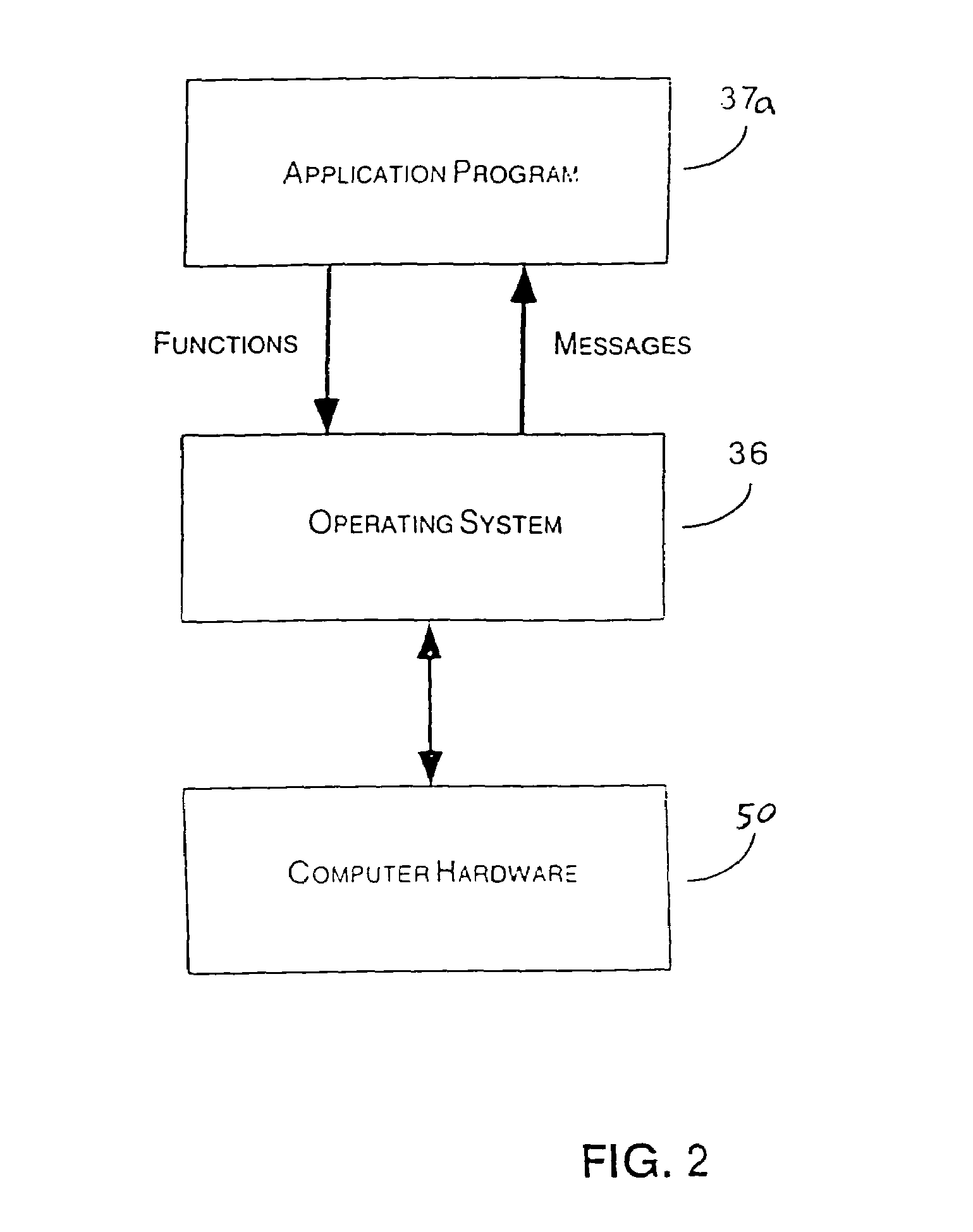
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
316 results about "Resource constraints" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
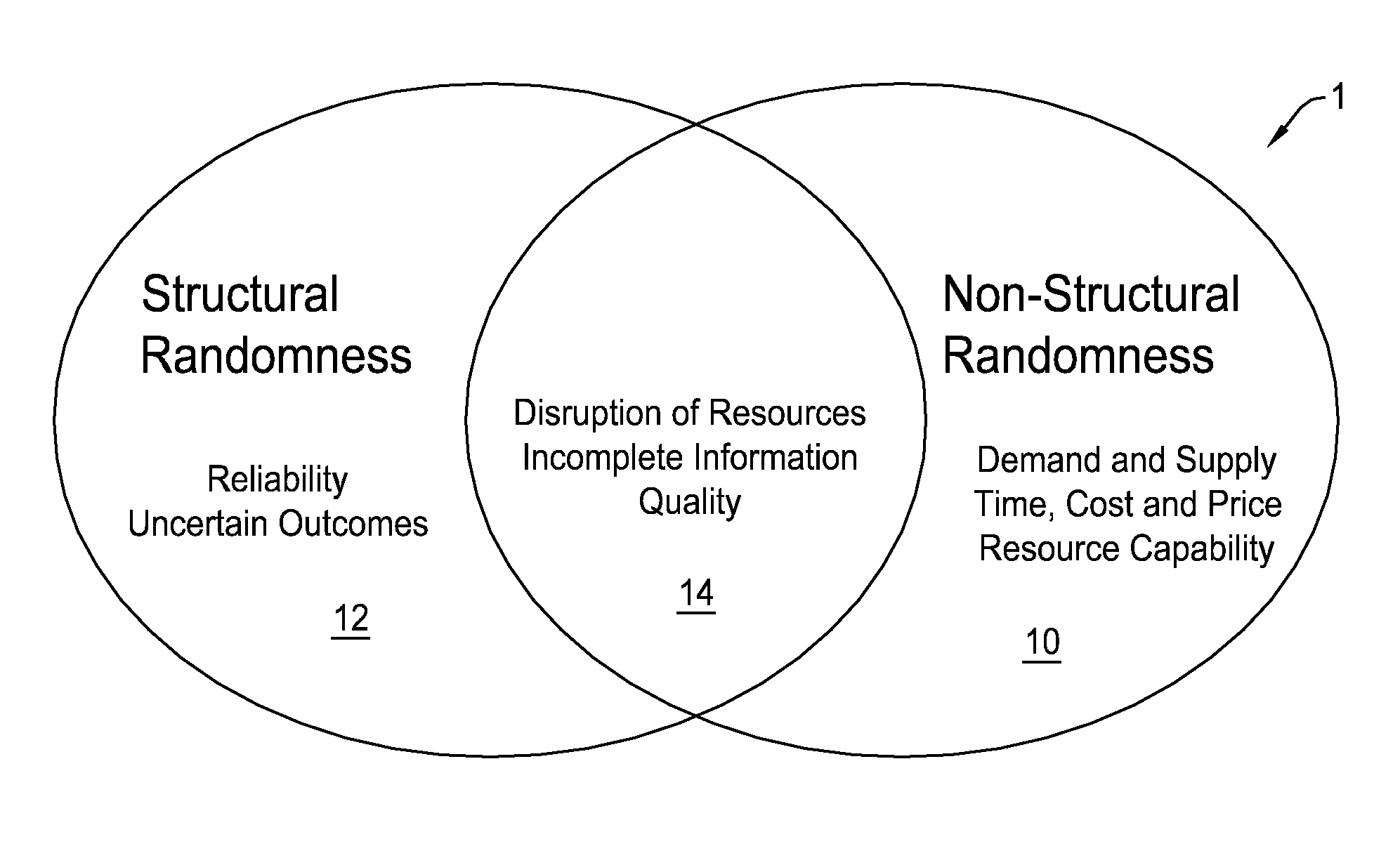
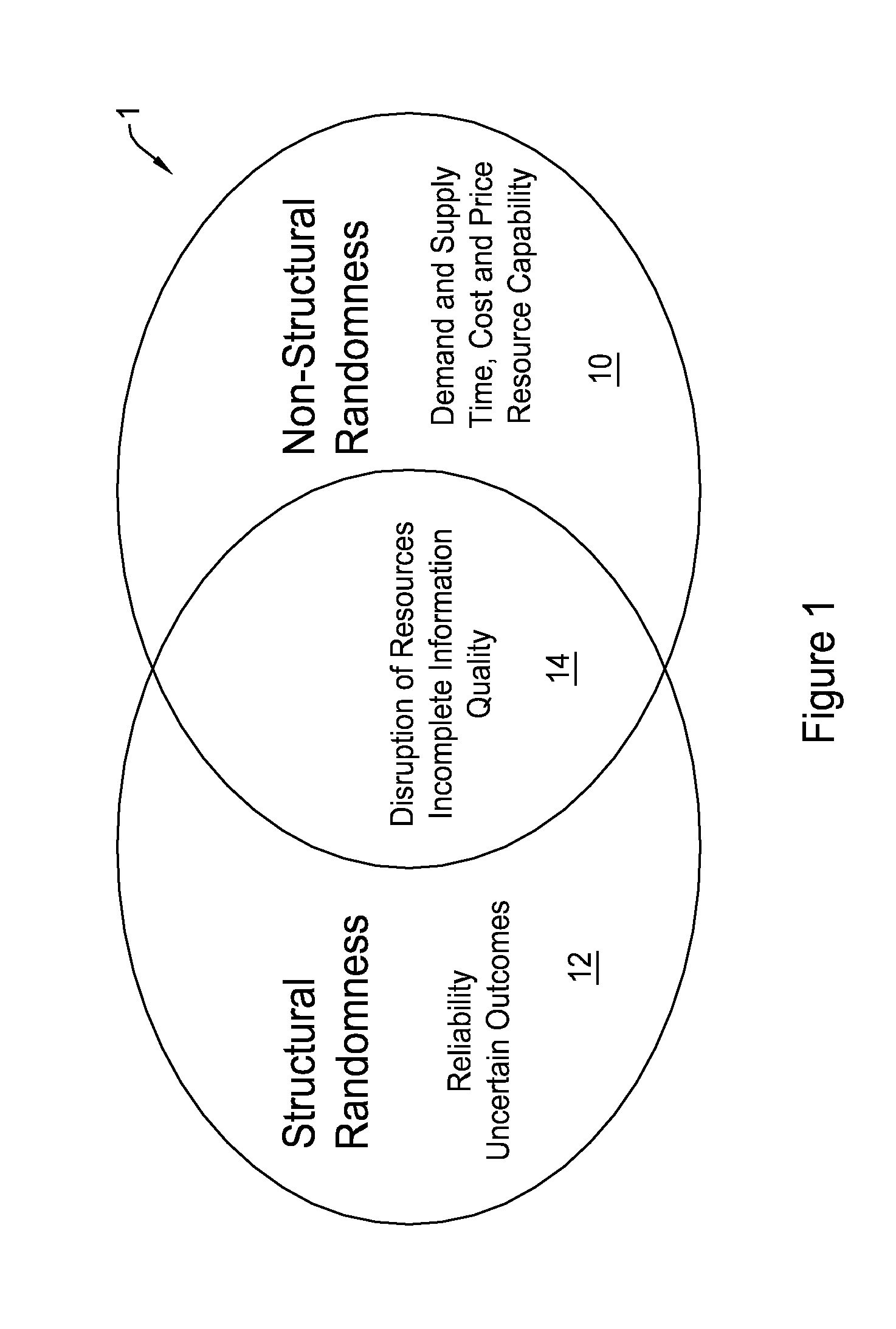
The resource constraint definition refers to the limitations of inputs available to complete a particular job: primarily people time, equipment and supplies. Every project you accept will require some combination of time and resources.
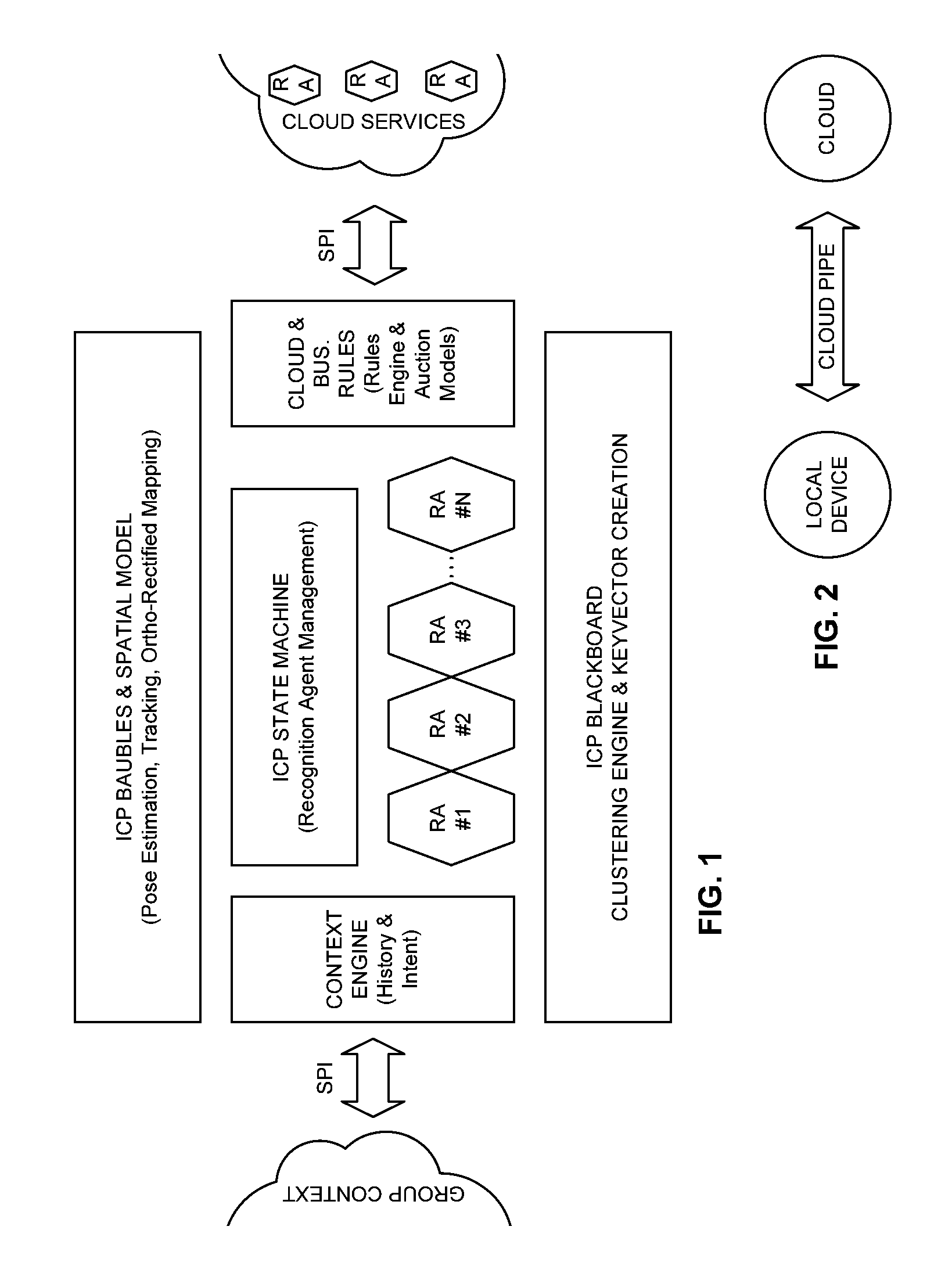
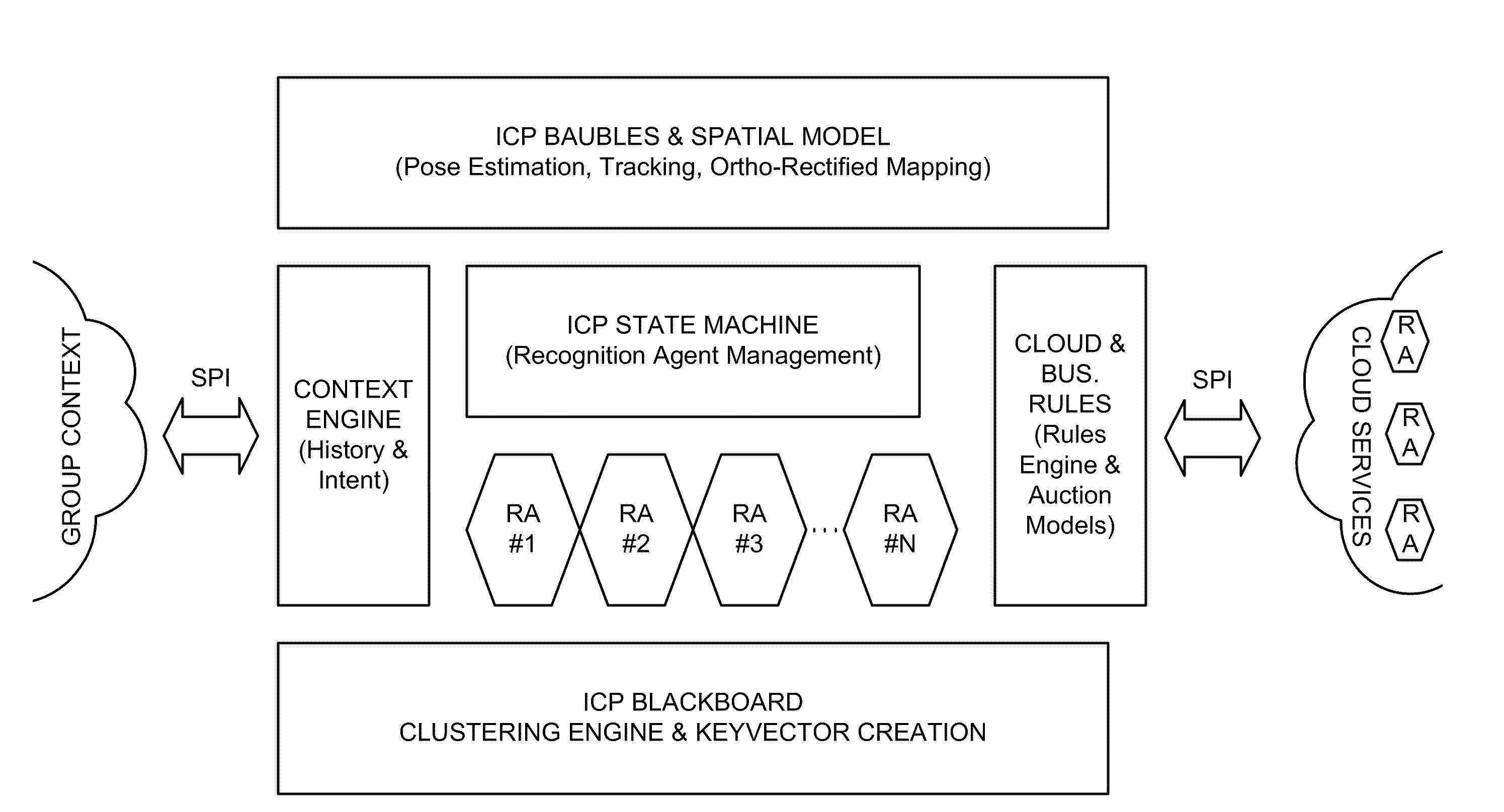
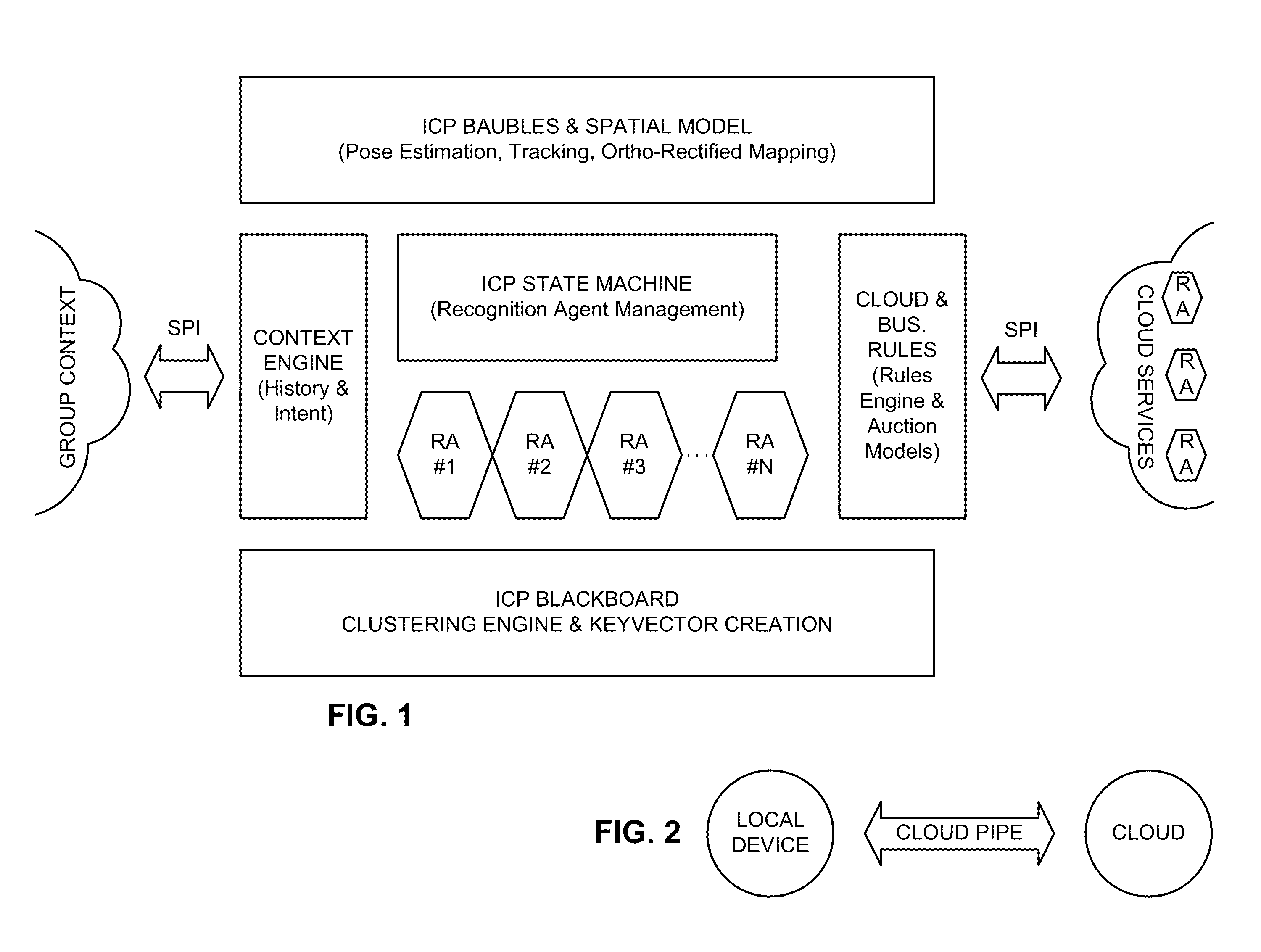
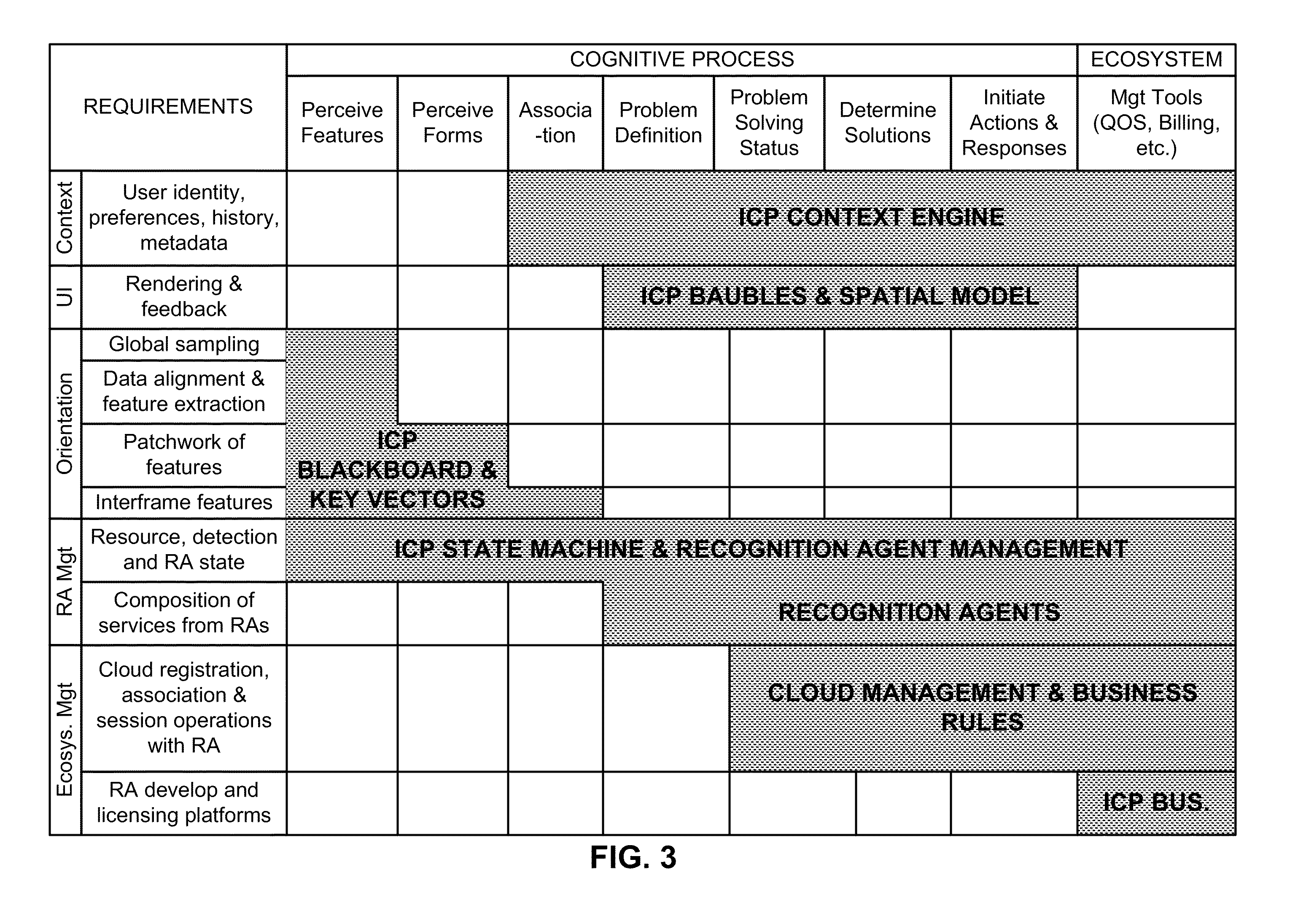
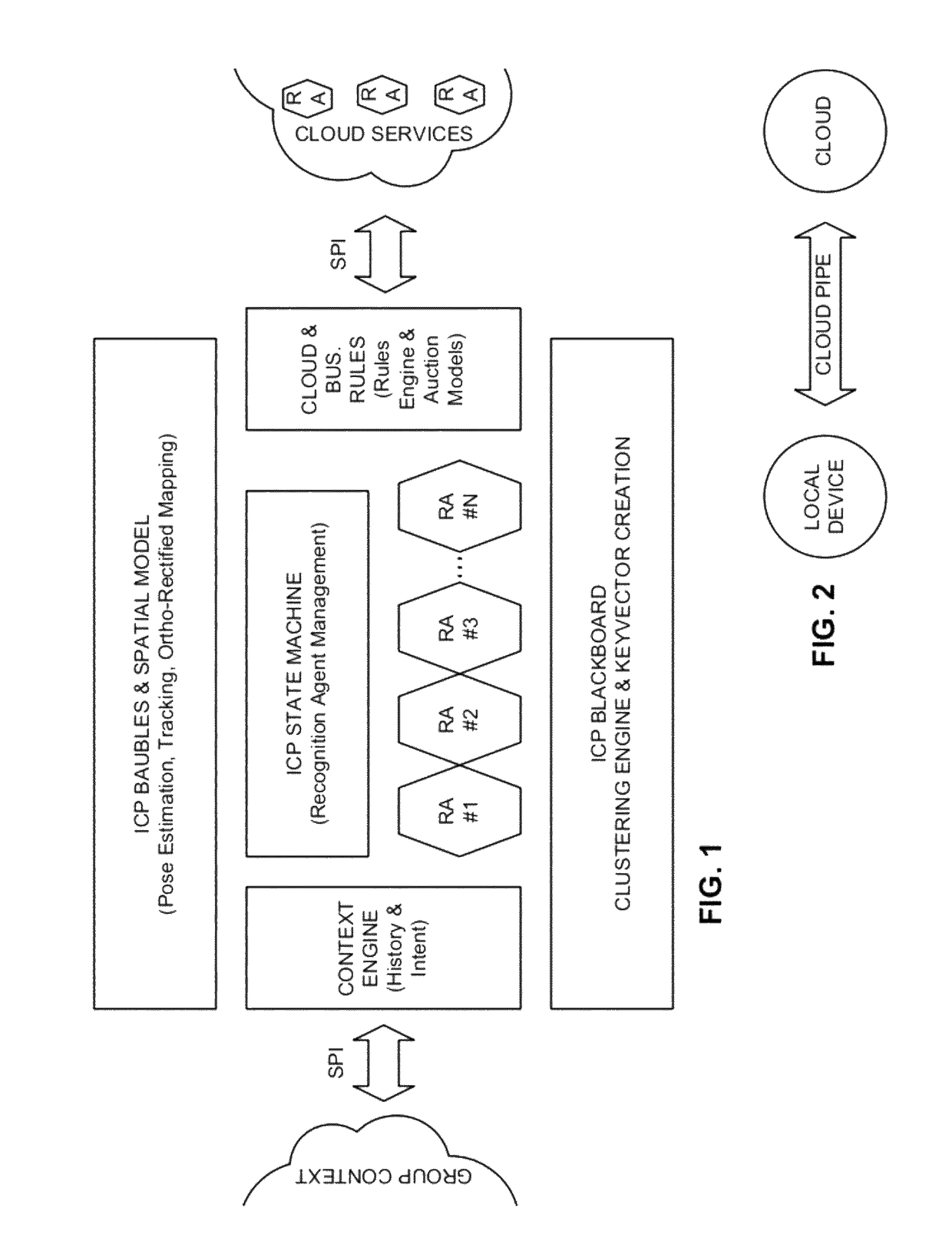
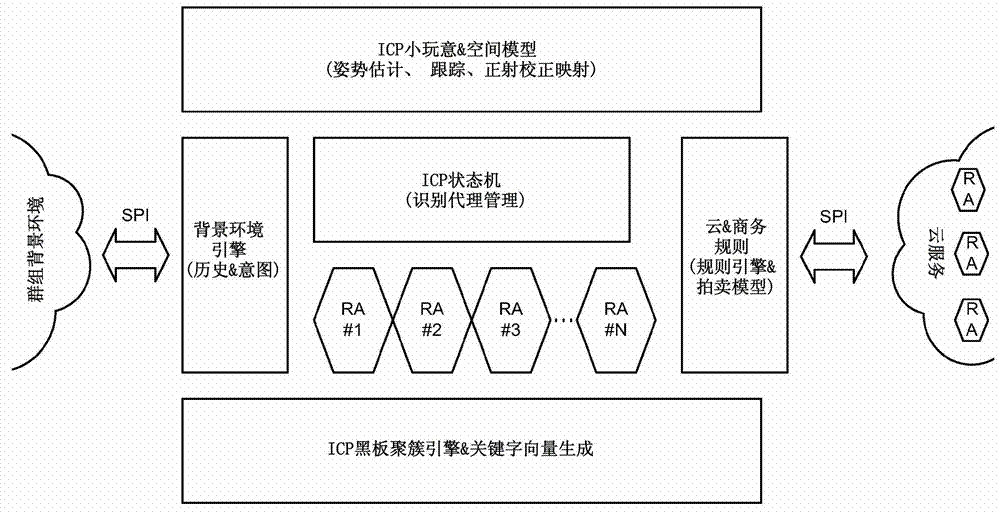
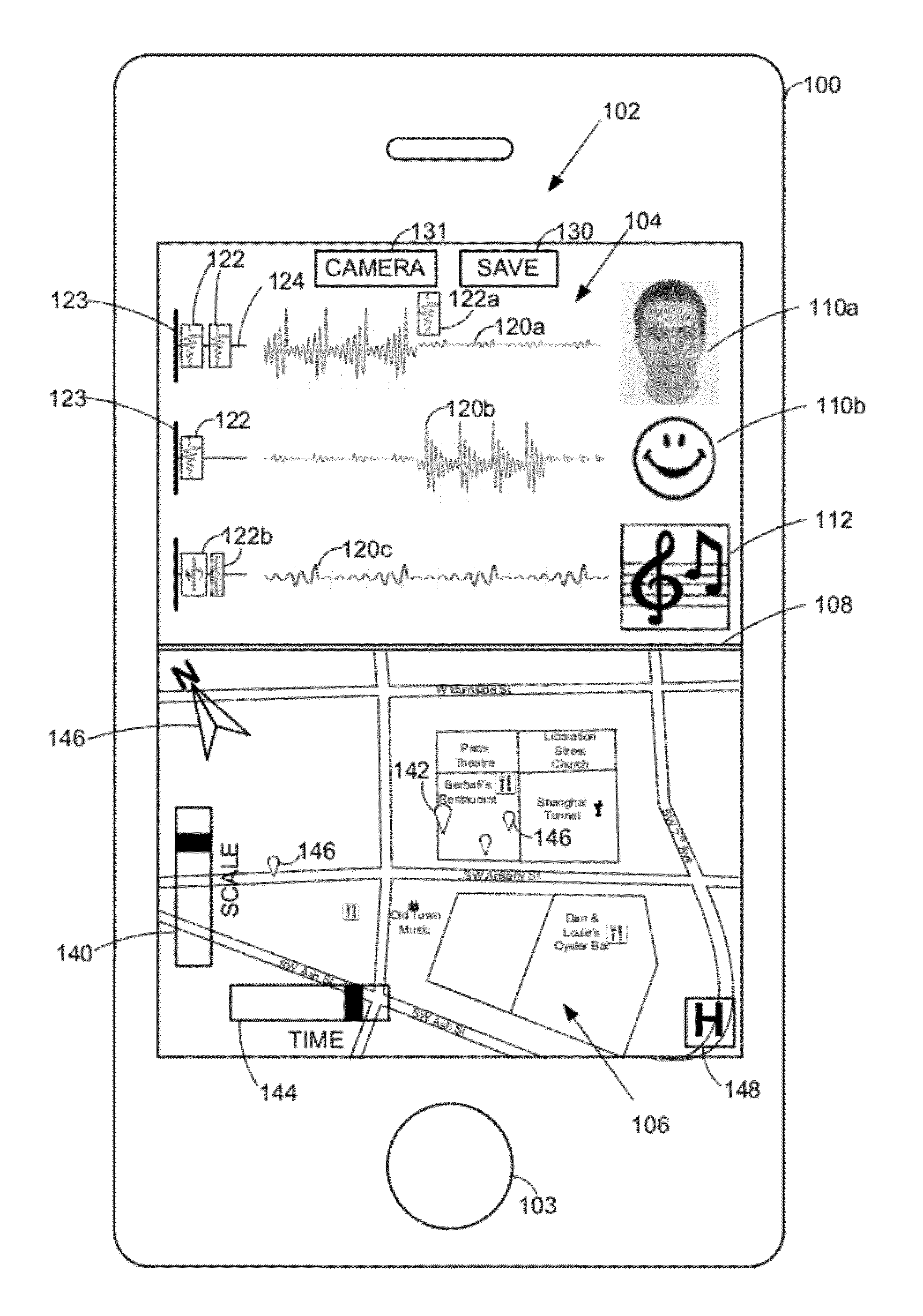
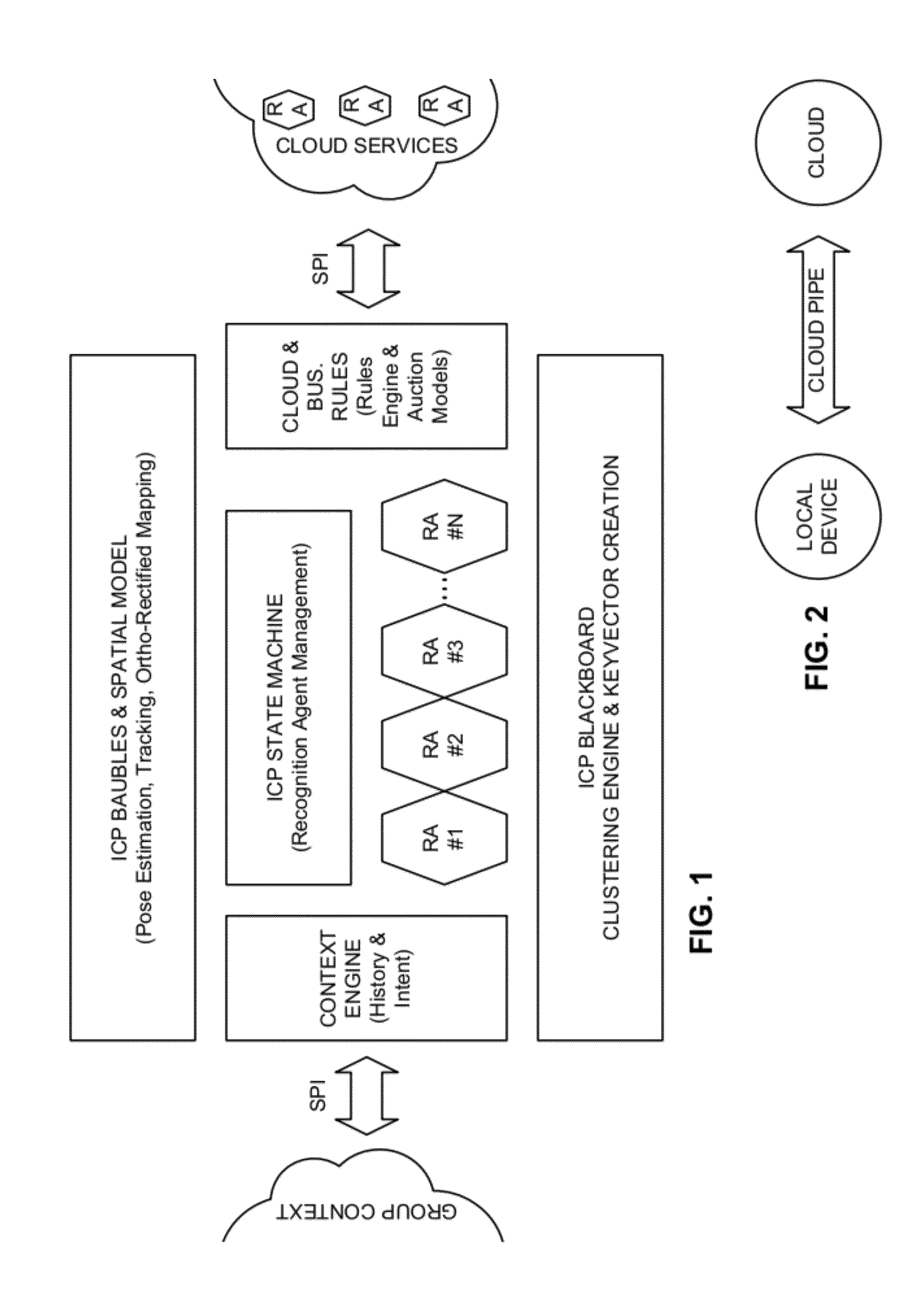
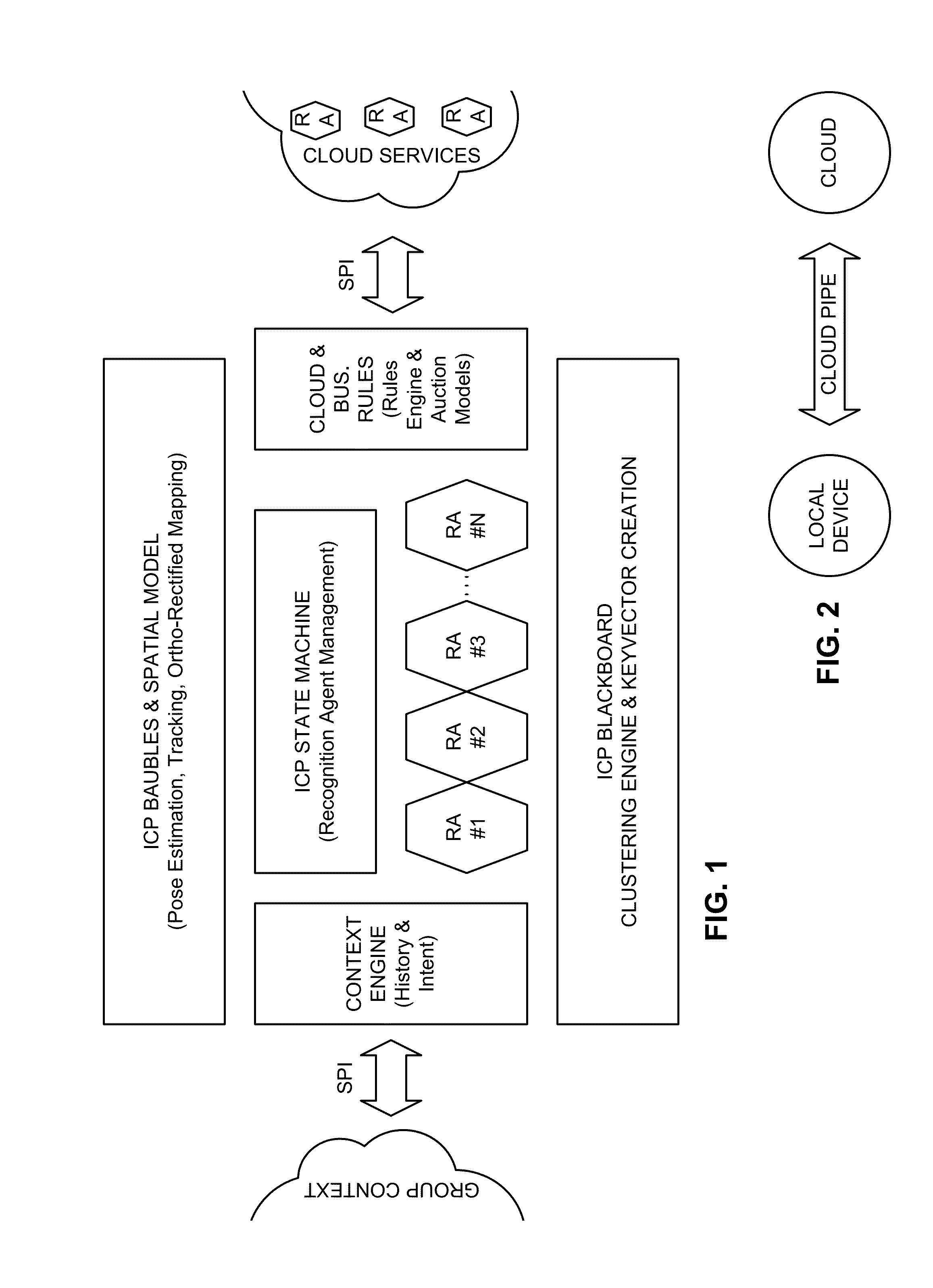
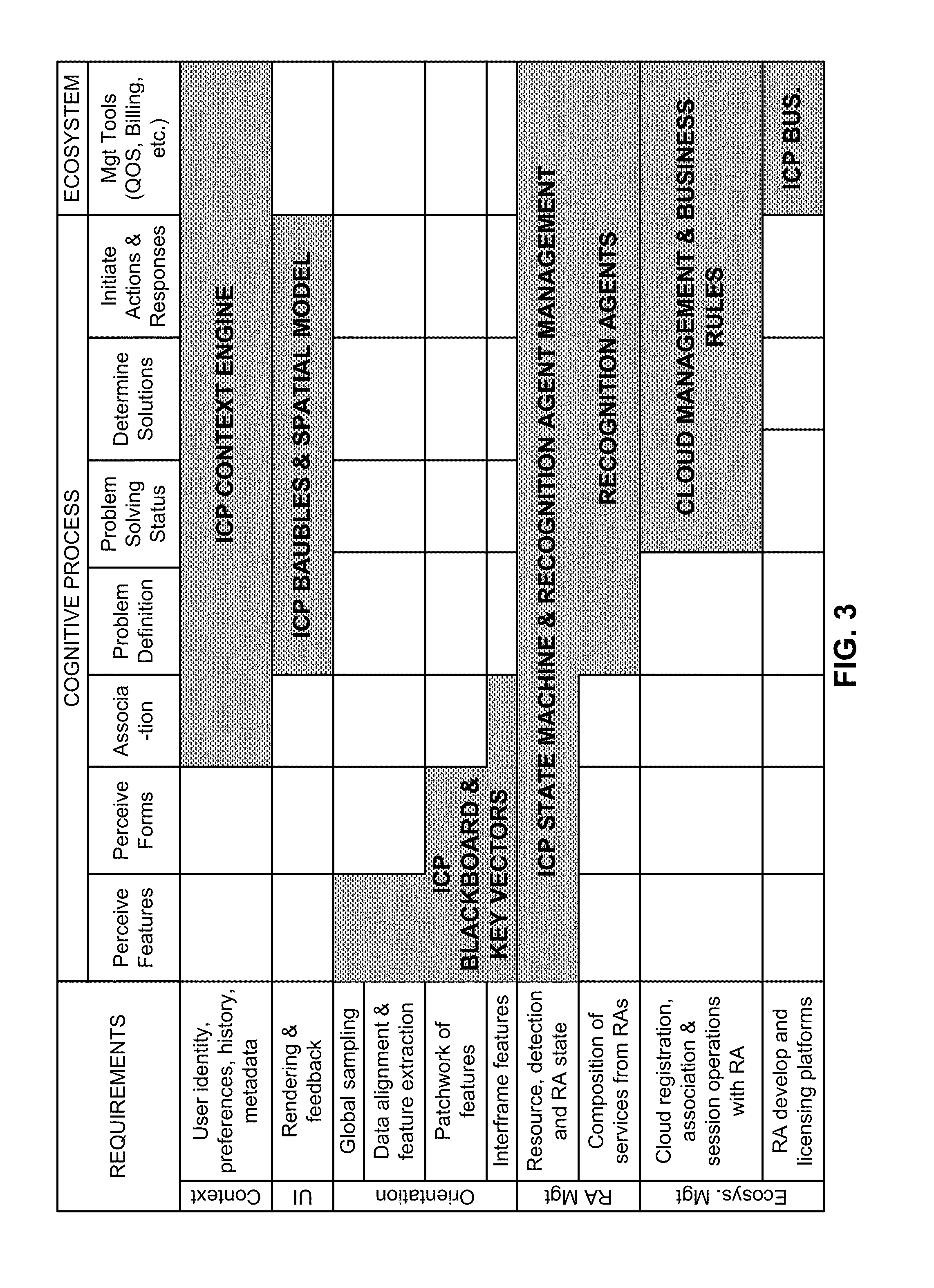
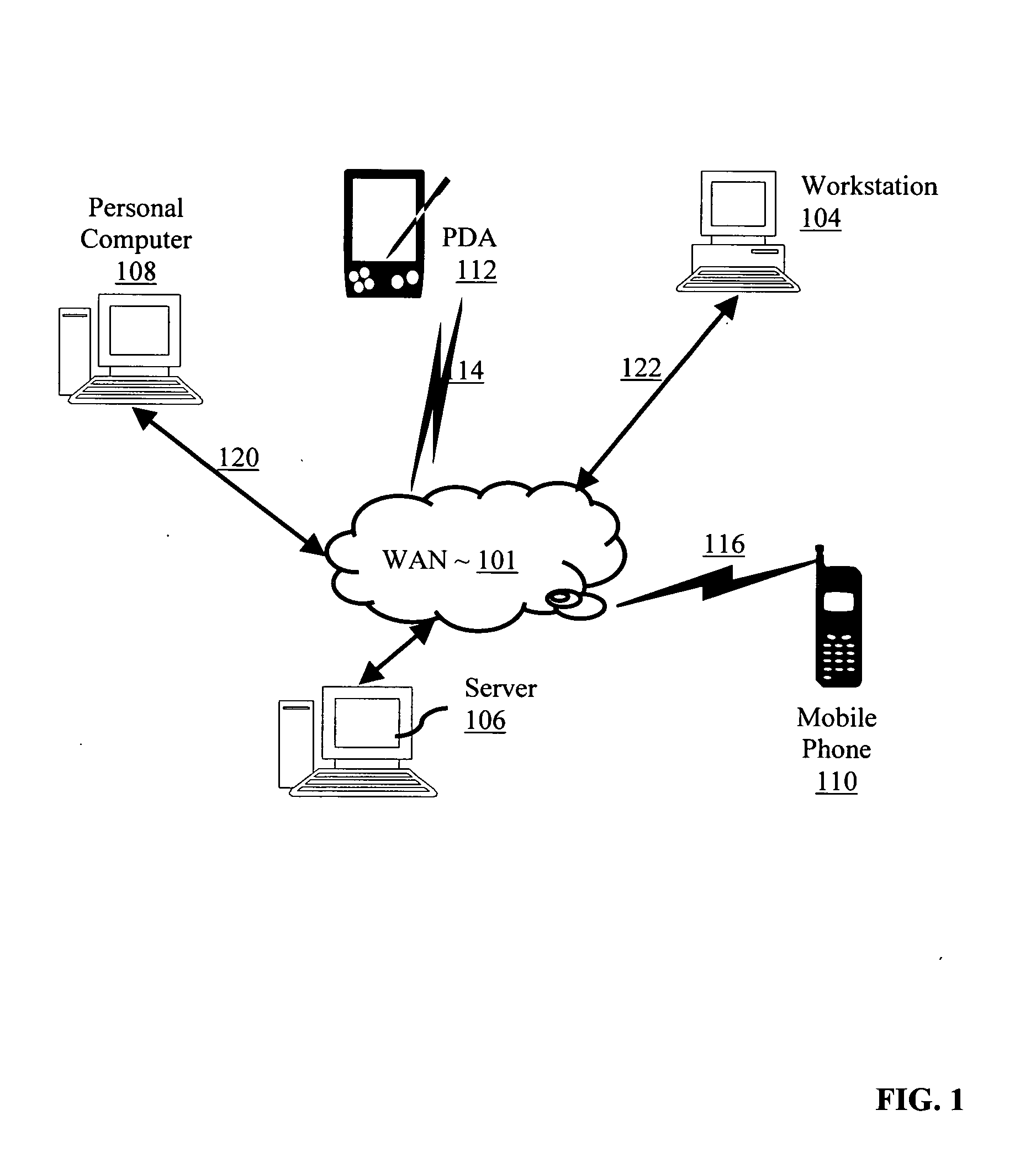
Intuitive computing methods and systems
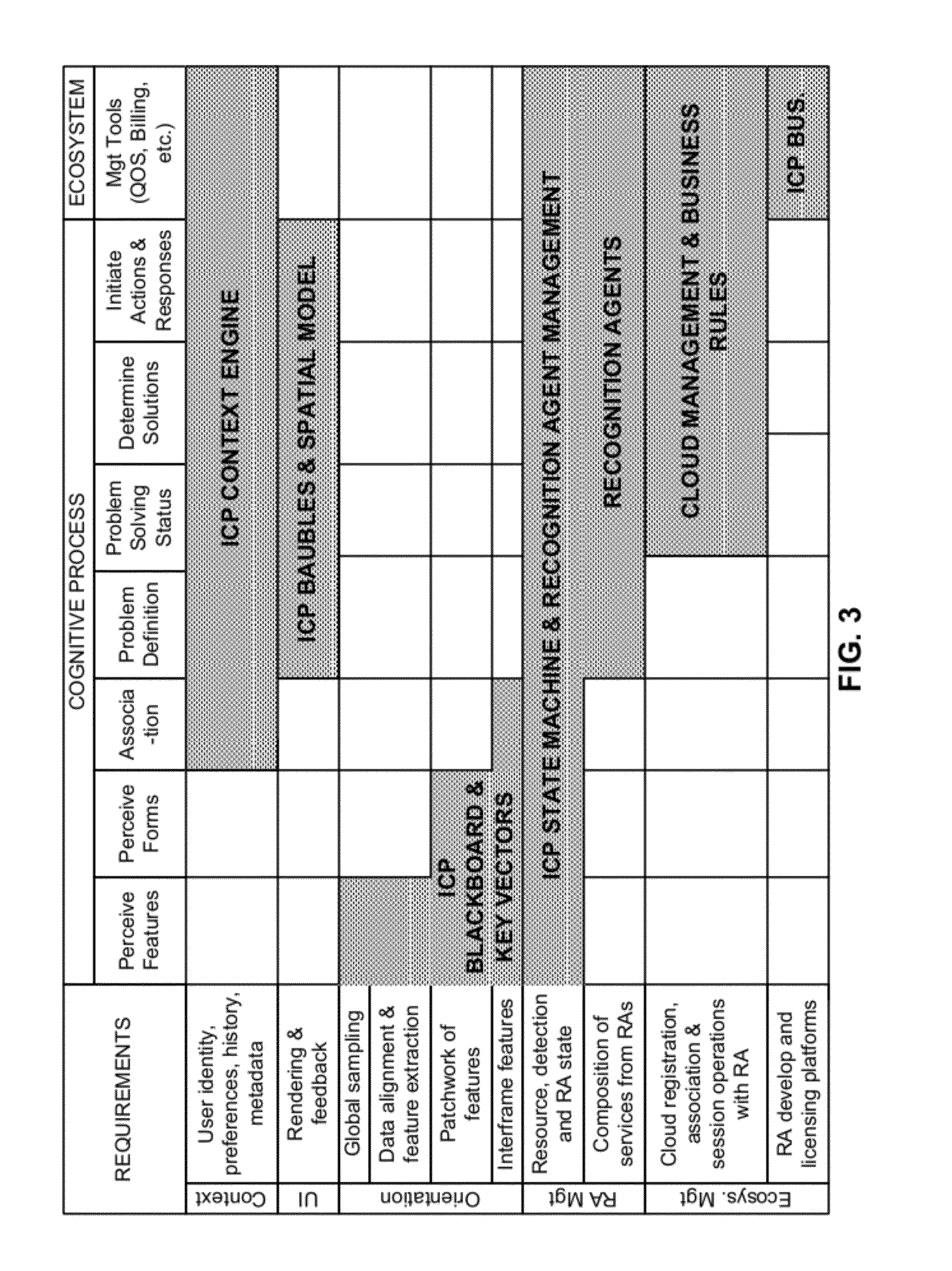
ActiveUS20110098056A1Wide applicabilityTelevision system detailsInstruments for road network navigationImaging processingCognition.knowledge
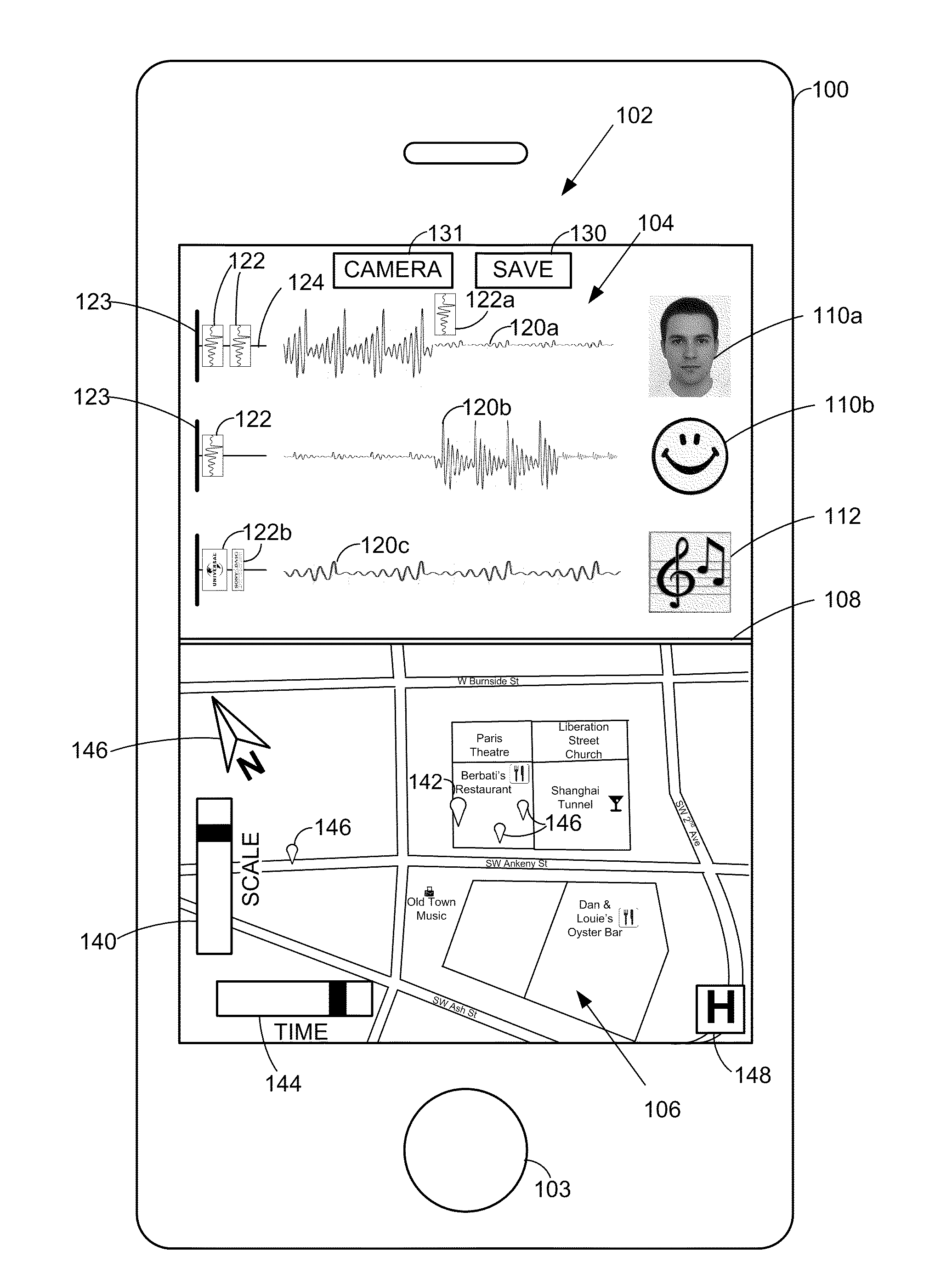
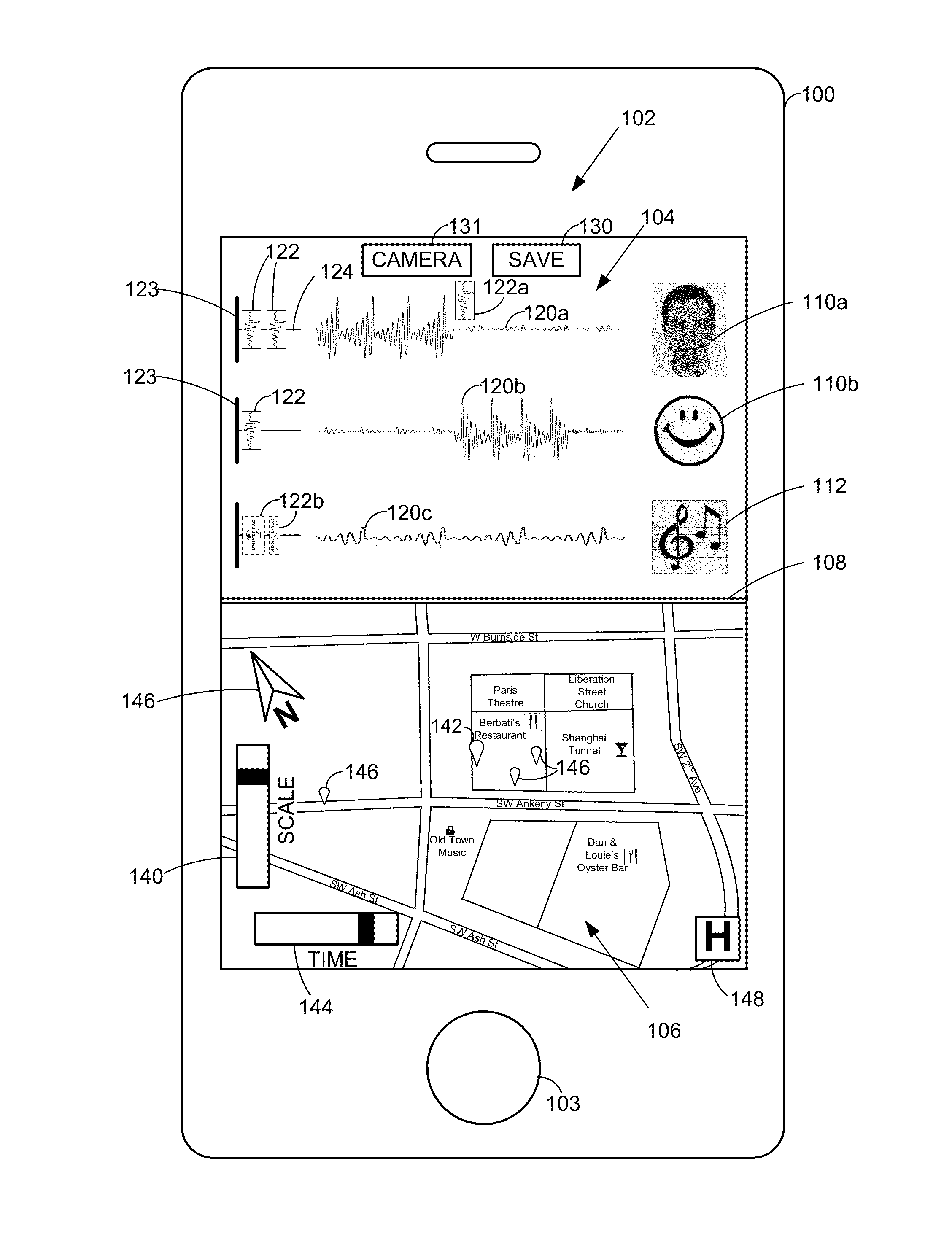
A smart phone senses audio, imagery, and / or other stimulus from a user's environment, and acts autonomously to fulfill inferred or anticipated user desires. In one aspect, the detailed technology concerns phone-based cognition of a scene viewed by the phone's camera. The image processing tasks applied to the scene can be selected from among various alternatives by reference to resource costs, resource constraints, other stimulus information (e.g., audio), task substitutability, etc. The phone can apply more or less resources to an image processing task depending on how successfully the task is proceeding, or based on the user's apparent interest in the task. In some arrangements, data may be referred to the cloud for analysis, or for gleaning. Cognition, and identification of appropriate device response(s), can be aided by collateral information, such as context. A great number of other features and arrangements are also detailed.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
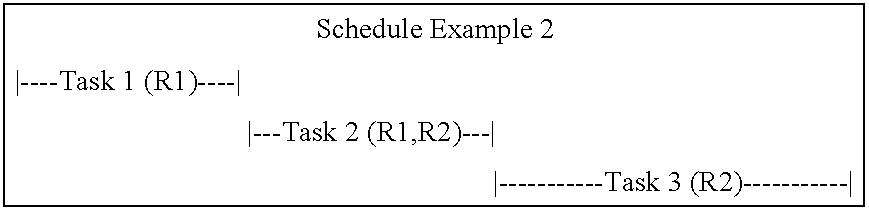
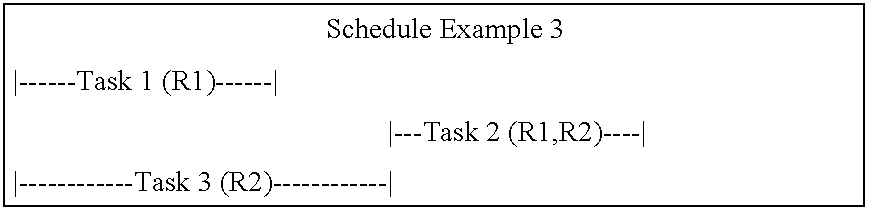
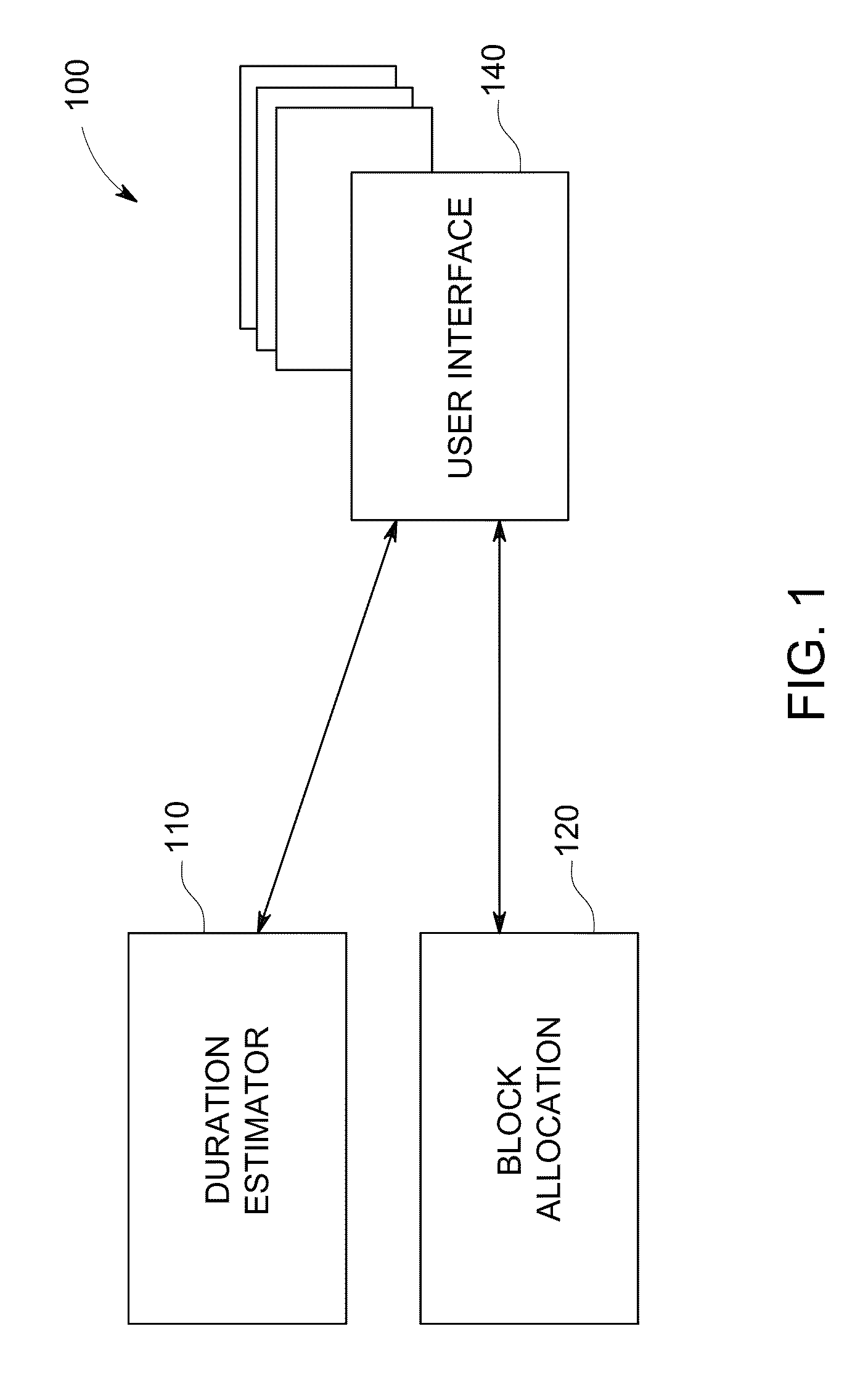
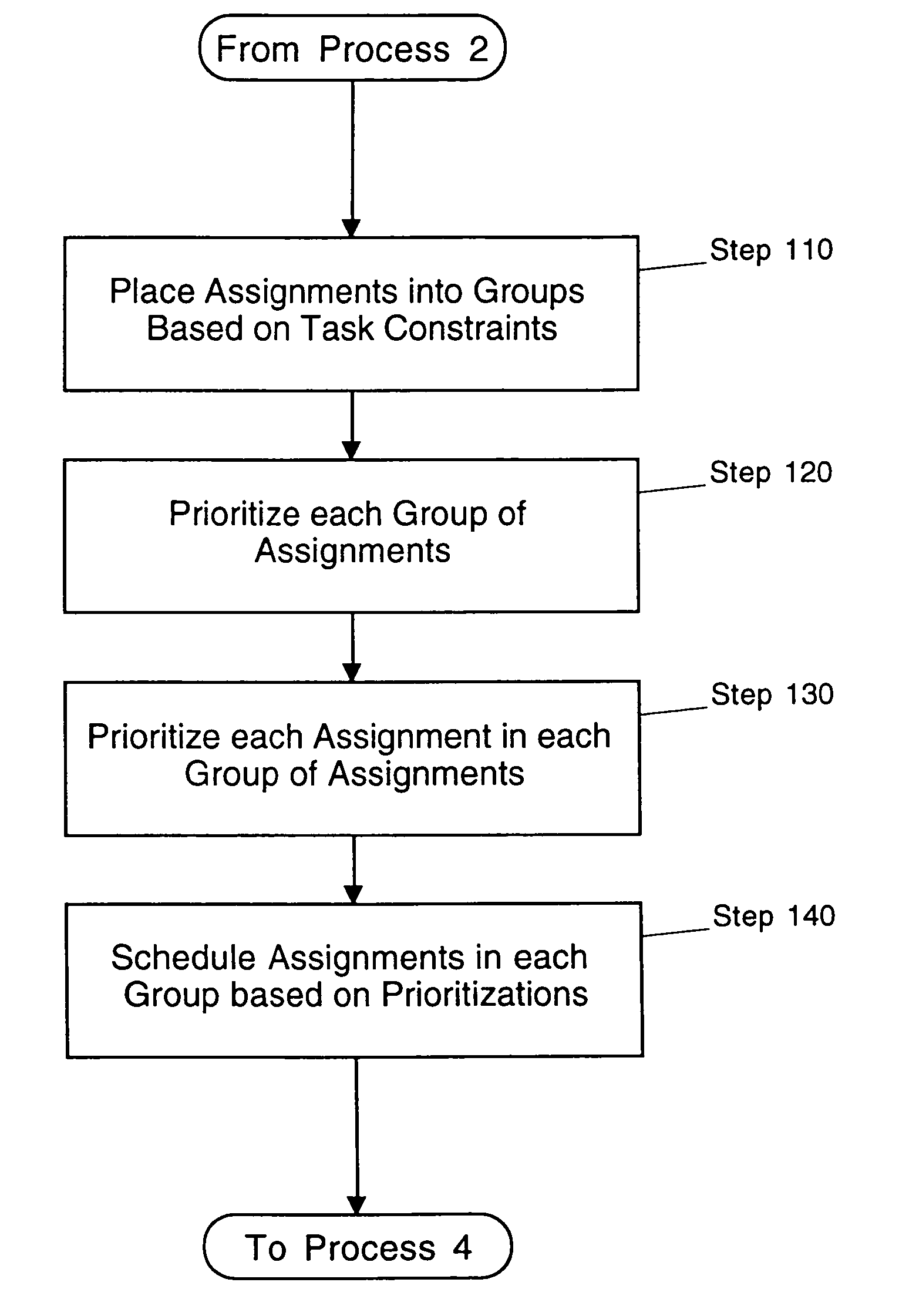
System and method for generating a schedule based on resource assignments
A system for generating a schedule by generating assignments for the tasks of a project and sequentially scheduling the individual assignments to available resources. First, input information is received which includes a resource calendar and a task list. A resource calendar identifies the resources available to work on a project and any constraints that are associated with the resources. A task list identifies the tasks that must be performed and any constraints that are associated with the tasks. At a minimum, the constraints associated with the tasks must identify each of the resources assigned to the task, and the work-amount that each resource must perform. Next, assignments are generated for each of the tasks. Each of the assignments identifies a specific resource and the work-amount required by the specific resource. Finally, each of the assignments are scheduled in accordance with the provided resource constraints identified in the resource calendar. The resulting schedule maximizes the utilization of the resources by scheduling on an assignment basis. The assignments are individually scheduled into the next available time-slot of the resources, thus, eliminating idle time where a resource is under-utilized.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
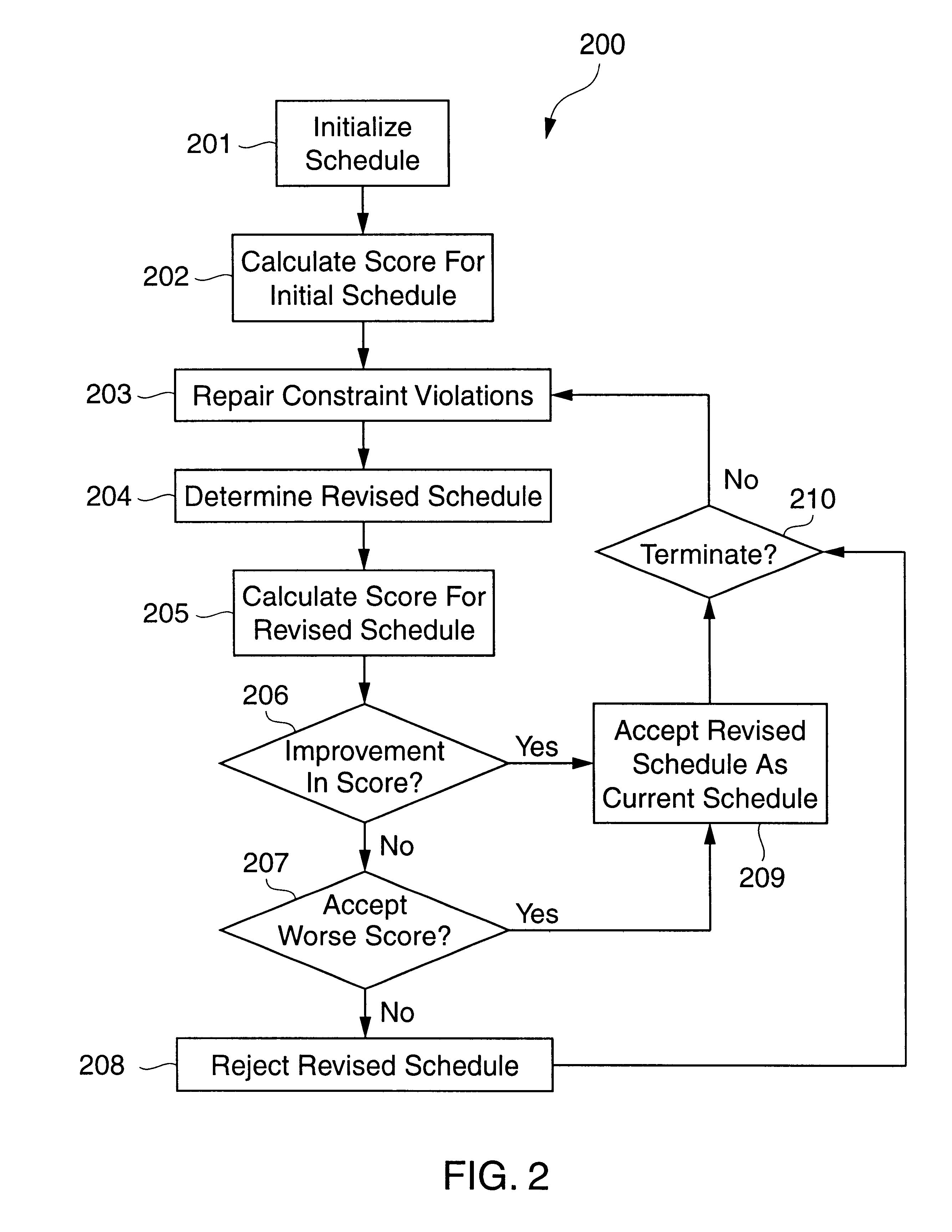
Iterative repair optimization with particular application to scheduling for integrated capacity and inventory planning
A schedule for a complex activity is obtained by a scheduling system using a method of constraint-based iterative repair. A predetermined initial schedule is iteratively repaired, repairs being made during each iteration only to portions of the schedule that produce a constraint violation, until an acceptable schedule is obtained. Since repairs are made to the schedule only to repair violated constraints, rather than to the entire schedule, schedule perturbations are minimized, thereby reducing problems with the dynamic performance of the scheduling system and minimizing disruption to the smooth operation of the activity. All constraints on the scheduling activity can be evaluated simultaneously to produce a solution that is near optimal with respect to all constraints. In particular, consumable resource constraints can be evaluated simultaneously with other constraints such as, for example, reusable resource constraints, temporal constraints, state constraints, milestone constraints and preemptive constraints. The scheduling system of the invention is much quicker than previous scheduling systems that use, for example, constructive scheduling method. The system of the invention can also be easily modified to add, delete or modify constraints. Because of the minimization of schedule perturbation, coupling of all constraints, speed of operation, and ease of modification, the scheduling system of the invention is particularly useful for scheduling applications that require frequent and rapid rescheduling.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Sensor-based mobile search, related methods and systems
ActiveUS20110098029A1Wide applicabilityTelevision system detailsDevices with sensorMobile searchImaging processing
A smart phone senses audio, imagery, and / or other stimulus from a user's environment, and acts autonomously to fulfill inferred or anticipated user desires. In one aspect, the detailed technology concerns phone-based cognition of a scene viewed by the phone's camera. The image processing tasks applied to the scene can be selected from among various alternatives by reference to resource costs, resource constraints, other stimulus information (e.g., audio), task substitutability, etc. The phone can apply more or less resources to an image processing task depending on how successfully the task is proceeding, or based on the user's apparent interest in the task. In some arrangements, data may be referred to the cloud for analysis, or for gleaning. Cognition, and identification of appropriate device response(s), can be aided by collateral information, such as context. A great number of other features and arrangements are also detailed.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
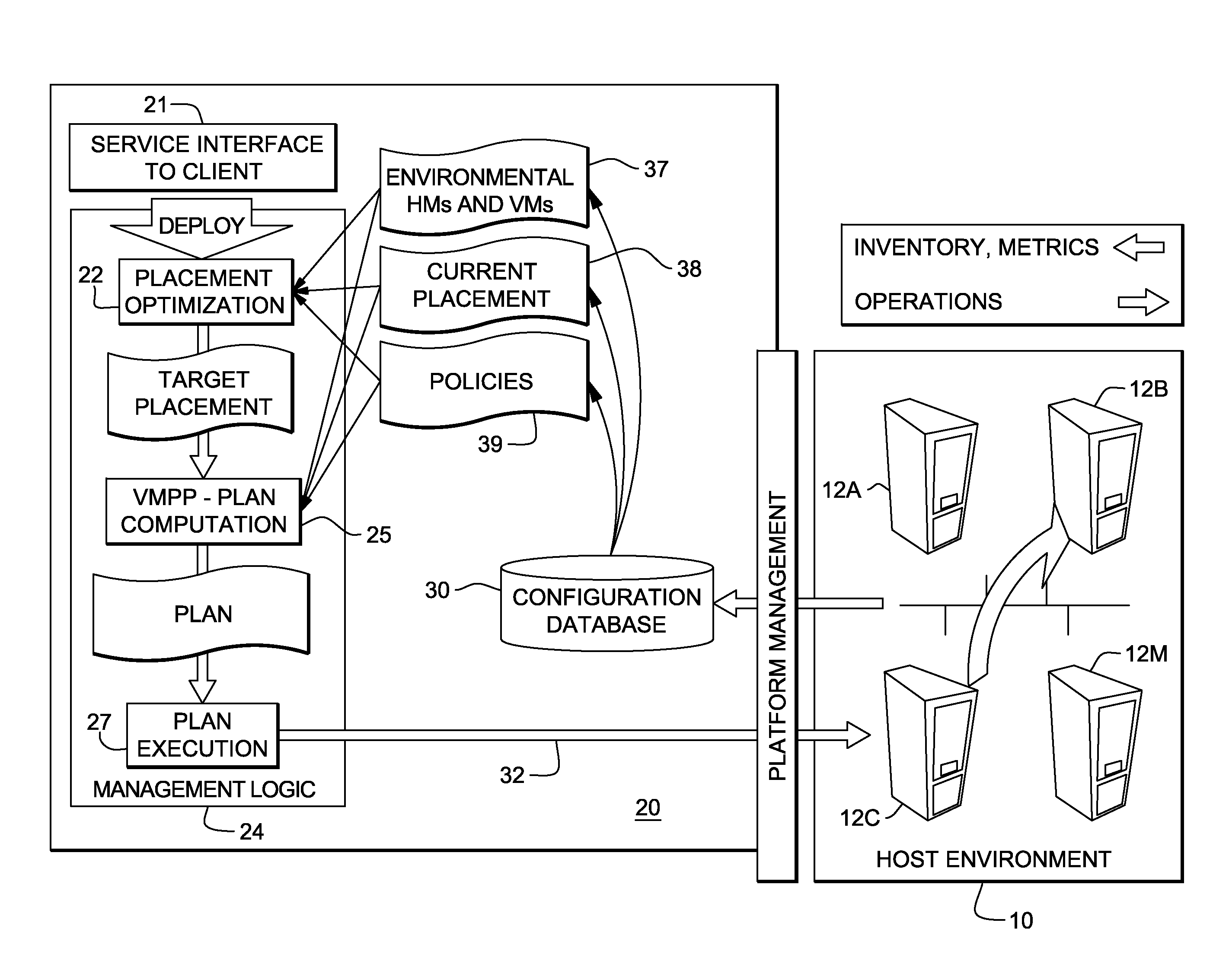
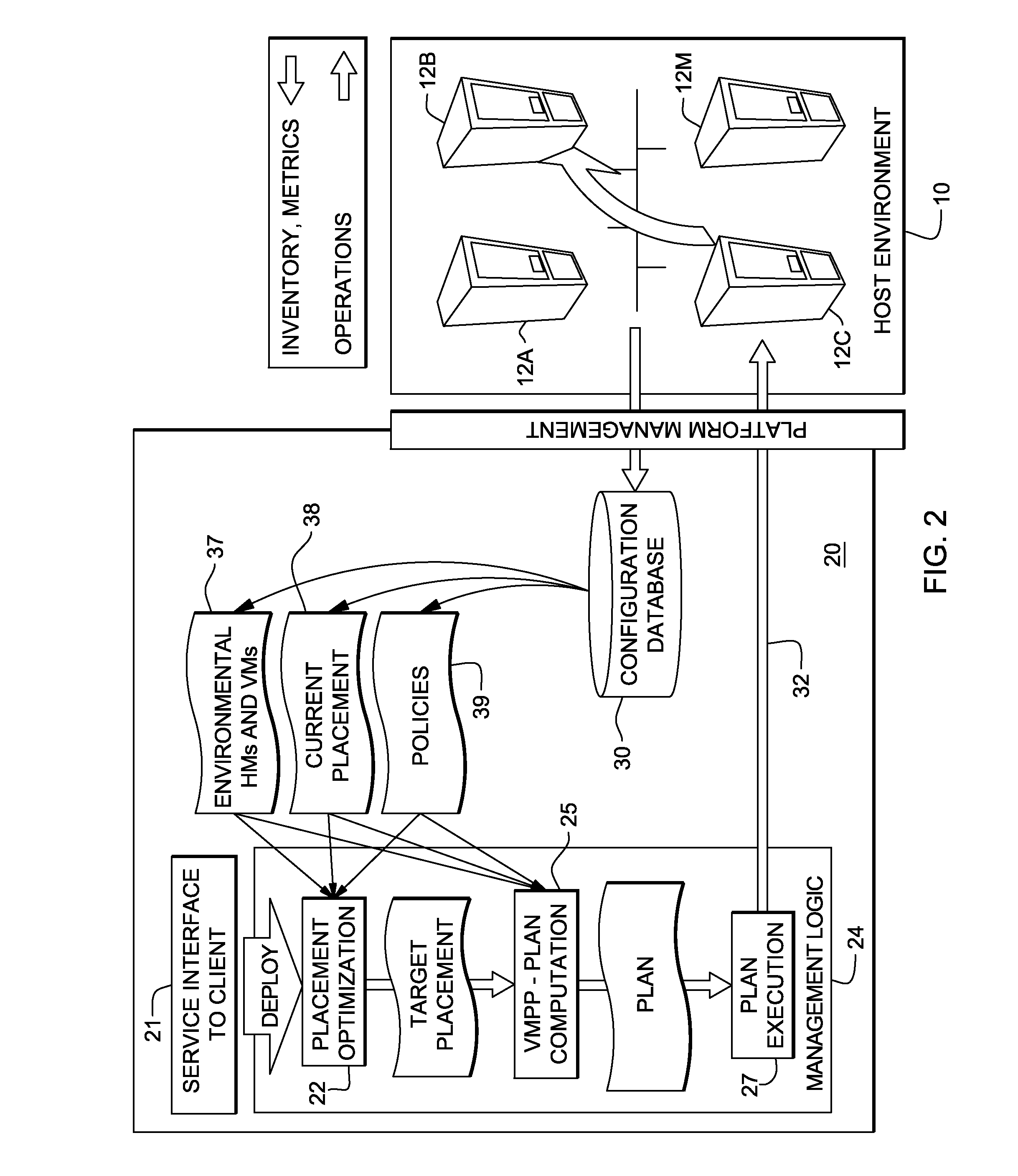
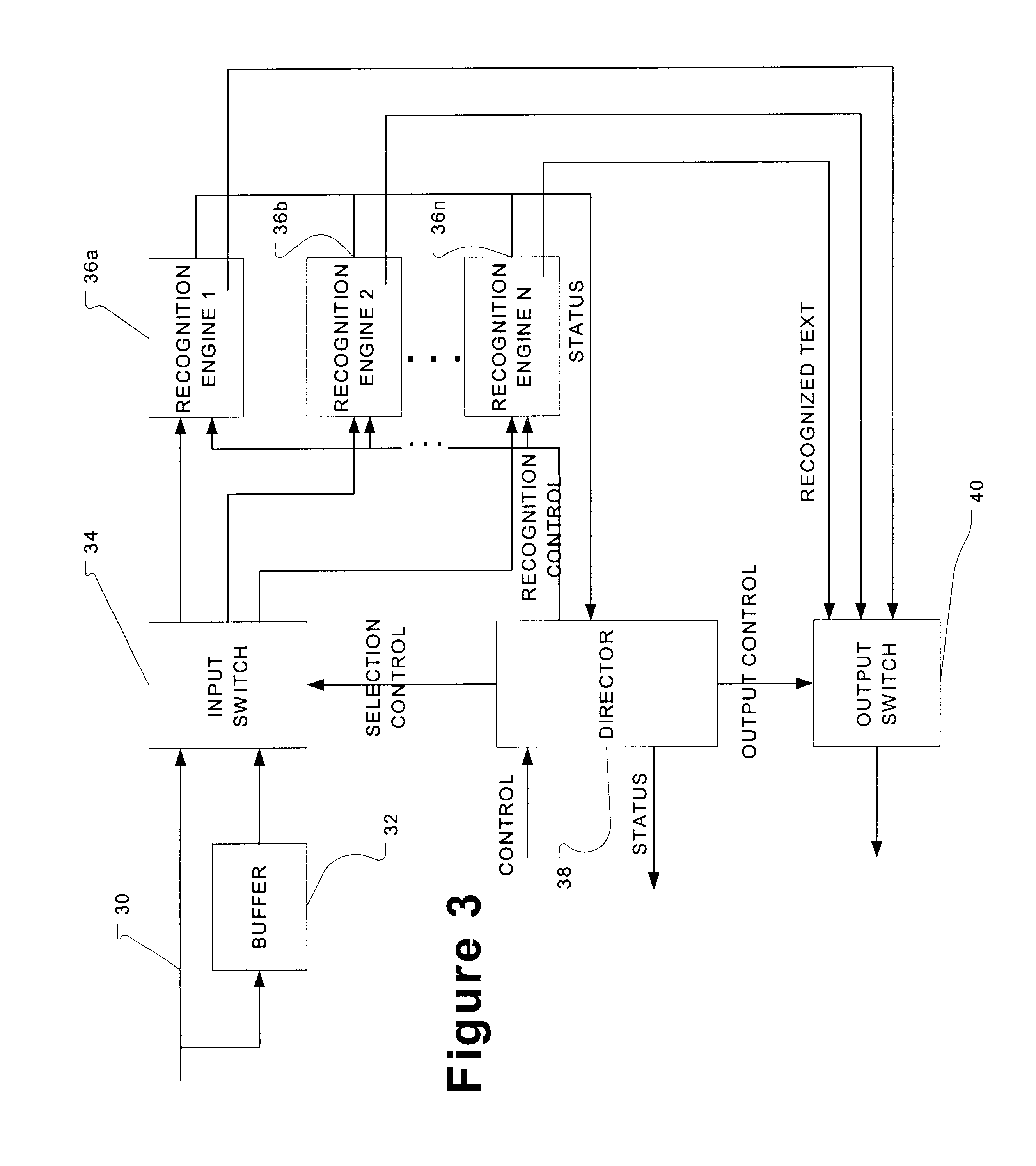
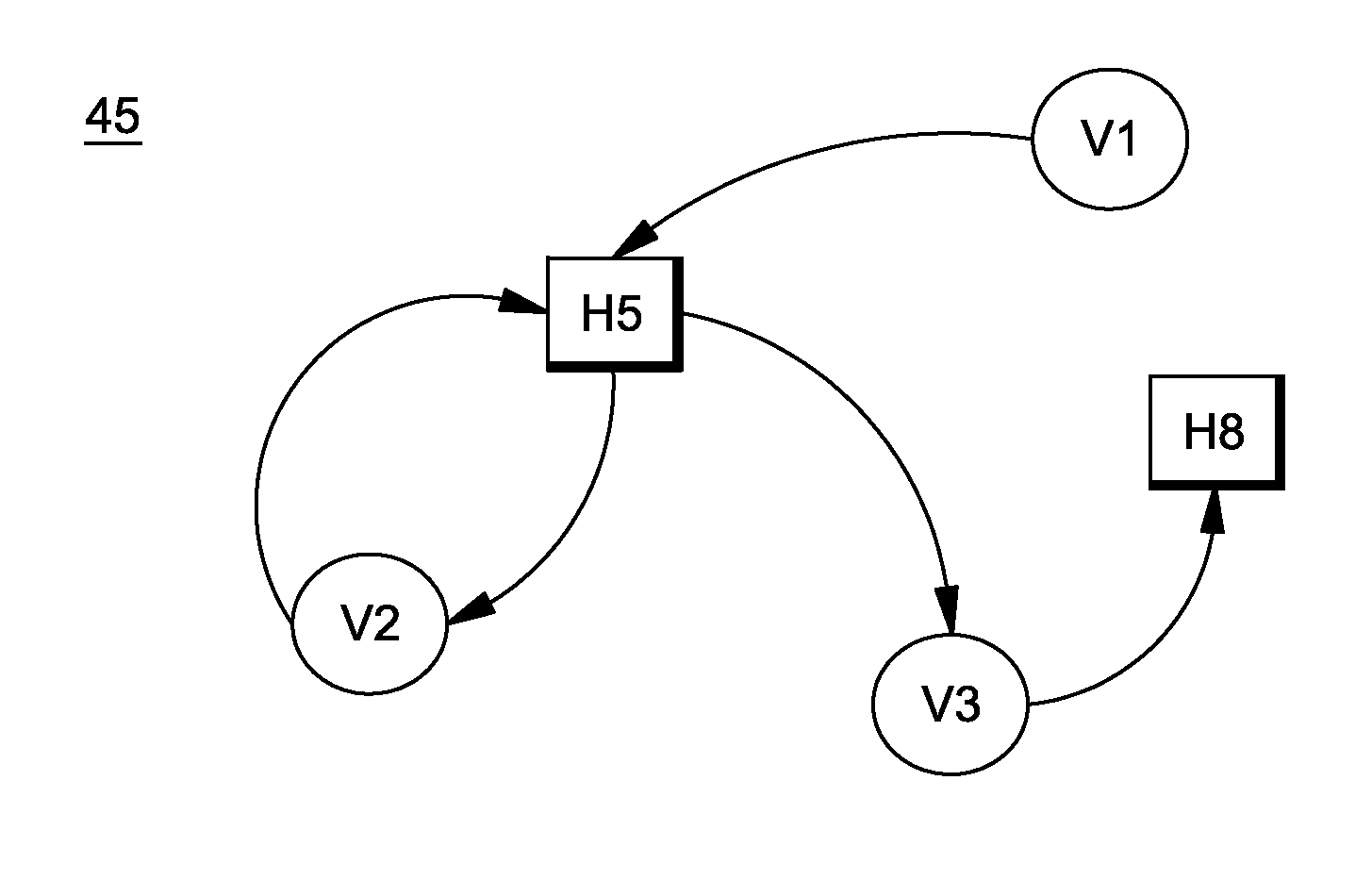
System and method for deploying virtual machines in a computing environment
InactiveUS20100250744A1Cycle brokenEffect is temporaryDigital data processing detailsAnalogue computers for electric apparatusGraphicsDirected graph
A system and method for planning placement of virtual machines VMs in a computing environment comprising a set of hosting machines HM. The method includes constructing a bipartite directed graph-based model that represents both a current and a target placement states, both including virtual machine nodes v in VM and nodes h in HM. Using a technique of graph pruning, the method iteratively generates a plan for achieving a desired target placement starting from the current placement without temporarily violating any policy or resource constraint. The application of the pruning algorithm to VM deployment automation necessarily defines a new model. The methodology employed safely manages concurrent changes in a datacenter, so that the environment can adjust faster to changing constraints. Furthermore, the present invention allows detection of migration cycles, caused by deadlocked combinations of capacity and policy constraints, and resolving them.
Owner:IBM CORP
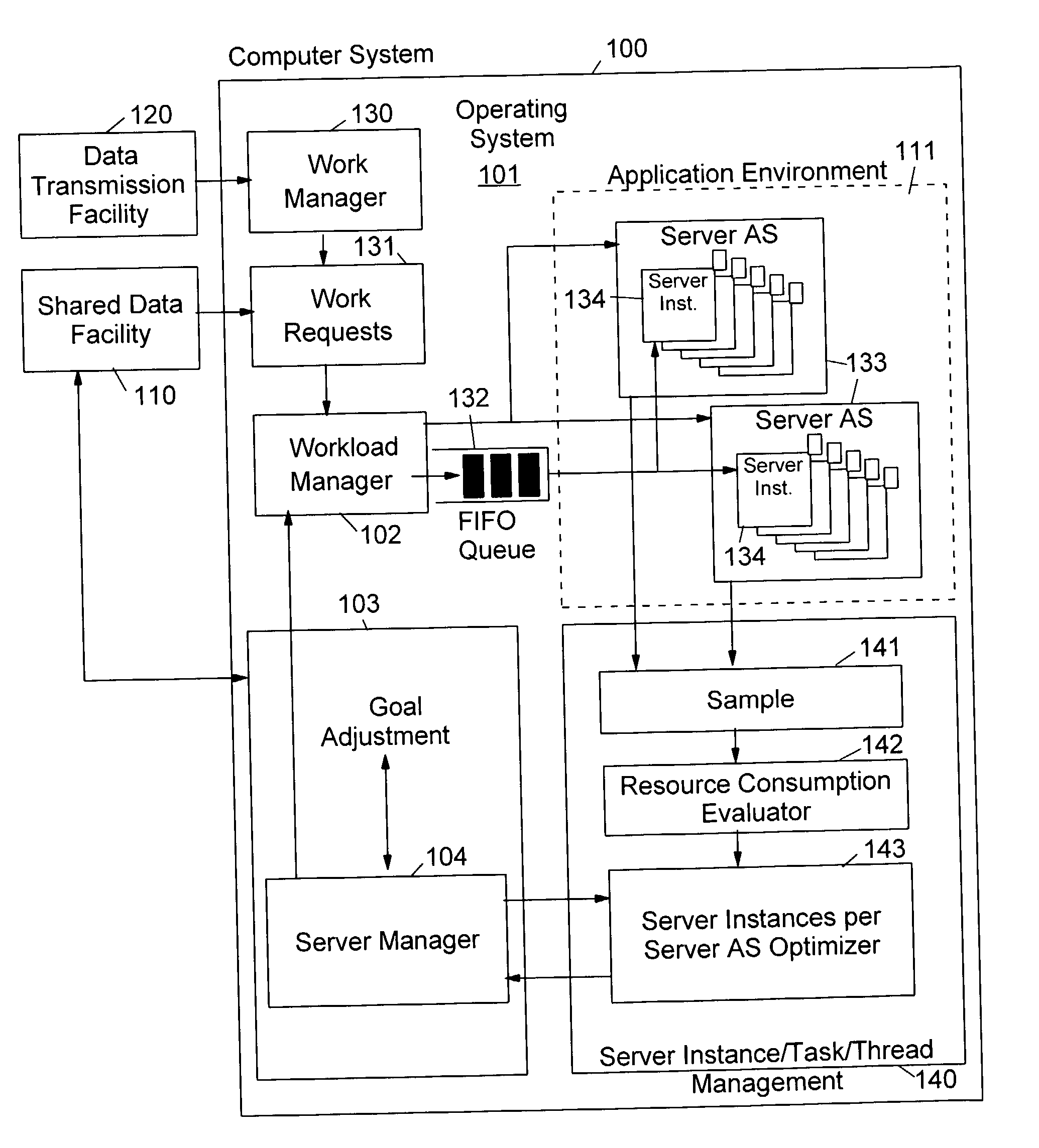
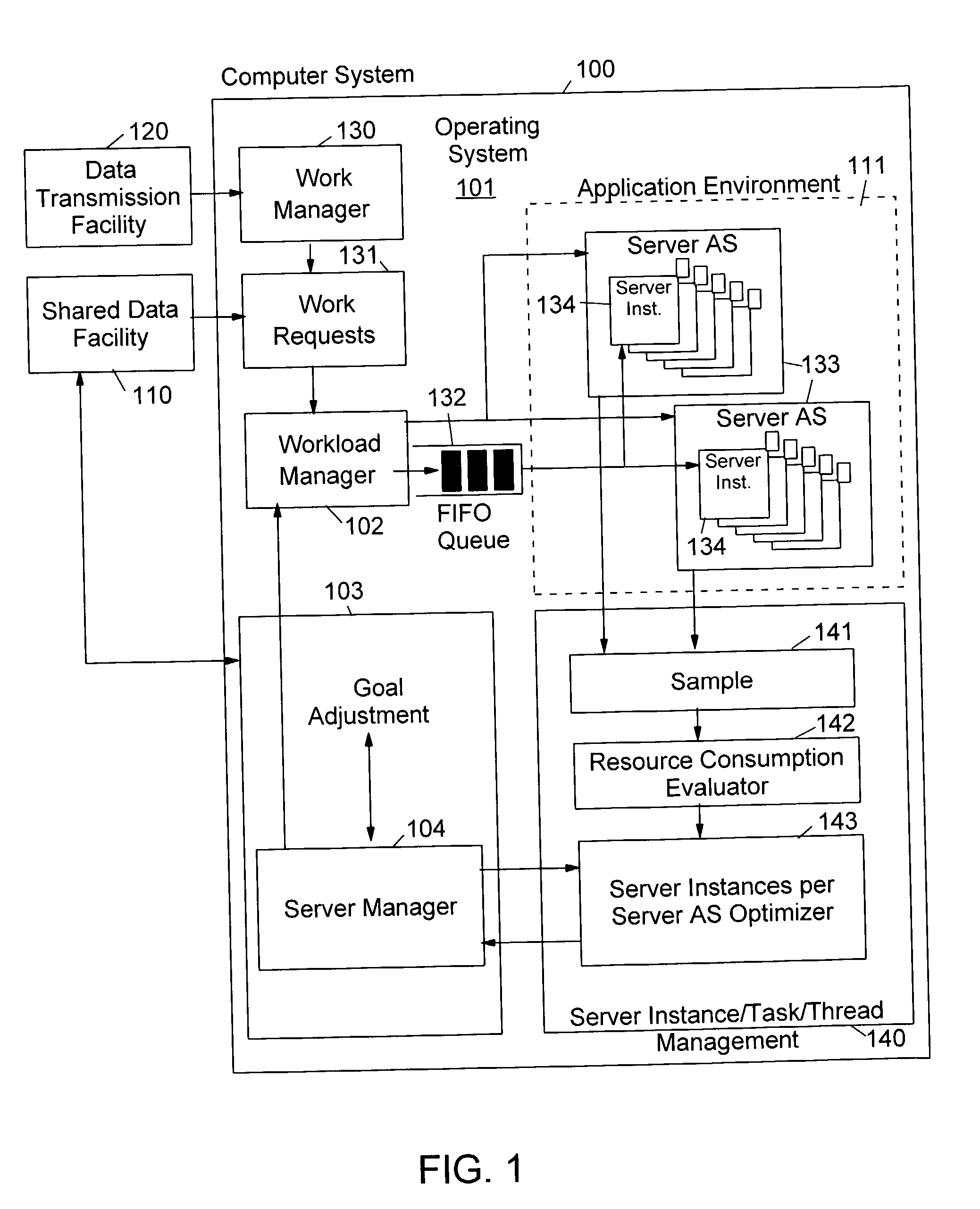
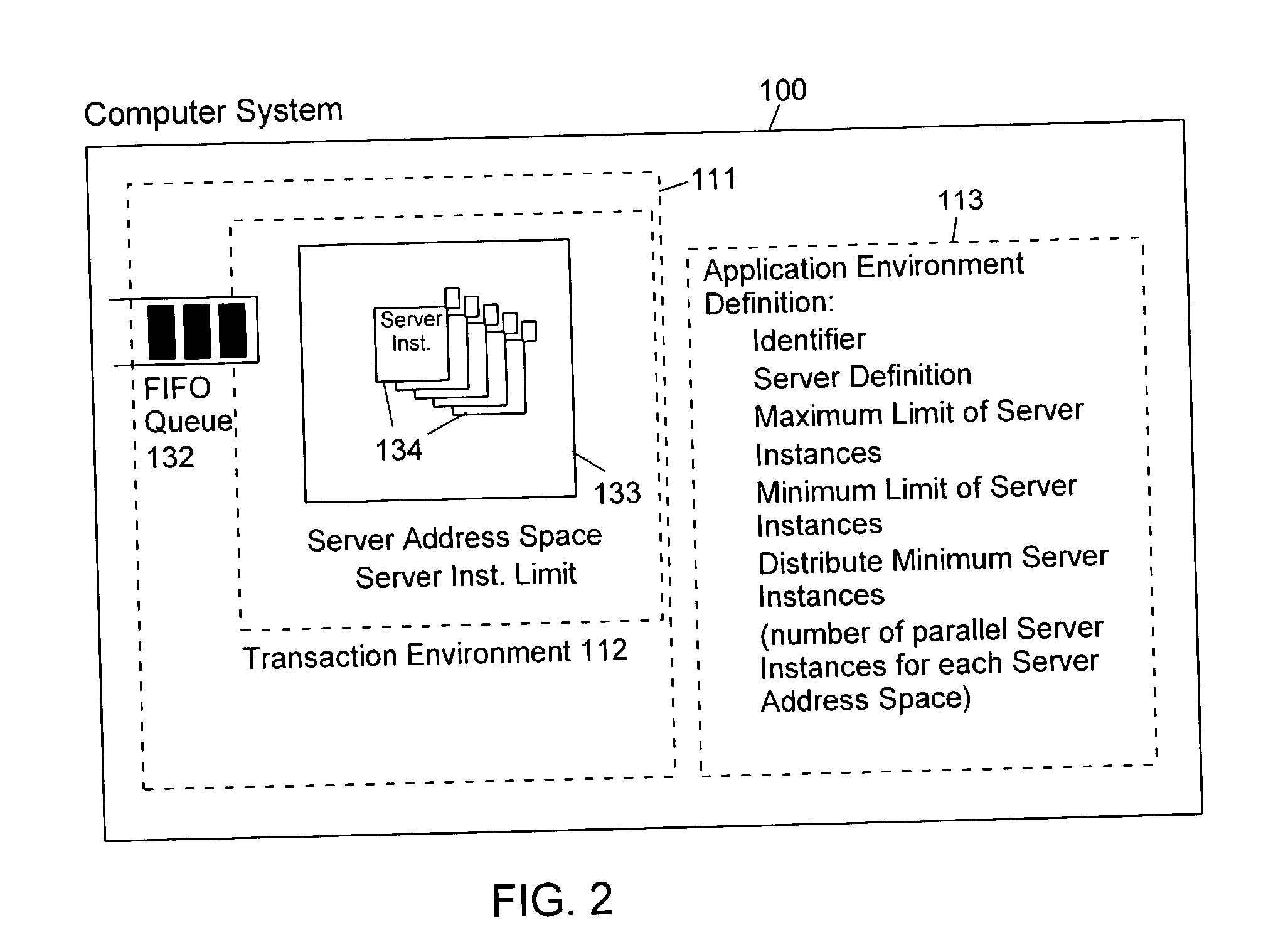
Method and apparatus for controlling the number of servers in a hierarchical resource environment
InactiveUS20030005028A1Improve overall utilizationImprove system performanceResource allocationMemory systemsResource consumptionComputerized system
The invention relates to the control of servers which process client work requests in a computer system on the basis of resource consumption. Each server contains multiple server instances (also called "execution units") which execute different client work requests in parallel. A workload manager determines the total number of server containers and server instances in order to achieve the goals of the work requests. The number of server instances started in each server container depends on the resource consumption of the server instances in each container and on the resource constraints, service goals and service goal achievements of the work units to be executed. At predetermined intervals during the execution of the work units the server instances are sampled to check whether they are active or inactive. Dependent on the number of active server instances the number of server address spaces and server instances is repeatedly adjusted to achieve an improved utilization of the available virtual storage and an optimization of the system performance in the execution of the application programs.
Owner:IBM CORP
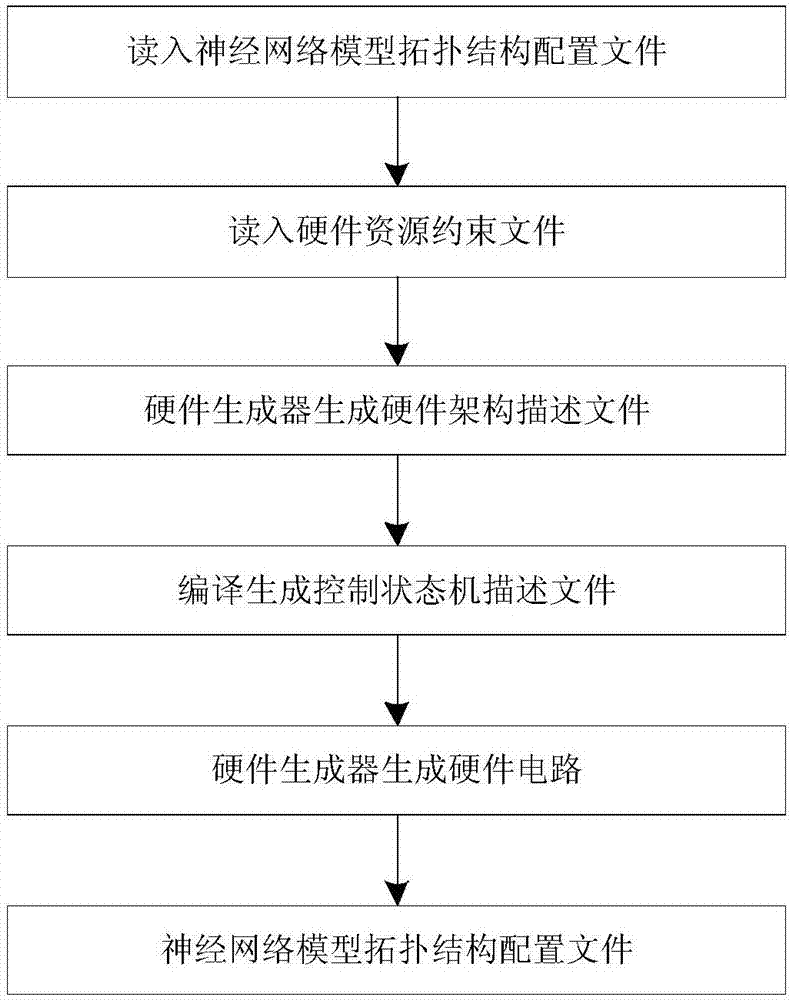
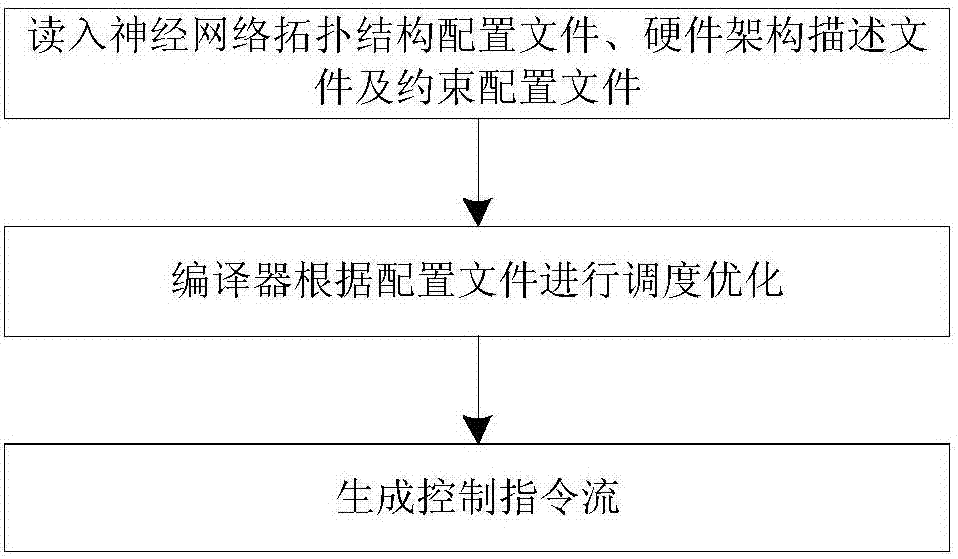
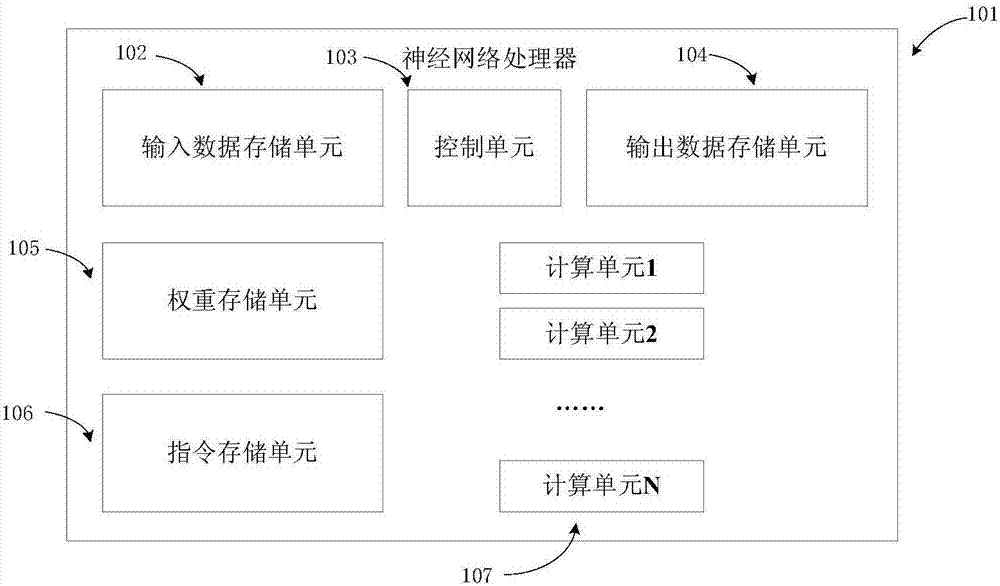
Automated design method, device and optimization method applied for neural network processor
ActiveCN107016175ABiological neural network modelsCAD circuit designComputer architectureHardware architecture
The invention discloses an automated design method, device and optimization method applied for a neural network processor. The method comprises the steps that neural network model topological structure configuration files and hardware resource constraint files are obtained, wherein the hardware resource constraint files comprise target circuit area consumption, target circuit power consumption and target circuit working frequency; a neural network processor hardware architecture is generated according to the neural network model topological structure configuration files and the hardware resource constraint files, and hardware architecture description files are generated; according to a neural network model topological structure, the hardware resource constraint files and the hardware architecture description files, modes of data scheduling, storage and calculation are optimized, and corresponding control description files are generated; according to the hardware architecture description files and the control description files, cell libraries meet the design requirements are found in constructed reusable neural network cell libraries, corresponding control logic and a corresponding hardware circuit description language are generated, and the hardware circuit description language is transformed into a hardware circuit.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
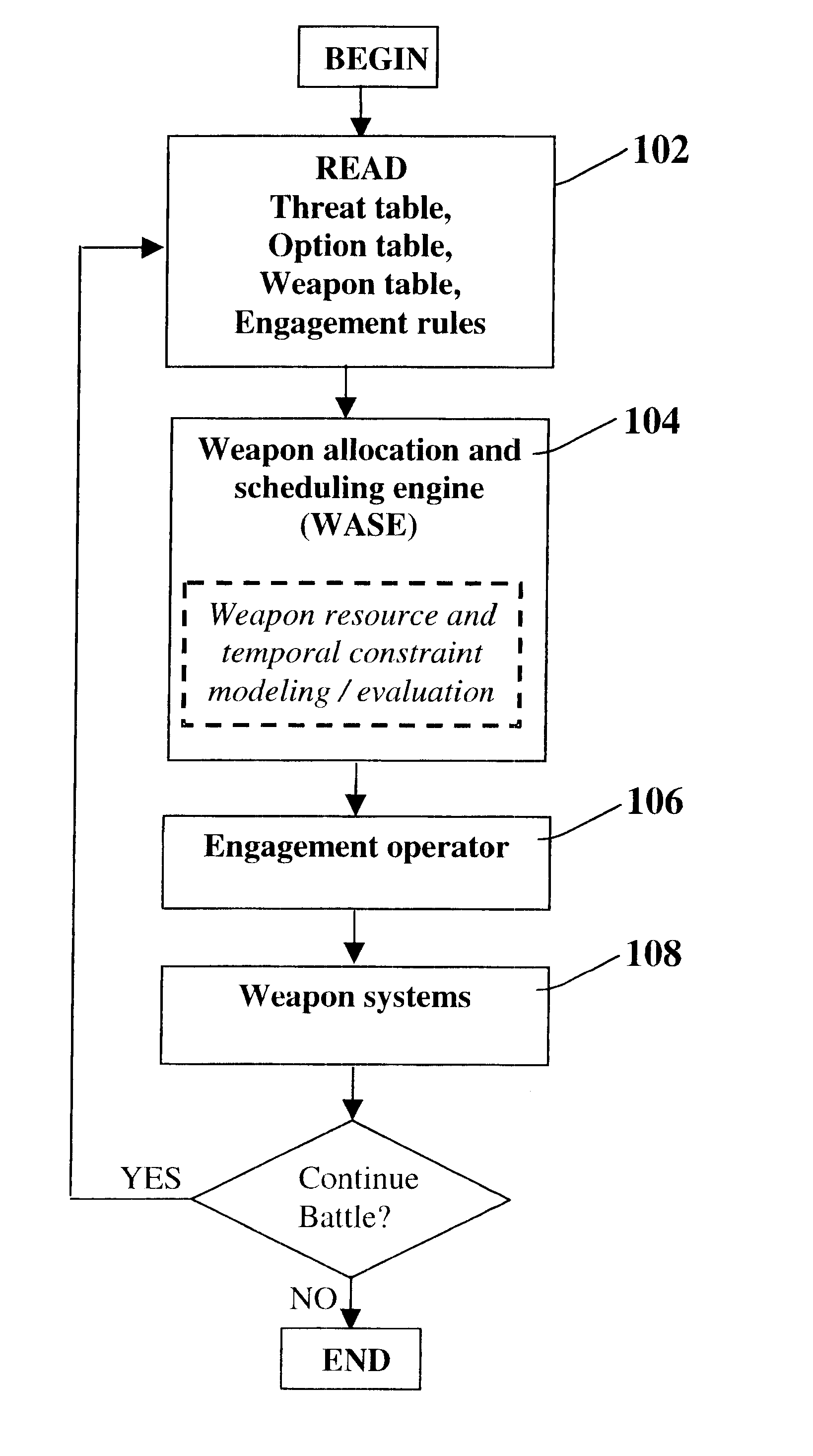
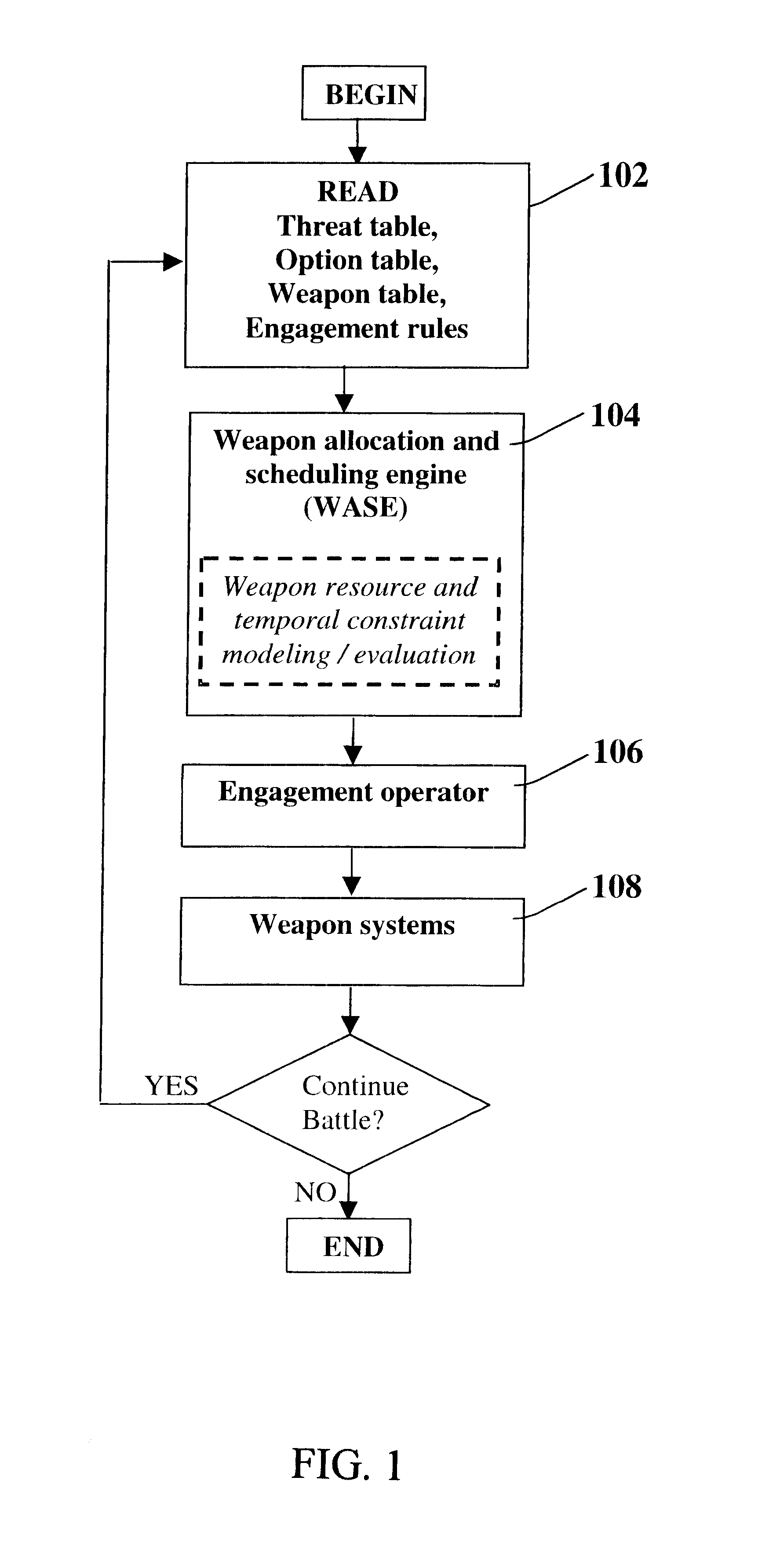
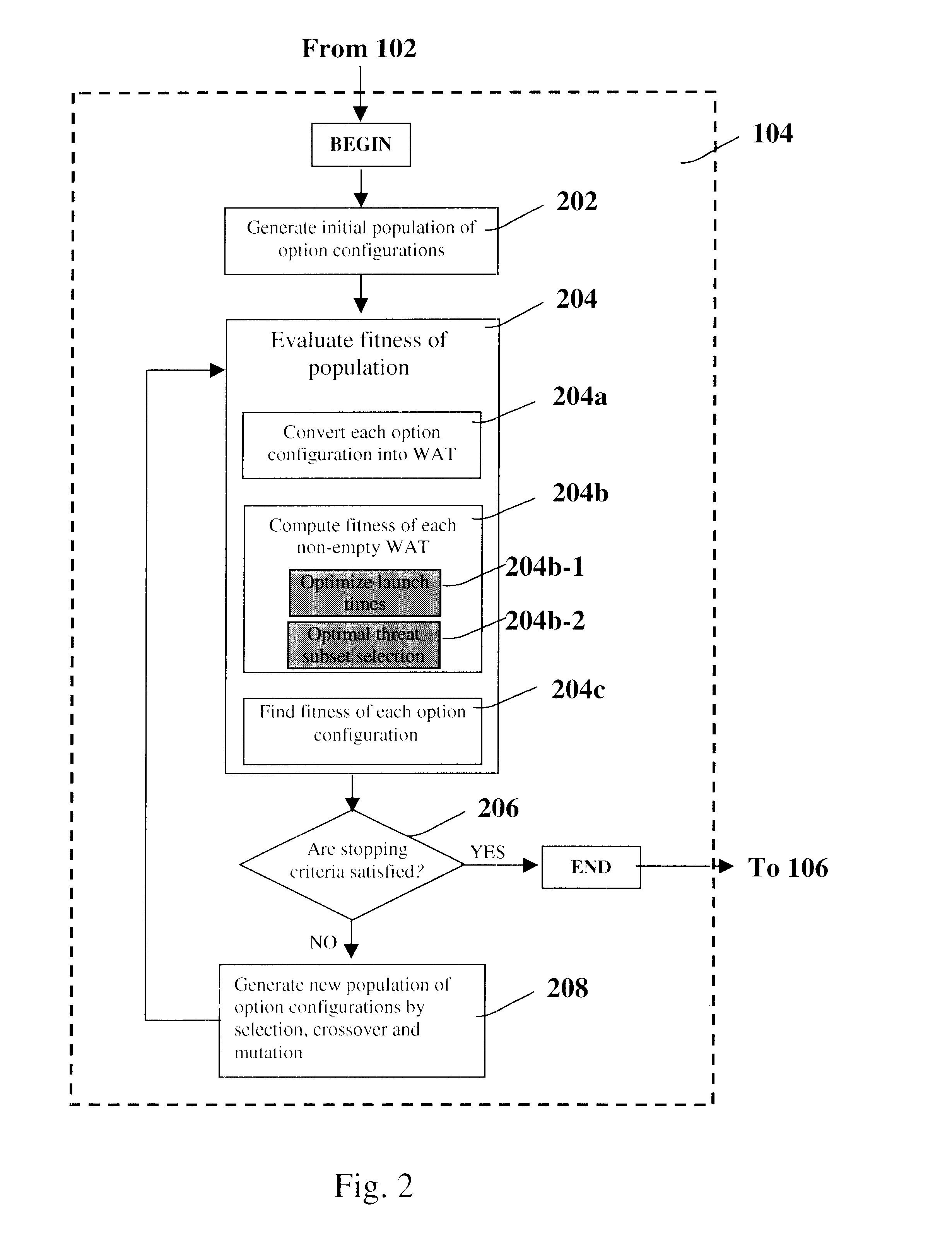
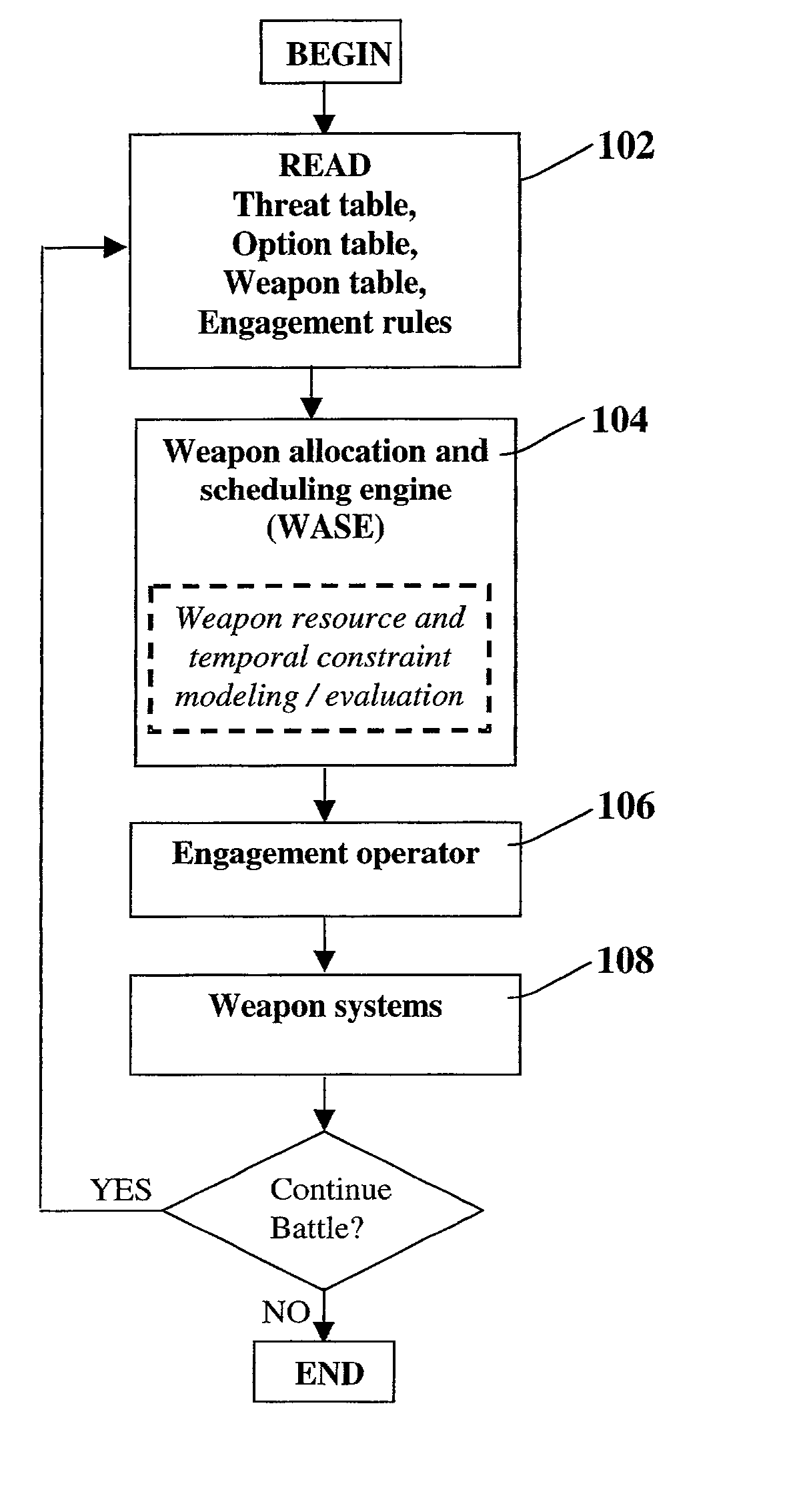
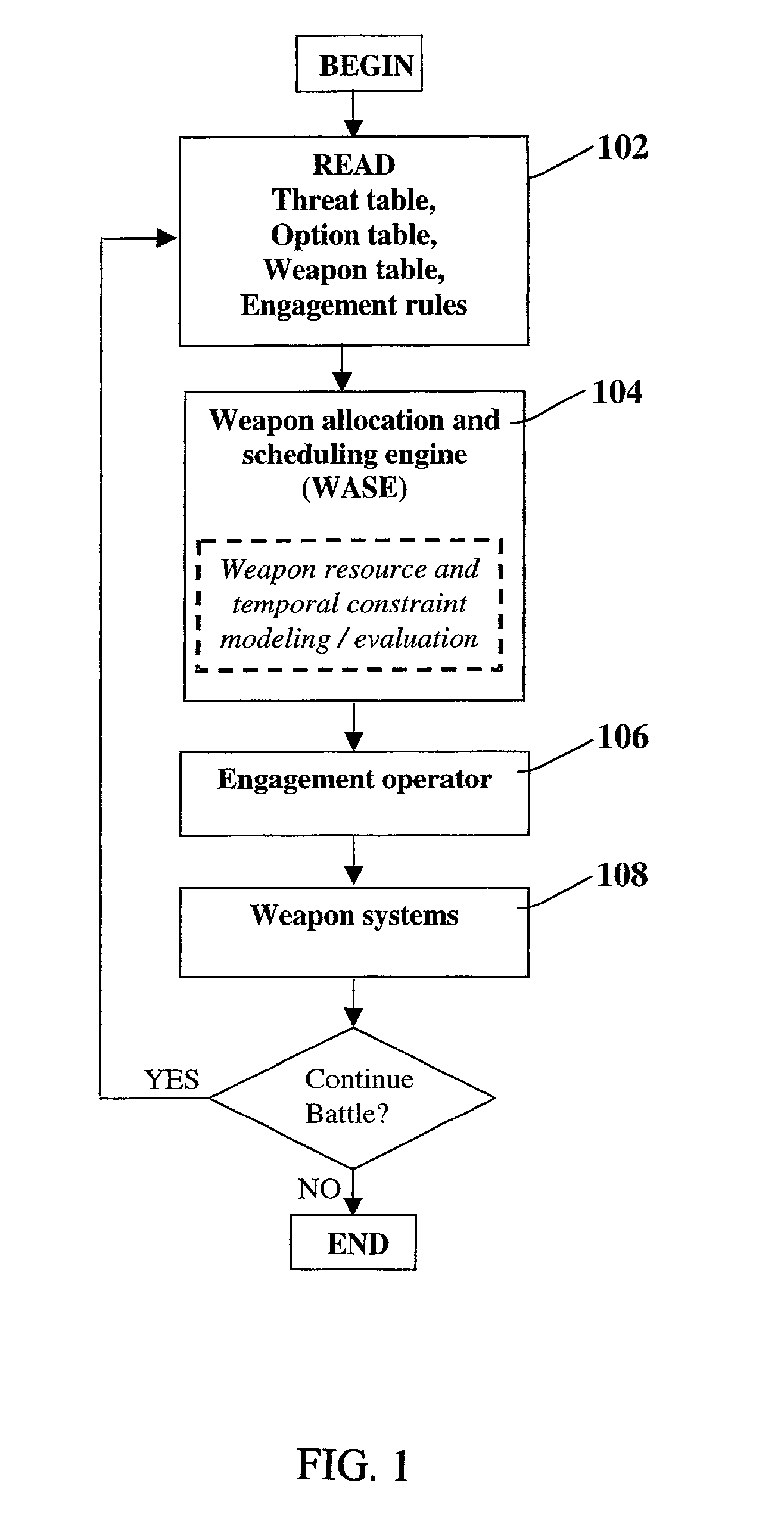
Method for automatic weapon allocation and scheduling against attacking threats
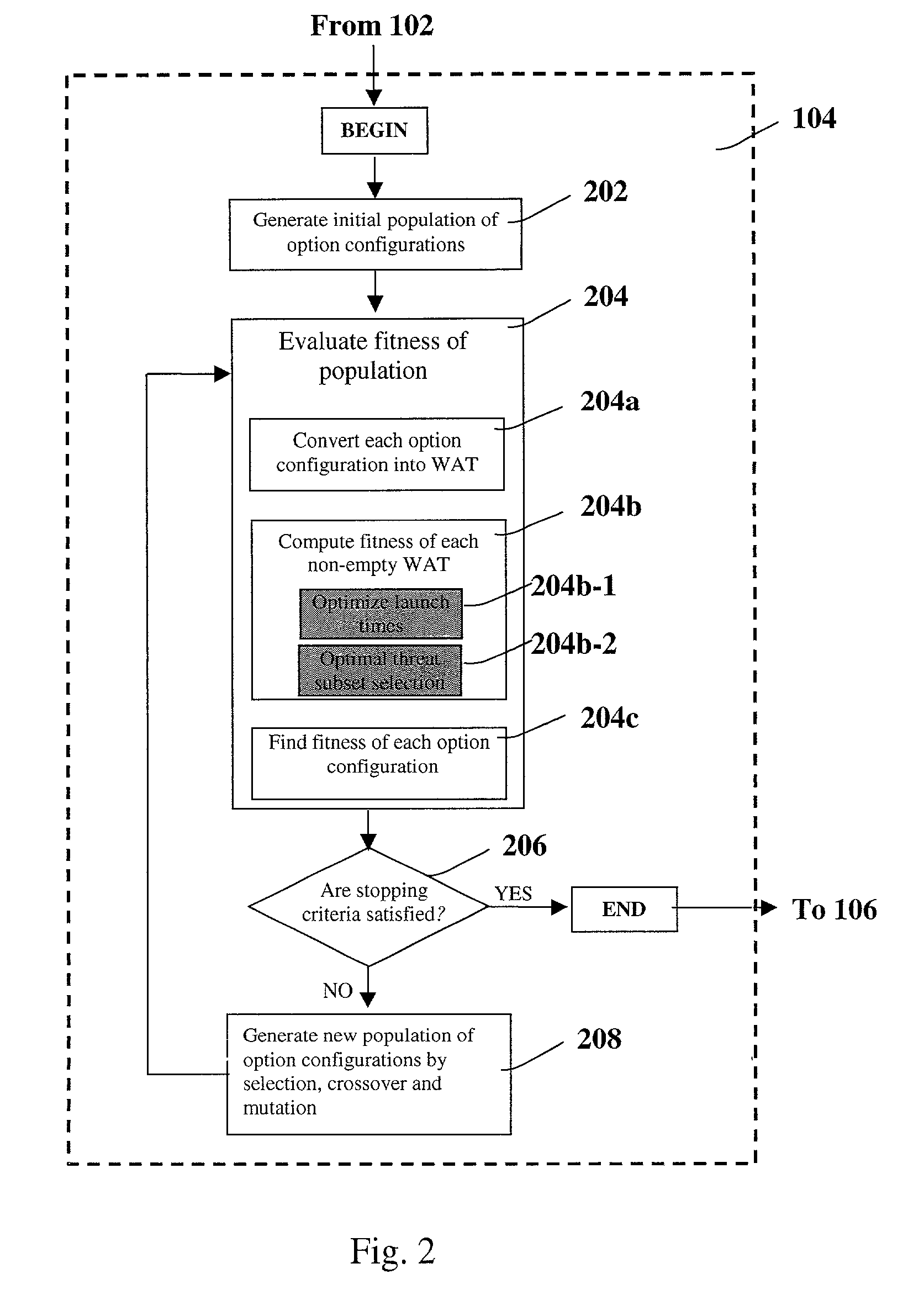
A system and method for automatic weapon allocation and scheduling of the present invention. The inventive method includes the steps of providing data with respect to threats, weapons, weapon allocation options; weapon allocation rules; and temporally dependent constraints with respect thereto; evaluating the data; and temporally allocating the weapons to the threats automatically in accordance with the evaluation. The invention computes the optimal pairing and the best time to deploy each weapon system against threat(s) it is paired with in arriving at the pairing. This results in an optimal assignment where weapon resource constraints are not exceeded and therefore guarantee availability of sufficient resources for engagement of every threat that is paired with a weapon system.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Intuitive computing methods and systems
ActiveUS8121618B2Wide applicabilityTelevision system detailsInstruments for road network navigationImaging processingCognition.knowledge
A smart phone senses audio, imagery, and / or other stimulus from a user's environment, and acts autonomously to fulfill inferred or anticipated user desires. In one aspect, the detailed technology concerns phone-based cognition of a scene viewed by the phone's camera. The image processing tasks applied to the scene can be selected from among various alternatives by reference to resource costs, resource constraints, other stimulus information (e.g., audio), task substitutability, etc. The phone can apply more or less resources to an image processing task depending on how successfully the task is proceeding, or based on the user's apparent interest in the task. In some arrangements, data may be referred to the cloud for analysis, or for gleaning. Cognition, and identification of appropriate device response(s), can be aided by collateral information, such as context. A great number of other features and arrangements are also detailed.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
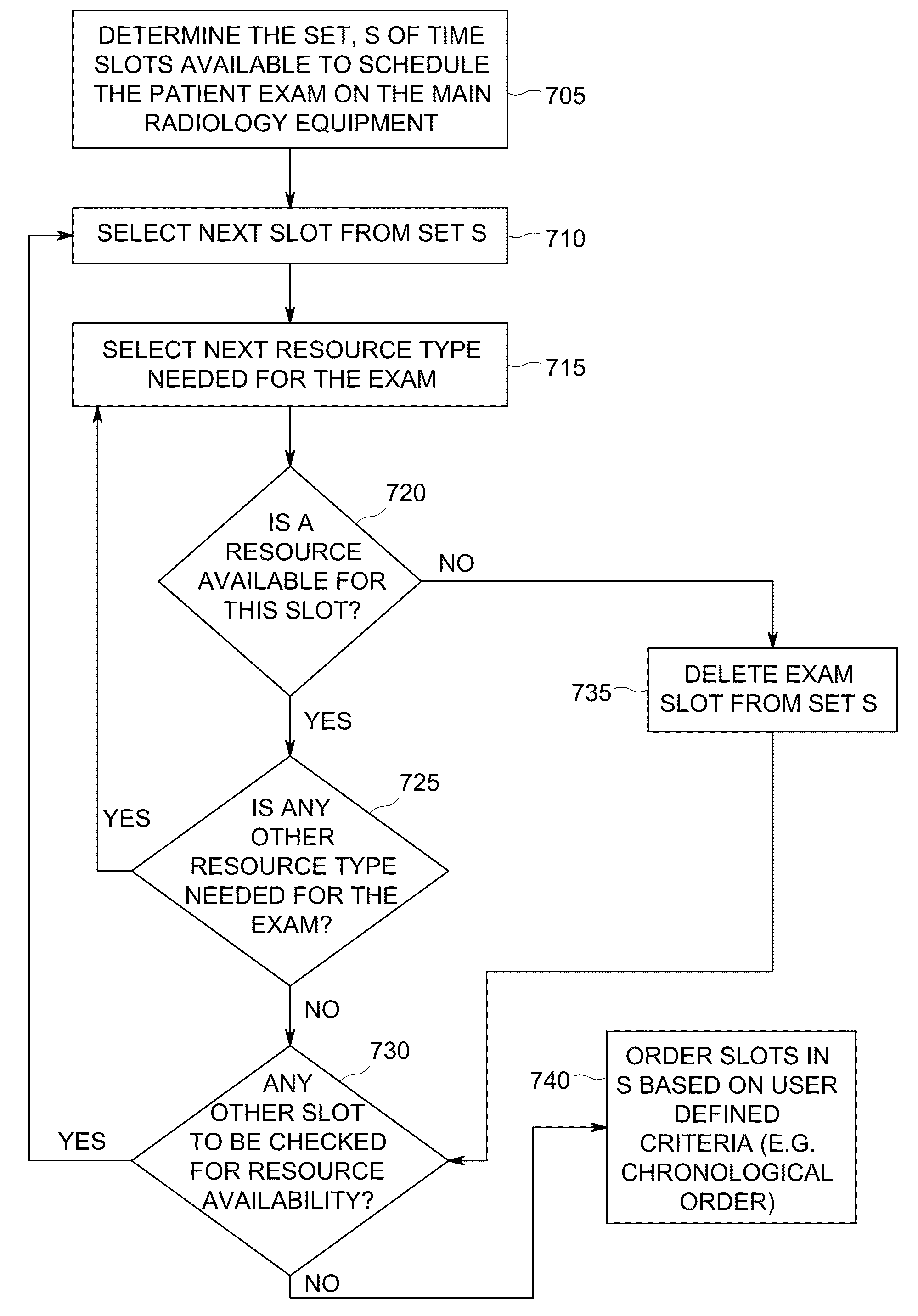
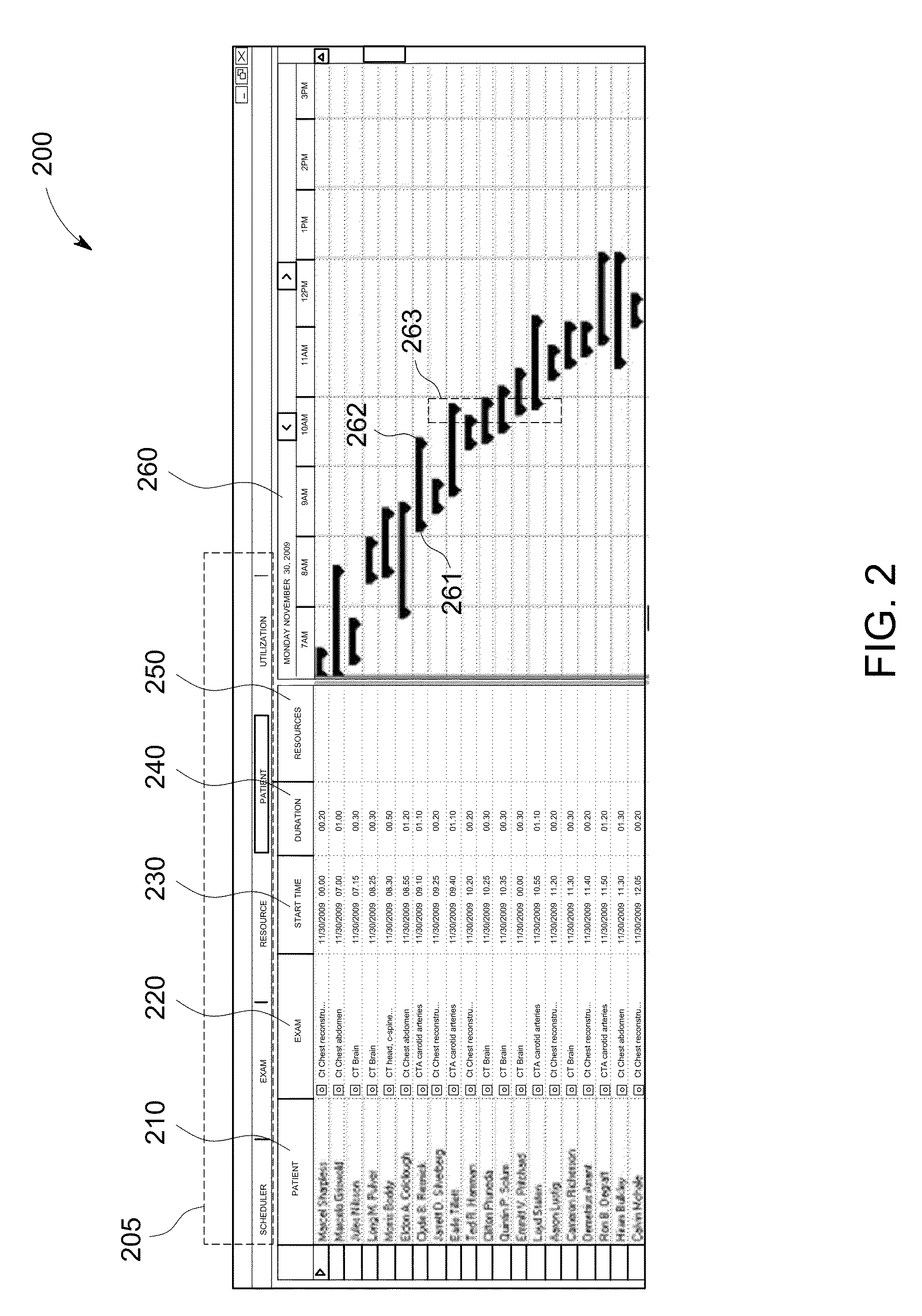
Systems and methods for multi-resource scheduling
Systems and methods are provided to schedule clinical tasks involving multiple sub-tasks and multiple resources in a clinical enterprise. An example method includes identifying a slot for a task defined by a task duration and one or more resources, the task including a plurality of sub-tasks, each sub-task having a sub-task duration utilizing one or more of the one or more resources, wherein each sub-task to be performed consecutively based on resource constraints; selecting a time slot for the task based on resource availability, the plurality of sub-tasks in the task, and a duration associated with each sub-task, wherein resource availability information is obtained from a clinical information system, and wherein each resource is scheduled only for one or more sub-tasks in which the resource is involved; displaying the schedule including the task and the plurality of sub-tasks; and facilitating access to view and modify the schedule.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
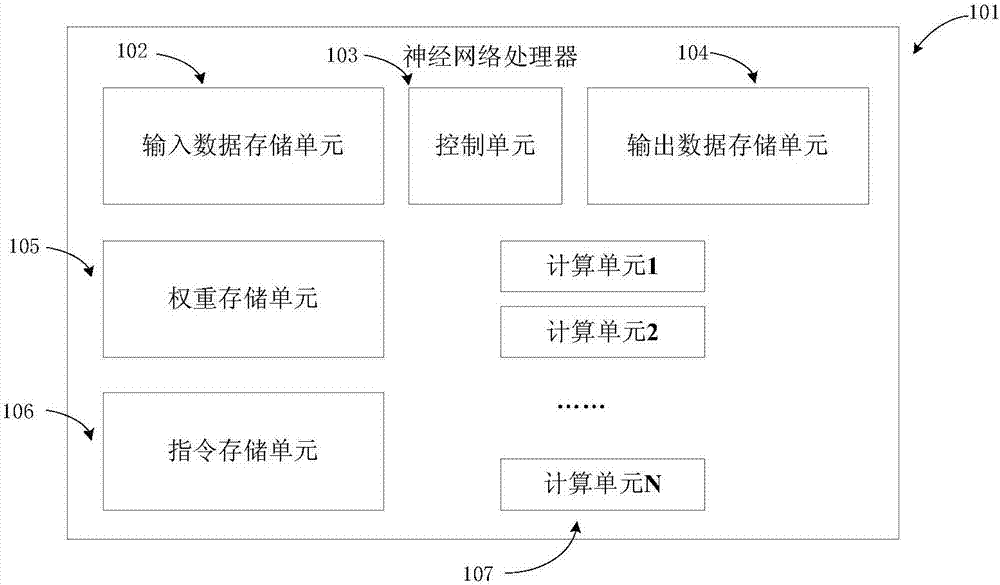
Neural network processor oriented automatic design method, device and optimization method
ActiveCN107103113AAutomate collaborative designShorten the design cycleBiological neural network modelsCAD circuit designNerve networkAlgorithm
The invention provides a neural network processor oriented automatic design method, device and optimization method. The automatic design method includes: a first step, acquiring a neural network model description file and a hardware resource constraint parameter, wherein the hardware resource constraint parameter includes the hardware resource size and the target operation speed; a second step, searching a unit library from an established neural network assembly library according to the neural network model description file and the hardware resource constraint parameter, and generating a hardware description language code corresponding to a neural network processor of the neural network model according to the unit library; and a step 3, converting the hardware description language code into a hardware circuit of the neural network processor.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Intuitive computing methods and systems
ActiveCN102893327AWide applicabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionSpeech recognitionImaging processingCognition
A smart phone senses audio, imagery, and / or other stimulus from a user's environment, and acts autonomously to fulfill inferred or anticipated user desires. In one aspect, the detailed technology concerns phone-based cognition of a scene viewed by the phone's camera. The image processing tasks applied to the scene can be selected from among various alternatives by reference to resource costs, resource constraints, other stimulus information (e.g., audio), task substitutability, etc. The phone can apply more or less resources to an image processing task depending on how successfully the task is proceeding, or based on the user's apparent interest in the task. In some arrangements, data may be referred to the cloud for analysis, or for gleaning. Cognition, and identification of appropriate device response(s), can be aided by collateral information, such as context. A great number of other features and arrangements are also detailed.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
Sensor-based mobile search, related methods and systems
ActiveUS8175617B2Wide applicabilityTelevision system detailsDevices with sensorImaging processingMobile search
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
Multidimensional resource scheduling system and method for cloud environment data center
InactiveCN102932279AAccurate abstractionIncrease weightData switching networksResource poolVirtualization
The invention provides a multidimensional resource scheduling system and method for a cloud environment data center, belonging to the field of cloud computing. The system provided by the invention comprises a user application request submitting module, a resource status acquiring module, a resource scheduling module, an application request priority queuing module and a virtualized physical resource pool. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: firstly detecting the status information of multidimensional resources in the virtualized physical resource pool and a current application request set in the user application request submitting module, which are acquired by the resource status acquiring module; then defining an application request priority queue which is suitable for the status balanced consumption of the current multidimensional resources in the virtualized physical resource pool by using a multiple-attribute-decision-making application priority scheduling algorithm; and finally submitting the application request which has the highest priority and meets resource constraints to the cloud environment data center for execution.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method for automatically and dynamically switching between speech technologies
InactiveUS6704707B2Low costHigh level of and performanceSpeech recognitionSpeech identificationSpeech technology
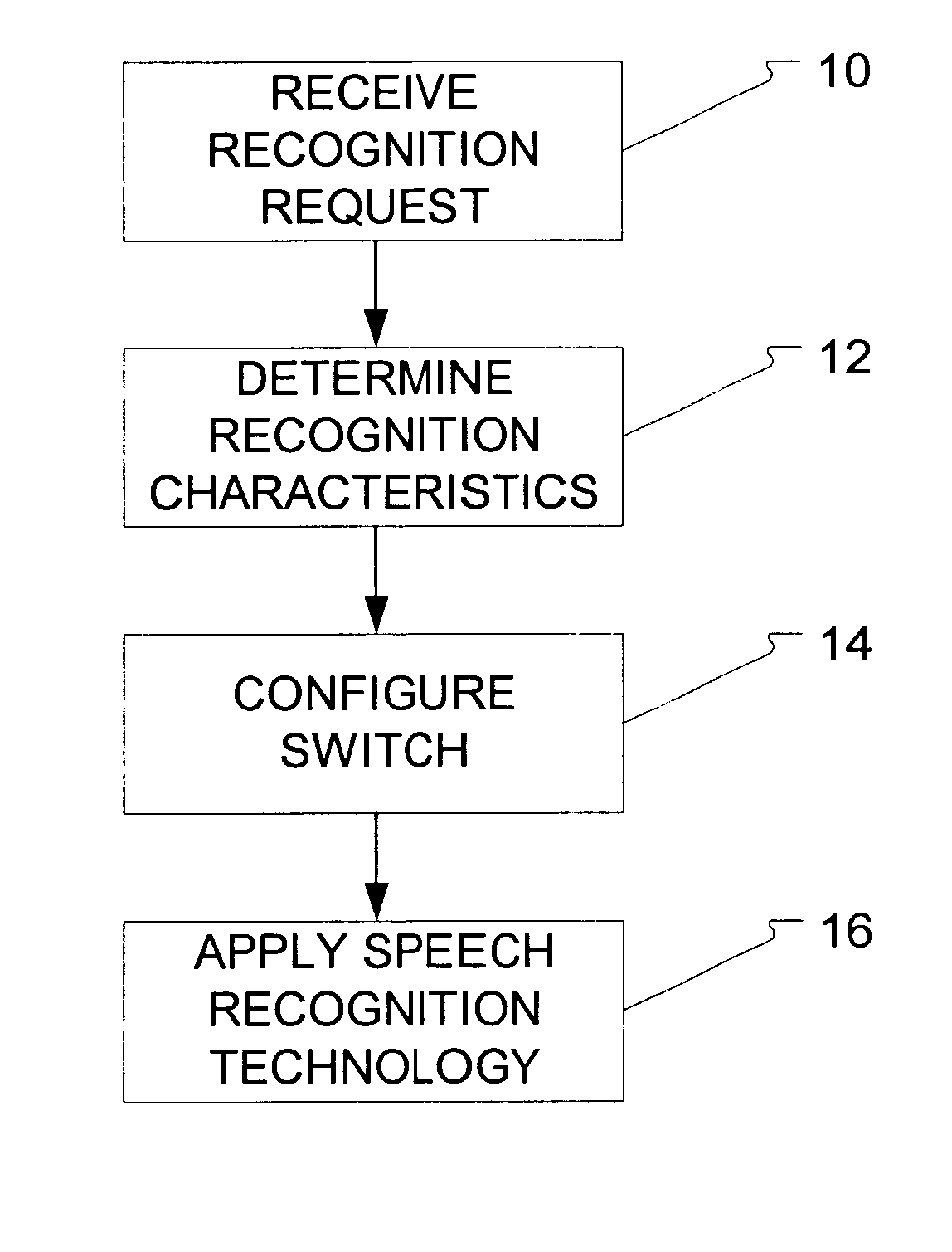
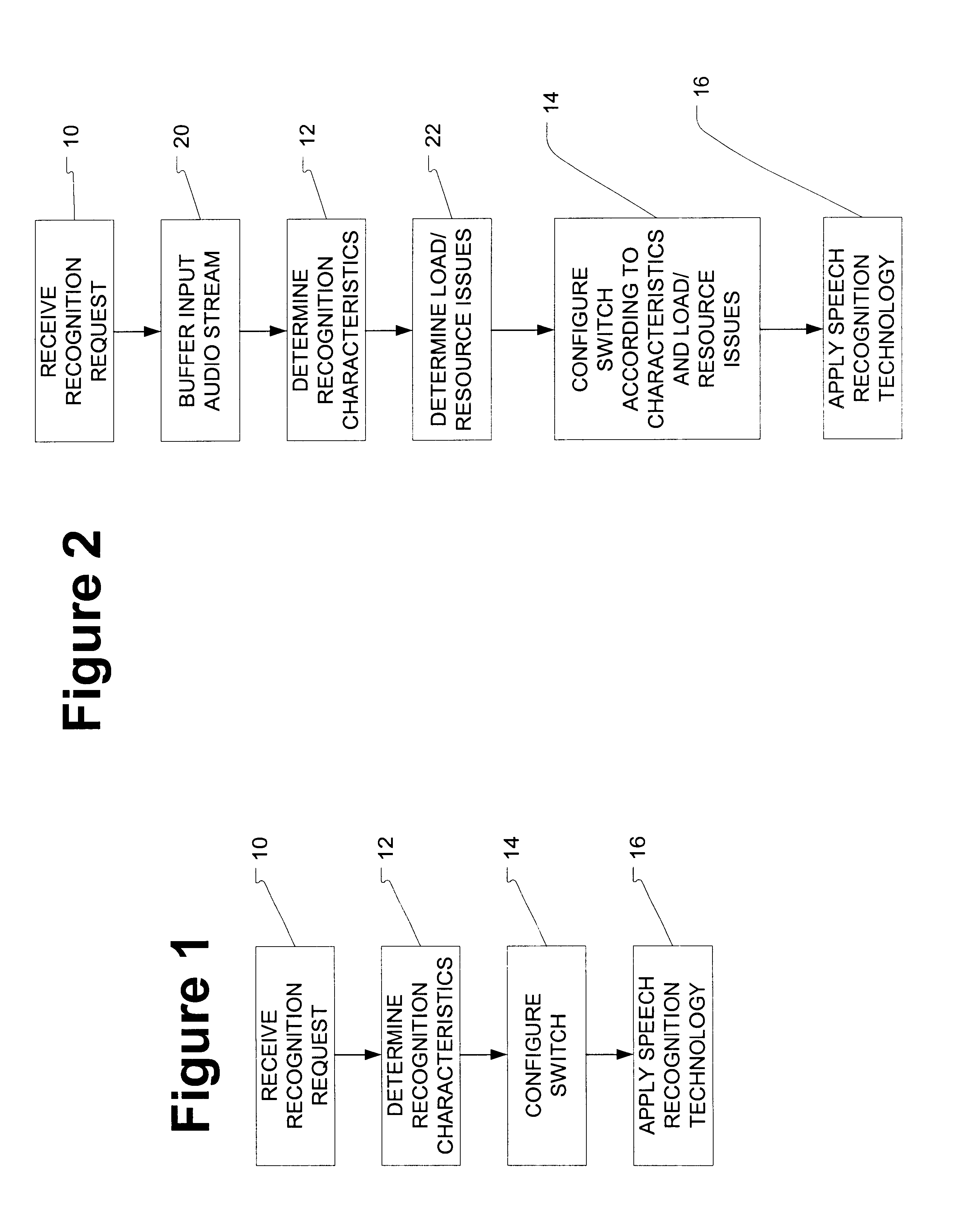
A method for switching between speech recognition technologies. The method includes reception of an initial recognition request accompanied by control information. Recognition characteristics are determined using the control information and then a switch is configured based upon the particular characteristic. Alternatively, the switch may be configured based upon system load levels and resource constraints.
Owner:INTEL CORP
System and method for deploying virtual machines in a computing environment
InactiveUS7904540B2Digital data processing detailsAnalogue computers for electric apparatusGraphicsDirected graph
A system and method for planning placement of virtual machines VMs in a computing environment comprising a set of hosting machines HM. The method includes constructing a bipartite directed graph-based model that represents both a current and a target placement states, both including virtual machine nodes v in VM and nodes h in HM. Using a technique of graph pruning, the method iteratively generates a plan for achieving a desired target placement starting from the current placement without temporarily violating any policy or resource constraint. The application of the pruning algorithm to VM deployment automation necessarily defines a new model. The methodology employed safely manages concurrent changes in a datacenter, so that the environment can adjust faster to changing constraints. Furthermore, the present invention allows detection of migration cycles, caused by deadlocked combinations of capacity and policy constraints, and resolving them.
Owner:IBM CORP
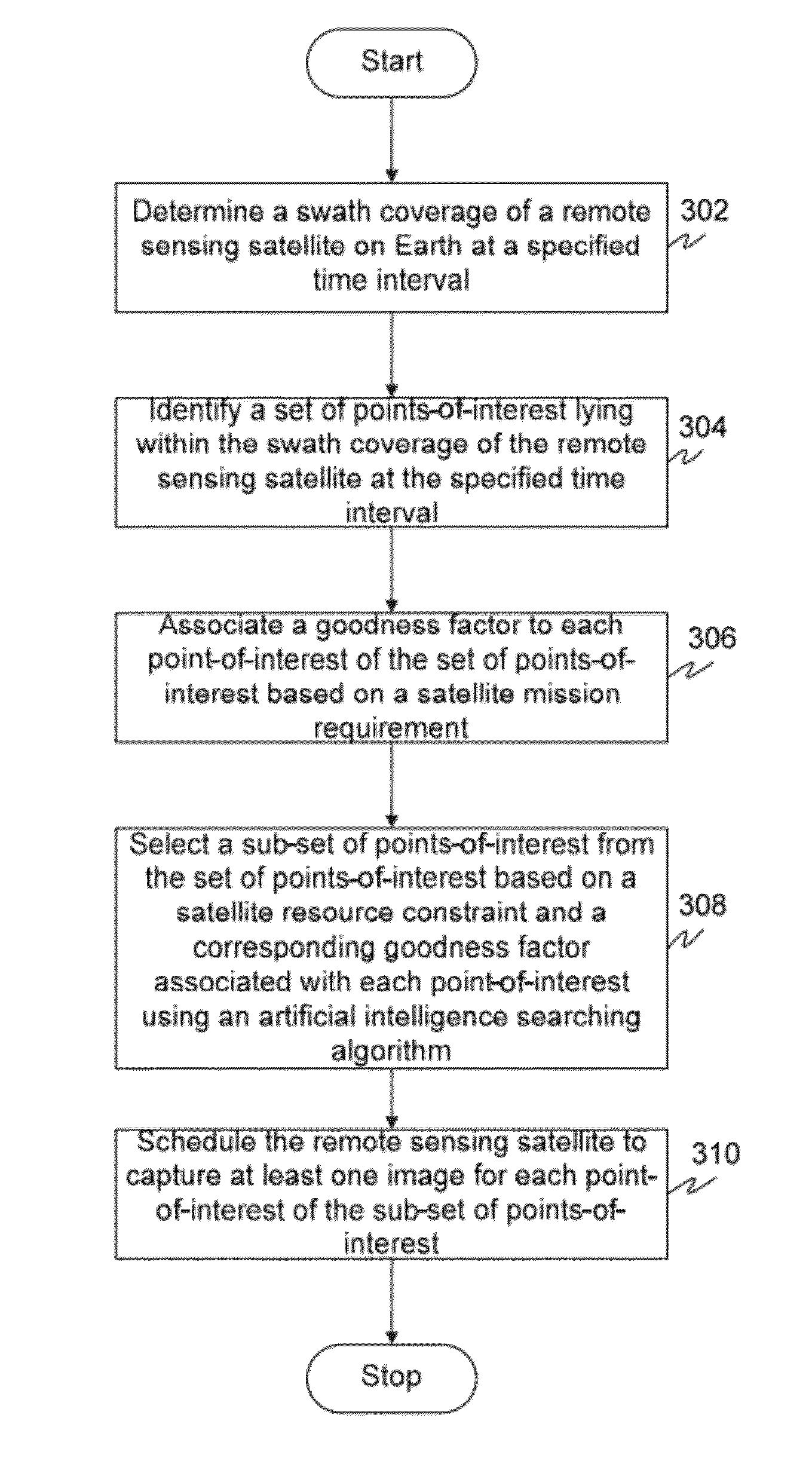
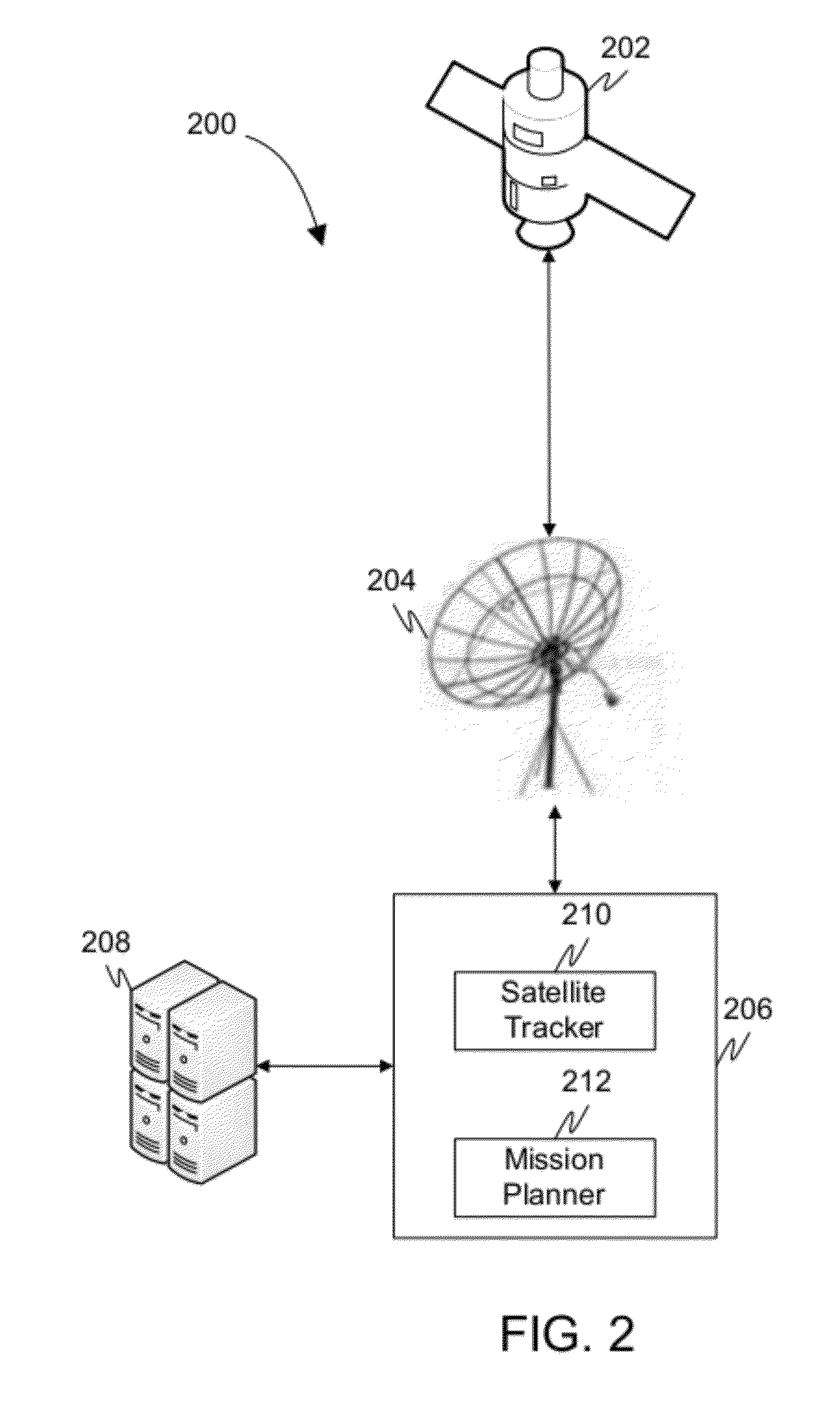
Method and system for automatically planning and scheduling a remote sensing satellite mission
InactiveUS20120029812A1Cosmonautic vehiclesInstruments for comonautical navigationGround stationResource constraints
The present invention provides method and system for automatically planning and scheduling a remote sensing satellite mission. A swath coverage of a remote sensing satellite at a specified time interval is determined from a ground station. Thereafter, a set of points-of-interest lying within the swath coverage of the remote sensing satellite at the specified time interval is identified. The method further includes associating a goodness factor to each point-of-interest of the set of points-of-interest based on a satellite mission requirement. An artificial intelligence searching algorithm is utilized to select a sub-set of points-of-interest from the set of points-of-interest based on a satellite resource constraint and a corresponding goodness factor associated with each point-of-interest. Finally, the method schedules the remote sensing satellite to capture at least one image for each point-of-interest of the sub-set of points-of-interest.
Owner:KING ABDULAZIZ CITY FOR SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
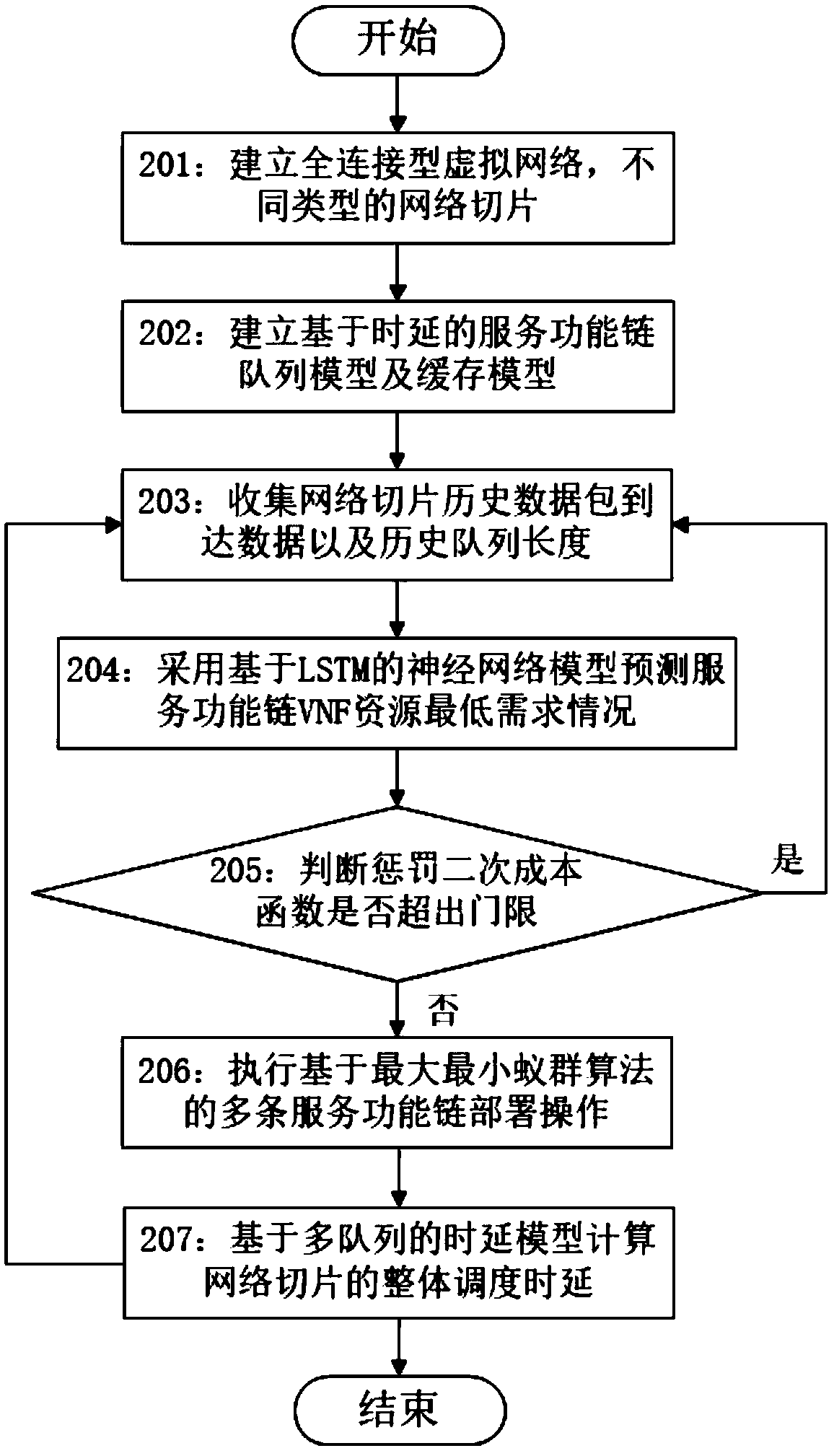
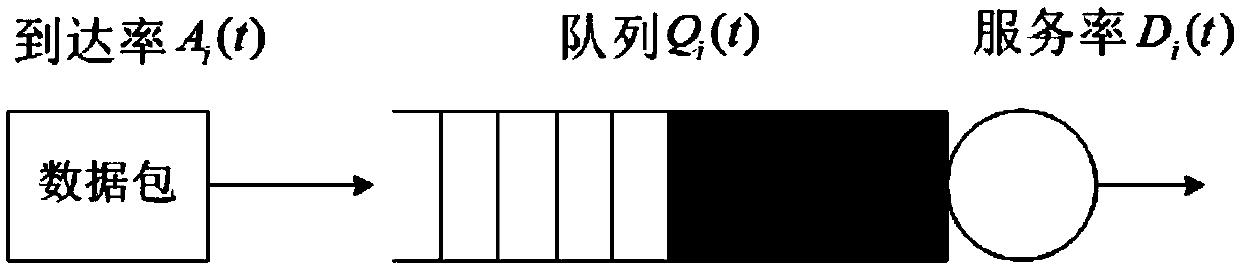
Prediction-based virtual network function scheduling method for 5G network slices
The invention relates to a prediction-based virtual network function scheduling method for 5G network slices, and belongs to the field of mobile communication. The method specifically comprises: establishing a delay-based service function chain queue model for service function chain features having dynamically changing service traffic; establishing a multi-queue cache model, and determining, at different time, priorities requested by the slices and a lowest service rate that should be provided, according to the size of a slice service queue; discretizing the time into a series of consecutive time windows, and establishing a prediction-based traffic perception model by using the queue information in the time windows as a training data set sample; and searching a scheduling method for the best service function chain VNF under the resource constraint that the caching of the slice service queue does not overflow according to the predicted size of each slice service queue and the corresponding lowest service rate. The method realizes on-line mapping of network slices, reduces the overall average scheduling delay of multiple network slices, and improves the performance of network services.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Intuitive Computing Methods and Systems
ActiveUS20120165046A1Wide applicabilityTelevision system detailsInstruments for road network navigationImaging processingCognition.knowledge
A smart phone senses audio, imagery, and / or other stimulus from a user's environment, and acts autonomously to fulfill inferred or anticipated user desires. In one aspect, the detailed technology concerns phone-based cognition of a scene viewed by the phone's camera. The image processing tasks applied to the scene can be selected from among various alternatives by reference to resource costs, resource constraints, other stimulus information (e.g., audio), task substitutability, etc. The phone can apply more or less resources to an image processing task depending on how successfully the task is proceeding, or based on the user's apparent interest in the task. In some arrangements, data may be referred to the cloud for analysis, or for gleaning. Cognition, and identification of appropriate device response(s), can be aided by collateral information, such as context. A great number of other features and arrangements are also detailed.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
Measure of analysis performed in property checking
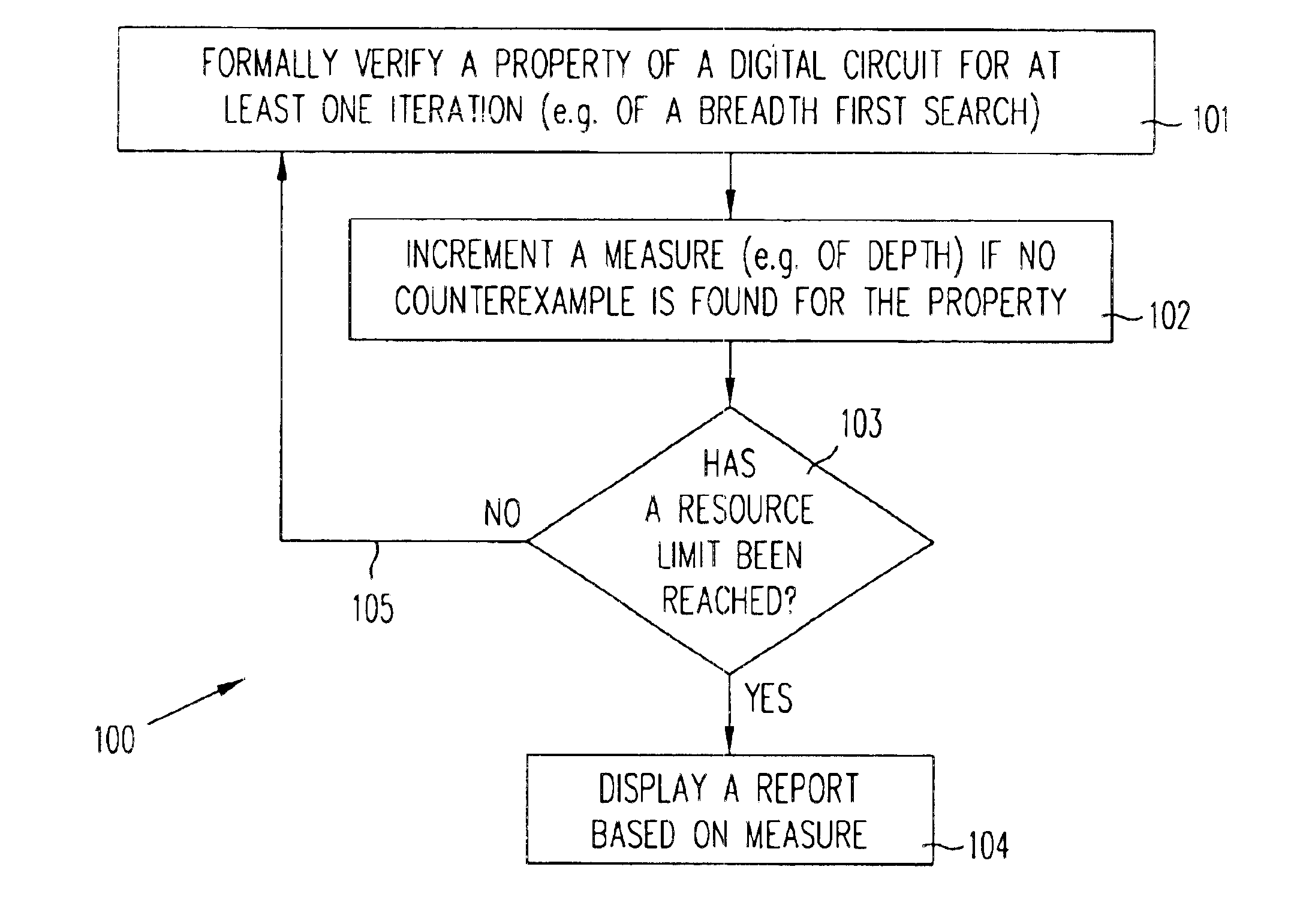
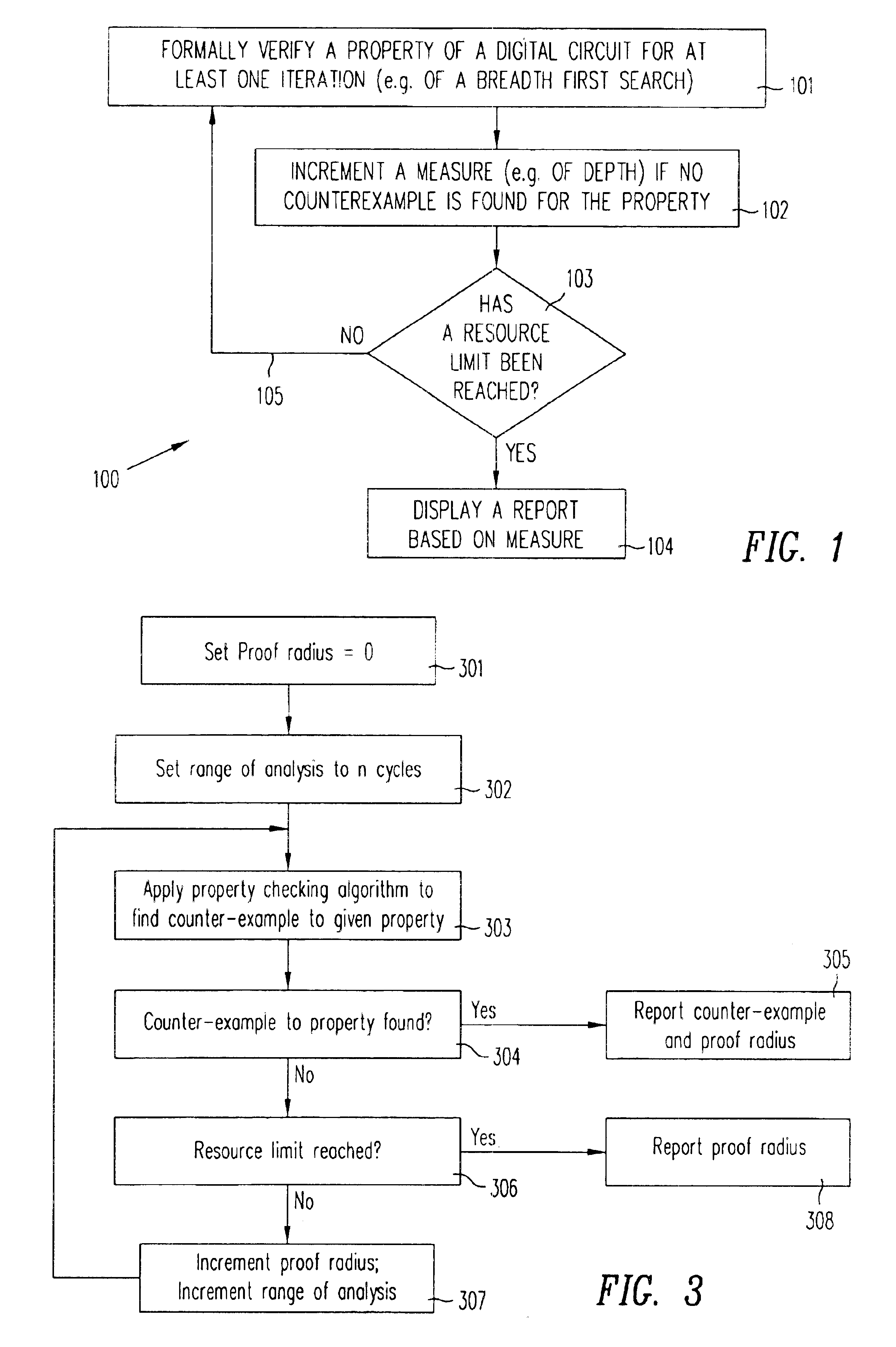
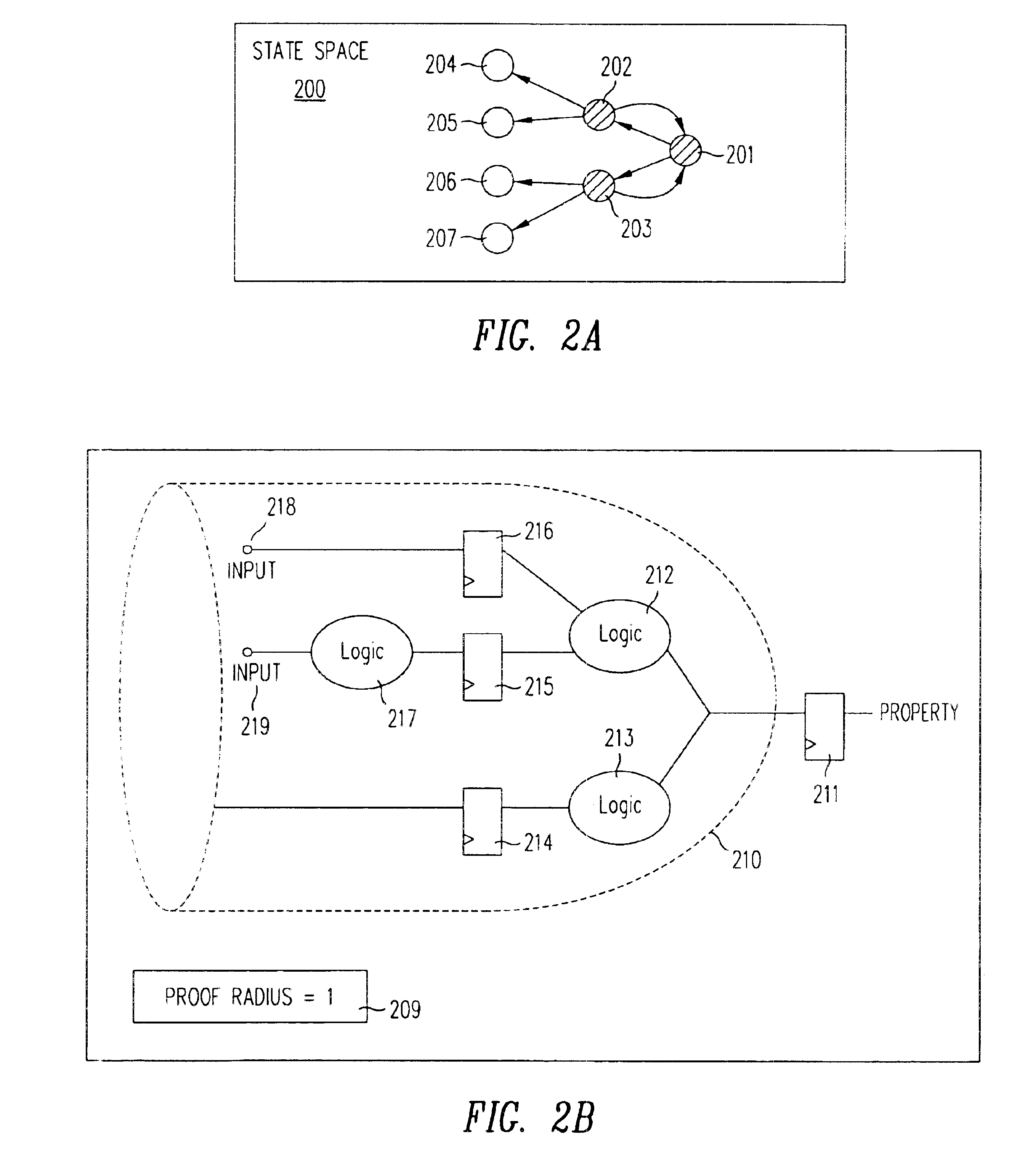
InactiveUS6848088B1Computation using non-denominational number representationComputer aided designDistance analysisComputer science
The amount of analysis performed in determining the validity of a property of a digital circuit is measured concurrent with performance of the analysis, and provided as an output when a true / false answer cannot be provided e.g. when stopped due to resource constraints. In some embodiments, a measure of value N indicates that a given property that is being checked will not be violated within a distance N from an initial state from which the analysis started. Therefore, in such embodiments, a measure of value N indicated that the analysis has implicitly or explicitly covered every possible excursion of length N from the initial state, and formally proved that no counter-example is possible within this length N.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
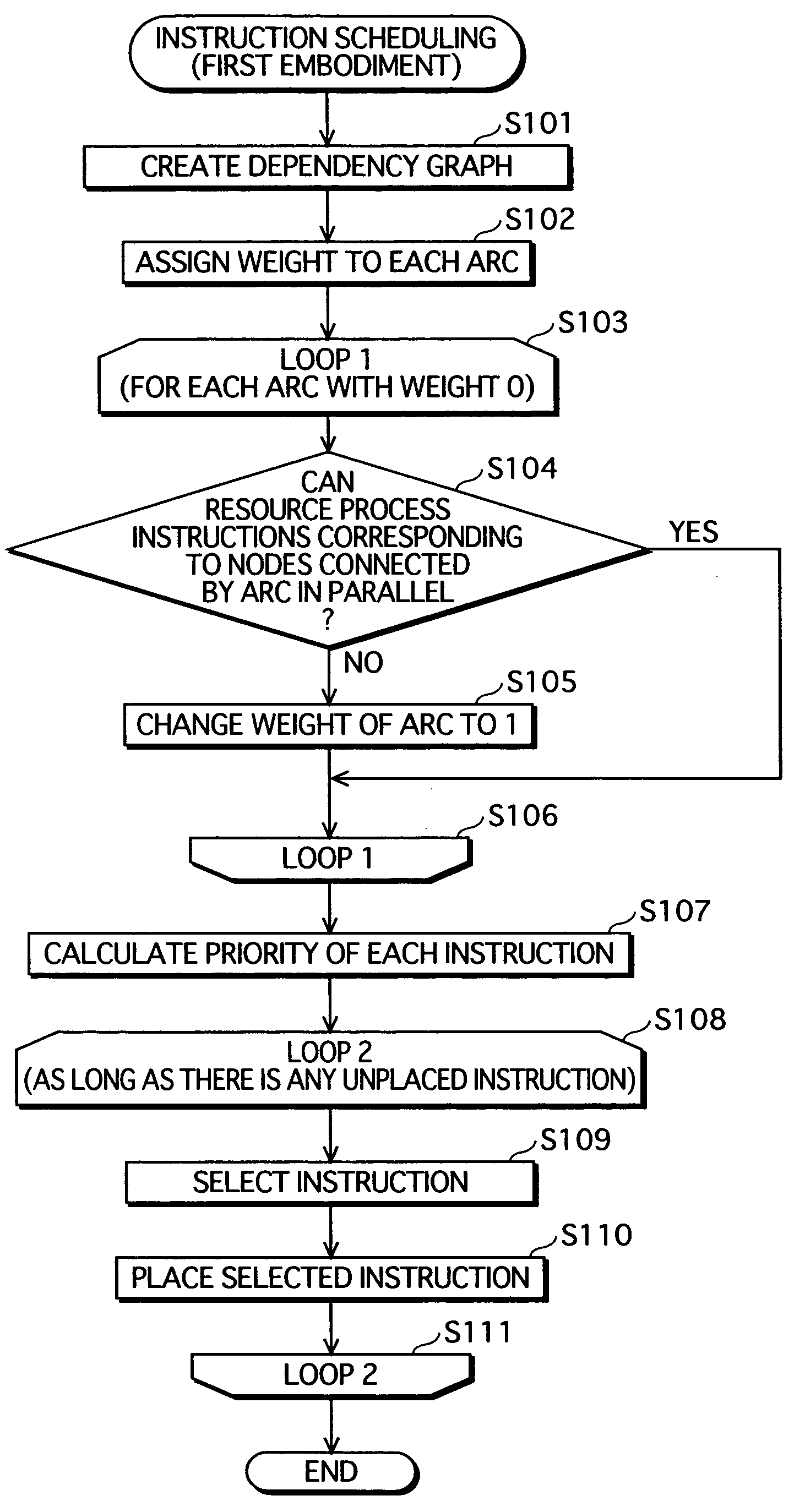
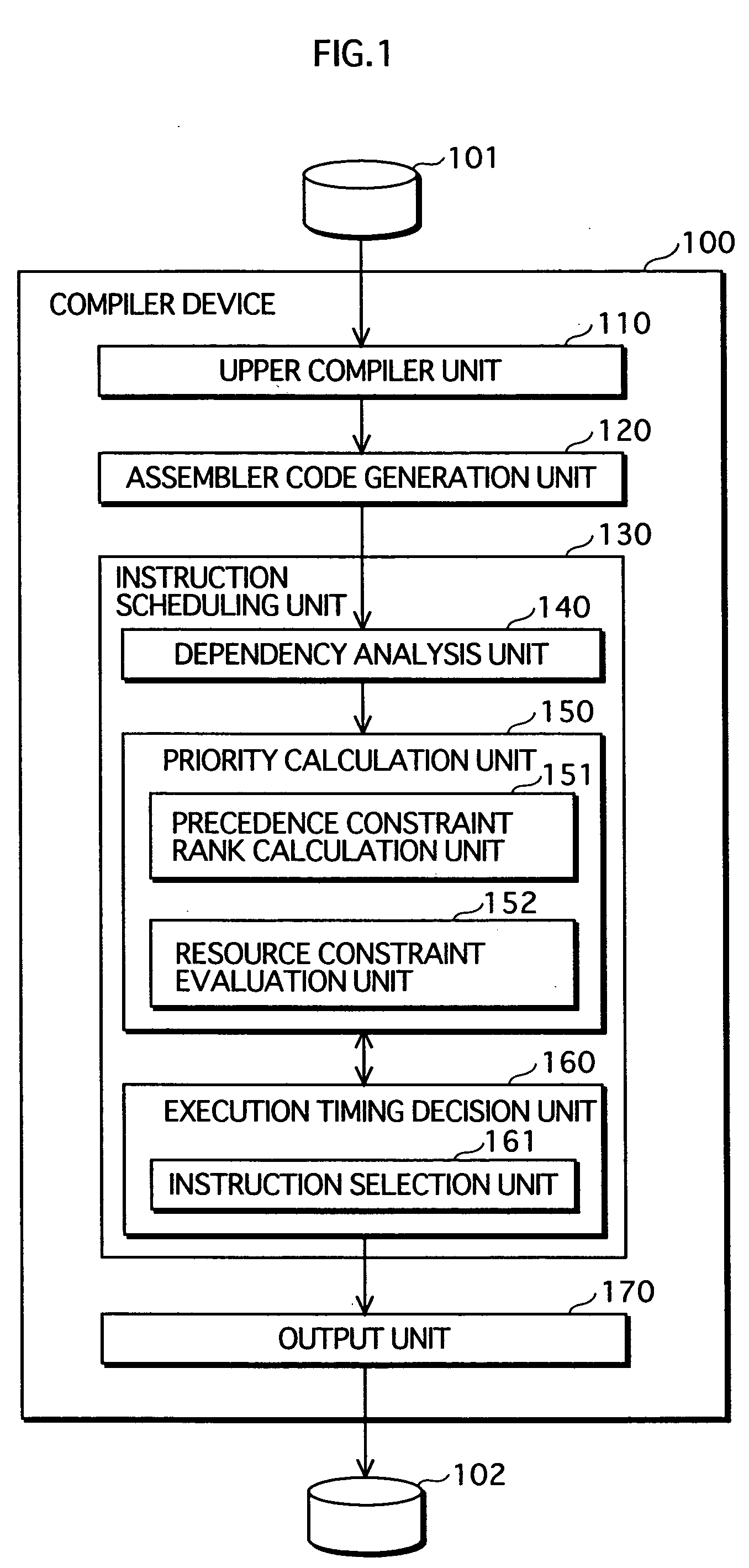
Instruction scheduling method, instruction scheduling device, and instruction scheduling program
InactiveUS20040083468A1Software engineeringProgram controlScheduling instructionsParallel processing
A dependency analysis unit creates a dependency graph showing dependencies between instructions acquired from an assembler code generation unit. A precedence constraint rank calculation unit assigns predetermined weights to arcs in the graph, and adds up weights to calculate a precedence constraint rank of each instruction. When a predecessor and a successor having a dependency and an equal precedence constraint rank cannot be processed in parallel due to a resource constraint, a resource constraint evaluation unit raises the precedence constraint rank of the predecessor. A priority calculation unit sets the raised precedence constraint rank as a priority of the predecessor. An instruction selection unit selects an instruction having a highest priority. An execution timing decision unit places the selected instruction in a clock cycle. The selection by the instruction selection unit and the placement by the execution timing decision unit are repeated until all instructions are placed in clock cycles.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
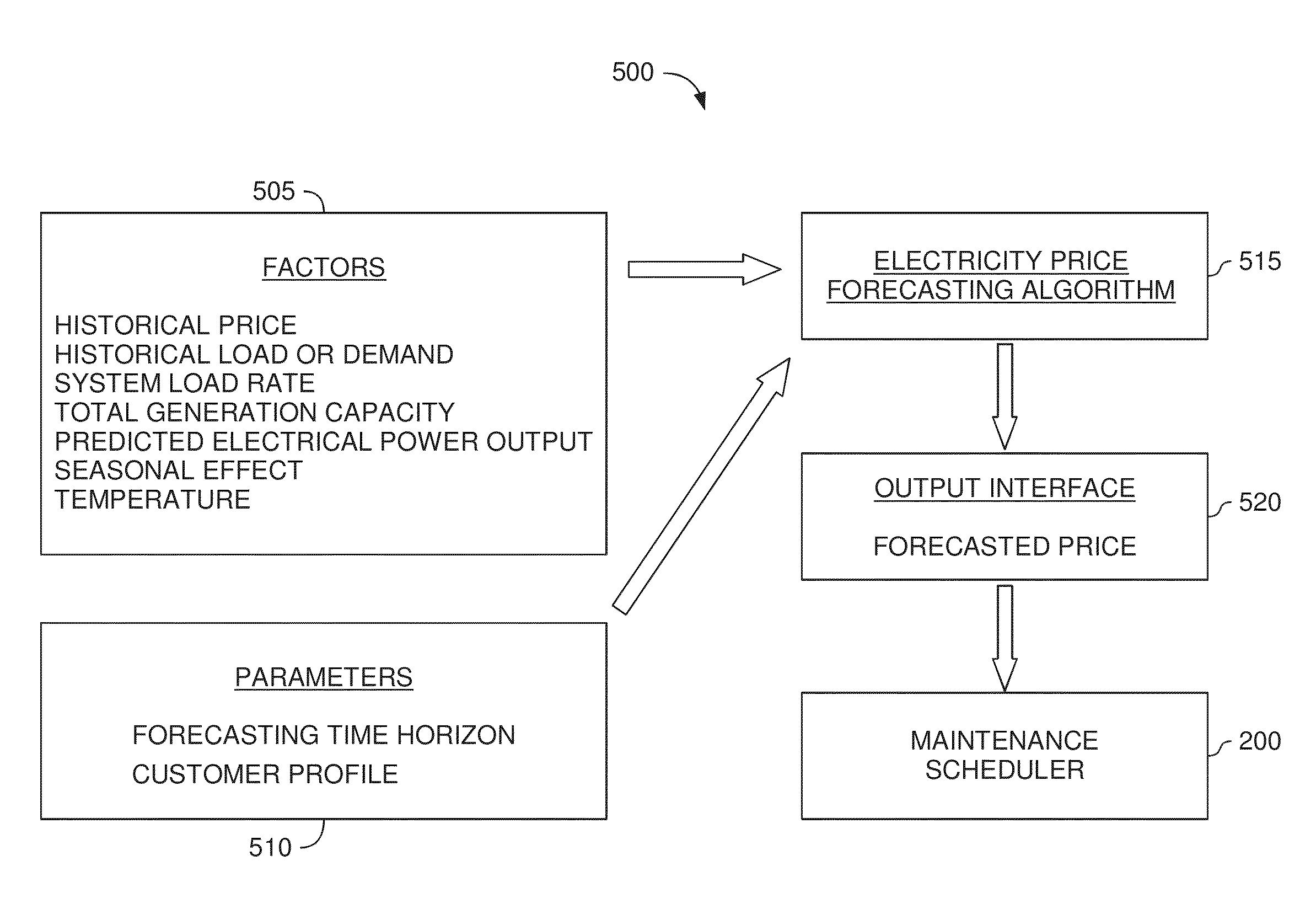
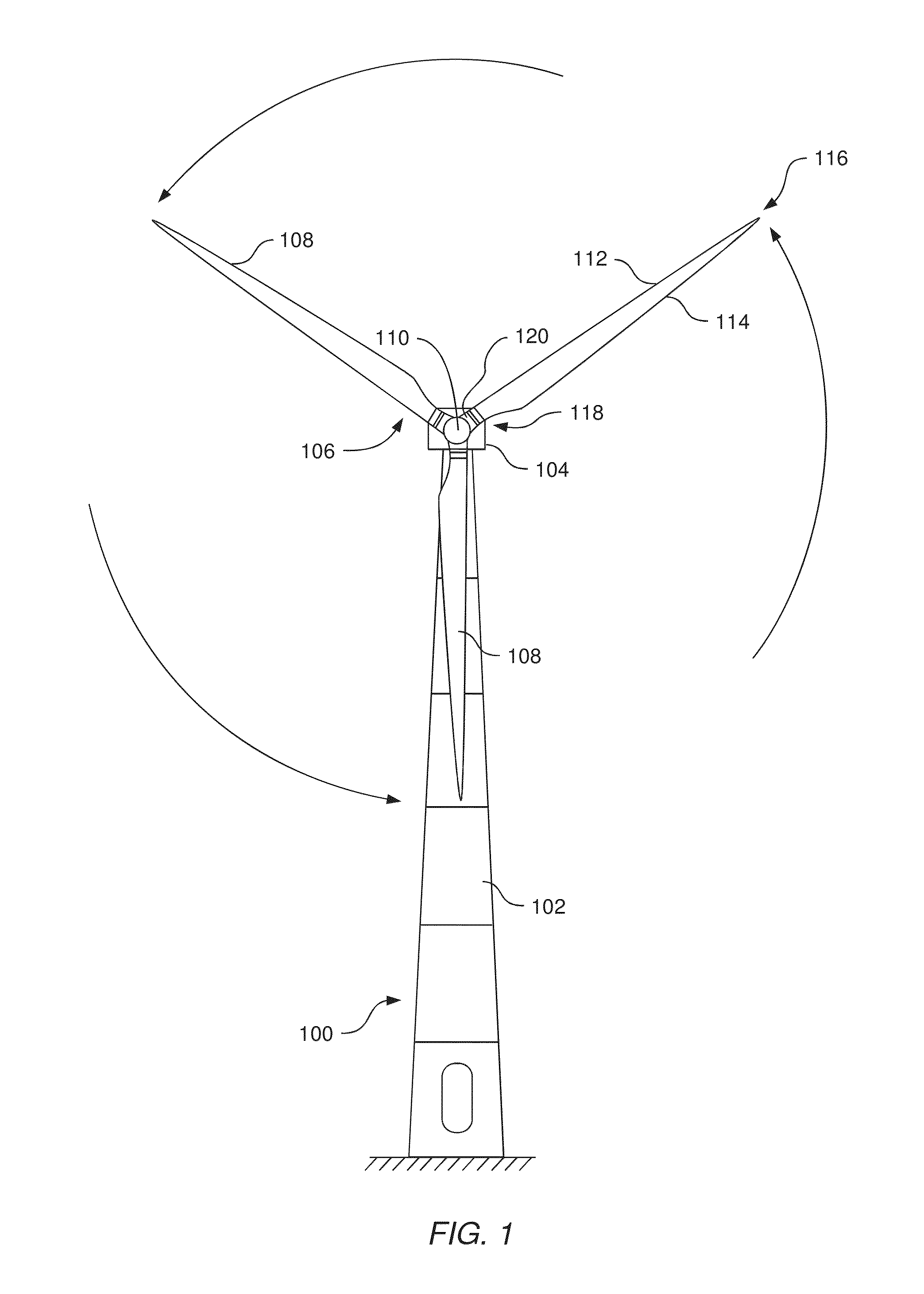
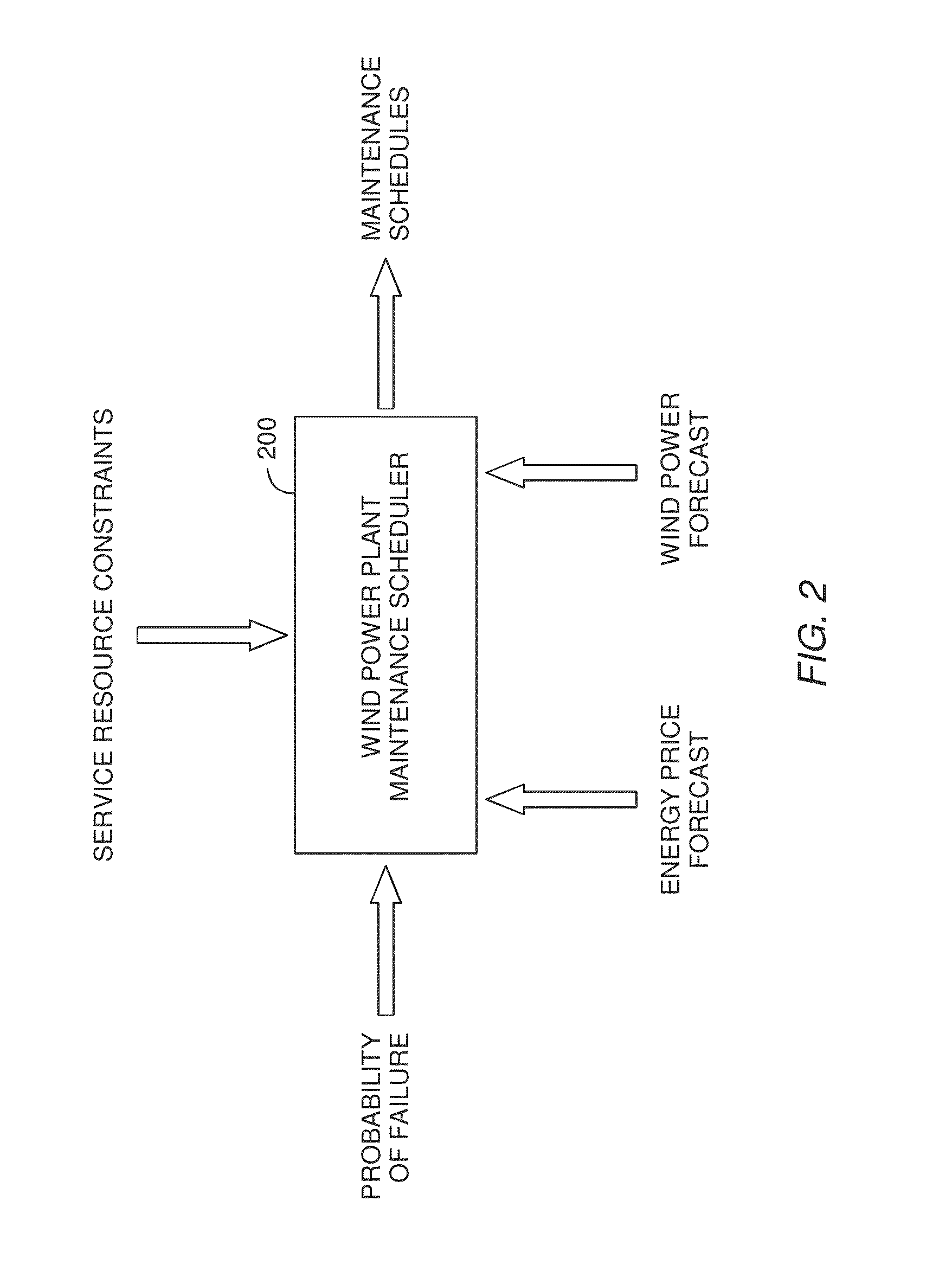
Wind turbine maintenance optimizer
Determining when to perform preventative maintenance is an important consideration for maximizing the revenue of a wind turbine. For example, performing preventative maintenance may be cheaper than replacing turbine components when they fail. When determining to perform preventative maintenance, a maintenance scheduler may consider multiple factors. These factors may include the probability of failure, the predicted price of energy, predicted wind power production, resource constraints, and the like. Specifically, the maintenance scheduler may predict the future values of these factors which are then integrated into a net present value (NPV) for each of the components. Based on the respective NPVs, the maintenance scheduler may determine which maintenance actions to perform and in what order.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Method for automatic weapon allocation and scheduling against attacking threats
A system and method for automatic weapon allocation and scheduling of the present invention. The inventive method includes the steps of providing data with respect to threats, weapons, weapon allocation options; weapon allocation rules; and temporally dependent constraints with respect thereto; evaluating the data; and temporally allocating the weapons to the threats automatically in accordance with the evaluation. The invention computes the optimal pairing and the best time to deploy each weapon system against threat(s) it is paired with in arriving at the pairing. This results in an optimal assignment where weapon resource constraints are not exceeded and therefore guarantee availability of sufficient resources for engagement of every threat that is paired with a weapon system.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Intuitive computing methods and systems
InactiveUS20140337733A1Resource allocationCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingCognition.knowledge
A smart phone senses audio, imagery, and / or other stimulus from a user's environment, and acts autonomously to fulfill inferred or anticipated user desires. In one aspect, the detailed technology concerns phone-based cognition of a scene viewed by the phone's camera. The image processing tasks applied to the scene can be selected from among various alternatives by reference to resource costs, resource constraints, other stimulus information (e.g., audio), task substitutability, etc. The phone can apply more or less resources to an image processing task depending on how successfully the task is proceeding, or based on the user's apparent interest in the task. In some arrangements, data may be referred to the cloud for analysis, or for gleaning. Cognition, and identification of appropriate device response(s), can be aided by collateral information, such as context. A great number of other features and arrangements are also detailed.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
Method for performing oilfield production operations
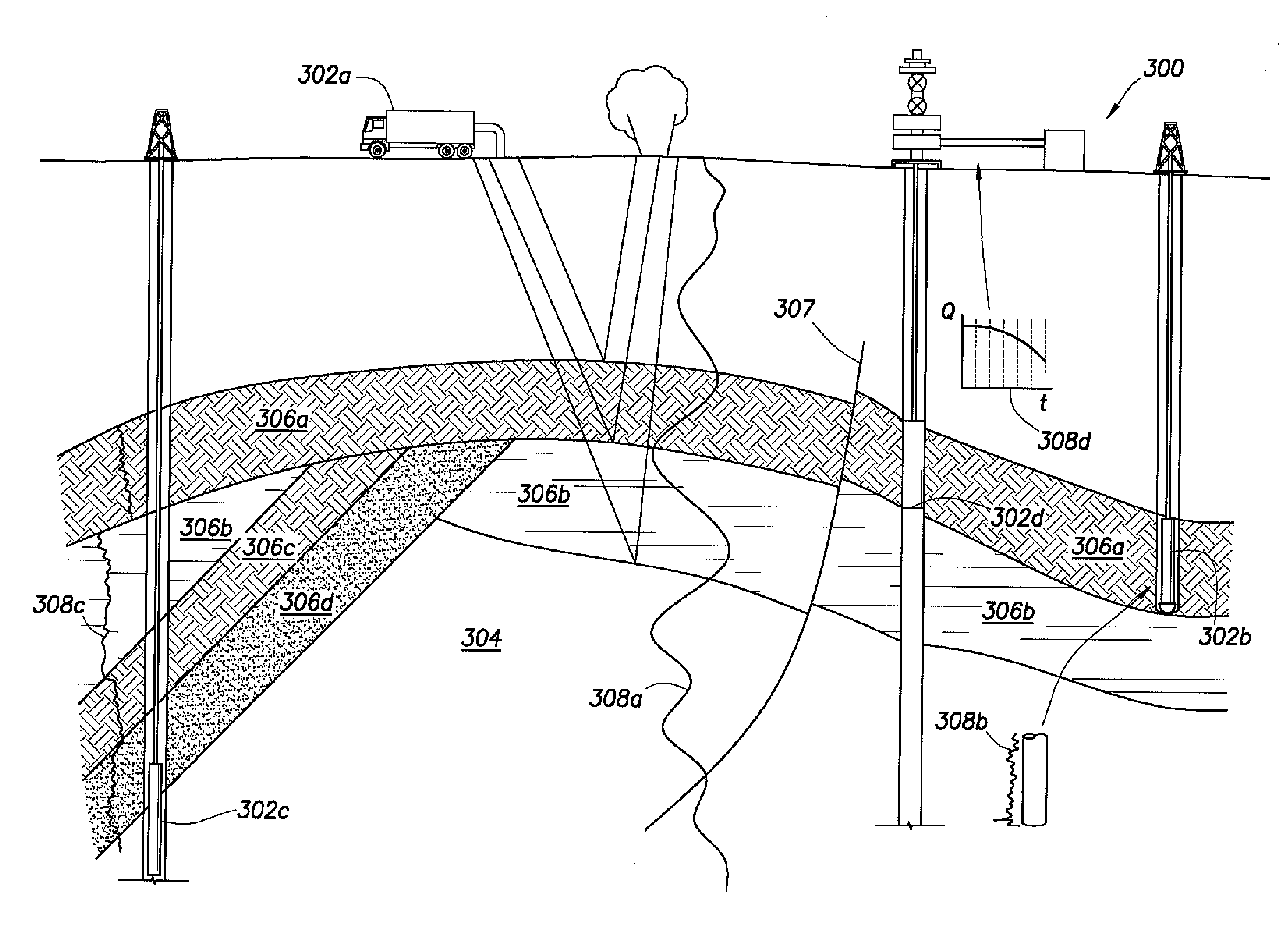
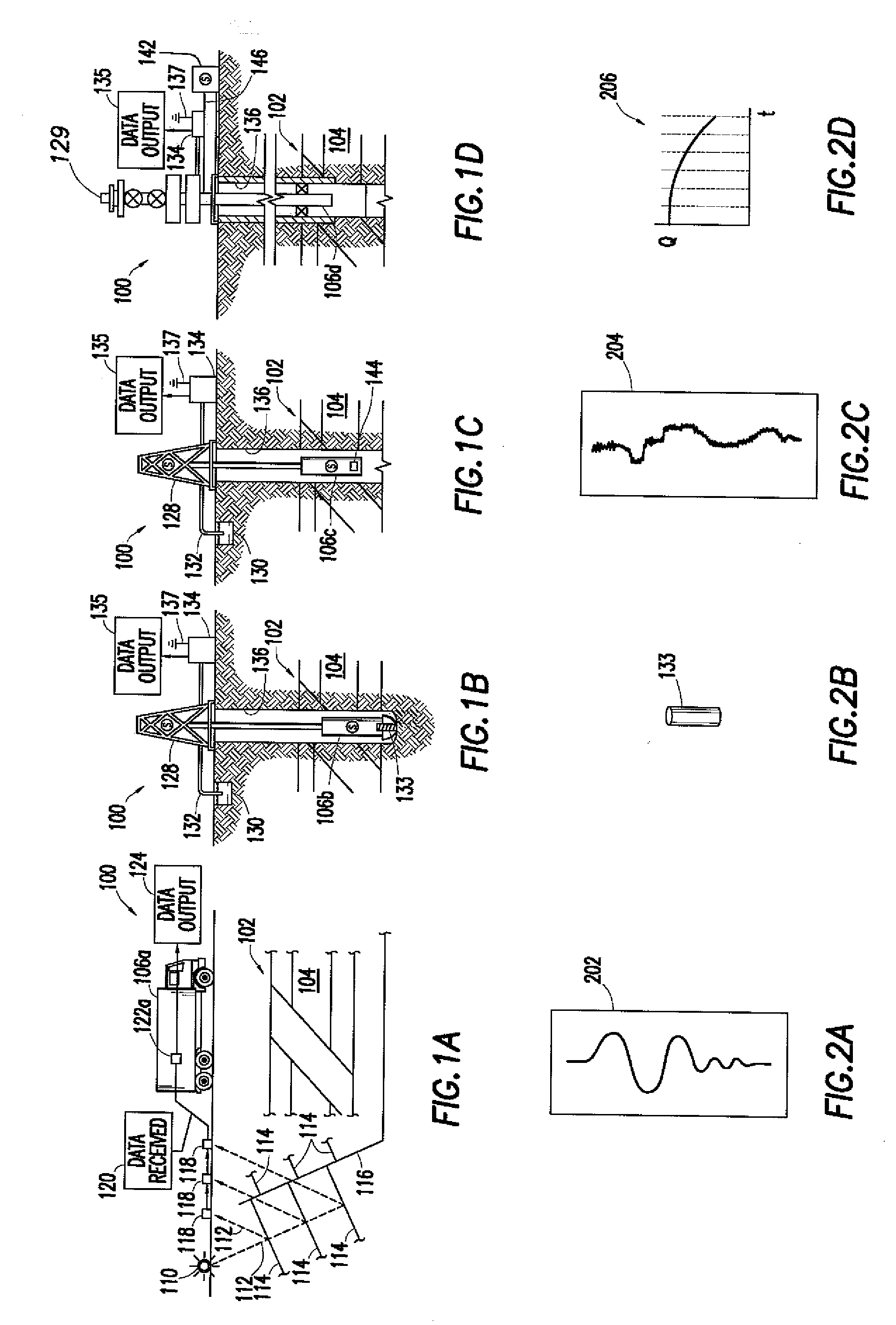
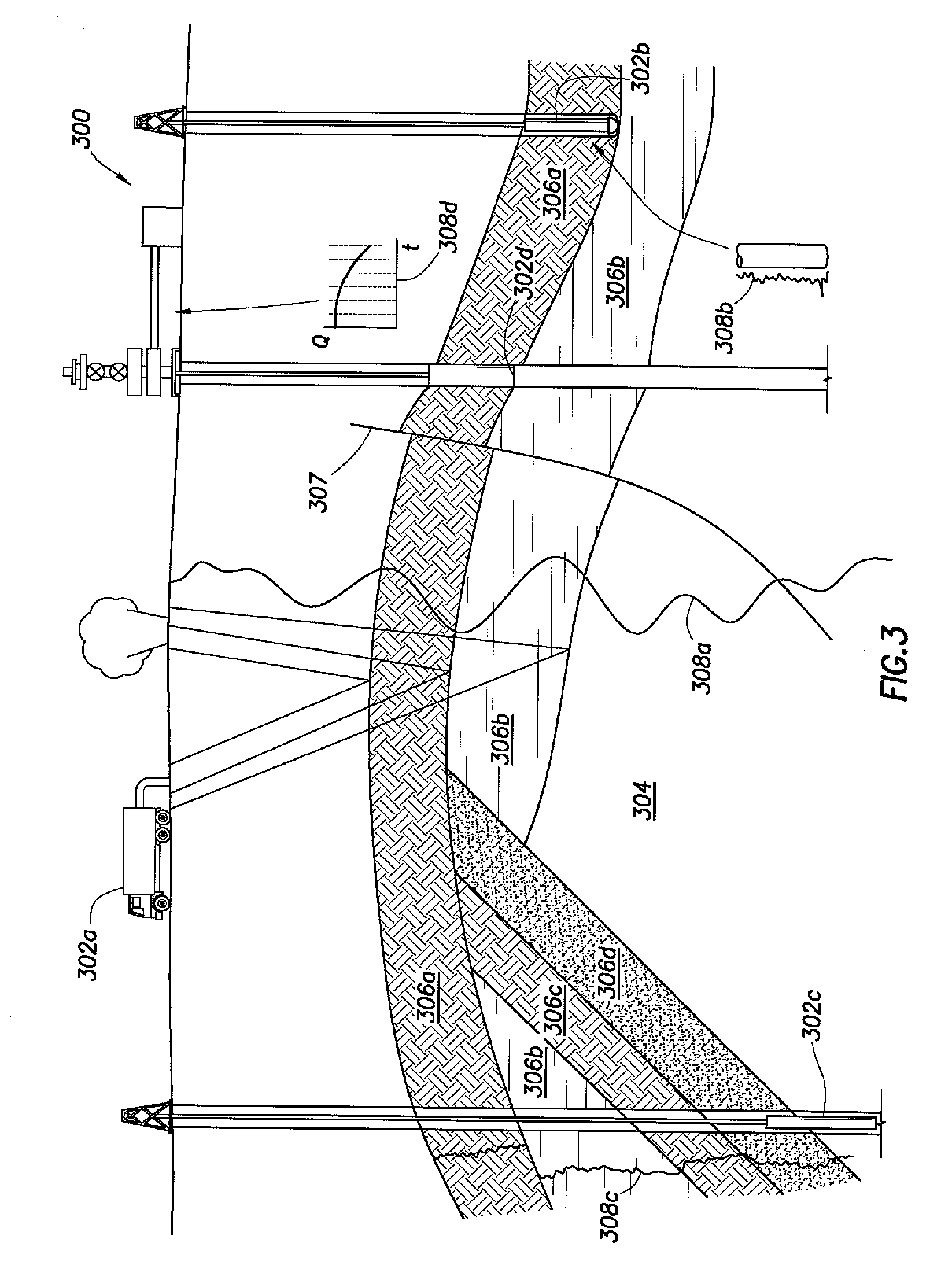
ActiveUS20080140369A1Speed maximizationMaximize liquid/oilSurveyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationEngineeringResource allocation
A method is disclosed for optimal lift resource allocation, which includes optimally allocating lift resource under a total lift resource constraint or a total production constraint, the allocating step including distributing lift resource among all lifted wells in a network so as to maximize a liquid / oil rate at a sink.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
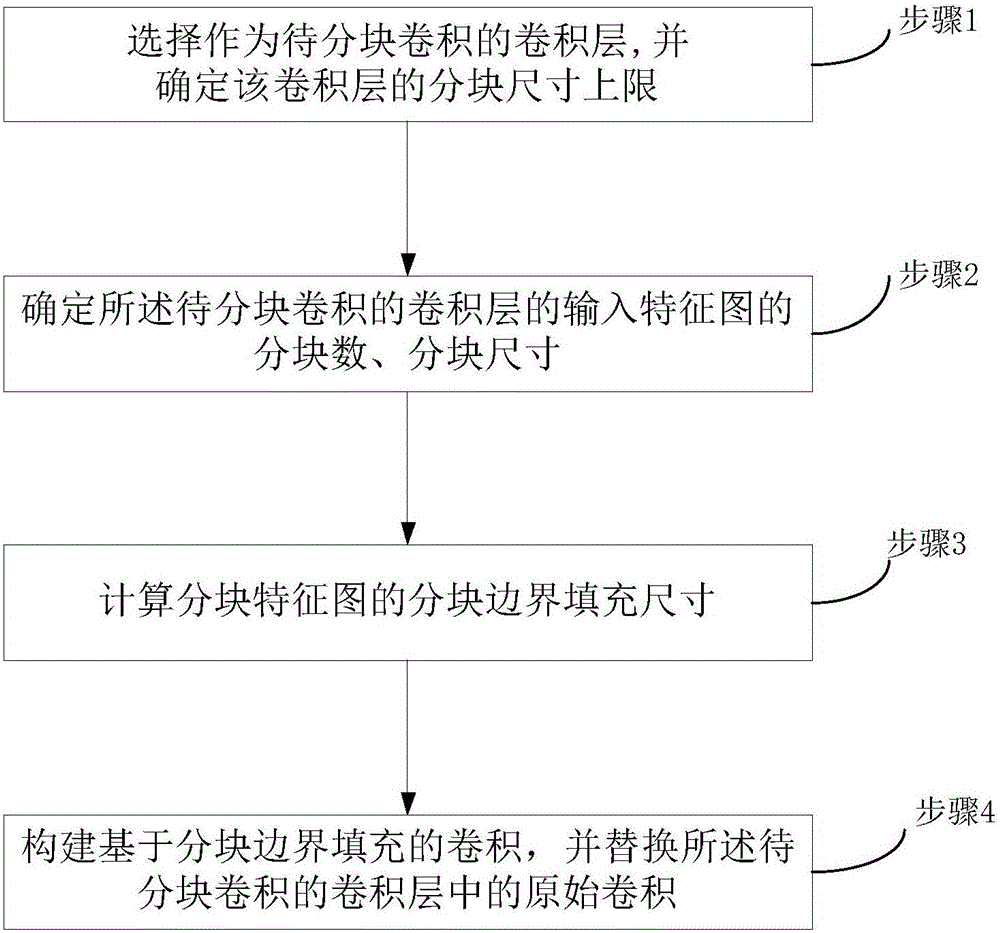
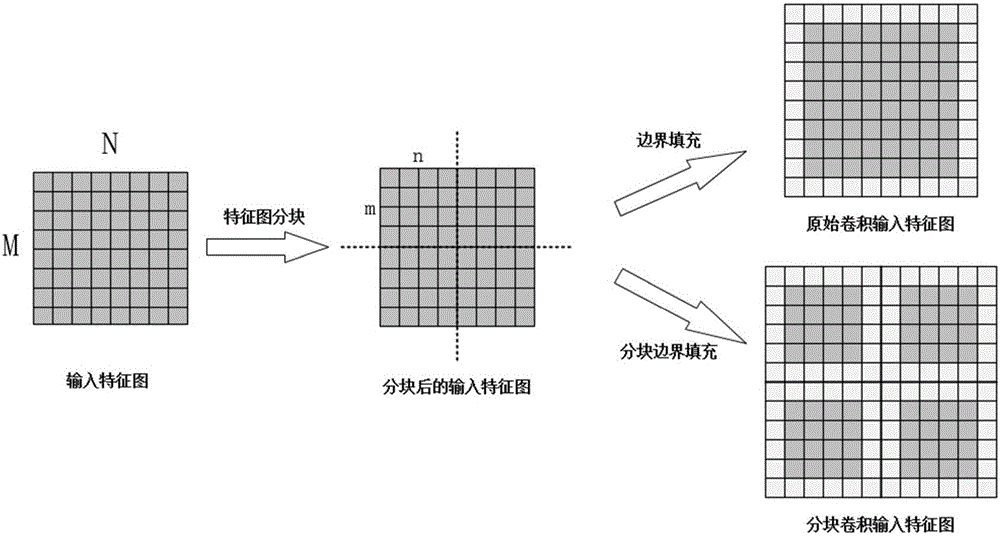
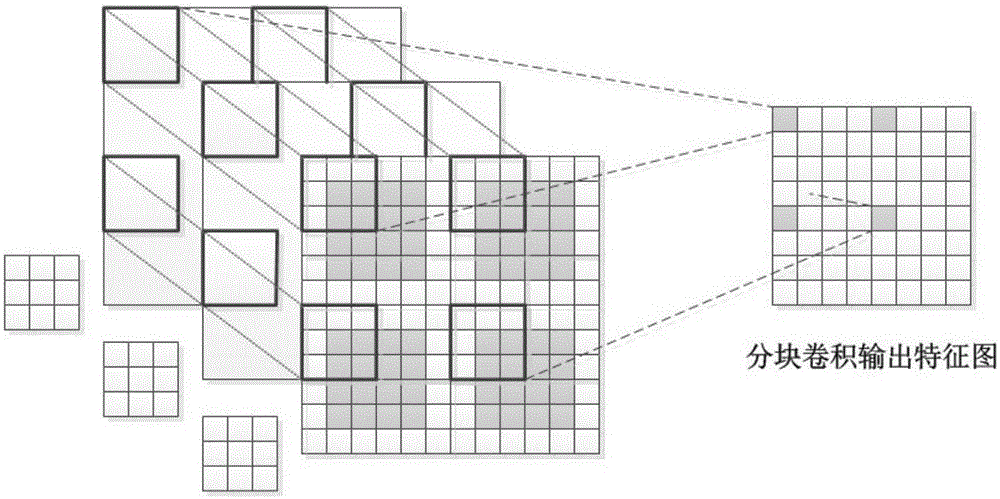
Blocked convolution optimization method and device for convolution neural network
ActiveCN107437110AResource Constraint Issues EliminatedAlleviate resource constraintsNeural architecturesPhysical realisationNerve networkAlgorithm
The invention relates to the field of deep neural networks and provides a blocked convolution optimization method and a device for a convolution neural network, so as to solve the bottleneck problem of convolution operation in a hardware processing system in the neural network. The optimization method comprises steps: a to-be-blocked convolution layer is selected, and the upper limit of the block size is determined; according to the upper limit of the block size, a block number and the block size of an input feature map are determined; based on the block number, the block size, the size of a convolution kernel, the size of the input feature map and the filling size of an input feature map boundary, the block boundary filling size of a block feature map is calculated; and based on the block number, the block size and the block boundary filling size, a convolution based on the block boundary filling is built to replace the original convolution. The resource constraint problem of the convolution neural network during operation of an embedded hardware platform is greatly alleviated, the burst length is improved maximally when a memory is read and written, the throughput is improved, the time delay is reduced, and the efficiency is improved.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
System and method for generating a schedule based on resource assignments
InactiveUS7379888B1Maximize utilizationRestricted in mannerMultiprogramming arrangementsResourcesResource assignmentIdle time
A system for generating a schedule by generating assignments for the tasks of a project and sequentially scheduling the individual assignments to available resources. First, input information is received which includes a resource calendar and a task list. A resource calendar identifies the resources available to work on a project and any constraints that are associated with the resources. A task list identifies the tasks that must be performed and any constraints that are associated with the tasks. At a minimum, the constraints associated with the tasks must identify each of the resources assigned to the task, and the work-amount that each resource must perform. Next, assignments are generated for each of the tasks. Each of the assignments identifies a specific resource and the work-amount required by the specific resource. Finally, each of the assignments are scheduled in accordance with the provided resource constraints identified in the resource calendar. The resulting schedule maximizes the utilization of the resources by scheduling on an assignment basis. The assignments are individually scheduled into the next available time-slot of the resources, thus, eliminating idle time where a resource is under-utilized.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Techniques for application tuning
ActiveUS20120310618A1Error detection/correctionAnalogue computers for electric apparatusParallel computingResource constraints
Techniques for tuning systems generate configurations that are used to test the systems to determine optimal configurations for the systems. The configurations for a system are generated to allow for effective testing of the system while remaining within budgetary and / or resource constraints. The configurations may be selected to satisfy one or more conditions on their distributions to ensure that a satisfactory set of configurations are tested. Machine learning techniques may be used to create models of systems and those models can be used to determine optimal configurations.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
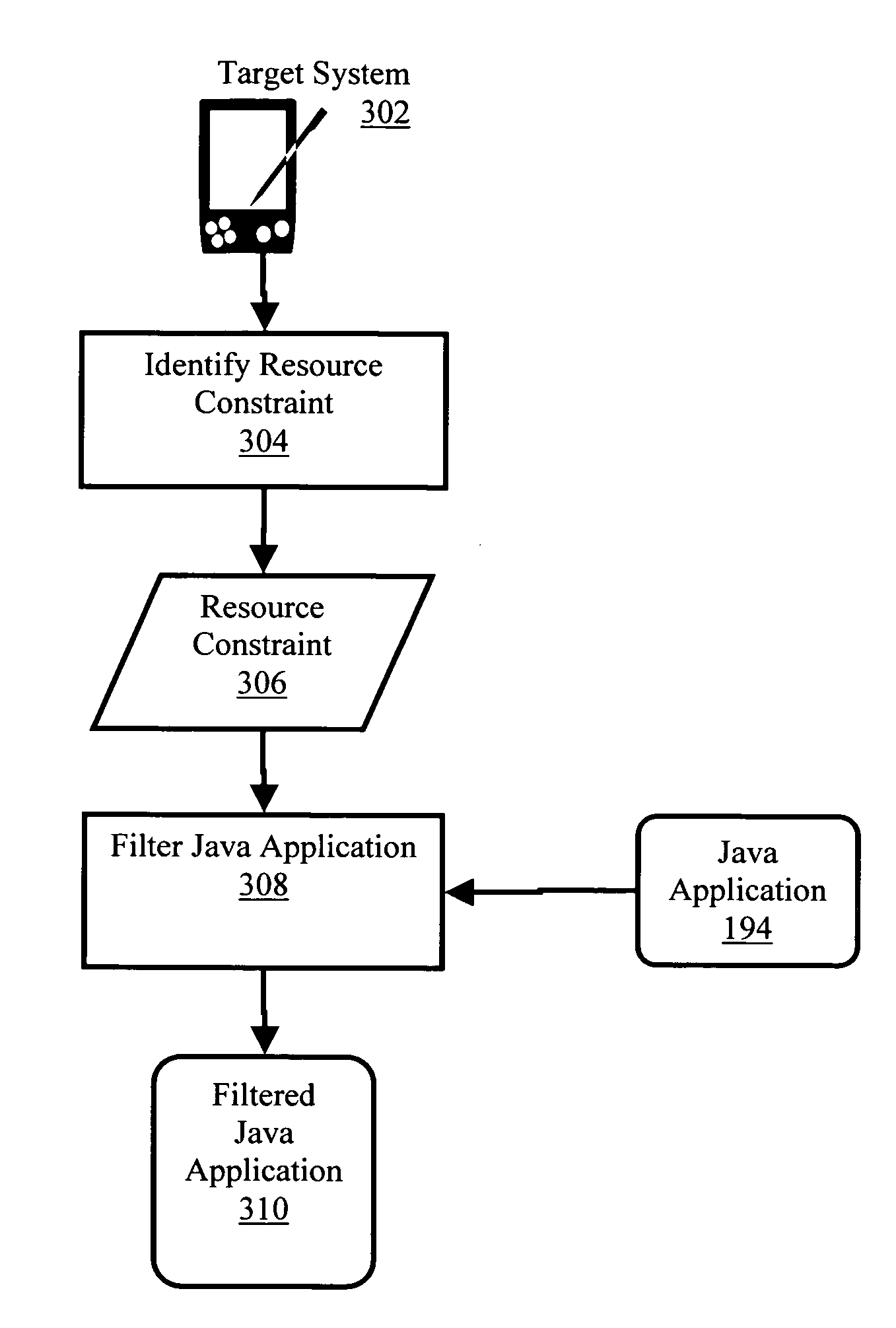
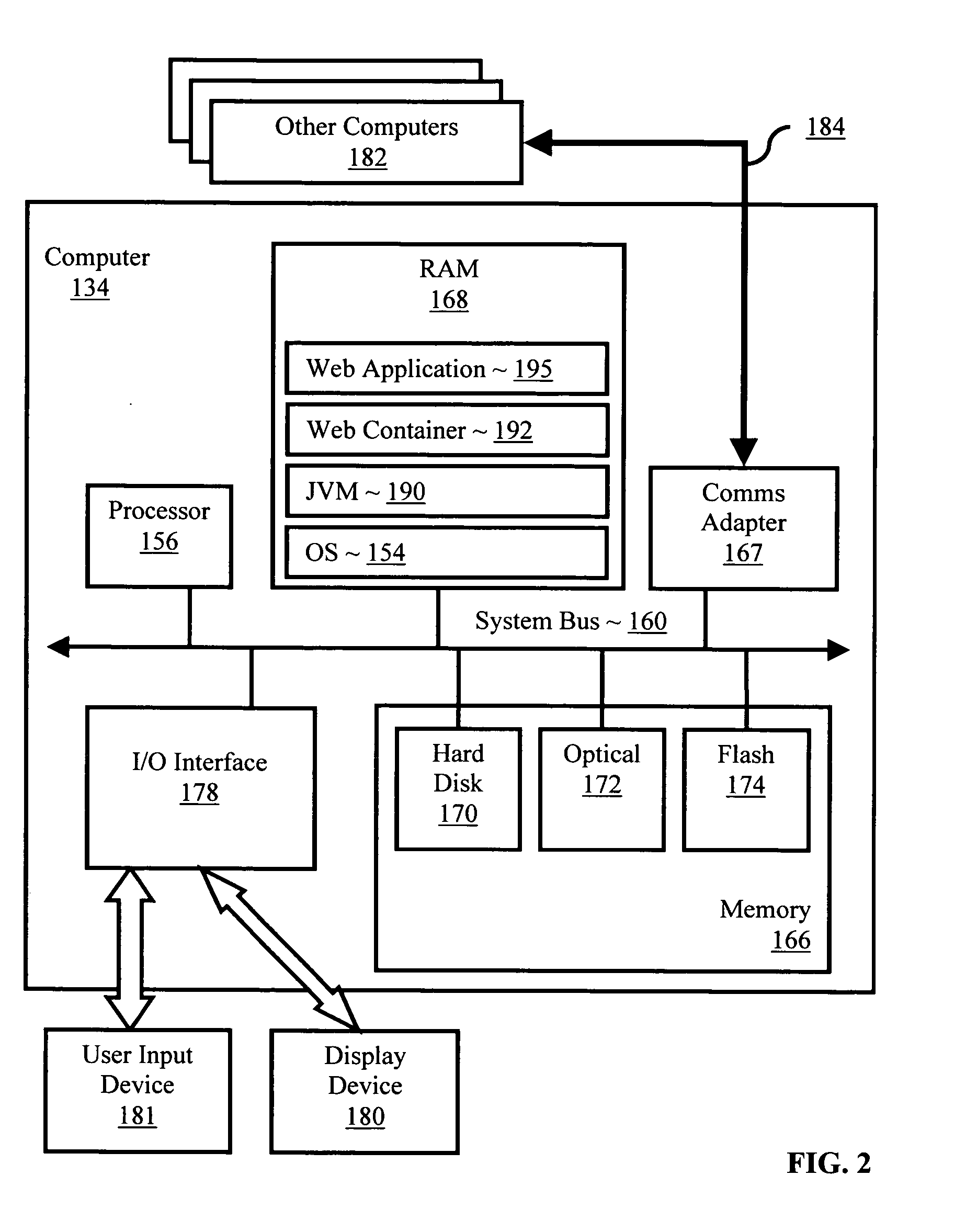
Deploying Java applications in resource constrained environments
Methods, systems, and products are provided for deploying Java applications in resource constrained environments. Embodiments include identifying a resource constraint of a target system and filtering the Java application in dependence upon the identified resource constraint. In many embodiments, identifying a resource constraint of a target system includes identifying limited runtime processing capabilities of the target system and filtering the Java application in dependence upon the identified resource constraint includes preprocessing a tag library of the Java application. In some embodiments, preprocessing a tag library is carried out by identifying a tag library descriptor of the Java application and copying a listener from the tag library descriptor to a deployment descriptor for the Java application.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and Method of Stochastic Resource-Constrained Project Scheduling
A method or system of optimally scheduling projects with resource constraints and stochastic task durations. This is a new framework in order to solve real world problems of uncertainties and computational dilemma in project scheduling and management. This new framework is devised with a constraint programming (CP) procedure as an approximate dynamic programming (ADP) to reduce the size of domain.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com