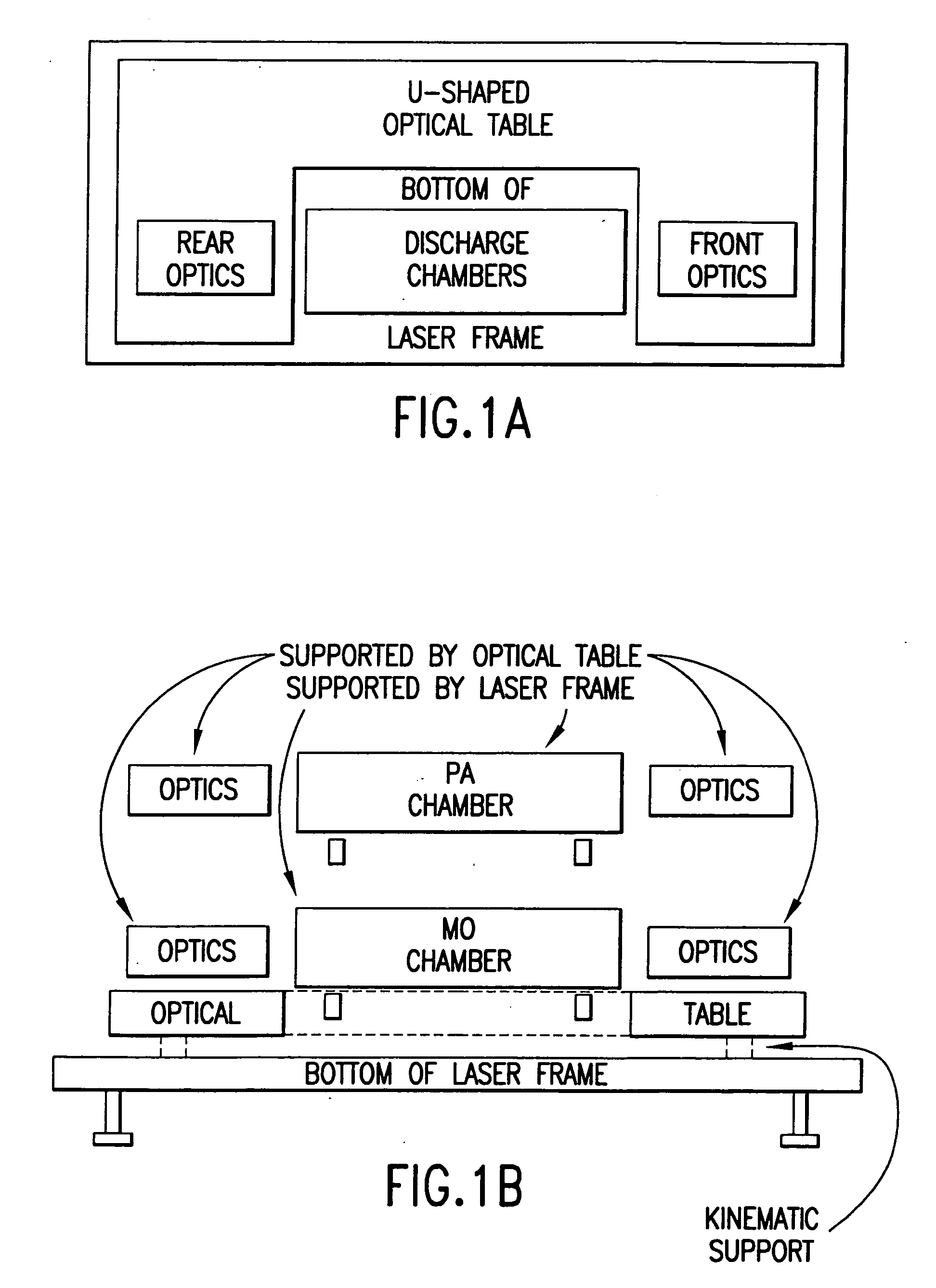
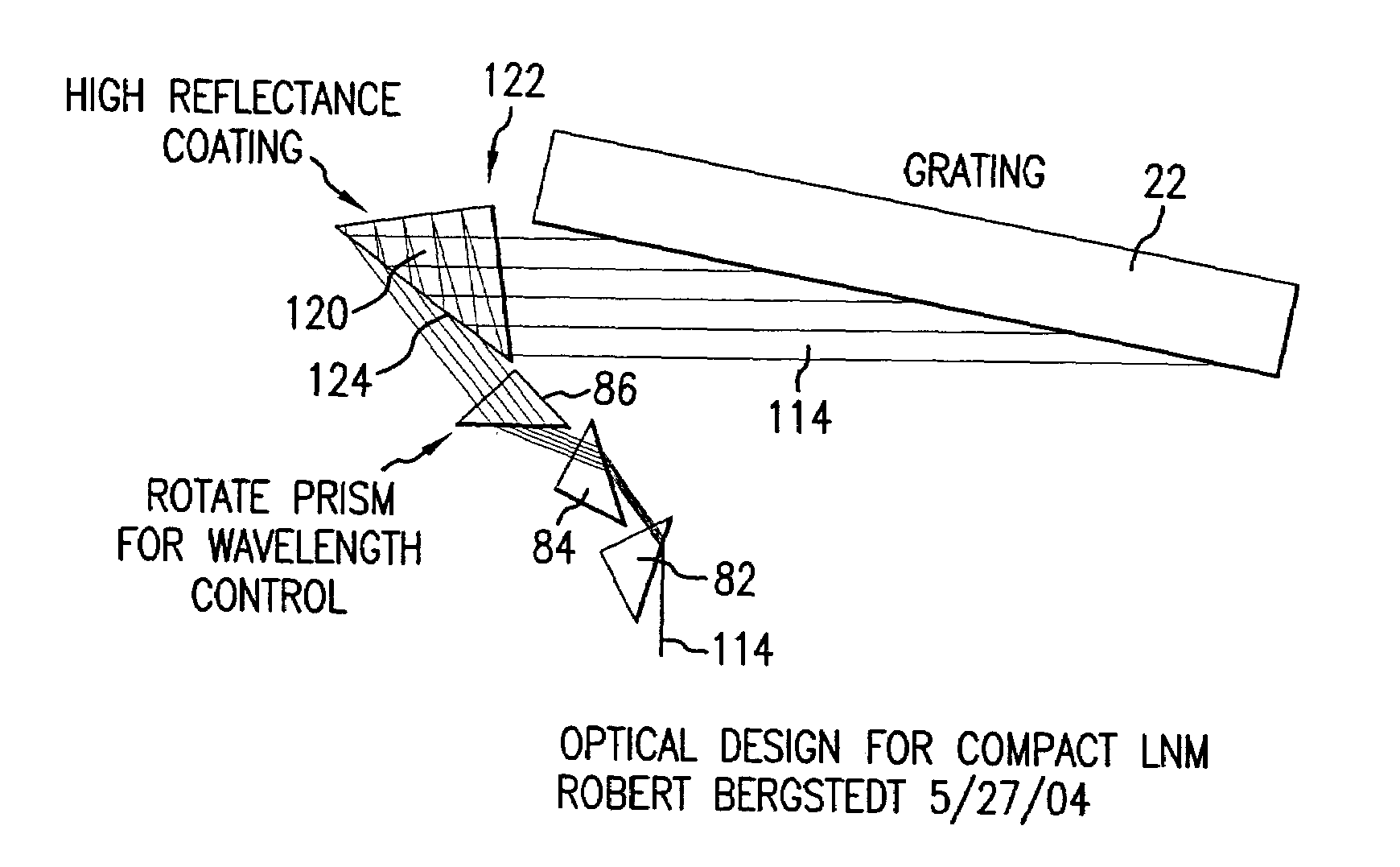
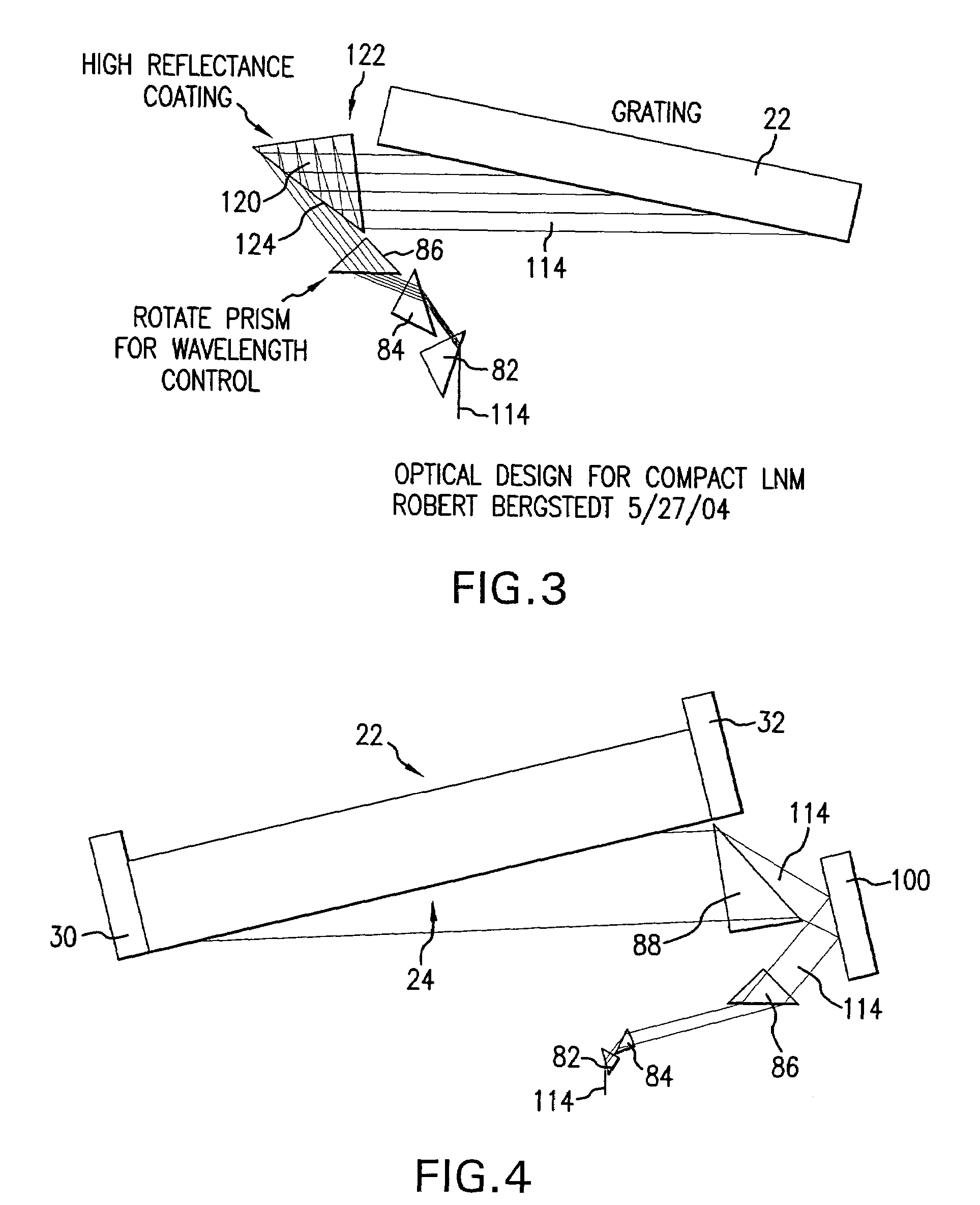
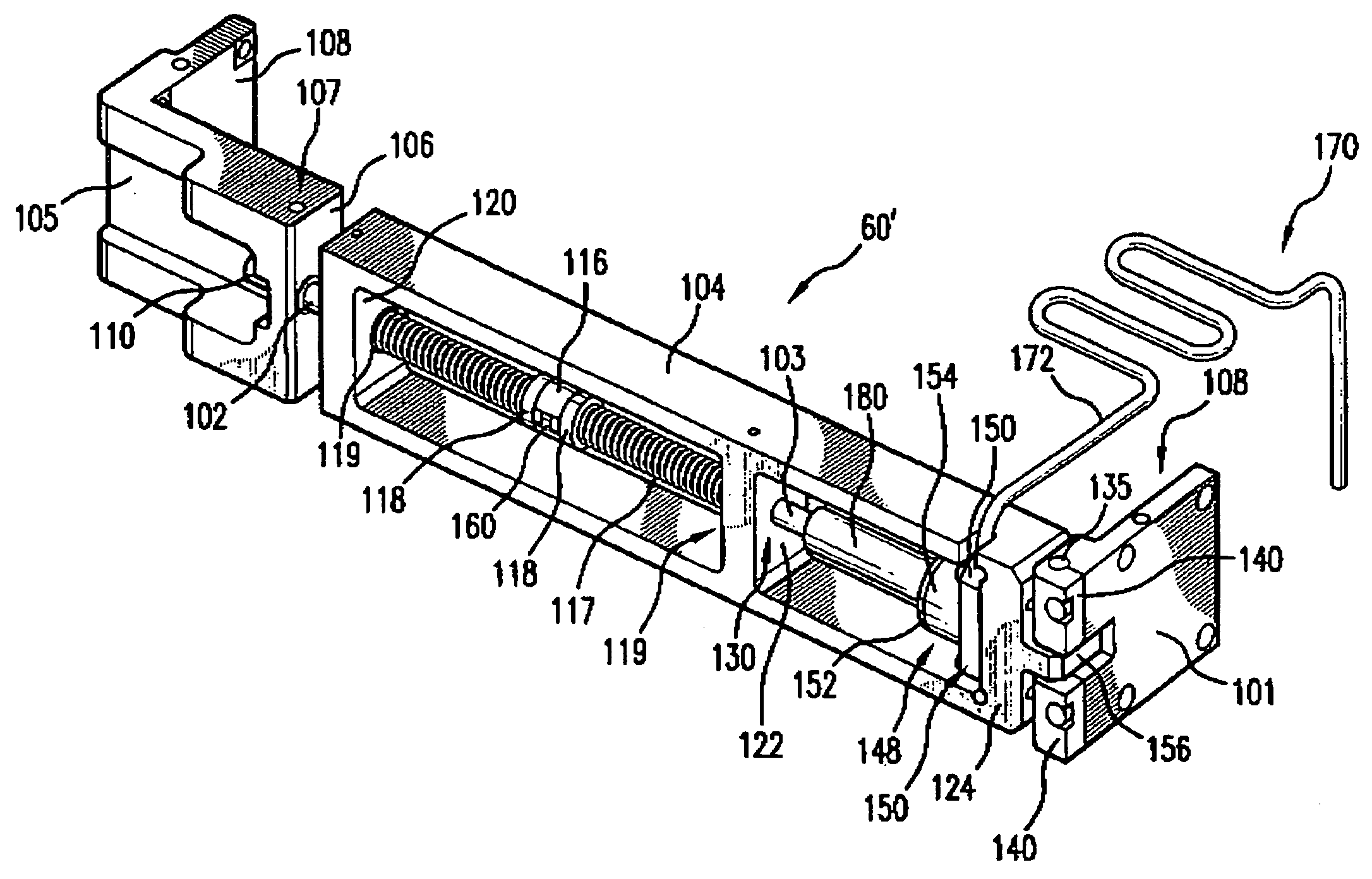
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
37 results about "Line narrowing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
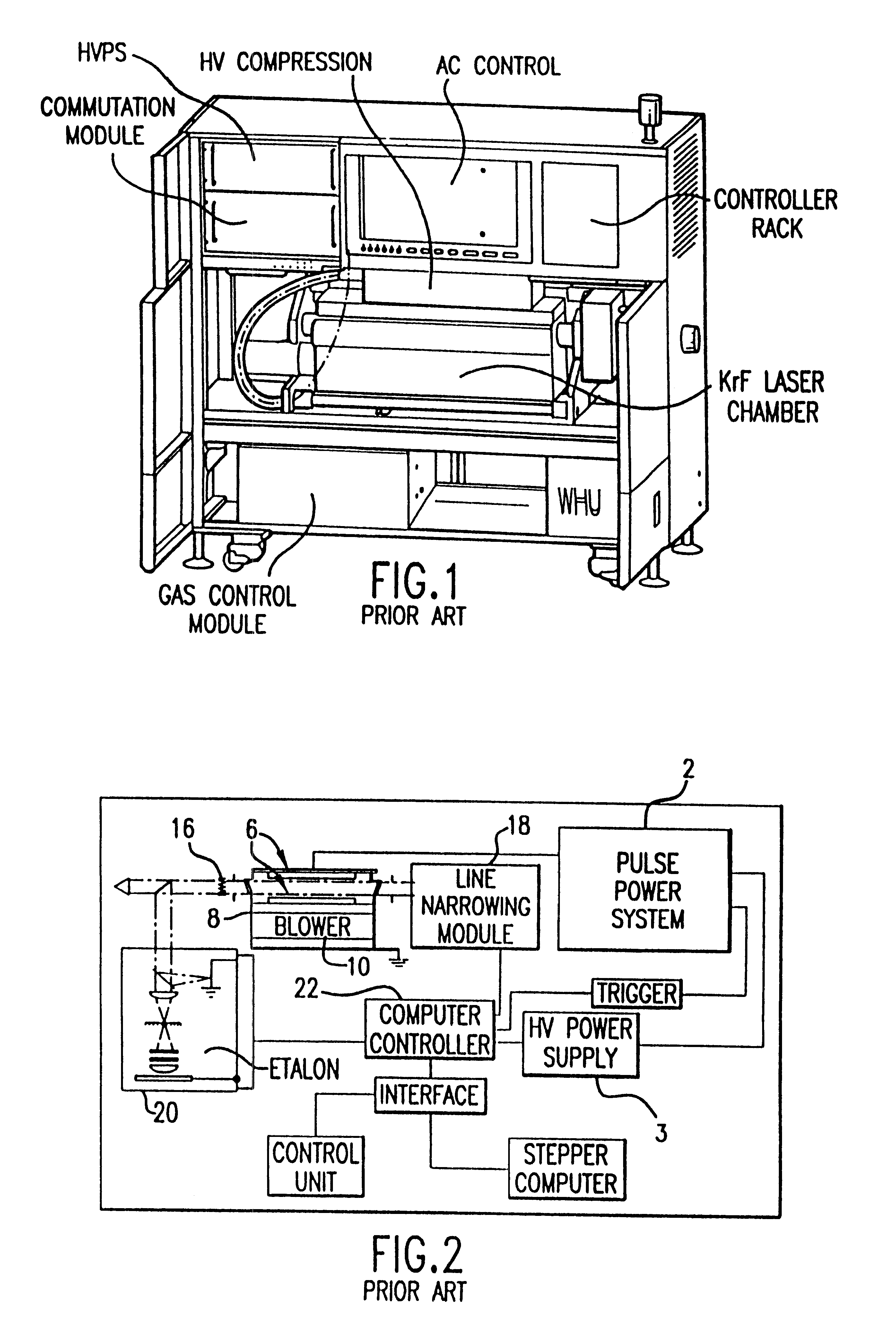
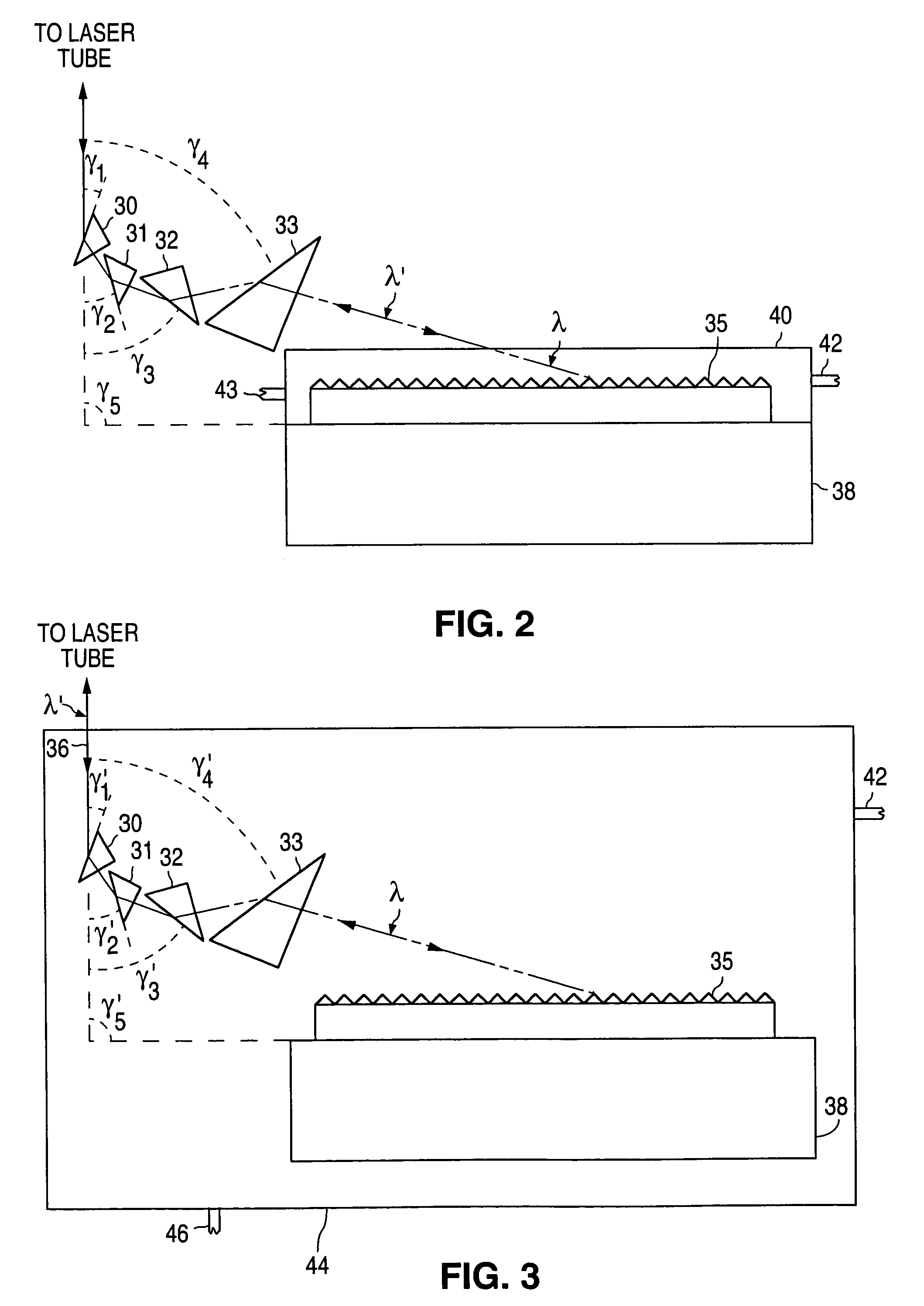
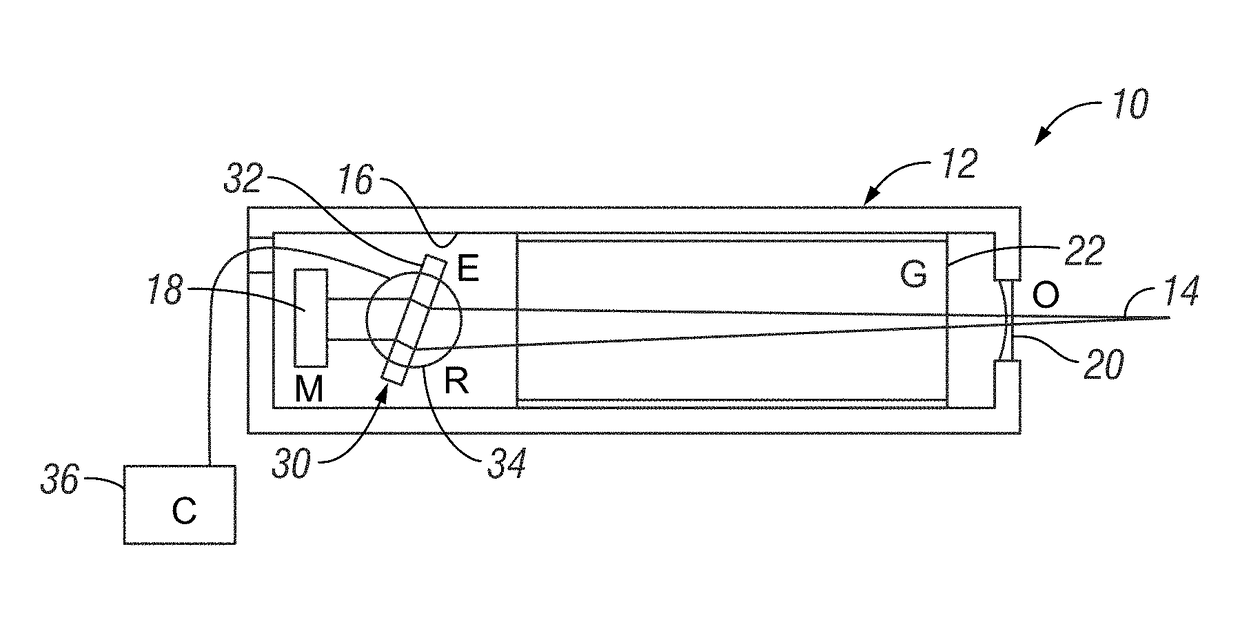
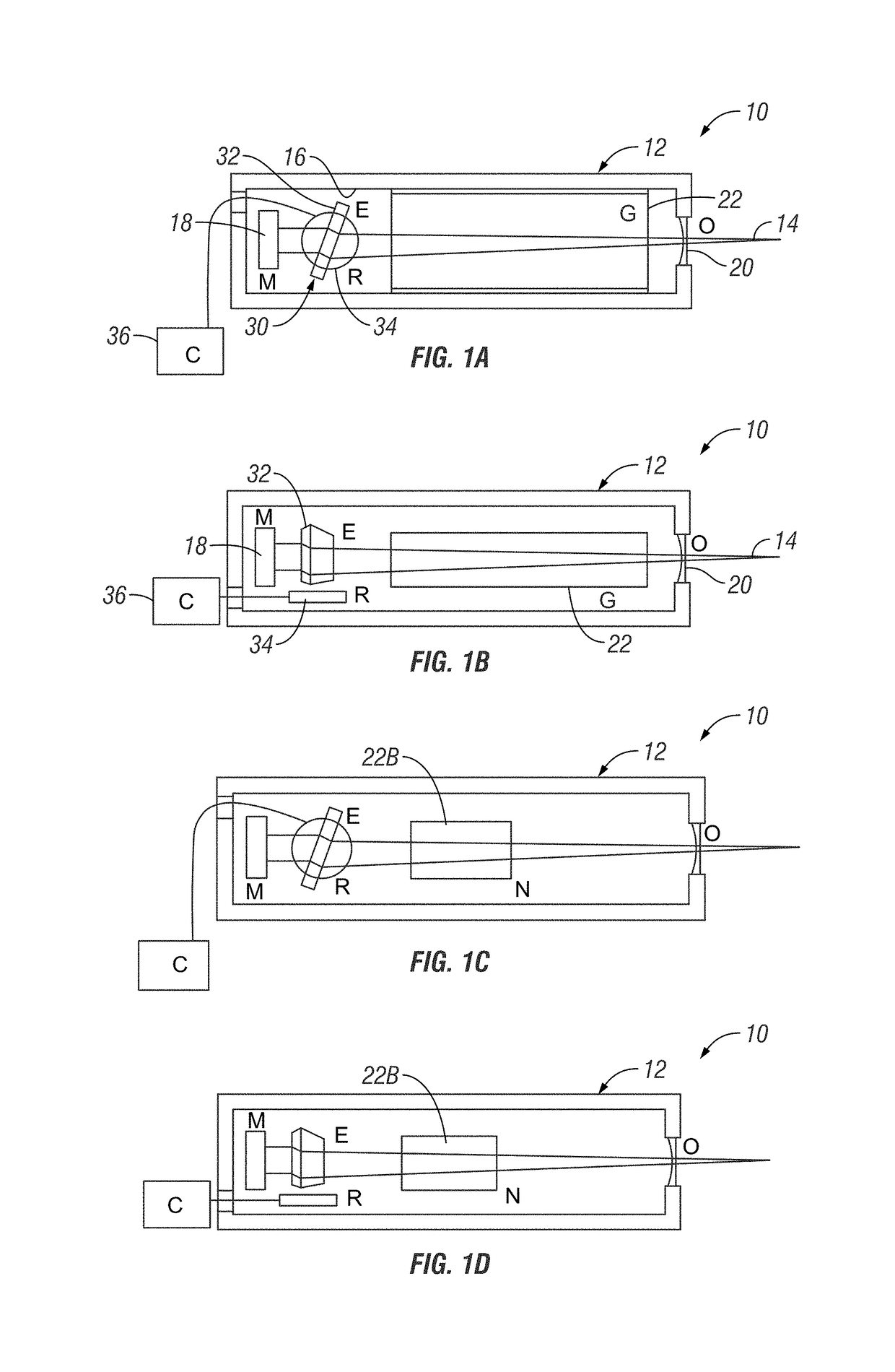
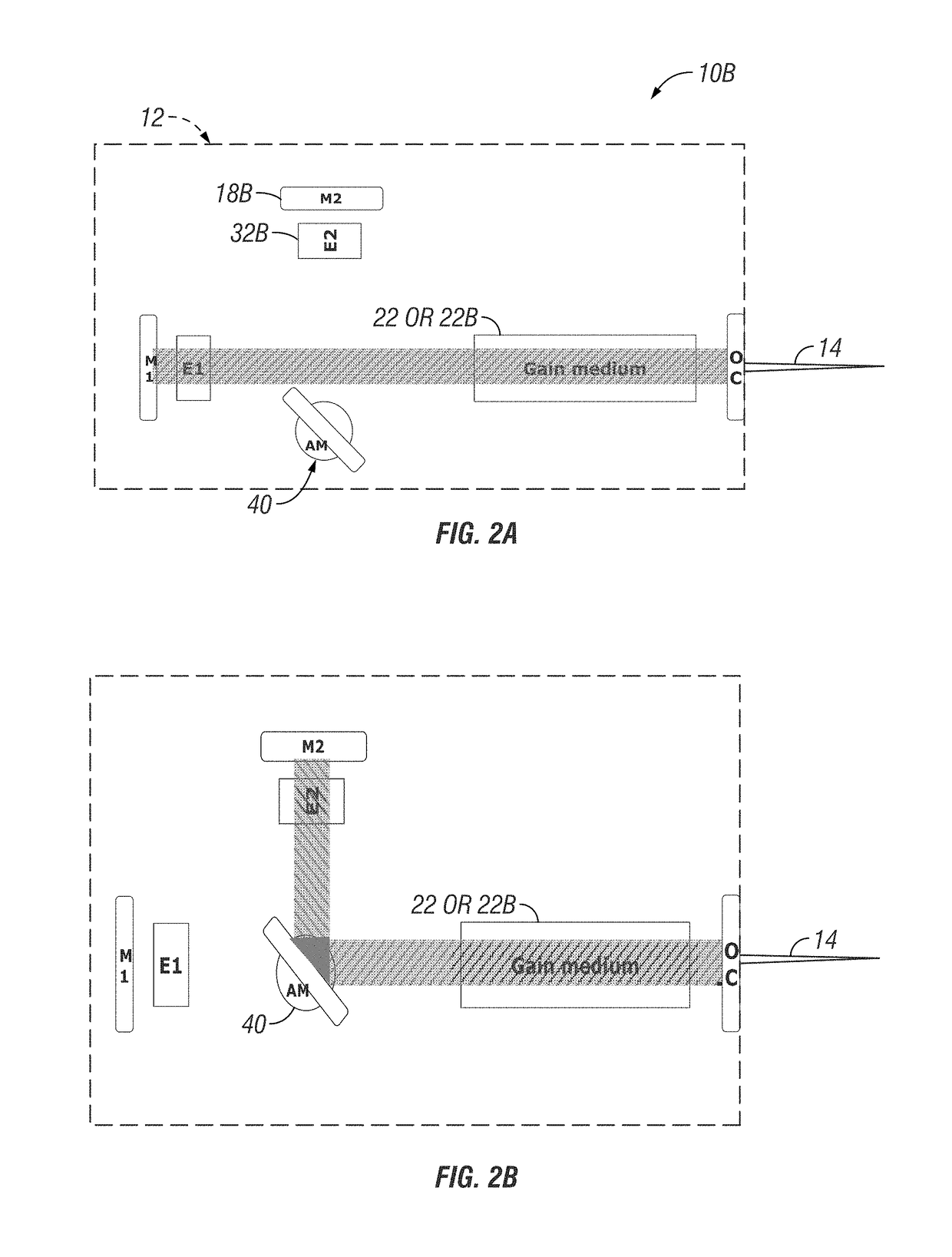
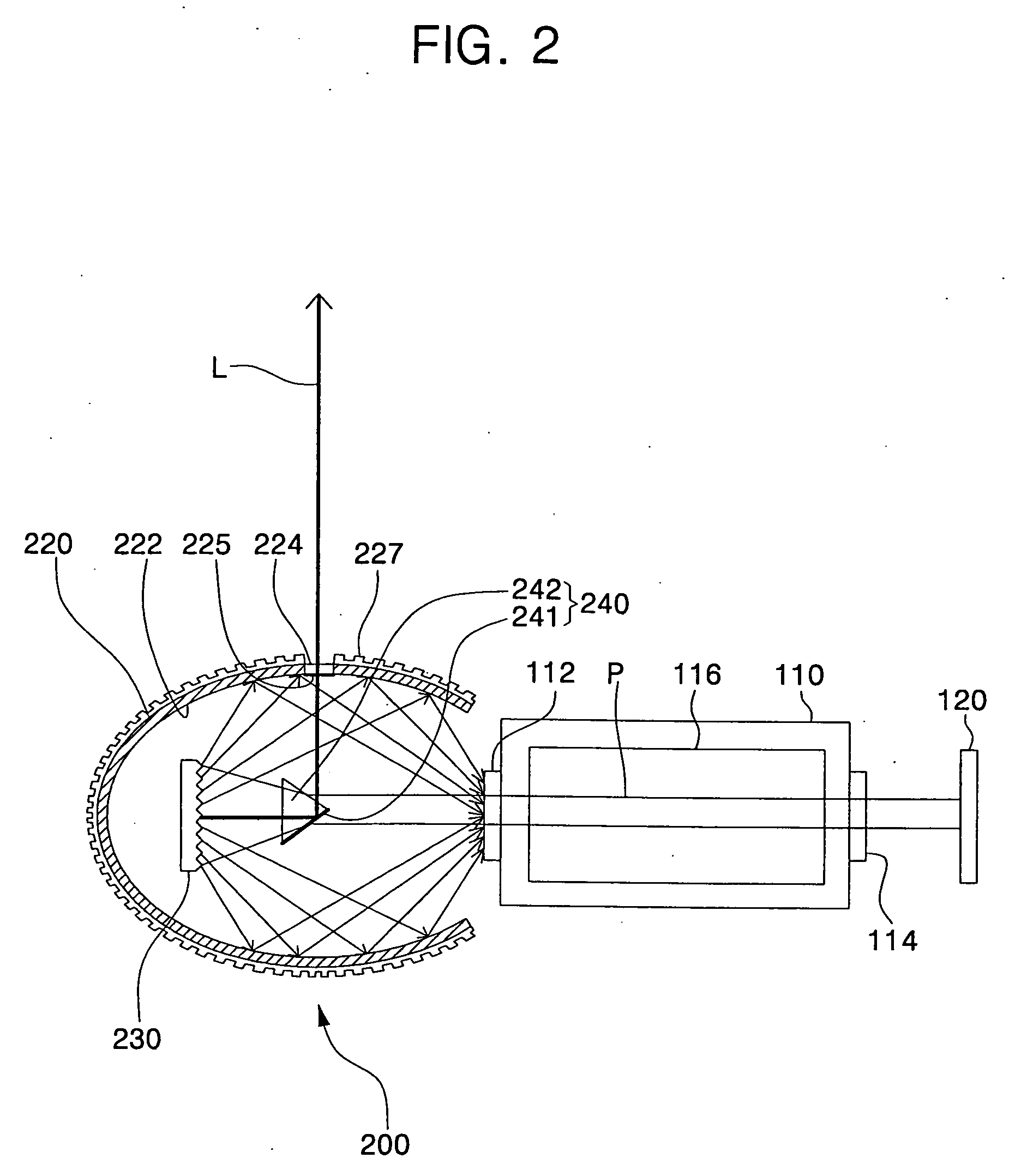
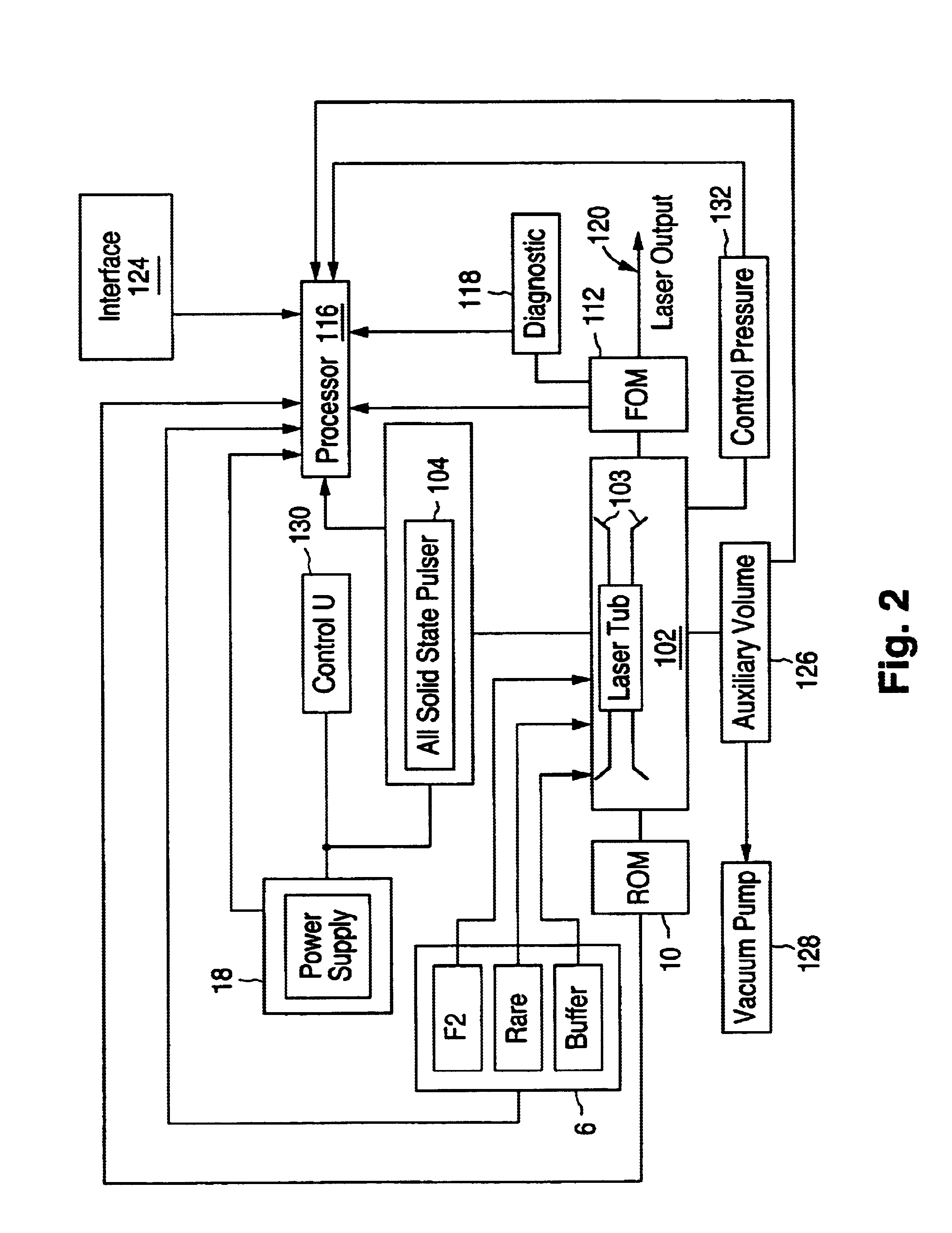
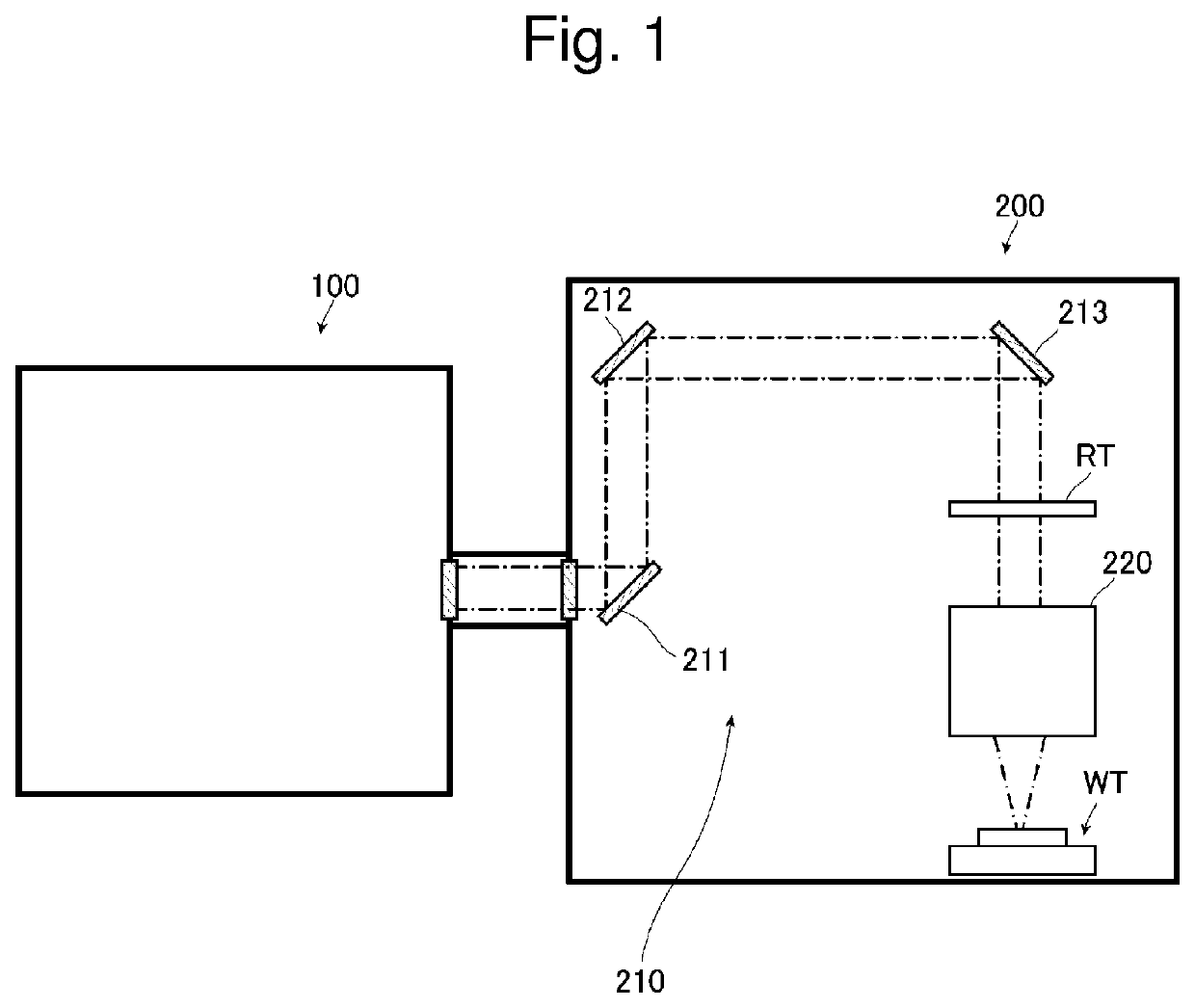
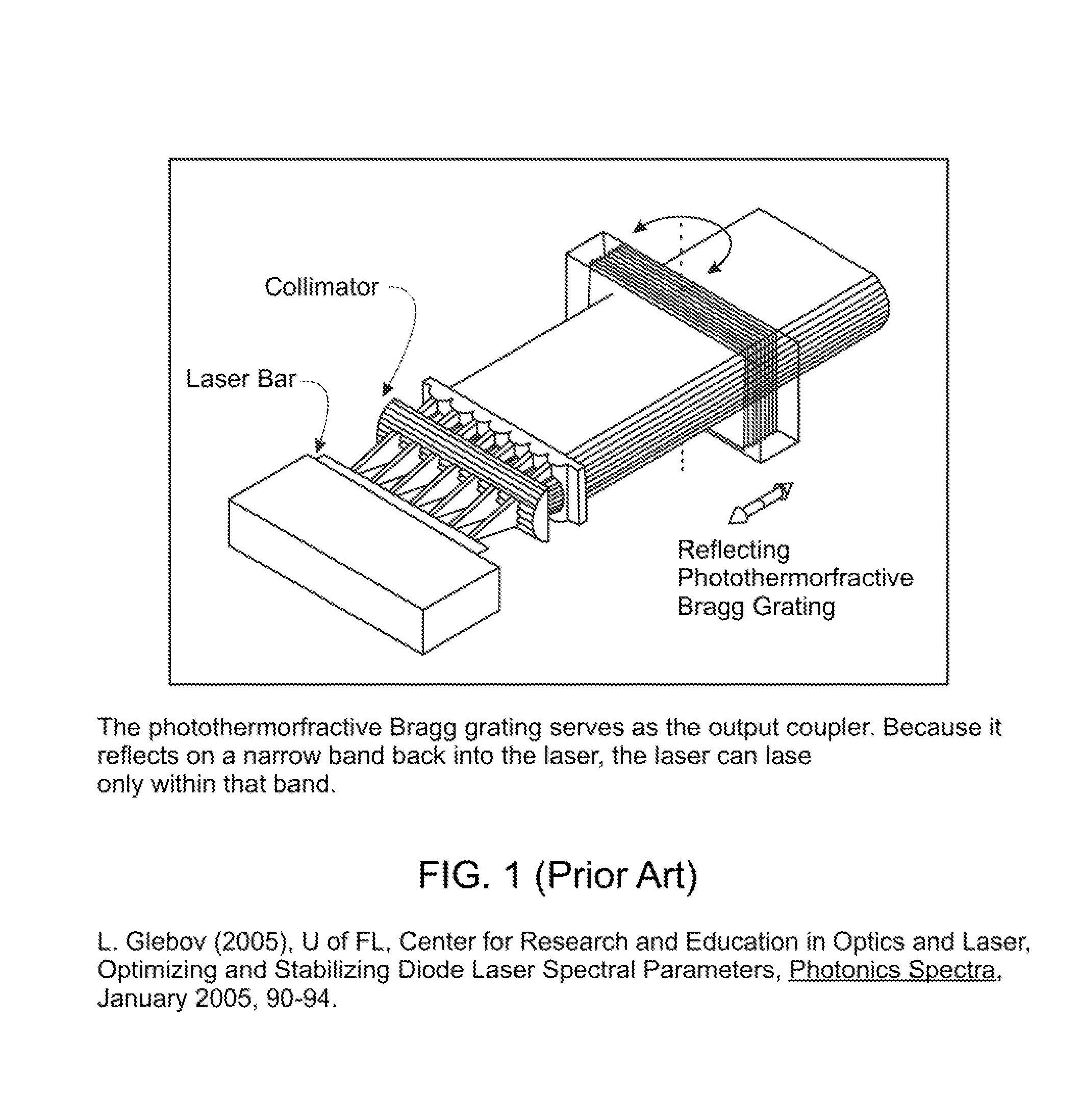
Injection seeded F2 lithography laser
InactiveUS6370174B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser arrangementsLithographic artistModular design
A tunable injection seeded very narrow band F2 lithography laser. The laser combines modular design features of prior art long life releasable lithography lasers with special F2 line narrowing and tuning techniques applied to a seed beam operated in a first gain medium which beam is used to stimulate narrow band lasing in a second gain medium to produce a very narrow band laser beam useful for integrated circuit lithography.
Owner:CYMER INC
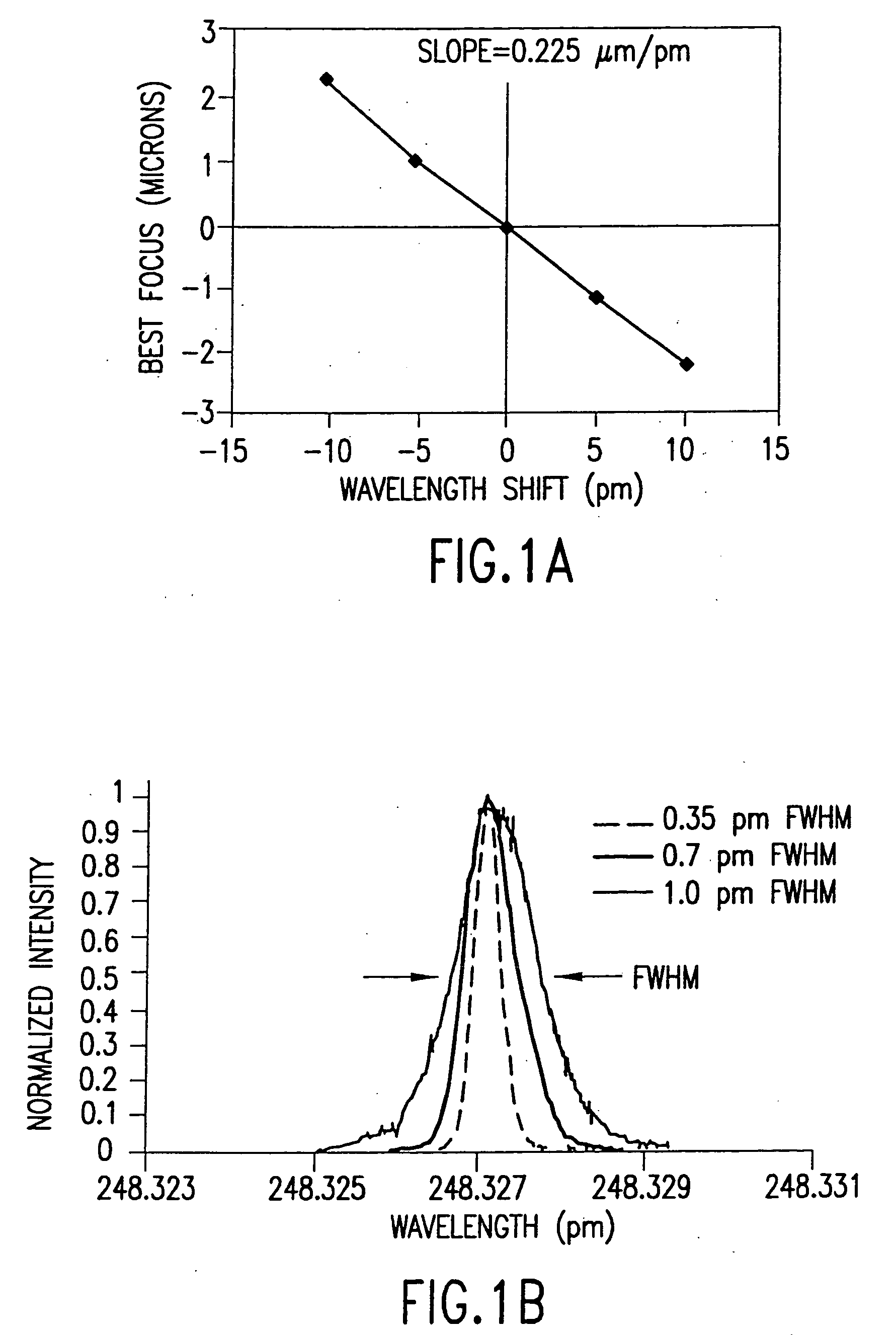
Laser spectral engineering for lithographic process
InactiveUS6853653B2Improved pattern resolutionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical resonator shape and constructionResistElectric discharge
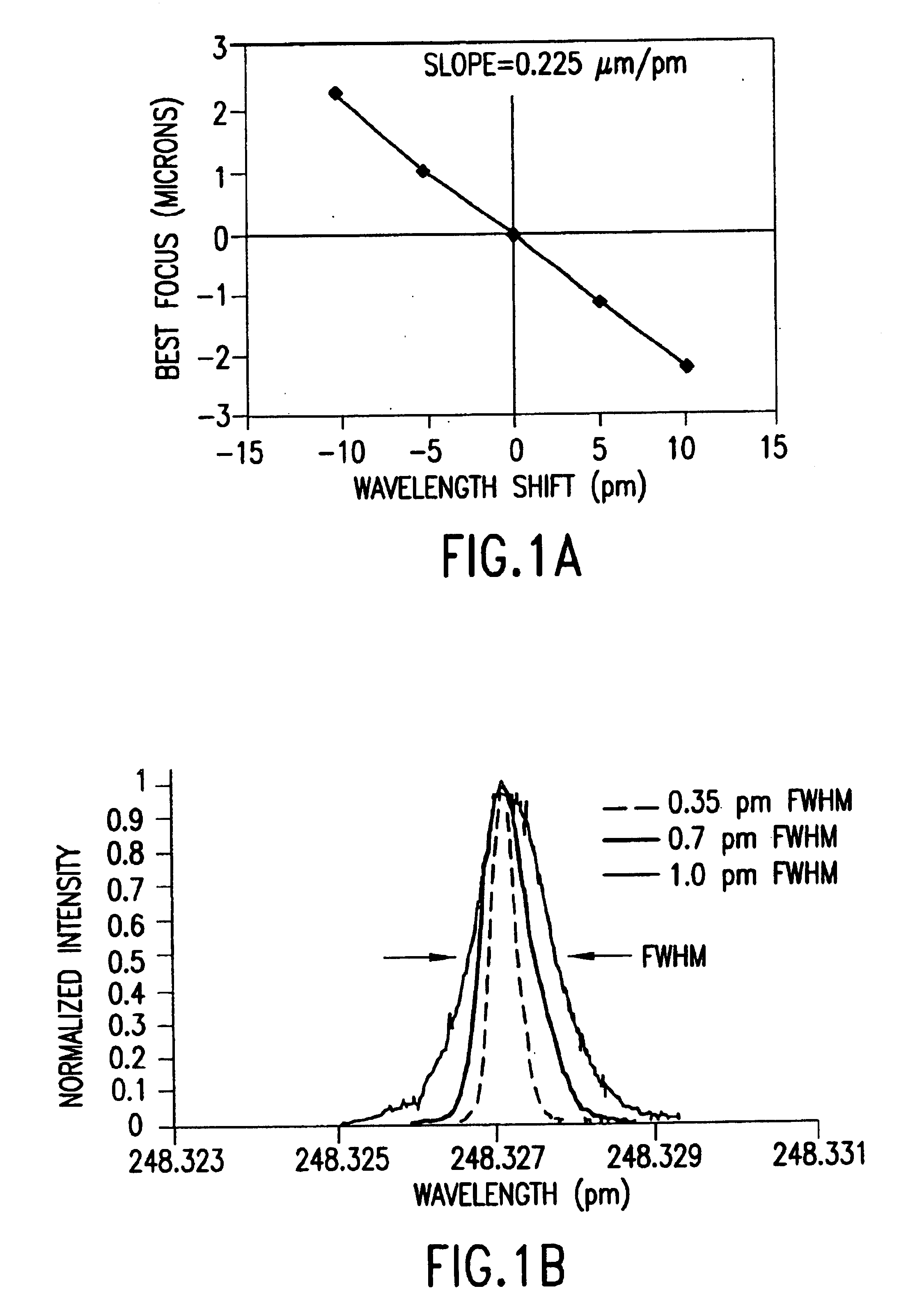
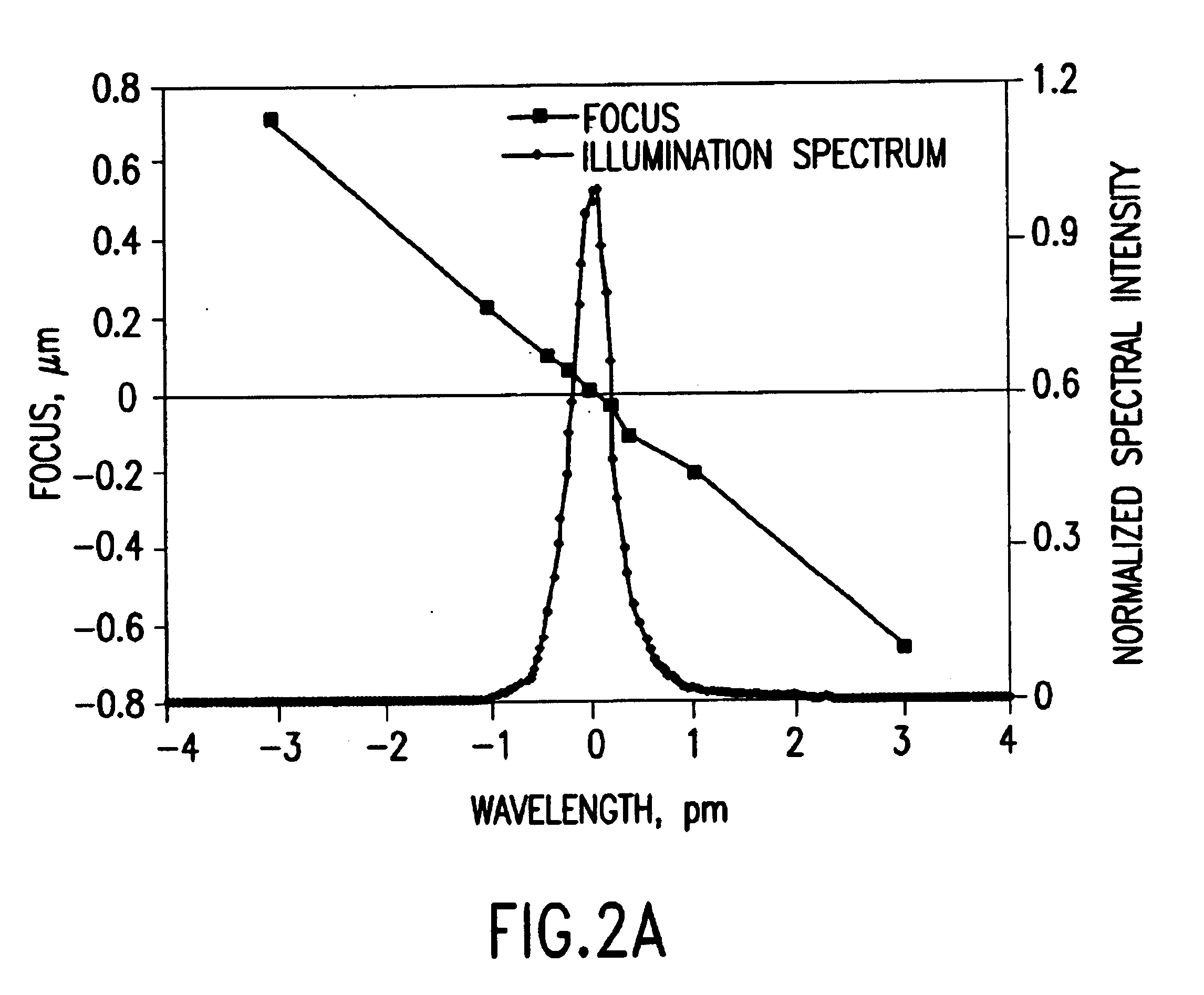
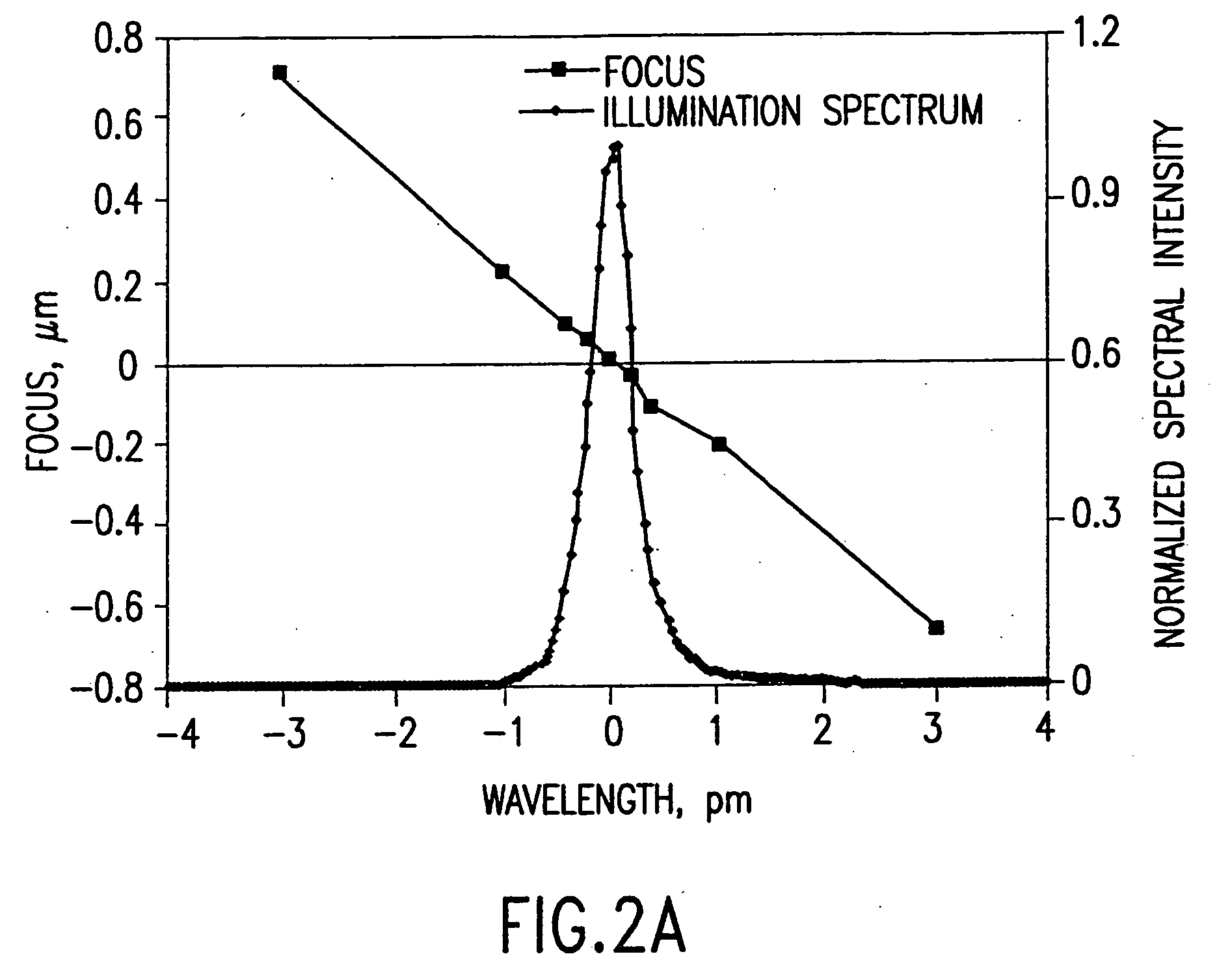
An integrated circuit lithography technique called spectral engineering by Applicants, for bandwidth control of an electric discharge laser. In a preferred process, a computer model is used to model lithographic parameters to determine a desired laser spectrum needed to produce a desired lithographic result. A fast responding tuning mechanism is then used to adjust center wavelength of laser pulses in a burst of pulses to achieve an integrated spectrum for the burst of pulses approximating the desired laser spectrum. The laser beam bandwidth is controlled to produce an effective beam spectrum having at least two spectral peaks in order to produce improved pattern resolution in photo resist film. Line narrowing equipment is provided having at least one piezoelectric drive and a fast bandwidth detection control system having a time response of less than about 2.0 millisecond. In a preferred embodiment, a wavelength tuning mirror is dithered at dither rates of more than 500 dithers per second in phase with the repetition rate of the laser. In one case, the piezoelectric drive was driven with a square wave signal and in a second case it was driven with a sine wave signal. In another embodiment, the maximum displacement was matched on a one-to-one basis with the laser pulses in order to produce a desired average spectrum with two peaks for a series of laser pulses. Other preferred embodiments utilize three separate wavelength tuning positions producing a spectrum with three separate peaks.
Owner:CYMER INC
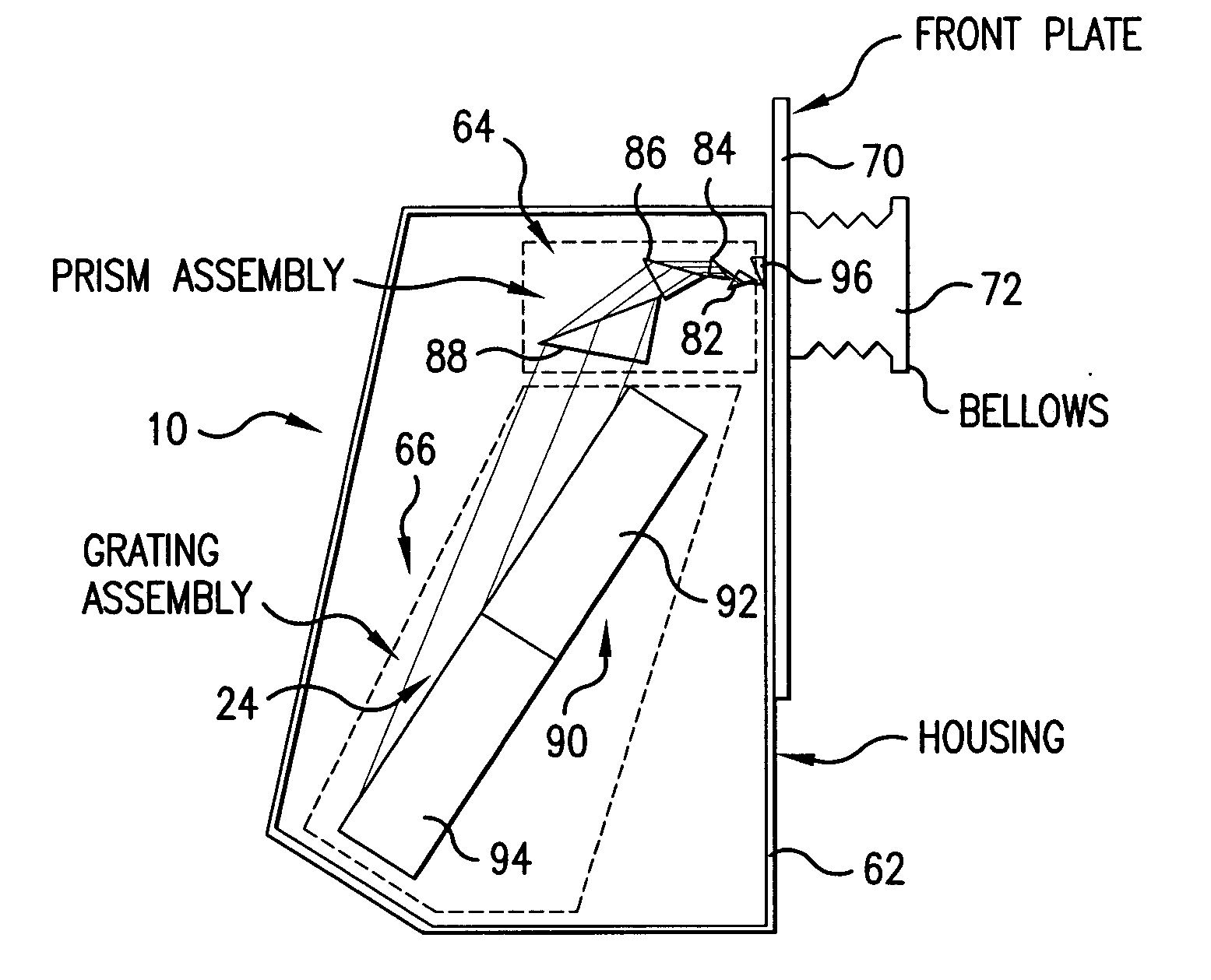
Large diffraction grating for gas discharge laser
InactiveUS20020127497A1Increased beam expansionSmall bandwidthPhotomechanical apparatusDiffraction gratingsBeam expanderLithography process
A grating based line narrowing unit for gas discharge lasers with increased beam expansion to produce smaller bandwidths. The grating has a grating surface larger than 100 cm.sup.2 and is a replica grating produced from a master grating produced with a lithography process on a single crystal substrate. In preferred embodiments, a beam from the chamber of the laser is expanded with four prism beam expanders. The large grating, much larger than gratings historically produced from diamond lined gratings, permit substantial reductions in bandwidth while maintaining laser efficiency. A narrow band of wavelengths in the expanded beam is reflected from a grating in a Littrow configuration back via the bi-directional beam expanders into the laser chamber for amplification.
Owner:CYMER INC
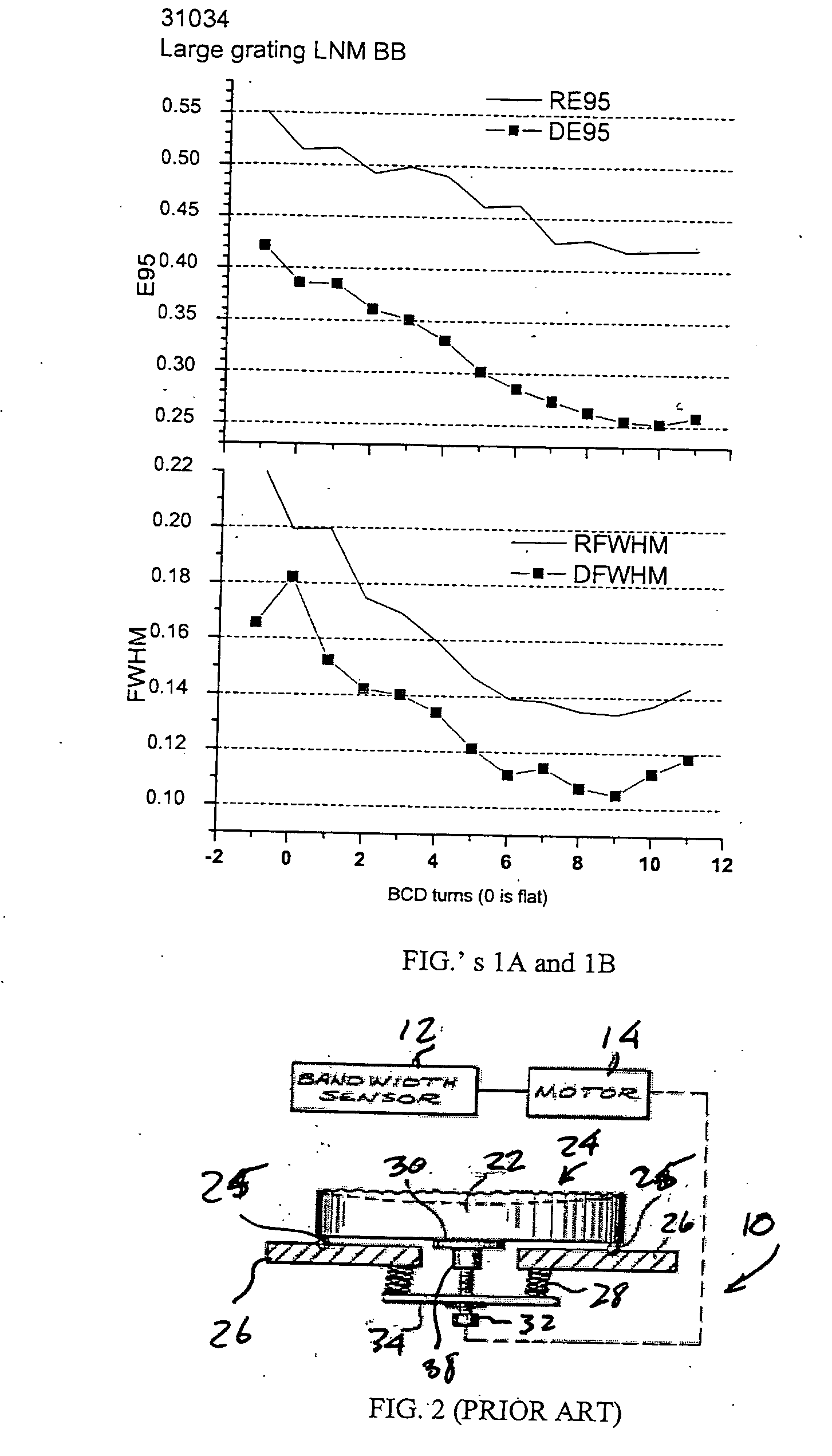
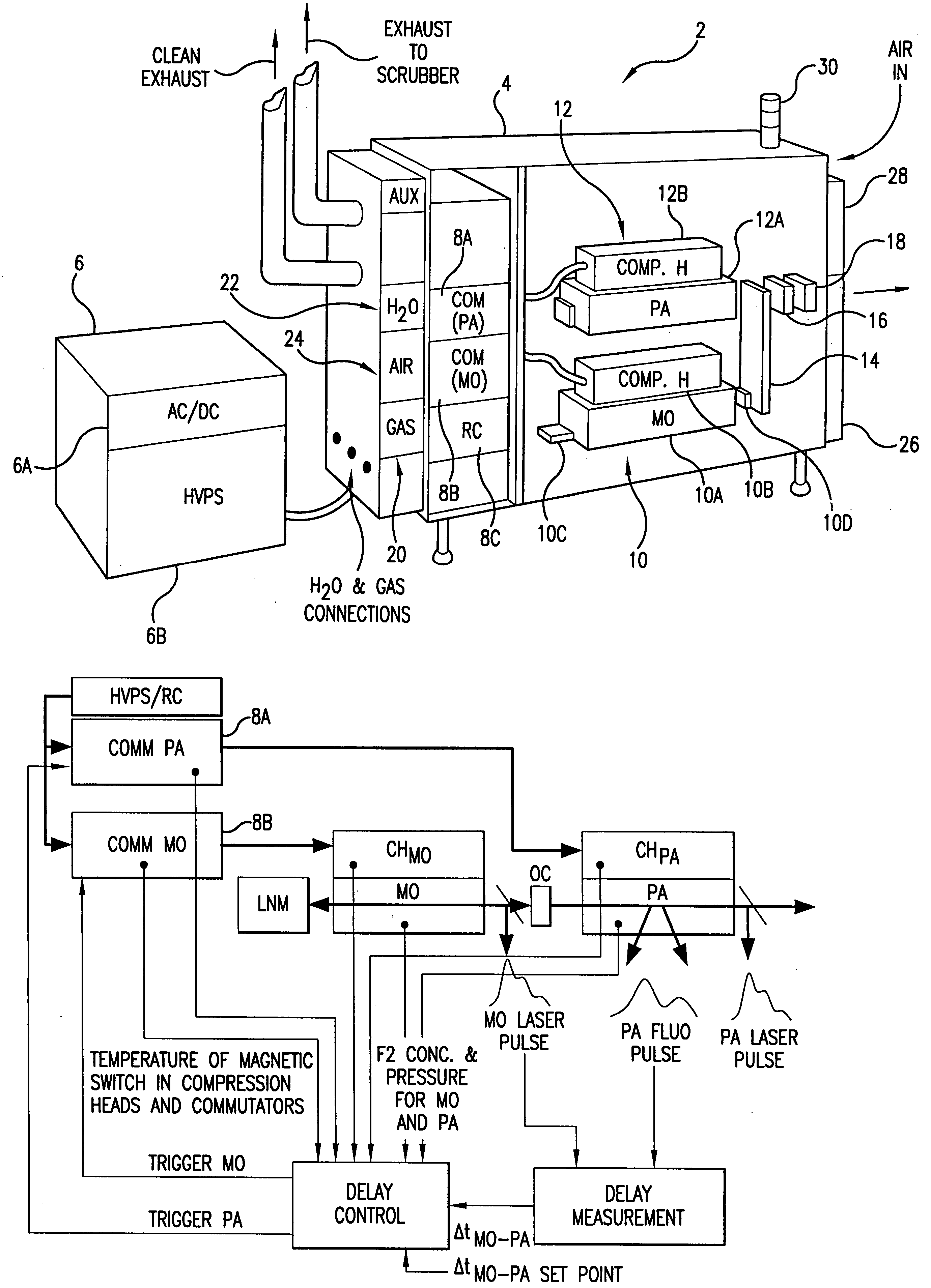
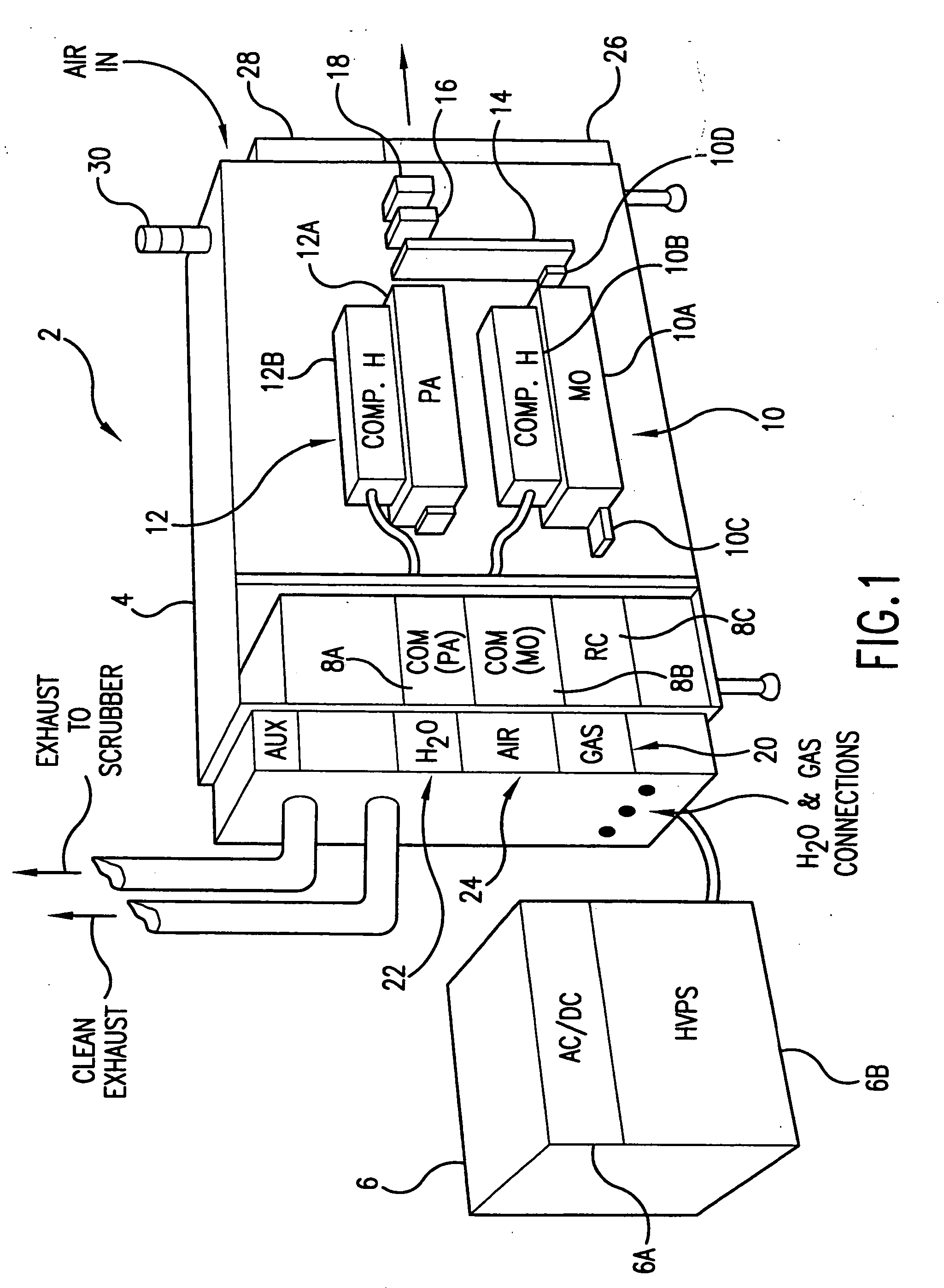
High power high pulse repetition rate gas discharge laser system bandwidth management
InactiveUS20060114956A1Minimize Fresnel lossHigh repetition rateActive medium materialPulse beamAngle of incidence
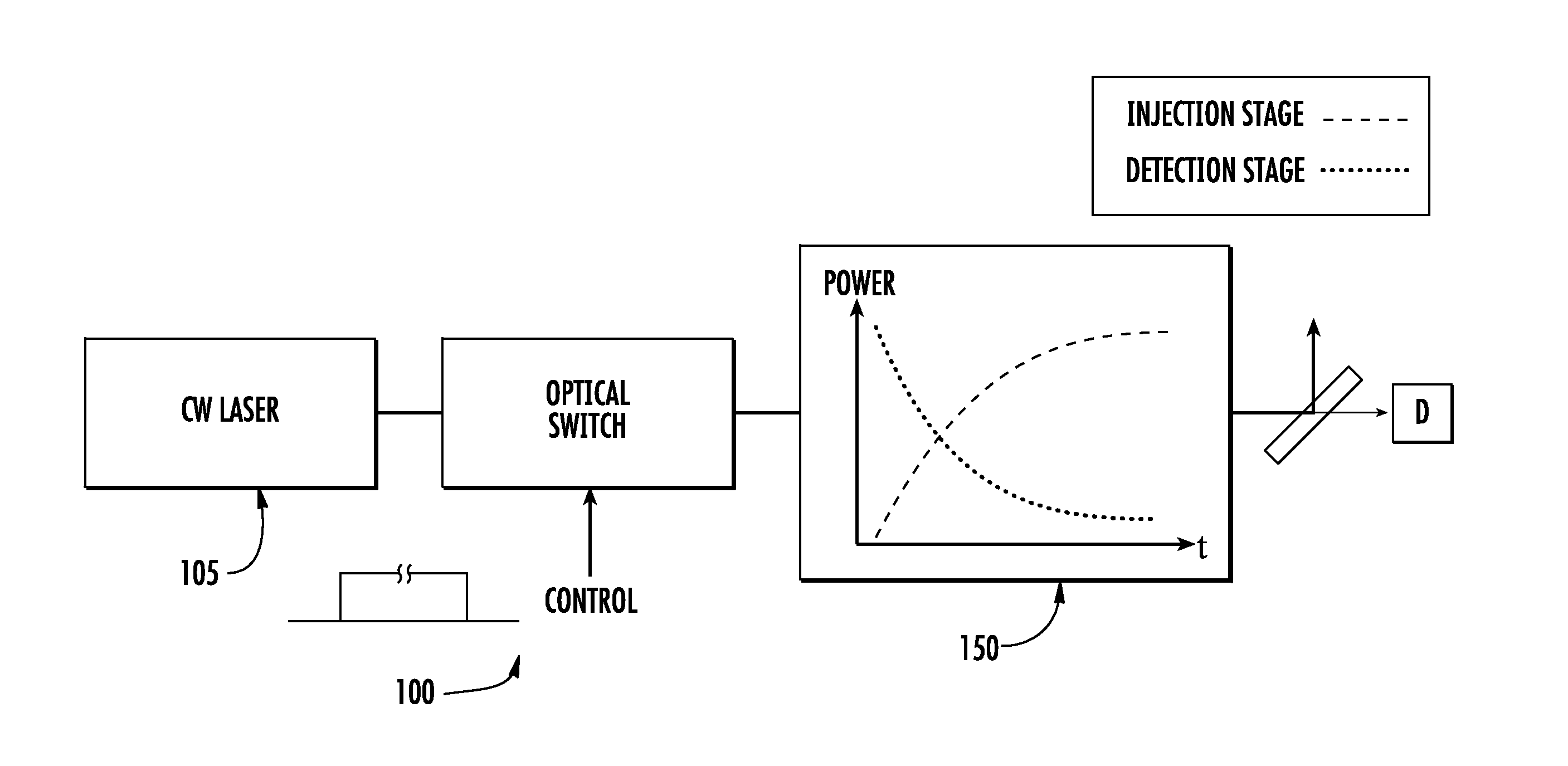
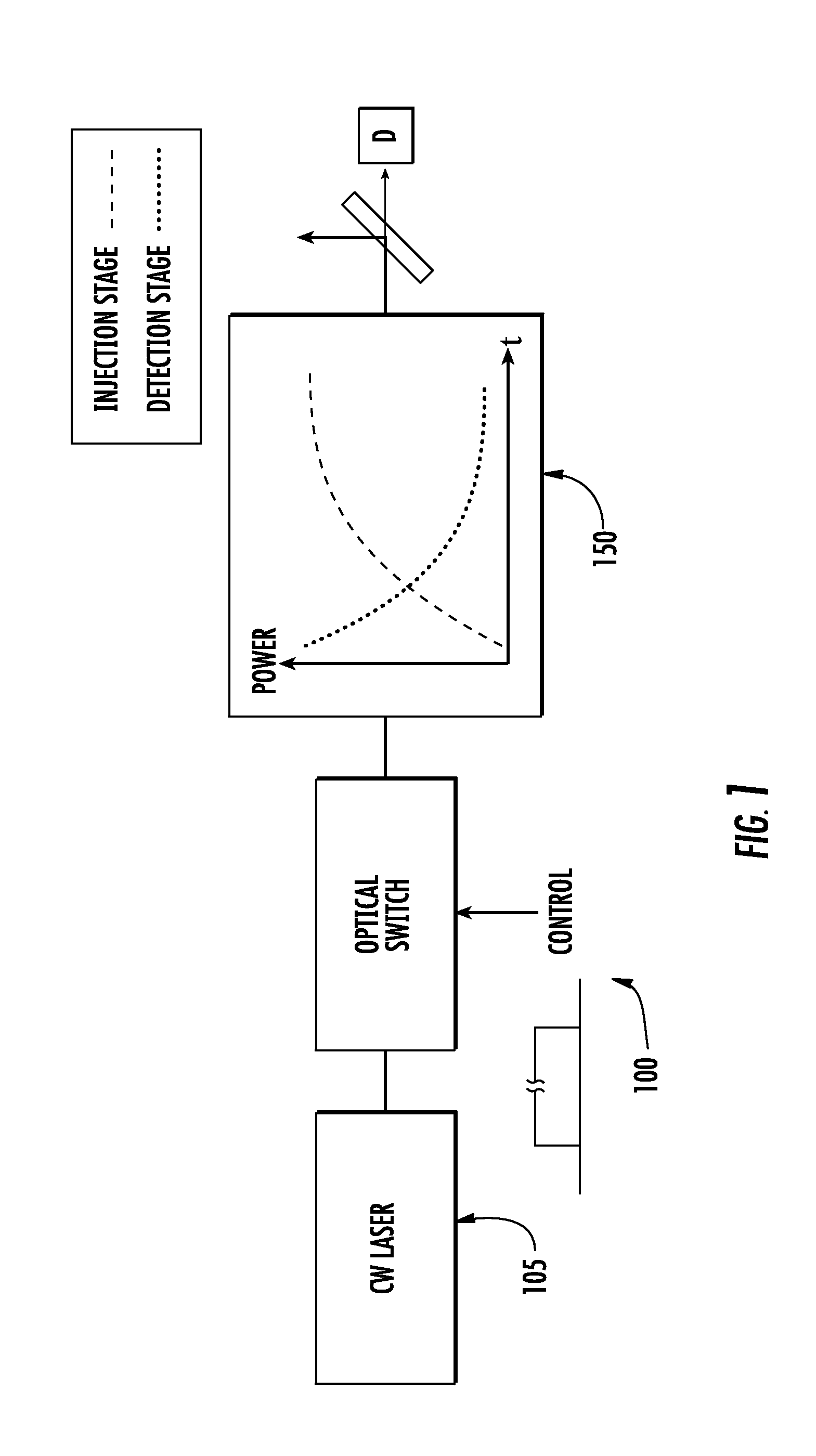
A line narrowing apparatus and method for a narrow band DUV high power high repetition rate gas discharge laser producing output laser light pulse beam pulses in bursts of pulses is disclosed, which may comprise a dispersive center wavelength selection optic contained within a line narrowing module, selecting at least one center wavelength for each pulse determined at least in part by the angle of incidence of the laser light pulse beam containing the respective pulse on a dispersive wavelength selection optic dispersive surface; a first dispersive optic bending mechanism operatively connected to the dispersive center wavelength selection optic and operative to change the curvature of the dispersive surface in a first manner; and, a second dispersive optic bending mechanism operatively connected to the dispersive center wavelength selection optic and operative to change the curvature of the dispersive surface in a second manner. The first manner may modify a first measure of bandwidth and the second manner may modify a second measure of bandwidth such that the ratio of the first measure to the second measure substantially changes. The first measure may be a spectrum width at a selected percentage of the spectrum peak value (FWX % M) and the second measure may be width within which some selected percentage of the spectral intensity is contained (EX %). The first dispersive optic bending mechanism may change the curvature of the dispersive surface in a first dimension and the second in a second dimension generally orthogonal to the first dimension. The laser system may comprise a beam path insert comprising a material having an different index of refraction and an index of refraction thermal gradient opposite from that of a neighboring optical element. The first dispersive optic bending mechanism may change the curvature of the dispersive surface in a first dimension and the second a second dimension generally parallel to the first dimension. An optical beam twisting element in the lasing cavity may optically twist the laser light pulse beam to present a twisted wavefront to the dispersive center wavelength selection optic. Bending may change the curvature and wavelength selection, e.g., in a burst may create two center wavelength peaks to select FWX % M and EX % independently.
Owner:CYMER INC
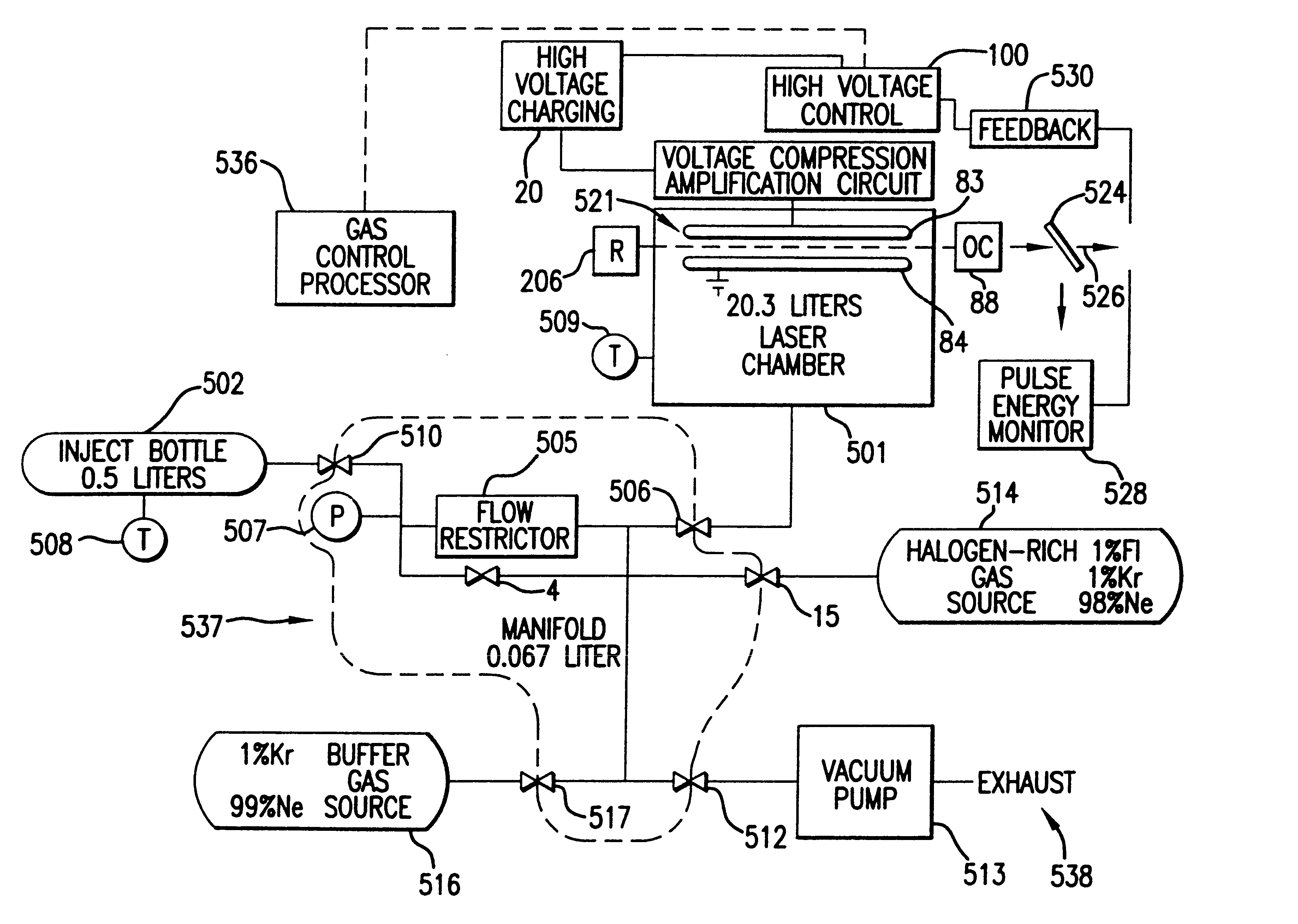
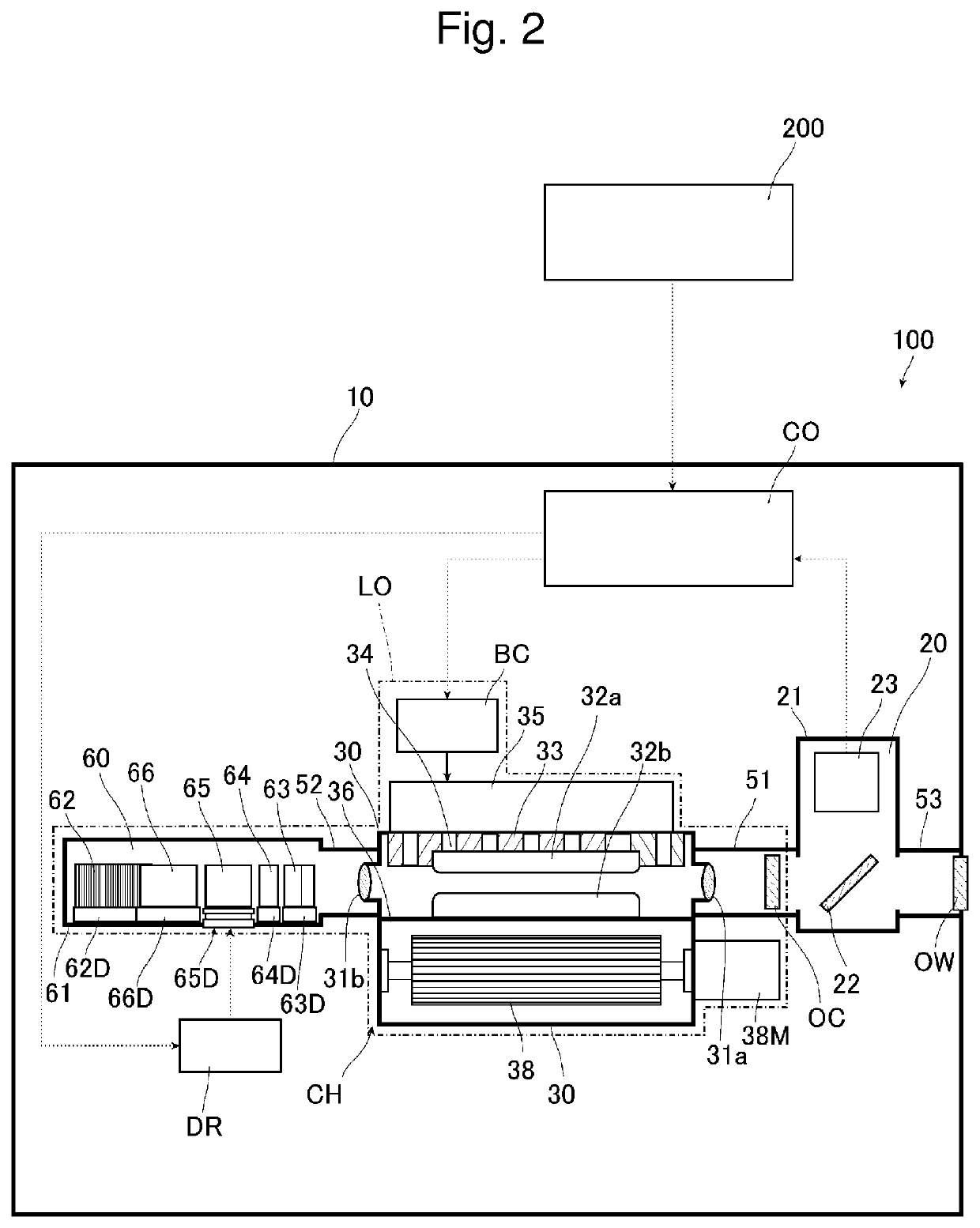
Reliable, modular, production quality narrow-band high rep rate F2 laser
InactiveUSRE38054E1Improve product qualityFast chargingVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingEngineeringHigh pressure
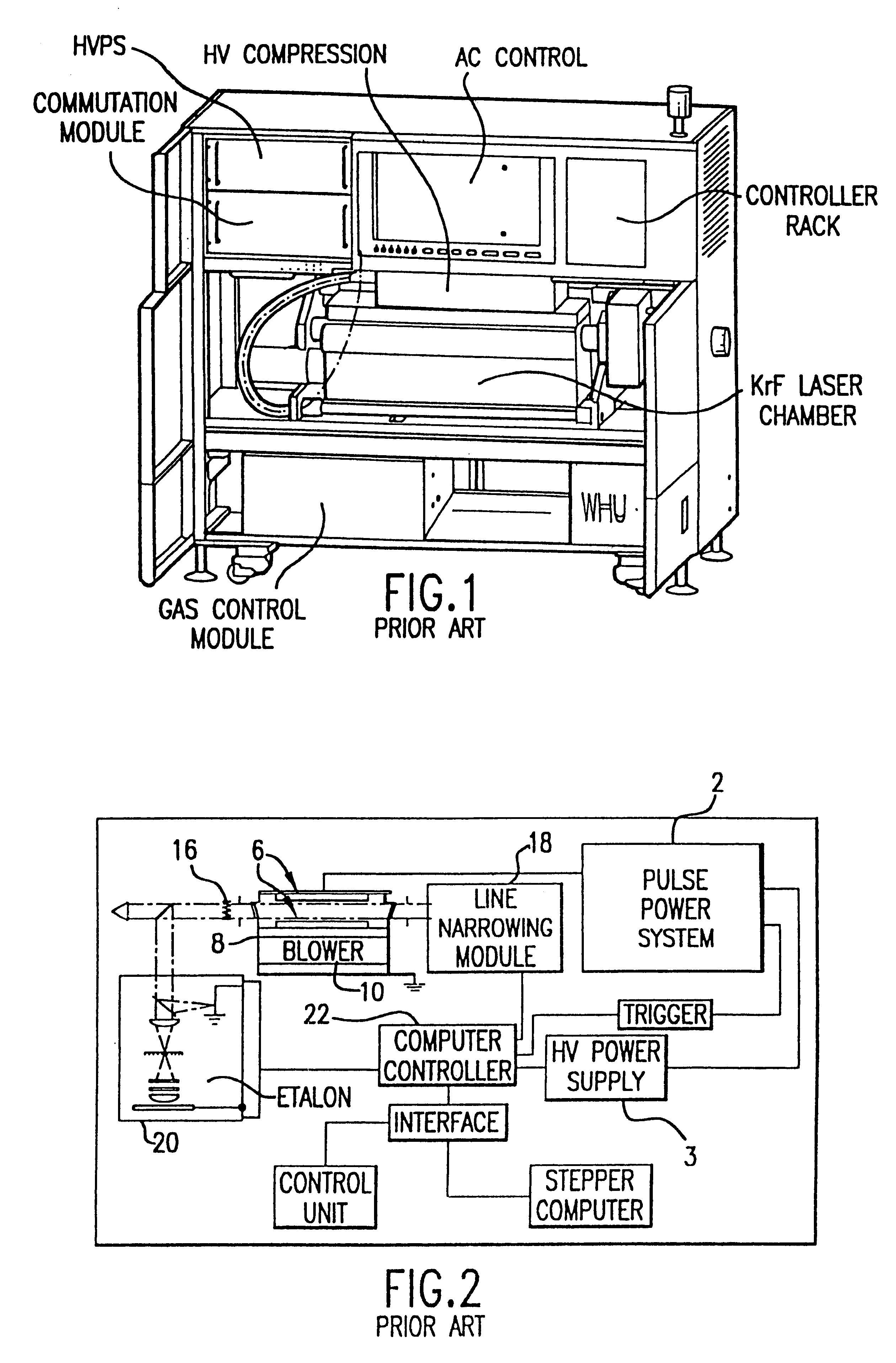
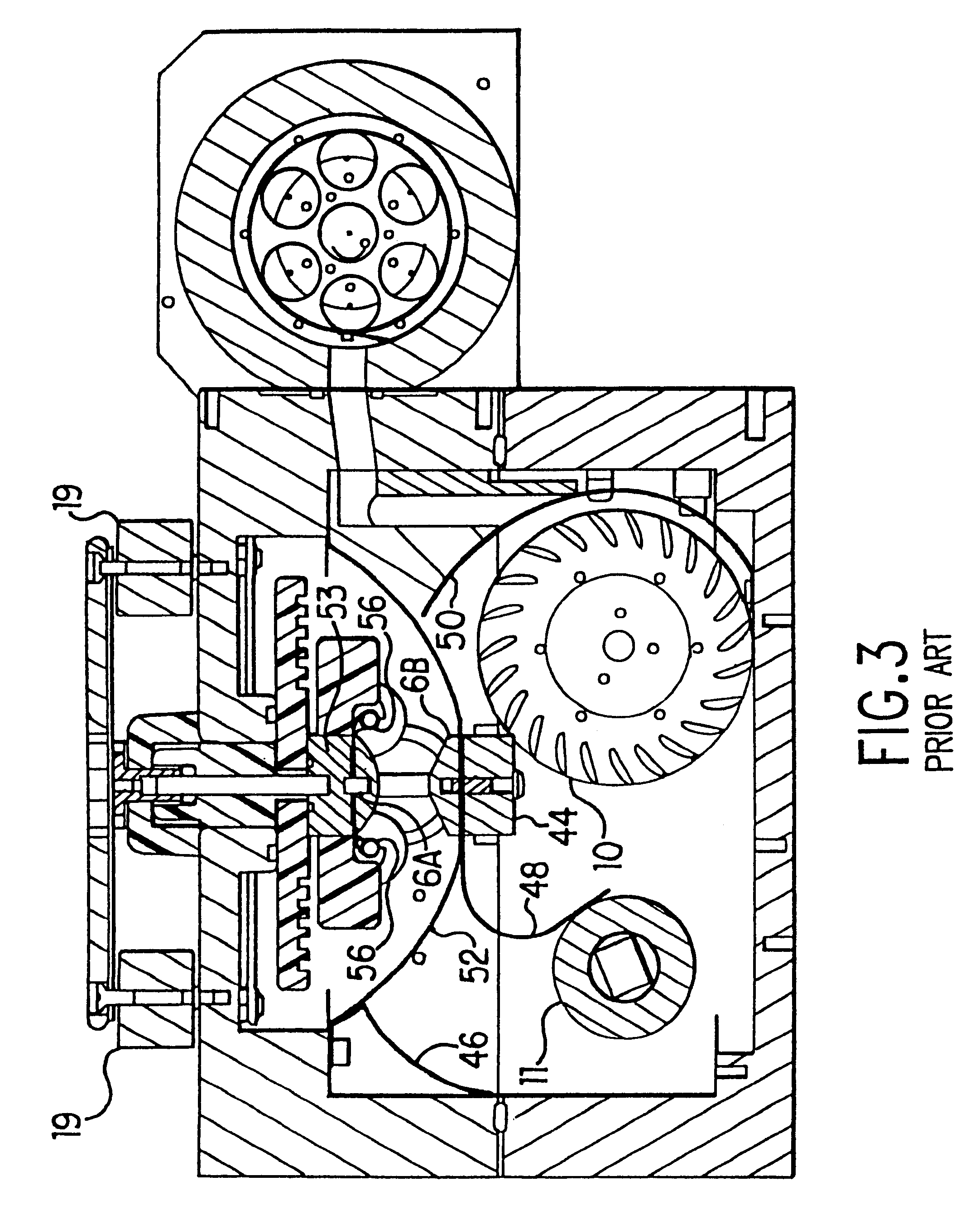
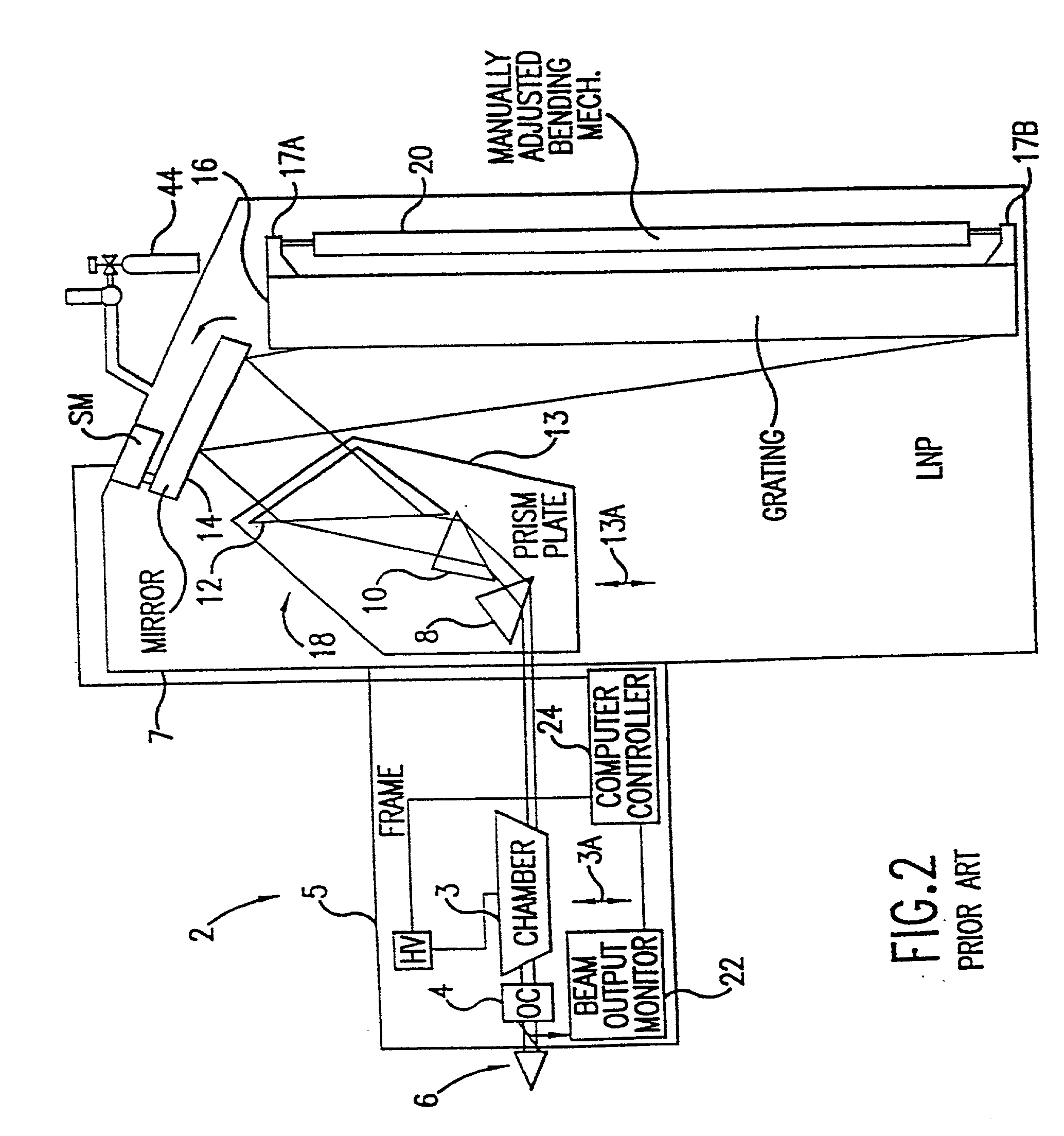
The present invention provides a reliable modular production quality excimer laser capable of producing 10 mJ laser pulses in the range of 1000 Hz to 2000 Hz or greater. Replaceable modules include a laser chamber; a pulse power system comprised of three modules; an optical resonator comprised of a line narrowing module and an output coupler module; a wavemeter module, an electrical control module, a cooling water module and a gas control module. Important improvements have been provided in the pulse power unit to produce faster rise time and improved pulse energy control. These improvements include an increased capacity high voltage power supply with a voltage bleed-down circuit for precise voltage trimming, an improved communication module that generates a high voltage pulse from the capacitors charged by the high voltage power supply and amplifies the pulse voltage 23 times with a very fast voltage transformer having a secondary winding consisting of a single four-segment stainless steel rod. A novel design for the compression head saturable inductor greatly reduces the quantity of transformer oil required and virtually eliminates the possibility of oil leakage which in the past has posed a hazard.
Owner:CYMER INC
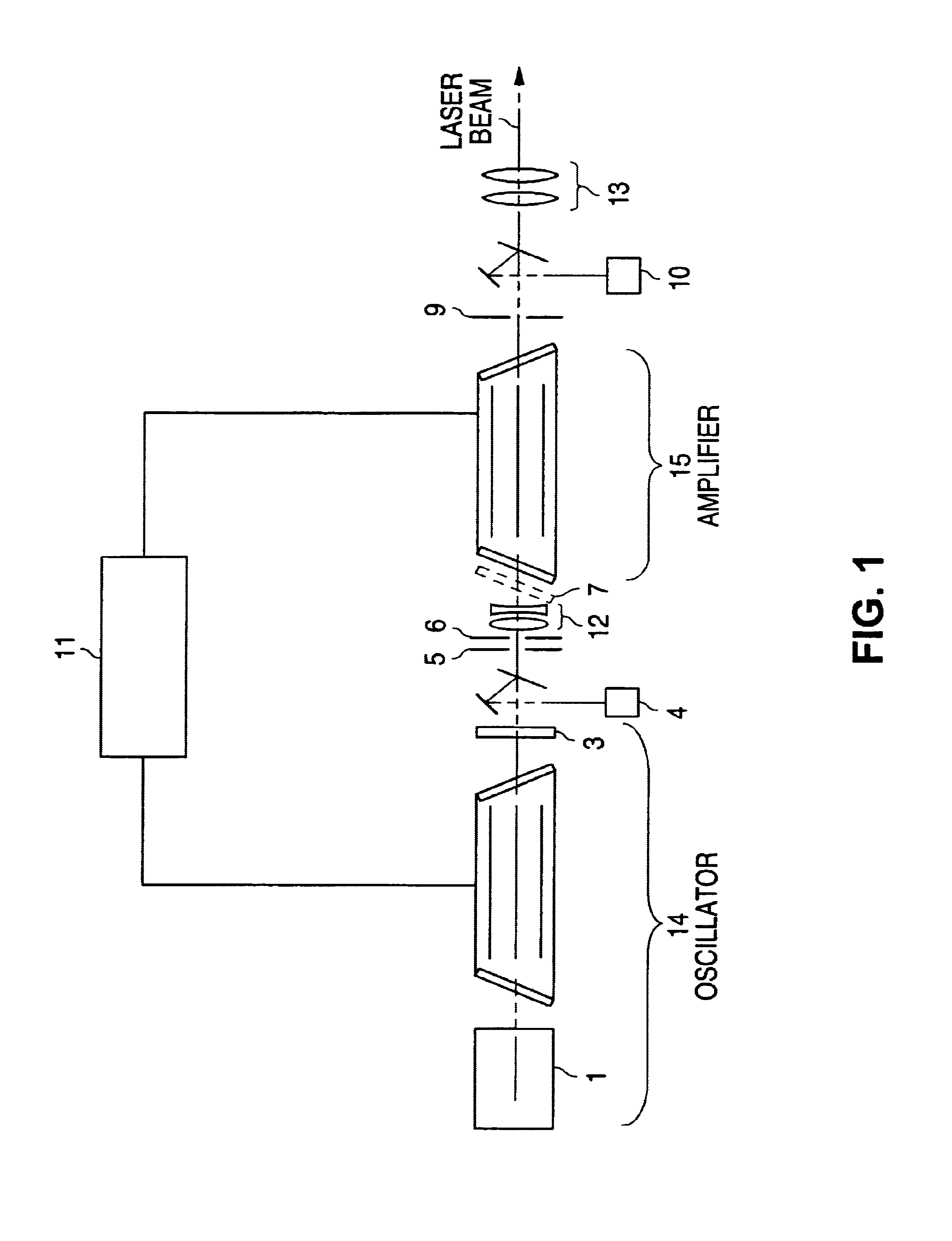
Very narrow band, two chamber, high rep-rate gas discharge laser system
InactiveUS20050271109A1Output powerBeam quality specificationOptical measurementsOptical resonator shape and constructionPulse beamSpectral bands
An oscillator-amplifier gas discharge laser system and method is disclosed which may comprise a first laser unit which may comprise a first discharge region which may contain an excimer or molecular fluorine lasing gas medium; a first pair of electrodes defining the first discharge region containing the lasing gas medium, a line narrowing unit for narrowing a spectral bandwidth of output laser light pulse beam pulses produced in said first discharge region; a second laser unit which may comprise a second discharge chamber which may contain an excimer or molecular fluorine lasing gas medium; a second pair of electrodes defining the second discharge region containing the lasing gas medium; a pulse power system providing electrical pulses to the first pair of electrodes and to the second pair of electrodes producing gas discharges in the lasing gas medium between the respective first and second pair of electrodes, and laser parameter control mechanism modifying a selected parameter of a selected laser output light pulse beam pulse produced by said gas discharge laser system by controlling the timing of the occurrence of the gas discharge between the first pair of electrodes and the occurrence of the gas discharge between the second pair of electrodes.
Owner:CYMER INC
Very narrow band, two chamber, high reprate gas discharge laser system
InactiveUS6985508B2Optical measurementsOptical resonator shape and constructionBand shapeLine narrowing
An injection seeded modular gas discharge laser system capable of producing high quality pulsed laser beams at pulse rates of about 4,000 Hz or greater and at pulse energies of about 5 mJ or greater. Two separate discharge chambers are provided, one of which is a part of a master oscillator producing a very narrow band seed beam which is amplified in the second discharge chamber. The chambers can be controlled separately permitting separate optimization of wavelength parameters in the master oscillator and optimization of pulse energy parameters in the amplifying chamber. A preferred embodiment in an ArF excimer laser system configured as a MOPA and specifically designed for use as a light source for integrated circuit lithography. In the preferred MOPA embodiment, each chamber comprises a single tangential fan providing sufficient gas flow to permit operation at pulse rates of 4000 Hz or greater by clearing debris from the discharge region in less time than the approximately 0.25 milliseconds between pulses. The master oscillator is equipped with a line narrowing package having a very fast tuning mirror capable of controlling centerline wavelength on a pulse-to-pulse basis at repetition rates of 4000 Hz or greater to a precision of less than 0.2 pm.
Owner:CYMER INC
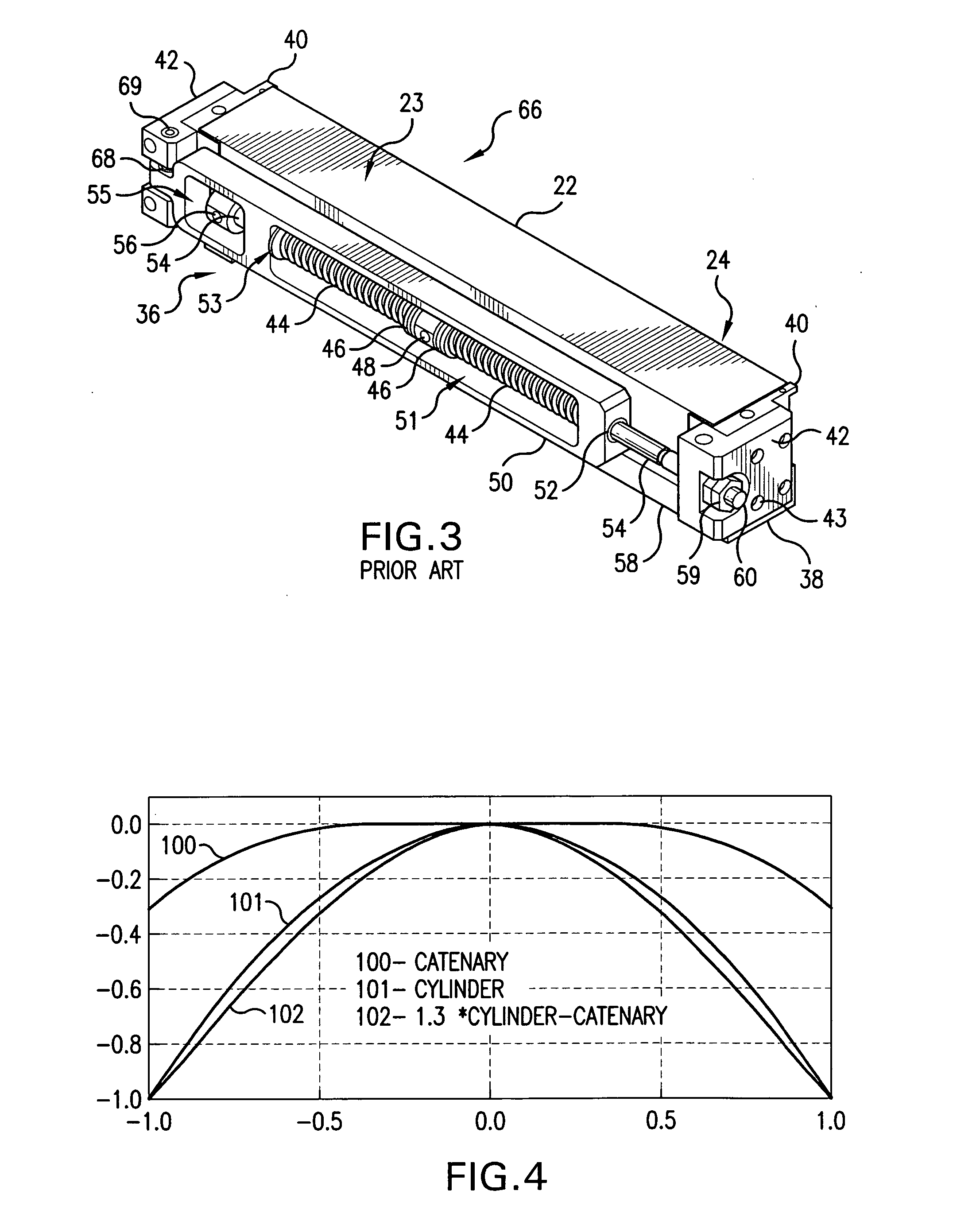
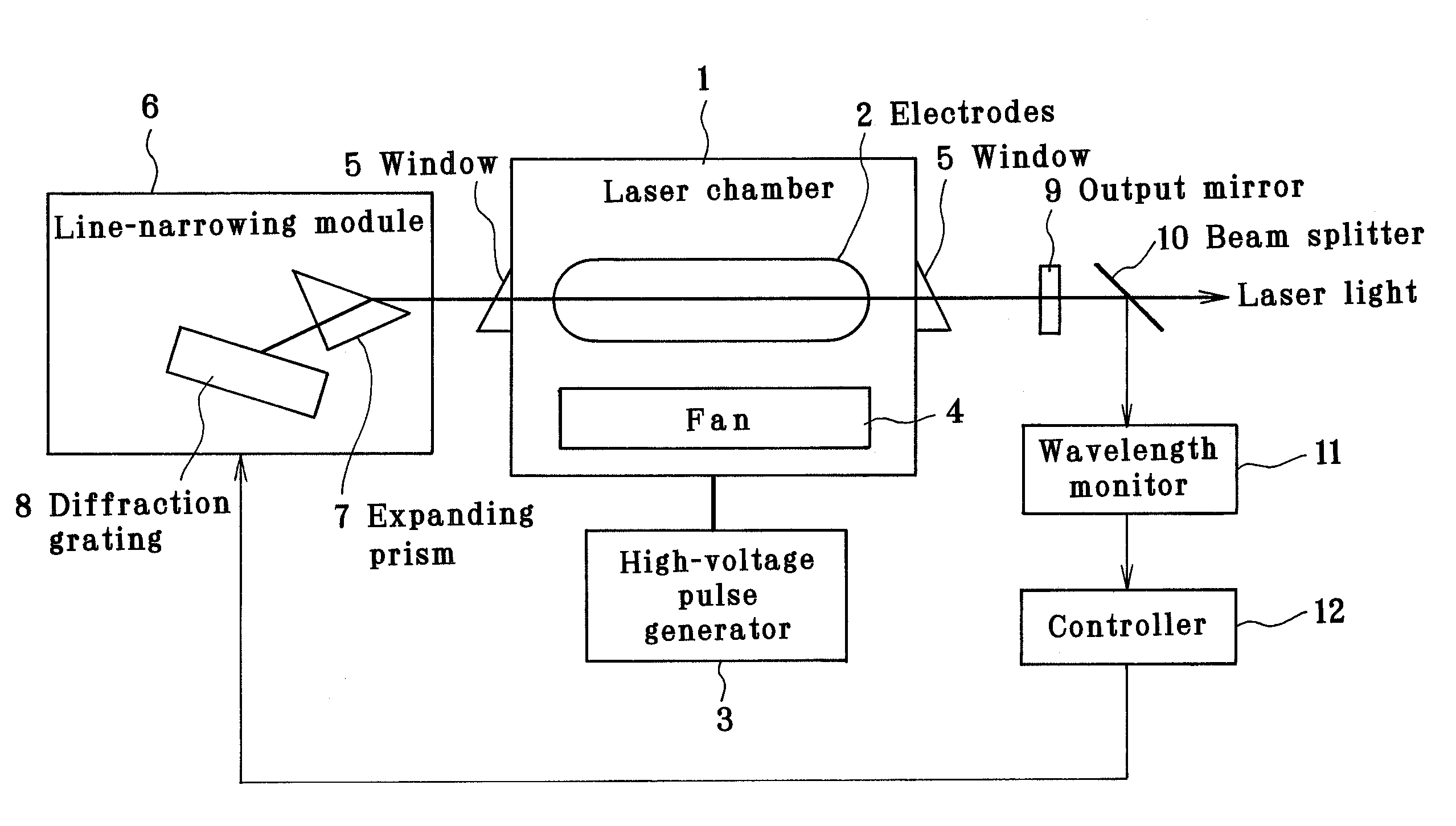
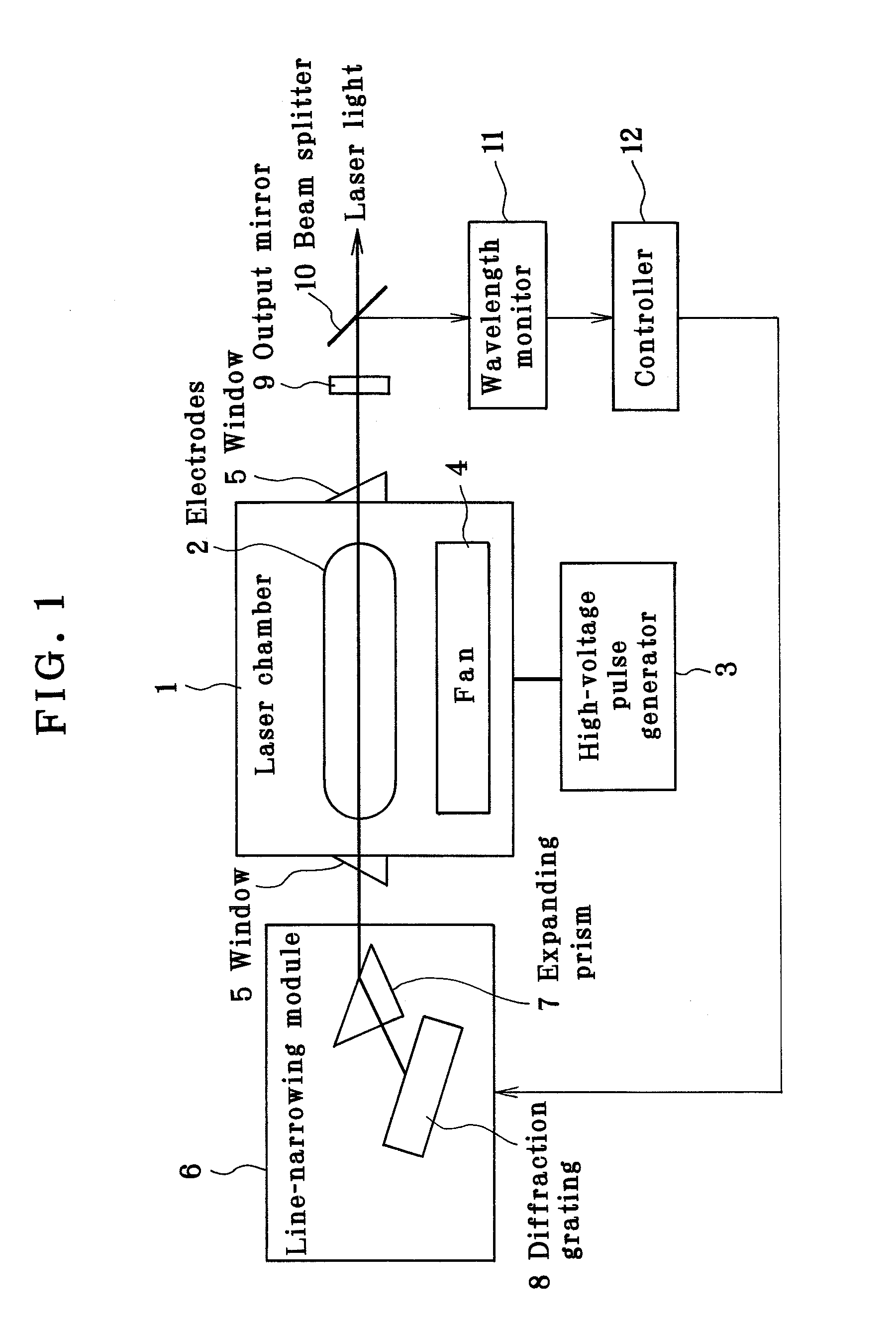
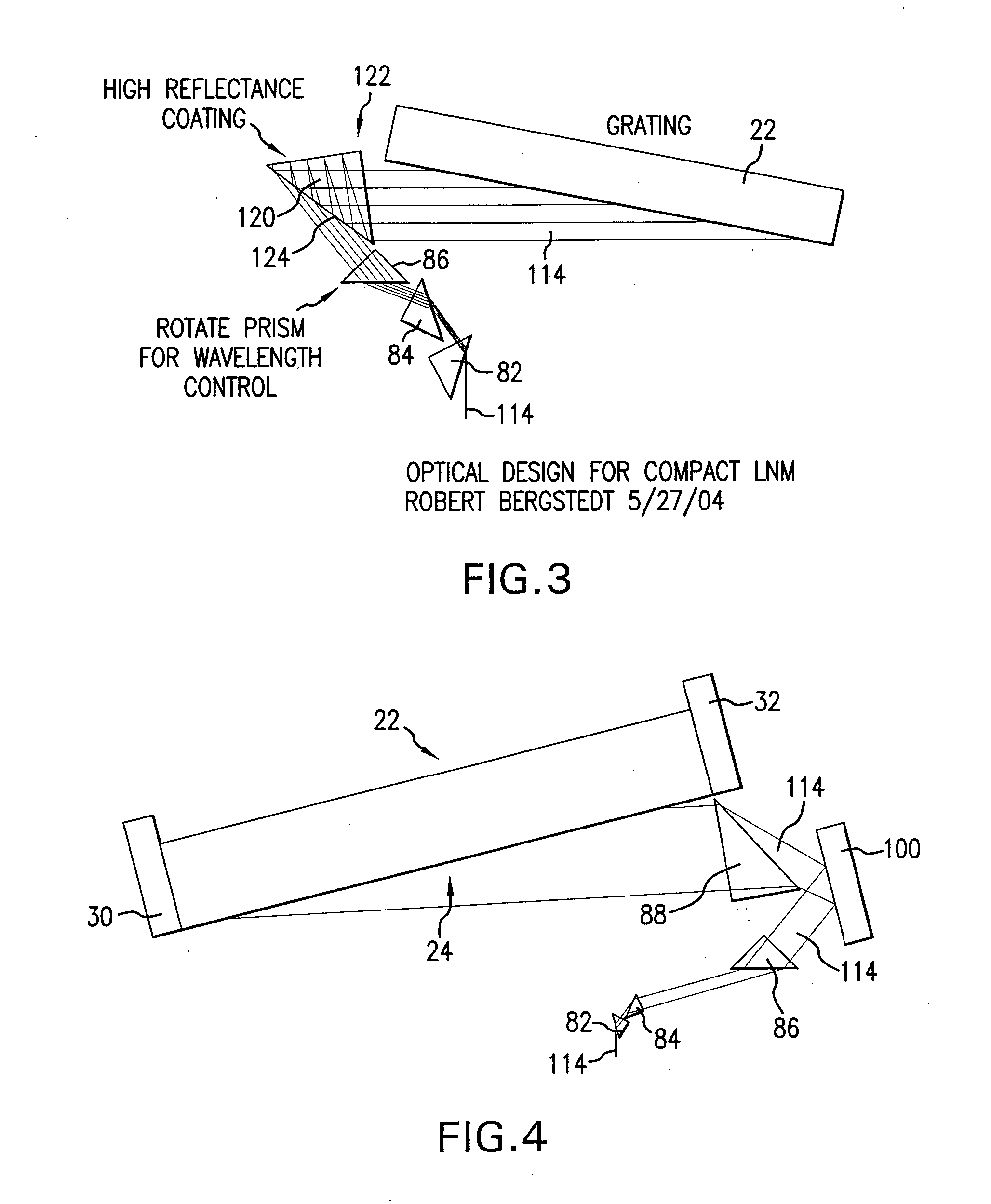
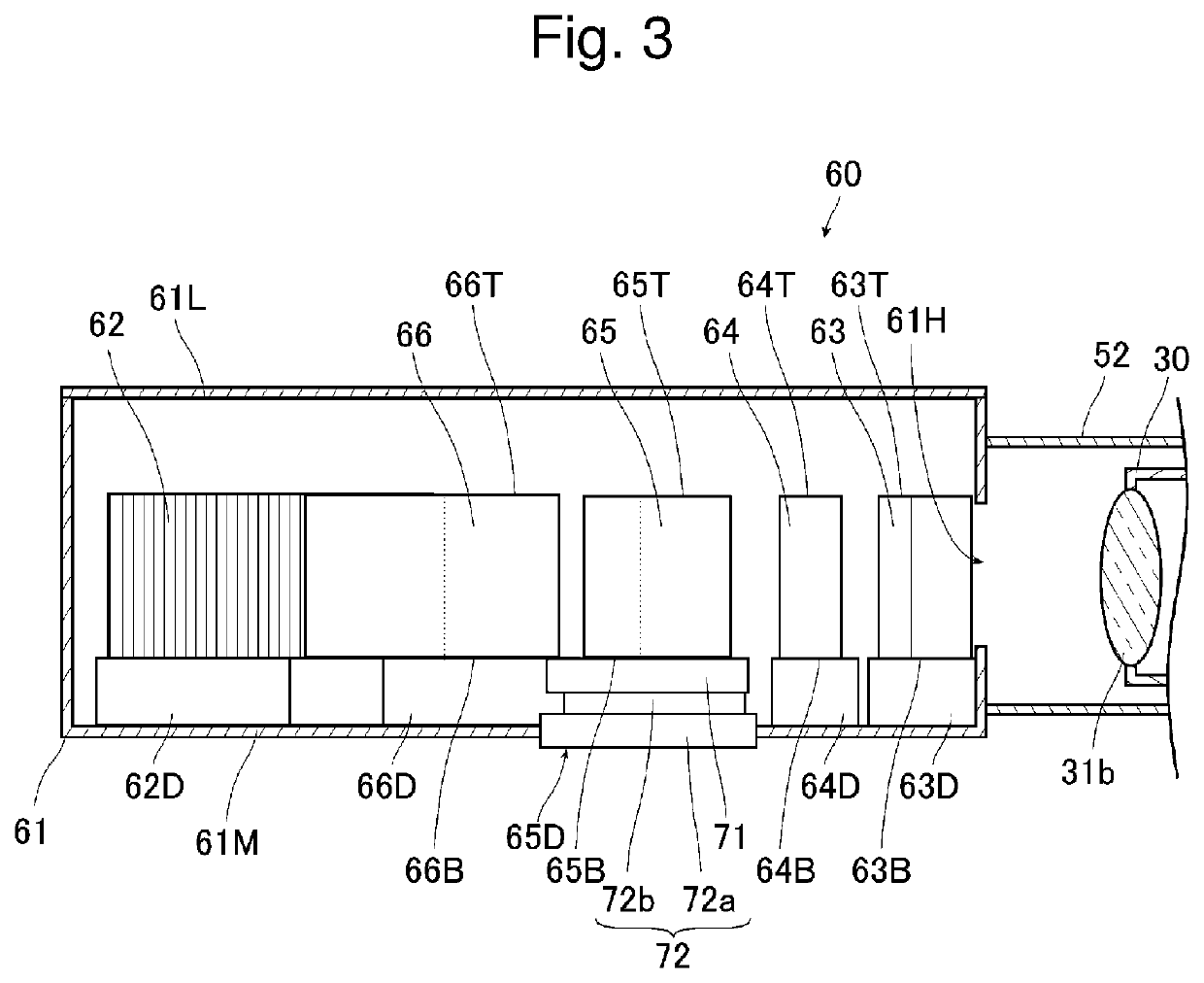
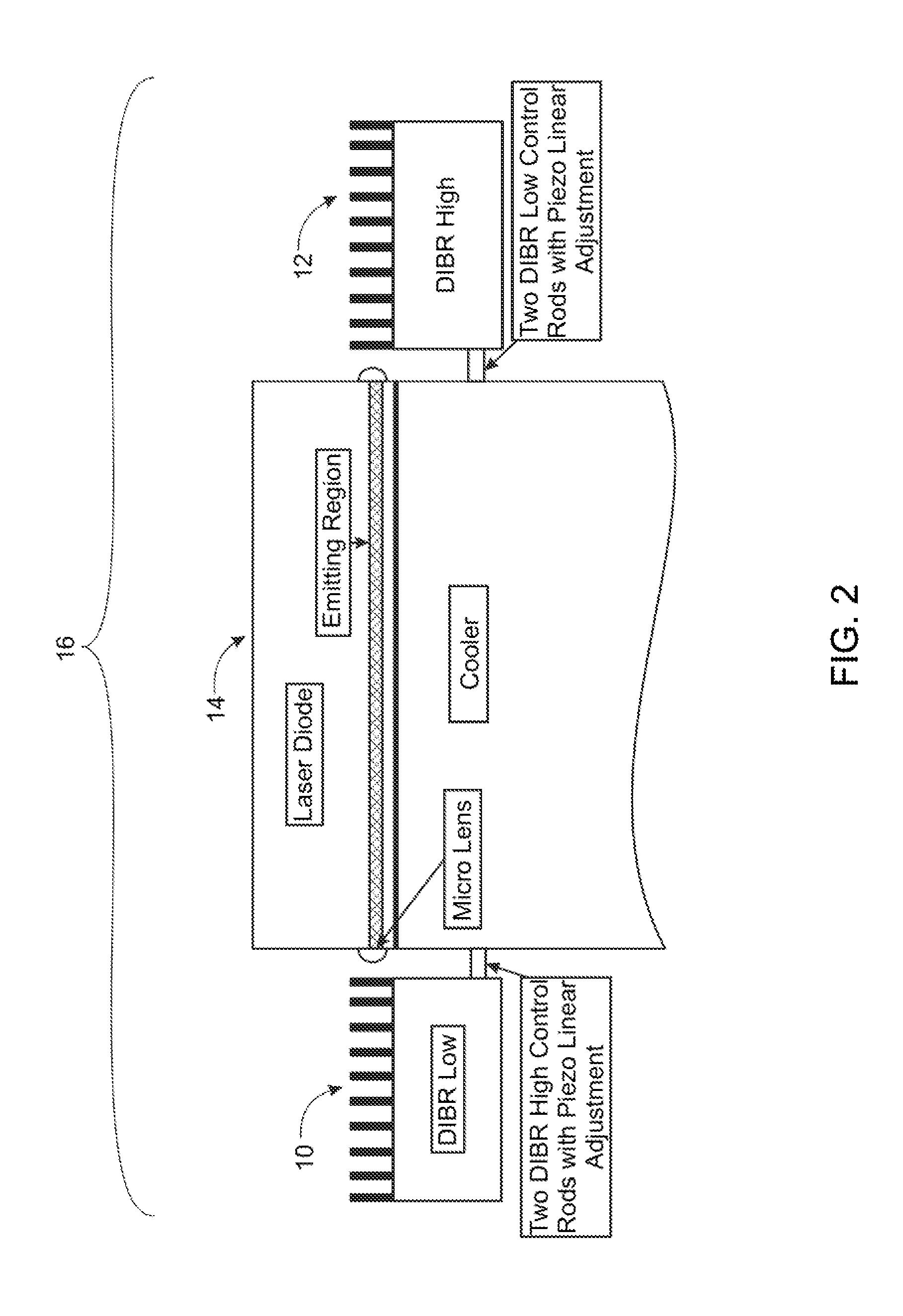
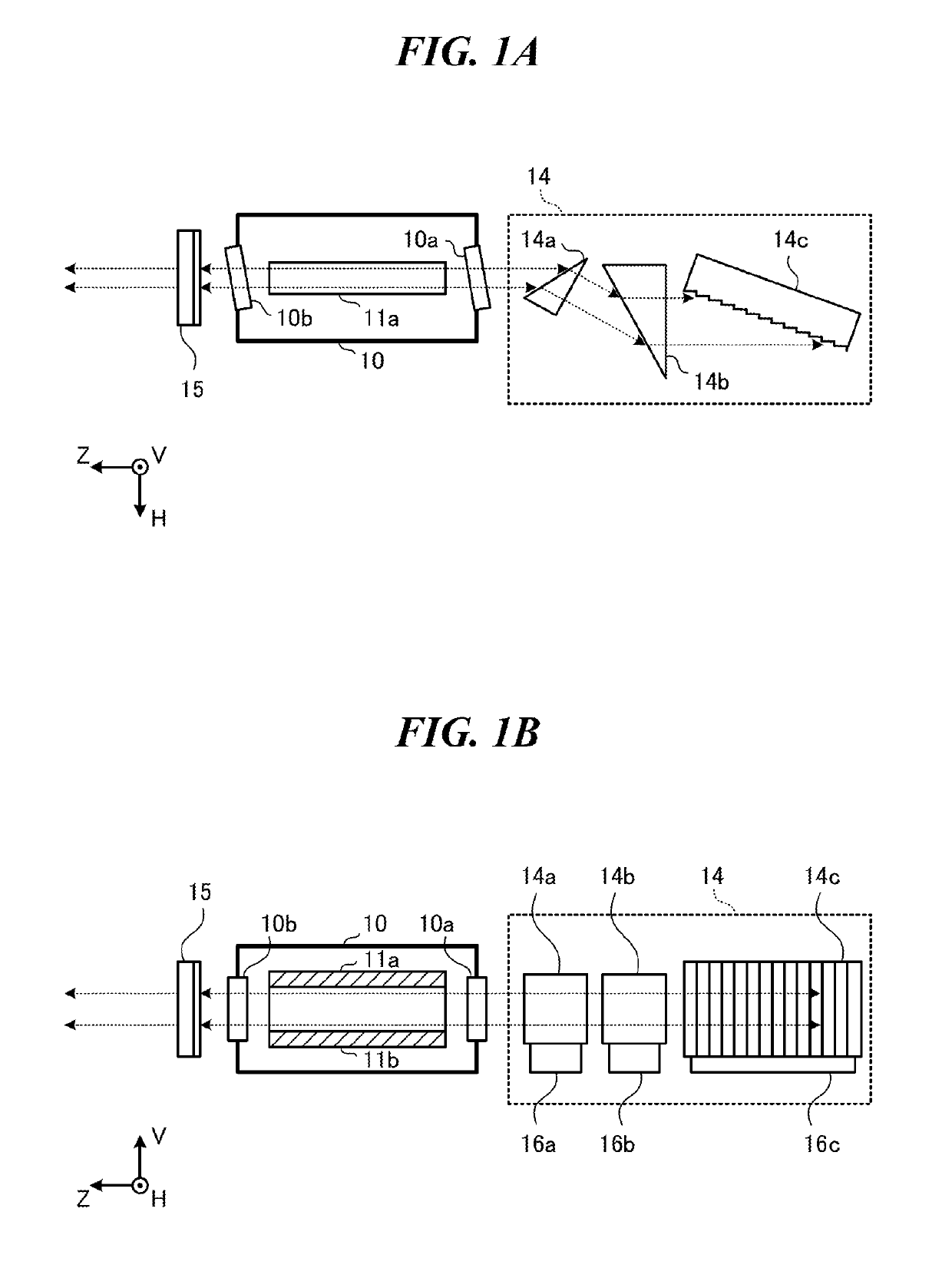
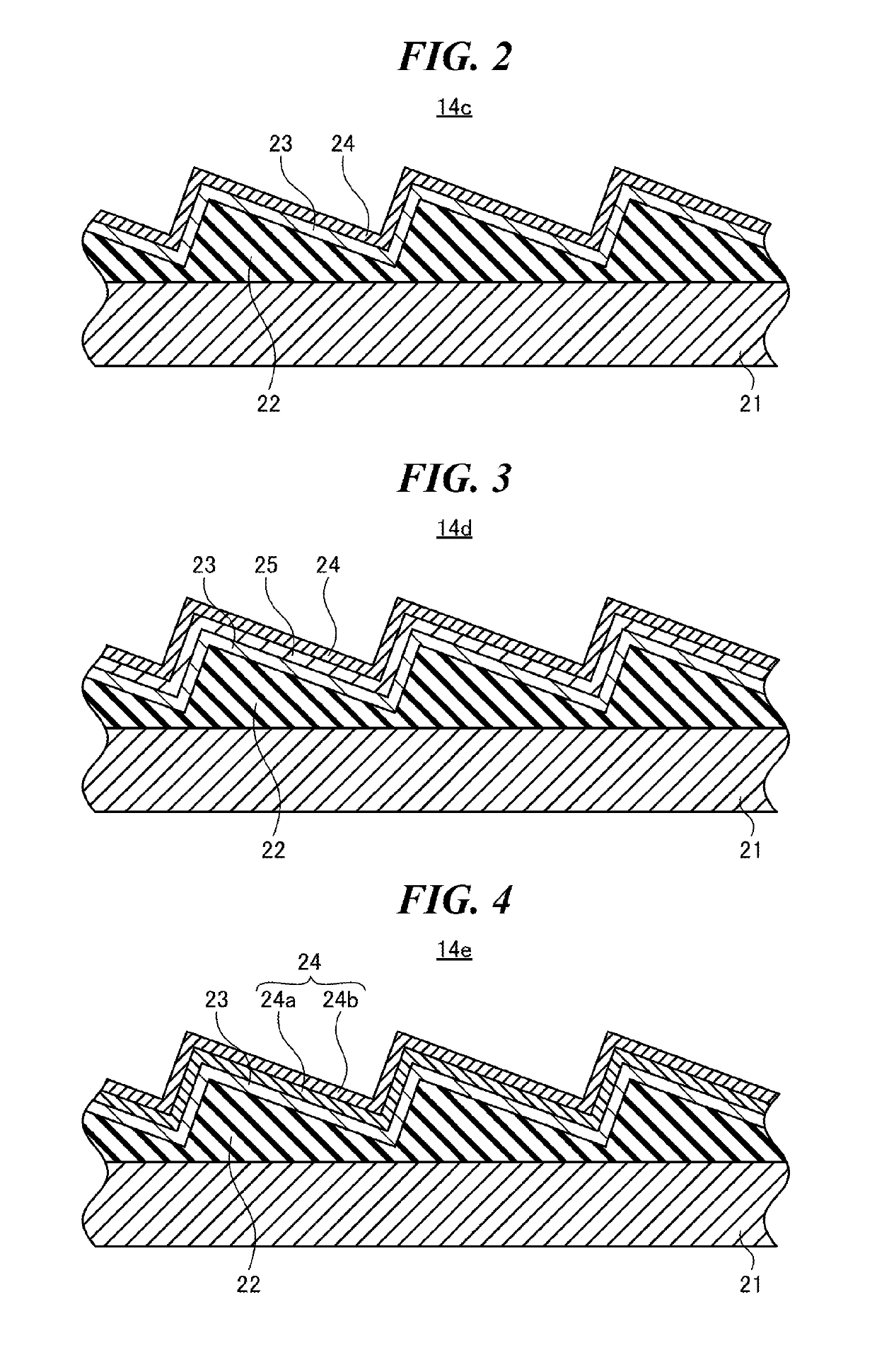
Line narrowing module
ActiveUS7366219B2Photomechanical apparatusOptical resonator shape and constructionPulse beamAngle of incidence
A line narrowing method and module for a narrow band DUV high power high repetition rate gas discharge laser producing output laser light pulse beam pulses in bursts of pulses, the module having a nominal optical path are disclosed which may comprise: a dispersive center wavelength selection optic moveably mounted within an optical path of the line narrowing module, selecting at least one center wavelength for each pulse determined at least in part by the angle of incidence of the laser light pulse beam containing the respective pulse on the dispersive wavelength selection optic; a first tuning mechanism operative in part to select the angle of incidence of the laser light pulse beam containing the respective pulse upon the dispersive center wavelength selection optic, by selecting an angle of transmission of the laser light pulse beam containing the pulse toward the dispersive center wavelength selection optic; a second tuning mechanism operative in part to select the angle of incidence of the laser light pulse beam containing the respective pulse by changing the position of the dispersive center wavelength selection optic relative to the nominal optical path of the line narrowing module; wherein the second tuning mechanism coarsely selects a value for the center wavelength and the first tuning mechanism more finely selects the value for the center wavelength. The apparatus and method may further comprise at least one beam expanding and redirecting prism in the optical path of the line narrowing module; the first tuning mechanism selecting an angle of incidence of the at least a first spatially defined portion of the laser light pulse beam by changing the position of the at least one beam expanding prism relative to the nominal optical path of the line narrowing module. The first and second tuning mechanisms may be controlled by a center wavelength controller during a burst based upon feedback from a center wavelength detector detecting the center wavelength of at least one other pulse in the burst of pulses and the controller providing the feedback based upon an algorithm employing the detected center wavelength for the at least one other pulse in the burst. The first tuning mechanism may comprise an electro-mechanical course positioning mechanism and a fine positioning mechanism comprising an actuatable material that changes position or shape when actuated.
Owner:CYMER INC
Bandwidth control device
A method and apparatus is disclosed for operating a laser output light beam pulse line narrowing mechanism that may comprise a nominal center wavelength and bandwidth selection optic; a static wavefront compensation mechanism shaping the curvature of the selection optic; an active wavefront compensation mechanism shaping the curvature of the selection optic and operating independently of the static wavefront compensation mechanism. The method and apparatus may comprise the nominal center wavelength and bandwidth selection optic comprises a grating; the static wavefront compensation mechanism applies a pre-selected bending moment to the grating; the active wavefront compensation mechanism applies a separate selected bending moment to the grating responsive to the control of a bending moment controller based on bandwidth feedback from a bandwidth monitor monitoring the bandwidth of the laser output light beam pulses. The active wavefront compensation mechanism may comprise a pneumatic drive mechanism.
Owner:CYMER INC
Resonator arrangement for bandwidth control
A line-narrowed excimer or molecular fluorine laser system includes a discharge chamber filled with a gas mixture at least including molecular fluorine and a buffer gas, multiple electrodes within the discharge chamber connected to a discharge circuit for energizing the gas mixture, a resonator including a pair of resonator reflecting surfaces disposed on either side of the discharge chamber for generating a laser beam, and a line-narrowing / selection unit within the resonator for narrowing the bandwidth of the laser beam. The resonator further includes a third reflecting surface which is deformable and disposed between the pair of resonator reflecting surfaces. The line-narrowing / selection unit preferably includes a beam expander and a dispersive element, wherein the deformable third reflecting surface is disposed between the beam expander and the dispersive element.
Owner:COHERENT GMBH
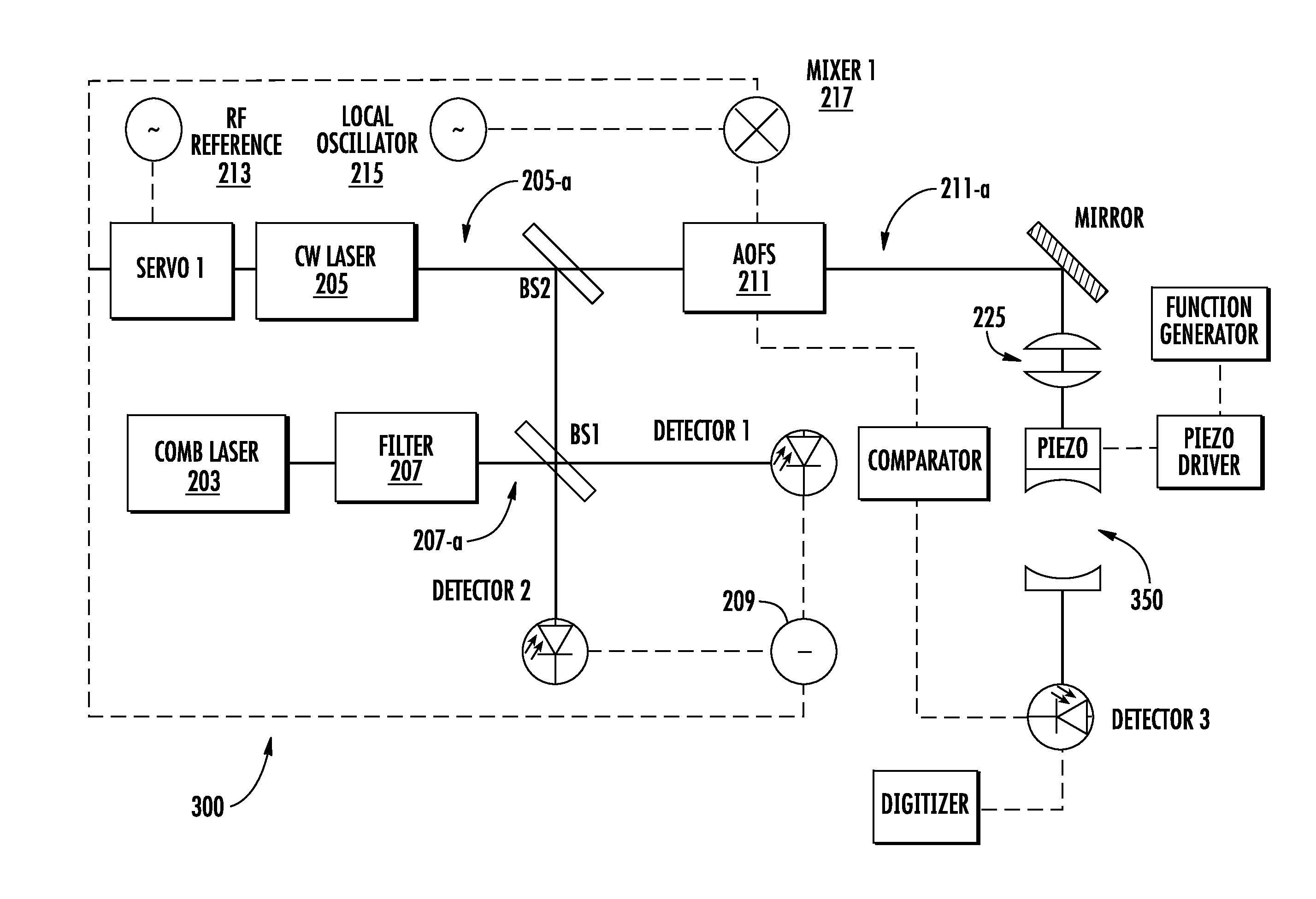
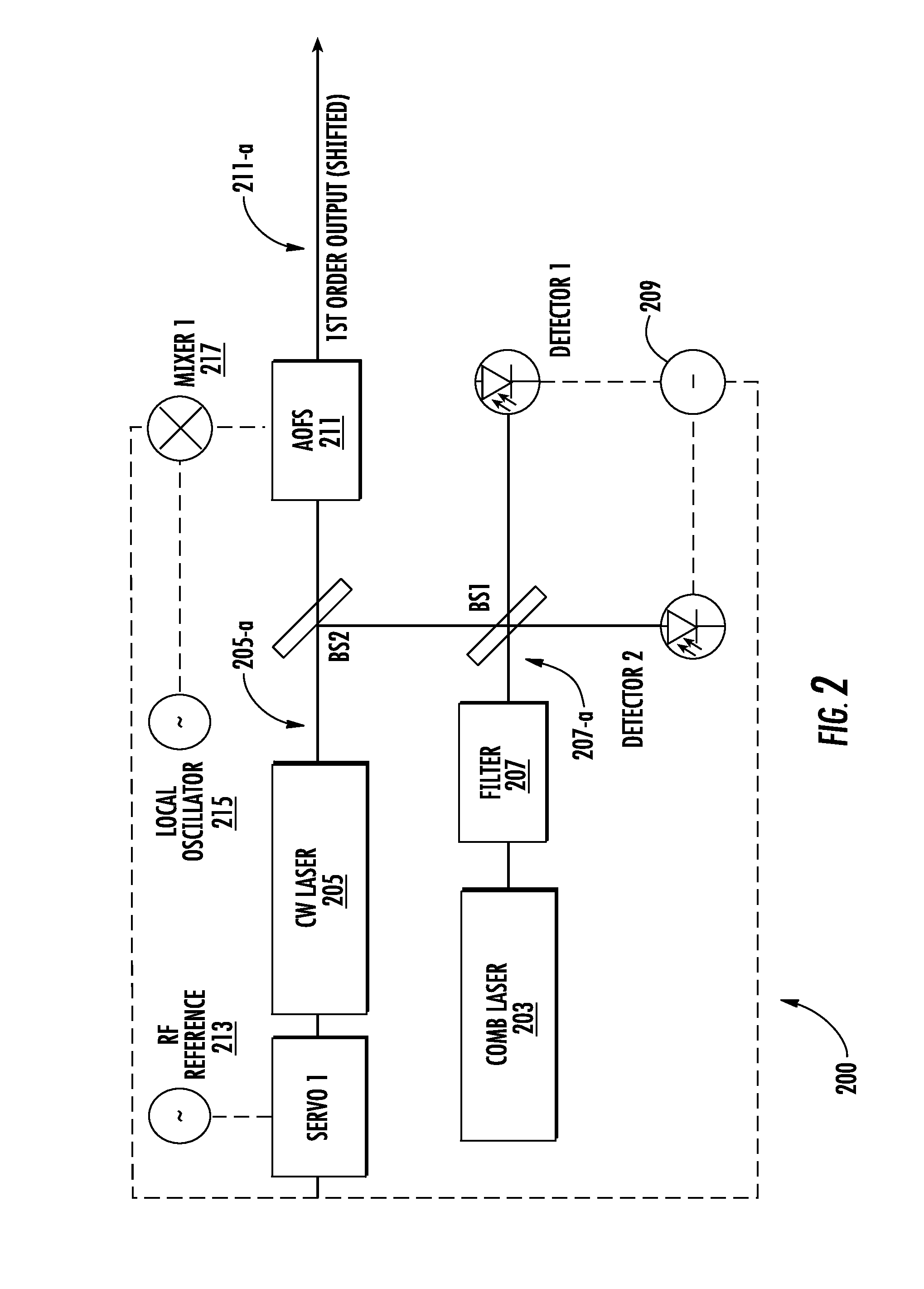
Methods for precision optical frequency synthesis and molecular detection
InactiveUS20150185141A1Quick correctionEfficiently coupled into cavityOptical measurementsLaser detailsFrequency measurementsOptical frequencies
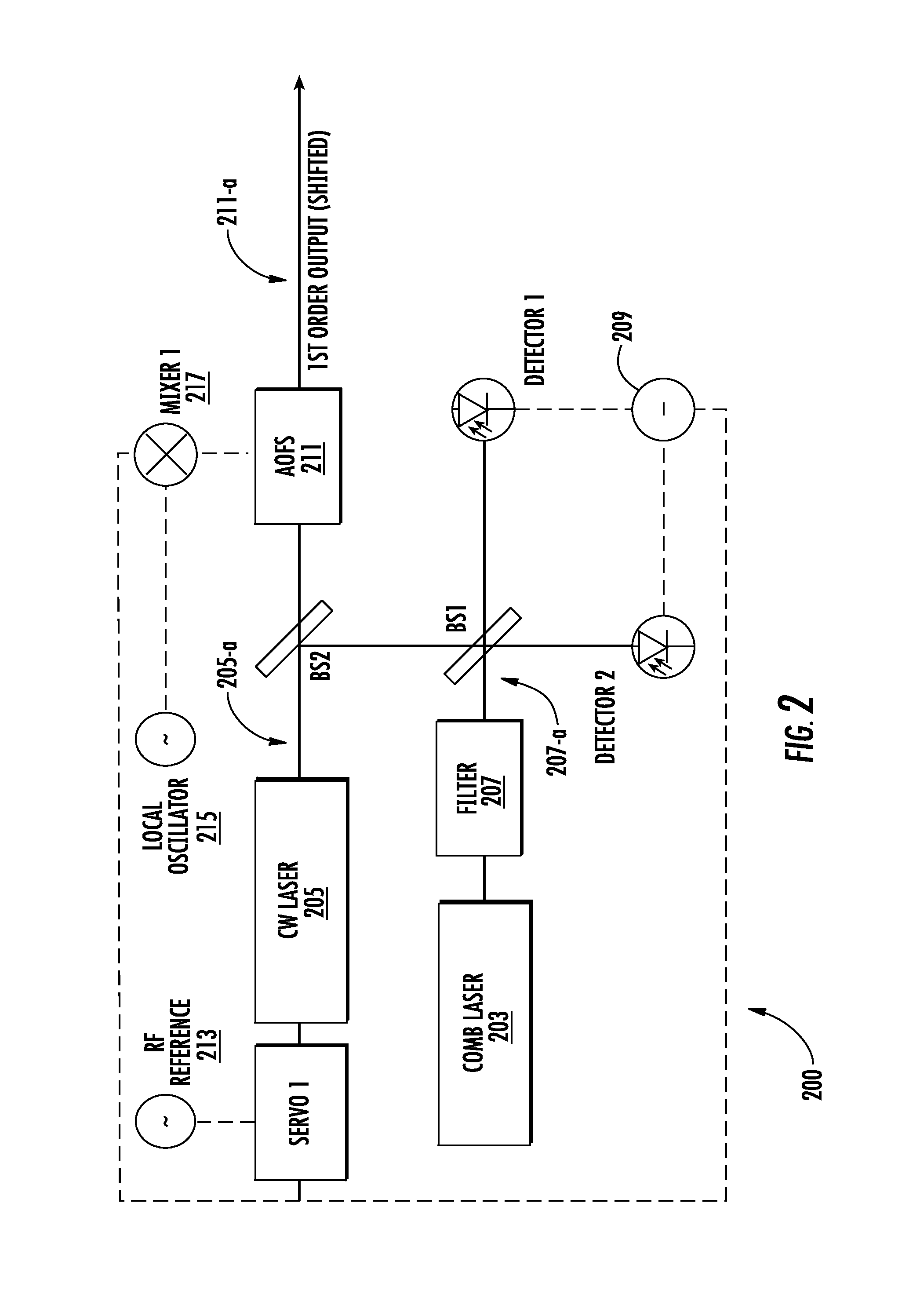
The present invention relates to precision linewidth control and frequency measurements of continuous wave lasers for the near to far IR spectral regions, precision frequency synthesizers and exemplary applications in molecular detection. Methods and systems are disclosed for simultaneous line narrowing of cw lasers, as well as referencing the desired emission wavelength to a frequency comb laser.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Line-narrowed gas laser system
ActiveUS7072375B2Improve abilitiesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingActive medium materialLine widthPeak value
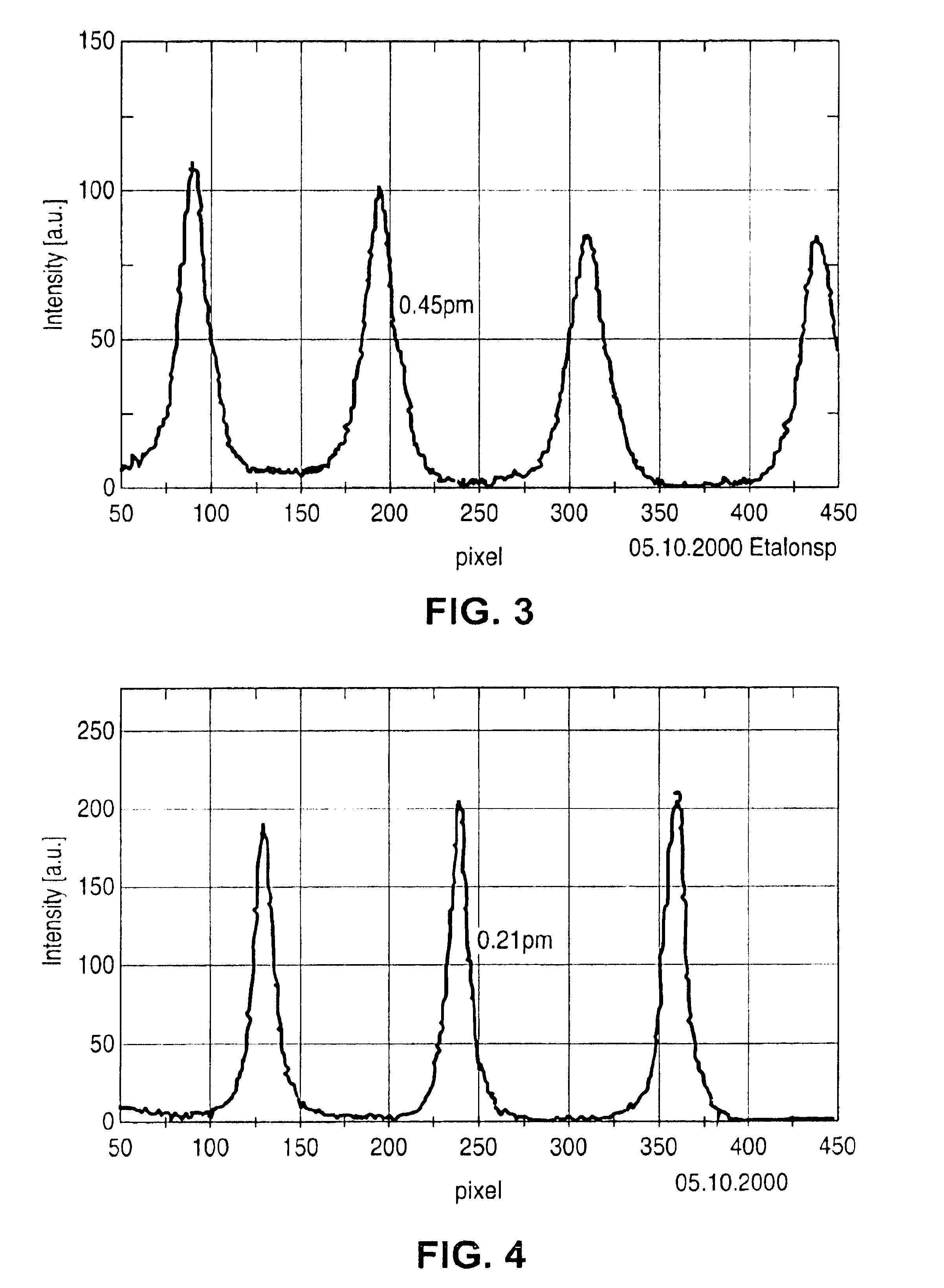
In a line-narrowed gas laser system such as a line-narrowed molecular fluorine laser system, ASE is cut off to obtain a spectral linewidth of 0.2 pm or lower and a spectral purity of 0.5 pm or lower. The laser system comprises a laser chamber filled with an F2-containing laser gas, discharge electrodes located in the laser chamber, a laser resonator and a line-narrowing module located in the laser resonator with a wavelength selection element, so that a line-narrowed laser beam emerges from the laser resonator. To cut off ASE from the laser beam emerging from the laser resonator, the duration from laser emission by discharge to generation of a laser beam is preset. Rise of the sidelight is made so gentle that the starting point of a laser pulse can exist after the time of the first sidelight peak.
Owner:GIGAPHOTON +1
Line narrowing module
ActiveUS20060114957A1Photomechanical apparatusOptical resonator shape and constructionPulse beamAngle of incidence
A line narrowing method and module for a narrow band DUV high power high repetition rate gas discharge laser producing output laser light pulse beam pulses in bursts of pulses, the module having a nominal optical path are disclosed which may comprise: a dispersive center wavelength selection optic moveably mounted within an optical path of the line narrowing module, selecting at least one center wavelength for each pulse determined at least in part by the angle of incidence of the laser light pulse beam containing the respective pulse on the dispersive wavelength selection optic; a first tuning mechanism operative in part to select the angle of incidence of the laser light pulse beam containing the respective pulse upon the dispersive center wavelength selection optic, by selecting an angle of transmission of the laser light pulse beam containing the pulse toward the dispersive center wavelength selection optic; a second tuning mechanism operative in part to select the angle of incidence of the laser light pulse beam containing the respective pulse by changing the position of the dispersive center wavelength selection optic relative to the nominal optical path of the line narrowing module; wherein the second tuning mechanism coarsely selects a value for the center wavelength and the first tuning mechanism more finely selects the value for the center wavelength. The apparatus and method may further comprise at least one beam expanding and redirecting prism in the optical path of the line narrowing module; the first tuning mechanism selecting an angle of incidence of the at least a first spatially defined portion of the laser light pulse beam by changing the position of the at least one beam expanding prism relative to the nominal optical path of the line narrowing module. The first and second tuning mechanisms may be controlled by a center wavelength controller during a burst based upon feedback from a center wavelength detector detecting the center wavelength of at least one other pulse in the burst of pulses and the controller providing the feedback based upon an algorithm employing the detected center wavelength for the at least one other pulse in the burst. The first tuning mechanism may comprise an electro-mechanical course positioning mechanism and a fine positioning mechanism comprising an actuatable material that changes position or shape when actuated.
Owner:CYMER INC
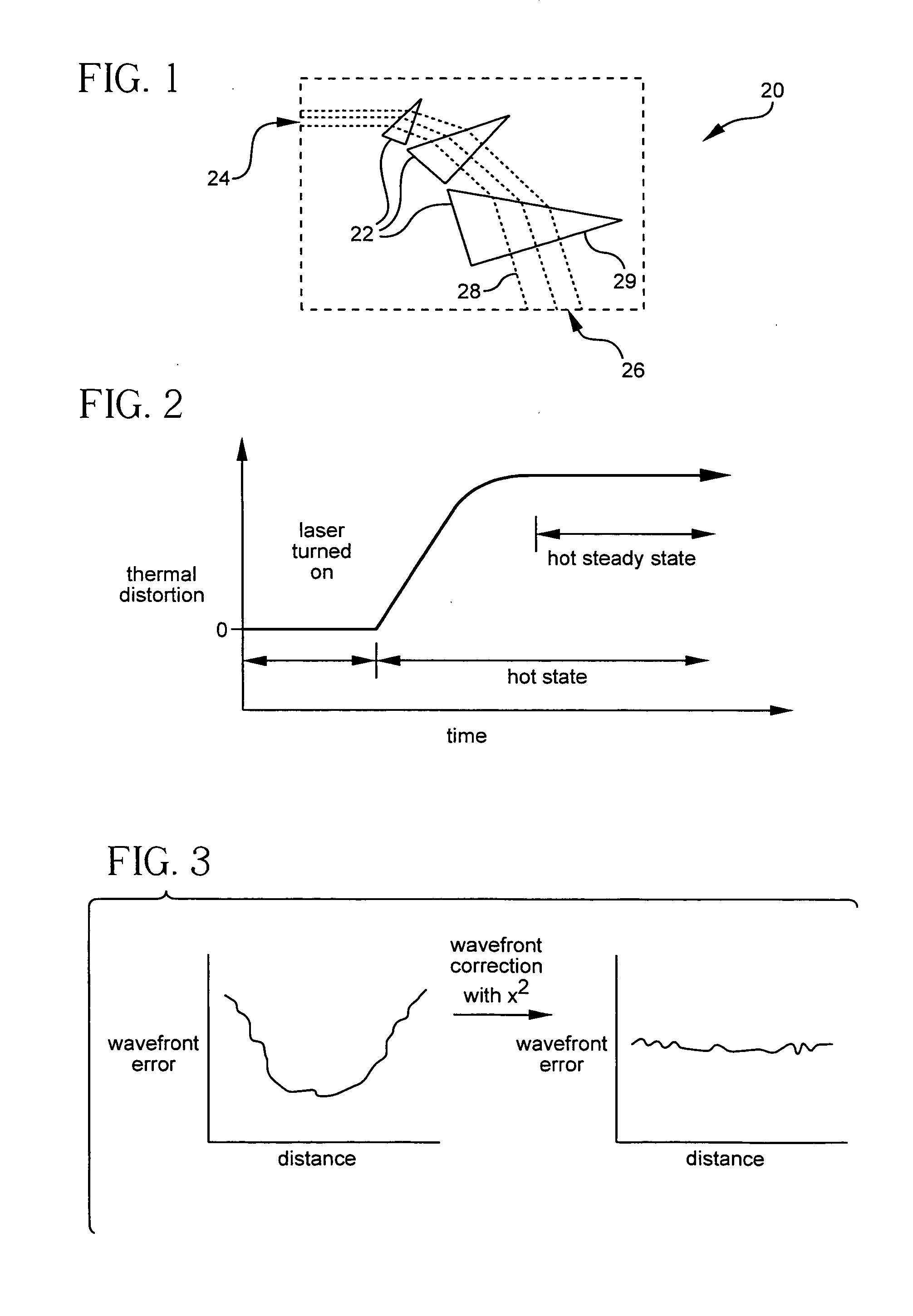
Optical systems including wavefront correcting optical surfaces
InactiveUS20060023277A1Improve performanceImprove stabilityOptical resonator shape and constructionMountingsWavefrontOptical property
The present invention relates to optical systems, beam expanding assemblies, line narrowing modules, and lasers having refractive optical elements with wavefront correcting optical surfaces. The present invention enables the skilled artisan to provide optical systems, beam expanding assemblies, line narrowing modules, and lasers having improved optical properties, such as, in the case of lasers, narrow linewidth at high power, and substantially planar wavefronts.
Owner:CORNING INC
Laser spectral engineering for lithographic process
InactiveUS20050041701A1Improved pattern resolutionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical resonator shape and constructionResistPeak value
An integrated circuit lithography technique called spectral engineering by Applicants, for bandwidth control of an electric discharge laser. In a preferred process, a computer model is used to model lithographic parameters to determine a desired laser spectrum needed to produce a desired lithographic result. A fast responding tuning mechanism is then used to adjust center wavelength of laser pulses in a burst of pulses to achieve an integrated spectrum for the burst of pulses approximating the desired laser spectrum. The laser beam bandwidth is controlled to produce an effective beam spectrum having at least two spectral peaks in order to produce improved pattern resolution in photo resist film. Line narrowing equipment is provided having at least one piezoelectric drive and a fast bandwidth detection control system having a time response of less than about 2.0 millisecond. In a preferred embodiment, a wavelength tuning mirror is dithered at dither rates of more than 500 dithers per second in phase with the repetition rate of the laser. In one case, the piezoelectric drive was driven with a square wave signal and in a second case it was driven with a sine wave signal. In another embodiment, the maximum displacement was matched on a one-to-one basis with the laser pulses in order to produce a desired average spectrum with two peaks for a series of laser pulses. Other preferred embodiments utilize three separate wavelength tuning positions producing a spectrum with three separate peaks.
Owner:CYMER INC
Bandwidth control device
A method and apparatus is disclosed for operating a laser output light beam pulse line narrowing mechanism that may comprise a nominal center wavelength and bandwidth selection optic; a static wavefront compensation mechanism shaping the curvature of the selection optic; an active wavefront compensation mechanism shaping the curvature of the selection optic and operating independently of the static wavefront compensation mechanism. The method and apparatus may comprise the nominal center wavelength and bandwidth selection optic comprises a grating; the static wavefront compensation mechanism applies a pre-selected bending moment to the grating; the active wavefront compensation mechanism applies a separate selected bending moment to the grating responsive to the control of a bending moment controller based on bandwidth feedback from a bandwidth monitor monitoring the bandwidth of the laser output light beam pulses. The active wavefront compensation mechanism may comprise a pneumatic drive mechanism.
Owner:CYMER INC
Tunable laser with stabilized grating
InactiveUS7075963B2Improve stabilityAttenuation bandwidthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical resonator shape and constructionBeam expanderGrating
A line-narrowing module for a laser includes a prism beam expander and a grating preferably attached to a heat sink. A pressure-controlled enclosure filled with an inert gas seals the grating and / or other elements of the line-narrowing module. The pressure in the enclosure is adjusted for tuning the wavelength. Preferably, the pressure is controlled by controlling the flow of an inert gas through the enclosure. A pump may be used, or an overpressure flow may be used. Alternatively, a prism of the beam expander or an etalon may be rotatable for tuning the wavelength.
Owner:COHERENT GMBH
Background removal from Raman spectra by an intracavity active-tuning element for a laser
ActiveUS9905990B1Easy to detectSimple and effective and compact and economical multiple wavelength Raman spectra acquisitionRaman/scattering spectroscopyRaman scatteringWavelength interrogationLength wave
A system, apparatus, and method for multiple wavelength Raman interrogation laser generation and Raman spectra acquisition. An intracavity laser tuning subsystem is integrated into the laser cavity. The tuning subsystem allows switching between at least two laser output frequencies in a manner effective for good identification and separation of Raman spectra from non-Raman spectra, including auto-fluorescence from the sample and background. The tuning subsystem can be implemented in different ways in the cavity. It does not require material alteration of the line-narrowing components. Also, processing of acquired raw signal from the multiple wavelength interrogation can further assist effective Raman spectra identification and separation.
Owner:ALAKAI DEFENSE SYST
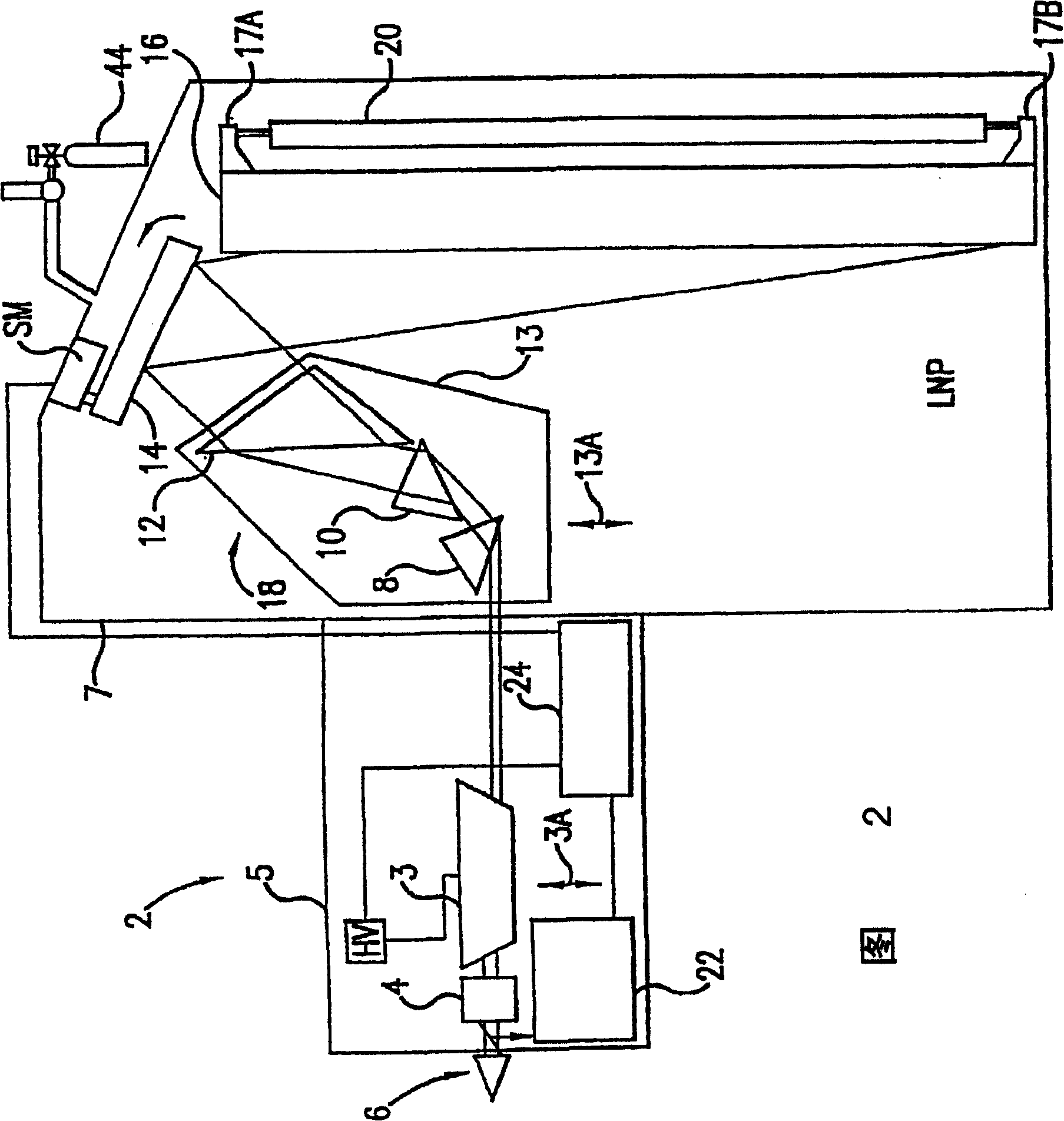
Line narrowing module, light source of exposure apparatus comprising the same, and method of producing exposure light using line narrowing
ActiveUS20070036183A1Improve light energy efficiencyNarrow bandwidthPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLight beamLine narrowing
A line narrowing module includes an elliptical mirror having first and second foci and having an opening adjacent to the second focus, a diffraction grating disposed at the first focus so as to separate an incident beam into different lines, and a laser beam dispersion and extraction unit. The laser beam dispersion and extraction unit is situated in the module and composed to disperse a laser beam, incident thereon from a region containing the second focus of the elliptical mirror, over the diffraction grating and selectively extract from the resulting lines a laser beam having a desired narrowed bandwidth. Most of the remainder of the light is reflected by the elliptical mirror to the region having the second focus. A light source that employs the line narrowing module also includes a laser oscillator for generating the beam whose bandwidth is narrowed by the module, and light returning unit that returns one fraction of the beam extracted fron the laser oscillator back to the laser oscillator. Another fraction of the beam is extracted from the laser oscillator through a front window of the laser oscillator, and undergoes line narrowing in the module. The laser beam having the narrowed bandwidth is immediately output as the exposure light from the module, whereas the remainder of the light is returned from the module back to the laser oscillator.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Methods for precision optical frequency synthesis and molecular detection
InactiveUS9097656B2Quick correctionEfficiently coupled into cavityOptical measurementsRadiation pyrometryFrequency measurementsLine width
The present invention relates to precision linewidth control and frequency measurements of continuous wave lasers for the near to far IR spectral regions, precision frequency synthesizers and exemplary applications in molecular detection. Methods and systems are disclosed for simultaneous line narrowing of cw lasers, as well as referencing the desired emission wavelength to a frequency comb laser.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Bandwidth control technique for a laser
InactiveUS7079556B2Excitation process/apparatusOptical resonator shape and constructionTime responseNarrow range
A technique for bandwidth control of an electric discharge laser. Line narrowing equipment is provided having at least one piezoelectric drive and a fast bandwidth detection means and a bandwidth control having a time response of less than about 1.0 millisecond. In a preferred embodiment wavelength tuning mirror is dithered at dither rates of more than 500 dithers per second within a very narrow range of pivot angles to cause a dither in nominal wavelength values to produce a desired effective bandwidth of series of laser pulses.
Owner:CYMER INC
Excimer laser and line narrowing module
InactiveUS20070171952A1Avoid failureYield maximizationPhotomechanical apparatusOptical resonator shape and constructionBeam expanderLight beam
An excimer laser and a line-narrowing module capable of increasing and maximizing production yield in semiconductor manufacturing are disclosed. The line-narrowing module utilizes a beam expander that passes laser light, produced by and incident from a generator of the excimer laser and collimates the laser light in one direction. A diffraction grating receives the collimated laser light and diffracts the laser light and causes a traveling direction of the laser light to be separated according to an associated wavelength of the laser light. A multi-wavelength reflector located at a reflecting position on one side between the diffraction grating and the beam expander in order to re-enter the laser light having a multi-wavelength into the generator through the beam expander. The multi-wavelength reflector reflects the laser light consisting of a plurality of wavelengths among the laser light whose traveling direction is separated from the diffraction grating onto the beam expander.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Excimer laser and line narrowing module
An excimer laser and a line-narrowing module capable of increasing and maximizing production yield in semiconductor manufacturing are disclosed. The line-narrowing module utilizes a beam expander that passes laser light, produced by and incident from a generator of the excimer laser and collimates the laser light in one direction. A diffraction grating receives the collimated laser light and diffracts the laser light and causes a traveling direction of the laser light to be separated according to an associated wavelength of the laser light. A multi-wavelength reflector located at a reflecting position on one side between the diffraction grating and the beam expander in order to re-enter the laser light having a multi-wavelength into the generator through the beam expander. The multi-wavelength reflector reflects the laser light consisting of a plurality of wavelengths among the laser light whose traveling direction is separated from the diffraction grating onto the beam expander.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Line narrowing of molecular fluorine laser emission
InactiveUS6763048B2Optical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialLength waveLine narrowing
A molecular fluorine laser system includes a discharge tube filled with a gas mixture including molecular fluorine and at least one buffer gas and having a total pressure of less than substantially 2500 mbar, multiple electrodes within the discharge tube, a pulsed discharge circuit connected to the electrodes for energizing the gas mixture, a line-selection optic for selecting one of multiple closely-spaced lines around 157 nm emitted from the discharge tube, and a laser resonator including the line-selection optic and the discharge tube for generating a beam of laser pulses having a wavelength around 157 nm at a bandwidth of less than 0.6 pm.
Owner:LAMBDA PHYSIK
Molecular fluorine laser system
InactiveUS6690703B1Optical resonator shape and constructionLaser arrangementsNoble gasLine narrowing
A molecular fluorine laser includes a discharge chamber filled with a gas mixture including molecular fluorine and a buffer gas and not including a laser active rare gas, multiple electrodes within the discharge chamber defining a discharge region therebetween connected to a pulsed discharge circuit for applying discharge pulses to the electrodes for energizing the gas mixture, and a resonator including the discharge chamber for generating an oscillator laser beam at a wavelength around 157 nm and a bandwidth of less than 0.6 pm. The laser further includes a power amplifier for increasing the energy of the attenuated oscillator laser beam to a second predetermined energy for lithographic processing, a line-narrowing unit for reducing the bandwidth, a low intensity suppressor module to suppress the weaker lines of the F2-laser, and a synchronization unit to synchronize the oscillator and amplifier.
Owner:LAMBDA PHYSIK
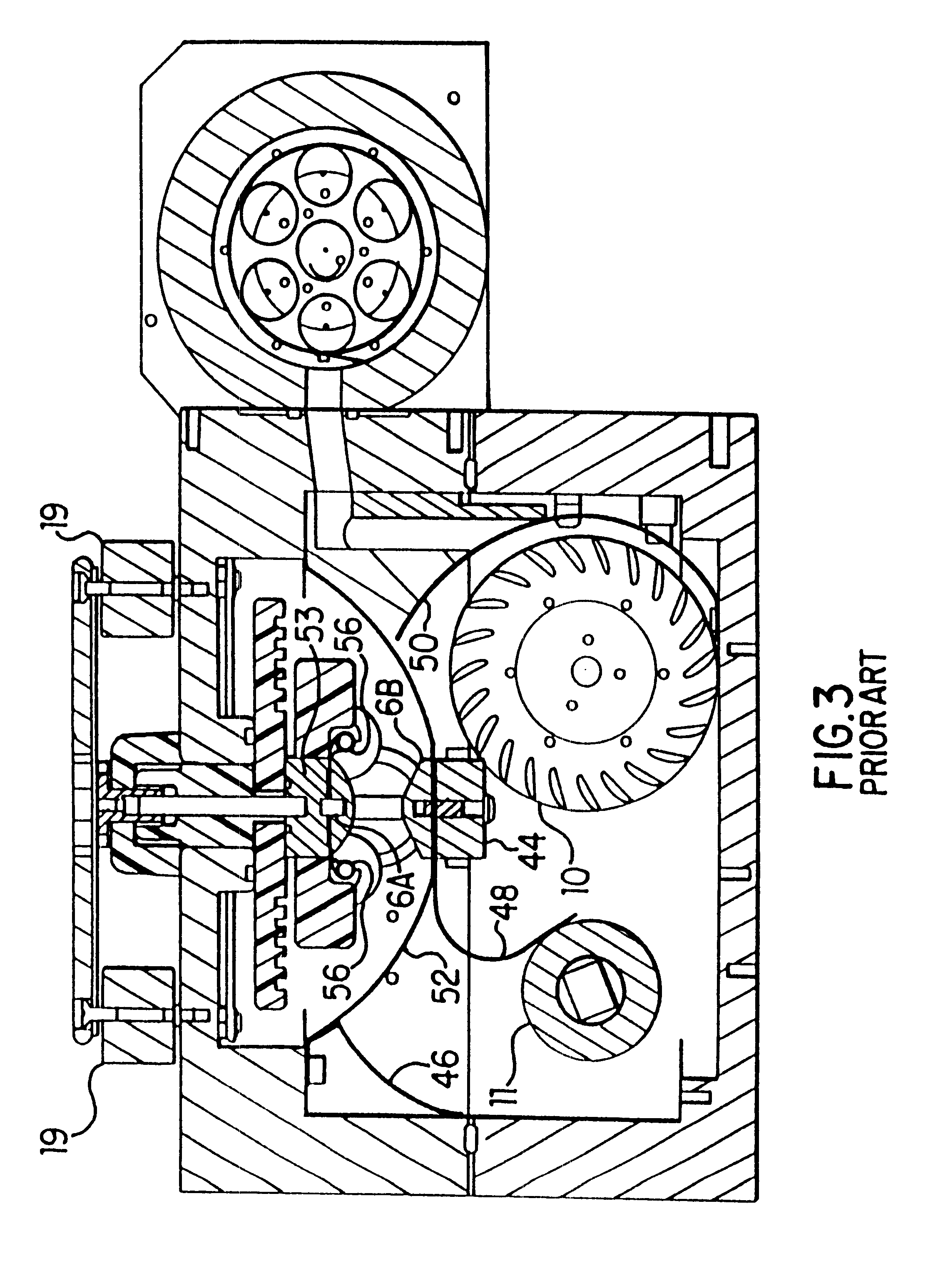
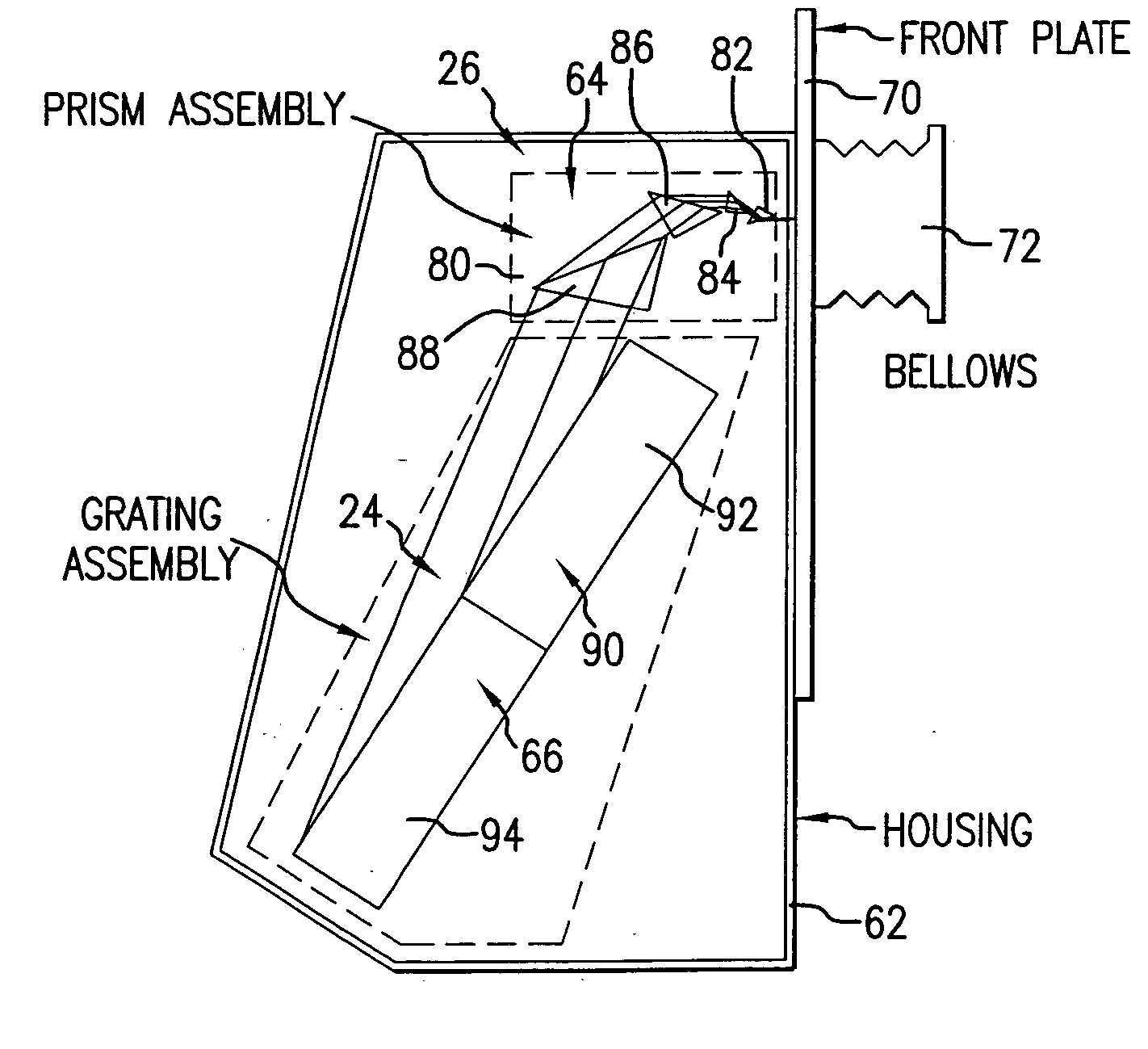
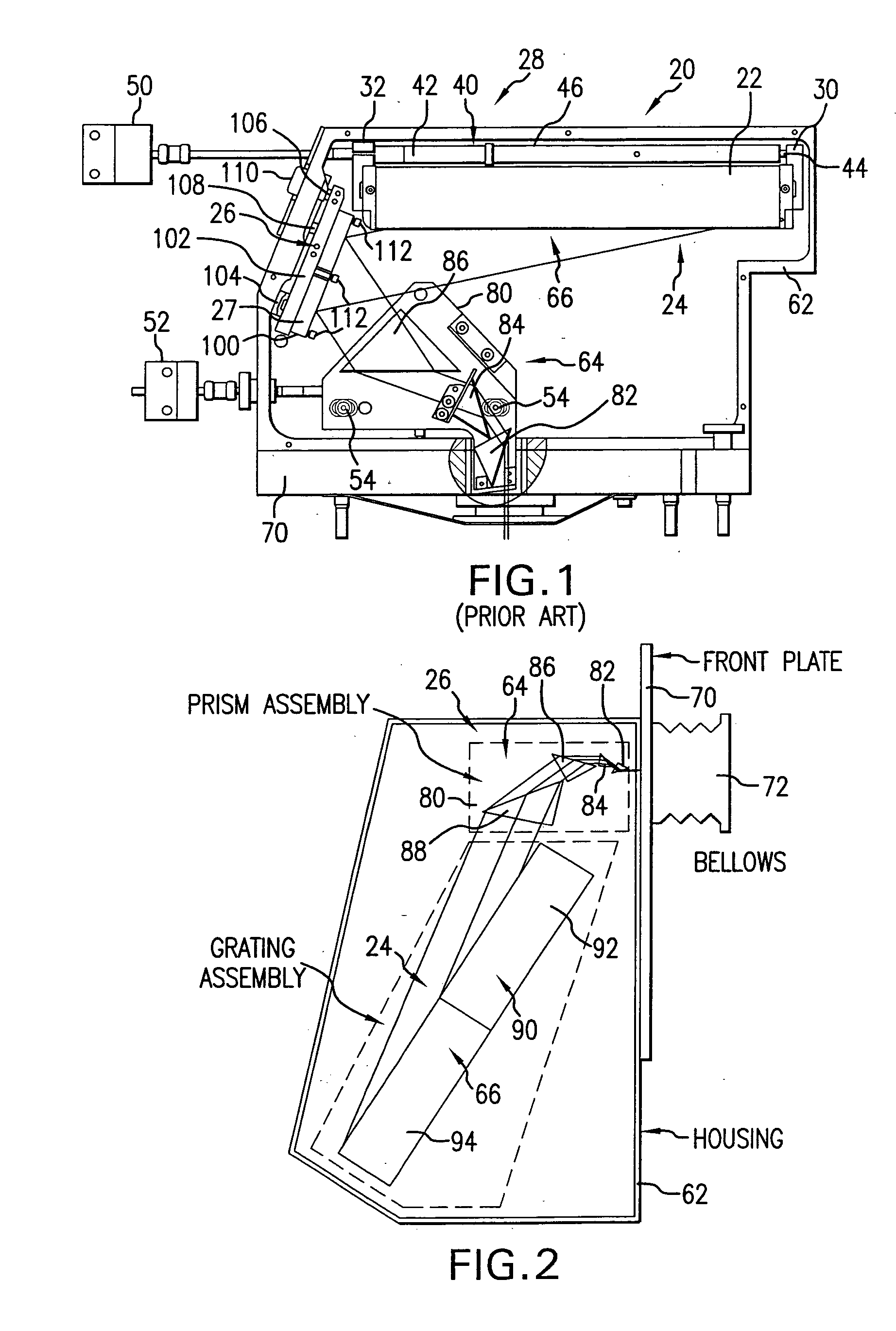
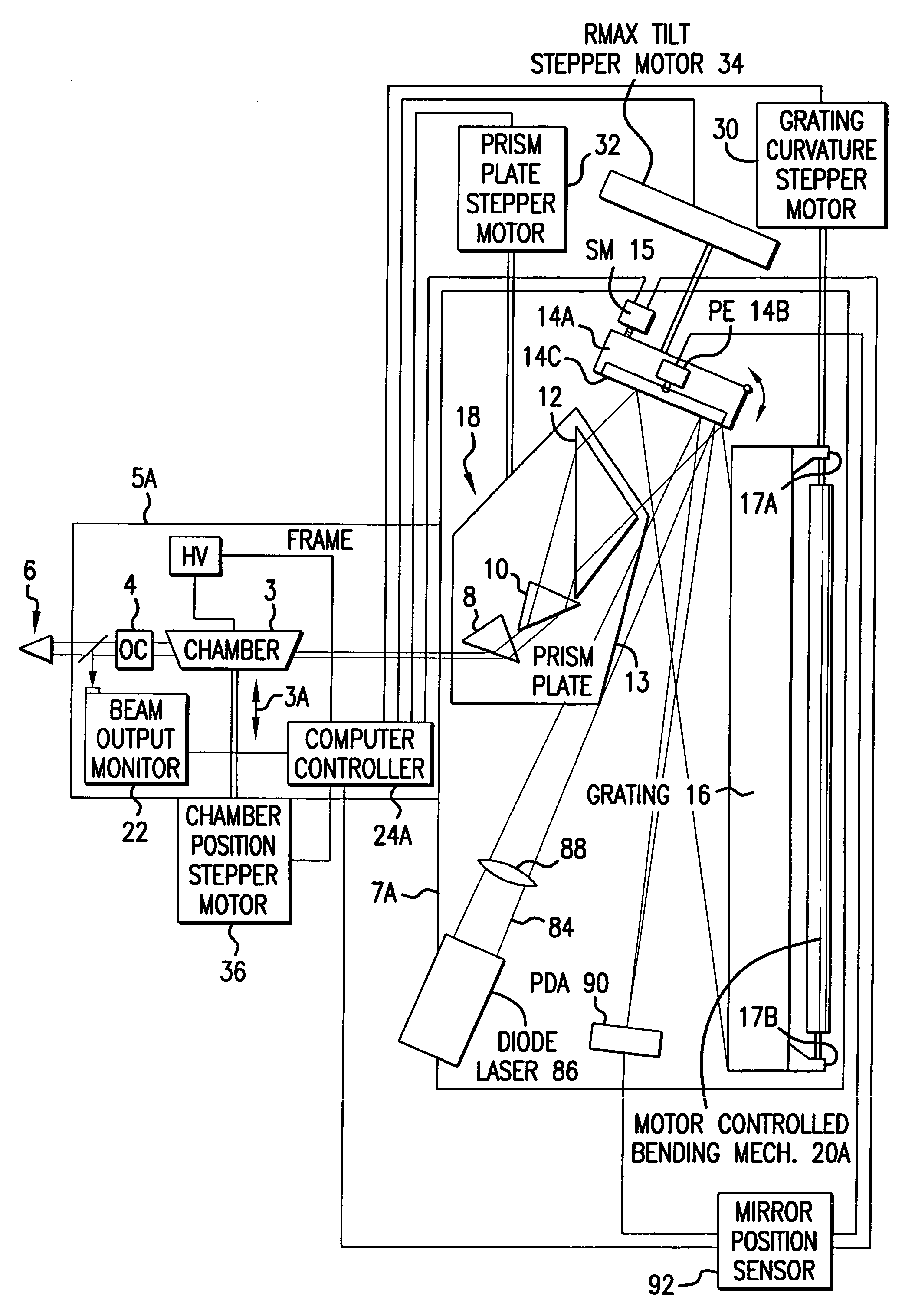
Line narrowing unit with flexural grating mount
InactiveCN100416950CRelieve pressureEliminate the effects ofPrismsOptical resonator shape and constructionGratingHigh energy laser beam
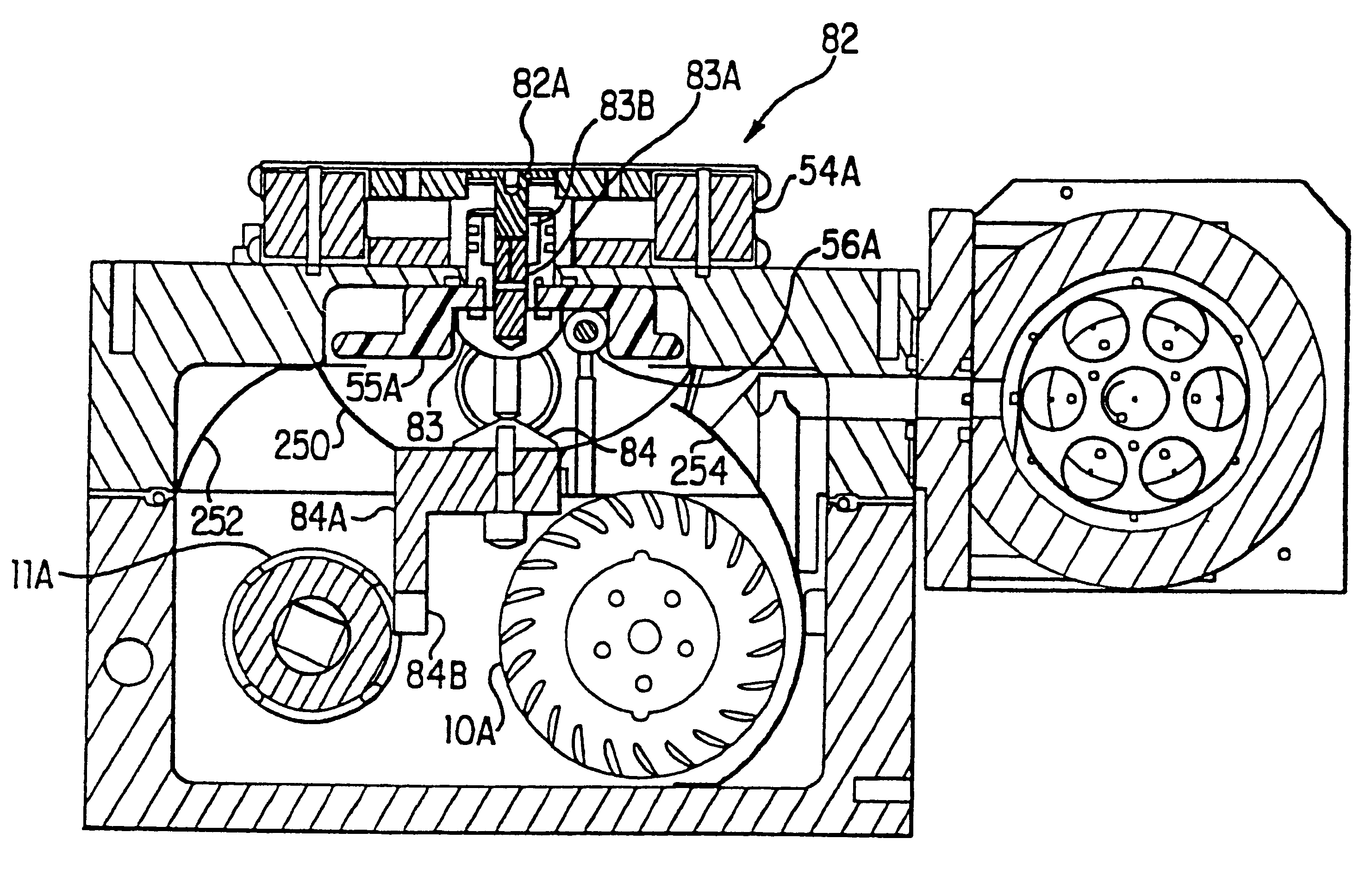
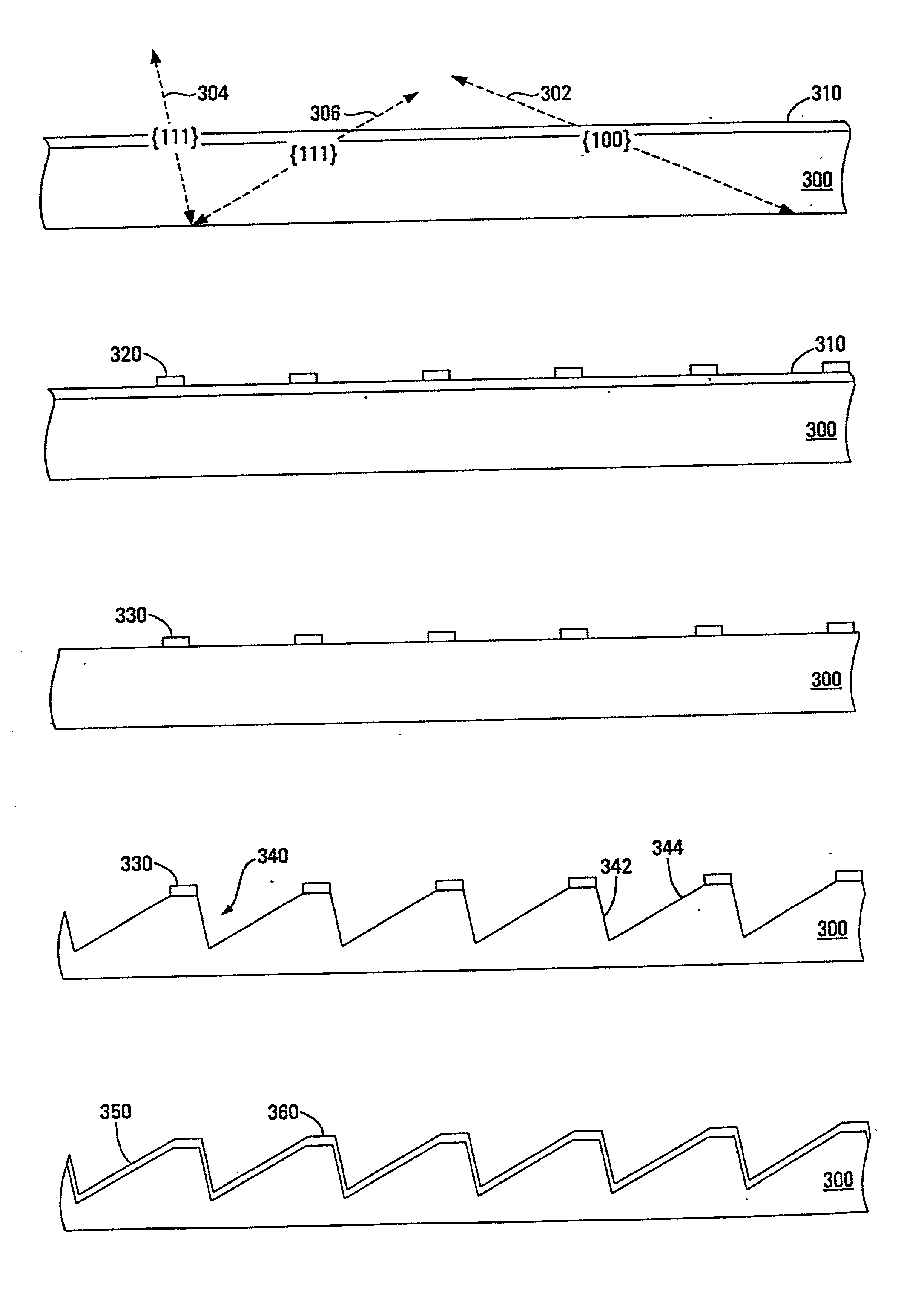
A grating based line narrowing device for line narrowing lasers producing high energy laser beams. A flexure grating mount is provided which virtually eliminates stress on the grating caused by differential thermal expansion between the grating and the housing structure. The grating which is comprised of a very thin aluminum surface on a thick ultra low expansion glass substrate is attached to an aluminum housing structure using a flexure grating mount. At least one flexure joint is provided in the grating mount which permits thermal expansion and contraction of the substrate. In some embodiments the mount comprises a metal plate and the flexure joint is a H-Flex joint (124) with four legs (126) which is machined into the metal plate. In another embodiment two H-Flex joints are provided. In other embodiments, the flexure joint is a dovetail joint permitting one end of the mount to slip relative to the other.
Owner:西默有限公司
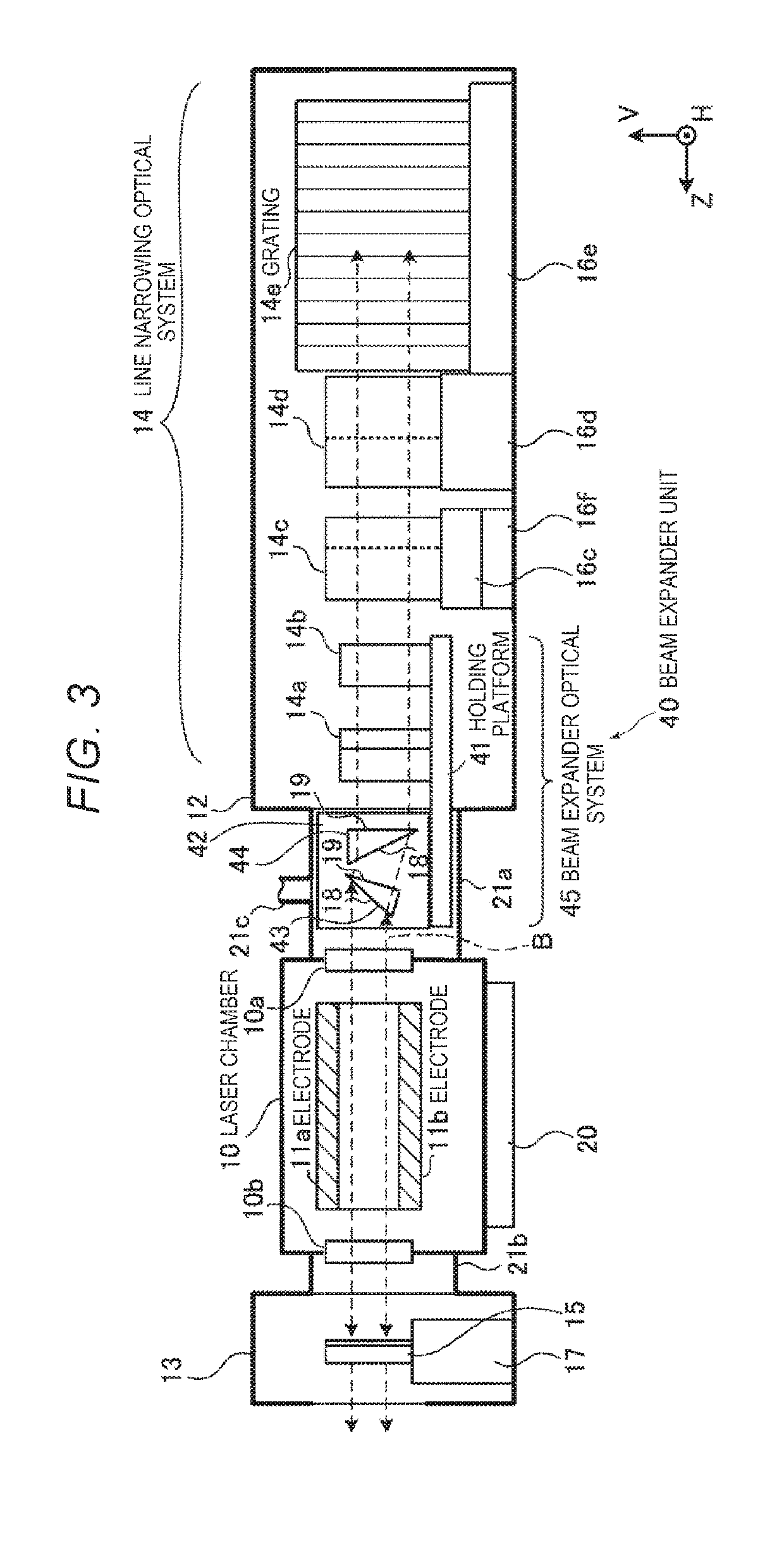
Laser device
ActiveUS20190173258A1Optical resonator shape and constructionGas laser constructional detailsBeam expanderGrating
Provided is a laser device that includes a laser chamber in which a pair of discharge electrodes are disposed; a line narrowing optical system including a grating disposed in a position outside the laser chamber; a beam expander optical system that increases a diameter of a light beam, outputted from the laser chamber and traveling toward the grating, in a first direction parallel to a discharge direction between the discharge electrodes and in a second direction orthogonal to the discharge direction; and a holding platform that is formed as a component separate from the laser chamber and the grating, holds the beam expander optical system, and forms along with the beam expander optical system a beam expander unit.
Owner:GIGAPHOTON
Line narrowing module, gas laser apparatus, and electronic device manufacturing method
A line narrowing module includes a prism including an entrance side surface that light enters, an exit side surface from which the light is emitted, and a bottom surface, and configured to wavelength-disperse the light having entered the entrance side surface and to emit the light from the exit side surface; a holder portion having a stationary surface on which the bottom surface of the prism is secured; a rotary mechanism portion including a rotary stage on which the holder portion is secured, the rotary stage being configured to rotate the prism around an axis perpendicular to a dispersion plane of the light emitted from the prism; a drive unit configured to rotate the rotary stage; and a grating configured to reflect the light emitted from the prism, centroids of the prism, the holder portion, and the rotary stage being located on the axis.
Owner:GIGAPHOTON
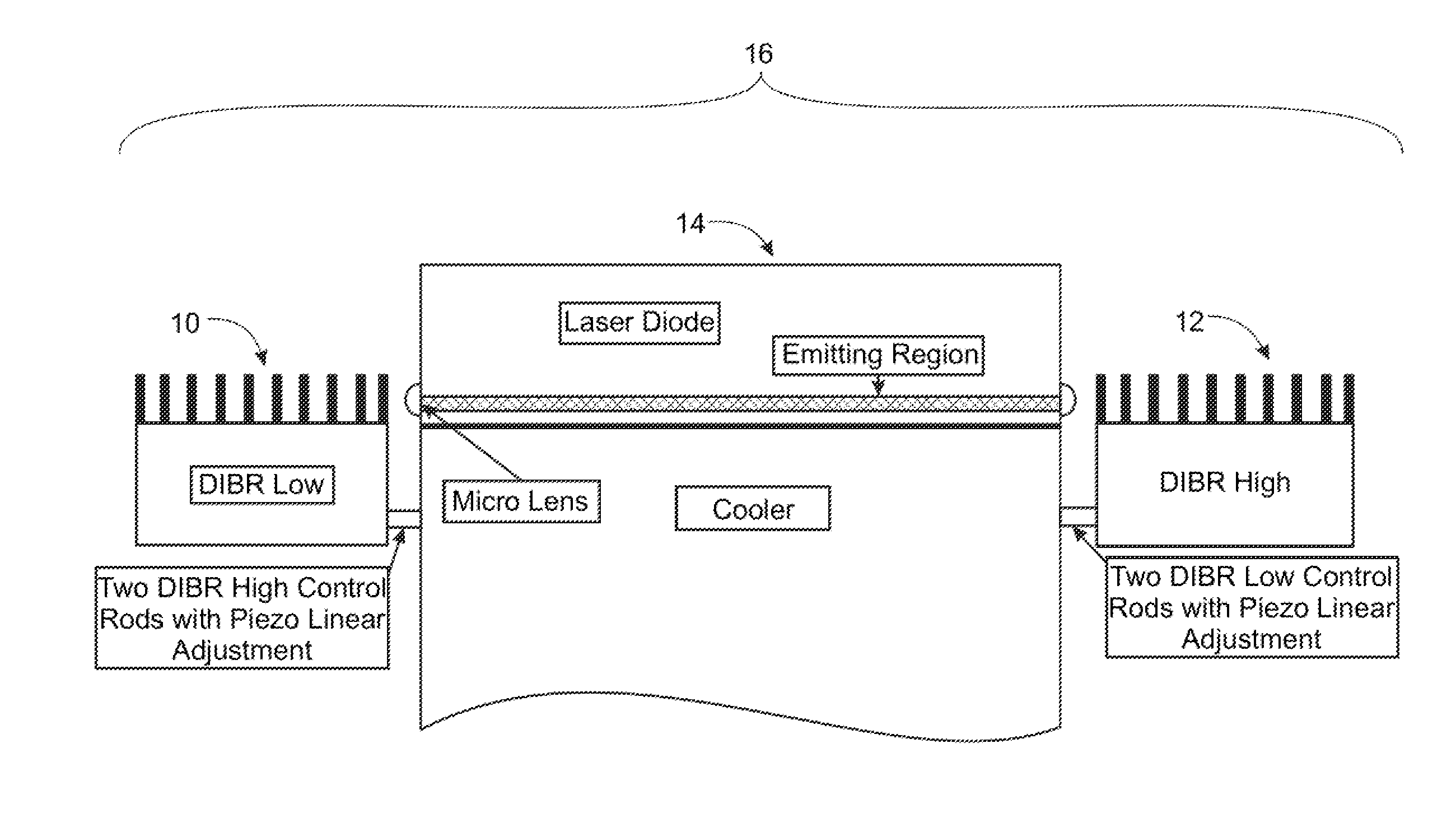
Method and Apparatus for the Line Narrowing of Diode Lasers
A system for narrowing the spectral output of diode lasers through the use of dielectric stacks in the laser cavity comprising an alternating sequence of layers of dielectric material and air, which dielectric stacks are fabricated through the controlled laser ablation of the dielectric material.
Owner:TRANSLITH SYST
Grating, method for manufacturing grating, and method for recycling grating
A grating for line-narrowing a laser beam that is outputted from a laser apparatus at a wavelength in a vacuum ultraviolet region may include: a grating substrate; a first aluminum metal film formed above the grating substrate, the first aluminum metal film having grooves in a surface thereof; and a first protective film formed by an ALD method above the first aluminum metal film.
Owner:GIGAPHOTON
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com