Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
324 results about "Instruction scheduling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In computer science, instruction scheduling is a compiler optimization used to improve instruction-level parallelism, which improves performance on machines with instruction pipelines. The pipeline stalls can be caused by structural hazards (processor resource limit), data hazards (output of one instruction needed by another instruction) and control hazards (branching).
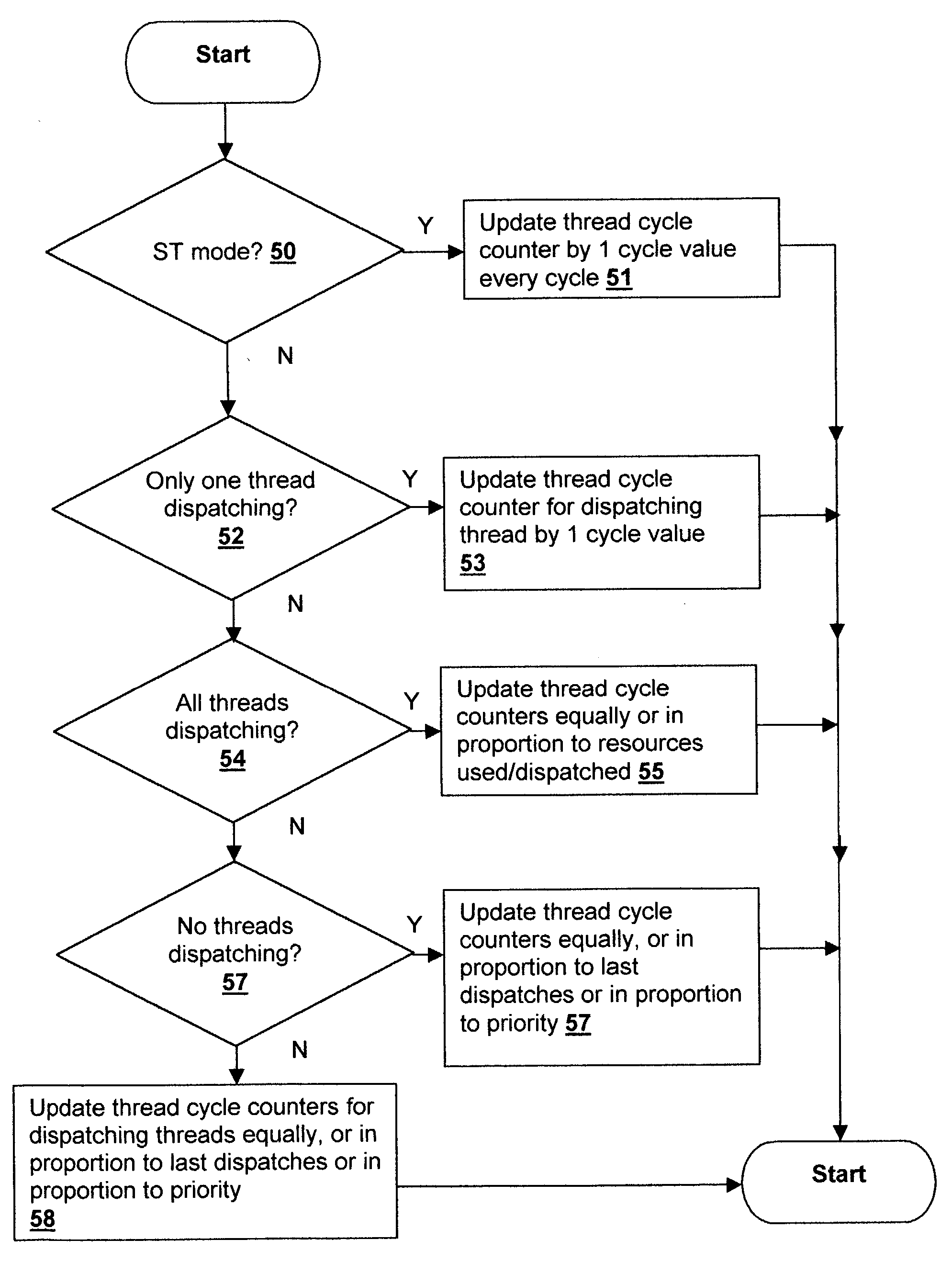
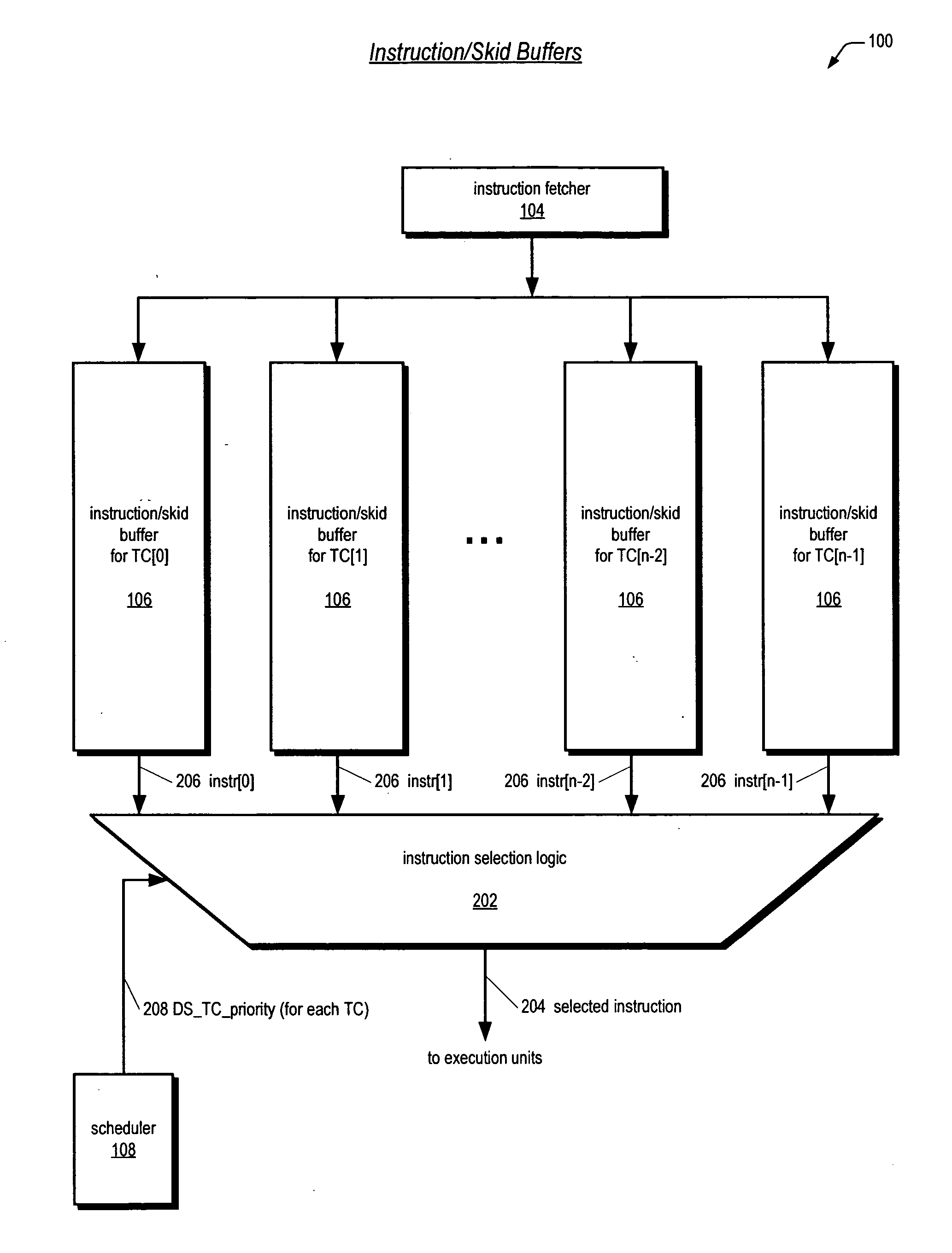
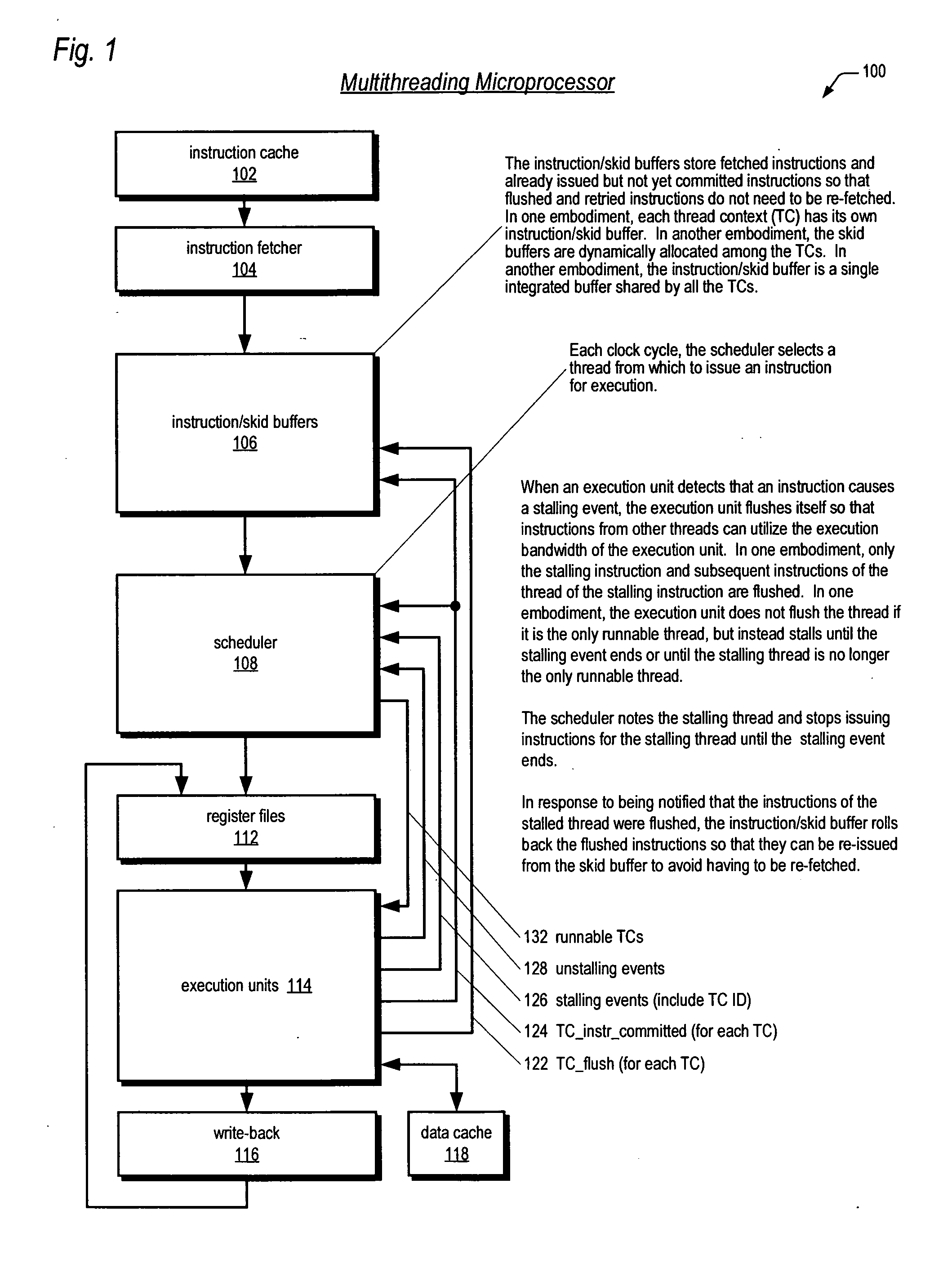
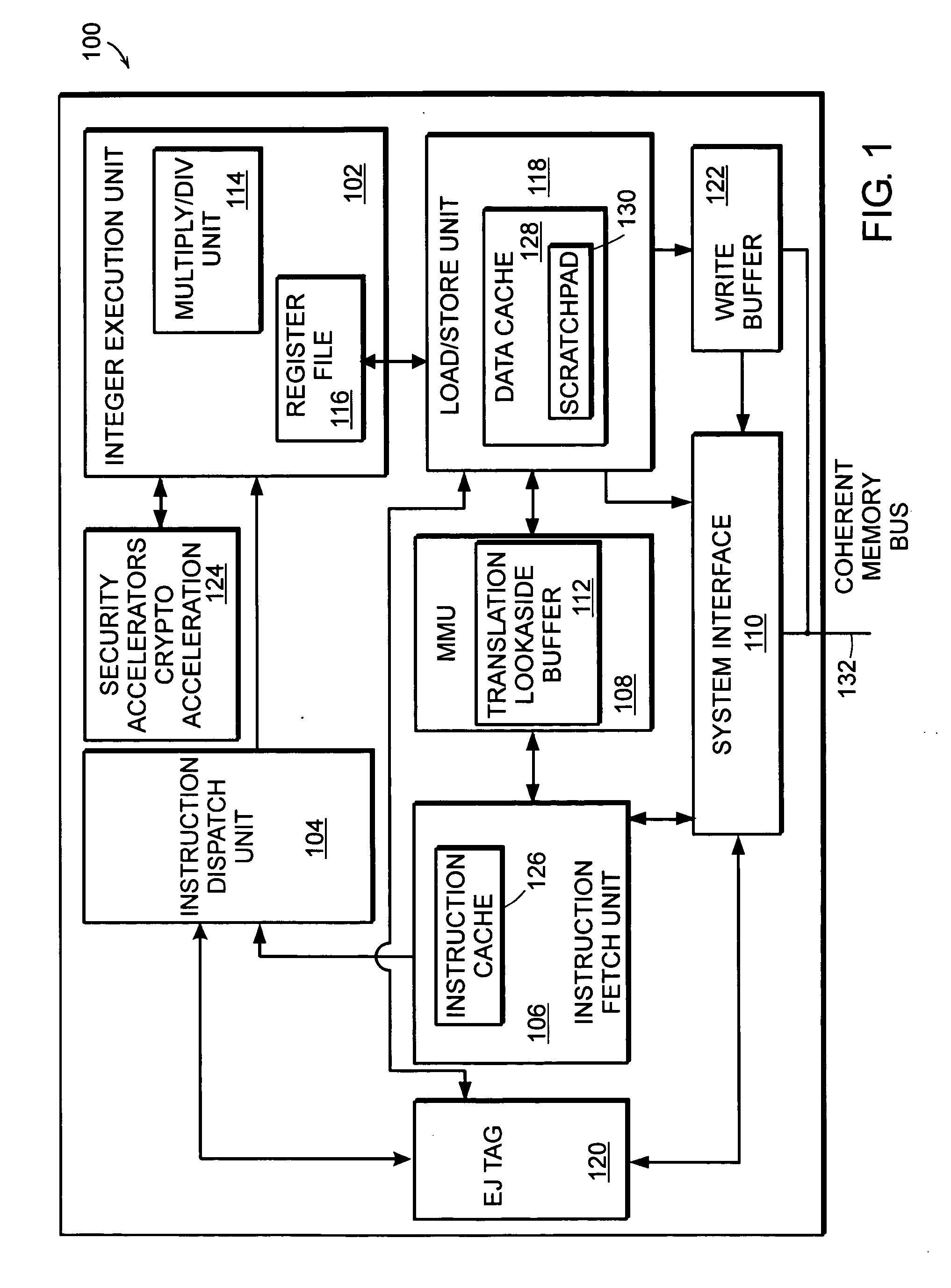
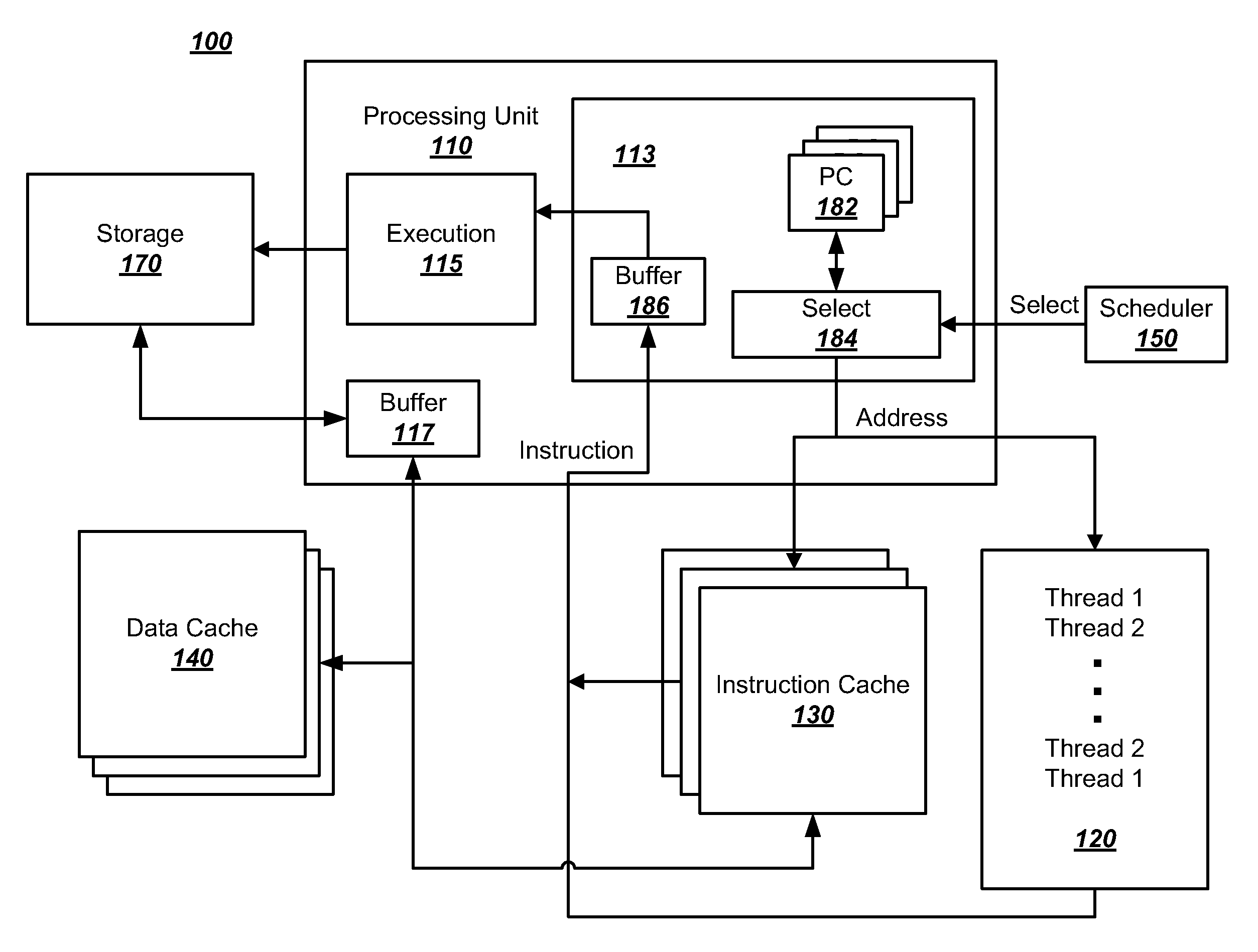
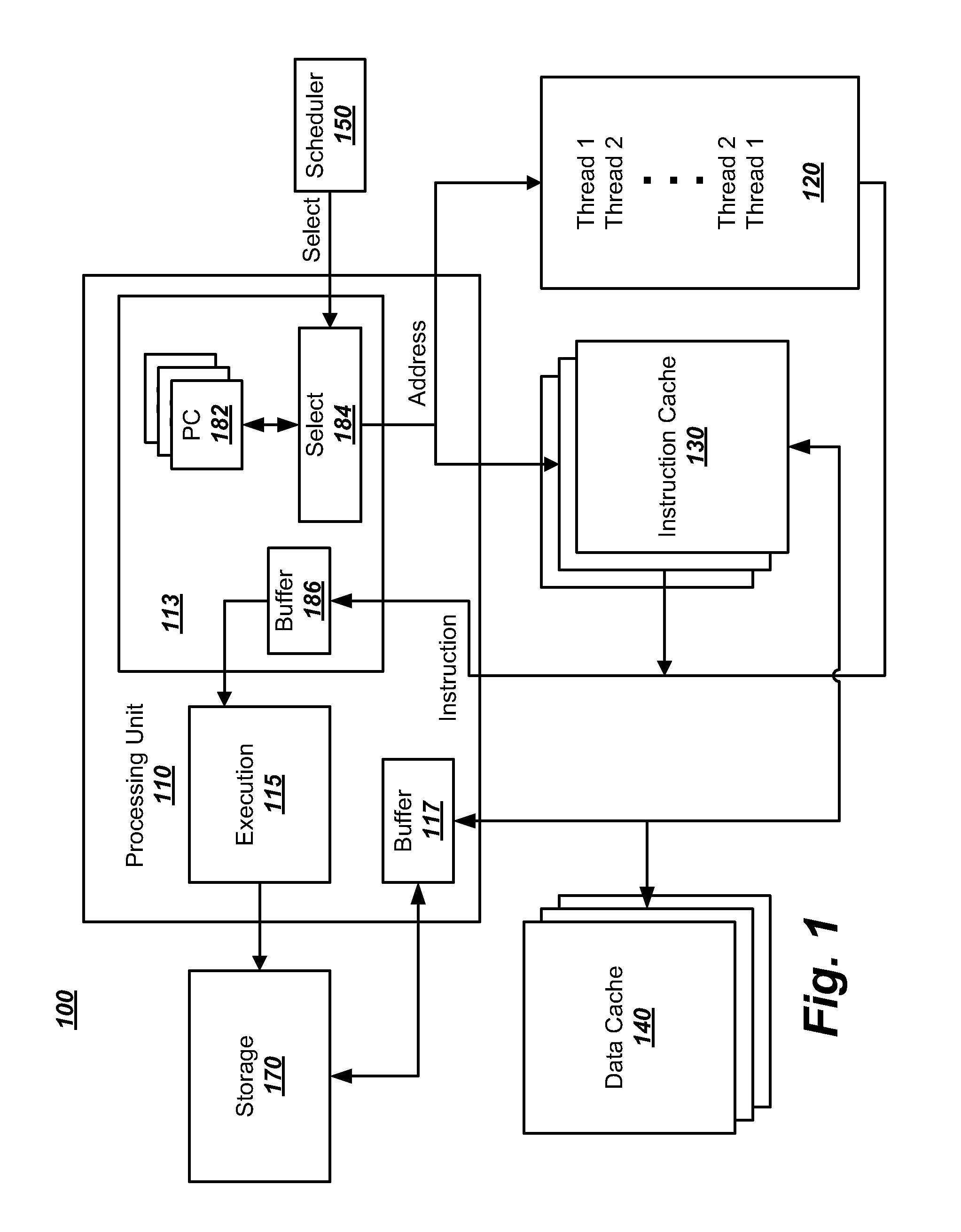
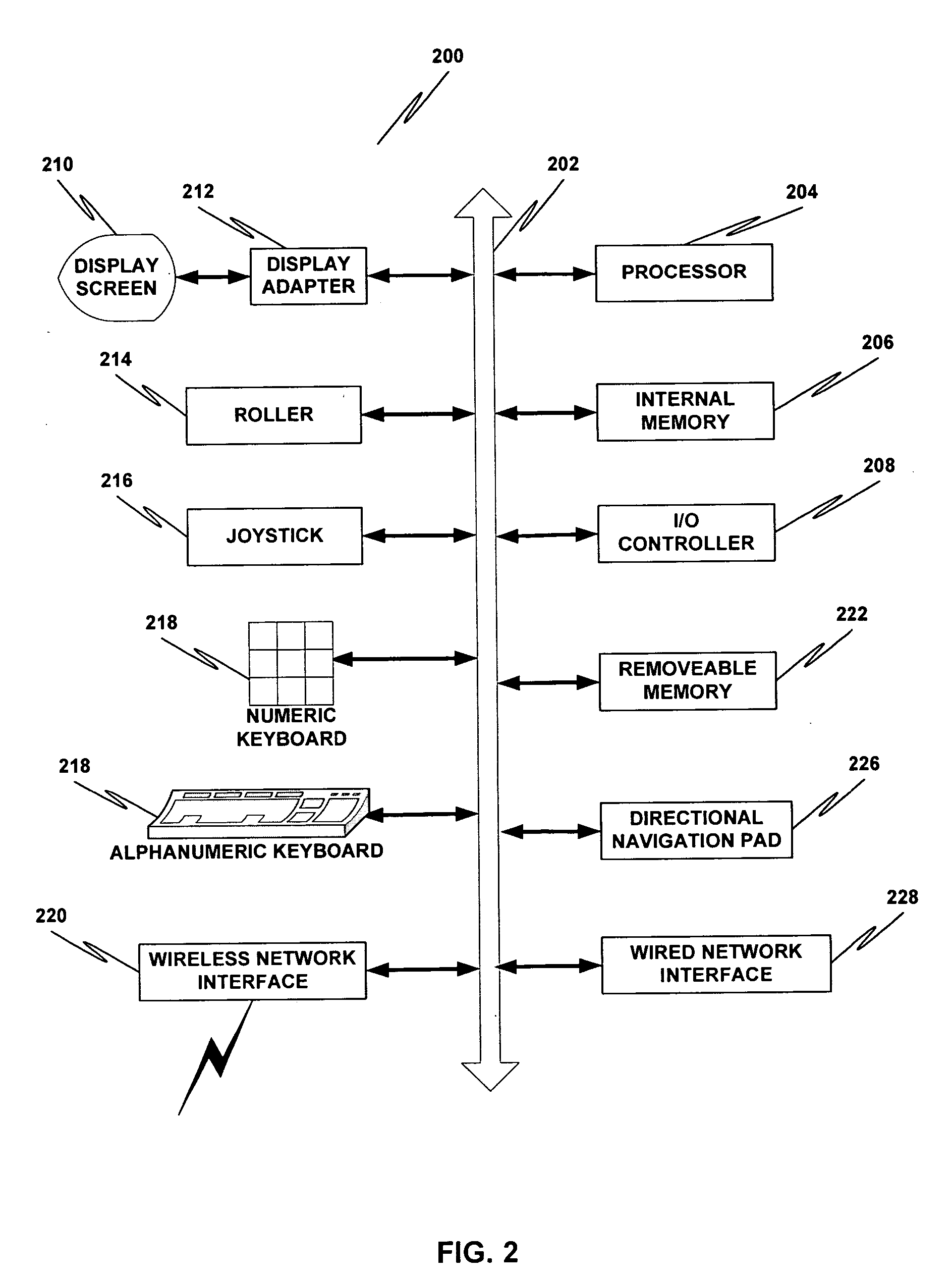
Accounting method and logic for determining per-thread processor resource utilization in a simultaneous multi-threaded (SMT) processor
InactiveUS20040216113A1Resource allocationProgram control using stored programsResource utilizationScheduling instructions
An accounting method and logic for determining per-thread processor resource utilization in a simultaneous multi-threaded (SMT) processor provides a mechanism for accounting for processor resource usage by programs and threads within programs. Relative resource use is determined by detecting instruction dispatches for multiple threads active within the processor, which may include idle threads that are still occupying processor resources. If instructions are dispatched for all threads or no threads, the processor cycle is accounted equally to all threads. Alternatively if no threads are in a dispatch state, the accounting may be made using a prior state, or in conformity with ratios of the threads' priority levels. If only one thread is dispatching, that thread is accounted the entire processor cycle. If multiple threads are dispatching, but less than all threads are dispatching (in processors supporting more than two threads), the processor cycle is billed evenly across the dispatching threads. Multiple dispatches may be detected for the threads and a fractional resource usage determined for each thread and the counters may be updated in accordance with their fractional usage.
Owner:IBM CORP
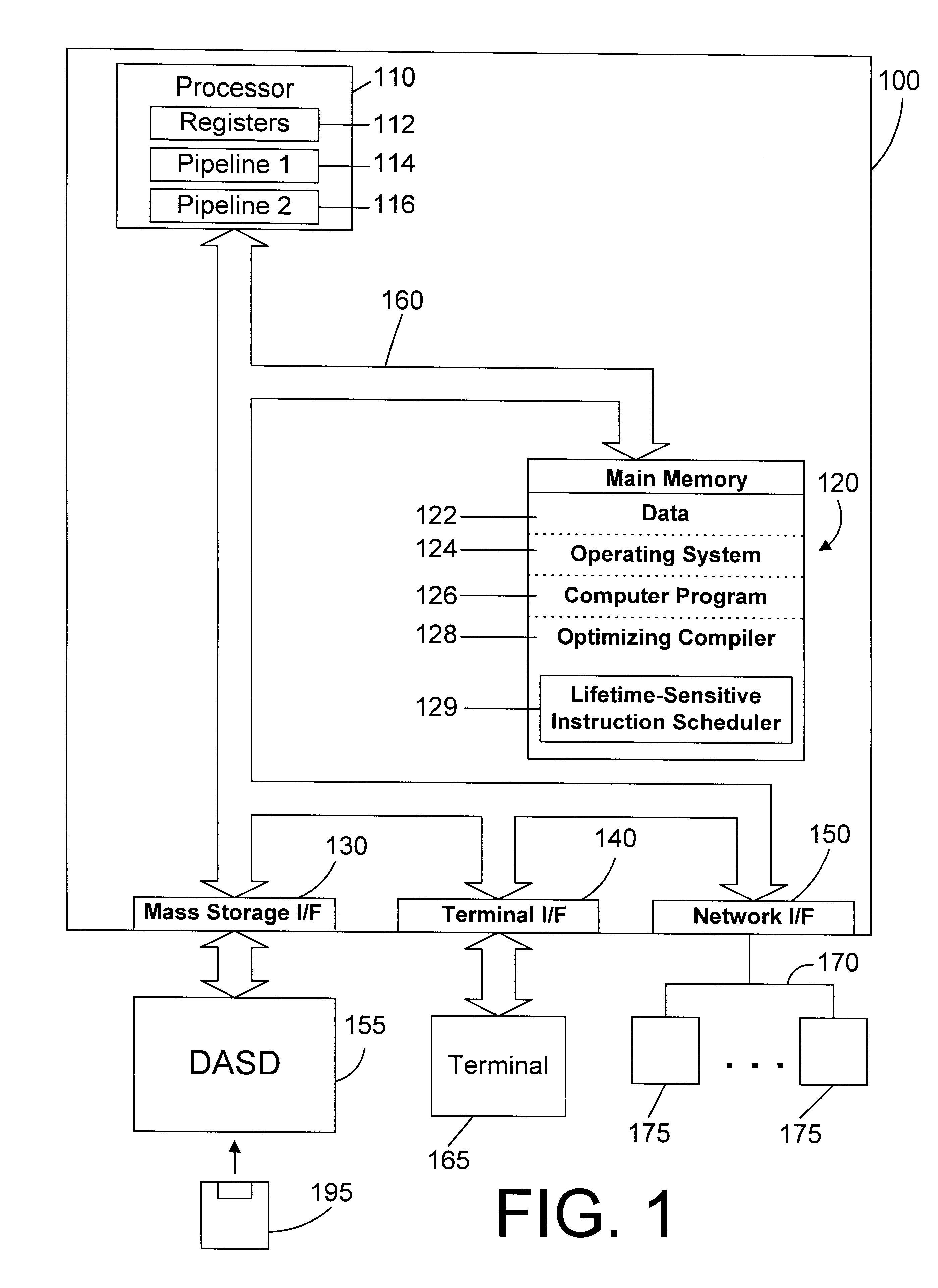
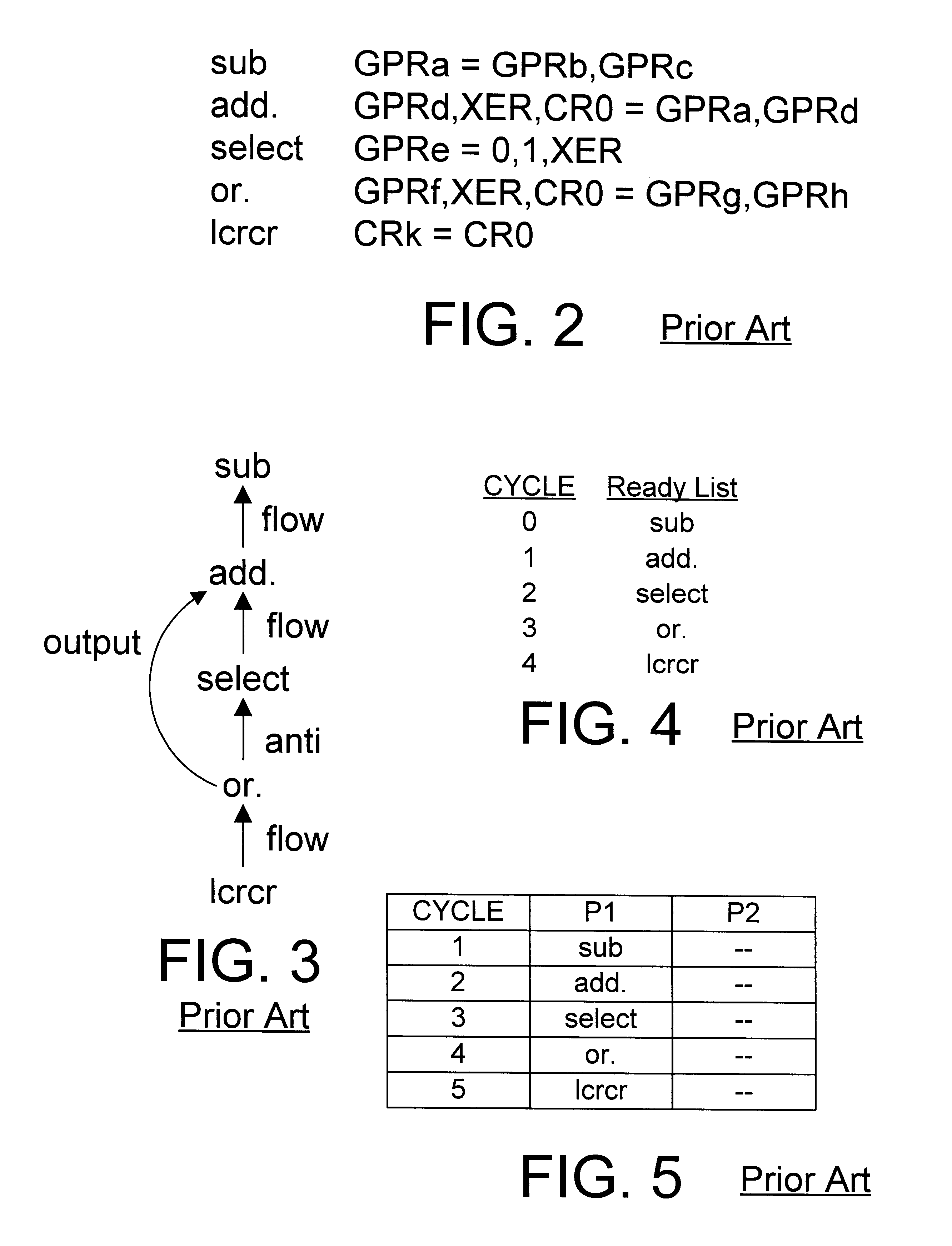
Lifetime-sensitive instruction scheduling mechanism and method
InactiveUS6305014B1Effective instructionHigh degree of parallelismSoftware engineeringSpecific program execution arrangementsScheduling instructionsDegree of parallelism
An instruction scheduler in an optimizing compiler schedules instructions in a computer program by determining the lifetimes of fixed registers in the computer program. By determining the lifetimes of fixed registers, the instruction scheduler can achieve a schedule that has a higher degree of parallelism by relaxing dependences between instructions in independent lifetimes of a fixed register so that instructions can be scheduled earlier than would otherwise be possible if those dependences were precisely honored.
Owner:IBM CORP
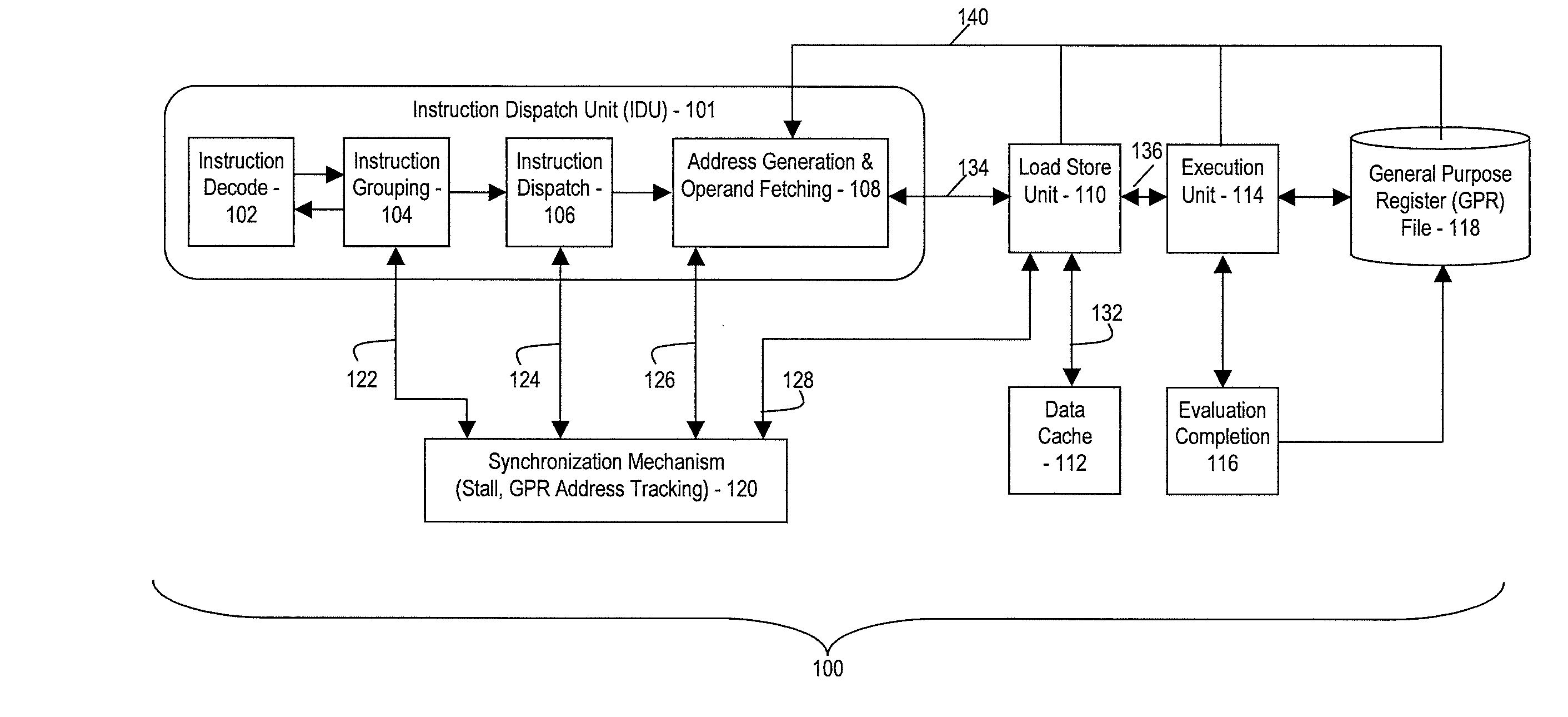
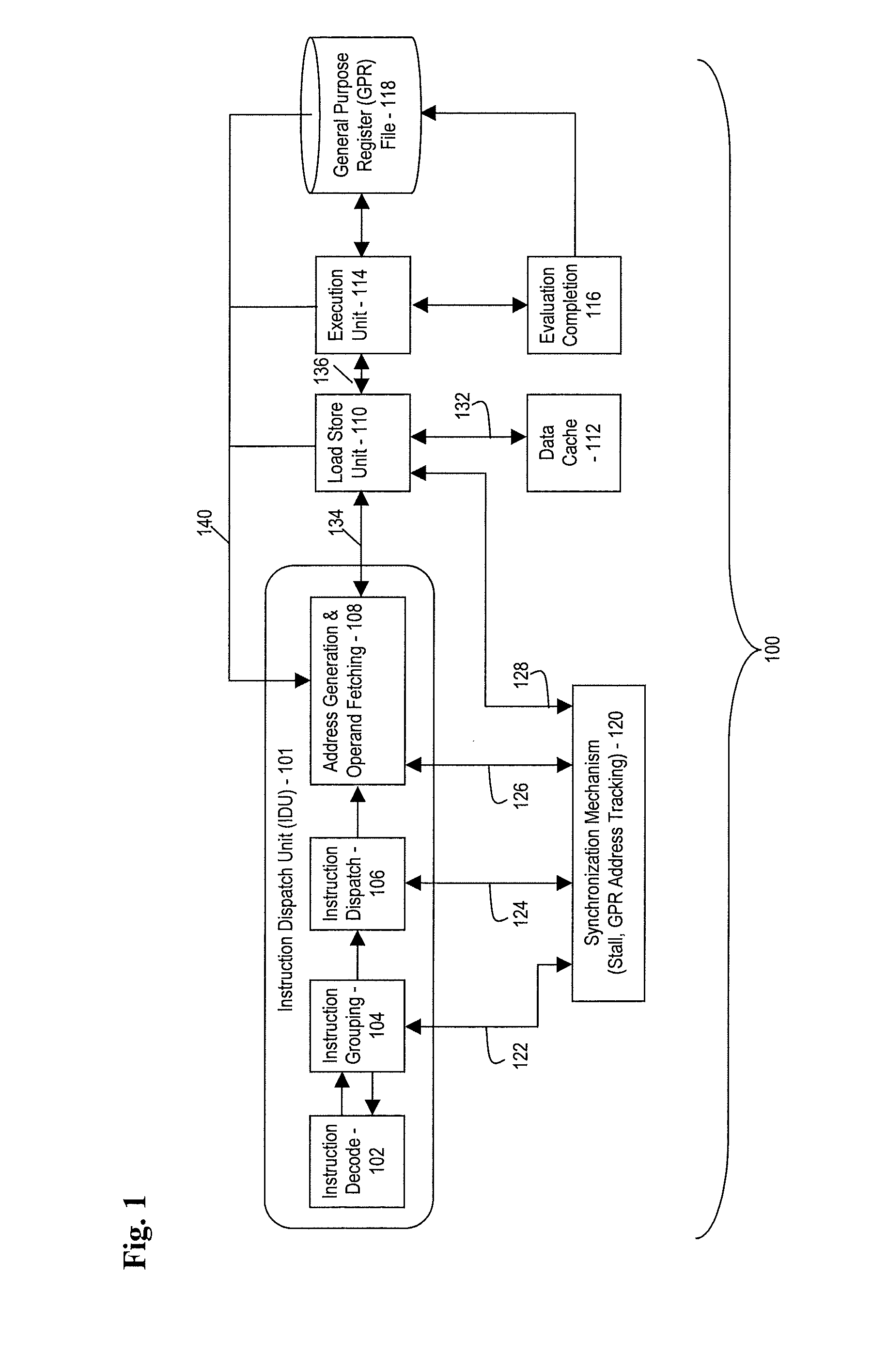
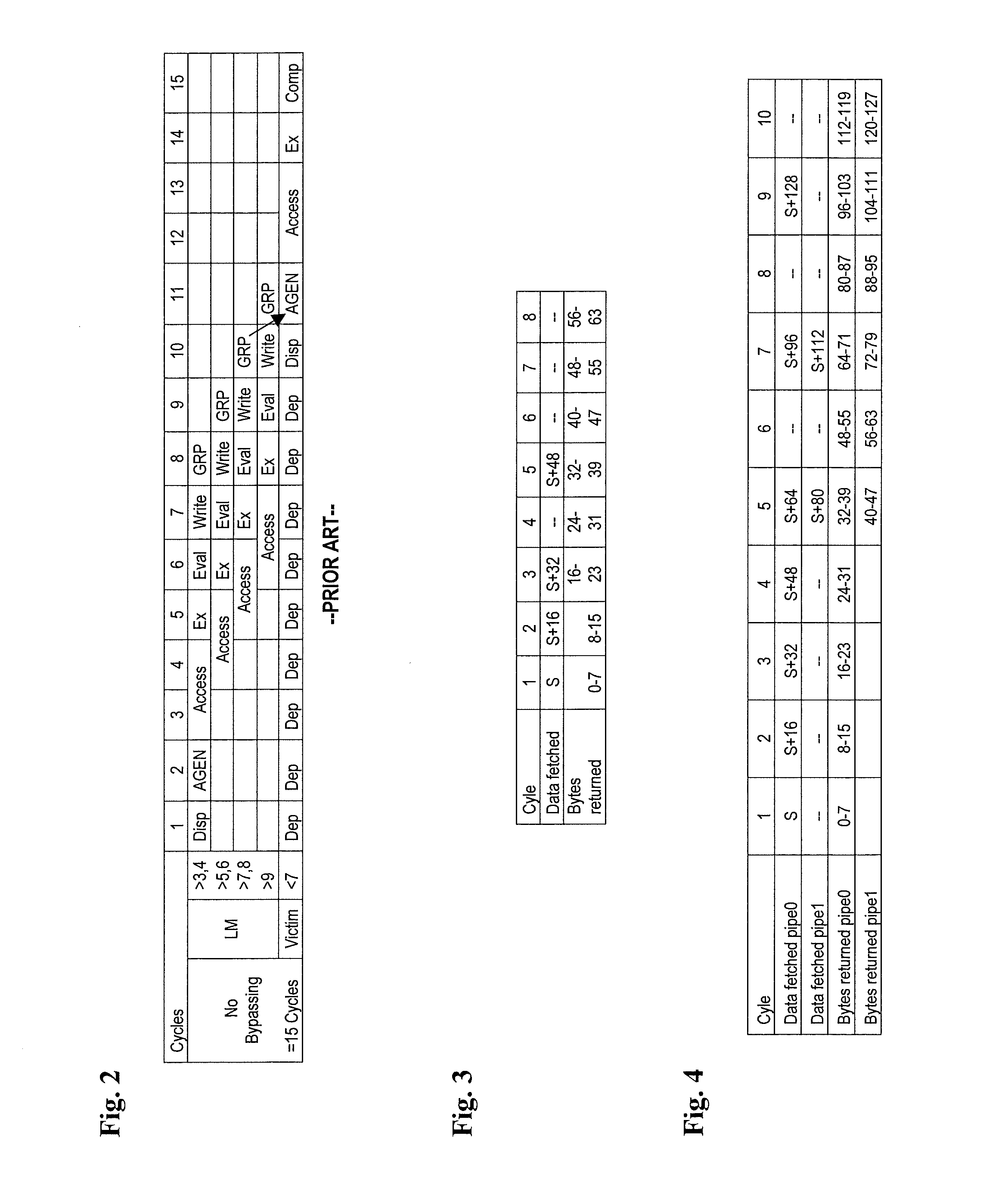
Processor and method for synchronous load multiple fetching sequence and pipeline stage result tracking to facilitate early address generation interlock bypass
A pipelined processor including an architecture for address generation interlocking, the processor including: an instruction grouping unit to detect a read-after-write dependency and to resolve instruction interdependency; an instruction dispatch unit (IDU) including address generation interlock (AGI) and operand fetching logic for dispatching an instruction to at least one of a load store unit and an execution unit; wherein the load store unit is configured with access to a data cache and to return fetched data to the execution unit; wherein the execution unit is configured to write data into a general purpose register bank; and wherein the architecture provides support for bypassing of results of a load multiple instruction for address generation while such instruction is executing in the execution unit before the general purpose register bank is written. A method and a computer system are also provided.
Owner:IBM CORP
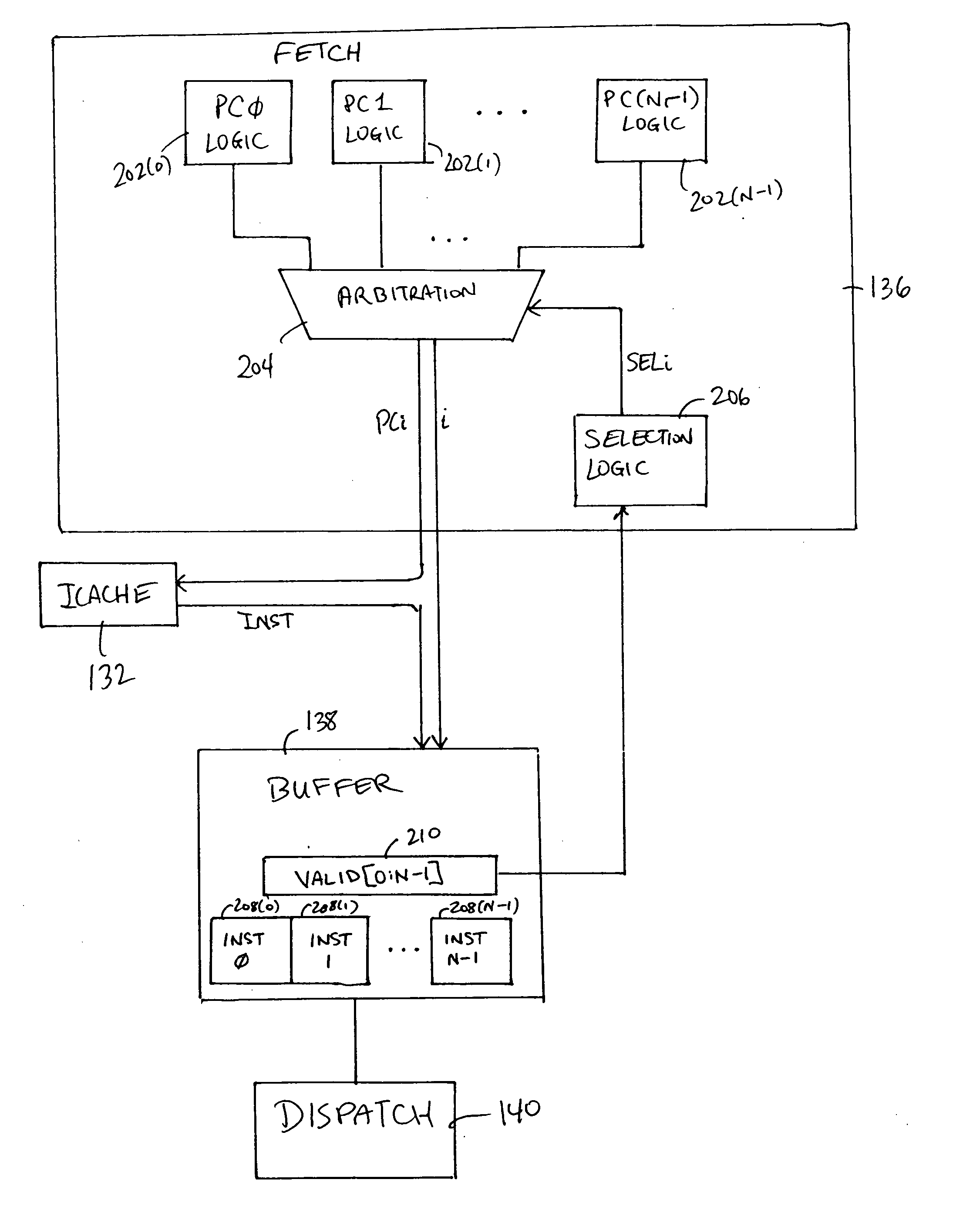
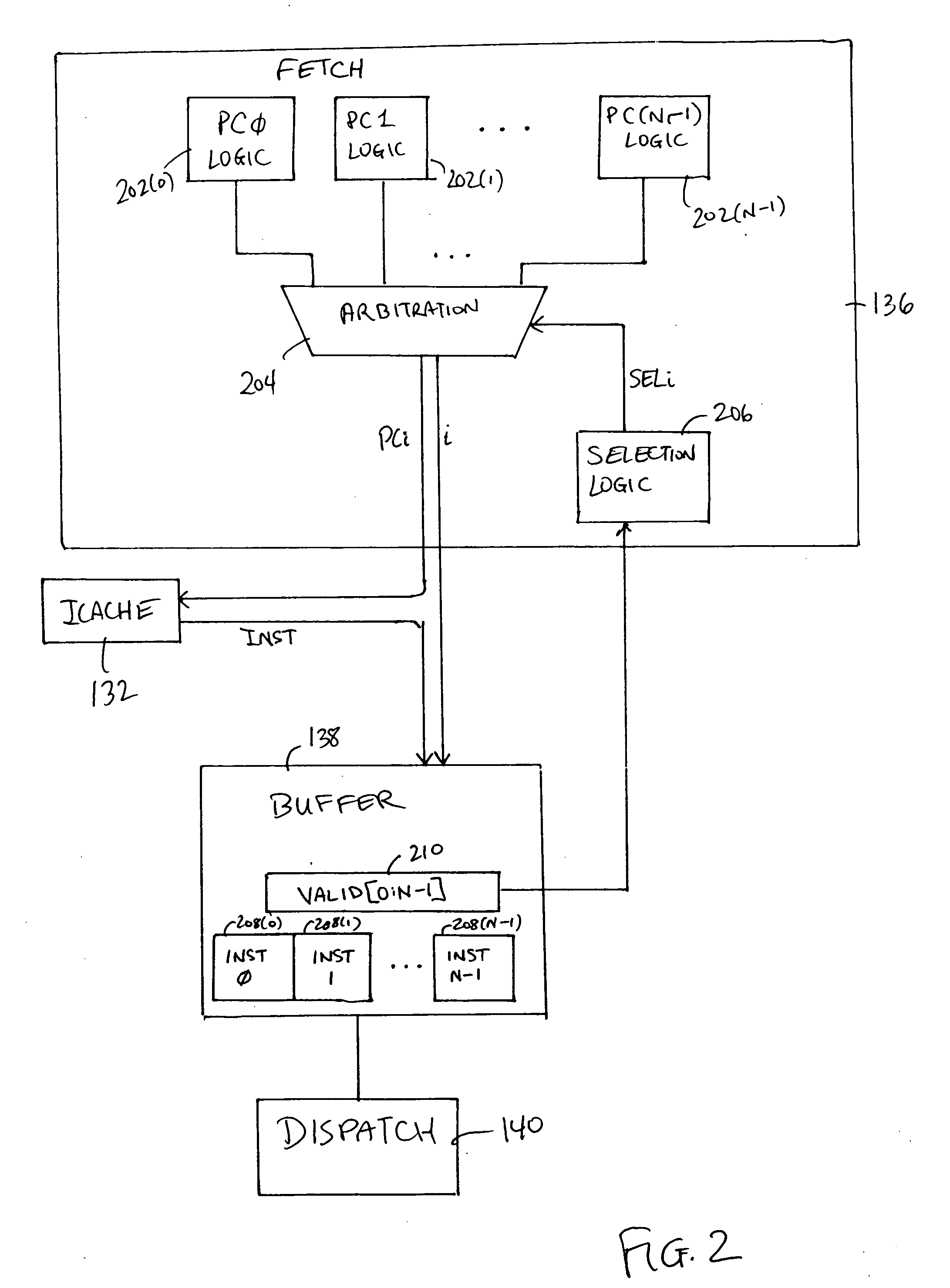
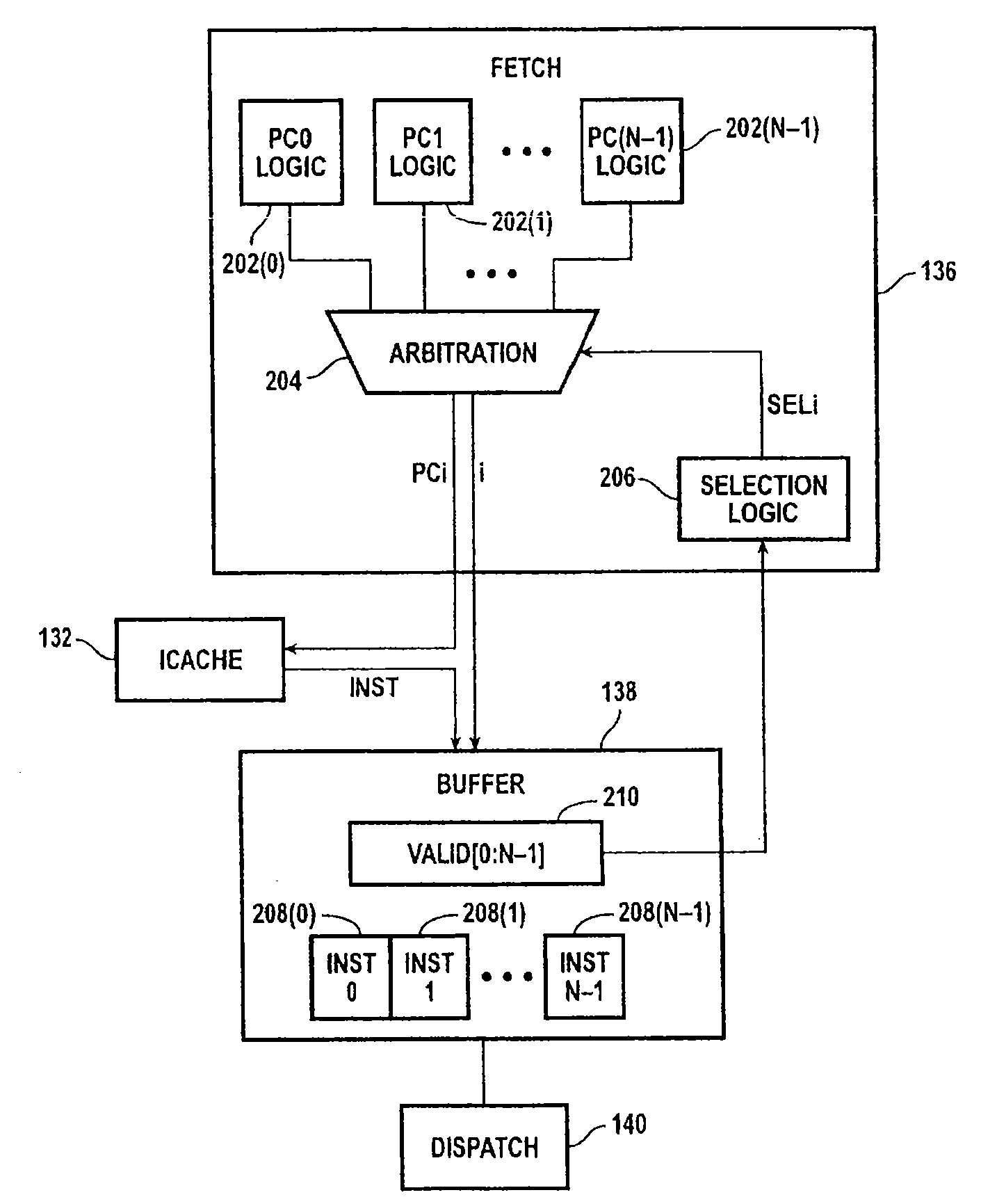
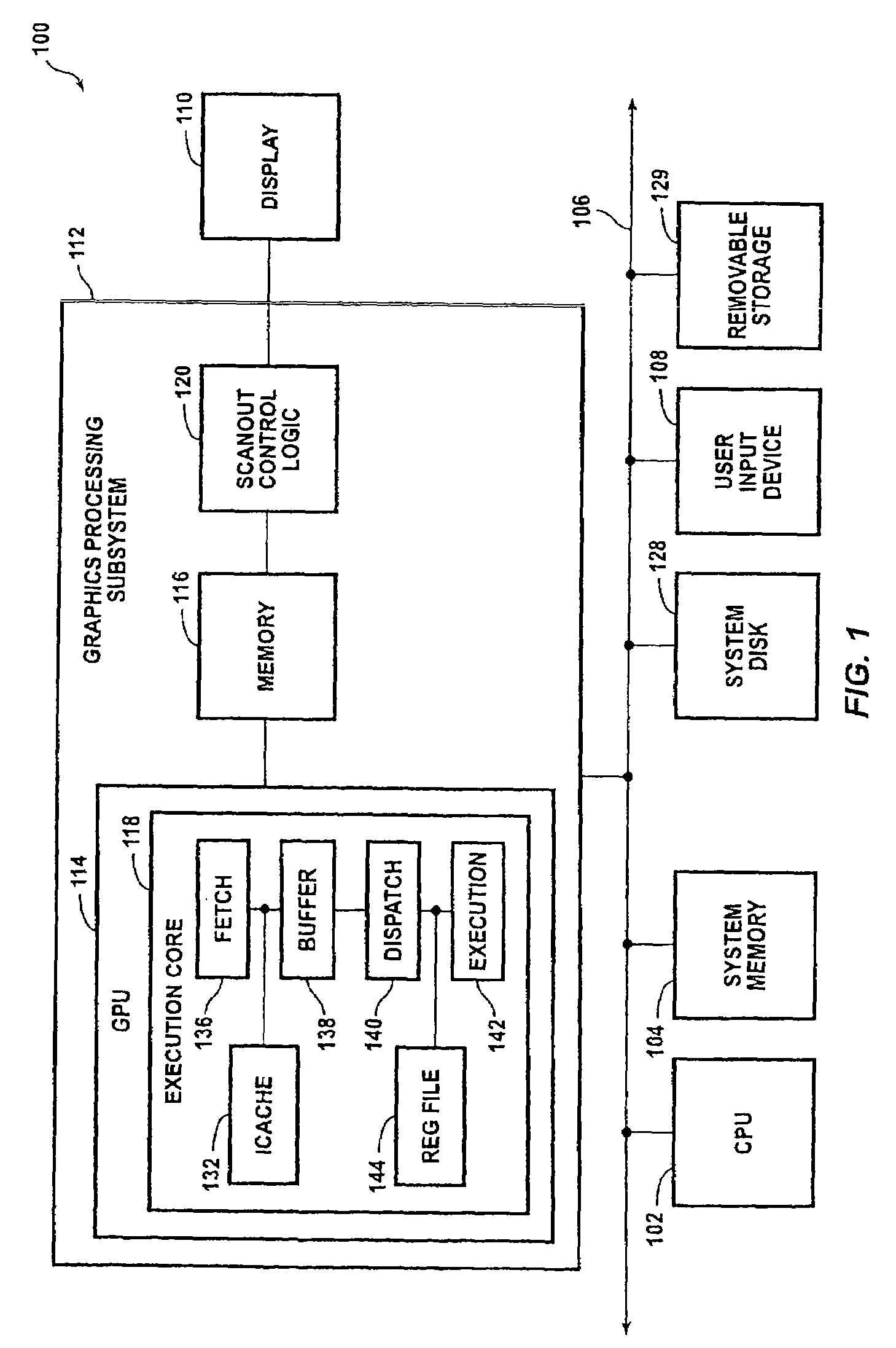
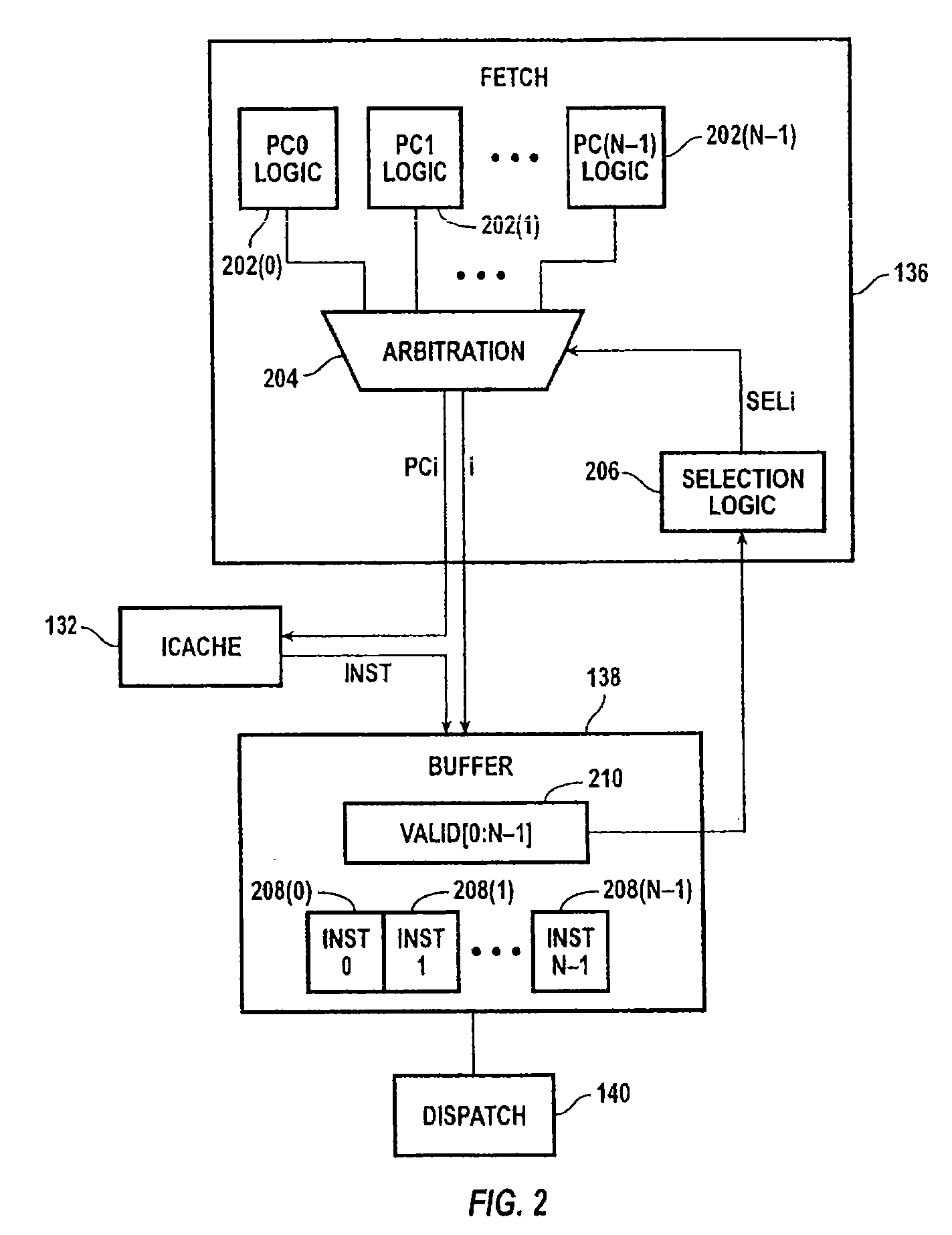
Across-thread out of order instruction dispatch in a multithreaded graphics processor
ActiveUS20050138328A1Digital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsGraphicsInstruction buffer
Instruction dispatch in a multithreaded microprocessor such as a graphics processor is not constrained by an order among the threads. Instructions are fetched into an instruction buffer that is configured to store an instruction from each of the threads. A dispatch circuit determines which instructions in the buffer are ready to execute and may issue any ready instruction for execution. An instruction from one thread may be issued prior to an instruction from another thread regardless of which instruction was fetched into the buffer first. Once an instruction from a particular thread has issued, the fetch circuit fills the available buffer location with the following instruction from that thread.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
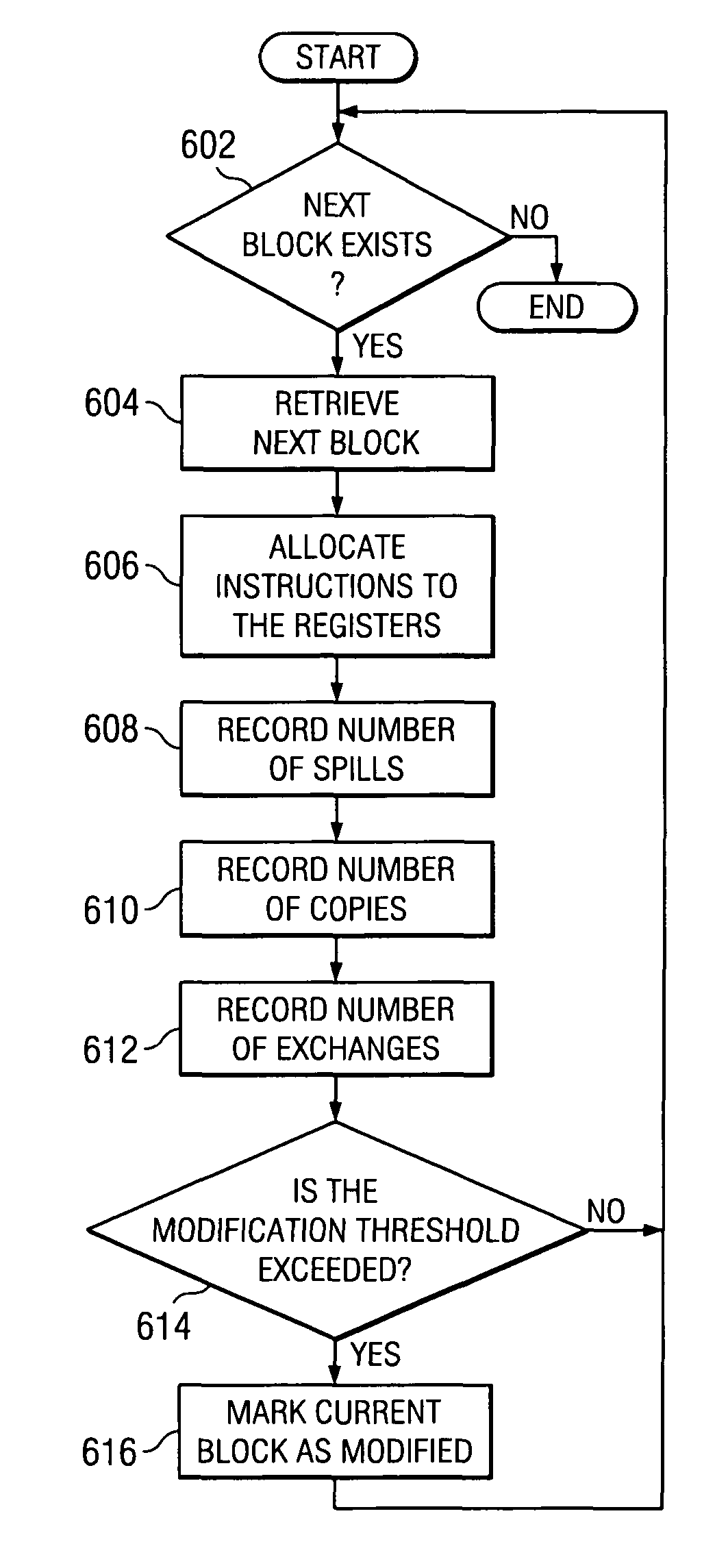
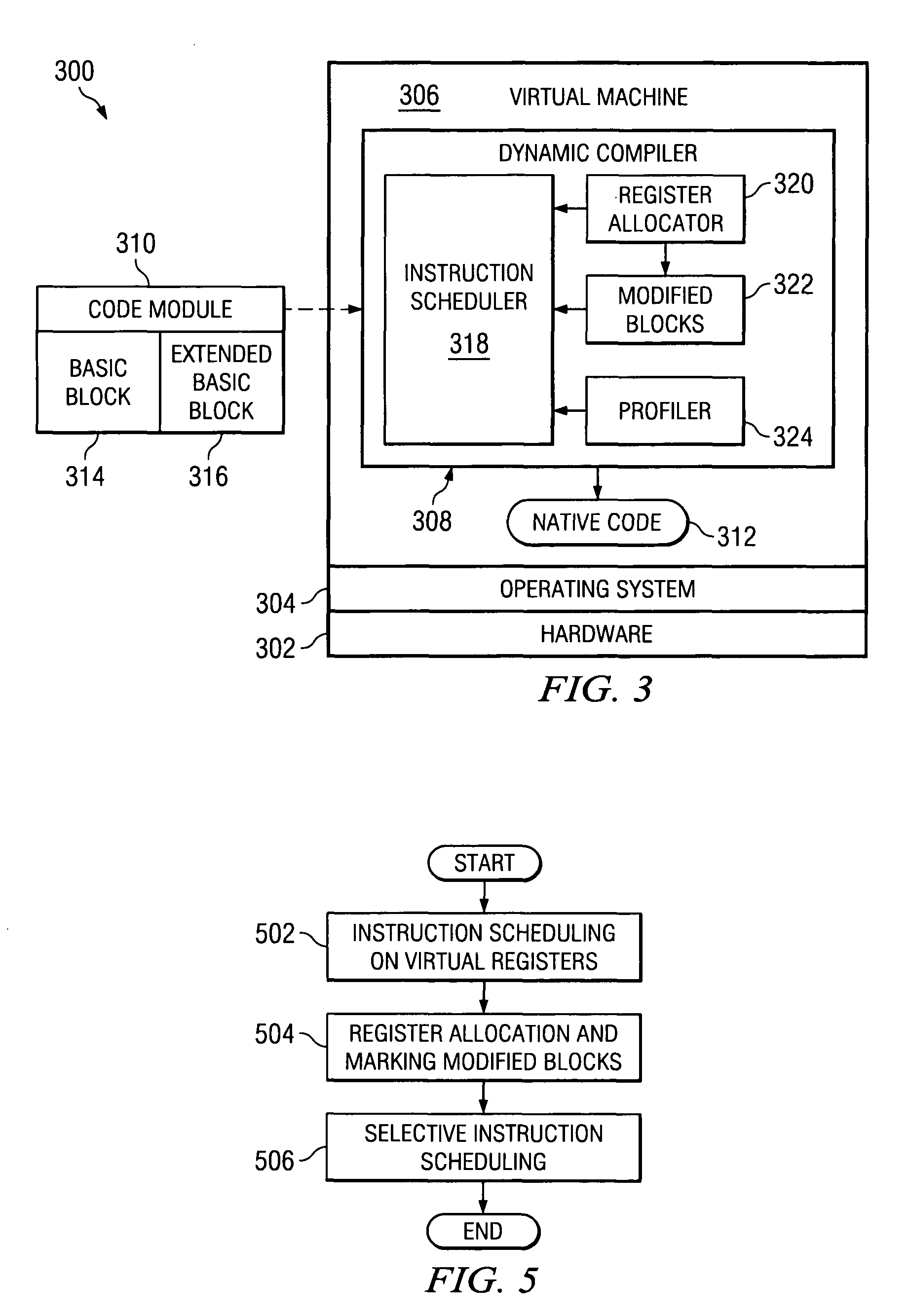
Post-register allocation profile directed instruction scheduling
ActiveUS7770161B2Software engineeringSpecial data processing applicationsRegister allocationProcessor register
A computer implemented method, system, and computer usable program code for selective instruction scheduling. A determination is made whether a region of code exceeds a modification threshold after performing register allocation on the region of code. The region of code is marked as a modified region of code in response to the determination that the region of code exceeds the modification threshold. A determination is made whether the region of code exceeds an execution threshold in response to the determination that the region of code is marked as a modified region of code. Post-register allocation instruction scheduling is performed on the region of code in response to the determination that the region of code is marked as a modified region of code and the determination that the region of code exceeds the execution threshold.
Owner:TWITTER INC
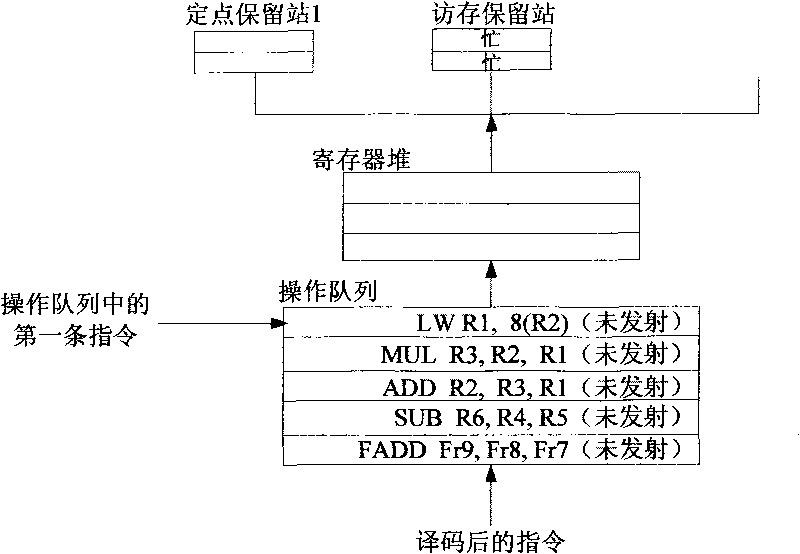
Device and method for instruction scheduling
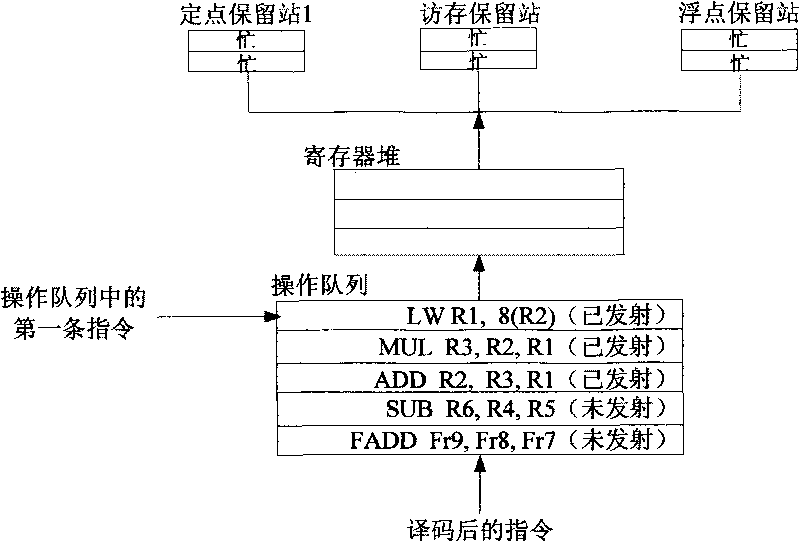
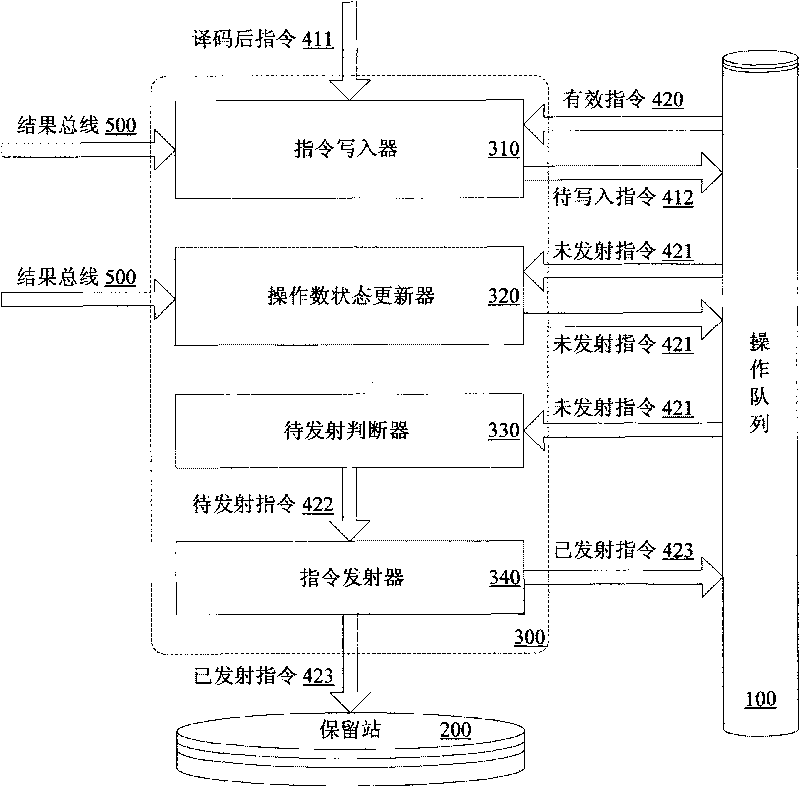
ActiveCN101710272AImprove efficiencyImprove performanceConcurrent instruction executionReservation stationScheduling instructions
The invention provides a device and a method for dynamically scheduling instructions transmitted from an operation queue to a reservation station in a microprocessor. The method comprises the following: a step of writing instructions, which is to set and then write the operand states of the decoded instructions on the basis of data correlation between the decoded instructions to be written into the operation queue and effective instructions in the operation queue, as well as instruction execution results which have been written back and are being written; a step of updating the operand states, which is to update the operand state of each instruction not transmitted on the basis of the data correlation between each instruction not transmitted and the instructions being written back of instruction execution results; a step of judging to-be-transmitted instructions, which is to judge whether the to-be-transmitted instructions with all operands ready exist on the basis of the operand state of each instruction not transmitted; and a step of transmitting instructions, which is to transmit the judged to-be-transmitted instructions to the reservation station when the reservation station has vacancies. Pipeline efficiency can be effectively improved by transmitting the instructions with the operands ready to the reservation station on the basis of the data correlation between the instructions.
Owner:LOONGSON TECH CORP
Construction method of GPU and CPU combined processor
InactiveCN101526934AWork is not tiredDigital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionVideo memoryOperational system
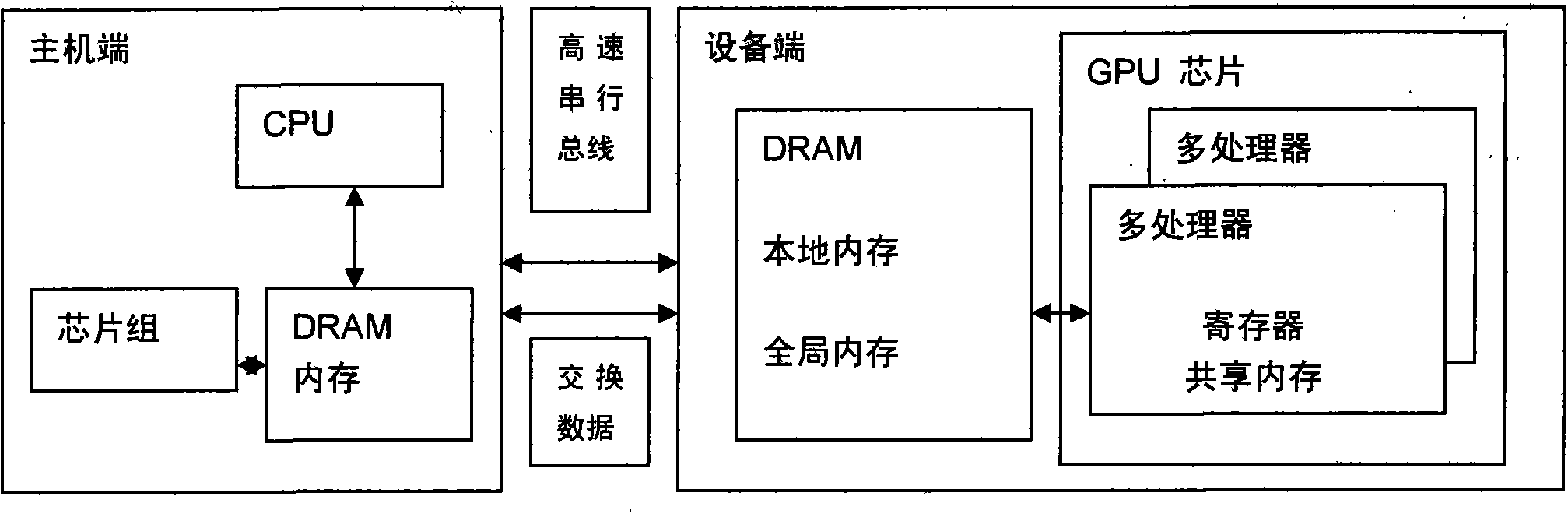
The invention provides a construction method of a GPU and CPU combined processor, which comprises the following steps: a CPU and a GPU are coupled to construct a combined processor, wherein the CPU is responsible for the general-purpose processing tasks of an operation system, system software, general-purpose application program, and the like which have complex instruction scheduling, circulation, branches and logical judgment; and the GPU is responsible for the highly-parallel calculating processing of large-scale data without logical relation; and the CPU and the GPU jointly finish the same large-scale parallel calculating application. In the GPU and CPU combined processor, a plurality of cores of CPU are communicated with each other by a memory bus and carry out calculation, and the cores of the GPU exchange data and are calculated by a uniform shared memory (a video memory on the GPU); the GPU and the CPU are connected by a high-speed serial bus and exchange calculating data by the memory of the CPU and the shared memory of the GPU; and the construction method can fully utilize the parallel processing capacity of the cores of the GPU and realize the rapid parallel calculation of enormous data volume.
Owner:LANGCHAO ELECTRONIC INFORMATION IND CO LTD
Across-thread out of order instruction dispatch in a multithreaded graphics processor
ActiveUS7310722B2Digital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsGraphicsScheduling instructions
Instruction dispatch in a multithreaded microprocessor such as a graphics processor is not constrained by an order among the threads. Instructions are fetched into an instruction buffer that is configured to store an instruction from each of the threads. A dispatch circuit determines which instructions in the buffer are ready to execute and may issue any ready instruction for execution. An instruction from one thread may be issued prior to an instruction from another thread regardless of which instruction was fetched into the buffer first. Once an instruction from a particular thread has issued, the fetch circuit fills the available buffer location with the following instruction from that thread.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
System, method, and program product for loop instruction scheduling hardware lookahead
InactiveUS6044222ASoftware engineeringDigital computer detailsScheduling instructionsComputerized system
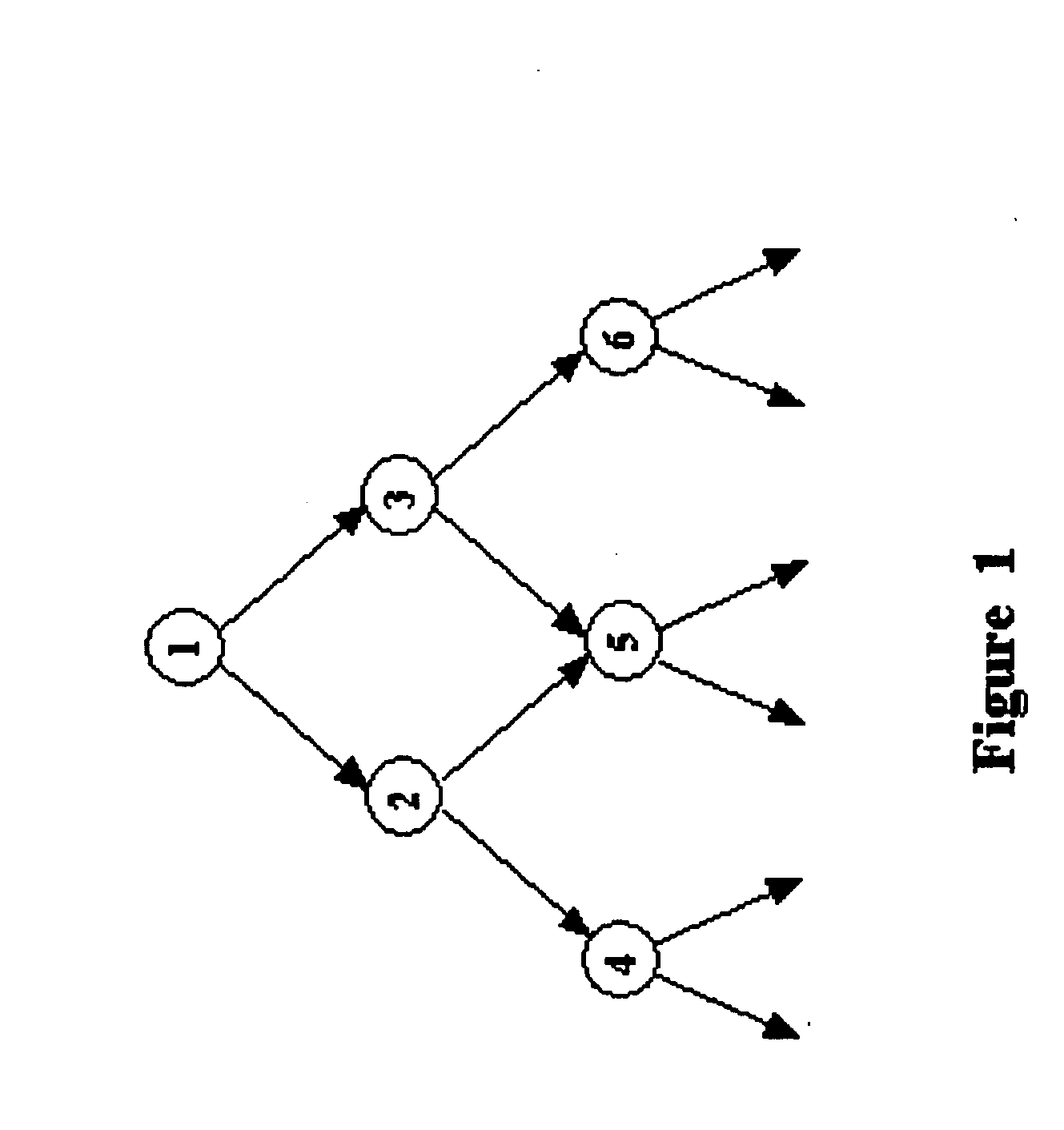
Improved scheduling of instructions within a loop for execution by a computer system having hardware lookahead is provided. A dependence graph is constructed which contains all the nodes of a dependence graph corresponding to the loop, but which only contains loop-independent dependence edges. A start node simulating a previous iteration of the loop may be added to the dependence graph, and an end node simulating a next iteration of the loop may also added to the dependence graph. A loop-independent edge between a source node and the start node is added to the dependence graph, and a loop-independent edge between a sink node and the end node is added to the dependence graph. Loop-carried edges which satisfy a computed lower bound on the time required for a single loop iteration are eliminated from a dependence graph, and loop-carried edges which do not satisfy the computed lower bound are replaced by a pair of loop-independent edges. Instructions may be scheduled for execution based on the dependence graph.
Owner:IBM CORP
Bifurcated thread scheduler in a multithreading microprocessor
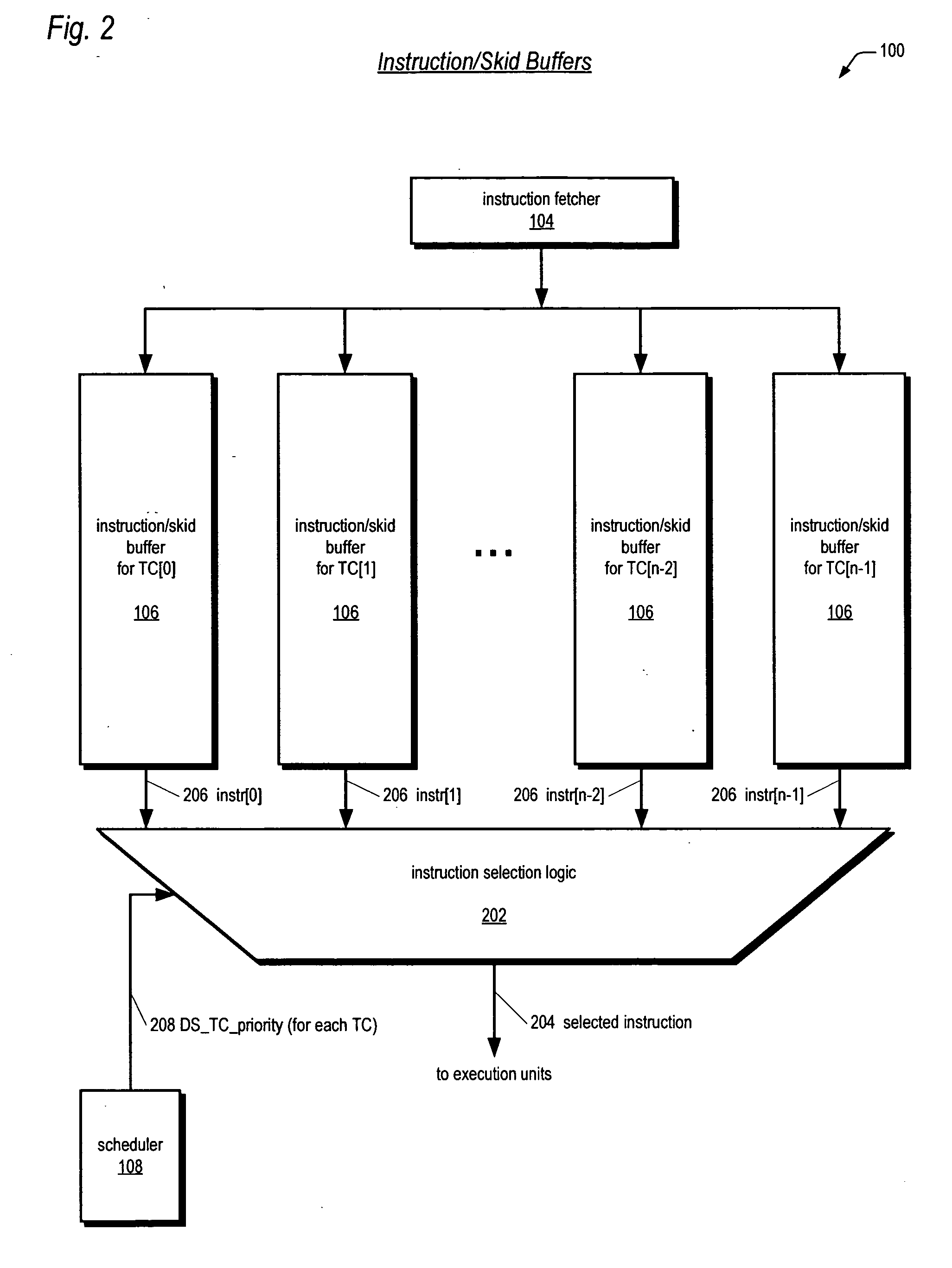
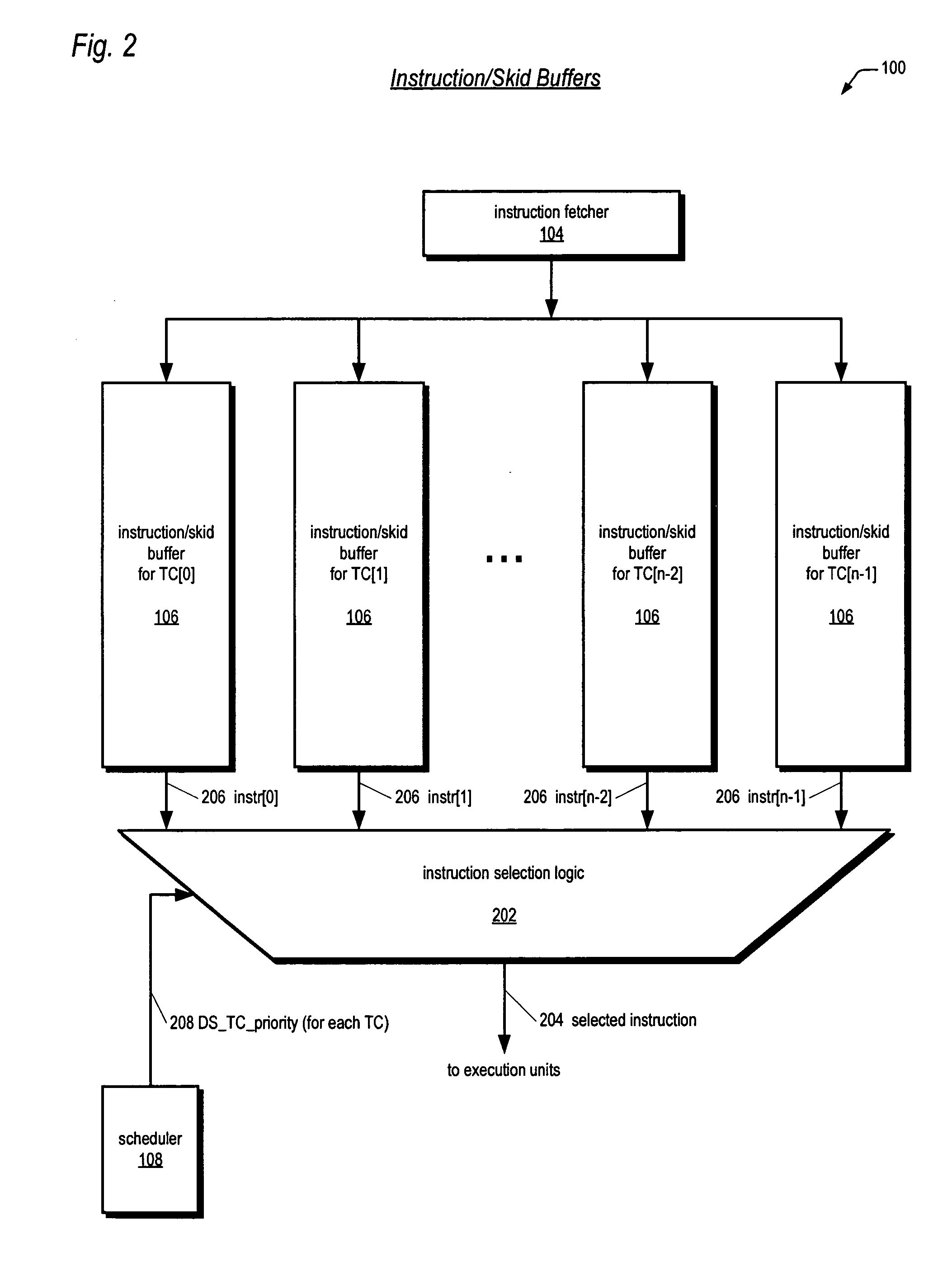
ActiveUS20060179279A1Accurate operationSafely modified by the customerProgram control using stored programsDigital computer detailsThread schedulingExecution unit
A bifurcated instruction scheduler for dispatching instructions of multiple threads concurrently executing in a multithreading processor is provided. The scheduler includes a first portion within a reusable core that is not customizable by a customer, a second portion outside the core that is customizable, and an interface coupling the second portion to the core. The second portion implements a thread scheduling policy that may be customized to the customer's particular application. The first portion may be scheduling policy-agnostic and issues instructions of the threads each clock cycle to execution units based on the scheduling policy communicated by the second portion. The second portion communicates the scheduling policy via a priority for each of the threads. When the core commits an instruction for execution, the core communicates to the second portion which thread the committed instruction is in to enable the second portion to update the priorities in response thereto.
Owner:MIPS TECH INC
Instruction dispatch scheduler employing round-robin apparatus supporting multiple thread priorities for use in multithreading microprocessor
ActiveUS20060206692A1Short clock cycleThe process is simple and fastDigital computer detailsMemory systemsParallel computingLeast significant bit
A dispatch scheduler in a multithreading microprocessor is disclosed. Each of N concurrently executing threads has one of P priorities. P N-bit round-robin vectors are generated, each being a 1-bit left-rotated and subsequently sign-extended version of an N-bit 1-hot input vector indicating the last thread selected for dispatching at the priority. N P-input muxes each receive a corresponding one of the N bits of each of the P round-robin vectors and selects the input specified by the thread priority. Selection logic selects an instruction for dispatching from the thread having a dispatch value greater than or equal to any of the threads left thereof in the N-bit input vectors. The dispatch value of each of the threads comprises a least-significant bit equal to the corresponding P-input mux output, a most-significant bit that is true if the instruction is dispatchable, and middle bits comprising the priority of the thread.
Owner:ARM FINANCE OVERSEAS LTD
Barrel-incrementer-based round-robin apparatus and instruction dispatch scheduler employing same for use in multithreading microprocessor
InactiveUS20060179194A1Selectively disableDigital data processing detailsProgram controlProcessor schedulingShared resource
A circuit for selecting one of N requestors in a round-robin fashion is disclosed. The circuit 1-bit left rotatively increments a first addend by a second addend to generate a sum that is ANDed with the inverse of the first addend to generate a 1-hot vector indicating which of the requestors is selected next. The first addend is an N-bit vector where each bit is false if the corresponding requester is requesting access to a shared resource. The second addend is a 1-hot vector indicating the last selected requester. A multithreading microprocessor dispatch scheduler employs the circuit for N concurrent threads each thread having one of P priorities. The dispatch scheduler generates P N-bit 1-hot round-robin bit vectors, and each thread's priority is used to select the appropriate round-robin bit from P vectors for combination with the thread's priority and an issuable bit to create a dispatch level used to select a thread for instruction dispatching.
Owner:ARM FINANCE OVERSEAS LTD
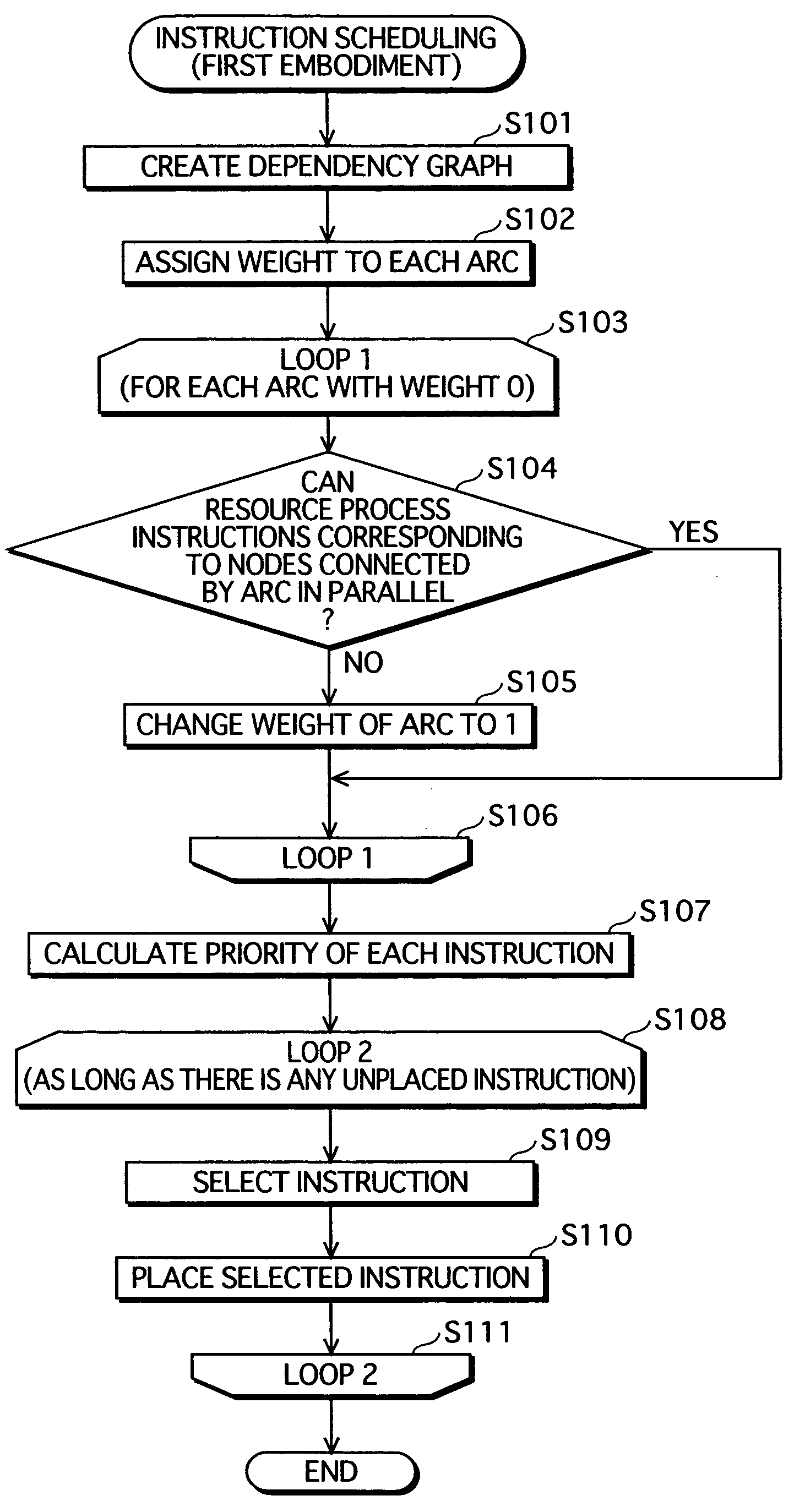
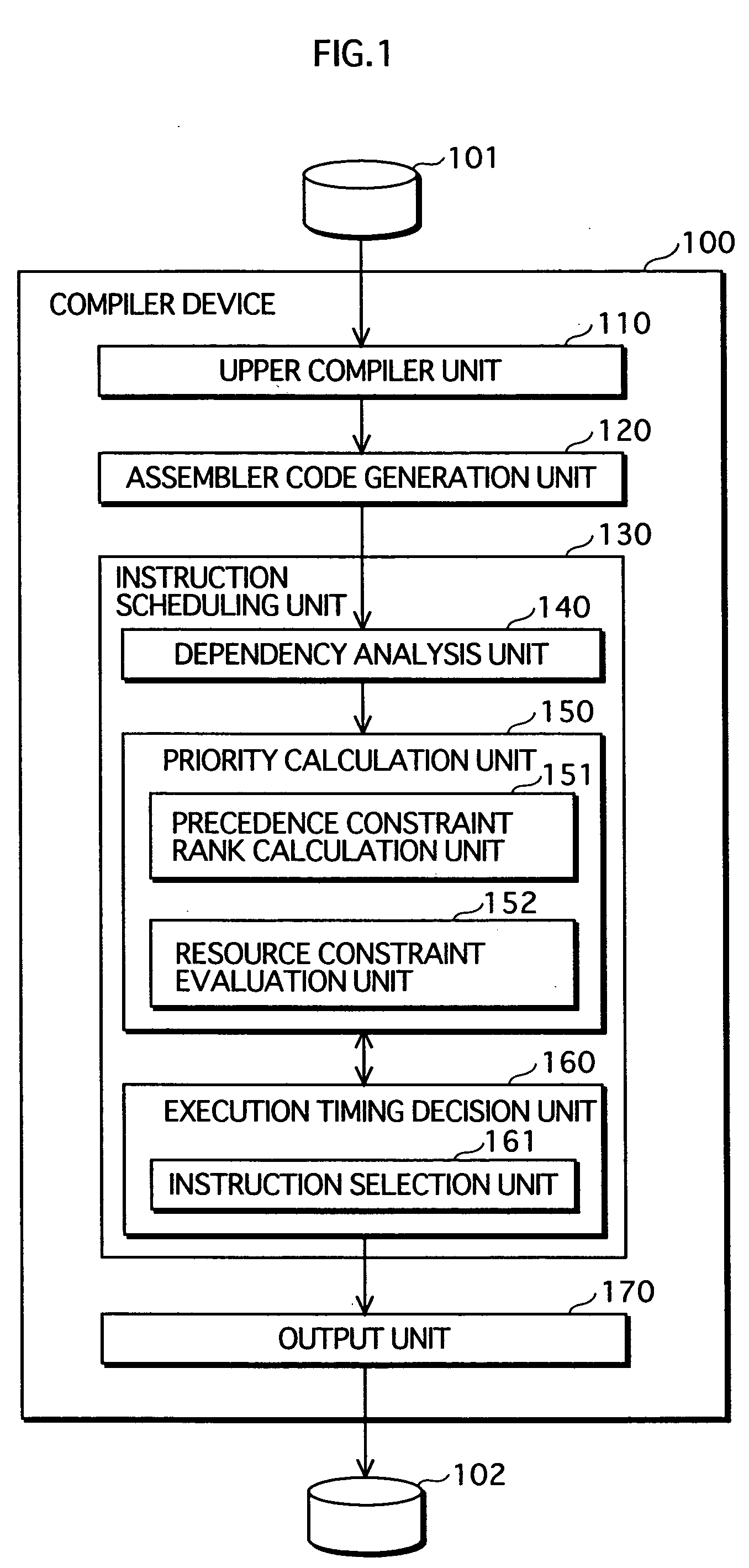
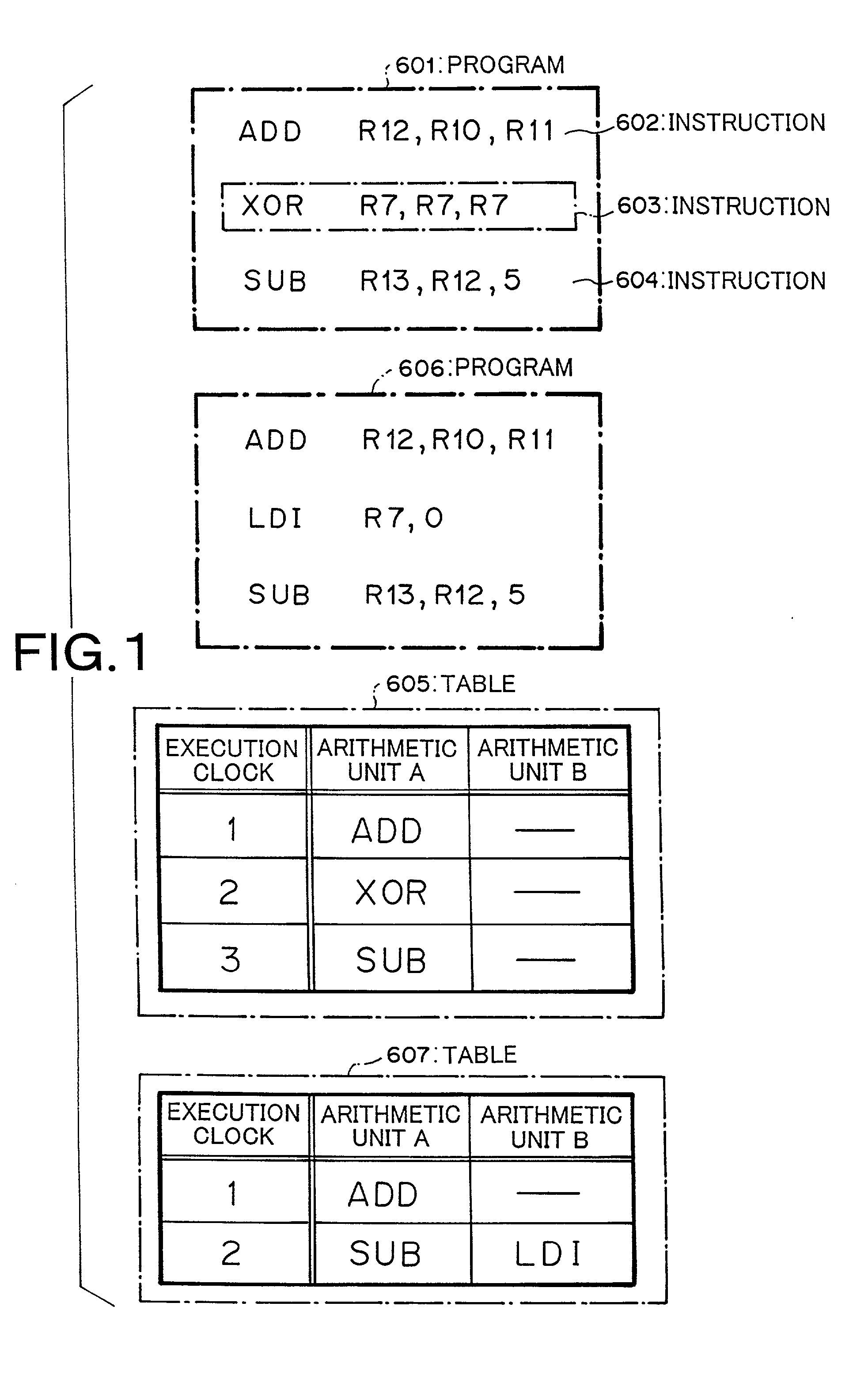
Instruction scheduling method, instruction scheduling device, and instruction scheduling program
InactiveUS20040083468A1Software engineeringProgram controlScheduling instructionsParallel processing
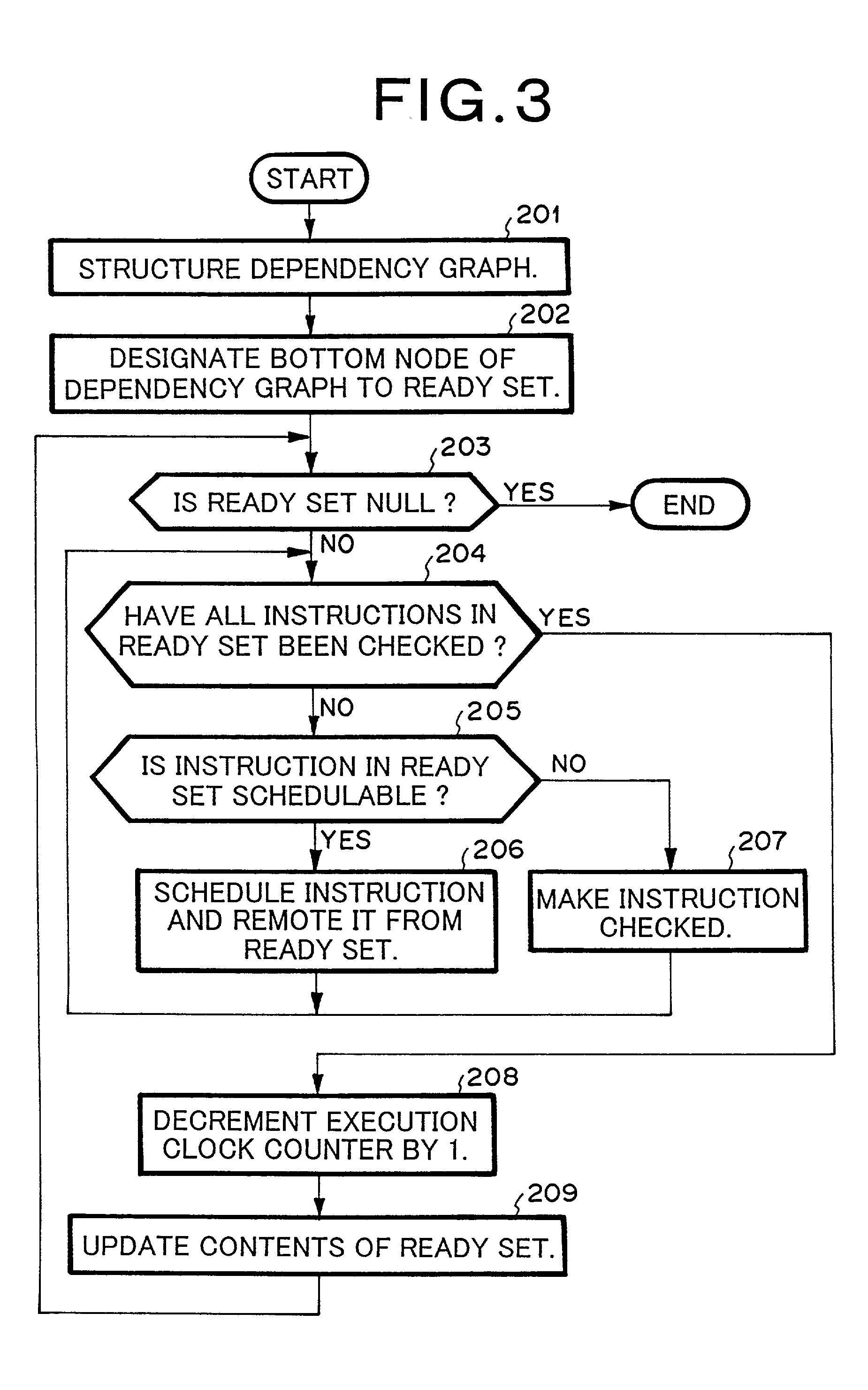
A dependency analysis unit creates a dependency graph showing dependencies between instructions acquired from an assembler code generation unit. A precedence constraint rank calculation unit assigns predetermined weights to arcs in the graph, and adds up weights to calculate a precedence constraint rank of each instruction. When a predecessor and a successor having a dependency and an equal precedence constraint rank cannot be processed in parallel due to a resource constraint, a resource constraint evaluation unit raises the precedence constraint rank of the predecessor. A priority calculation unit sets the raised precedence constraint rank as a priority of the predecessor. An instruction selection unit selects an instruction having a highest priority. An execution timing decision unit places the selected instruction in a clock cycle. The selection by the instruction selection unit and the placement by the execution timing decision unit are repeated until all instructions are placed in clock cycles.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method for executing structured symbolic machine code on a microprocessor
InactiveUS20060090063A1Software engineeringInstruction analysisScheduling instructionsHigh probability
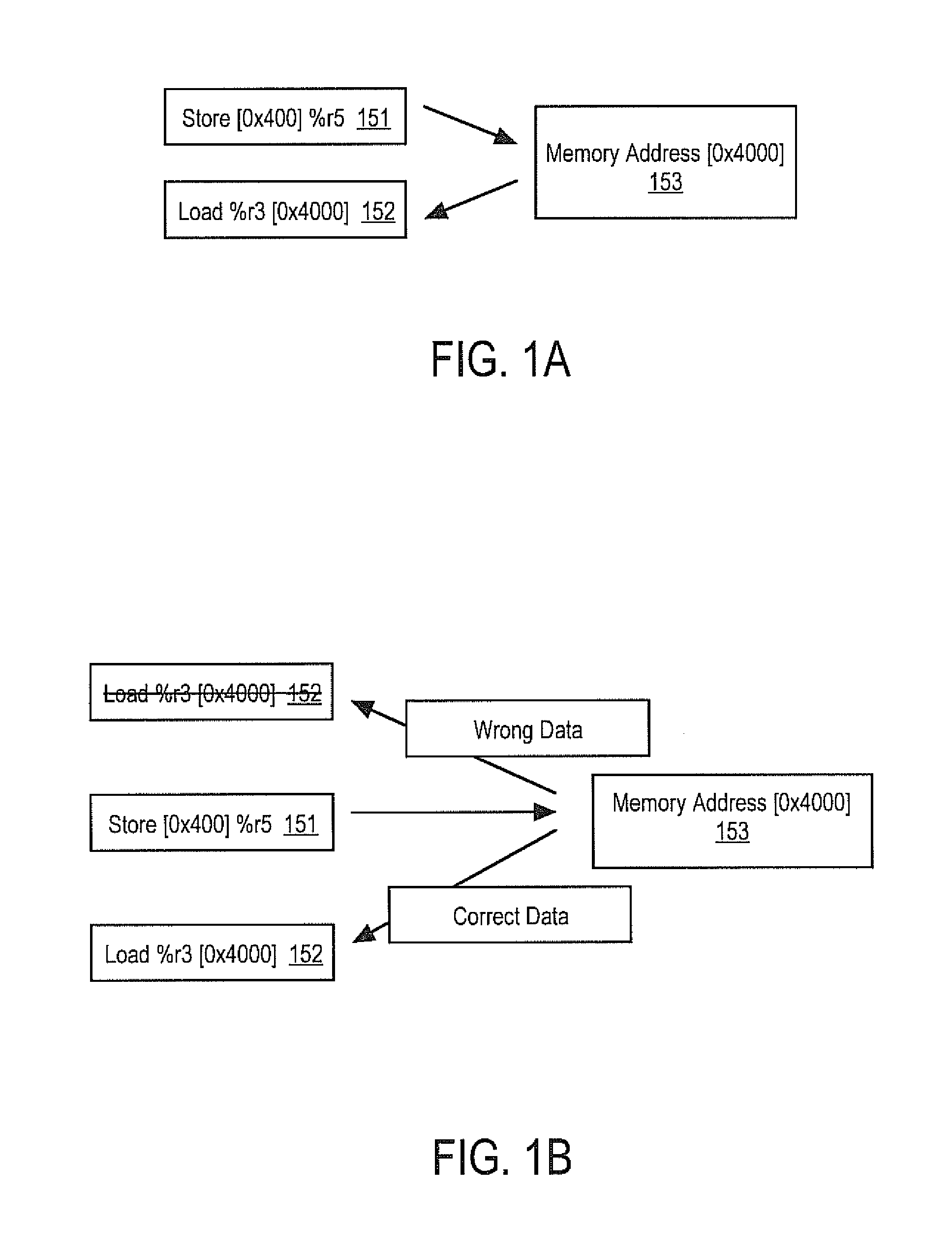
The invention describes a method for executing structured symbolic machine code on a microprocessor. Said structured symbolic machine code contains a set of one or more regions, where each of said regions contains symbolic machine code containing, in addition to the proper instructions, information about the symbolic variables, the symbolic constants, the branch tree, pointers and functions arguments used within each of said regions. This information is fetched by the microprocessor from the instruction cache and stored into dedicated memories before the proper instructions of each region are fetched and executed. Said information is used by the microprocessor in order to improve the degree of parallelism achieved during instruction scheduling and execution. Among other purposes, said information allows the microprocessor to perform so-called speculative branch prediction. Speculative branch prediction does branch prediction along a branch path containing several dependent branches in the shortest time possible (in only a few clock cycles) without having to wait for branches to resolve. This is a key issue which allows to apply region scheduling in practice, e.g. treegion scheduling, where machine code must be fetched and speculatively executed from the trace having highest probability or confidence among several traces. This allows to use the computation resources (e.g. the FUs) of the microprocessor in the most efficient way. Finally, said information allows to re-execute instructions in the right order and to overwrite wrong data with the correct ones when miss-predictions occur.
Owner:THEIS JEAN PAUL
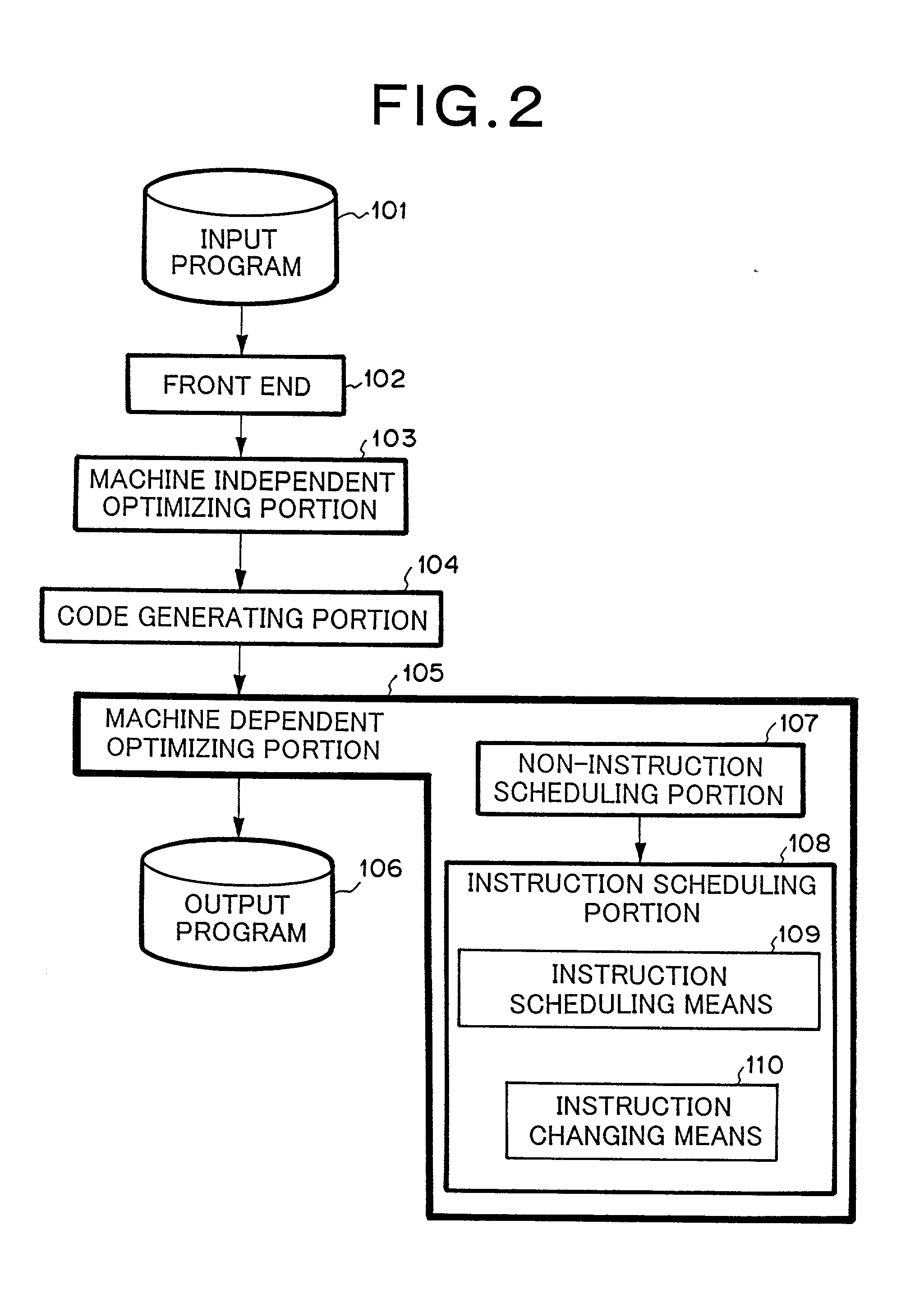
Compiler processing system for generating assembly program codes for a computer comprising a plurality of arithmetic units
InactiveUS20010039654A1Software engineeringConcurrent instruction executionScheduling instructionsProgram code
Provided is a compiler processing system for generating assembly program codes from a source program for a computer comprising a plurality of arithmetic units, the system comprising: a front end; a machine-independent optimization portion; a code generating portion; and a machine-dependent optimization portion; wherein the machine-dependent optimization portion comprises: a non-instruction scheduling portion; and an instruction scheduling portion comprising: means for determining if an arithmetic unit is available for an inspected instruction at an execution clock concerned; means for determining if there is a substitutional instruction which performs the equivalent function as the inspected instruction if an arithmetic unit is not available for the inspected instruction; means for determining if an arithmetic unit is available at the execution clock for the substitutional instruction, if any; and means for changing the inspected instruction to the substitutional instruction if an arithmetic unit is available for the substitutional instruction.
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
Method and apparatus for efficient scheduling for asymmetrical execution units
ActiveUS20140373022A1Efficient schedulingOptimizes dispatch throughputProgram initiation/switchingConcurrent instruction executionScheduling instructionsParallel computing
A method for performing instruction scheduling in an out-of-order microprocessor pipeline is disclosed. The method comprises selecting a first set of instructions to dispatch from a scheduler to an execution module, wherein the execution module comprises two types of execution units. The first type of execution unit executes both a first and a second type of instruction and the second type of execution unit executes only the second type. Next, the method comprises selecting a second set of instructions to dispatch, which is a subset of the first set and comprises only instructions of the second type. Next, the method comprises determining a third set of instructions, which comprises instructions not selected as part of the second set. Finally, the method comprises dispatching the second set for execution using the second type of execution unit and dispatching the third set for execution using the first type of execution unit.
Owner:INTEL CORP
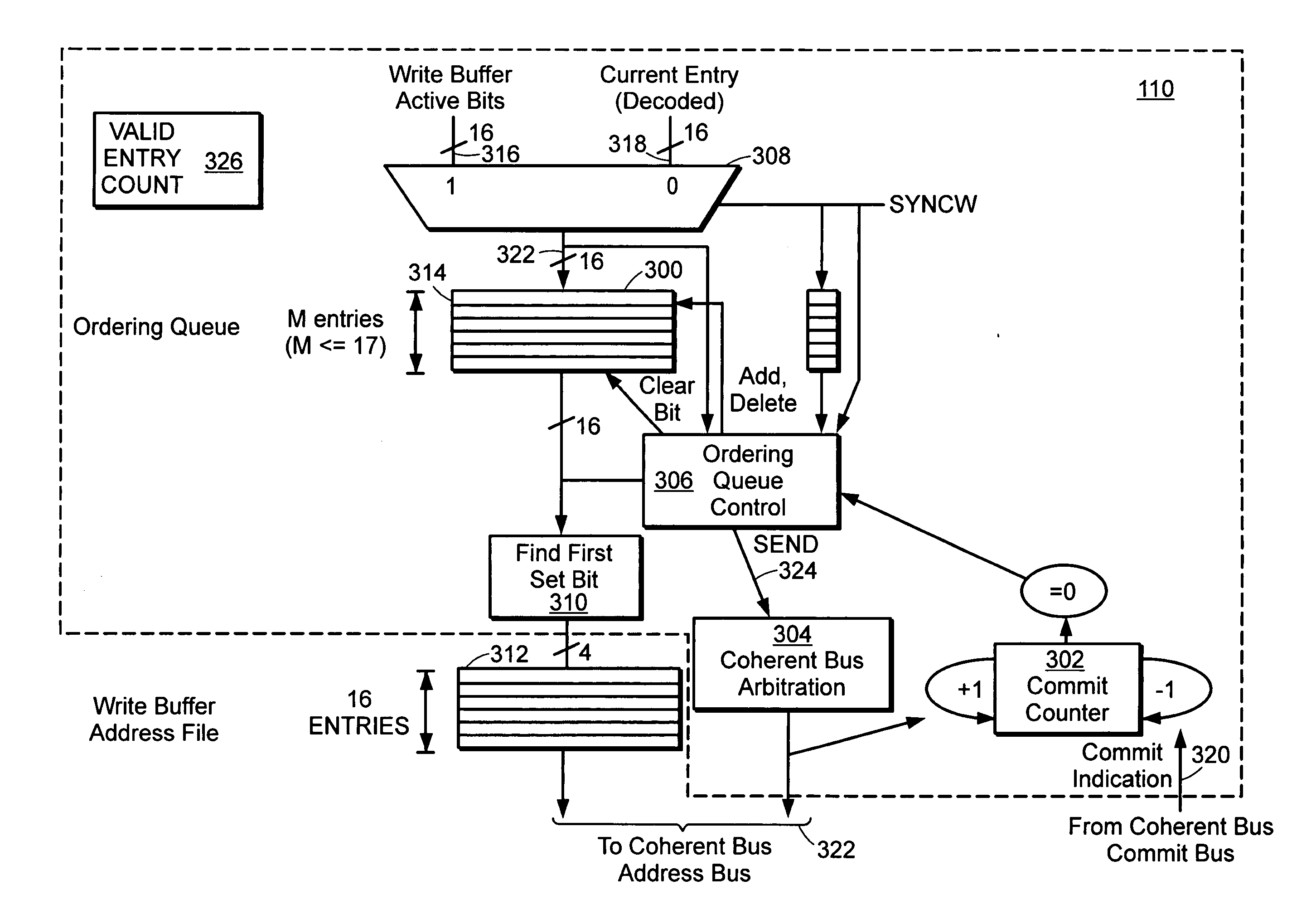
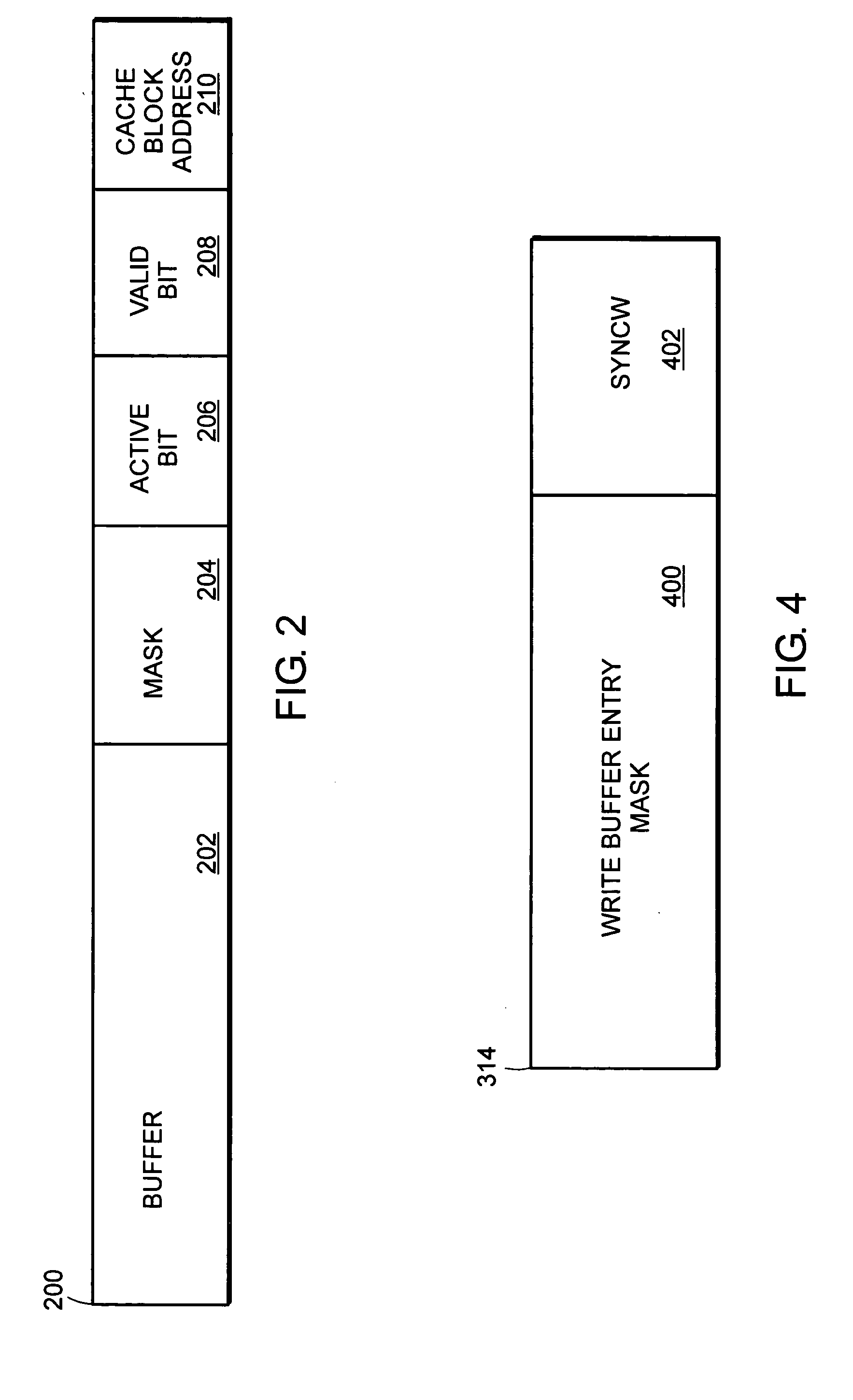
Store instruction ordering for multi-core processor
ActiveUS20060095741A1Minimizes stallingStalling of a store ordering instruction can be eliminatedDigital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsExternal storageMulti-core processor
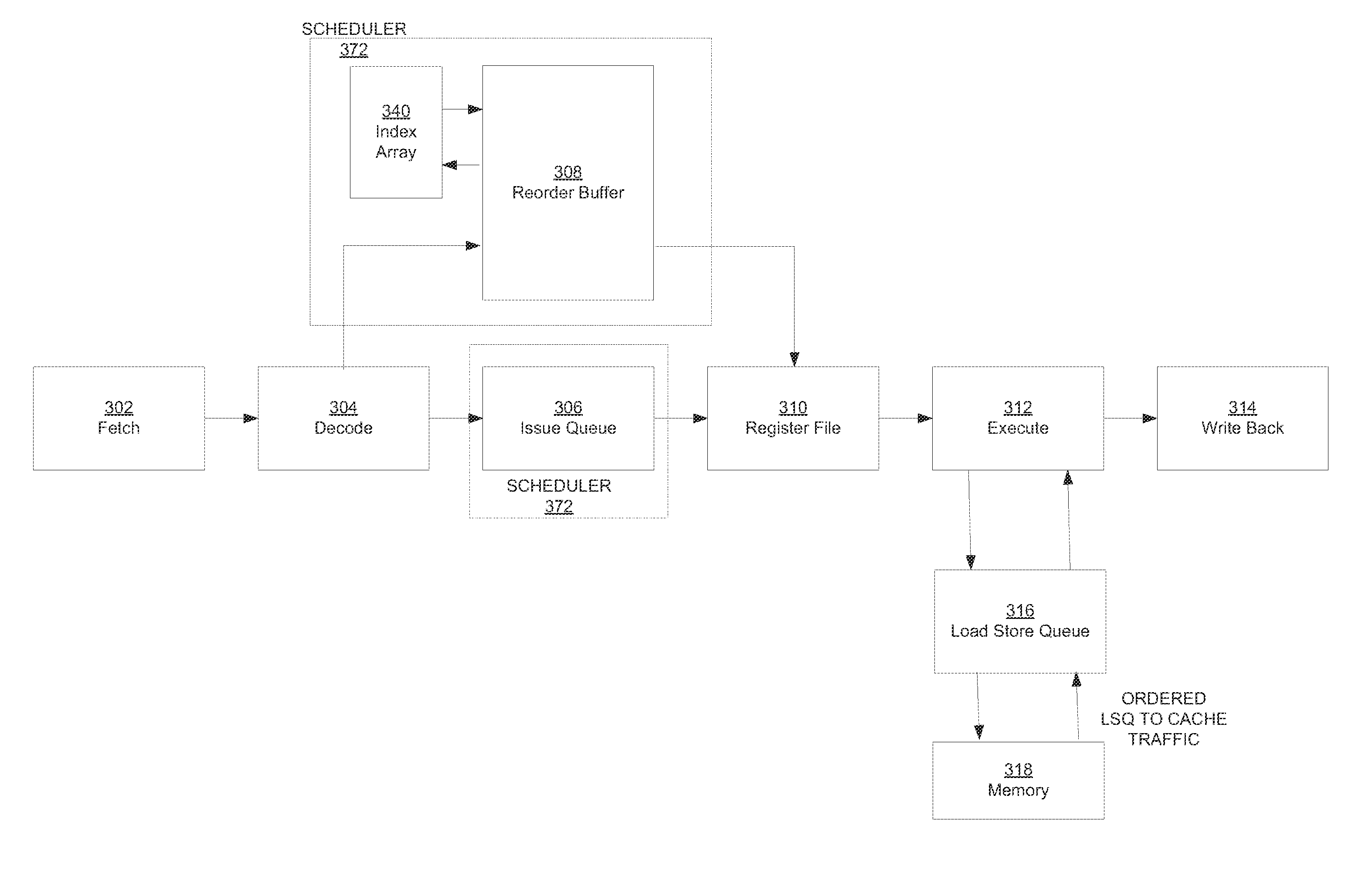
A method and apparatus for minimizing stalls in a pipelined processor is provided. Instructions in an out-of-order instruction scheduler are executed in order without stalling the pipeline by sending store data to external memory through an ordering queue.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
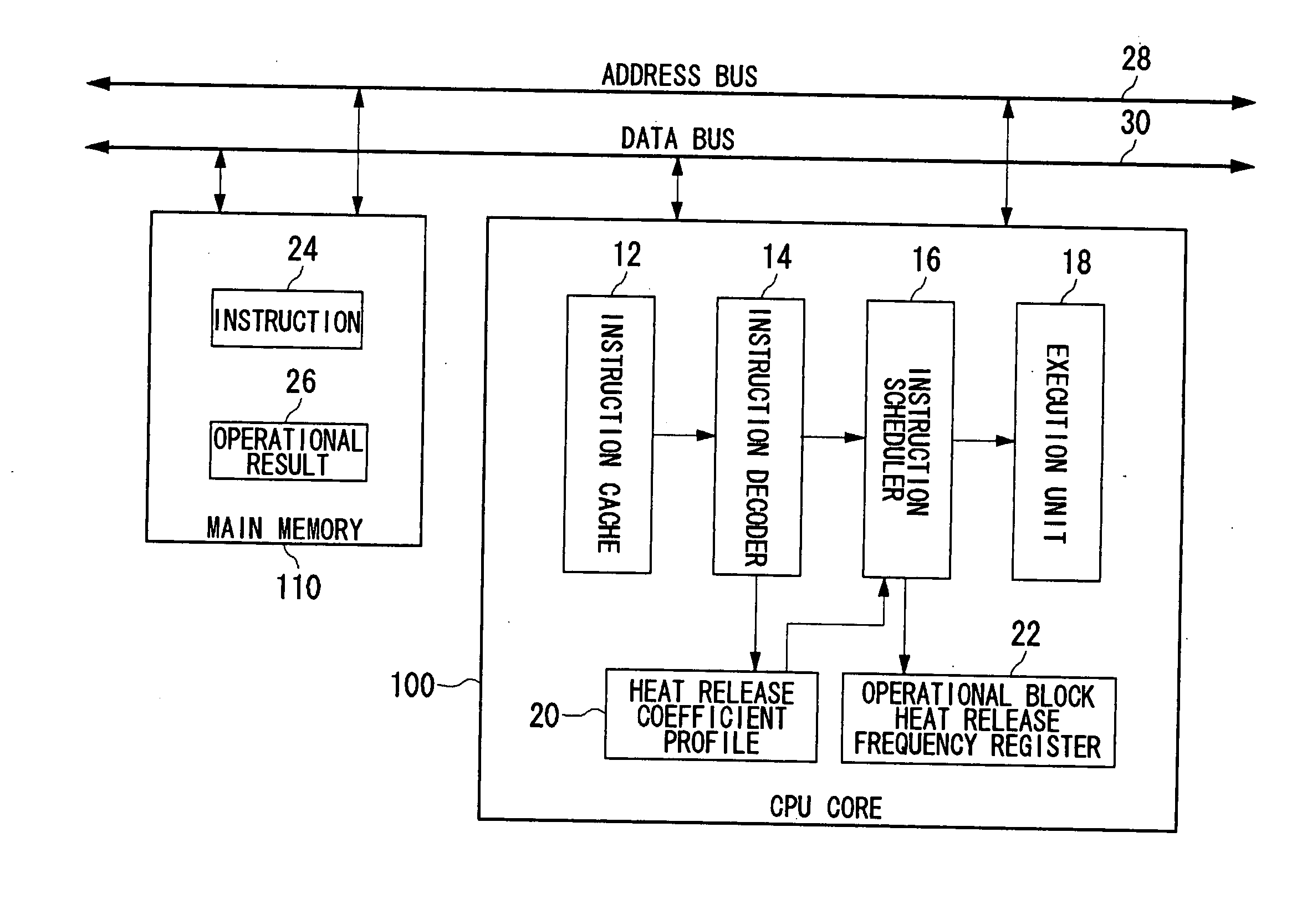
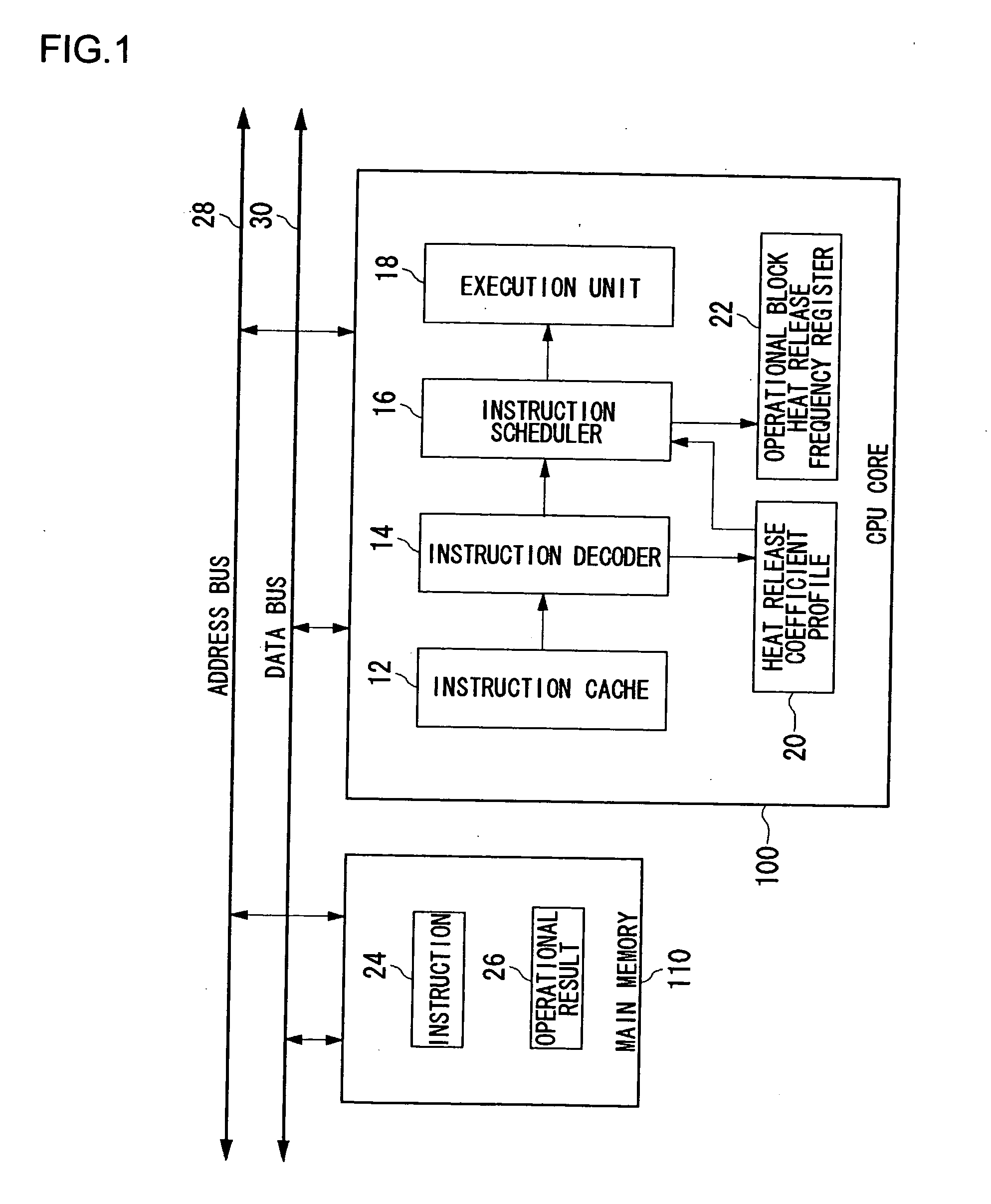
Processor, multiprocessor system, processor system, information processing apparatus, and temperature control method
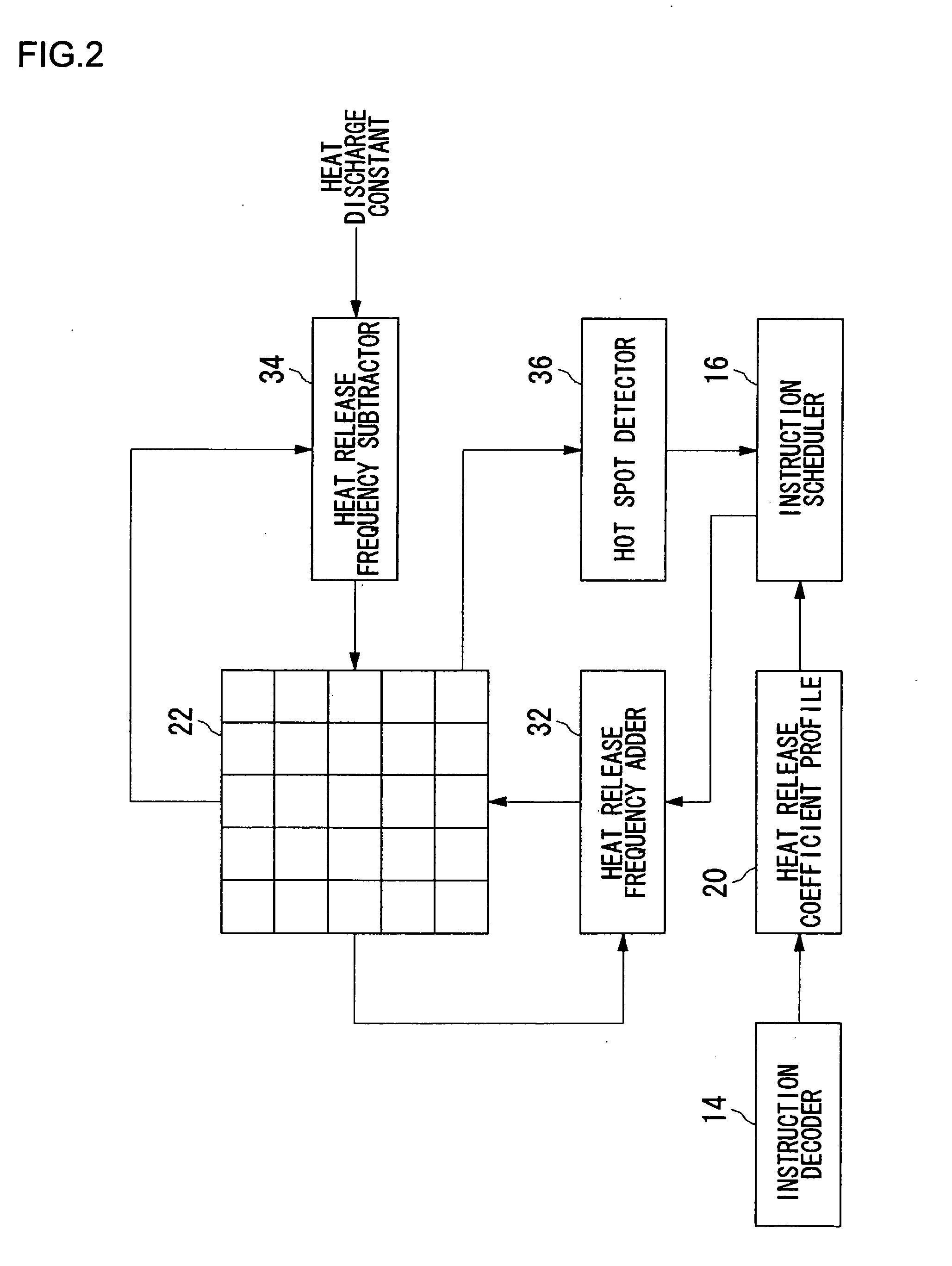
InactiveUS20070198134A1Avoid misuseWithout incurring degradation in processor performanceEnergy efficient ICTResource allocationTemperature controlInformation processing
An instruction decoder identifies, for each instruction, an operational block involved in the execution of the instruction and an associated heat release coefficient. The instruction decoder stores identified information in a heat release coefficient profile. An instruction scheduler schedules the instructions in accordance with the dependence of the instructions on data. A heat release frequency adder cumulatively adds the heat release coefficient to the heat release frequency of the operational block held in the operational block heat release frequency register as the execution of the scheduled instructions proceeds. A heat release frequency subtractor subtracts from the heat release frequency of the operational blocks in the operational block heat release frequency register in accordance with heat discharge that occurs with time. A hot spot detector detects an operational block with its heat release frequency, held in the operational block heat release frequency register, exceeding a predetermined threshold value as a hot spot. The instruction scheduler delays the execution of the instruction involving for its execution the operational block identified as a hot spot.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
Across-thread out-of-order instruction dispatch in a multithreaded microprocessor
InactiveUS20070214343A1Digital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsGraphicsComputer architecture
Instruction dispatch in a multithreaded microprocessor such as a graphics processor is not constrained by an order among the threads. Instructions for each thread are fetched, and a dispatch circuit determines which instructions in the buffer are ready to execute. The dispatch circuit may issue any ready instruction for execution, and an instruction from one thread may be issued prior to an instruction from another thread regardless of which instruction was fetched first. If multiple functional units are available, multiple instructions can be dispatched in parallel.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Instruction dispatching method and apparatus
InactiveUS20080040724A1Avoid delayGeneral purpose stored program computerMultiprogramming arrangementsScheduling instructionsParallel computing
A system, apparatus and method for instruction dispatch on a multi-thread processing device are described herein. The instruction dispatching method includes, in an instruction execution period having a plurality of execution cycles, successively fetching and issuing an instruction for each of a plurality of instruction execution threads according to an allocation of execution cycles of the instruction execution period among the plurality of instruction execution threads. Remaining execution cycles are subsequently used to successively fetch and issue another instruction for each of the plurality of instruction execution threads having at least one remaining allocated execution cycle of the instruction execution period. Other embodiments may be described and claimed.
Owner:MARVELL WORLD TRADE LTD
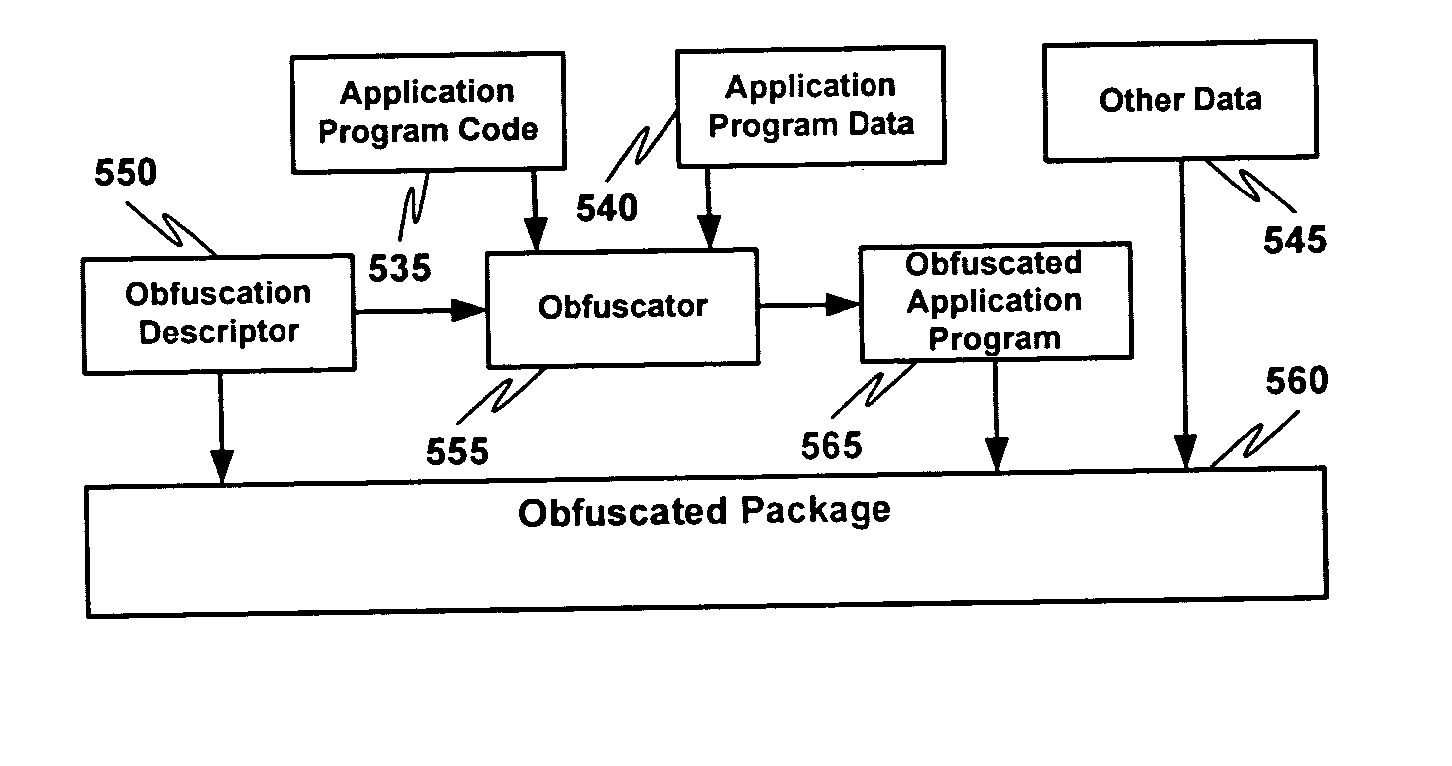
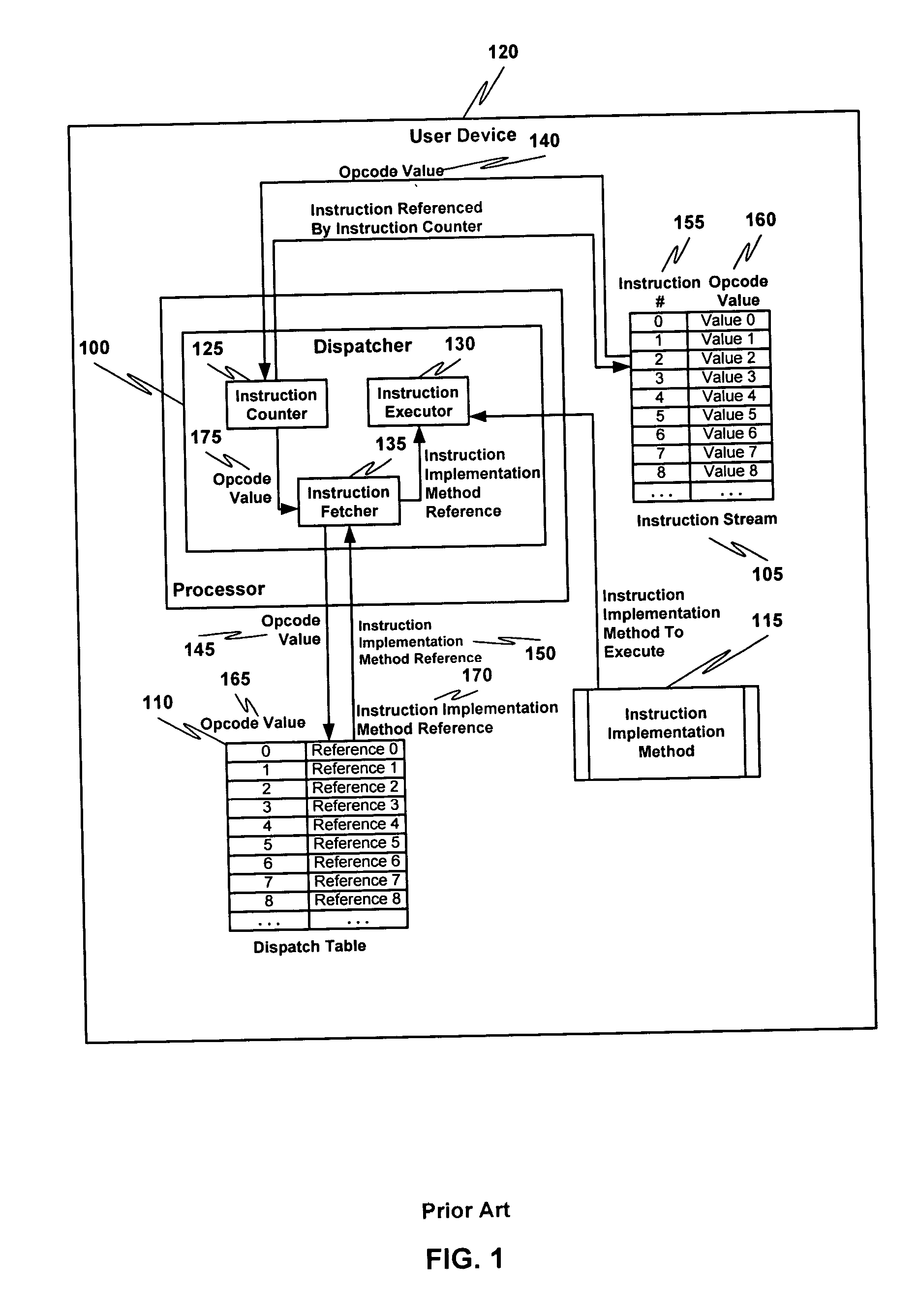
Multiple instruction dispatch tables for application program obfuscation
ActiveUS20050071652A1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsProgram instructionInstruction set
Obfuscating an application program comprises reading an application program comprising code, determining multiple dispatch tables associated with the application program, transforming the application program into application program code configured to utilize the dispatch tables during application program execution to determine the location of instruction implementation methods to be executed based at least in part on a current instruction counter value, and sending the application program code. Executing an obfuscated application program comprises receiving an obfuscated application program comprising at least one instruction opcode value encoded using one of multiple instruction set opcode value encoding schemes, receiving an application program instruction corresponding to a current instruction counter value, selecting an instruction dispatch table based at least in part on the current instruction counter value, and executing the application program instruction using the selected instruction dispatch table.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
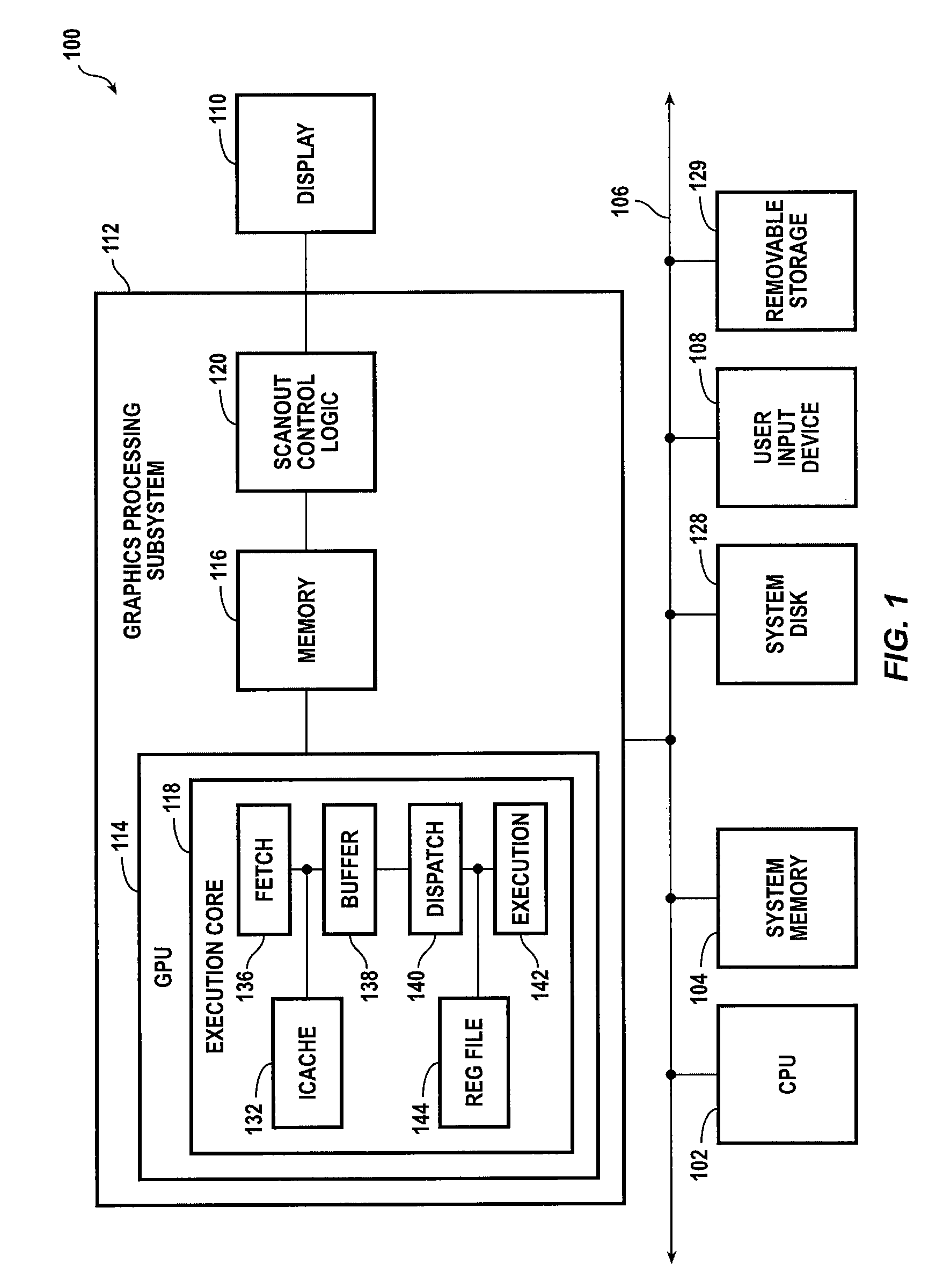
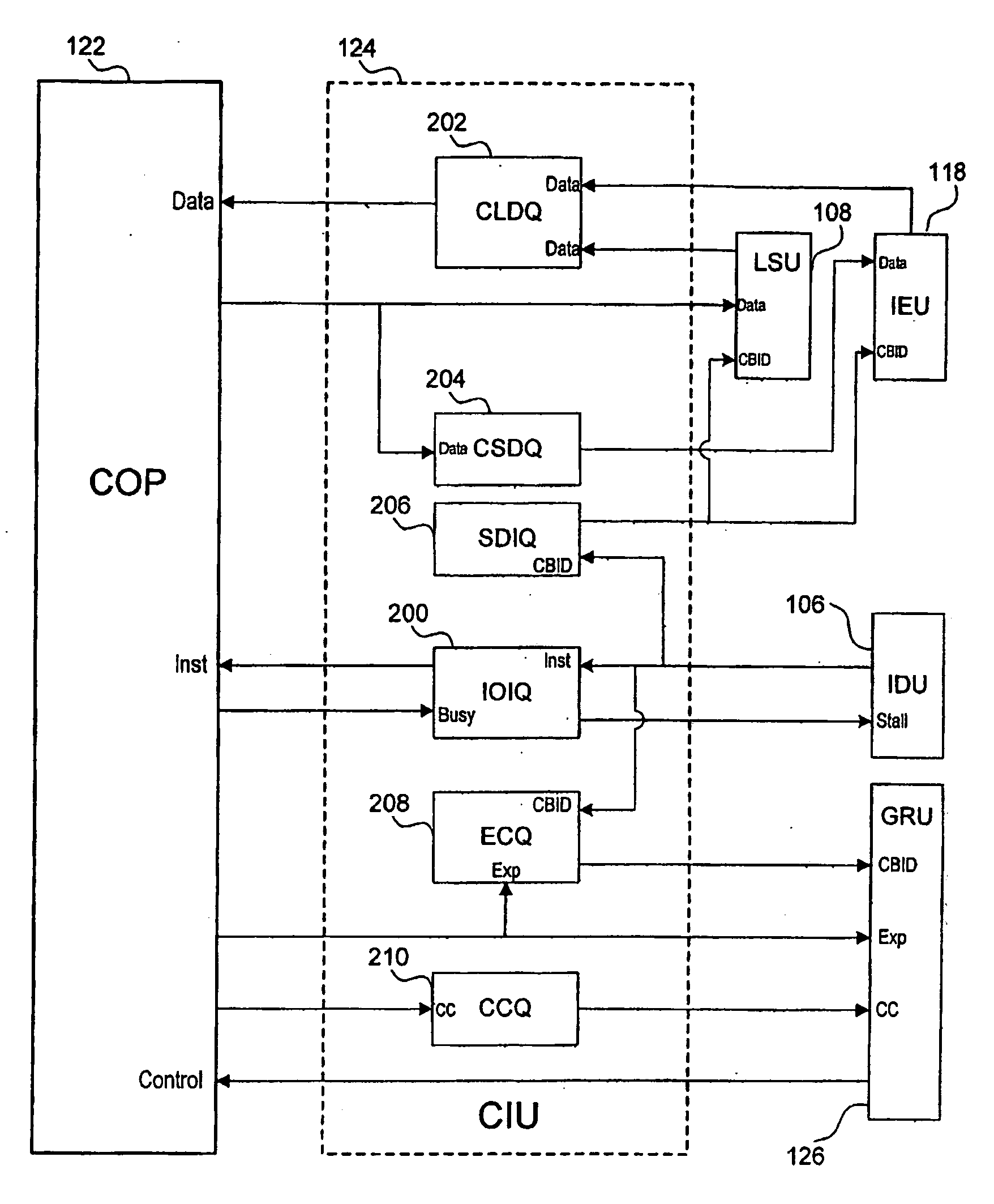
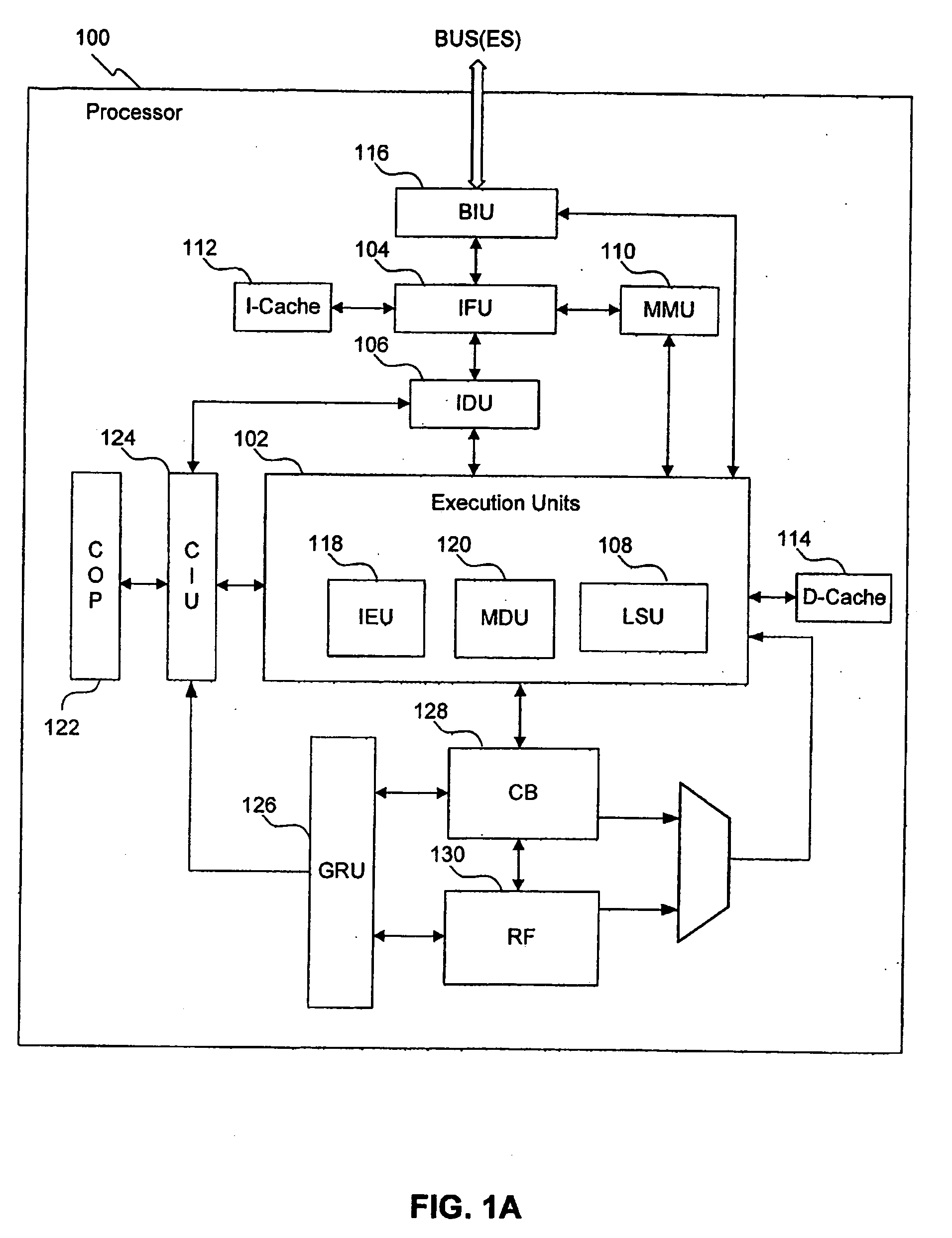
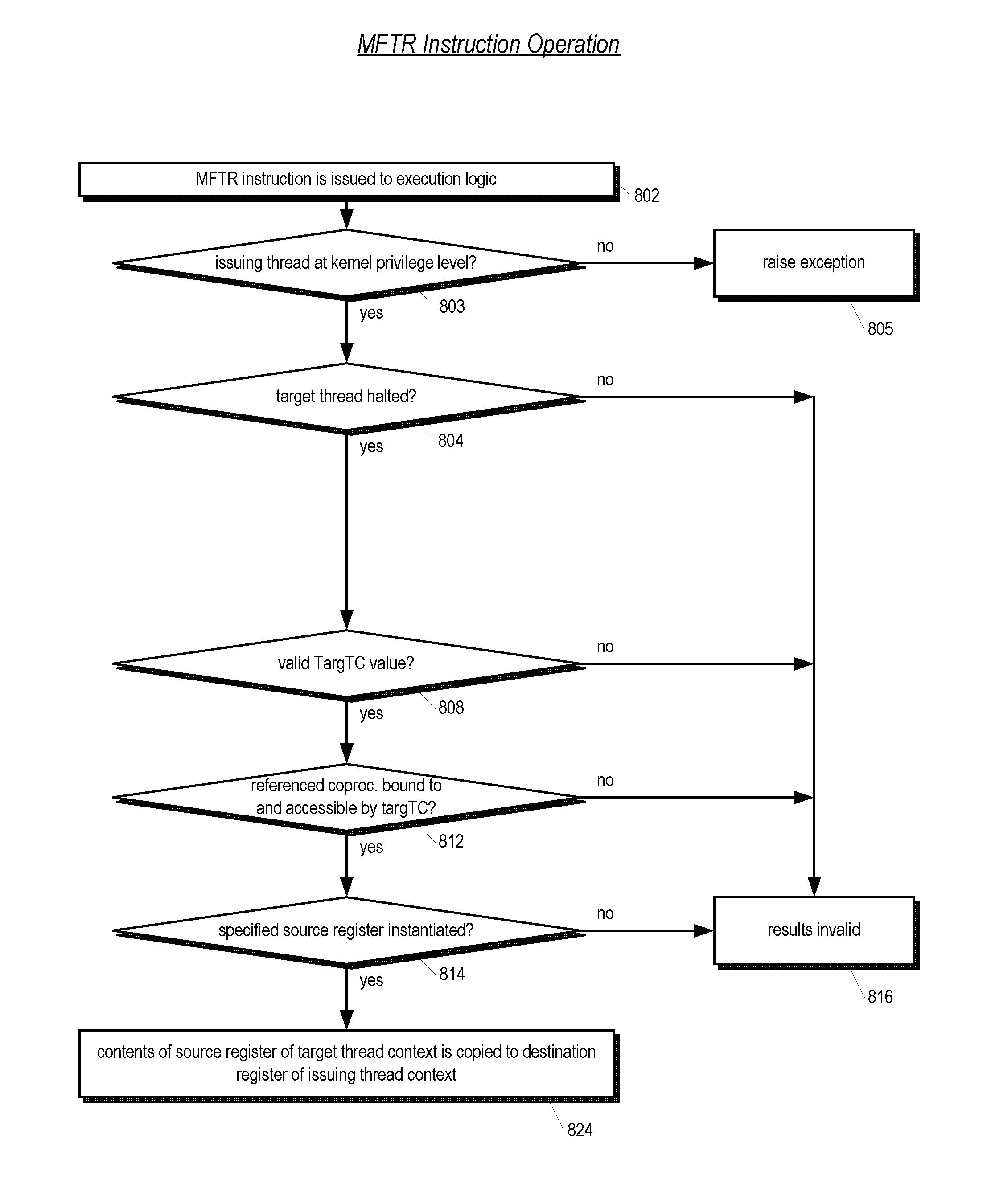
Out-of-order processor having an in-order coprocessor, and applications thereof
ActiveUS20080059771A1Runtime instruction translationGeneral purpose stored program computerCoprocessorScheduling instructions
An in-order coprocessor is interfaced to an out-of-order execution pipeline. In an embodiment, the interfacing is achieved using a coprocessor interface unit that includes an in-order instruction queue, a coprocessor load data queue, and a coprocessor store data queue. Instructions are written into the in-order instruction queue by an instruction dispatch unit. Instructions exit the in-order instruction queue and enter the coprocessor. In the coprocessor, the instructions operate on data read from the coprocessor load data queue. Data is written back, for example, to memory or a register file by inserting the data into the out-of-order execution pipeline, either directly or via the coprocessor store data queue, which writes back the data.
Owner:ARM FINANCE OVERSEAS LTD
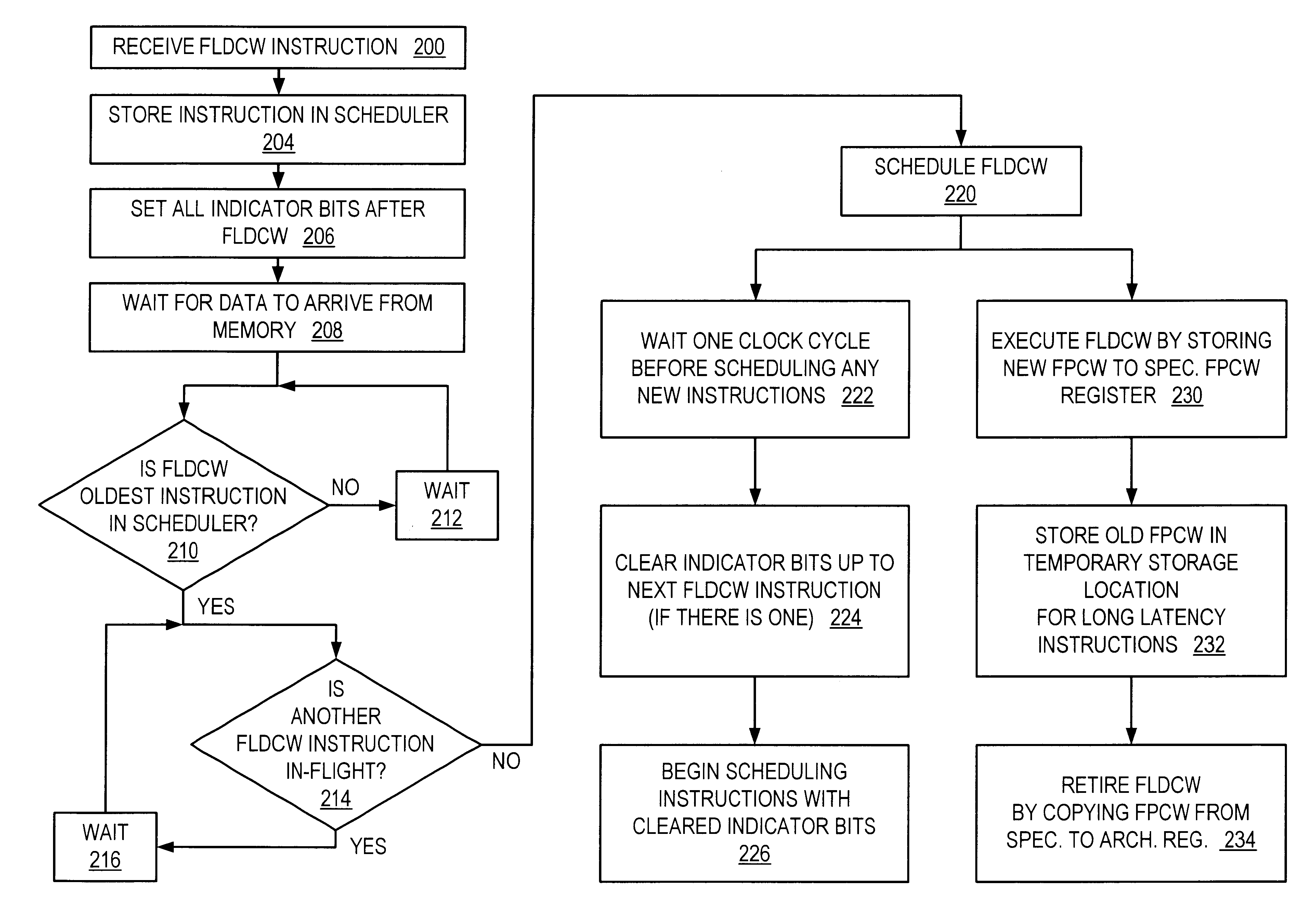
Rapid execution of floating point load control word instructions
InactiveUS6405305B1Conditional code generationDigital computer detailsScheduling instructionsParallel computing
A microprocessor with a floating point unit configured to rapidly execute floating point load control word (FLDCW) type instructions in an out of program order context is disclosed. The floating point unit is configured to schedule instructions older than the FLDCW-type instruction before the FLDCW-type instruction is scheduled. The FLDCW-type instruction acts as a barrier to prevent instructions occurring after the FLDCW-type instruction in program order from executing before the FLDCW-type instruction. Indicator bits may be used to simplify instruction scheduling, and copies of the floating point control word may be stored for instruction that have long execution cycles. A method and computer configured to rapidly execute FLDCW-type instructions in an out of program order context are also disclosed.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
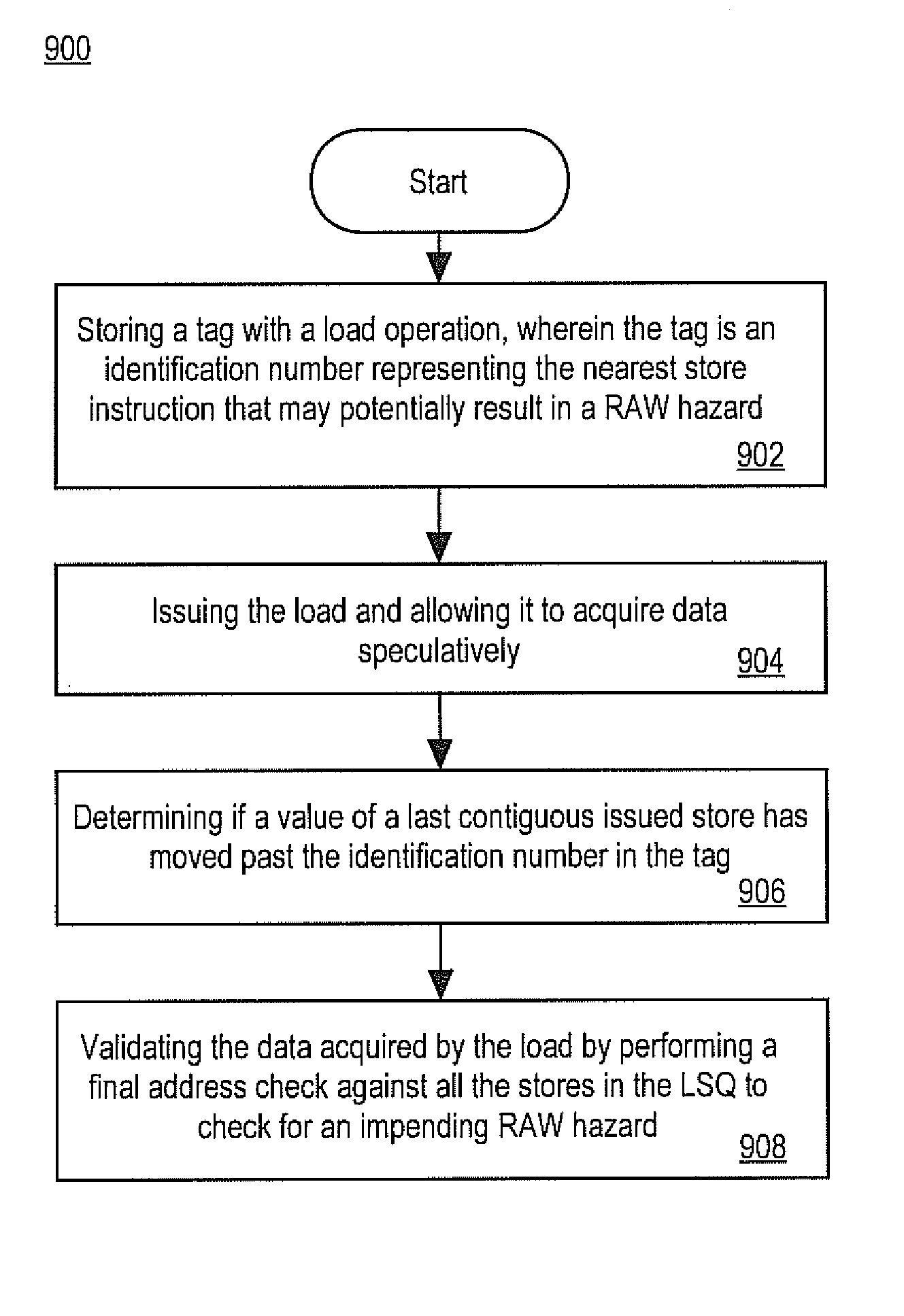
Method and apparatus for nearest potential store tagging
ActiveUS20140281409A1Easy to understandDigital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionScheduling instructionsParallel computing
A method for performing memory disambiguation in an out-of-order microprocessor pipeline is disclosed. The method comprises storing a tag with a load operation, wherein the tag is an identification number representing a store instruction nearest to the load operation, wherein the store instruction is older with respect to the load operation and wherein the store has potential to result in a RAW violation in conjunction with the load operation. The method also comprises issuing the load operation from an instruction scheduling module. Further, the method comprises acquiring data for the load operation speculatively after the load operation has arrived at a load store queue module. Finally, the method comprises determining if an identification number associated with a last contiguous issued store with respect to the load operation is equal to or greater than the tag and gating a validation process for the load operation in response to the determination.
Owner:INTEL CORP
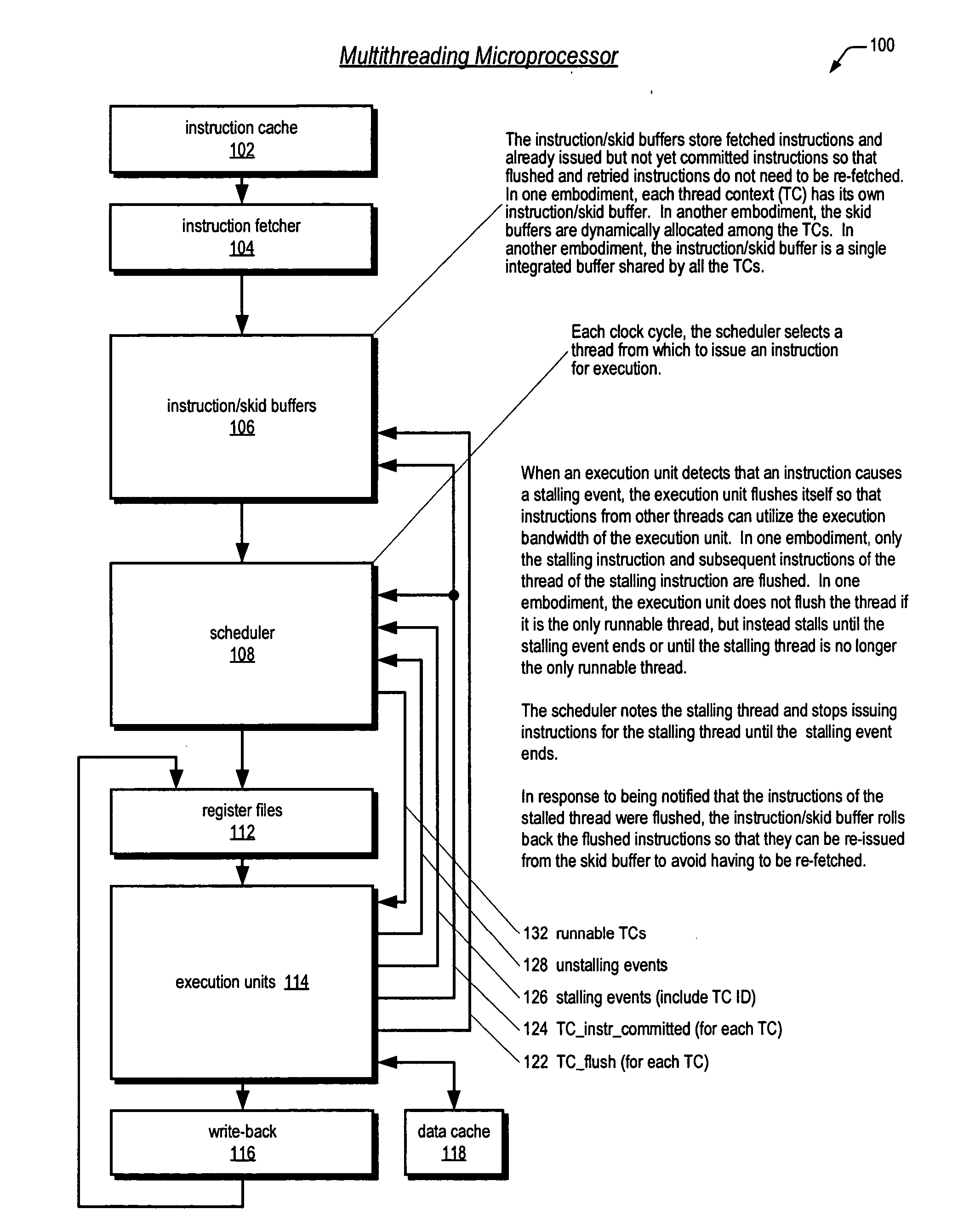
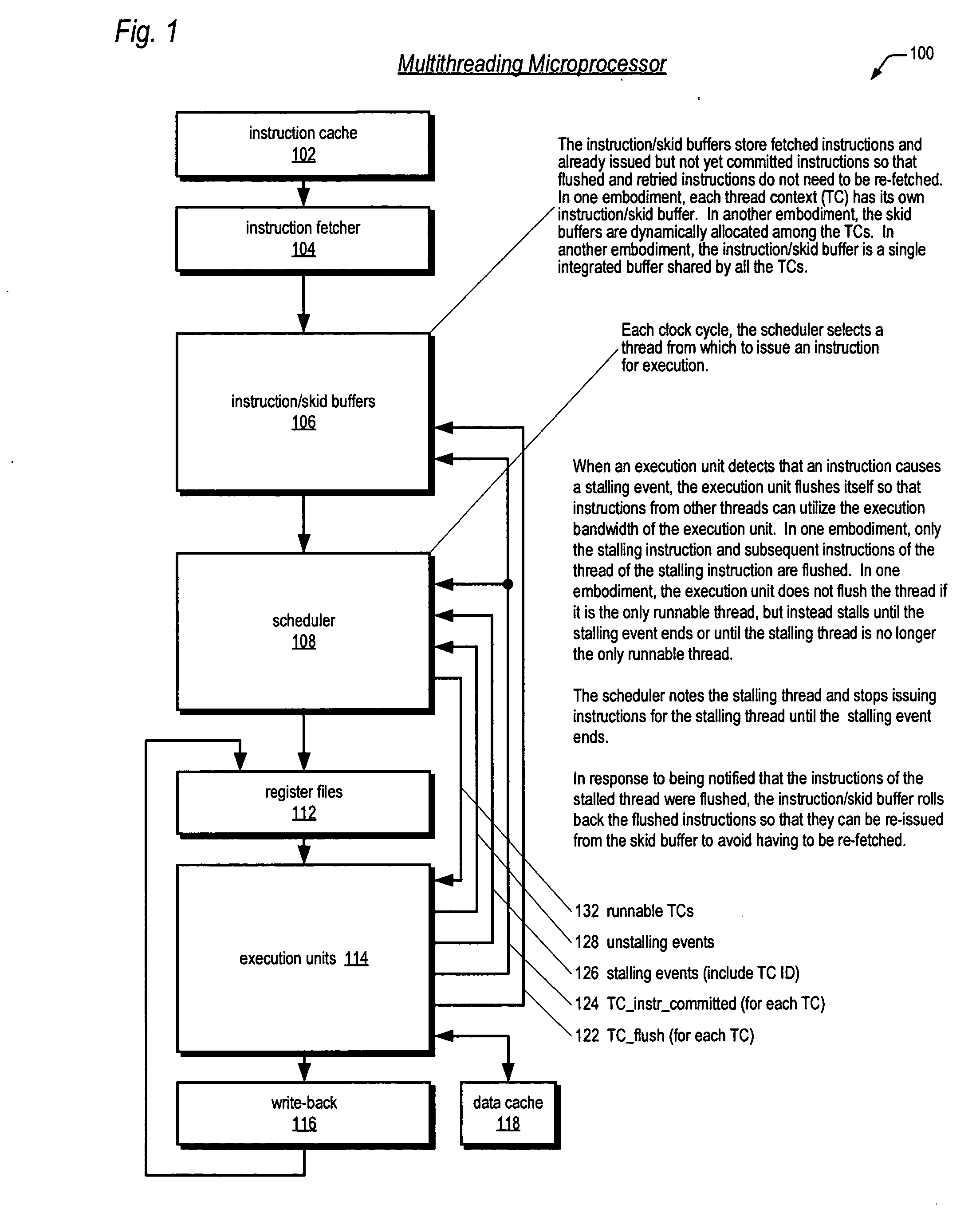
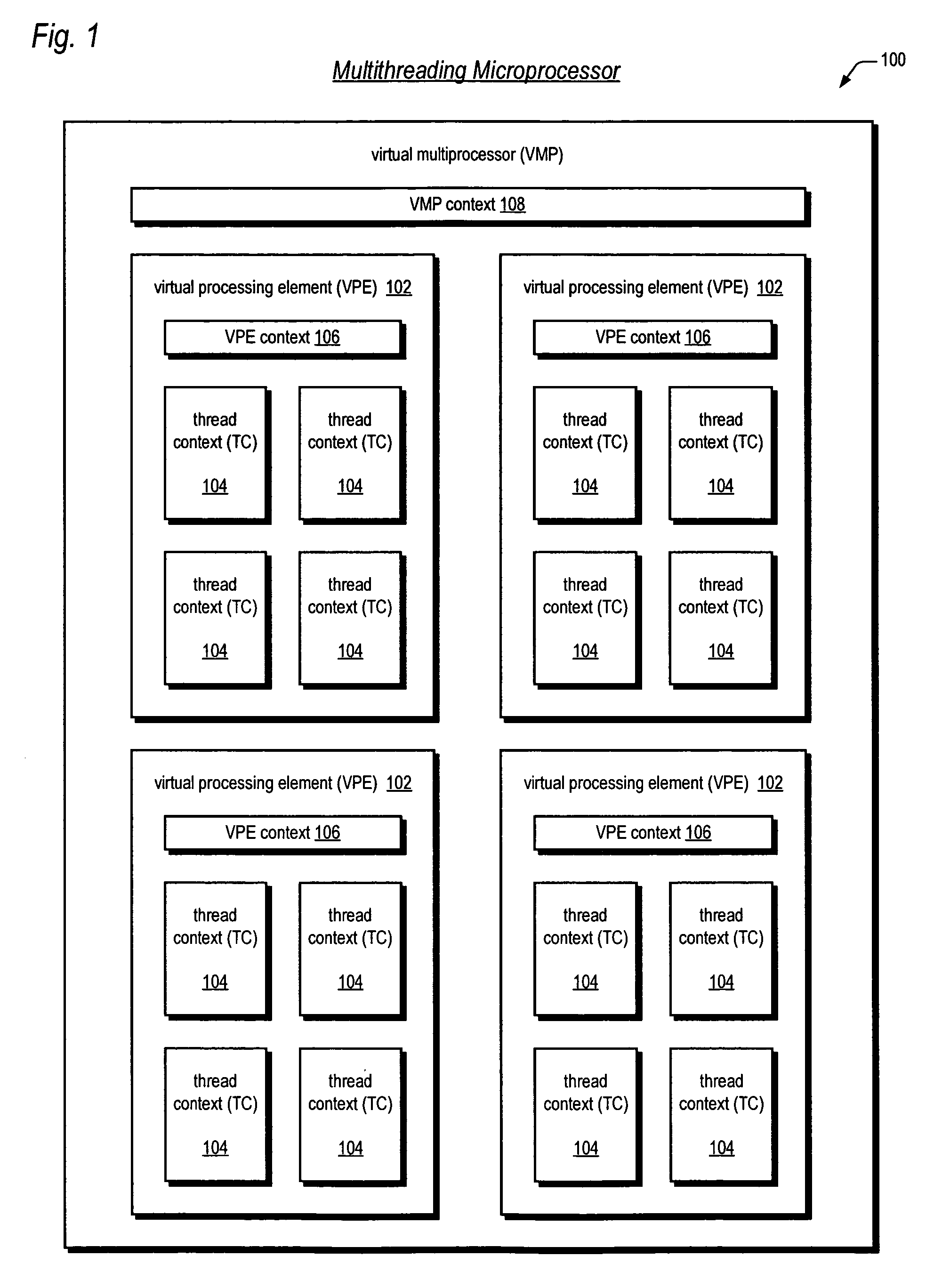
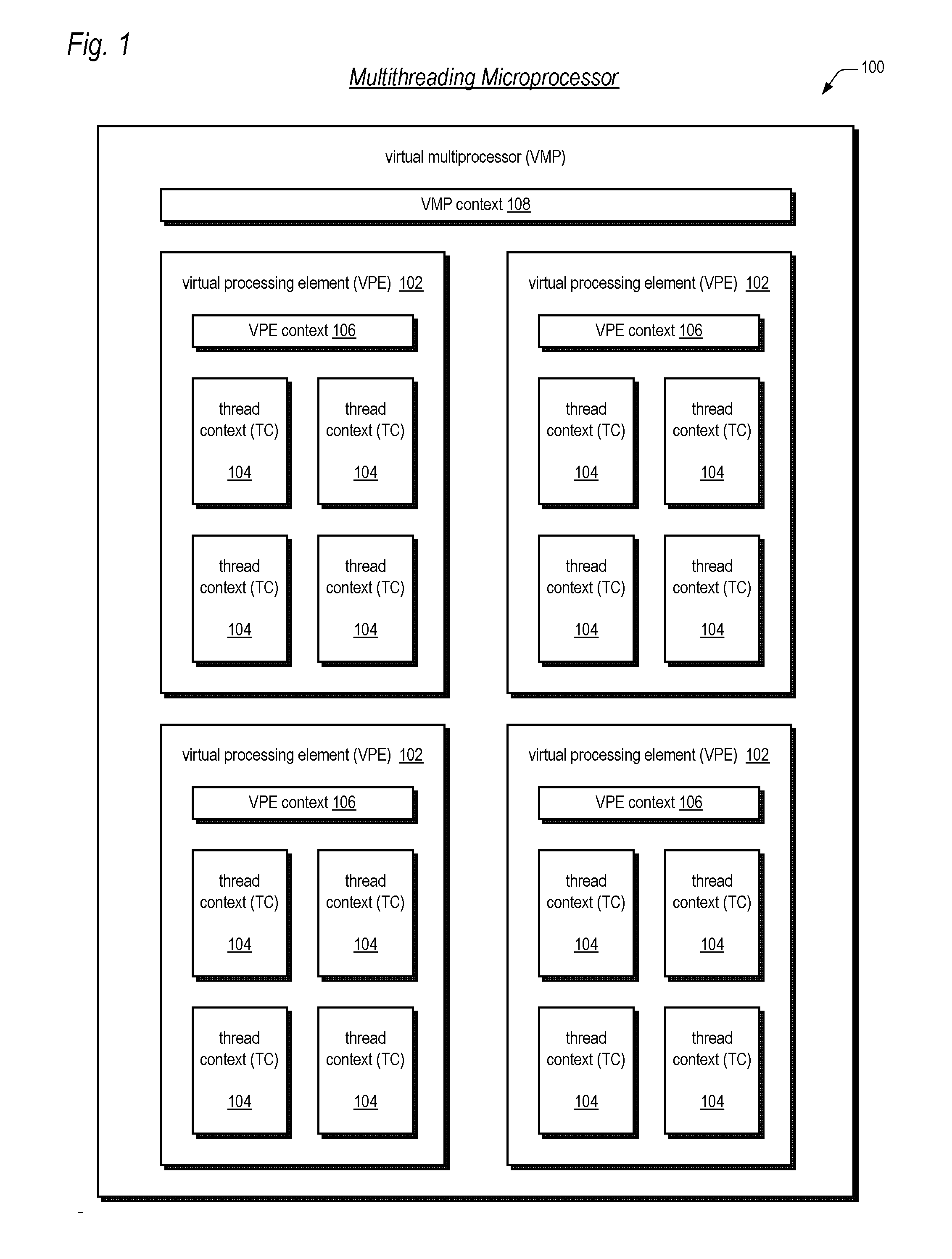
Symmetric multiprocessor operating system for execution on non-independent lightweight thread context
ActiveUS20060190946A1Lightweight in of chip areaLightweight in of power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTMultiprogramming arrangementsOperational systemMulti processor
A multiprocessing system is disclosed. The system includes a multithreading microprocessor having a plurality of thread contexts (TCs), a translation lookaside buffer (TLB) shared by the plurality of TCs, and an instruction scheduler, coupled to the plurality of TCs, configured to dispatch to execution units, in a multithreaded fashion, instructions of threads executing on the plurality of TCs. The system also includes a multiprocessor operating system (OS), configured to schedule execution of the threads on the plurality of TCs, wherein a thread of the threads executing on one of the plurality of TCs is configured to update the shared TLB, and prior to updating the TLB to disable interrupts, to prevent the OS from unscheduling the TLB-updating thread from executing on the plurality of TCs, and disable the instruction scheduler from dispatching instructions from any of the plurality of TCs except from the one of the plurality of TCs on which the TLB-updating thread is executing.
Owner:MIPS TECH INC
Symmetric multiprocessor operating system for execution on non-independent lightweight thread contexts
ActiveUS20070044106A2Lightweight in of areaLightweight in of powerMultiprogramming arrangementsMemory systemsOperational systemMulti processor
A multiprocessing system is disclosed. The system includes a multithreading microprocessor having a plurality of thread contexts (TCs), a translation lookaside buffer (TLB) shared by the plurality of TCs, and an instruction scheduler, coupled to the plurality of TCs, configured to dispatch to execution units, in a multithreaded fashion, instructions of threads executing on the plurality of TCs. The system also includes a multiprocessor operating system (OS), configured to schedule execution of the threads on the plurality of TCs, wherein a thread of the threads executing on one of the plurality of TCs is configured to update the shared TLB, and prior to updating the TLB to disable interrupts, to prevent the OS from unscheduling the TLB-updating thread from executing on the plurality of TCs, and disable the instruction scheduler from dispatching instructions from any of the plurality of TCs except from the one of the plurality of TCs on which the TLB-updating thread is executing.
Owner:MIPS TECH INC
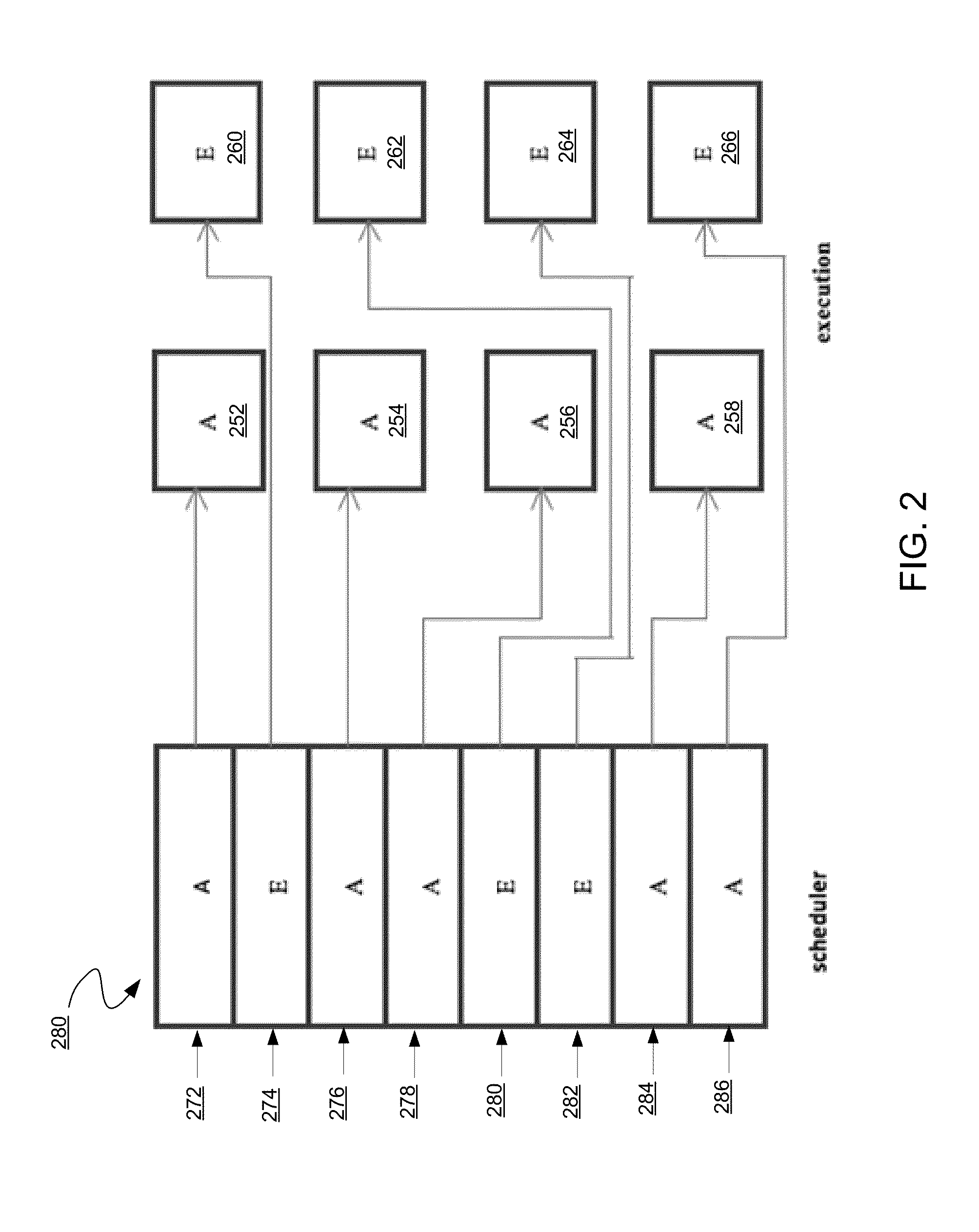
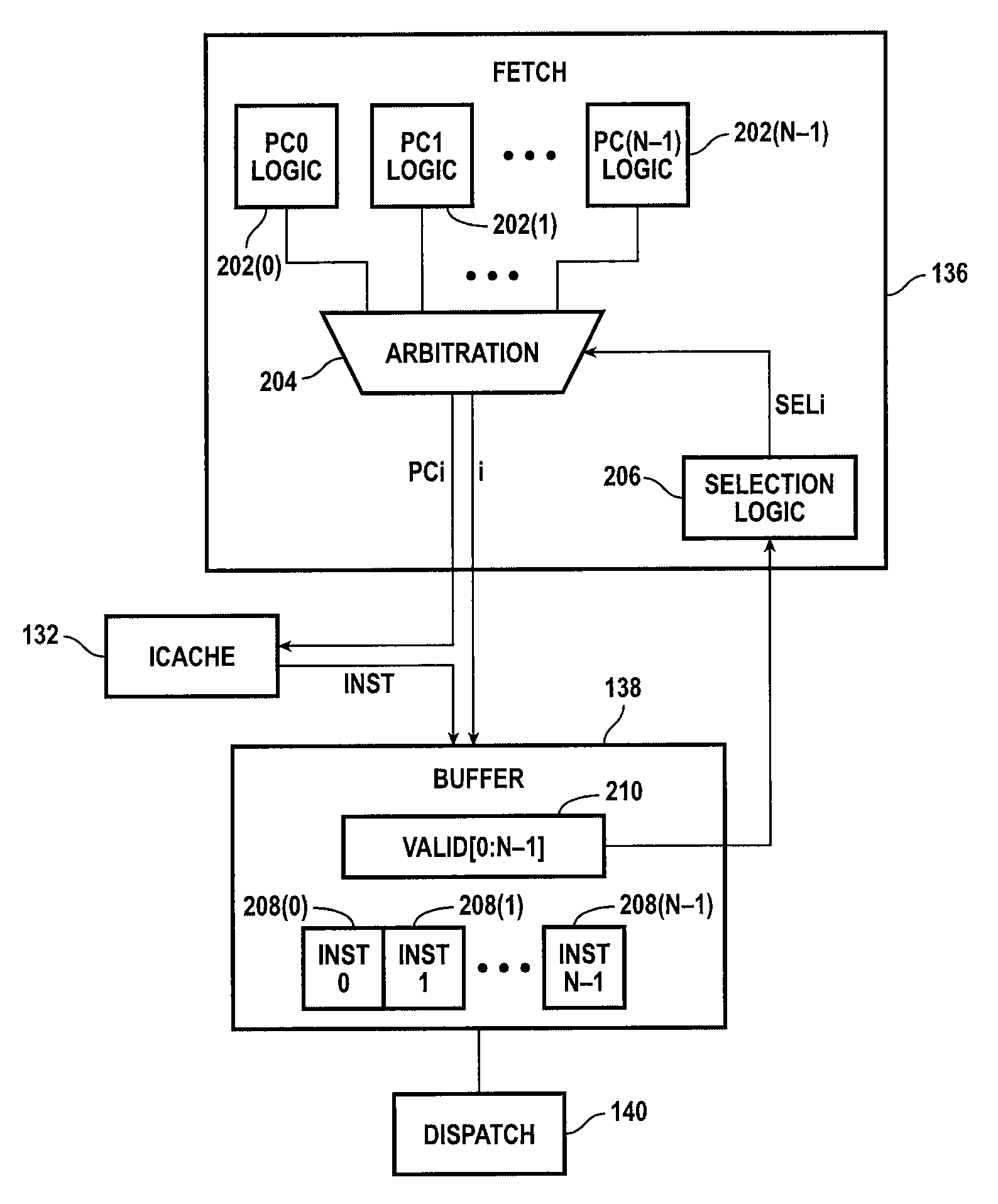
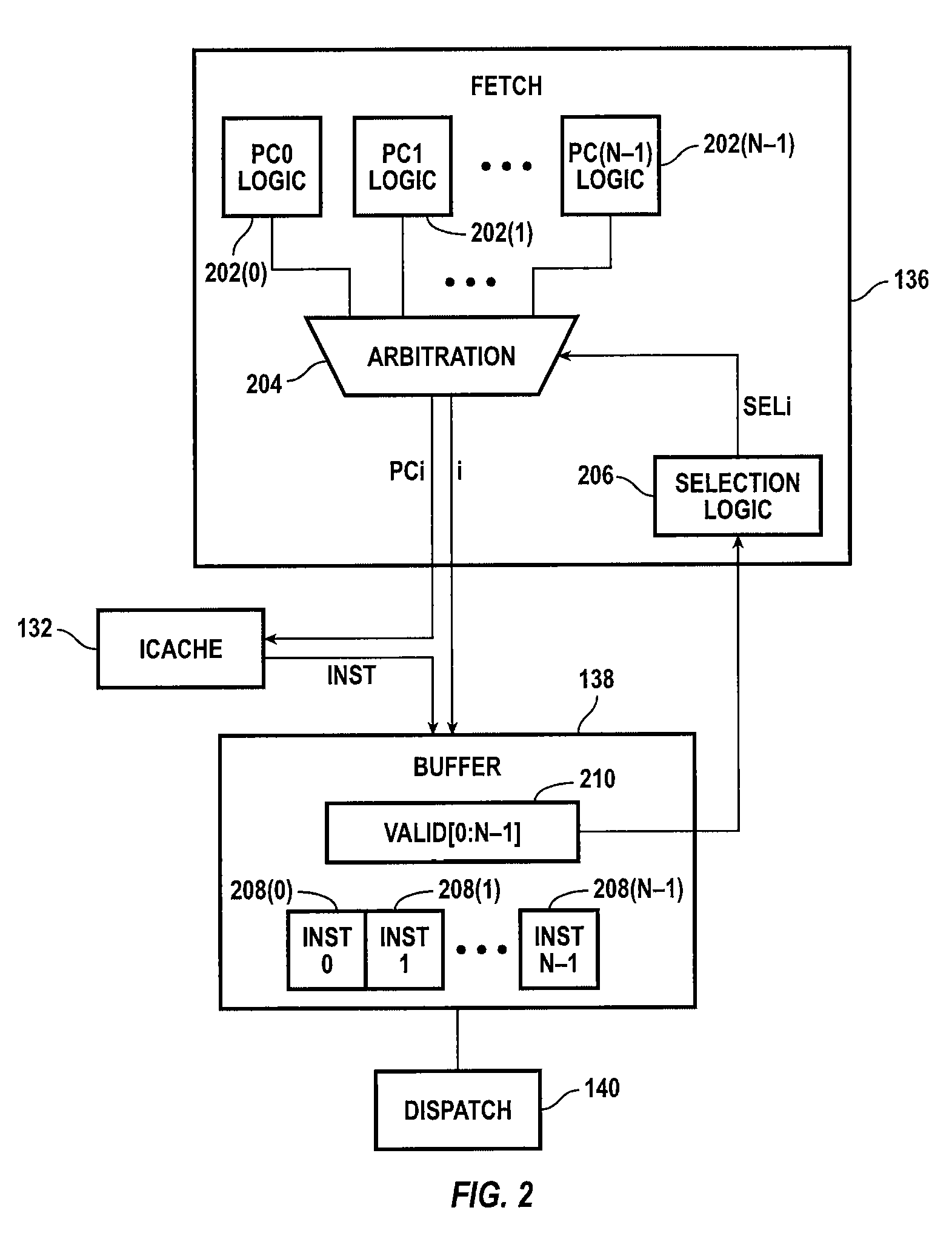
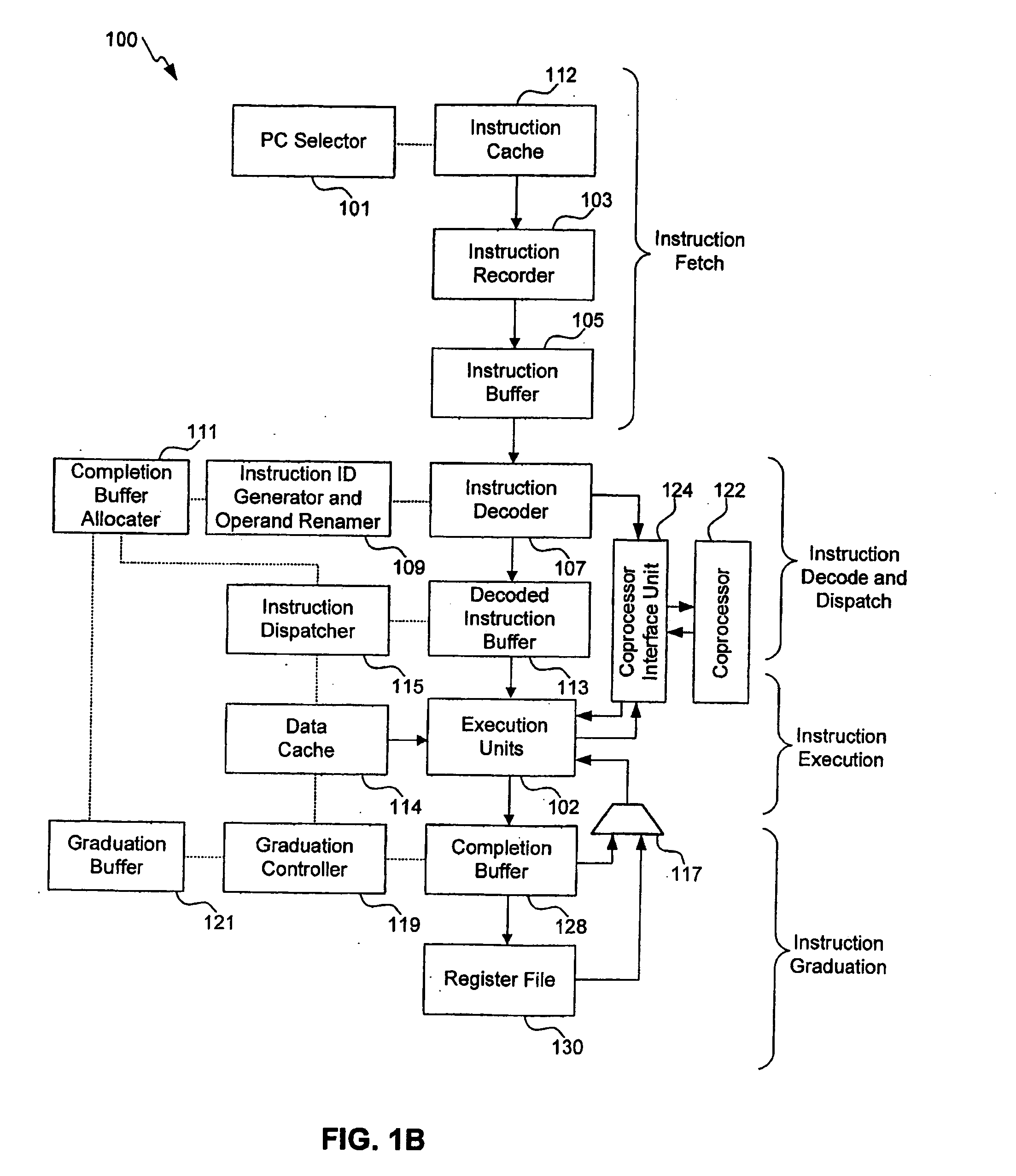
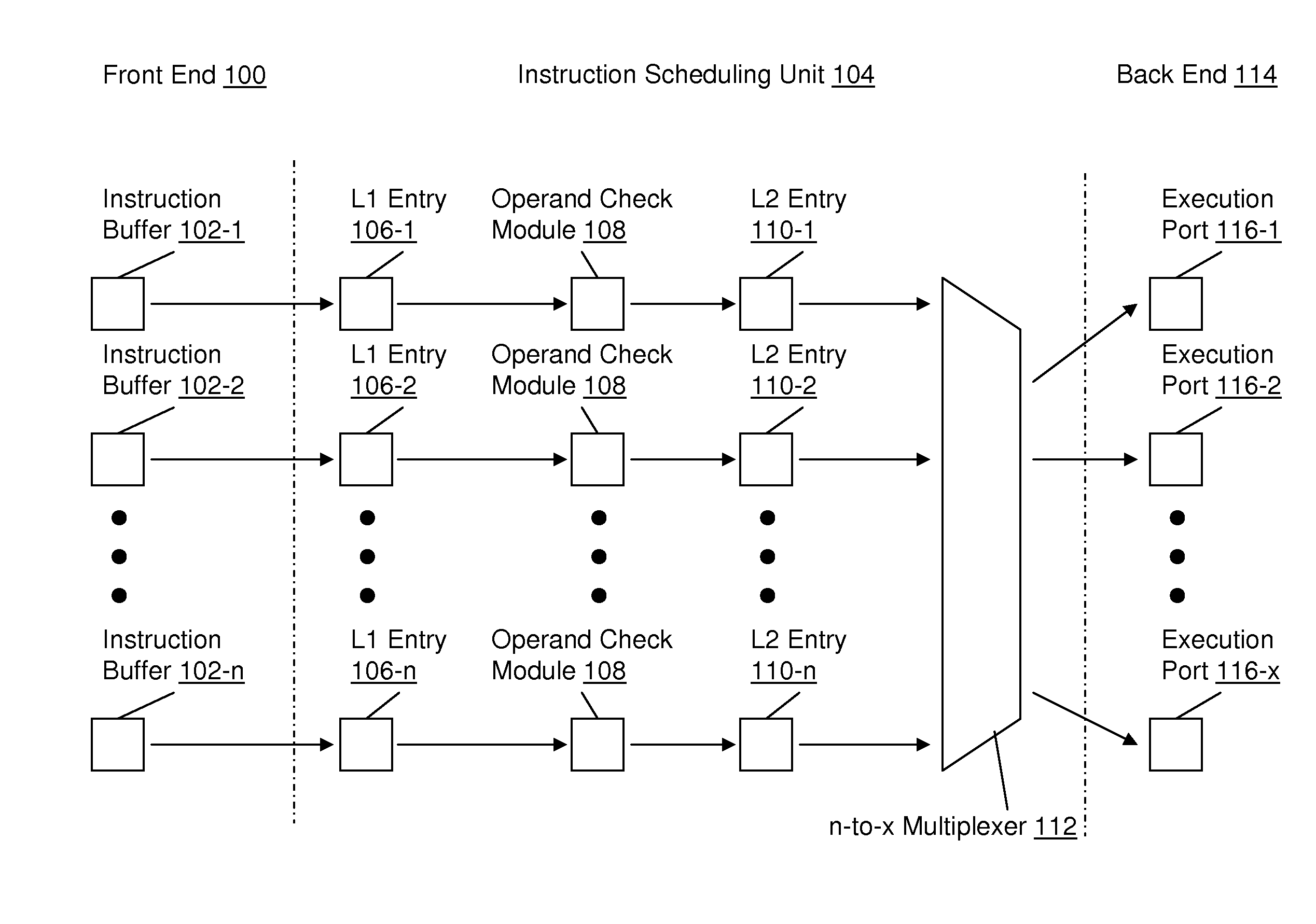
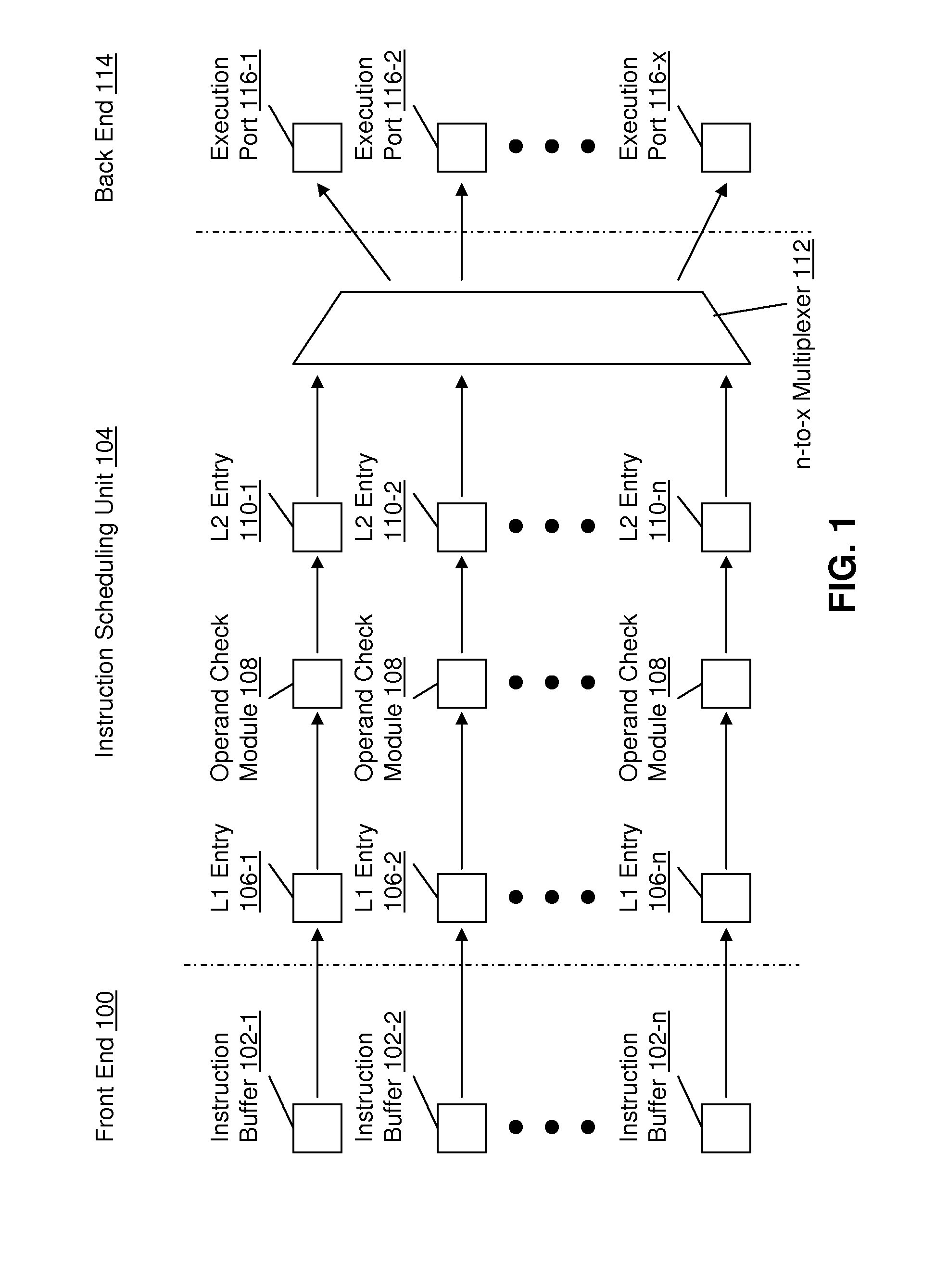
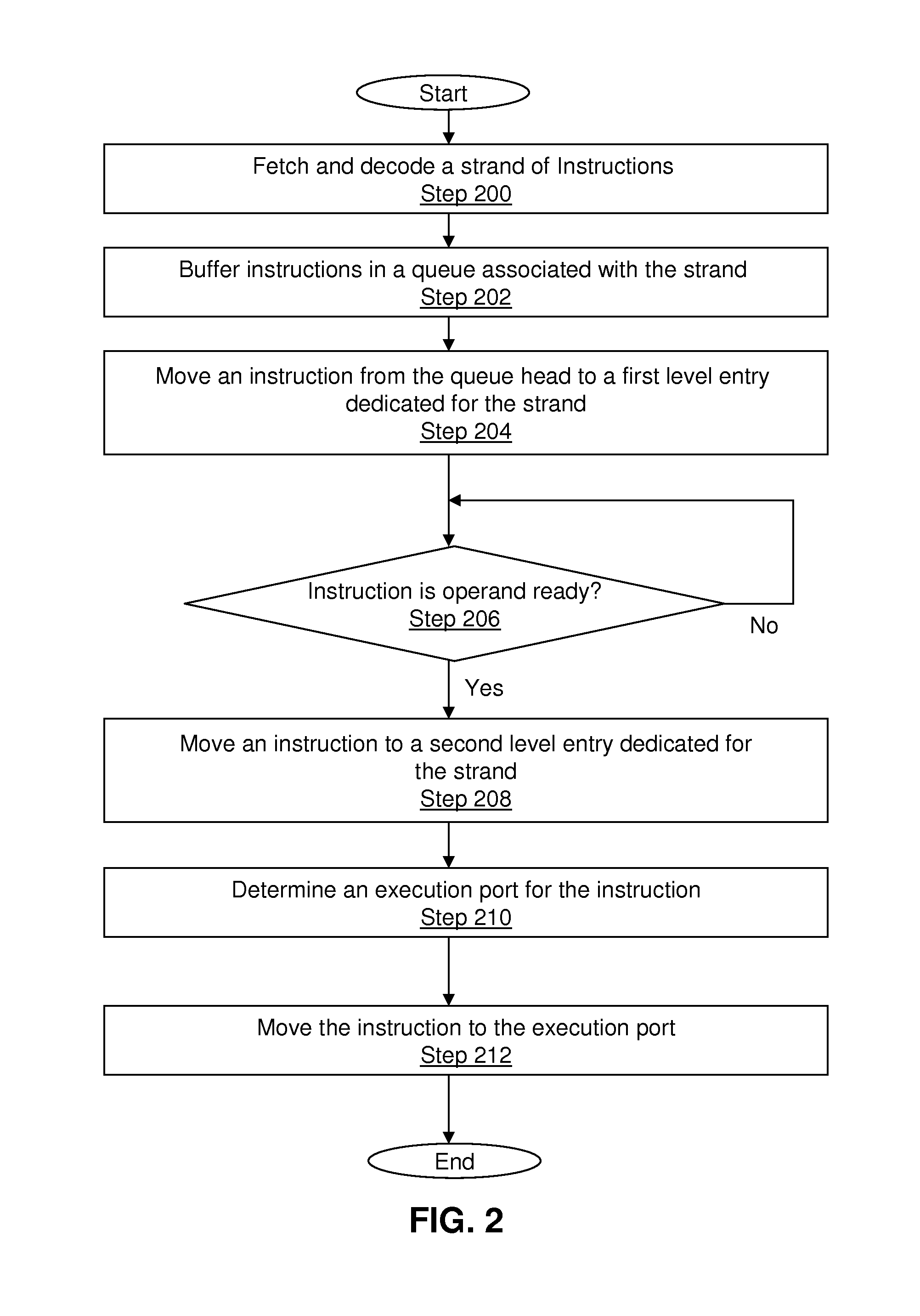
Instruction scheduling for a multi-strand out-of-order processor
In one embodiment, a multi-strand system with a pipeline includes a front-end unit, an instruction scheduling unit (ISU), and a back-end unit. The front-end unit performs an out-of-order fetch of interdependent instructions queued using a front-end buffer. The ISU dedicates two hardware entries per strand for checking operand-readiness of an instruction and for determining an execution port to which the instruction is dispatched. The back-end unit receives instructions dispatched from the hardware device and stores the instructions until they are executed. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Multiple instruction dispatch tables for application program obfuscation
ActiveUS7353499B2Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsProgram instructionScheduling instructions
Obfuscating an application program comprises reading an application program comprising code, determining multiple dispatch tables associated with the application program, transforming the application program into application program code configured to utilize the dispatch tables during application program execution to determine the location of instruction implementation methods to be executed based at least in part on a current instruction counter value, and sending the application program code. Executing an obfuscated application program comprises receiving an obfuscated application program comprising at least one instruction opcode value encoded using one of multiple instruction set opcode value encoding schemes, receiving an application program instruction corresponding to a current instruction counter value, selecting an instruction dispatch table based at least in part on the current instruction counter value, and executing the application program instruction using the selected instruction dispatch table.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method and apparatus for integrated instruction scheduling and register allocation in a postoptimizer
The present invention describes a method of efficiently optimizing instruction scheduling and register allocation in a post optimizer. The method removes false register dependencies between pipelined instructions by building an incremental (partial) interference graph of register allocation for scheduled instructions. False dependency graph indicates the amount of parallelism in the data flow graph. The incremental interference graph uses a mix of virtual and physical registers. The interference graph is built incrementally as an instruction schedular schedules each instruction. The optimization is done incrementally on localized code. The physical register mapping is maximized and virtual registers are created on demand basis.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
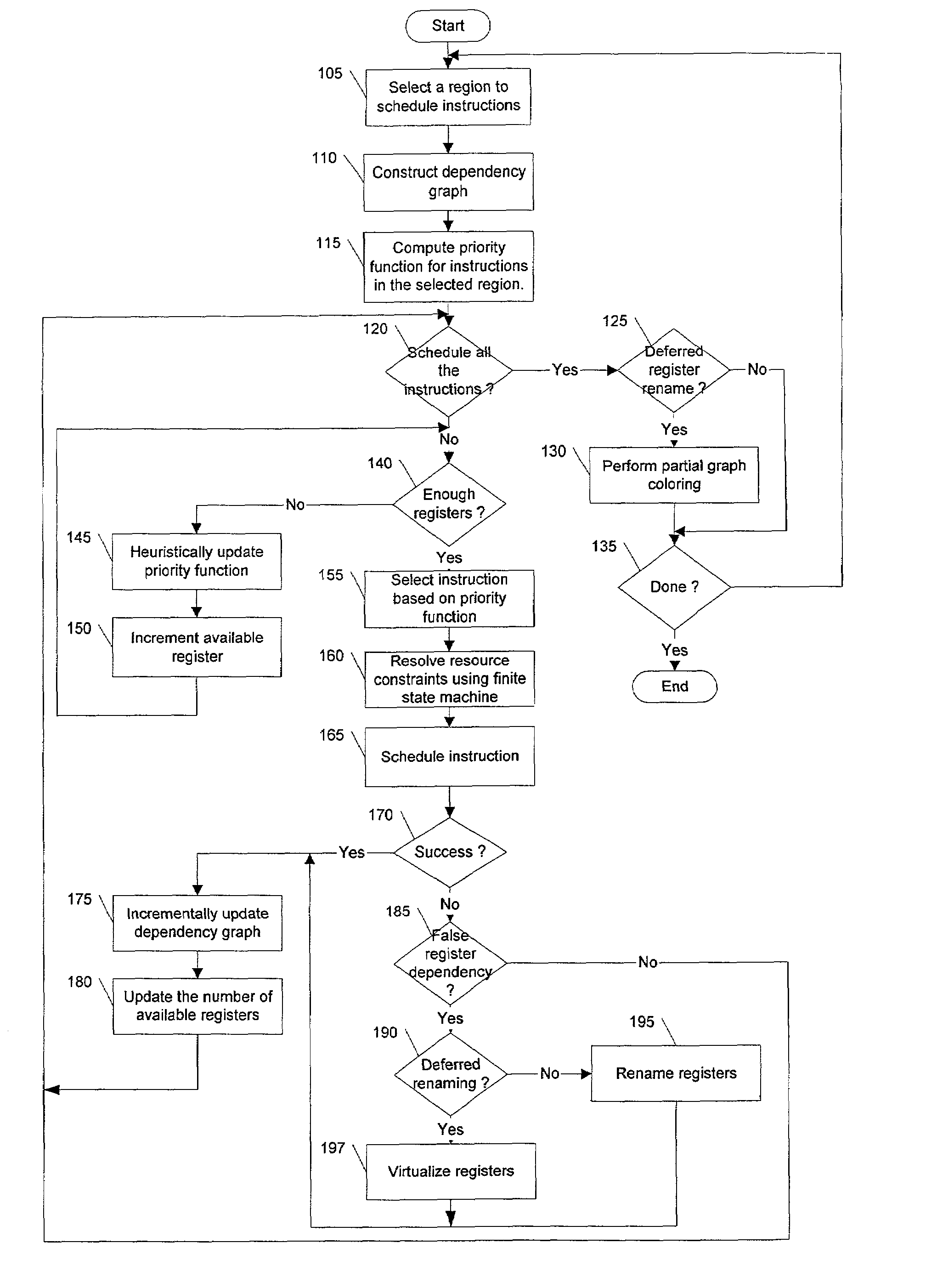
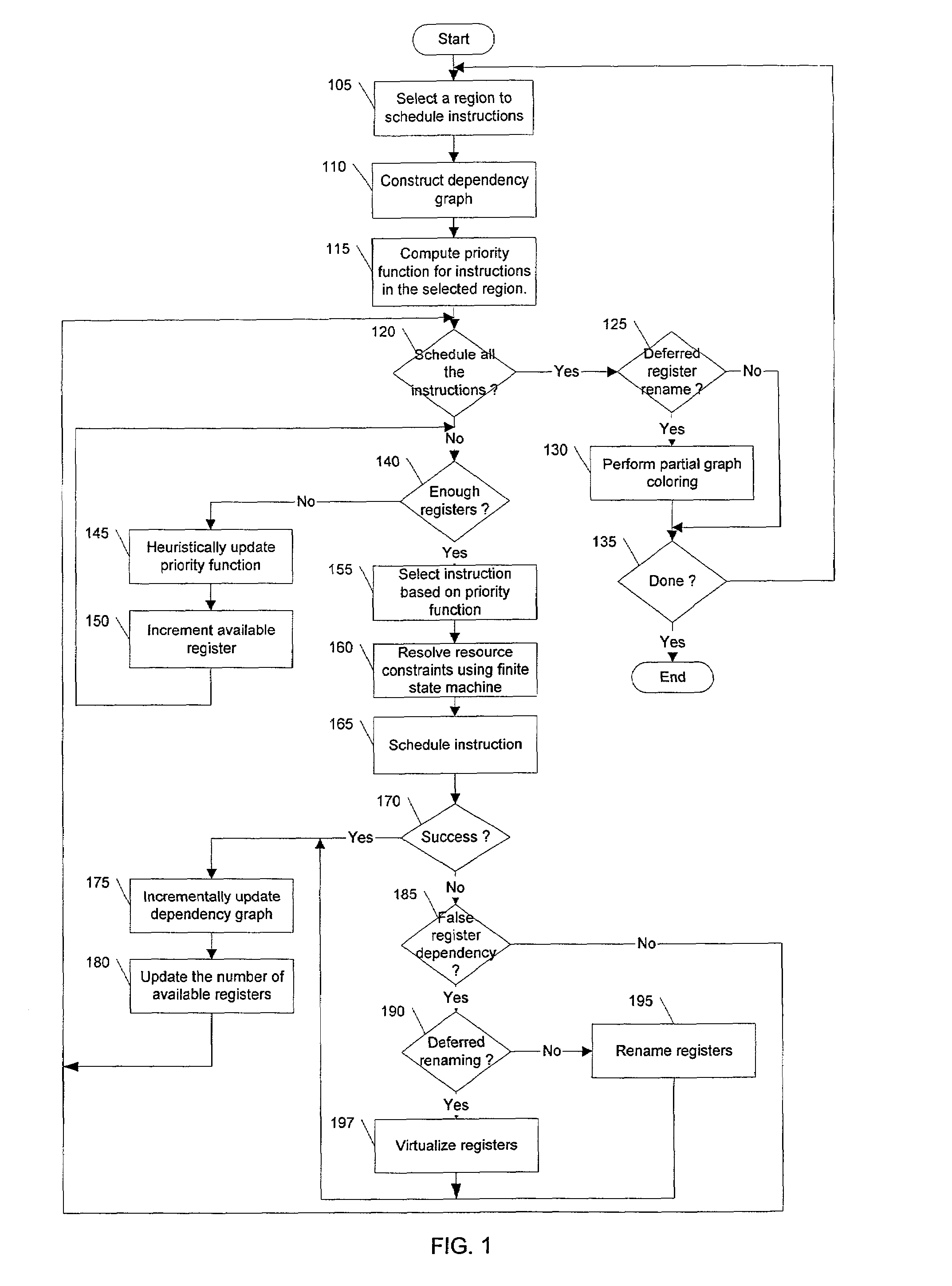
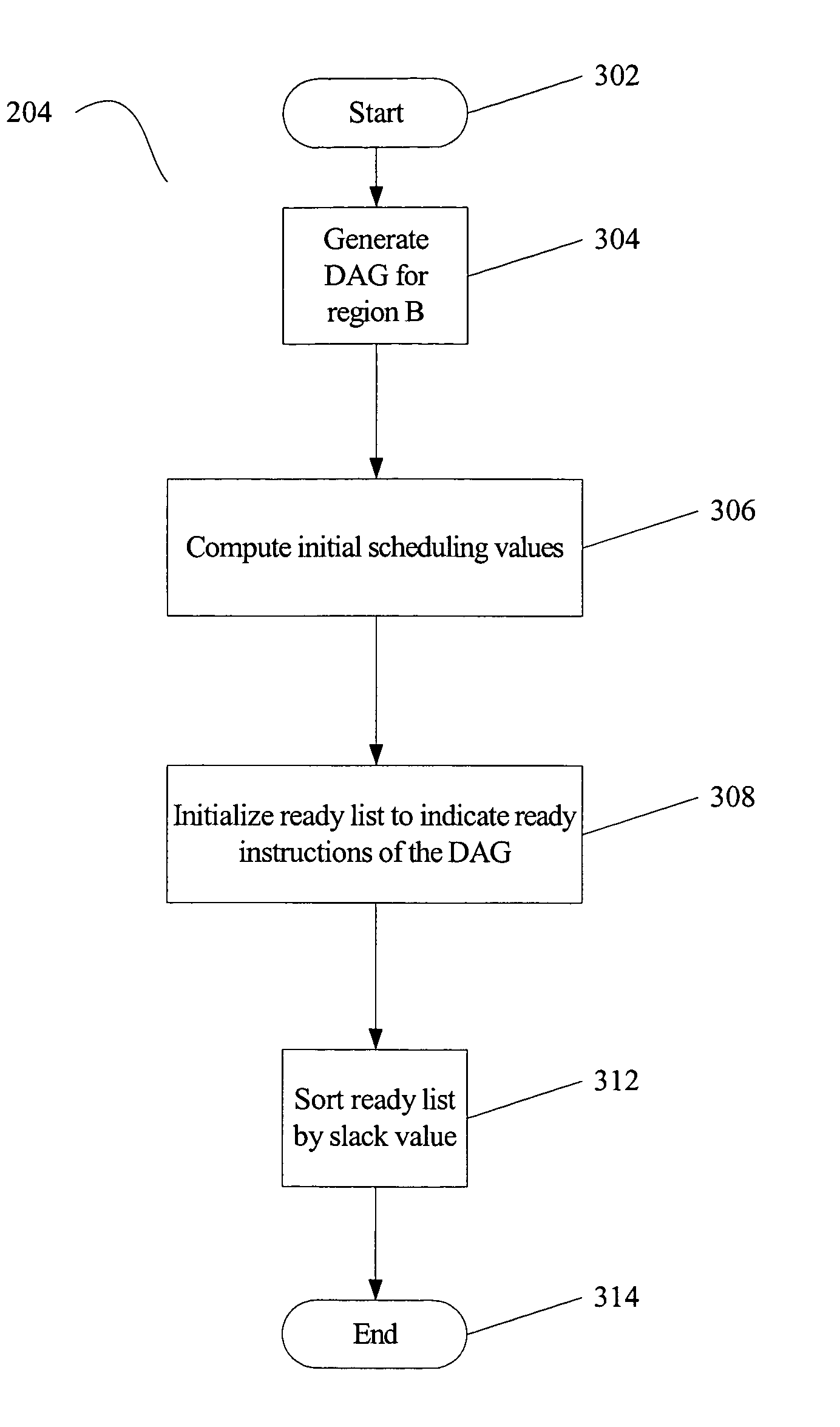
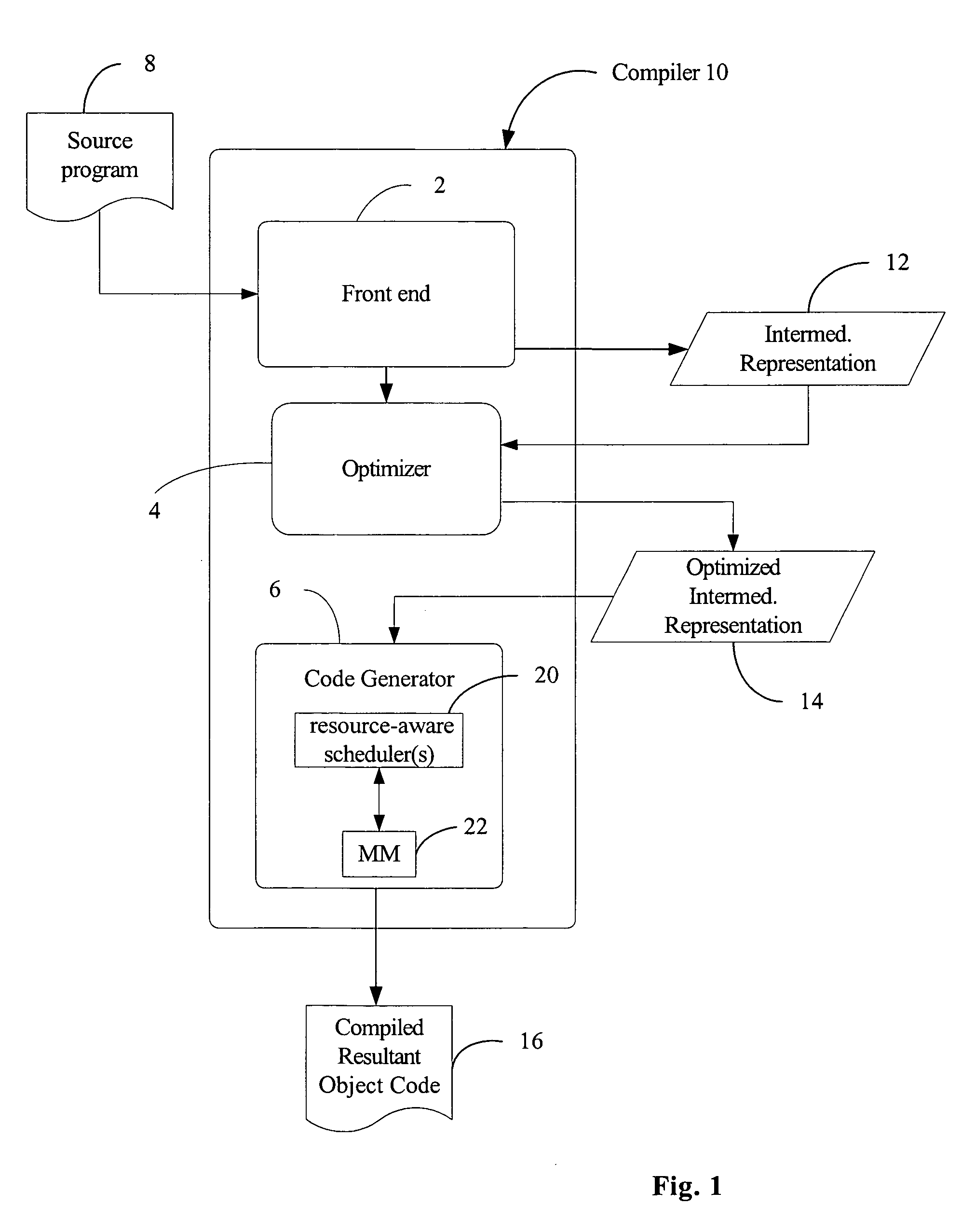
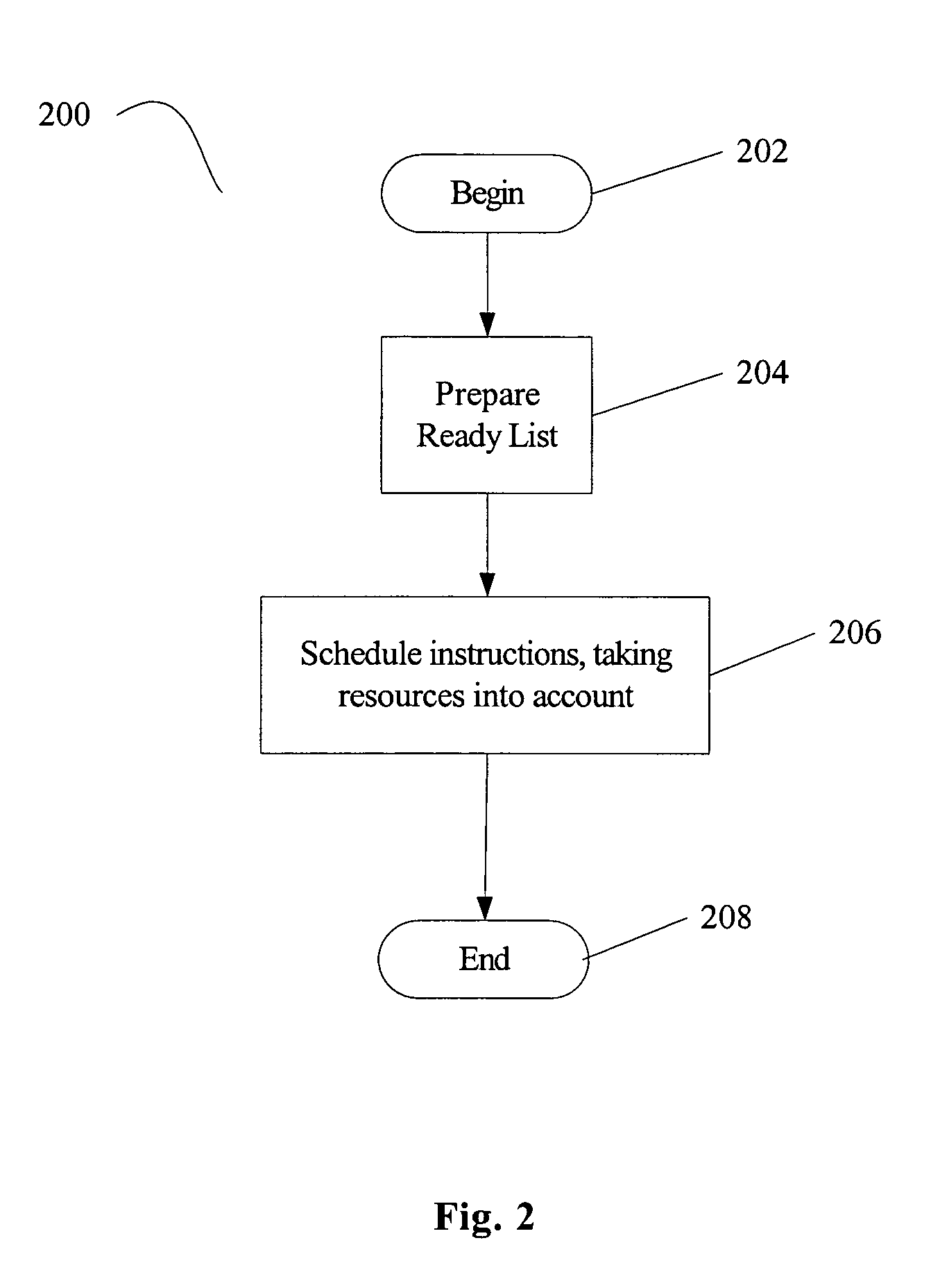
Resource-aware scheduling for compilers
Disclosed are embodiments of a compiler, methods, and system for resource-aware scheduling of instructions. A list scheduling approach is augmented to take into account resource constraints when determining priority for scheduling of instructions. Other embodiments are also described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com