Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
50 results about "Optical transport unit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method and apparatus for forming an image that shows information about a subject
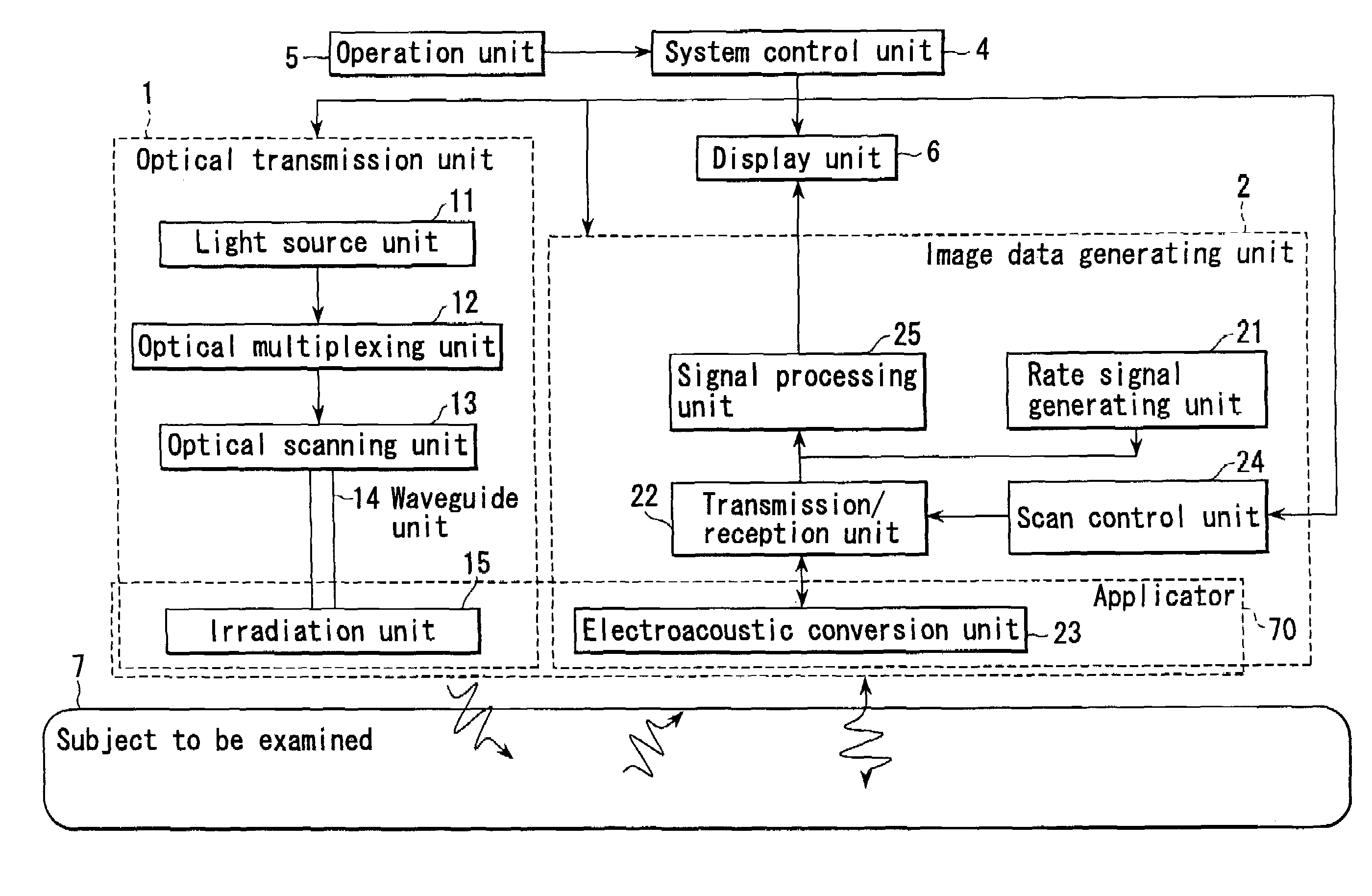
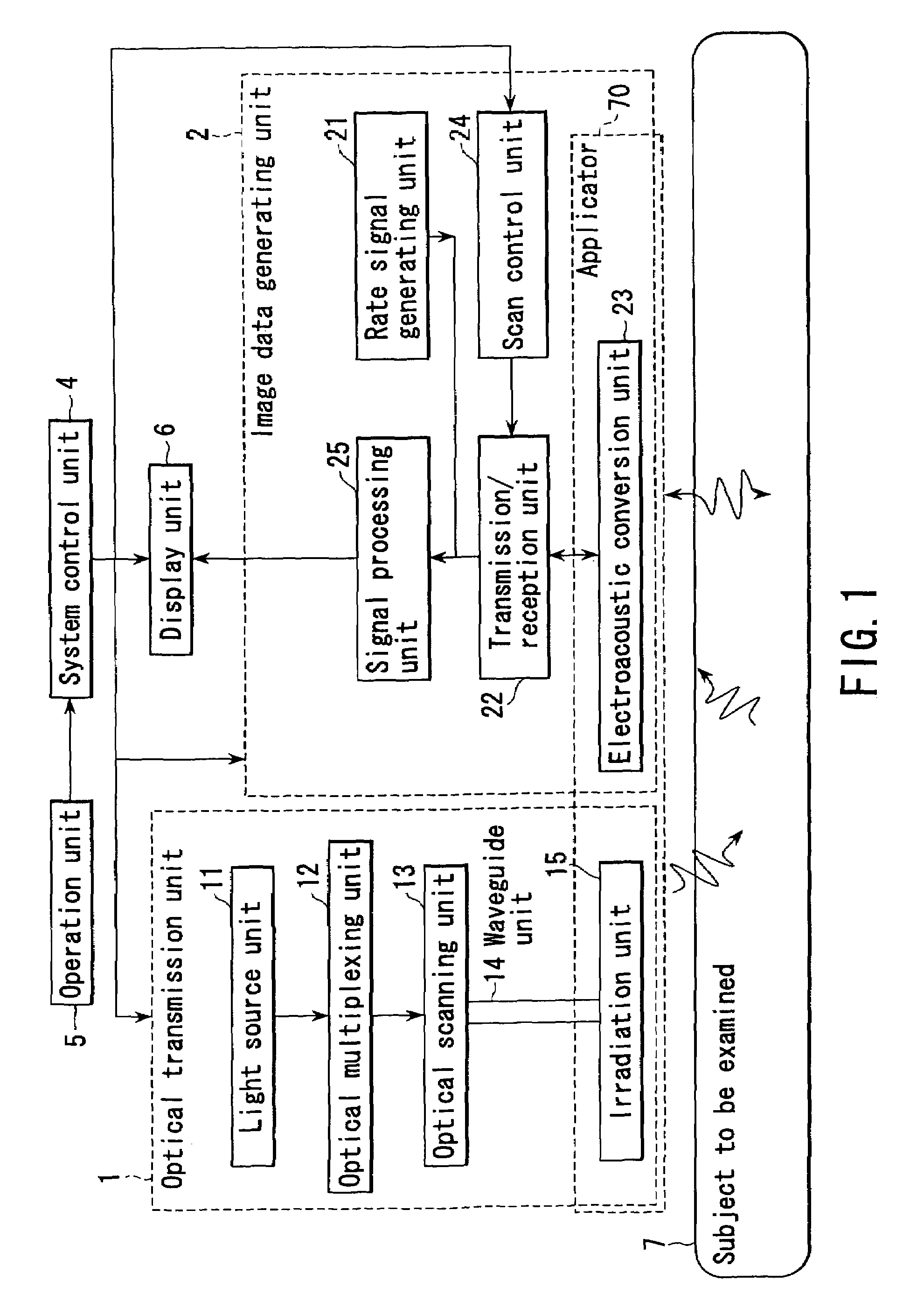
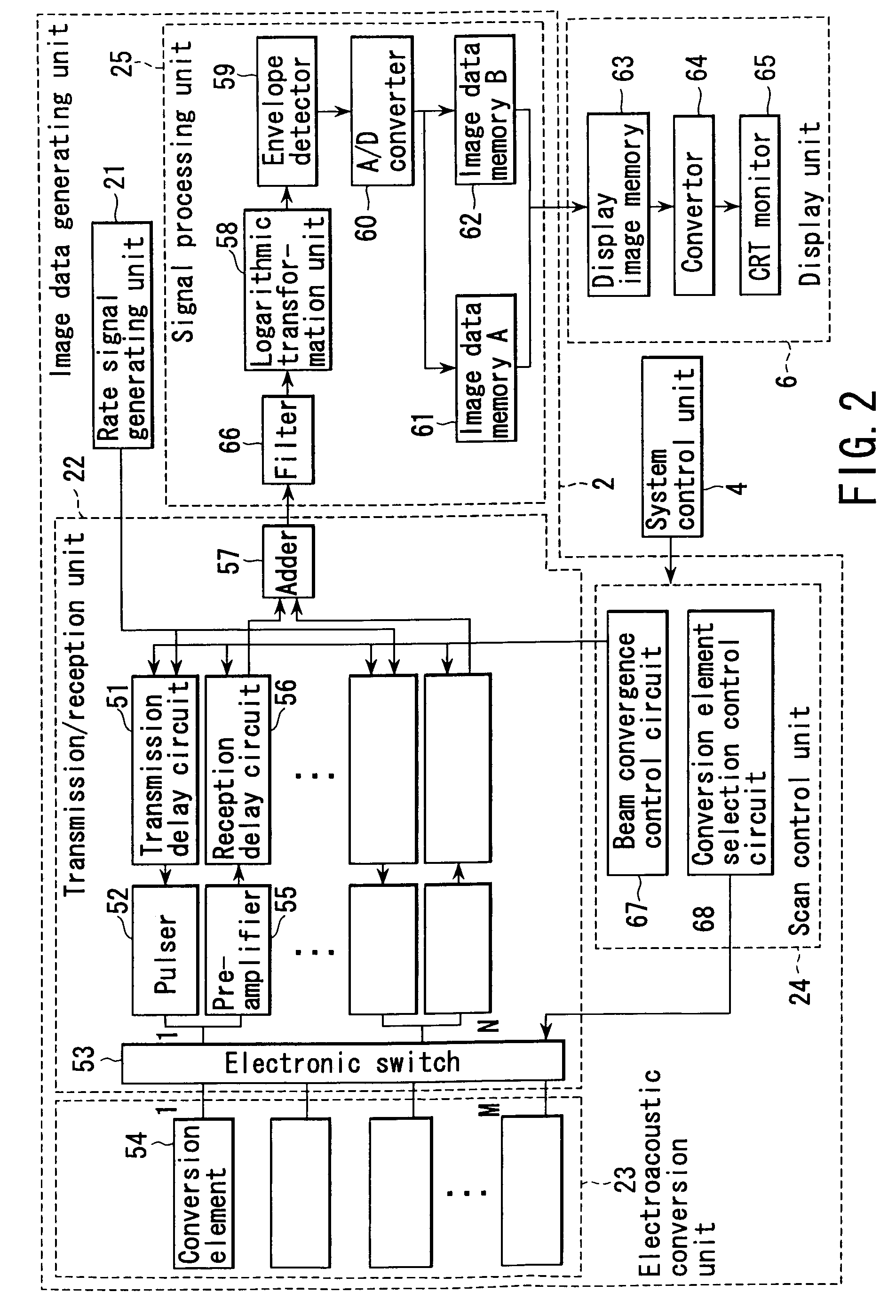
InactiveUS6979292B2Easy to operateImprove spatial resolutionAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesOrgan movement/changes detectionElectricitySonification
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
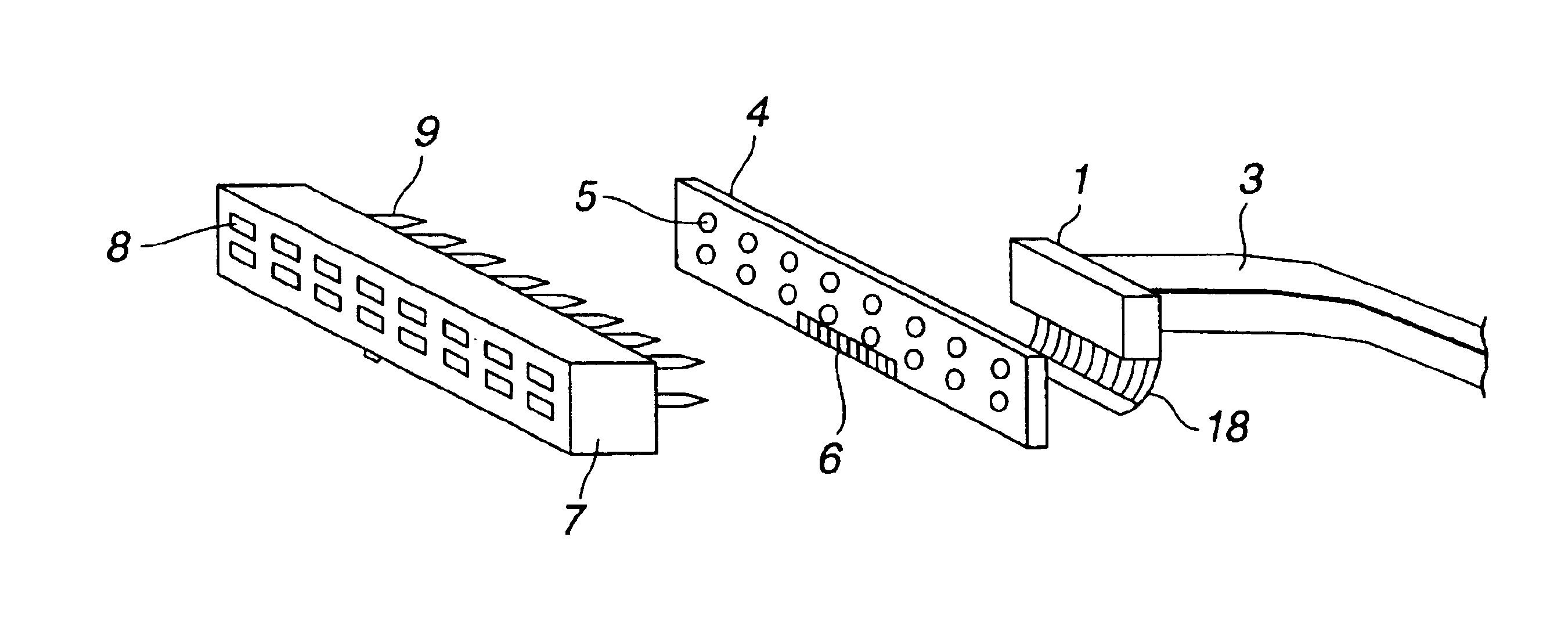
Optical wiring device
InactiveUS6854901B1Easy to adaptLow costLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionElectricityOptical data transmission
An optical wiring device includes an electric connecting portion, an optical transmission unit for transmitting an optical signal, and an optical device for conducting an optoelectric conversion. The optical device is provided between the electric connecting portion and the optical transmission unit. The optical device includes at least one of a surface light emitting device, which is modulated by an electric signal supplied through the electric connecting portion, and a surface light receiving device, which converts an optical signal transmitted through the optical transmission unit to an electric signal.
Owner:CANON KK
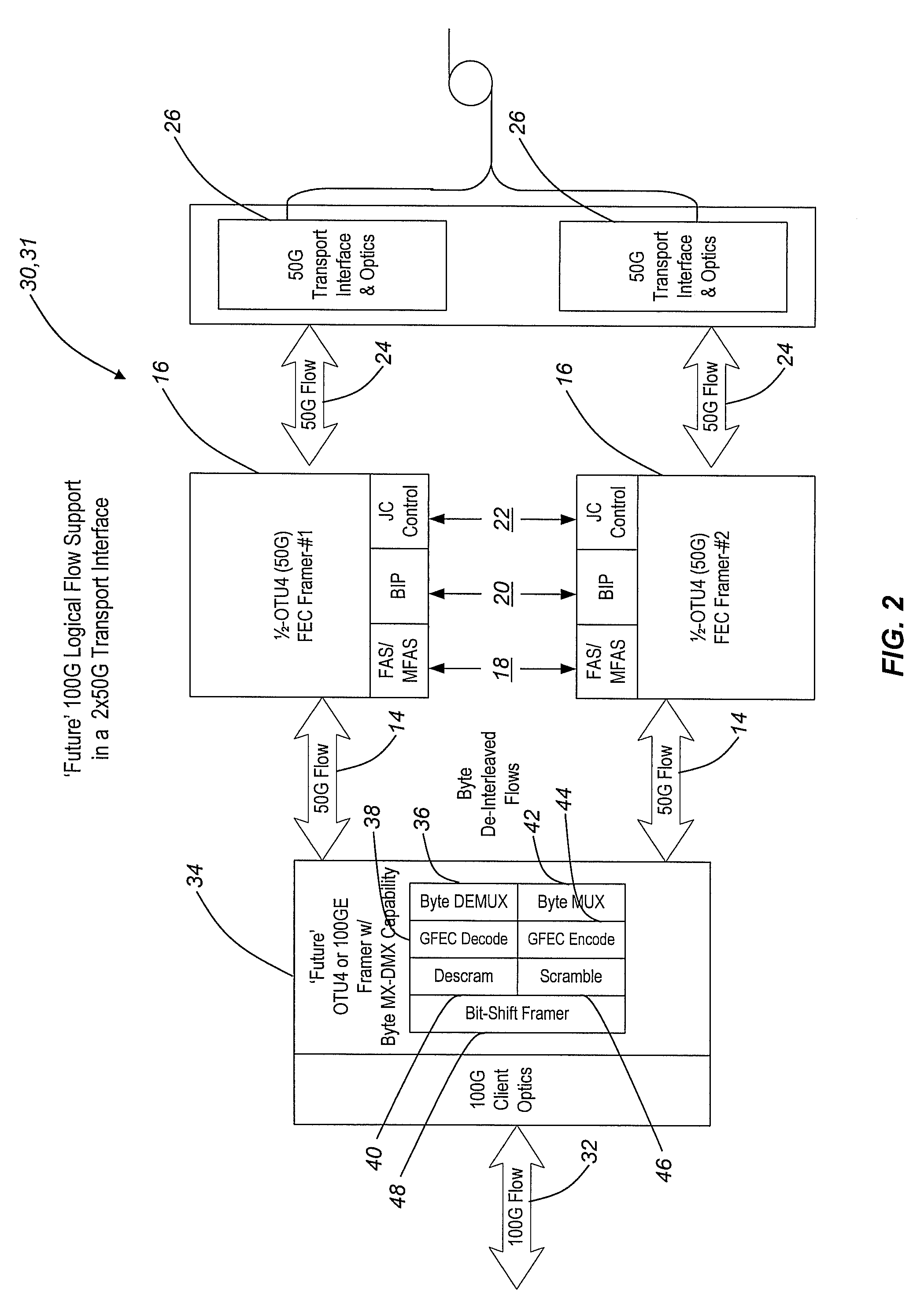
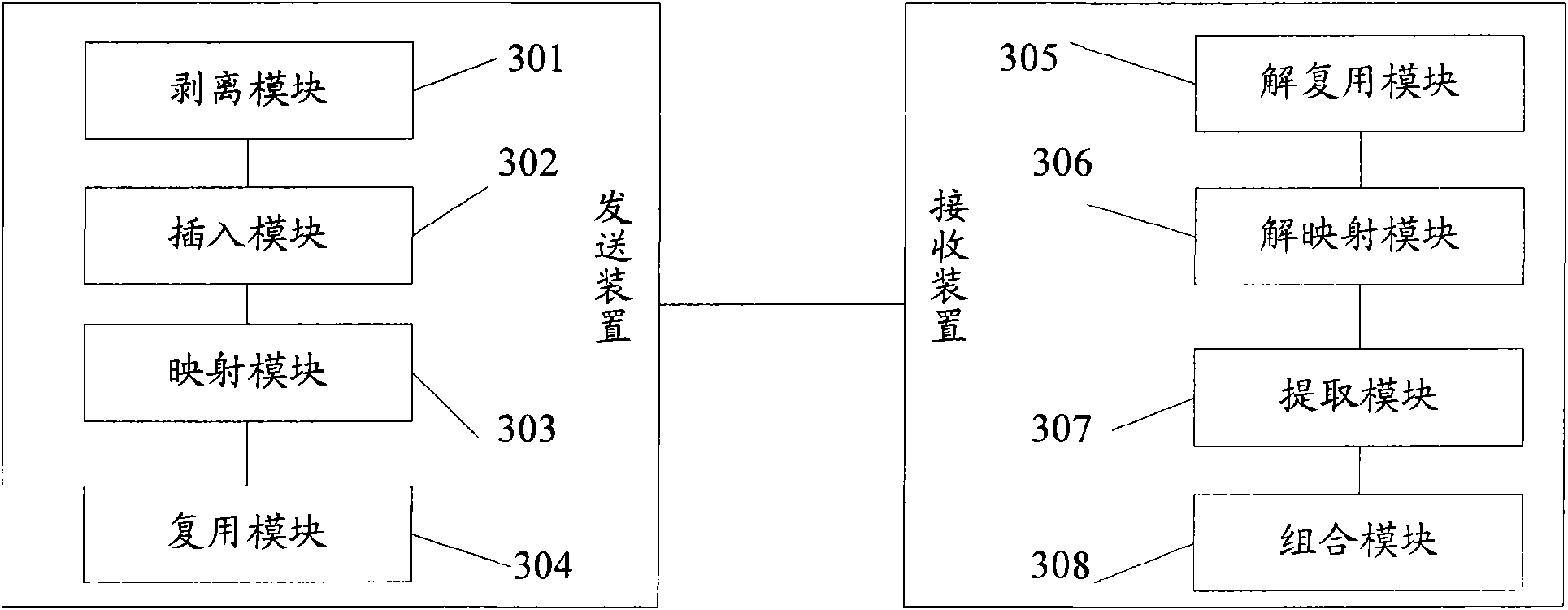
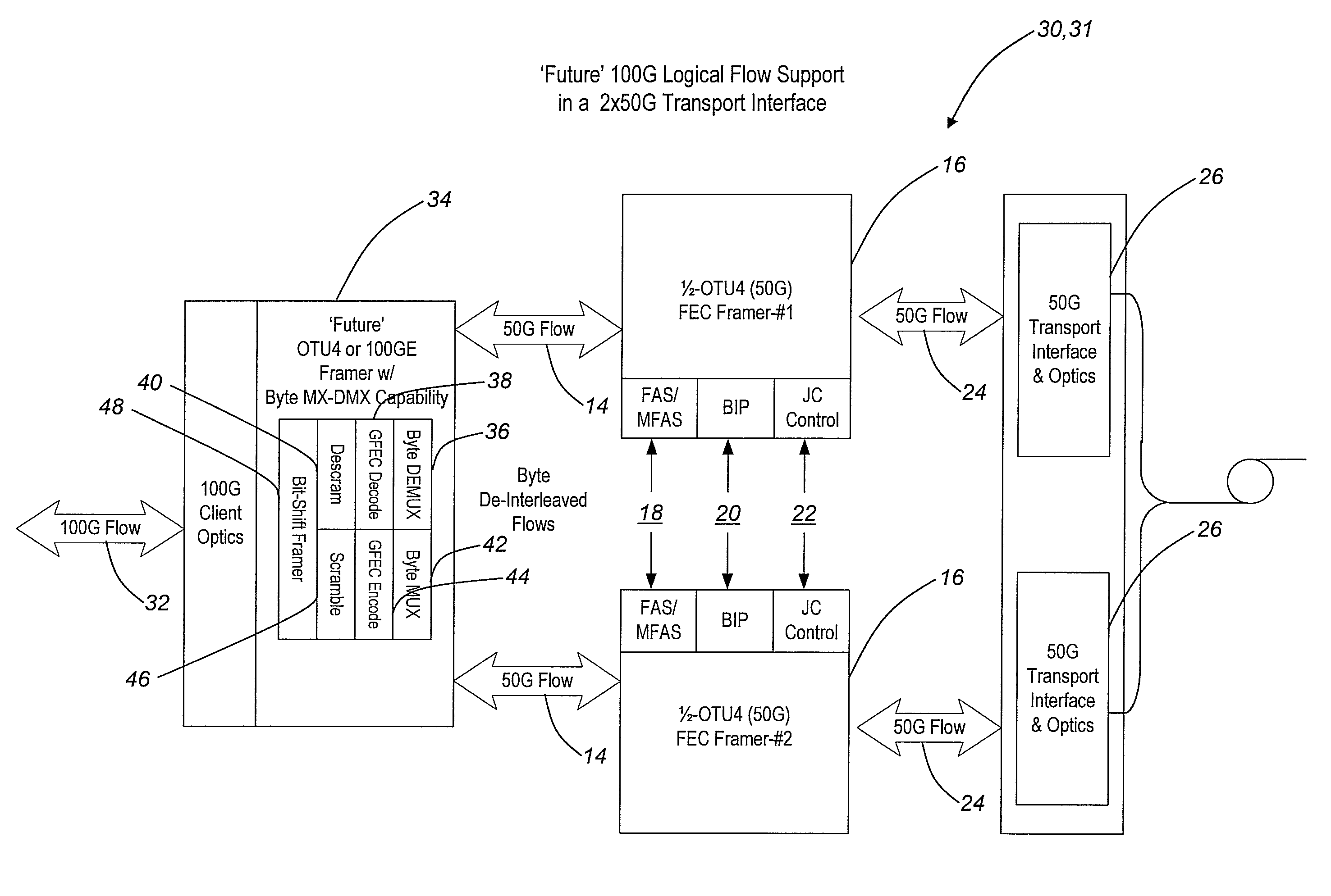
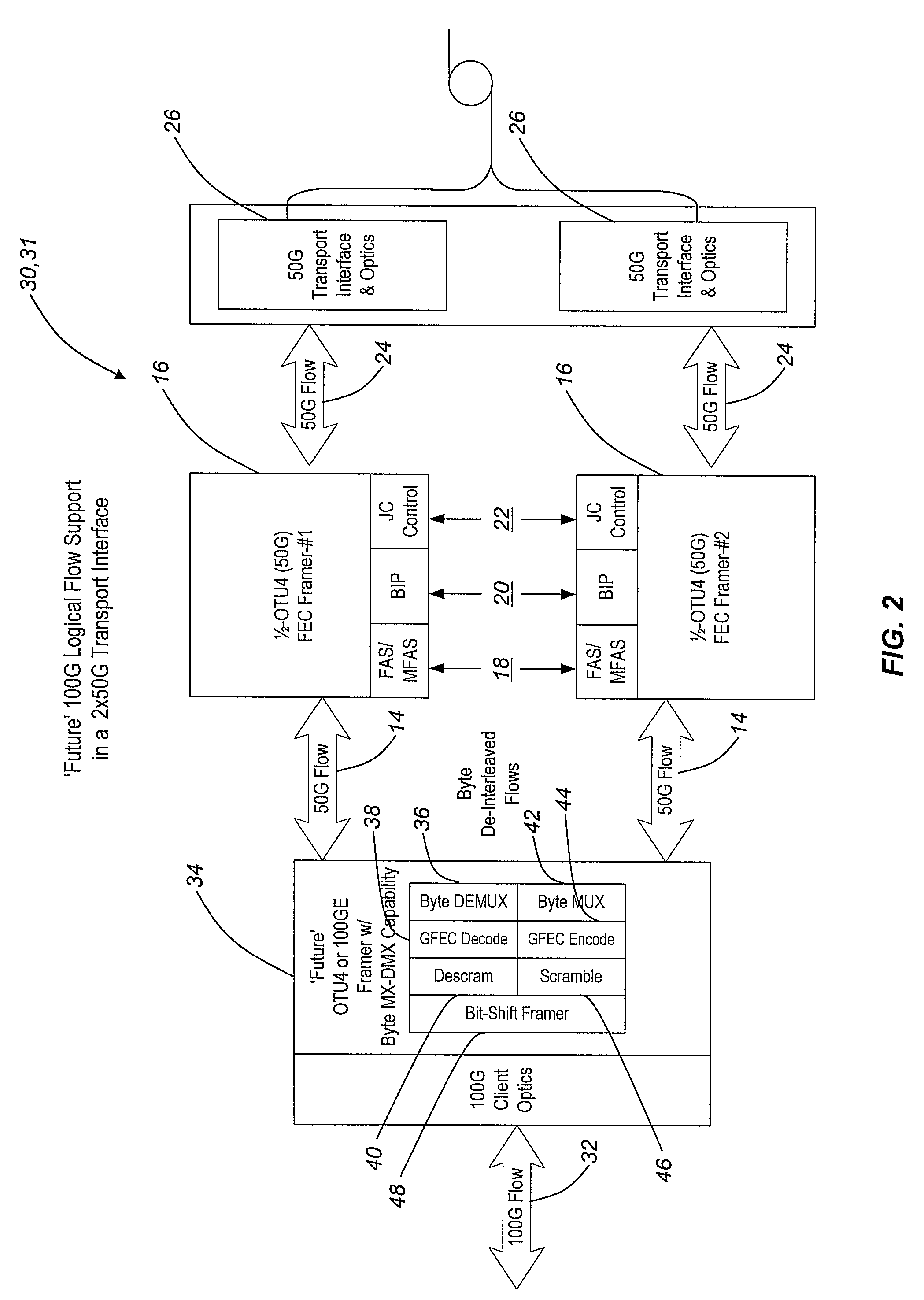
Byte-interleaving systems and methods for 100g optical transport enabling multi-level optical transmission
ActiveUS20090169217A1Useful and efficient and cost-effectiveTime-division multiplexElectromagnetic transmittersMultiplexingForward error correction
The present invention provides byte-interleaving systems and methods for Optical Transport Unit N (OTUN) (i.e. Optical Transport Unit 4 (OTU4)) and 100 Gb / s (100 G) optical transport enabling multi-level optical transmission. The byte-interleaving systems and methods of the present invention support the multiplexing of sub-rate clients, such as 10 Gb / s (10 G) clients, 40 Gb / s (40 G) clients, etc., into two 50 Gb / s (50 G) logical flows, for example, that can be forward error correction (FEC) encoded and carried on a single wavelength to provide useful, efficient, and cost-effective 100 G optical transport today. Signaling format support allows these two 50 G logical flows to be forward compatible with an evolving OTU4 and 100 G signaling format without waiting for optical and electronic technology advancement. Signaling format support also allows an evolving standard 100 G logical flow (i.e. OTU4, 100 Gb / s Ethernet (100 GbE), etc.) to be carried as 2×50 G logical flows, 4×25 G logical flows, or other lower rate formats on a single wavelength.
Owner:CIENA
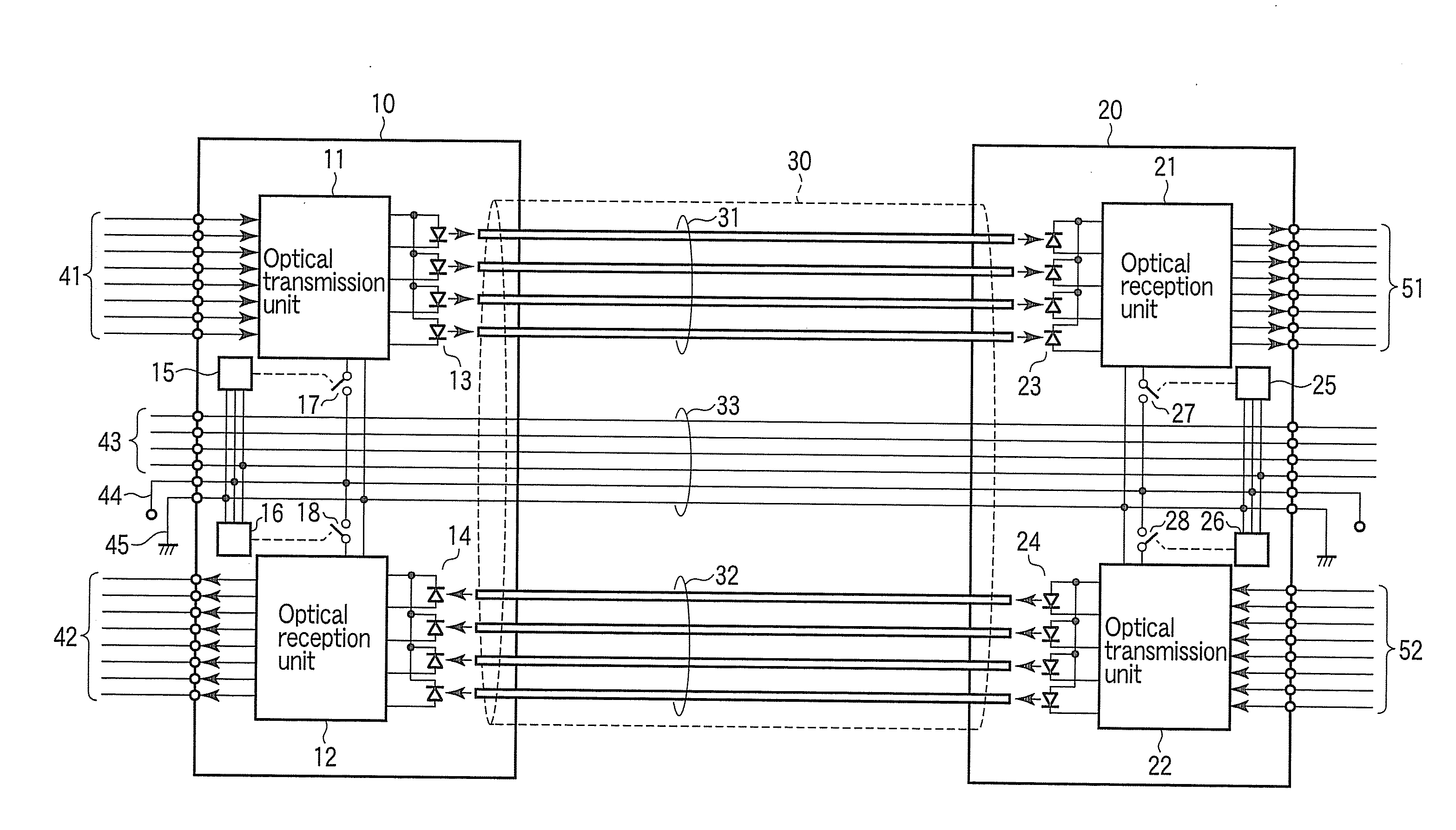
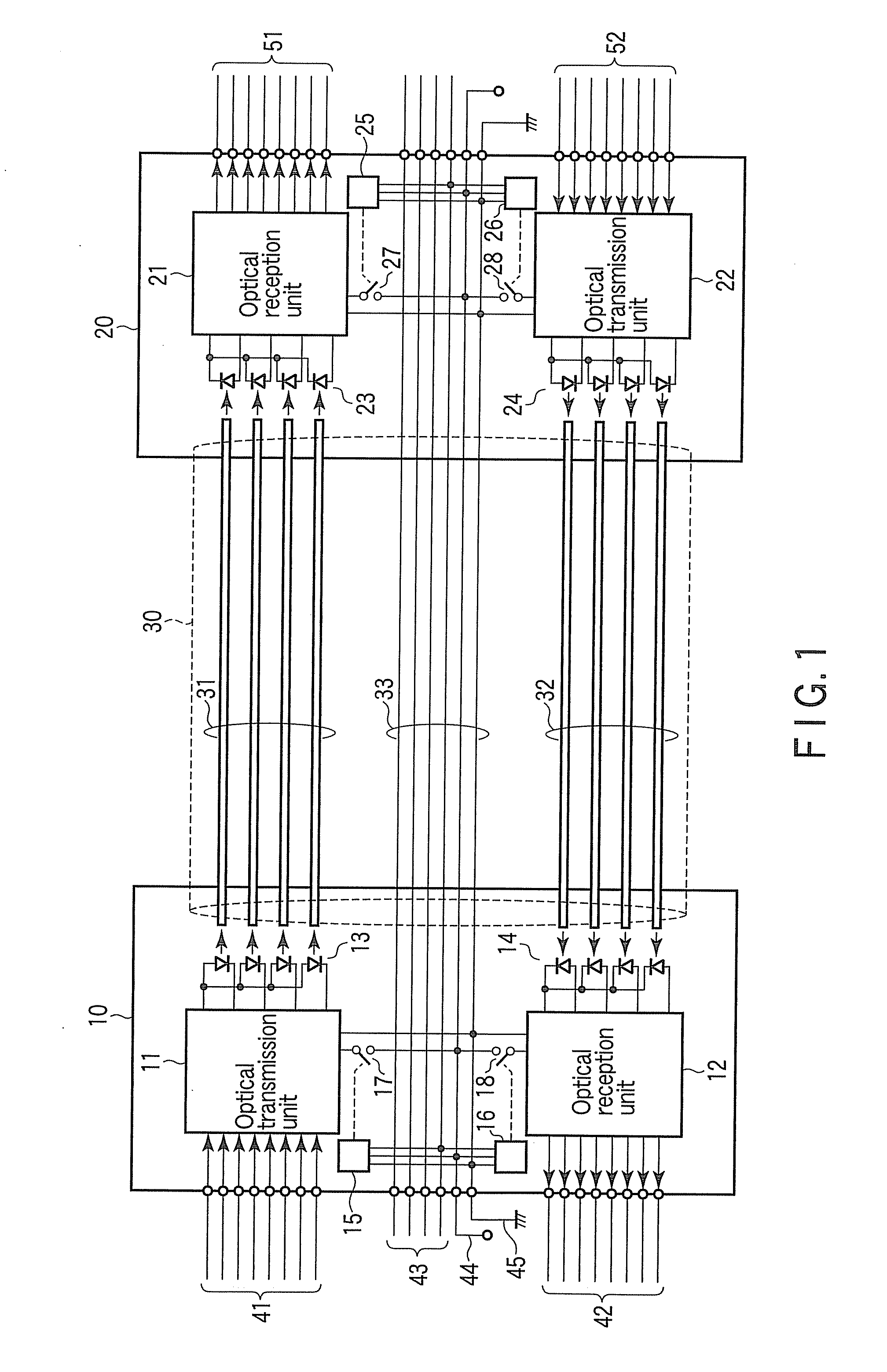
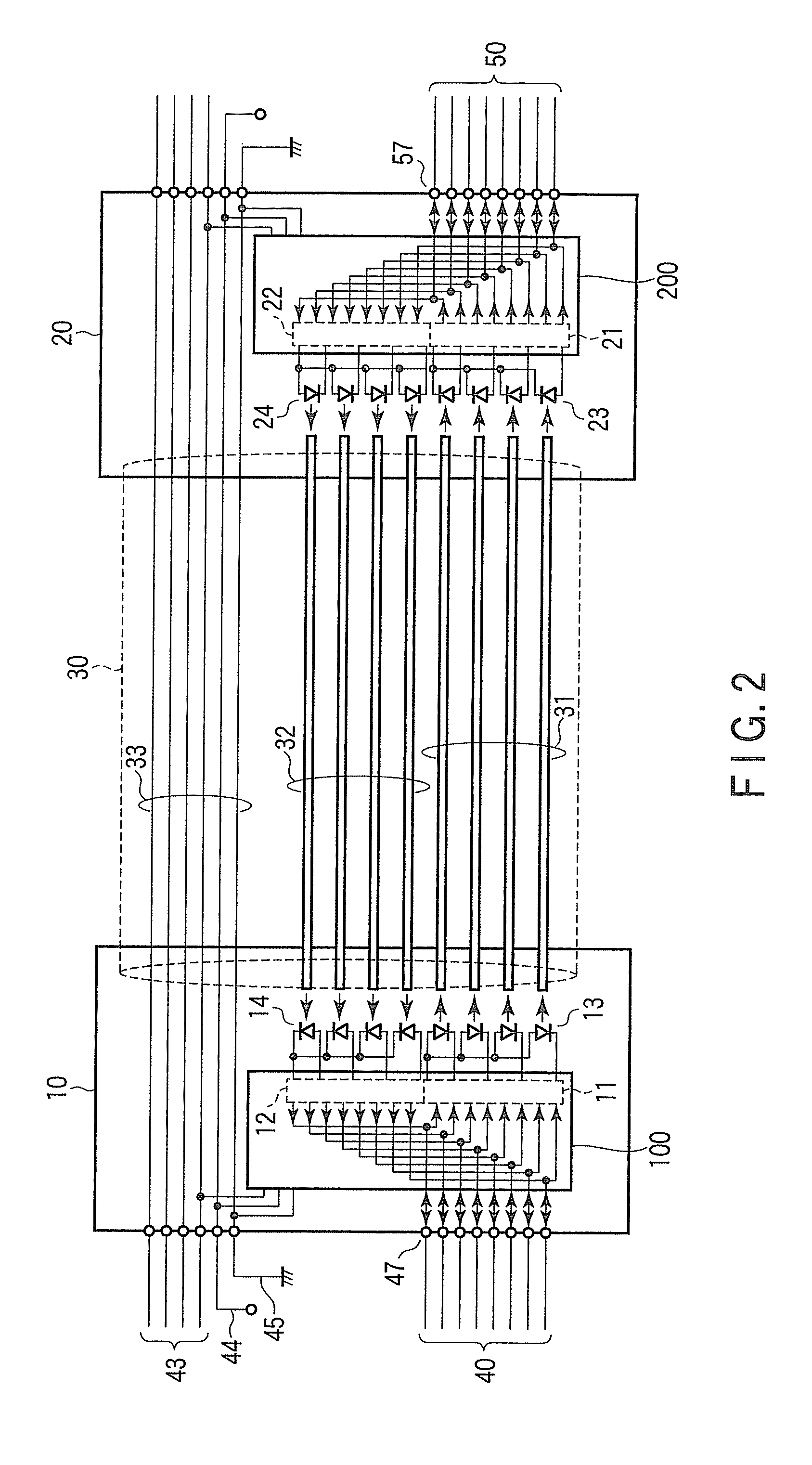
Optical wiring cable
According to one embodiment, an optical wiring cable including a first optical interconnection paths, a first optical transmission unit incorporated in a first connector, and configured to transmit an optical signal to the first optical interconnection paths, a first optical reception unit incorporated in a second connector, and configured to receive an optical signal from the first optical interconnection paths, a second optical interconnection paths, a second optical transmission unit incorporated in the second connector, and configured to transmit an optical signal to the second optical interconnection paths, a second optical reception unit incorporated in the first connector, and configured to receive an optical signal from the second optical interconnection paths, and a control unit configured to detect a combination of electronic apparatuses to which the first and the second connector are to be connected, and control power supply to the optical transmission units and the optical reception units.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
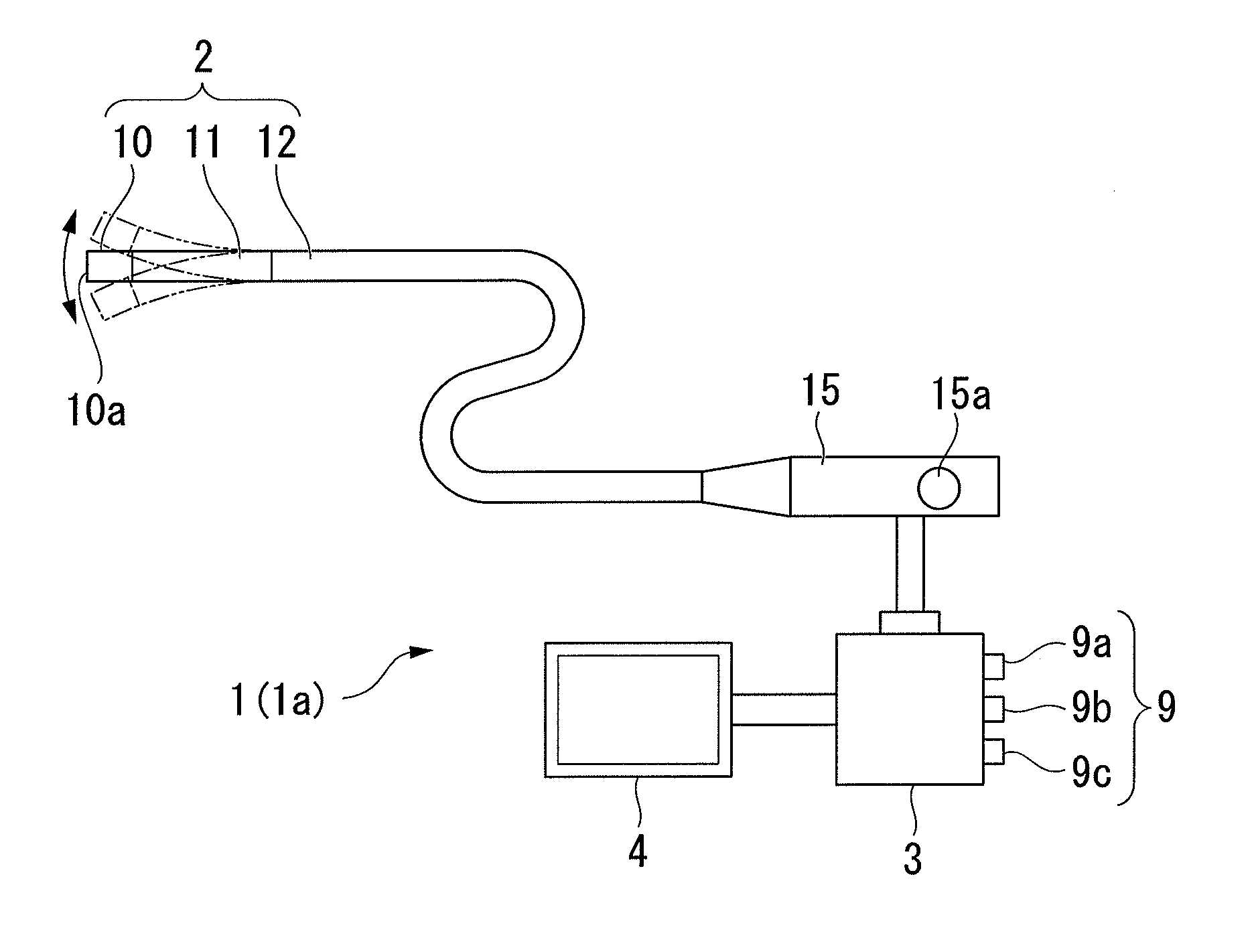
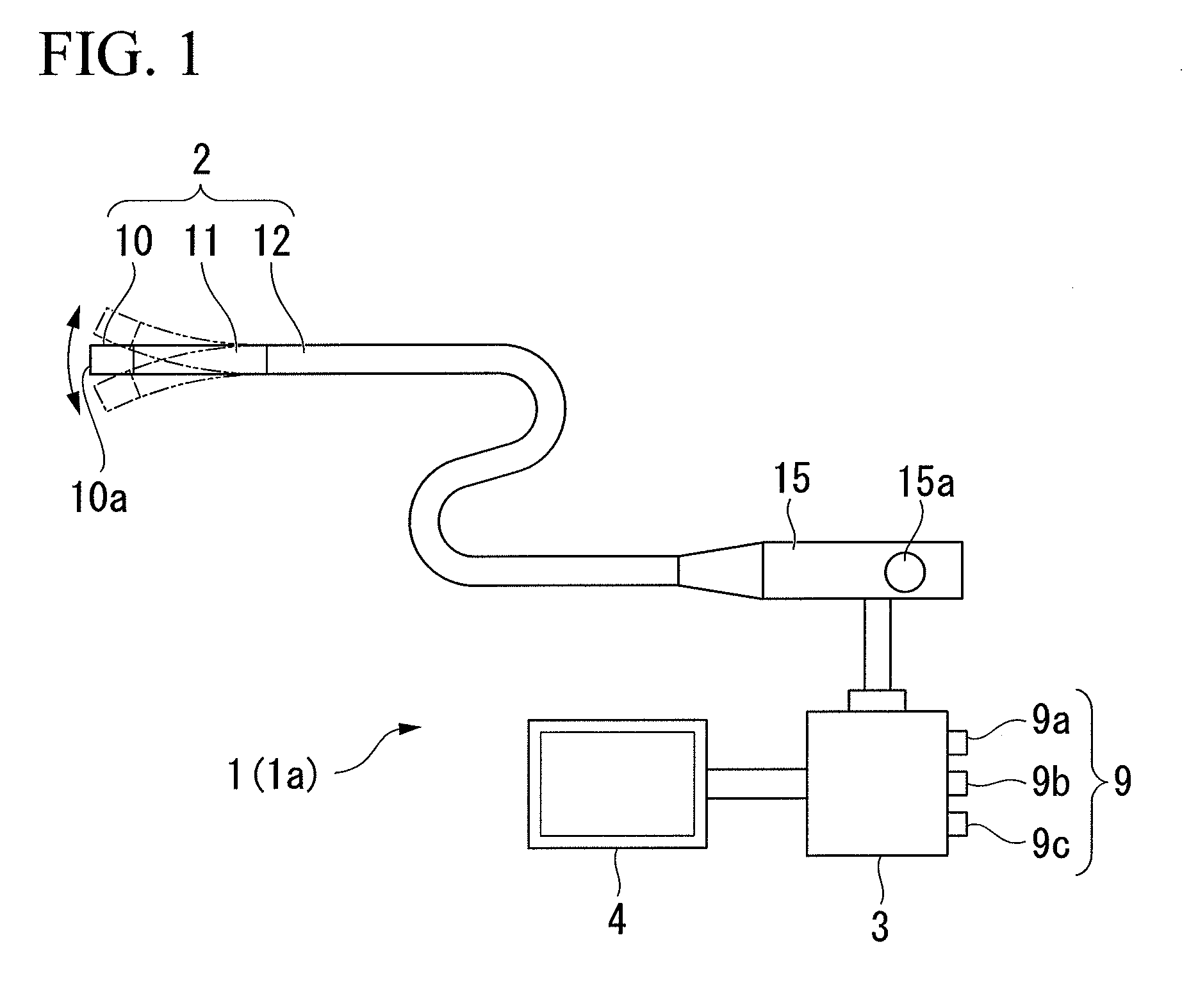
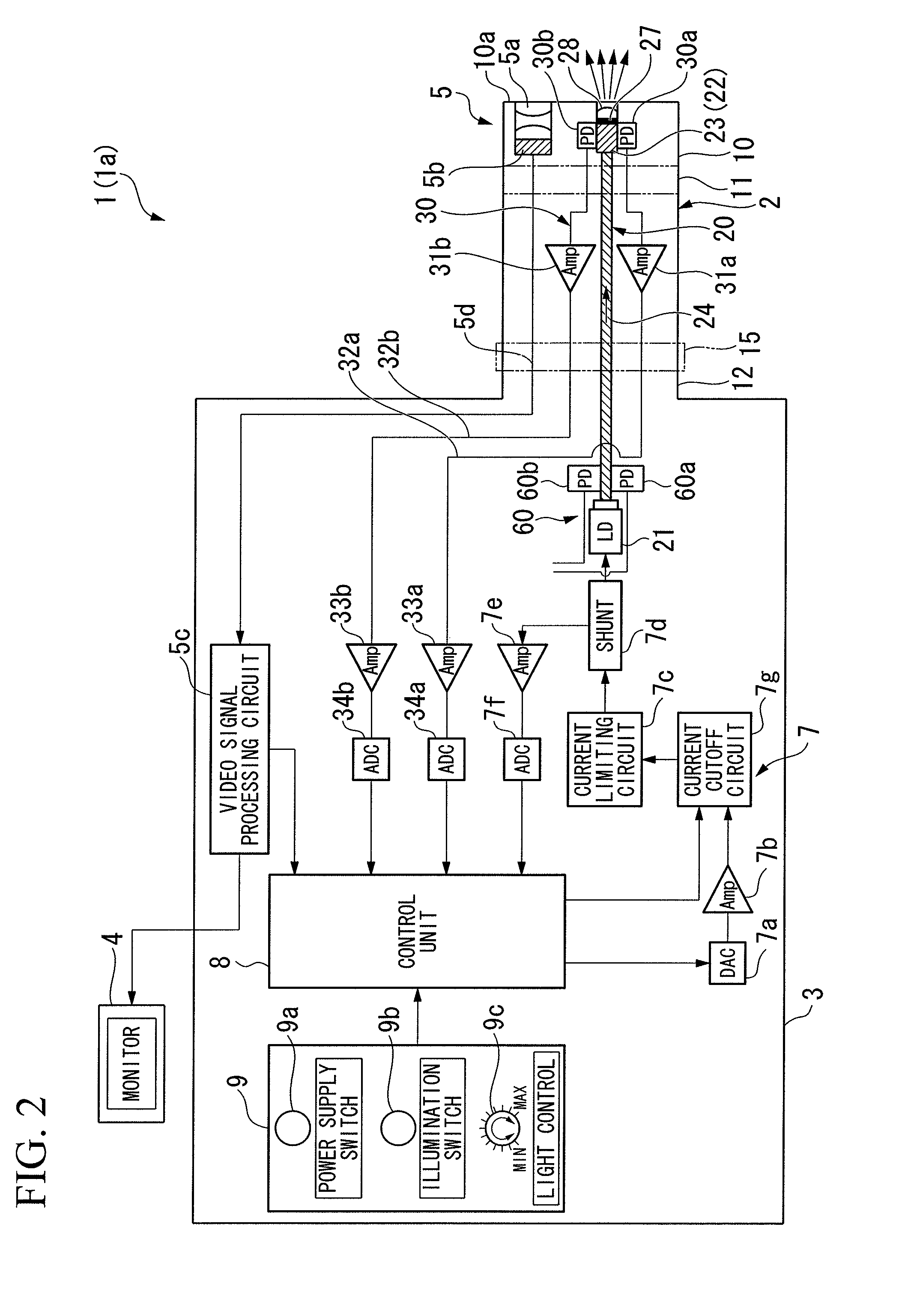
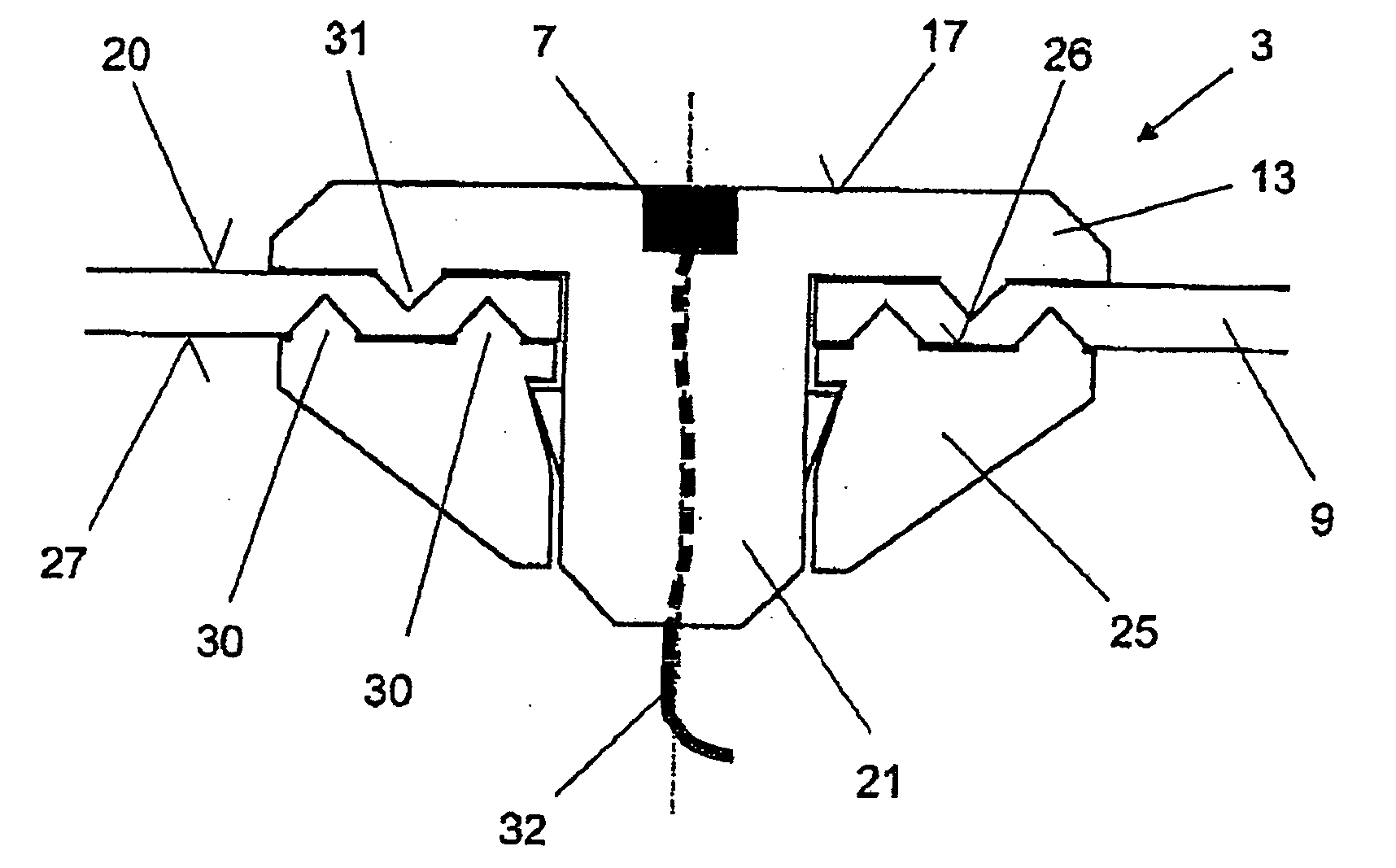
Illumination device and endoscope apparatus
An illumination device (1a) includes a light source unit (21) which is provided on the base end side of an insertion portion (2) to emit excitation light, a first optical transmission unit (24) which is provided from the base end side toward the front end side in the insertion portion (2) to guide excitation light from the light source unit (21) to the front end side, a fluorescent member (22) which is provided at the front end of the first optical transmission unit (24) and is excited by excitation light to emit illumination light, and a light determination unit (30) which is provided near the fluorescent member (22) to determine the amount of illumination light emitted from the fluorescent member (22) and output a determination signal. With this configuration, when laser light is irradiated from the light source unit (21) onto the fluorescent member such that illumination light is emitted from the fluorescent member (22) and is irradiated to the outside, it is possible to provide an illumination device (1a) and an endoscope apparatus (1) capable of quantitatively evaluating the amount of illumination light accurately.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Device for fastening a sensor on containers
ActiveUS20070157748A1Simple and reliable connectionImprove connection securityMeasurement apparatus componentsTransportation and packagingOptical transport unitBearing surface
Device for fastening a sensor on containers with a flexible container wall, in particular mixing bags, comprising a sensor support which is fitted with a sensor, bears against an inner wall of the container wall at least with a rear subsurface averted from the sensor, and is guided with a central piece through an opening in the container wall in which the sensor support is fixed on the container wall by a clamping part which can be connected to the central piece, in which the container wall is clamped between the rear subsurface of the sensor support and on a bearing surface, facing an outer wall of the container, of the clamping part, and in which the rear subsurface bears sealingly against the inner wall of the container wall. The sensor support can also have an electronic or optical transmit unit which is connected to the sensor, in which case the transmit unit communicates in a wireless fashion with a receive unit arranged outside the container.
Owner:SARTORIUS STEDIM BIOTECH GMBH
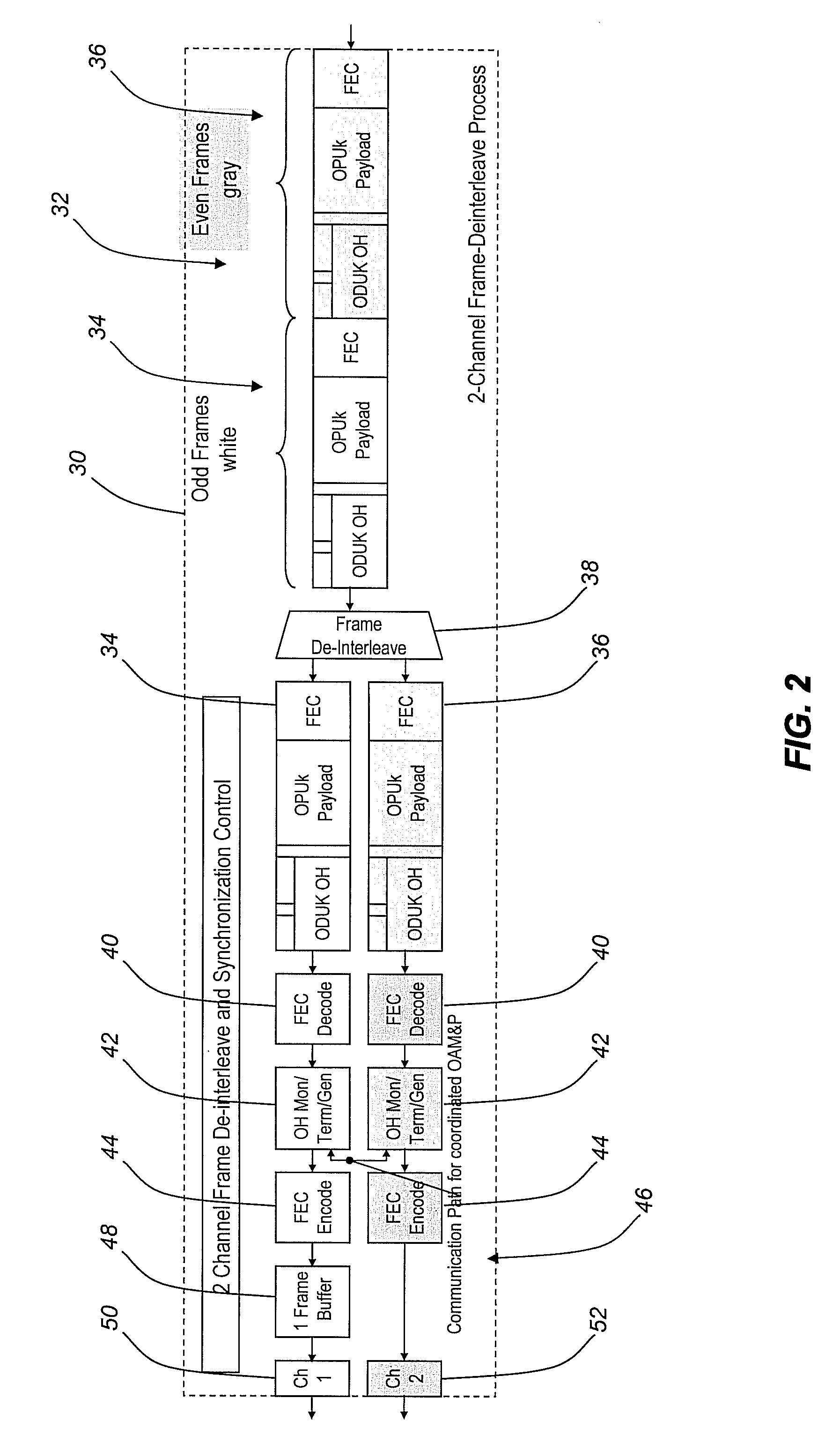
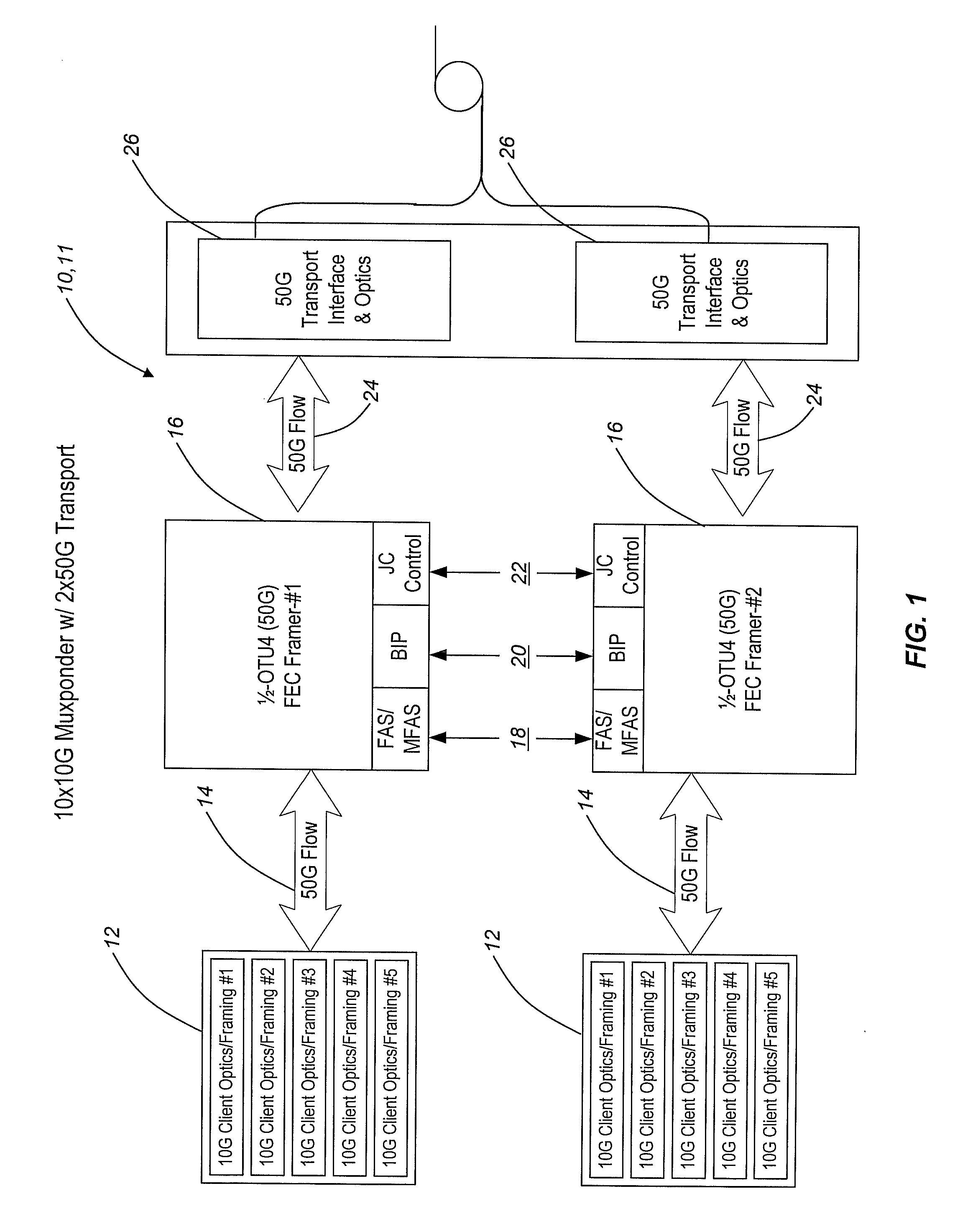
Frame-interleaving systems and methods for 100g optical transport enabling multi-level optical transmission
ActiveUS20090169204A1Useful and efficient and cost-effectiveTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationMultiplexingEngineering
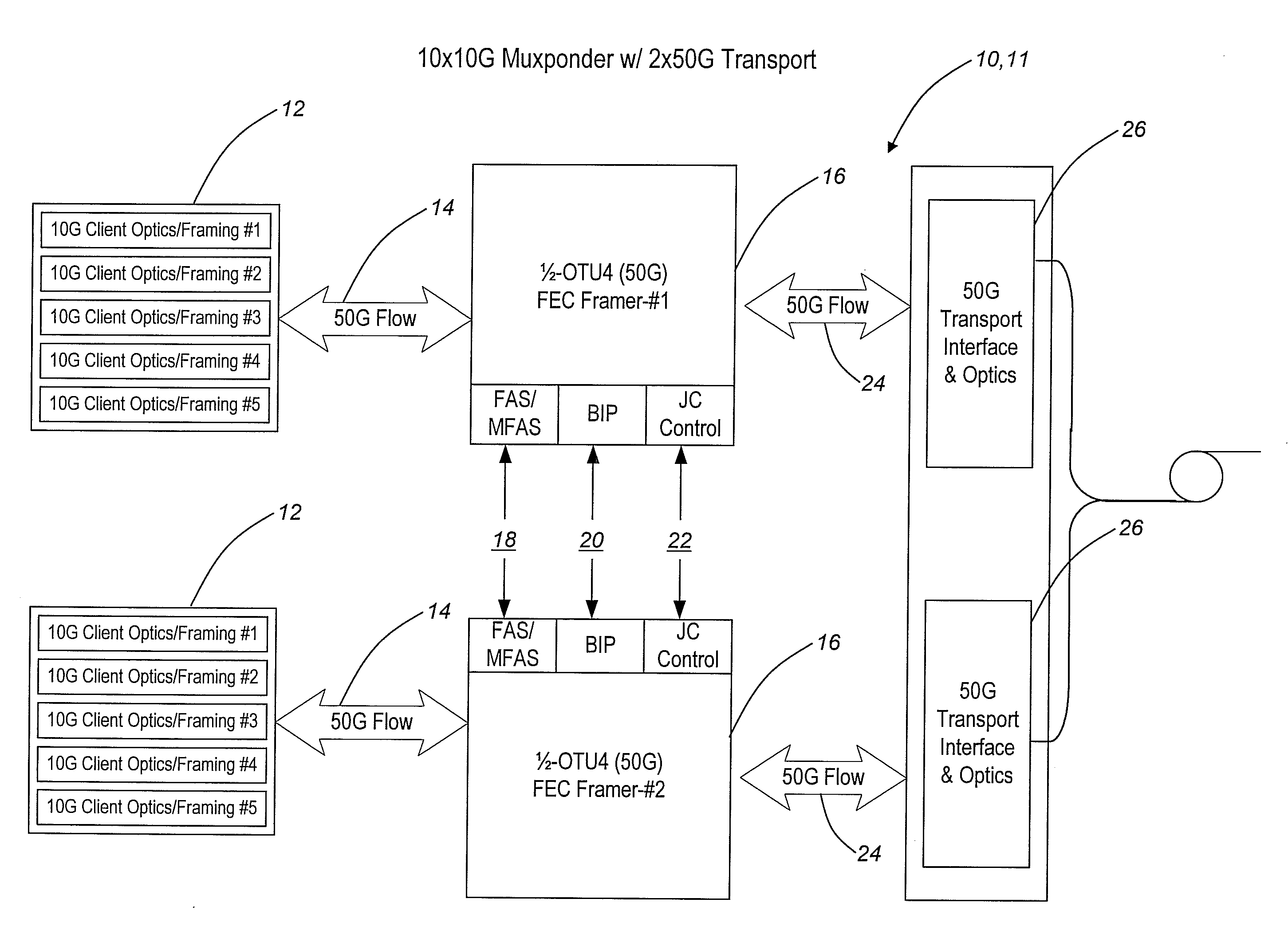
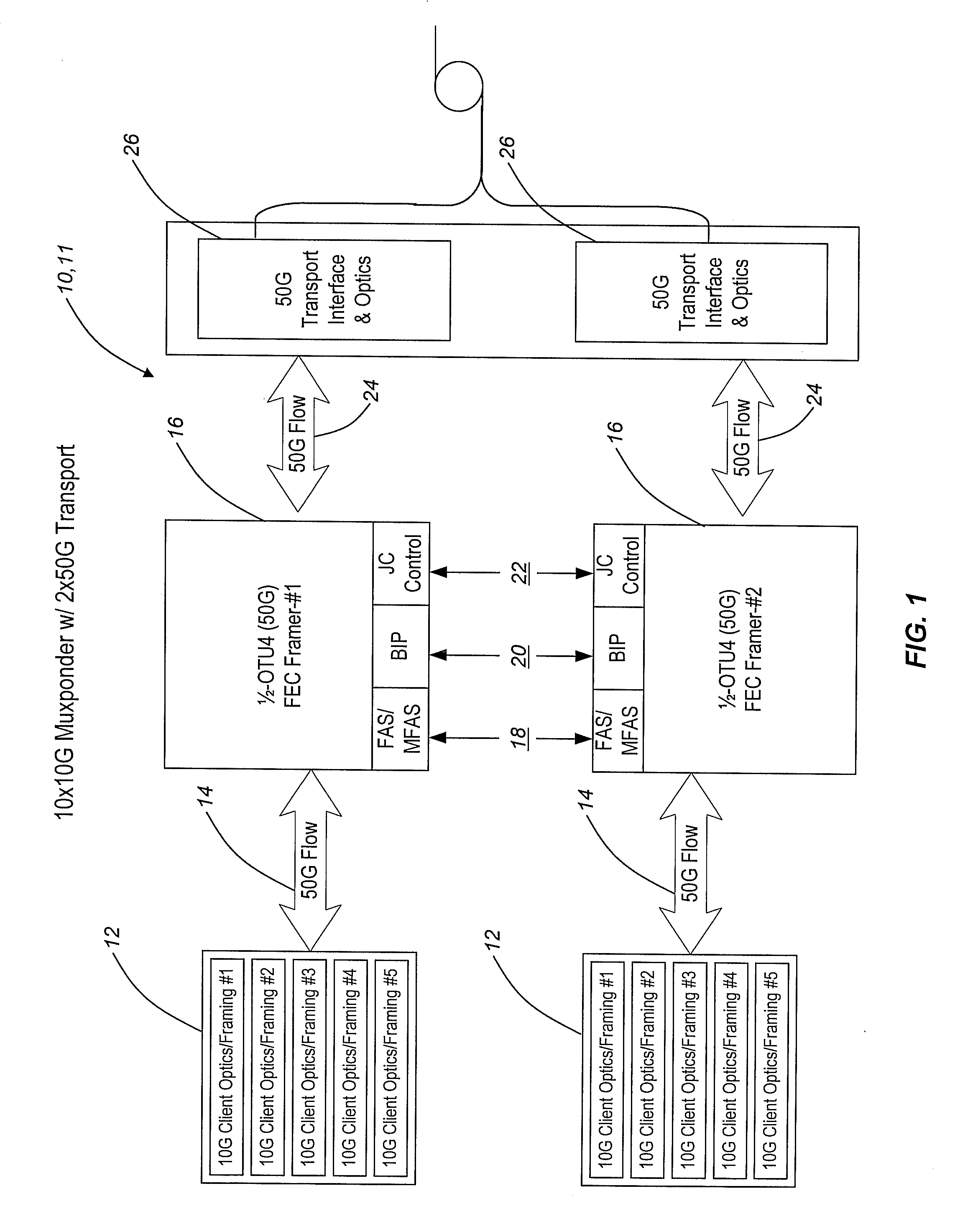
The present invention provides frame-interleaving systems and methods for Optical Transport Unit K (OTUK) (i.e. Optical Transport Unit 4 (OTU4)), 100 Gb / s Ethernet (100 GbE), and other 100 Gb / s (100 G) optical transport enabling multi-level optical transmission. The frame-interleaving systems and methods of the present invention support the multiplexing of sub-rate clients, such as 10×10 Gb / s (10 G) clients, 2×40 Gb / s (40 G) plus 2×10 G clients, etc., into two 50 Gb / s (50 G) transport signals, four 25 Gb / s (25 G) transport signals, etc. that are forward error correction (FEC) encoded and carried on a single wavelength to provide useful, efficient, and cost-effective 100 G optical transport solutions today. In one exemplary configuration, a 100 G client signal or 100 G aggregate client signal carried over two or more channels is frame-deinterleaved, followed by even / odd sub-channel FEC encoding and framing. In another exemplary configuration, a 100 G client signal or 100 G aggregate client signal carried over two or more channels is received and processed by a single 100 G FEC framer, followed by frame-deinterleaving into two or more sub-rate channels.
Owner:CIENA
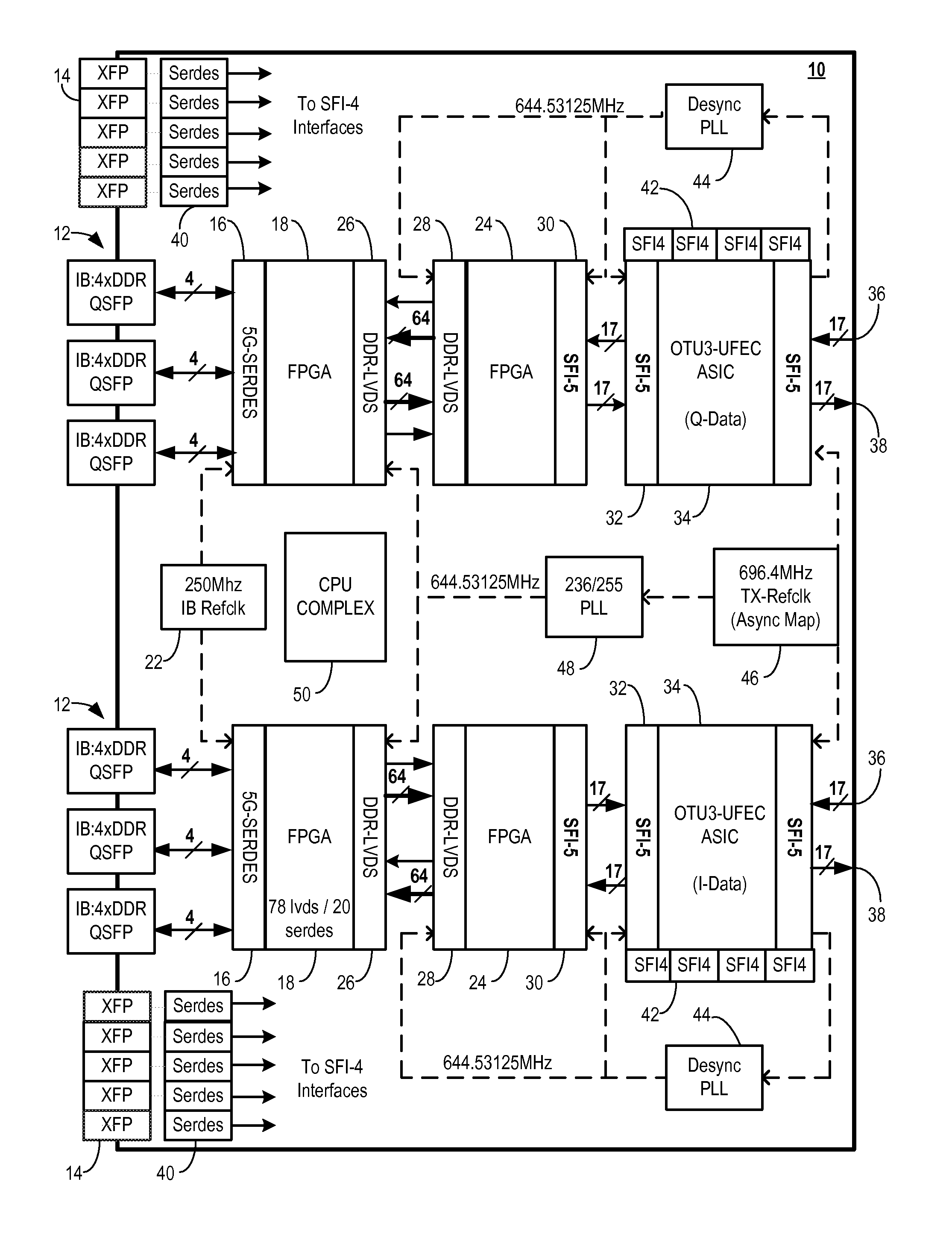
High-speed optical transceiver for InfiniBand and Ethernet
ActiveUS8805195B2Modulated-carrier systemsElectromagnetic network arrangementsTransceiverEthernet protocol
Owner:CIENA
Device for fastening a sensor on containers
ActiveUS7603921B2Mounted easily and cost-effectivelyImprove securityMeasurement apparatus componentsTransportation and packagingOptical transport unitBearing surface
Device for fastening a sensor on containers with a flexible container wall, in particular mixing bags, comprising a sensor support which is fitted with a sensor, bears against an inner wall of the container wall at least with a rear subsurface averted from the sensor, and is guided with a central piece through an opening in the container wall in which the sensor support is fixed on the container wall by a clamping part which can be connected to the central piece, in which the container wall is clamped between the rear subsurface of the sensor support and on a bearing surface, facing an outer wall of the container, of the clamping part, and in which the rear subsurface bears sealingly against the inner wall of the container wall. The sensor support can also have an electronic or optical transmit unit which is connected to the sensor, in which case the transmit unit communicates in a wireless fashion with a receive unit arranged outside the container.
Owner:SARTORIUS STEDIM BIOTECH GMBH
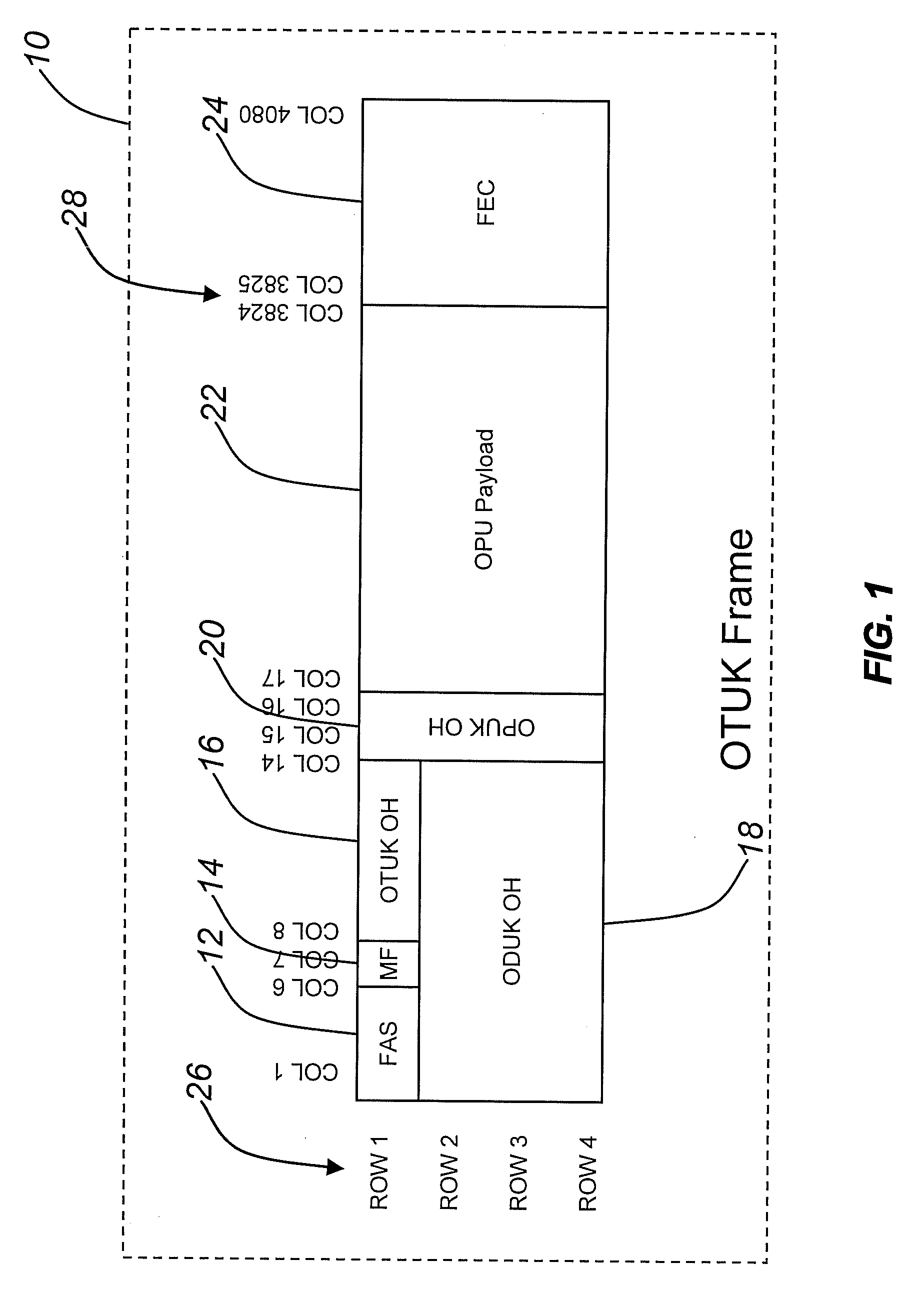
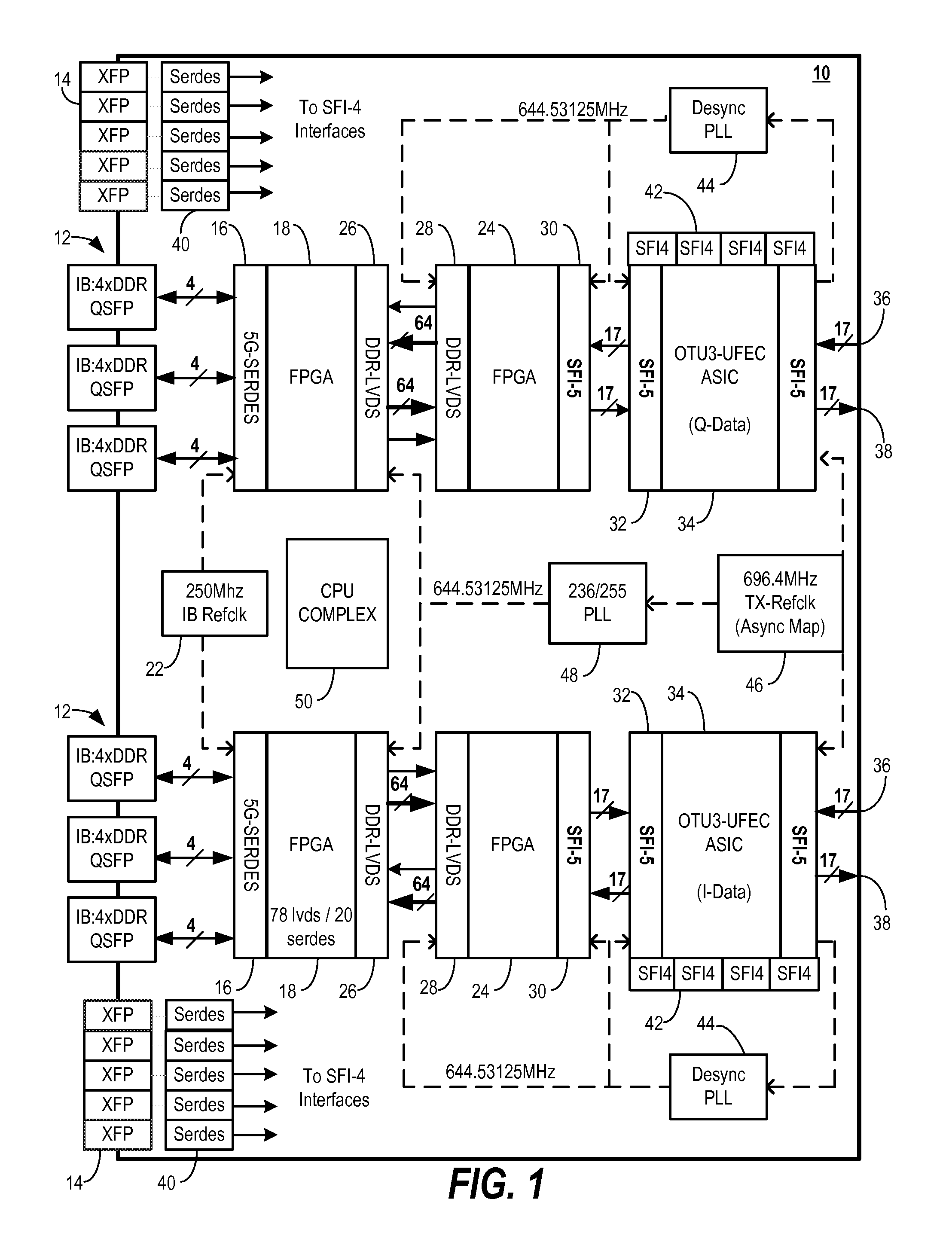
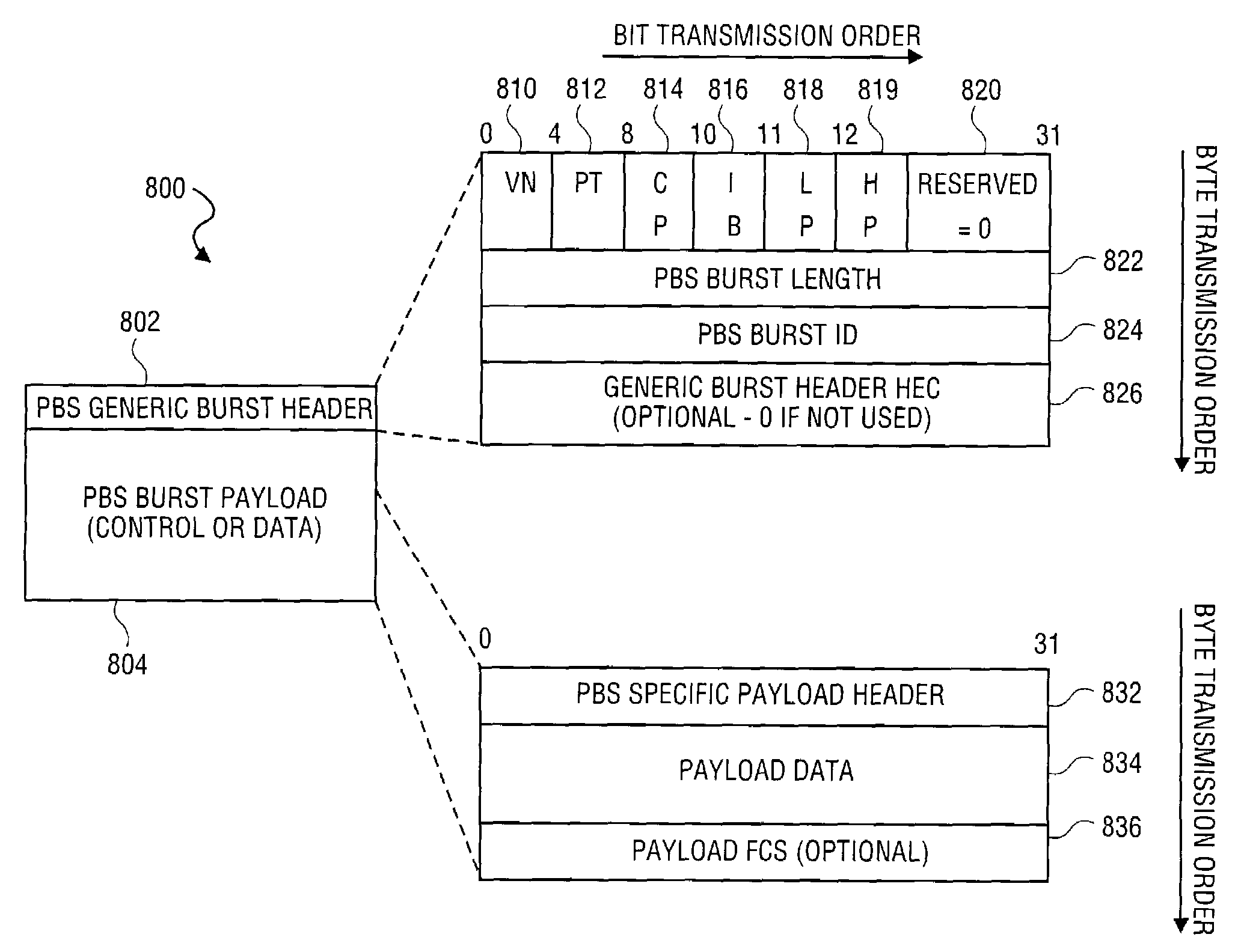
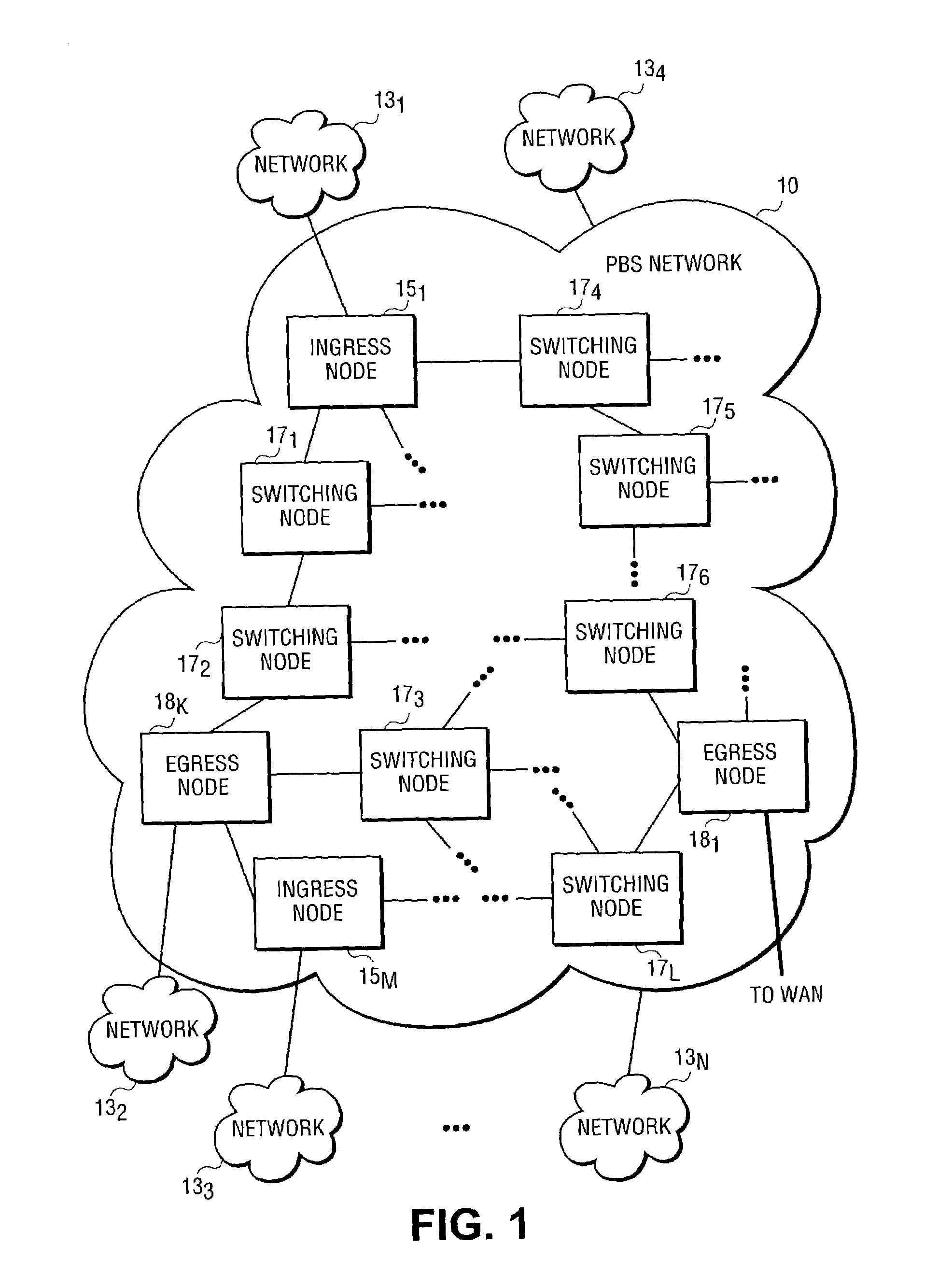
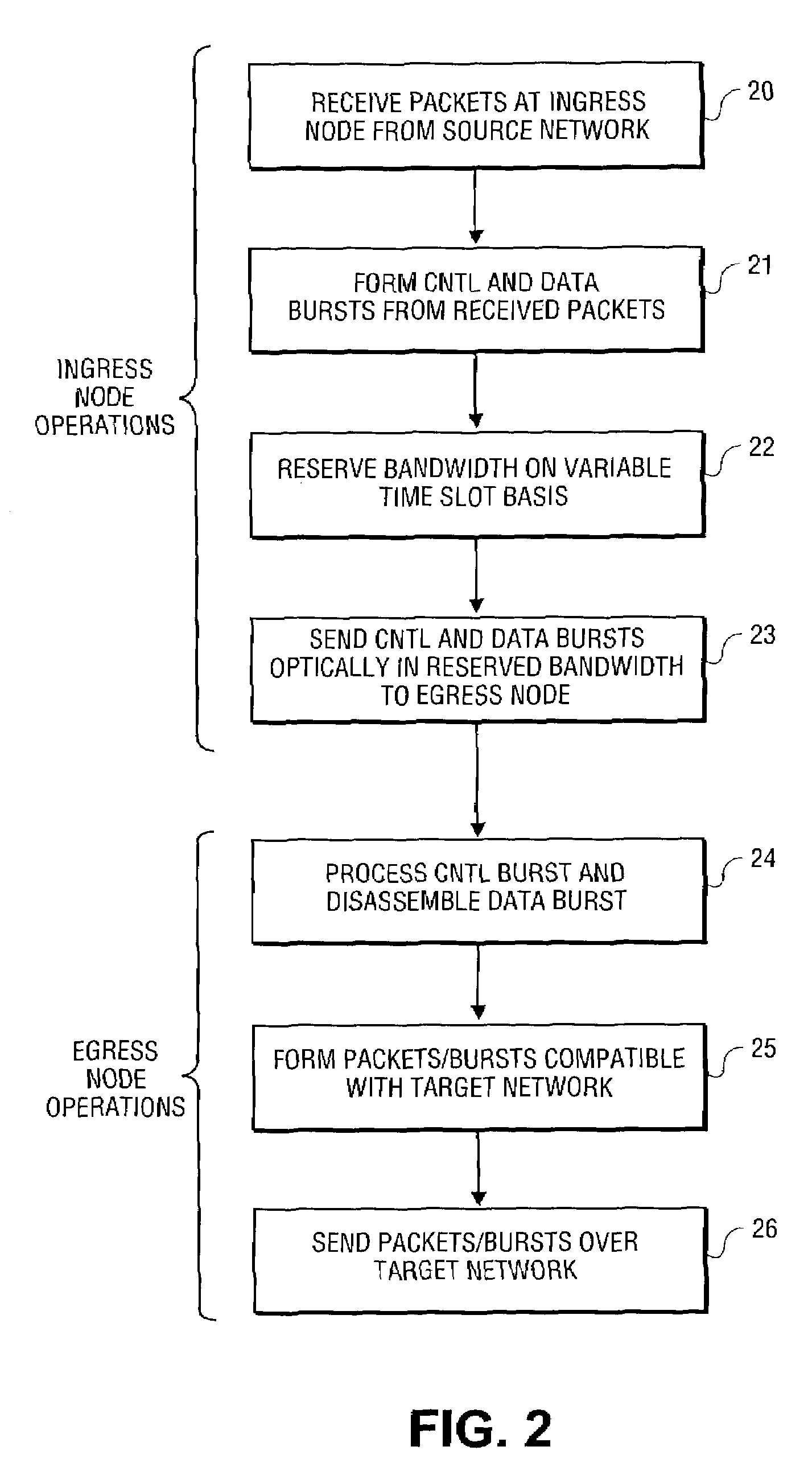
Architecture and method for framing optical control and data bursts within optical transport unit structures in photonic burst-switched networks
InactiveUS7526202B2Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationPhotonic crystalExchange network
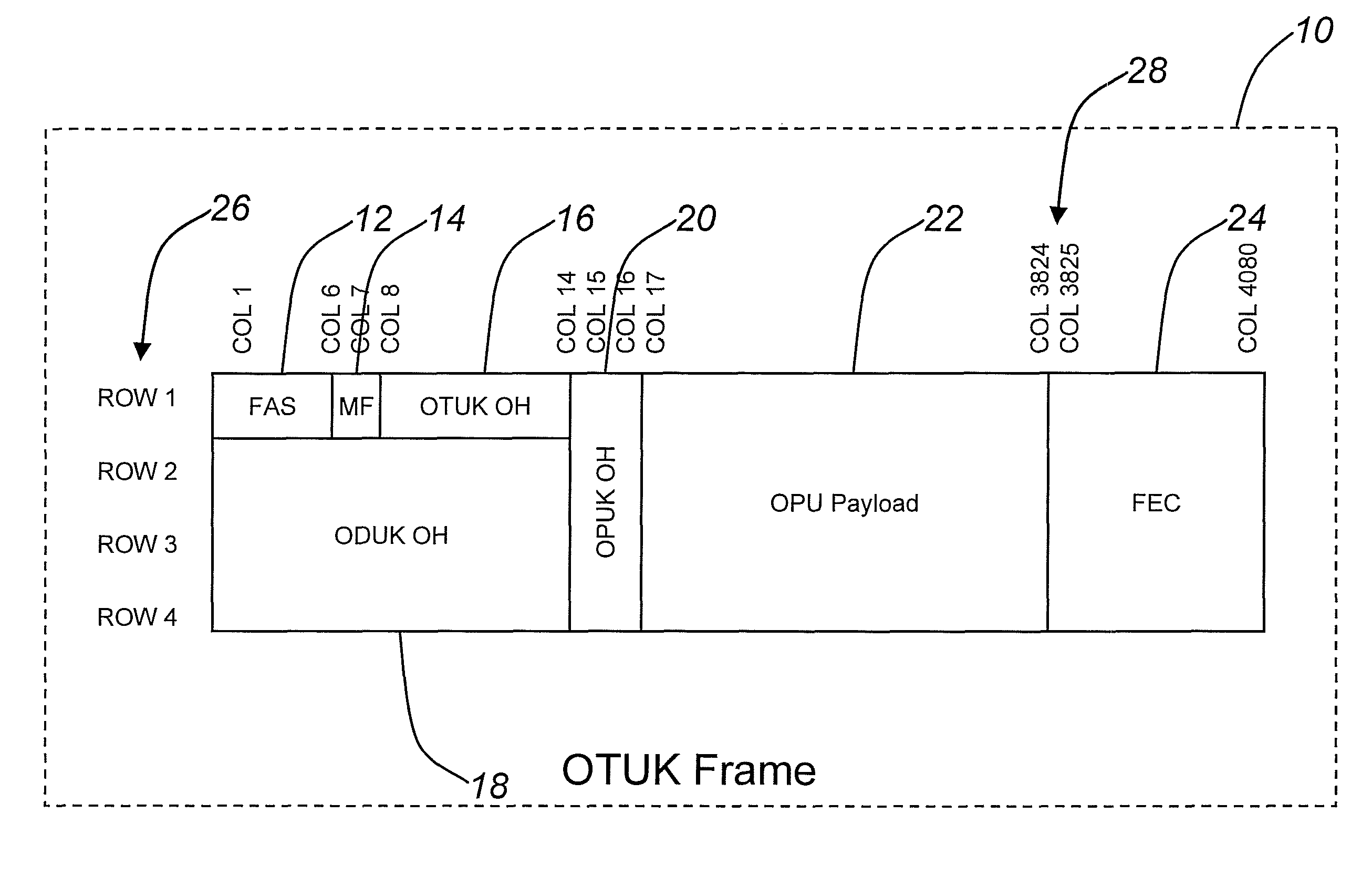
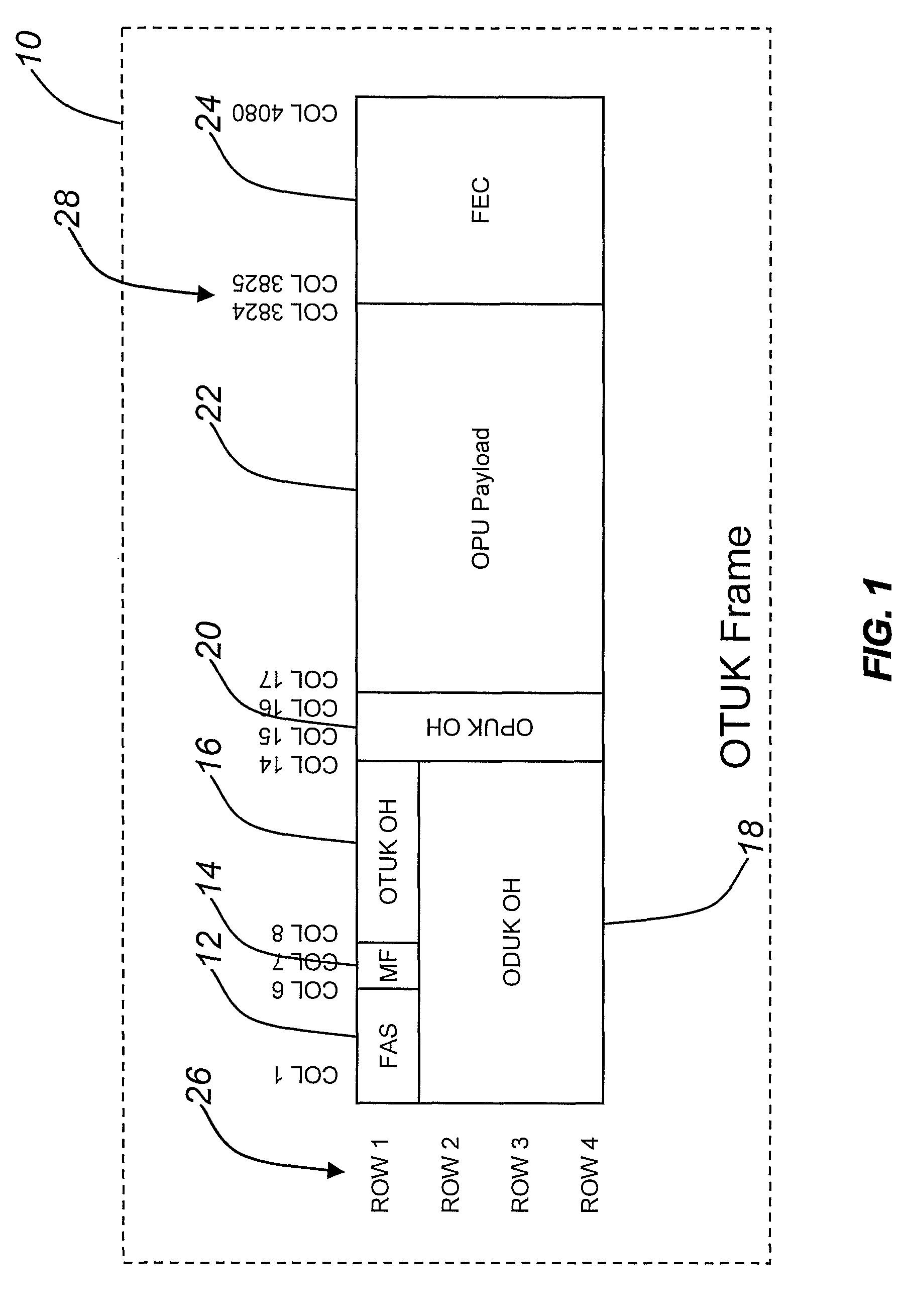
An optical network, which includes edge and switching nodes, optically communicate information formatted into bursts that are included in one or more optical channel transport unit (OTU) frames that are based on ITU-T recommendation G.709. The overhead portion of the OTU frame can include all of the fields defined in the G.709 standard, except that the two reserved bits are used to define an OTU frame type. When the FEC function is not used, the OTU frame can be arbitrarily partitioned to carry optical burst information. The information can be either control and / or data bursts or metadata related to the optical network and / or optical burst flow. When the FEC function is used, the OTU frame is used to include optical control or data bursts or optical metadata in the payload portion of the G.709 OTU frame.
Owner:INTEL CORP
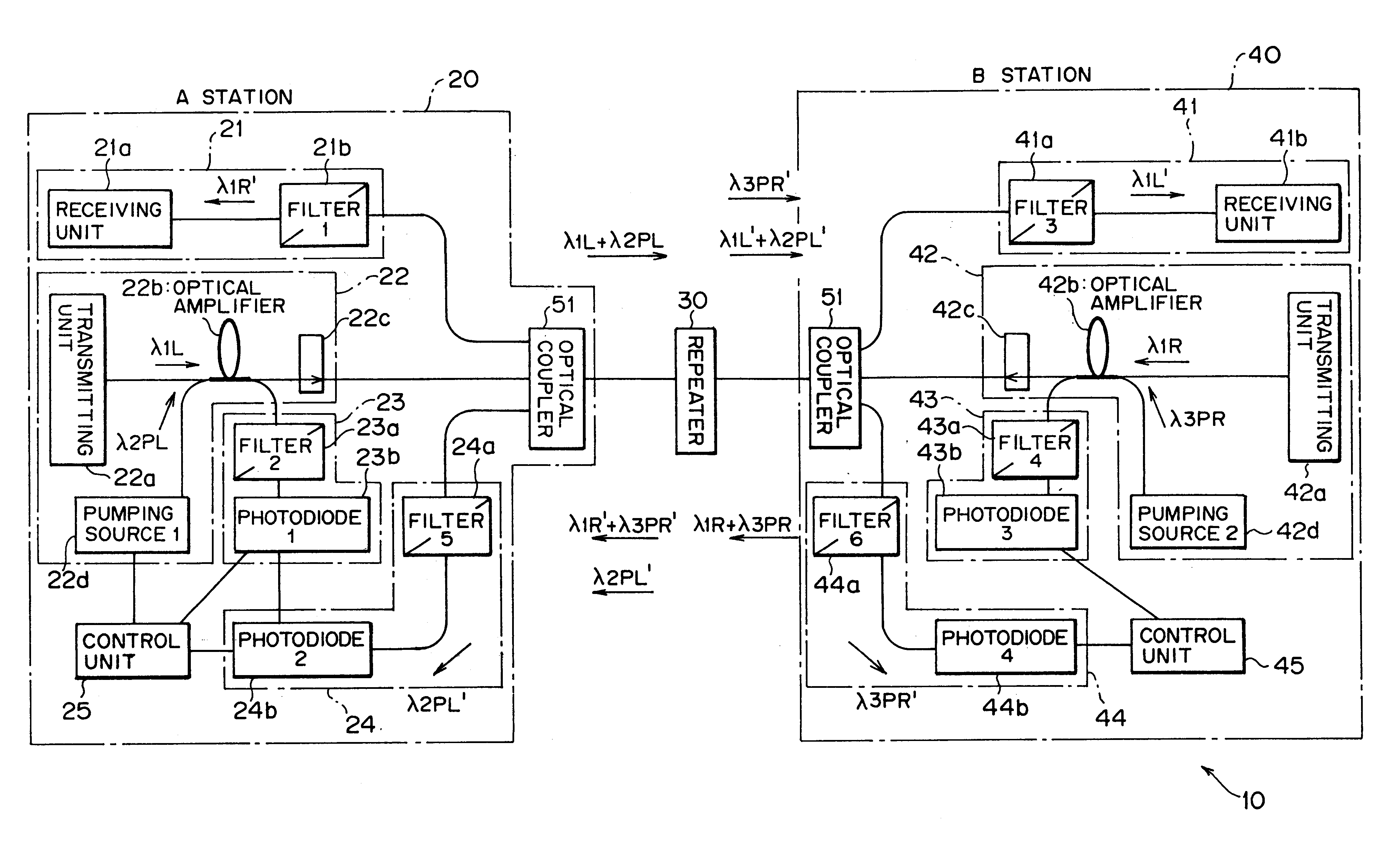
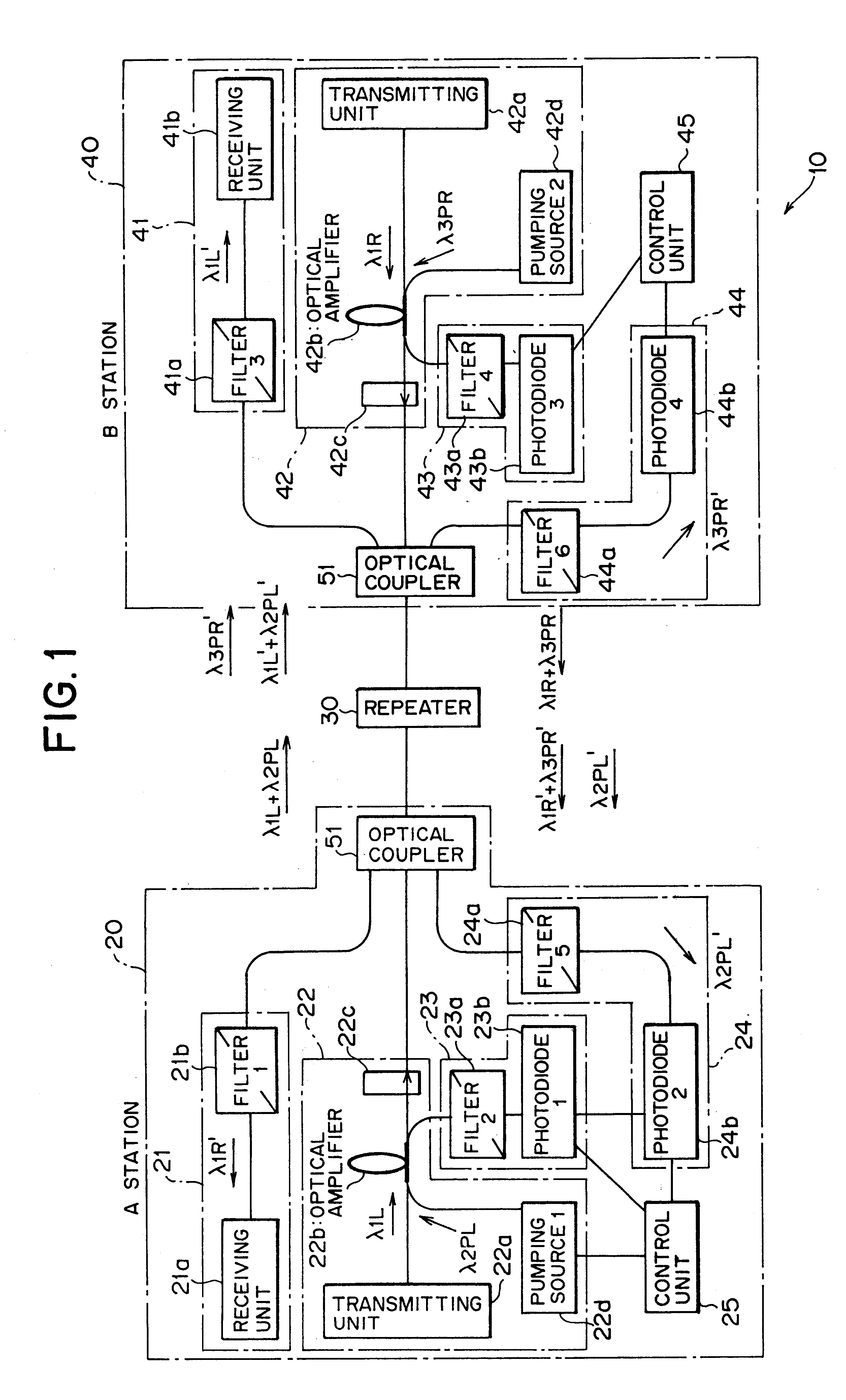
Optical transmitting apparatus and optical repeating apparatus
InactiveUS6661947B2Low costReduce maintenanceExcitation process/apparatusWavelength-division multiplex systemsEngineeringOptical transport unit
In an optical amplifying technique using remote pumping, an optical transmitting apparatus and an optical repeating apparatus are provided. An optical repeating apparatus comprises a first optical transmitting unit, a first loopback unit, a second optical transmitting unit, a second loopback unit, and four optical couplers, wherein transmission light and reception light are transmitted through one optical fiber cable, whereby the installation cost and maintenance cost of the optical cable are decreased. Disconnect of the optical cable is detected by a monitoring function using pumping light and residual pumping light, whereby reliability and safety of the system are remarkably improved. Additionally, adjustment of the optical output level of the repeating station can be most suitably set according to an actual transmission distance.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
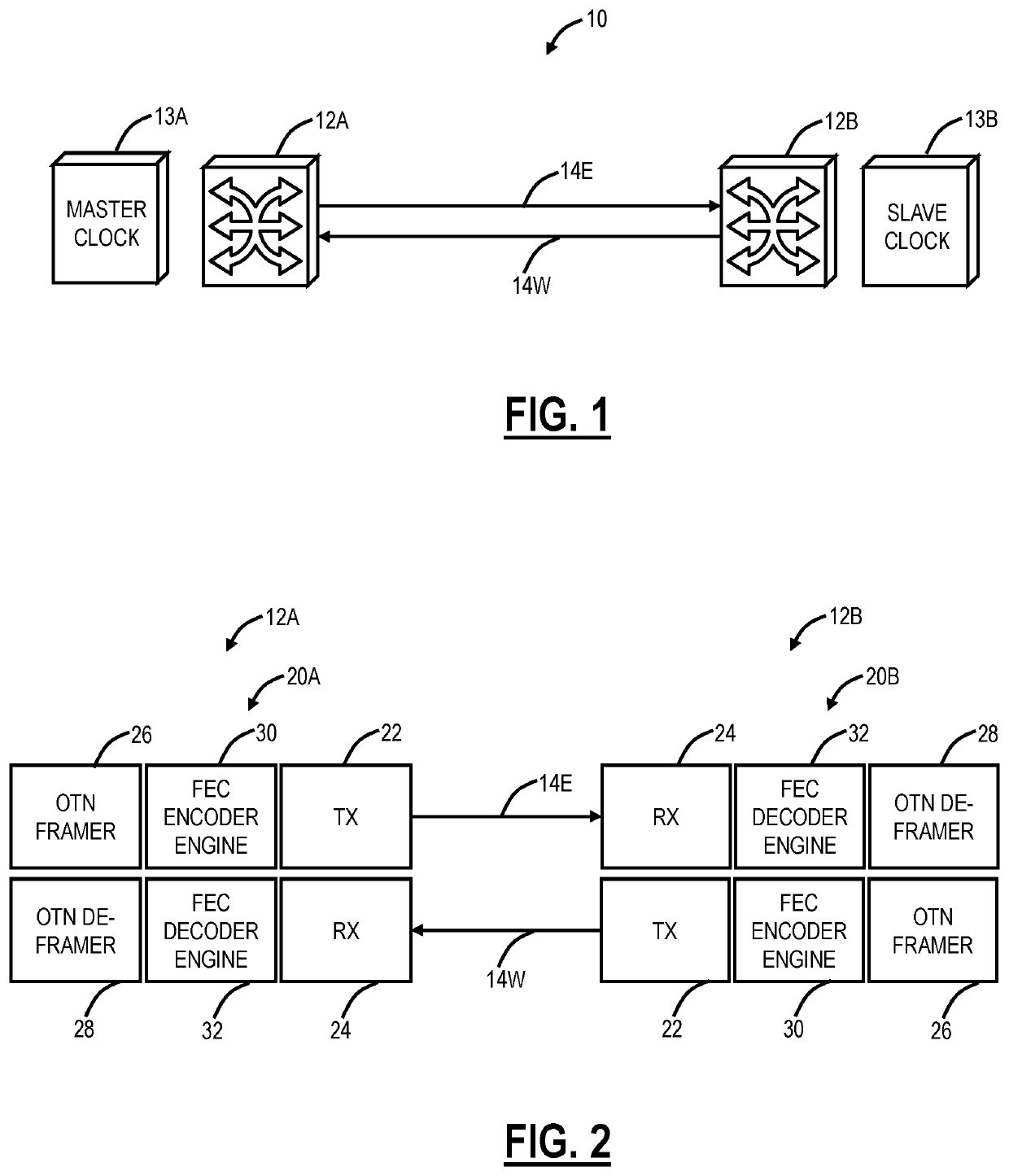
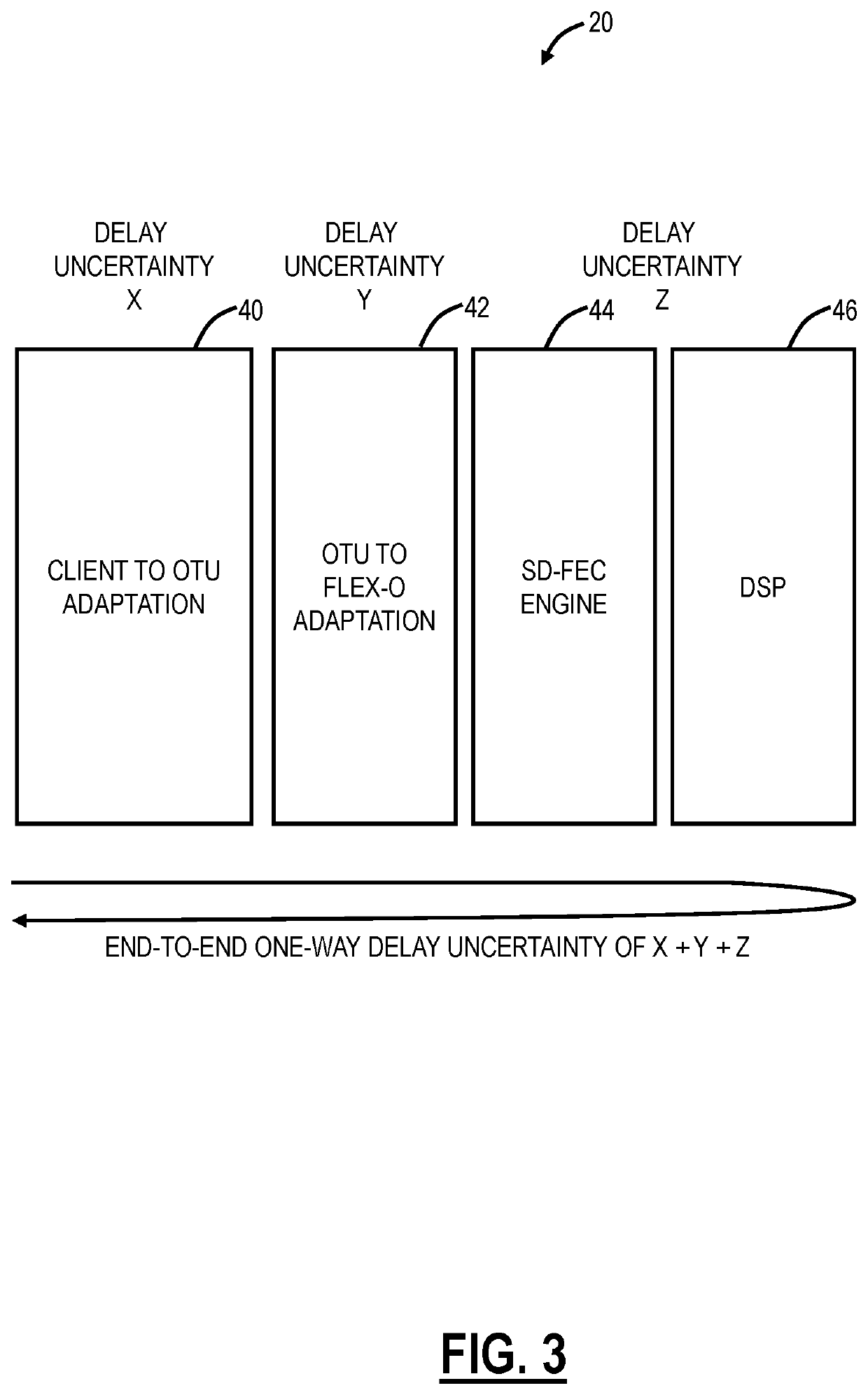
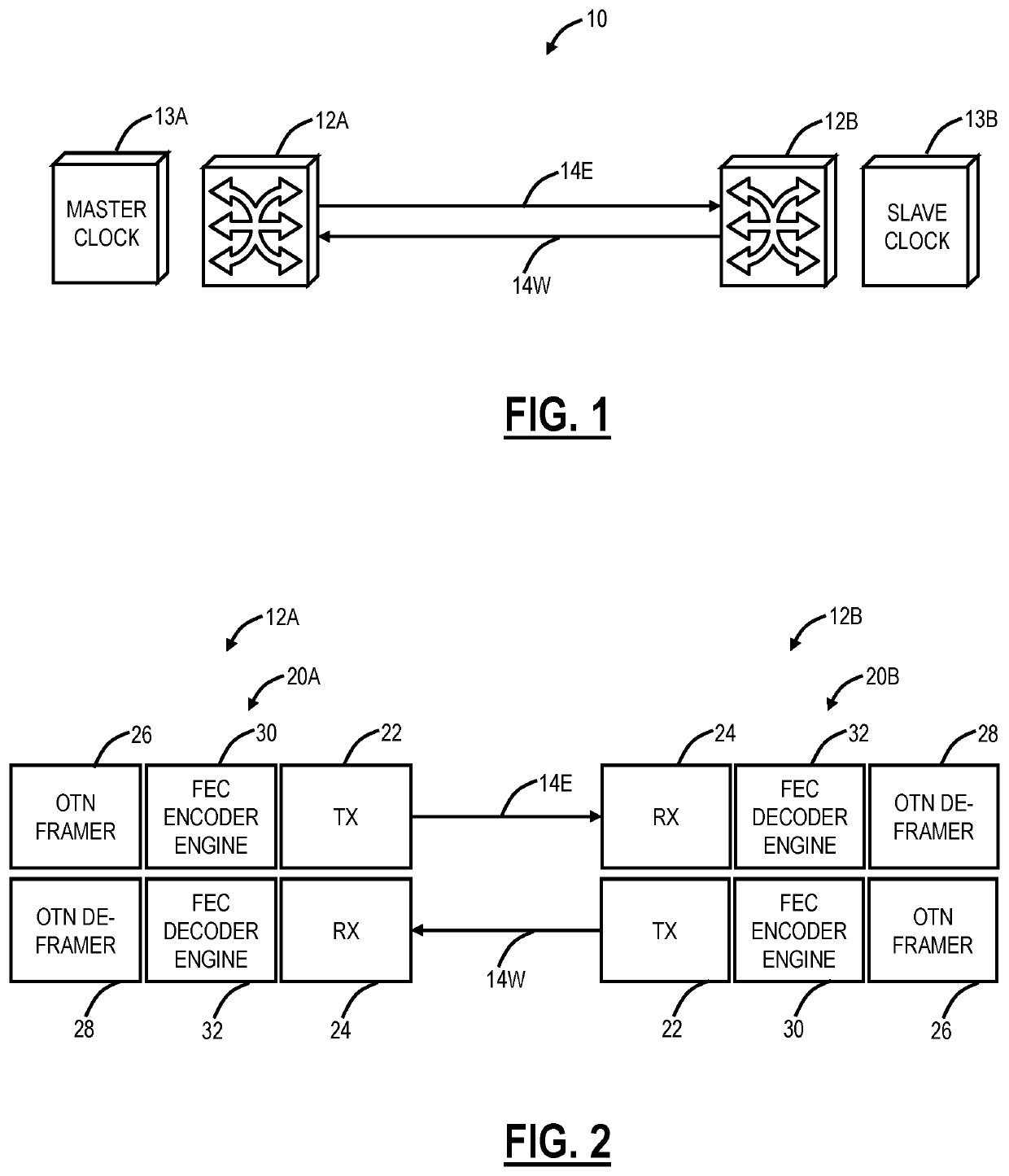
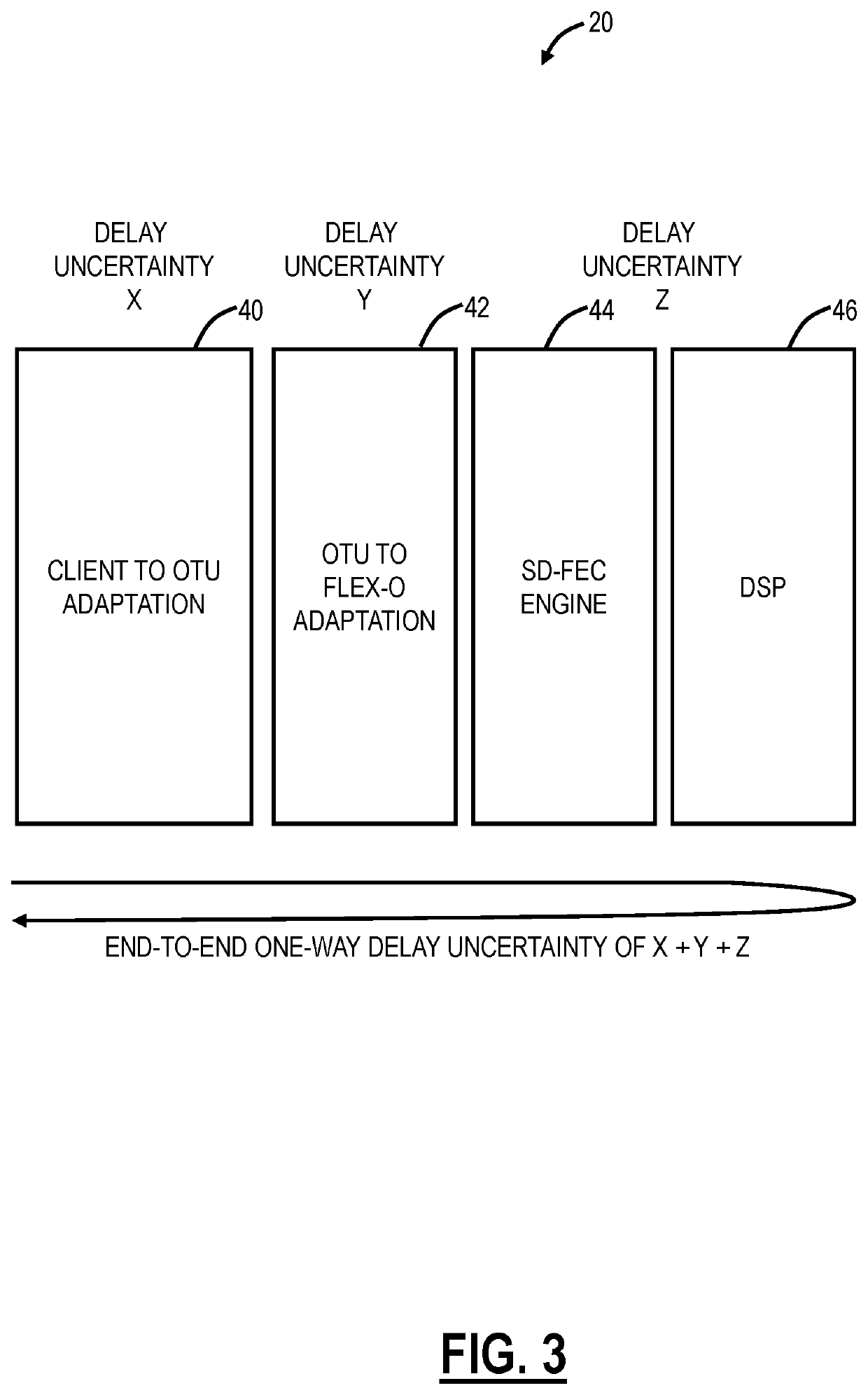
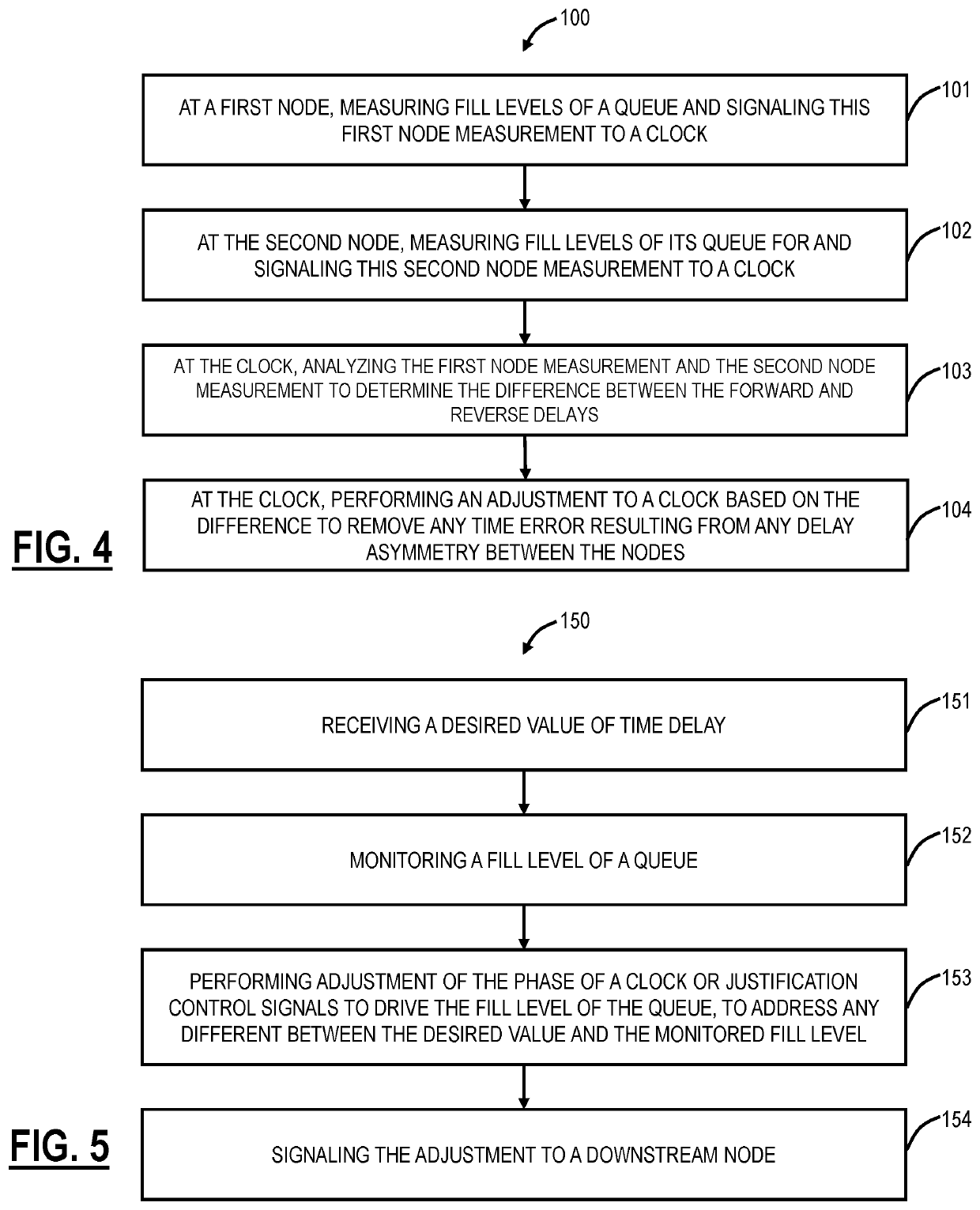
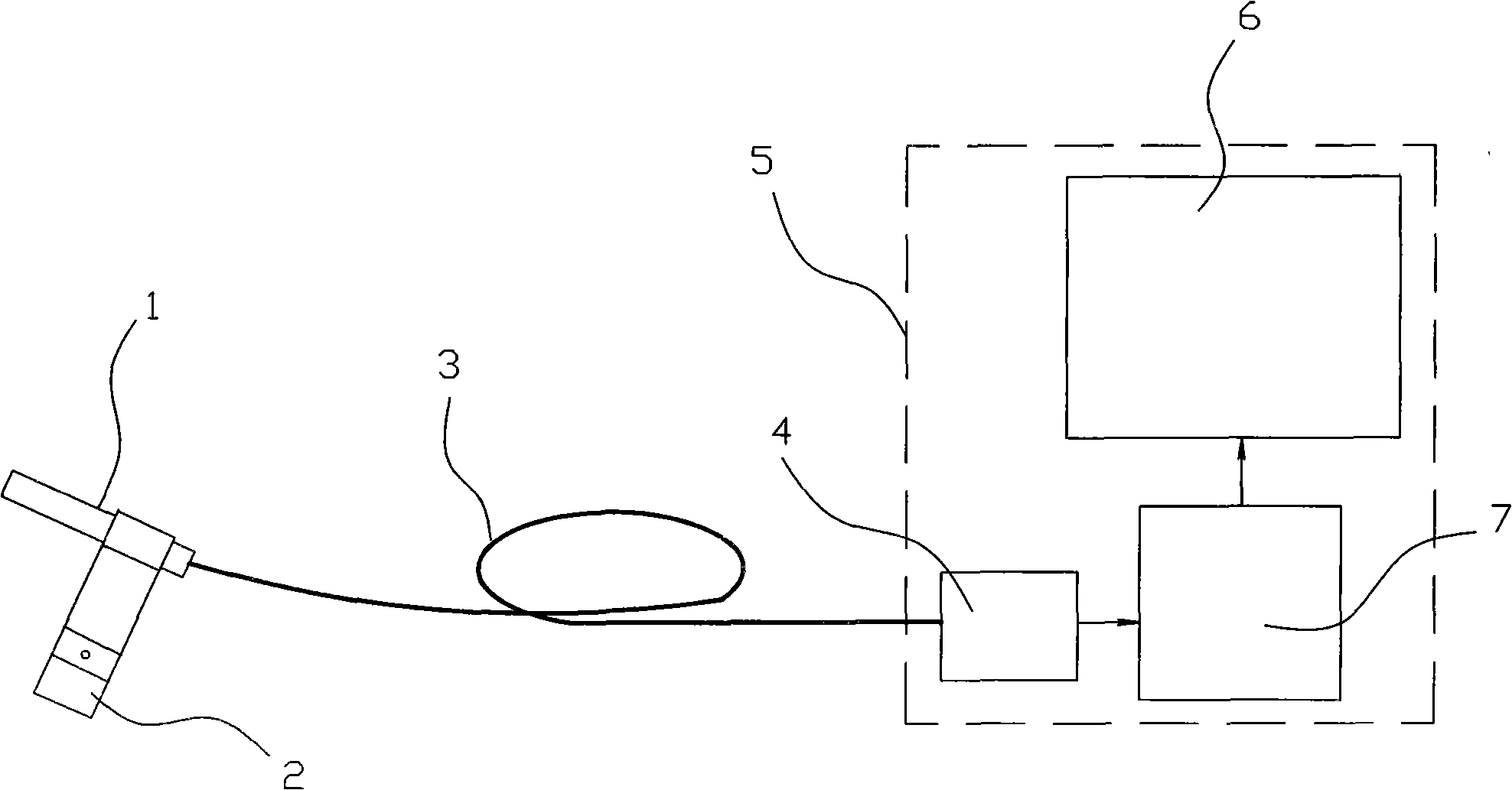
Systems and methods for compensating coherent optics delay asymmetry in a packet optical network
ActiveUS20200028585A1Reduce delay asymmetryMultiplex system selection arrangementsSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansModem deviceHemt circuits
Systems and methods of compensating for the delay asymmetry of coherent optical modems in a packet optical network include measuring fill levels of one or more queues each including an elastic First-In-First-Out (FIFO) circuit used in a transport mapping scheme, wherein the transport mapping scheme is one or more of client mapping to Optical Transport Unit (OTU) and OTU mapping to Flexible OTN (FlexO); and performing adjustments in a clock based in part on the measured fill levels, wherein the adjustments are configured to reduce a Time Error (TE) in the packet network based on delay asymmetry between two nodes.
Owner:CIENA
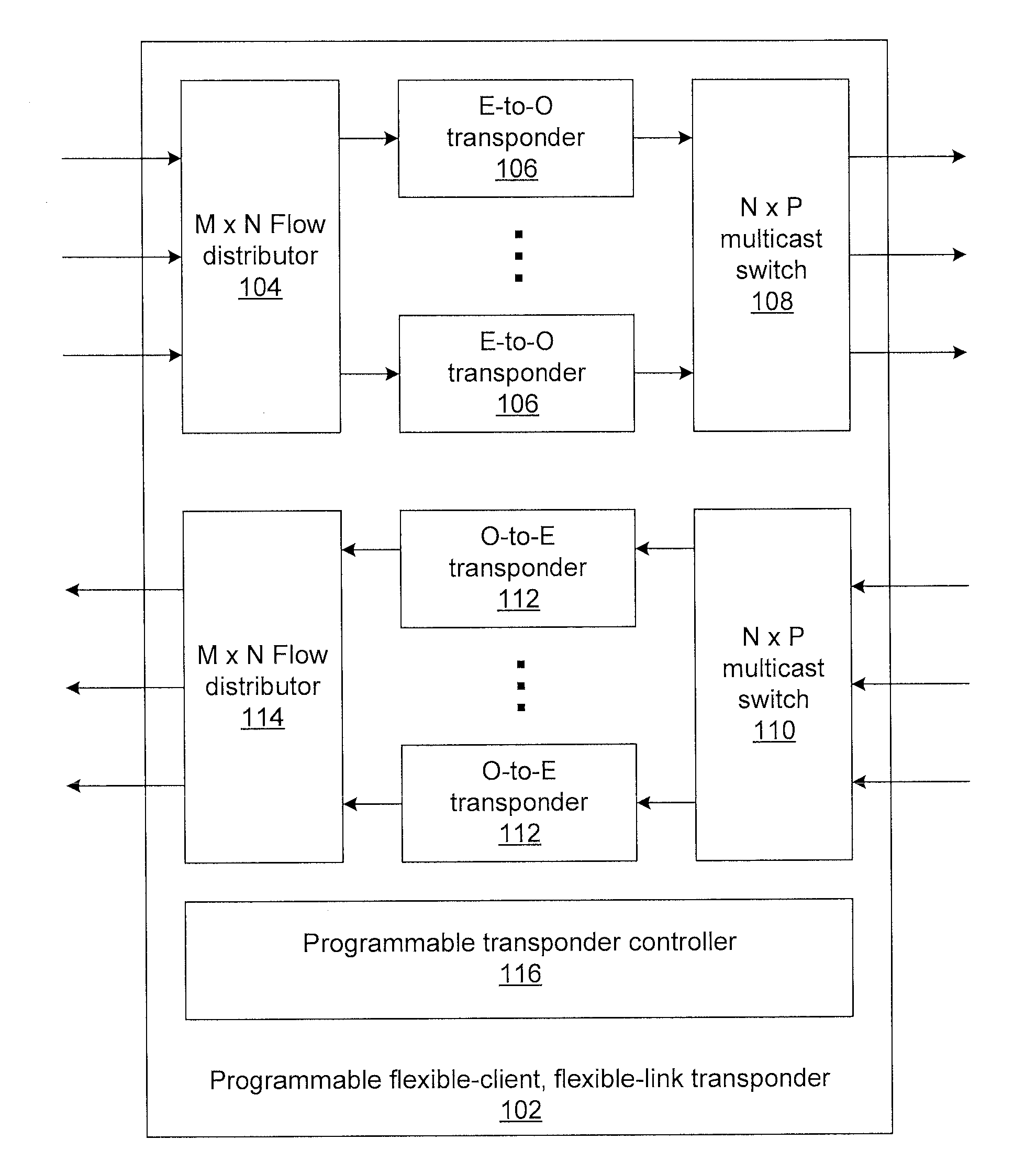
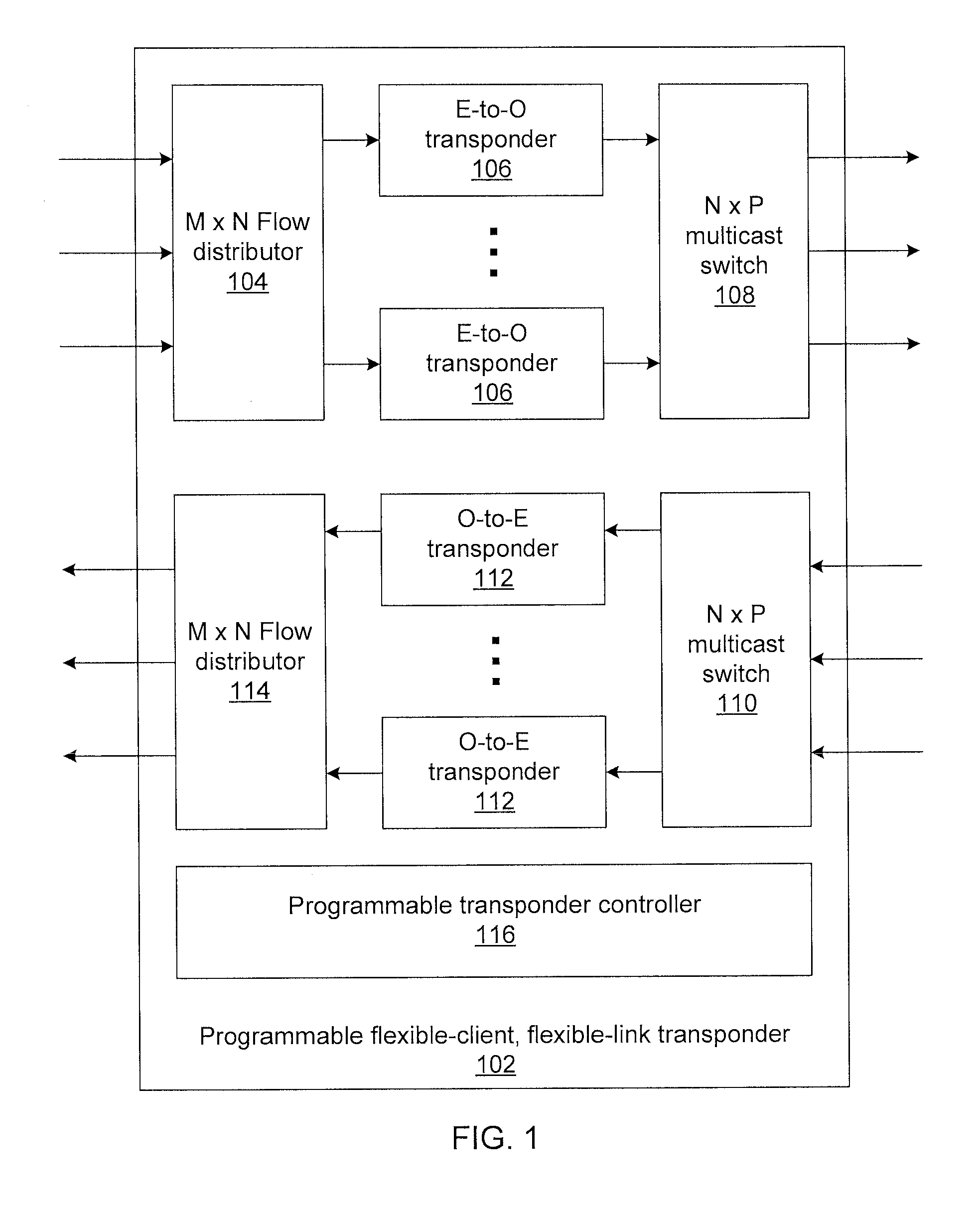
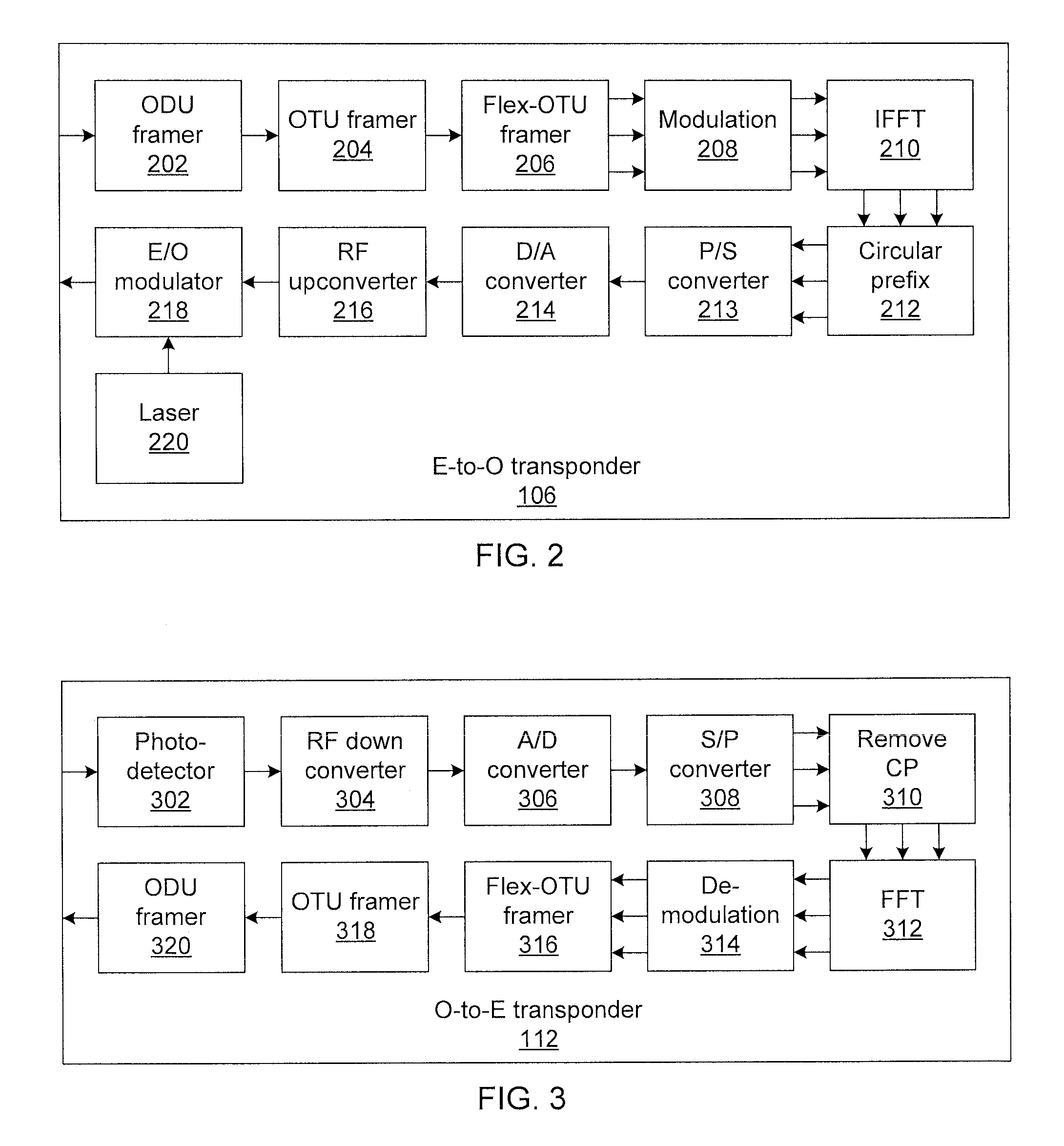
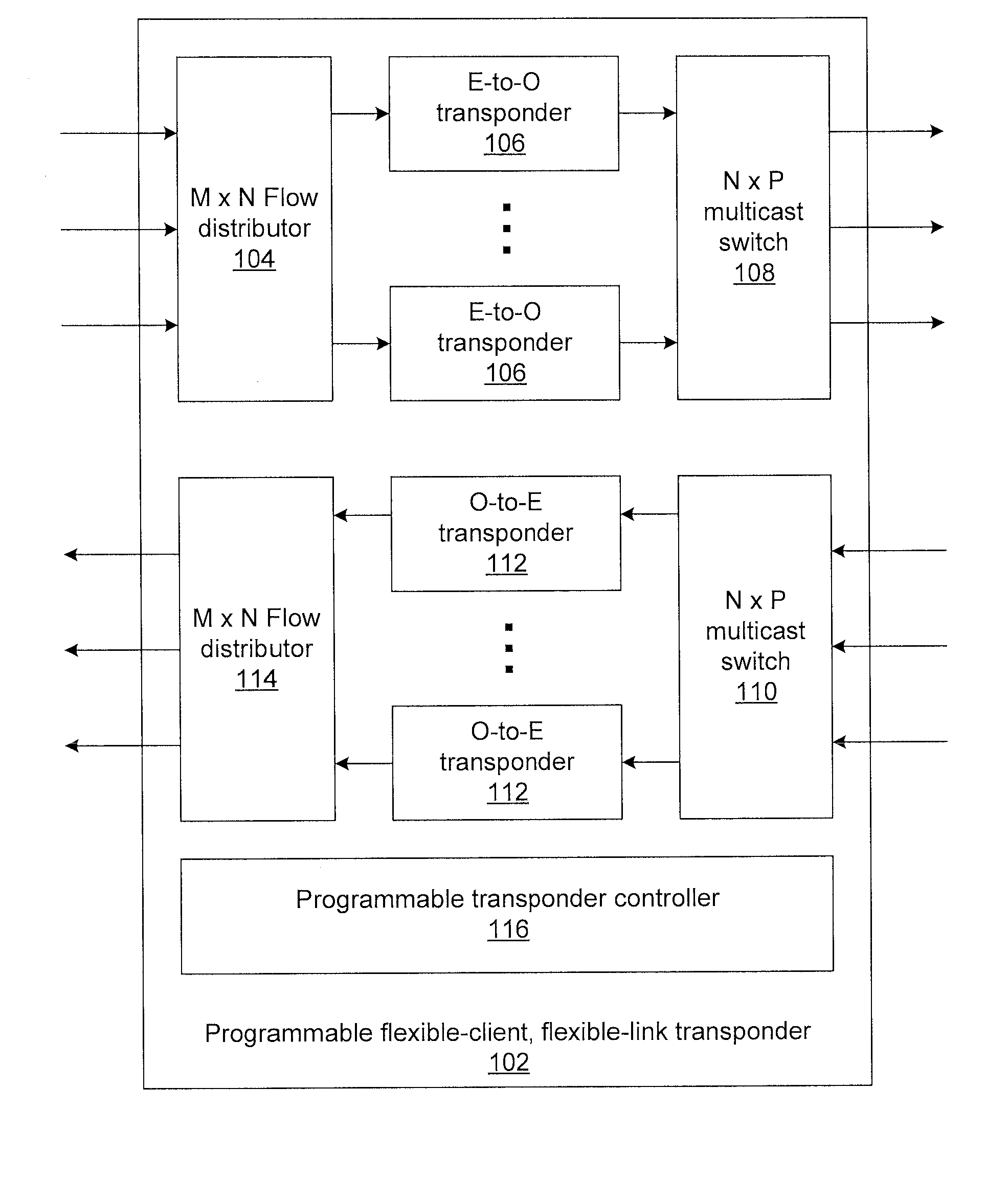
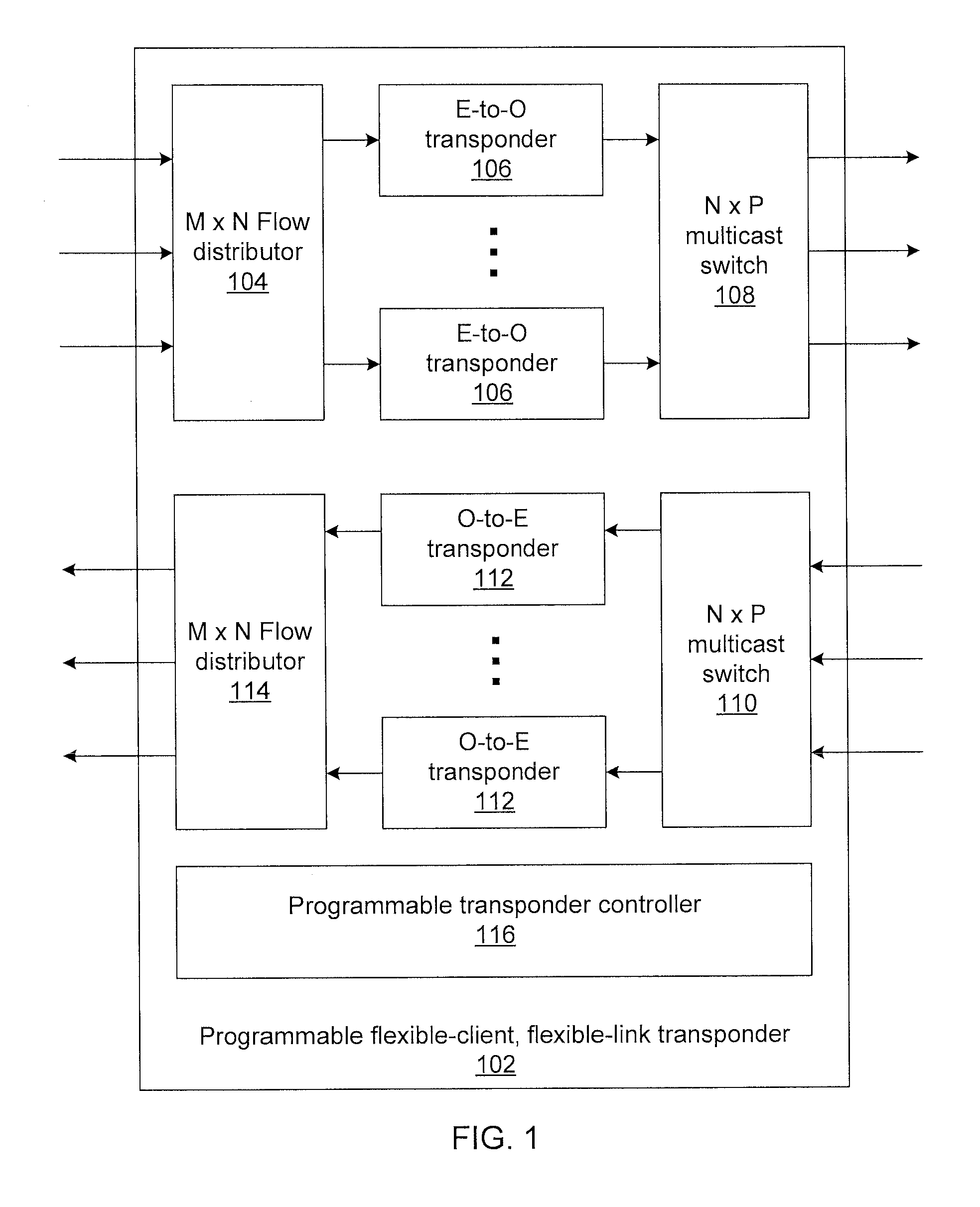
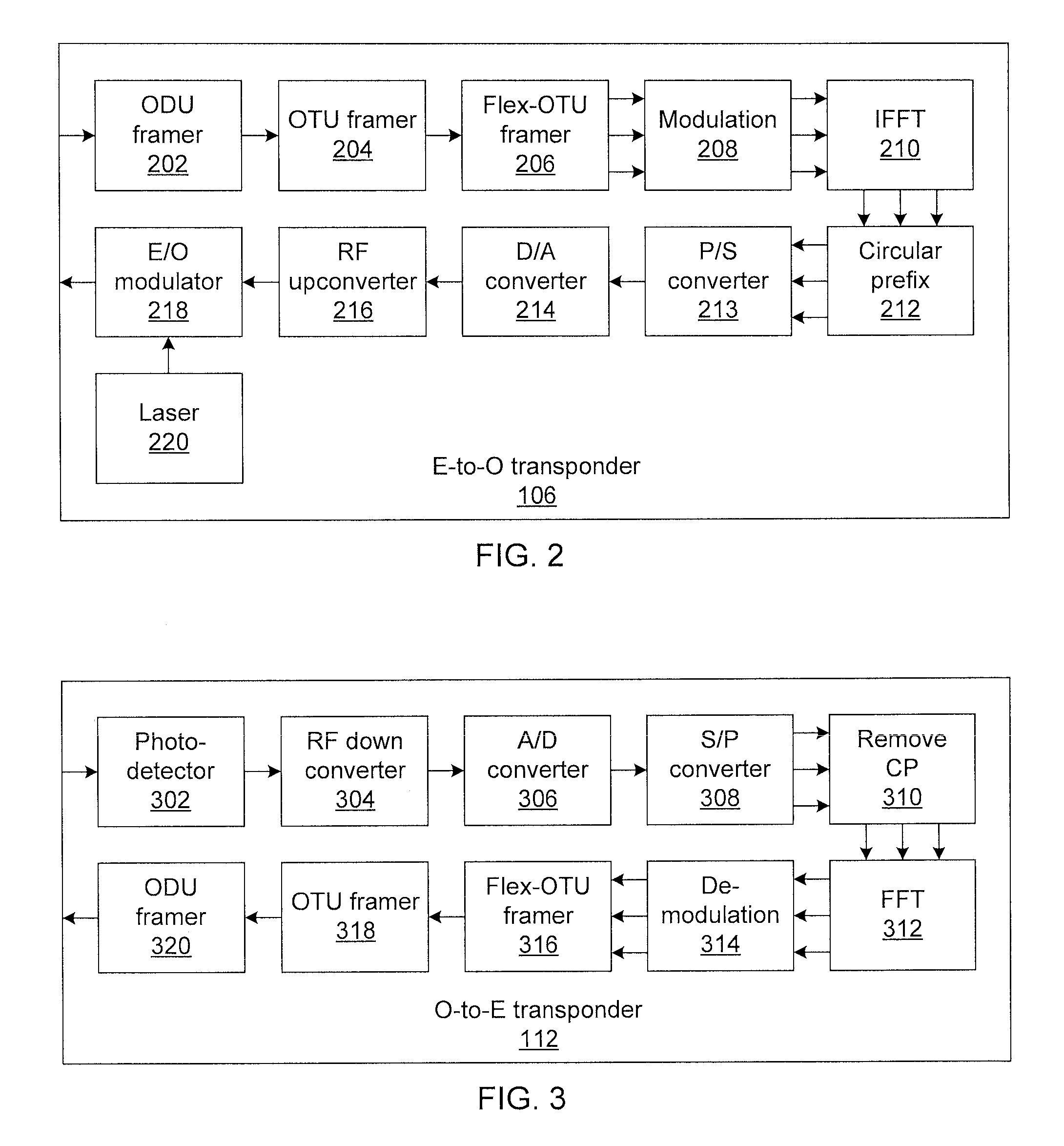
Flexible-client, flexible-line interface transponder
ActiveUS20150181316A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexMultiplexingPhotodetector
Methods and systems for flexible-client, flexible-link optical transponders include electrical-to-optical transponders, which accept client data from a flow distributor, and a first multiplexing switch that connects modulated optical carriers from the transponders to line interfaces. The electrical-to-optical transponders each include a flexible optical transport unit (OTU) framer module that compresses multiple optical data units (ODUs) into a single ODU having a higher order than any of the input ODUs to form an optical transport network (OTN) frame. An electrical-to-optical modulator modulates OTN frames onto a carrier. The transponder includes a second multiplexing switch that accepts optical carriers from line interfaces and optical-to-electrical transponders that accept modulated optical carriers from the second multiplexing switch. Each optical-to-electrical transponder includes a photodetector to convert the modulated optical carriers to the electrical domain and a flexible OTU framer module that decompresses received ODUs in OTN frames into multiple ODUs to form a bit stream.
Owner:NEC CORP
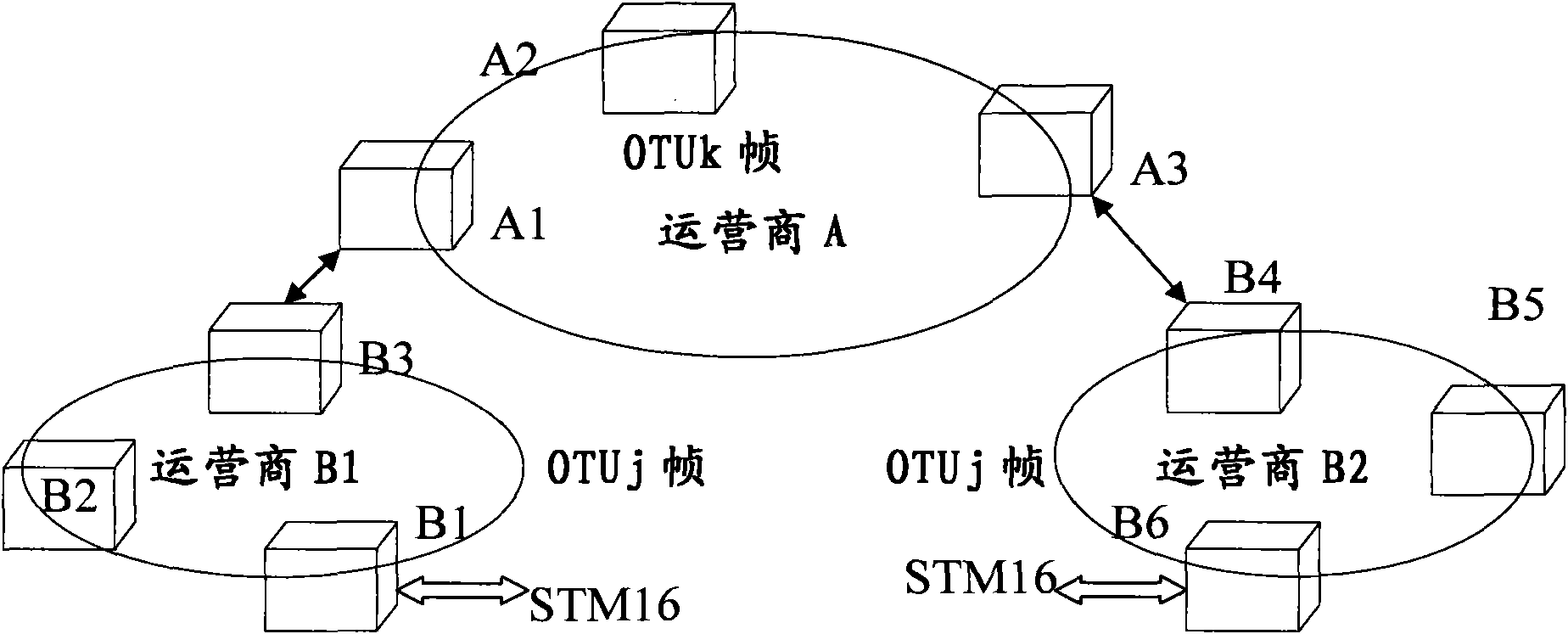
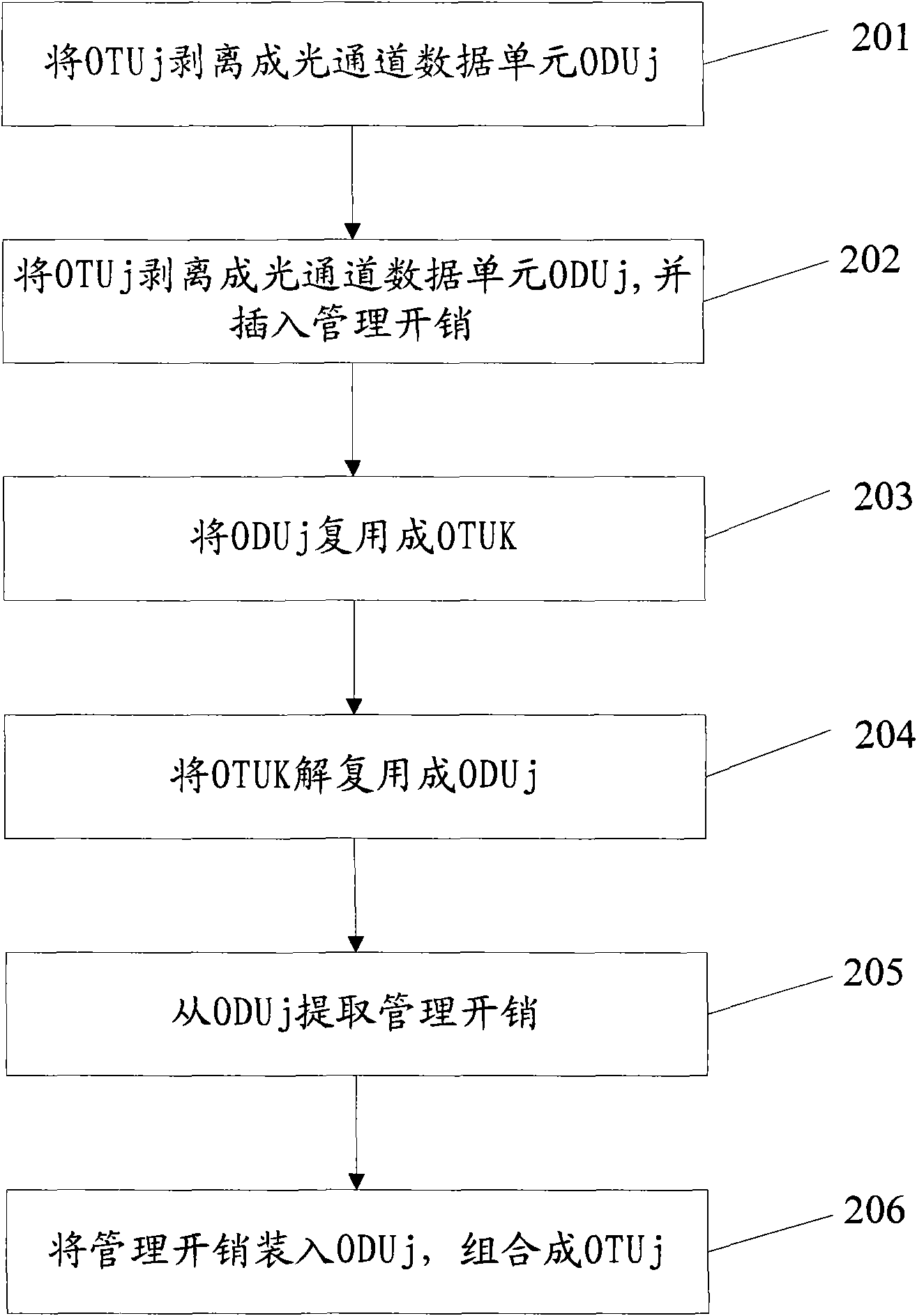
Method, device and network system for transporting optical transport unit (OTU) by optical transport network (OTN)
InactiveCN101686416AConvenient and accurate transmissionAddressing quality degradationMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionOptical data transmissionNetworked system
The invention discloses a method, a device and a network system for transporting an optical transport unit (OTU) by an optical transport network (OTN), relating to the network field and solving the problems of slide code channel quality degradation, and the like caused by different overload rates of optical data transmission frames in the prior art. The method provided by the technical scheme comprises the following steps: at a source node, mapping a received OTUj and data to be sent by a local OTN into an OTUk of the local OTN for transmission; and at a host node, de-mapping and transformingthe OTUk into the OTUj and extracting the carried data, wherein j and k respectively represent the rate grades of the OTU. The invention can be applied to transporting information among networks.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
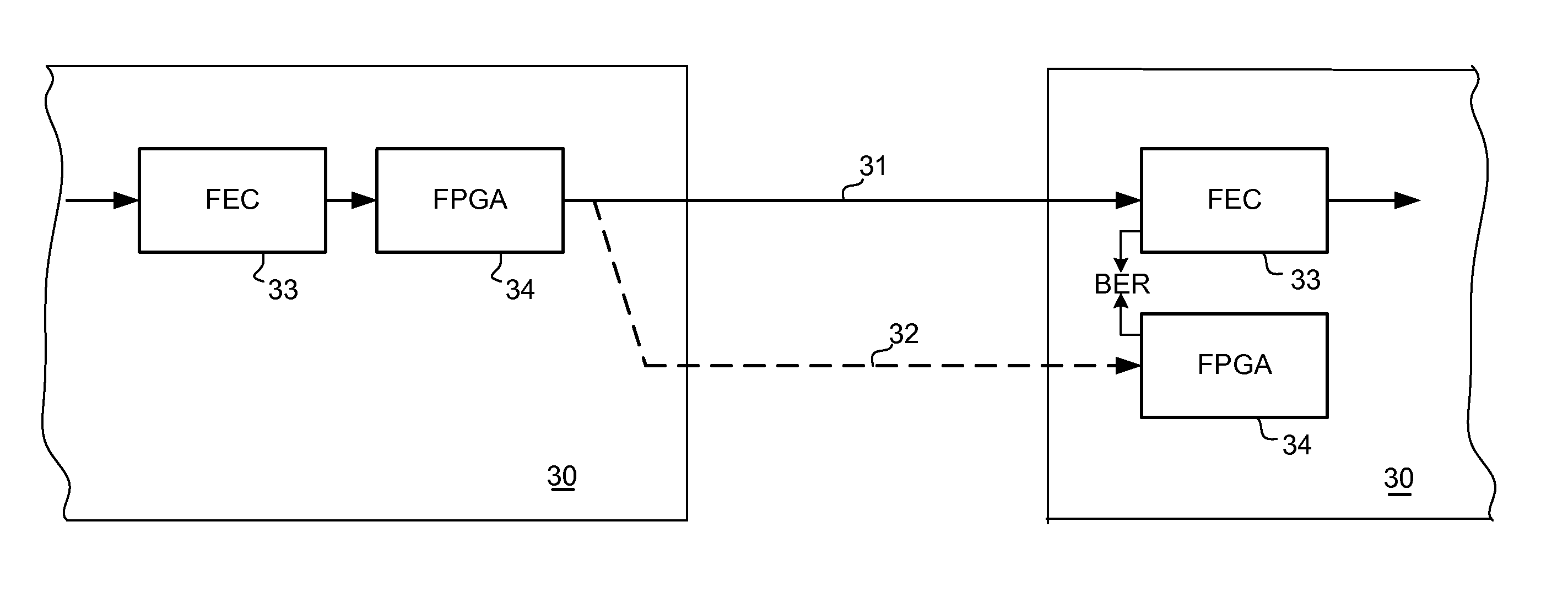
Efficient and simple bit error rate calculation on optical transport layer
Transport network interfaces operate to transport for Optical Transport Unit frames over an Optical Transport Network. Besides FEC bits for the Optical Transport Unit frames, the transmitting transport network interface provides sequences of error-determining bits for the Optical Transport Unit frames sent on working and protection communications channels. There is at least one sequence for each Optical Transport Unit frame, the number of bits in the at least one sequence much smaller than the number of bits in the Optical Transport Unit frame. The receiving transport network interface determines the bit error rates for the working and protection channels from the sequences of error-determining bits without decoding said Forward Error Correction bits and can select the working and protection channels accordingly.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Byte-interleaving systems and methods for 100G optical transport enabling multi-level optical transmission
ActiveUS8045863B2Time-division multiplexElectromagnetic transmittersMultiplexingForward error correction
Owner:CIENA
Video endoscope
InactiveUS20150065800A1Minimal installationImprove data transfer rateSurgeryEndoscopesOptical transport unitEndoscope
A video endoscope including: an elongated housing; an image sensor unit arranged in the elongated housing; an optical transmitting unit arranged in the elongated housing and connected to the image sensor unit; and a through contact device, wherein the optical transmitting unit is arranged at a proximal end of the elongated housing on the through-contact device, the through-contact device penetrates through a wall of the elongated housing and the through-contact device is arranged such that it is mounted in a hermetically sealed manner in the wall of the elongated housing.
Owner:OLYMPUS WINTER & IBE
Frame-interleaving systems and methods for 100G optical transport enabling multi-level optical transmission
The present invention provides frame-interleaving systems and methods for Optical Transport Unit K (OTUK) (i.e. Optical Transport Unit 4 (OTU4)), 100 Gb / s Ethernet (100 GbE), and other 100 Gb / s (100 G) optical transport enabling multi-level optical transmission. The frame-interleaving systems and methods of the present invention support the multiplexing of sub-rate clients, such as 10×10 Gb / s (10 G) clients, 2×40 Gb / s (40 G) plus 2×10 G clients, etc., into two 50 Gb / s (50 G) transport signals, four 25 Gb / s (25 G) transport signals, etc. that are forward error correction (FEC) encoded and carried on a single wavelength to provide useful, efficient, and cost-effective 100 G optical transport solutions today. In one exemplary configuration, a 100 G client signal or 100 G aggregate client signal carried over two or more channels is frame-deinterleaved, followed by even / odd sub-channel FEC encoding and framing. In another exemplary configuration, a 100 G client signal or 100 G aggregate client signal carried over two or more channels is received and processed by a single 100 G FEC framer, followed by frame-deinterleaving into two or more sub-rate channels.
Owner:CIENA
Optical sensing device for restraining voltage sensor temperature error
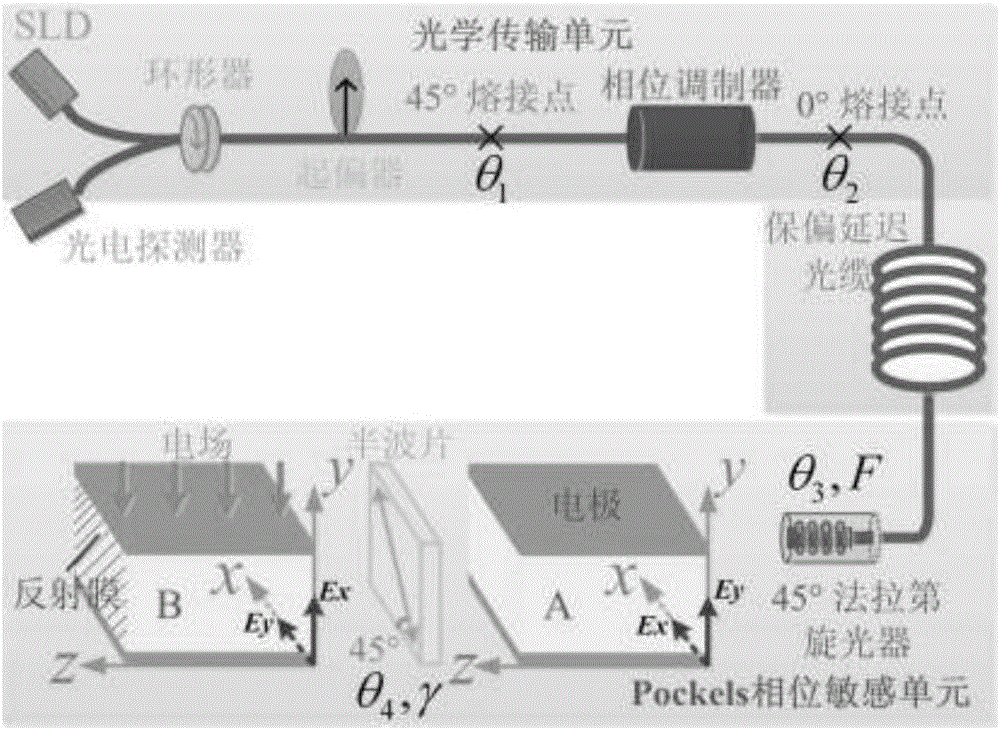
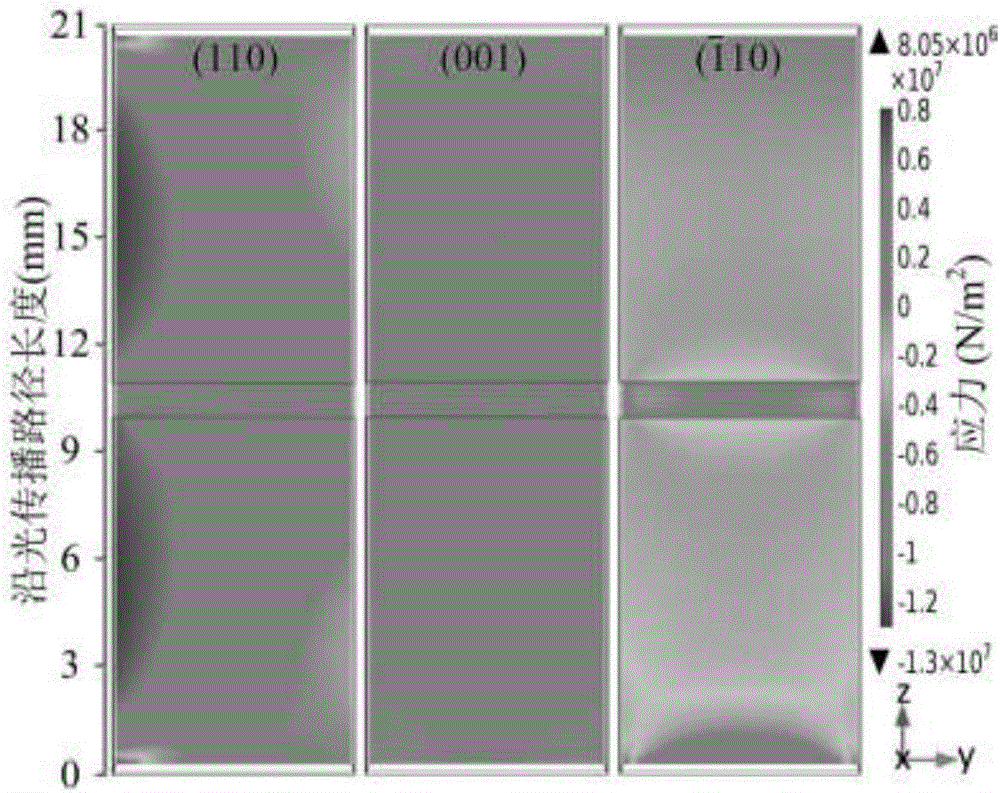
ActiveCN105911324AImprove temperature stabilityReduce stress distributionVoltage/current isolationSpecial purpose recording/indication apparatusOptical sensingOptical transport unit
The invention discloses an optical sensing device for restraining a voltage sensor temperature error and belongs to the field of an optical voltage sensor. The optical sensing device comprises an optical transmission unit and a Pockels phase sensing unit. The reciprocity degeneration of the Pockels phase sensing unit is caused by the inconsistency of the temperature fields and stress fields of two crystals; and the generation of a measuring error of the optical voltage sensor is caused by the influence of the non-ideal welding angle and counter shaft angle of the optical transmission unit on the magnitude of interference light intensity and feedback phase. By establishing a temperature error model of the optical transmission unit and the Pockels phase sensing unit, a novel optical base structure for counteracting additional stress birefringence in the two crystals is designed, and an angle error compensating method is provided, so that the measuring precision and temperature stability of the optical voltage sensor are increased.
Owner:安徽华驰动能科技有限公司
Packet-optical integrated switch without optical transponder
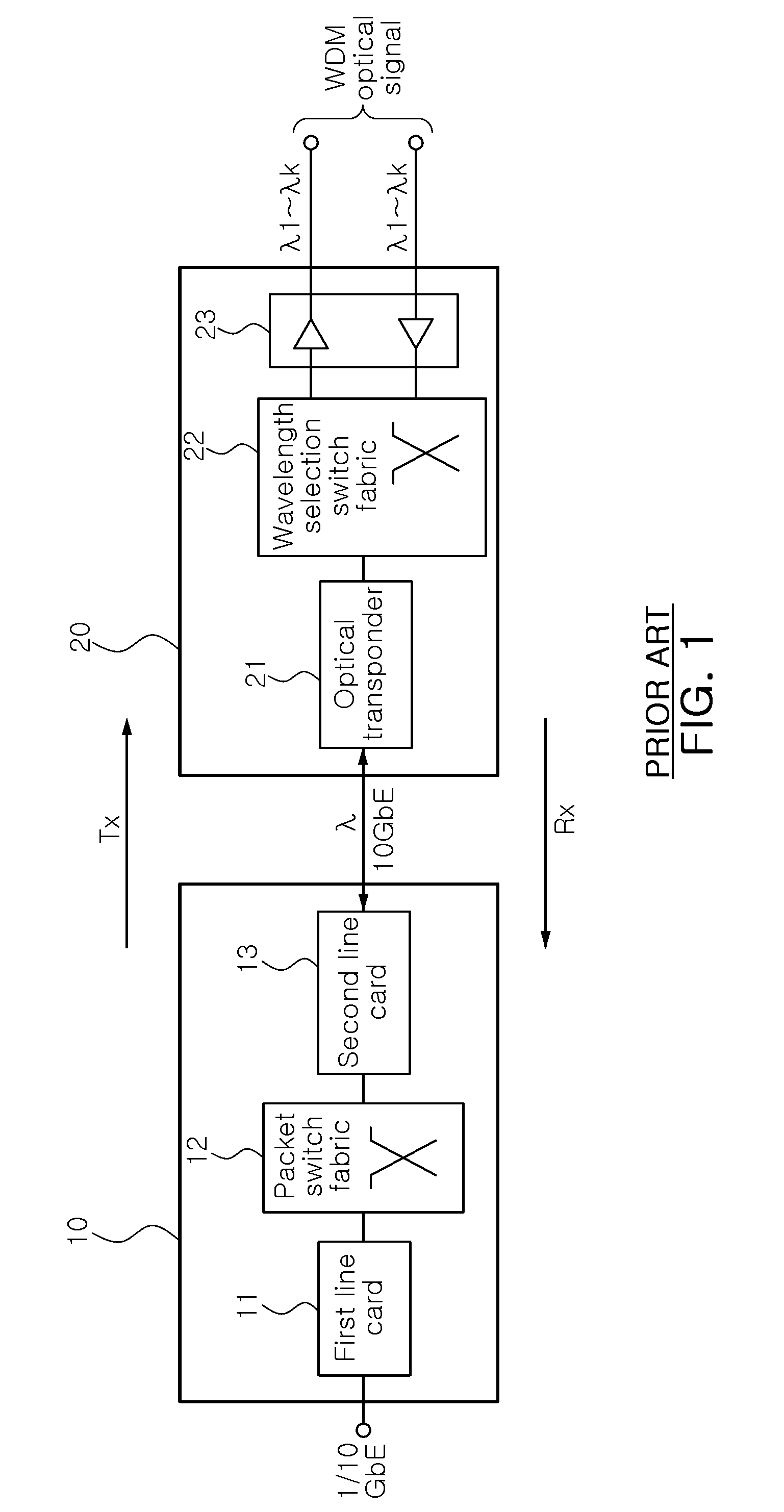
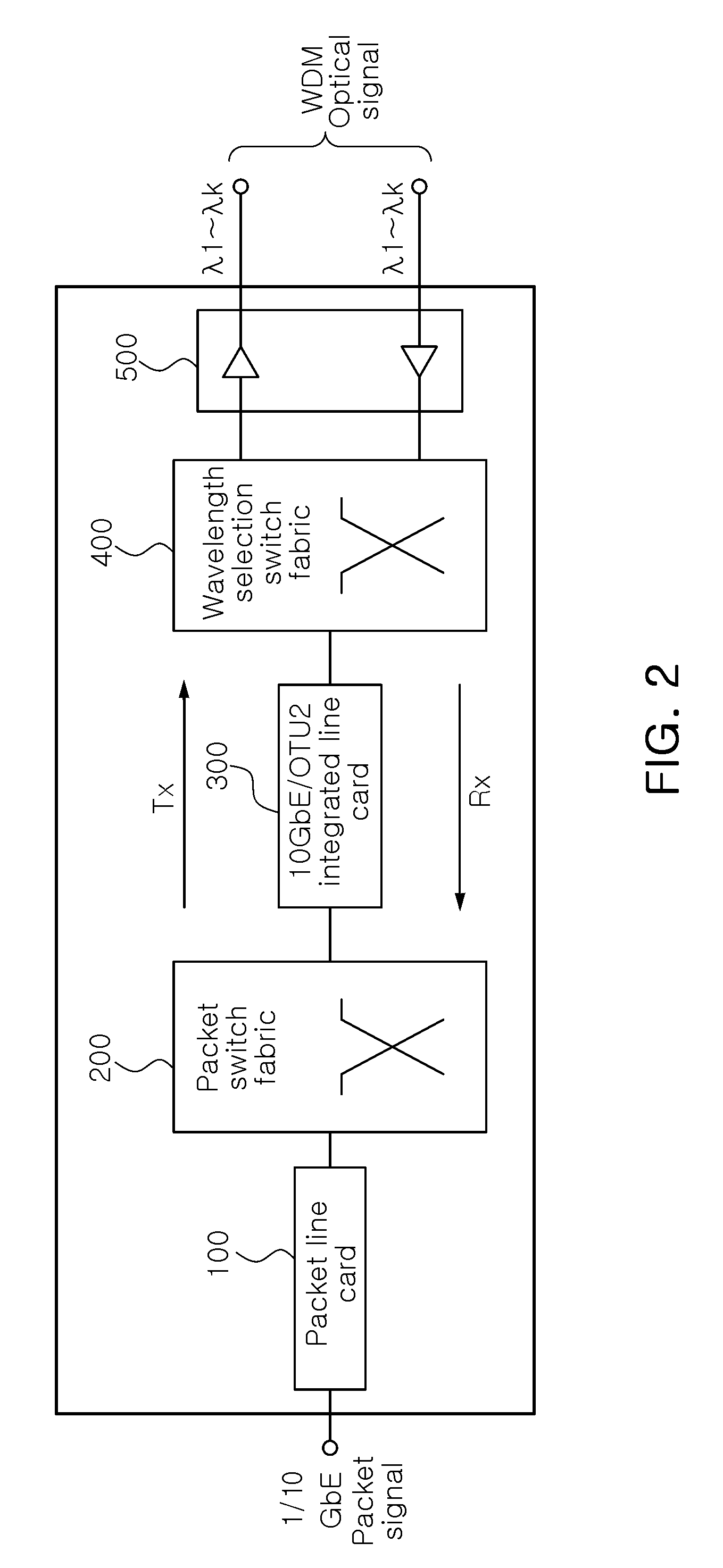
InactiveUS20100135659A1Promote conversionLow production costMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systems10 Gigabit EthernetWavelength selective switching
A packet-optical integrated switch without an optical transponder, includes: a packet line card configured to output an Ethernet packet signal to a pre-set output port; a packet switch fabric configured to transfer the packet signal from the packet line card to the output port previously set in a destination address included in the packet signal; a 10 gigabit Ethernet (10 GbE) / optical transport unit level 2 (OTU2) integrated line card configured to convert the packet signal from the packet switch fabric into an OTU2 optical signal having a pre-set wavelength; and a wavelength selection switch fabric configured to allocate the optical signal from the 10 GbE / OTU2 integrated line card to a pre-set wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) port by pre-set wavelength to exchange the optical signal to each port by wavelength, wherein the packet line card, the packet switch fabric, the 10 GbE / OTU2 integrated line card, and the wavelength selection switch fabric perform the reverse operations of the process, respectively.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Efficient and simple bit error rate calculation on optical transport layer
Transport network interfaces operate to transport for Optical Transport Unit frames over an Optical Transport Network. Besides FEC bits for the Optical Transport Unit frames, the transmitting transport network interface provides sequences of error-determining bits for the Optical Transport Unit frames sent on working and protection communications channels. There is at least one sequence for each Optical Transport Unit frame, the number of bits in the at least one sequence much smaller than the number of bits in the Optical Transport Unit frame. The receiving transport network interface determines the bit error rates for the working and protection channels from the sequences of error-determining bits without decoding said Forward Error Correction bits and can select the working and protection channels accordingly.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
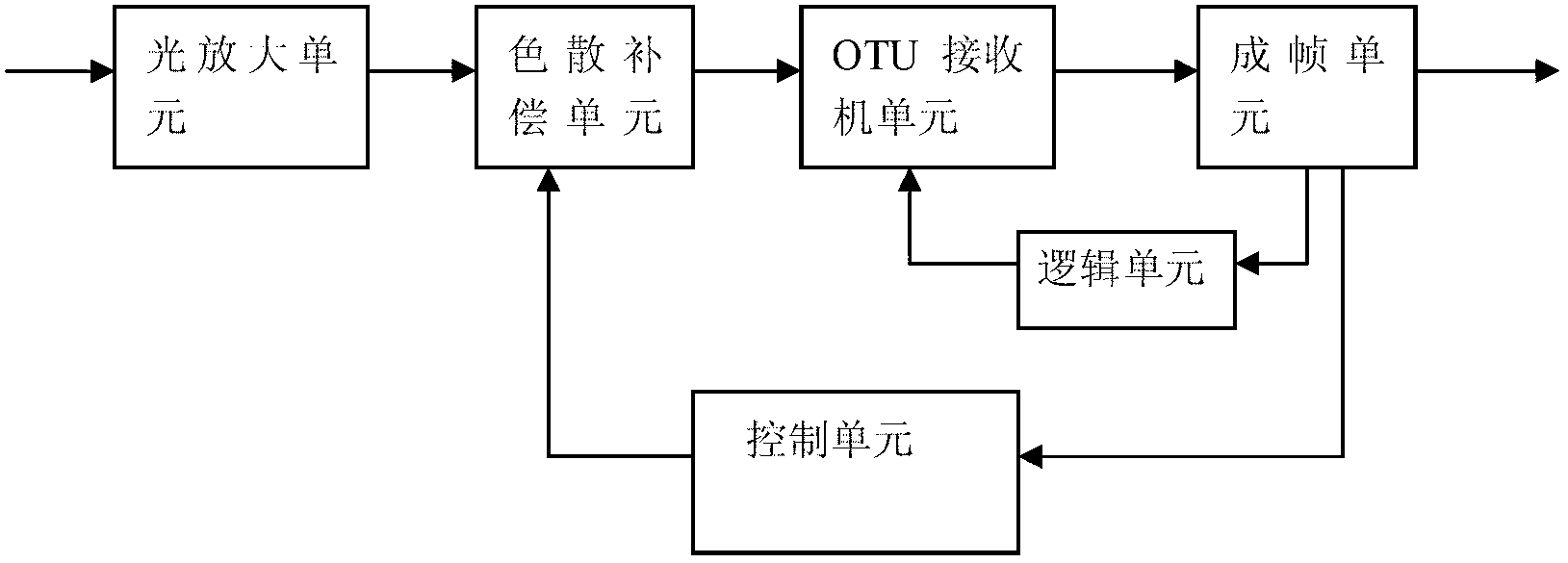
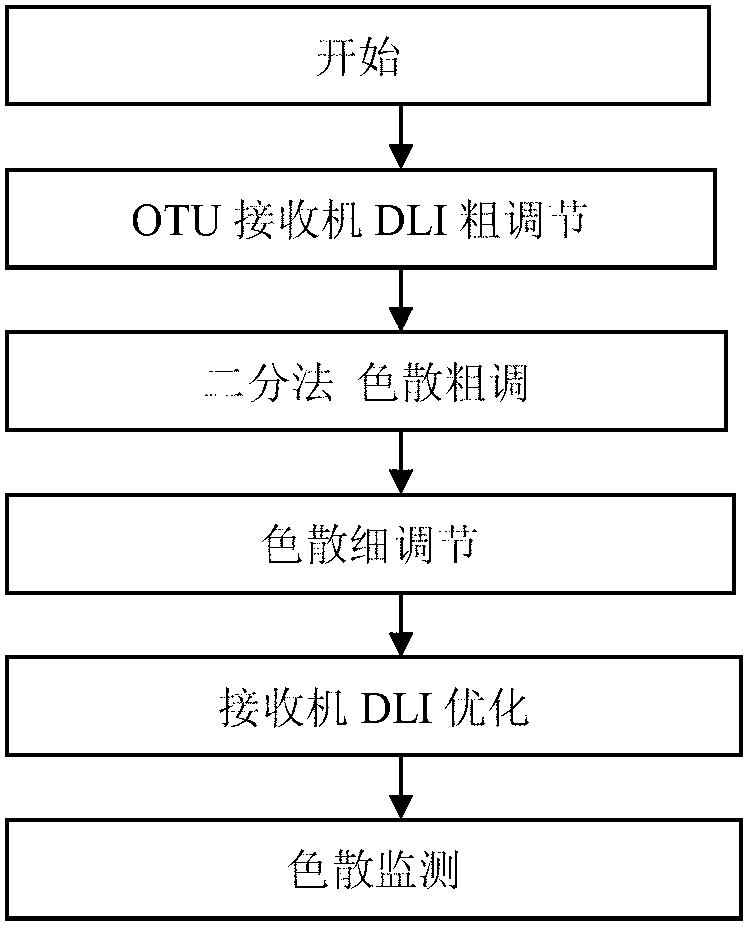
Fast self-adaptive dispersion compensation method in 40Gbps DWDM (dense wavelength division multiplexing) system
ActiveCN103188017AShorten the timeImprove efficiencyElectromagnetic transmissionLocal optimumEngineering
The invention relates to a fast self-adaptive dispersion compensation method in a 40Gbps DWDM (dense wavelength division multiplexing) system. The fast self-adaptive dispersion compensation method specifically comprises the following steps: step A) delaying coarse regulation of an interferometer DLI (delay line interferometer) by an OTU (optical transport unit) receiver; step B) performing dispersion coarse regulation through a dichotomic method; step C) performing fine regulation through a TDC (time-to-digital converter); step D): optimizing the DLI through the receiver; and step E) monitoring through the TDC, judging whether dispersion changes or not by FEC (forward error control) error correction counting or warning and entering step B) or C) if the dispersion changes. According to the method disclosed by the invention, a coarse regulation point is fast found by using the dichotomic method, the optimal dispersion is found by adopting a mid-point method after entering the fine regulation step, the dispersion compensation time is effectively reduced, the efficiency is improved, and the defects of local optimization can be simultaneously avoided.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD
Systems and methods for compensating coherent optics delay asymmetry in a packet optical network
ActiveUS10594395B2Reduce delay asymmetryMultiplex system selection arrangementsSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansModem deviceHemt circuits
Systems and methods of compensating for the delay asymmetry of coherent optical modems in a packet optical network include measuring fill levels of one or more queues each including an elastic First-In-First-Out (FIFO) circuit used in a transport mapping scheme, wherein the transport mapping scheme is one or more of client mapping to Optical Transport Unit (OTU) and OTU mapping to Flexible OTN (FlexO); and performing adjustments in a clock based in part on the measured fill levels, wherein the adjustments are configured to reduce a Time Error (TE) in the packet network based on delay asymmetry between two nodes.
Owner:CIENA
Method for measuring oscillation frequency and oscillation frequency measuring device
InactiveCN101526393AGood effectRealize online detectionSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansFiberFrequency measurements
The invention provides a method for measuring oscillation frequency and the technical proposal of an oscillation frequency measuring device. The method comprises: the change of scattered light is transmitted to a photomuitplier specially used for photon counting through optical fiber when objects vibrate, the photomuitplier transforms optical signals into electrical signals, and then the electrical signals are transmitted to a photoelectric pulse counter; data output by the photoelectric pulse counter is transmitted to a data processing computer, and the data processing computer utilizes a photon correlation method to process the data; after that, the data is transformed by Fourier, so that power spectrum image and data of oscillation frequency distribution can be obtained. The device is provided with an optical probing unit, an optical transport unit and a data processing unit, wherein, the optical probing unit is connected with the optical transport unit which is connected with the data processing unit, the data processing unit is provided with a photomuitplier module that is electrically connected with an photoelectric pulse counting module, and the photoelectric pulse counting module is electrically connected with the data processing computer; the optical transport unit is optical fiber; the optical probing unit is an optical probing head which is a light input end of the optical fiber.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Flexible-client, flexible-line interface transponder
ActiveUS9414135B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexMultiplexingPhotovoltaic detectors
Methods and systems for flexible-client, flexible-link optical transponders include electrical-to-optical transponders, which accept client data from a flow distributor, and a first multiplexing switch that connects modulated optical carriers from the transponders to line interfaces. The electrical-to-optical transponders each include a flexible optical transport unit (OTU) framer module that compresses multiple optical data units (ODUs) into a single ODU having a higher order than any of the input ODUs to form an optical transport network (OTN) frame. An electrical-to-optical modulator modulates OTN frames onto a carrier. The transponder includes a second multiplexing switch that accepts optical carriers from line interfaces and optical-to-electrical transponders that accept modulated optical carriers from the second multiplexing switch. Each optical-to-electrical transponder includes a photodetector to convert the modulated optical carriers to the electrical domain and a flexible OTU framer module that decompresses received ODUs in OTN frames into multiple ODUs to form a bit stream.
Owner:NEC CORP
Optical signal transmission method and related device
PendingCN113099323AMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionComputer hardwareHigh bandwidth
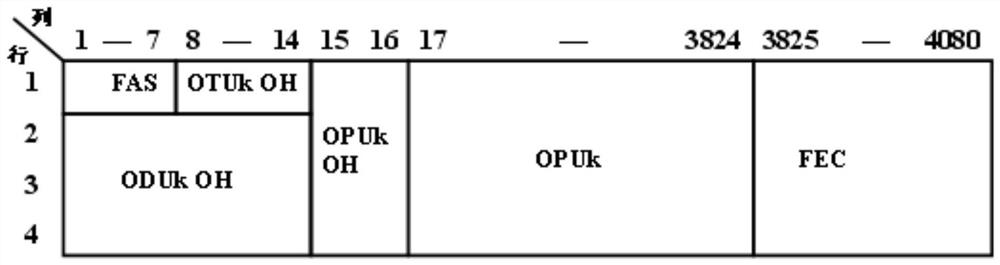
The embodiment of the invention provides an optical signal transmission method and a related device. An optical signal transmission method may include mapping a first optical data unit frame to a first flexible branch unit frame, the first flexible branch unit frame including a plurality of payload blocks; mapping the first flexible branch unit frame to a first optical payload unit frame, wherein a plurality of payload blocks included in the first flexible branch unit frame are distributed in a payload area of the first optical payload unit frame; mapping the first optical payload unit frame to a second optical data unit frame, the bit rate of the second optical data unit frame being greater than the bit rate of the first optical data unit frame; mapping the second optical data unit frame to a first optical transport unit frame; and transmitting the first optical transmission unit frame. According to the technical scheme of the embodiment of the invention, the bandwidth utilization rate and the adjustment flexibility of the transmission rate of the customer service are improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for transmitting signals in an optical transport network
InactiveUS20150295840A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsTime-division multiplexEngineeringA domain
An exemplary method and apparatus are provided for a remapping of Optical Data Units of fixed size into lower order Optical Data Units of flexible size. More particularly, a transport signal which has a frame structure referred to as Optical Transport Units may be transmitted through an Optical Transport Network domain. Each Optical Transport Unit contains at least one Optical Data Unit of fixed size with an overhead section and a payload section. An edge network node of the Optical Transport Network domain receives the transport signal and remaps the at least one Optical Data Unit of fixed size into a domain-internal lower order Optical Data Unit of flexible size. Within the Optical Transport Network domain, the remapped domain-internal lower order Optical Data Unit of flexible size is transmitted as payload of a domain-internal higher order Optical Data Unit of fixed size.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
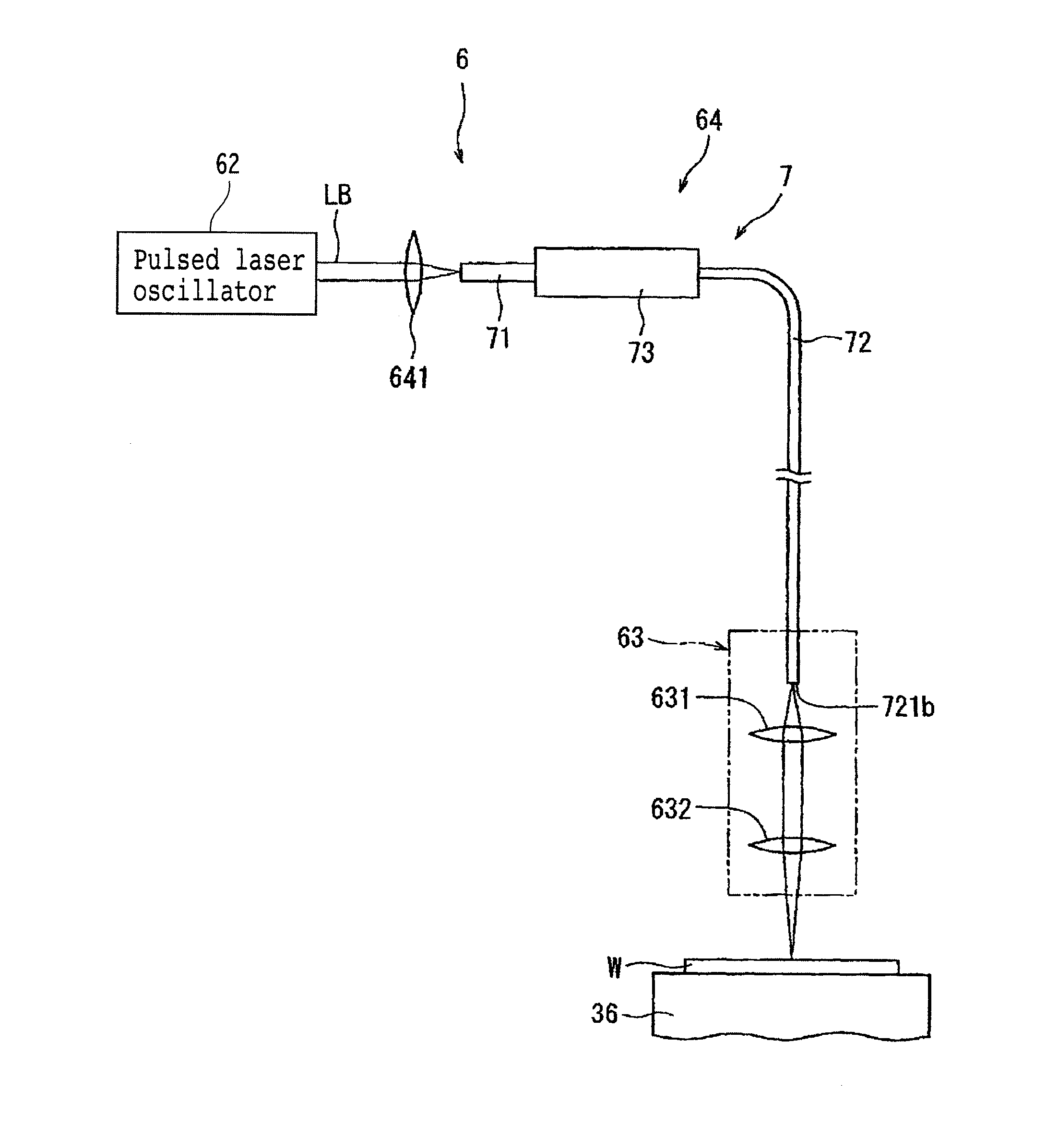
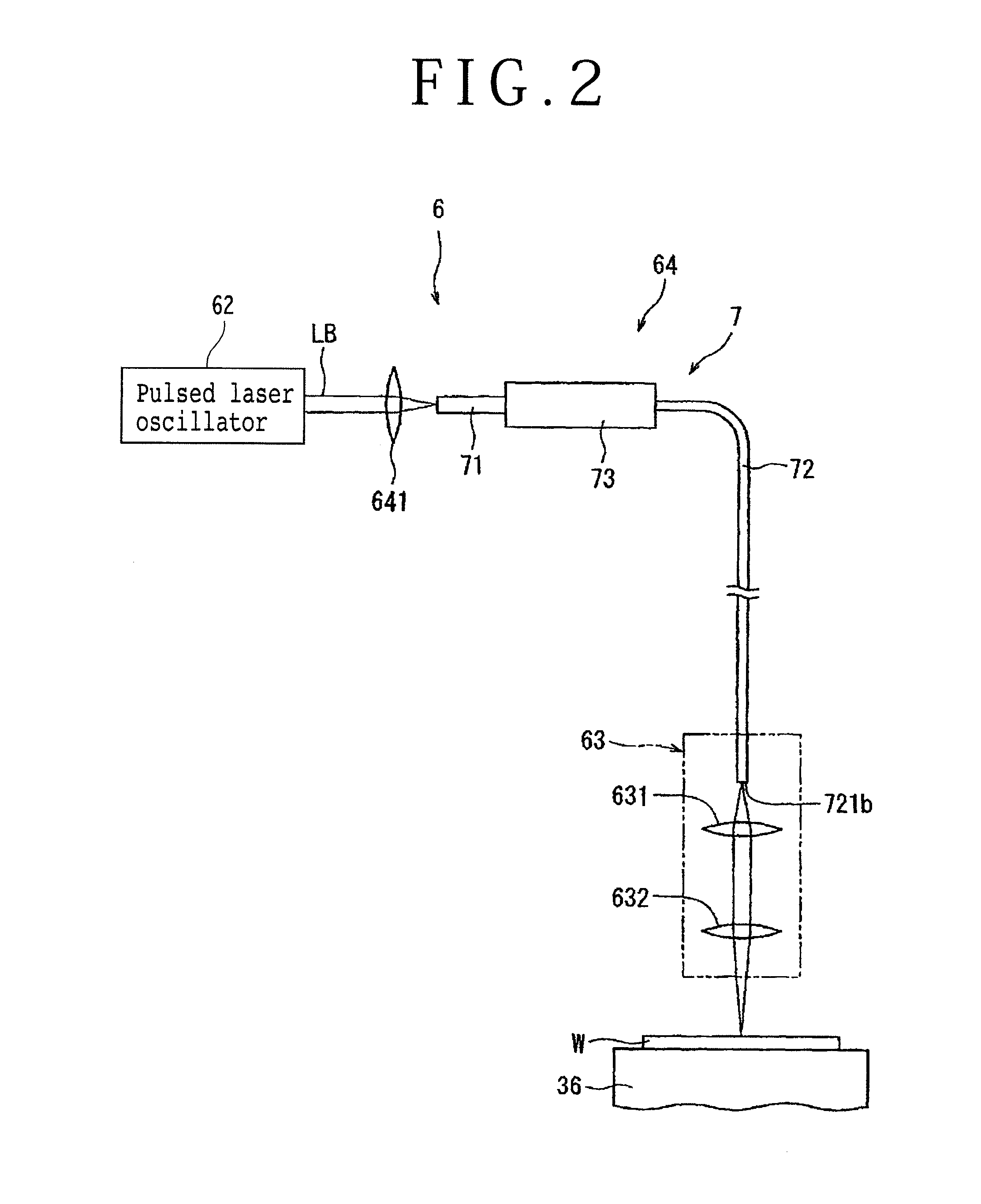
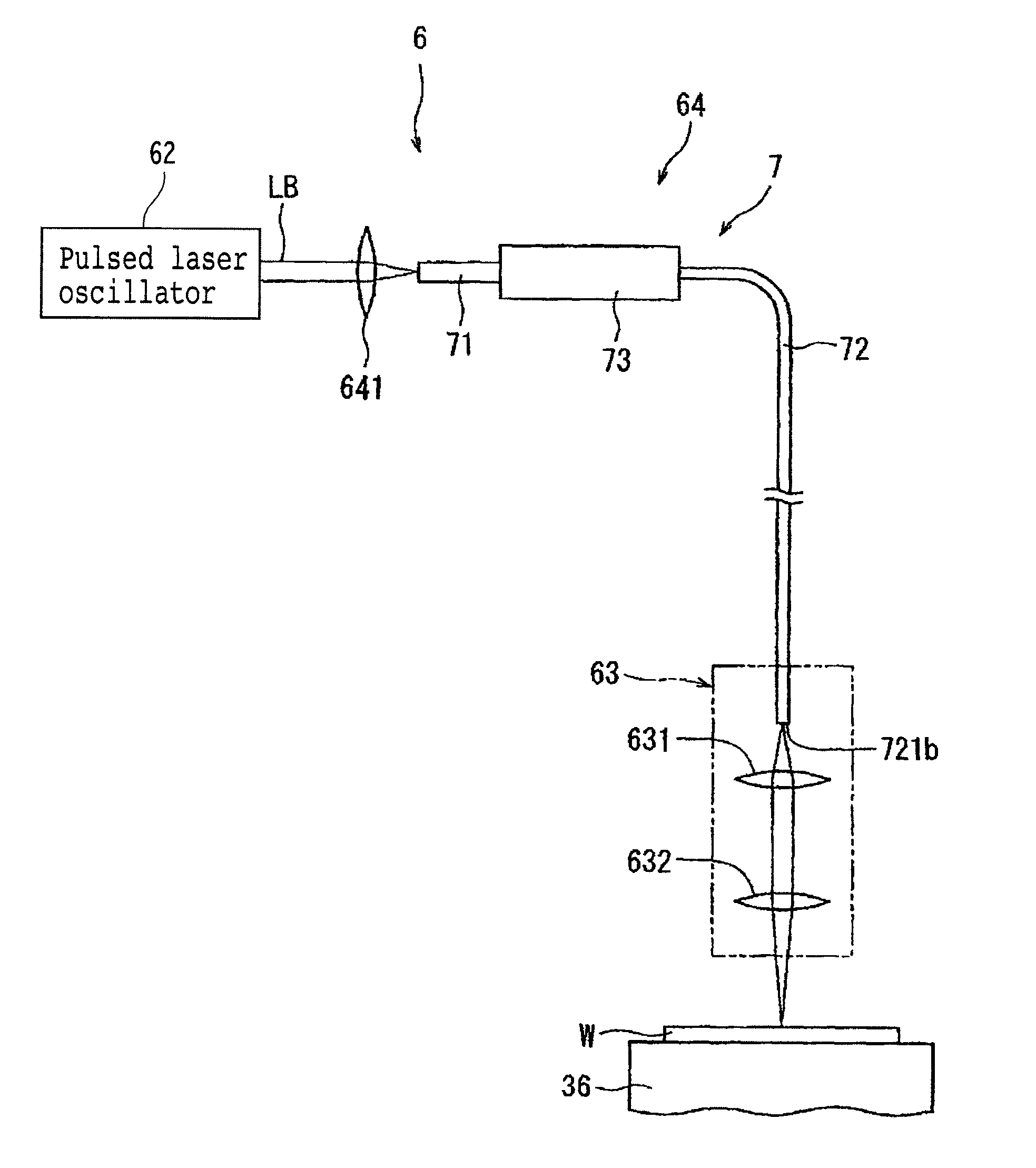
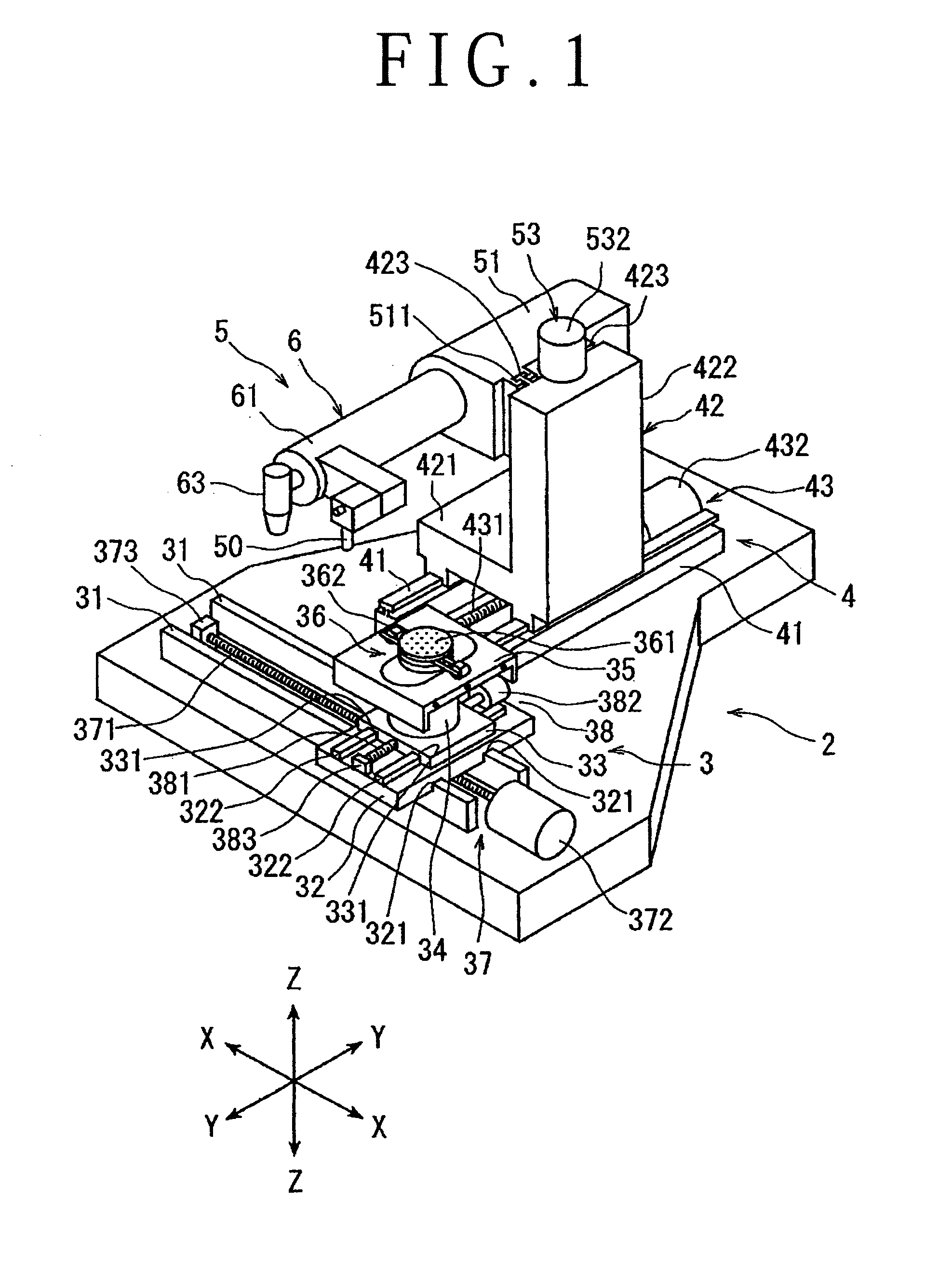
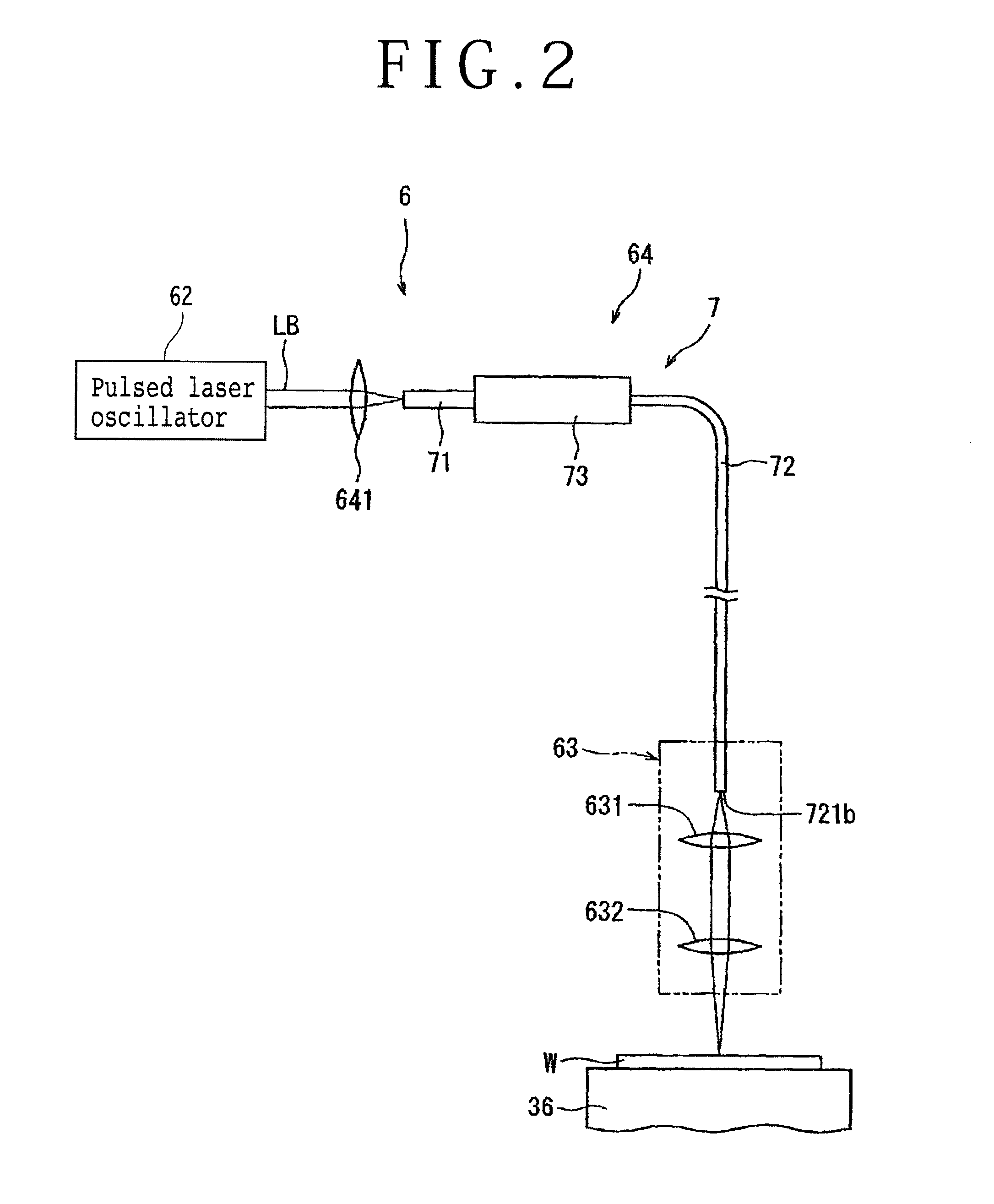
Laser processing apparatus
ActiveUS20140034624A1Reliable settingsMaintenance conditionCoupling light guidesWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser processingOptical transport unit
A laser processing apparatus has an optical transmitting unit for guiding a laser beam to a focusing unit. The optical transmitting unit includes a focusing lens for focusing the laser beam, an optical fiber unit for inputting the focused laser beam and guiding it to the focusing unit. The optical fiber unit includes an LMA fiber for inputting the focused laser beam. The LMA fiber has a large-diameter core covered with a cladding, a transmitting fiber provided by an SM fiber or a PM fiber. The transmitting fiber has a small-diameter core covered with a cladding, the small-diameter core having a diameter corresponding to the wavelength of the laser beam oscillated by the laser oscillator. A connector connects the LMA fiber and the transmitting fiber so that these fibers are axially aligned with each other.
Owner:DISCO CORP
Laser processing apparatus
ActiveUS9289857B2Reliable settingsMaintenance conditionCoupling light guidesWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser processingLength wave
Owner:DISCO CORP
Conductor line, current collector, conductor line system, and method for contactlessly transmitting data
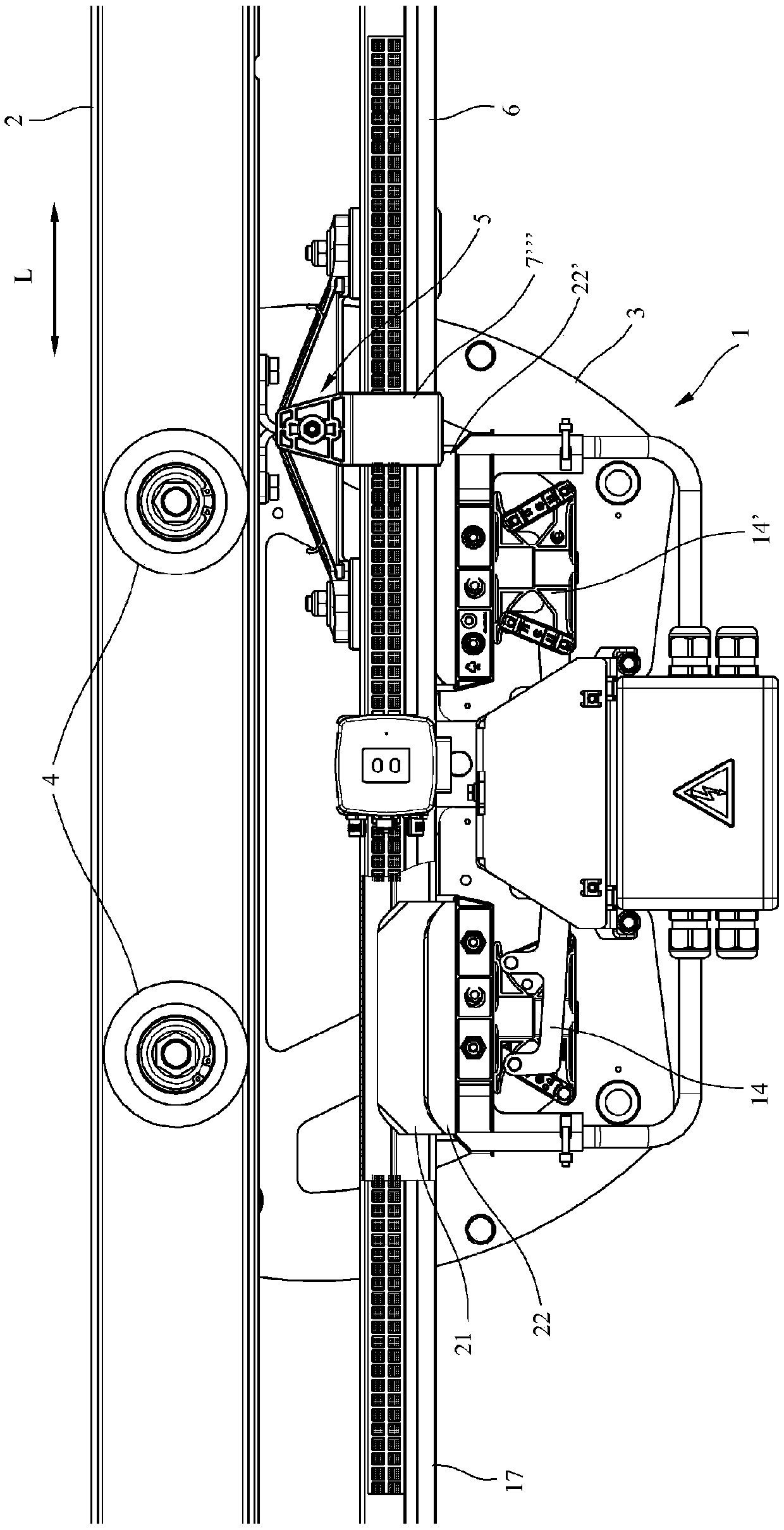
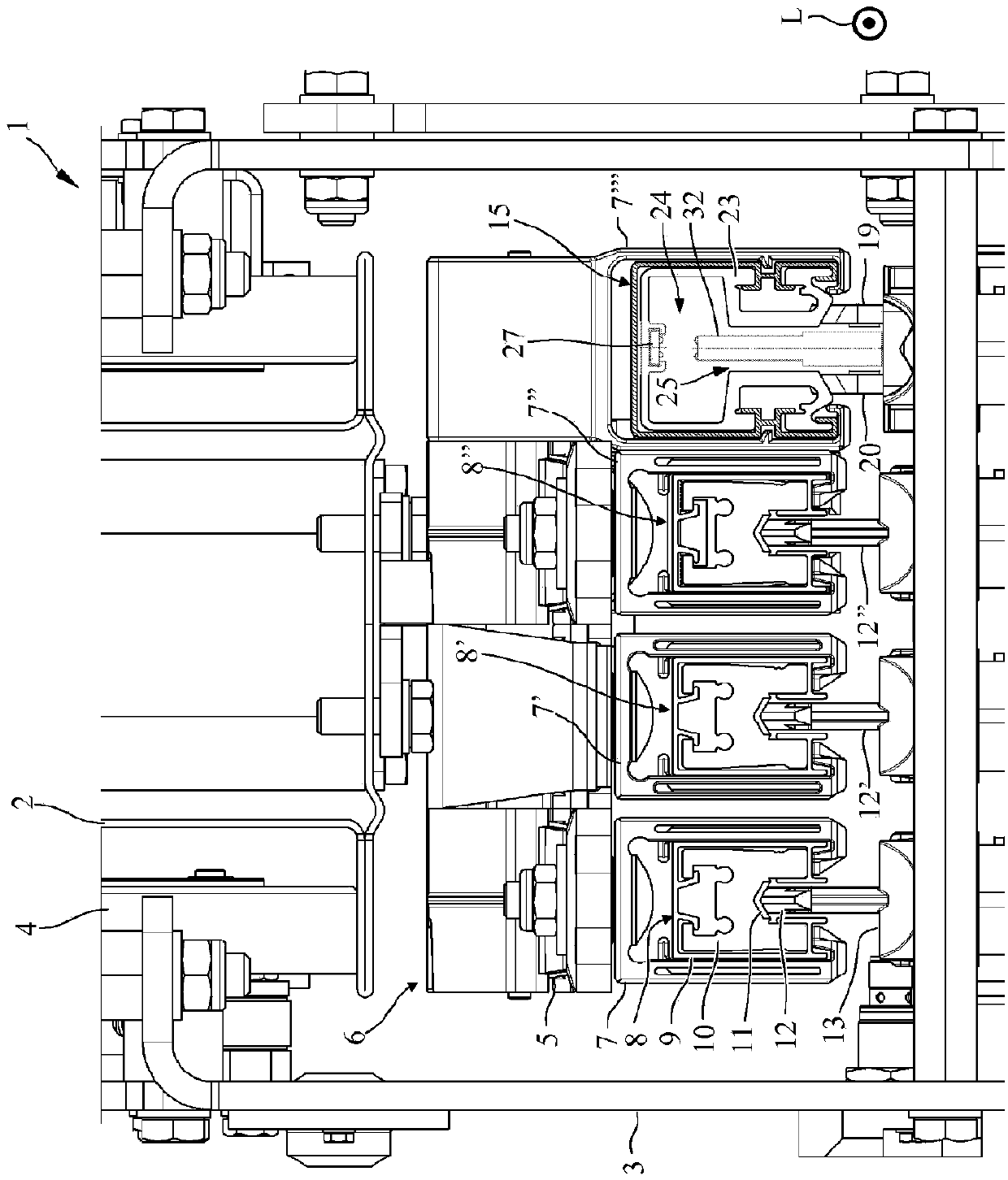
ActiveCN109641529AClose-range type systemsRoute devices for controlling vehiclesElectrical conductorOptical transport unit
The invention relates to a conductor line (6; 35) for supplying electric energy to at least one electric load which can be moved on the conductor line (6; 35) in the longitudinal direction (L) of theconductor line, comprising at least one conductor strand (15) which runs in the longitudinal direction and which comprises an electrically conductive profiled conductor section (10, 16) for contactinga conductor contact (21, 22) of the load, and a current collector (3) for supplying electric energy to the at least one load, wherein the current collector (3) has at least one conductor contact (21,22) for contacting an electrically conductive profiled conductor section (10, 16) of a conductor strand (15) of the conductor line (6; 35). The aim of the invention is to allow a simple, secure, andextremely reliable data transmission which has as little interference as possible or is as interference-free as possible, is insensitive to external influences, and has a high transmission volume. This is achieved in that a first optical transmission unit (27) which runs in the longitudinal direction (L) is arranged on the conductor line (6; 35) for contactlessly transmitting data to a second optical transmission unit (30) which can be moved relative to the conductor line (6; 35), and a second optical transmission unit (30) which can be moved in the longitudinal direction (L) relative to the conductor line (6; 35) is arranged on the current collector (3) for contactlessly transmitting data to a first optical transmission unit (27) arranged on the conductor line (6; 35).
Owner:CONDUCTIX WAMPFLER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com