Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
345 results about "Articulated robot" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
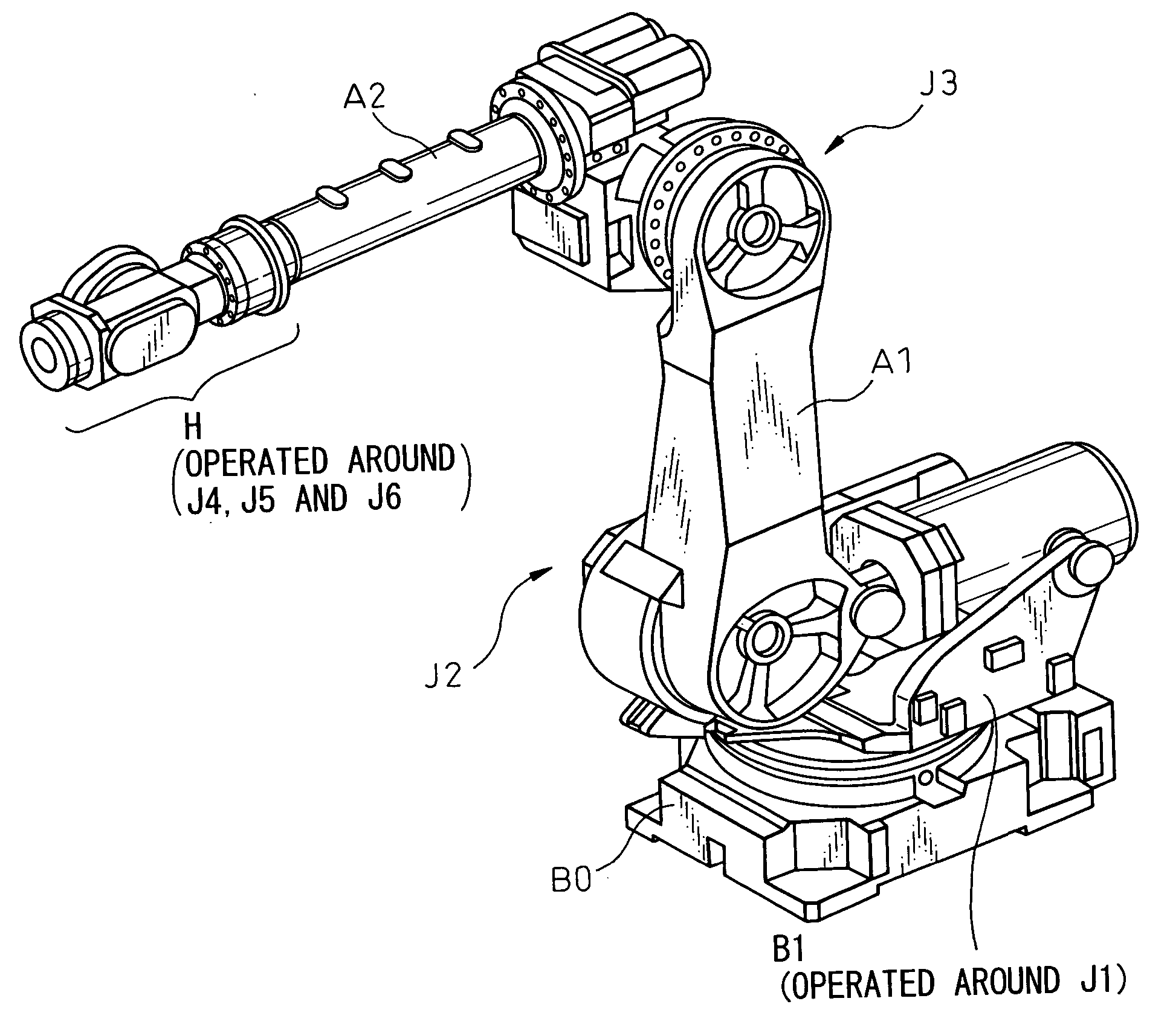
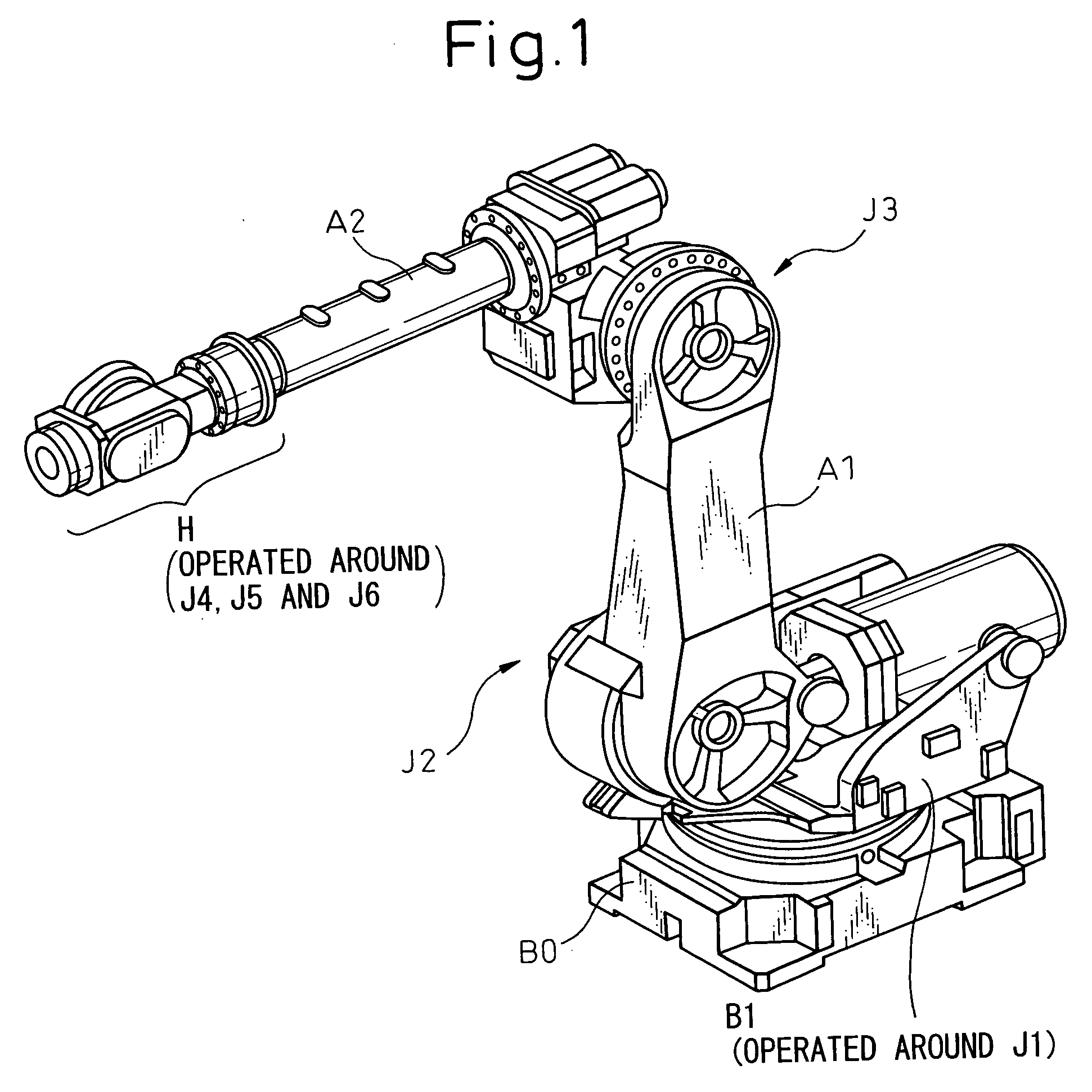
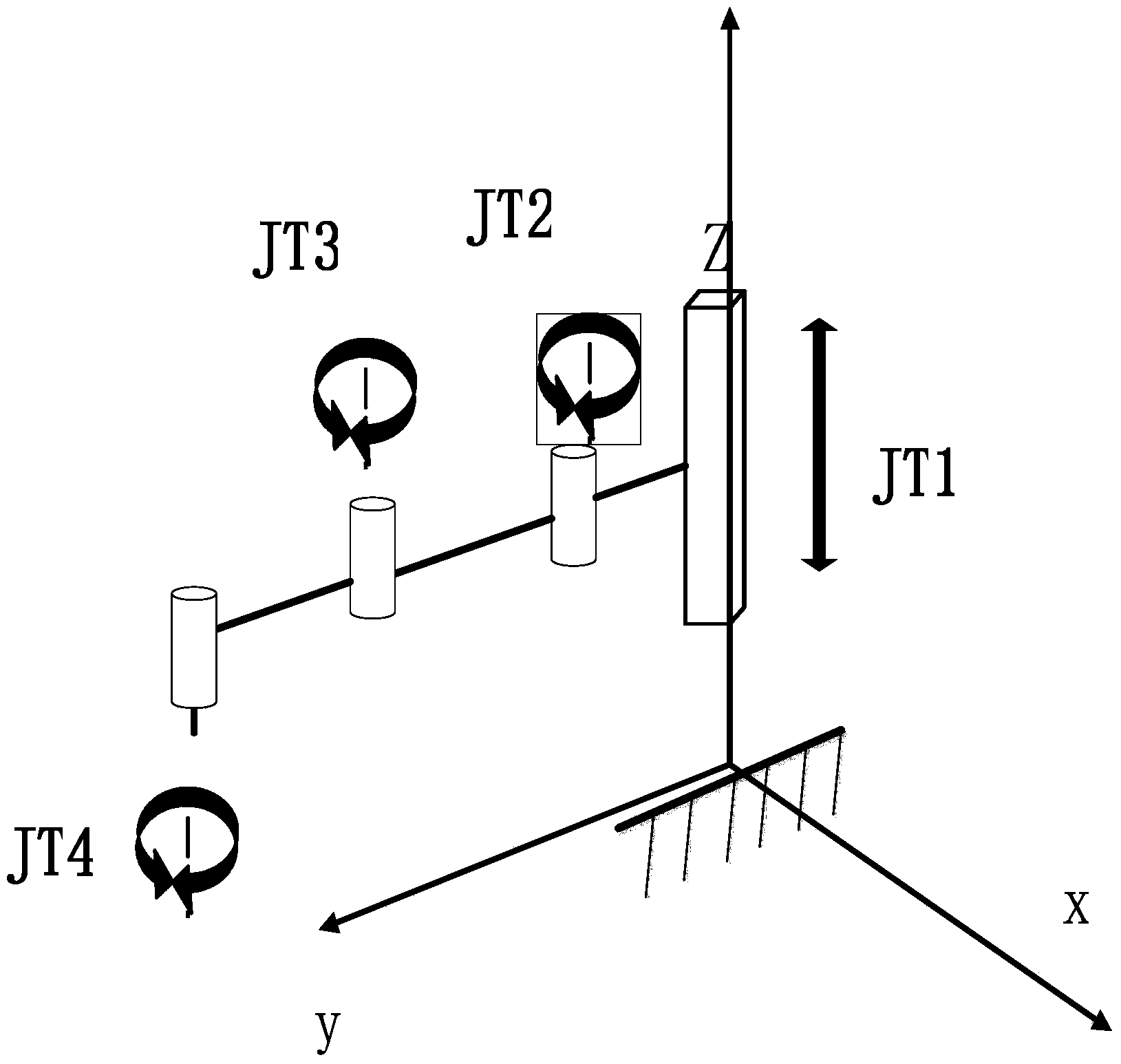
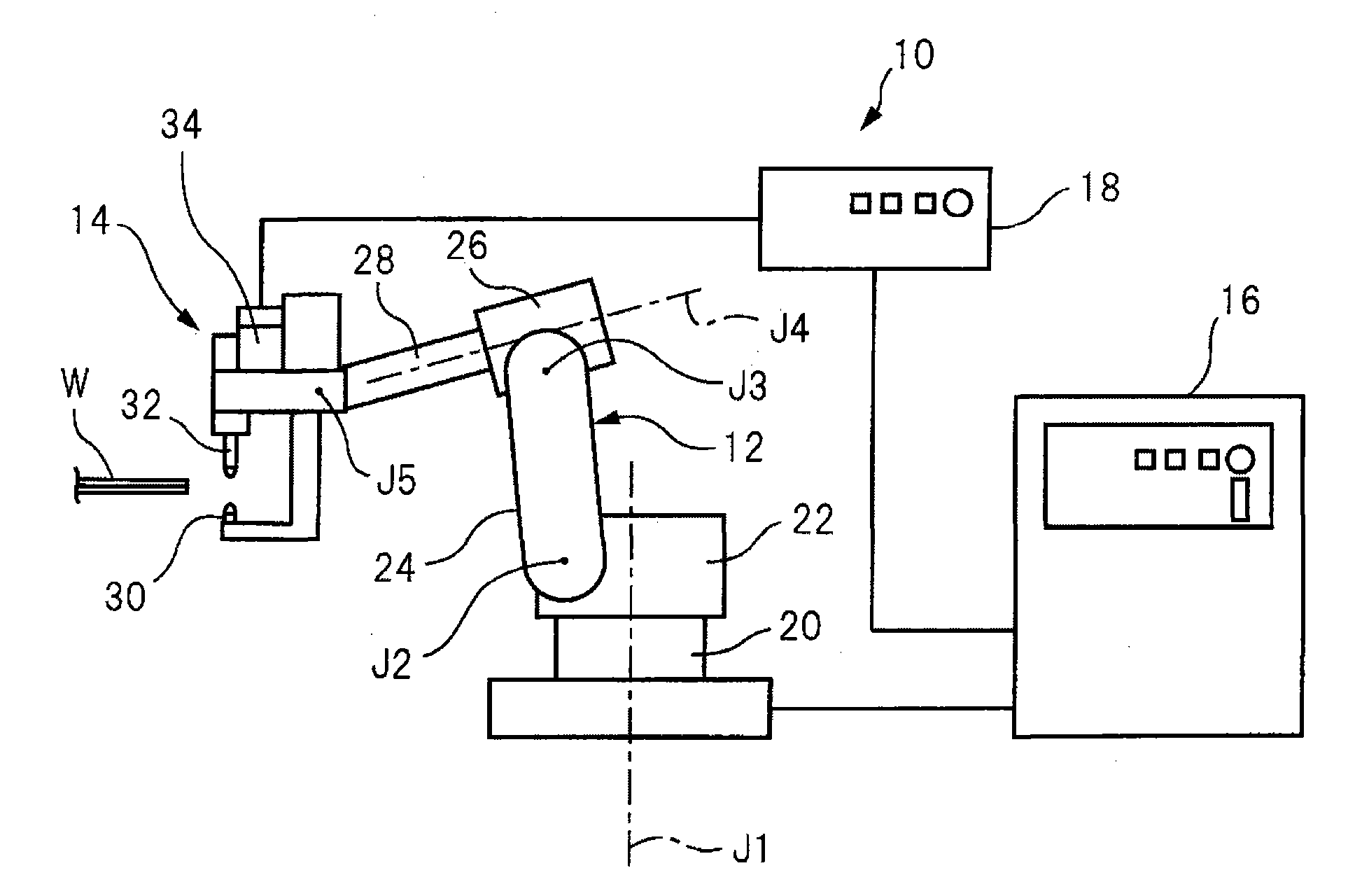
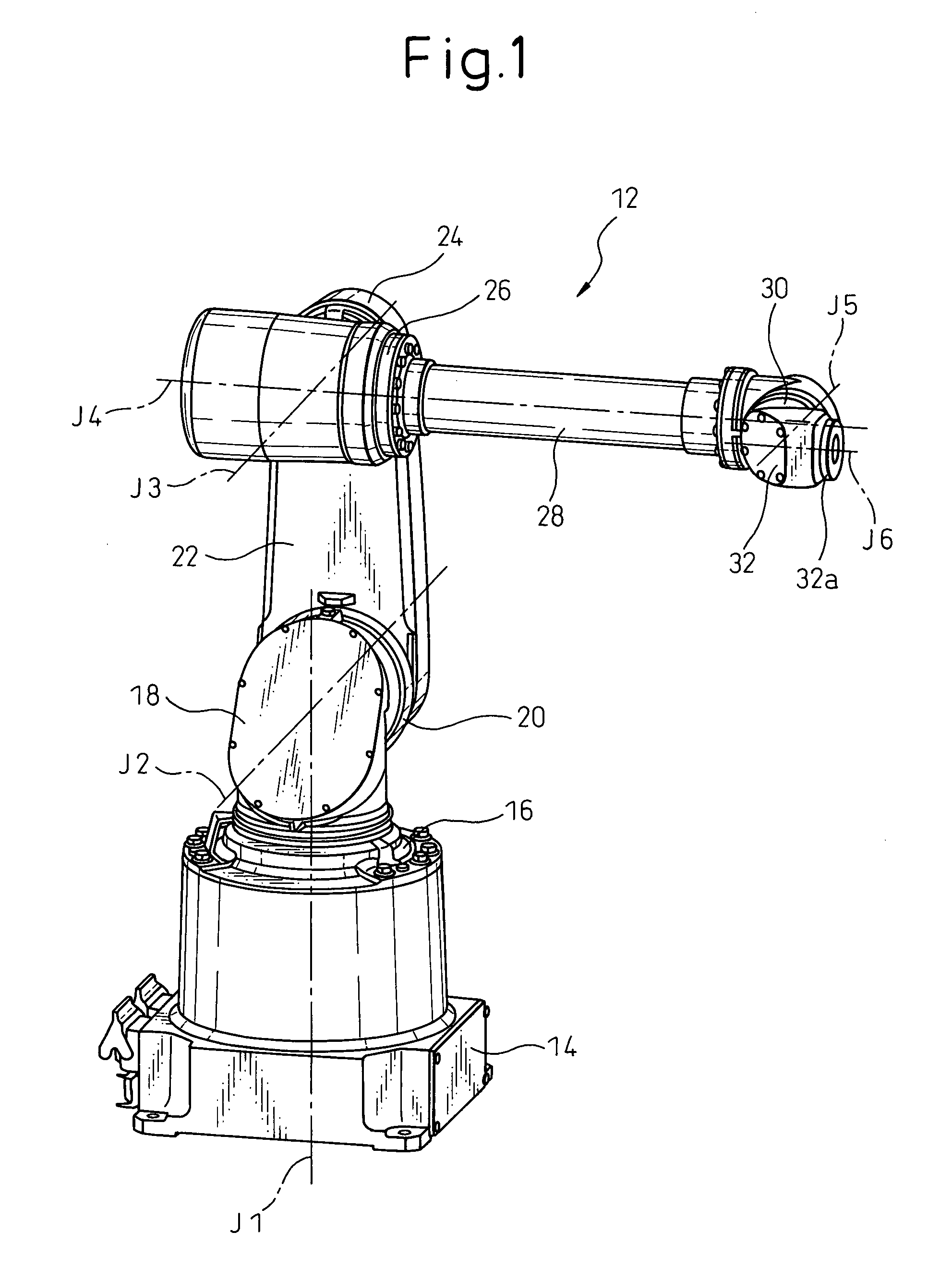
An articulated robot is a robot with rotary joints (e.g. a legged robot or an industrial robot). Articulated robots can range from simple two-jointed structures to systems with 10 or more interacting joints. They are powered by a variety of means, including electric motors.
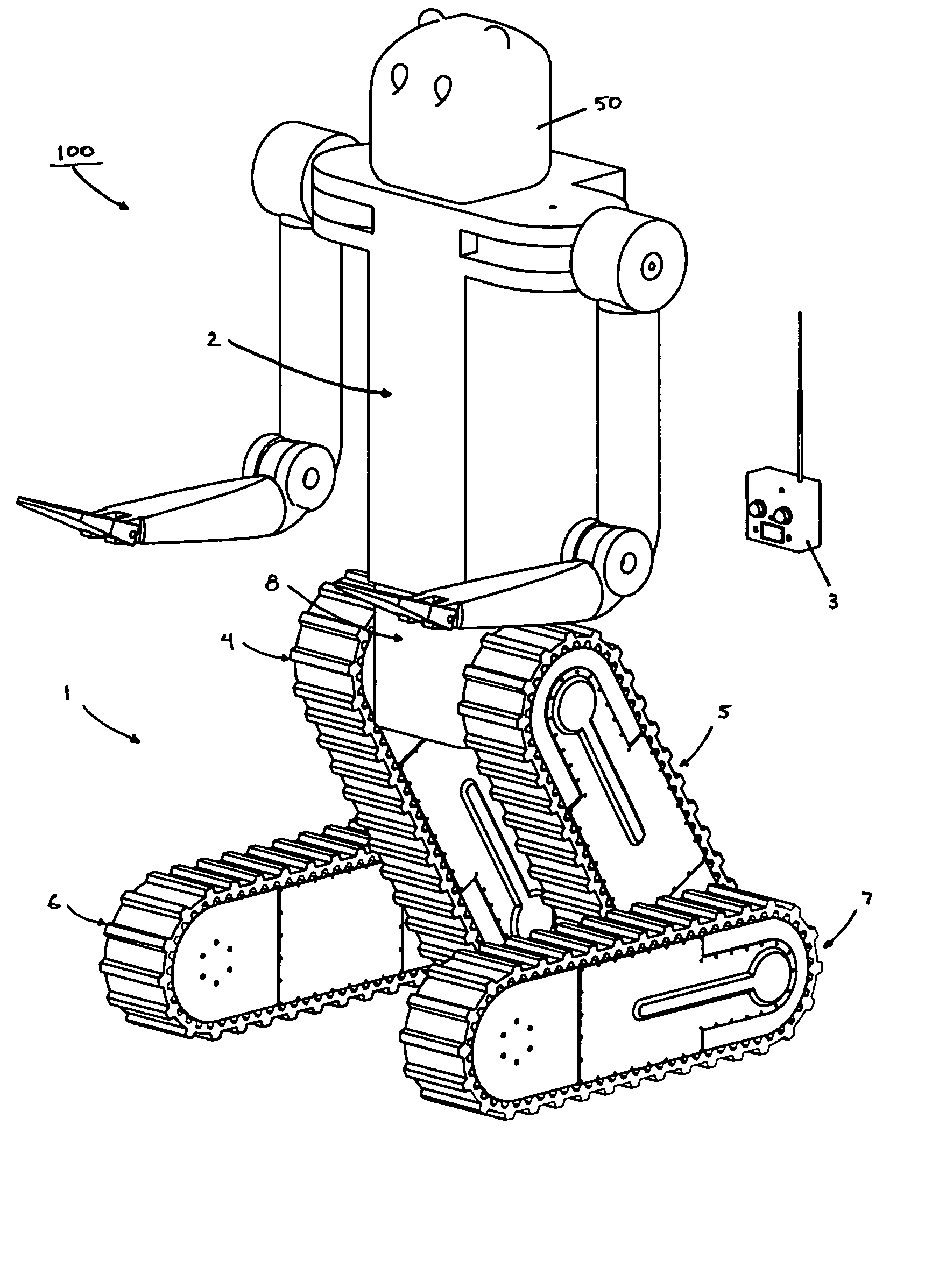
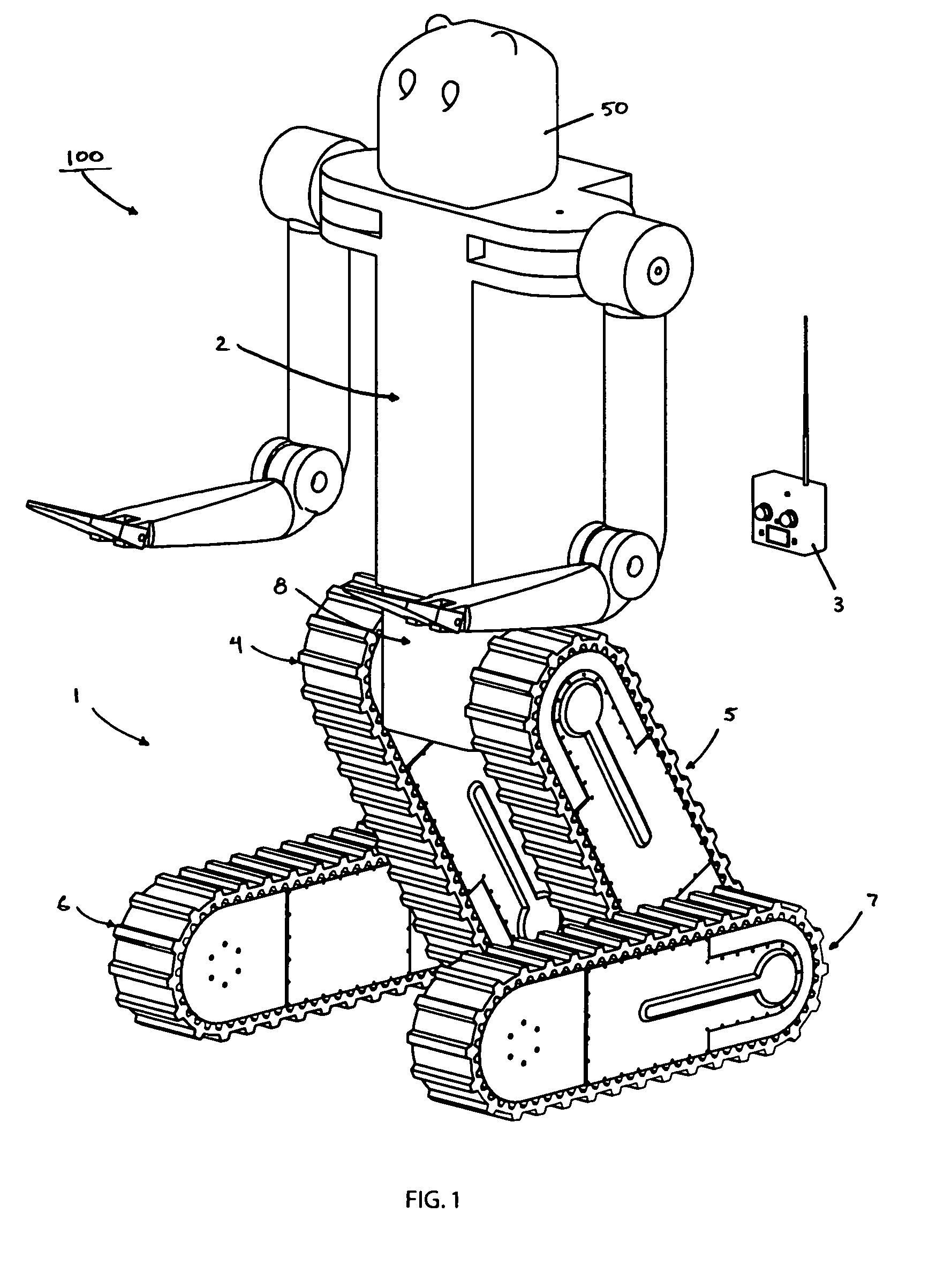
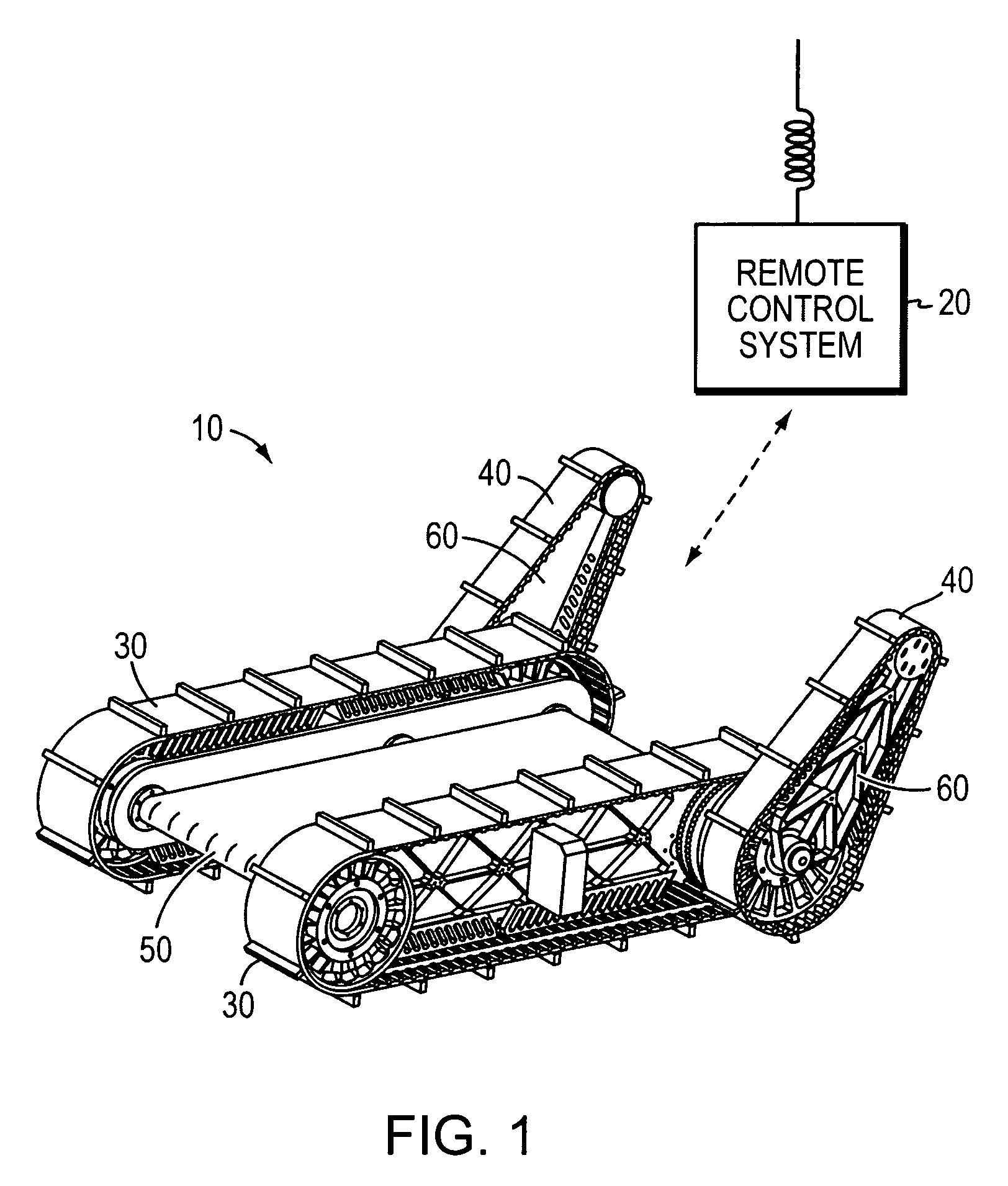
Mobile robot platform
InactiveUS7348747B1Improve agilityImprove battery lifeProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlEngineeringRight lower leg
A mobile articulated robot platform is provided where the platform comprises a payload base hip section for attaching a torso, the platform having two opposing sides, where the platform includes a right leg assembly and a left leg assembly, with each leg assembly having an upper leg and a lower leg section, where the right and left leg assemblies each comprise a right upper leg being pivotally coupled on one side of said payload base hip section and a left upper leg being pivotally coupled to the other side of the payload base hip section, and a right lower leg being independently and pivotally connected to the right upper leg, and a left lower leg being independently and pivotally connected to the left upper leg, allowing rotation of each of the lower legs about each of the upper legs.
Owner:VECNA
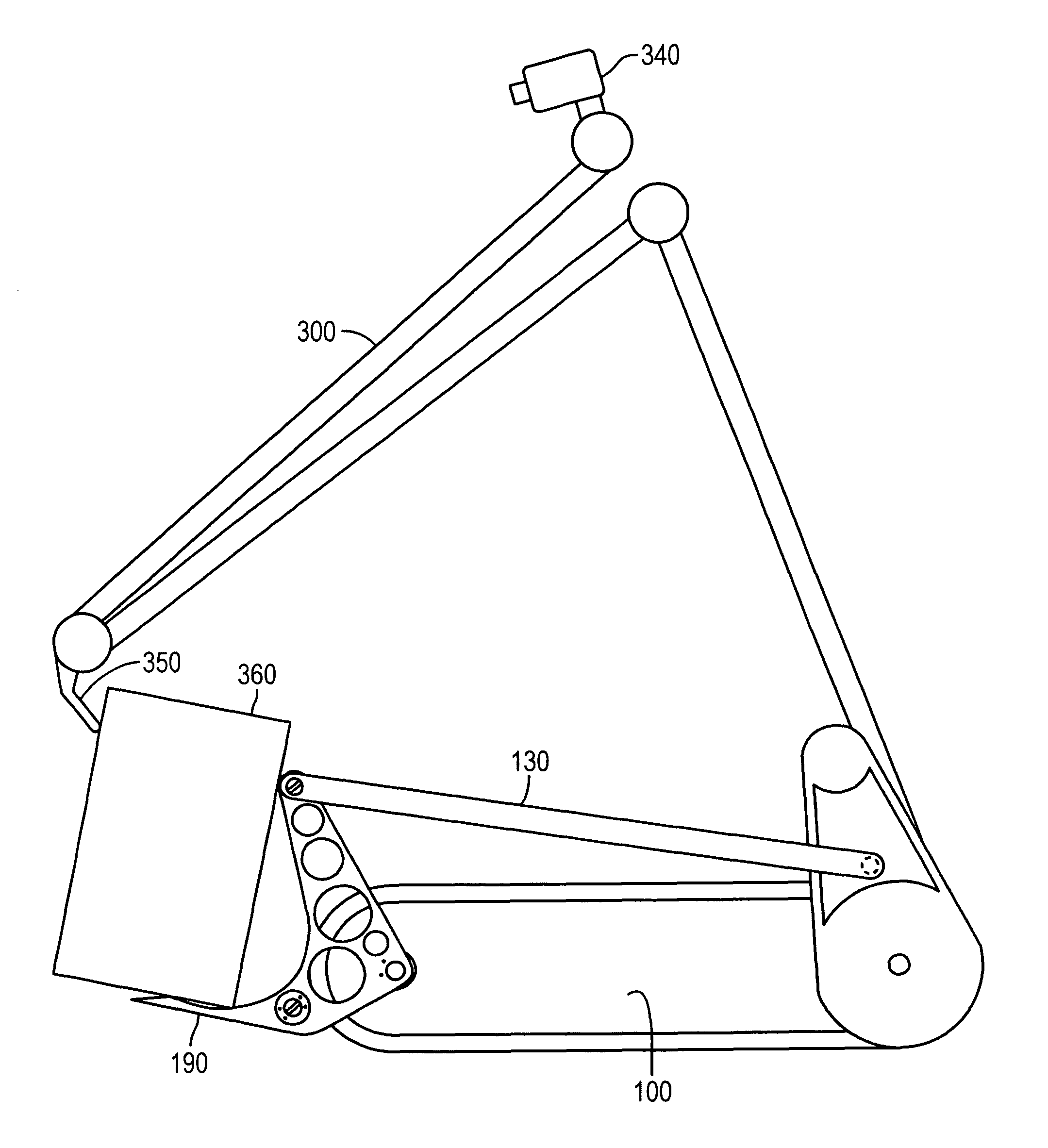
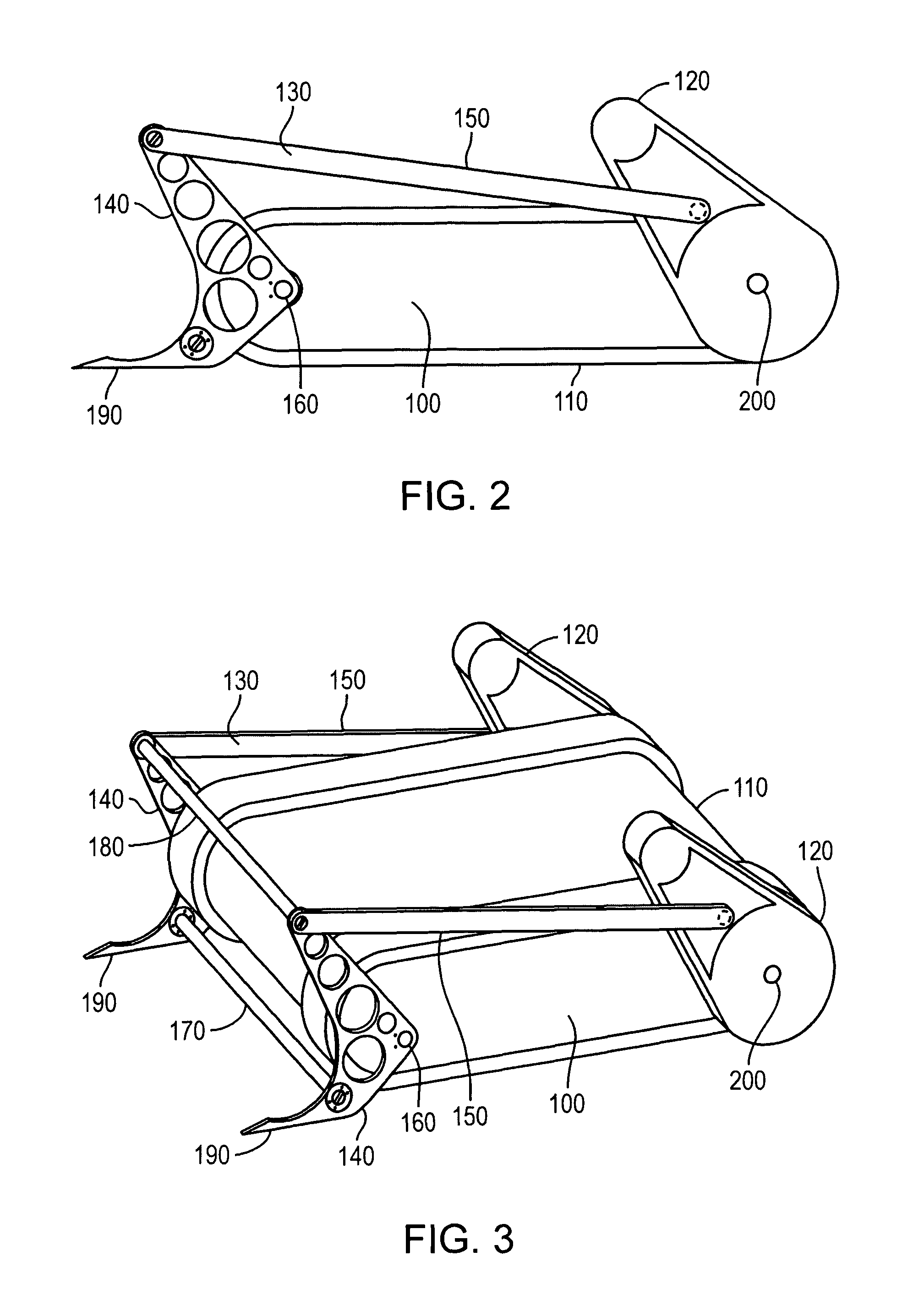
Lifting apparatus for remote controlled robotic device
InactiveUS8007221B1Substantial mechanical advantageIncreased mechanical advantageSoil-shifting machines/dredgersLifting devicesRemote controlTeleoperated robot
A retrofittable lifting apparatus for use on an articulated robotically controlled device is disclosed. The lifting apparatus includes a structure for mating the apparatus to the robotic device and a mechanism for the remotely controlled lifting of an ordnance or other object. Actuation of the lifting mechanism may be provided by existing sources of motion on the robotic device, or by additional sources of motion attached to the robotic device.
Owner:FLIR DETECTION
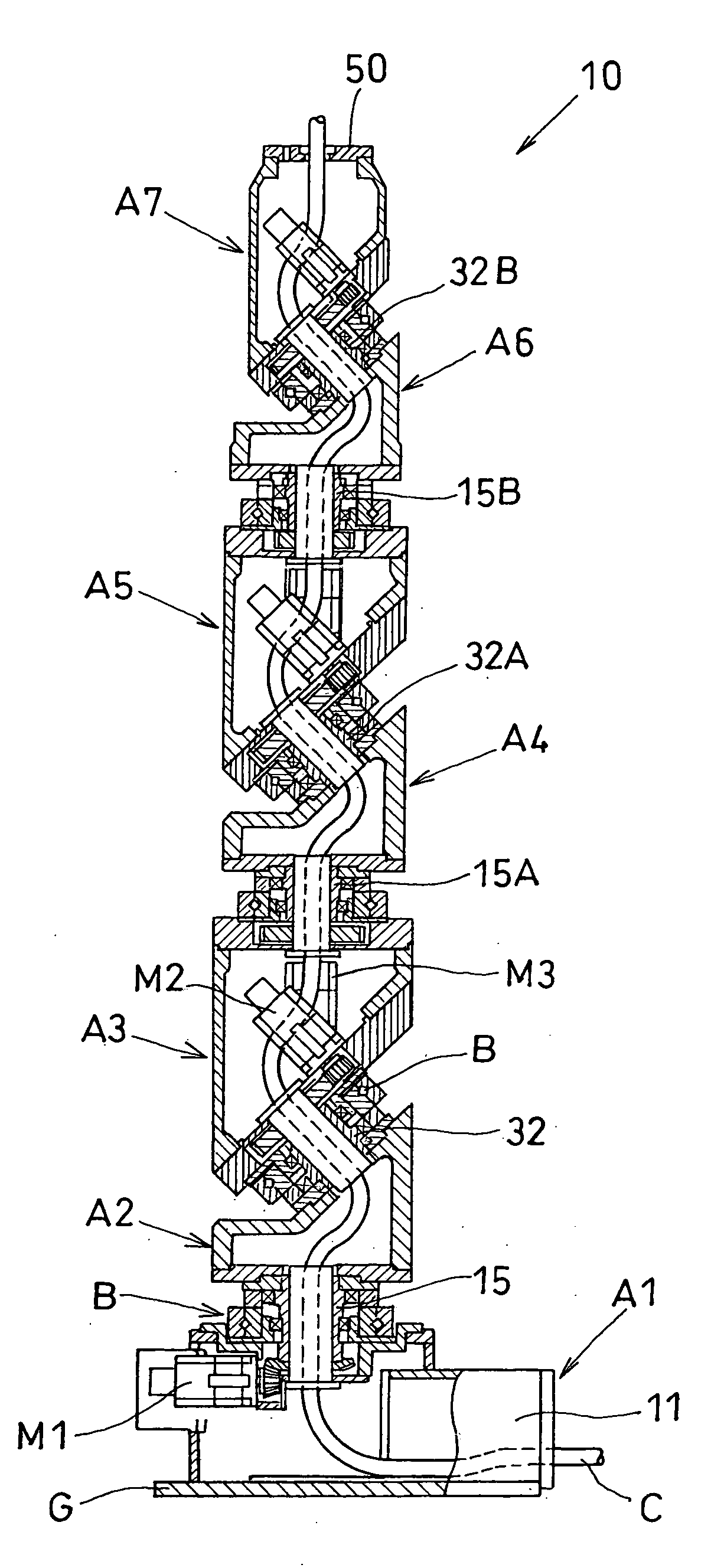
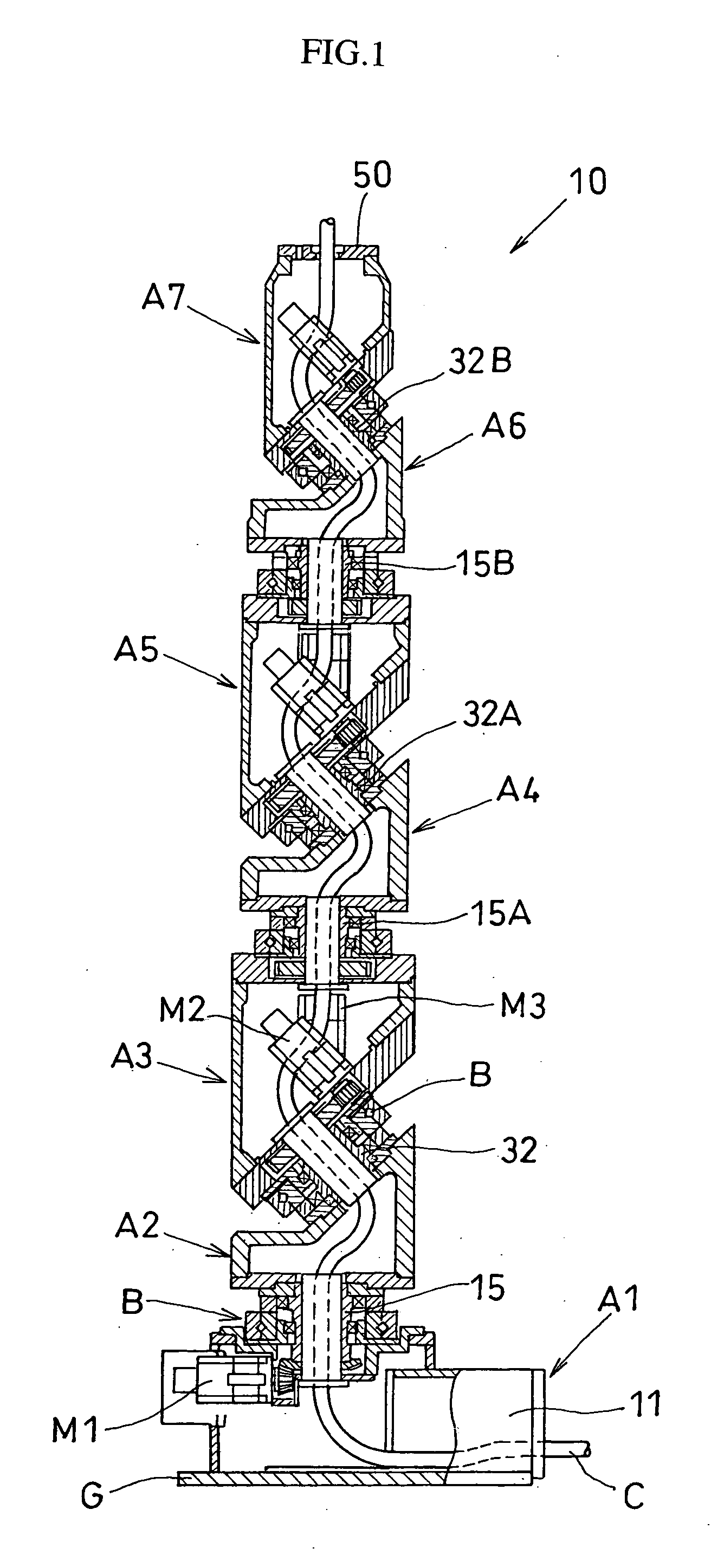
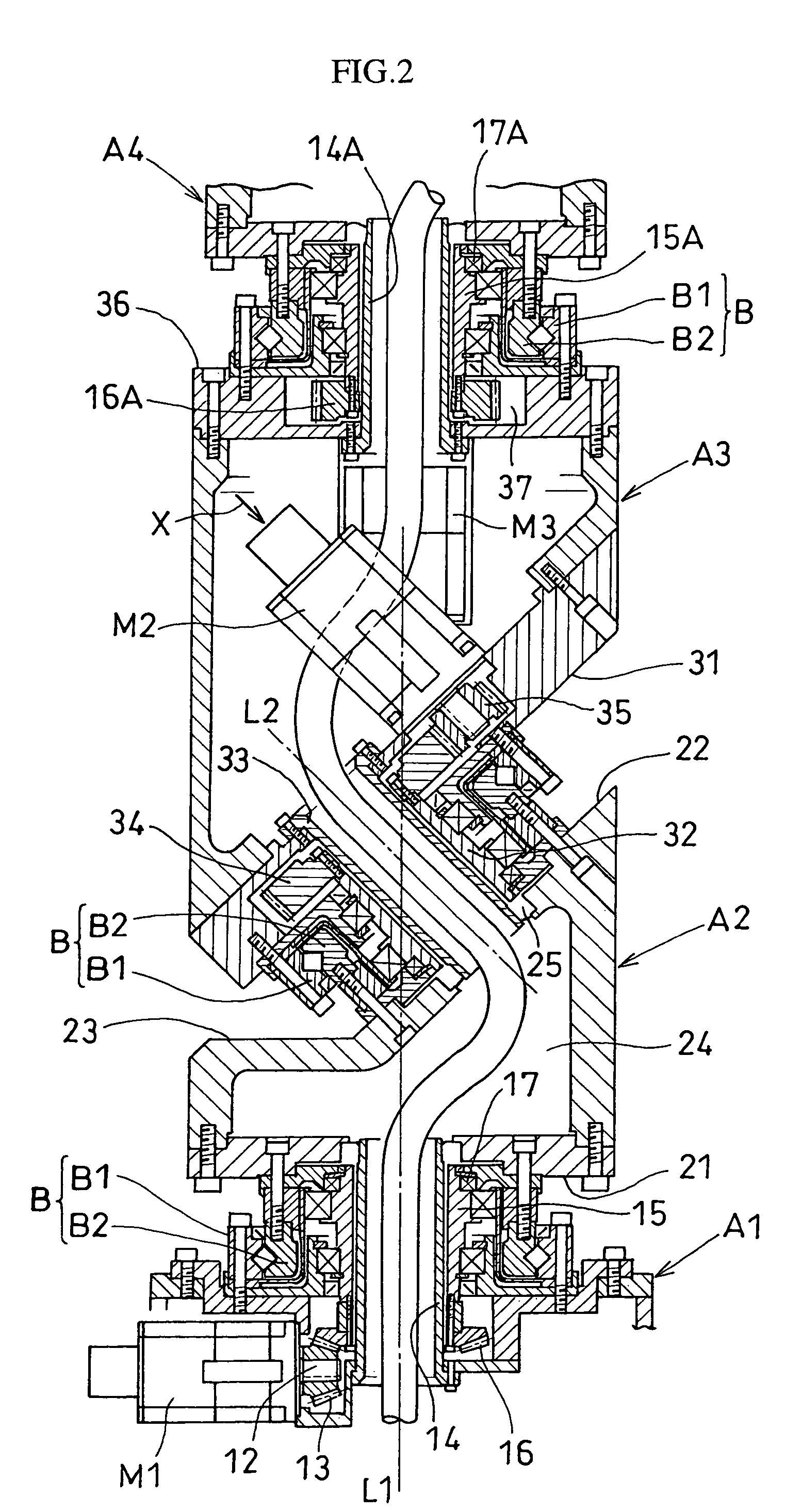
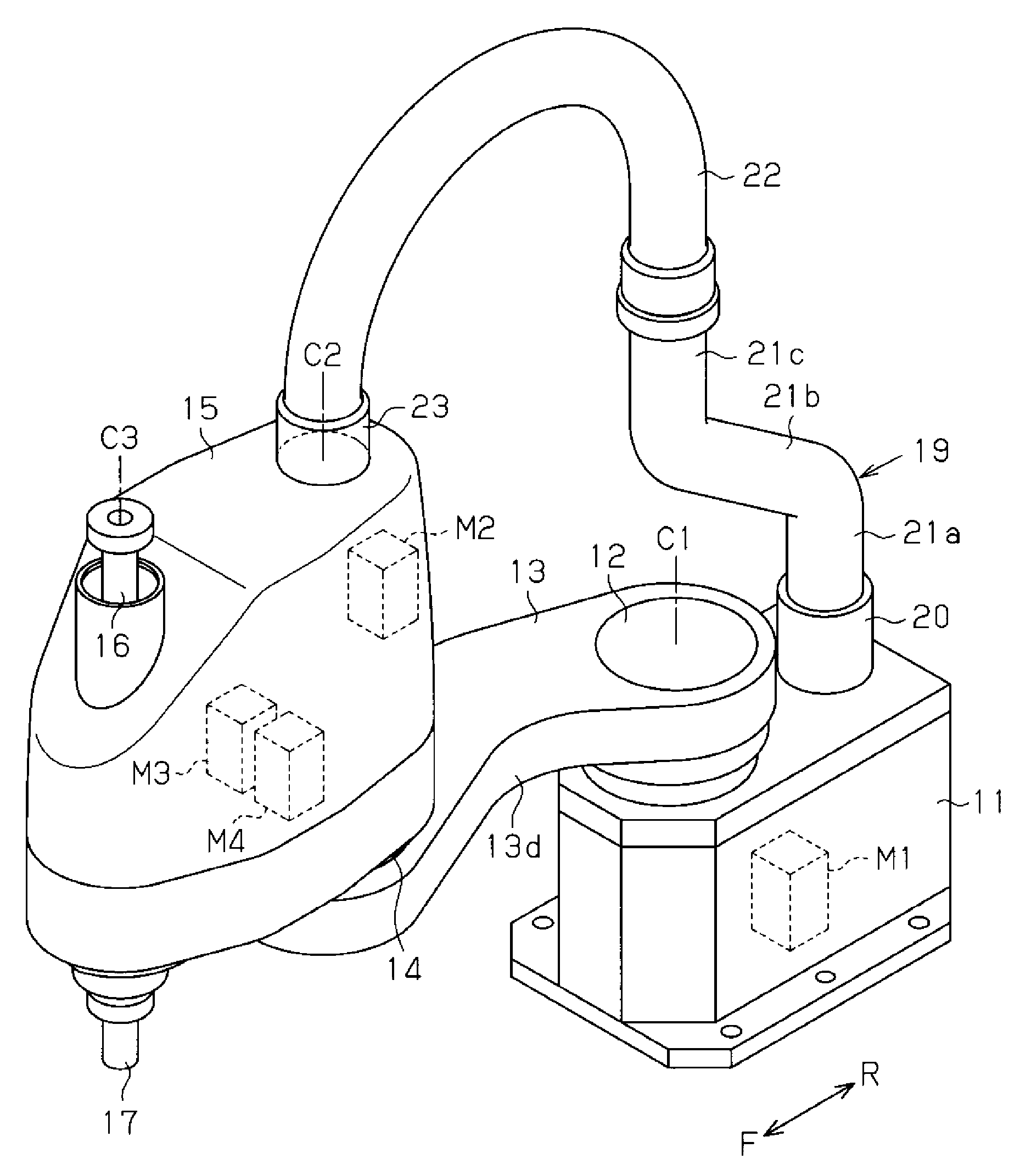
Articulated robot
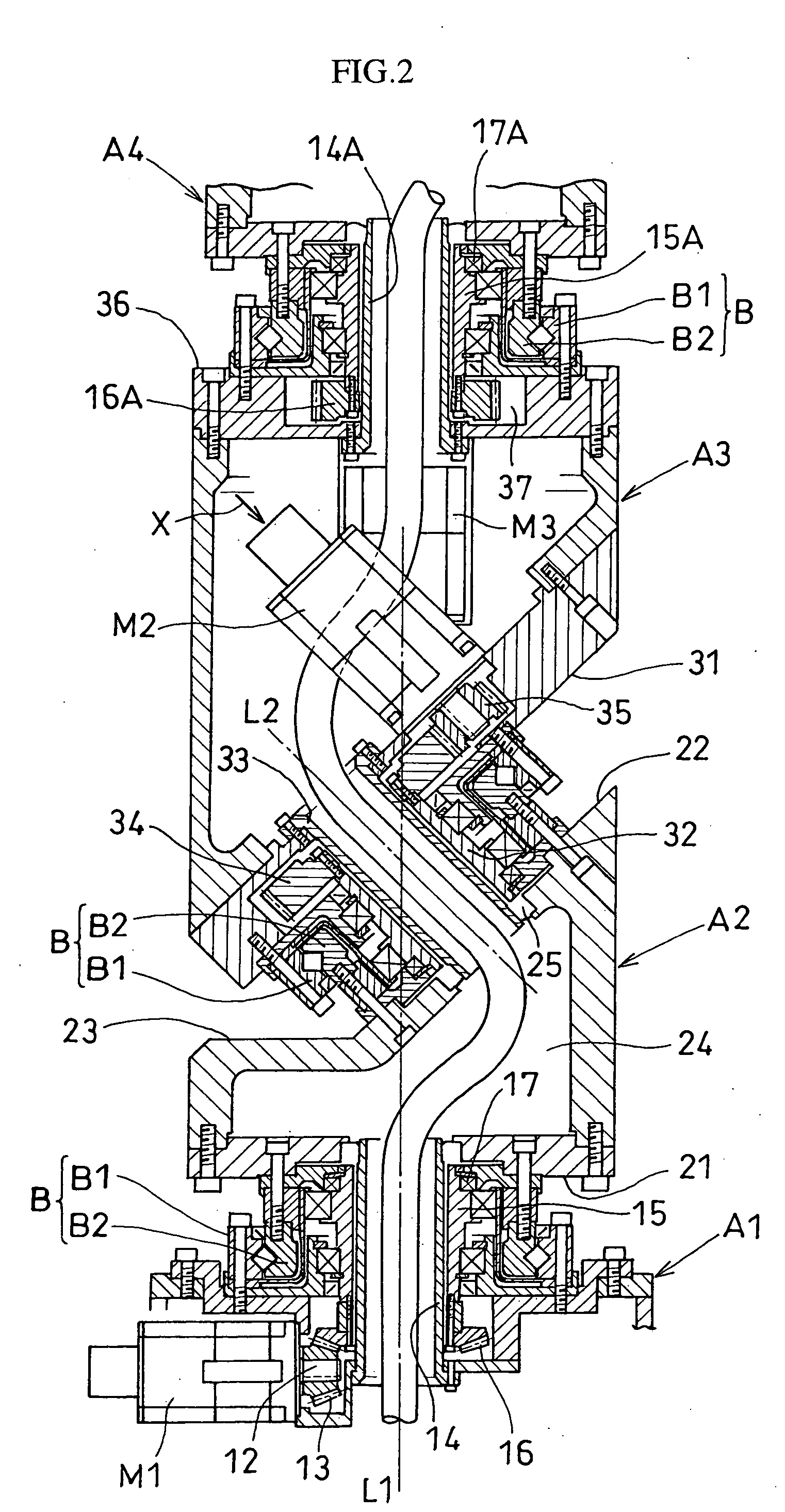
ActiveUS20040149064A1Programme-controlled manipulatorMechanical apparatusElectric power transmissionRotational axis
An articulated robot capable of reducing dead space while maintaining a wide operating area and simplifying a power transmission system necessary for moving each joint. A plurality of joint arms A1 to A7 are connected via first rotating shafts 15, 15A, and 15B as horizontal rotating shafts and via second rotating shafts 32, 32A, and 32B as inclined rotating shafts alternately. A motor M for driving the rotating shaft and a speed-reducing mechanism are provided for each rotating shaft.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Industrial robot
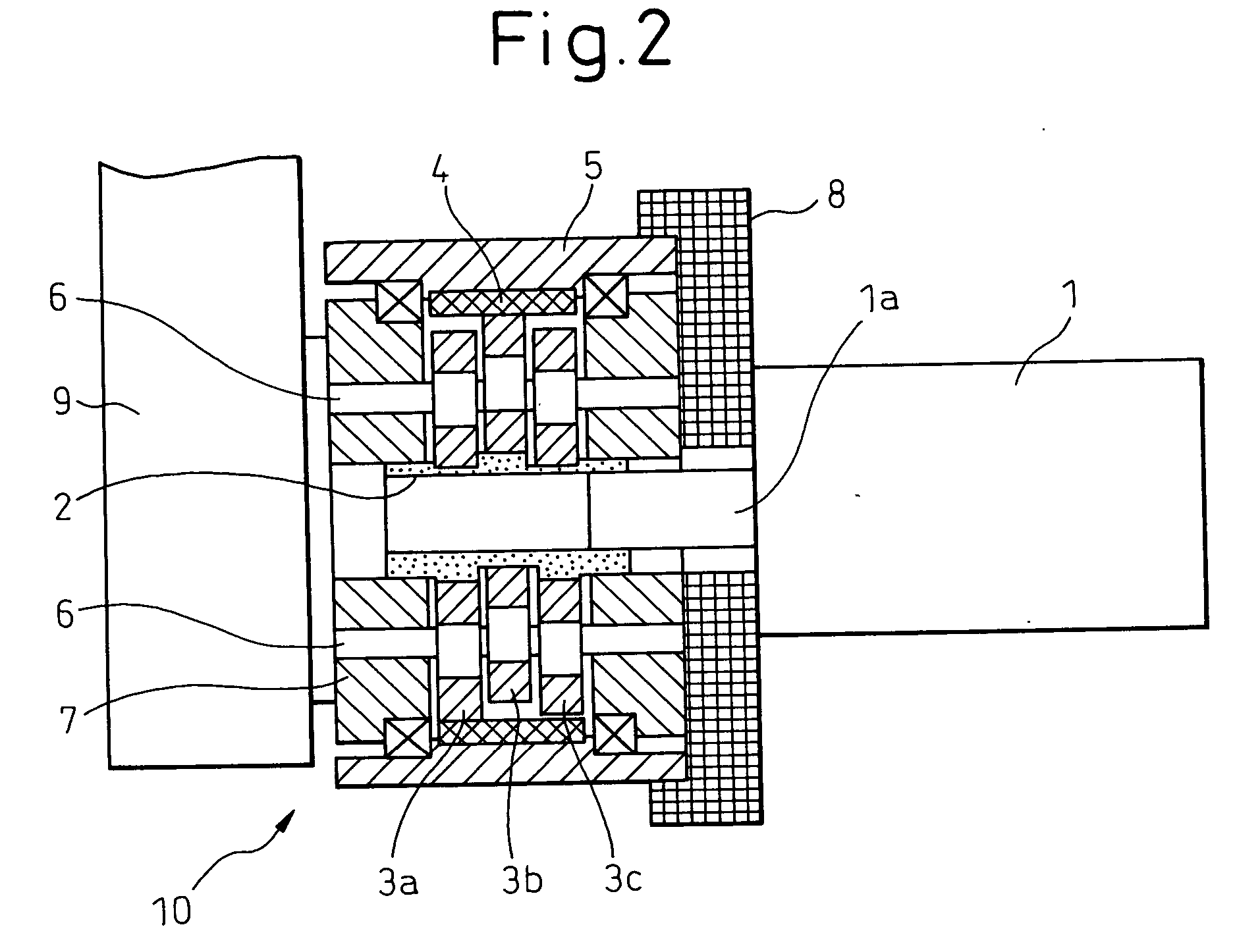
InactiveUS20050204850A1Simple structureImprove machining accuracyProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsEngineeringControl theory
A joint structure is employed for an articulated type robot in which a speed reducer of one-stage speed reducing structure and a servo motor are directly connected to each other for the joint of the rotary base B1 and the lower arm A1 and for the joint of the lower arm A1 and the upper arm A2. The input shaft 2 of the speed reducer 10 directly connected to the output shaft of the servo motor 1 attached to the first member 8 (B1 / A2) is a crank shaft composing a cam, and the external gears 3a, 3b, 3c are meshed with the cam surfaces. When the servo motor 1 is driven and the input shaft 2 is rotated, the external gears 3a, 3b, 3c are eccentrically revolved and rotated while the external gears 3a, 3b, 3c are meshed with the internal gear 4 provided inside the case 5 of the speed reducer 10. The rotation is taken out by a plurality of pin members 6 engaged to the external gears 3a, 3b, 3c and transmitted to the output shaft 7 of the speed reducer 10. Therefore, the second member 9 (A1) is relatively pivoted with respect to the first member 8. Due to the foregoing, the robot structure in which a plurality of joint devices for connecting the adjoining links via the speed reducer are connected in series to each other can be simplified.
Owner:FANUC LTD
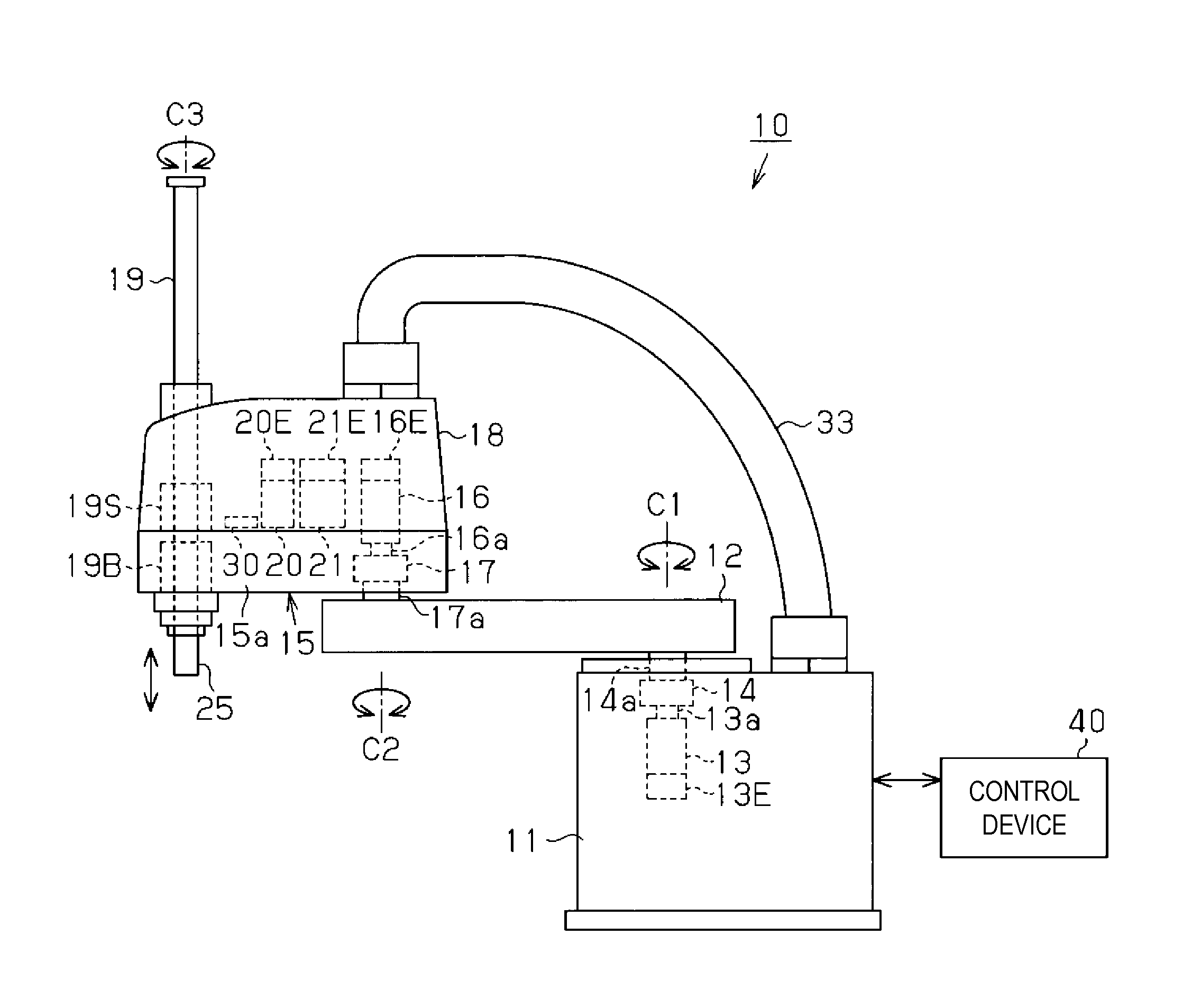
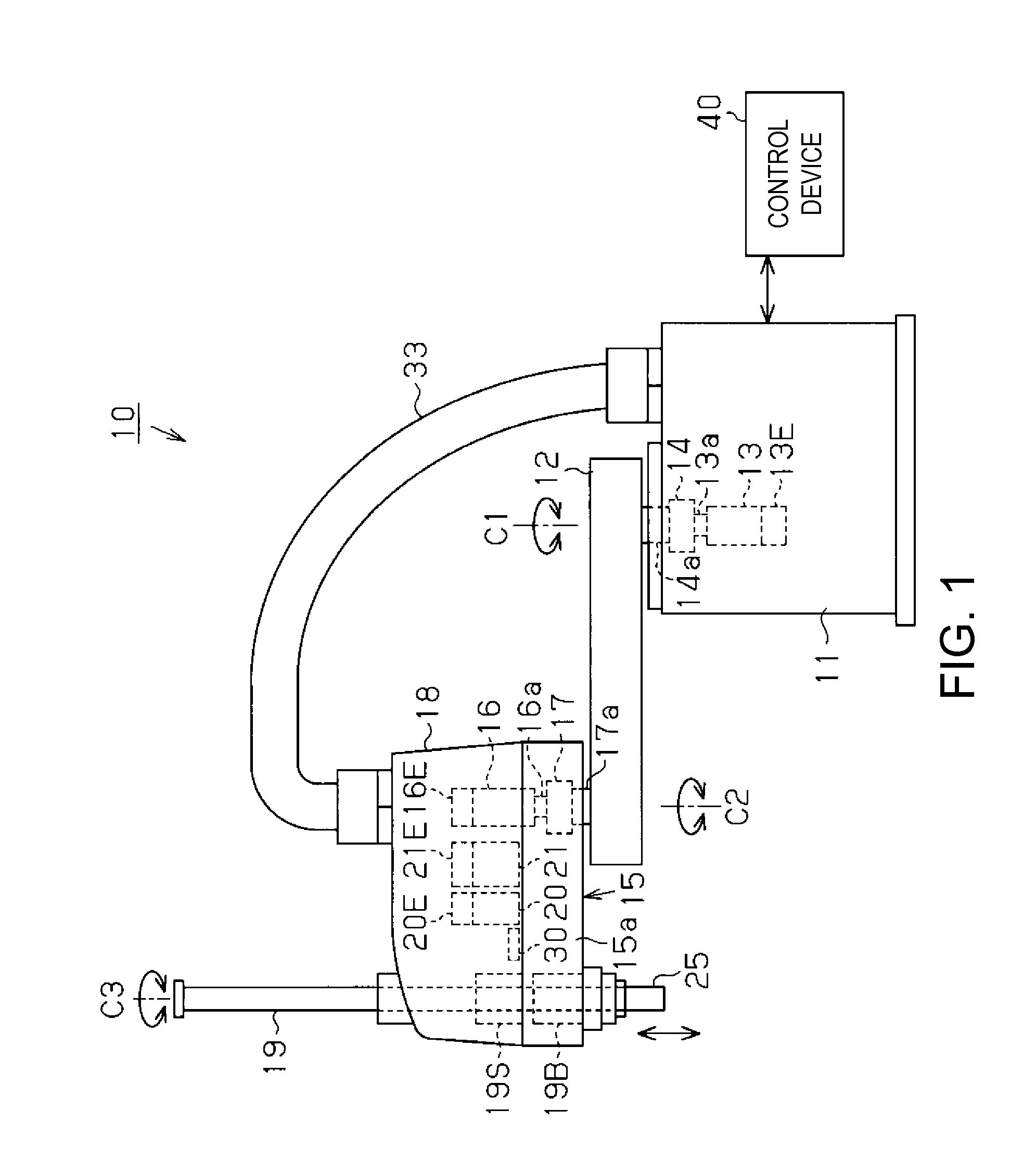
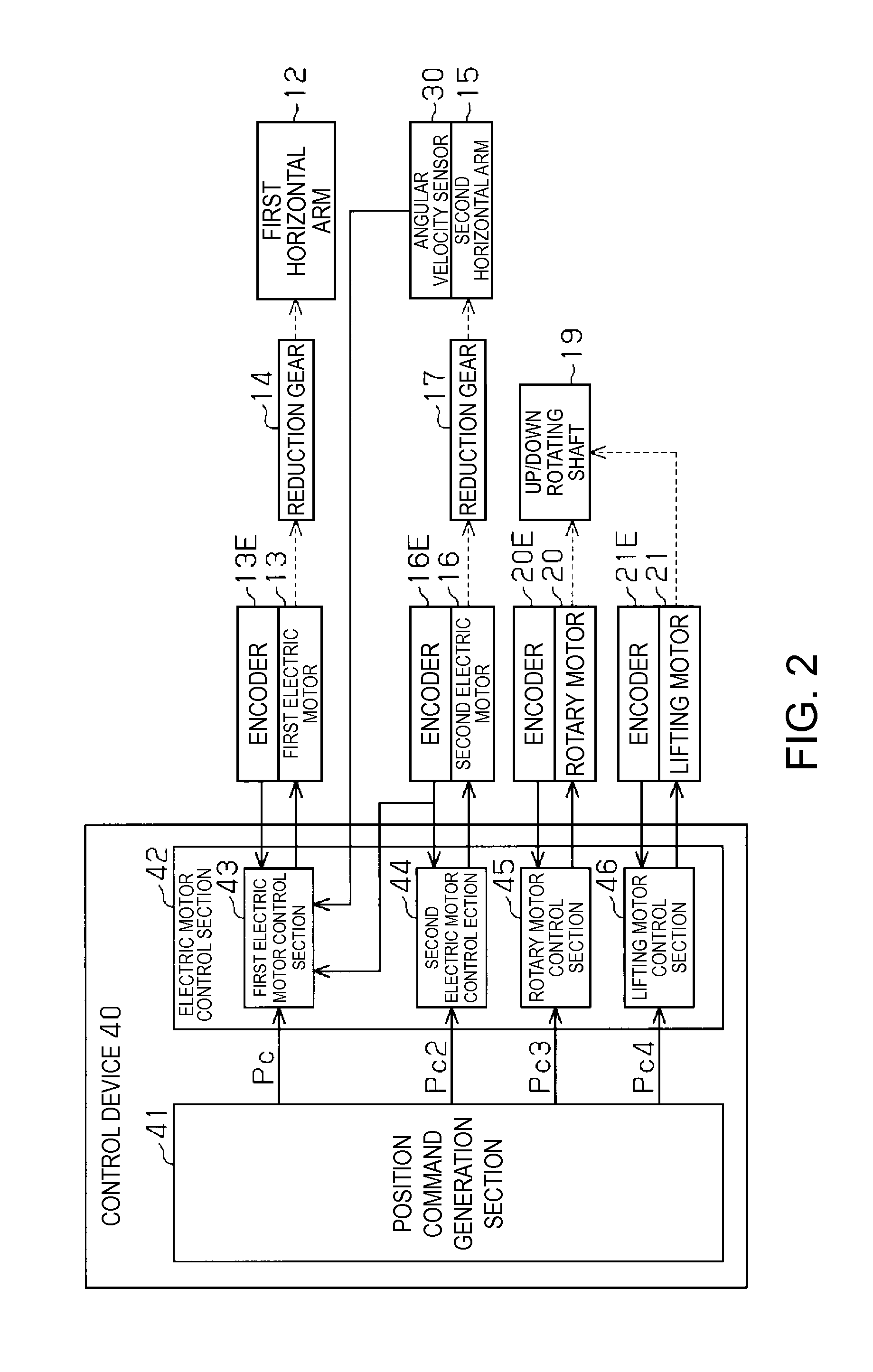
Horizontal articulated robot, and method of controlling the same
ActiveUS20120215357A1Reduce in quantityReduced durabilityProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorRotation velocityAngular velocity
A robot includes a first horizontal arm coupled to a base, a second horizontal arm coupled to the base via the first horizontal arm, first and second motors adapted to rotate the respective arms, and first and second encoders adapted to calculate rotational angles and rotational velocities of the respective motors. A first motor control section subtracts first and second angular velocities based on the first and second encoders from a sensor angular velocity detected by an angular sensor, and controls the first motor so that a velocity measurement value obtained by adding a vibration velocity based on a vibration angular velocity as the subtraction result and a first rotational velocity becomes equal to a velocity command value.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
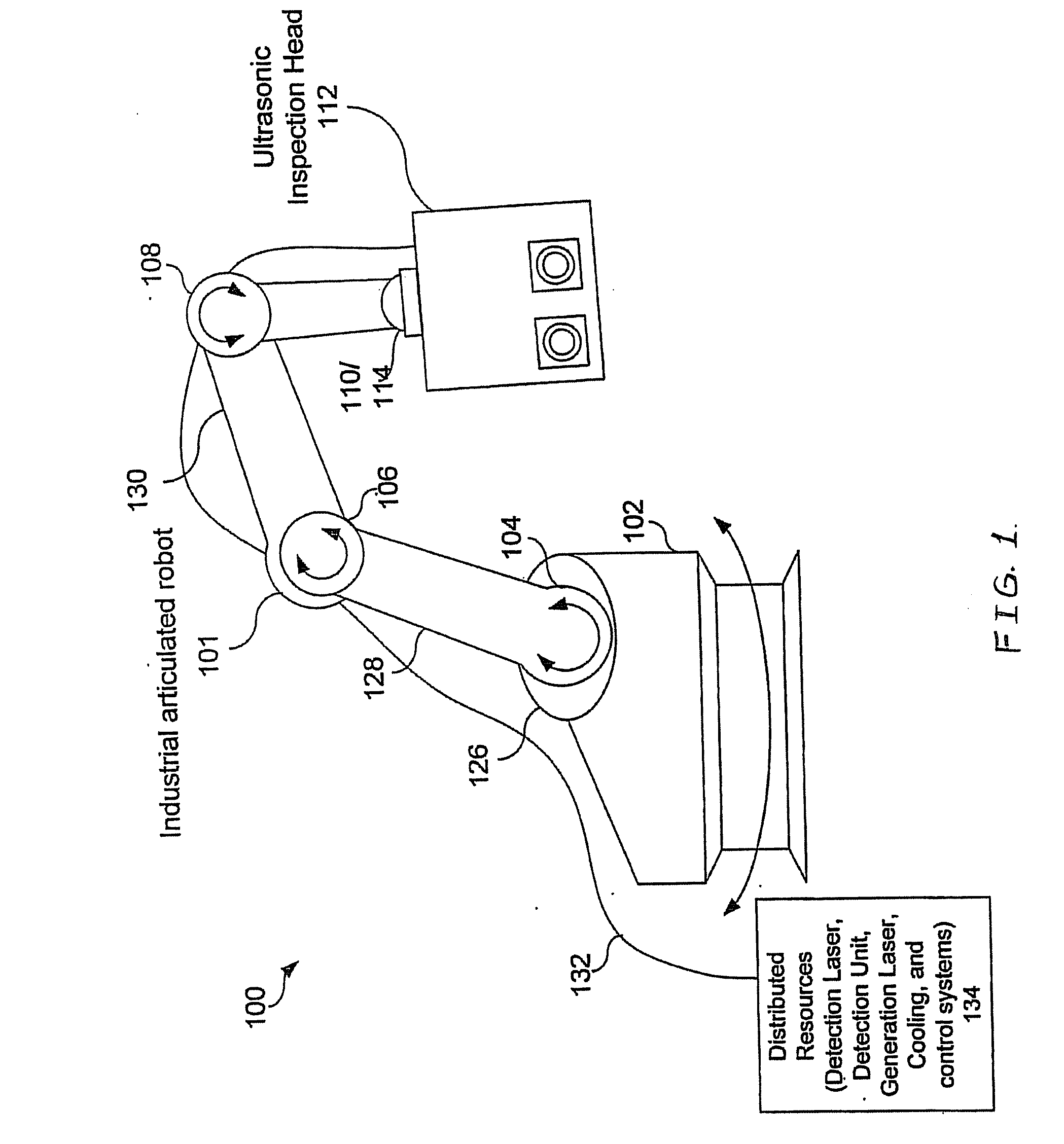
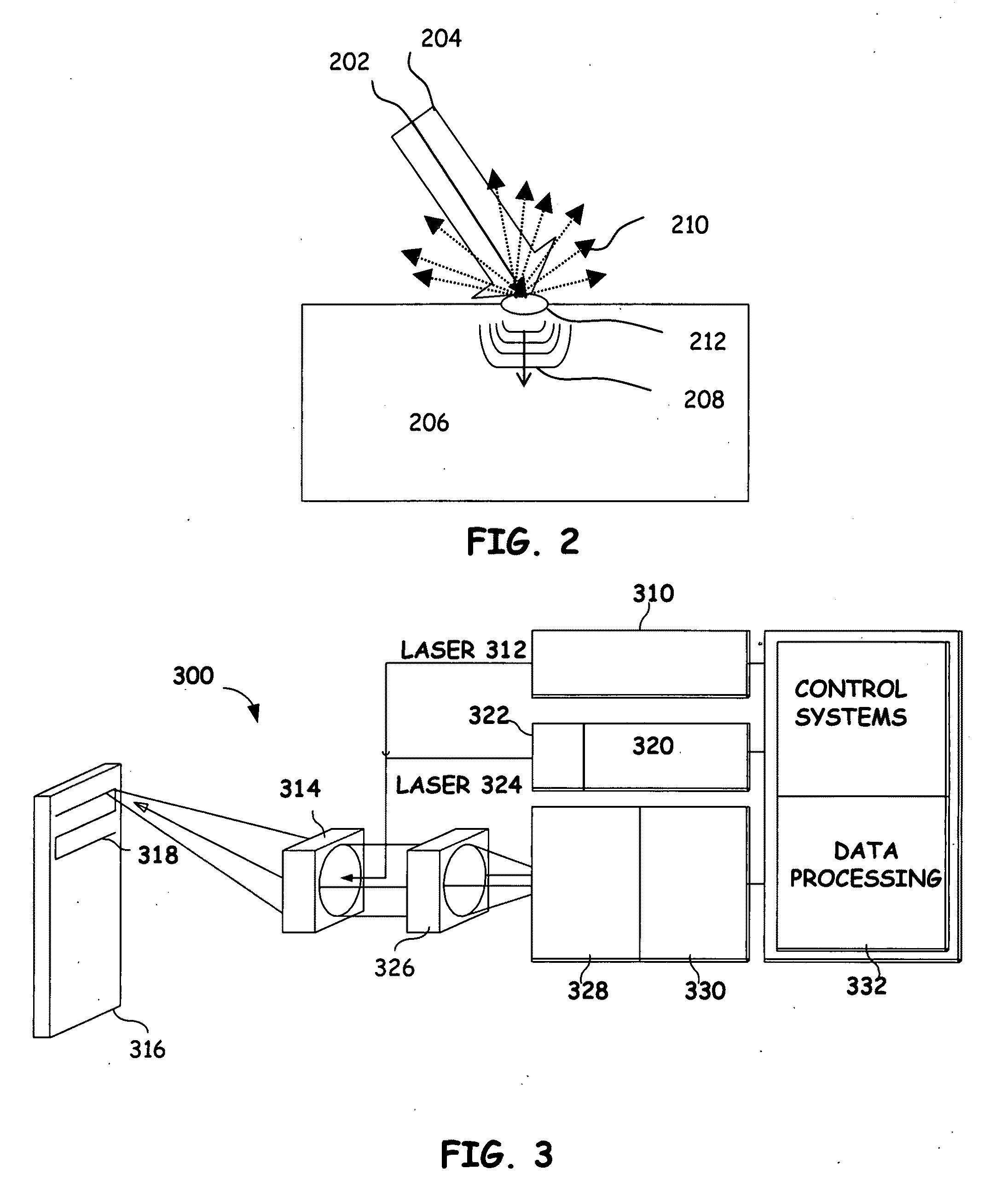
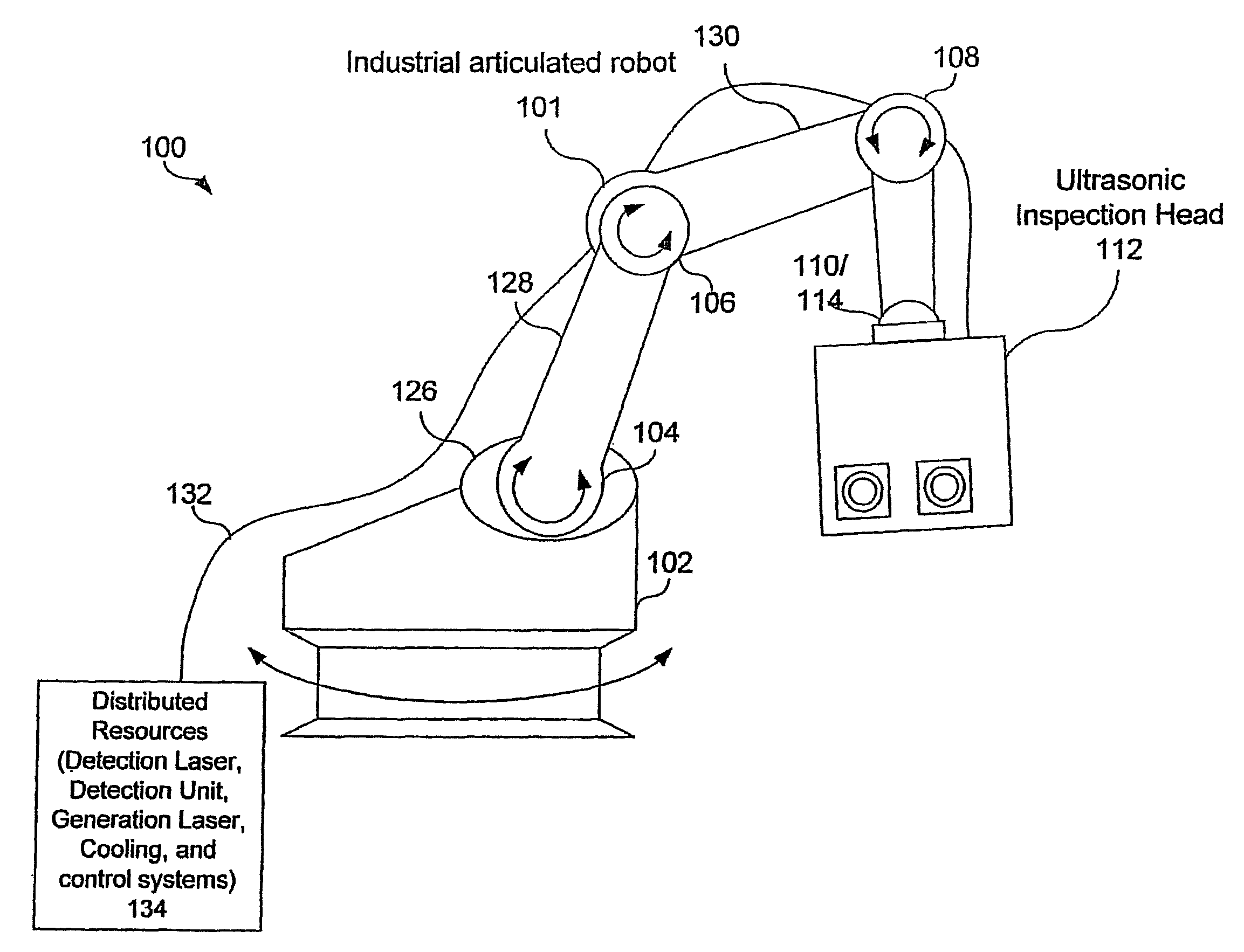
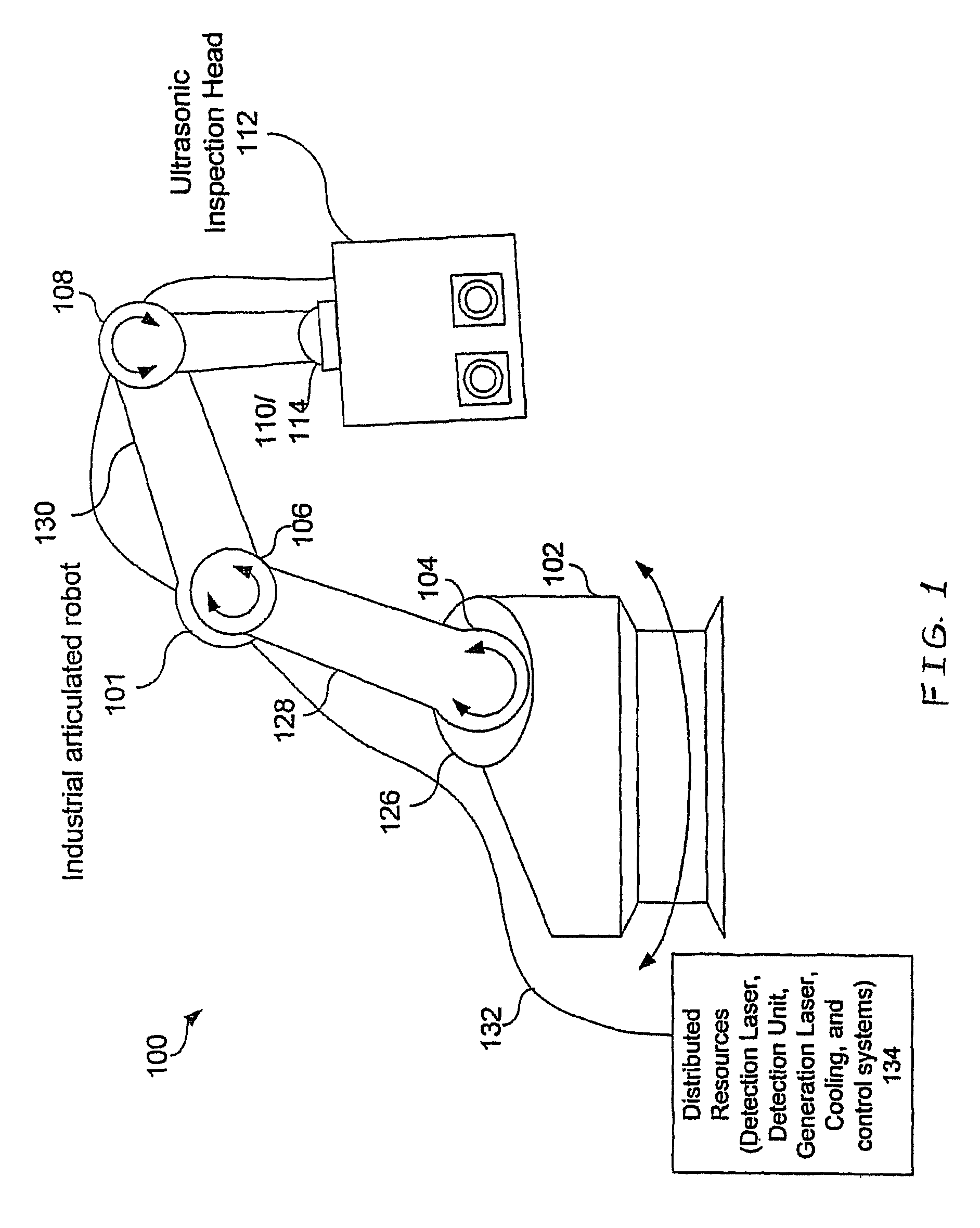
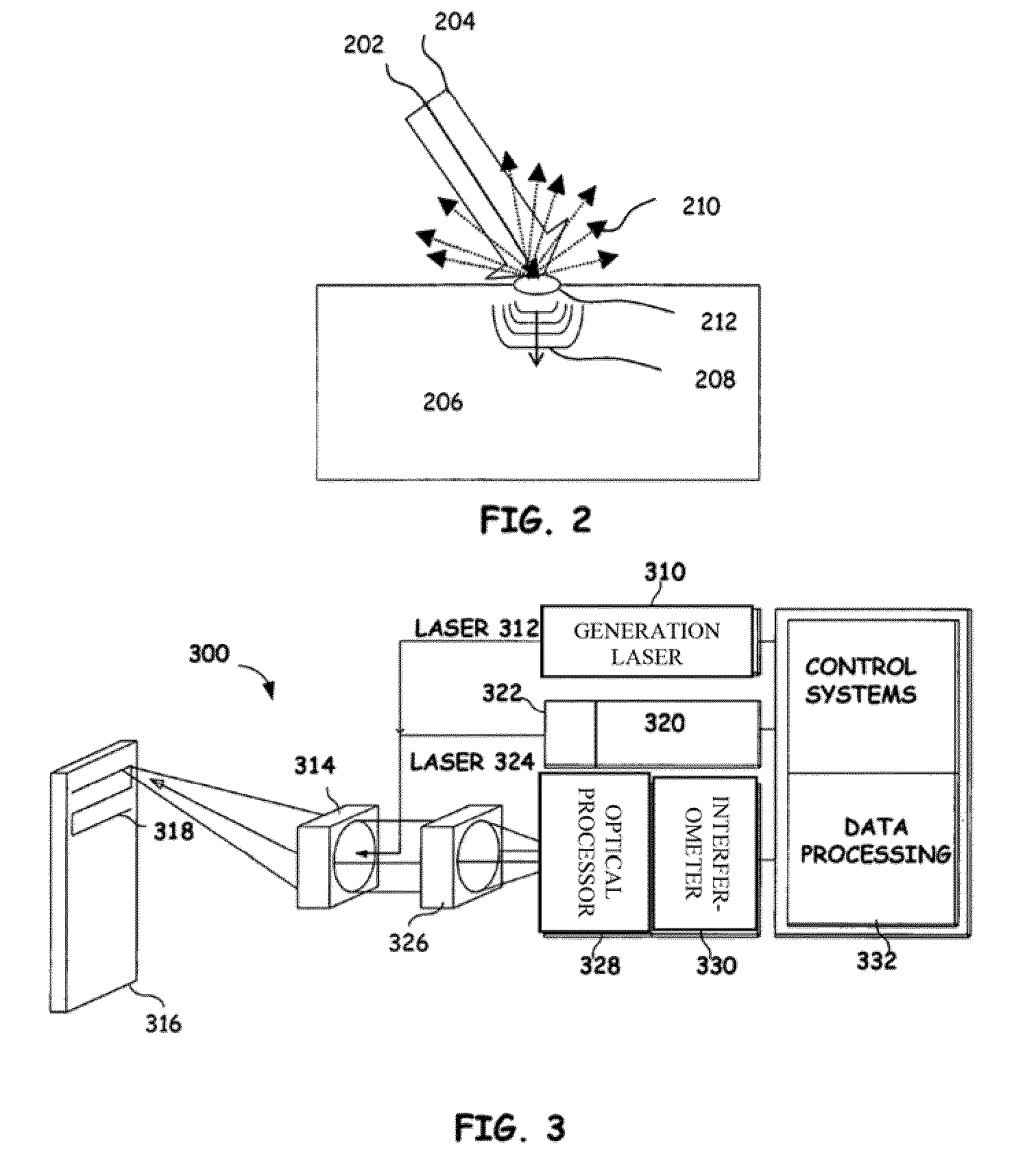
Articulated robot for laser ultrasonic inspection
ActiveUS20090010285A1Cost-effectiveMore compact robotsLaser using scattering effectsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesNon destructiveUltrasound sonography
An ultrasonic non-destructive evaluation (NDE) system operable to inspect target materials is provided. This ultrasonic NDE system includes an articulated robot, an ultrasound inspection head, a processing module, and a control module. The ultrasound inspection head couples to or mounts on the articulated robot. The ultrasound inspection head is operable to deliver a generation laser beam, a detection laser beam, and collect phase modulated light scattered by the target materials. The processing module processes the phase modulated light and produces information about the internal structure of the target materials. The control module directs the articulated robot to position the ultrasound inspection head according to a pre-determined scan plan.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Motor, robot, substrate loader, and exposure apparatus
An apparatus that reduces vibration generation and magnetic leakage, wherein the apparatus is a motor, an articulated serial robot that has a motor built in, a substrate loader that includes the articulated robot, and a related exposure apparatus equipped with the substrate loader. The motor includes a drive shaft to drive the motor; a rotor attached with the shaft; and a stator that opposes the rotor and causes an electromagnetic force to act between the rotor and the stator to drive the drive shaft; an RC stator, for reaction force cancellation attached with the stator; an RC rotor for reaction force cancellation, opposing the RC stator; and a counterweight sleeve attached with the RC rotor, wherein the reaction force, which is applied to the stator via the drive shaft when the counterweight sleeve rotates in a direction opposite that of the drive shaft, is cancelled.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Surgical robotic systems and methods thereof
ActiveUS20170071685A1Surgical navigation systemsSurgical systems user interfaceSupporting systemEngineering
An automated medical system and method for using the automated medical system. The automated medical system may comprise a robot support system. The robot support system may comprise a robot body. The robot support system may further comprise a selective compliance articulated robot arm coupled to the robot body and operable to position a tool at a selected position in a surgical procedure. The robot support system may further comprise an activation assembly operable to transmit a move signal to the selective compliance articulated robot arm allowing an operator to move the selective compliance articulated robot arm. The automated medical system may further comprise a camera tracking system and an automated imaging system.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Iron tower climbing articulated robot
InactiveCN102001089AImprove obstacle performanceSolve labor intensityProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsEngineeringTower
The invention provides an electric iron tower climbing robot which mainly comprises a pair of mechanical arms, an electric cylinder, a pitching mechanism and a mechanical clamping device, wherein the mechanical clamping device can clamp steel angles of different specifications; the upper ends of the two mechanical arms are connected by an installing shaft; a motor stand and an ejector rod of the electric cylinder are respectively connected with the two arms through pin columns; the electric cylinder telescopically drives the two arms to rotate around the installing shaft at the upper ends; the lower ends of the mechanical arms are connected with a rotating shaft of the pitching mechanism; the pitching mechanism enables the mechanical arms to rotate around the rotating shaft to realize an obstacle detouring function; and a worm-gear case of the pitching mechanism is fixedly connected with wrist joints of mechanical hands, so that the mechanical arms can also rotate around the wrist joints of the mechanical hands to realize a turning function. The invention has compact structure; complex actions such as obstacle detouring, turning and the like can be completed by linkage of multiple joints; and the robot can climb different structure types of iron towers, has wide range of use and certain loading capacity, and can carry necessary overhaul equipment, substitute for workers to climb the electric iron tower and complete the corresponding overhaul task.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
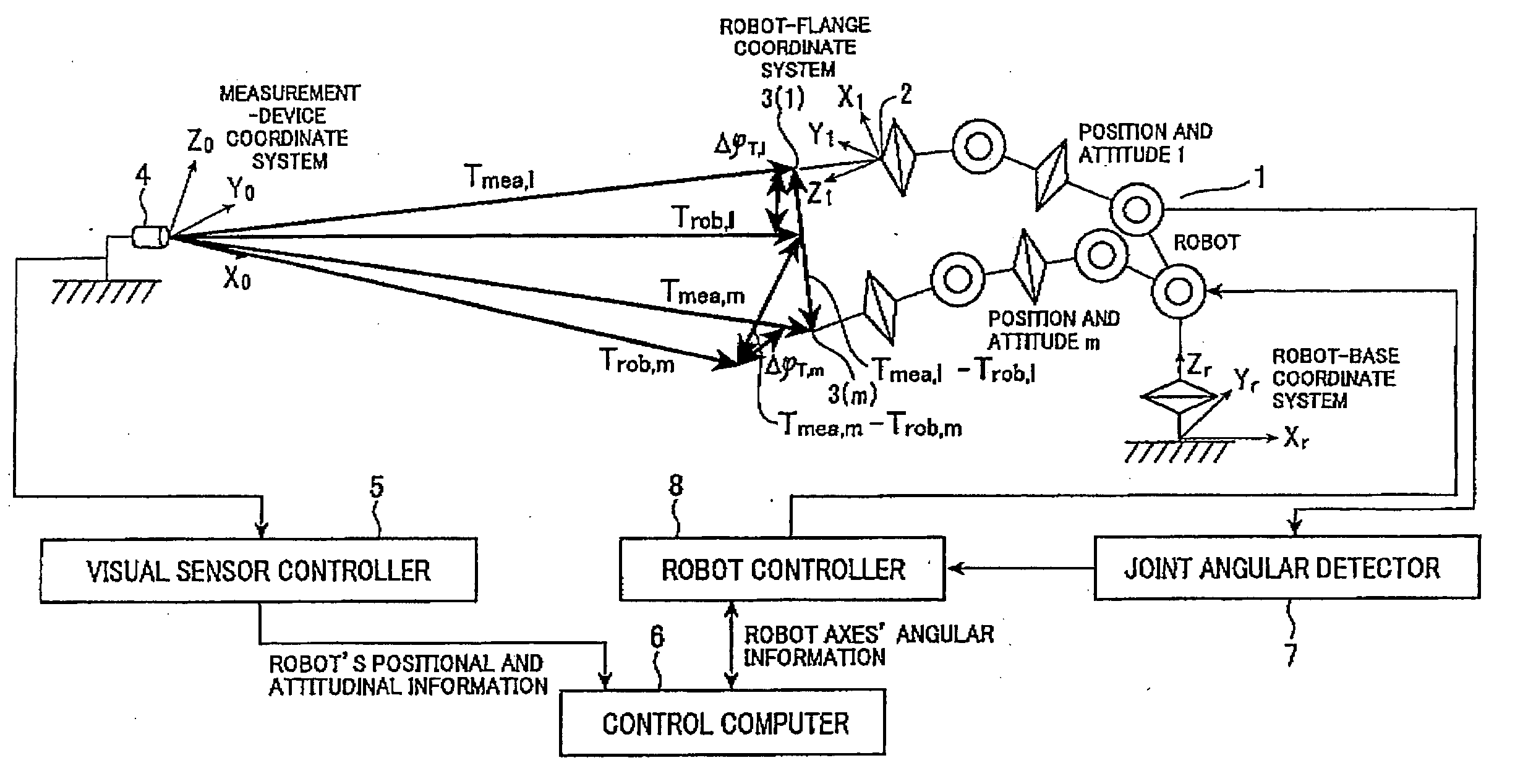
Method and apparatus for calibrating position and attitude of arm tip of robot
ActiveUS20100168915A1Improve accuracyImprove calibration accuracyProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlEngineeringArticulated robot
A calibrating technique is provided for the position / attitude or only the position of an arm tip of a robot, such as an articulated type of robot. At plural positions, respective n pieces of errors (Δφn, wherein n is a positive integer larger than a value obtained by dividing the number of unknown parameters by 6 or 3) are calculated. Each error is a difference between a position of the arm tip measured and a position commanded by control. An inter-error difference (Δεy (1≦y≦n−1)) between a reference error (Δφm (1≦m≦n)) arbitrarily selected from the n-piece errors (Δφn) and other errors (Δφx (x≦n, except for m)) other than the reference error (Δφm) is calculated. A parameter, which is a basis for calculating the inter-error differences (Δεy), is made to converge until a sum of absolute values of the inter-error differences (Δεy) becomes within a given threshold (ε0 (ε0>0)).
Owner:DENSO WAVE INC
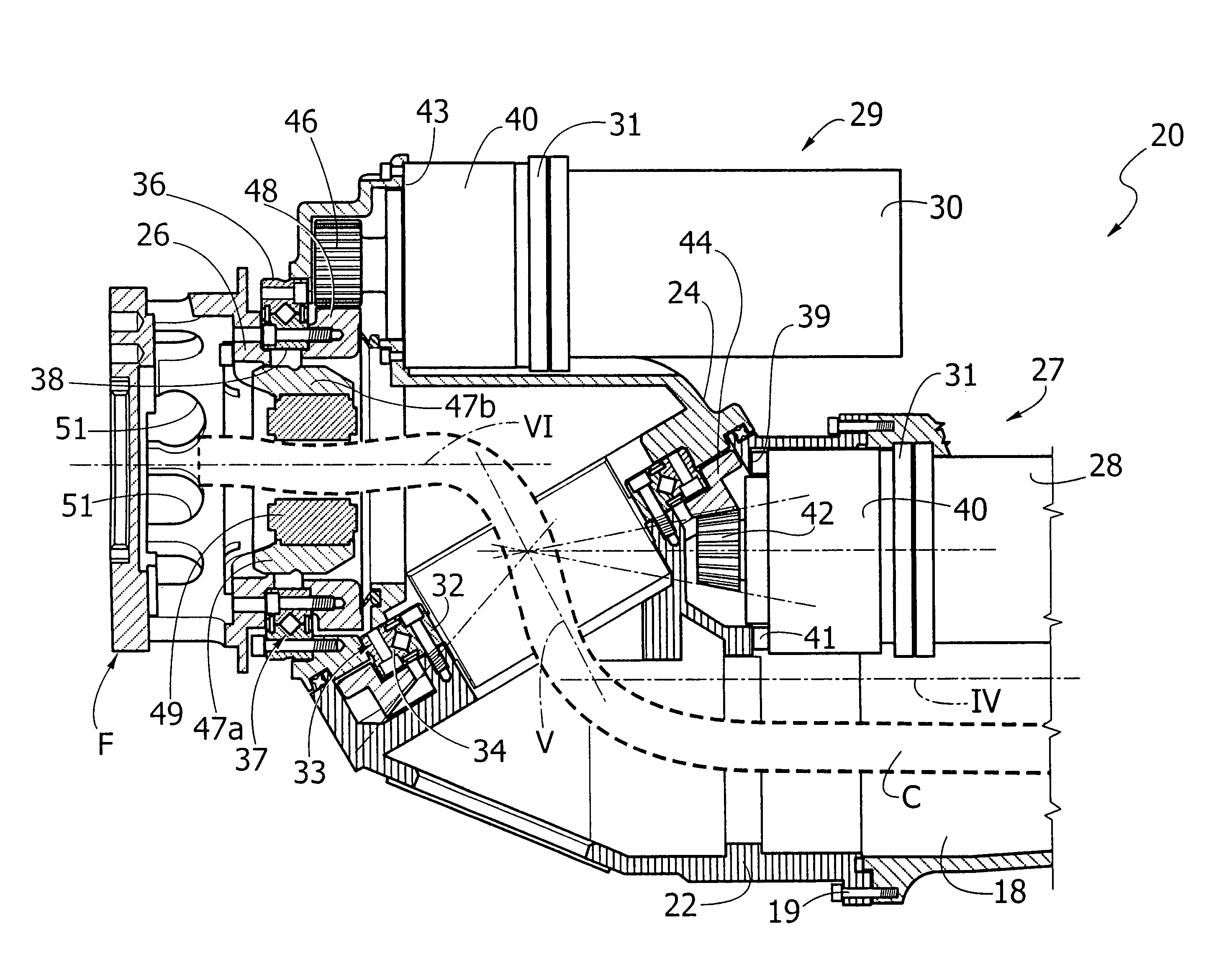
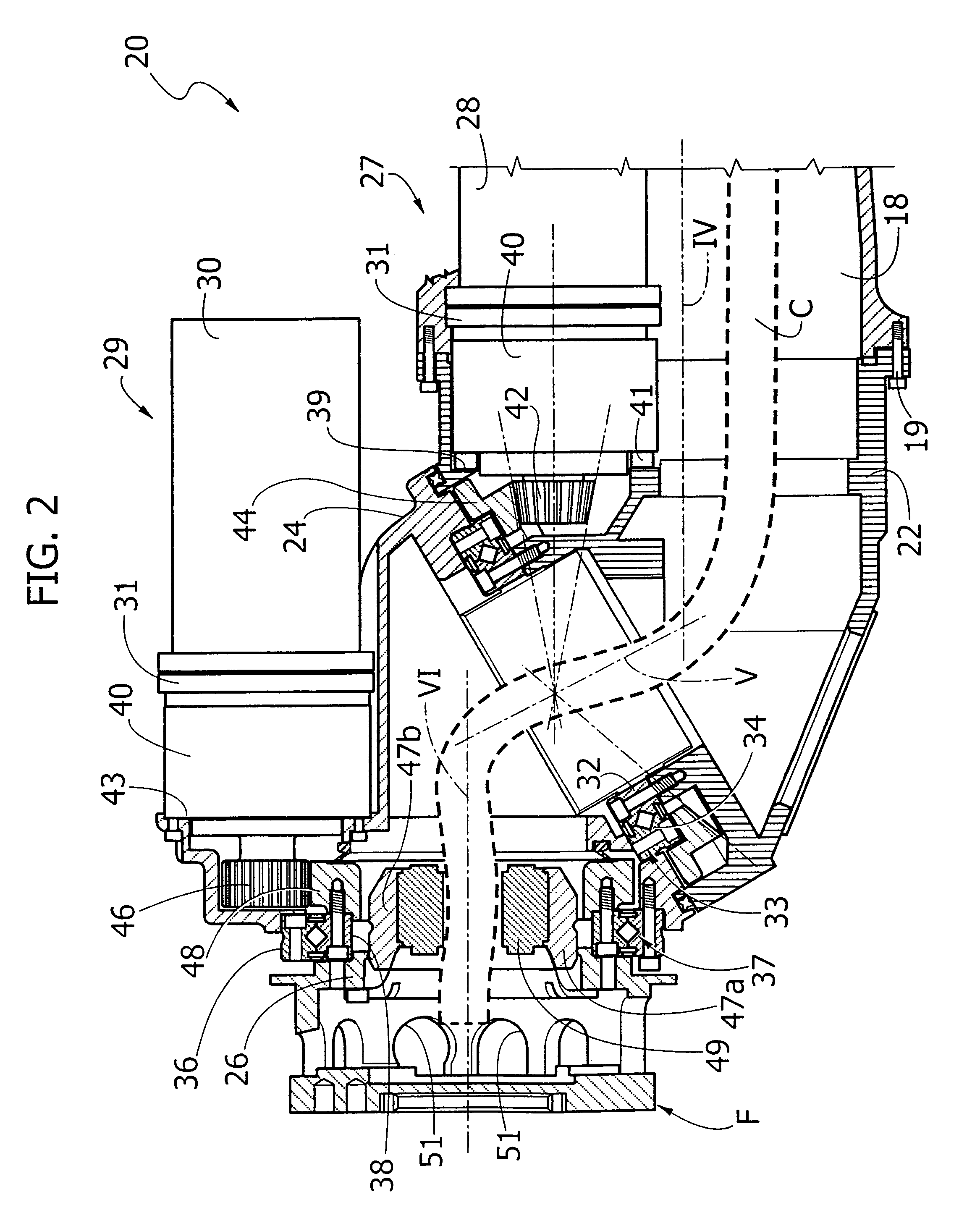
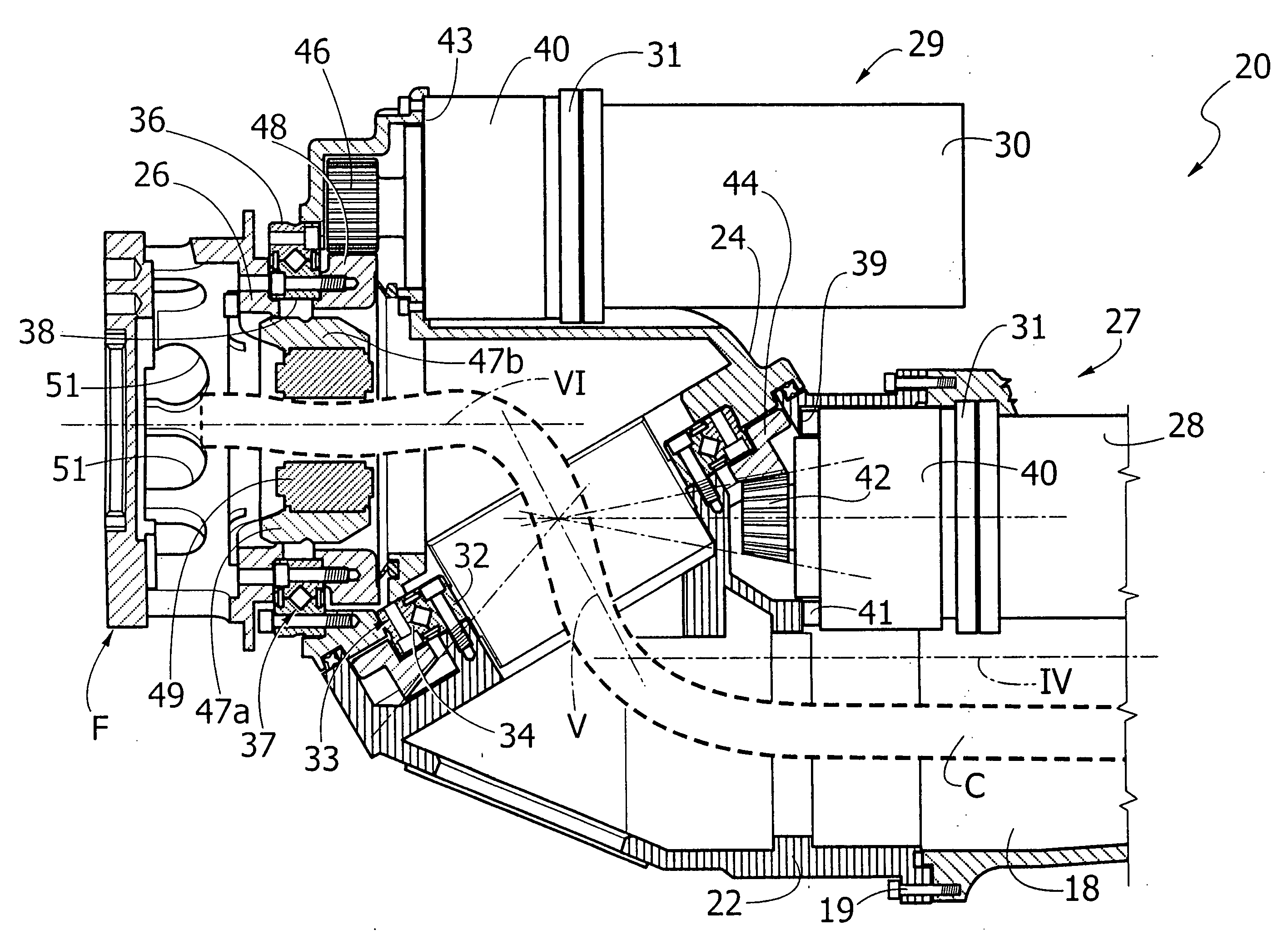
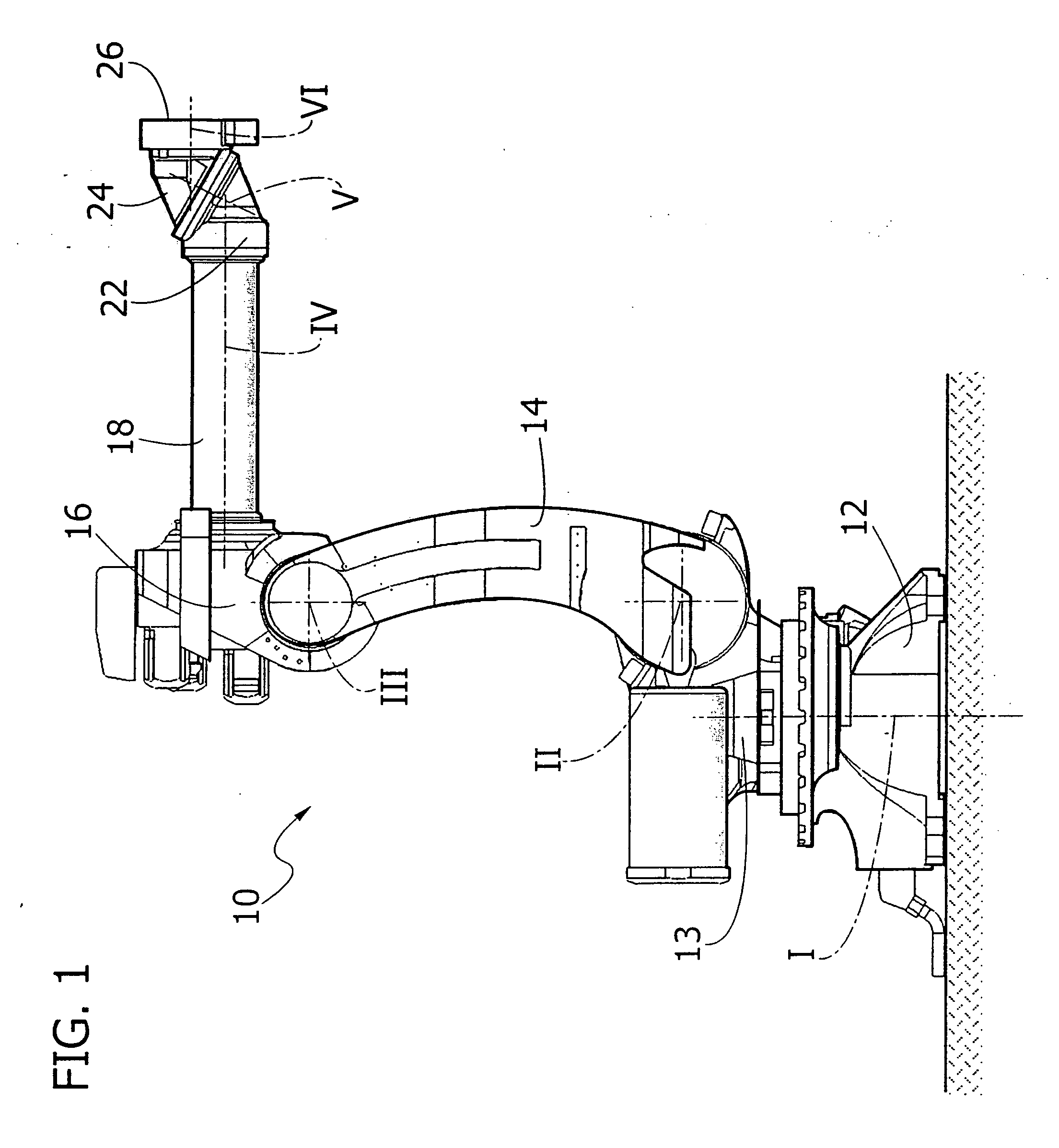
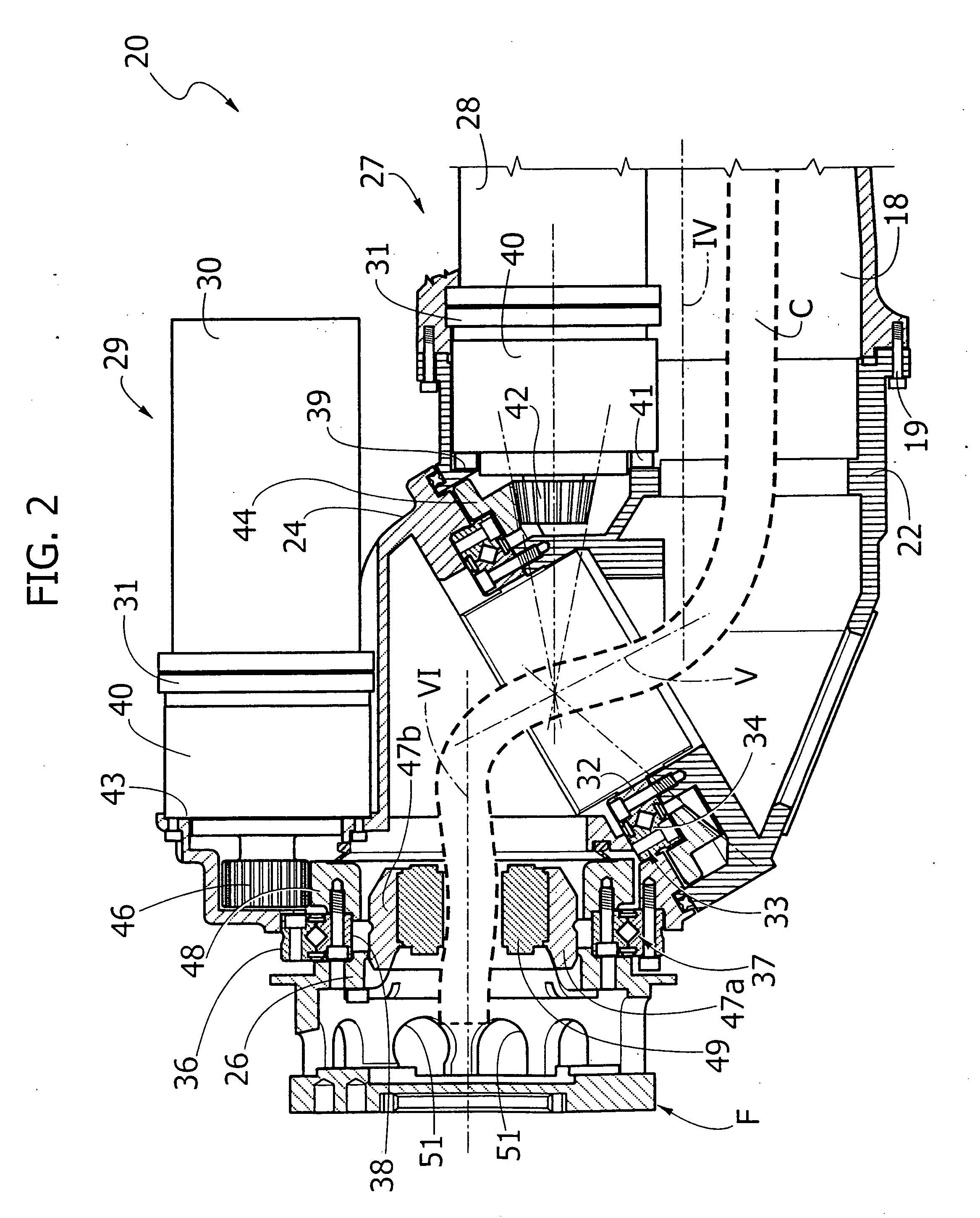
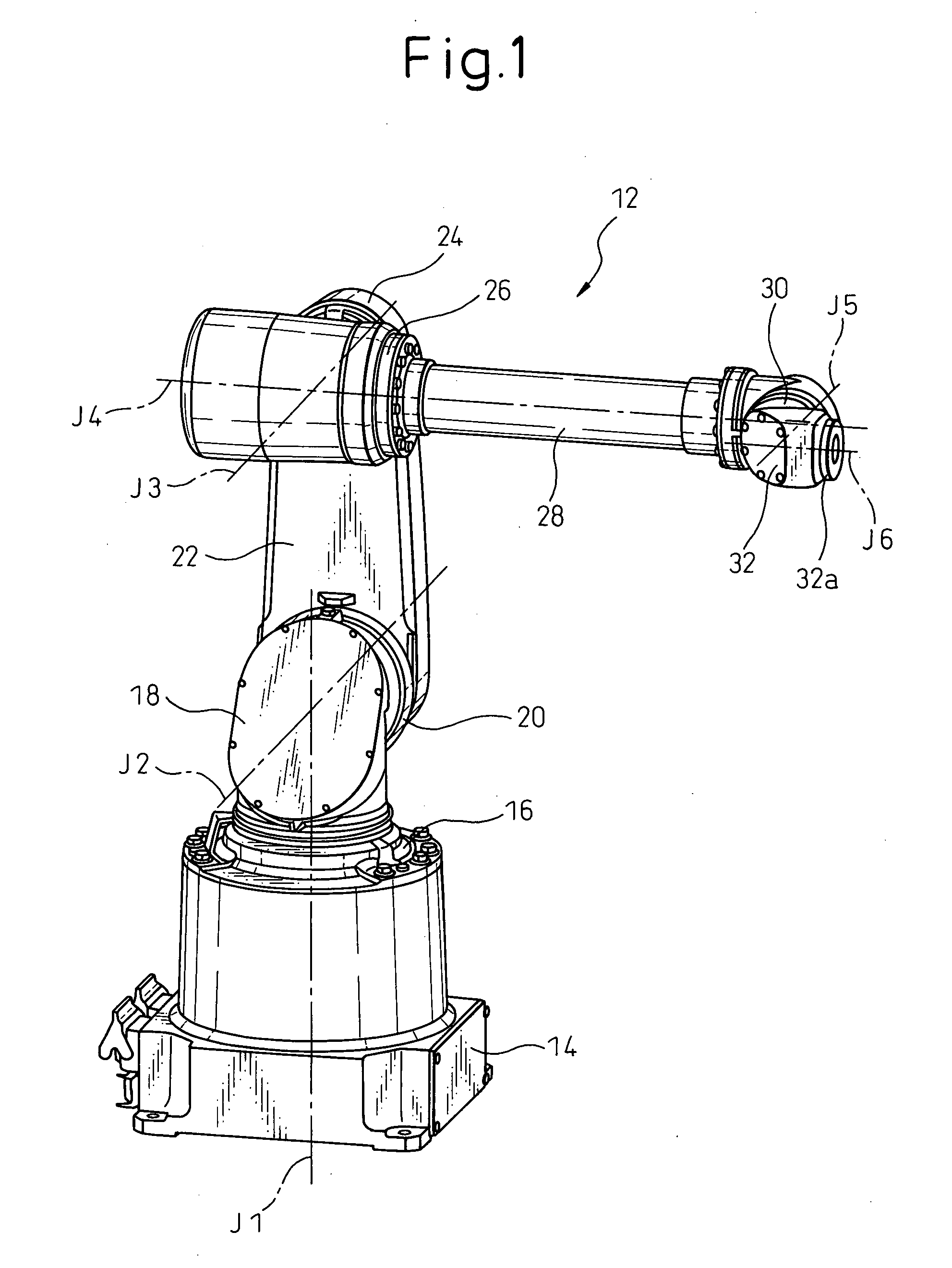
Articulated robot wrist
An articulated robot includes a wrist carrying a flange for attachment of an apparatus to be carried by the robot. The wrist comprises a first support mounted on a robot component that is rotatable about a first axis, a second support rotatably mounted on the first support about a second axis inclined with respect to the first axis, and a third support rotatably mounted on the second support about a third axis, inclined with respect to the second axis. A first motor carried by the first support drives the rotation of the second support, and a second motor carried by the second support drives the rotation of the third support, which ends with the flange for attachment of the apparatus to be carried by the robot.
Owner:COMAU SPA
Horizontal articulated robot
ActiveUS7422412B2Compact and economicalProgramme-controlled manipulatorMechanical apparatusEngineeringActuator
A horizontal articulated robot has a plurality of horizontal arms coupled by joint shafts, and a working shaft disposed at the extreme end of an extreme end arm among the horizontal arms has mounting portions of an end effector formed to both the upper and lower ends thereof. With this arrangement, there can be provided a horizontal articulated robot that can cope with various work transport forms and various types of works by one type of a robot by selectively using the upper and lower sides of a working shaft.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Articulated robot
ActiveUS7597025B2Reduce dead spaceWide areaProgramme-controlled manipulatorMechanical apparatusElectric power transmissionRotational axis
An articulated robot capable of reducing dead space while maintaining a wide operating area and simplifying a power transmission system necessary for moving each joint. A plurality of joint arms A1 to A7 are connected via first rotating shafts 15, 15A, and 15B as horizontal rotating shafts and via second rotating shafts 32, 32A, and 32B as inclined rotating shafts alternately. A motor M for driving the rotating shaft and a speed-reducing mechanism are provided for each rotating shaft.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
A traditional Chinese medicine massage robot combining rectangular coordinates and joints
ActiveCN102283765AImprove rigidityHigh positioning accuracyDevices for locating reflex pointsVibration massagePhysical medicine and rehabilitationRectangular coordinates
The invention relates to a rectangular coordinate and joint type combined traditional Chinese massage robot which is characterized by comprising a bed body provided with a support frame, wherein a mechanical arm is arranged on the support frame; and a massage device comprising a thumb rubber assembly, a metacarpus massage assembly and a roller is arranged at the tail end of the mechanical arm. The mechanical arm in the rectangular coordinate and joint type combined traditional Chinese massage robot is a rectangular coordinate and joint type combined mechanical device and has the characteristics of favorable rigidity and high positioning precision endowed by a rectangular coordinate type mechanical device as well as the characteristic of flexible action endowed by a joint type mechanical device; and the massage device is arranged at the tail end of the mechanical arm. The massage device can be used for realizing various traditional Chinese massage methods such as kneading, finger rolling, finger pressing, palm pushing, palm kneading, palm pressing, vibrating, rolling, rapping and the like under the matching of the mechanical arm.
Owner:SHANDONG KANGTAI INDAL
Four-shaft mechanical arm for grabbing sheet metal parts
ActiveCN103707296ASmall sizeNot suitable for working in tight spacesProgramme-controlled manipulatorEngineeringPerpendicular direction
The invention provides a four-shaft mechanical arm for grabbing sheet metal parts, and belongs to the technical field of four-shaft mechanical arms. The four-shaft mechanical arm for grabbing the sheet metal parts is used for solving the problems that according to a traditional four-freedom-degree articulated robot, a linear movement portion which ascends and descends perpendicularly is arranged at the tail end of a robot body, the mechanism size in the perpendicular direction is large, and the robot is not applicable to operation in a narrow and small space. The four-shaft mechanical arm for grabbing the sheet metal parts is formed by a first shaft unit, a second shaft unit, a third shaft unit, a fourth shaft unit and an electronic control cabinet in a combined mode, wherein the first shaft unit is used for implementing ascent and descent movement of a mechanical arm body, the second shaft unit is used for implementing rotation movement of a large arm, the third shaft unit is used for implementing rotation movement of a small arm, the fourth shaft unit is used for implementing rotation movement of a sucker support, the four shaft units can be used in cooperation, the working range of each shaft is wide, and the four-shaft mechanical arm is quite applicable to operation in the narrow and small space. According to the four-shaft mechanical arm for grabbing the sheet metal parts, the stroke of a first shaft ranges from 0mm to 400mm, the stroke of a second shaft is within the range of + / -180 degrees, the stroke of a third shaft is within the range of + / -135 degrees, the stroke of a fourth shaft is within the range of + / -110 degrees, and repeated positioning accuracy is within the range of + / -0.5mm.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Horizontal articulated robot
ActiveUS20100050806A1Extended range of motionMinimize increase in massProgramme-controlled manipulatorMechanical apparatusEngineeringArticulated robot
A horizontal articulated robot includes a base, a first arm provided rotatably around a first rotation axis on the base, a second arm provided rotatably around a second rotation axis on the first arm, the second rotation axis being parallel to the first rotation axis, and a main shaft provided in the second arm to be extended in a direction parallel to the second rotation axis. A distance between the second rotation axis and the main shaft is shorter than a length of a straight line connecting the first and the second rotation axes. Additionally, the first arm has a recessed portion formed so as to include a position on a rotation path where a rotation radius around the second rotation axis is equivalent to the distance between the second rotation axis and the main shaft.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Articulated robot wrist
Described herein is an articulated robot wrist, comprising: a first support, which is to be mounted on a robot component that is rotatable about a first axis; a second support, mounted on said first support in a rotatable way about a second axis inclined with respect to said first axis; a first motor, carried by said first support, the shaft of which is connected in rotation to said second support via a first gear transmission; a third support, mounted on said second support in a rotatable way about a third axis, inclined with respect to said second axis; and a second motor, carried by the second support, the shaft of which is connected in rotation to said third support via a second gear transmission.
Owner:COMAU SPA
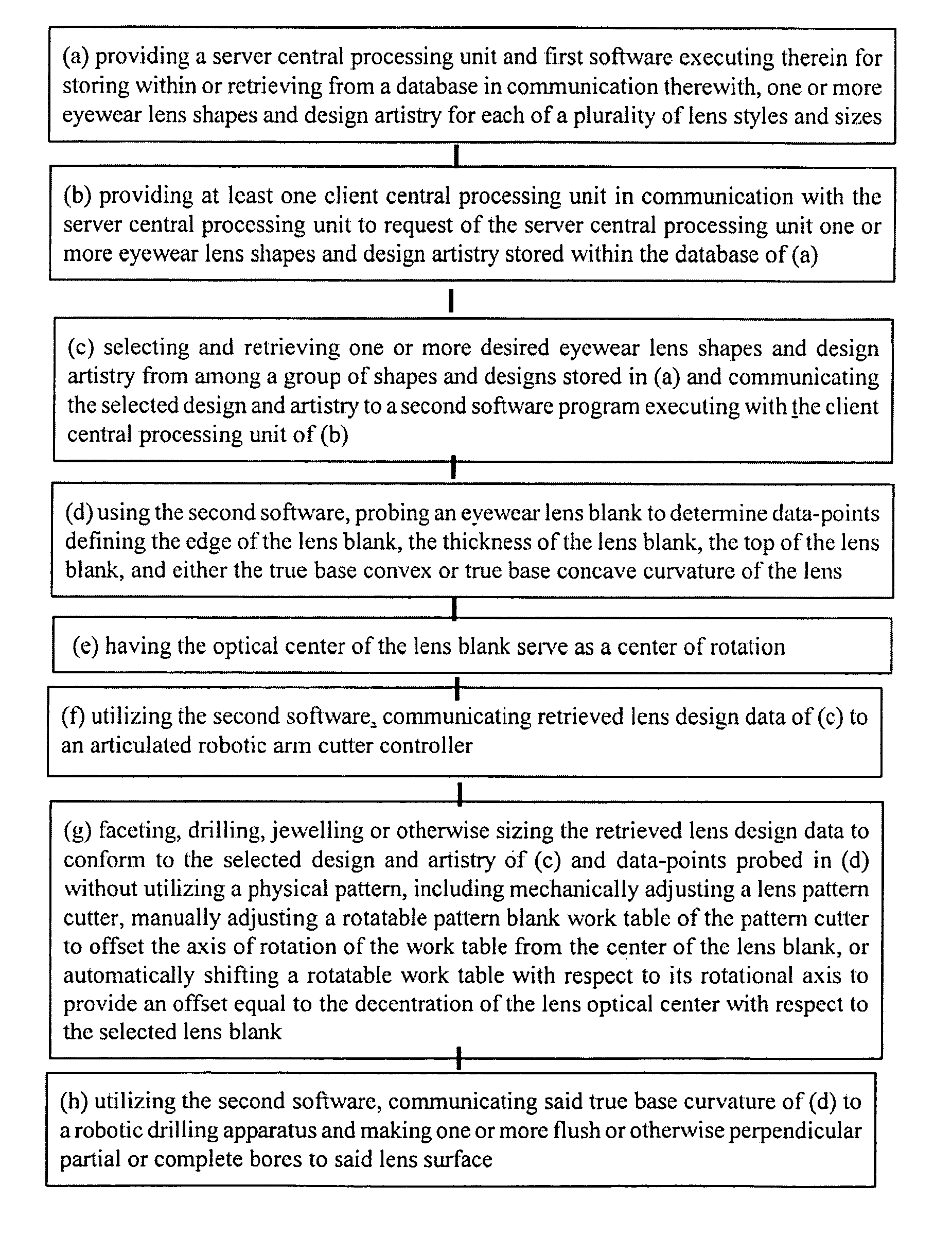
E-facet optical lens
A method and system design and manufacture of the monogrammed faceted and stone adorned eyeglass lenses via a computer program allowing a design, intricate facet cuts and stone placement on a computer lens model. Software may utilize a touch probe or laser scanner to gather point data from a previously designed lens, converting the data to a computer model. The data is then used to send signals to an articulated robotic arm holding a lens shape. The robotic arm receives the commands from the computer, moving and rotating the lens shape against an abrasive wheel, rotating cutter blade or rotating drill thereby duplicating the facet cuts, slots notches or depressions or other designs contained in the computer lens model. Varying pressure is applied by the articulated arm and various degrees of abrasiveness of the abrasive wheel.
Owner:YANCY VIRGIL T
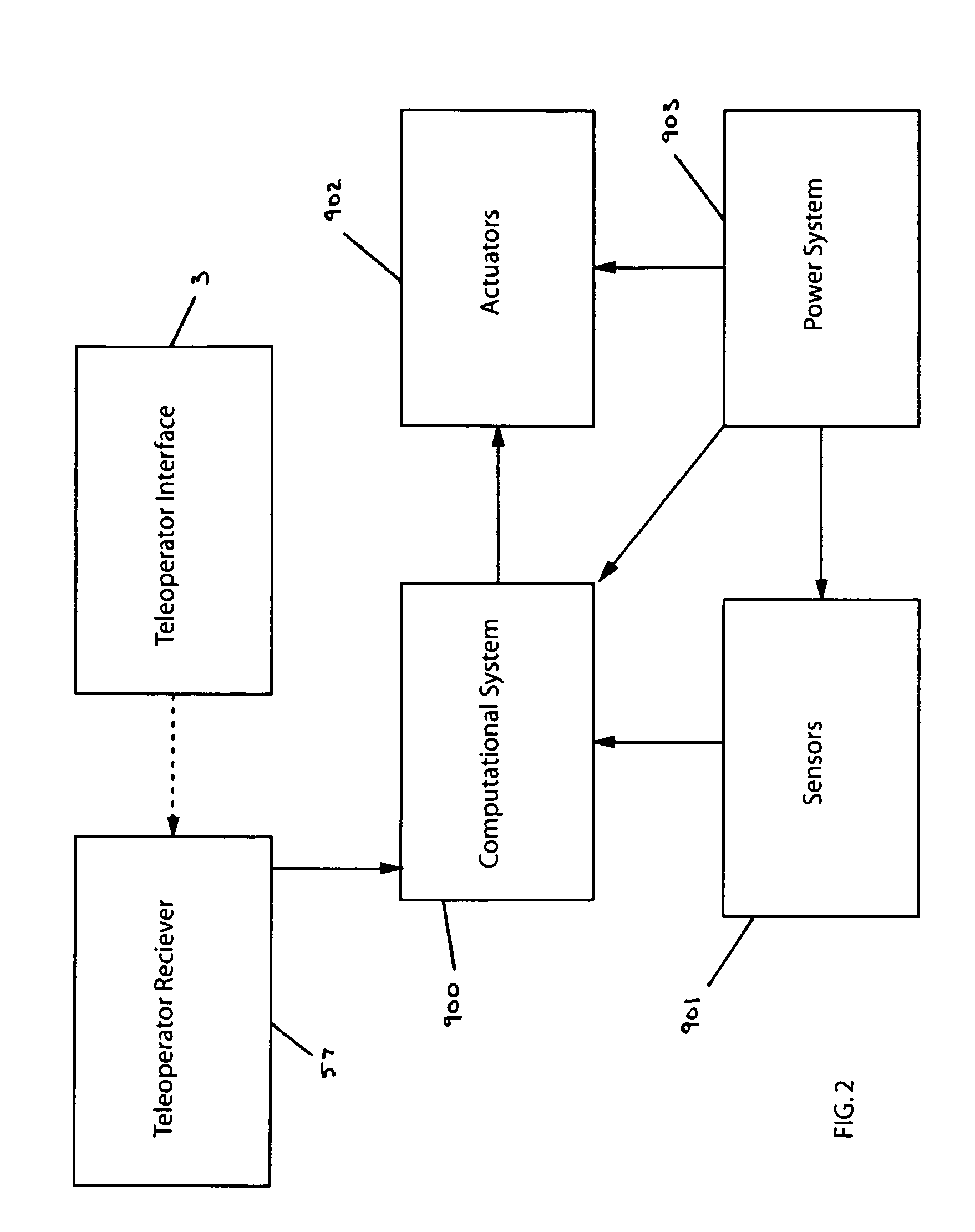
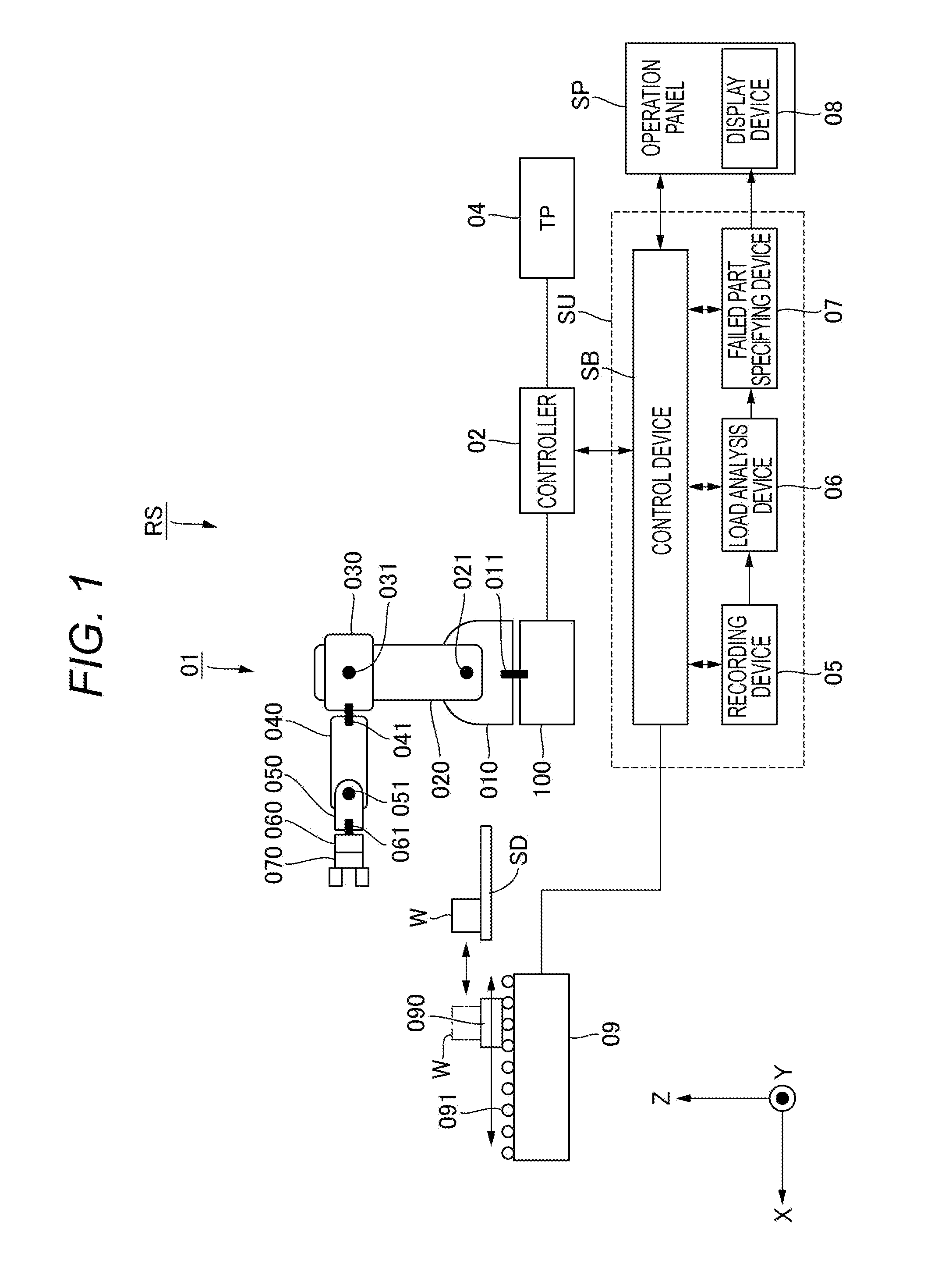
Robot system controlling method, program, recording medium, robot system, and diagnosis apparatus
ActiveUS20150328774A1Accurate estimateLess errorProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorRobotic systemsSimulation
A method of controlling a robot system including an articulated robot and a control device is provided. The articulated robot includes links connected by joints, motors configured to drive the joints respectively, and detection devices configured to detect rotation amounts of the joints respectively. The control device controls the motors. The method includes the steps of, by the control device, recording movement information of the joints based on outputs of the detection devices; when detecting an abnormality in the operation of the articulated robot, determining presence or absence of a failure in the articulated robot based on the movement information recorded in at least a period from before detection of the abnormality until detection of the abnormality; and specifying a failure portion of the articulated robot if it is determined that there is a failure in the articulated robot in the step of determining.
Owner:CANON KK
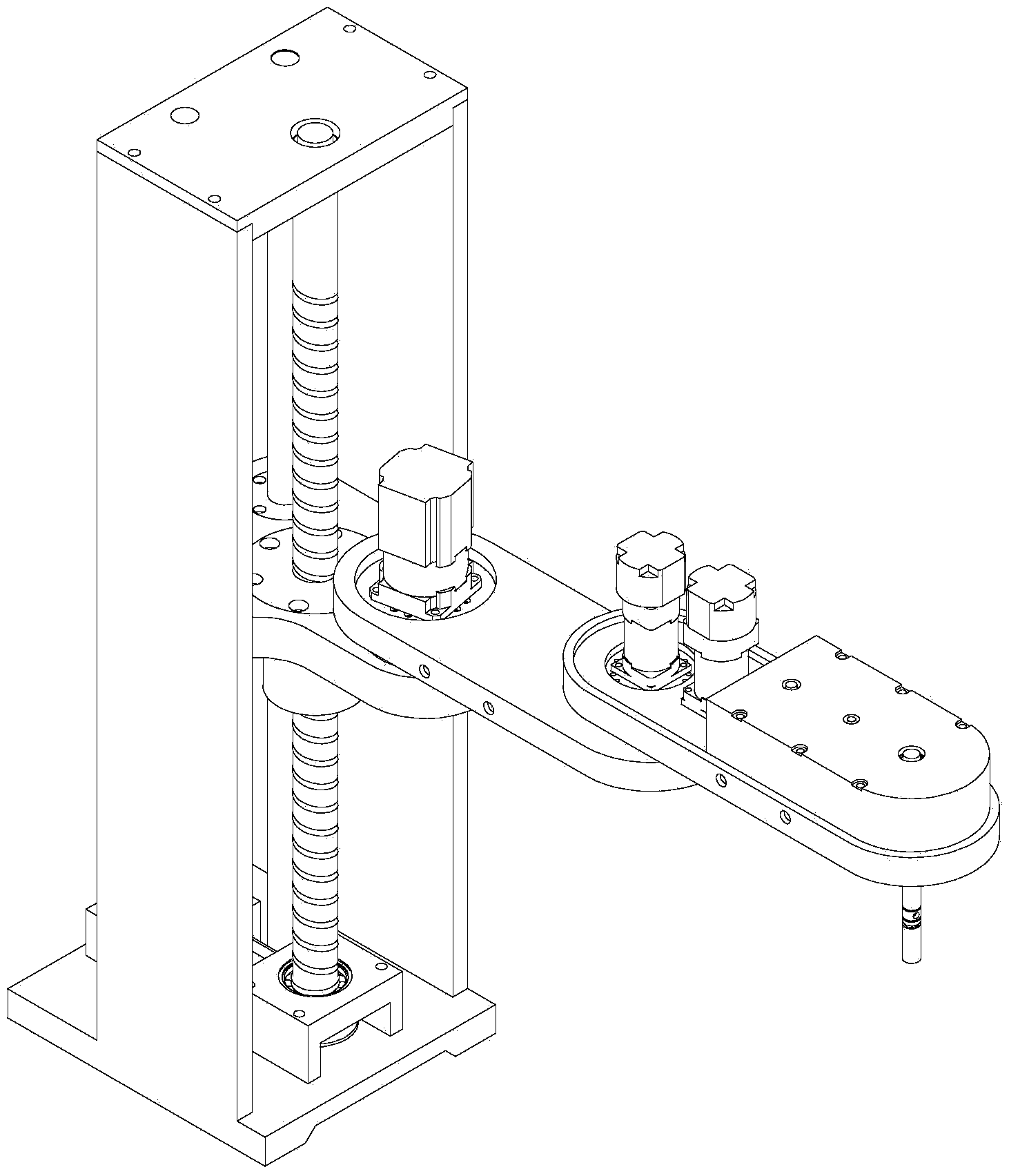
Novel plane articulated robot structure
InactiveCN103640028ACompact structureConvenient ArrangementProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsCantilevered beamOptical axis
The invention provides a novel plane articulated robot structure which comprises a base, a lifting seat, a first mechanical arm, a second mechanical arm and an operation spindle. The base functions in supporting and reducing vibration; the lifting seat vertically moves along a Z-axis direction under the limiting action of a lead screw and a polished shaft; the first mechanical arm is rotatably mounted on the lifting seat by taking an X axis parallel to a Z axis as a rotating center; the second mechanical arm is rotatably mounted on the first mechanical arm by taking a Y axis parallel to the X axis as a rotating center; the operation spindle is rotatably mounted on the second mechanical arm by taking an R axis parallel to the Y axis as a rotating center. The vertically moving Z axis of a plane articulated robot with four degrees of freedom moves to the base of the robot, so that the inertia of the mechanical arms of the industrial robot can be decreased by the design, stress of the mechanical arms serving as cantilever beams is improved, the running speed and control stability of the robot are effectively improved, and the working space of the industrial robot is enlarged.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
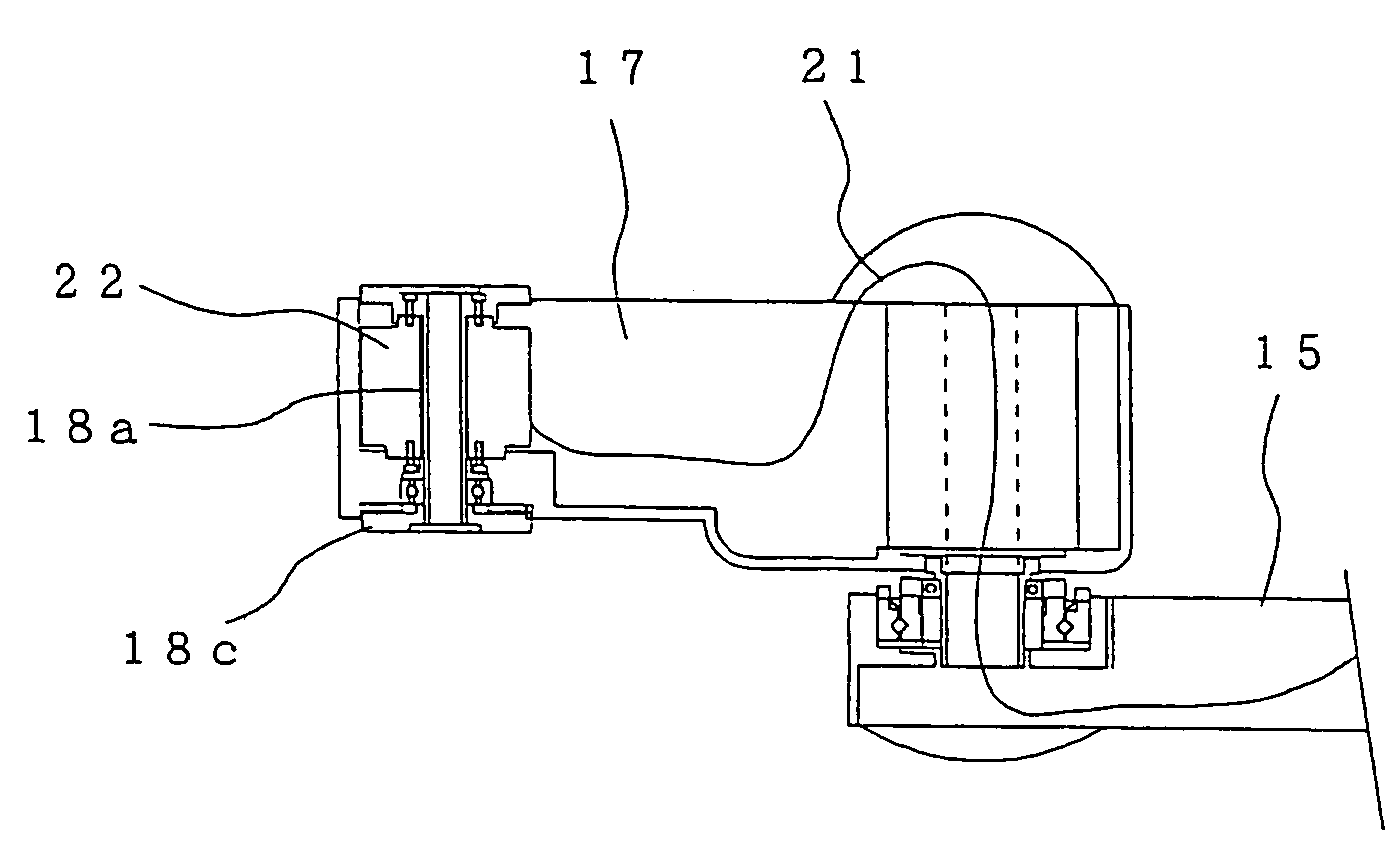
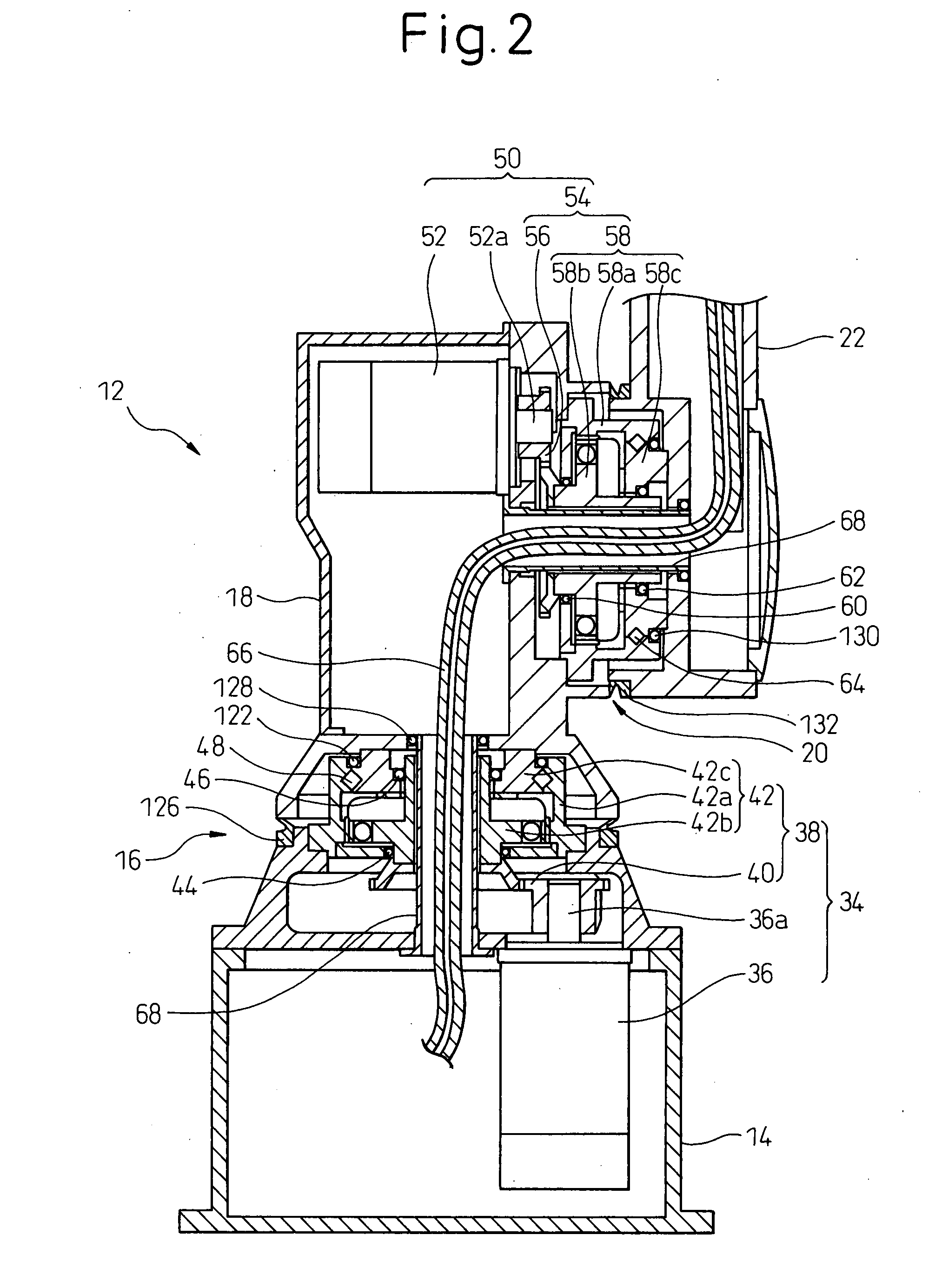
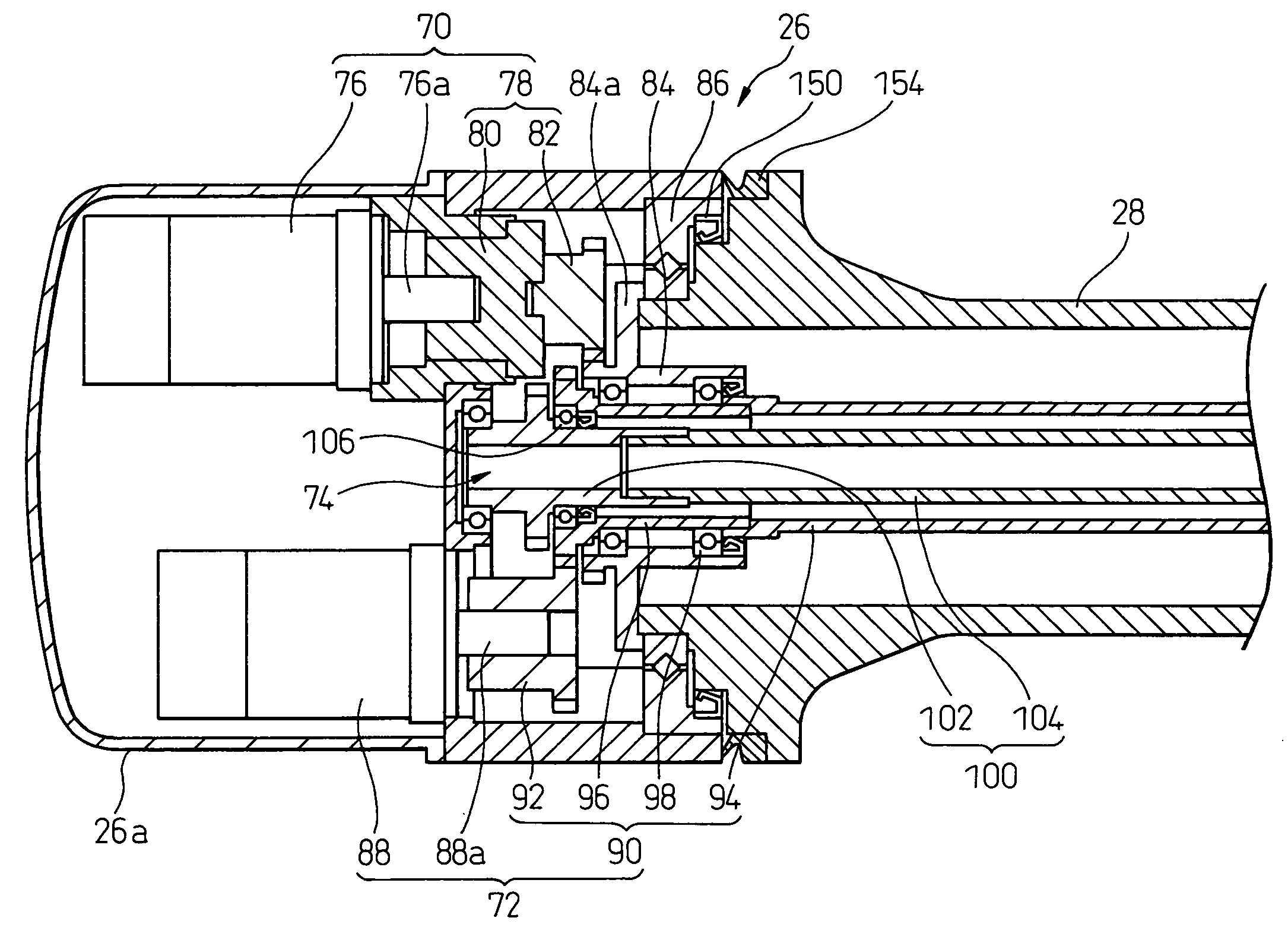
Sealing device for joint section of robot and articulated robot having the same
A sealing device provided to a joint section of a robot. The sealing device includes overlapped seal portions having a multi-stage configuration, provided for a driving mechanism incorporated into the joint section. The overlapped seal portions include a first seal portion including a first contact seal element sealing a first inter-member gap defined adjacent to a lubricant retaining section provided in the driving mechanism; and a second seal portion arranged outside the first seal portion and including a second contact seal element sealing a second inter-member gap defined in a circumferential wall of the joint section, the circumferential wall defining an accommodation space for accommodating the driving mechanism.
Owner:FANUC LTD
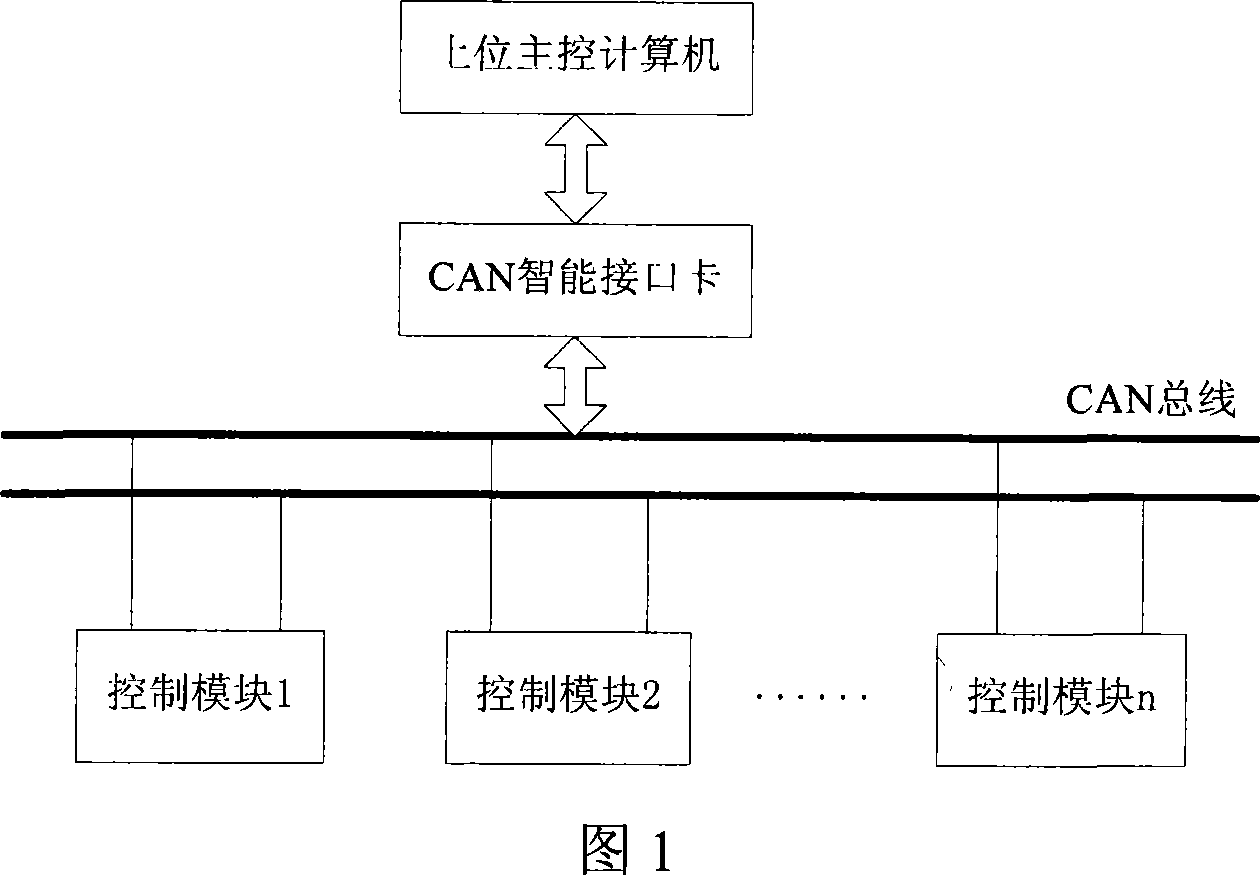
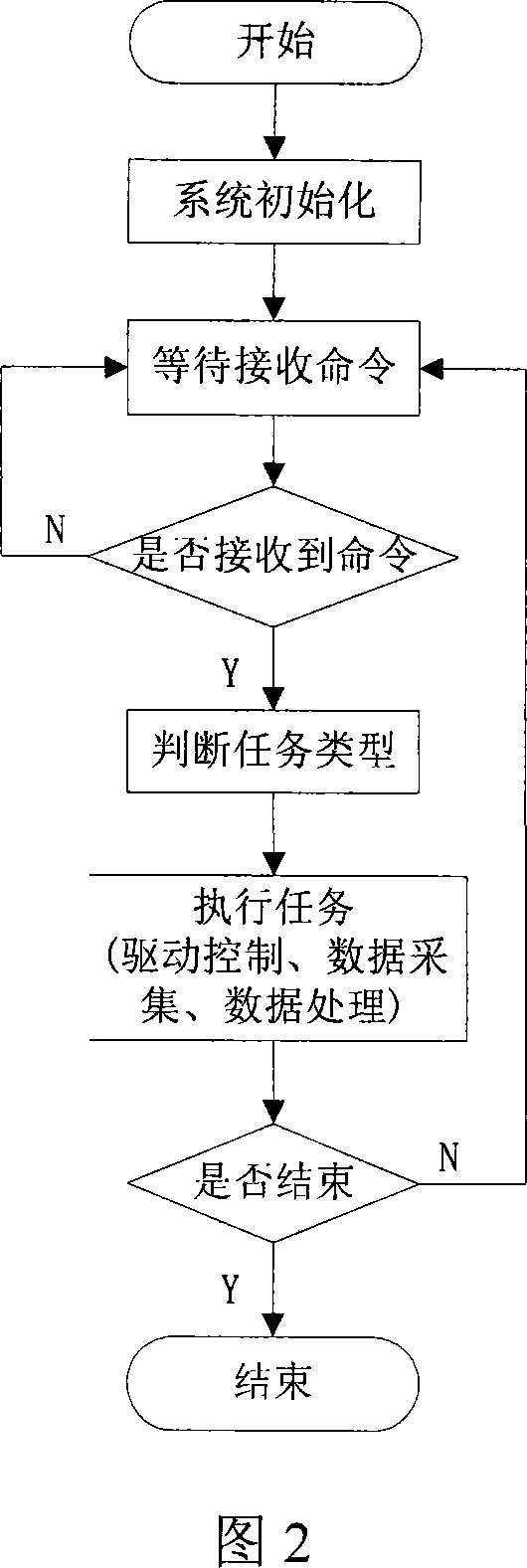
Control system for modular robot based on CAN bus
InactiveCN101053954AImprove portabilityIncrease or decrease quantityProgramme-controlled manipulatorTotal factory controlControl systemComputer module
The present invention relates to a modularized control system for an articulated robot, which is based on CAN bus. The present invention is characterized in that the control system comprises a PC, a CAN intelligence interface card, a plurality of control modules (wherein, each control module controls one articulation of the robot), and a CAN bus for connecting the modules and the CAN intelligence interface card. In the control system of the present invention, a two circuit CAN intelligence interface card is connected to the PC by an USB interface at one end, and is connected to the CAN bus by a CAN bus interface at the other end; the control module is connected to the CAN bus. The system and method of the present invention has excellent portability, short development cycle, low cost, regrouping property, fungible property, openness and high stability, and can execute on-line monitoring to robot.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
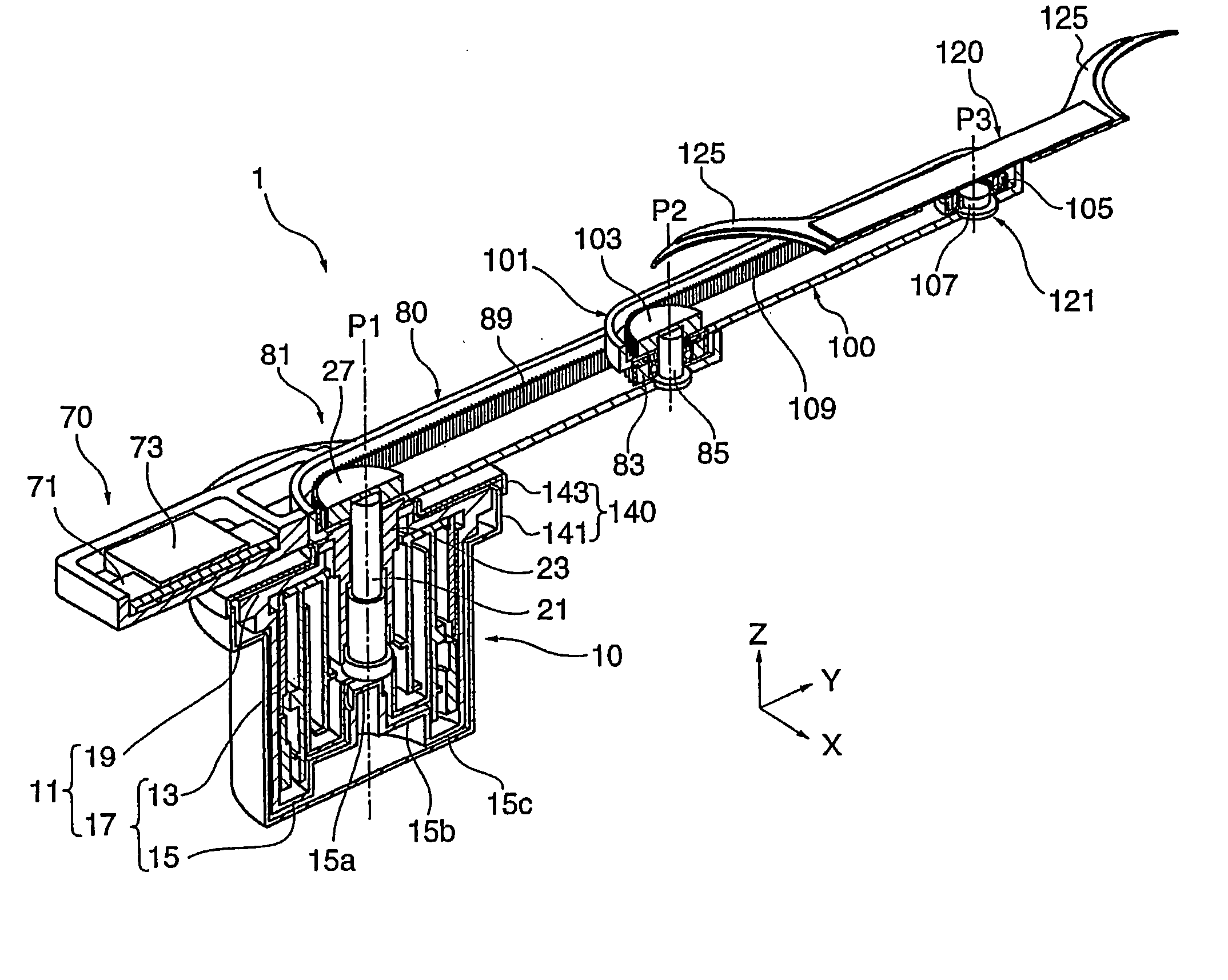
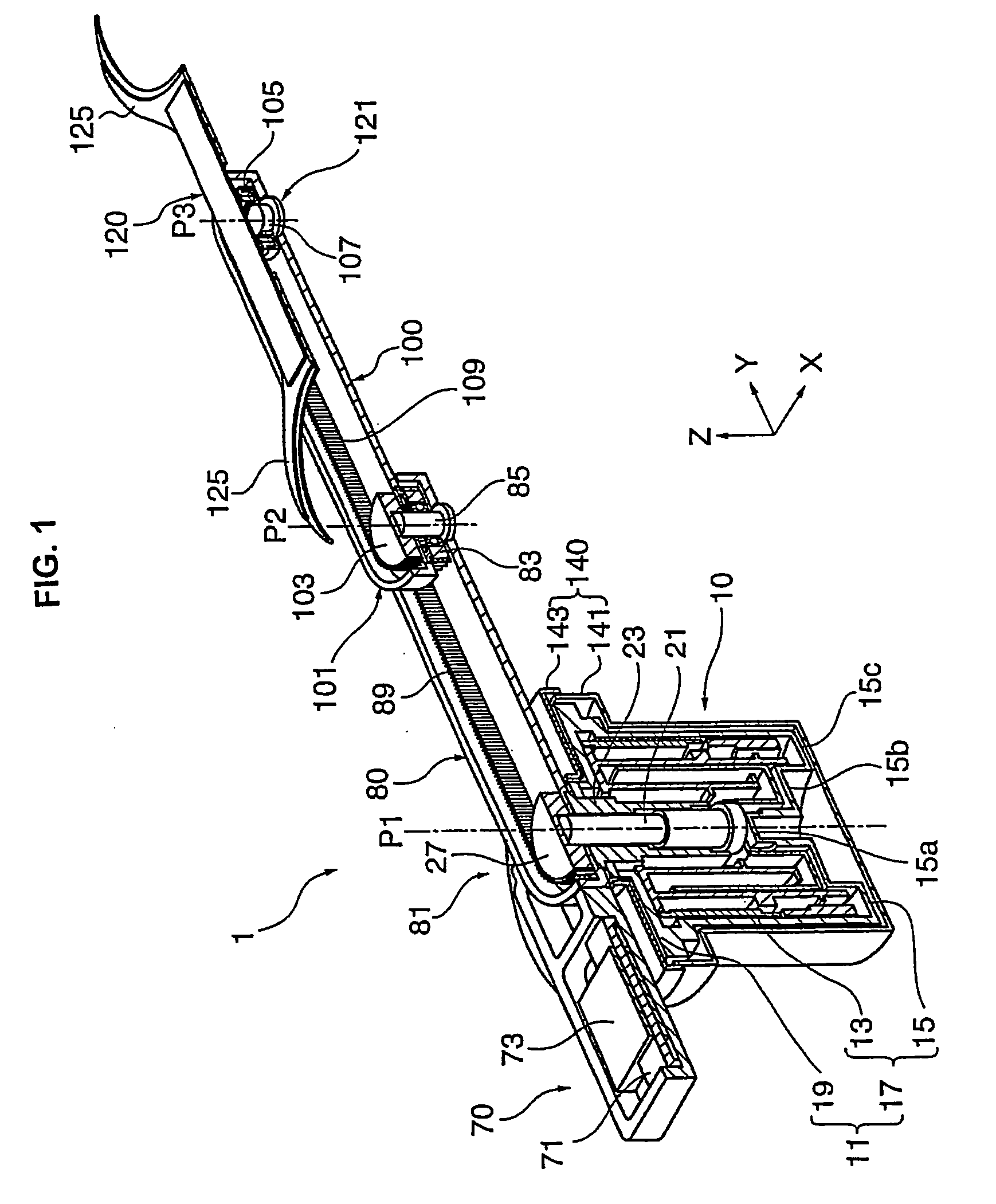
Wrist structure for an articulated robotic arm
ActiveUS20160114491A1Reduce in quantityIncrease in sizeJointsRobotSignal processing circuitsRobotic arm
A wrist structure for an articulated robotic arm includes: a wrist body, a rotary member, a signal processing circuit board, a connector, a control unit and a drive unit. The wrist body includes a front end portion, a rear end portion, a receiving portion, and a wiring hole formed in the rear end portion. The rotary member is rotatably connected to the front end portion. The signal processing circuit board is removably disposed at the rear end portion, located inside the receiving portion and includes a gap aligned with the wiring hole. The connector is disposed in the wrist body and signal connected to the signal processing circuit board. The control unit is disposed inside the receiving portion and signal connected to the signal processing circuit board. The drive unit is disposed in the receiving portion to control the rotary member to swing with respect to the wrist body.
Owner:HIWIN TECH
Articulated robot for laser ultrasonic inspection
ActiveUS7784348B2Cost-effectiveMore compact robotsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesLaser using scattering effectsNon destructiveUltrasound sonography
An ultrasonic non-destructive evaluation (NDE) system operable to inspect target materials is provided. This ultrasonic NDE system includes an articulated robot, an ultrasound inspection head, a processing module, and a control module. The ultrasound inspection head couples to or mounts on the articulated robot. The ultrasound inspection head is operable to deliver a generation laser beam, a detection laser beam, and collect phase modulated light scattered by the target materials. The processing module processes the phase modulated light and produces information about the internal structure of the target materials. The control module directs the articulated robot to position the ultrasound inspection head according to a pre-determined scan plan.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
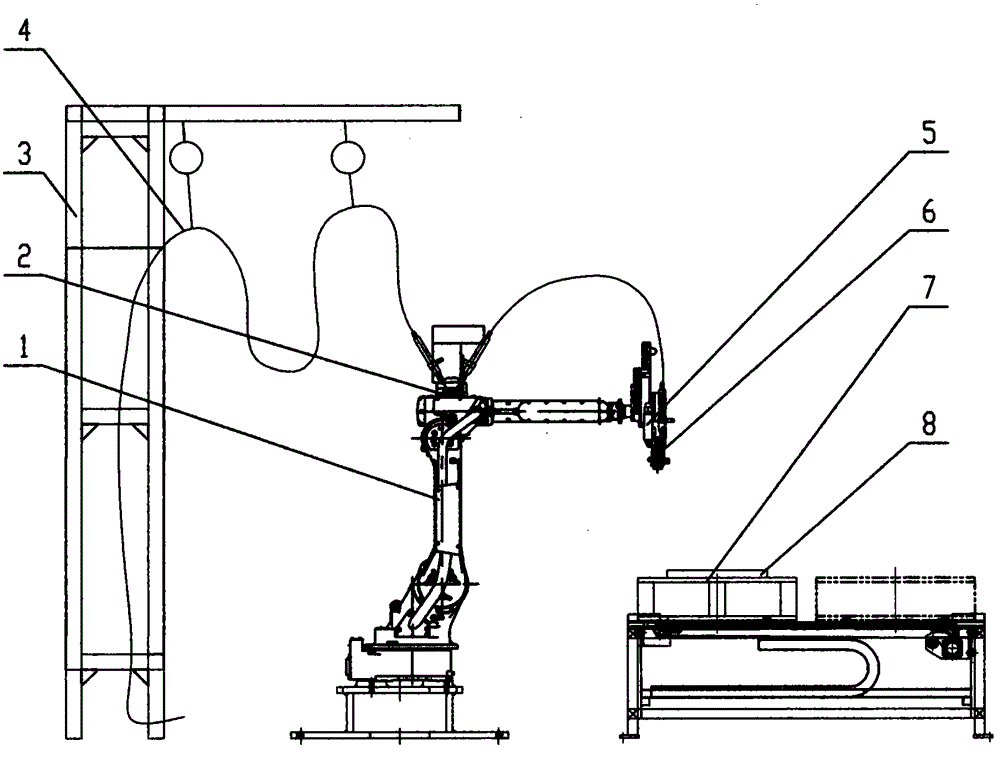
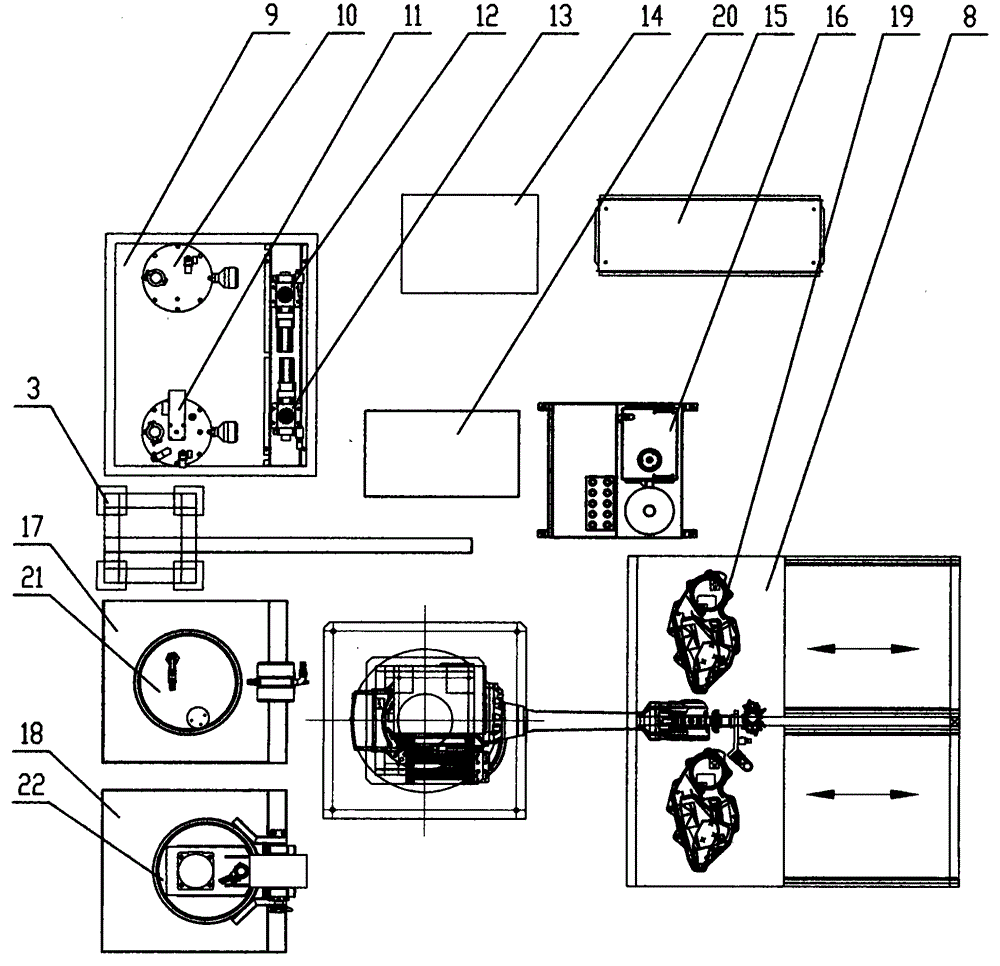
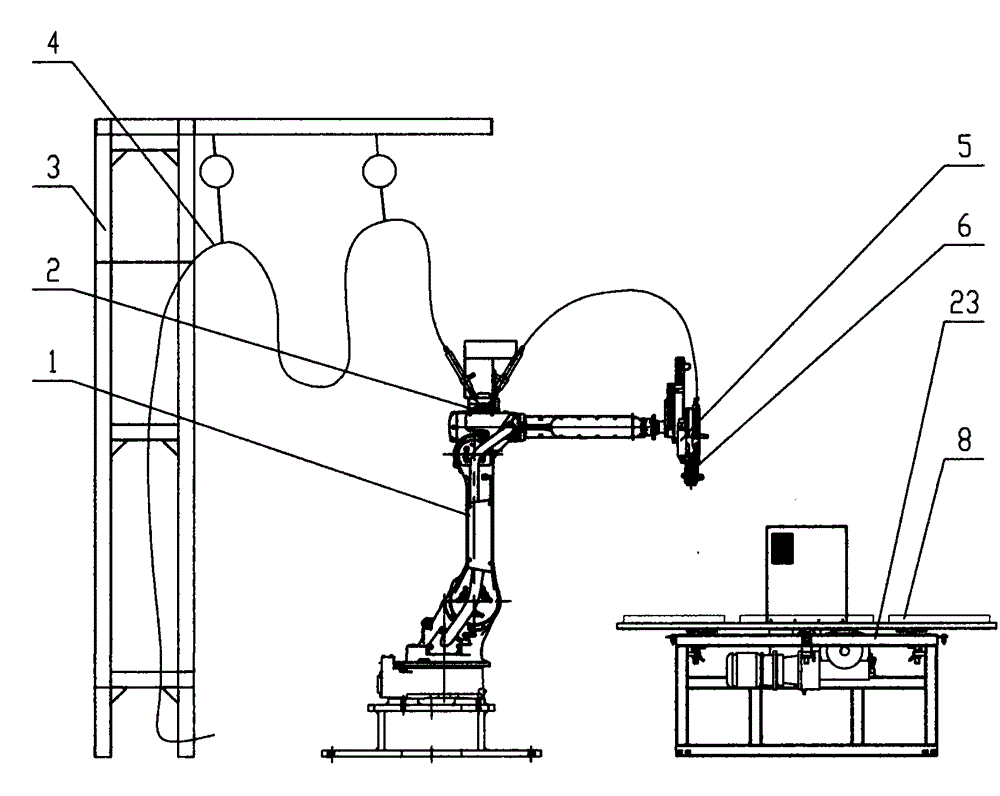
Full-automatic robot gluing equipment and process technology
The invention relates to the technical field of gluing, in particular to full-automatic robot gluing equipment and a process technology which are used for two-component polyurethane gluing. The full-automatic robot gluing equipment is characterized in that the equipment comprises a three-axis robot or a four-axis robot or a five-axis robot or a six-axis robot, a glue supply device, a two-component gluing head, a two-station automatic gluing workbench or a multi-station automatic rotary gluing workbench, plasma treatment equipment, a waste cleaning solution recovery device and an intelligent control system. The three-axis robot or the four-axis robot is of a gantry type or cantilever type structure. The two-component gluing head and a plasma treatment head are fixed to the three-axis robot or the four-axis robot and can be linked in the X axis, the Y axis and the Z axis. The five-axis robot or the six-axis robot is an articulated robot, and five-axis linkage or six-axis linkage of the two-component gluing head and the plasma treatment head can be achieved. According to the novel polyurethane gluing equipment and the process technology, the proportion is precise, glue tape performance is stable, and the sealing effect is good.
Owner:DALIAN HUAGONG INNOVATION TECH
Method of detection of welding workpiece position using movable electrode
A method of detection of a welding workpiece position using a movable electrode, in a spot welding system, a welding workpiece and a spot welding gun are moved relatively by a multi-articulated robot, such that the movable electrode is closed to the welding workpiece or the movable electrode is separated from the welding workpiece, simultaneously, a current or torque of a servo motor is monitored, and a surface position of the welding workpiece is detected from the position of the movable electrode and the position of the multiarticulated robot when the trend of the current or torque changes.The spot welding system comprises: the spot welding gun having the movalbe electrode driven by the servo motor and a counter electrode arranged facing the movable electrode, and the multiarticulated robot for holding one of the welding workpiece and the spot welding gun. Thereby, the precision of detection of the surface position of the welding workpiece by the movable electrode in the spot welding system can now be improved without lengthening the time required for detection of the surface position of the welding workpiece.
Owner:FANUC LTD
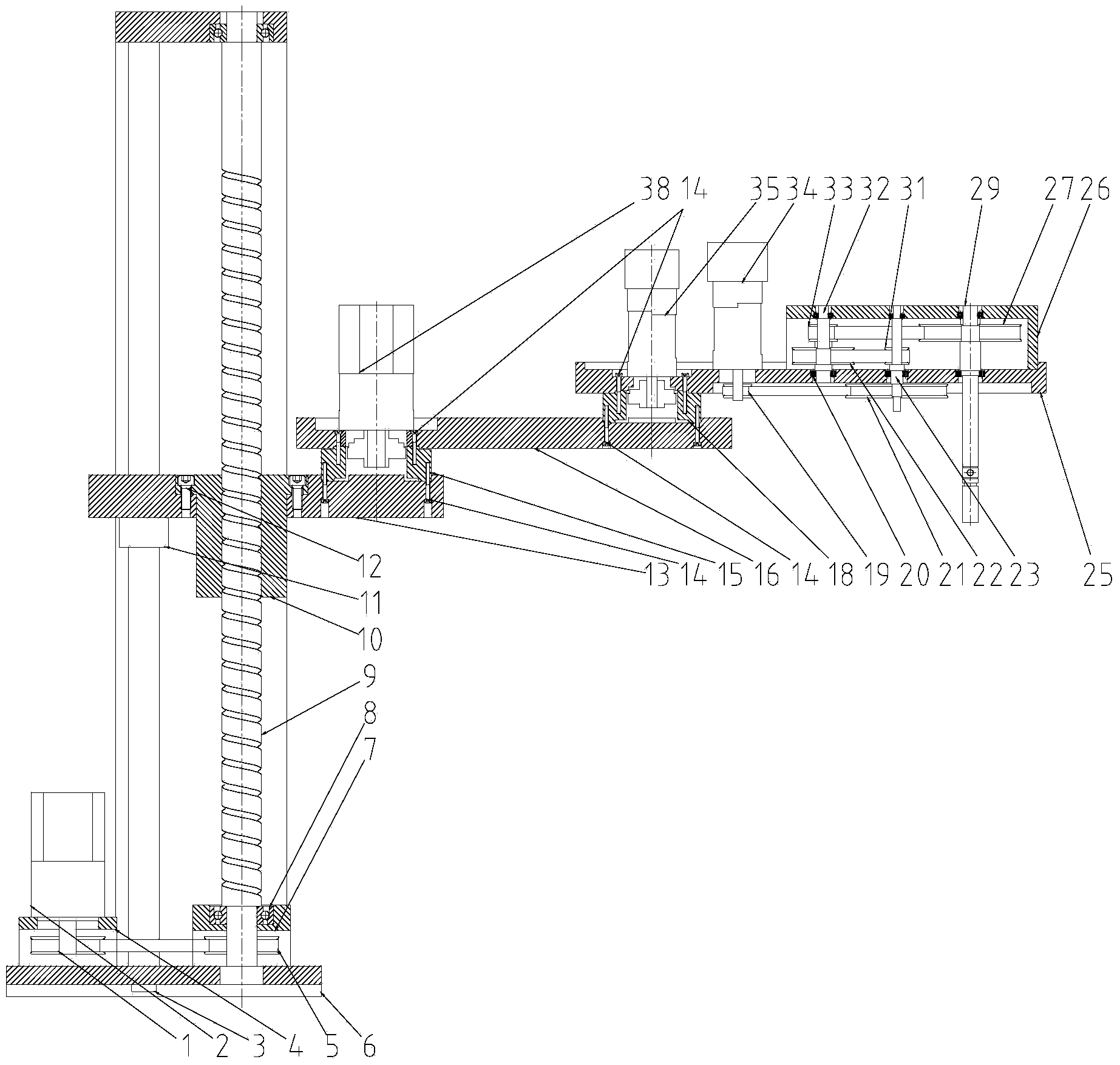
Novel four-degree-of-freedom articulated robot structure
ActiveCN104385260ACompact structureConvenient ArrangementProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsDegrees of freedomEngineering
The invention discloses a novel four-degree-of-freedom articulated robot structure. The novel four-degree-of-freedom articulated robot structure comprises a base, a lifting seat, a first mechanical arm, a Y-axis cover, a second mechanical arm, and an operation main shaft, wherein the lifting seat vertically moves in the direction of a Z-axis under the limiting actions of a lead screw, a lead screw, and a guide rail pair, the first mechanical arm can rotate around an X-axis parallel to the Z-axis to be installed on the lifting seat, the Y-axis cover is installed on the first mechanical arm, bears a first Y-axis speed reduction device shaft and a second Y-axis speed reduction device shaft, and is provided with through holes for a Y-axis servo motor shaft, the first Y-axis speed reduction device shaft and the second Y-axis speed reduction device shaft to penetrate, the second mechanical arm can rotate around the Y-axis parallel to the X-axis to be installed on the first mechanical arm, and the operation main shaft can rotate around an R-axis parallel to the Y-axis to be installed on the second mechanical arm. The novel four-degree-of-freedom articulated robot structure is simple in structure, low in cost, large in operation space, and high in operation accuracy.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
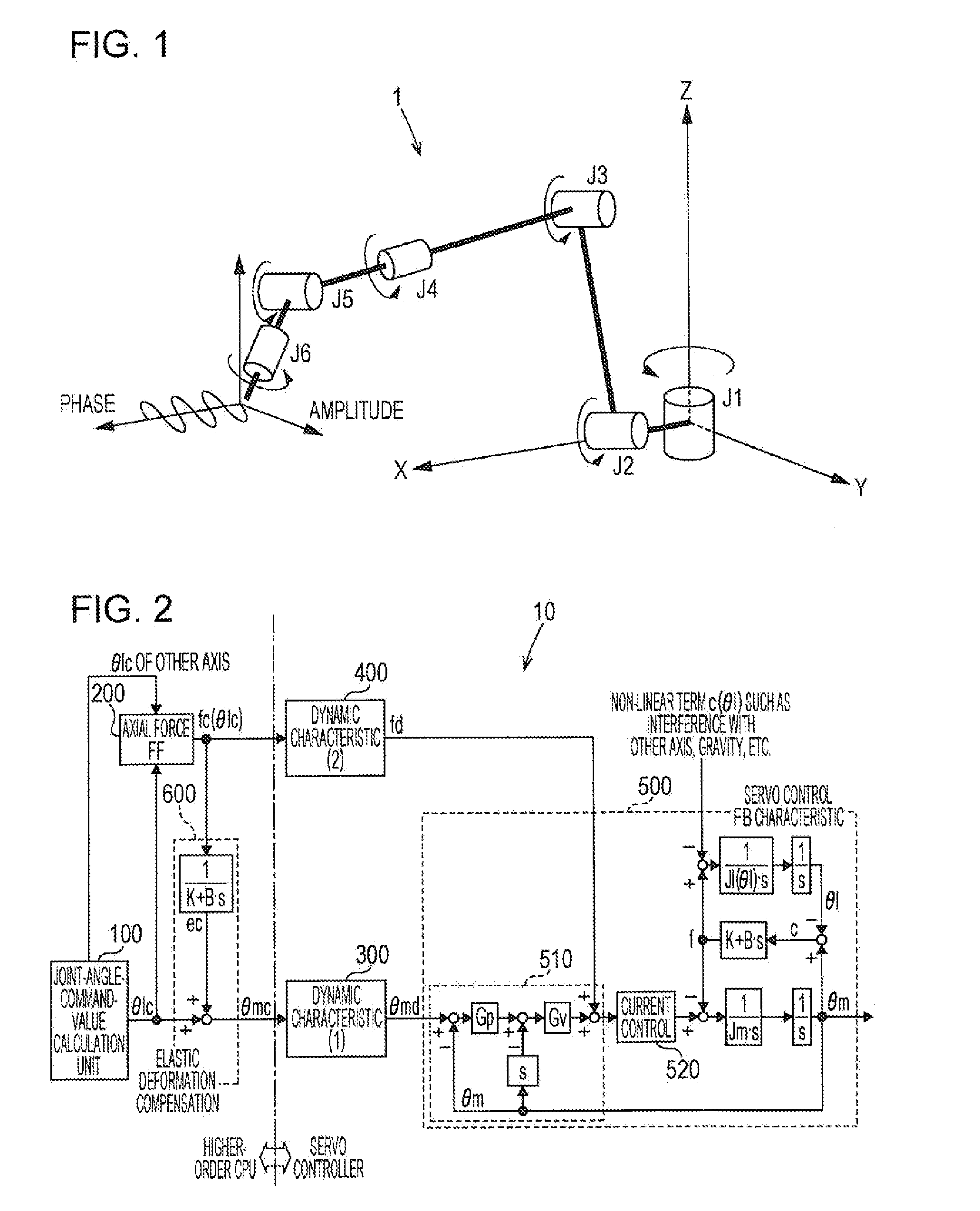
Elastic-deformation-compensation control device and control method for articulated robot
ActiveUS20150105905A1Improve trajectory accuracyImprove accuracyProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlAxial forceControl theory
In an elastic-deformation-compensation control device (10), a first dynamic characteristic calculation unit (300) performs filtering processing with respect to a motor-angle command value (θmc) outputted from a motor-angle-command-value calculation unit (600), and outputs a processed motor-angle target value (θmd). A second dynamic characteristic calculation unit (400) is provided with a high-frequency cutoff characteristic having a cutoff frequency which is lower than that of the first dynamic characteristic calculation unit (300), performs filtering processing with respect to the output from an axial force torque calculation unit (200), and outputs a processed axial force torque compensation value (fd).
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Sealing device for joint section of robot and articulated robot having the same
A sealing device provided to a joint section of a robot. The sealing device includes overlapped seal portions having a multi-stage configuration, provided for a driving mechanism incorporated into the joint section. The overlapped seal portions include a first seal portion including a first contact seal element sealing a first inter-member gap defined adjacent to a lubricant retaining section provided in the driving mechanism; and a second seal portion arranged outside the first seal portion and including a second contact seal element sealing a second inter-member gap defined in a circumferential wall of the joint section, the circumferential wall defining an accommodation space for accommodating the driving mechanism.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Method for calibrating structural parameters of robot using double-ball-bar
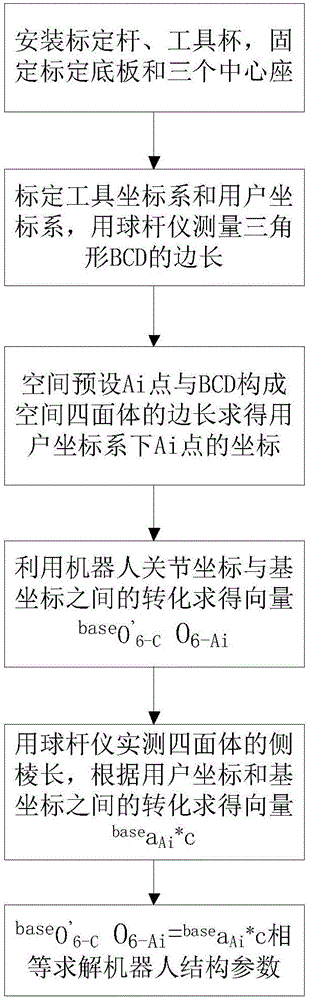
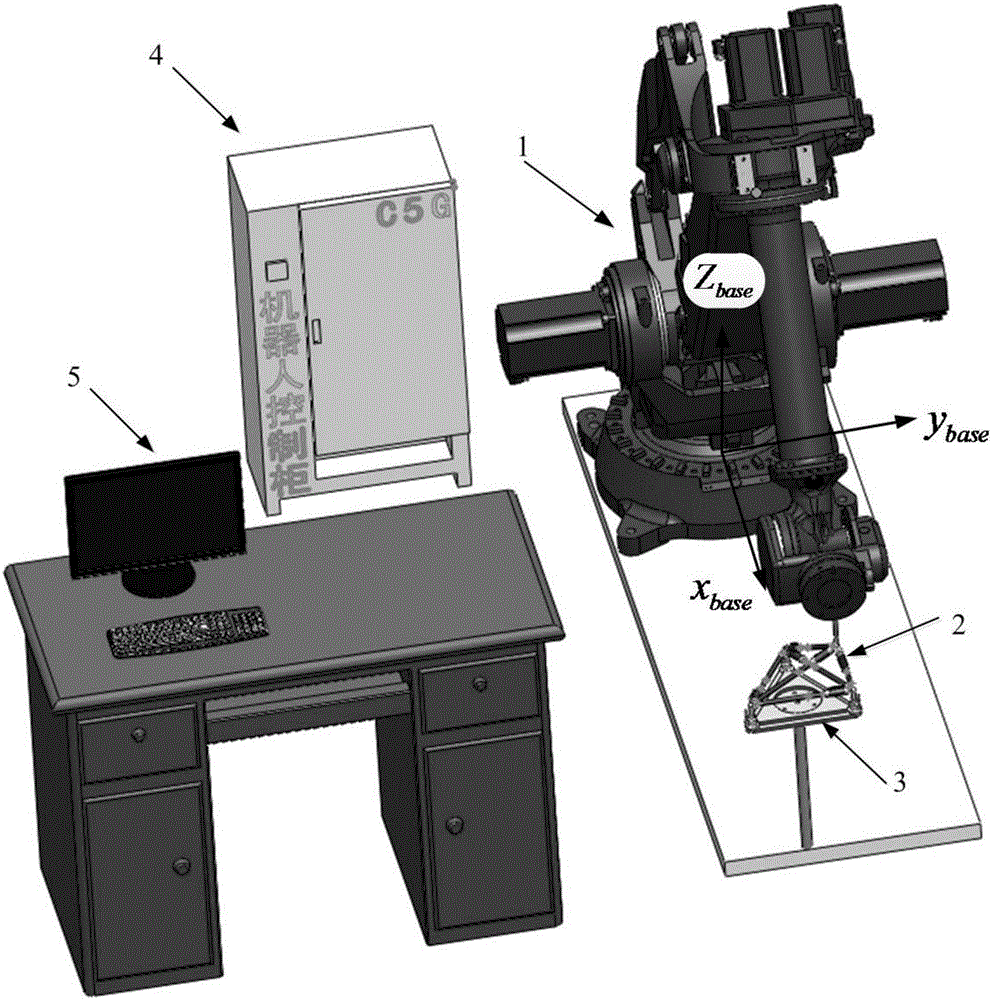
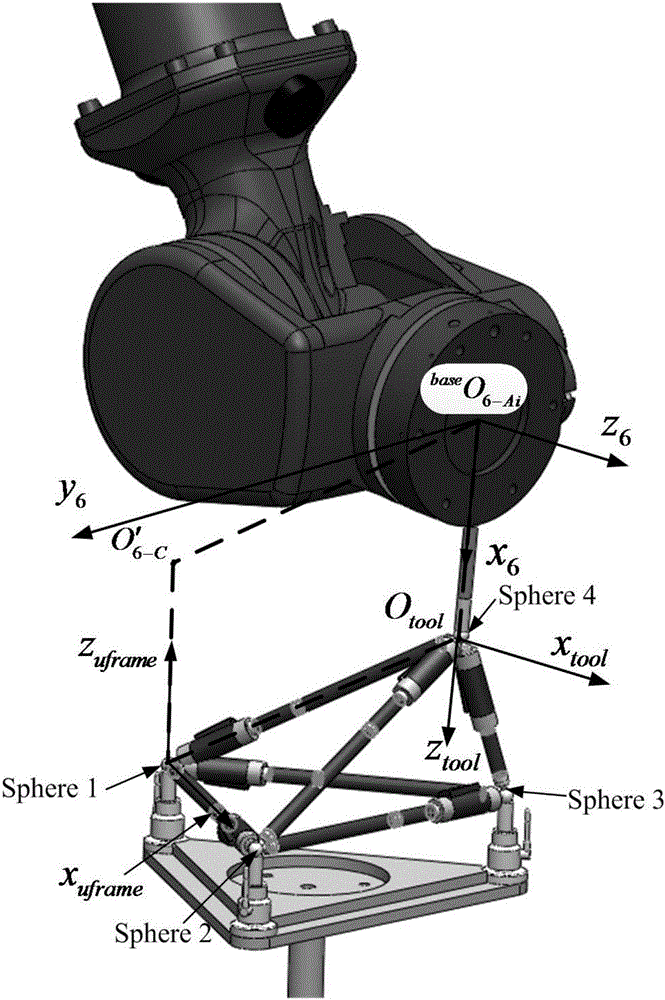
ActiveCN106393174ARealize CalibrationEliminate the effect of errorManipulatorEngineeringCalibration result
The present invention belongs to the field of robot structural parameter calibration, and discloses a method for calibrating structural parameters of a robot using a double-ball-bar. The method comprises the following steps: (a) mounting a calibration rod and a tool cup, and fixing a calibration baseplate and three central seats; (b) calibrating a tool coordinate system and a user coordinate system, and measuring the lengths of the sides of a triangle BCD using the double-ball-bar; (c) presetting a point A in space to form a spatial tetrahedron with the BCD, and obtaining the coordinates of point A under the user coordinate system according to the lengths of the sides of the tetrahedron; (d) obtaining vector <base>O'6-CO6-Ai through conversion of coordinates of robot joints to base coordinates; (e) measuring the lengths of the lateral sides of the tetrahedron using the double-ball-bar, and obtaining vector <base>aAi*c according to conversion of user coordinates to base coordinates; and (f) obtaining the structural parameters of the robot according to the parallelogram principle. According to the present invention, the calibration of the structural parameters of a six-degree-of-freedom articulated robot using the double-ball-bar is achieved simply and quickly, and the calibration result has high accuracy.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com