Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1188 results about "Adaptive routing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
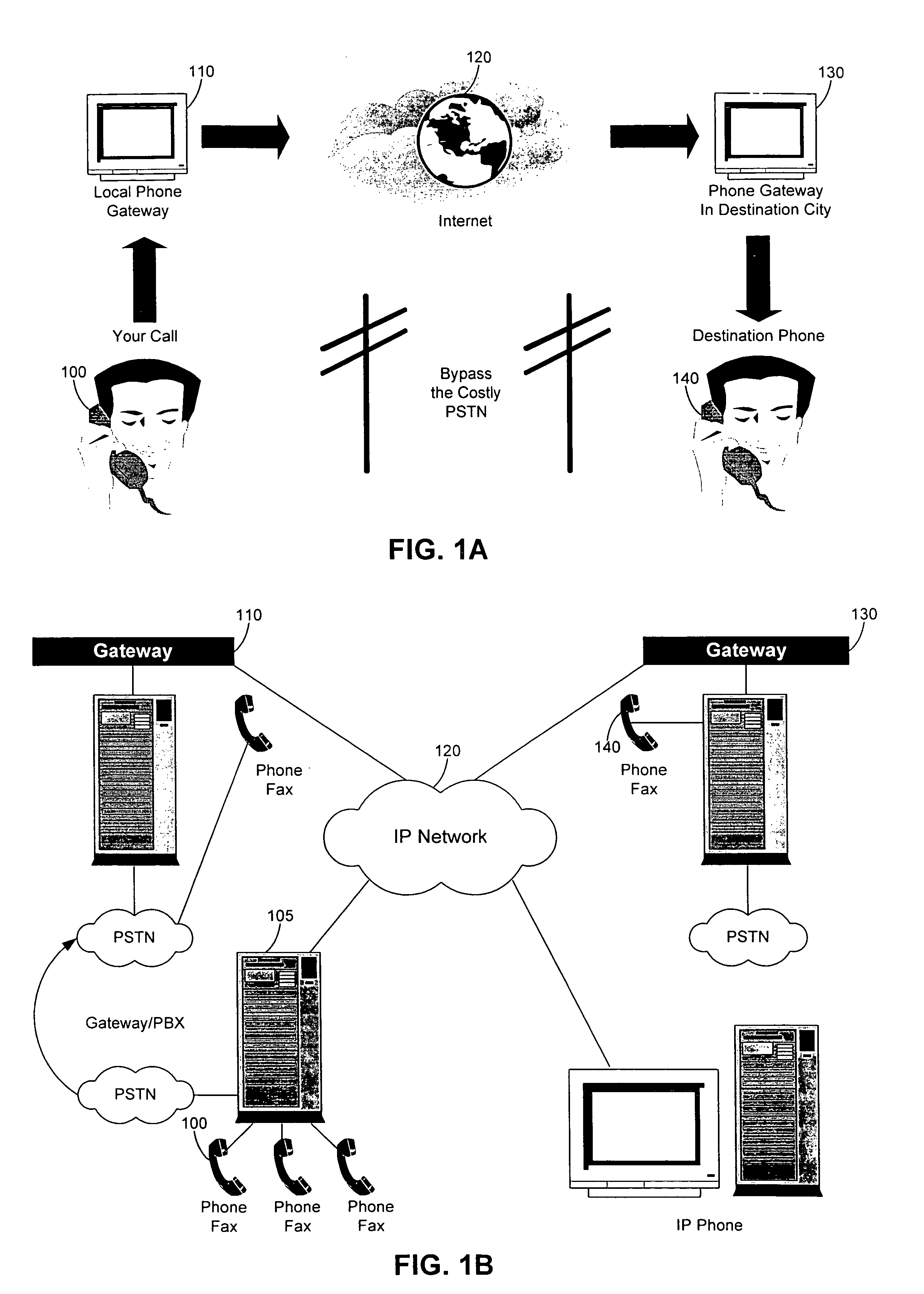
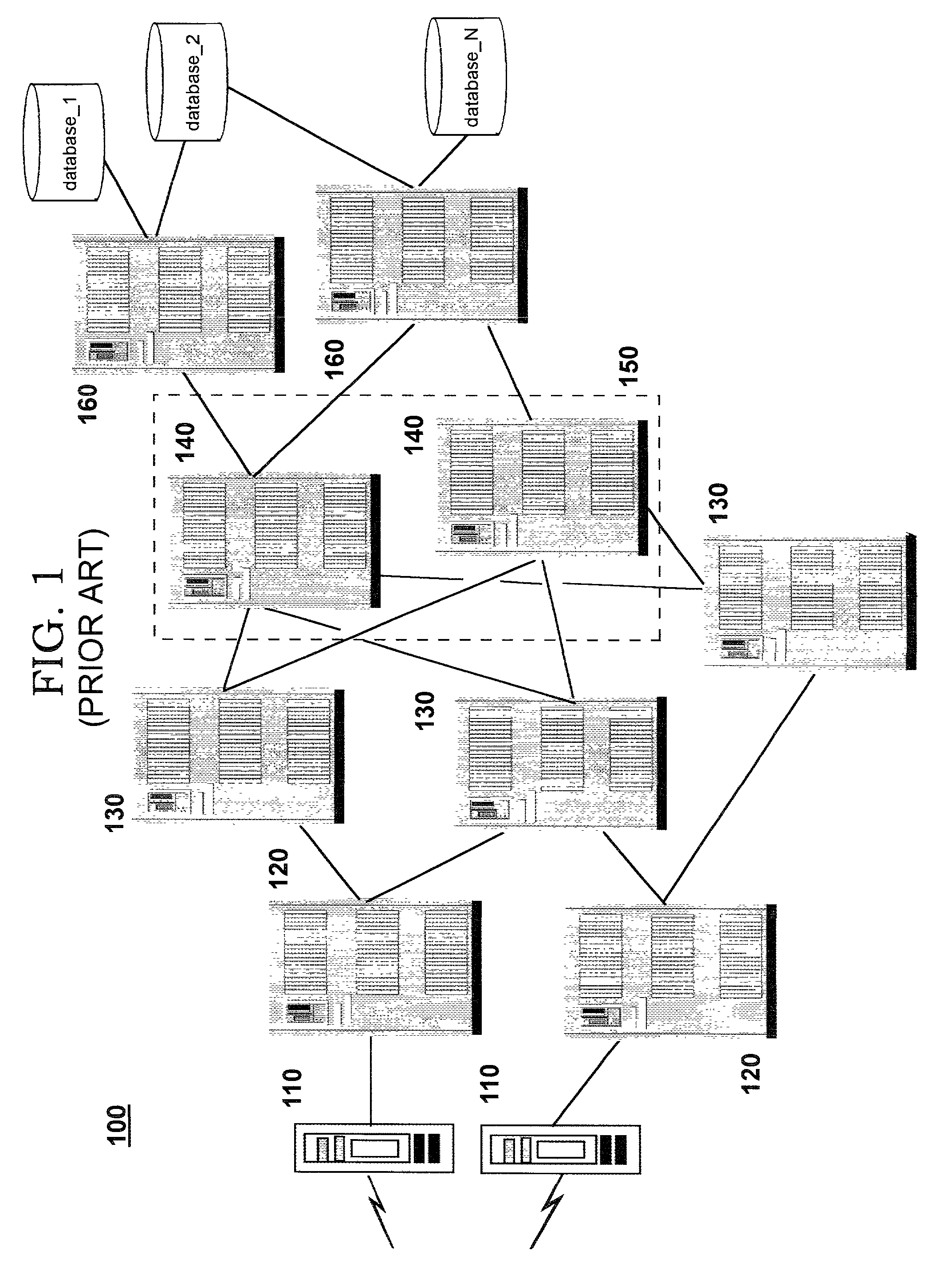
Dynamic routing, also called adaptive routing, is a process where a router can forward data via a different route or given destination based on the current conditions of the communication circuits within a system. The term is most commonly associated with data networking to describe the capability of a network to 'route around' damage, such as loss of a node or a connection between nodes, so long as other path choices are available. Dynamic routing allows as many routes as possible to remain valid in response to the change.
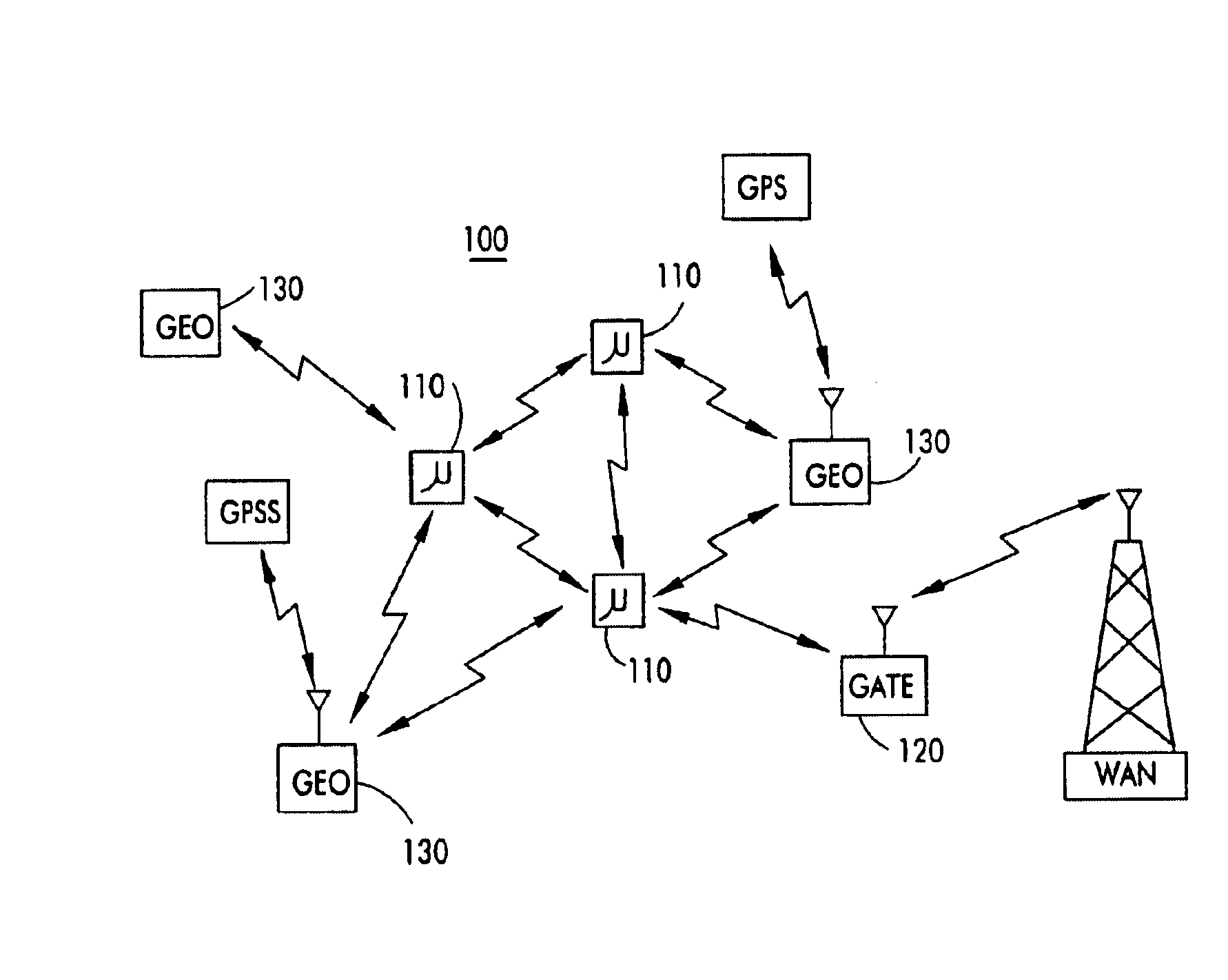
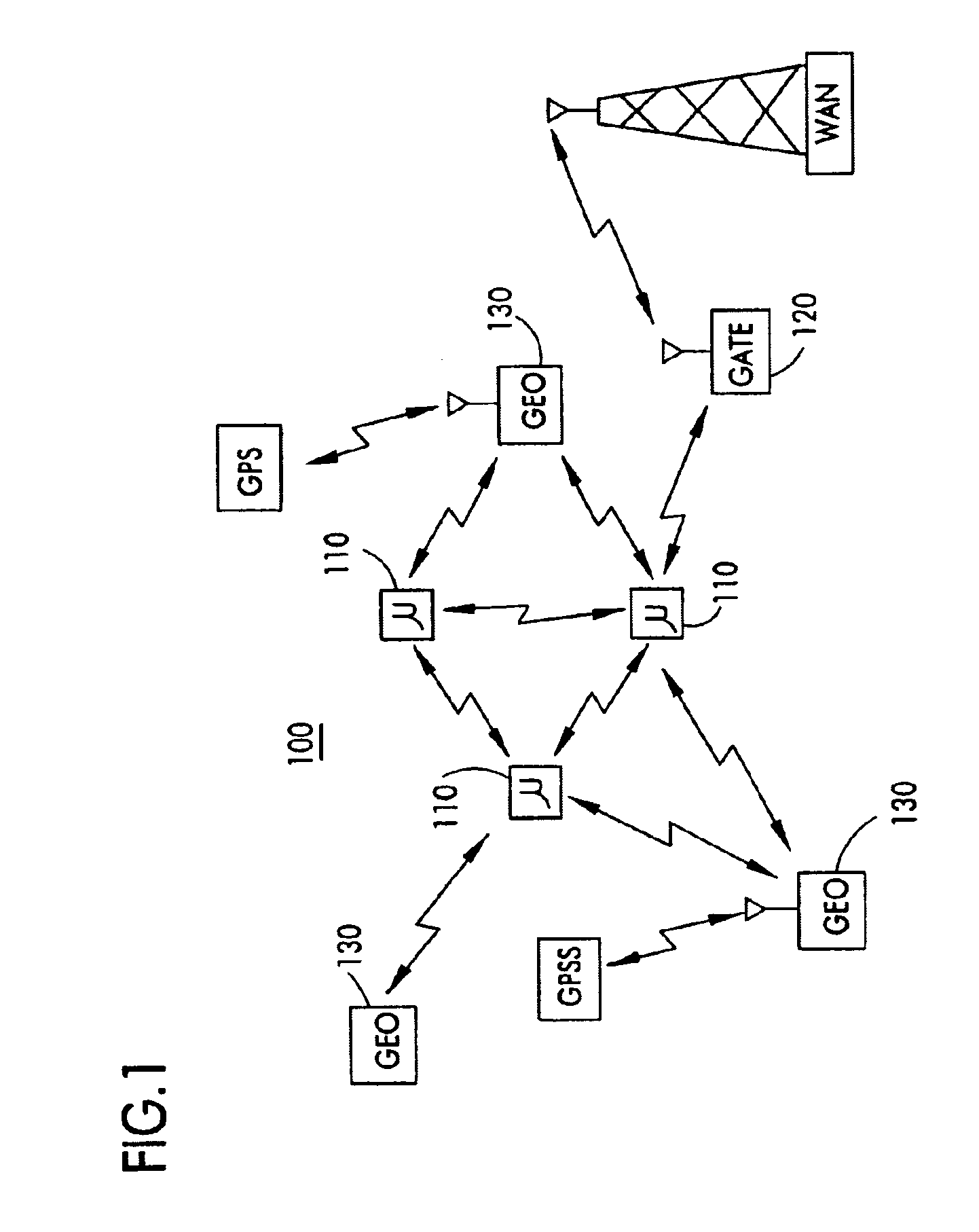
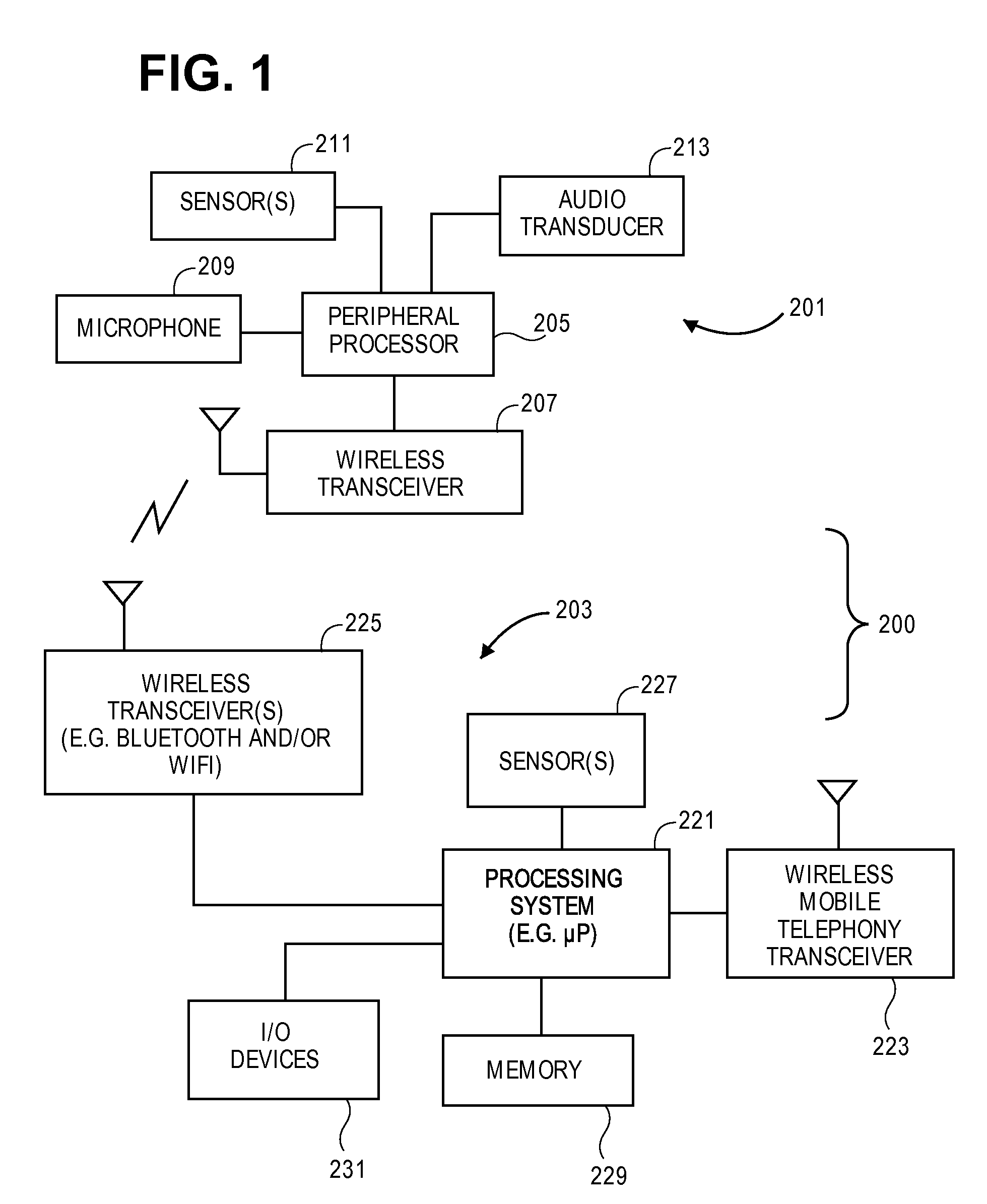
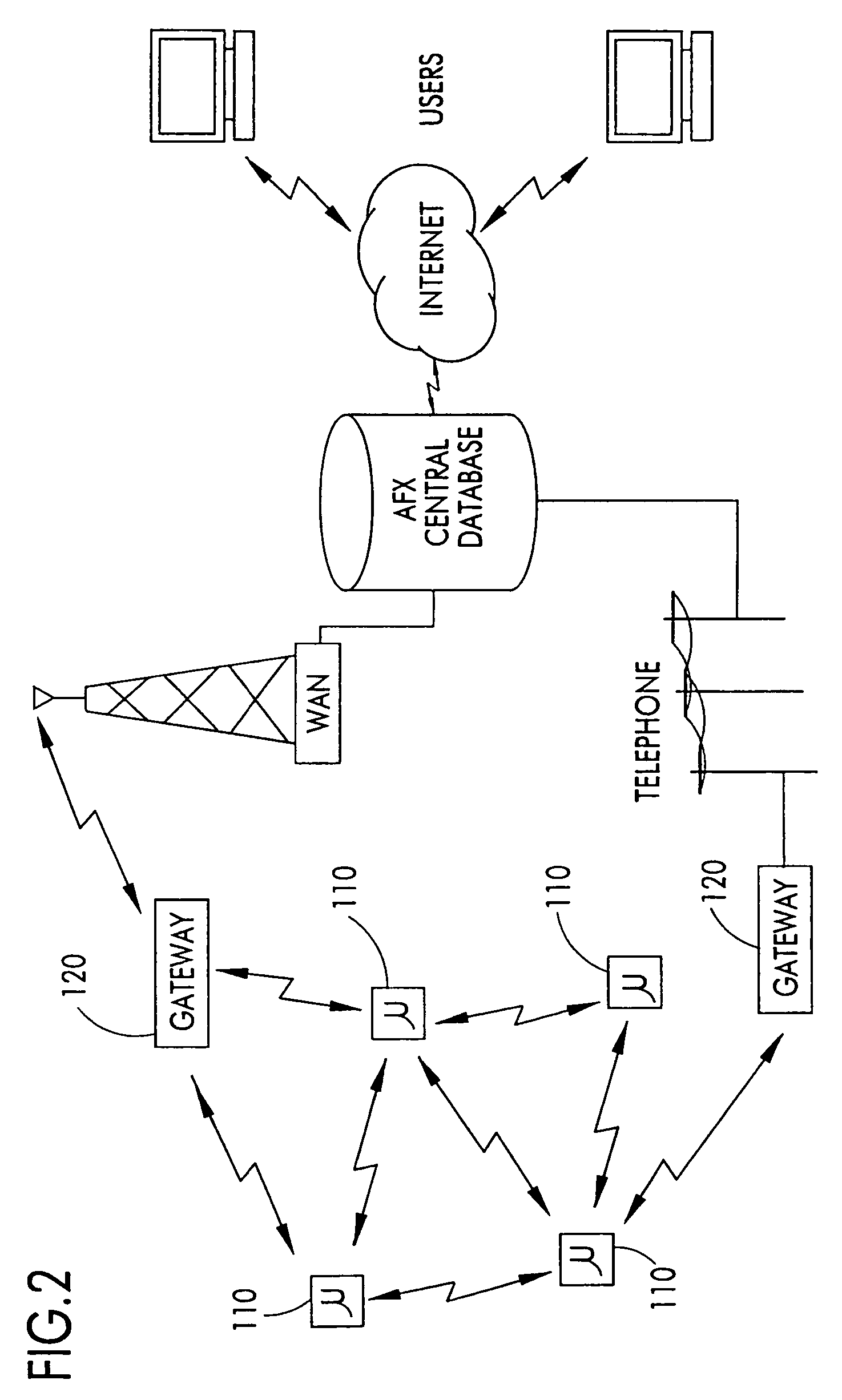
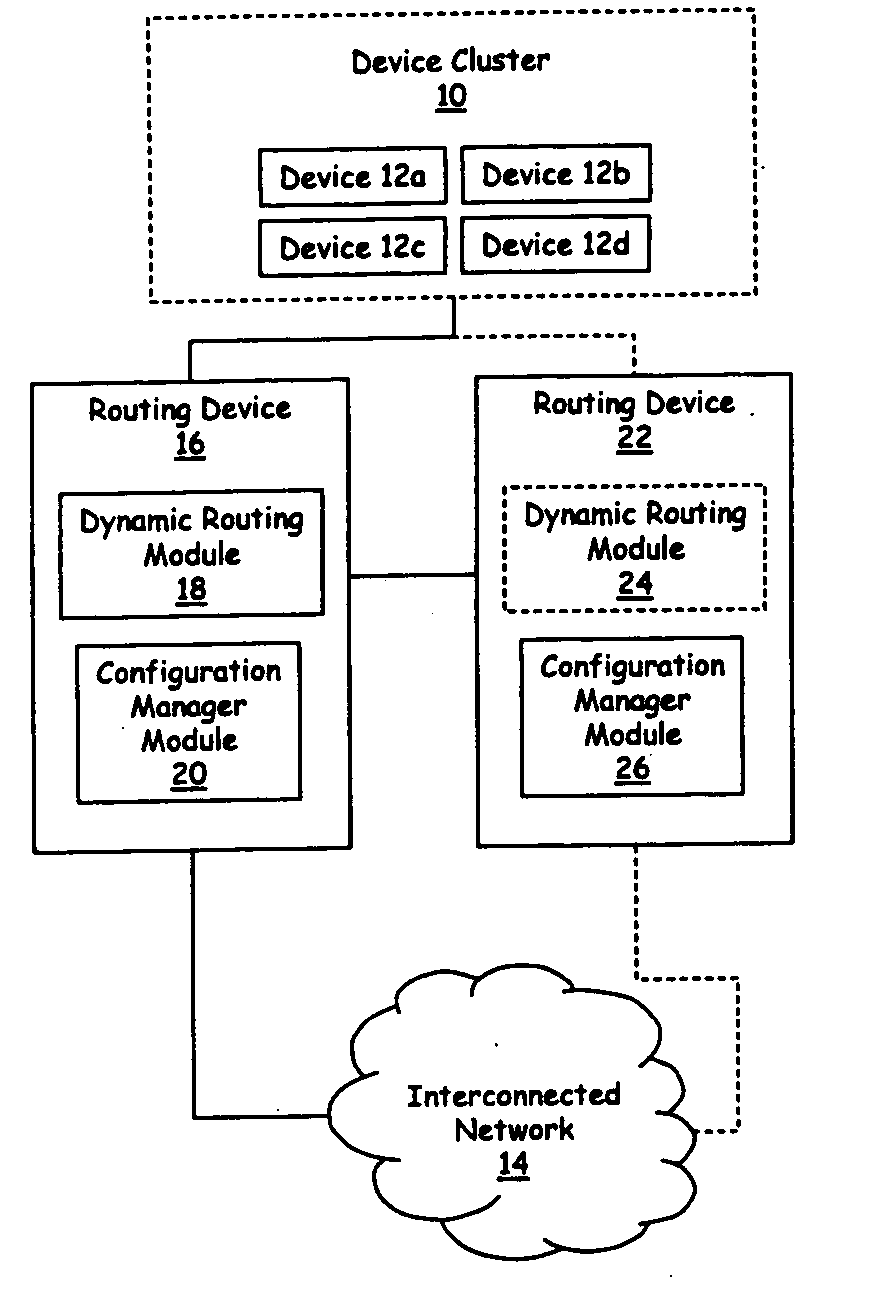
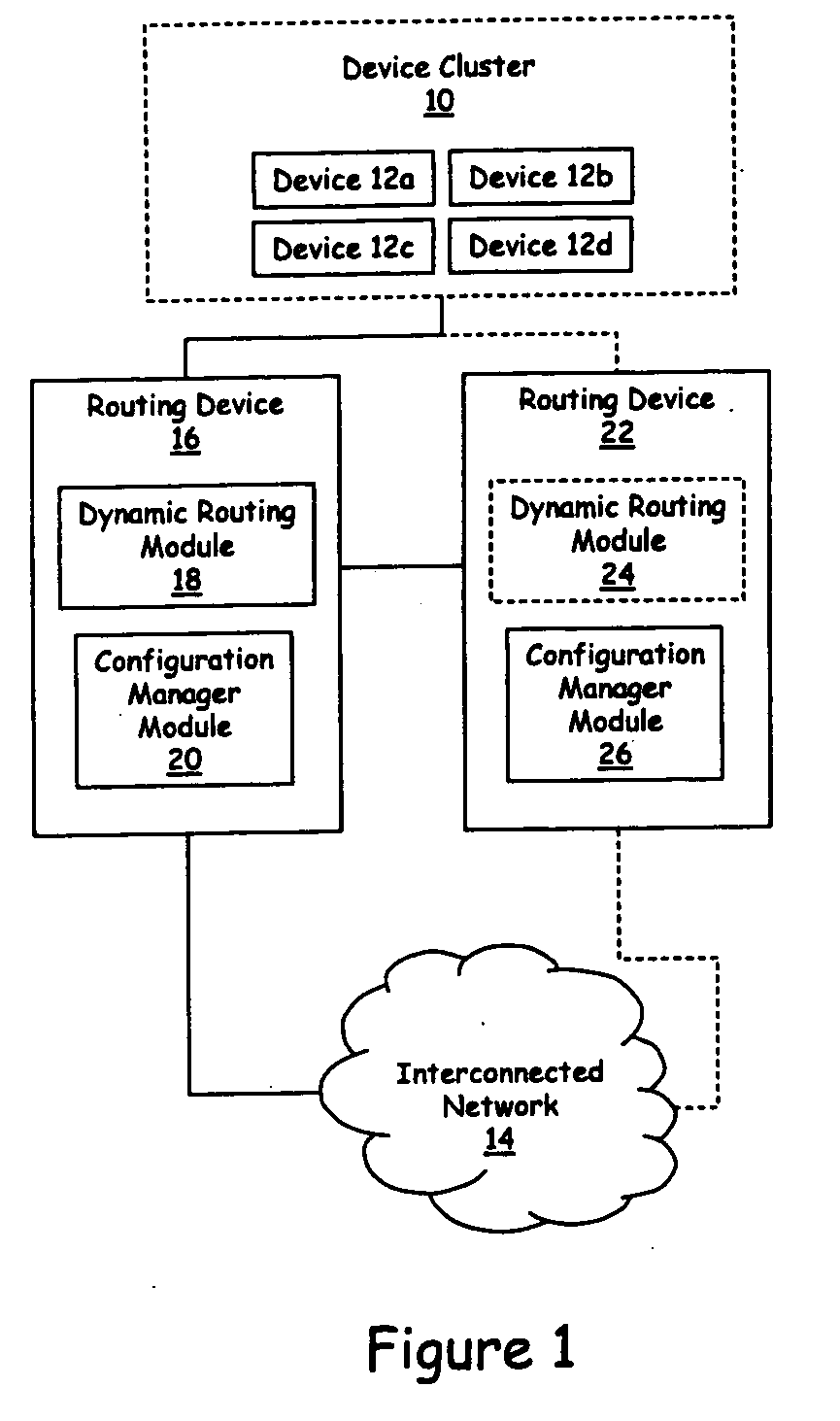
On/off keying node-to-node messaging transceiver network with dynamic routing and configuring
InactiveUS7027773B1Low costReduce trafficNear-field transmissionError preventionTransceiverAdaptive routing
The invention is a system operating on a reference frequency. The system comprises a plurality of at least three nodes. Each node hands off a message received from another node to a subsequent node. Each of the nodes comprises a transceiver receiving a message on the reference frequency from another node and transmitting the received message on the reference frequency to a subsequent node, and a controller controlling operation of the transceiver to receive the.. message transmitted by another node and to transmit the received message to a subsequent node.
Owner:AFX TECH GRP INT
Dynamic routing of audio among multiple audio devices
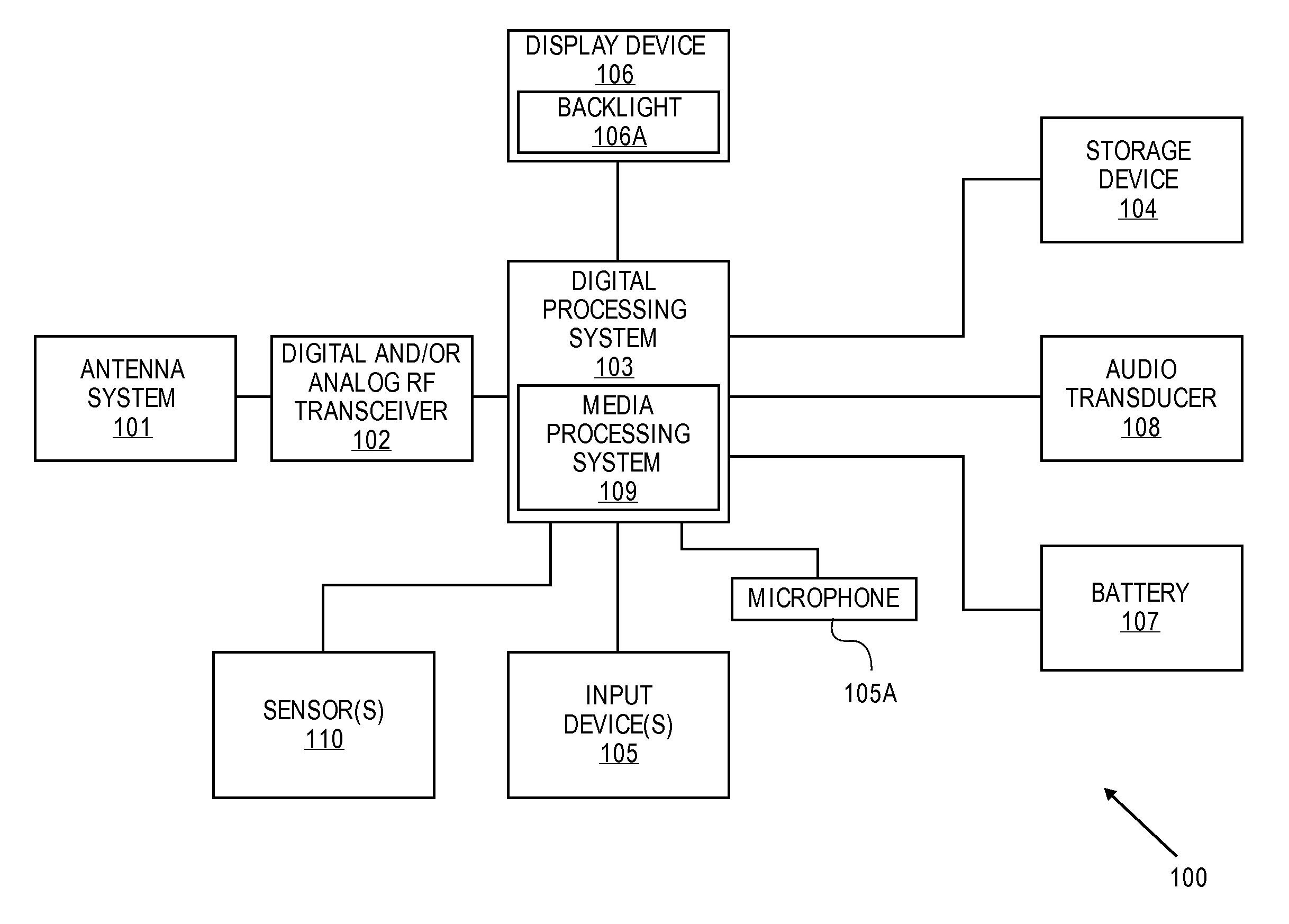
ActiveUS20090003620A1Devices with sensorDevices with wireless LAN interfaceHuman–computer interactionAdaptive routing
A routing screen is presented on an electronic device by a user interface application in response to receiving a notification that an external audio device is connected to the electronic device. The routing screen displays representations of an internal audio device and the external audio device. In one aspect, the representations are buttons. In another aspect, the representations are entries in a list. If a user selects one of representations, the user interface application causes the audio signals to be routed to the audio device represented by the selection. An application control screen having a set of objects that represent functions for an audio application may also be displayed. One of the objects on the application control screen is modified in response status changes in the external audio device. A user may select this object to access the routing screen when the external audio device is connected.
Owner:APPLE INC
Node-to node messaging transceiver network with dynamic routing and configuring
InactiveUS7653394B2Low costReduce trafficEnergy efficient ICTData switching by path configurationTransceiverAdaptive routing
The invention is a system operating on a reference frequency. The system comprises a plurality of at least three nodes. Each node hands off a message received from another node to a subsequent node. Each of the nodes comprises a transceiver receiving a message on the reference frequency from another node and transmitting the received message on the reference frequency to a subsequent node, and a controller controlling operation of the transceiver to receive the message transmitted by another node and to transmit the received message to a subsequent node.
Owner:AFX TECH GRP INT
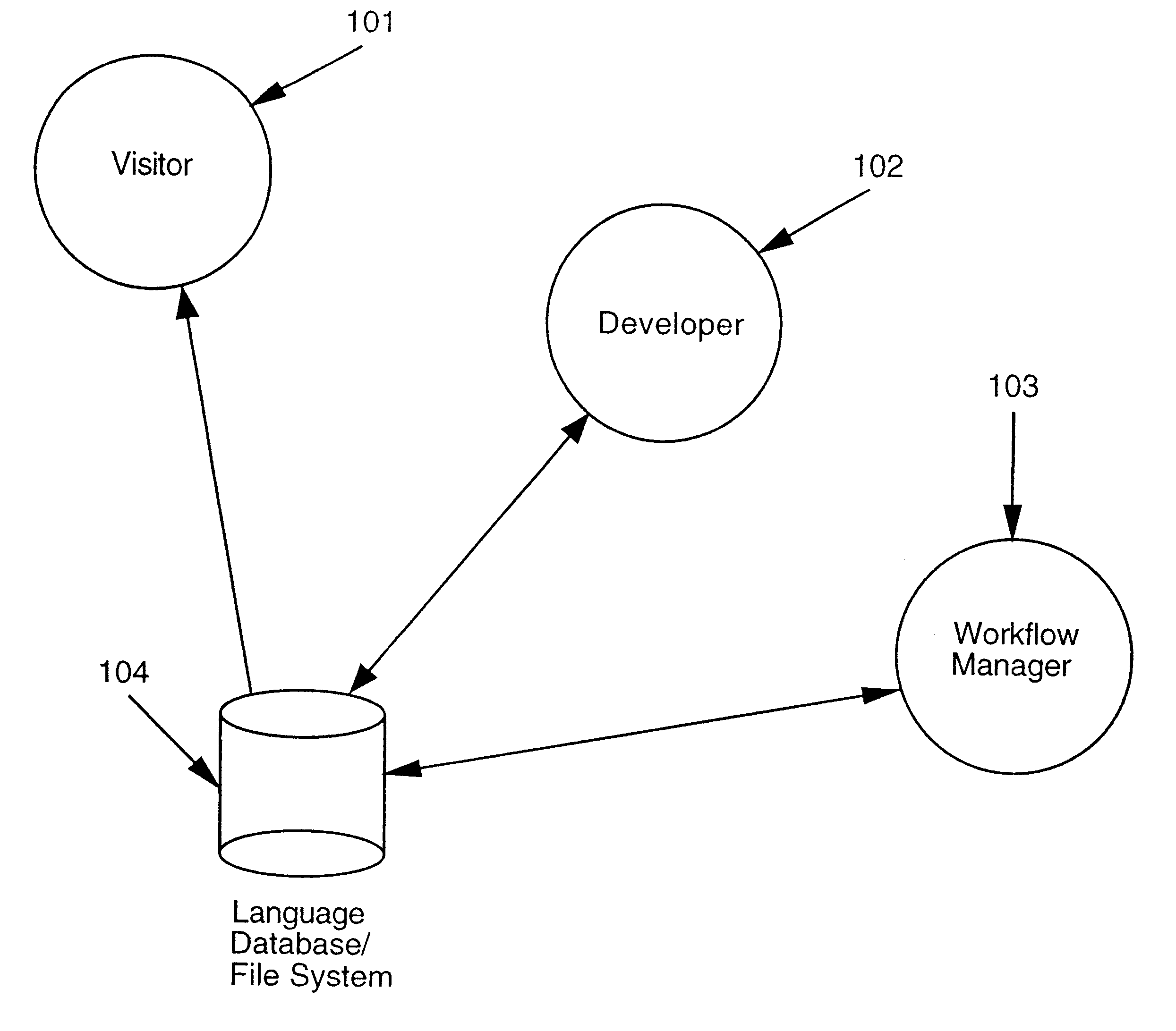
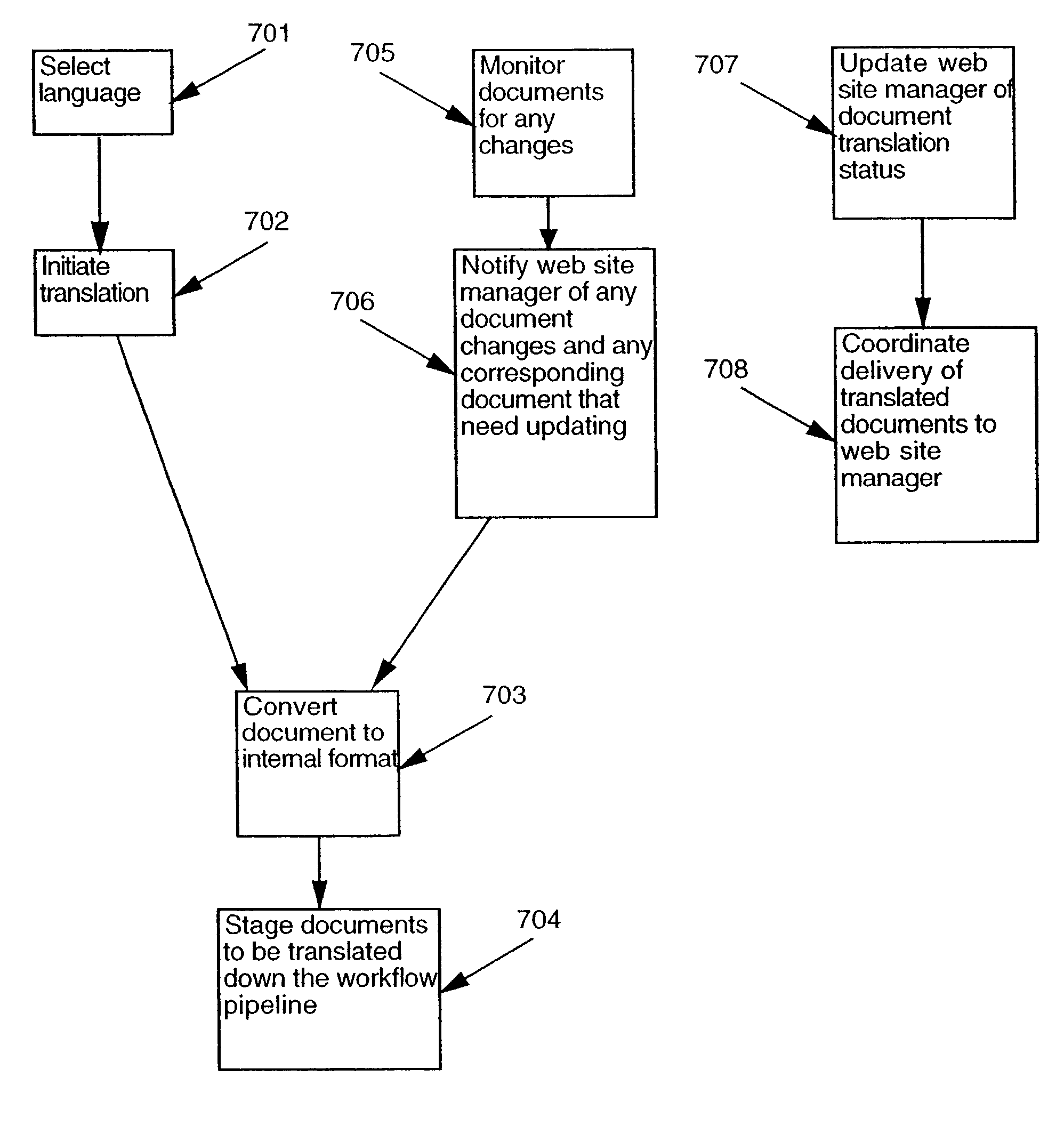
Translation management system
InactiveUS6526426B1Natural language translationMultiple digital computer combinationsData streamProgram planning
A translation management system in a computer environment. A preferred embodiment of the invention automatically detects when a document, data stream, or non-text file in the master language has been updated and notifies the user which corresponding documents, data streams, or non-text files in the other languages require translation which are then staged and dynamically routed and sequenced to individual translation resources where the actual translation is performed. Management status, reporting, scheduling, and accounting information is sent to the user as the translation process ensues. The user is notified of the completion of translation and the invention coordinates the delivery of the translated documents, data streams, or non-text files back to the user's site for installation and optional review.
Owner:TRANSPERFECT TECH LLC +1
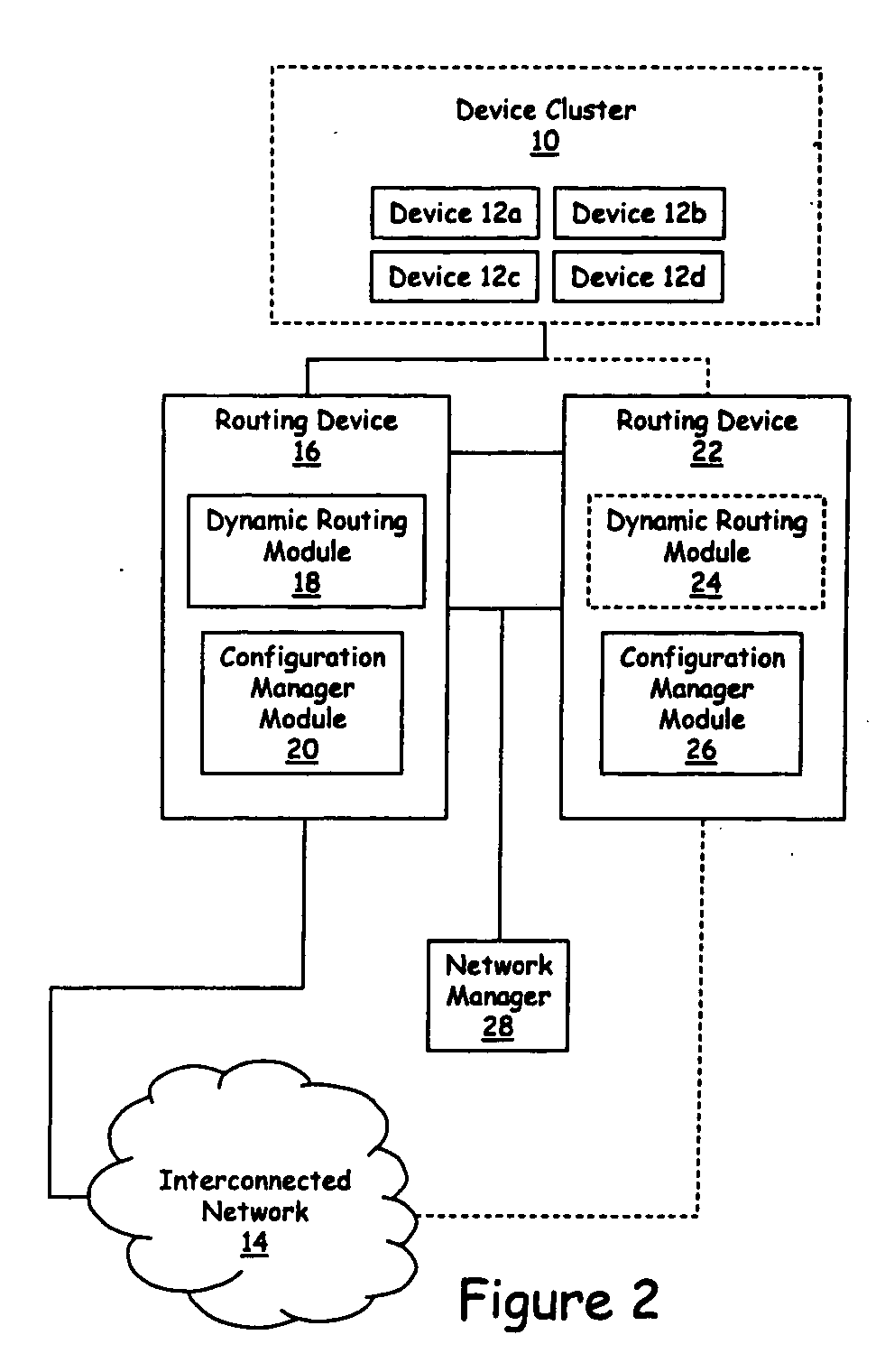
System and method for providing redundant routing capabilities for a network node
Owner:IP INFUSION INC
Virtual private network having automatic reachability updating
InactiveUS20050138204A1Easy to createCommunication securityEnergy efficient ICTDigital data protectionPrivate networkReachability
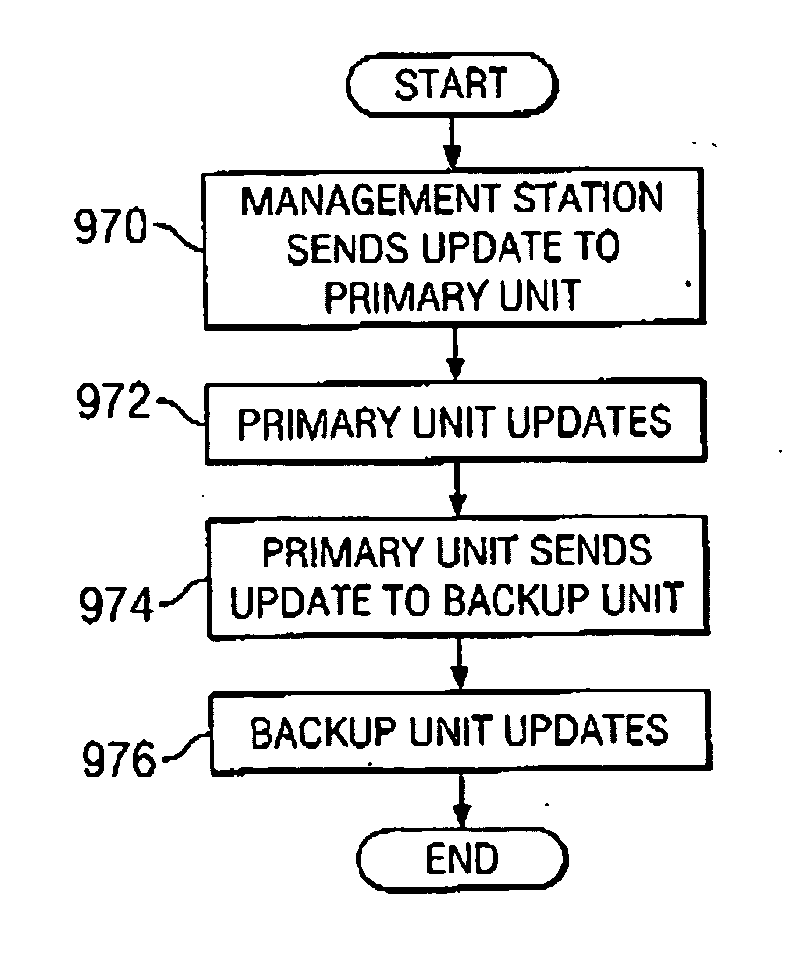
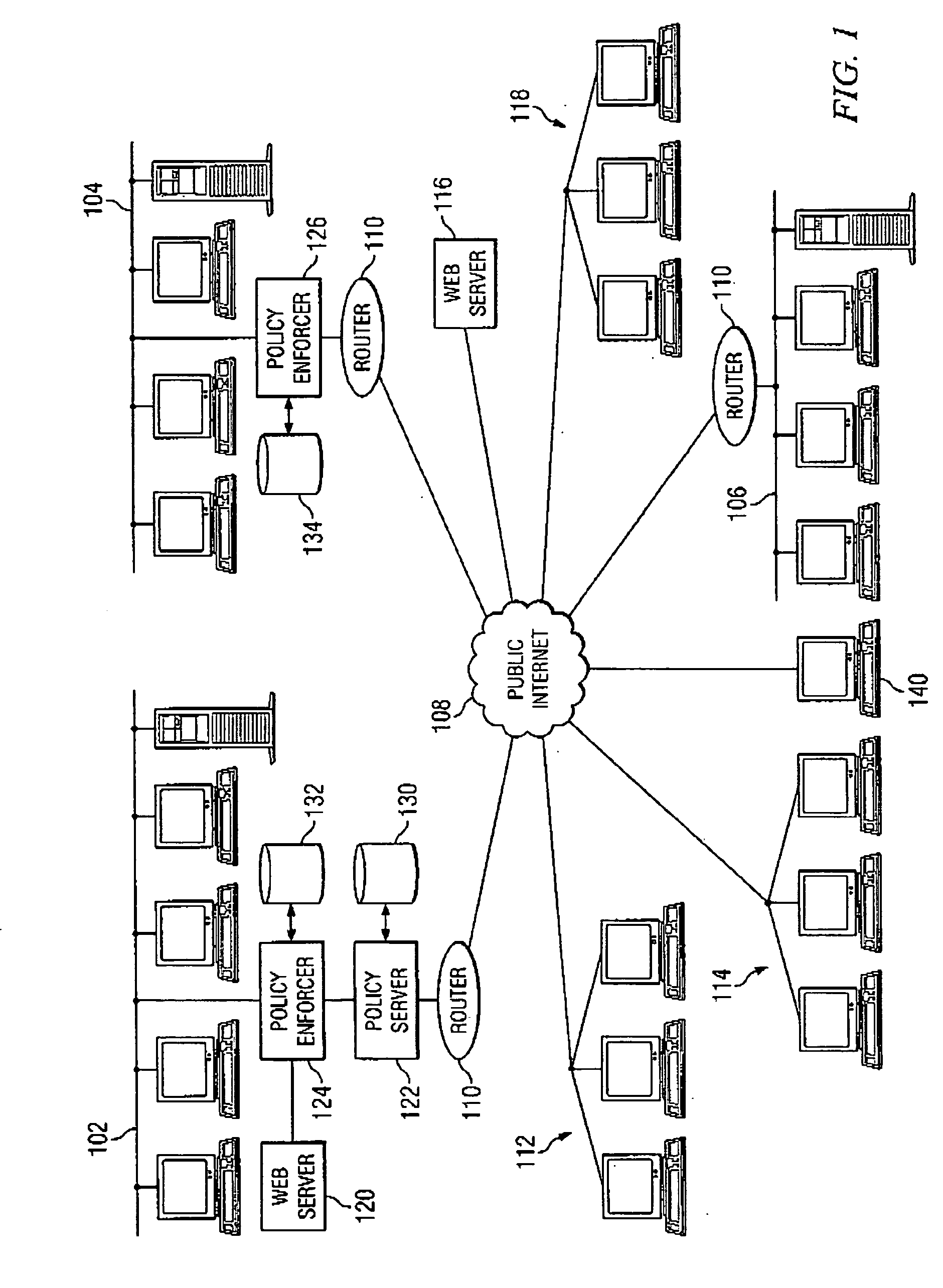
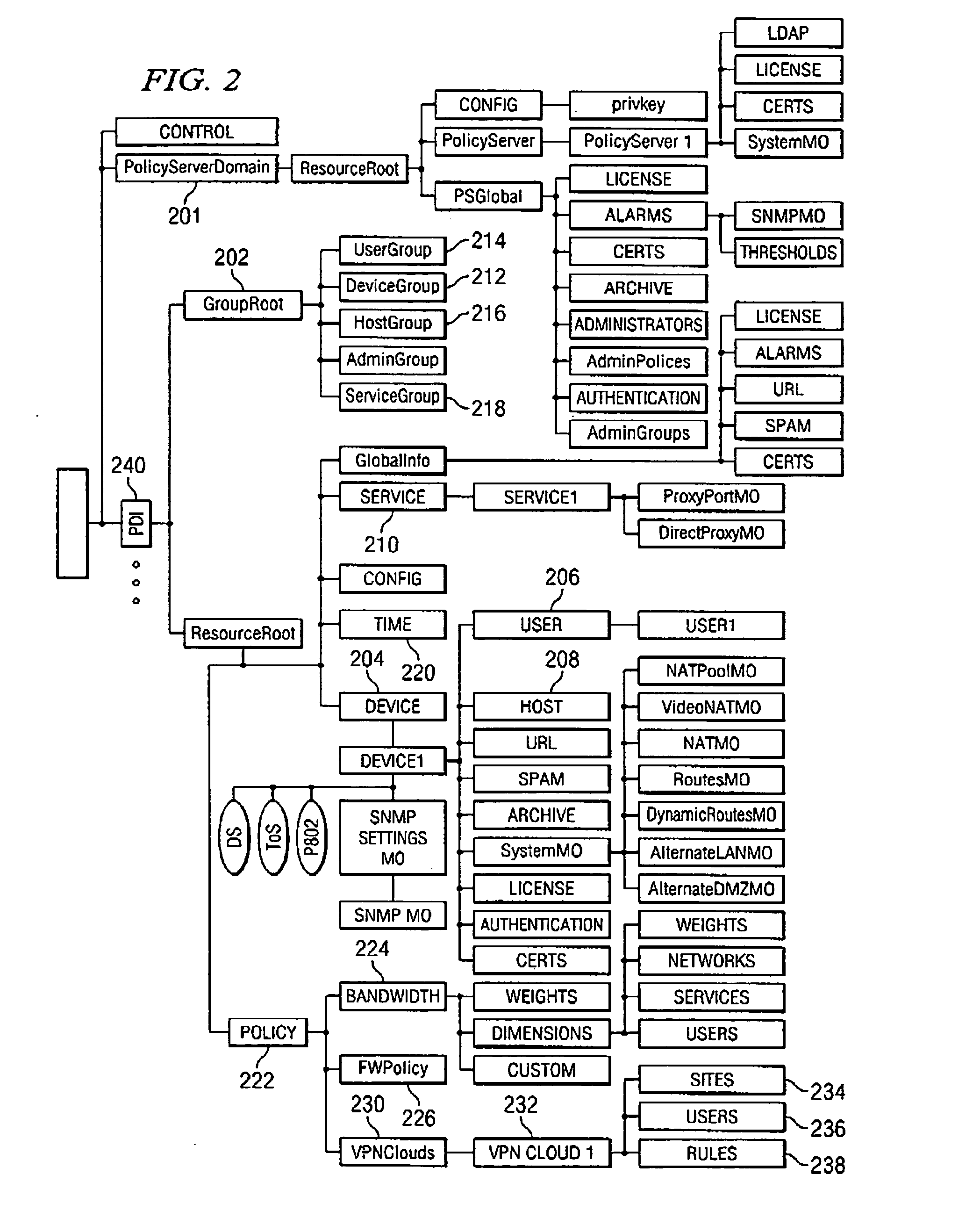
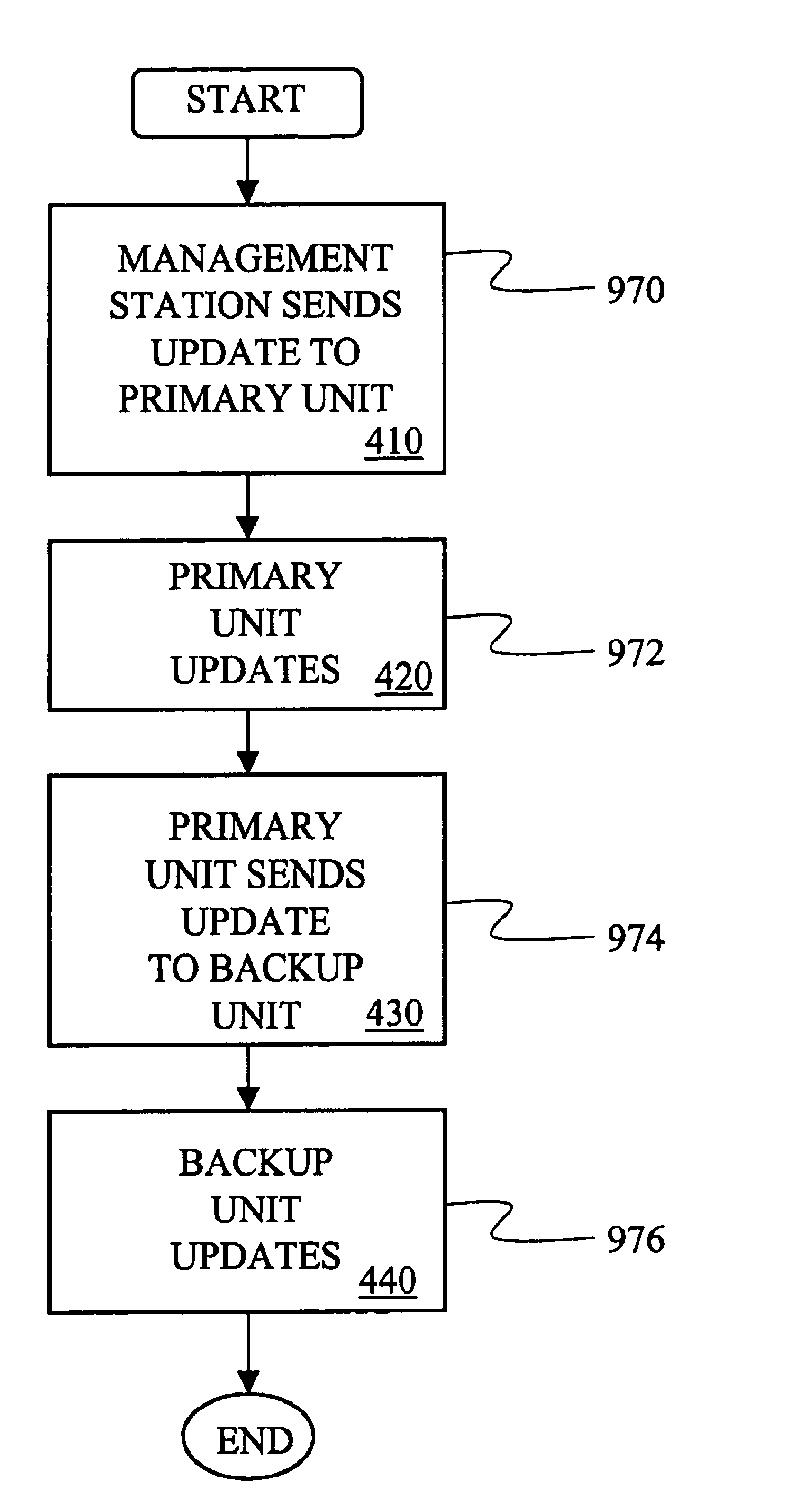
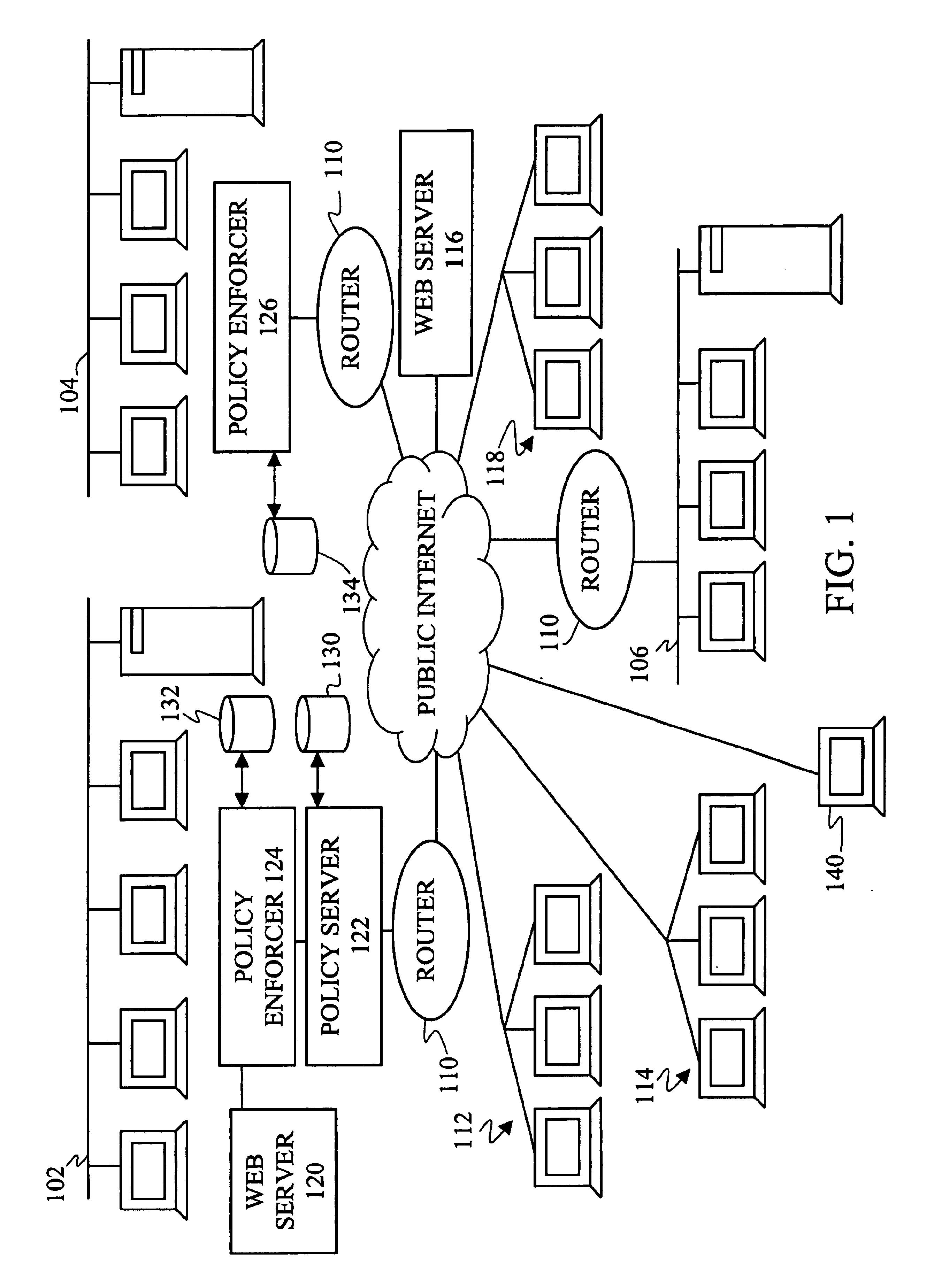
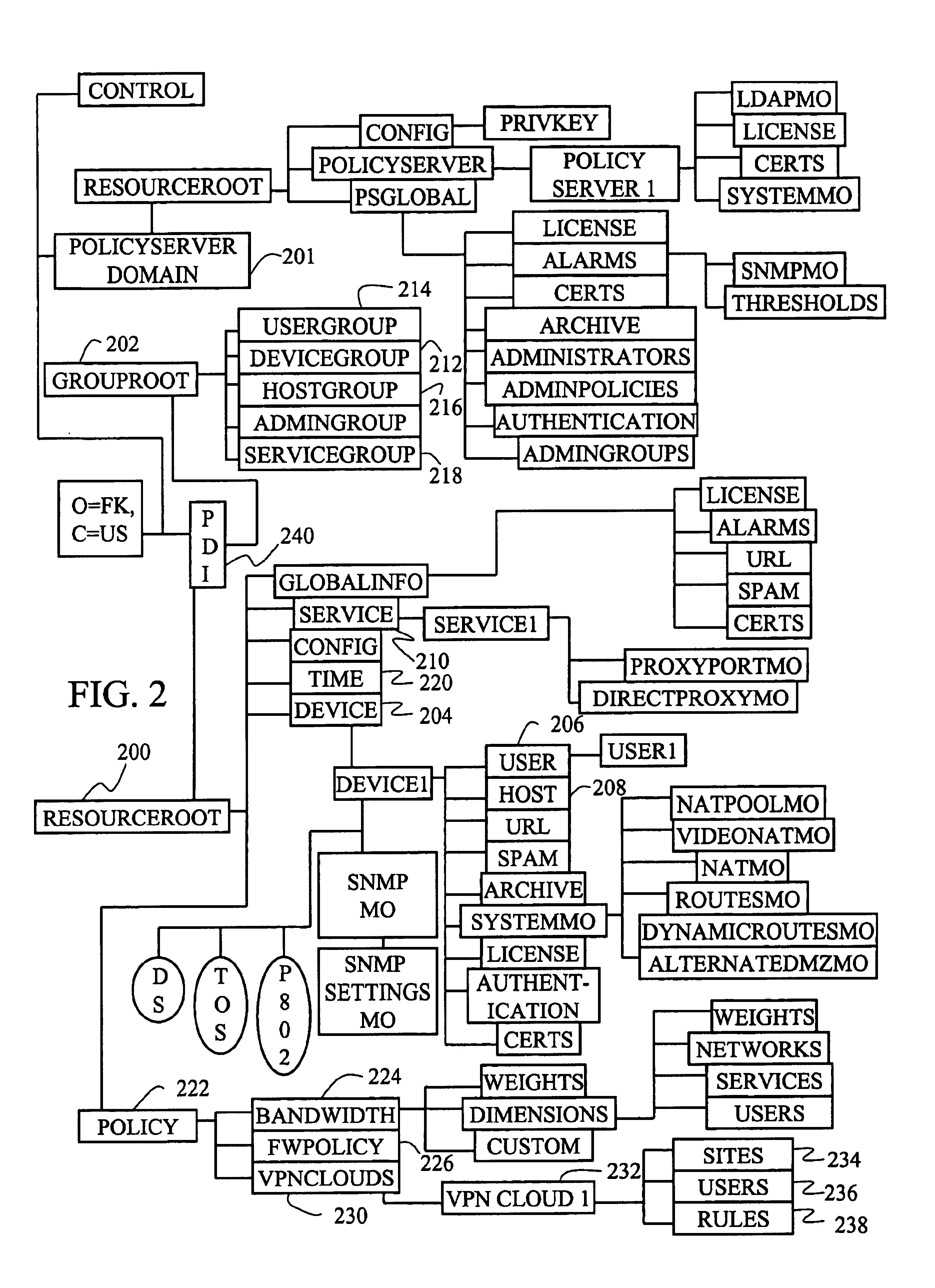
A unified policy management system for an organization including a central policy server and remotely situated policy enforcers. A central database and policy enforcer databases storing policy settings are configured as LDAP databases adhering to a hierarchical object oriented structure. Such structure allows the policy settings to be defined in an intuitive and extensible fashion. Changes in the policy settings made at the central policy server are automatically transferred to the policy enforcers for updating their respective databases. Each policy enforcer collects and transmits health and status information in a predefined log format and transmits it to the policy server for efficient monitoring by the policy server. For further efficiencies, the policy enforcement functionalities of the policy enforcers are effectively partitioned so as to be readily implemented in hardware. The system also provides for dynamically routed VPNs where VPN membership lists are automatically created and shared with the member policy enforcers. Updates to such membership lists are also automatically transferred to remote VPN clients. The system further provides for fine grain access control of the traffic in the VPN by allowing definition of firewall rules within the VPN. In addition, policy server and policy enforcers may be configured for high availability by maintaining a backup unit in addition to a primary unit. The backup unit become active upon failure of the primary unit.
Owner:IYER SHANKER V +3
Object model for network policy management
InactiveUS6944183B1Simplified managementEnergy efficient ICTDigital computer detailsNetwork managementAdaptive routing
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
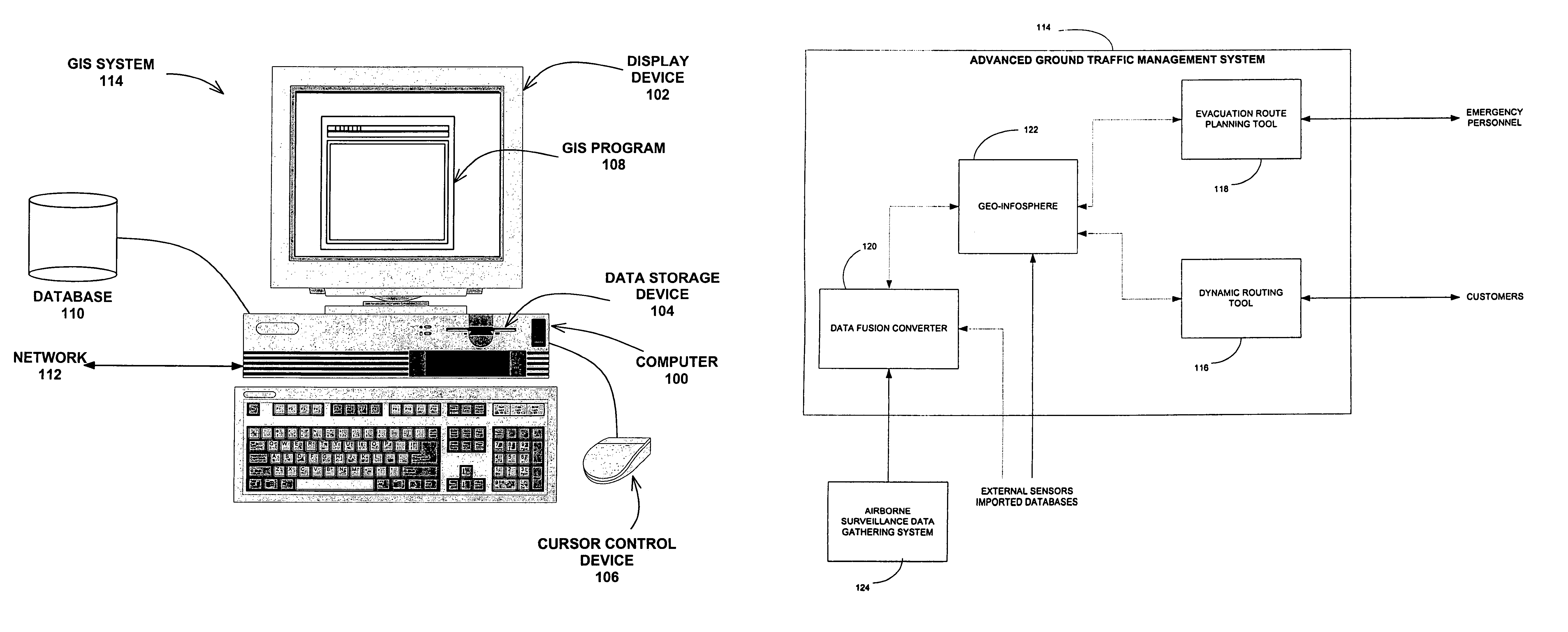
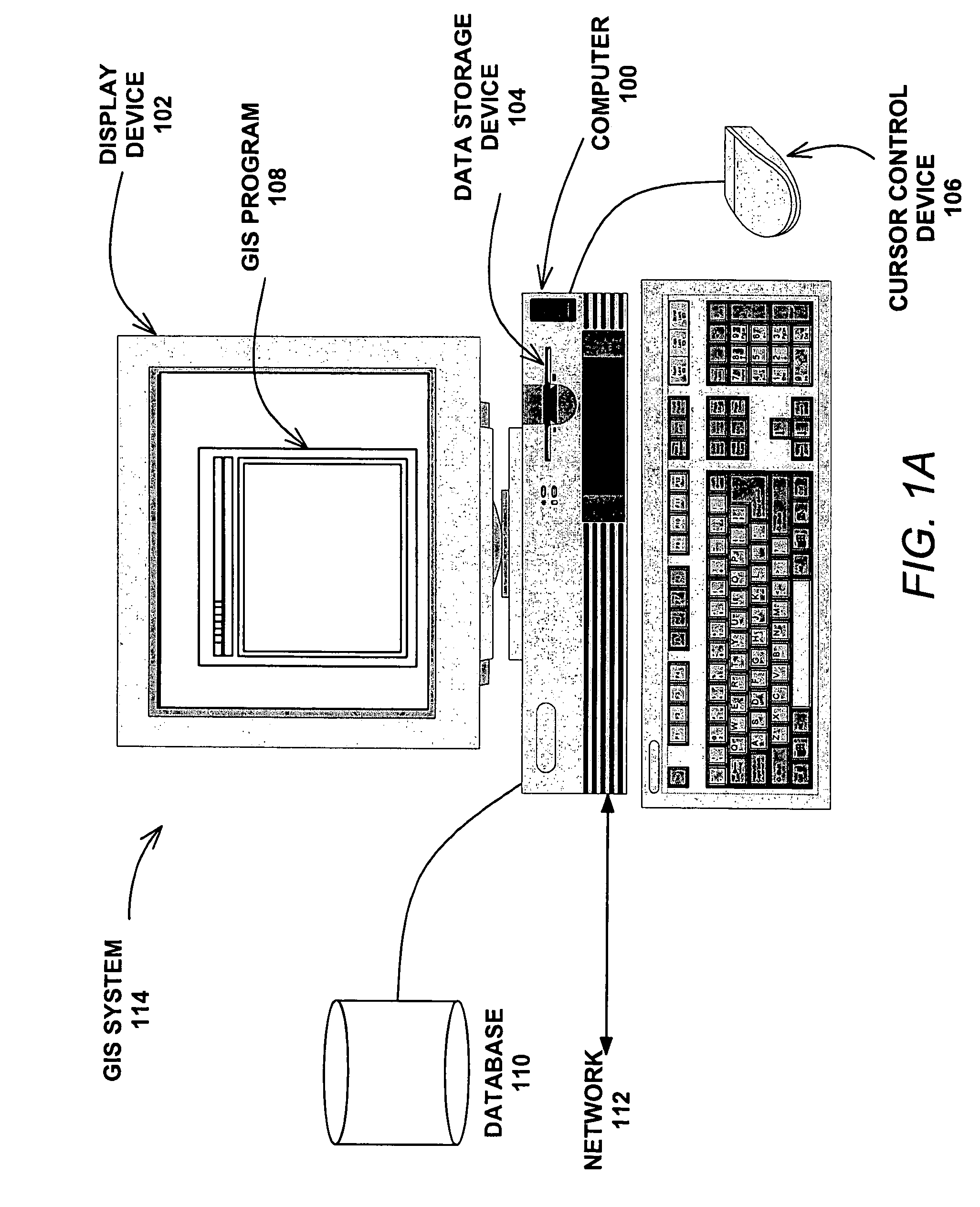
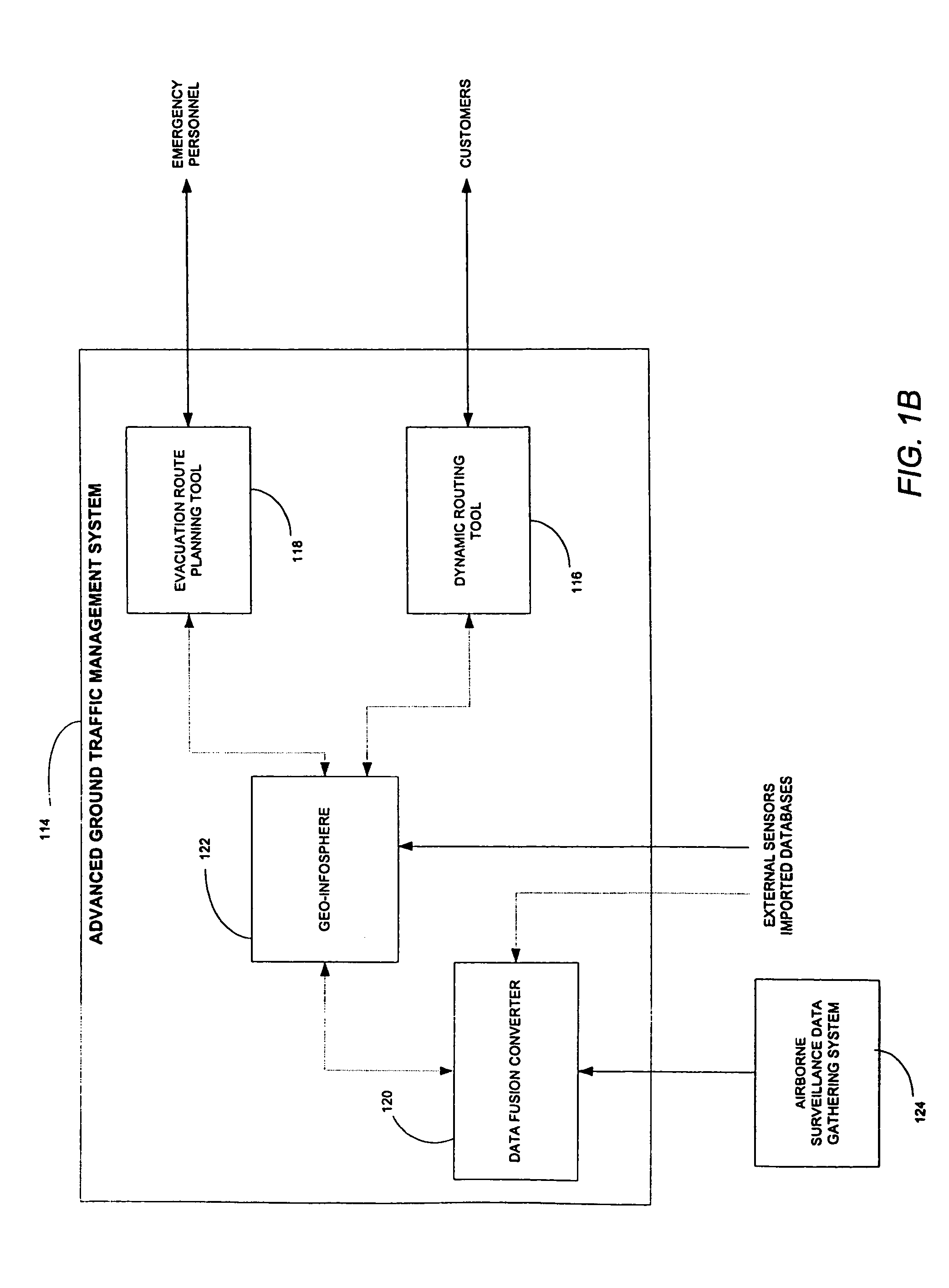
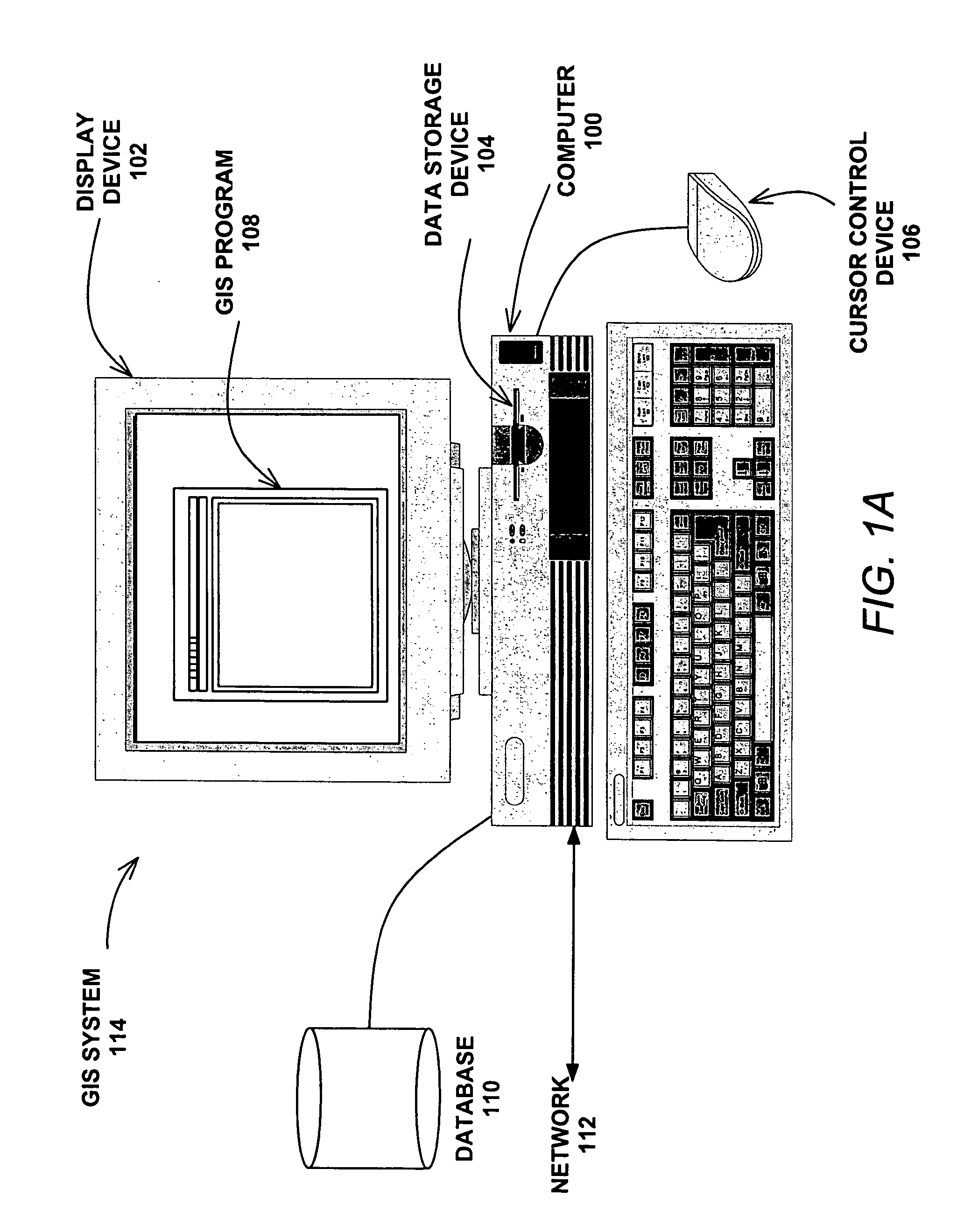
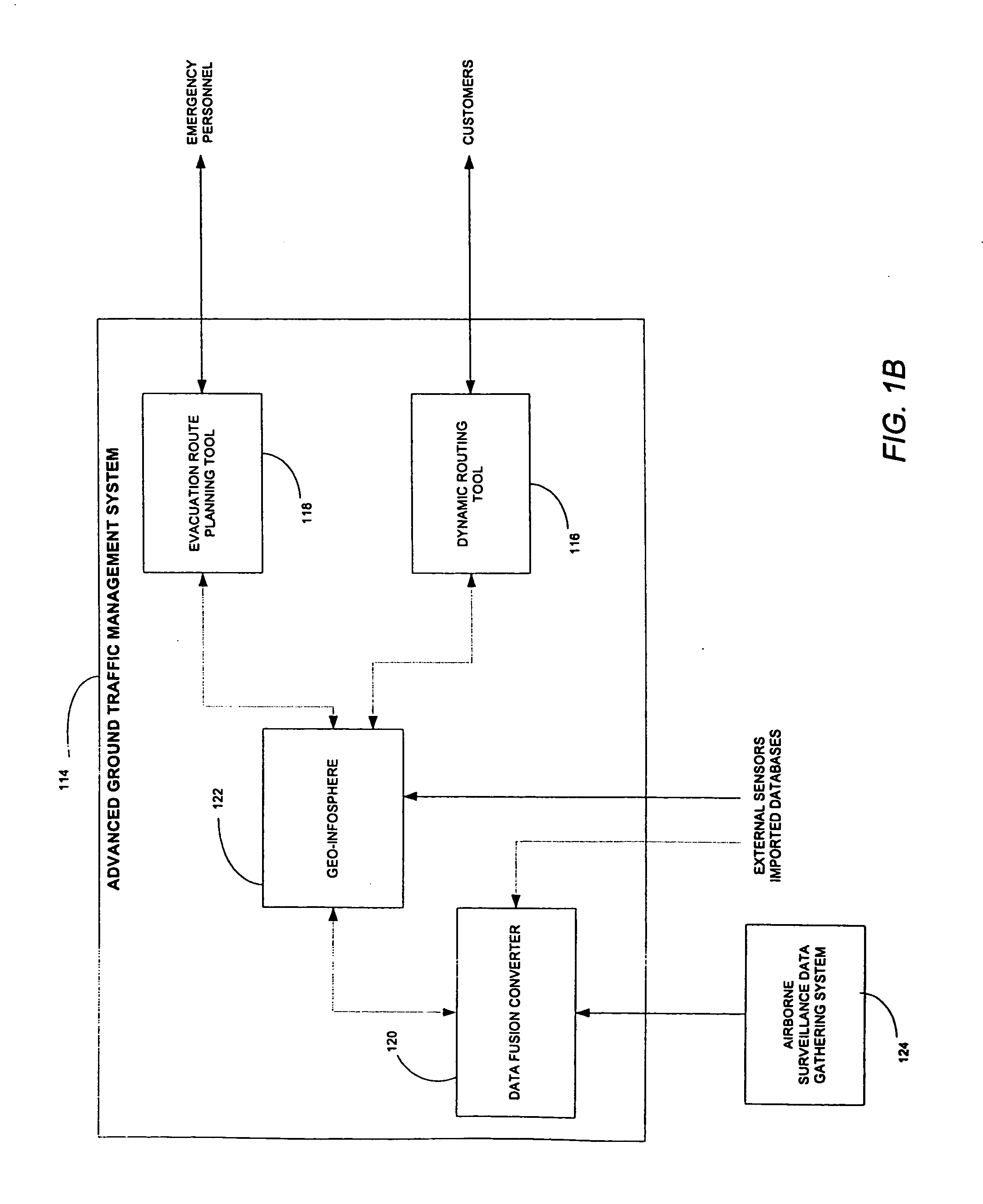
AGTM airborne surveillance
ActiveUS7650231B2Analogue computers for vehiclesInstruments for road network navigationGeolocationAdaptive routing
Systems, methods and apparatuses for managing ground transportation in a geographical area are disclosed. A system for managing ground transportation in a geographical area in accordance with the present invention comprises at least one airborne surveillance platform, a graphical information systems (GIS) database, receiving information from the airborne surveillance platform, the GIS database storing data that represents the geographical area, the GIS database including at least one node representing at least one geographical location within the geographic area and at least one arc representing at least one street within the geographic area, and a routing tool, coupled to the GIS database, wherein the dynamic routing tool accepts data from the GIS database and determines a transportation route for at least one vehicle within the geographical area using at least the data from the GIS database and the information from the airborne surveillance platform.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
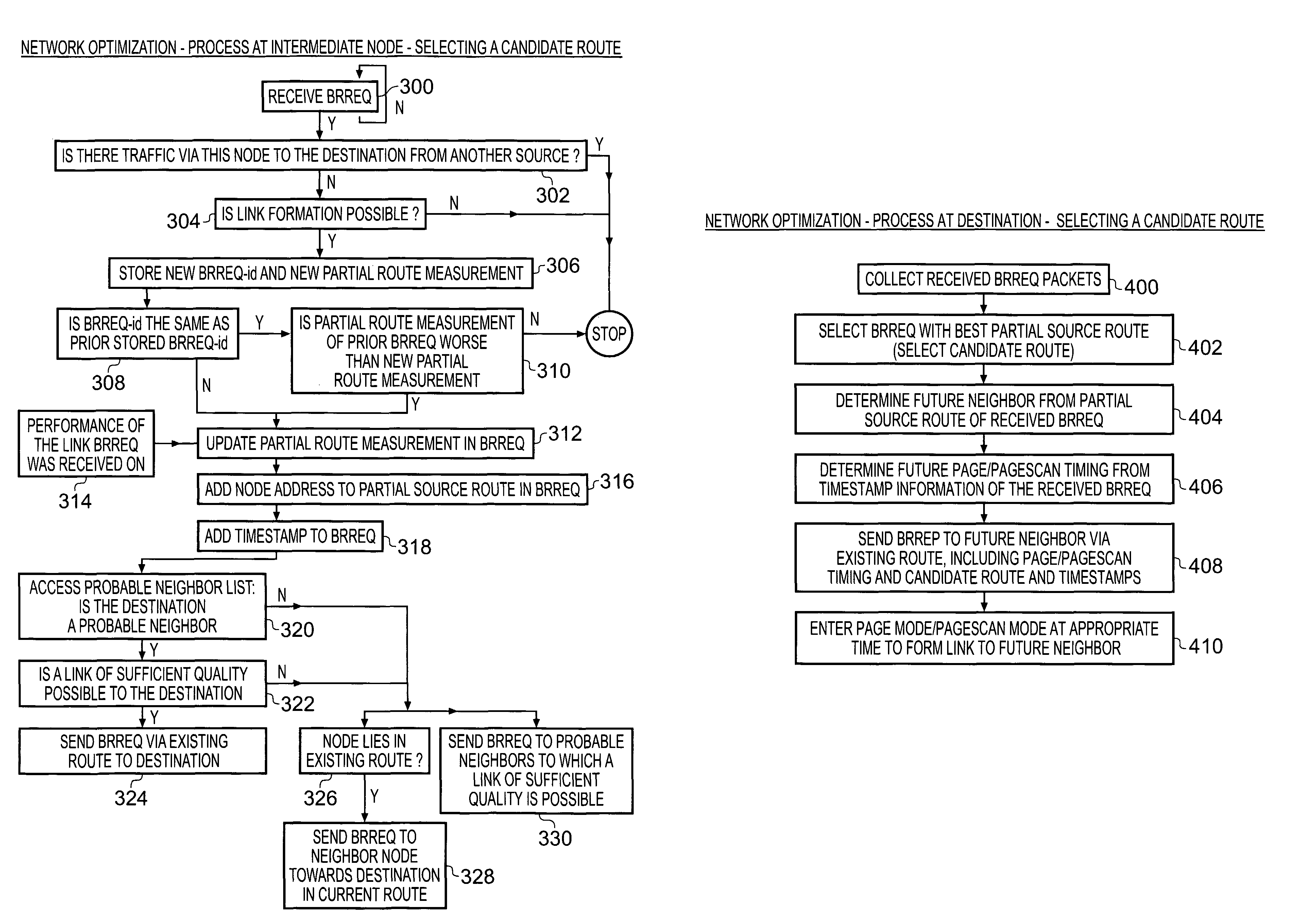
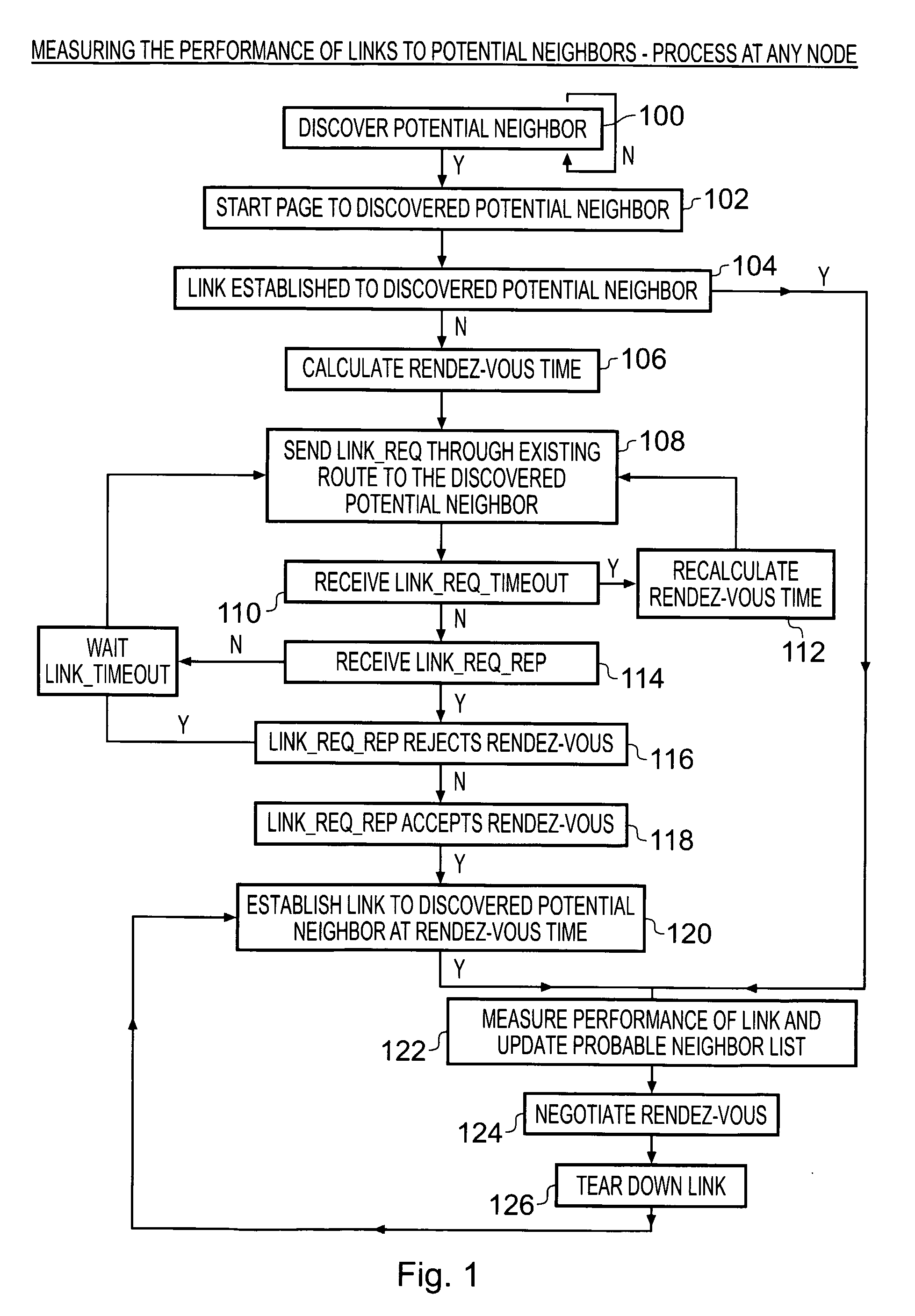
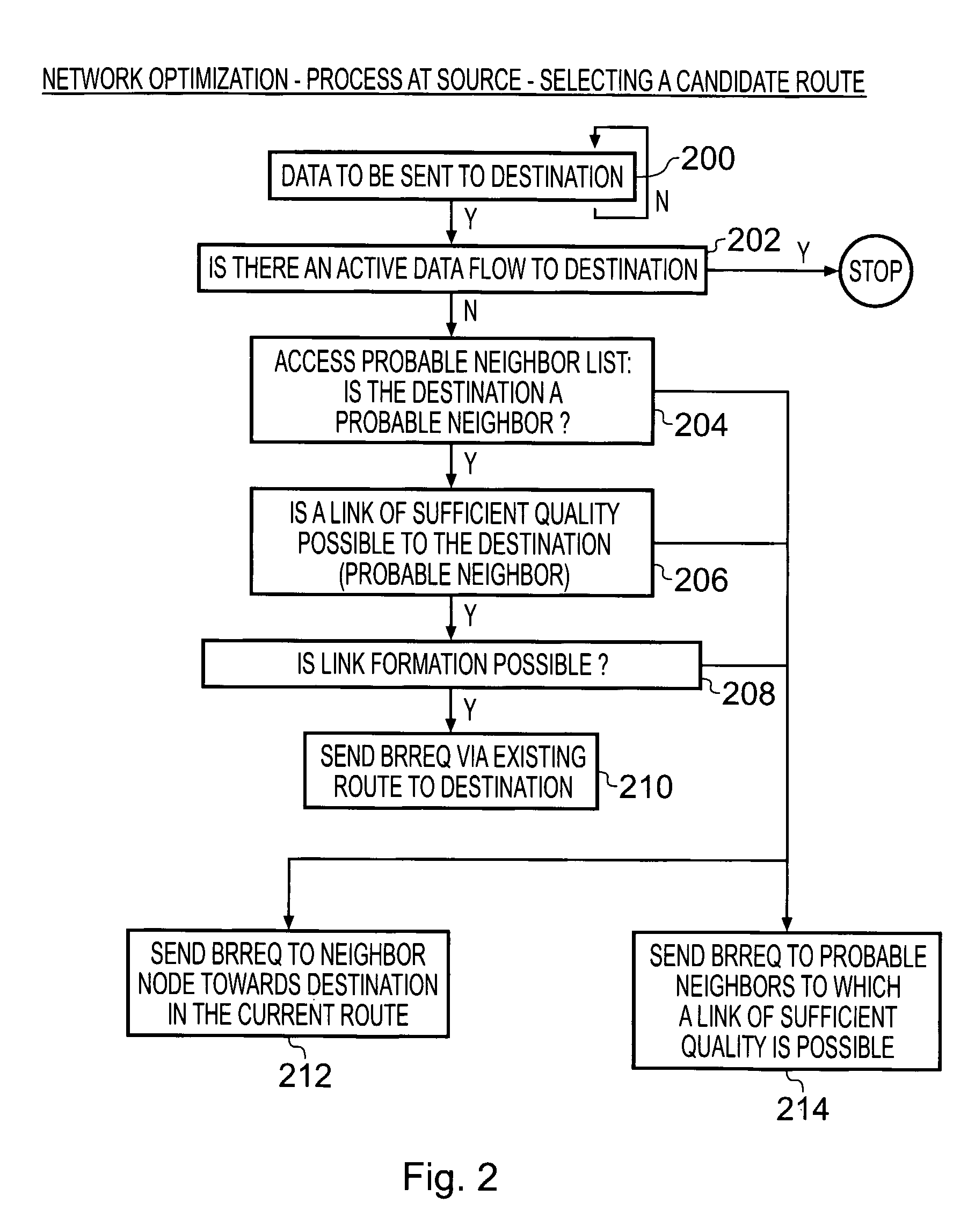
Adaptive routing
ActiveUS8036207B2Maintain performanceImprove utilizationError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsSelf adaptiveAdaptive routing
Methods and devices are shown for improving an existing route between a first node and a second node in a first ad-hoc network that includes a plurality of nodes, the method and devices selecting based on a predetermined performance criterion or criteria one of a plurality of candidate routes between the first node and the second node, wherein each candidate route includes at least one inter-node link that is not included within the first ad-hoc network and at least one candidate route including multiple inter-node links; initializing, via the existing route, the use of the inter-node links of the selected candidate route; and switching from using the existing route to using the candidate route.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
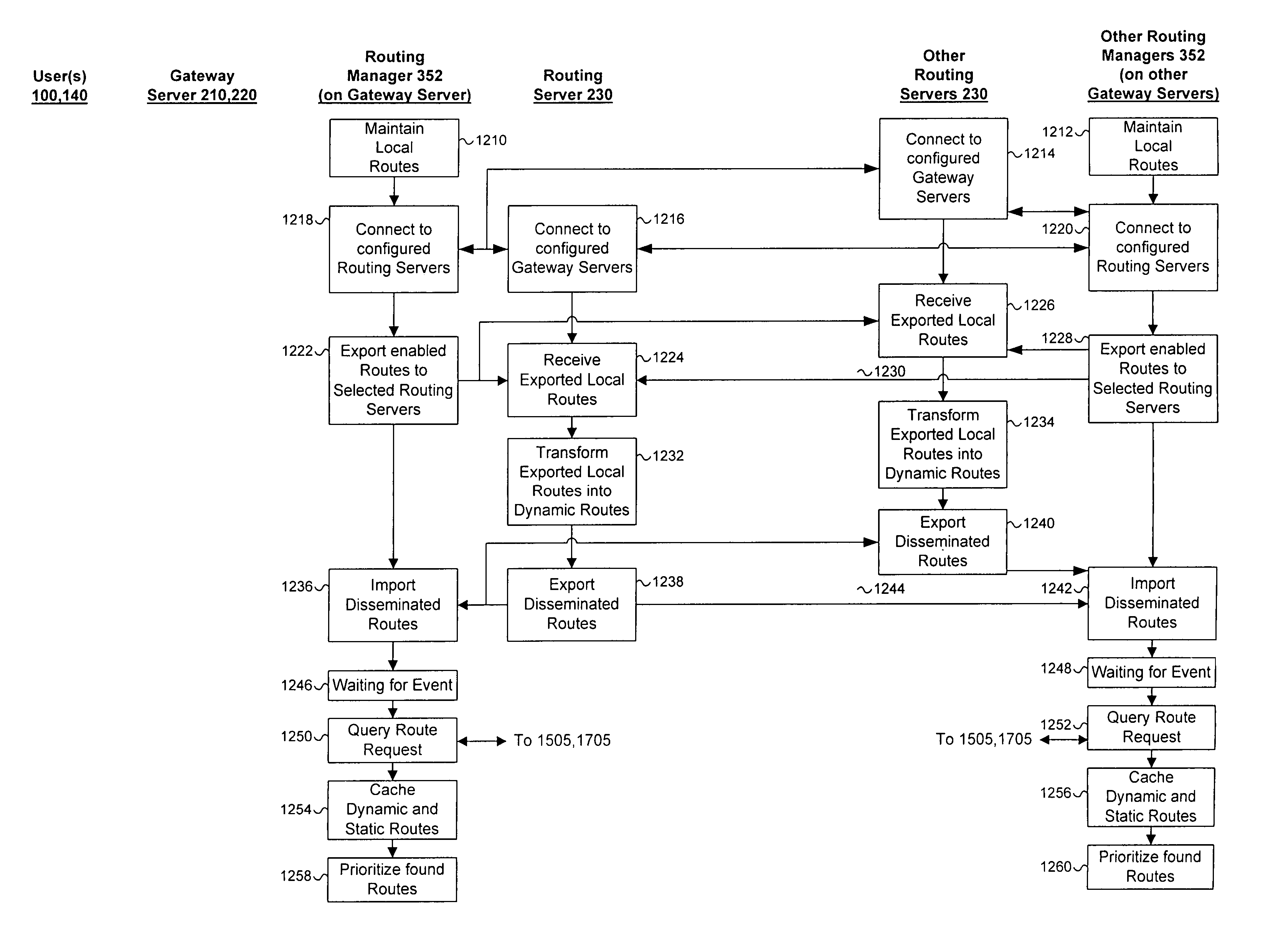
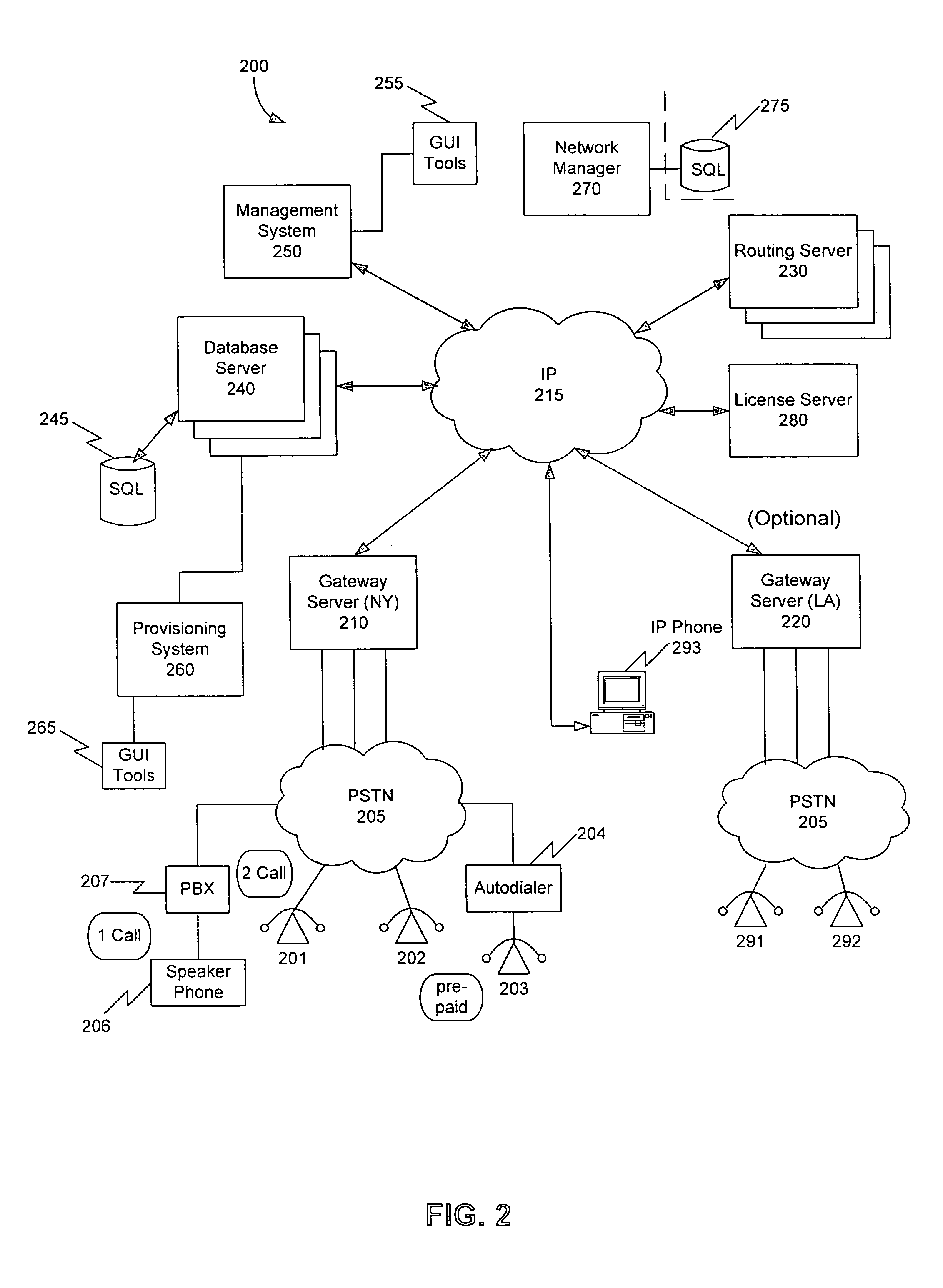
Method, system, and computer program product for managing routing servers and services
InactiveUS7457279B1Interconnection arrangementsData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityTelephone network
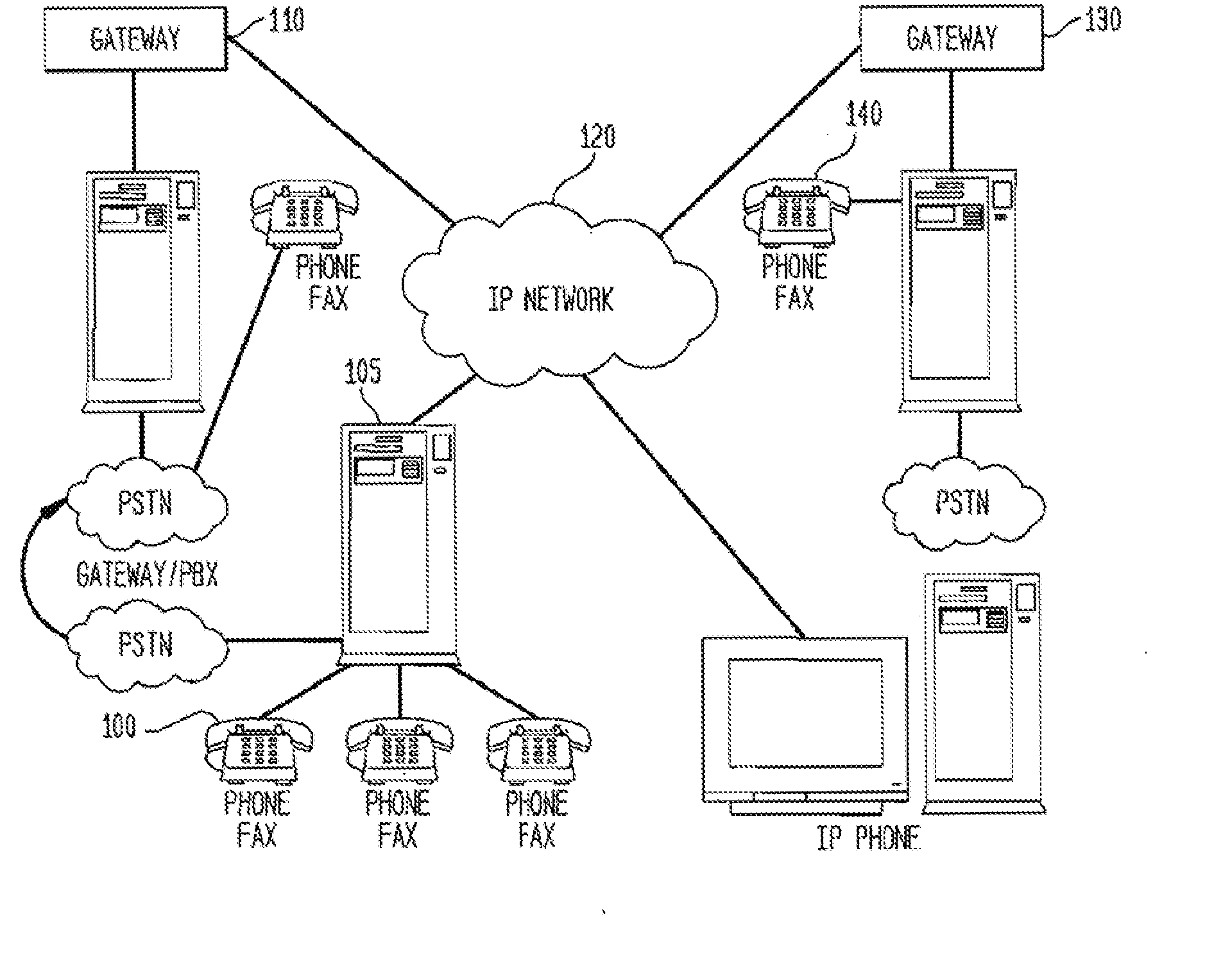
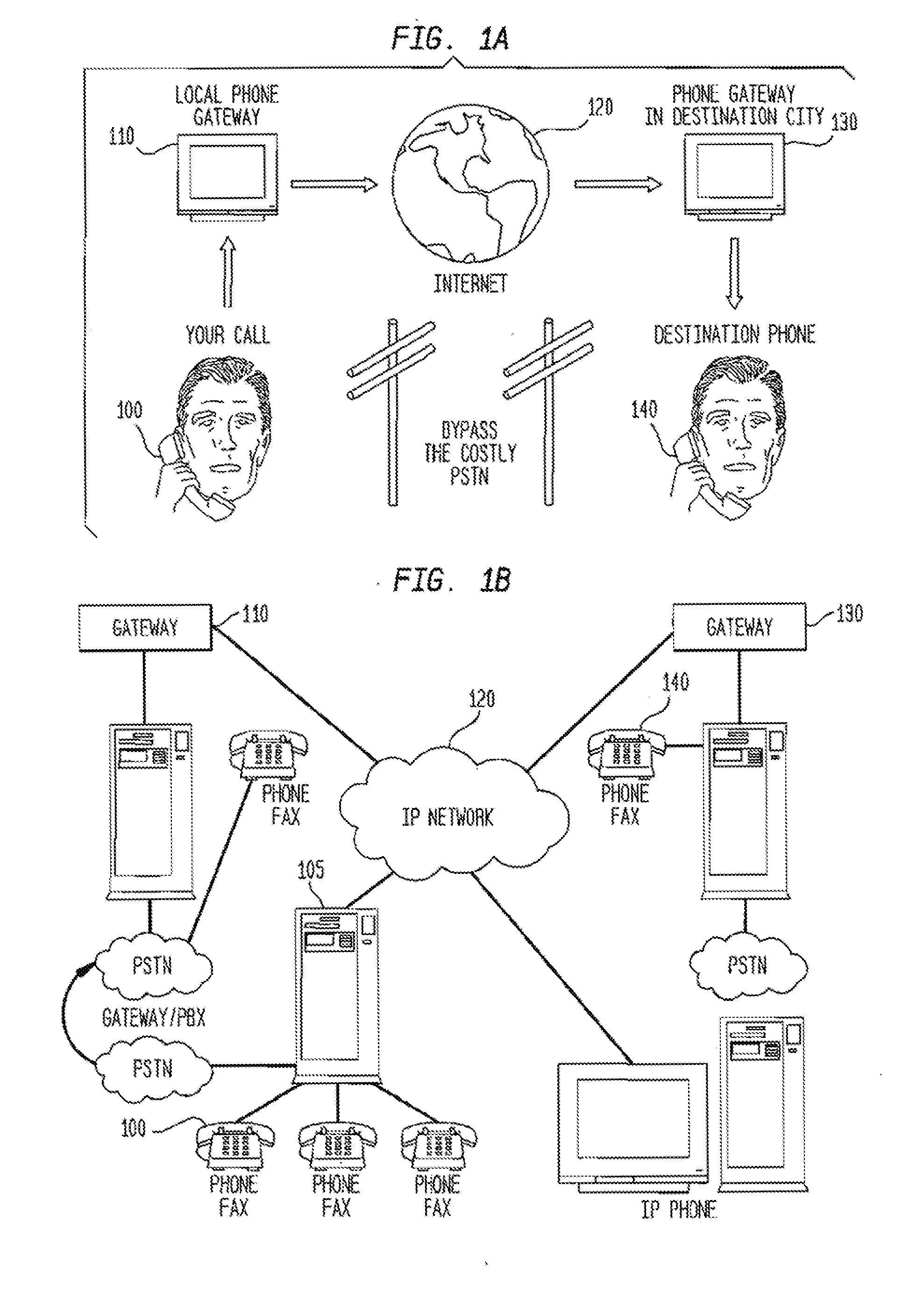
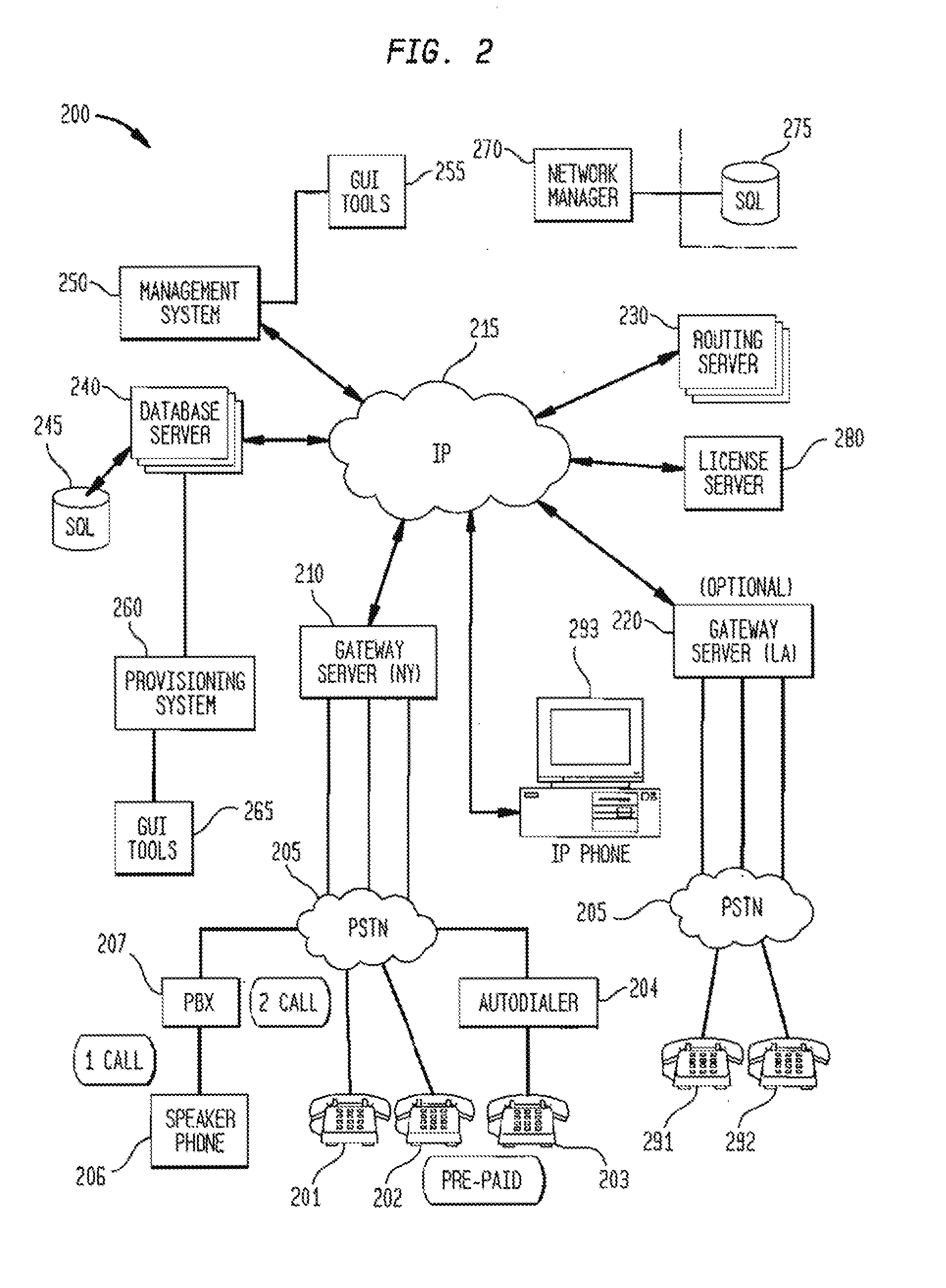
A method, system, and computer program product for routing network traffic (calls in a Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)), which expands the capabilities of existing systems by providing faster and more efficient direction of network traffic, is disclosed. A routing management system includes a routing manager which maintains a list of local routes, establishes and manages connections to the routing server(s), exports routes to the routing server(s), imports disseminated routes from the routing server(s), obtains static global and dynamic routes from the routing server(s), caches those routes for future use, finds all matching routes for a particular number dialed by the user, and prioritizing those routes based on timing, access and ordering information. An additional embodiment contains at least one routing server which provides look-up services for gateway server(s), allows export of local routes from gateway server(s), and distributes translation data, and at least one gateway server which handles calls received on either the Internet protocol (IP) or traditional telephony networks. The gateway server bridges calls between the different kinds of networks, interacts with users, interfaces with the routing system.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
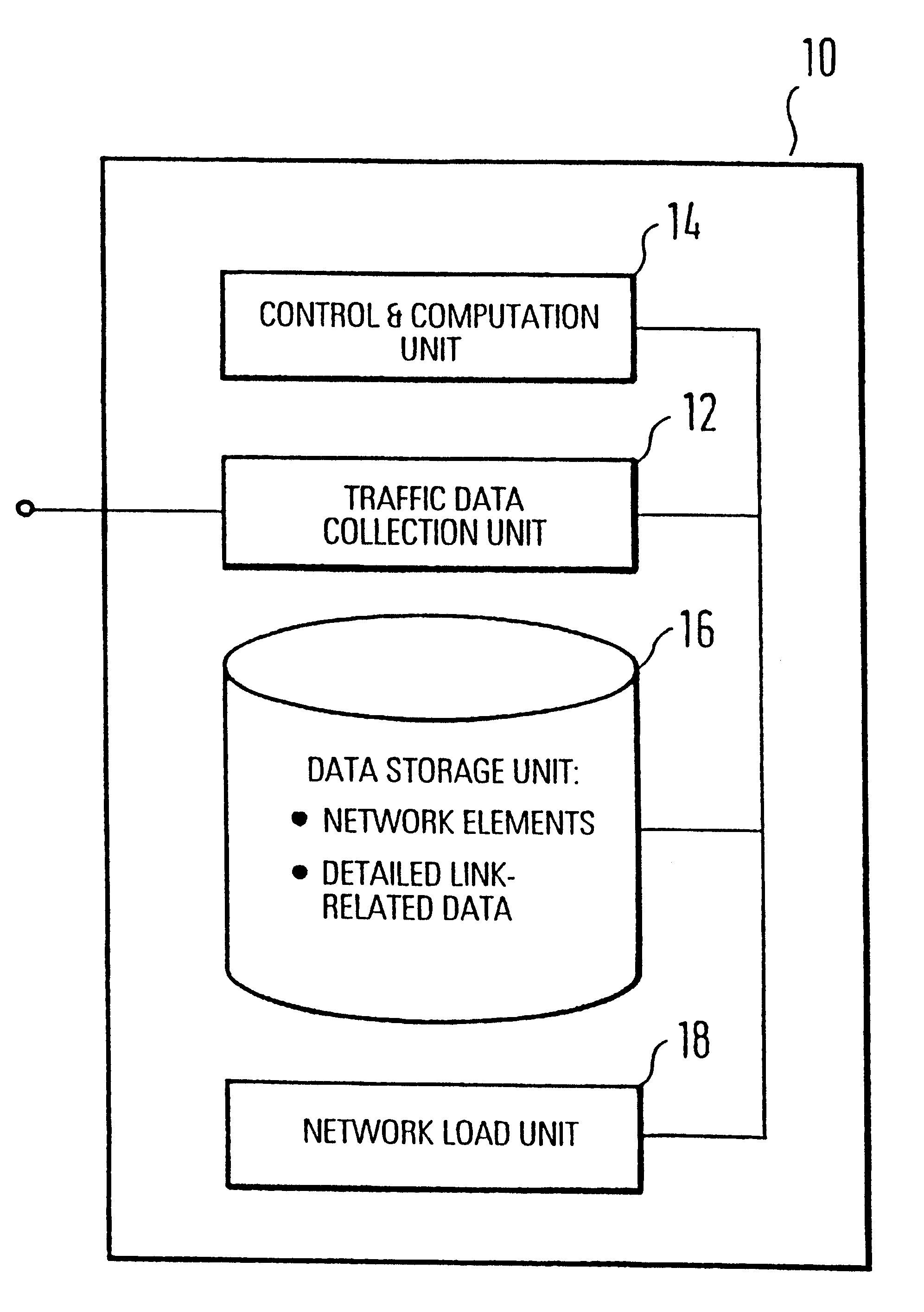
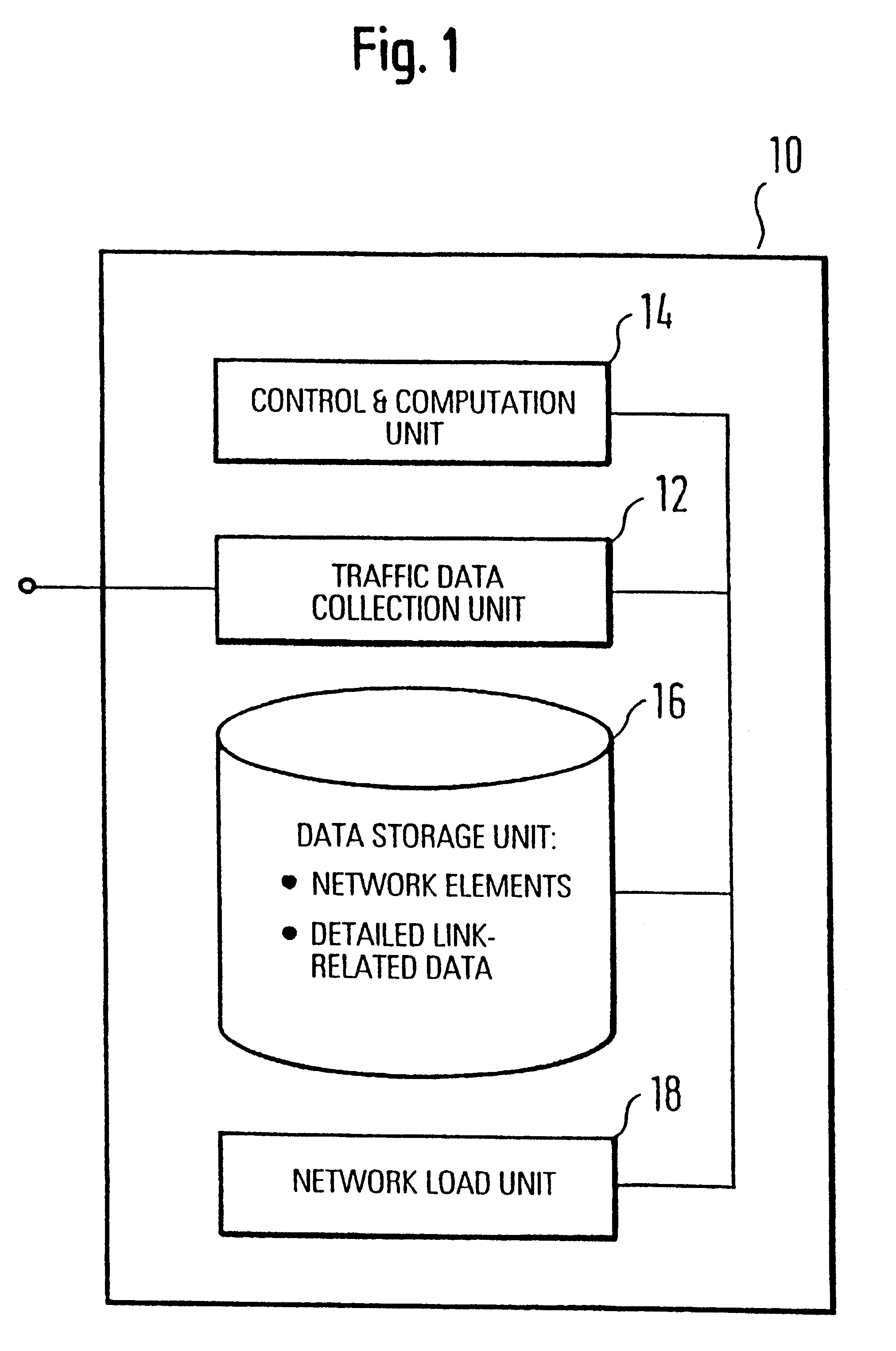
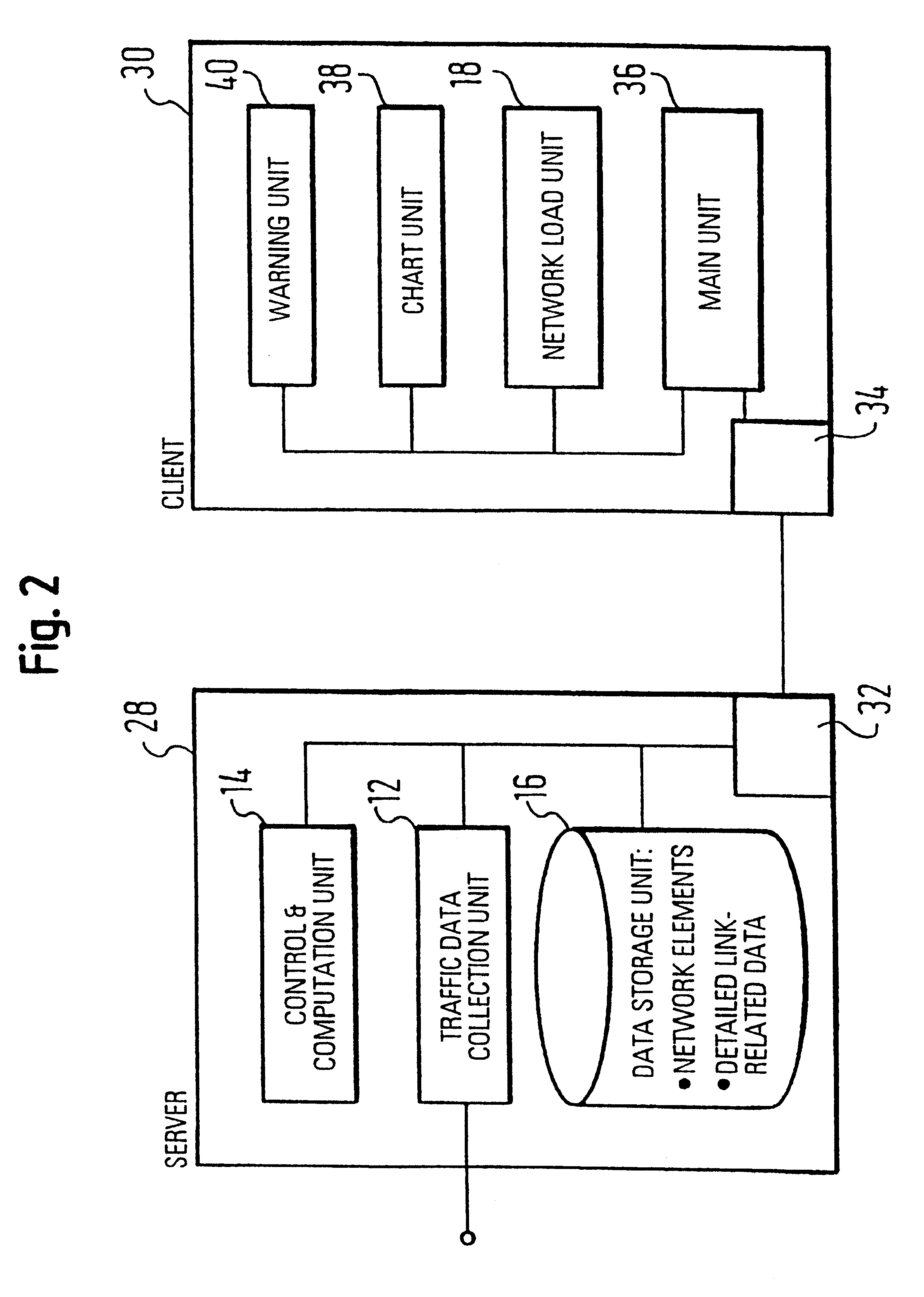
System for traffic data evaluation of real network with dynamic routing utilizing virtual network modelling
InactiveUS6442615B1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksNetwork modelAdaptive routing
To provide an improved approach to traffic data evaluation in a network using dynamic routing there is provided a traffic data evaluation apparatus for a network using dynamic routing comprising traffic data collection means (12) to collect data with respect to a real traffic flow in the network. Further, the traffic data evaluation apparatus comprises a network modelling unit (14, 16) to model the network through a virtual network having virtual links without capacity restrictions imposed thereon. Still further, there is provided a network load evaluation means (18) to map the real traffic flow onto the virtual network assuming optimal routing and to compare the capacity used for each virtual link with the capacity assigned thereto. Thus, it is possible to draw conclusions on the network load by real network measurements also for a network using a dynamic routing protocol.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
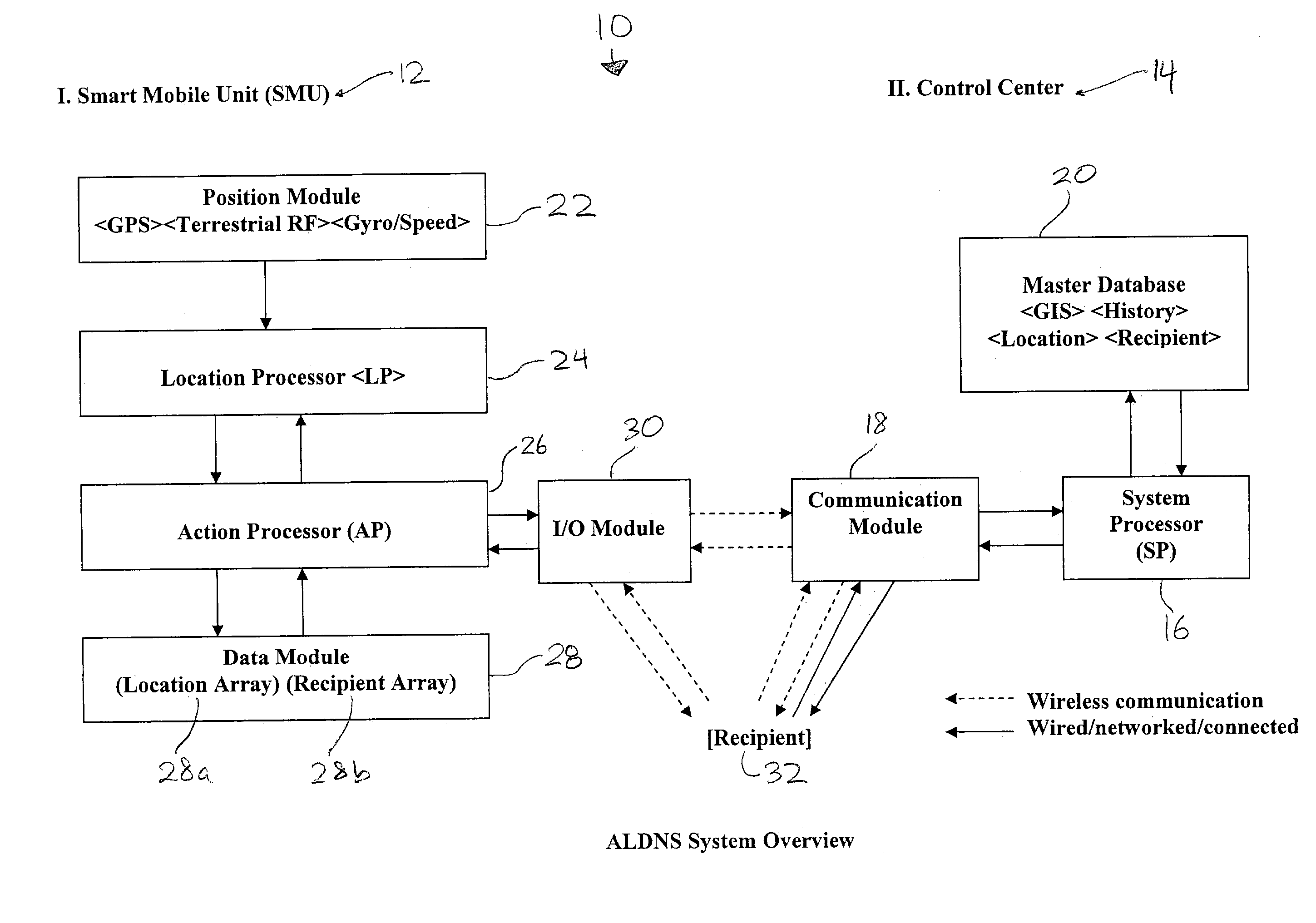
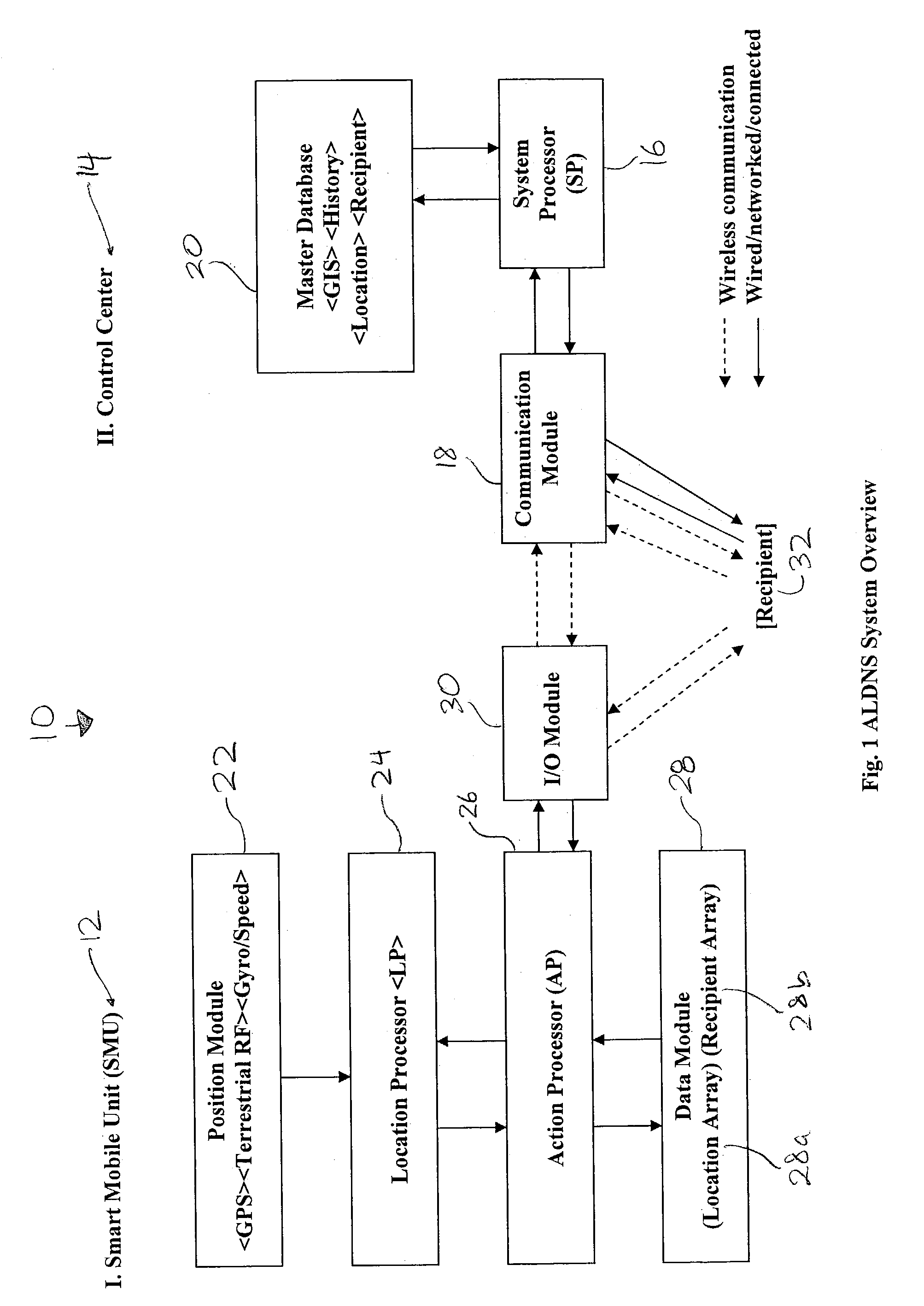
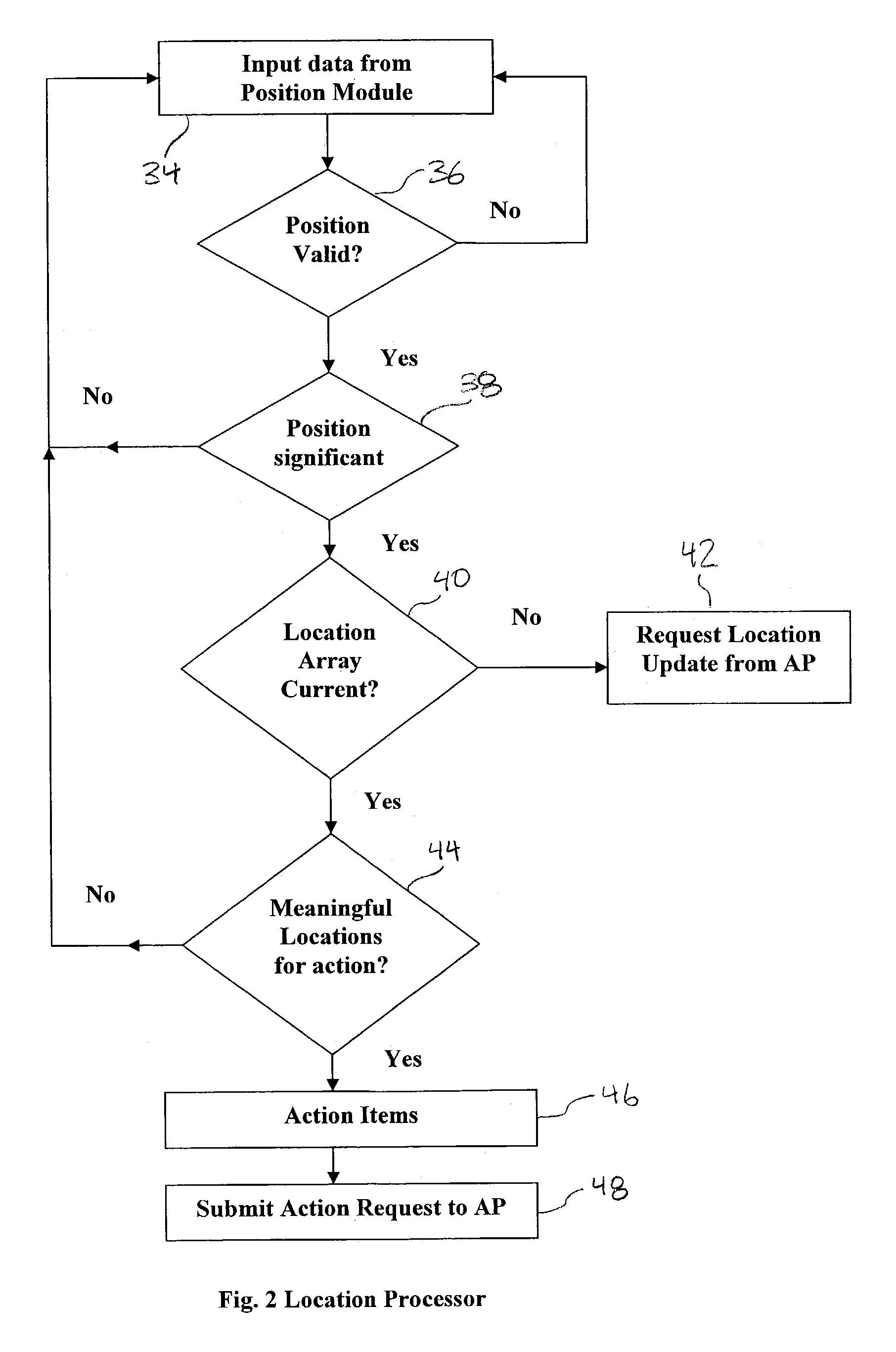
Method and apparatus for an automated location-based, dynamic notification system (ALDNS)
An automated, location-based, dynamic notification system comprises a mobile unit hardware device and a control center computer facility with communication capabilities. The mobile unit comprises a position module, a location processor, an action processor, a data module, and an I / O module. The control center comprises a system processor, a communication module, and a master database. The system provides notifications of arriving, approaching, leaving, entering, and any other types of location-related notifications, which are issued in an automatic, unattended manner. The illustrated embodiments of the invention are based on location and thus are used in a dynamic routing situation where both route patterns and stop locations change frequently while the object is moving. The system requires no interaction from the driver or the dispatcher, requires no on-board checking or manipulation of a schedule, and applies in many situations including special-education transportation, prisoner transportation, airport shuttle service.
Owner:GEOSPATIAL TECH
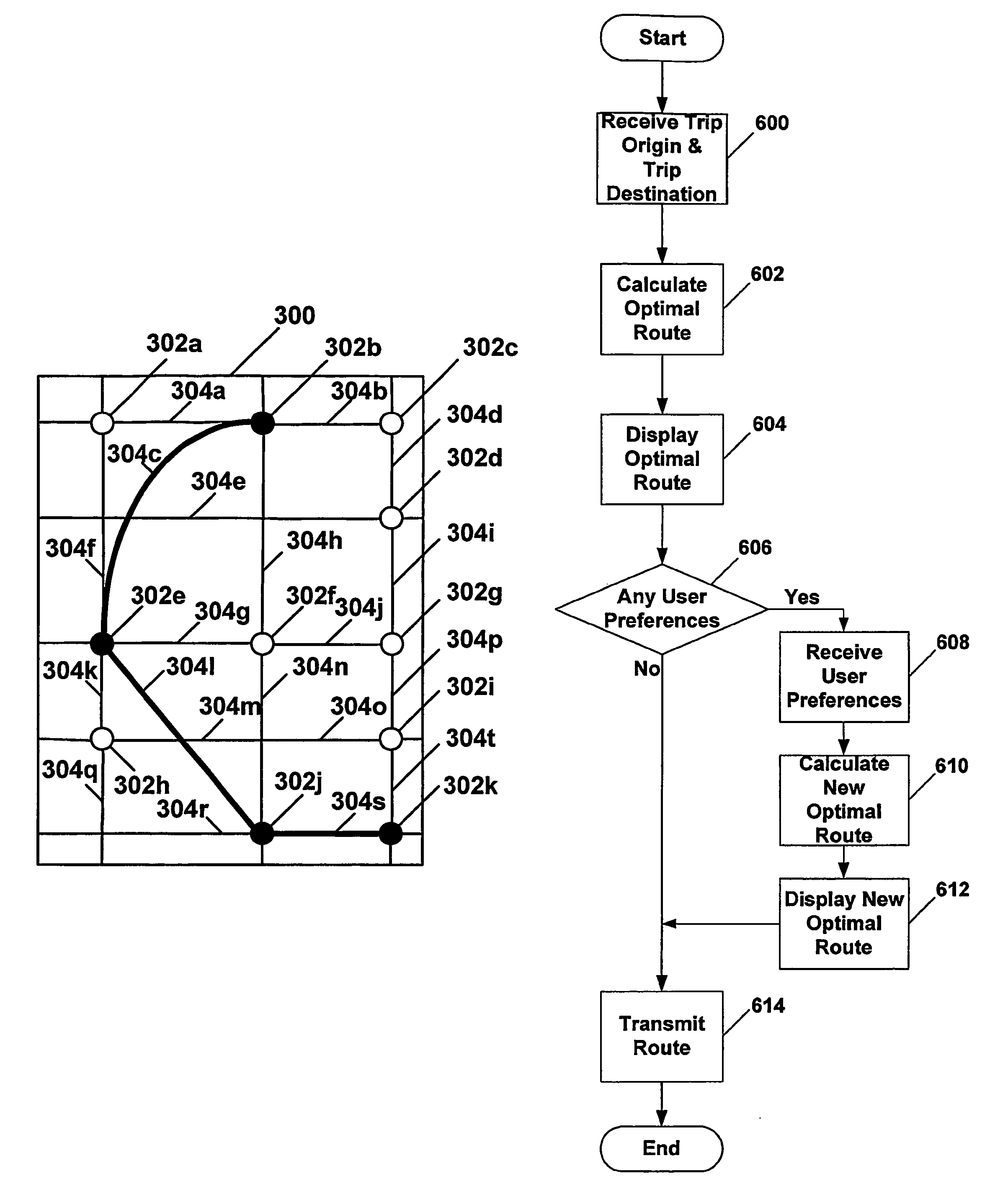
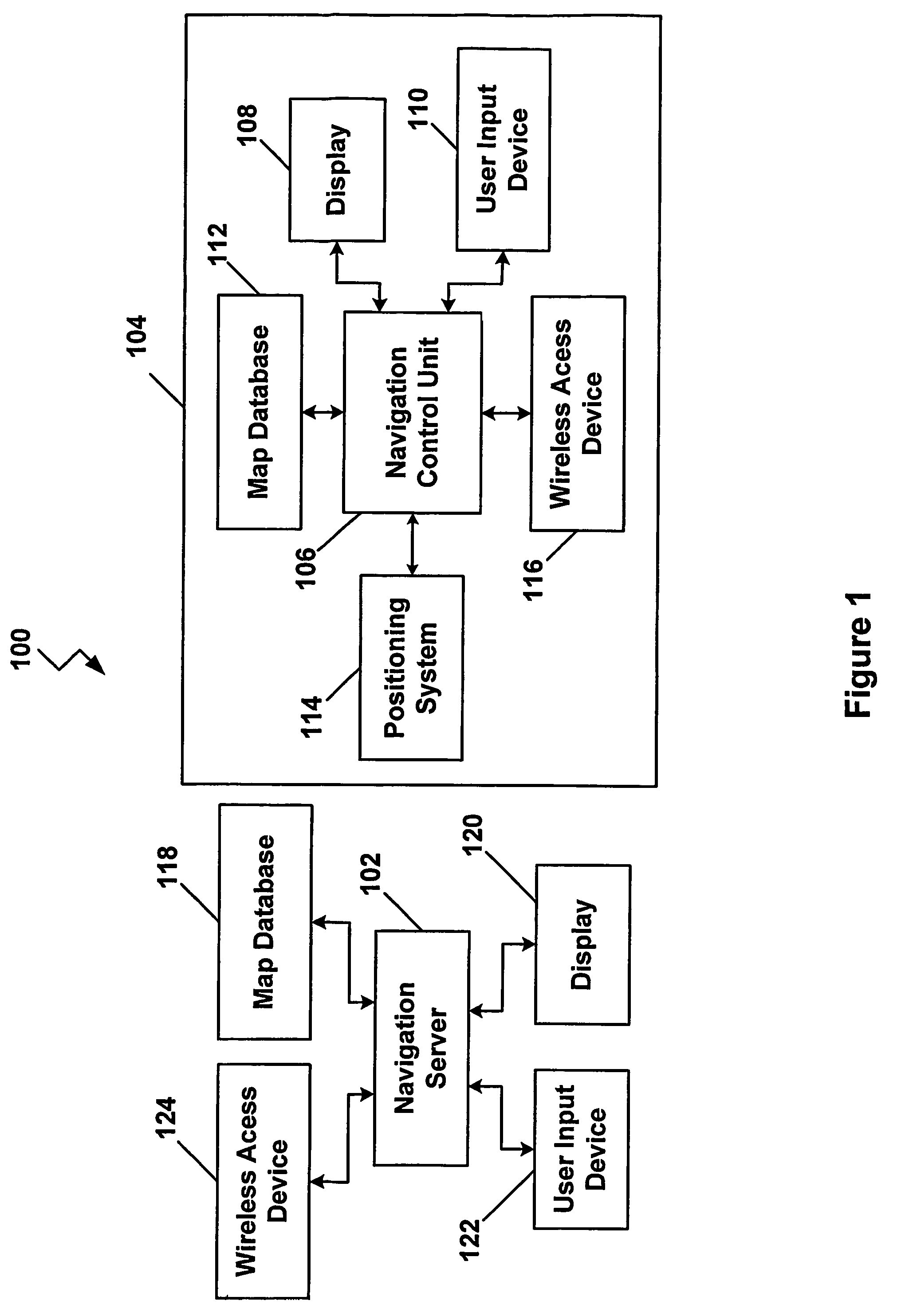
Transmission of special routes to a navigation device
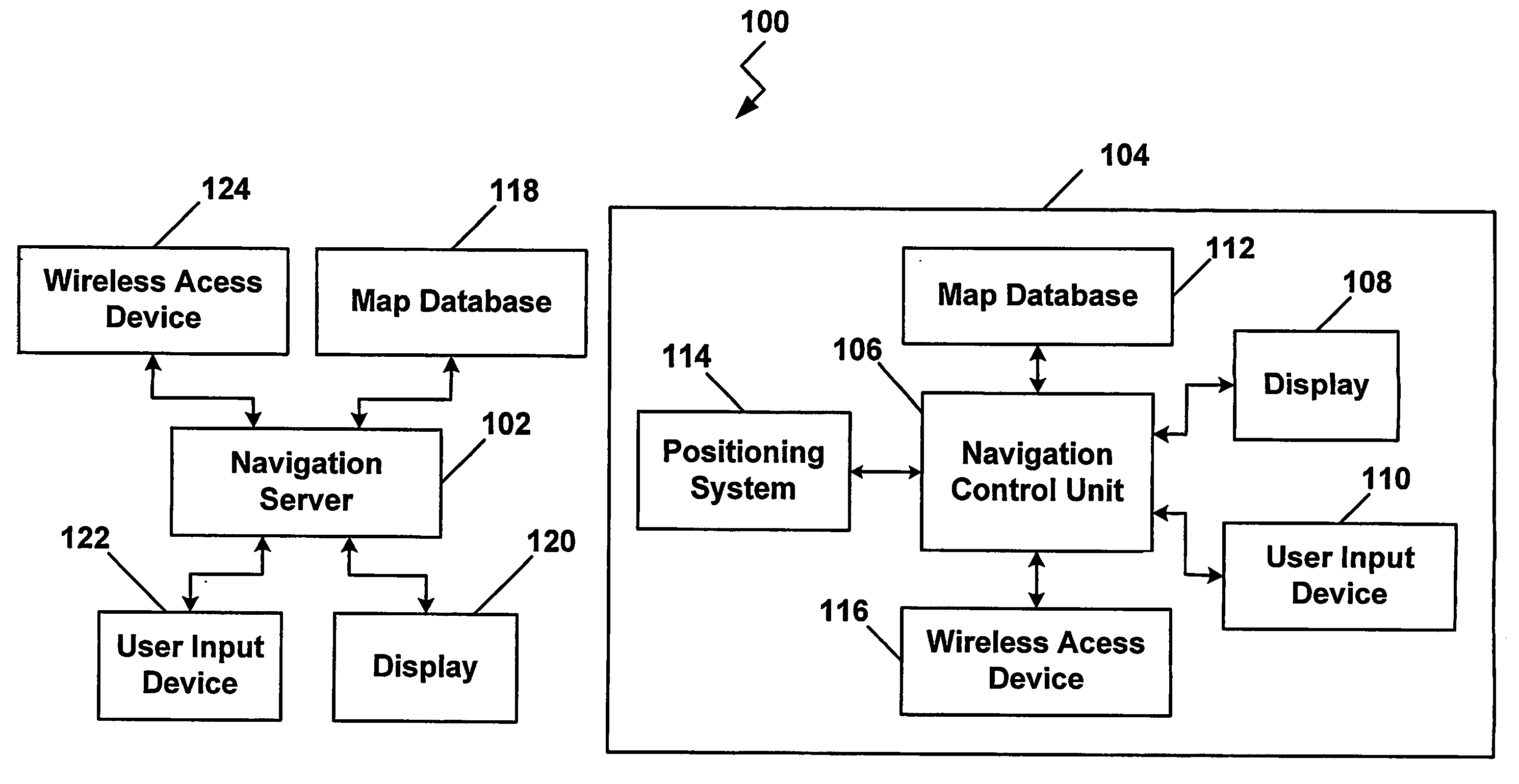
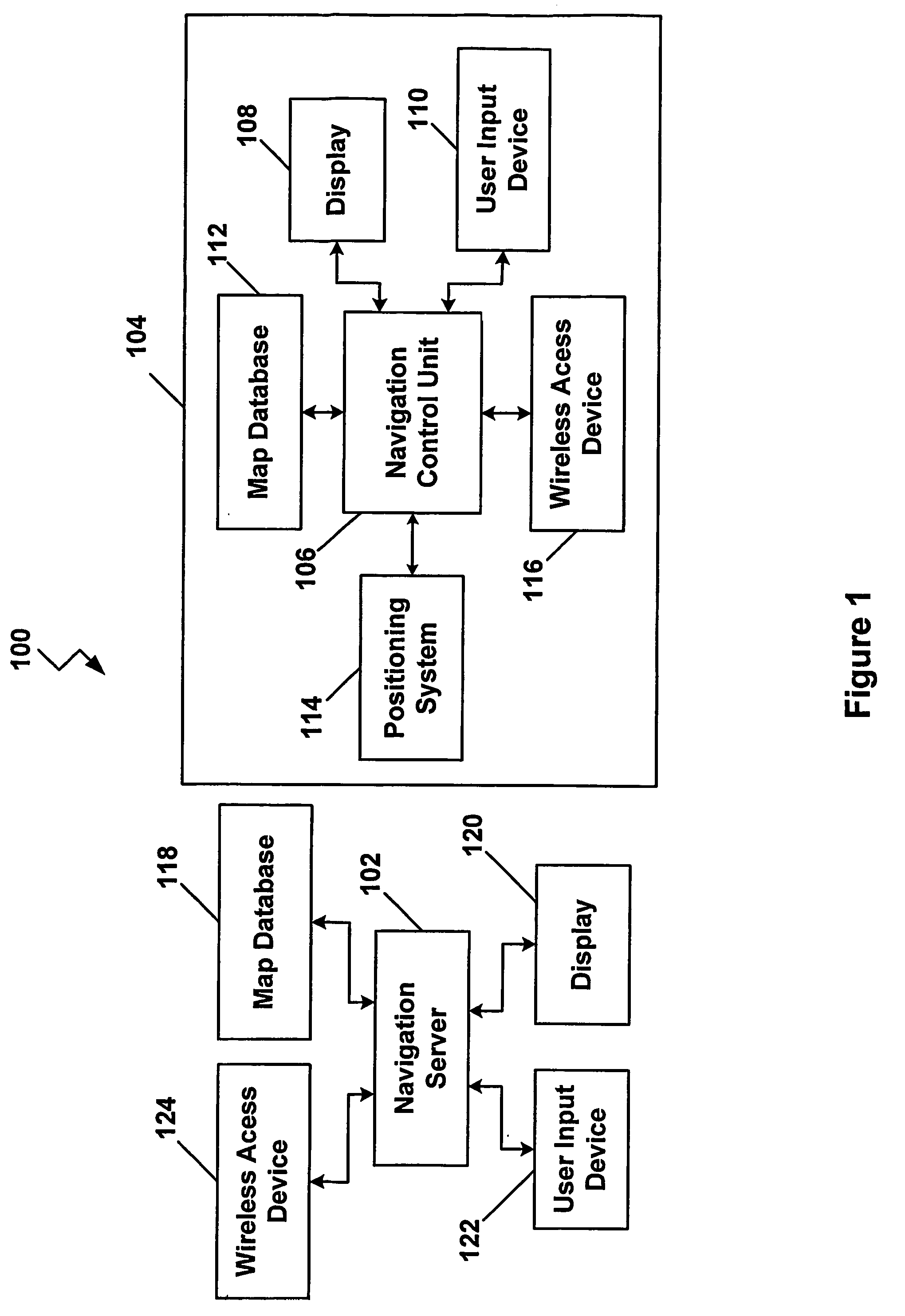
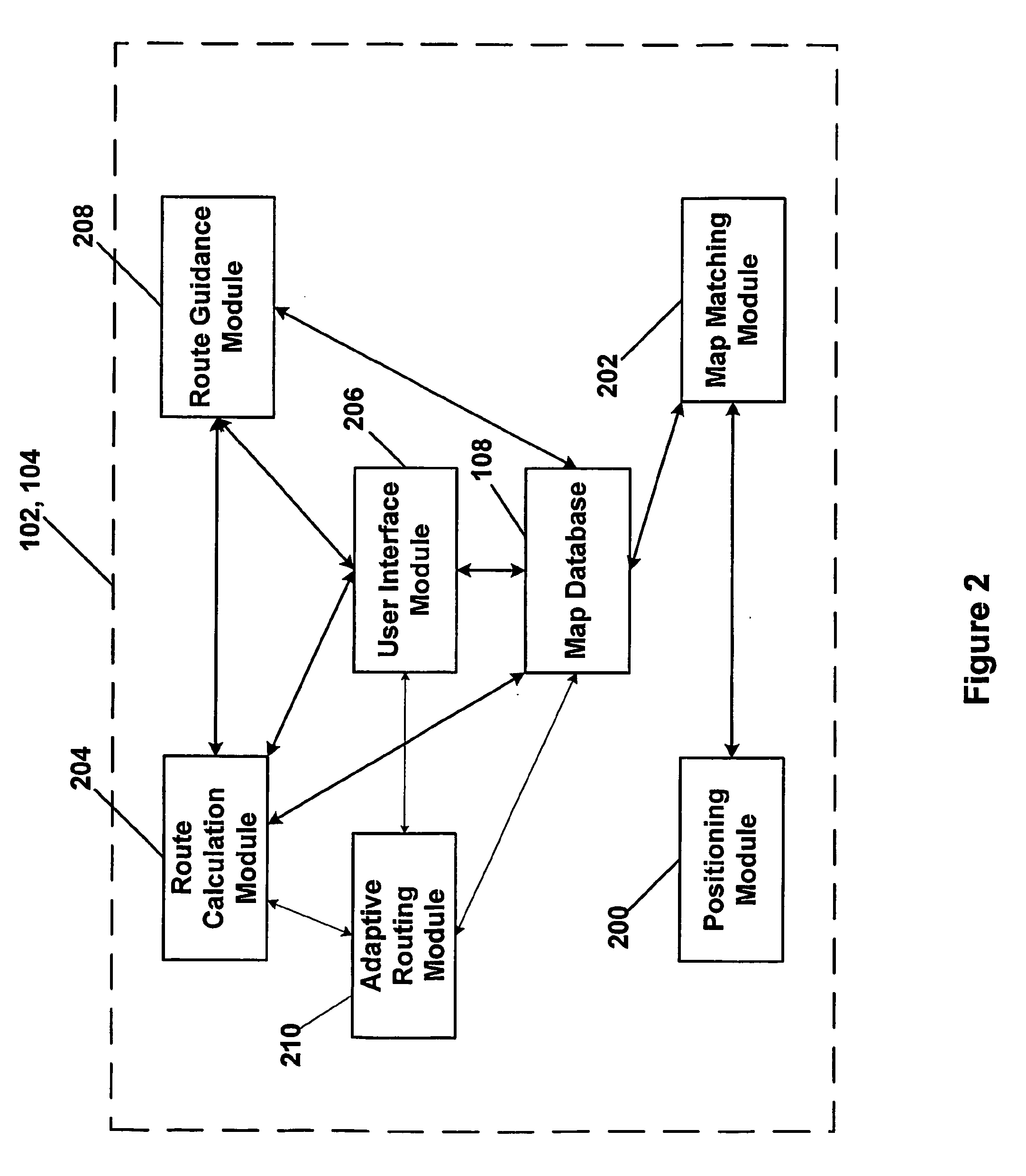
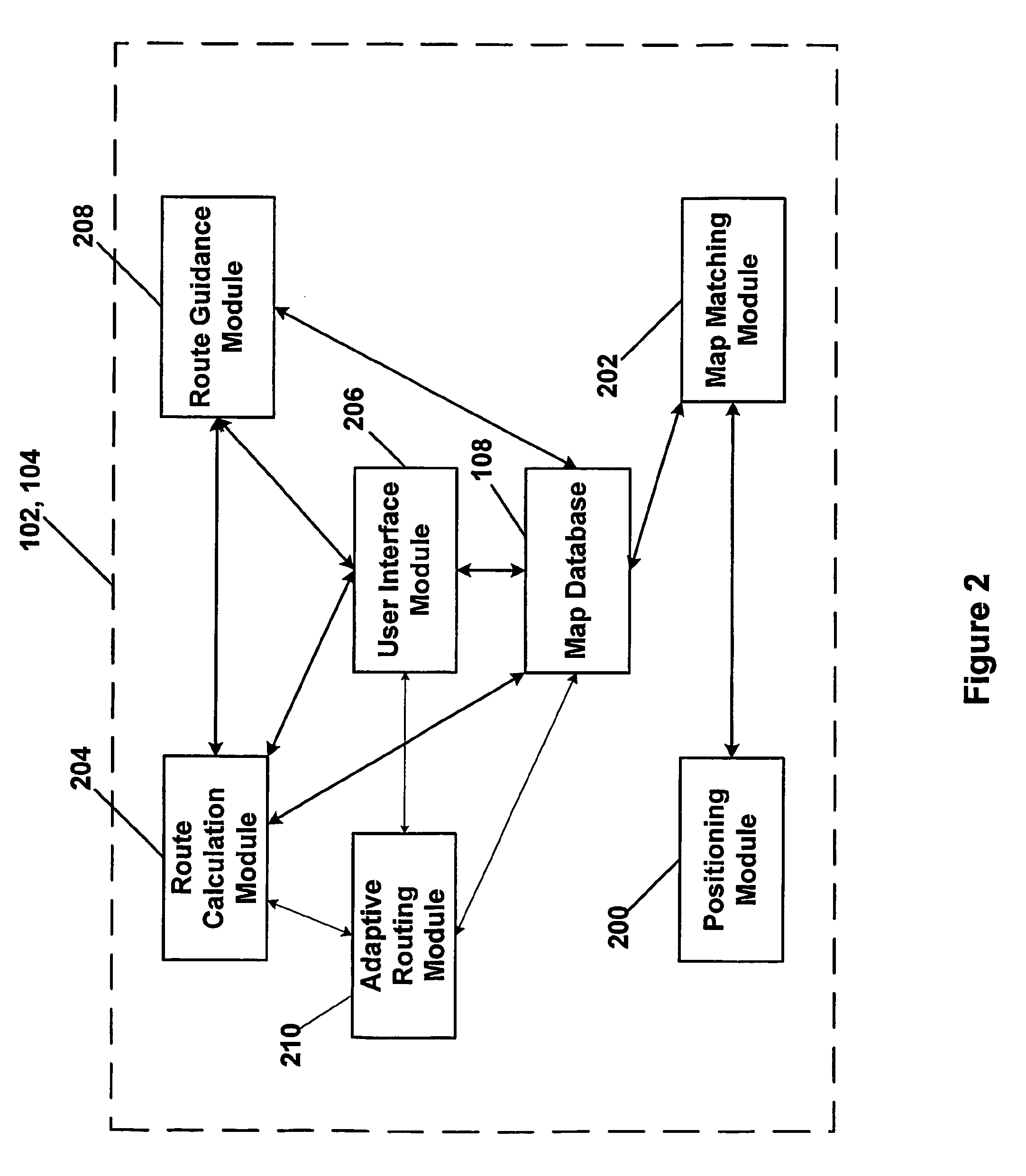
ActiveUS20060015249A1Instruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsUser inputNavigation system
A vehicle navigation system includes an adaptive routing module (210) that allows a user to provide inputs that influence routes that are calculated to predetermined destinations. A route calculation module (204) executed by a navigation server (102) is operable to calculate a first route from the trip origin to the trip destination. An adaptive route calculation (204) executed by the navigation server (102) is operable to allow the user to enter a user modification of the first route. After the user modification is entered by the user, a second route to the trip destination is calculated as a function of the user modification. The second route is then transmitted to a vehicle navigation system (104).
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
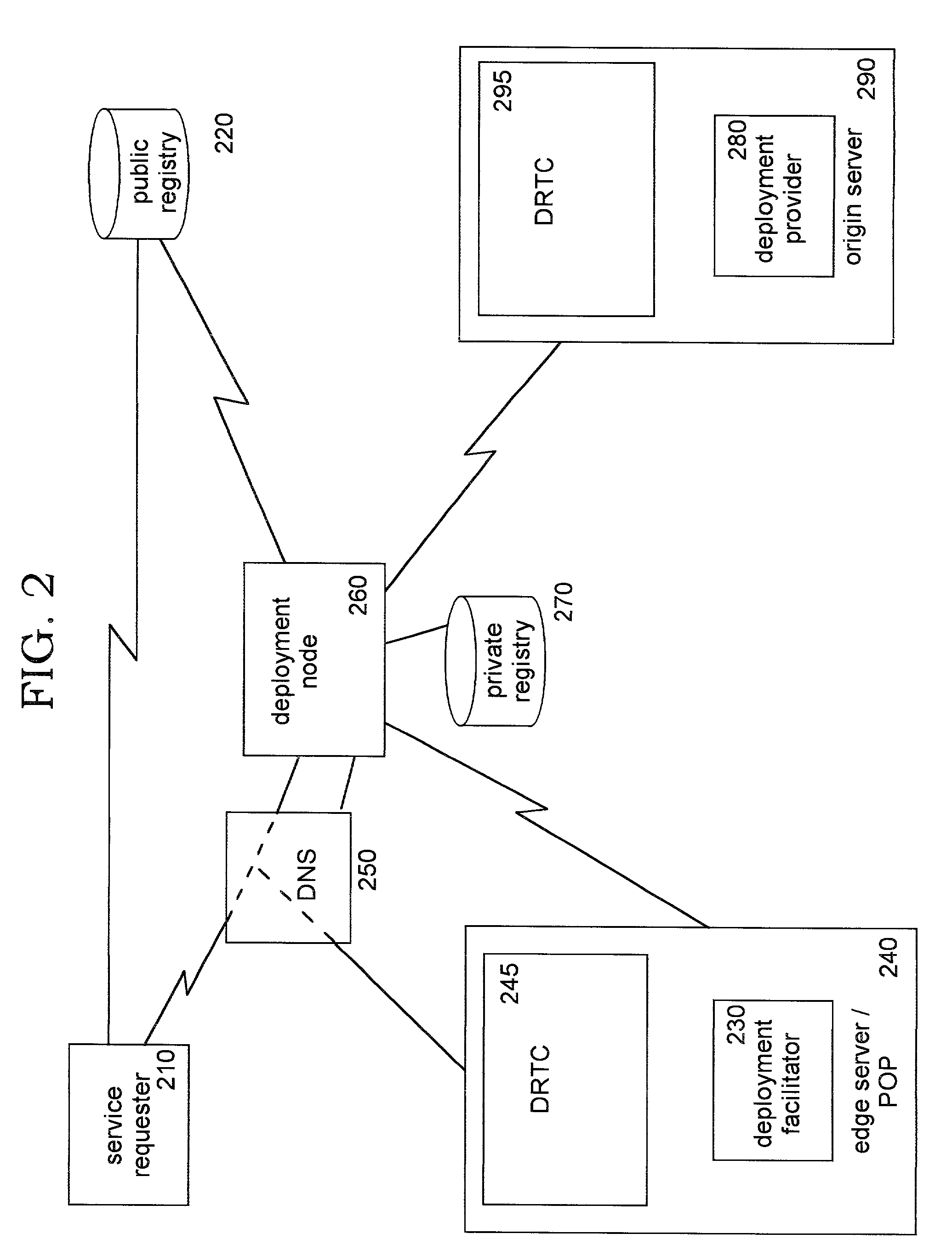
Dynamic deployment of services in a computing network
InactiveUS20020178254A1Improve efficiencyMore efficient web hosting sitesResource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork conditionsClient-side
Methods, systems, and computer program products for improving network operations by dynamically deploying services (such as web services or other network-accessible services) in a computing network. A process is defined whereby conditions such as usage metrics for incoming client requests (or other network conditions such as load balancing considerations) are monitored, and used to trigger dynamic deployment of web services to locations in the network in order to improve efficiency (e.g. by reducing response time to the client and / or reducing the burden on the back-end computing system resources). Service requests are dynamically routed to the destination where the service resides, in a manner which is transparent to the client. In an optional aspect, programmatic replication of system upgrades may be implemented by redeploying services using this same dynamic deployment approach, enabling the complexity of upgrading previously-deployed software to be reduced significantly. As another optional aspect, previously-deployed software may also be automatically and programmatically undeployed using disclosed techniques.
Owner:IBM CORP
Digraph based mesh communication network
ActiveUS20060029060A1Data switching by path configurationWireless communicationNetwork packetAdaptive routing
In a packet communication network, a method of packet switched transport is provided using digraphs defining paths among nodes in which a graph identifier, instead of a literal destination address, is used to determine paths through the network. The nodes themselves implement a real-time mesh of connectivity. Packets flow along paths that are available to them, flowing around obstructions such as dead nodes and lost links without need for additional computation, route request messages, or dynamic routing tree construction.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
Dynamic route requests for multiple clouds
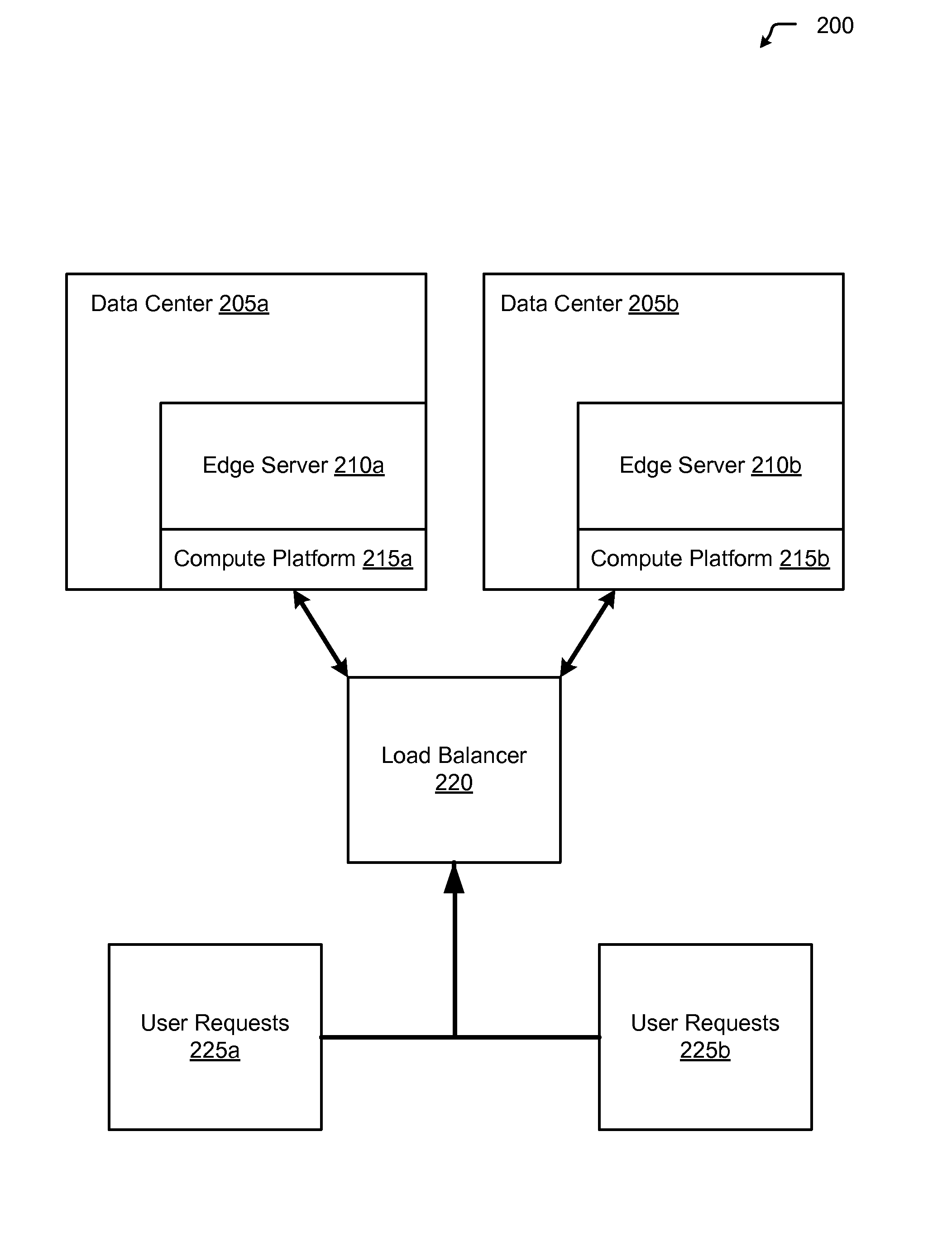
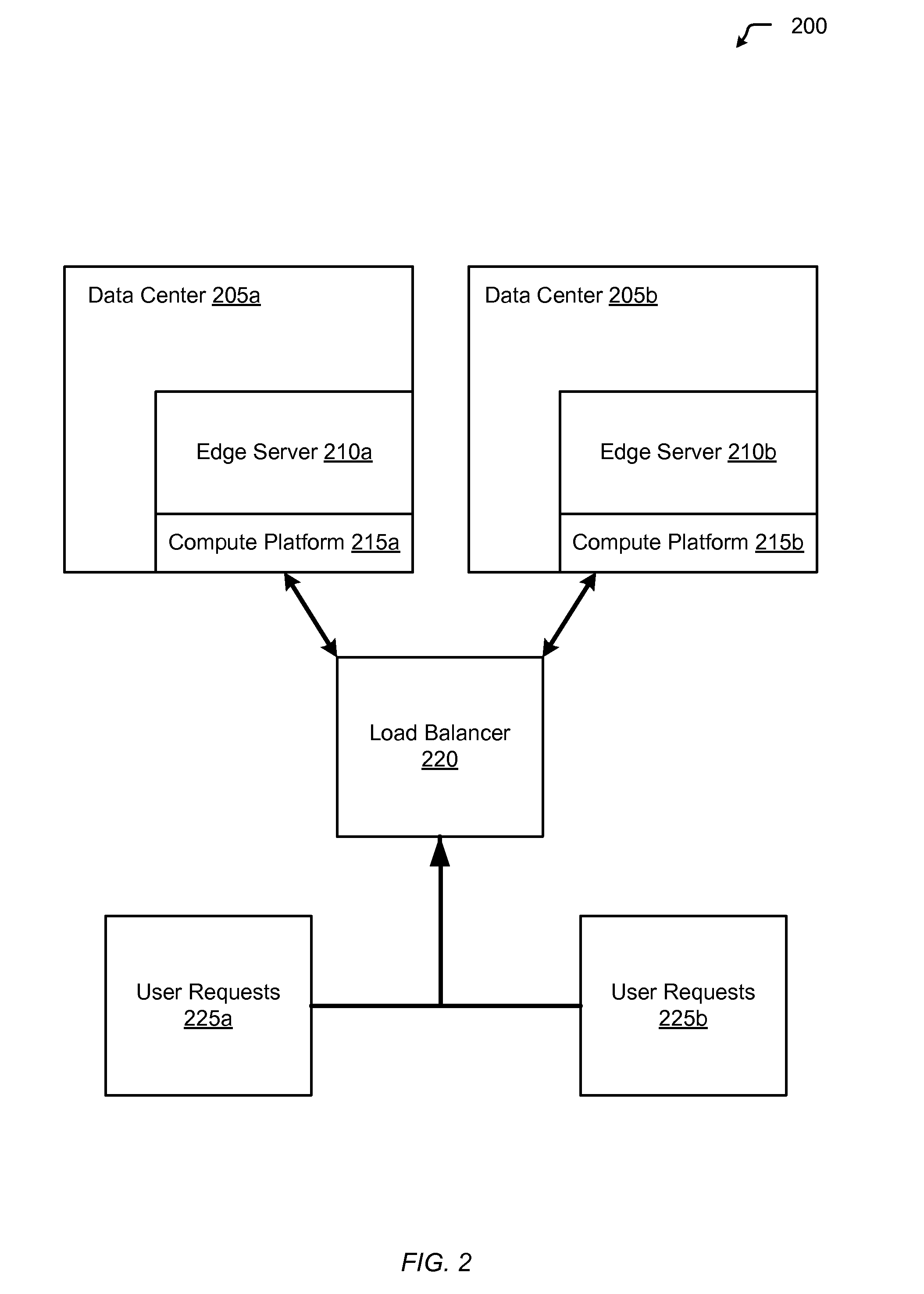
InactiveUS20130080623A1Affect service qualityImprove application performanceDigital computer detailsProgram controlEdge serverUser device
Aspects of the present invention include a method of dynamically routing requests within multiple cloud computing networks. The method includes receiving a request for an application from a user device, forwarding the request to an edge server within a content delivery network (CDN), and analyzing the request to gather metrics about responsiveness provided by the multiple cloud computing networks running the application. The method further includes analyzing historical data for the multiple cloud computing networks regarding performance of the application, based on the performance metrics and the historical data, determining an optimal cloud computing network within the multiple cloud computing networks to route the request, routing the request to the optimal cloud computing network, and returning the response from the optimal cloud computing network to the user device.
Owner:LIMELIGHT NETWORKS
Method and system for mapping traffic predictions with respect to telematics and route guidance applications
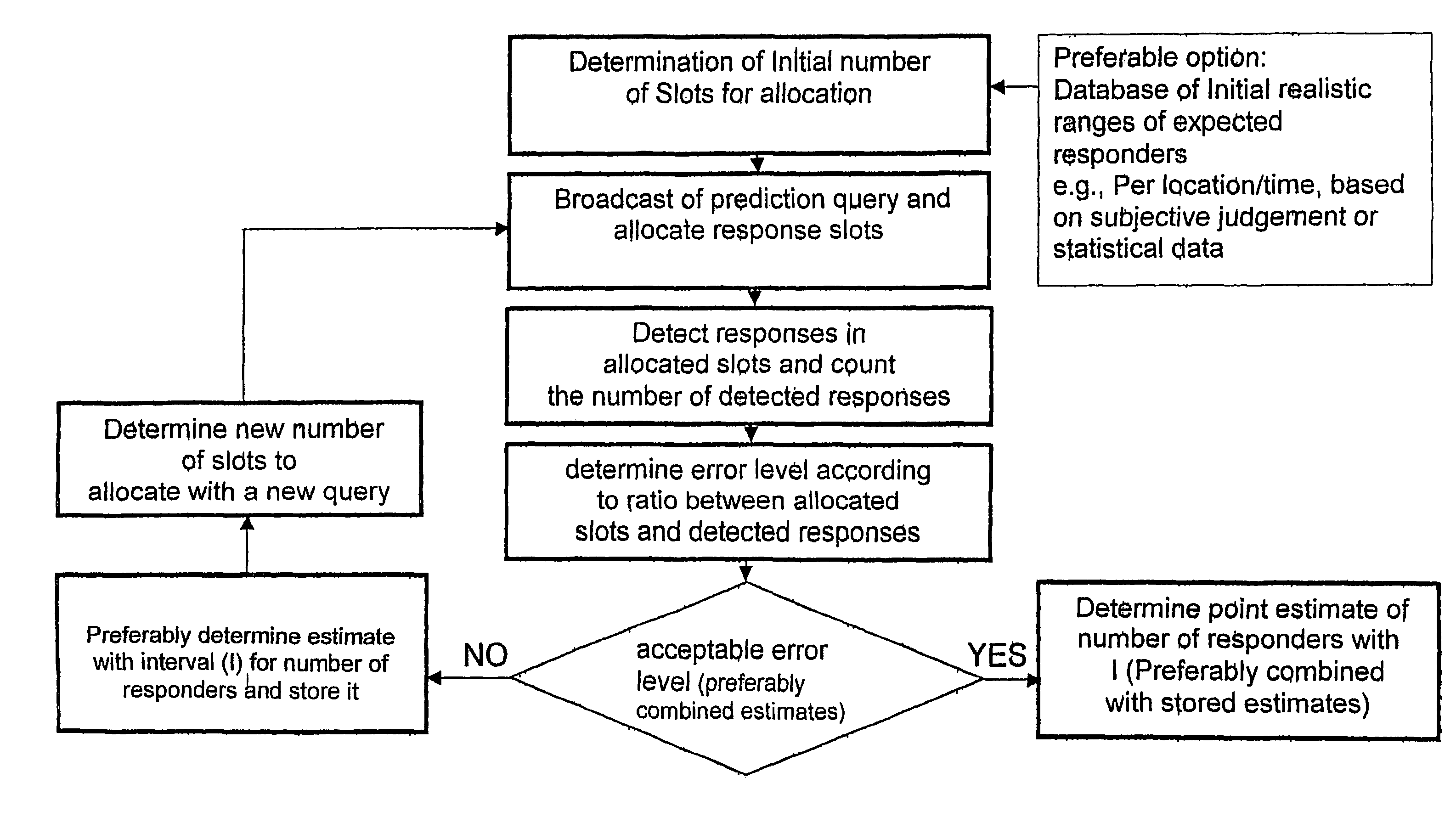
InactiveUS7103470B2Accurate and prediction capability of useImprove accuracyAnalogue computers for vehiclesInstruments for road network navigationTraffic capacityResponse process
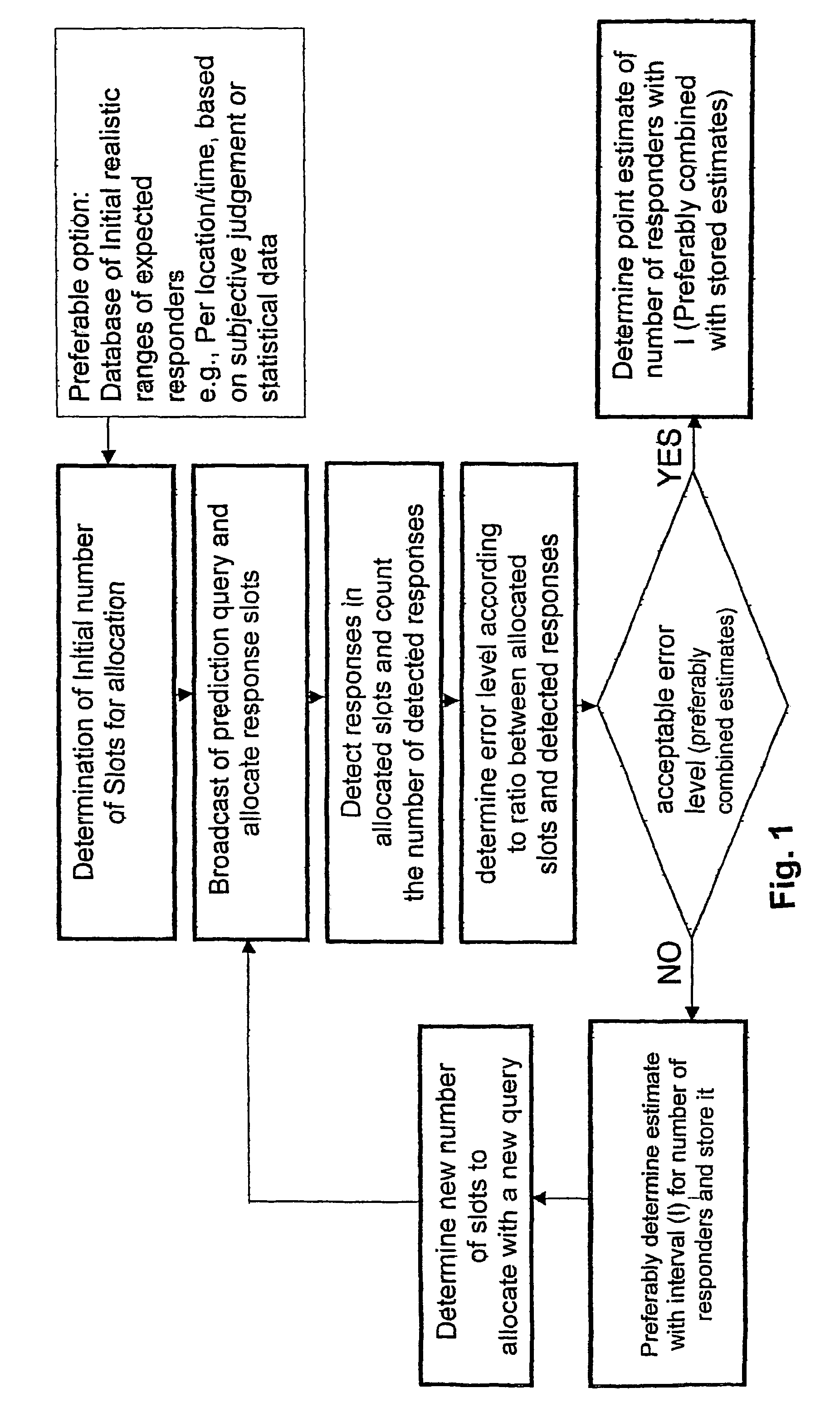
A method is provided for predicting load of traffic of vehicles that are travelling according to non reference route plan, provided with Dynamic Route Guidance capability of their PMMS, in a Forward Time Interval related Route Segment and according to a predetermined protocol between mobile systems and a non mobile system platform of a SODMS. Using mobile units, a traffic prediction query is receiving according to a predetermined differential traffic load match process. A match process is performed by each of the mobile units and, according to a match, a predetermined response procedure is enabled, wherein a response procedure in each mobile unit uses a predetermined random process to select an allocated slot in which to transmit a predetermined signal, which provides an improved way to predict traffic in conjunction with off line database statistics, preferably with such that are being adaptively corrected by prior data and method to predict traffic which do not include, or lack sufficient erratic traffic information.
Owner:MINTZ JOSEF
Dynamic route discovery for optical switched networks using peer routing
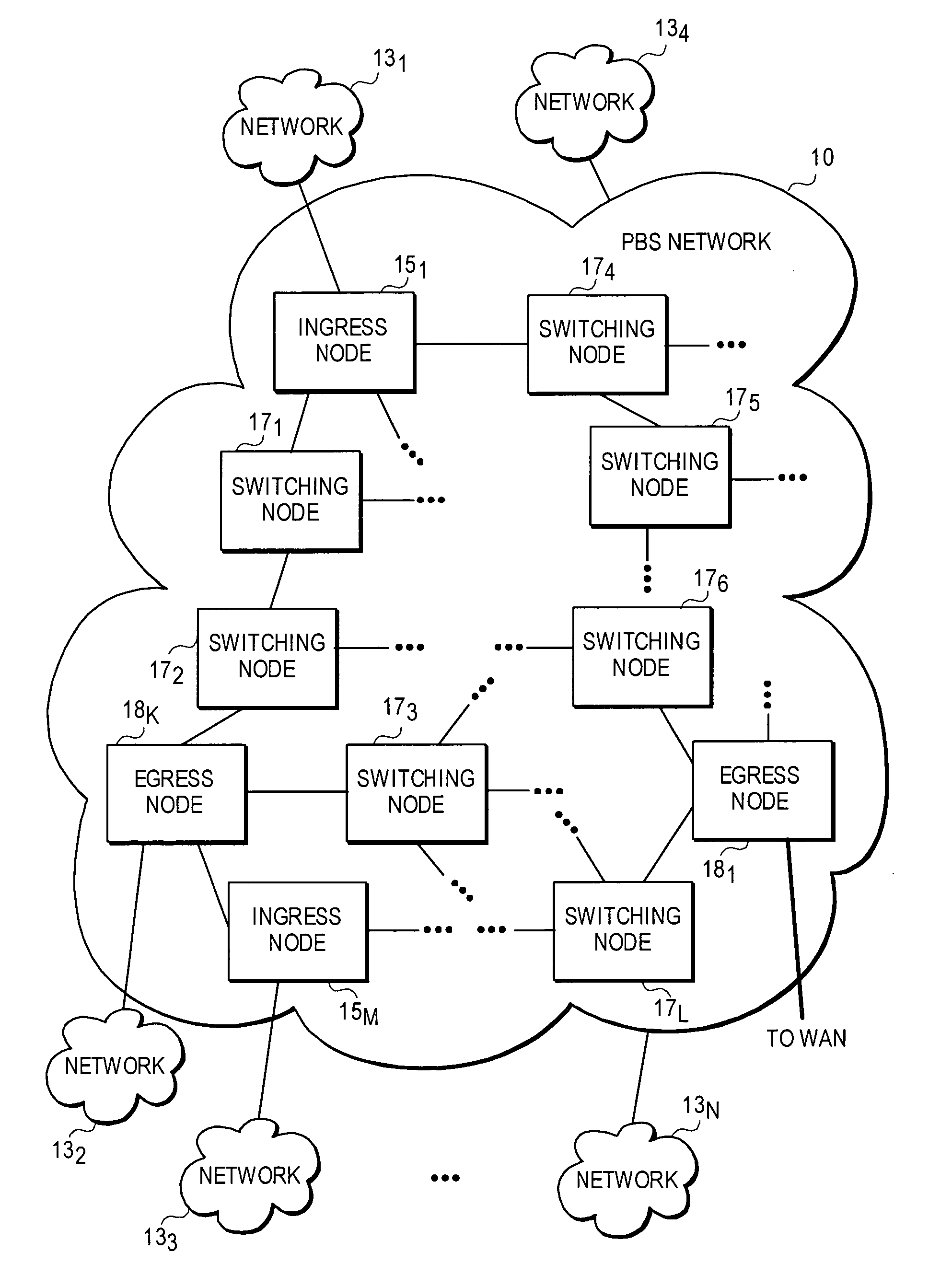
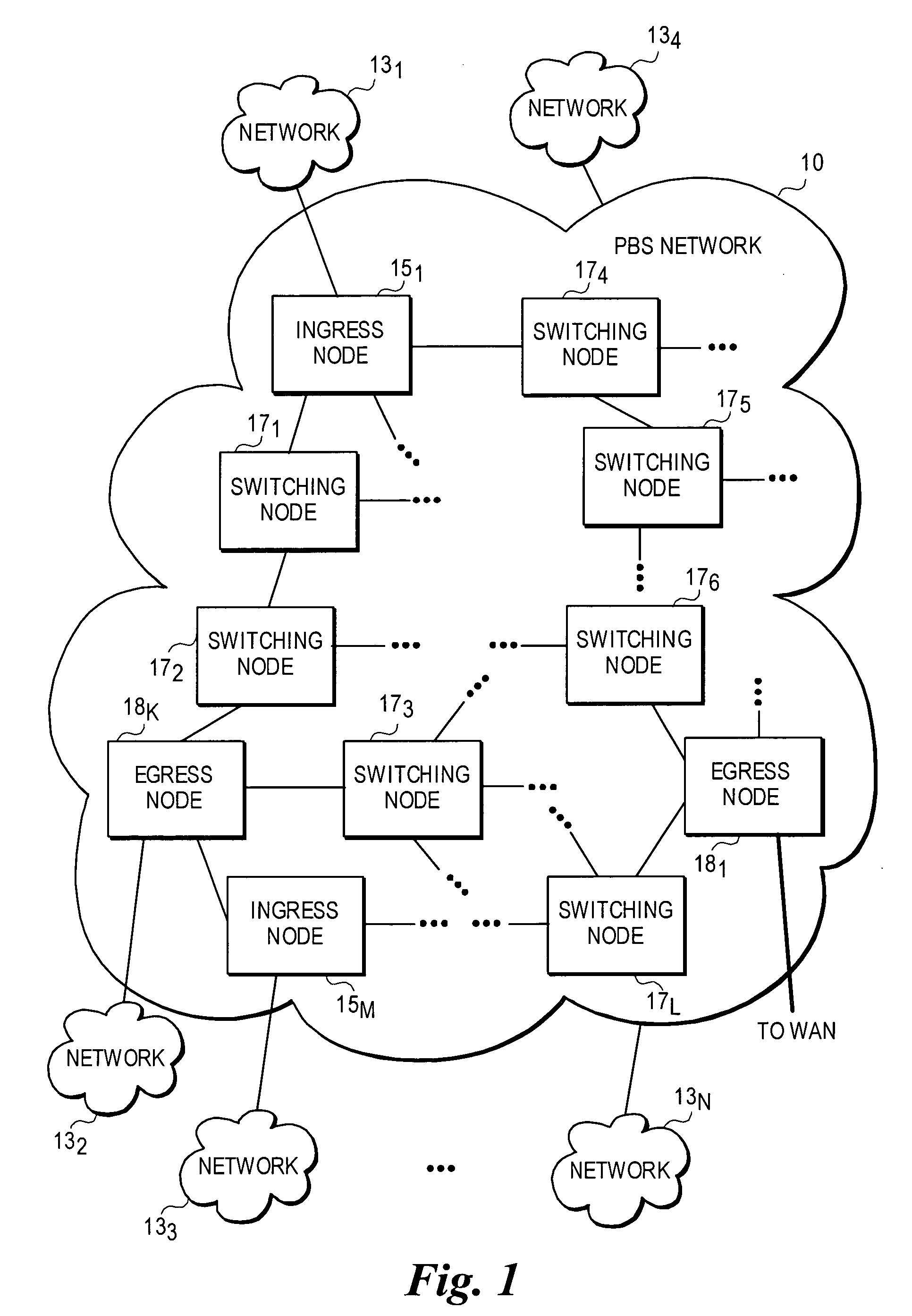
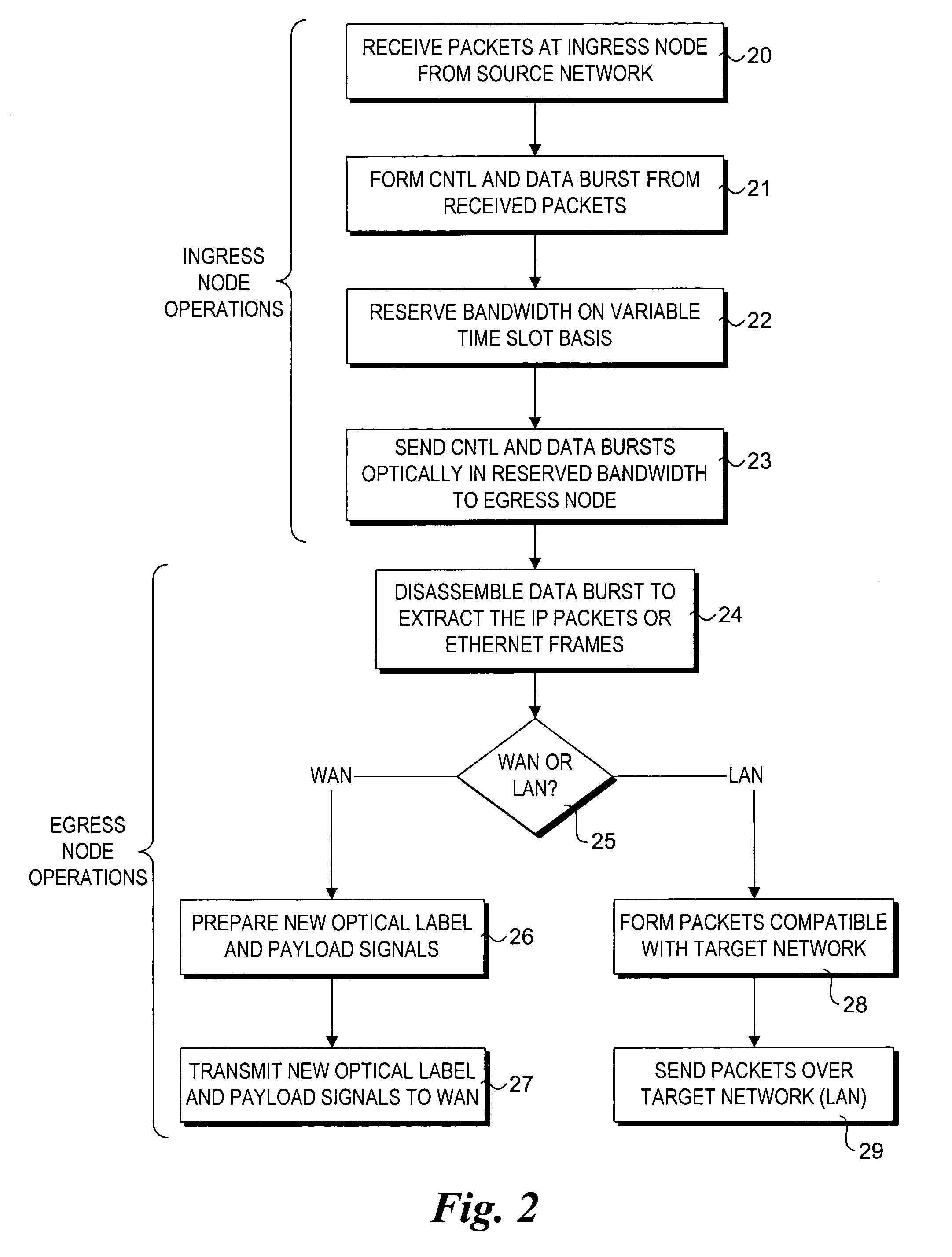
ActiveUS20050105905A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexExchange networkEdge node
An architecture and method for performing dynamic route discovery and time slot reservation provisioning within optical-switched networks. The method employs extensions to the RSVP-TE signaling protocol, which uses various messages to reserve resources. Under a peer routing embodiment, routing trees and resource availability data are maintained by the edge nodes. A lightpath route is dynamically selected based on selection criteria applied to the routing tree data and the availability of resources along the lightpath. Link state information, including resource reservation data, is broadcast by the switching nodes to update the edge nodes of their resource availability. A resource reservation message is passed between nodes defined by an explicit route contained in the message, and resource availability is confirmed for the entire lightpath prior to confirming the resource reservations.
Owner:INTEL CORP
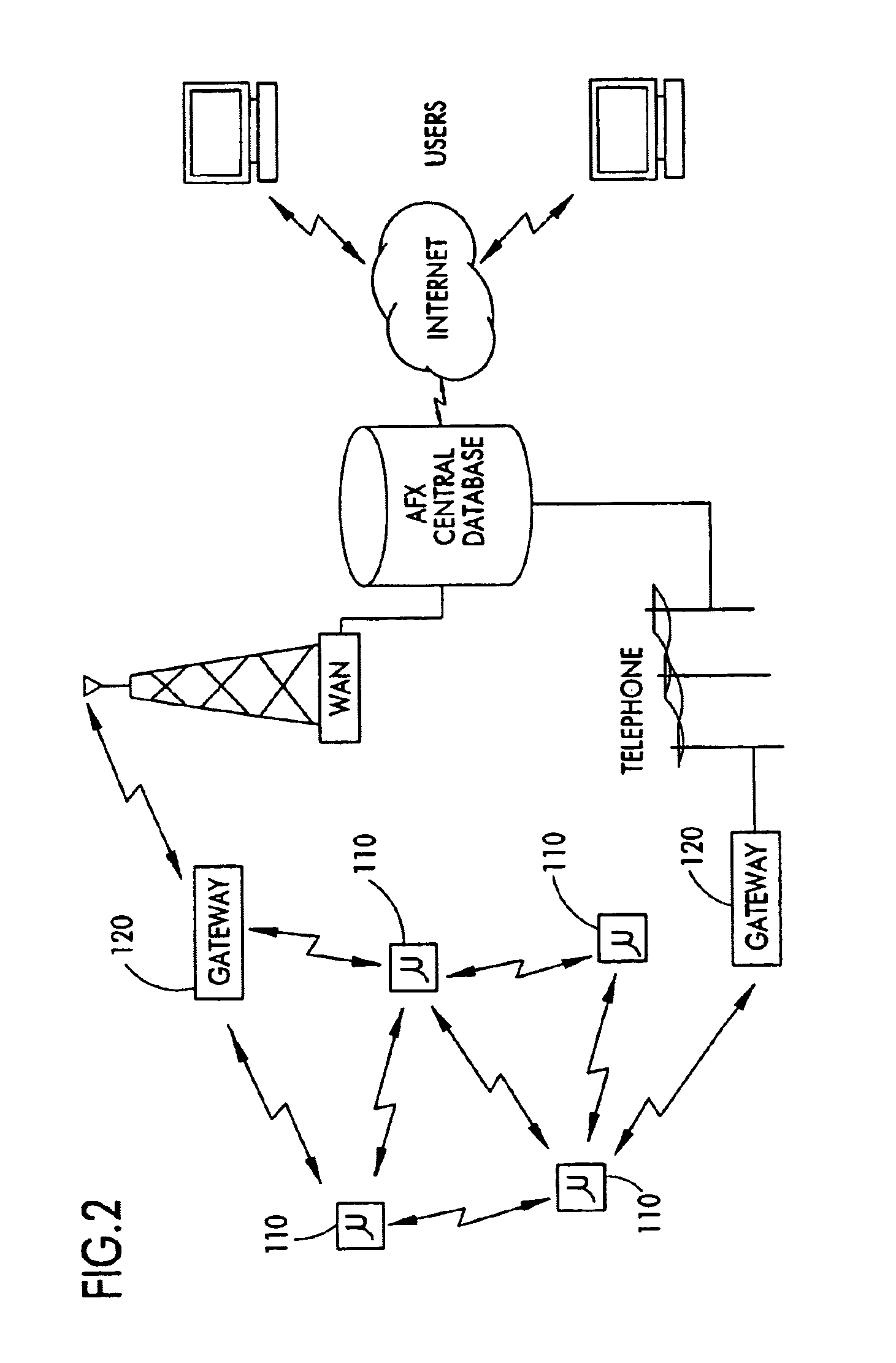
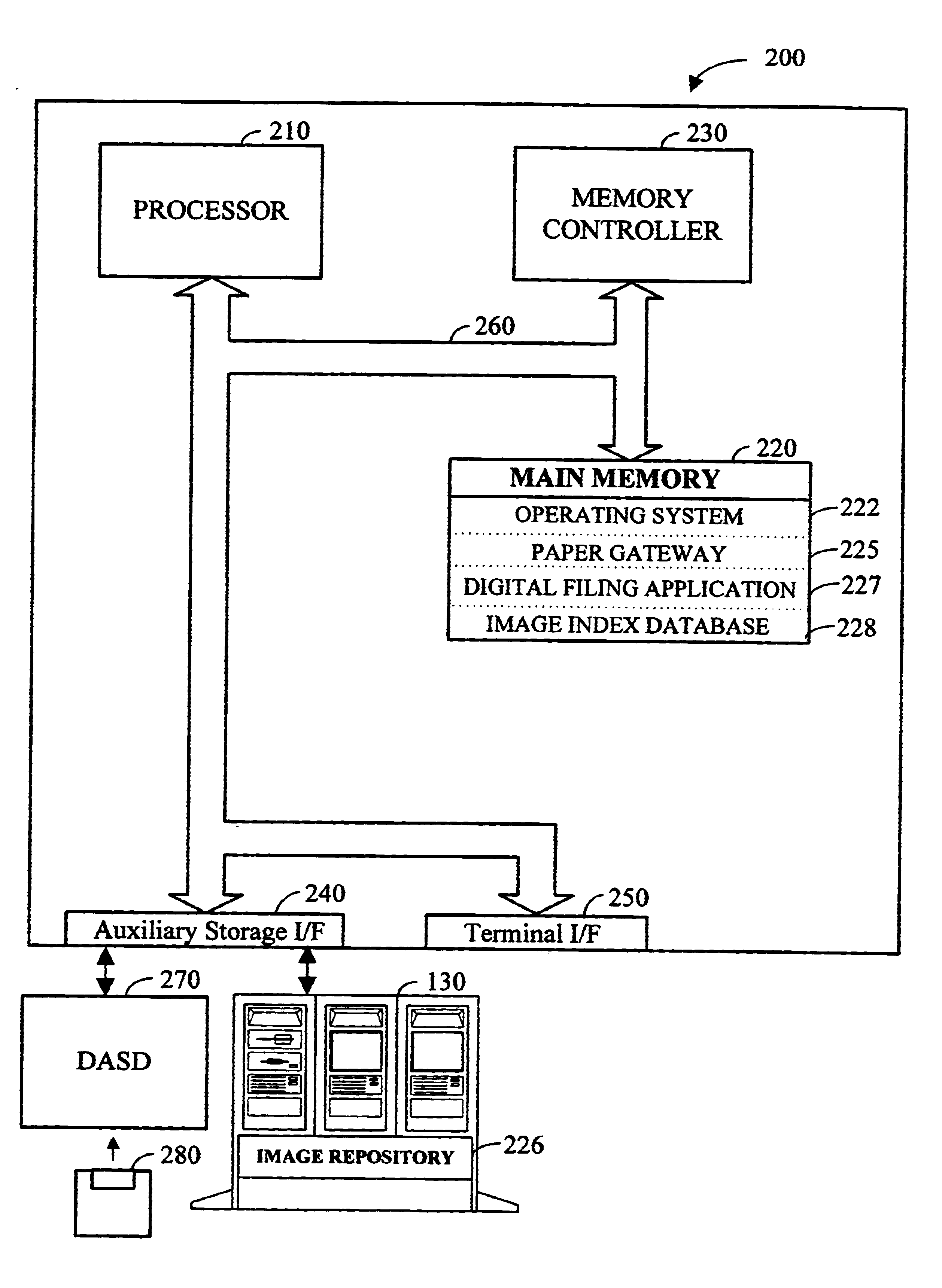
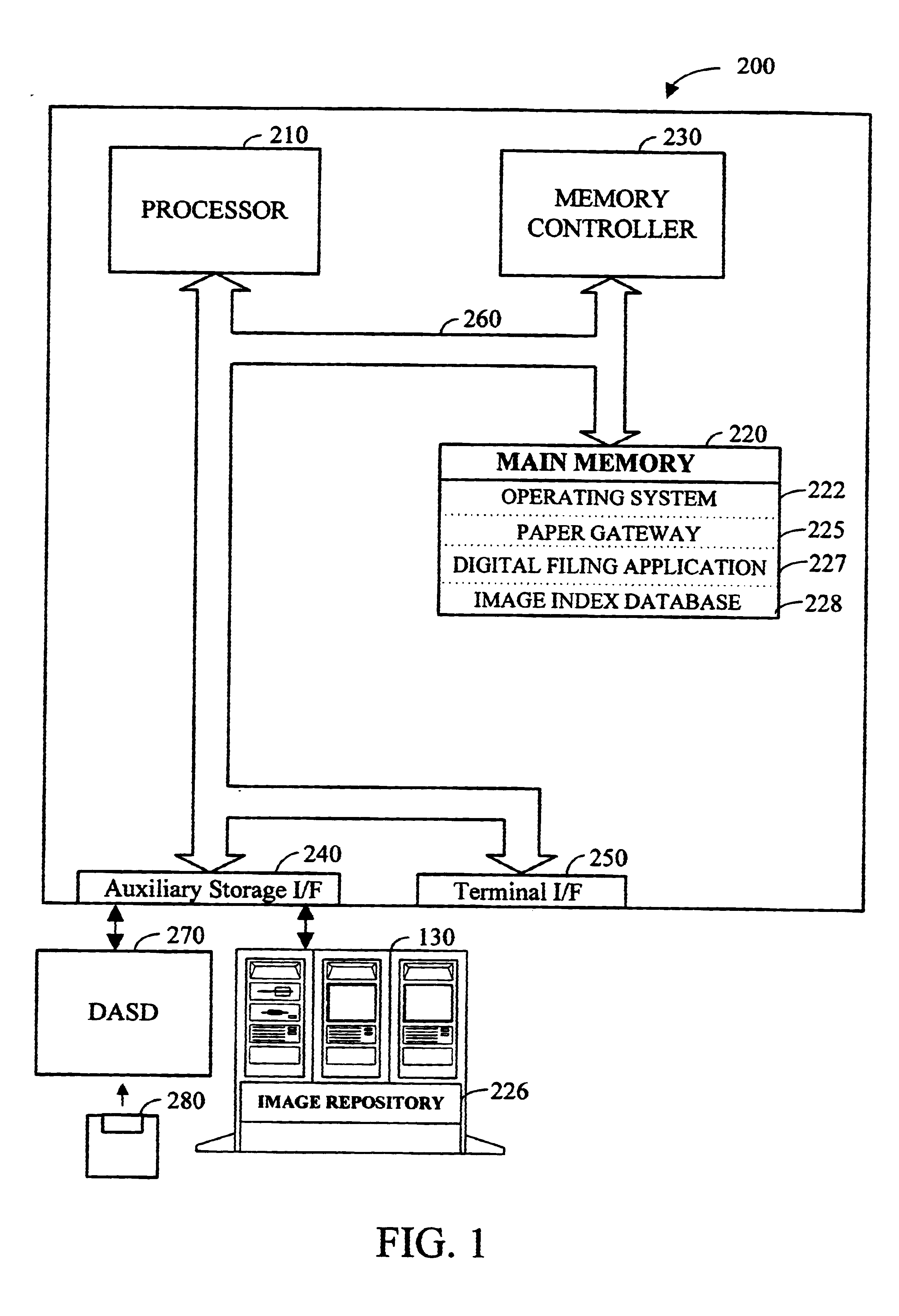
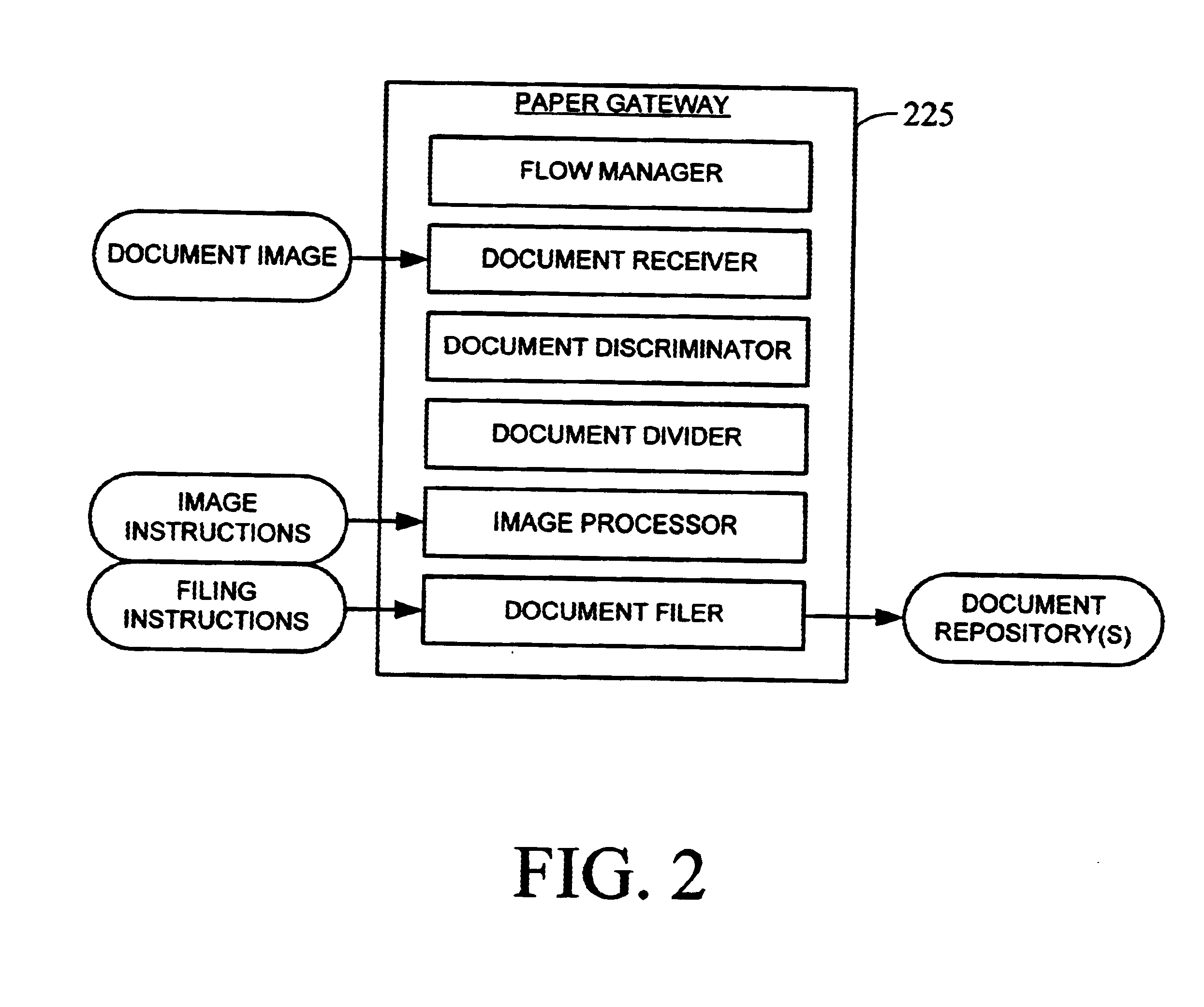
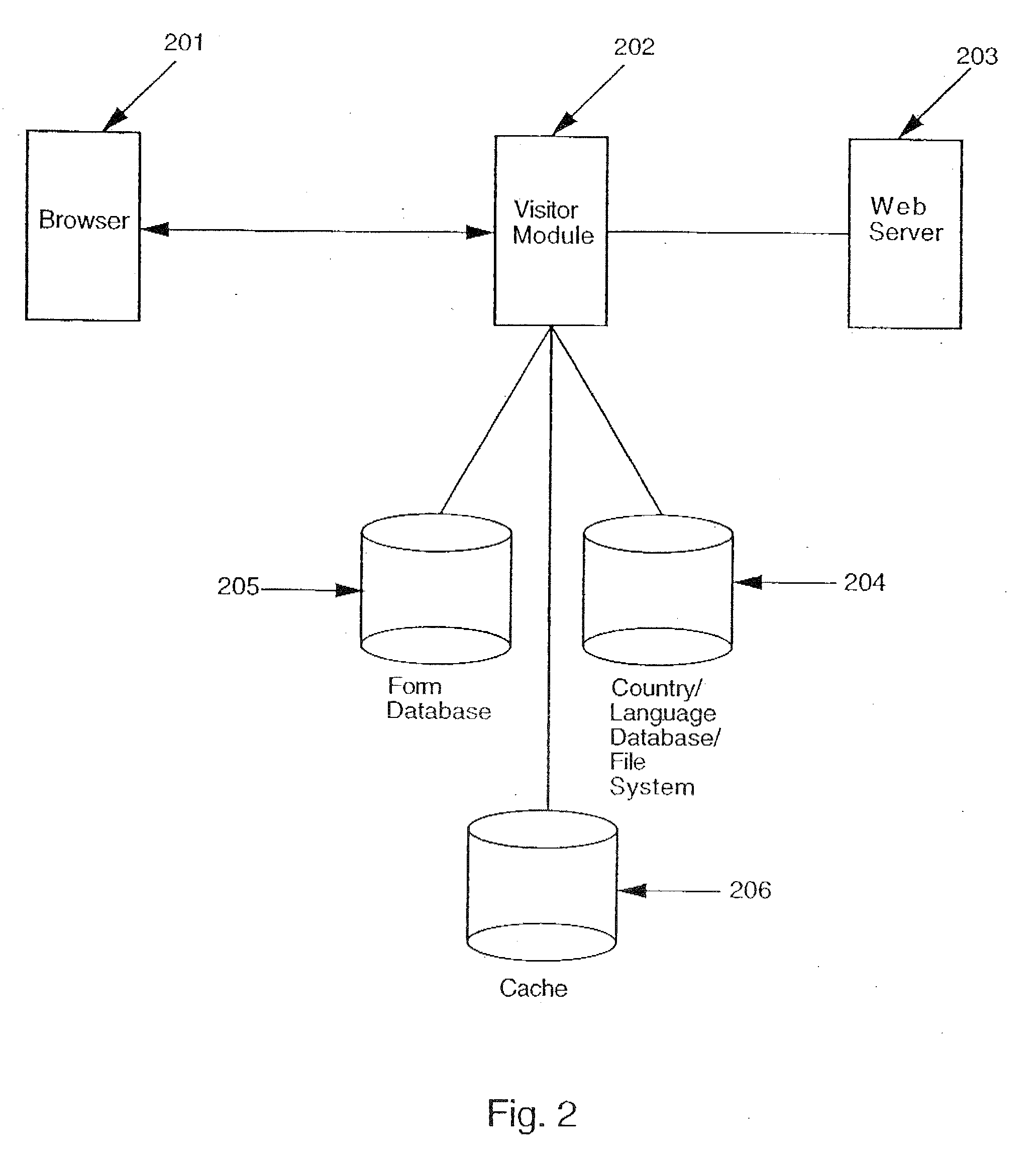
Apparatus and method for dynamically routing documents using dynamic control documents and data streams
InactiveUS6674924B2Easy to operateEasy to createData processing applicationsDigital computer detailsData streamPaper based
According to the preferred embodiments, an apparatus and method for dynamic routing using dynamic data streams is disclosed. Dynamic routing using dynamic data streams facilitates the creation of a flexible paper gateway in a digital filing system that provides for receiving, processing and storing document images from a wide variety of sources. When thus implemented, dynamic routing allows the digital filing system to efficiently operate while providing digital filing services to a wide variety of users with different needs. Thus, the preferred embodiments provide for the efficient digital filing and efficient management of paper-based information from its receipt at the desktop through an indexing, scanning, image storage and image retrieval process.
Owner:WRIGHT STEVEN F +2
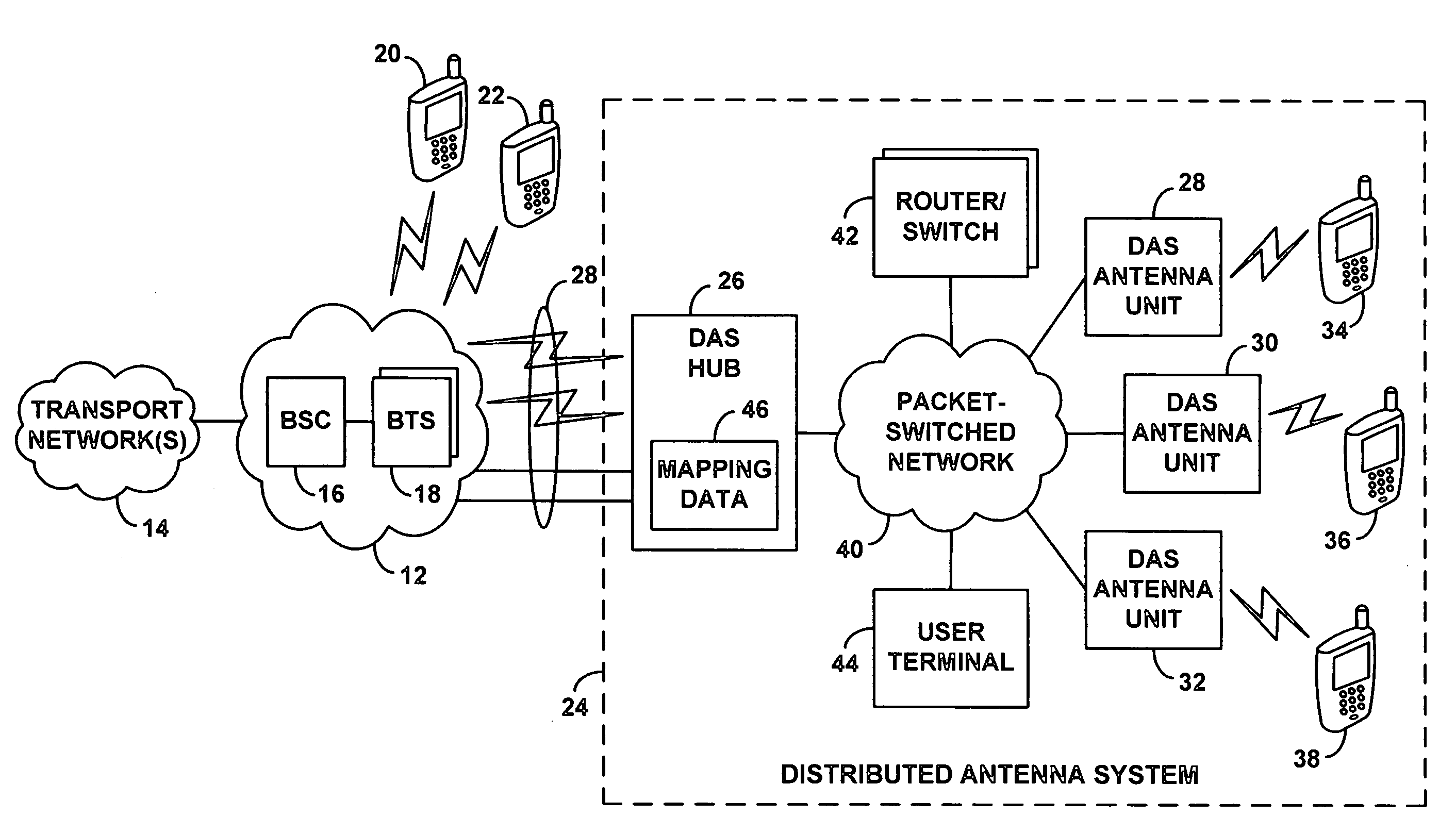
Method and system for dynamically routing between a radio access network and distributed antenna system remote antenna units
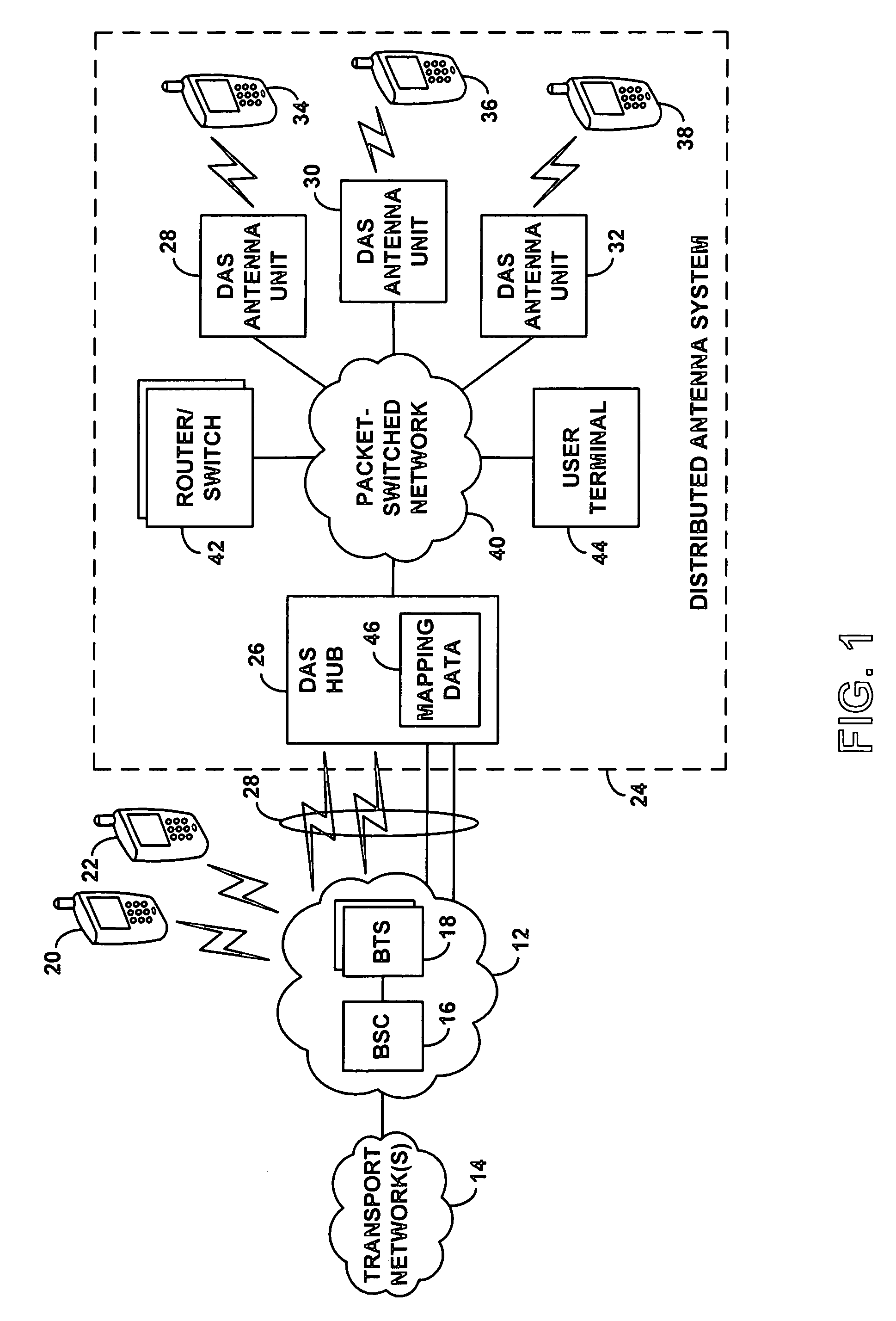
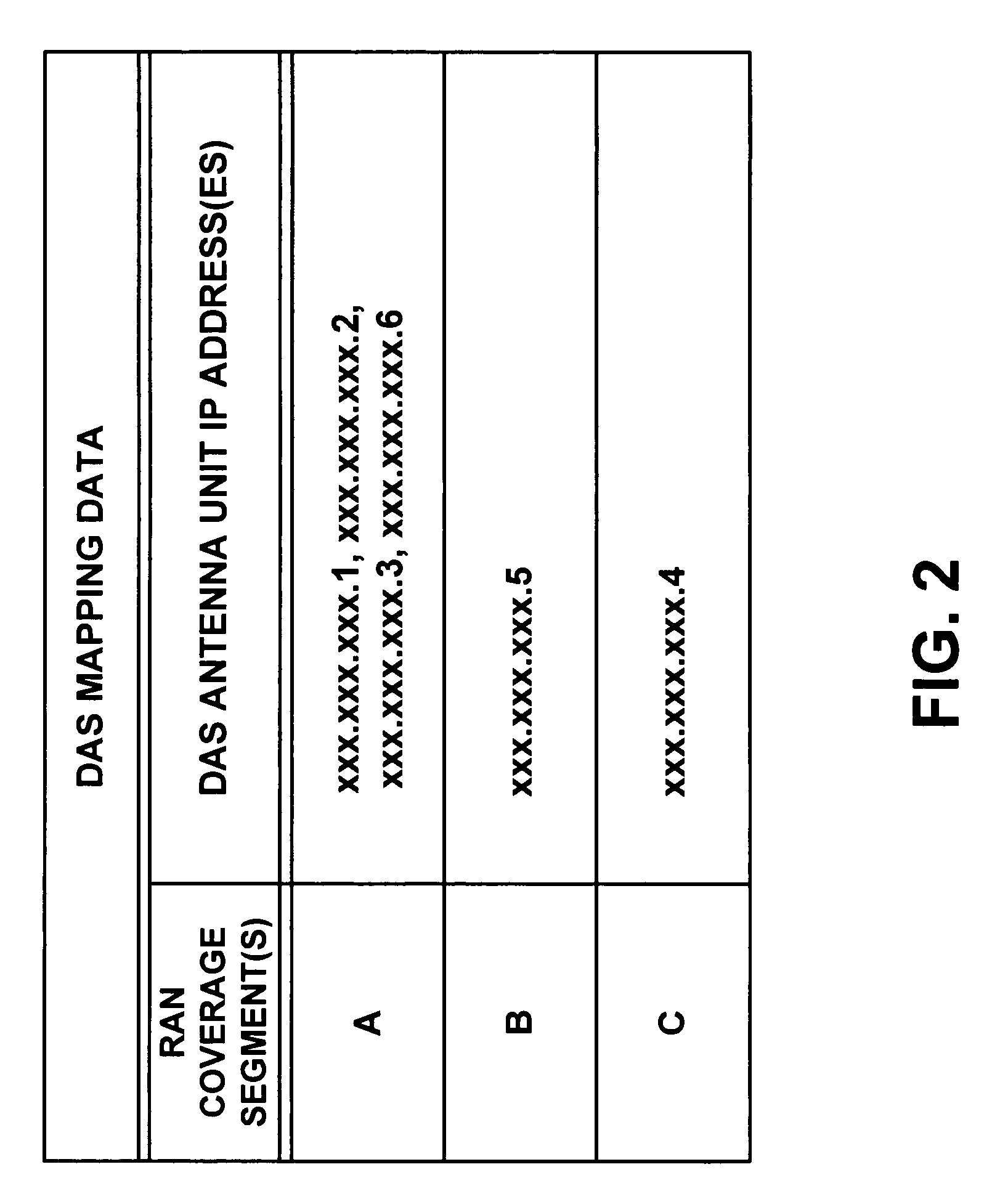
ActiveUS7286507B1Conveniently changedOptimization mechanismBroadcast transmission systemsTelephonic communicationAccess networkDistributed antenna system
An improved mechanism for routing communication traffic between a radio access network and distributed antenna system (DAS) remote antenna units. In accordance with an exemplary embodiment of the invention, a DAS hub and each DAS antenna unit served by the DAS hub will sit as a respective node on a packet-switched network. Further, the DAS hub will maintain or otherwise have access to a set of mapping data that correlates one or more radio access network coverage segments (e.g., cell sectors) with one or more DAS antenna unit addresses on the packet-switched network (e.g., IP addresses). Advantageously, an administrator of the DAS can then configure or alter the mapping data whenever desired, to conveniently set the RAN-DAS correlations and to thereby distribute RAN coverage in a desired manner throughout the DAS.
Owner:SPRINT SPECTRUM LLC
Transmission of special routes to a navigation device
ActiveUS7873471B2Instruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsUser inputNavigation system
A vehicle navigation system includes an adaptive routing module (210) that allows a user to provide inputs that influence routes that are calculated to predetermined destinations. A route calculation module (204) executed by a navigation server (102) is operable to calculate a first route from the trip origin to the trip destination. An adaptive route calculation (204) executed by the navigation server (102) is operable to allow the user to enter a user modification of the first route. After the user modification is entered by the user, a second route to the trip destination is calculated as a function of the user modification. The second route is then transmitted to a vehicle navigation system (104).
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
Translation management system
InactiveUS7207005B2Enhancing maintainability and storageNatural language translationDigital computer detailsData streamDocumentation procedure
A translation management system in a computer environment. A preferred embodiment of the invention automatically detects when a document, data stream, or non-text file in the master language has been updated and notifies the user which corresponding documents, data streams, or non-text files in the other languages require translation which are then staged and dynamically routed and sequenced to individual translation resources where the actual translation is performed. Management status, reporting, scheduling, and accounting information is sent to the user as the translation process ensues. The user is notified of the completion of translation and the invention coordinates the delivery of the translated documents, data streams, or non-text files back to the user's site for installation and optional review. The invention makes a variety of translation resources instantly available to the user which include both automated translation tools as well as human translators. The translation resources are connected to the invention using a flexible architecture that can be deployed on intranets as well as the Internet.
Owner:TRANSPERFECT GLOBAL INC +1
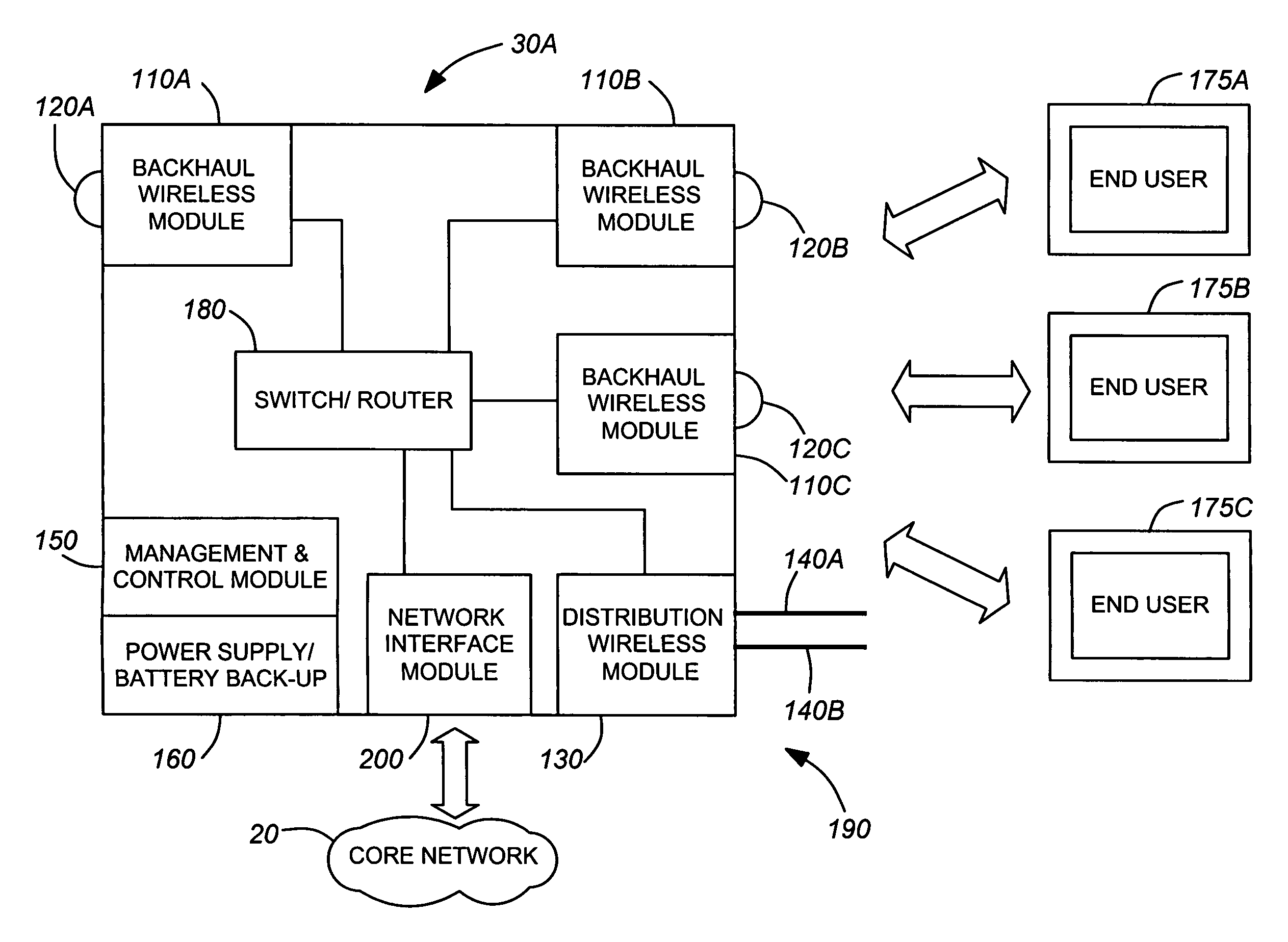
Integrated wireless distribution and mesh backhaul networks
ActiveUS7164667B2Low costError preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementWireless mesh networkDirectional antenna
Networks, devices and methods related to wireless networking. A wireless network using nodes that perform both distribution and backhaul functions is provided. These nodes constitute the key elements of a wireless network that would be deployed and controlled by a wireless network operator. Each node contains a distribution wireless module which is wirelessly coupled to the wireless end user device using a point to multipoint scheme. Also integrated into each node is at least one backhaul wireless module with a directional wireless antenna. Each backhaul wireless module communicates by way of a point to point wireless link with the backhaul module of one other node. The nodes in the wireless network are interconnected to form a mesh backhaul network. Because of the nature of a mesh network, data traffic can be routed around obstacles that may prevent line of site links. Furthermore, the mesh network allows dynamic routing of data traffic to avoid congestion points or downed links in the network.
Owner:WI FI ONE
Method and system for dynamic estimation and predictive route generation
InactiveUS7565155B2Instruments for road network navigationData processing applicationsGraphicsAdaptive routing
The preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to methods and systems for dynamic route estimation and prediction using discrete sampled location updates from various mobile devices for the purpose of providing a graphical representation of a mobile device's route along a known network path of map data. The embodiments also provide supplemental route metrics, such as traveled distance, elapsed time, etc., and the capability to assign destination points for the purpose of providing the ability to modify location update points in an application, such as a route planner, and / or to store the dynamically generated route based on various preferences for later retrieval.
Owner:BLUESTONE VENTURES
Translation management system
InactiveUS20060200766A1Enhancing maintainability and storageNatural language translationDigital computer detailsData streamProgram planning
A translation management system in a computer environment. A preferred embodiment of the invention automatically detects when a document, data stream, or non-text file in the master language has been updated and notifies the user which corresponding documents, data streams, or non-text files in the other languages require translation which are then staged and dynamically routed and sequenced to individual translation resources where the actual translation is performed. Management status, reporting, scheduling, and accounting information is sent to the user as the translation process ensues. The user is notified of the completion of translation and the invention coordinates the delivery of the translated documents, data streams, or non-text files back to the user's site for installation and optional review. The invention makes a variety of translation resources instantly available to the user which include both automated translation tools as well as human translators. The translation resources are connected to the invention using a flexible architecture that can be deployed on intranets as well as the Internet.
Owner:TRANSPERFECT TECH LLC +1
Method for real-time traffic analysis on packet networks
An architecture for capture and generation, and a set of methods for characterization, prediction, and classification of traffic in packet networks are disclosed. The architecture consists of a device that stores packet timing information and processes the data so that characterization, prediction, and classification algorithms can perform operations in real-time. A methodology is disclosed for real-time traffic analysis, characterization, prediction, and classification in packet networks. The methodology is based on the simultaneous aggregation of packet arrival times at different times scales. The traffic is represented at the synchronous carrier level by the arrival or non-arrival of a packet. The invention does not require knowledge about the information source, nor needs to decode the information contents of the packets. Only the arrival timing information is required. The invention provides a characterization of the traffic on packet networks suitable for a real-time implementation. The methodology can be applied in real-time traffic classification by training a neural network from calculated second order statistics of the traffic of several known sources. Performance descriptors for the network can also be obtained by calculating the deviation of the traffic distribution from calculated models. Traffic prediction can also be done by training a neural network from a vector of the results of a given processing against a vector of results of the subsequent processing unit; noticing that the latter vector contains information at a larger time scale than the previous. The invention also provides a method of estimating an effective bandwidth measure in real time which can be used for connection admission control and dynamic routing in packet networks. The invention provides appropriate traffic descriptors that can be applied in more efficient traffic control on packet networks.
Owner:TELECOMM RES LAB
Method, System, and Computer Program Product for Managing Routing Servers and Services
InactiveUS20090245236A1Interconnection arrangementsData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityTelephone network
A method, system, and computer program product for routing network traffic (calls in a Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)), which expands the capabilities of existing systems by providing faster and more efficient direction of network traffic, is disclosed. A routing management system includes a routing manager which maintains a list of local routes, establishes and manages connections to the routing server(s), exports routes to the routing server(s), imports disseminated routes from the routing server(s), obtains static global and dynamic routes from the routing server(s), caches those routes for future use, finds all matching routes for a particular number dialed by the user, and prioritizing those routes based on timing, access and ordering information. An additional embodiment contains at least one routing server which provides look-up services for gateway server(s), allows export of local routes from gateway server(s), and distributes translation data; and at least one gateway server which handles calls received on either the Internet protocol (IP) or traditional telephony networks. The gateway server bridges calls between the different kinds of networks, interacts with users, interfaces with the routing system.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
Interference mitigation and adaptive routing in wireless ad-hoc packet-switched networks
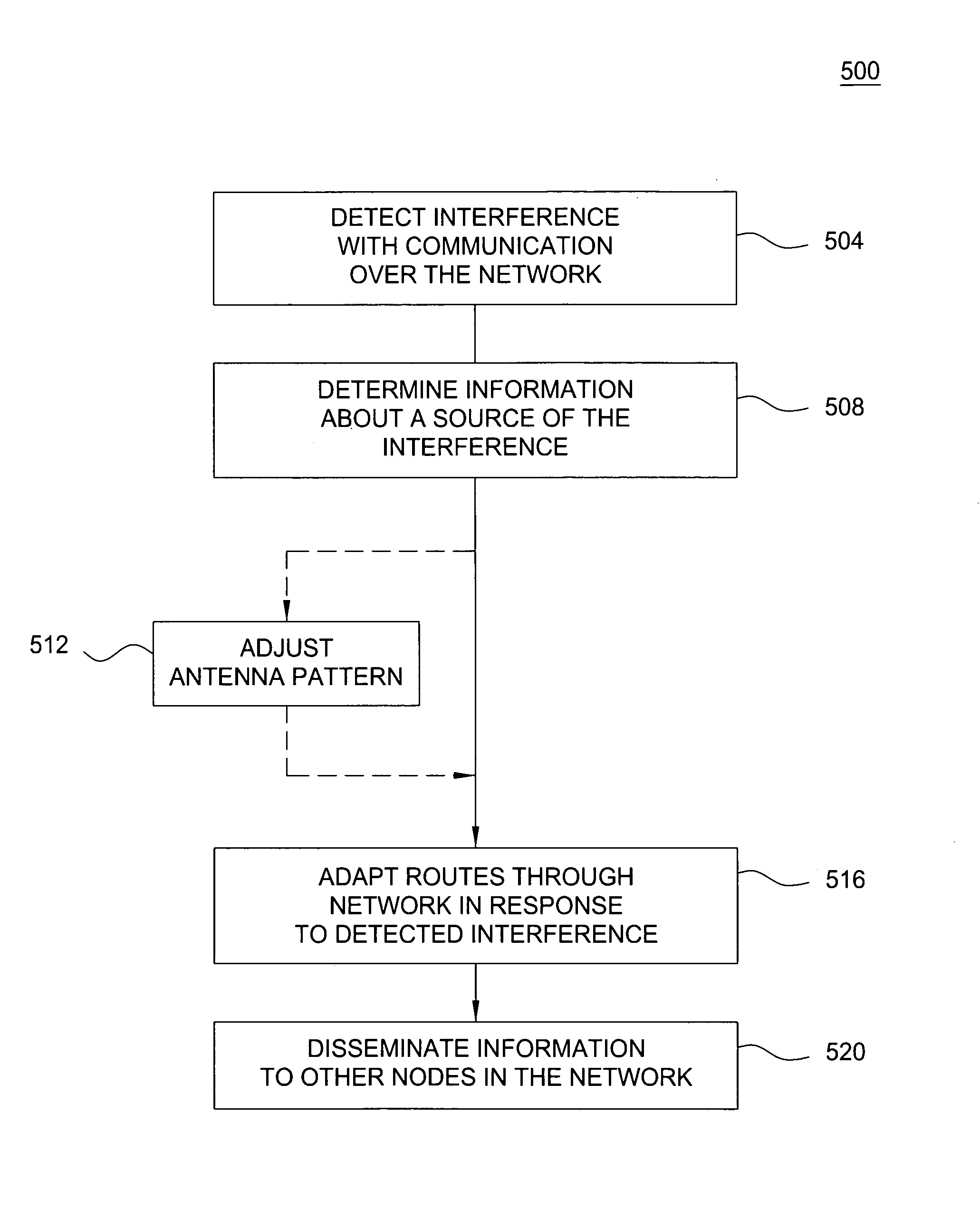
ActiveUS7342876B2Reduce the impact of interferenceError preventionTransmission systemsExchange networkRadio frequency
Described are an apparatus and method for routing packets through a multiple-hop wireless communications network. Interference with packet switched communications carried by radio frequency (RF) over the multiple-hop wireless communications network is detected. In response to information related to the detected interference, a route is adaptively determined for transmitting packets through the multiple-hop wireless communications network that mitigates the effect of the interference on the packets.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
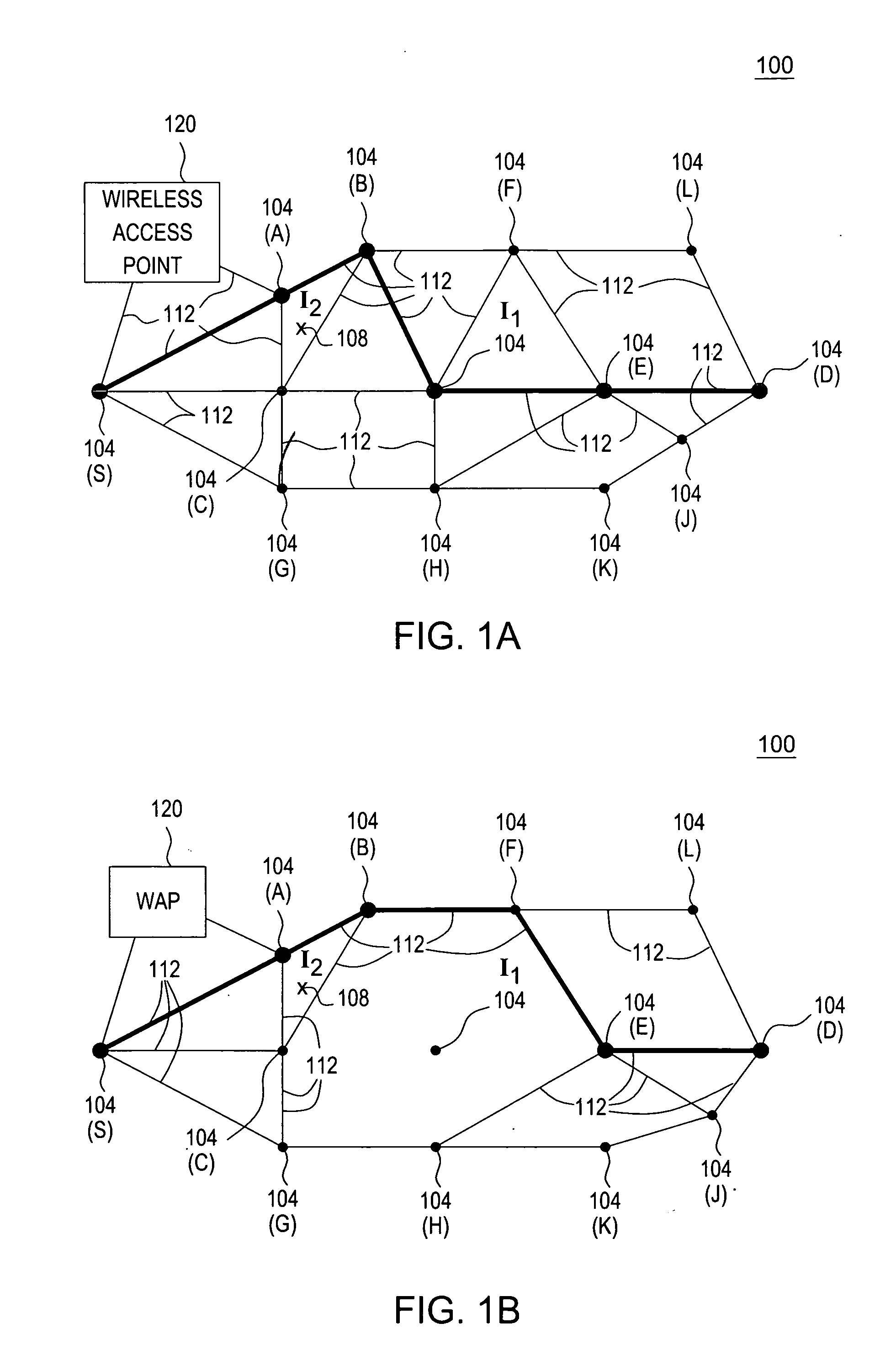
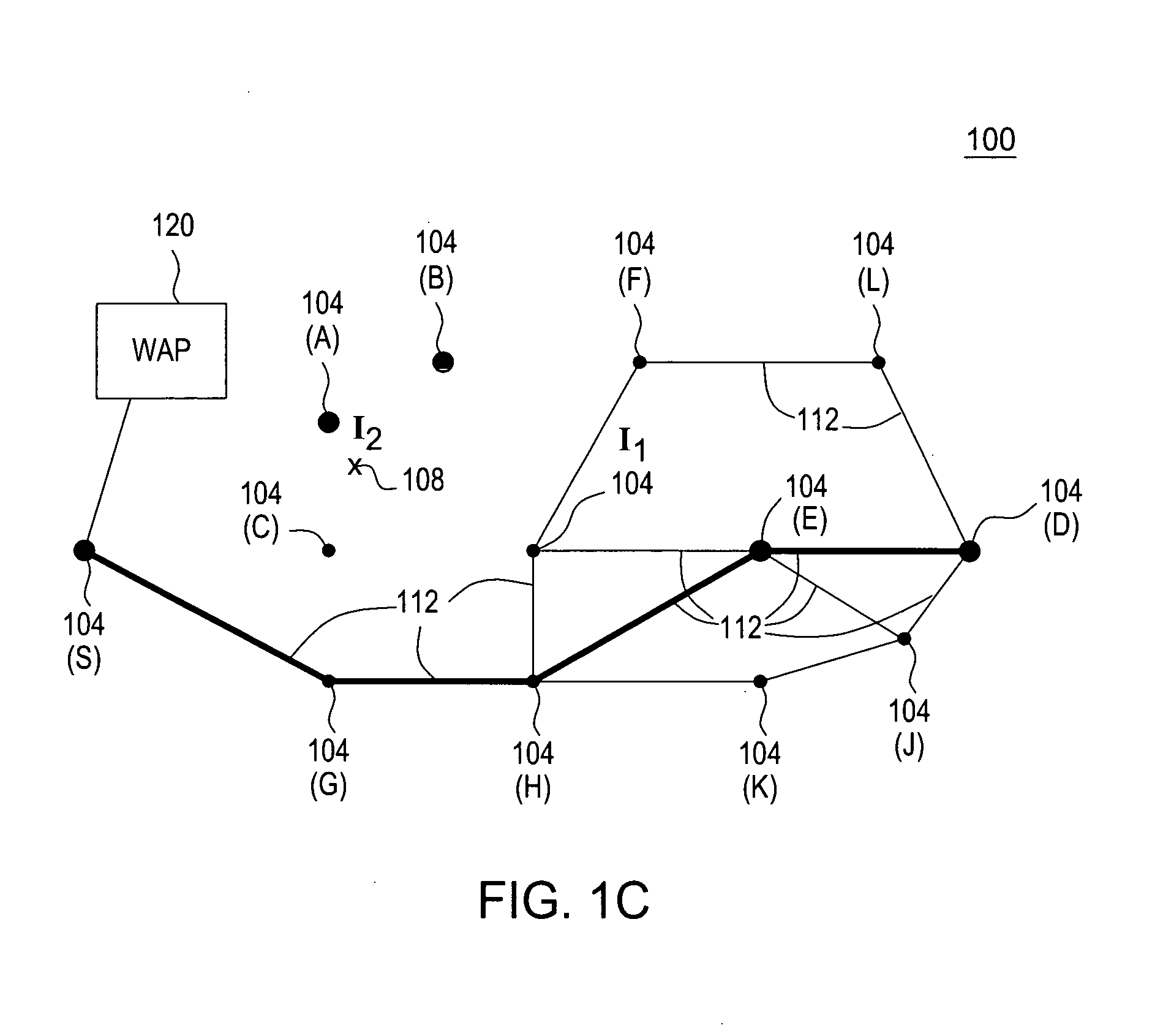
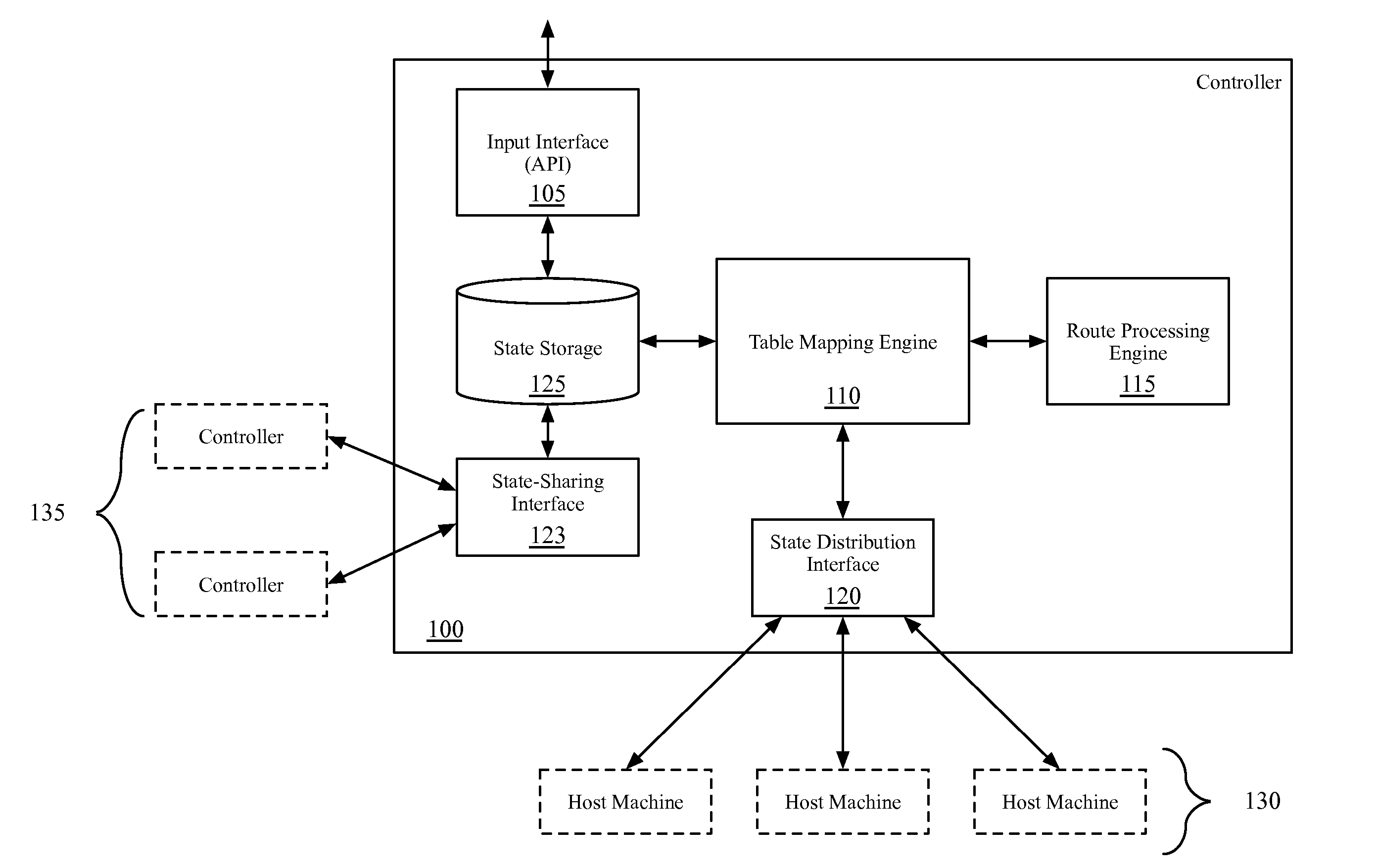
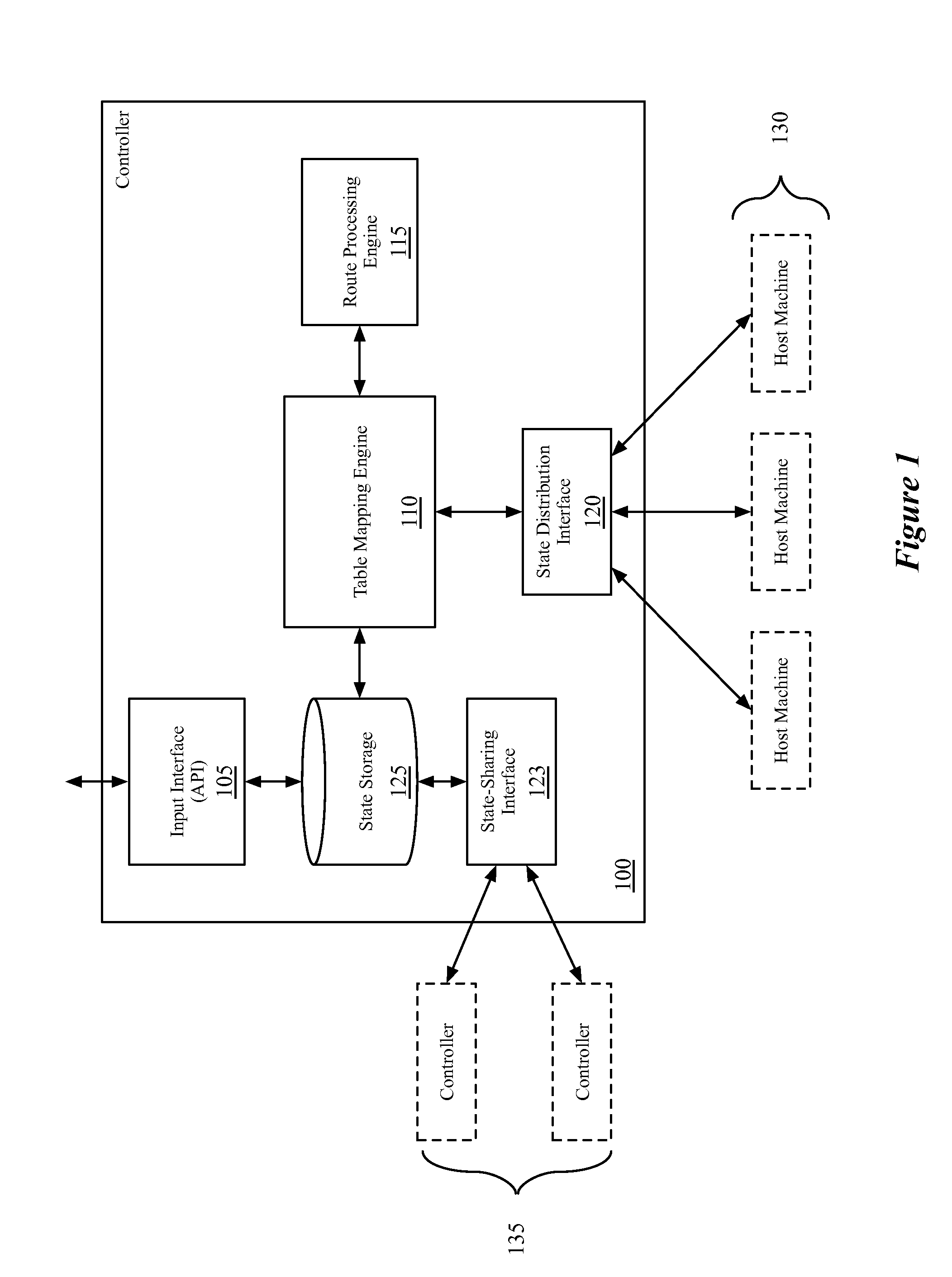
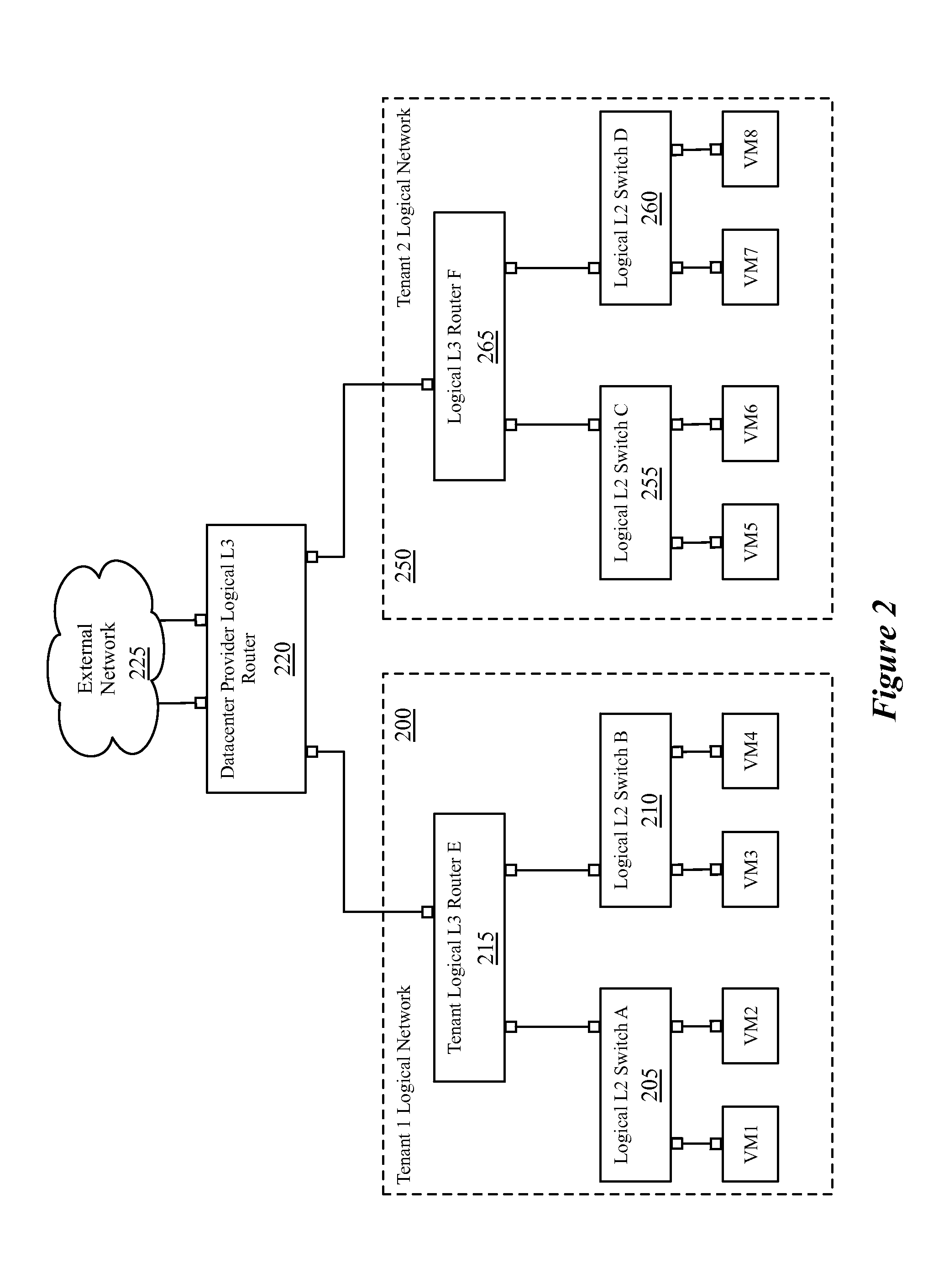
Dynamic routing for logical routers
Some embodiments provide a method for a network controller that manages a first logical router of a logical network that is implemented across several managed network elements. The method receives input data specifying a first route for a second logical router. Based on a connection between the first logical router and a second logical router in the logical network, the method dynamically generates a second route for the first logical router based on the first route. The method distributes data to implement the first logical router, including the second route, to a set of the managed network elements.
Owner:NICIRA
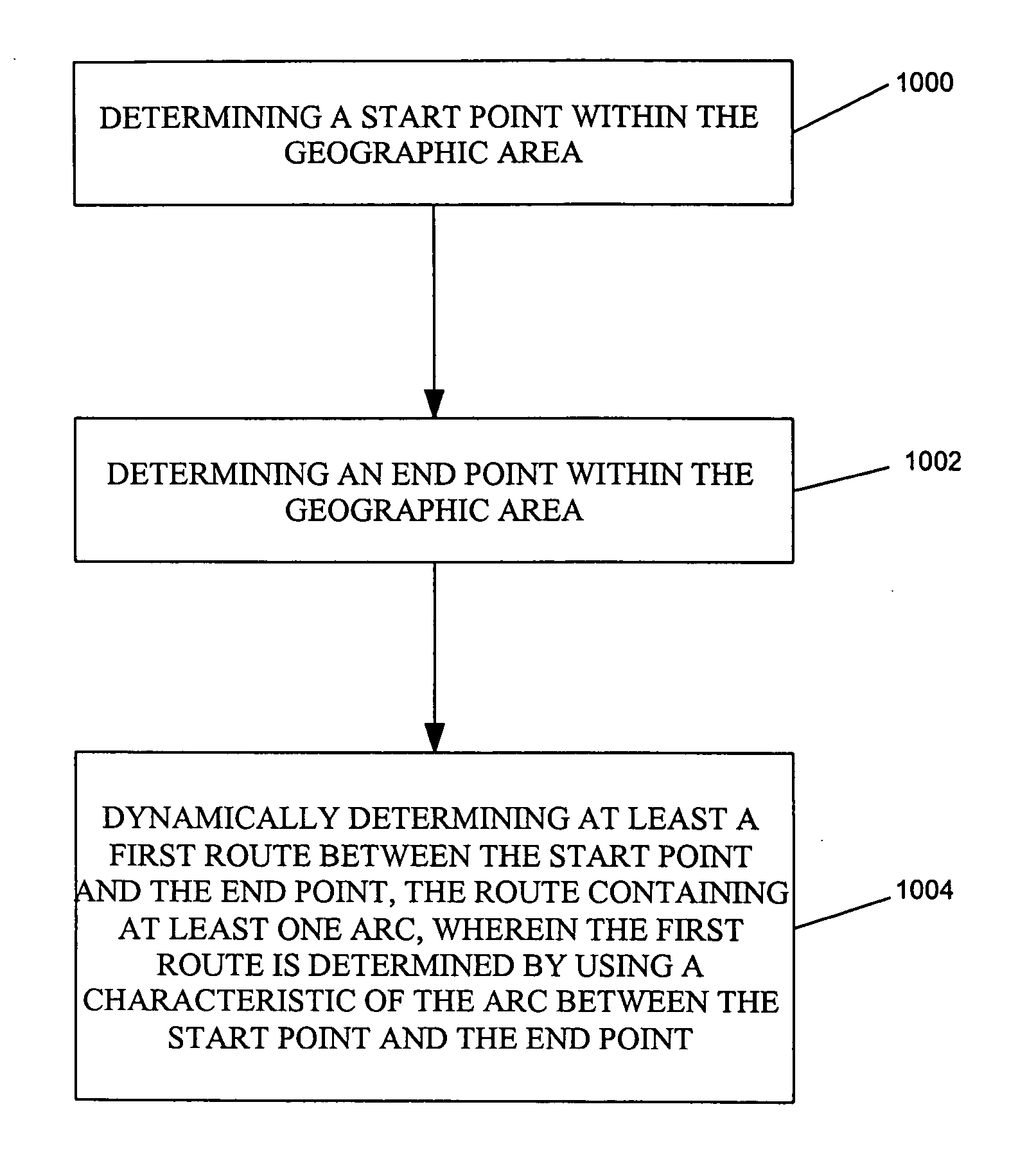
Dynamic routing tool
InactiveUS20060241855A1Maximizing traffic flowMinimize timeInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlAdaptive routingComputer science
GIS-based methods and apparatuses for determining transportation routes are disclosed. A method in accordance with the present invention comprises determining a transportation route using a geographical information systems (GIS) database that represents a geographical area, wherein the GIS database includes at least one node representing at least one geographical location within the geographic area and at least one arc representing at least one street within the geographic area. The method further comprises determining a start point within the geographic area, determining an end point within the geographic area, and dynamically determining at least a first route between the start point and the end point, the route containing at least one arc, wherein the first route is determined by using a characteristic of the arc between the start point and the end point.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com