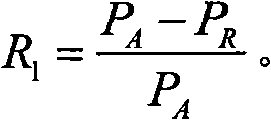Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
151 results about "Shortest-path tree" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
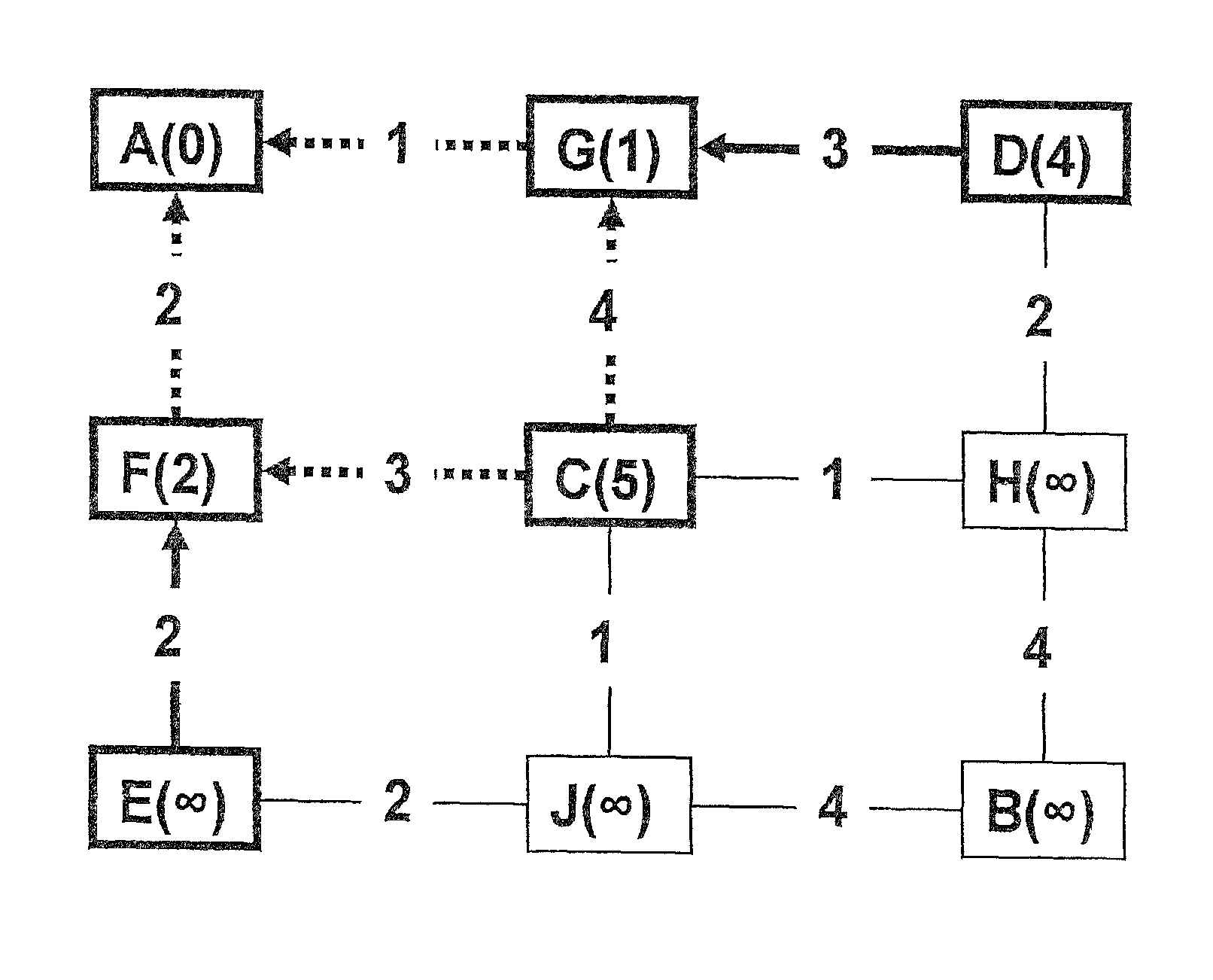
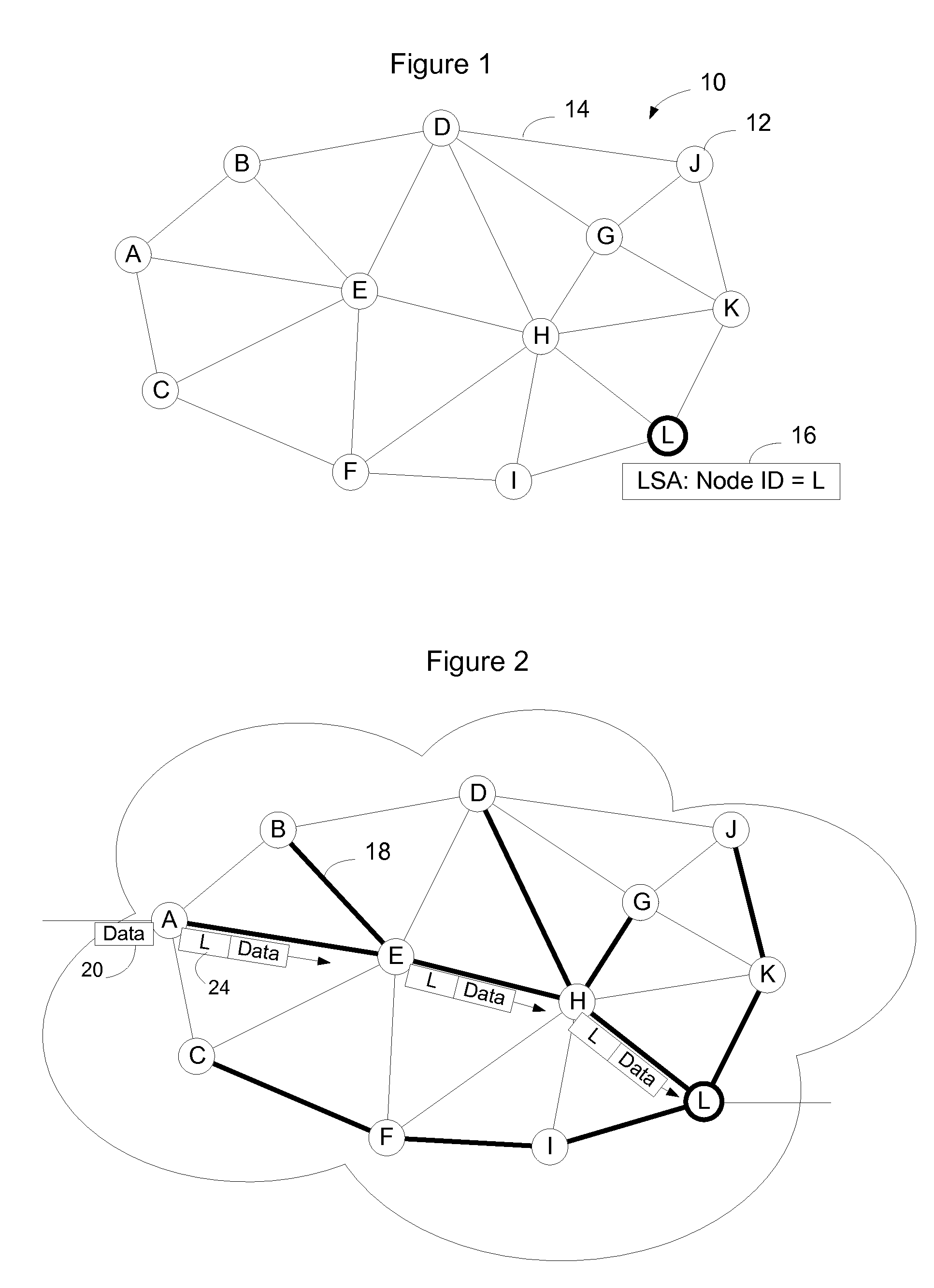
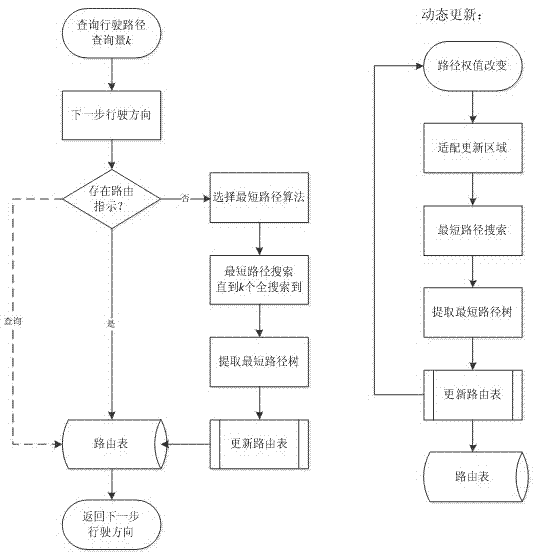
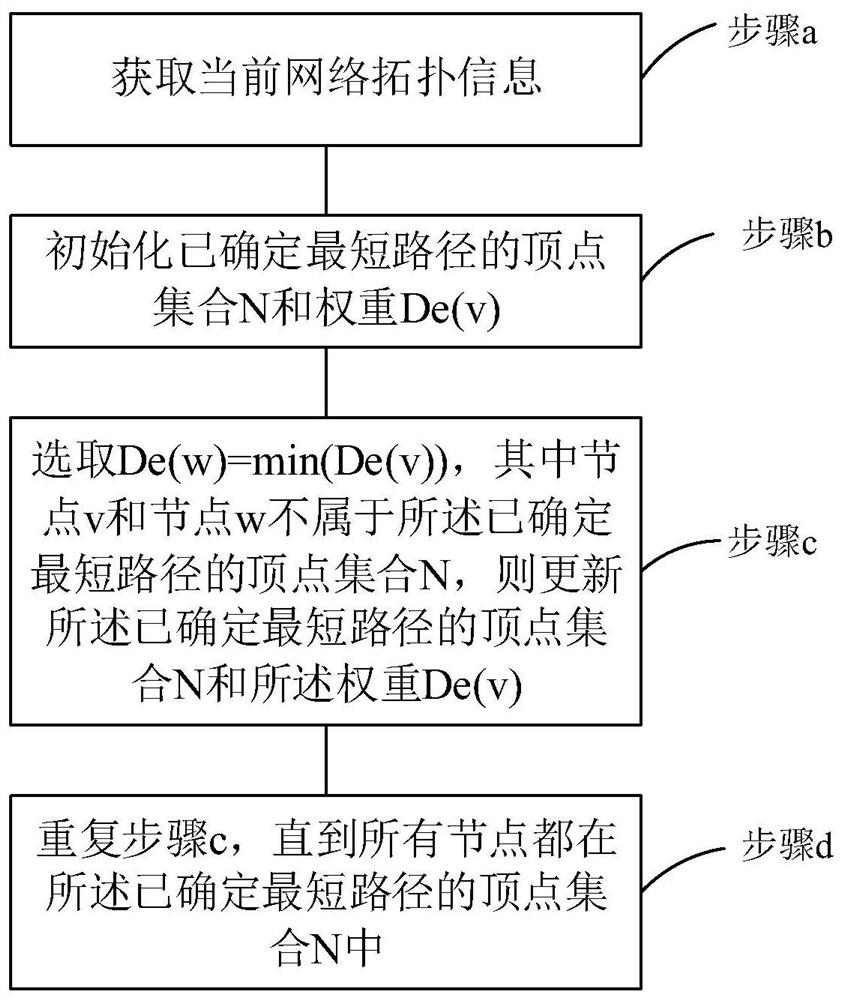
Given a connected, undirected graph G, a shortest-path tree rooted at vertex v is a spanning tree T of G, such that the path distance from root v to any other vertex u in T is the shortest path distance from v to u in G.
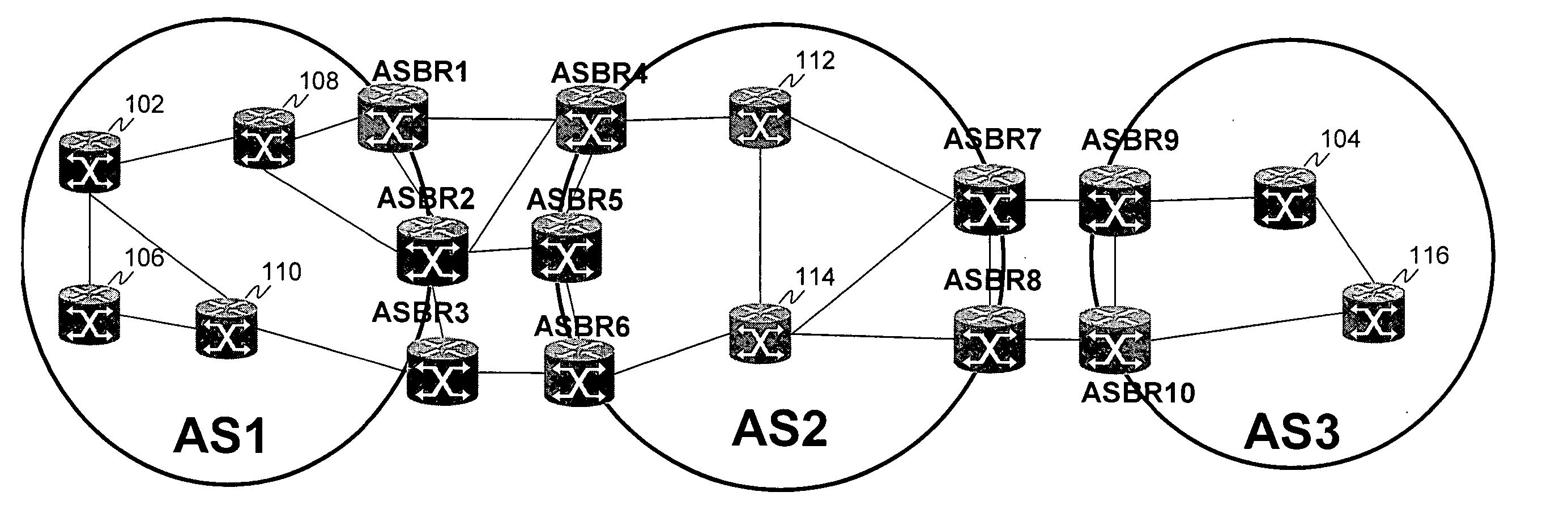
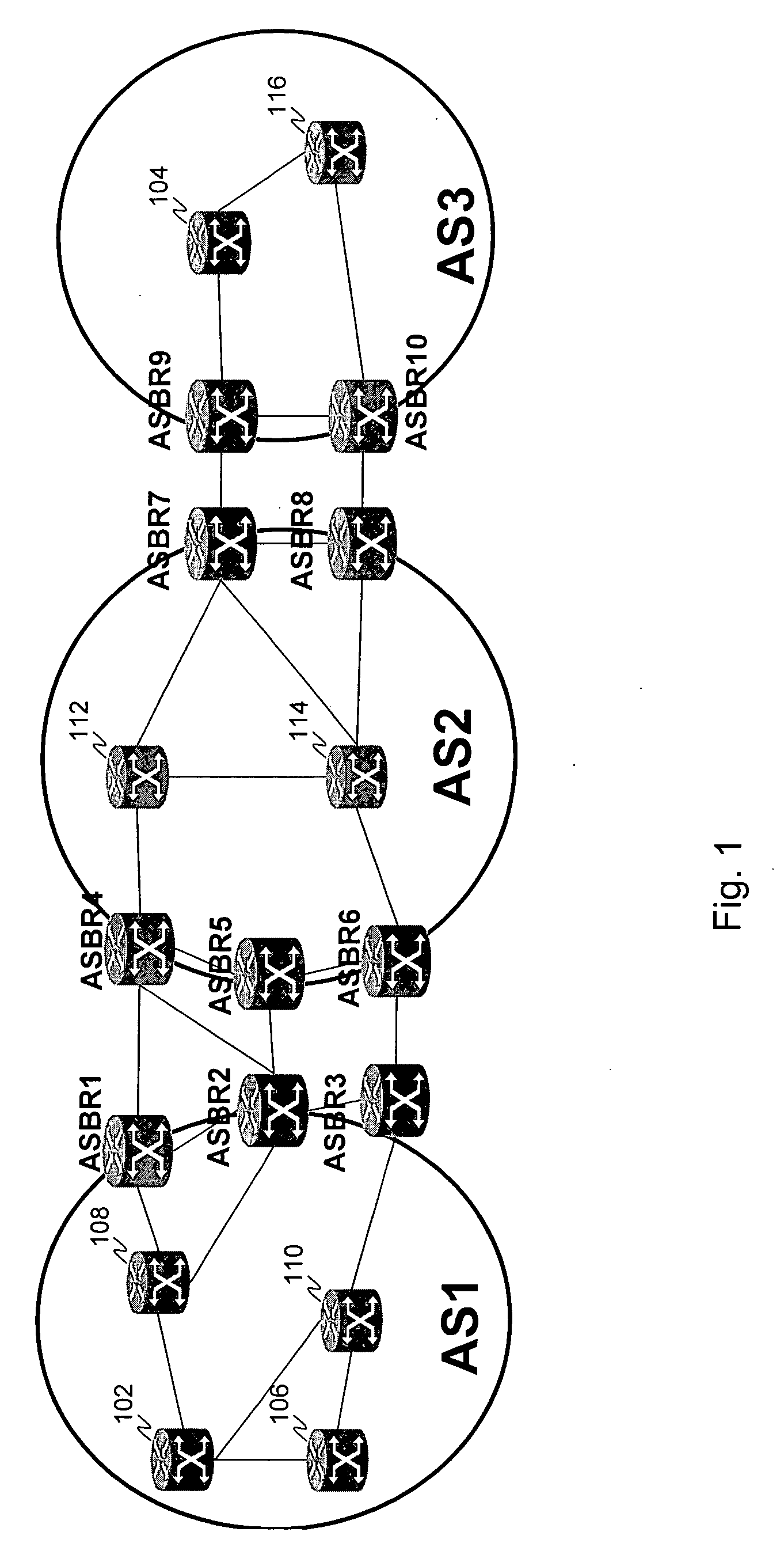
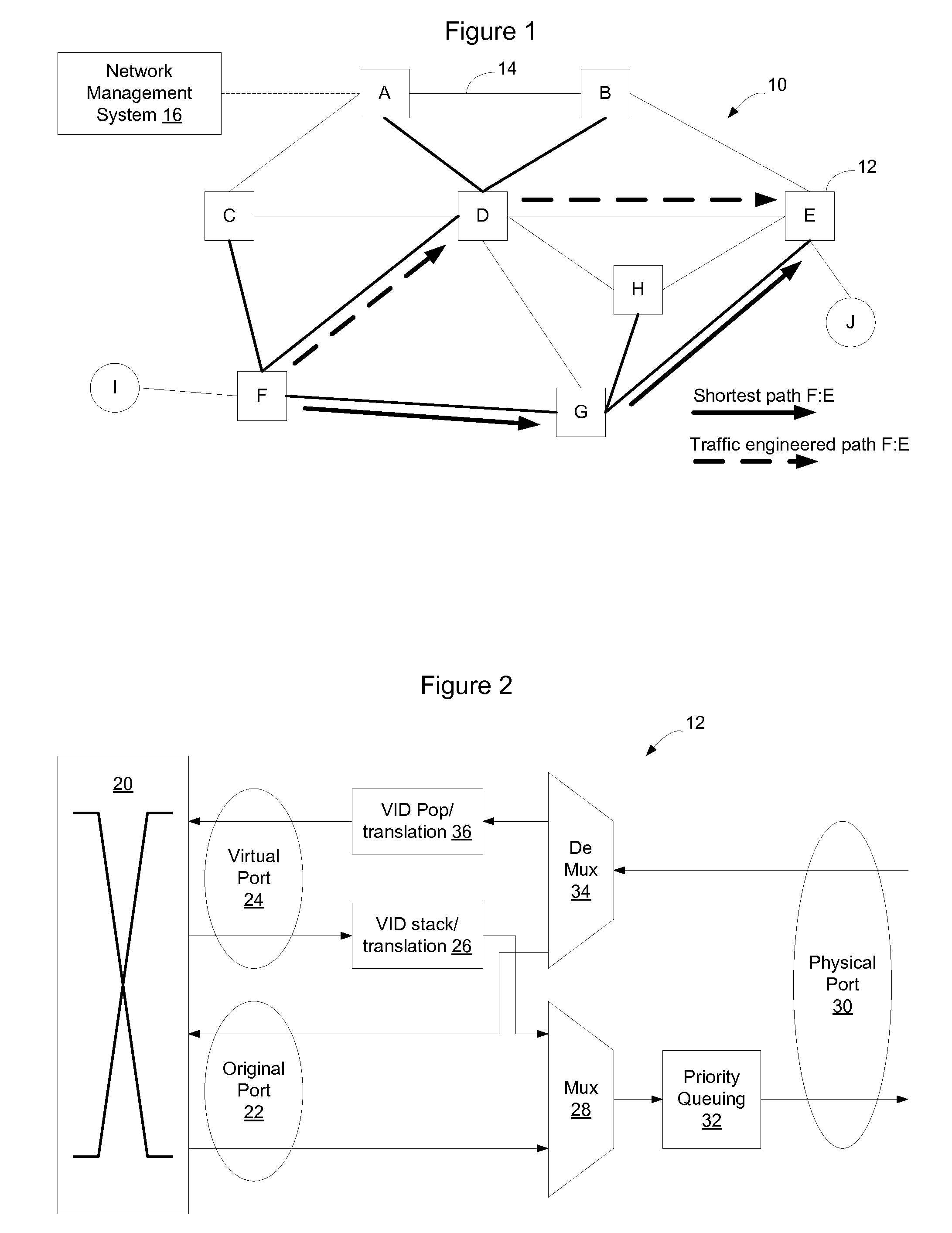
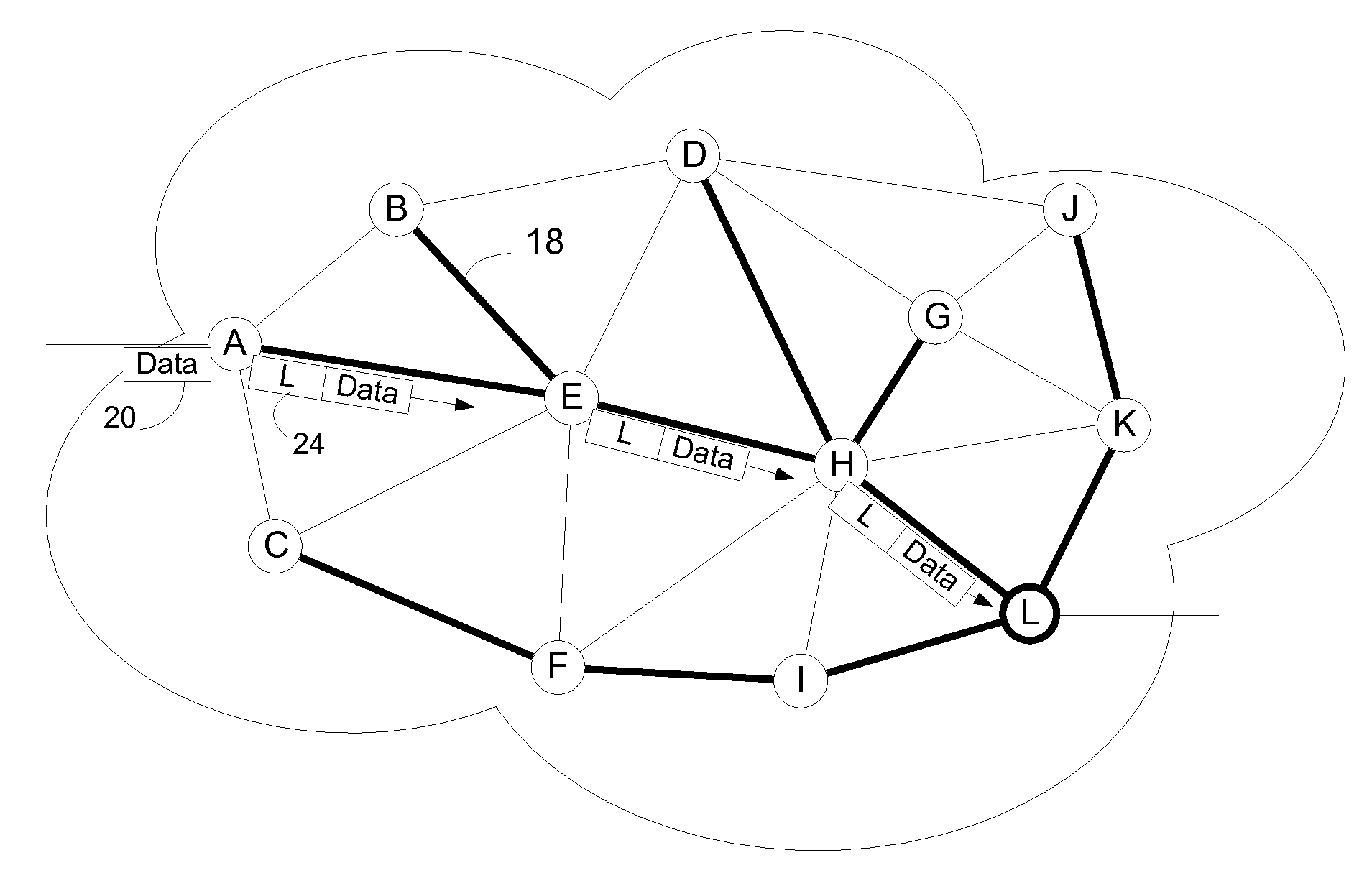
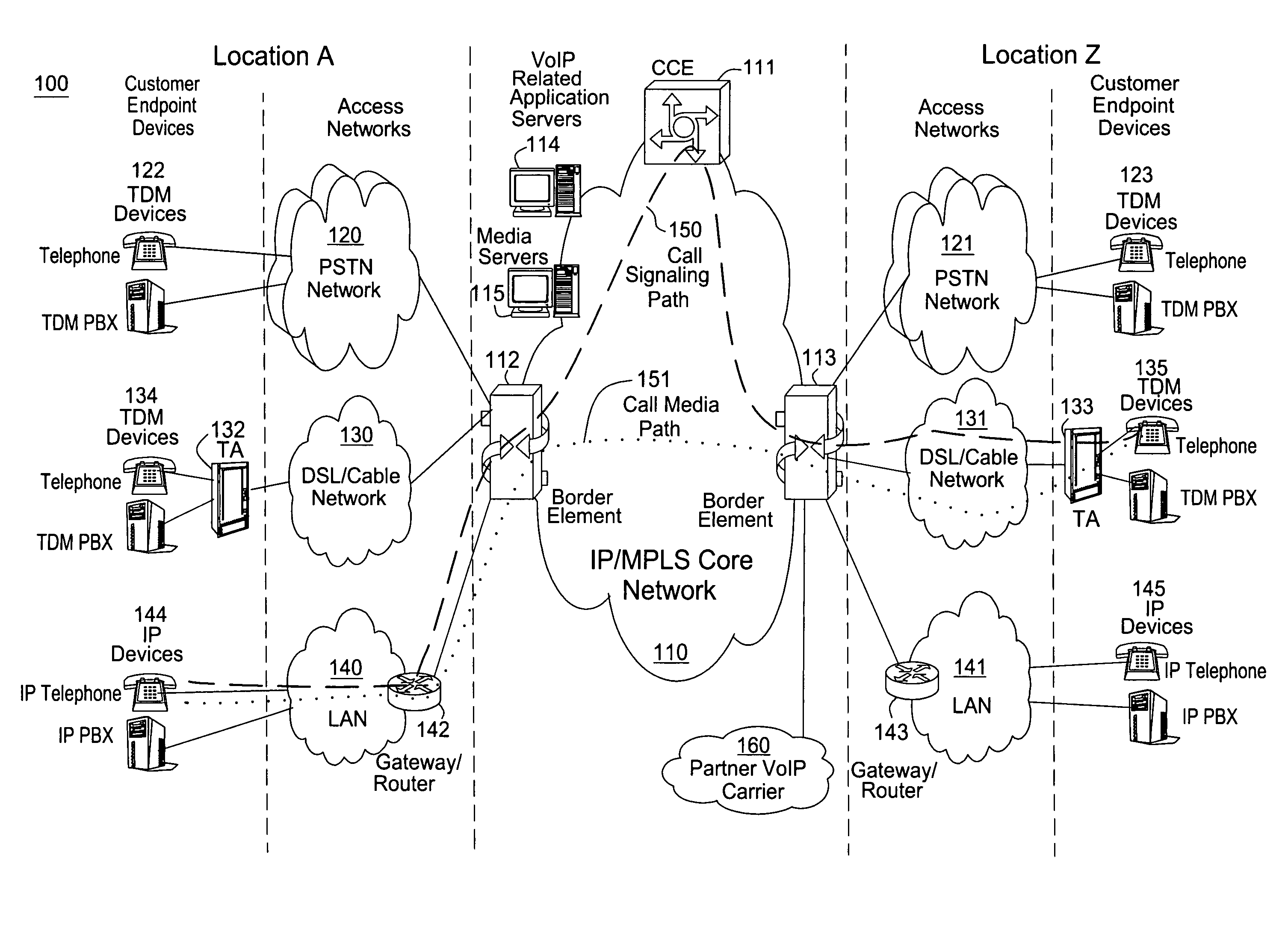
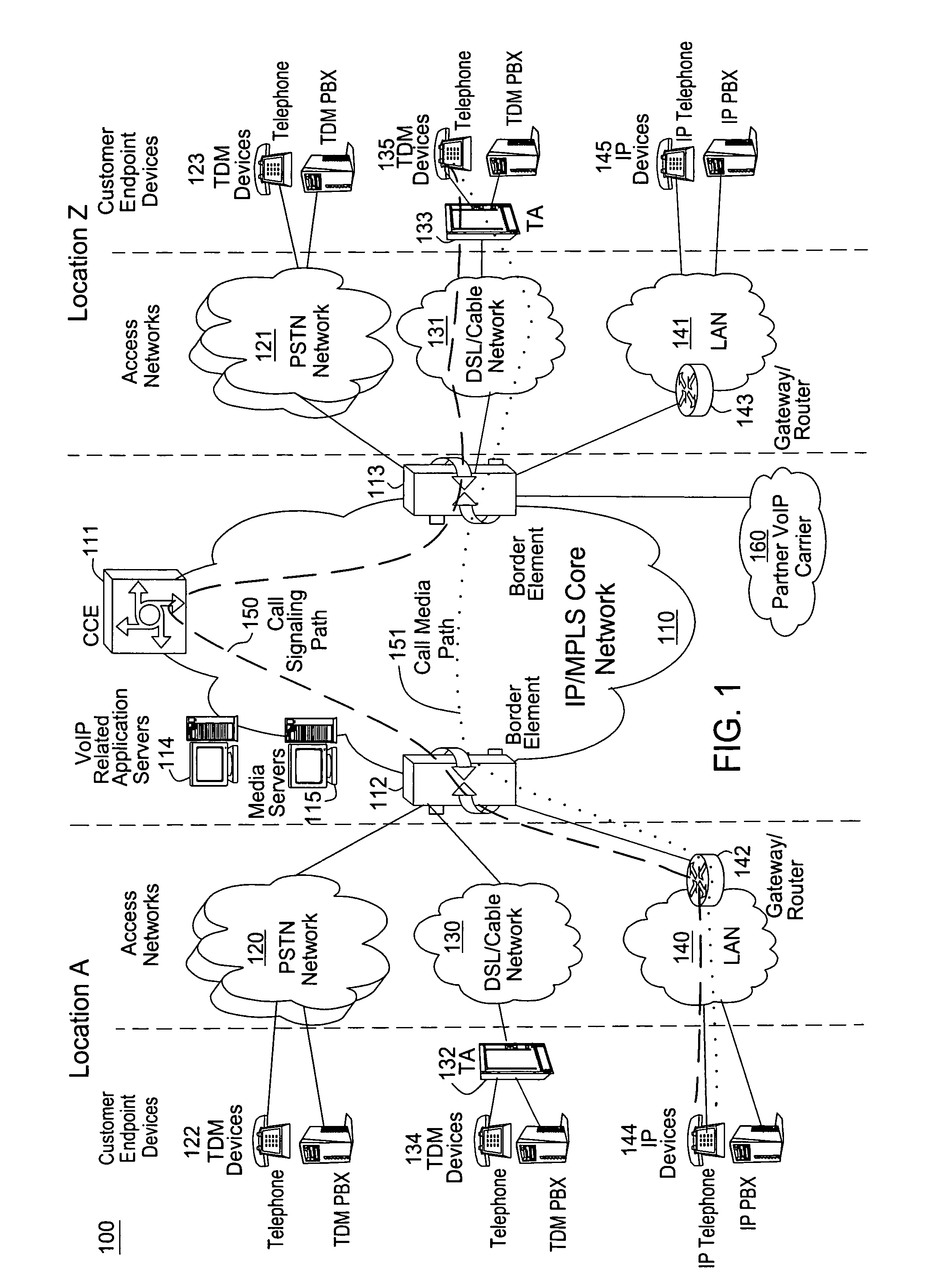
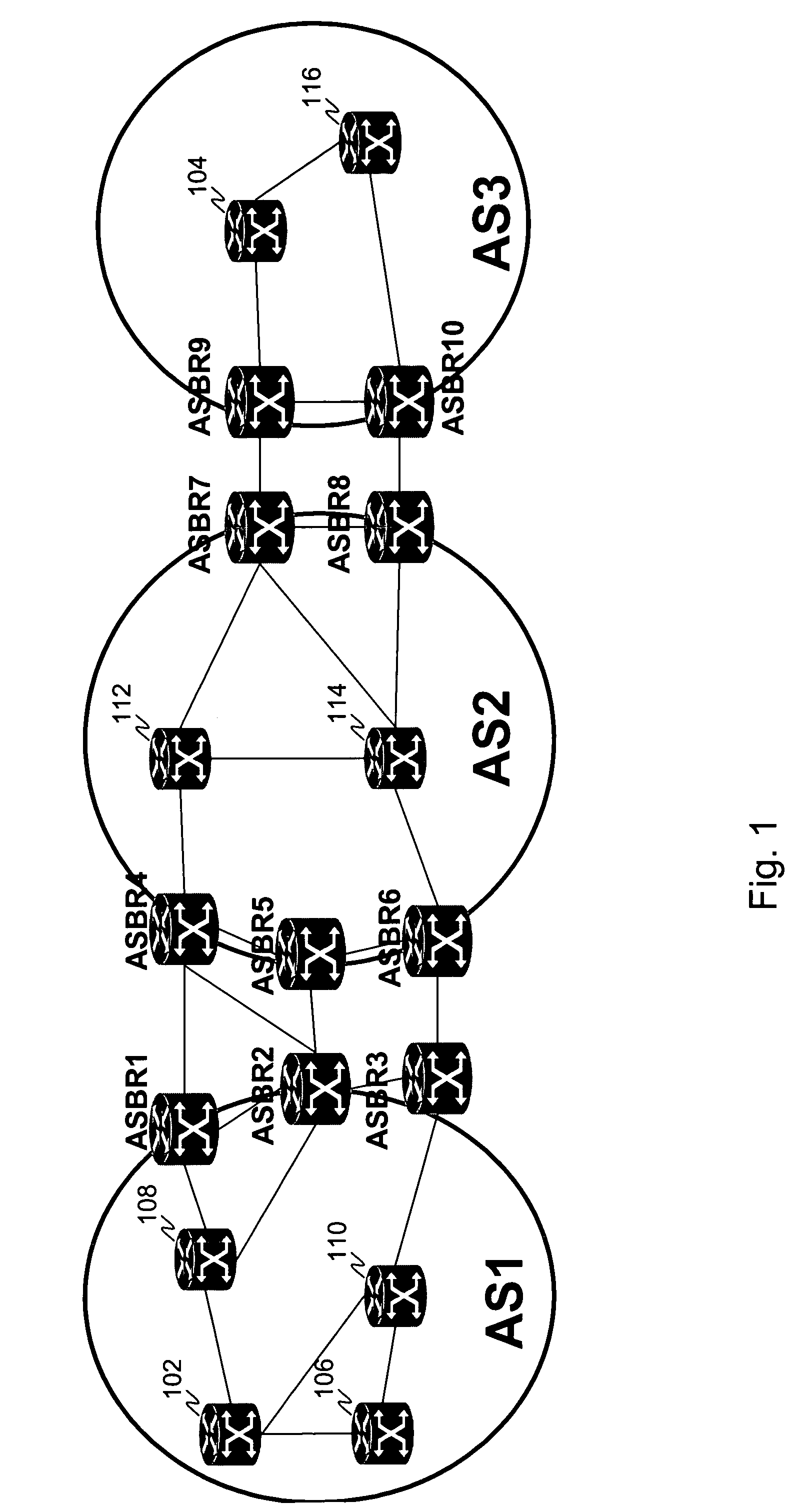
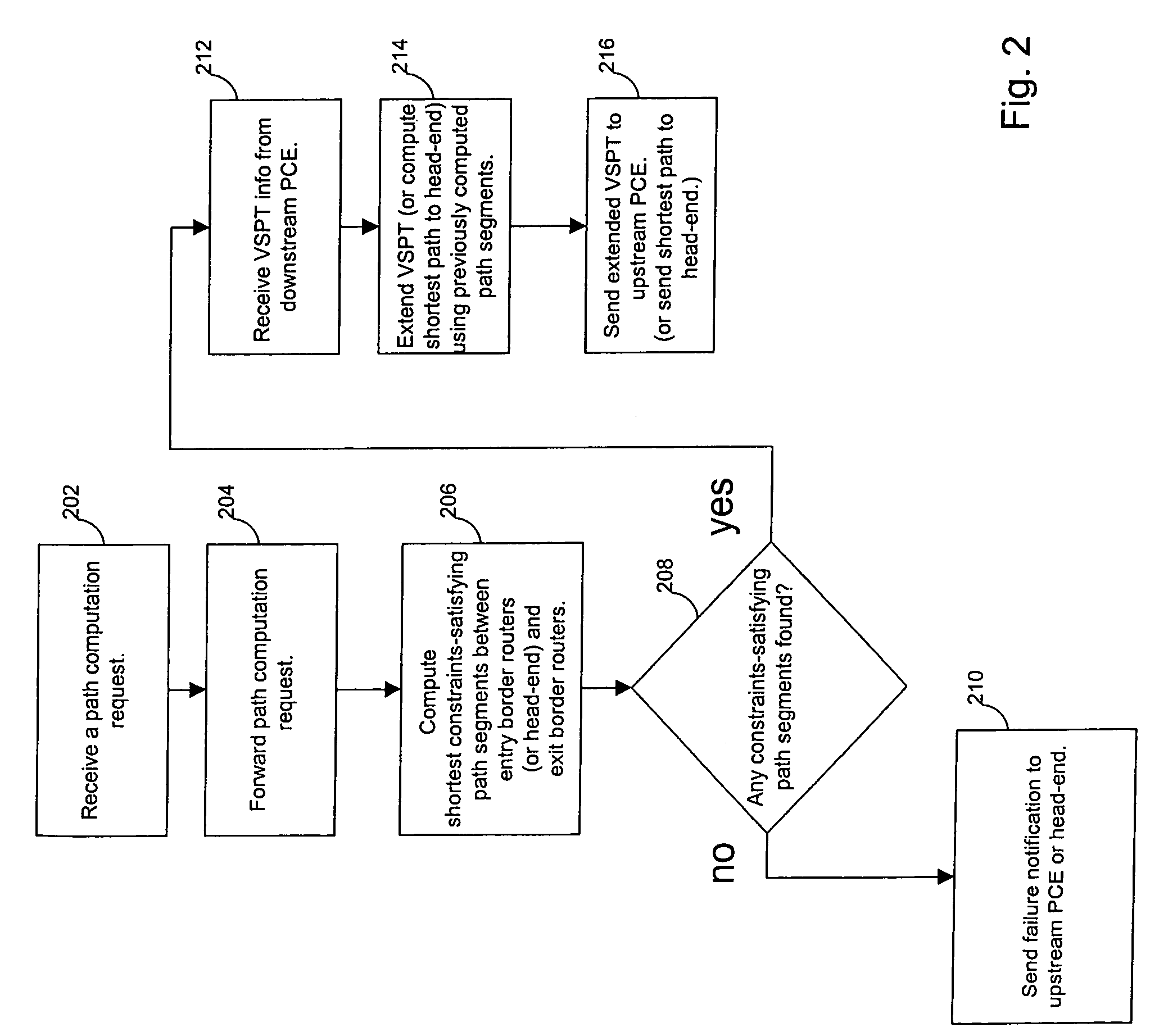
Computing inter-autonomous system MPLS traffic engineering LSP paths
InactiveUS20060039391A1Data switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsPath computation elementMpls traffic engineering
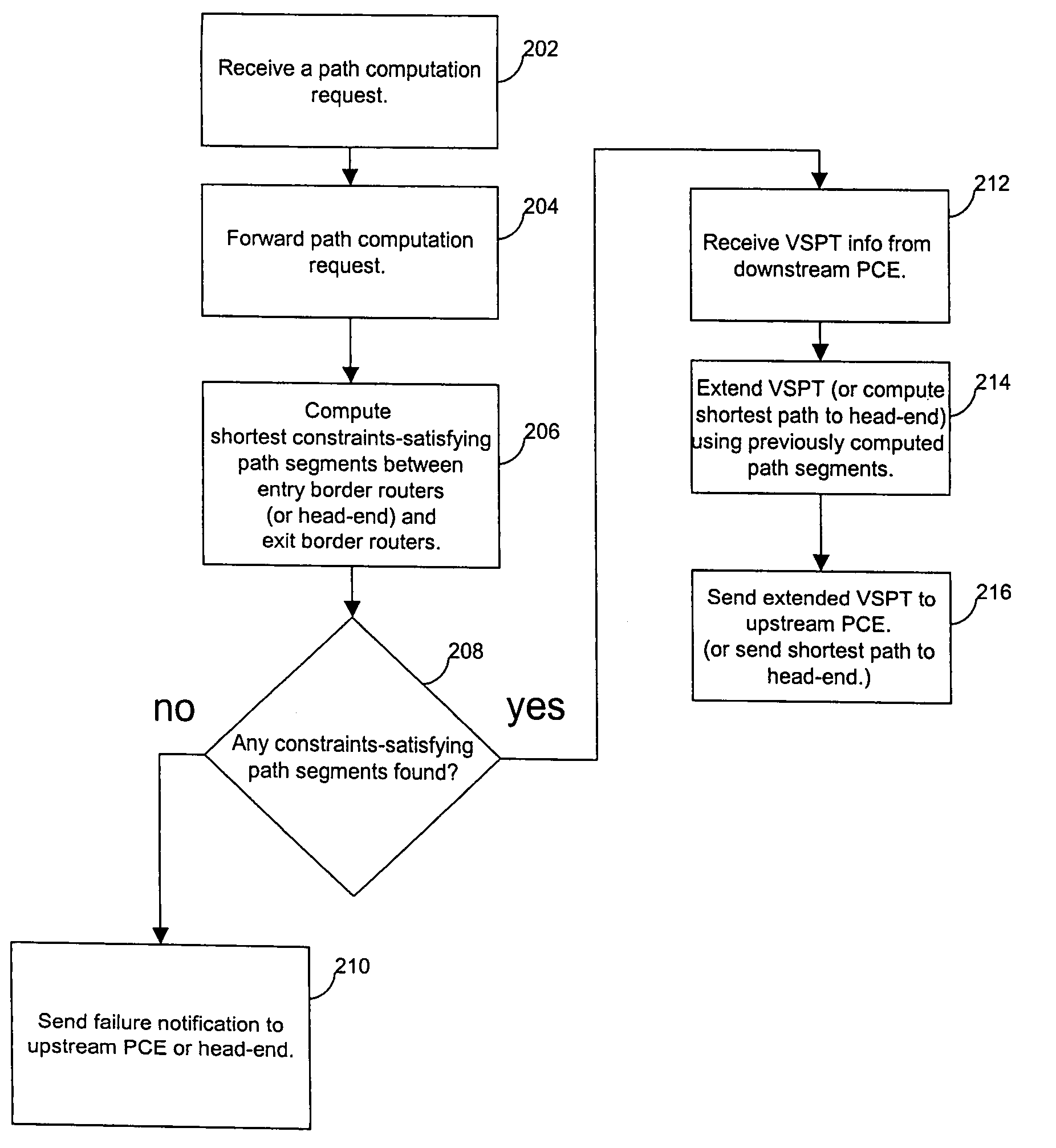
Systems and methods for computing the paths of MPLS Traffic Engineering LSPs across Autonomous System and / or area boundaries. A distributed path computation algorithm exploits multiple path computation elements (PCEs) to develop a virtual shortest path tree (VSPT) resulting in computation of an end-to-end optimal (shortest) path. In some implementations, the VSPT is computed recursively across all the Autonomous Systems and / or areas between the head-end and tail-end of the Traffic Engineering LSP.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
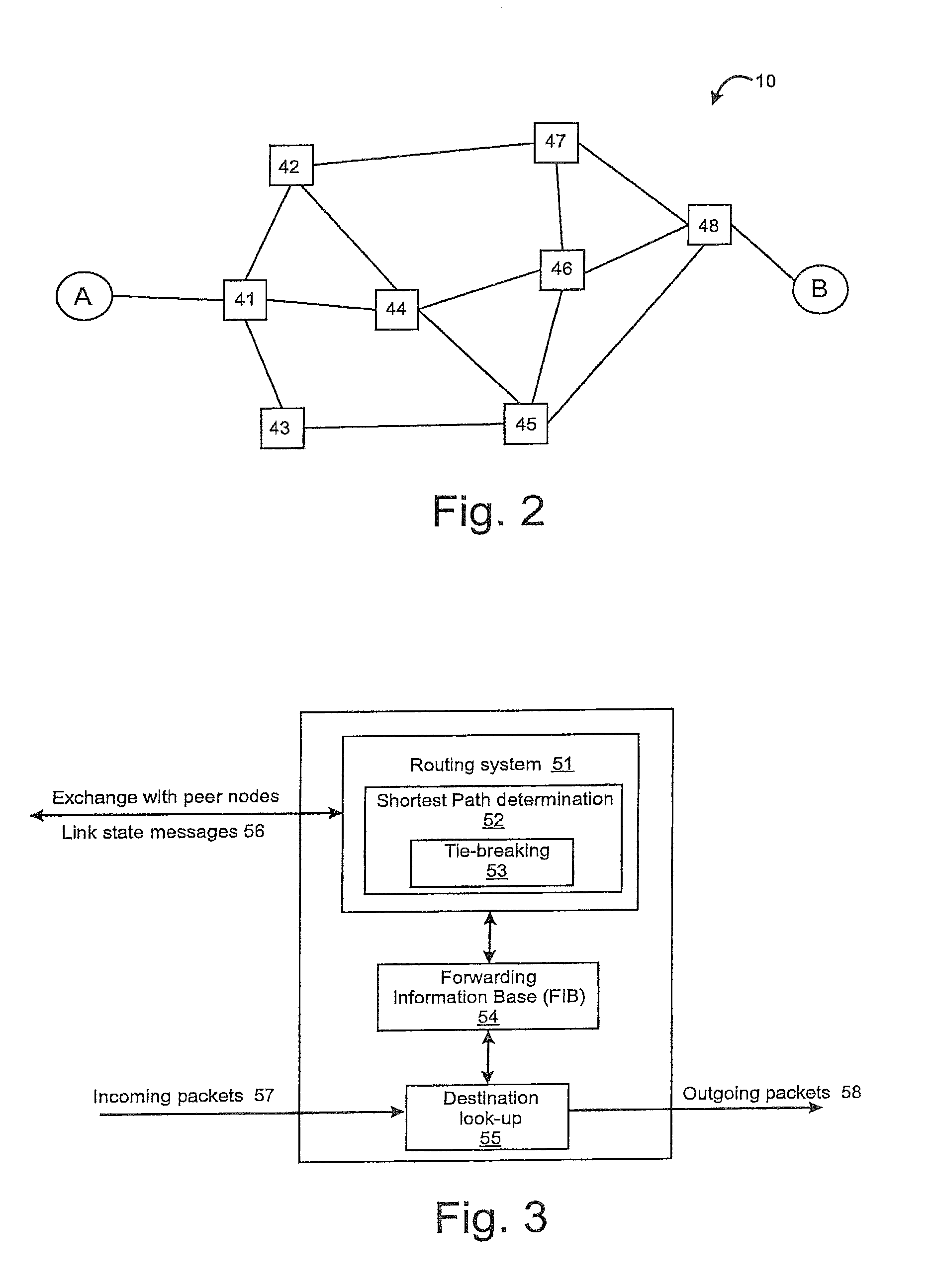
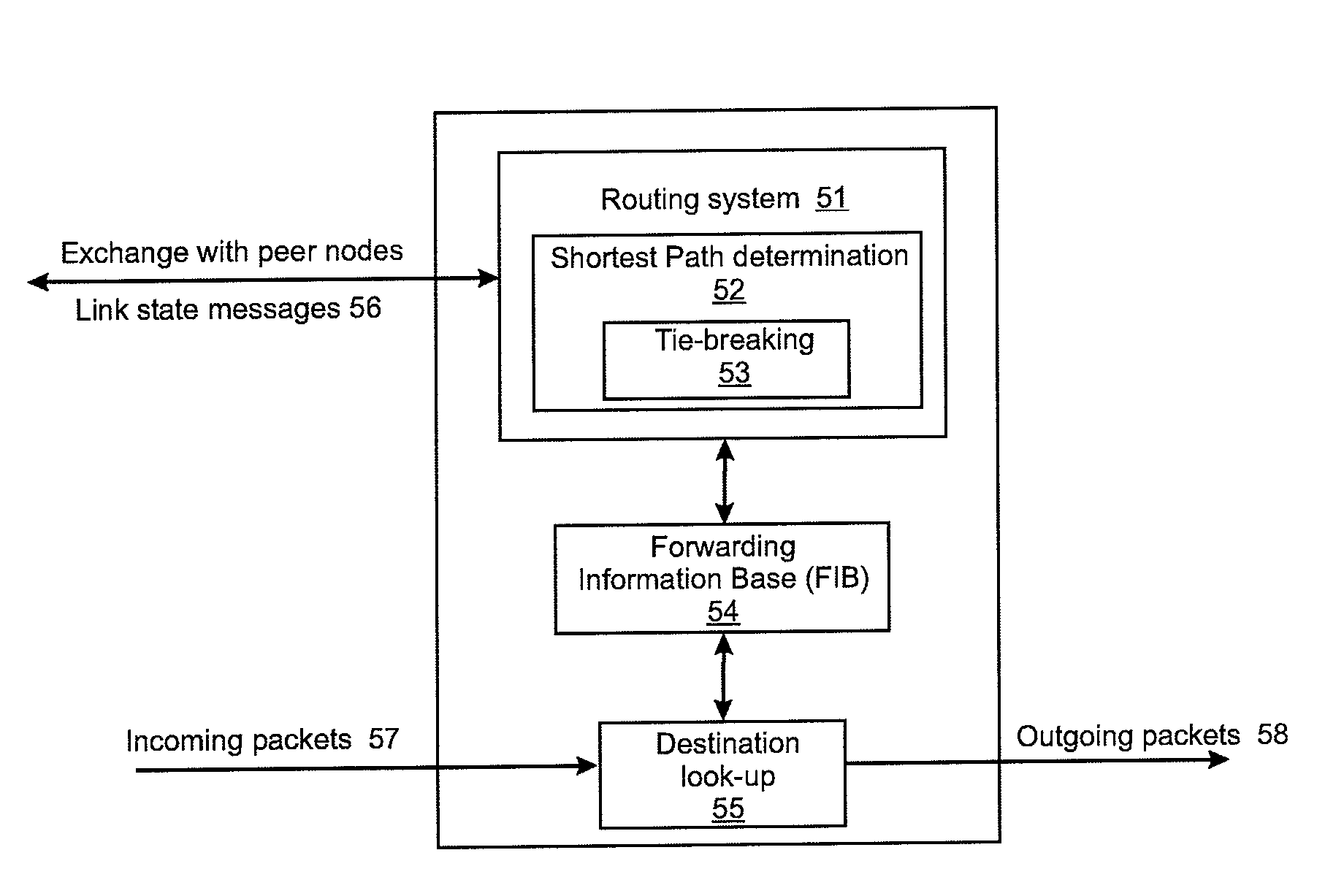
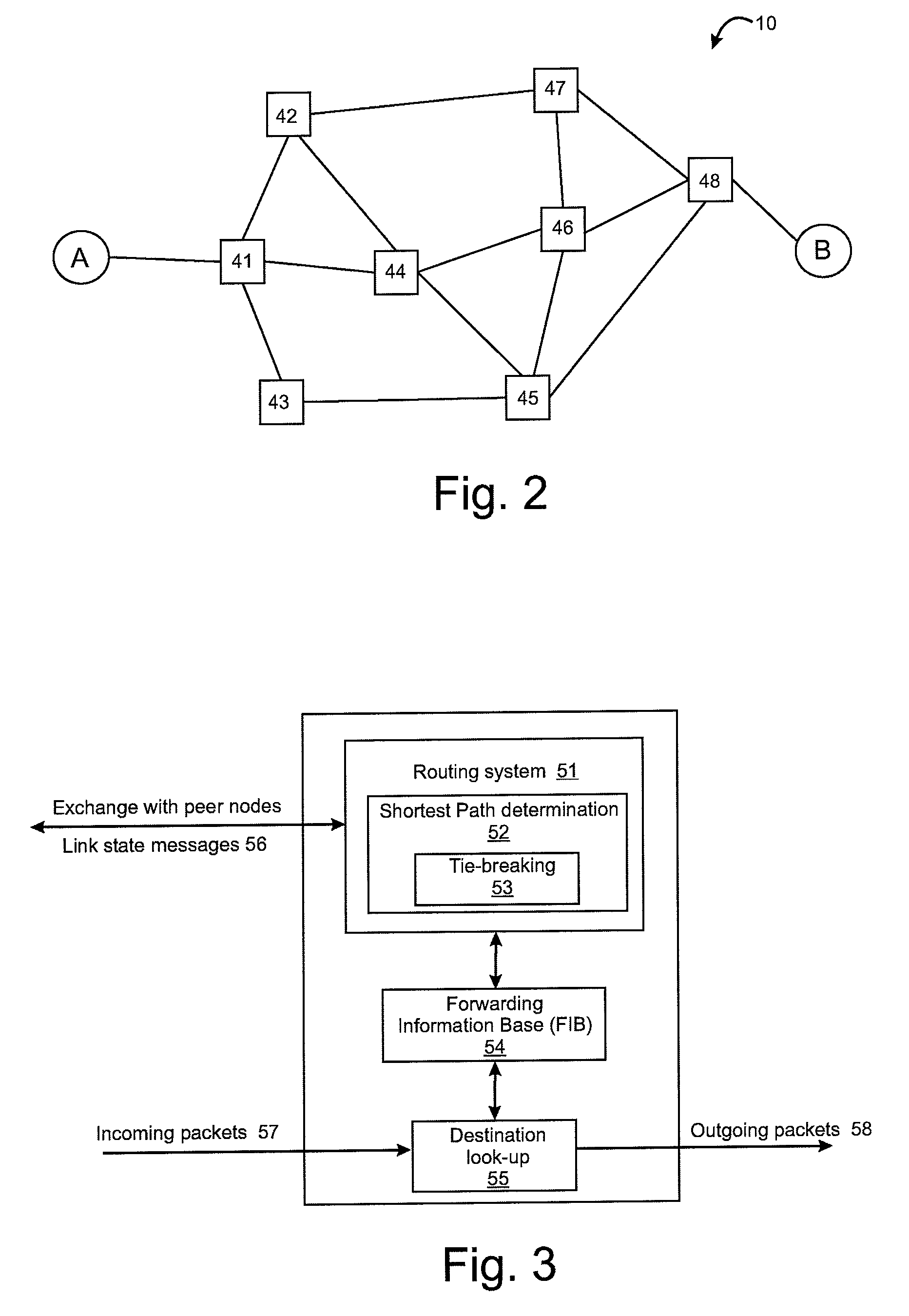
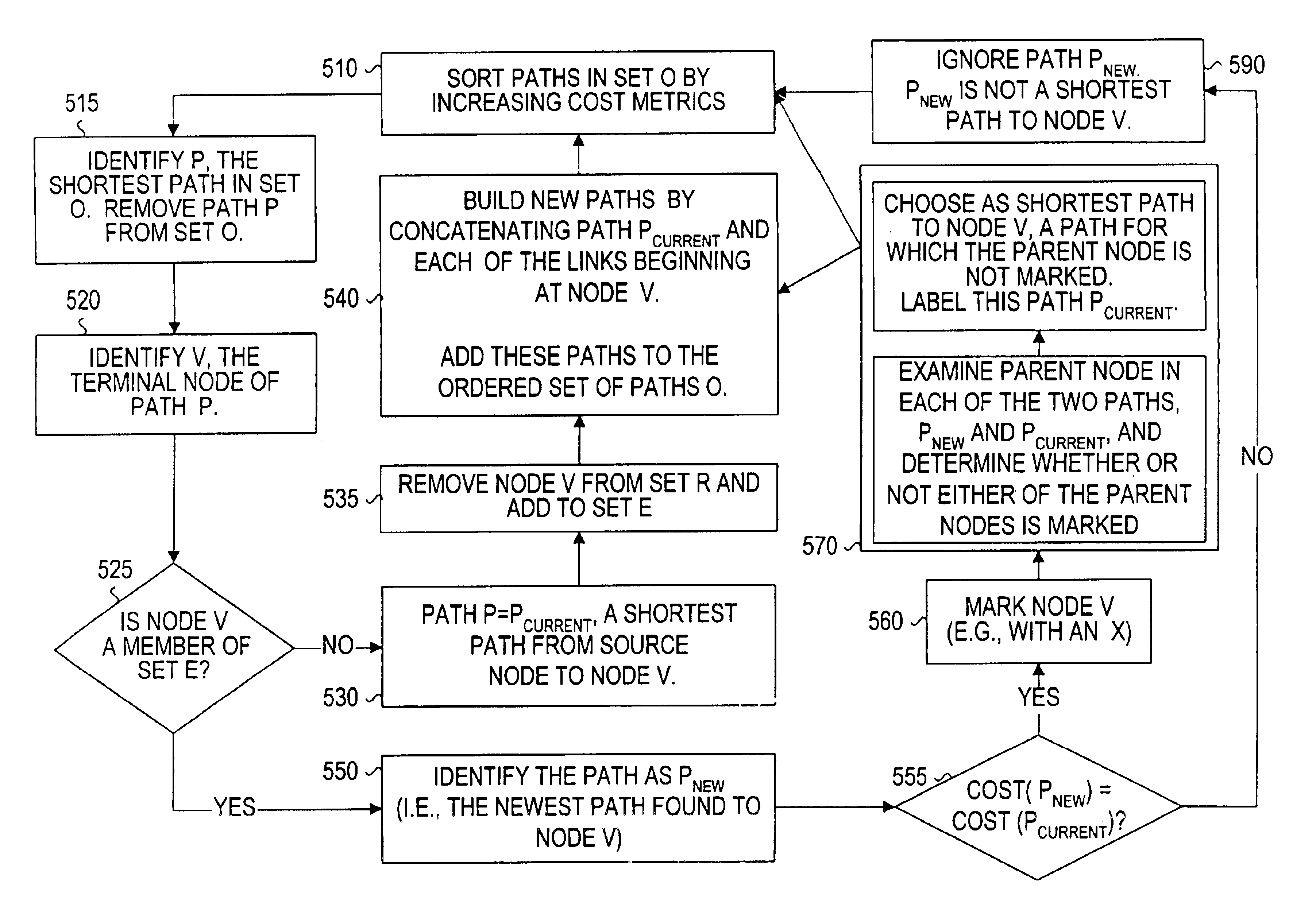
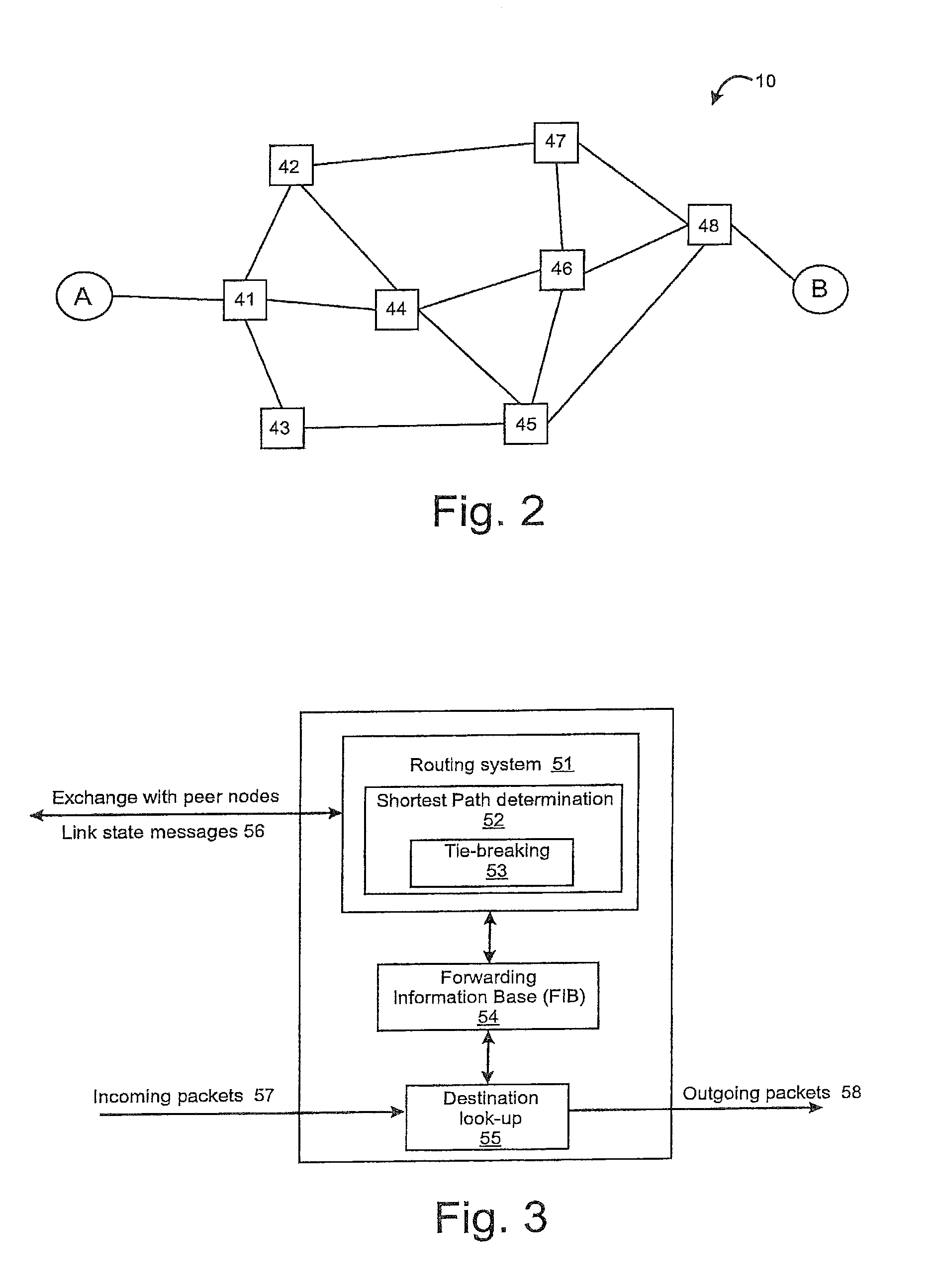
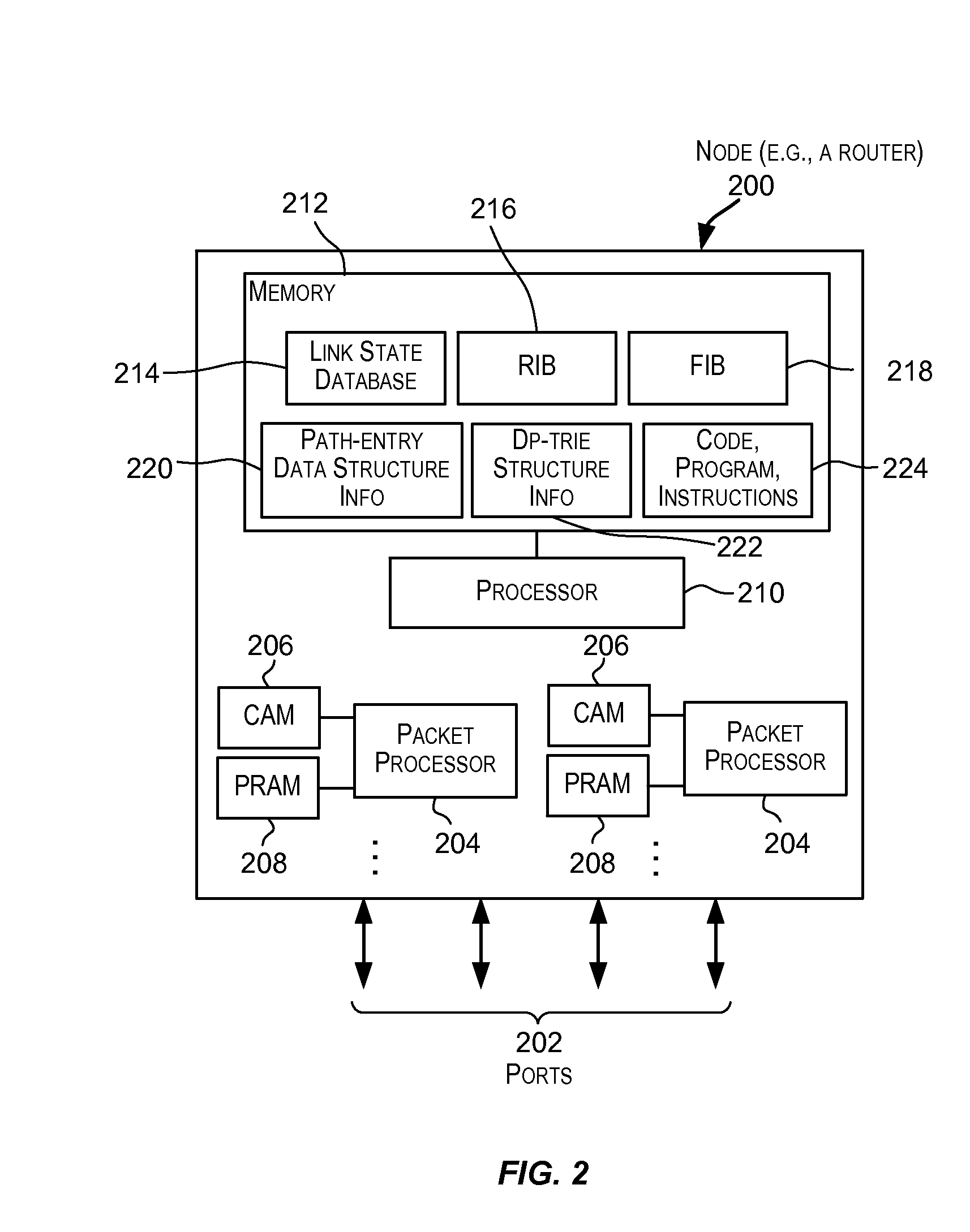
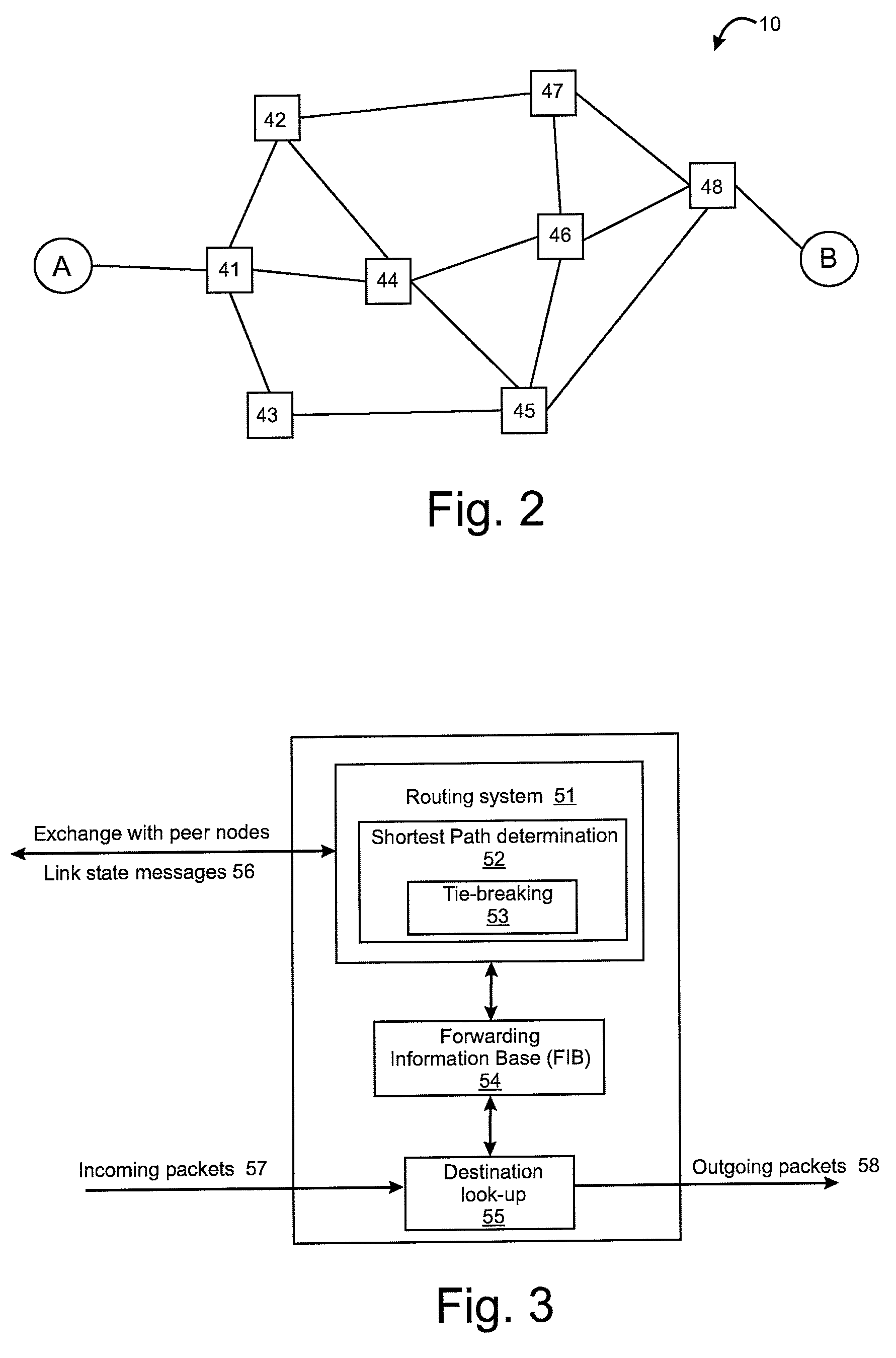
Tie-breaking in shortest path determination
InactiveUS8761022B2Simple calculationLower requirementError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic flowOrder set
A consistent tie-breaking decision between equal-cost shortest (lowest cost) paths is achieved by comparing an ordered set of node identifiers for each of a plurality of end-to-end paths. Alternatively, the same results can be achieved, on-the-fly, as a shortest path tree is constructed, by making a selection of an equal-cost path using the node identifiers of the diverging branches of the tree. Both variants allow a consistent selection to be made of equal-cost paths, regardless of where in the network the shortest paths are calculated. This ensures that traffic flow between any two nodes, in both the forward and reverse directions, will always follow the same path through the network.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Tie-Breaking in Shortest Path Determination
InactiveUS20090168768A1Simple calculationLower requirementData switching by path configurationTraffic flowDistributed computing
A consistent tie-breaking decision between equal-cost shortest (lowest cost) paths is achieved by comparing an ordered set of node identifiers for each of a plurality of end-to-end paths. Alternatively, the same results can be achieved, on-the-fly, as a shortest path tree is constructed, by making a selection of an equal-cost path using the node identifiers of the diverging branches of the tree. Both variants allow a consistent selection to be made of equal-cost paths, regardless of where in the network the shortest paths are calculated. This ensures that traffic flow between any two nodes, in both the forward and reverse directions, will always follow the same path through the network.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
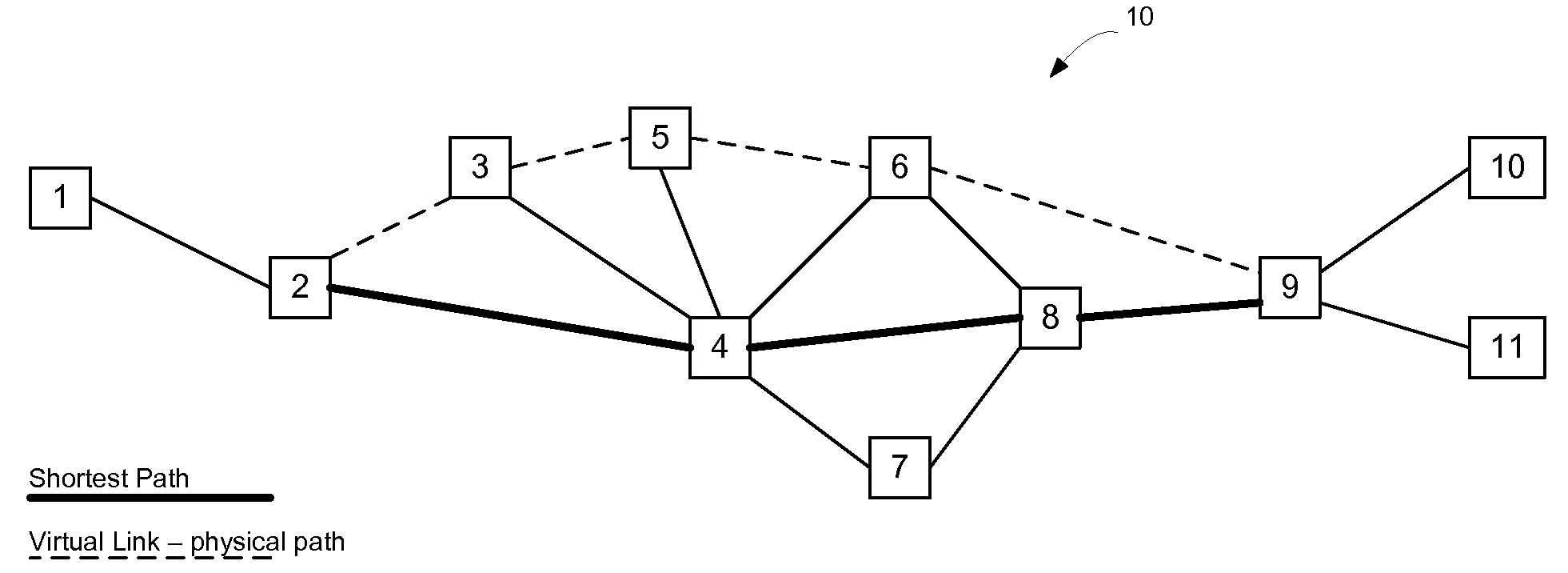
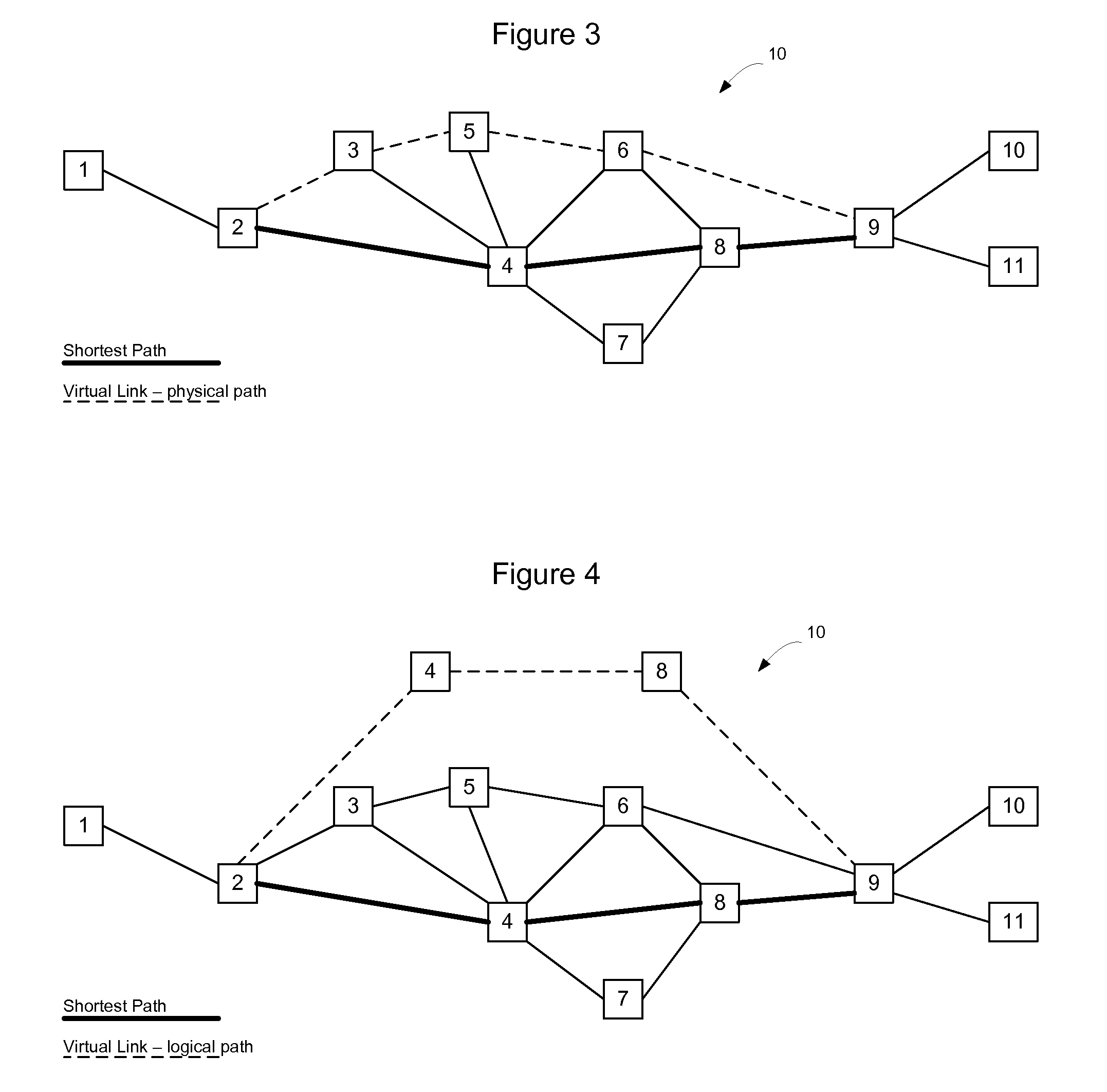
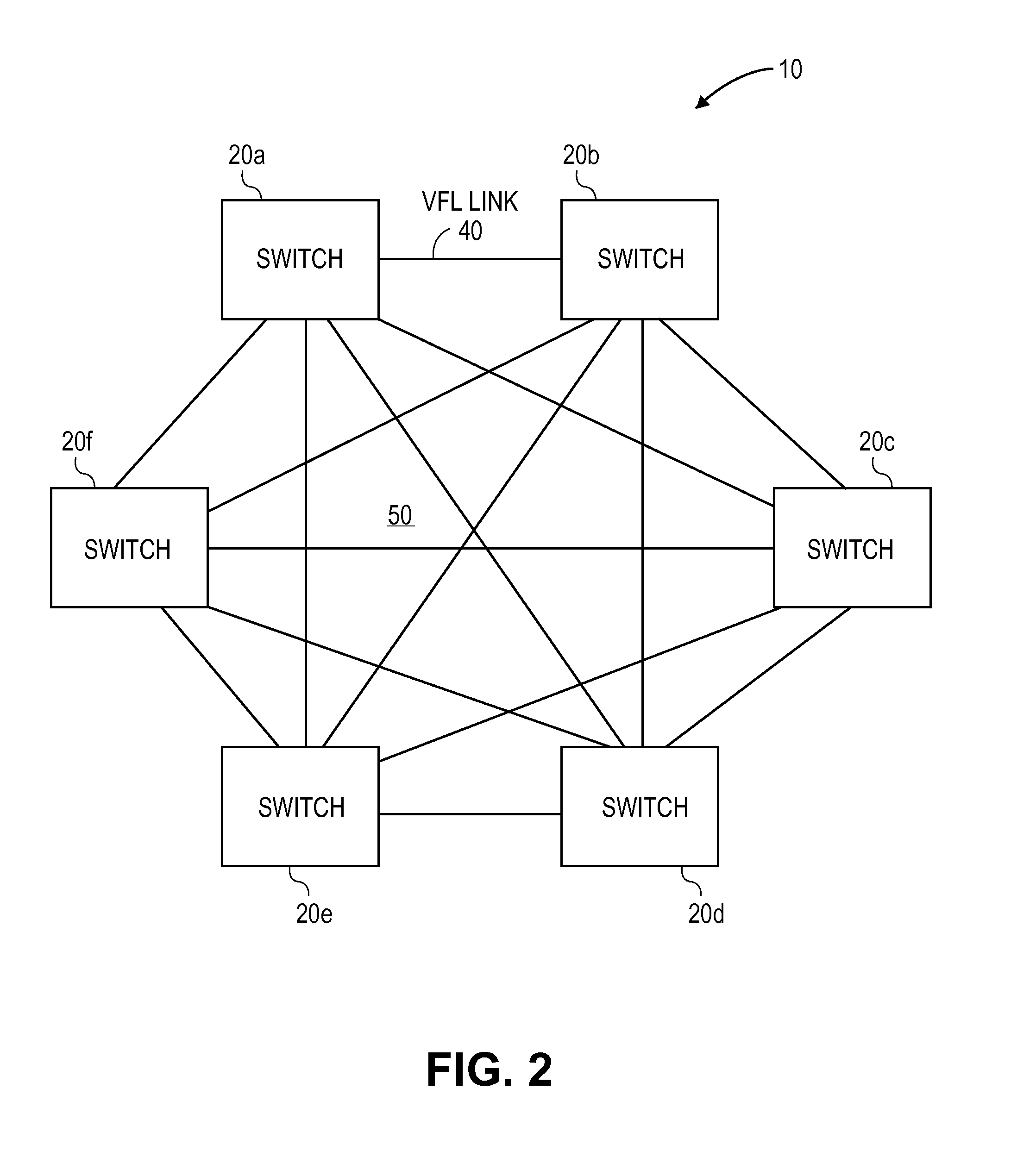
Virtual Links in a Routed Ethernet Mesh Network
ActiveUS20100272110A1Broad spectrum of traffic manipulationSame costData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityLogical view
Virtual links may be used to divert traffic within an Ethernet network without affecting overall traffic patterns on the Ethernet network. In one embodiment, the virtual link may be established on the network via a routing system in use on the network. Nodes on a defined path for the virtual link will install forwarding state for the virtual link so that traffic may follow the defined path through the network. The logical view of the virtual link, from a routing perspective however, has the same cost as the shortest path between the endpoints of the virtual link and, accordingly, does not affect other traffic patterns on the network. Once established, the end nodes on the virtual path will have two equal cost paths through the network—one following the shortest path tree and one along the path for the virtual link. The end nodes may use a tie breaking process in an Equal Cost Multi Path (ECMP) selection process to preferentially select the virtual link over the shortest path.
Owner:CIENA
Method and apparatus for discovering edge-disjoint shortest path pairs during shortest path tree computation
InactiveUS6928484B1Improve efficiencyReduced computing resourceError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsMethod selectionPath protection
A method for identifying and choosing a shortest path segment that has an alternate edge disjoint path segment. While routing Unidirectional Path Switched Ring (UPSR) path segments in a graph, there may be several equal distance paths to choose the shortest path from. Choosing a certain path as the shortest path may minimize or eliminate the chance of finding an alternative path segment. A method is provided such that if multiple shortest paths from the source node to a particular destination node exist, the method selects the shortest path which has an alternate edge disjoint path, and which can be used for path protection. The particular shortest path chosen by the method is not necessarily the first shortest path constructed.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Co-existing static and dynamic IP multicast
InactiveUS20060262792A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationAccess timeIp address
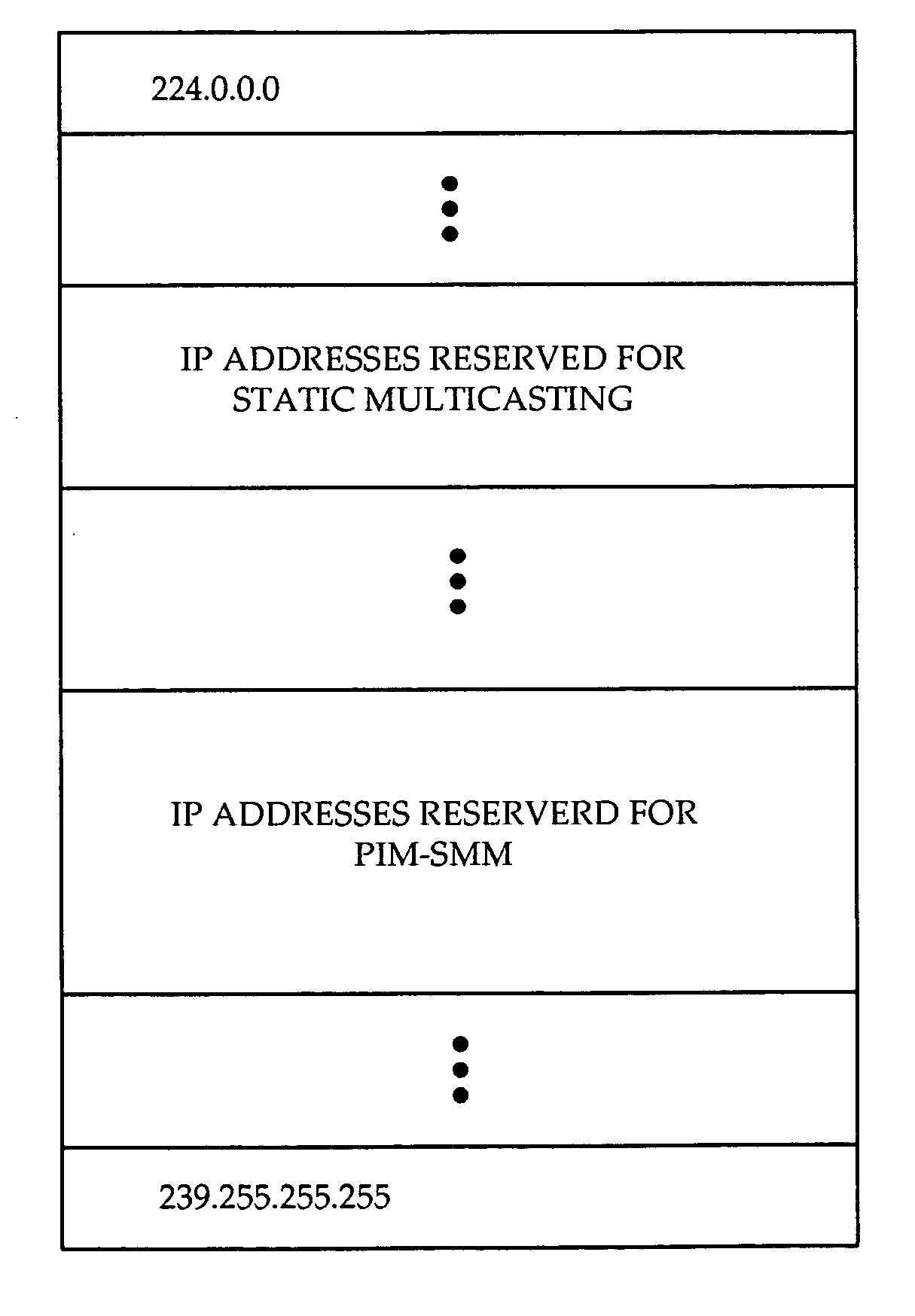
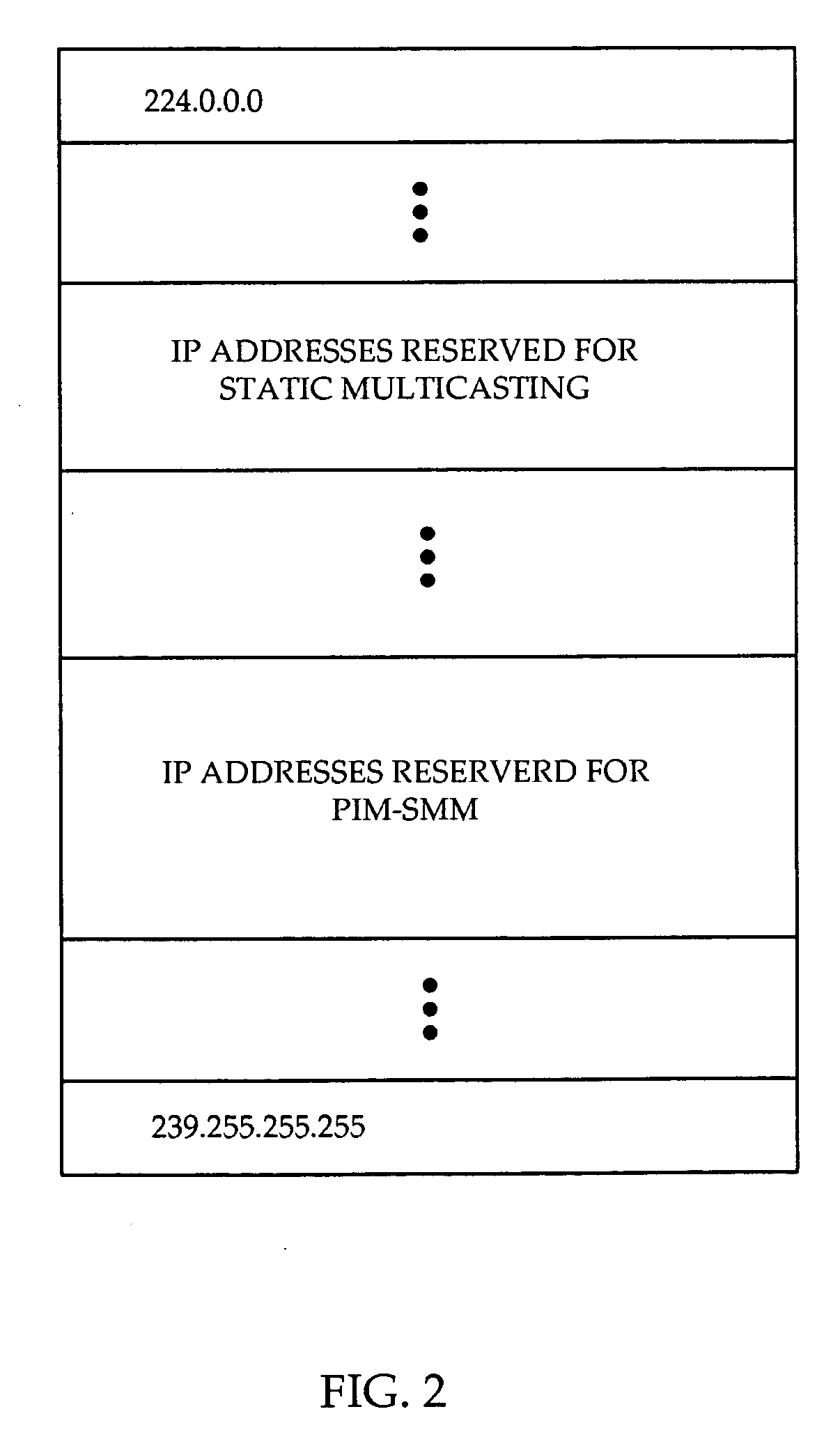
A system and method are provided for providing both static and dynamic IP multicasting. The concept of a multicast Static-Range is introduced which allows the coexistence of static and dynamic IP multicast. The multicast Static-Range is a set of Class D IP addresses which is reserved for static multicasting, and is configured at all routers. When a router receives a PIM message or an IGMP message, the router determines whether the group specified in the message is within the multicast Static-Range. If the group pertains to a static multicasting group, the router does not propagate the message to upstream routers using PIM-SM or PIM-SSM protocols, and only connects or disconnects interfaces internal to the router. If the multicast group address in the message is not within the multicast Static-Range, the router recognizes that the message pertains to a dynamic multicasting group and implements PIM or IGMP protocols as usual. If the invention is used for broadcasting TV, the low end of TB channels or commonly used channels can be created as static IP multicast. This way, a user can access or leave such channels without an entire shortest path tree being created or torn down, improving access time and channel surfing for a user. Also, pay-per-view, digital or less frequently used channels can be created using dynamic IP multicast with traditional PIM-SSM protocol, in order to make efficient use of router resources.
Owner:RPX CORP
Log-based traceback system and method using centroid decomposition technique
InactiveUS20100212013A1Reduce loadAttacked easilyMemory loss protectionData taking preventionShort path algorithmDecomposition
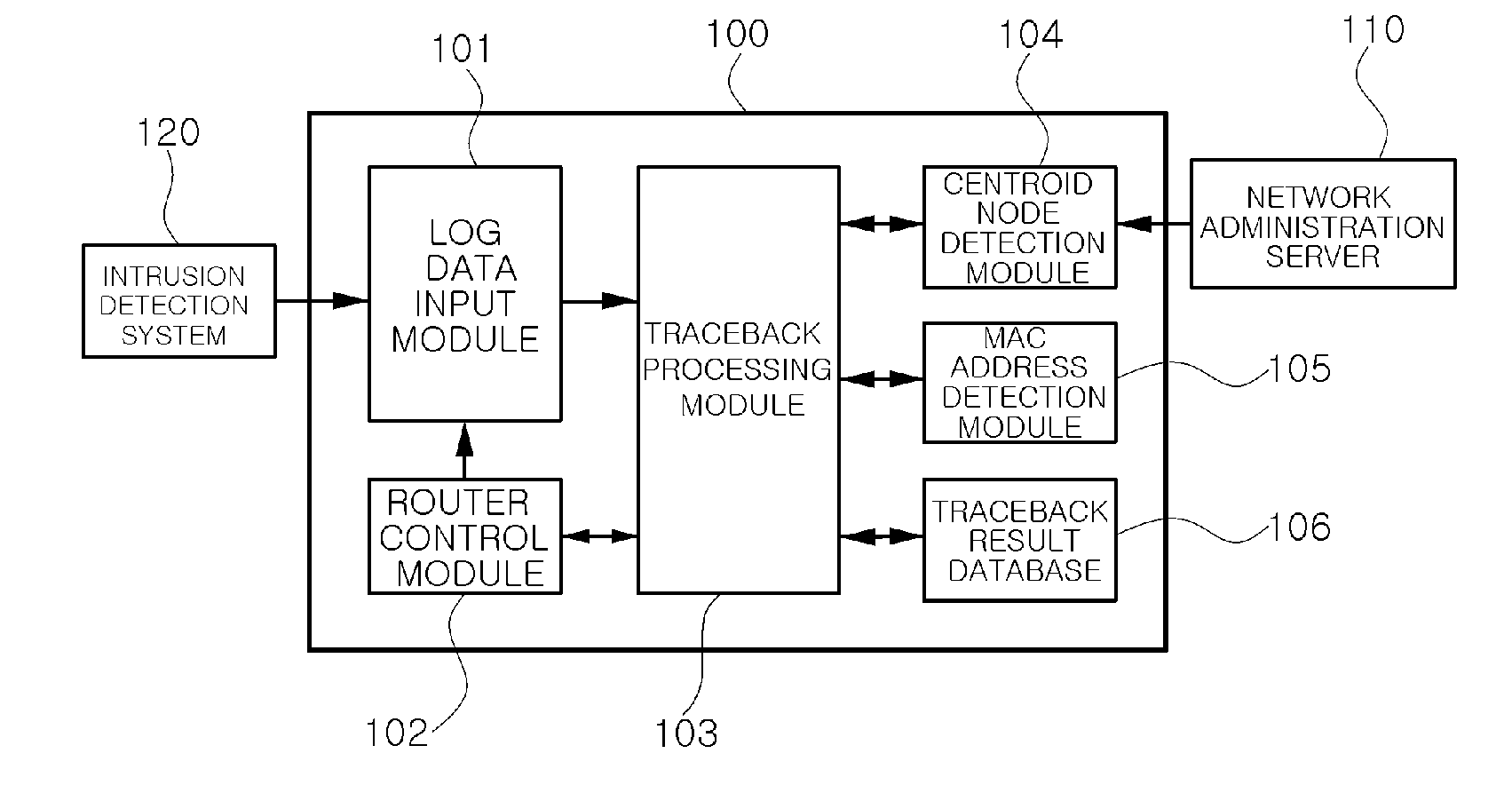
There are provided a system and method for tracing back an attacker by using centroid decomposition technique, the system including: a log data input module collecting log data of an intrusion alarm from an intrusion detection system; a centroid node detection module generating a shortest path tree by applying a shortest path algorithm to network router connection information collected by a network administration server, detecting a centroid node by applying centroid decomposition technique removing a leaf-node to the shortest path tree, and generating a centroid tree whose node of each level is the detected centroid node; and a traceback processing module requesting log data of a router matched with the node of each level of the centroid tree, and tracing back a router identical to the log data of the collected intrusion alarm as a router connected to a source of an attacker by comparing the log data of the router with the log data of the collected intrusion alarm. According to the system and method, an attacker causing a security intrusion event may be quickly detected, a load on the system is reduced, and a passage host exposed to a danger or having weaknesses may be easily recognized, thereby easily coping with an attack.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
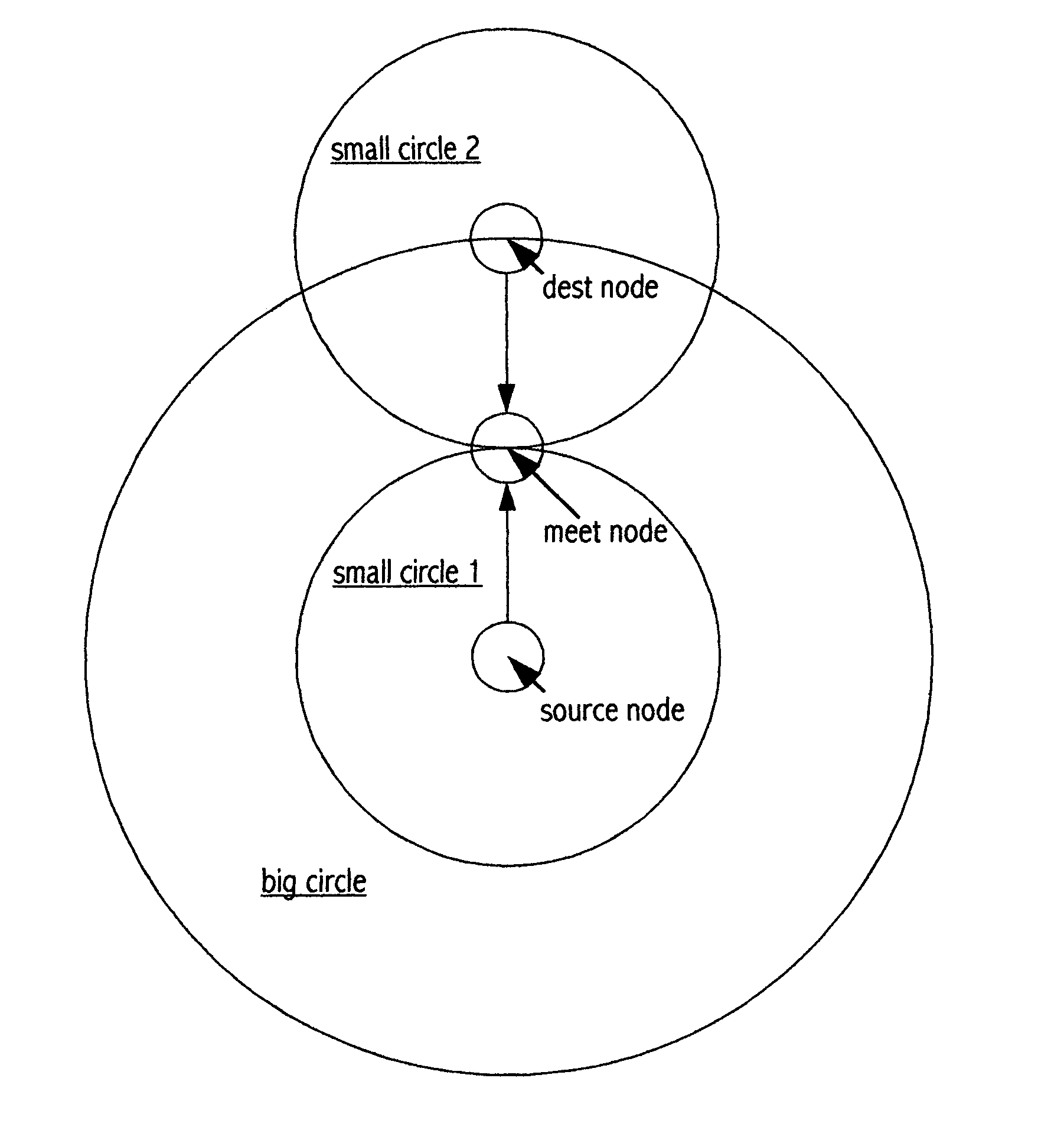
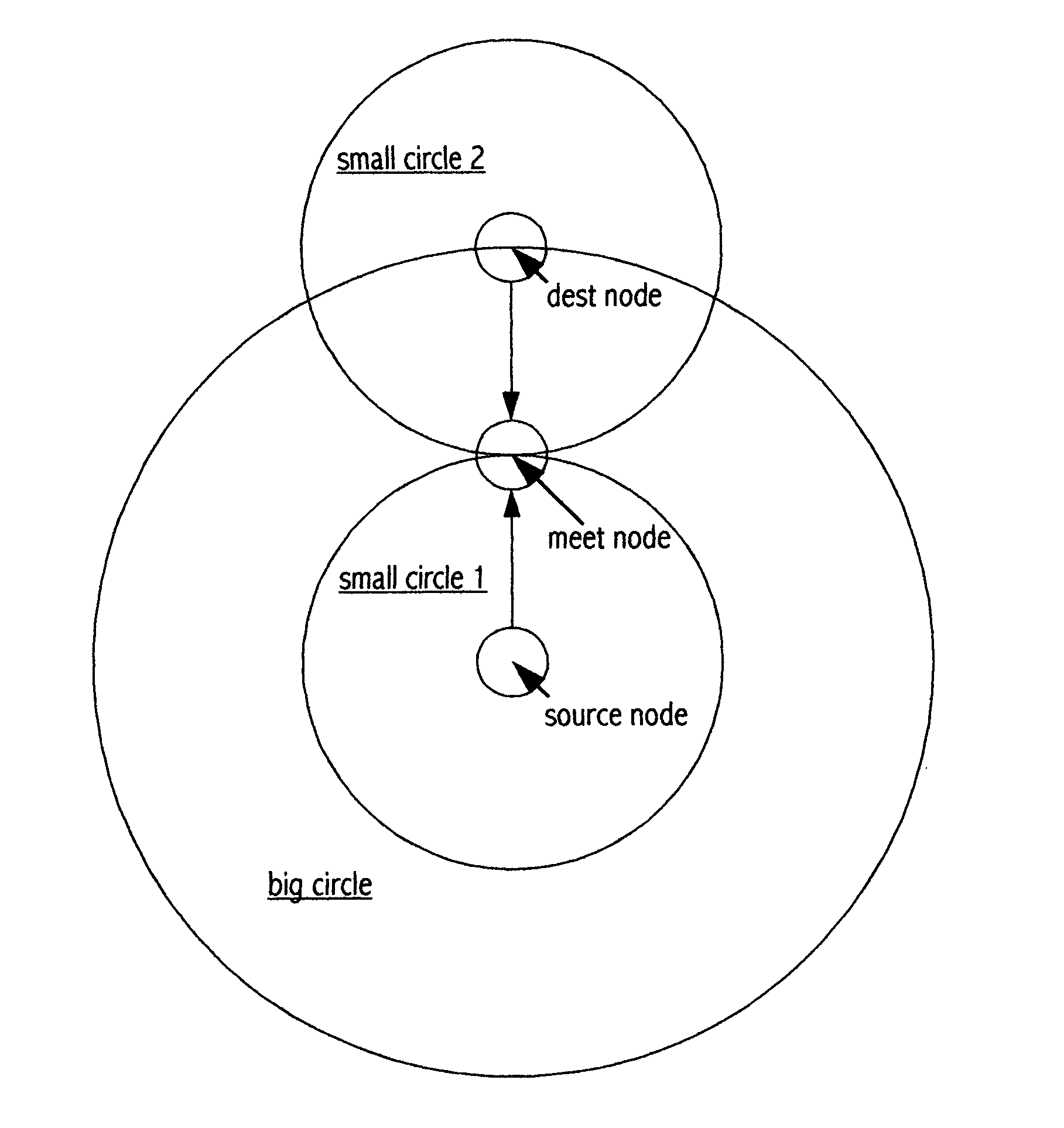
Shortest path search method "Midway"
InactiveUS7280481B2Reduce overheadLess timeError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsShort path algorithmShortest path search
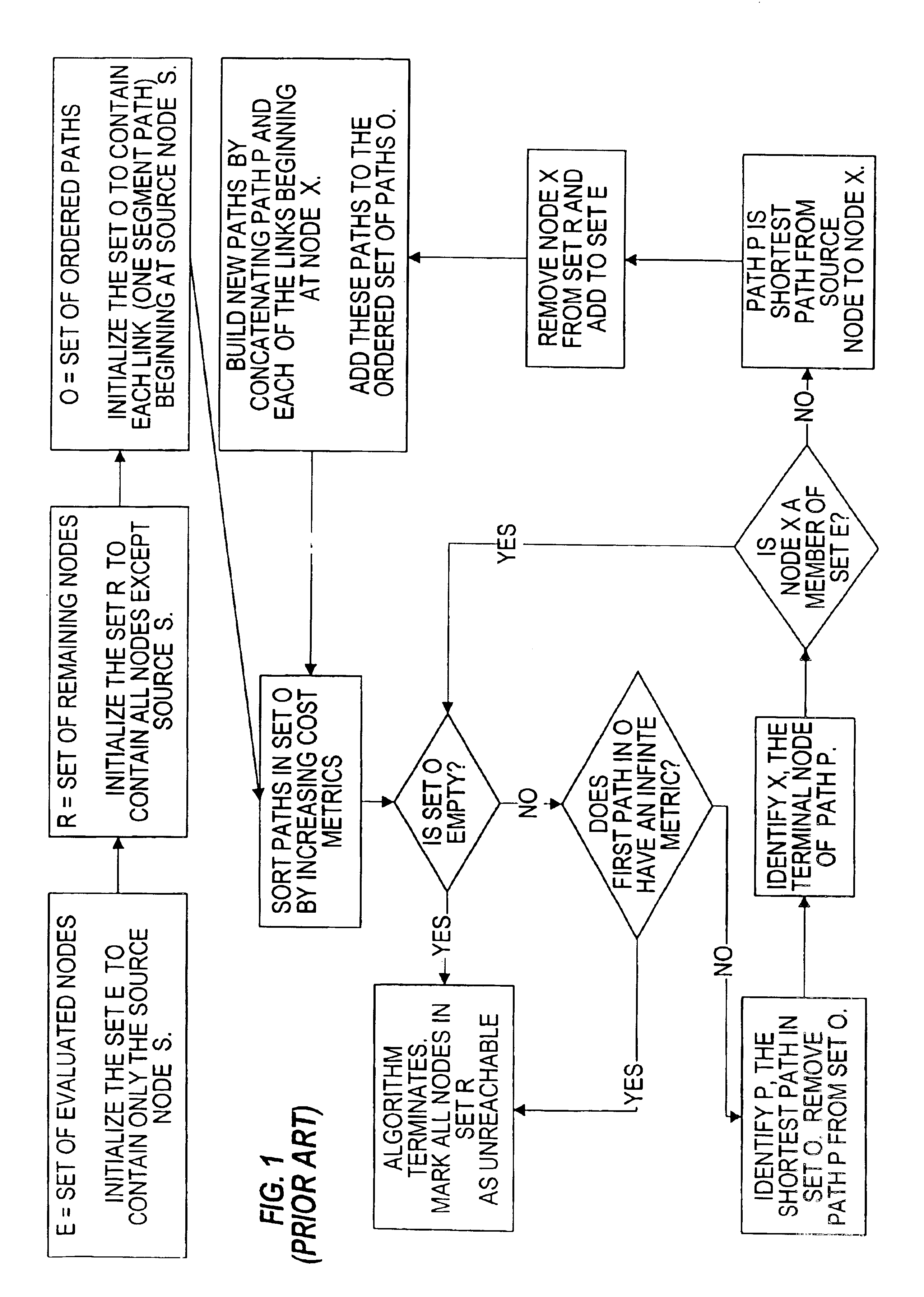
A method of searching for a shortest path from a single source node to a single destination node in a two dimensional computer network. The method is similar to Dijkstra shortest path algorithm (“Dijkstra”) in the way it builds a shortest path tree. However, instead of starting from the source node and searching through to the destination node as Dijkstra does, the method runs a shortest path search from both ends (i.e. source and destination) simultaneously or alternatively, until a shortest path tree from one end meets a shortest path tree from the other end at an intermediate node, and the concatenated path (source node intermediate node-destination node) satisfies a condition. Conditions other than those used by Dijkstra determine when the search should terminate, and whether the search has succeeded or failed. It has been verified that the new method requires less overhead and time than Dijkstra.
Owner:RONG GUANGYI DAVID
Service Instance Applied to MPLS Networks
InactiveUS20100124225A1Data switching by path configurationSecuring communicationShort path treeNetwork domain
Domain-wide unique node identifiers and domain-wide unique service identifiers are distributed within a MPLS domain using routing system LSAs. Nodes on the MPLS network compute shortest path trees for each destination and install unicast forwarding state based on the calculated trees. Nodes also install multicast connectivity between nodes advertising common interest in a common service identifier. Rather than distributing labels to be used in connection with unicast and multicast connectivity, the nodes deterministically calculate the labels. Any number of label contexts may be calculated. The labels may either be domain wide unique per unicast path or per multicast, or may be locally unique and deterministically calculated to provide forwarding context for the associated path. Multicast and unicast paths may be congruent, although this is not a requirement.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Shortest path search method "Midway"
InactiveUS20040073702A1Error preventionTransmission systemsShortest path searchTheoretical computer science
"Midway" is a new method to search for a shortest path from a single source node to a single destination node in a two dimensional computer network. It is similar to Dijkstra shortest path search algorithm in the way to build a shortest path tree, but it is different from Dijkstra algorithm in the following points. Instead of starting from the source node and searching all the way through to the destination node as what Dijkstra algorithm does, Midway runs shortest path search from both ends (i.e. source and destination) simultaneously or alternatively, until a shortest path from one end meets a shortest path from the other end on midway. Algorithms are designed to run shortest path search from both ends, and conditions other than those used by Dijkstra are defined to determine when the search should terminate. It has been verified that the new search method takes much less overhead and time than Dijkstra to find a shortest path.
Owner:RONG GUANGYI DAVID
Computing inter-autonomous system MPLS traffic engineering LSP paths
Systems and methods for computing the paths of MPLS Traffic Engineering LSPs across Autonomous System and / or area boundaries. A distributed path computation algorithm exploits multiple path computation elements (PCEs) to develop a virtual shortest path tree (VSPT) resulting in computation of an end-to-end optimal (shortest) path. In some implementations, the VSPT is computed recursively across all the Autonomous Systems and / or areas between the head-end and tail-end of the Traffic Engineering LSP.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
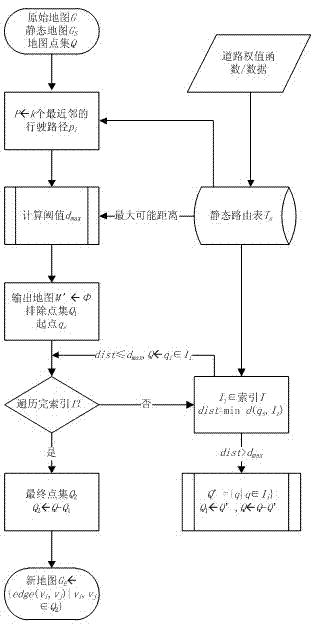
K nearest neighbor search method for variable weight network
InactiveCN102810118AReduce in quantityNarrow searchSpecial data processing applicationsPathPingRouting table
The invention relates to a k nearest neighbor search method for a variable weight network. The method comprises the steps as follows: routing thinking in a computer network is led in k nearest neighbor query, and predecessor / subsequent information in shortest path tree obtained in computation is taken as history data and is saved in a routing table by designing an update strategy of the routing table. Due to the dynamical update strategy of the routing table, the routing mechanism can adapt to dynamic changes of local road weights in a road net. The k nearest neighbor search method provides the candidate set screening rule and the road net area cutting rule of a non-mobile object as well as the position prediction method and the candidate set screening rule of a mobile object in the dynamical road net, effectively reduces the number of candidate points and narrows down the search range of the k nearest neighbor query, and avoids the defect that indexing and constraint conditions are adjusted frequently because the changes of a k nearest neighbors algorithm are caused by the road weights continuously in the conventional dynamical road net extended from a static road net.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
Tie-breaking in shortest path determination
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Method, head node and tail node of forwarding multicasting message
InactiveCN101588296ASpecial service provision for substationNetworks interconnectionComputer networkLabel switching
The invention provides a method, head node and tail node of a forwarding multicasting message, where the method includes: the head node the multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) traffic engineering (TE) tunnel transmits the path message to the tail node of the MPLS TE tunnel through the main label switching path of the MPLS TE tunnel; the tail node acquires the range of the multicasting address supported by the MPLS TE tunnel from the path message; the tail node transmits the adding message in the multicasting address range by the requested multicasting address through the MPLS TE tunnel; after the head node receives the adding message transmitted by the tail node, the head node adds the MPLS TE tunnel interface to the shortest path tree (SPT) outlet interface list corresponding to the multicasting address requested by the adding message; after the head node receives the multicasting message, the head node transmits the multicasting message according to the SPT outlet interface list corresponding to the multicasting address of the multicasting message.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
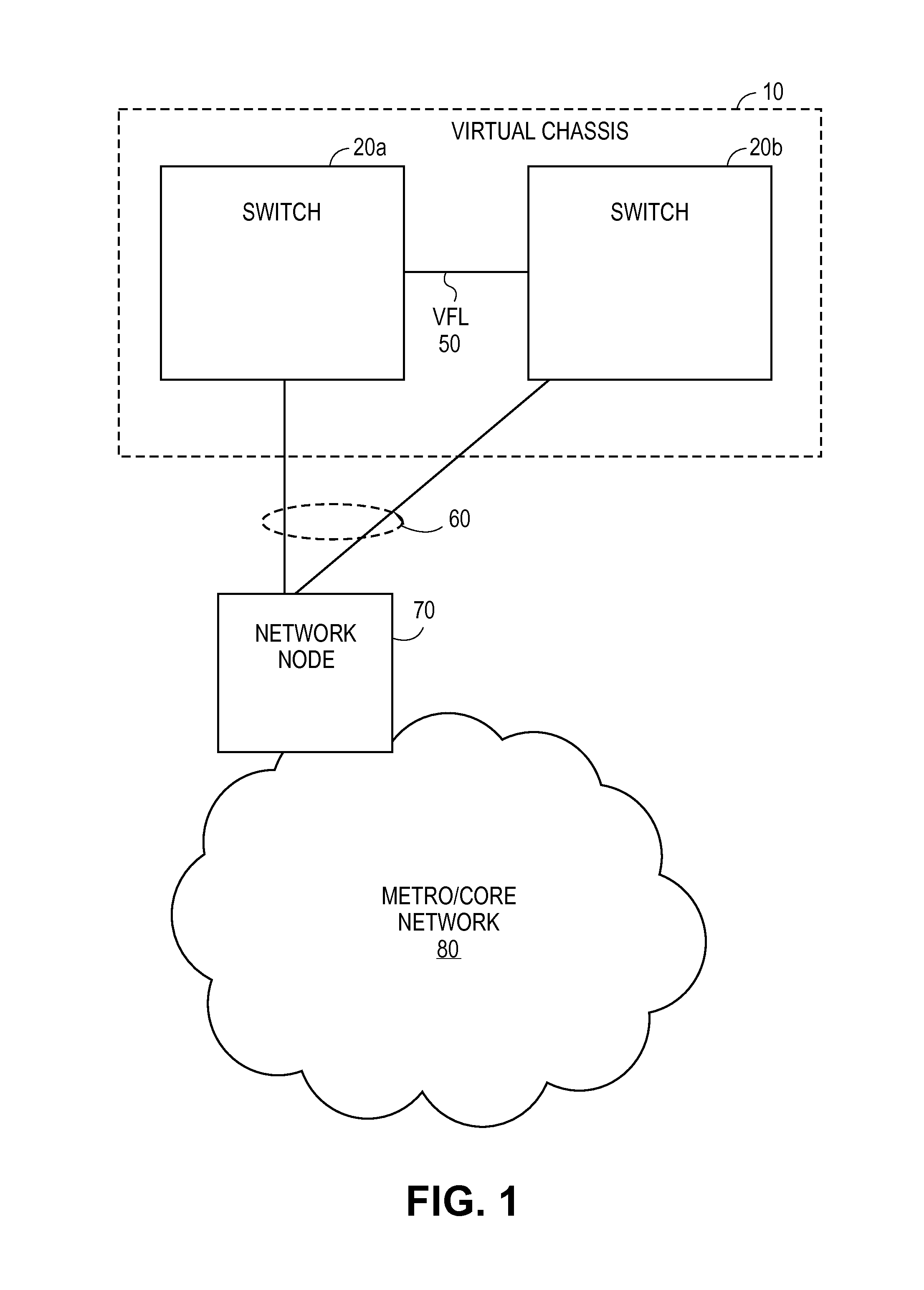
Virtual Chassis Topology Management
Topology management within a virtual chassis is achieved by communicating virtual chassis topology information between switches within the virtual chassis within protocol extensions of customized protocol data units (PDUs) associated with a VC-ISIS protocol. The virtual chassis topology information can be used, for example, to detect the topology of the virtual chassis and generate a shortest path tree within each switch of the virtual chassis for use in routing between switches within the virtual chassis.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Method and apparatus for updating a shortest path graph
InactiveUS7593341B1Error preventionTransmission systemsTheoretical computer scienceDijkstra's algorithm
A method and apparatus for updating a shortest path graph or a shortest path tree are disclosed. For example, an arc weight is changed for an arc in the network, where a plurality of affected nodes in the network is determined. The distance of each of the affected nodes is determined, where a subset of the plurality of affected nodes is then placed in a heap. One aspect of the present invention is that not all the affected nodes are placed in the heap. In one embodiment, the present reduced heap approach only applies the Dijkstra's algorithm to those affected nodes whose distances change in a smaller amount that the change in the arc weight. In turn, the shortest path graph or the shortest path tree is updated in accordance with the affected nodes placed in the heap.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Dynamic routing of optical signals in optical networks
InactiveUS20100086306A1Risk minimizationReduced availabilityWavelength-division multiplex systemsData switching by path configurationUltrasound attenuationShort path algorithm
A method for dynamic routing an optical signal in an optical network is provided, including: executing a shortest-path algorithm receiving input concerning a source node, a destination node and the topology of the network, providing a shortest-path tree comprising nodes and arcs connecting the nodes, the shortest-path tree comprising branches along which an effective attenuation is no greater than a predetermined limit, each branch comprising an end node and each end node being associated with a corresponding set of wavelengths; checking, for each end node having no wavelength conversion resources and for each wavelength, if the end node is connected to at least another node external to the branch through the wavelength; excluding, for any end node if the result of the checking is negative for at least one wavelength, the at least one wavelength from the corresponding set of wavelengths, thus updating the topology; and re-executing the shortest-path algorithm.
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
Techniques for efficiently updating routing information upon shortest path tree computation
ActiveUS20110044351A1Efficient updateShorten the timeData switching by path configurationShortest-path treeDistributed computing
Techniques for efficiently updating routing information in a network device such as a router. According to an embodiment of the present invention, information is stored identifying one or more nodes and leaves owned or advertised by the nodes. When a change occurs in a network environment, information is stored identifying one or more nodes and leaves that have changes associated with them. The routing information in the network device is then updated for only those nodes and leaves that have changes associated with them.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Tie-breaking in shortest path determination
InactiveUS7911944B2Simple calculationLower requirementError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsNODALTraffic flow
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Route bridging method, network bridge equipment and bridging network
The invention discloses a path bridging method, network bridge equipment and a bridged network. The route bridging method comprises the steps that: all nodes in the bridged network respectively calculate the shortest path tree which takes the node as a root; a first node determines an output port reaching a second node according to the shortest path tree which takes the first node as the root and is calculated by the first node, and transmits a notification protocol message through the output port so as to lead the nodes receiving the notification protocol message to acquire that an input port of the notification protocol message belongs to a shortest path tree topology which takes the second node as the root; the first node determines the input port of the notification protocol message transmitted by other nodes; the first node adds the determined output port and input port to the shortest path tree topology which takes the second node as the root; and the first node transmits data frames according to the ports contained in the shortest path tree topology which takes the second node as the root. The shortest path tree topology can be based on VLAN, and also multicast MAC address. The implementation mode perfects the shortest path bridging technology.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
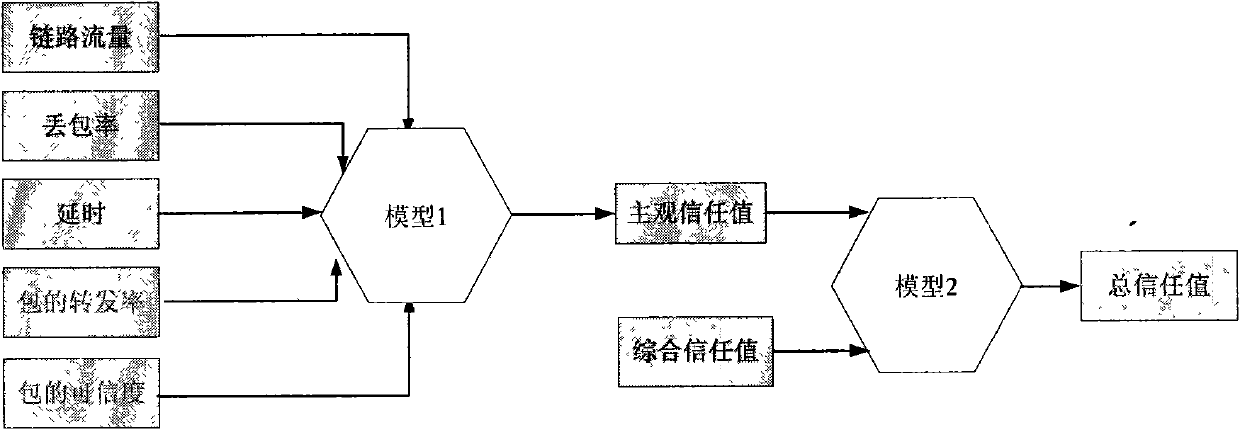
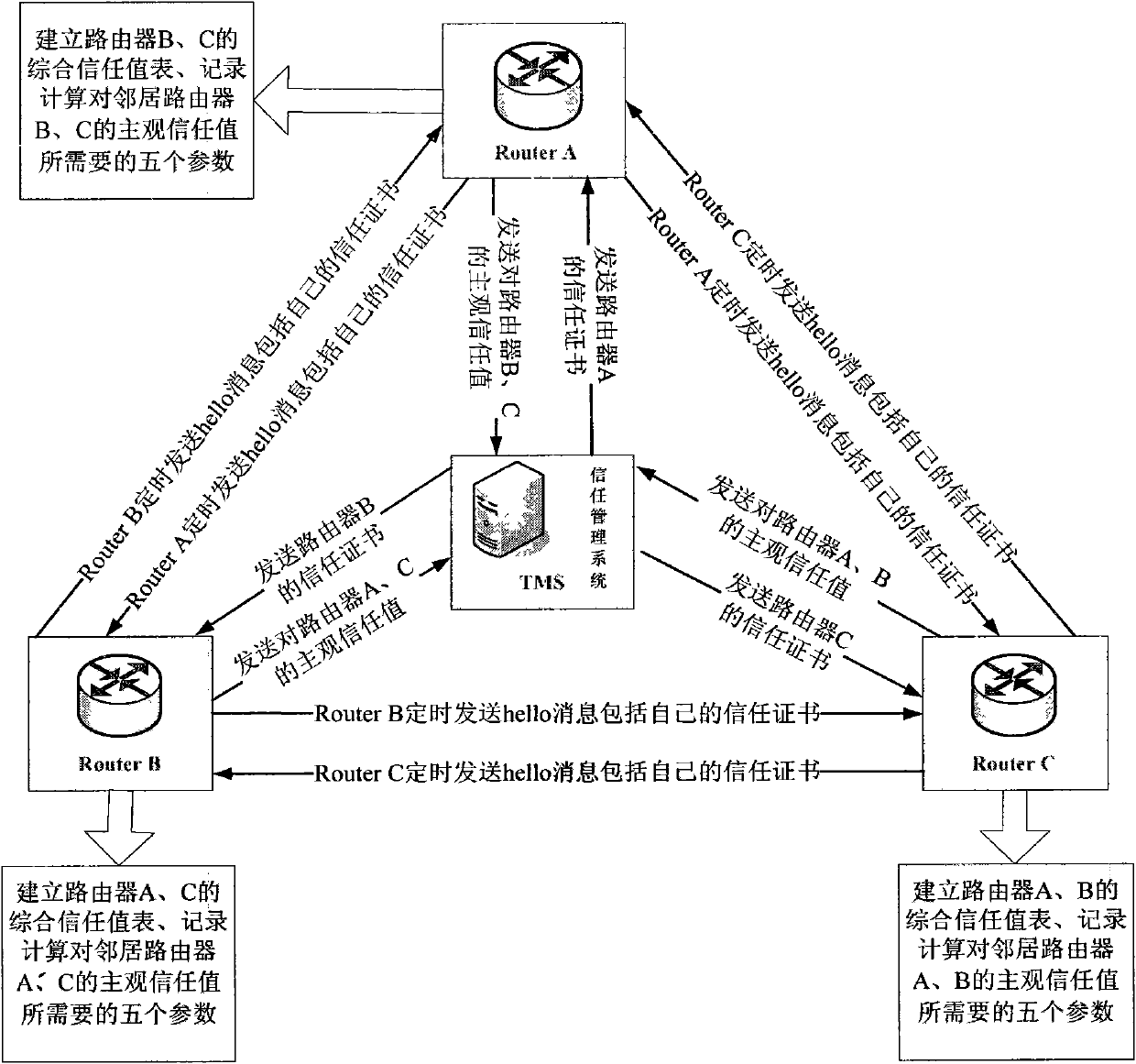
Trust management system based trusted reconstructing method of IP routing protocol
The invention discloses a trust management system based trusted reconstructing method of an Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol, which comprises the following steps of: (1) before each router is added into a network, registering to the trust management system, and sending corresponding trust certificates to the routers by the trust management system, the trust certificates including comprehensive trust values of the routers and each being calculated according to safe parameters and configuration parameters of the routers and all the subjective trust value of the neighbor router to the routers by the trust management system; (2) transferring the trust certificates among the routers through hello information, wherein an adjacency relation is not established for the router without the trust certificate, all the routers in the network are ensured to have own trust certificates; (3) each router calculating the subjective trust value of the neighbor router based on network real time parameters including link flow, packet loss probability, retardation, transmission rate of the packet and reliability of the packet, during an interactive work with the neighbor router, calculating a total trust value of the neighbor router by using the comprehensive trust value and the subjective trust value of the neighbor router, and modifying a metric field of a link-state announcement Router_LSA packet as the total trust value and synchronizing a link-state data base;(4) modifying a Dijkstra algorithm, using a reciprocal of the total trust value between the routers as the parameter for the arithmetic computation, selecting the router with higher trust value to generate a shortest path tree, and forming a trust routing list; (5) periodically reporting the subjective trust value of the neighbor routers to the trust management system by each router, simultaneously obtaining the parameter required for computing the subjective trust value, updating the trust certificate of each router at fixed time, and eliminating the router with the overdue trust certificate out of the network to maintain the topological structure of the whole network.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Analyzing method of grid fault current shock topological graph
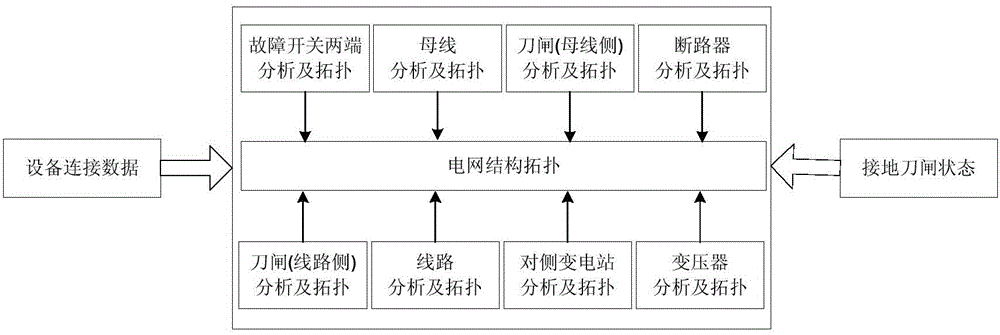
ActiveCN106021596AAccurate Calculation BasisFor real-time analysisData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsGrid faultTopological graph
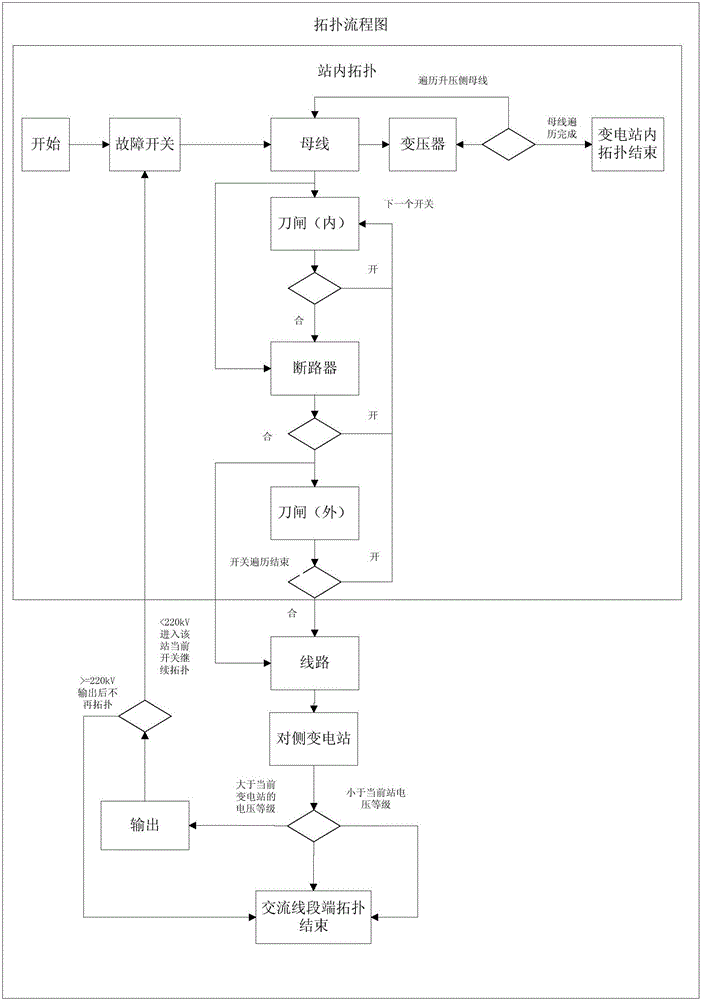
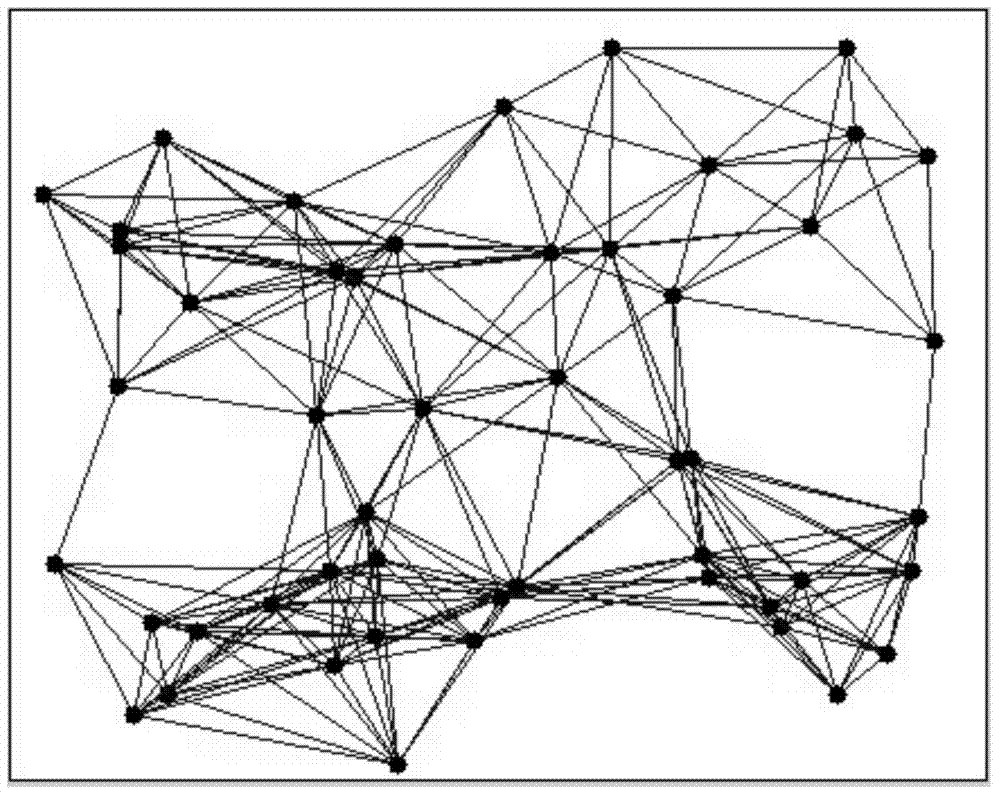
The invention discloses an analyzing method of a grid fault current shock topological graph. The method comprises the following steps that 1, wiring diagram information and real-time status information of plant stations and primary equipment in all transformer substations are obtained; 2, topology is conducted on the intra-station primary equipment from the position of a breakdown switch in one transformer substation by means of a tree graph algorithm according to the wiring diagram information and the real-time status information, and then topology is conducted from intra-station to the side transformer substations till topology of all the transformer substations is completed; 3, a tree graph formed through topology is output to be the grid fault current shock topological graph in a tree mode by the shortest path. According to the analyzing method of the grid fault current shock topological graph, a shock path of a fault current to a main grid at the fault occurring moment is vividly shown in a grid fault current shock topological graph mode, and an accurate calculation basis is provided for the quantitative research aspect of fault current cumulative shock.
Owner:STATE GRID JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER CO ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
Method, device and system for creating bidirectional multicast distribution trees on basis of interior gateway protocol
ActiveCN103546381ASimple operation and maintenanceSolve complex operation and maintenance problemsData switching networksDistribution treeProtocol Independent Multicast
An embodiment of the invention discloses a method, a device and a system for creating bidirectional multicast distribution trees on the basis of an interior gateway protocol, and relates to the technical field of communication. The technical scheme includes that the method comprises receiving a root address of at least one first node and a multicast group range supported by the first node; generating shortest paths from each first node, which is used as a source node, to other nodes according to the corresponding root address and a shortest path tree algorithm, and creating flooding trees according to the shortest paths; determining flooding trees corresponding to various three-layer multicast groups according to three-layer multicast group information and the multicast group ranges supported by the first nodes when the three-layer multicast group information is received, and generating the bidirectional multicast distribution trees for the flooding trees corresponding to the various three-layer multicast groups according to the three-layer multicast group information. The root addresses of the first nodes are transmitted by the first nodes by means of flooding. The three-layer multicast group information is transmitted by edge nodes by means of flooding. The method, the device and the system have the advantage that the problem of complexity in operation and maintenance due to the fact that a PIM (protocol independent multicast) routing protocol and a unicast routing protocol which is an IGP (interior gateway protocol) need to be simultaneously operated and maintained in multipoint-to-multipoint multicast scenes can be solved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Multicast method based on SDN
InactiveCN106209622AReal-time dynamic adjustment managementAvoid consumptionData switching networksHigh level techniquesComputer networkResource consumption
The invention discloses a multicast method based on an SDN. A member in a multicast group sends multicast group addition information to an SDN controller; a multicast source sends registration information to the SDN controller; the SDN controller forms a shortest path tree by taking the multicast source as a root node according to the addition information of the member in the multicast group, departure information of the member in the multicast group and the network situation; information of the shortest path tree is sent to forwarding equipment; therefore, a multicast forwarding table item is established on the forwarding equipment; and a multicast forwarding path is formed. The multicast method disclosed by the invention is superior to a sharing tree formed by a PIM-SM in the forwarding path aspect; and simultaneously, unnecessary network resource consumption due to a flooding mechanism in a PIM-DM is avoided.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HAIGE COMM GRP INC
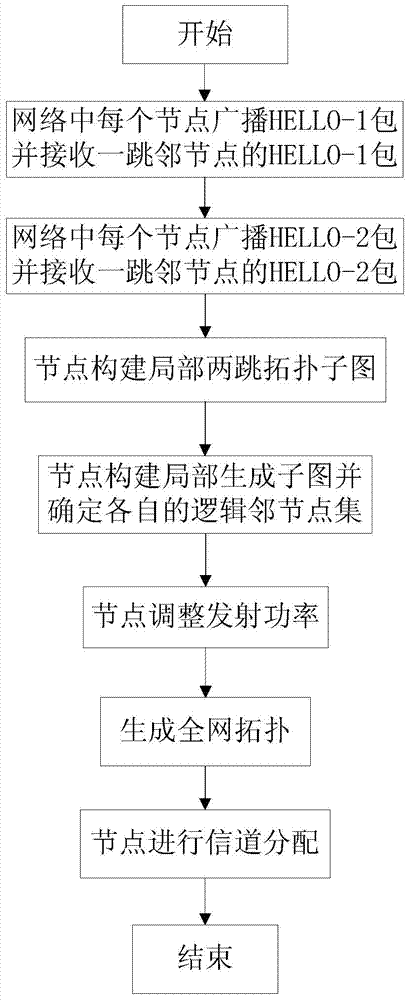
Distributed topology control method for cognitive Ad Hoc network
ActiveCN104507168AEliminate distractionsGuaranteed connectivityNetwork topologiesHigh level techniquesEnergy consumptionTopology construction
The invention discloses a distributed topology control method for a cognitive Ad Hoc network, and mainly solves the problems of mutual interference of secondary users and failure in guarantee of connectivity of networks of the secondary users in the prior art. An implementation process of the distributed topology control method for the cognitive Ad Hoc network includes: enabling each node in the network to sequentially broadcast a HELLO packet twice, and receiving the HELLO packet of initial neighbor nodes to set up a local two-hop topology subgraph; constructing a shortest path tree according to energy consumption link cost weight on the basis of the local two-hop topology subgraph, and on the basis of the shortest path tree, constructing a local generation subgraph capable of guaranteeing user communication; adjusting transmission power according to one-hop neighbor nodes in the local generation subgraph; enabling all nodes in the network and links between the nodes and the logical neighbor nodes thereof to form a whole network topology; after topology construction is finished, performing independent channel selection for the nodes in the network. The distributed topology control method for the cognitive Ad Hoc network has the advantages of low complexity and realization of guaranteeing communication of user networks and eliminating user interference, and is applicable to the cognitive Ad Hoc network.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV +1
Method for providing QoS (quality of service)-guaranteeing multi-path and method for providing disjoint path using the same
InactiveUS7366114B2Guarantee service reliabilityData switching by path configurationQuality of serviceTheoretical computer science
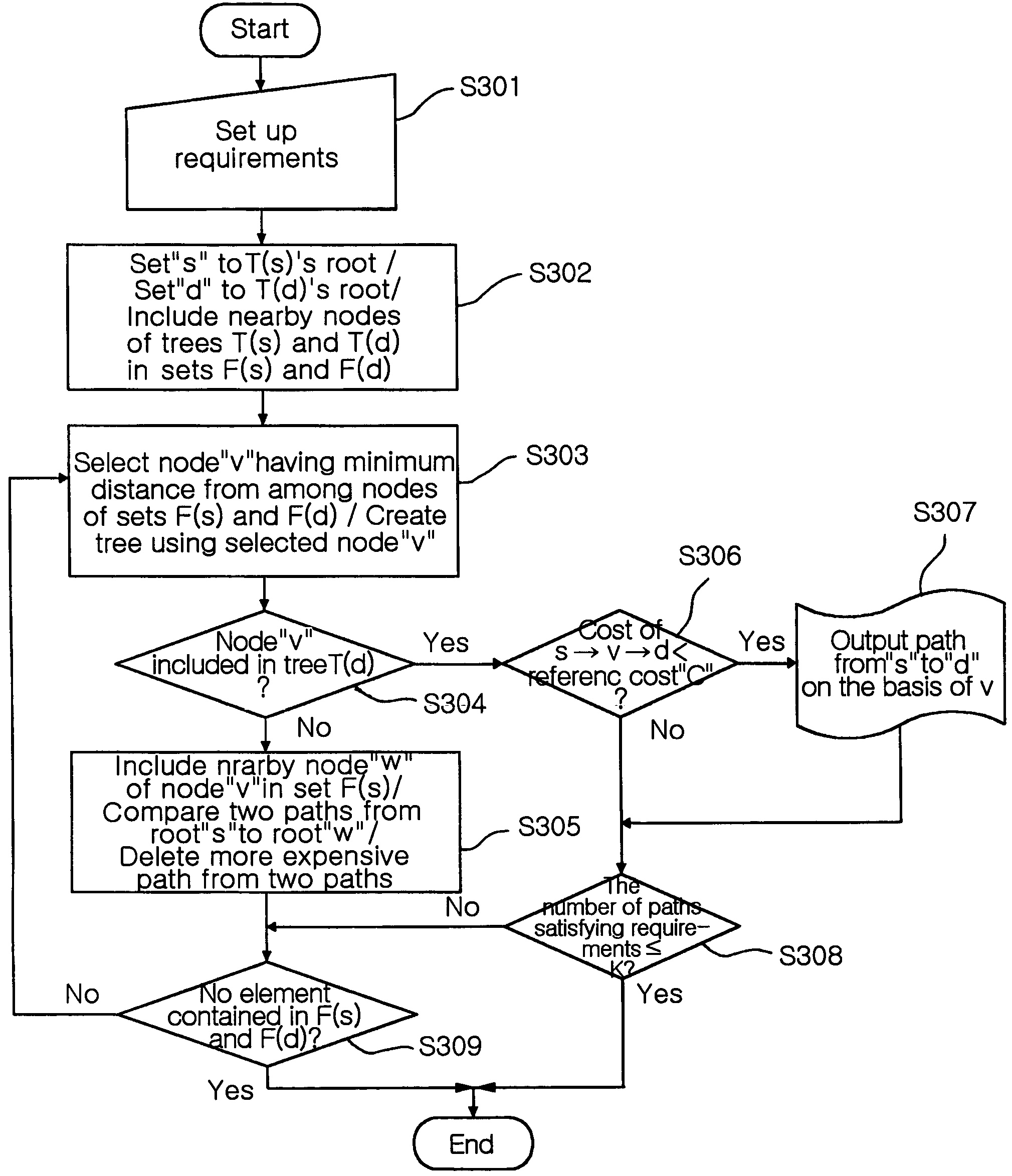
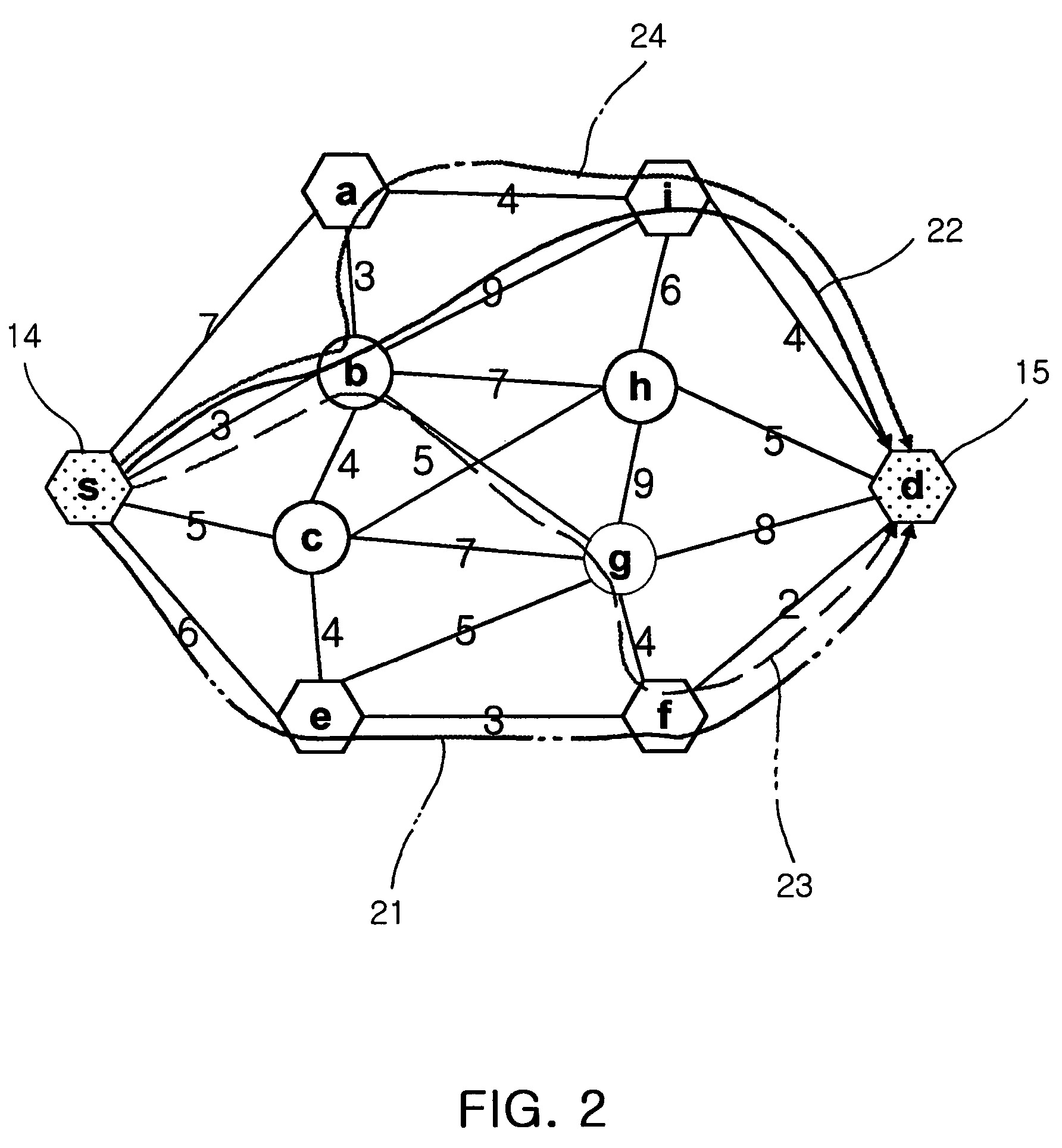
A method for providing a QoS-guaranteeing multi-path and a method for providing disjoint paths using the same are provided. The method configures the shortest path tree by adapting the start node “s” and the destination node “d”. When a new node is selected as a tree node in a tree configuration process according to the “s” or the “d”, the closest node to either the “s” or the “d” is selected. If a specified node “v” is contained in both a tree oriented from the “s” and another tree oriented from the “d”, one path of “s”-“v”-“d” is created. If all nodes are contained in either the tree of “s” or the other tree of “d”, then a program of path creation process is terminated. Further, the method further includes a step for determining two disjoint paths from the “s” to the “d” among the found multiple paths above.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Distributed fault-tolerant topology control method based on dump energy sensing
InactiveCN103200643AProlong survival timeImprove robustnessNetwork topologiesHigh level techniquesSelf-organizing networkNetwork topology
The invention discloses a distributed fault-tolerant topology control method based on dump energy sensing. The distributed fault-tolerant topology control method based on the dump energy sensing mainly solves the problem that balance of dump energy between nodes and network topology fault-tolerant capability can not be guaranteed at the same time in the prior art. The distributed fault-tolerant topology control method based on the dump energy sensing comprises the steps of broadcasting a HELLO package of each node in a network and receiving the HELLO package of an initial neighbor node, and establishing a local topology subgraph; construing a shortest path tree based on the local topology subgraph and according to link cost weight and constructing a local k communication generation subgraph by traversing all directed edges according to distance weight from small to large; adjusting emission power according to a one-hop neighbor node in the local k communication generation subgraph, and connecting non-logic neighbor nodes within the emission power range; and finally construing a whole network topology according to all the nodes in the network and links between the nodes and the logic neighbor nodes. The process can be repeatedly executed according to the updating cycle T of the topology. The distributed fault-tolerant topology control method based on the dump energy sensing has the advantages that life cycle of the network is prolonged, and fault-tolerant capability of the network is enhanced. The distributed fault-tolerant topology control method based on the dump energy sensing can be applied to a wireless self-organizing network.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Concurrent path computation using virtual shortest path tree
ActiveUS7801048B1Increase the amount of calculationVerify feasibilityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPath computation elementMpls traffic engineering
Parallelism is exploited to accelerate the distributed computation of an MPLS Traffic Engineering LSP across multiple Autonomous Systems or areas using a virtual shortest path tree. After relaying a path computation request, a path computation element immediately begins local path segment computations even before a response to the request is received. When a response including virtual shortest path tree information is received, the tree is extended using the previously computed path segments. Also, a path computation element can verify the local feasibility of the requested path after receiving a request so that a requesting head-end or upstream path computation element can be quickly informed that a constraints-satisfying path is not available.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Shortest path tree and spanning tree combined energy-saving routing method
The invention discloses a shortest path tree and spanning tree combined routing method and belongs to the technical field of network topology. The method is characterized in that on the basis of a standard link state routing protocol, a dormant state is added to each link which is connected with a router node in a network, a shared spanning tree is selected on a given network topology, links on the spanning tree are in a working state all the time so as to guarantee network connectivity, other links which are not on the spanning tree enter into dormant states if no flow passes, each router stores a shortest path routing list of the whole network path and a routing list of a corresponding spanning tree, as for a data packet, an ingress router determines that the data packet uses a path therein according to current link loads, a label identification is added, and a non ingress router selects a corresponding routing list according to a label to perform forwarding.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Q-learning optical network-on-chip adaptive routing planning method based on Dijkstra algorithm
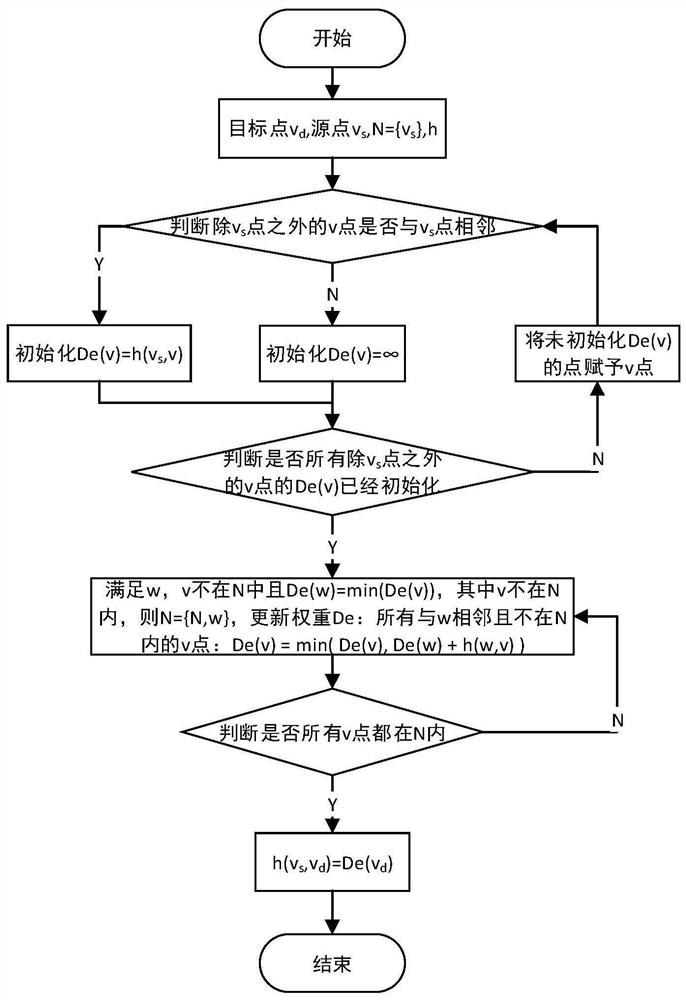
ActiveCN111770019AOvercome the disadvantage of only generating one shortest pathAutomatic planning path controllableMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching networksPathPingEngineering
The invention relates to a Q-learning optical network-on-chip adaptive routing planning method based on a Dijkstra algorithm, and the method comprises the steps: S1, constructing a network model, anddefining the parameters of the network model; S2, constructing a shortest path tree from each node to other nodes according to a Dijkstra algorithm and a network model, storing a plurality of shortestpaths from the node to a target node vd in each node according to a preset value, and obtaining a routing hop count h (vs, vd) of the shortest path from a source node vs to the target node vd; S3, according to a Q-learning algorithm, performing path planning by adopting a link selection mechanism based on an epsilon-greedy strategy to obtain a plurality of planned paths from the source node vs tothe target node vd, and obtaining reward values of the planned paths, the routing hop count of the planned paths not exceeding the routing hop count h (vs, vd) of the shortest path; and S4, obtainingan optimal path according to the reward value of the planned path. According to the method, the defect that each target point of the Dijkstra algorithm can only generate one shortest path is overcome.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com