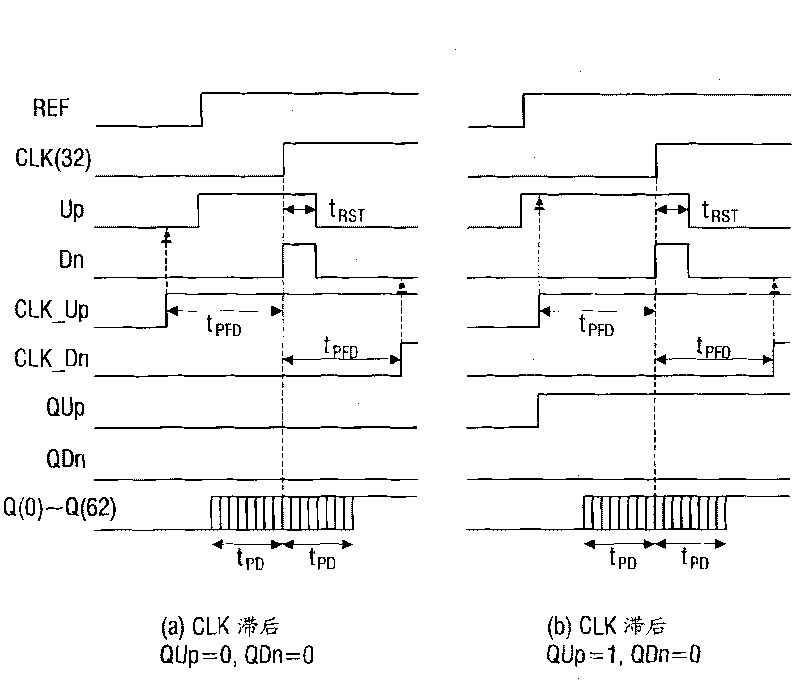
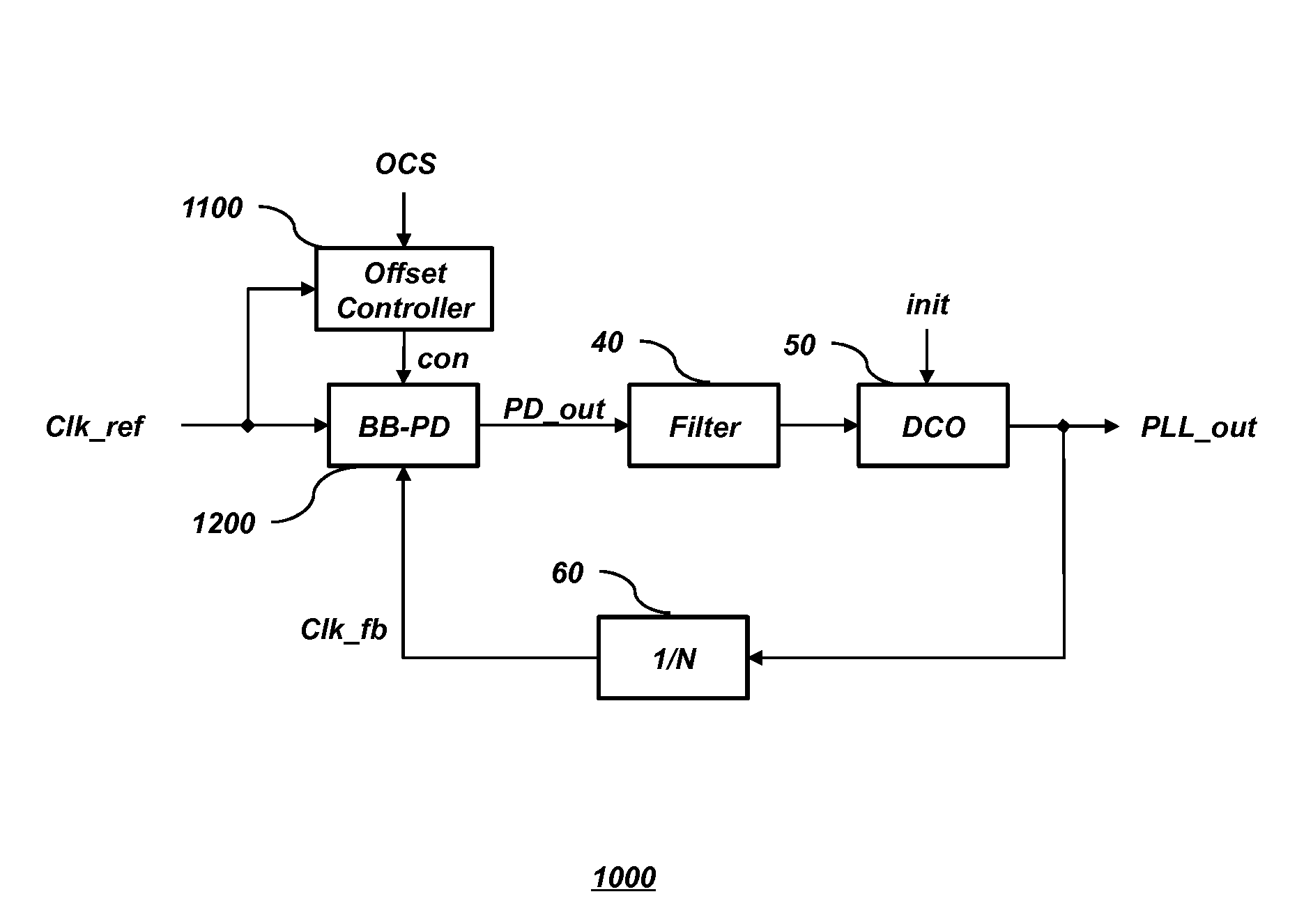
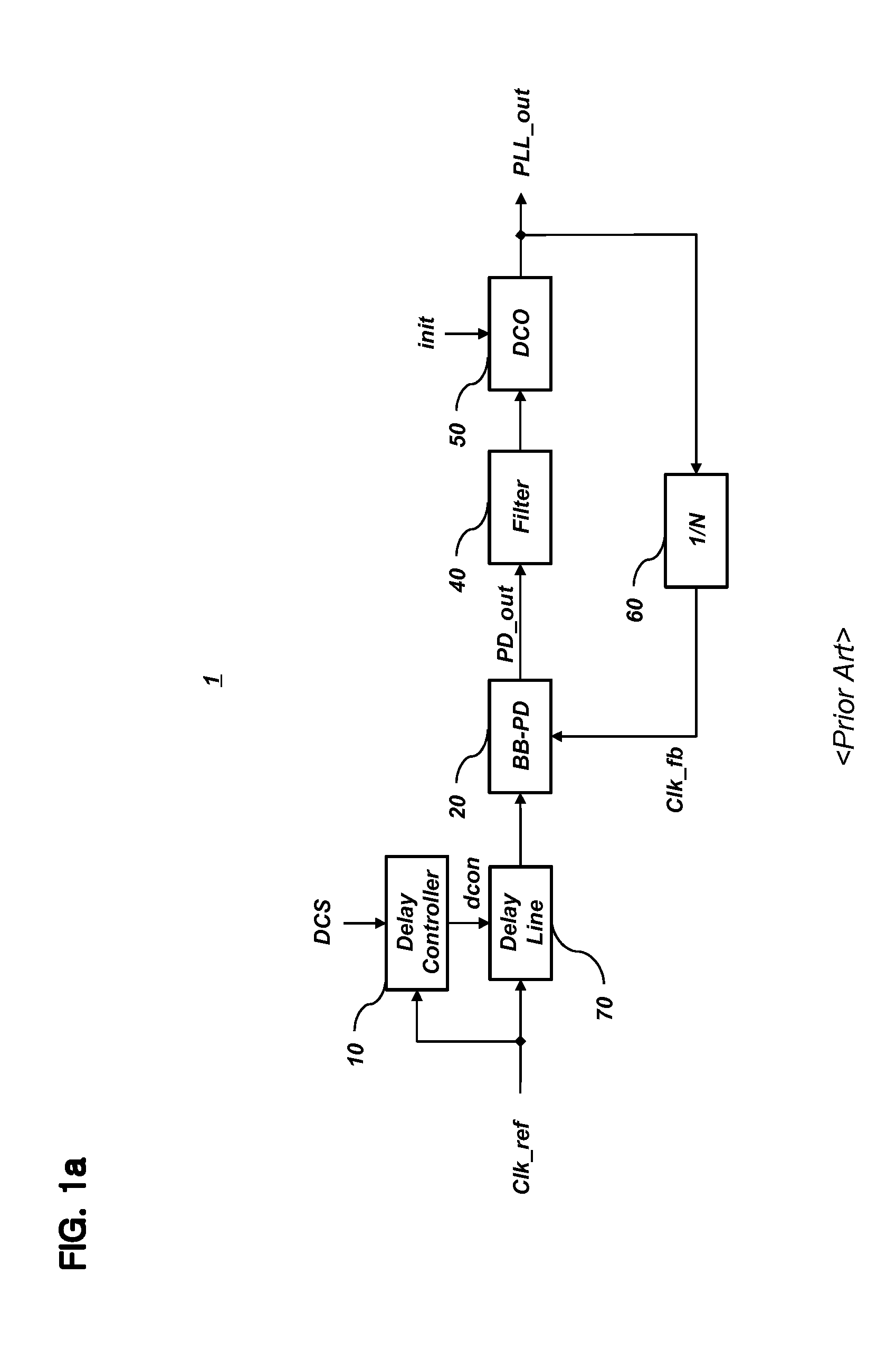
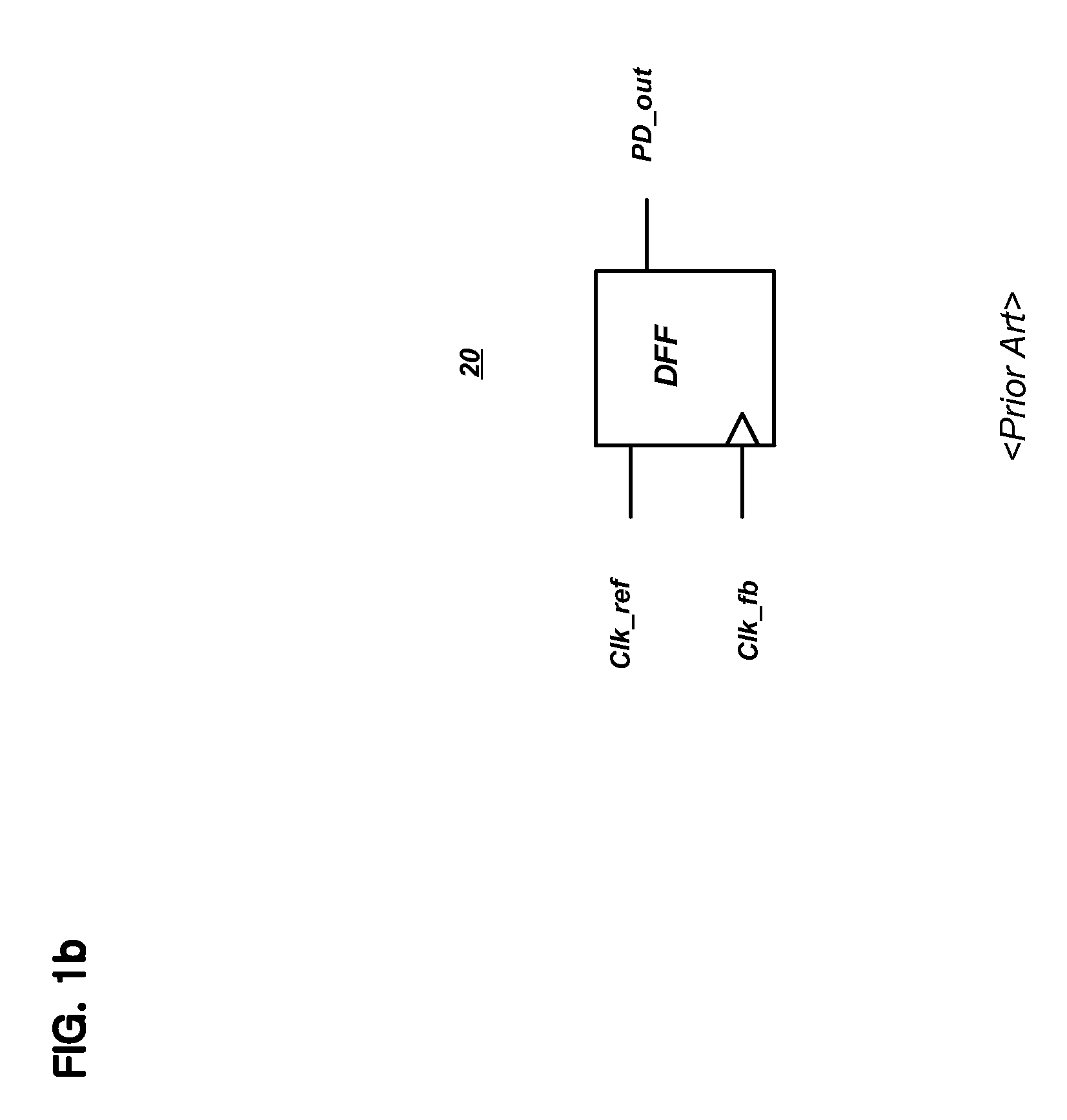
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
762 results about "Phase frequency detector" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
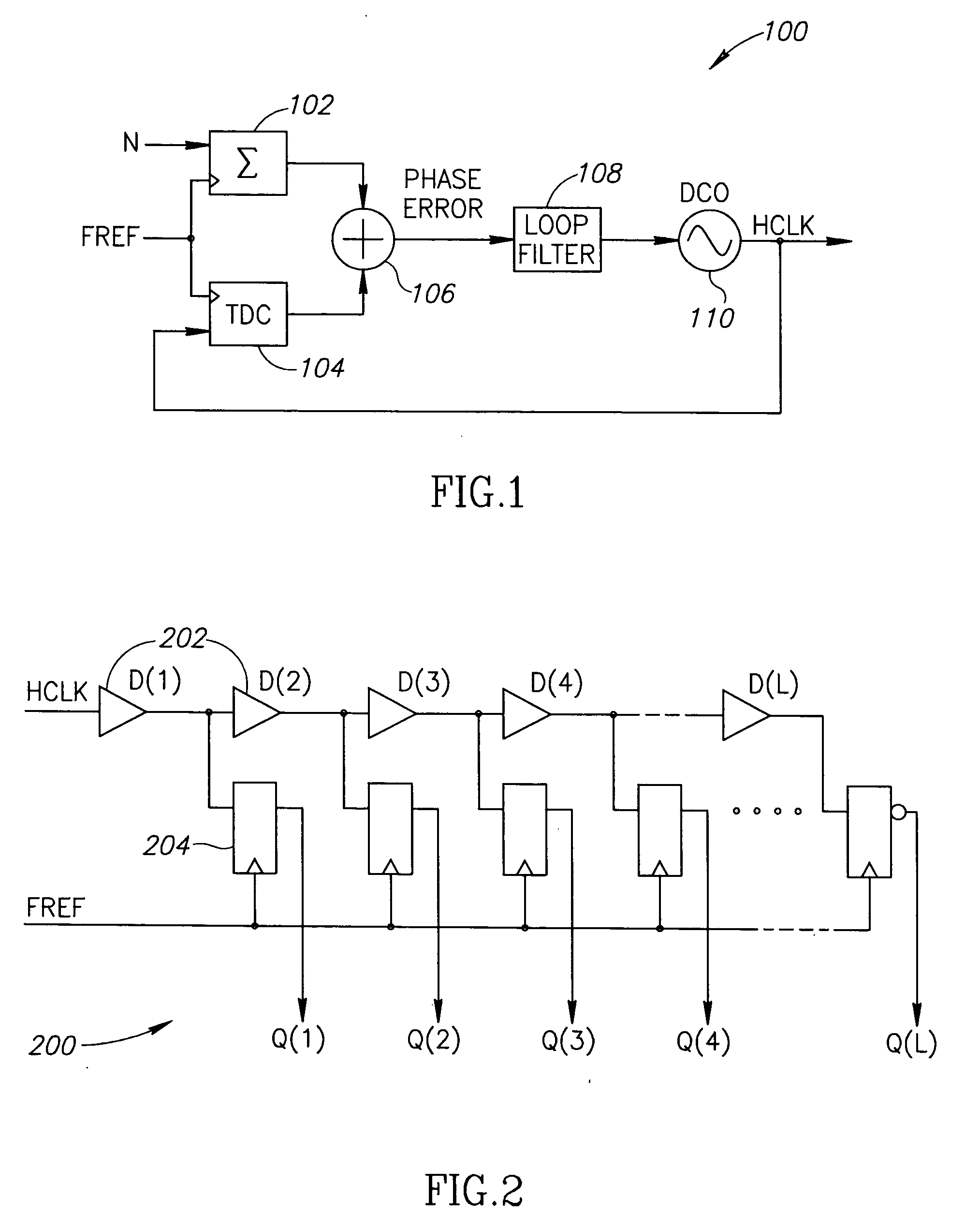
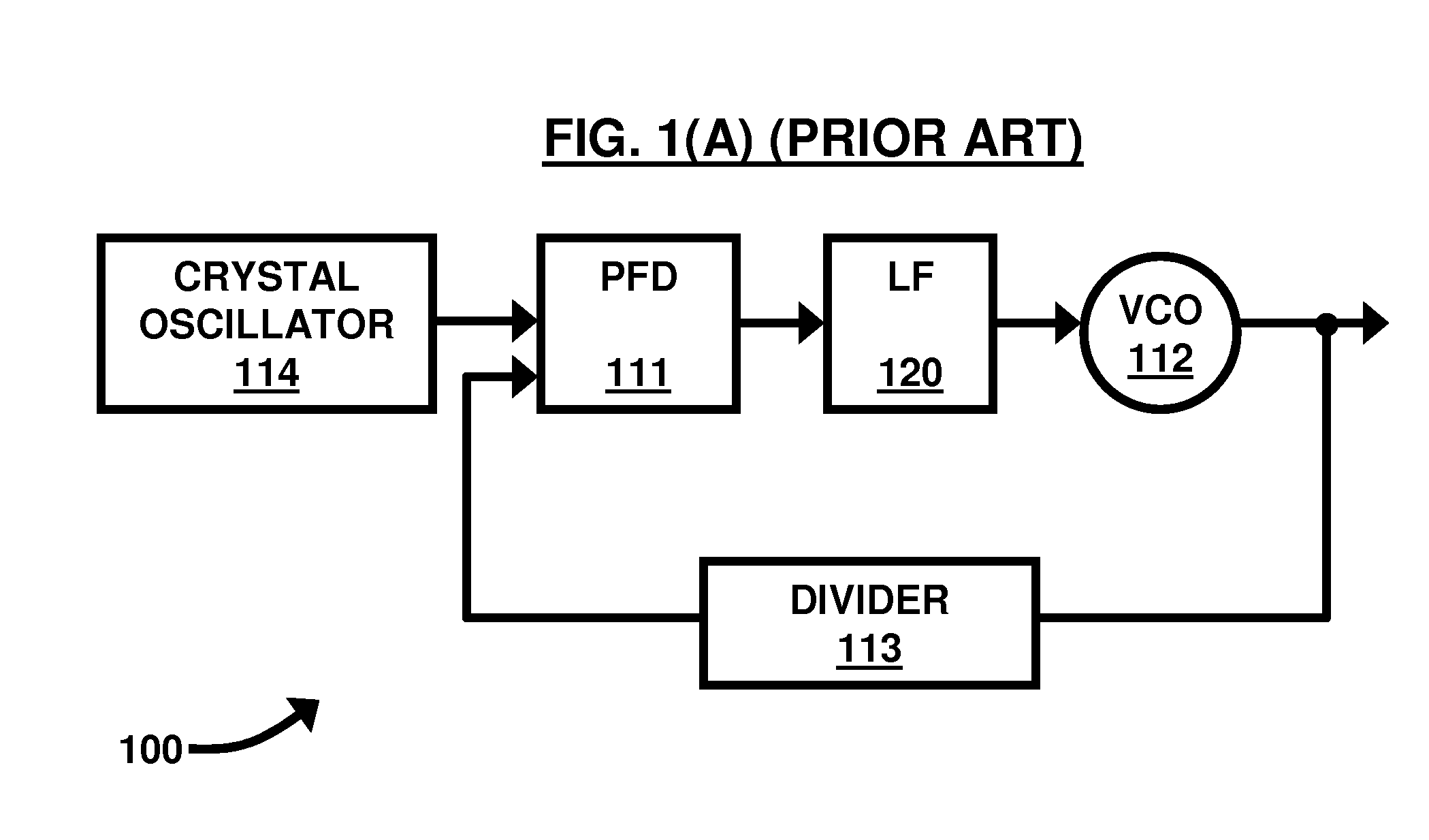
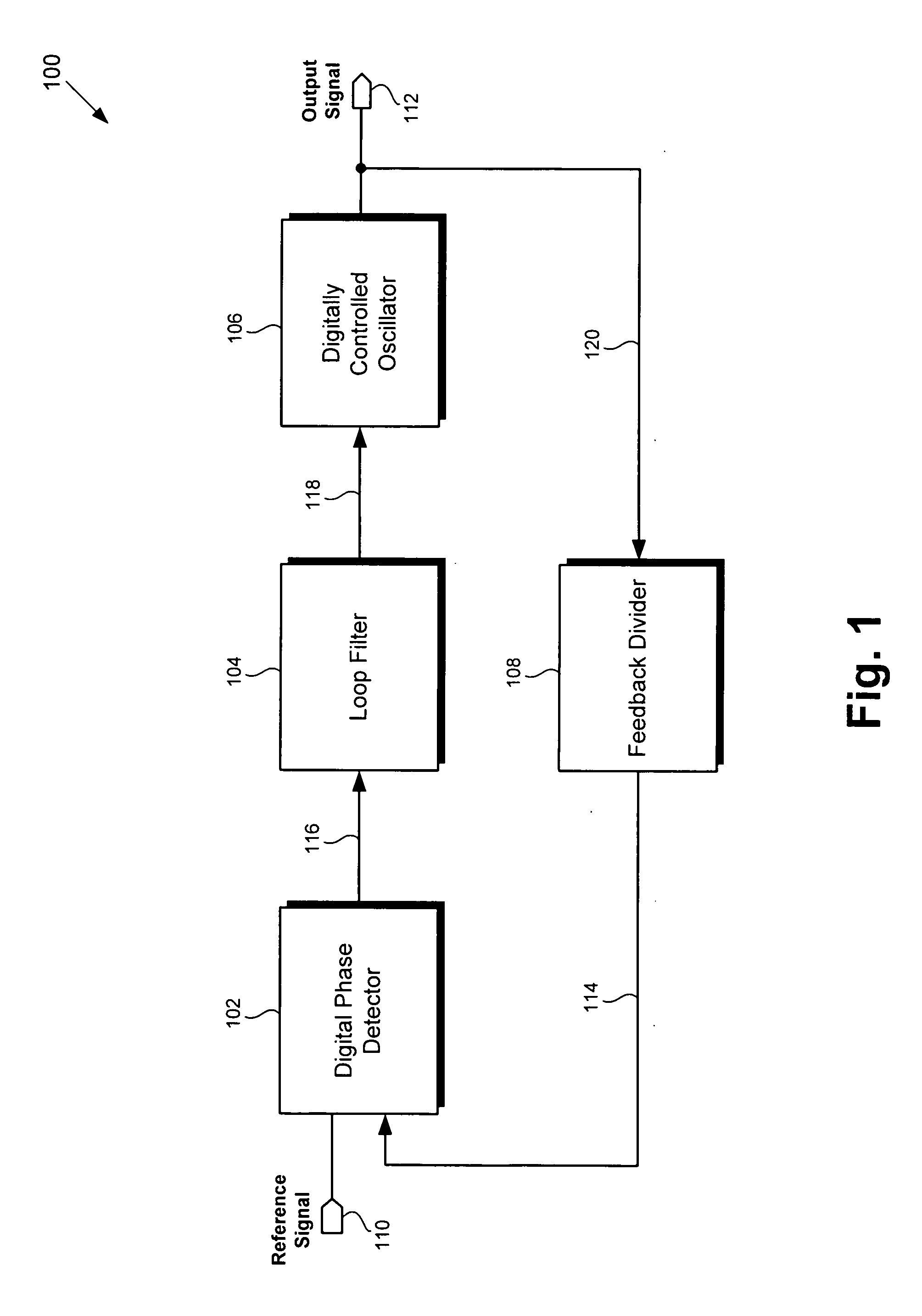
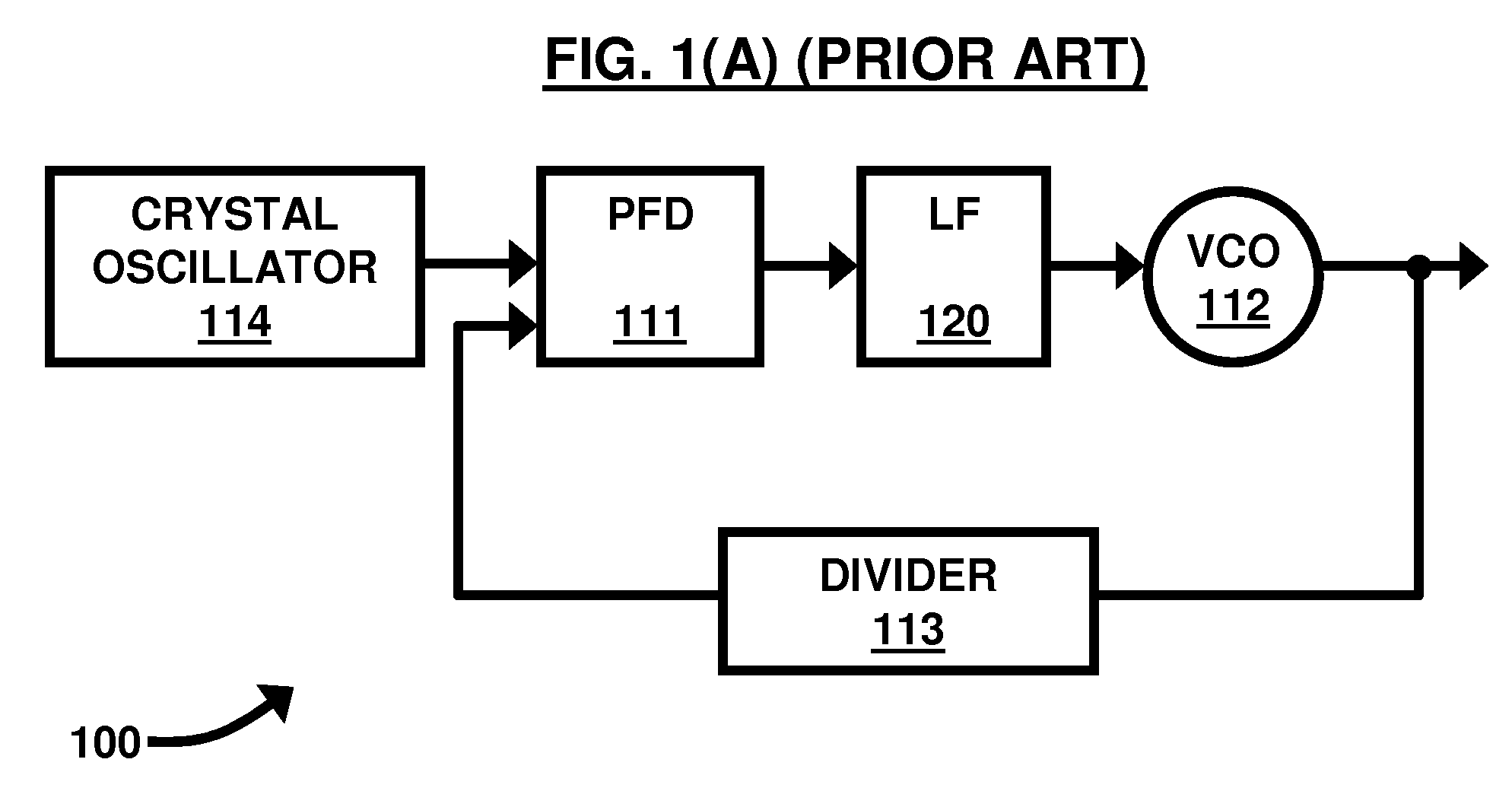
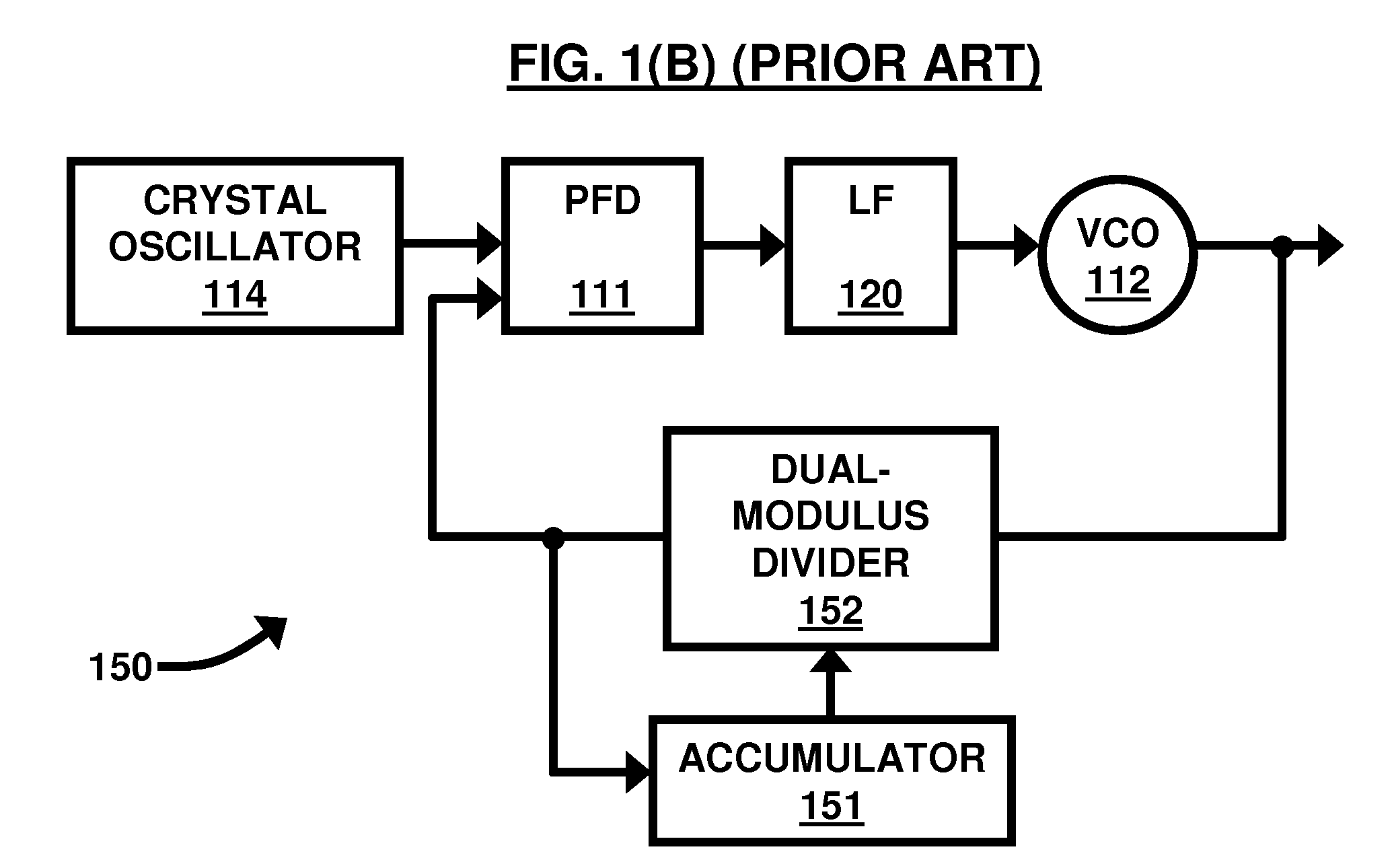
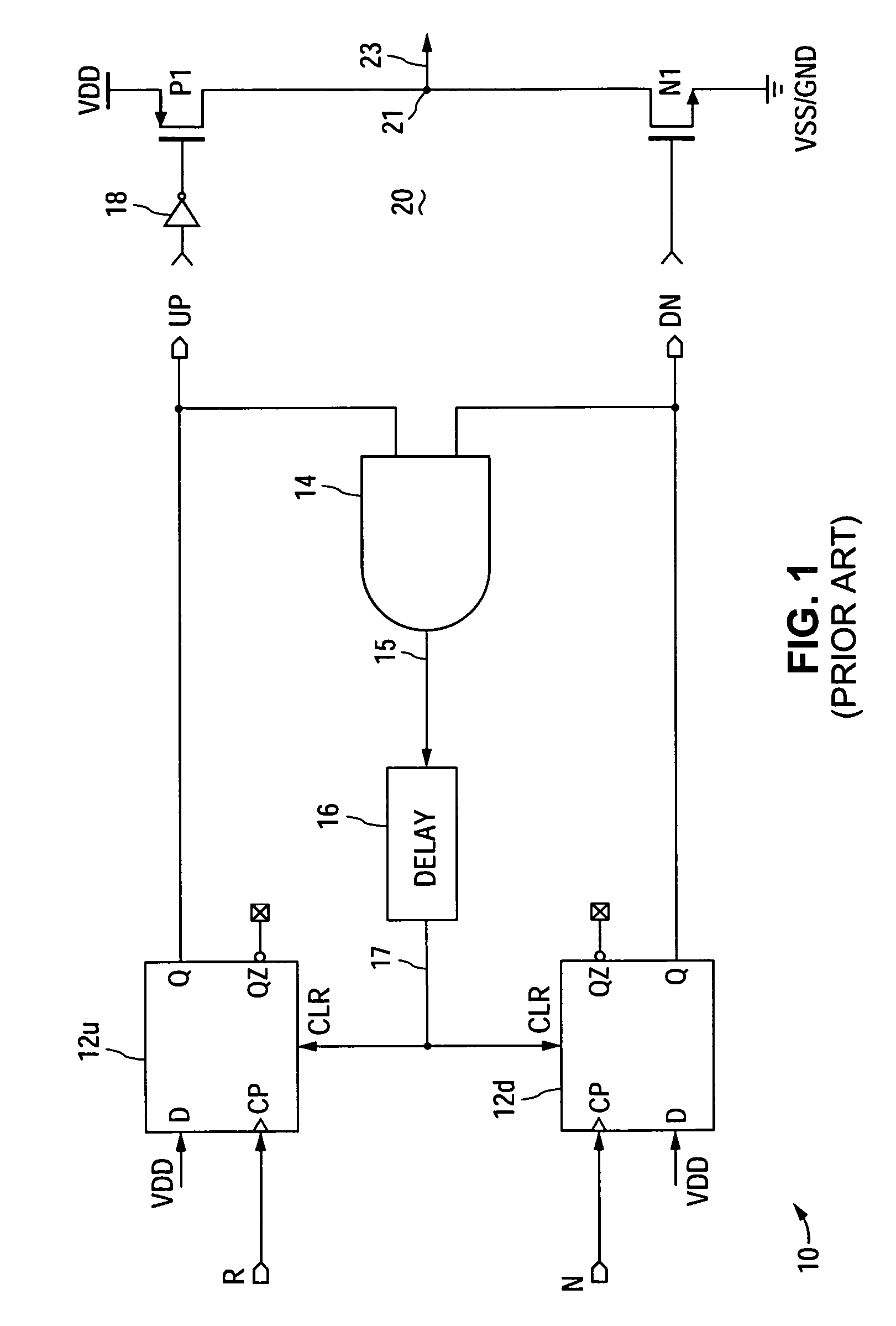
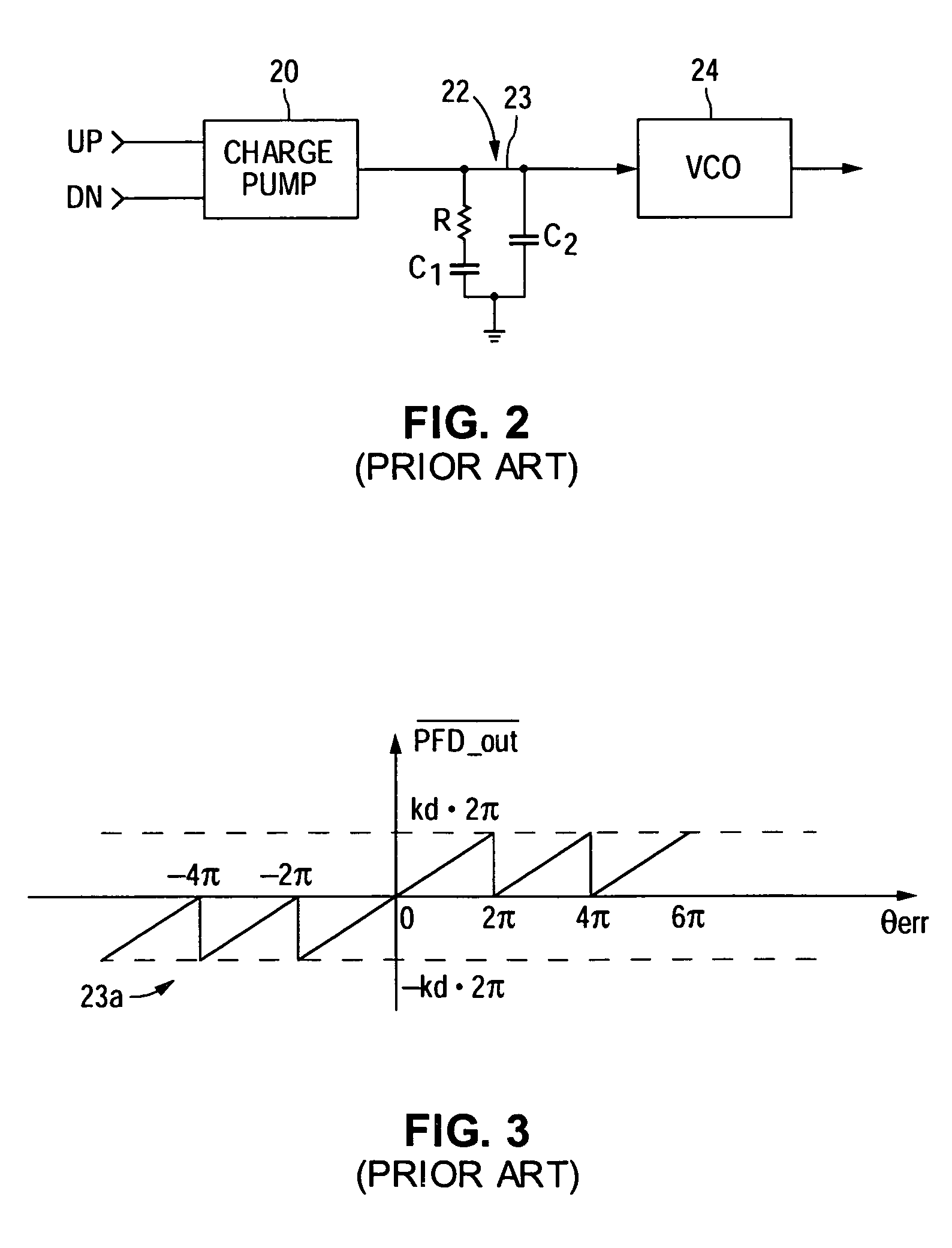
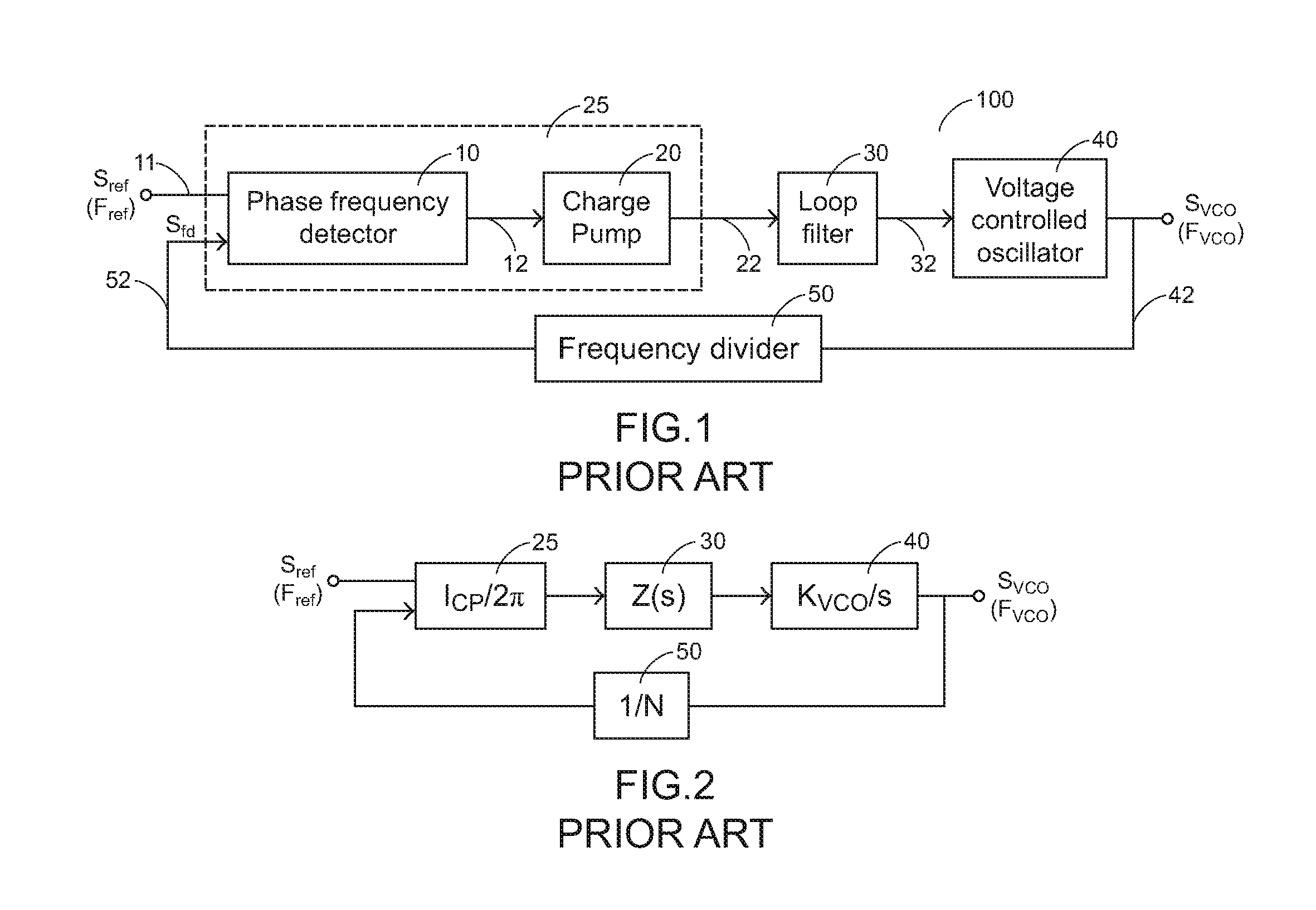
A phase frequency detector, in electronics, is a device which compares the phase of two input signals. It has two inputs which correspond to two different input signals, usually one from a voltage-controlled oscillator and another from some external source. It has two outputs which instruct subsequent circuitry on how to adjust to lock onto the phase. To form a Phase-locked loop the PFD phase error output is fed to a loop filter which integrates the signal to smooth it. This smoothed signal is fed to a voltage-controlled oscillator which generates an output signal with a frequency that is proportional to the input voltage. The VCO output is also fed back to the PFD to form the PLL circuit. The PFD is an improvement over the phase comparators of early PLLs in that it also provides a frequency error output as well as a phase error signal.
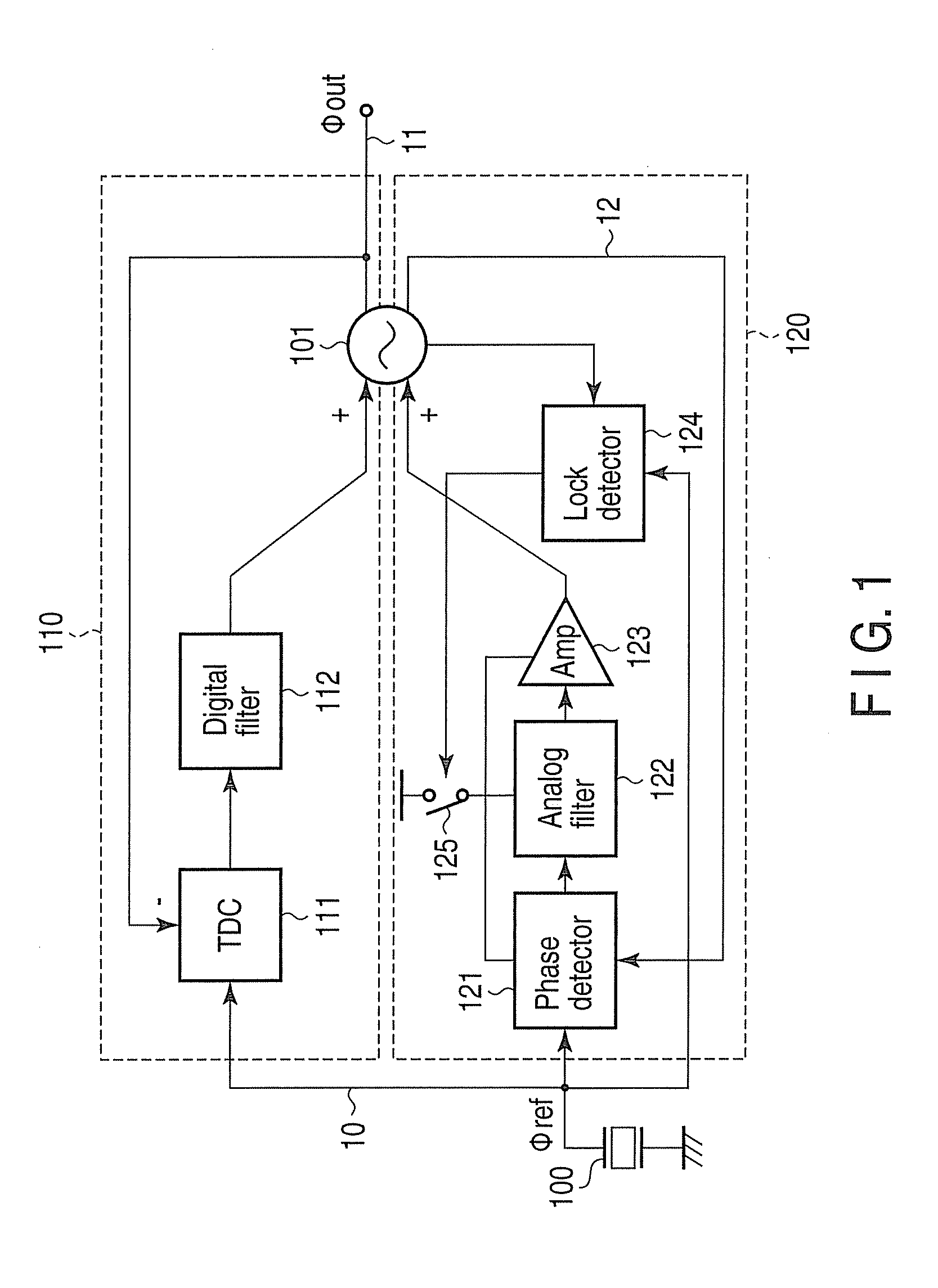
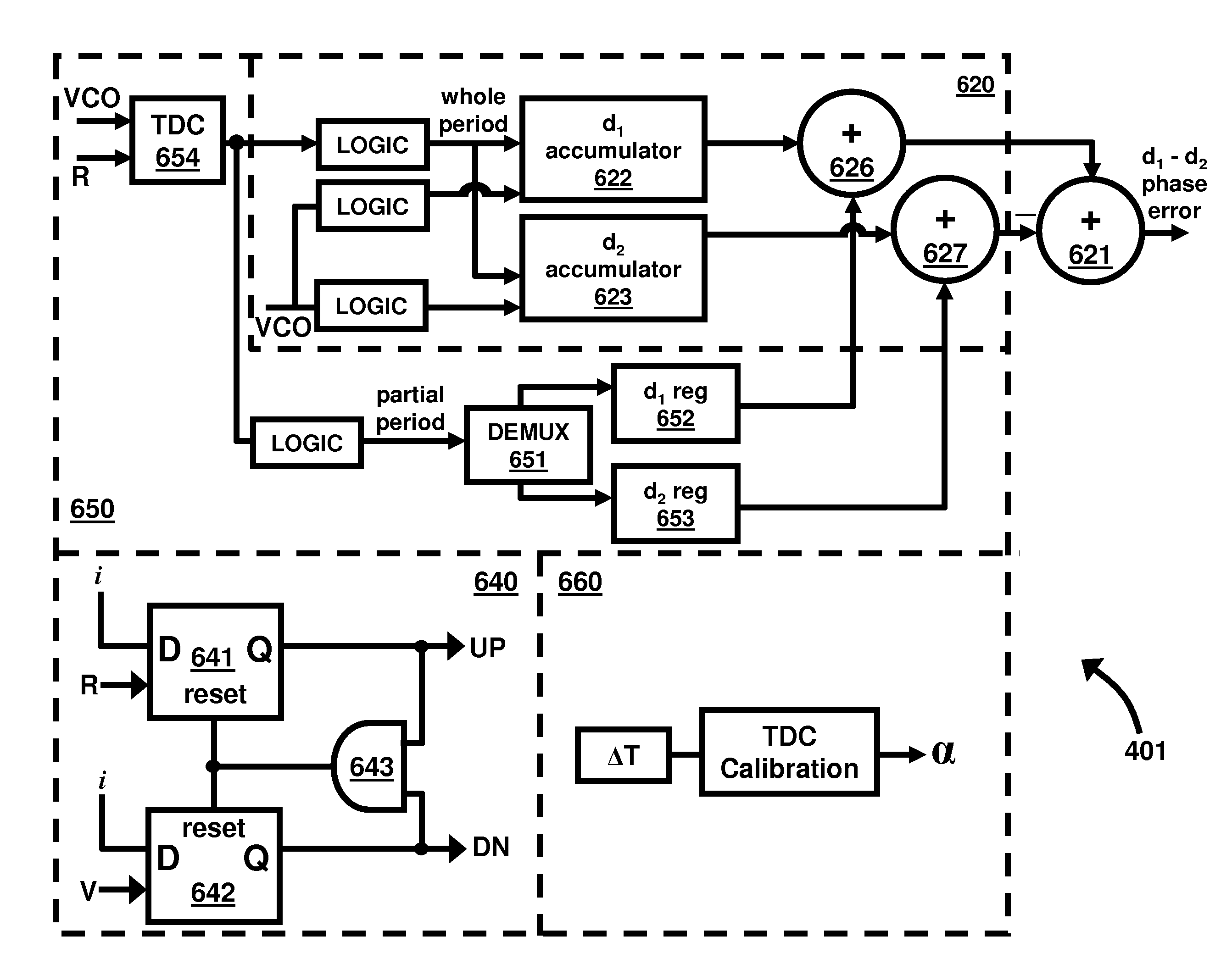
Circuit for high-resolution phase detection in a digital RF processor
ActiveUS20060103566A1Less sensitiveReduce power consumptionElectric signal transmission systemsPulse automatic controlEngineeringDigital converter
A novel time-to-digital converter (TDC) used as a phase / frequency detector and charge pump replacement in an all-digital PLL within a digital radio processor. The TDC core is based on a pseudo-differential digital architecture making it insensitive to NMOS and PMOS transistor mismatches. The time conversion resolution is equal to an inverter propagation delay, e.g., 20 ps, which is the finest logic-level regenerative timing in CMOS. The TDC is self calibrating with the estimation accuracy better than 1%. The TDC circuit can also serve as a CMOS process strength estimator for analog circuits in large SoC dies. The circuit also employs power management circuitry to reduce power consumption to a very low level.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
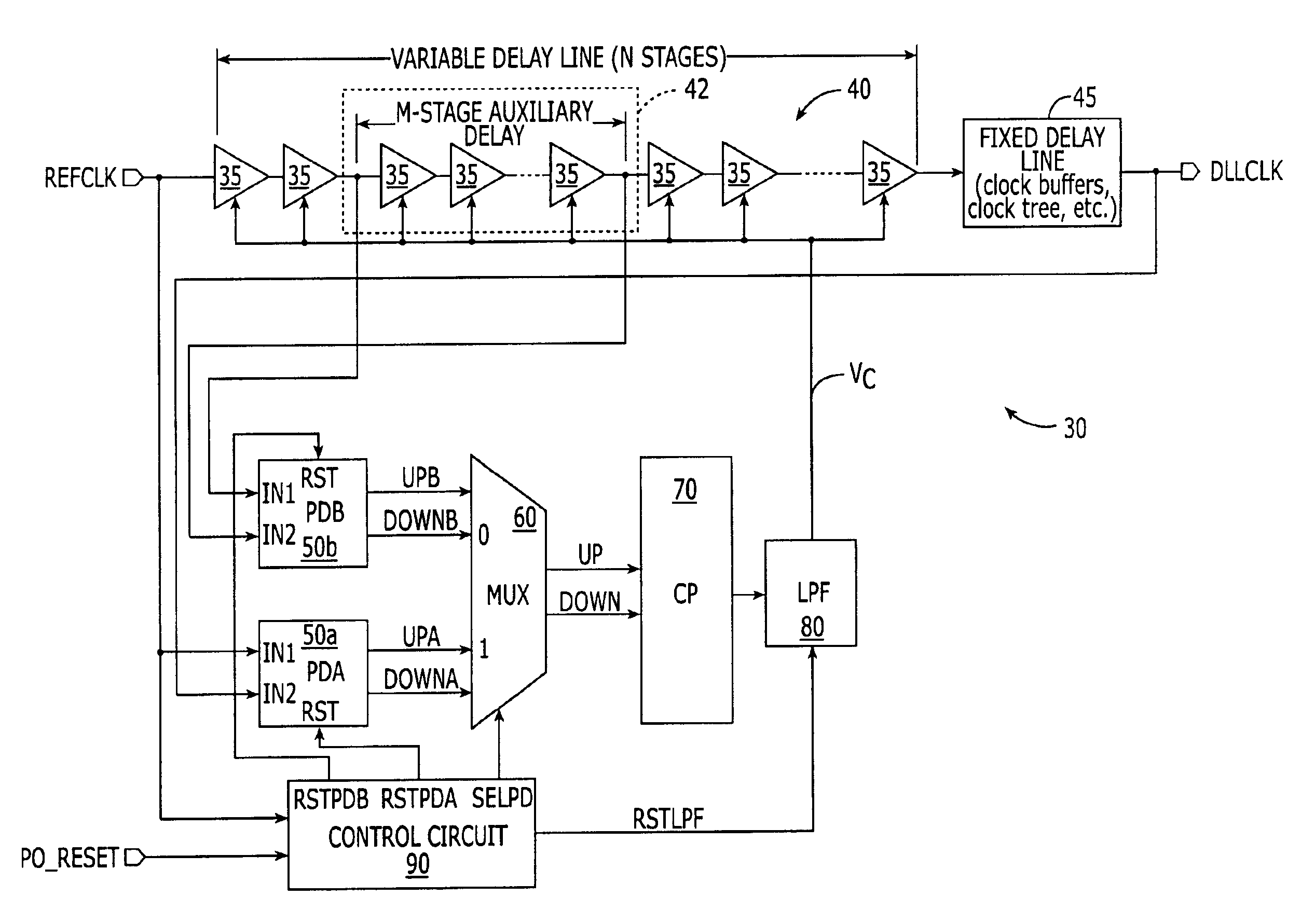
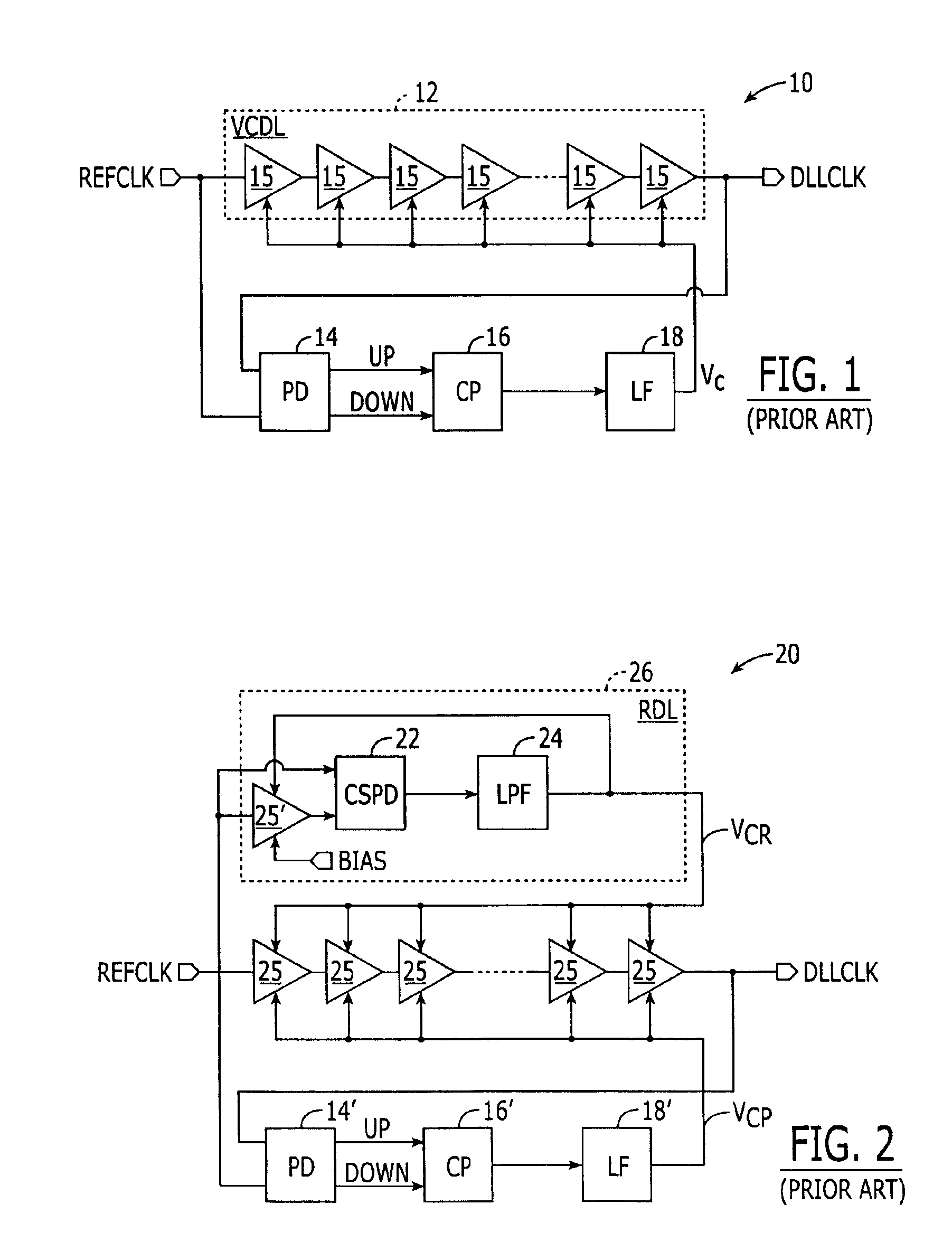
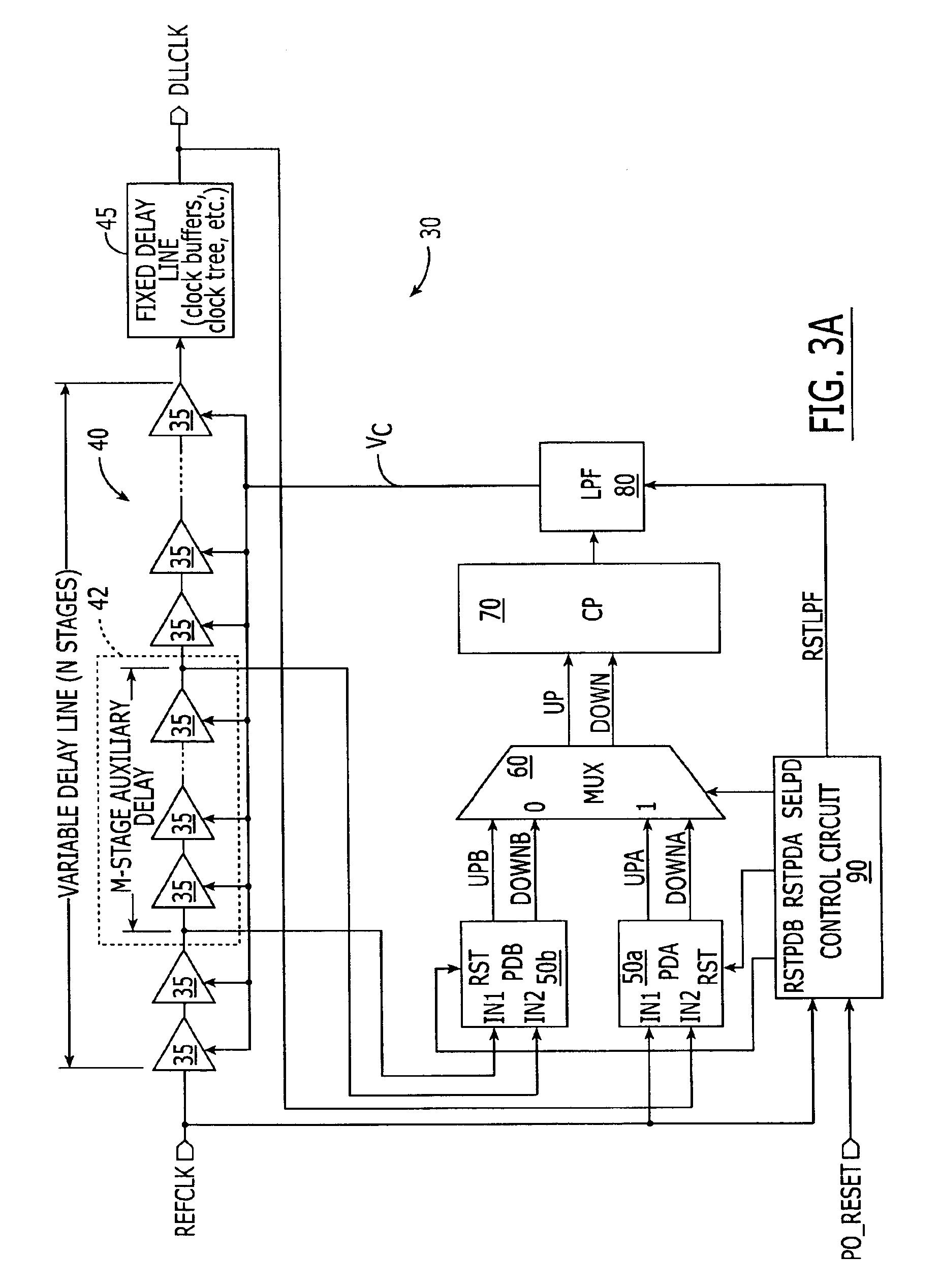
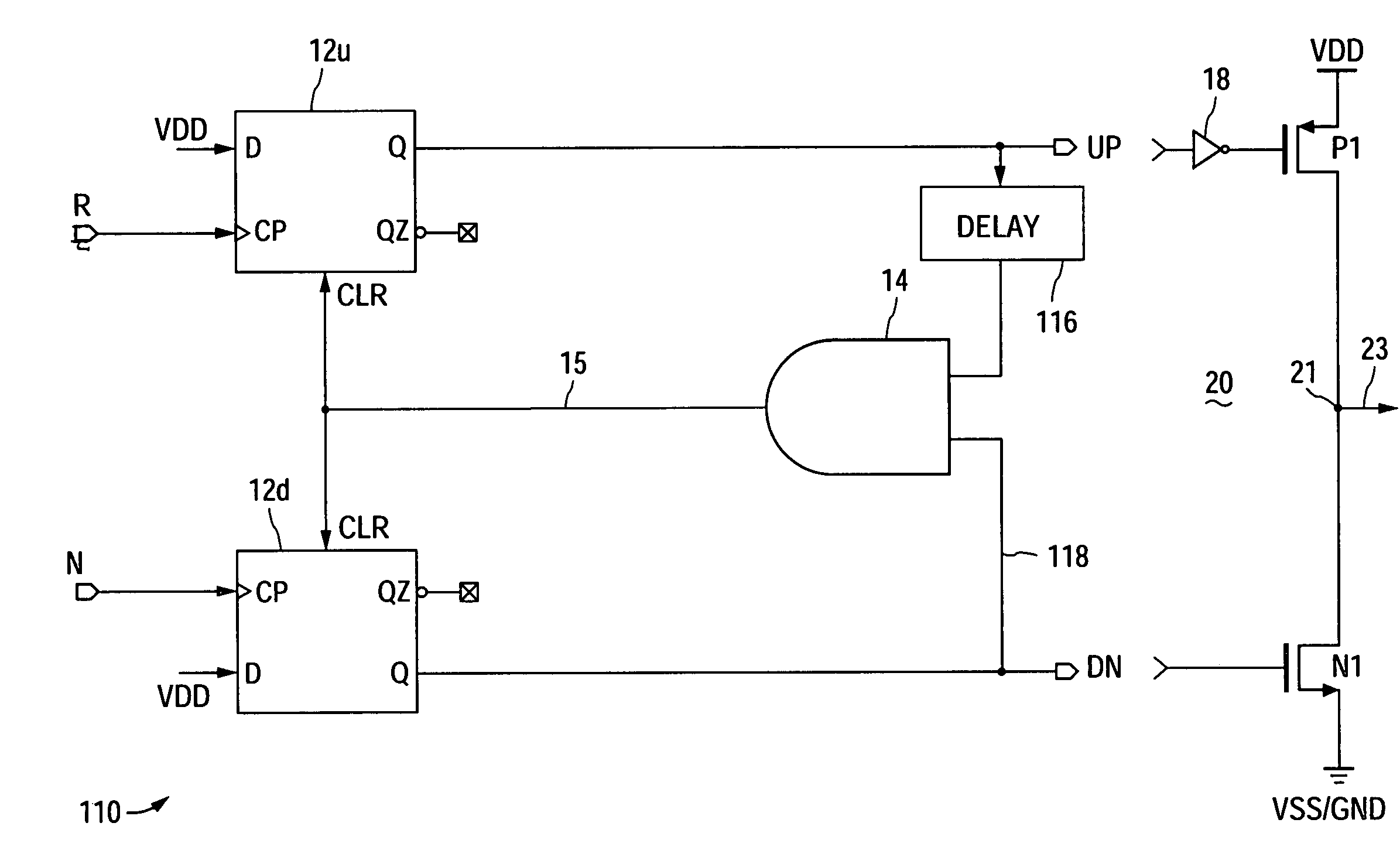
Delay-locked loop (DLL) integrated circuits having high bandwidth and reliable locking characteristics
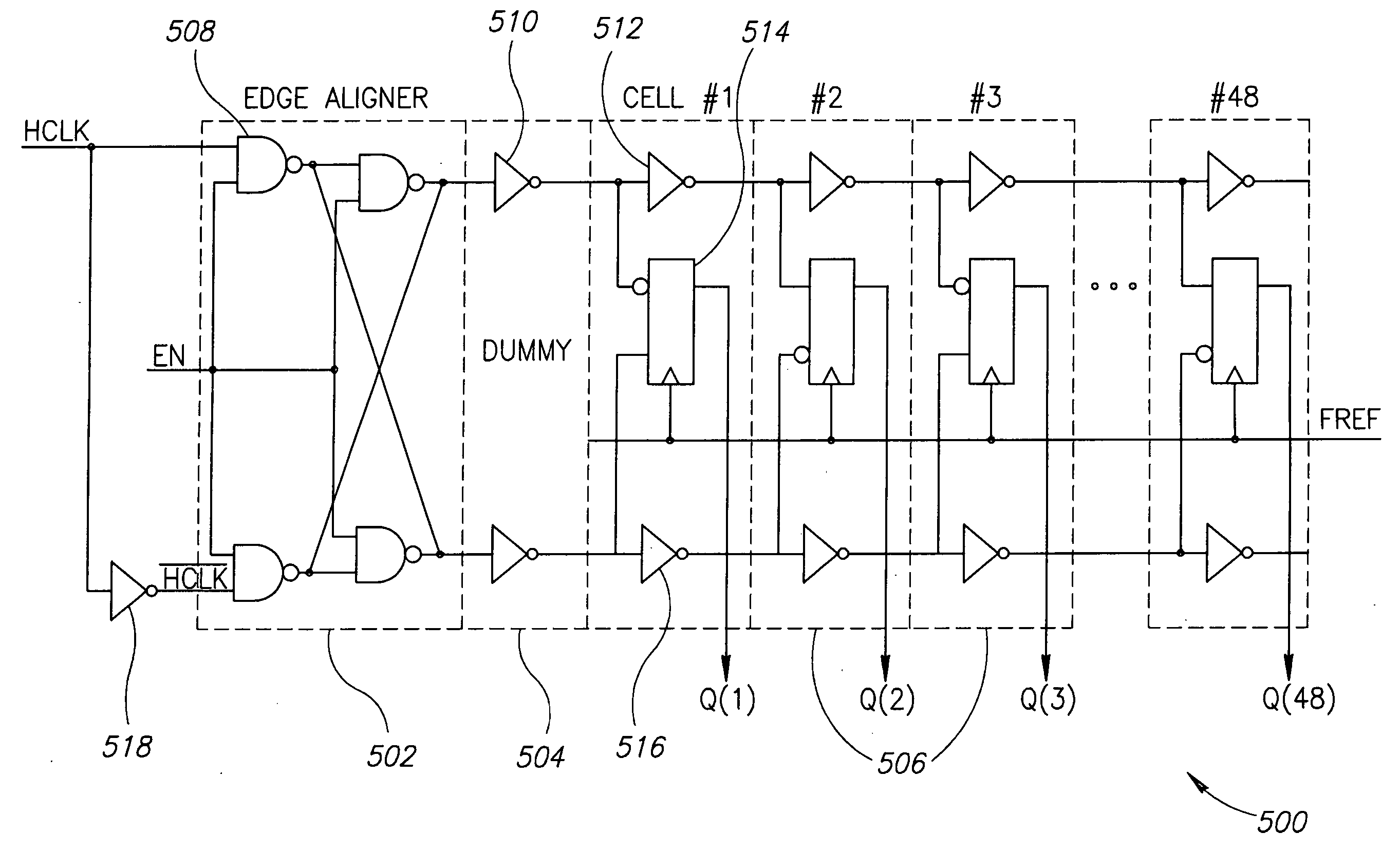
Delay-locked loops have high bandwidth locking characteristics that are less susceptible process, voltage and temperature (PVT) variations. These DLLs are configured to support transition from a partial feedback loop lock condition to a full feedback loop lock condition during a start-up time interval, in order to insure that a multi-cycle lock condition is established at the time the DLL's clock signal output becomes available. The DLL may include a variable delay line that is responsive to a reference clock signal, an auxiliary phase detector that is electrically coupled to the variable delay line, and a main phase detector that is responsive to the reference clock signal and a feedback clock signal (DLLCLK). The auxiliary phase detector may be an edge-triggered SR-type phase detector and the main phase detector may be a three-state phase frequency detector.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
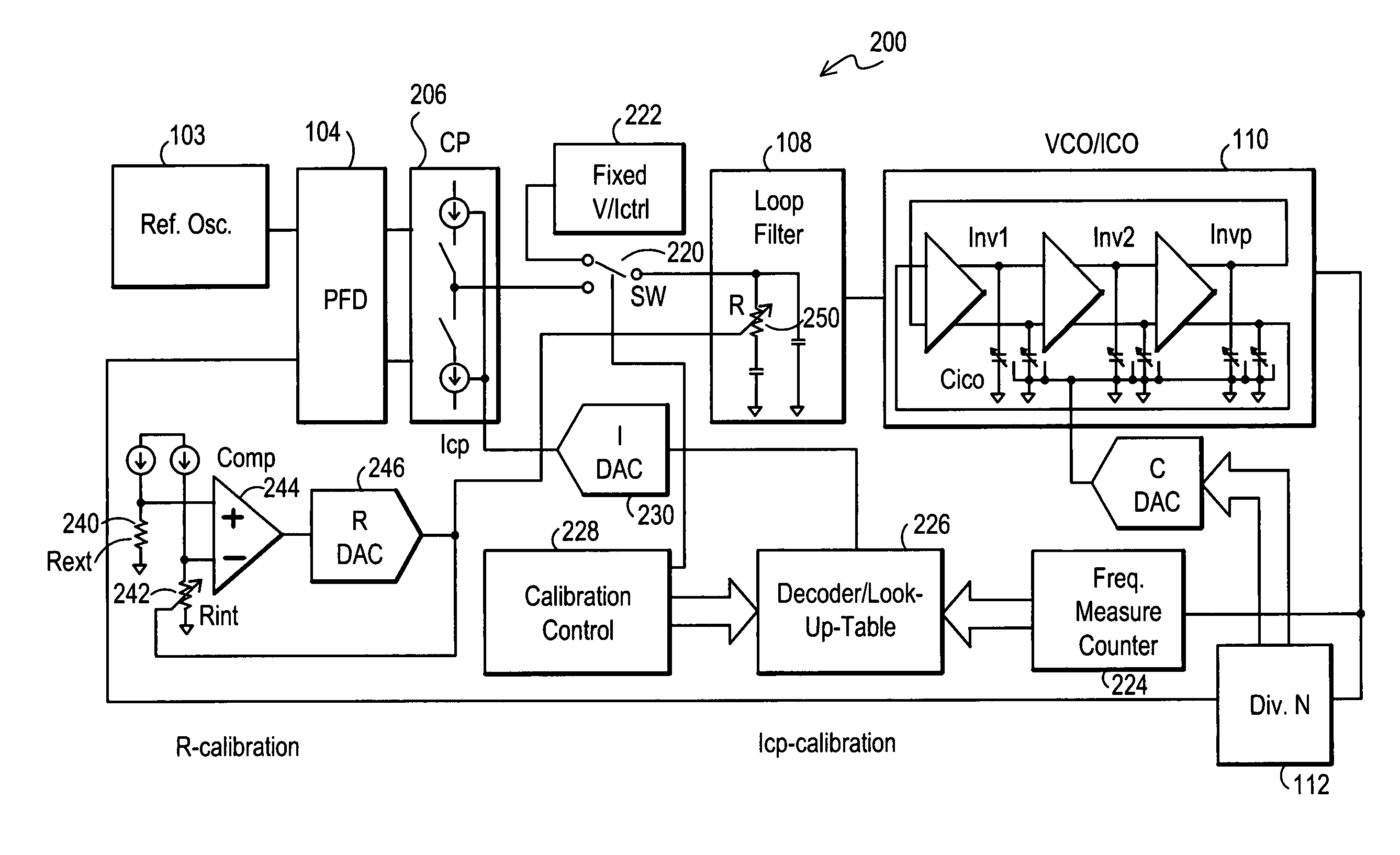
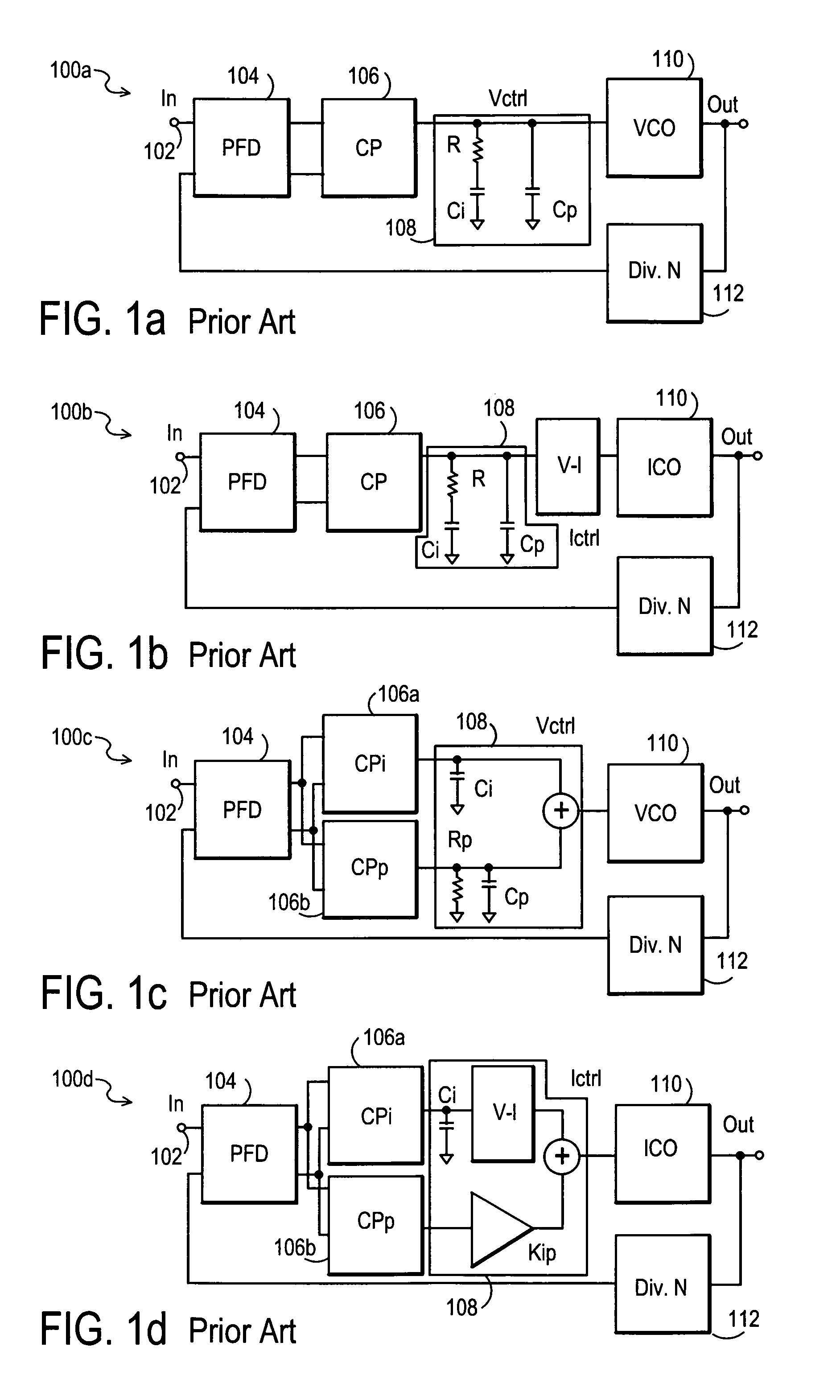
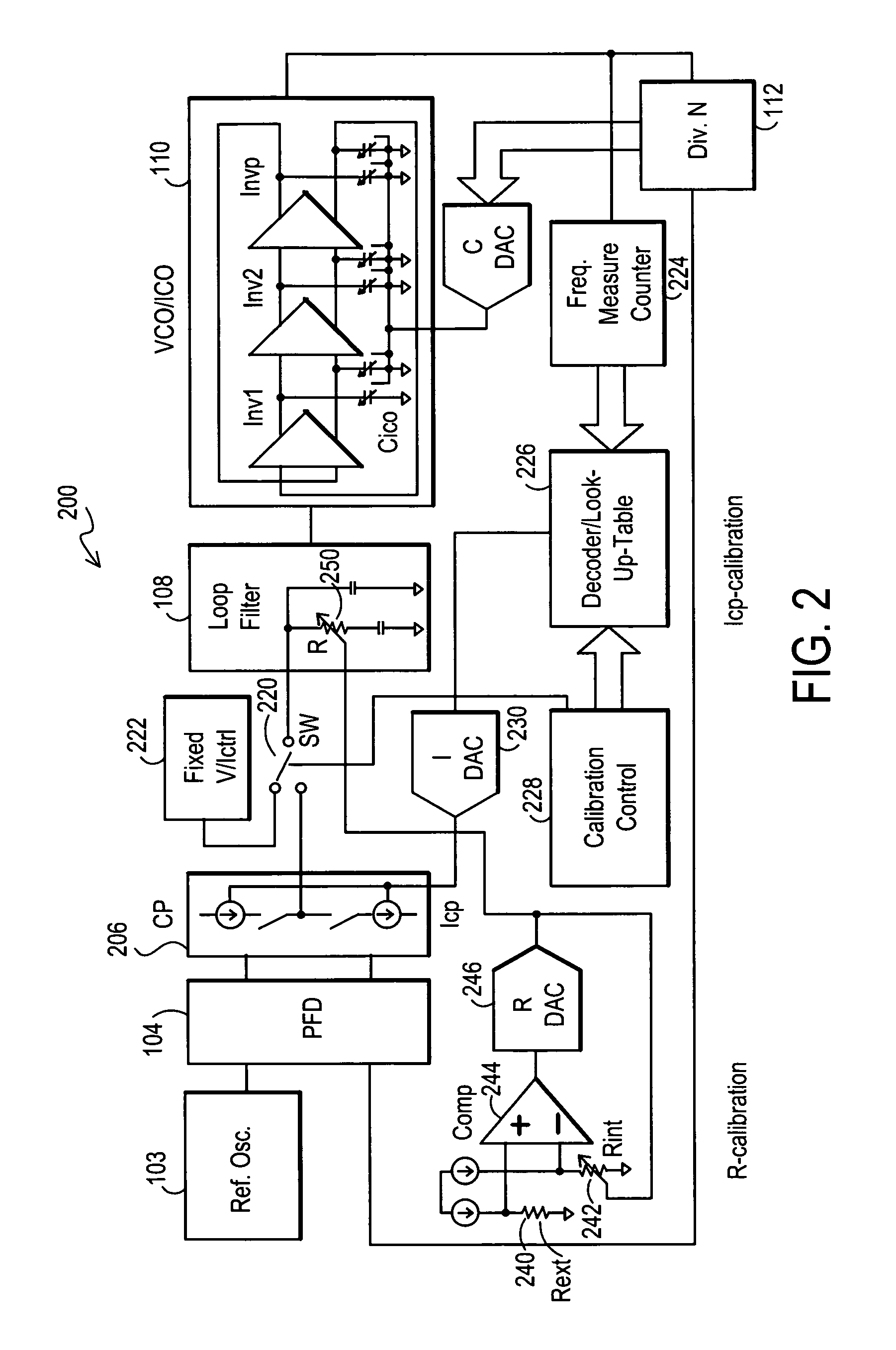
Method and apparatus to achieve a process, temperature and divider modulus independent PLL loop bandwidth and damping factor using open-loop calibration techniques
InactiveUS7095287B2Reduce complexityImprove accuracyPulse automatic controlFrequency analysisDamping factorProportional control
Several open-loop calibration techniques for phase-locked-loop circuits (PLL) that provide a process, temperature and divider modulus independence for the loop bandwidth and damping factor are disclosed. Two categories of open-loop techniques are presented. The first method uses only a single measurement of the output frequency from the oscillator and adjusts a single PLL loop element that performs a simultaneous calibration of both the loop bandwidth and damping factor. The output frequency is measured for a given value of the oscillator control signal and the charge-pump current is adjusted such that it cancels the process variation of the oscillator gain. The second method uses two separate and orthogonal calibration steps, both of them based on the measurement of the output frequency from the oscillator when a known excitation is applied to the open loop signal path. In the first step the loop bandwidth is calibrated by adjusting the charge-pump current based on the measurement of the forward path gain when applying a constant phase shift between the two clocks that go to the phase frequency detector, while the integral path is hold to a constant value. During the second step the damping factor is calibrated by adjusting the value of the integral loop filter capacitor based on the measurement of the oscillator output frequency when excited with a voltage proportional with the integral capacitor value, while the proportional control component is zeroed-out.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
High frequency low noise phase-frequency detector and phase noise reduction method and apparatus
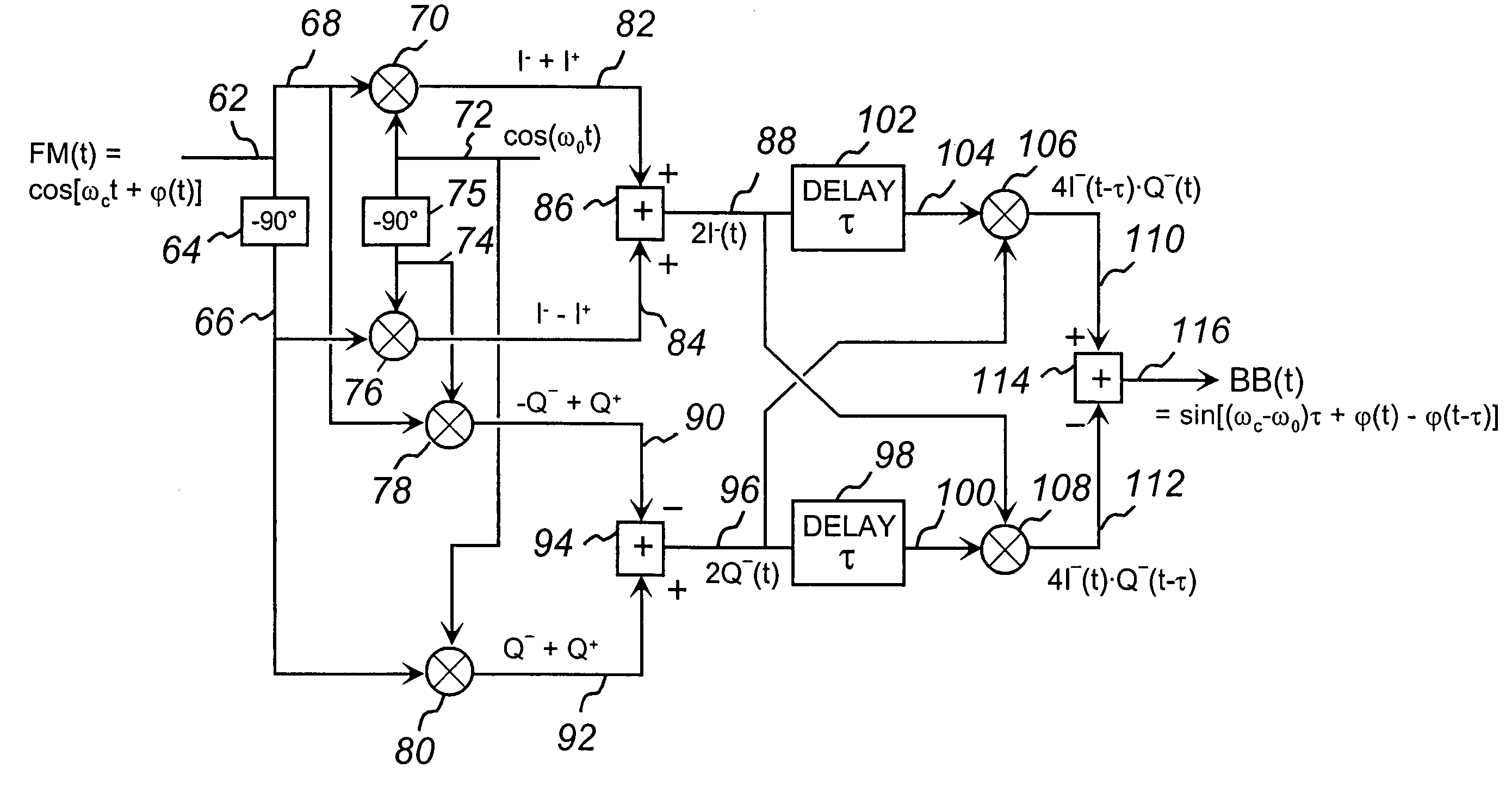
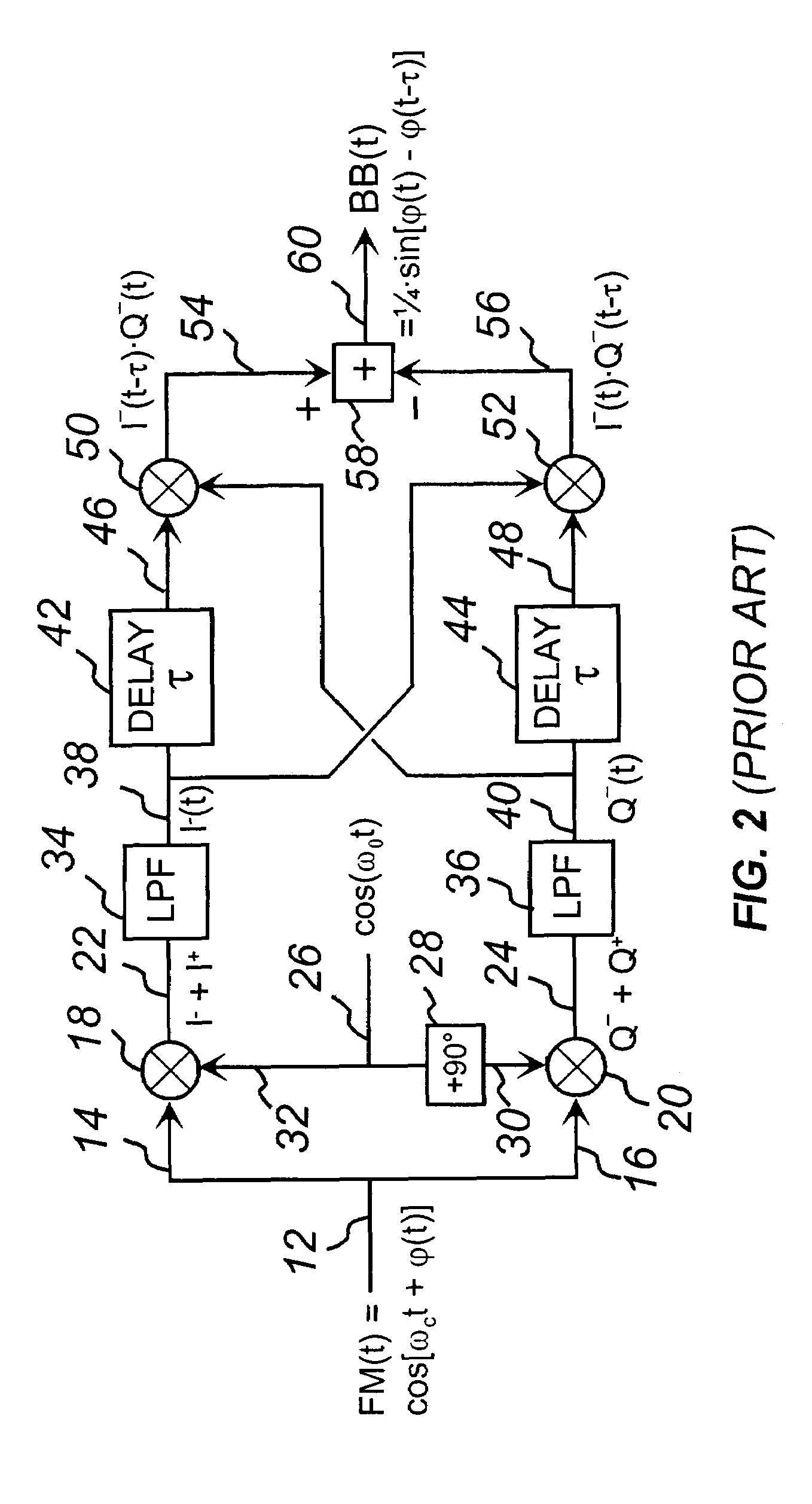
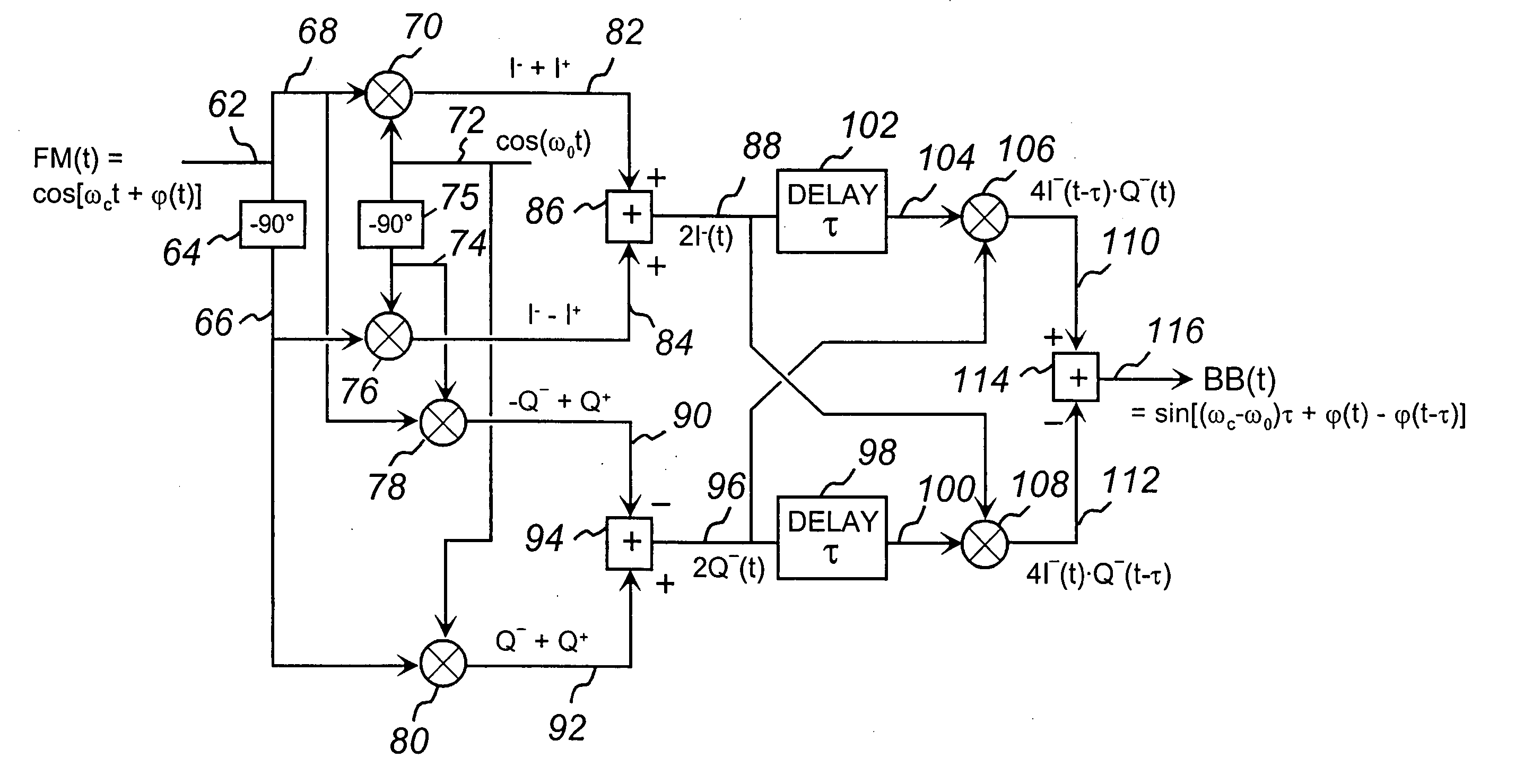
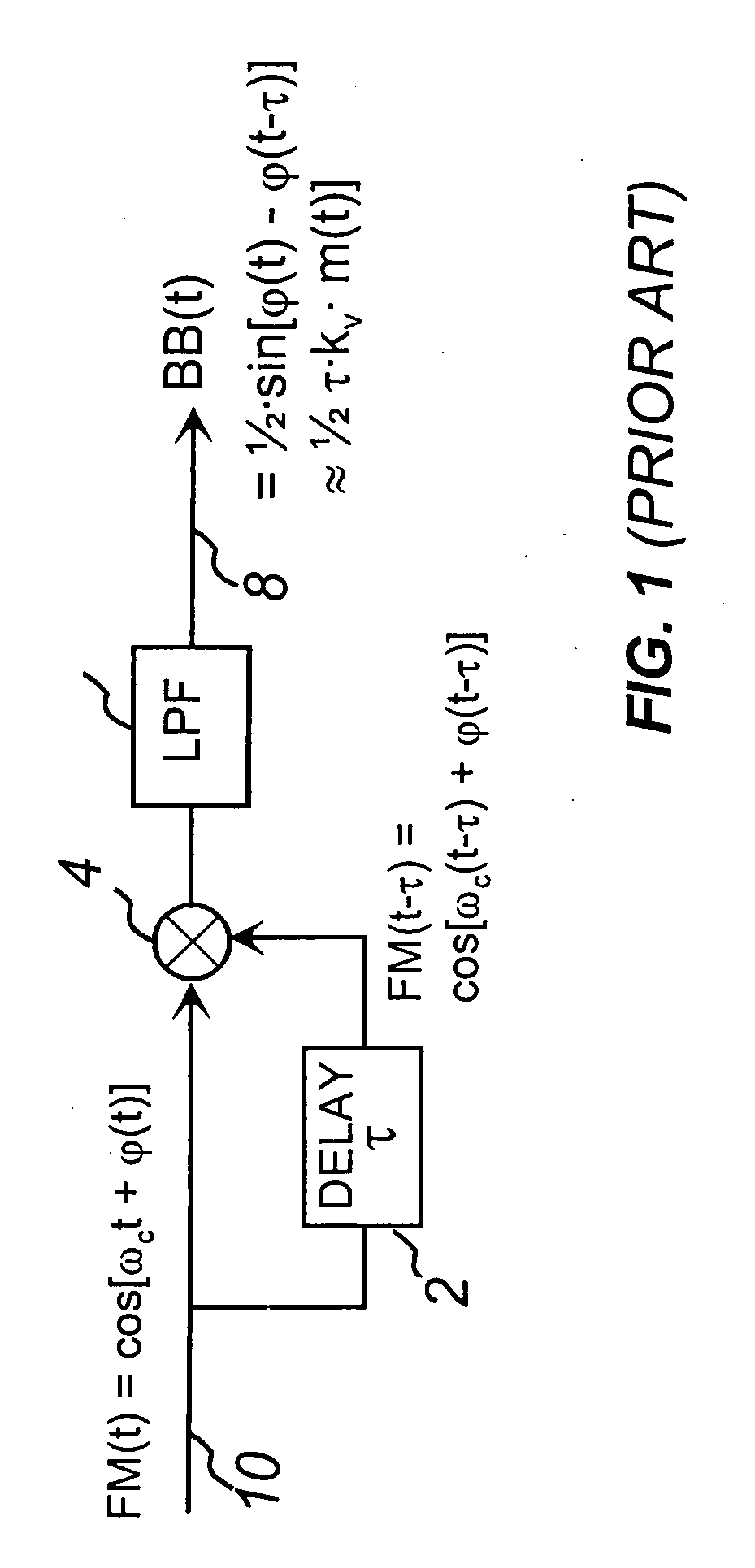
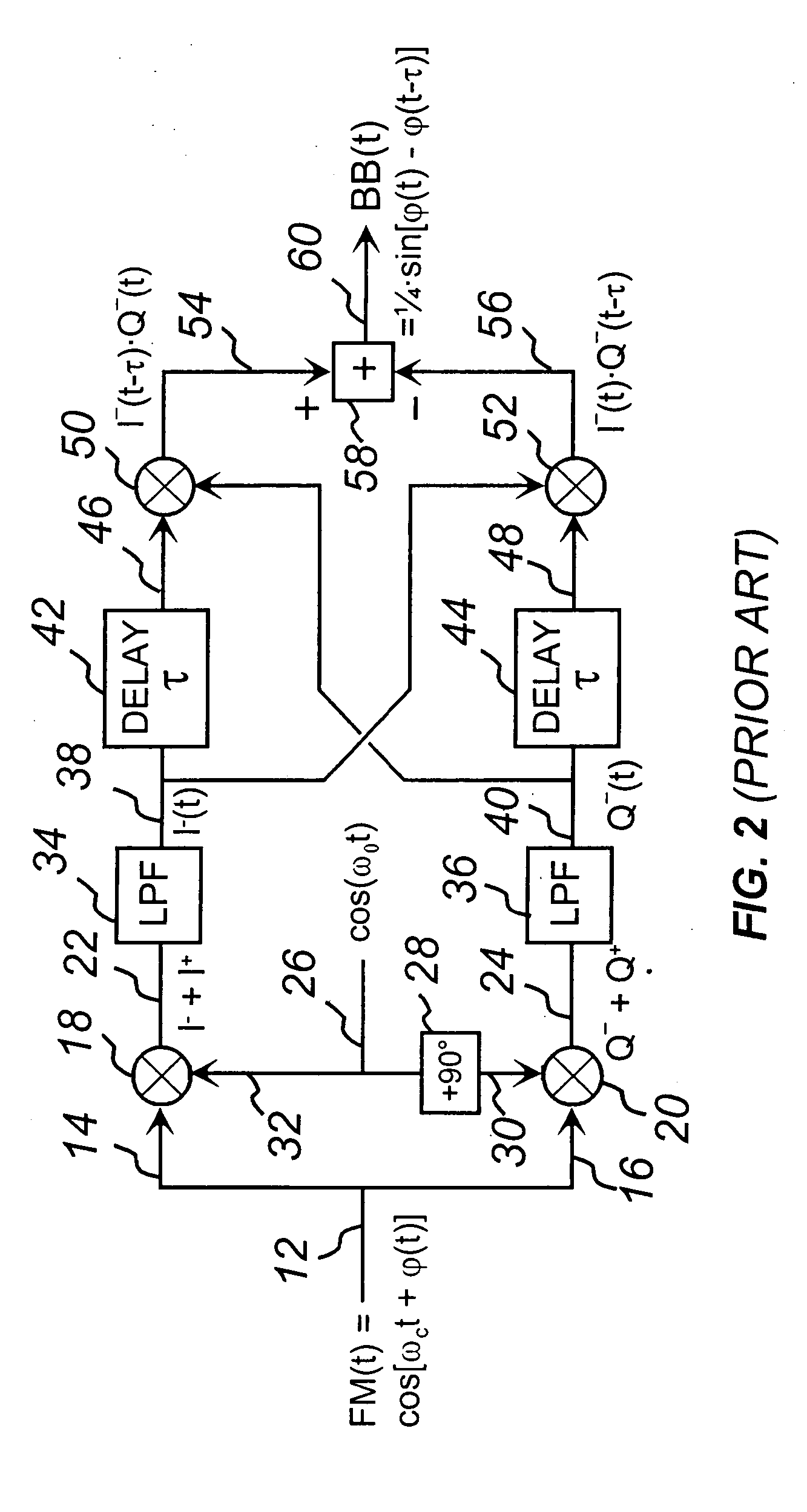
The present invention discloses a new type of extremely low-noise phase-frequency detector (PFD) 500, broadband from DC to multi-GHz RF frequencies for PLL synthesizer applications. Free of any feedback mechanisms, thus inherently fast, it operates close to transition frequency fT of IC processes or frequency limits of discrete mixers. The PFD 500 utilizes complex SSB conversion in both the in-phase and quadrature arms, delaying the in-phase arm in 530, beating the delayed signal 124 with the un-delayed quadrature signal 122 in mixer 126. The output 128 contains both the frequency difference and the phase difference information between the two signals 118 and 520, providing both the frequency-discrimination (FD) and the phase detection (PD) functions. Utilizing standard mixers the PFD 500 can achieve superior CNRs of 180 dBc / Hz at multi-GHz RF. Additionally, utilizing the FD / FM demodulation capability, the present invention improves phase noise of various signals and linearity of FM modulators.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
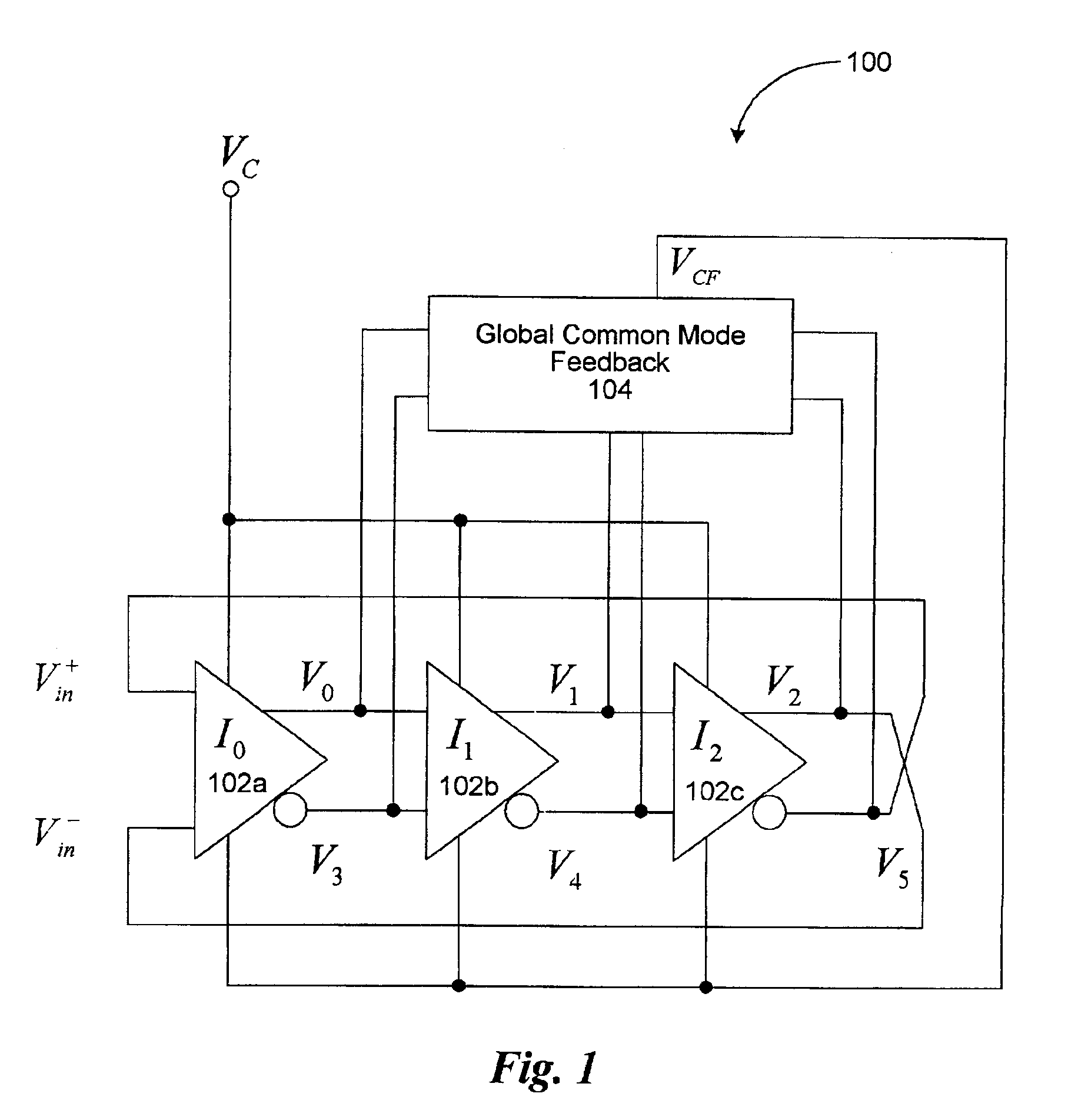
Multi-phase voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) with common mode control
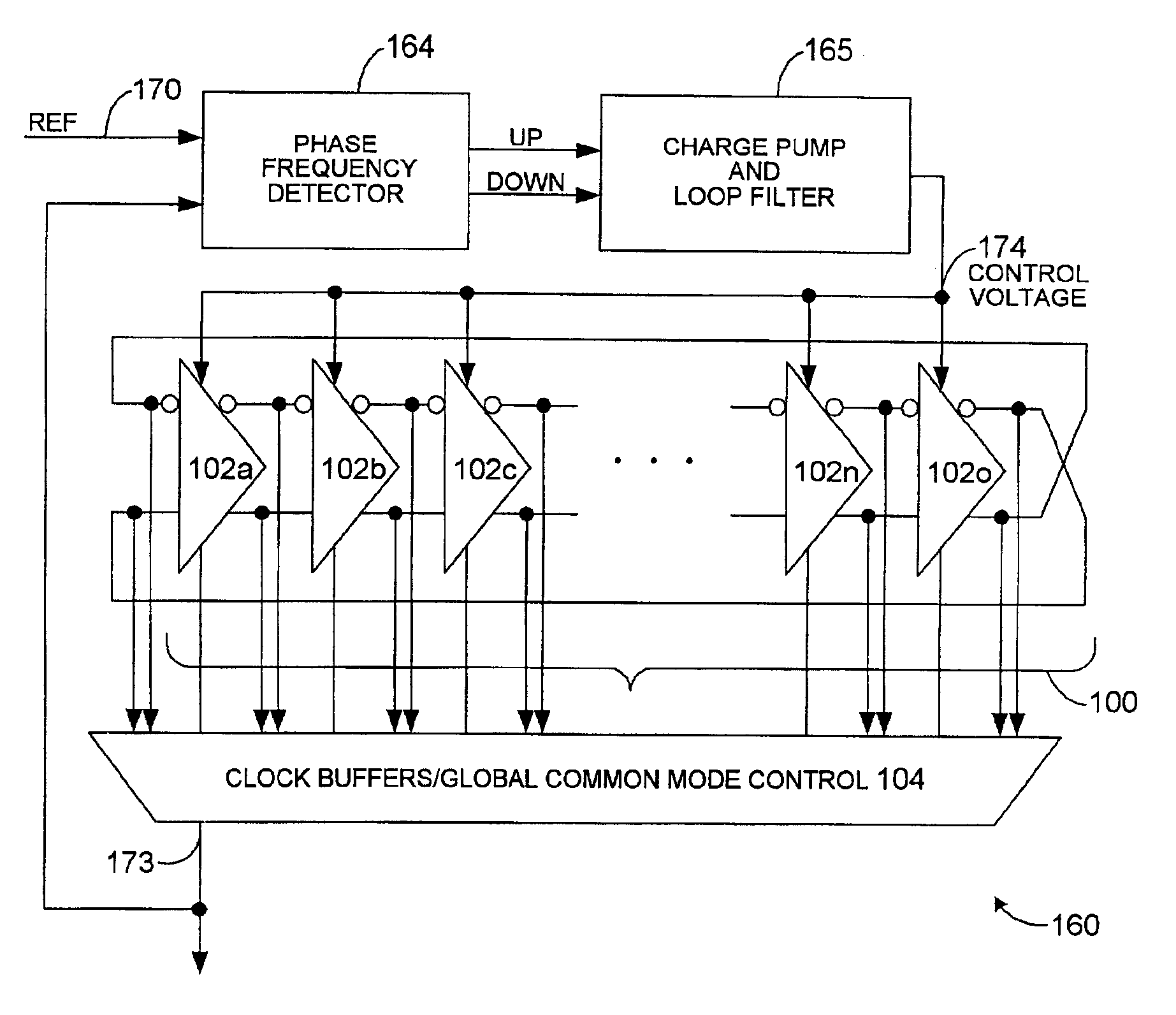
A voltage controlled oscillator ("VCO") circuit capable of generating signals with reduced jitter and / or low-phase noise is provided. One embodiment provides a plurality of cascaded VCO cells, where each VCO cell can include a source coupled differential pair, a bias transistor connected to the differential pair for biasing the differential pair, a resistive load pair connected to the differential pair, and a voltage controlled capacitor pair or varactor pair connected to the differential pair. The varactors provide control over the frequency of the oscillations produced by the VCO circuit in combination with a control voltage. A phase frequency detector combined with a charge pump and loop filter provide the control voltage.
Owner:UNIVERSAL CONNECTIVITY TECH INC
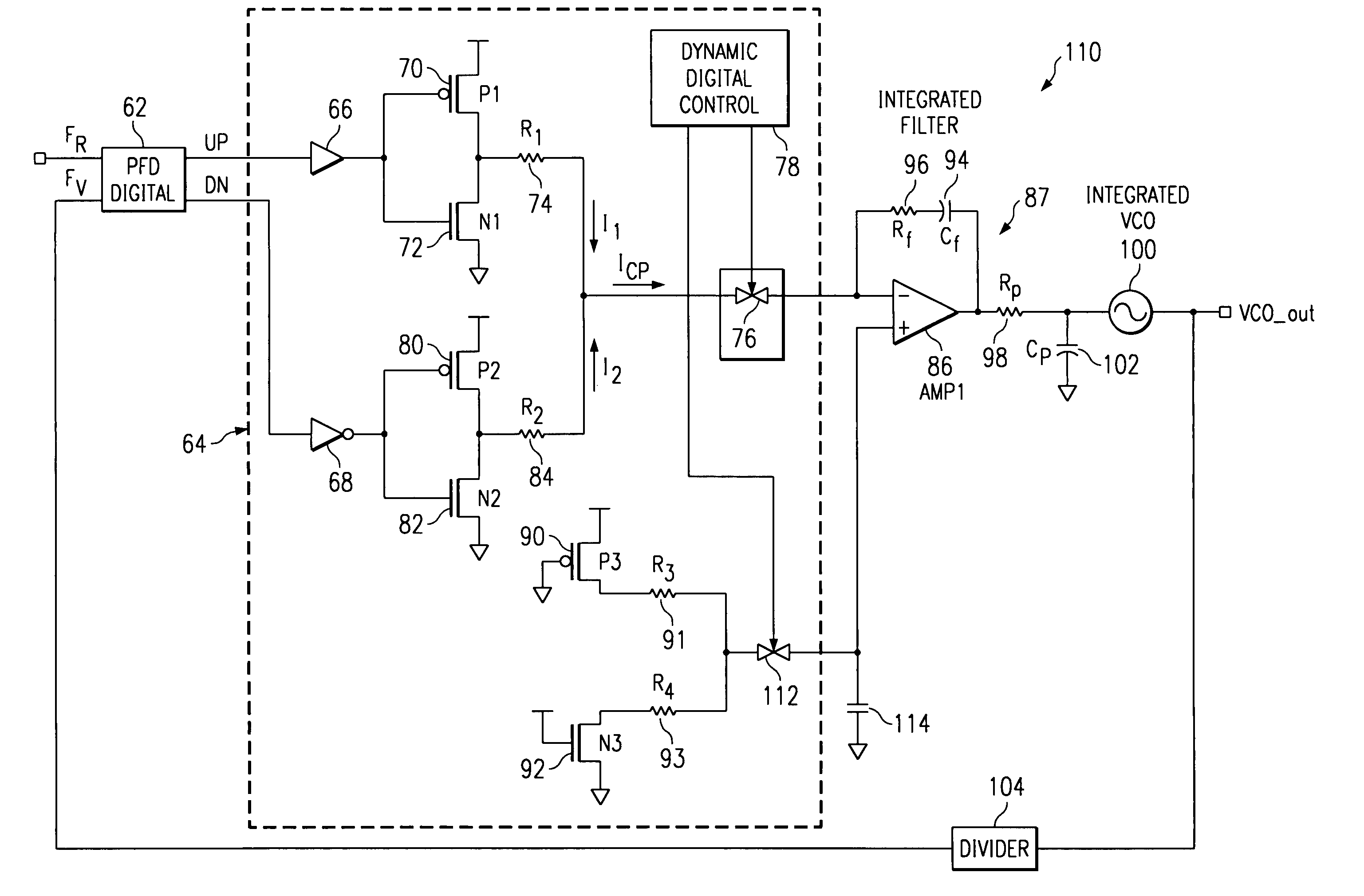
Charge pump phase locked loop with improved power supply rejection
ActiveUS6963233B2Improve power supply rejection ratioVoltage variationPulse automatic controlElectric variable regulationPhase detectorElectricity
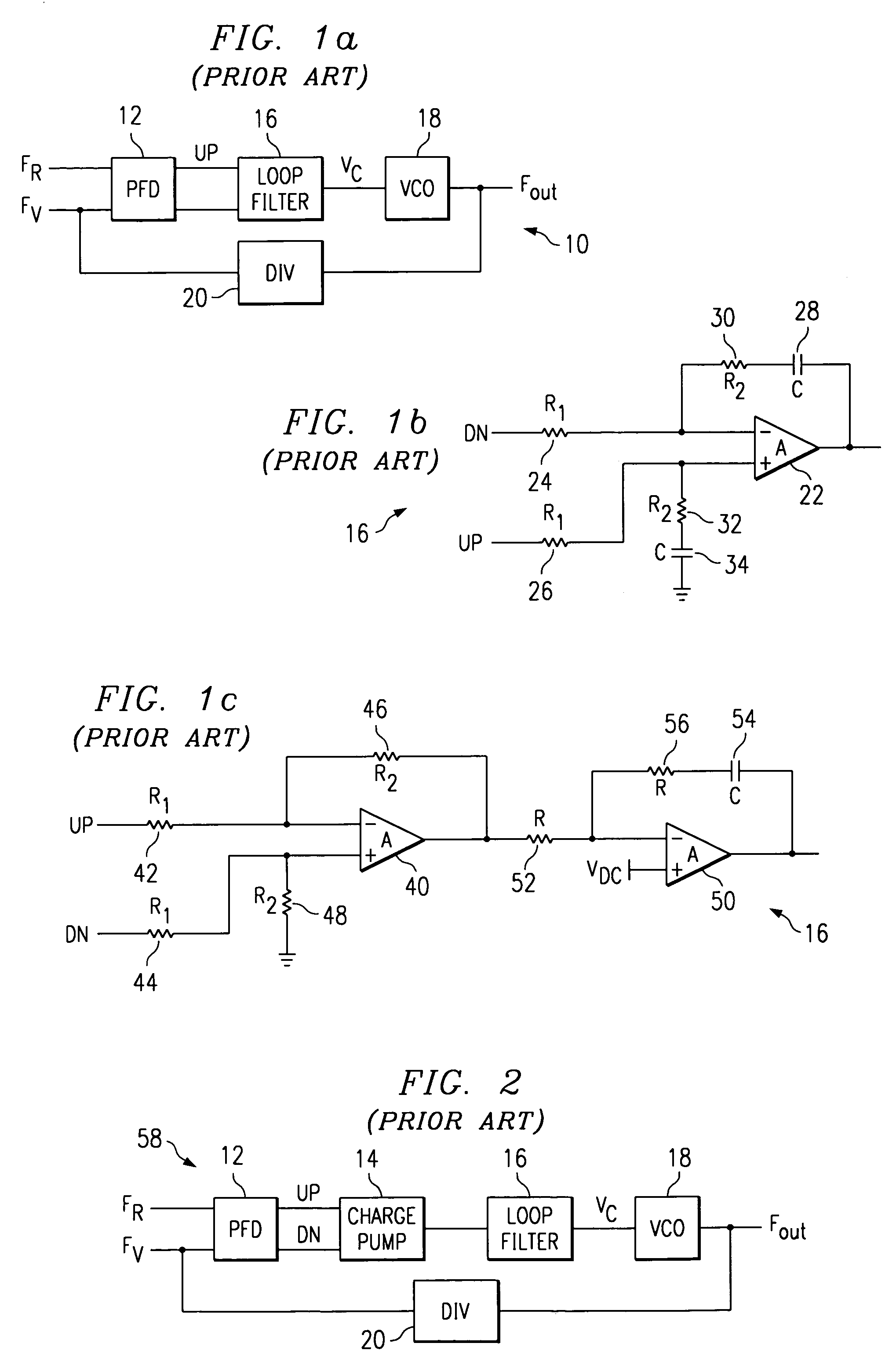
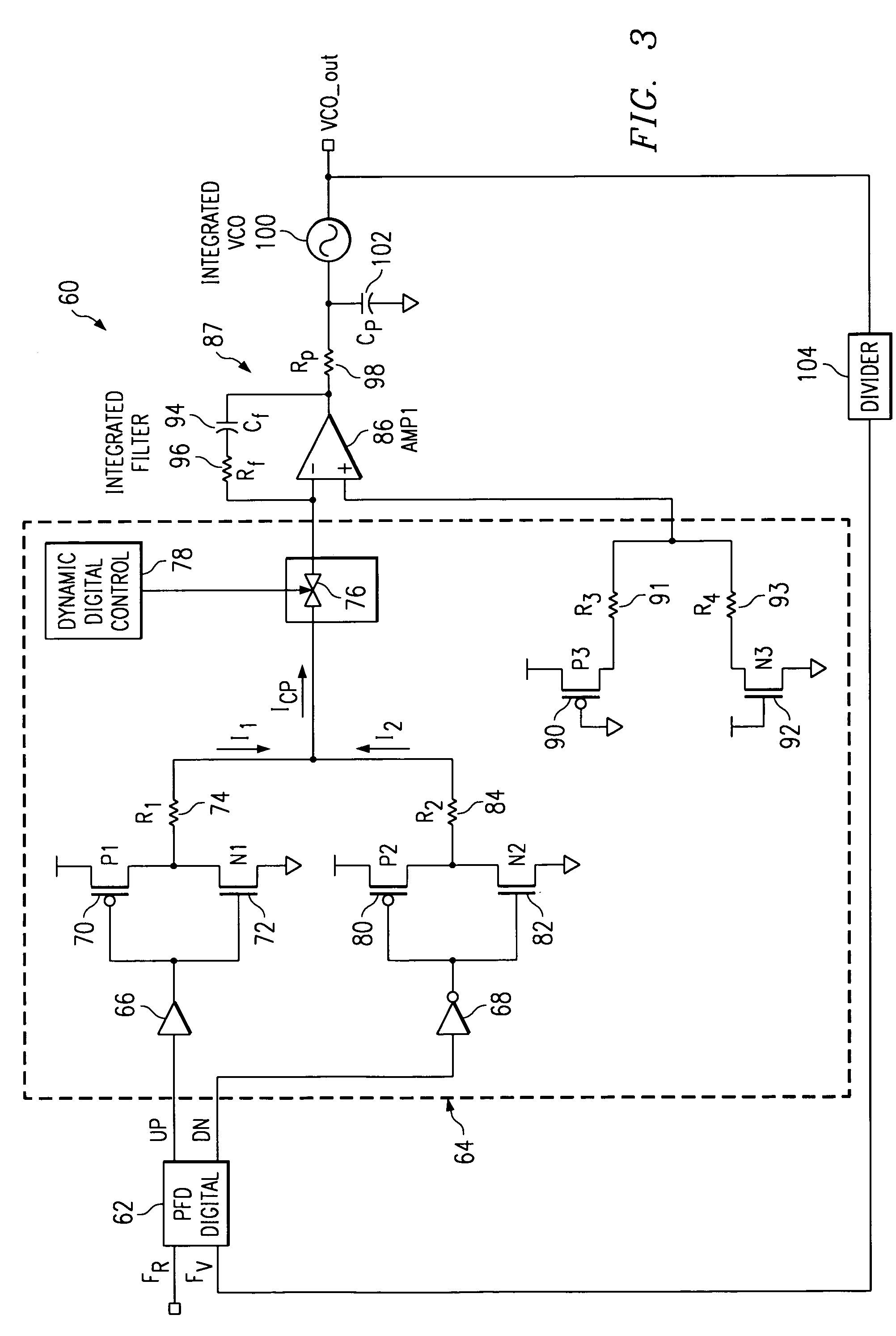
A phase lock loop circuit (60) has a phase frequency detector (62), a charge pump (64), an active filter (87) and a voltage-controlled oscillator (100). The phase detector generates signals responsive to reference signal FR and VCO output signal FV. A charge pump generates a voltage at the input of a first transmission gate (76) according to the values of the phase detector signals. A predetermined voltage is generated at the input of a second transmission gate (112). When the transmission gates (76, 110) are closed (low impedance) the charge pump may sink or source current to the inverting input of the operational amplifier (86) of the active filter 86 and the predetermined voltage is applied to the non-inverting input. When the transmission gates are open (high impedance state) the inverting input is electrically isolated from the node and the non-inverting output is isolated from the power supply.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
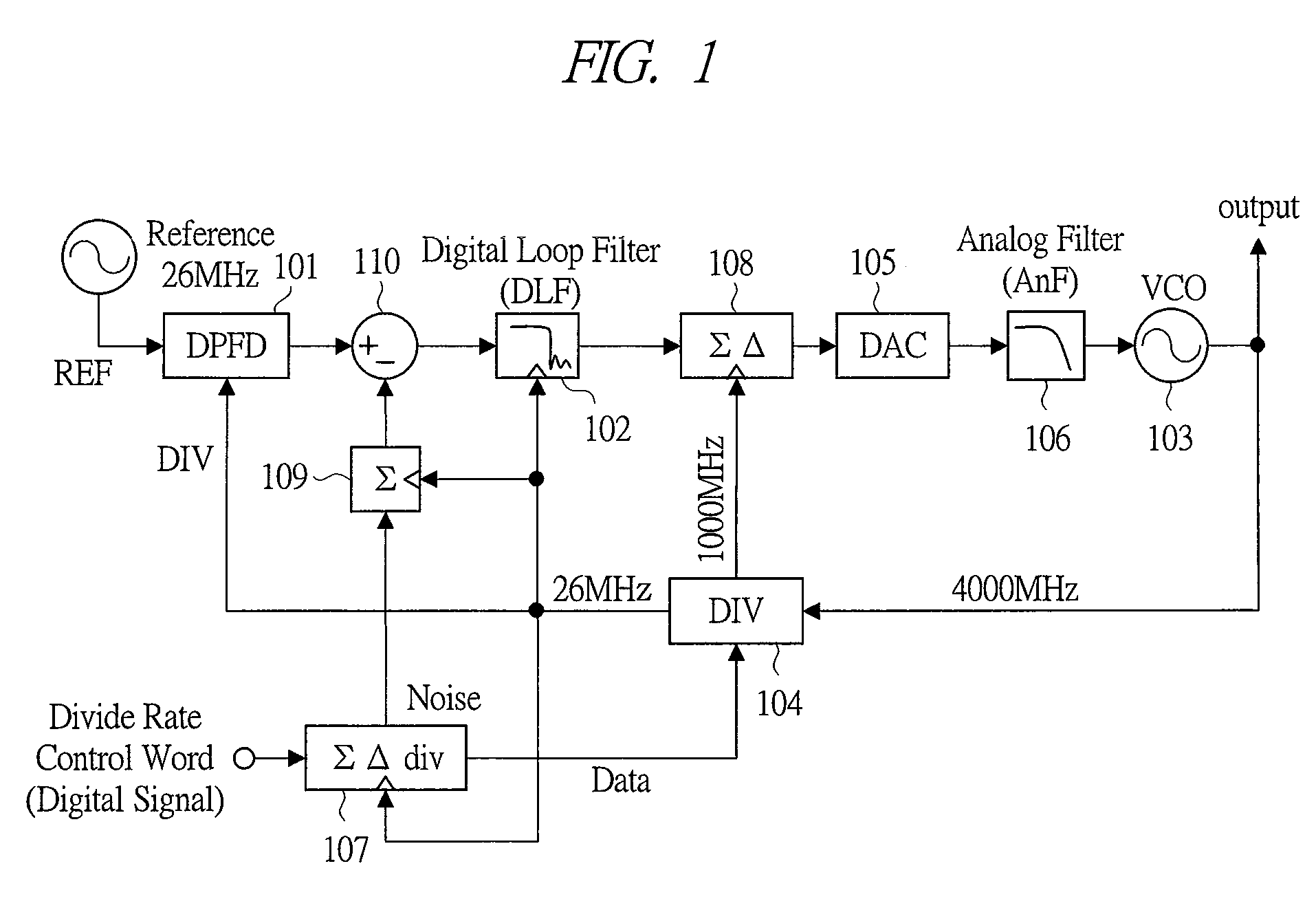
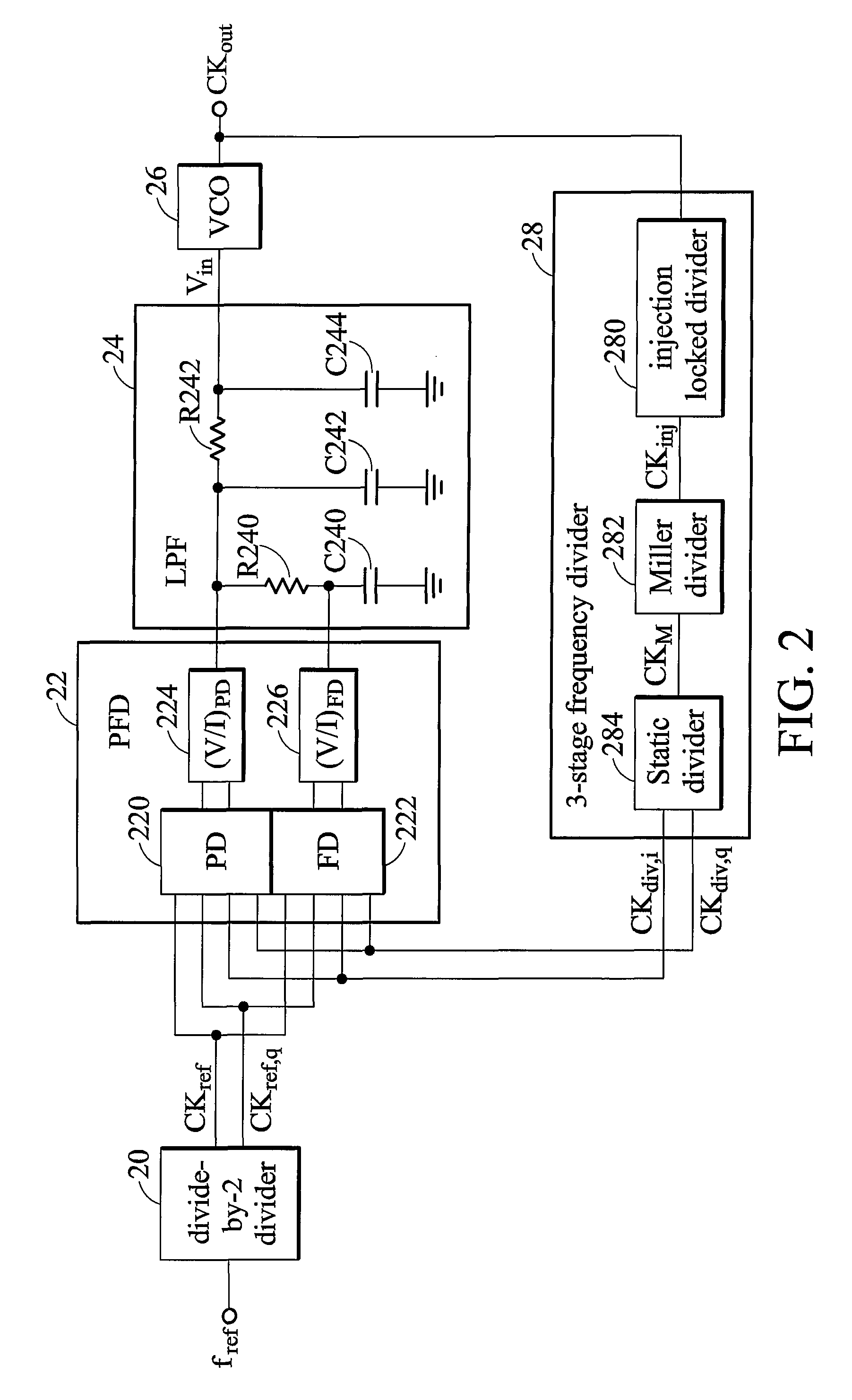
Low-power, low-jitter, fractional-n all-digital phase-locked loop (PLL)
ActiveUS20080048791A1Pulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionLoop filterReference Period
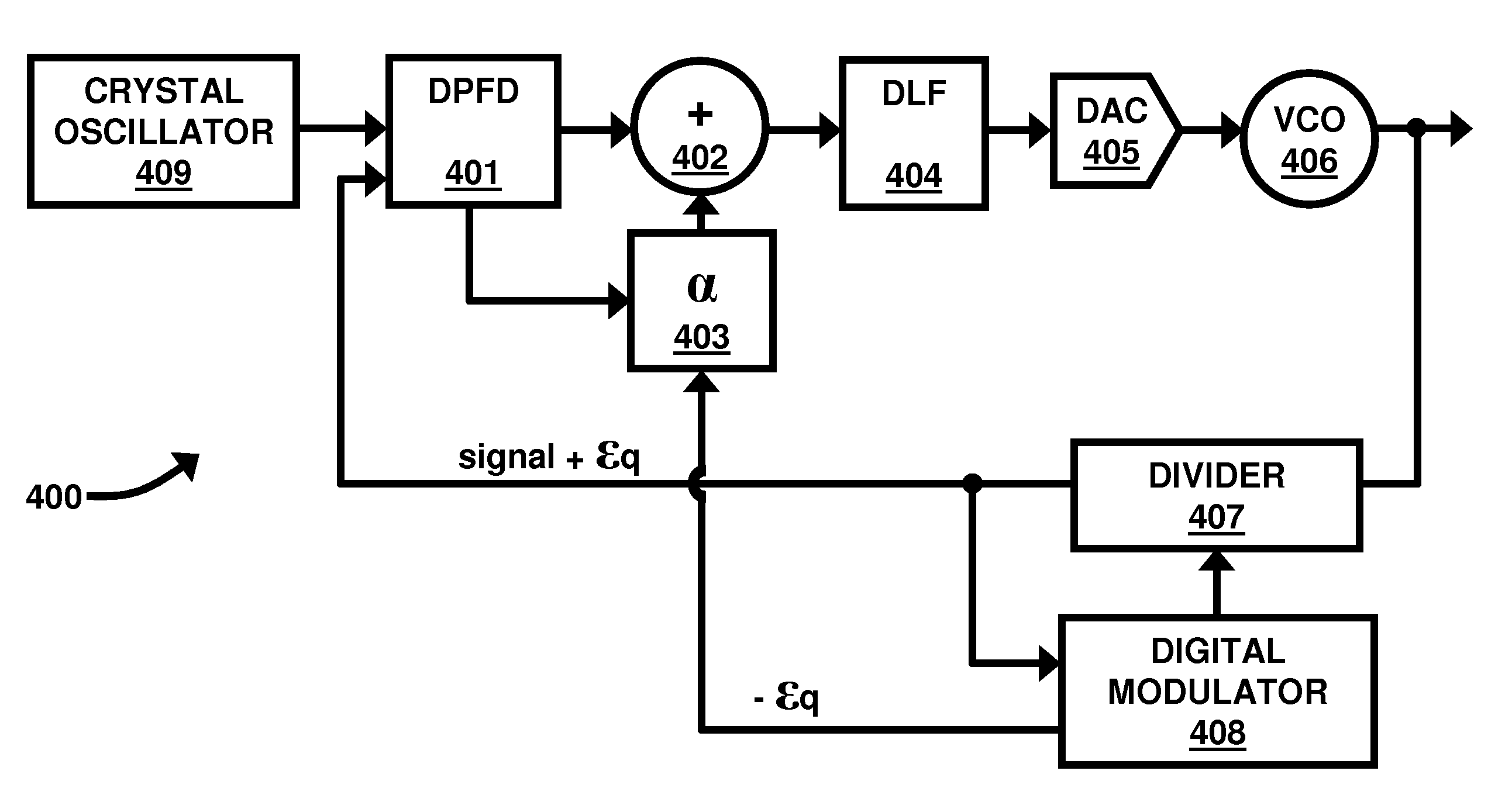
A method for synthesizing frequencies with a low-jitter an all-digital fractional-N phase-locked loop (PLL) electronic circuit adapted to synthesize frequencies with low-jitter, wherein the electronic circuit comprises a digital phase-frequency detector (DPFD) operatively connected to a digital loop filter (DLF), wherein the DPFD adapted to receive a reference signal and a feedback signal; compare a phase and frequency of the reference and feedback signals to determine a phase and frequency error between the reference and feedback signals; and provide a DPFD output comprising a multi-bit output; wherein the DLF is adapted to receive and filter the DPFD output and provide a DLF output, and wherein the DLF output is updated at each reference period.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
Clock generator and data recovery circuit using the same
ActiveUS20060078079A1Reduce tracking timePulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionPhase detectorLoop filter
A clock generator and a data recovery circuit. The clock generator includes a voltage control oscillator (VCO) for generating a sampling clock and multi-phase clocks, a multiplexer for receiving the multi-phase clocks and selecting one of the multi-phase clocks to generate a selected clock according to a selection signal, a phase-frequency detector for receiving the selected clock and a reference clock and generating a phase-frequency error signal, a charge pump and loop filter for receiving the phase-frequency error signal and generating a control voltage, a phase detector for receiving the sampling clock and an input signal and generating a phase error signal, and a digital low-pass filter for receiving the phase error signal and generating the selection signal. The digital low-pass filter clears an accumulated phase error when it generates the selection signal to force the multiplexer to change the phase.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
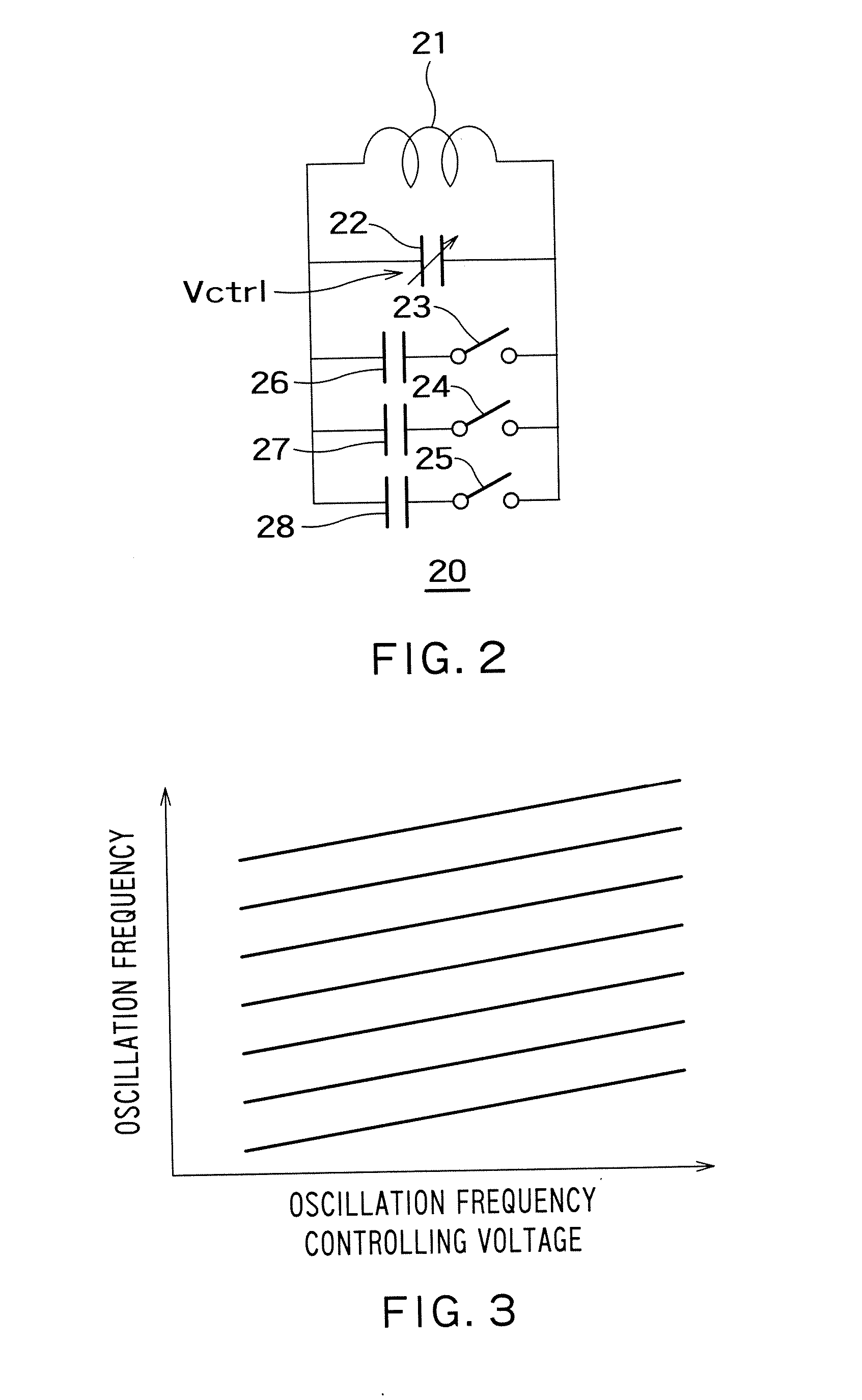
Controller for oscillator
An oscillator controller, has a phase frequency detector that compares a reference signal and a frequency-divided signal and outputs a phase difference signal; a charge pump that outputs a phase error signal according to the phase difference signal output from said phase frequency detector; a loop filter that filters the phase error signal output from said charge pump and outputs an oscillation frequency controlling voltage; a voltage-controlled oscillator that has an LC resonator having a coil, a variable capacitor connected to the opposite ends of the coil at the opposite ends thereof, and a capacitor connected in series with a switch between the opposite ends of said variable capacitor, the oscillation frequency of the voltage-controlled oscillator being controlled through adjustment of the capacitance value of said variable capacitor by said oscillation frequency controlling voltage; a frequency divider that divides the frequency of the output of said voltage-controlled oscillator and outputs said frequency-divided signal; a first counter that counts the number of waves of said reference signal to a desired number and outputs a first flag signal; a second counter that counts the number of waves of said frequency-divided signal to said desired number and outputs a second flag signal; a first comparator that compares said first flag signal and said second flag signal and outputs a frequency comparison signal; and a control circuit that controls said voltage-controlled oscillator, said first counter, said second counter and said frequency divider by outputting signals thereto.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Pll circuit
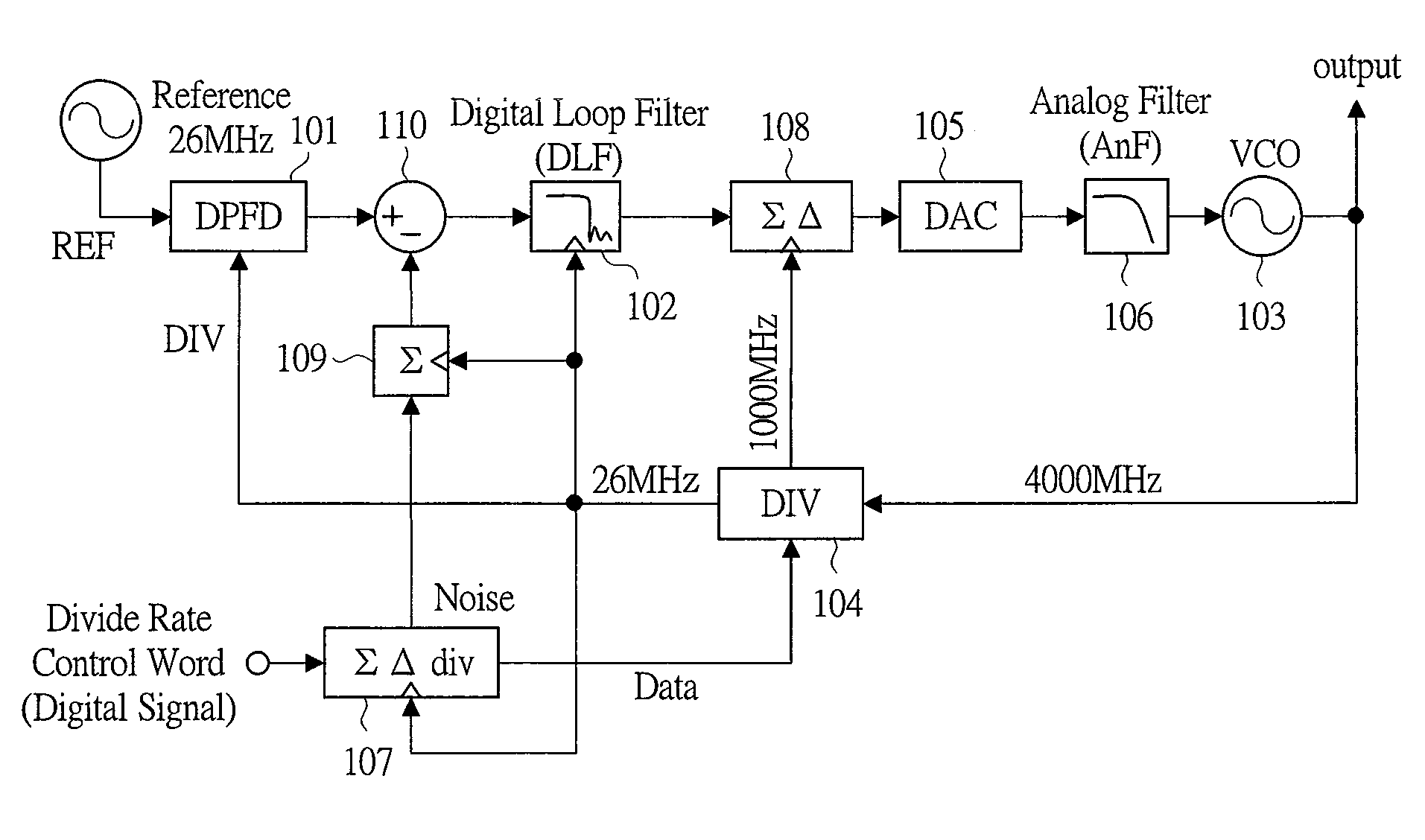
InactiveUS20100097150A1Suppressing quantization noiseReduce areaPulse automatic controlLoop filterDigital analog converter
A technique for suppressing quantization noise generated due to digitizing an analog circuit in a PLL circuit is provided. The PLL circuit comprises: a digital phase frequency detector which detects (compares) phases and frequencies of a reference signal and a frequency-divided signal and converts the same to a digital value; a digital loop filter which eliminates high-frequency noise components from an output of the digital phase frequency comparator; a digital-analog converter which converts a digital value of an output of the digital loop filter to an analog value; an analog filter which eliminates a high-frequency noise component from an output of the digital-analog converter; a voltage controlled oscillator whose frequency is controlled based on an output of the analog filter; and a frequency divider which divides the frequency of the voltage controlled oscillator and outputs the frequency-divided signal.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP +1
High frequency low noise phase-frequency detector and phase noise reduction method and apparatus
InactiveUS20060057996A1Less noisyFaster topologyPulse automatic controlRadio transmissionLow noiseDBc
The present invention discloses a new type of extremely low-noise phase-frequency detector (PFD) 500, broadband from DC to multi-GHz RF frequencies for PLL synthesizer applications. Free of any feedback mechanisms, thus inherently fast, it operates close to transition frequency fT of IC processes or frequency limits of discrete mixers. The PFD 500 utilizes complex SSB conversion in both the in-phase and quadrature arms, delaying the in-phase arm in 530, beating the delayed signal 124 with the un-delayed quadrature signal 122 in mixer 126. The output 128 contains both the frequency difference and the phase difference information between the two signals 118 and 520, providing both the frequency-discrimination (FD) and the phase detection (PD) functions. Utilizing standard mixers the PFD 500 can achieve superior CNRs of 180 dBc / Hz at multi-GHz RF. Additionally, utilizing the FD / FM demodulation capability, the present invention improves phase noise of various signals and linearity of FM modulators.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
Phase synchronization circuit and receiver having the same
InactiveUS20090207961A1Pulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionPhase detectorPhase difference
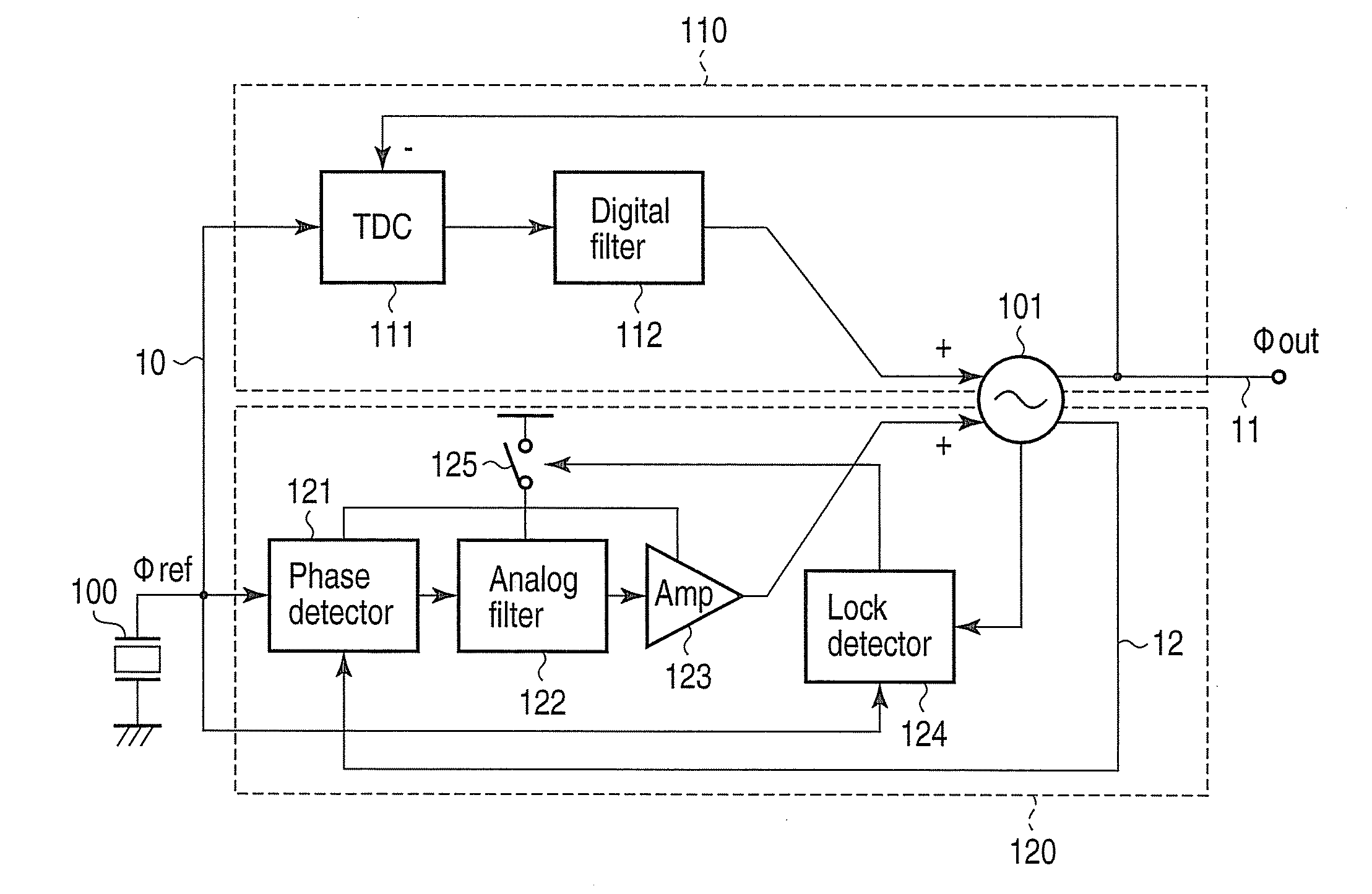
A phase synchronization circuit includes a controlled oscillator configured to generate a first oscillation signal and a second oscillation signal that have a common frequency but different phase controlled by a combination of a first control signal and a second control signal, a digital phase frequency detector configured to detect a frequency difference and a first phase difference between a reference signal and the first oscillation signal to generate the first control signal, an analog phase detector configured to detect a second phase difference between the second oscillation signal and the reference signal to generate the second control signal, and a lock detection unit configured to detect a lock of the first oscillation signal with the reference signal in terms of frequency and phase, in order to set the analog phase detector in an active state.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
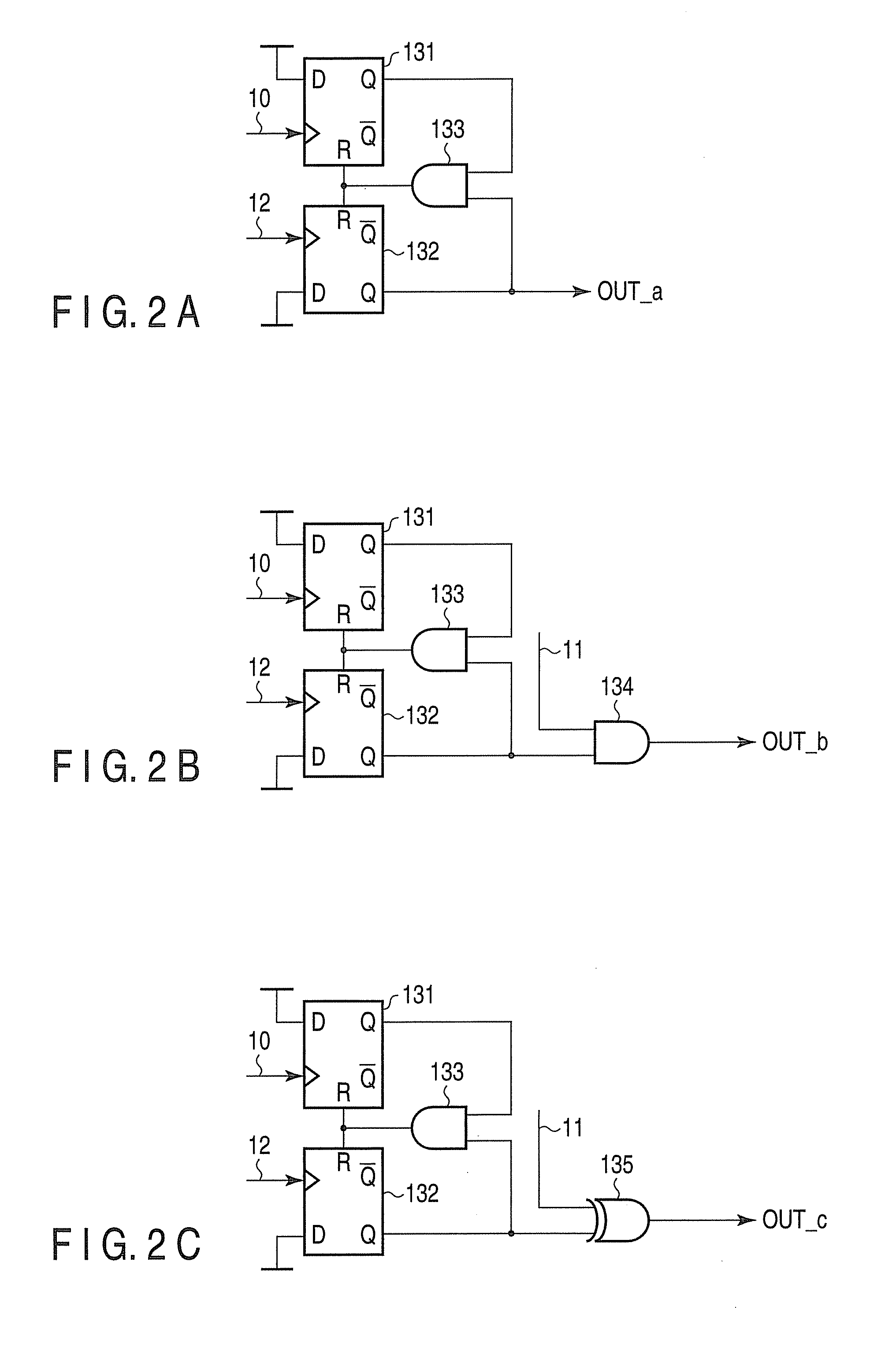
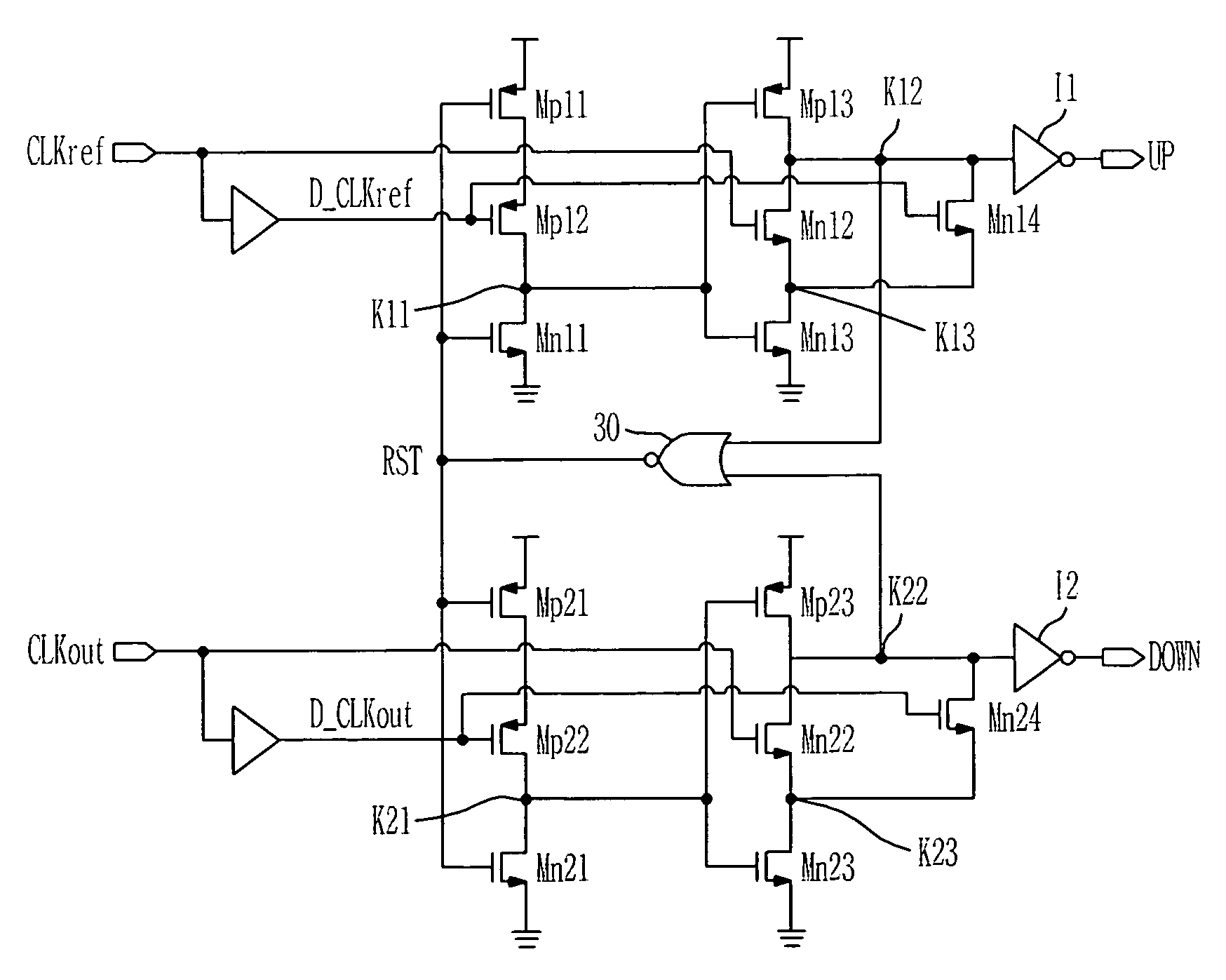
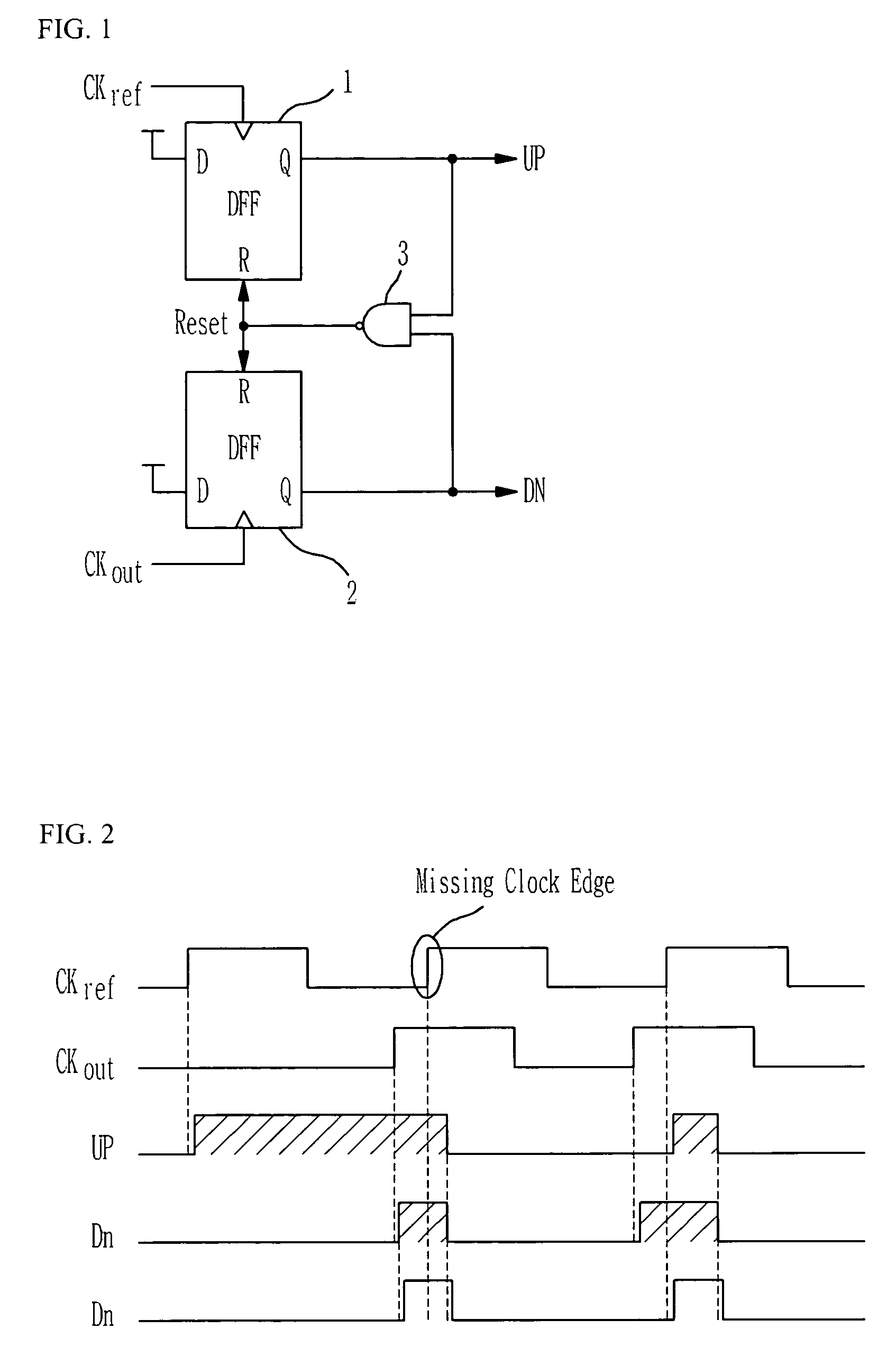
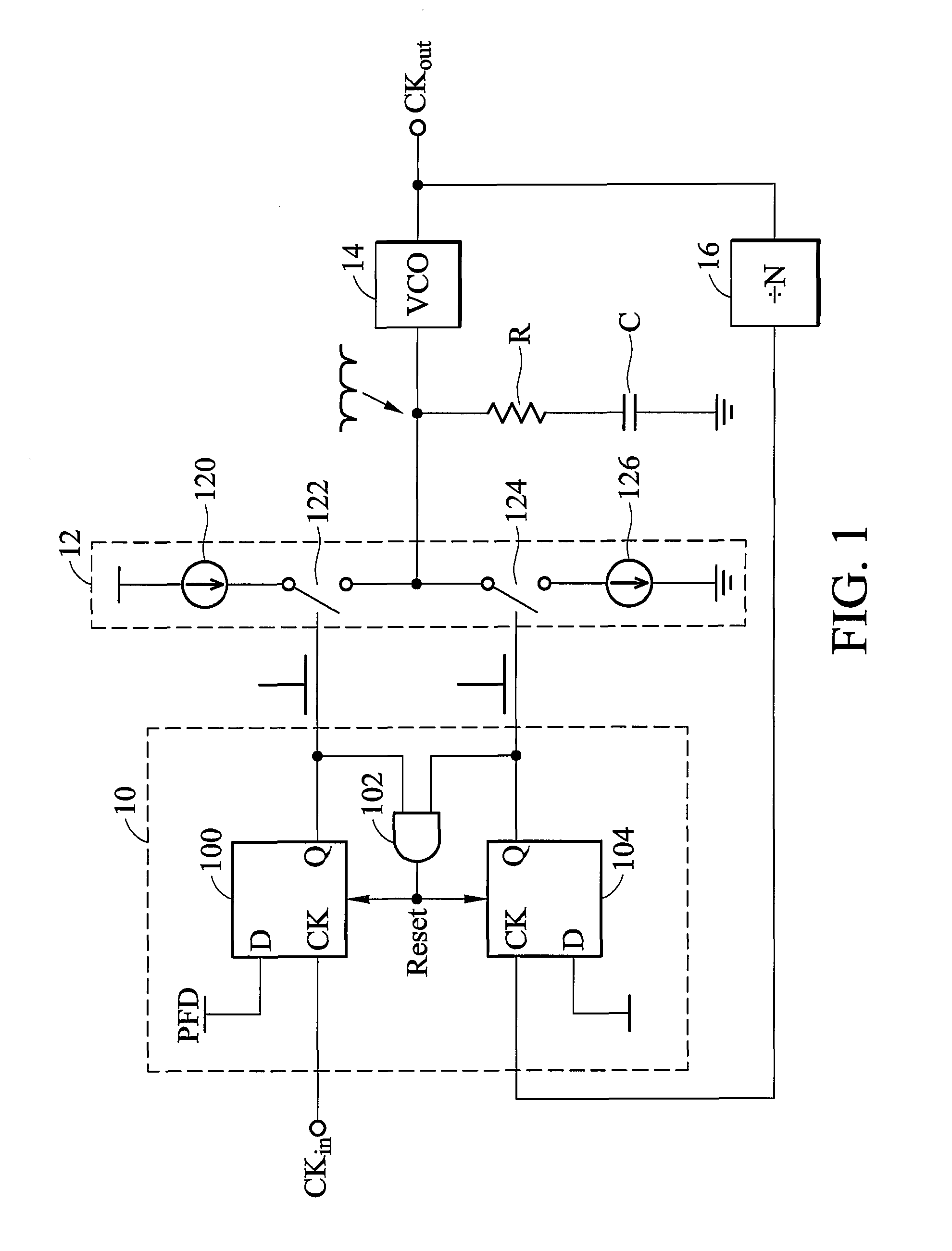
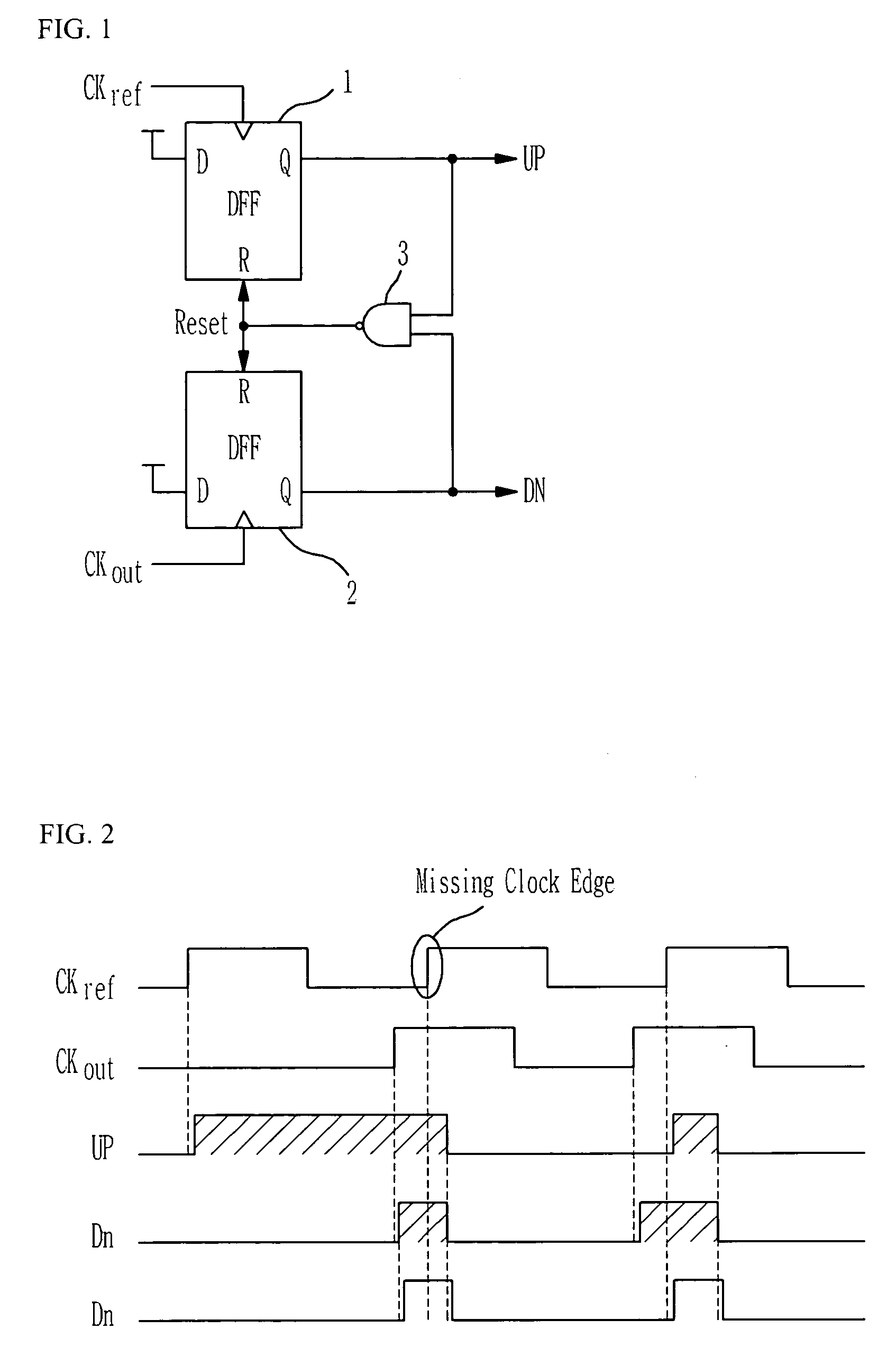
Phase frequency detector
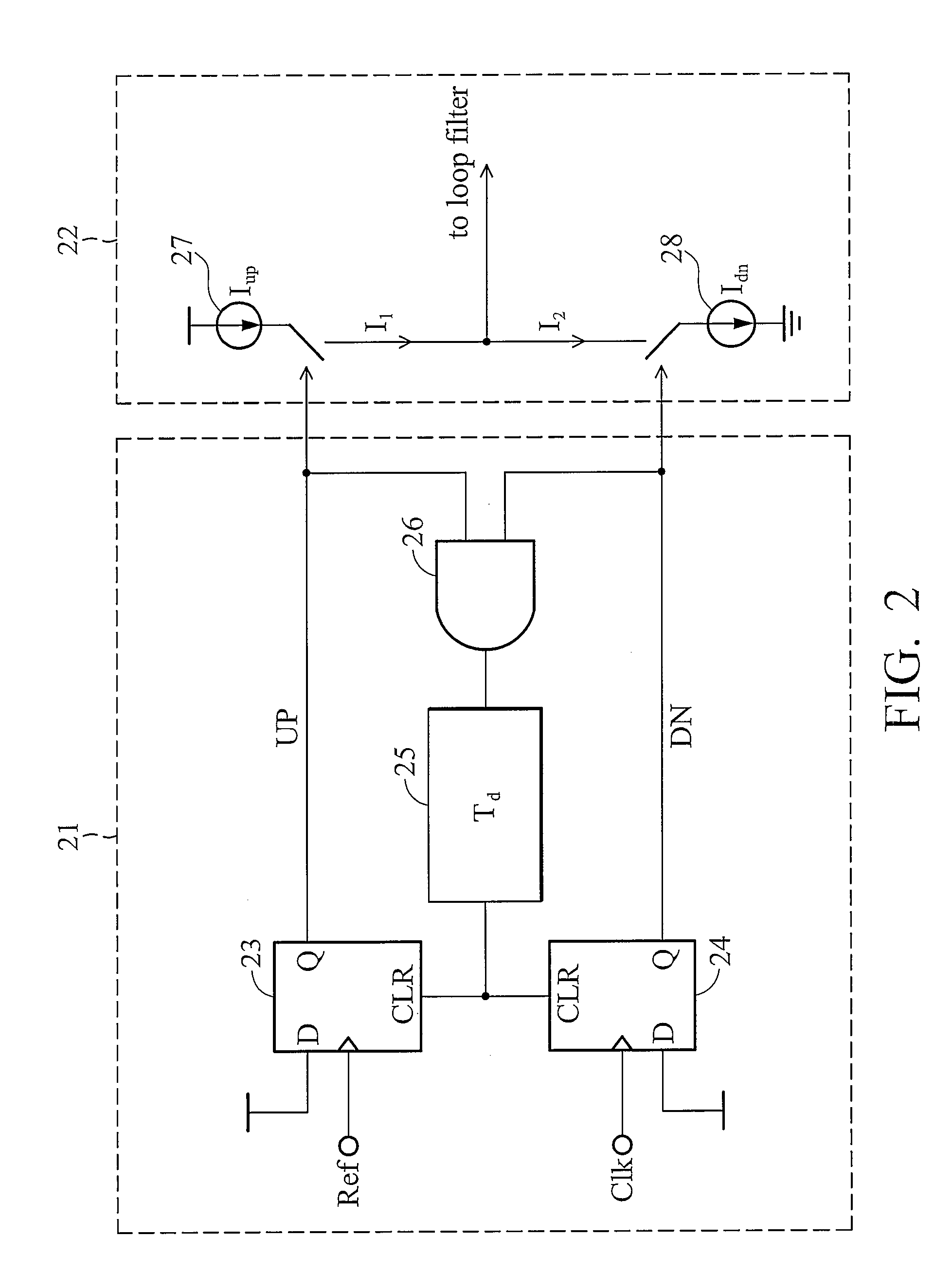
InactiveUS7053666B2Fast phase lockReduce power consumptionPulse automatic controlVoltage-current phase angleLow noiseControl signal
Provided is a phase frequency detector for use in a phase locked loop (PLL) or a delay locked loop (DLL), the phase frequency detector including: an UP signal output unit having a first stage operated according to a reference clock delayed by a predetermined time and a reset signal, a second stage operated according to the reference clock and an output of the first stage, and an inverter for inverting an output of the second stage; a DOWN signal output unit having: a first stage operated according to an outer clock delayed by a predetermined time and the reset signal, a second stage operated according to the outer clock and an output of the first stage, and an inverter for inverting an output of the second stage; and a logic gate logically combining the output of the second stage of the UP signal output unit and the output of the second stage of the DOWN signal output unit to generate the reset signal, thereby a phase range of the input signal with which an effective control signal can be obtained is wide so that low power consumption and low noise characteristics can be obtained due to fast phase lock, low power consumption of a dynamic logic, and fast signal transmission.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Digital loop circuit for programmable logic device
InactiveUS7633322B1Reduced size and complexityIncrease rangePulse automatic controlPhase detectorLoop filter
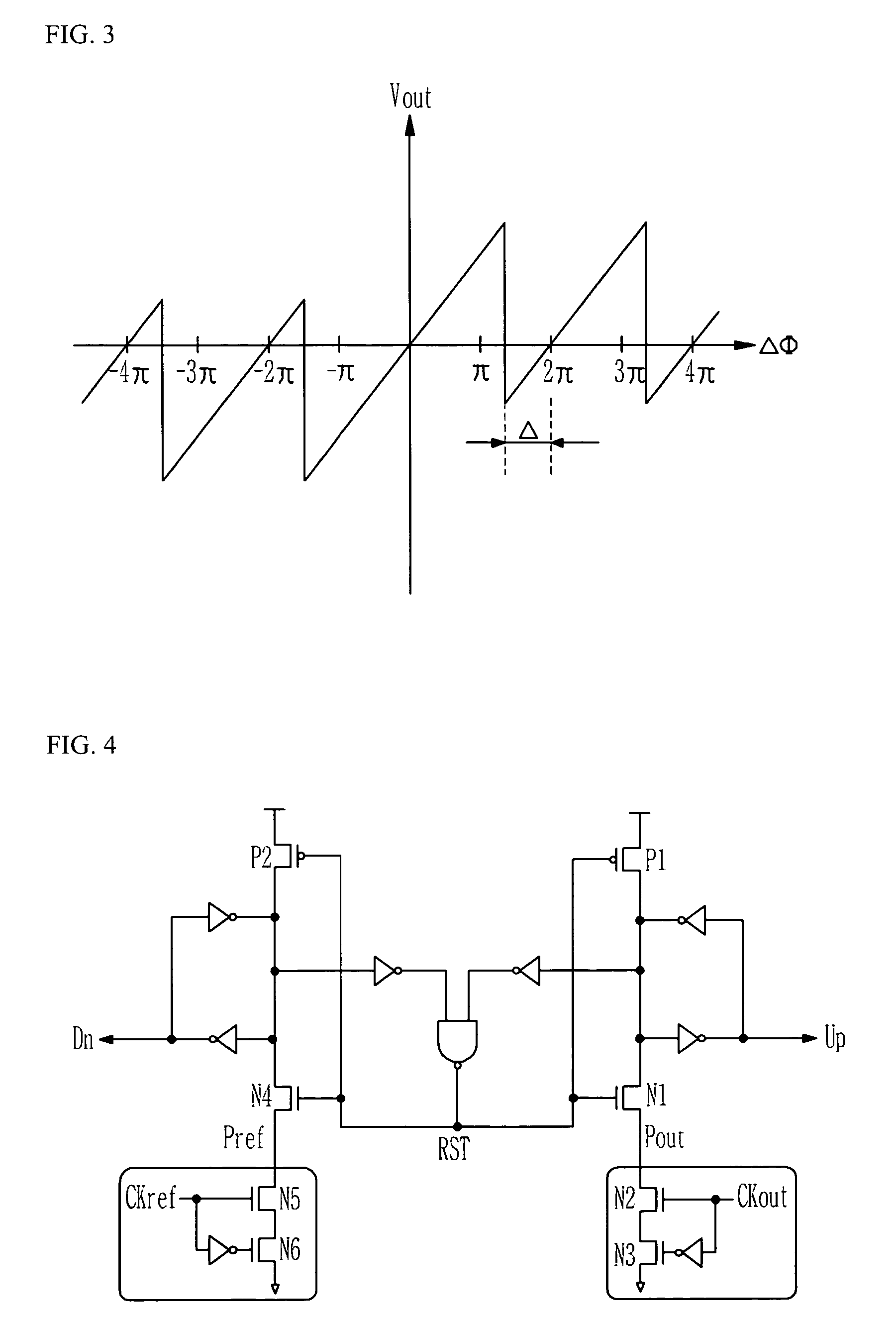
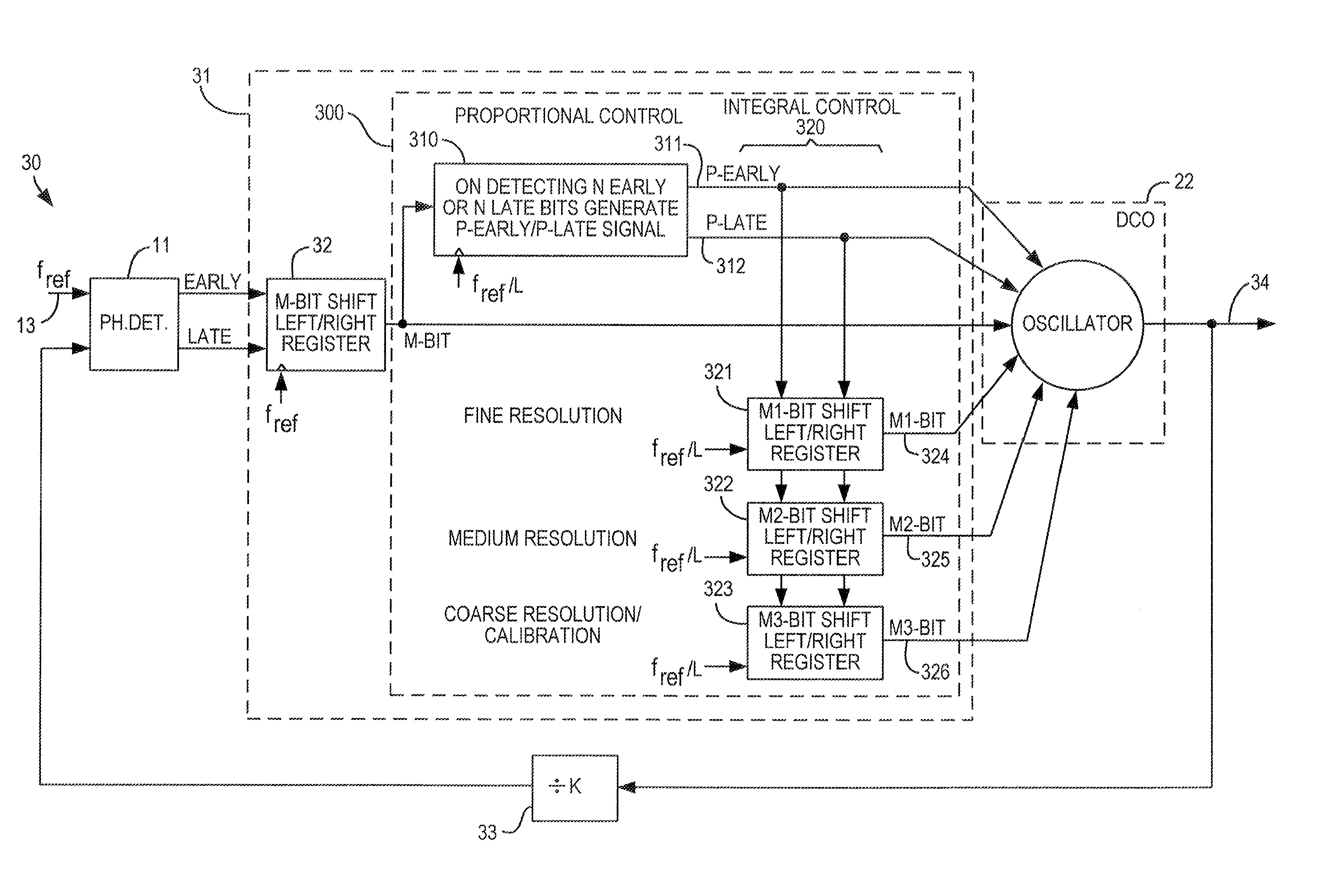
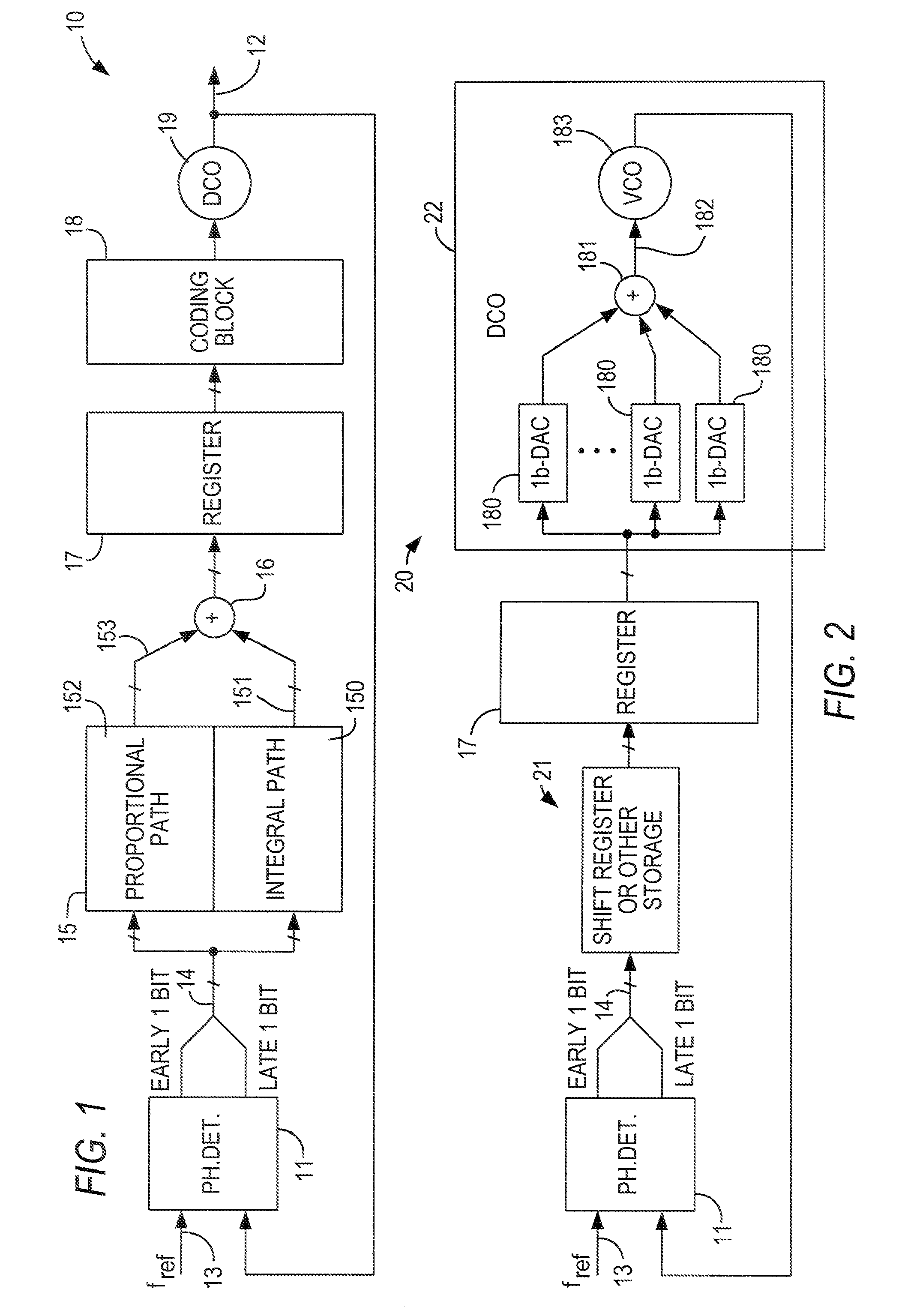
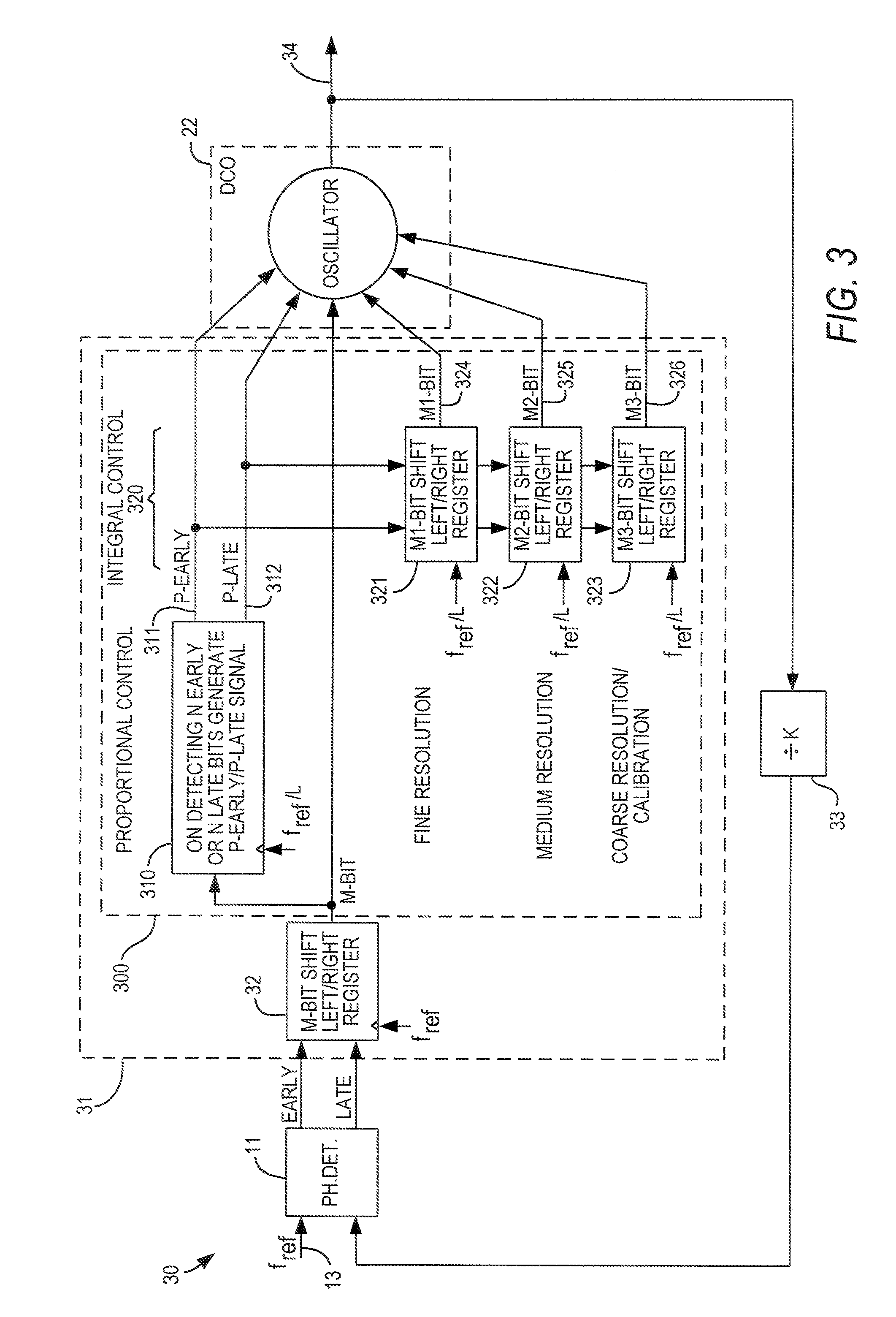
A digital loop circuit—i.e., a phase-locked loop (“PLL”) or delay-locked loop (“DLL”)—having a simplified digital loop filter, is particularly well-suited for a programmable logic device (“PLD”). The loop filter may be a memory (e.g., a shift register) which counts the early / late or up / down signals from a phase detector or phase-frequency detector (“error detector”) and outputs a signal when the count exceeds a threshold. Separate integral and proportional paths of the loop may include chained shift registers, with each outputting a signal only when the previous shift register overflows into it. A digital error detector may respond nonlinearly, with outputs of different bit widths, to different amounts of phase or frequency error.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Method and apparatus for on-chip phase error measurement to determine jitter in phase-locked loops
ActiveUS20080172193A1Noise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementElectrical testingPhase locked loop circuitPhase frequency detector
An apparatus includes a phase-locked loop (PLL) circuit including a phase-frequency detector configured to output phase error signals. A phase error monitor circuit is configured to determine instantaneous peak phase error by logically combining the phase error signals and comparing pulse widths of the logically combined phase error signals to a programmable delay time at each reference clock cycle to determine instantaneous phase error change. A storage element is configured to store the instantaneous phase error change.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
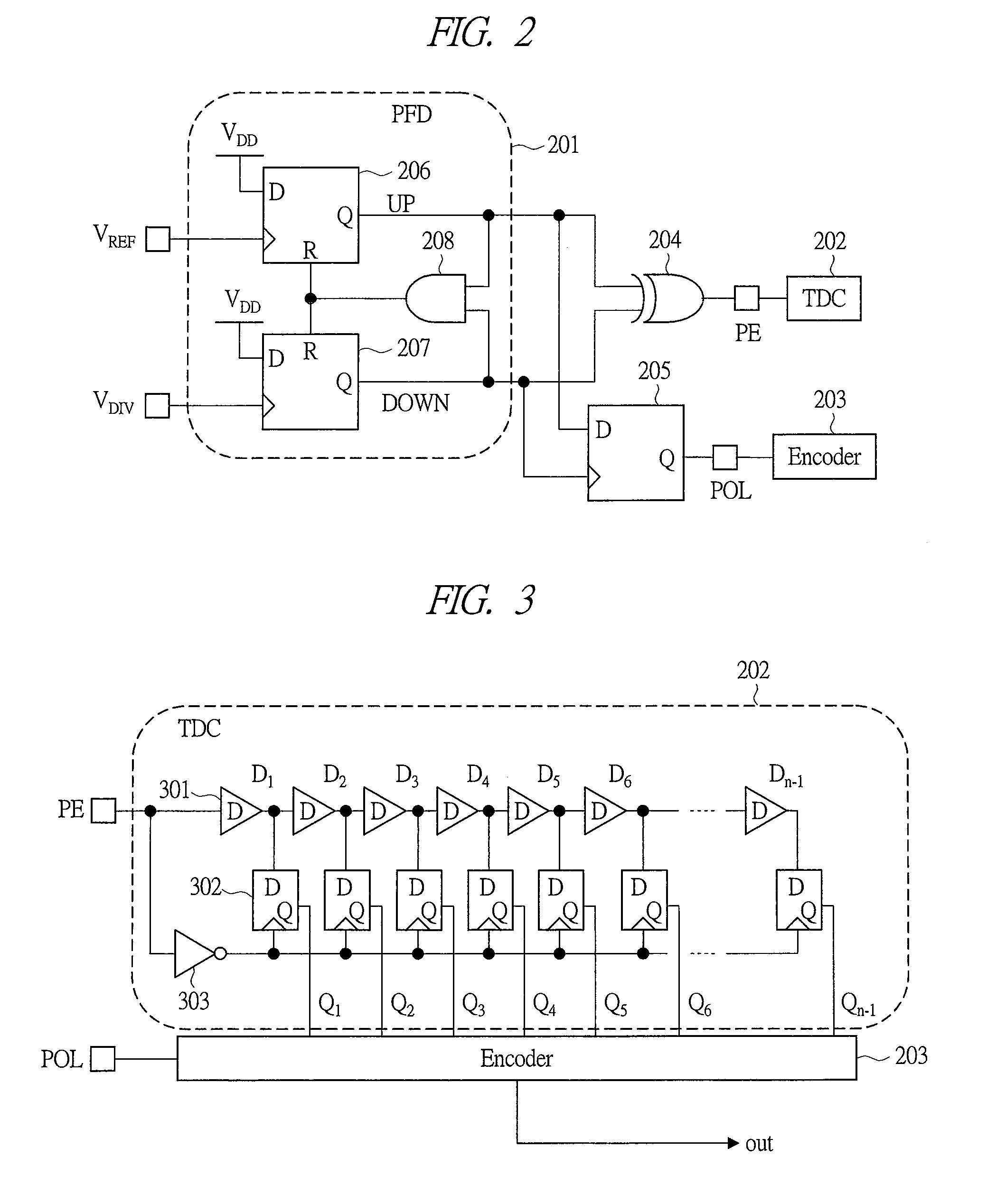
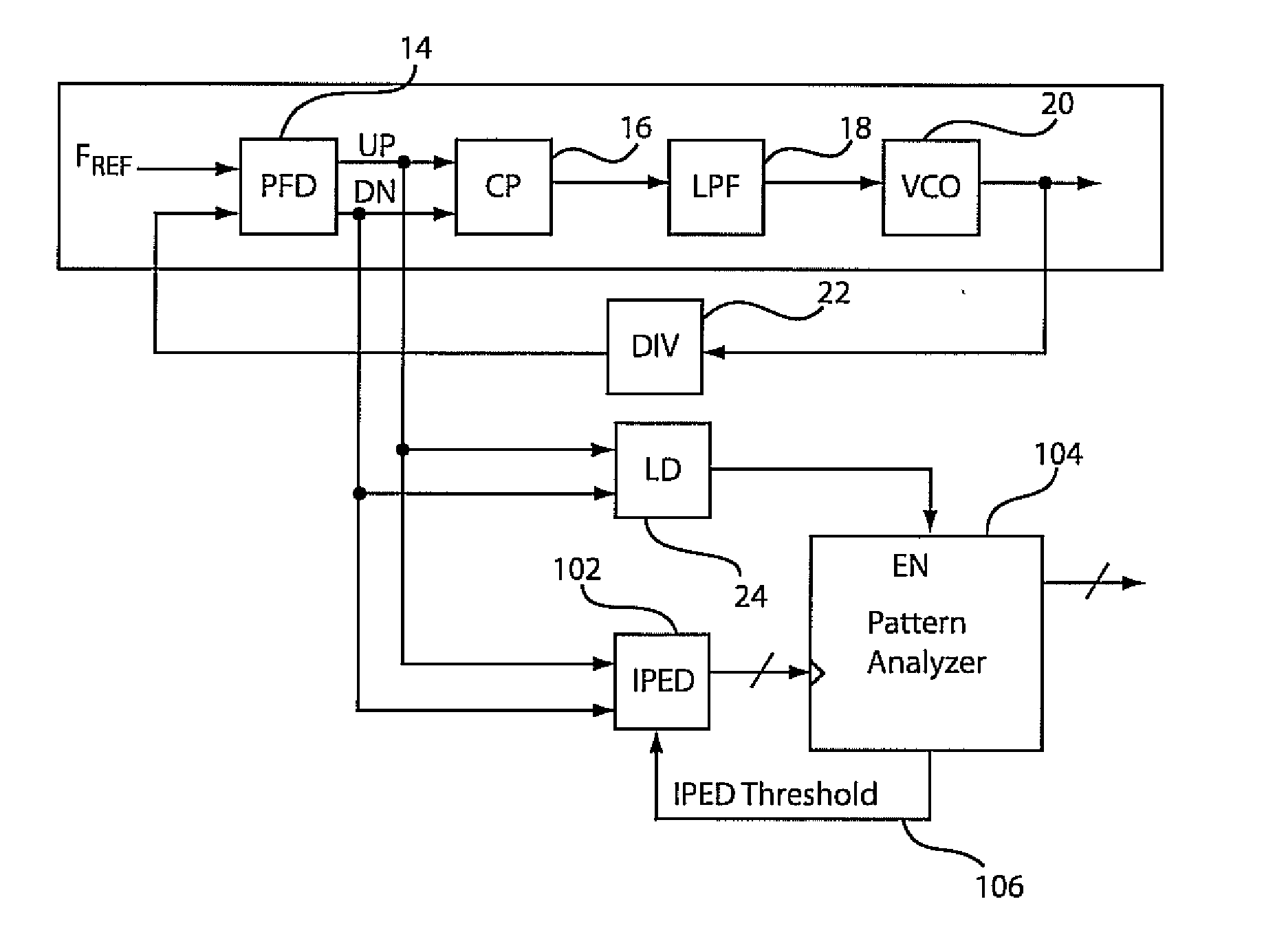
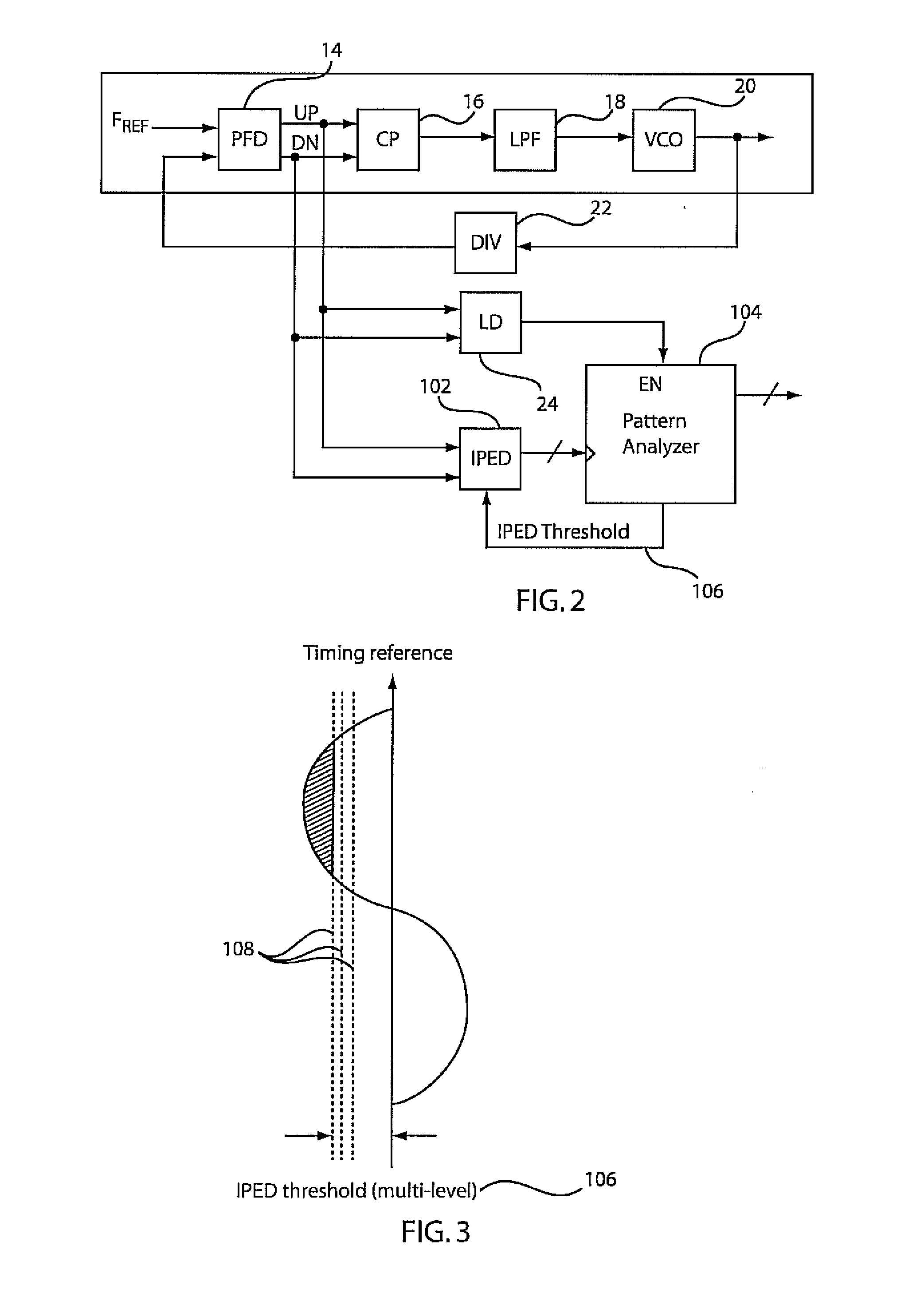
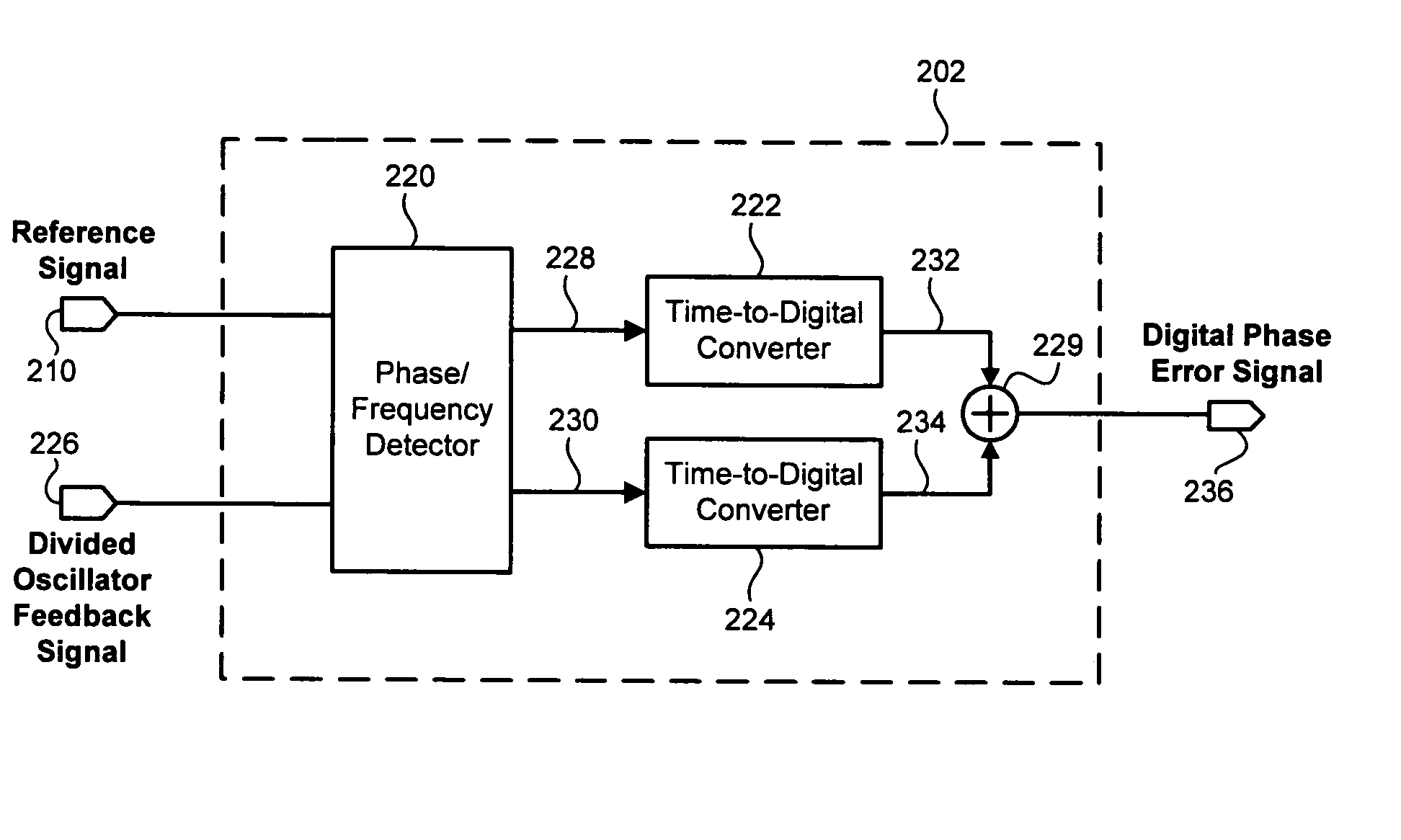
Digital phase detector for a phase locked loop
ActiveUS20060171495A1Readily apparentPulse automatic controlOscillations comparator circuitsPhase detectorDigital number
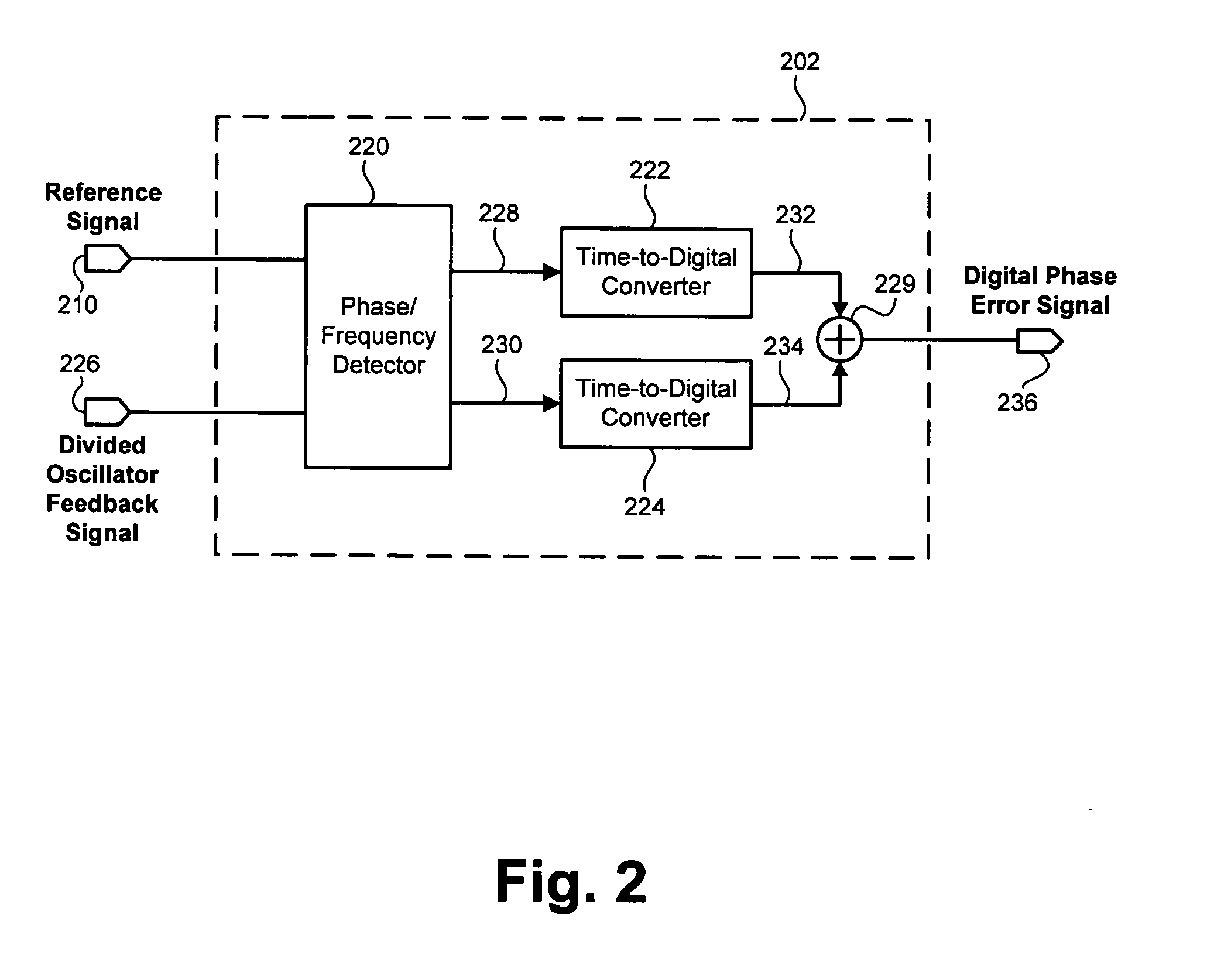
According to one exemplary embodiment, a digital phase detector includes a phase / frequency detector, where the phase / frequency detector is configured to receive a reference signal and a divided oscillator feedback signal and output a first pulse-width modulated signal and a second pulse-width modulated signal. The digital phase detector also includes a first time-to-digital converter, where the first time-to-digital converter is coupled to the phase / frequency detector. The first time-to-digital converter is configured to receive and convert the first pulse-width modulated signal to a first digital number. The digital phase detector further includes a second time-to-digital converter coupled to the phase / frequency detector and configured to receive and convert the second pulse-width modulated signal to a second digital number. The digital phase detector further includes a summation element, where the summation element is configured to subtract the second digital number from the first digital number and output a digital phase error signal.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
Delay-compensated fractional-N frequency synthesizer
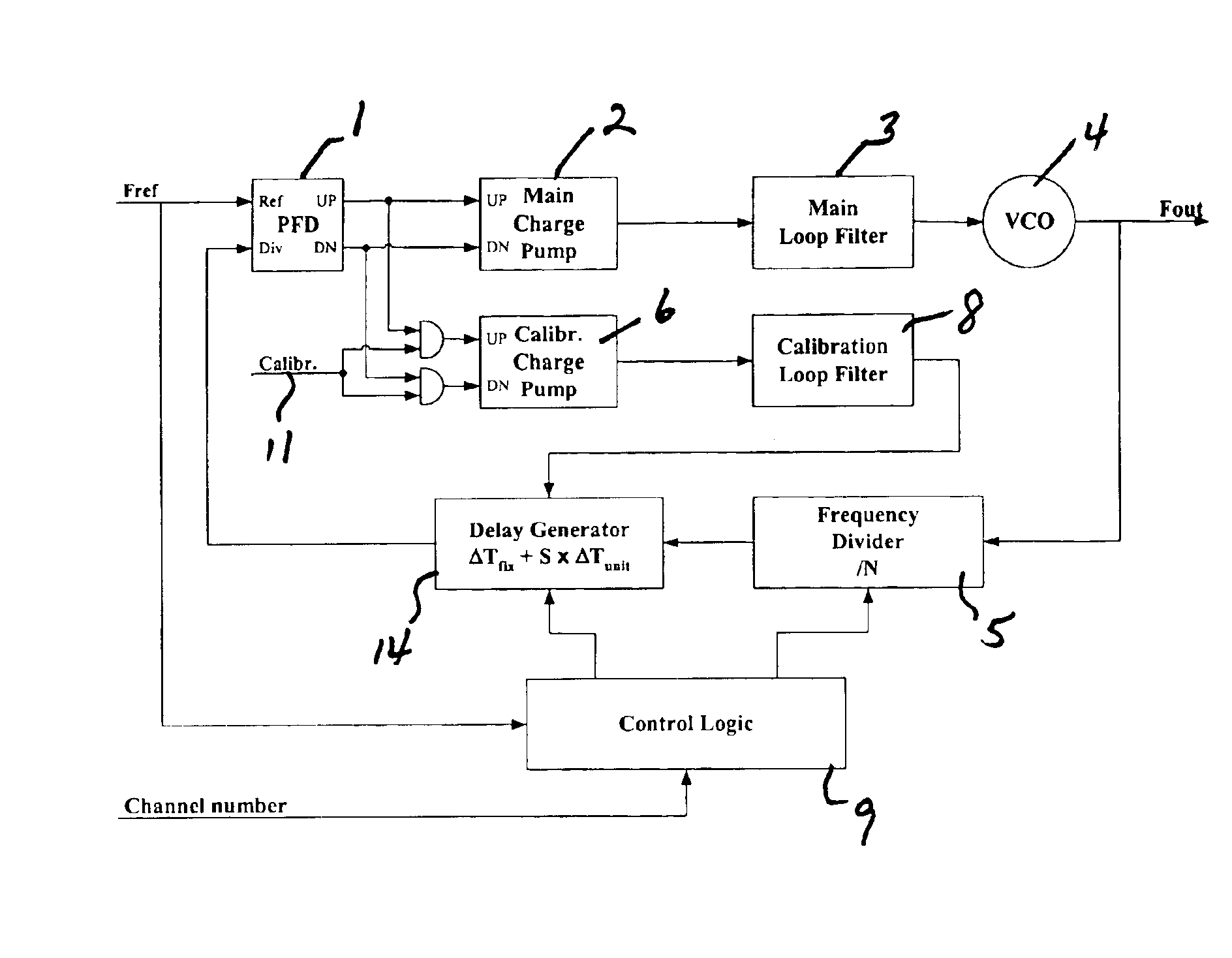
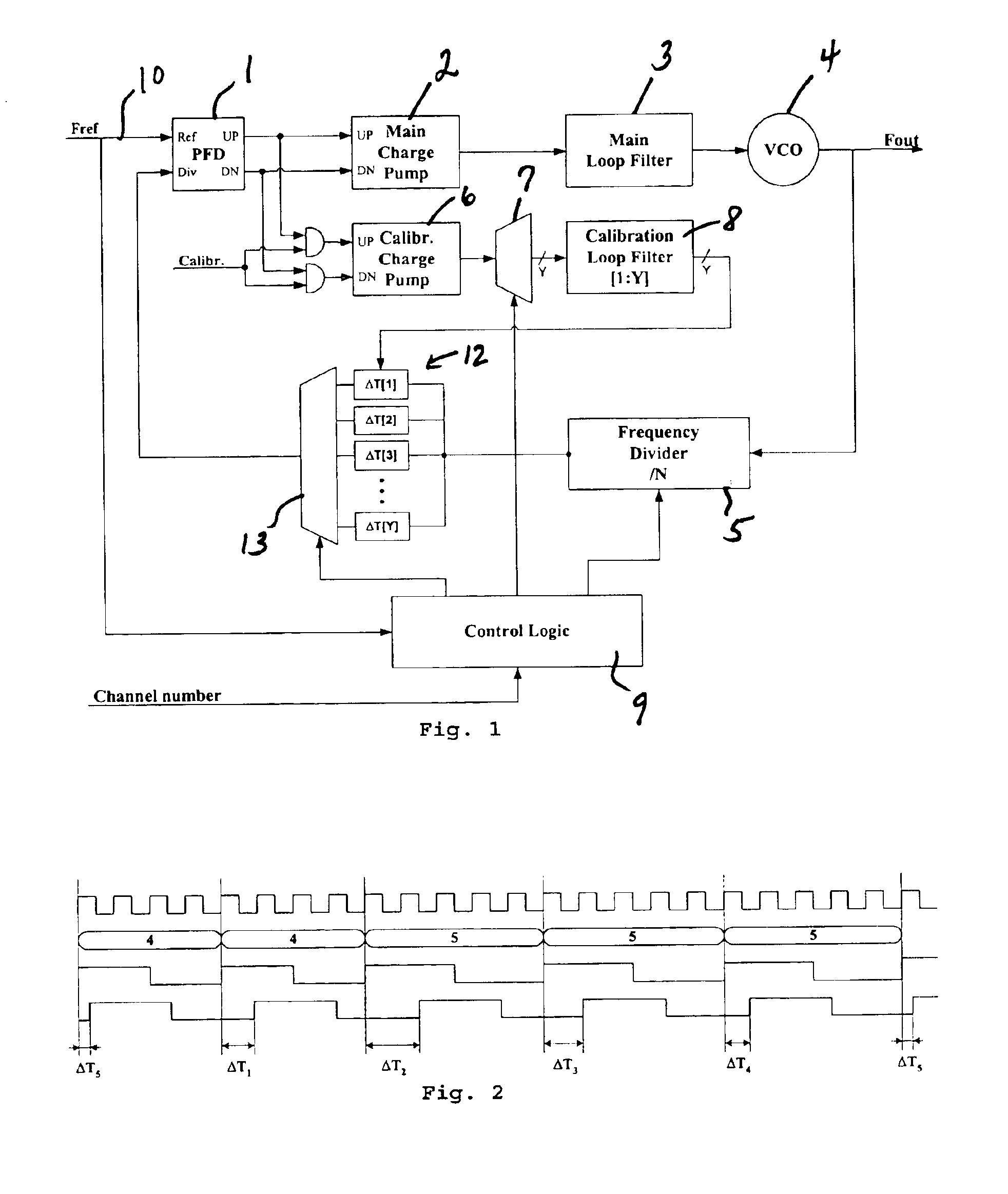
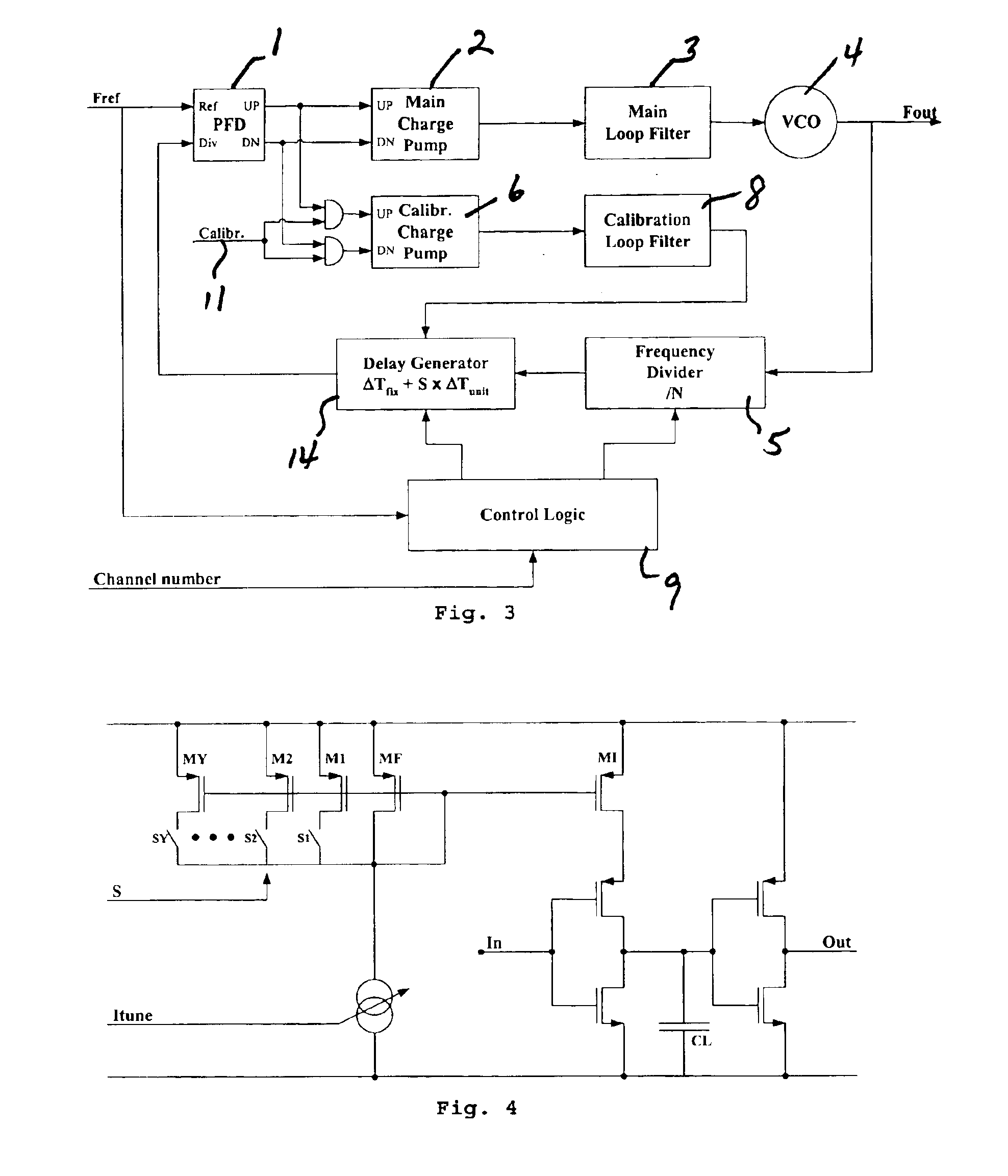
A Phase-Locked Loop is provided that includes a main loop, a calibration loop, and Control Logic. The main loop comprises, coupled in series, a Phase Frequency Detector, a Main Charge Pump, a Main Loop Filter, a Voltage Controlled Oscillator and a Frequency Divider. The calibration loop is coupled to the Phase Frequency Detector and comprises a Calibration Charge Pump and a Calibration Loop Filter. The Control Logic controls the Frequency Divider and receives a control input signal. A Reference Frequency Signal is coupled to the Phase Frequency Detector and the Control Logic, and a calibration signal is coupled to the calibration loop. Additionally, the main loop further comprises a delay generator controlled by the Control Logic and arranged to receive correction signals from the calibration loop and to send an output signal to the Phase Frequency Detector.
Owner:PROTON WORLD INT
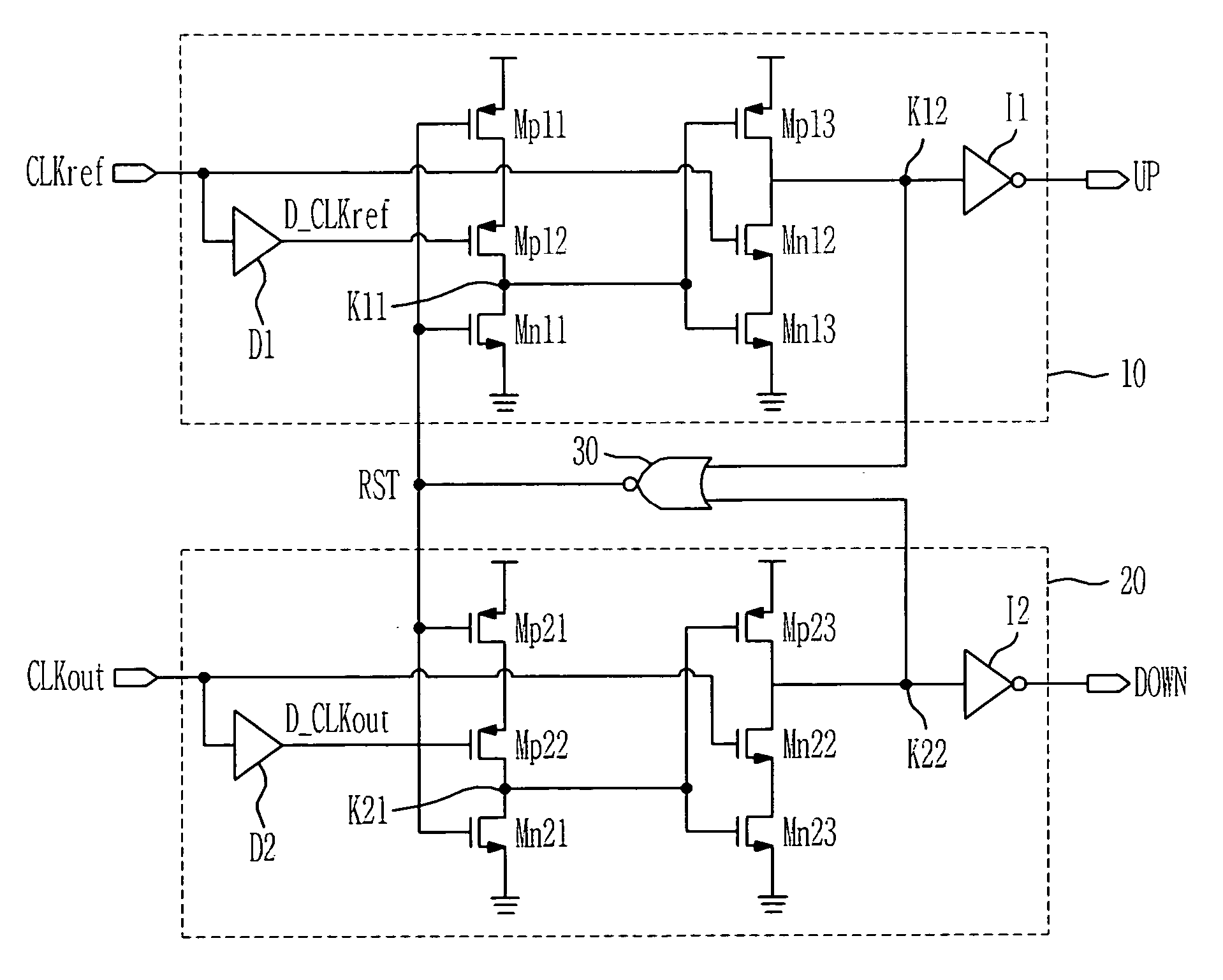
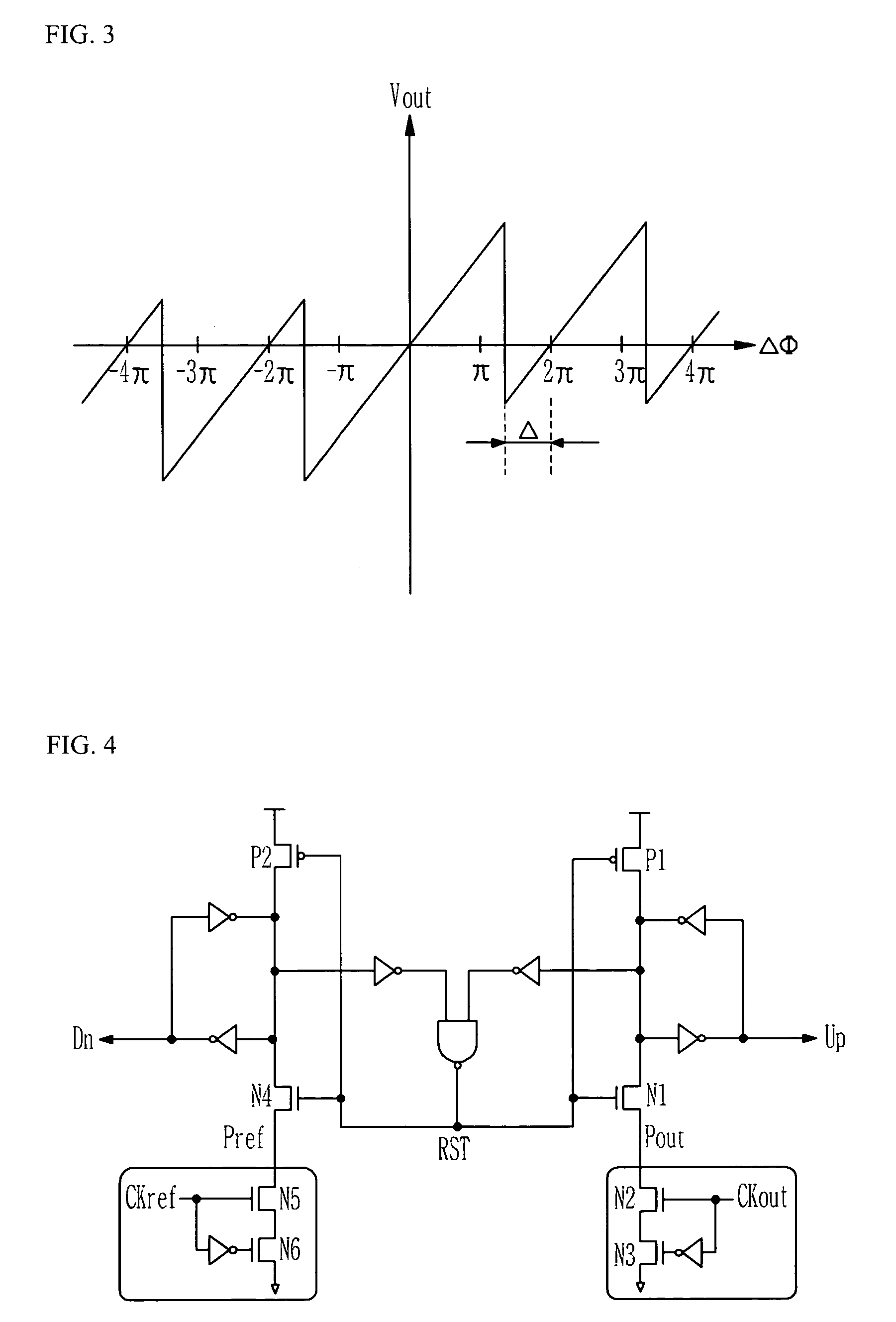
Phase frequency detector and phase-locked loop
ActiveUS7592847B2Pulse automatic controlVoltage-current phase anglePhase detectorPhase frequency detector
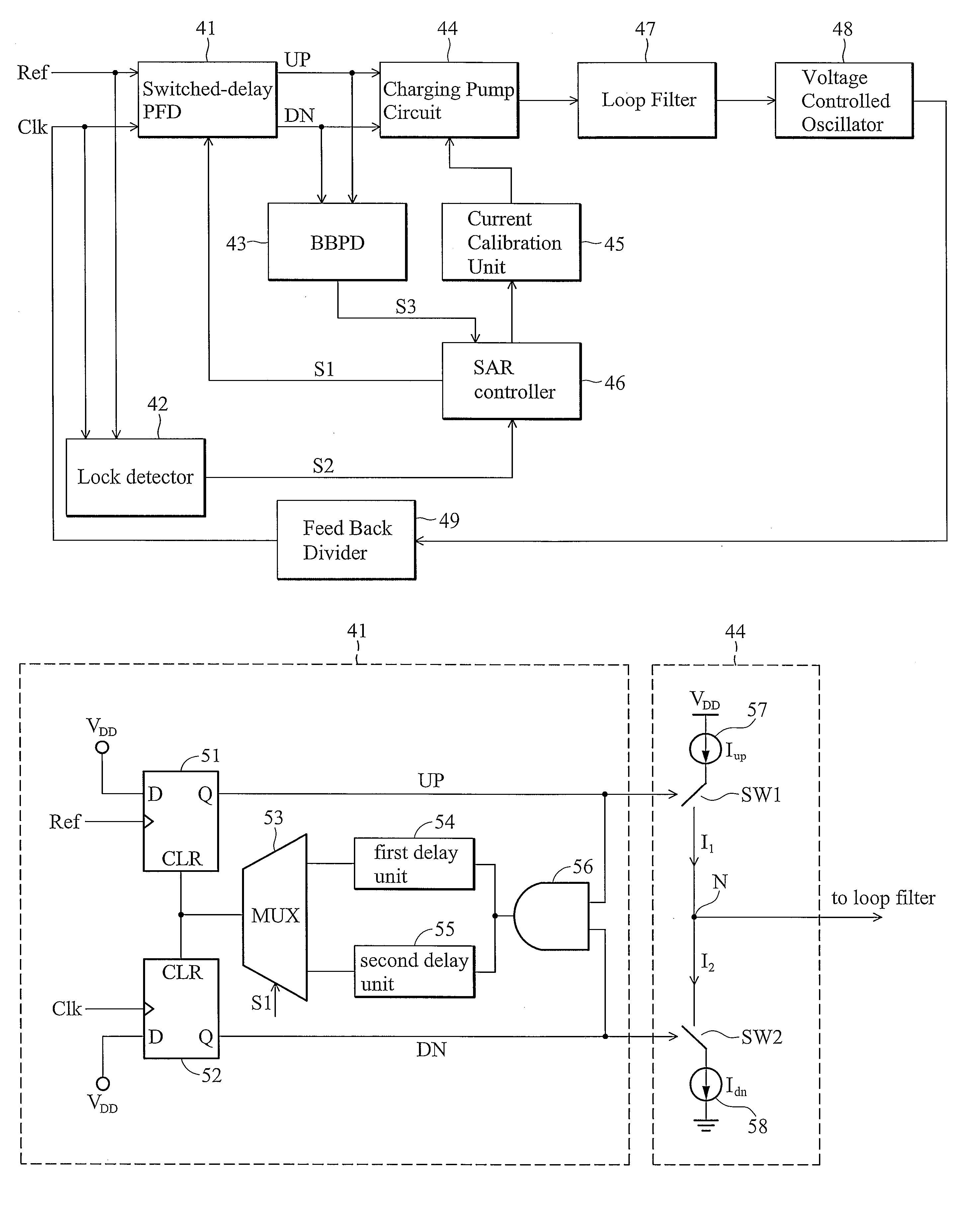
A phase frequency detector with two different delays is disclosed herein. The phase detector comprises a first D flip-flop, a second D flip-flop, a first delay unit and a second delay unit. The first D flip-flop receives a reference signal to output an up signal. The second D flip-flop receives a clock signal to output a down signal. The first delay unit delays the received signal with a first delay. The second delay unit delays the received signal with a second delay. When the reference signal synchronizes with the clock signal and the charge pump currents are calibrated, the high-level pulse widths of the up signal and the down signal are determined based on the first delay, and when the reference signal does not synchronize with the clock signal and the charge pump currents are not calibrated, the high-level pulse widths of the up signal and the down signal are determined based on the second delay.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC +1
Low-power, low-jitter, fractional-N all-digital phase-locked loop (PLL)
ActiveUS7365607B2Pulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionLoop filterReference Period
A method for synthesizing frequencies with a low-jitter an all-digital fractional-N phase-locked loop (PLL) electronic circuit adapted to synthesize frequencies with low-jitter, wherein the electronic circuit comprises a digital phase-frequency detector (DPFD) operatively connected to a digital loop filter (DLF), wherein the DPFD adapted to receive a reference signal and a feedback signal; compare a phase and frequency of the reference and feedback signals to determine a phase and frequency error between the reference and feedback signals; and provide a DPFD output comprising a multi-bit output; wherein the DLF is adapted to receive and filter the DPFD output and provide a DLF output, and wherein the DLF output is updated at each reference period.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
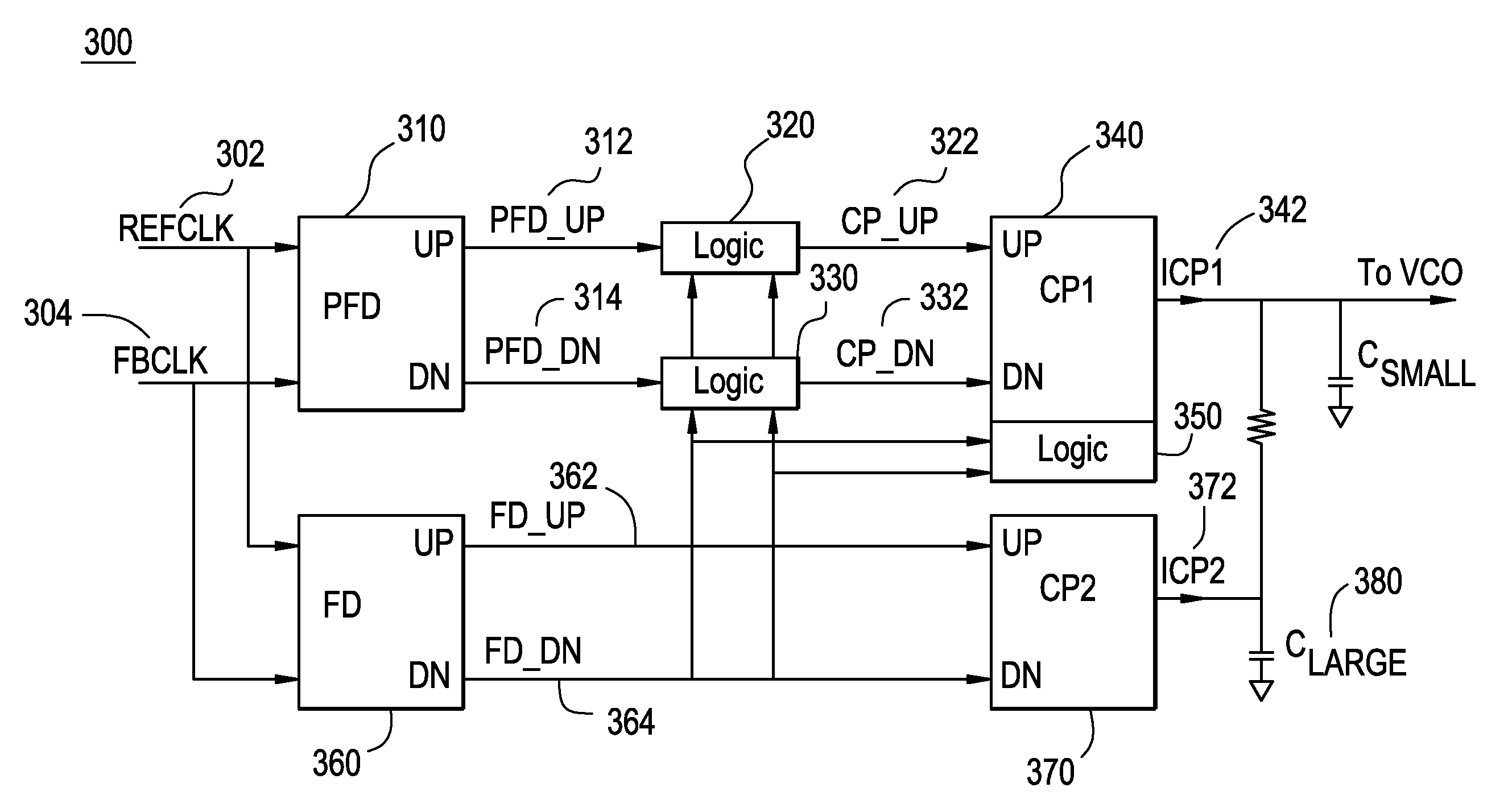
Fast lock circuit for a phase lock loop
InactiveUS7728675B1Increase volumeSlow chargingPulse automatic controlOscillator tubesLoop filterDetector circuits
A fast lock circuit for phase lock loop comprising a frequency detector, a phase frequency detector, a logic unit and a corresponding charge pump for the frequency and the phase frequency detectors. Embodiments of the present invention use the logic unit to relay signals from the phase frequency detector circuit to the charge pump when the PLL is in lock. The logic circuit relay signals from the frequency detector circuit before the PLL is in lock. As a result, a constant current is supplied to a large loop filter capacitor before lock. In one embodiment, additional logic circuit may be used to maximize the output current. Therefore, using the logic circuit to supply constant current charges the large loop filter capacitor continuously and avoids a slow down in charging the large loop filter. Accordingly, current is no longer wasted and the lock time is improved.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Phase locked loop
InactiveUS8063707B2Improve stabilityIncrease chip areaPulse automatic controlControl signalPhase locked loop circuit
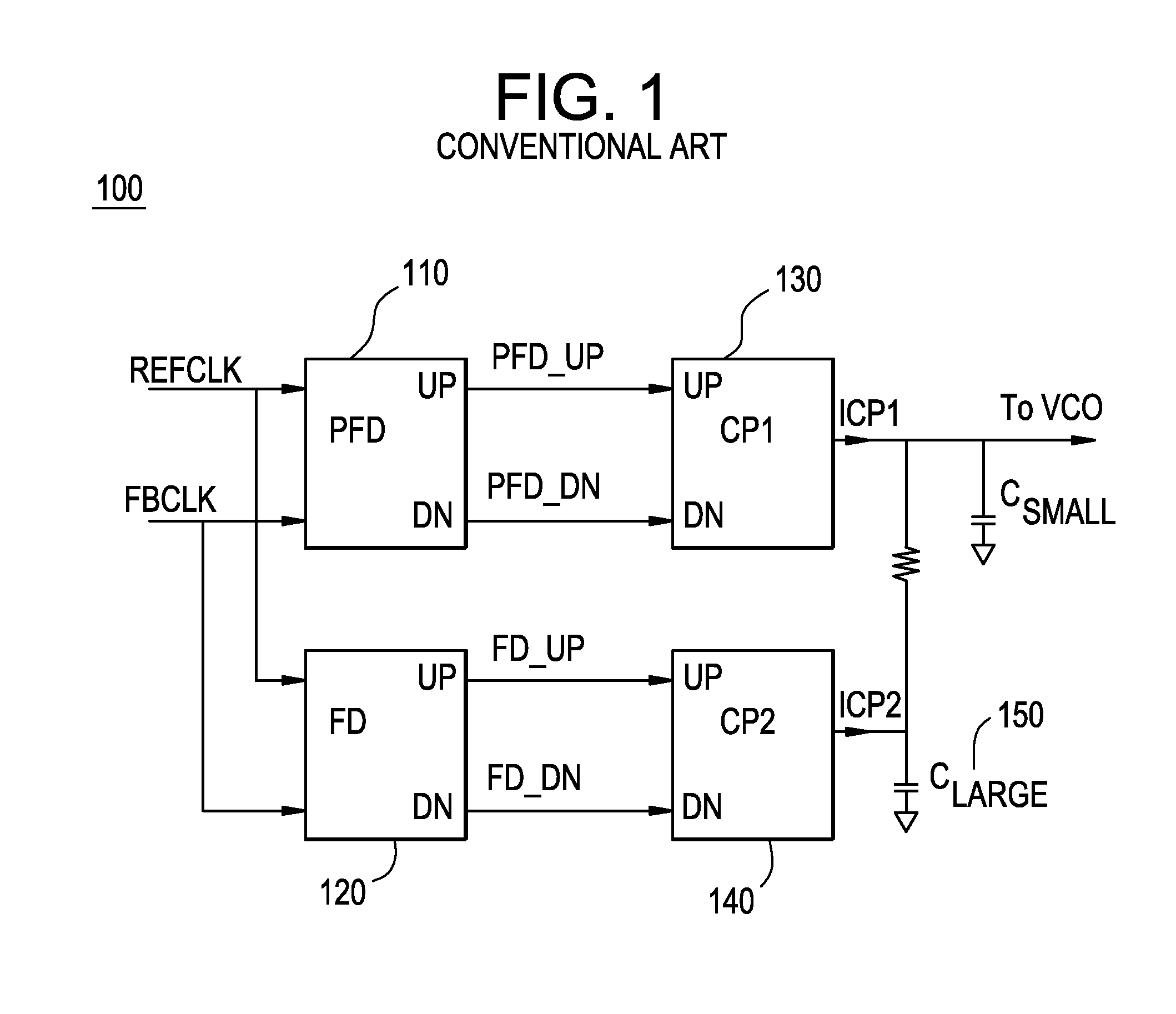
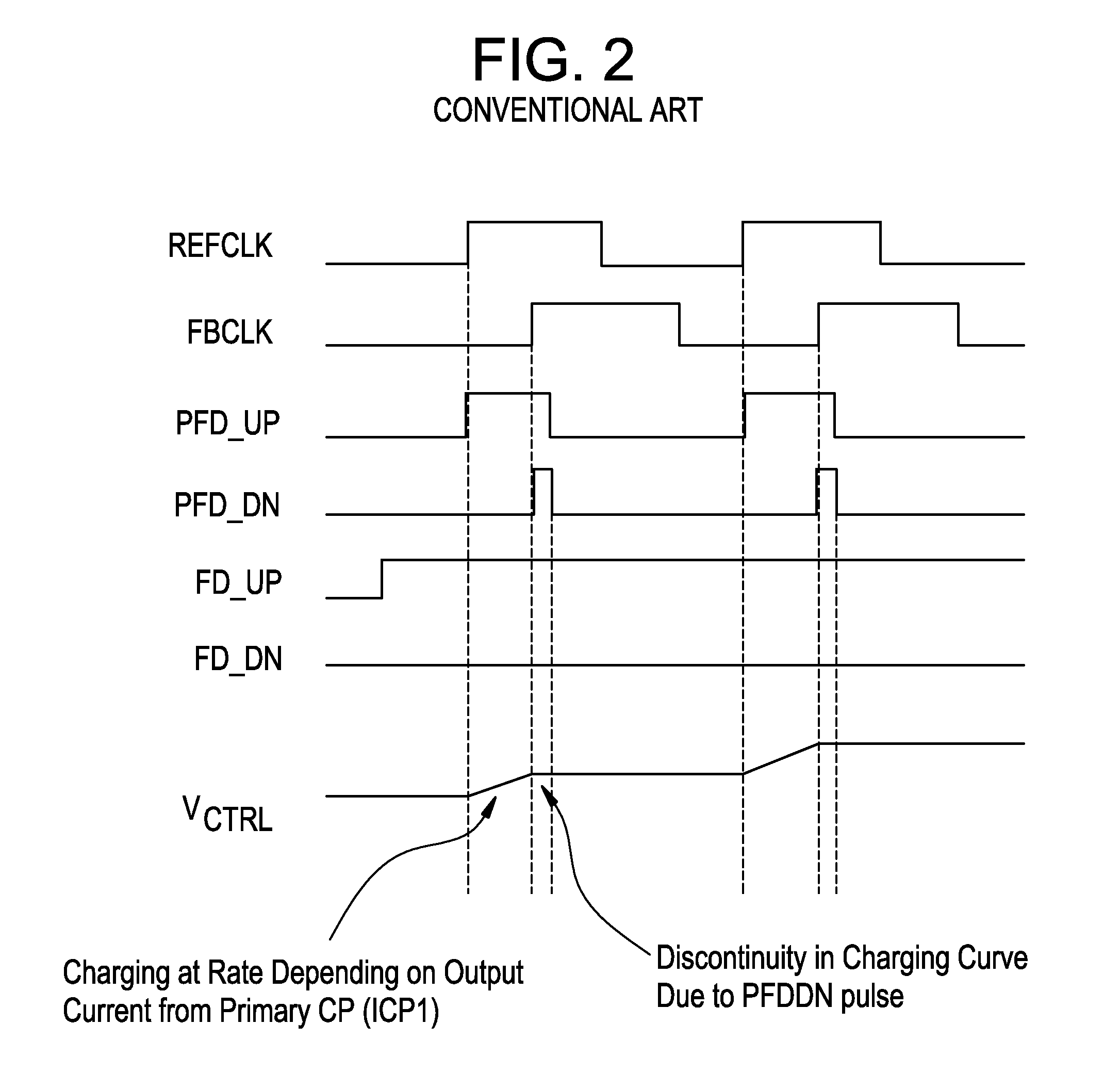
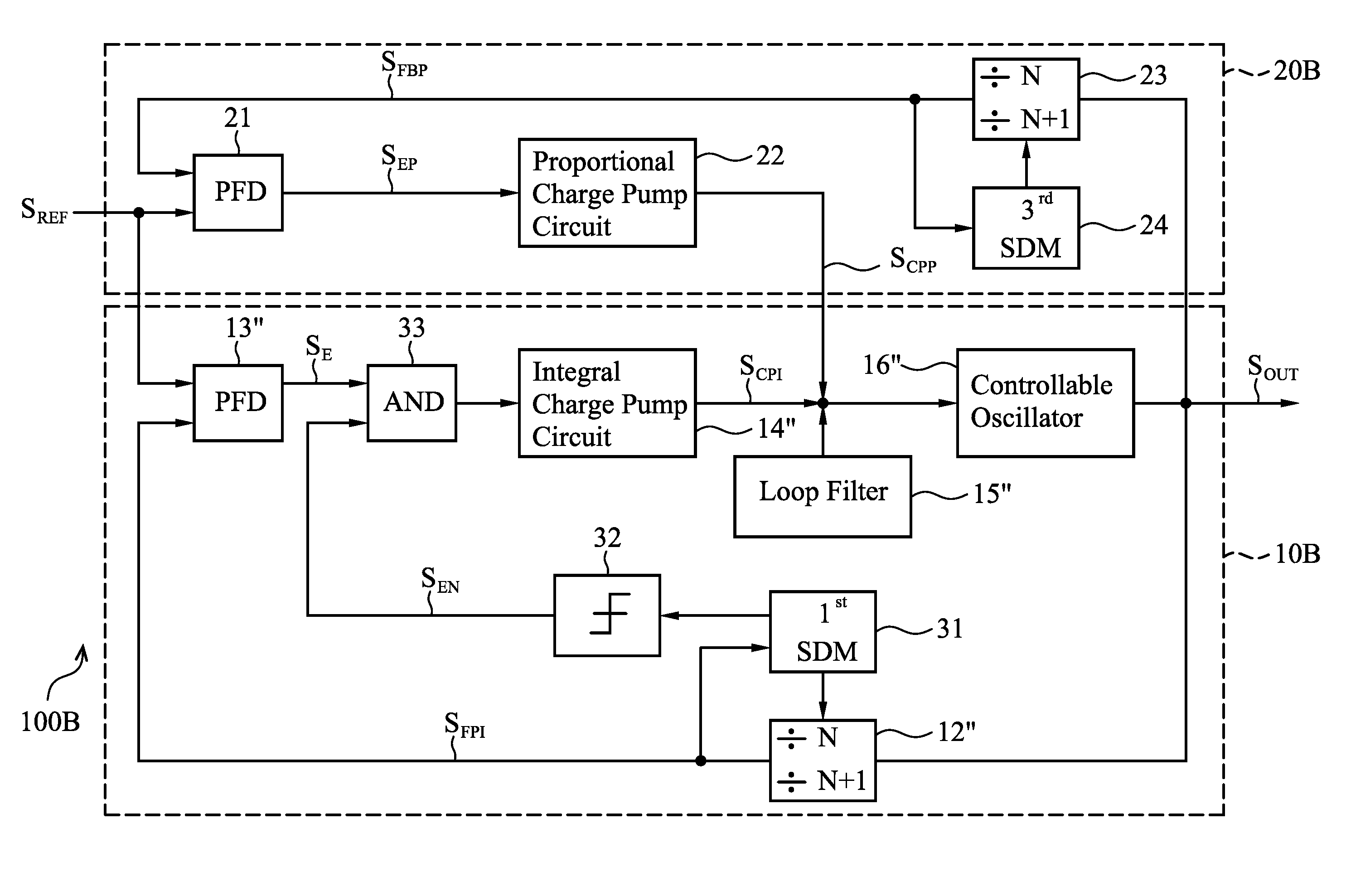
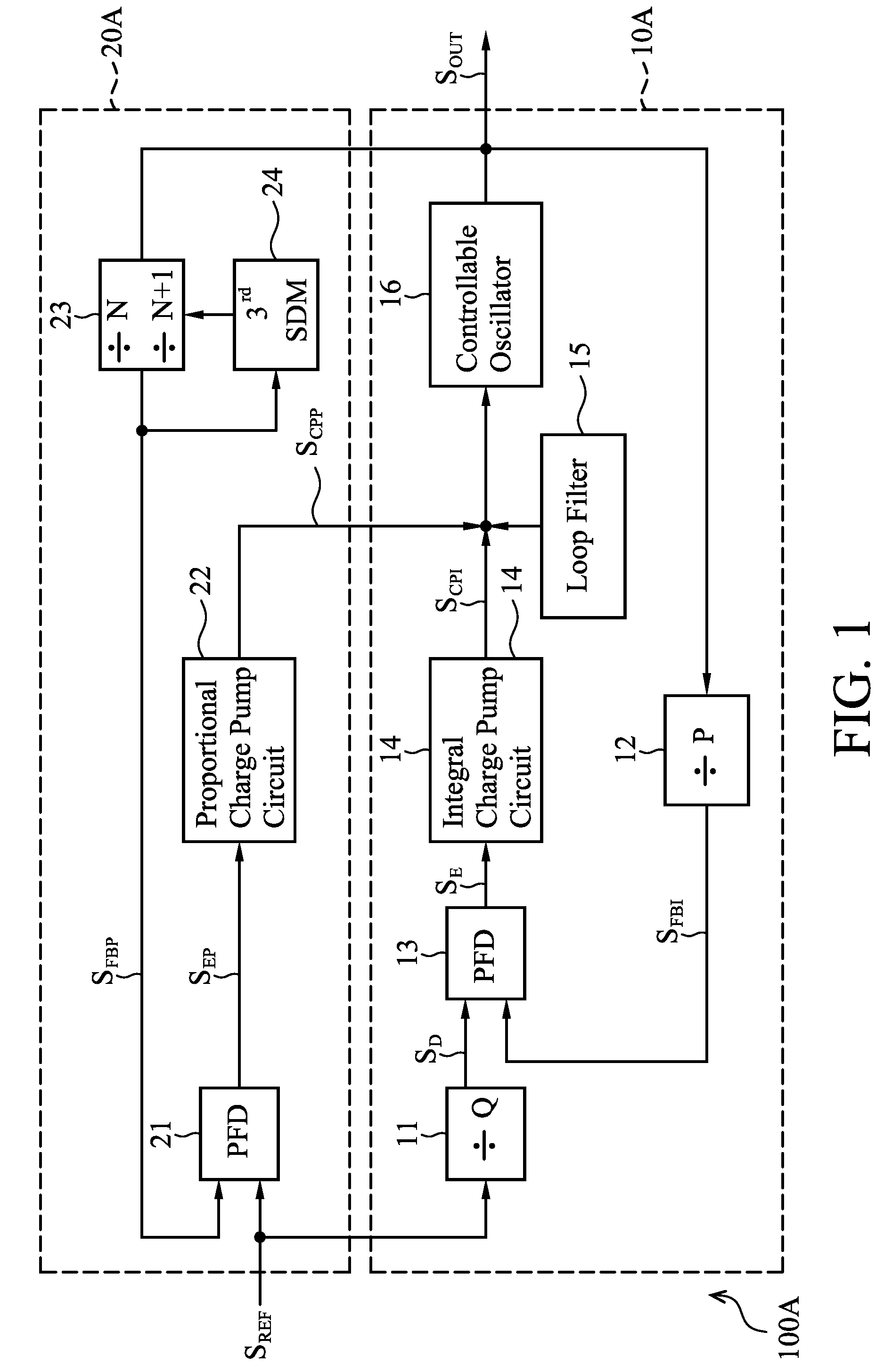
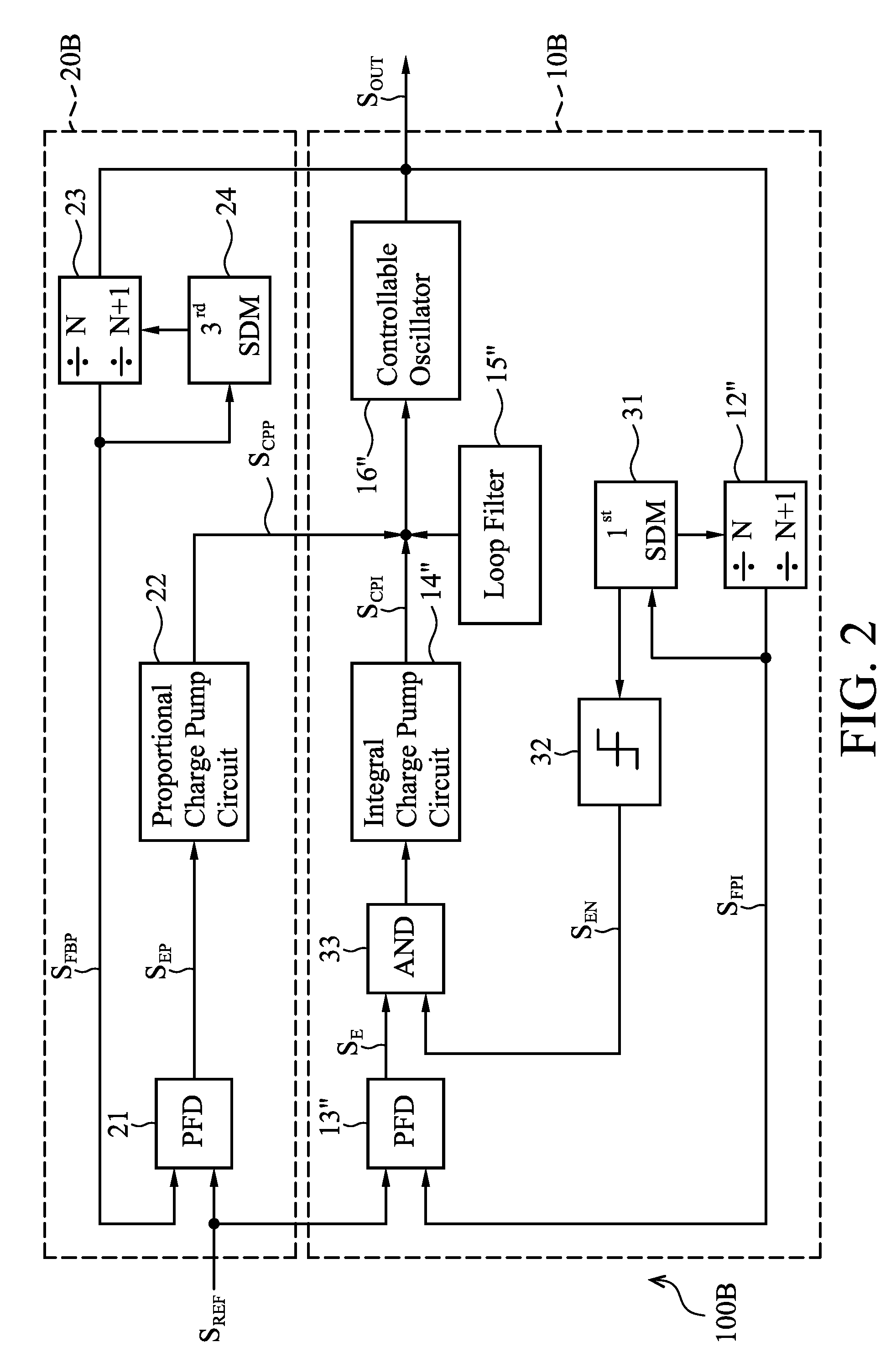
Phase locked loop circuits capable of increasing an equivalent capacitance thereof to improve stability are provided, in which an integral part comprises a first phase frequency detector providing a phase error signal, a first charge pump circuit generating a control signal according to the phase error signal, a controllable oscillator providing an output clock according to the control signal, and a sampling adjustment unit decreasing the number of times the control signal is updated according to the phase error signal. A proportional part is coupled between the controllable oscillator and a reference clock and operated in a fraction mode.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Phase-frequency detector with linear phase error gain near and during phase-lock in delta sigma phase-locked loop
ActiveUS7092475B1Pulse automatic controlOscillations comparator circuitsNon symmetricPhase difference
A phase-frequency detector (PFD) having substantially linear phase error gain within a predetermined phase error range centered about zero phase error when used in a delta sigma phase-locked loop (PLL). The output signals (e.g., charge pump control signals), which are also used to reset the input circuitry, are fed back with asymmetrical signal delays, thereby causing one of the output signals to remain in an asserted state for a substantially constant time duration at least during when a difference between the reference and feedback signal phases is within a predetermined phase difference range centered about zero phase difference.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
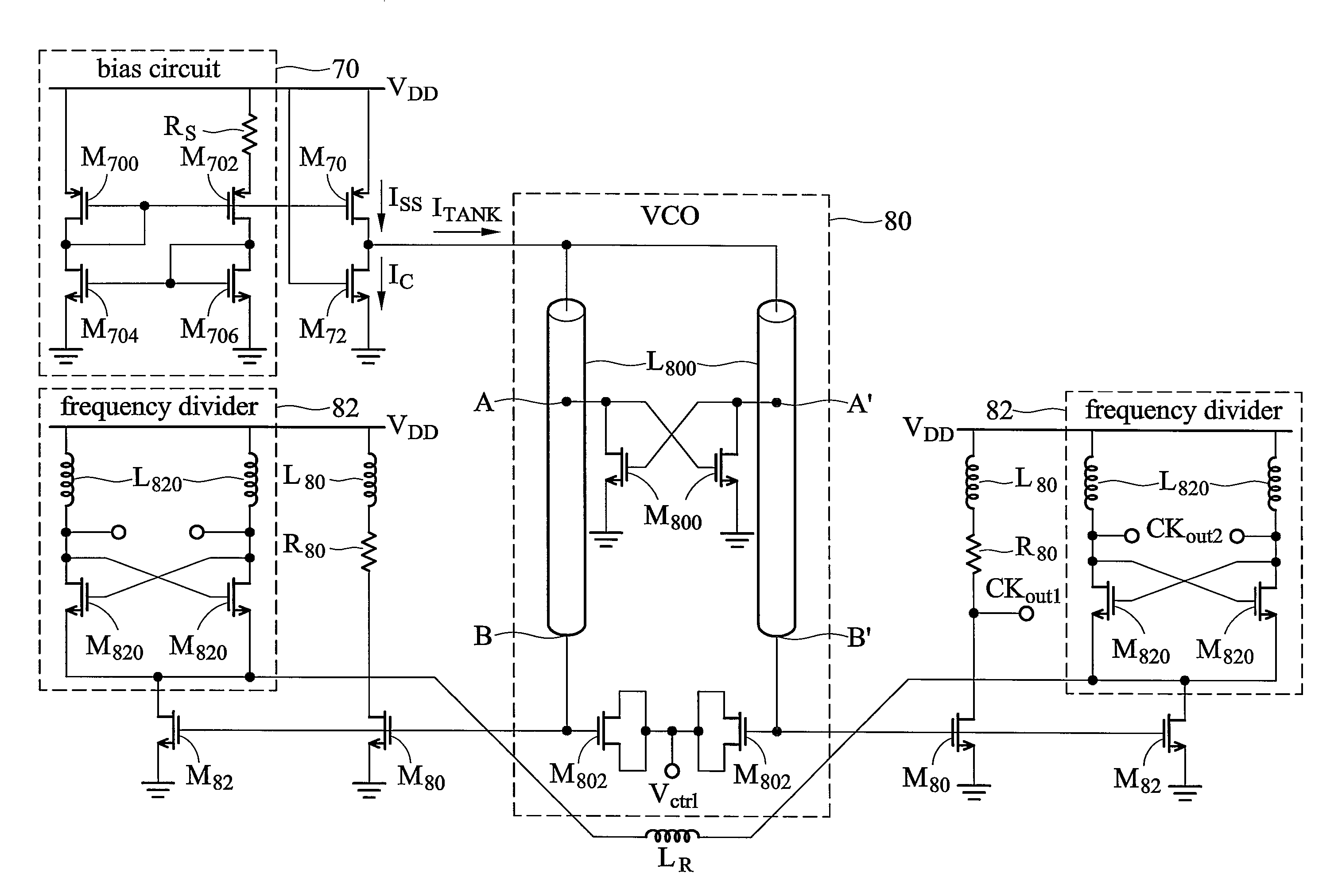
Phase locked loop, voltage controlled oscillator, and phase-frequency detector
ActiveUS7830212B2Pulse automatic controlSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLoop filterPhase frequency detector
A phase locked loop, voltage controlled oscillator, and phase-frequency detector are provided. The phase locked loop comprises a phase-frequency detector (PFD), a loop filter (LF), a voltage controlled oscillator (VCO), and a 3-stage frequency divider. The PFD receives a reference signal and a feedback signal to determine phase and frequency errors. The LF), coupled to the phase-frequency detector, filters the phase and frequency errors to generate a control voltage. The VCO, coupled to the loop filter, generates a VCO output signal according to the control voltage. The 3-stage frequency divider, coupled to the voltage controlled oscillator, divides the frequency of the VCO output signal 3 times to generate the feedback signal.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC +1
Phase frequency detector
InactiveUS20060055434A1Fast phase lockReduce power consumptionPulse automatic controlVoltage-current phase angleLow noiseControl signal
Provided is a phase frequency detector for use in a phase locked loop (PLL) or a delay locked loop (DLL), the phase frequency detector including: an UP signal output unit having a first stage operated according to a reference clock delayed by a predetermined time and a reset signal, a second stage operated according to the reference clock and an output of the first stage, and an inverter for inverting an output of the second stage; a DOWN signal output unit having: a first stage operated according to an outer clock delayed by a predetermined time and the reset signal, a second stage operated according to the outer clock and an output of the first stage, and an inverter for inverting an output of the second stage; and a logic gate logically combining the output of the second stage of the UP signal output unit and the output of the second stage of the DOWN signal output unit to generate the reset signal, thereby a phase range of the input signal with which an effective control signal can be obtained is wide so that low power consumption and low noise characteristics can be obtained due to fast phase lock, low power consumption of a dynamic logic, and fast signal transmission.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
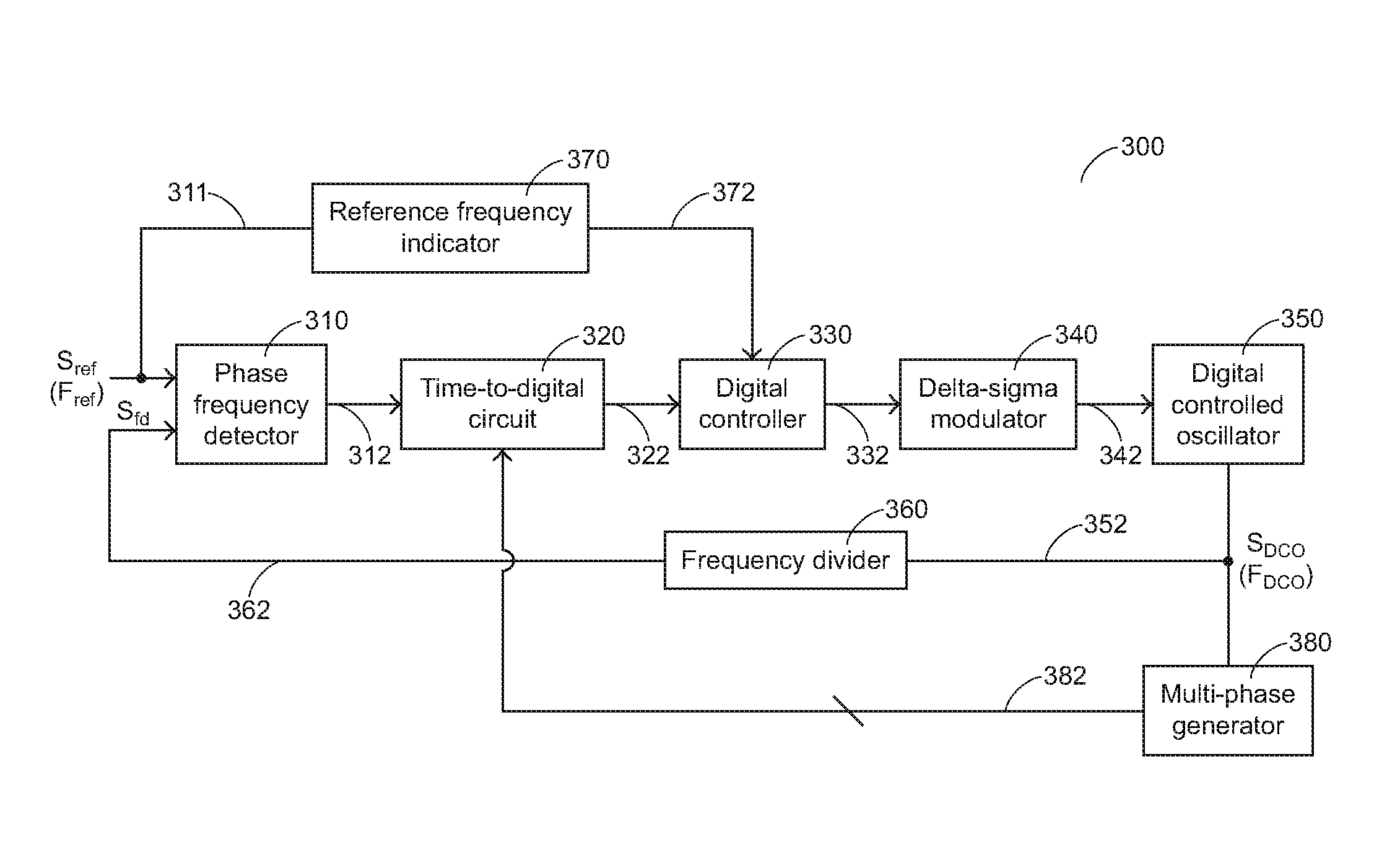
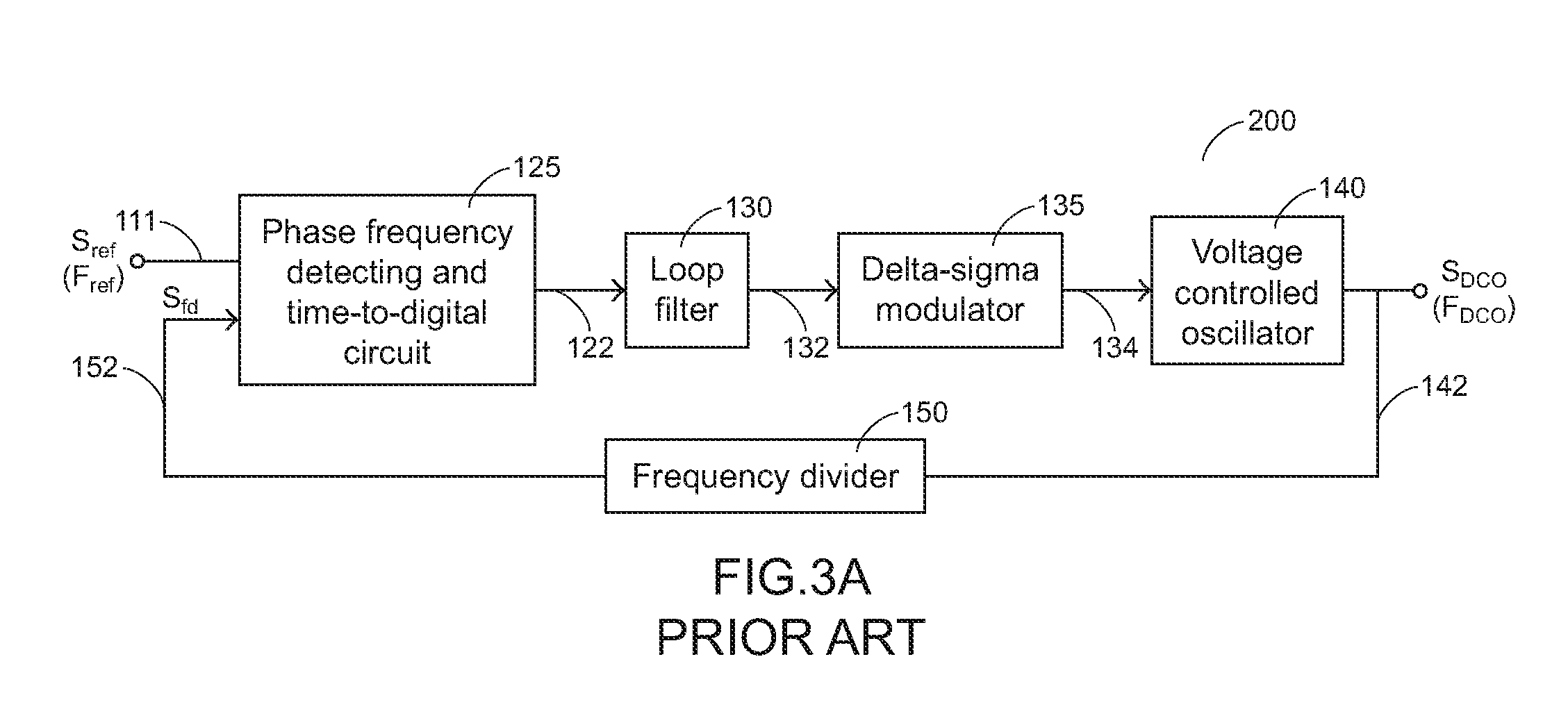
All digital phase locked loop circuit
InactiveUS20100141314A1Easily maintain its loop dynamicPulse automatic controlPhase locked loop circuitPhase difference
An all digital phase locked loop circuit includes a reference frequency indicator for receiving a reference signal with a reference frequency and generating a frequency indicating value; a phase frequency detector for comparing the reference signal with a frequency divided signal and generating a phase difference pulse; a time-to-digital circuit for receiving the phase difference pulse and a plurality of output signals and generating a phase difference value; a digital controller for receiving the frequency indicating value and the phase difference value and generating a control value; a delta-sigma modulator for modulating the control value and generating a modulated control value; a DCO for receiving the modulated control value and generating an output oscillating signal with a digital controlled frequency; a frequency divider for dividing the digital controlled frequency to generate the frequency divided signal; and a multi-phase generator for receiving the output oscillating signal and generating the output signals.
Owner:SUNPLUS TECH CO LTD
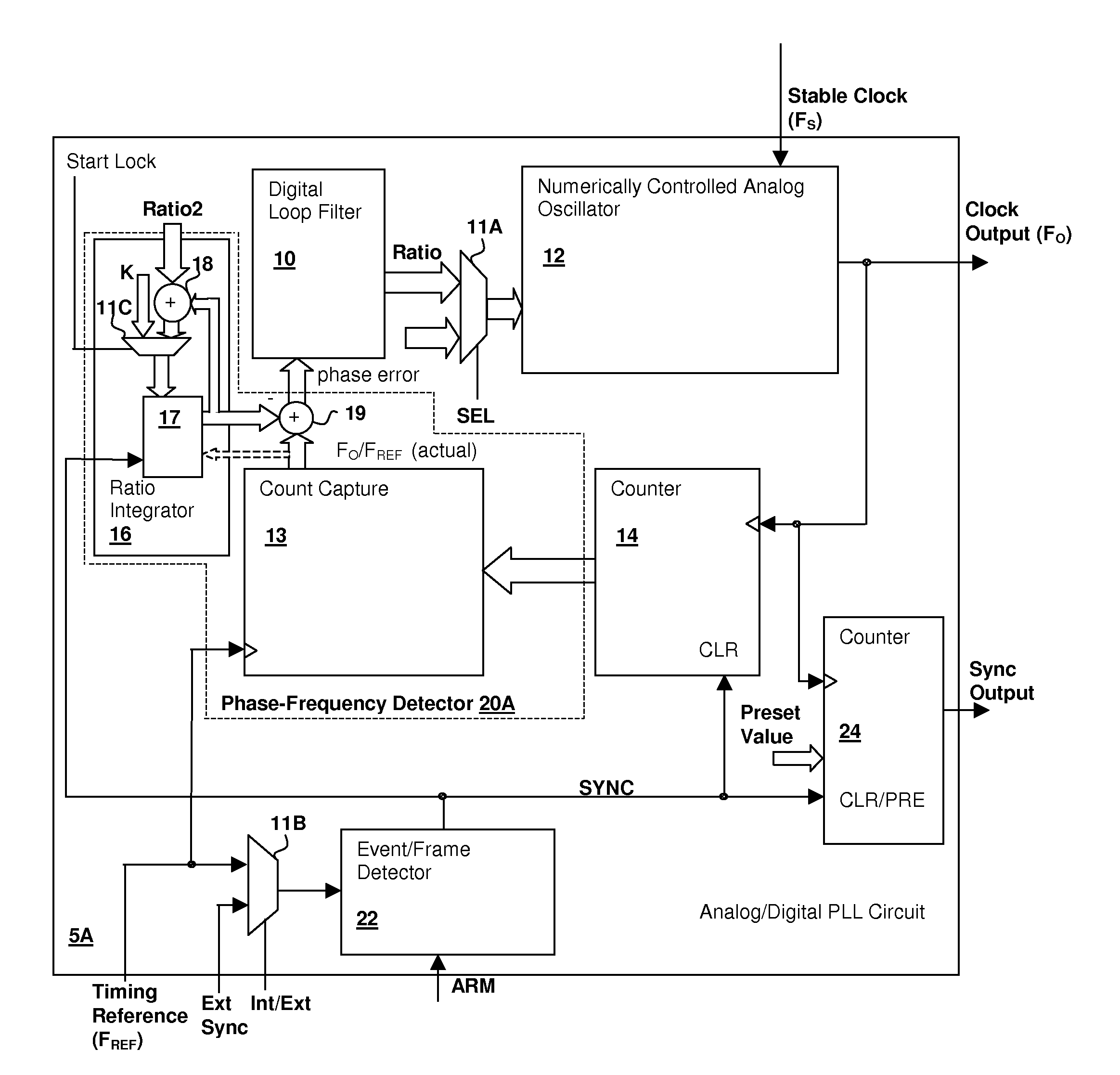
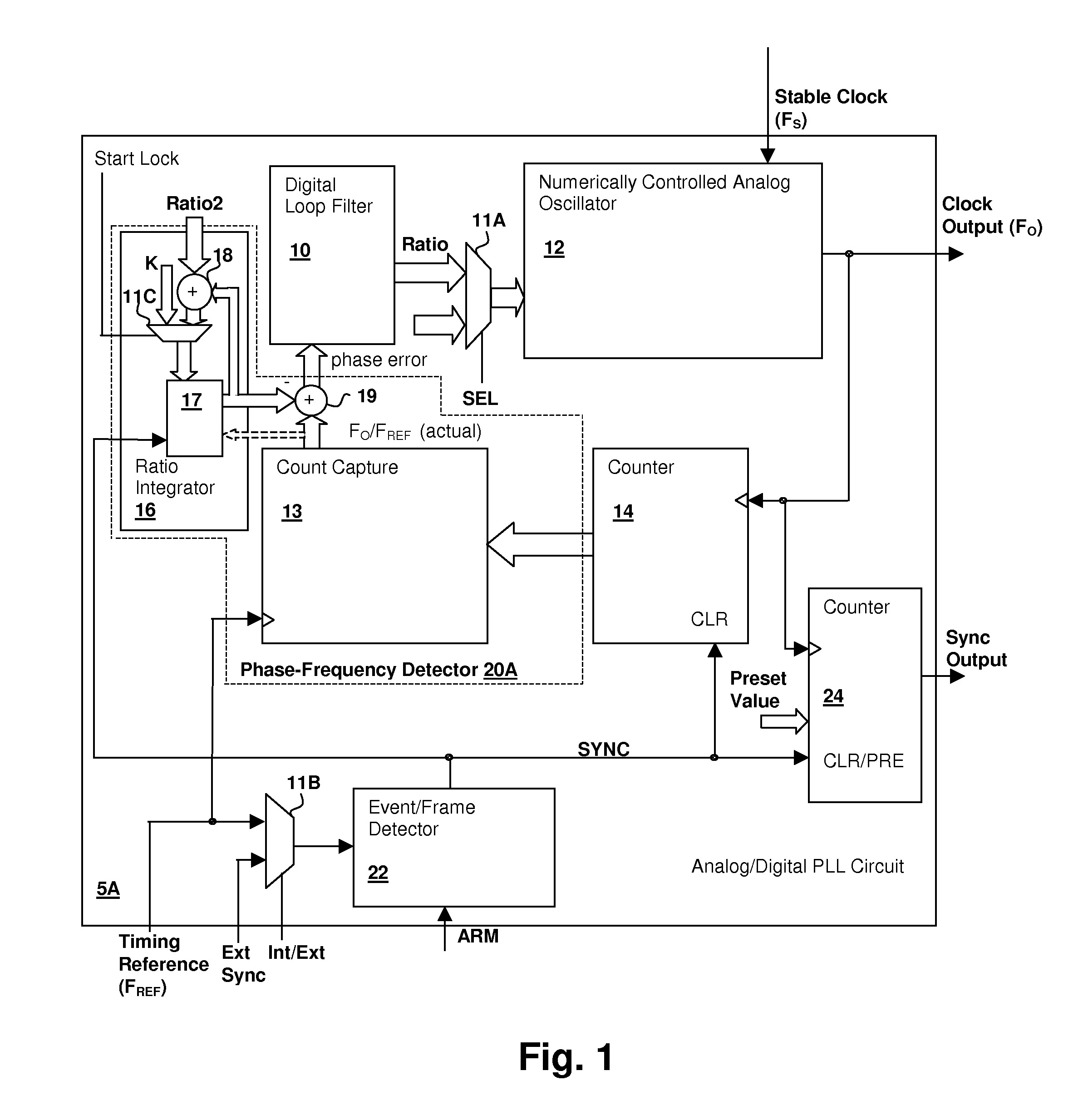
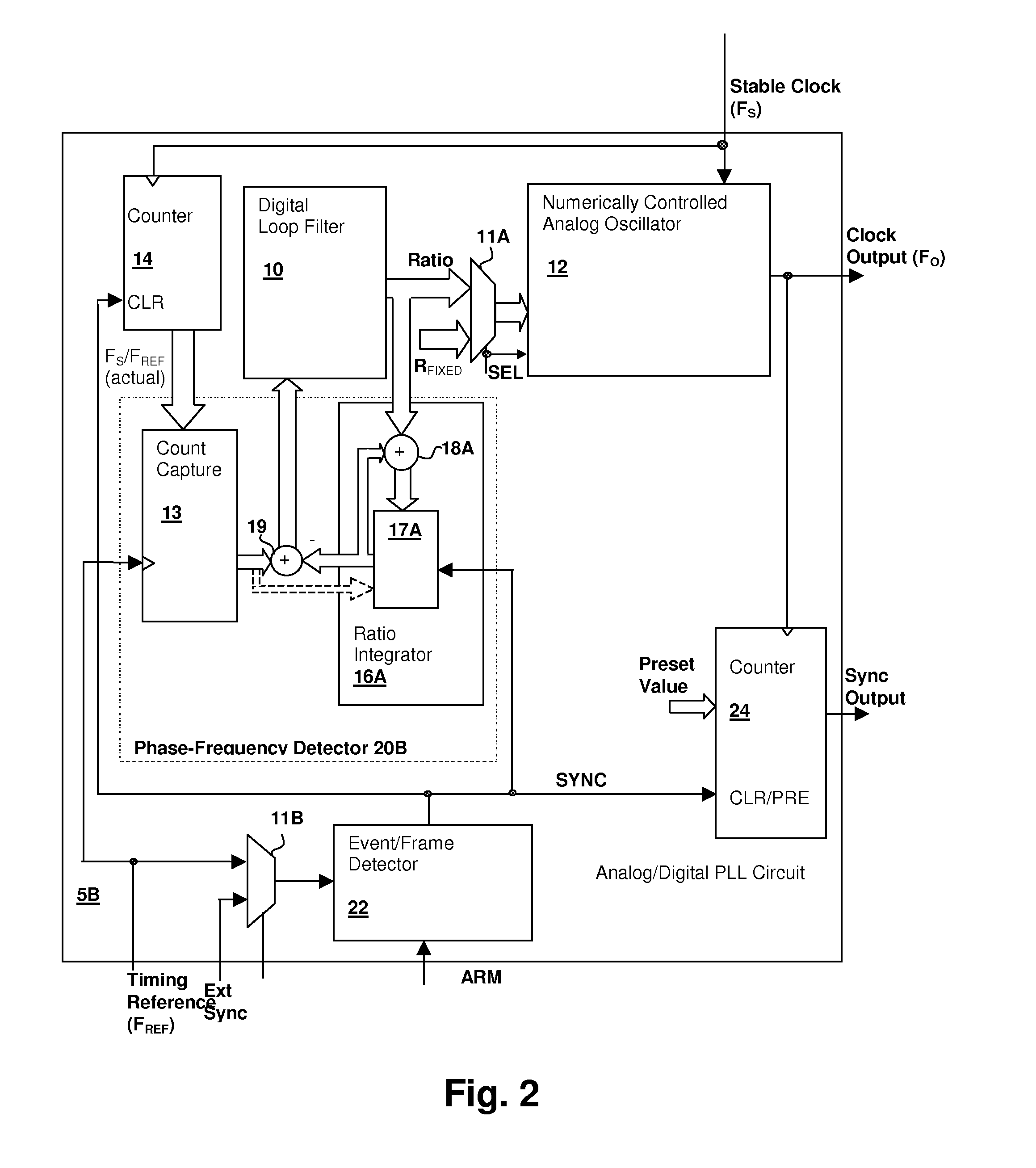
Hybrid analog/digital phase-lock loop with high-level event synchronization
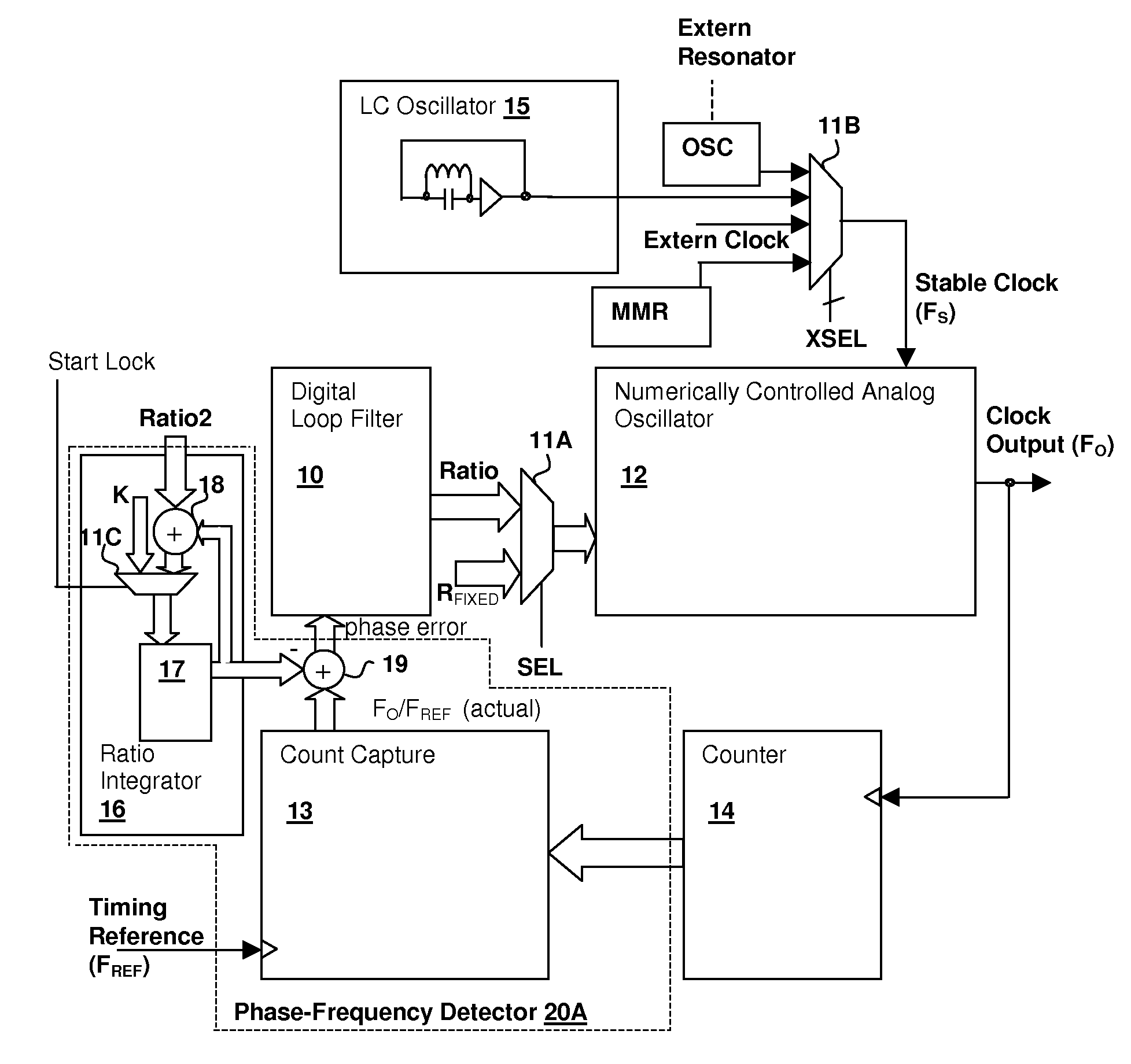
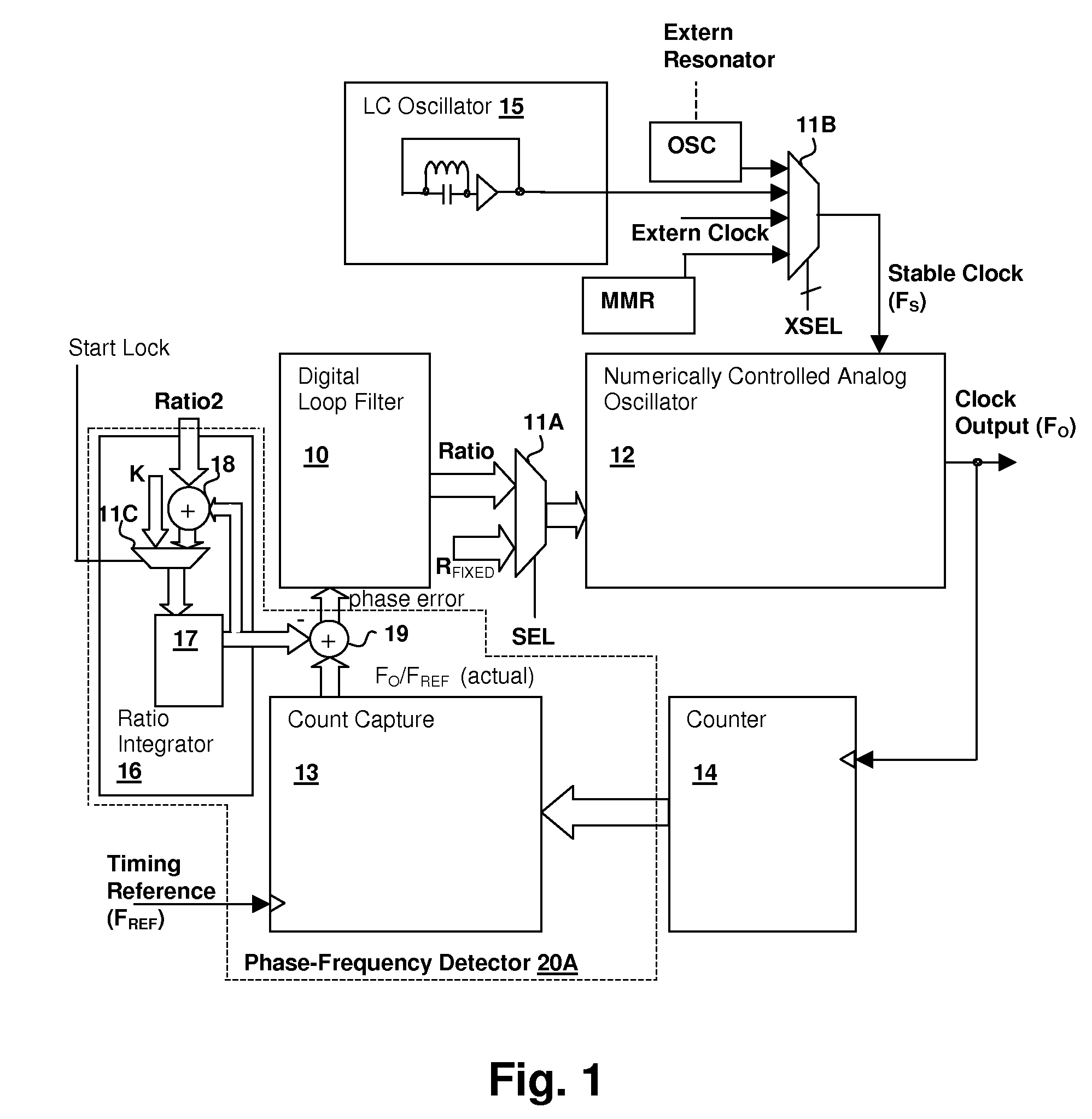
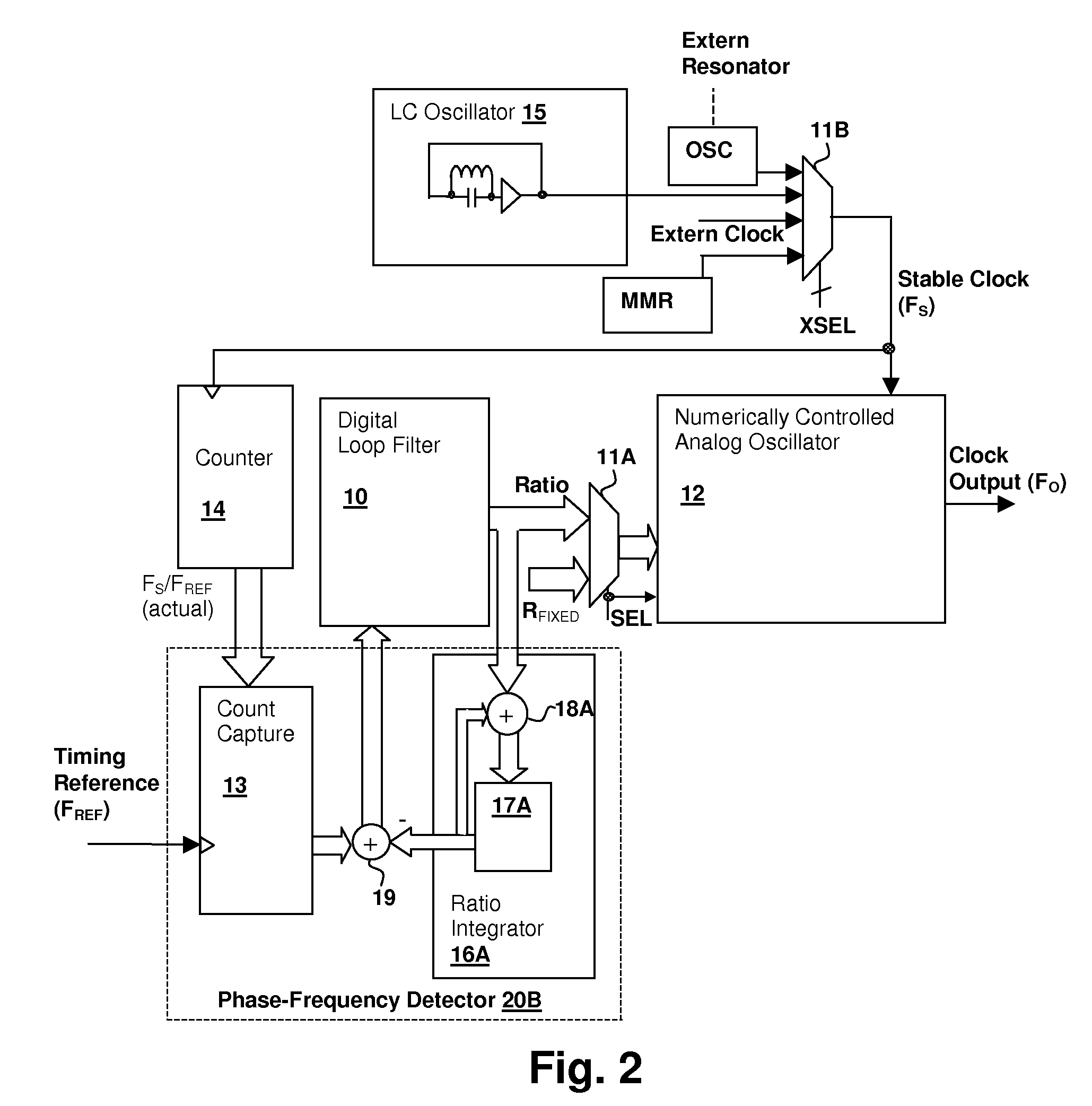
ActiveUS20080075152A1Modulated-carrier systemsPulse automatic controlEvent synchronizationLow jitter
A hybrid analog / digital phase-lock loop with high-level event synchronization provides a mechanism for generating a low-jitter clock from a timing reference that has a high jitter level and synchronizing the output clock to high-level events. A numerically-controlled analog oscillator provides a clock output and a counter divides the frequency of the clock output to provide input to a digital phase-frequency detector for detecting an on-going phase-frequency difference between the timing reference and the output of the counter. A synchronization circuit detects or receives a high-level event signal, and resets the on-going phase-frequency difference and optionally the counter to synchronize the clock output with the events. The synchronization circuit may have an arming input to enable the synchronization circuit to signal a next event. Another clock output divider may be included to generate a timing reference output, and the other clock divider also reset in response to a detected event.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Digital-data receiver synchronization
InactiveUS6925135B2Error minimizedFrequency minimizedPulse automatic controlTime-division multiplexData synchronizationDigital data
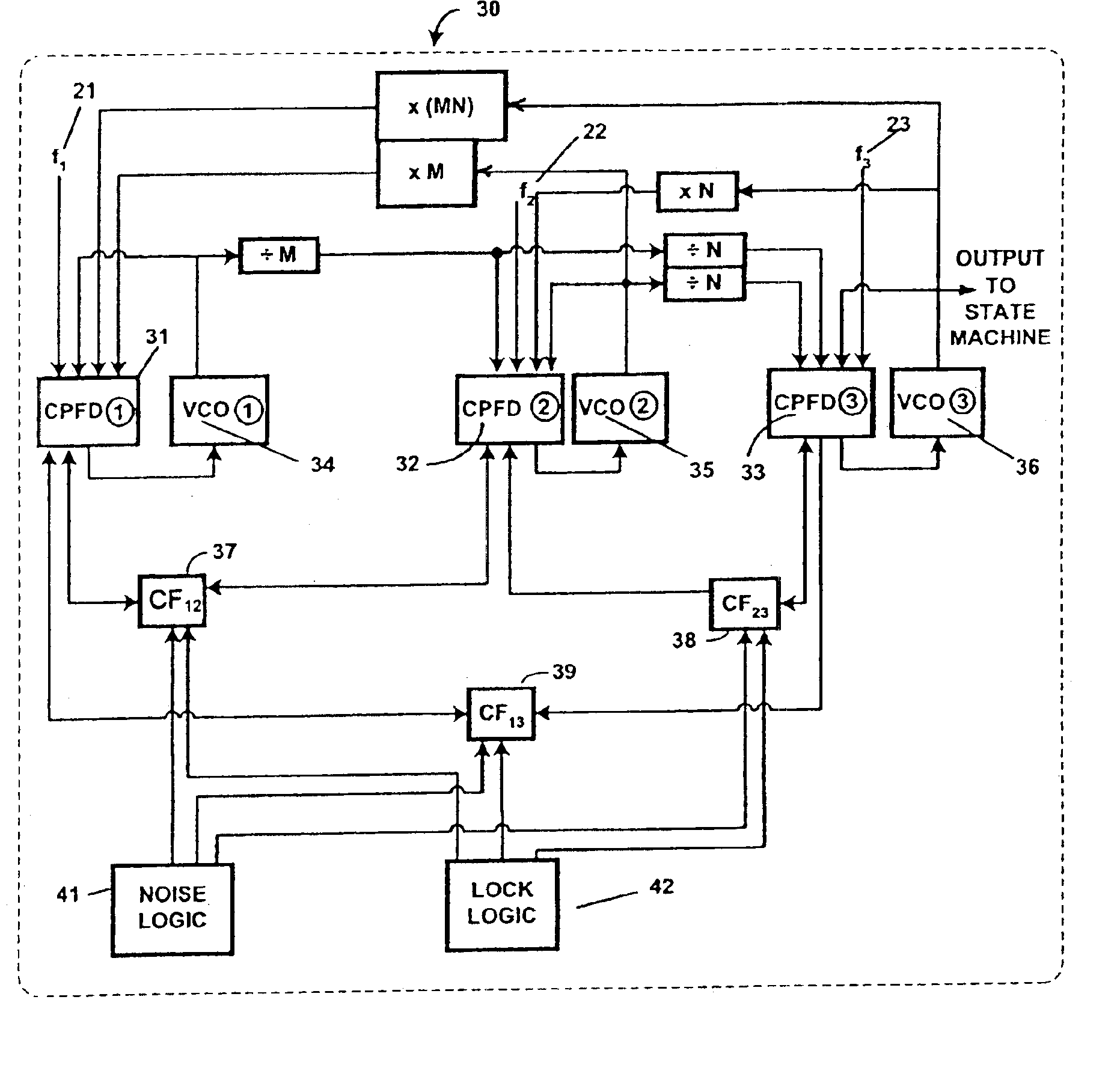
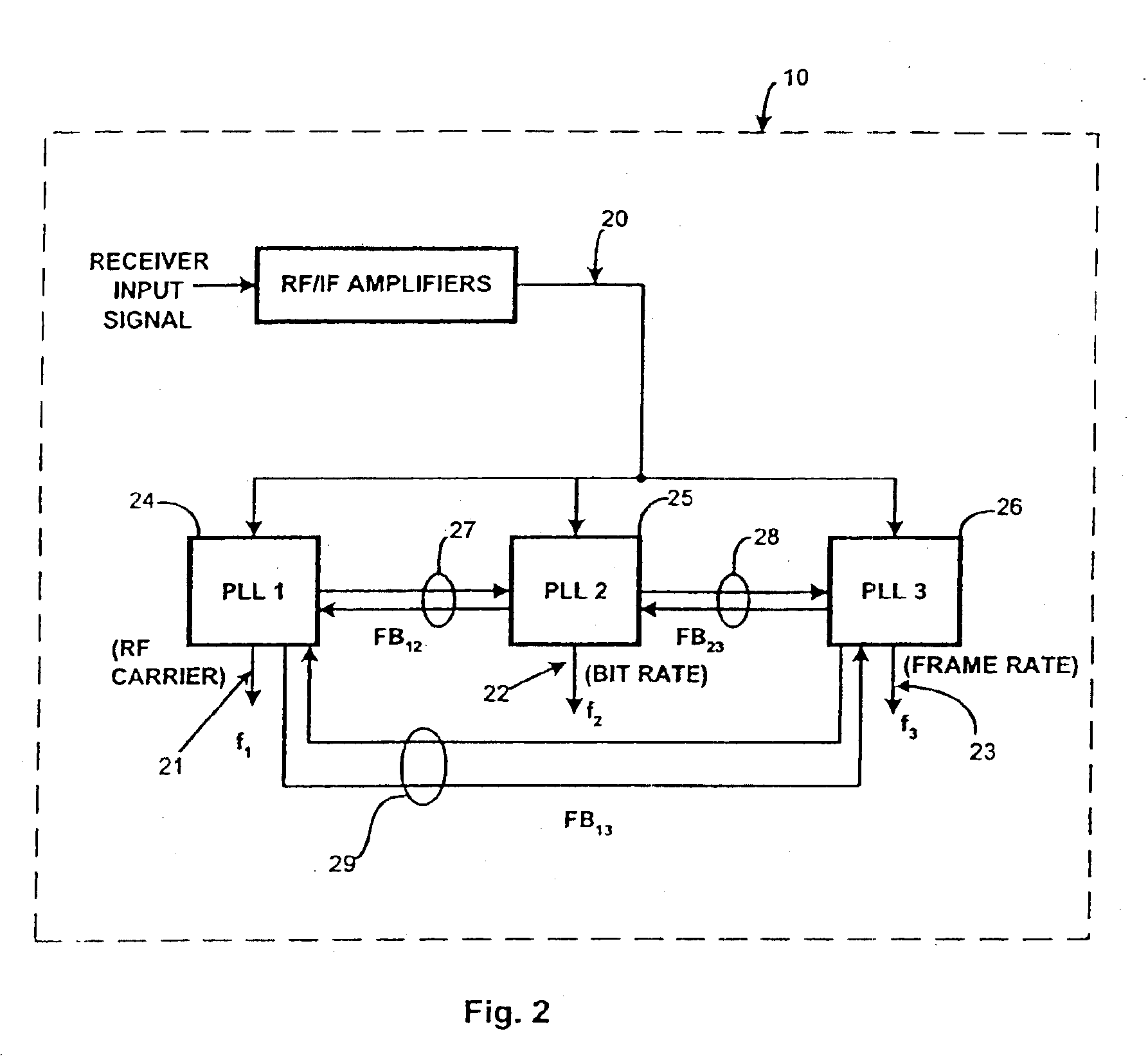
Digital-data receiver synchronization is provided with composite phase-frequency detectors, mutually cross-connected comparison feedback or both to provide robust reception of digital data signals. A single master clock can be used to provide frequency signals. Advantages can include fast lock-up time in moderately to severely noisy conditions, greater tolerance to noise and jitter when locked, and improved tolerance to clock asymmetries.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Hybrid analog/digital phase-lock loop for low-jitter synchronization
ActiveUS7680236B1Pulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionLoop filterPhase frequency detector
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Time-to-digital convertoer and all-digital phase locked loop
ActiveCN101753142AAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsPhase differencePhase frequency detector
A time-to-digital converter (TDC) includes a converter which receives a first signal and a second signal, delays the second signal in phases using a plurality of delay elements which are coupled in series, compares the delayed second signal with the first signal, and outputs a phase error of the second signal with respect to the first signal, a phase frequency detector which receives the first signal, and a third signal from one of the nodes in the plurality of delay elements, and outputs a phase difference between the first signal and the third signal, and a frequency detector which outputs a frequency error of the second signal with respect to the first signal as a digital code using an output signal of the phase frequency detector and the second signal.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
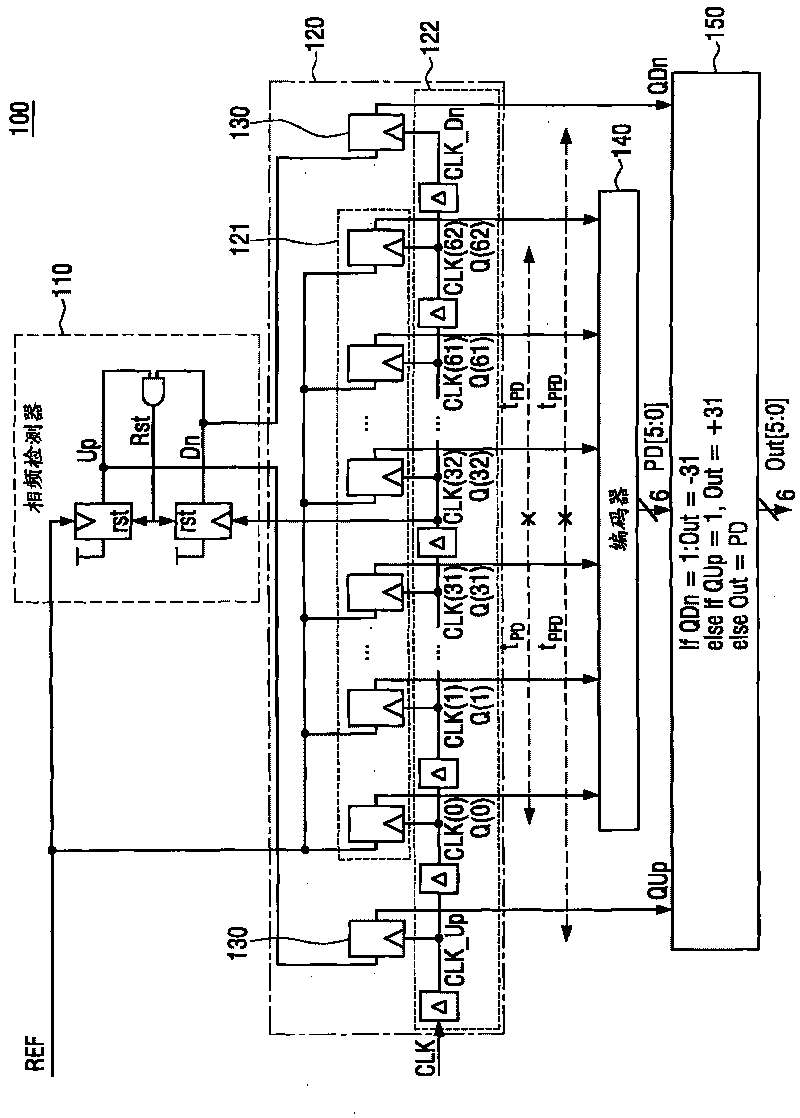
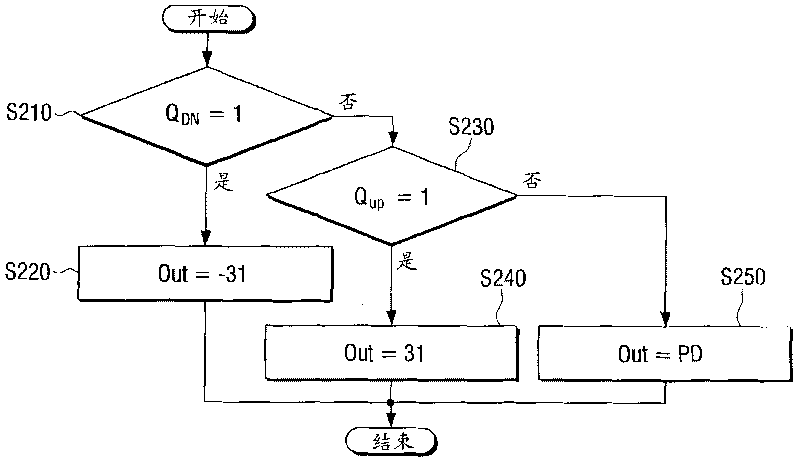
Phase detector, phase-frequency detector, and digital phase locked loop
A phase detector includes a phase comparing circuit configured to detect and output a phase difference between a first clock signal and a second clock signal, a latch circuit configured to latch an output signal of the phase comparing circuit and output a phase detection signal, and an initial voltage control circuit configured to control an initial voltage of an input terminal of the latch circuit according to a control signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com