Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
571 results about "Memory bus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
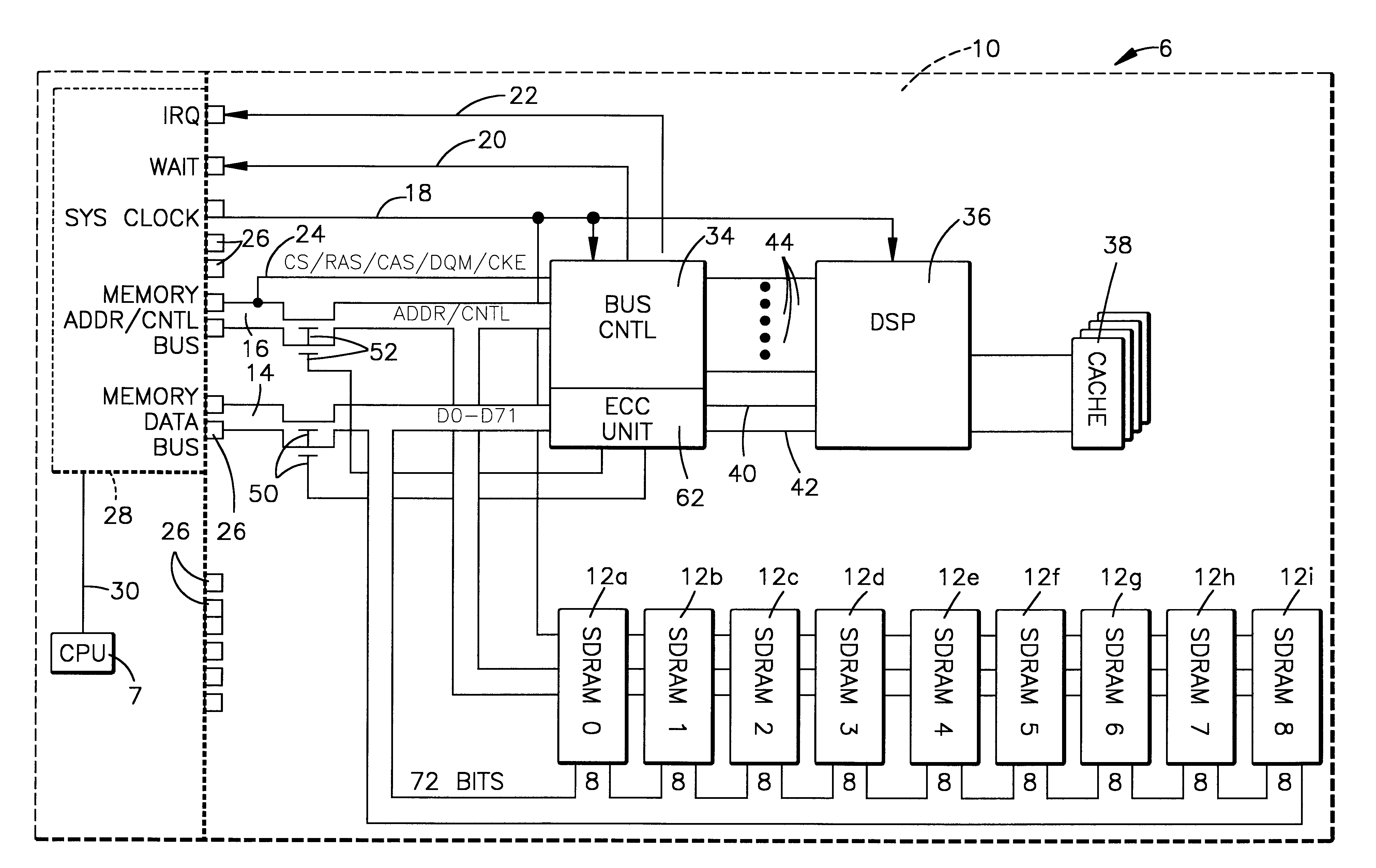
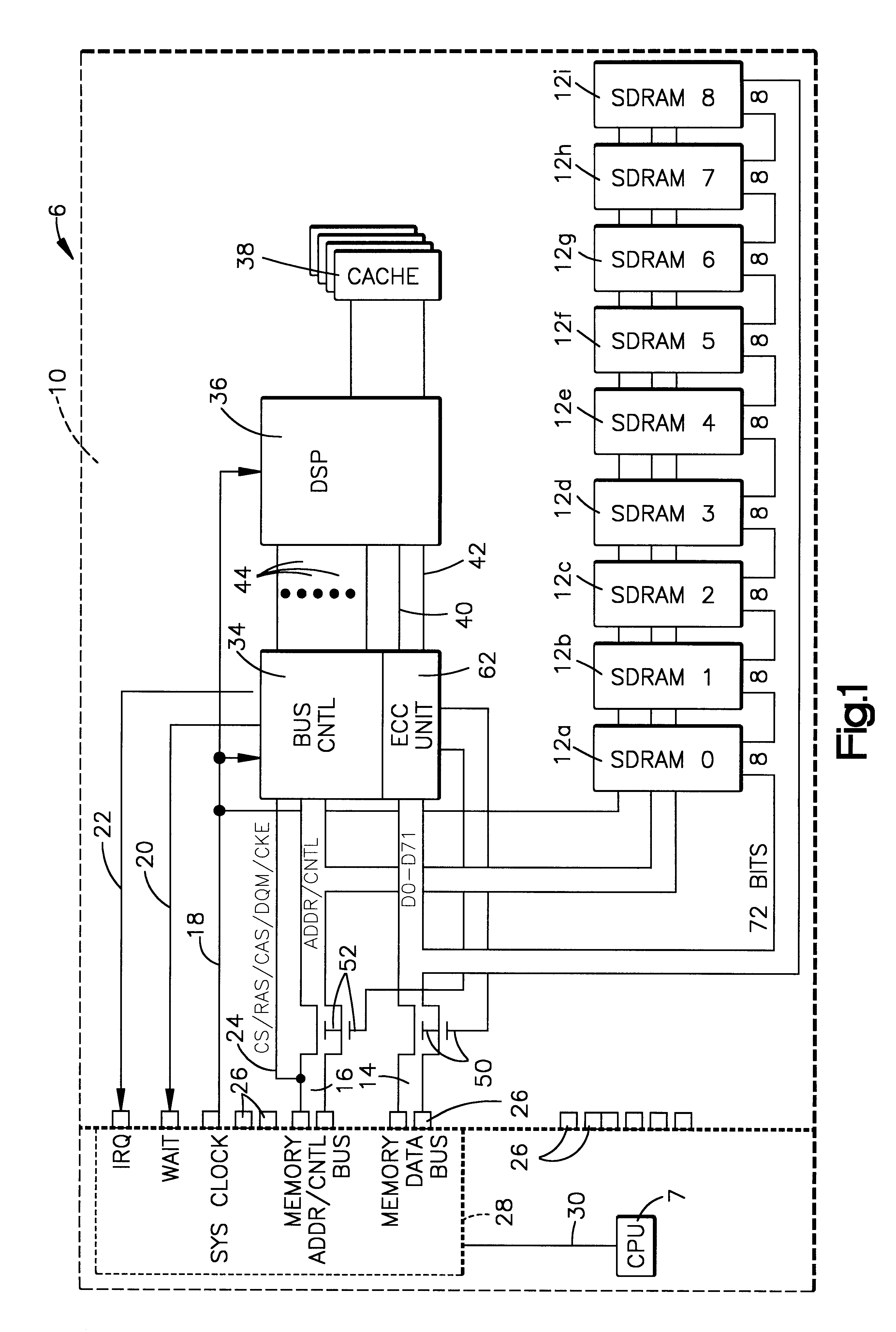
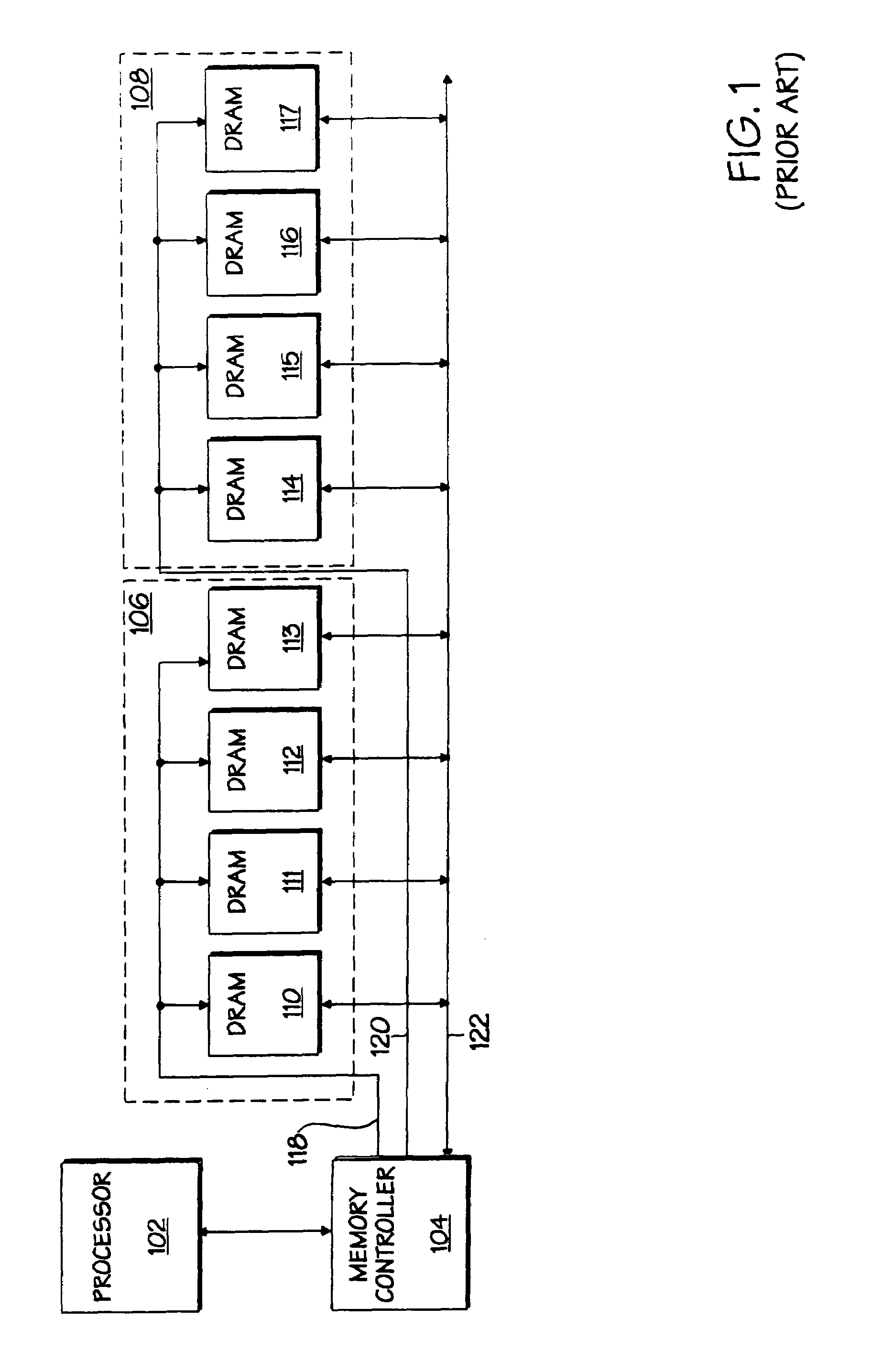
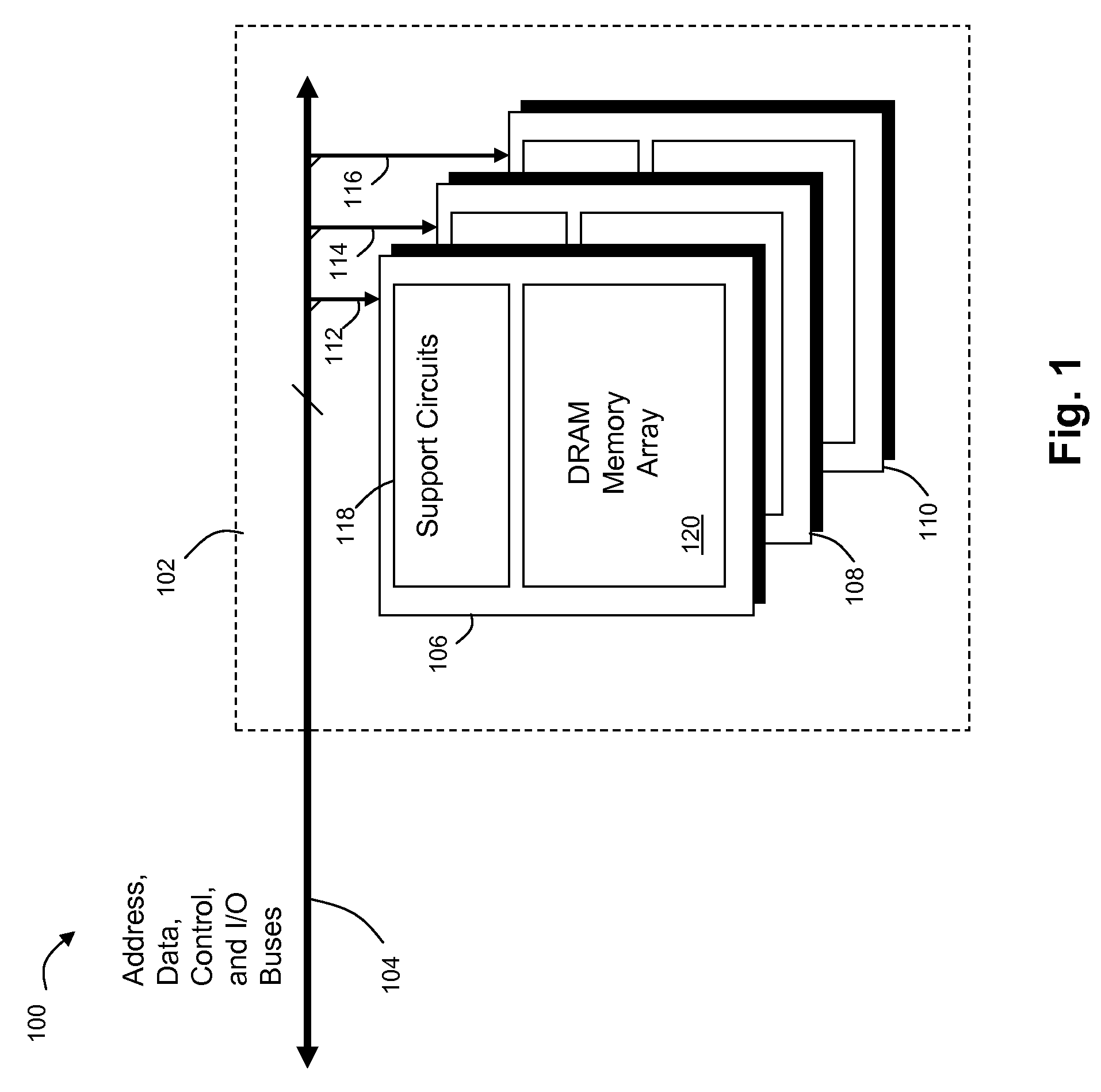
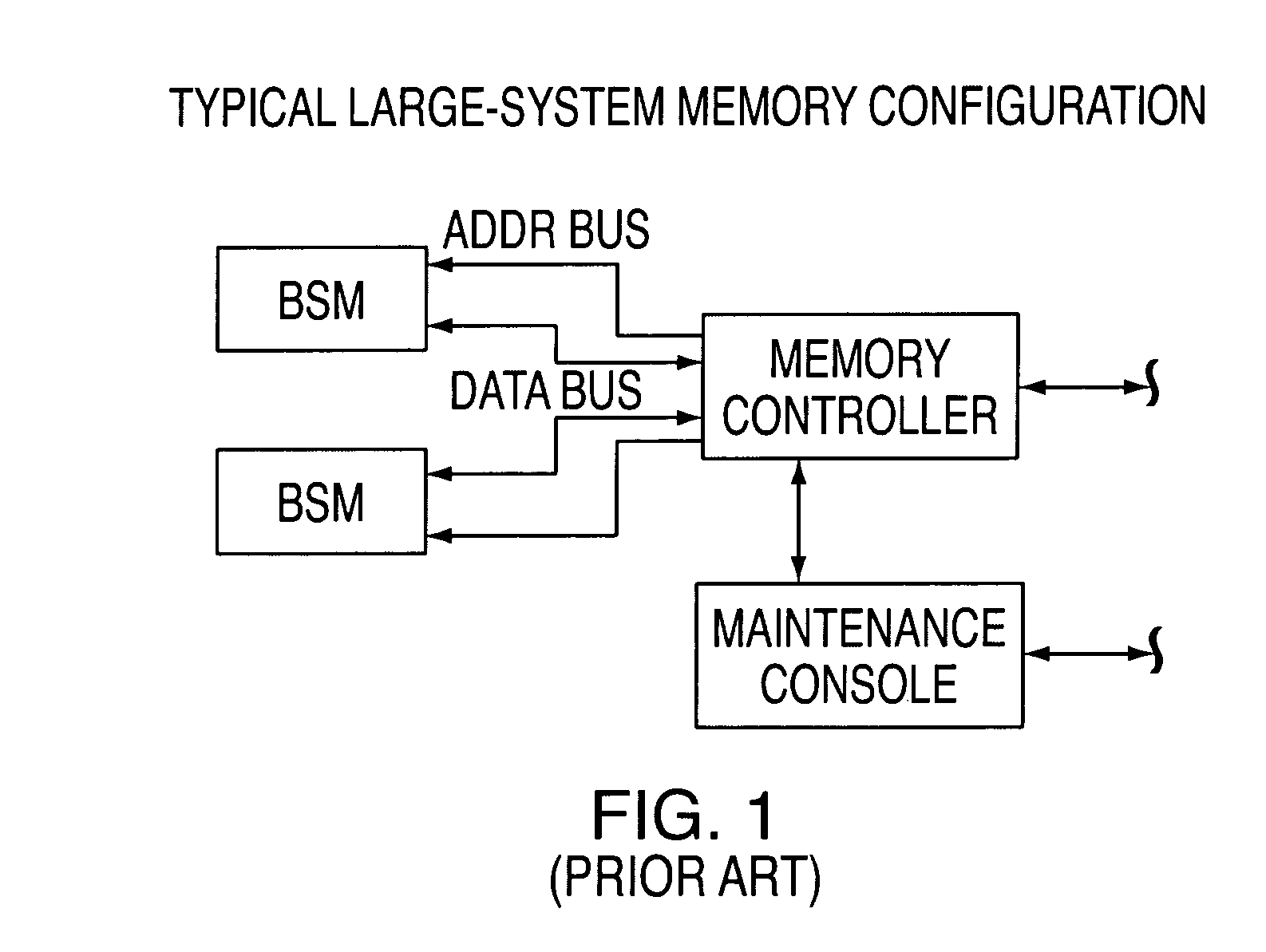
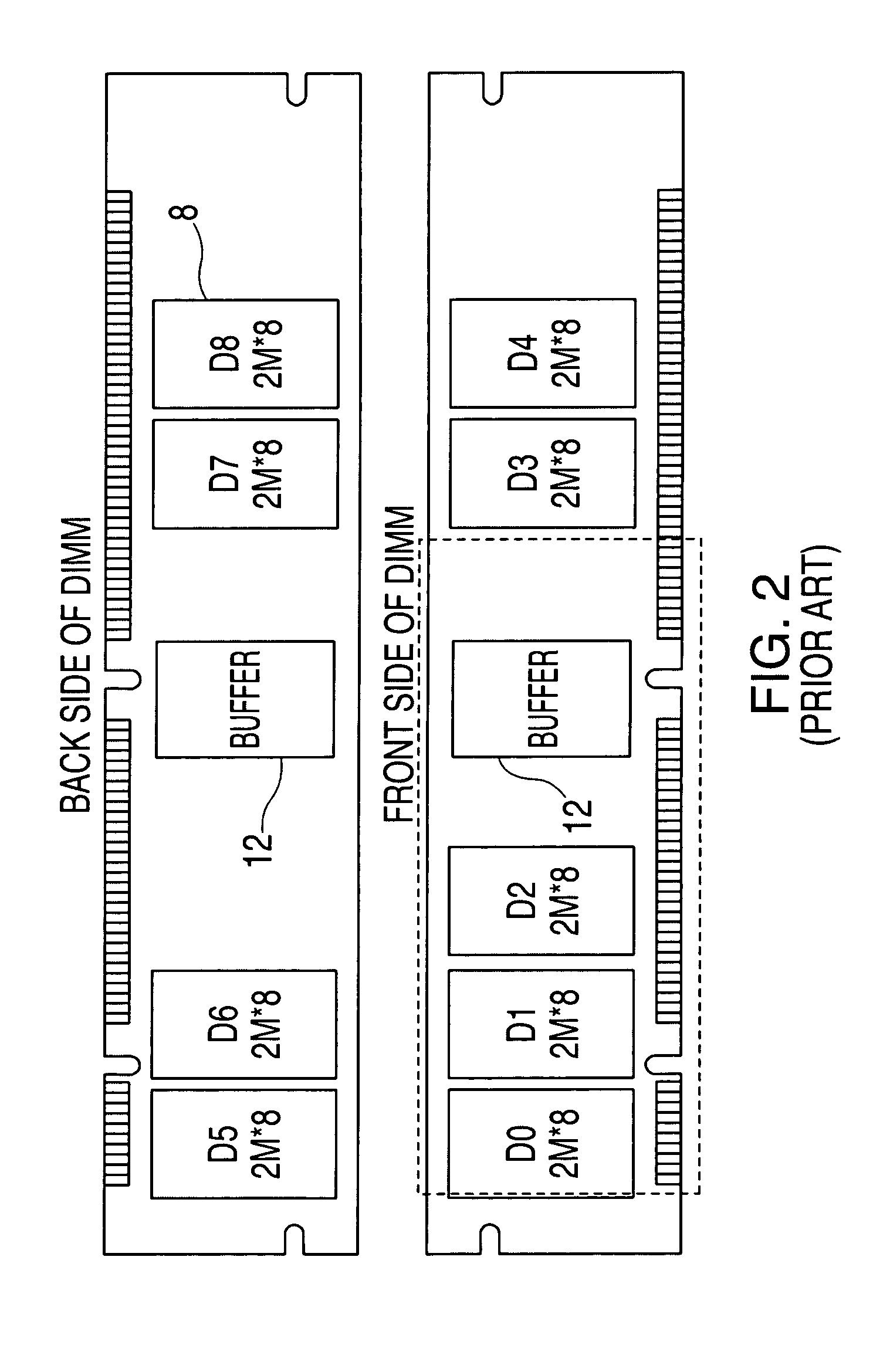
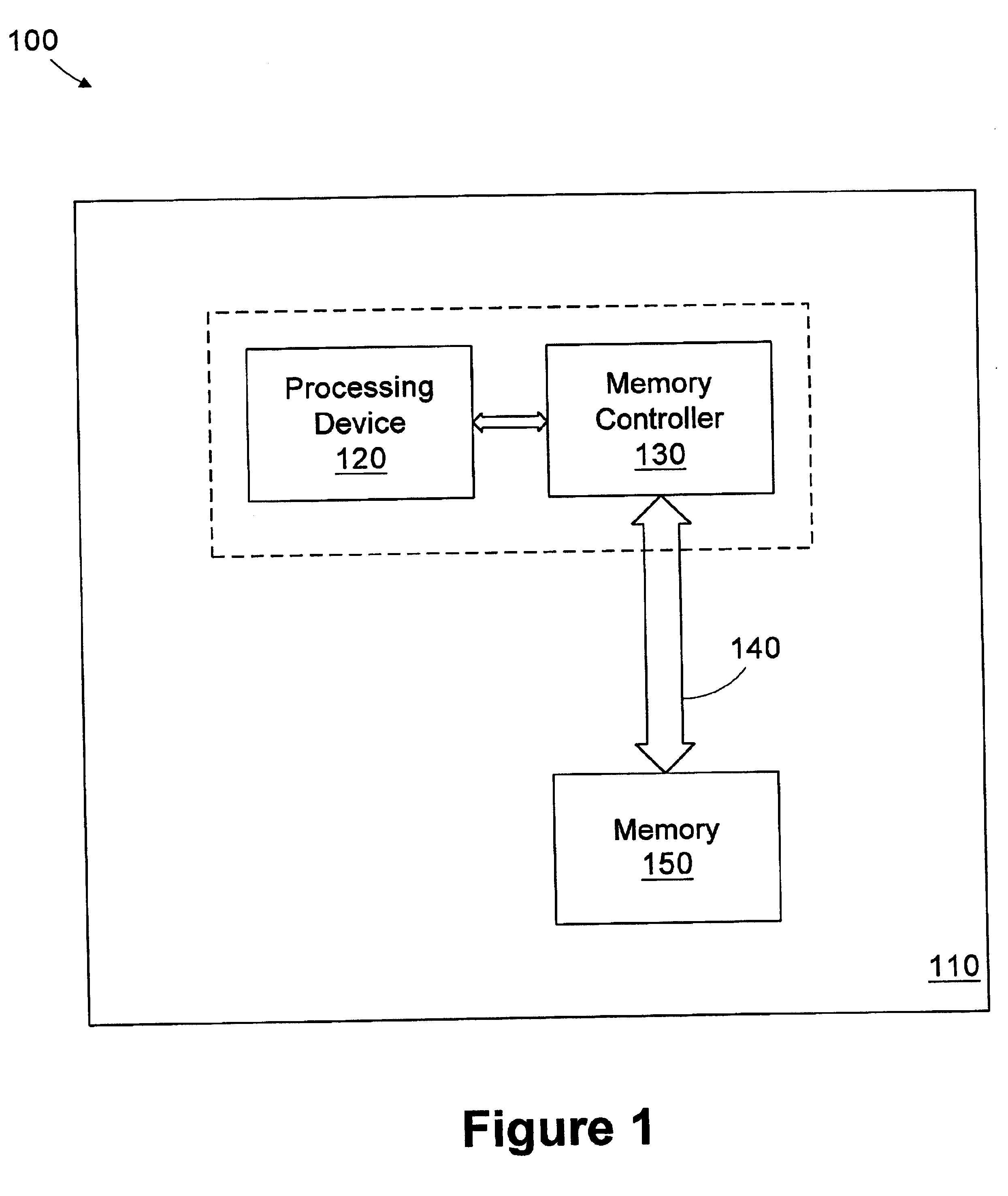
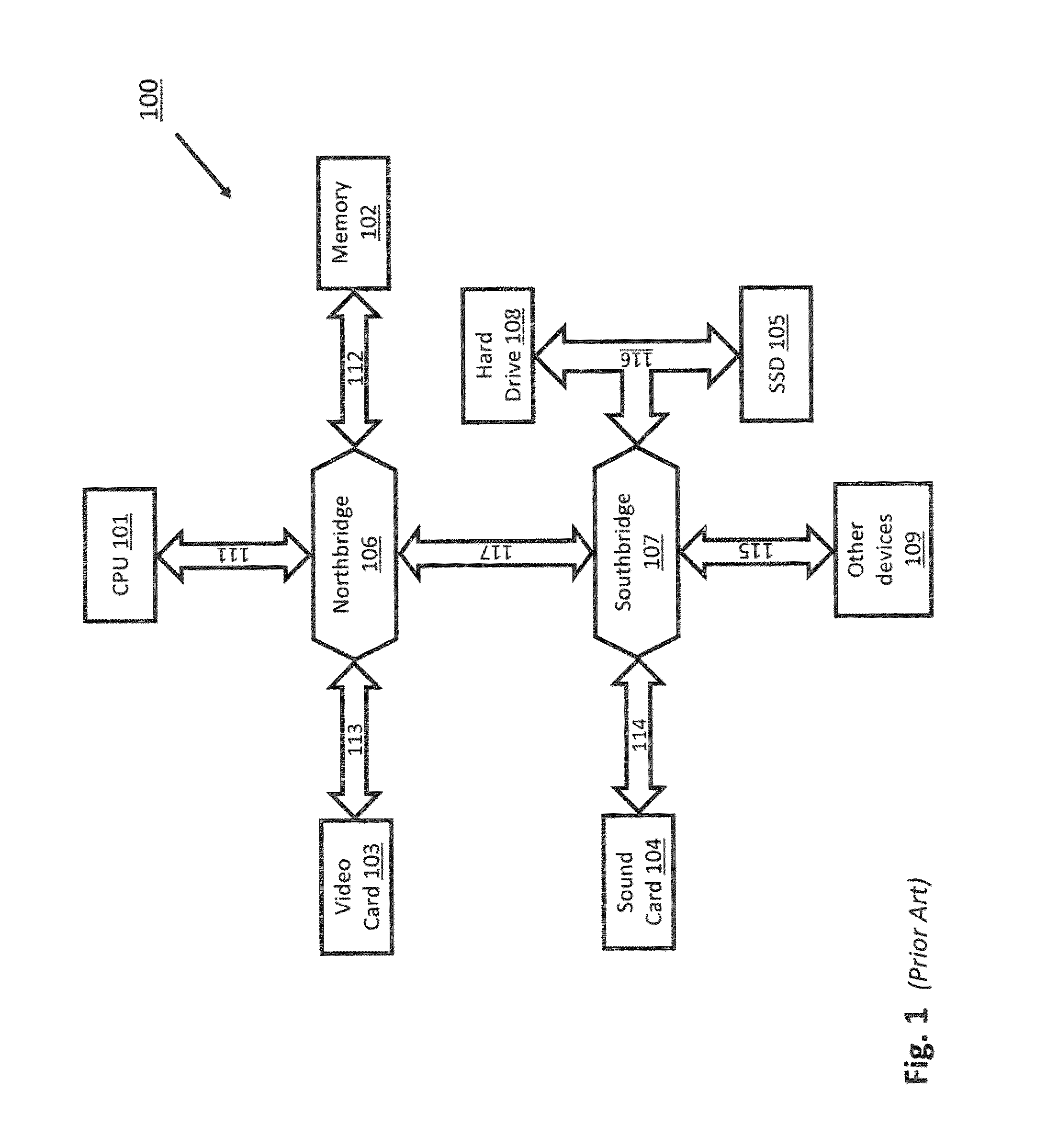
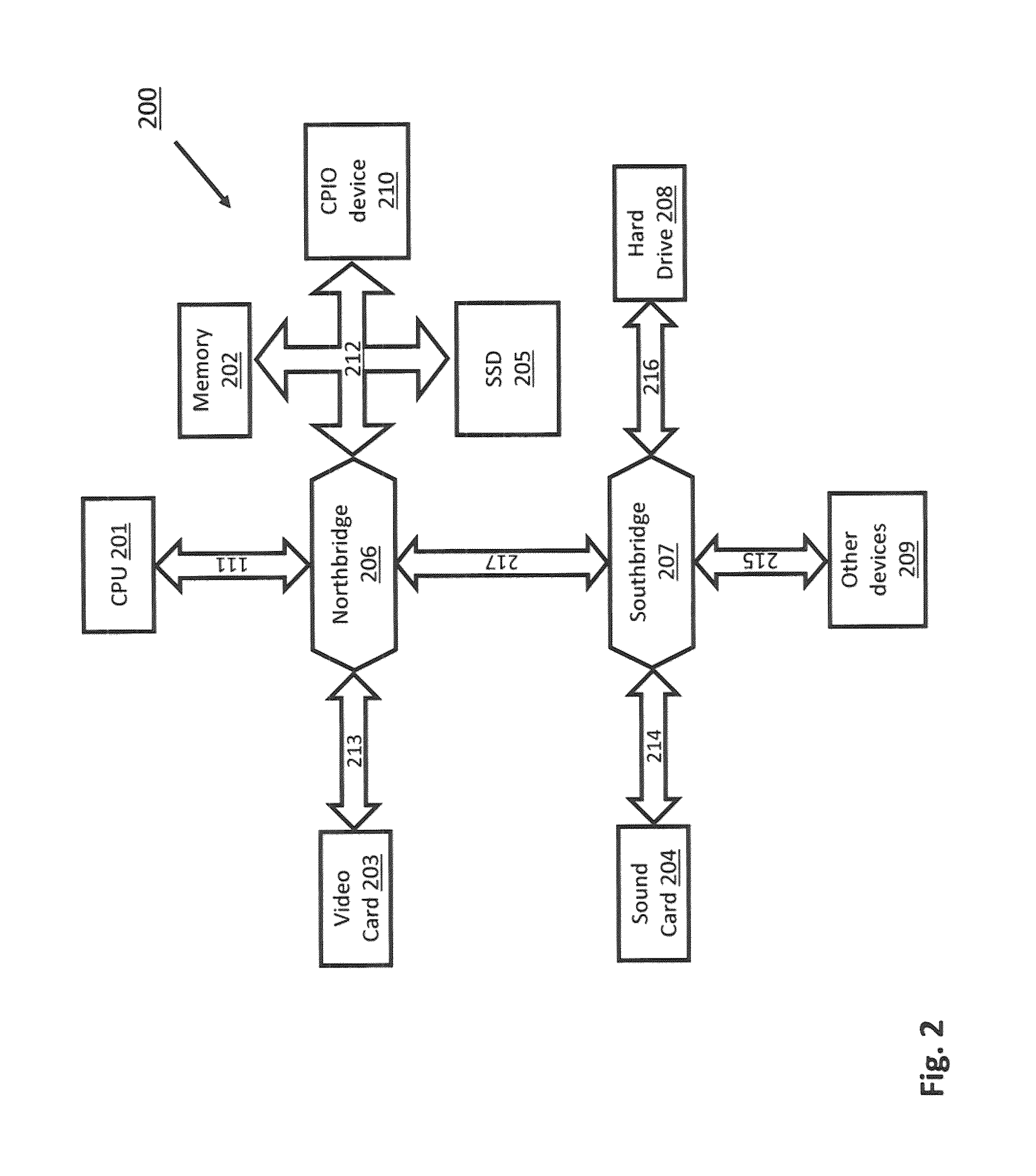
The memory bus is the computer bus which connects the main memory to the memory controller in computer systems. Originally, general-purpose buses like VMEbus and the S-100 bus were used, but to reduce latency, modern memory buses are designed to connect directly to DRAM chips, and thus are designed by chip standards bodies such as JEDEC. Examples are the various generations of SDRAM, and serial point-to-point buses like SLDRAM and RDRAM. An exception is the Fully Buffered DIMM which, despite being carefully designed to minimize the effect, has been criticized for its higher latency.
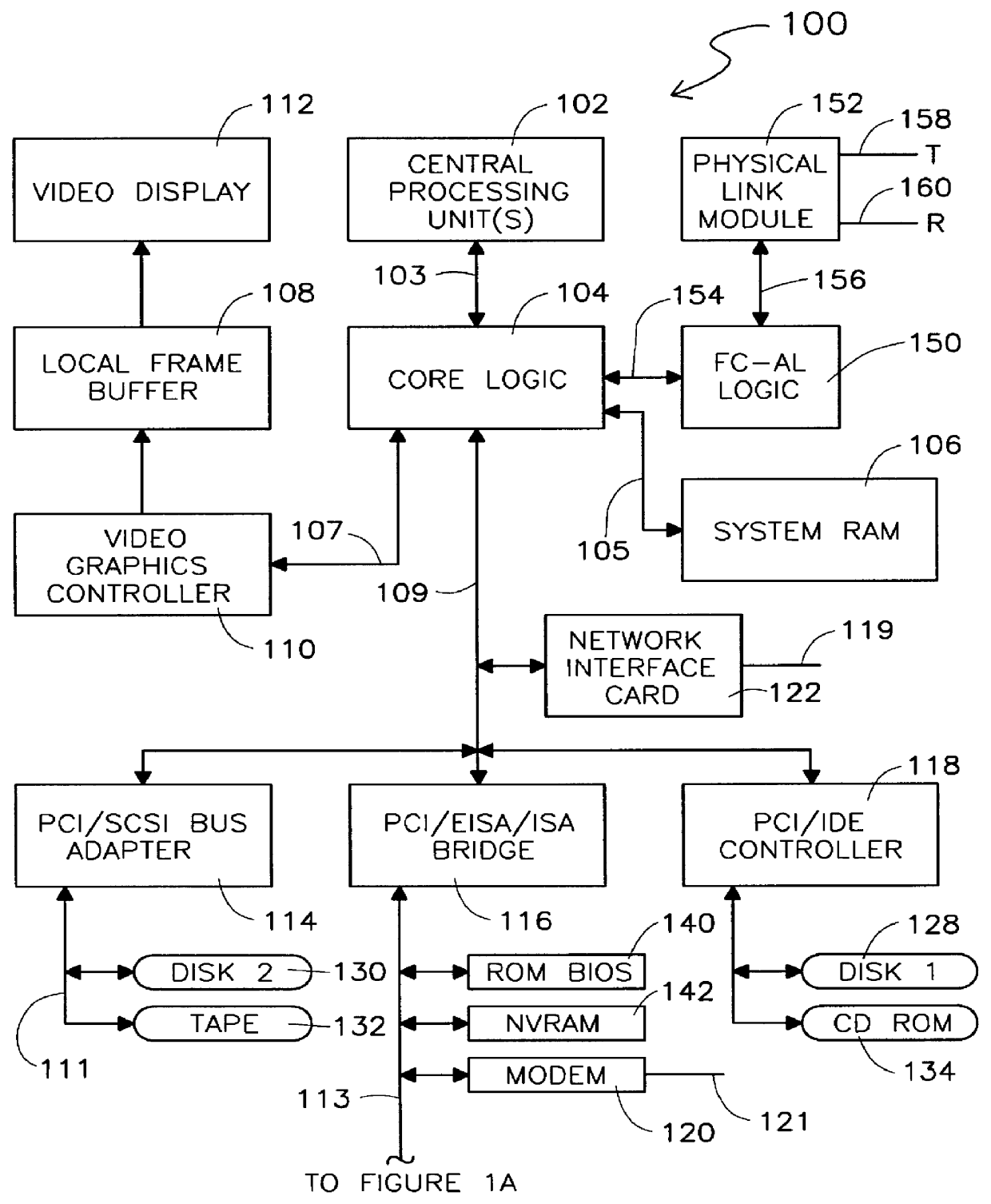
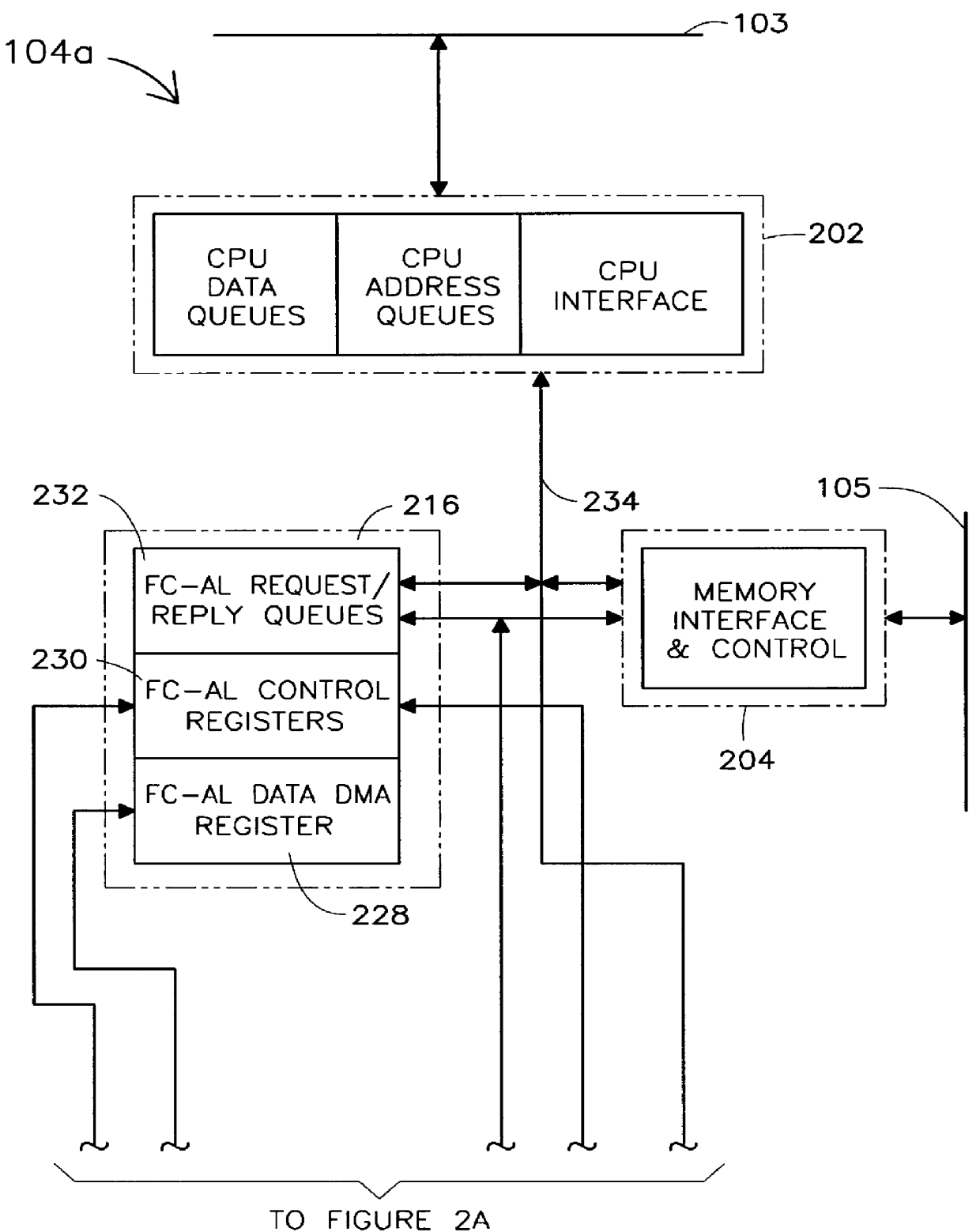
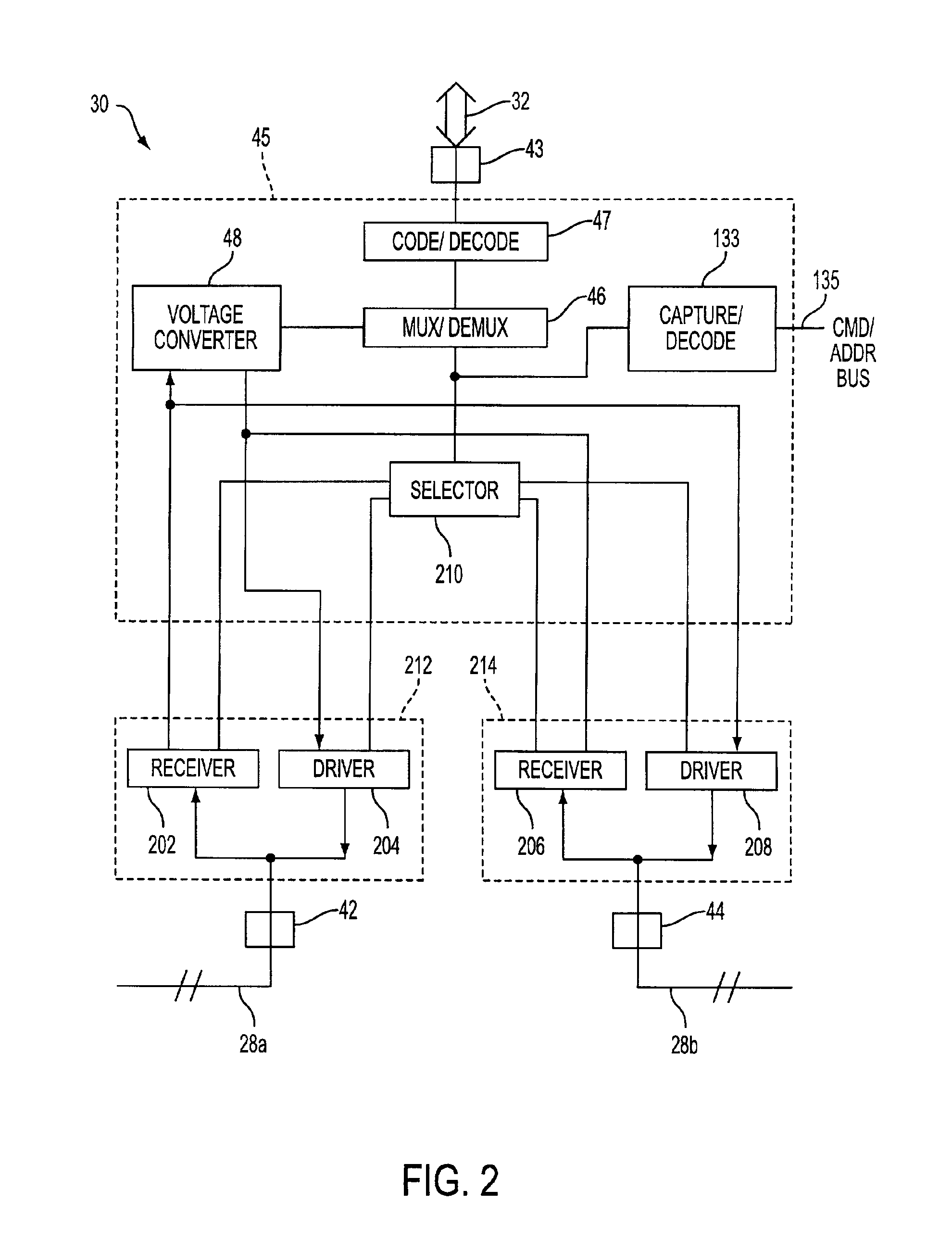
Dual purpose apparatus, method and system for accelerated graphics port and fibre channel arbitrated loop interfaces
InactiveUS6057863ALow costIncrease the number ofDigital computer detailsImage data processing detailsFiberComputer hardware
A multiple use core logic chipset is provided in a computer system that may be configured either as a bridge between an accelerated graphics port ("AGP") bus and host and memory buses, or as an interface bridge between a Fibre Channel Arbitrated Loop ("FC-AL") interface and the host and memory buses. The function of the multiple use chipset is determined at the time of manufacture of the computer system or in the field whether an AGP bus bridge or an FC-AL bridge interface is to be implemented. Selection of the type of bus bridge (AGP or FC-AL bridge interface) in the multiple use core logic chipset may be made by a hardware signal input, or by software during computer system configuration or power on self test ("POST"). Software configuration may also be determined upon detection of either an AGP or a FC-AL bridge interface device connected to the common AGP / FC-AL bus. FC-AL information may be stored in the computer system main memory using the high speed FC-AL bridge interface.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP +1
System and method of interfacing co-processors and input/output devices via a main memory system
ActiveUS20120204079A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionComputer moduleMemory bus
A system for interfacing with a co-processor or input / output device is disclosed. According to one embodiment, the system includes a computer processing unit, a memory module, a memory bus that connects the computer processing unit and the memory module, and a co-processing unit or input / output device, wherein the memory bus also connects the co-processing unit or input / output device to the computer processing unit.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
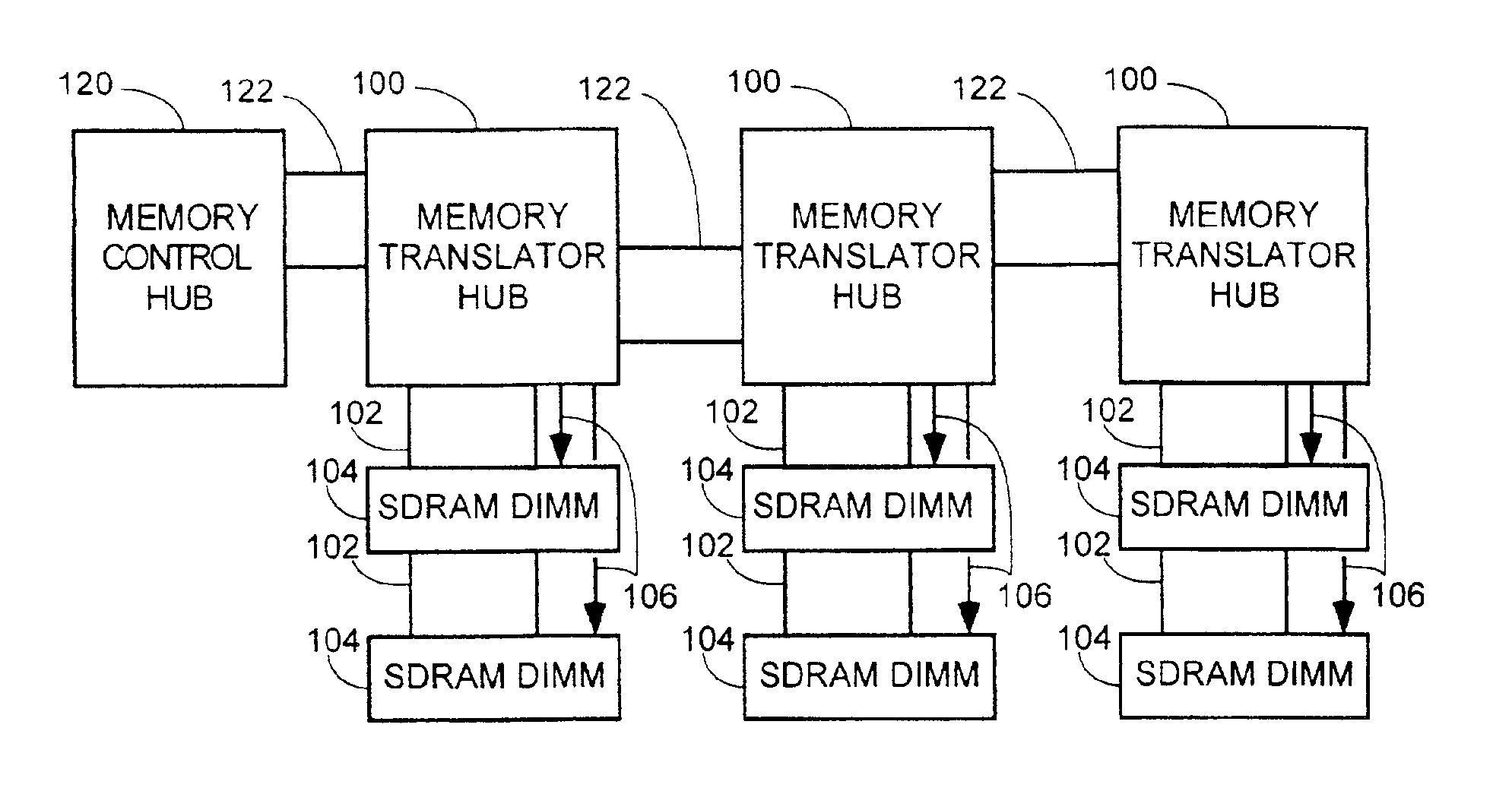
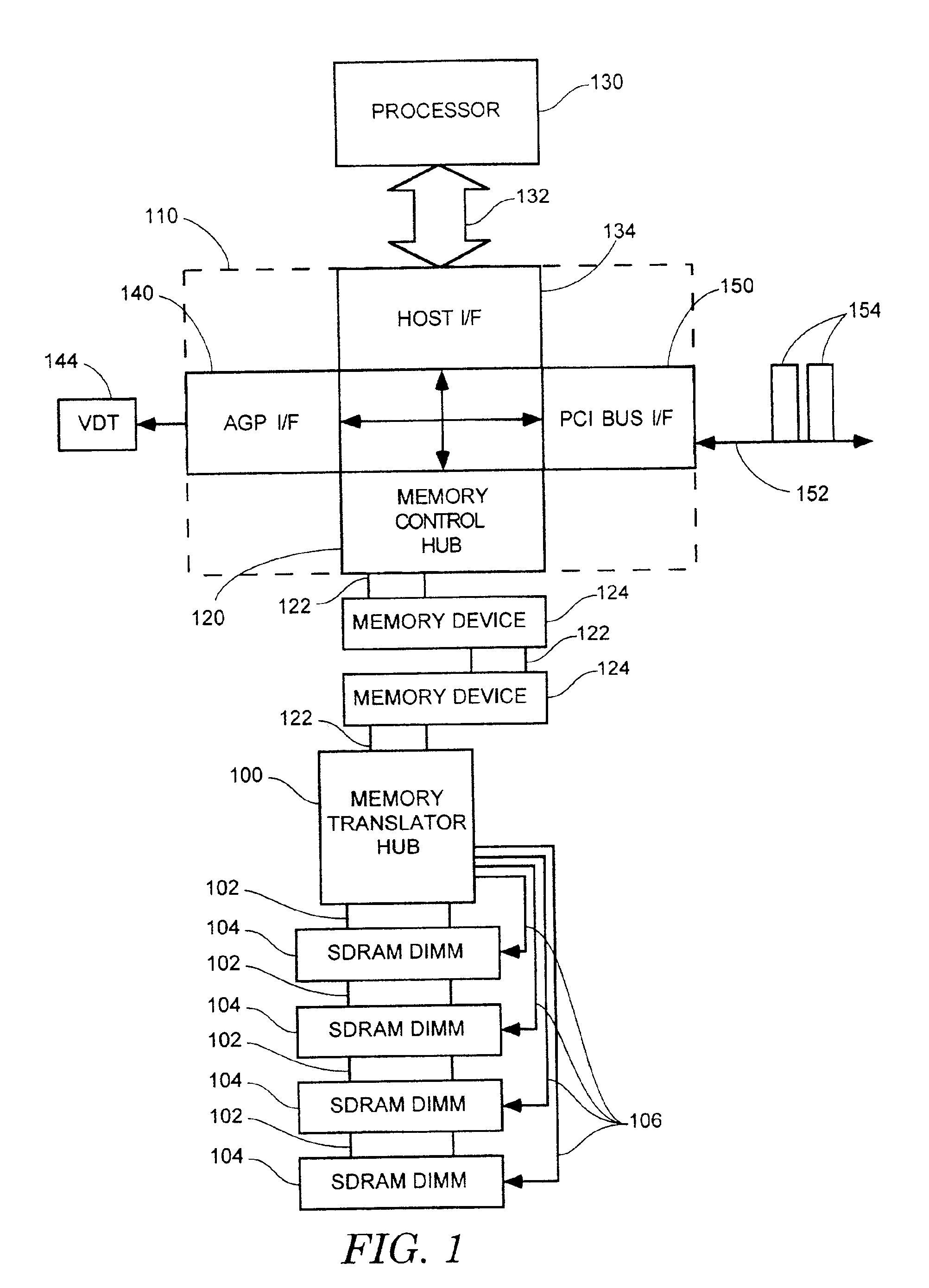
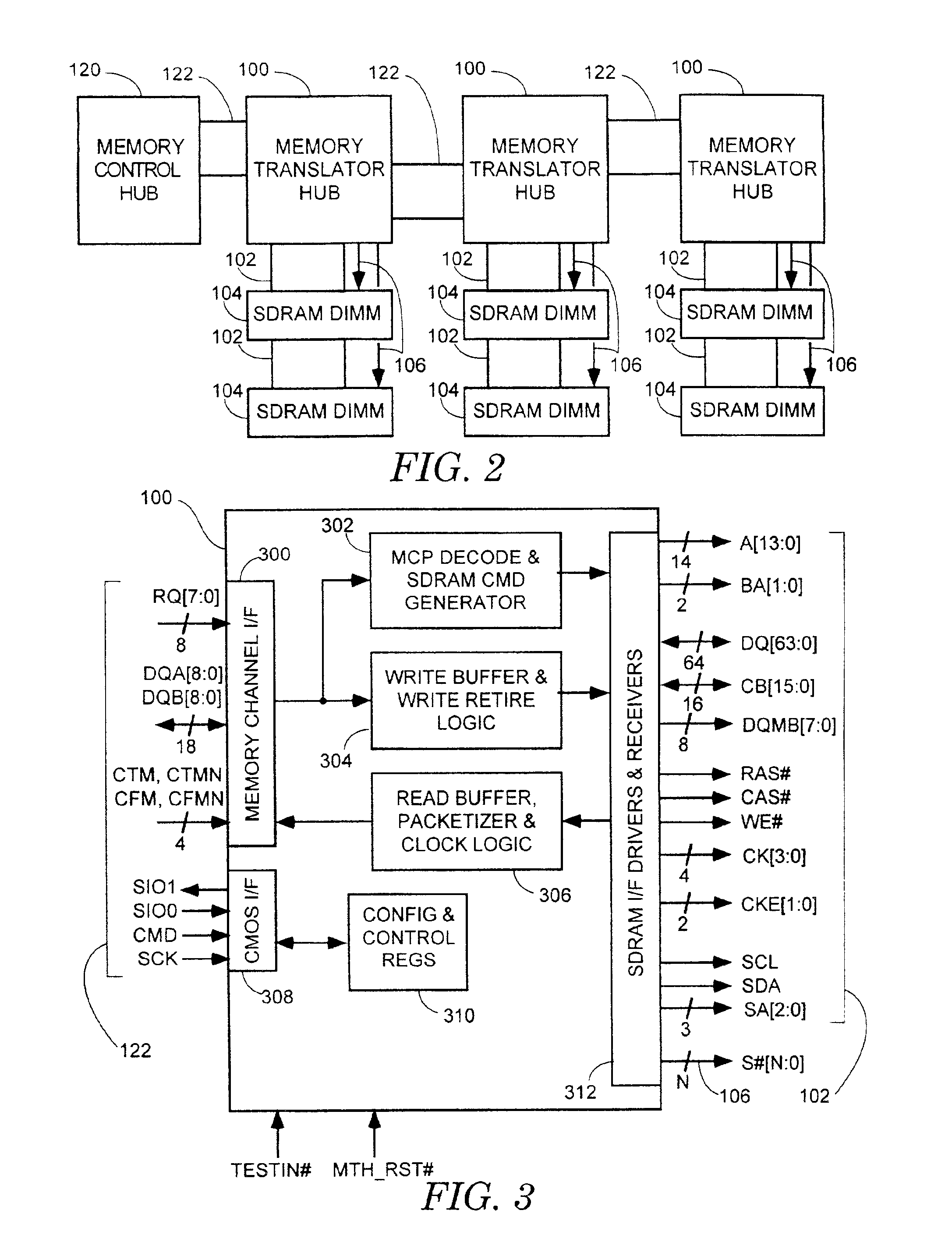
Method and apparatus for supporting SDRAM memory
A memory translation hub comprising a memory channel interface, a memory bus interface, and a command generator coupled to the memory channel interface and to the memory bus interface. The memory channel interface receives a memory control packet from a memory channel. The memory bus interface provides a memory bus. The command generator causes the memory bus interface to provide memory control signals on the memory bus responsive to the memory control packet.
Owner:INTEL CORP
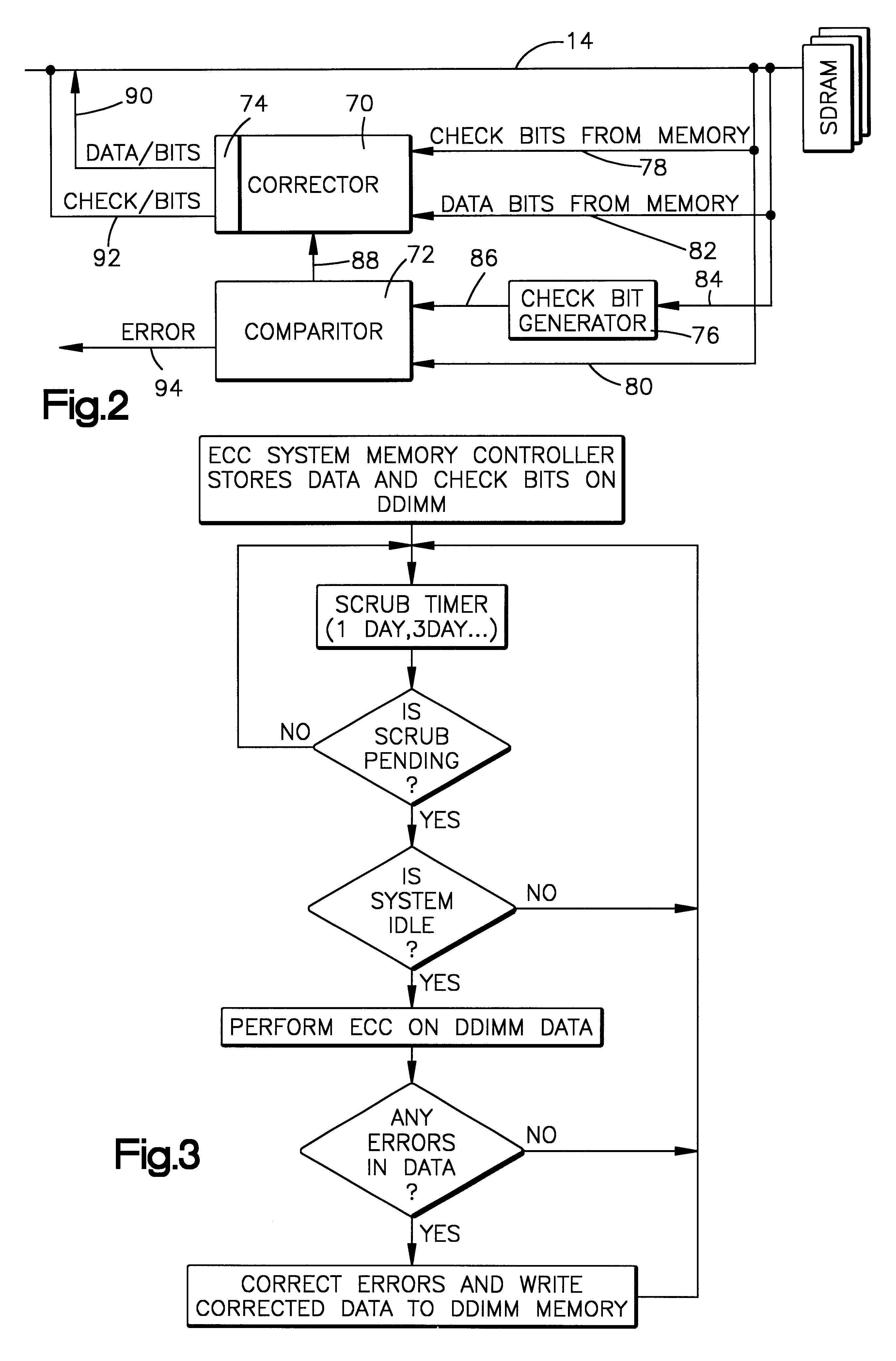
On-board scrubbing of soft errors memory module
A memory module for attachment to a computer system having a memory bus and a method of using the memory module for error correction by scrubbing soft errors on-board the module is provided. The module includes a printed circuit card with memory storage chips on the card to store data bits and associated ECC check bits. Tabs are provided on the circuit card to couple the card to the memory bus of the computer system. Logic circuitry selectively operatively connects and disconnects the memory chip and the memory bus. A signal processor is connected in circuit relationship with the memory chips. The logic circuitry selectively permits the signal processor to read the stored data bits and associated check bits from the memory chips, recalculate the check bits from the read stored data bits, compare the recalculated check bits with the stored check bits, correct all at least one bit errors in the store data bits and stored associated check bits and re-store the correct data bits and associated check bits in the memory chips. When the memory chips and the memory bus are disconnected, single bit soft errors occurring during storage of the data bits and check bits are corrected periodically before the data is read from the memory chips to the data bus on a read operation.
Owner:IBM CORP
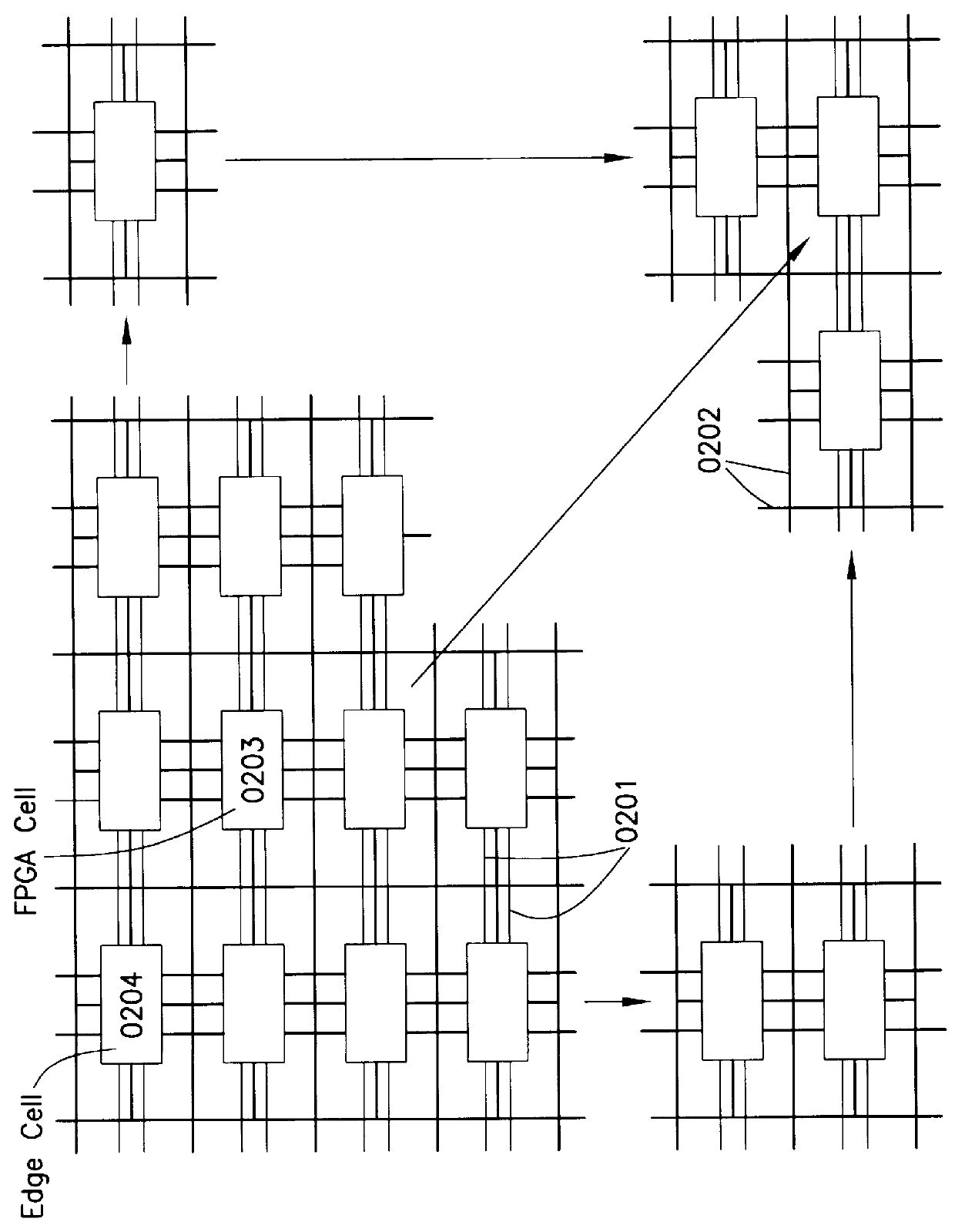
I/O and memory bus system for DFPs and units with two- or multi-dimensional programmable cell architectures
InactiveUS6119181ADigital storageArchitecture with single central processing unitComputer architectureMemory bus
A uniform bus system is provided which operates without any special consideration by a programmer. Memories and peripheral may be connected to this bus system without any special measures. Likewise, units may be cascaded with the help of the bus system. The bus system combines a number of internal lines, and leads them as a bundle to terminals. The bus system control is predefined and does not require any influence by the programmer. Any number of memories, peripherals or other units can be connected to the bus system.
Owner:SCIENTIA SOL MENTIS AG
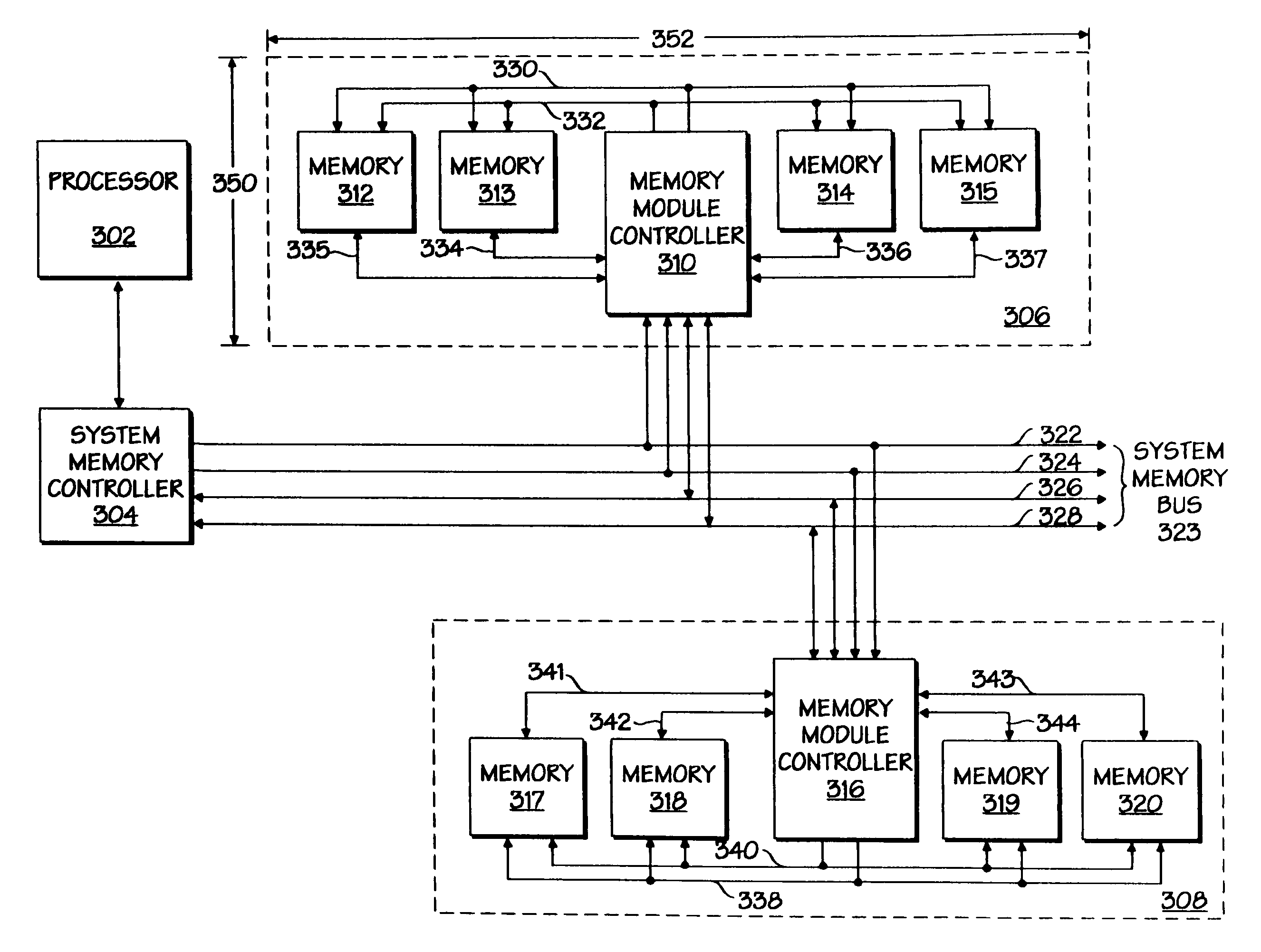
Memory module having a memory module controller controlling memory transactions for a plurality of memory devices
InactiveUS6968419B1Energy efficient ICTMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory busControl memory
A memory module that has a plurality of memory devices and a memory module controller configured to receive a memory transaction from a first memory bus and to control access to the plurality of memory devices.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Rdma-ssd dual-port unified memory and network controller
ActiveUS20150254003A1Increase storage capacityLower latencyMemory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersMagnetic reluctanceData memory
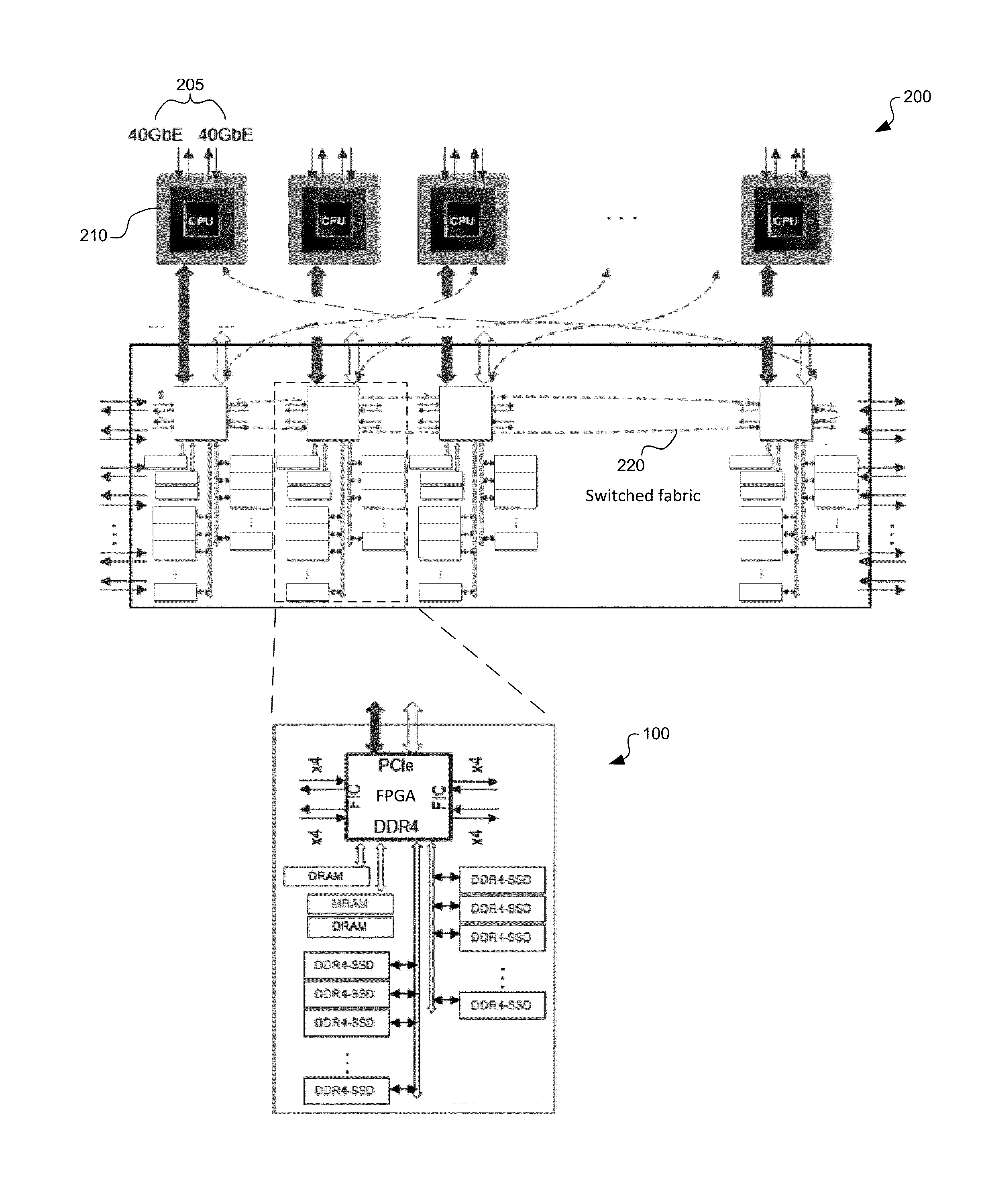
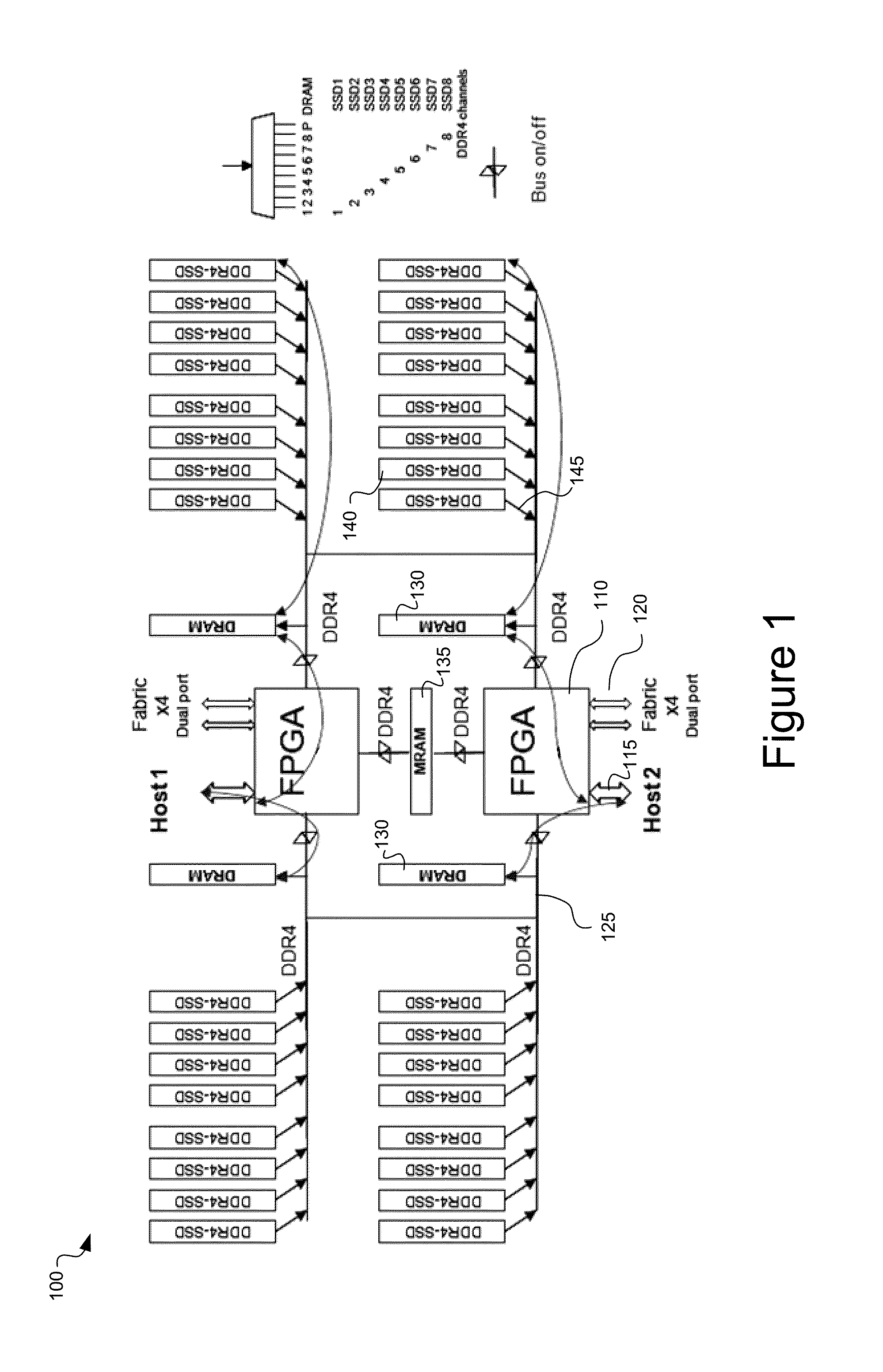
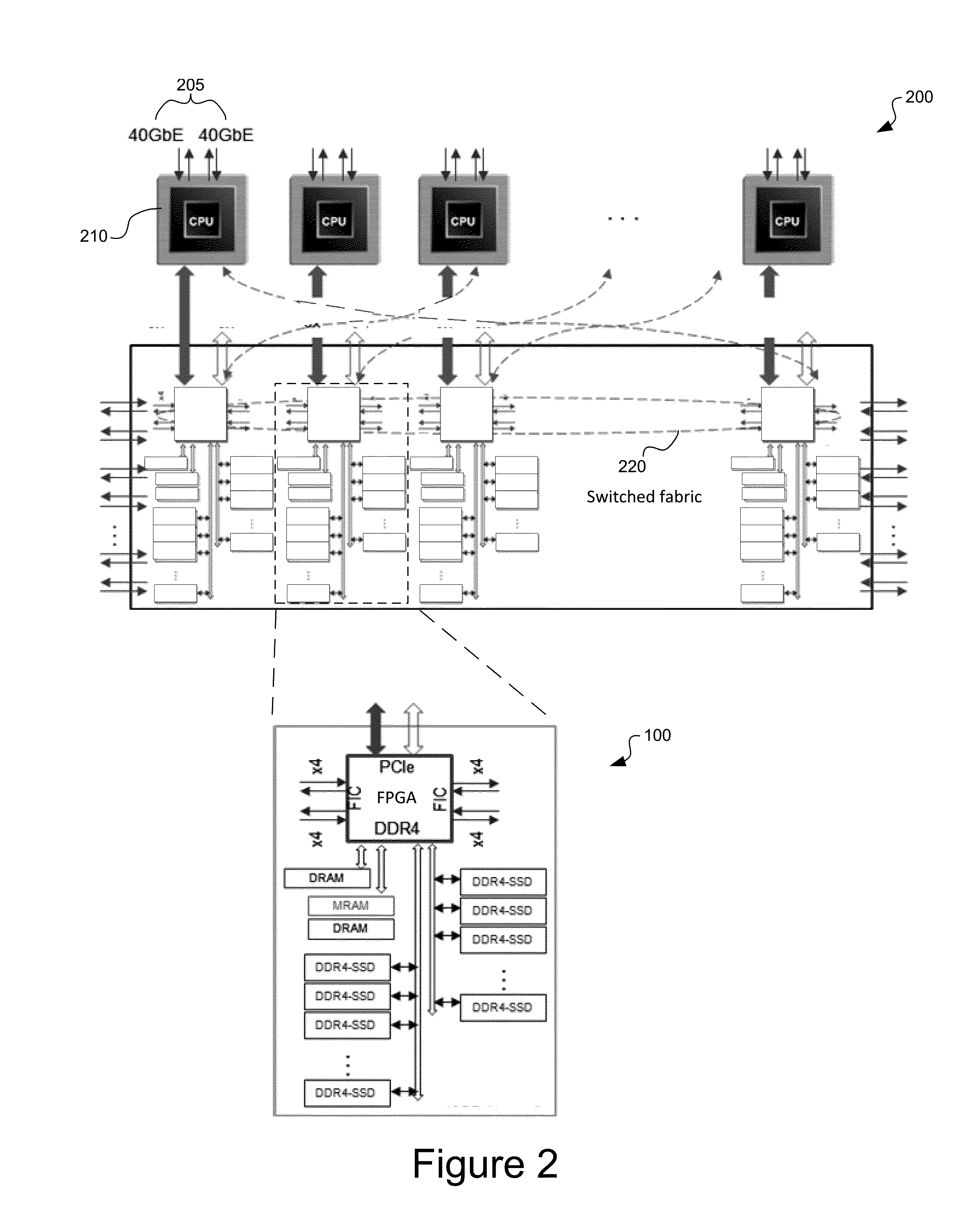
System and method for a unified memory and network controller for an all-flash array (AFA) storage blade in a distributed flash storage clusters over a fabric network. The unified memory and network controller has 3-way control functions including unified memory buses to cache memories and DDR4-AFA controllers, a dual-port PCIE interconnection to two host processors of gateway clusters, and four switch fabric ports for interconnections with peer controllers (e.g., AFA blades and / or chassis) in the distributed flash storage network. The AFA storage blade includes dynamic random-access memory (DRAM) and magnetoresistive random-access memory (MRAM) configured as data read / write cache buffers, and flash memory DIMM devices as primary storage. Remote data memory access (RDMA) for clients via the data caching buffers is enabled and controlled by the host processor interconnection(s), the switch fabric ports, and a unified memory bus from the unified controller to the data buffer and the flash SSDs.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
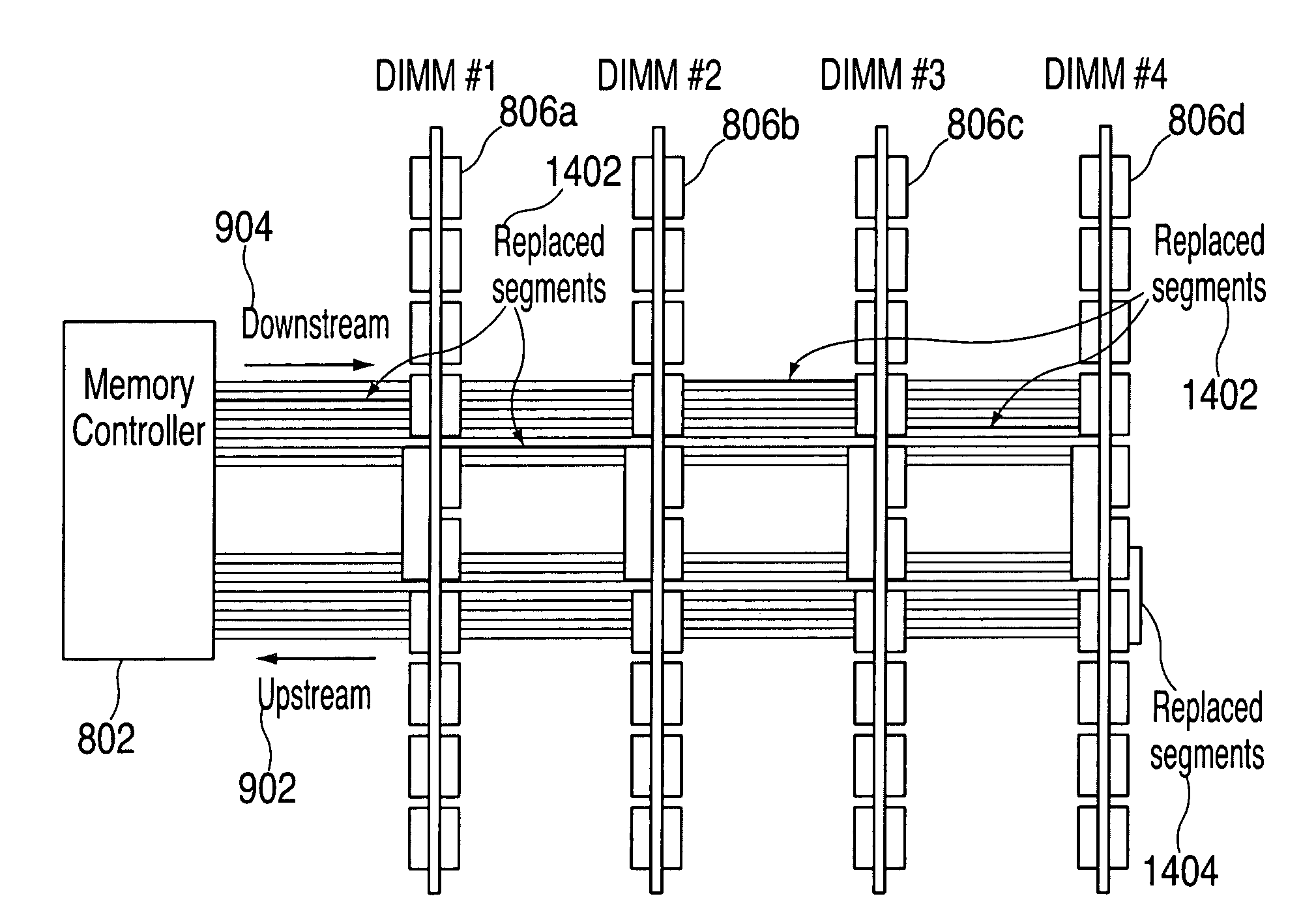
System, method and storage medium for providing segment level sparing
A memory subsystem that includes segment level sparing. The memory subsystem includes a cascaded interconnect system with segment level sparing. The cascaded interconnect system includes two or more memory assemblies and a memory bus. The memory bus includes multiple segments and the memory assemblies are interconnected via the memory bus.
Owner:IBM CORP
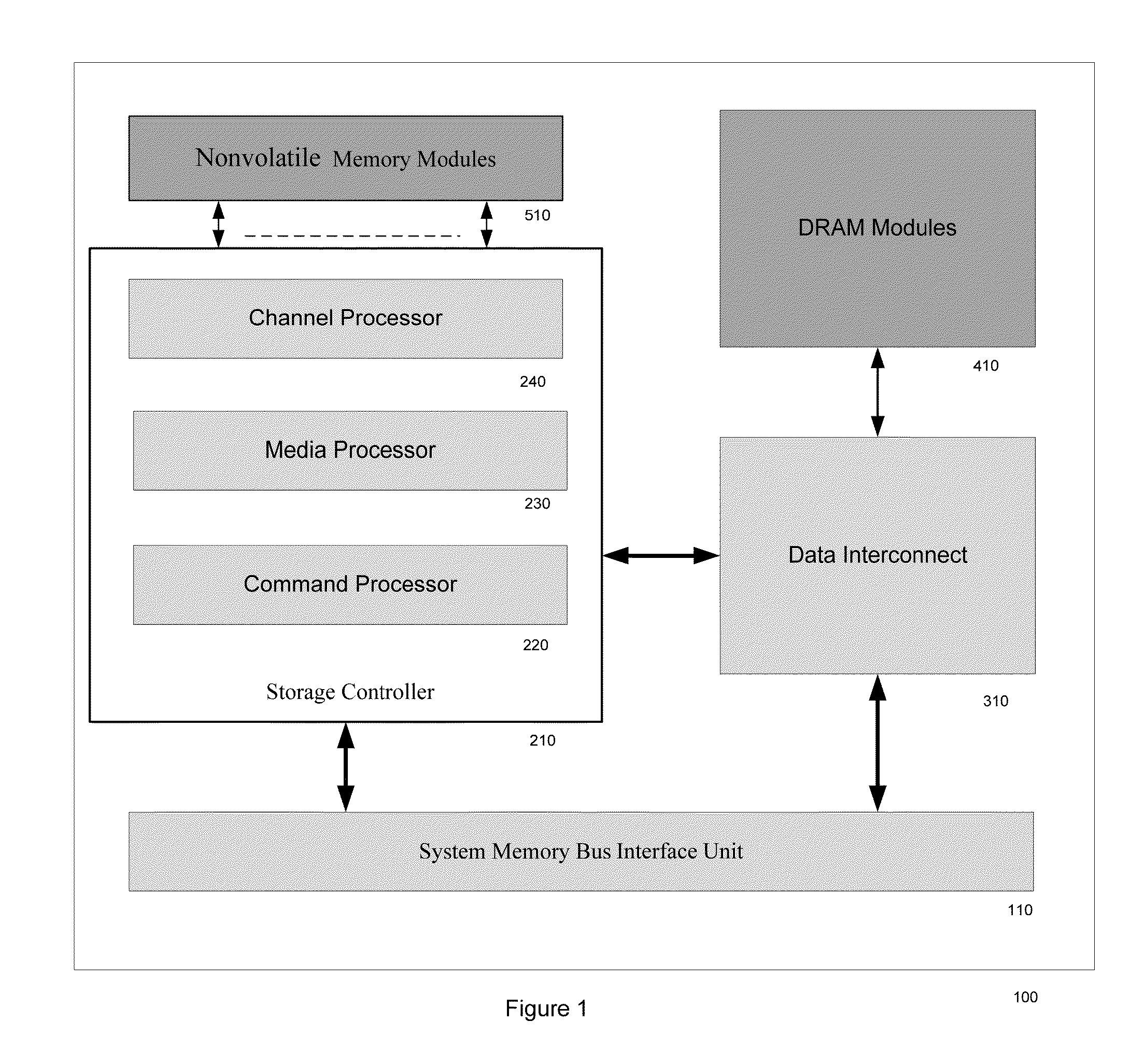
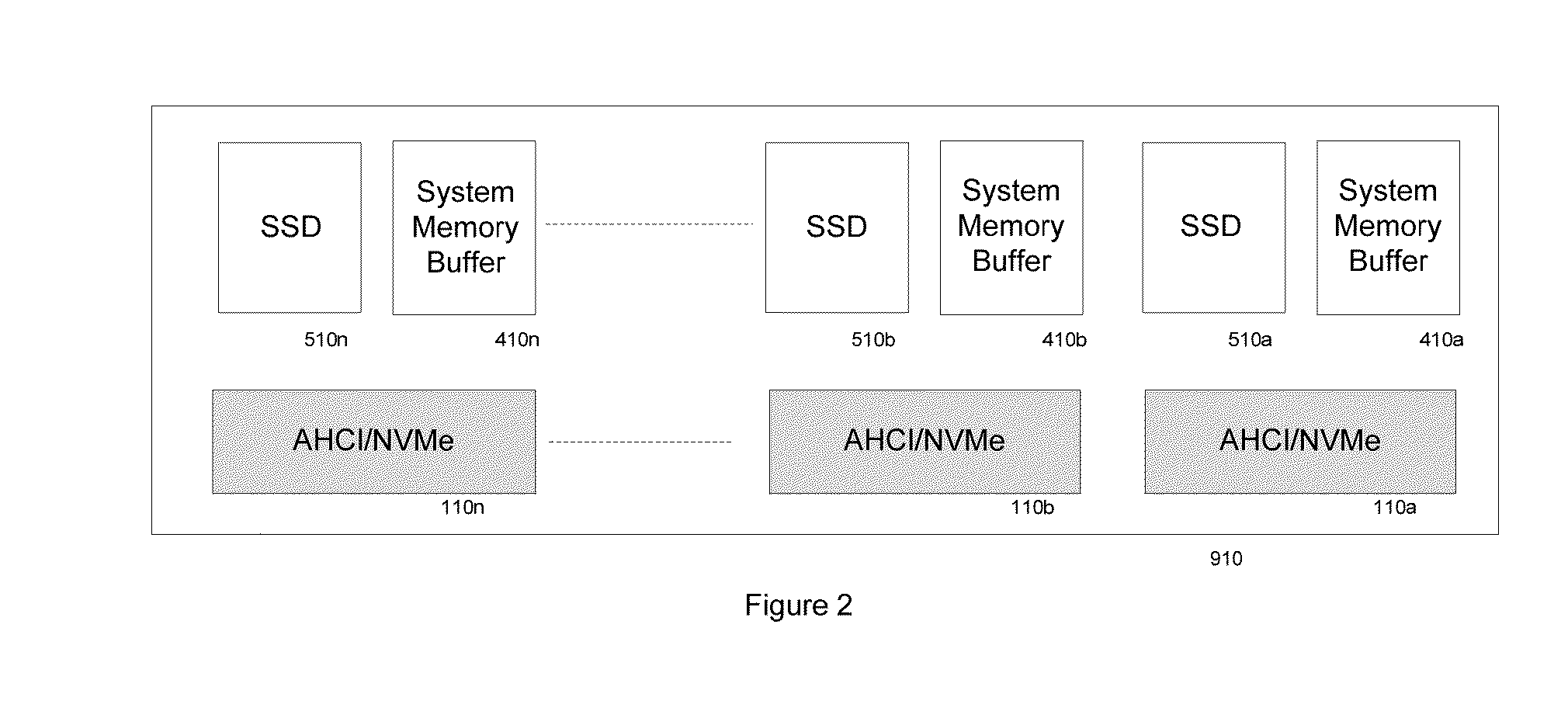
METHOD OF DIRECT CONNECTING AHCI OR NVMe BASED SSD SYSTEM TO COMPUTER SYSTEM MEMORY BUS
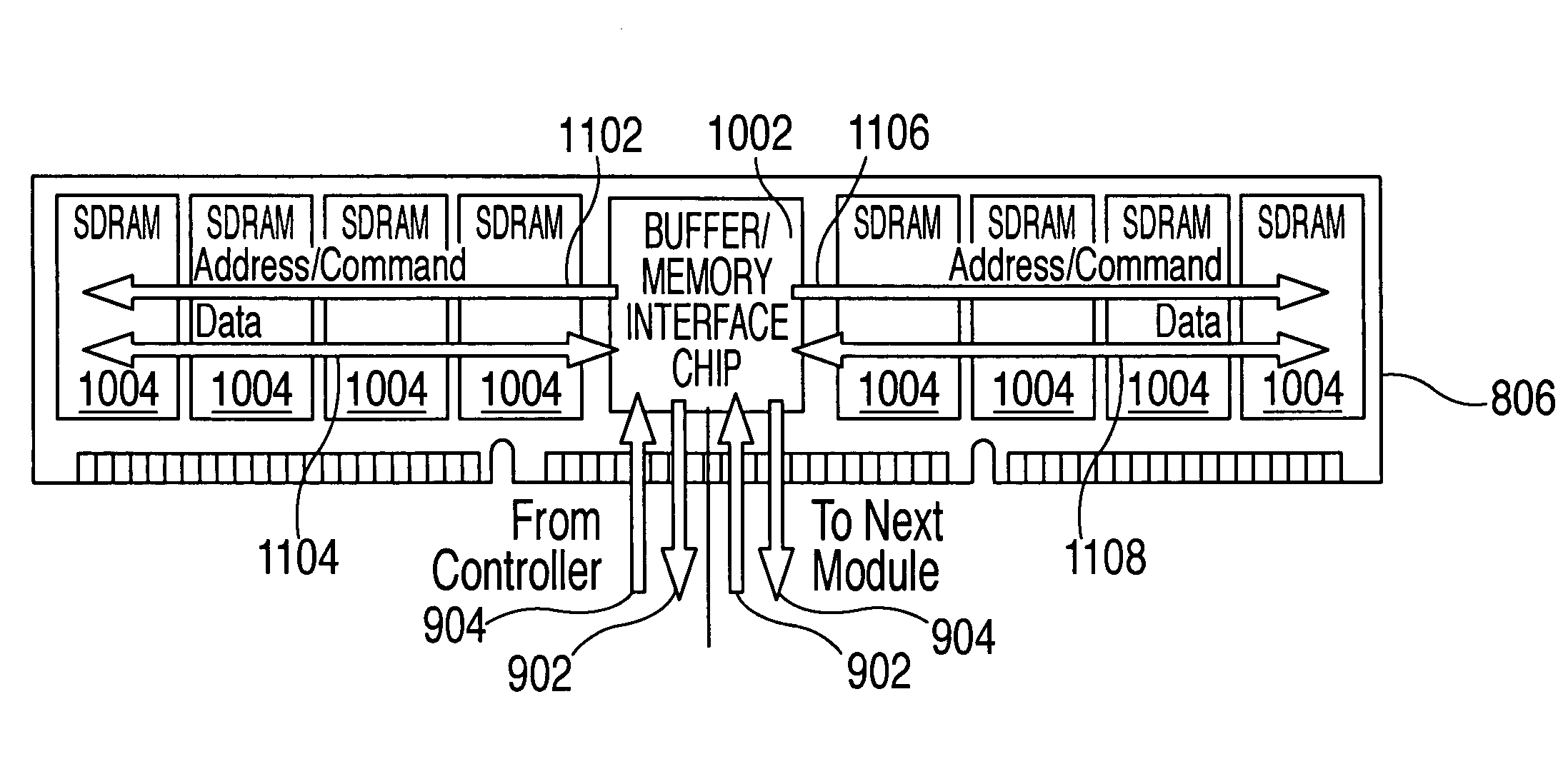
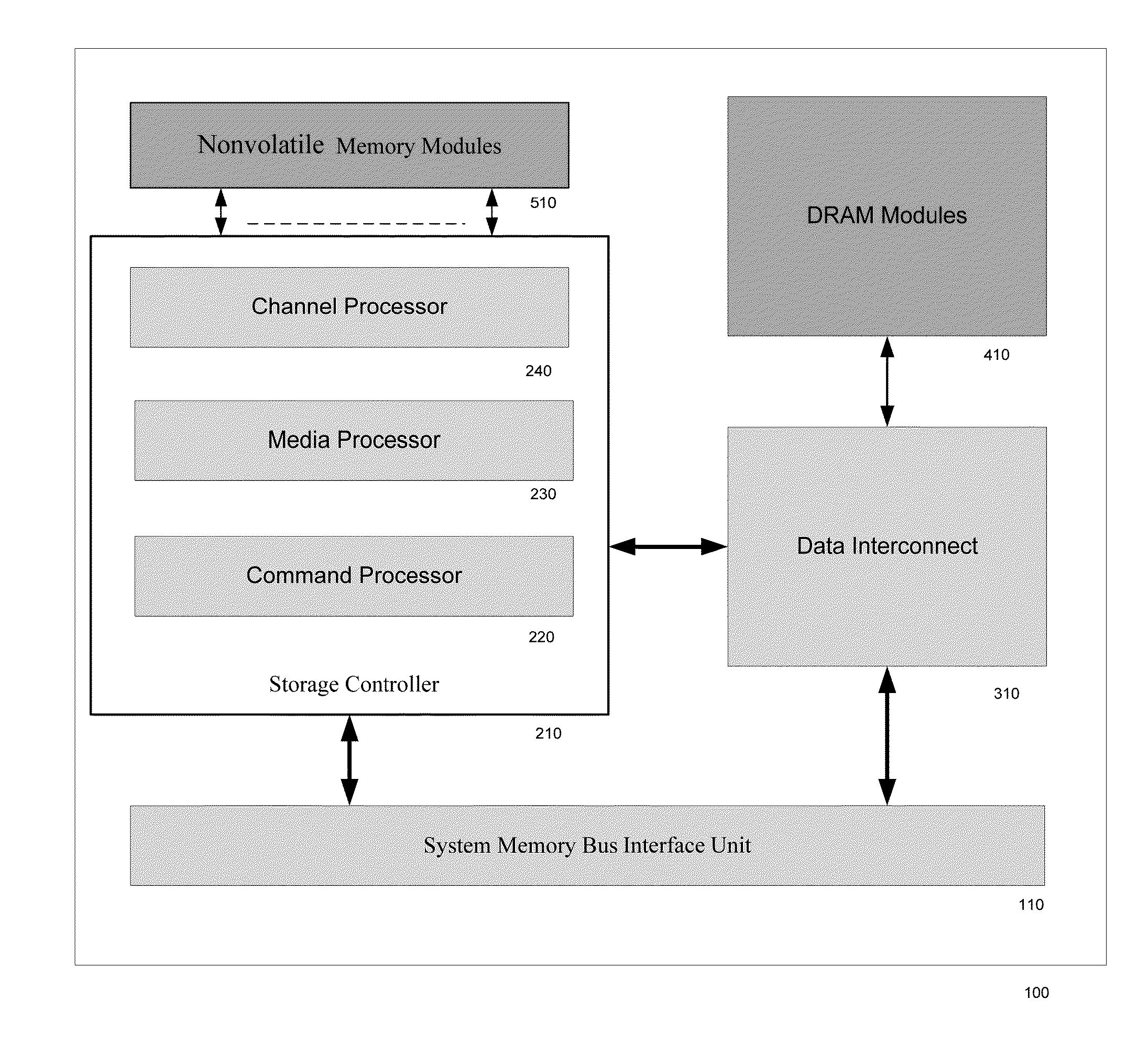
A SSD system directly connected to the system memory bus includes at least one system memory bus interface unit, one storage controller with associated data buffer / cache, one data interconnect unit, one nonvolatile memory (NVM) module, and flexible association between storage commands and the NVM module. A logical device interface, the Advanced Host Controller Interface (AHCI) or NVM Express (NVMe), is used for the SSD system programming. The SSD system appears to the computer system physically as a dual-inline-memory module (DIMM) attached to the system memory controller, and logically as an AHCI device or an NVMe device. The SSD system may sit in a DIMM socket and scaling with the number of DIMM sockets available to the SSD applications. The invention moves the SSD system from I / O domain to the system memory domain.
Owner:HUANG MING +1
Memory repeater
InactiveUS6882082B2Improve acceleration performanceMemory adressing/allocation/relocationUnauthorized memory use protectionCommunications systemMemory bus
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
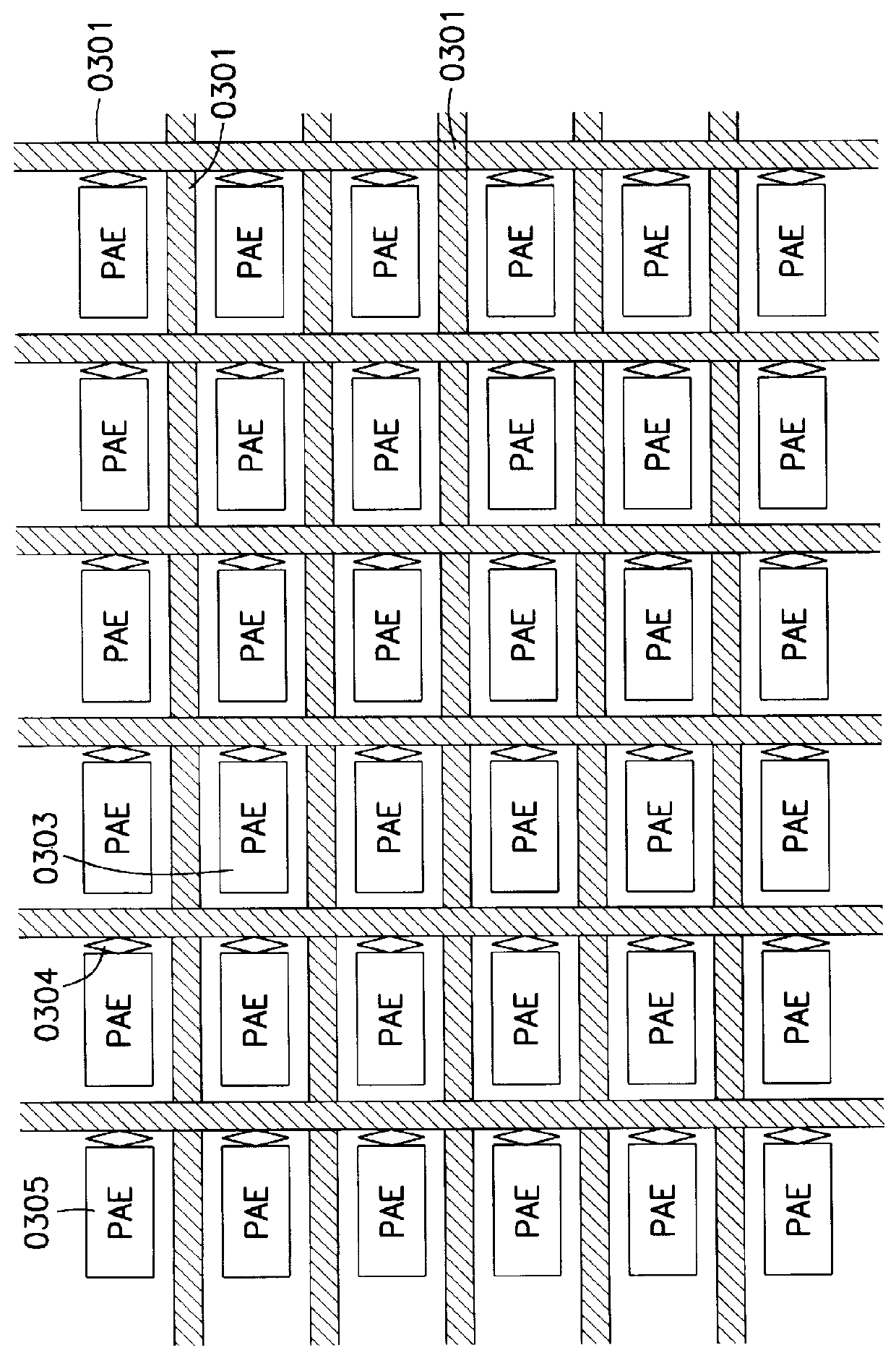
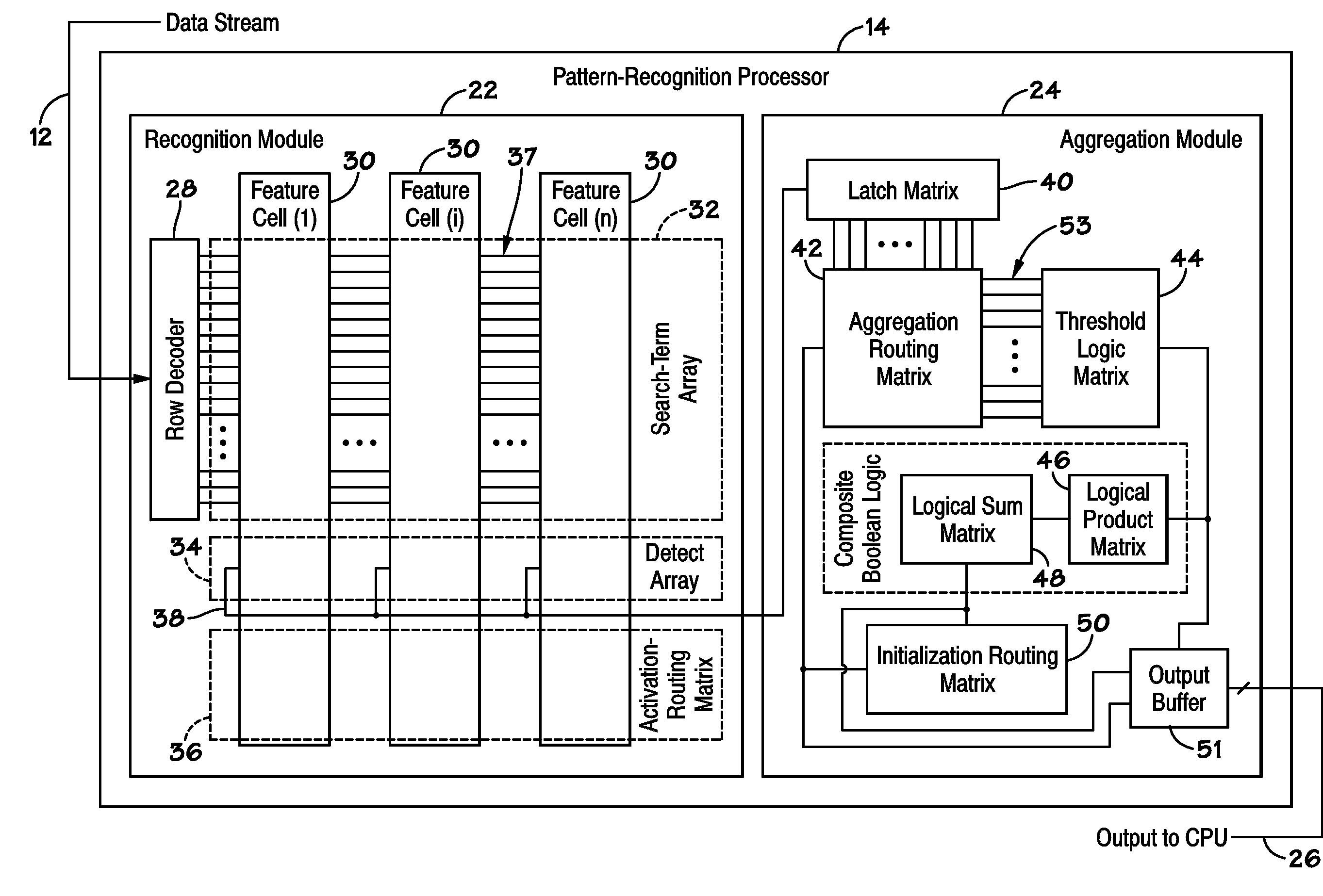
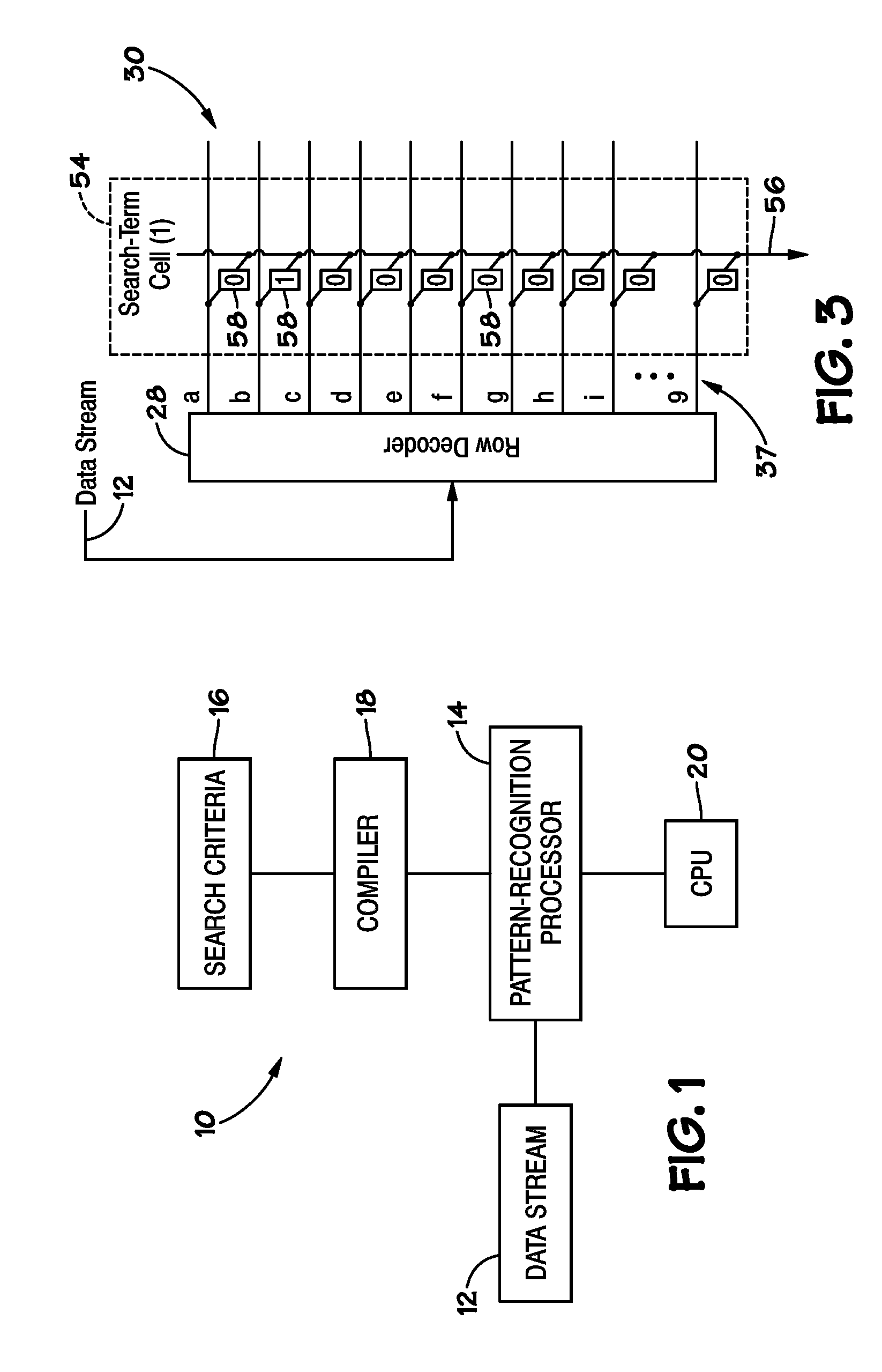
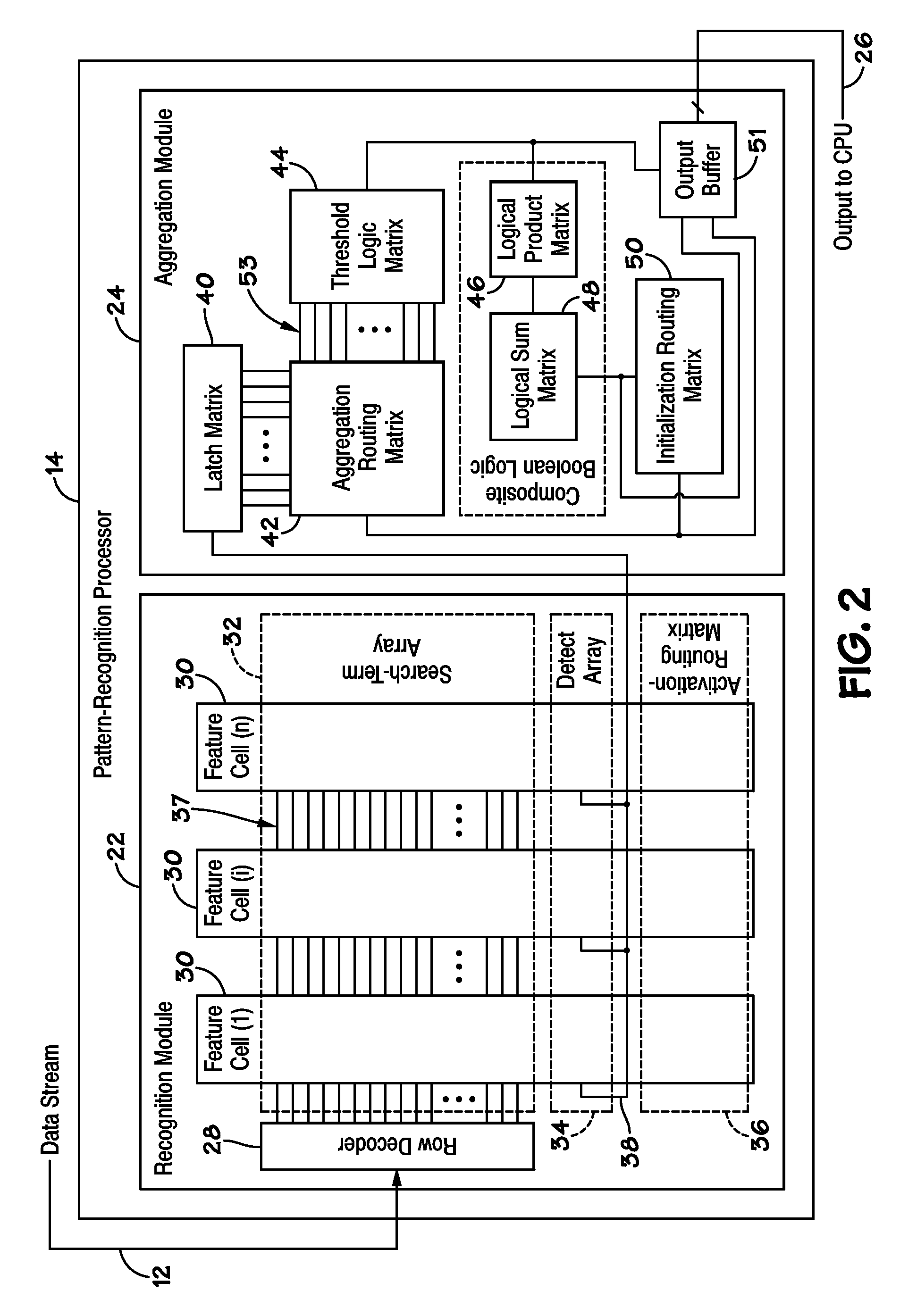
Buses for Pattern-Recognition Processors
InactiveUS20100174887A1General purpose stored program computerCharacter and pattern recognitionMemory busParallel computing
Disclosed are methods and systems, among which is a system that includes a pattern-recognition processor, a central processing unit (CPU) coupled to the pattern-recognition processor via a pattern-recognition bus, and memory coupled to the CPU via a memory bus. In some embodiments, the pattern-recognition bus and the memory bus form about the same number of connections to the pattern-recognition processor and the memory, respectively.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
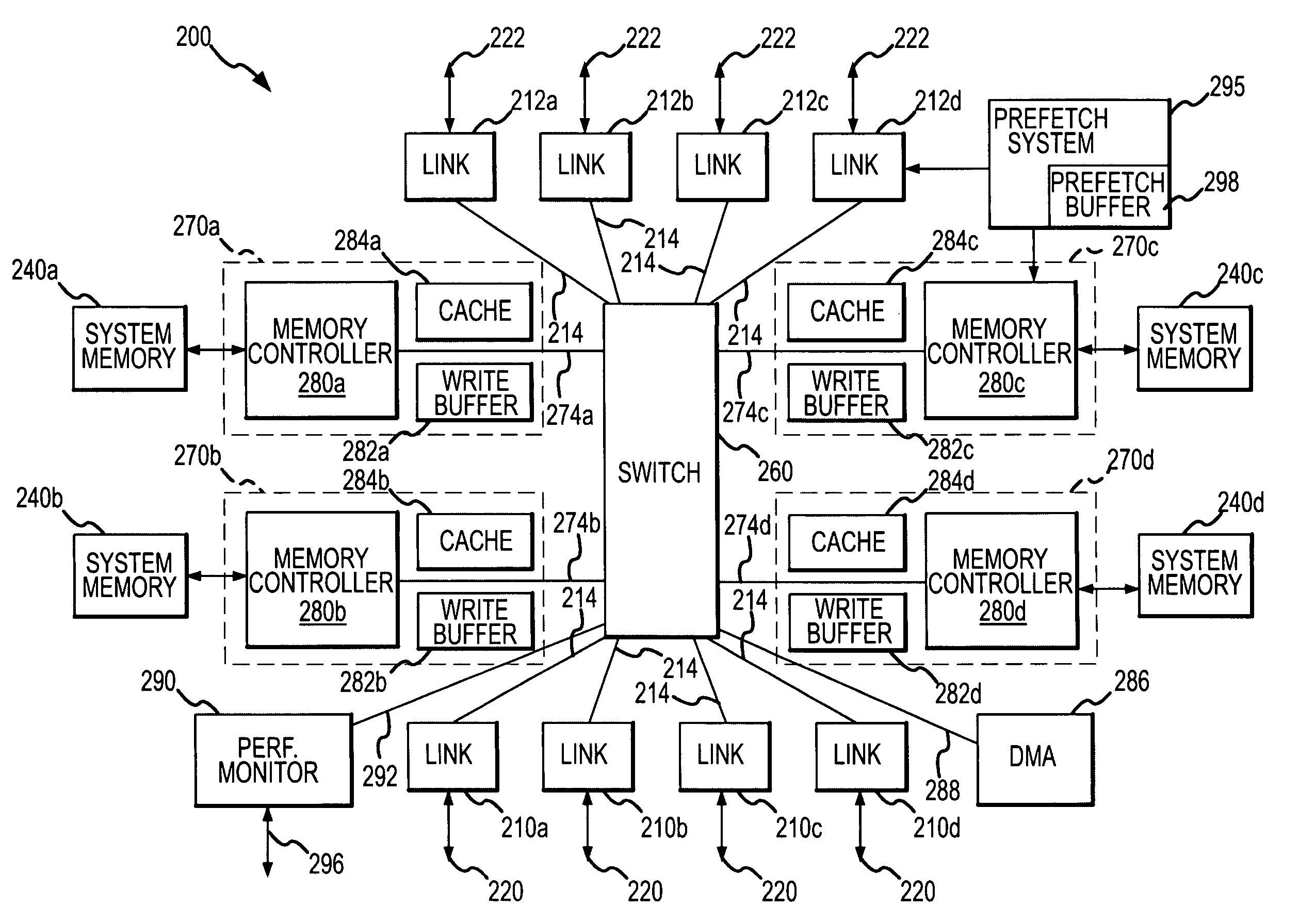
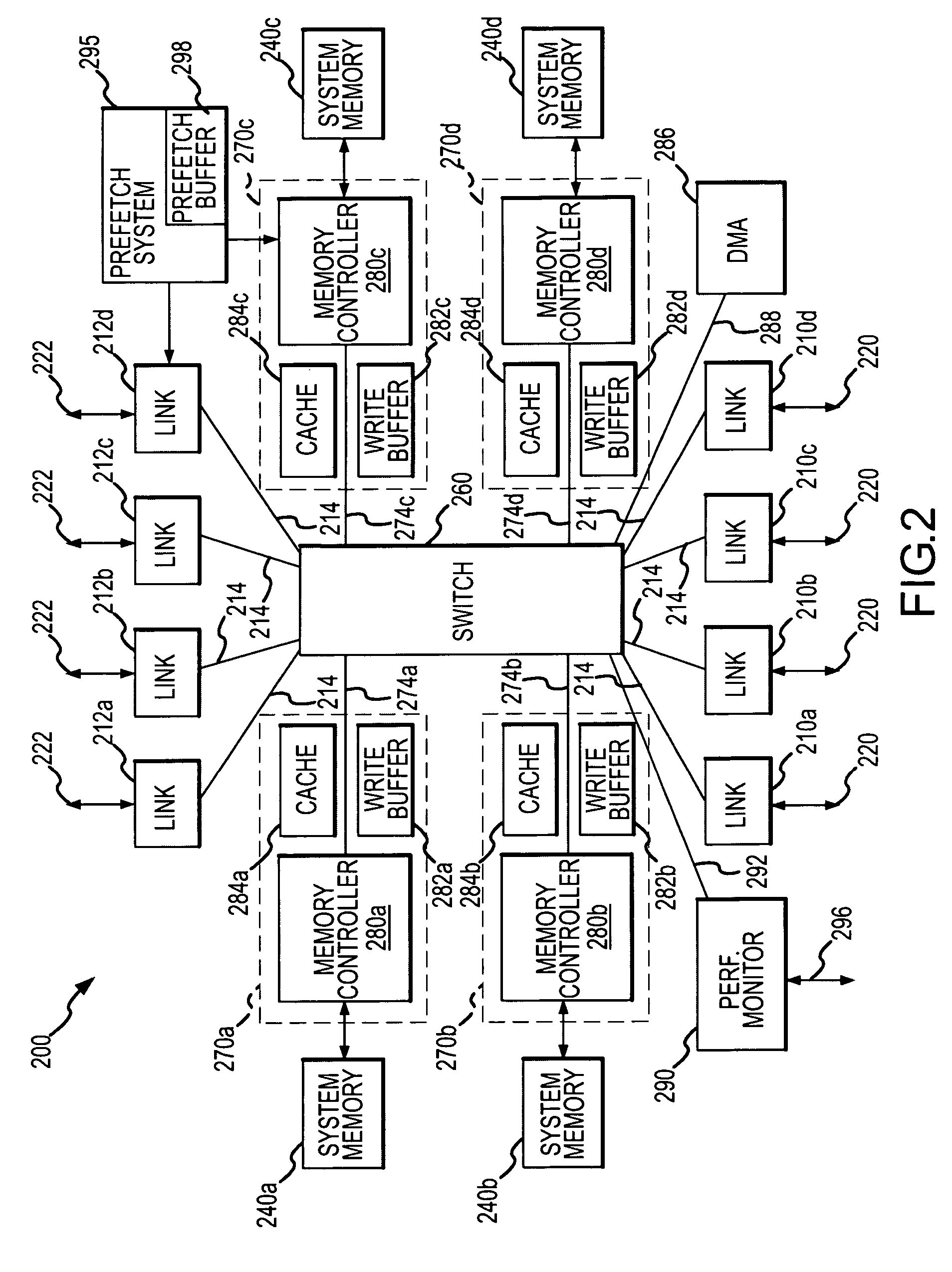
Memory hub and method for memory system performance monitoring
InactiveUS7216196B2Error detection/correctionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory busCache hit rate
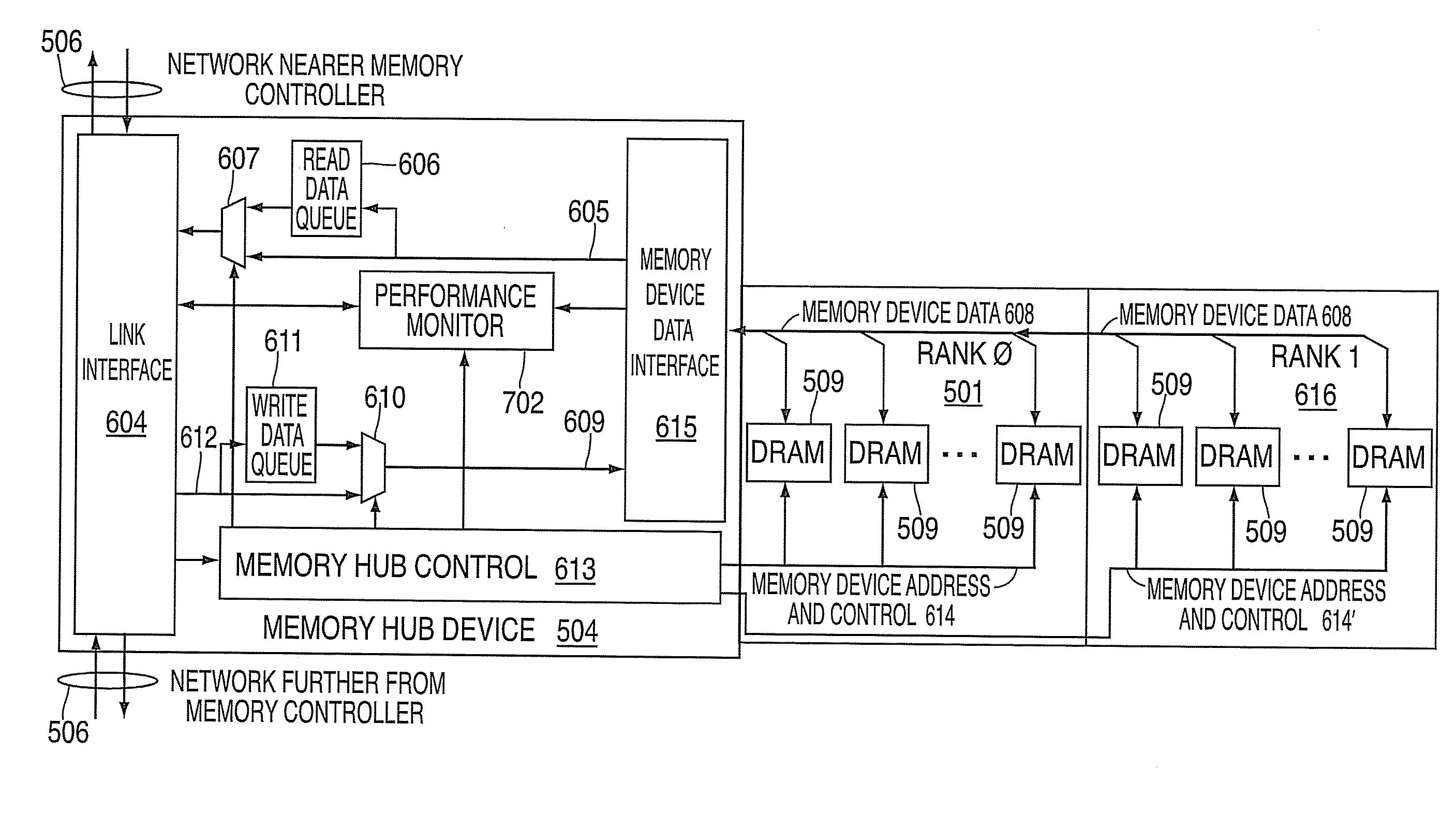
A memory module includes a memory hub coupled to several memory devices. The memory hub includes at least one performance counter that tracks one or more system metrics—for example, page hit rate, number or percentage of prefetch hits, cache hit rate or percentage, read rate, number of read requests, write rate, number of write requests, rate or percentage of memory bus utilization, local hub request rate or number, and / or remote hub request rate or number.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Memory bus termination with memory unit having termination control
Methods and apparatus for a memory system using line termination circuits in each memory unit (e.g., integrated circuit memory device) are disclosed. The memory unit contains termination control logic that sets the state of a controllable termination circuit to control reflections on the data bus. The termination control logic determines the proper state for the termination circuit from the state of its memory unit, and in some cases, from the approximate state of the data bus as gleaned from commands decoded from the command / address bus. A termination configuration register on the unit can be used to define the appropriate termination state for each unit state and / or data bus state.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
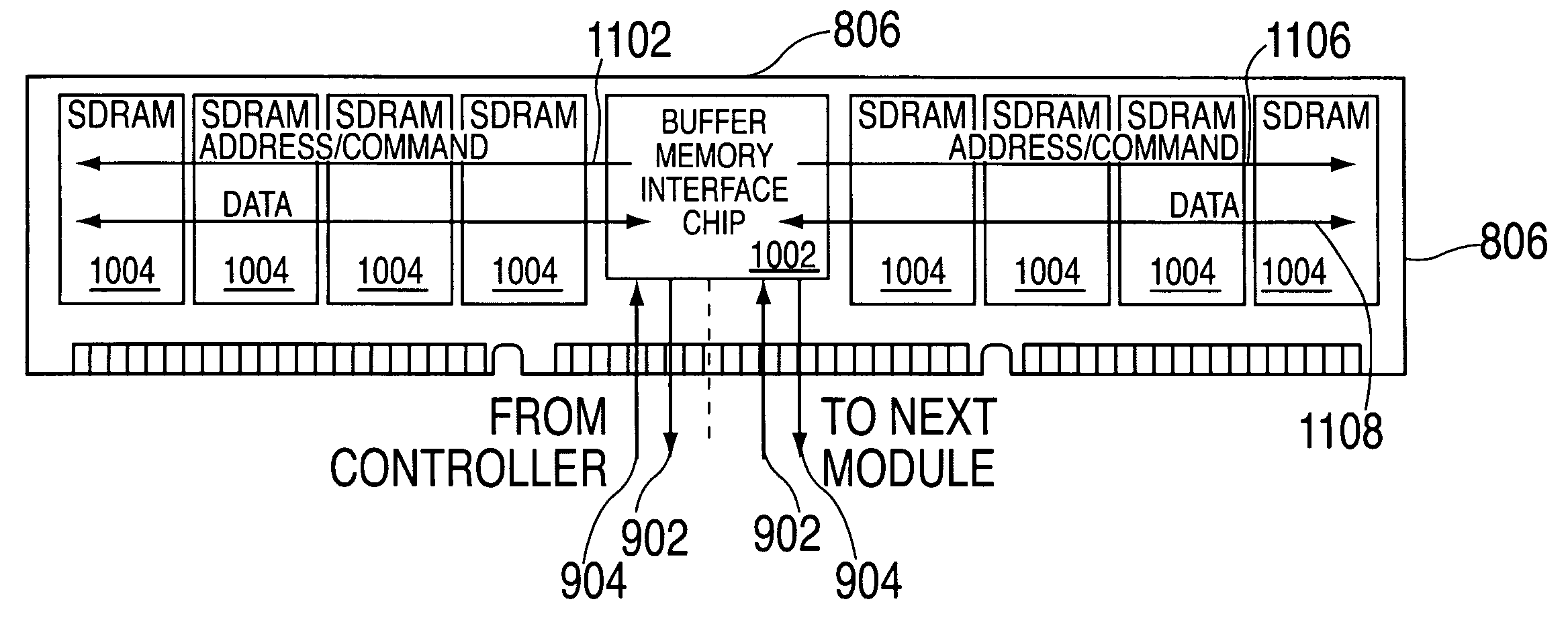
System and Method for Packaged Memory
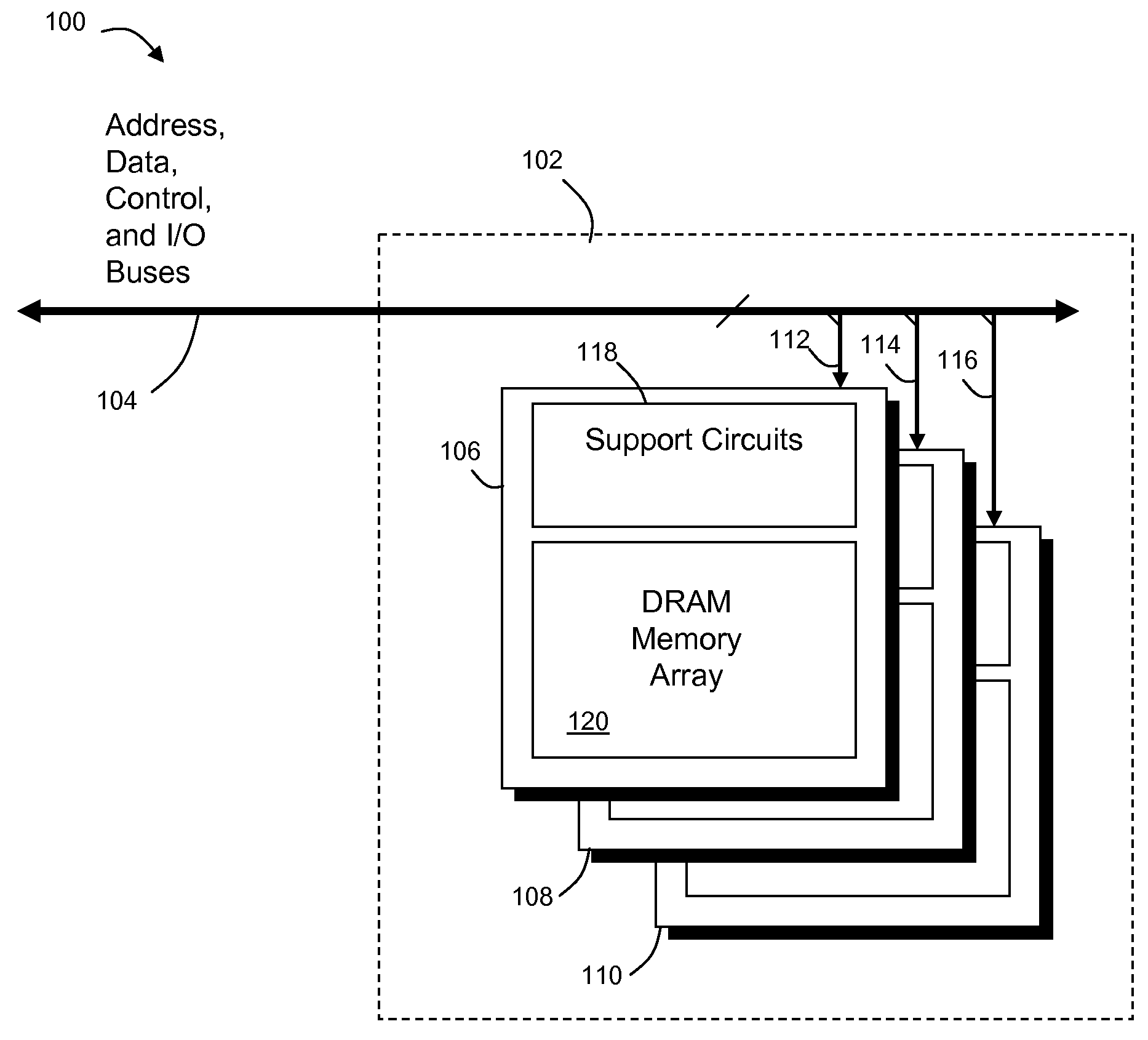
ActiveUS20100070696A1Energy efficient ICTMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory chipMemory bus
In one embodiment, a memory system is disclosed. The memory system has at least one memory chip having an address and data interface coupled to an internal address and data bus, and a memory controller and interface chip also having a an address and data interface coupled to the address and data interface of the at least one memory chip via an internal address and data bus. The at least one memory chip, the memory controller and interface chip and the internal address and data bus are disposed within a common chip package. The memory controller and interface chip has an external interface configured to be coupled to a standard memory bus via external contacts of the common chip package.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS
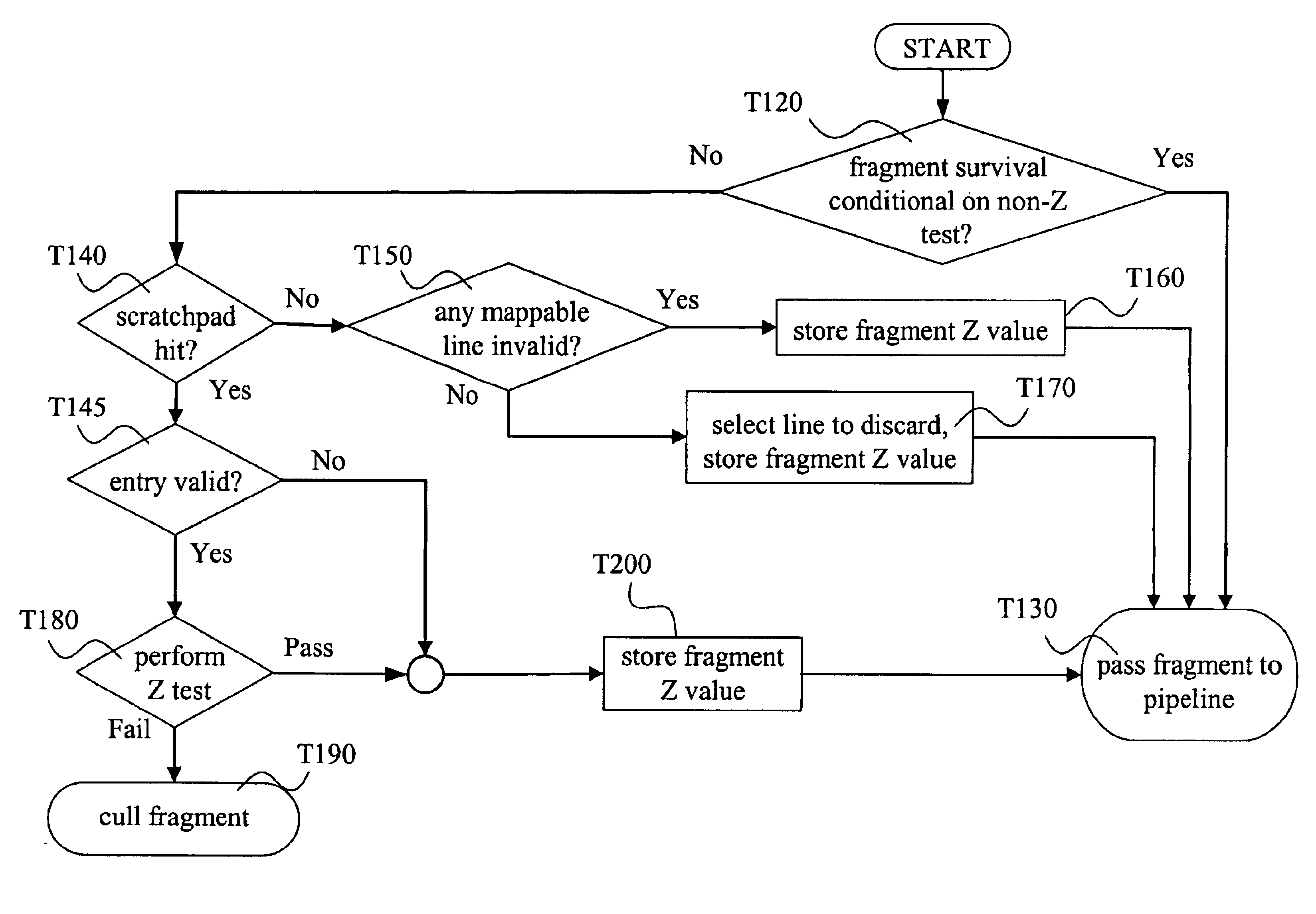
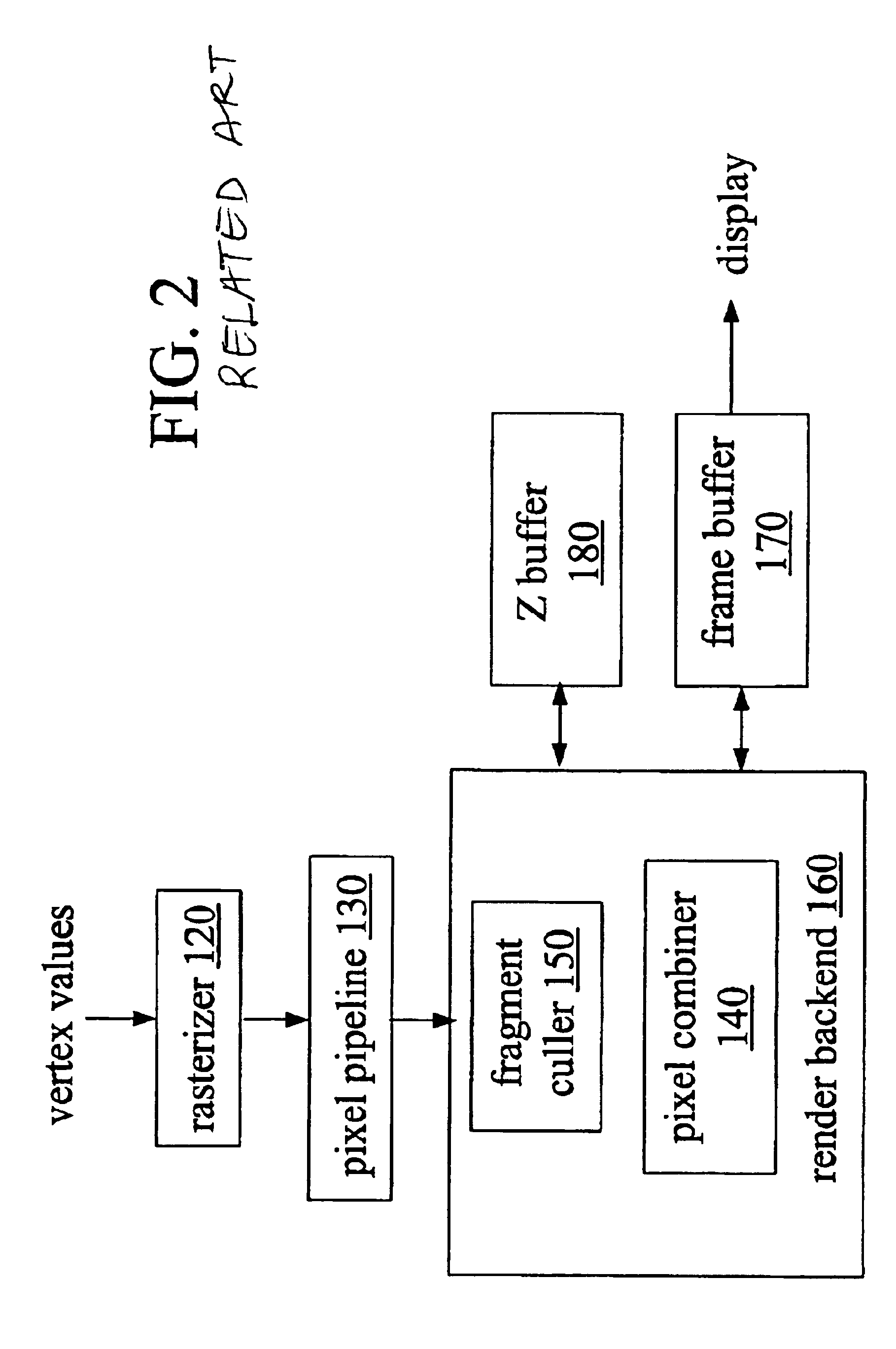
System, method, and apparatus for early culling
InactiveUS6999076B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsDetails involving image processing hardwareComputational scienceGraphics
A method of graphics processing includes determining a non-depth conditional status and an occlusion status of a fragment. Such a method may be used in culling occluded fragments before expending resources such as processing cycles and memory bus usage. In one example, a scratchpad stores depth values of robust fragments and is used for occlusion testing. Graphics architectures, and methods that include use of representative Z values, are also disclosed.
Owner:ADVANCED SILICON TECH
System, method and storage medium for providing segment level sparing
A memory subsystem that includes segment level sparing. The memory subsystem includes a cascaded interconnect system with segment level sparing. The cascaded interconnect system includes two or more memory assemblies and a memory bus. The memory bus includes multiple segments and the memory assemblies are interconnected via the memory bus.
Owner:IBM CORP
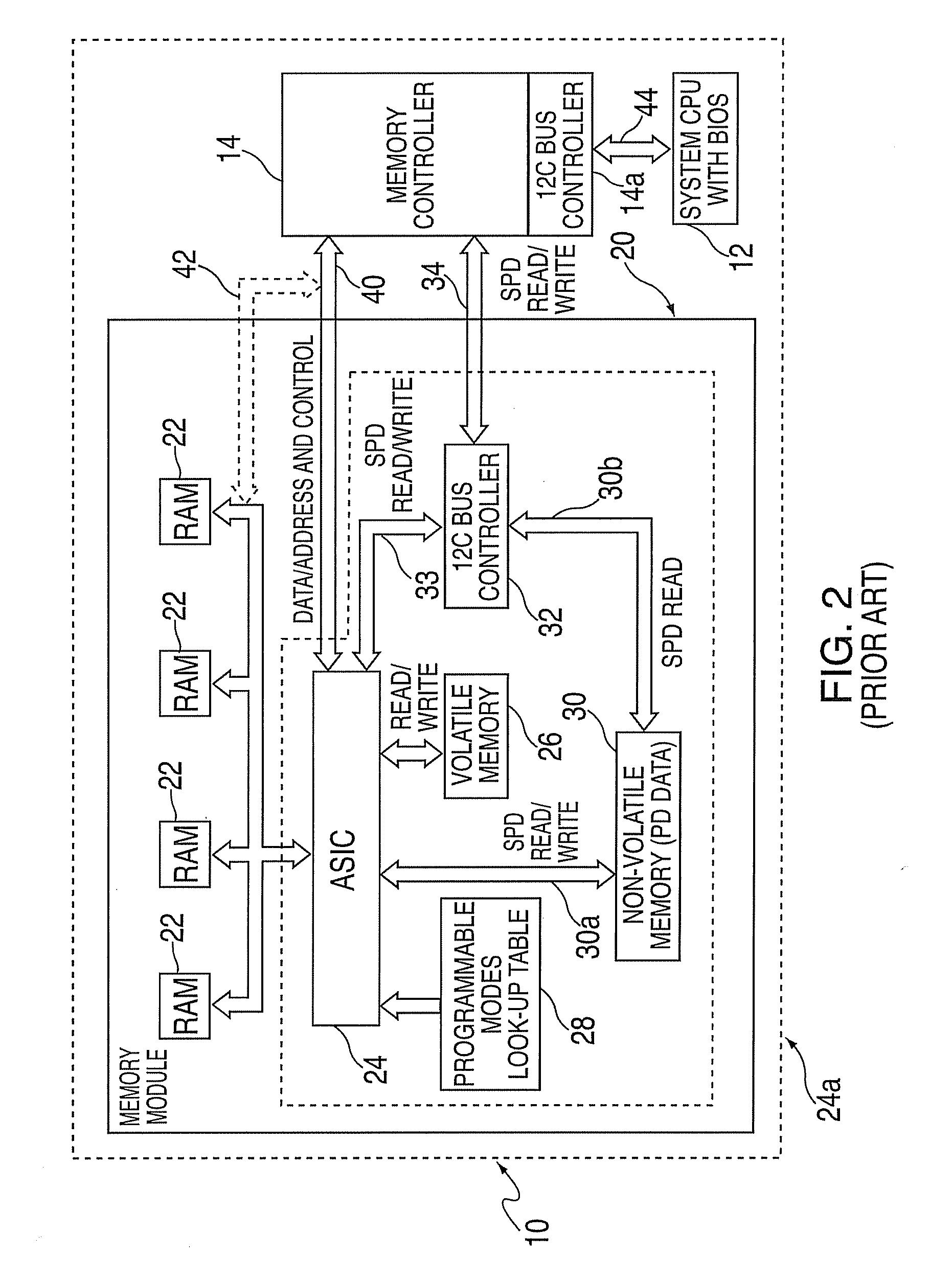
Method and apparatus for detecting insertion and removal of a memory module using standard connectors
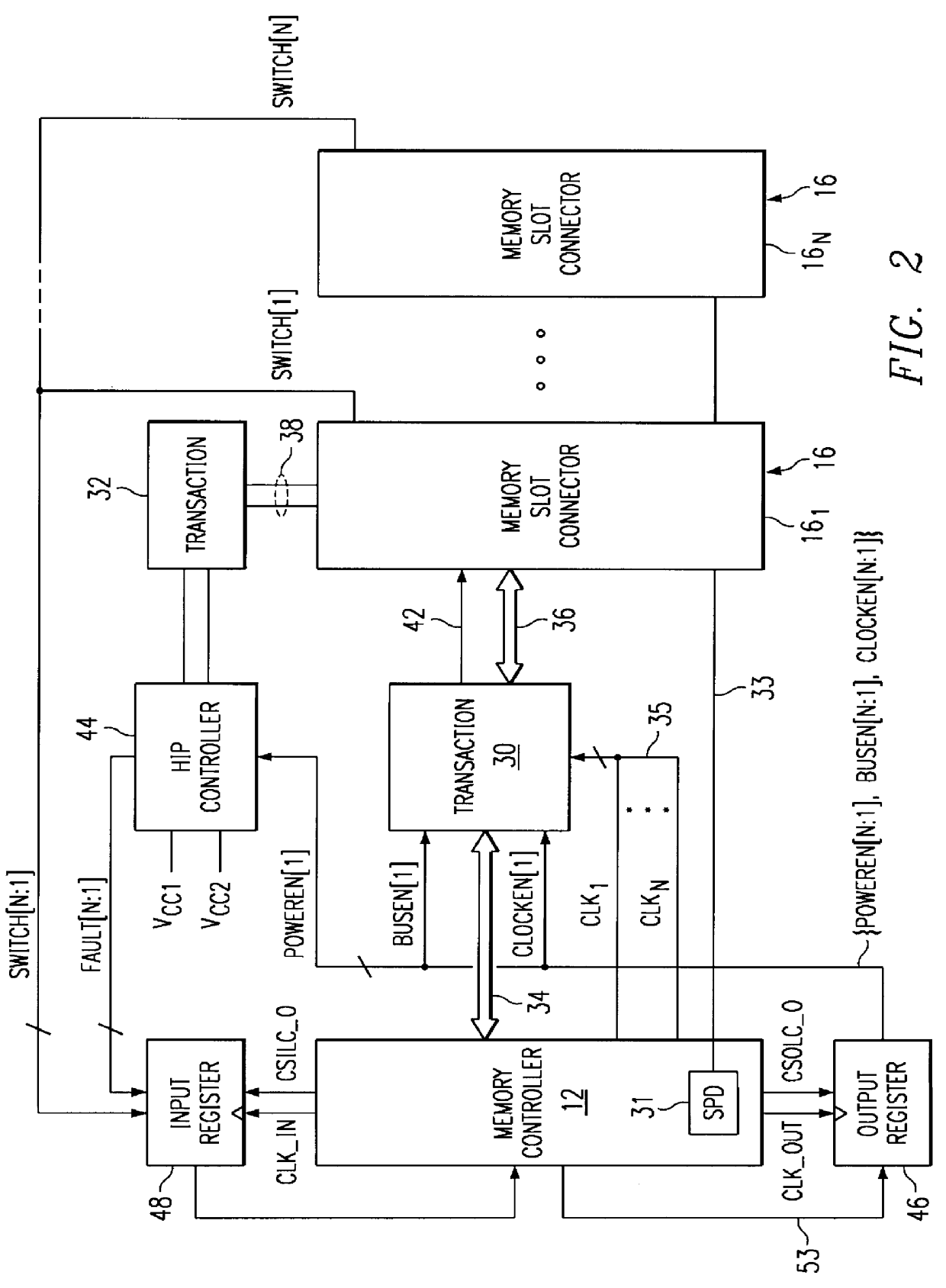
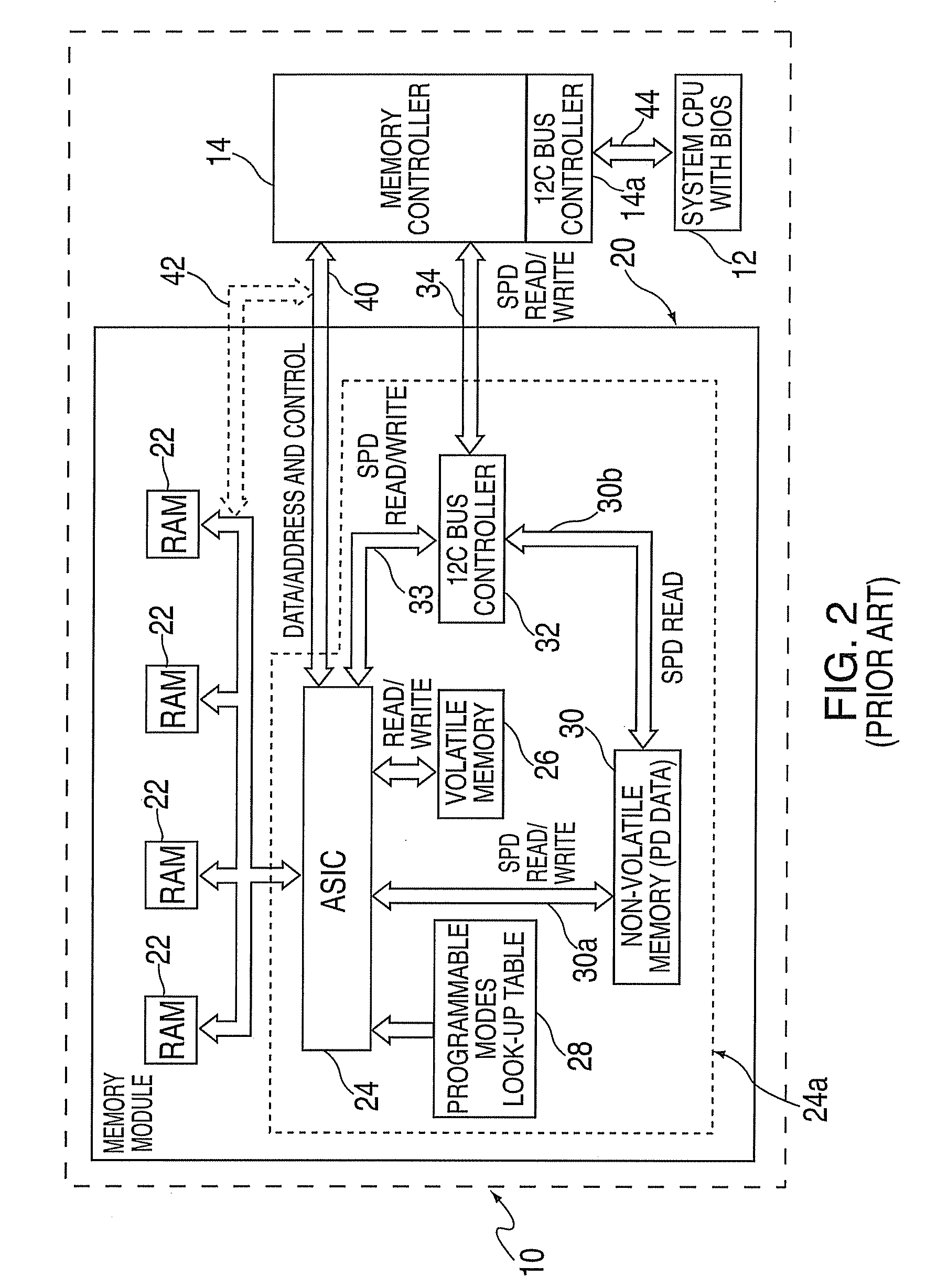
A method and apparatus for detecting insertion and removal of memory modules in a computer system using standard connectors is disclosed. A memory controller includes logic to read serial presence bits from memory modules incorporating such serial presence features. In response to system software the memory controller monitors a particular slot connector where a memory module is to be inserted or removed. Changes in the serial presence bits indicate insertion or removal. Each slot connector is further connectable to a memory bus for insertion and removal of memory modules while the computer system is operational.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Systems and methods for providing performance monitoring in a memory system
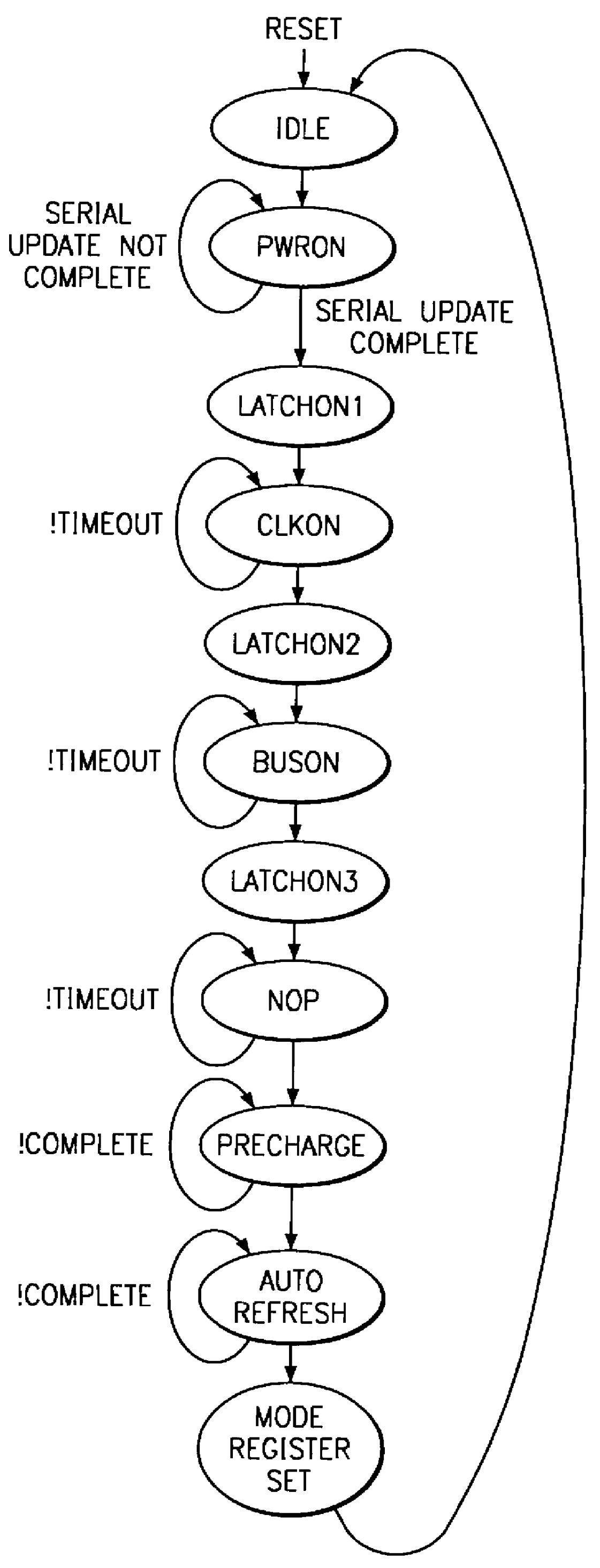
Systems and methods for providing performance monitoring in a memory system. Embodiments include a memory system for storing and retrieving data for a processing system. The memory system includes a memory controller, a plurality of memory devices, a memory bus and a memory hub device. The memory controller receives and responds to memory access requests. The memory bus is in communication with the memory controller. The memory hub device is in communication with the memory bus. The memory hub device includes a memory interface for transferring one or more of address, control and data information between the memory hub device and the memory controller via the memory bus. The memory hub device also includes a memory device interface for communicating with the memory devices. The memory hub device further includes a performance monitor for monitoring and reporting one or more of memory bus utilization, memory device utilization, and performance characteristics over defined intervals during system operation.
Owner:IBM CORP
High-speed data-rate converting and switching circuit
InactiveUS6854042B1Extended durationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital storageSignal onMemory bus
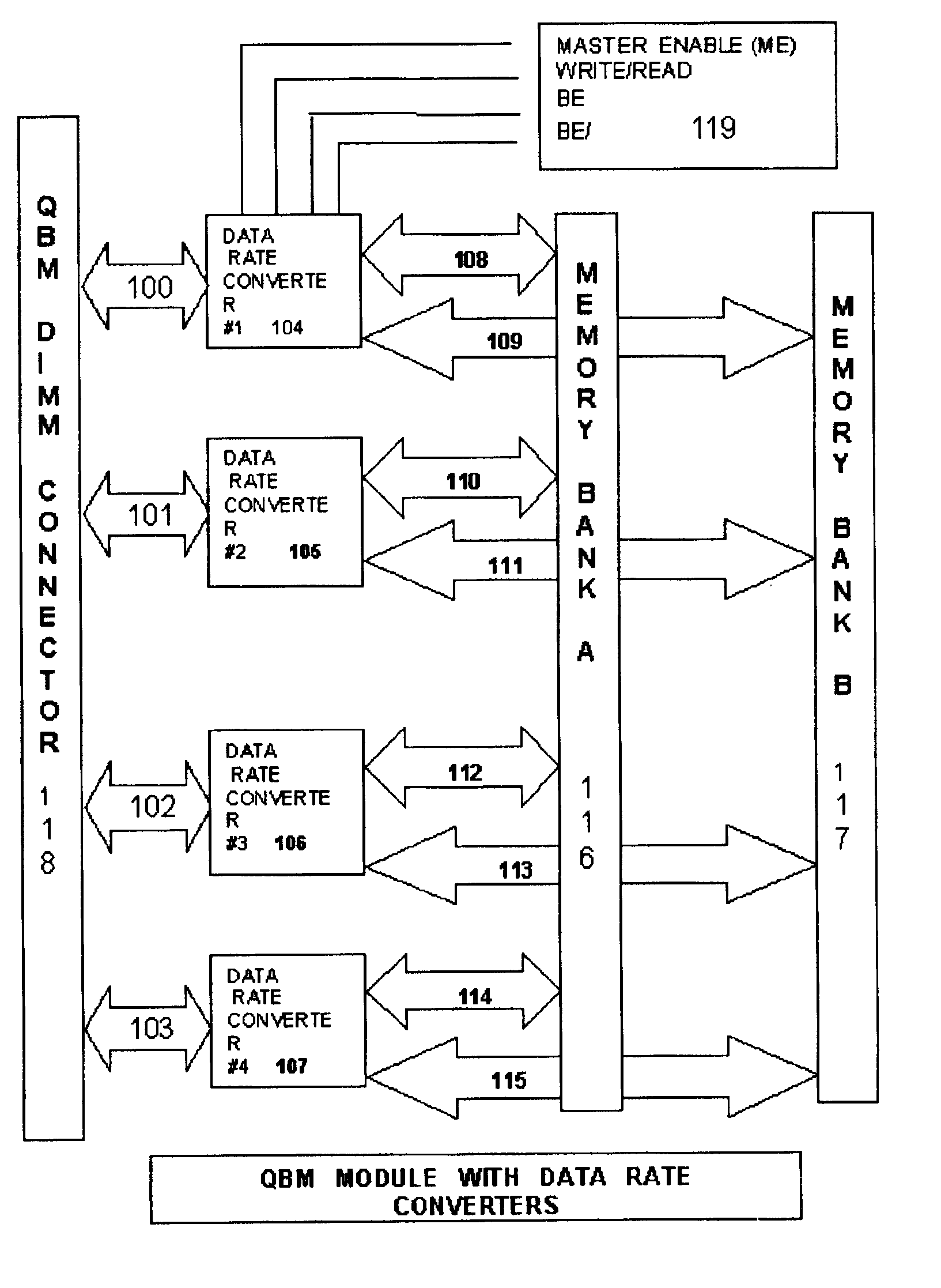
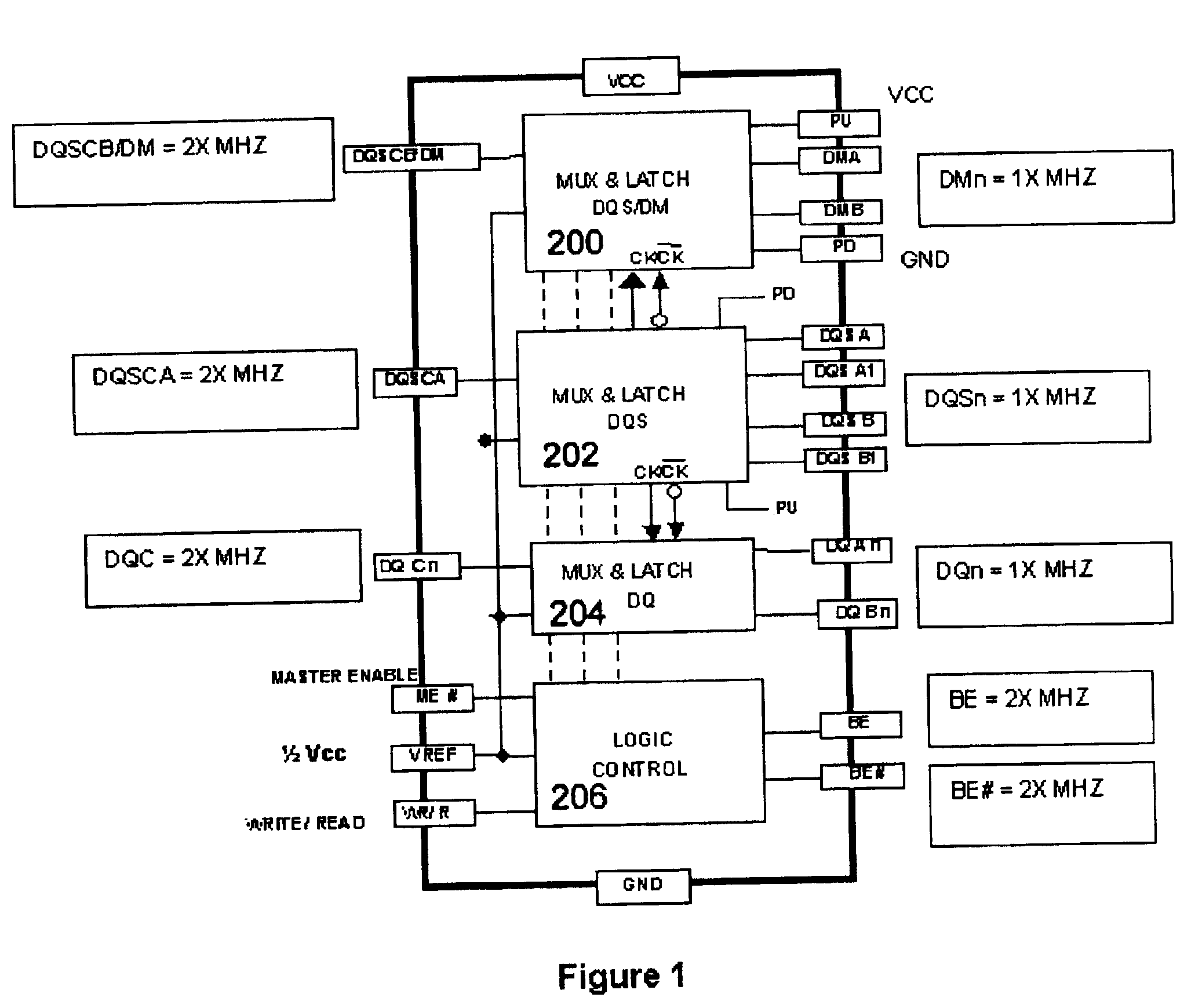
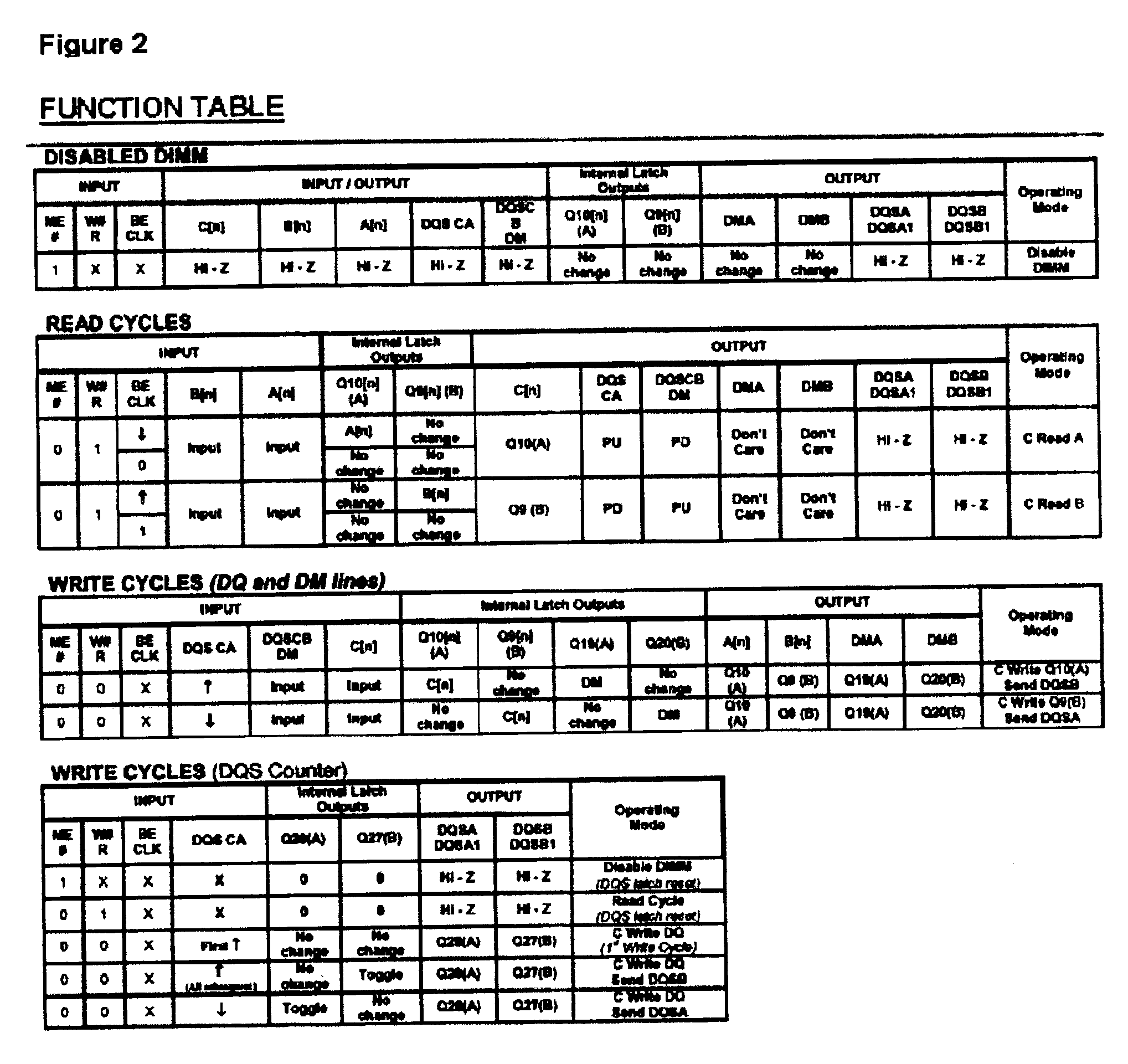
A high speed bidirectional data rate conversion circuit converts 1× data rate signals from attached devices on port A and port B to 2× data rate signals on bus C and further converts 2× high speed data rate signals on bus C to 1× data rate signals on ports A and B for memory devices attached to ports A and B. The usage of pass gate switches and combination of latches and counters is used to permit proper synchronization of the data signals, and to further generate strobe signals at both system bus and memory bus sides, and to further generate data mask signals for writing to the memory bus side of the circuit. The collection of such switching elements and latches are provided on a single silicon chip which includes of the functions of the invention.
Owner:URENSCHI ASSETAB LIABILITY
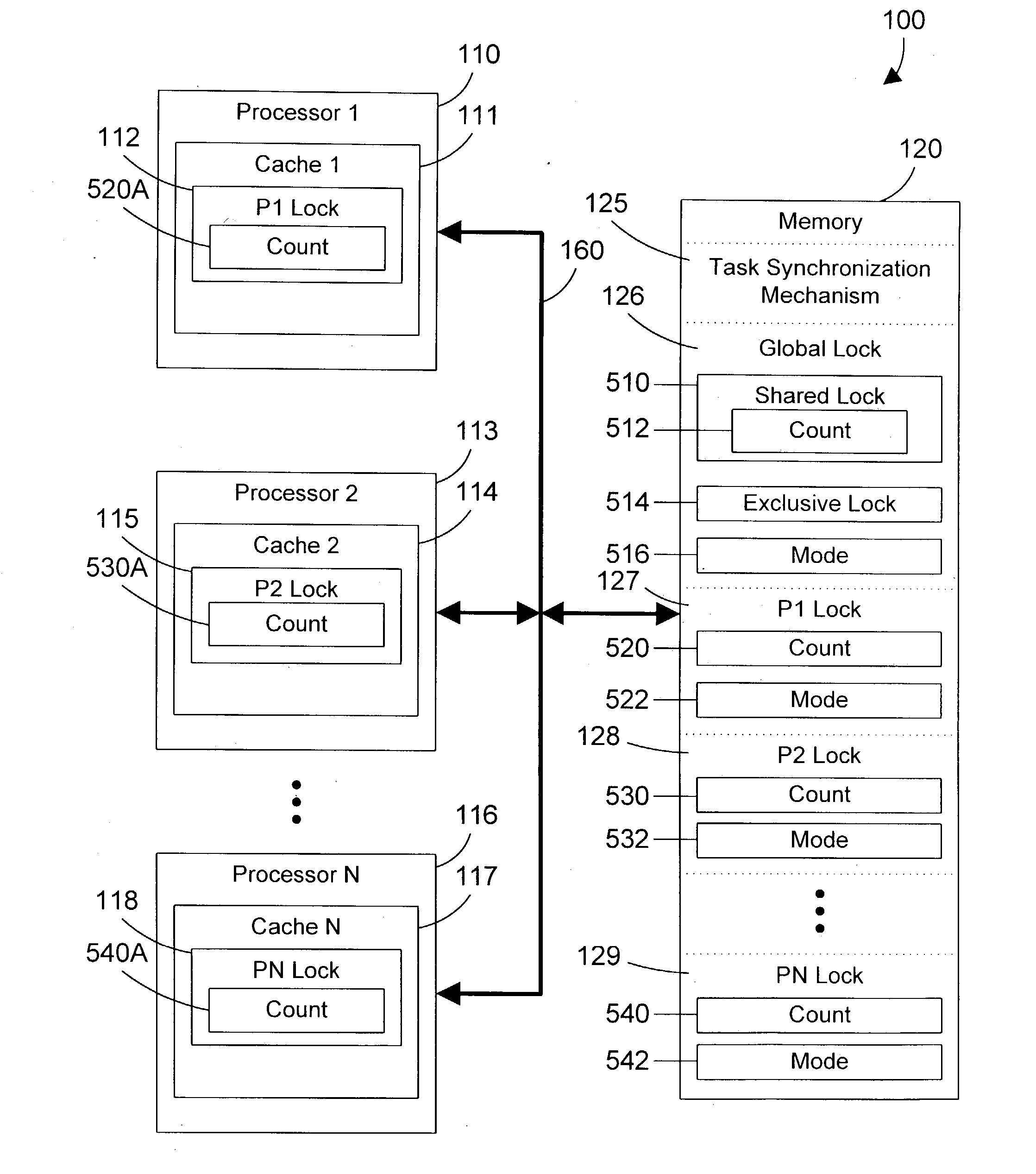
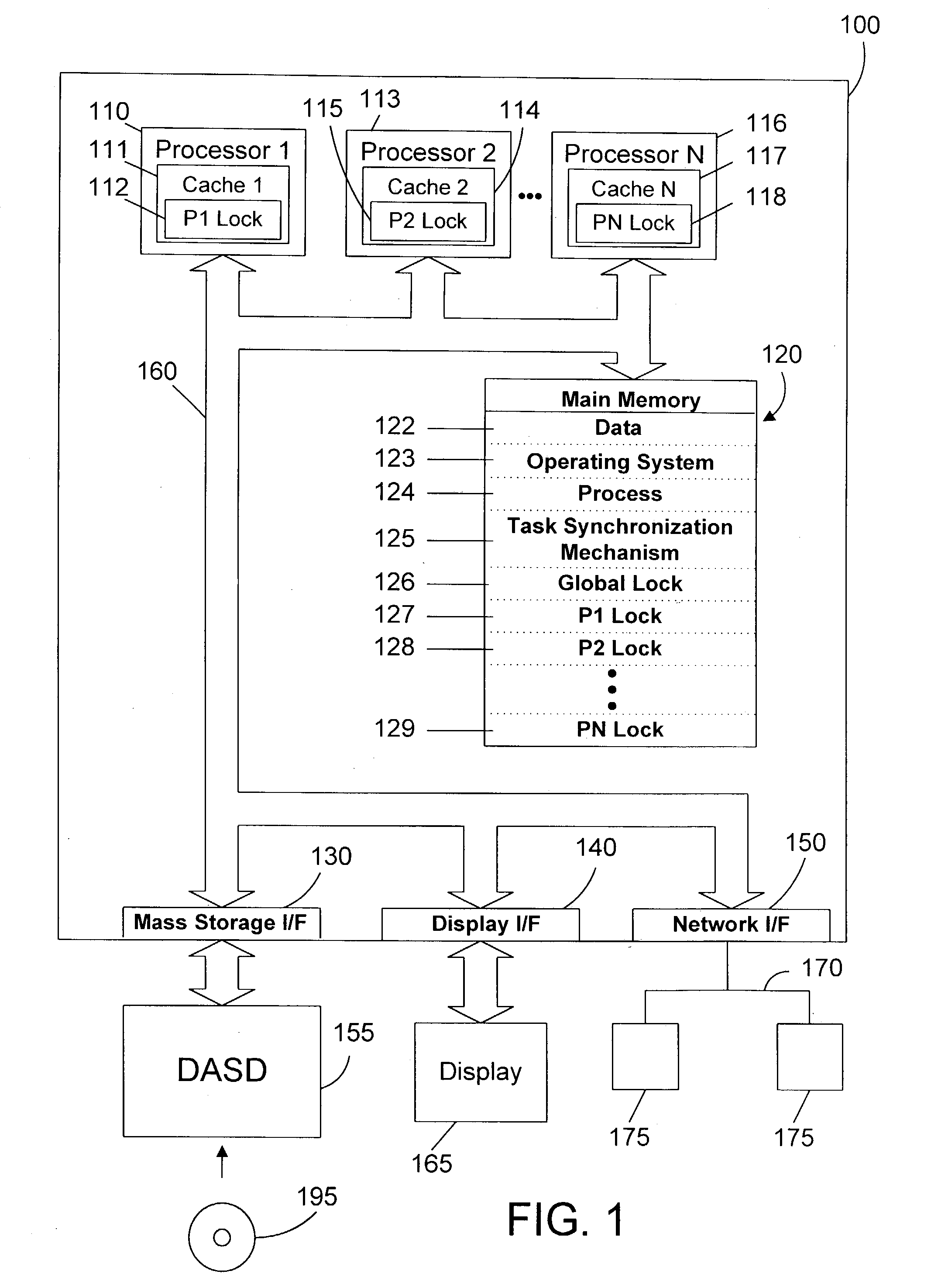
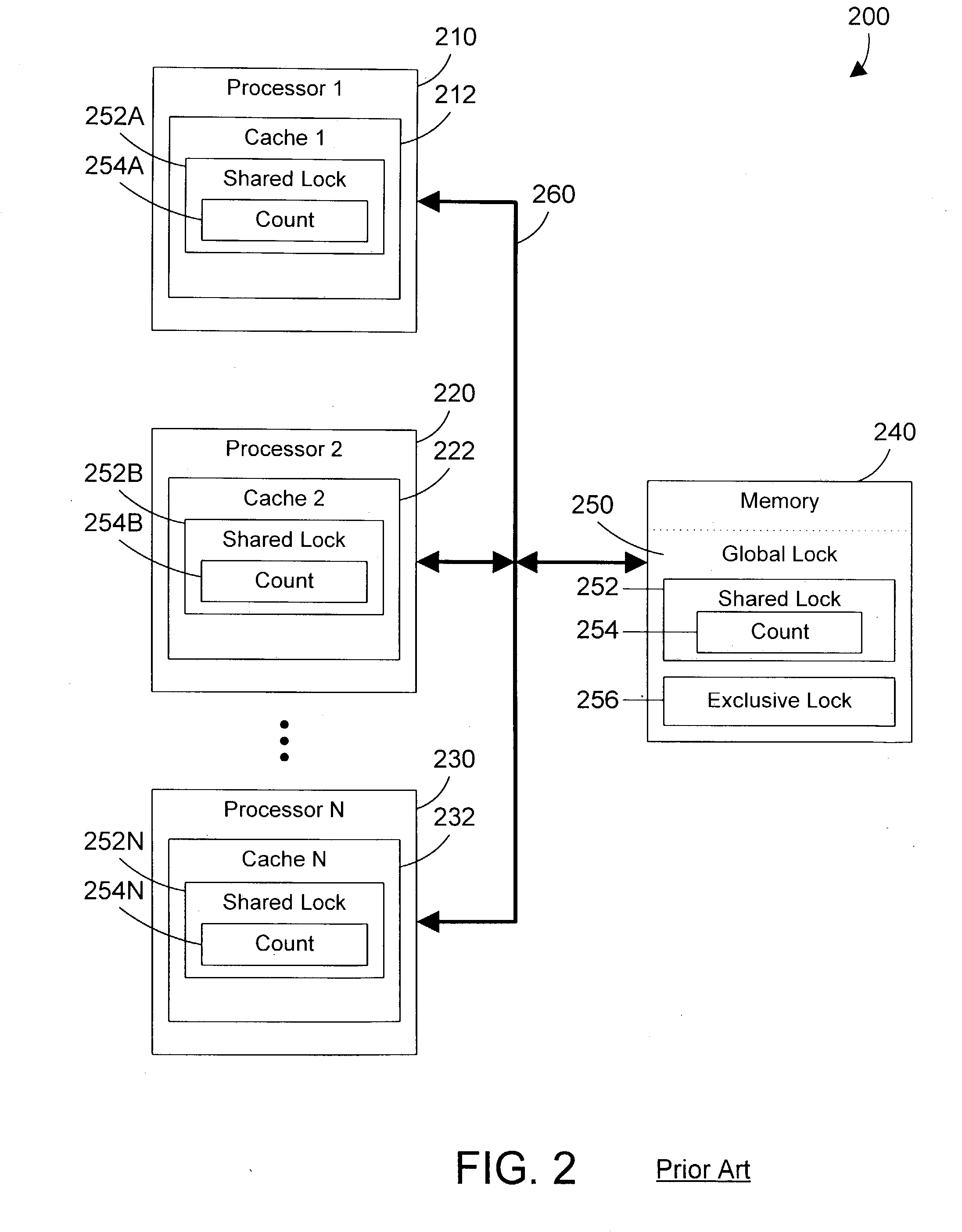
Task synchronization mechanism and method
ActiveUS20040143712A1Significant overheadSignificant performanceUnauthorized memory use protectionMultiprogramming arrangementsComputer architectureMemory bus
A task synchronization mechanism operates on a global lock that is shared between processors an on local locks that are not shared between processors. The local locks are processor-specific locks. Each processor-specific lock is dedicated to a particular processor in the system. When shared access to a resource is required, a processor updates its processor-specific lock to indicate the processor is sharing the resource. Because each processor-specific lock is dedicated to a particular processor, this eliminates a significant portion of the memory bus traffic associated with all processors reading and updating the same lock. When exclusive access to a resource is required, the requesting processor waits until the count of all processor-specific locks indicate that none of these processors have a lock on the resource. Once no processor has a lock on the resource, exclusive access to the resource may be granted. By changing from a single lock to multiple processor-specific locks, significant performance benefits are achieved by eliminating the memory bus traffic associated with caching a single lock to multiple processors.
Owner:IBM CORP
Memory module with integrated bus termination
A memory module includes a memory device, a connector, a plurality of lines coupling the memory device and the connector, and termination circuitry coupled to at least a subset of the lines. A method for terminating a memory bus includes providing at least two expansion sockets coupled to the memory bus; interfacing two expansion memory modules including termination circuitry with the expansion sockets; and disabling the termination circuitry for one of the expansion memory modules.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Synchronous flash memory emulating the pin configuration of SDRAM
InactiveUS6892270B2Improves operation of systemImprove operationRead-only memoriesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRandom access memoryComputerized system
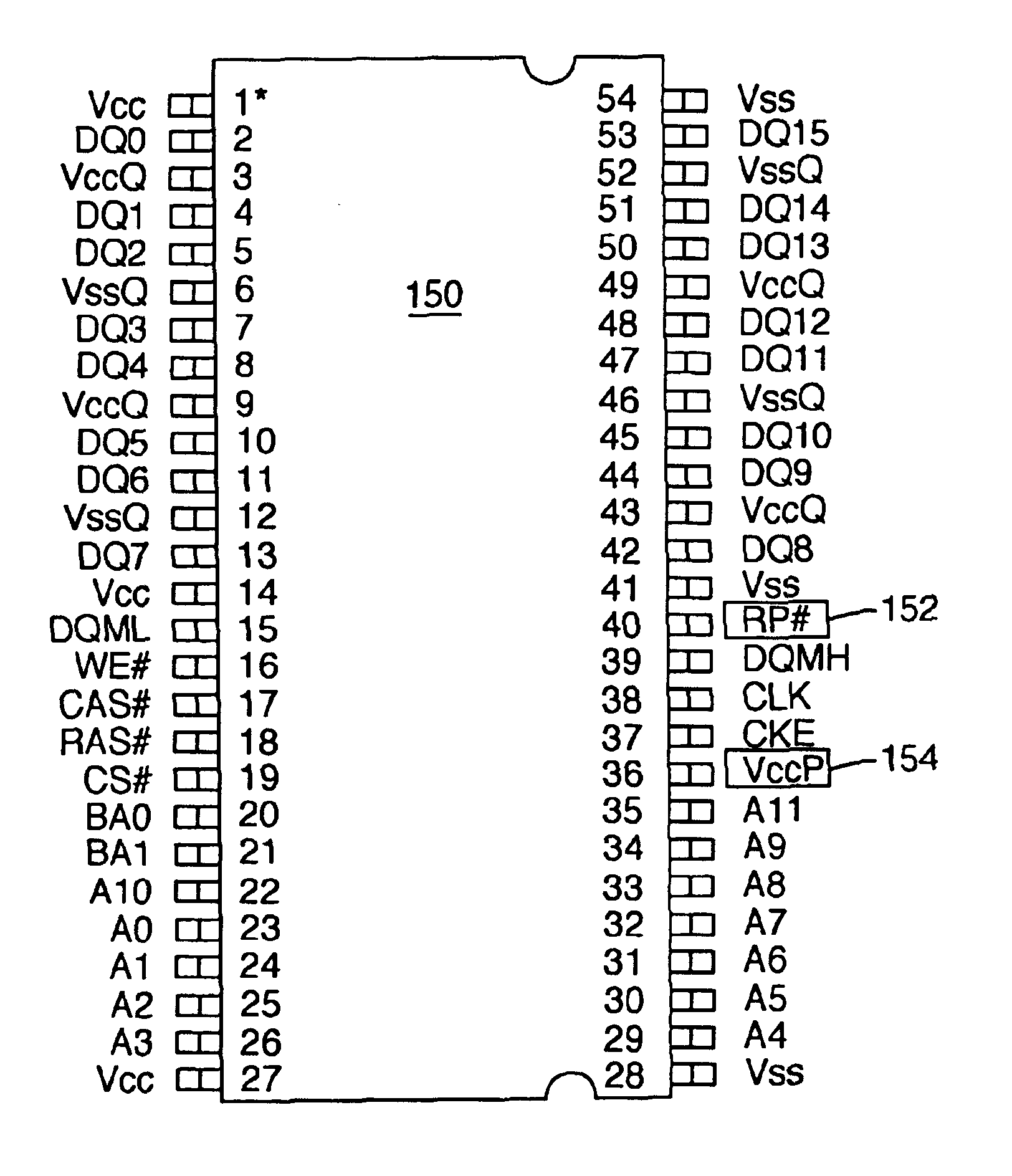
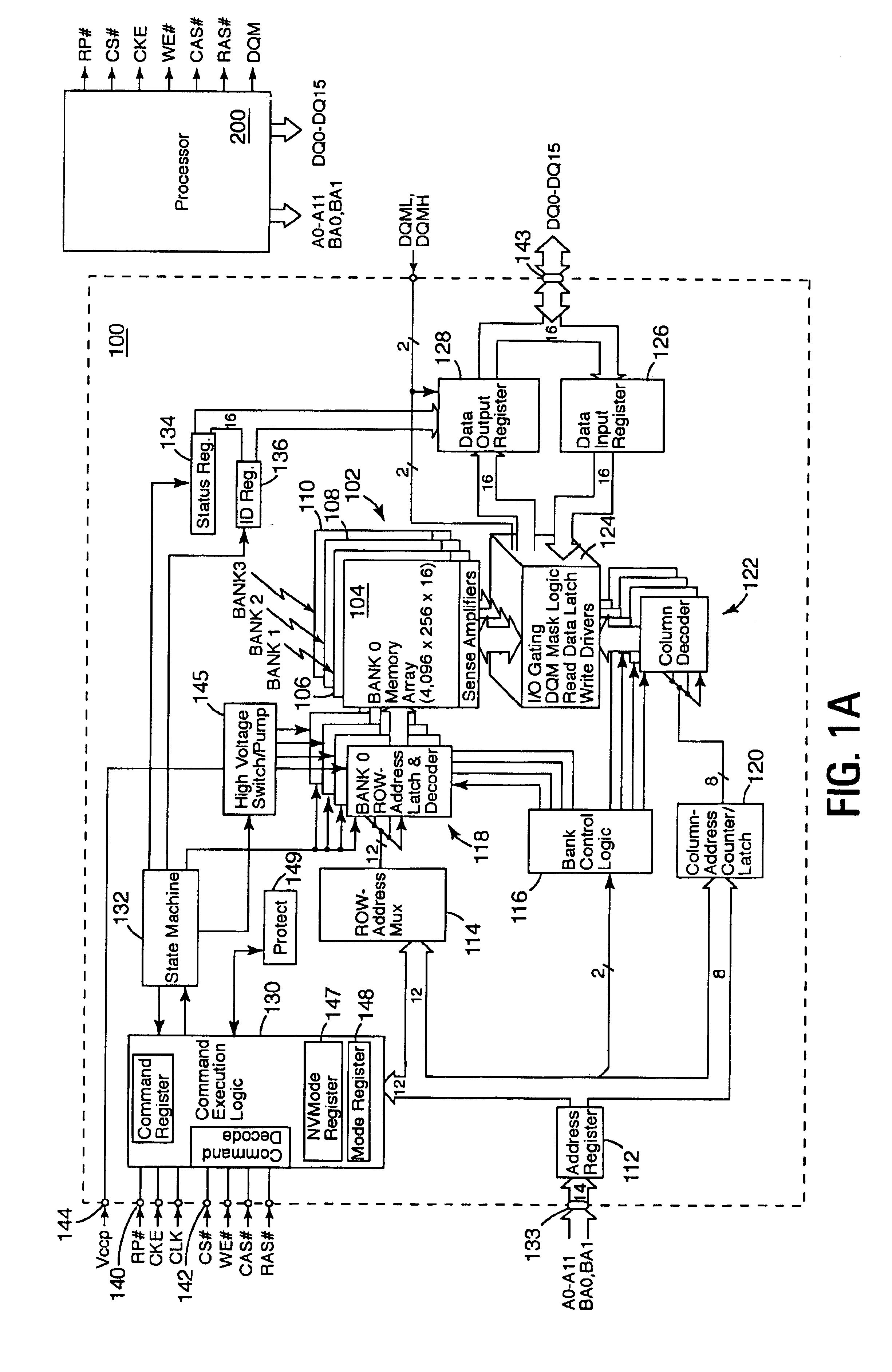
A computer system comprises a memory controller and a synchronous non-volatile memory device coupled to the memory controller via a main memory bus. The synchronous non-volatile memory device has external interconnects arranged in a manner that corresponds to interconnects of a synchronous dynamic random access memory device. The synchronous flash memory device, however, comprises a reset connection, and a Vccp power supply connection correspond to first and second no-connect (NC) interconnect pins of the synchronous dynamic random access memory. In one embodiment, the synchronous non-volatile memory device has a command interface comprising a write enable connection (WE#) to receive a write enable signal, a column address strobe connection (CAS#) to receive a column address strobe signal, a row address strobe connection (RAS#) to receive a row address strobe signal, and a chip select connection (CS#) to receive a chip select signal.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Wireless flash memory card expansion system
ActiveUS20070239929A1Multiple digital computer combinationsMemory systemsMemory busFlash memory controller
A Flash memory card system is disclosed. The Flash memory card system comprises a Flash memory wireless host adapter and a Flash memory bus wireless device. The Flash memory wireless host adapter comprises a Flash memory card connector and a Flash memory controller coupled to the Flash memory card connector. The Flash-52 memory card signals are converted to standard Flash memory internal bus signals by the Flash memory controller. The host adapter further comprises a Flash memory wireless module coupled to the Flash memory controller for receiving and transmitting the standard Flash memory bus signals wirelessly. The Flash-51 memory bus wireless device comprises a Flash memory bus wireless device adapter coupled to a Flash memory. The device adapter is paired to the wireless module for receiving and transmitting the standard Flash memory bus signals wirelessly. A host device storage capacity utilizing the Flash memory card system is expanded.
Owner:KINGSTON DIGITAL CO LTD
System and method of interfacing co-processors and input/output devices via a main memory system
ActiveUS8713379B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionCoprocessorMemory bus
A system for interfacing with a co-processor or input / output device is disclosed. According to one embodiment, the system includes a computer processing unit, a memory module, a memory bus that connects the computer processing unit and the memory module, and a co-processing unit or input / output device, wherein the memory bus also connects the co-processing unit or input / output device to the computer processing unit.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
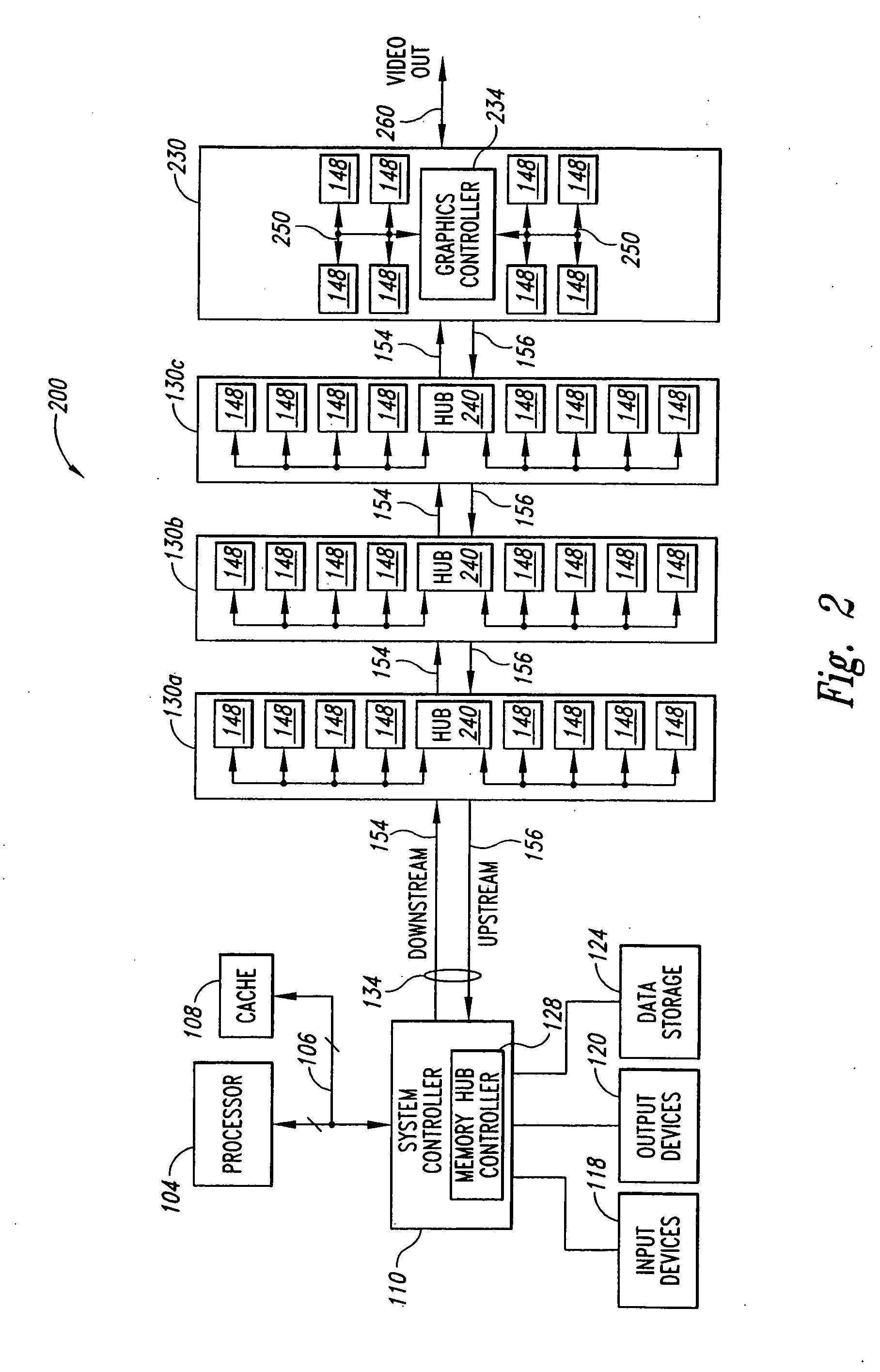
System and method for memory hub-based expansion bus
InactiveUS20060179208A1Multiplex communicationUnauthorized memory use protectionMemory busTerm memory
A system memory includes a memory hub controller, a memory module accessible by the memory hub controller, and an expansion module having a processor circuit coupled to the memory module and also having access to the memory module. The memory hub controller is coupled to the memory hub through a first portion of a memory bus on which the memory requests from the memory hub controller and memory responses from the memory hub are coupled. A second portion of the memory bus couples the memory hub to the processor circuit and is used to couple memory requests from the processor circuit and memory responses provided by the memory hub to the processor circuit.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
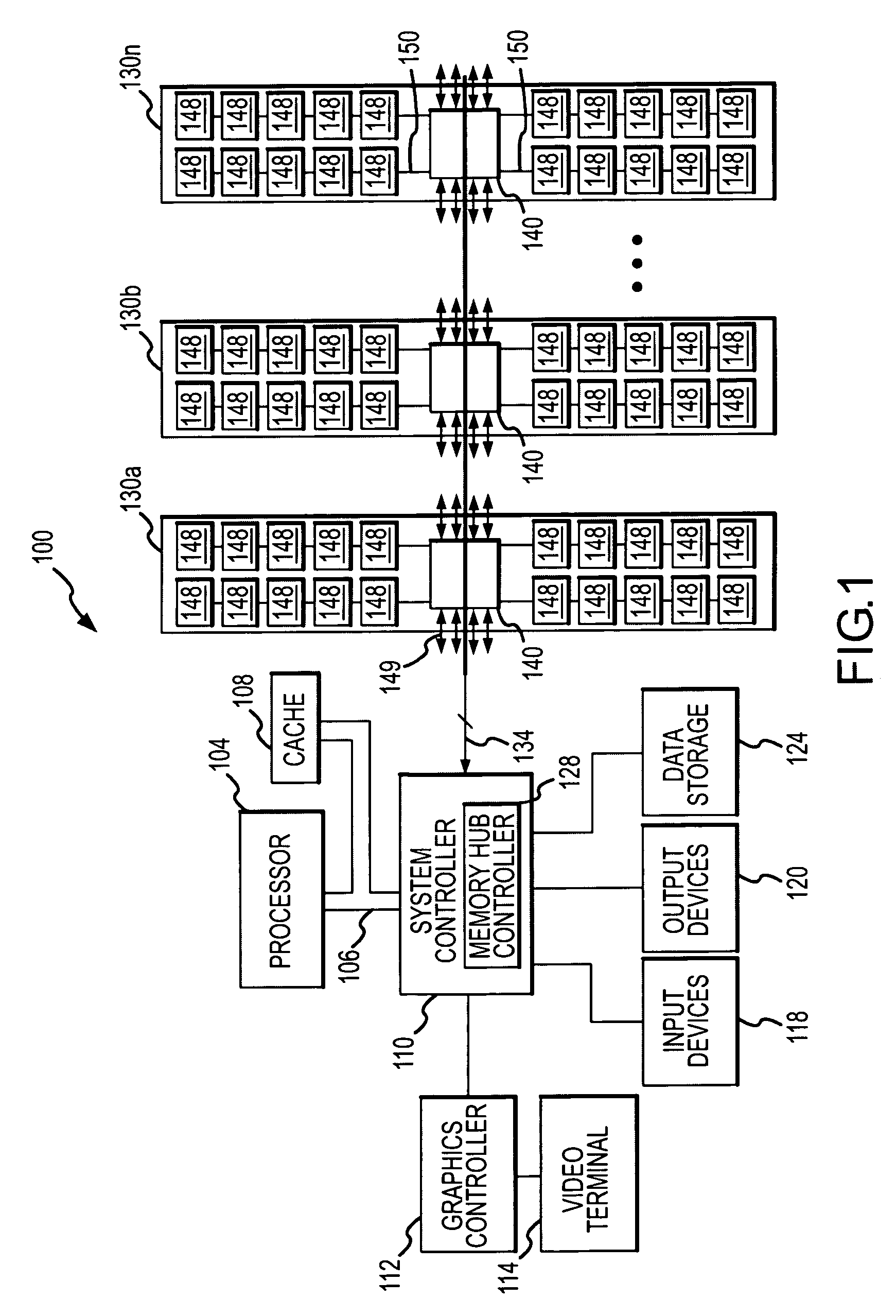
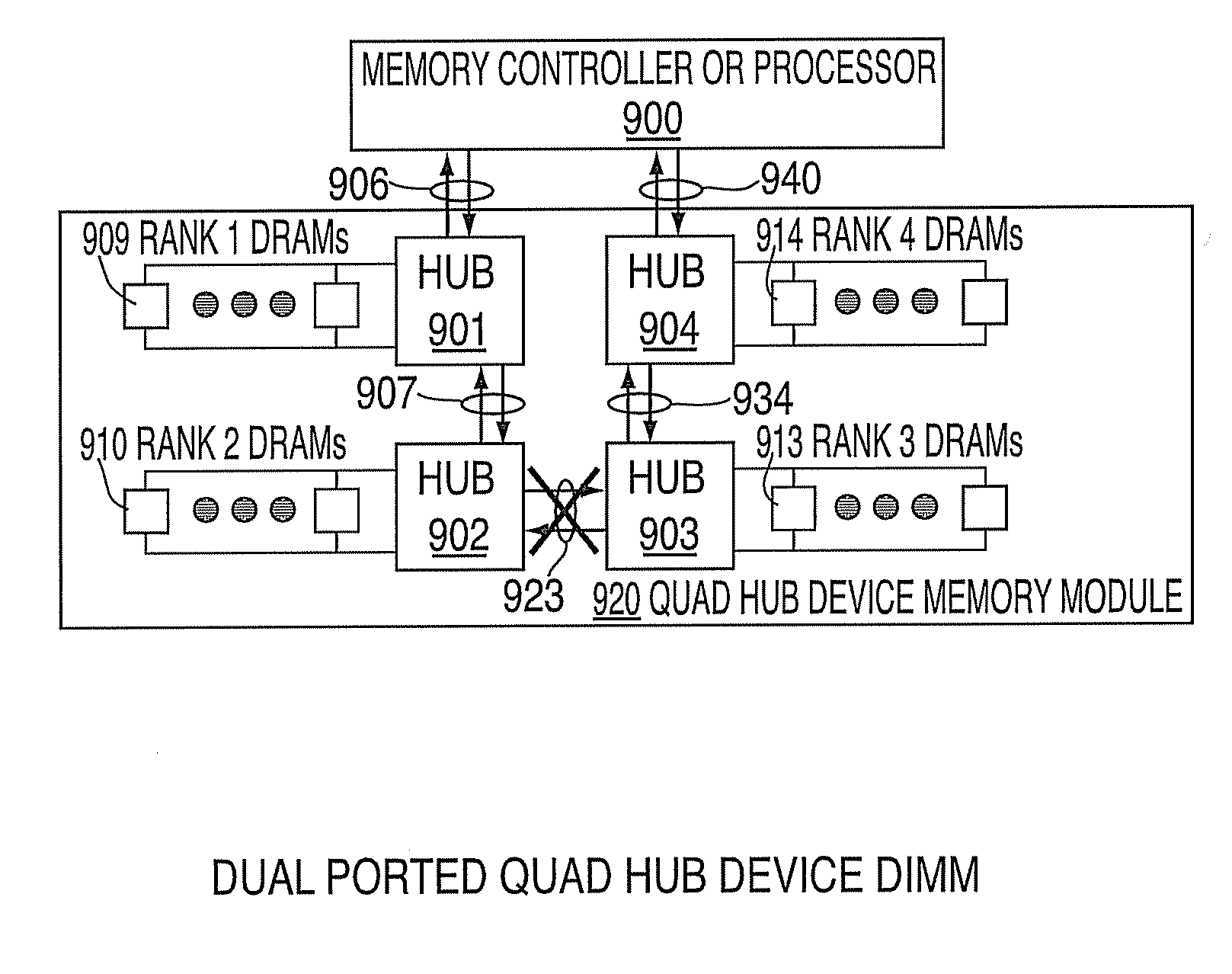
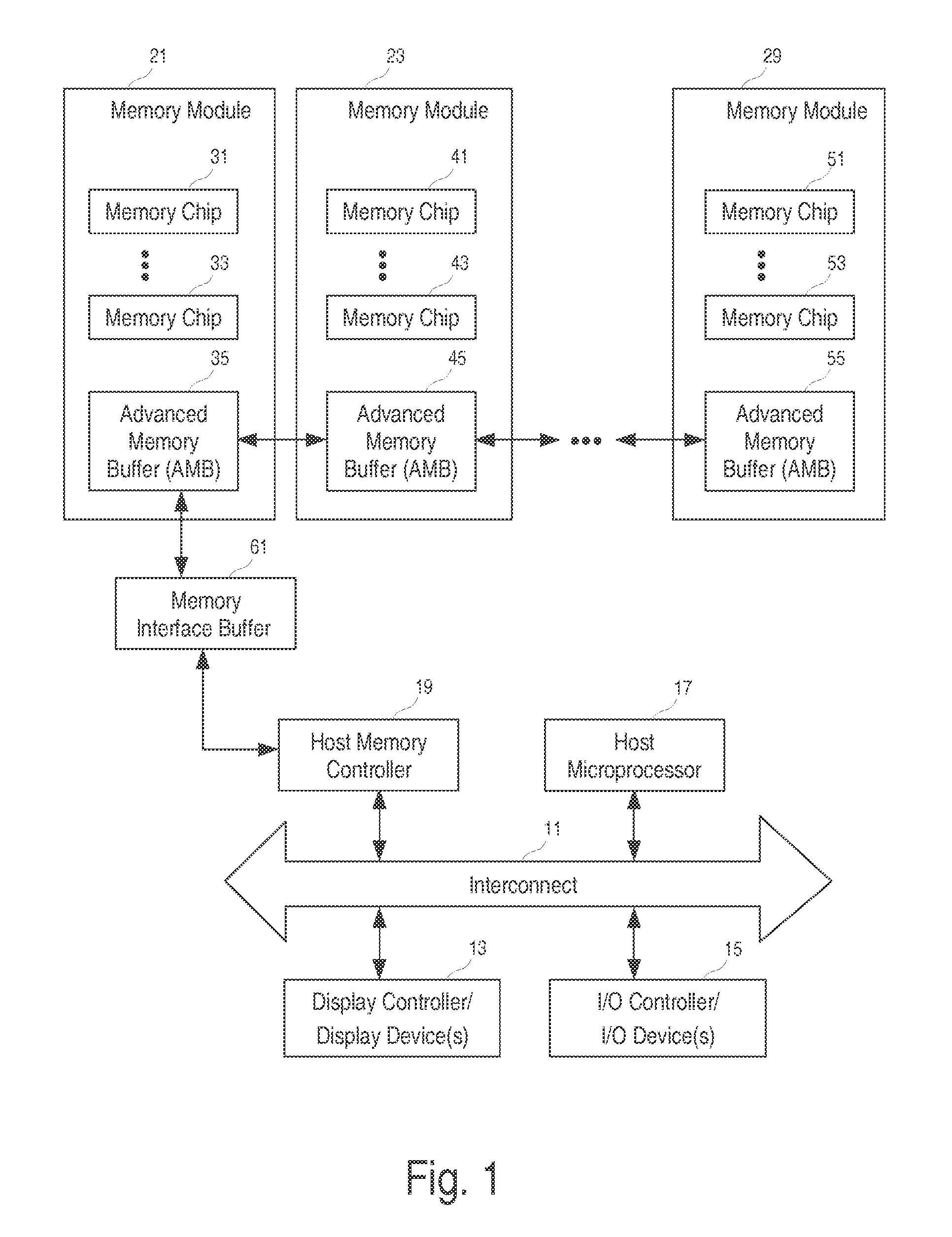
Branching Memory-Bus Module with Multiple Downlink Ports to Standard Fully-Buffered Memory Modules
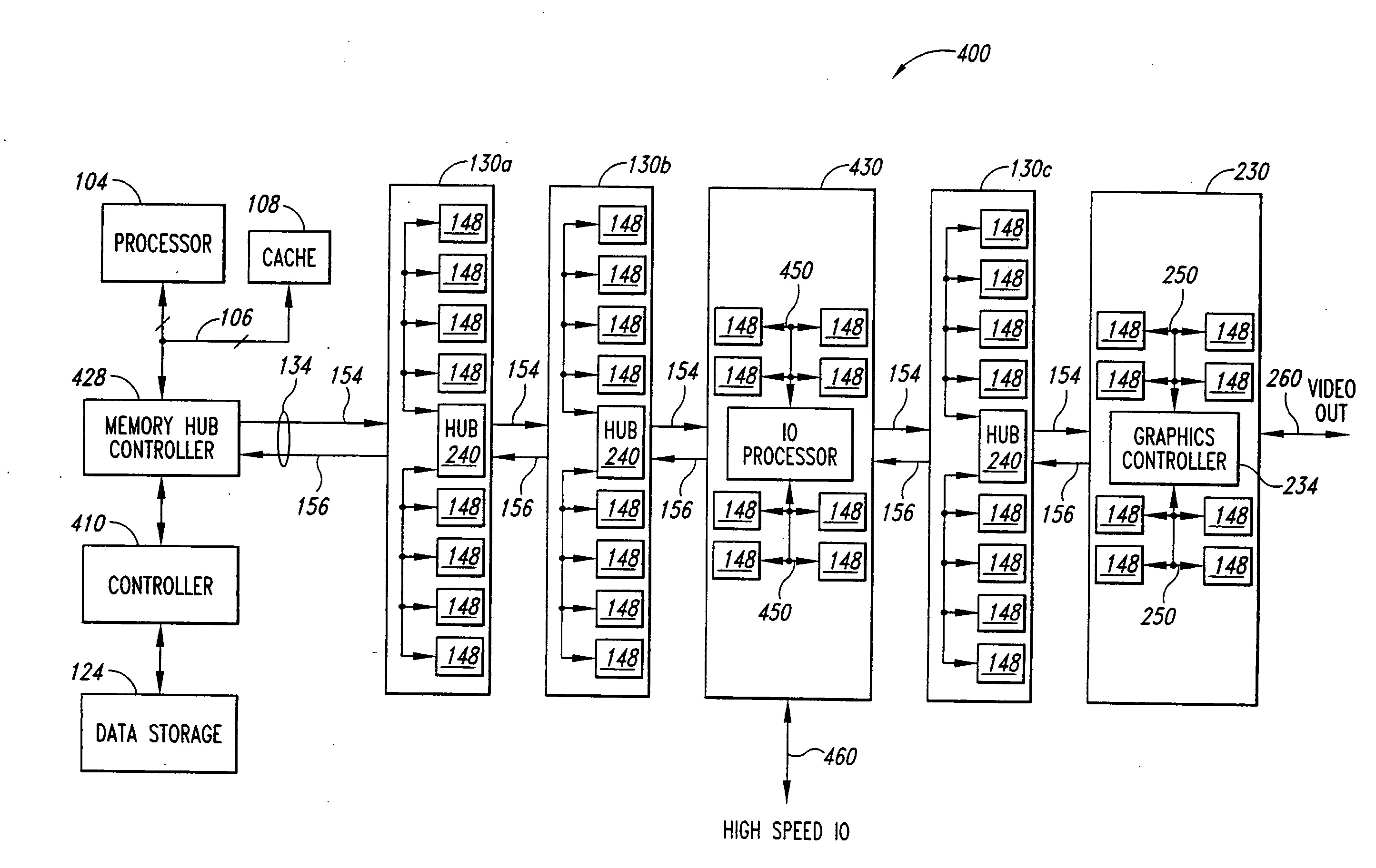
A branching memory-bus module has one uplink port and two or more downlink ports. Frames sent downstream by a host processor are received on the uplink port and repeated to the multiple downlink ports to two or more branches of memory modules. Frames sent upstream to the processor by a memory module on a downlink port are repeated to the uplink port. A branching Advanced Memory Buffer (AMB) on the branching memory-bus module has re-timing and re-synchronizing buffers that repeat frames to the multiple downlink ports. Elastic buffers can merge and synchronize frames from different downlink branches. Separate northbound and southbound lanes may be replaced by bidirectional lanes to reduce pin counts. Latency from the host processor to the farthest memory module is reduced by branching compared with a serial daisy-chain of fully-buffered memory modules. Point-to-point bus segments have only two endpoints despite branching by the branching AMB.
Owner:MONTAGE TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Systems and methods for providing memory modules with multiple hub devices
InactiveUS20070276977A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationInput/output processes for data processingMemory busMemory controller
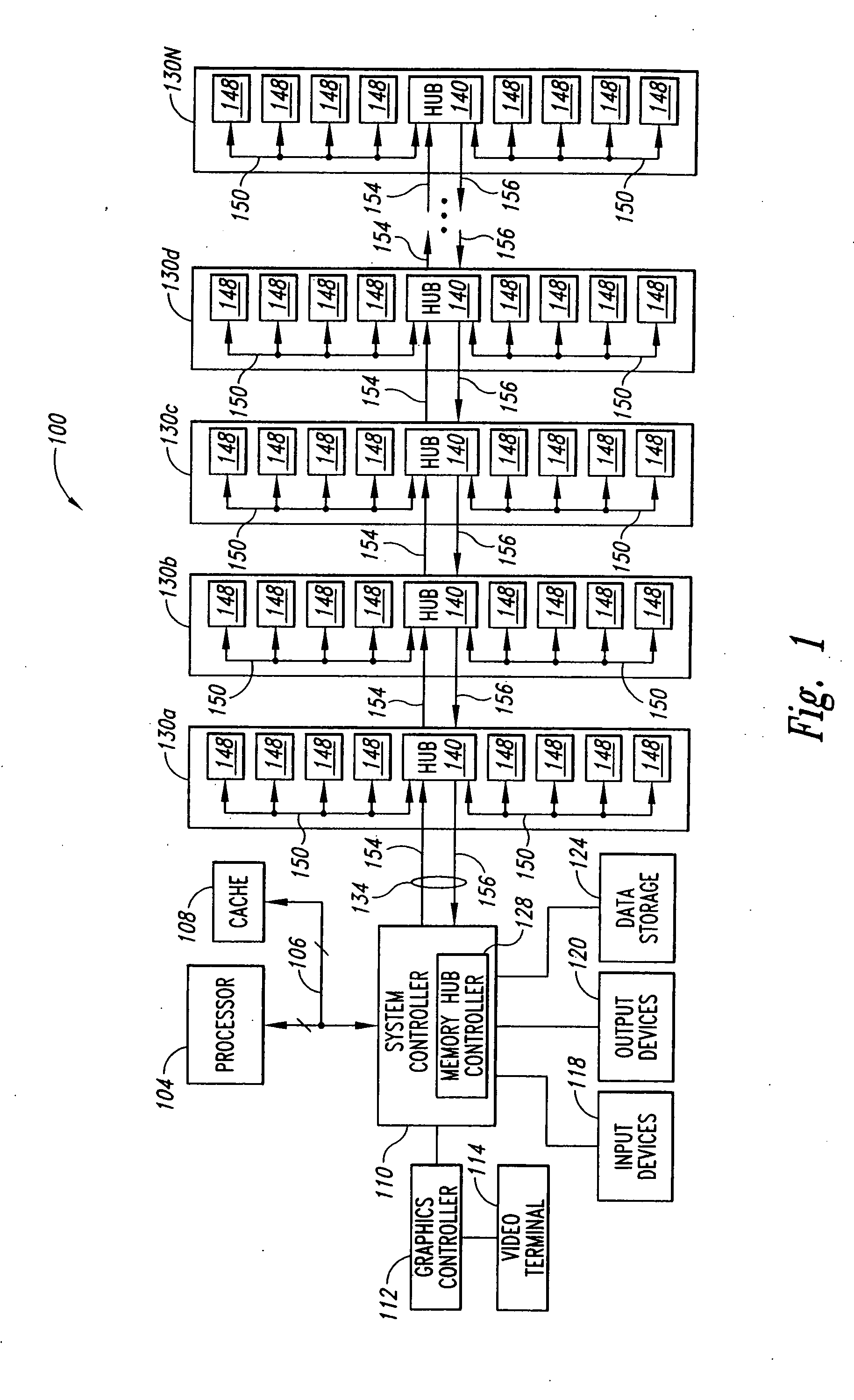
Systems and methods for providing memory modules with multiple hub devices. Exemplary systems include a cascade-interconnect memory system with a memory bus, a memory controller and a memory module. The memory controller is in communication with the memory bus for generating, receiving and responding to memory access requests. The memory module includes a first hub device with three or more ports and a second hub device with three or more ports. A first port on the first hub device is in communication with the memory controller via the memory bus, a second port on the first hub device is in communication with a first set of memory devices, and a third port on the first hub device is cascade connected to a first port on the second hub device. A second port on the second hub device is in communication with a second set of memory devices and a third port on the second hub device supports a cascaded connection to a subsequent hub device in the memory system.
Owner:IBM CORP
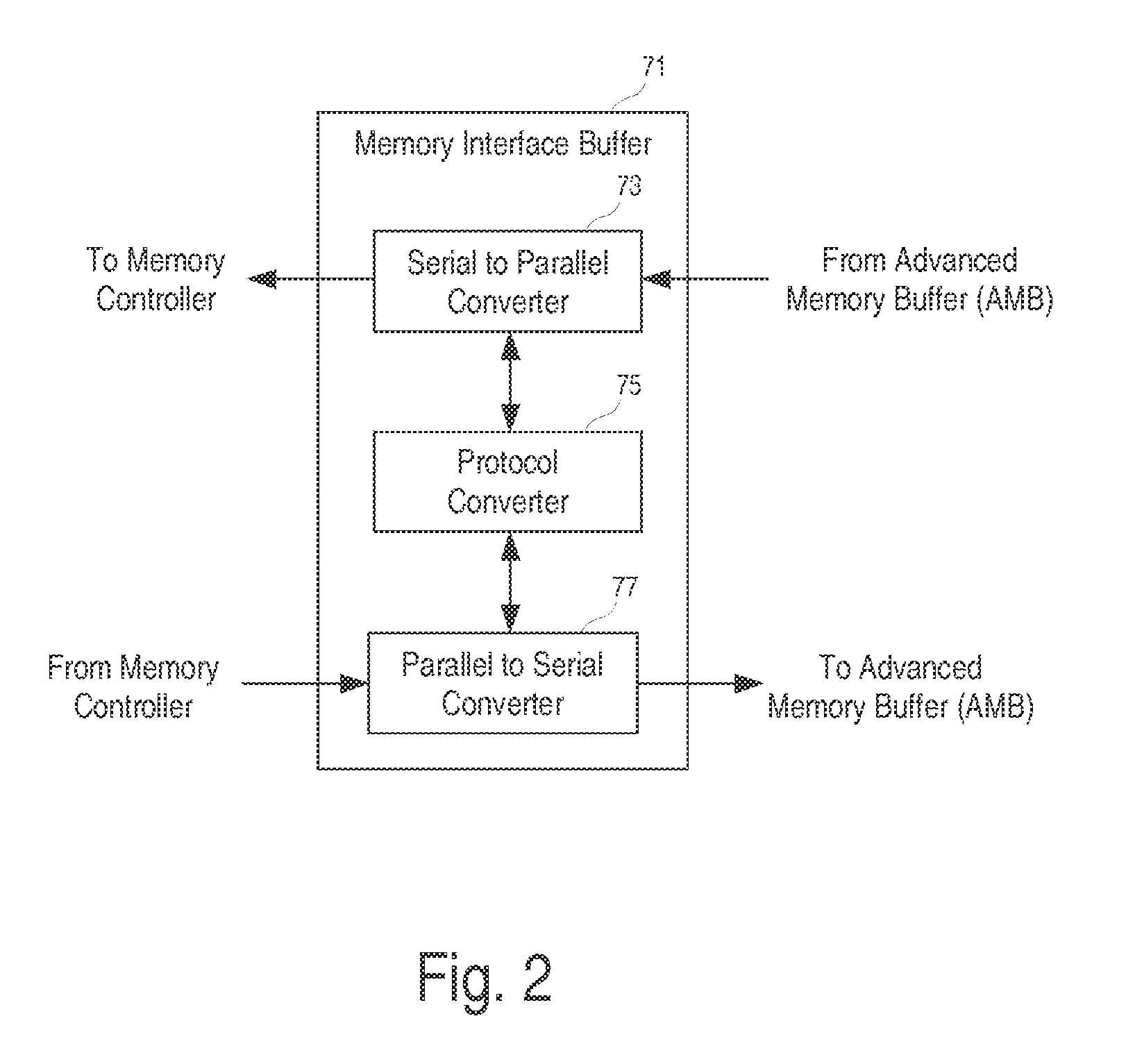
Memory interface to bridge memory buses
A memory interface to bridge a parallel memory bus and a serial memory bus. One embodiment includes a printed circuit board, comprising: at least one memory interface buffer chip to connect an advanced memory buffer (AMB) interface and one or more non-fully buffered memory modules.
Owner:MONTAGE TECH HLDG CO LTD
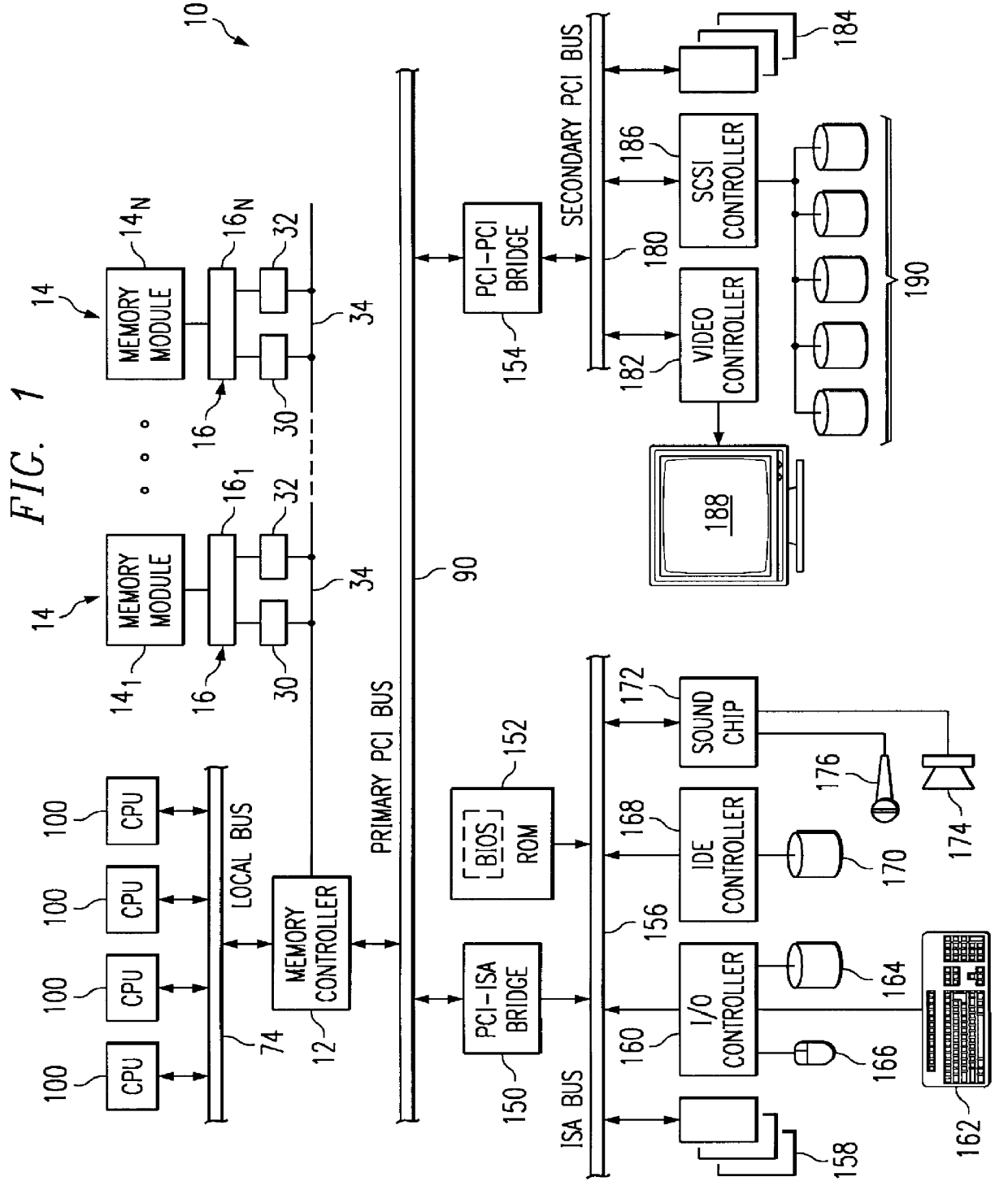
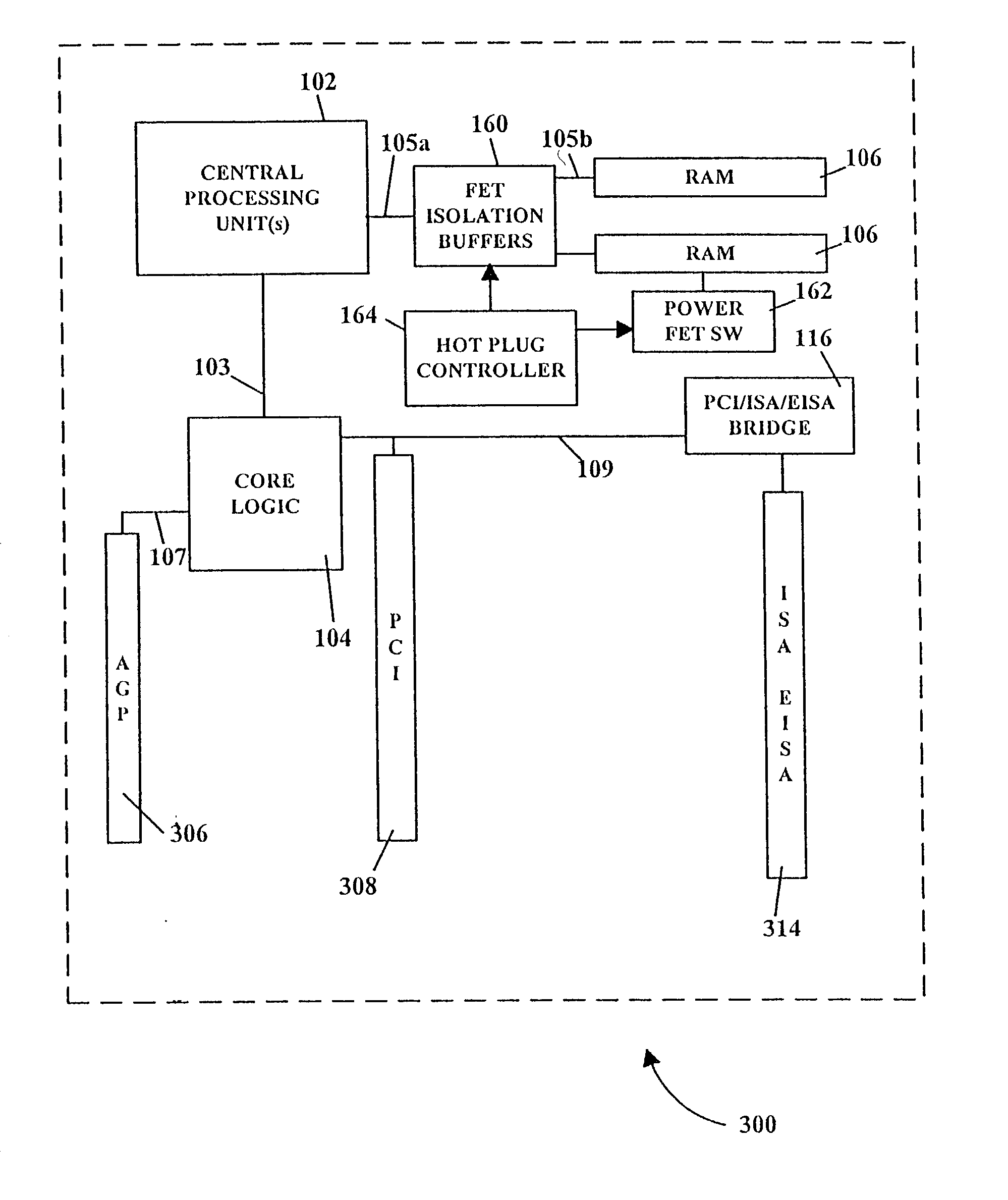
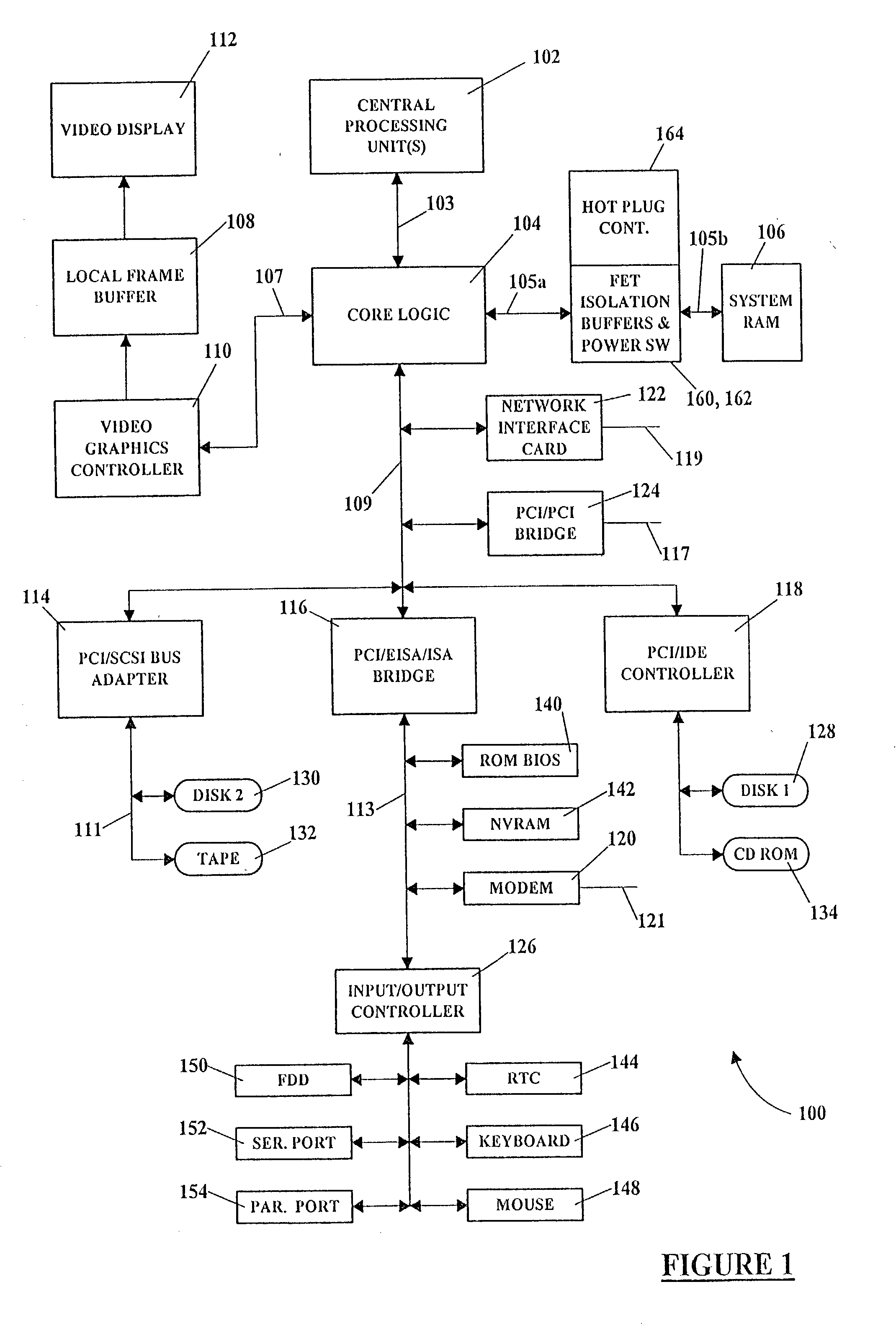
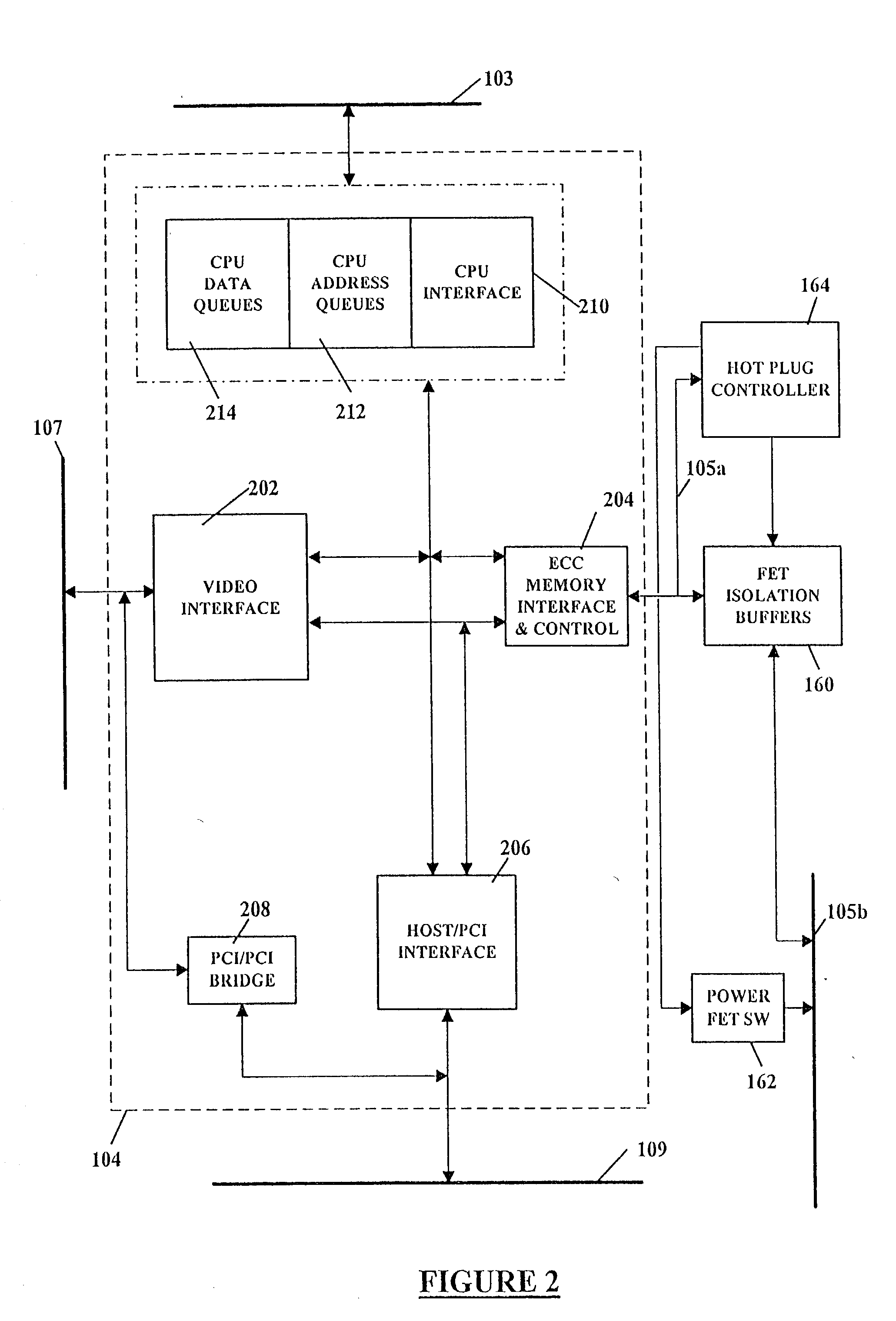
Replacement, upgrade and/or addition of hot-pluggable components in a computer system
InactiveUS20020129186A1Component plug-in assemblagesElectric digital data processingOperational systemMemory bus
A computer system adapted for hot-pluggable components such as memory modules that may be replaced, upgraded and / or added without disturbing normal operation of the computer system. A failing memory module may be replaced by copying its contents to a new memory module in a background operation while the computer system runs its operating system and applications programs. When all contents are copied to the new memory module, the failing memory module may be removed without having to shut down the computer system. Computer system memory may be upgraded or added to by inserting the new memory module(s) into vacant disconnected memory connectors, whereupon the computer system automatically recognizes the new memory module(s), synchronously connects the new memory module(s) to the computer system memory bus, initializes the new memory module(s), and then notifies the operating system that the new memory module(s) is available, all without disturbing normal operation of the computer system.
Owner:COMPAQ COMP CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com