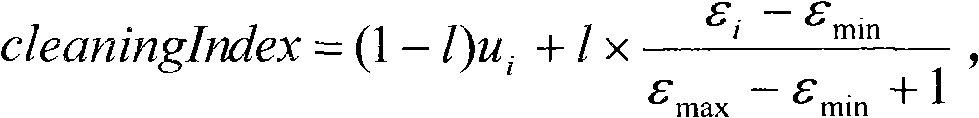Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1355 results about "Invalid Data" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
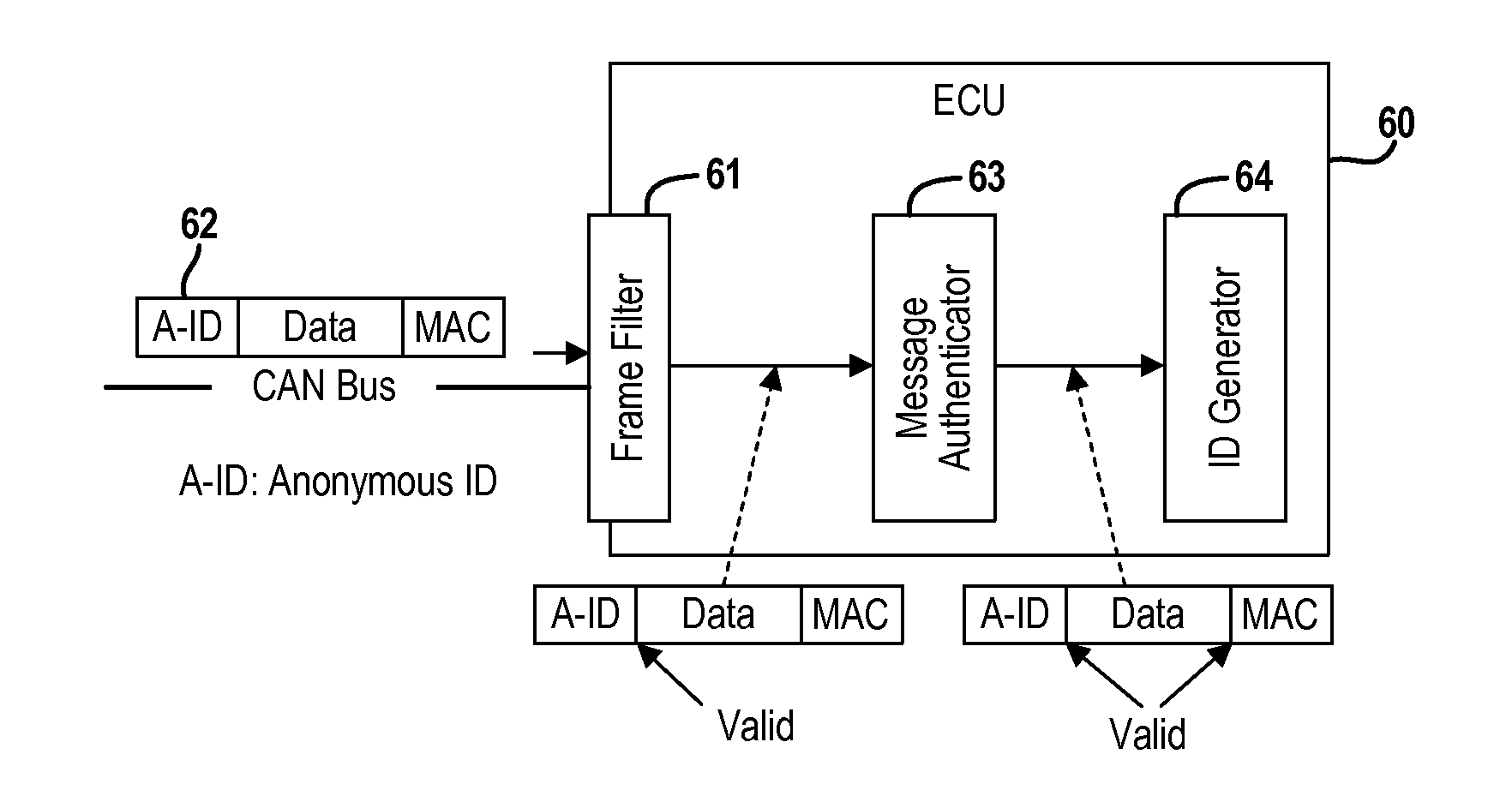
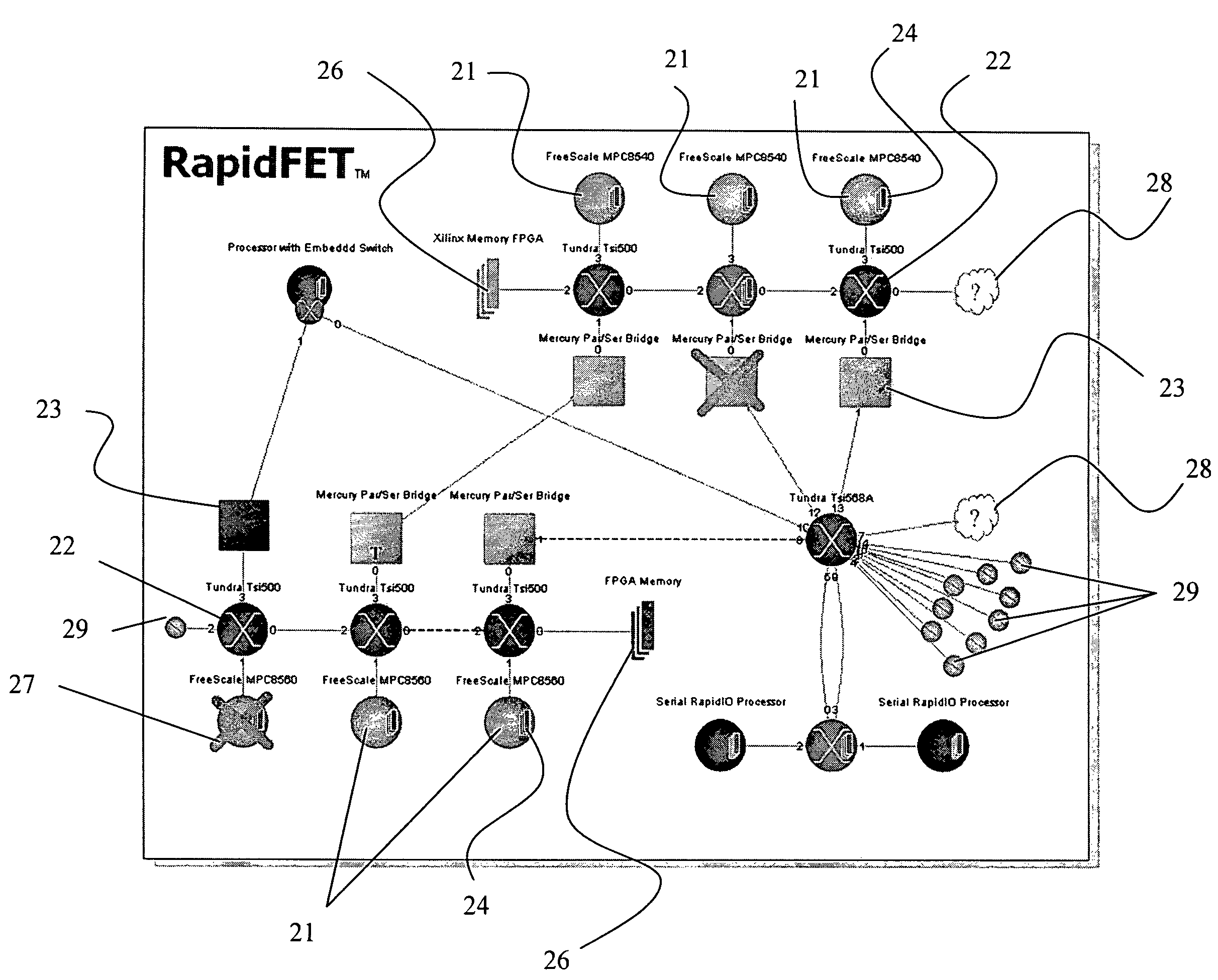
Real-Time Frame Authentication Using ID Anonymization In Automotive Networks
ActiveUS20150089236A1Reduce message authentication delay tmReduce delaysKey distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesComputer networkData integrity
A real-time frame authentication protocol is presented for in-vehicle networks. A frame identifier is made anonymous to unauthorized entities but identifiable by the authorized entities. Anonymous identifiers are generated on a per-frame basis and embedded into each data frame transmitted by a sending ECU. Receiving ECUs use the anonymous identifiers to filter incoming data frames before verifying data integrity. Invalid data frame are filtered without requiring any additional run-time computations.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
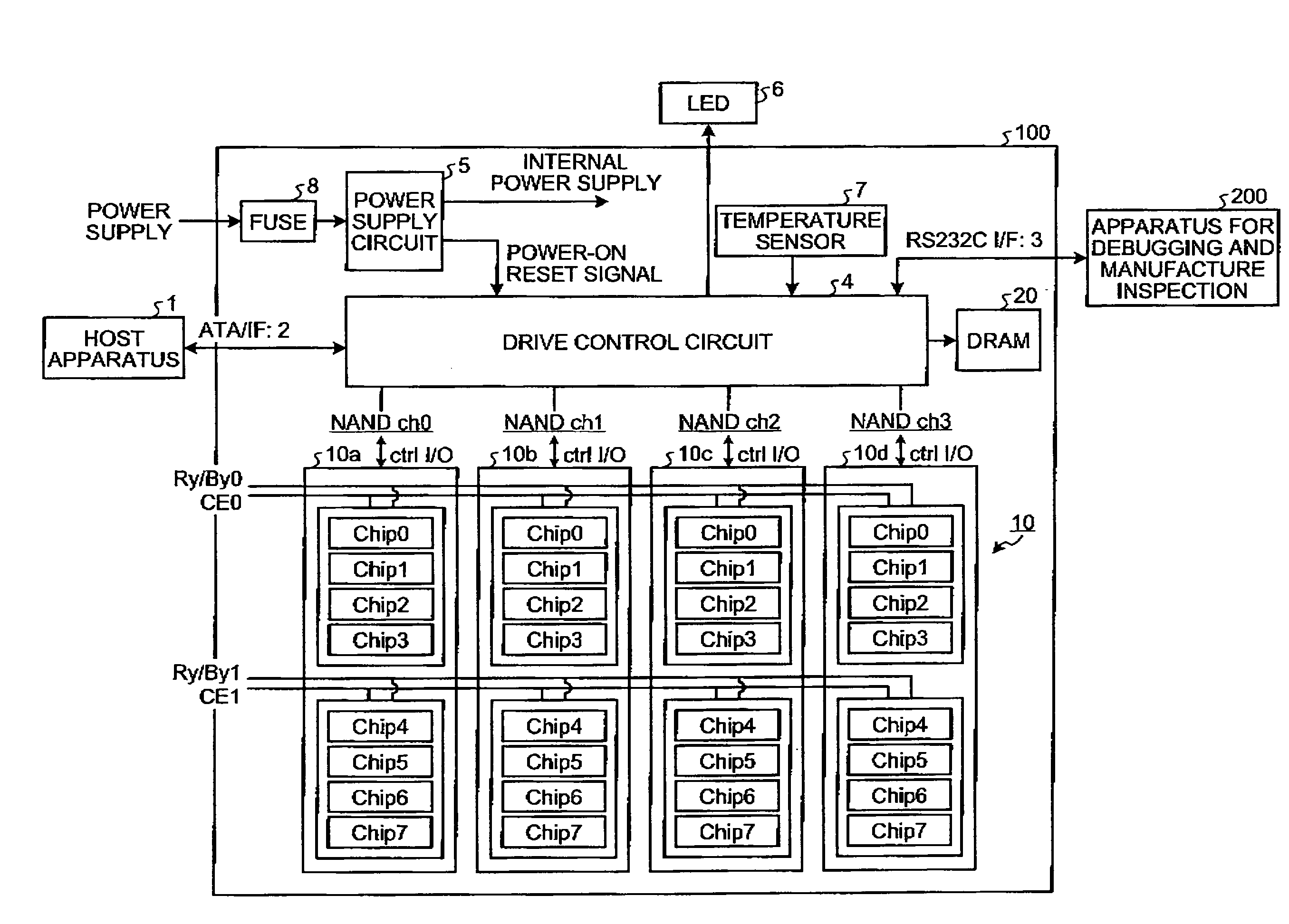
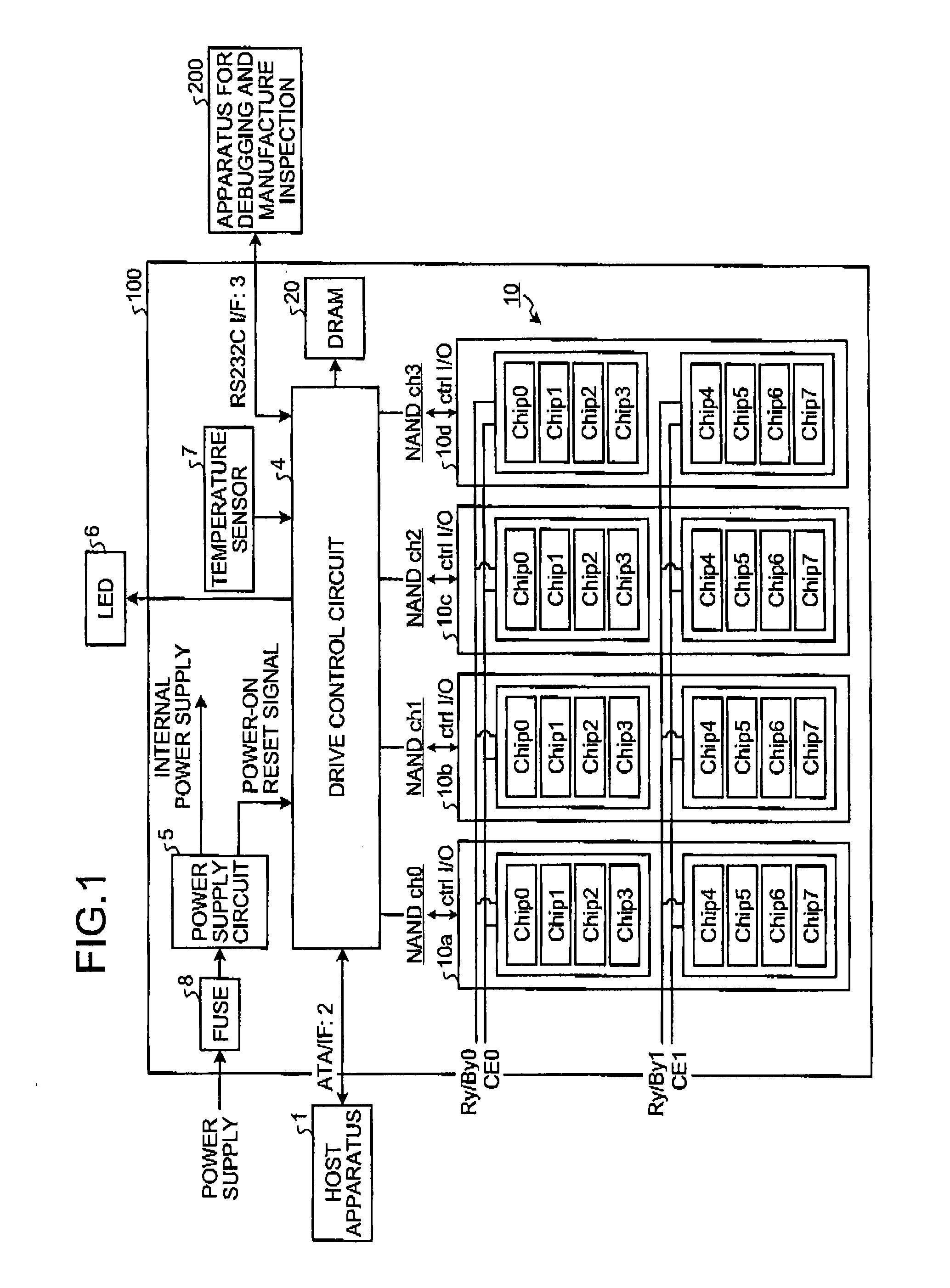
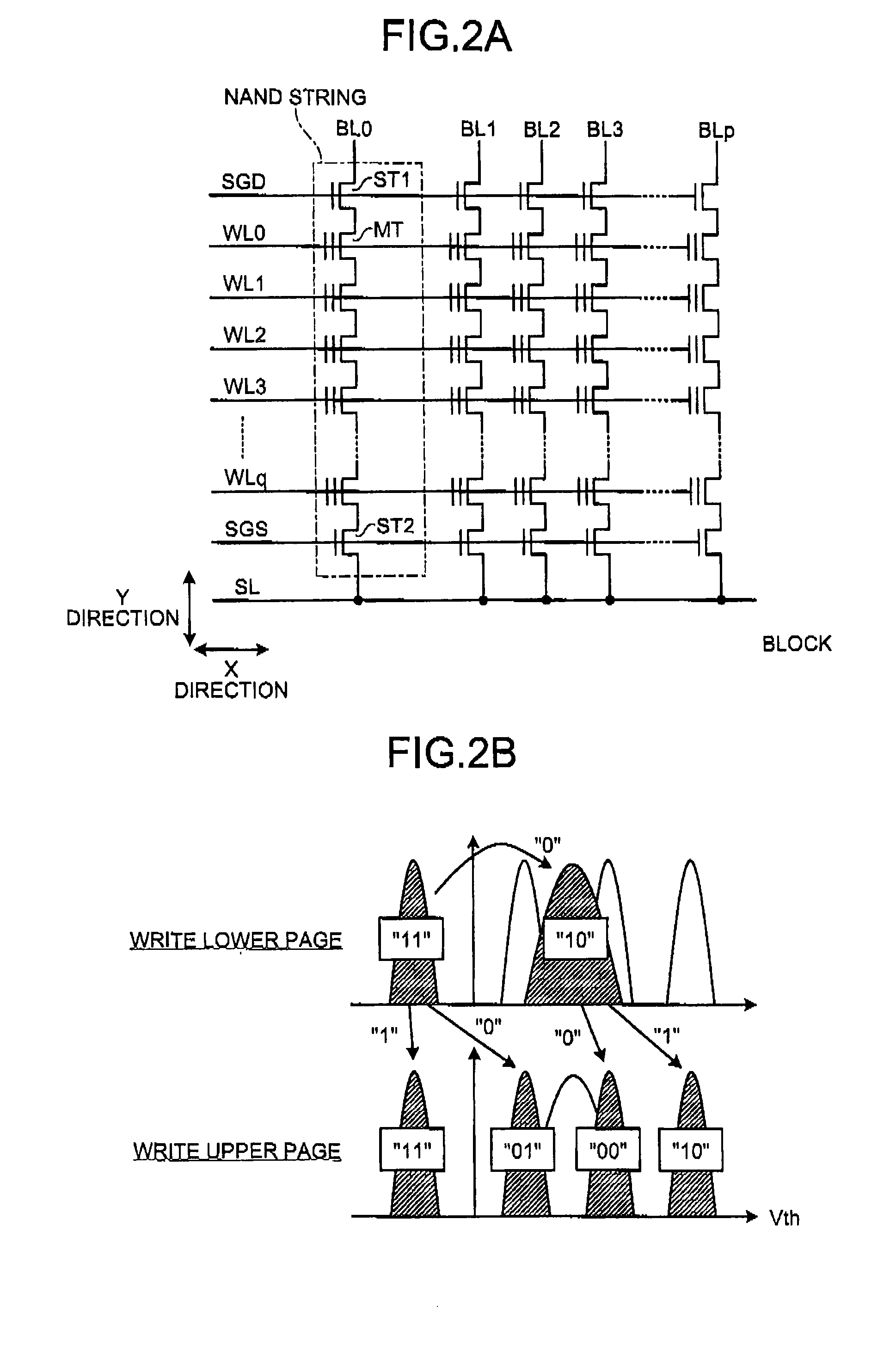
Method for restoring and maintaining solid-state drive performance
InactiveUS20110119462A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInvalid DataTerm memory
A method of maintaining a solid-state drive so that free space within memory blocks of the drive becomes free usable space to the drive. The drive comprises cells organized in pages that are organized in memory blocks in which at least user files are stored. A defragmentation utility is executed to cause at least some of the memory blocks that are partially filled with data and contain file fragments to be combined or aligned and to cause at least some of the memory blocks that contain only invalid data to be combined or aligned. A block consolidation utility is then executed to eliminate at least some of the partially-filled blocks by consolidating the file fragments into a fewer number of the memory blocks. The consolidation utility also increases the number of memory blocks that contain only invalid memory. All of the memory blocks containing only invalid data are then erased.
Owner:OCZ STORAGE SOLUTIONS
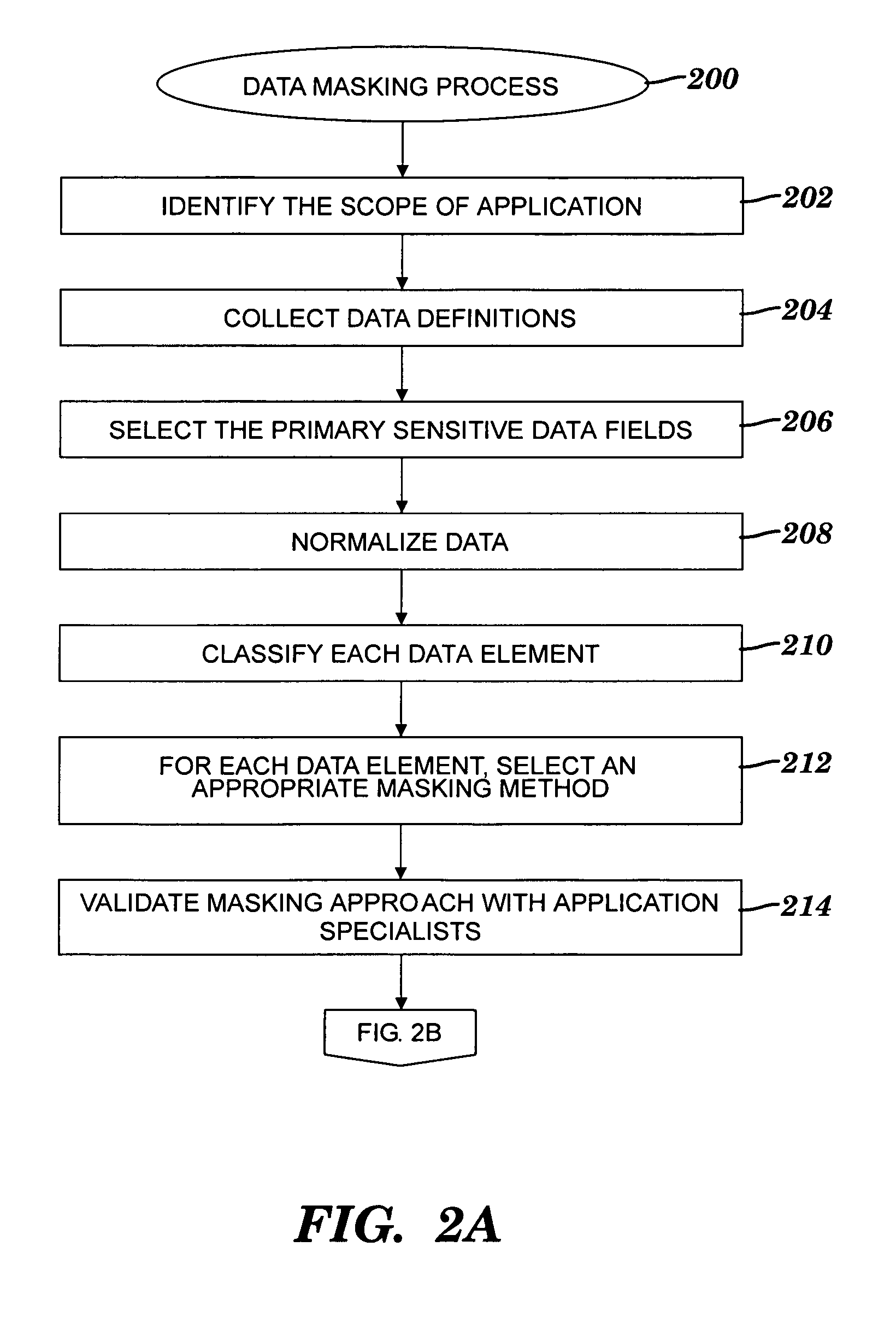
Obfuscating sensitive data while preserving data usability
InactiveUS20090132419A1Computer security arrangementsSecuring communicationConfidentialityData field
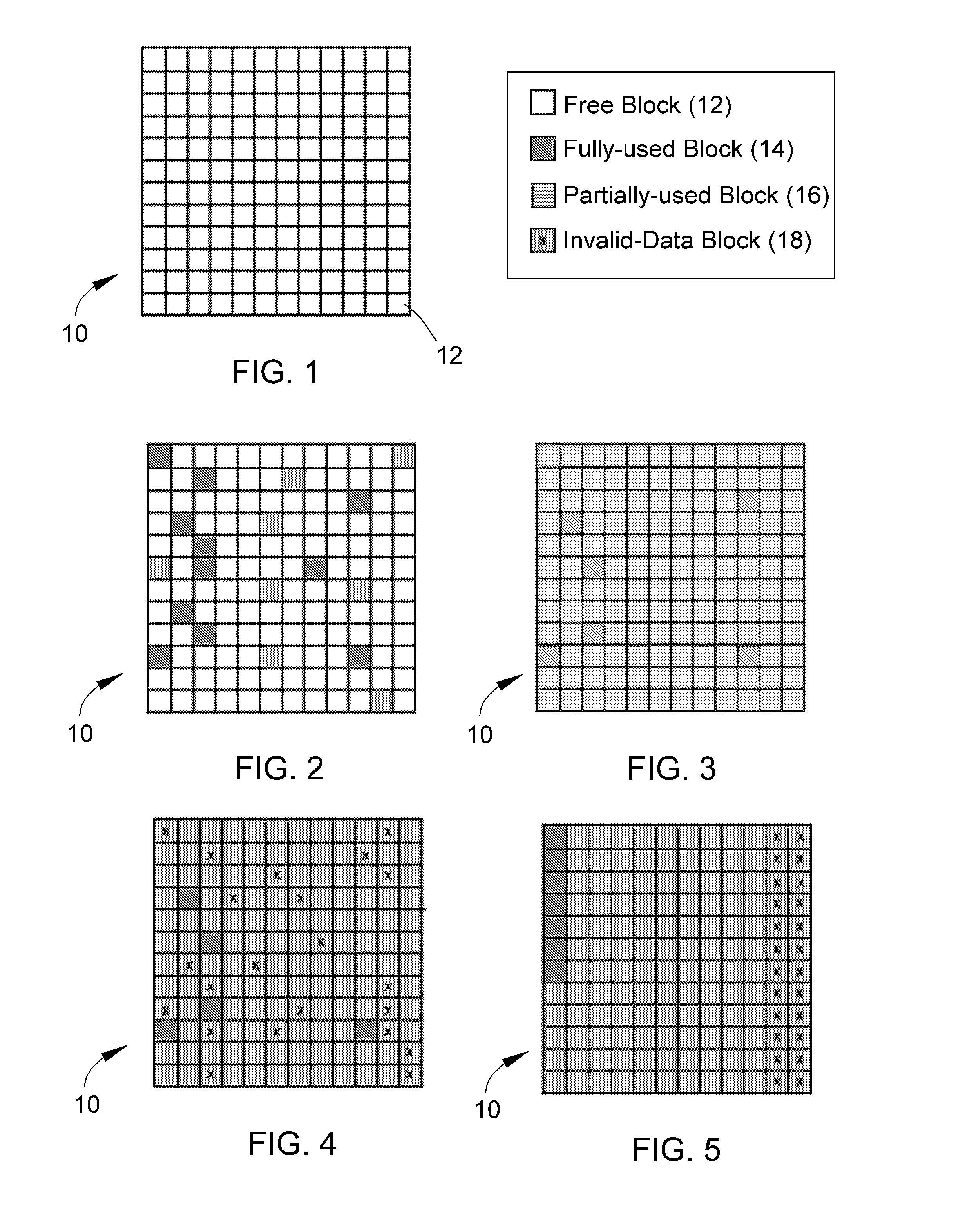
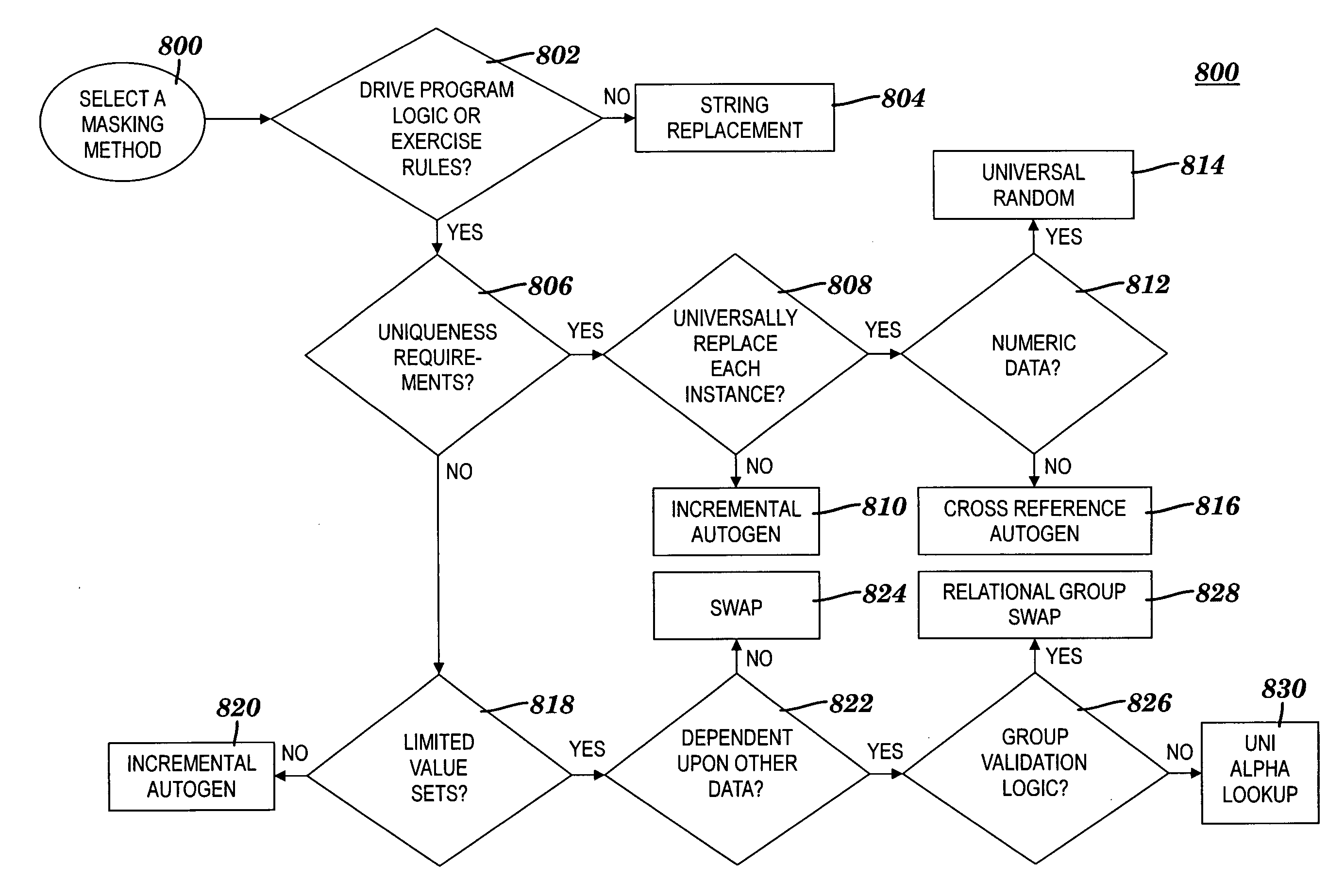
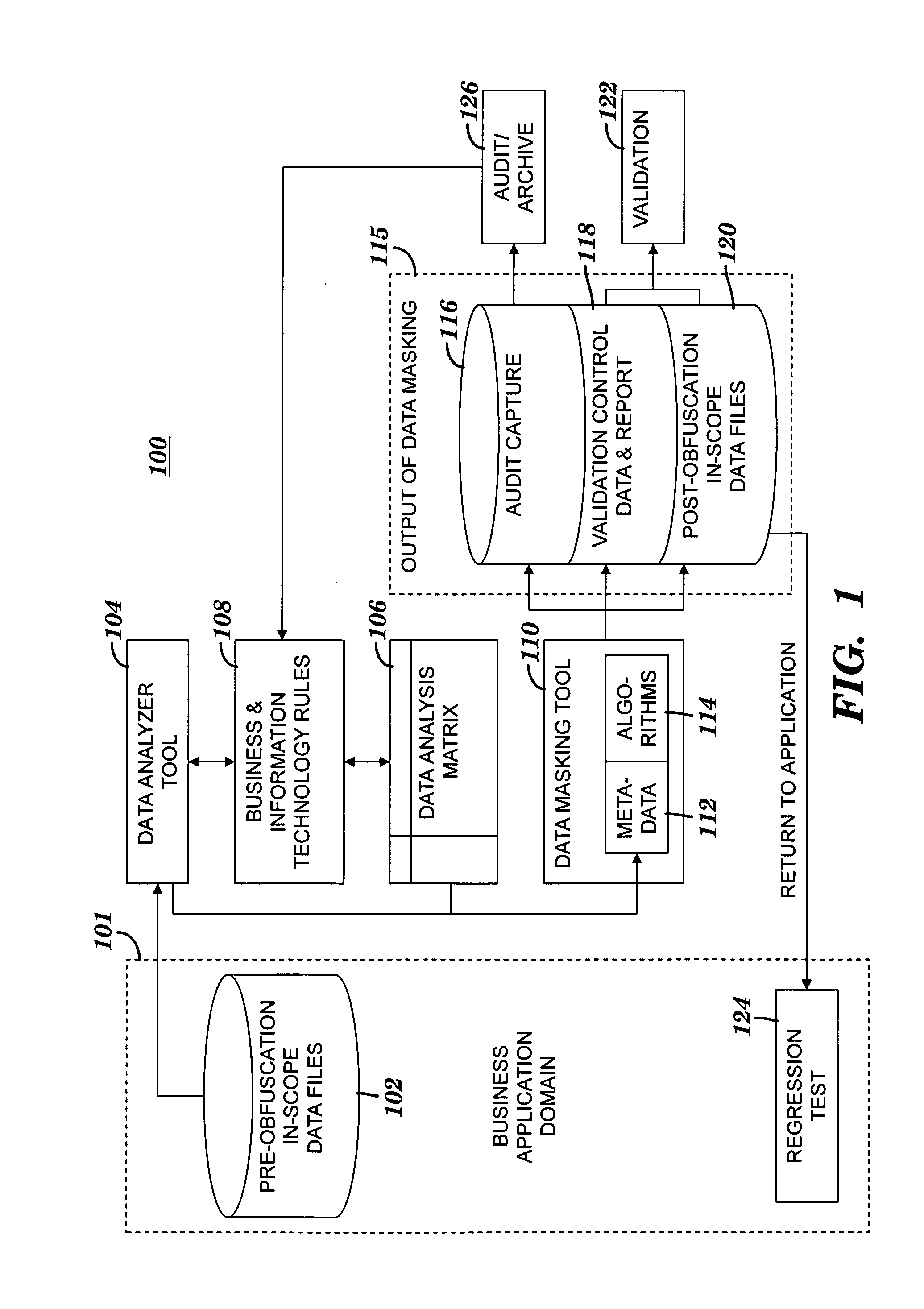
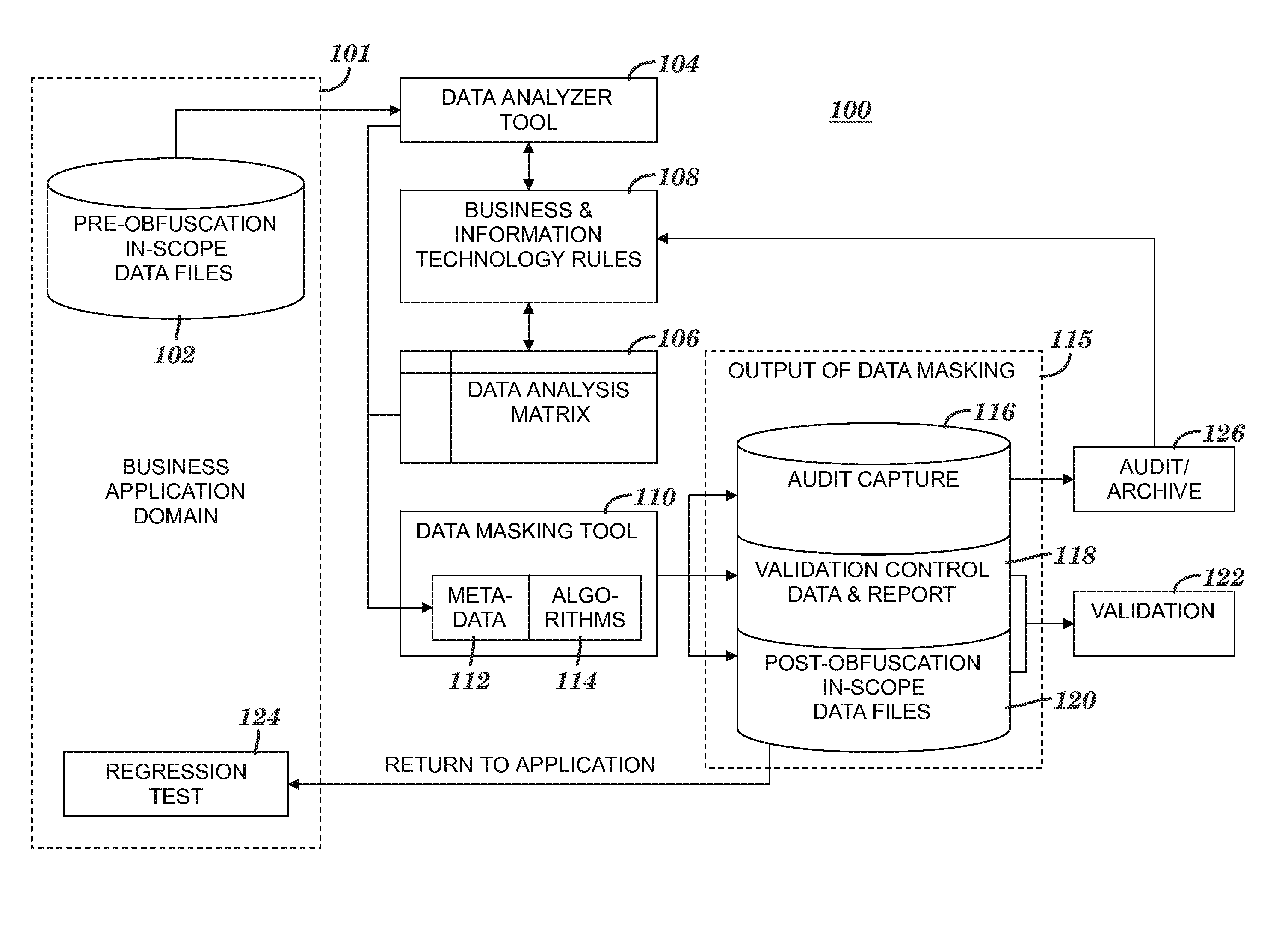
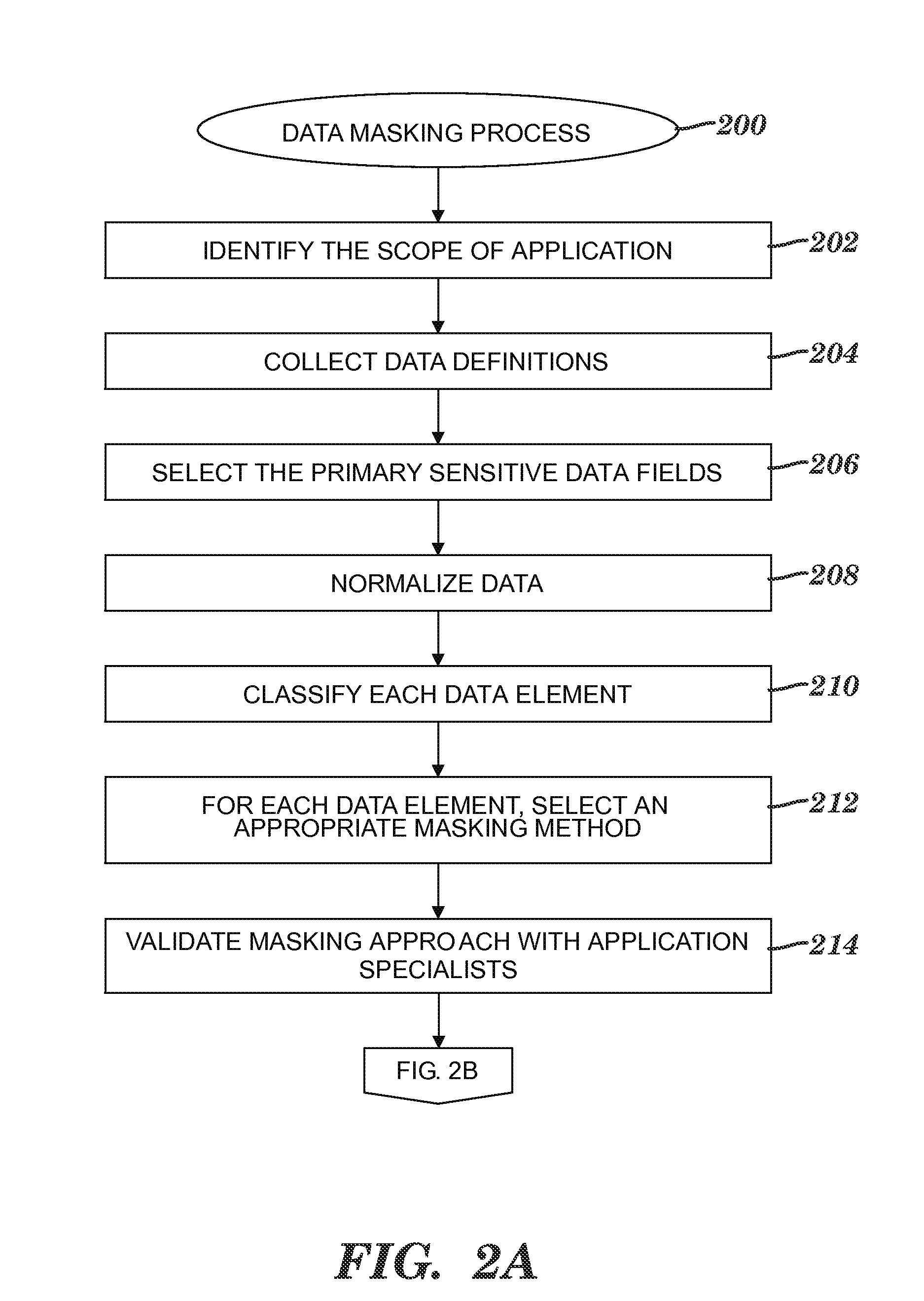
A method and system for obfuscating sensitive data while preserving data usability. The in-scope data files of an application are identified. The in-scope data files include sensitive data that must be masked to preserve its confidentiality. Data definitions are collected. Primary sensitive data fields are identified. Data names for the primary sensitive data fields are normalized. The primary sensitive data fields are classified according to sensitivity. Appropriate masking methods are selected from a pre-defined set to be applied to each data element based on rules exercised on the data. The data being masked is profiled to detect invalid data. Masking software is developed and input considerations are applied. The selected masking method is executed and operational and functional validation is performed.
Owner:IBM CORP
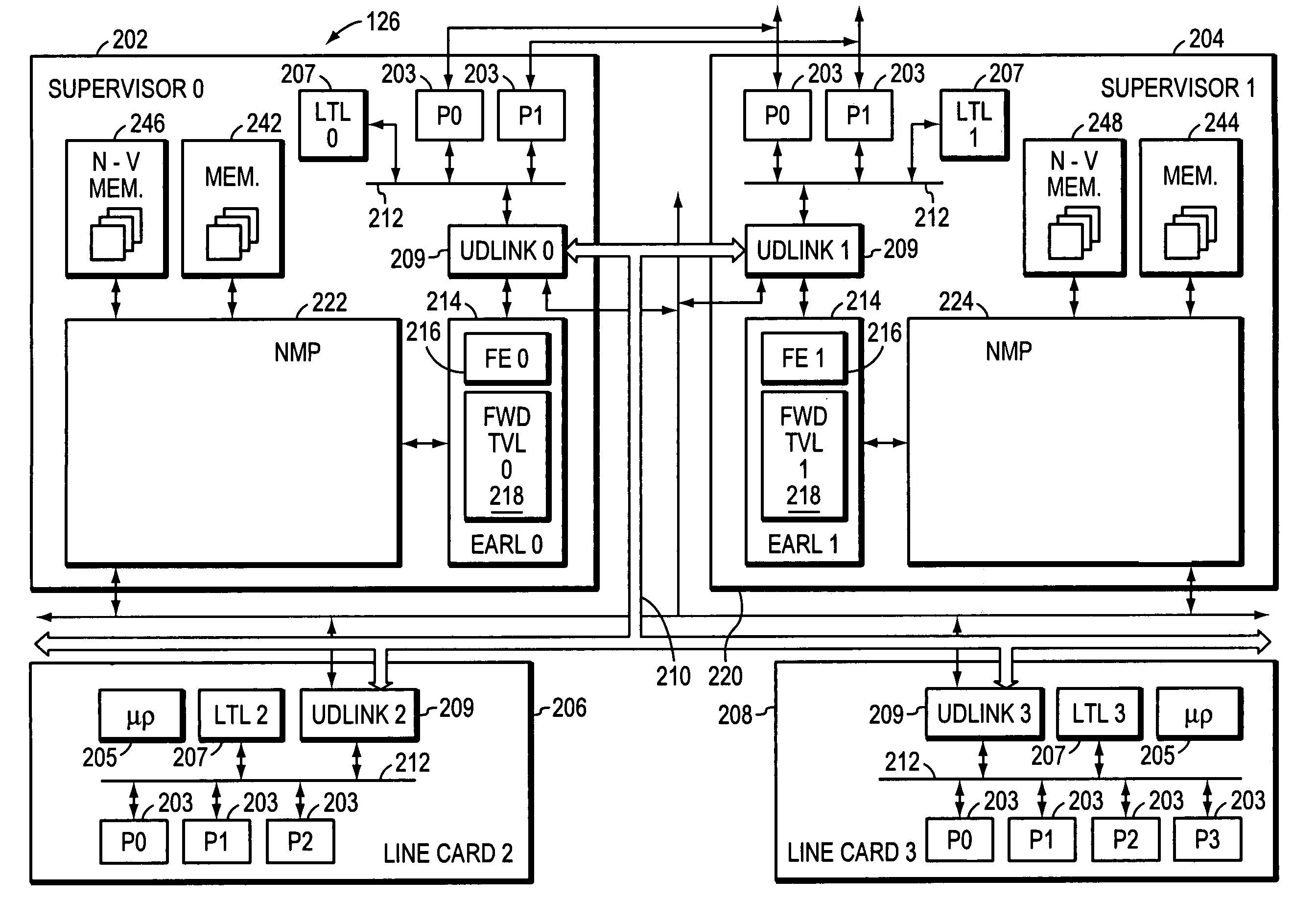
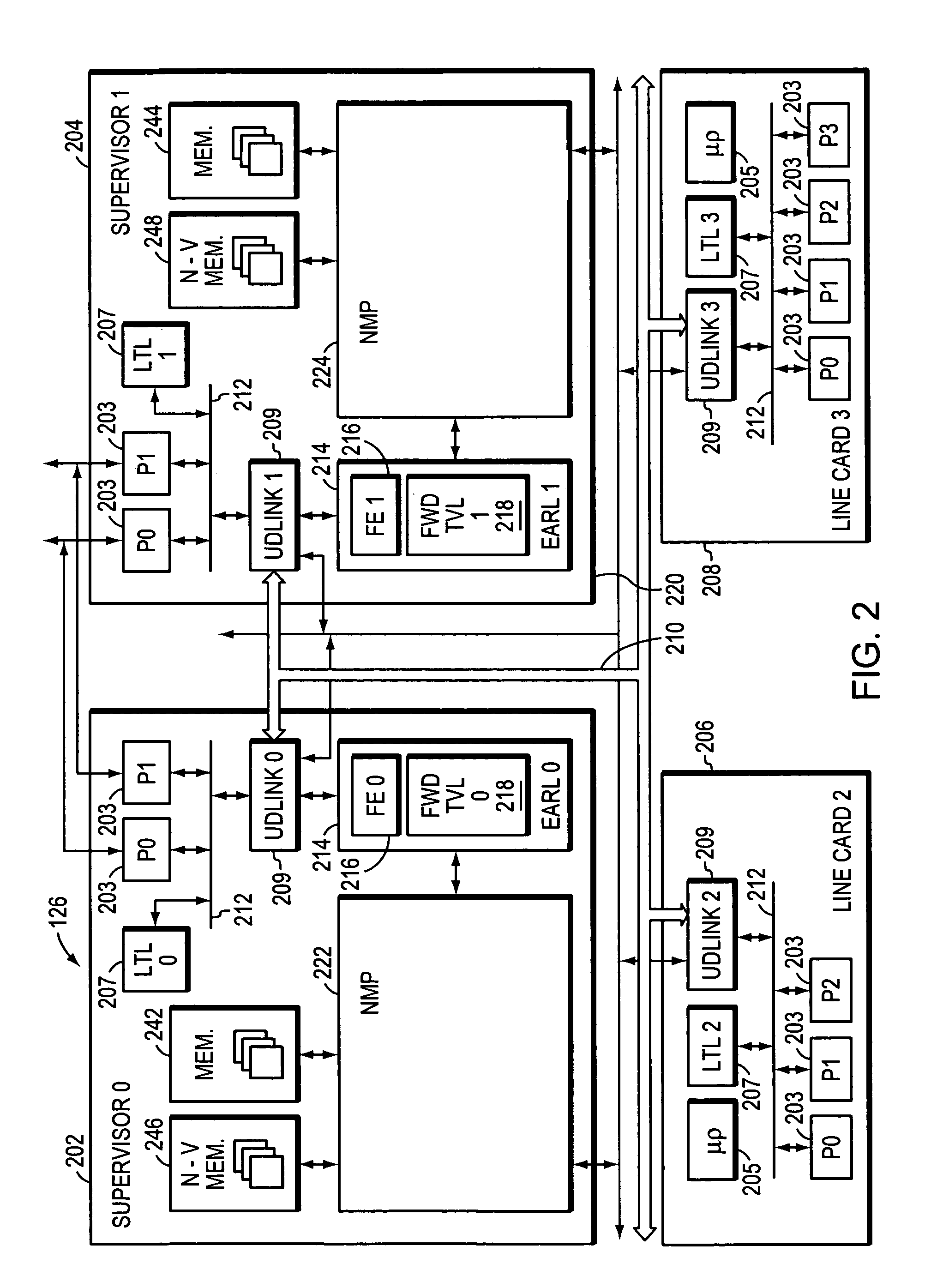
High availability architecture for network devices
InactiveUS7061858B1Avoiding significant disruptionError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsLine cardHigh availability
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
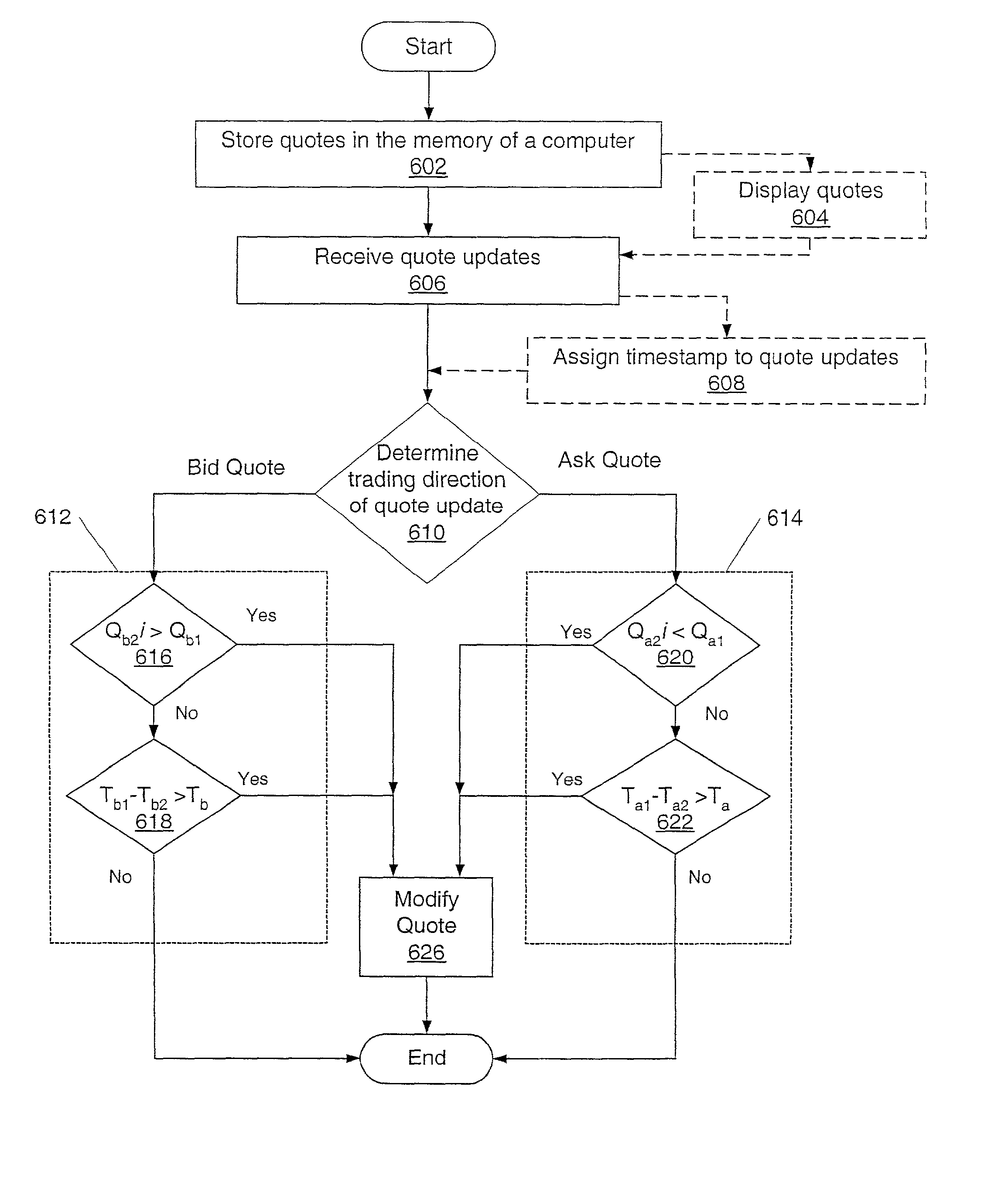
Methods and systems for suppression of stale or invalid data in a securities quotation display
Methods and systems for displaying information related to securities to a user are provided. In an embodiment, a method may include storing securities quotes in a memory of a computer. The method may include receiving quote updates information. The received quote update information and the quotes stored in the memory of the computer may be compared via one or more criteria. For bid quotes, a first criterion may include determining if a quote stored in the memory of the computer is greater than the price of a quote update. For ask quotes, the first criterion may include determining if a quote stored in the memory of the computer is less than the price of a quote update. A second criterion may include determining if a timestamp associated with the quote update minus a timestamp associated with the quote stored in the memory of the computer is greater than a predetermined threshold time. If one or more of the criteria are met, the method may modify the quote in the memory of the computer. Modifying the quote may include, but is not limited to: changing a display color, changing a font style, inhibiting the quote from being displayed, and deleting the quote from the memory of the computer.
Owner:INSTINET GRP INC +2
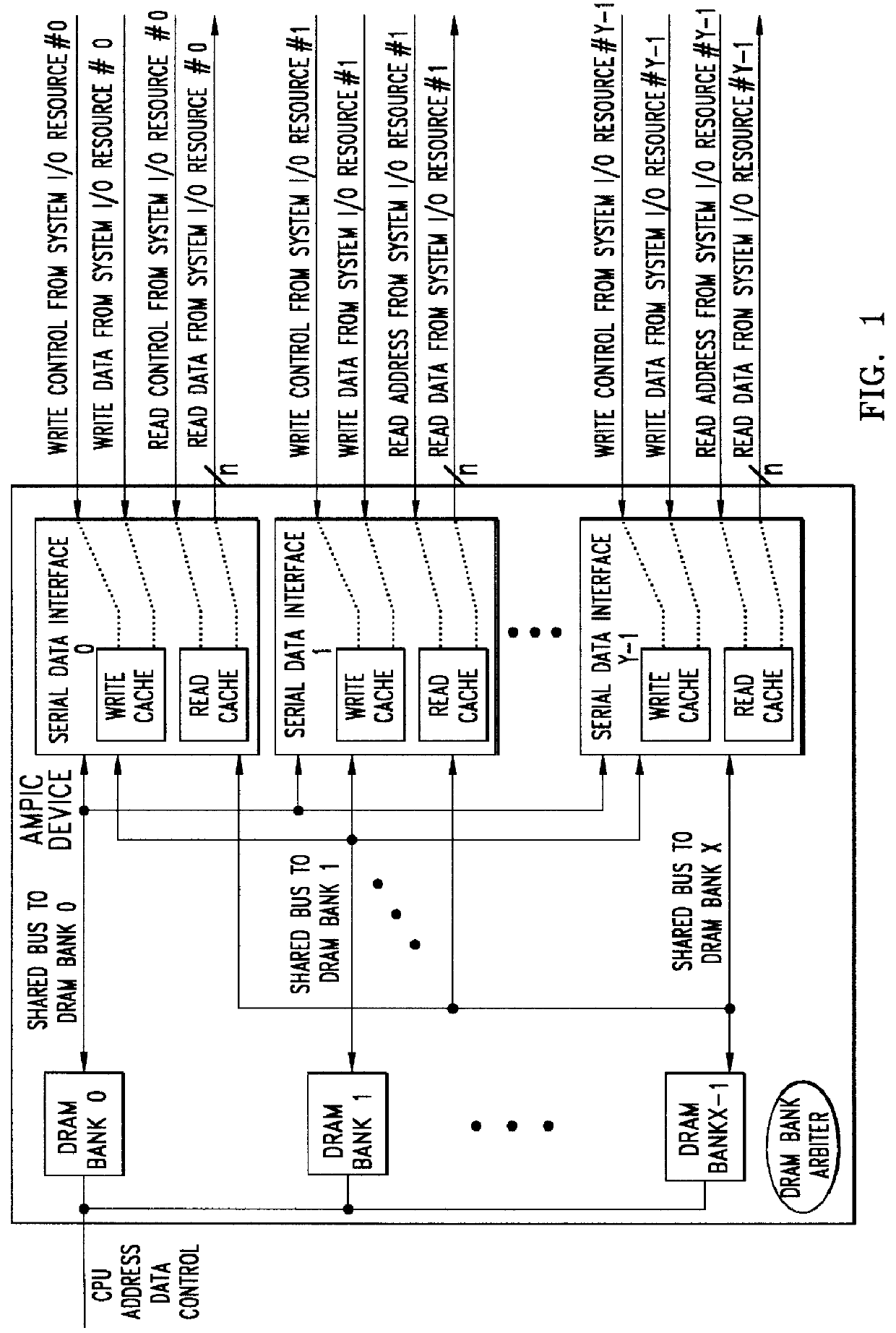
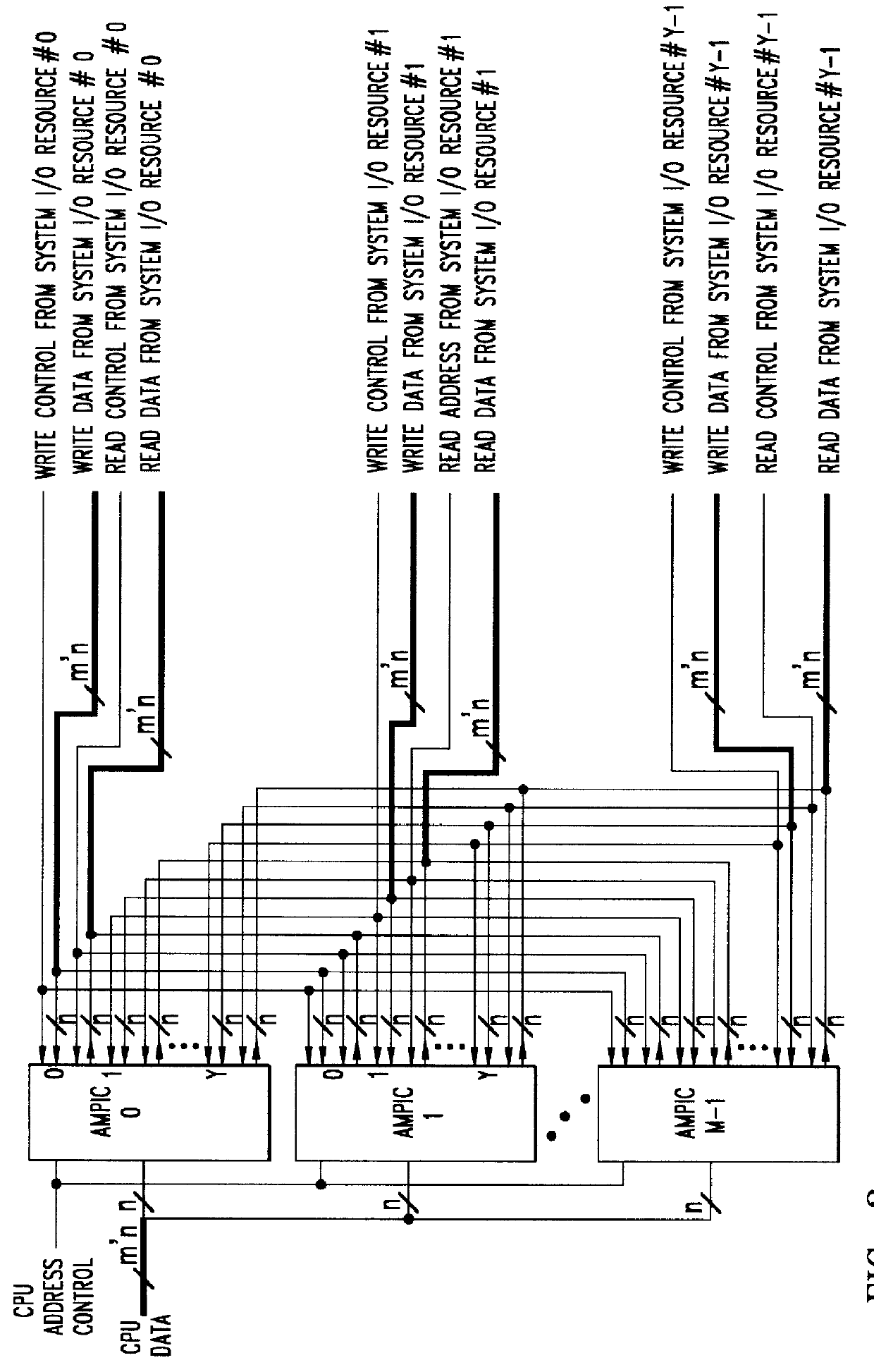
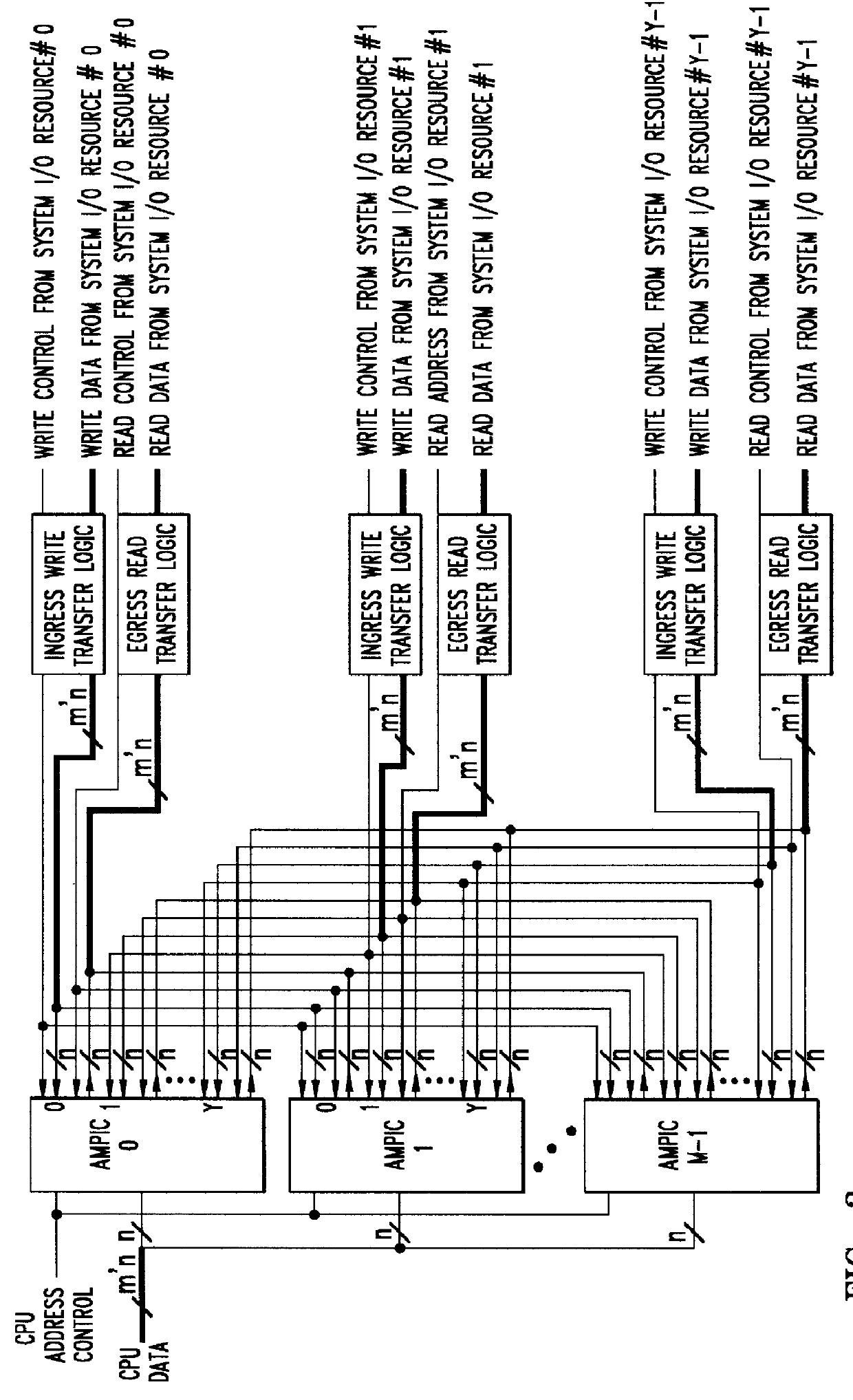
Method of and apparatus for validating data read out of a multi port internally cached dynamic random access memory (AMPIC DRAM)
InactiveUS6085290AEliminates race conditionMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData validationStatic random-access memory
An apparatus for and method of enhancing the performance of a multi-port internal cached DRAM (AMPIC DRAM) by providing an internal method of data validation within the AMPIC memories themselves to guarantee that only valid requested data is returned from them, or properly marked invalid data. A modified technique for identifying bad data that has been read out of AMPIC memory devices in the system.
Owner:NEXABIT NETWORKS +1
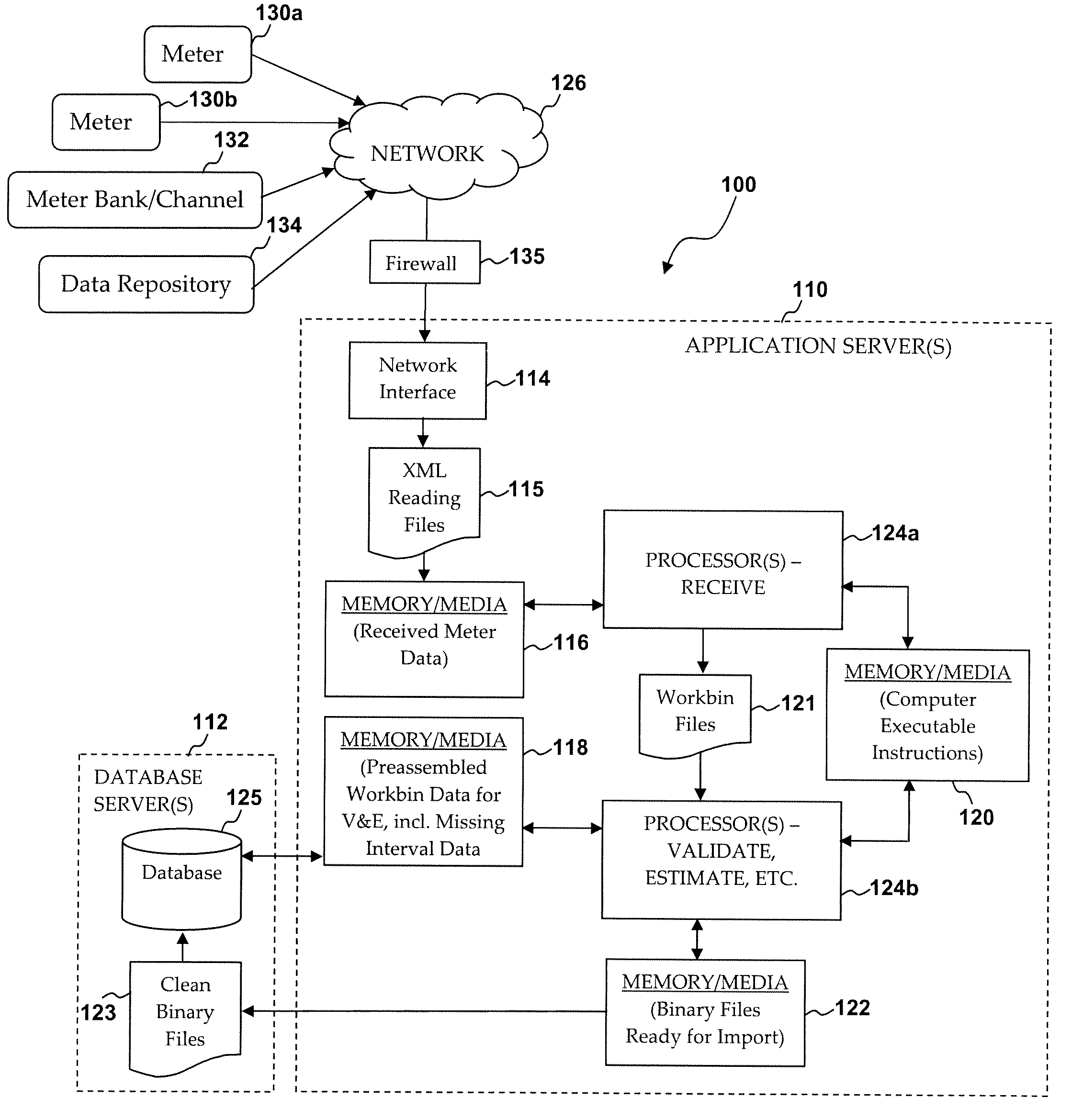
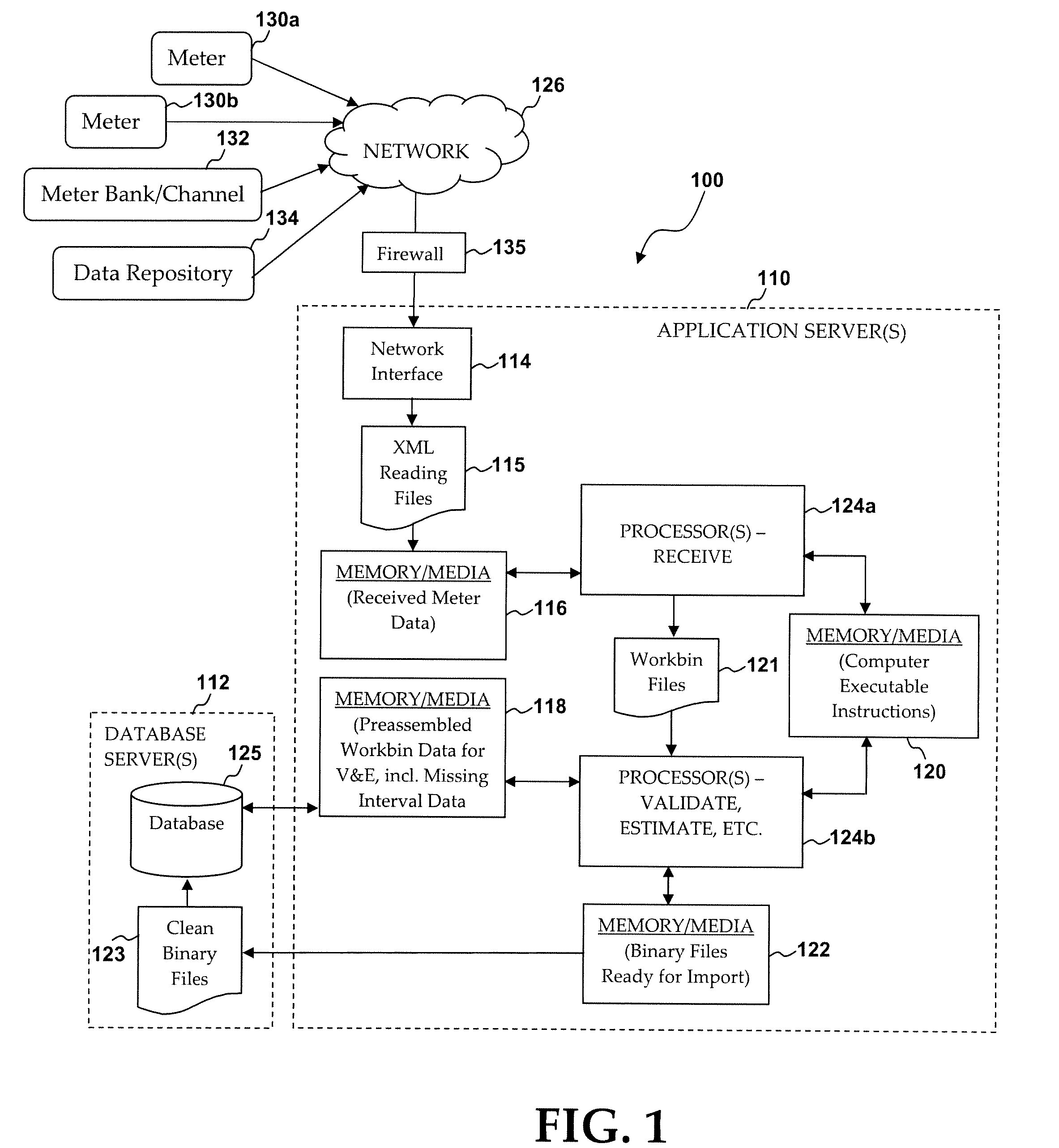
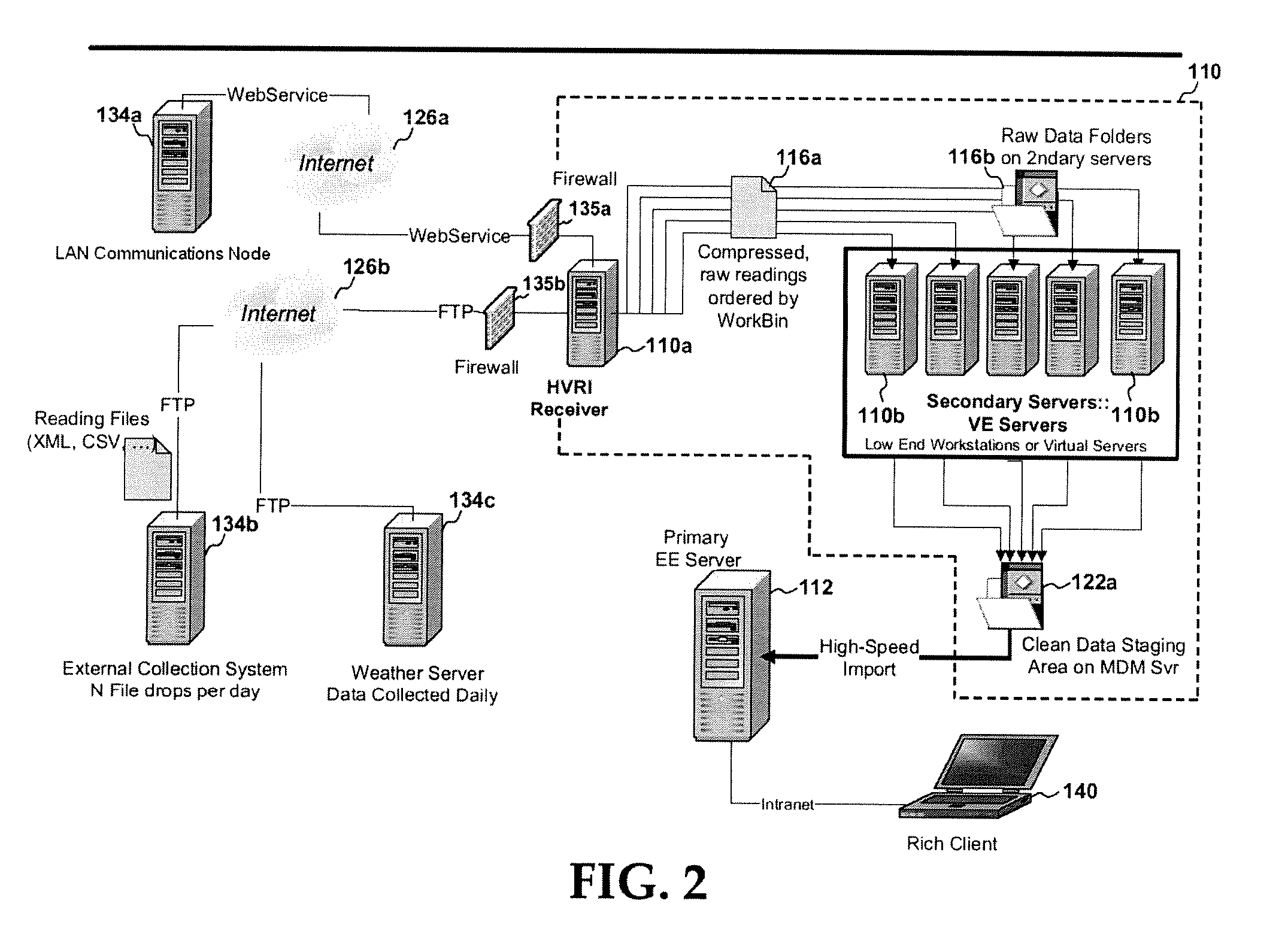
System and method of high volume import, validation and estimation of meter data
ActiveUS20100117856A1Efficient collectionReduce the amount of solutionElectric signal transmission systemsTariff metering apparatusApplication serverMeter data management system
A meter data management system includes one or more application servers configured to receive, validate and estimate received meter data. The one or more application servers may include various memory / media elements for storing raw and transformed meter data as well as software in the form of computer-executable instructions, which are executed by a processor to implement a variety of functions, including establishing a mapping between the plurality of external devices and a plurality of preconfigured processing workbins (e.g., collections of meter channels in the same time zones), transforming the received meter data into a plurality of data files identified by timing parameter and workbin, validating data provided in each data file, estimating missing or invalid data, and automatically writing validated (and optionally estimated) data as import files to a database server. Such clean data files are then imported to one or more dedicated databases installed on the database server.
Owner:ITRON
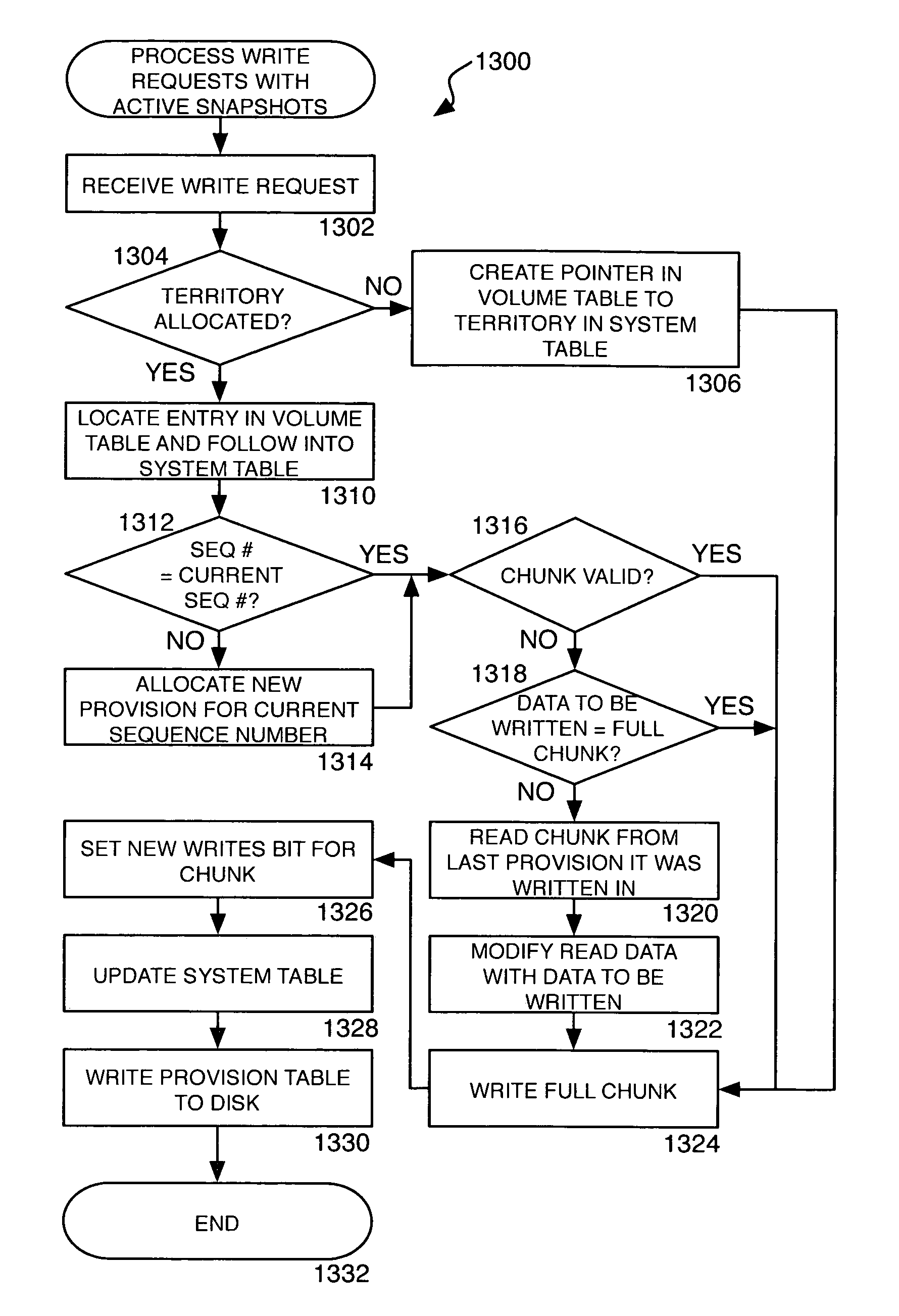
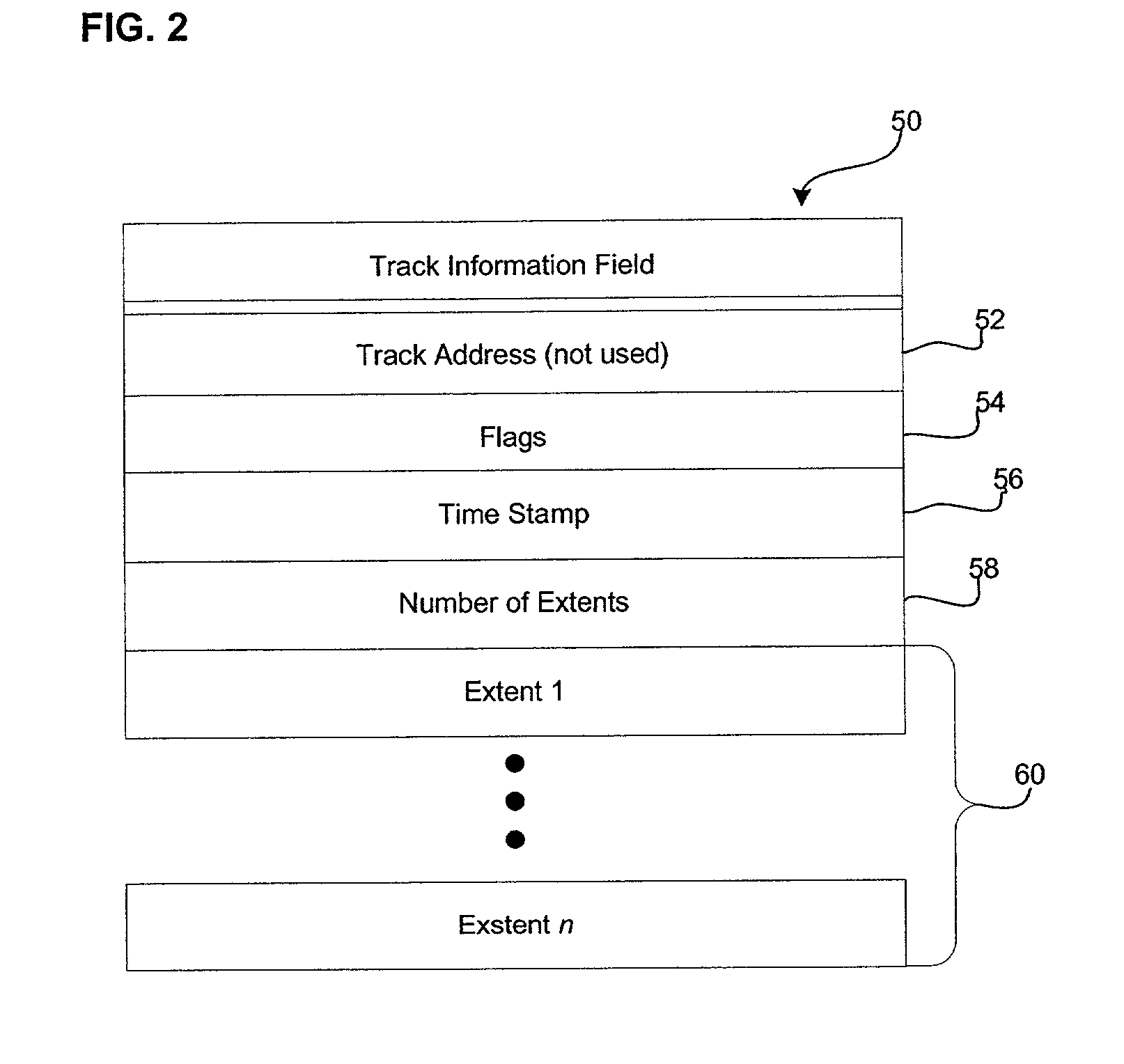
Method, system, apparatus, and computer-readable medium for taking and managing snapshots of a storage volume
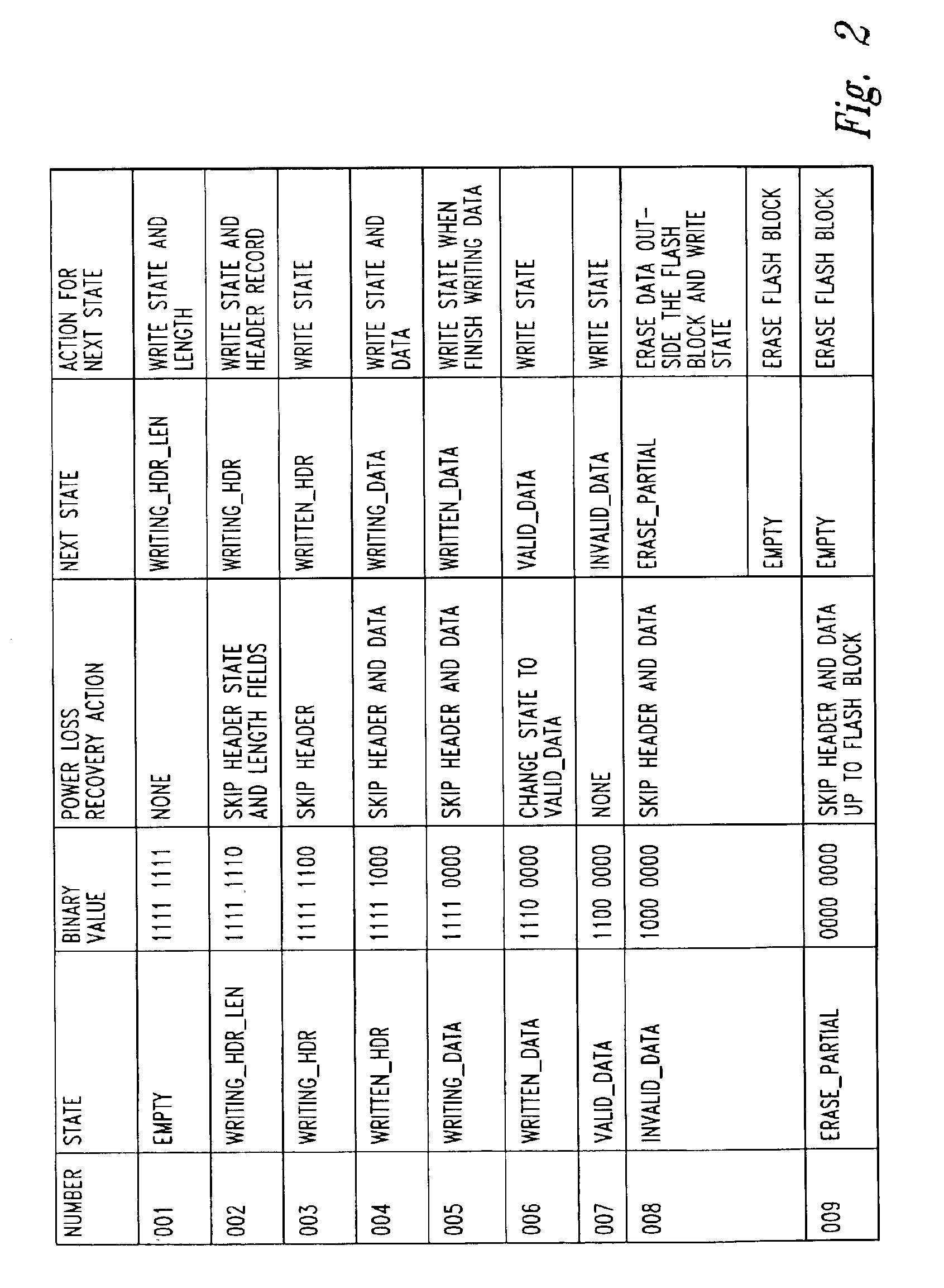
ActiveUS7373366B1No performance lossScroll fastError detection/correctionSpecial data processing applicationsGranularityInvalid Data
A method, system, apparatus, and computer-readable medium are provided for taking snapshots of a storage volume. According to aspects of one method, each snapshot is represented as a unique sequence number. Every fresh write access to a volume in a new snapshot lifetime is allocated a new section in the disk, called a provision, which is labeled with the sequence number. Read-modify-write operations are performed on a sub-provision level at the granularity of a chunk. Because each provision contains chunks with valid data and chunks with invalid data, a bitmap is utilized to identify the valid and invalid chunks with each provision. Provisions corresponding to different snapshots are arranged in a linked list. Branches from the linked list can be created for storing writable snapshots. Provisions may also be deleted and rolled back by manipulating the contents of the linked lists.
Owner:AMZETTA TECH LLC
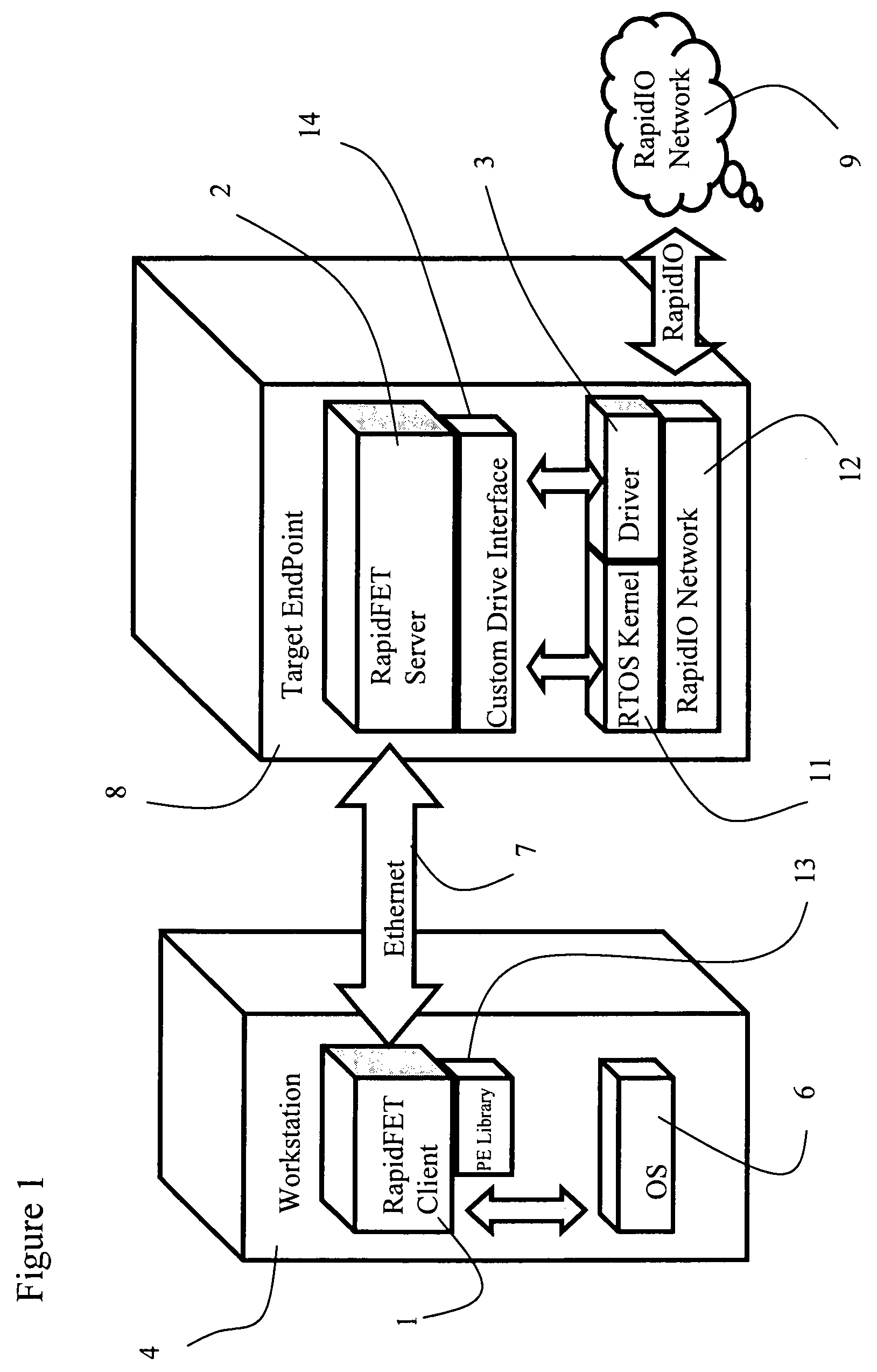
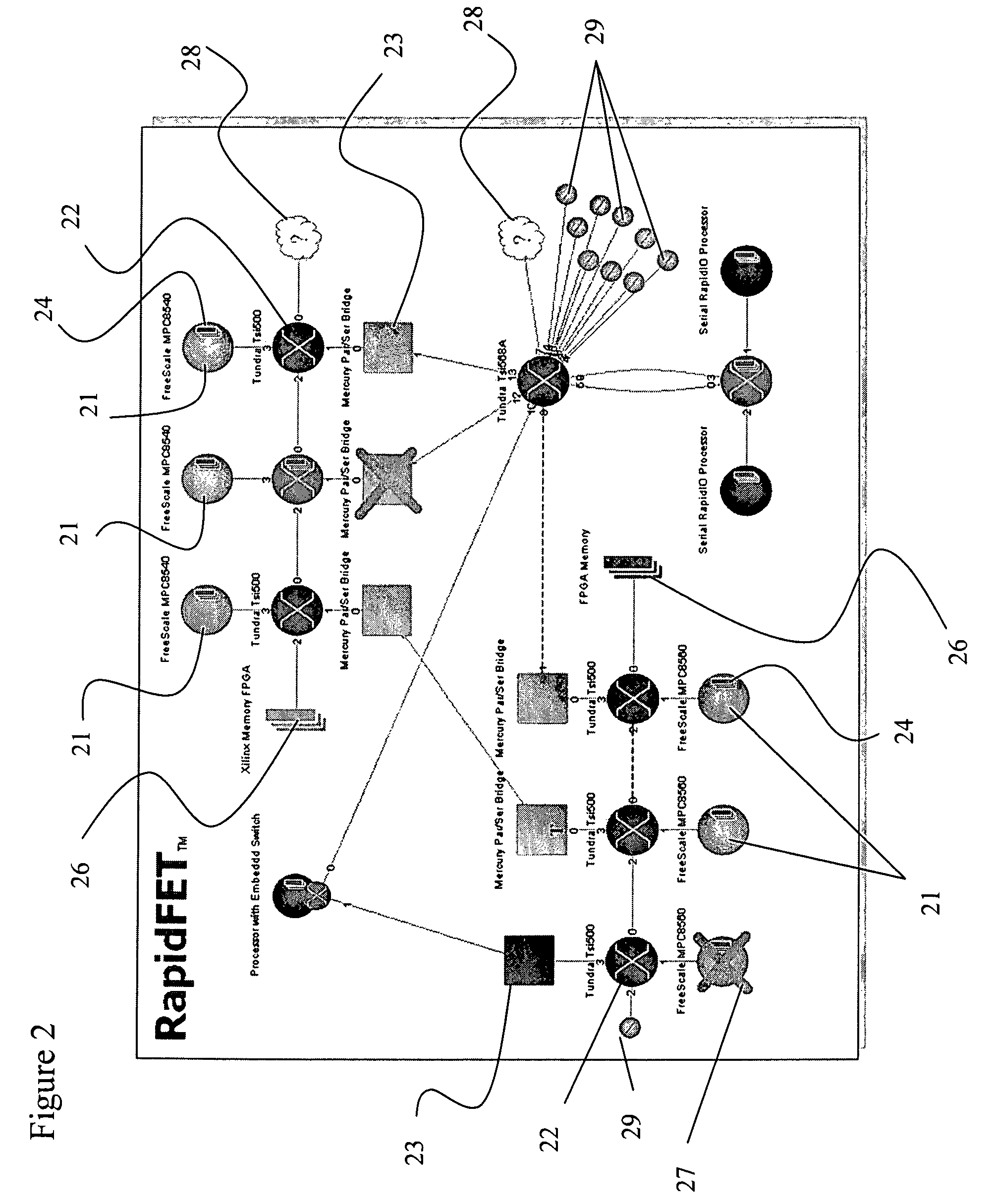
Fabric network management and diagnostic tool
The invention relates to a maintenance and diagnostic tool for embedded fabric (EF) networks providing an interactive graphical user interface for displaying, monitoring and managing processing elements, such as microprocessors, switches, bridges and memory, within the EF network. The computer software tool identifies the various processing elements in the system along with the data routes therebetween, gives each processing element a unique identification label, and then initializes each switch with routing tables. All of the aforementioned information is then used to construct an interactive graphical user interface of the network map illustrating the various processing elements and the active and inactive data paths extending therebetween.
Owner:FABRIC EMBEDDED TOOLS CORP
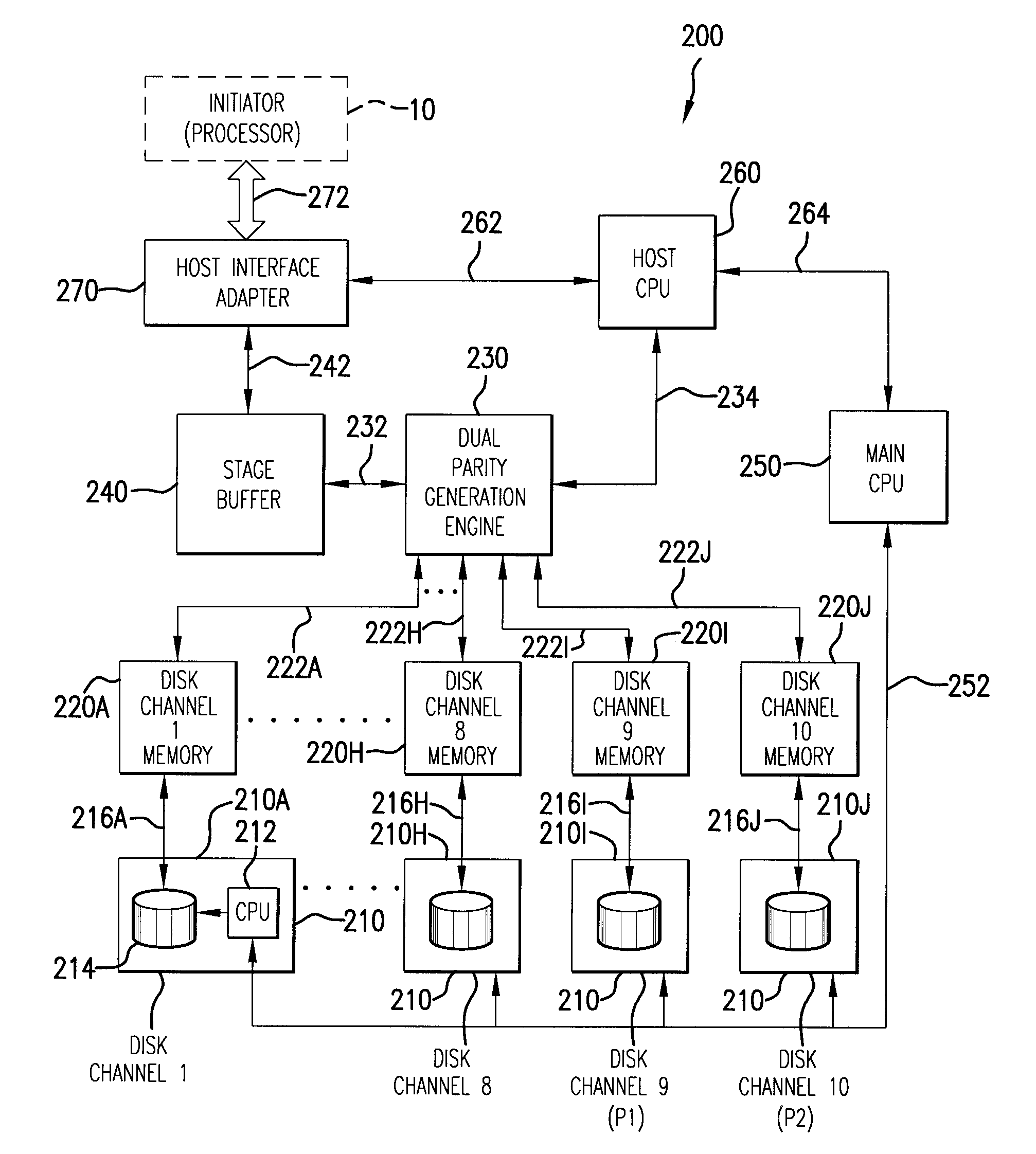
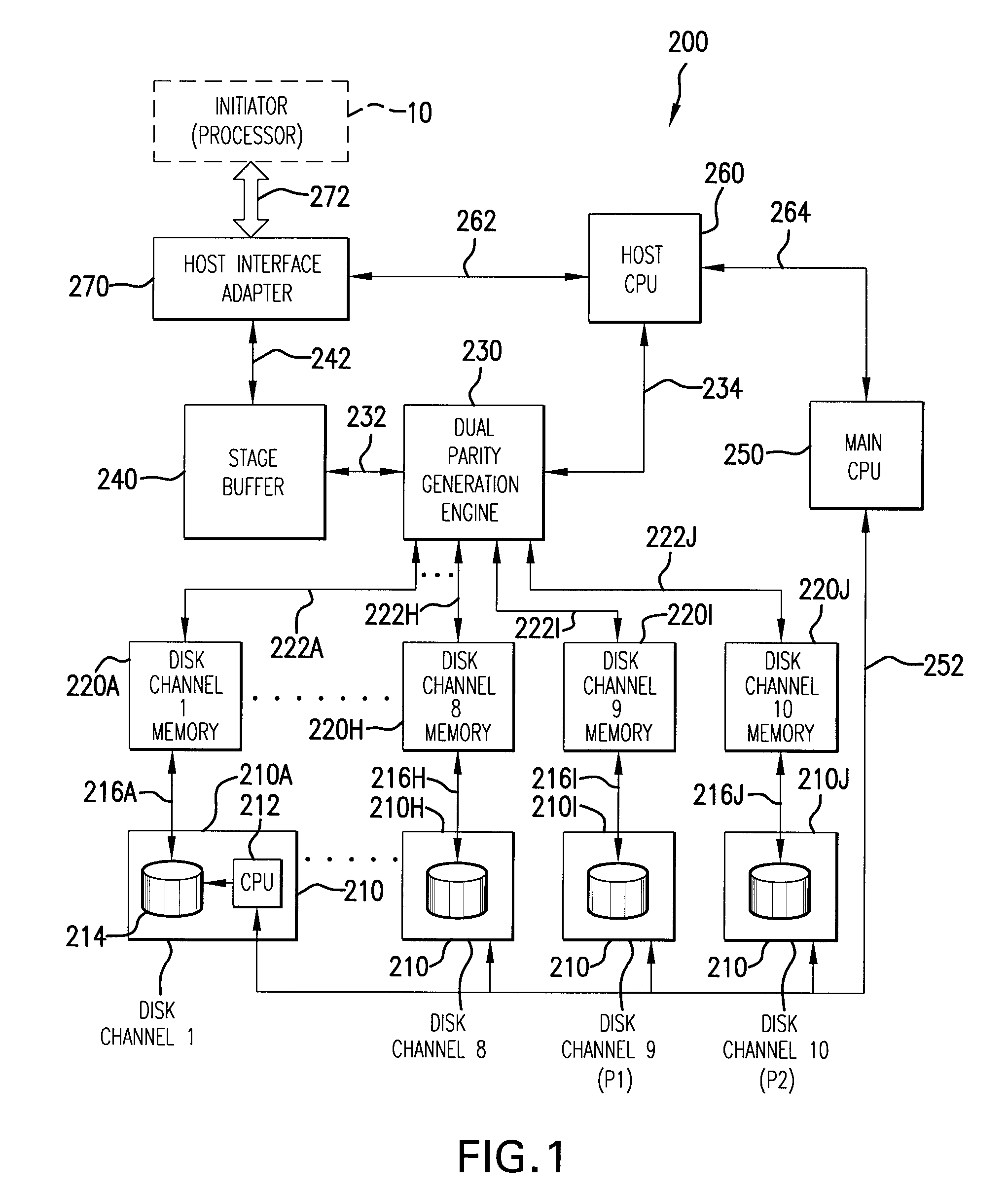
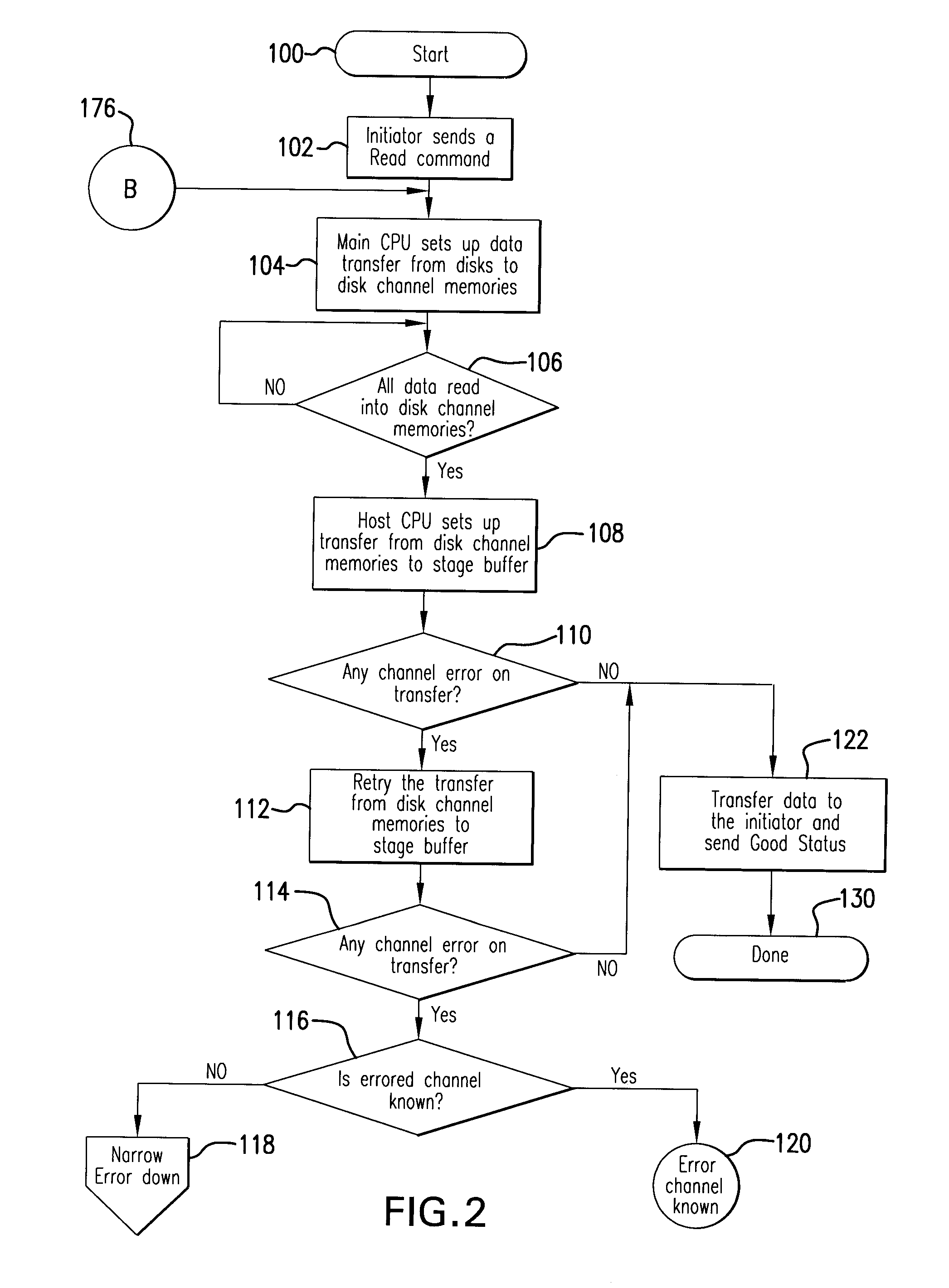
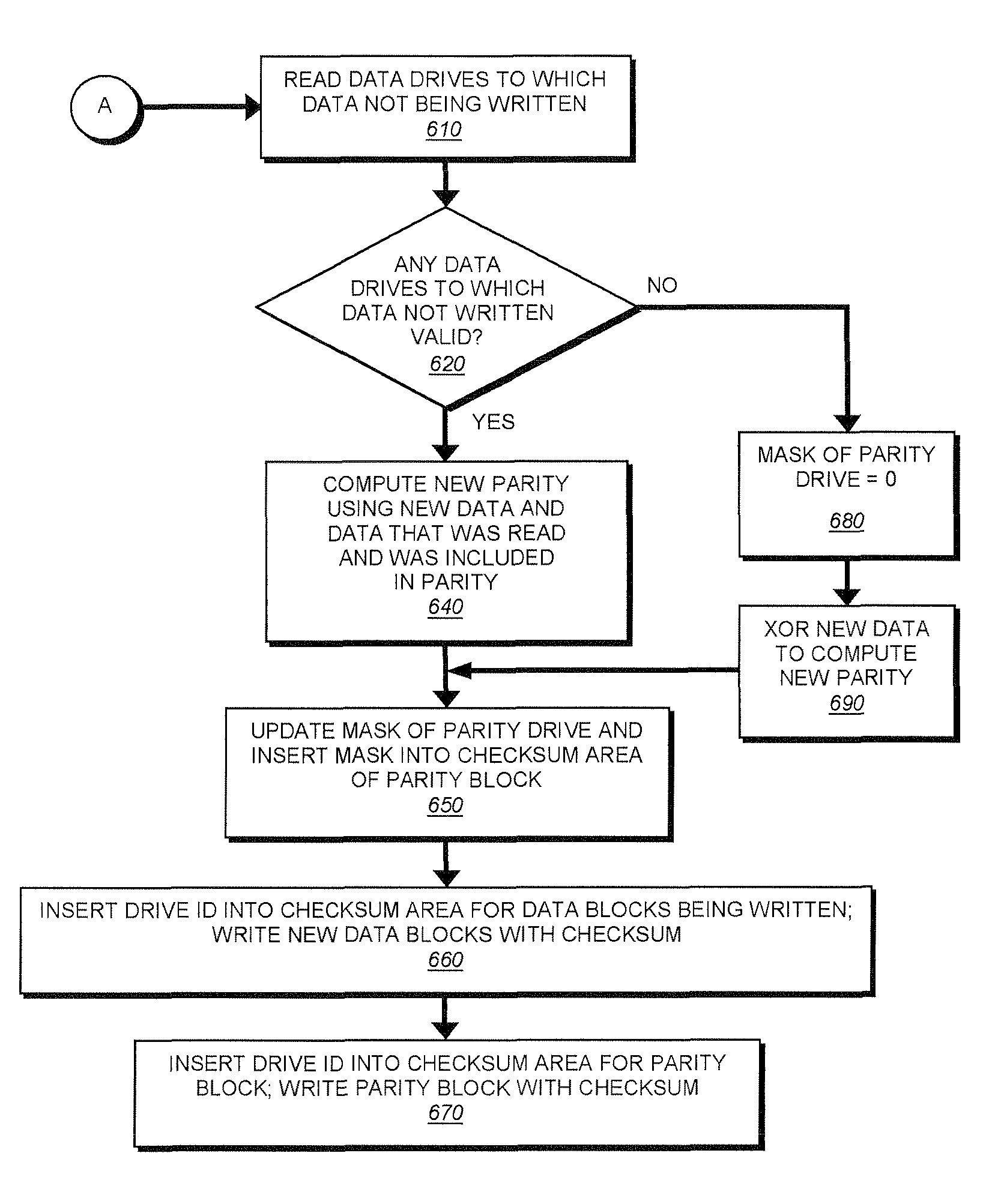
Method for auto-correction of errors in a raid memory system
A method for auto-correction of errors in an array of disk storage devices (210) having a plurality of disk storage devices (210I, 210J) dedicated to storing parity data to provide fault tolerance for a loss of at least two of the plurality of disk storage devices (210A-210J). A read operation from the storage channels (210A-210J) transfers data to a plurality of disk channel memories (220A-220J). The data in the disk channel memories (220A-220J) is checked to confirm the data is valid. Responsive to detection of invalid data, the data may be tested to identify the disk storage channel in error, including sequentially excluding data read from a different one of the plurality of disk channel memories (220A-220J) from a parity check and determining the validity of data from remaining disk channel memories. If valid data is obtained, the disk storage channel from which the data was excluded is identified as the disk storage channel in error.
Owner:DATADIRECT NETWORKS
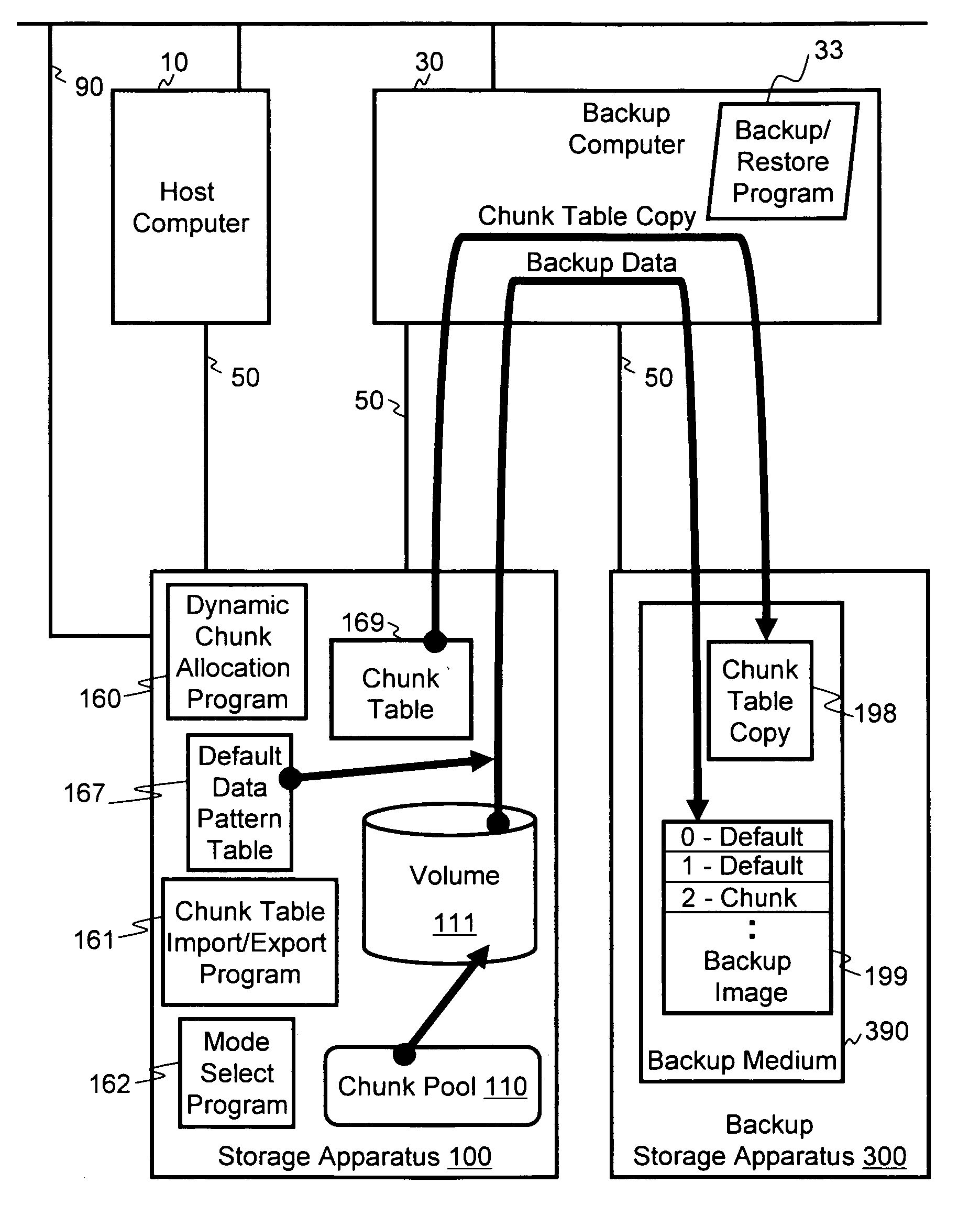
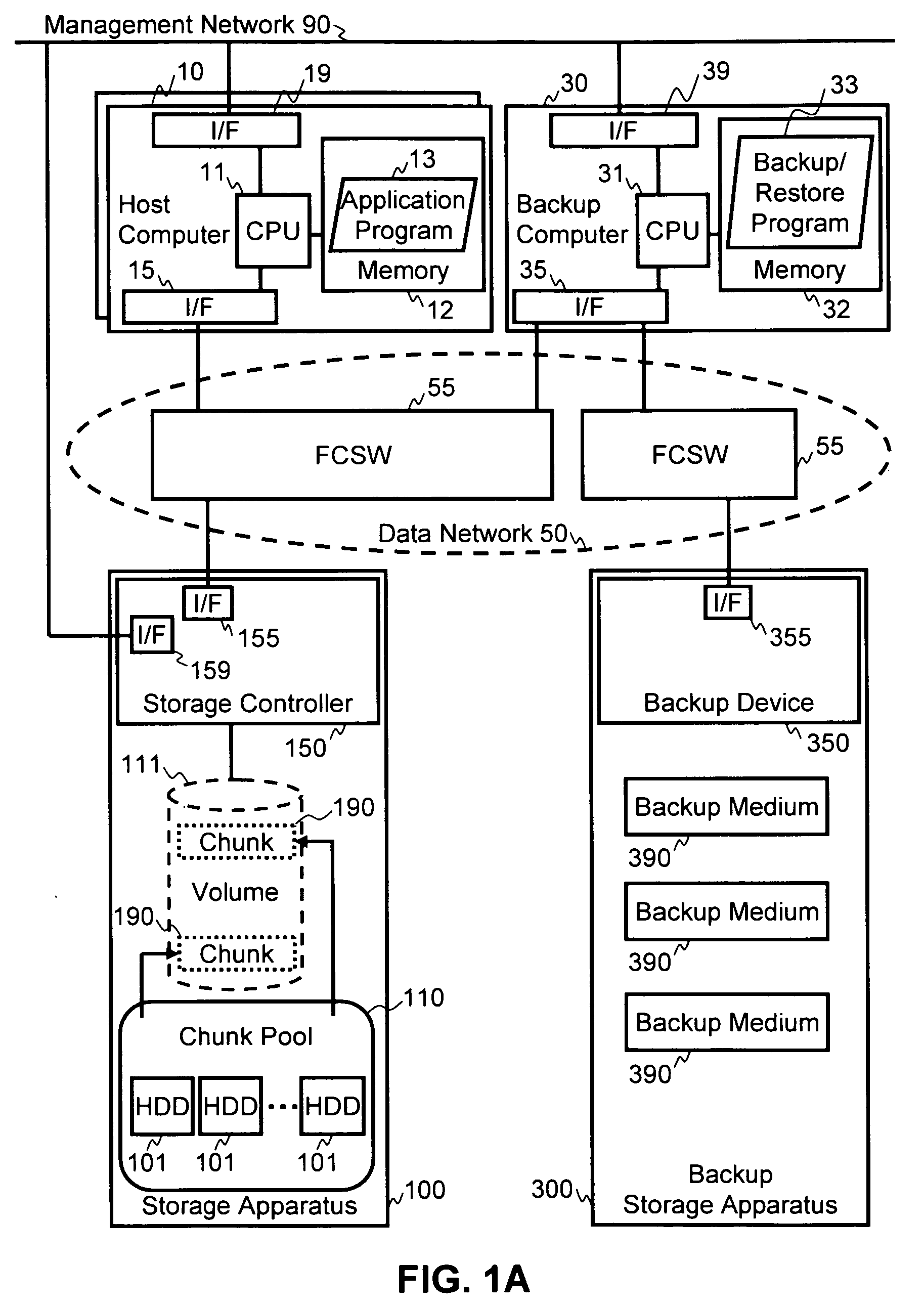
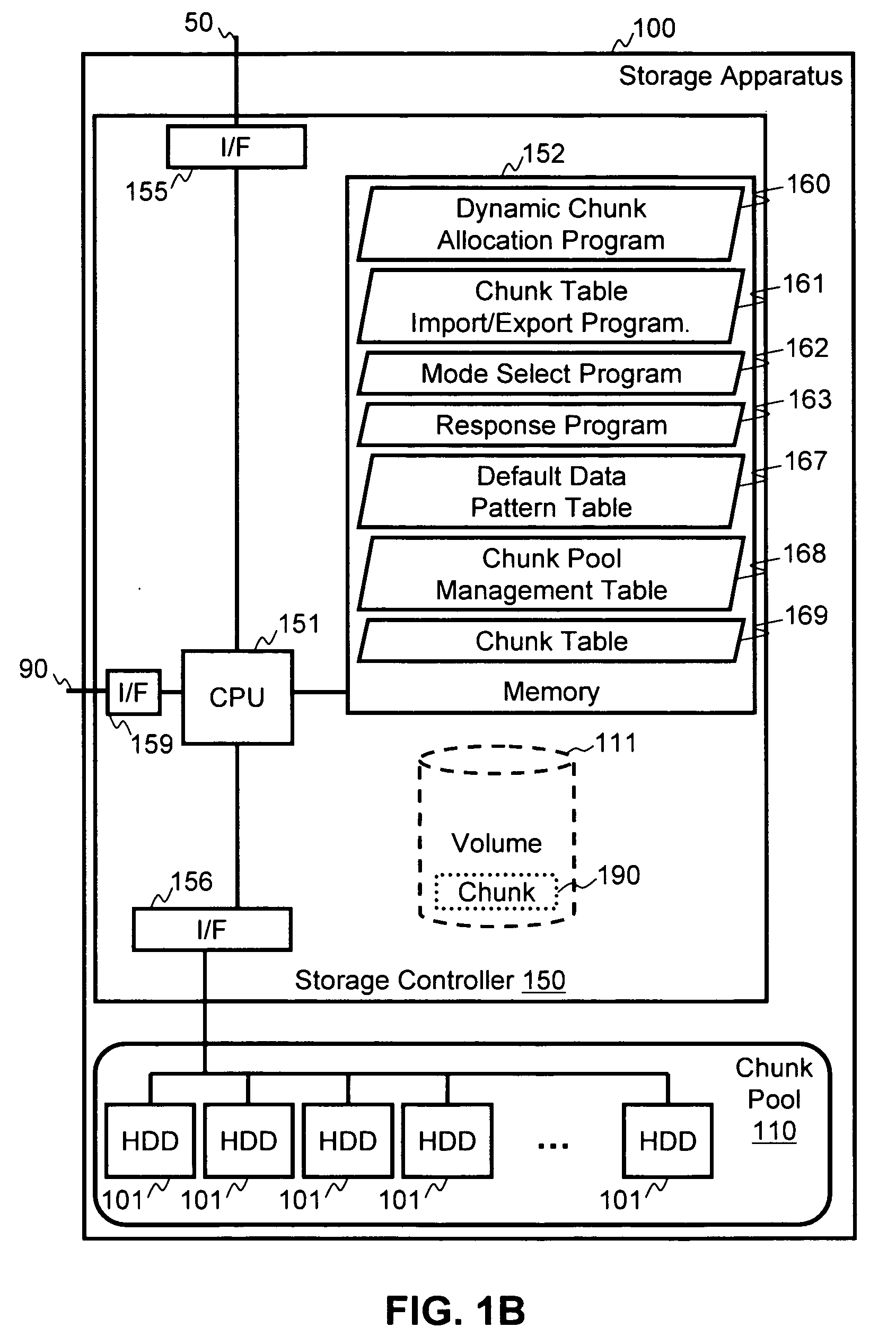
Method and apparatus for backup and restore in a dynamic chunk allocation storage system
Backup and restore operations are made possible in a storage system that has dynamic chunk allocation (DCA) capability. In a DCA storage system, a chunk of physical storage area is not allocated to a segment of a volume until a write command is received targeting the segment of the volume. During a restore operation of the volume in the DCA storage system, the wasting of storage capacity when a backup image of the volume is restored is mitigated by preventing allocation of physical storage areas to segments of restore data that are only void data.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Communication processing apparatus, data communication system, and communication processing method
InactiveUS20060218264A1Reliable transmissionNetwork traffic/resource managementDigital computer detailsCommunications systemTransceiver
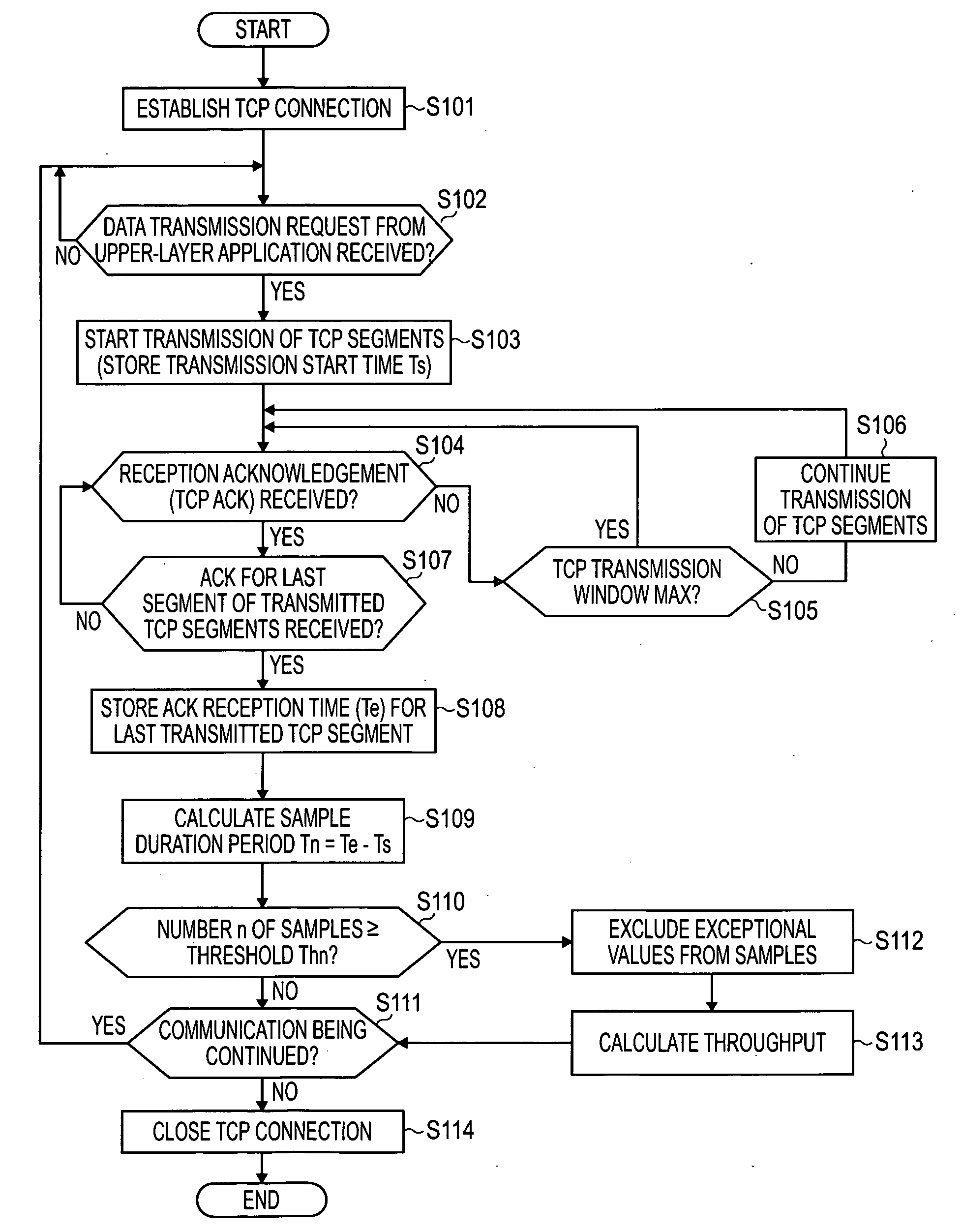
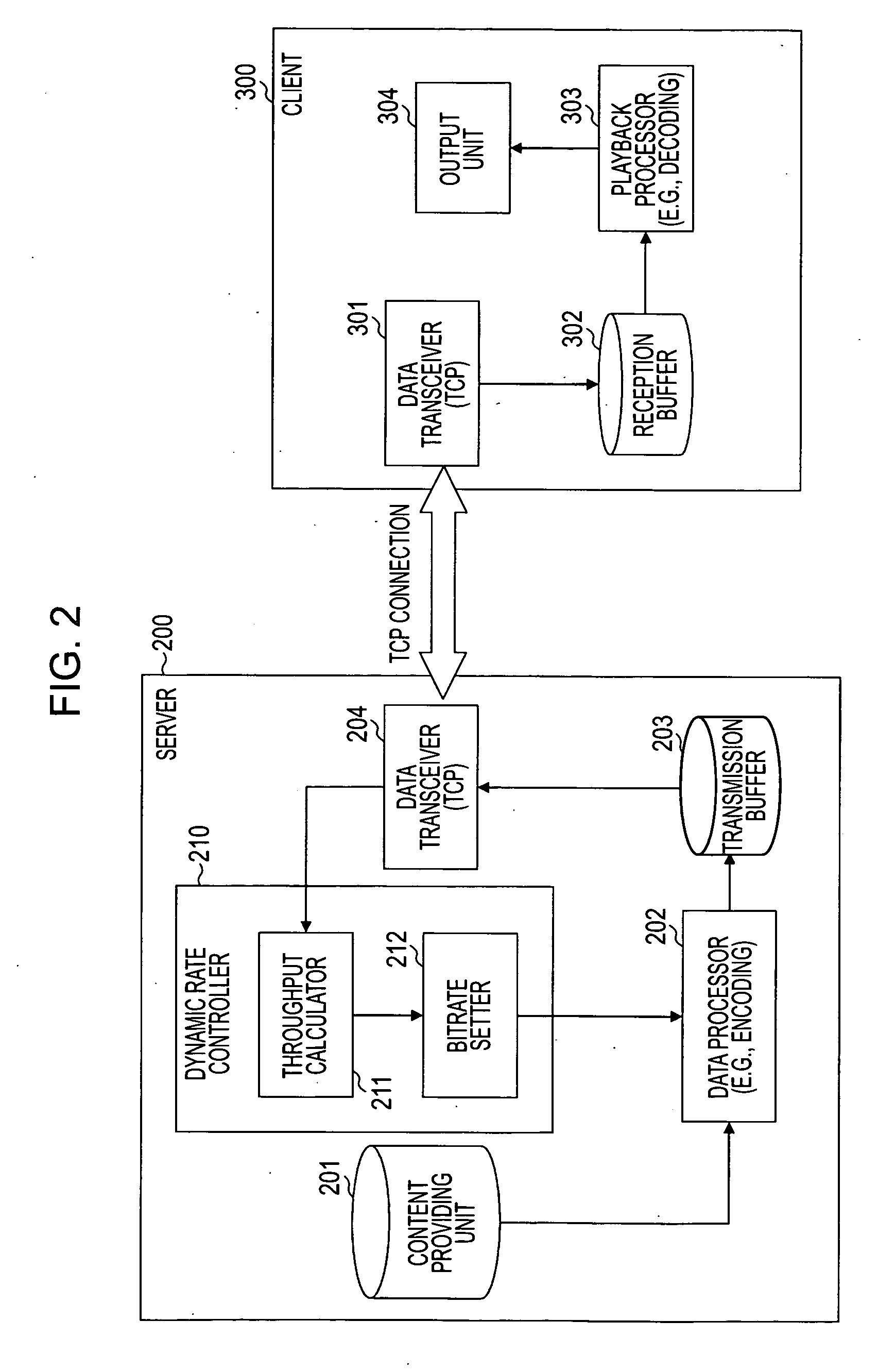
A communication processing apparatus that acts as a server for transmitting data to a client includes a data transceiver configured to carry out communications with the client; a rate controller configured to control a bitrate of data transmitted to the client; and a data processor configured to prepare data to transmit in accordance with the bitrate. The rate controller includes a throughput calculator configured to extract an effective data transmission and reception period not including an ineffective data transmission and reception period in a period during which a communication connection is maintained between the server and the client, and to calculate a maximum throughput on the basis of the length of the effective data transmission and reception period and the amount of data transmitted; and a bitrate setter configured to set a bitrate within a range of up to a maximum allowable bitrate corresponding to the maximum throughput calculated by the throughput calculator.
Owner:SONY CORP
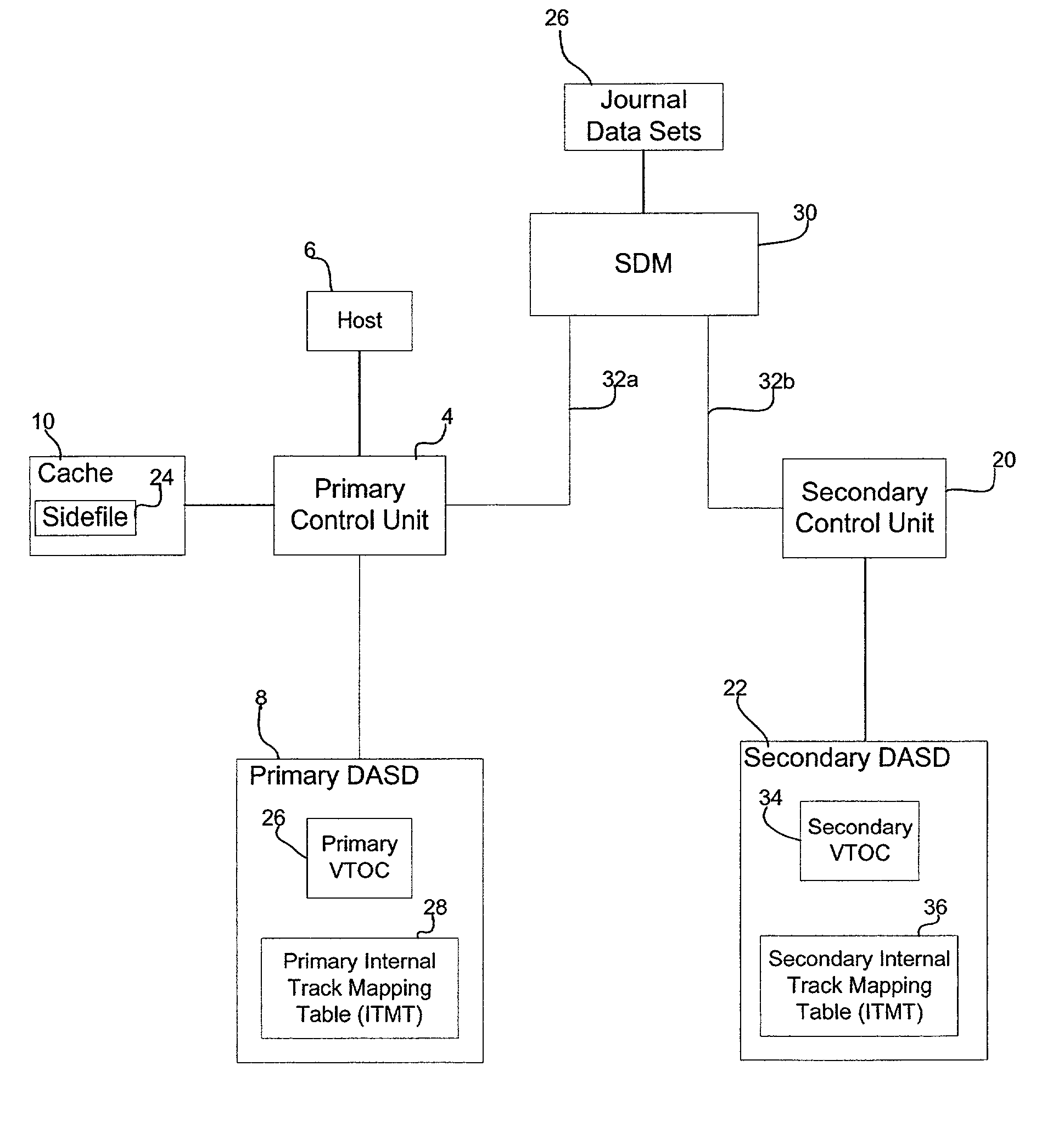
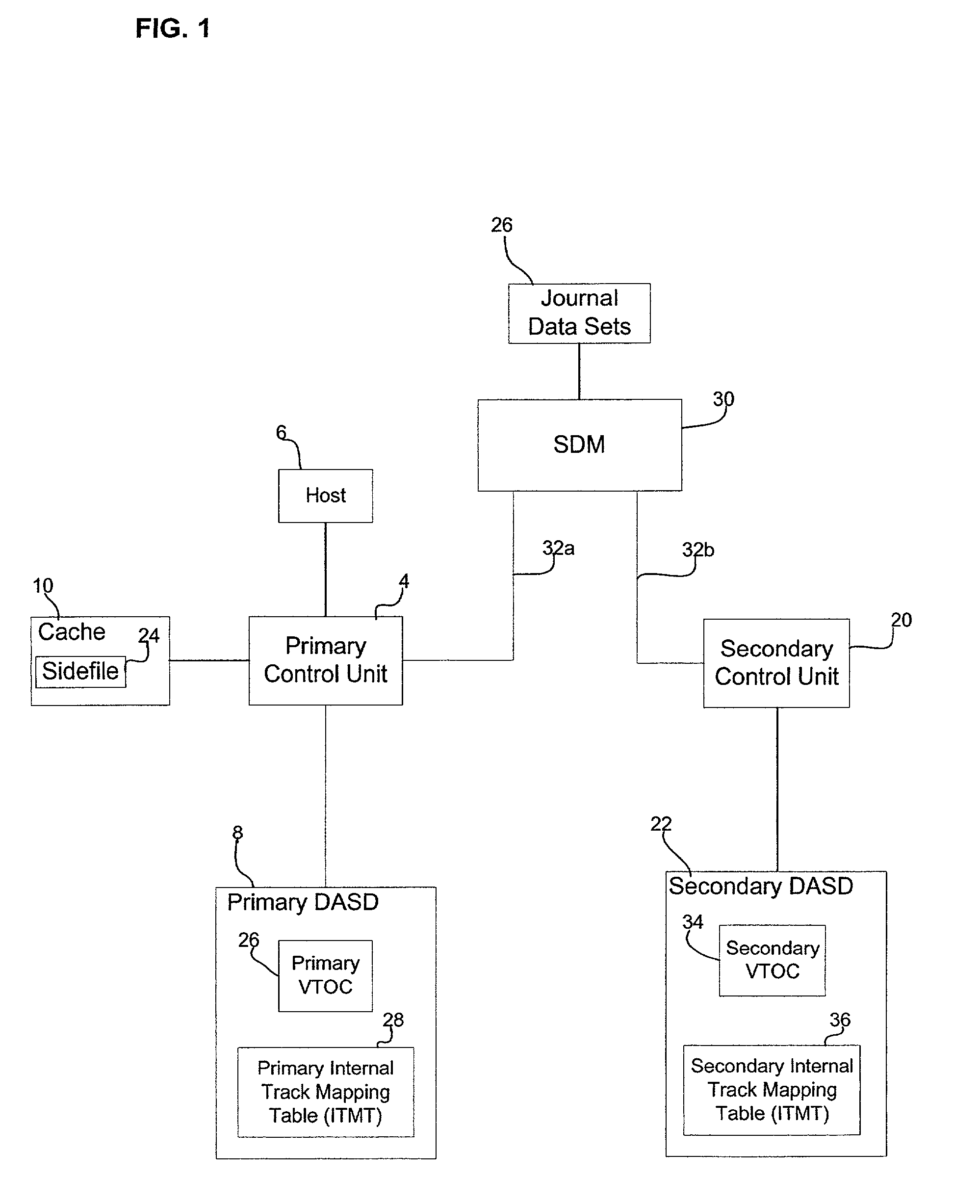
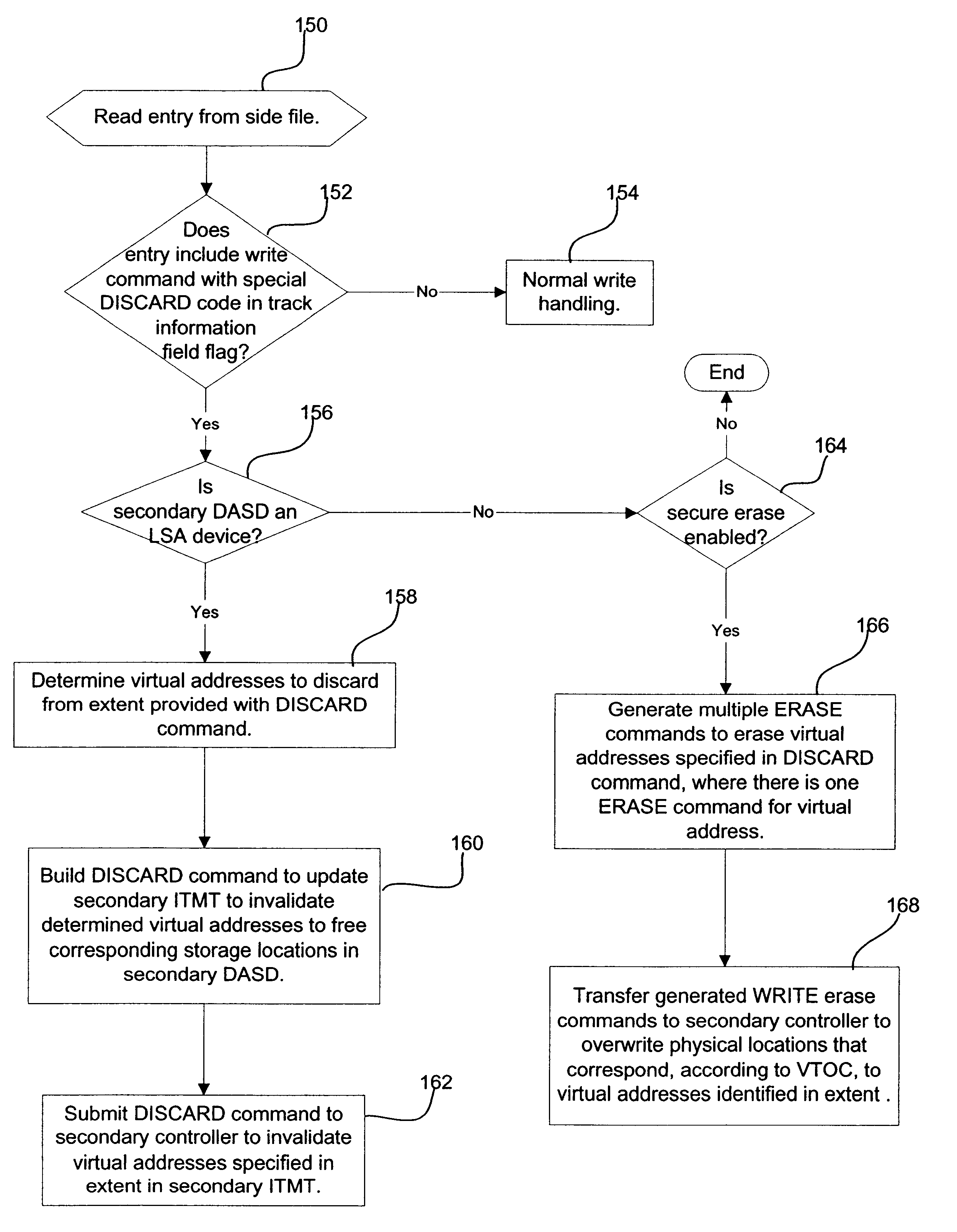
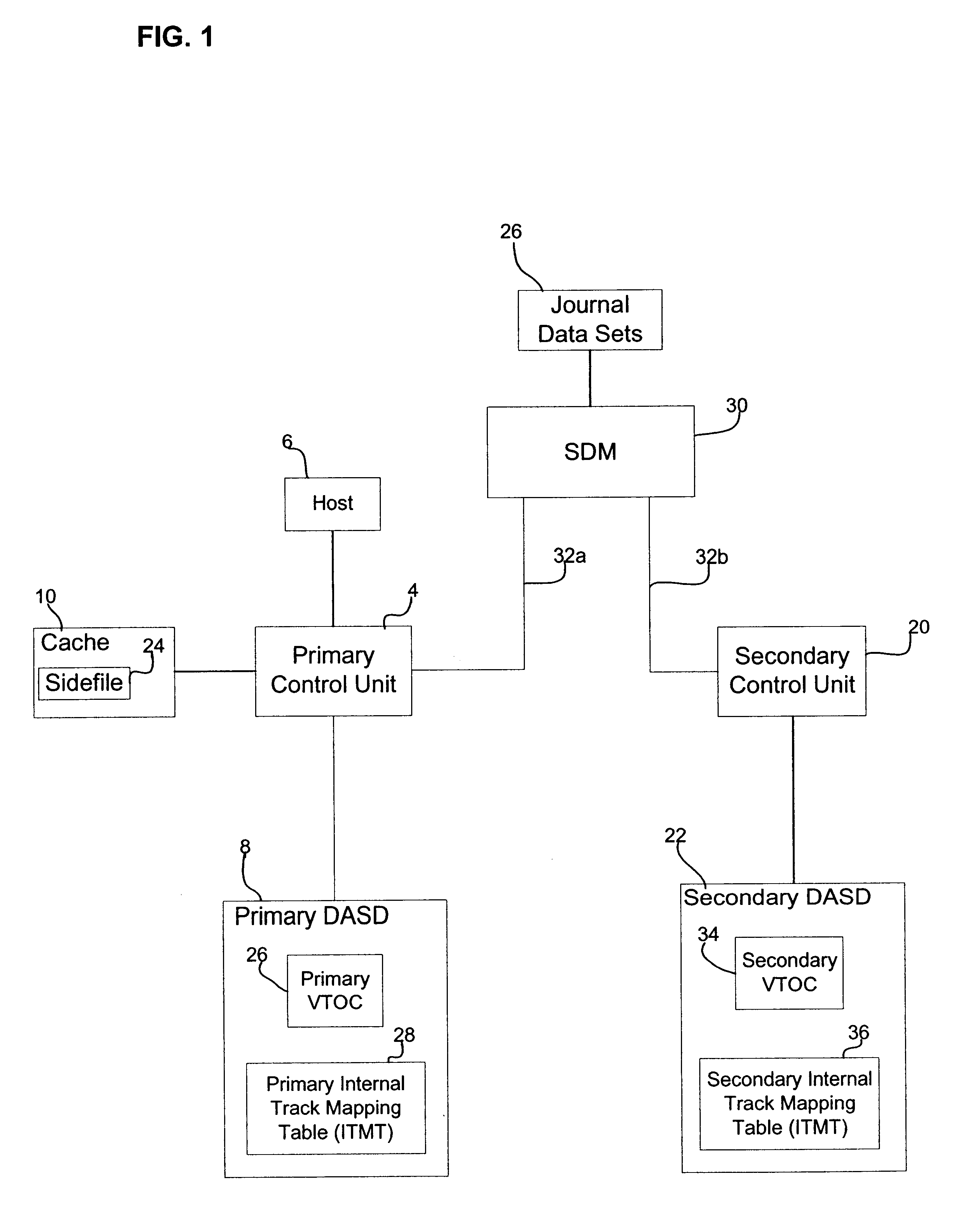
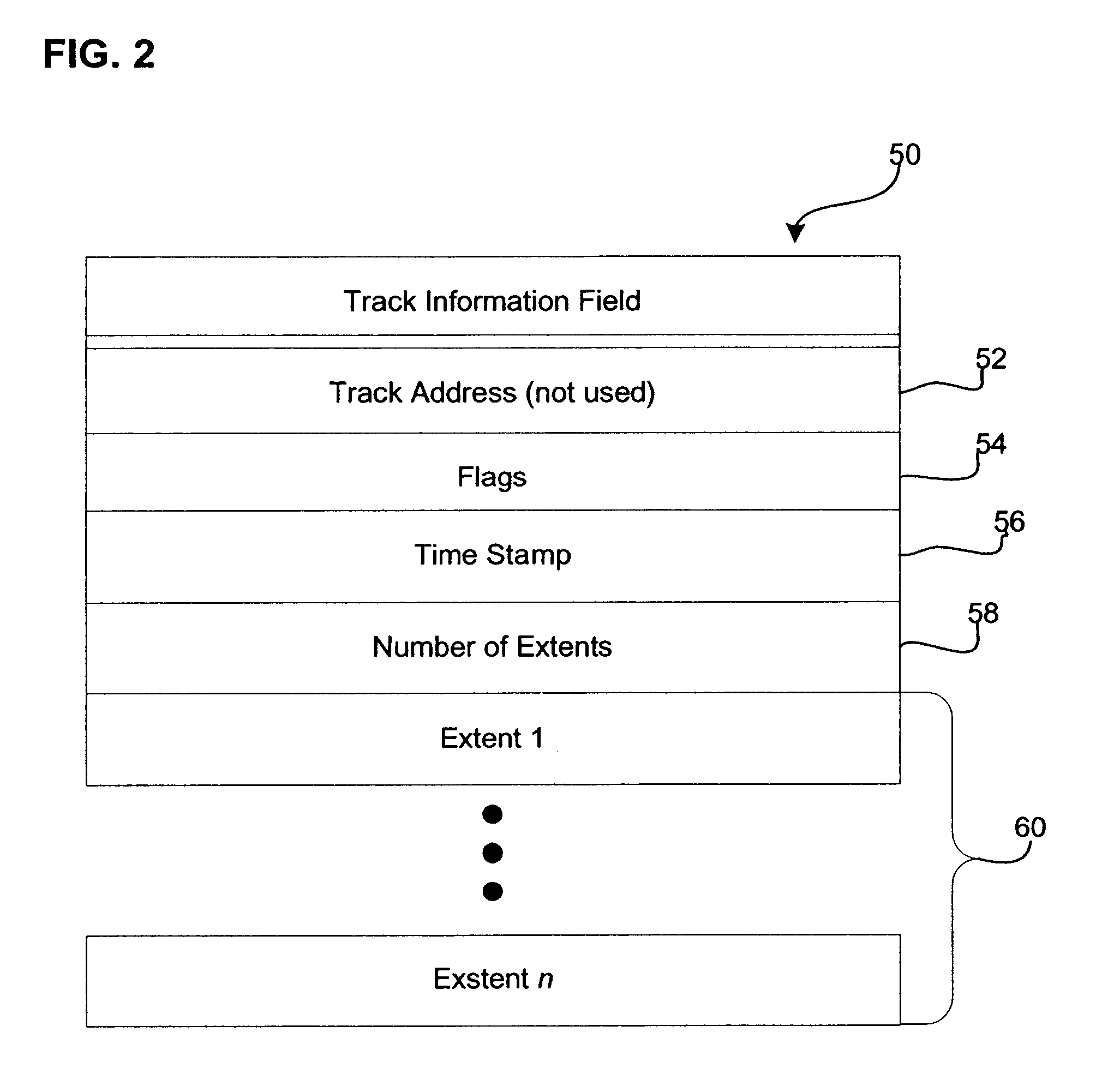
Method, system, and program for discarding data in a storage system where uptdates to a primary storage device are shadowed in a secondary storage device
InactiveUS20020103980A1Operation moreMany timesInput/output to record carriersMemory loss protectionData setInvalid Data
Provided is a method, system, and program for releasing storage space in a first and second storage devices. Updates to the first storage device are copied to the second storage device to provide secondary storage for the updates. A first and second tables map data sets to addresses in the first and second storage devices, respectively. A first command is detected to invalidate data sets in the first table. The addresses in the first table comprise virtual addresses, and a third table provides a mapping of the virtual addresses to physical storage locations in the first storage device. A second command is generated to update the second table to invalidate the data sets in the second storage device invalidated in the first table by the first command. A third command is detected to invalidate the virtual addresses in the third table used by the data sets invalidated in the first table to free the physical storage locations in the first storage device pointed to by the invalidated virtual addresses. A fourth command is generated that is directed to the physical storage locations in the second storage device used by the invalidated data sets.
Owner:IBM CORP
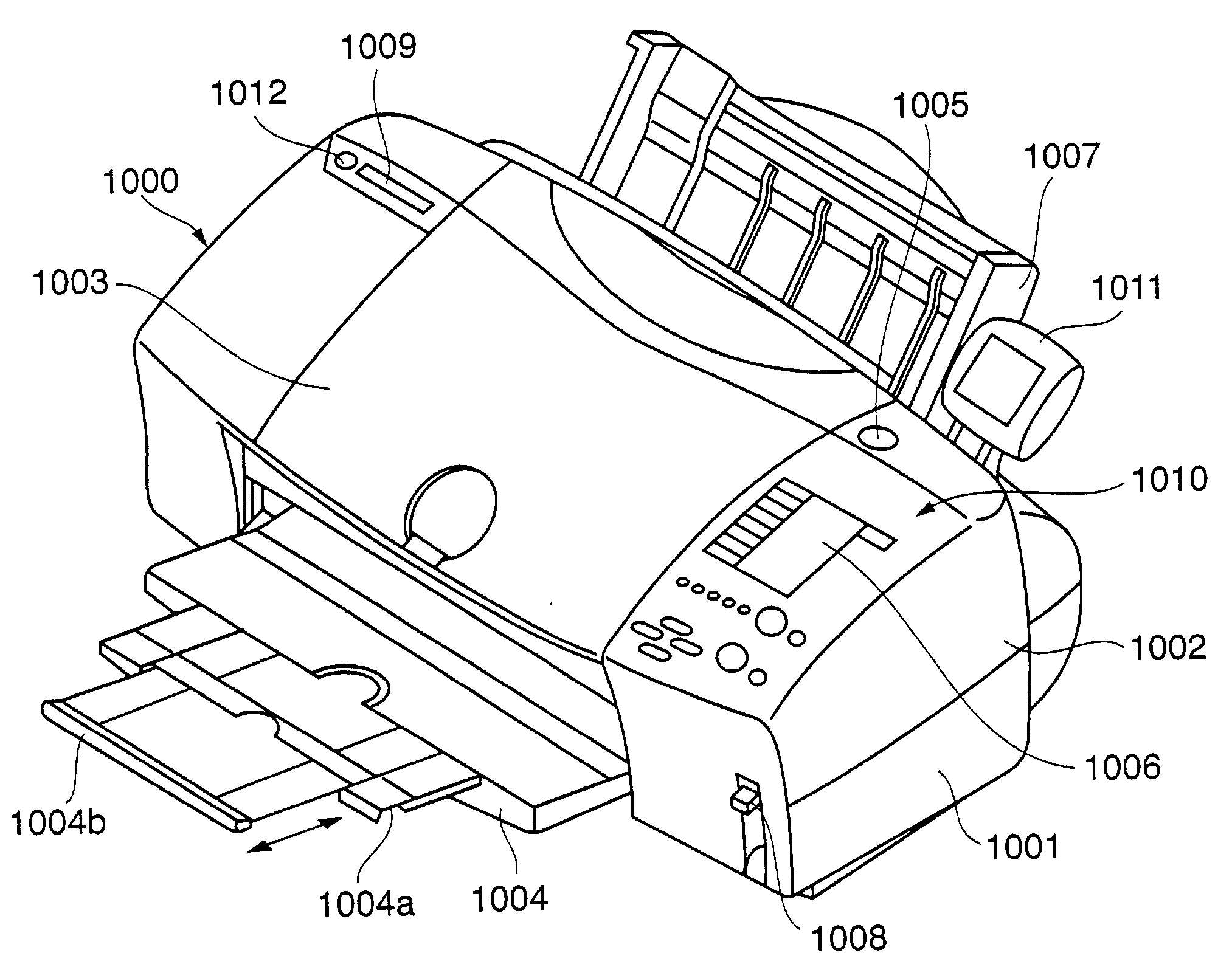
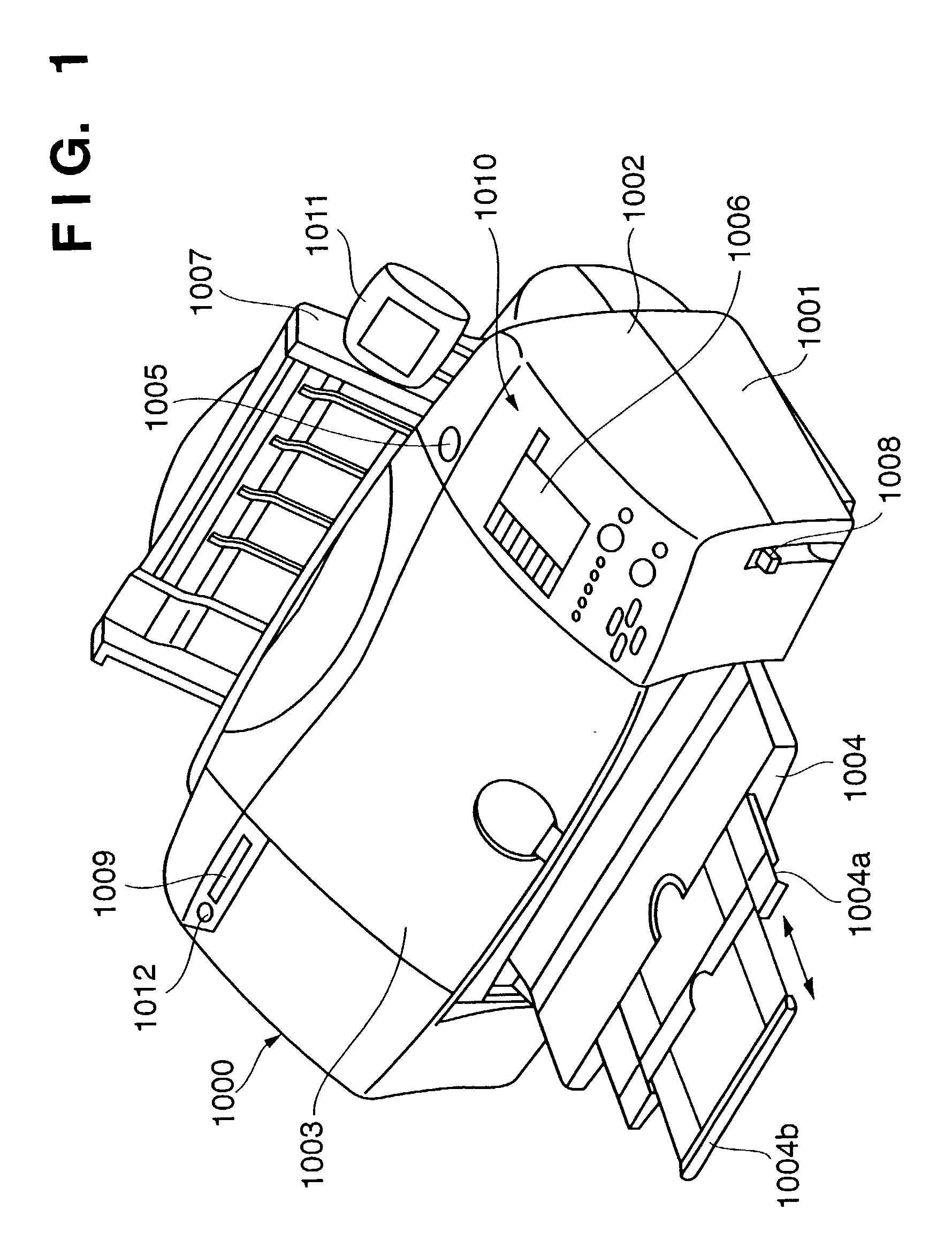
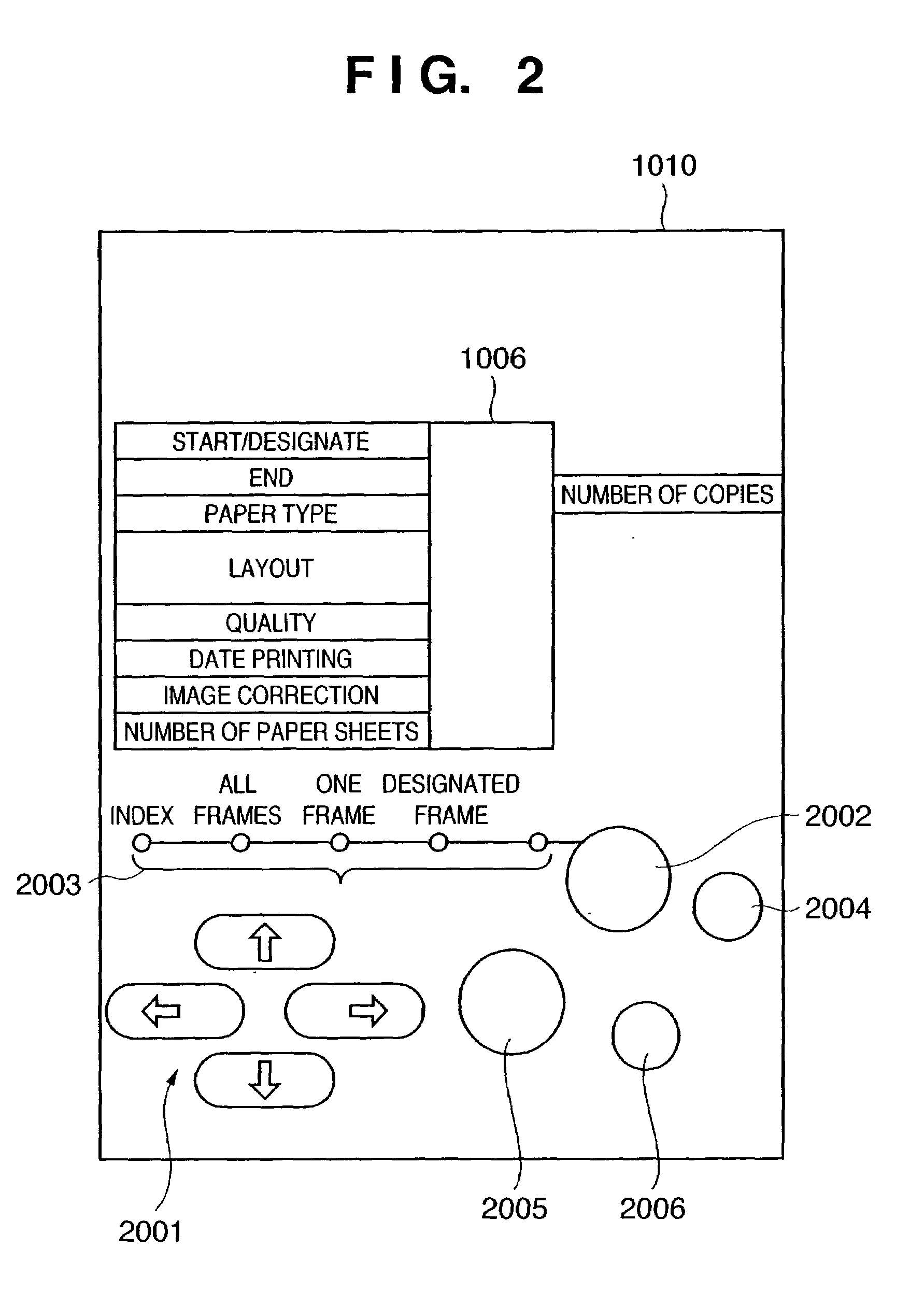
Imaging apparatus, system having imaging apparatus and printing apparatus, and control method therefor
An imaging apparatus capable of outputting a sensed image to a printing apparatus issues a print request command containing a parameter for designating a print mode to a PD printer apparatus connected via an interface. The imaging apparatus transmits image data corresponding to the print mode on the basis of a data request from the PD printer apparatus. The imaging apparatus transmits, to the PD printer apparatus, the print request command in which the parameter is changed to invalid data, thereby designating printing of the transmitted image data.
Owner:CANON KK
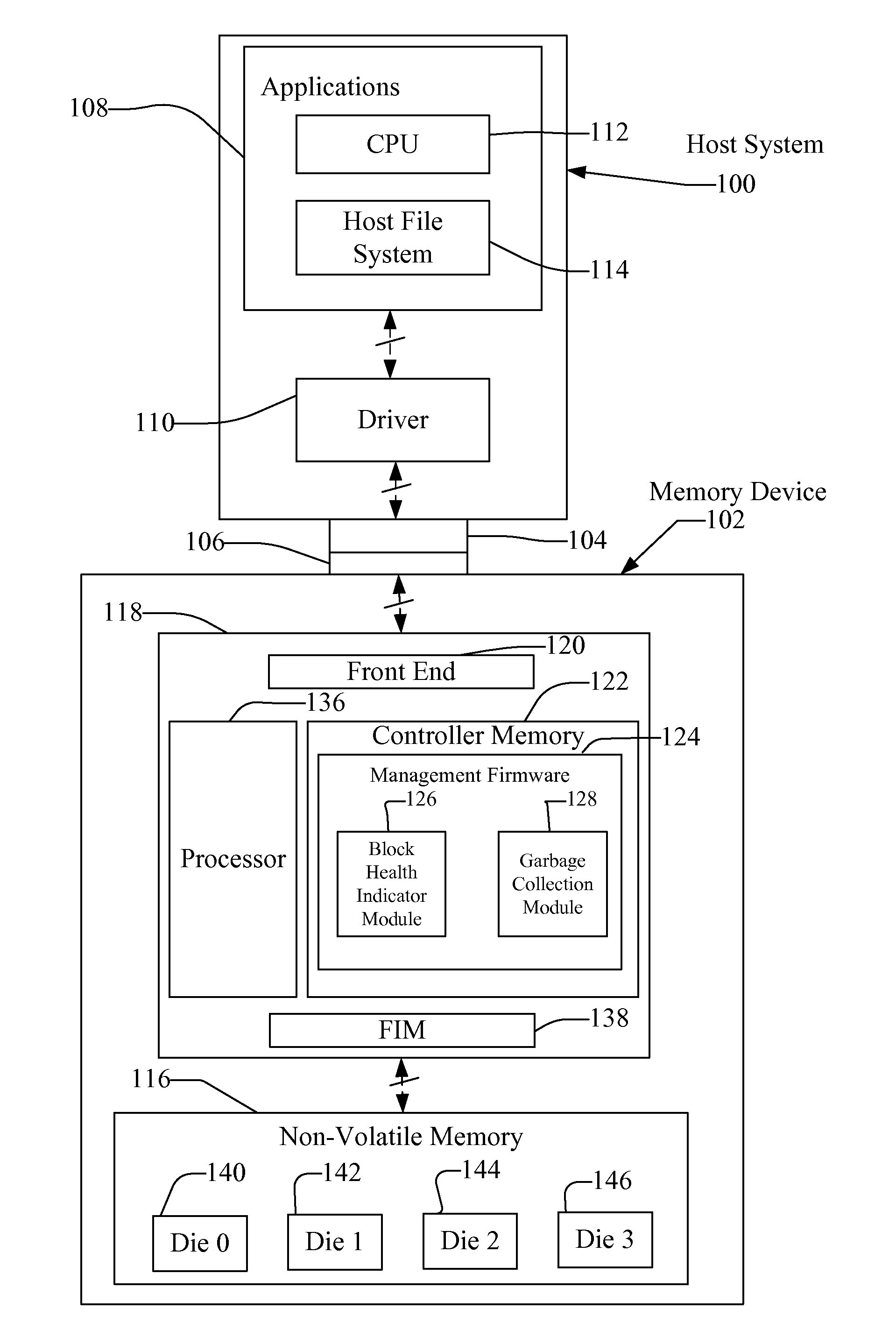
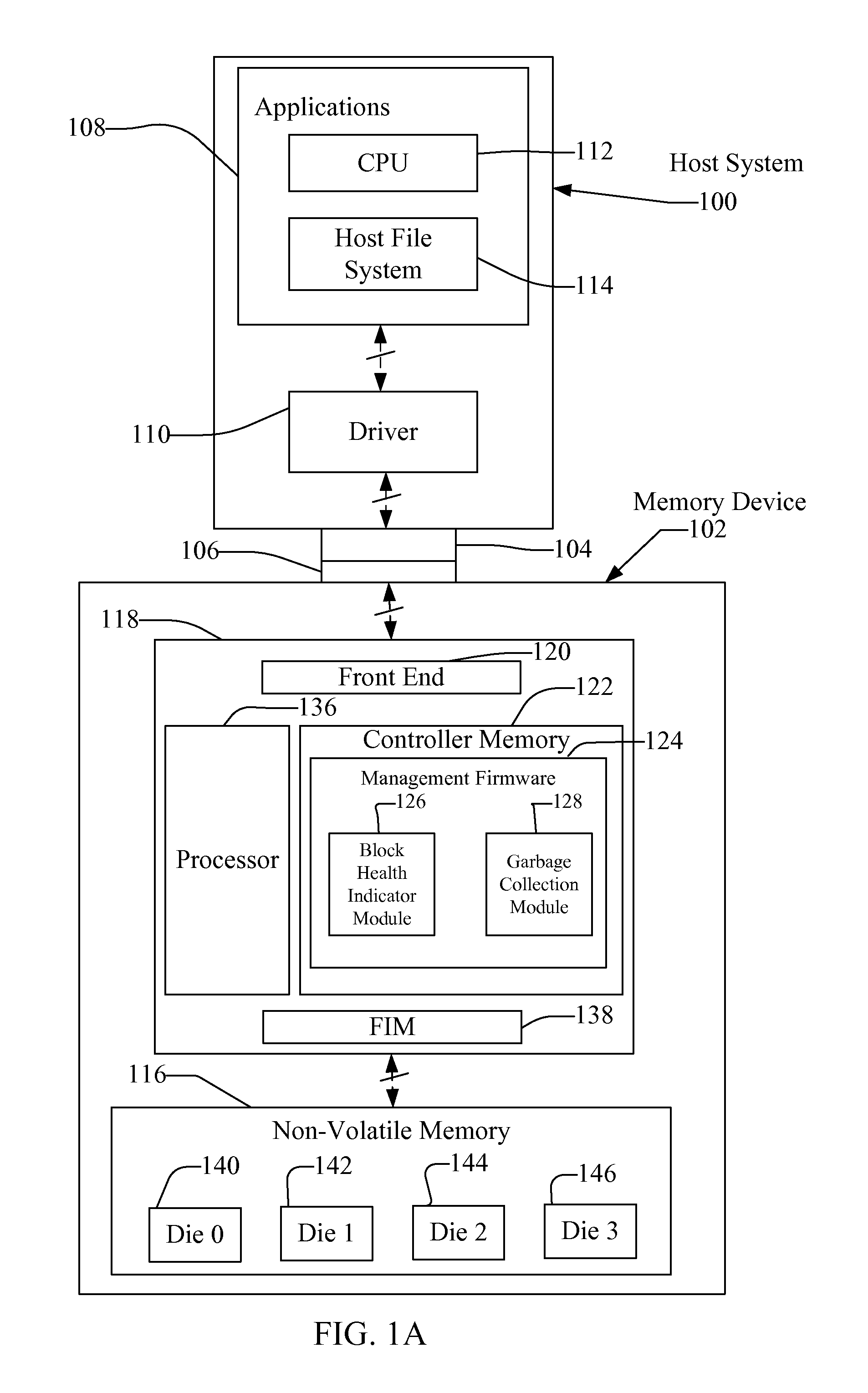
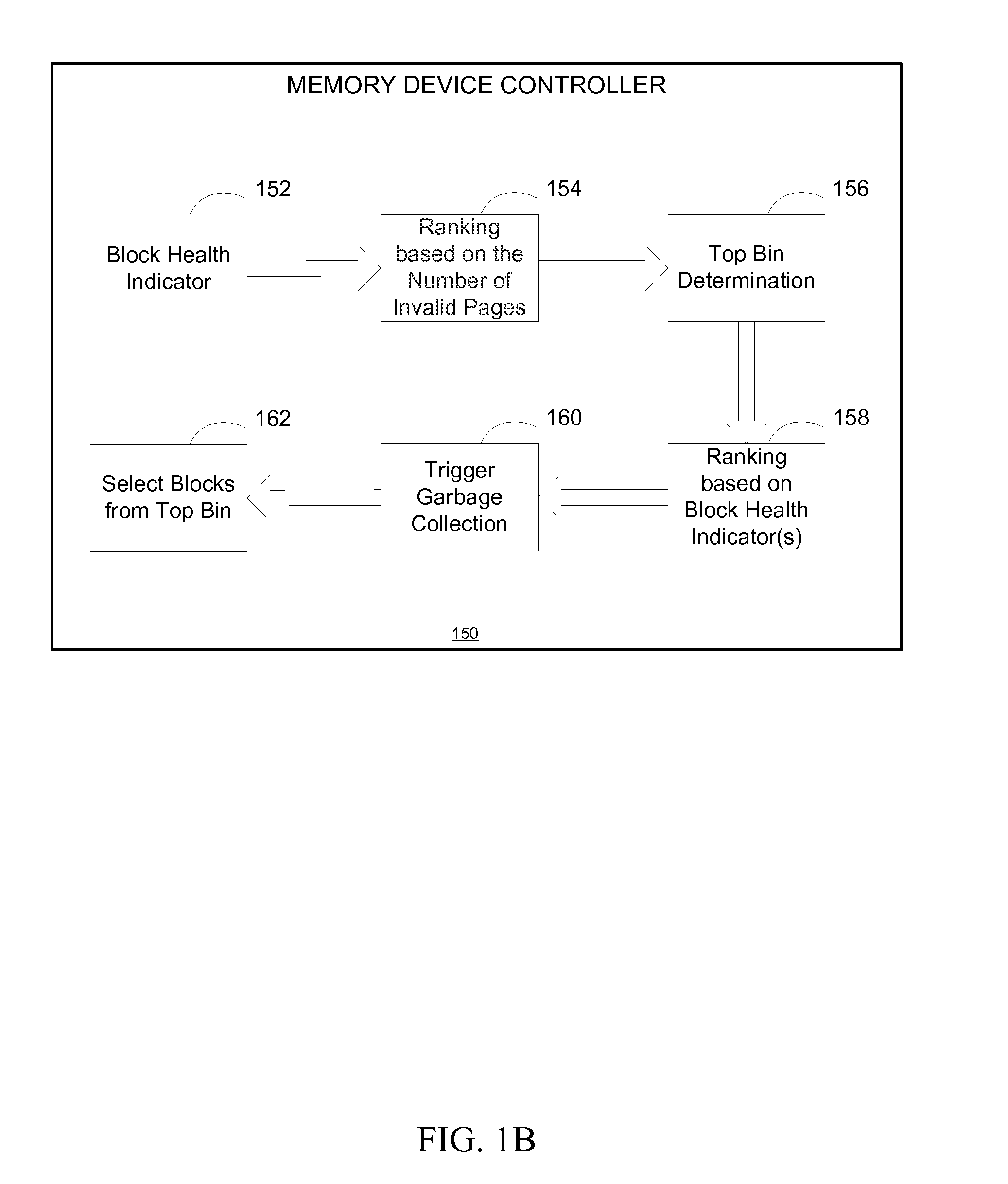
System and Method for Selecting Blocks for Garbage Collection Based on Block Health
Systems and methods for garbage collection in a memory device are disclosed. The memory device includes a plurality of blocks that may be filled with data. In the event that the memory device needs to remove invalid data stored in the blocks, the memory device may perform a garbage collection process. To select the blocks for garbage collection, the memory device may examine both the number of invalid pages in the blocks and the health of the blocks (e.g., the program / erase cycles, erase speed, and program speed). Thus, the memory device may select the blocks for garbage collection that have the most invalid pages and are the healthiest. In this manner, the memory device may more evenly wear the blocks in the memory device.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Memory system and method for controlling a nonvolatile semiconductor memory
ActiveUS20090248964A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInvalid DataLinked list
A memory system includes a nonvolatile semiconductor memory having blocks, the block being data erasing unit; and a controller configured to execute; an update processing for; writing superseding data in a block, the superseding data being treated as valid data; and invalidating superseded data having the same logical address as the superseding data, the superseded data being treated as invalid data; and a compaction processing for; retrieving blocks having invalid data using a management tablet the management table managing blocks in a linked list format for each number of valid data included in the block; selecting a compaction source block having at least one valid data from the retrieved blocks; copying a plurality of valid data included in the compaction source blocks into a compaction target block; invalidating the plurality of valid data in the compaction source blocks; and releasing the compaction source blocks in which all data are invalidated.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
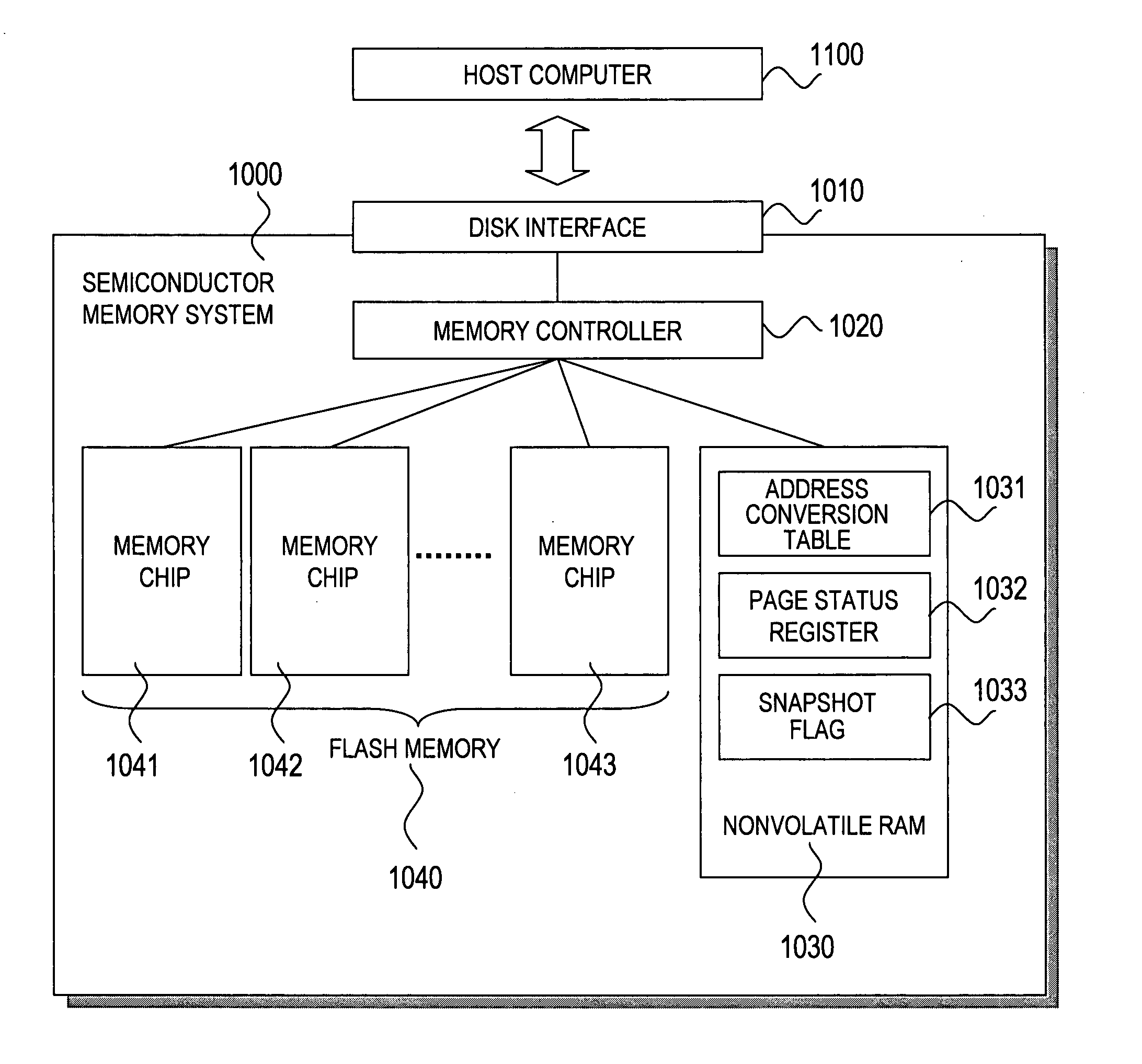
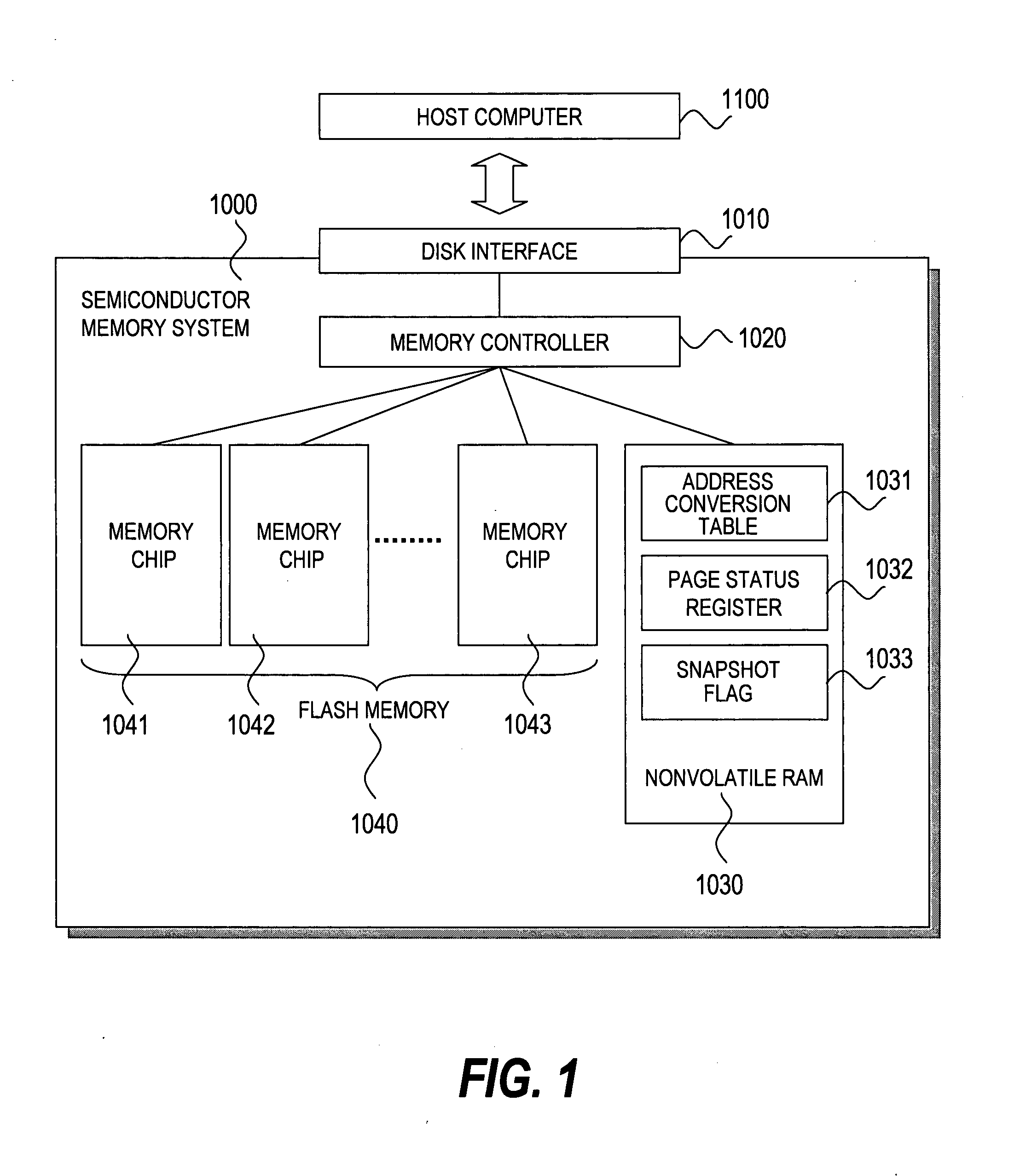
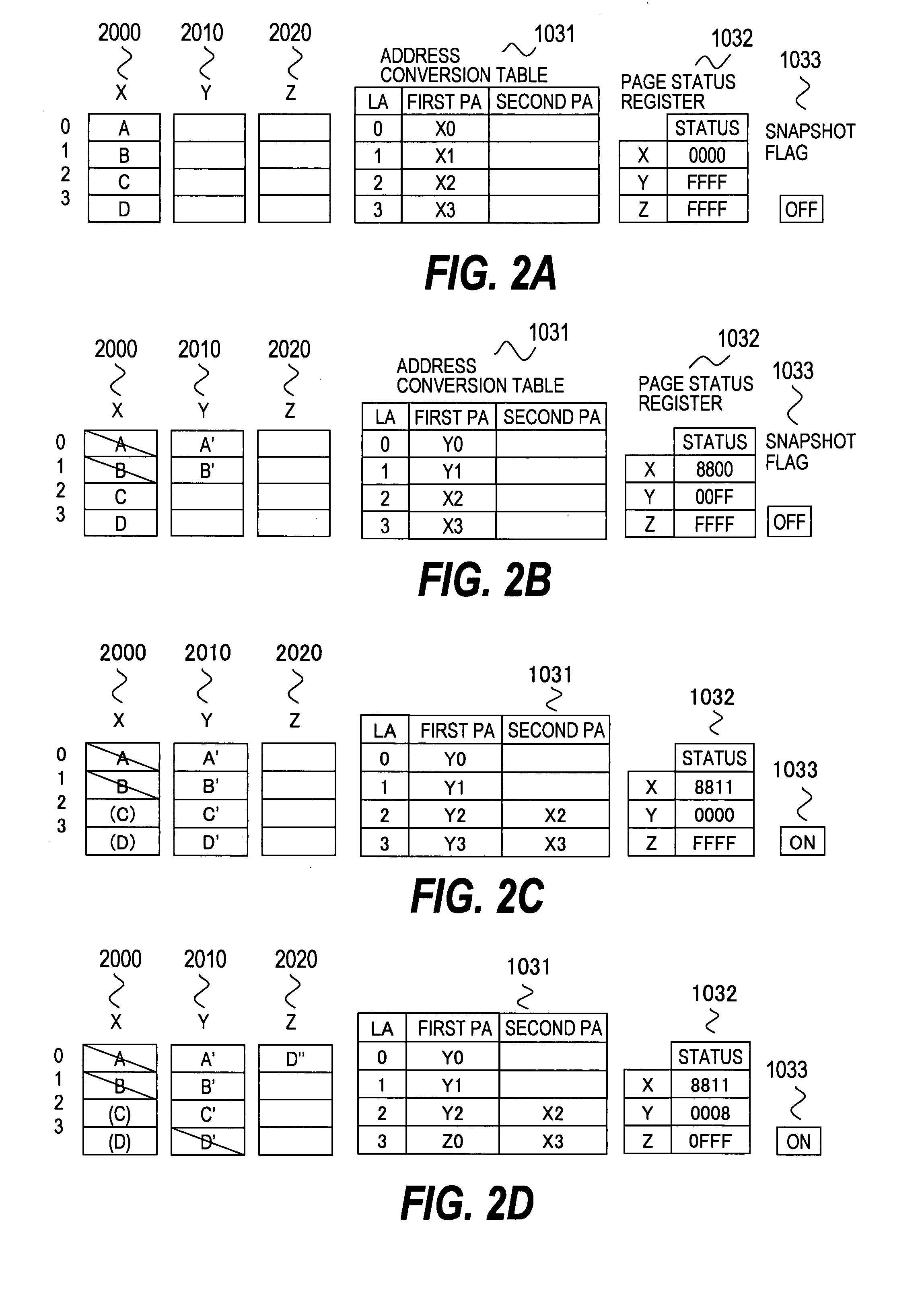
Semiconductor memory system having a snapshot function
ActiveUS20080126712A1Reduce loadImprove usabilityError detection/correctionMemory systemsInvalid DataData store
In a semiconductor memory computer equipped with a flash memory, use of backed-up data is enabled. The semiconductor memory computer includes an address conversion table for detecting physical addresses of at least two pages storing data by designating a logical address from one of logical addresses to be designated by a reading request. The semiconductor memory computer includes a page status register for detecting one page status allocated to each page, and page statuses to be detected include the at least following four statuses: (1) a latest data storage status, (2) a not latest data storage status, (3) an invalid data storage status, and (4) an unwritten status. By using the address conversion table and the page status register, at least two data s (latest data and past data) can be read for one designated logical address from a host computer.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
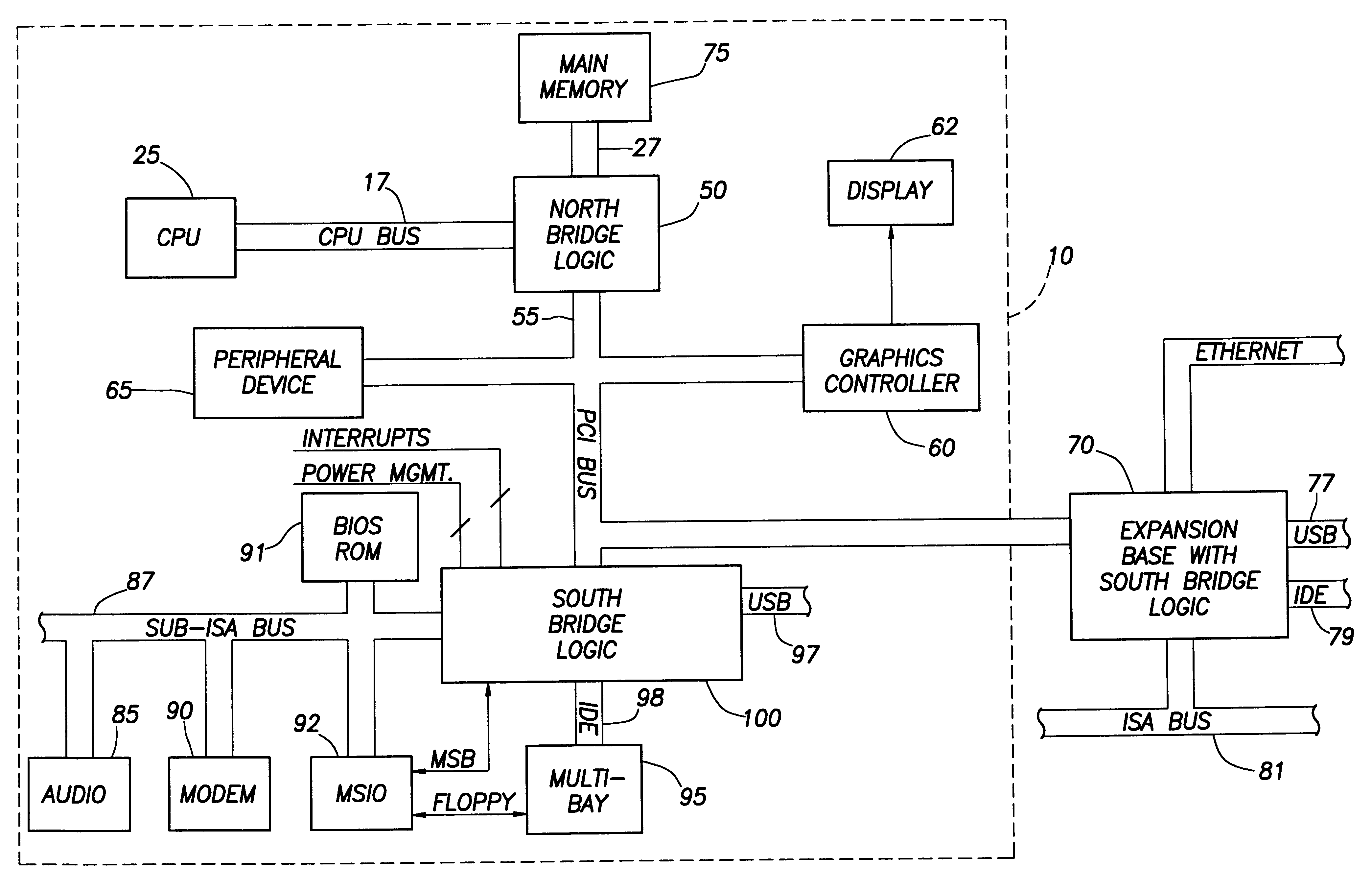
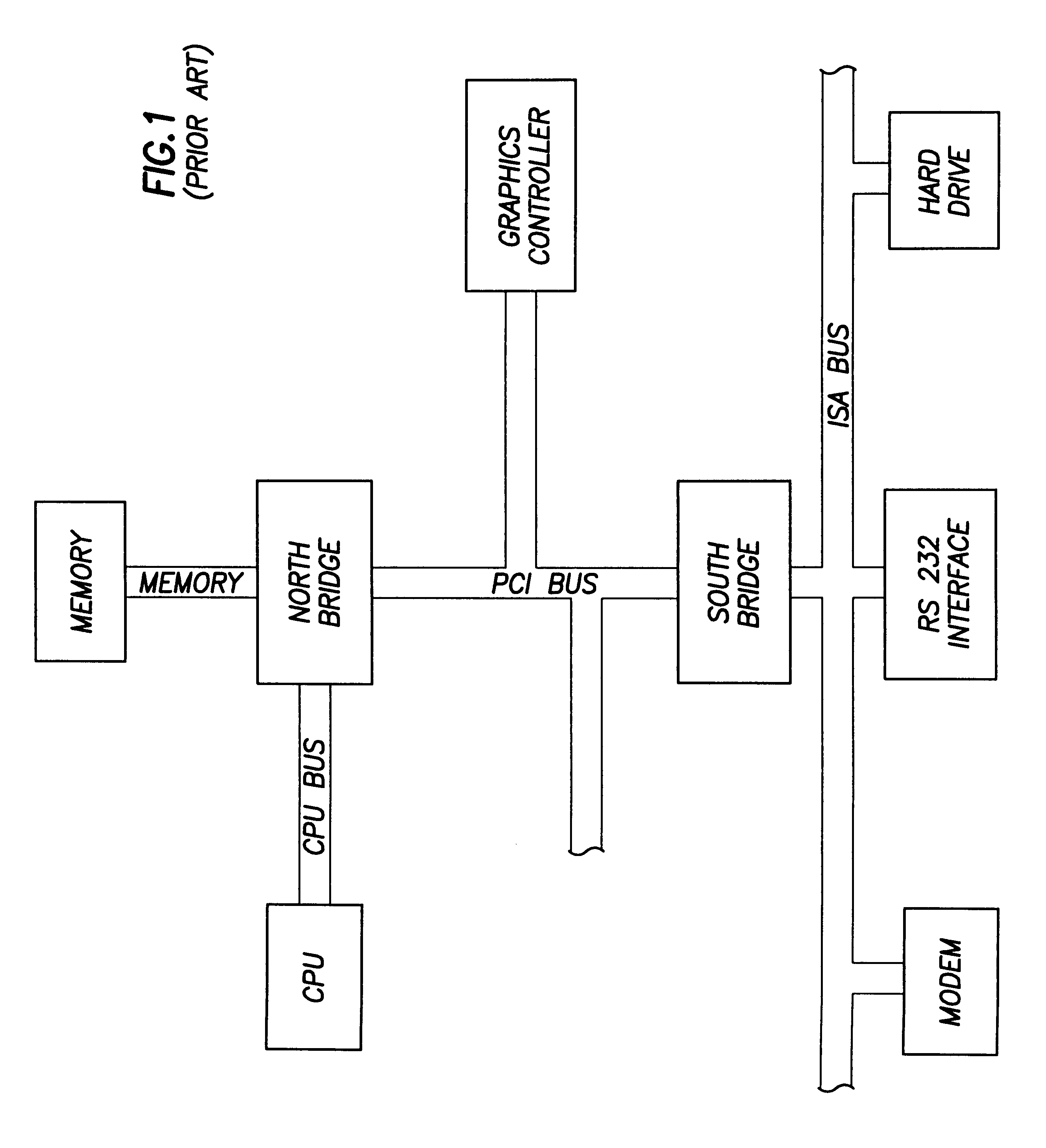
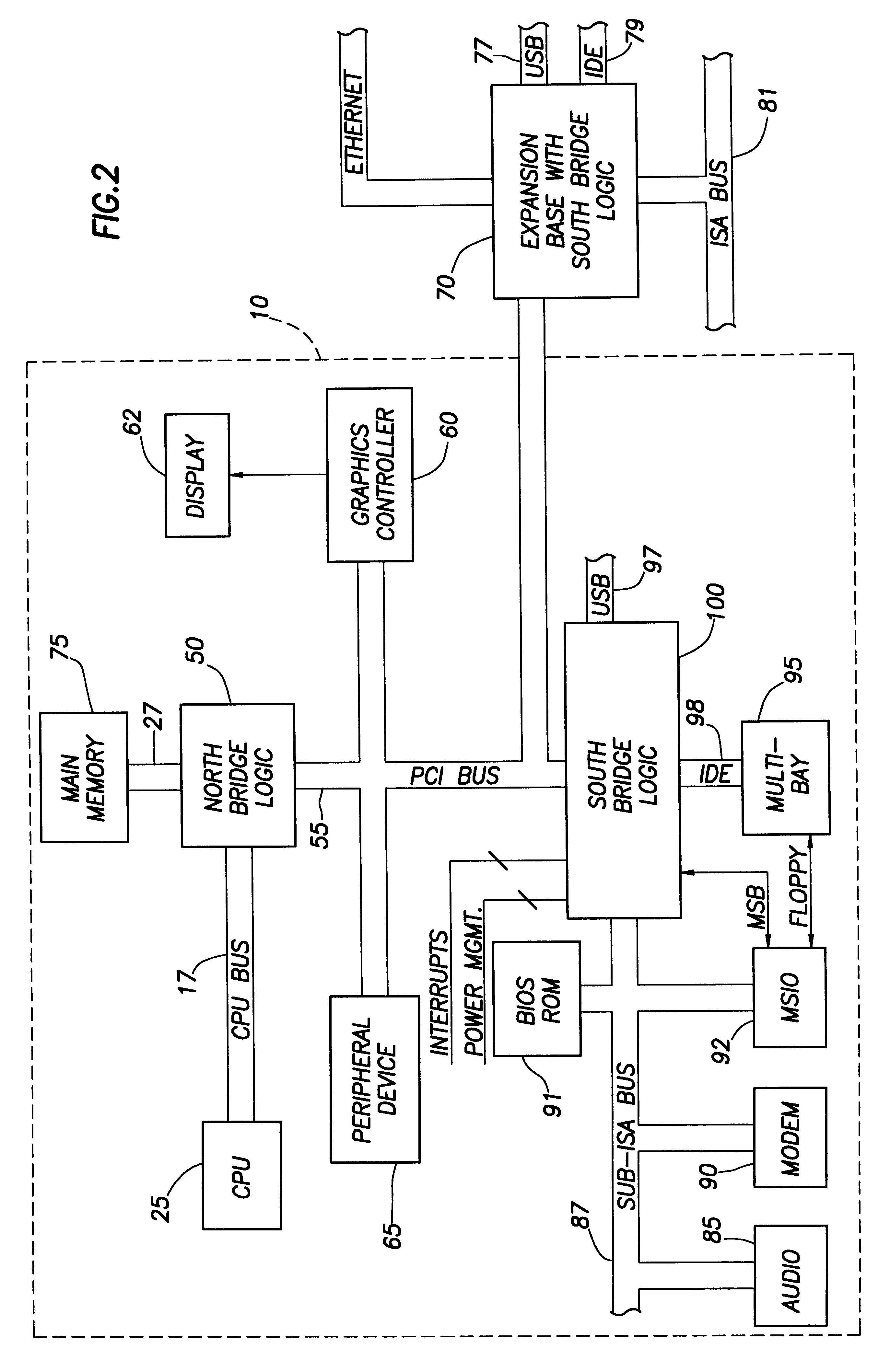
Computer system with bridge logic that asserts a system management interrupt signal when an address is made to a trapped address and which also completes the cycle to the target address
A computer system includes a South bridge logic that connects an expansion bus to one or more secondary expansion busses and peripheral devices. The South bridge logic includes internal control devices that are targets for masters on the expansion bus. The target devices couple to the expansion bus through a common expansion target interface, which monitors and translates master cycles on the expansion bus on behalf of the target devices. The South bridge includes an ACPI / power management logic capable of supporting a Device Idle mode in which selected I / O device may be placed in a low power state. To prevent cycles from being run to a device in a low power state, the ACPI / power management includes status registers that are used to determine when a device in low power mode is the target of an expansion bus cycle. If such a cycle occurs, the cycle is intercepted and an SMI signal is transmitted to the CPU. In addition, the target interface responds to the master by asserting a retry signal. When the transaction is retried, the cycle is passed to the target, which responds with an invalid data signal. The CPU by this time, or at some subsequent time realizes that the target was asleep based upon processing of the SMI signal. The CPU then either re-executes the cycle when the device is removed form the low power state, or else simply rejects the invalid data.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
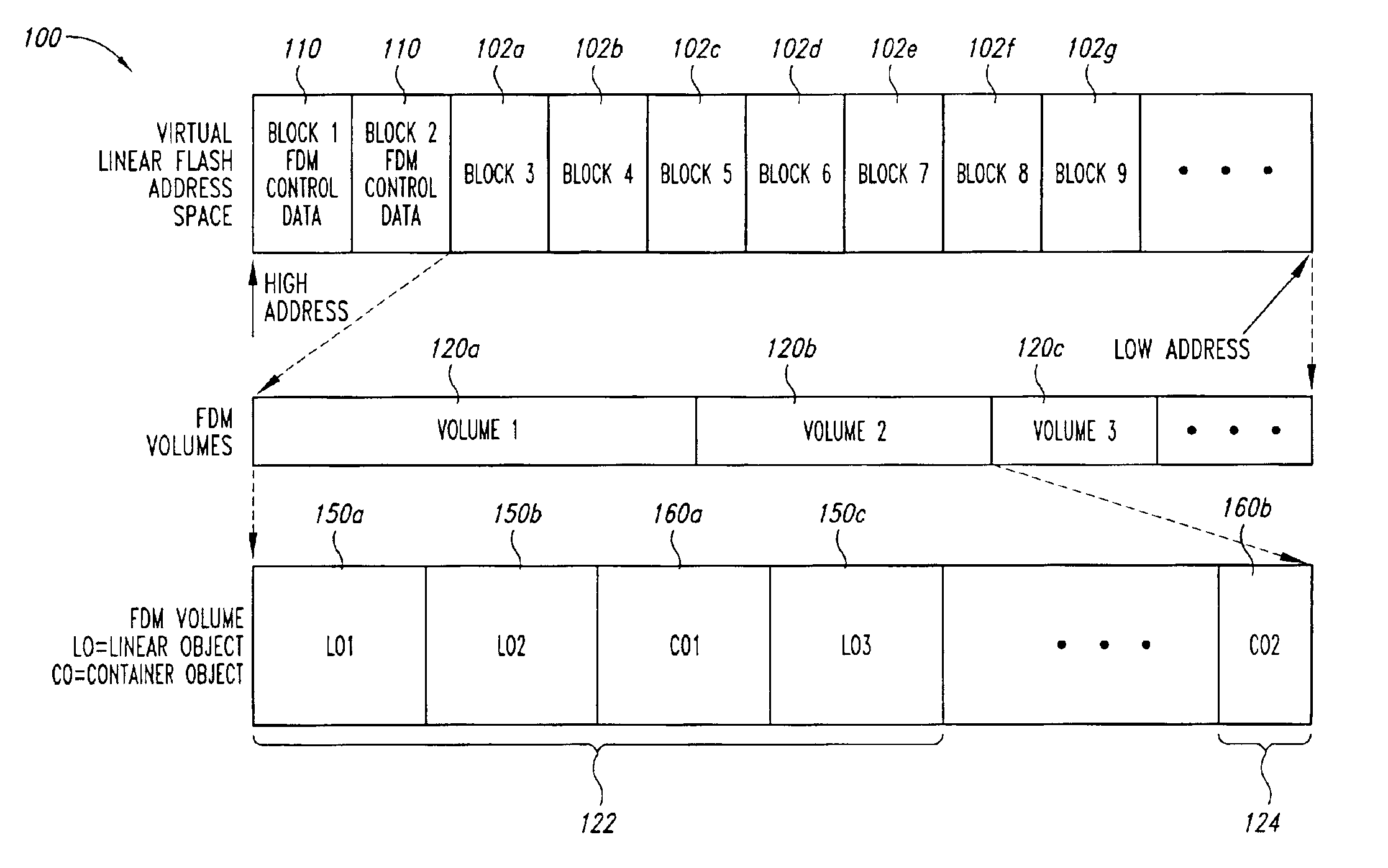
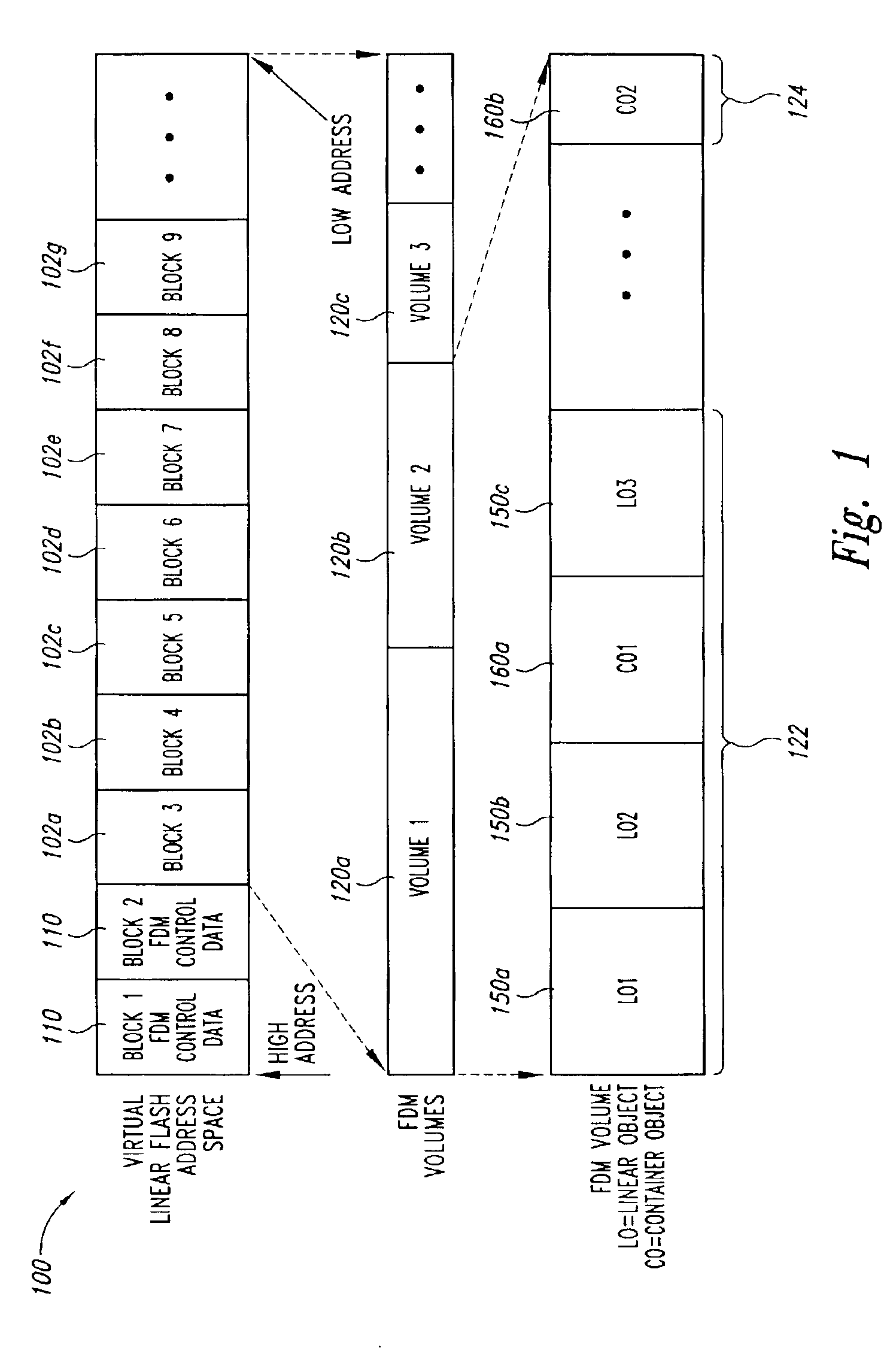
Linear object management for a range of flash memory
InactiveUS6895486B2Memory adressing/allocation/relocationMicro-instruction address formationInvalid DataParallel computing
Data object management for a range of memory. The range of memory has first and second opposite ends. A plurality of data objects are written to a first contiguous region of memory located at the first end of the range of memory. At least one of the valid data objects of the plurality of data objects are copied to a second contiguous region of memory located at the second end of the range of memory when a reclamation process is requested. The valid data objects copied from the first contiguous region of memory are marked as invalid data in the first contiguous region of memory subsequent to the valid data objects being copied to the second end of the range of memory, and the memory in which invalid data objects in the first contiguous region of memory are located is erased.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Method, system, and program for discarding data in a storage system where updates to a primary storage device are shadowed in a secondary storage device
InactiveUS6587933B2Operation moreMany timesInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData setInvalid Data
Provided is a method, system, and program for releasing storage space in a first and second storage devices. Updates to the first storage device are copied to the second storage device to provide secondary storage for the updates. A first and second tables map data sets to addresses in the first and second storage devices, respectively. A first command is detected to invalidate data sets in the first table. The addresses in the first table comprise virtual addresses, and a third table provides a mapping of the virtual addresses to physical storage locations in the first storage device. A second command is generated to update the second table to invalidate the data sets in the second storage device invalidated in the first table by the first command. A third command is detected to invalidate the virtual addresses in the third table used by the data sets invalidated in the first table to free the physical storage locations in the first storage device pointed to by the invalidated virtual addresses. A fourth command is generated that is directed to the physical storage locations in the second storage device used by the invalidated data sets.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Erasing method and apparatus of memory block
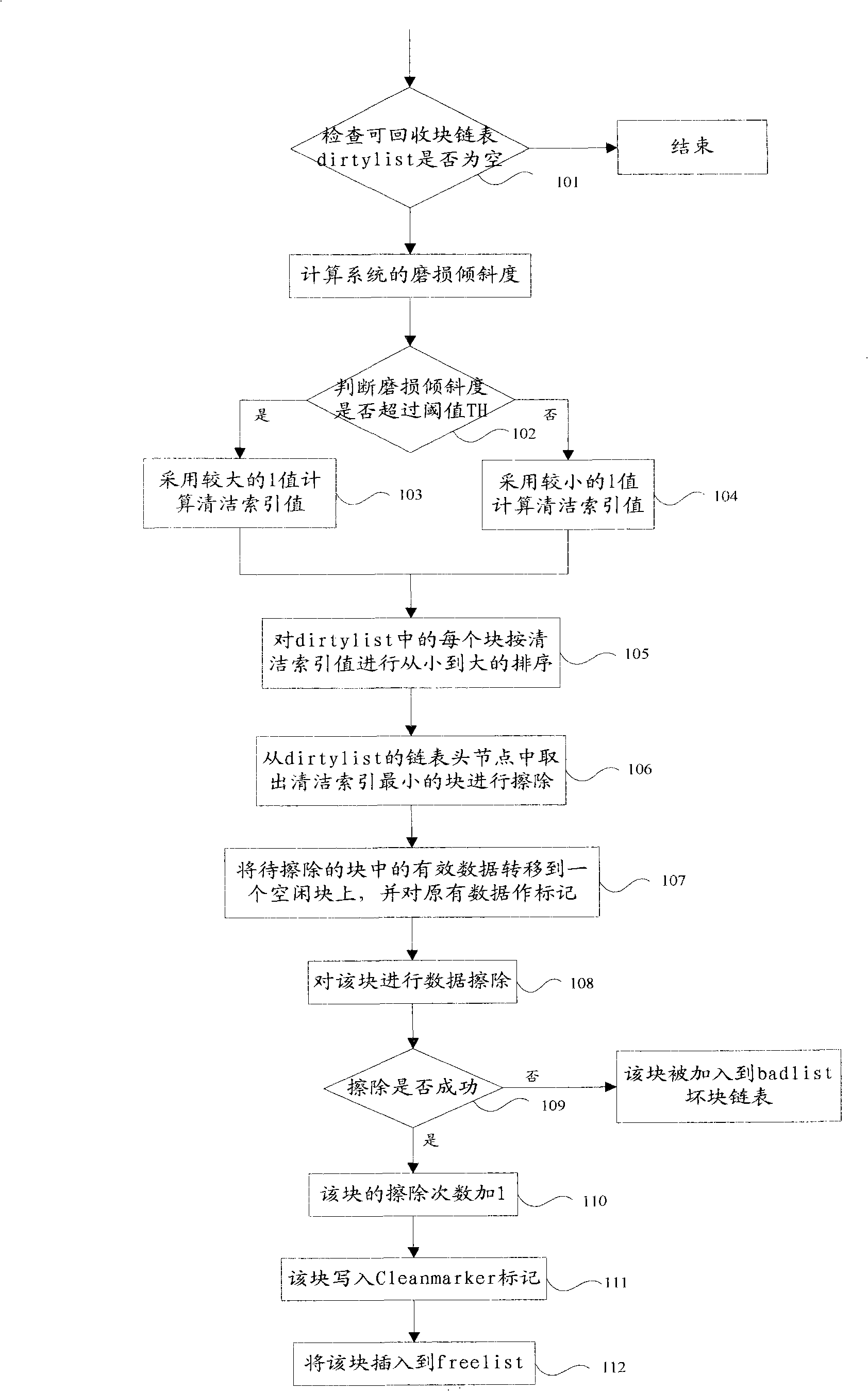
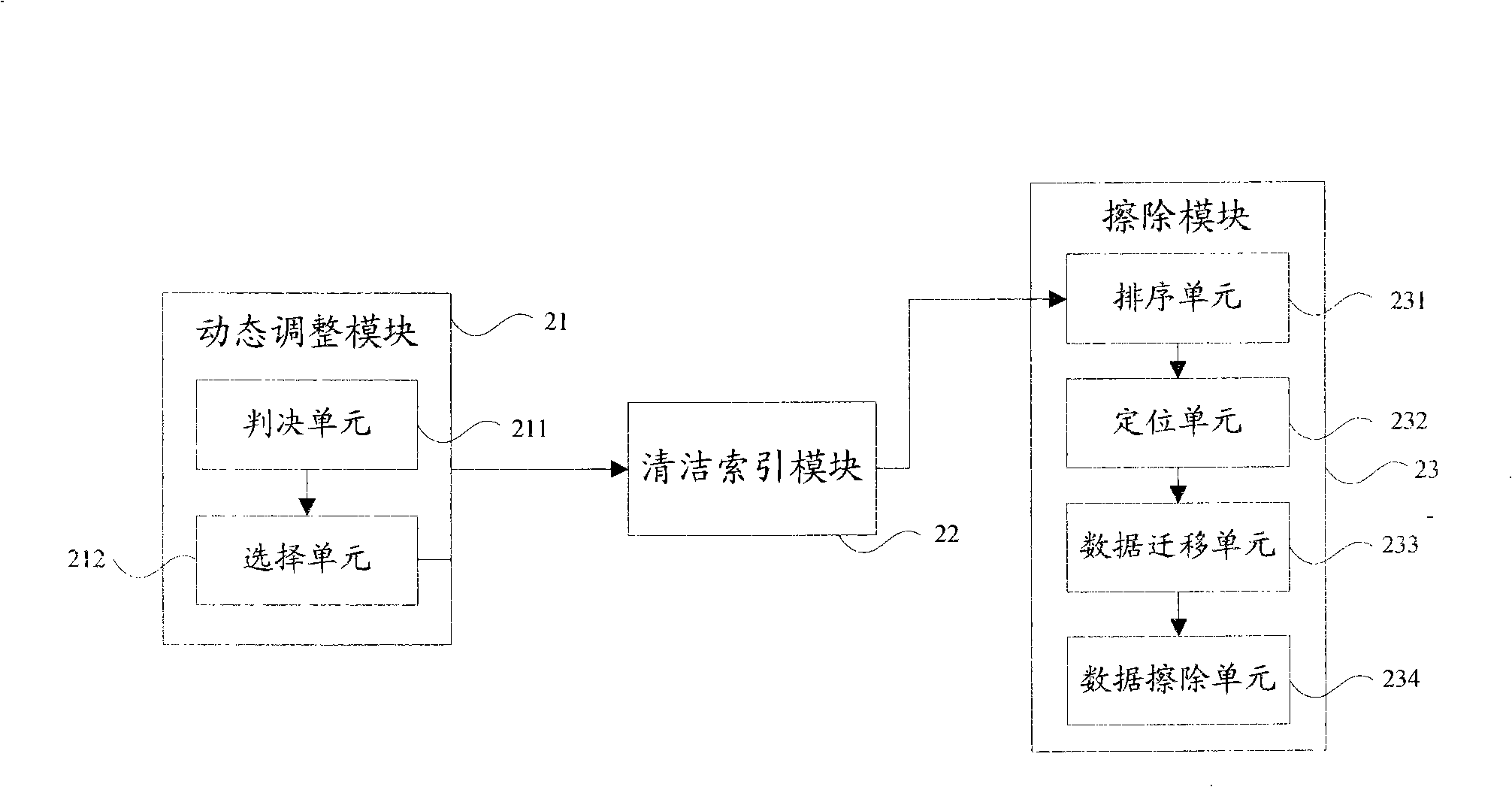
InactiveCN101339808ASolve the problem of increased wear and tearAvoid negative effectsMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInvalid DataParallel computing
The invention discloses an erasing method of a memory block, which comprises the steps as follows: tendency between recovery efficiency and wear leveling is dynamically regulated according to degree of wear uniformity of a memory block containing invalid data to acquire a cleanness index value of the memory block, and then the memory block to be erased is determined according to the cleanness index value for data erasing. The invention further discloses an erasing device of the memory block, which comprises a dynamic regulation module, a cleanness index module and an erasing module. By providing a new calculation method of the cleanness index, the invention introduces a new parameter, which causes the wear leveling among blocks to be still effectively calculated when erasing times of the block approximates the erasing limit. Meanwhile, a dynamic regulation method is provided to dynamically regulate the tendency between the recovery efficiency and the wear leveling according to the degree of wear uniformity, thus ensuring that the garbage collection of a flash memory has more balanced performance and adaptive ability.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
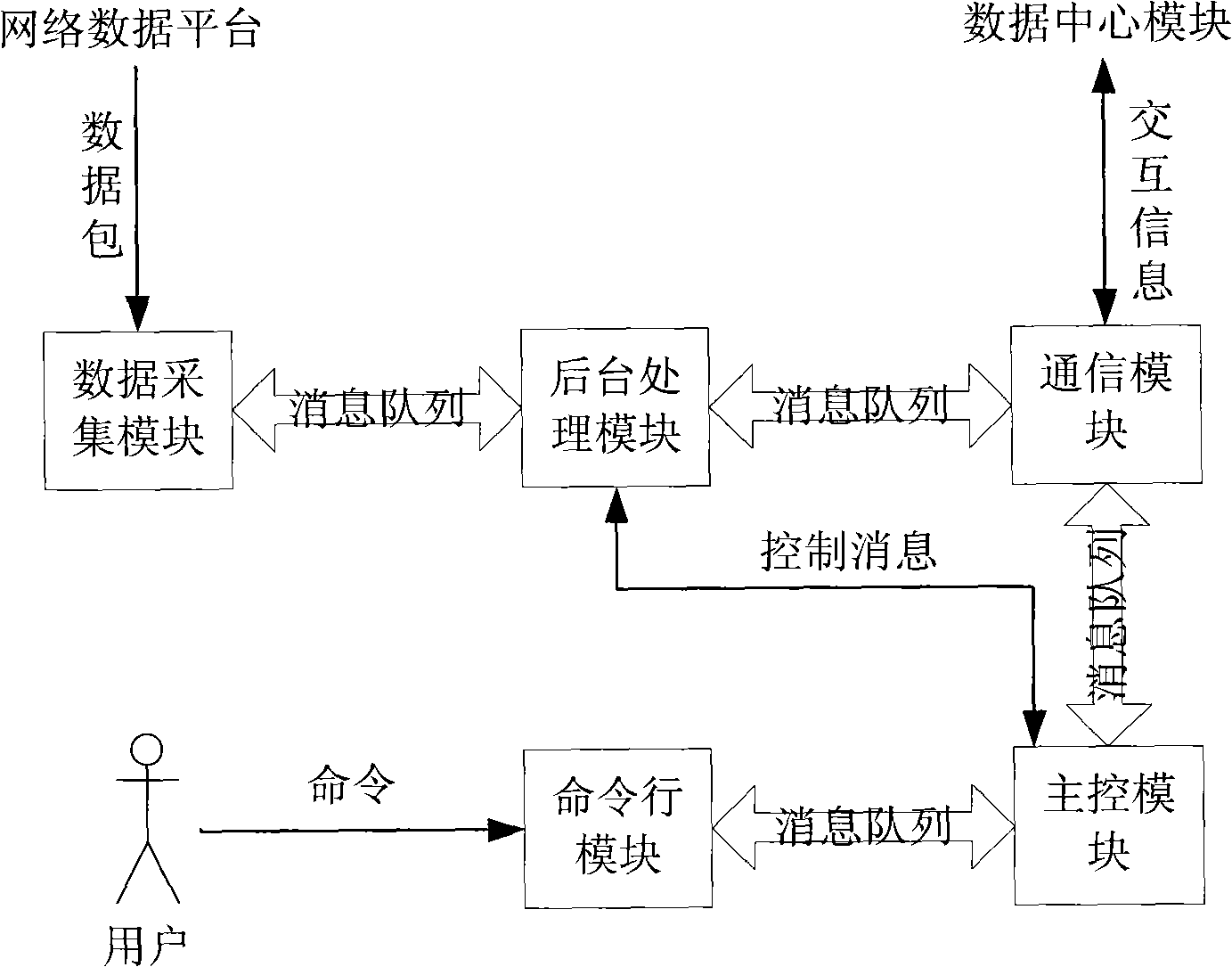
Dynamic configurable data monitoring system and method for distributed network
The invention relates to a system and a method for monitoring distributed network data with dynamic configuration in the technical field of computer network. In the invention, an agent module of data acquisition collects the data of an affiliated network data platform according to the configuration files set by users and carries out preprocessing of the collected data; the preprocessing comprises operations of data packet filtration and data packet disassembly, wherein, the data packet filtration refers to protocol filtration operation, namely, the invalid data pocket is discarded according to the filtration mechanism defined by the users; the data packet disassembly operation refers to that useful information in the data packets is extracted according to presented content by the users and the data required by the users is reported to a data center module in the form of XML document; the data center module is responsible for processing the data files reported by the agent module of data acquisition and in the form of XML, and carries out dynamic management on the agent module of data acquisition by inquiring, configuring and updating the XML documents. The system and the method of the invention simplify the design of the system, and improve the ability of the system to process data as well as usability and robustness of the system.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Obfuscating sensitive data while preserving data usability
InactiveUS20120272329A1Digital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsConfidentialityData file
An approach for obfuscating sensitive data while preserving data usability is presented. The in-scope data files of an application are identified. The in-scope data files include sensitive data that must be masked to preserve its confidentiality. Data definitions are collected. Primary sensitive data fields are identified. Data names for the primary sensitive data fields are normalized. The primary sensitive data fields are classified according to sensitivity. Appropriate masking methods are selected from a pre-defined set to be applied to each data element based on rules exercised on the data. The data being masked is profiled to detect invalid data. Masking software is developed and input considerations are applied. The selected masking method is executed and operational and functional validation is performed.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
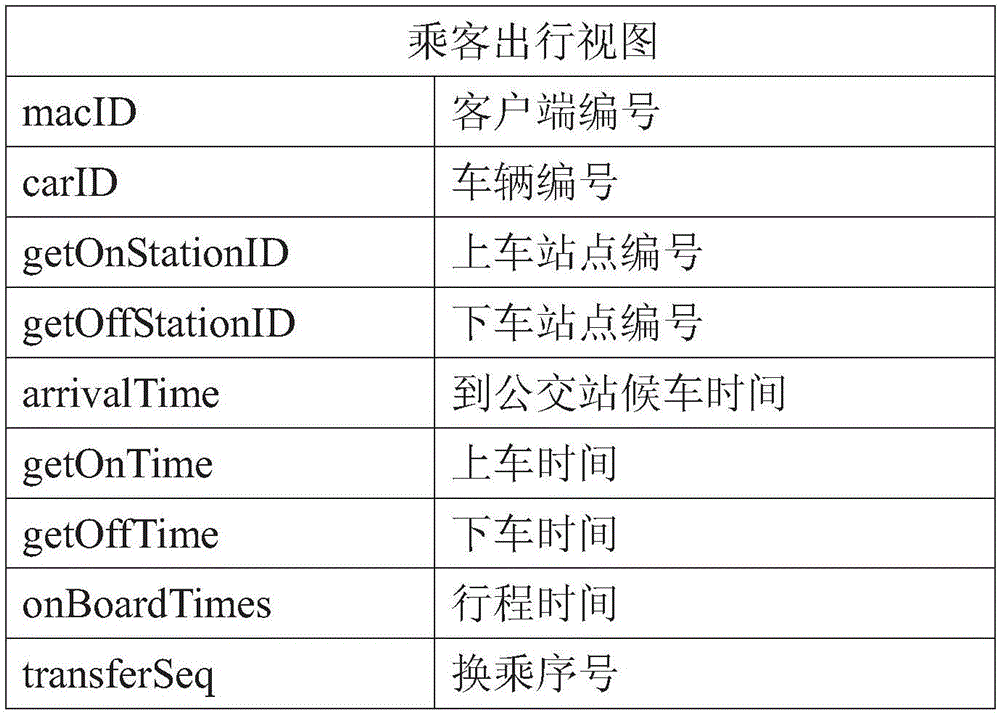
Bus passenger flow data collection and origin-destination point analysis method and system
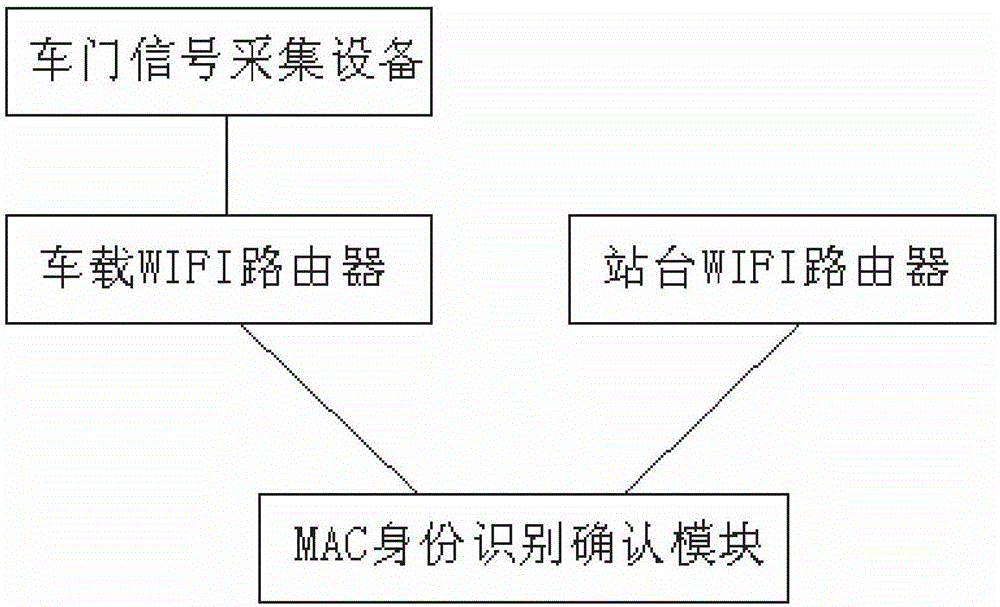
ActiveCN105869388AImprove accuracyUnreliable solutionRoad vehicles traffic controlWireless communicationIdentity recognitionInvalid Data
The invention discloses a bus passenger flow data collection and origin-destination point analysis method. The method comprises the steps that corresponding WIFI routers are arranged in a bus and a bus stop at the same time, MAC address data of intelligent terminals carried by passengers in the bus and passengers waiting for a bus on the bus stop is detected and collected, and according to the bus door opening and closing signals collected by a bus door signal collecting device, passenger identity confirmation and invalid data filtering are carried out. The invention further discloses a bus passenger flow data collection and origin-destination point analysis system which comprises the vehicle-mounted WIFI router, a bus door signal collecting device, the bus stop router and an MAC identity recognition and confirmation module. Bus passenger flow analysis is carried out based on various data sources, and high accuracy of WIFI identity recognition information for bus passenger flow and OD analysis is ensured.
Owner:SUZHOU LANGJIETONG INTELLIGENT TECH
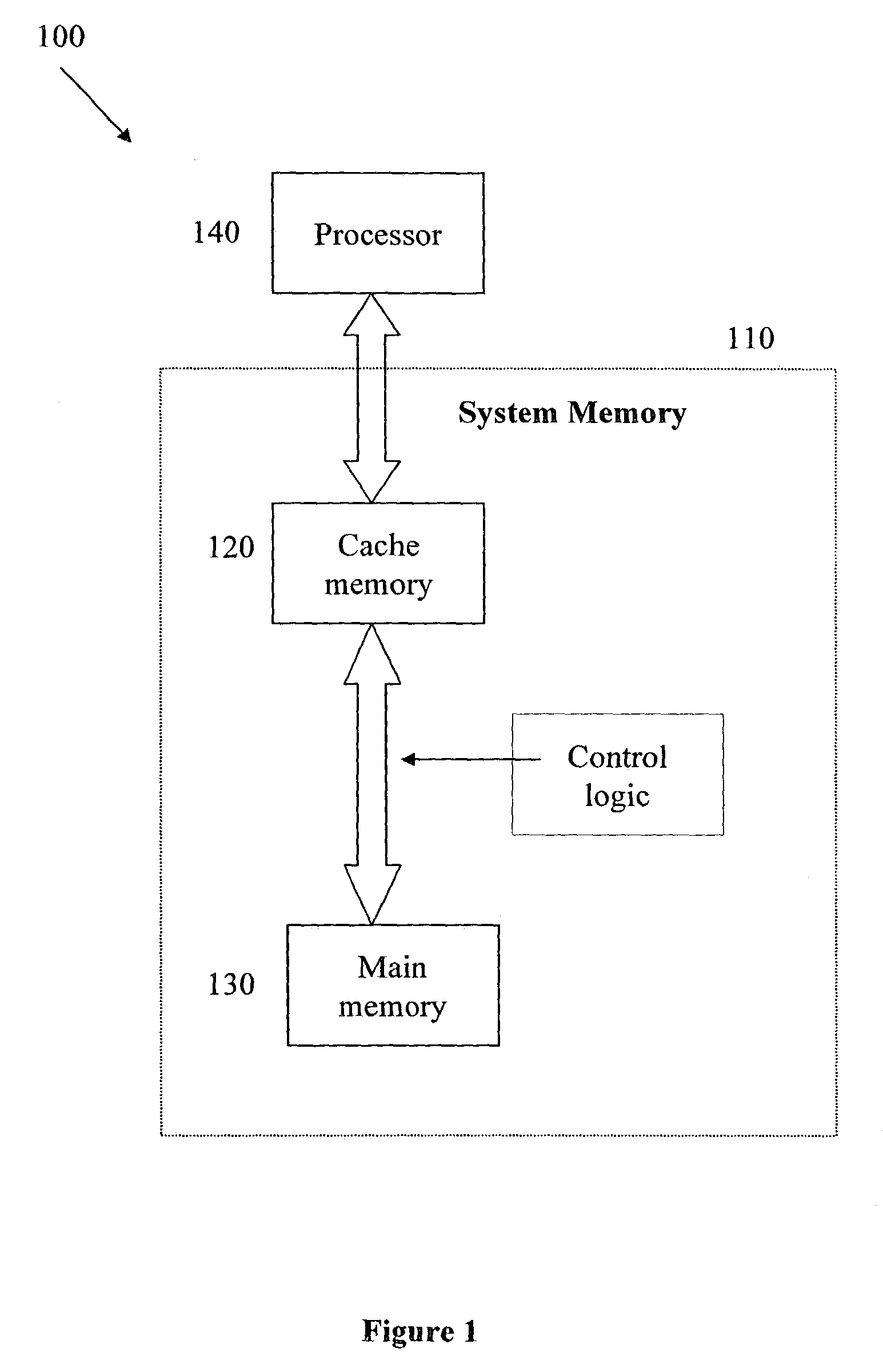
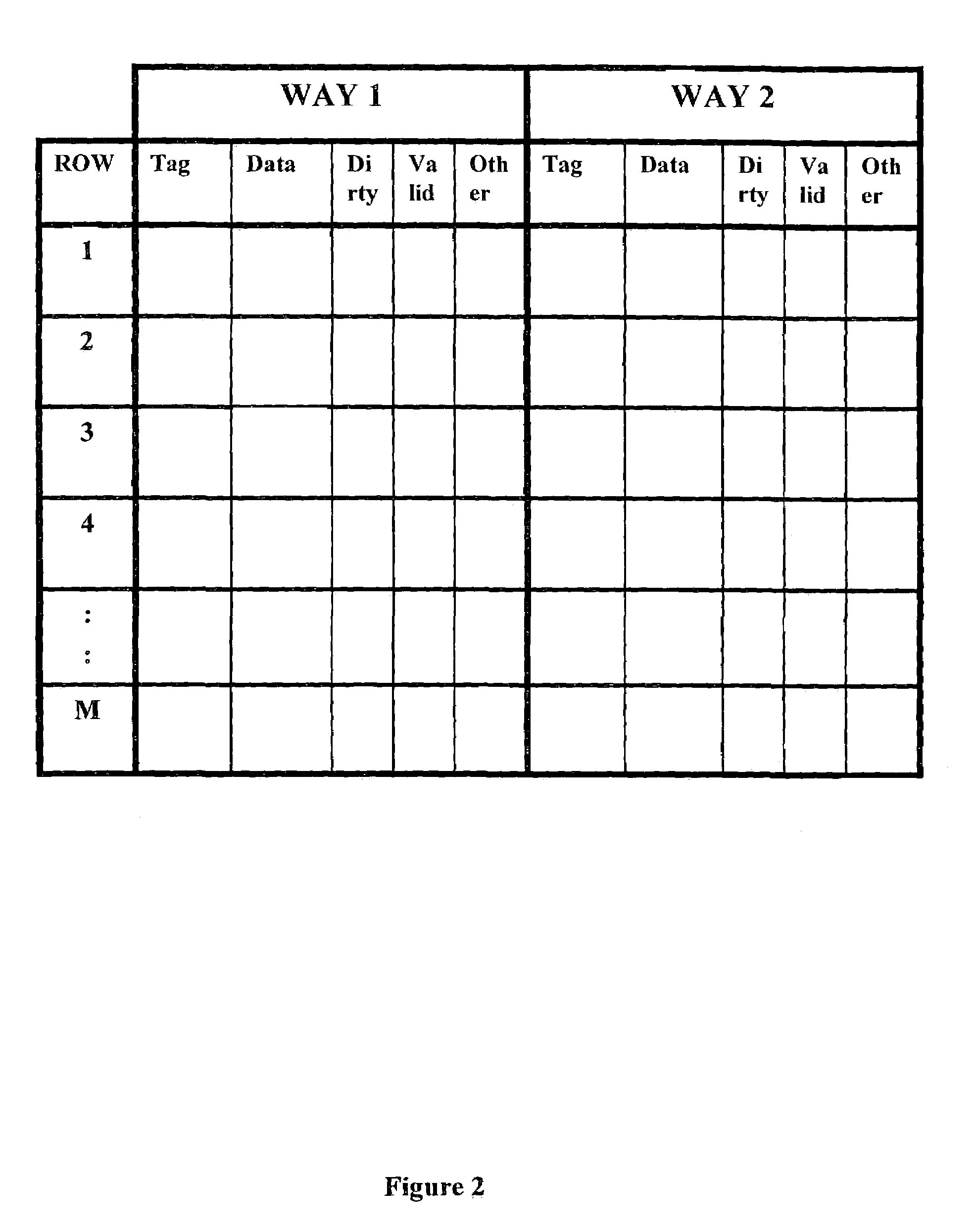
Cache memory data replacement strategy
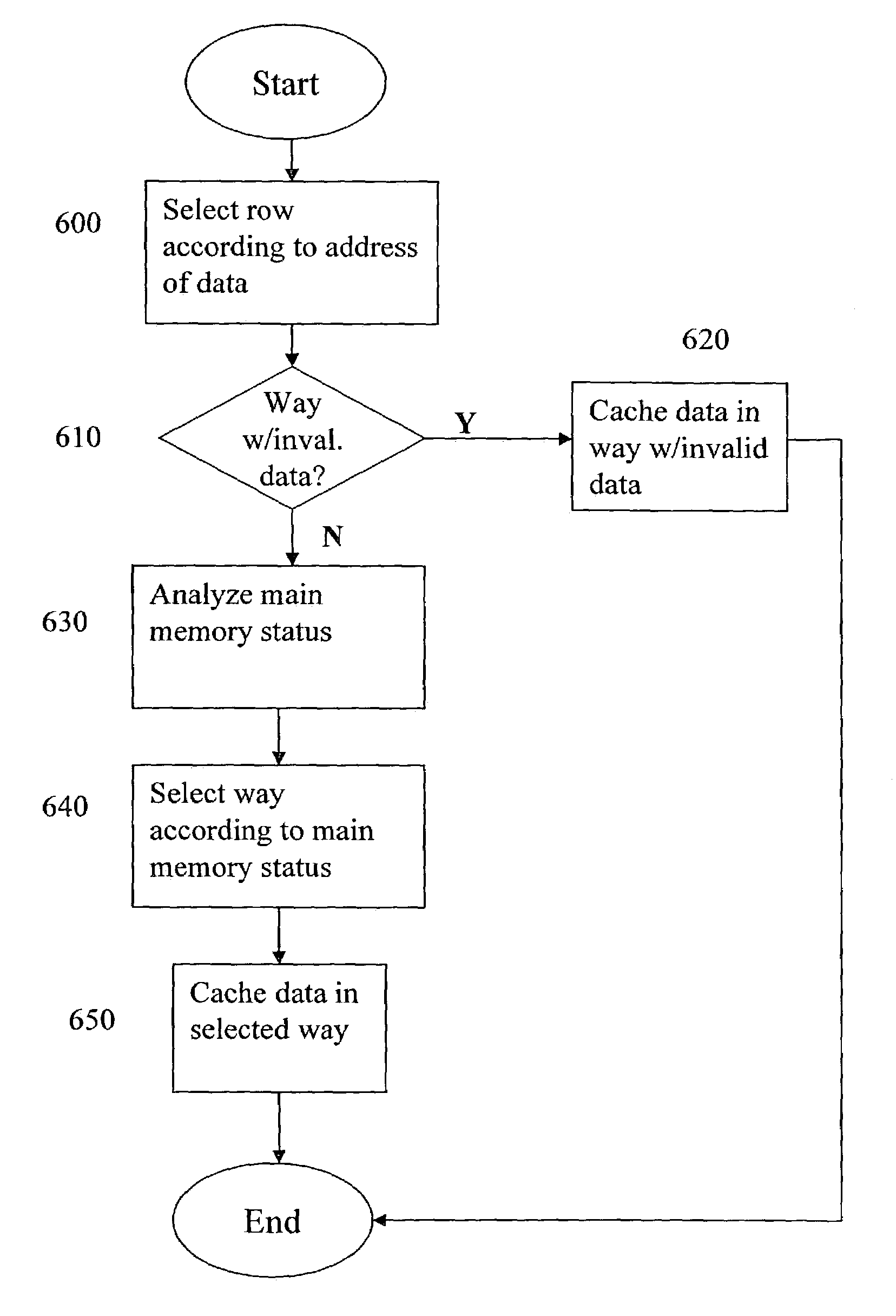
ActiveUS7069388B1Shorten the timeAvoid cachingMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory addressInvalid Data
A method for caching specified data in an n-way set associative memory with a copy-back update policy consists of the following steps. First, a row of the associative memory, organized as a plurality of rows and having n ways per row, is selected according to the main memory address of the specified data. The main memory provides primary storage for the data being cached. If one of the ways of the selected row holds invalid data, the specified data is cached in the way holding the invalid data and the data caching process is discontinued. If all n ways of the selected row hold valid data, the following steps are performed. First, a replacement strategy is used to select a way from the selected row. If the way selected in accordance with the replacement strategy holds unmodified data, the specified data is cached in the way selected by the replacement strategy and the data caching process is discontinued. However, if the way selected by the replacement strategy holds modified data, the ways of the selected row are examined again to find a way that holds data from the currently open page of the main memory. If such at least one such way is found, the specified data is cached in one of the ways holding data from the open page, and the data caching process is discontinued. Finally, if none of the ways in the selected row meet the above criteria, the specified data is cached in the way previously selected by the replacement algorithm, and the method terminates.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
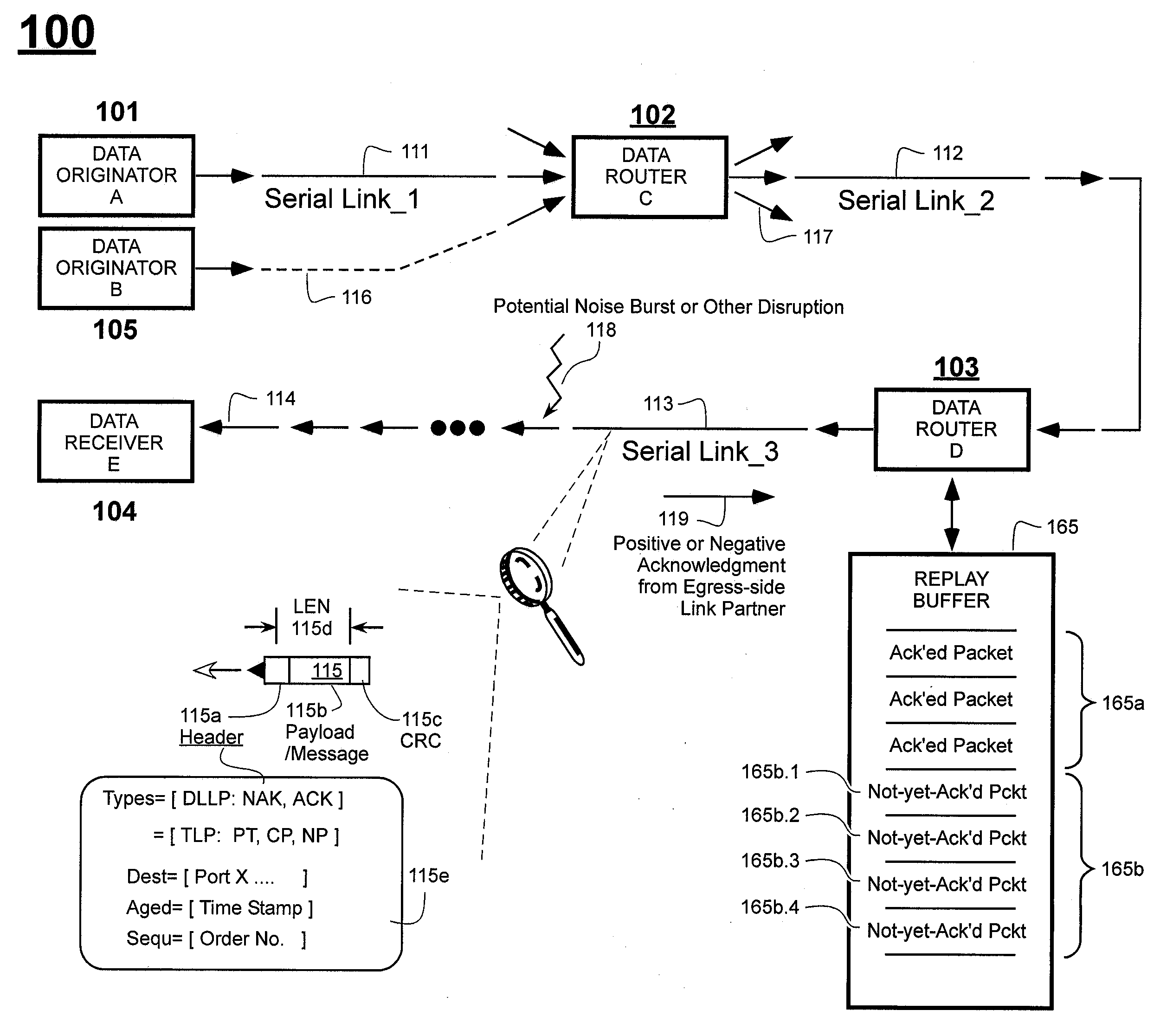
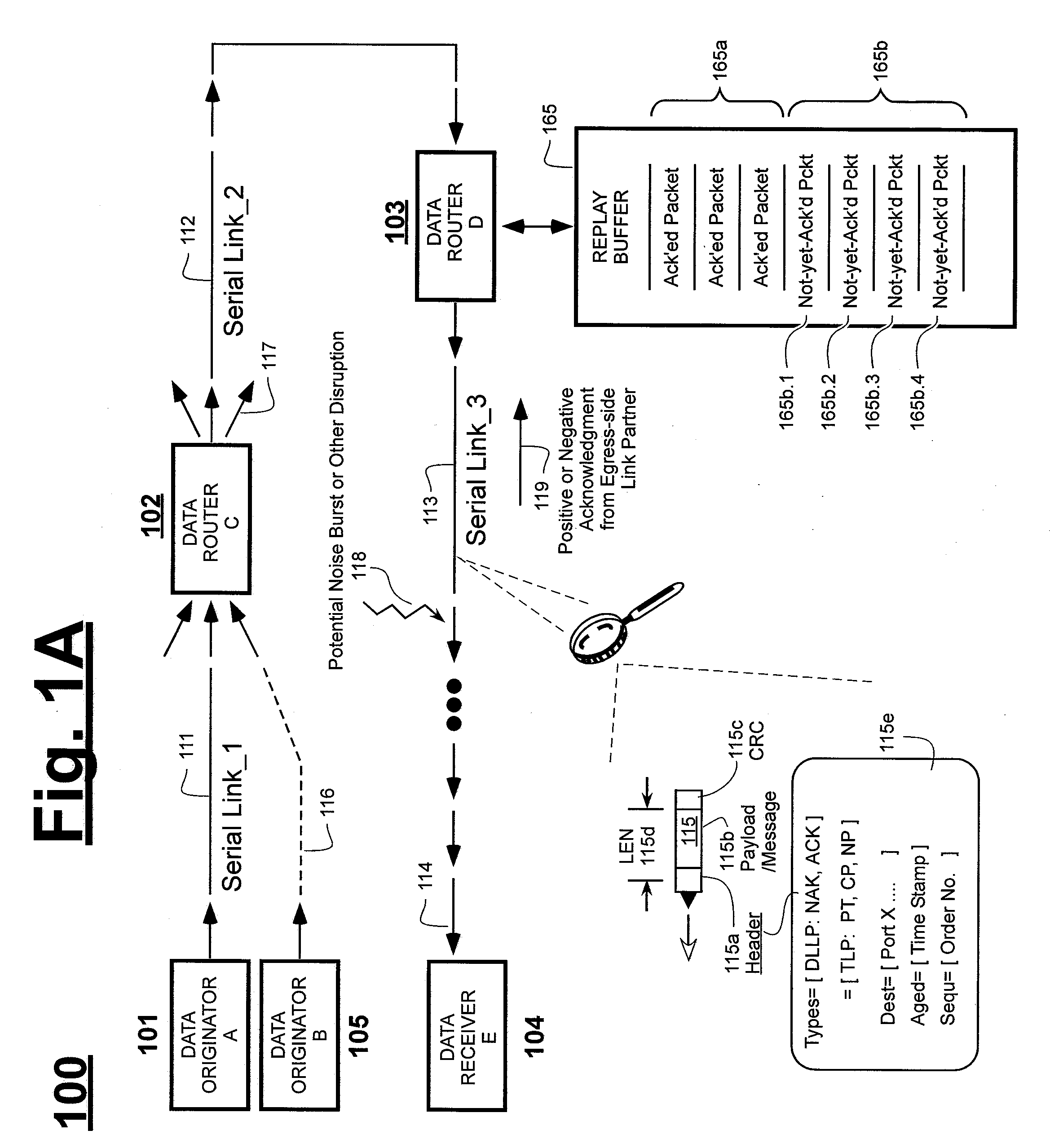
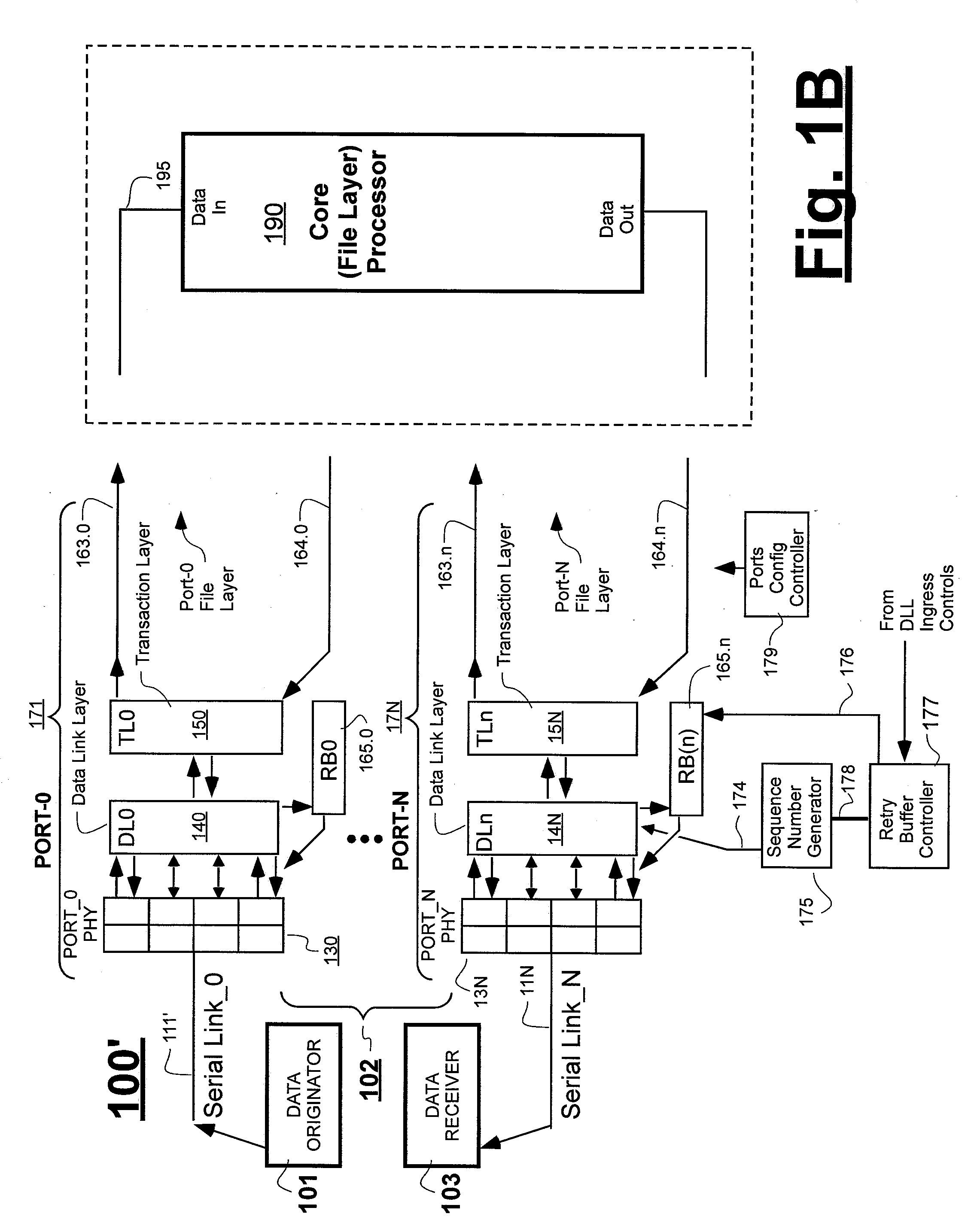
Method of Skipping Nullified Packets During Mass Replay from Replay Buffer
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS US INC
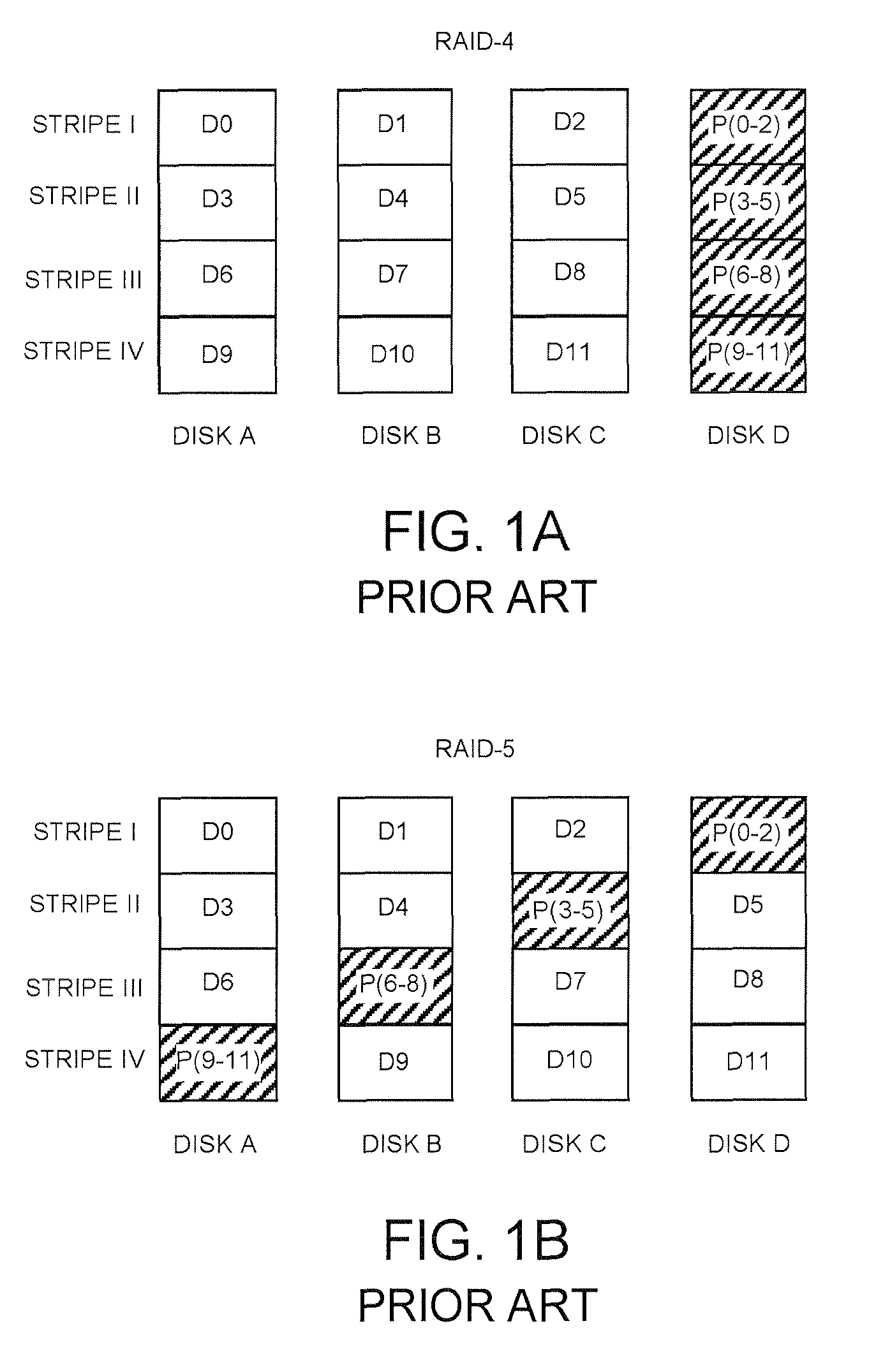
System and method for eliminating zeroing of disk drives in RAID arrays
ActiveUS8209587B1Eliminate needEfficient reconstructionError detection/correctionStatic storageRAIDInvalid Data
Embodiments of the present invention disclose a technique for providing an indication whether data stored on a disk drive are invalid. As used herein, invalid data are data written prior to the disk drive being added to an array of the disk drives or data in a block that has become free and which has been removed from the corresponding parity block of the stripe. Knowing that the disk drive was written prior to the drive being added to the existing array or having data which has become invalid allows a storage server to ignore the invalid data and not to use it when computing parity (i.e., a data protection value computed as a result of a logical operation on data blocks in a stripe in the array of disk drives). This, in turn, eliminates the need to zero disk drives or to perform parity re-computation prior to using the disk drives.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Test circuit capable of testing embedded memory with reliability
InactiveUS7007215B2Accurate conditionAccurate measurementError preventionTransmission systemsAccess timeControl signal
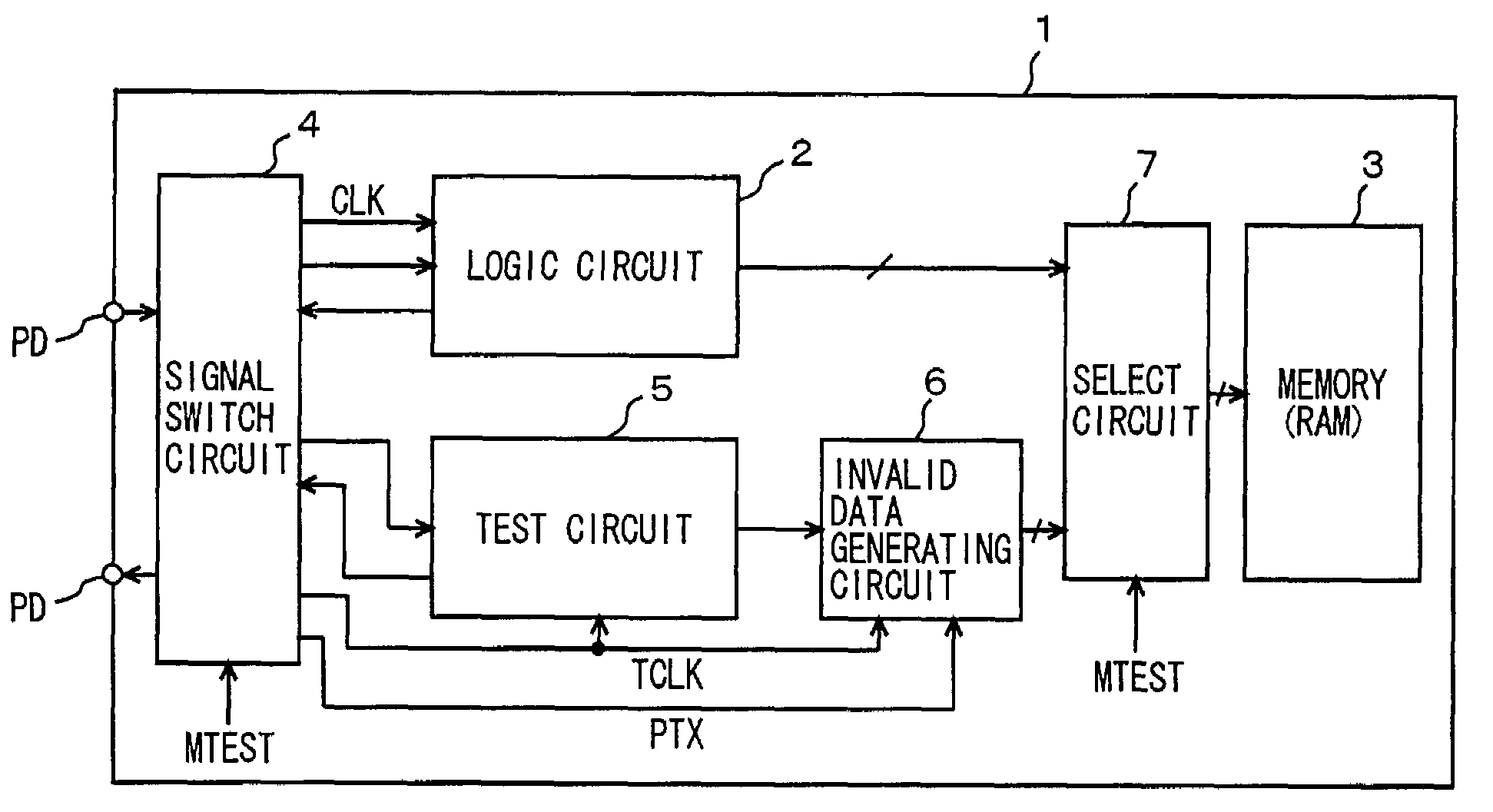
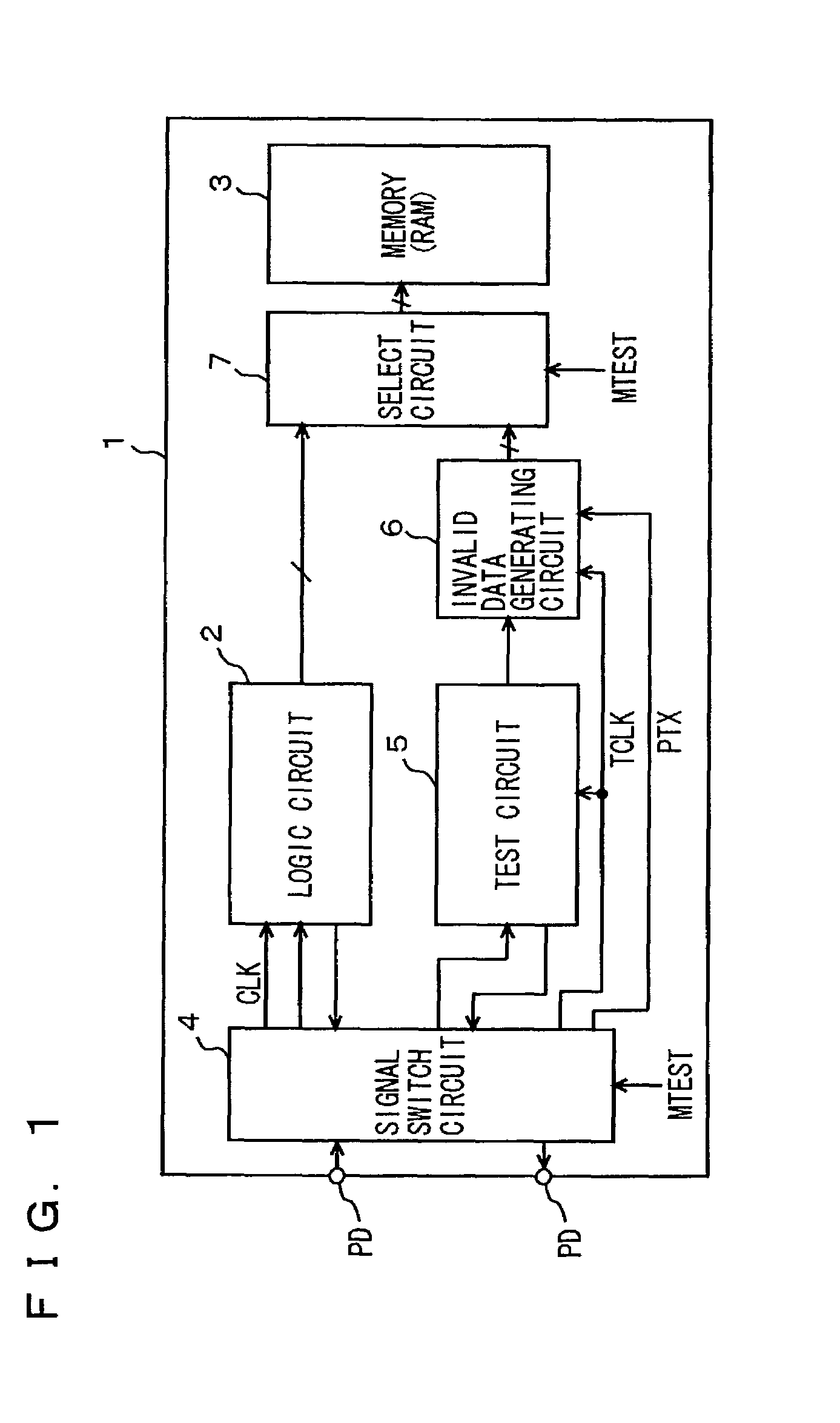
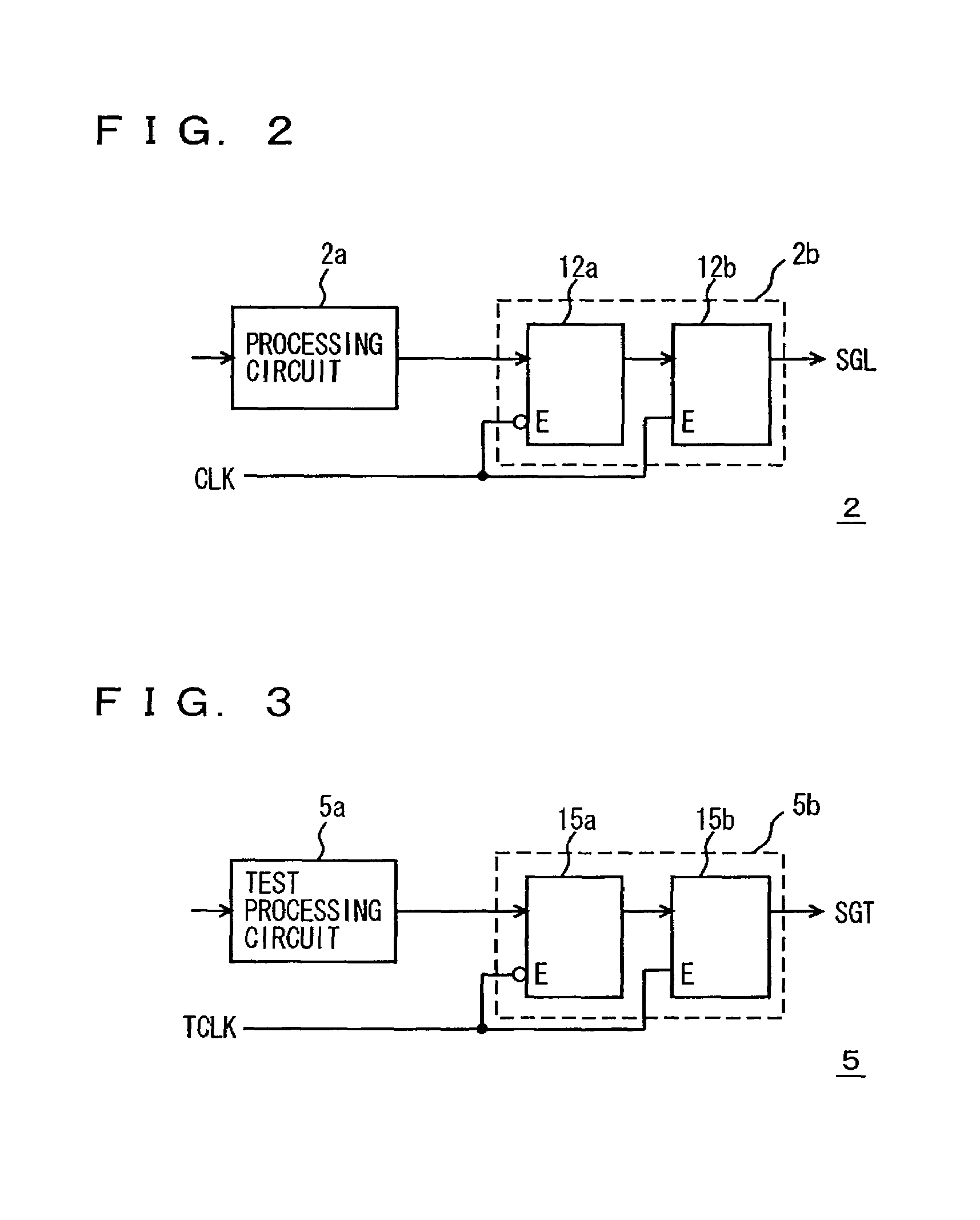
A test signal applied to an embedded memory is changed in synchronization with a test clock signal, set to an invalidated state by an asynchronous control signal asynchronous to the test clock signal and then is applied to a memory. The memory takes in a received signal in synchronization with a memory clock signal. An invalid data generating circuit modifies the test signal in accordance with the asynchronous control signal and generates a test signal and to apply the test signal to the memory. A period of an invalid state of the modified test signal can be adjusted and therefore, by monitoring a changing timing of the asynchronous control signal PTX with an external tester, setup and hold times of a signal for the memory can be measured. Setup and hold times and an access time for an embedded memory can be correctly measured.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
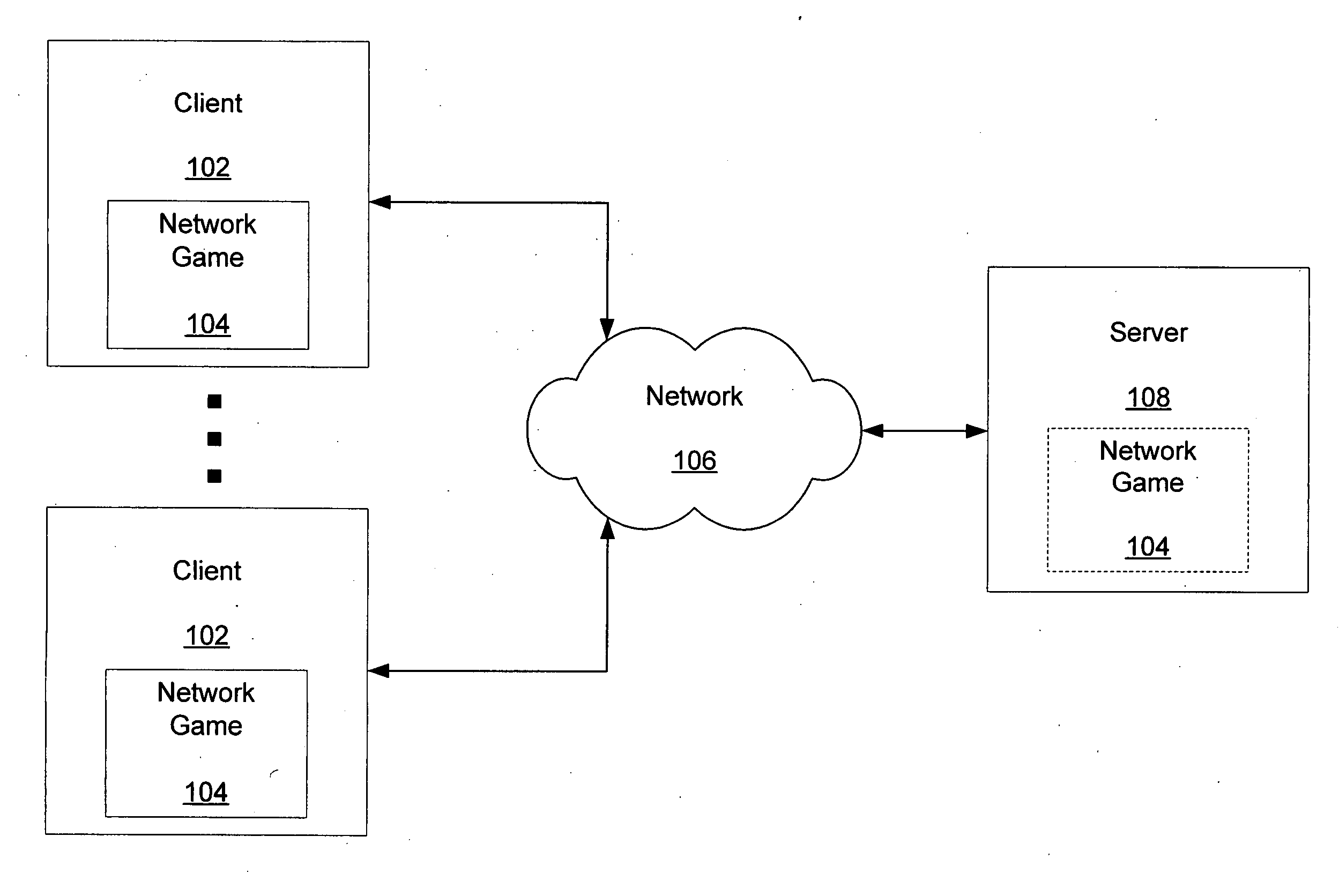
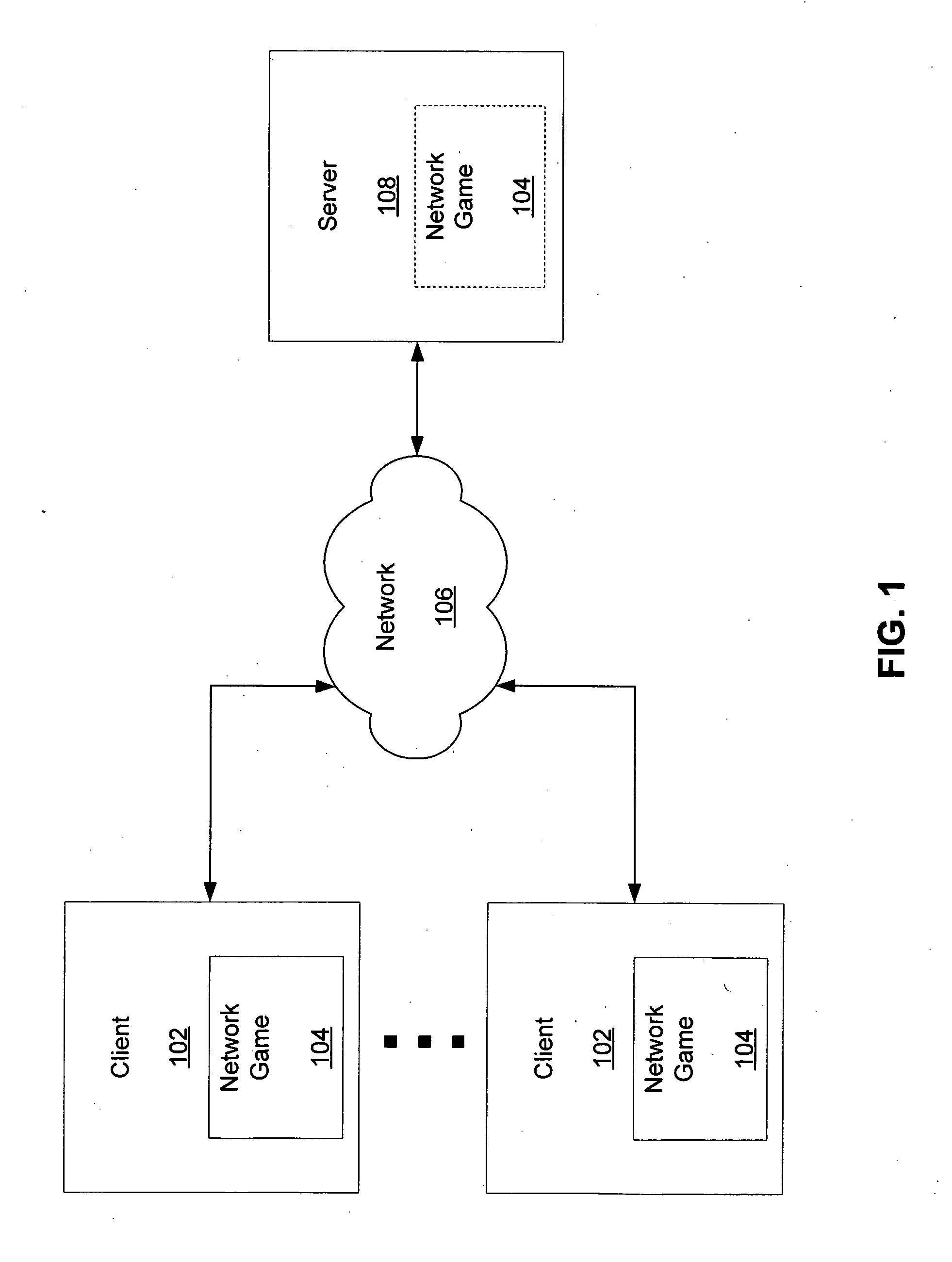
Active validation of network devices
A system and method for actively validating a network device is provided. Nodes in a network game community are prompted to engage in interrogation and response to facilitate the identification of nodes operating with hacked, modified and non-typical game configurations. In one embodiment, a query is presented to a user's machine which triggers a response, and where the response indicates whether certain data at the user is valid and wherein invalid data is suggestive of illegal community behavior. Functions are triggered and data is queried to determine whether the state of game environment is operating according to known metrics or constraints. Various queries to test user integrity include memory peeks, confirmation of location of functions in memory, memory hashing, profiling of threads operating on the user machine, and combinations thereof. Queries may be actively initiated by a server, peer, peer group or combinations thereof and may be scheduled on a routine basis, triggered in response to passive listening, and via collaborating users who suspect cheat activity.
Owner:SONY INTERACTIVE ENTRTAINMENT LLC
Automated and customizable generation of efficient test programs for multiple electrical test equipment platforms
InactiveUS20050273685A1Electronic circuit testingError detection/correctionDevice materialTest algorithm
Automating techniques provide a way to create efficient test programs for characterizing semiconductor devices, such as those on a silicon die sample. Typically, test program creation is a drawn out process involving data entry for every test to be run as part of the test program. The described techniques improve test algorithm selection and automatically populate the test algorithm data in creating the test program. The automatic population may occur by accessing test structure, header, and test algorithm catalogs. The test structure catalog contains physical data for the test program, while the header catalog contains global parameter values. The test algorithm catalog has all of the various test algorithms that may be run in a given test, where these test algorithms may be in a template form and specific to any number of different test language abstractions. After test program creation, a validation process is executed to determine if the test program data is valid. Invalid data may be flagged, in an example. Once validated, techniques are described for converting the validated test program into an executable form, by formatting the various test algorithm data in the test program into a form compatible with the applicable test language abstraction selected by the user or the tester.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com