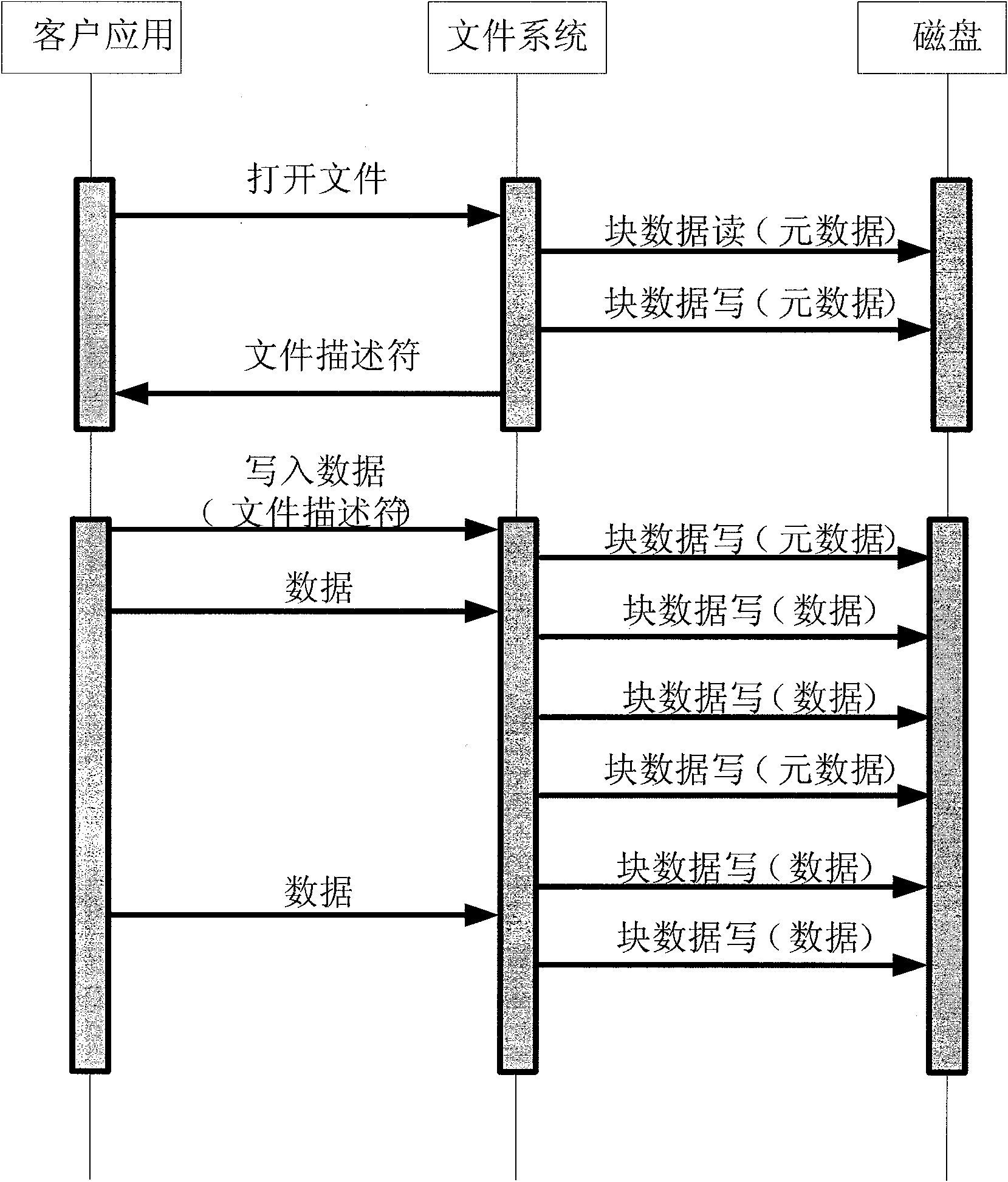
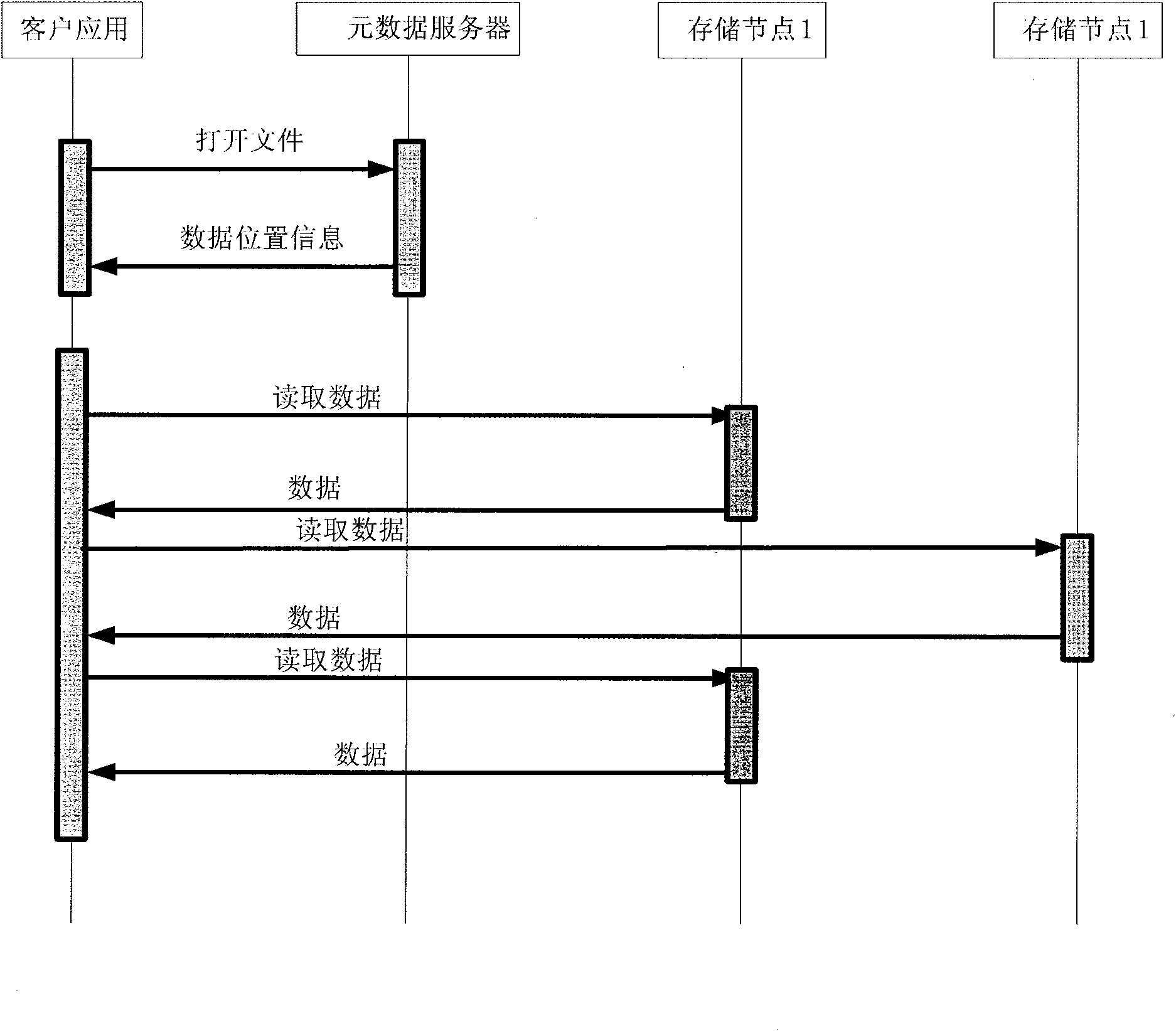
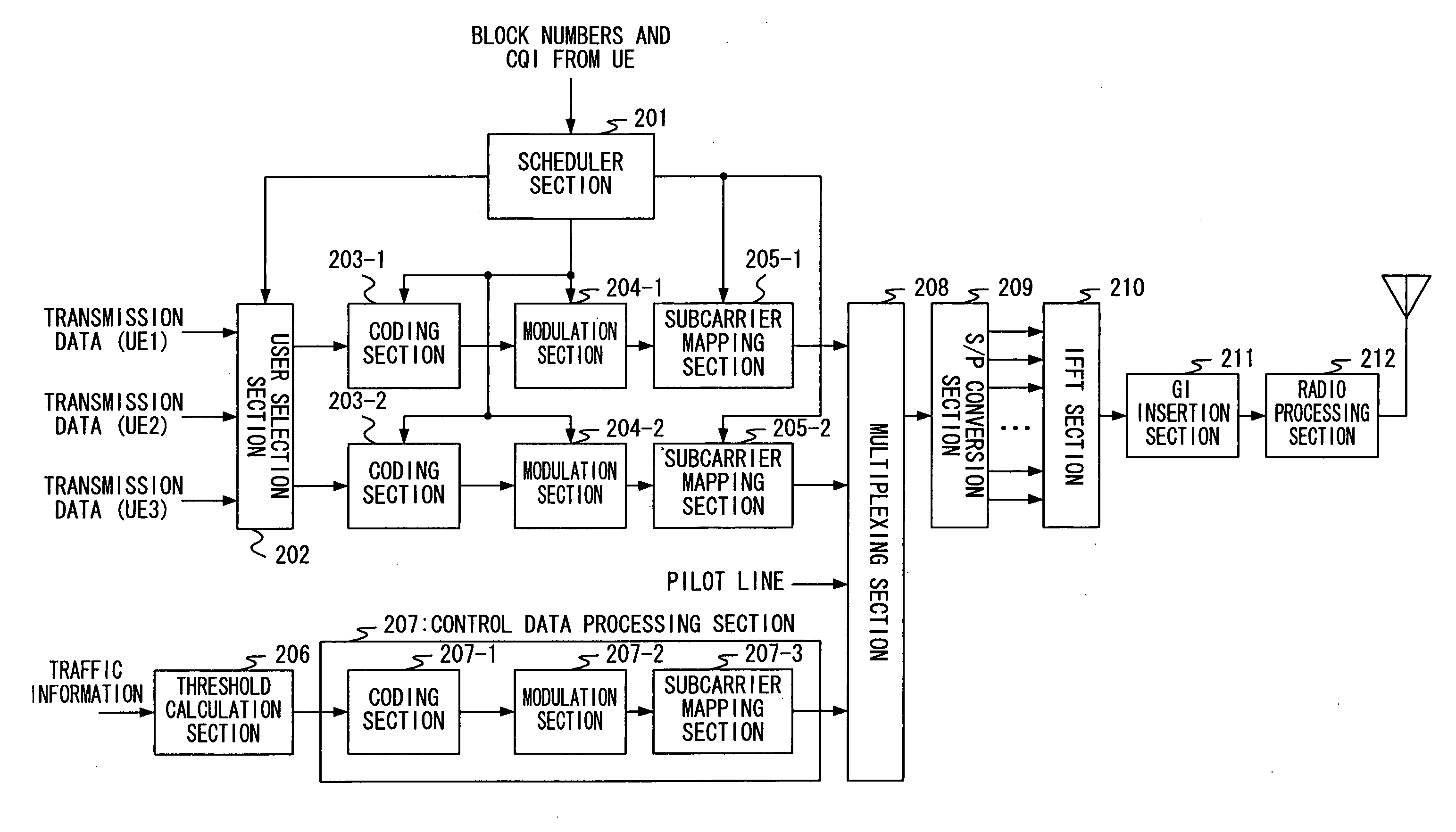
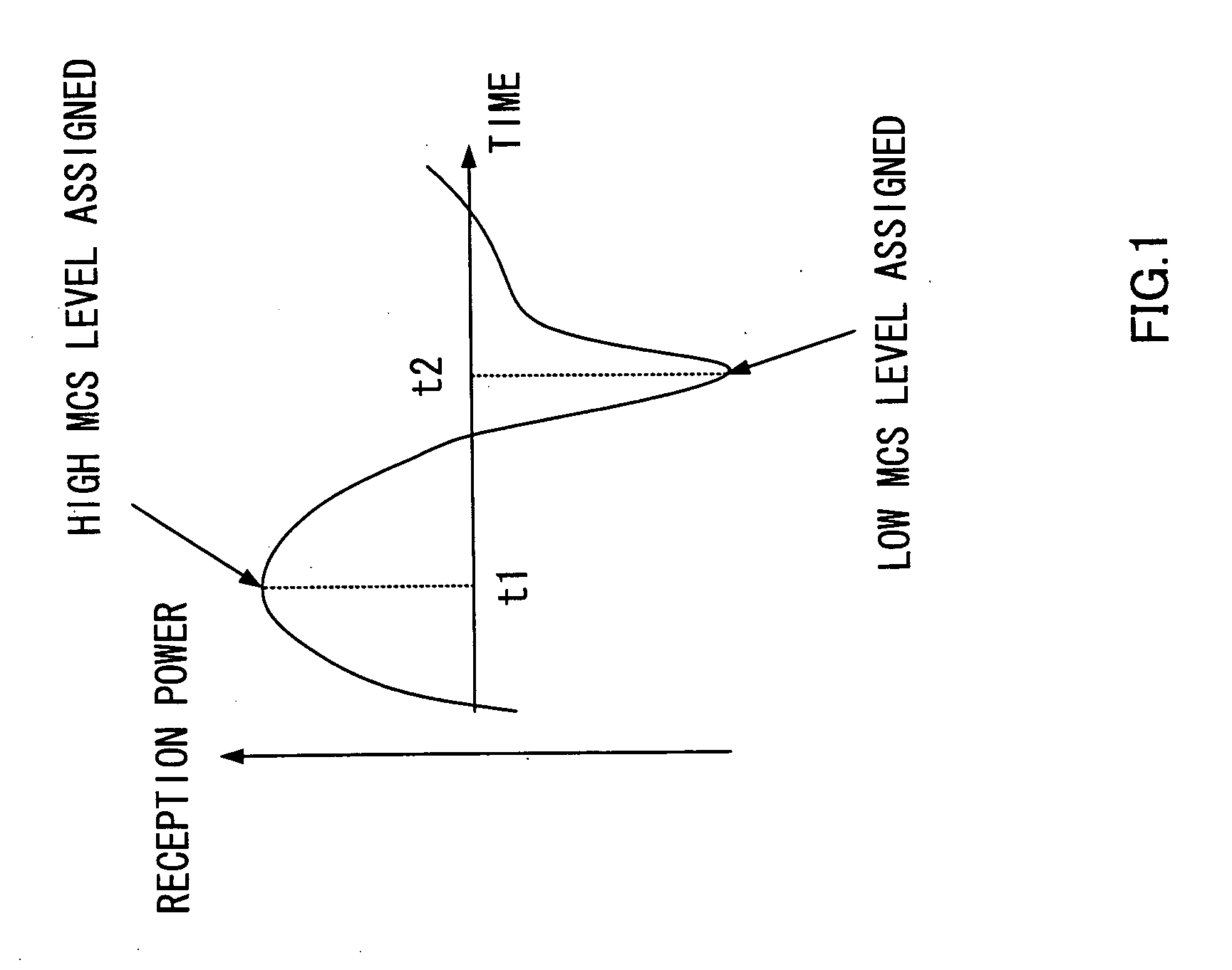
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
734 results about "Block number" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
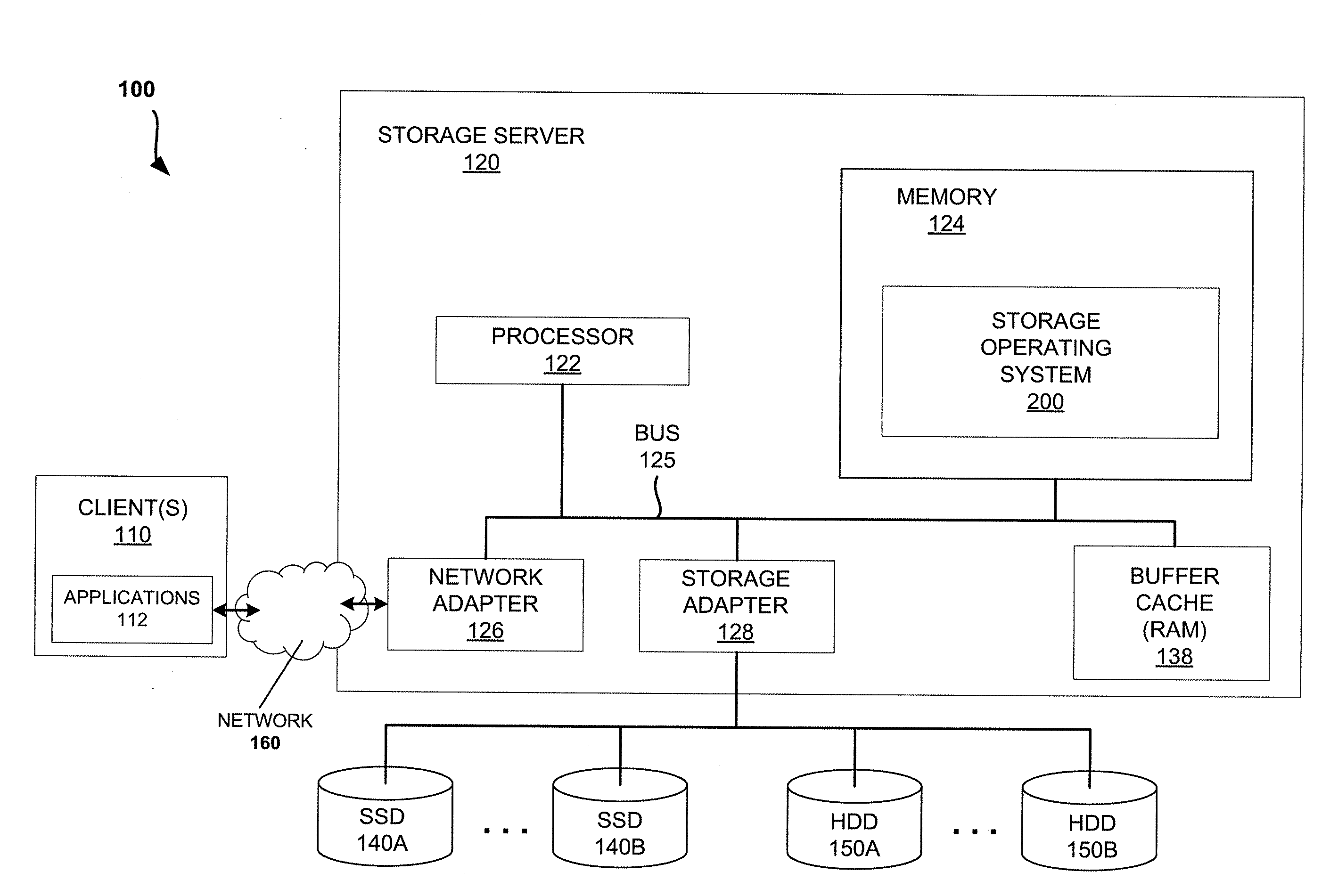
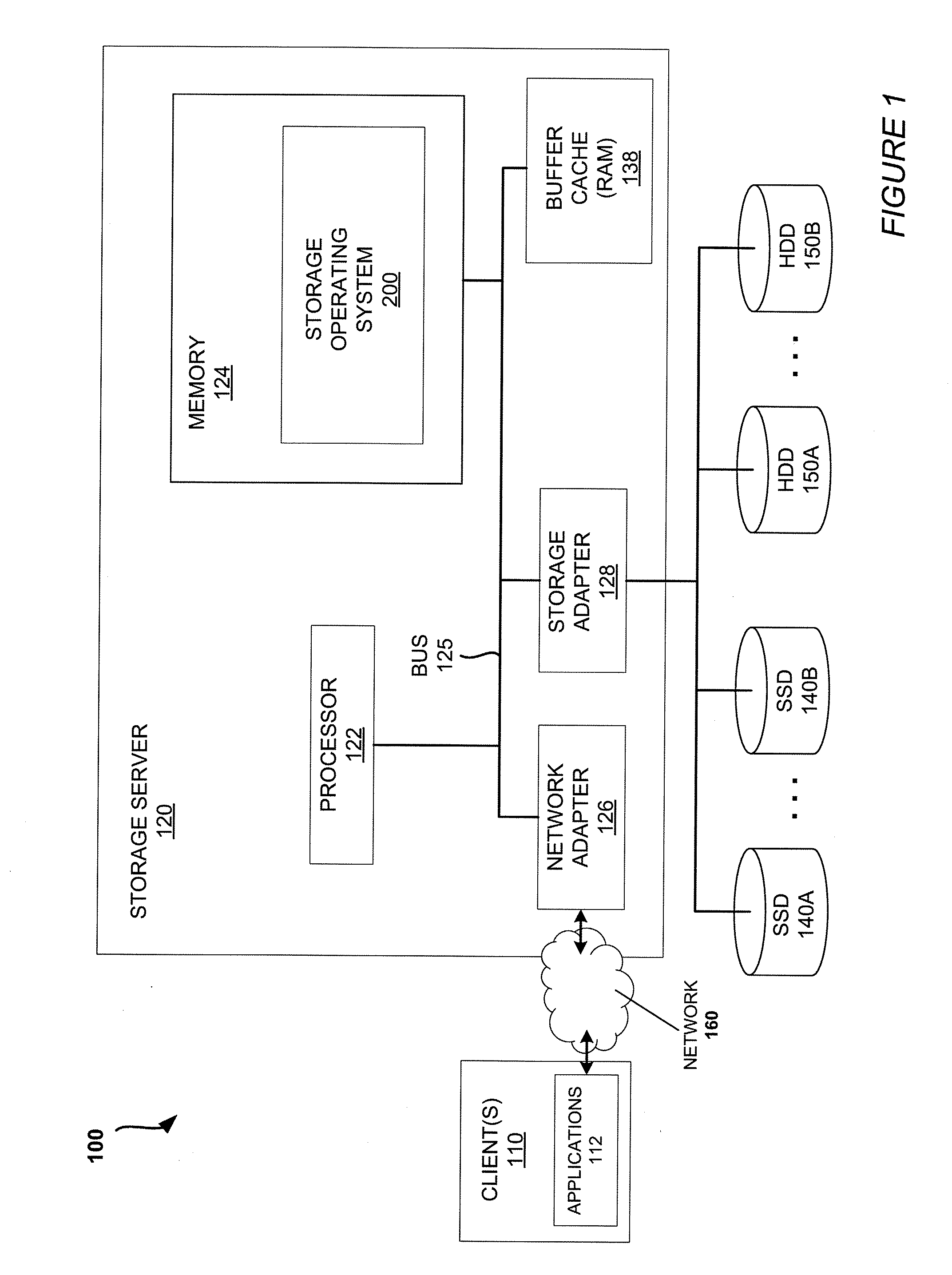
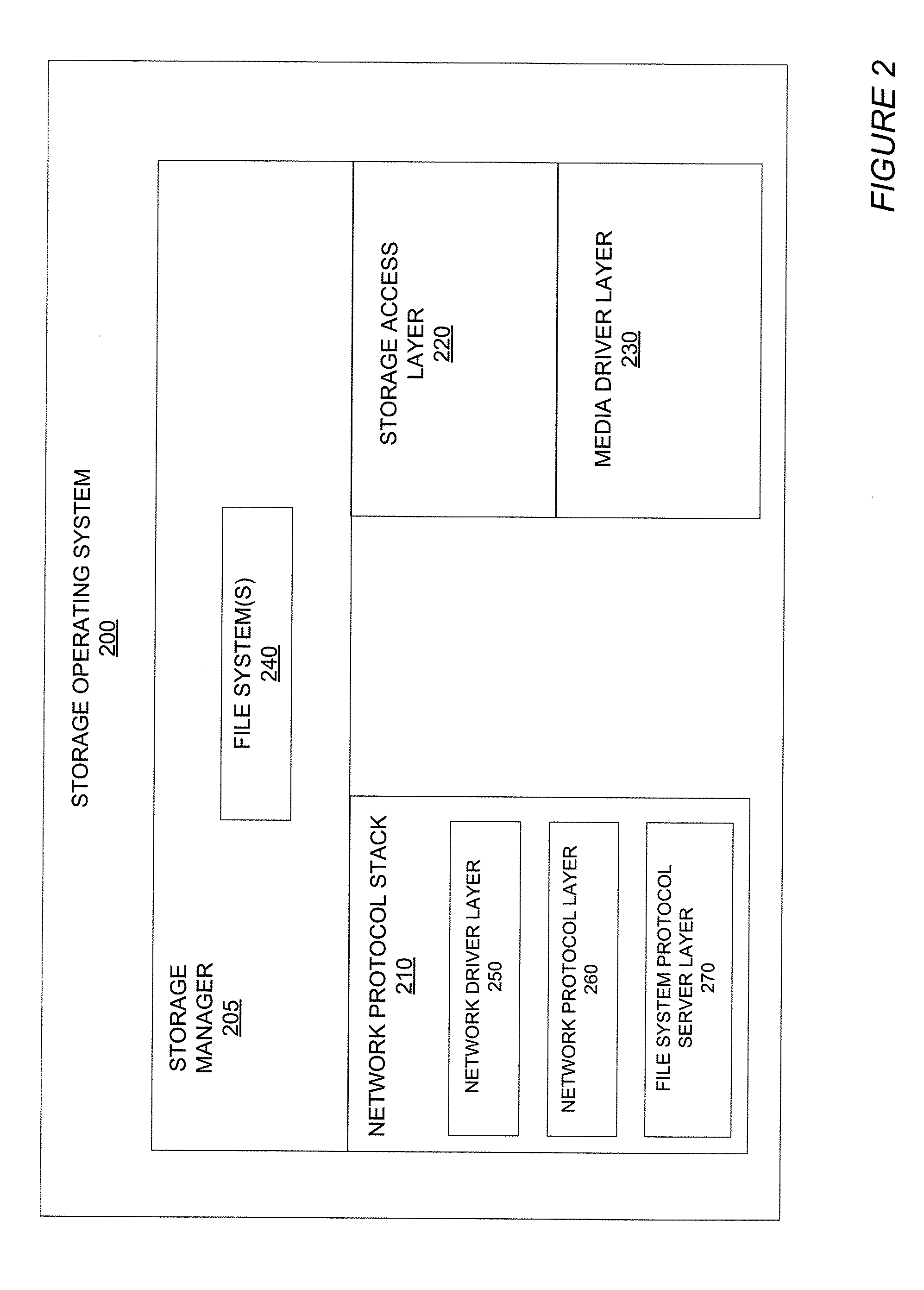
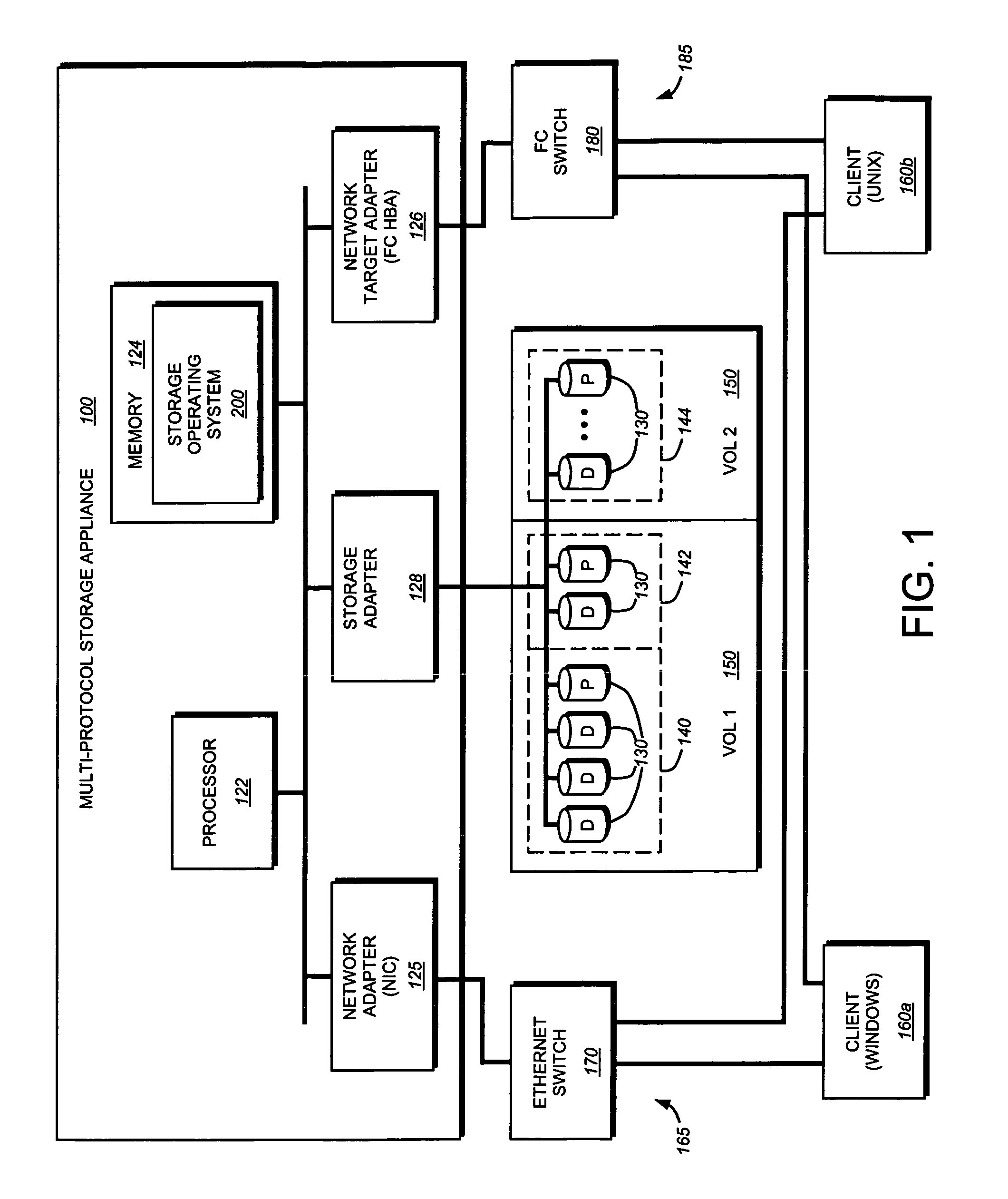
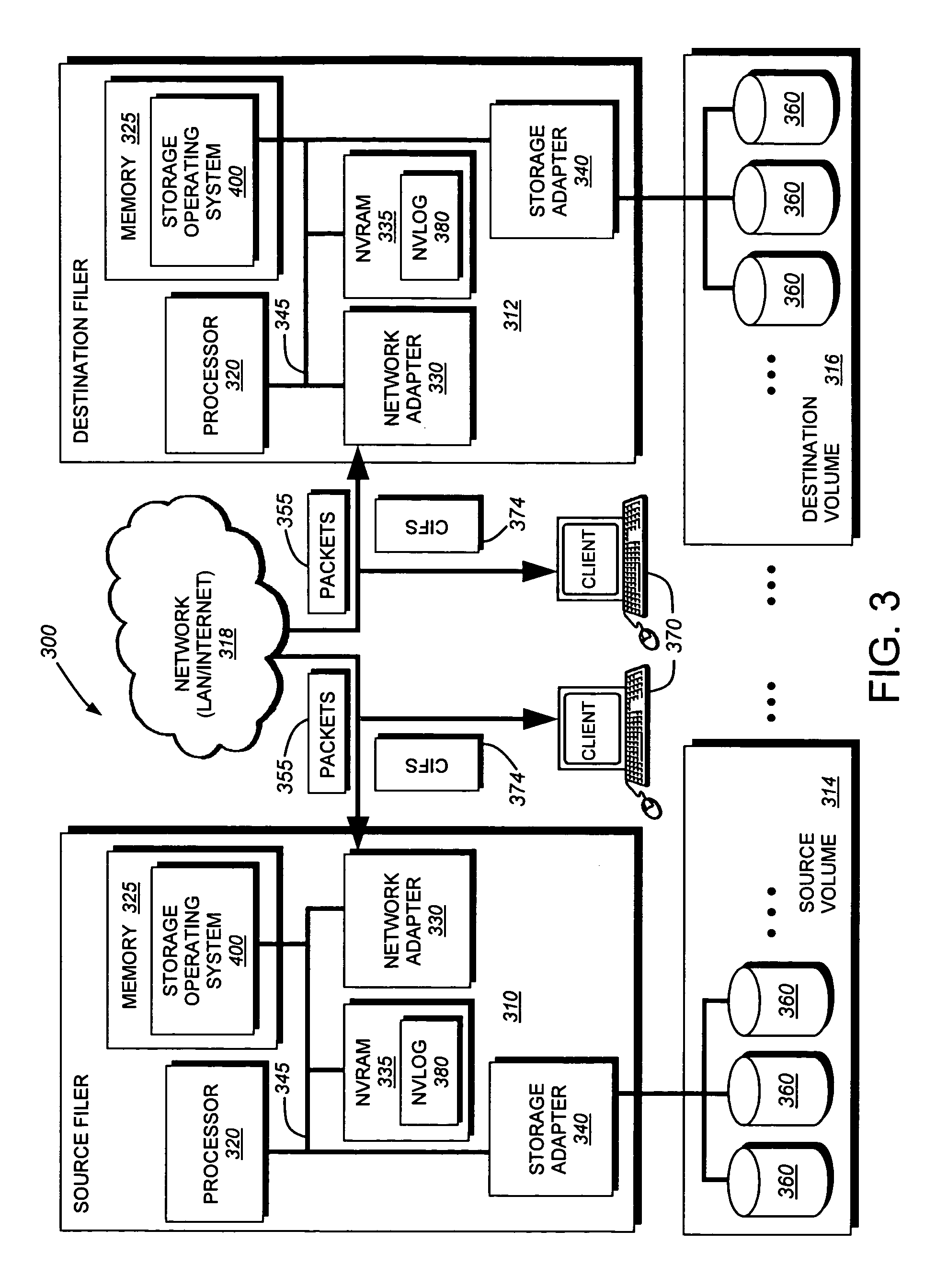
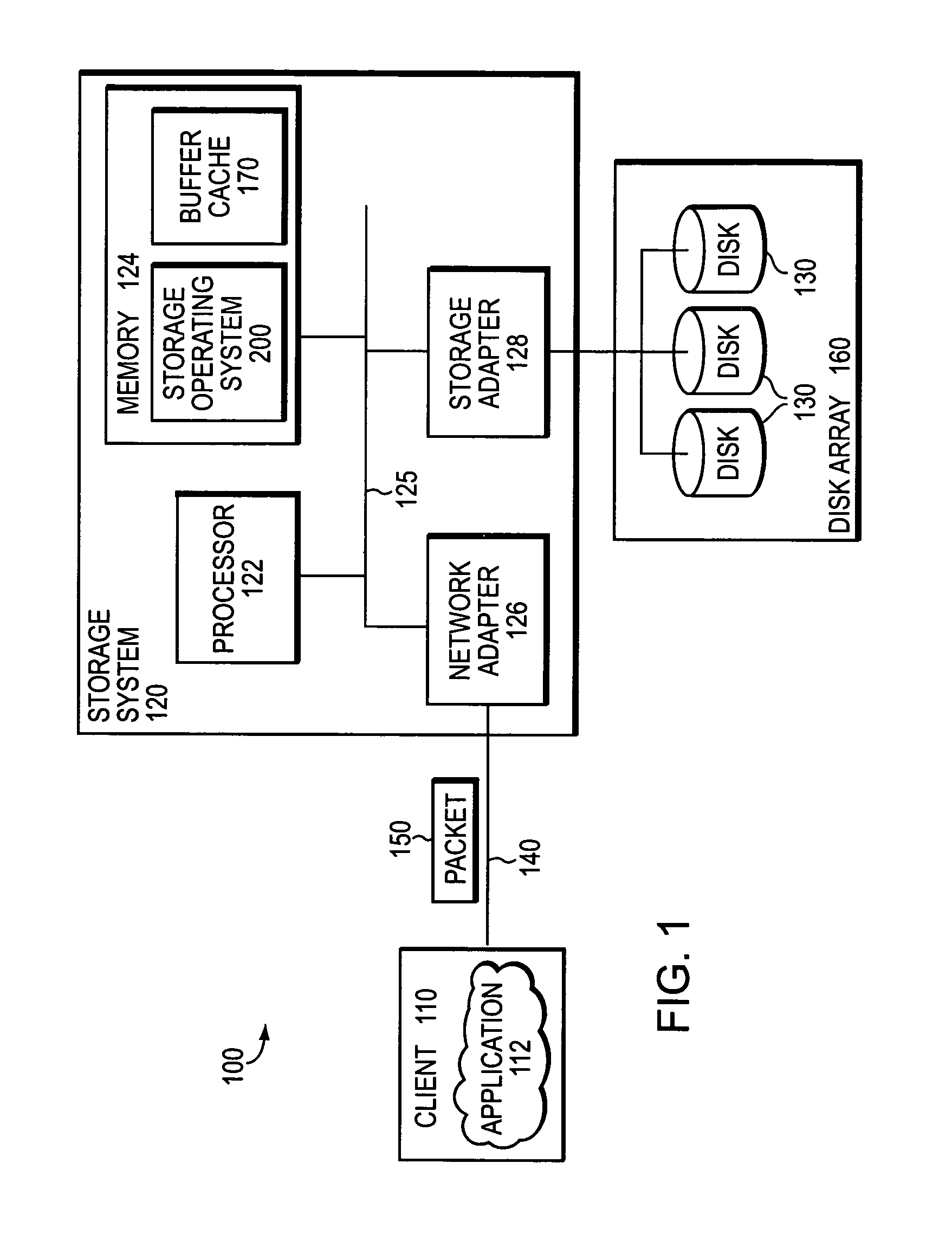
Mechanisms for moving data in a hybrid aggregate
ActiveUS20100281230A1Improved performance characteristicsMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationPolicy decisionFile system
At least certain embodiments disclose a method, system and apparatus for relocating data between tiers of storage media in a hybrid storage aggregate encompassing multiple tiers of heterogeneous physical storage media including a file system to automatically relocate the data between tiers. The hybrid storage aggregate includes one or more volumes, each volume including a volume block number space spanning at least a first-tier of storage media and a second tier of storage media of the multiple tiers of heterogeneous physical storage media and the hybrid storage aggregate further includes a control module to cooperatively manage the tiers of the multiple tiers of heterogeneous physical storage media and a file system coupled with the control module, the file system including a policy module configured to make policy decisions based on a set of one or more policies and configured to automatically relocate data between different tiers of the multiple tiers of heterogeneous physical storage media based on the set of policies.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
System and method for mapping file block numbers to logical block addresses
ActiveUS7437530B1Improve performanceRaise transfer toMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionOperational systemLogical block addressing
A system and method for mapping file block numbers (FBNs) to logical block addresses (LBAs) is provided. The system and method performs the mapping of FBNs to LBAs in a file system layer of a storage operating system, thereby enabling the use of clients in a storage environment that have not been modified to incorporate mapping tables. As a result, a client may send data access requests to the storage system utilizing FBNs and have the storage system perform the appropriate mapping to LBAs.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
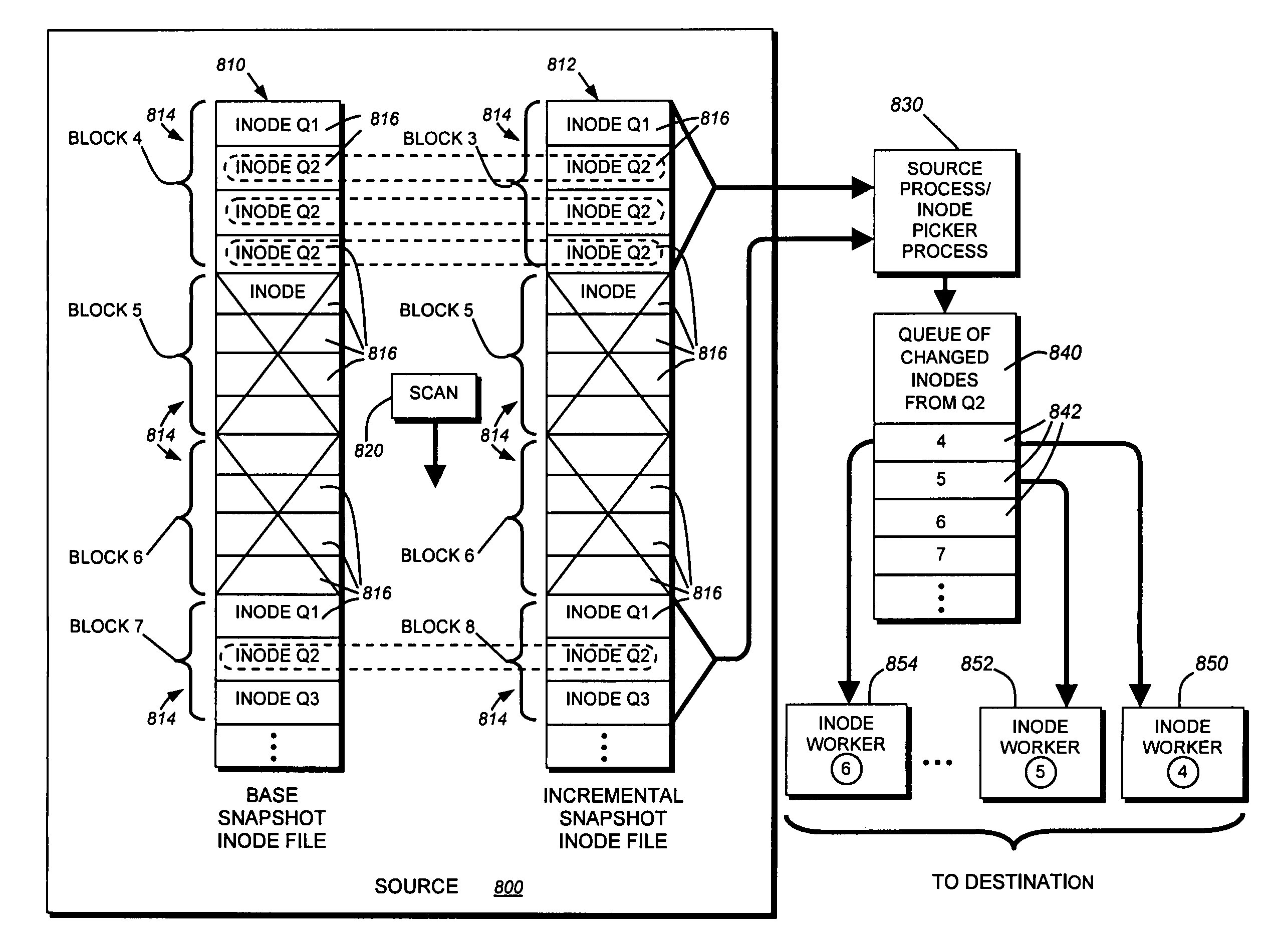
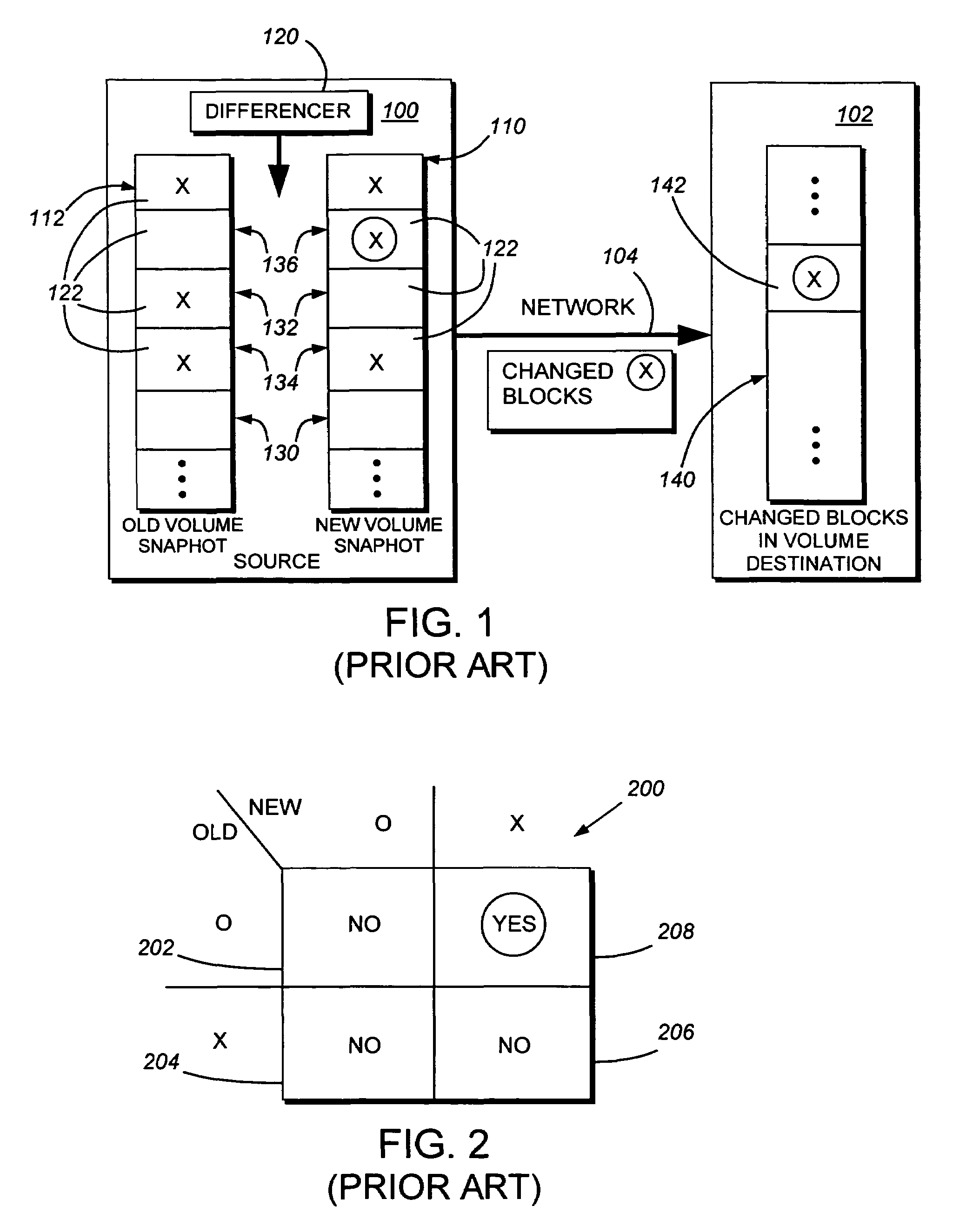
System and method for determining changes in two snapshots and for transmitting changes to destination snapshot
InactiveUS6993539B2Efficient scanningOvercome disadvantagesData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsData streamInode
A system and method for remote asynchronous replication or mirroring of changes in a source file system snapshot in a destination replica file system using a scan (via a scanner) of the blocks that make up two versions of a snapshot of the source file system, which identifies changed blocks in the respective snapshot files based upon differences in volume block numbers identified in a scan of the logical file block index of each snapshot. Trees of blocks associated with the files are traversed, bypassing unchanged pointers between versions and walking down to identify the changes in the hierarchy of the tree. These changes are transmitted to the destination mirror or replicated snapshot. This technique allows regular files, directories, inodes and any other hierarchical structure to be efficiently scanned to determine differences between versions thereof. The changes in the files and directories are transmitted over the network for update of the replicated destination snapshot in an asynchronous (lazy write) manner. The changes are described in an extensible, system-independent data stream format layered under a network transport protocol. At the destination, source changes are used to update the destination snapshot. Any deleted or modified inodes already on the destination are moved to a temporary or “purgatory” directory and, if reused, are relinked to the rebuilt replicated snapshot directory. The source file system snapshots can be representative of a volume sub-organization, such as a qtree.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
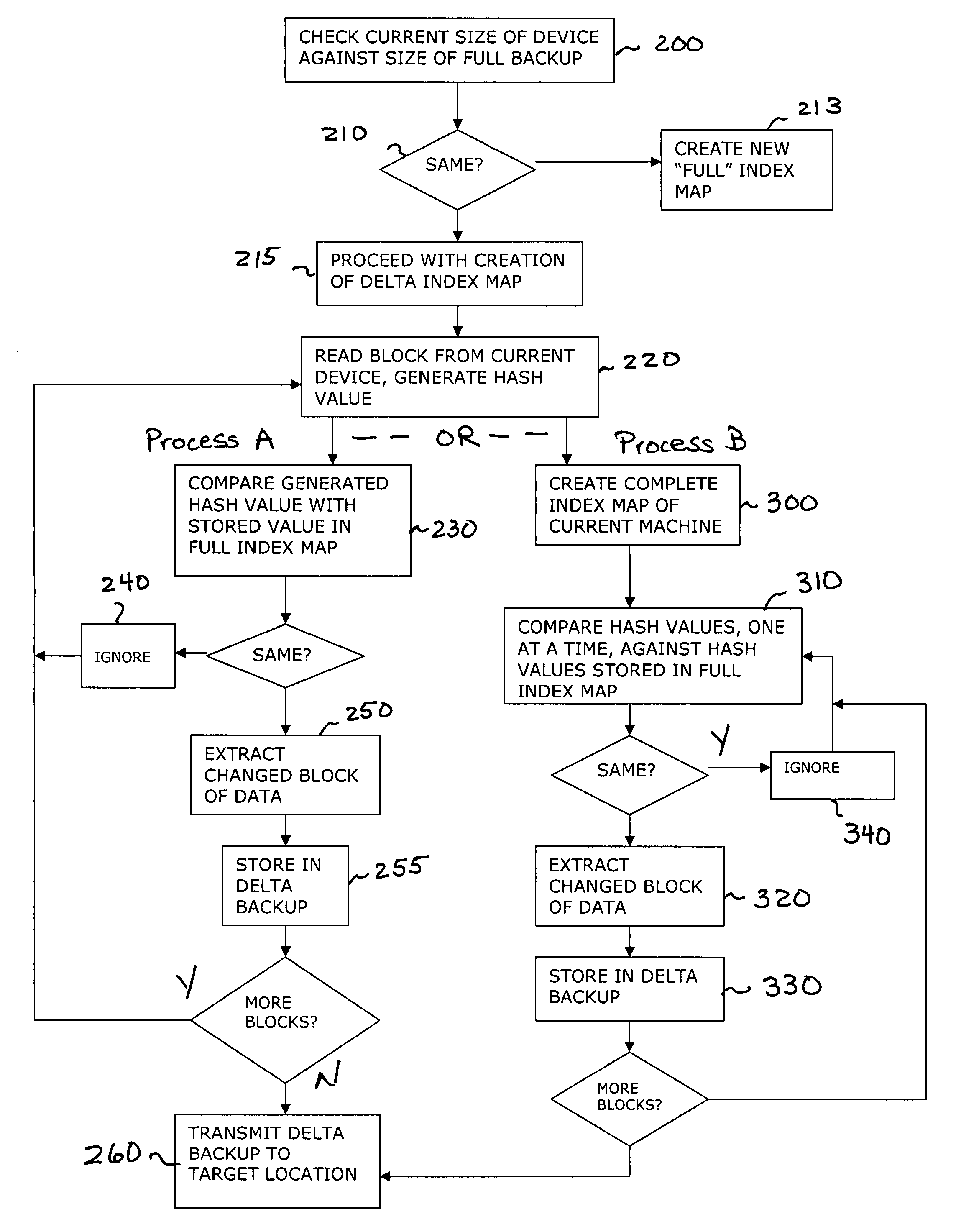
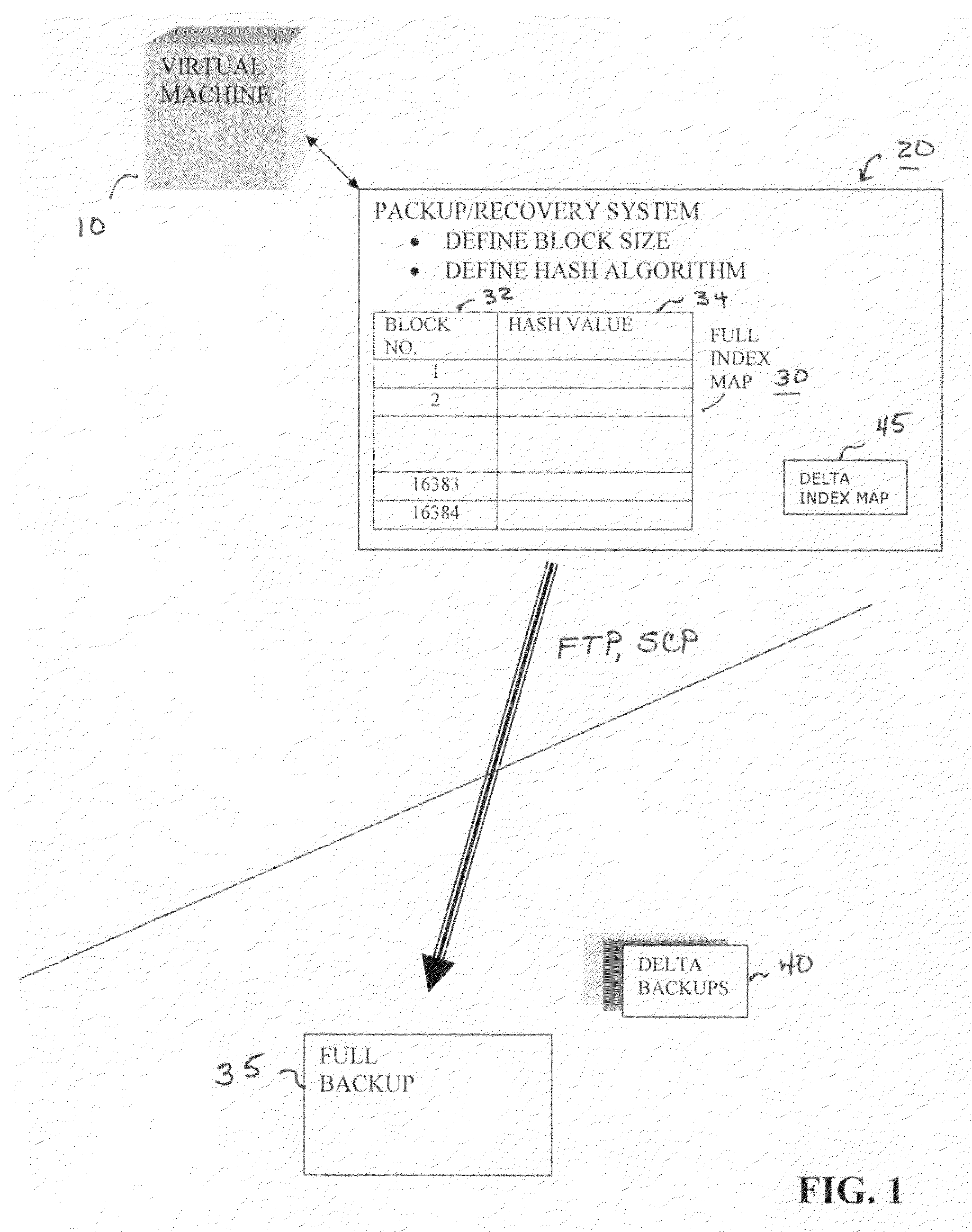
Method and apparatus for providing virtual machine backup
InactiveUS20070208918A1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionComputerized systemComputer science
A system and method for creating computer system backups, particularly well-suited for performing backups of virtual machines. The method starts by reading the current state of the machine, in blocks of a constant size, and creates a “FULL” index of block numbers and a hash value associated with the data within that block, while at the same time creating a FULL backup of the machine (the FULL backup then stored at an off-site target location). Once the FULL index map is defined, subsequent DELTA backups are created by reading the current state of the device in the same block fashion and generating updated hash values for each data block. The newly-generated hash values are compared against the values stored in the FULL index map. If the hash numbers for a particular block do not match, this is an indication that the data within that block has changed since the last FULL backup was created. Once all of the “changed” data blocks have been identified to form a DELTA backup, a communication connection is opened in the network and the DELTA backup is sent to the off-site target location.
Owner:PHD TECH
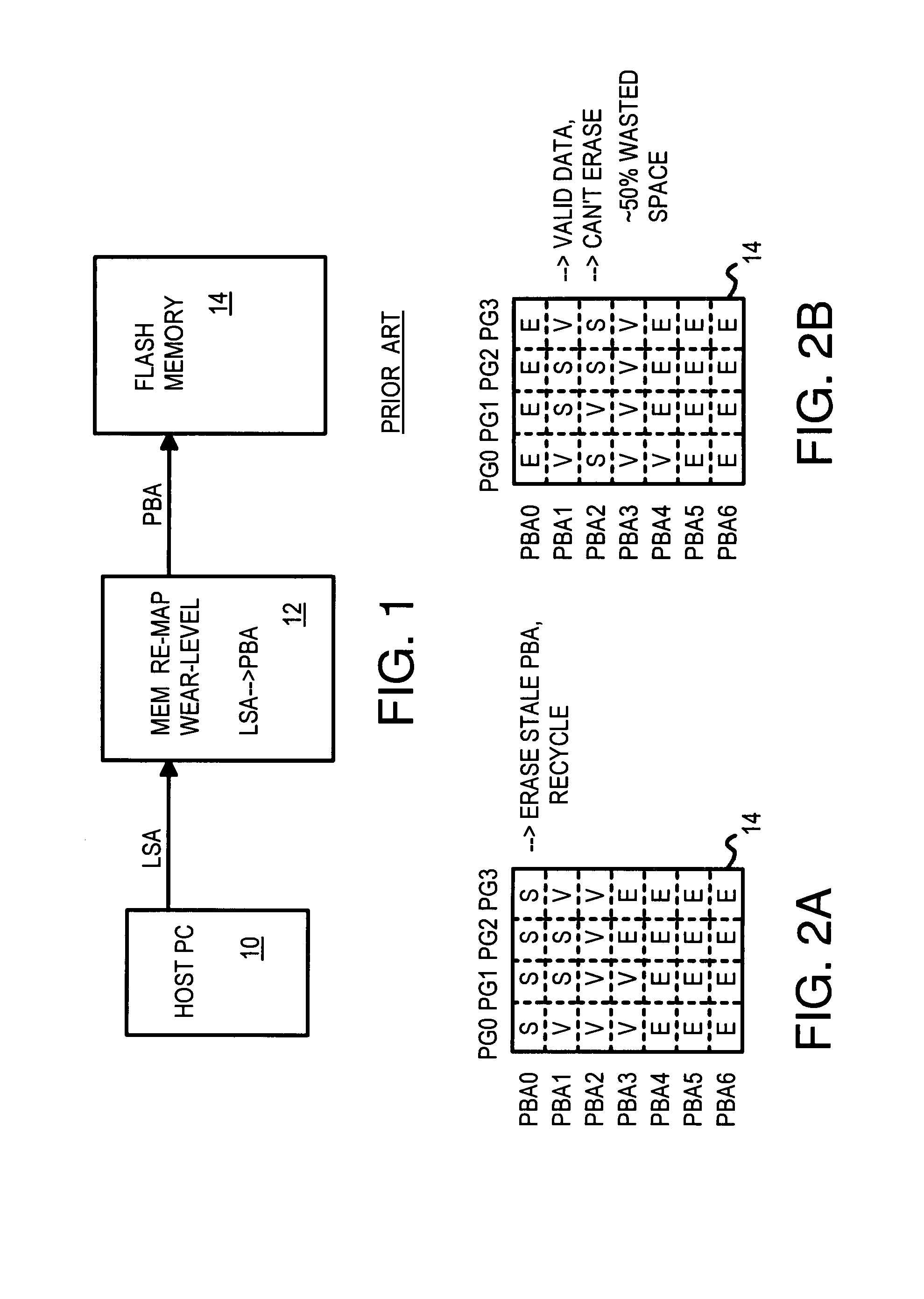
Flash Module with Plane-Interleaved Sequential Writes to Restricted-Write Flash Chips
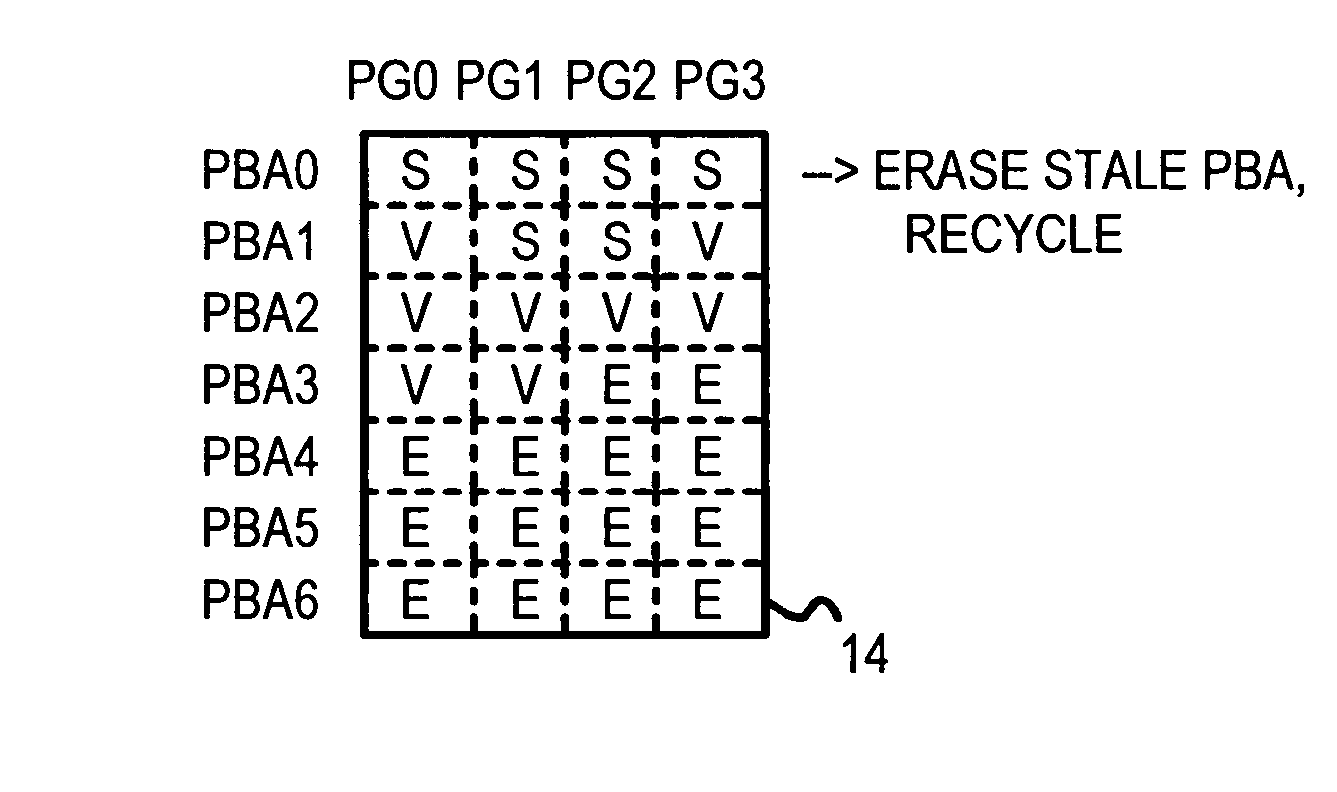
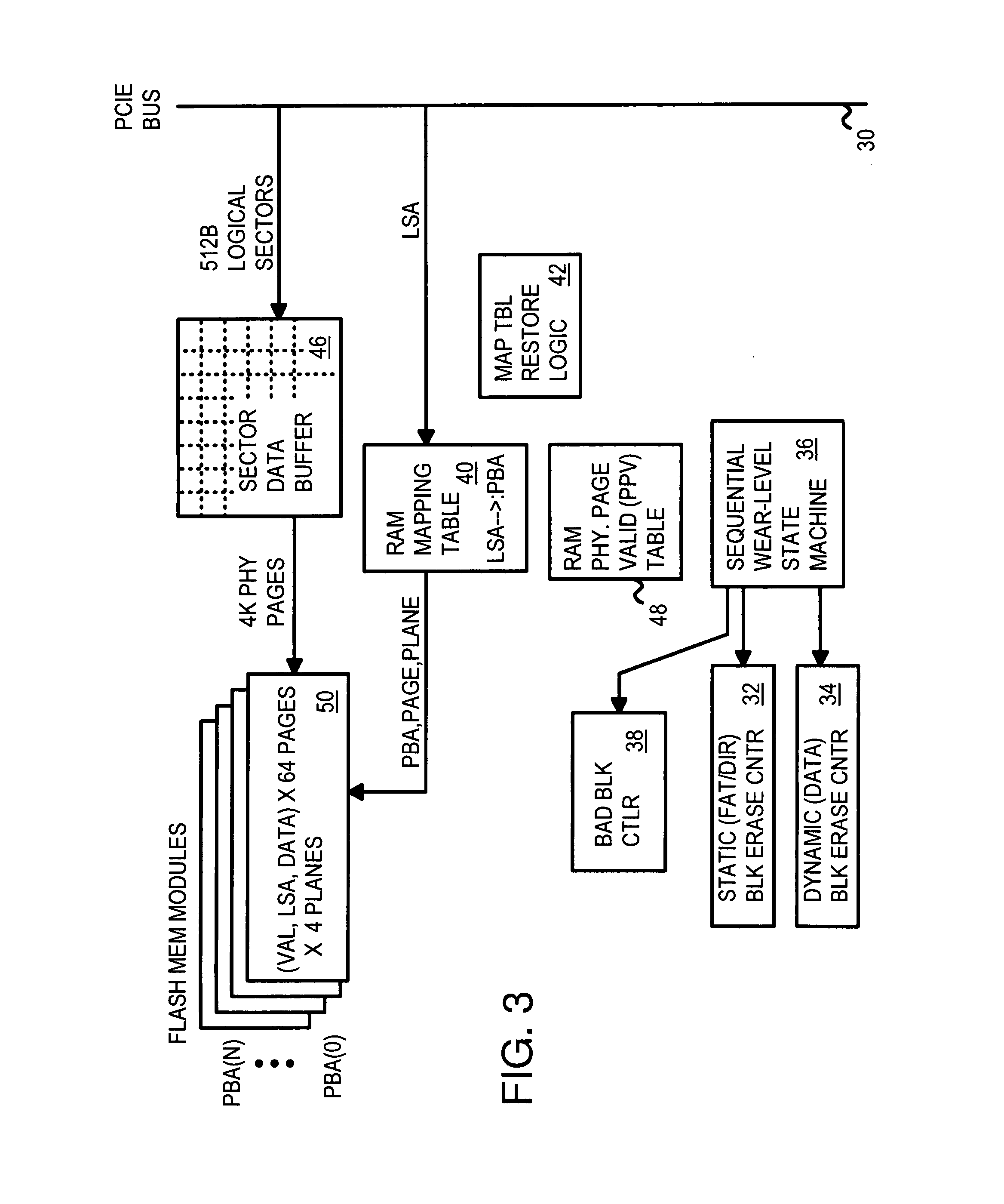
InactiveUS20080034153A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesFlash memory controllerBlock number
A flash memory controller on a PCIE bus controls flash-memory modules on a flash bus. The flash-memory modules are plane-interleaved using interleaved bits extracted from the lowest bits of the logical block index. These plane-interleave bits are split into a LSB and a MSB, with middle physical block bits between the LSB and MSB. A physical sequential address counter generates a physical block number by incrementing the plane-interleave bits before the middle physical block bits, and then relocating the MSB to above the middle physical block bits. This causes blocks to be accessed in a low-high sequence of 0, 1, 4096, 4097, 2, 3, 4098, 4099, etc. in the four planes of flash memory. A RAM physical page valid table tracks valid pages in the four planes, while a RAM mapping table stores the plane, block, and page addresses for logical sectors generated by the physical sequential address counter.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
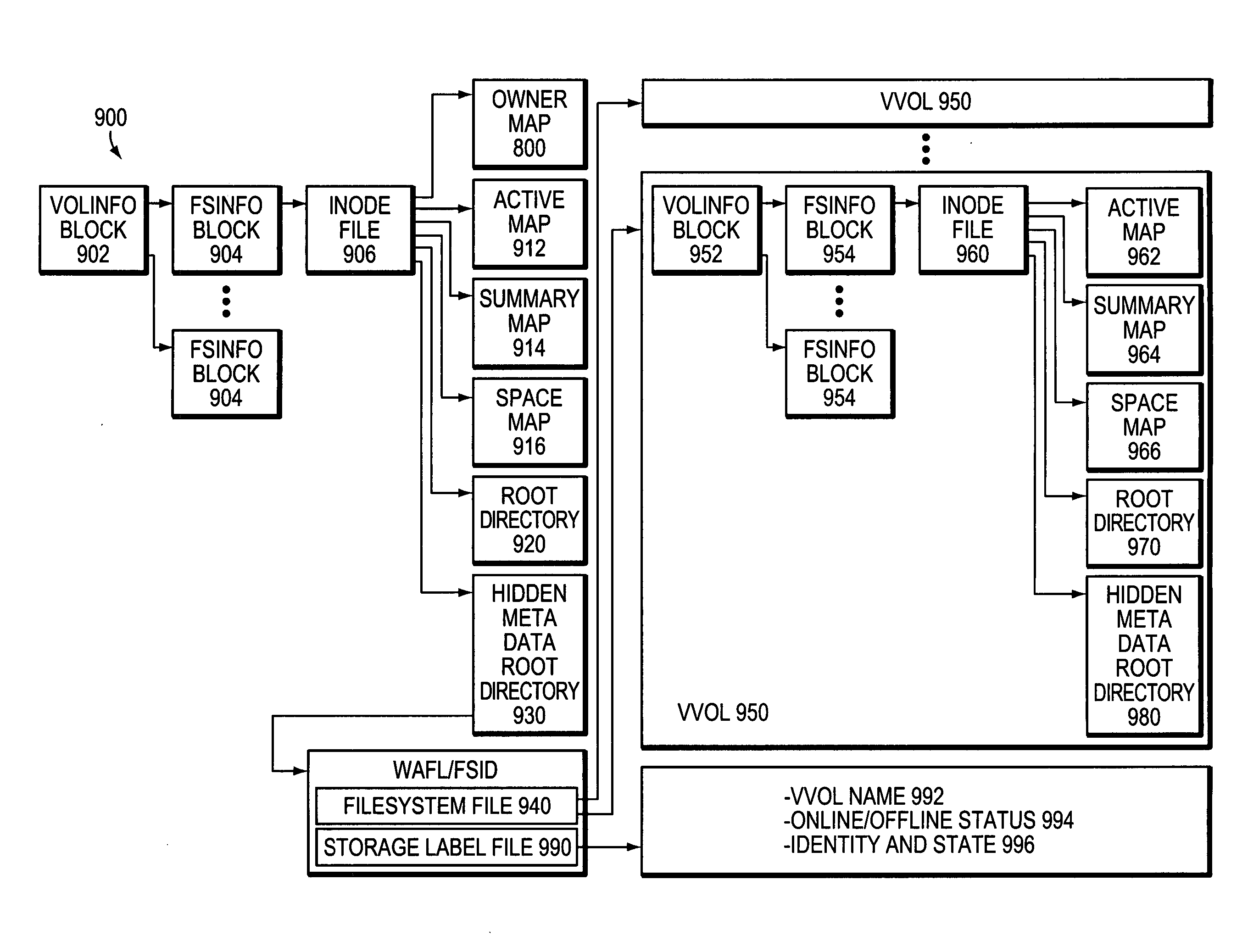
Extension of write anywhere file system layout
ActiveUS20050246401A1Avoid partialFlexible sizeDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsRAIDFile system
A file system layout apportions an underlying physical volume into one or more virtual volumes (vvols) of a storage system. The underlying physical volume is an aggregate comprising one or more groups of disks, such as RAID groups, of the storage system. The aggregate has its own physical volume block number (pvbn) space and maintains metadata, such as block allocation structures, within that pvbn space. Each vvol has its own virtual volume block number (vvbn) space and maintains metadata, such as block allocation structures, within that vvbn space. Notably, the block allocation structures of a vvol are sized to the vvol, and not to the underlying aggregate, to thereby allow operations that manage data served by the storage system (e.g., snapshot operations) to efficiently work over the vvols. The file system layout extends the file system layout of a conventional write anywhere file layout system implementation, yet maintains performance properties of the conventional implementation.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
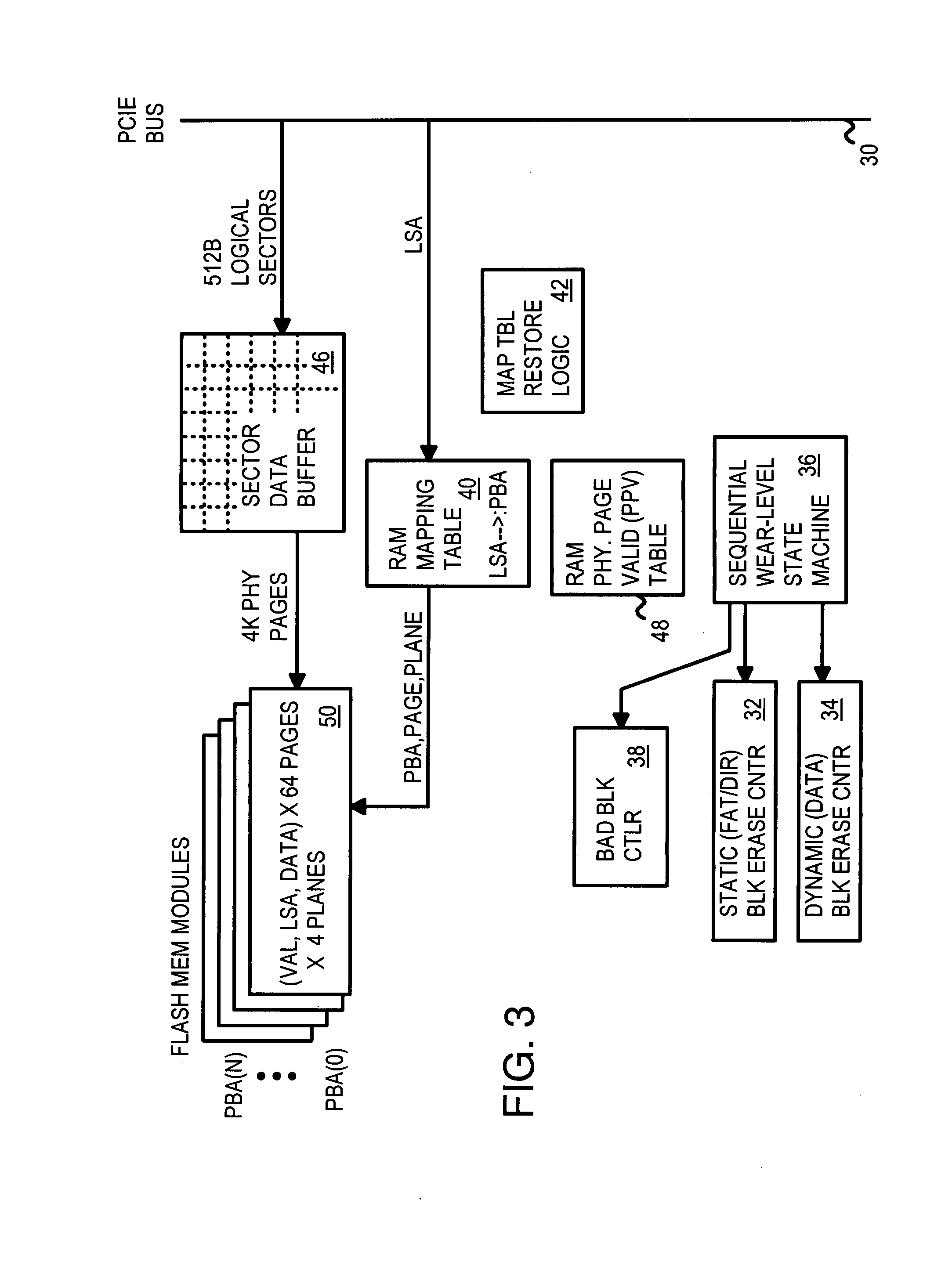
Multi-Channel Flash Module with Plane-Interleaved Sequential ECC Writes and Background Recycling to Restricted-Write Flash Chips
InactiveUS20080034154A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesInterleave sequenceBlock number
A RAM mapping table is restored from flash memory using plane, block, and page addresses generated by a physical sequential address counter. The RAM mapping table is restored following a plane-interleaved sequence generated by the physical sequential address counter using interleaved bits extracted from the lowest bits of the logical block index. These plane-interleave bits are split into a LSB and a MSB, with middle physical block bits between the LSB and MSB. The physical sequential address counter generates a physical block number by incrementing the plane-interleave bits before the middle physical block bits, and then relocating the MSB to above the middle physical block bits. This causes blocks to be accessed in a low-high sequence of 0, 1, 4096, 4097, 2, 3, 4098, 4099, etc. in the four planes of flash memory. Background recycling and ECC writes are also performed.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
Extension of write anywhere file system layout
ActiveUS7409494B2Guaranteed to workOvercome disadvantagesDigital data information retrievalRedundant operation error correctionRAIDFile system
A file system layout apportions an underlying physical volume into one or more virtual volumes (vvols) of a storage system. The underlying physical volume is an aggregate comprising one or more groups of disks, such as RAID groups, of the storage system. The aggregate has its own physical volume block number (pvbn) space and maintains metadata, such as block allocation structures, within that pvbn space. Each vvol has its own virtual volume block number (vvbn) space and maintains metadata, such as block allocation structures, within that vvbn space. Notably, the block allocation structures of a vvol are sized to the vvol, and not to the underlying aggregate, to thereby allow operations that manage data served by the storage system (e.g., snapshot operations) to efficiently work over the vvols. The file system layout extends the file system layout of a conventional write anywhere file layout system implementation, yet maintains performance properties of the conventional implementation.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
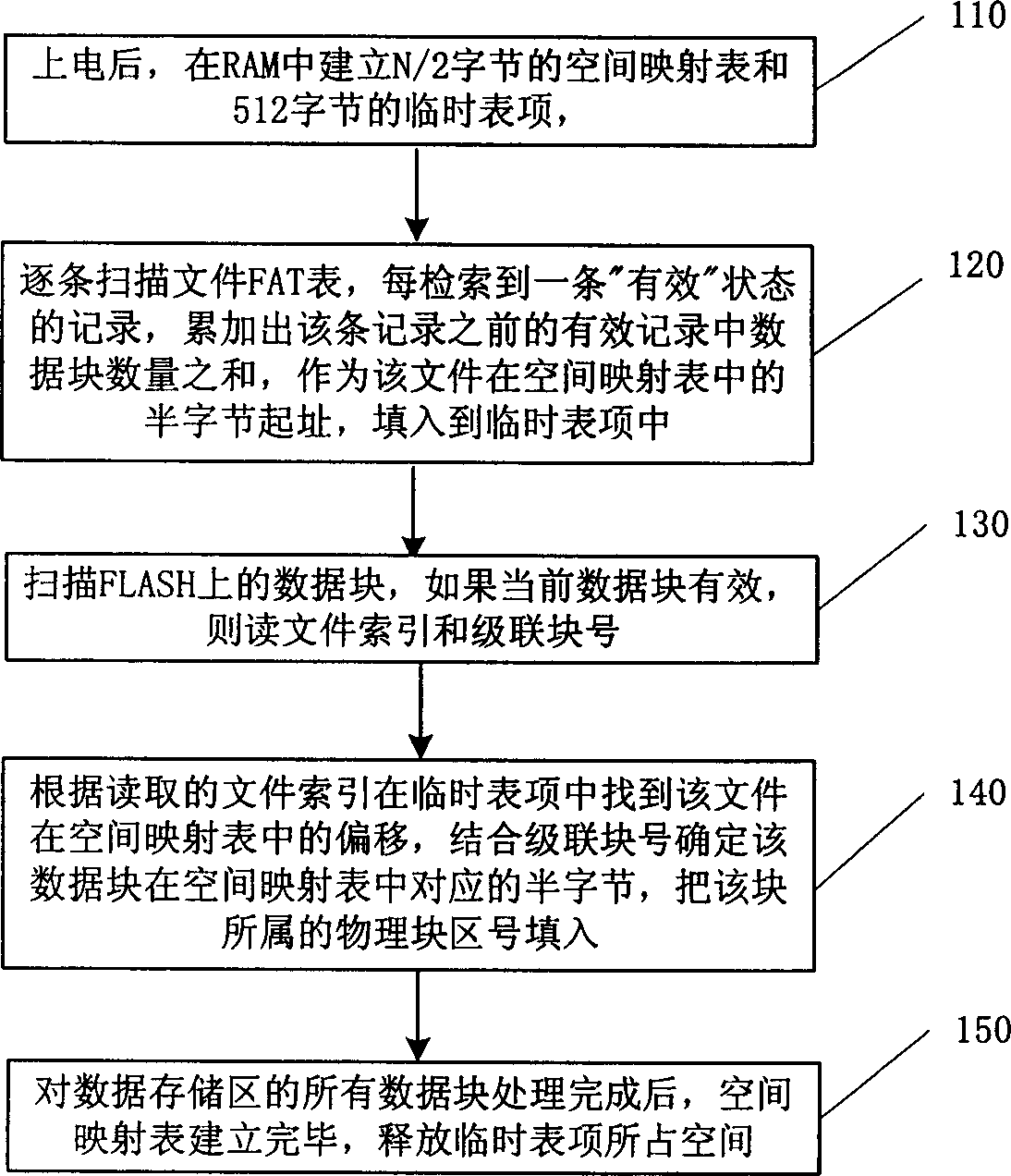
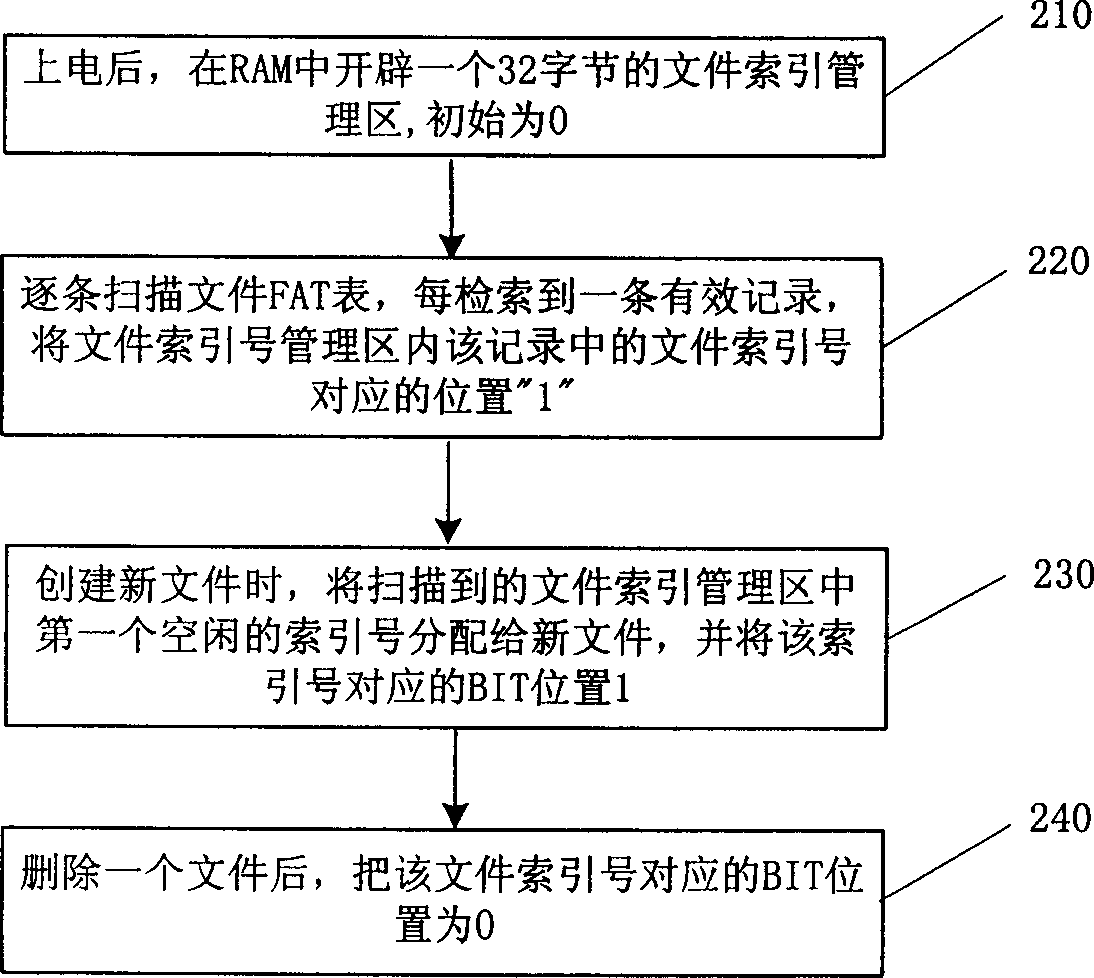
A flash memory file system management method
ActiveCN1632765AImprove retrieval efficiencyEnsure safetyRead-only memoriesMemory systemsFlash file systemFile system
This invention discloses a flash file system management method, which comprises the following steps: to divide the flash memory into FAT area and data memory area; to establish the space mapping form and to write the data block of each file into the block; to write the new file ID, block number, file researching number into the record; then to orderly write each data block into the spare block and to write each data block number into relative positions of the space mapping form; only to operate the file data memory area when updating file data; to identify the place of the data to be read when reading the data for searching the data block.
Owner:DATANG MICROELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
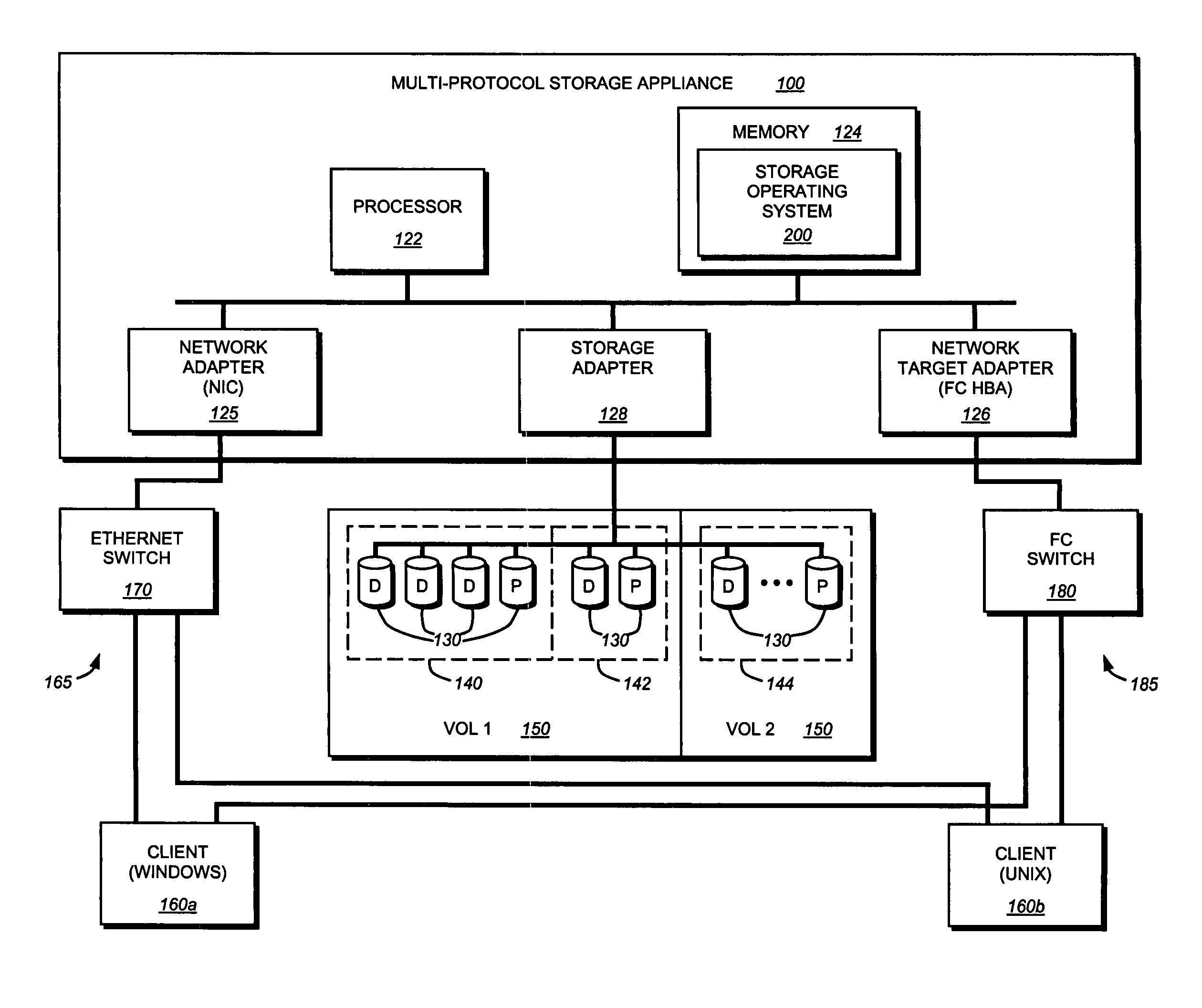
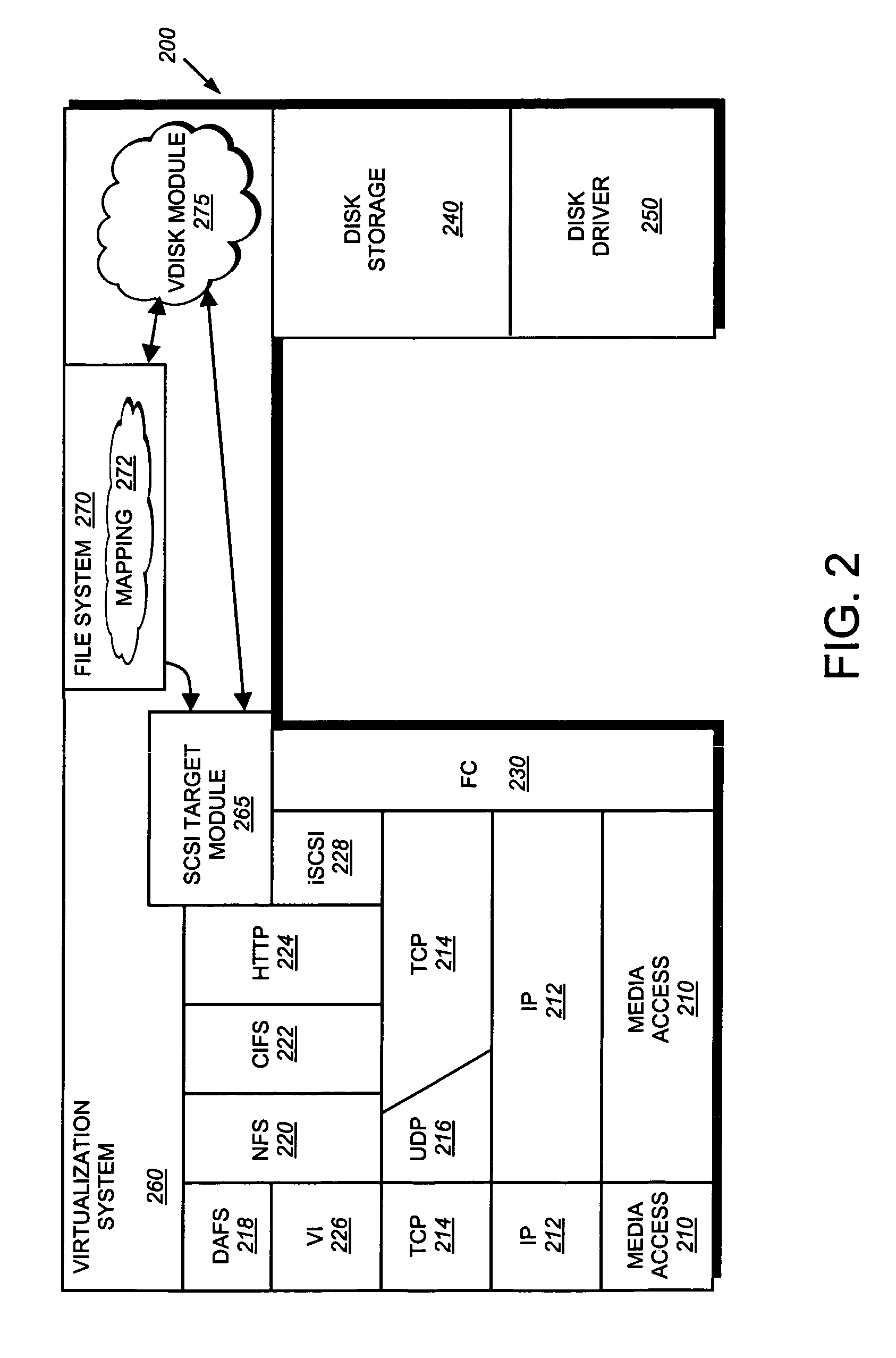
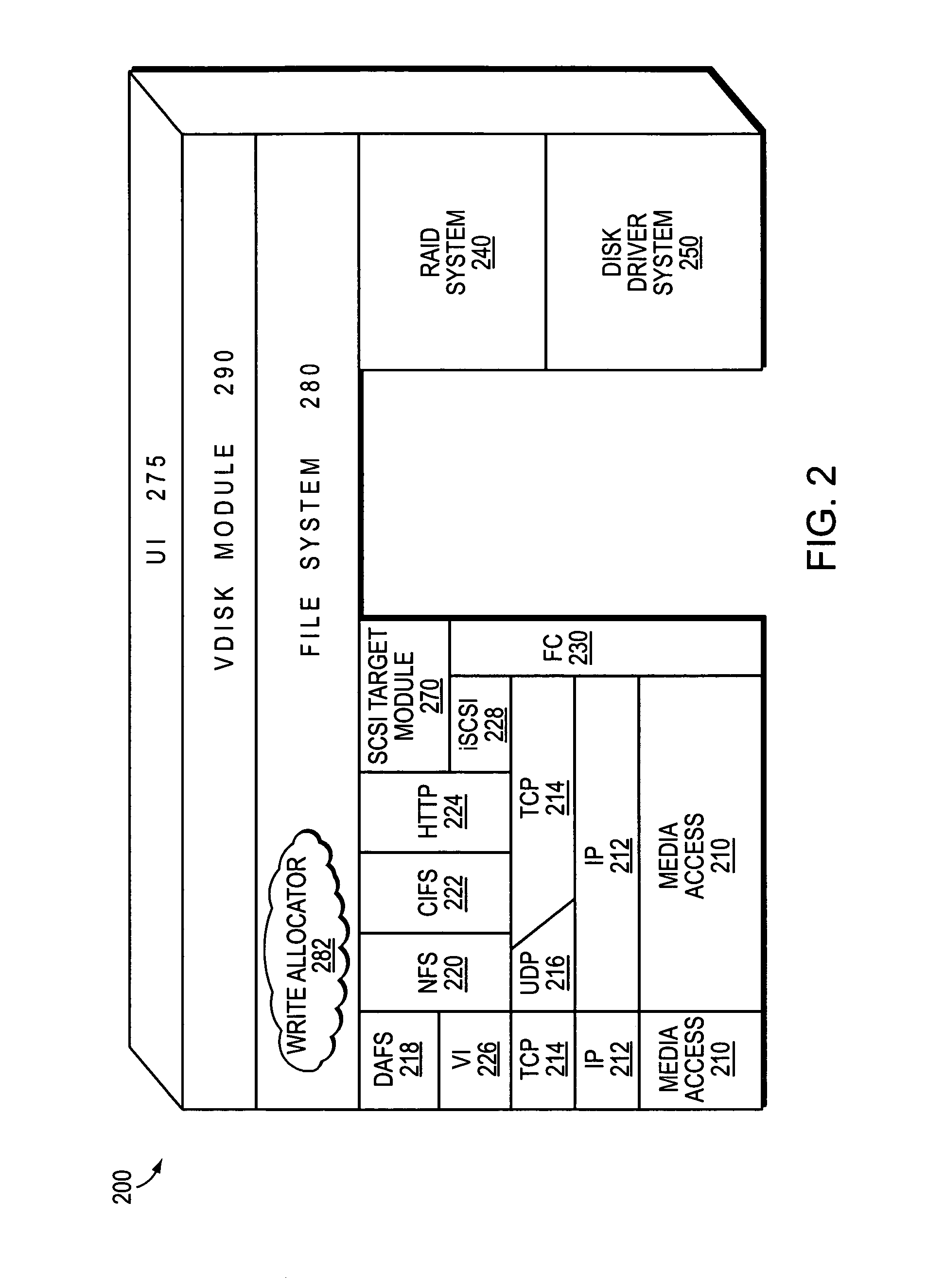
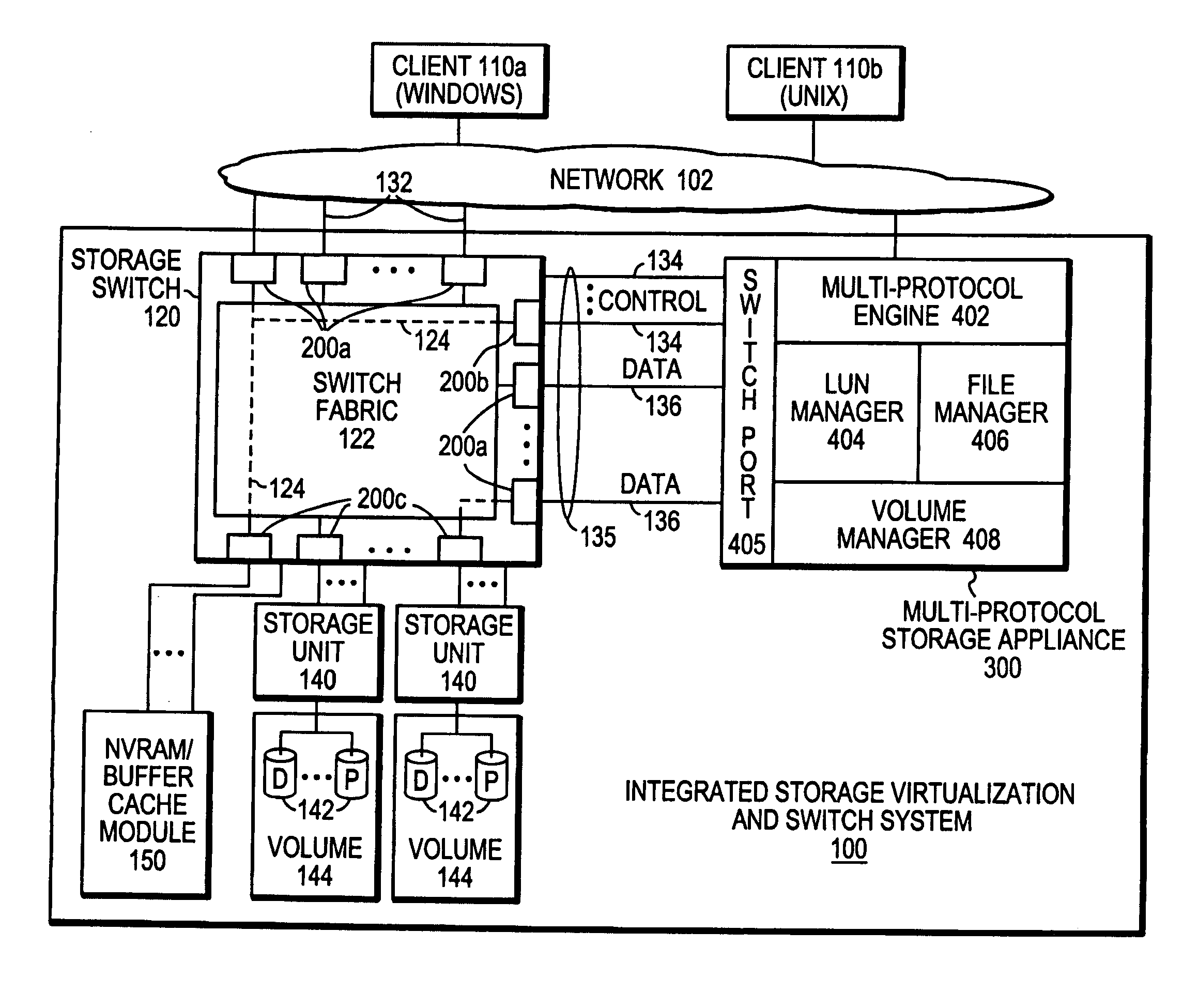
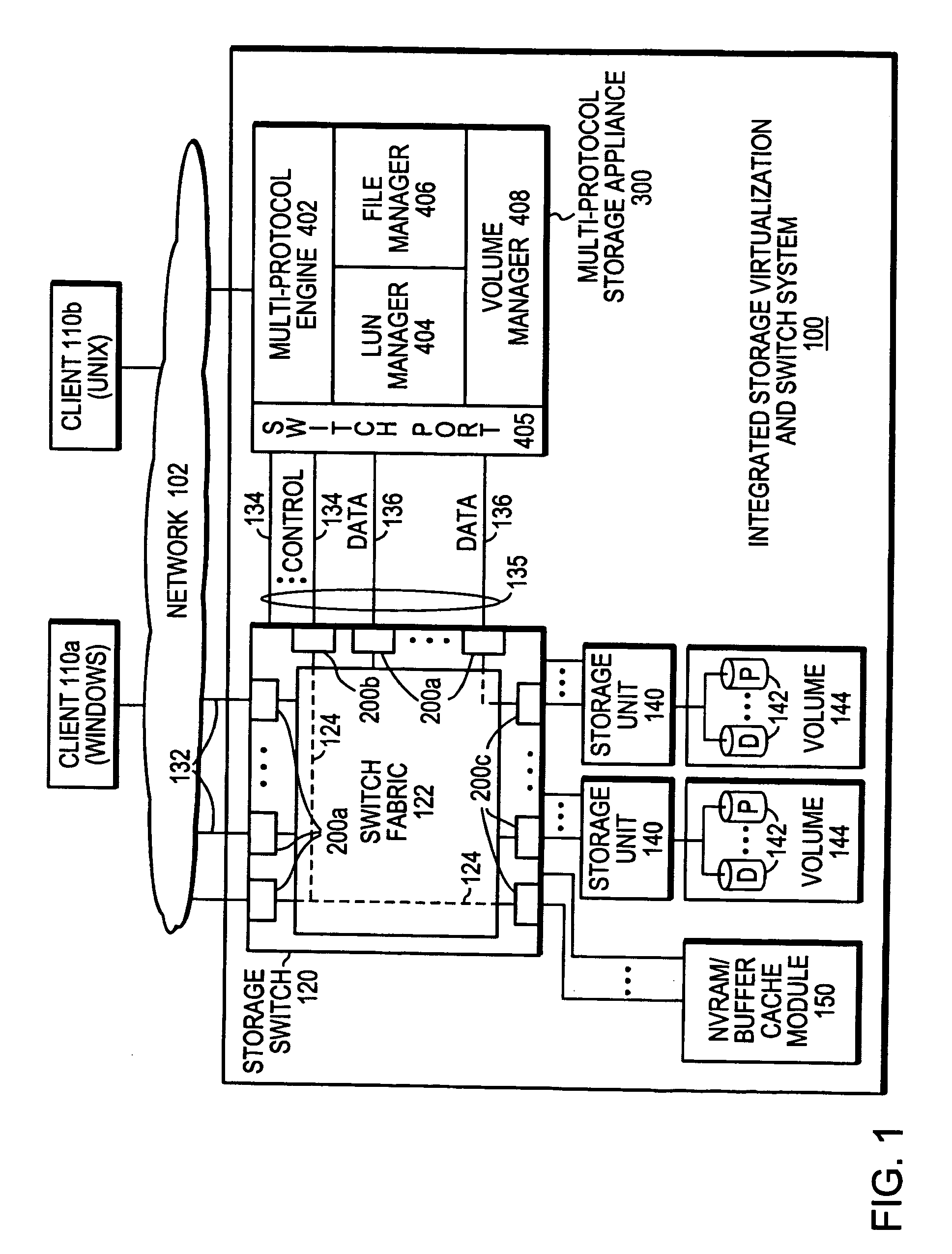
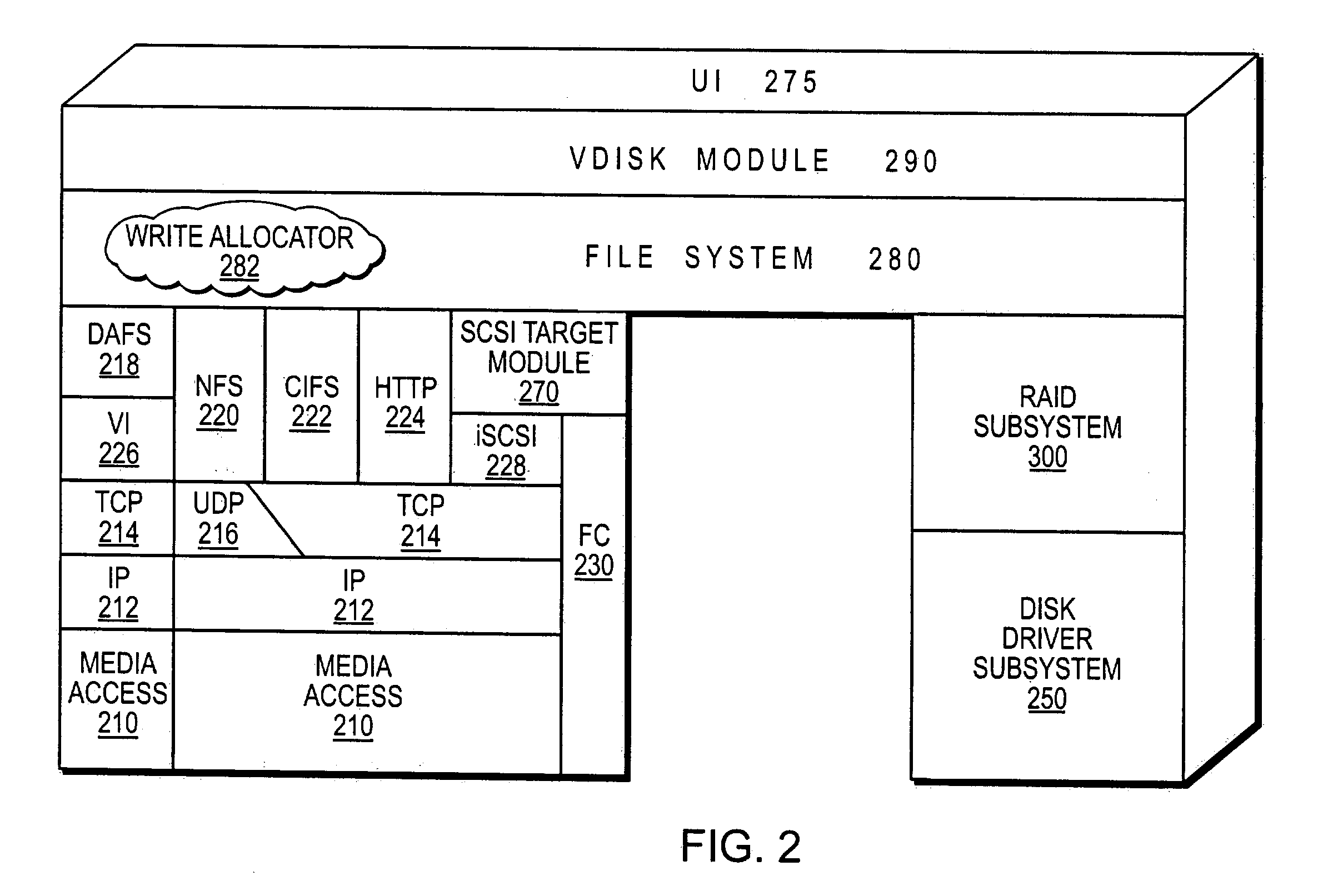
Integrated storage virtualization and switch system
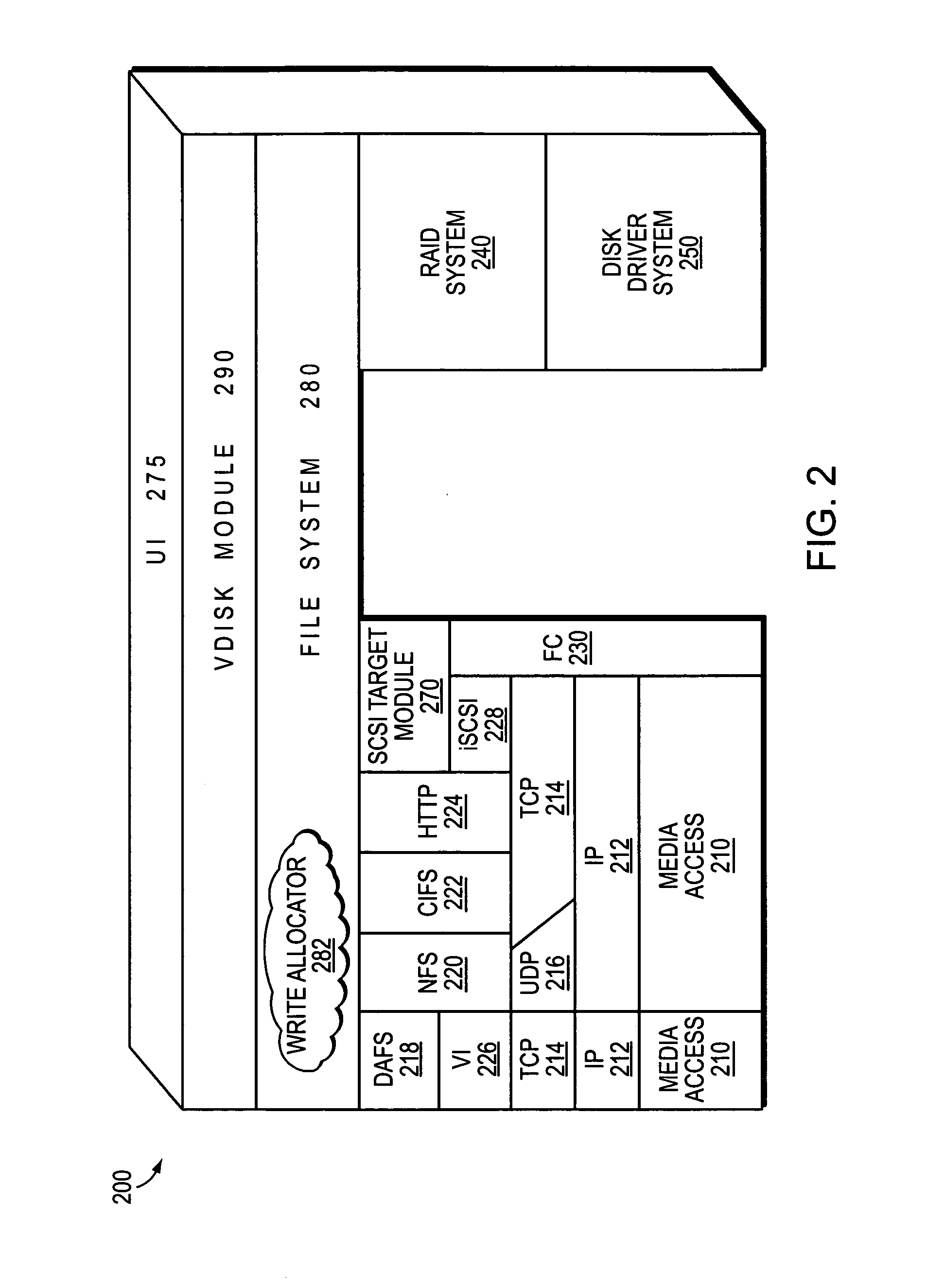
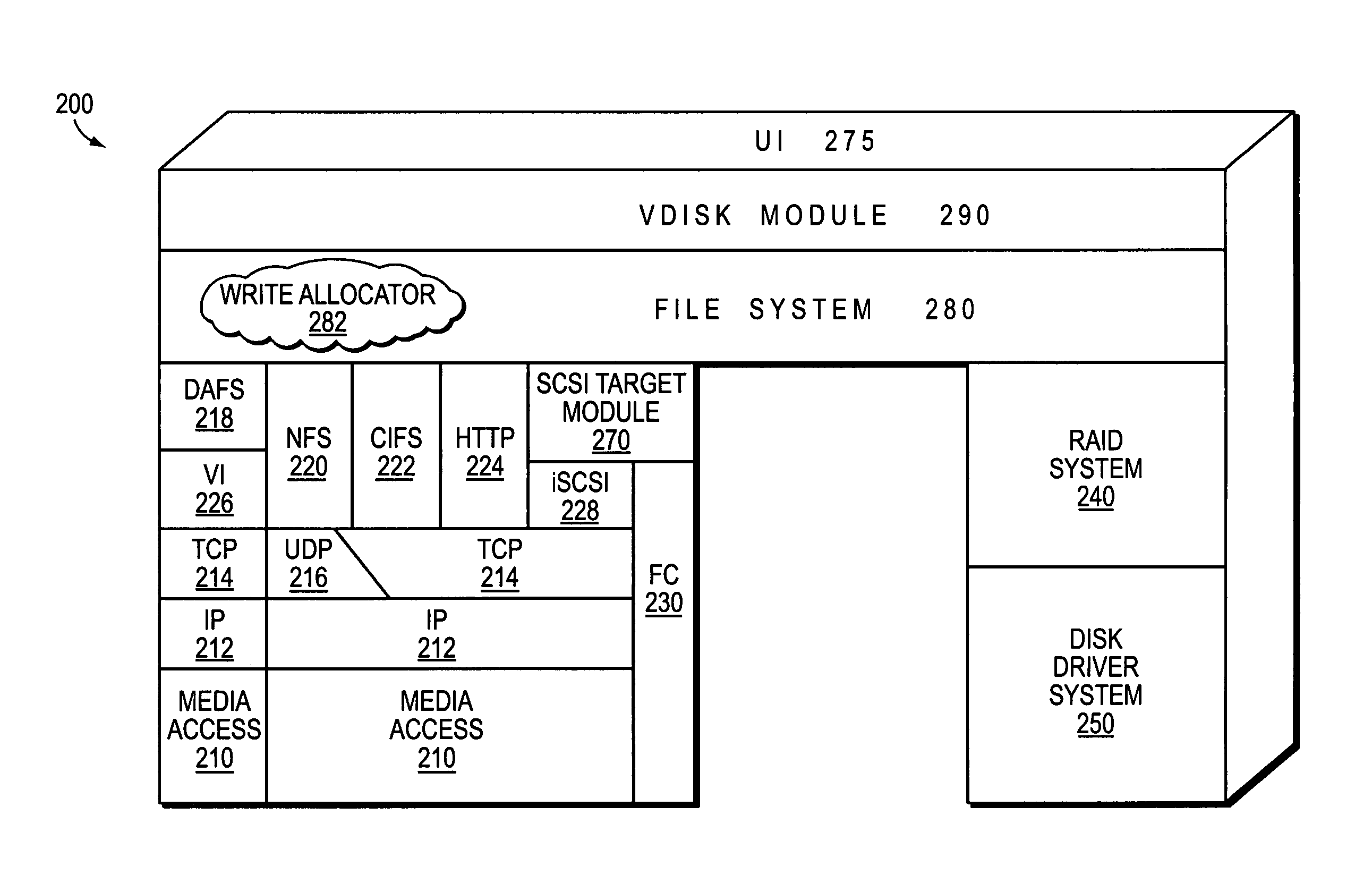
ActiveUS20060206603A1Reduce sizeImprove connectivityDigital computer detailsTransmissionOperational systemFile system
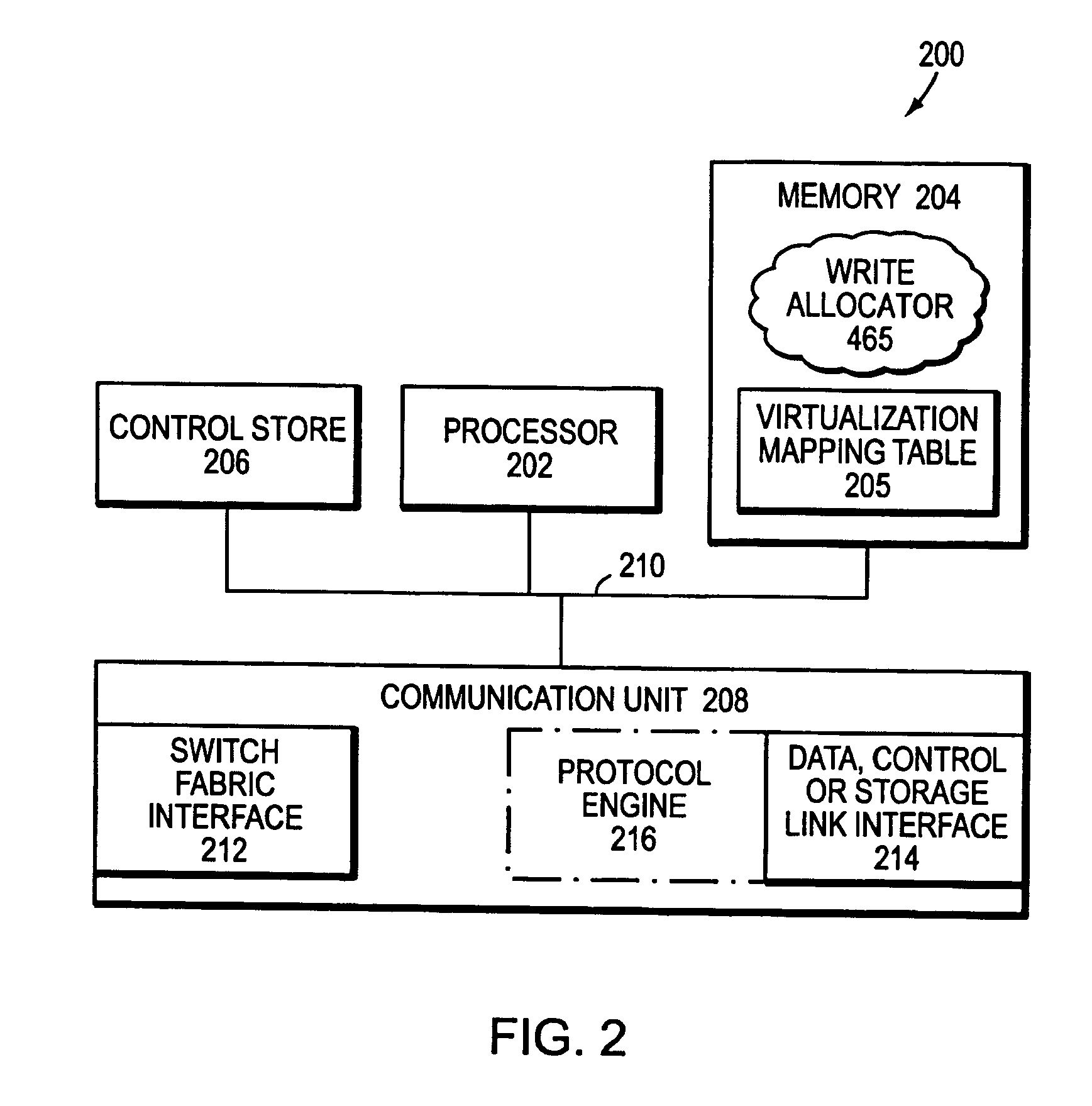
A system integrates an intelligent storage switch with a flexible virtualization system to enable efficient service of file and block protocol data access requests for information stored on the system. A storage operating system executing on a storage system coupled to the switch implements the virtualization system to provide a unified view of storage to clients by logically organizing the information as named files, directories and logical unit numbers. The virtualization system is illustratively embodied as a file system having a write allocator configured to provide a flexible block numbering policy that addresses volume management capabilities, such as storage virtualization, at a finer granularity (e.g., a single block) than that of previous non-flexible storage virtualization schemes. The flexible block numbering policy also yields substantial benefits in terms of increased write efficiency and elimination of storage “hot spots”, as well as a compelling point-in-time read-only data image (snapshot) mechanism.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
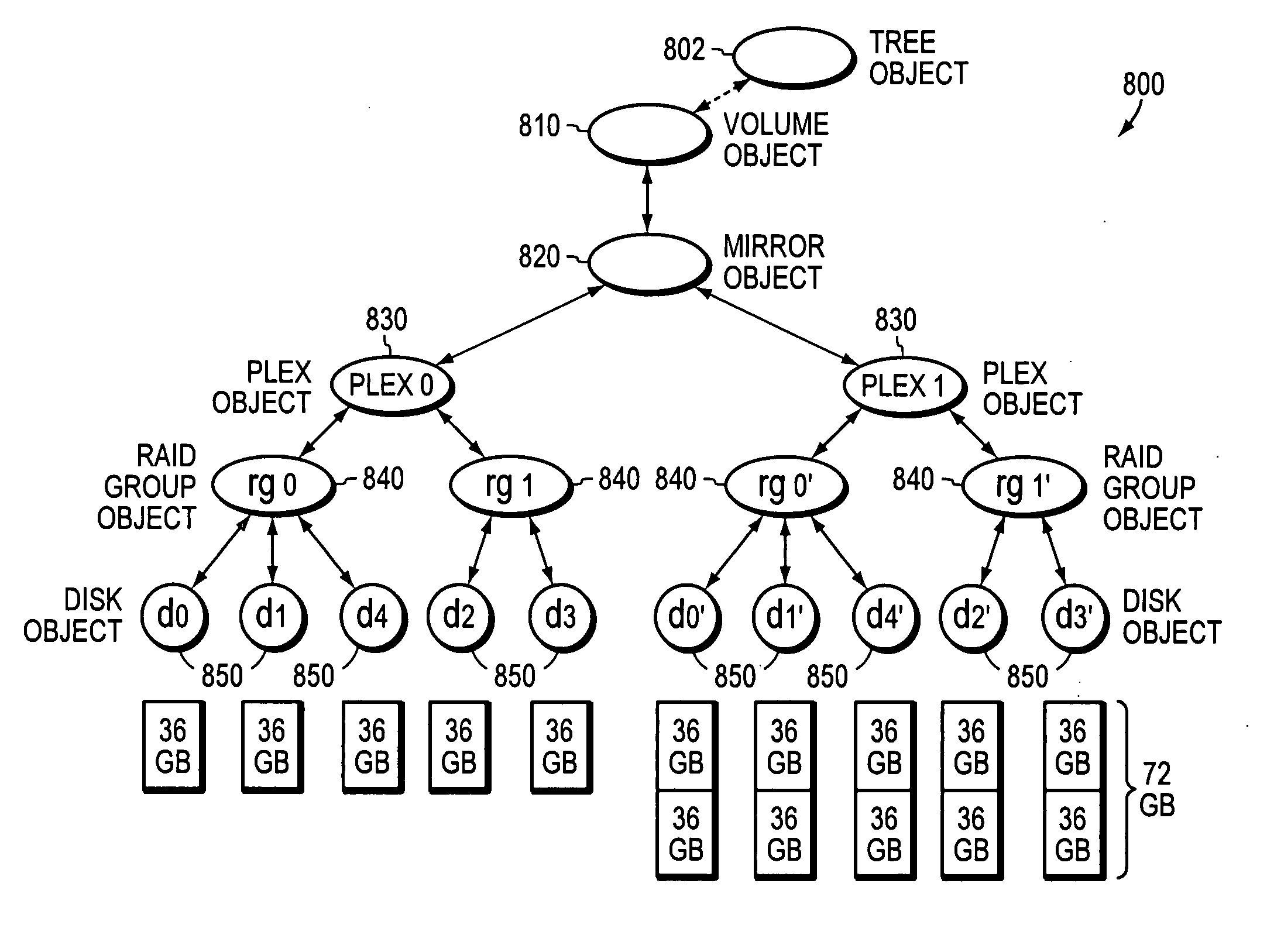
Location-independent RAID group virtual block management
ActiveUS7111147B1Facilitating instantiationProvide flexibilityMemory loss protectionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationTopology managementRAID
A technique maps the capacity of storage devices, such as disks, into any RAID group of a volume of a storage system regardless of the location of the RAID group within a volume block number (VBN) space of the volume. The technique separates disks and mapped VBN ranges, allowing for flexibility in the description and extension of RAID group capacities, while providing disk addition policies that support location-independent disk insertion into RAID groups. The technique also provides a disk label structure that supports the provision of multiple VBN ranges within a RAID group and within individual disks. Moreover, the technique provides file system support for allocation and topology management of the multiple mapped VBN ranges within disks and RAID groups, as well as noncontiguous VBN ranges across the RAID groups in the volume.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
System and method for determining changes in two snapshots and for transmitting changes to a destination snapshot
InactiveUS7603391B1Efficient scanningOvercome disadvantagesData processing applicationsRedundant operation error correctionData streamInode
A system and method for remote asynchronous replication or mirroring of changes in a source file system snapshot in a destination replica file system using a scan (via a scanner) of the blocks that make up two versions of a snapshot of the source file system, which identifies changed blocks in the respective snapshot files based upon differences in volume block numbers identified in a scan of the logical file block index of each snapshot. Trees of blocks associated with the files are traversed, bypassing unchanged pointers between versions and walking down to identify the changes in the hierarchy of the tree. These changes are transmitted to the destination mirror or replicated snapshot. This technique allows regular files, directories, inodes and any other hierarchical structure to be efficiently scanned to determine differences between versions thereof. The changes in the files and directories are transmitted over the network for update of the replicated destination snapshot in an asynchronous (lazy write) manner. The changes are described in an extensible, system-independent data stream format layered under a network transport protocol. At the destination, source changes are used to update the destination snapshot. Any deleted or modified inodes already on the destination are moved to a temporary or “purgatory” directory and, if reused, are relinked to the rebuilt replicated snapshot directory. The source file system snapshots can be representative of a volume sub-organization, such as a qtree.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
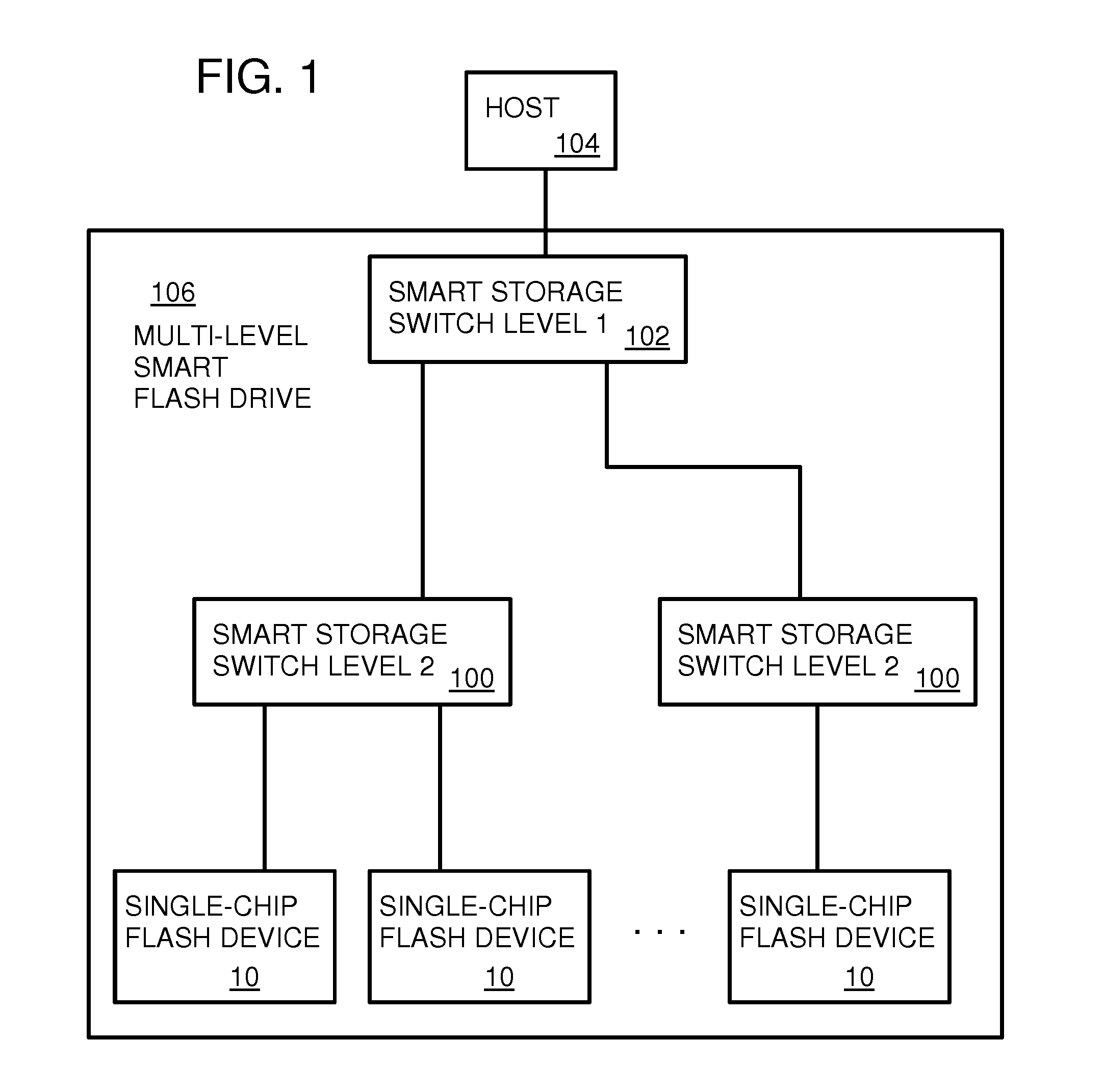
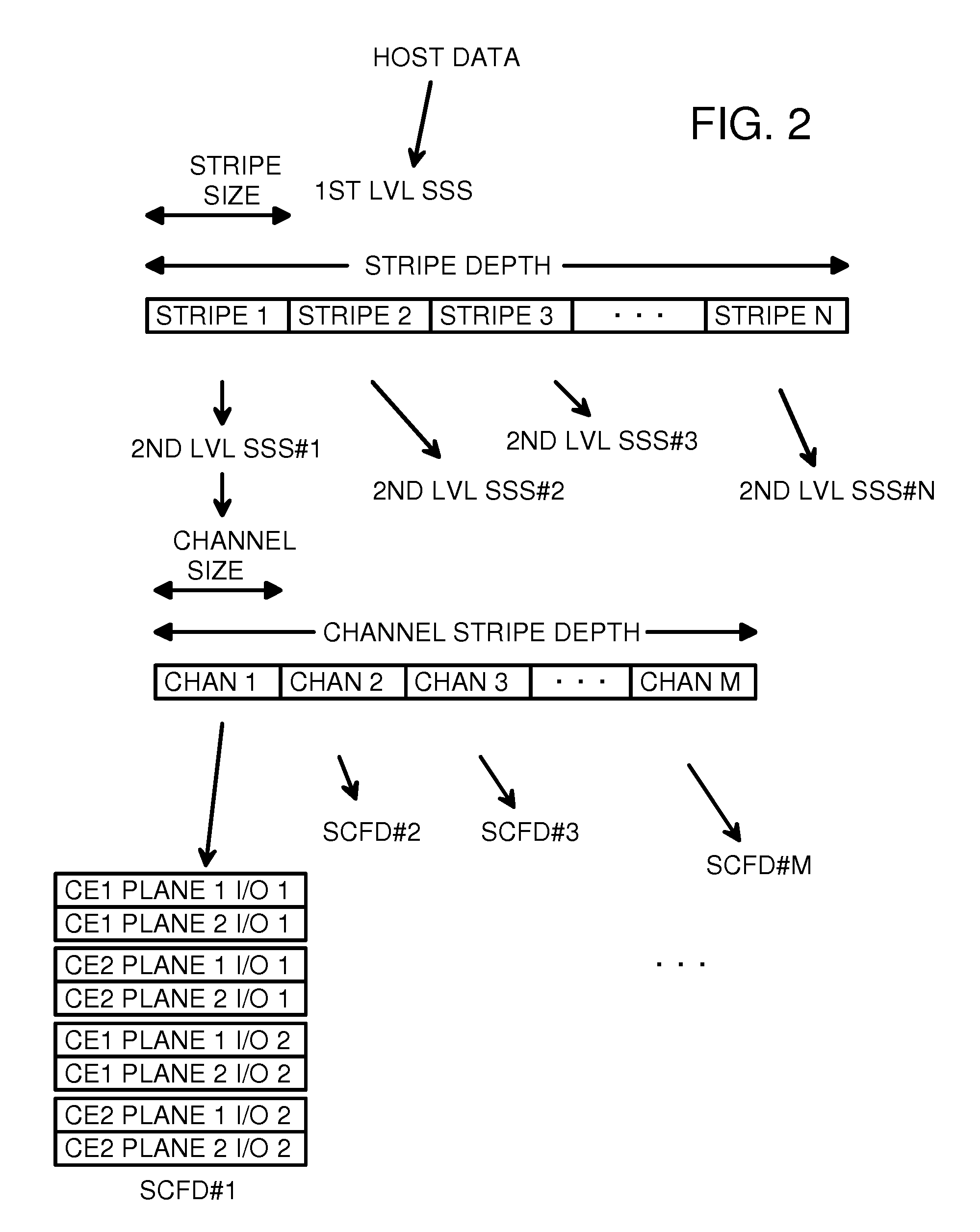
Flash-Memory Device with RAID-type Controller
InactiveUS20120278543A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionRAIDDisk array
A smart flash drive has one or more levels of smart storage switches and a lower level of single-chip flash devices (SCFD's). A SCFD contains flash memory and controllers that perform low-level bad-block mapping and wear-leveling and logical-to-physical block mapping. The SCFD report their capacity, arrangement, and maximum wear-level count (WLC) and bad block number (BBN) to the upstream smart storage switch, which stores this information in a structure register. The smart storage switch selects the SCFD with the maximum BBN as the target and the SCFD with the lowest maximum WLC as the source of a swap for wear leveling when a WLC exceeds a threshold that rises over time. A top-level smart storage switch receives consolidated capacity, arrangement, WLC, and BBN information from lower-level smart storage switch. Data is striped and optionally scrambled by Redundant Array of Individual Disks (RAID) controllers in all levels of smart storage switches.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
Hybrid storage system
ActiveUS8315995B1Large capacityLow costMemory architecture accessing/allocationDigital data information retrievalGranularityFile system
Roughly described, a tiered storage system has a filesystem that promotes and demotes data among tiers at block granularity. It maintains a logical-to-physical mapping which indicates for each block in a file both the assigned tier and the physical block number within the tier. Methods for performing file- and block-level manipulations are described. In an embodiment, a nominal tier is managed by a native filesystem, and higher tiers are managed by a super filesystem. The super filesystem manages promotion and demotion among the tiers, interfacing with higher tiers directly but interfacing with the nominal tier only through the native filesystem. The native filesystem defines the file namespace in the system, and the logical-to-physical block mapping for blocks in the nominal tier. The super filesystem defines the logical-to-physical mapping for blocks in the higher tiers, but retains the file identification information as defined by the native filesystem.
Owner:PEER FUSION
Cheap signatures for synchronous broadcast communication
InactiveUS20050182932A1Keep in syncSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesUser identity/authority verificationHash functionClient-side
A method and system are configured for synchronous broadcast communications by applying signature keys using hashing functions. Each subsequent transmission in a sequence includes a signature key that can be verified by hashing to a preceding signature key from a previous portion of the sequence. The first transmission in the sequence is signed using a signature key that is known by the client device, typically verified using some other mechanism such as asymmetric key signatures. Each client device can utilize an internal counter for the current time or the block number in the transmission sequence to maintain synchronized transmissions in the even that a particular portion of the sequence is missed, and to validate signature keys. Since the signature keys can be validated when they are received but not predicted before they are received, the transmission is difficult to attack while synchronization is maintained.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Data access method, node and system
ActiveCN102594852AReduce access overheadImprove access efficiencyTransmissionAccess methodDistributed File System
The invention discloses a data access method, a data access device and a data access system. The method comprises the following steps that: an access request containing a block number identifier is received; a pre-established local block unit searches the corresponding relation between the block number of the local block unit and storage node resource information providing storage services according to the block number to obtain a storage node position corresponding to the block number identifier and a block data identifier; and the local block unit sends the data access request to the storage node according to the storage node position corresponding to the block number identifier and the block data identifier, wherein the storage node resource information comprises the storage node position information and the block number identifier of a storage node. By the method, the device and the system, the problem that a metadata server becomes a bottleneck of the system because the current distributed file system is required to address through the metadata server at every access is solved, and the access efficiency is low is overcome.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM GRP CO LTD
Radio communication apparatus and radio communication method
ActiveUS20060089102A1Improve throughputReceivers monitoringError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorEngineeringThroughput
A CIR measuring section 307 measures CIRs of all blocks received and a block selection section 308 makes a threshold decision based on the CIR measurement result and threshold information according to an amount of traffic in the own cell and neighboring cells. As a result of the threshold decision, blocks whose CIRs exceed the threshold are regarded as usable blocks. A CIR averaging section 309 averages the CIRs of the usable blocks and a CQI generation section 310 generates a CQI based on the CIR average value. The CQI generated and selected block numbers are reported to a base station apparatus. This allows the throughput of the own cell and neighboring cells to be improved.
Owner:OPTIS WIRELESS TECH LLC
Restructuring of executable computer code and large data sets
InactiveUS20030014741A1Software engineeringSpecific program execution arrangementsData setParallel computing
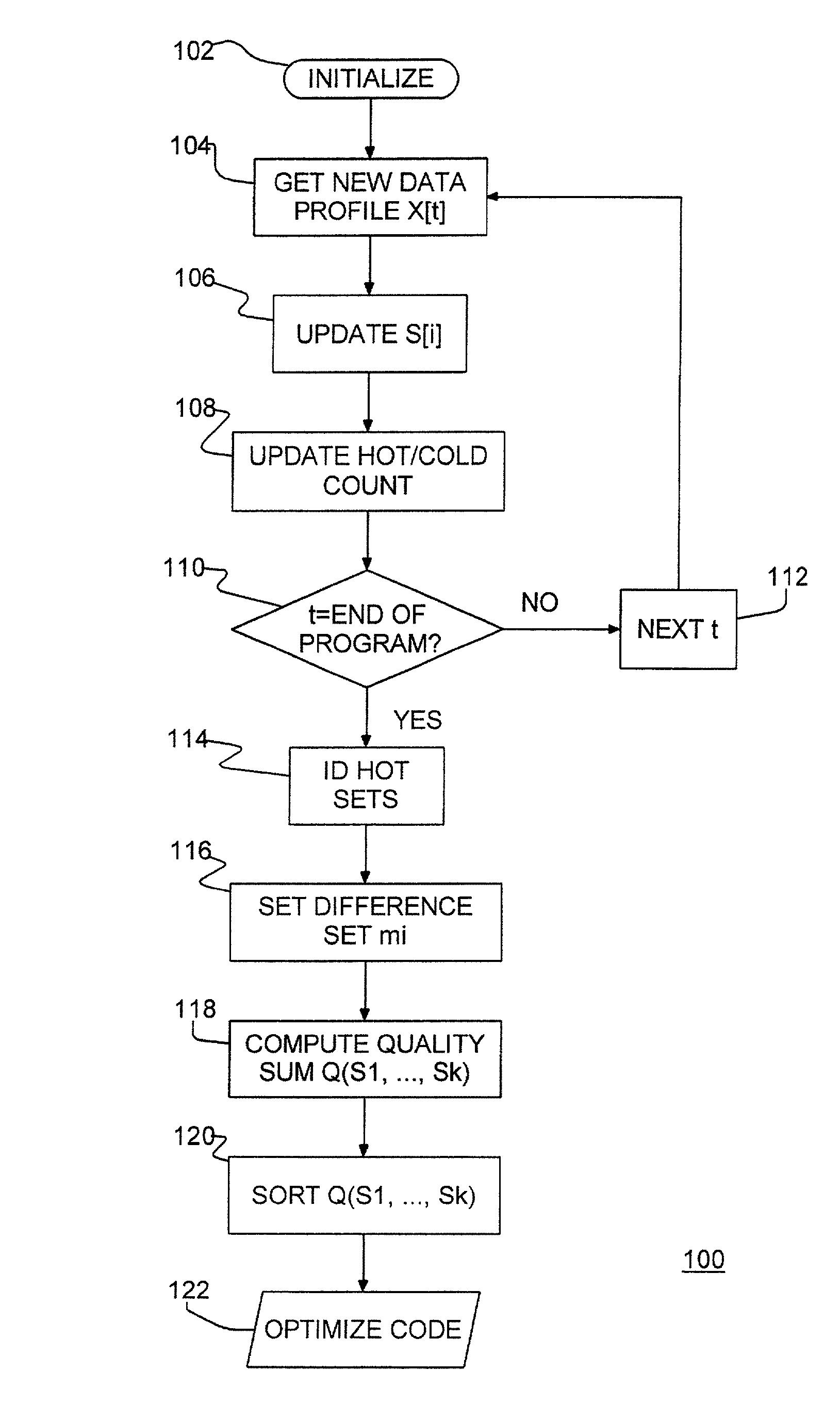
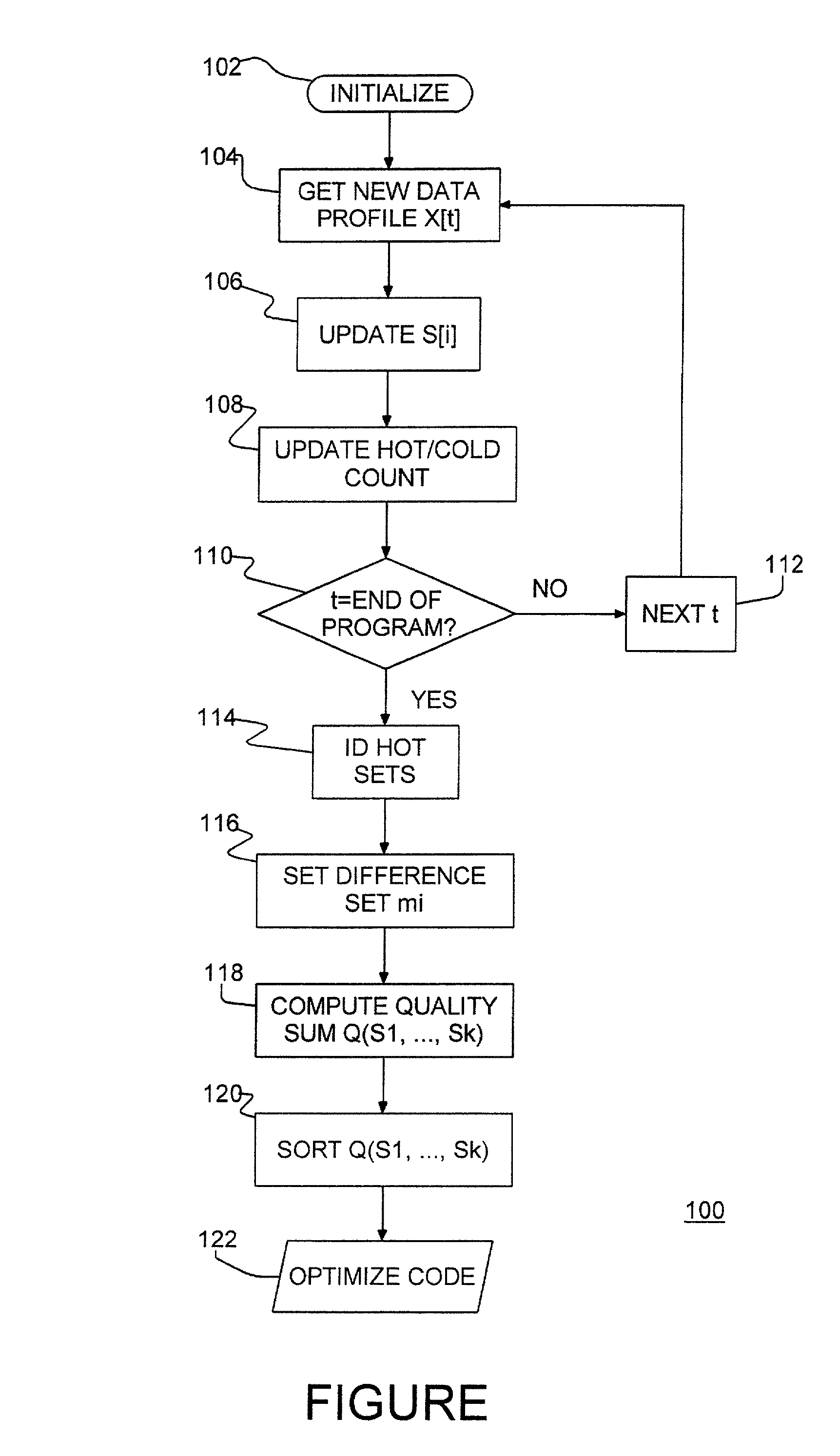
A program product and method of compiling a computer program to optimize performance of a computer program. First, after initialization, a profiling run is done on computer code which may include program code blocks and program data. Execution of each computer program step is monitored and each occurrence of each individual code unit is logged, e.g. each instruction block or block of data. Frequently occurring code units are identified periodically as hot blocks. An initial snapshot of hot blocks is logged, e.g., when identified hot blocks exceed an initial block number. Profiling continues until the profiling run is complete, updating identified hot blocks and logging a new current snapshot whenever a current set of identified hot blocks contains a selected percentage of different hot blocks. Snapshots are selected as representative to different program modes. The program is optimized according to program modes.
Owner:IBM CORP
Efficient source blocking algorithm for FEC for MBMS streaming
InactiveUS20060077890A1Frequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission systemsBlock numberCorrection code
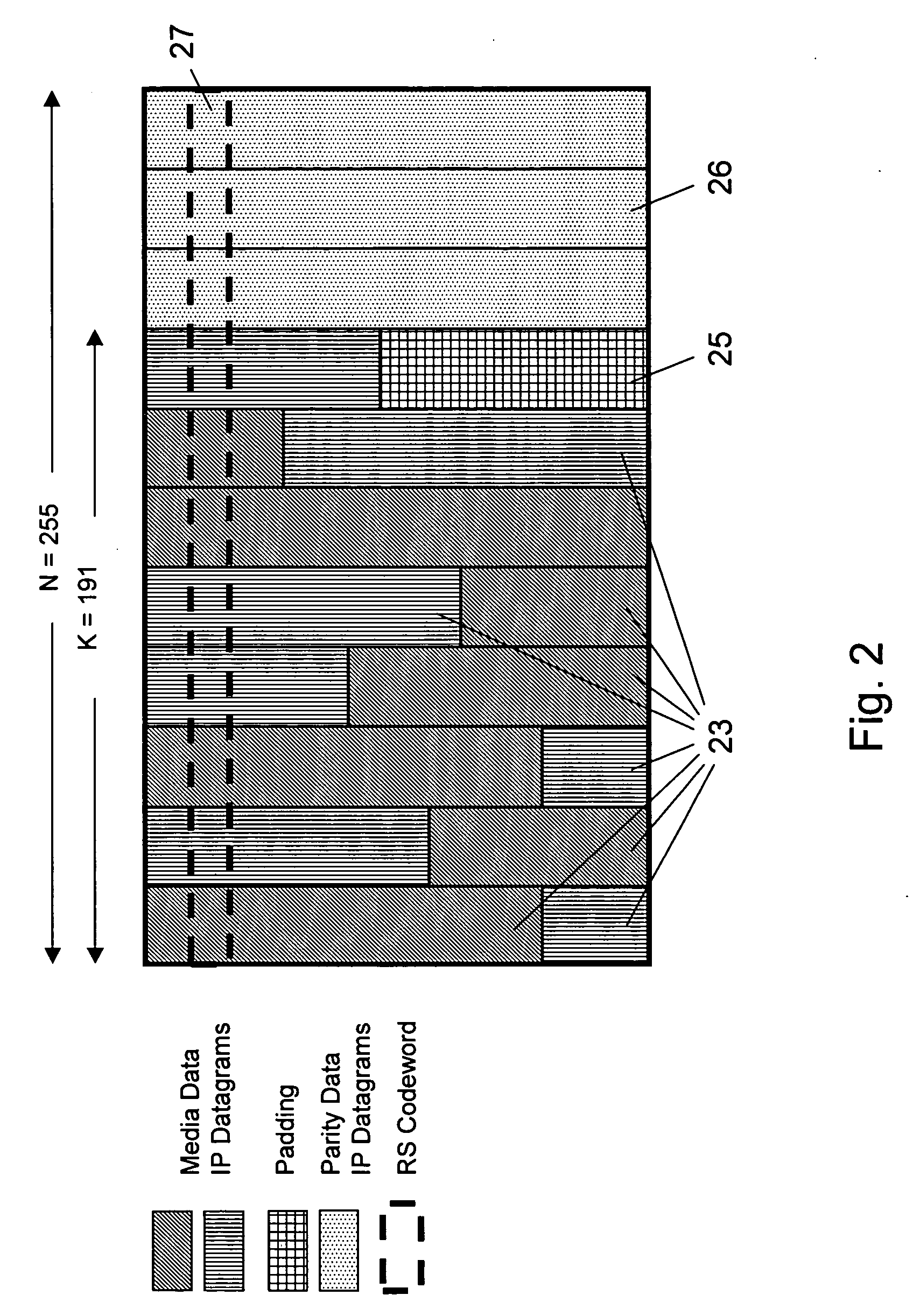
A hybrid-padding approach for arranging variable size data packets for error correction encoding and decoding is disclosed. The approach can involve arranging the data packets in columns and rows and selecting the row size to minimize the amount of padding required. If data packet is smaller than the number of rows the data packet is inserted into the column and the remaining rows are padded. If the data packet is larger than the number of rows, the data packet is allowed to span multiple columns with the last column being padded if necessary. The data packets can include parameters, such as a source block number, packet length, and starting column number, and the error correction packets can include parameters, such as, a source block number an N, a K, the starting column number, and the number of row, to signal the hybrid-padding message.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Method of encryption and decryption with block number dependant key sets, each set having a different number of keys
InactiveUS6917684B1Increase speedSimilar level of securityEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesSecret communicationKey generationBlock number
The subkey data generating unit 101 has two different subkey key generation processes. When encrypting a (T*n)th plaintex block (where T denotes a predetermined cycle and n is a positive integer), sixteen sets of subkey data are generated. In all other cases, two sets of subkey data are generated. The encrypting unit 100 encrypts the plaintex using the generated sixteen or two sets of subkey data.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
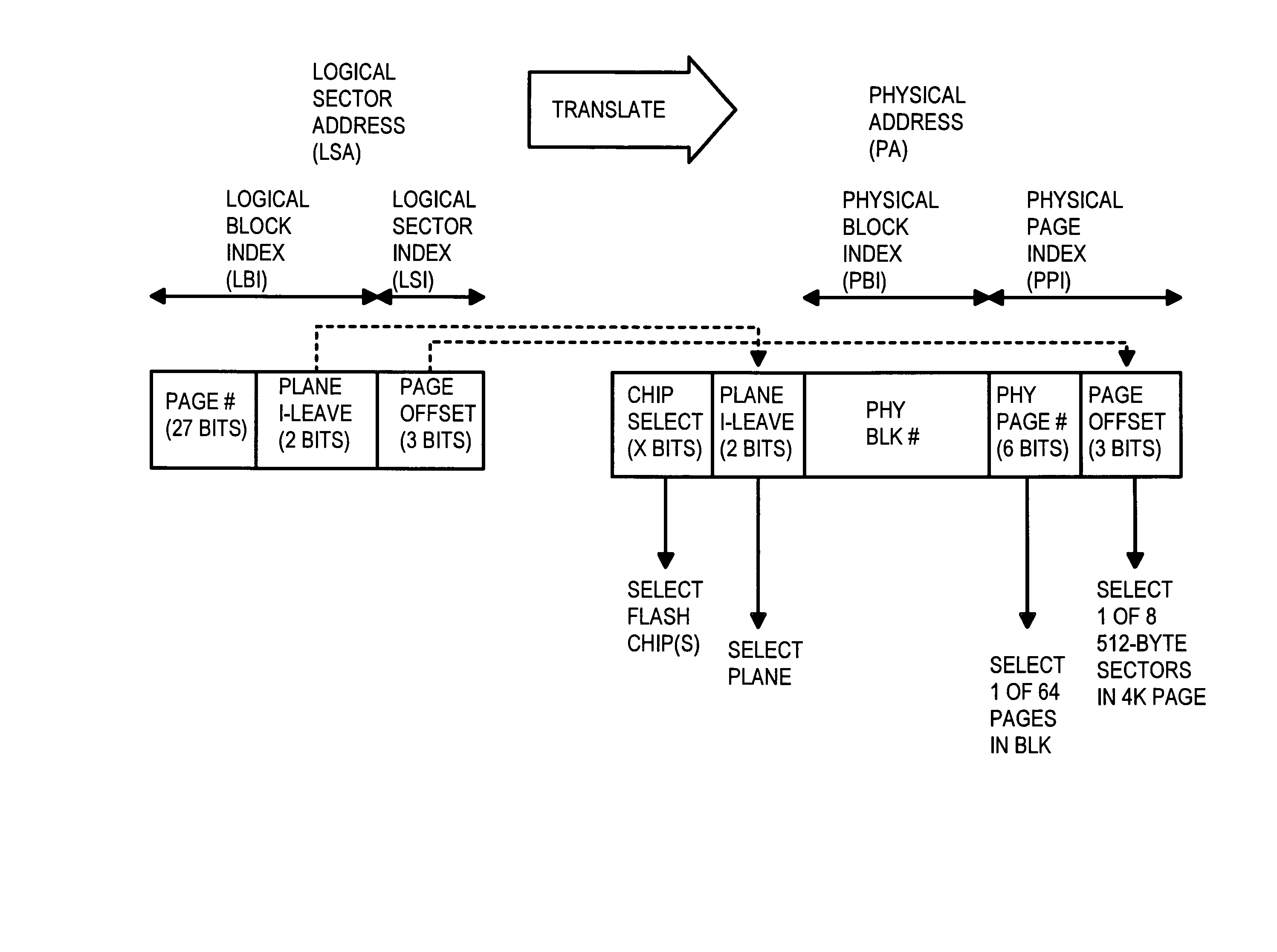
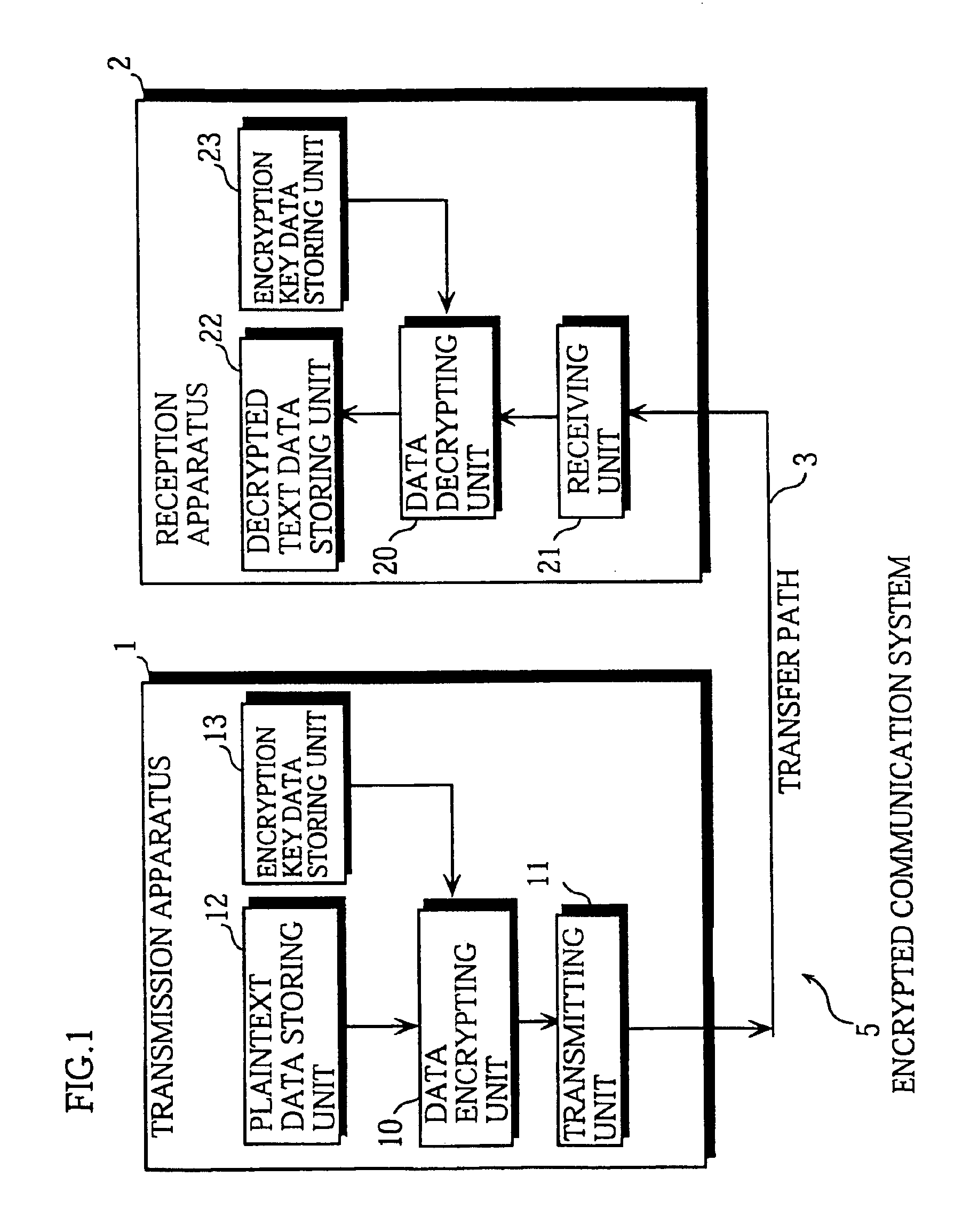
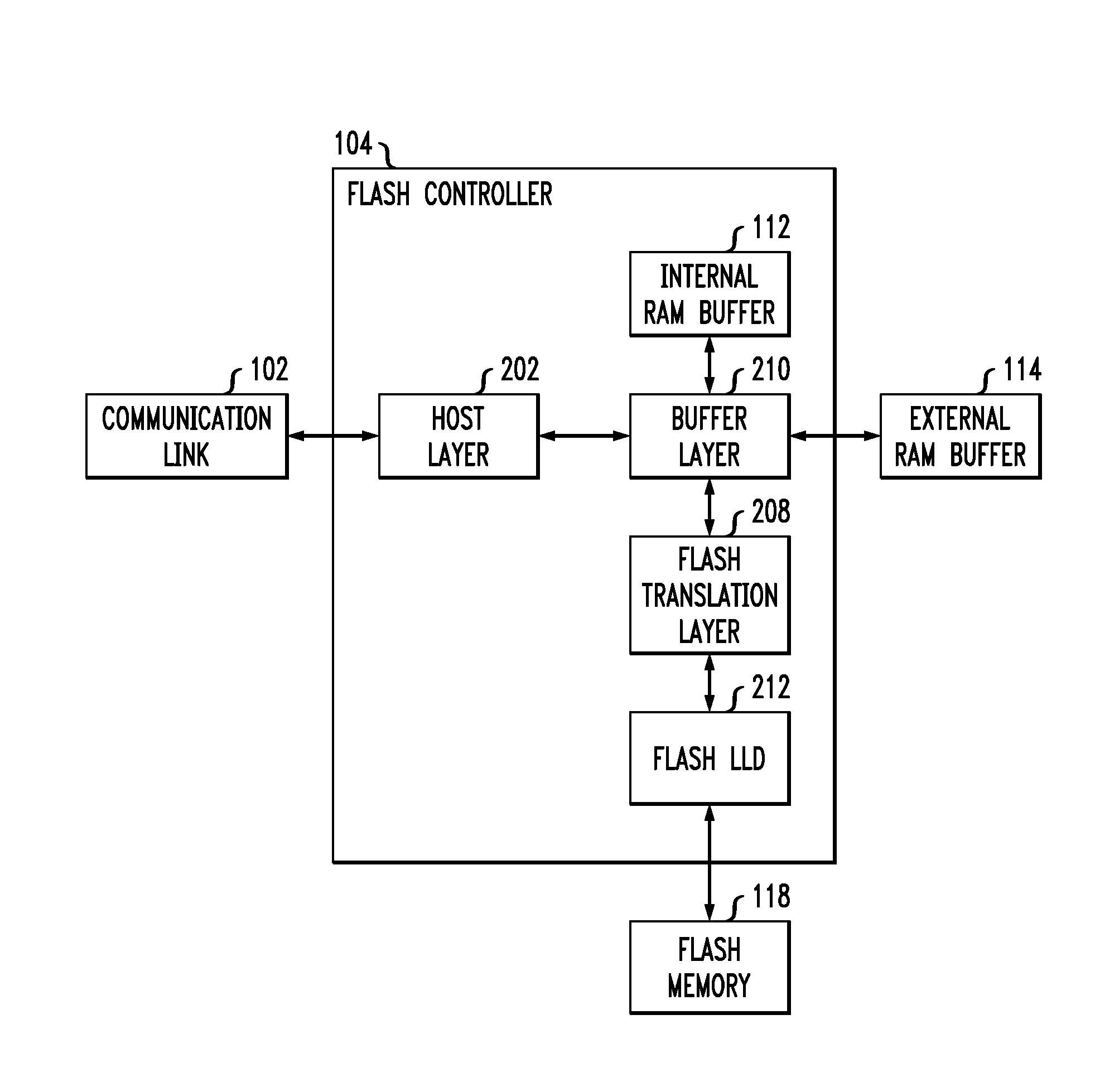
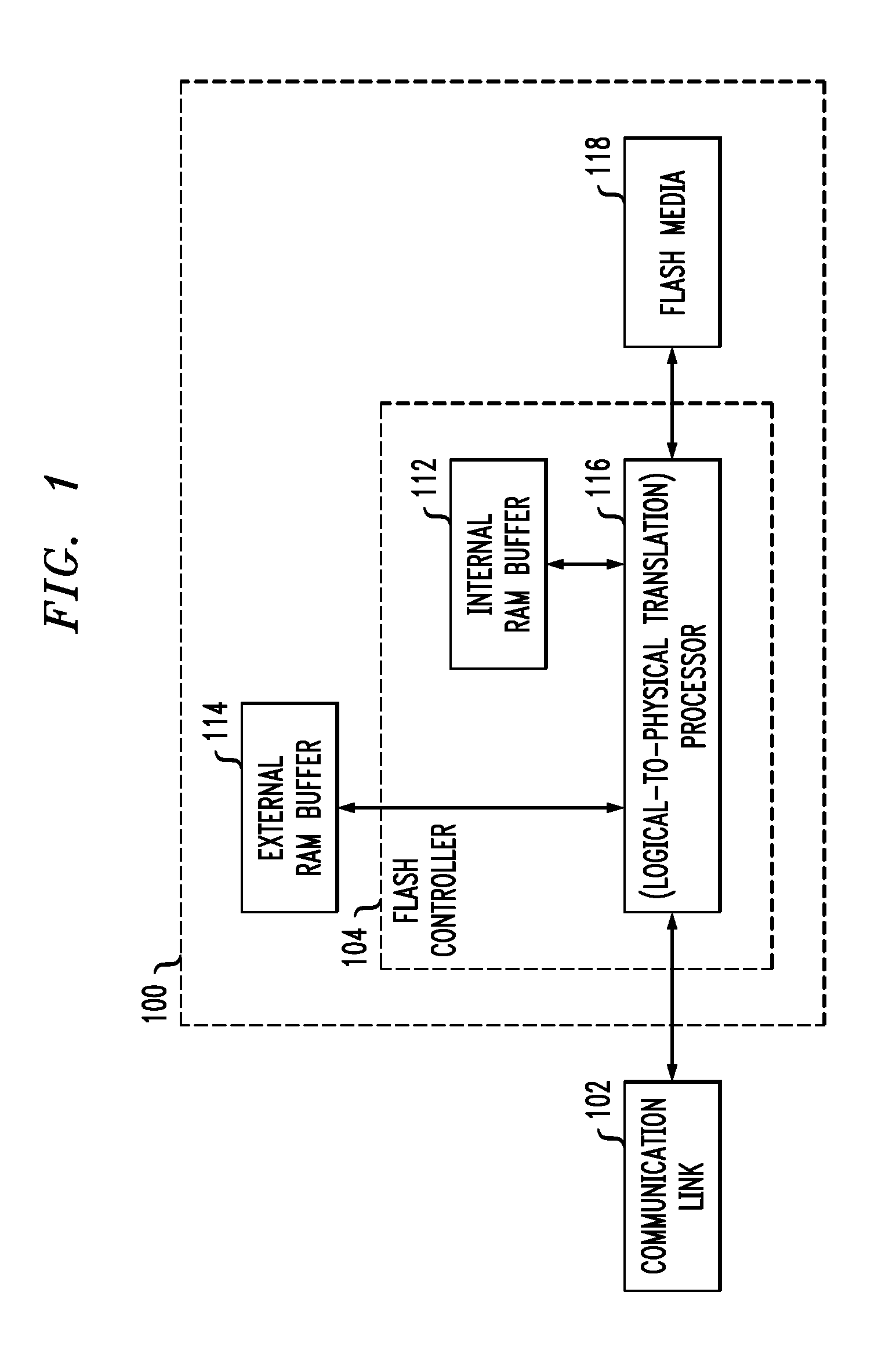
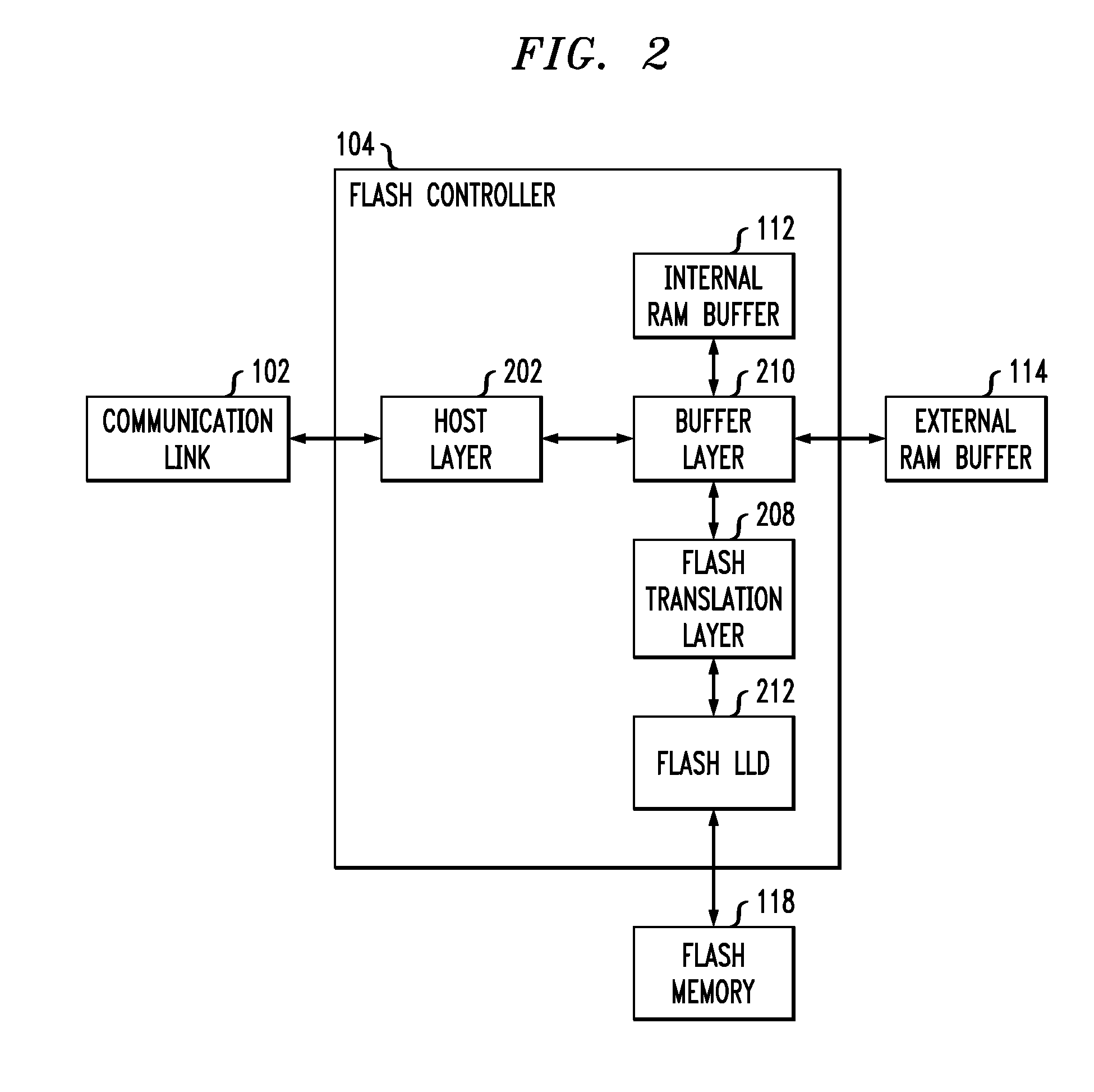
Logical-to-physical address translation for solid state disks
ActiveUS8219776B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesPhysical addressData storing
Described embodiments provide logical-to-physical address translation for data stored on a storage device having sectors organized into blocks and superblocks. A flash translation layer maps a physical address in the storage device to a logical sector address. The logical sector address corresponds to mapping data that includes i) a page index, ii) a block index, and iii) a superblock number. The mapping data is stored in at least one summary page corresponding to the superblock containing the physical address. A block index and a page index of a next empty page in the superblock are stored in a page global directory corresponding to the superblock. A block index and a page index of the at least one summary page and the at least one active block table for each superblock are stored in at least one active block table of the storage device.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
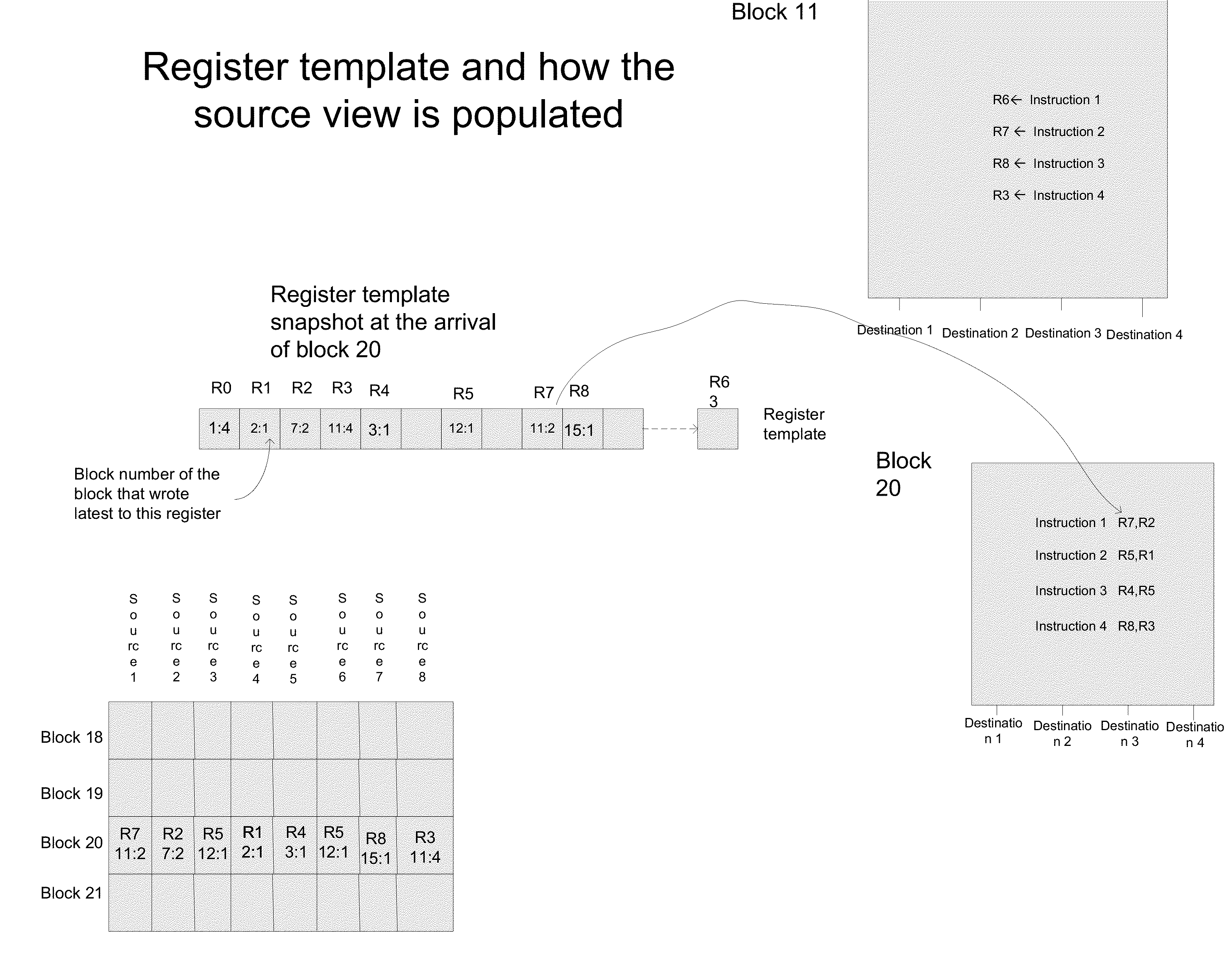
Method for dependency broadcasting through a block organized source view data structure
ActiveUS20140282601A1Conditional code generationProgram initiation/switchingParallel computingInstruction sequence
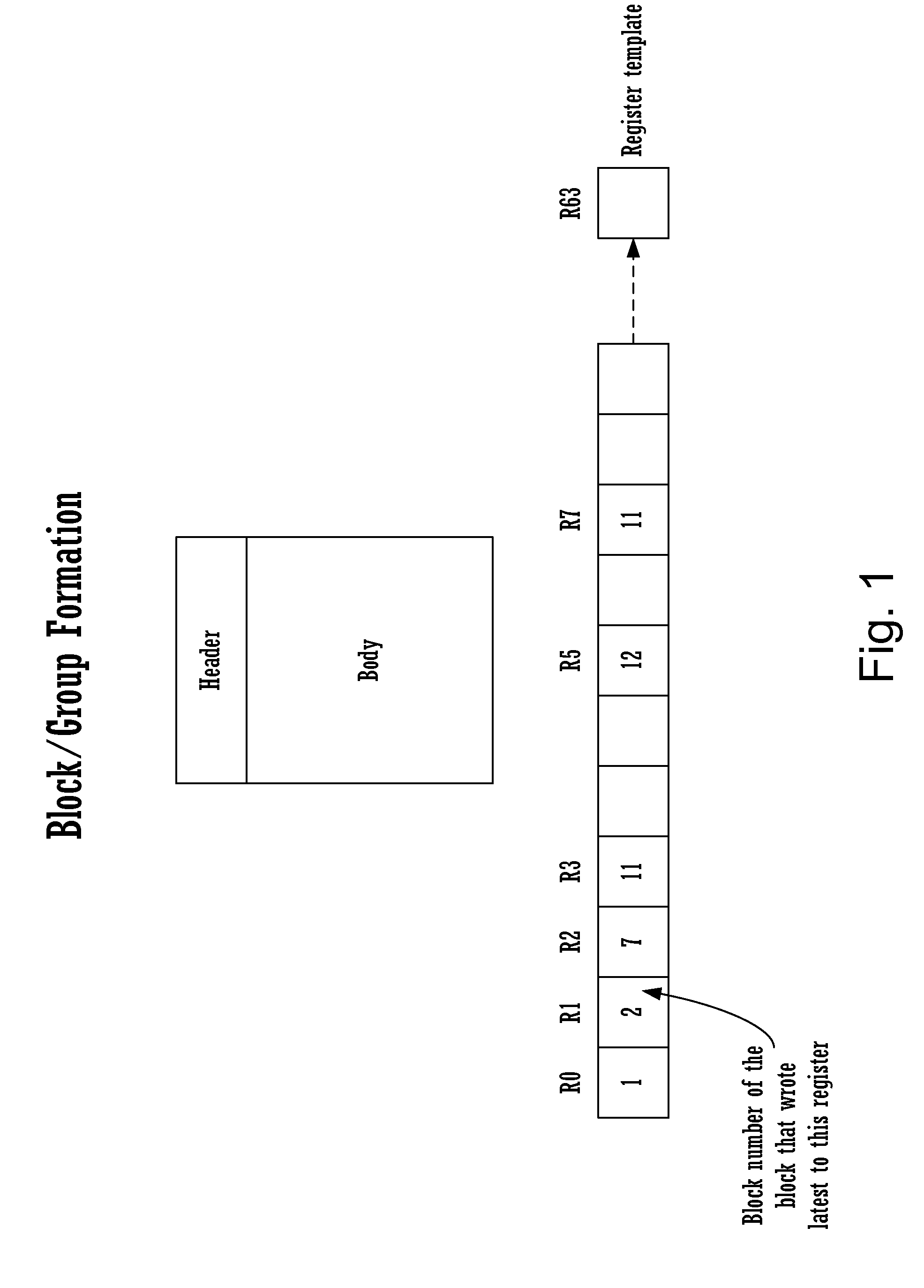
A method for dependency broadcasting through a block organized source view data structure. The method includes receiving an incoming instruction sequence using a global front end; grouping the instructions to form instruction blocks; using a plurality of register templates to track instruction destinations and instruction sources by populating the register template with block numbers corresponding to the instruction blocks, wherein the block numbers corresponding to the instruction blocks indicate interdependencies among the blocks of instructions; populating a block organized source view data structure, wherein the source view data structure stores sources corresponding to the instruction blocks as recorded by the plurality of register templates; upon dispatch of one block of the instruction blocks, broadcasting a number belonging to the one block to a column of the source view data structure that relates that block and marking the column accordingly; and updating the dependency information of remaining instruction blocks in accordance with the broadcast.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Location-independent RAID group virtual block management
InactiveUS20060271734A1Overcome disadvantagesFacilitating instantiationMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionRAIDOperational system
A storage operating system is configured to assign volume block numbers (VBNs) to a volume. The system has a plurality of disks, and each disk of the plurality of disks is assigned disk block numbers (DBNs). A raidmap is configured to map the VBNs to the DBNs of the plurality of physical disks, the mapping for a particular disk stored in a disk label for the particular disk. The disk label for the particular disk is then written to the particular disk.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Hybrid CNC control system
InactiveUS20020091460A1Accurate recordReliable processingSpecial data processing applicationsNumerical controlVisual BasicNumerical control
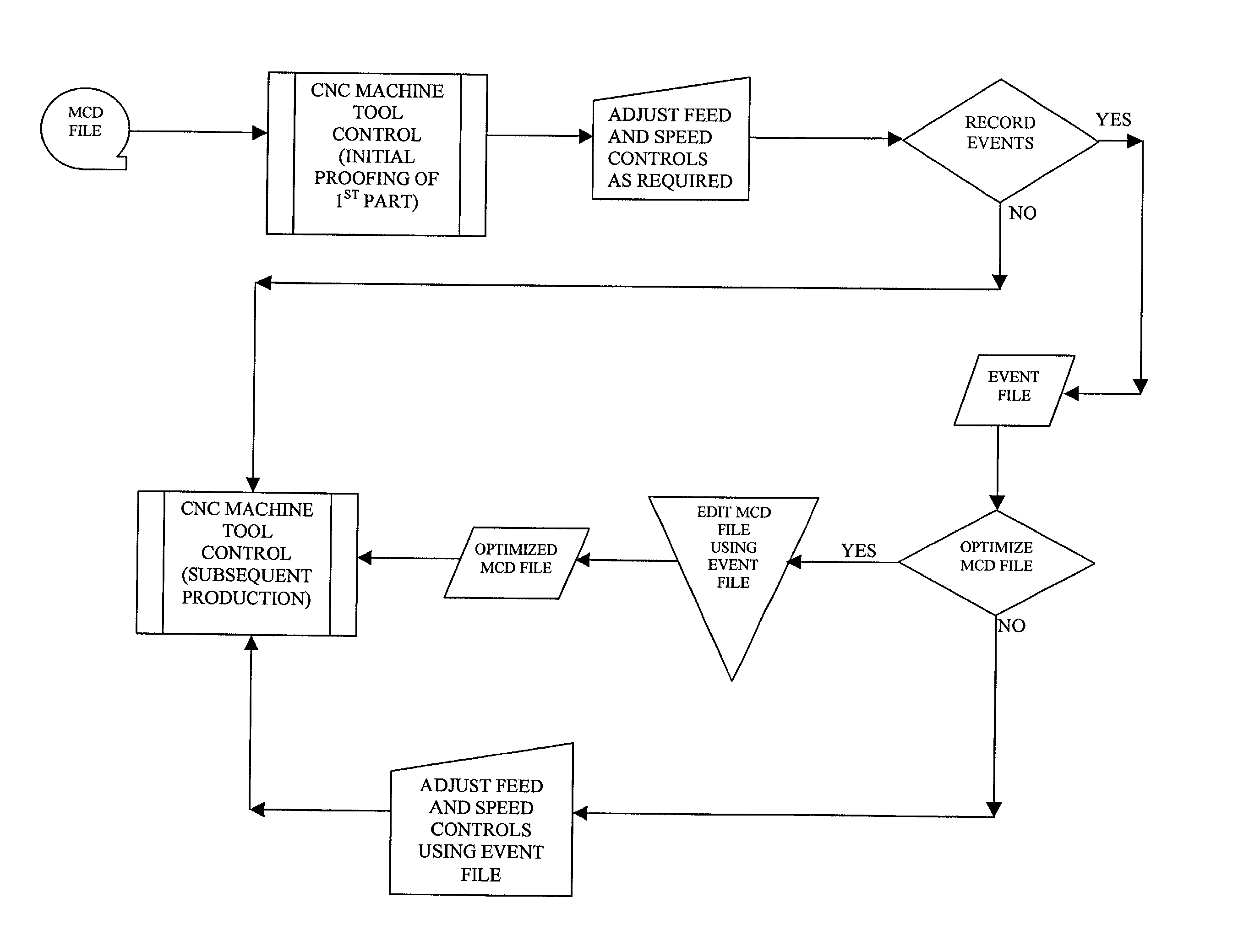
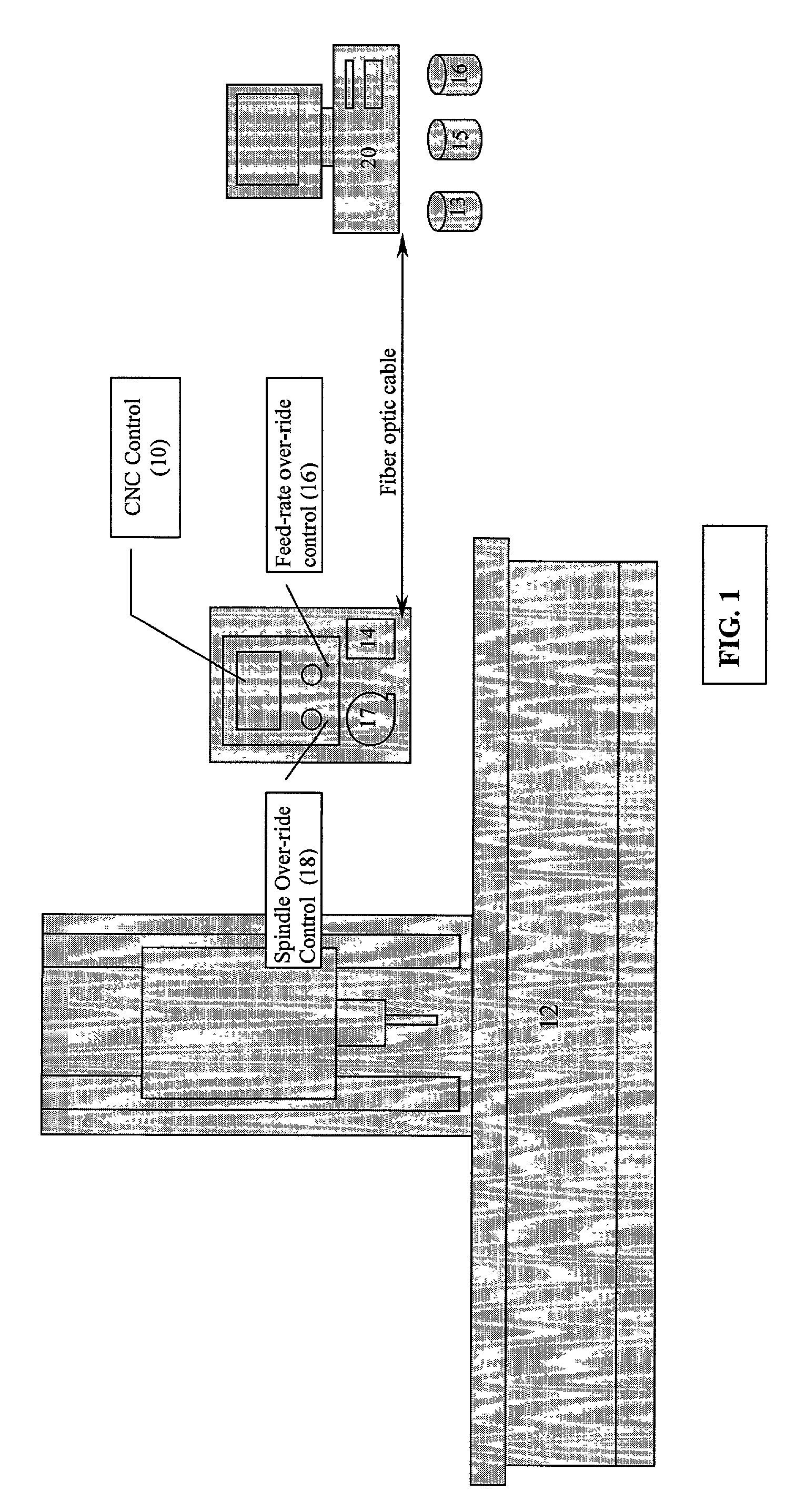
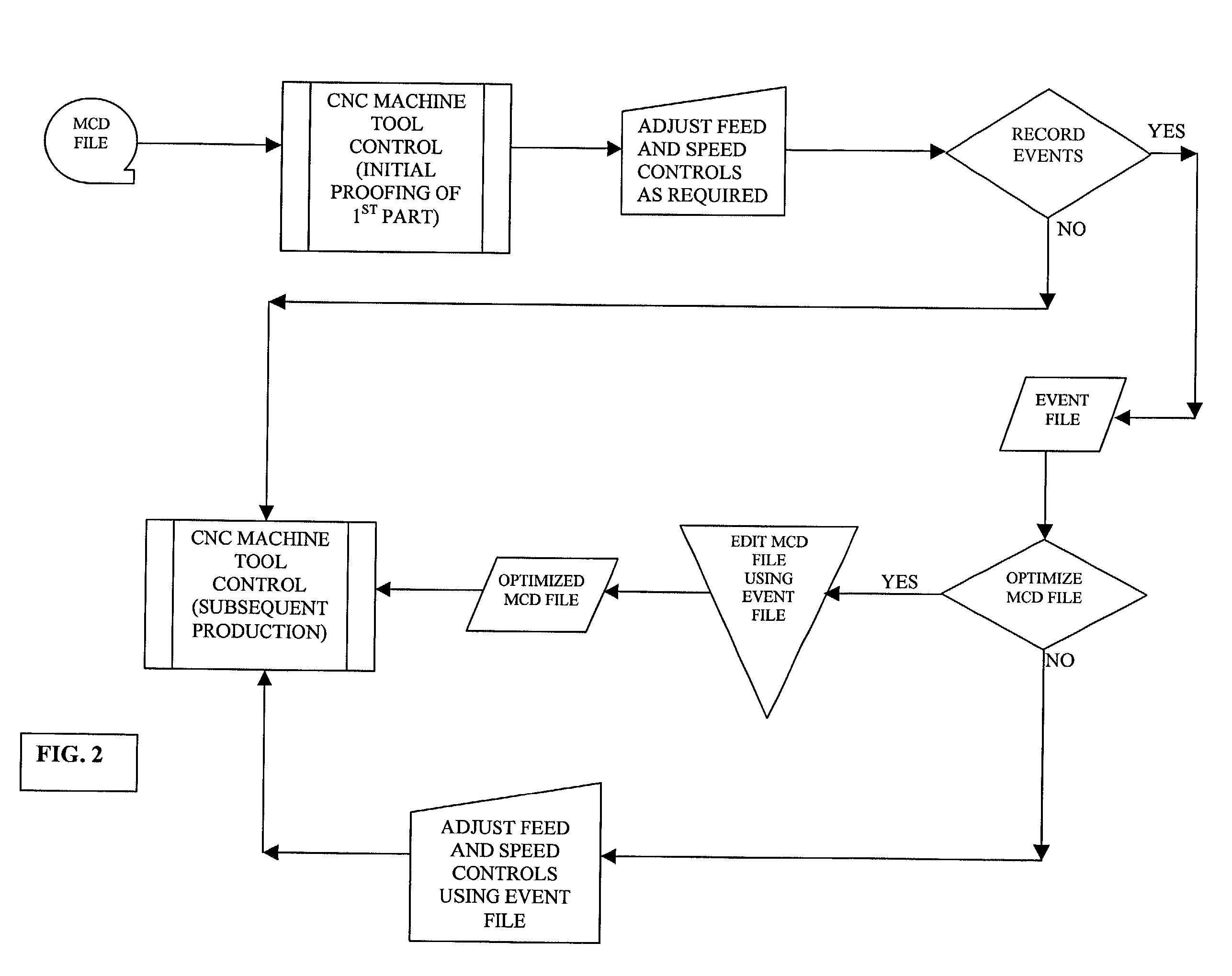
The present invention demonstrates an improved CNC Control system, which integrates operator-induced changes into the pre-programmed CNC machining process. The improved CNC Control system develops a Human Activity Storage Program (HASP), which is used for subsequent production in conjunction with and simultaneously with the Numerical Control Program thereby enhancing the production process by integrating the skilled machinist's input into the production process. The numerical control program of a CNC machine is interfaced with an IBM compatible personal computer (PC) to make information relative to the block number, feed-rate and / or spindle speed over-ride values available at the personal computer. If the CNC Control has been re-configured properly (with regard to the ladder interface and operating system) a PC computer is not required. During the machining of a part the machine operator will manually over-ride the feed-rate and / or the spindle speed to optimize machining performance. Through the use of VISUAL BASIC OR C++programming modules and routines, the spindle speed and feed-rate controls (located at the CNC Control) are polled at frequent or 5OO ms intervals. The status or over-ridden values of these controls are correlated to the active block number in use during each polled sequence and this information is written to an "event file". After the subject part has been completed, one of two options can be used. An "edit phase" is initiated which utilizes the information in the "event file" to reconstruct the MCD file. After the edit phase is complete, the resultant output "Optimized MCD" can be used to produce like parts with confidence that all motion is running at peak performance and all programmed trajectories are maintained. The cycle can be repeated again (if desired) to ensure even greater efficiency while cutting. In the alternative, the event file can be employed to "command" the CNC Control with respect to feed-rate and / or spindle speed over-ride settings.
Owner:ALLEN WILLIAM D
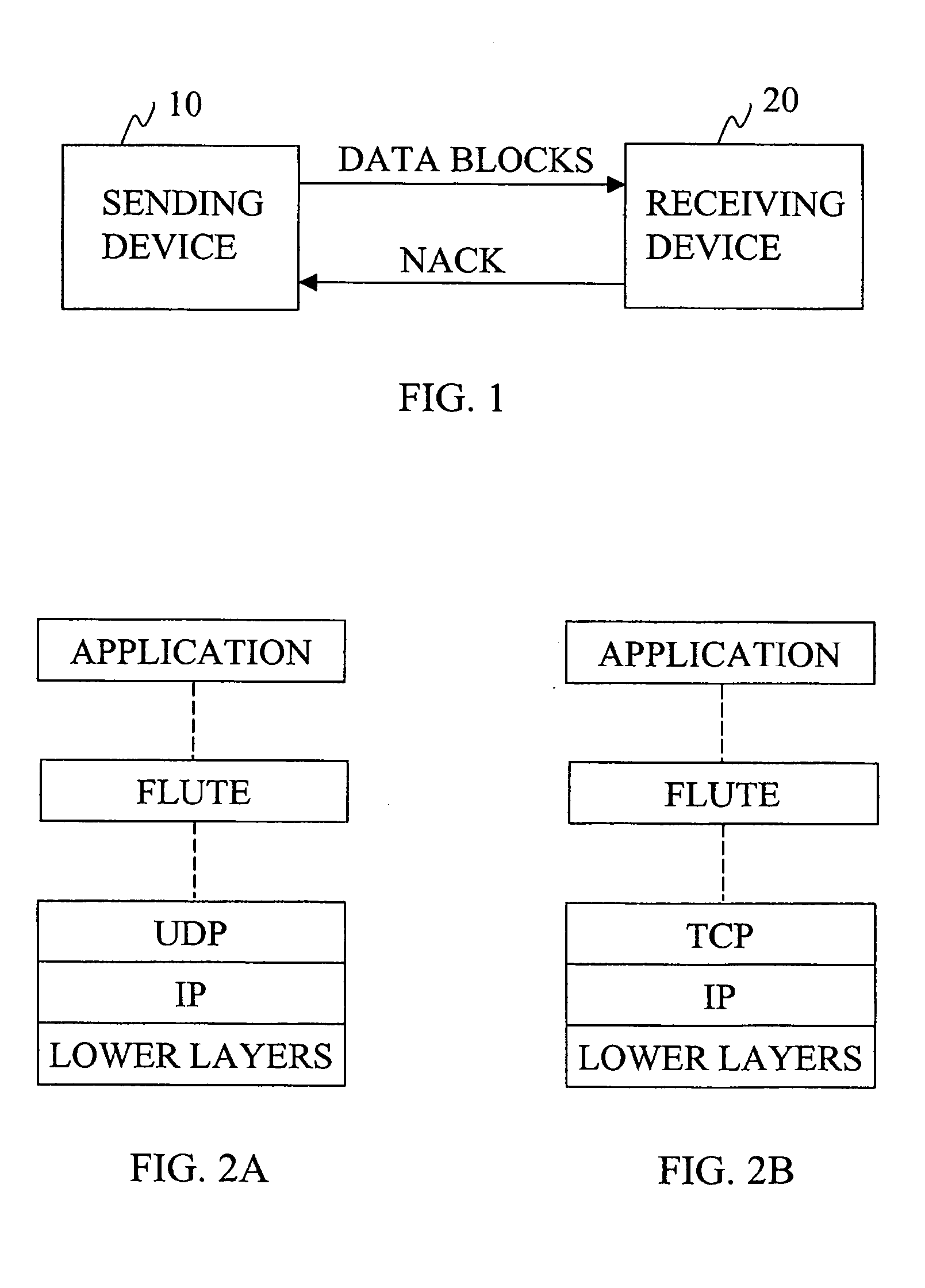
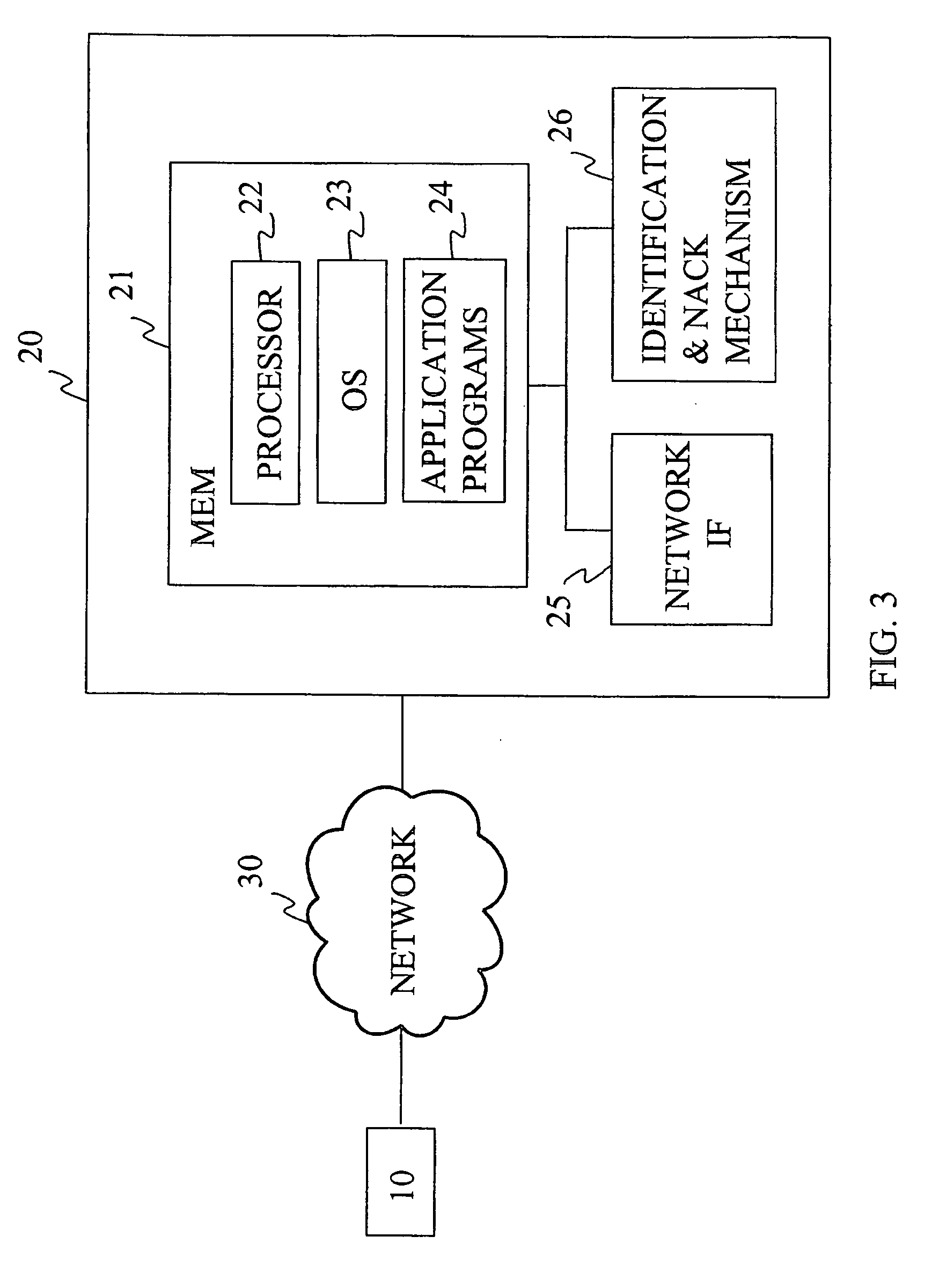
Identification and re-transmission of missing parts
ActiveUS20050182842A1Accurate identificationSpecial service provision for substationBroadcast with distributionDatabaseBlock number
The invention relates to a method for file delivery in a system capable of one-to-many transmission, the method comprising transferring one or more data blocks from a sender to at least one receiver, identifying a data block expected to be received but not received at all or incorrectly received at the receiver, and taking action to re-transmit said data block. In the method, said identification is performed on the basis of a block number, an encoding identifier and certain other identification information.
Owner:CONVERSANT WIRELESS LICENSING LTD
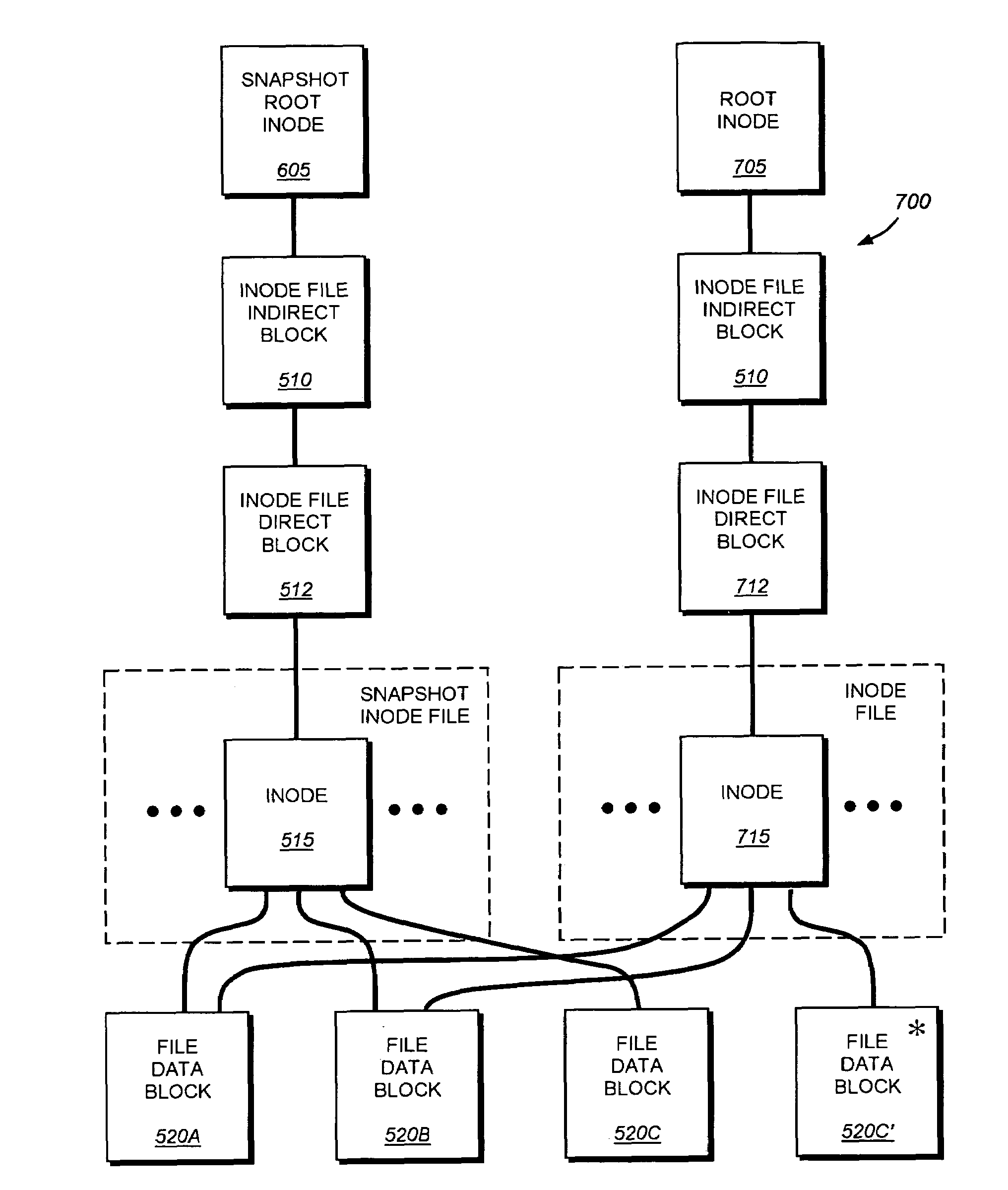
Identifying snapshot membership for blocks based on snapid
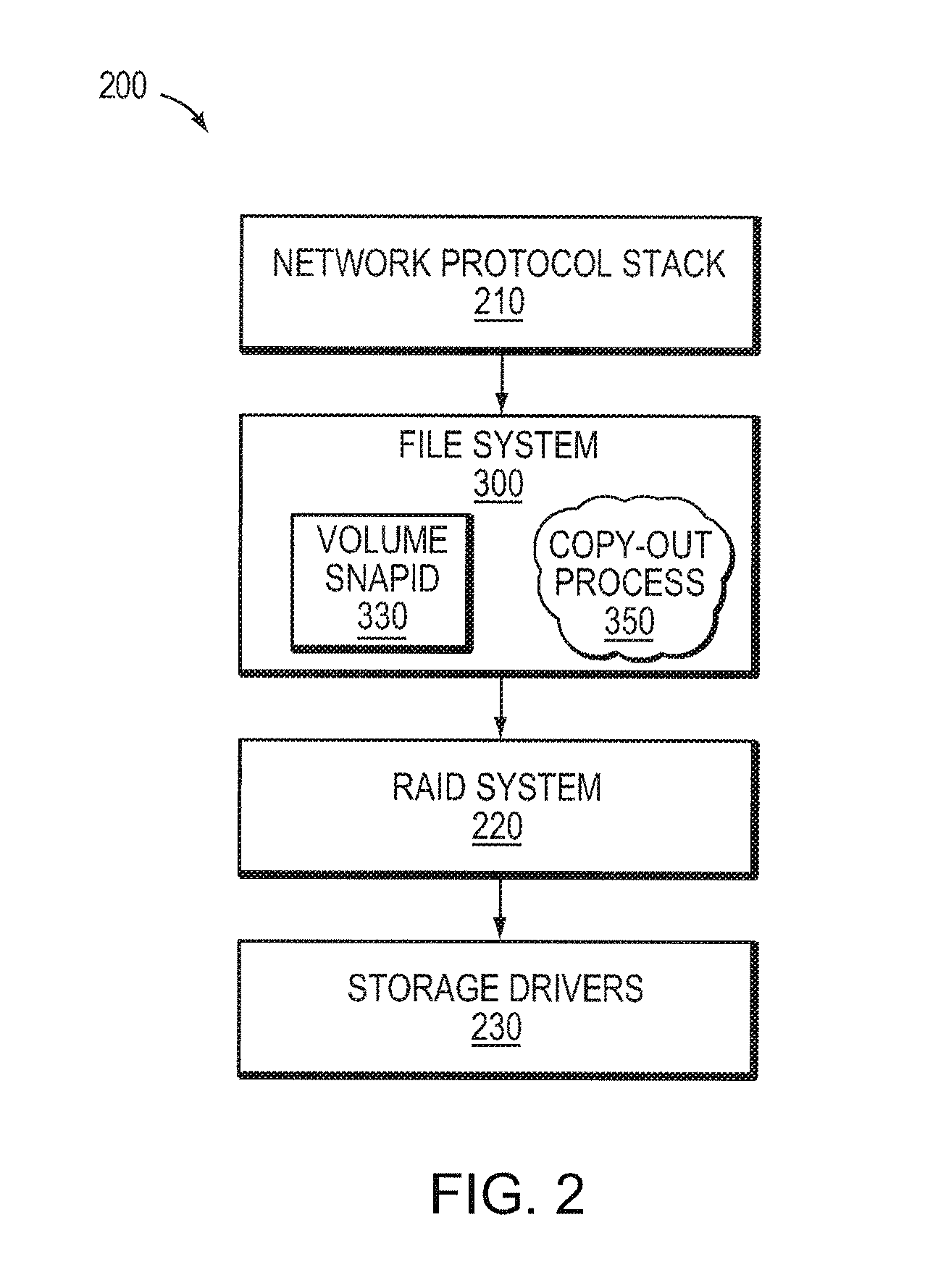
ActiveUS7849057B1Efficiently manage and organizeEasy to operateDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsFile systemSelf-balancing binary search tree
An on-disk structure of a file system has the capability to efficiently manage and organize data containers, such as snapshots, stored on a storage system. A multi-bit, monotonically increasing, snapshot identifier (“snapid”) is provided that represents a snapshot and that increases every time a snapshot is generated for a volume of the storage system. The snapid facilitates organization of snapshot metadata within, e.g., a data structure used to organize metadata associated with snapshot data. In the illustrative embodiment, the data structure is a balanced tree structure configured to index the copy-out snapshot data blocks. The snapid is also used to determine which blocks belong to which snapshots. To that end, every block that is used in a snapshot has an associated “valid-to” snapid denoting the newest snapshot for which the block is valid. The oldest snapshot for which the block is valid is one greater than the valid-to field of the next older block at the same file block number.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Method and apparatus for accessing a striped configuration of disks
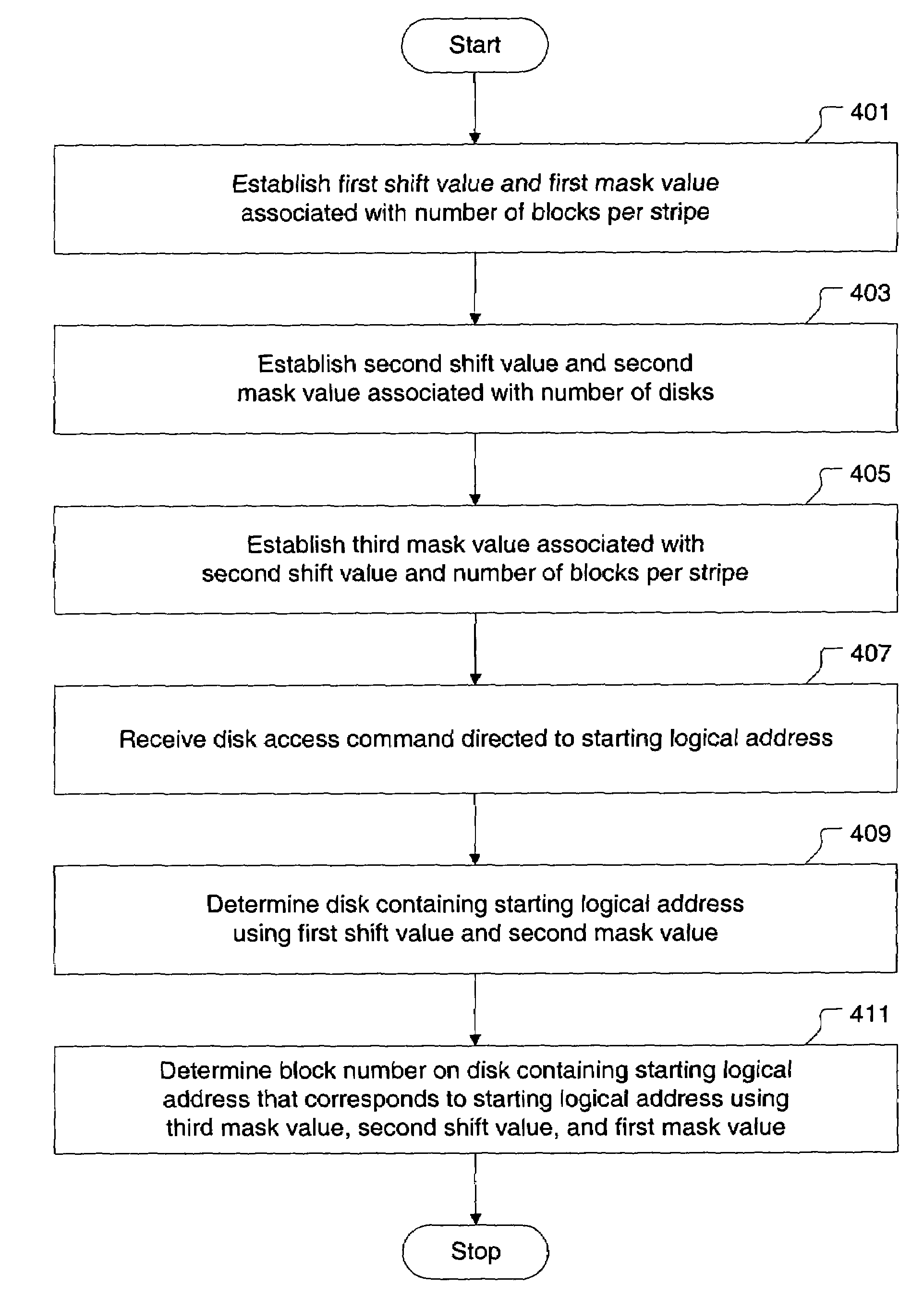
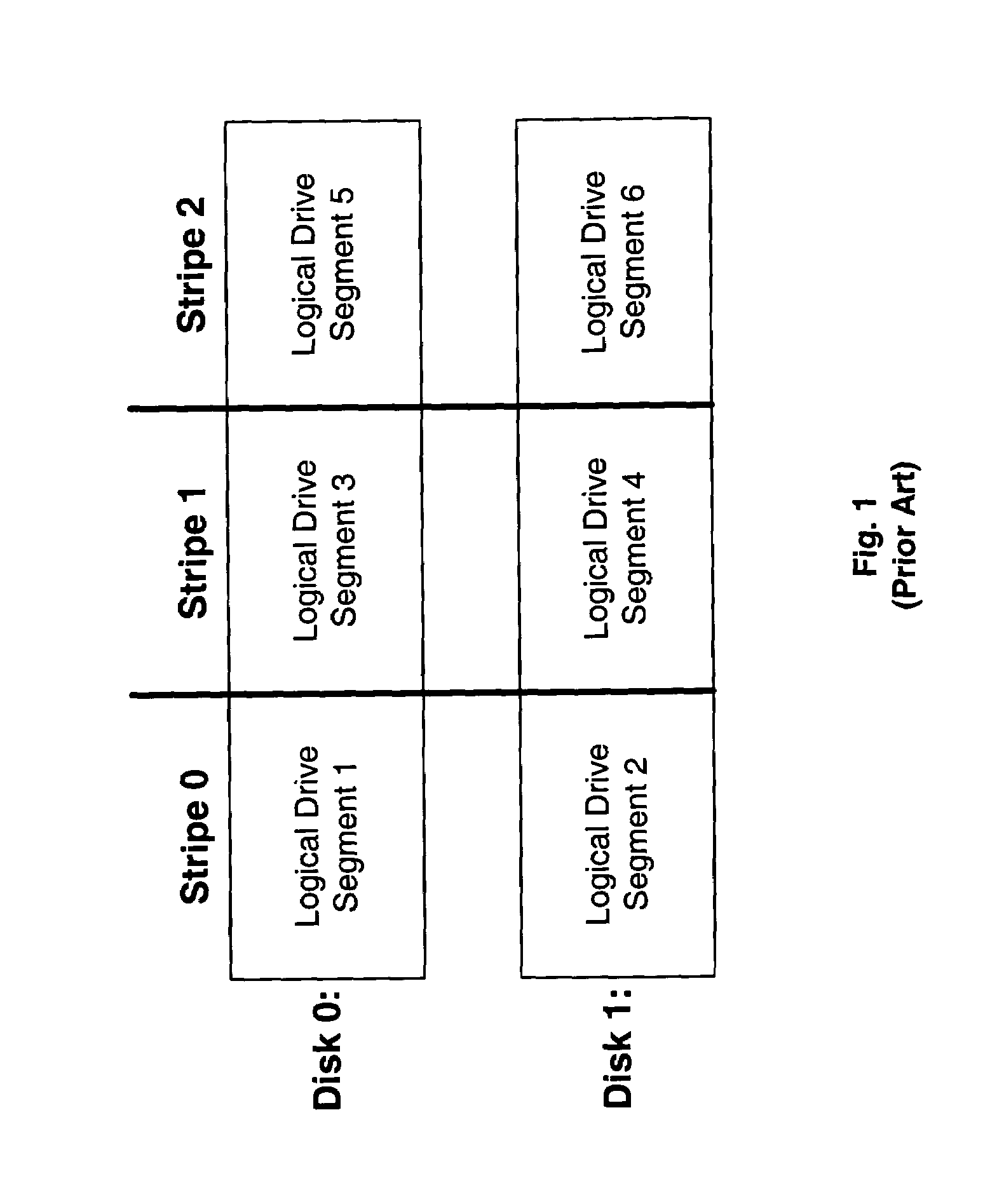
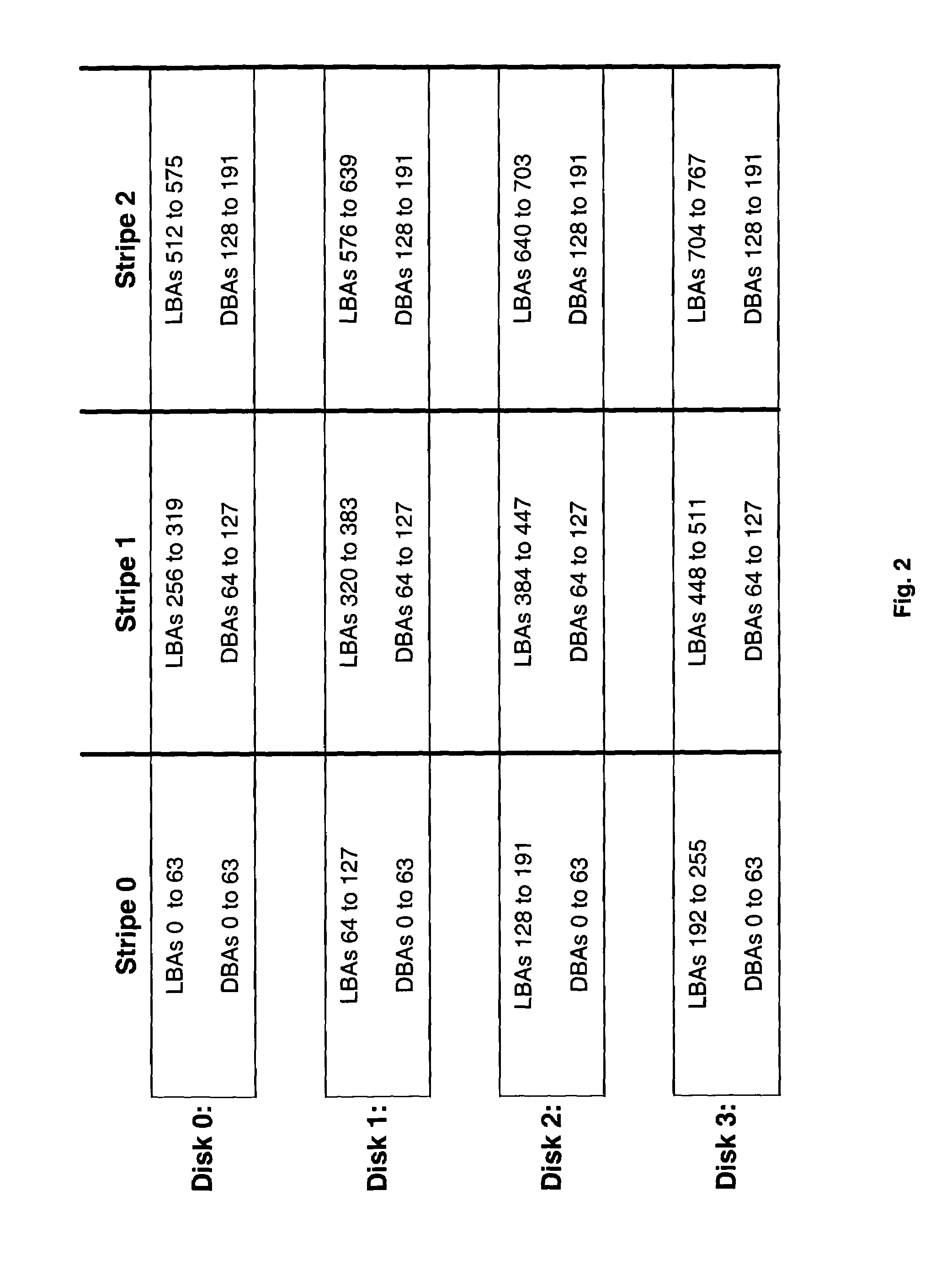
InactiveUS7406563B1Efficient processingEasy to implementMemory loss protectionInput/output processes for data processingRAIDModulo operation
Broadly speaking, a method and an apparatus is provided for processing access commands directed to a striped configuration of disks. More specifically, the method and apparatus determines a physical block address corresponding to a logical address in a redundant array of independent disks level 0 (RAID 0) system. Bit-level operations are incorporated to determine a disk in the RAID 0 system and a block number on the disk that corresponds to a particular logical address. Since the bit-level operations replace traditionally required division and modulo operations, the method and apparatus provides for more efficient processing of access commands directed to the RAID 0 system.
Owner:PMC-SIERRA
Snapshot storage and data recovery method of continuous data protection system
ActiveCN101777016AImprove storage efficiencySave storage spaceMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRedundant operation error correctionRecovery methodBinary tree
The invention discloses a snapshot storage and data recovery method of a continuous data protection system. In a block-level continuous data protection (CDP) system, each write operation of a disk data block has a CDP metadata for recording the write operation. The CDP metadata is taken as a chain table node, and besides a block number containing the data block, the node also sets up three fields of forward link, uplink and downlink. On the basis, a binary tree is constructed to record the table head of each key chain table node, thereby forming a key node set, and the chain table starting from the table heads can reflect the mapping relation from each block address of the disk of the current time to the log data block. The invention can store the mapping relation of the snapshot time by using less storage space, thereby supporting more intensive data snapshot and being beneficial to shortening the data recovery time.
Owner:TOYOU FEIJI ELECTRONICS
Method for executing blocks of instructions using a microprocessor architecture having a register view, source view, instruction view, and a plurality of register templates
InactiveUS20150046686A1Register arrangementsDigital computer detailsProcessor registerParallel computing
A method for executing blocks of instructions using a microprocessor architecture having a register view, source view, instruction view, and a plurality of register templates. The method includes receiving an incoming instruction sequence using a global front end; grouping the instructions to form instruction blocks; using a plurality of register templates to track instruction destinations and instruction sources by populating the register template with block numbers corresponding to the instruction blocks, wherein the block numbers corresponding to the instruction blocks indicate interdependencies among the blocks of instructions; using a register view data structure, wherein the register view data structure stores destinations corresponding to the instruction blocks; using a source view data structure, wherein the source view data structure stores sources corresponding to the instruction blocks; and using an instruction view data structure, wherein the instruction view data structure stores instructions corresponding to the instruction blocks.
Owner:INTEL CORP
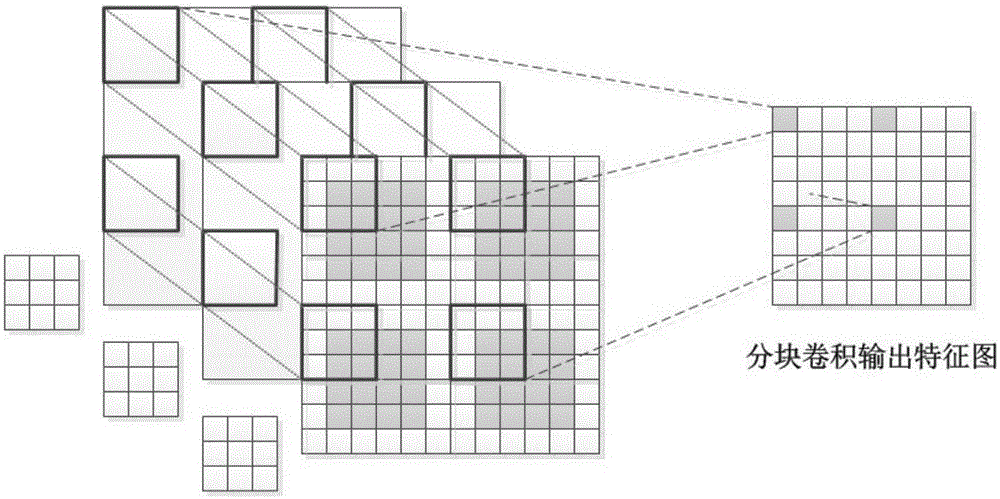
Blocked convolution optimization method and device for convolution neural network
ActiveCN107437110AResource Constraint Issues EliminatedAlleviate resource constraintsNeural architecturesPhysical realisationNerve networkAlgorithm
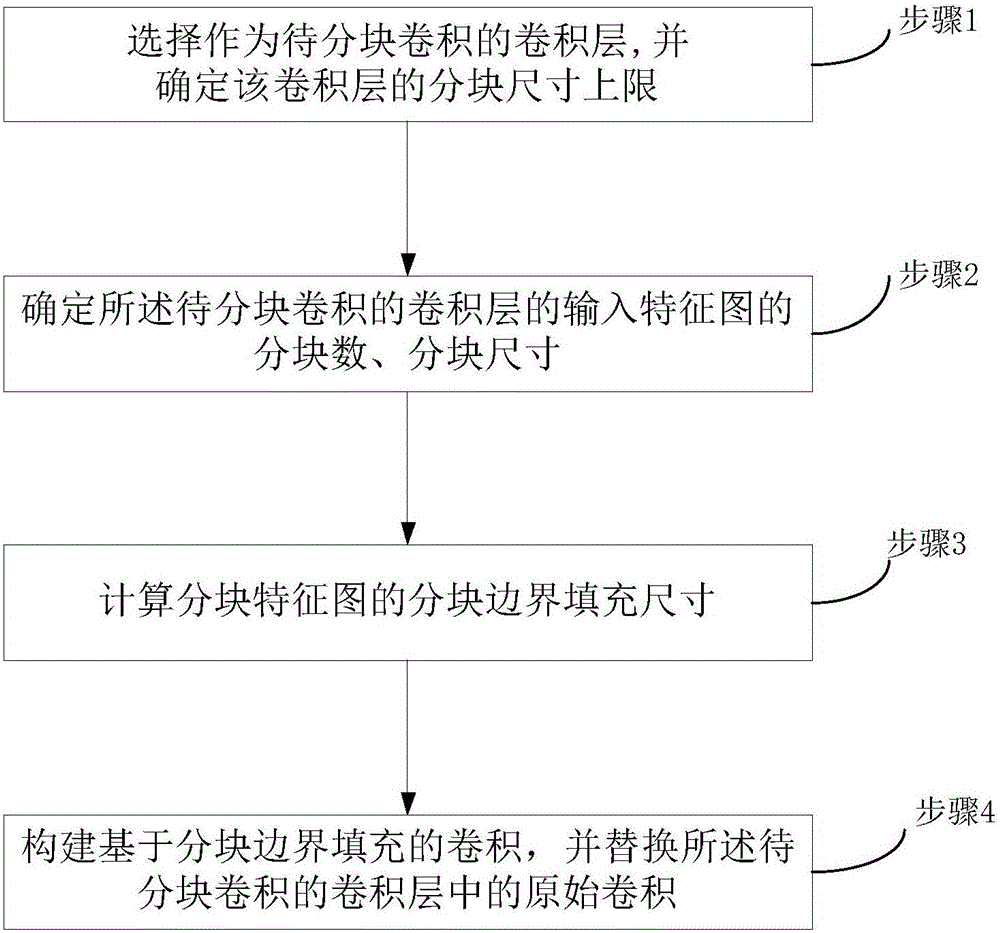
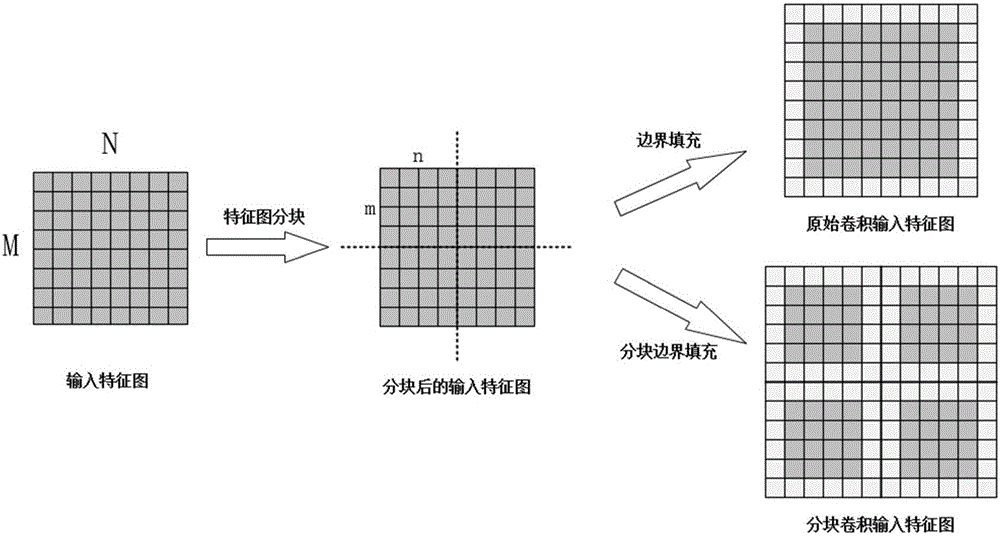
The invention relates to the field of deep neural networks and provides a blocked convolution optimization method and a device for a convolution neural network, so as to solve the bottleneck problem of convolution operation in a hardware processing system in the neural network. The optimization method comprises steps: a to-be-blocked convolution layer is selected, and the upper limit of the block size is determined; according to the upper limit of the block size, a block number and the block size of an input feature map are determined; based on the block number, the block size, the size of a convolution kernel, the size of the input feature map and the filling size of an input feature map boundary, the block boundary filling size of a block feature map is calculated; and based on the block number, the block size and the block boundary filling size, a convolution based on the block boundary filling is built to replace the original convolution. The resource constraint problem of the convolution neural network during operation of an embedded hardware platform is greatly alleviated, the burst length is improved maximally when a memory is read and written, the throughput is improved, the time delay is reduced, and the efficiency is improved.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com