Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
707 results about "Degree of parallelism" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
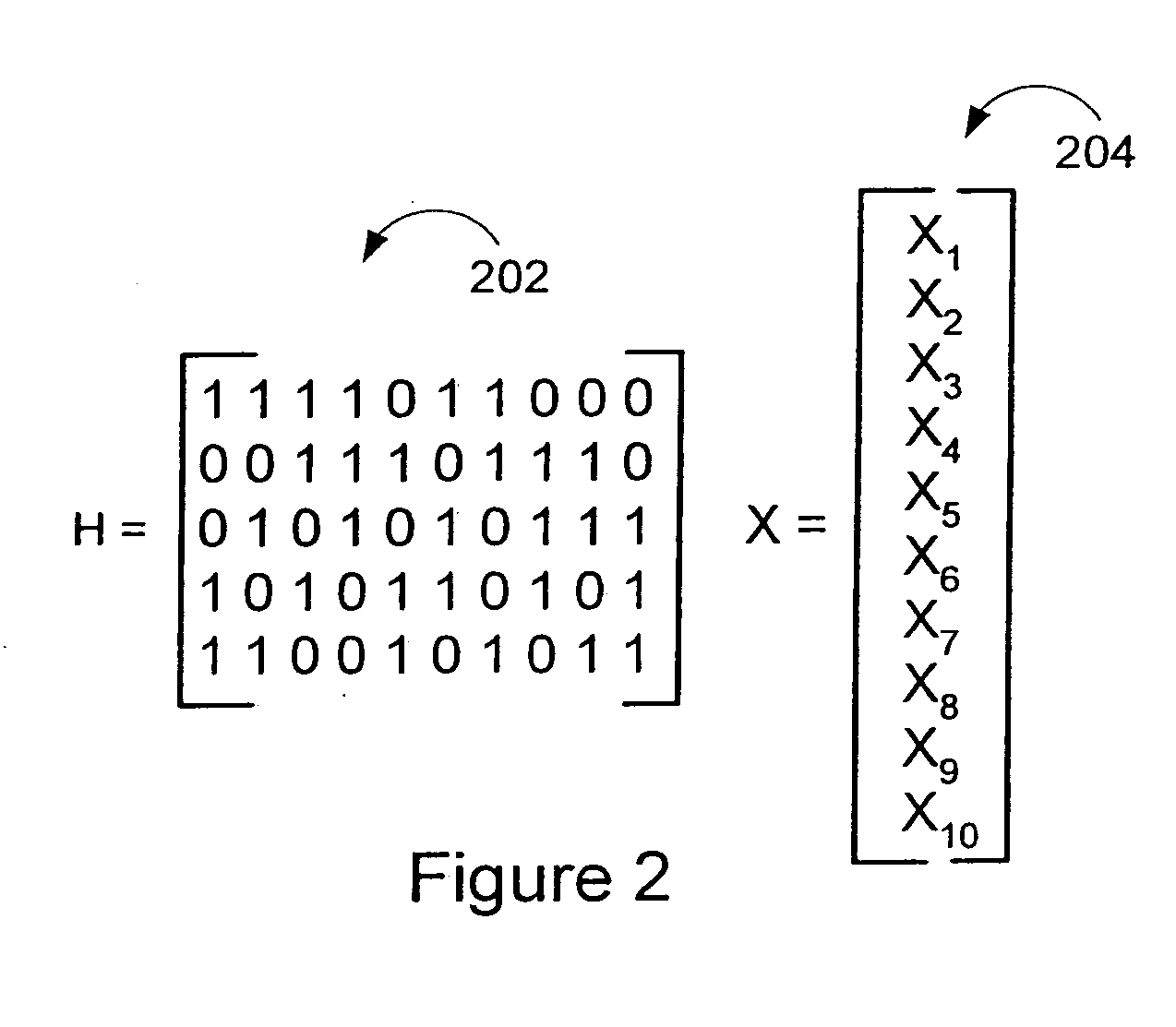
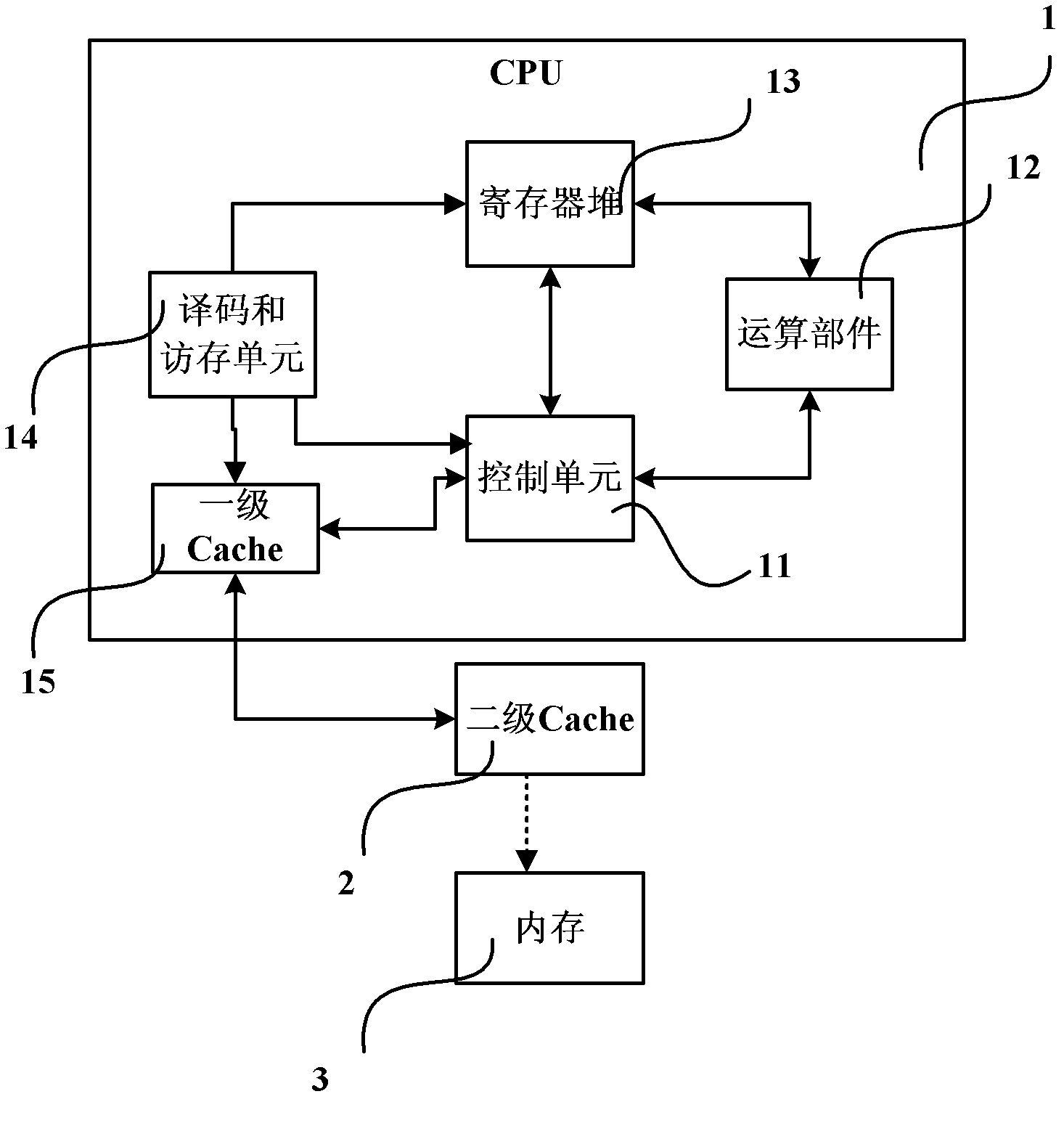
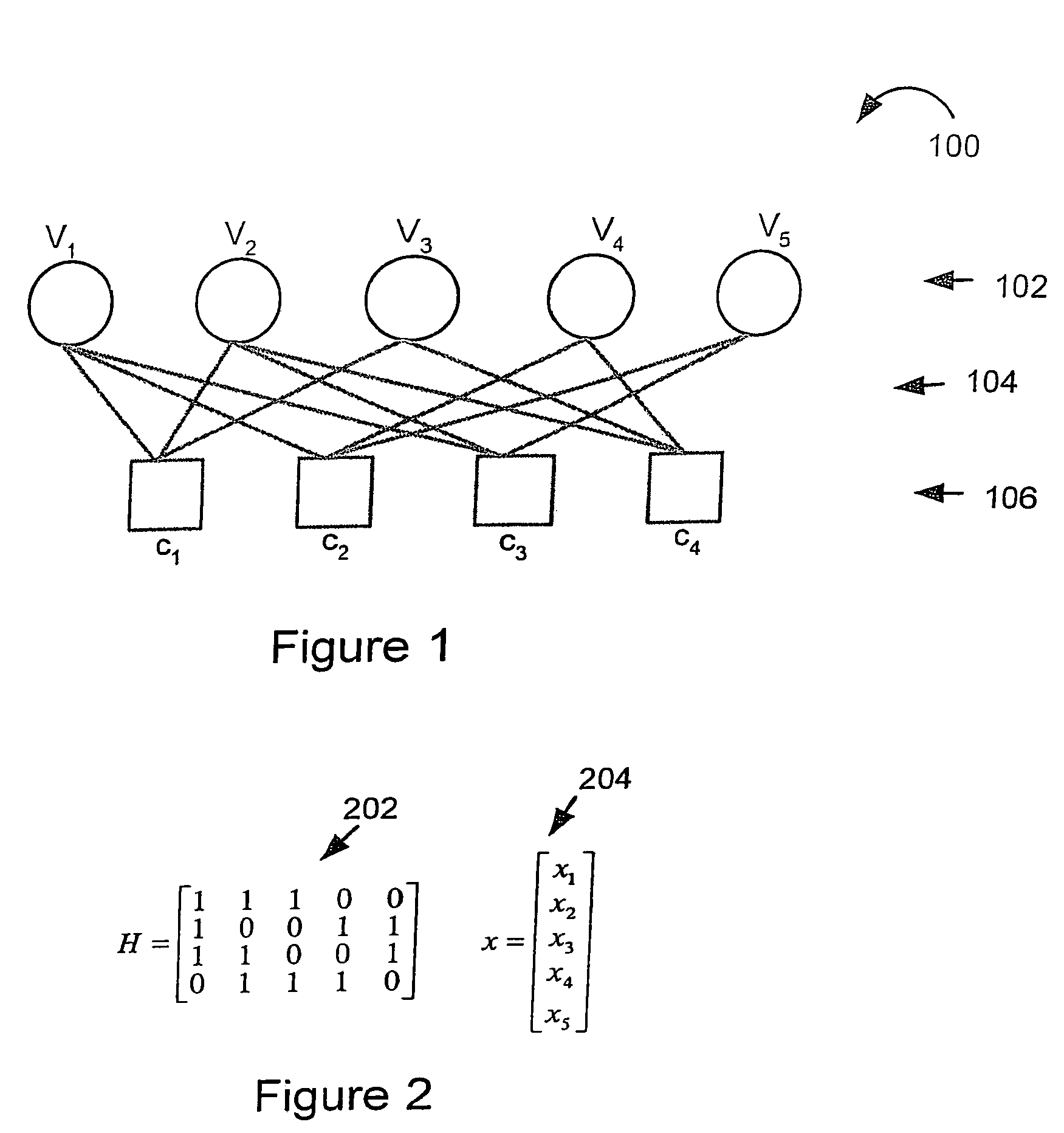
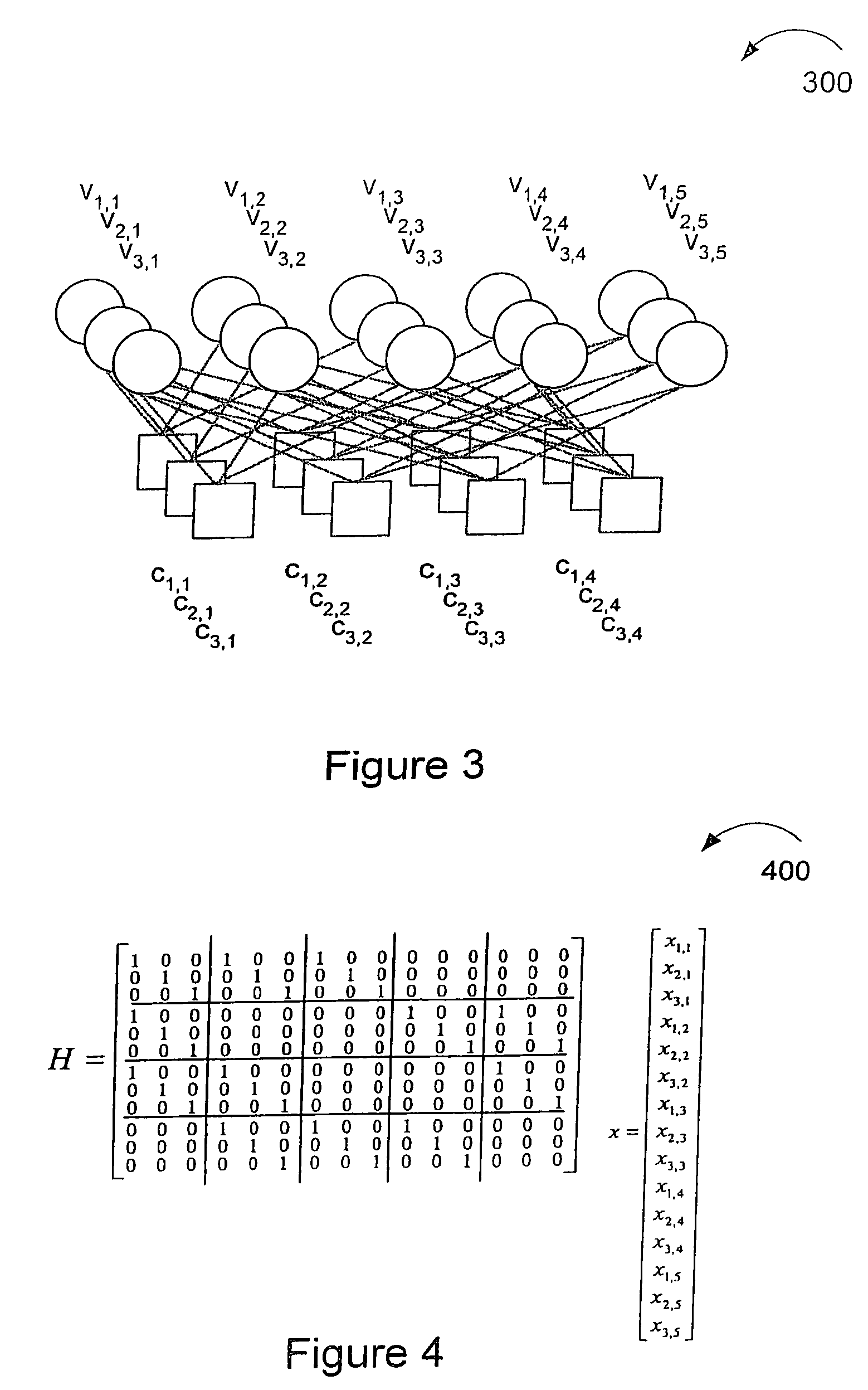
The degree of parallelism (DOP) is a metric which indicates how many operations can be or are being simultaneously executed by a computer. It is especially useful for describing the performance of parallel programs and multi-processor systems.
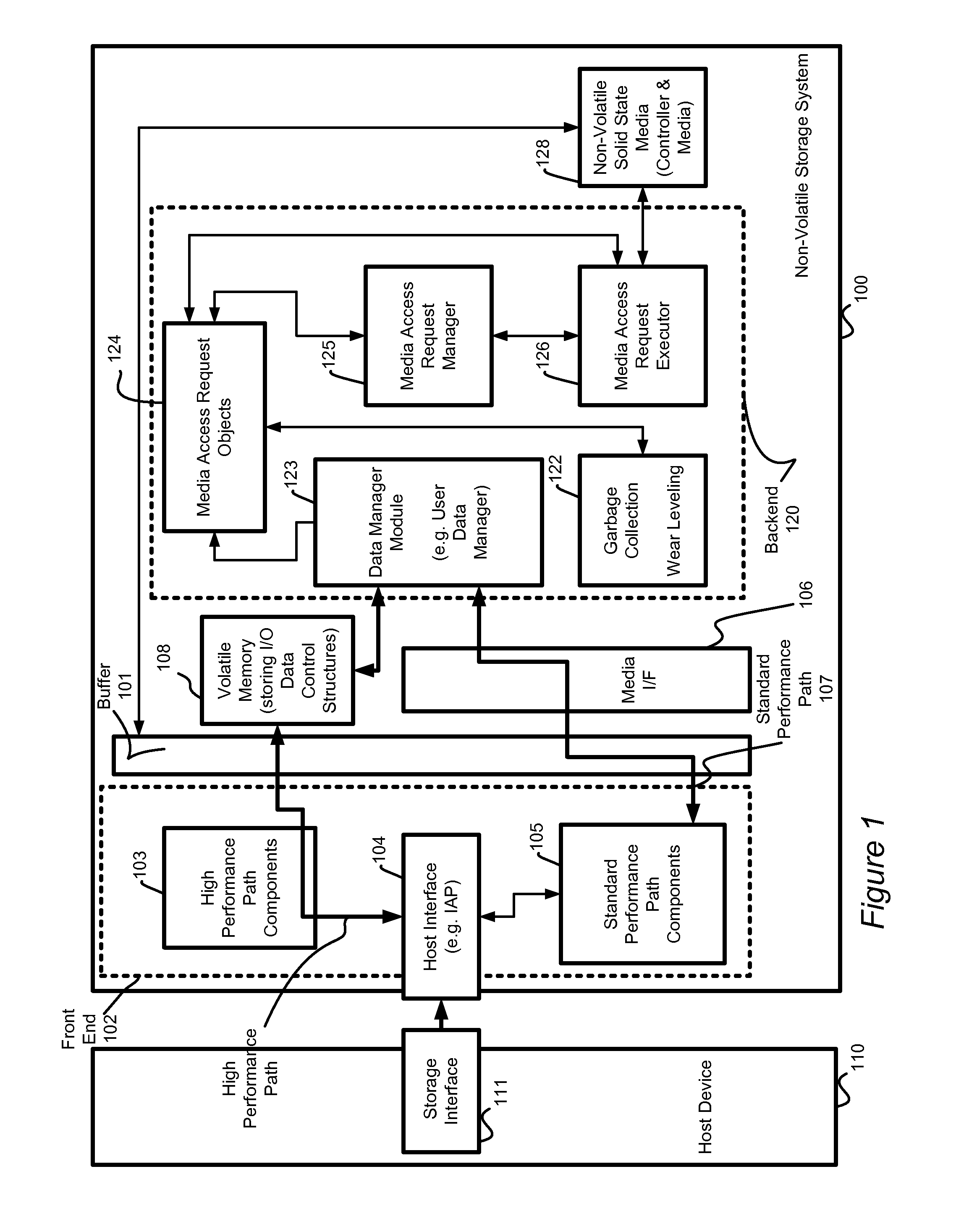
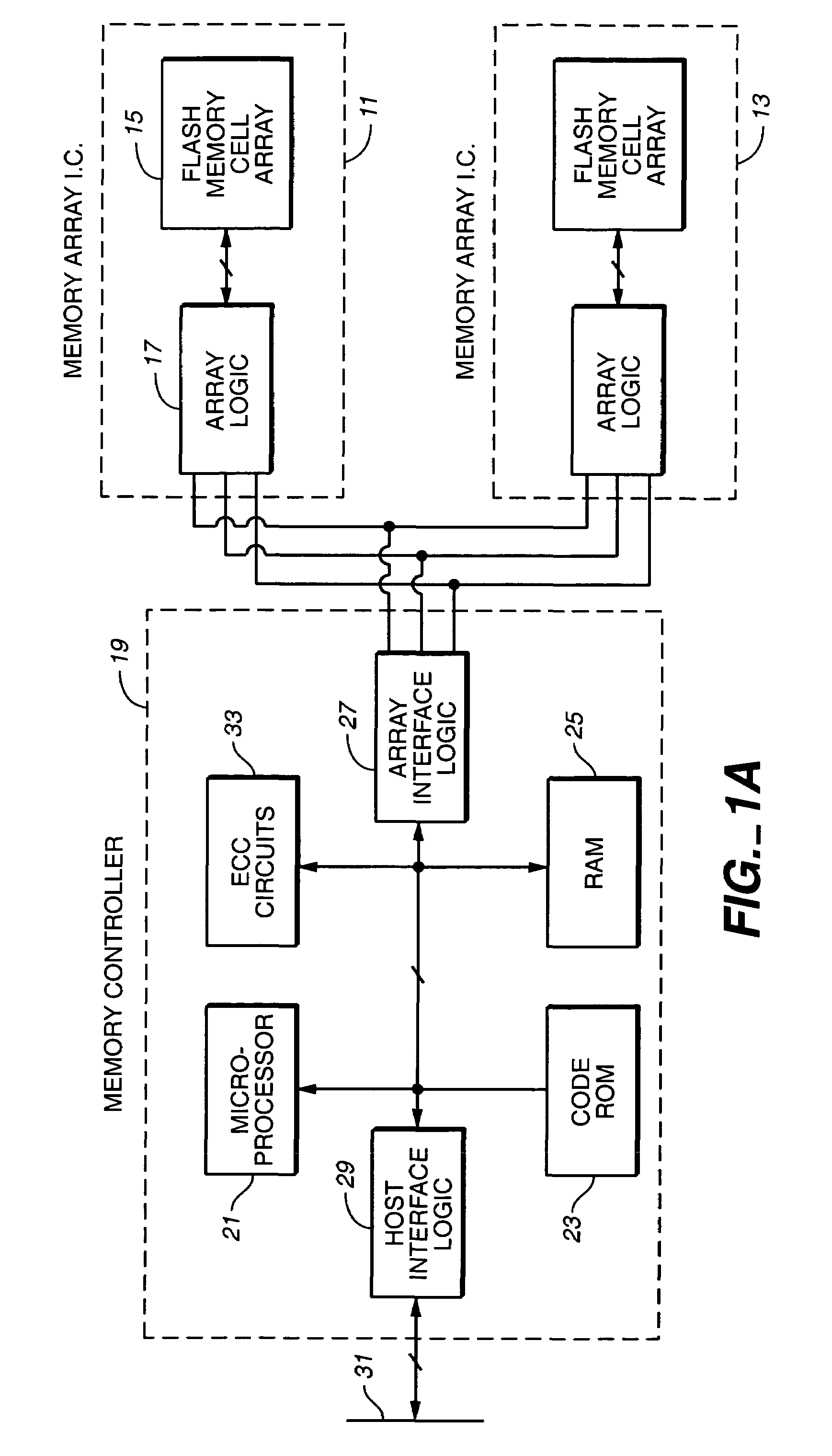
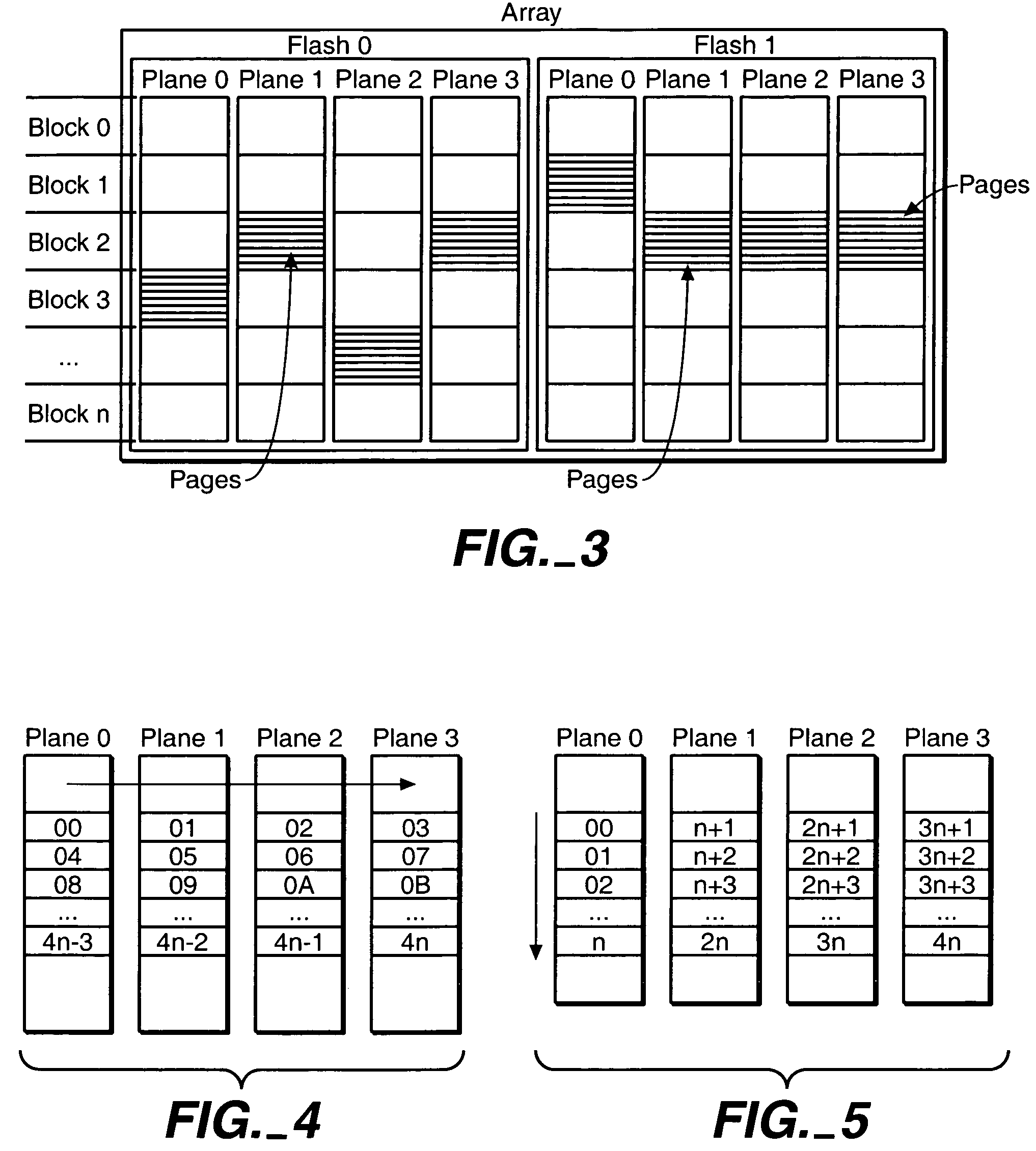
Adaptive mode switching of flash memory address mapping based on host usage characteristics
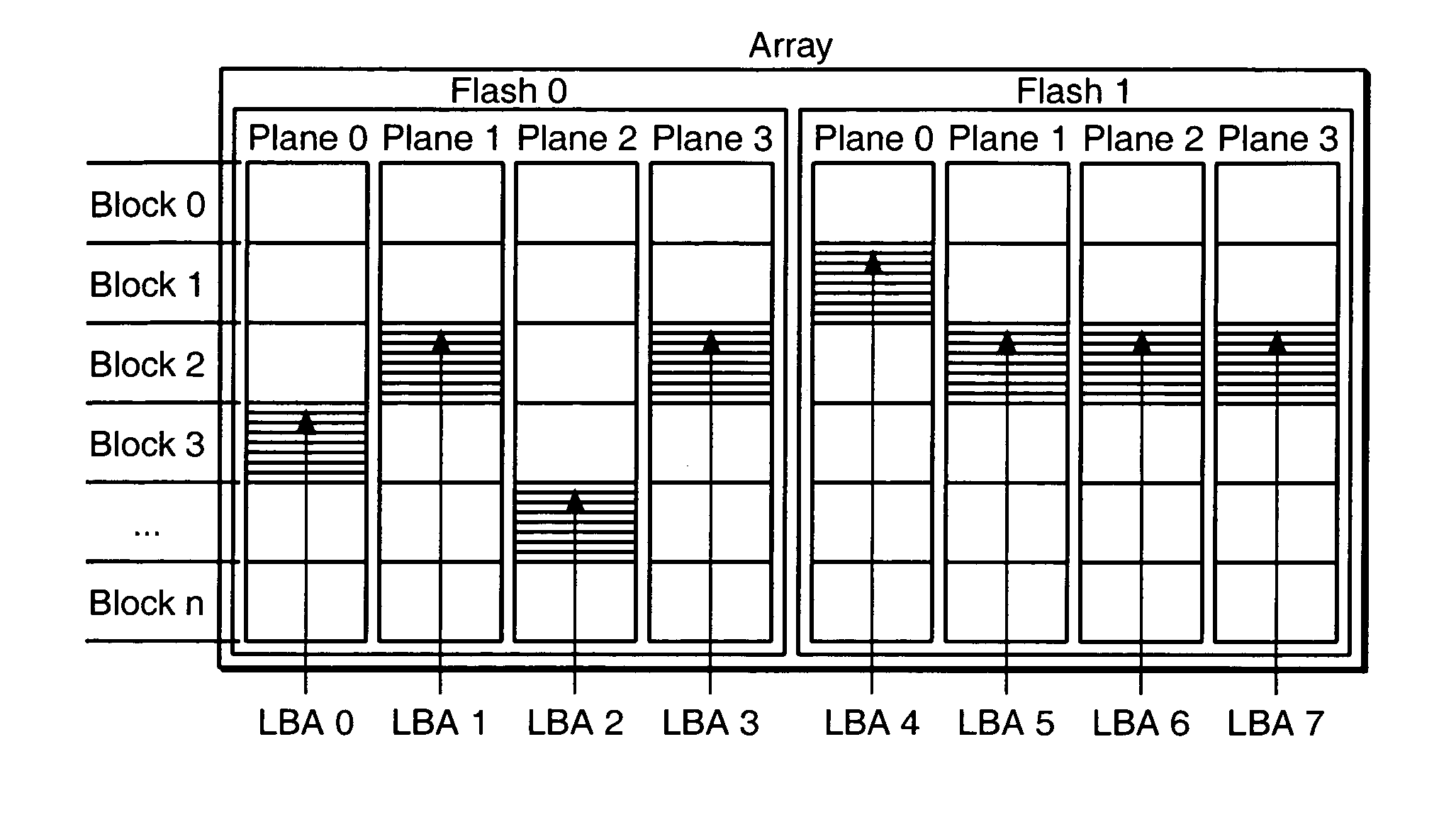
ActiveUS20050144361A1Reduced useful lifeOptimal performance characteristicMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDegree of parallelismSelf adaptive
In a non-volatile memory storage system such as a flash EEPROM system, a controller switches the manner in which data sectors are mapped into blocks and metablocks of the memory in response to host programming and controller data consolidation patterns, in order to improve performance and reduce wear. Data are programmed into the memory with different degrees of parallelism.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
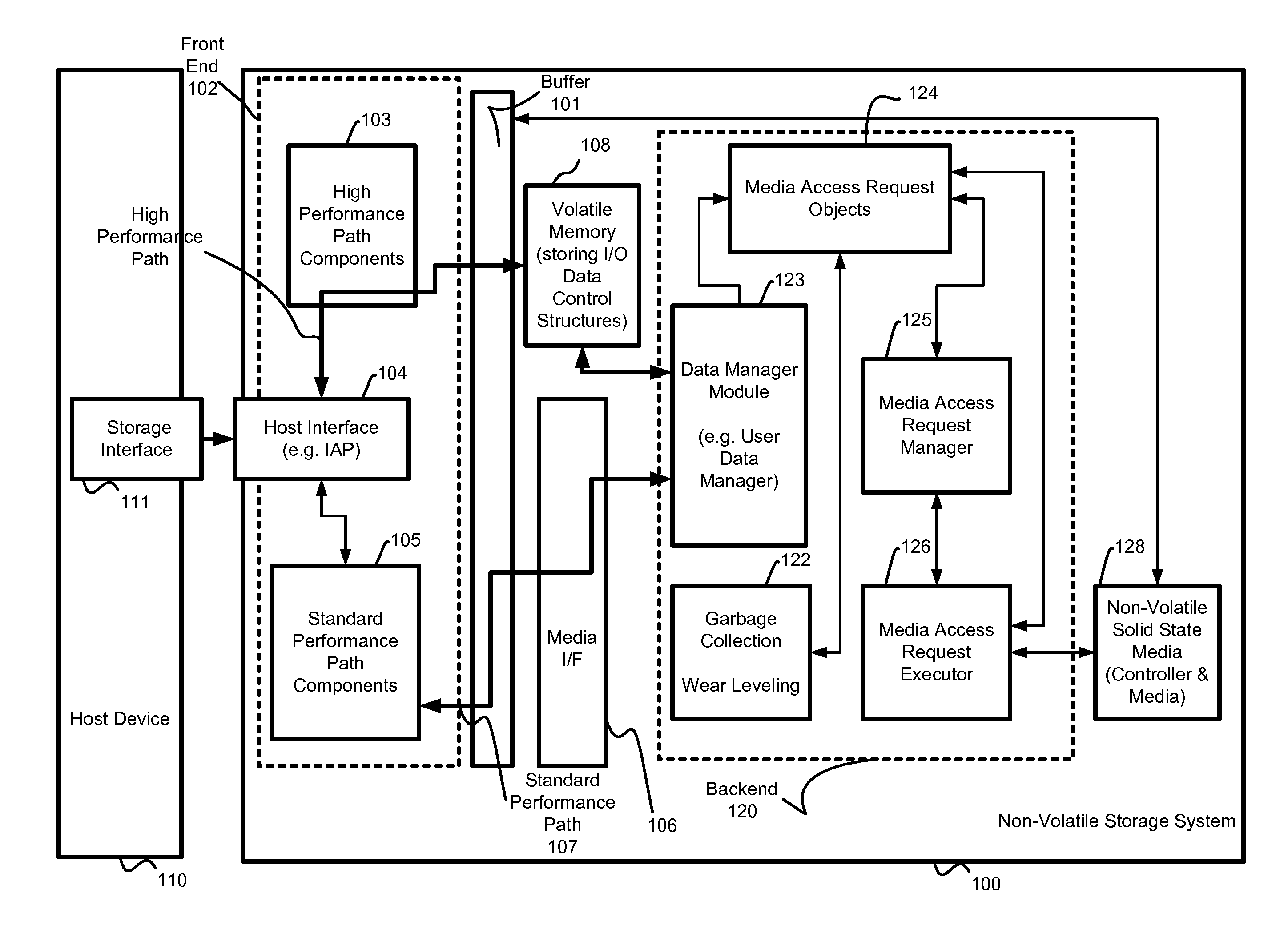
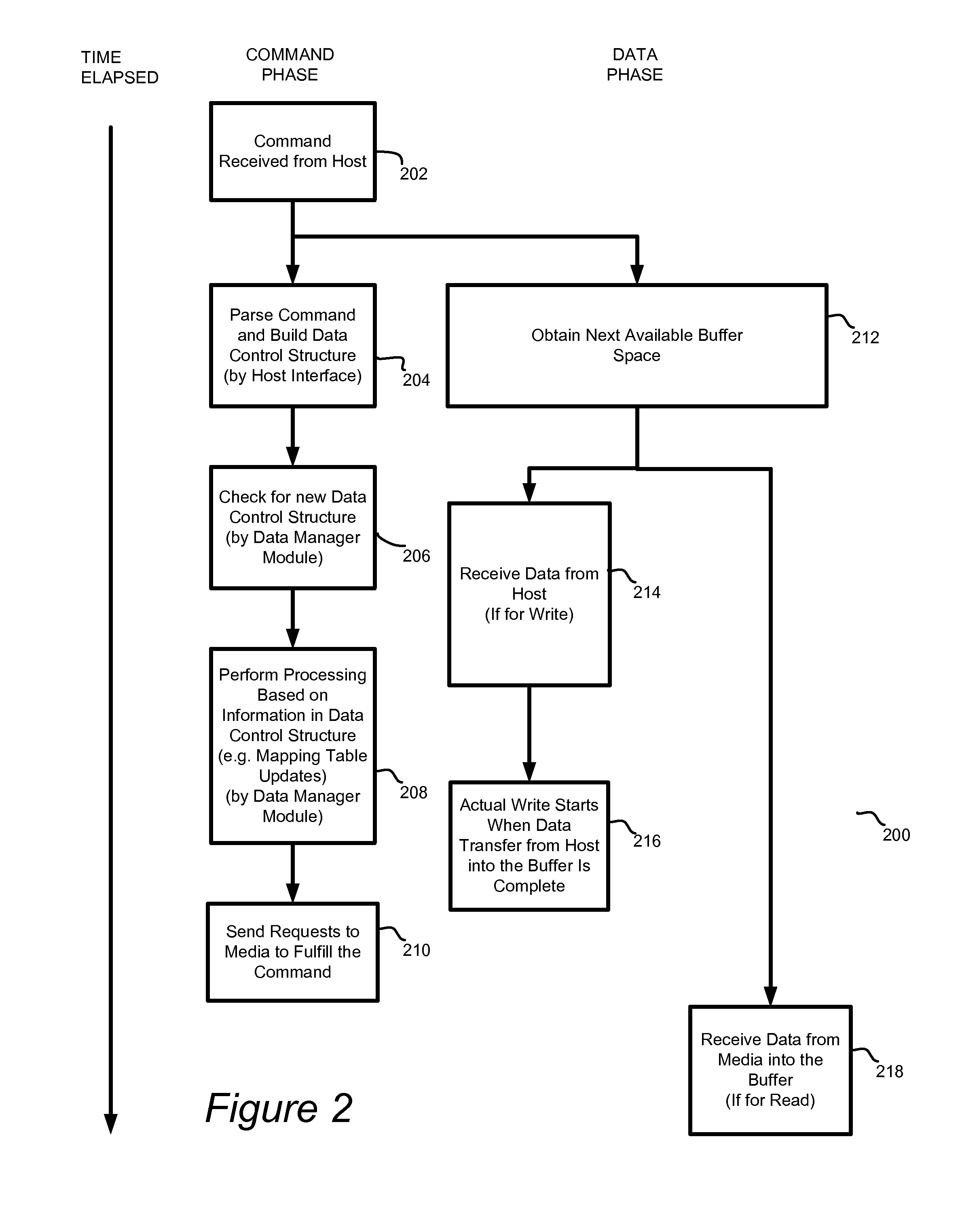
System and method for high performance command processing in solid state drives
ActiveUS8423722B1Improve performanceHigh bandwidthMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsHard disc driveHigh bandwidth
Solid State Drives (SSD) can yield very high performance if it is designed properly. A SSD typically includes both a front end that interfaces with the host and a back end that interfaces with the flash media. Typically SSDs include flash media that is designed with a high degree of parallelism that can support a very high bandwidth on input / output (I / O). A SSD front end designed according to a traditional hard disk drive (HDD) model will not be able to take advantage of the high performance offered by the typical flash media. Embodiments of the invention provide improved management of multiple I / O threads that take advantage of the high performing and concurrent nature of the back end media, so the resulting storage system can achieve a very high performance.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
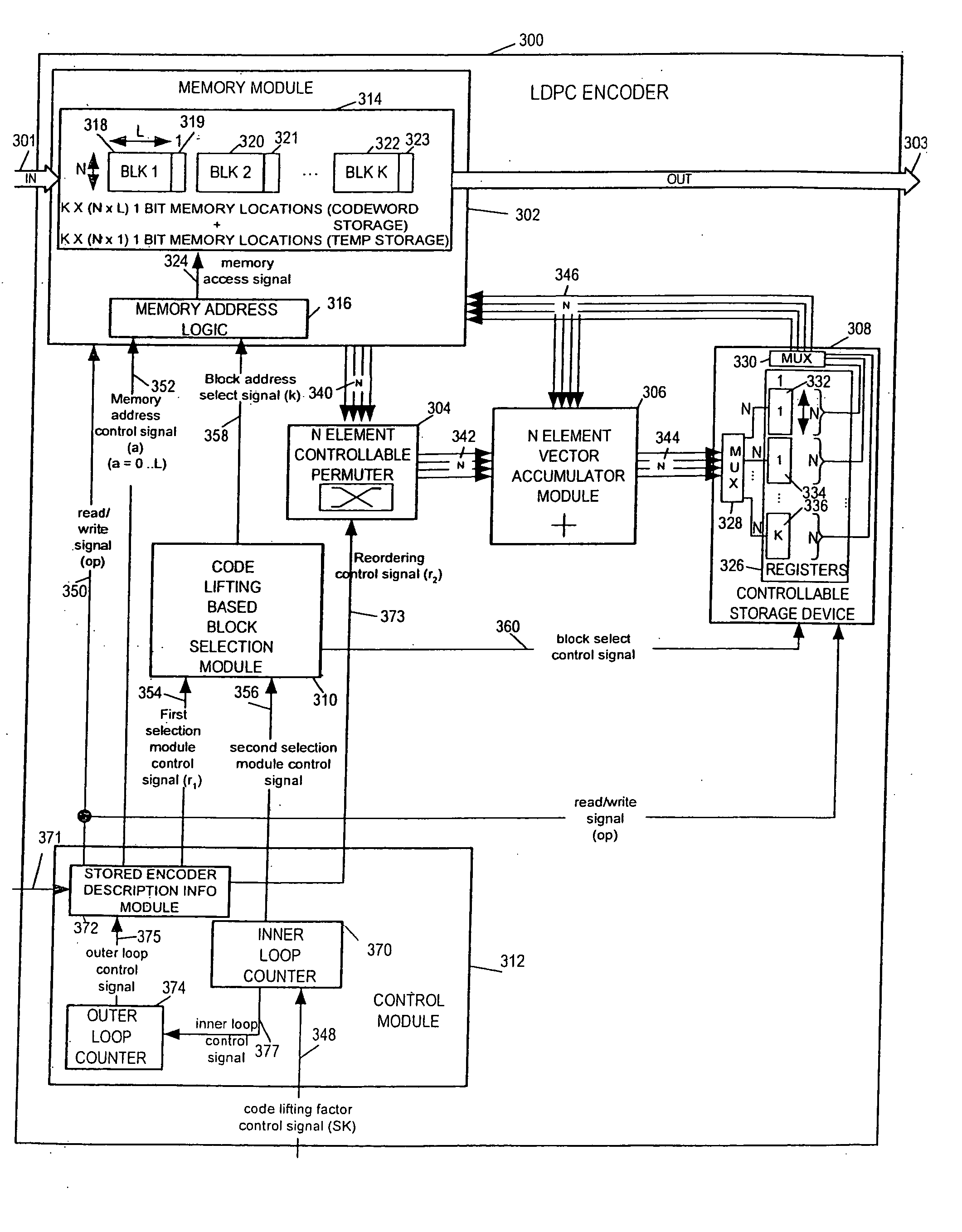
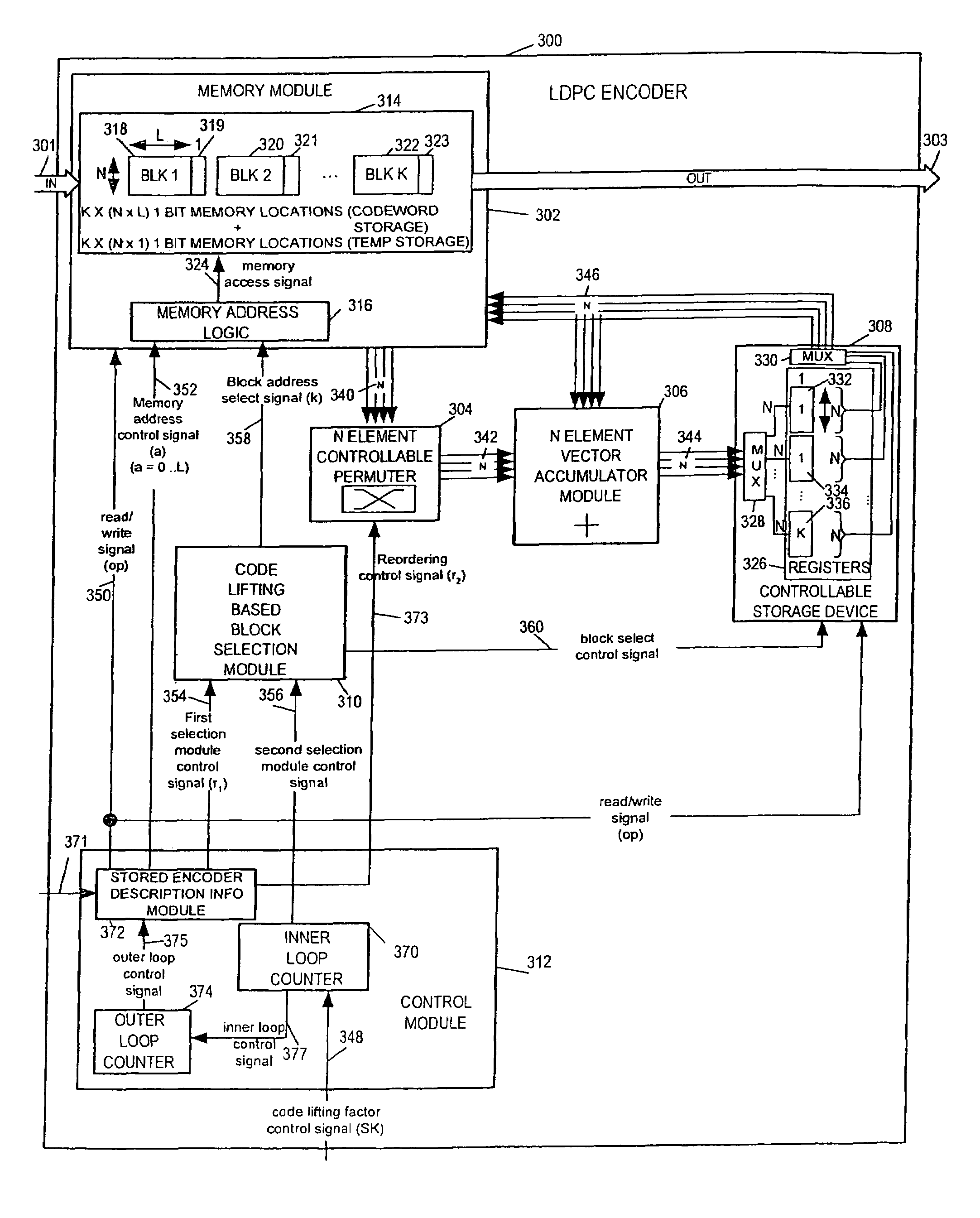
LDPC encoding methods and apparatus
ActiveUS20060020872A1Simple microcodeEasy to modifyError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionDegree of parallelismInstruction set
A flexible and relatively hardware efficient LDPC encoder is described. The encoder can be implemented with a level of parallelism which is less than the full parallelism of the code structure used to control the encoding process. Each command of a relatively simple microcode used to describe the code structure can be stored and executed multiple times to complete the encoding of a codeword. Different codeword lengths can be supported using the same set of microcode instructions but with the code being implemented a different number of times depending on the lifting factor selected to be used. The LDPC encoder can switch between encoding codewords of different lengths, without the need to change the stored code description information, by simply changing a code lifting factor used to control the encoding processes. When coding codewords shorter than the maximum supported codeword length some block storage locations and / or registers may go unused.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
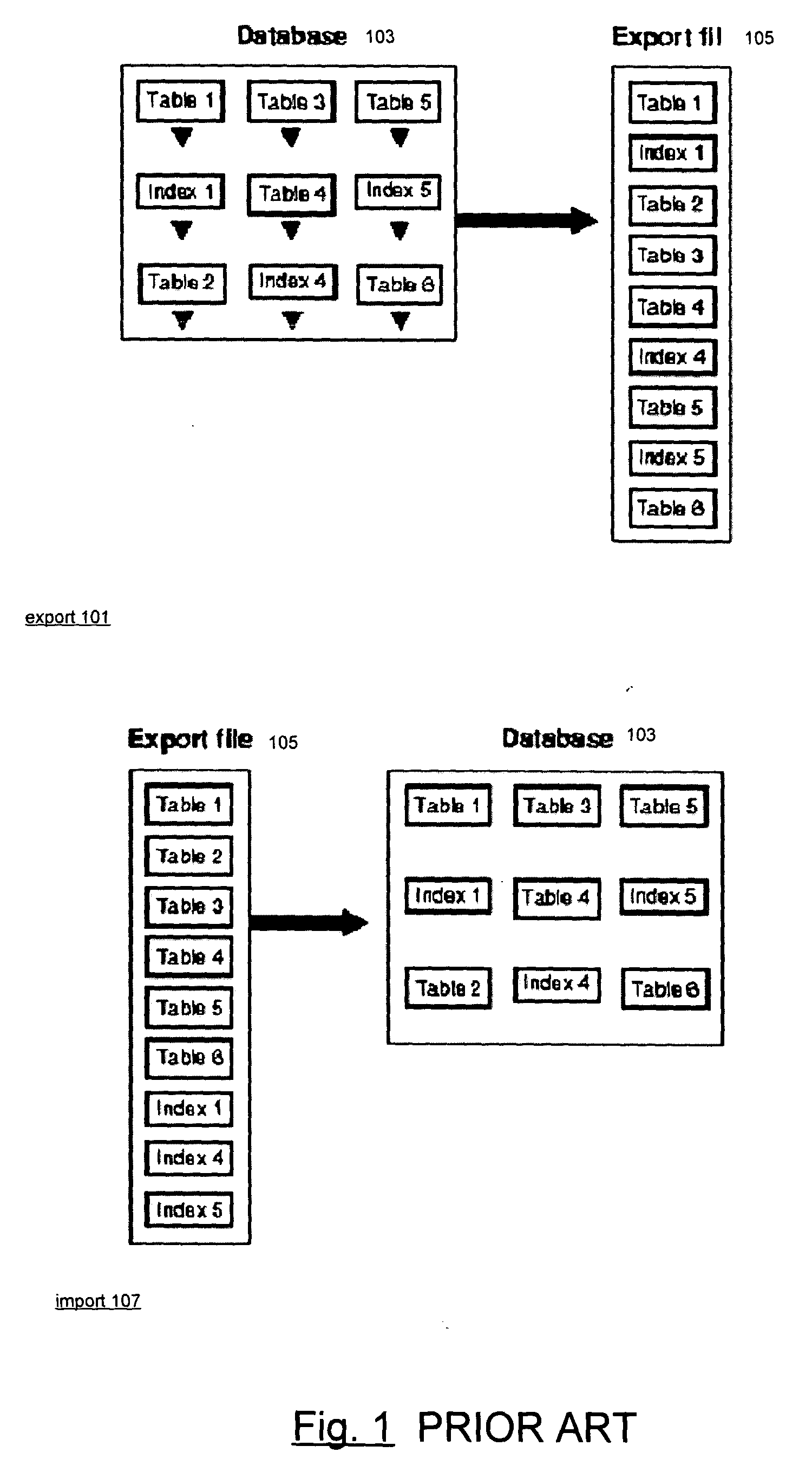
Apparatus and methods for transferring database objects into and out of database systems
ActiveUS20050055351A1Control performanceDatabase updatingDatabase management systemsRelational database management systemTransfer mechanism
Techniques for transferring objects between database systems. As implemented in a relational database management system, the techniques employ a data transfer mechanism that operates under control of a master table in the RDBMS that is performing the transfer operation. The master table specifies the kind of transfer operation to be performed, a set of objects to be transferred, operations to be performed on the objects as they are being transferred, and filters for selecting a subset of the objects. During execution of the transfer, the transfer mechanism maintains and updates state in the master table such that queries may be made on the master table to determine the current status of the operation and such that the transfer mechanism may restart the operation after it has been stopped either at the request of a client that is performing the operation or because of an error in the transfer. The master table's persistence and the status information it contains permit the client that is performing the operation to detach from the operation without stopping the operation and later again attach to the operation to determine the operation's status or to perform operations such as creating new files for the operation or changing the degree of parallelism with which the transfer operation is being performed. Another feature of the transfer mechanism is using an object's metadata to determine the most efficient way of transferring the object.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Scratch pad block
ActiveUS7315916B2Improve performanceWrite efficientlyMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesHigh densityHigh velocity
In a memory array having a minimum unit of erase of a block, a scratch pad block is used to store data that is later written to another block. The data may be written to the scratch pad block with a low degree of parallelism and later written to another location with a high degree of parallelism so that it is stored with high density. Data may be temporarily stored in the scratch pad block until it can be more efficiently stored elsewhere. This may be when some other data is received. Unrelated data may be stored in the same page of a scratch pad block.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Enabling intra-partition parallelism for partition-based operations
InactiveUS6954776B1Without incurring overhead costImprove parallelismDigital data information retrievalResource allocationHash functionTheoretical computer science
Techniques are provided for increasing the degree of parallelism without incurring overhead costs associated with inter-nodal communication for performing parallel operations. One aspect of the invention is to distribute-phase partition-pairs of a parallel partition-wise operation on a pair of objects among the nodes of a database system. The -phase partition-pairs that are distributed to each node are further partitioned to form a new set of-phase partition-pairs. One -phase partition-pair from the set of new-phase partition-pairs is assigned to each slave process that is on a given node. In addition, a target object may be partitioned by applying an appropriate hash function to the tuples of the target object. The parallel operation is performed by broadcasting each tuple from a source table only to the group of slave processes that is working on the static partition to which the tuple is mapped.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
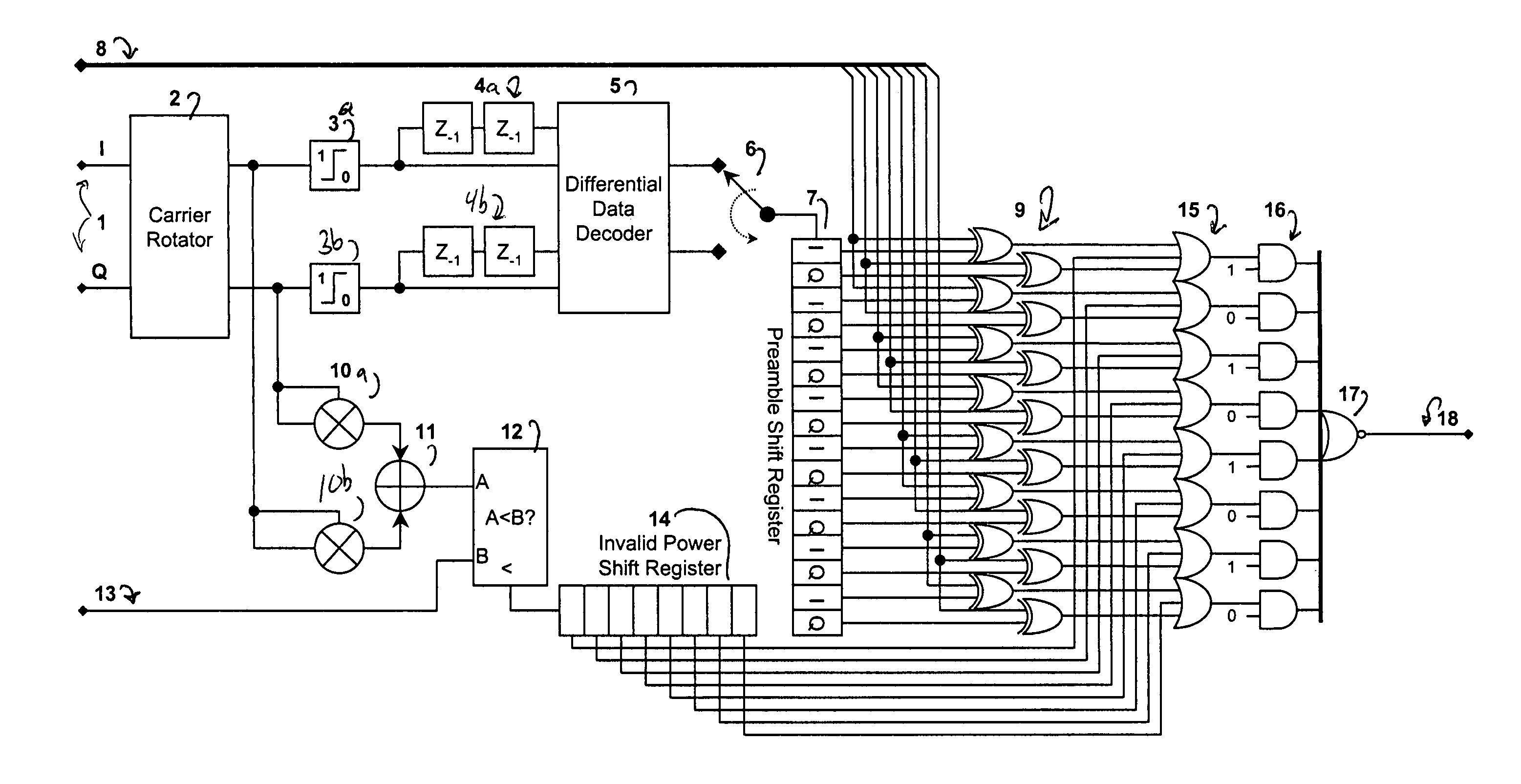
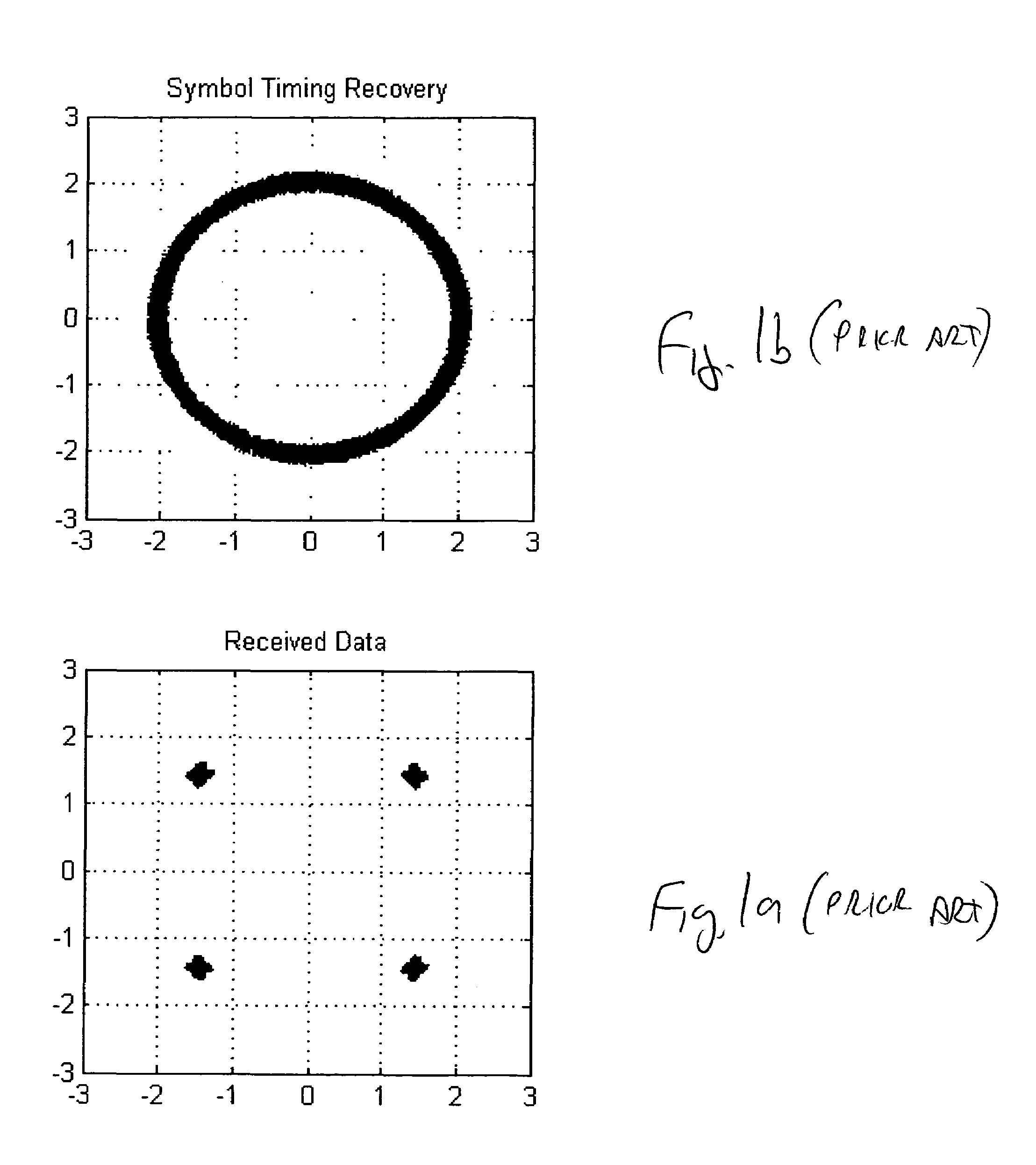
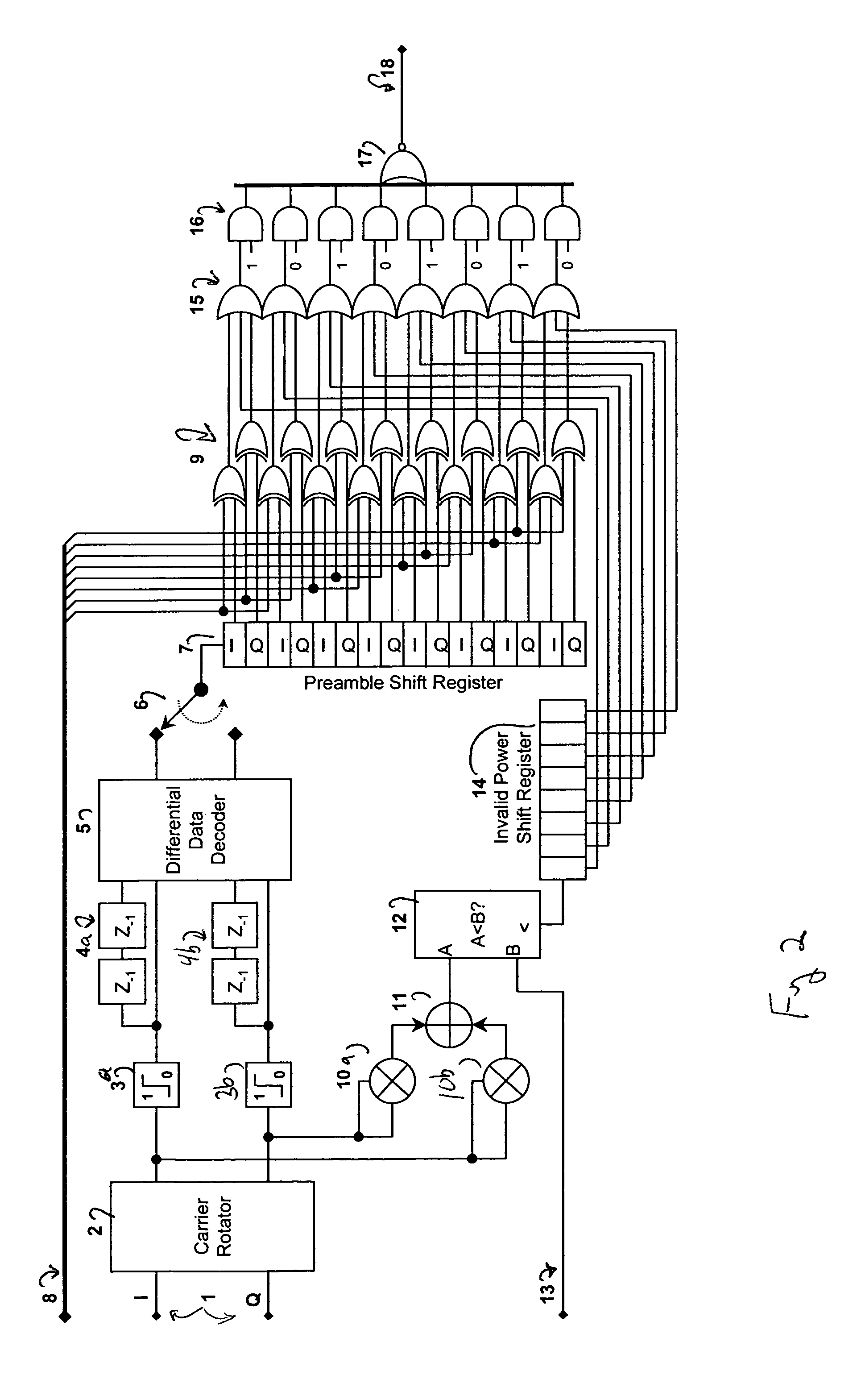
Method and apparatus for efficient preamble detection in digital data receivers
InactiveUS7428273B2Improve data throughputBroad potential applicabilityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsFrequency-modulated carrier systemsDigital dataComputer science
Traditional techniques for data reception in burst-mode receivers are of significant complexity. To aid detection, most burst-mode systems transmit a preamble, or predetermined data pattern, at the start of each new block of data. Using current methods, the detection of a new preamble, indicating the arrival of a new burst of data, is particularly complex. A method and apparatus is disclosed that significantly reduces this detection complexity, while maintaining superior signaling performance. This simplification can lead to higher data throughput within processing-limited receivers, and / or a greater degree of parallelism in multiple channel receivers.
Owner:PROMPTU SYST CORP
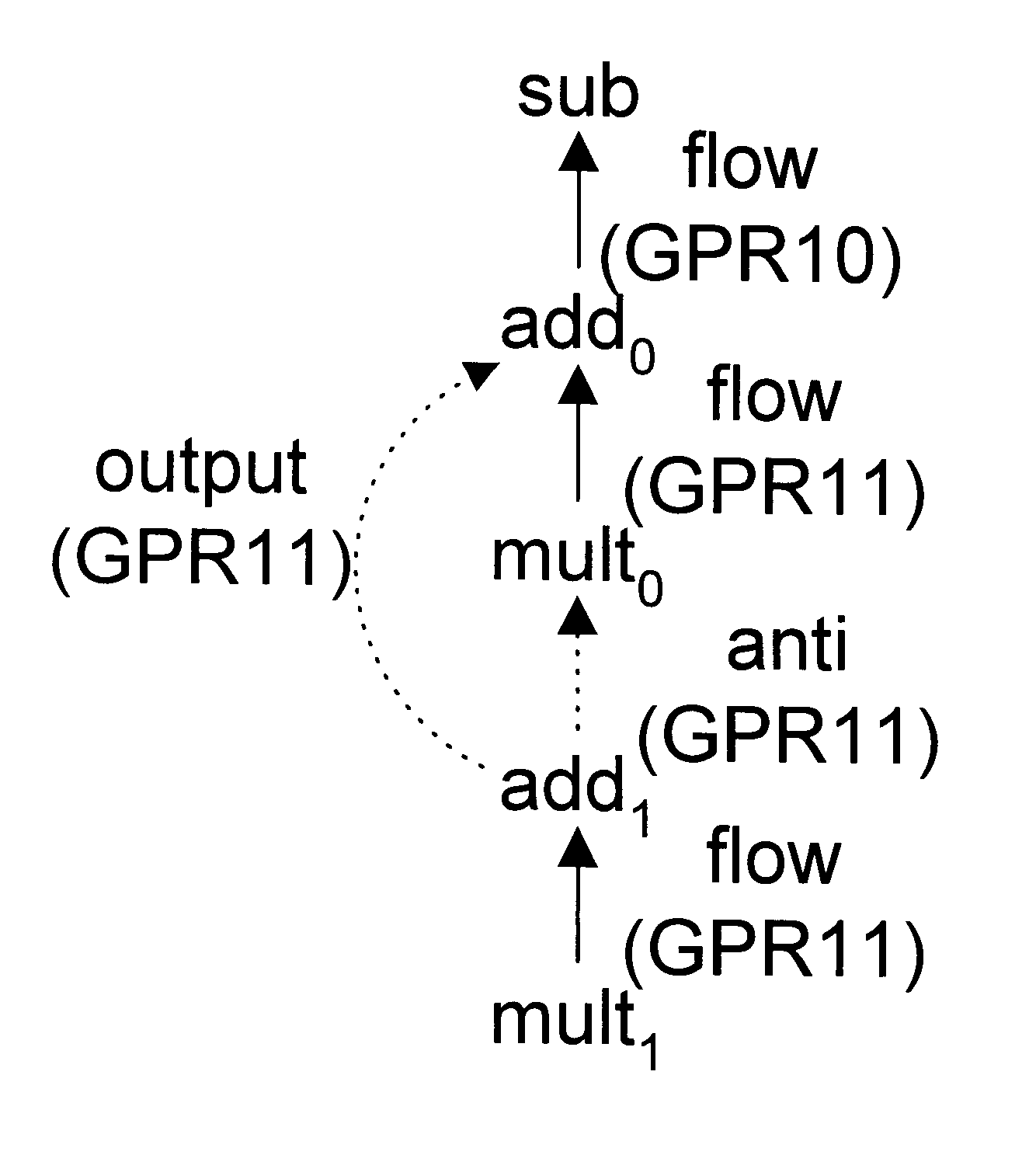
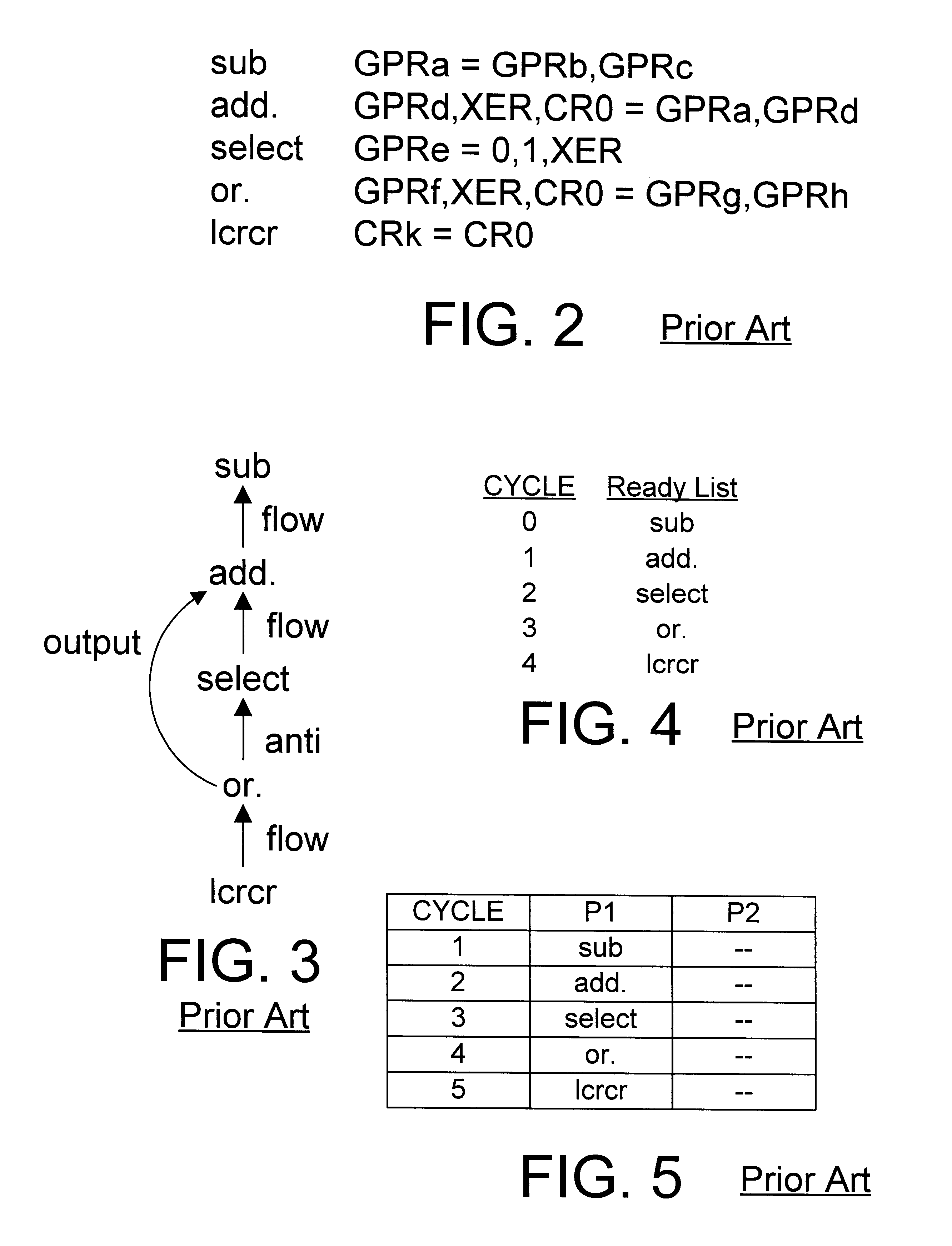
Lifetime-sensitive instruction scheduling mechanism and method
InactiveUS6305014B1Effective instructionHigh degree of parallelismSoftware engineeringSpecific program execution arrangementsScheduling instructionsDegree of parallelism
An instruction scheduler in an optimizing compiler schedules instructions in a computer program by determining the lifetimes of fixed registers in the computer program. By determining the lifetimes of fixed registers, the instruction scheduler can achieve a schedule that has a higher degree of parallelism by relaxing dependences between instructions in independent lifetimes of a fixed register so that instructions can be scheduled earlier than would otherwise be possible if those dependences were precisely honored.
Owner:IBM CORP
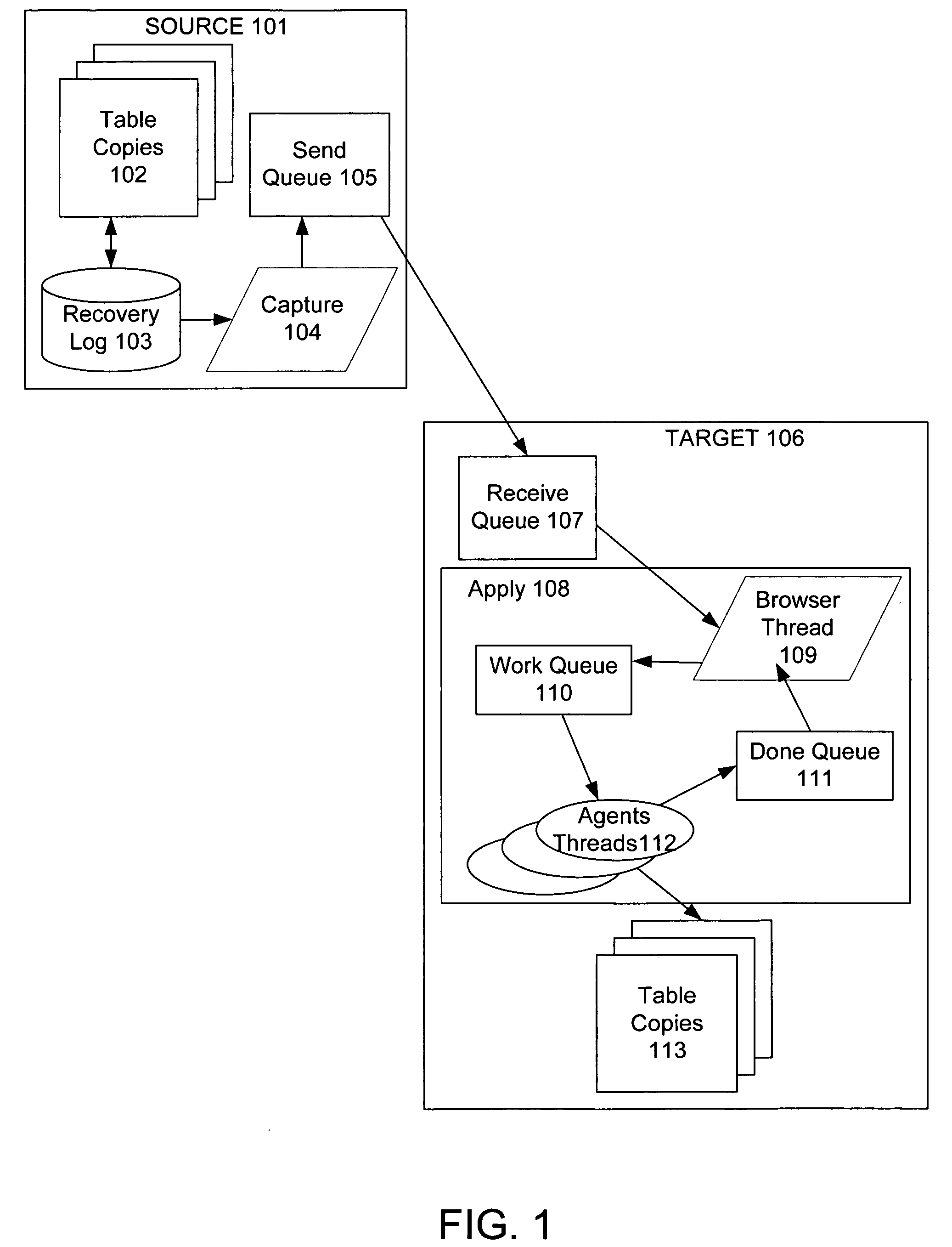
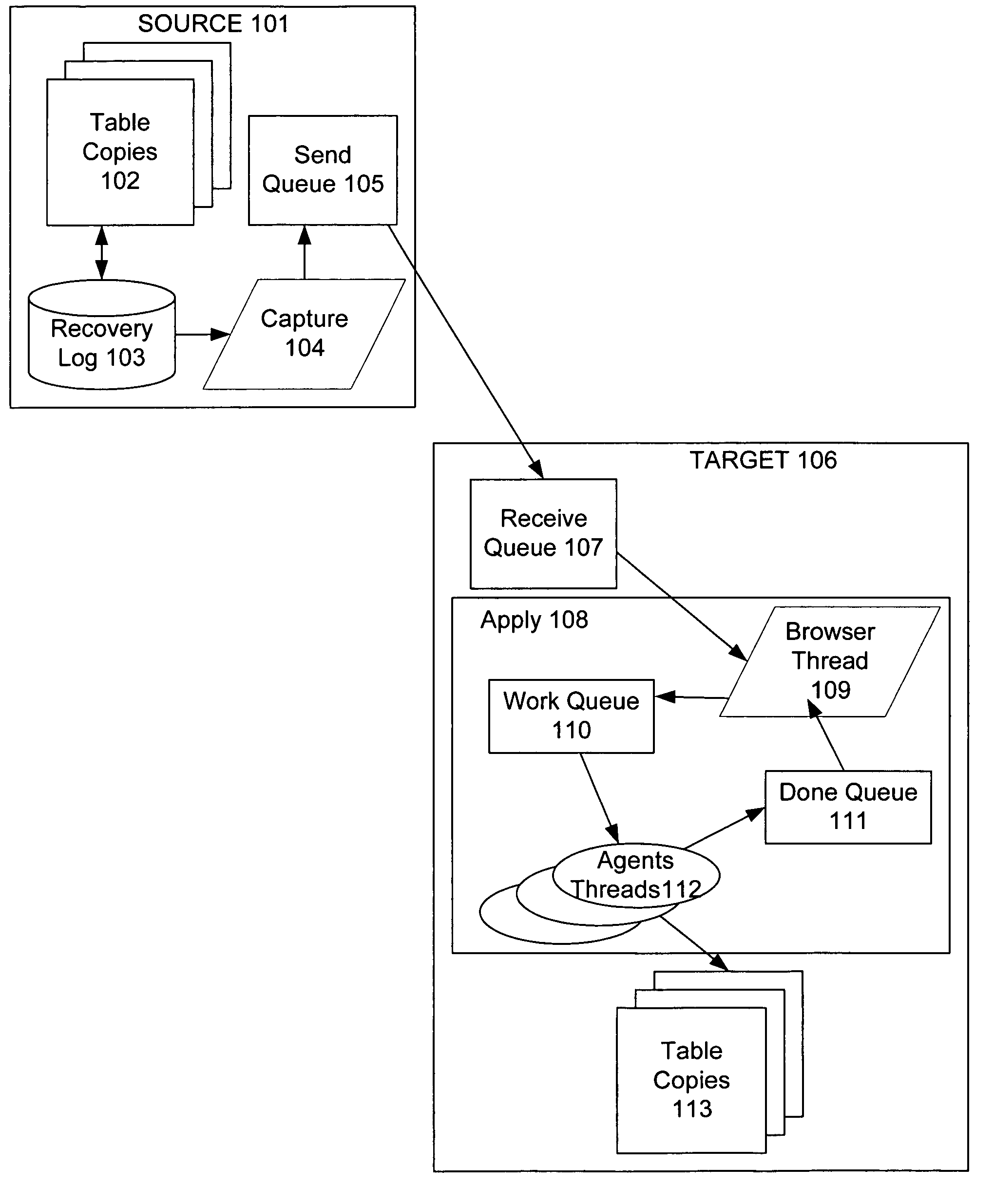
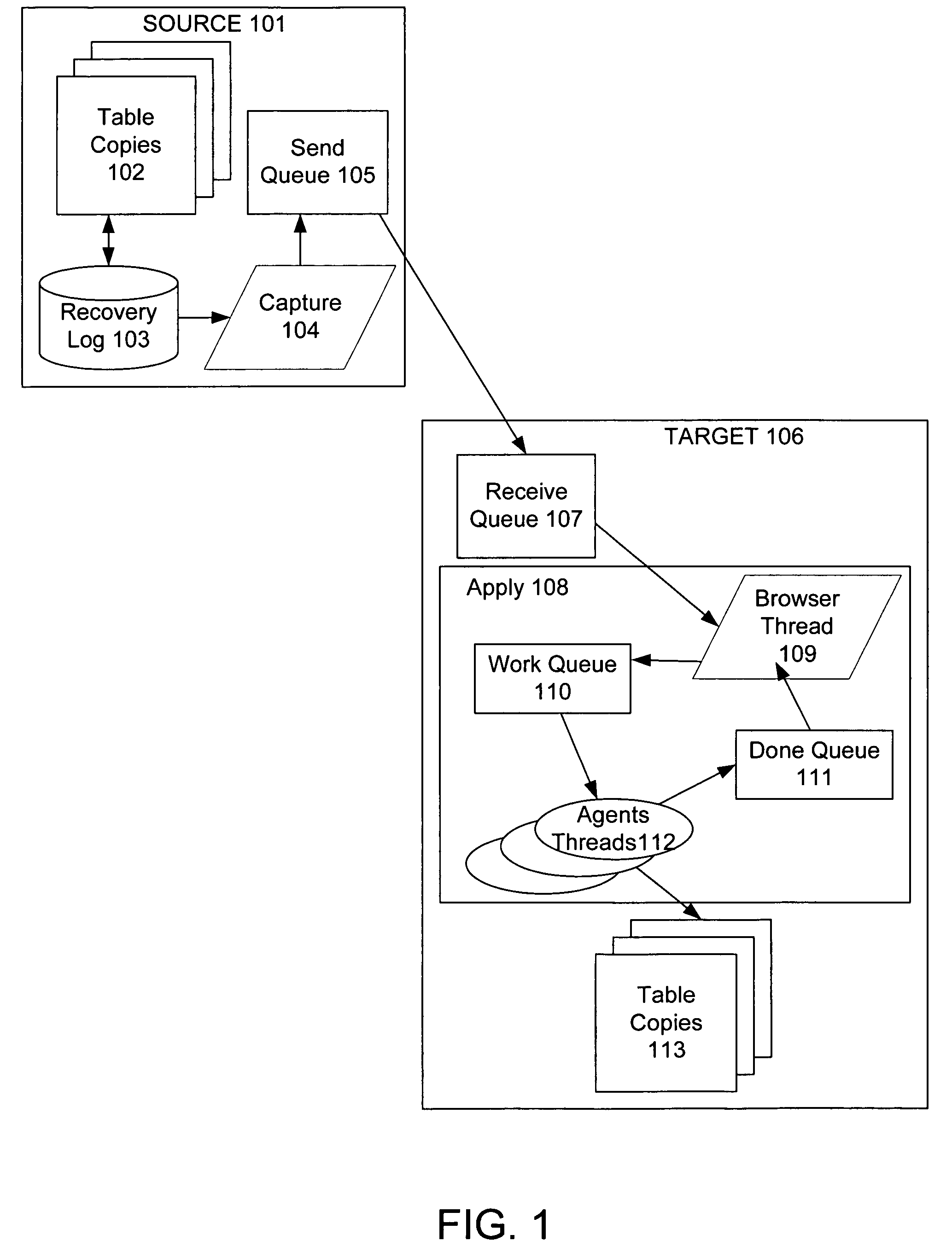
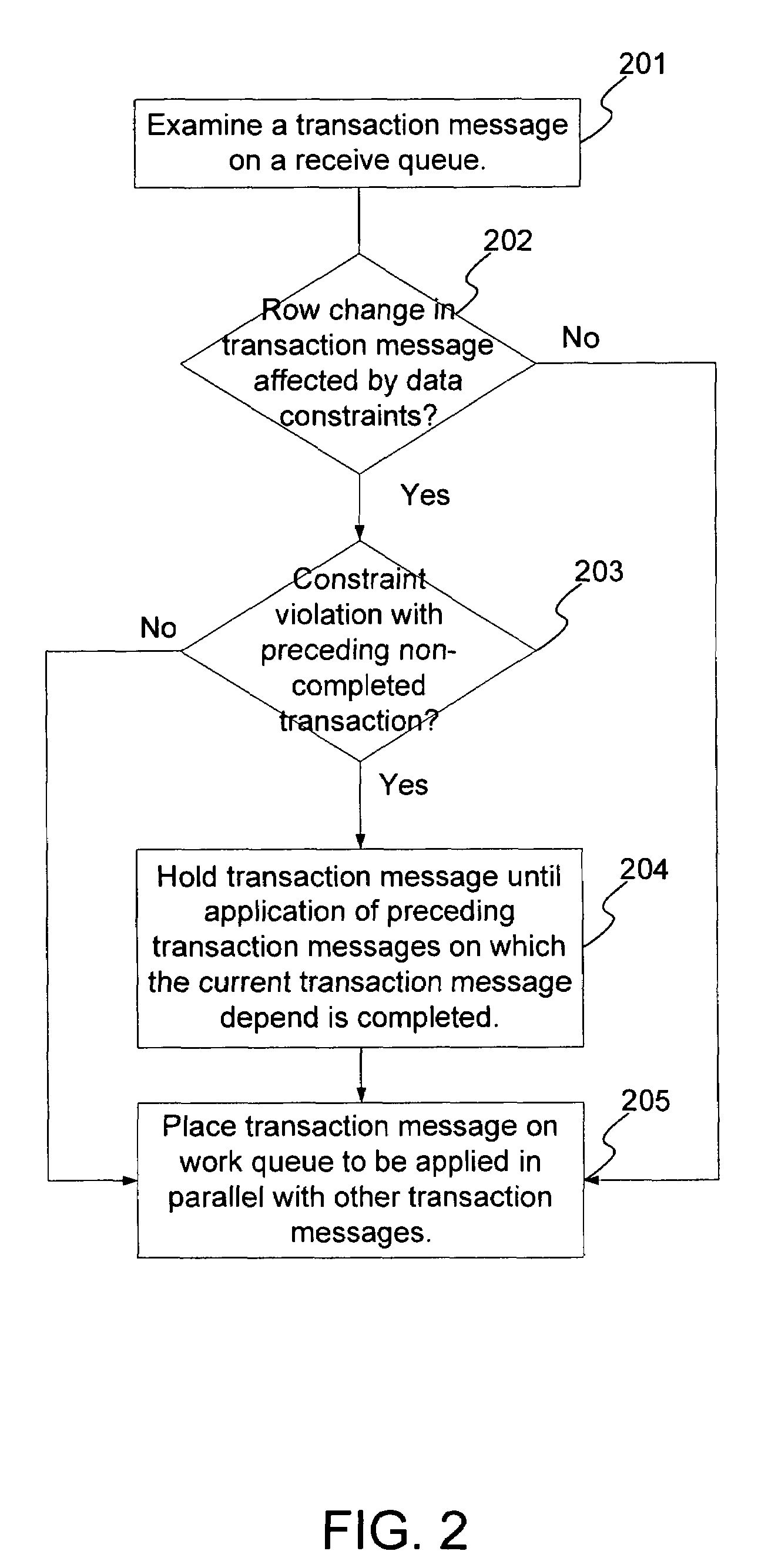
Techniques to preserve data constraints and referential integrity in asynchronous transactional replication of relational tables
InactiveUS20050192989A1High degree of parallelismData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalComputer hardwareImproved method
An improved method and system for preserving data constraints during parallel apply in asynchronous transaction replication in a database system have been disclosed. The method and system preserves secondary unique constraints and referential integrity constraints, while also allowing a high degree of parallelism in the application of asynchronous replication transactions. The method and system also detects and resolves ordering problems introduced by referential integrity cascade deletes, and allows the parallel initial loading of parent and child tables of a referential integrity constraint.
Owner:IBM CORP
Adaptive mode switching of flash memory address mapping based on host usage characteristics
ActiveUS7631138B2Short lifeImprove performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSelf adaptiveDegree of parallelism
In a non-volatile memory storage system such as a flash EEPROM system, a controller switches the manner in which data sectors are mapped into blocks and metablocks of the memory in response to host programming and controller data consolidation patterns, in order to improve performance and reduce wear. Data are programmed into the memory with different degrees of parallelism.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Wavescalar architecture having a wave order memory
InactiveUS20050166205A1Reduce communication costsMaximizing processor utilizationSingle instruction multiple data multiprocessorsProgram synchronisationTerm memoryLow complexity
A dataflow instruction set architecture and execution model, referred to as WaveScalar, which is designed for scalable, low-complexity / high-performance processors, while efficiently providing traditional memory semantics through a mechanism called wave-ordered memory. Wave-ordered memory enables “real-world” programs, written in any language, to be run on the WaveScalar architecture, as well as any out-of-order execution unit. Because it is software-controlled, wave-ordered memory can be disabled to obtain greater parallelism. Wavescalar also includes a software-controlled tag management system.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Techniques to preserve data constraints and referential integrity in asynchronous transactional replication of relational tables
InactiveUS7240054B2High degree of parallelismData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalComputer hardwareImproved method
An improved method and system for preserving data constraints during parallel apply in asynchronous transaction replication in a database system have been disclosed. The method and system preserves secondary unique constraints and referential integrity constraints, while also allowing a high degree of parallelism in the application of asynchronous replication transactions. The method and system also detects and resolves ordering problems introduced by referential integrity cascade deletes, and allows the parallel initial loading of parent and child tables of a referential integrity constraint.
Owner:IBM CORP
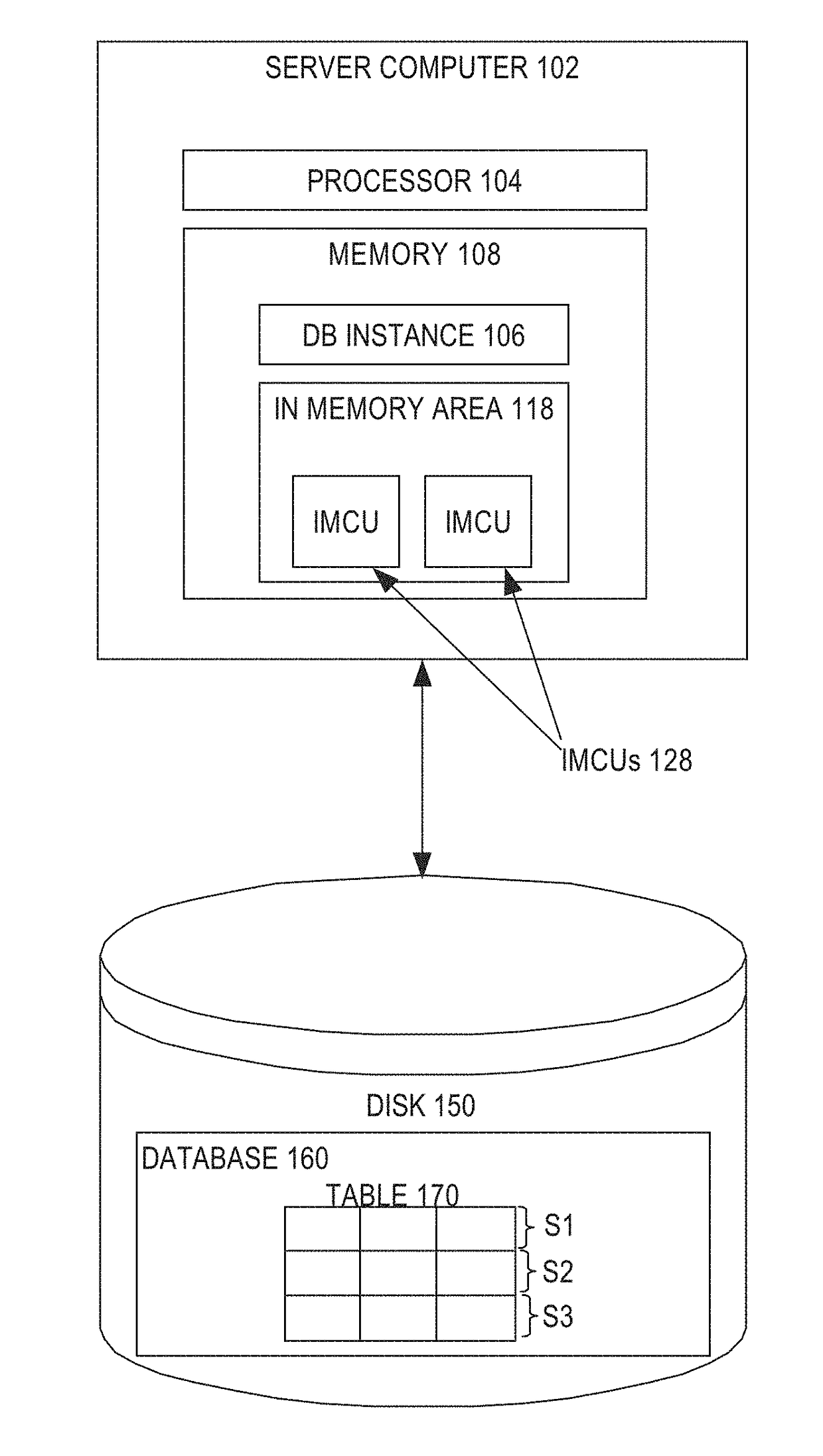
Efficient hybrid parallelization for in-memory scans
ActiveUS20180060399A1Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsDegree of parallelism
Techniques are described herein for hybrid parallelization of in-memory table scans. Work for an in-memory scan is divided into granules based on a degree of parallelism. The granules are assigned to one or more processes. The work for each granule is further parallelized by dividing the work granule into one or more tasks. The tasks are assigned to one or more threads, the number of which can be dynamically adjusted.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method for executing structured symbolic machine code on a microprocessor
InactiveUS20060090063A1Software engineeringInstruction analysisScheduling instructionsHigh probability
The invention describes a method for executing structured symbolic machine code on a microprocessor. Said structured symbolic machine code contains a set of one or more regions, where each of said regions contains symbolic machine code containing, in addition to the proper instructions, information about the symbolic variables, the symbolic constants, the branch tree, pointers and functions arguments used within each of said regions. This information is fetched by the microprocessor from the instruction cache and stored into dedicated memories before the proper instructions of each region are fetched and executed. Said information is used by the microprocessor in order to improve the degree of parallelism achieved during instruction scheduling and execution. Among other purposes, said information allows the microprocessor to perform so-called speculative branch prediction. Speculative branch prediction does branch prediction along a branch path containing several dependent branches in the shortest time possible (in only a few clock cycles) without having to wait for branches to resolve. This is a key issue which allows to apply region scheduling in practice, e.g. treegion scheduling, where machine code must be fetched and speculatively executed from the trace having highest probability or confidence among several traces. This allows to use the computation resources (e.g. the FUs) of the microprocessor in the most efficient way. Finally, said information allows to re-execute instructions in the right order and to overwrite wrong data with the correct ones when miss-predictions occur.
Owner:THEIS JEAN PAUL
Systems and methods for efficient scheduling of concurrent applications in multithreaded processors
ActiveUS20130332711A1Efficient executionEasy to addInstruction analysisDigital computer detailsInstruction set designConcurrency control
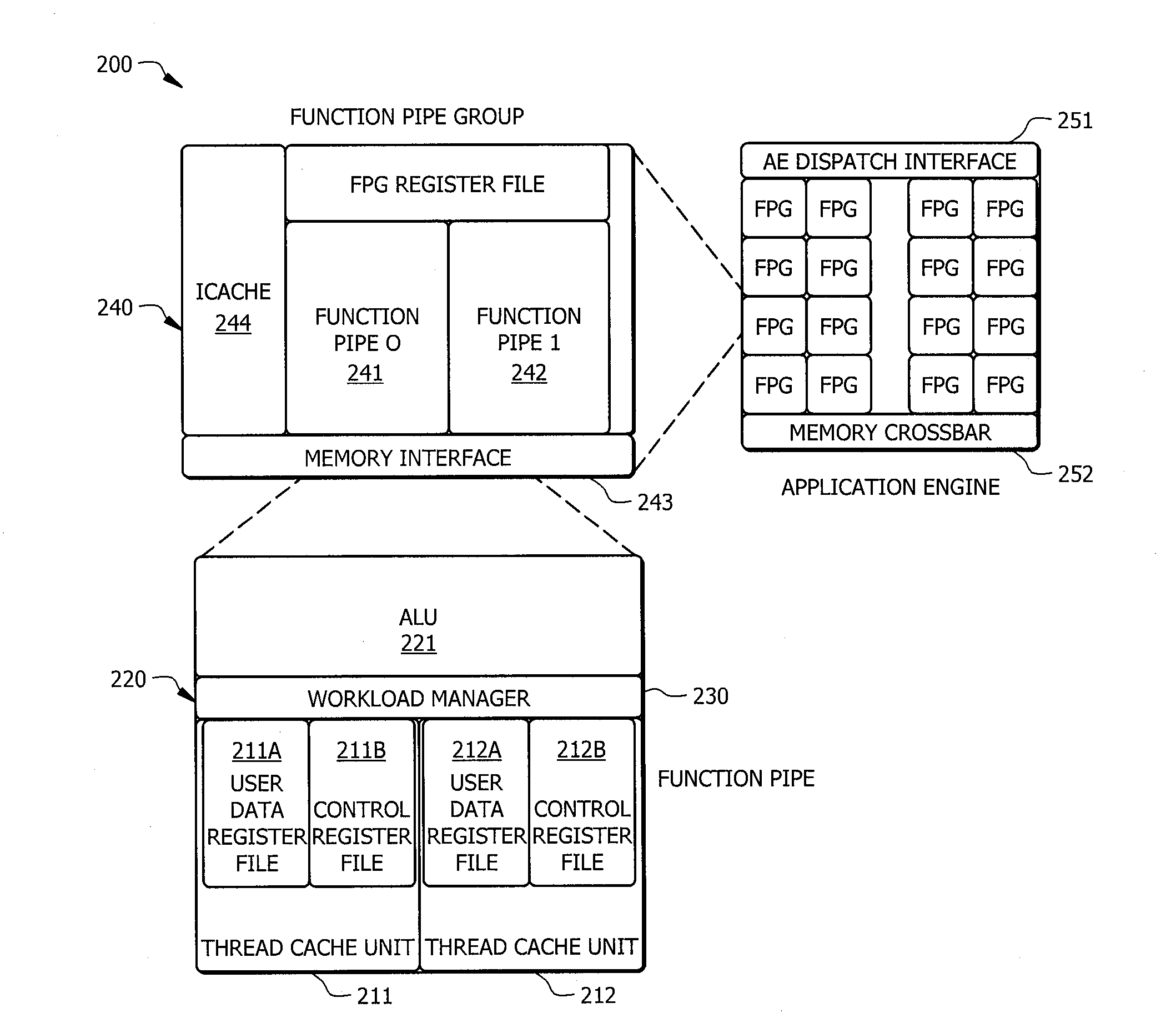
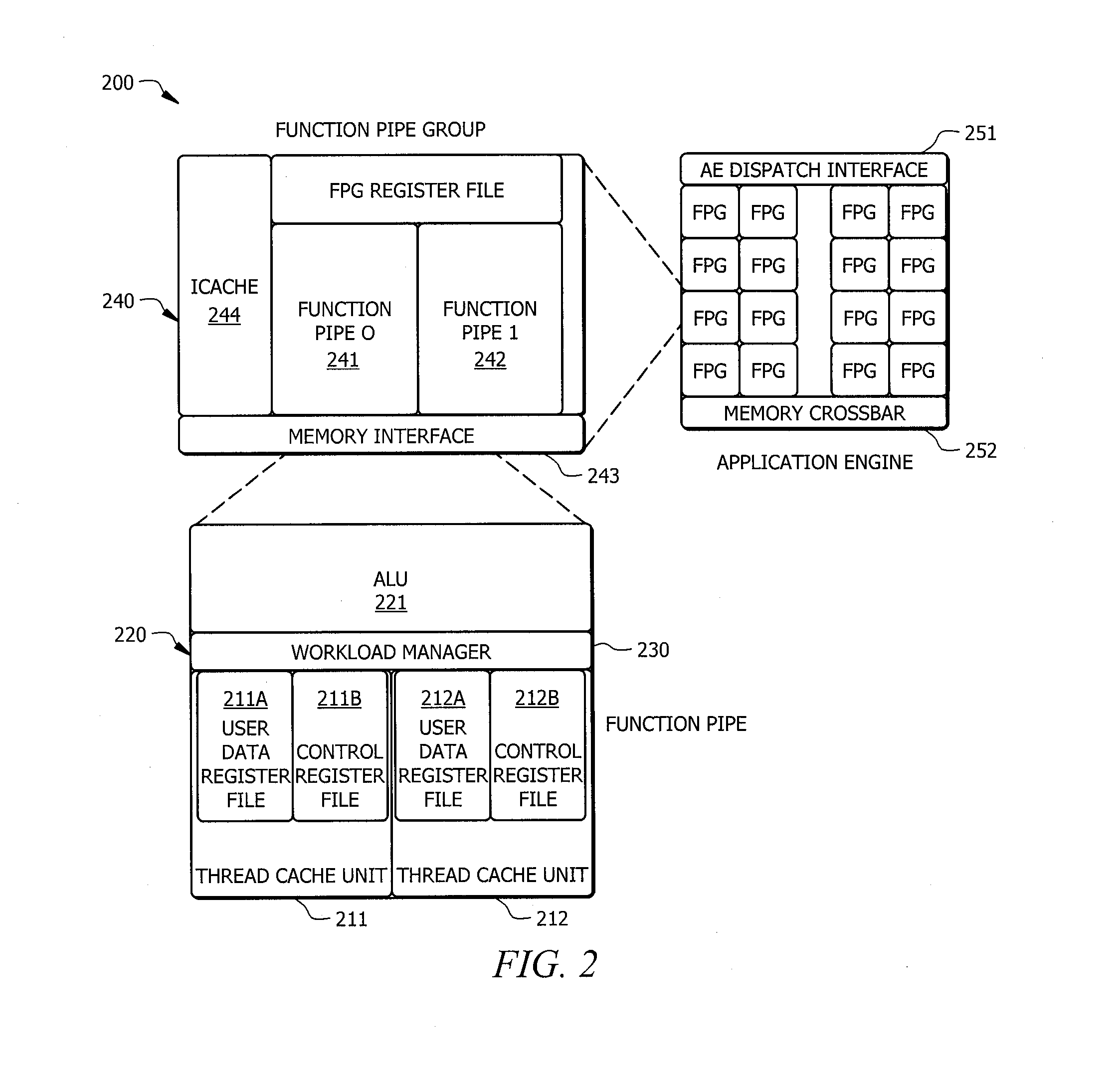
Systems and methods which provide a modular processor framework and instruction set architecture designed to efficiently execute applications whose memory access patterns are irregular or non-unit stride as disclosed. A hybrid multithreading framework (HMTF) of embodiments provides a framework for constructing tightly coupled, chip-multithreading (CMT) processors that contain specific features well-suited to hiding latency to main memory and executing highly concurrent applications. The HMTF of embodiments includes an instruction set designed specifically to exploit the high degree of parallelism and concurrency control mechanisms present in the HMTF hardware modules. The instruction format implemented by a HMTF of embodiments is designed to give the architecture, the runtime libraries, and / or the application ultimate control over how and when concurrency between thread cache units is initiated. For example, one or more bit of the instruction payload may be designated as a context switch bit (CTX) for expressly controlling context switching.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
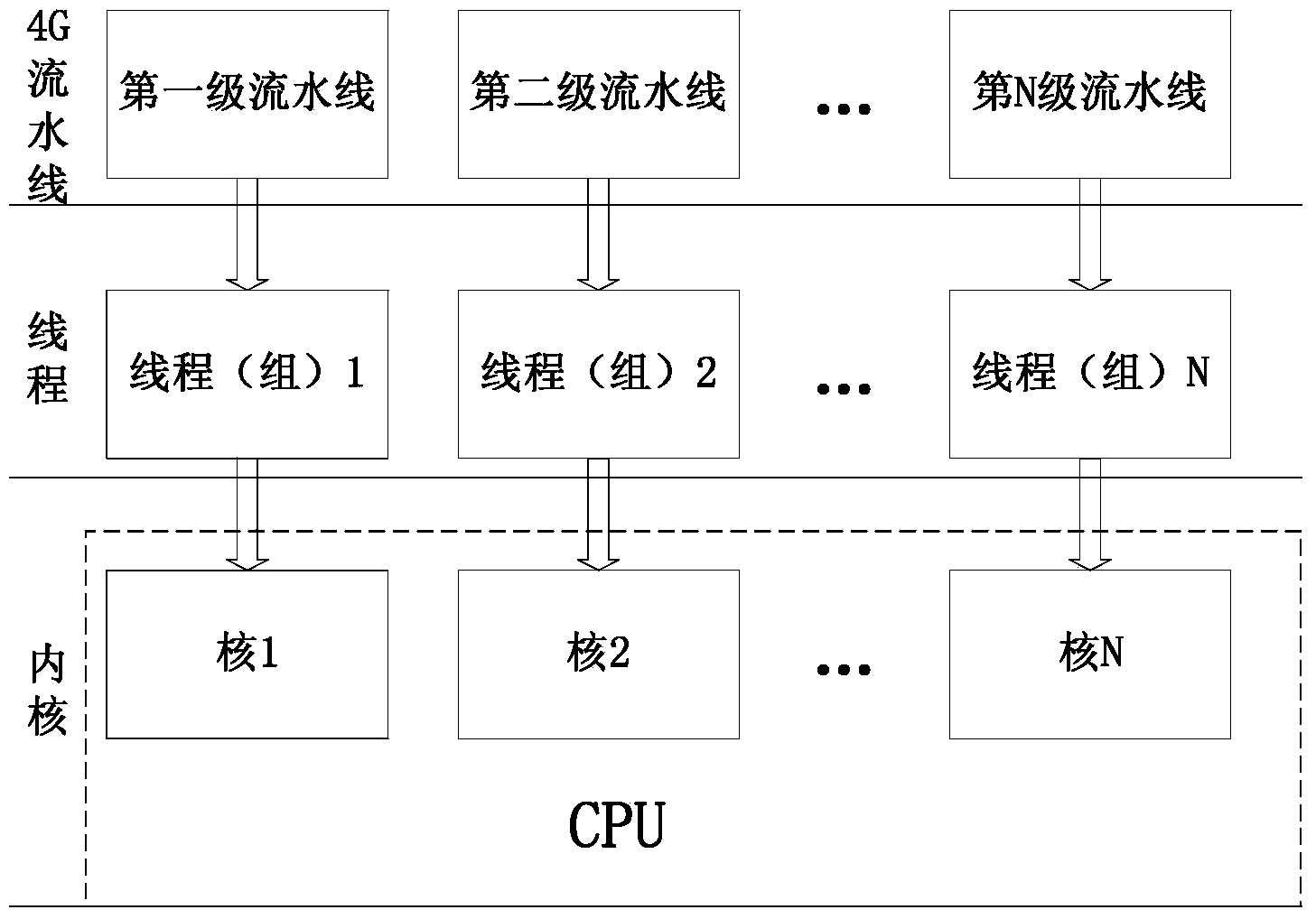
System and method for processing multi-core parallel assembly line signals of 4G broadband communication system
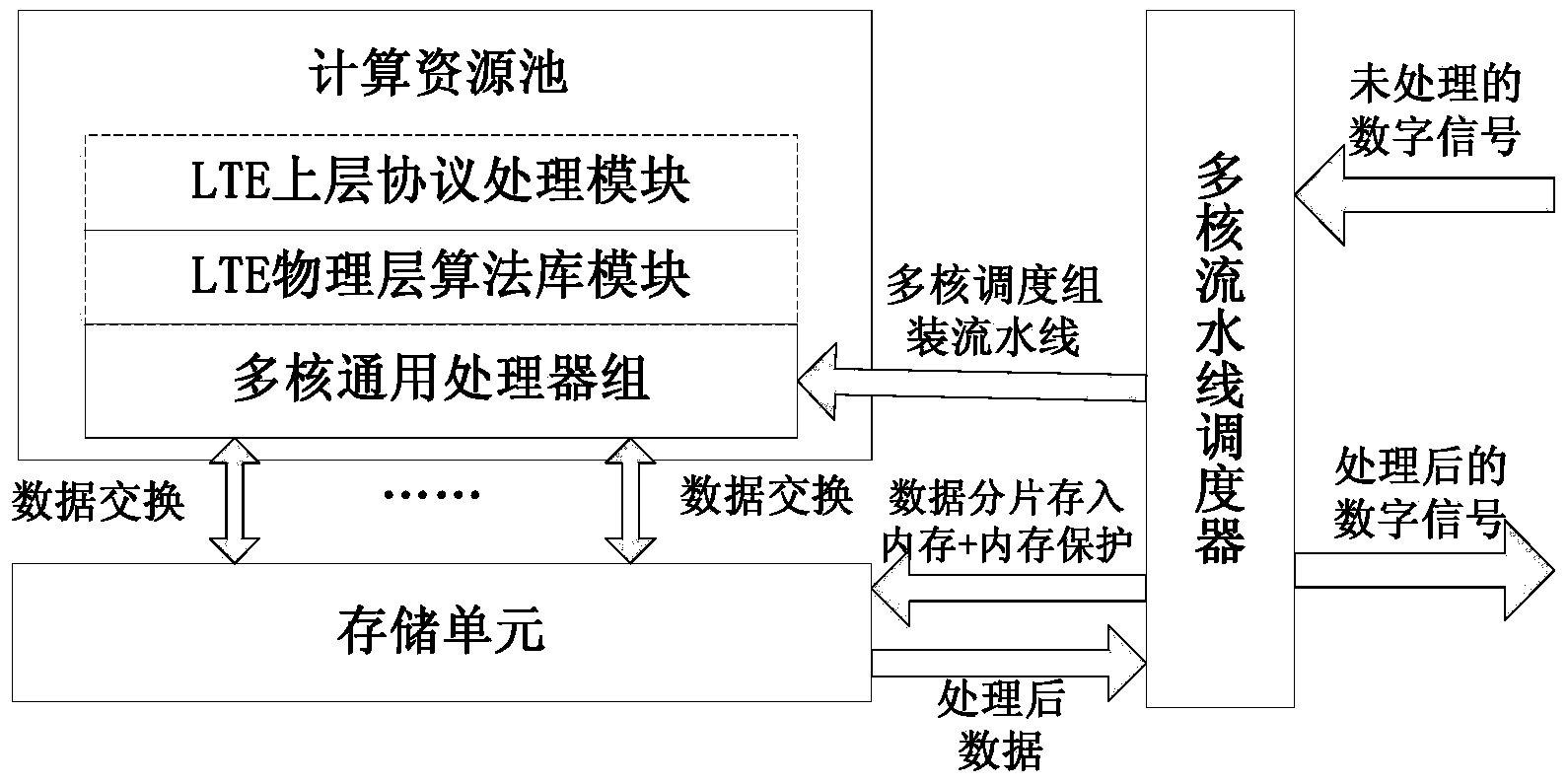
InactiveCN103838552ASafe handlingOptimize traditional processing methodsConcurrent instruction executionCommunications systemGranularity
The invention discloses a system and method for processing multi-core parallel assembly line signals of a 4G broadband communication system based on a GPP. In order to meet the strict requirement for the real-time performance of the 4G communication system, the cloud computing idea is utilized, the GPP serves as a computing resource, communication data are processed by utilizing an assembly line processing mode based on the GPP, and a large volume of data and computing tasks are divided into reasonable granularities through a scheduler and are distributed to assembly lines of all levels to be processed respectively. Under the condition that hardware performance is limited, the assembly line mode can meet the requirement for the real-time performance more easily, meanwhile, the time affluence amount is led in, and large delay variation can be borne by the system. Computing resources are fully utilized through reasonable dispatching. According to the system and method for processing the 4G broadband communication system multi-core parallel assembly line signals, three kinds of assembly lines are designed totally, one assembly line is suitable for processing a large data volume and higher in reliability, another assembly line is suitable for processing a small data volume and high in speed and flexibility, and the third assembly line is a composite assembly line based on twp application scenes and with a high degree of parallelism, wherein the performance of the third assembly line is obviously improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
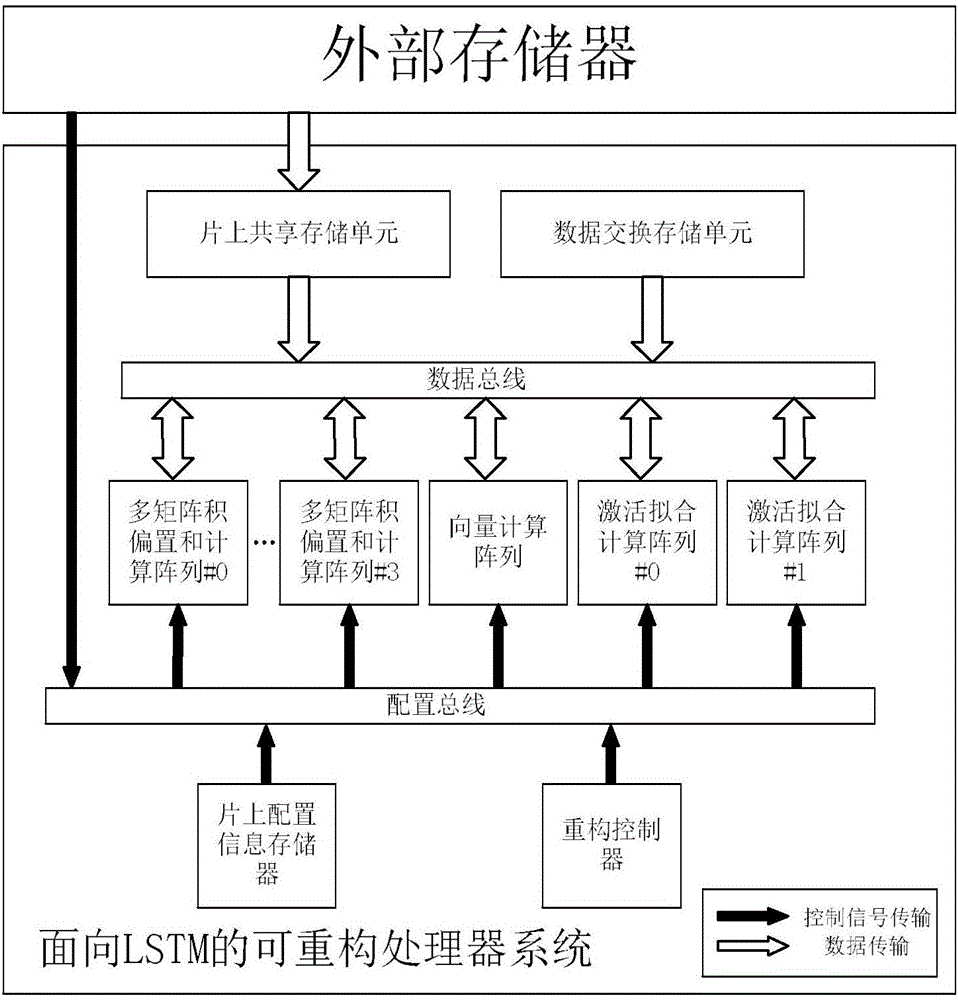
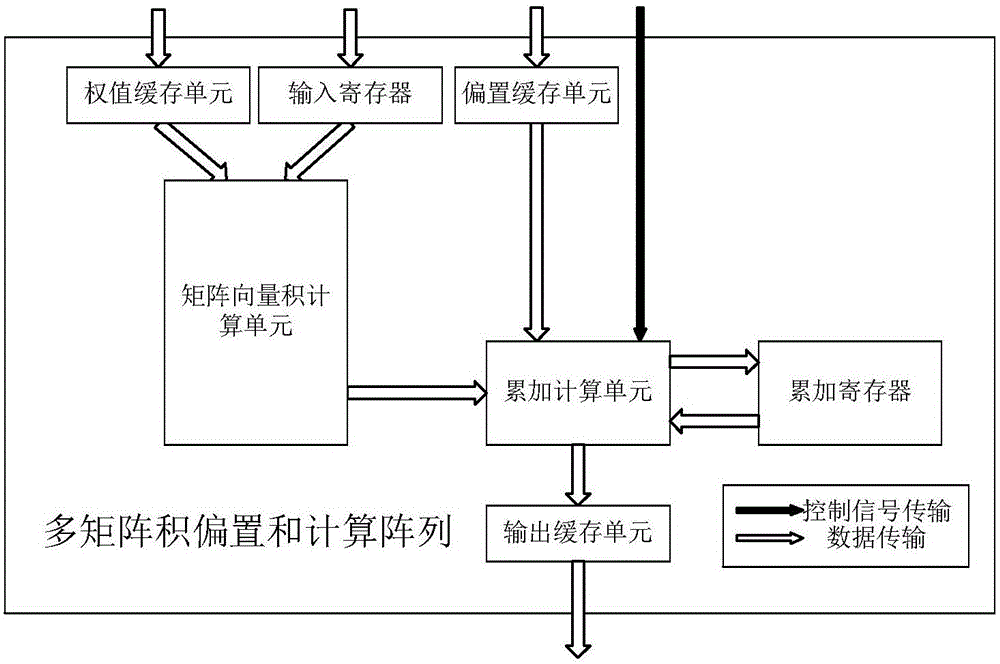
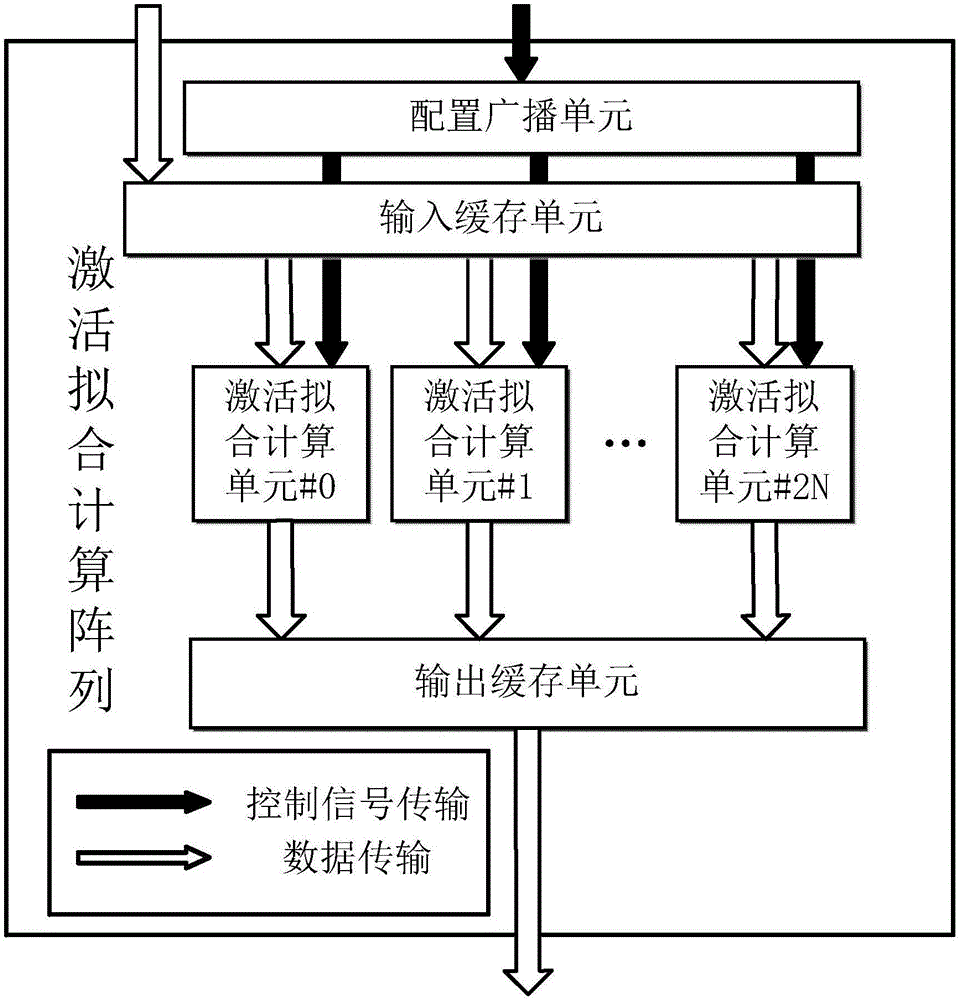
Multi-computing-unit coarse-grained reconfigurable system and method for recurrent neural network
ActiveCN106775599AConcurrent instruction executionPhysical realisationActivation functionControl signal
The invention discloses a multi-computing-unit coarse-grained reconfigurable system and method for a recurrent neural network LSTM (long short-term memory). The system comprises multi-matrix-product bias and calculation arrays, activation fitting calculation arrays and vector quantity calculation arrays. The multi-matrix-product bias and calculation arrays are used for realizing calculation and accumulation operation of multiple matrix vector products in the recurrent neural network and perform addition bias calculation under control of control signals, and output values are outputted through corresponding output cache units. The activation fitting calculation arrays are used for realizing a piecewise linear fitting calculation function of activation functions in the recurrent neural network LSTM, activation fitting calculation units are controlled by the control signals to perform corresponding activation function piecewise linear fitting calculation when input values enter input cache units, and output values are outputted through corresponding output cache units. The vector quantity calculation arrays are used for realizing dimension-based vector multiplication and vector addition calculation, and after multiplication units finish calculation, data are transmitted to vector addition units or directly outputted under control of the control signals. Parallelism degree, calculation speed and array utilization rate of the reconfigurable system are increased.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
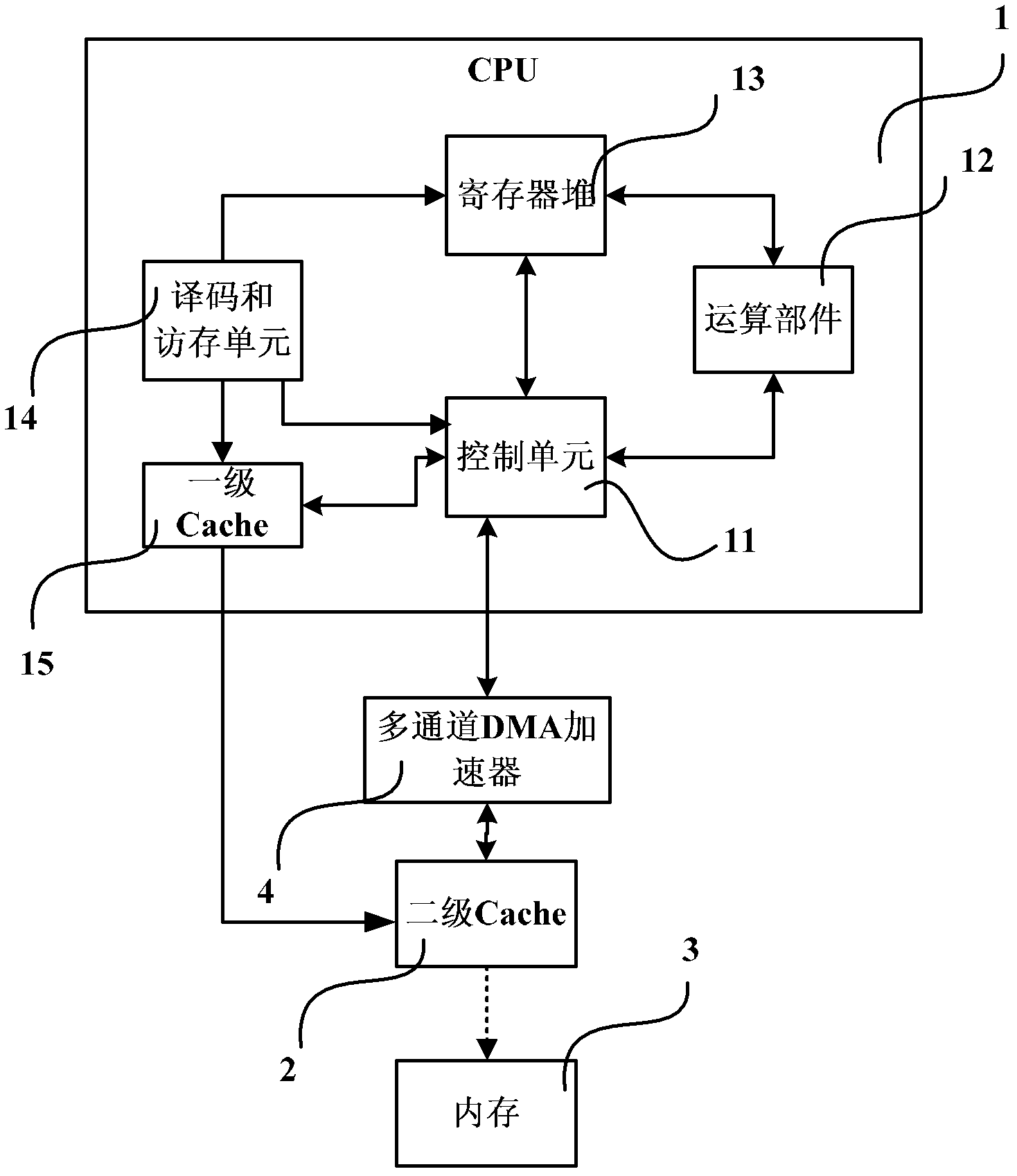
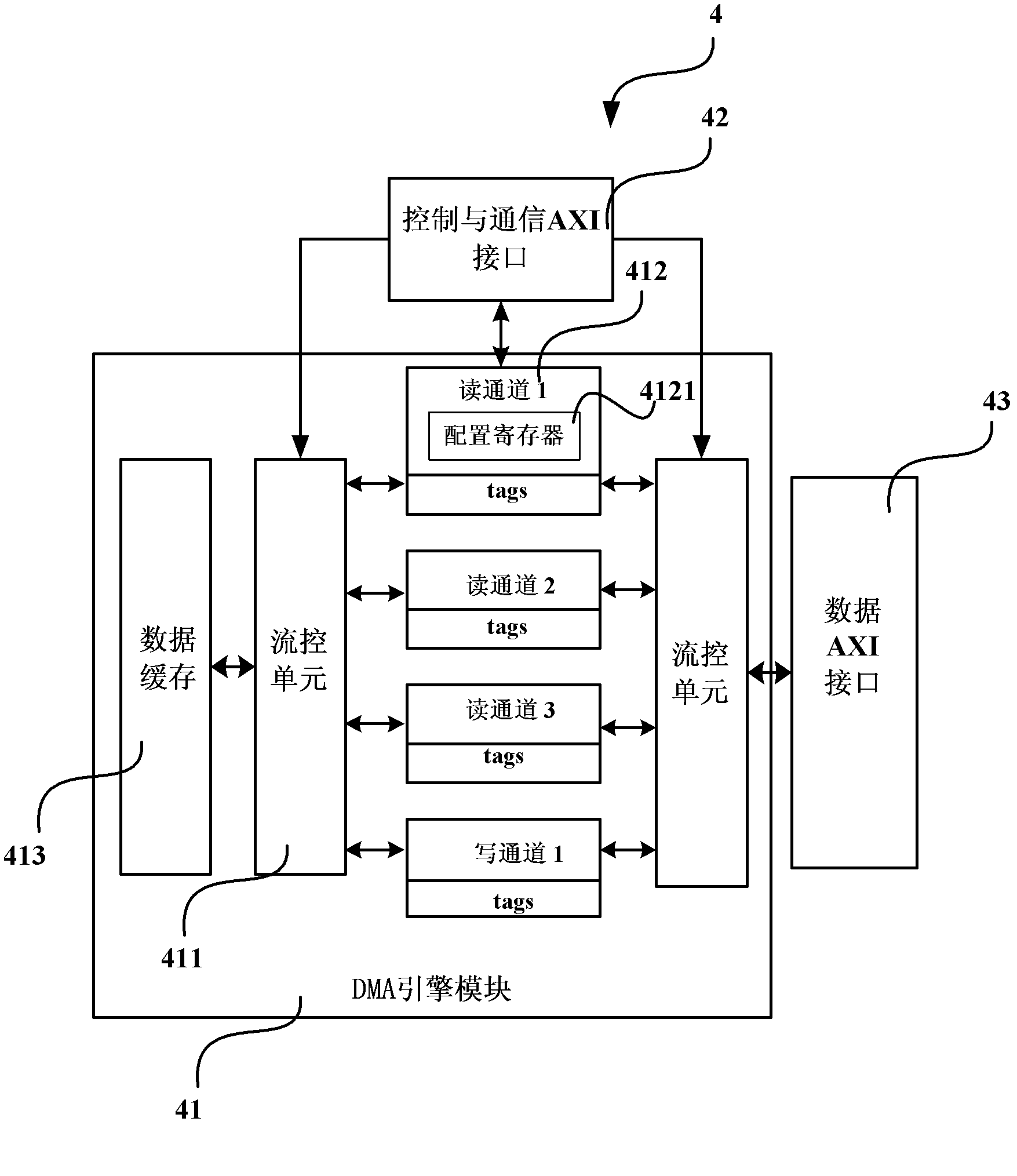
Processor system, as well as multi-channel memory copying DMA accelerator and method thereof
ActiveCN102567256AHigh bandwidthLower latencyElectric digital data processingReconfigurabilityDirect memory access
The invention provides a processor system, as well as a multi-channel memory copying DMA (direct memory access) accelerator and a method thereof. The processor system comprises a multi-channel direct memory access (DMA) accelerator connected between a processor core and a memory through a data bus, and the multi-channel DMA accelerator is used for judging and decomposing task information of a data reading and writing request according to the task information of the data reading and writing request when the processor core emits the data reading and writing request of a memory copying command, controlling a plurality of reading and writing channels to emit the multiple reading and writing requests to the memory in parallel according to the task information of the data reading and writing request after decomposition, the reading and writing frequencies and the priorities of the plurality of the reading and writing channels in the task information and values of marker bits of the reading and writing channels, and further completing data reading and writing. The processor system has the advantages of high bandwidth, low latency, high degree of parallelism, reconfigurability and platform independence.
Owner:LOONGSON TECH CORP
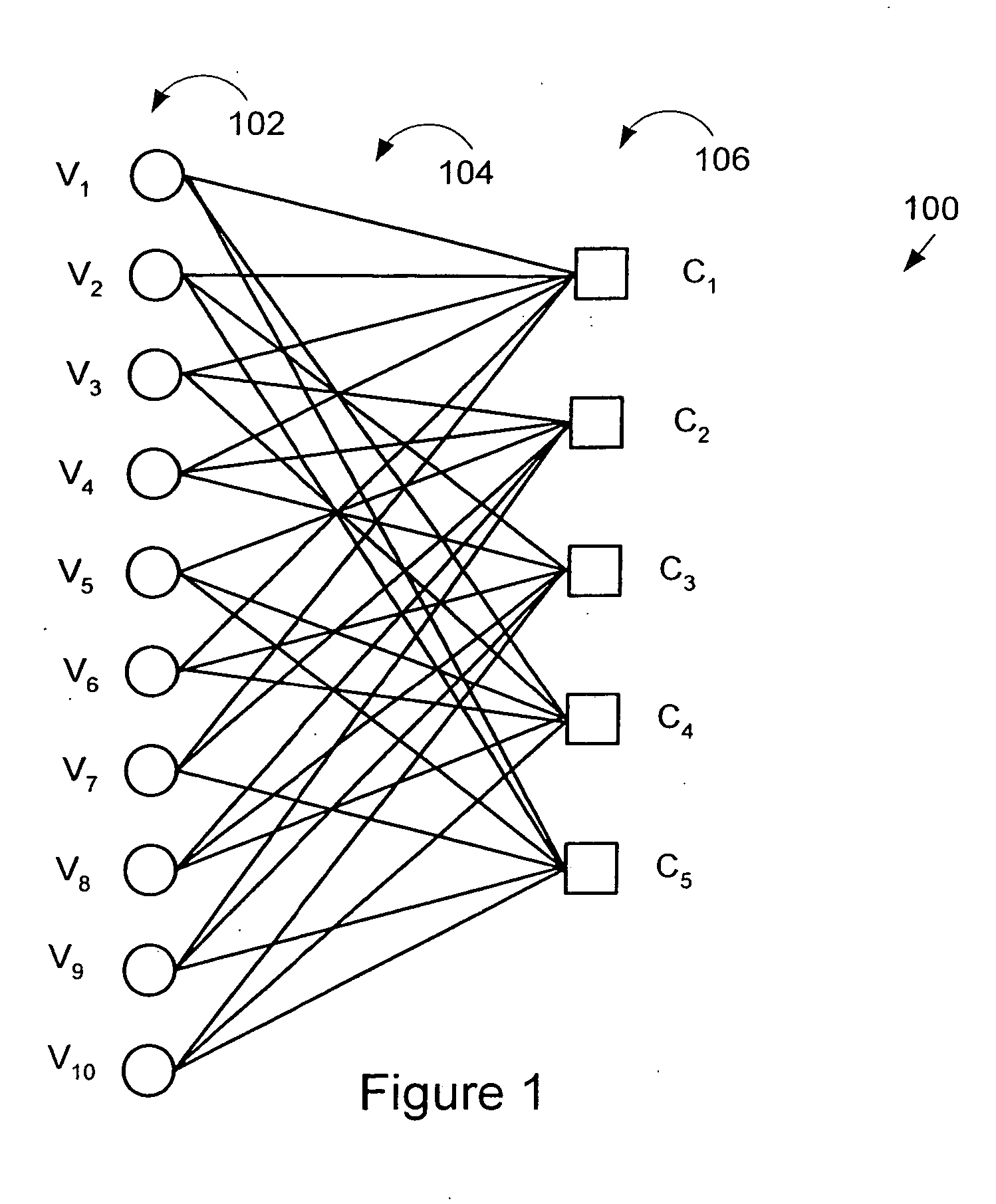
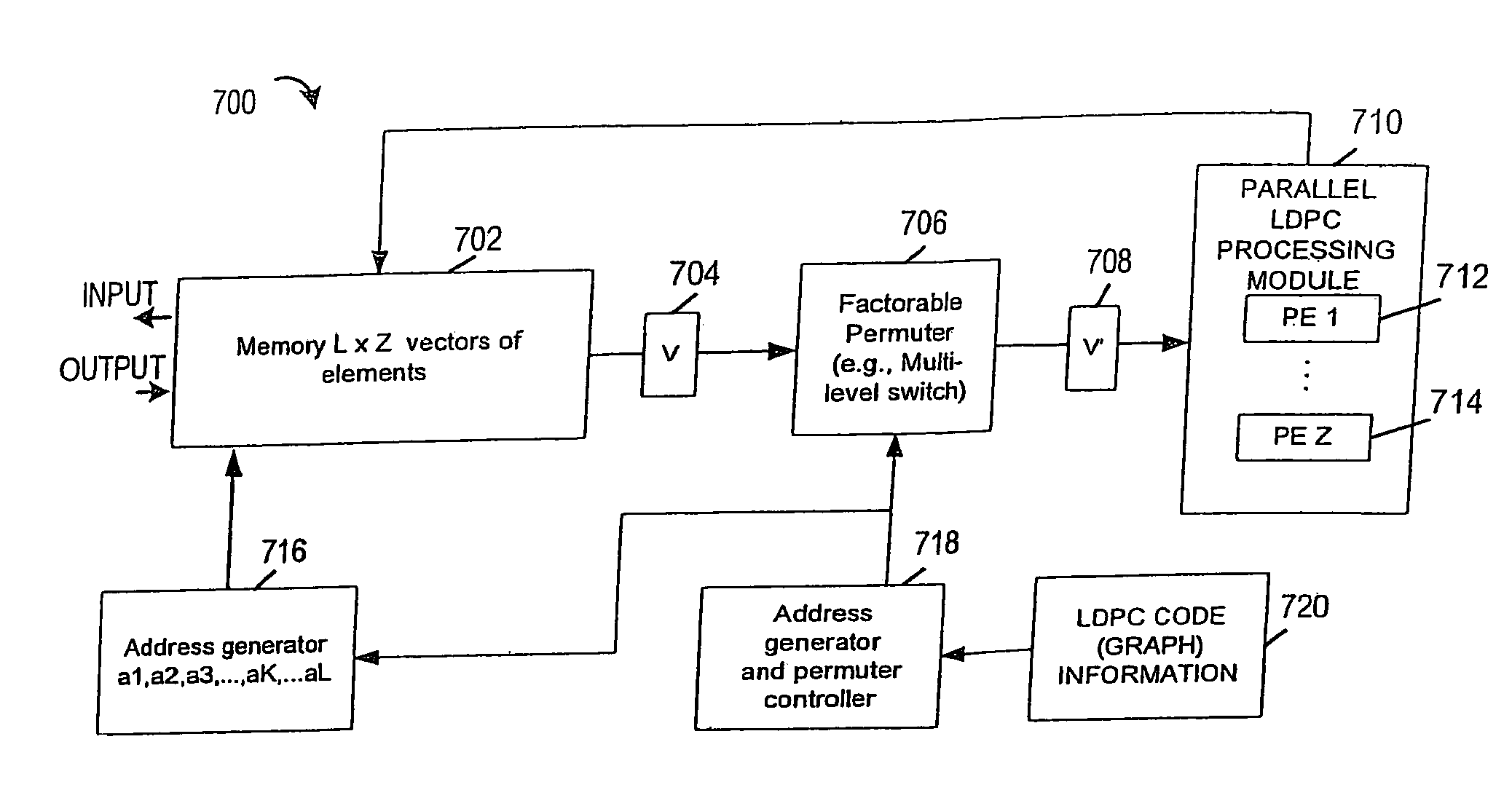
Method and apparatus for performing low-density parity-check (LDPC) code operations using a multi-level permutation
InactiveUS7237171B2Easy to implementError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionGraphicsCommunications system
Methods and apparatus of the present invention can be used to implement a communications system wherein different devices using the same LDPC code can be implemented using different levels of parallelism. The use of a novel class of LDPC codes makes such differences in parallelism possible. Use of a factorable permuter in various embodiments of the invention make LDPC devices with different levels of parallelism in the encoder and decoder relatively easy to implement when using the codes in the class of LDPC codes discussed herein. The factorable permuter may be implemented as a controllable multi-stage switching devices which performs none, one, or multiple sequential reordering operations on a Z element vector passed between memory and a Z element vector processor, with the switching one individual vectors being controlled in accordance with the graph structure of the code being implemented.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
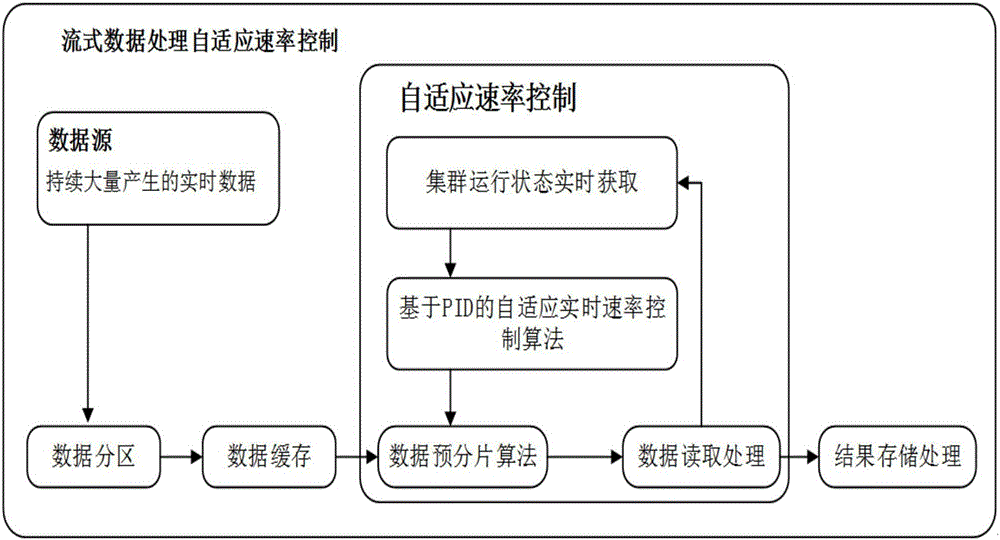
Self-adaptive rate control method for stream data processing
InactiveCN106648904AAvoid bandwidth consumptionAvoid reading and writing consumptionResource allocationSpecial data processing applicationsProgramming complexityStream data
The invention belongs to the technical field of computer applications and relates to a self-adaptive rate control method for stream data processing. According to the method, based on a common data receiving message queue and a big data distributor calculating framework, the degree of parallelism of data processing is adjusted through a pre-fragmentation mode according to the condition of a current calculating colony and the quantity of current processed data of the colony is dynamically adjusted according to a self adaptive real time rate control method, so that the stability of the calculating colony is ensured, and the delay of data stream processing is reduced. Along with gradual penetration of big data into the industries, the application range of the real-time processing of mass data is gradually expanded. The real time property and the stability of a mass data processing system are quite important. On the premise of not increasing the quantity of the colony hardware and the task programming complexity, the stability and the processing efficiency of the calculating colony are enhanced to a certain extent.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Two-stage scheduling method of parallel test tasks facing spacecraft automation test
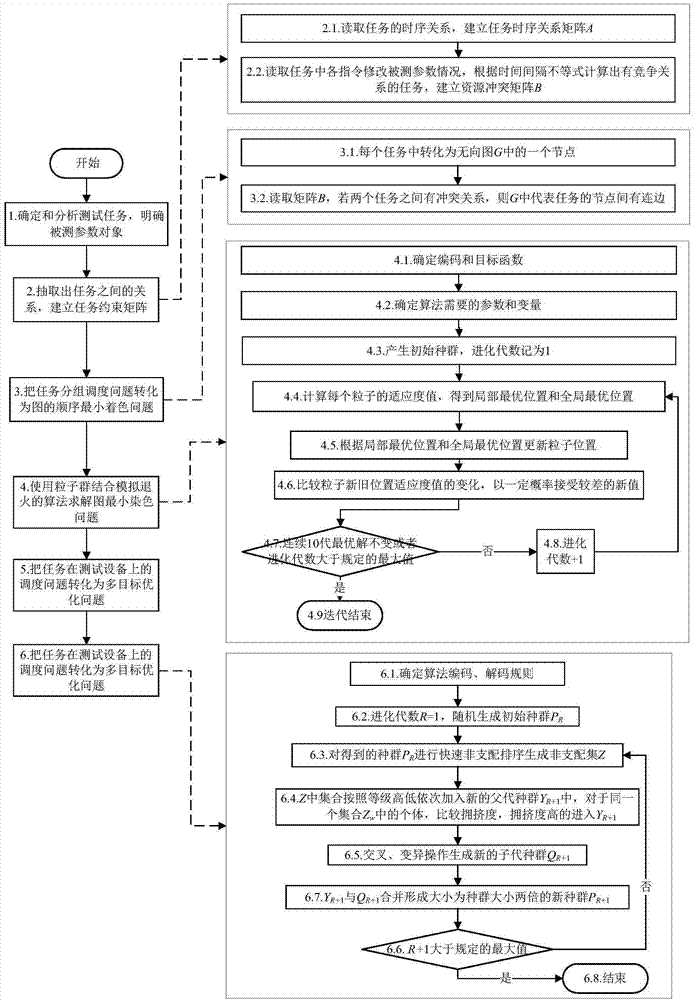
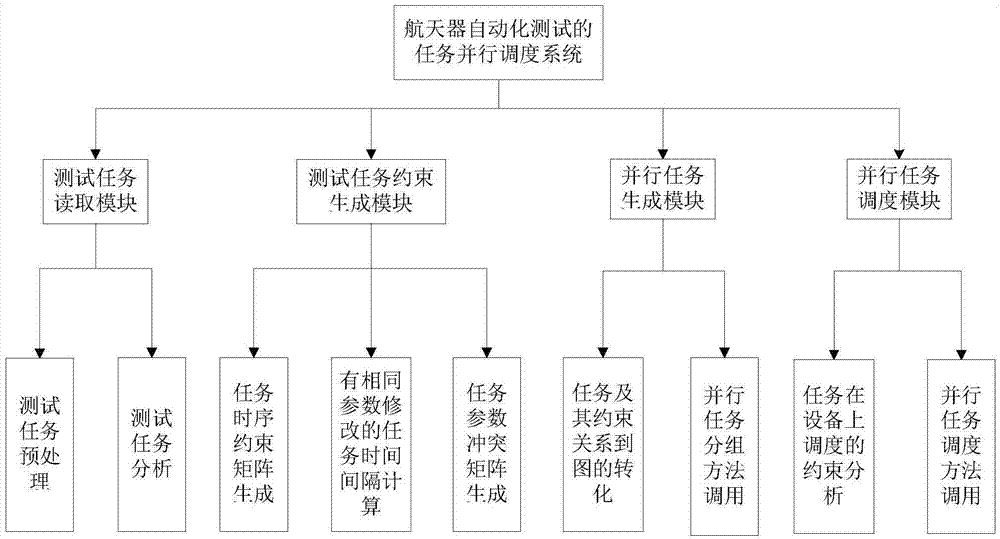
InactiveCN104239213AEasy to callEasy to handleConcurrent instruction executionSoftware testing/debuggingColoring problemDegree of parallelism
The invention relates to a two-stage scheduling method of parallel test tasks facing a spacecraft automation test, which belongs to the field of parallel tests. The method comprises the following stages: in the first stage, the test tasks, task instructions and tested parameters are analyzed and determined, a constraint relation between the tasks is defined, a time sequence constraint matrix and a parameter competitive relation matrix are established, the tasks and the constraint relation between the tasks are changed into undirected graphs, a parallel task scheduling problem is changed into a minimum coloring problem in the sequence of the tops of the graphs, a method based on the combination of a particle swarm and simulated annealing is used for solving, and then a test task group with the maximal degree of parallelism is obtained; in the second stage, the obtained test task group with the maximal degree of parallelism is distributed on limited test equipment, and then an optimal scheduling scheme is obtained. According to the two-stage scheduling method, the constraint relation among a plurality of test tasks is quickly established, the independence between the test tasks is analyzed, the degree of parallelism of the test tasks is increased, the optimal scheduling of the tasks on the equipment is realized when constraint conditions are satisfied, and the test efficiency is improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
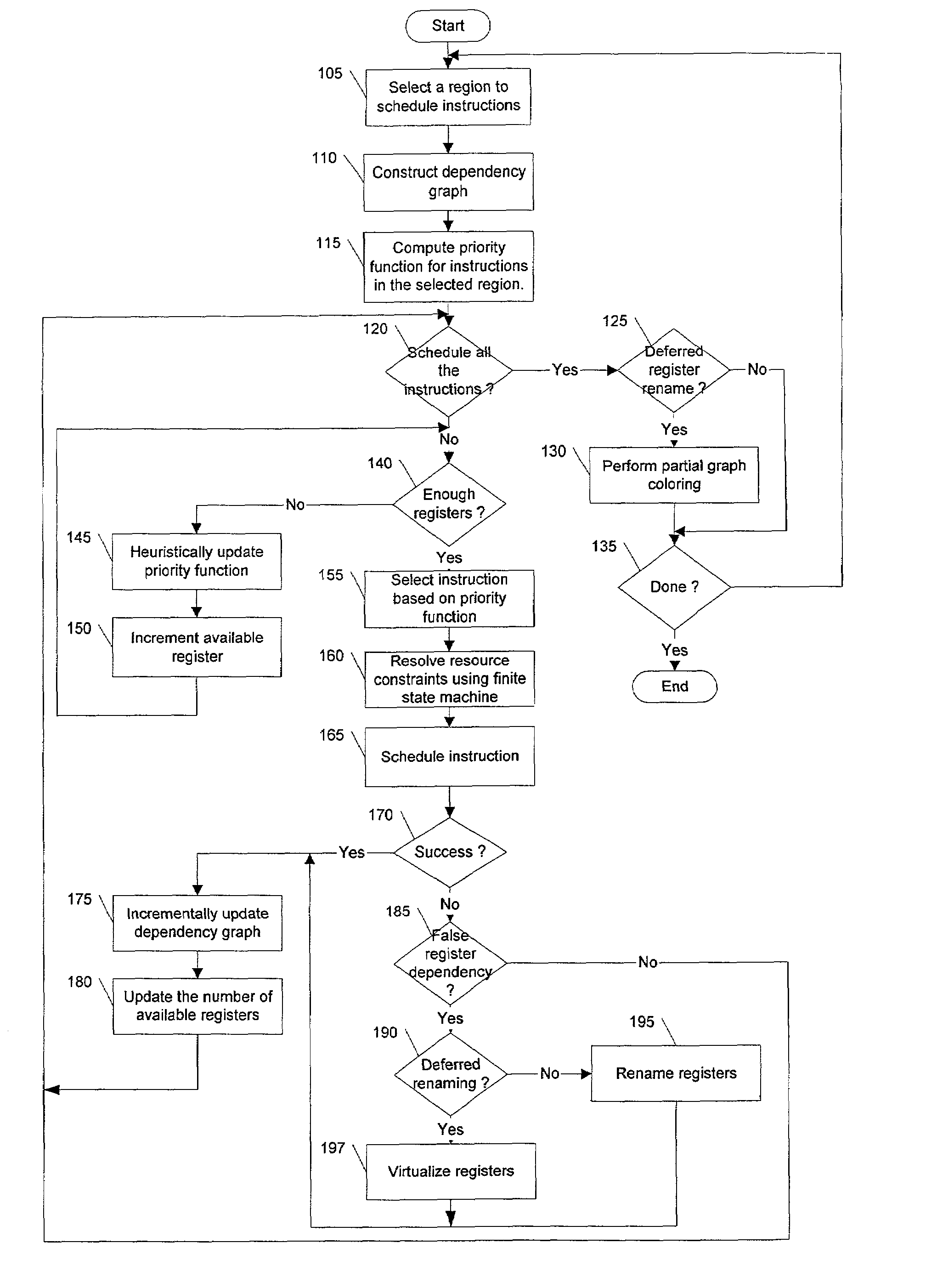
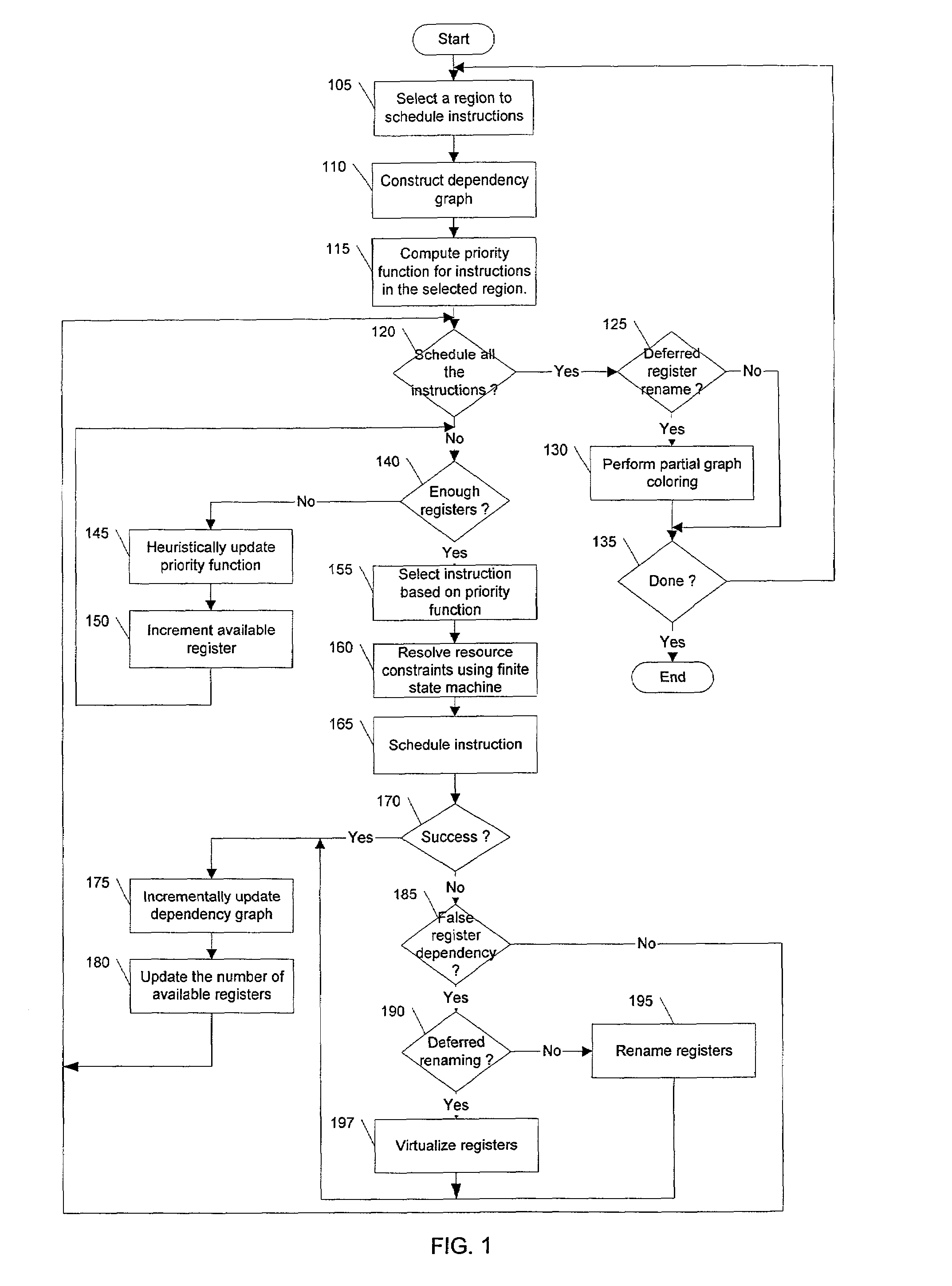
Method and apparatus for integrated instruction scheduling and register allocation in a postoptimizer
The present invention describes a method of efficiently optimizing instruction scheduling and register allocation in a post optimizer. The method removes false register dependencies between pipelined instructions by building an incremental (partial) interference graph of register allocation for scheduled instructions. False dependency graph indicates the amount of parallelism in the data flow graph. The incremental interference graph uses a mix of virtual and physical registers. The interference graph is built incrementally as an instruction schedular schedules each instruction. The optimization is done incrementally on localized code. The physical register mapping is maximized and virtual registers are created on demand basis.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
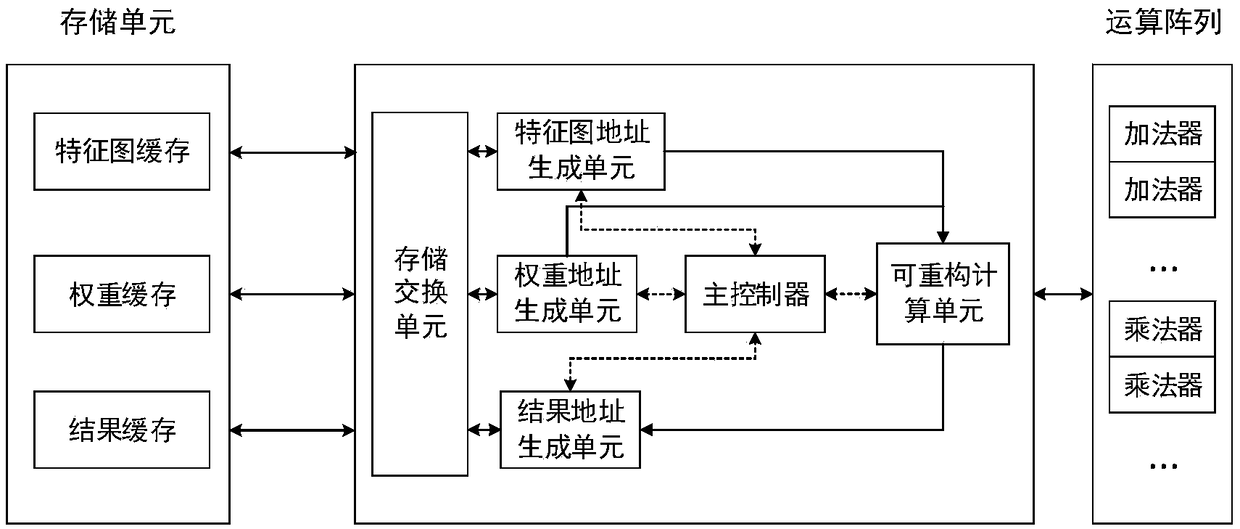
Reconfigurable CNN (Convolutional Neural Network) high concurrency convolution accelerator
ActiveCN108805266AIncrease profitImprove parallelismNeural architecturesAddress generation unitReconfigurable computing
The invention provides a reconfigurable CNN (Convolutional Neural Network) high concurrency convolution accelerator, which comprises a weight address generation unit, a result address generation unit,a reconfigurable calculation unit, a characteristic pattern address generation unit, a master controller and a memory exchange unit, wherein the weight address generation unit generates the address of convolution kernel data in a cache; the result address generation unit generates the address of result data in the cache; the reconfigurable calculation unit can reconfigure a calculation array intotwo multiply-accumulation tree circuits with different particle sizes; the characteristic pattern address generation unit generates the address of characteristic pattern data in the cache; the mastercontroller generates an accumulator resetting signal synchronous with the address, carries out gating on a corresponding circuit in the reconfigurable calculation unit, and generates an interrupt signal for the end of the whole operation; and the memory exchange unit converts an effective characteristic pattern read address and a weight read address into the read operation of a memory unit, and converts an effective result write address and data into a write operation for the memory unit. The accelerator has the beneficial effects that a control part is simplified, the degree of parallelism of a multi-channel convolution operation and memory access efficiency can be greatly improved, and occupied resources are reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
LDPC encoding methods and apparatus
ActiveUS7346832B2Simple microcodeEasy to modifyError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionProcessor registerDegree of parallelism
A flexible and relatively hardware efficient LDPC encoder is described. The encoder can be implemented with a level of parallelism which is less than the full parallelism of the code structure used to control the encoding process. Each command of a relatively simple microcode used to describe the code structure can be stored and executed multiple times to complete the encoding of a codeword. Different codeword lengths can be supported using the same set of microcode instructions but with the code being implemented a different number of times depending on the lifting factor selected to be used. The LDPC encoder can switch between encoding codewords of different lengths, without the need to change the stored code description information, by simply changing a code lifting factor used to control the encoding processes. When coding codewords shorter than the maximum supported codeword length some block storage locations and / or registers may go unused.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
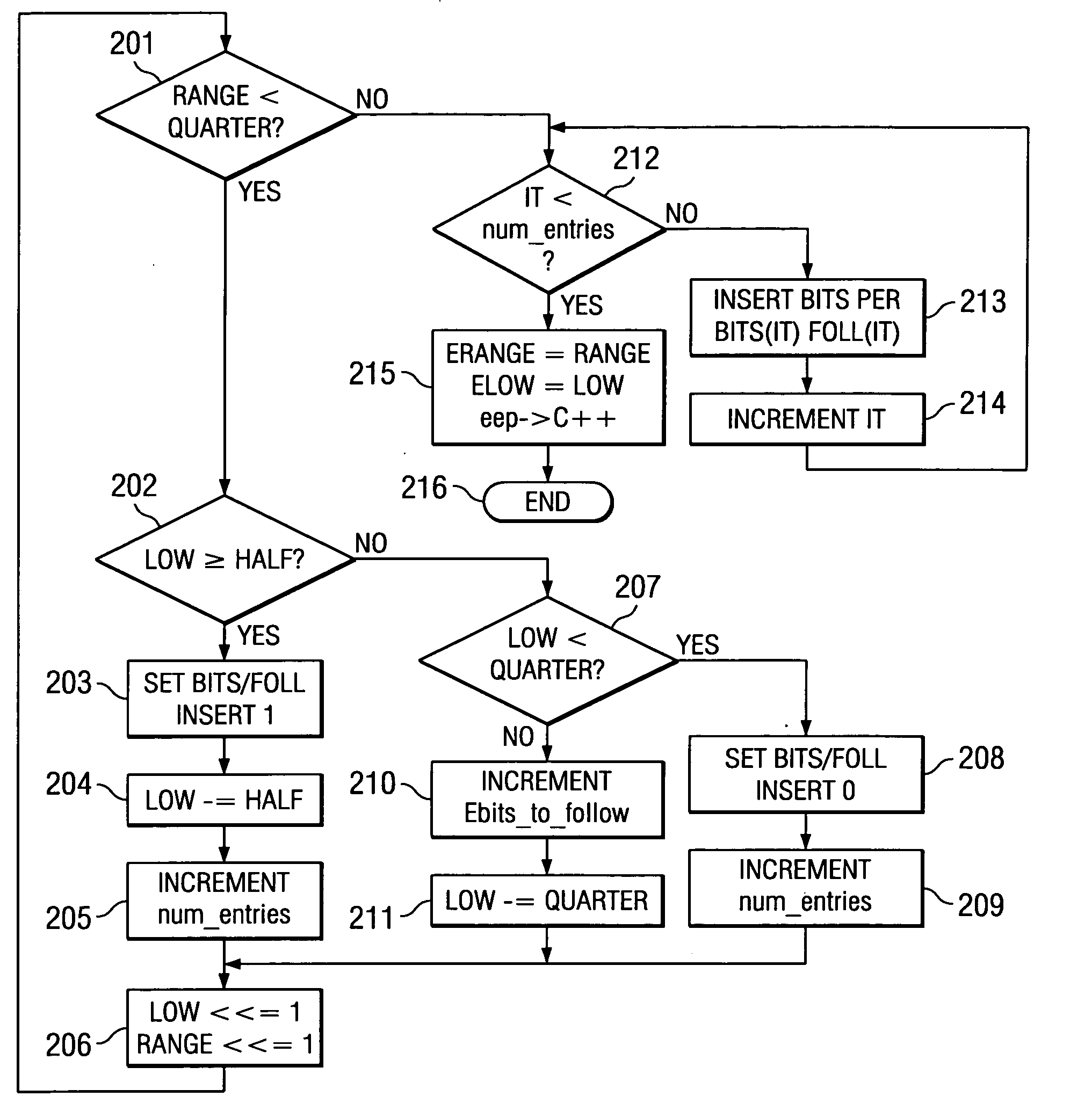
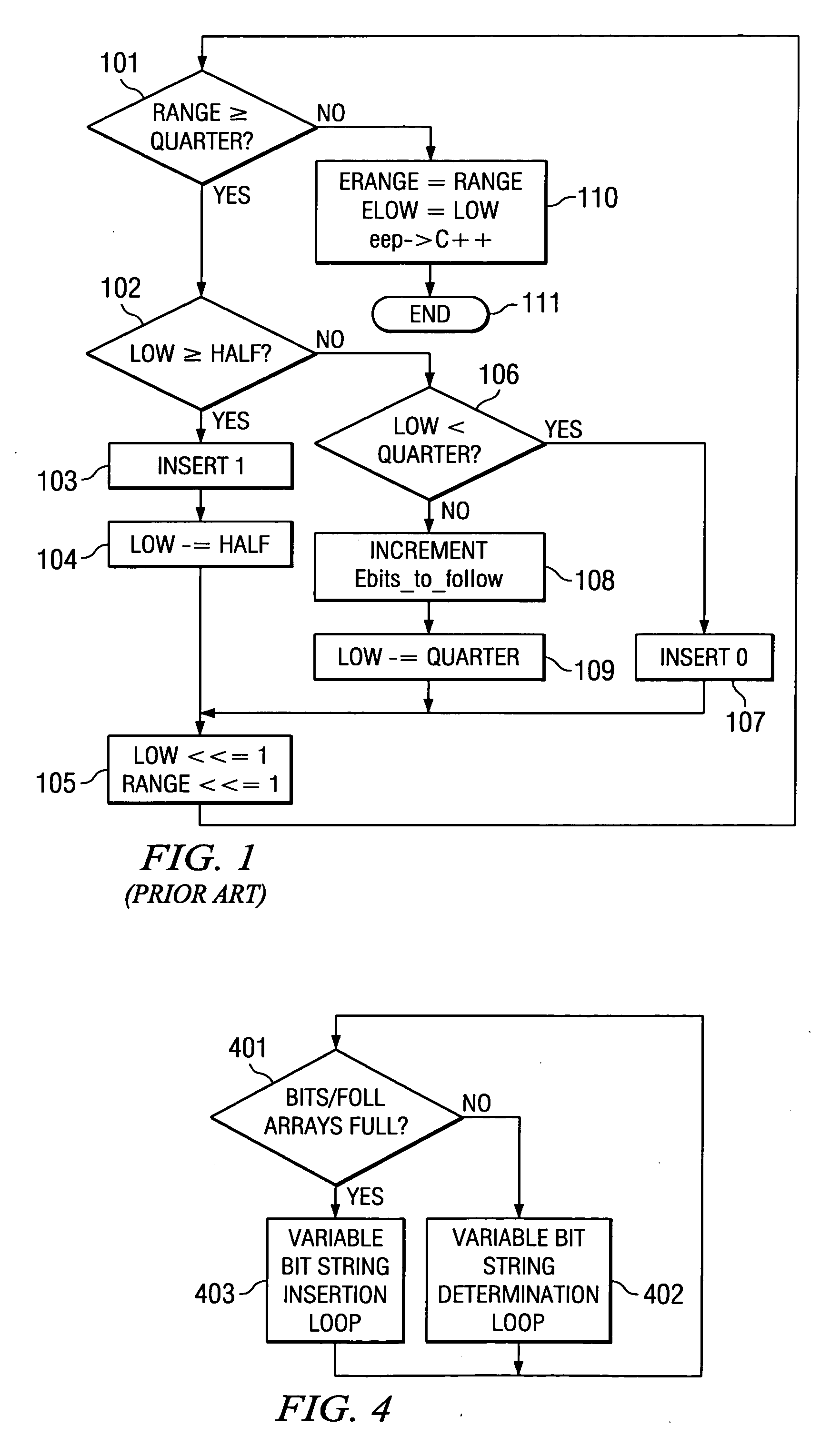
Method of context based adaptive binary arithmetic encoding with decoupled range re-normalization and bit insertion
ActiveUS20050001745A1Increases the available instruction level parallelism (IPC)Improve performanceDigital computer detailsCode conversionCouplingVariable length
This invention increases the available instruction level parallelism (IPC) of CABAC encoding by decoupling the re-normalization loop and the bit-insertion task required to create the encoded bit-stream. This makes all software implementations of CABAC based encoding significantly faster on digital signal processors that can exploit instruction level parallelism such as very long instruction word (VLIW) digital signal processors. In a joint hardware / software implementation, this invention employs existing Huffman variable length encoding hardware with minimum modifications. The de-coupling of these two tasks of this invention exposes previously hidden underlying instruction level parallelism and task level parallelism.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
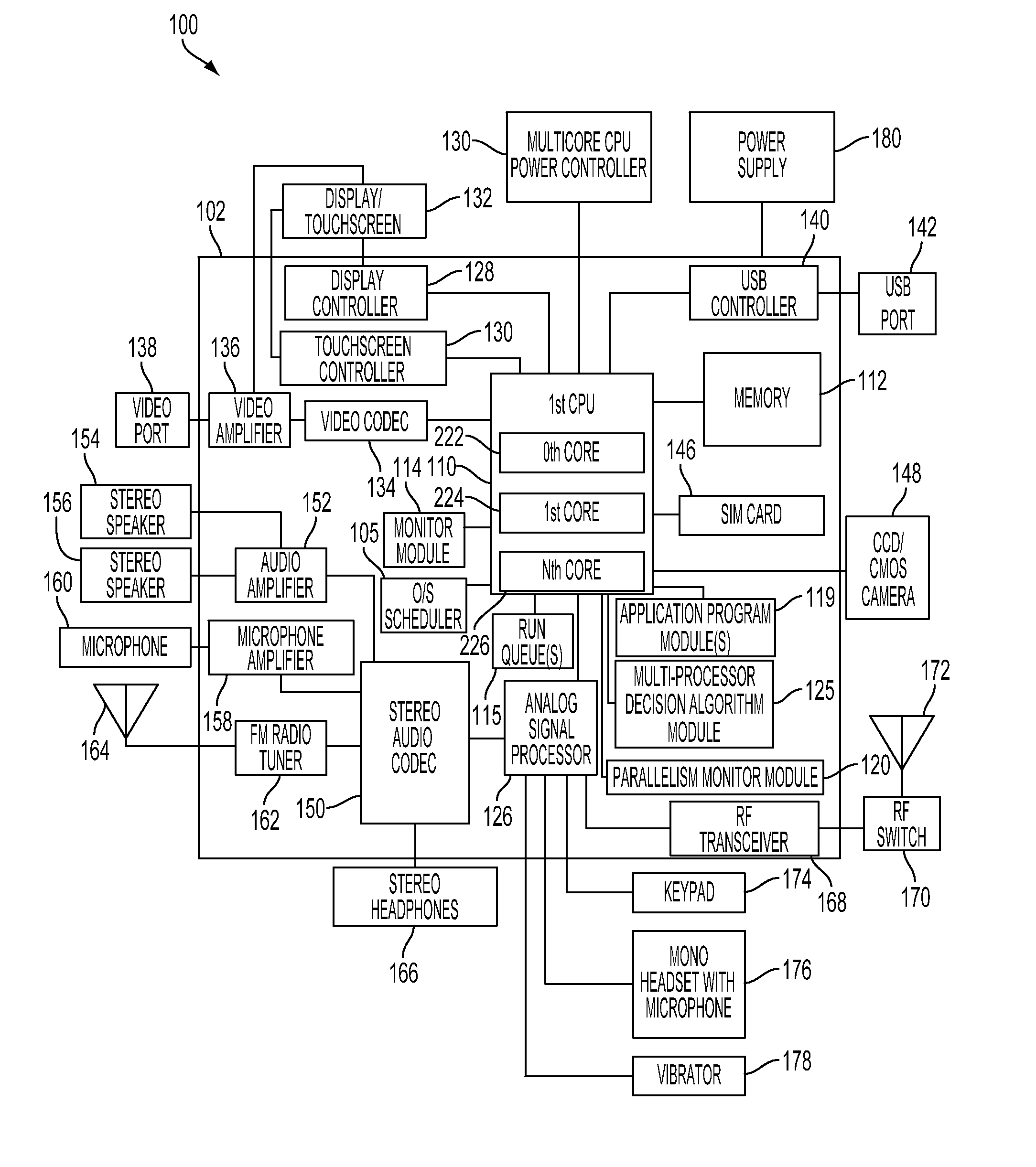
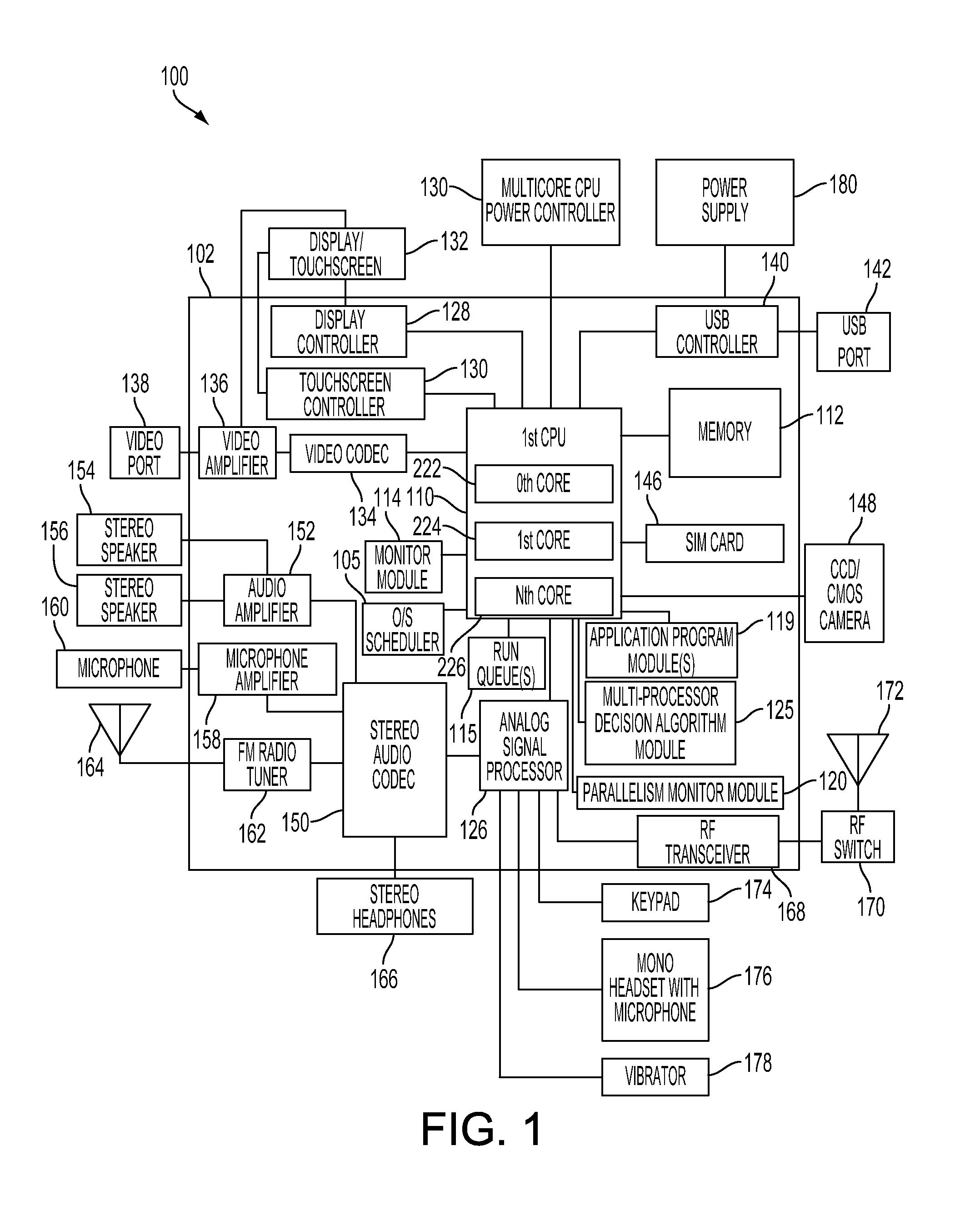
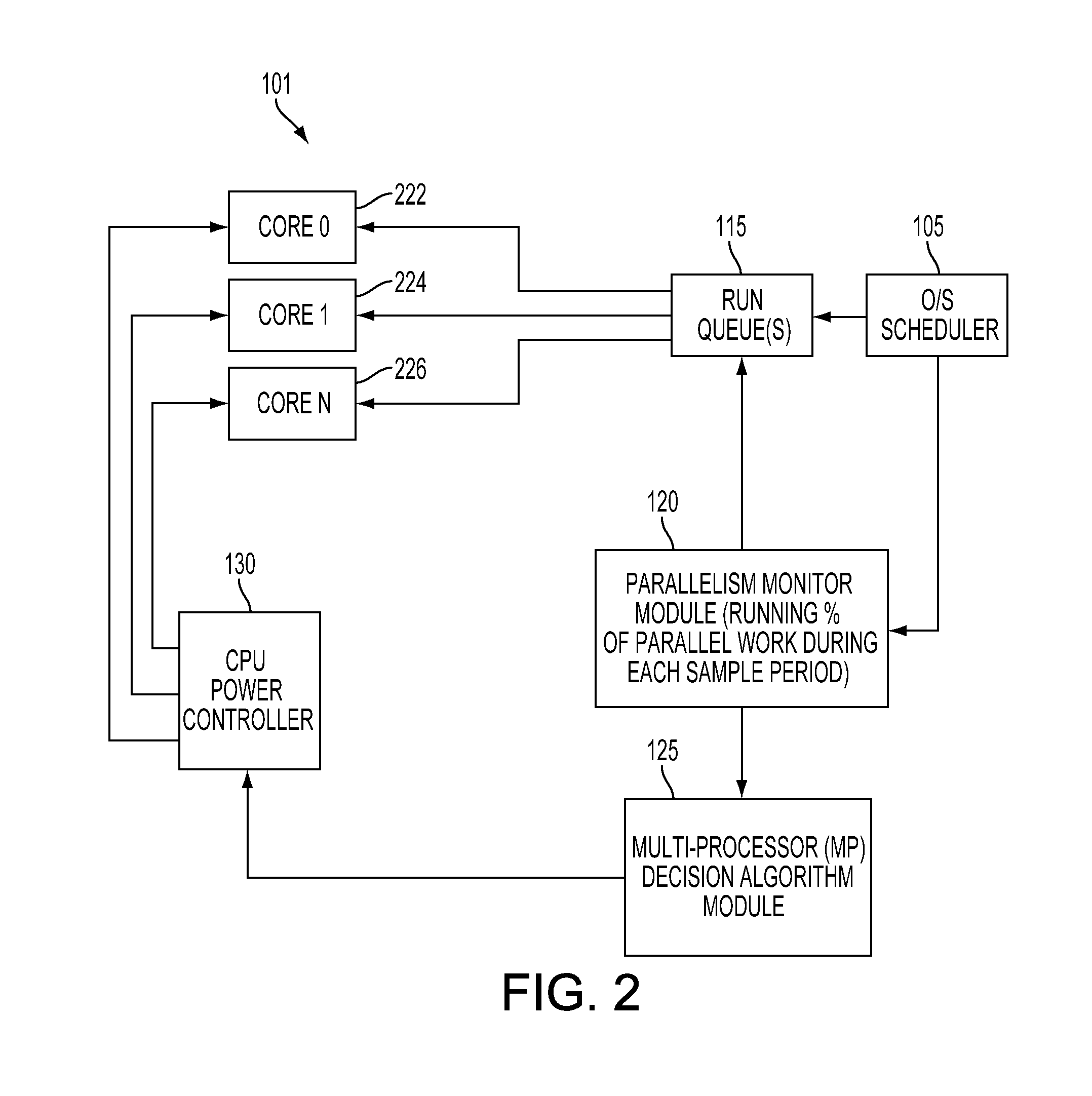
Method and system for dynamically controlling power to multiple cores in a multicore processor of a portable computing device
A method and system for dynamically determining the degree of workload parallelism and to automatically adjust the number of cores (and / or processors) supporting a workload in a portable computing device are described. The method and system includes a parallelism monitor module that monitors the activity of an operating system scheduler and one or more work queues of a multicore processor and / or a plurality of central processing units (“CPUs”). The parallelism monitor may calculate a percentage of parallel work based on a current mode of operation of the multicore processor or a plurality of processors. This percentage of parallel work is then passed to a multiprocessor decision algorithm module. The multiprocessor decision algorithm module determines if the current mode of operation for the multicore processor (or plurality of processors) should be changed based on the calculated percentage of parallel work.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
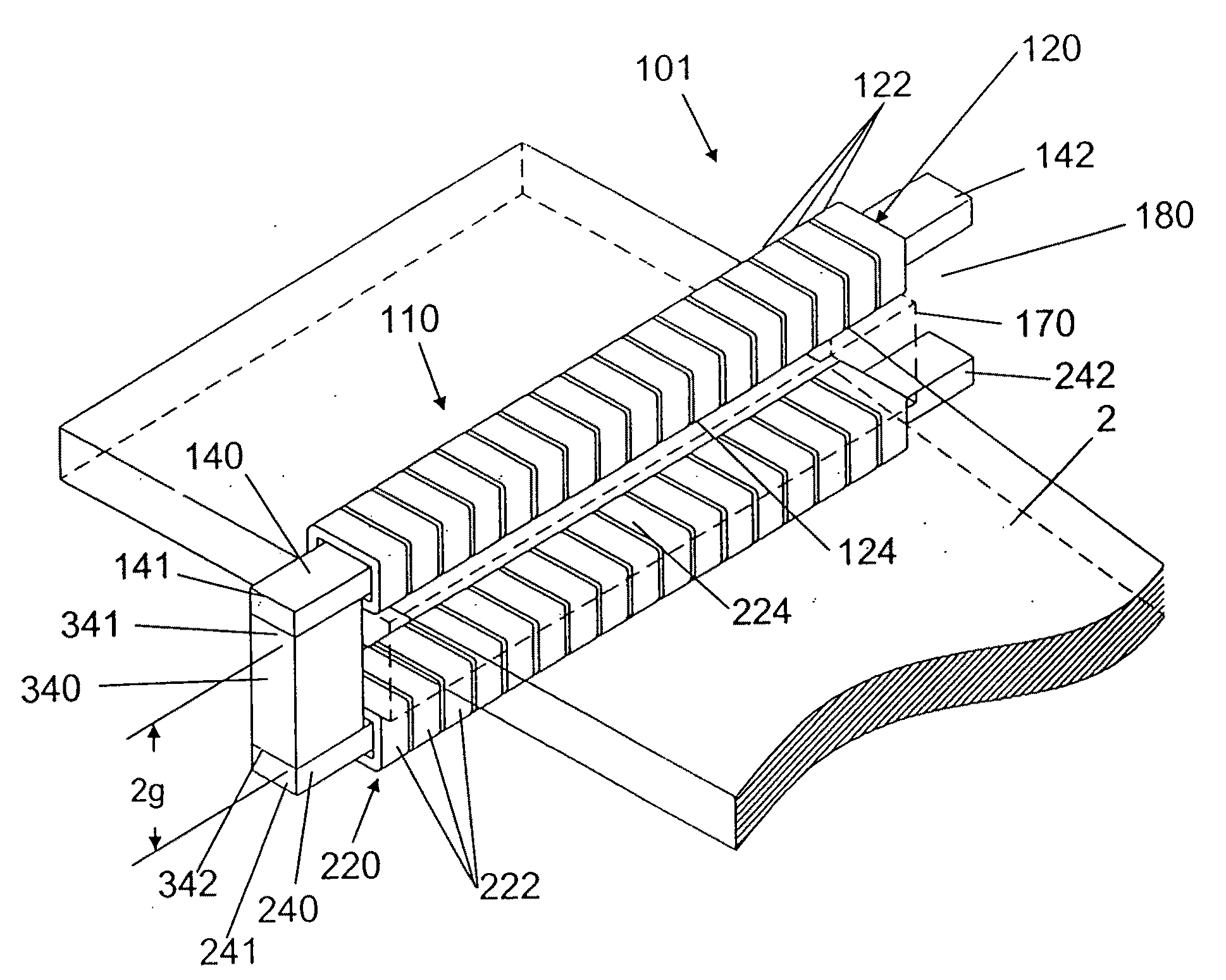
Open-ended electromagnetic corrector assembly and method for deflecting, focusing, and controlling the uniformity of a traveling ion beam
ActiveUS20100001204A1Improve uniformityImprove parallelismThermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersDegree of parallelismFlat glass
The present invention is an electromagnetic controller assembly for use in ion implantation apparatus, and provides a structural construct and methodology which can be employed for three recognizably separate and distinct functions: (i) To adjust the trajectory of charged particles carried within any type of traveling ion beam which is targeted at a plane of implantation or a work surface for the placement of charged ions into a prepared workpiece (such as a silicon wafer or flat glass panel); (ii) concurrently, to alter and change the degree of parallelism of the ions in the traveling beam; and (iii) concurrently, to control the uniformity of the current density along the transverse direction of traveling ion beams, regardless of whether the beams are high-aspect, continuous ribbon ion beams or alternatively are scanned ribbon ion beams.
Owner:WHITE NICHOLAS R
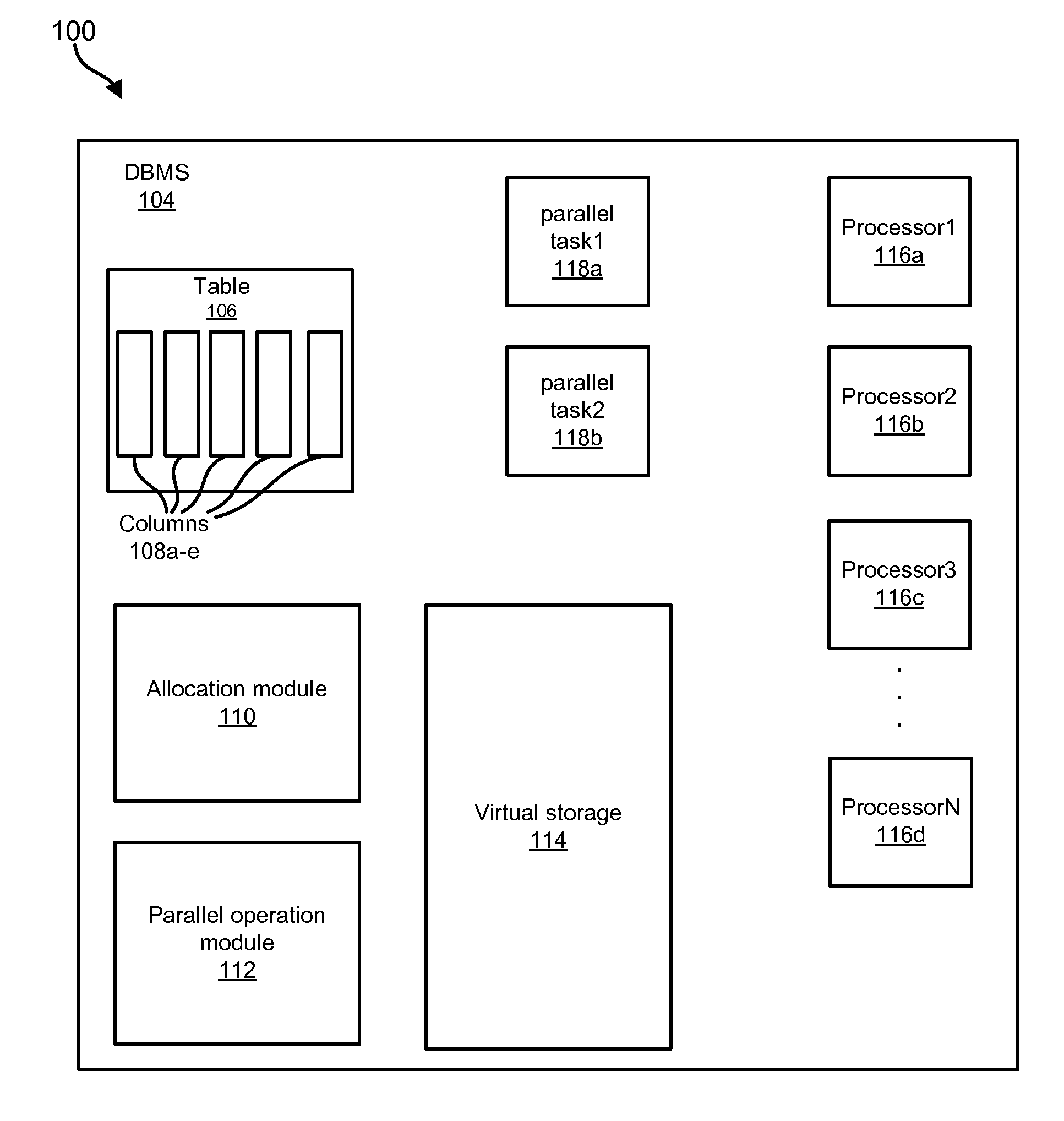
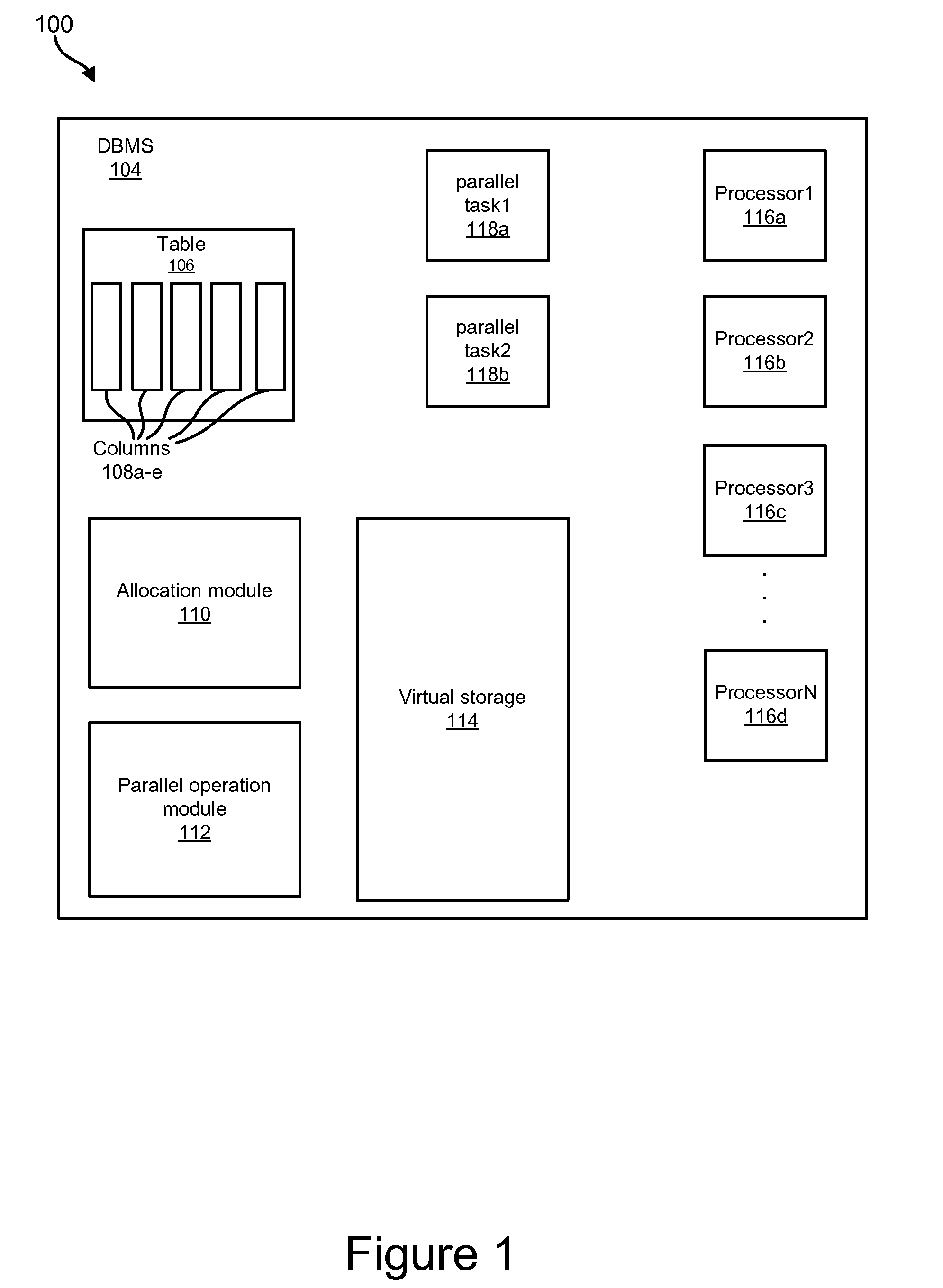
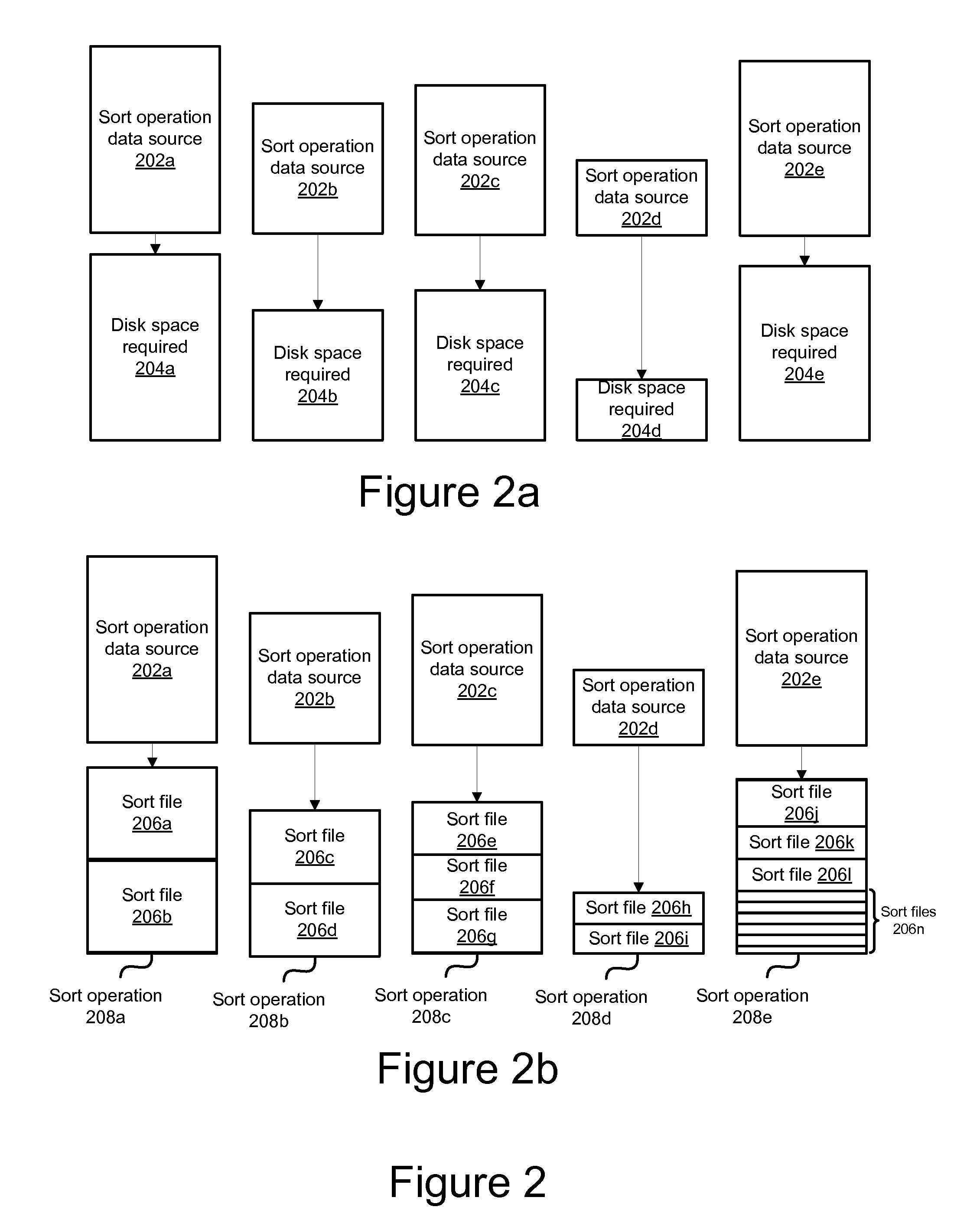
Apparatus, system, and method for deterministic file allocations for parallel operations
InactiveUS20090063591A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsFile allocationMulti processor
An apparatus, system, and method for determining the maximum supported degree of parallel sort operations in a multi-processor computing environment. An allocation module allocates a minimum number of sort files to a sort operation for each data source that participates in the parallel sort. The allocation module attempts to allocate sort files of one-half the sort operation data source file size, and iteratively reduces the sort file size requests in response to determinations that sort files of the requested size are not available. After allocation, a parallel operation module determines whether there is sufficient virtual storage to execute the sort operations in parallel. If there is not, the parallel operations module collapses the two smallest sort operations, thereby reducing the degree of parallelism by one, and repeats the request. The parallel operation module repeats the process until the sorts are executed or the process fails for lack of virtual storage.
Owner:IBM CORP
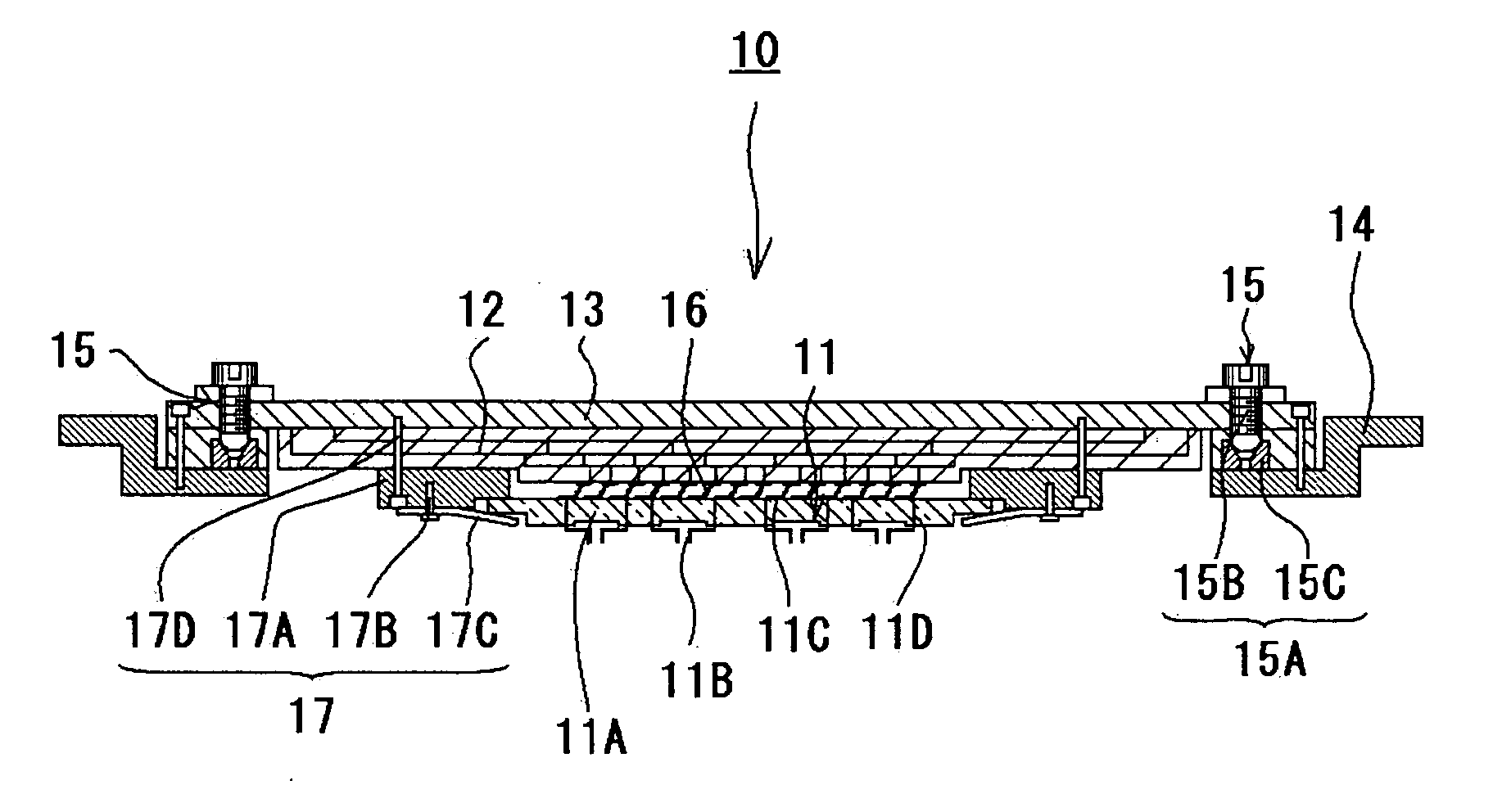
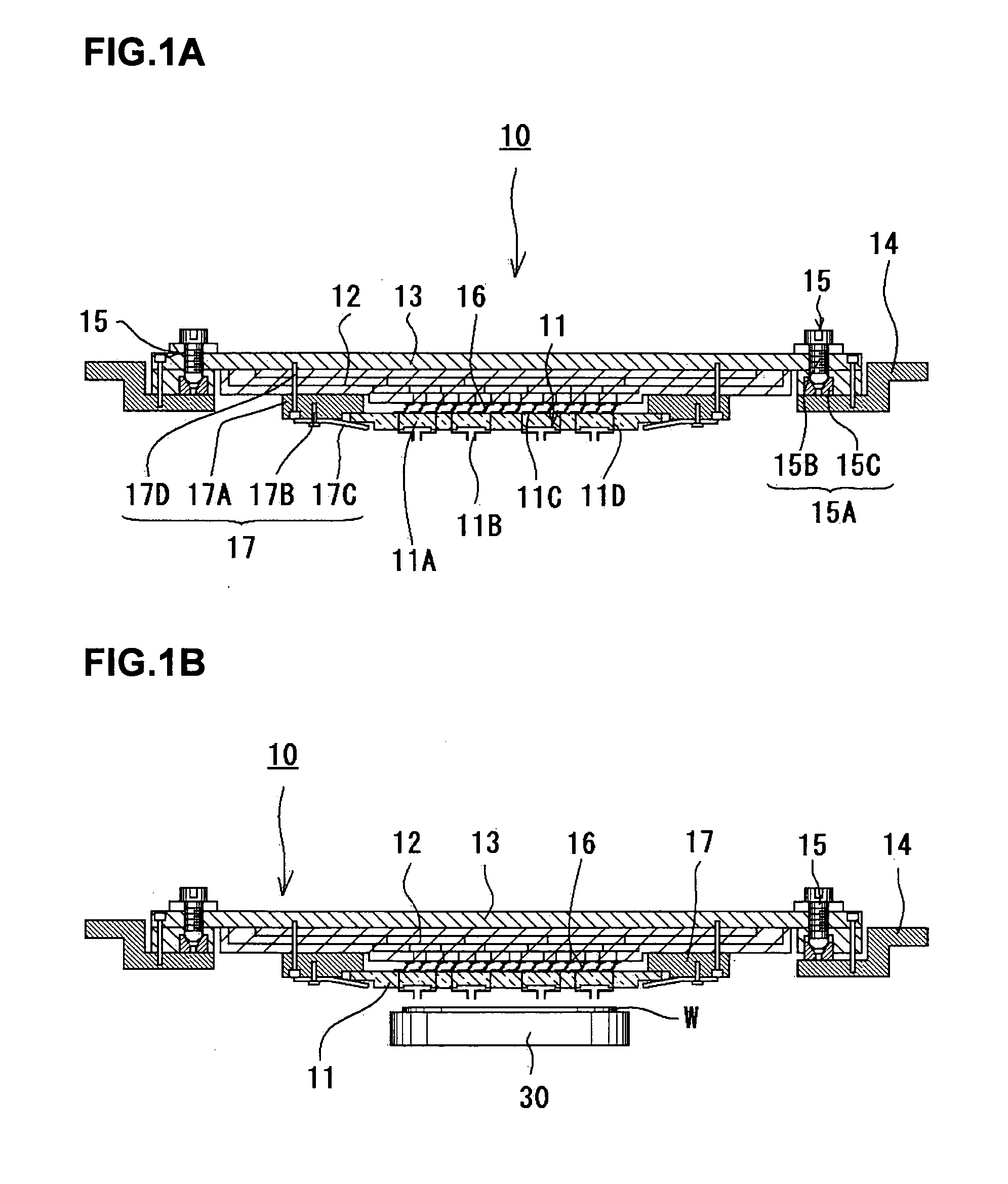
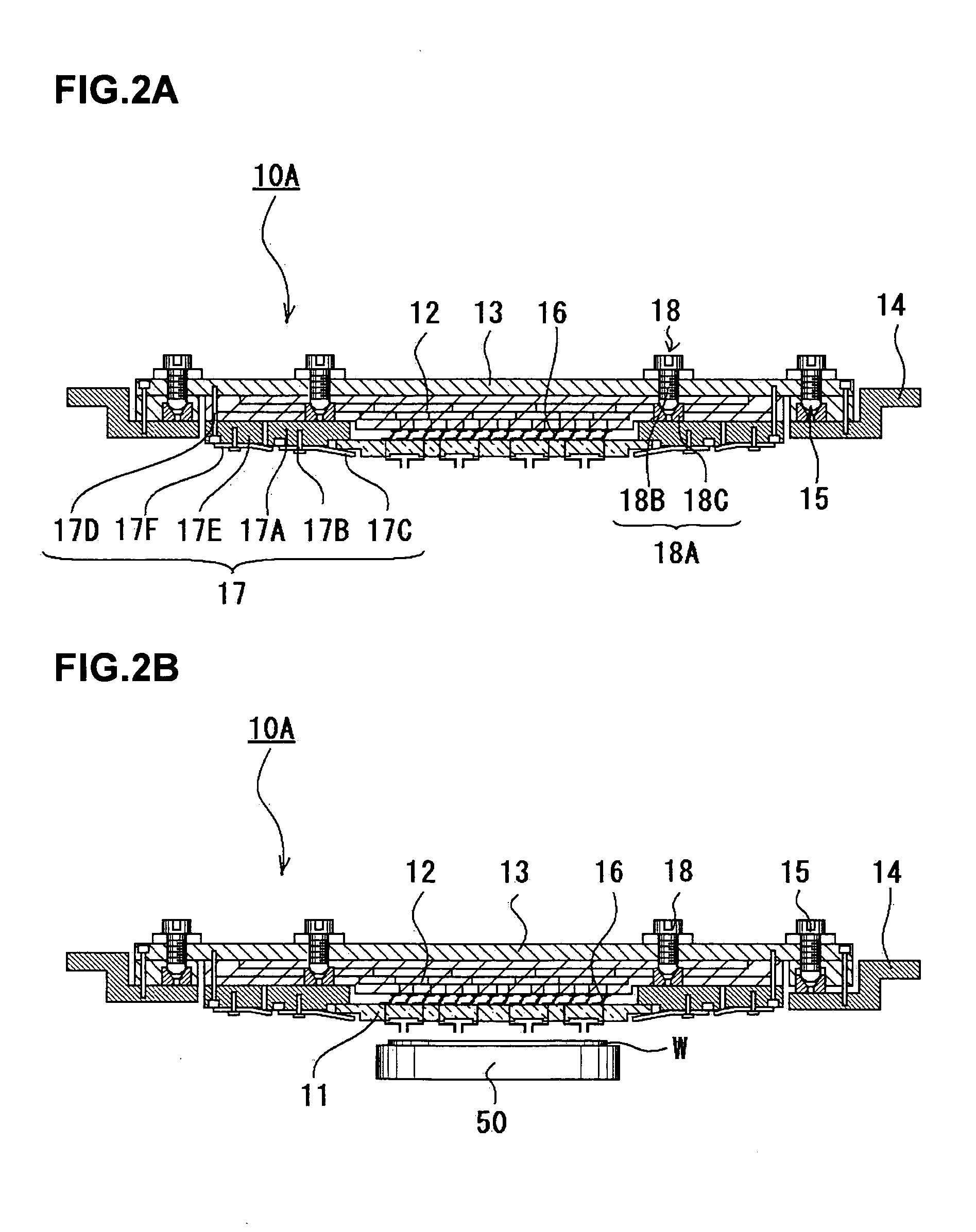
Probe Card
InactiveUS20080048698A1Highly reliable inspectionReliable inspectionSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectrical measurement instrument detailsProbe cardEngineering
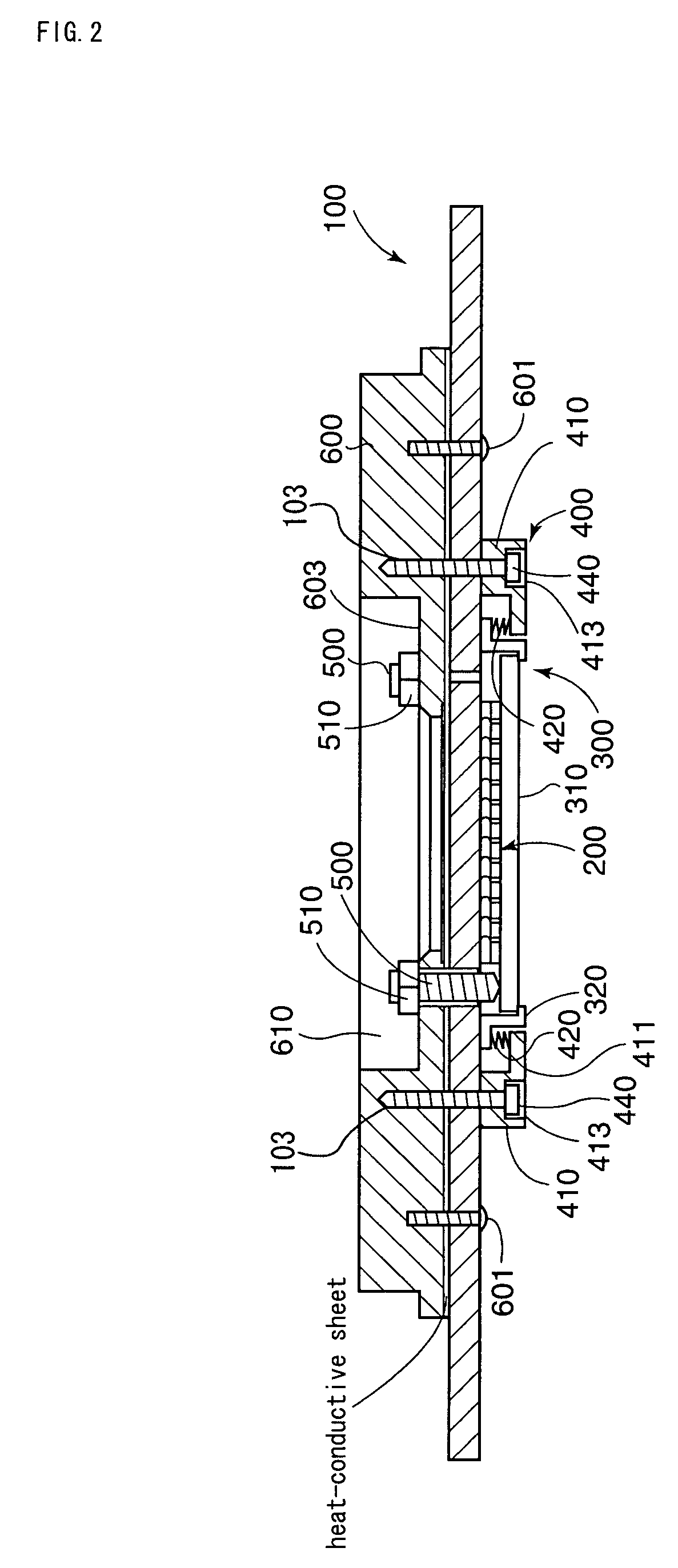
It is an object of the present invention to conduct highly reliable inspection by adjusting a contactor of a probe card and an inspection object in a prober to a parallel state even if the contactor and the inspection object become not parallel to each other. The present invention is a probe card mounted in a prober via a holder, the probe card including: a contactor; a circuit board electrically connected to the contactor; a reinforcing member reinforcing the circuit board; and a parallelism adjustment mechanism adjusting a degree of parallelism between the contactor and an inspection object disposed in the prober.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
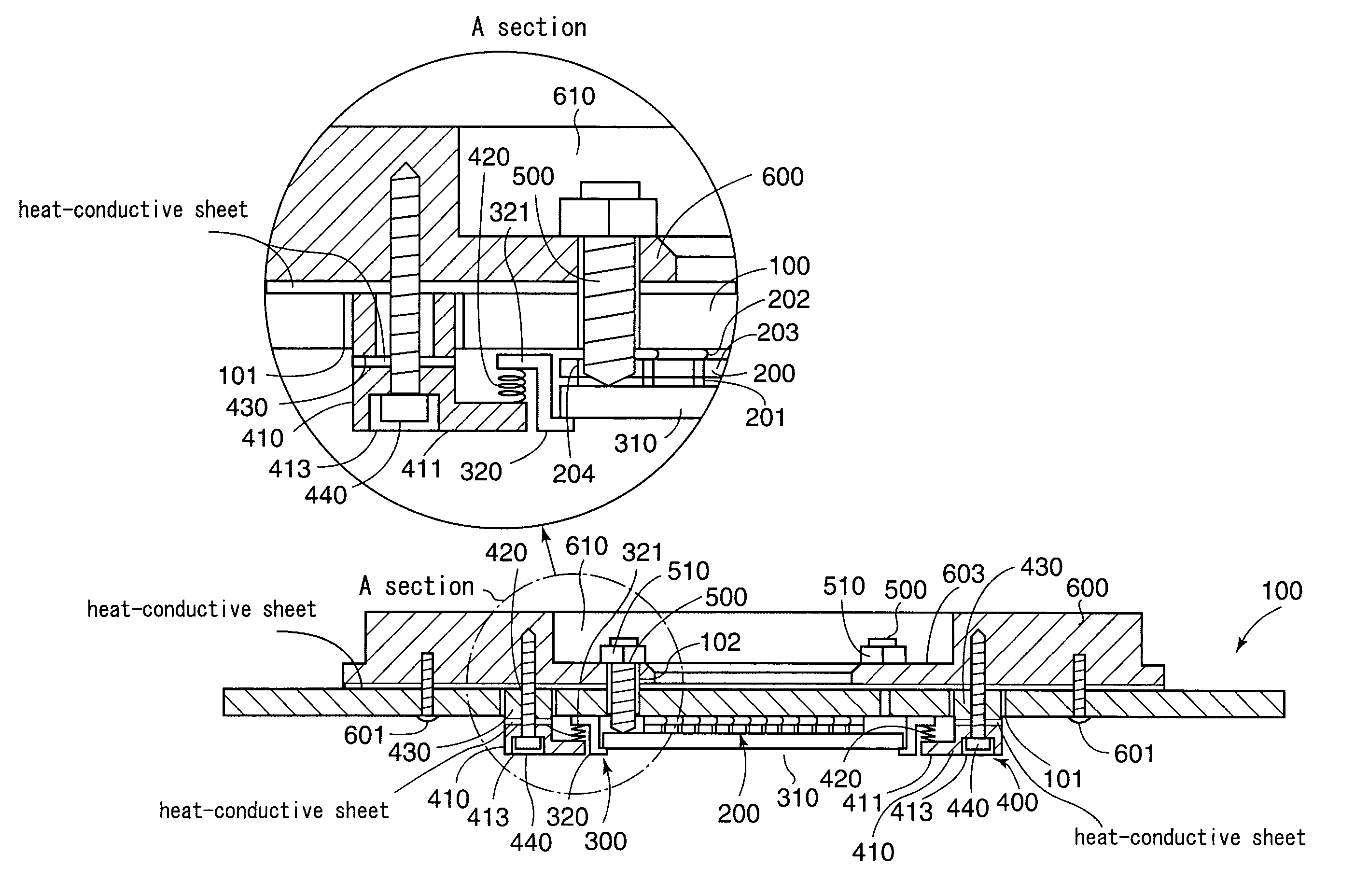
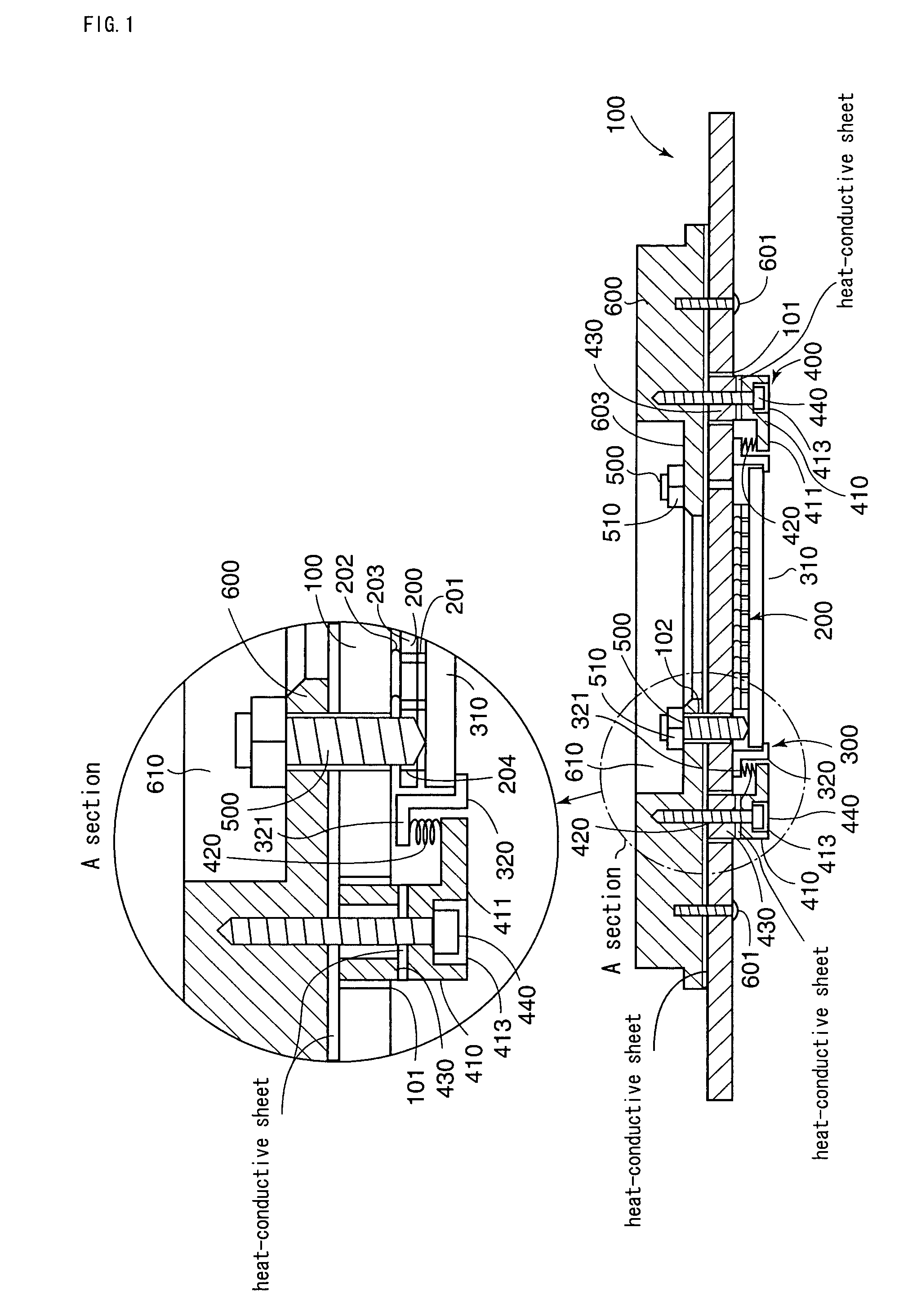
Probe card having a coil spring interposed between a support member and a contactor unit
InactiveUS7075319B2Avoid deformationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectronic circuit testingElectricityProbe card
A probe card including a substrate body, a contactor unit provided below the substrate body for establishing an electrical contact with the subject to be tested as well as for establishing an electrical contact with the substrate body, a supporting device for supporting the contactor unit from below with elastic force and parallelism adjusting screws that come in contact with the contactor unit from above in a vertical direction for adjusting a degree of parallelism of the contactor unit. In particular, the supporting device is configured to include a coil spring interposed toward a vertical direction between a flange section provided at the inside section of the support member arranged below the substrate body and a flange section provided at the outside section of the contactor unit.
Owner:NIHON DENSHIZAIRYO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com