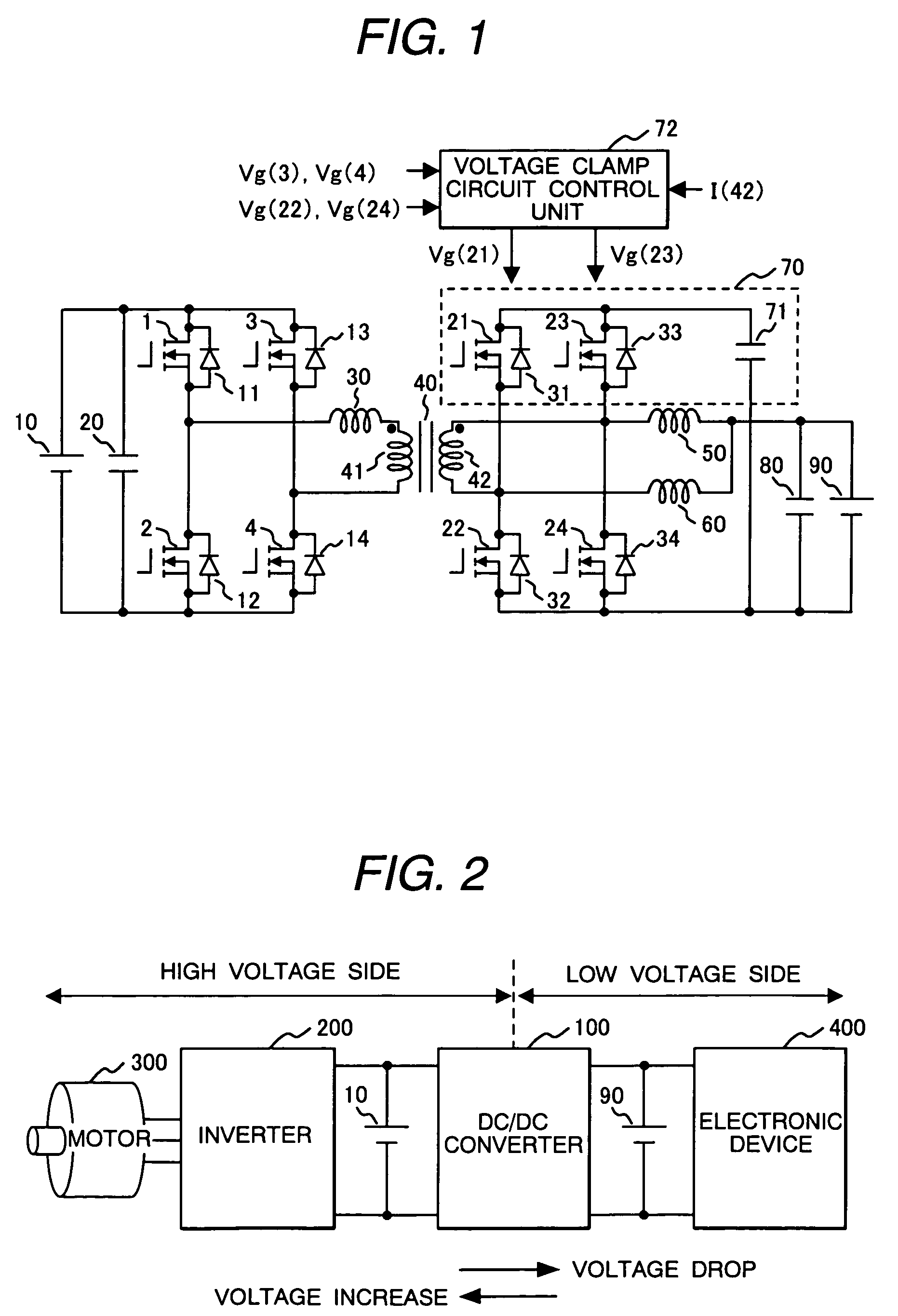
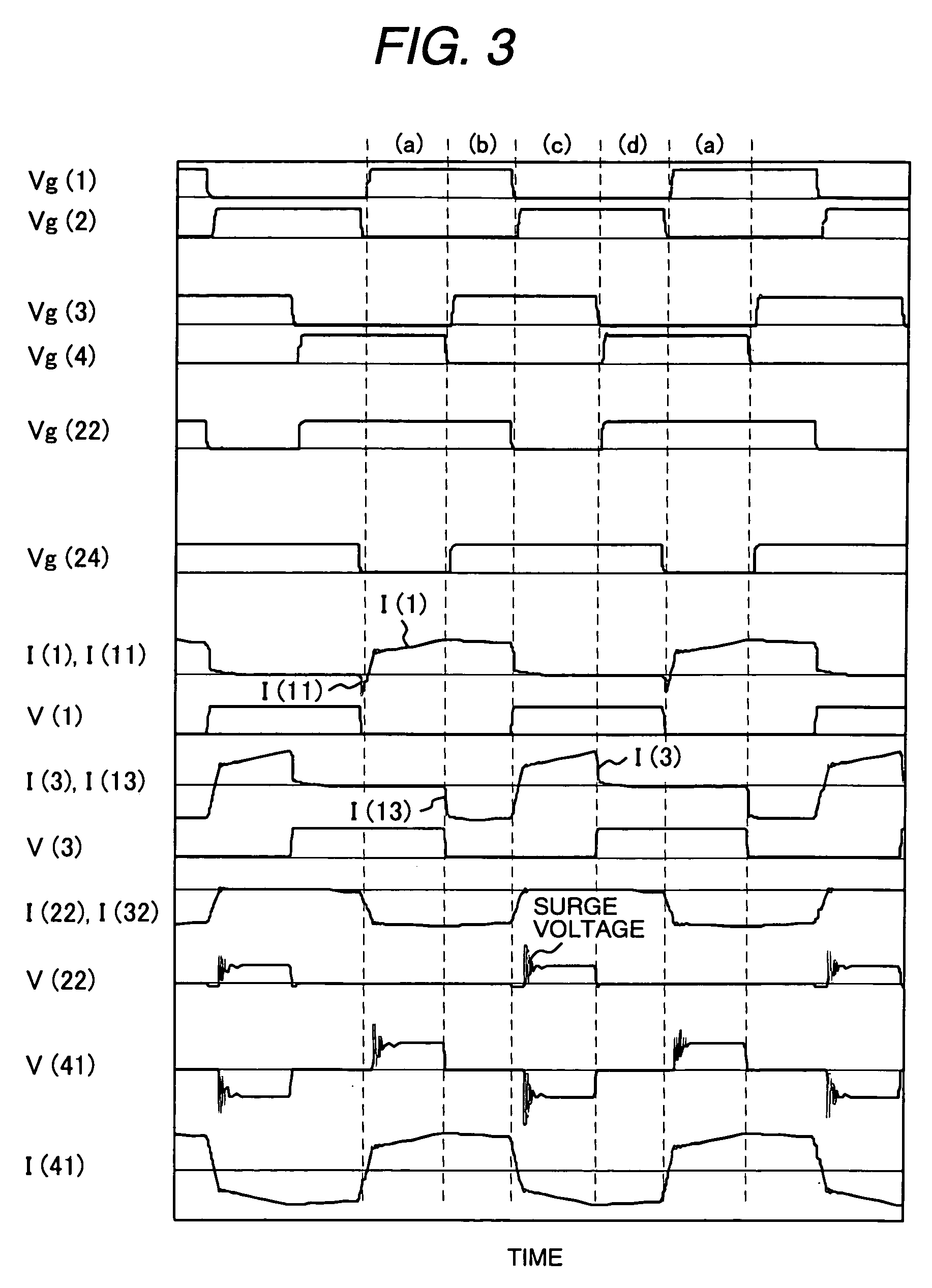
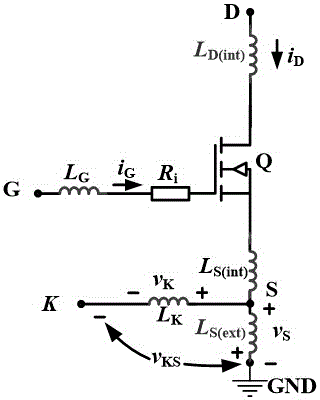
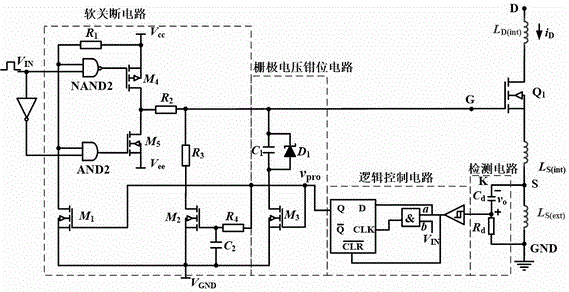
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
853 results about "Voltage clamp" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
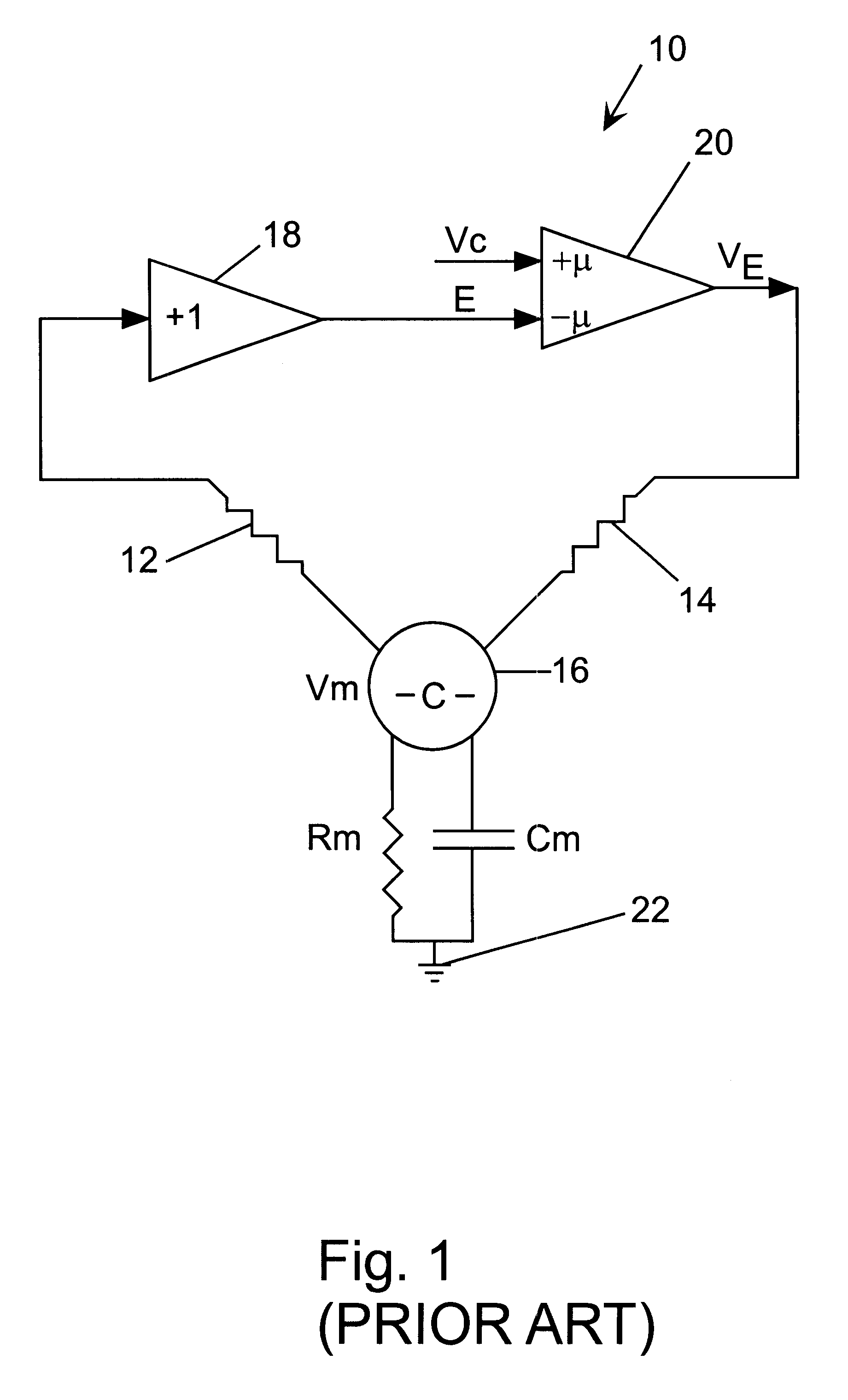
The voltage clamp is an experimental method used by electrophysiologists to measure the ion currents through the membranes of excitable cells, such as neurons, while holding the membrane voltage at a set level. A basic voltage clamp will iteratively measure the membrane potential, and then change the membrane potential (voltage) to a desired value by adding the necessary current. This "clamps" the cell membrane at a desired constant voltage, allowing the voltage clamp to record what currents are delivered. Because the currents applied to the cell must be equal to (and opposite in charge to) the current going across the cell membrane at the set voltage, the recorded currents indicate how the cell reacts to changes in membrane potential. Cell membranes of excitable cells contain many different kinds of ion channels, some of which are voltage-gated. The voltage clamp allows the membrane voltage to be manipulated independently of the ionic currents, allowing the current-voltage relationships of membrane channels to be studied.
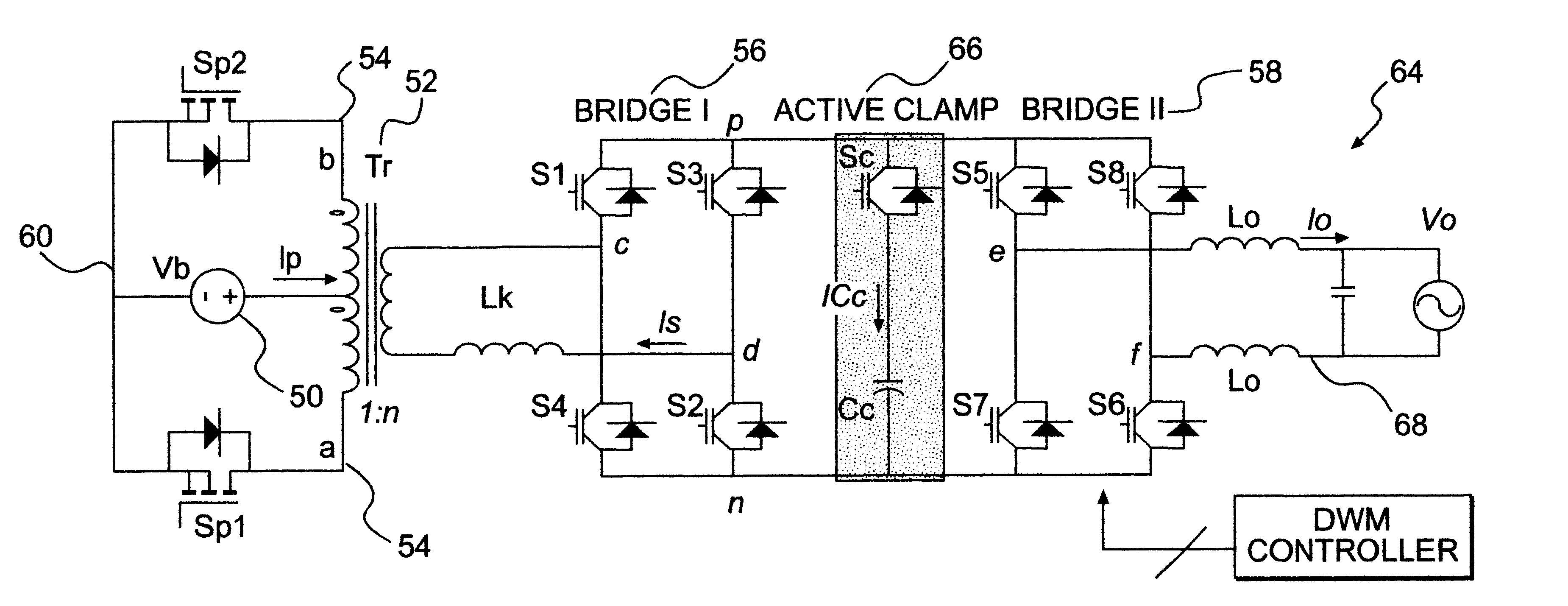
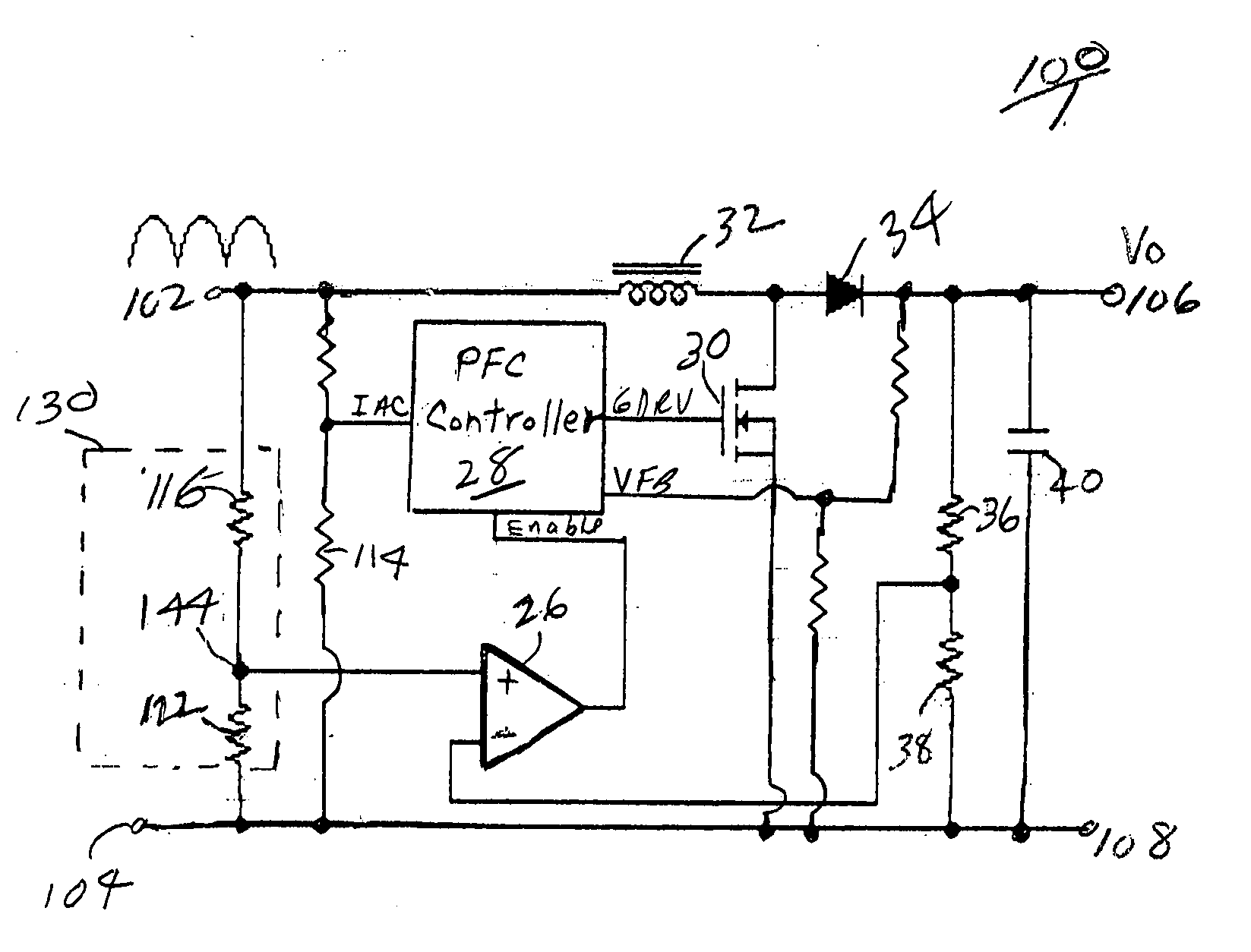
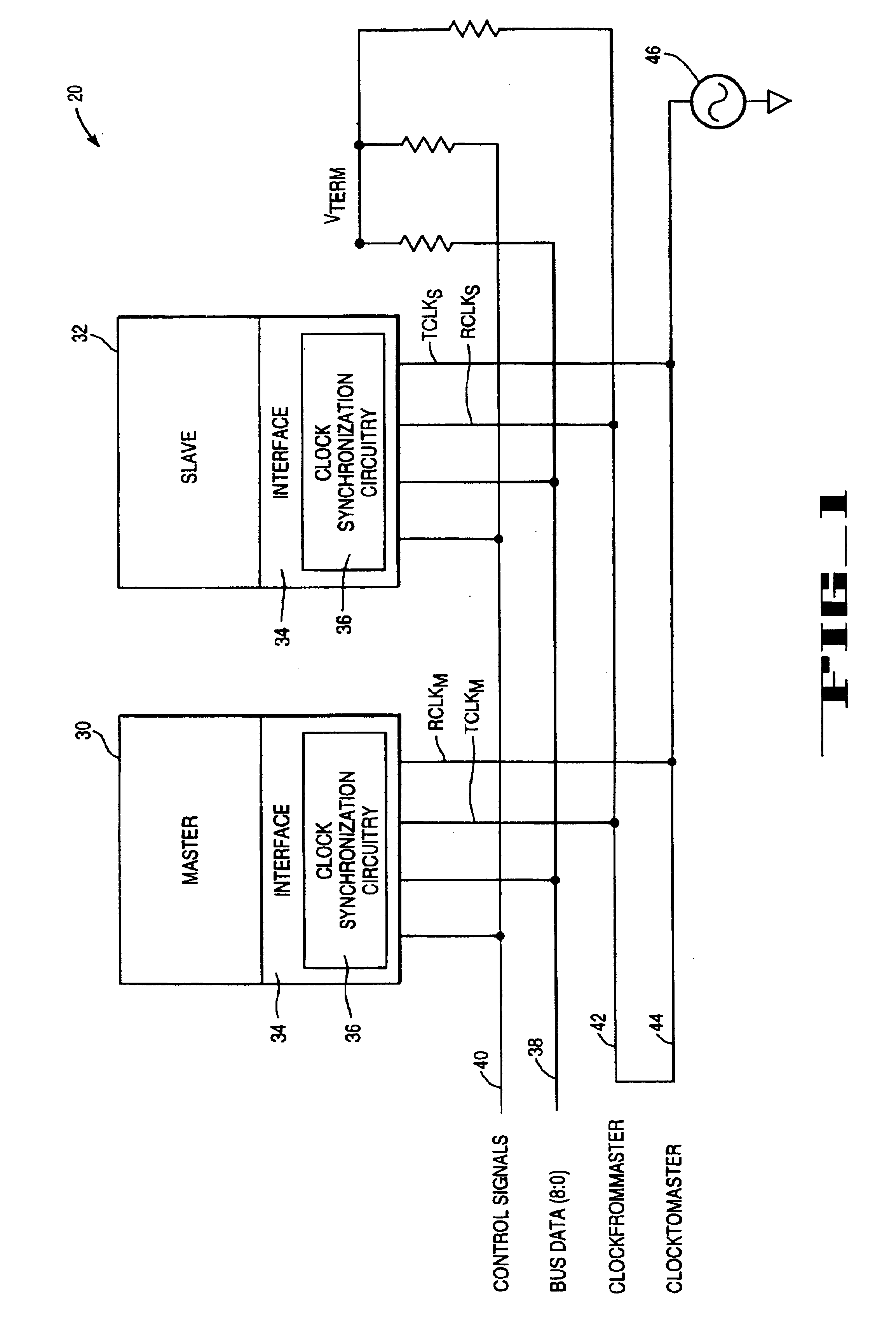
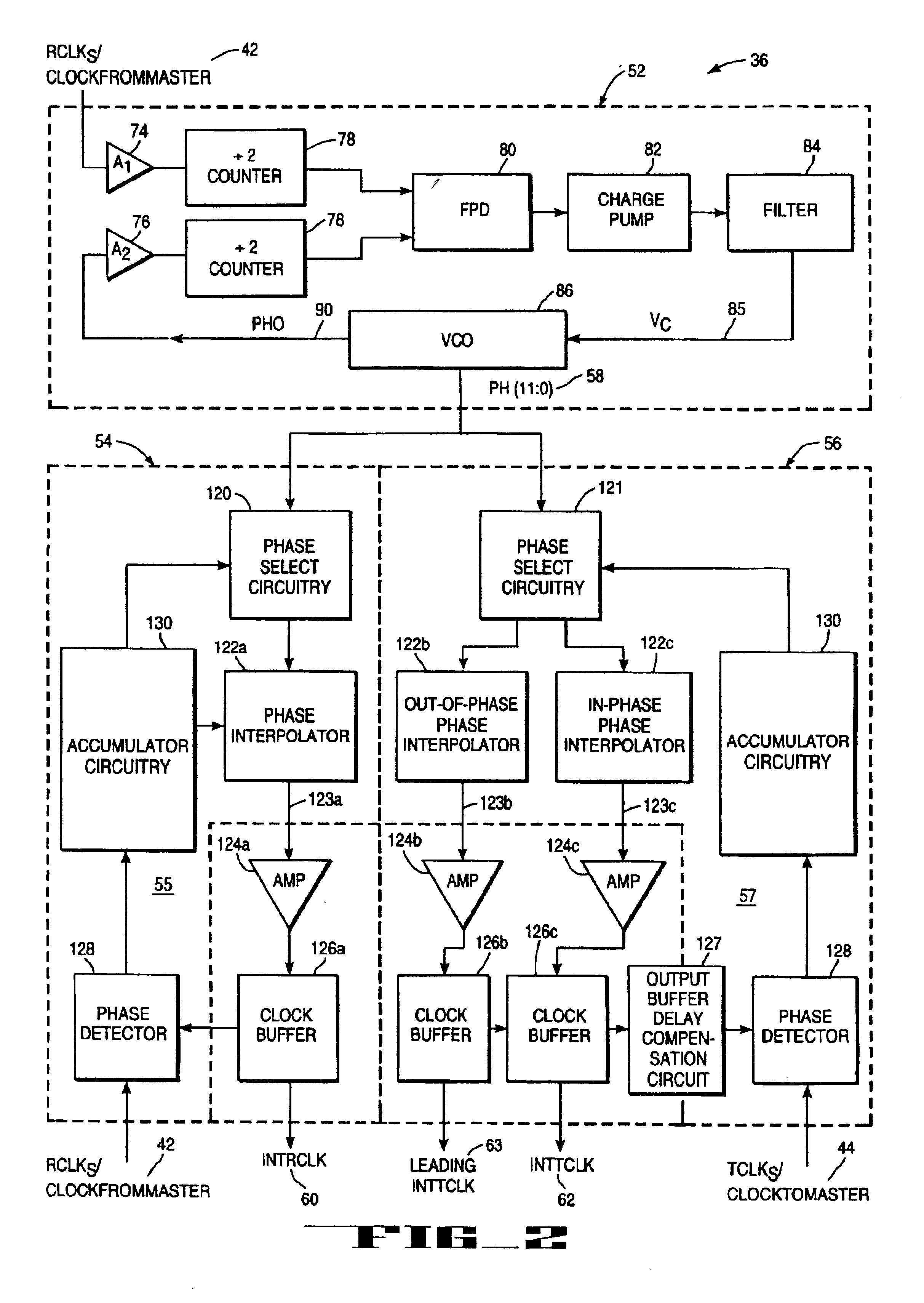
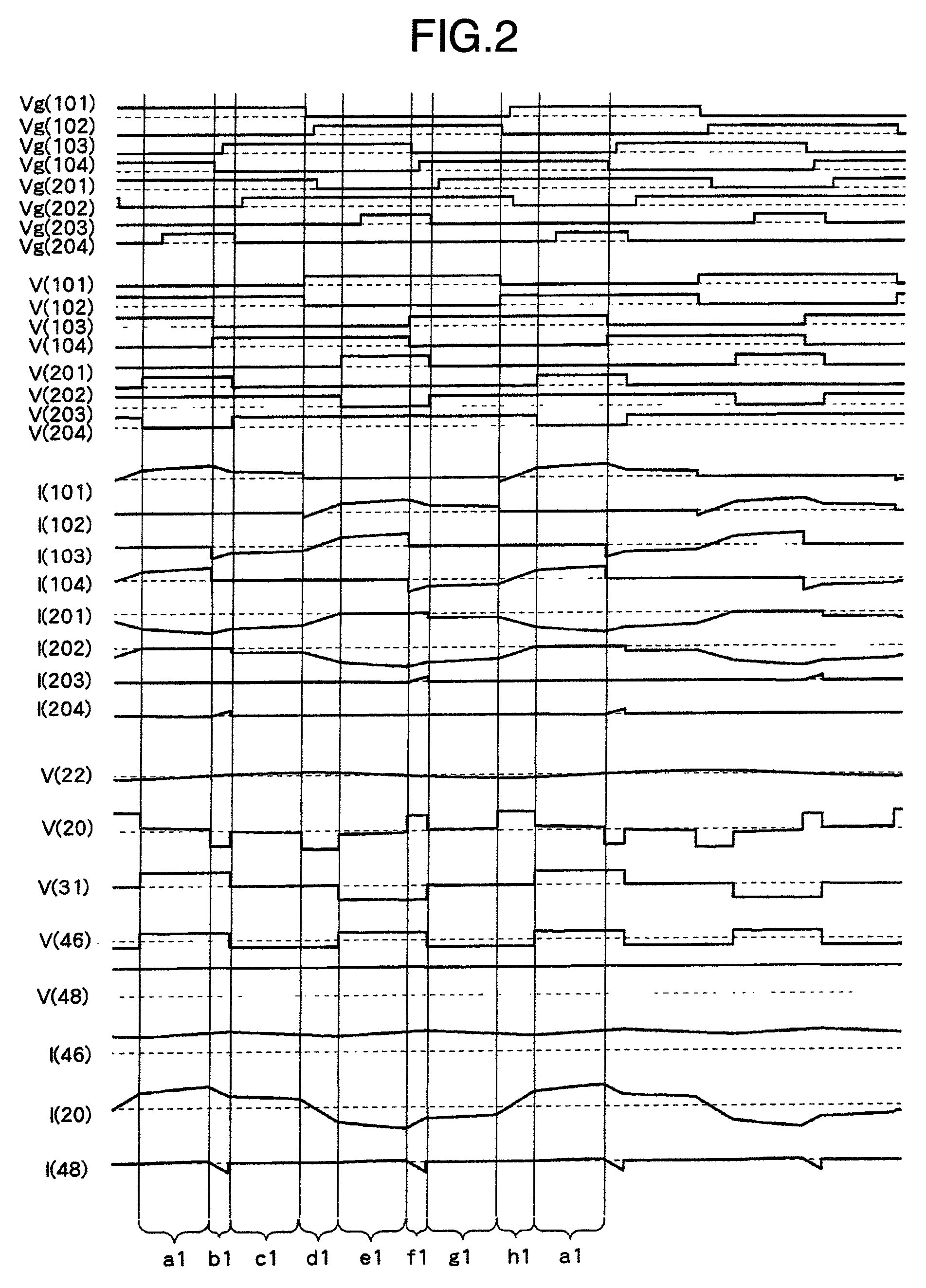
Soft-switched quasi-single-stage (QSS) bi-directional inverter/charger
A soft-switched single-phase quasi-single-stage (QSS) bi-directional inverter / charger converts AC-DC or DC-AC. The inverter / charger comprises a push-pull inverter / rectifier on the dc-side, an isolation transformer which provides ohmic isolation and voltage scaling, two full-bridges on the ac side in cascade, a voltage clamp branch comprising a capacitive energy storage element in series with an active switch with its anti-parallel diode, a passive filter at the ac side to smooth out the high frequency switching voltage ripple at the output, and a corresponding PWM scheme to seamlessly control the converter to operate in all four quadrant operation modes in the output voltage and output current plane, and is capable of converting power in both directions.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Charge perturbation detection system for DNA and other molecules
ActiveUS7785785B2Material nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCapacitanceChemical reaction
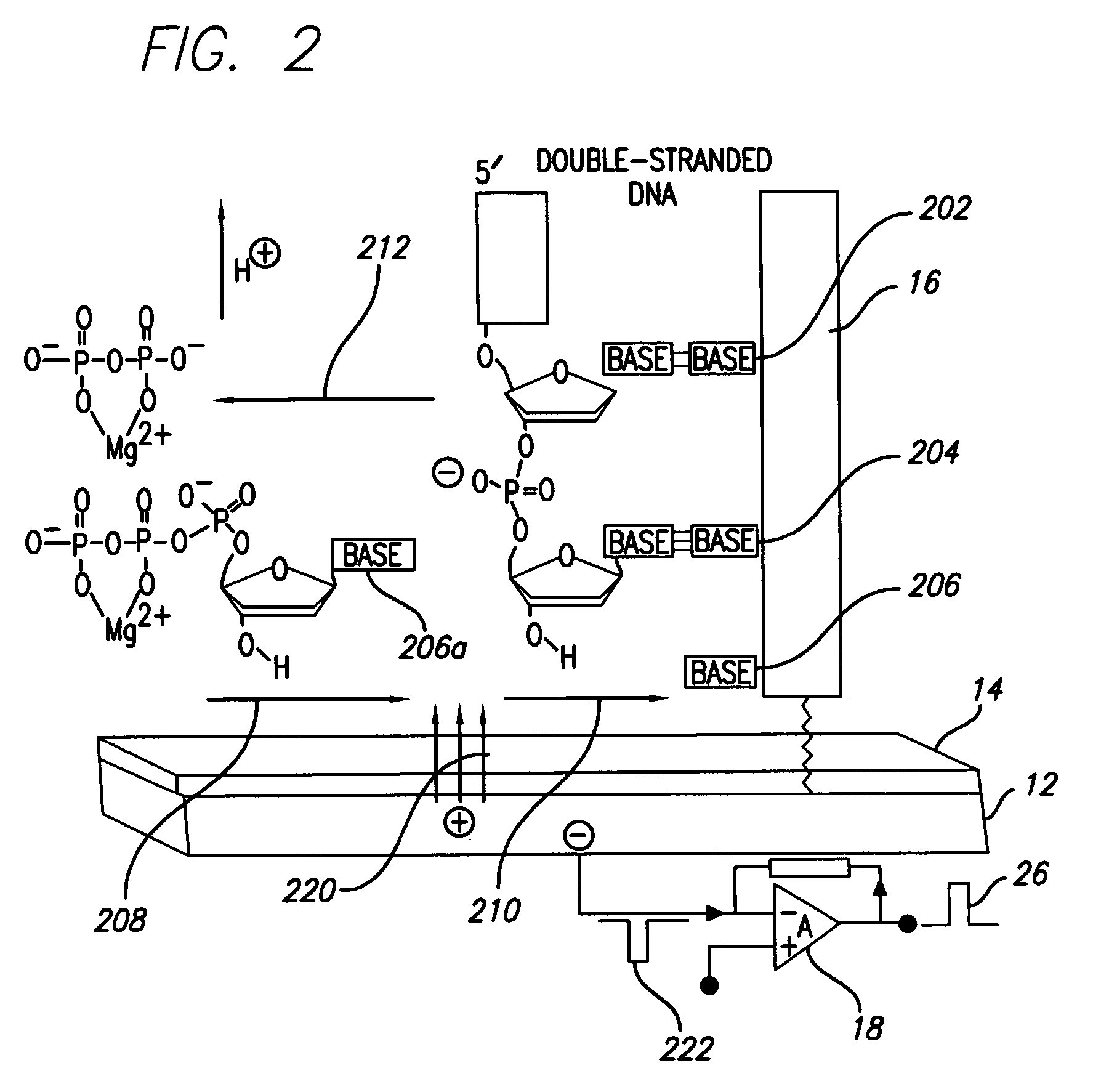
Methods and apparatus for direct detection of chemical reactions are provided. In a preferred embodiment, electric charge perturbations of the local environment during enzyme-catalyzed reactions are sensed by an electrode system with an immobilized target molecule. The target molecule is preferably DNA. The charge perturbation caused by the polymerase reaction can uniquely identify a DNA sequence. The polymerization process generates local perturbations of charge in the solution near the electrode surface and induces a charge in a polarazible gold electrode. This event is detected as a transient current by a voltage clamp amplifier. Detection of single nucleotides in a sequence can be determined by dispensing individual dNTPs to the electrode solution and detecting the charge perturbations. Alternatively, multiple bases can be determined at the same time using a mix of all dNTPs with subsequent analysis of the resulting signal. The initial enzyme attachment to the DNA molecule can be detected prior to polymerization, with electrode capacitance measurement using the same voltage-clamp amplifier. This technique and device may be adapted to other reaction determinations, such as enzymatic reactions, other electrode configurations, and other amplifying circuits.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
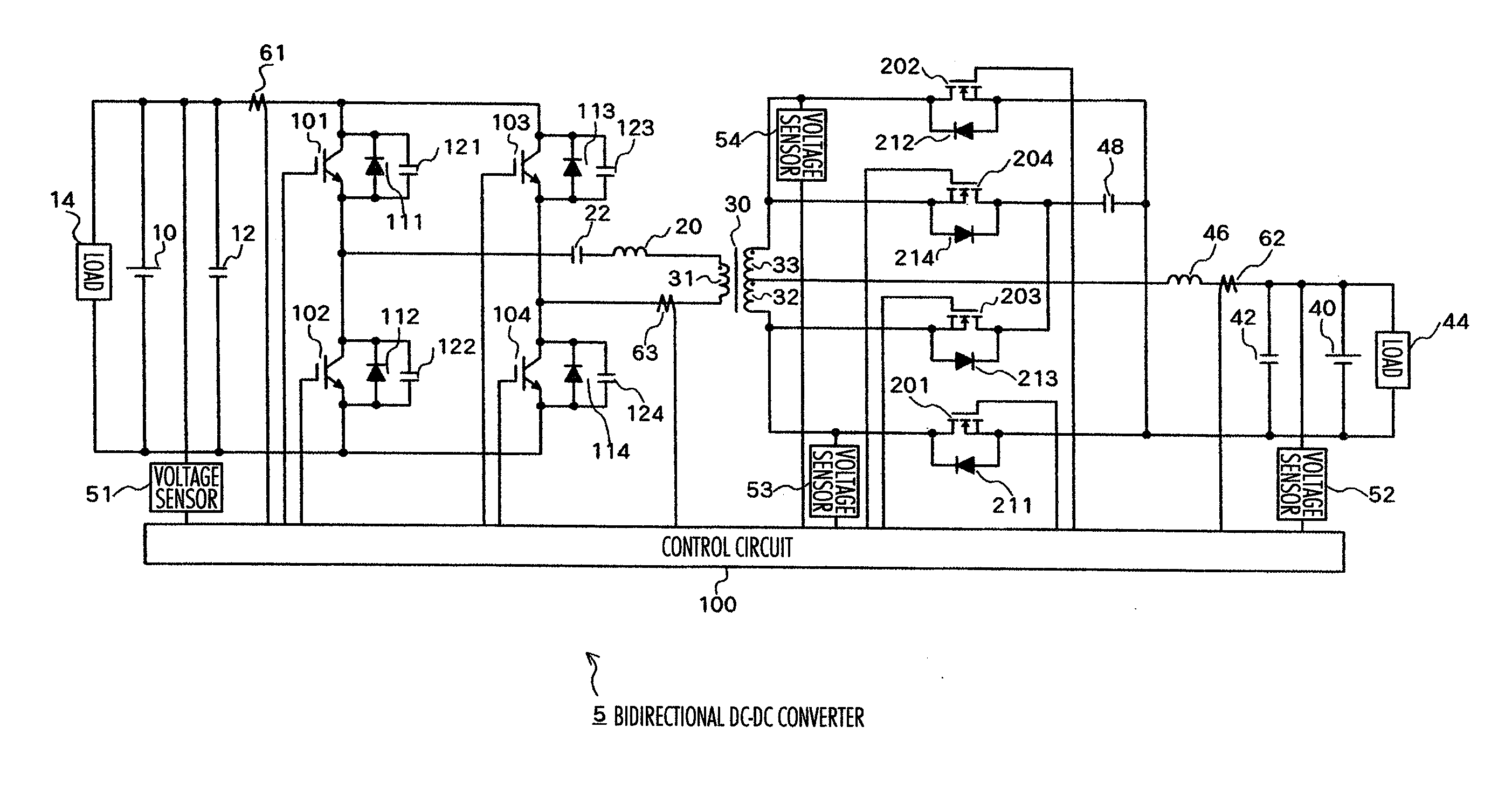
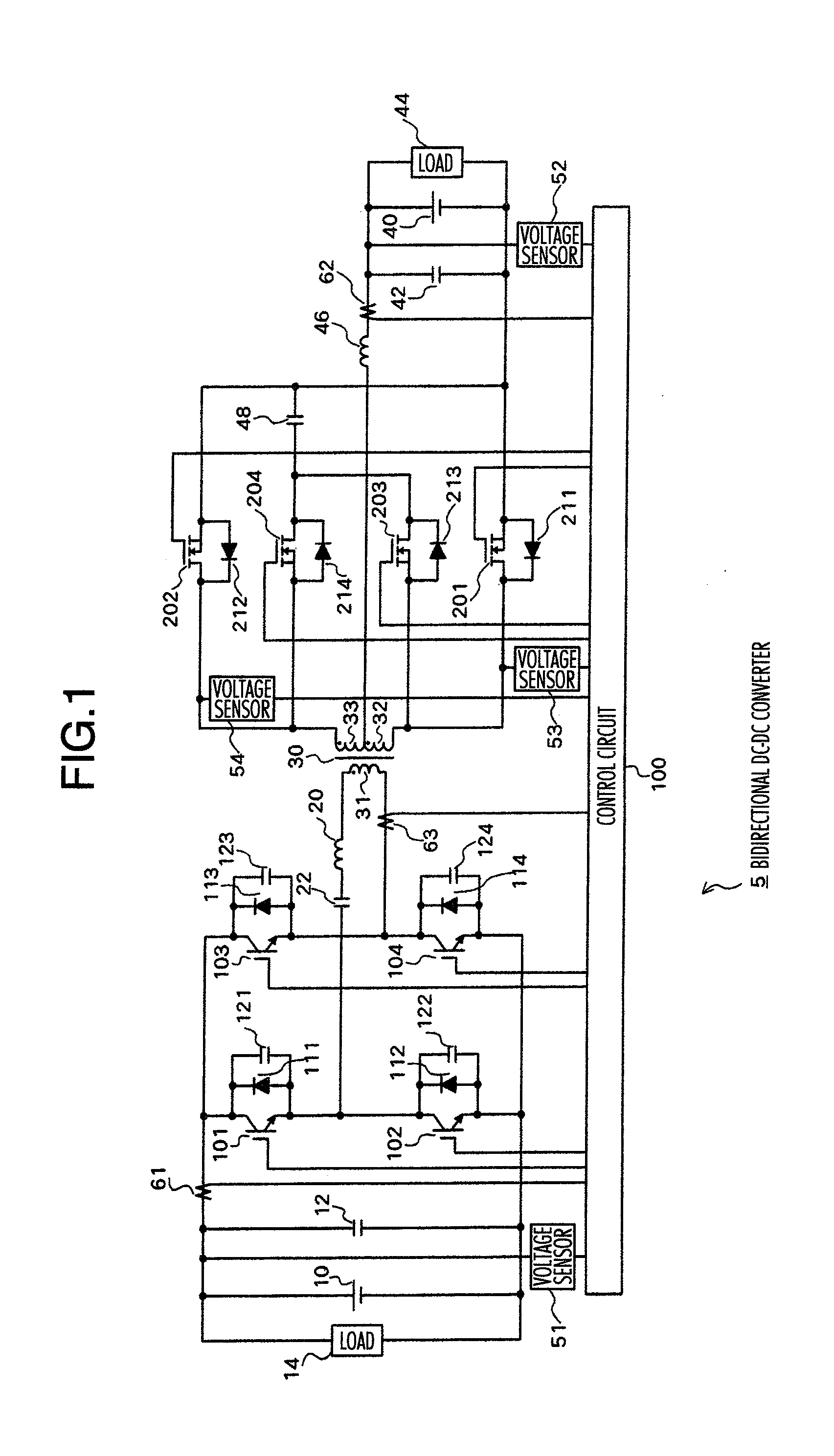
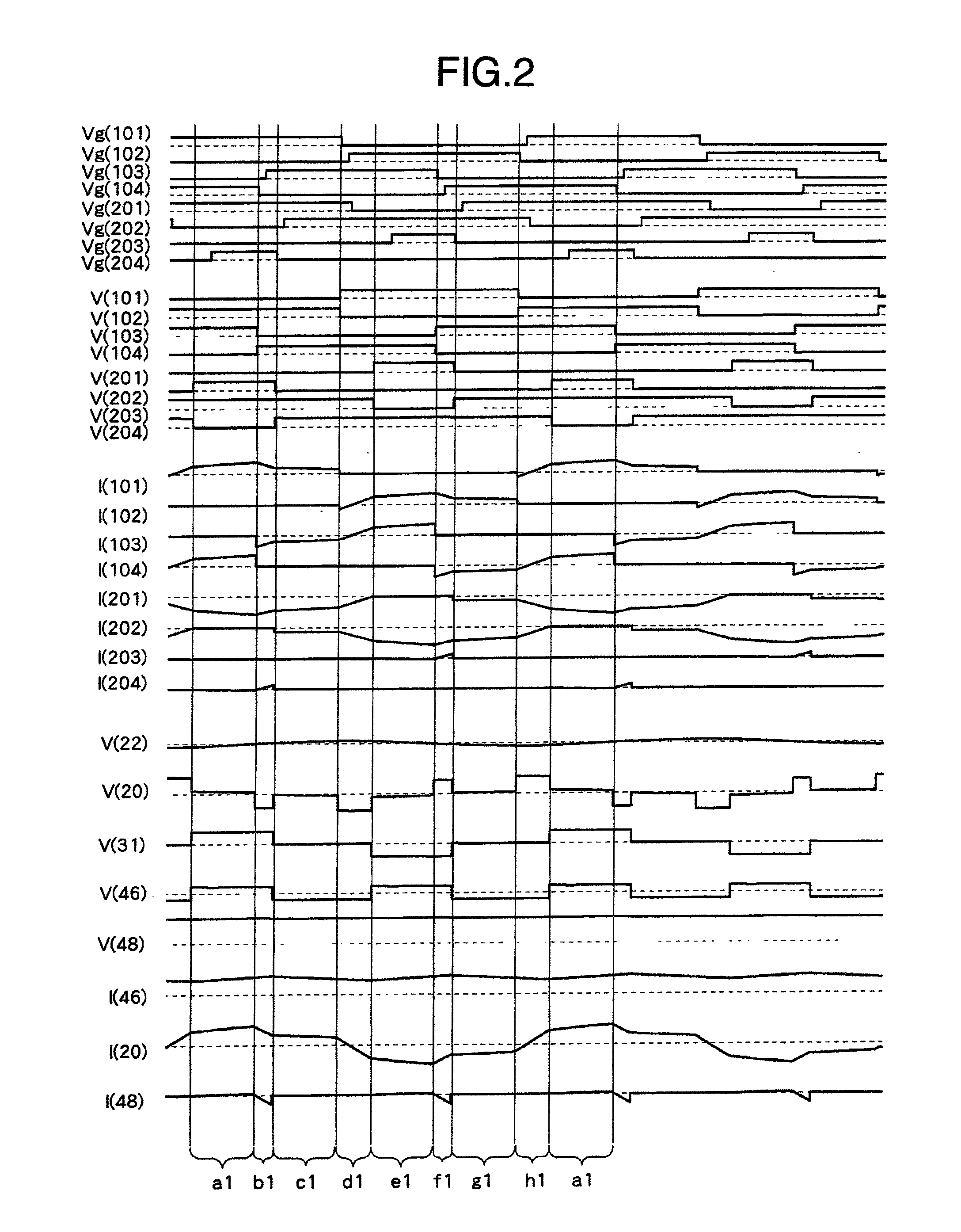
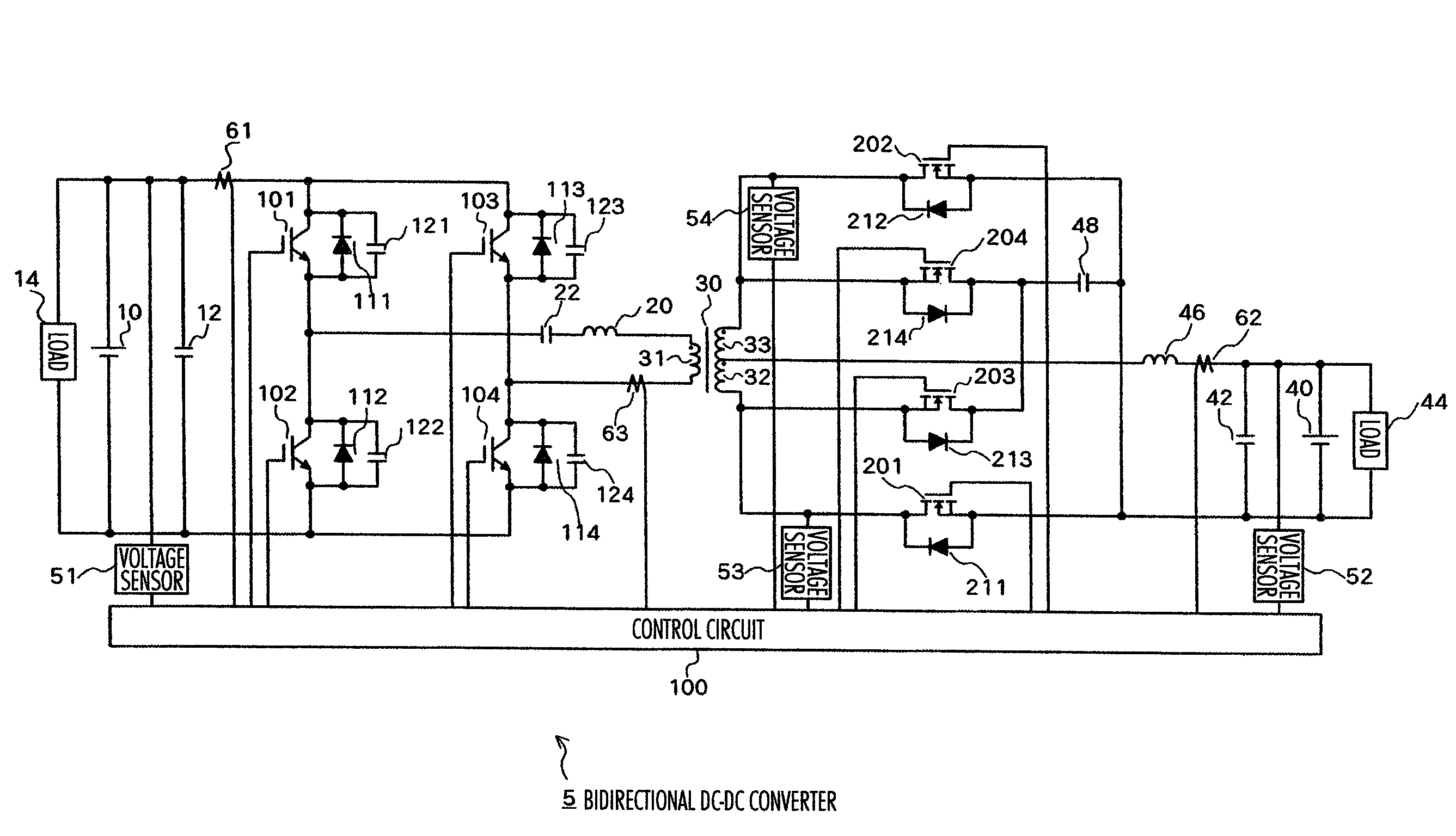
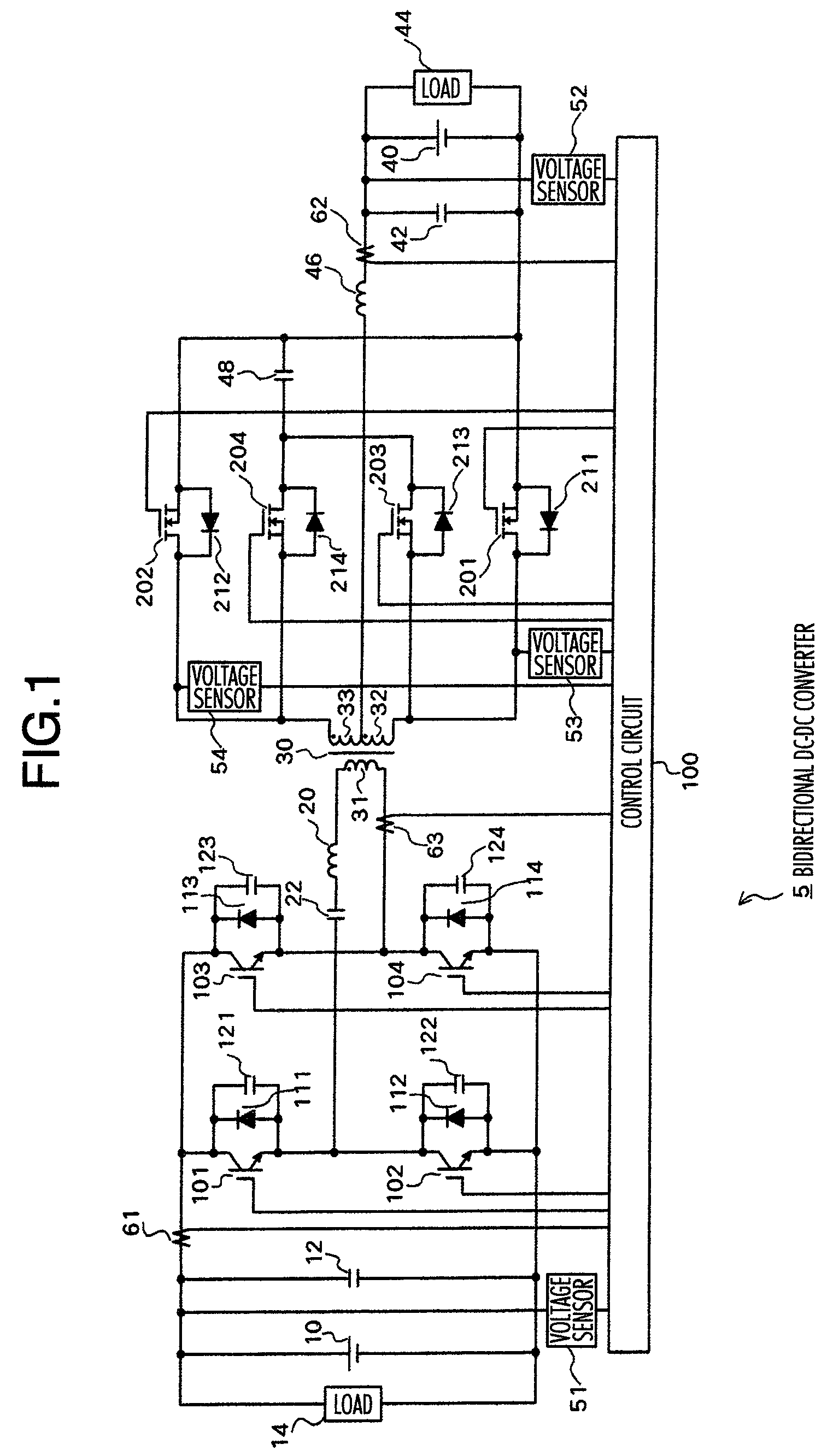
Isolated bidirectional DC-DC converter
ActiveUS20060139823A1Total current dropReduce lossesEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionClamp capacitorLow noise
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
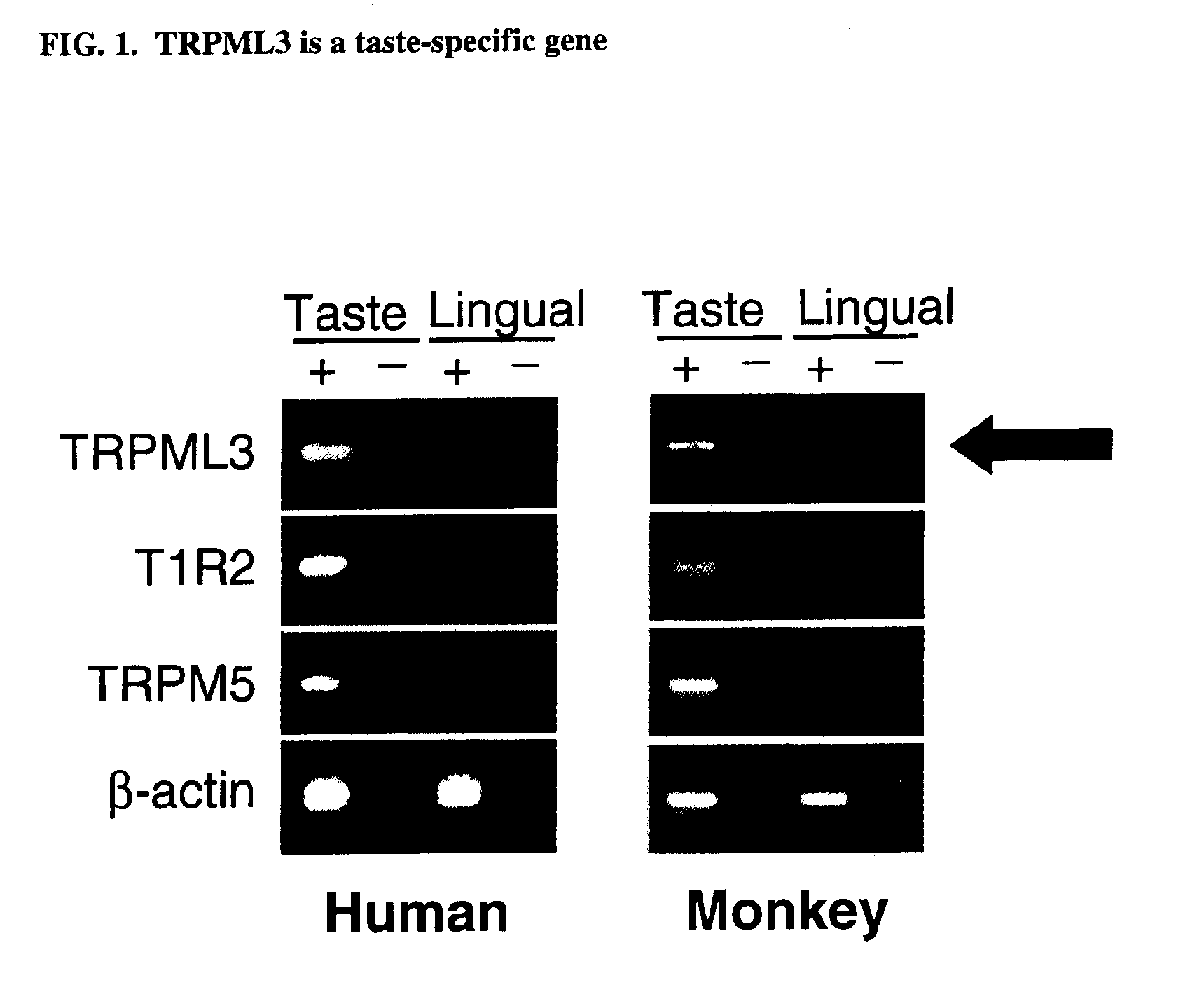
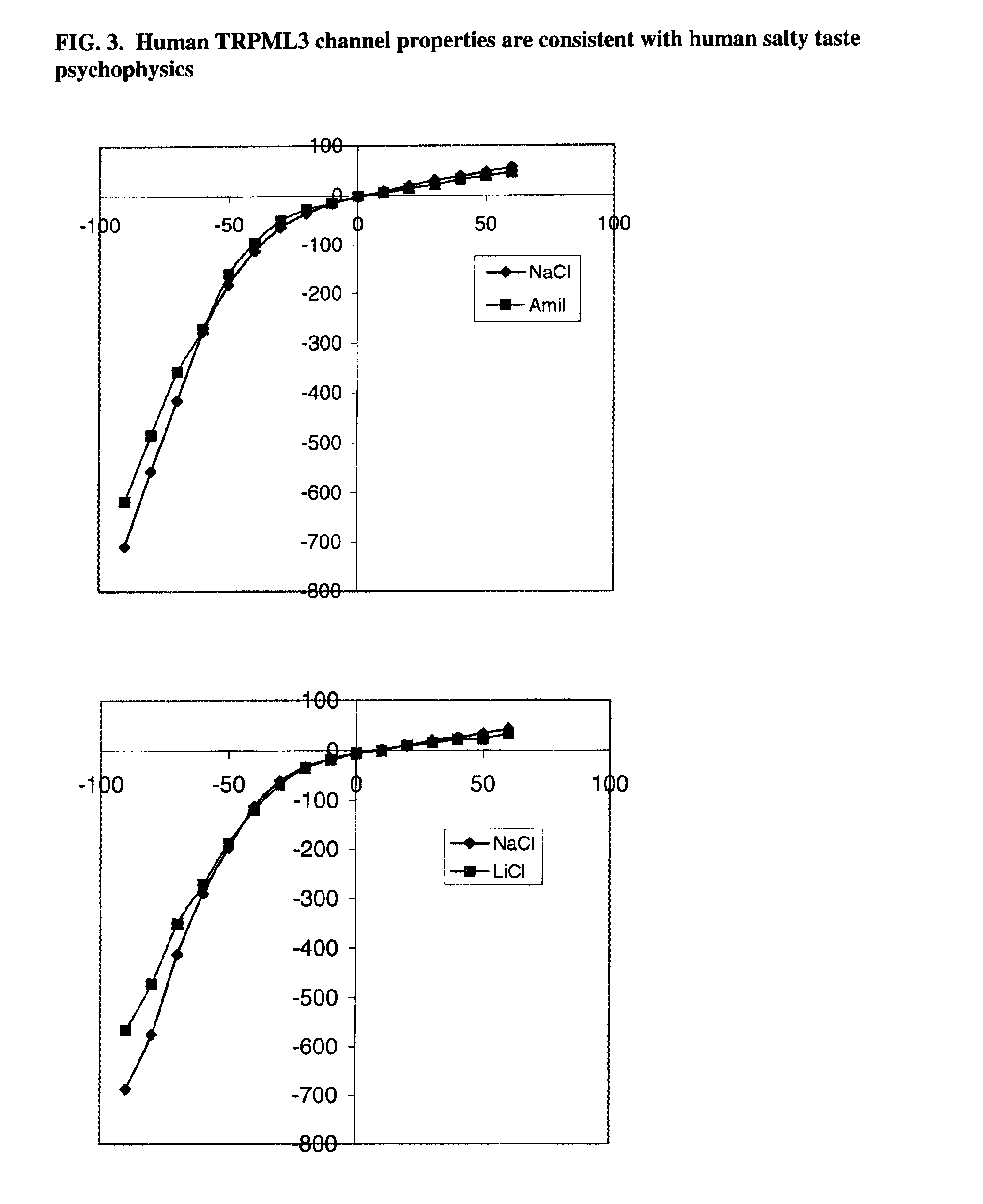
Identification of TRPML3 (MCOLN3) as a salty taste receptor and use in assays for identifying taste (salty) modulators and/or therapeutics that modulate sodium transport, absorption or excretion and/or aldosterone, and/or vasopressin production or release
InactiveUS20090210953A1Reduce volumeIncrease pressureCompound screeningApoptosis detectionSalty taste perceptionReceptor
The present invention relates to the elucidation that TRPML3 is involved in salty taste perception in primates including humans and likely other mammals and based thereon high-throughput mammalian and medium-throughput oocyte-based electrophysiological assays for identifying human TRPML3 modulators, preferably TRPML3 enhancers. Compounds that modulate TRPML3 function in the assay are expected to affect salty taste in humans. The inventive electrophysiological assays, such as the two-electrode voltage-clamp technique, facilitate the identification of compounds which specifically modulate human TRPML3. The assays of the invention provide a robust screen useful to detect compounds that facilitate (enhance) or inhibit TRPML3 function. Compounds that enhance or block TRPML3 channel activity should thereby modulate salty taste. In addition, these compounds may be used to regulate sodium excretion, urinary output and other biological functions relating to sodium levels and TRPML3 related functions.
Owner:SENOMYX INC
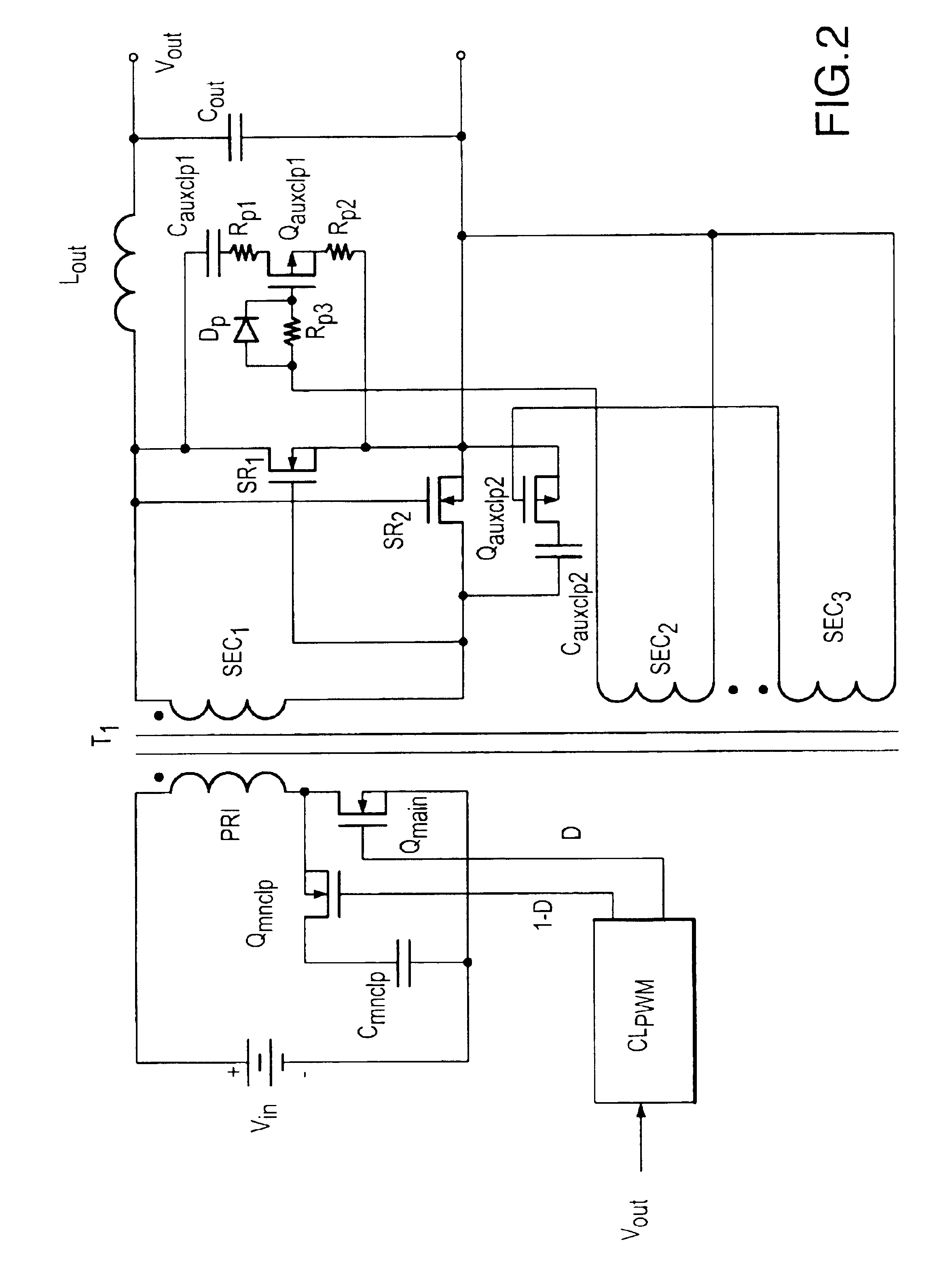
Auxiliary active clamp circuit, a method of clamping a voltage of a rectifier switch and a power converter employing the circuit or method
InactiveUS6882548B1Easy to useTransistorEfficient power electronics conversionActive clampClamp capacitor
The present invention is directed to an auxiliary active clamp circuit and a method of clamping a voltage of a rectifier switch associated with a power converter. The power converter includes a main active clamp circuit associated with a main power switch coupled to a primary winding of a transformer and a rectifier switch coupled to a secondary winding of the transformer. The main power switch conducts during a main conduction period of the power converter and the rectifier switch conducts during an auxiliary conduction period of the power converter. In one embodiment, the auxiliary active clamp circuit includes an auxiliary clamp capacitor, coupled across the rectifier switch, that stores a clamping voltage substantially equal to an off-state voltage of the rectifier switch. The auxiliary active clamp circuit also includes an auxiliary clamp switch, coupled in series with the auxiliary clamp capacitor, that receives a drive signal from a secondary winding and conducts during the main conduction period thereby clamping a voltage across the rectifier switch at about the clamping voltage.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Bi-directional dc-dc converter and method for controlling the same
InactiveUS20090059622A1Large electric powerEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionClamp capacitorDc dc converter
A bi-directional DC-DC converter has a transformer for connecting a voltage type full bridge circuit connected to a first power source and a current type switching circuit connected to a second power source. A voltage clamping circuit constructed by switching elements and a clamping capacitor is connected to the current type switching circuit. The converter has a control circuit for cooperatively making switching elements operative so as to control a current flowing in a resonance reactor.
Owner:HITACHI INFORMATION & TELECOMM ENG LTD
Soft transition converter
InactiveUS6862195B2Total current dropReduce reverse recovery lossEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcSoft switchingFull bridge
The present invention is a circuit and method for reducing switching and reverse recovery losses in the output rectifiers while creating zero voltage switching conditions for the primary switchers. There are described two output configurations, one employing a soft commutation inductor element a bridge rectifier and a output filter capacitor, the second using a soft commutation inductor element a rectification-filtering bridge composed by two capacitors and two capacitors. Both secondary circuits can be driven by three primary circuits. A first circuit is a full bridge with phase shift control, and a second circuit is a half bridge topology with an additional bydirectional switch which achieves two goals, on to get soft switching commutation across all the primary switches, the second to create the right waveforms in the secondary suitable with the claims in this invention. The third topology is a phase shifted two transistors forward. The circuits claimed in this invention can provide soft commutation across the primary switching elements and secondary rectifier means, clamping the voltage across the rectifiers to the output voltage eliminating the need for snubbers circuits both in primary and the secondary section.
Owner:DELTA ENERGY SYST SWITZERLAND
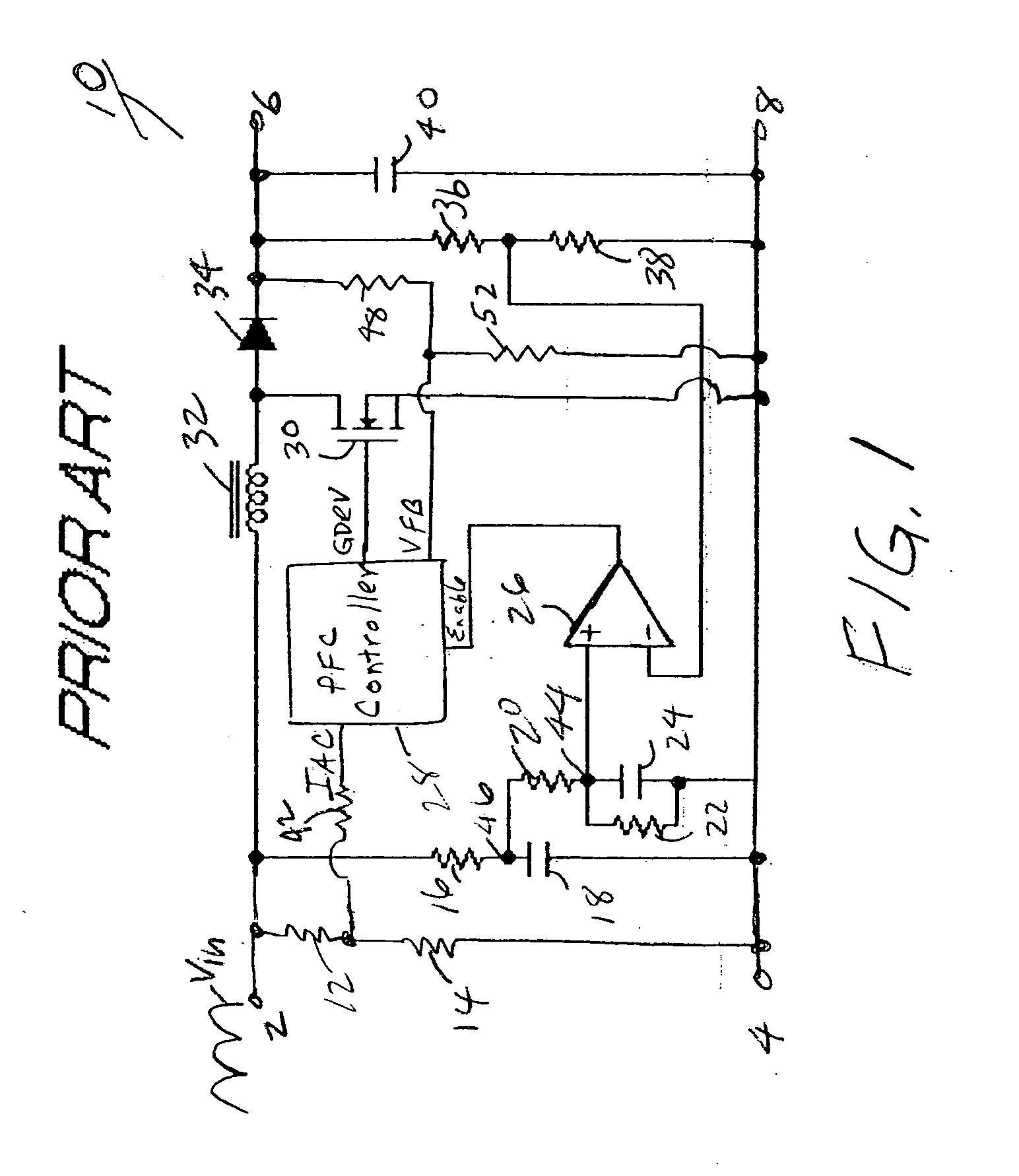
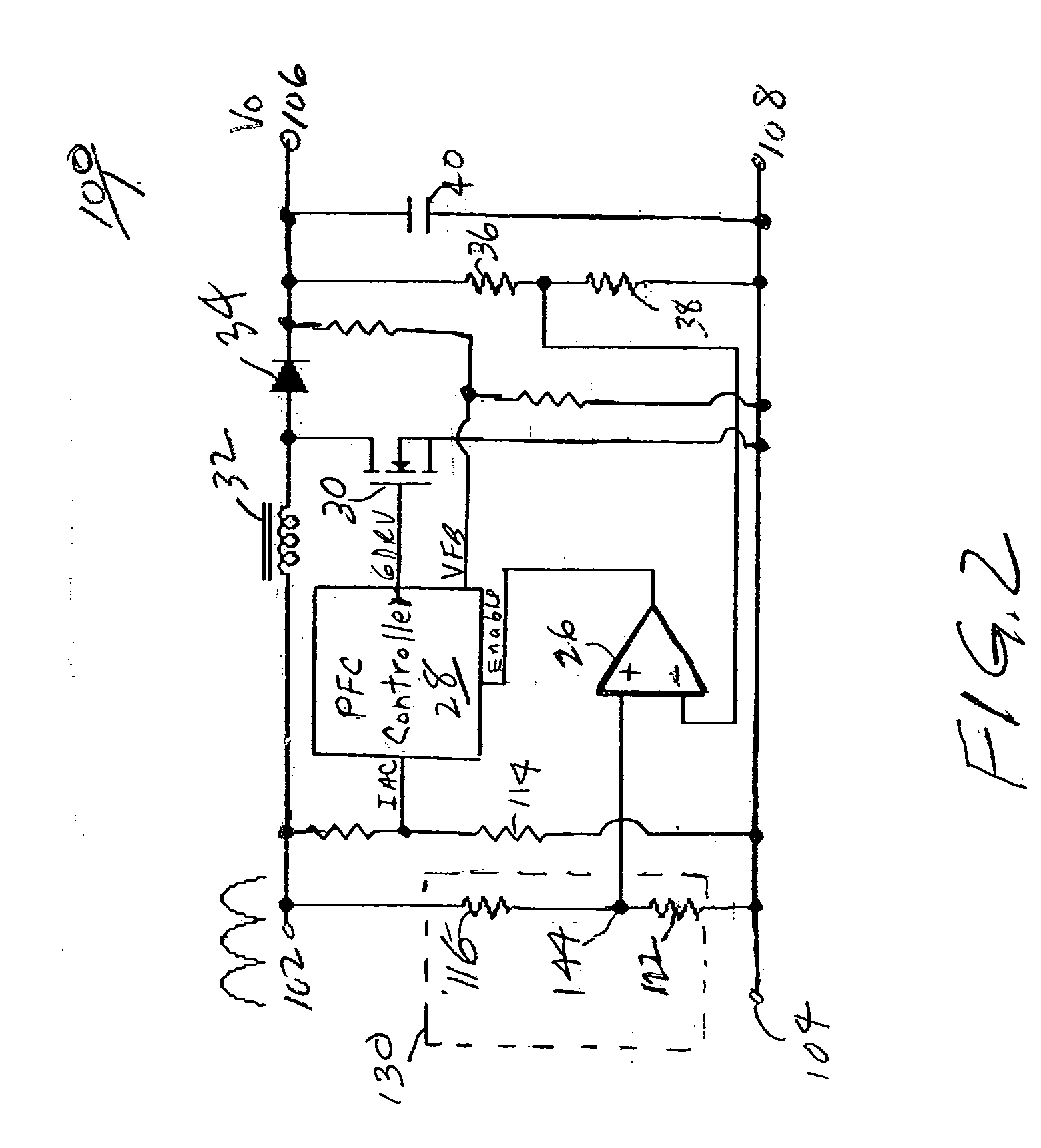
Real-time voltage detection and protection circuit for PFC boost converters
InactiveUS20050269999A1Avoid unnecessary down timeOvercomes drawbackEnergy industryElectric variable regulationPower factorPeak value
A circuit for protection of the operation of power factor correction (PFC) converters from conditions such as input voltage surges that can otherwise cause failure, and to prevent unnecessary down time of the boost converter after a power failure or on startup. The circuit detects the real time rectified input voltage and provides real time comparison of the detected input voltage and the output voltage. The boost function of the PFC is controlled as a function of the output of the comparison circuit so as to quickly inhibit the boost function of the PFC controller thereby disabling boost and protecting the circuit from burning out. The circuit enables the PFC to starts and restart more quickly, even before the output voltage becomes stabilized, since boost is permitted as soon as the output voltage exceeds the real time sampled input voltage. By enabling boost during this period, the circuit eliminates the need to wait at least a few cycle times until the output voltage is higher than the peak of rectified input voltage. In a preferred embodiment, a complementary protection circuit having a voltage clamp is also provided to prevent unnecessary shutdown of the converter.
Owner:ASTEC INT LTD
Delay stage circuitry for a ring oscillator
InactiveUSRE38482E1Easy to optimizePulse automatic controlTime-division multiplexEngineeringVoltage clamp
A ring oscillator includes an even-numbered plurality of ring coupled delay stages. Each delay stage includes a differential amplifier, a voltage clamping circuit, and a current source. The differential amplifier receives first and second input signals from a preceding delay stage. The differential amplifier provides a first output signal and a complementary second output signal at first and second nodes, respectively. The voltage clamping circuit is coupled between the first and second nodes to limit a peak-to-peak voltage swing of each of the first and second output signals. The current source is coupled to the differential amplifier and varies a bias current in accordance with a delay bias voltage.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Clamp circuit
InactiveUS6737905B1Reduce areaLow costPulse automatic controlSolid-state devicesLevel shiftingLinear region
Owner:DENSO CORP
Biological membrane voltage estimator
InactiveUS6163719ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectrical resistance and conductanceExcitable cell
A method and apparatus for estimating the membrane voltage of a cell that is independent of cell conductance. This estimated voltage is used to implement stable, complete (100%) series resistance compensation for a single electrode voltage clamp amplifier, enabling the recording of rapid ionic currents in single, excitable cells.
Owner:ALEMBIC INSTR
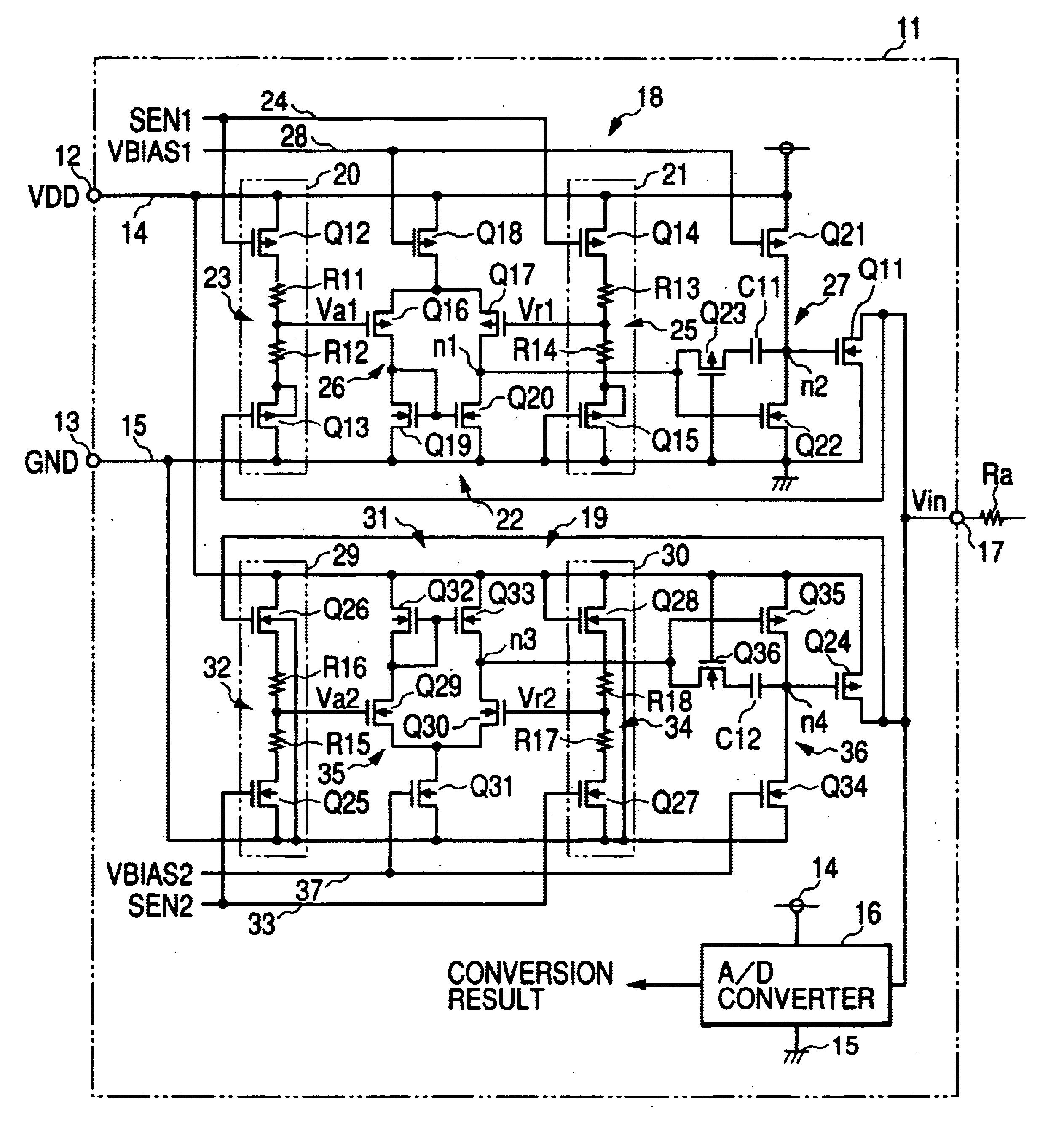
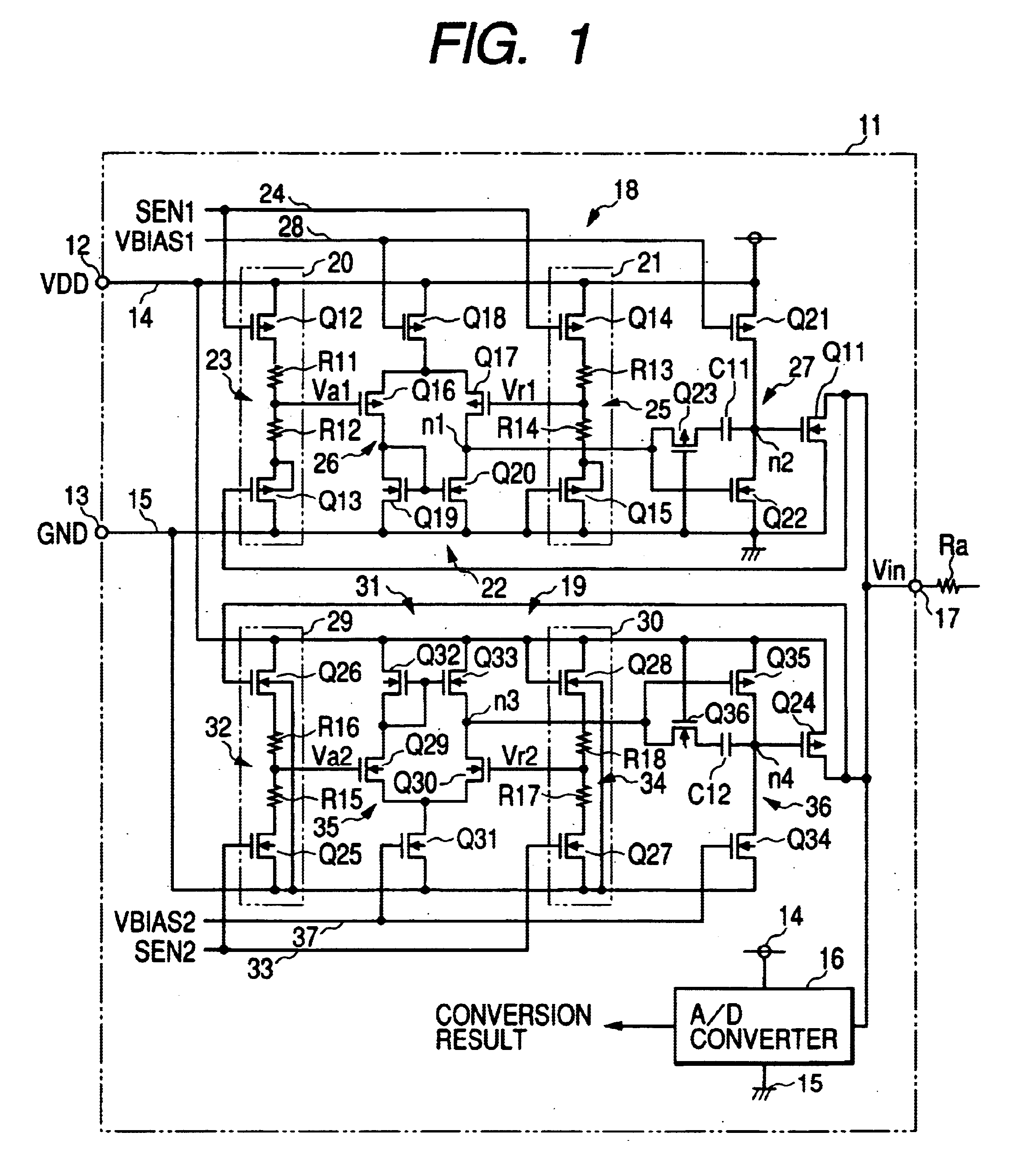
Clamp circuit
InactiveUS20040080352A1Reduce areaLow costPulse automatic controlSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceLevel shifting
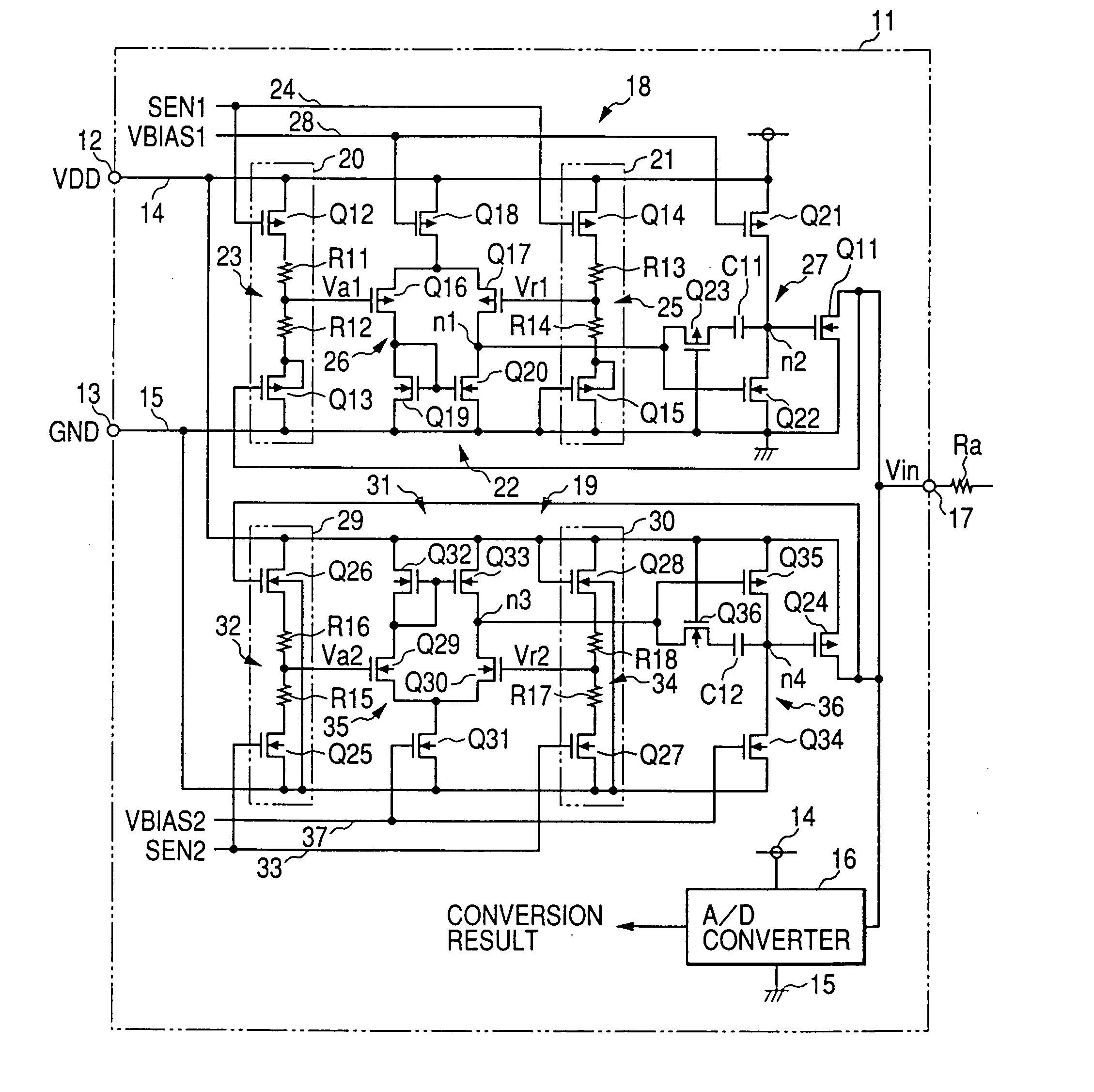
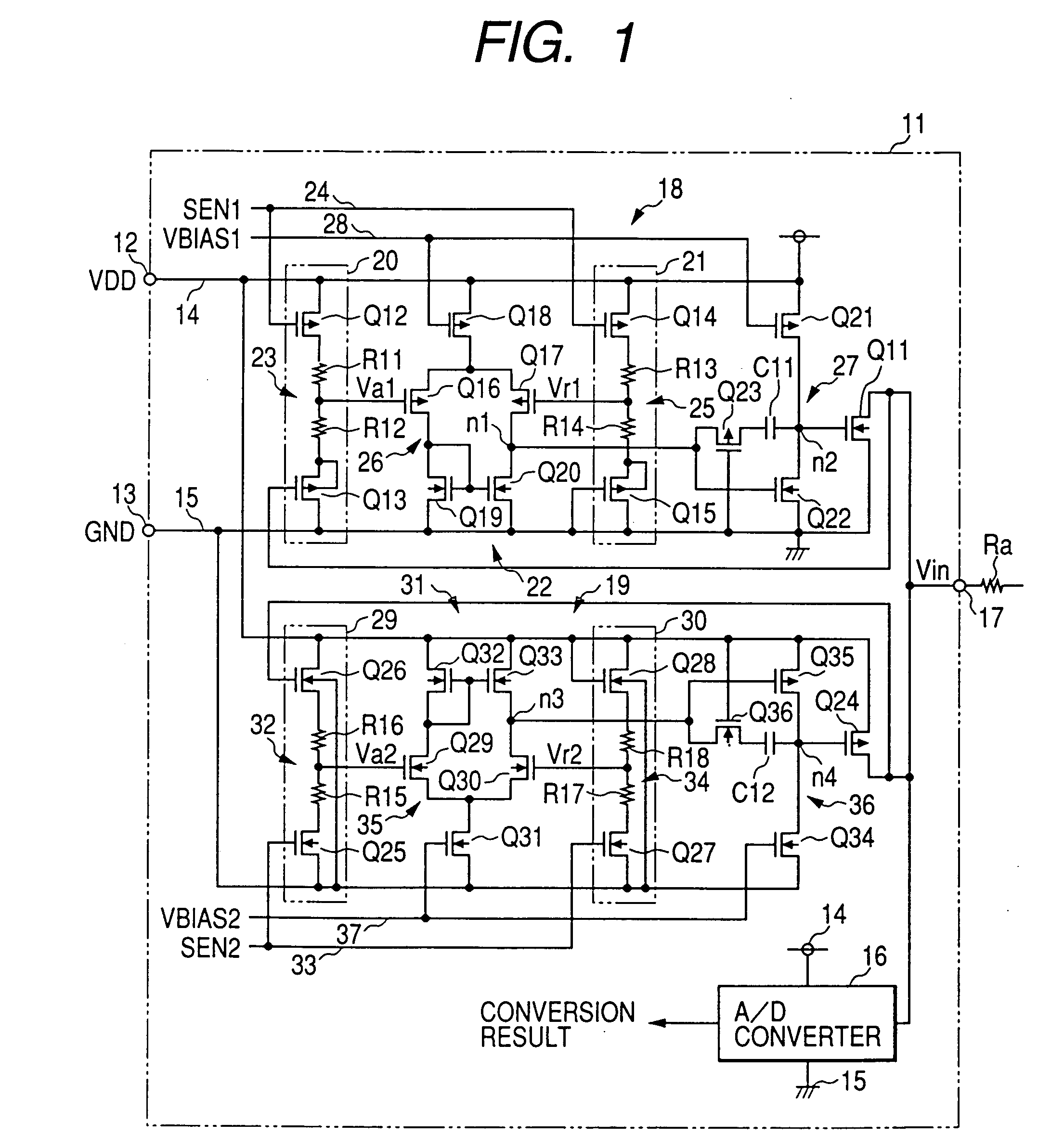
The clamp circuit clamps an input voltage at prescribed higher and lower clamp voltages which are stabilized under a temperature fluctuation. Transistors Q12 and Q14 are switched on in their linear region. In a lower voltage clamp circuit 18, an Vin detecting circuit 20 outputs Va1 by level-shifting Vin by Q13 and voltage-divides by series resistance circuit 23 the level-shifted Vin, while a reference voltage generating circuit 21 outputs Vr1 by level-shifting 0 V by Q15 and voltage-divides by series resistance circuit 25 the level-shifted voltage. Q11 is switched on, when a comparator 22 determines that Va1 descends and goes across Vr1. Here, Q12 is of the same characteristics as Q14, while Q13 is of the same characteristics as Q15. Further, the resistance of the circuits 23 is the same as that of the circuit 25. The higher voltage clamp circuit 19 is similar to the circuit 18.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Reverse-connection preventing circuit, reverse-connection preventing processing method and communication equipment
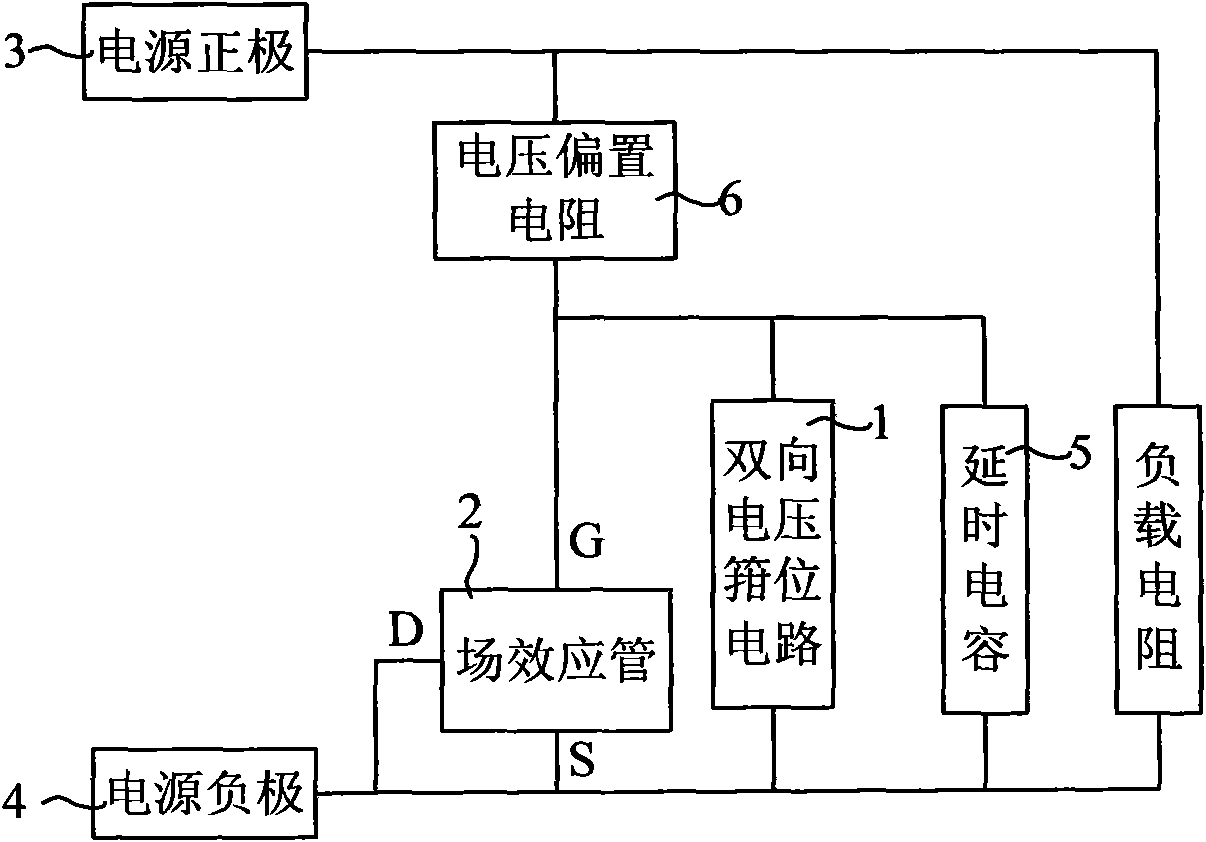
InactiveCN101872971AExpand the application voltage rangeImprove reliabilityEmergency protective circuit arrangementsOvervoltageElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention provides a reverse-connection preventing circuit, a reverse-connection preventing processing method and communication equipment. The circuit comprises a voltage bias resistor connected between the anode and the cathode of the power supply, a bidirectional voltage-lamping circuit and at least one field-effect tube, wherein the voltage bias resistor is connected with the grid electrode of the field-effect tube and is used for conducting and biasing the field-effect tube; the bidirectional voltage-lamping circuit is connected in parallel at two ends of the grid electrode and the source electrode of the field-effect tube and is used for taking a grid electrode and source electrode voltage clamp of the field-effect tube as a first protective voltage when inputting overvoltage in the forward direction; and the first protective voltage is the normal work voltage of the field-effect tube. The invention also provides the reverse-connection preventing processing method and the communication equipment. The invention achieves the input overvoltage protection function of the direct current input reverse-connection preventing circuit and improves the reliability of the circuit.
Owner:BEIJING XINWANG RUIJIE NETWORK TECH CO LTD
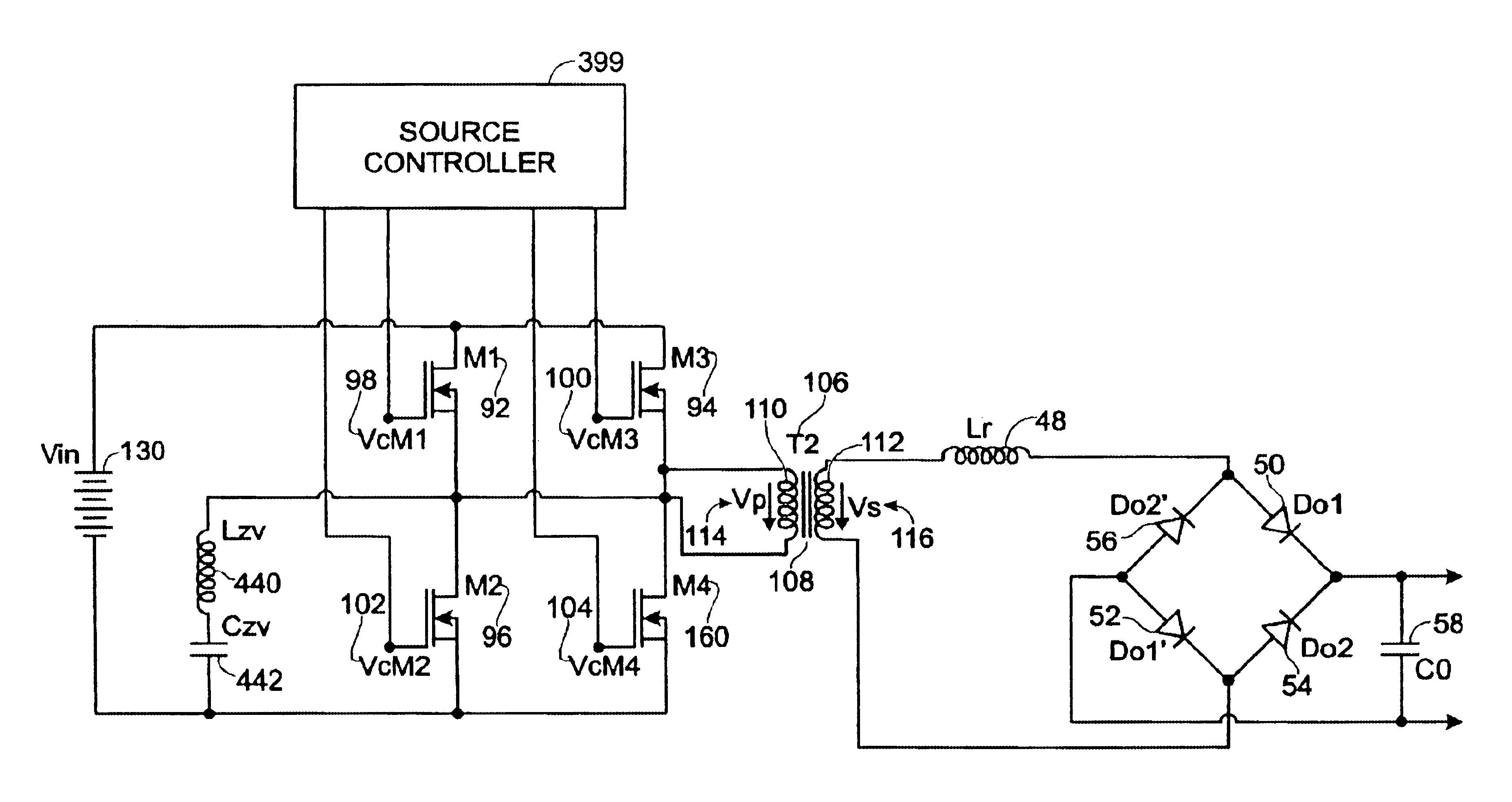
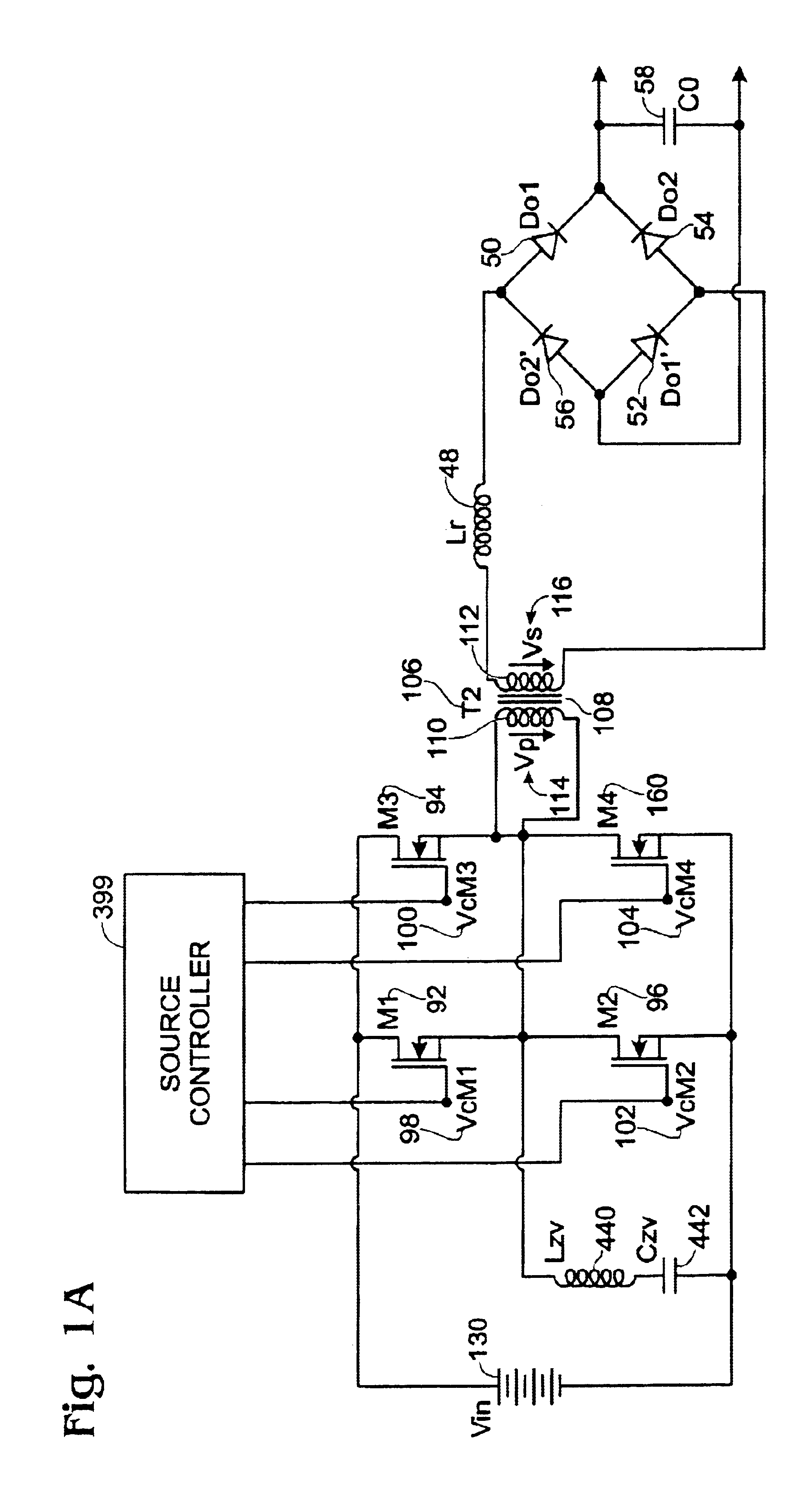
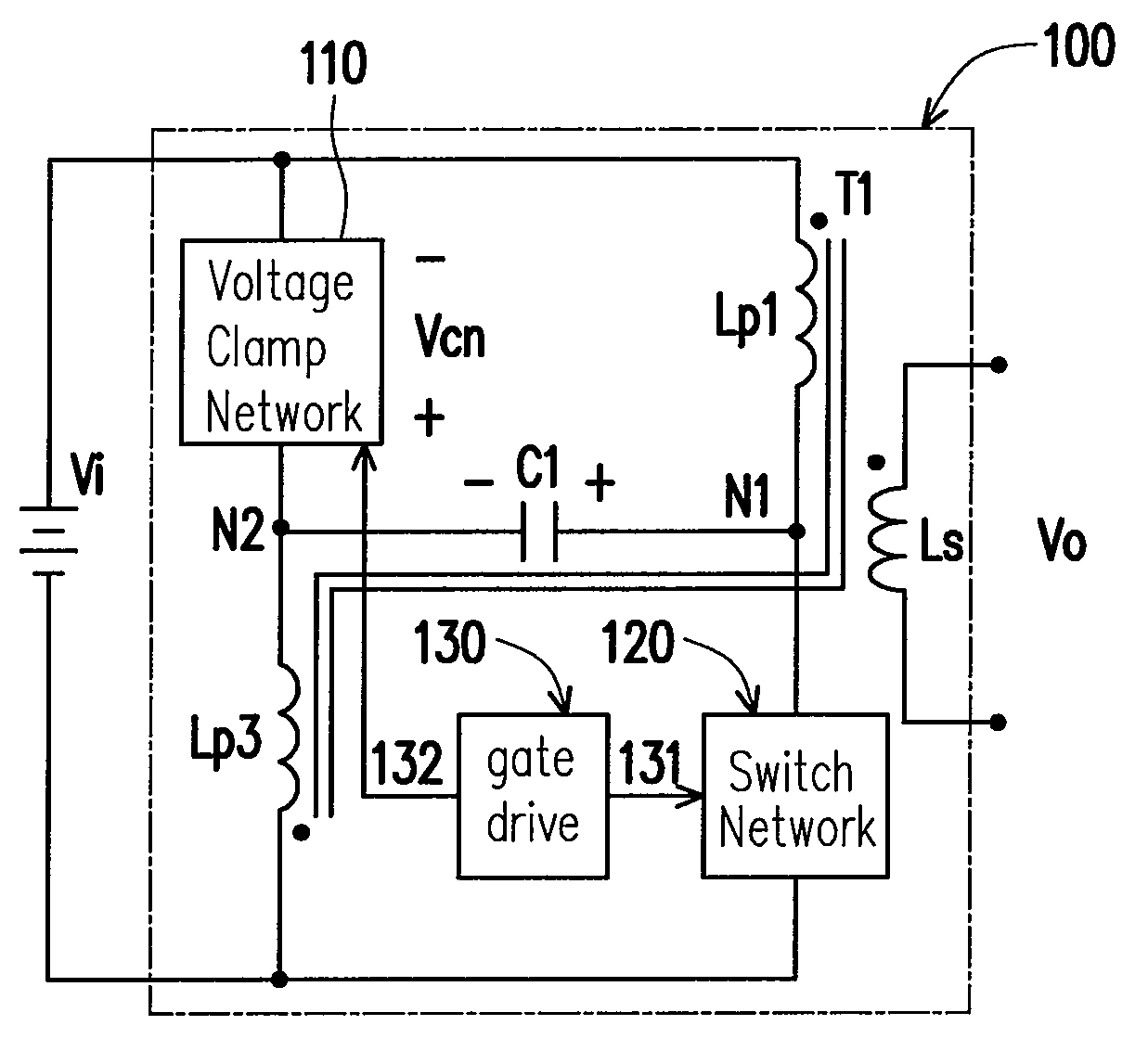
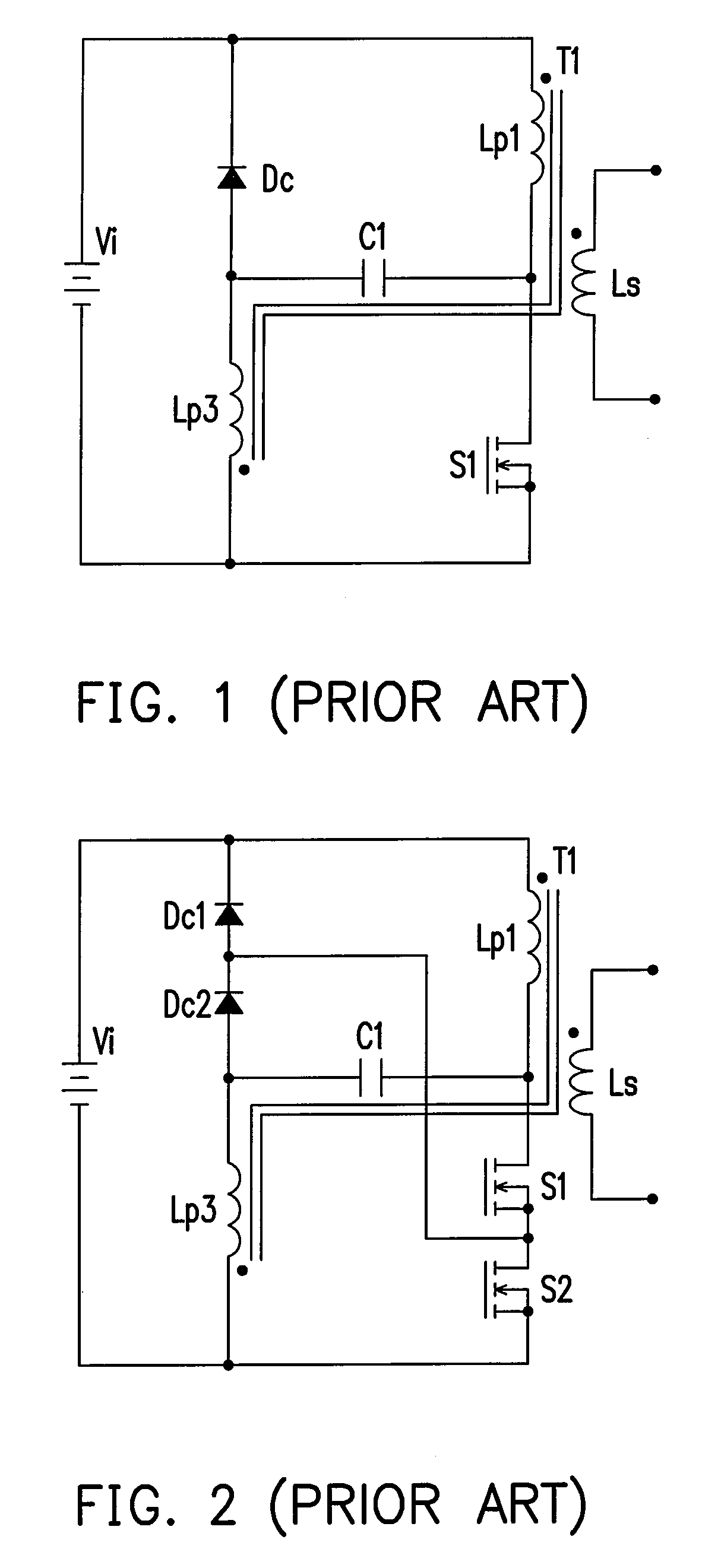
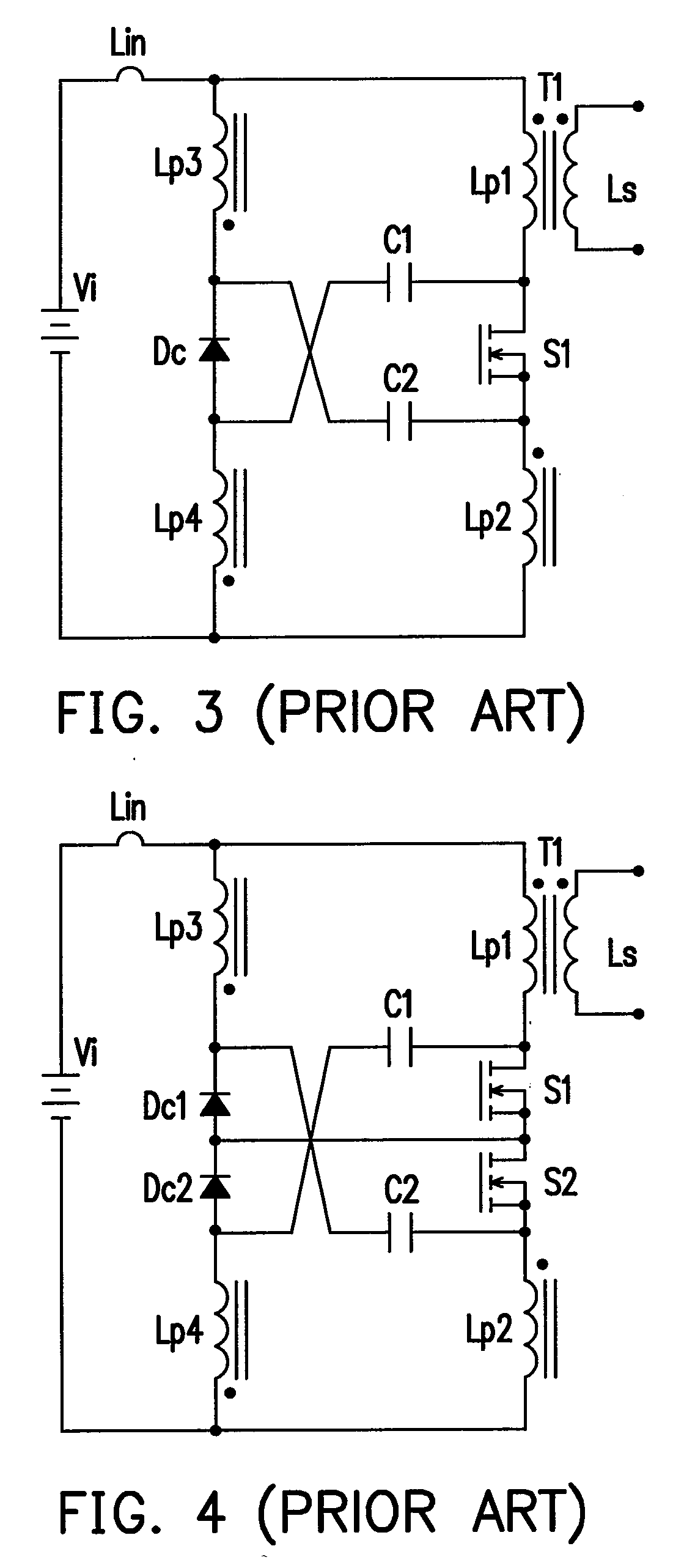
Voltage-clamp power converters
InactiveUS20090257254A1Reduced input current rippleReduce EMI problemsEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionMOSFETClamp capacitor
Several inversion circuits used to convert a DC input to an AC output comprise two series circuits, at least one clamp capacitor, and at least one transformer. Each of the series circuits is in parallel with the DC input. The first series circuit includes one switch network and at least one transformer primary. The second series circuit includes one voltage-clamp network and at least one transformer primary. At least one clamp capacitor couples the first and the second series circuits, and is attached to each series circuit at a node between the respective transformer primary winding. The voltage-clamp network may be implemented with two of the three sub-circuits connected in series: a diode, a resister-capacitor-diode, and a MOSFET-capacitor.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Input protection circuit
ActiveUS8259428B2Sufficient amount of heatAvoid narrow scopeBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerOvervoltageVoltage clamp
Owner:PHILIPS IP VENTURES BV
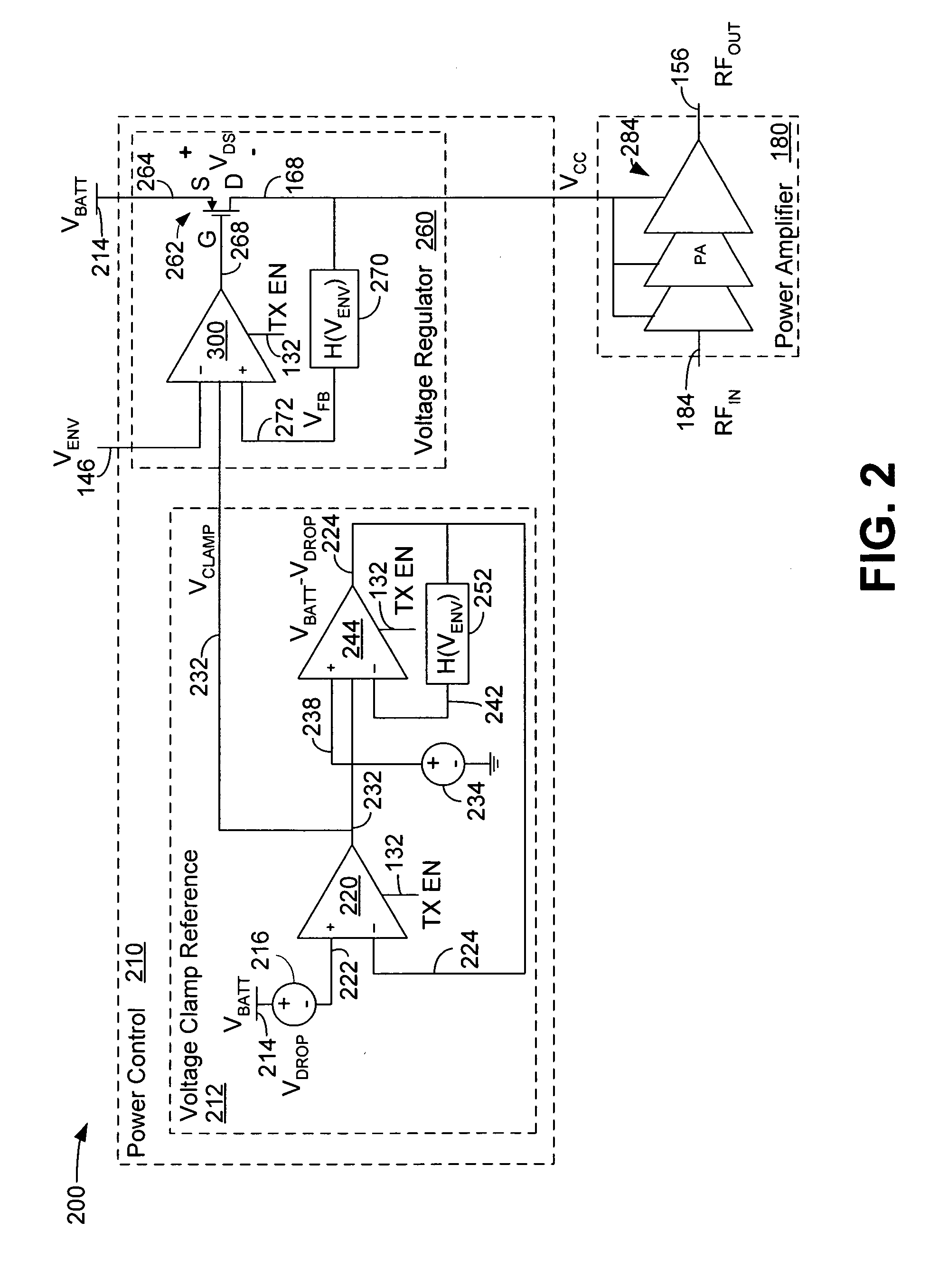
Voltage clamp for improved transient performance of a collector voltage controlled power amplifier
ActiveUS20060119425A1Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsSupply voltage varying controlAudio power amplifierControl signal
A power control circuit for a power amplifier comprises a voltage regulator having a first input configured to receive a envelope control signal, a second input configured to receive a feedback signal, and a third input configured to receive a voltage clamp signal; and a clamp voltage reference circuit configured to generate the voltage clamp signal.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
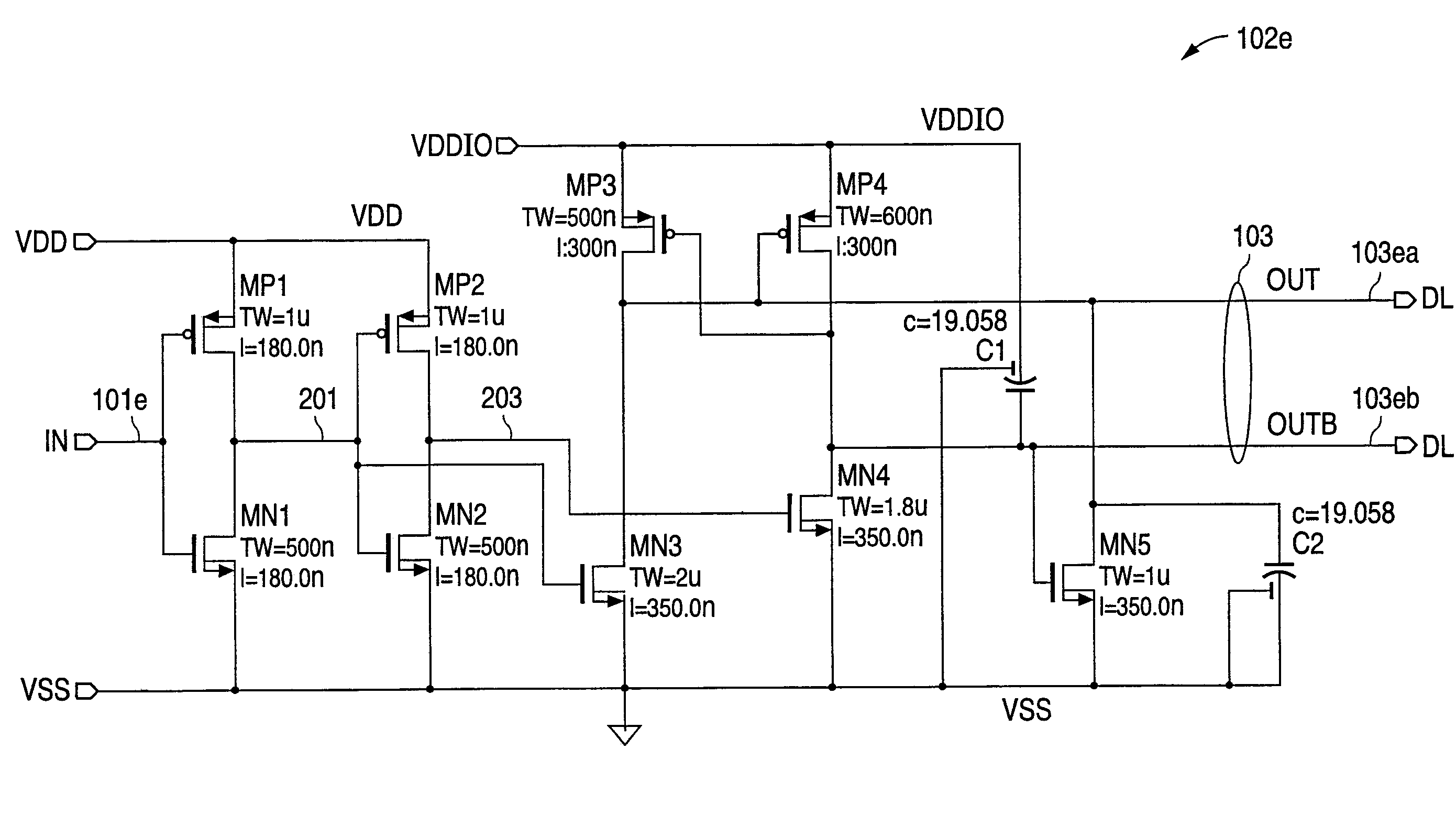
Power supply detection circuit biased by multiple power supply voltages for controlling a signal driver circuit
ActiveUS7397296B1Power reduction by control/clock signalPulse automatic controlDriver circuitCapacitance
A power supply detection circuit biased by at least two power supply voltages for controlling a signal driver circuit. Upstream and downstream amplifiers, powered by upstream and downstream power supply voltages, respectively, process an original control signal to produce a differential signal via output signal electrodes. Capacitances coupling respective ones of the output signal electrodes to the downstream power supply voltage and the circuit reference potential discharge and charge respective ones of the output signal electrodes in relation to initial receptions of the upstream and downstream power supply voltages and original control signal, following which voltage clamp circuitry maintains such discharged and charged states pending reception of the original control signal in a predetermined state.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Power gating techniques able to have data retention and variability immunity properties
ActiveUS7126370B2Reduce power consumptionReliability increasing modificationsPower reduction by control/clock signalManufacturing variabilityEngineering
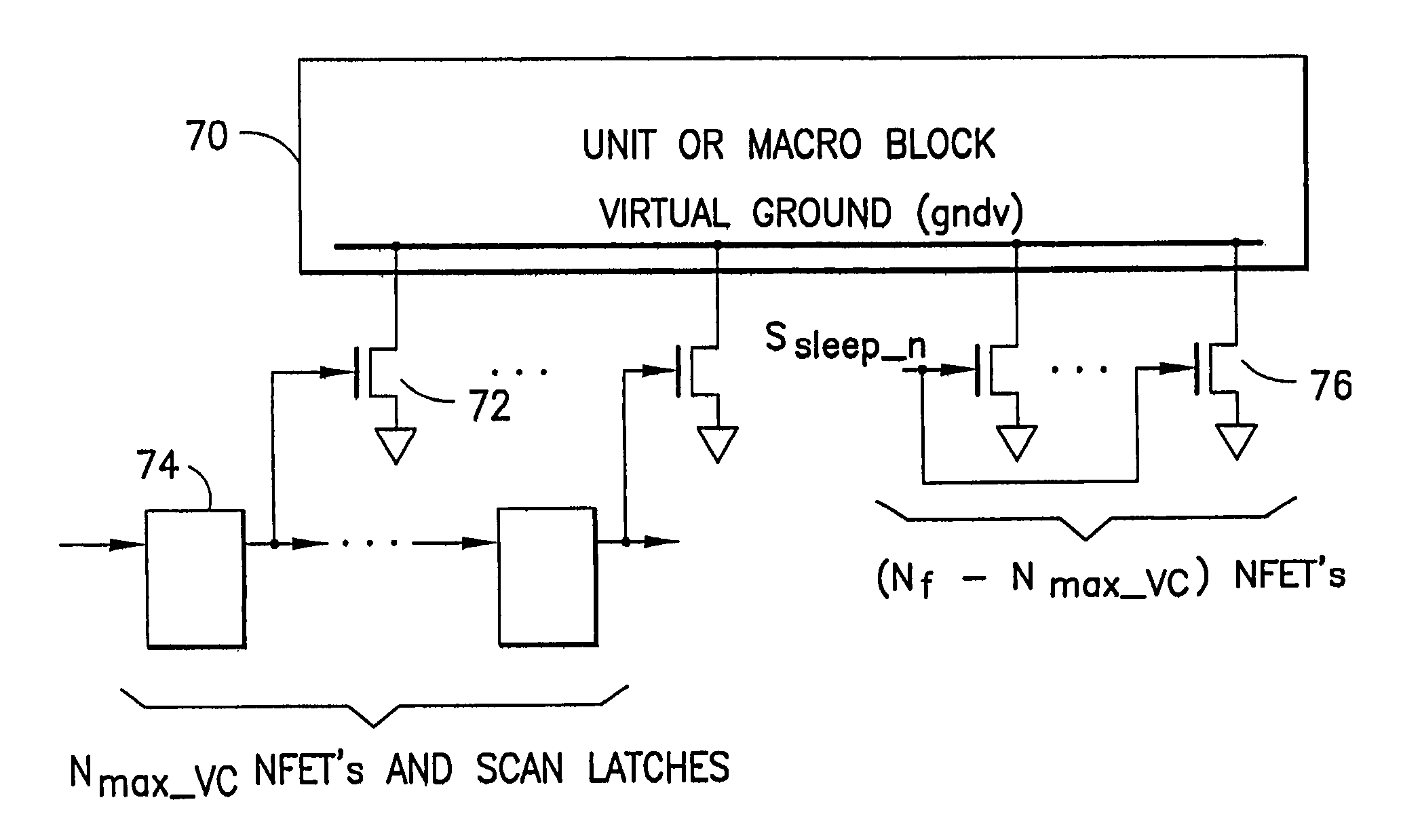
A power gated semiconductor integrated circuit comprises: (1) logic circuit to be power gated, said logic circuit having a virtual ground rail; (2) footer device disposed between said virtual ground rail and a ground rail for reducing power consumption of said logic circuit; and (3) virtual rail voltage clamp disposed electrically in parallel with said footer device for limiting the voltage at the virtual ground rail, the virtual rail voltage clamp comprising at least one NFET. A total of Nf NFETs are connected to the virtual ground rail of the integrated circuit for use as both virtual rail voltage clamps and footer devices. A quantity of Nmax-VC NFETs are scanned and perform the function of voltage clamps and the remaining (Nf−Nmax-VC) NFETs perform power gating. Manufacturing variability immunity and tuning of the variability immunity is achieved by adjusting the quantity Nmax-VC based upon testing of the manufactured integrated circuit.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Isolated bidirectional DC-DC converter
ActiveUS7638904B2Effectively miniaturizedTotal current dropEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionClamp capacitorConverters
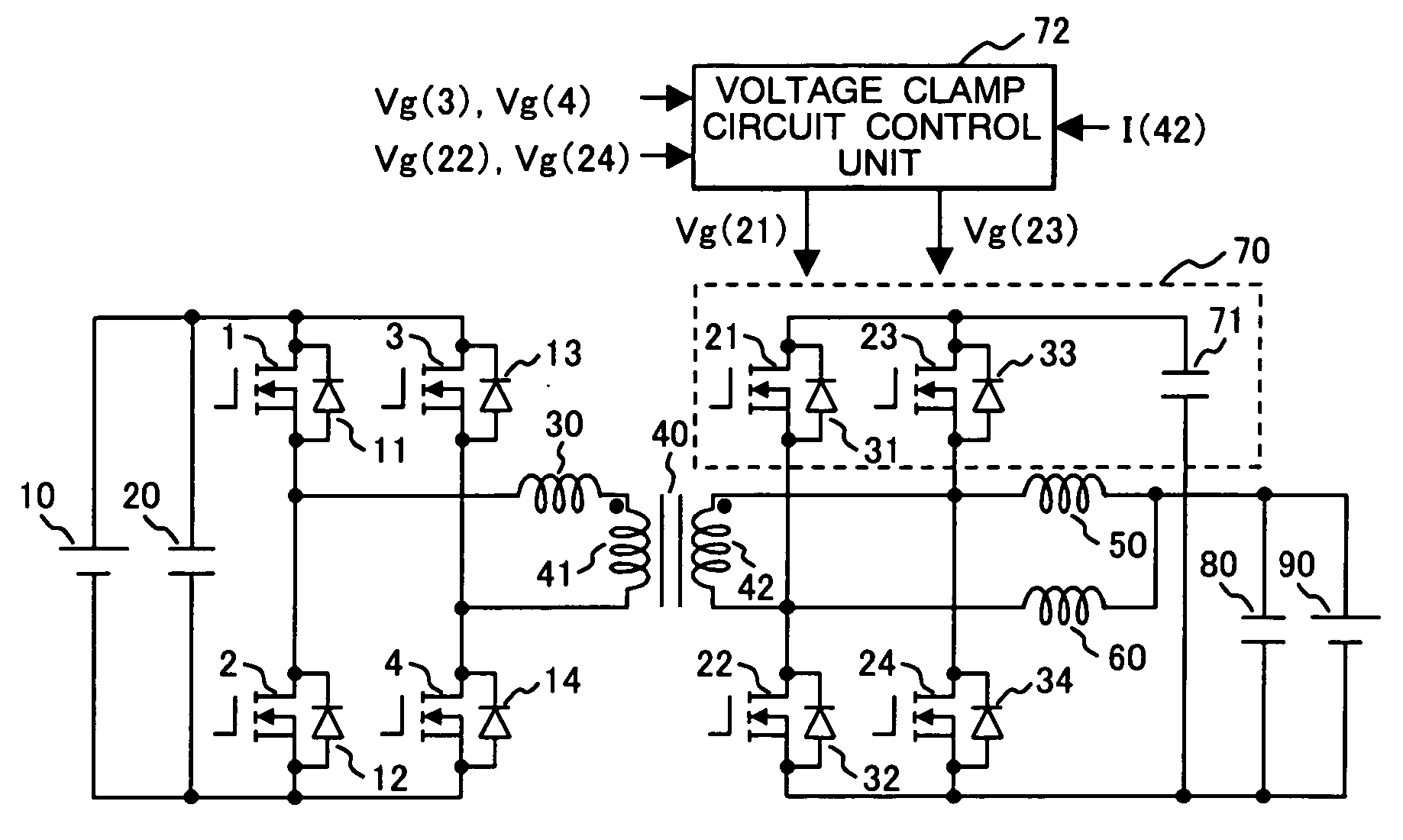
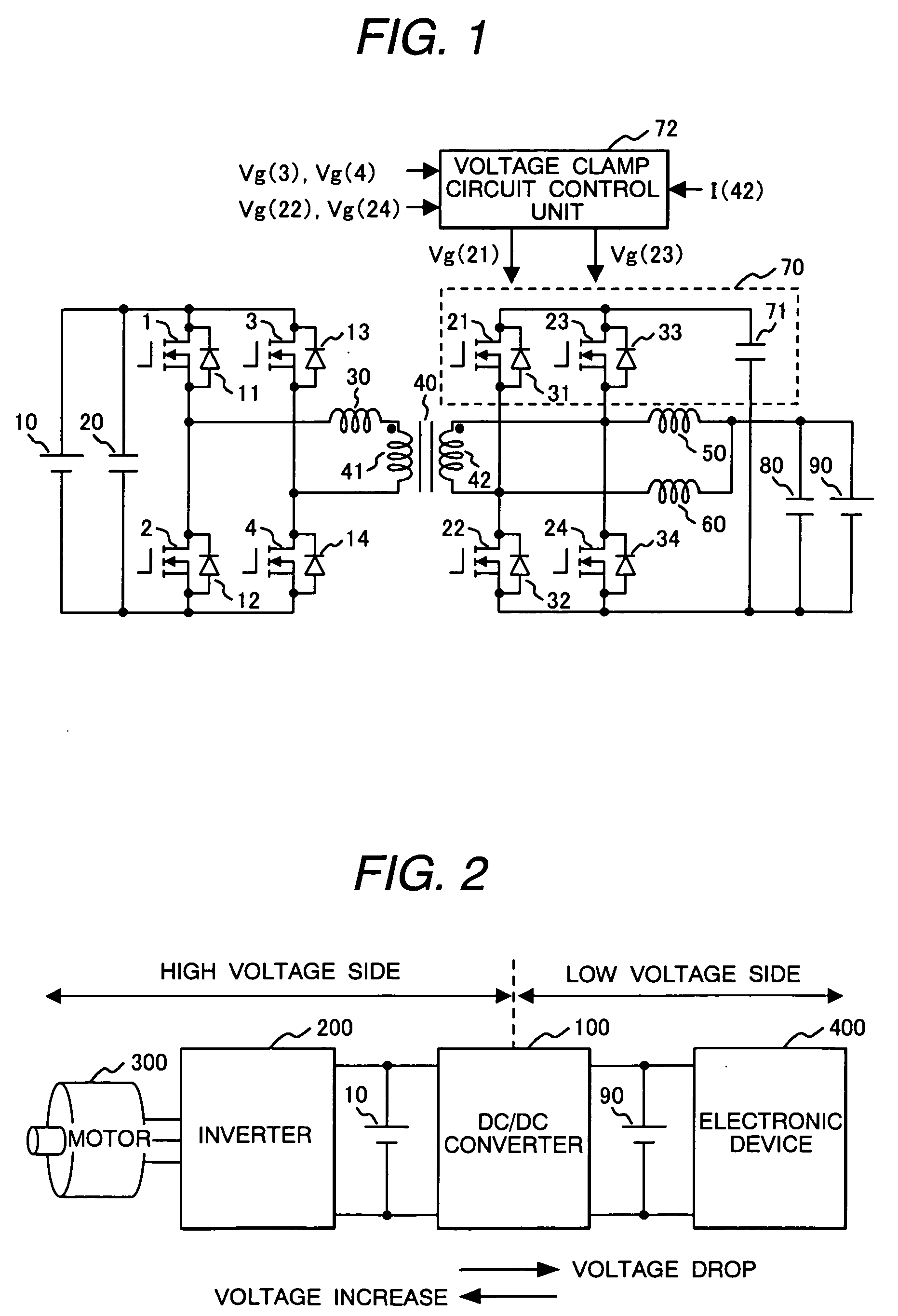
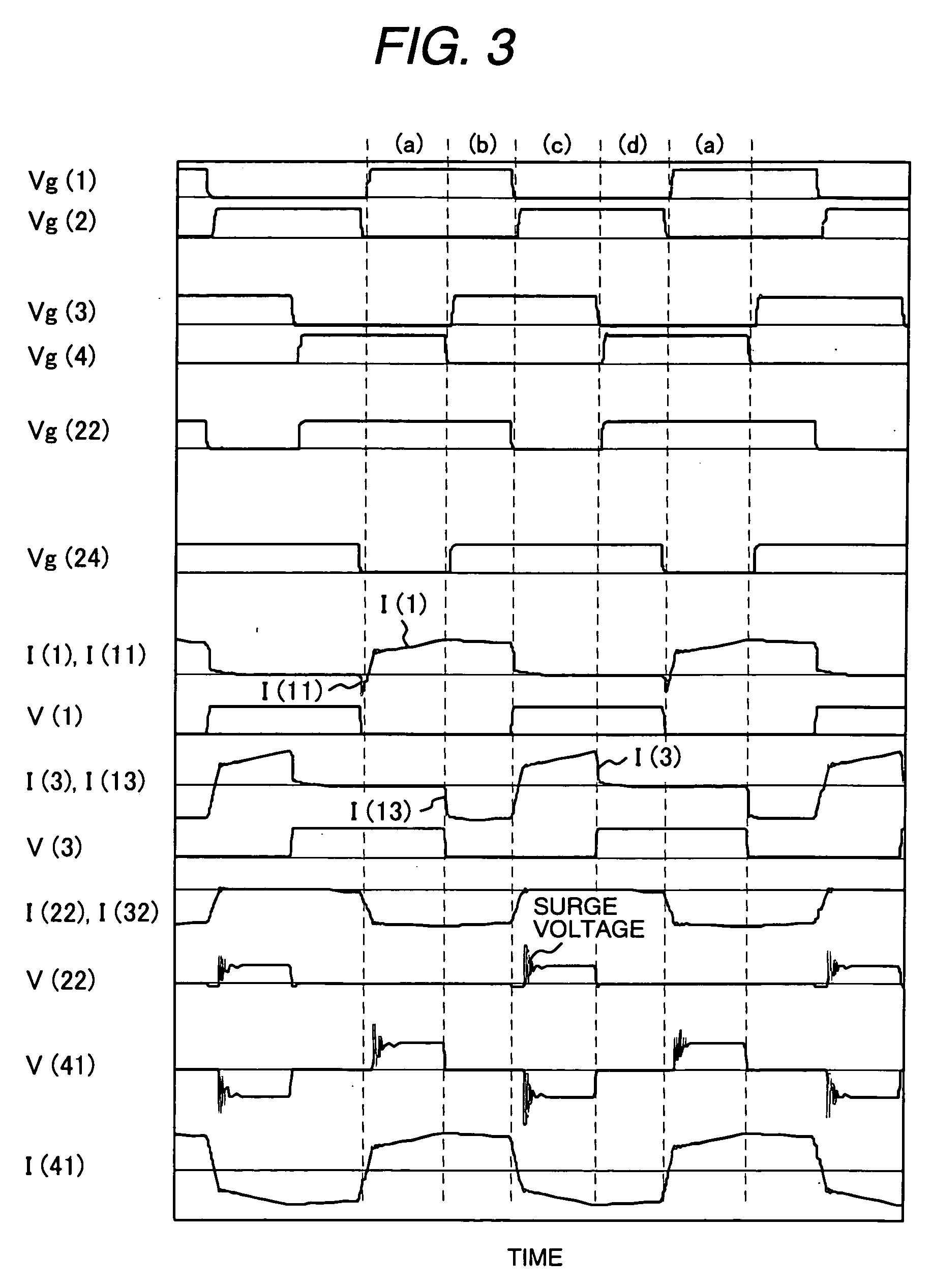
The DC-DC converter connects a first and a second switching circuit for converting power mutually between direct current and alternating current respectively to a first DC power source and a second DC power source and has a transformer between the AC terminals thereof. Here, between the AC terminals of the second switching circuit and the negative pole terminal of the DC power source, a voltage clamp circuit composed of a series unit of switching devices with a reverse parallel diode and a clamp condenser is connected.An isolated bidirectional DC-DC converter which prevents a reduction in a circulating current at time of buck and an occurrence of a surge voltage at time of voltage boost and realizes highly efficiency, low noise, and miniaturization is provided.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Current detection method based on parasitic inductance and application of current detection method
ActiveCN106027011AProtection securityReduce voltage spikesTransistorElectronic switchingVoltage spikeSignal on
The invention provides a current detection method based on parasitic inductance and application of the current detection method. Voltage signals on two ends of the parasitic inductance at a connecting line between a source pin of a switch tube and a power ground are detected to judge whether overcurrent occurs, an overcurrent turn-off instruction is sent through a logic control circuit, and the grid-source voltage of the switch tube is limited to protect the switch tube through a grid voltage clamp circuit when the overcurrent condition occurs. According to the method and the application thereof, a soft turn-off function is integrated, the speed for overcurrent turn-off is slowed down, the voltage spike at the turn-off moment is reduced, and the rapidity of short circuit protection of a SiC device is realized while an EMI (Electro-Magnetic Interference) problem is reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Segmented slope compensation circuit applicable to BUCK converter
ActiveCN107707103AHigh precisionStable jobAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyPower conversion systemsCapacitanceSystem stability
A segmented slope compensation circuit applicable to a BUCK converter belongs to the technical field of an electronic circuit. An oscillator circuit is used for introducing output voltage informationof the BUCK converter, a negative input end voltage of an operational amplifier is clamped to a positive input end voltage thereof, a first capacitor is charged by a current mirror, the negative inputend voltage, namely a slop voltage signal, of the operational amplifier is obtained, the slop voltage signal is compared with a second reference voltage to obtain a periodic slope voltage signal, a slope current generation circuit is used for generating compensation slopes with different slope rates under different duty ratios, a slope voltage correlated to the duty ratios is generated on a sampling resistor after passing through a slope summing circuit, and a base current compensation circuit is used for stabilizing a system. Compared with a traditional slope compensation circuit, the segmented slope compensation circuit has the advantages that the system stability is improved by employing different slope compensation rates under different duty ratios; and with the adoption of a triode as a buffer, the segmentation accuracy is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
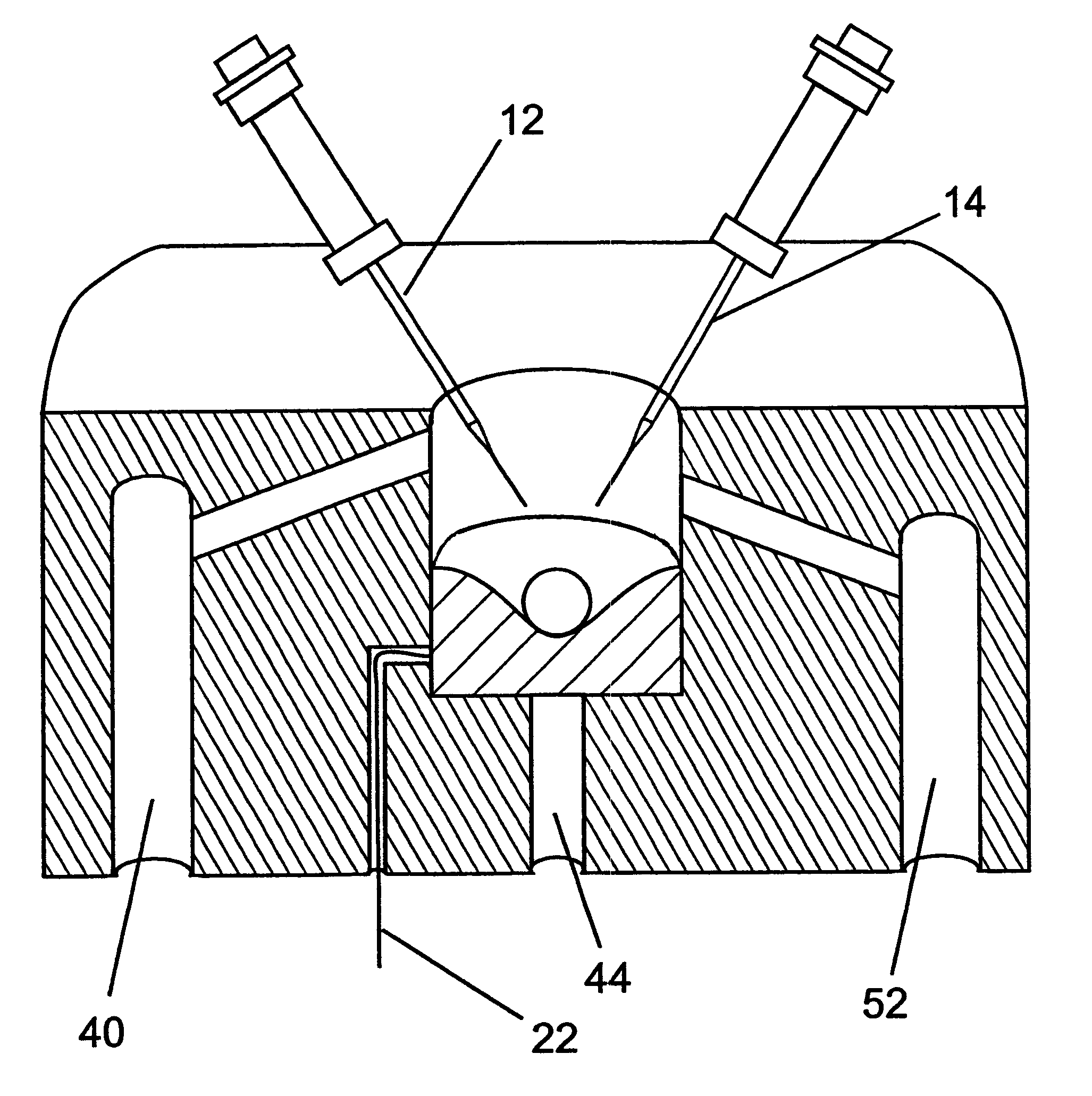
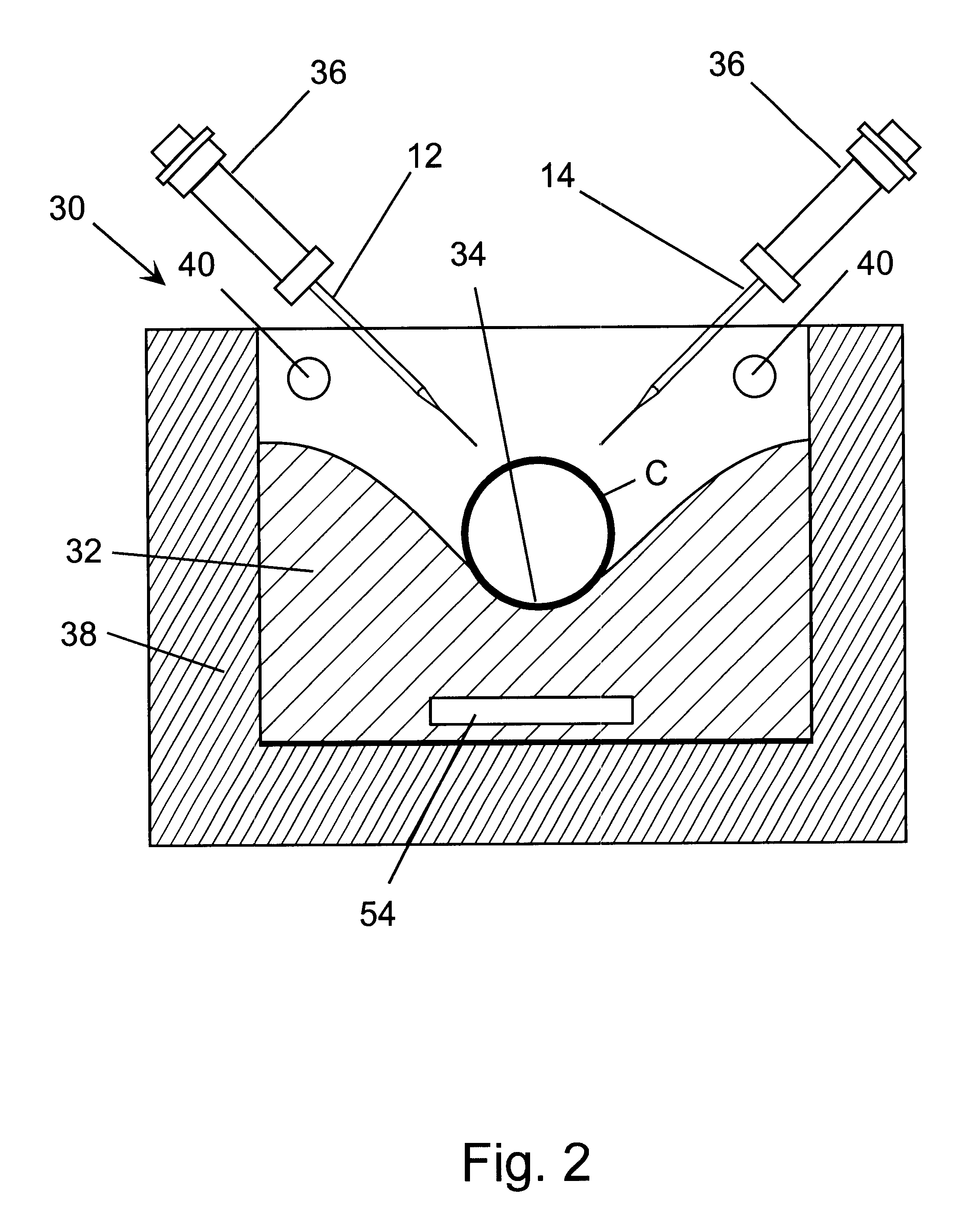
Perfusion chamber for electrophysiological testing of oocytes
InactiveUS6541243B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPorosityEngineering
A perfusion chamber includes a porous oocyte support structure. A continuously sloped top surface and a receiving well in the support structure entrap the underside of the oocyte, thereby localizing the cell in a predetermined fixed position within the reach of dedicated voltage-clamp microelectrodes. A test solution is delivered continuously at the top of the chamber, above the oocyte, and withdrawn from the bottom of the chamber, below the oocyte. The porosity of the support material enables the continuous perfusion of test solution around the membrane of the oocyte, including its bottom portion that is held firmly in contact with the holding well. The geometry of the holding well is selected such as to ensure the automatic and precise placement of the oocyte by gravity and to optimize the pressure distribution over its membrane, thereby minimizing the probability of rupture or other damage to the cell. The entire top surface of the support structure is sloped inward toward the substantially central well, and the bottom of the well is contoured to conform to the shape of an oocyte of average size.
Owner:MDS ANALYTICAL TECH US
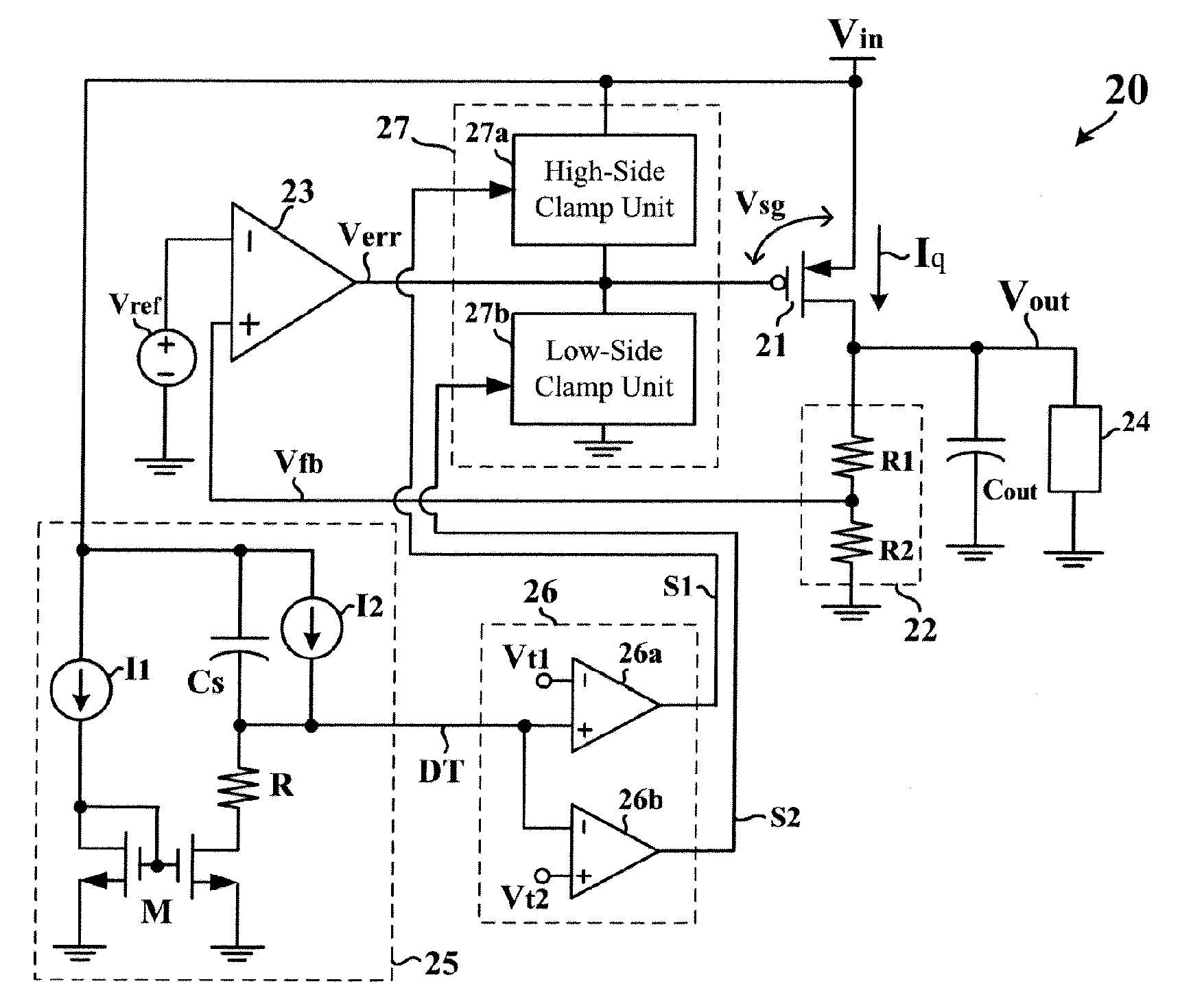
Linear voltage regulator with improved responses to source transients
ActiveUS20070053115A1Improve control regulationImproving regulation control over output voltageEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentArrangements responsive to excess voltageLinear regulatorEngineering
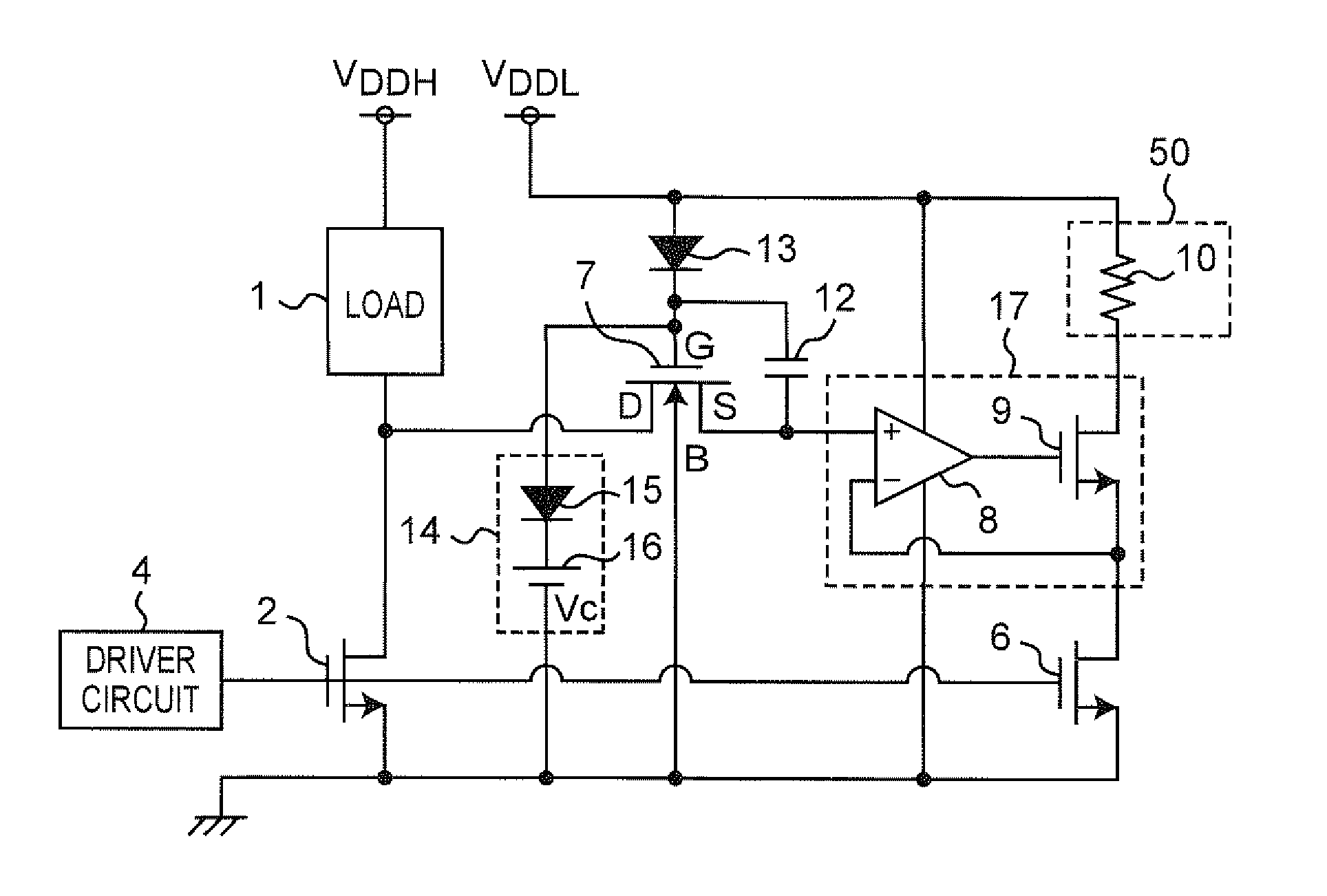
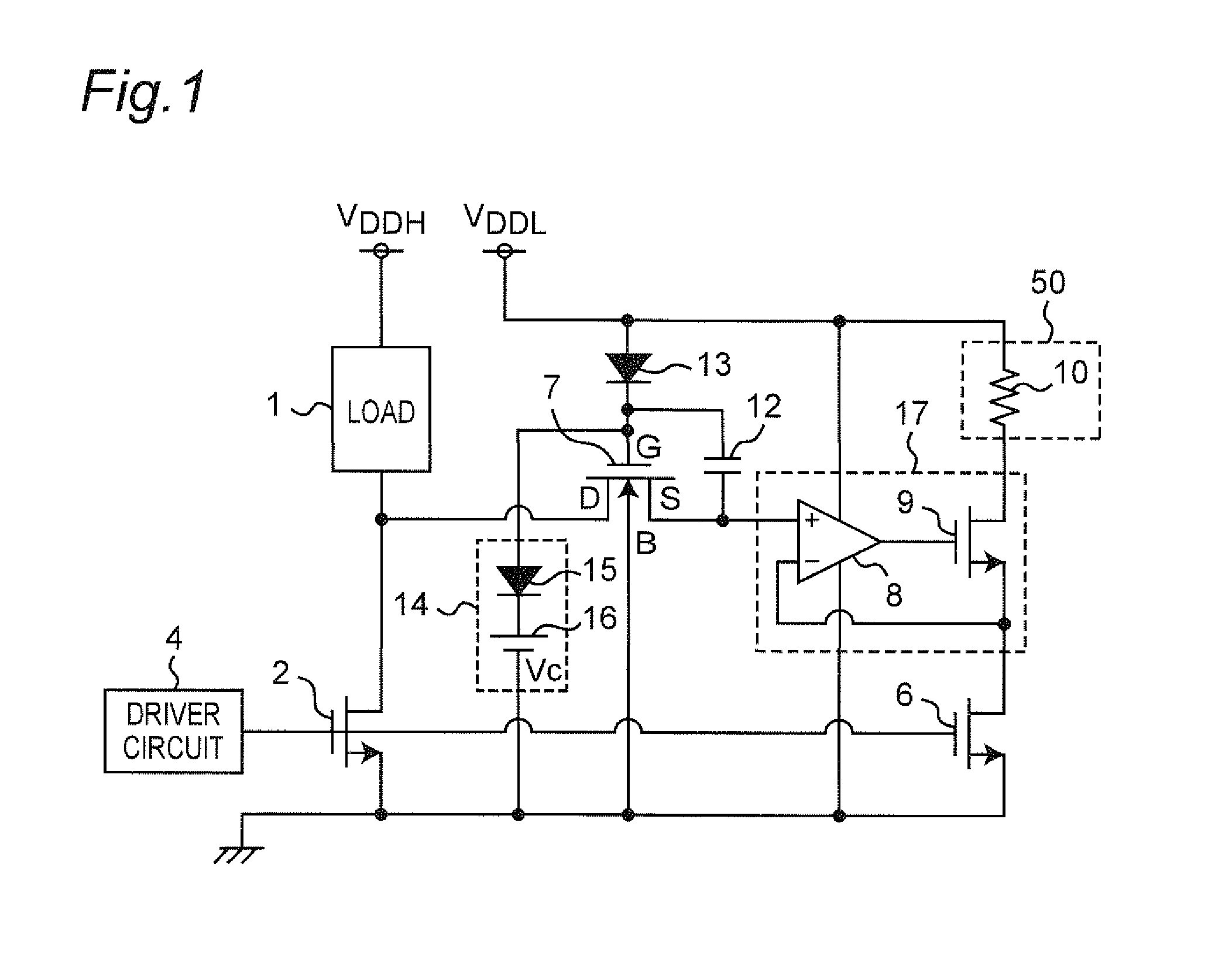
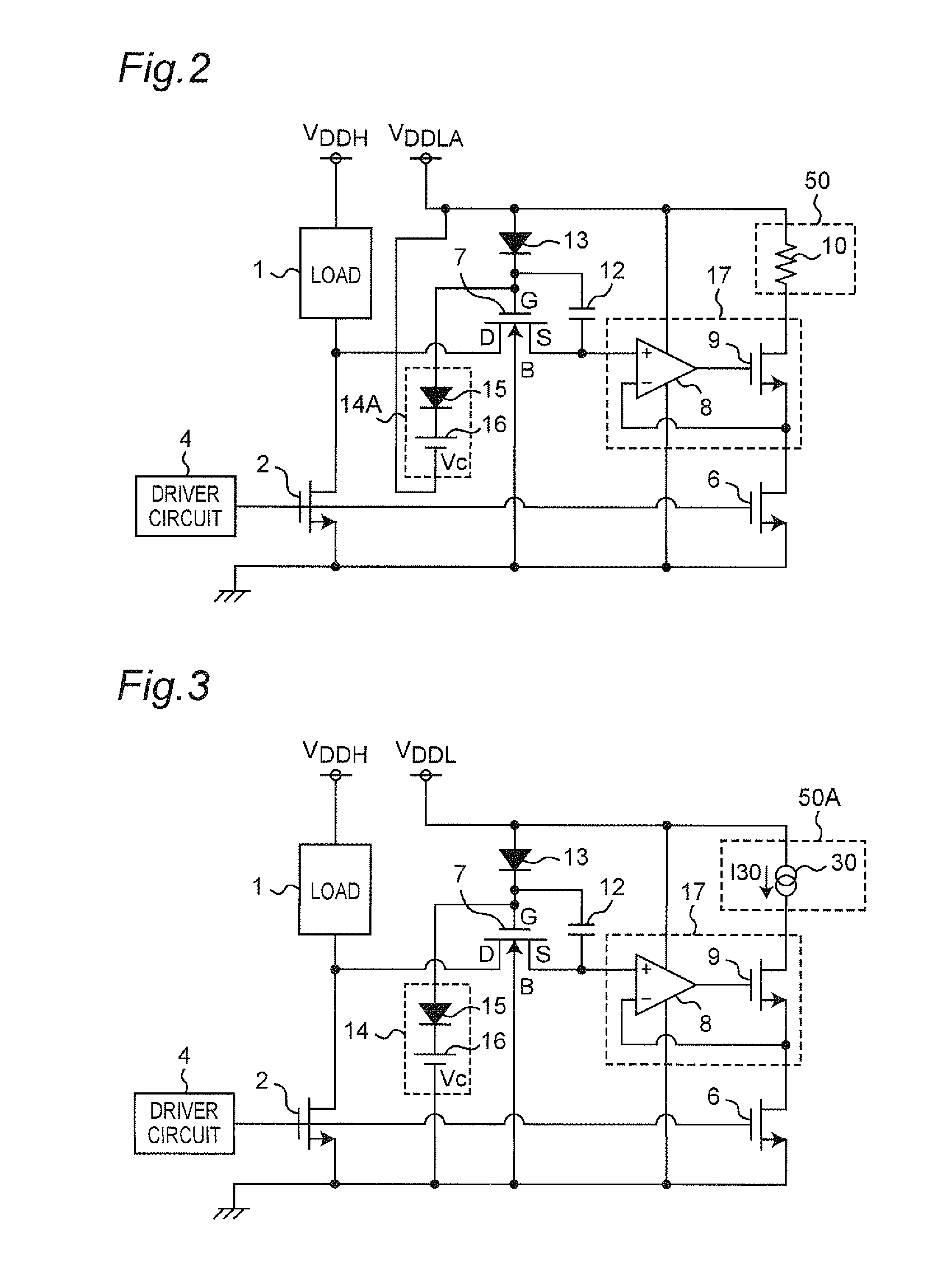
A linear voltage regulator has a regulating transistor with a first channel electrode receiving an input voltage source and a second electrode providing an output voltage. A control electrode of the regulating transistor is controlled by an error amplifying circuit based on comparison between a feedback signal of the output voltage and a reference voltage. An event detecting circuit is coupled to the input voltage source for detecting occurrence of a transient in the input voltage source. In response to the detected transient event, an enable controlling circuit generates an enable signal for determining an effective operation time of a voltage clamping circuit. During such effective operation time, a potential difference between the first channel electrode and the control electrode is limited within a predetermined clamp voltage for preventing the regulating transistor from being dramatically changed in operation.
Owner:GLOBAL MIXED MODE TECH
Open drain driver, and a switch comprising the open drain driver
ActiveUS20060255852A1Good overvoltage protectionSuitable for useTransistorElectrical testingMOSFETCapacitance
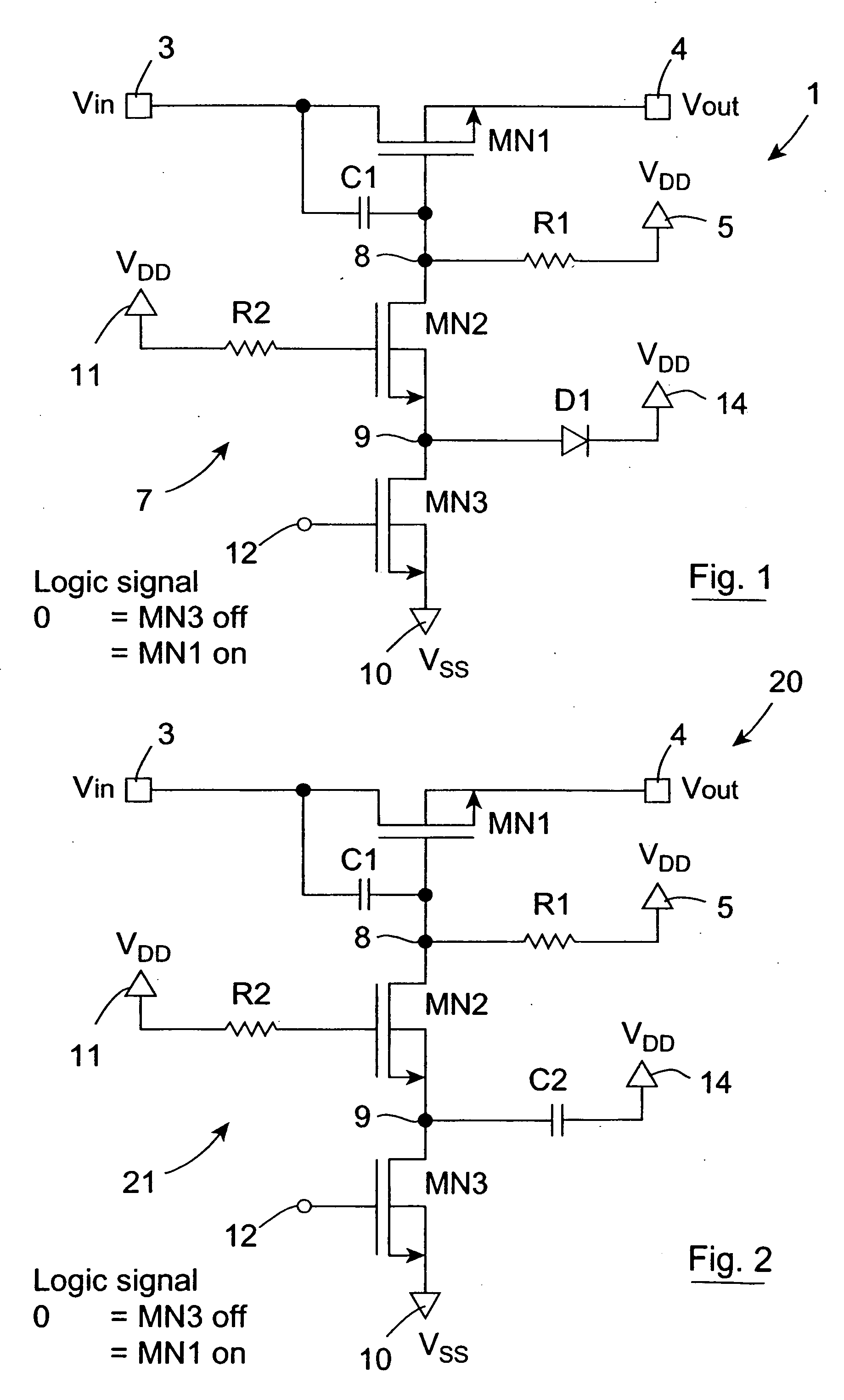
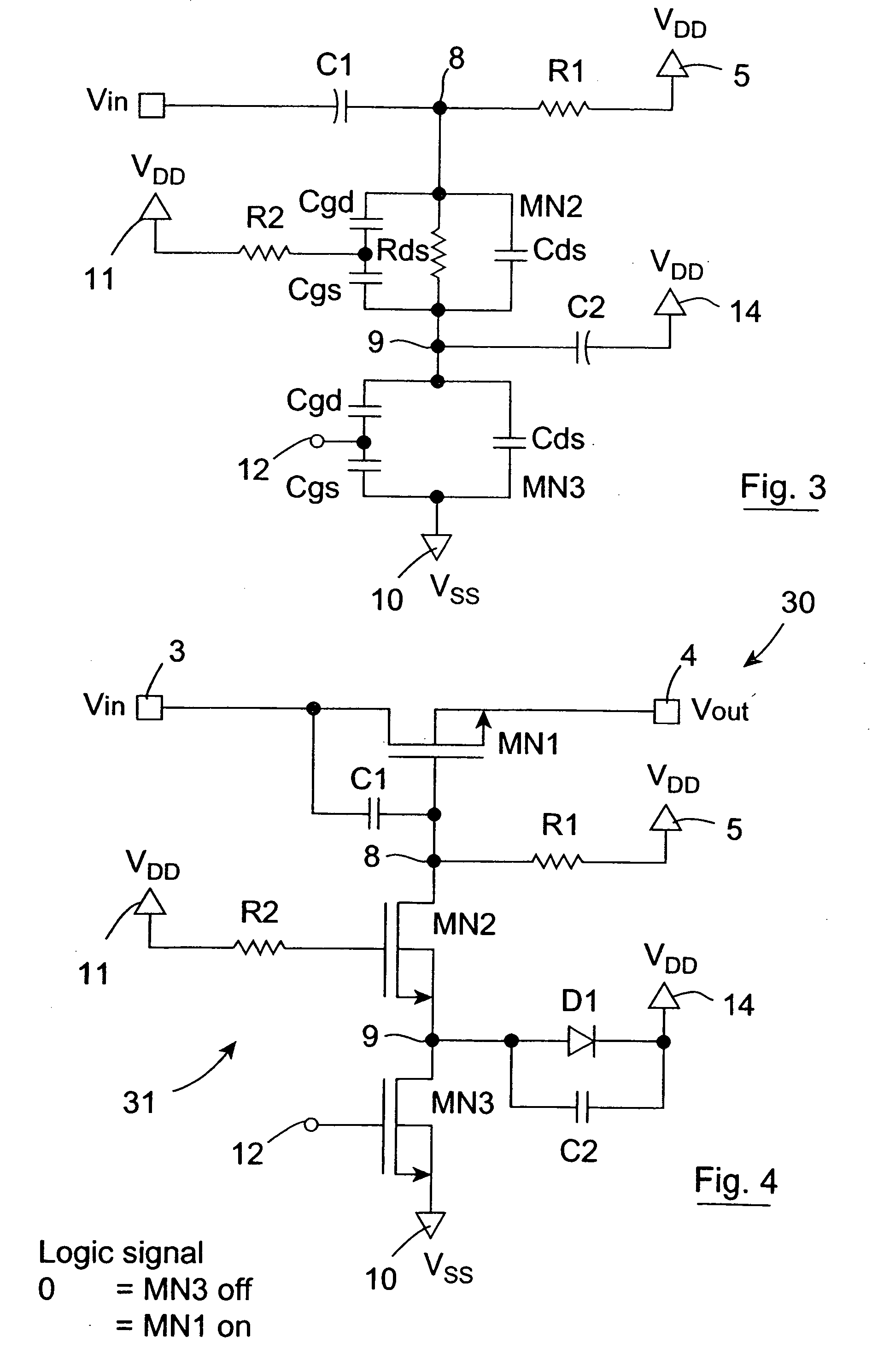
An open drain driver (7) selectively switches a MOSFET switch (MN1) which is passively held in the conducting state into the non-conducting state. The MOSFET switch (MN1) switches an AC analogue input signal on a main input terminal (3) to a main output terminal (4) and the gate of the MOSFET switch (MN1) is AC coupled by a capacitor (C1) to the drain thereof. The open drain driver (7) comprises a first MOSFET (MN2) and a second MOSFET (MN3) through which the gate of the MOSFET switch (MN1) is pulled to ground (Vss). The gate of the first MOSFET (MN2) is coupled to the supply voltage (VDD) for maintaining the first MOSFET (MN2) in the open state. A control signal is applied to the gate of the second MOSFET (MN3) for selectively operating the open drain driver (7) in the conducting state for operating the MOSFET switch (MN1) in the non-conducting state. When the second MOSFET (MN3) is in the non-conducting state, the first MOSFET (MN2) remains in the conducting state until the voltage on a coupling node (9) between the first and second MOSFETs (MN2,MN3) equals the difference between its gate voltage and its threshold voltage, at which stage, any over-voltages applied to the gate of the MOSFET switch (MN1) are divided between the first and second MOSFETs (MN2,MN3). A coupling diode (D1) coupling the coupling node (9) to the supply voltage (VDD) clamps the voltage on the coupling node (9) at the supply voltage (VDD) plus the conducting voltage of the diode (D1), in the event of the voltage on the coupling node (9) rising after the first MOSFET (MN2) has gone into the non-conducting state. The coupling node (9) may be capacitively coupled to the supply voltage (VDD) by a coupling capacitor instead of or as well as the diode (D1) for limiting the voltage on the coupling node (9).
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
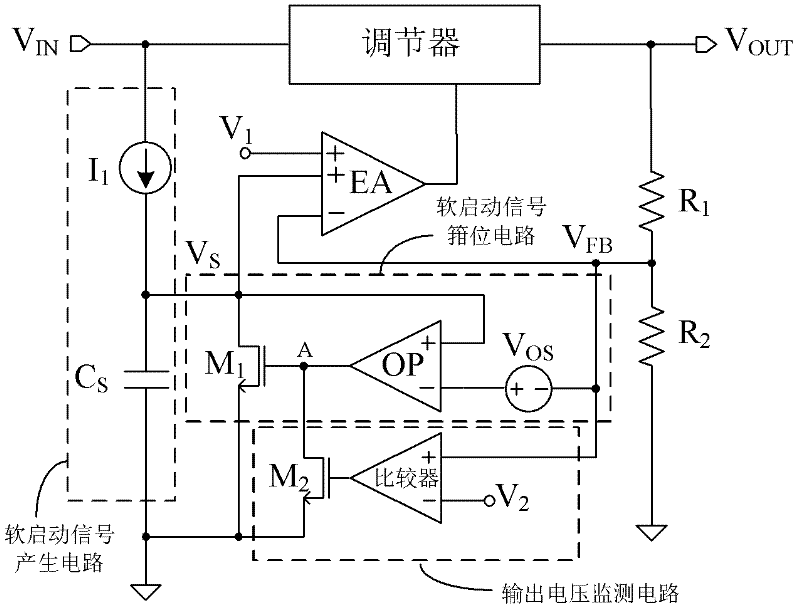
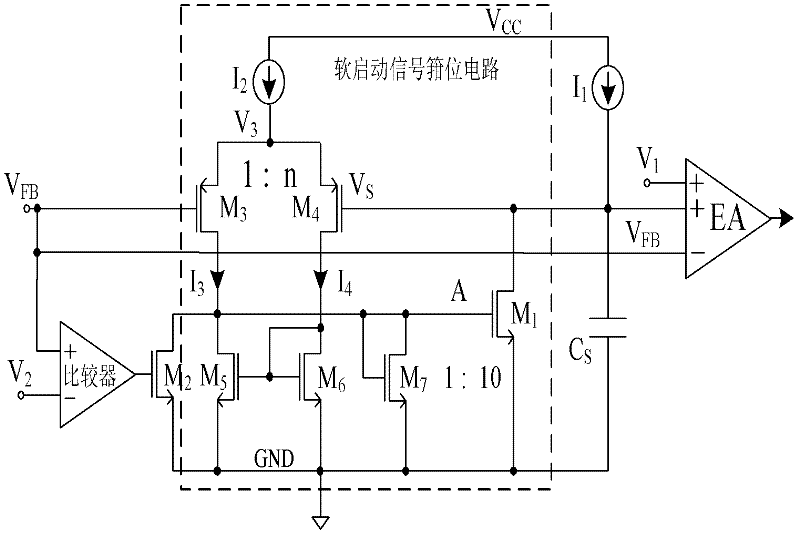
Soft start circuit based on feedback voltage clamping soft start signal
The invention discloses a soft start circuit based on a feedback voltage clamping soft start signal, and mainly aims to overcome the drawback that soft start protection cannot be provided in the process that output voltage recovers from an abnormal condition in the prior art. The circuit comprises a constant current source I1 and a capacitor Cs, wherein the constant current source I1 charges the capacitor Cs to generate a soft start signal VS which climbs upward with a slope for replacing a reference voltage upon start so as to allow an output voltage to rise smoothly; the output end of the constant current source I1 and the output end of the capacitor Cs are connected with a soft start signal clamping circuit which performs clamping on the soft start signal Vs under the abnormal condition; and the control end A of the clamping circuit is connected with an output voltage monitoring circuit which is used for monitoring the output voltage and controlling the operation condition of the clamping circuit. When the method is used, the condition of the output voltage can be monitored under different conditions such as a condition that the output voltage climbs to a normal value or recovers from the abnormal condition, and the active soft start protection is provided for a voltage regulator circuit and can be used in different voltage regulator circuits.
Owner:深圳德信微电子有限公司
Bi-directional DC-DC converter and method for controlling the same
InactiveUS7848118B2Efficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionClamp capacitorDc dc converter
A bi-directional DC-DC converter has a transformer for connecting a voltage type full bridge circuit connected to a first power source and a current type switching circuit connected to a second power source. A voltage clamping circuit constructed by switching elements and a clamping capacitor is connected to the current type switching circuit. The converter has a control circuit for cooperatively making switching elements operative so as to control a current flowing in a resonance reactor.
Owner:HITACHI INFORMATION & TELECOMM ENG LTD
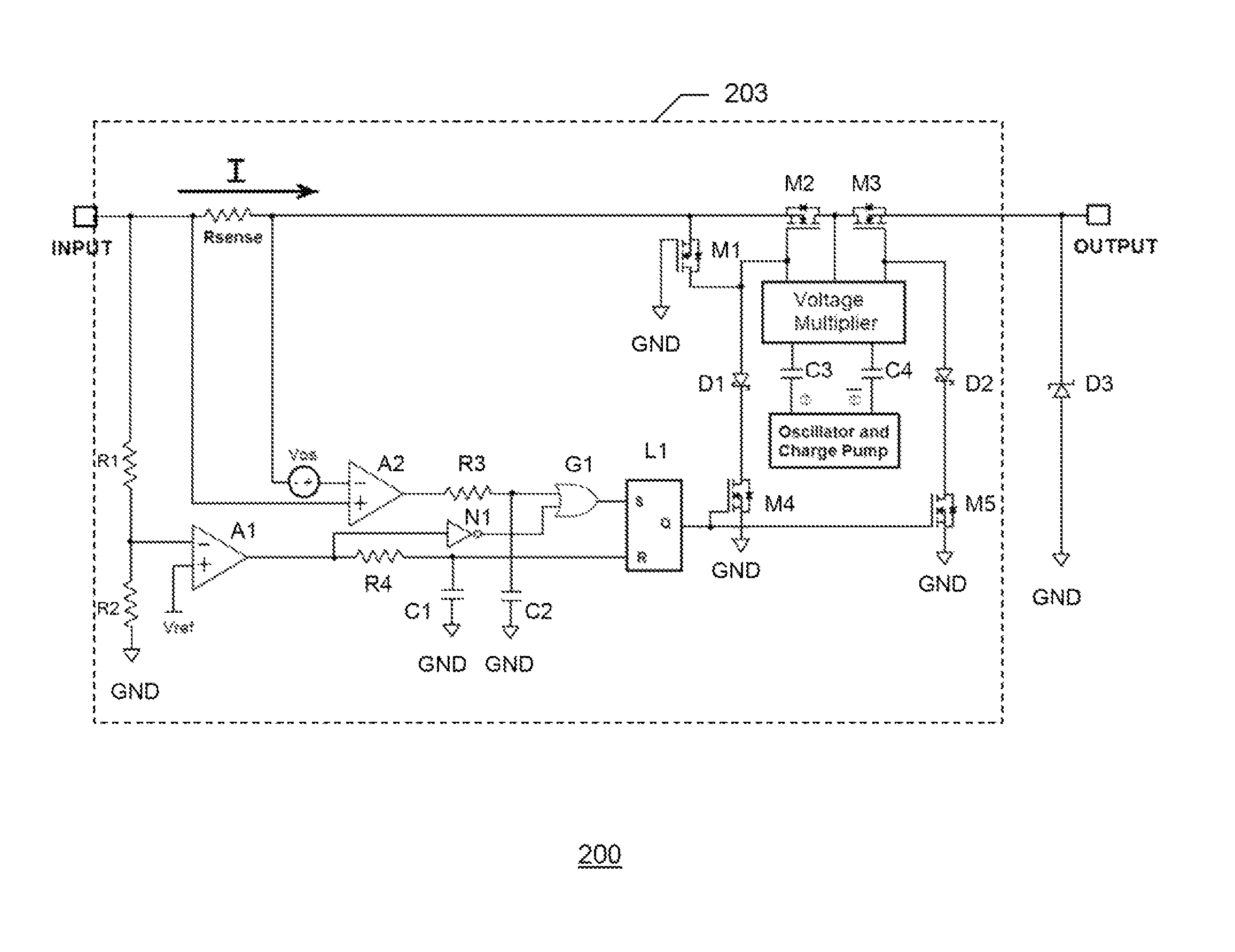
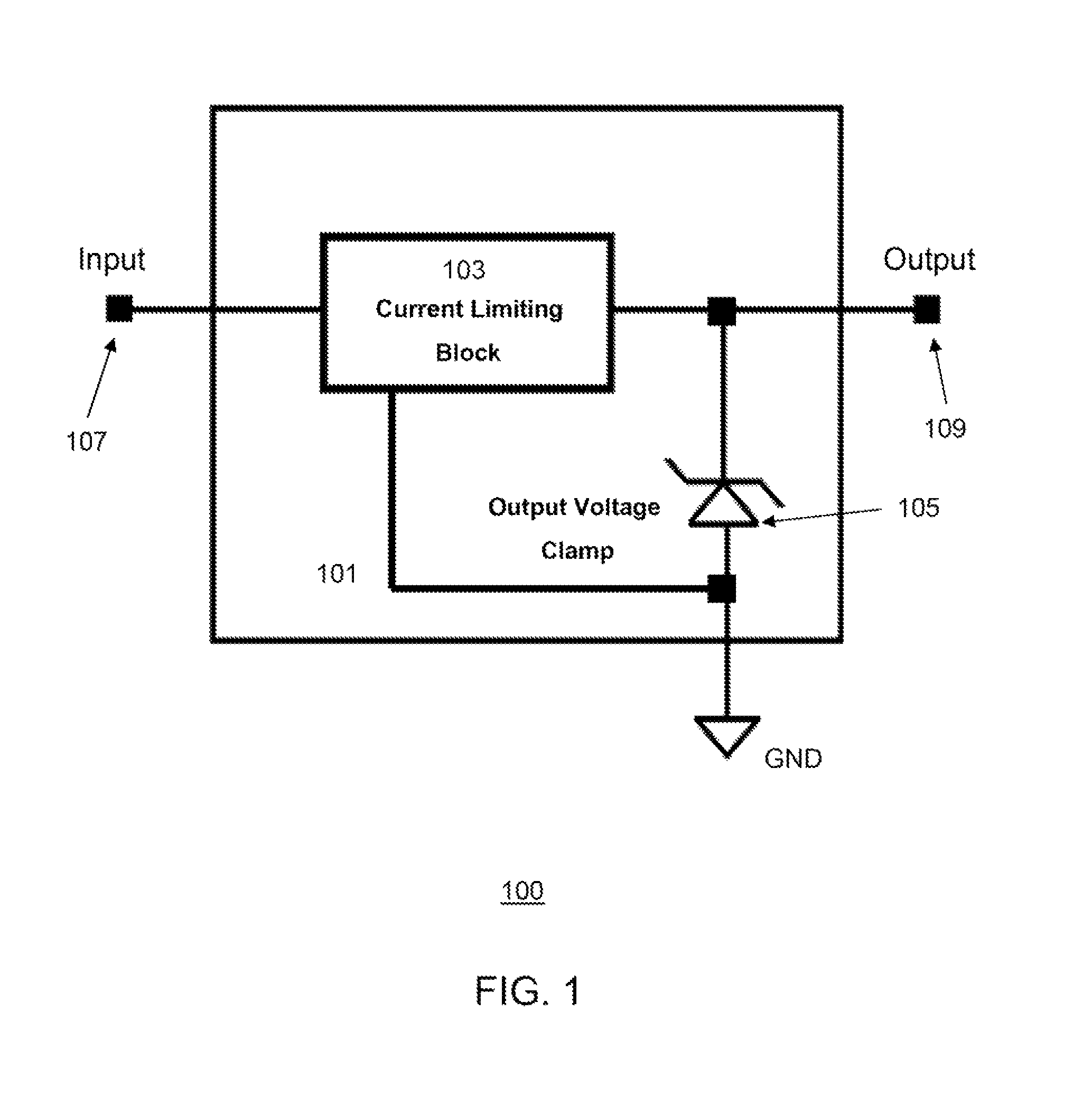
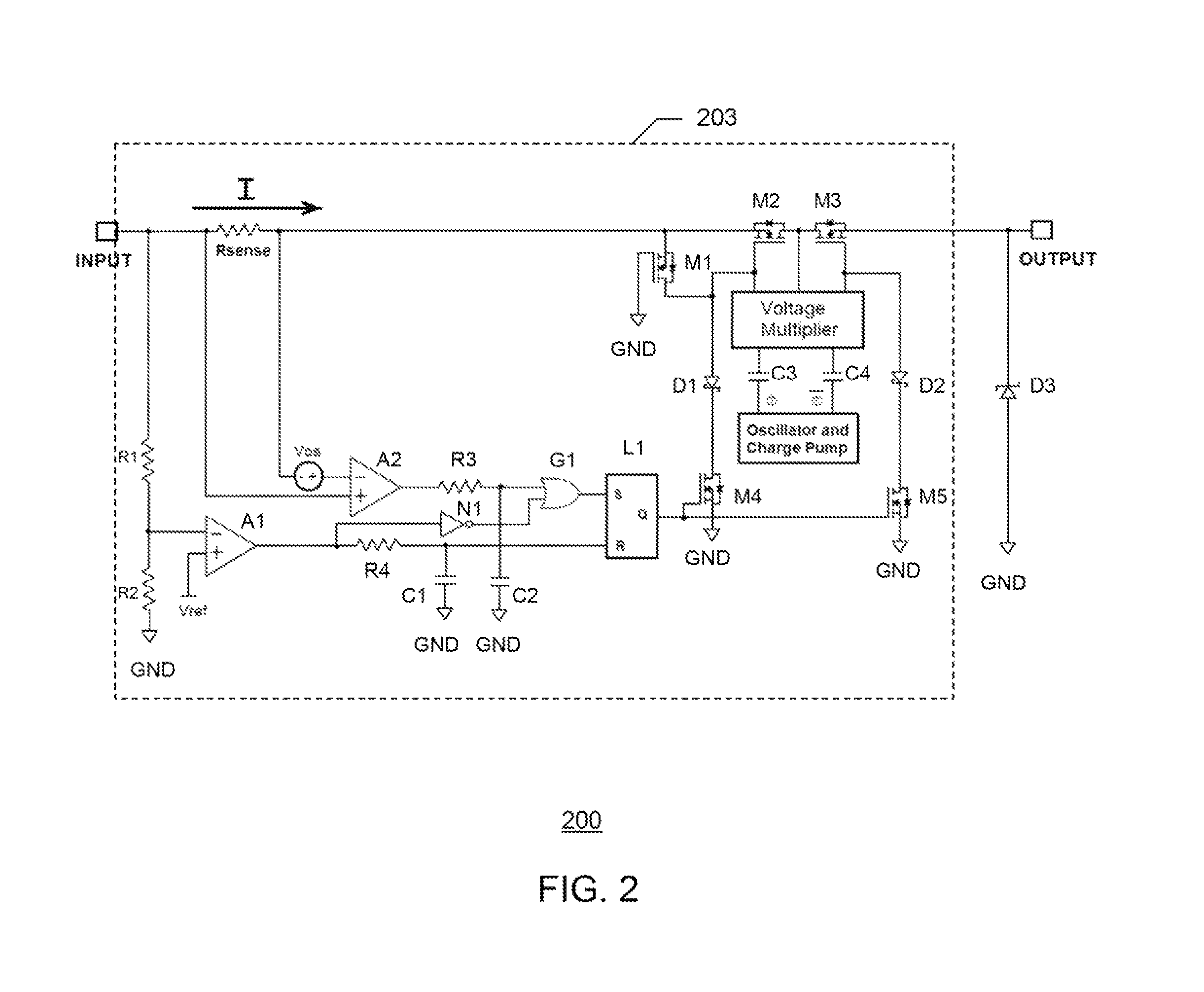
System and method for fast-acting power protection
InactiveUS8537517B1Arrangements responsive to excess currentEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentMOSFETSemiconductor materials
A fast-acting power protection system and a related method of power protection are disclosed. In one embodiment of the invention, the fast-acting power protection system includes a current limiting block capable of reducing or shutting down an unwanted current or voltage surge at an input terminal of the fast-acting power protection system. The fast-acting power protection system also integrates an output voltage clamp and the current limiting block in one piece of monolithic semiconductor material, wherein the output voltage clamp protects an electrical device connected to an output terminal of the fast-acting power protection system from an unwanted voltage surge by rapidly clamping an output voltage to a clamp voltage. Furthermore, the fast-acting power protection system also protects from a reverse polarity input voltage and dielectrically isolates a MOSFET for reverse polarity protection from other current-limiting MOSFET's inside the current limiting block.
Owner:MFG NETWORKS INC MNI
High voltage clamps with transient activation and activation release control
ActiveUS20180026440A1Protection from damageTransistorEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentTime delaysSemiconductor chip
High voltage clamps with active activation and activation-release control are provided herein. In certain configurations, a clamp can have scalable operating clamping voltage level and can be used to protect the electrical circuit connected to a power supply of a semiconductor chip from damage from an overstress event, such as electrostatic discharge (ESD) events. The pins of the power supply are actively monitored to detect when an overstress event is present, and the clamp is turned-on in response to detecting the overstress event. A timer is used to shut down the clamp after a time delay from detecting the overstress event, thereby providing a false detection shutdown mechanism that prevents the protection clamp from getting falsely activated and remain in the on-state during normal circuit operation.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Process-variation tolerant diode, standard cells including the same, tags and sensors containing the same, and methods for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20070128760A1Improve forward stabilityReadily apparentMaterial nanotechnologySolid-state devicesVoltage generatorComplementary pair
Process variation-tolerant diodes and diode-connected thin film transistors (TFTs), printed or patterned structures (e.g., circuitry) containing such diodes and TFTs, methods of making the same, and applications of the same for identification tags and sensors are disclosed. A patterned structure comprising a complementary pair of diodes or diode-connected TFTs in series can stabilize the threshold voltage (Vt) of a diode manufactured using printing or laser writing techniques. The present invention advantageously utilizes the separation between the Vt of an NMOS TFT (Vtn) and the Vt of a PMOS TFT (Vtp) to establish and / or improve stability of a forward voltage drop across a printed or laser-written diode. Further applications of the present invention relate to reference voltage generators, voltage clamp circuits, methods of controlling voltages on related or differential signal transmission lines, and RFID and EAS tags and sensors.
Owner:ENSURGE MICROPOWER ASA
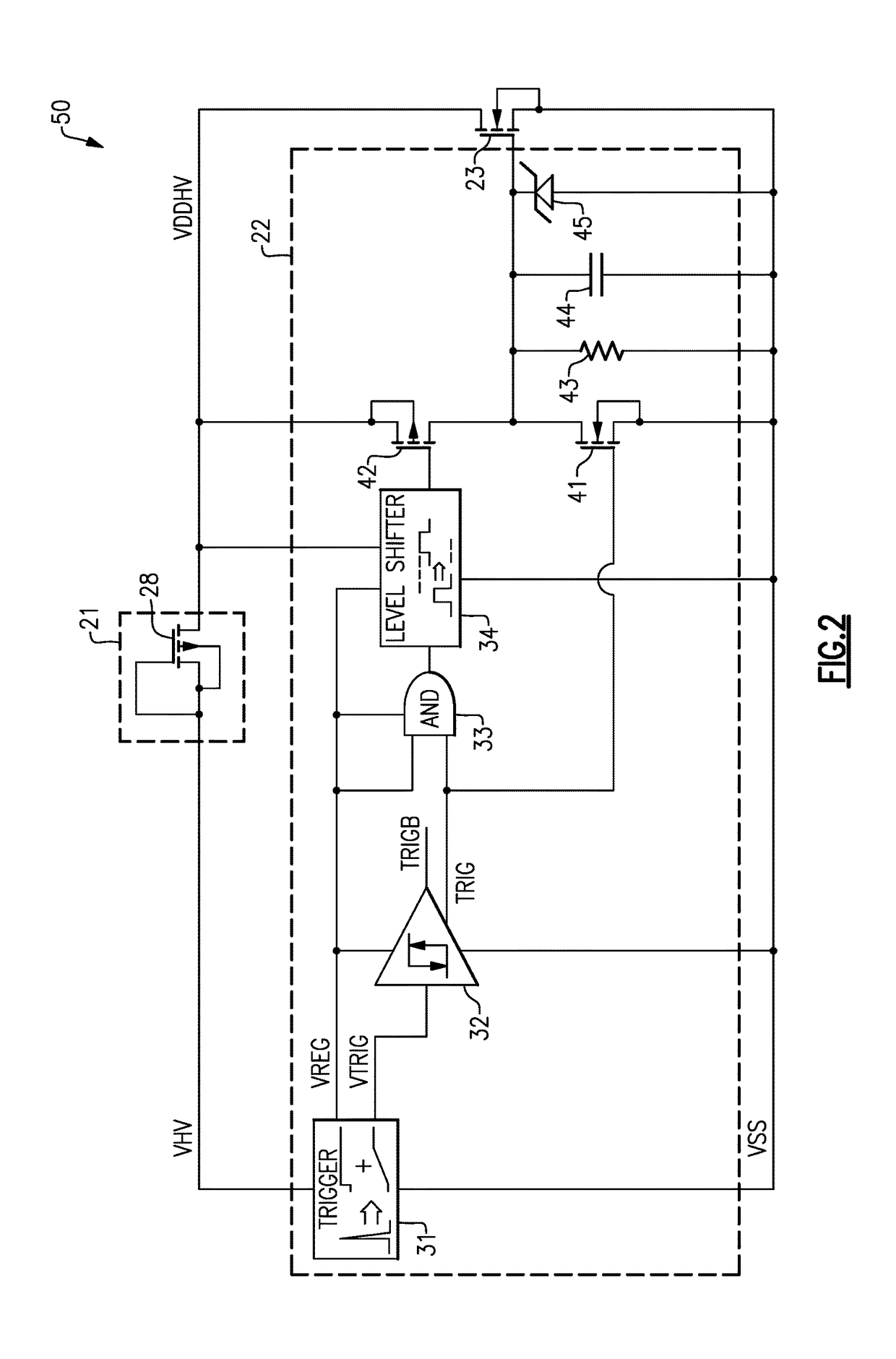
Current detection circuit including electrostatic capacitor and rectifying element for increasing gate voltage of protecting mosfet
Using a electrostatic capacitor and a diode, a gate voltage of a protecting MOSFET is increased when a drain voltage of a power transistor increases. A voltage clamp circuit clamps the maximum voltage of the gate voltage of the protecting MOSFET to a predetermined clamp voltage. A voltage control circuit controls a drain voltage of a sense transistor so as to substantially coincide with a source voltage of the protecting MOSFET.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com