Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38 results about "Accelerated Graphics Port" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
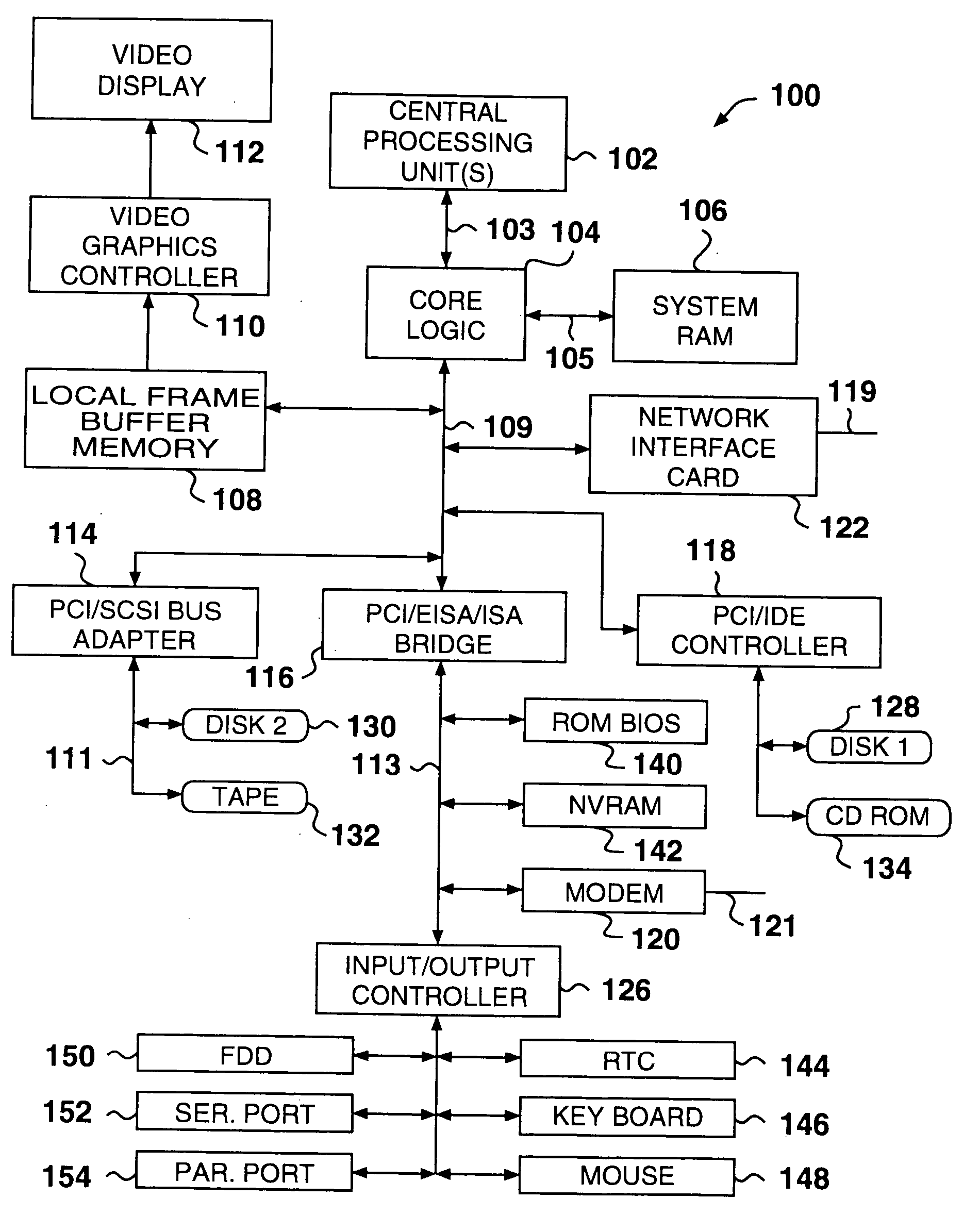
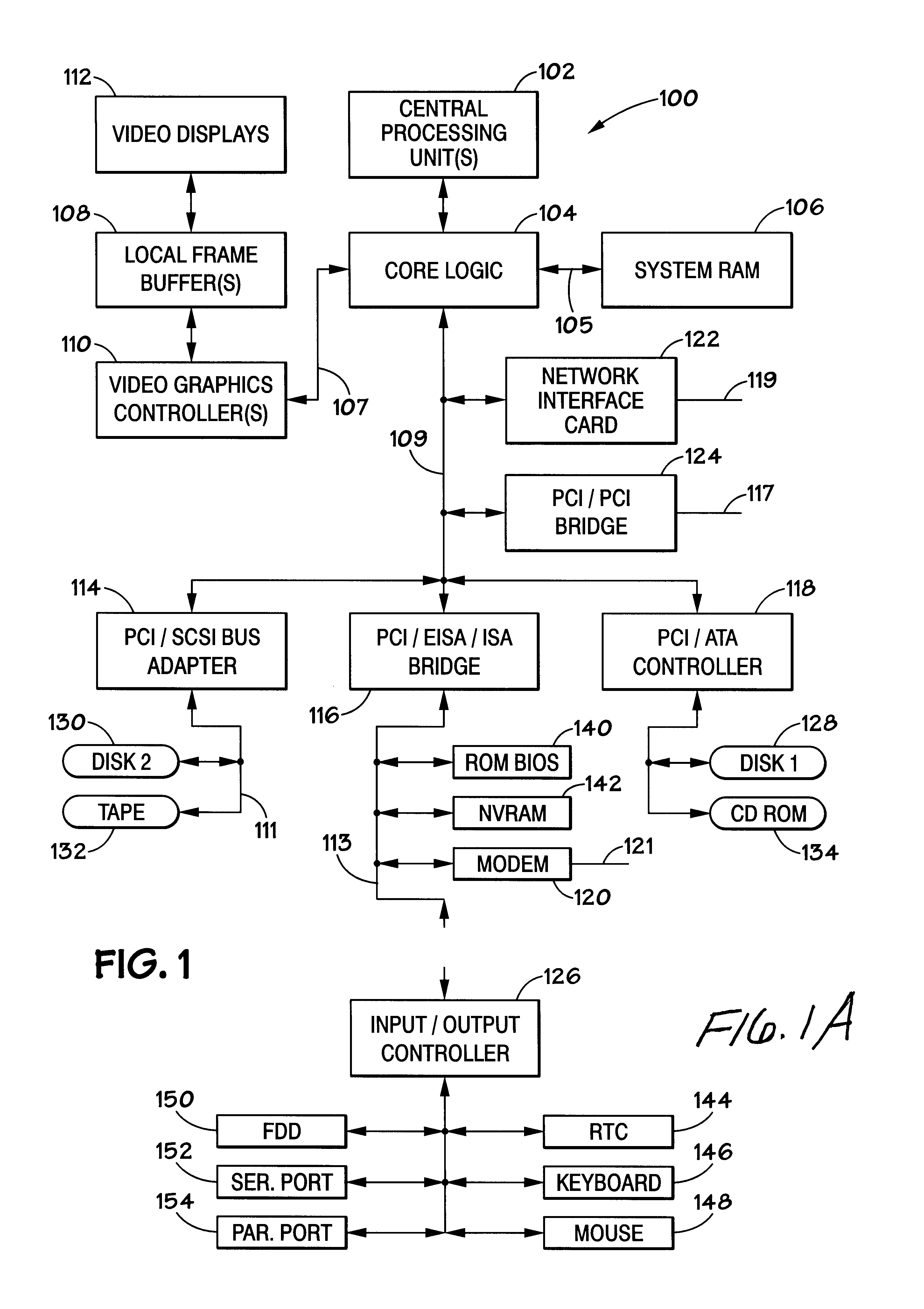
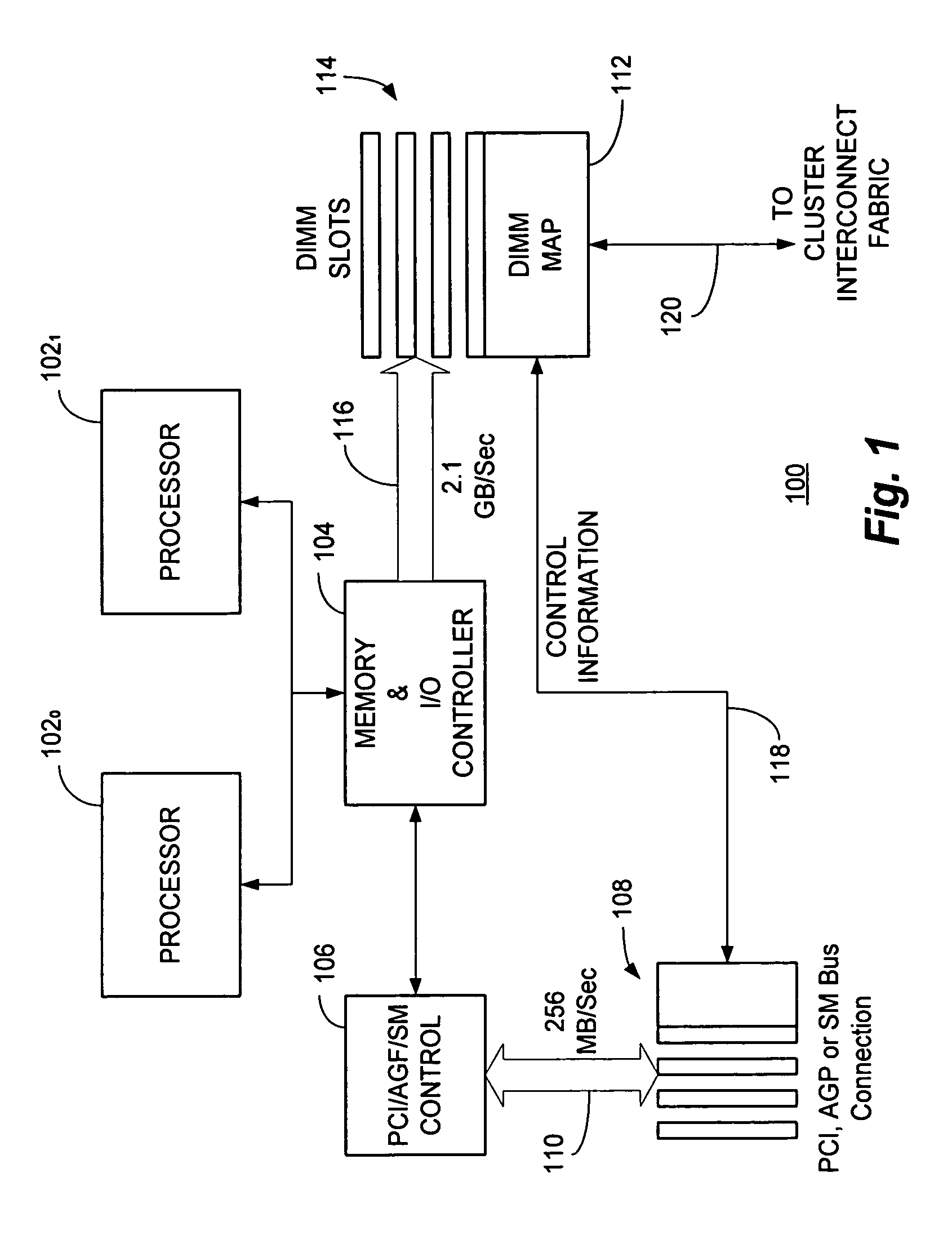
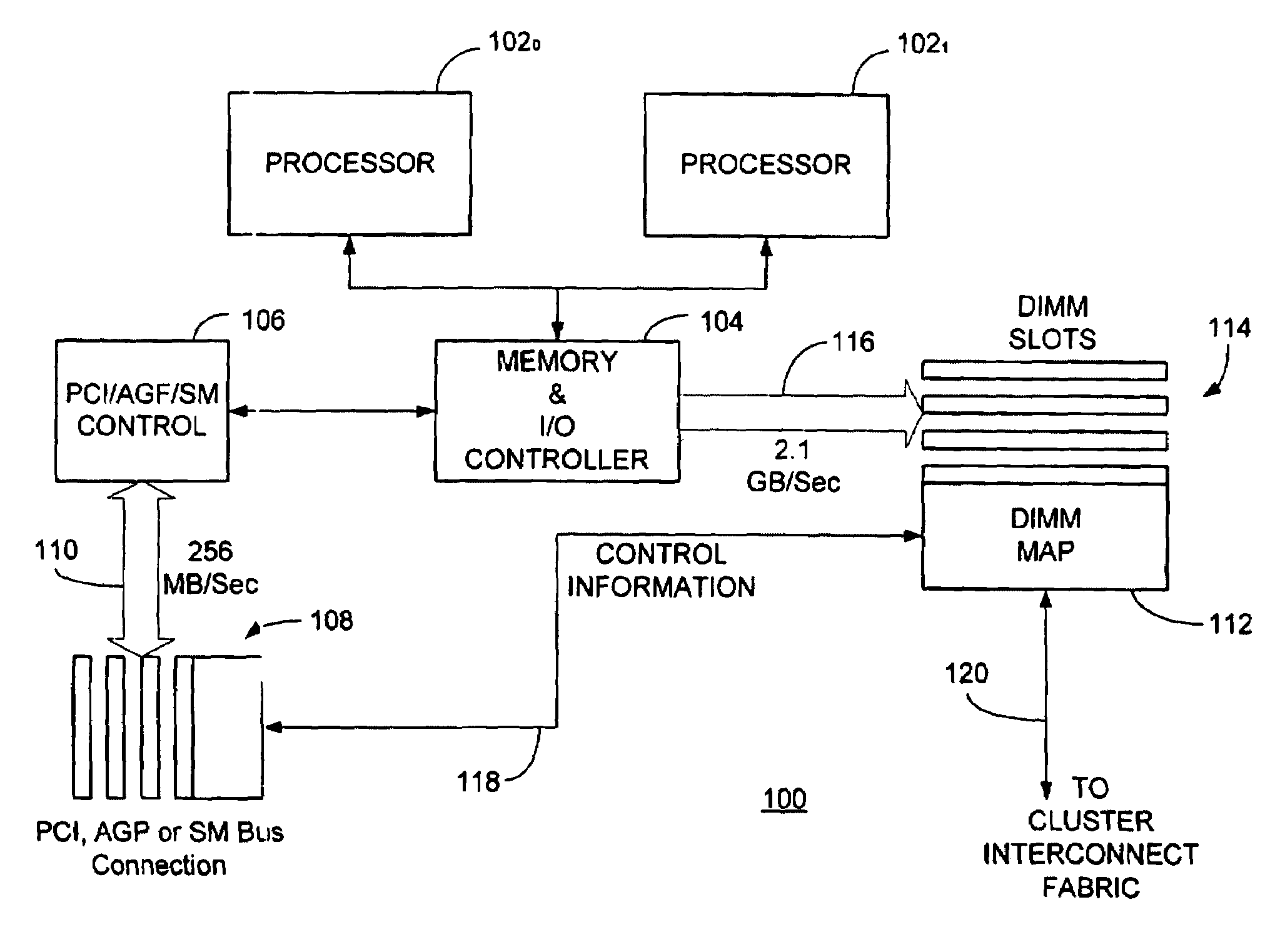
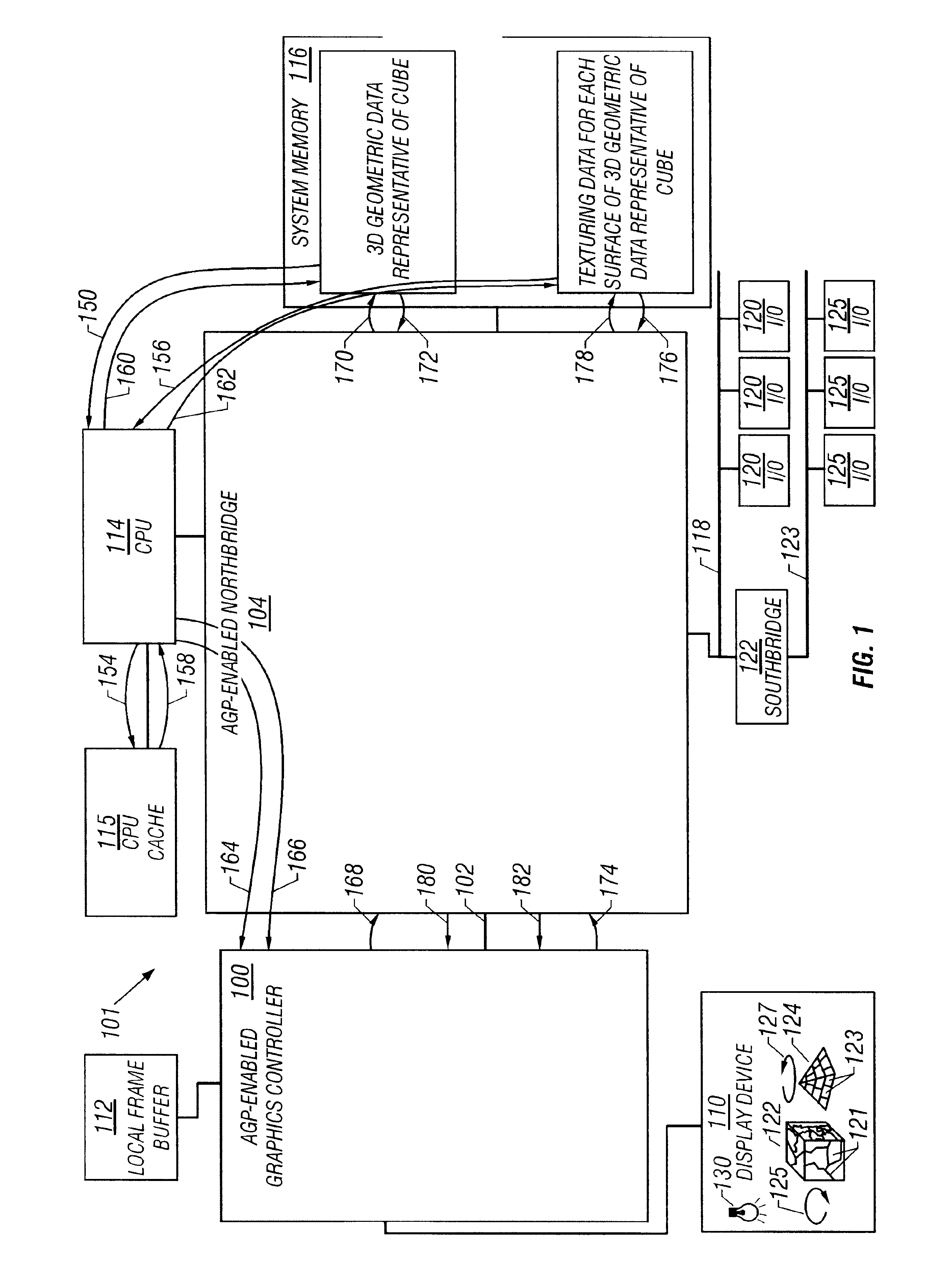
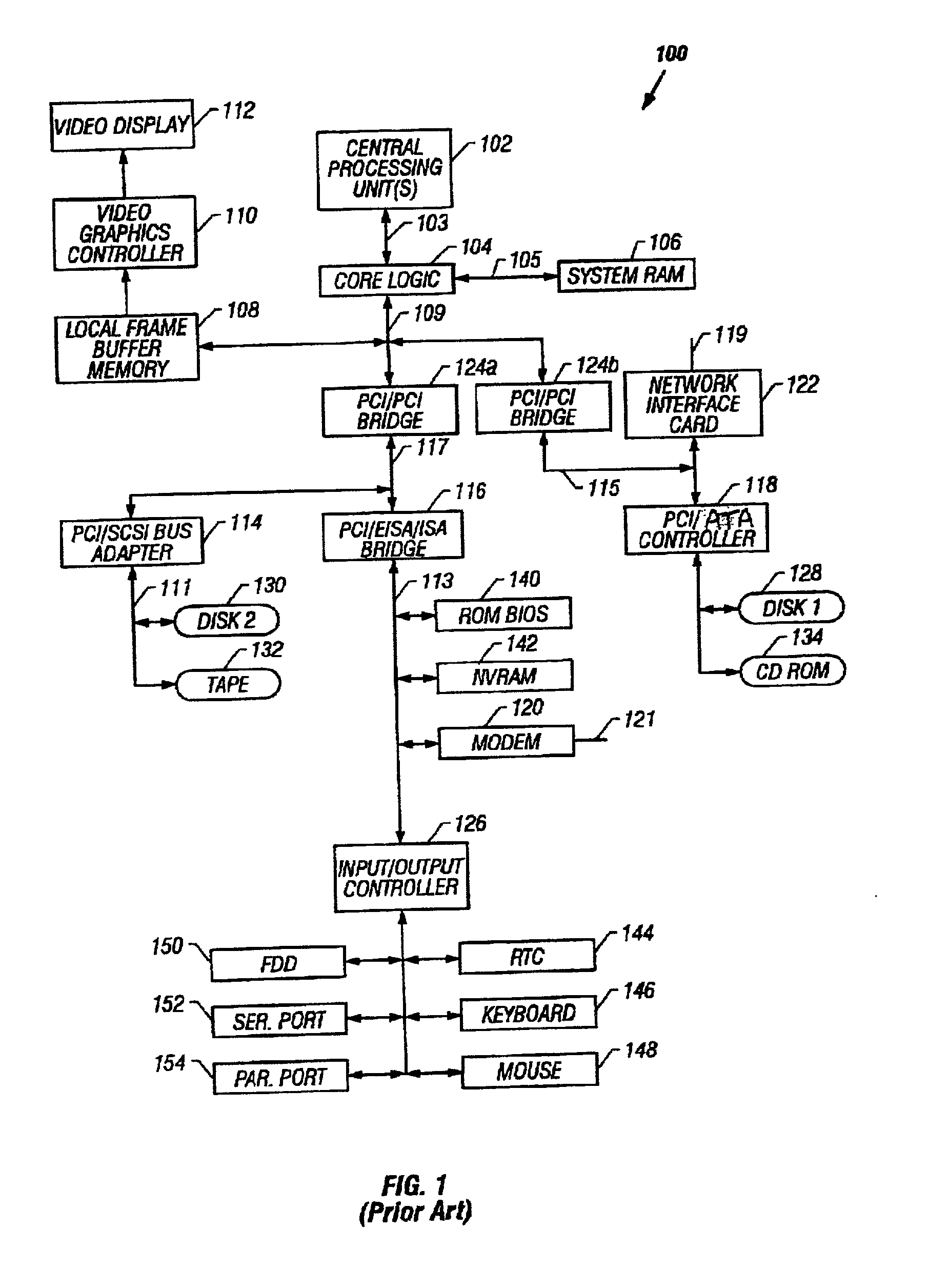
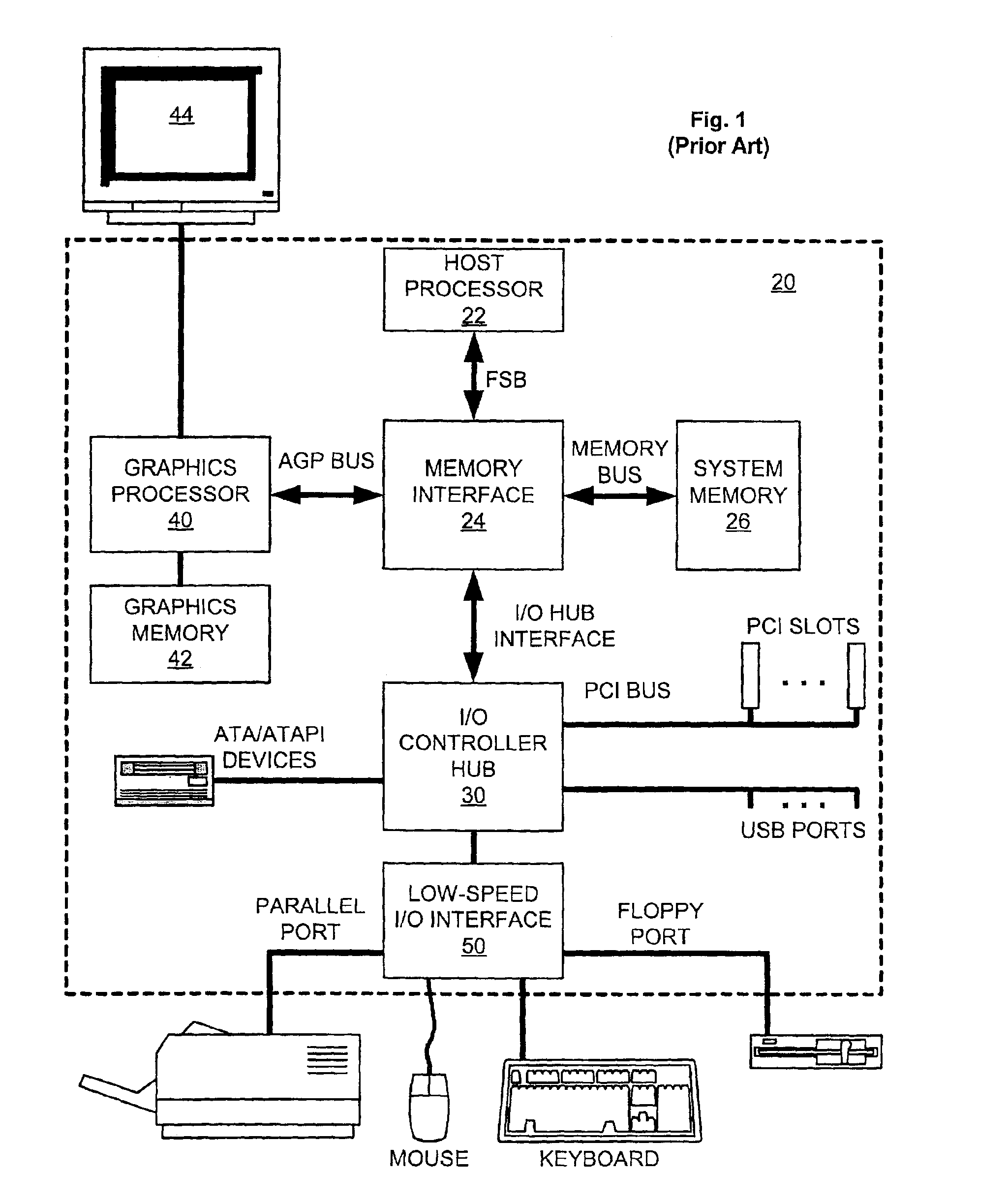
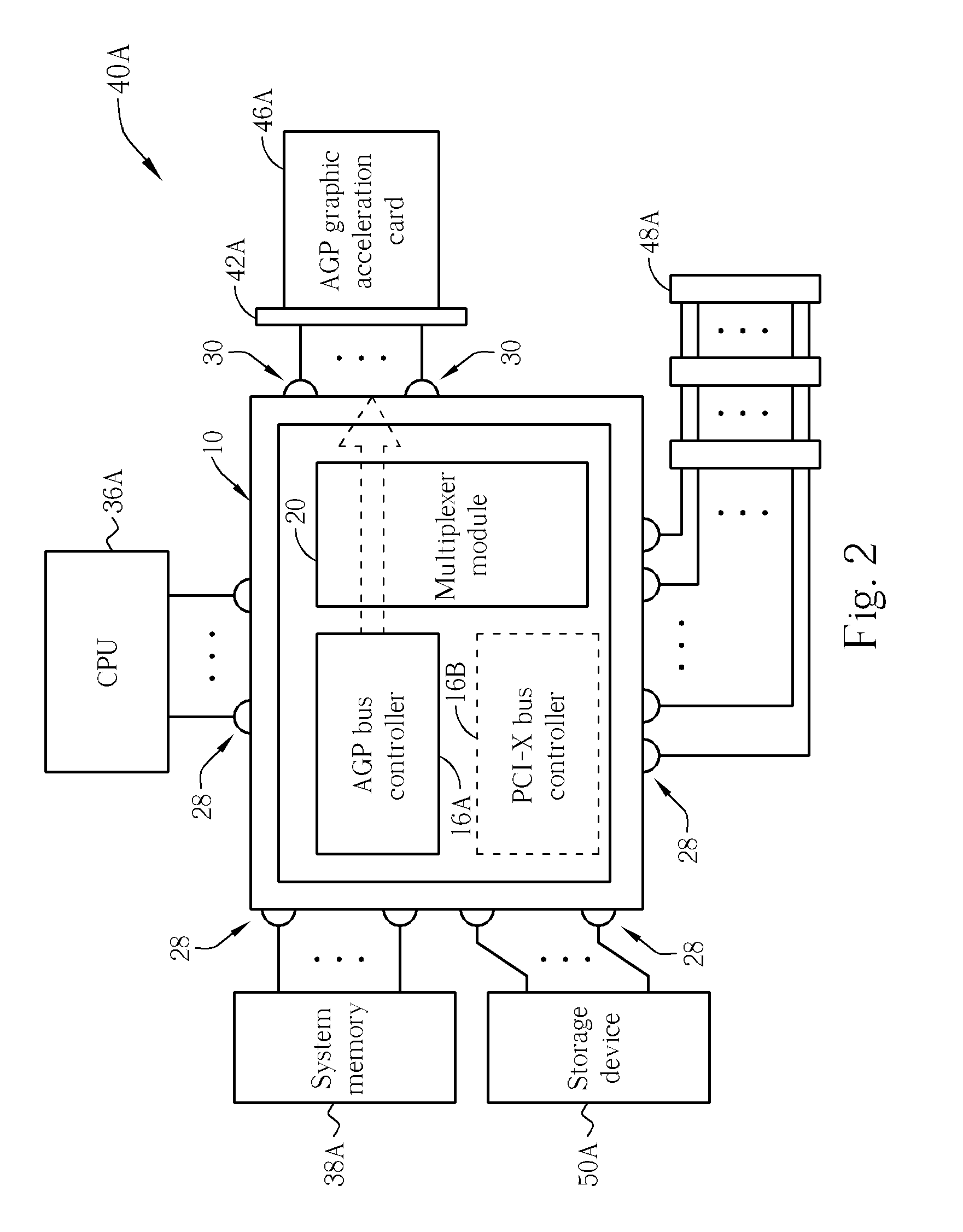
The Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP) was designed as a high-speed point-to-point channel for attaching a video card to a computer system, primarily to assist in the acceleration of 3D computer graphics. It was originally designed as a successor to PCI-type connections for video cards. Since 2004, AGP has been progressively phased out in favor of PCI Express (PCIe); by mid-2008, PCI Express cards dominated the market and only a few AGP models were available, with GPU manufacturers and add-in board partners eventually dropping support for the interface in favor of PCI Express.
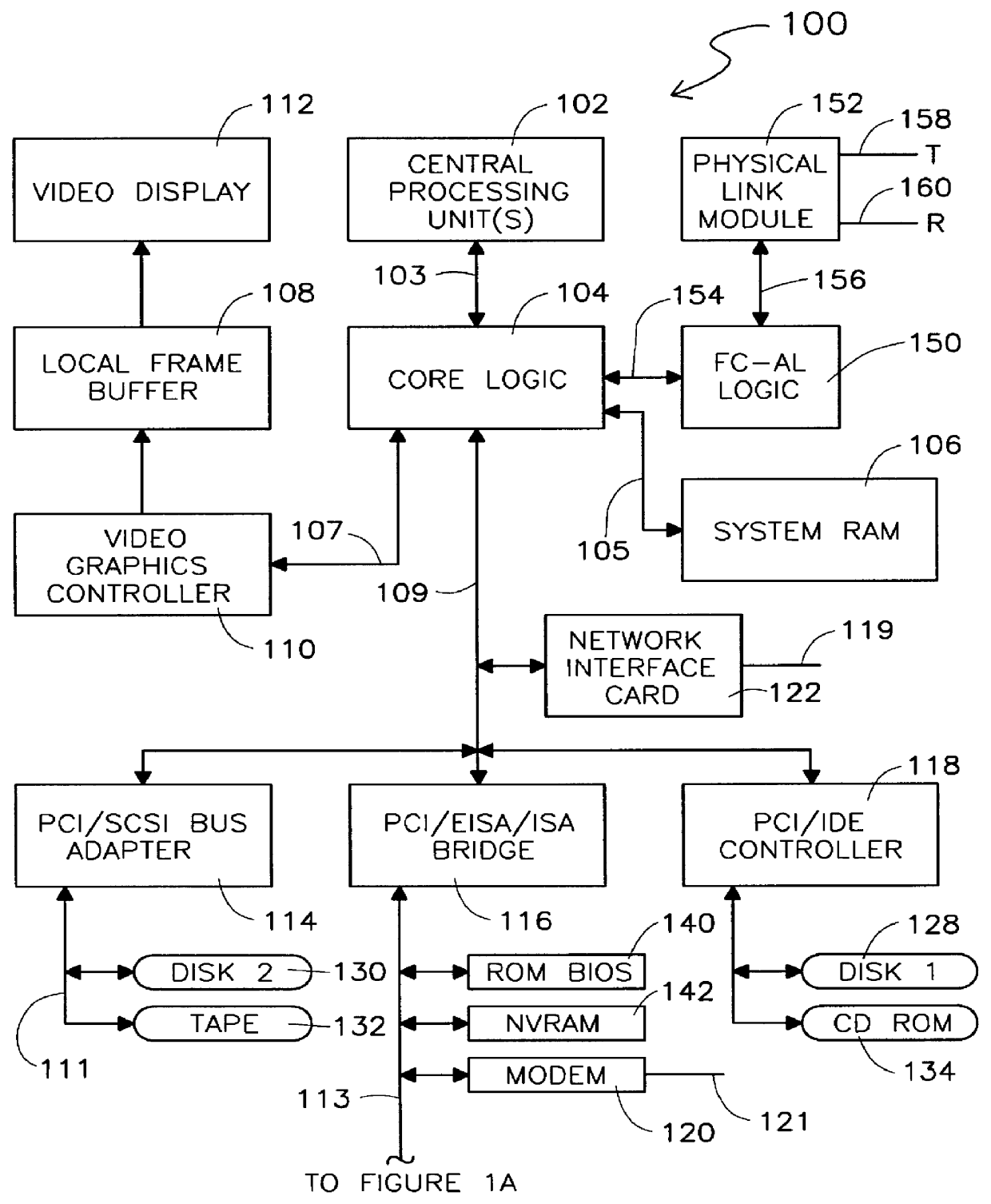
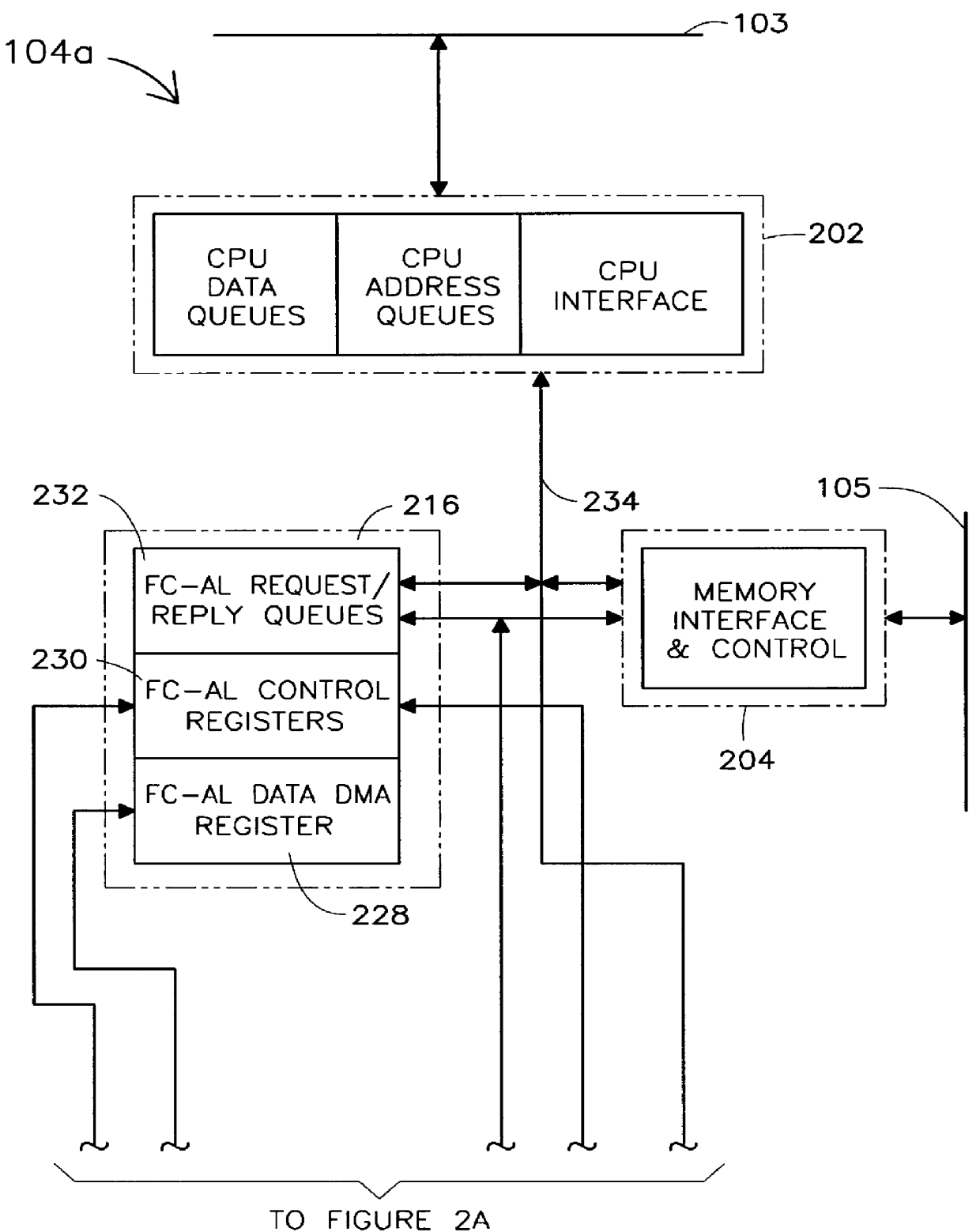
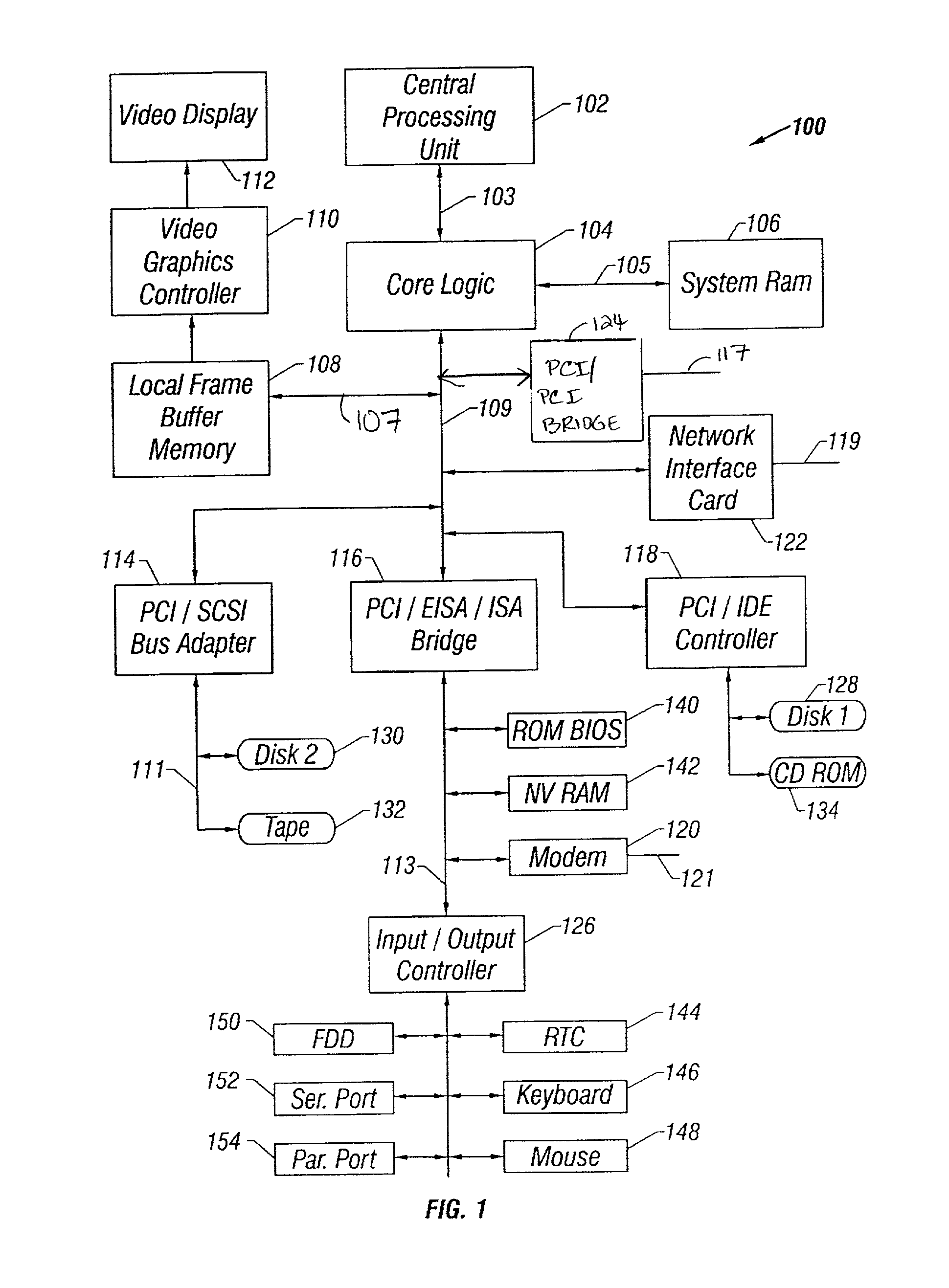
Dual purpose apparatus, method and system for accelerated graphics port and fibre channel arbitrated loop interfaces
InactiveUS6057863ALow costIncrease the number ofDigital computer detailsImage data processing detailsFiberComputer hardware
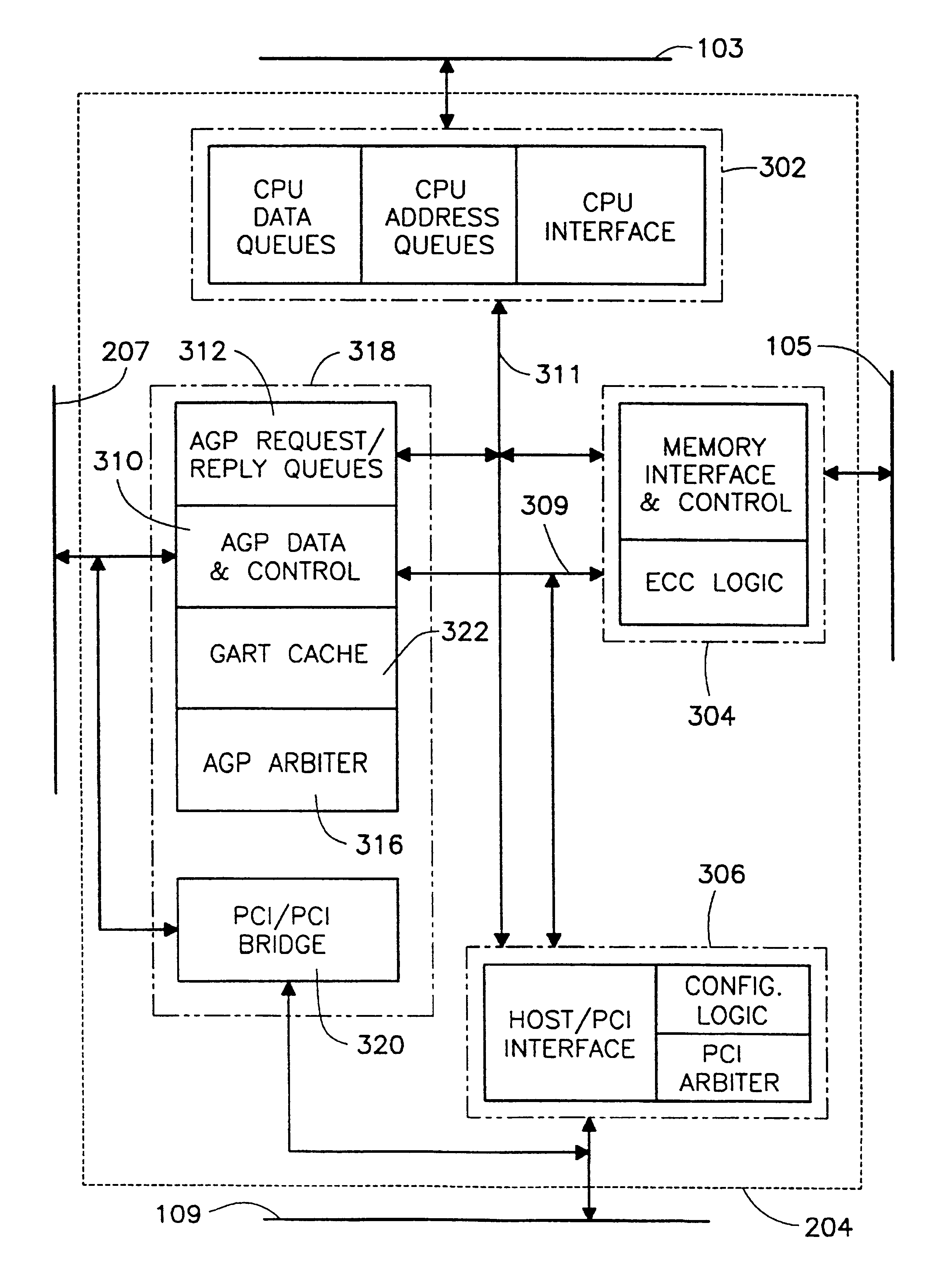
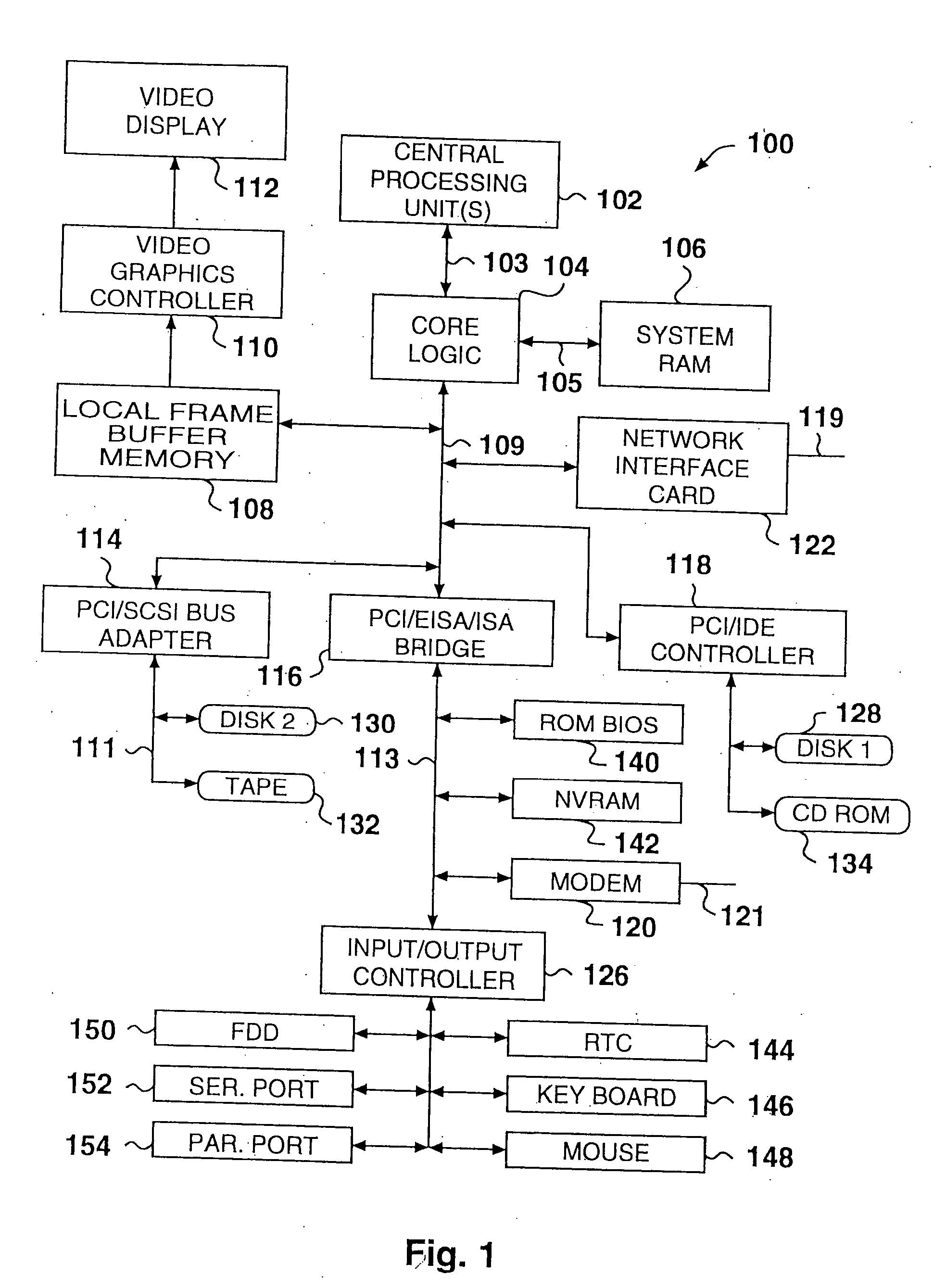
A multiple use core logic chipset is provided in a computer system that may be configured either as a bridge between an accelerated graphics port ("AGP") bus and host and memory buses, or as an interface bridge between a Fibre Channel Arbitrated Loop ("FC-AL") interface and the host and memory buses. The function of the multiple use chipset is determined at the time of manufacture of the computer system or in the field whether an AGP bus bridge or an FC-AL bridge interface is to be implemented. Selection of the type of bus bridge (AGP or FC-AL bridge interface) in the multiple use core logic chipset may be made by a hardware signal input, or by software during computer system configuration or power on self test ("POST"). Software configuration may also be determined upon detection of either an AGP or a FC-AL bridge interface device connected to the common AGP / FC-AL bus. FC-AL information may be stored in the computer system main memory using the high speed FC-AL bridge interface.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP +1
Computer system having configurable core logic chipset for connection to a fault-tolerant accelerated graphics port bus and peripheral component interconnect bus
InactiveUS20020099980A1Increase security and reliabilityRedundant hardware error correctionInput/output processes for data processingGraphicsComputerized system
A core logic chipset for a computer system is provided which can be configured as a bridge between either an accelerated graphics port (AGP) bus or an additional peripheral component interconnect (PCI) bus. A common bus having provisions for the PCI and AGP interface signals is connected to the core logic chipset and either an AGP or PCI device(s). The common bus, which is part of a fault-tolerant interconnect system, includes a first bus portion and a lower bus portion. When an error (e.g., a parity error) is detected on the first bus portion, the transaction is transferred over the second bus portion. When an error is detected on the second bus portion, the transaction is transferred over the first bus portion. If errors are detected on both portions, the transaction may be terminated.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
High speed peripheral interconnect apparatus, method and system
InactiveUS20050033893A1High degreeMeet the requirementsElectric digital data processingGraphicsMemory bus
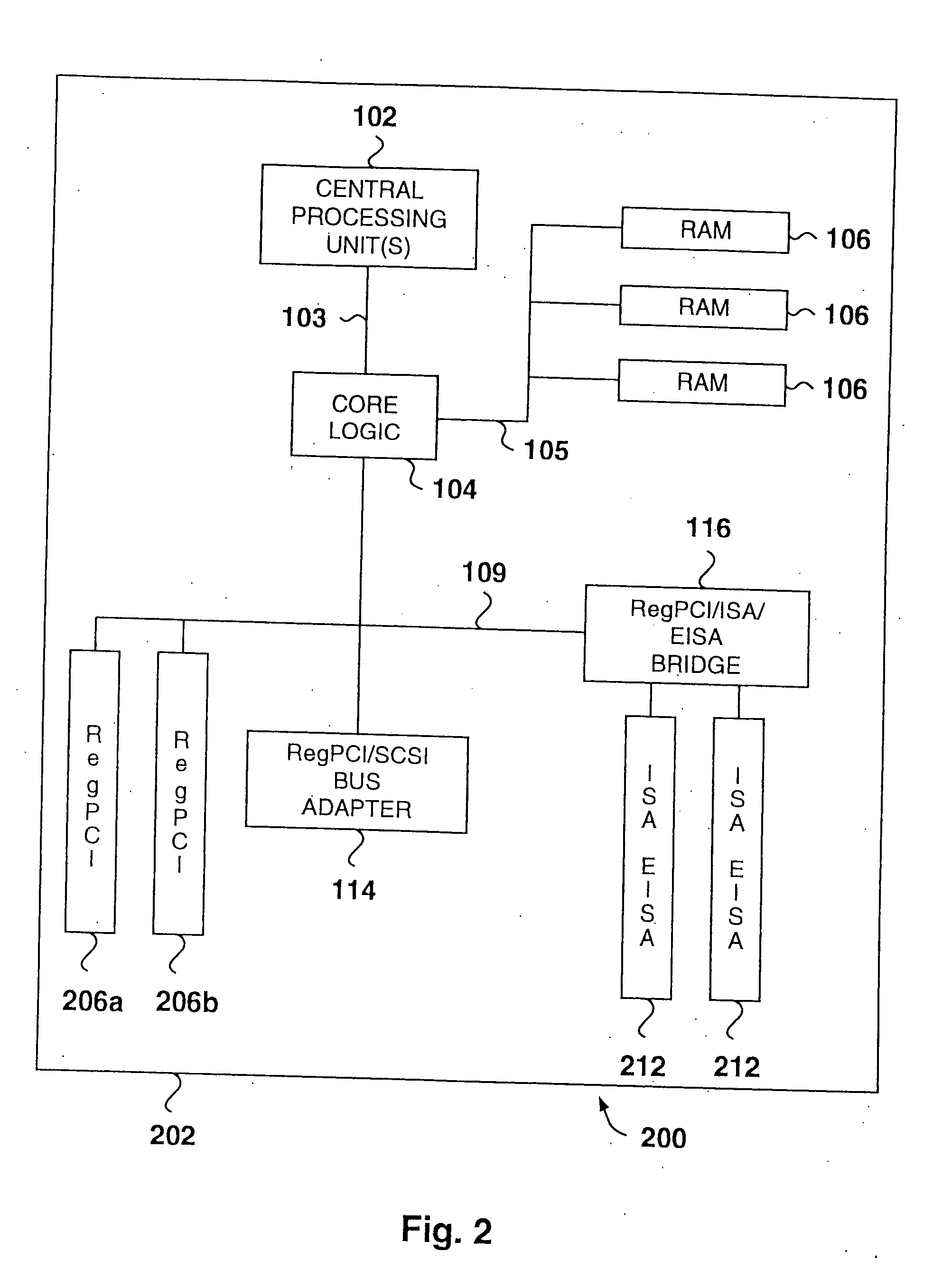
**A multiple use core logic chip set is provided in a computer system that may be configured either as a bridge between an accelerated graphics port (“AGP”) bus and host and memory buses, as a bridge between an additional registered peripheral component interconnect (“RegPCI”) bus and the host and memory buses, or as a bridge between a primary PCI bus and an additional RegPCI bus. The function of the multiple use chip set is determined at the time of manufacture of the computer system or in the field whether an AGP bus bridge or an additional registered PCI bus bridge is to be implemented. The multiple use core logic chip set has an arbiter having Request (“REQ”) and Grant (“GNT”) signal lines for each PCI device utilized on the additional registered PCI bus. Selection of the type of bus bridge (AGP or RegPCI) in the multiple use core logic chip set may be made by a hardware signal input, or by software during computer system configuration or power on self test (“POST”). Software configuration may also be determined upon detection of either an AGP or a RegPCI device connected to the common AGP / RegPCI bus.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Multi-mode graphics address remapping table for an accelerated graphics port device
InactiveUS6750870B2Memory adressing/allocation/relocationCathode-ray tube indicatorsMemory addressParallel computing
A computer system having a core logic chipset that functions as a bridge between an Accelerated Graphics Port ("AGP") bus device such as a graphics controller, and a host processor and computer system memory wherein a Graphics Address Remapping Table ("GART table") is used by the core logic chipset to remap virtual memory addresses used by the AGP graphics controller into physical memory addresses that reside in the computer system memory. The GART table enables the AGP graphics controller to work in contiguous virtual memory address space, but actually use non-contiguous blocks or pages of physical system memory to store textures, command lists and the like. The GART table is made up of a plurality of entries, each entry comprising an address pointer to a base address of a memory page, and feature flags that may be used to customize the associated memory page. The size of the GART table entries is selectively dependent on the addressing capability of the AGP bus device and the amount of system memory allocated to the AGP bus device.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
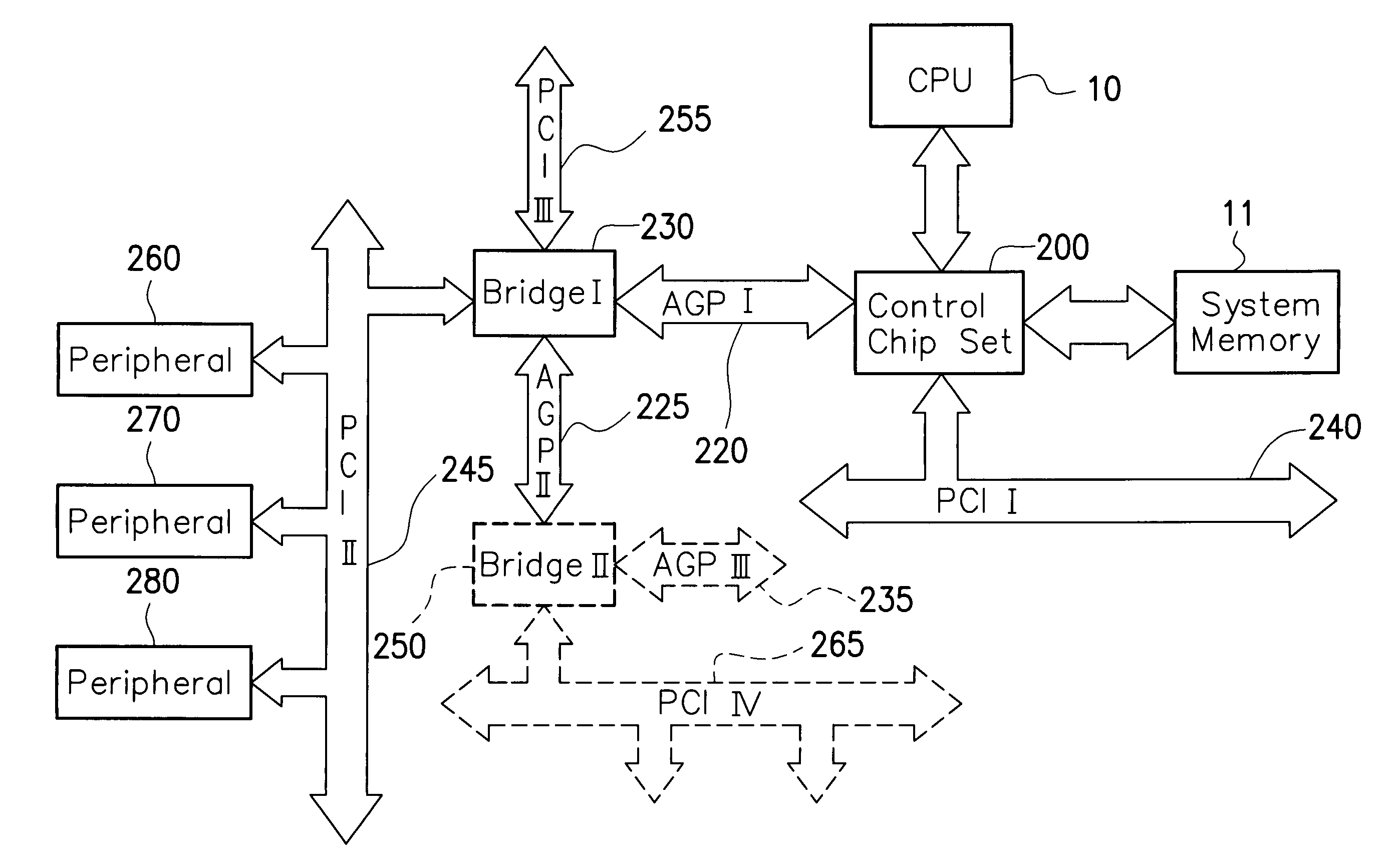
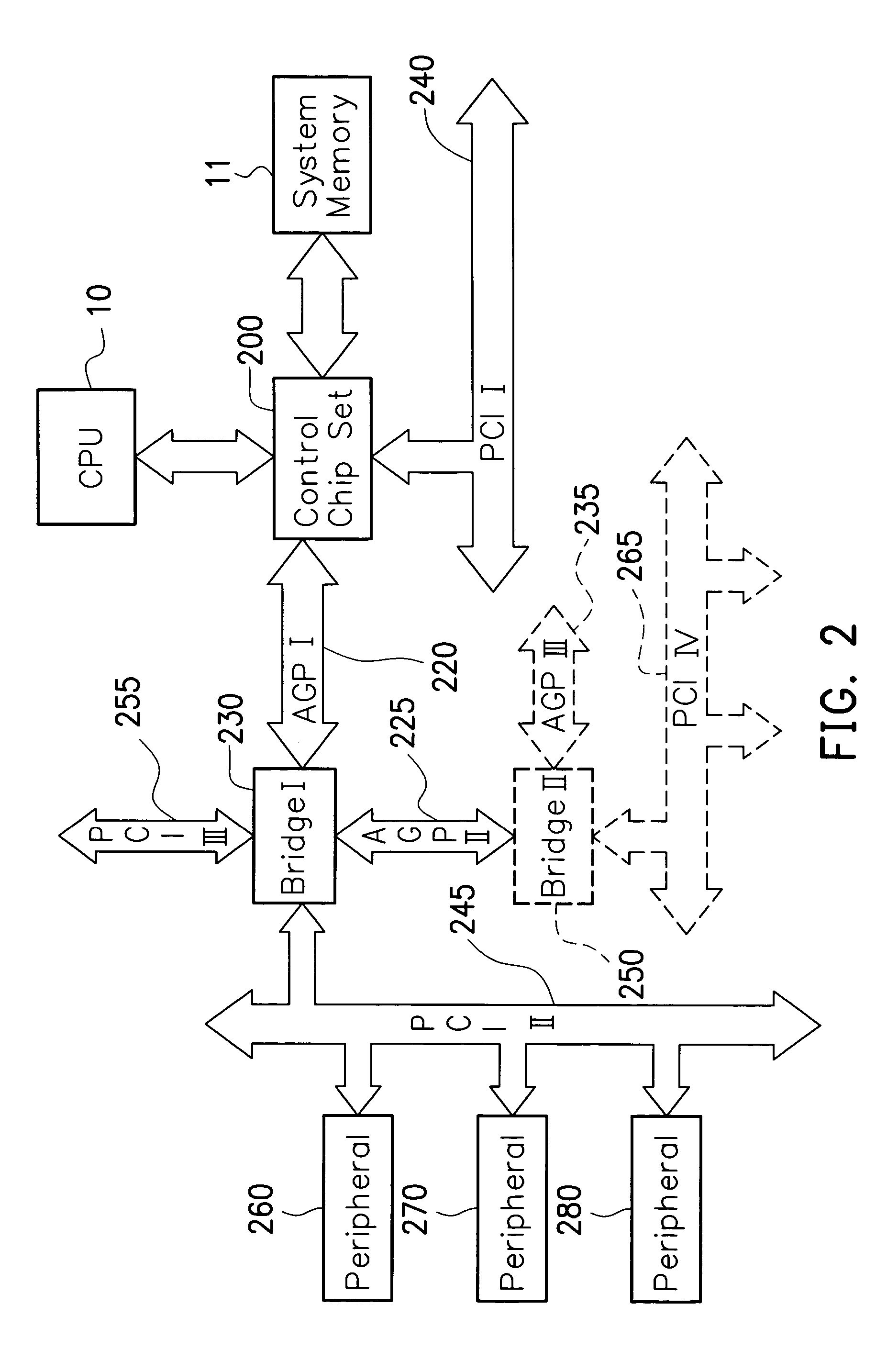
System, method, and device for accelerated graphics port linking
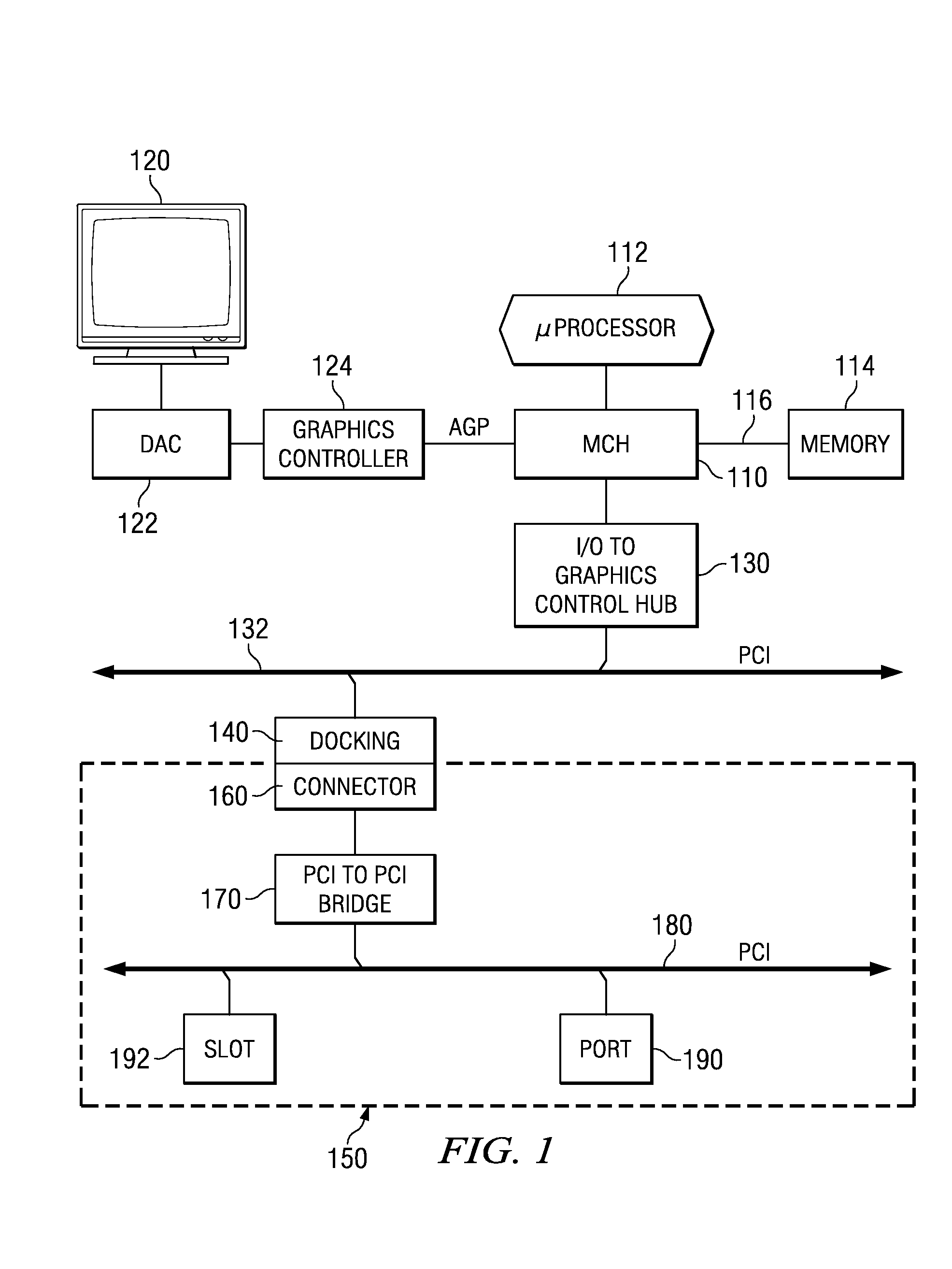
The invention provides systems, devices, and methods for using more than one Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP) to process graphics for a single computer monitor (282). In one embodiment, the invention is a method of providing advanced / high-performance AGP capabilities to a laptop computer by intercepting AGP signals from a laptop having a low-power AGP (224) and converting the AGP signals to signals for a high-performance AGP (270).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Systems and methods for efficiently updating complex graphics in a computer system by by-passing the graphical processing unit and rendering graphics in main memory
InactiveUS20050012751A1Avoids data flow problemIncrease computing speedCathode-ray tube indicatorsDigital output to display deviceGraphicsAnti-aliasing
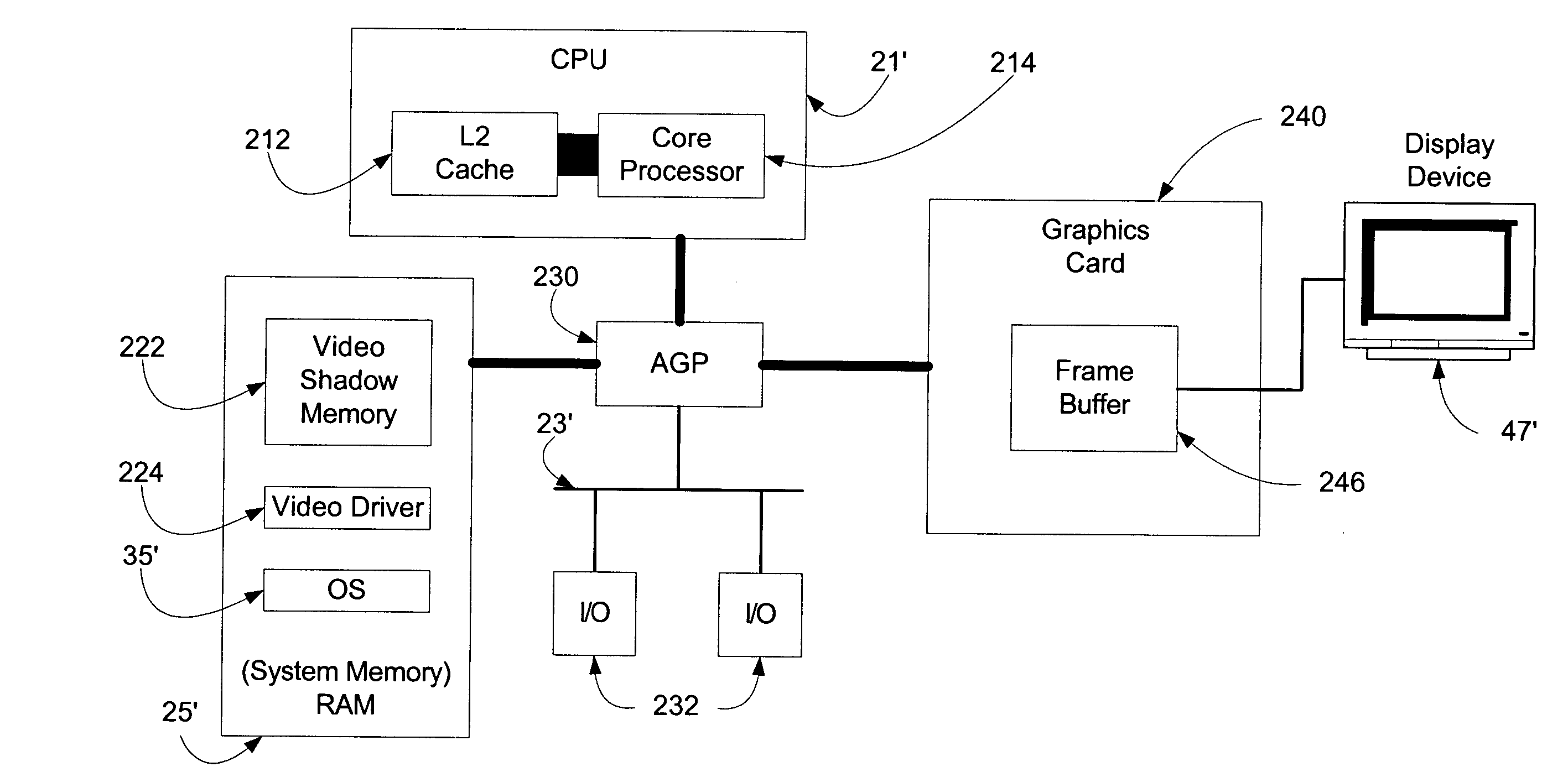
In one embodiment of the present invention, a method for rendering complex graphics —comprising “orientation-change graphics” for display on display devices in alternate orientations (e.g., portrait or inverse landscape); compositing of overlays; shading; texturing; anti-aliasing: alpha-blending; and / or sub-pixel manipulation technologies—is disclosed wherein the graphical processing unit (GPU) and video RAM shadow memory (VRAMSM) are bypassed and graphics are rendered in video shadow memory (VSM) by the central processing unit (CPU) and copied directly to the frame buffer. This method avoids the data flow problems of computer systems favoring system-to-video flow of data (that is, systems using an accelerated graphics port (AGP)) and leverages modern CPUs' increased computational speeds wherein the burden of rendering graphics in the CPU is no longer a significant resource cost such that the gains in graphics rendering more than offset any such CPU processing cost.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
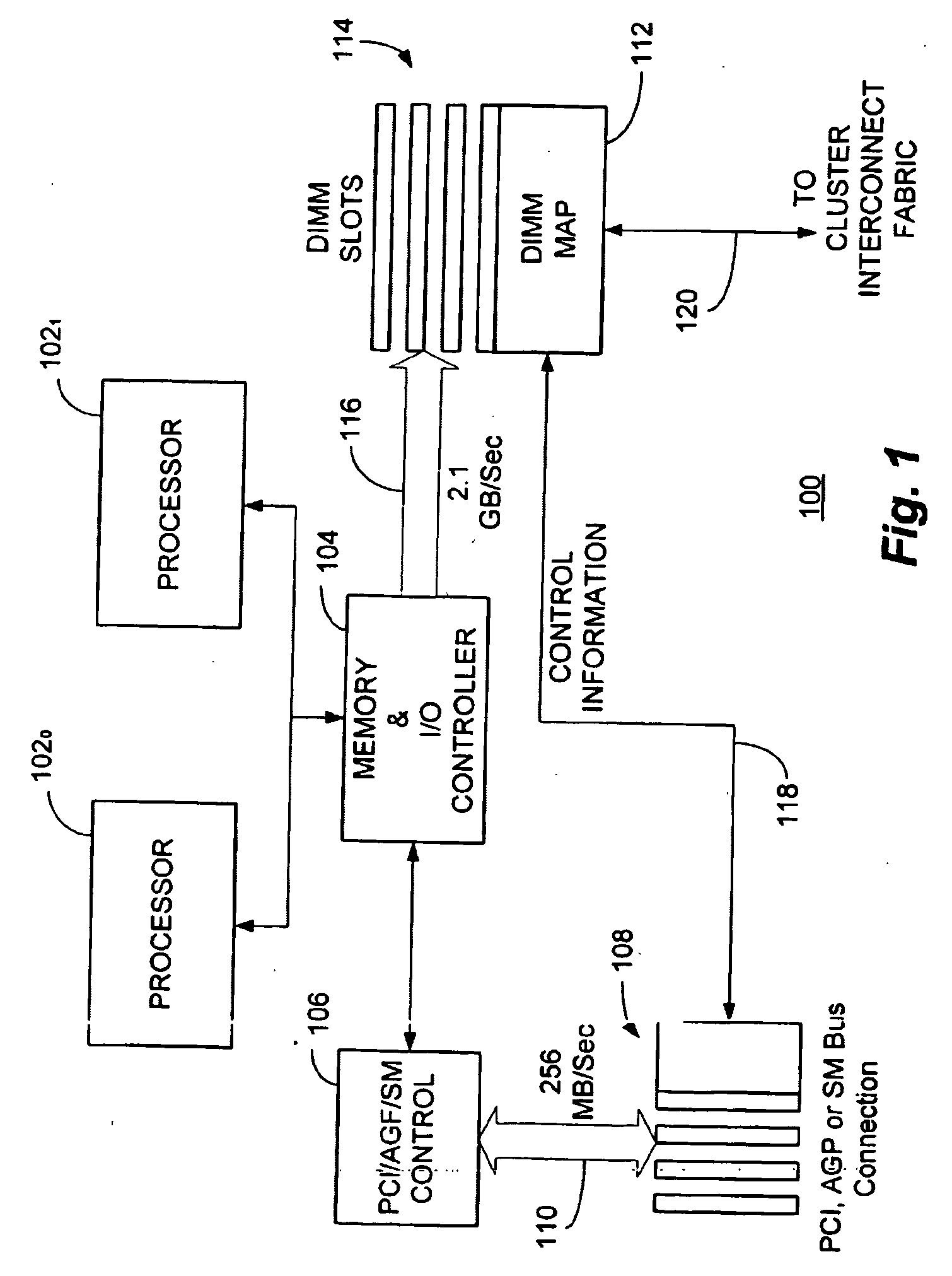
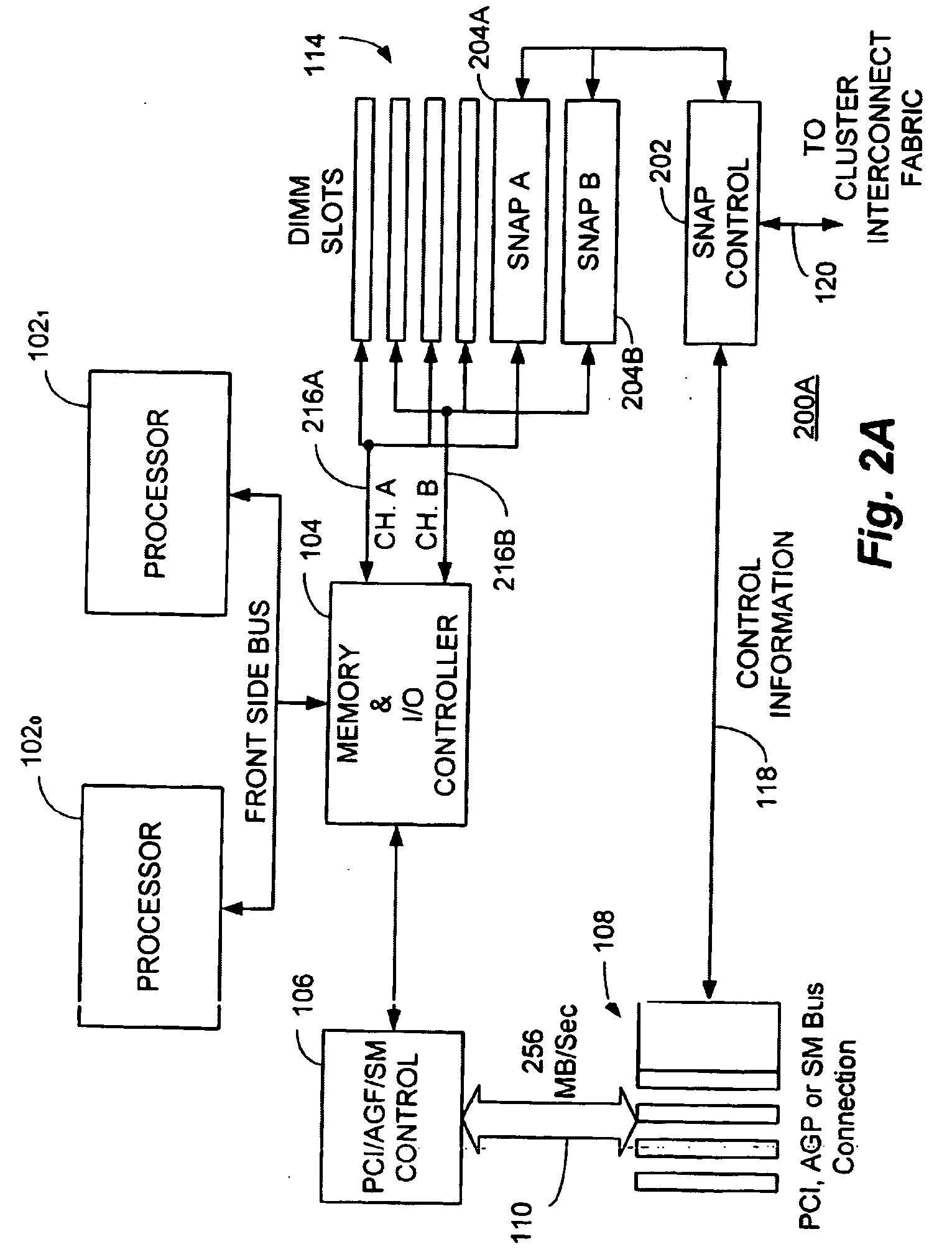
Switch/network adapter port for clustered computers employing a chain of multi-adaptive processors in a dual in-line memory module format
InactiveUS7373440B2Improve data transfer rateLower latencyMultiple digital computer combinationsArchitecture with single central processing unitTrademarkSystem maintenance
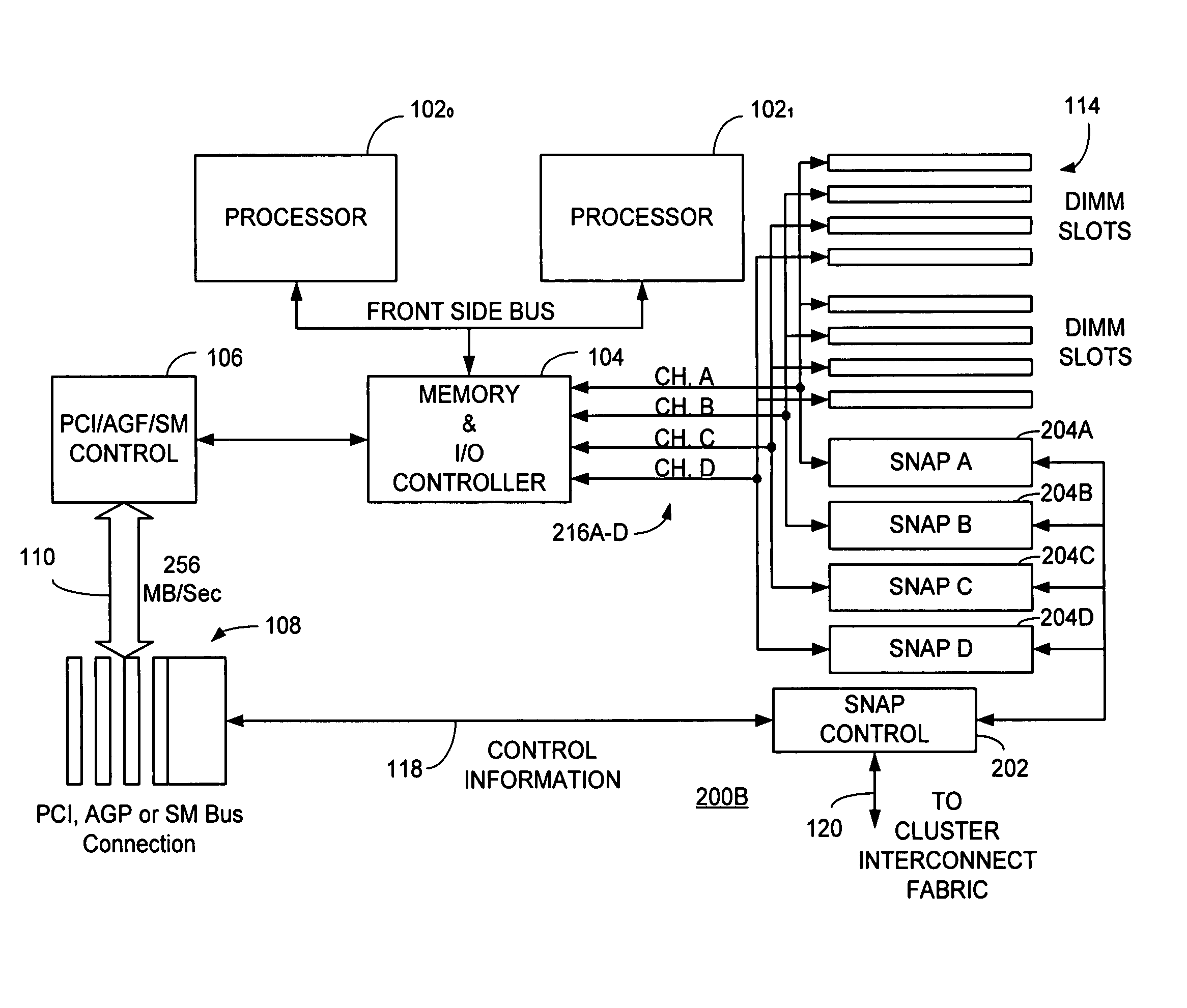
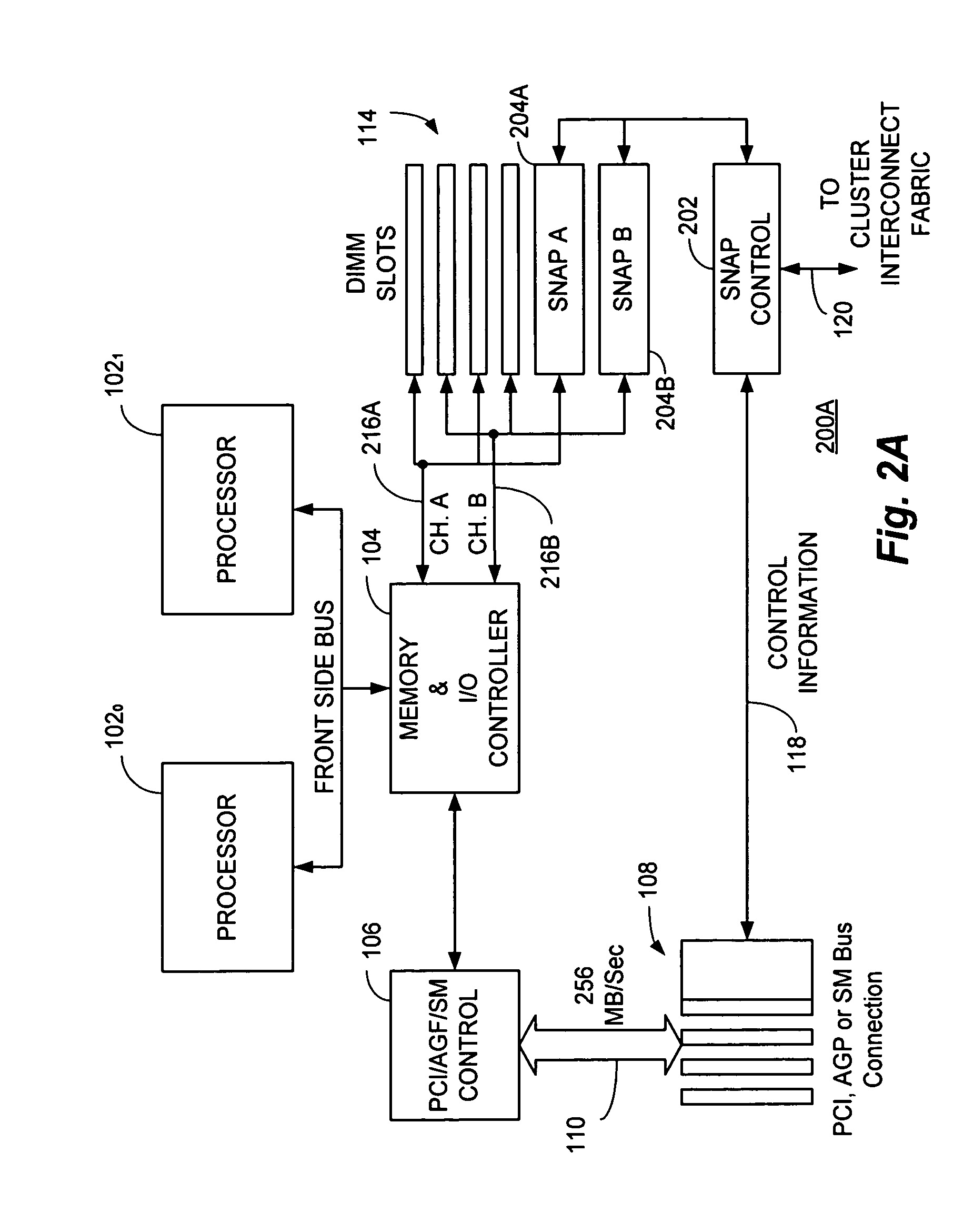
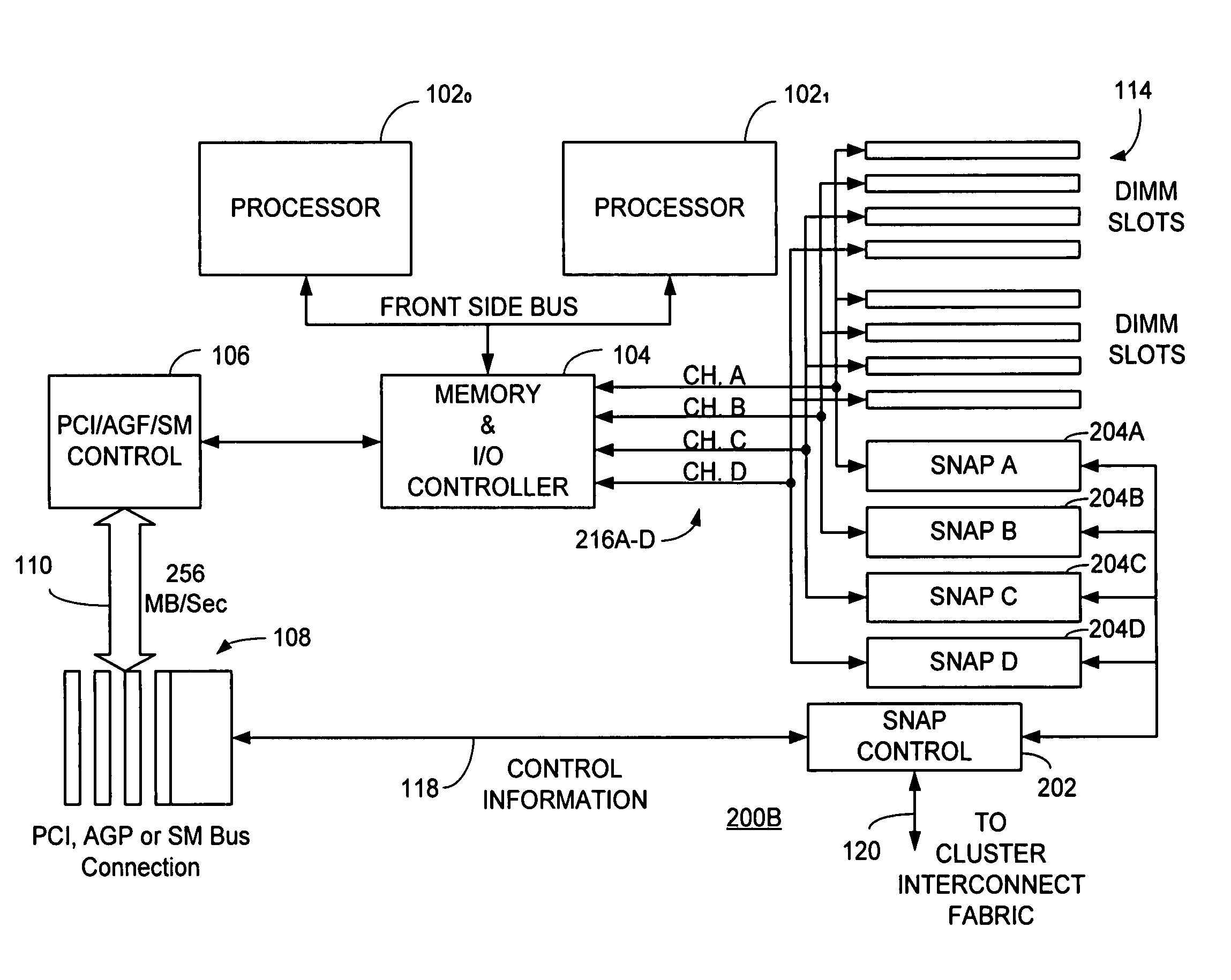
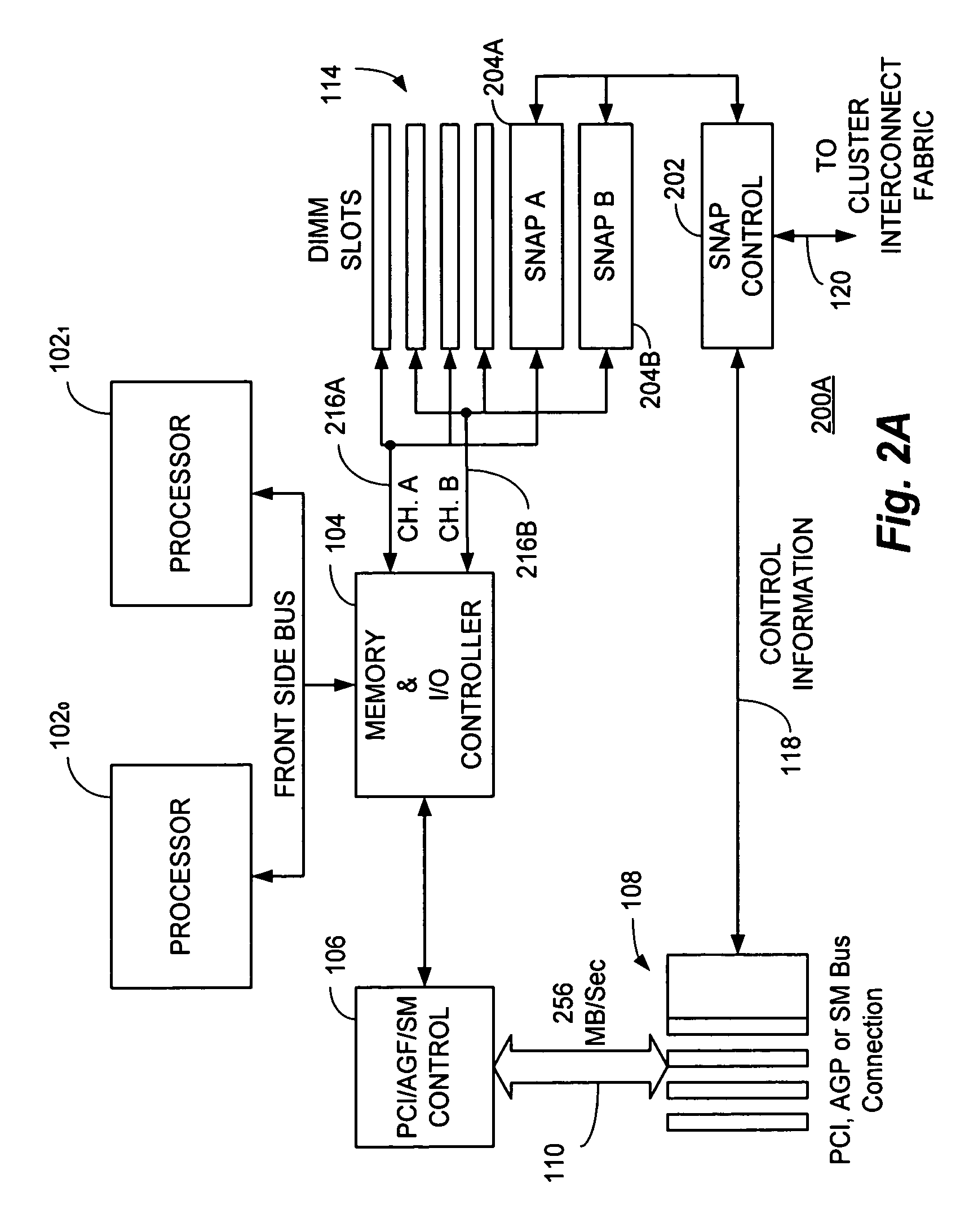
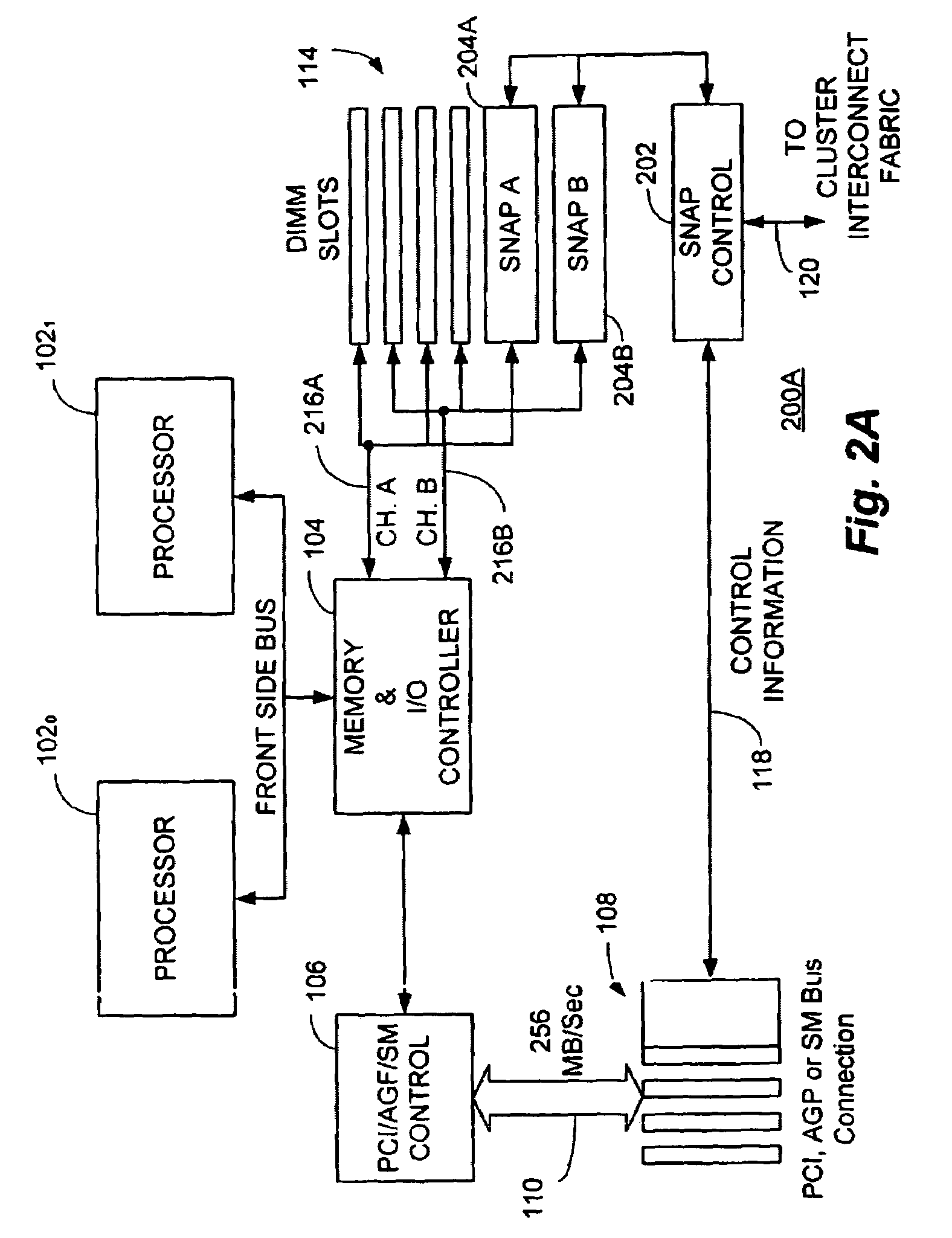
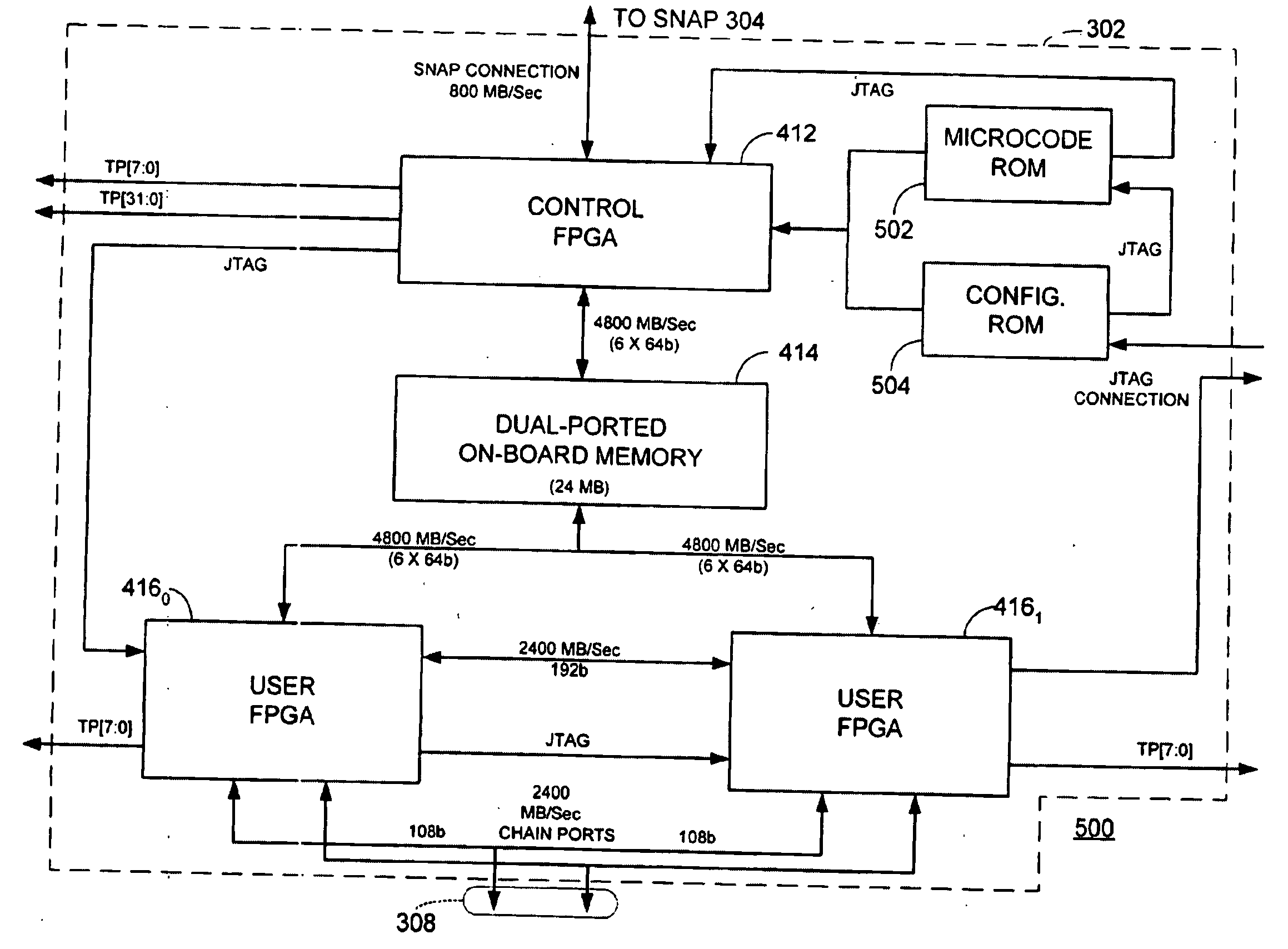
A switch / network adapter port (“SNAP”) for clustered computers employing multi-adaptive processor (“MAP™”, a trademark of SRC Computers, Inc.) elements in a dual in-line memory module (“DIMM”) or Rambus™ in-line memory module (“RIMM”) format to significantly enhance data transfer rates over that otherwise available through use of the standard peripheral component interconnect (“PCI”) bus. Particularly disclosed is a microprocessor based computer system utilizing either a DIMM or RIMM physical format processor element for the purpose of implementing a connection to an external switch, network, or other device. In a particular embodiment, connections may be provided to either the PCI, accelerated graphics port (“AGP”) or system maintenance (“SM”) bus for purposes of passing control information to the host microprocessor or other control chips. The field programmable gate array (“FPGA”) based processing elements have the capability to alter data passing through it to and from an external interconnect fabric or device.
Owner:SRC COMP
Computer bridge interfaces for accelerated graphics port and peripheral component interconnect devices
InactiveUS6567880B1Not to excessively loadGeneral purpose stored program computerDigital output to display deviceGraphicsMemory bus
A core logic chip set is provided in a computer system to provide a bridge between host and memory buses and an accelerated graphics port ("AGP") bus adapted for operation of two AGP devices, or one AGP device and one peripheral component interconnect ("PCI") device. A common AGP bus having provisions for the PCI and AGP interface signals is connected to the core logic chip set and the AGP and / or PCI device(s). The core logic chip set has an AGP / PCI arbiter having Request ("REQ") and Grant ("GNT") signal lines for each AGP and / or PCI device connected to the AGP bus. Another embodiment has a plurality of AGP buses for a plurality of AGP devices. This allows concurrent operation for AGP devices connected to different AGP buses. Two of the AGP buses may be combined to connect to one 64 bit PCI device.
Owner:COMPAQ COMP CORP
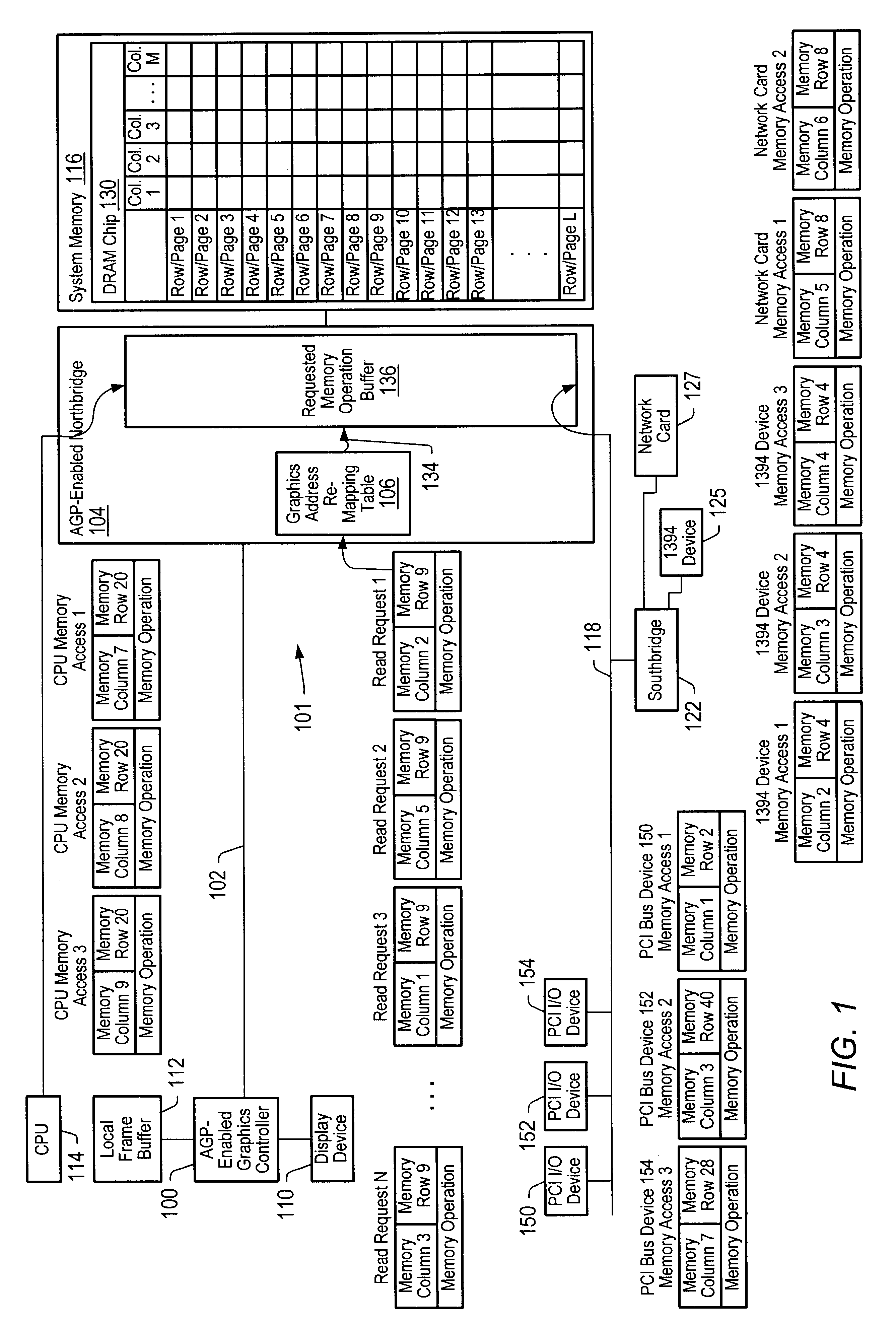
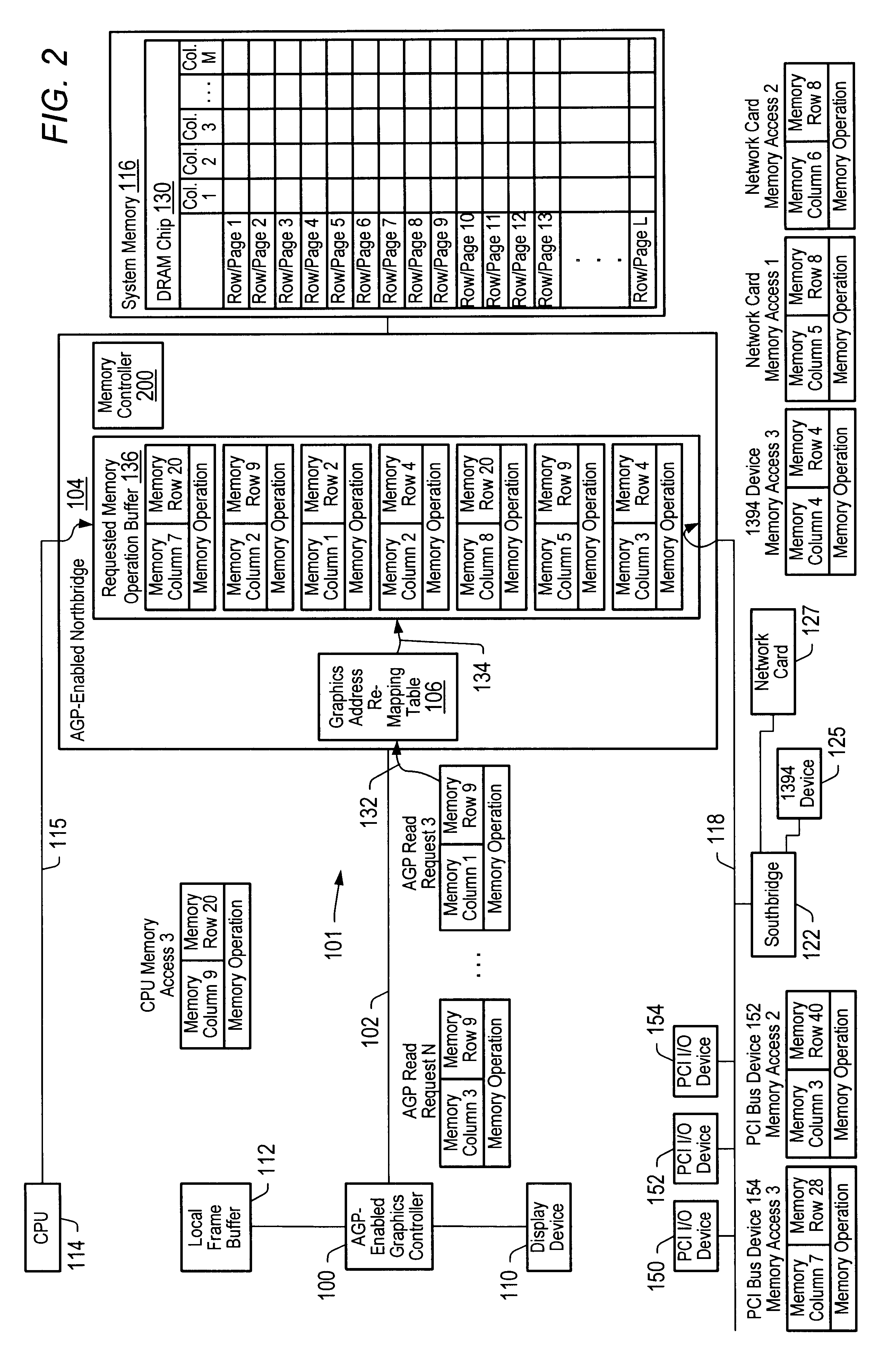
Method and system for improved data access
A method and system which will increase the ability of memory controllers to intelligently schedule accesses to system memory. The method and system provide a memory controller and a requested memory operation buffer structured so that at least one source attribute of a requested memory operation can be identified. In one instance, the requested memory operation buffer has queues, associated with data buses, which can be utilized to identify source attributes of requested memory operations. Examples of such queues are an Accelerated Graphics Port Interconnect queue associated with an Accelerated Graphics Port interconnect, a system bus queue associated with a system bus, and a Peripheral Component Interconnect bus queue associated with a Peripheral Component Interconnect bus where the queues can be utilized by a memory controller to identify the specific bus from which a requested memory operation originated. In another instance, the queues, associated with data buses, are structured such that one or more further source attributes-such as the identity of the request initiator, the priority of the request, whether the request is speculative, etcetera-of particular queued requested memory operations can be identified. In yet another instance, the requested memory operation buffer is structured such that one or more source attributes-such as the identity of the request initiator, the priority of the request, whether the request is speculative, etcetera-of particular queued requested memory operations can be identified.
Owner:ADVANCED SILICON TECH
Switch/network adapter port coupling a reconfigurable processing element to one or more microprocessors for use with interleaved memory controllers
InactiveUS20050283546A1Conveniently providedMultiple digital computer combinationsInput/output processes for data processingTrademarkControl store
A switch / network adapter port (“SNAP™”) in a dual in-line memory module (“DIMM”) or Rambus™ in-line memory module (“RIMM”) format for clustered computers employing multi-adaptive processor (“MAP®”, both trademarks of SRC Computers, Inc.) elements for use with interleaved memory controllers. Particularly disclosed is a microprocessor based computer system utilizing either a DIMM or RIMM physical format adapter port coupled to a reconfigurable processor element for the purpose of implementing a connection to an external switch, network, or other device. In a particular embodiment, connections may be provided to either the PCI, accelerated graphics port (“AGP”) or system maintenance (“SM”) bus for purposes of passing control information to the host microprocessor or other control chips. The field programmable gate array (“FPGA”) based processing elements have the capability to alter data passing through it to and from an external interconnect fabric or device.
Owner:SRC COMP
Switch/network adapter port coupling a reconfigurable processing element to one or more microprocessors for use with interleaved memory controllers
InactiveUS7565461B2Multiple digital computer combinationsInput/output processes for data processingTrademarkSystem maintenance
Owner:SRC COMP
Image rendering method applied to computer screen
The invention discloses an image rendering method applied to a computer screen, comprising the following steps: (1) a window for supporting a transparent channel is created; (2) display coordinates ofeach pixel in the image are computed, a three-dimensional accelerated graphics port is used for amplifying the image and rendering the image to a local video memory mapping, and background color is set into black ARGB; (3) chromatic values of a plurality of adjacent points in the image are averaged, and the rendered mapping is zoomed into output size; (4) the mapping in the local video memory isexchanged to an internal memory mapping by the operation of the three-dimensional accelerated graphics port:; (5) a two-dimensional Alpha mixed function is used for leading the internal memory mappingto be drawn on a desktop, so as to lead the image to be displayed on the desktop. The method can realize that three-dimensional cartoon images can be rendered out clearly and smoothly in a real-timemanner on any desktop background, thereby achieving good expressive form, eliminating sawtooth form at the edge part of the three-dimensional image, leading the image display to be real and achievingsmooth transition effect.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HUADUO NETWORK TECH
Computer system having configurable core logic chipset for connection to a fault-tolerant accelerated graphics port bus and peripheral component interconnect bus
InactiveUS6898740B2Increase security and reliabilityRedundant hardware error correctionInput/output processes for data processingGraphicsComputerized system
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
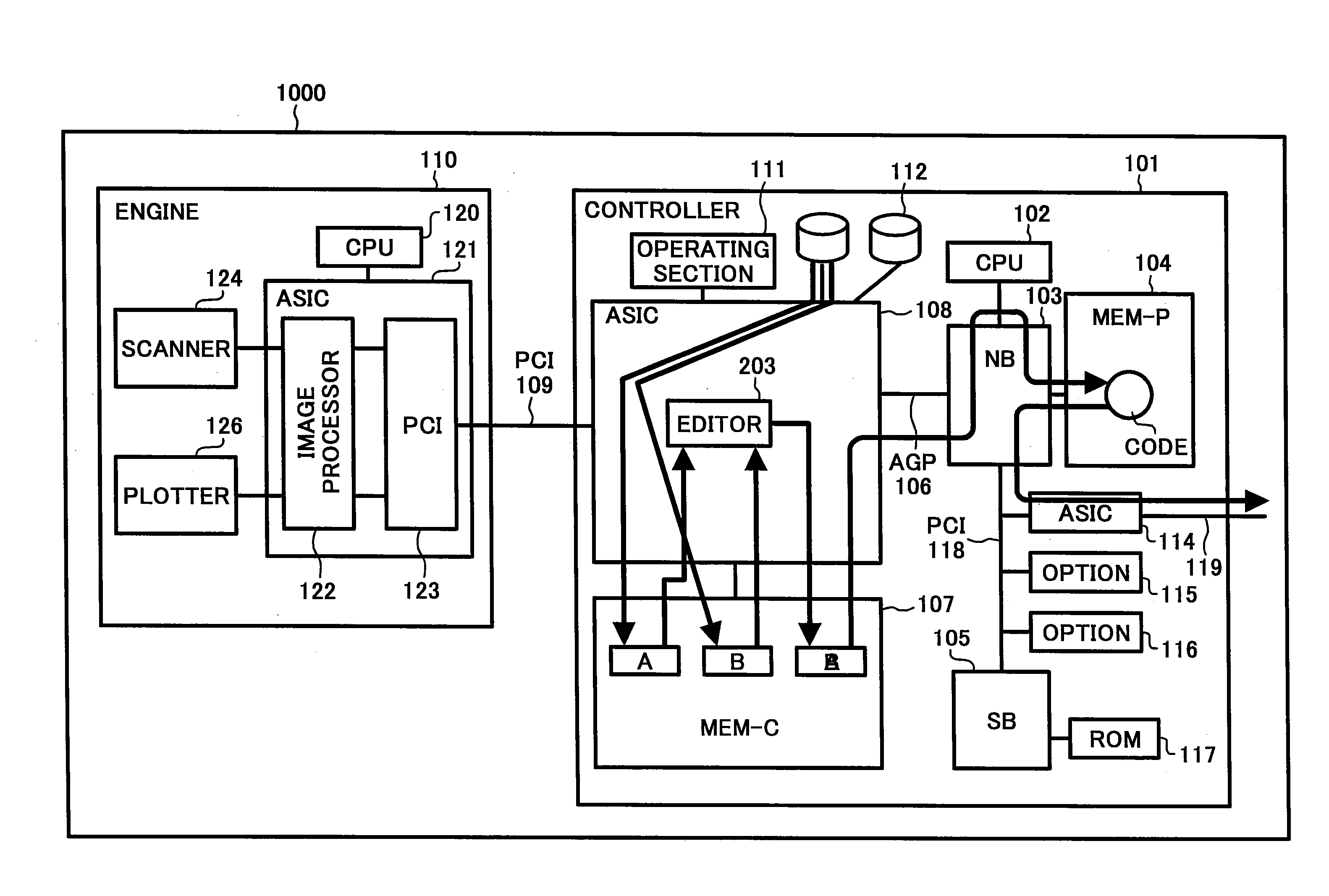
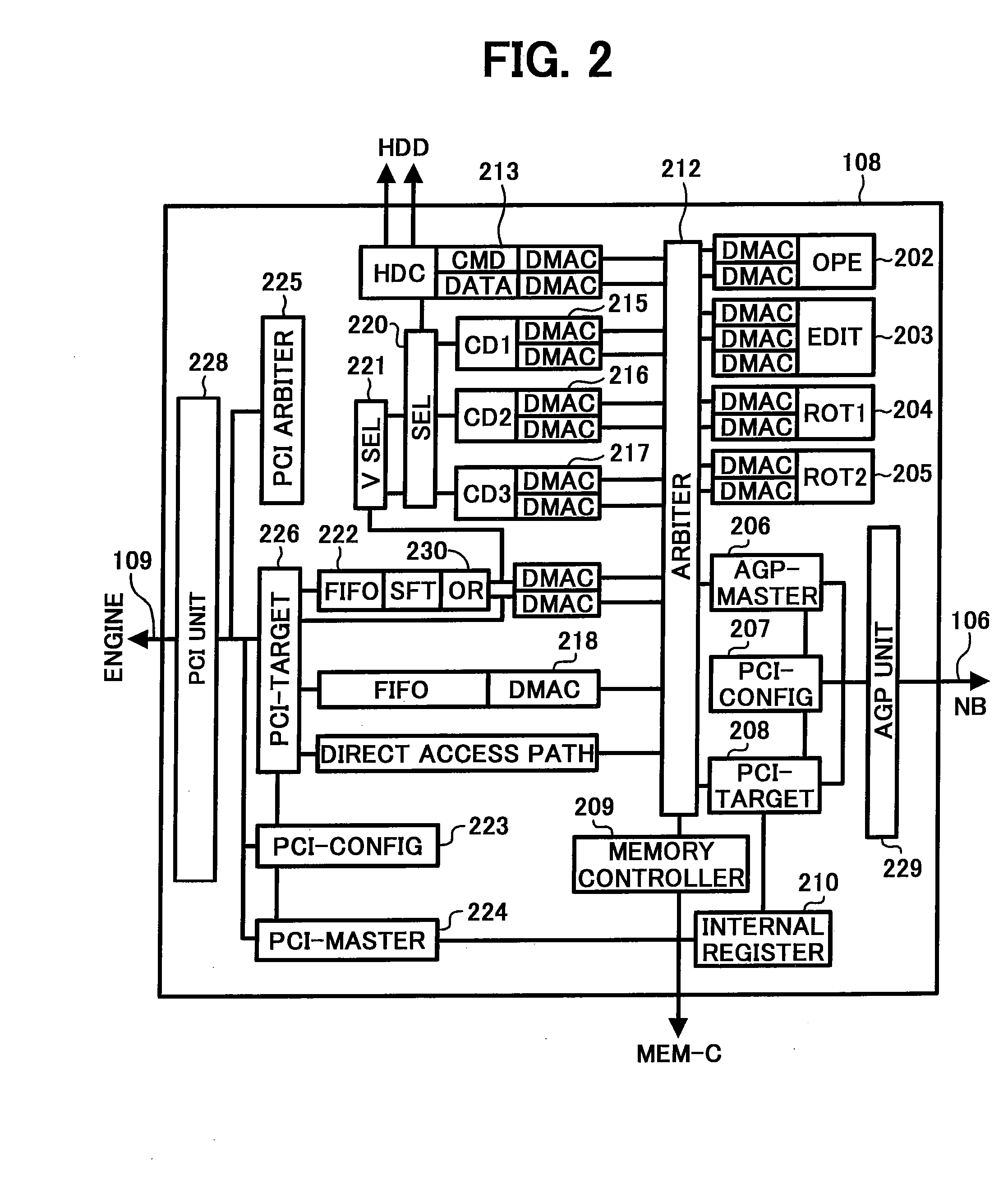
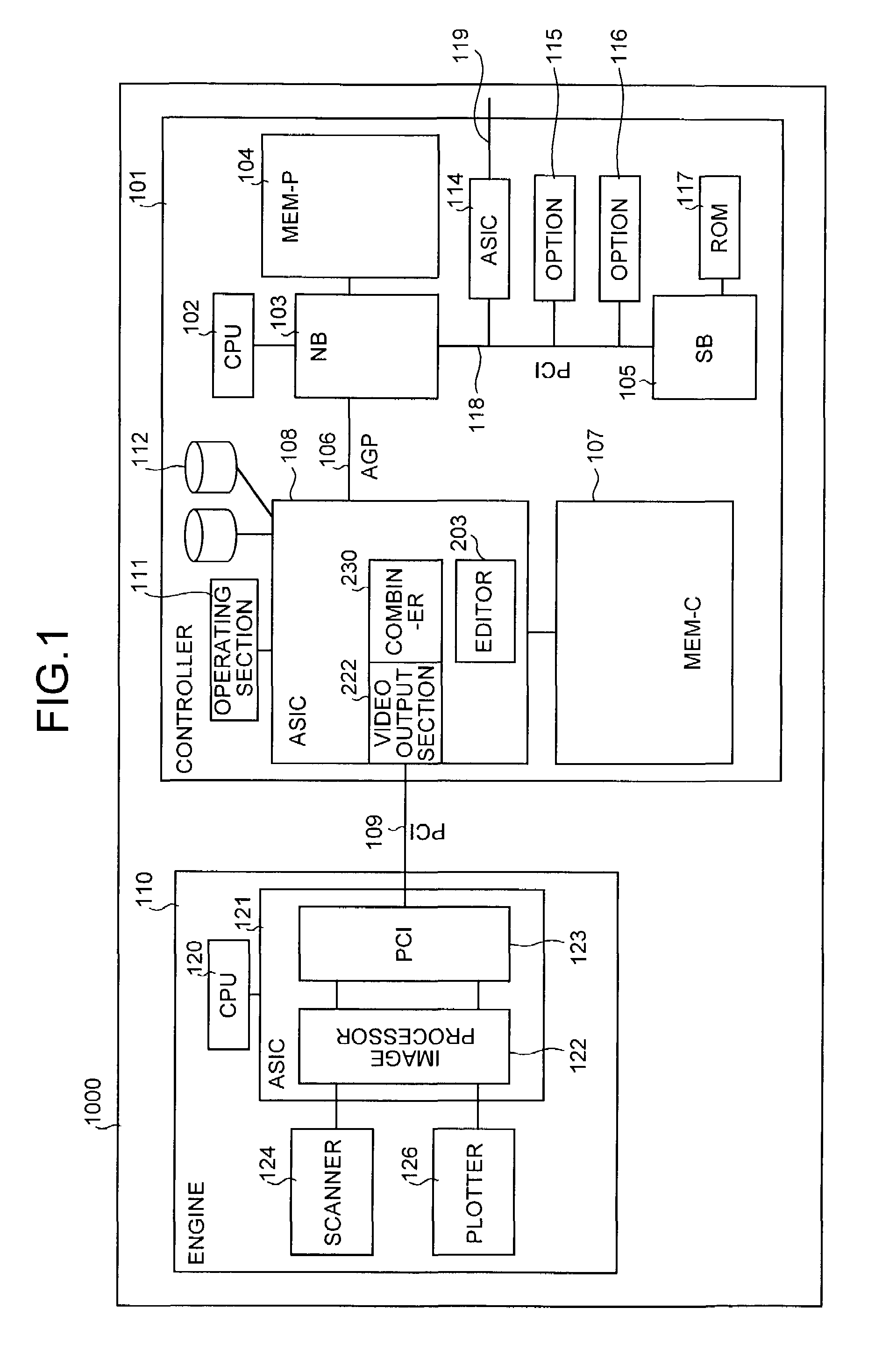
Image forming apparatus
ActiveUS20080165371A1Solve problemsDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsGraphicsImaging processing
An image forming apparatus includes a controller having an integrated circuit for image processing. The controller is connected to an engine via a peripheral component interconnect (PCI). The engine includes a plotter and a scanner. The controller includes a central processing unit (CPU) to which a chip-set is connected via an accelerated graphics port (AGP). The controller also includes an application specific integrated circuit (ASIC) that controls whether to output scanner image data, which is data acquired by the scanner, to the PCI as plotter data for the plotter, or to output the scanner image data to the AGP, or to output image data input through the AGP to the PCI as plotter data for the plotter. The ASIC includes a combiner that combines a plurality of image data.
Owner:RICOH KK
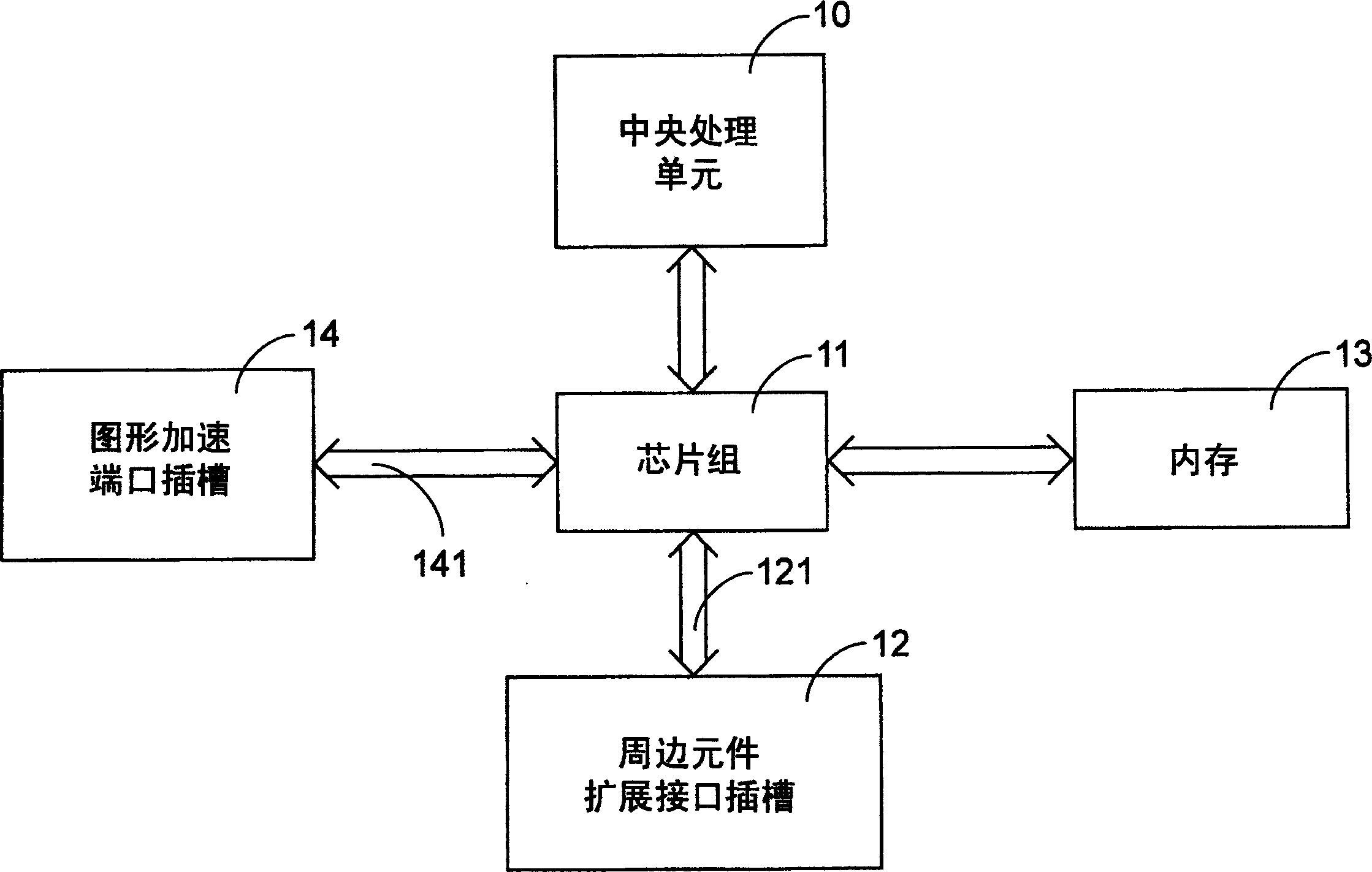
Computer backplane with an accelerated graphics port
InactiveUS6906929B2Speed up data transmissionImprove usabilityComponent plug-in assemblagesDigital processing power distributionGraphicsEngineering
A computer backplane is disposed with at least an AGP slot, a PCI slot and / or an EISA slot. The PCI slot can be used to electrically connect with PCI cards. The EISA slot and the PCI slot are in alignment to allow that a CPU card can be connected simultaneously to both the EISA slot and the PCI slot. The AGP slot is used to electrically connect with an AGP card. Such an arrangement allows for ease of replacement of the AGP card and a lower production cost.
Owner:ICP ELECTRONICS
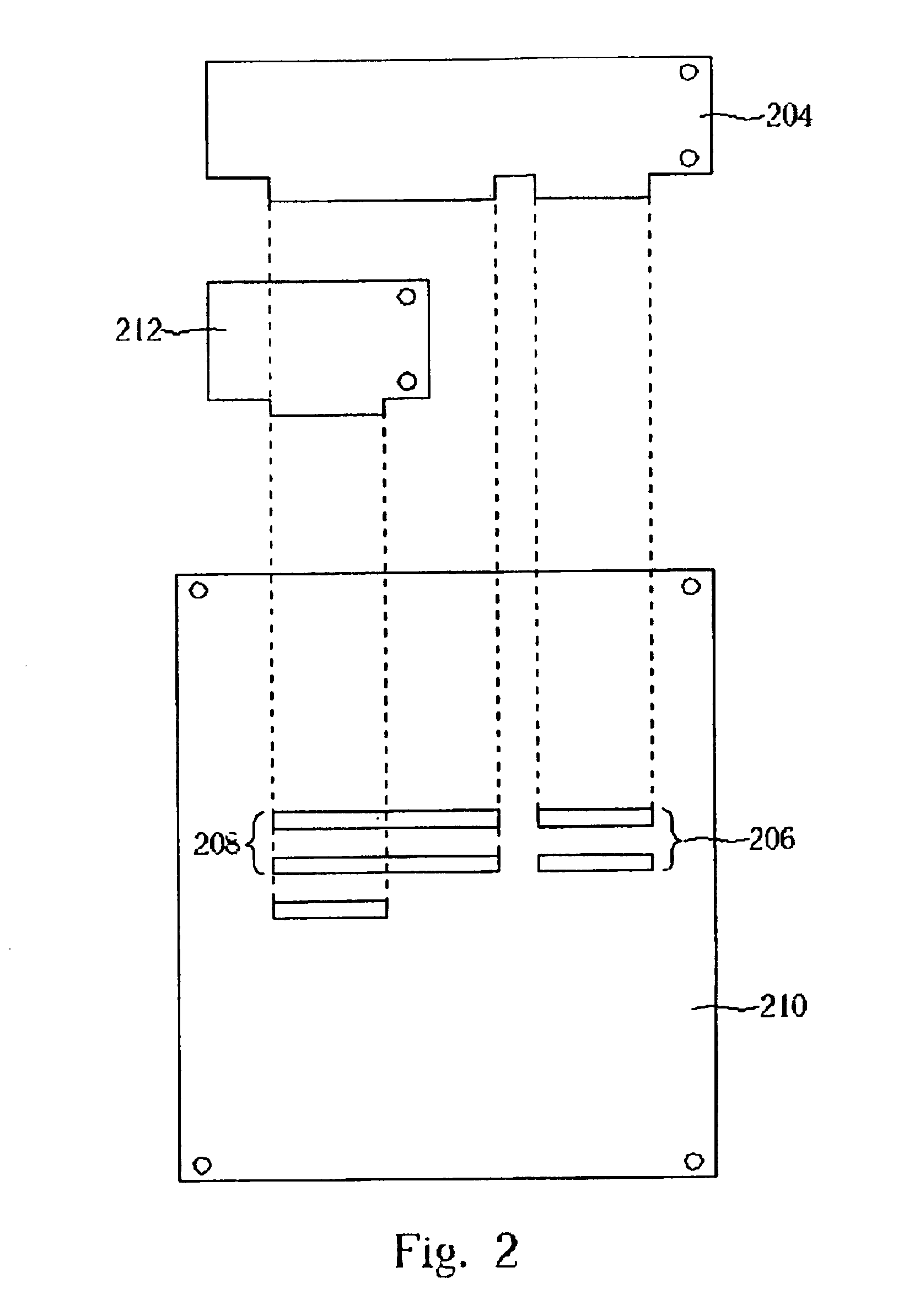
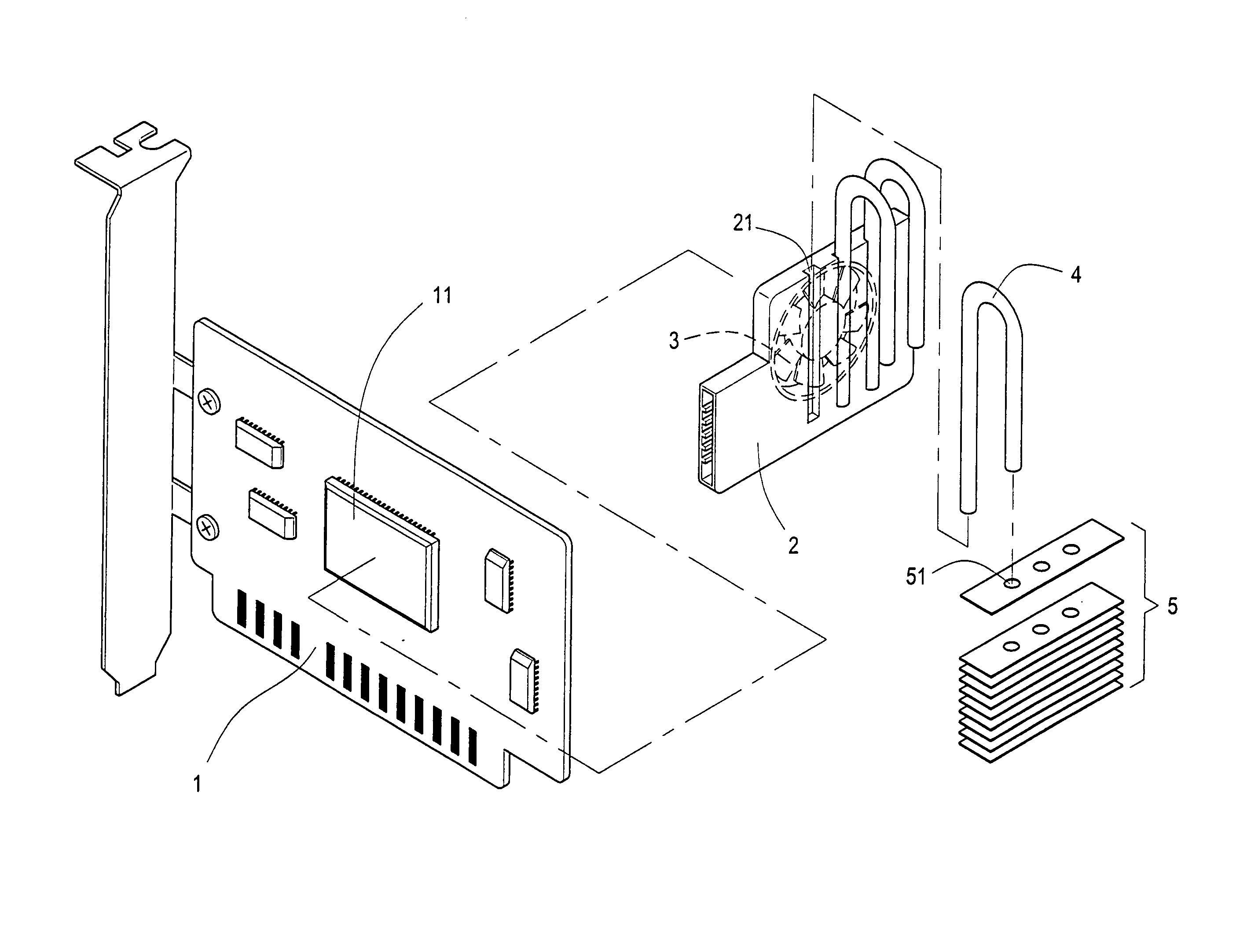
Heat dissipating structure of accelerated graphic port card
InactiveUS20050068727A1Increase the effective cooling areaImprove cooling effectDigital data processing detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsThermal energyGraphics
A heat dissipating structure of accelerated graphics port (AGP) card, disposed at the AGP card for dissipating heat with respect to a certain chip therein, at least includes an extruded aluminum heat dissipating section and a fan. The invention is characterized that, at least one heat conducting pipe is disposed at a lower portion of the extruded aluminum heat dissipating section, and extended to a rear side of the AGP card; and thermal energy produced by the AGP card chip is conducted by the heat conducting pipes to cooling fins at the rear side of the AGP card, thereby increasing an effective heat dissipating area for enhancing heat dissipation effects.
Owner:YU CHIEN CHUN +1
Method and system for data transmission in accelerated graphics port systems
InactiveUS6304935B1Software simulation/interpretation/emulationMemory systemsComputational scienceData processing system
A method and system for data transmission in data processing systems, especially in the context of data processing systems utilizing the Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP) interface standard. The method and system provide an AGP-enabled device wherein is contained a command queue. The AGP-enabled device is connected to and communicates with an AGP-enabled bridge through and over a data bus. The AGP-enabled bridge has an AGP-enabled device mimicking unit. In one instance, the AGP-enabled device is an AGP-enabled graphics controller, the command queue is a graphics controller command queue, the AGP-enabled bridge is an AGP-enabled Northbridge, and the data bus is an AGP interconnect. In this instance, the graphics controller has a graphics controller full signal unit which controls and utilizes the PIPE# signal of the AGP-enabled graphics controller to indicate whether the graphics controller command queue can accept data. Further in this instance, the AGP-enabled Northbridge has an AGP-enabled graphics controller mimicking unit. In another instance, the AGP-enabled Northbridge has a CPU mimicking unit.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Computer CPU and memory to accelerated graphics port bridge having a plurality of physical buses with a single logical bus number
InactiveUS20020109688A1Easy to handleImprove data throughputMemory adressing/allocation/relocationCathode-ray tube indicatorsMemory addressGraphics
A core logic chip set in a computer system provides a bridge between processor host and memory buses and a plurality of Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP) buses. Each of the plurality of AGP buses have the same logical bus number. The core logic chip set has an arbiter having Request ("REQ") and Grant ("GNT") signal lines for each AGP device connected to the plurality of AGP physical buses. Each of the plurality of AGP buses has its own read and write queues to provide transaction concurrency of AGP devices on different ones of the plurality of AGP buses when the transaction addresses are not the same or are M byte aligned. Upper and lower memory address range registers store upper and lower memory addresses associated with each AGP device. Whenever a transaction occurs, the transaction address is compared with the stored range of memory addresses. If a match between addresses is found then strong ordering is used. If no match is found then weak ordering may be used to improve transaction latency times. AGP device to AGP device transactions may occur without being starved by CPU host bus to AGP bus transactions.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
High speed peripheral interconnect apparatus, method and system
InactiveUS20050273534A1Increase clock frequencyHigh degreeElectric digital data processingGraphicsMemory bus
A multiple use core logic chip set is provided in a computer system that may be configured either as a bridge between an accelerated graphics port (“AGP”) bus and host and memory buses, as a bridge between an additional registered peripheral component interconnect (“RegPCI”) bus and the host and memory buses, or as a bridge between a primary PCI bus and an additional RegPCI bus. The function of the multiple use chip set is determined at the time of manufacture of the computer system or in the field whether an AGP bus bridge or an additional registered PCI bus bridge is to be implemented. The multiple use core logic chip set has an arbiter having Request (“REQ”) and Grant (“GNT”) signal lines for each PCI device utilized on the additional registered PCI bus. Selection of the type of bus bridge (AGP or RegPCI) in the multiple use core logic chip set may be made by a hardware signal input, or by software during computer system configuration or power on self test (“POST”). Software configuration may also be determined upon detection of either an AGP or a RegPCI device connected to the common AGP / RegPCI bus.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Switch/network adapter port coupling a reconfigurable processing element to one or more microprocessors for use with interleaved memory controllers
InactiveUS20050076152A1Conveniently providedMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork connectionsGraphicsDIMM
A switch / network adapter port (“SNAP™”) in a dual in-line memory module (“DIMM”) or Rambus™ in-line memory module (“RIMM”) format for clustered computers employing multi-adaptive processor (“MAP®”, both trademarks of SRC Computers, Inc.) elements for use with interleaved memory controllers. Particularly disclosed is a microprocessor based computer system utilizing either a DIMM or RIMM physical format adapter port coupled to a reconfigurable processor element for the purpose of implementing a connection to an external switch, network, or other device. In a particular embodiment, connections may be provided to either the PCI, accelerated graphics port (“AGP”) or system maintenance (“SM”) bus for purposes of passing control information to the host microprocessor or other control chips. The field programmable gate array (“FPGA”) based processing elements have the capability to alter data passing through it to and from an external interconnect fabric or device.
Owner:SRC COMP
Dynamic computation of chipset-supported accelerated graphics port aperture sizes
InactiveUS6933944B2Memory adressing/allocation/relocationCathode-ray tube indicatorsHard codingGraphics
Methods and apparatus for use with AGP-capable computer systems are disclosed. Since each AGP-capable chipset can have a unique range of graphics port aperture sizes that it supports, current graphics port aperture drivers are chipset-specific, with hard-coded tables of supported graphics aperture sizes. Described herein is a driver that dynamically ascertains the range of supported graphics aperture port sizes for an attached AGP-capable chipset, thus allowing this driver to be ported between different chipsets without manual reconfiguration and recompiling. The method employed in the driver sends one or more test aperture size values to a register resident in the chipset, and then reads what is written to see if the chipset changed any of the bits of the test value. The method infers supported sizes from examining which, if any bits, were changed by the chipset.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Switching extension equipment for computer system
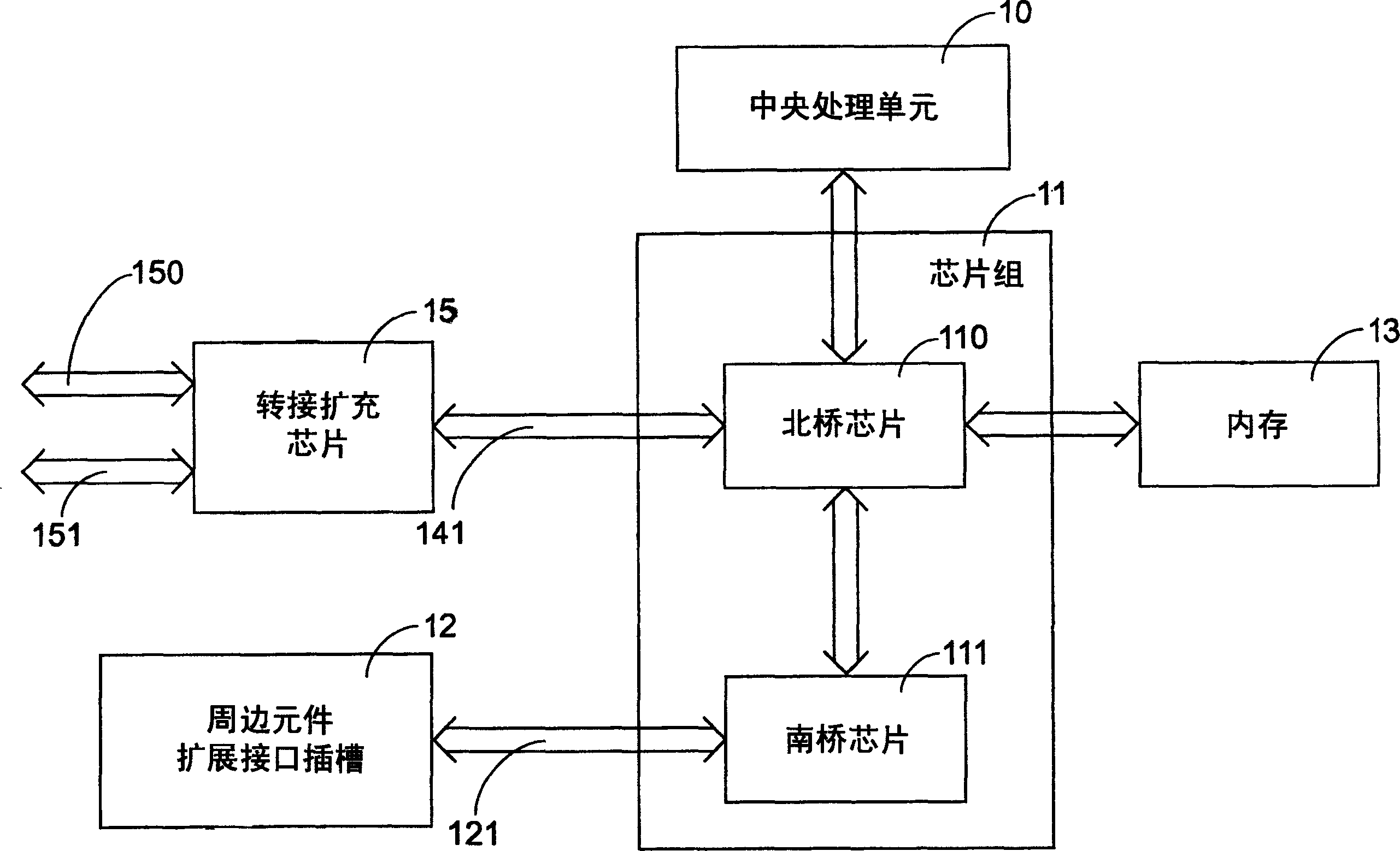
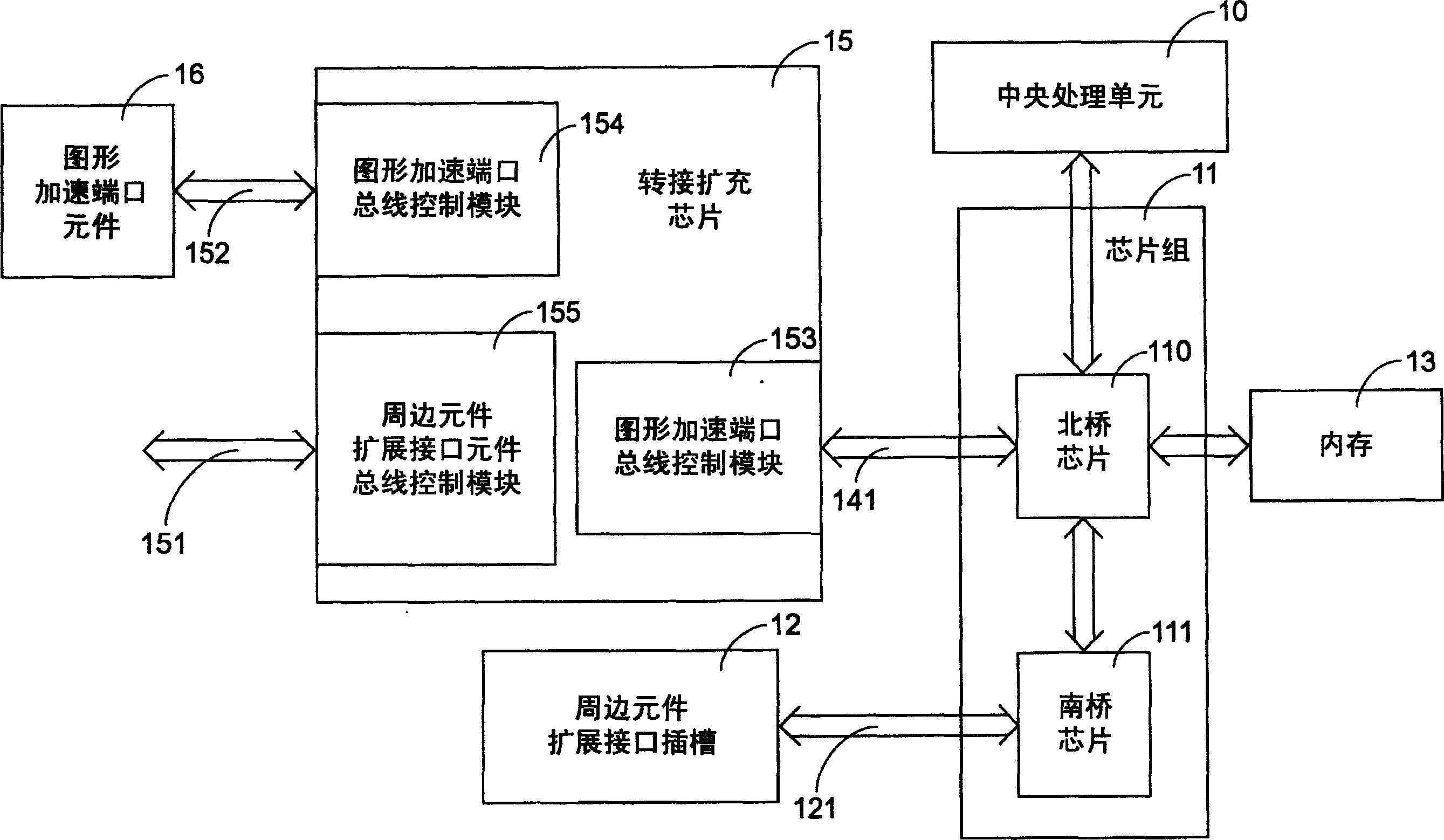
The invention provides a connecting and extending device, applied to a computer with an operating system, and comprising: a first accelerated graphics port (AGP) bus control module; a second AGP bus control module;; and a peripheral component interface (PCI) bus control module, where the signal lines are connected between the first AGP and PCI bus control modules to transmit signals. It can make full use of the function of rapid data transmission of the AGP socket.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Multi-function chipset and related method
Multi-function chipset and related design / manufacturing method for realizing different kinds of chipsets respectively supporting accelerated graphic port (AGP) bus and peripheral component interconnect extended (PCI-X) bus. The integrated circuit of the chipset includes both the AGP and PCI-X bus controllers, which share a common I / O pad configuration, and the chipset is selected to be an AGP-supported chipset or a PCI-X supported chipset by pin strapping. Also, the chipset can be packaged with different wire bonding configurations to alternatively realize chipsets supporting AGP bus or PCI-X bus.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Input/output structure and integrated circuit using the same
ActiveUS6972445B2Low costSimple designSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesInterconnectionExternal circuit
An input / output structure for a die to support an Accelerated Graphic Port (AGP) standard and a Peripheral Component Interconnection Express (PCIE) standard is provided. The I / O structureis suitable for the die pad. It comprises: a PCIE input / output pad for supporting PCIE standard; an AGP input / output pad for supporting AGP standard; a die pad coupled to an external circuit; a first conducting distributed wire coupled to the PCIE input / output pad and the die pad; and a second conducting distributed wire coupled to the AGP input / output pad and the die pad; wherein only one of the PCIE input / output pad and the AGP input / output pad is enabled at the same time.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Information recording method
ActiveCN104954749AImprove transfer storage speedReduce widthClosed circuit television systemsDigital video signal modificationFiltrationComplex programmable logic device
The invention provides an information recording method. The method comprises the following steps that a CPLD (Complex Programmable Logic Device) is used for transmitting image data to an encoding chip to be compressed and encrypted through format conversion and filtration after finishing reception of the image data; the encoding chip is used for sending the data back to the CPLD after finishing compression and encryption, and the CPLD controls a bus interface time sequence of an AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) and uploads the data to an upper computer. The invention provides an image signal acquiring and processing method which has the capabilities of improving the signal transmission and storage speed and reducing the requirements on the channel width and the size of a storage space.
Owner:SICHUAN TELUNTE TECH
Structure and method for extended bus and bridge in the extended bus
InactiveUS7054984B2Unauthorized memory use protectionElectric digital data processingGraphicsDatapath
A structure and a method for an extended bus and a bridge in the extended bus are disclosed. The structure of the extended bus has a first accelerated graphics port bus, a first bridge, a second accelerated graphics port bus and a first extended bus. The first bridge performs a compatible mutual conversion of the signal and data between the first accelerated graphics port bus and the first extended bus or the second accelerated graphics port bus, so that the first accelerated graphics port bus is extended for use. The invention extends and expands the current available high-speed and wide-bandwidth accelerated graphics port bus to obtain one or more extended buses. The data path through the south bridge chip is thus avoided. Furthermore, more expansion slots are provided to the system, and the flexibility of expanding the computer system is increased.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
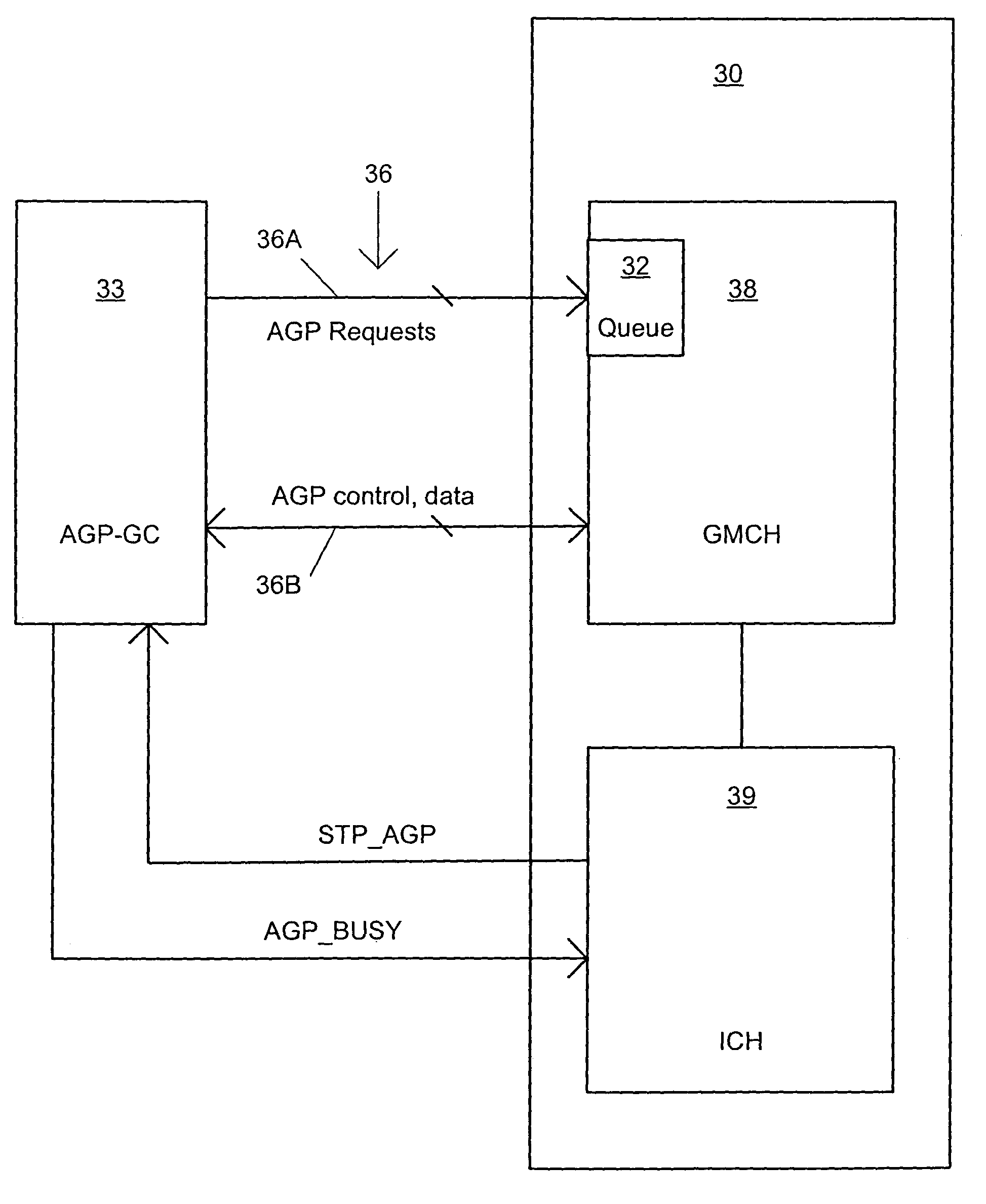
Entering and exiting power managed states without disrupting accelerated graphics port transactions
An interface between an accelerated graphics port graphics controller (AGP-GC) and a core controller to prevent entry into a low power state from interfering with transfers to or from the AGP-GC that have been requested but not completed. The core controller can communicate to the AGP-GC an intent to enter a low power state, while the AGP-GC can communicate to the core controller the busy status of the AGP-GC. When the AGP-GC receives notice of an intent to enter a low power state, it can stop issuing requests to the core controller. When the core controller detects that the AGP-GC is busy, the core controller can postpone entry into the low power state until the AGP-GC completes any requests that are in progress. In an alternate use of the interface, if the AGP-GC wishes to make a request during a low power state, it can signal the core controller of this need by indicating a busy status, which can trigger the core controller to initiate an exit from the low power state.
Owner:INTEL CORP
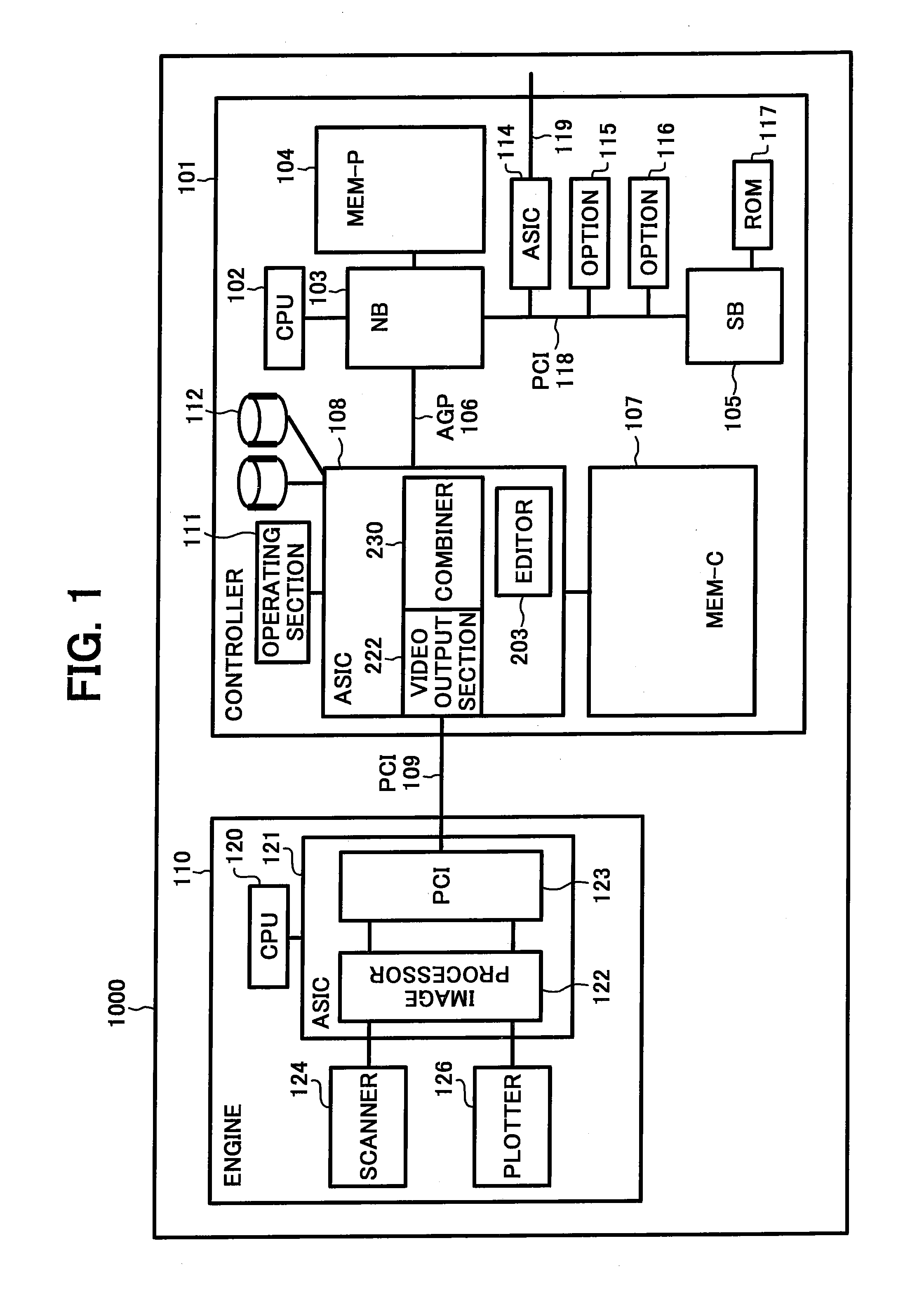
Image forming apparatus
ActiveUS7405843B2Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsGraphicsImaging processing
An image forming apparatus includes a controller having an integrated circuit for image processing. The controller is connected to an engine via a peripheral component interconnect (PCI). The engine includes a plotter and a scanner. The controller includes a central processing unit (CPU) to which a chip-set is connected via an accelerated graphics port (AGP). The controller also includes an application specific integrated circuit (ASIC) that controls whether to output scanner image data, which is data acquired by the scanner, to the PCI as plotter data for the plotter, or to output the scanner image data to the AGP, or to output image data input through the AGP to the PCI as plotter data for the plotter. The ASIC includes a combiner that combines a plurality of image data.
Owner:RICOH KK
Computer CPU and memory to accelerated graphics port bridge having a plurality of physical buses with a single logical bus number
InactiveUS6954209B2Easy to handleImprove data throughputMemory adressing/allocation/relocationCathode-ray tube indicatorsMemory addressGraphics
A core logic chip set in a computer system provides a bridge between processor host and memory buses and a plurality of Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP) buses. Each of the plurality of AGP buses have the same logical bus number. The core logic chip set has an arbiter having Request (“REQ”) and Grant (“GNT”) signal lines for each AGP device connected to the plurality of AGP physical buses. Each of the plurality of AGP buses has its own read and write queues to provide transaction concurrency of AGP devices on different ones of the plurality of AGP buses when the transaction addresses are not the same or are M byte aligned. Upper and lower memory address range registers store upper and lower memory addresses associated with each AGP device. Whenever a transaction occurs, the transaction address is compared with the stored range of memory addresses. If a match between addresses is found then strong ordering is used. If no match is found then weak ordering may be used to improve transaction latency times. AGP device to AGP device transactions may occur without being starved by CPU host bus to AGP bus transactions.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com