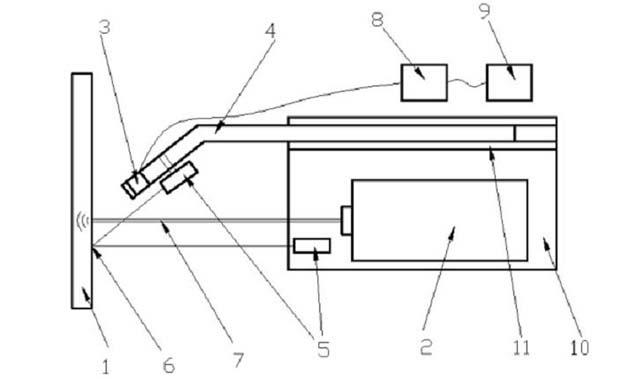
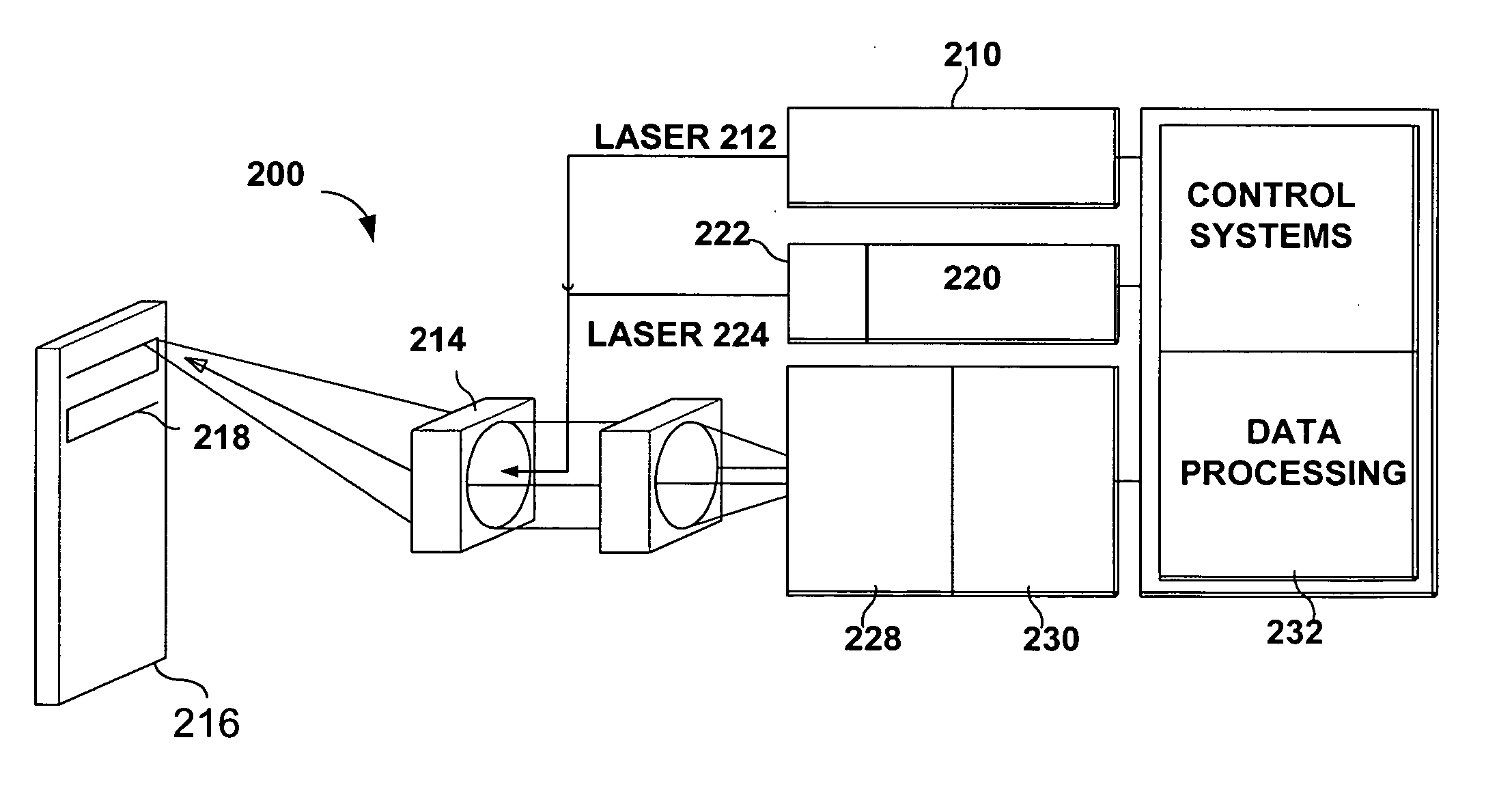
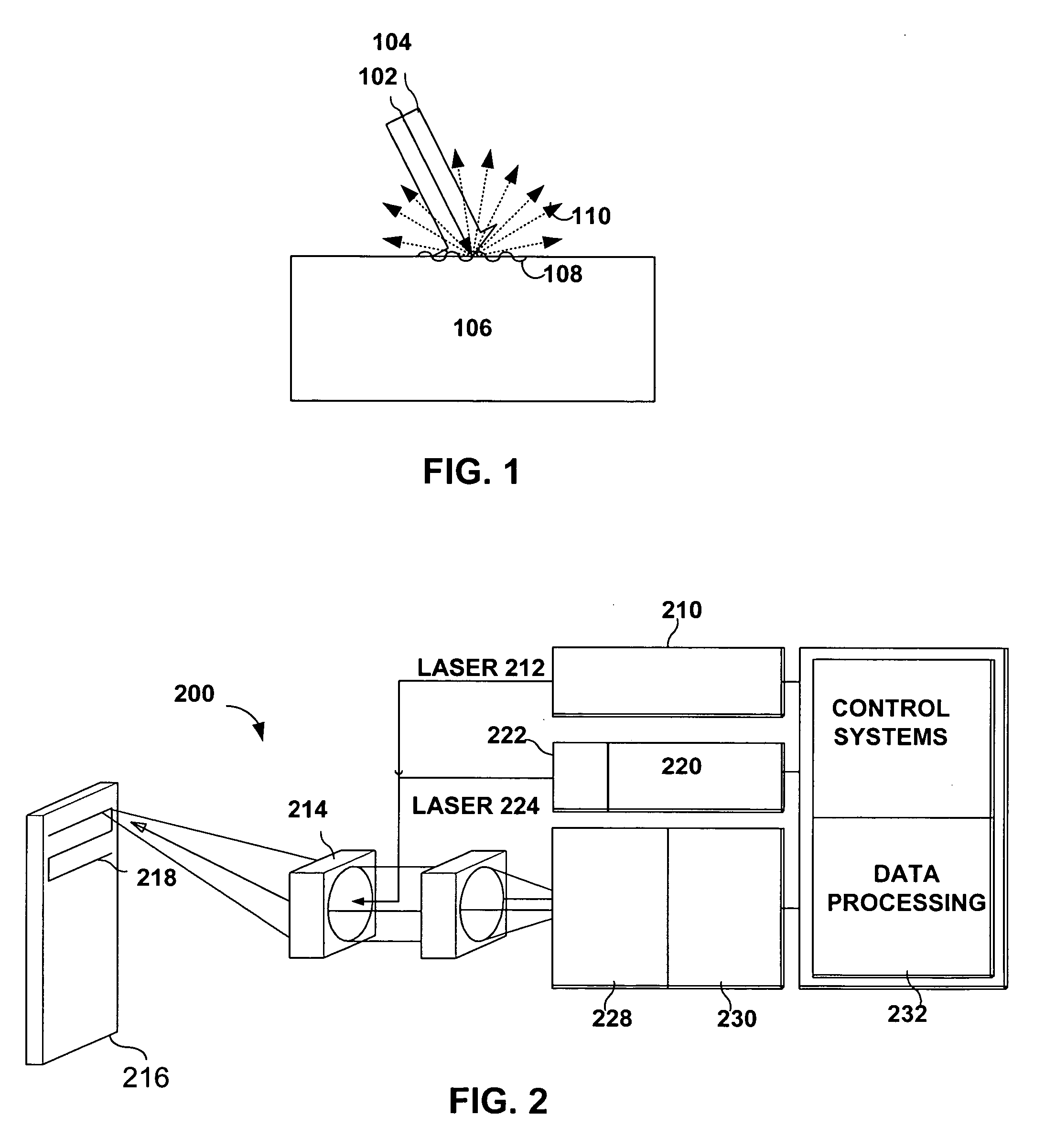
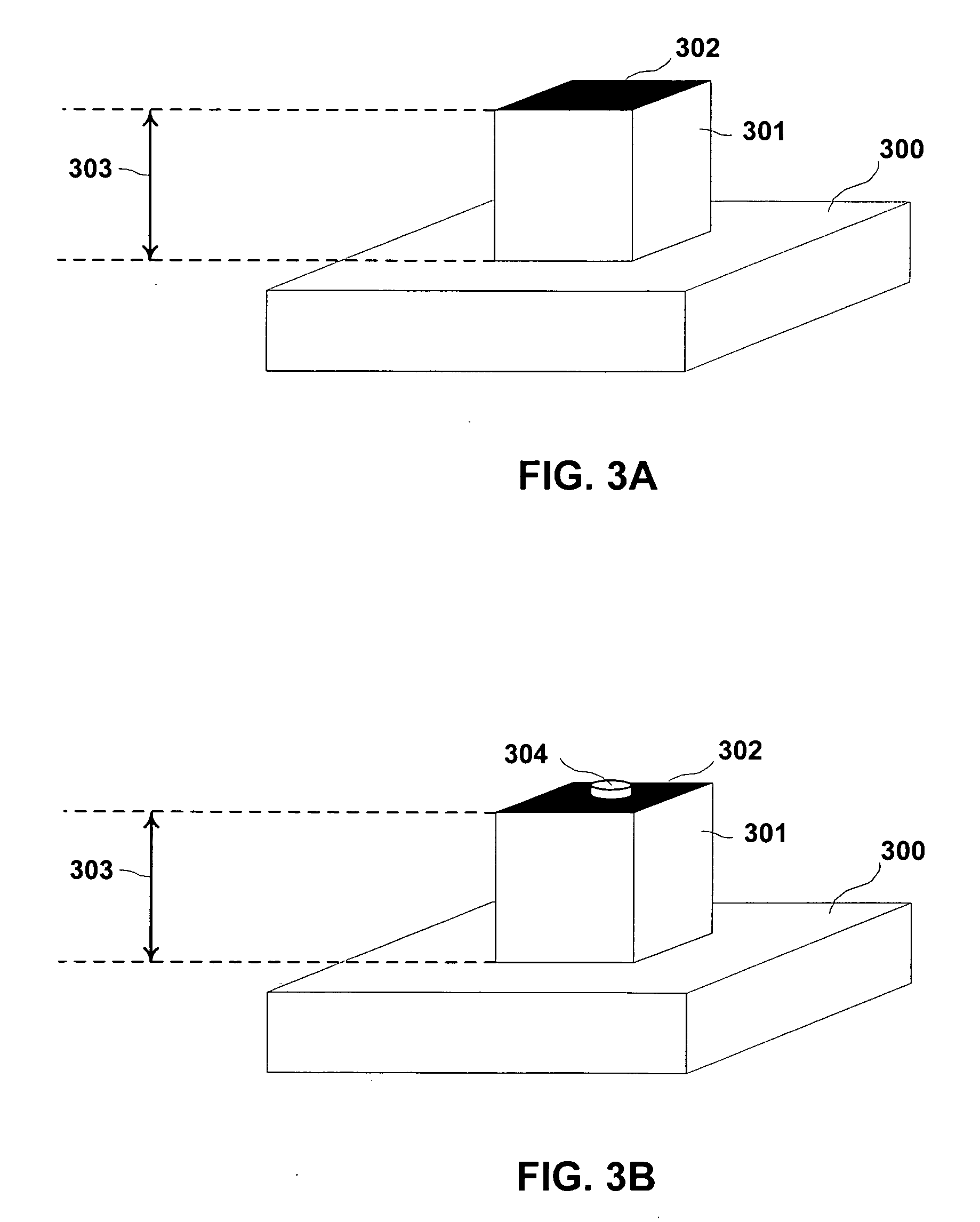
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
335 results about "Laser ultrasonics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
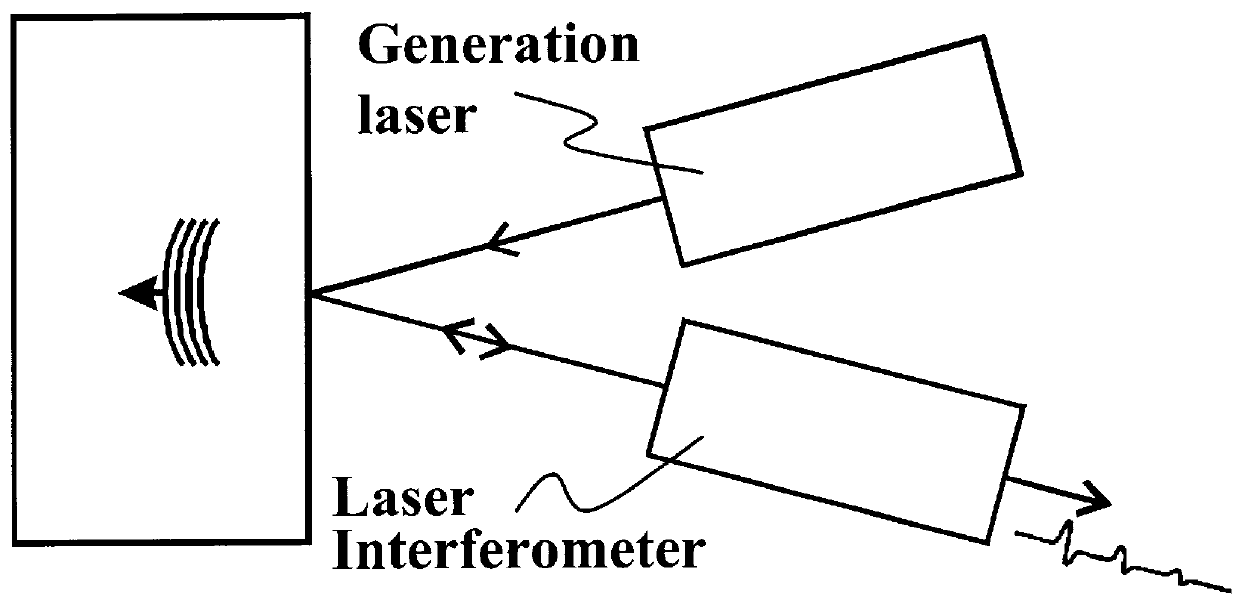
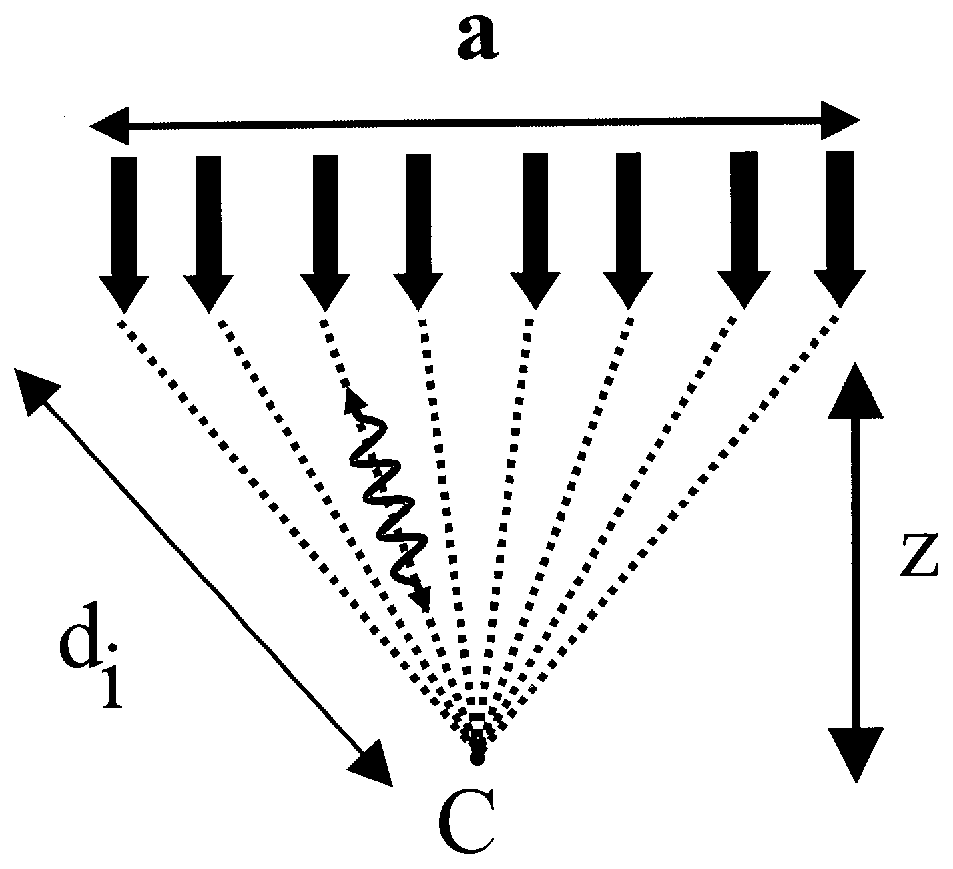
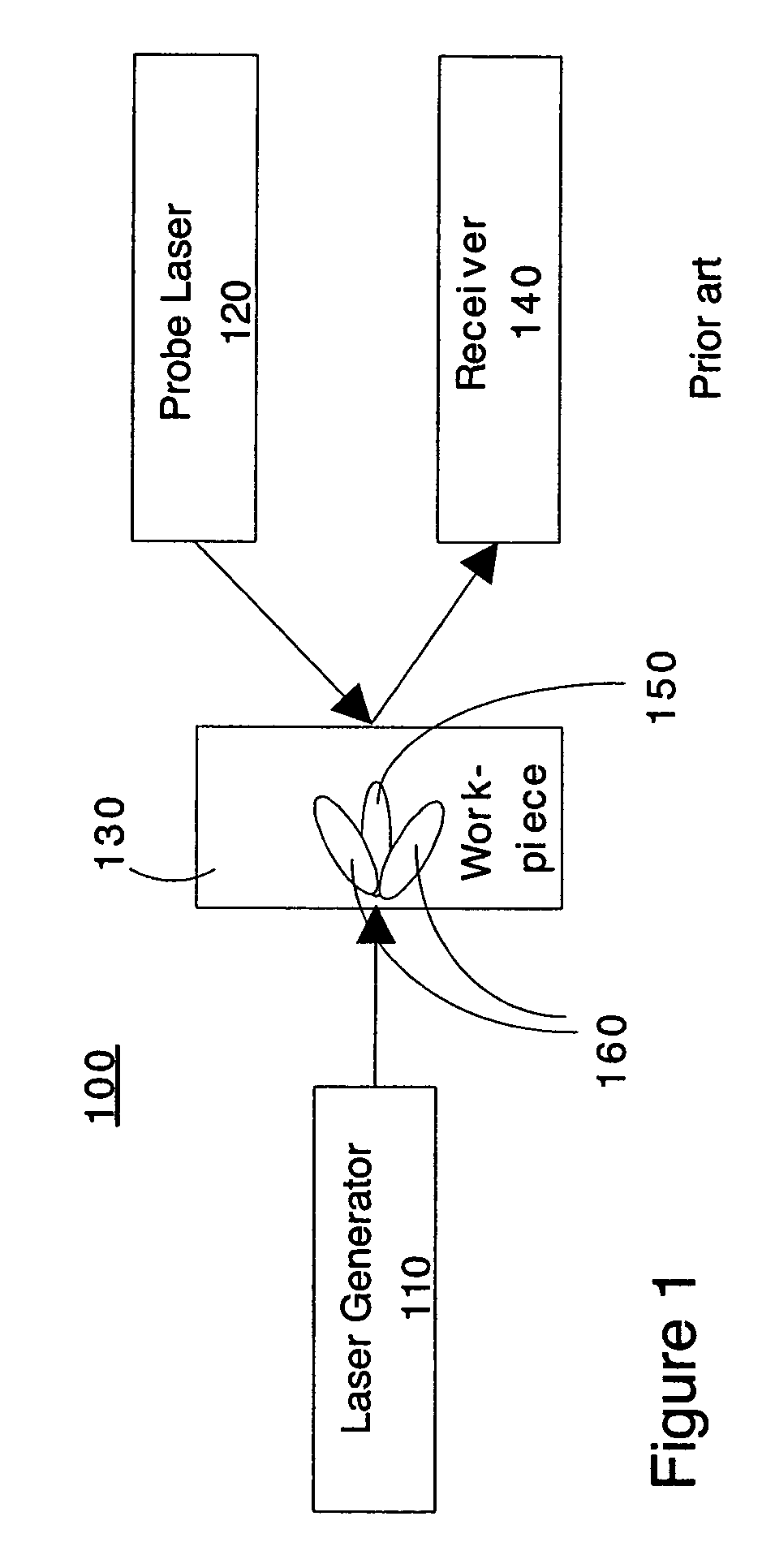
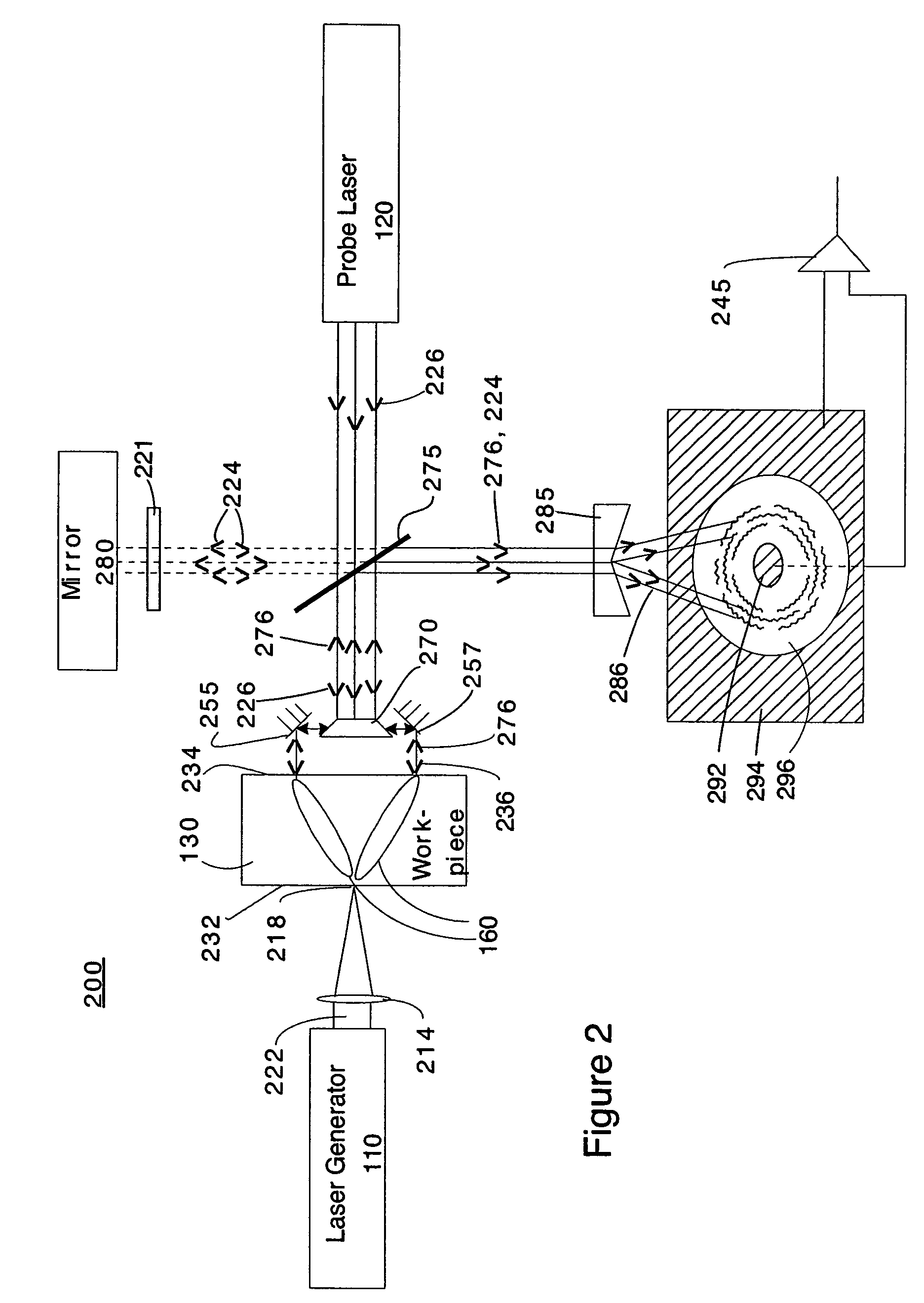
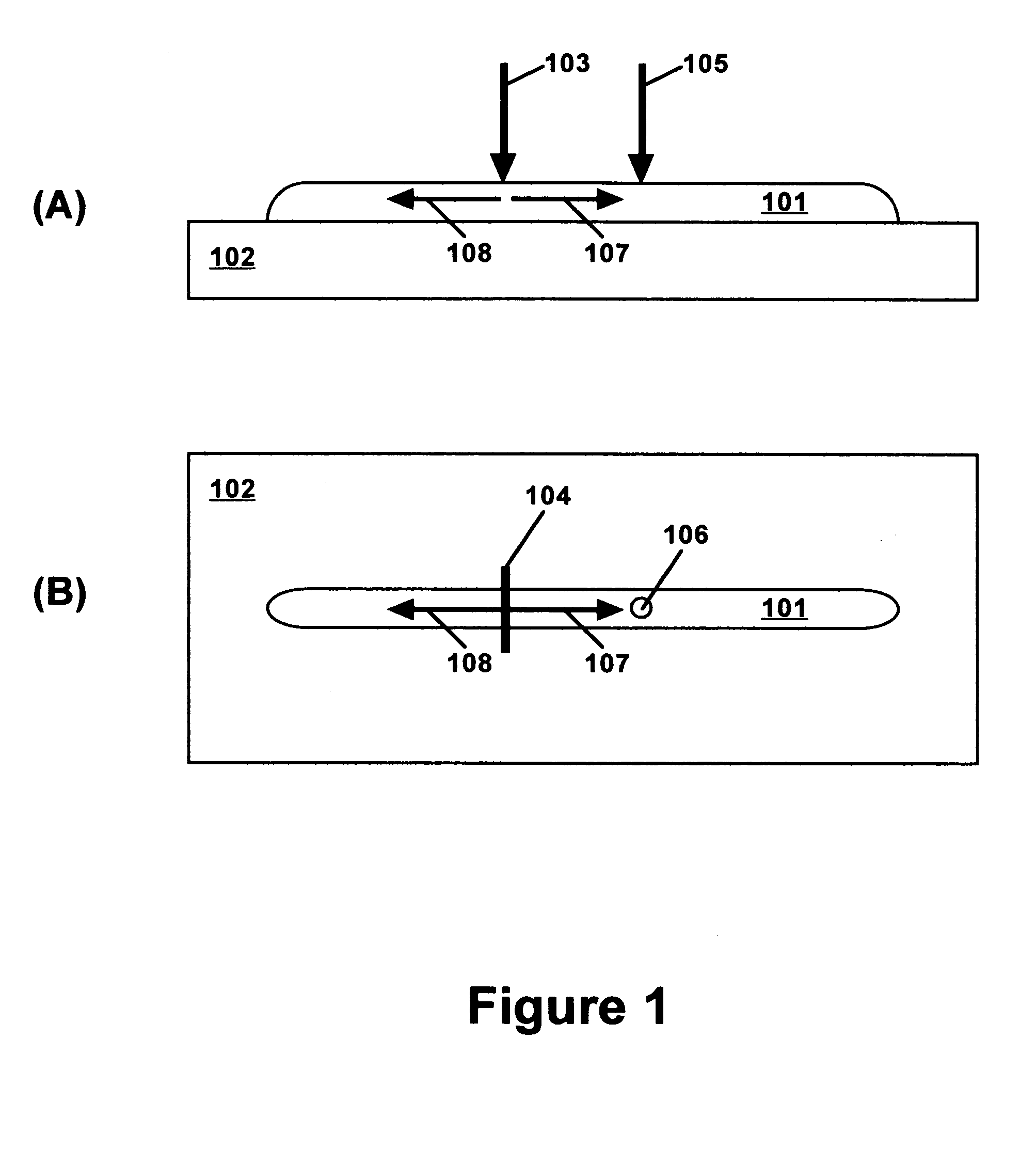
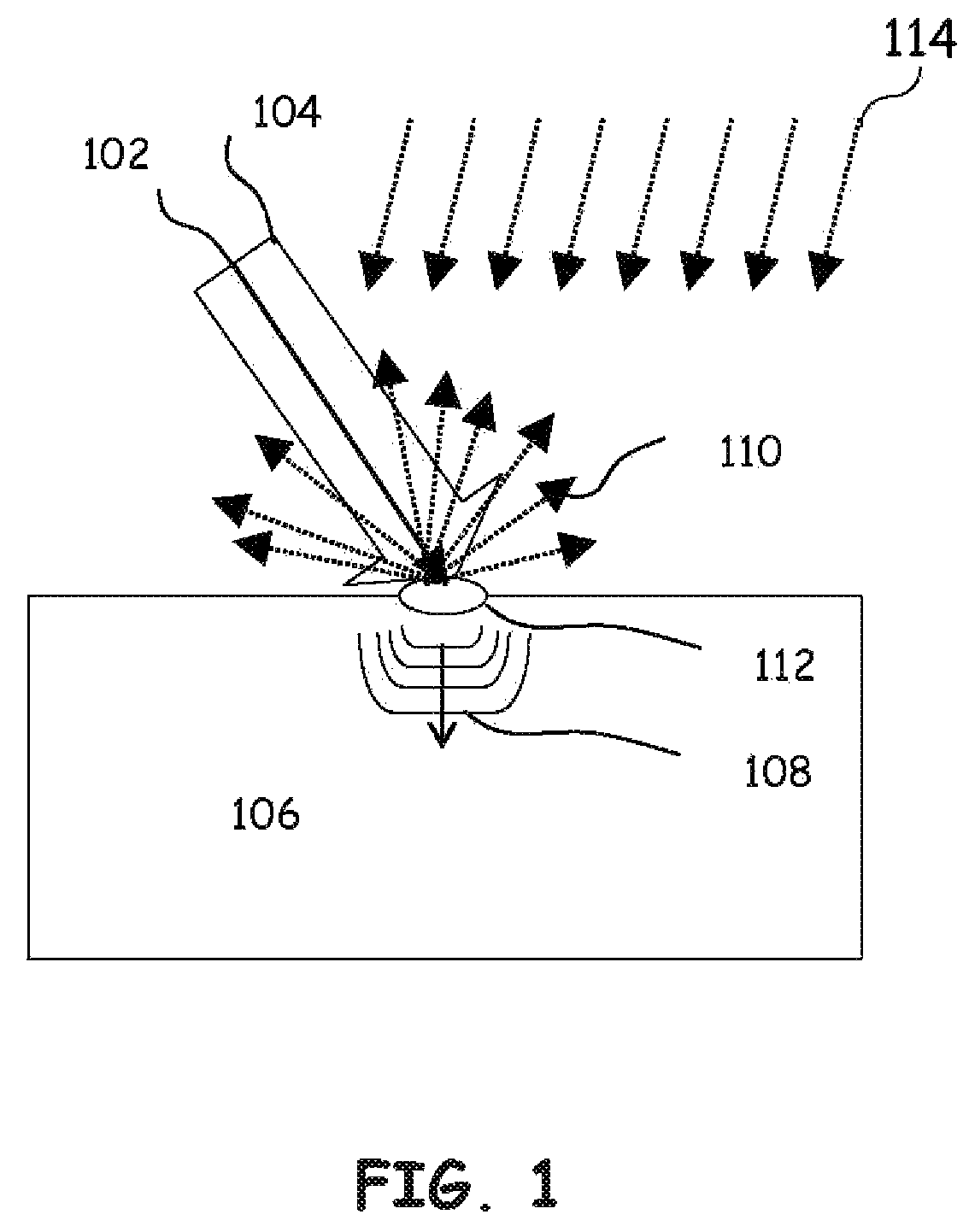
Laser-ultrasonics uses lasers to generate and detect ultrasonic waves. It is a non-contact technique used to measure materials thickness, detect flaws and carry out materials characterization. The basic components of a laser-ultrasonic system are a generation laser, a detection laser and a detector.
Laser Optoacoustic Ultrasonic Imaging System (LOUIS) and Methods of Use
ActiveUS20130190595A1Increase contrastImprove resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMedical imagingHelical computed tomographyContrast resolution
Provided herein are the systems, methods, components for a three-dimensional tomography system. The system is a dual-modality imaging system incorporates a laser ultrasonic system and a laser optoacoustic system. The dual-modality imaging system has means for generate tomographic images of a volume of interest in a subject body based on speed of sound, ultrasound attenuation and / or ultrasound backscattering and for generating optoacoustic tomographic images of distribution of the optical absorption coefficient in the subject body based on absorbed optical energy density or various quantitative parameters derivable therefrom. Also provided is a method for increasing contrast, resolution and accuracy of quantitative information obtained within a subject utilizing the dual-modality imaging system. The method comprises producing an image of an outline boundary of a volume of interest and generating spatially or temporally coregistered images based on speed of sound and / or ultrasonic attenuation and on absorbed optical energy within the outlined volume.
Owner:TOMOWAVE LAB INC
Method and system for high resolution ultrasonic imaging of small defects or anomalies.
InactiveUS6128092ARadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometrySonificationSynthetic aperture focusing
A method and system is provided for enhanced ultrasonic detection and imaging of small defects inside or at the surface of an object. The Synthetic Aperture Focusing Technique (SAFT) has been used to improve the detectability and to enhance images in conventional ultrasonics and this method has recently been adapted to laser-ultrasonics. In the present invention, an improved version of the frequency-domain SAFT (F-SAFT) based on the angular spectrum approach is described. The method proposed includes temporal deconvolution of the waveform data to enhance both axial and lateral resolutions, control of the aperture and of the frequency bandwidth to improve signal-to-noise ratio, as well as spatial interpolation of the subsurface images. All the above operations are well adapted to the frequency domain calculations and embedded in the F-SAFT data processing. The aperture control and the spatial interpolation allow also a reduction of sampling requirements to further decrease both inspection and processing times. This method is of particular interest when ultrasound is generated by a laser and detected by either a contact ultrasonic transducer or a laser interferometer.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Laser-ultrasound inspection using infrared thermography
InactiveUS20080137105A1Complete understandingUnderstanding of internal structureMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis by optical meansThermographic inspectionLaser
An inspection system is provided to examine internal structures of a target material. This inspection system combines an ultrasonic inspection system and a thermographic inspection system. The thermographic inspection system is attached to ultrasonic inspection and modified to enable thermographic inspection of target materials at distances compatible with laser ultrasonic inspection. Quantitative information is obtained using depth infrared (IR) imaging on the target material. The IR imaging and laser-ultrasound results are combined and projected on a 3D projection of complex shape composites. The thermographic results complement the laser-ultrasound results and yield information about the target material's internal structure that is more complete and more reliable, especially when the target materials are thin composite parts.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
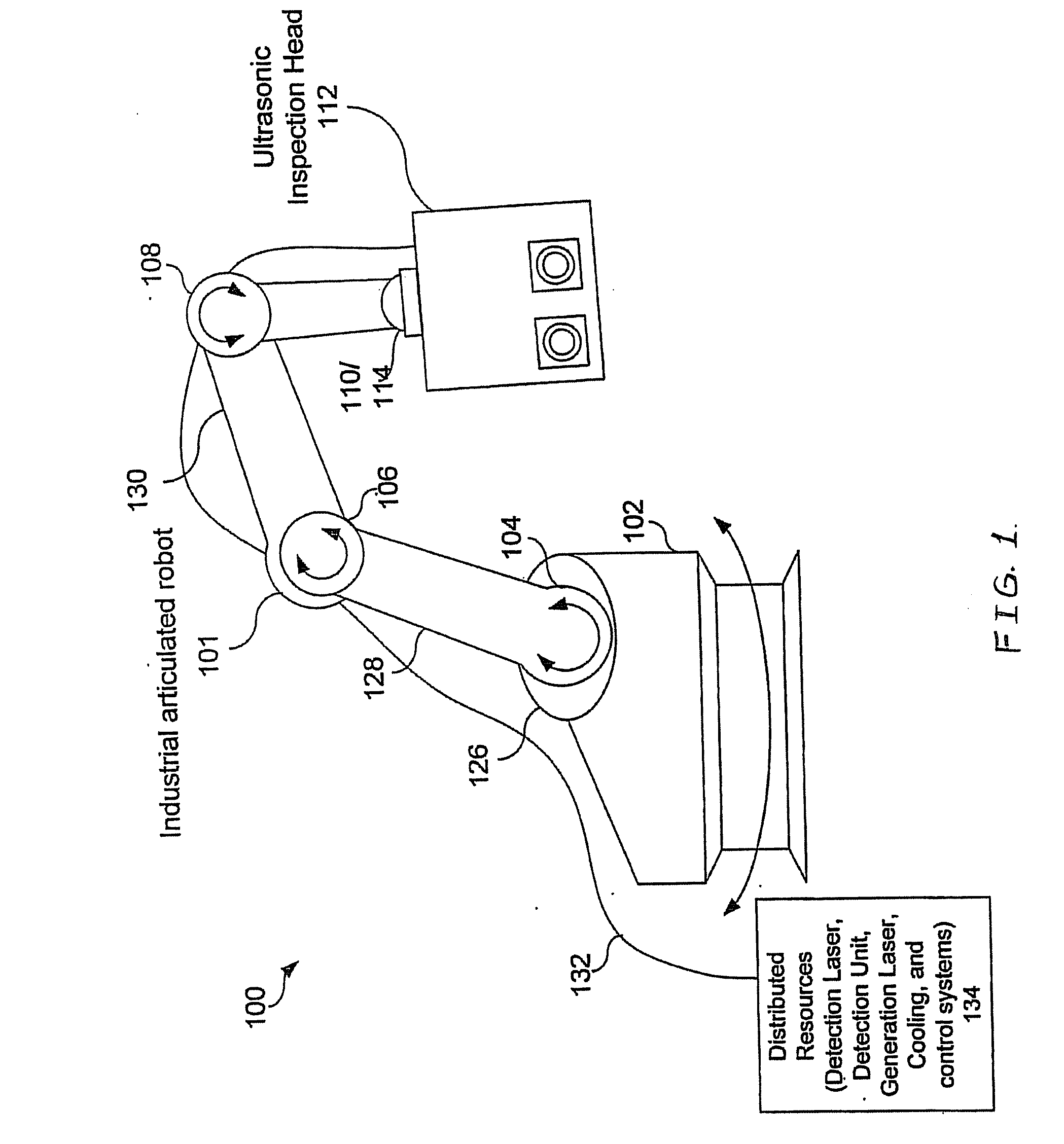
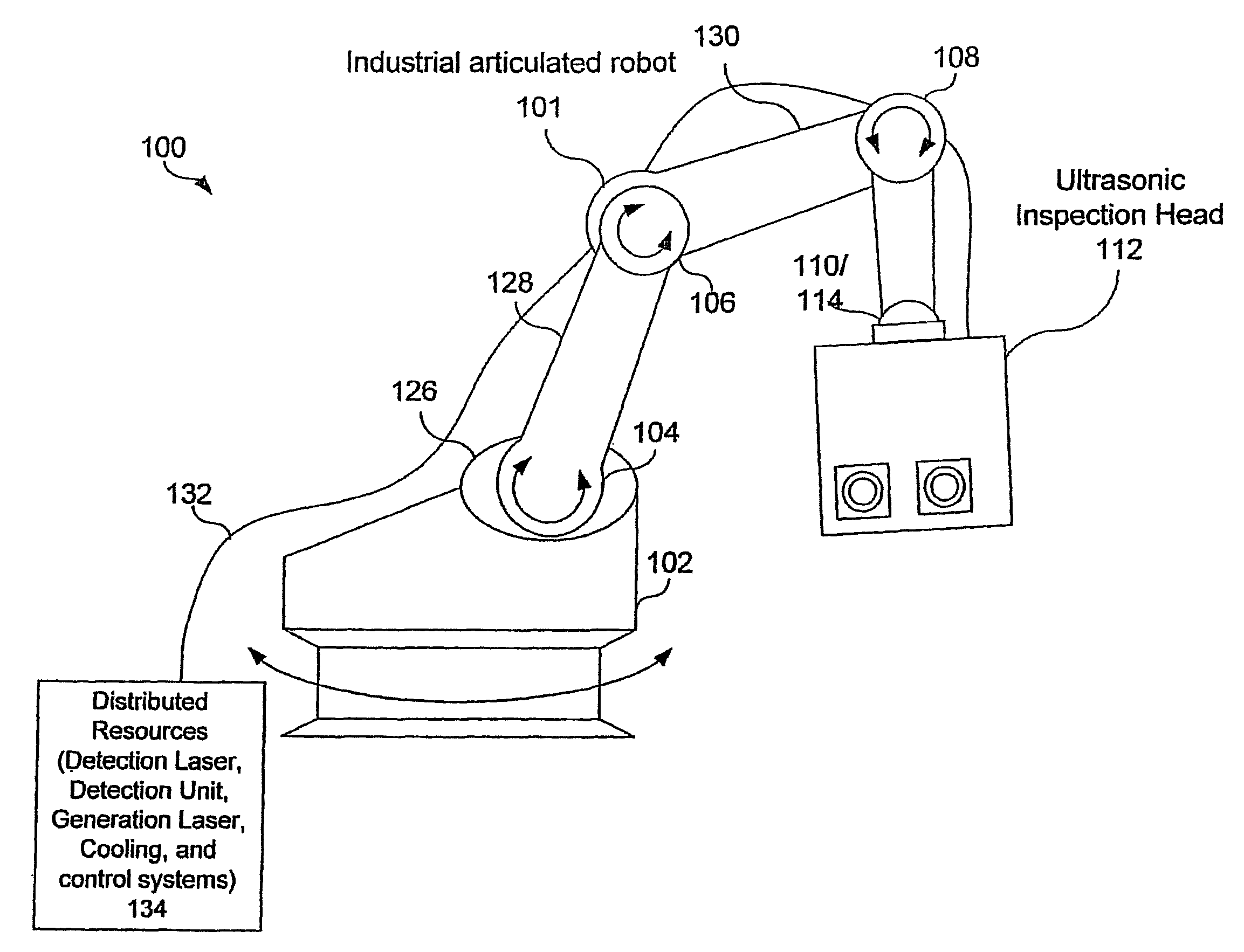
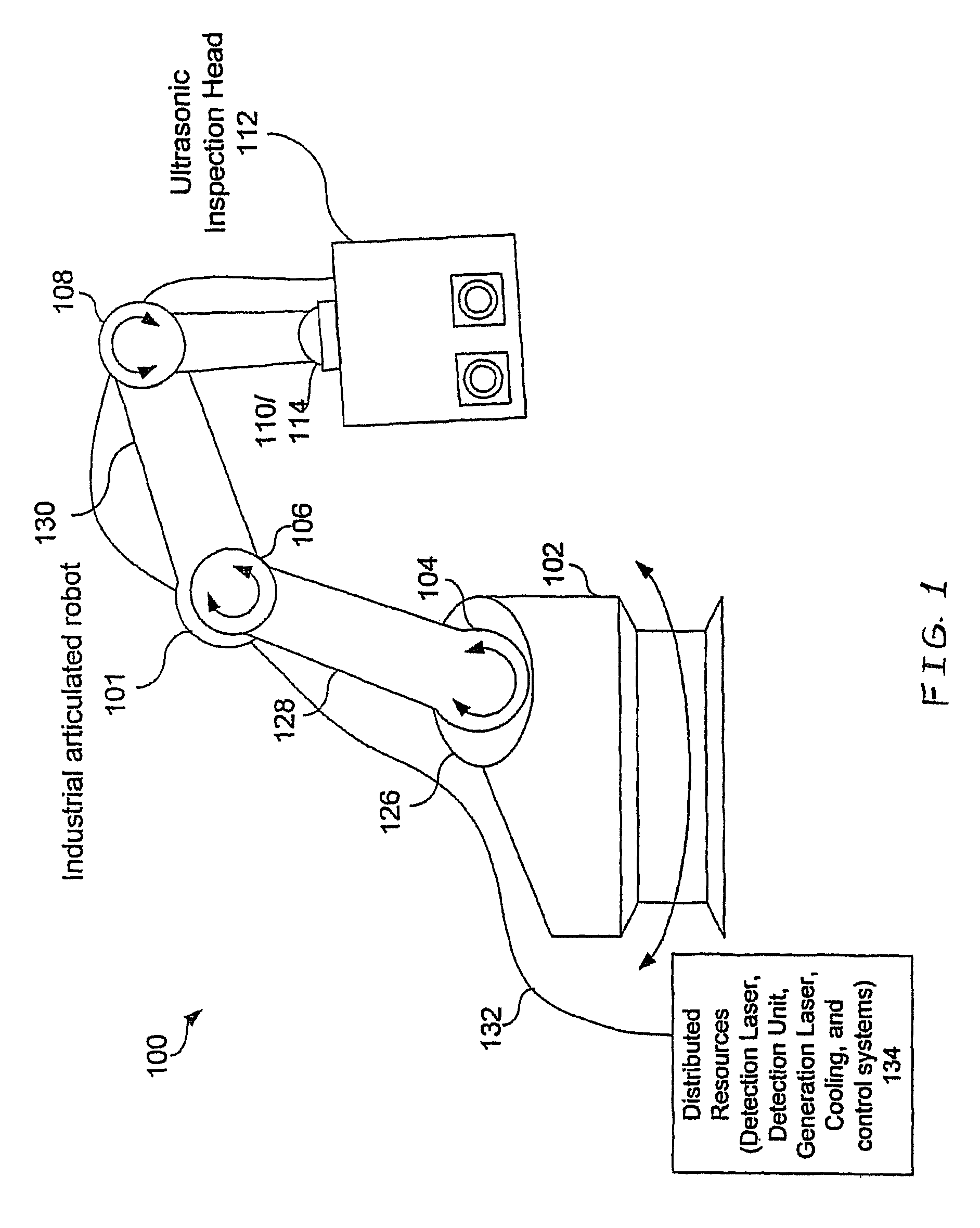
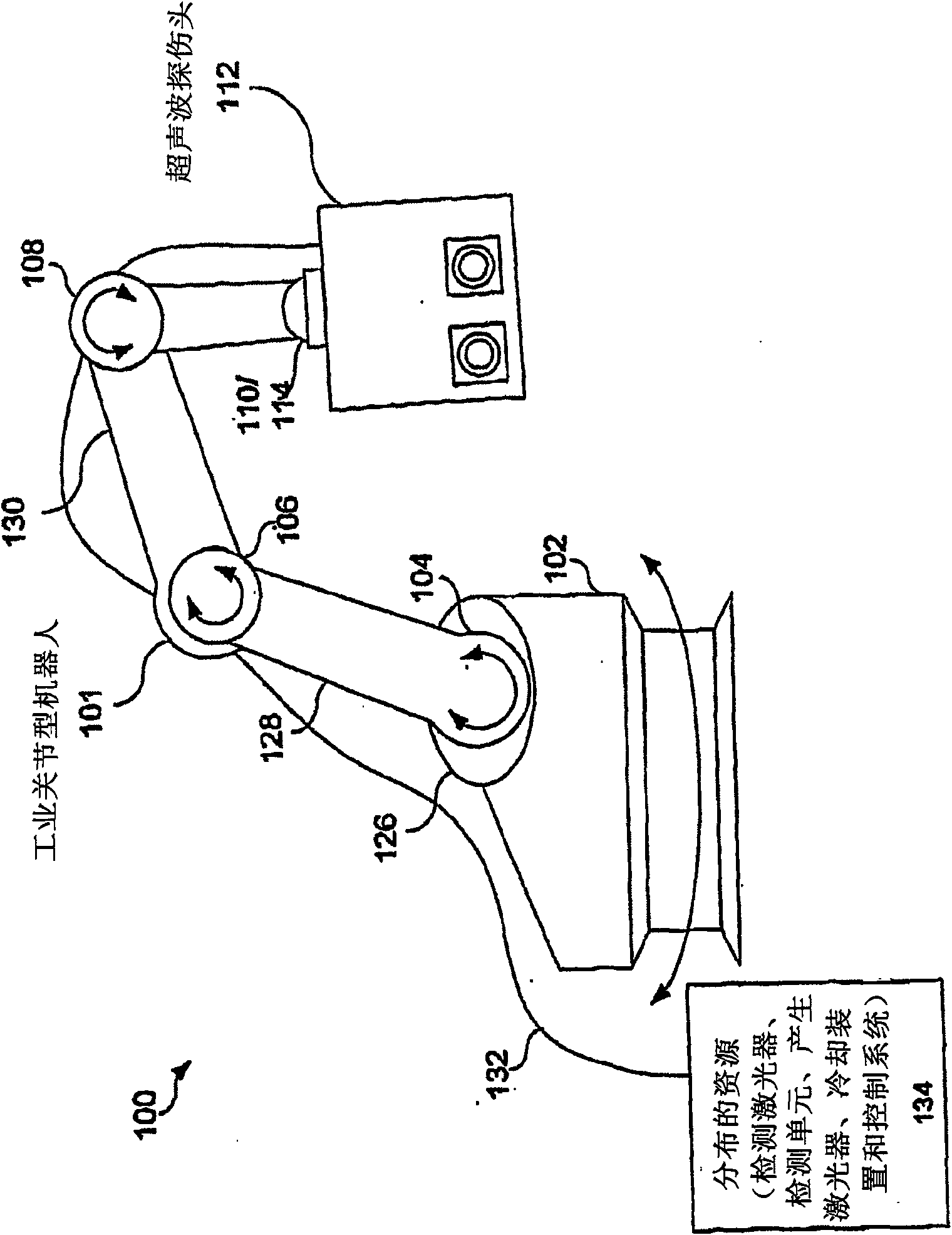
Articulated robot for laser ultrasonic inspection
ActiveUS20090010285A1Cost-effectiveMore compact robotsLaser using scattering effectsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesNon destructiveUltrasound sonography
An ultrasonic non-destructive evaluation (NDE) system operable to inspect target materials is provided. This ultrasonic NDE system includes an articulated robot, an ultrasound inspection head, a processing module, and a control module. The ultrasound inspection head couples to or mounts on the articulated robot. The ultrasound inspection head is operable to deliver a generation laser beam, a detection laser beam, and collect phase modulated light scattered by the target materials. The processing module processes the phase modulated light and produces information about the internal structure of the target materials. The control module directs the articulated robot to position the ultrasound inspection head according to a pre-determined scan plan.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
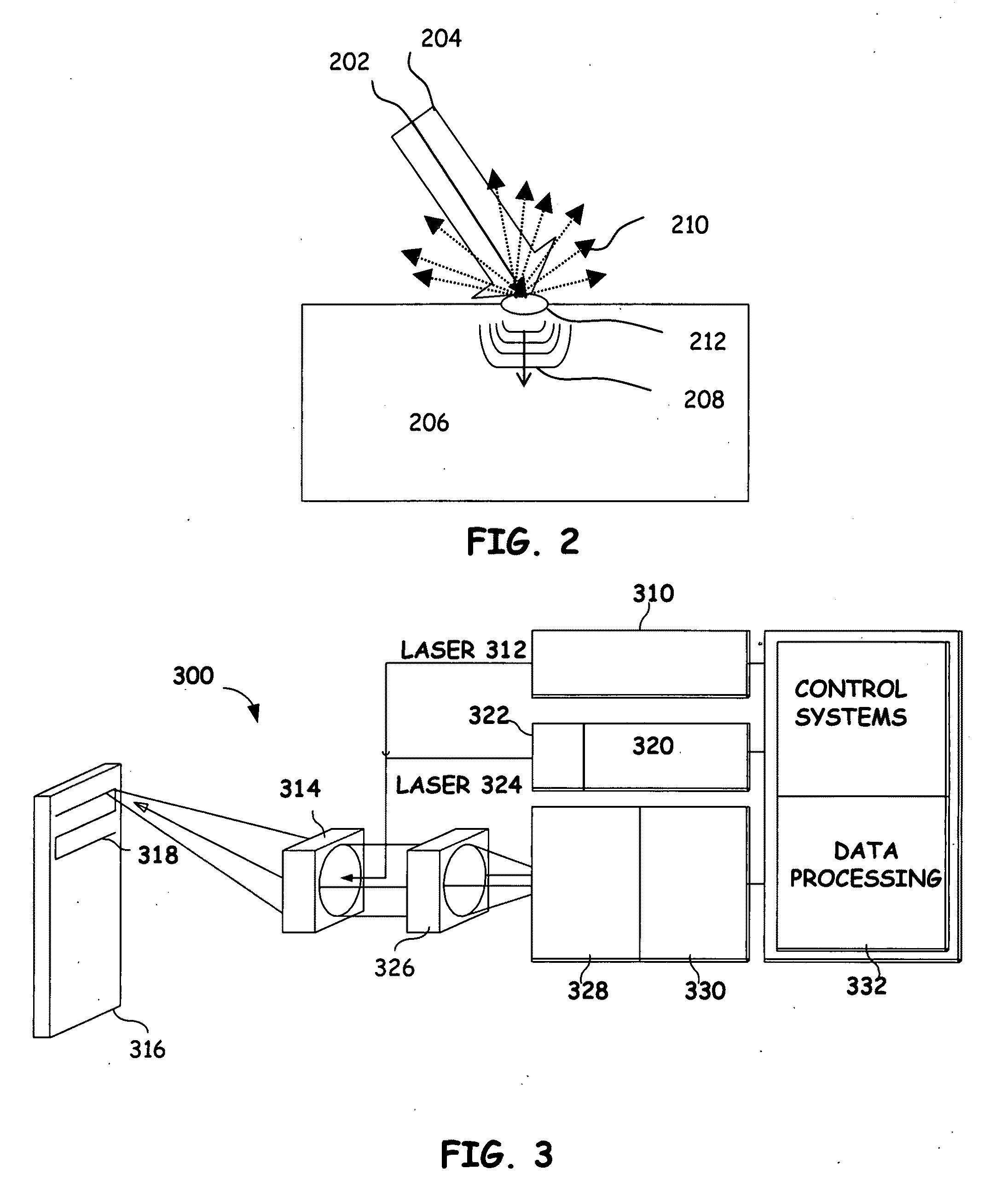
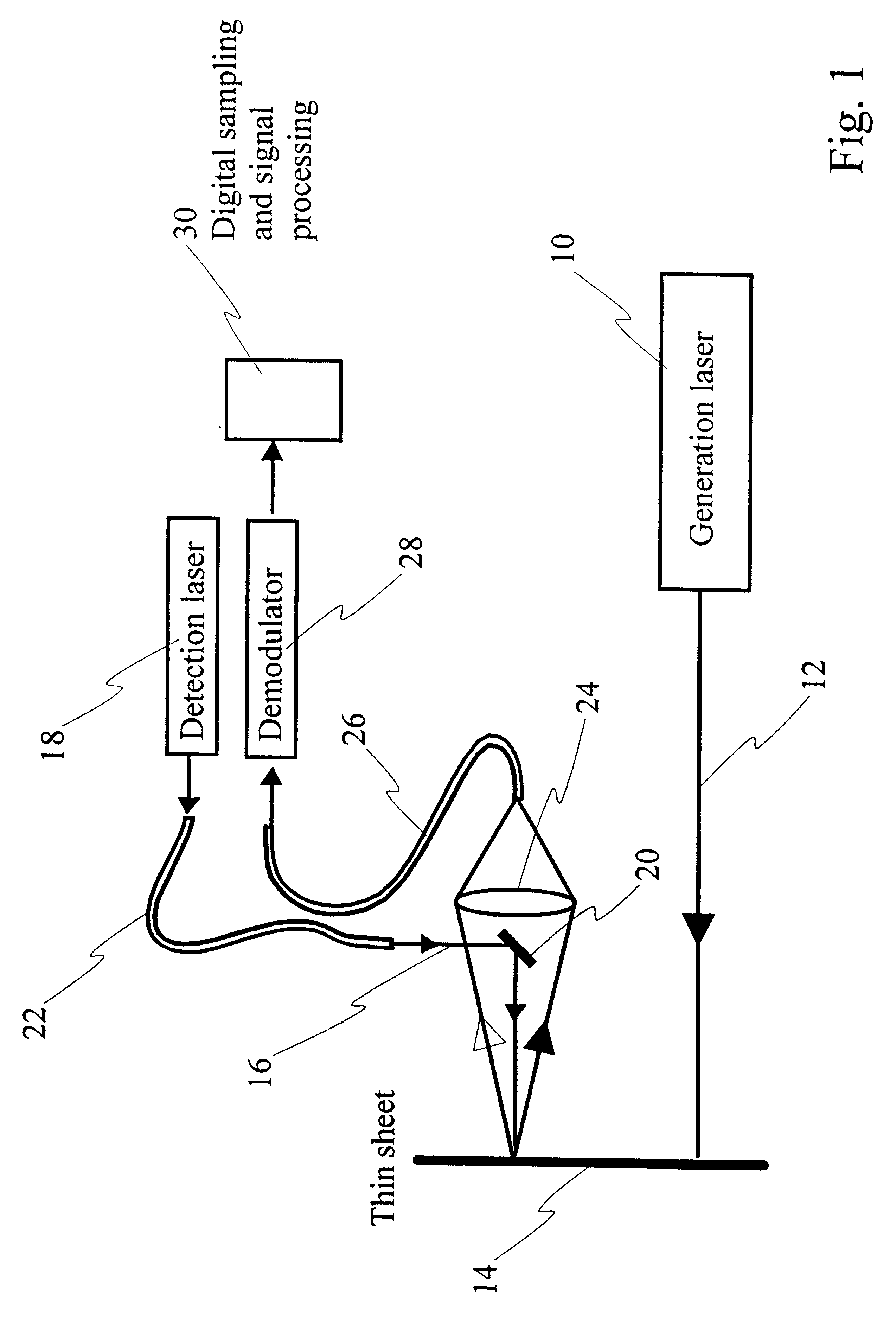
Laser-ultrasonic measurement of elastic properties of a thin sheet and of tension applied thereon
InactiveUS6543288B1Vibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesIn planeMeasurement device
A method and an apparatus for non-contact and non-invasive characterization of a moving thin sheet and in particular of a paper web on a production line. The method uses a laser for the generation of sonic and ultrasonic waves in the thin sheet and a speckle insensitive interferometric device for the detection of these waves. The generation is performed in conditions to avoid damage impeding further use of the sheet. When the generation and detection spots overlap, the method provides a measurement of the compression modulus. When the generation and detection spots are separated by a known distance and plate waves (Lamb waves) are generated and detected, the method provides a measurement of the in-plane modulus and of the tension applied to the sheet. By detecting waves propagating in various directions, either by rotating the detection sensor head or multiplexing the signals provided by several detection or generation locations, the anisotropy of the in-plane modulus is determined.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
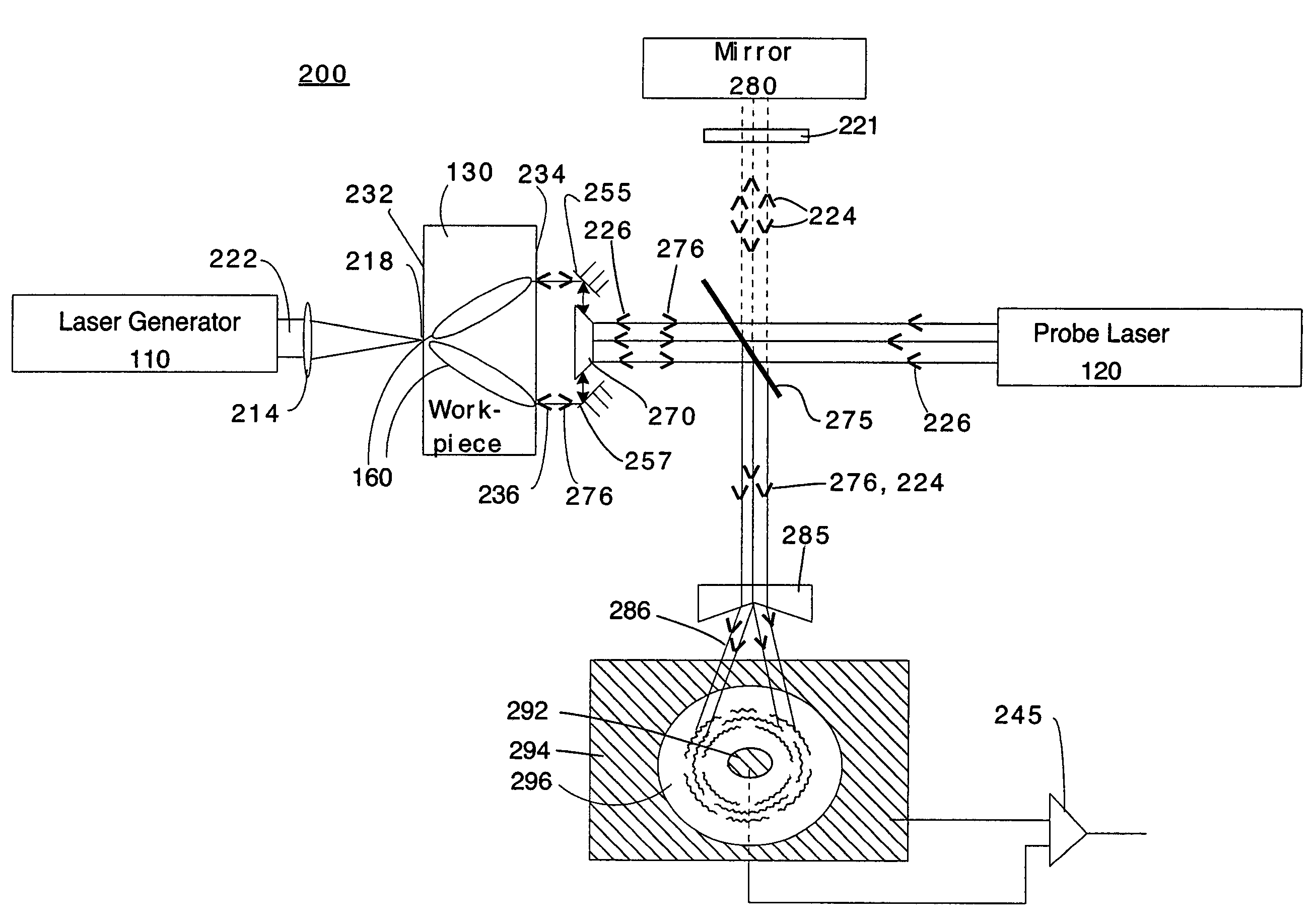
Ultrasound single-element non-contacting inspection system
InactiveUS7262861B1Low costReduce complexityVibration measurement in solidsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A laser ultrasonic inspection apparatus and method which enables remote sensing of thickness, hardness, temperature and / or internal defect detection is disclosed. A laser generator impinges a workpiece with light for generating a thermo-elastic acoustic reaction in a workpiece. A probe laser impinges the workpiece with an annularly-shaped probe light for interaction with the acoustic signal in the workpiece resulting in a modulated return beam. A photodetector having a sensitive region for detecting an annularly-shaped fringe pattern generated by an interaction of a reference signal and with the modulated return beam at said sensitive region.
Owner:HRL LAB
Laser ultrasonic online nondestructive material-increase manufacturing part detection method
ActiveCN106018288AAvoid detection blind spotsImprove reliabilityAdditive manufacturing apparatusMaterial analysis by optical meansNon detectionHigh energy beam
The invention provides a laser ultrasonic online nondestructive material-increase manufacturing part detection method and belongs to the field of nondestructive detection. The laser ultrasonic online nondestructive material-increase manufacturing part detection method utilizes the change of laser excited ultrasonic surface wave amplitude to detect metallurgical defects produced during material-increase manufacturing process, a detection device is integrated with a high-energy beam generating device of a material-increase manufacturing device to achieve synchronous part defect detection in the material-increase manufacturing process, non-detection zones brought due to complicated shapes after part manufacturing is completed are avoided, and the reliability of material-increase manufacturing parts is improved. In addition, the detection process and the manufacturing process are combined so that follow-up detection time can be omitted, and the production efficiency of the whole material-increase manufacturing part production process can be improved.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
Laser ultrasonic detection method and laser ultrasonic detection system for rapidly locating defects
InactiveCN104634741AReduce data processingReduce processingOptically investigating flaws/contaminationGalvanometerLaser light
The invention relates to a laser ultrasonic detection method and a laser ultrasonic detection system for rapidly locating defects. The laser ultrasonic detection method comprises the following steps: a laser emits pulse laser light, and a galvanometer scanning system is adopted to act on a workpiece to be detected; an air coupling surface wave probe is arranged at the same side of the workpiece to be detected and is used for receiving a scattered signal generated by the defect of a detected part; a subarea where the defect is located in the detected part is judged according to the received scattered wave, and the defect area can be rapidly located; and the defect of the defect area can be accurately located along with gradual reduction of the defect area according to the ultrasonic propagation imaging principle. According to the method and the system, the defect can be rapidly located, the data processing load is small and the detection efficiency is high.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Laser Ultrasonic Determination Method of Metal Third-Order Elastic Constant
InactiveCN102297898AAvoid overheatingAvoid axial length changesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesCorrelation functionStressed state
The invention discloses a method for utilizing a laser ultrasonic wave to precisely measure a third order elastic constant of metal. The method comprises the following steps: respectively measuring wave velocities of a longitudinal wave, a transverse wave and a surface wave excited by a laser under stress-free state and stress state; utilizing the wave velocities of the longitudinal wave, the transverse wave and the surface wave measured under stress-free state to calculate a second order elastic constant and a density of metal according to a sonic elasticity theory and a Rayleigh equation; utilizing the ultrasonic wave velocities of the longitudinal wave, the transverse wave and the surface wave measured under stress state to introduce an equivalent second order elastic constant and an independently measured linear coefficient of thermal expansion; and lastly, calculating the third order elastic constant according to the sonic elasticity theory. According to the method, a pulse laser source is utilized to excite a sound surface wave, non-contact exciting is performed under a thermal elastic system and an overheated phenomenon of materials is avoided, so as to realize nondestructive measurement. A large amount of sound surface wave data spread for different distances is collected and a correlation function is utilized to calculate a wave velocity of the sound surface wave and a spread distance of sound wave, thereby greatly reducing error of arriving time value of the sound surface wave and promoting the measuring precision of a sound wave velocity.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Scanning type laser ultrasonic detection method and system
InactiveCN104345092ABreak through the shortcomings of being unable to carry out quantitative detectionShorten detection timeAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial defectSonification
The invention discloses a scanning type laser ultrasonic detection method and system. The scanning type laser ultrasonic detection method comprises the following steps: controlling a laser to generate pulse laser beams by using host computer software; performing two-dimensional scanning on a tested material in the horizontal X-Y axis direction by using a galvanometer scanning device; receiving generated longitudinal wave signals by using a longitudinal wave sensor centered at a testing block; amplifying the received longitudinal wave signals, acquiring the generated longitudinal wave signals by using a digital A / D acquisition card, and performing band-pass filtering on acquired ultrasonic signals by using the host computer software; and controlling a scanning moving mirror system to perform two-dimensional scanning imaging on the surface of the material by using a computer control circuit system, and rapidly performing opto-acoustic imaging on the longitudinal wave signals received in the two-dimensional scanning process according to the fact that primary longitudinal wave peak value signals indicating whether the surface of the material has crack defects or not reach the sensor at different moments, thereby achieving rapid quantitative imaging detection on the defects of the detected material. The scanning type laser ultrasonic detection method is small in computer processing data amount, and the material defects can be directly quantitatively detected in a longitudinal wave transmitted image.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Laser-ultrasonic detection of subsurface defects in processed metals
InactiveUS20070234809A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansSonificationSurface acoustic wave
Subsurface defects in a processed metal are detected by a laser-ultrasonic method involving generation of a surface acoustic wave at one location on the processed metal surface, and detection of a scattered acoustic wave at another location on the processed metal surface. The method can be used in-line to provide real time monitoring of laser cladding and other metal processing operations.
Owner:OPTECH VENTURES
Adaptive additive manufacturing process using in-situ laser ultrasonic testing
InactiveUS20170059529A1Additive manufacturing apparatusAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesManufacturing technologyLaser heating
An additive manufacturing process, including: selectively-heating a layer of powder (18) to form a solid deposit layer (10) having a solid deposit (28), where the solid deposit layer constitutes part (24) of a component, via a selective laser heating process; propagating ultrasonic energy waves (50, 60) through the solid deposit prior to completion of the component by using a wave generating laser (40) set apart from a surface (44) of the solid deposit to direct a wave-generating laser beam (42) at the surface; detecting propagated ultrasonic energy waves (62); assessing the propagated ultrasonic waves for information about a physical characteristic of the solid deposit; and forming another solid deposit layer (80) in response to the information obtained about the solid deposit.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
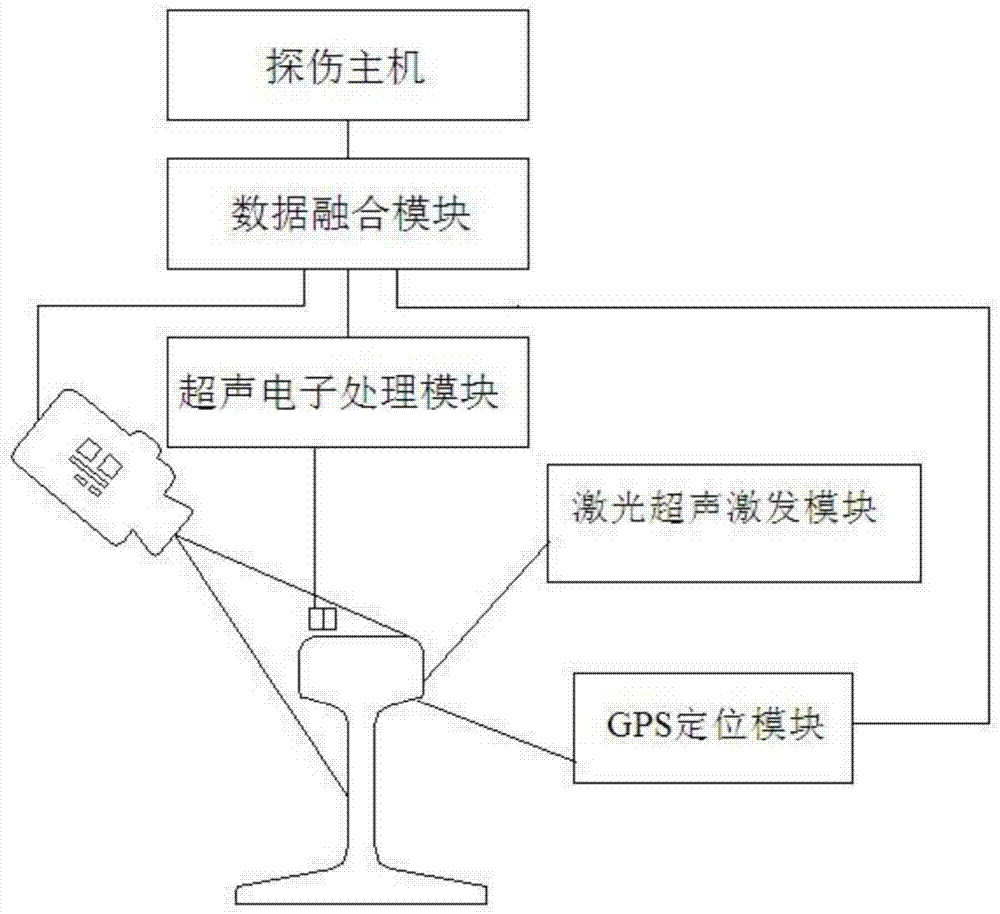
Steel rail flaw-detection method based on laser ultrasonic and high-speed photography image fusion
InactiveCN104237381AEfficient integrationAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesOptically investigating flaws/contaminationMetallurgyDigital image
The invention relates to the field of steel rail flaw-detection, in particular to a steel rail flaw-detection method based on laser ultrasonic and high-speed photography image fusion. The steel rail flaw-detection method comprises the following steps that: step 1, a laser ultrasonic excitation module and a high-speed photography module are installed on a steel rail flaw-detection car; step 2, the steel rail flaw-detection car moves along a steel rail to be detected, meanwhile, the laser ultrasonic excitation module transmits a pulse laser to the surface of the steel rail to be detected, so as to obtain laser ultrasonic detection data; moreover, the high-speed photography module photographs the surface of the steel rail to be detected to obtain digital image signal data; step 3, the laser ultrasonic detection data and the digital image signal data are fused together, and the flaw conditions of the steel rail to be detected are judged. The invention provides a flaw-detection method for obtaining the state of the actually-flawed surface of the steel rail and position information while carrying out flaw-detection on the steel rail, thus realizing the effective fusion of the laser ultrasonic detection data and the digital image signal data.
Owner:BEIJING SHEENLINE GRP CO LTD
Laser-ultrasound inspection using infrared thermography
InactiveUS7605924B2Complete understandingUnderstanding of internal structureMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis by optical meansThermographic inspectionLaser
An inspection system is provided to examine internal structures of a target material. This inspection system combines an ultrasonic inspection system and a thermographic inspection system. The thermographic inspection system is attached to ultrasonic inspection and modified to enable thermographic inspection of target materials at distances compatible with laser ultrasonic inspection. Quantitative information is obtained using depth infrared (IR) imaging on the target material. The IR imaging and laser-ultrasound results are combined and projected on a 3D projection of complex shape composites. The thermographic results complement the laser-ultrasound results and yield information about the target material's internal structure that is more complete and more reliable, especially when the target materials are thin composite parts.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Articulated robot for laser ultrasonic inspection
ActiveUS7784348B2Cost-effectiveMore compact robotsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesLaser using scattering effectsNon destructiveUltrasound sonography
An ultrasonic non-destructive evaluation (NDE) system operable to inspect target materials is provided. This ultrasonic NDE system includes an articulated robot, an ultrasound inspection head, a processing module, and a control module. The ultrasound inspection head couples to or mounts on the articulated robot. The ultrasound inspection head is operable to deliver a generation laser beam, a detection laser beam, and collect phase modulated light scattered by the target materials. The processing module processes the phase modulated light and produces information about the internal structure of the target materials. The control module directs the articulated robot to position the ultrasound inspection head according to a pre-determined scan plan.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Full-optical laser ultrasonic measuring method for internal defect of material
InactiveCN103808802AAvoid meltingRealize non-destructive testingAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesNon destructiveNondestructive testing
The invention discloses a full-optical laser ultrasonic measuring method for internal defects of a material. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, measuring the two-dimensional position and the size of the internal defect of a measured object on an x-y plane, and subsequently measuring the depth of the internal defect of the measured object in the z direction. By adopting the method, the three-dimensional position and the size information of the internal defect can be obtained by scanning, and the method is high in precision and efficiency, and is applicable to non-destructive detection on various materials.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
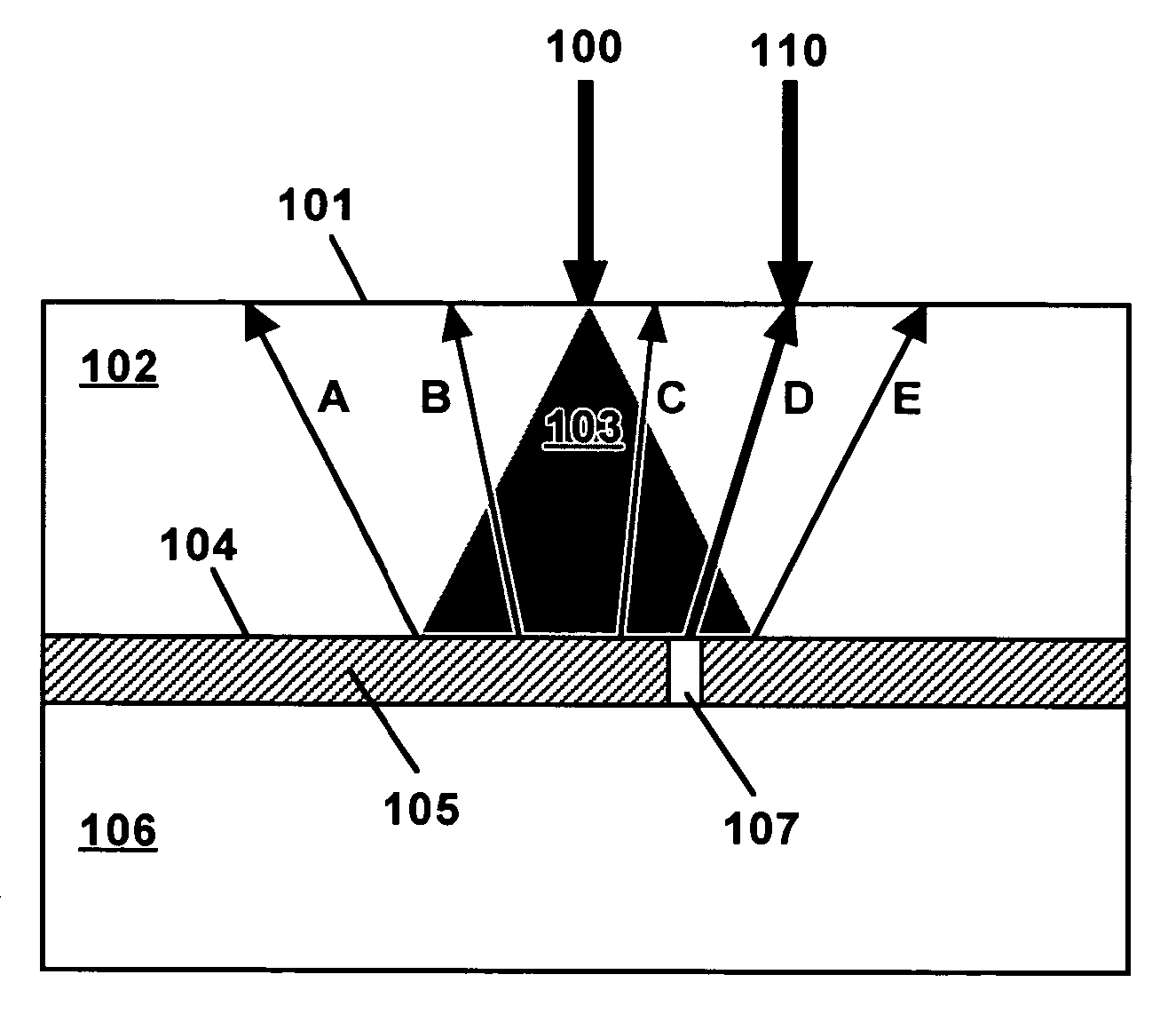
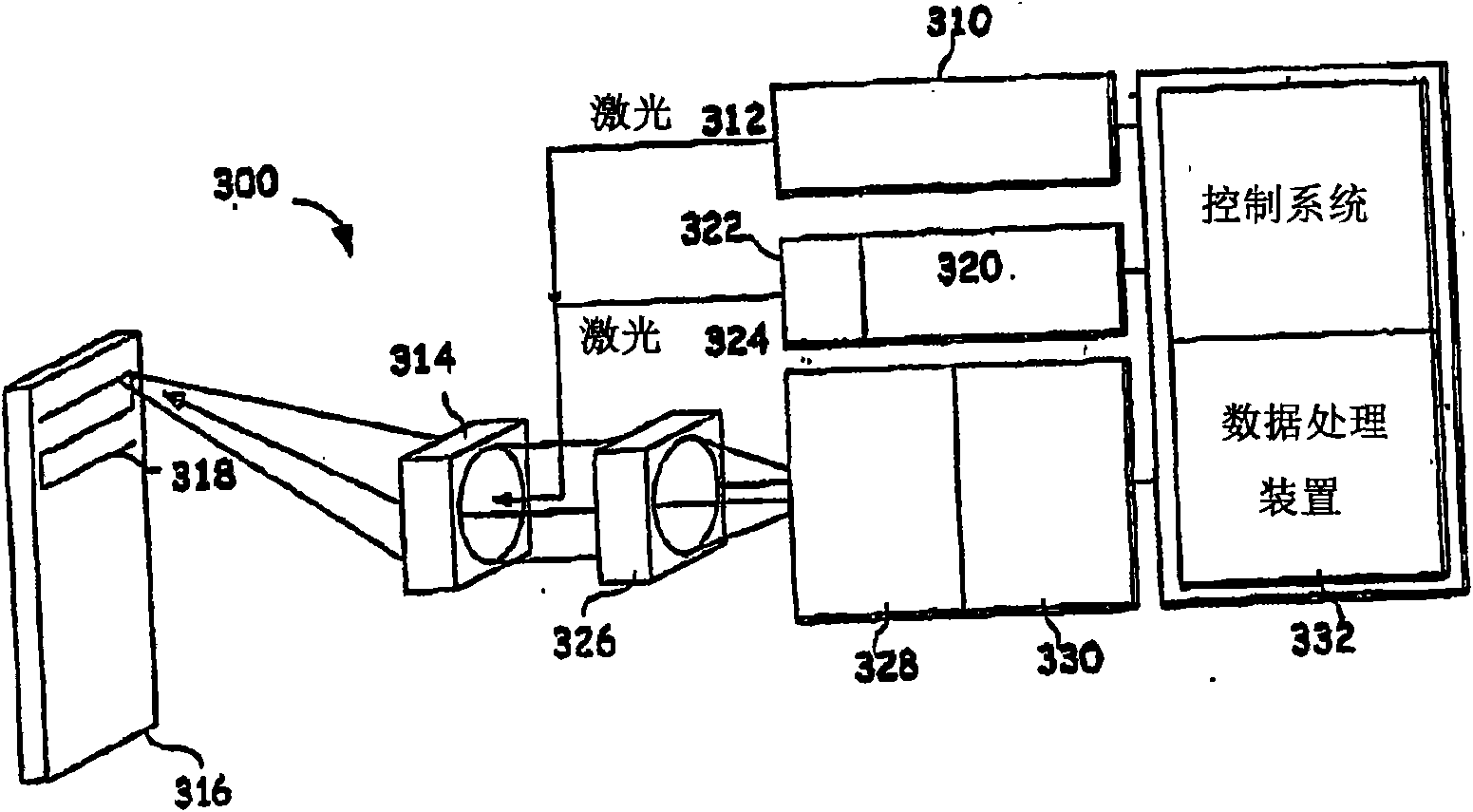
Laser-ultrasonic detection of flip chip attachment defects
InactiveUS20060021438A1Improve directivityIncrease intensityVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesLaser detectionLaser beams
Underfill voids and solder ball defects are detected via laser generation and laser detection of an ultrasonic wave at the top surface of flip chips. High resolution is provided by using small laser spot sizes and closely-spaced laser beams of wavelengths that are absorbed near the surface of the semiconductor. Alternatively, the generation laser beam may be absorbed in the bulk of the semiconductor. Improved spatial resolution and rejection of unwanted scattered waves can be attained by limiting the time frame of the ultrasonic waveform to the time required for the first longitudinal wave reflection from the bottom of the flip chip. The laser beam spacing can be reduced by using overlapping probe and detection beams of different wavelengths. Resolution of less than 100 μm features was demonstrated for silicon flip chips.
Owner:OPTECH VENTURES +1
Laser ultrasonic thickness measuring method and laser ultrasonic thickness measuring device capable of being used for field detection
ActiveCN102506781AAvoid conditional situationsLow costUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a laser ultrasonic thickness measuring method and a laser ultrasonic thickness measuring device capable of being used for field detection. The laser ultrasonic thickness measuring method is characterized in that a laser beam is sent out by a laser to excite an ultrasonic wave on the surface in a specific position of a measured object; meanwhile, an excited wave signal and an echo wave signal produced on the surface in the position are received by an air coupling sensor on the same side of the measured object as the laser; and the propagation distance of the ultrasonic wave is calculated according to the time difference between the excited wave signal and the echo wave signal, and a longitudinal wave propagation velocity of the measured object, so that thickness measurement of the specific position is realized. The device mainly comprises the laser, a main supporting seat, the air coupling sensor, a supporting rod, a centering device, a signal processing system and a display system. The device has a simple and light structure, and can meet the requirements of field detection; and through the adoption of the non-contact type detection method, the thicknesses of high temperature and high-corrosive measured objects can be measured.
Owner:启东市荣宇机械有限公司
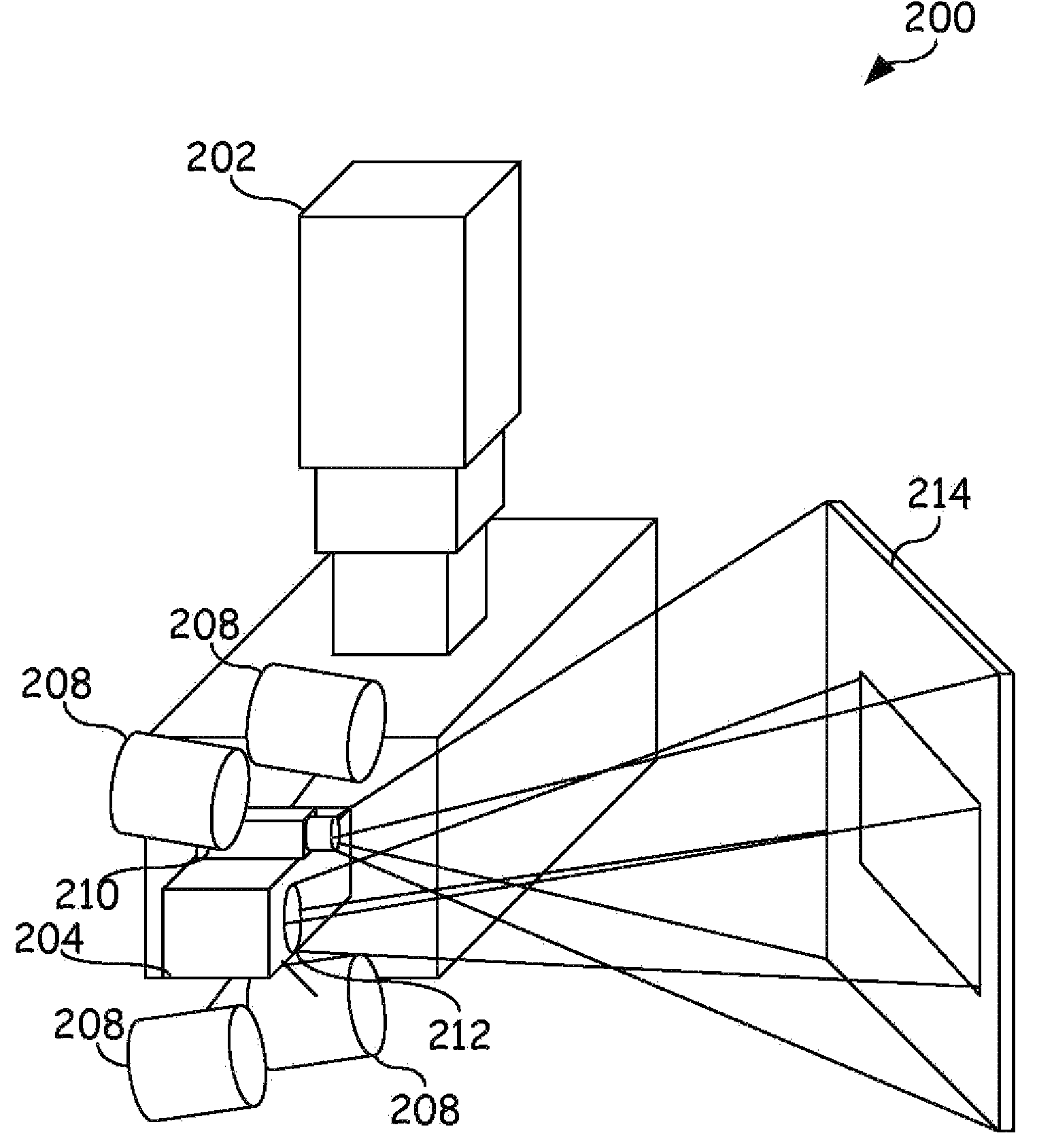
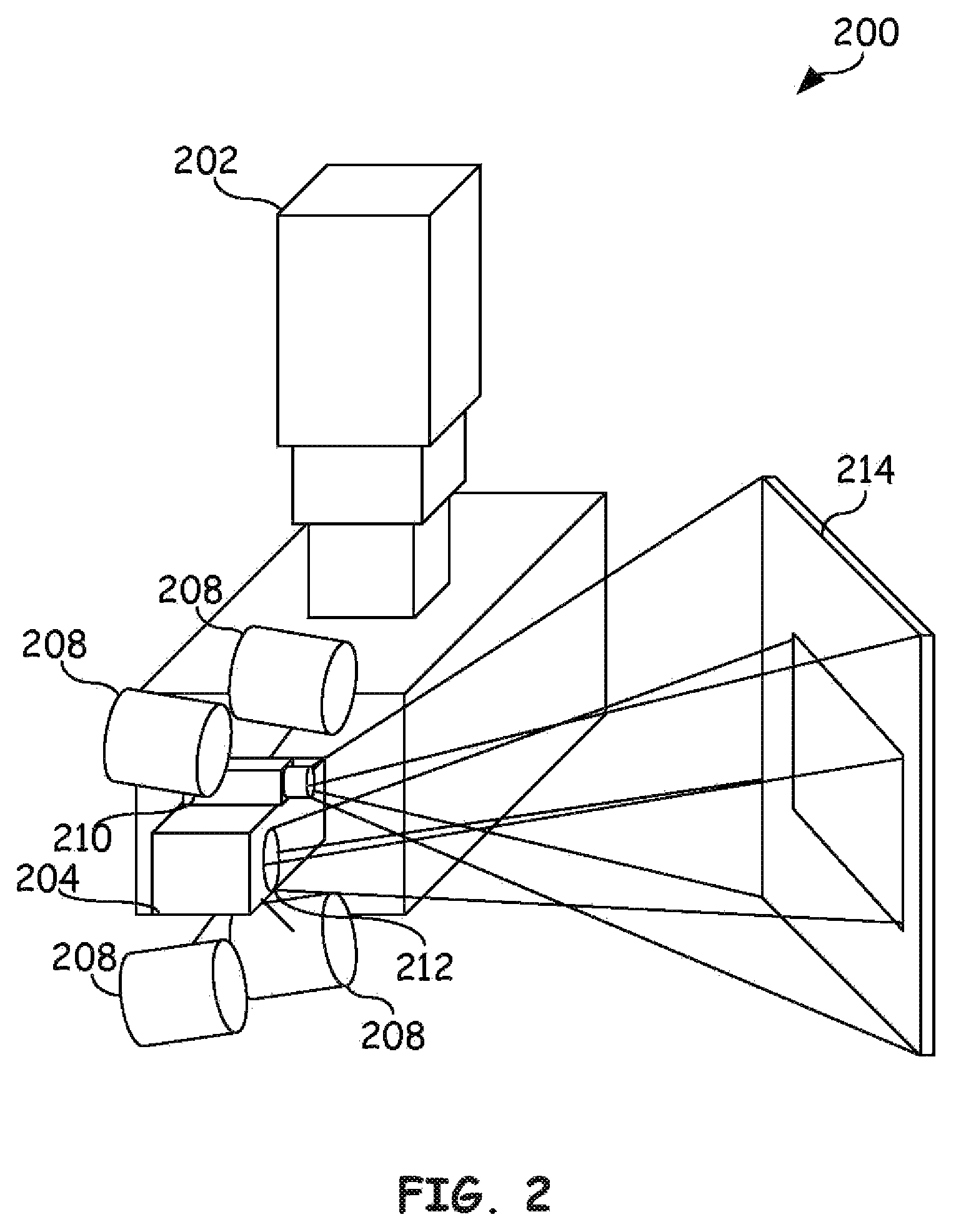
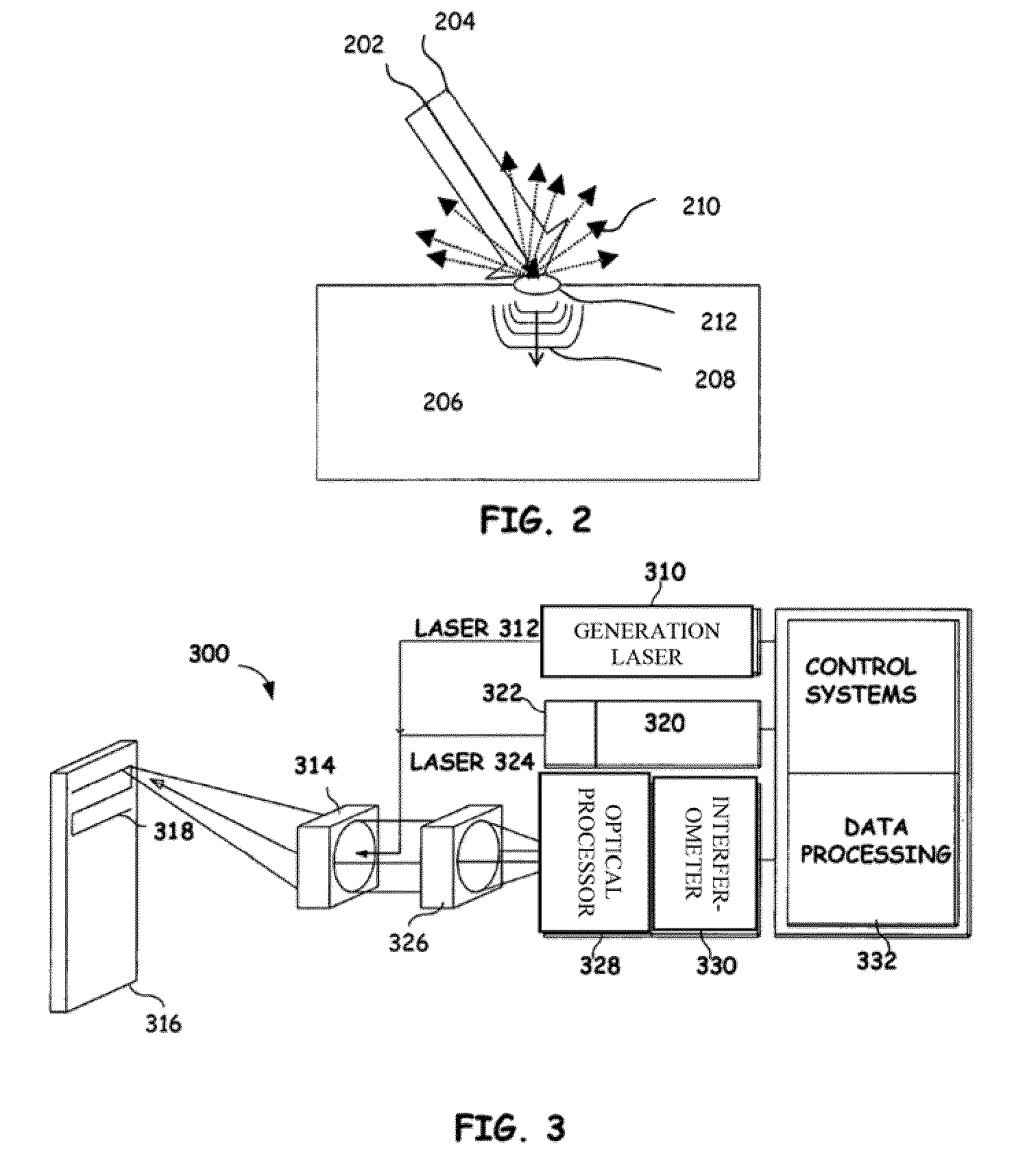
System and method to calibrate multiple sensors
ActiveUS20060219014A1Shorten the timeImprove accuracyAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesInvestigating composite materialsSonificationMultiple sensor
The present invention provides a multi-mode calibration target operable to calibrate multiple optical sensors. One embodiment has multiple planar surfaces, wherein the multiple planar surfaces are able to be distinguished by visual sensors based on their color, hue, shade, tint, or tone. Additionally, these planar surfaces may be raised or recessed from one another to provide depth contrast as well as visual contrast. Other embodiments may include narrow band emitters such as laser diodes located at predetermined locations within the multi-mode target. These targets may then be used to calibrate various sensors, such as optical sensors, within an inspection system such as a laser ultrasonic inspection system.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
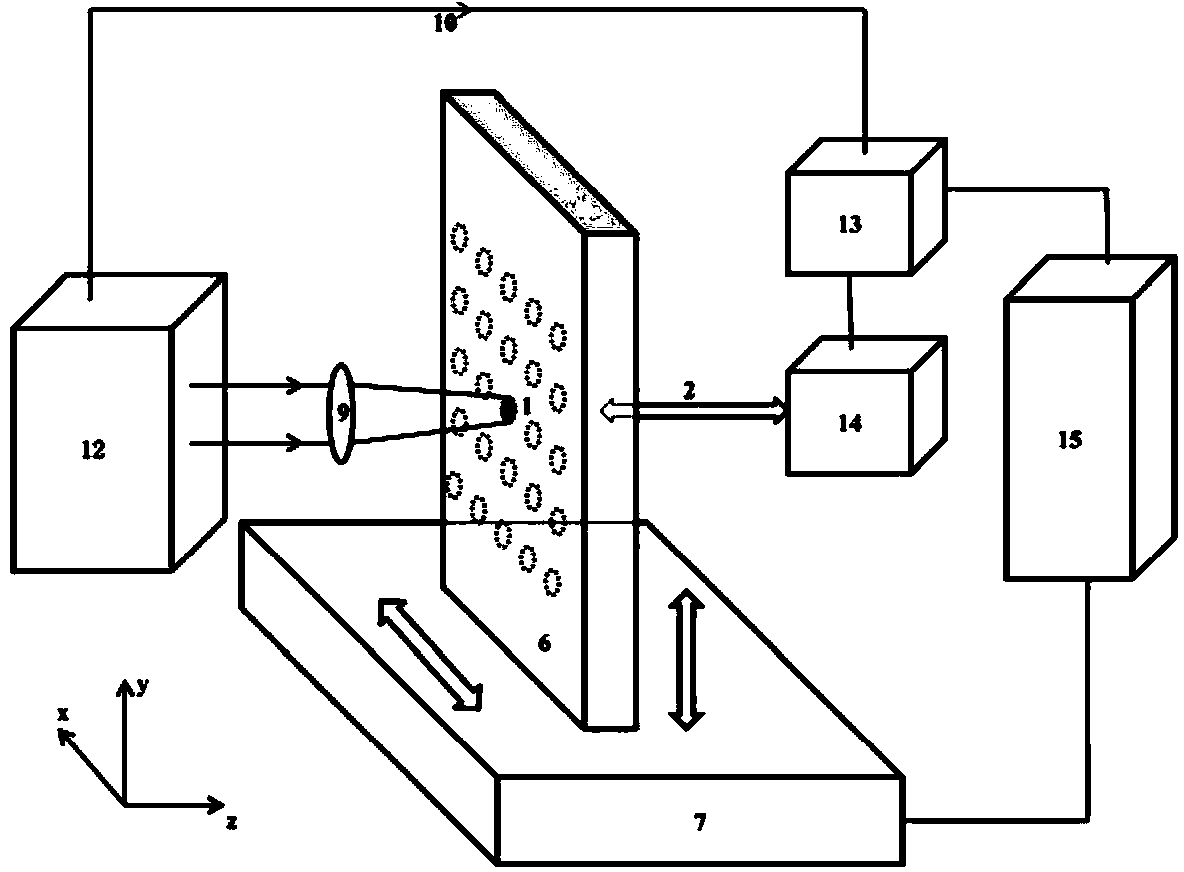
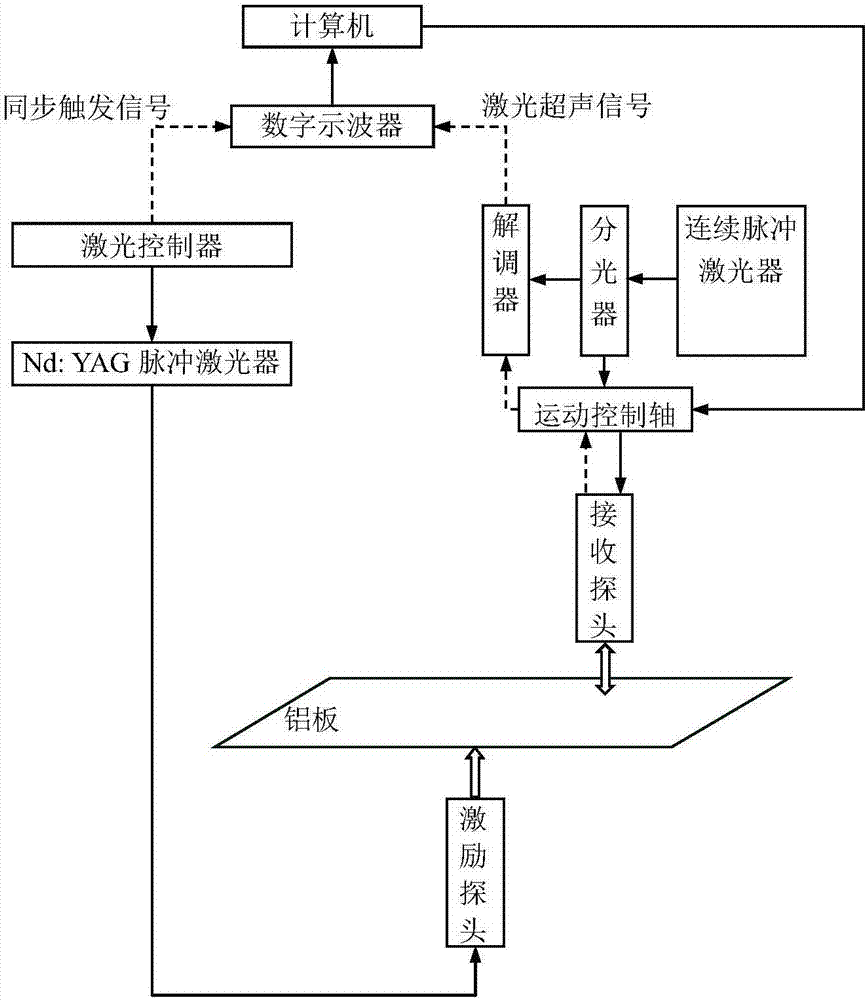
Laser ultrasonic detection device
InactiveCN102735615AEfficient detectionThe test result is accurateMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis by optical meansData processing systemProcess systems
The invention relates to a laser ultrasonic detection device and belongs to the technical field of laser ultrasonic detection. The device is composed of a crawling trolley, an optical fiber and an external control console, wherein the crawling trolley comprises a rotational scanning head, rolling wheels and stretching supporting bars, a box body and a fiber interface. A laser ultrasonic excitation source, a laser interference detection system and a data process system can be carried on the crawling trolley. Ultrasound is excited to generate on detected surfaces by lasers led into the trolley by the optical fiber or emitted by the laser ultrasonic excitation source carried on the crawling trolley. Ultrasonic signals are detected by the laser interference detection system carried on the crawling trolley and data are transmitted to the external control console for display by the data process system. The external control console is capable of monitoring the states of the trolley and controlling the trolley to conduct detection. The device of the invention is capable of conducting laser ultrasonic detection to pipelines on the problems of inwall surface damages, defects inside pipeline walls and the like. The device also has fast surface-scanning speed and high detection efficiency and is very practical.
Owner:ACAD OF OPTO ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Sheet material thickness online detection and adjustment system based on laser ultrasonic
ActiveCN104707871ARealize non-contact measurementMeasuring Thickness UniformityRoll mill control devicesMeasuring devicesProcess systemsBipolar signal
A sheet material thickness online detection and adjustment system based on laser ultrasonic comprises a sheet material rolling mechanism and a sheet material thickness online detection mechanism. The sheet material rolling mechanism comprises an upper roller, a lower roller, an upper-lower roller interval adjust mechanism and a PLC control system, the sheet material thickness online detection mechanism comprises an optics system assembly, a high temperature testing meter, a data collection system assembly and a data process system assembly, the data process system assembly transforms bipolar signals which are aliased in peak values and complex in background noise into unipolar signals which are clear in peak values and low in background noise, so that the time that longitudinal wave and transverse wave reach the center of the bottom surface of the sheet material for the first two times is obtained, and thereby the sheet material thickness value is calculated, the measured sheet material thickness value is compared with a preset sheet material thickness value in the PLC control system, the PLC control system transmits forward rotating / backward rotation movement commands to a servo motor, so that the interval between the upper roller and the lower roller is adjusted, and the sheet material thickness value is made to be consistent with the preset sheet material thickness value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
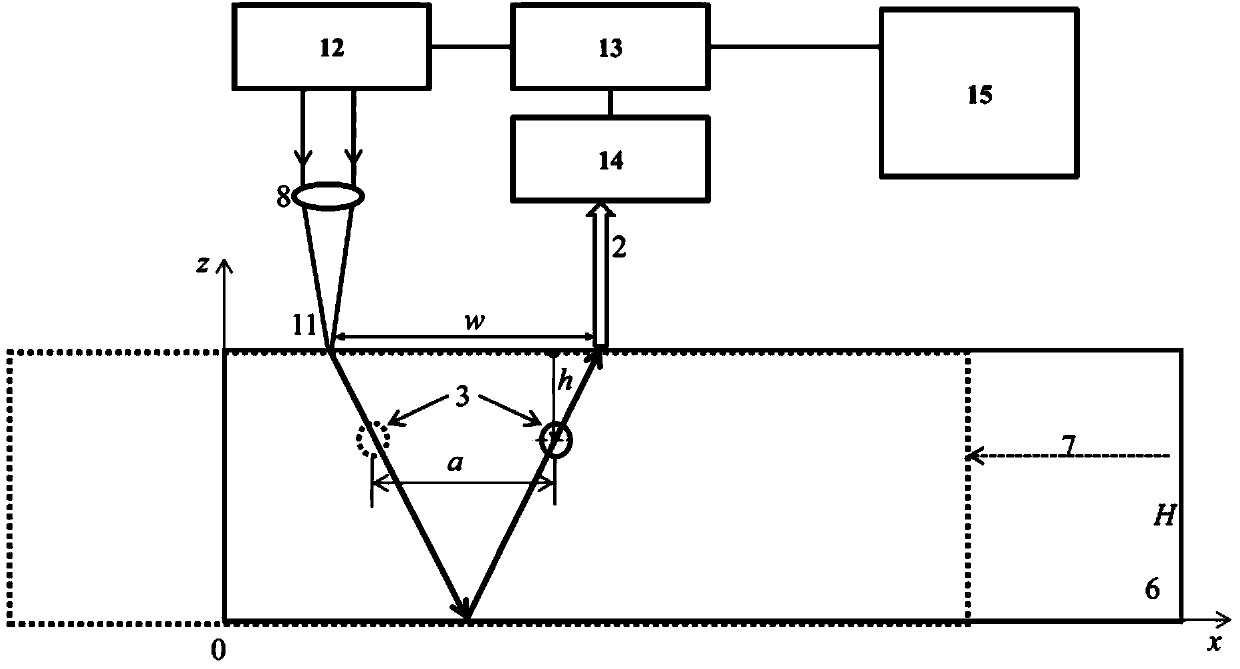
Rapid detection method and detection device for detecting diseases in tunnel
The invention relates to a rapid detection method and a detection device for detecting diseases in a tunnel. The detection method comprises the steps of: detecting the lining thickness and a back cavity through an acoustic emission and laser vibration measurement technology; detecting the lining strength and compactness through the laser ultrasonic technology; detecting underground water behind the lining by utilizing an infrared temperature detection technology; detecting the degradation degree of surrounding rock behind the lining by using a laser scanning and inversion technology; and determining the position of the disease by using inertial navigation and image registration technologies. The detection device for detecting diseases in the tunnel comprises an acoustic emission and laservibration measurement module, a laser ultrasonic module, an infrared temperature detection module, a surrounding rock parameter inversion module and the like. The device runs once in the tunnel to obtain the disease features such as lining thickness and the cavity at the back of the lining, the underwater, weakening degree, the concrete degree and the compactness of surrounding rock, and comparedwith the existing inspection technology, the rapid detection method and a detection device have the advantages that the detection efficiency and the identification precision are greatly improved, thedisease positioning is more accurate, and the influence on the normal traffic driving is obviously reduced.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV +1
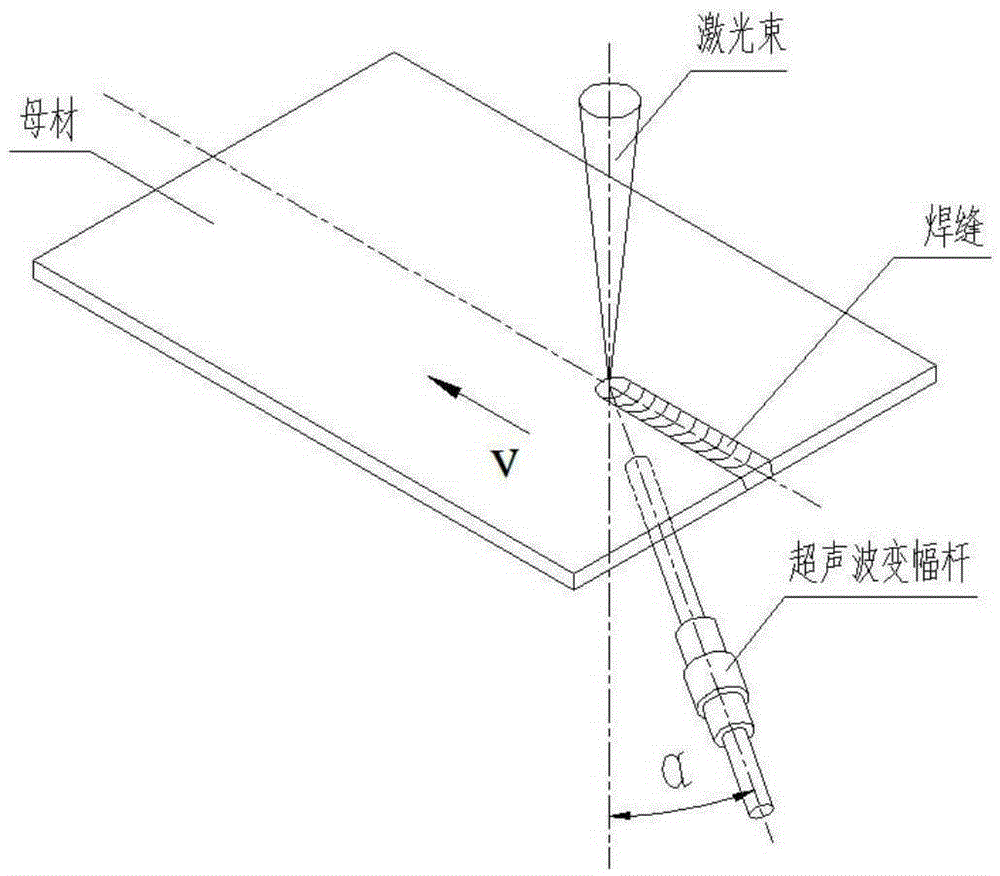
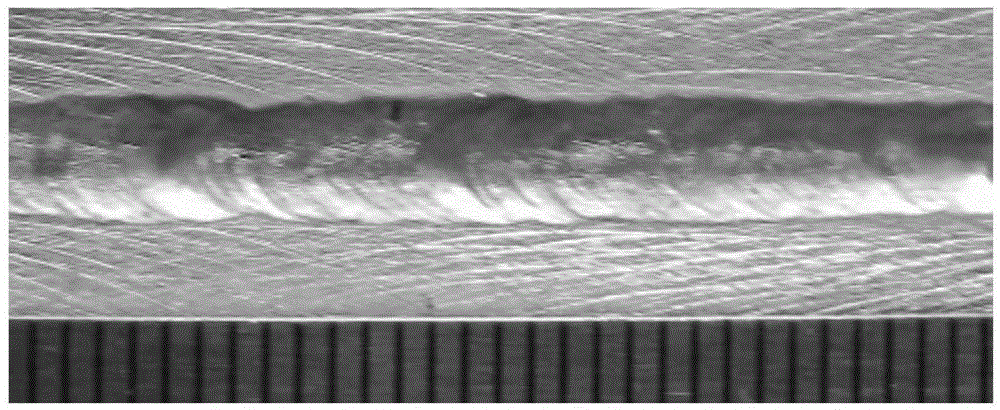
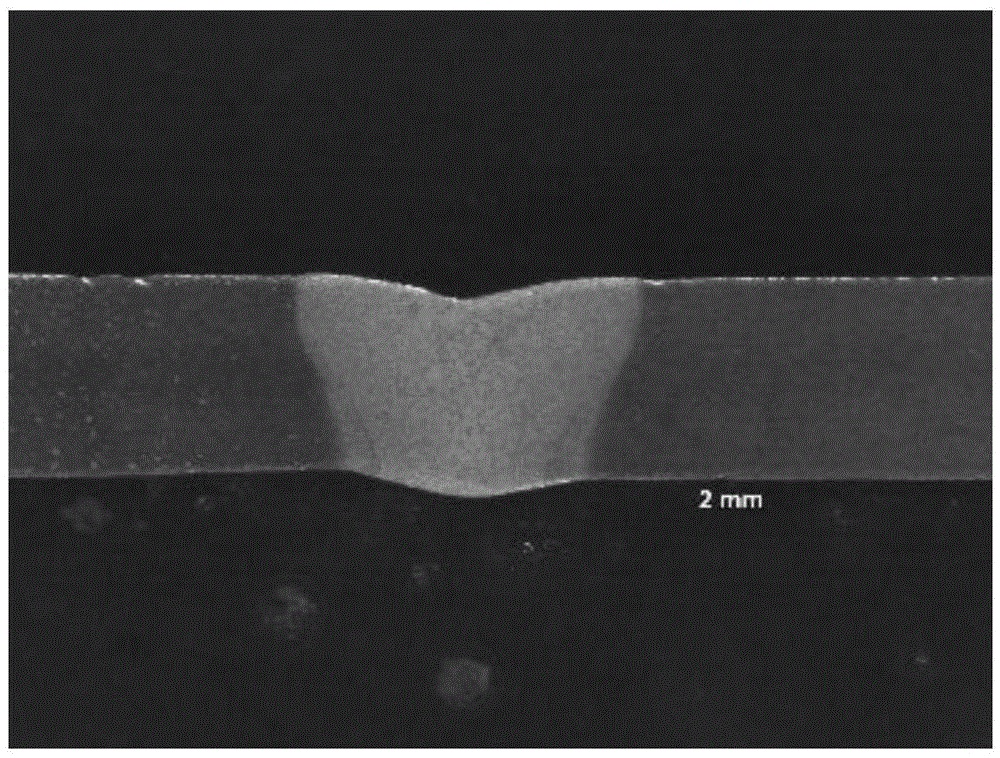
Magnesium alloy laser-ultrasonic double-side welding method
The invention discloses a magnesium alloy laser-ultrasonic double-side welding method and relates to a double-side welding method. The laser-ultrasonic double-side welding method comprises the following steps: firstly, cleaning and clamping a to-be-welded workpiece, setting the ultrasonic and laser position, further setting related processing parameters to carry out welding; compared with a conventional argon tungsten-arc welding (TIG welding) method, the laser-ultrasonic double-side welding method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the welding speed is higher, the magnesium alloy welding efficiency is improved, deficiencies like pores, slag inclusion and hot cracks which are easily produced in welding joints, as well as incomplete penetration are reduced, so that the welding joint can meet the using requirements; compared with the one side ultrasonic assisted laser welding method, the laser-ultrasonic double-side welding method disclosed by the invention further has the advantages that the temperature gradient in the molten pool is smaller under the actions of the heat sources, namely laser and ultrasonic, due to the fact that the ultrasonic wave is applied onto the back surface of a welding seam, the welding deformation and the thermal stress produced during the welding process are smaller, the tendency that the welding joint produces hot cracks within a brittle temperature range is effectively reduced, and the mechanical property of the welding seam is further improved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Metal plate defect location method based on laser Lamb wave frequency-wave number analysis
The invention discloses a metal plate defect location method based on laser Lamb wave frequency-wave number analysis and belongs to the field of laser ultrasonic non-destructive testing. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, excitation is performed by a laser excitation probe in a fixed position on a metal plate, a laser receiving probe scans defect lines to receive N groups of Lamb wave data, and a time-space wave field on a scanning path is obtained; secondly, signals under specific center frequency are extracted from the acquired N groups of Lamb wave data with a continuous wavelet transform method, and analyzability of a defect location result is guaranteed; finally, the extracted wave field signals are subjected to space-frequency-wave number imaging with short-space two-dimensional Fourier transform algorithm, and defect location is realized according to characteristics of a wave number spectrum on the scanning path. One completely non-contact type detection method is provided, and action rules between Lamb waves and defects in the wave number field are disclosed.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Multi-channel parallel laser ultrasonic detection system
InactiveCN102735614ASolve the problem of inconsistent ultrasound intensityDetection speedMaterial analysis by optical meansPrismHalf wave
The invention relates to a laser ultrasonic detection apparatus, belonging to the technical field of laser ultrasonic detection. The apparatus comprises a detection laser source, a front light-splitting structure, a collecting structure, a double-photorefractive lens, (a) polaroid(s), (a) detector(s), a half-wave plate, a front polarization splitting prism, an acoustic-optical modulator, a back polarization splitting prism, a back light-splitting structure, a detected piece, a laser ultrasonic excitation source, a beam-expanding structure, a bidirectional tunable aperture and a focusing mirror. The apparatus is capable of carrying out wide-range laser ultrasonic detections and the speed of the laser ultrasonic detection can be greatly raised. A linear ultrasonic excitation source is adopted to carrying out the excitation, enabling ultrasonic fields of each monitoring point to have the same distribution, and thus solving the problem that the ultrasonic intensity at each collecting point is inconsistent with each other when circular laser spots are adopted to excite the ultrasound. The apparatus has fast surface-scanning speed and high detection efficiency, and is very practical.
Owner:ACAD OF OPTO ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Residual stress nondestructive testing system and method based on transient grating laser ultrasonic surface wave
ActiveCN108871640AHigh sensitivityImprove spatial resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansApparatus for force/torque/work measurementBeam splitterFourier transform on finite groups
The present invention discloses a residual stress nondestructive testing system and method based on a transient grating laser ultrasonic surface wave. A laser beam generated by a pulse laser passes through a phase grating beam splitter and an imaging lens to form two laser sub-beams which intersect at a certain angle and irradiate the surface of a test sample to generate interference fringes witha fixed cycle [Lambda], and two coherent surface waves with wavelengths of [Lambda] propagated at two opposite directions are excited at the surface of the test sample under the action of the cycle hot elastic force; a laser interferometer is employed to receive generated surface wave signals generated at the excitation position to perform Fourier transform of the received signals to obtain a center frequency f, and a propagation velocity c of the surface wave of the detected position is calculated according to a formula of c=f*[Lambda]; and finally, a relative change amount of the wave speedof the surface wave is finally obtained in a condition of different stresses relative to the wave speed of the surface wave in a condition without stress to obtain a linear relation between the relative change amount of the wave speed of the surface wave and the stresses, and based on the linear relation, the wave speed of the surface wave propagated at the test sample surface in an unknown stressstate is measured through the method mentioned above to determine the magnitude of the stresses of the test sample surface.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Articulated robot for laser ultrasonic inspection
InactiveCN101680860AEasy to useCost-effective efficiencyProgramme-controlled manipulatorMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesNon destructiveLaser beams
An ultrasonic non-destructive evaluation (NDE) system operable to inspect target materials is provided. This ultrasonic NDE system includes an articulated robot, an ultrasound inspection head, a processing module, and a control module. The ultrasound inspection head couples to or mounts on the articulated robot. The ultrasound inspection head is operable to deliver a generation laser beam, a detection laser beam, and collect phase modulated light scattered by the target materials. The processing module processes the phase modulated light and produces information about the internal structure ofthe target materials. The control module directs the articulated robot to position the ultrasound inspection head according to a predetermined scan plan.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
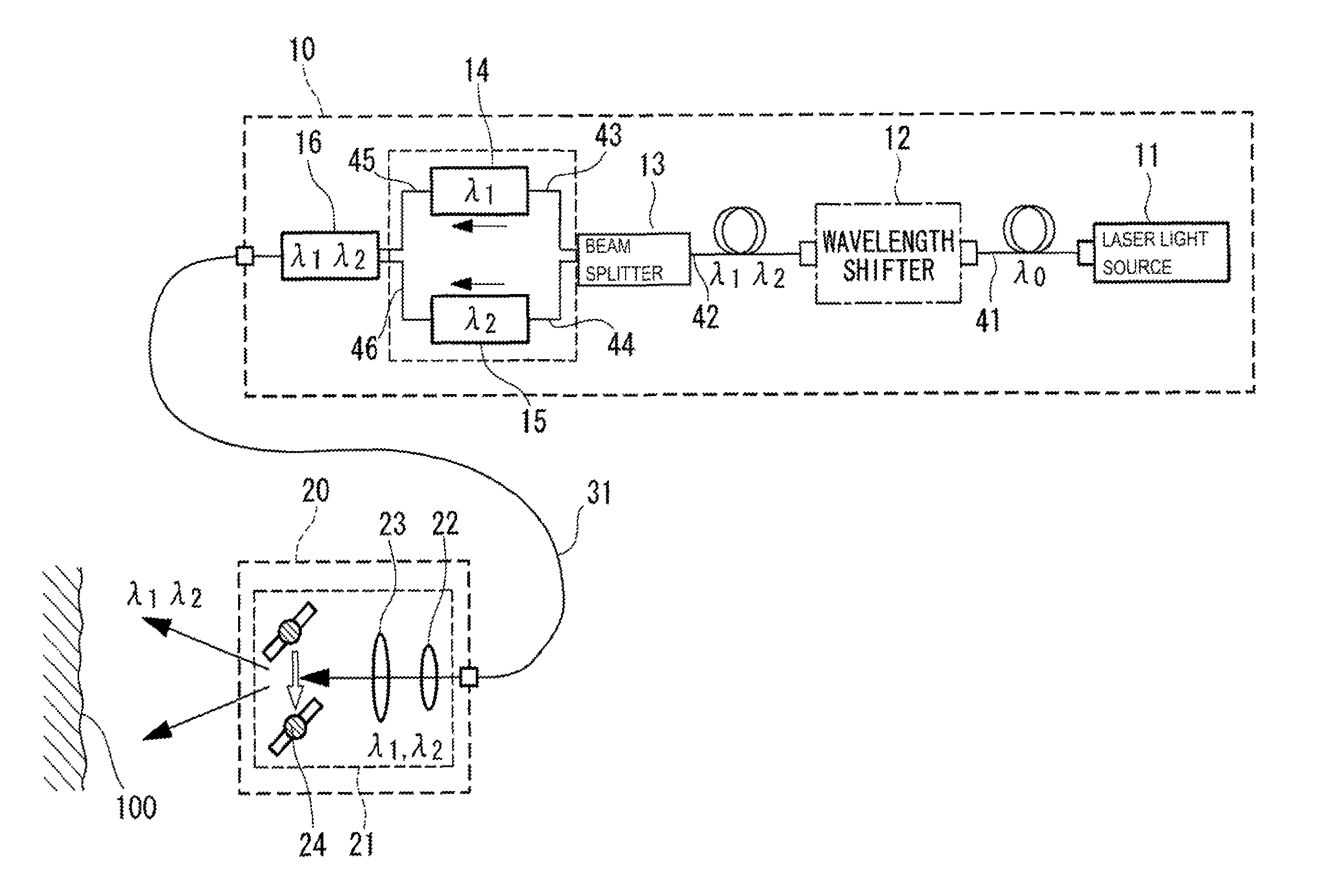
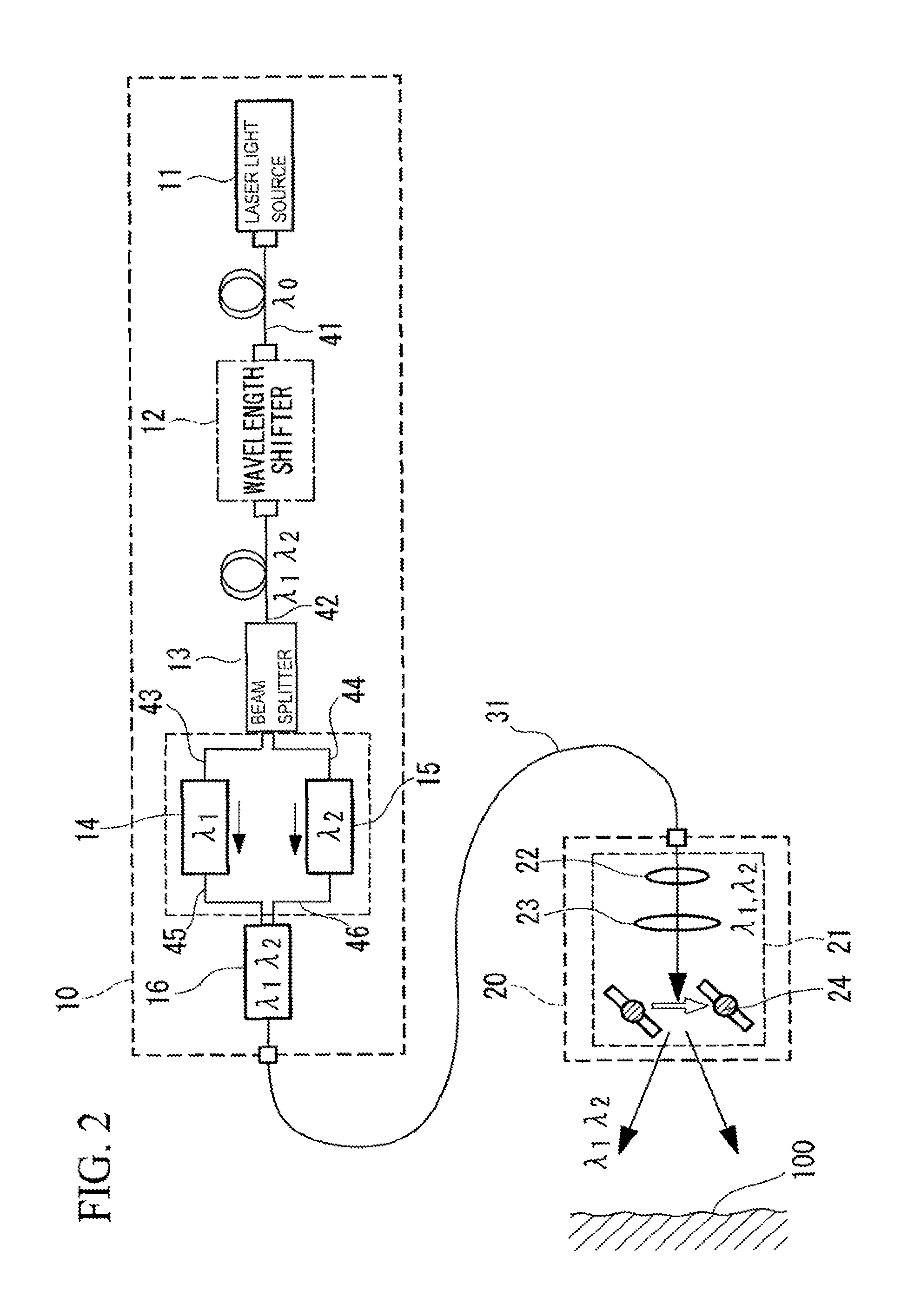
Laser ultrasonic flaw detection apparatus
ActiveUS8978478B2Easy to handleSimple configurationAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPhase-affecting property measurementsBeam splitterLaser light
A laser beam having a single wavelength emitted from a laser light source is converted at a wavelength shifter into a laser beam having at least two wavelengths, which is further demultiplexed at a beam splitter into a laser beam having a first wavelength and a laser beam having a second wavelength. The output power and pulse width of the laser beam having the first wavelength are adjusted by a first controller so as to reach levels appropriate for generating ultrasonic vibrations without causing damage to an inspection object. The output power and pulse width of the laser beam having the second wavelength are adjusted by a second controller so as to reach appropriate levels for detecting the above-described ultrasonic vibrations. These laser beams are multiplexed by a multiplexer into a single laser beam to be focused onto a surface of the inspection object.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Laser ultrasonic detection device and additive manufacturing and detection integrated equipment
PendingCN109387568AImprove defect detection performanceAdjust the step size in real timeAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAdditive layer manufacturingLaser
The invention relates to a laser ultrasonic detection device and additive manufacturing and detection integrated equipment. The laser ultrasonic detection device comprises a laser ultrasonic detectionprobe, an excited laser and a laser ultrasonic receiver, wherein the laser ultrasonic detection probe comprises a casing, a focusing probe arranged in the casing, a reflector, a receiving probe, a first lens, a second lens and an infrared thermometer. The temperature of workpieces is detected by the infrared thermometer in real time while defects are detected by ultrasonic waves, so that the defect detection accuracy is improved substantially. Meanwhile, the laser ultrasonic detection device cooperates with an industrial robot, a welding robot and a welding gun to realize independent operation of detection and additive manufacturing, and mutual interference is avoided.
Owner:NAT INST CORP OF ADDITIVE MFG XIAN
Device and method for measuring residual stress on surface of work piece based on laser ultrasonic
InactiveCN108168747AQuickly obtain residual stress distributionLow costForce measurementApparatus for force/torque/work measurementElectricityStress distribution
The invention discloses a device and a method for measuring the residual stress on the surface of a work piece based on laser ultrasonic. The method comprises the following steps: (1) placing a to-be-measured work piece under a vibrating mirror, and placing a piezoelectric sensor on the surface of the work piece and connecting the piezoelectric sensor to an oscilloscope; (2) using pulse laser to excite a surface wave on the surface of the work piece after the pulse laser is focused by the vibrating mirror, obtaining a surface wave signal R1 through the piezoelectric sensor, and obtaining the arrival time t1 of the surface wave; (3) making the pulse laser move longitudinally through scanning by the vibrating mirror, and repeating the step (2) to obtain a surface wave signal and obtain the arrival time of the surface wave; (4) obtaining the surface wave velocity distribution of the work piece on the longitudinal movement line through calculation; (5) laterally moving the piezoelectric sensor along the surface of the work piece, and after each lateral movement, repeating the steps (2)-(4) to obtain the surface wave velocity distribution of the surface of the work piece on different longitudinal movement lines; and (6) calculating the distribution of residual stress on the surface of the work piece according to the theory of acoustic elasticity and the surface wave velocity distribution. The residual stress on the surface of a work piece can be detected rapidly and nondestructively.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com