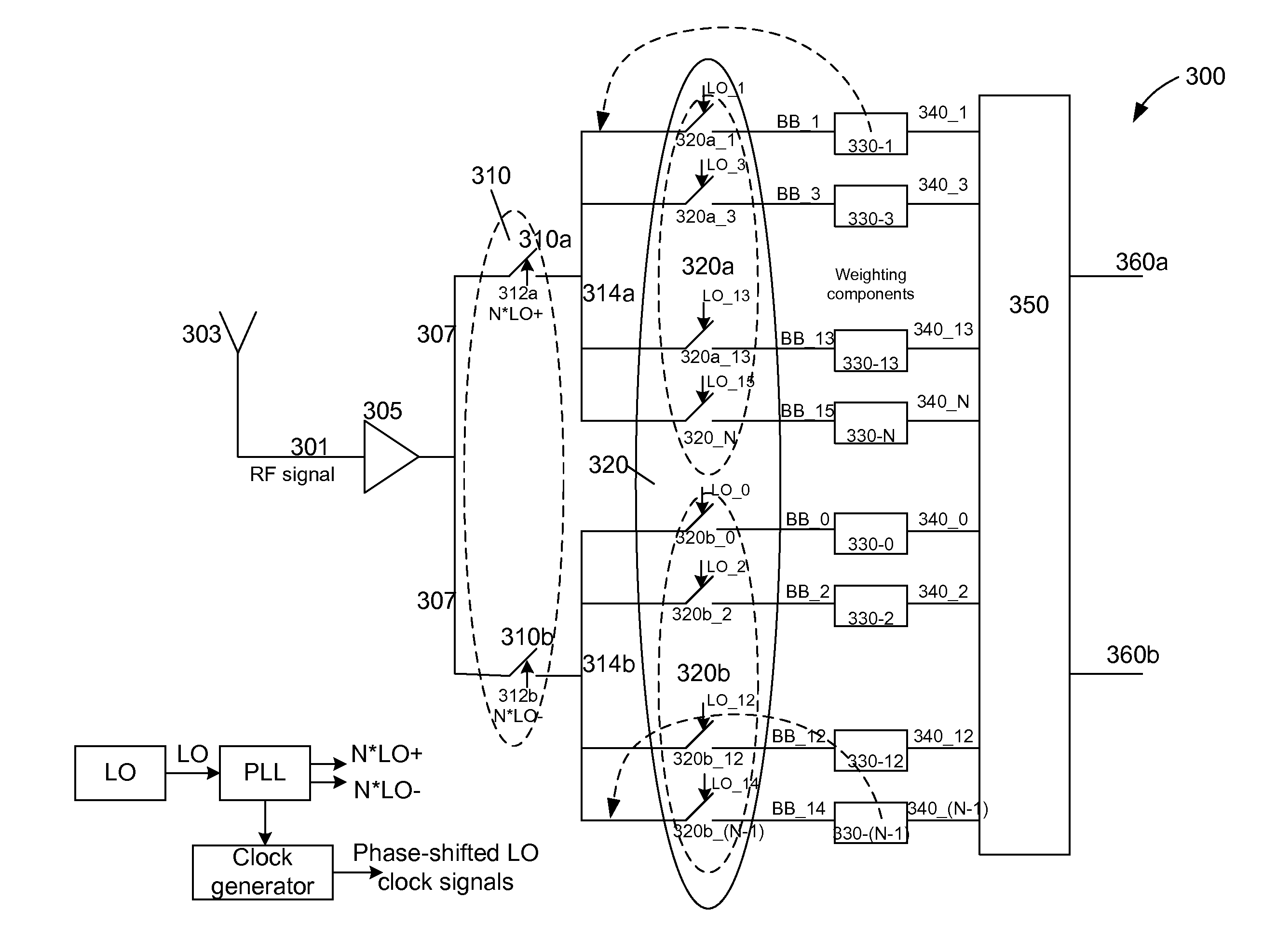
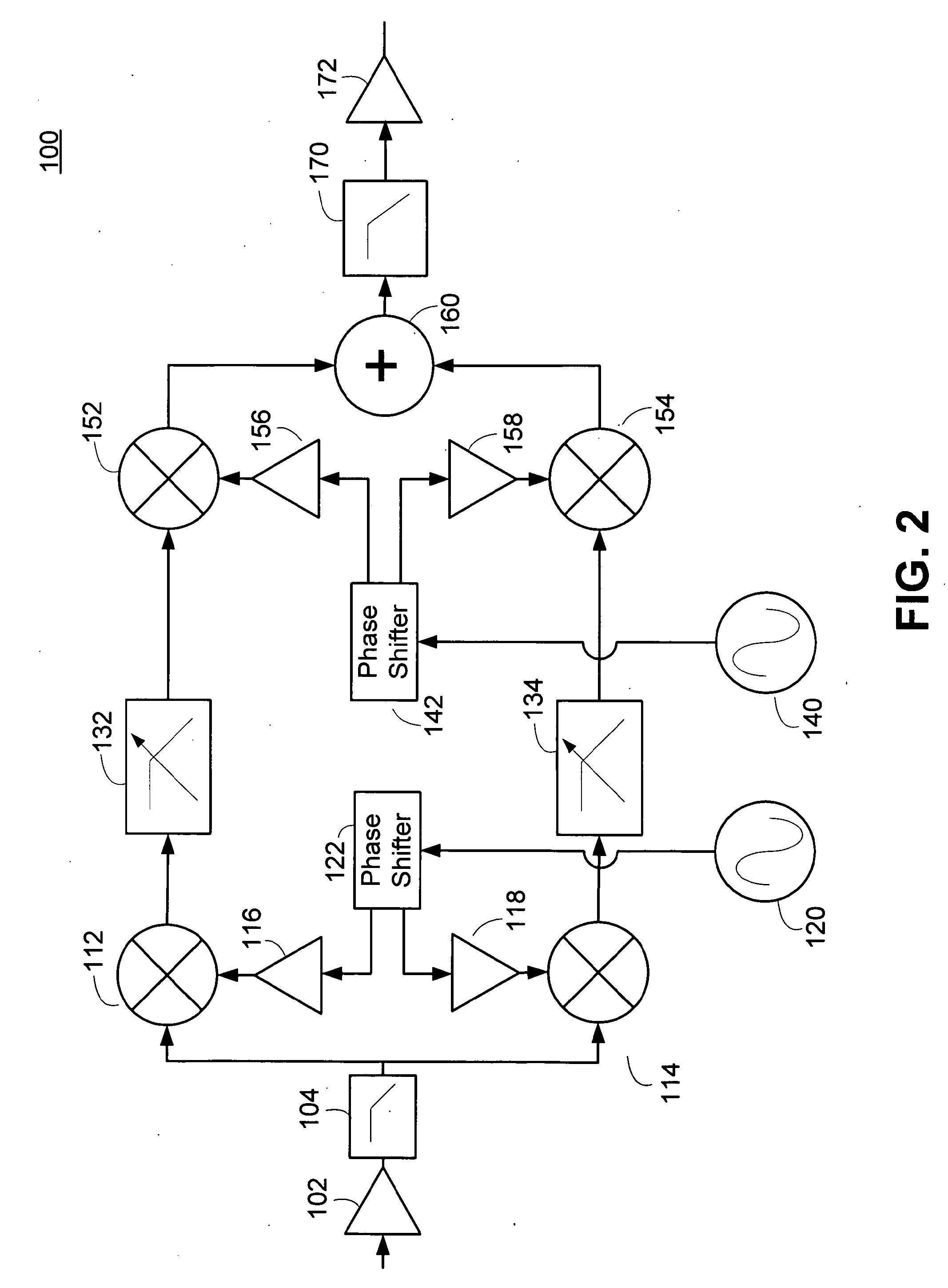
Harmonic Rejection Mixer Architecture with Reduced Sensitivity to Gain and Phase Mismatches
A harmonic rejection mixer includes a first scaling circuit for scaling an RF signal to generate a plurality of scaled RF signals, a first switching stage for sampling the scaled RF signals using a first plurality of switching signals, and a second mixing stage for mixing the sampled RF signals with a second plurality of switching signals to generate a plurality of frequency translated signals having different phases. A combiner adds the frequency translated signals together to generate a first plurality of baseband versions of the RF signal. A first amplifier stage processes the first plurality of baseband versions to generate a second plurality of baseband versions. The mixer further includes a second scaling circuit for scaling the second plurality of baseband versions and a second amplifier stage to generate an in-phase baseband signal and a quadrature baseband signal from the scaled second plurality of baseband versions.
Owner:MAXLINEAR INC
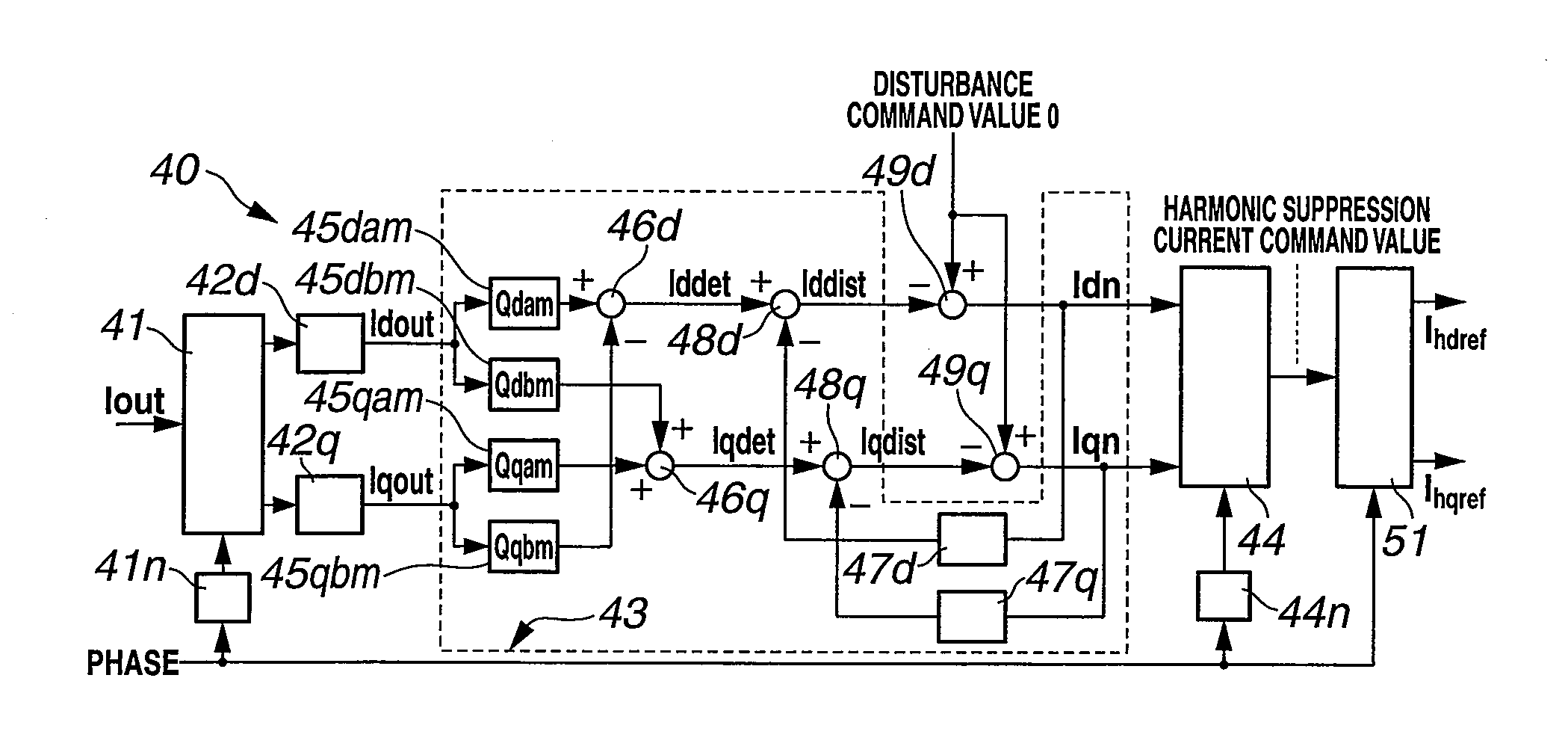
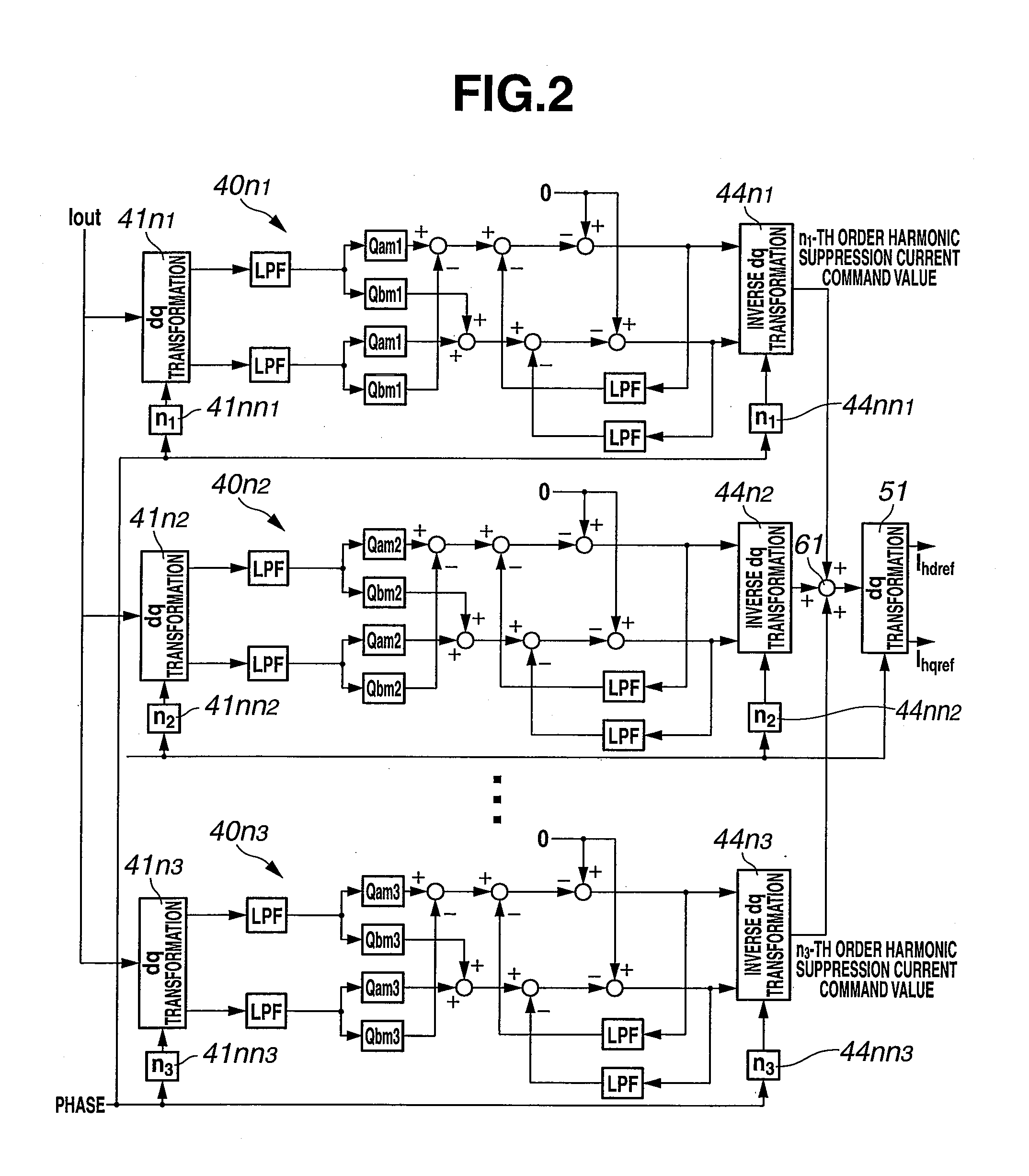
Harmonic current suppression method and harmonic current suppression device of power conversion device
InactiveUS20130135907A1Avoid flowStable harmonic suppressionDc-ac conversion without reversalHarmonic reduction arrangementHarmonicElectric power
A current control unit takes a deviation between a current command value and a current flowing through an inverter of a power conversion device, and controls the inverter based on the deviation. A harmonic sensing part receives input of an output current of an AC filter, and outputs a predetermined order harmonic of the input current in a direct current value form. A disturbance observer estimates the disturbance of the harmonic based on the output current and a coefficient defined as an inverse function of a transfer function from harmonic suppression current command value to filter output current detection value. A harmonic suppression control unit takes the deviation between the estimated harmonic disturbance and a disturbance command value that suppresses the disturbance, and calculates a harmonic suppression current command value. The harmonic suppression current command value is superimposed on the current command value of the current control unit.
Owner:MEIDENSHA ELECTRIC MFG CO LTD
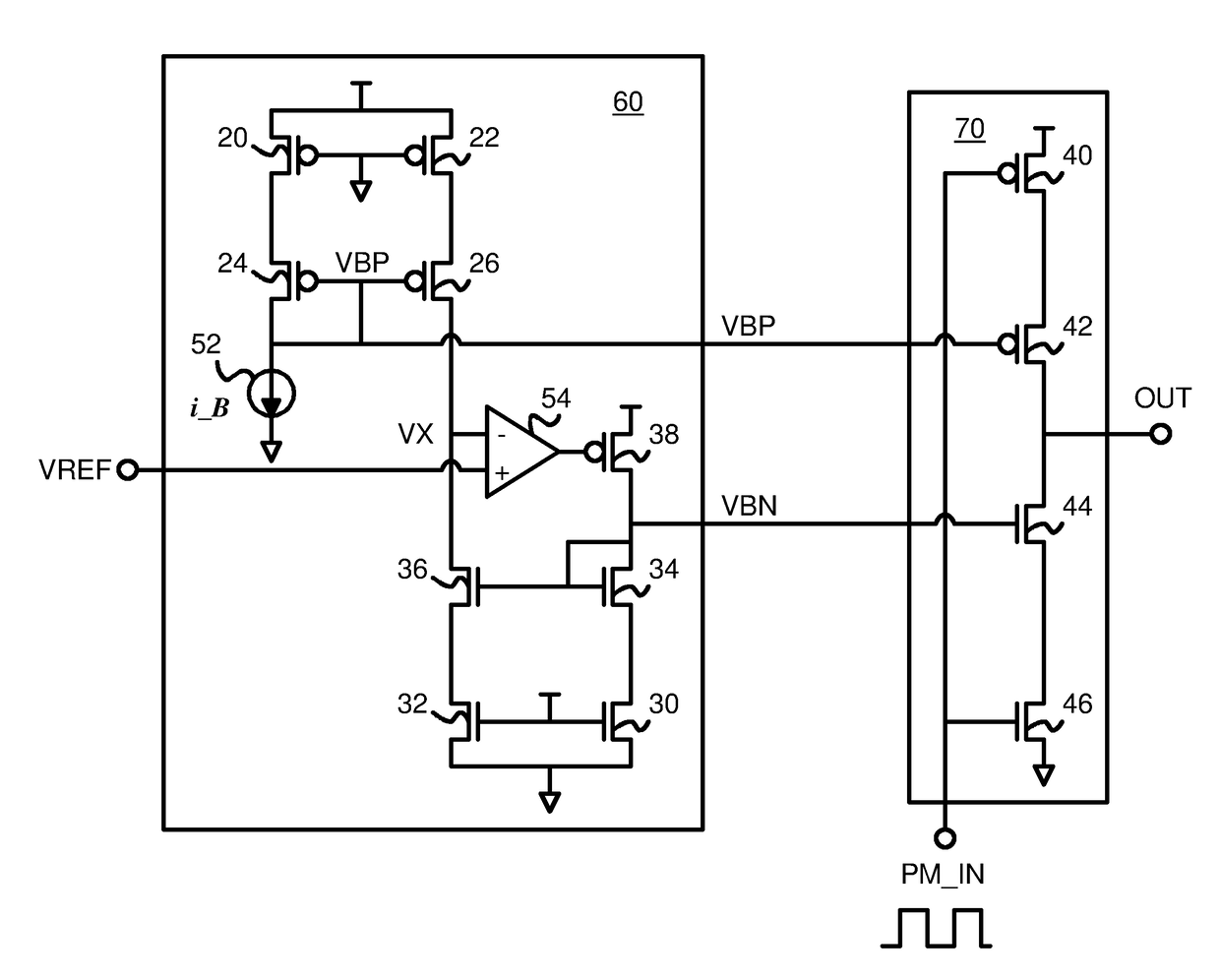
Harmonics suppression circuit for a switch-mode power amplifier
ActiveUS9641141B1Amplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesPower flowAudio power amplifier
Even harmonics are suppressed by a harmonics-reducing bias generator that drives bias voltages to cascode control transistors in series with driver transistors in a power amplifier. A first bias voltage is generated by mirroring pull-up currents in the power amplifier. A p-channel source transistor and a p-channel cascode current-mirror transistor also mirror the power amplifier pull-up current to a midpoint node. An n-channel sink transistor and an n-channel cascode current-mirror transistor mirror the pull-down current in the power amplifier to the midpoint node. An op amp compares the midpoint node to VDD / 2, and drives the gate of a p-channel feedback transistor. Current from the p-channel feedback transistor flows through an n-channel cascode current-mirror transistor that generates a second bias voltage. The second bias voltage is adjusted until the midpoint node reaches VDD / 2, causing the pull-up and pull-down currents in the power amplifier to better match, reducing even harmonics.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
Multi-pulse converter circuits
ActiveUS7148661B2Reduce harmonic interferenceOptimise levelDc network circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversion without reversalHarmonicEngineering
An AC to DC converter with harmonic suppression is provided. The harmonic suppression is provided by forcing an instantaneous current conflict between series connected rectifier bridges 54, 80, such that a voltage waveform at 6 times the AC supply frequency of the AC supply is automatically generated. This waveform is then injected via a injection circuit to give harmonic cancellation.
Owner:SAFRAN POWER UK
Dual-mode mixer circuit and method
ActiveUS20100120377A1Eliminate the problemIncrease rangeResonant long antennasComputations using contact-making devicesLocal oscillator signalPhase shifted
The present invention relates to a mixer circuit and method of frequency transformation, wherein an input signal is switched in accordance with a first local oscillator signal and in accordance with at least one second local oscillator signal having a smaller duty cycle than said first local oscillator signal, or having a respective predetermined phase shift with respect to said first local oscillator signal. Output signals obtained by the switching in accordance with the first and at least one second local oscillator signals are summed and the polarity of one of said first local oscillator signal and said at least one second local oscillator signal is switched in response to a control input, to thereby switch between a harmonic-rejection mode and a sub-harmonic mixing mode.
Owner:NXP BV
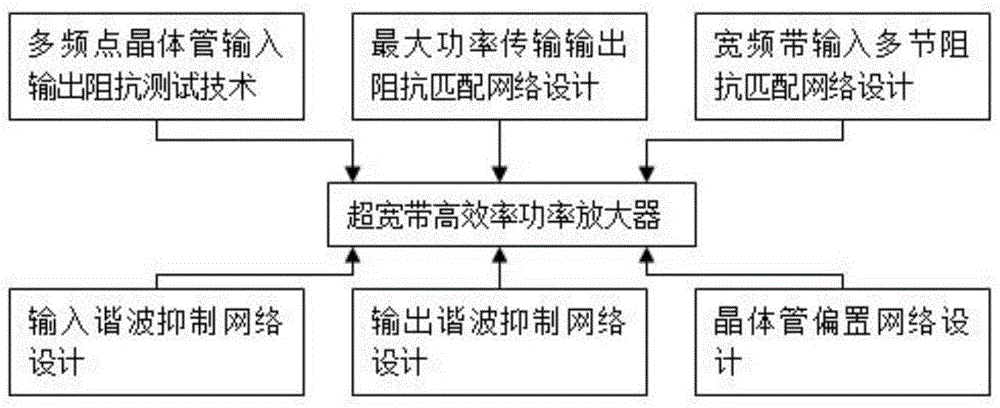
Design method for radio frequency ultra-wide band high-efficiency power amplifier and circuit
InactiveCN105631109AIncrease frequency bandwidthIncrease output powerCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsImpedance matchingEngineering
The invention discloses a design method for a radio frequency ultra-wide band high-efficiency power amplifier and a circuit. The design method includes the steps of a multi-frequency point transistor input and output impedance test, design of a maximum power transmission output impedance matching network, design of a wide band input multi-section impedance matching network, design of an input harmonic suppression network and an output harmonic suppression network and design of a transistor offset network. The transistor input and output impedance test technology achieves precise calculation of transistor input and output impedance. The maximum power transmission output impedance matching network achieves transistor impedance matching and maximum power transmission. The wide band input multi-section impedance matching network achieves wide band transistor input impedance matching. The design of the input harmonic suppression network and the output harmonic suppression network eliminates higher harmonic influences at the input end and the output end of a transistor, reduce losses and improve power additional efficiency of the amplifier. The design of the offset network provides working voltage of the transistor. The power amplifier can acquire higher frequency bandwidth, output power and power additional efficiency.
Owner:HEFEI NORMAL UNIV
Single chip GSM/EDGE transceiver architecture with closed loop power control
InactiveUS20070072577A1Resonant long antennasNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsClosed loopFrequency multiplier
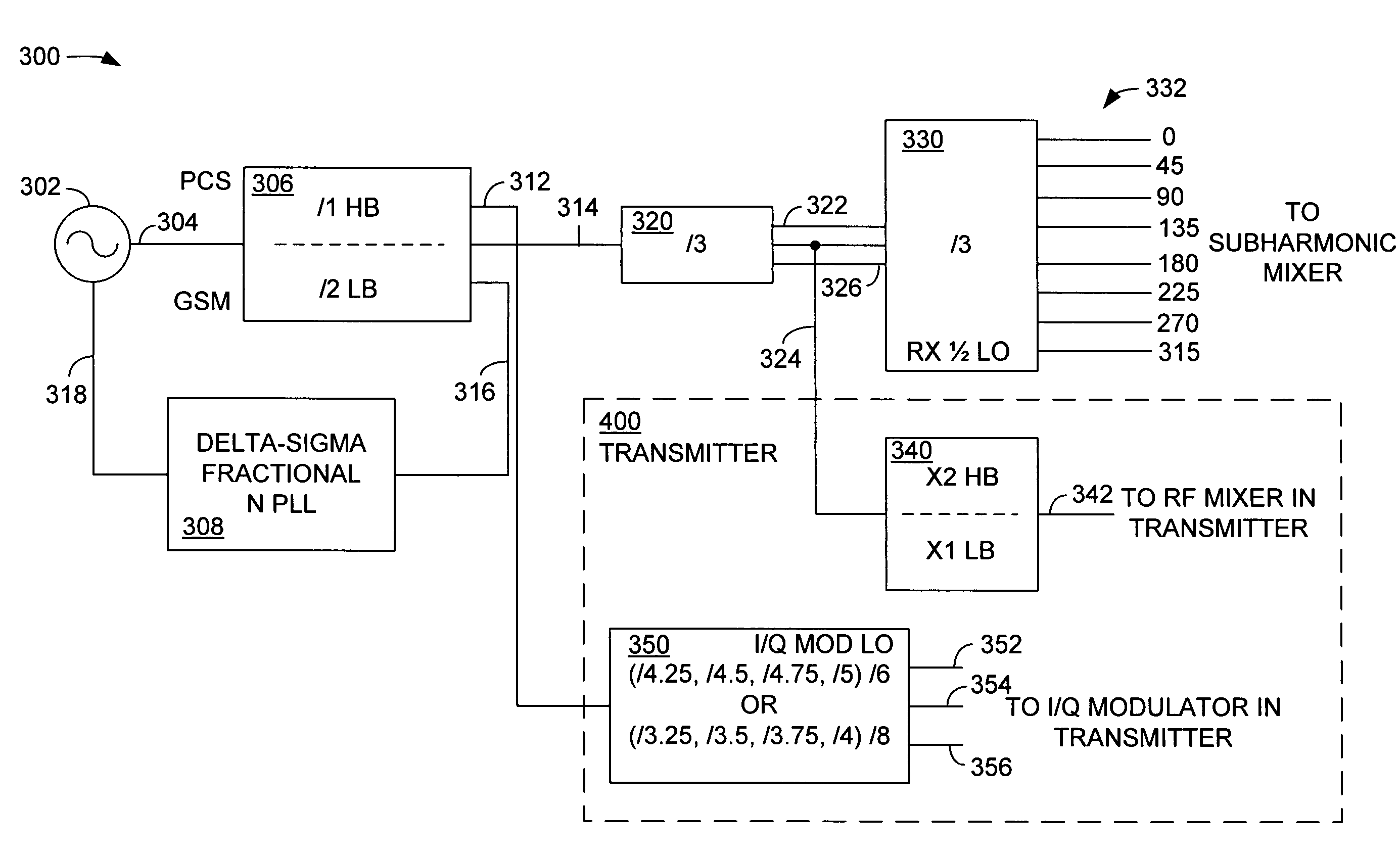
A single chip GSM / EDGE transceiver comprises a fully differential receive chain, a subharmonic mixer in the receive chain, the subharmonic mixer configured to receive a radio frequency (RF) input signal and a local oscillator (LO) signal that is phase-shifted by a nominal 45 degrees, and a synthesizer having a voltage controlled oscillator and having at least one frequency divider to generate desired transmit and receive LO signals. The transceiver also comprises a transmitter having a closed power control loop, and a harmonic rejection modulator, the use thereof made possible by a frequency plan designed to allow the synthesizer to develop the transmit and receive LO signals without a frequency multiplier.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Millimeter-wave frequency multiplier and cascaded frequency multipliers
InactiveCN102104362AReduce power consumptionReduce bias currentOscillations generatorsFrequency spectrumTransformer
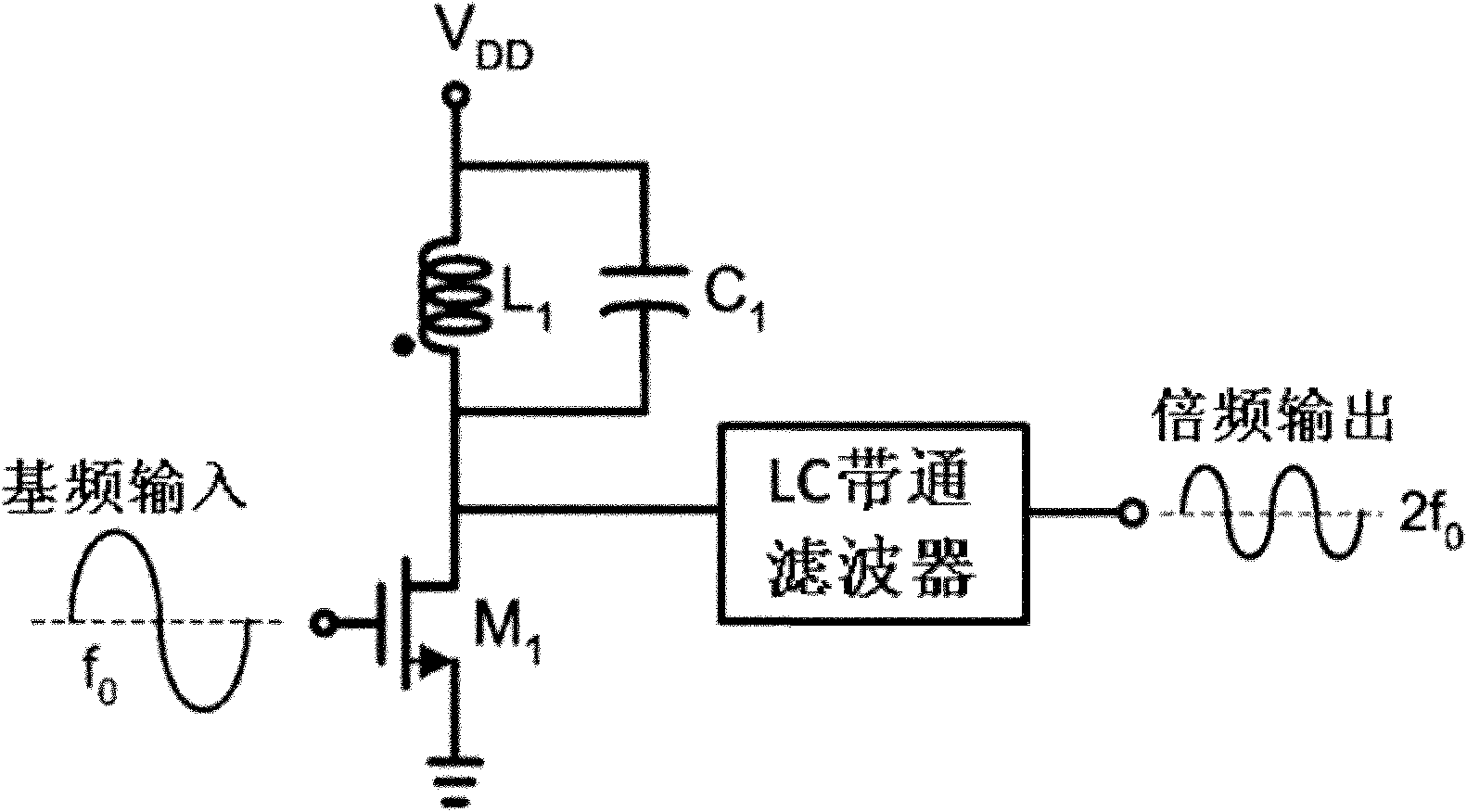
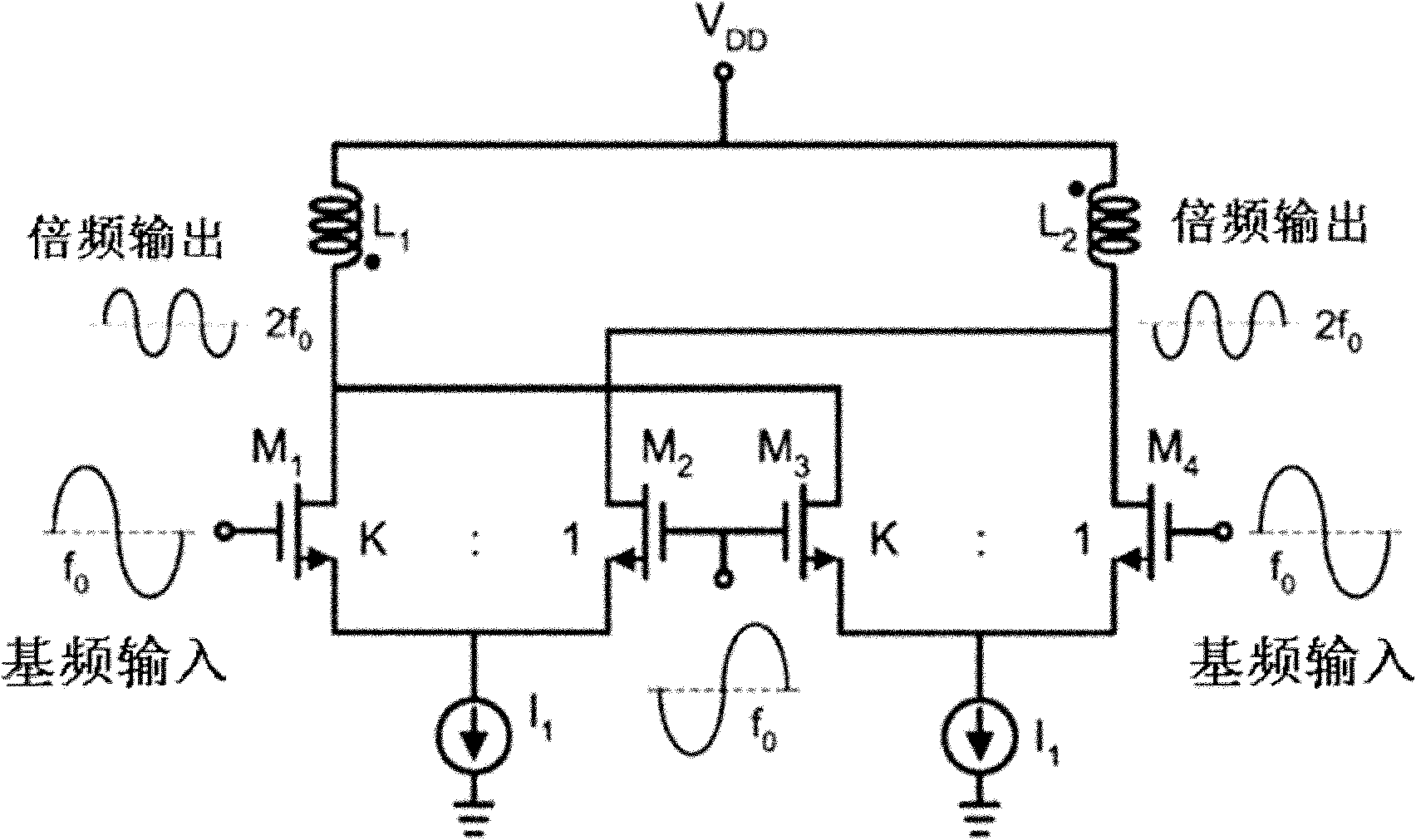
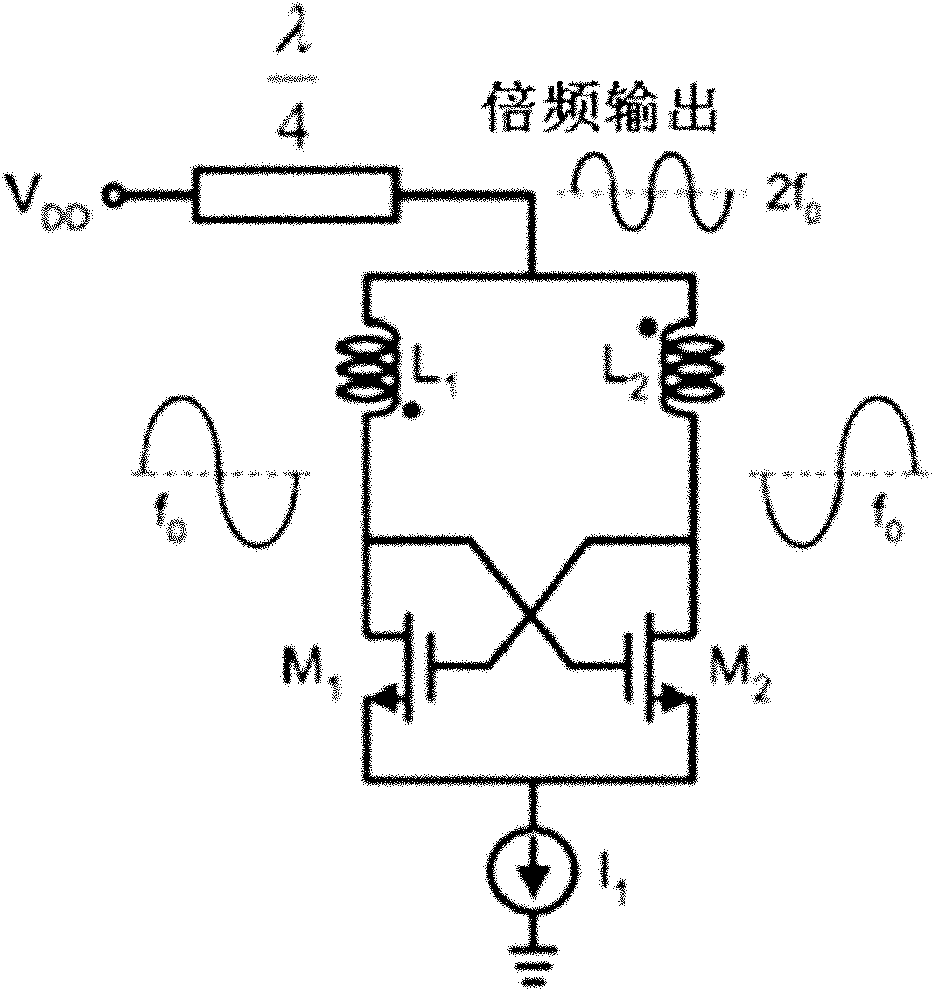
The invention discloses a millimeter-wave frequency multiplier and cascaded frequency multipliers, belonging to the technical field of radio frequency / millimeter wave integrated circuits. The frequency multiplier provided by the invention comprises a pseudo-differential amplifier, an LC parallel resonator cavity and an LC series resonator cavity, wherein the LC parallel resonator cavity is connected between the output end of the pseudo-differential amplifier and a power supply VDD (Voltage Drain Drain), the LC series resonator cavity is connected between the output end of the pseudo-differential amplifier and a ground wire, both input ends of the pseudo-differential amplifier are respectively connected with the positive end and the positive end of an input baseband signal (f0); and the LCparallel resonator cavity has the resonation frequency of 2f0, and the LC series resonator cavity has the resonation frequency of 4f0. The cascaded frequency multipliers provided by the invention comprise a plurality of the frequency multipliers which are sequentially connected through a single-to-double passive transformer. The millimeter-wave frequency multiplier and the cascaded frequency multipliers, provided by the invention, have the advantages of low power consumption, pure frequency spectrum of a frequency-multiplication output signal, good harmonic suppression performance, strong output signal, high frequency and easiness for single-chip integration on a silica-based process.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Direct-drive permanent magnet fan harmonic wave suppression optimizing method in asymmetric fault of power grid voltage
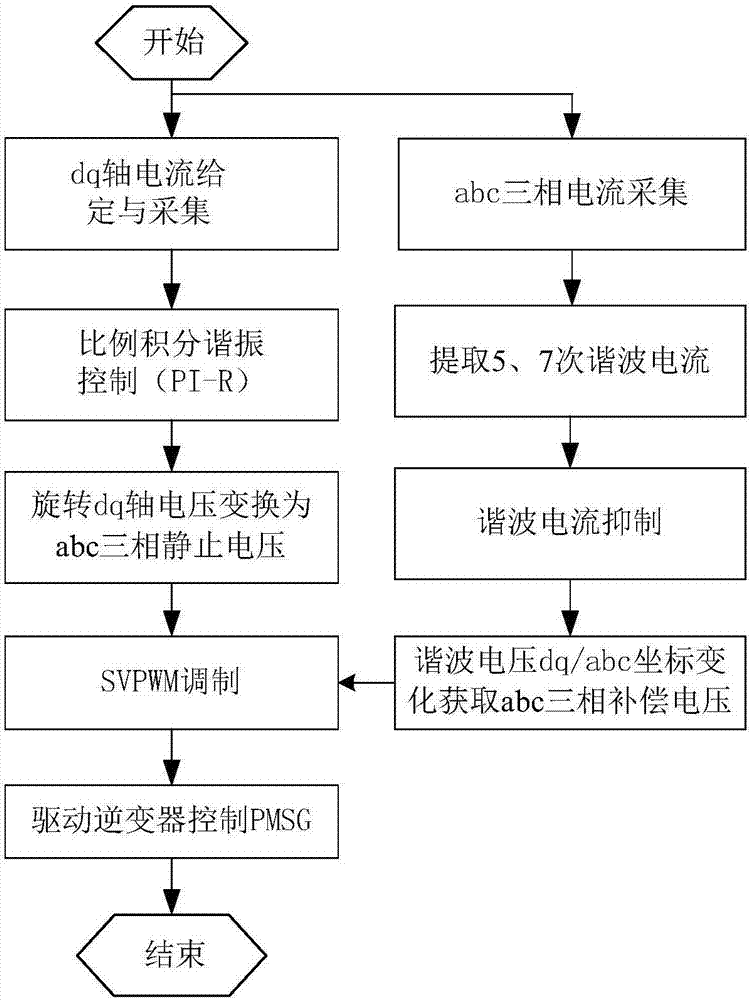
InactiveCN107453363AEliminate DC bus voltage fluctuationsSlow reaction speedElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsControl signalWave shape
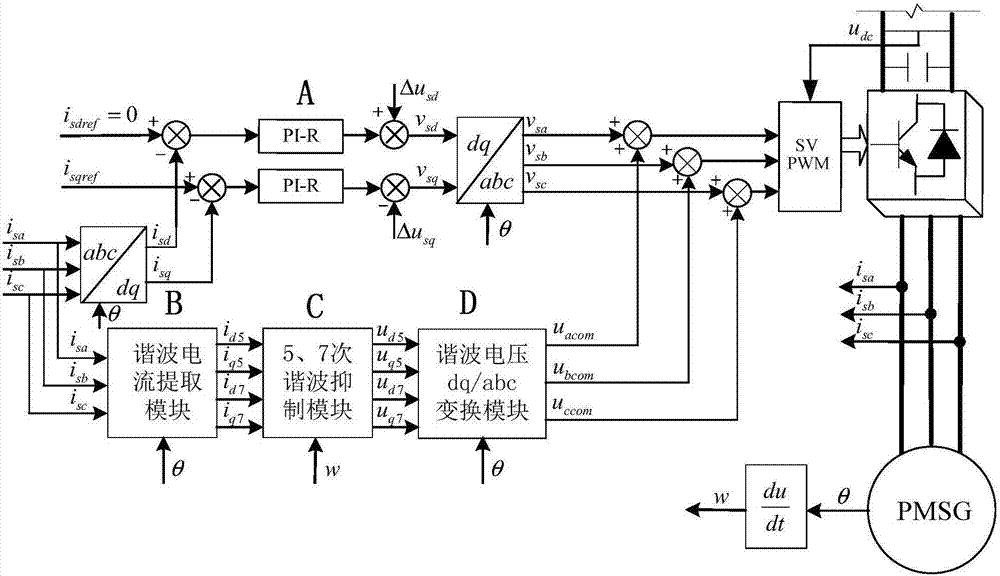
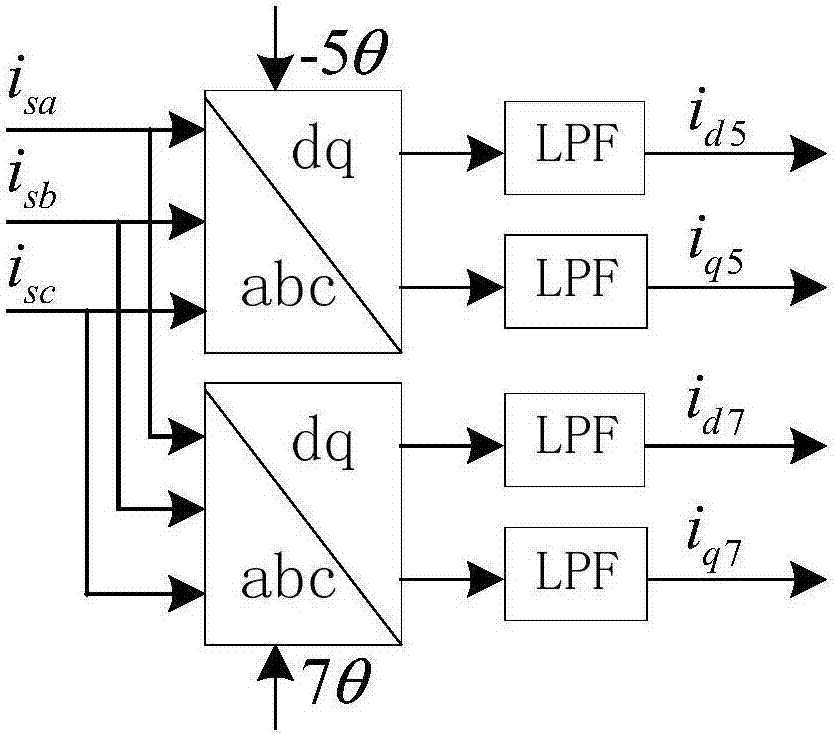
The invention discloses direct-drive permanent magnet fan harmonic wave suppression optimizing method in an asymmetric fault of power grid voltage. The method comprises the steps of acquiring abc three-phase static voltage according to abc three-phase current at the motor side; extracting harmonic current by 5-7 times according to the abc three-phase current at the motor side, performing harmonic current suppression, and acquiring abc three-phase compensation voltage; adding the abc three-phase static voltage and the abc three-phase compensation voltage for obtaining a control signal; performing SVPWM modulation on the control signal for obtaining a PWM wave, and controlling an inverter switch of the direct-driven permanent magnet fan through the PWM wave, thereby driving a permanent magnet synchronous generator (PMSG) of the drive-drive permanent magnet fan. According to the method of the invention, through acquiring the abc three-phase compensation voltage after extracting the harmonic current by 5-7 times and performing harmonic current suppression, the abc three-phase static voltage is compensated for generating a control signal, and a harmonic wave component in the motor current on the condition of asymmetric fault can be compensated, thereby greatly reducing influence of DC bus voltage to a motor-side current transformer, improving waveform of the motor current and performing a relatively high harmonic wave suppression effect.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Method and circuit structure for improving efficiency of wide-band radio frequency power amplifier
InactiveCN104716906AImprove efficiencyImprove output performanceAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionHigh frequency amplifiersAudio power amplifierHarmonic
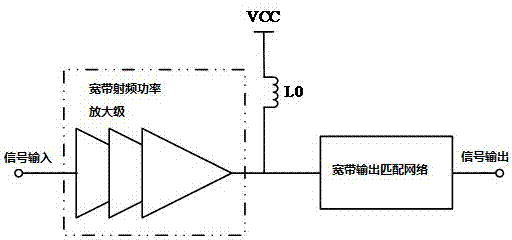
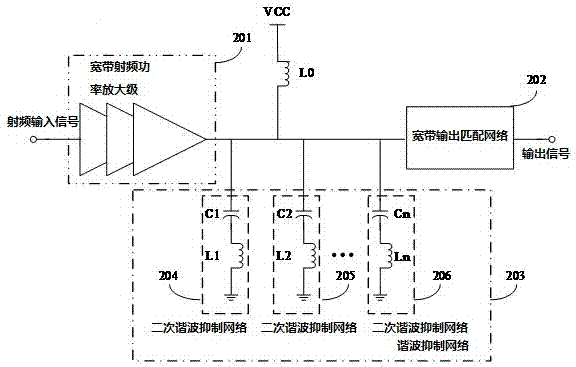
The invention discloses a method for improving efficiency of a wide-band radio frequency power amplifier, namely adding a harmonic source suppression network in output of the wide-band radio frequency power amplifier for improving efficiency. The invention also discloses a circuit structure for improving the efficiency of the wide-band radio frequency power amplifier. The circuit structure disclosed by the invention comprises a wide-band radio frequency power amplifier stage, a wide-band output matching network and a harmonic suppression network, wherein the wide-band output matching network is used for effectively outputting an output signal; the harmonic suppression network is used for carrying out harmonic suppression on a signal input into the wide-band output matching network, and the harmonic suppression network is formed by at least two second harmonic suppression networks which are connected between output of the wide-band radio frequency power amplifier stage and the ground in parallel. The method and the structure for improving the efficiency of the wide-band radio frequency power amplifier have the advantages that a second harmonic suppression circuit is adopted for being independent from an output matching network, a resonant frequency point can be flexibly controlled, second harmonic is effectively suppressed, efficiency and output capability of the power amplifier are improved, and wide-band matching is formed, so that the radio frequency power amplifier can operate in a wide range, and performances of the radio frequency power amplifier are improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
System and method for frequency translation with harmonic suppression using mixer stages
InactiveUS7190943B2Disadvantages and reduced eliminatedTranslation reduced eliminatedTransmission noise suppressionAmplitude to angle modulation conversionHarmonicControl signal
A circuit for frequency translating a radio frequency signal comprises a plurality of mixer stages, each stage associated with a particular range of frequencies of a radio frequency signal. The circuit further comprises a switching circuit that communicates the radio frequency signal to a selected one of the plurality of mixer stages in response to a control signal. The selected mixer stage comprises a phase generation circuit that generates a plurality of phase signals, and at least one mixer that combines the radio frequency signal with one of the plurality of phase signals to generate at least a portion of an intermediate frequency signal.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
Harmonic Reject Receiver Architecture and Mixer
ActiveUS20100003943A1Reduced responseModulation transference balanced arrangementsMultiplex with amplitude-modulated carrierLocal oscillator signalFrequency mixer
Receiver architectures and methods of processing harmonic rich input signals employing harmonic suppression mixers are disclosed herein. The disclosed receivers, mixers, and methods enable a receiver to achieve the advantages of switching mixers while greatly reducing the mixer response to the undesired harmonics. A harmonic mixer can include a plurality of mixers coupled to an input signal. A plurality of phases of a local oscillator signal can be generated from a single local oscillator output. Each of the phases can be used to drive an input of one of the mixers. The mixer outputs can be combined to generate a frequency converted output that has harmonic rejection.
Owner:MAXLINEAR INC
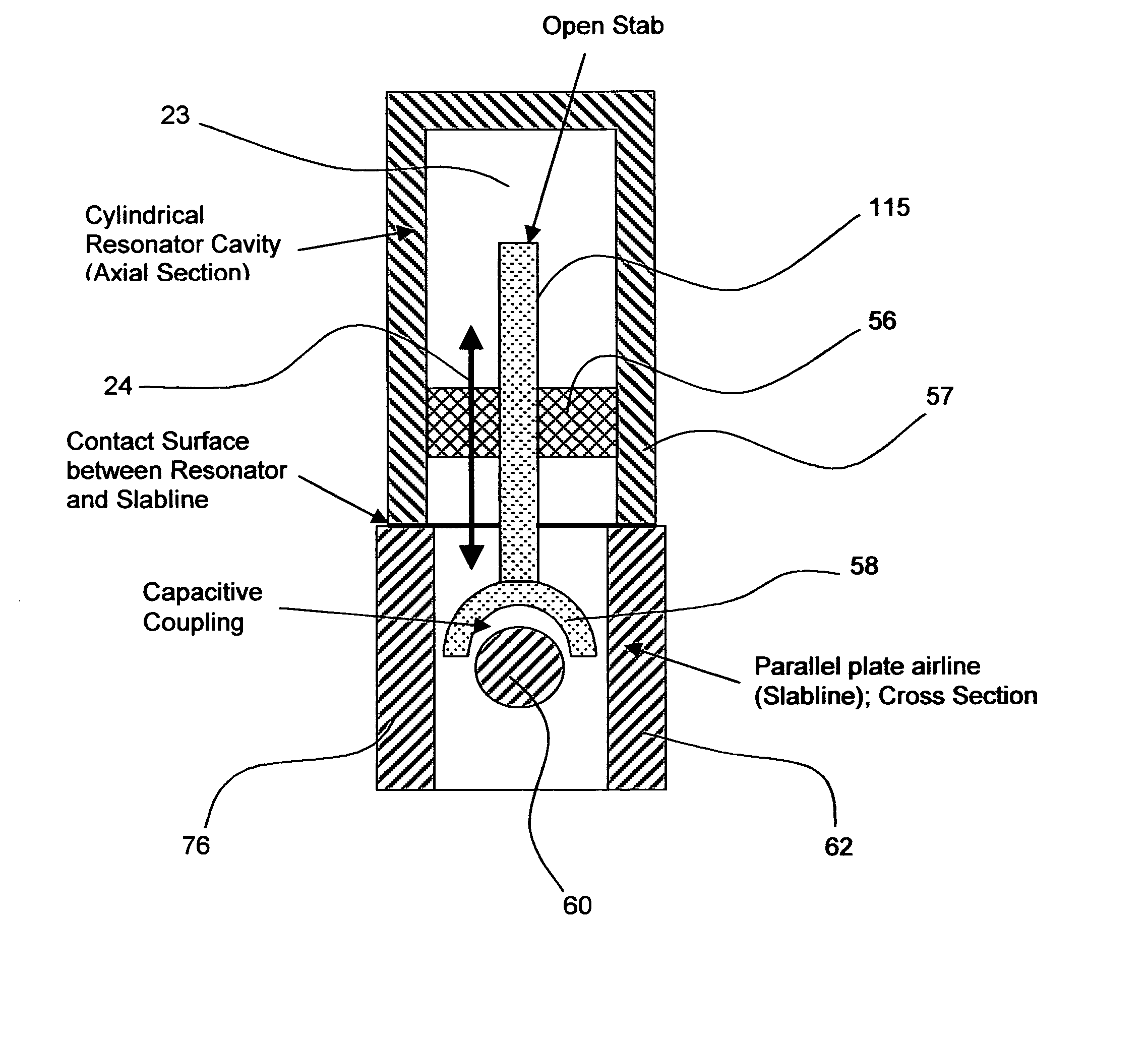
Harmonic load pull tuner with resonant prematching module
InactiveUS7449893B1Spectral/fourier analysisResistance/reactance/impedenceFundamental frequencyHarmonic impedance
Owner:TSIRONIS CHRISTOS
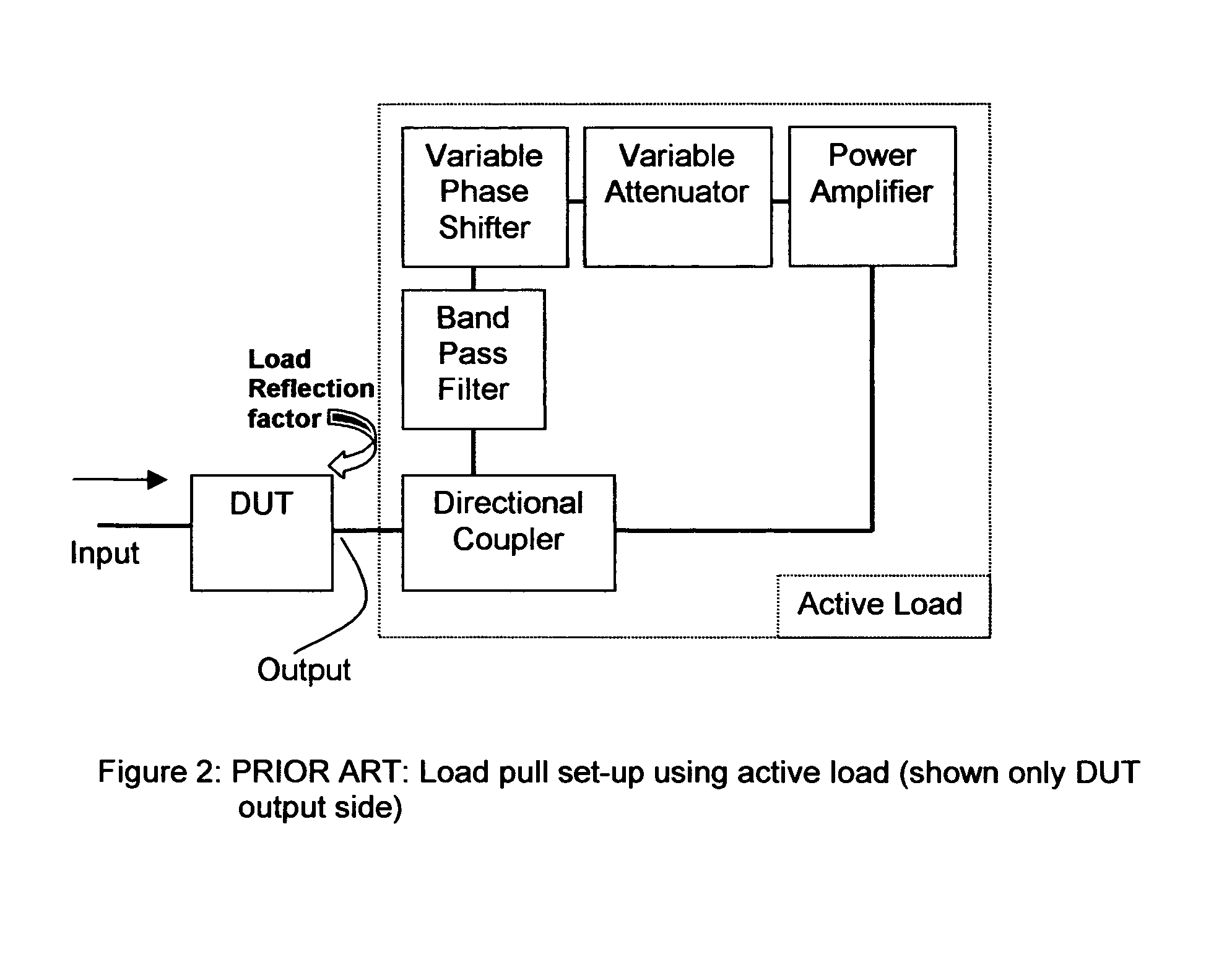
Method for reducing power requirements in active load pull system
InactiveUS8497689B1Resistance/reactance/impedenceWaveguide type devicesControl theoryRadio frequency
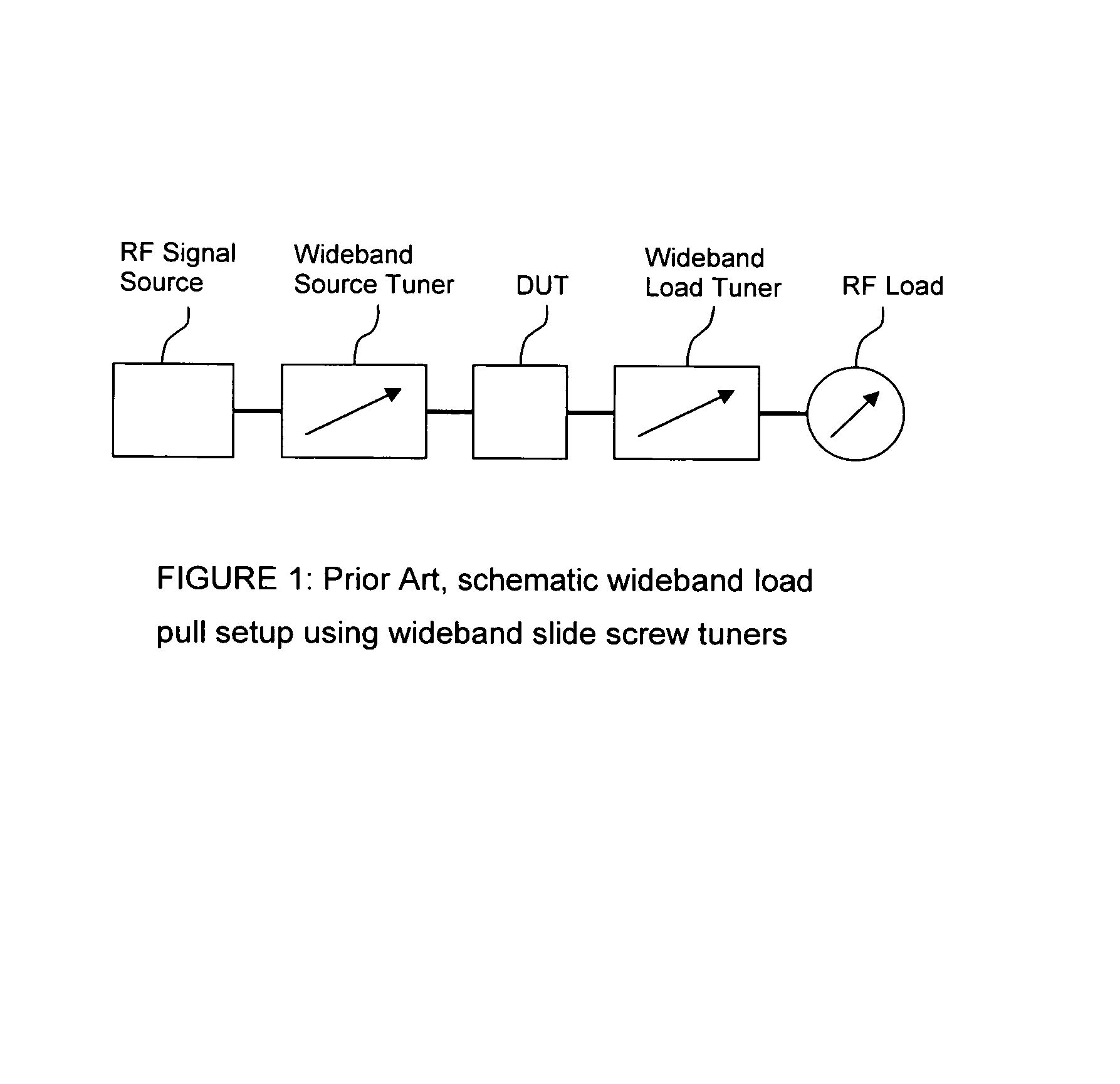
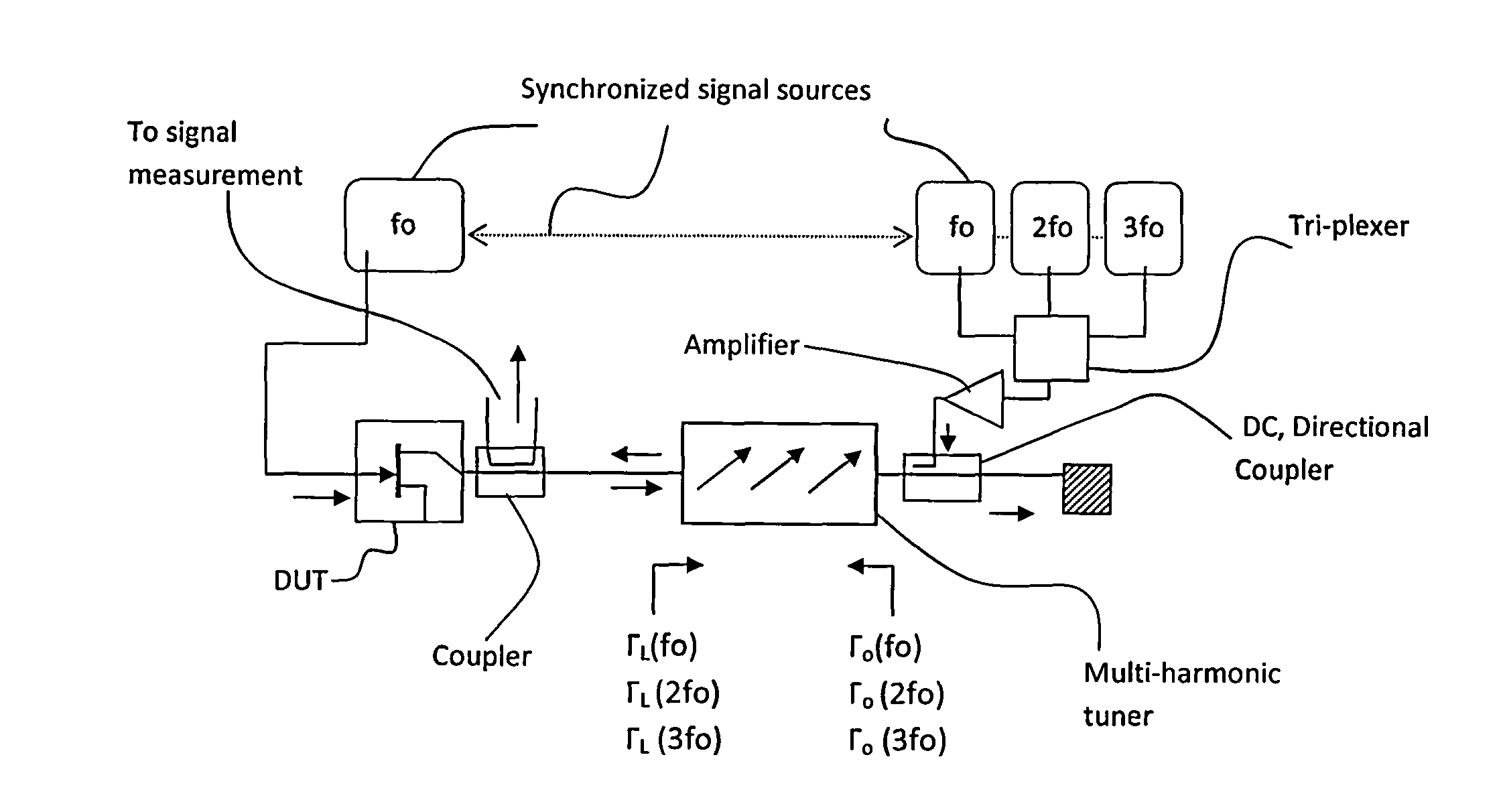
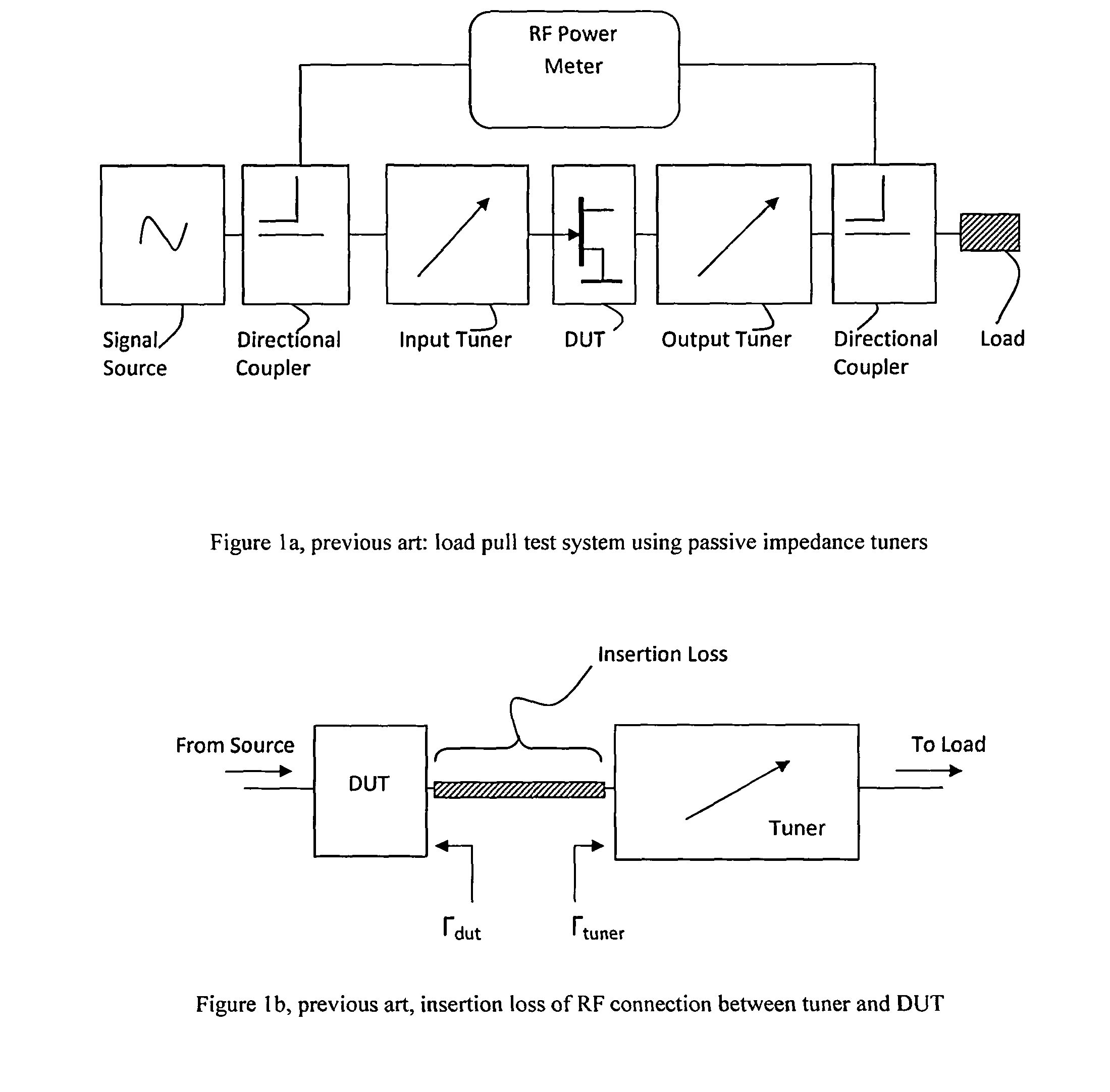
A method and test setup for reducing the RF power requirement in active load pull uses impedance tuners between the output of the test transistor and the active RF power injection network. The active network uses either a closed loop (active load) configuration or an open loop network employing split or synchronized signal sources. The impedance tuners are wideband (fundamental) tuners, harmonic rejection tuners or multi-harmonic tuners. A 7:1 transforming ratio of the tuners represents the best compromise between power matching and tuner loss, yielding a reduction of 11dB in power requirements from the active load or the synchronized source(s); if only the fundamental signal is injected at the output of the DUT, a multi-harmonic tuner or a harmonic rejection tuner is used for independent harmonic tuning; if multiple harmonic signals are injected, a multi-harmonic tuner is used and creates passive harmonic loads while reducing at the same time the power requirements from the harmonic injection sources.
Owner:TSIRONIS CHRISTOS
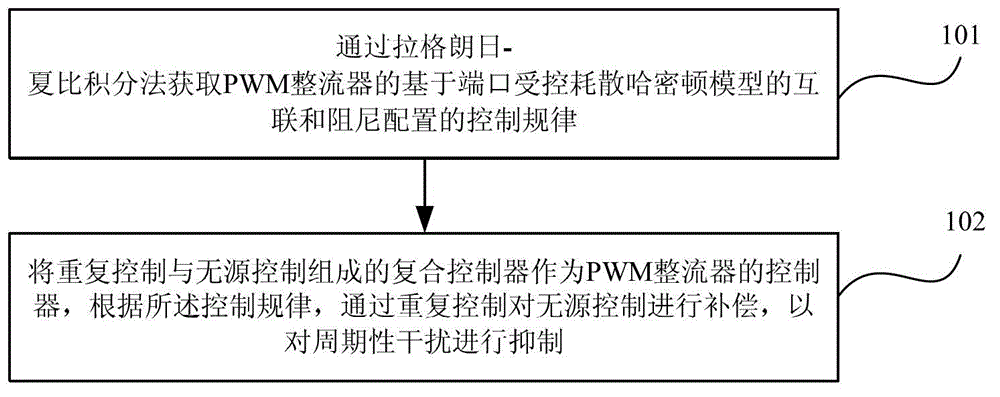
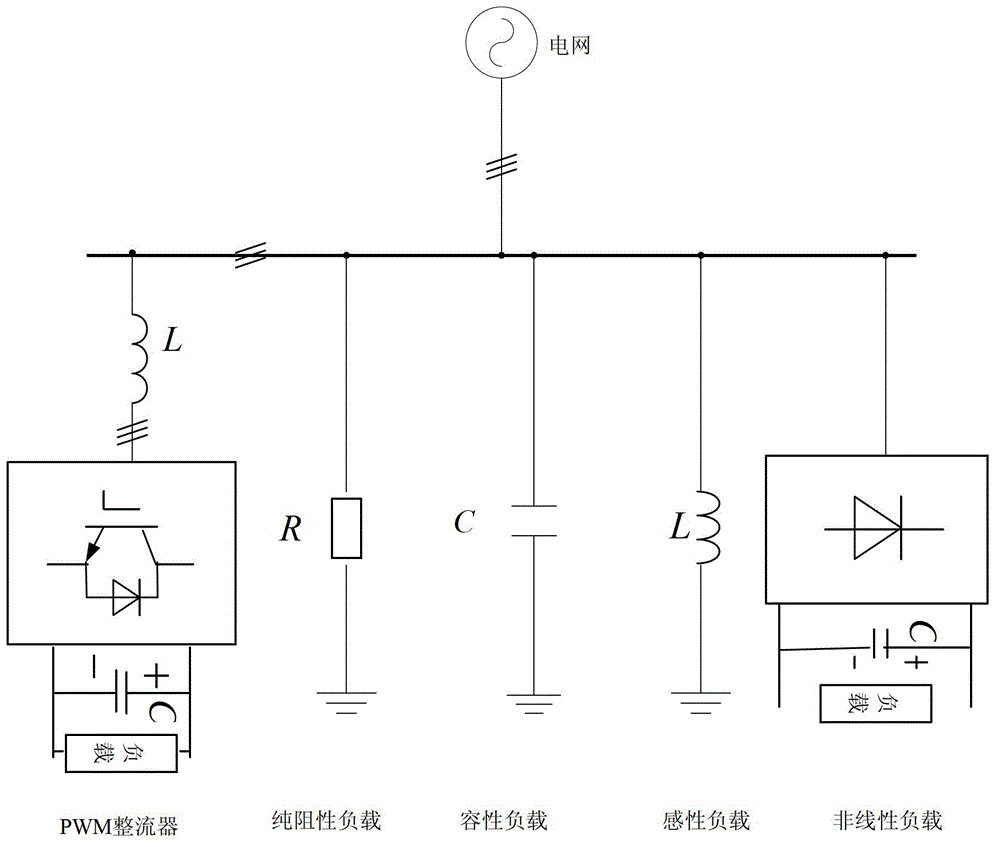
PWM (Pulse-Width Modulation) rectifier controlling method and PWM rectifier
InactiveCN102868309ASuppress harmonic interferenceImprove power qualityAc-dc conversionHarmonic reduction arrangementPower qualityPower grid
The embodiment of the invention provides a PWM (Pulse-Width Modulation) rectifier controlling method and a PWM rectifier. The PWM rectifier controlling method is a passivity control method based on repeated control and compensation, and comprises the following steps: a control law of the PWM rectifier based on the interconnection and damping configuration of port controlled dissipation Hamilton models is obtained with a Lagrange-Charpy integral method; and a composite controller including repeated control and passive control is used as a controller of the PWM rectifier, and the passive control is compensated by the repeated control according to the control law so as to suppress periodic interference. According to the embodiment of the invention, PWM rectification of a unit power factor can be realized, and at the same time the harmonic interference of a power grid is better suppressed under the condition of not detecting load harmonic current so as to improve power quality. Compared with the conventional PWM rectifier, the PWM rectifier disclosed by the invention has the functions of harmonic suppression and reactive compensation under the condition of not increasing hardware cost.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
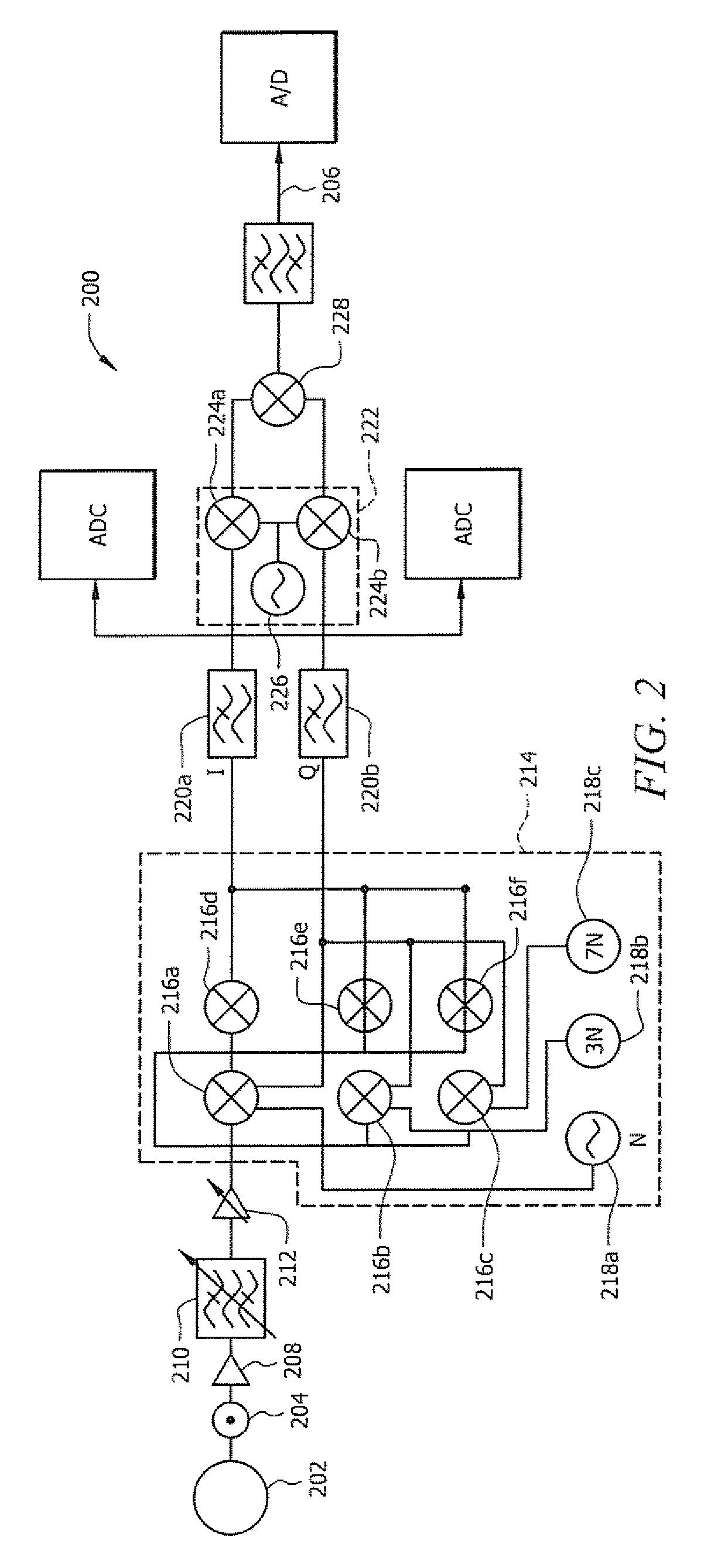
Broadband tuner for very wide signal conversion
InactiveUS20090258629A1Performance is not affectedDisadvantages and reduced eliminatedMultiple-port networksModulation transferenceHarmonicFrequency mixer
An agile RF tuner circuit capable of converting a wide portion of RF signal into an IF signal suitable for analog-to-digital conversion. The circuit up converts a received RF signal to a high IF signal and then down converts the high IF signal to a low IF signal. Embodiments of the RF circuit incorporate harmonic reject mixers to suppress harmonies and intermodulations typically associated with the frequency conversion process.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
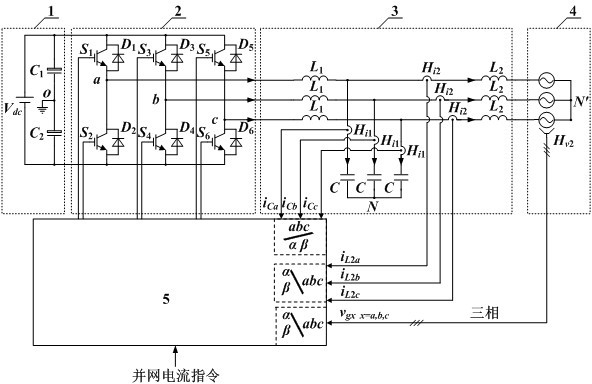
Method for suppressing and controlling current harmonics of three-phase LCL (Lower Control Limit) type grid-connected inverter
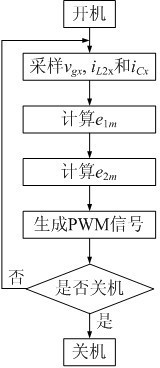
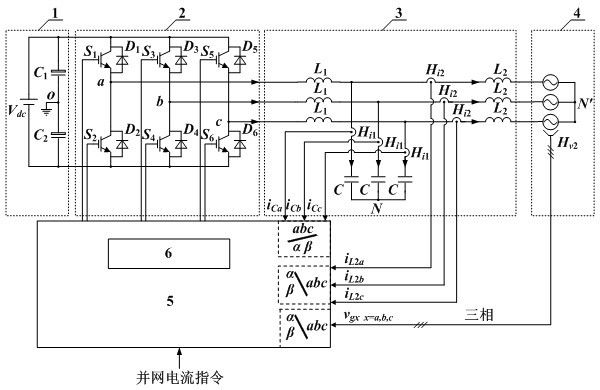
InactiveCN102118028AInhibition effectGood current waveform qualitySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPolyphase network asymmetry elimination/reductionCapacitanceControl signal
The invention discloses a method for controlling a three-phase LCL (Lower Control Limit) type grid-connected inverter, comprising the steps of: (1) detecting a capacitor current iCx and a grid-connected current iL2x by respectively utilizing a current sensor Hi1 of the capacitor current and a current sensor Hi2 of filter inductance, carrying out collection and coordinate transformation to obtain a capacitor current feedback signal iC-of-m and a grid-connected current feedback signal iL2-of-m, detecting a grid voltage vgx by utilizing a voltage sensor Hv2 of the grid voltage, carrying out collection and coordinate transformation, and computing to obtain a grid voltage feed-forward signal vg-fd-m via a grid voltage feed-forward function Gg-fd; (2) computing to obtain an error signal e1m according to the iL2-of-m and iref-m; (3) carrying out closed-loop processing on the e1m by a controller to obtain a reference signal iC-ref-m of the capacitor current feedback signal iC-of-m, wherein the error signal e2m is equal to (iC-ref-m)+(vg-fd-m)-(iC-of-m); and (4) generating a PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) control signal for controlling a switching tube of an inverter bridge by utilizing the e2m. Through the method, the influence of the grid voltage on the grid-connected current waveform quality can be effectively suppressed, the network-access power factors are improved, the grid-connected current waveform quality is good and balanced current can be still injected into the grid by the inverter when the voltage of the three-phase grid is imbalanced.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Balun transformer with improved harmonic suppression
ActiveUS7683733B2Good harmonic suppressionImprove performanceMultiple-port networksOne-port networksTransformerHarmonic
An electronic assembly includes a substrate (66), a balun transformer (42) formed on the substrate (66) and including a first winding (50) and a second winding (52), each having respective first and second ends, and a reaction circuit component (48) formed on the substrate (66) and electrically coupled to the second winding (52) between the first and second ends thereof. The balun transformer (42) and the reaction circuit component (48) jointly form a harmonically suppressed balun transformer having a fundamental frequency, and the reaction circuit component (48) is tuned such that the harmonically suppressed balun transformer resonates at a selected harmonic of the fundamental frequency.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com