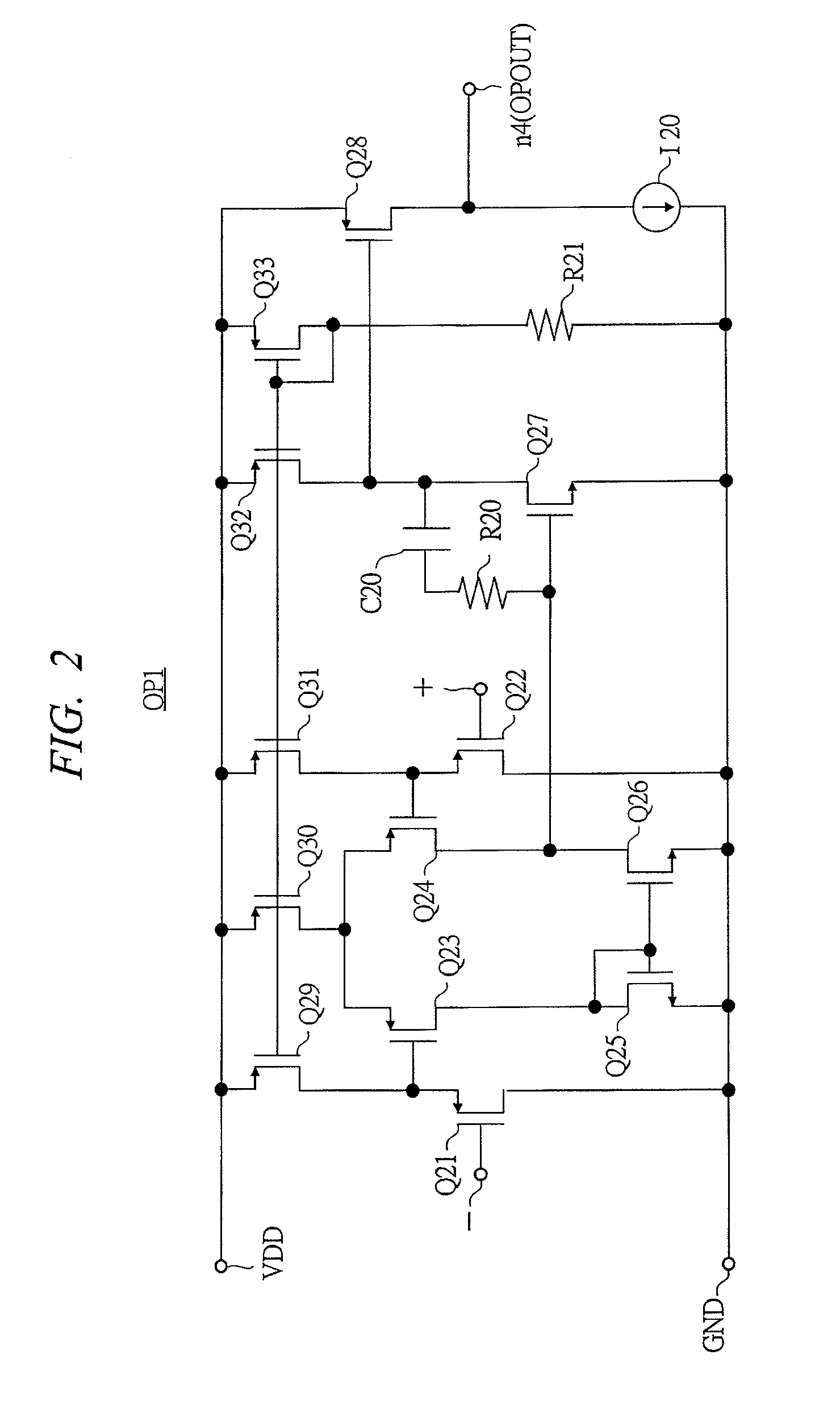
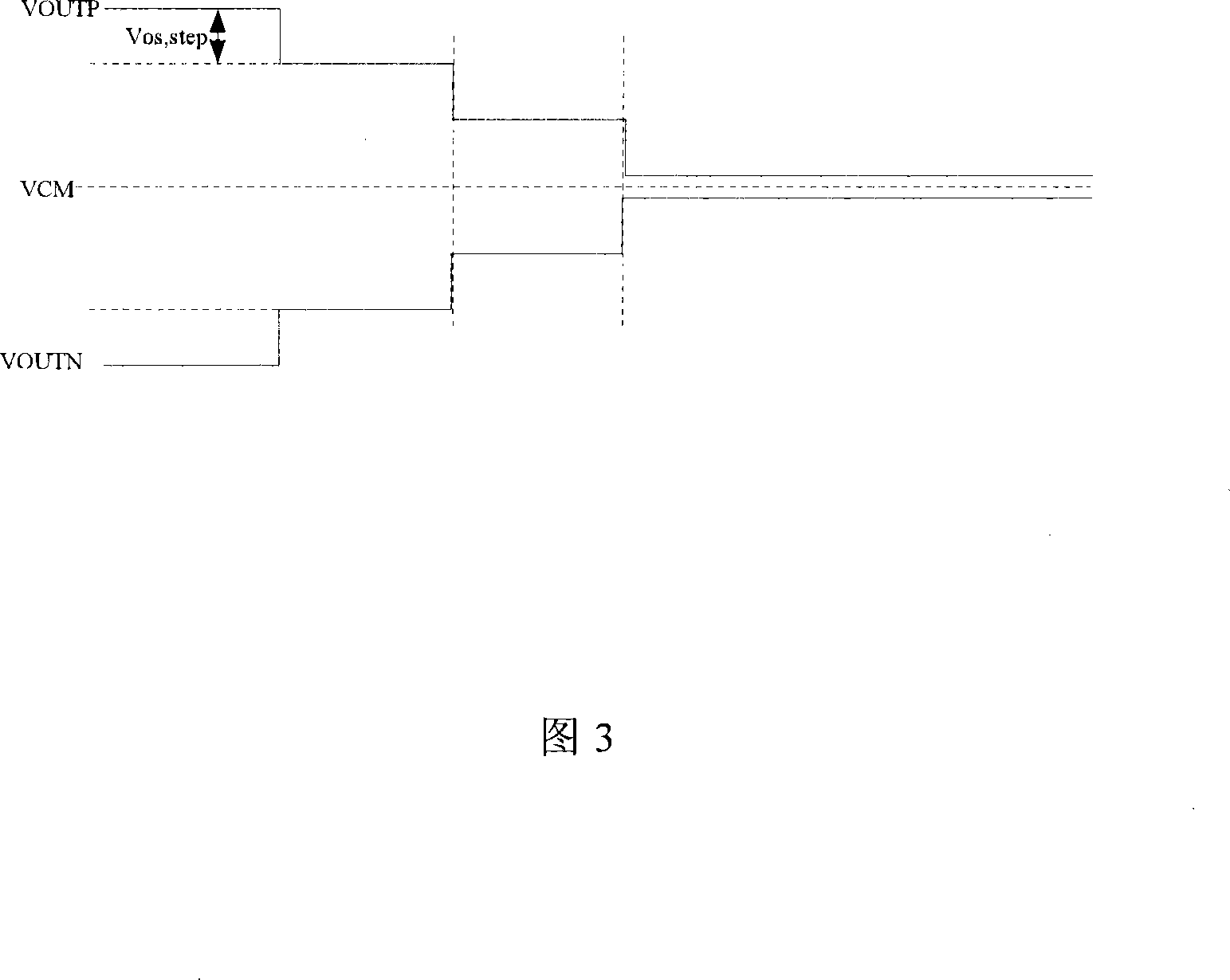
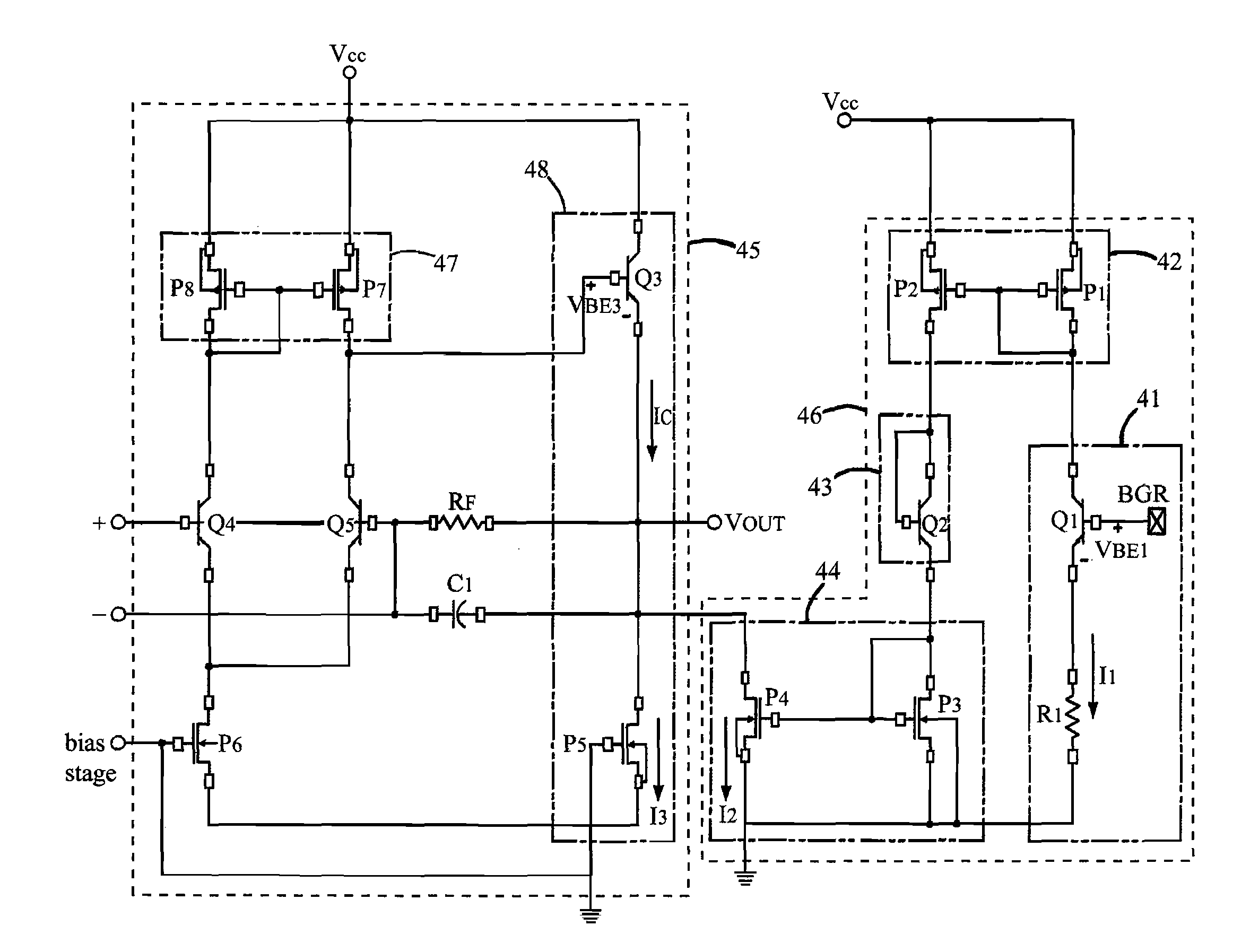
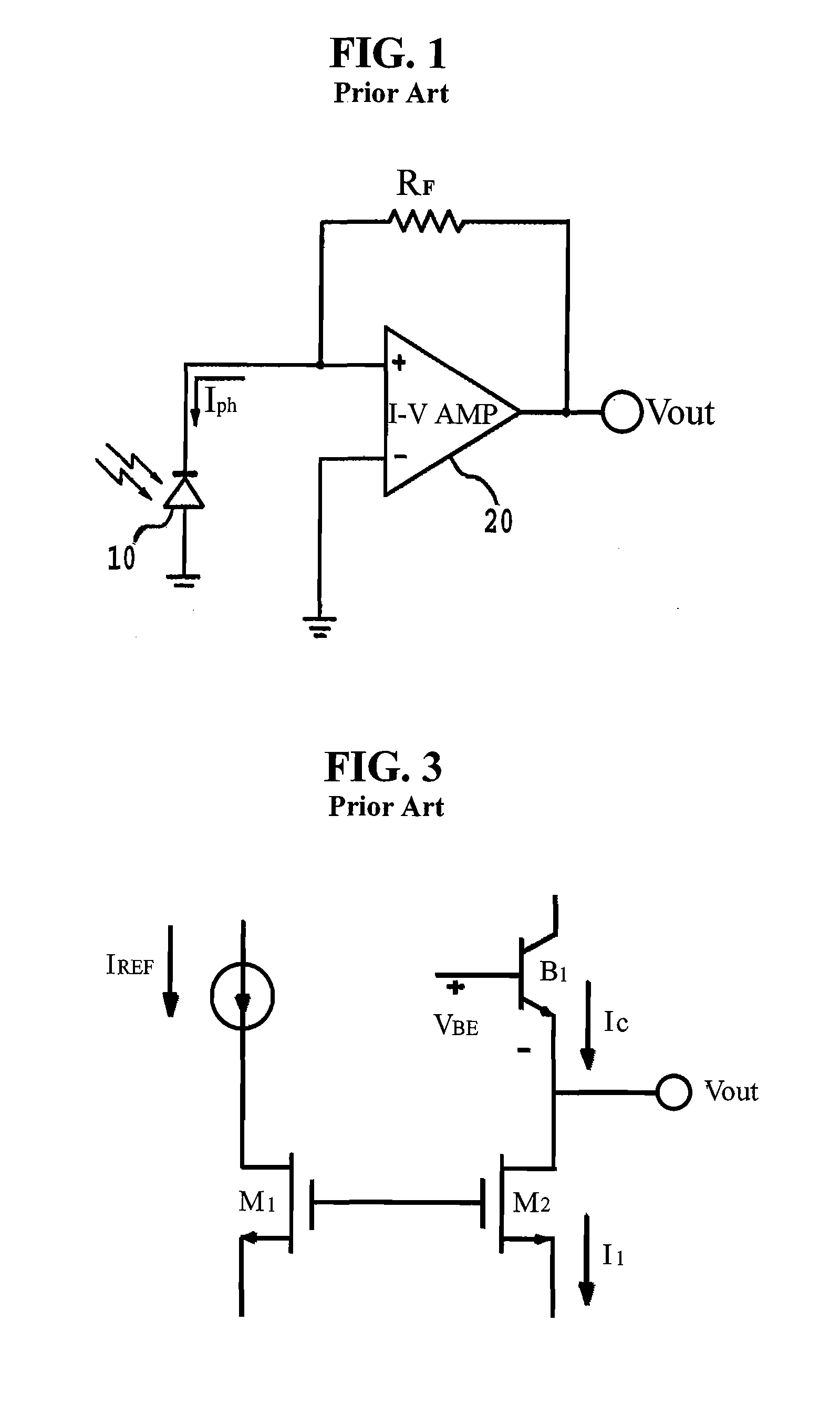
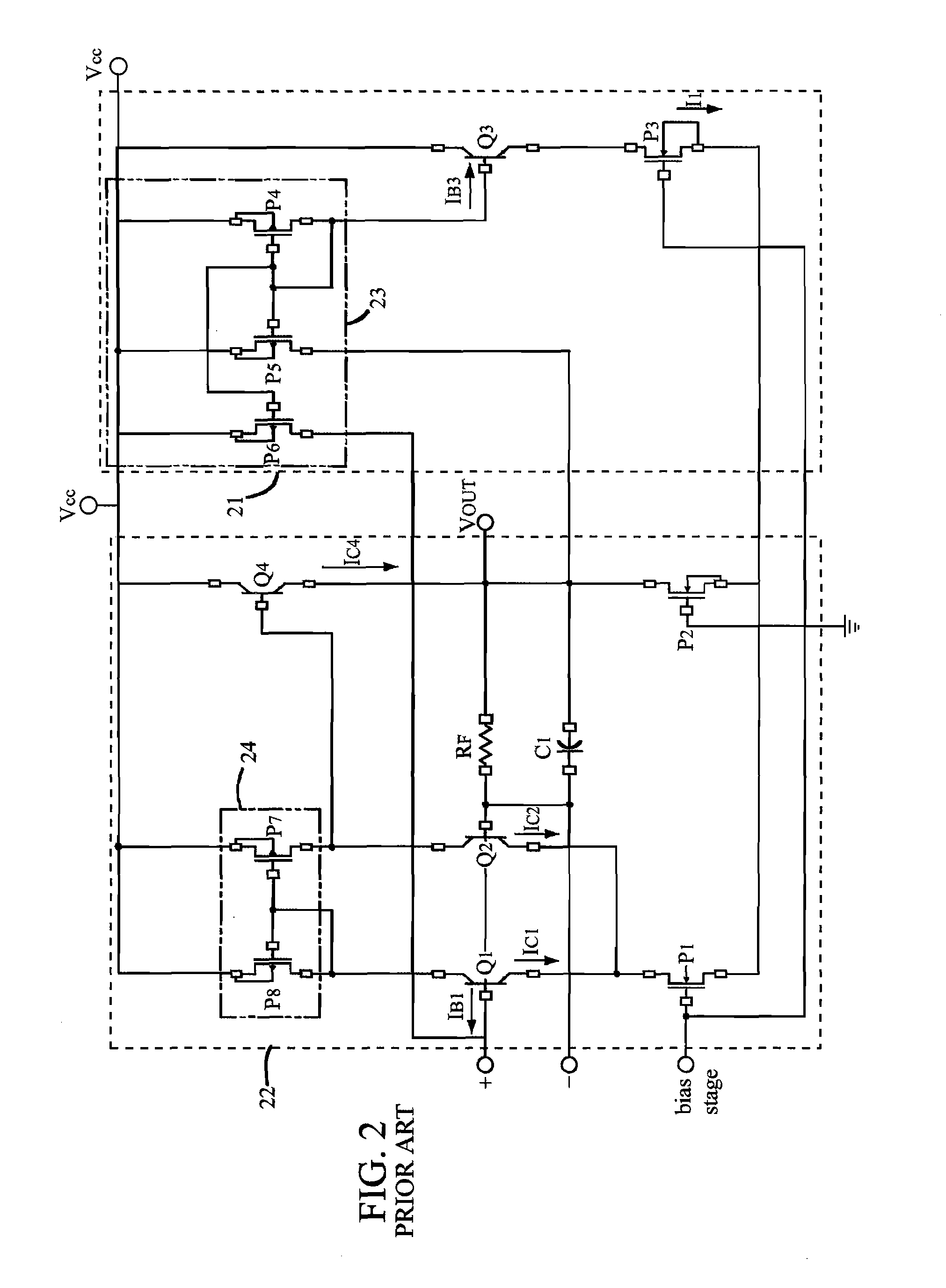
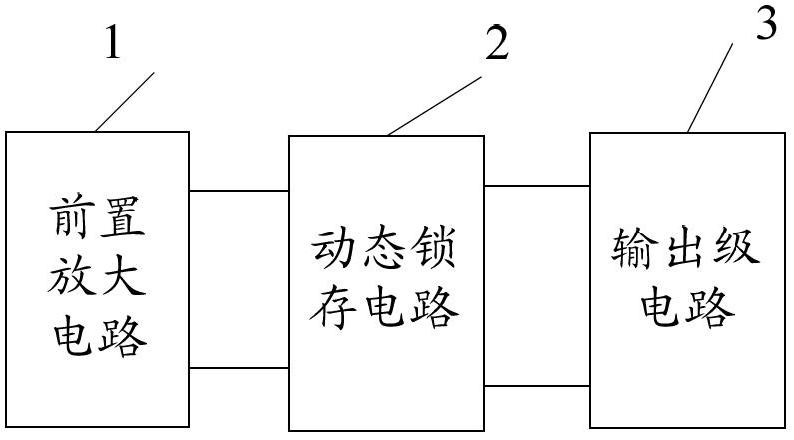
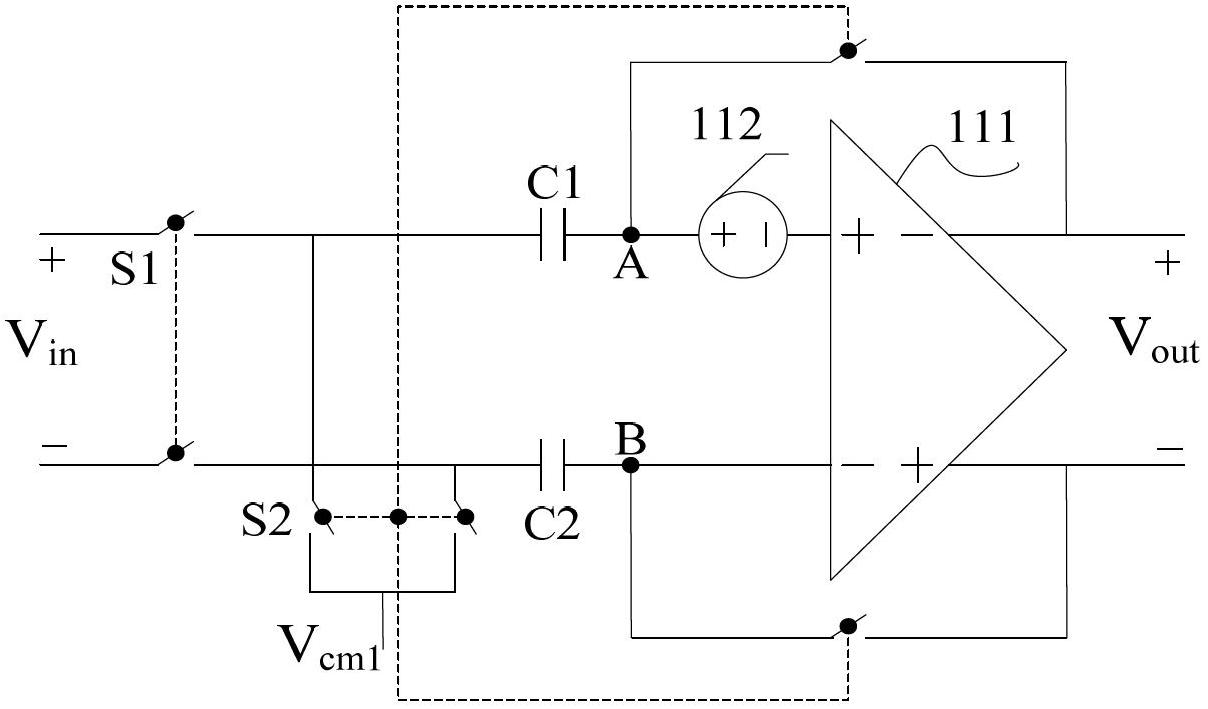
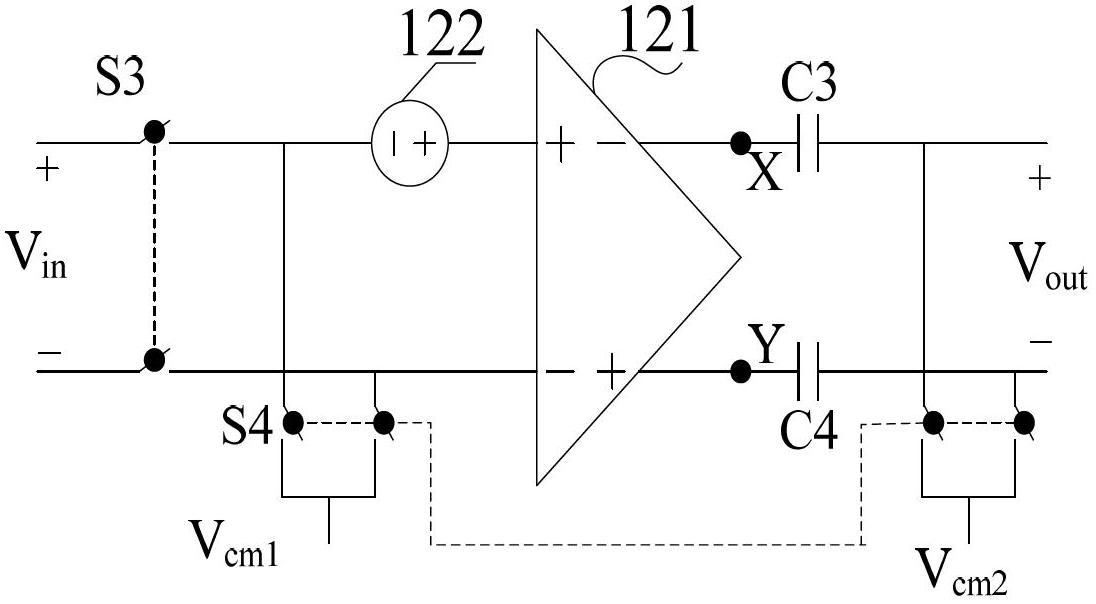
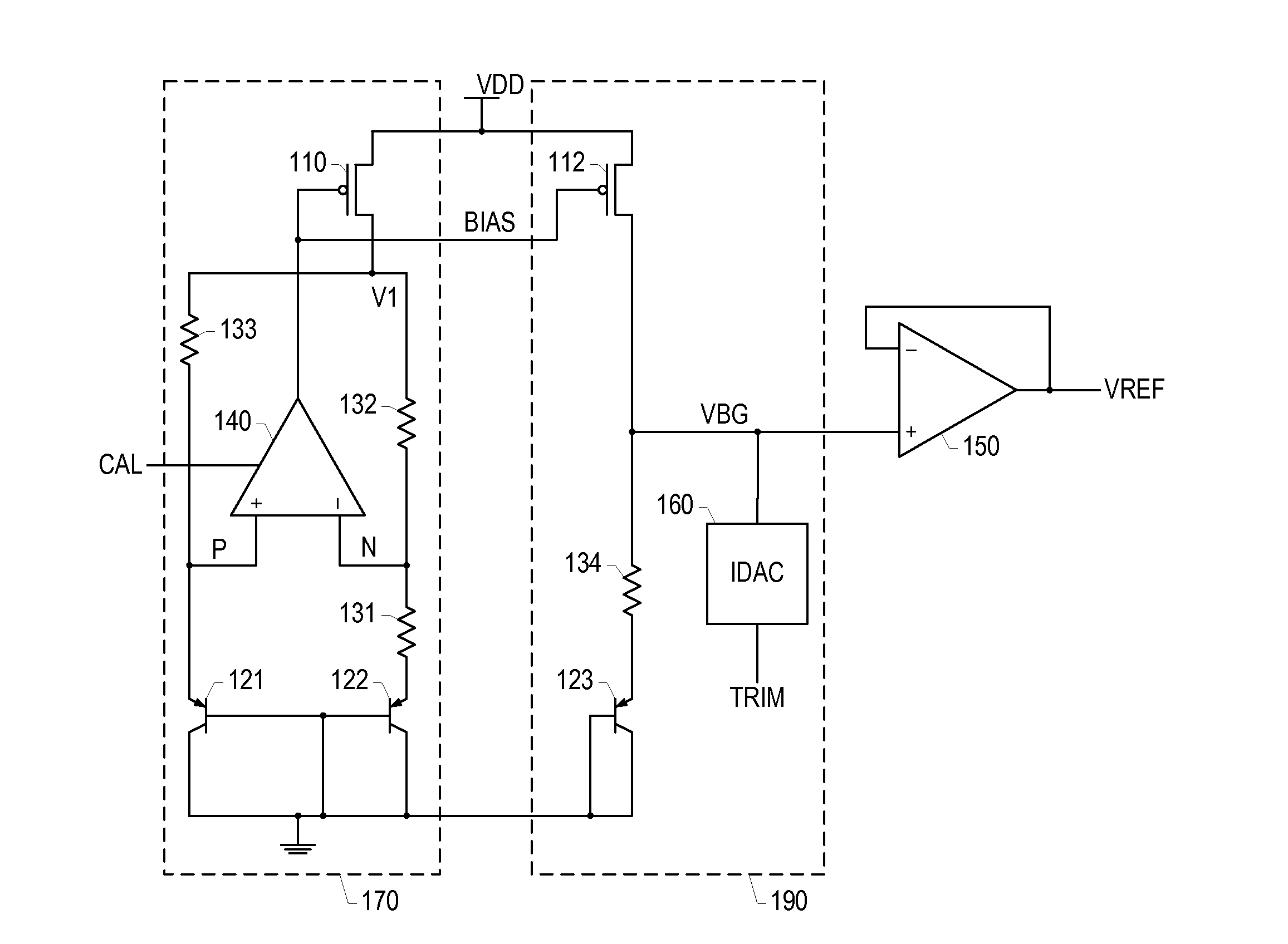
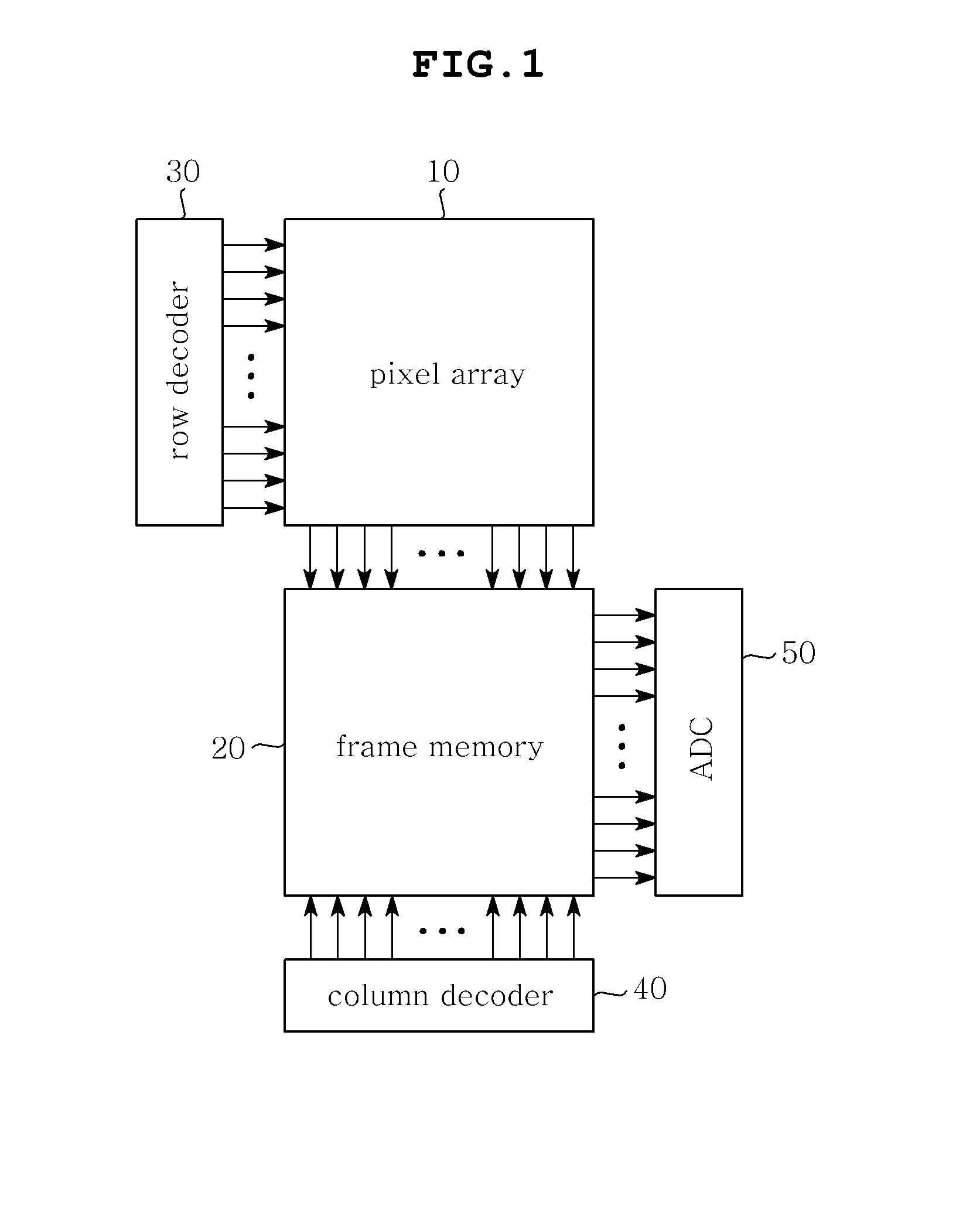Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
530 results about "Input offset voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
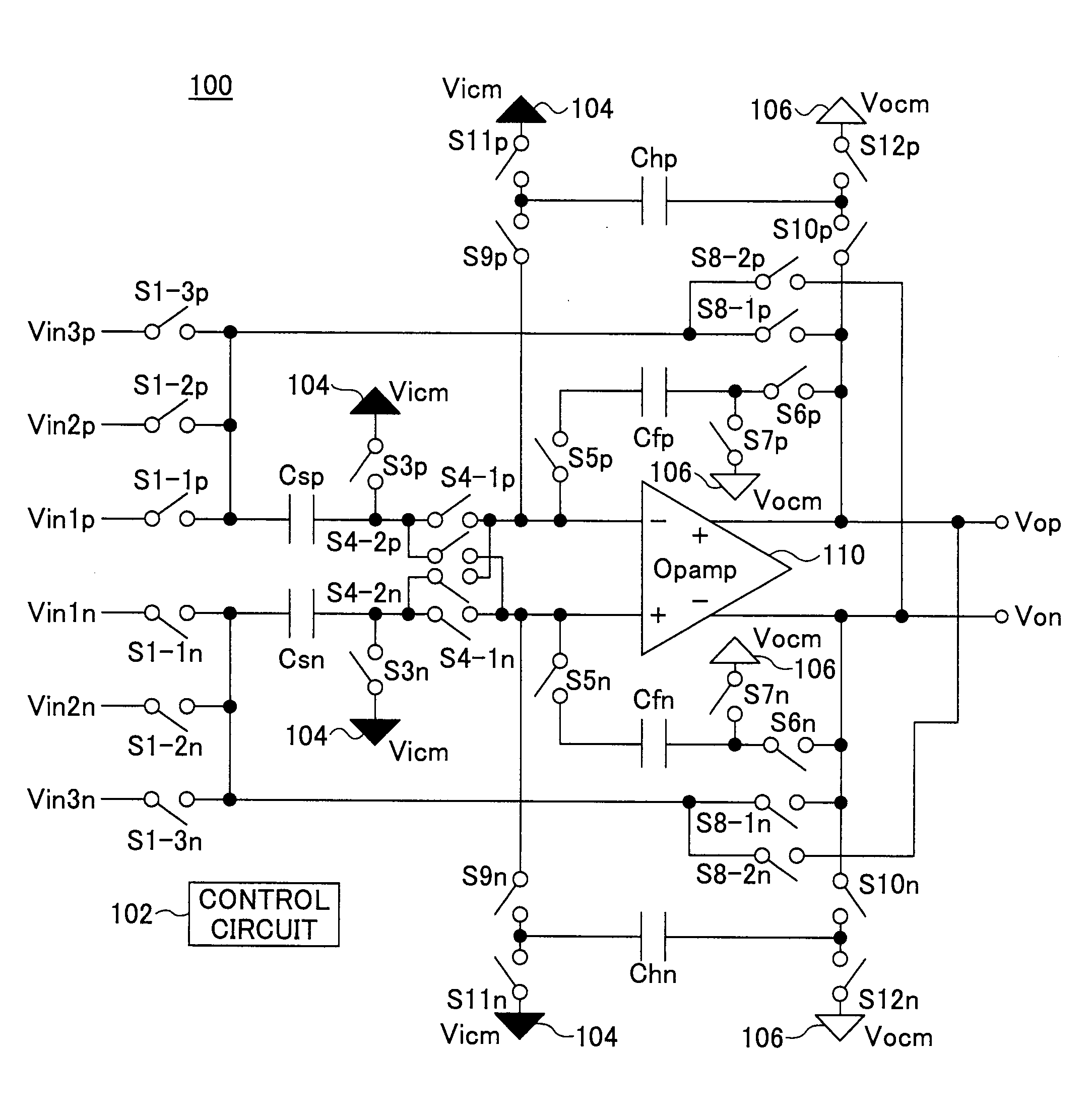
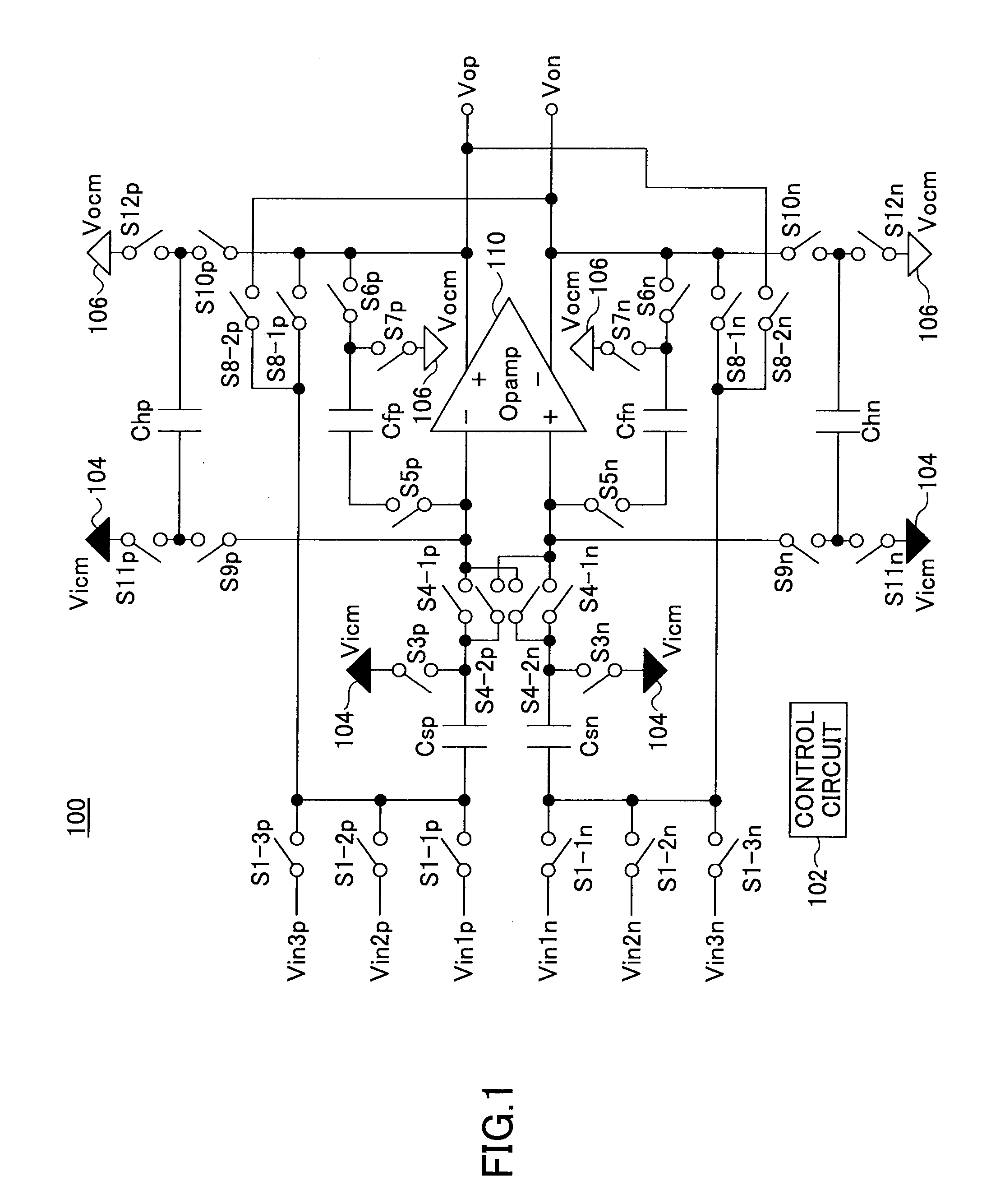
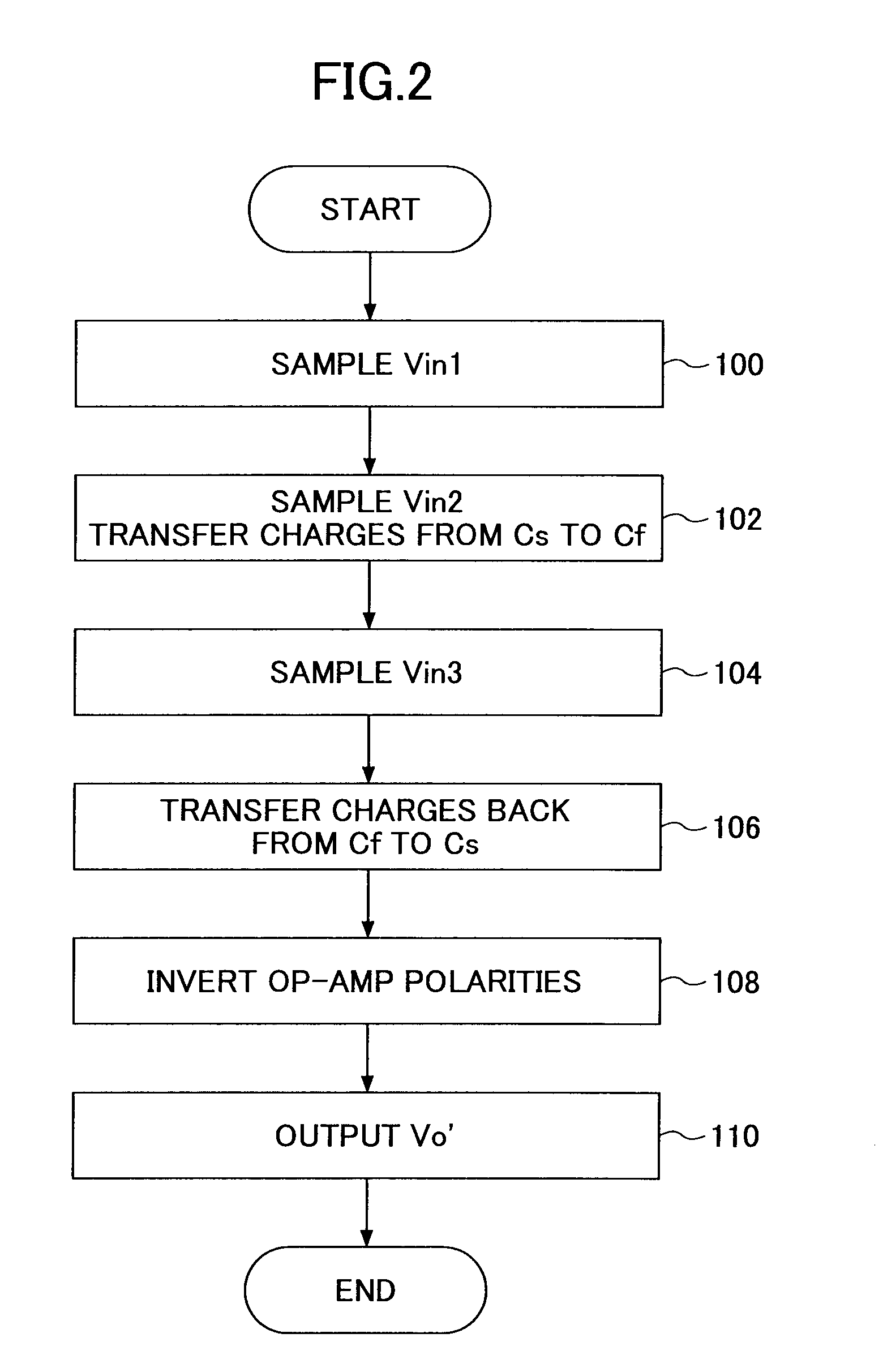
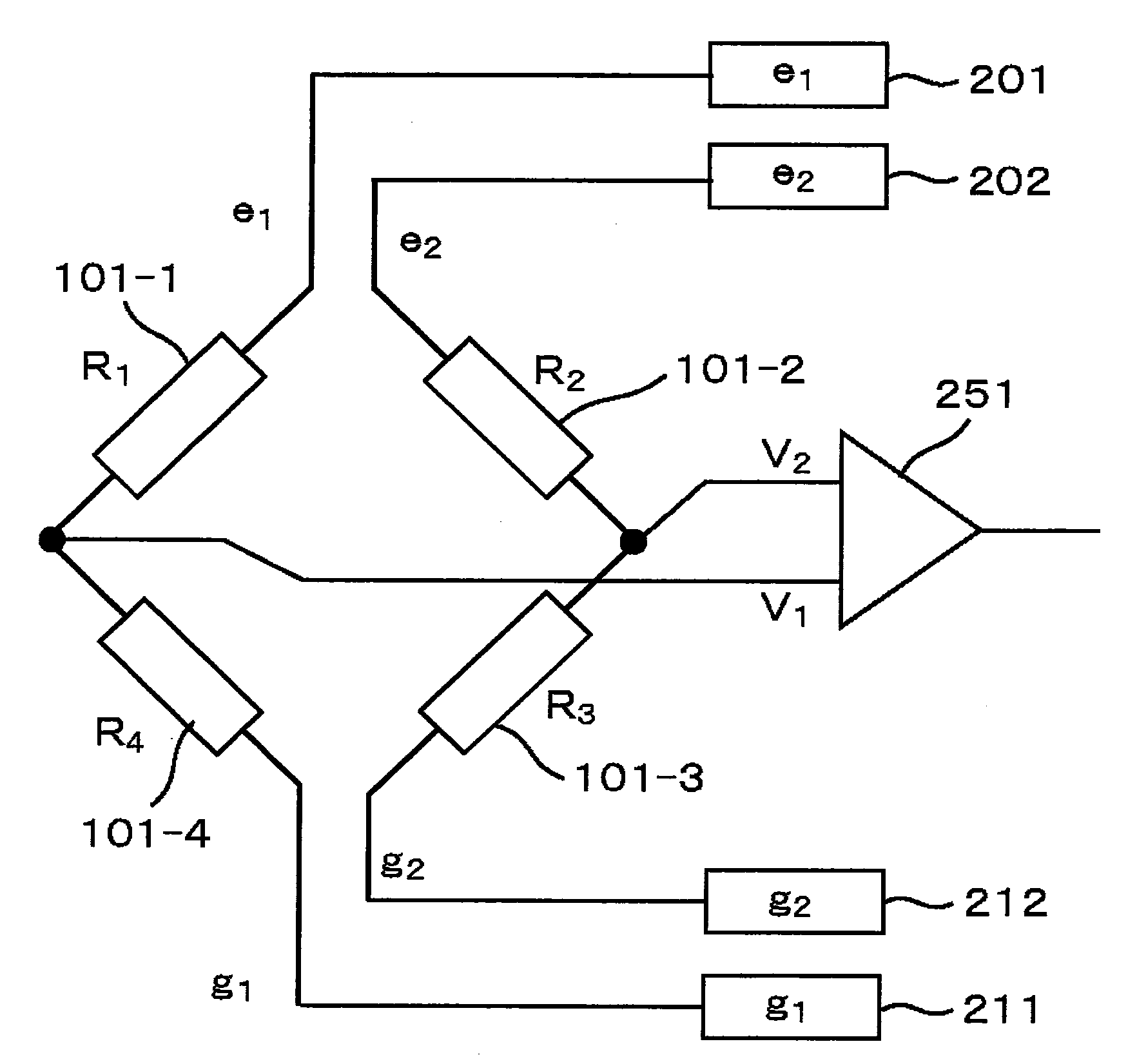
The input offset voltage (Vₒₛ) is a parameter defining the differential DC voltage required between the inputs of an amplifier, especially an operational amplifier (op-amp), to make the output zero (for voltage amplifiers, 0 volts with respect to ground or between differential outputs, depending on the output type). An ideal op-amp amplifies the differential input; if this input difference is 0 volts (i.e. both inputs are at the same voltage), the output should be zero.
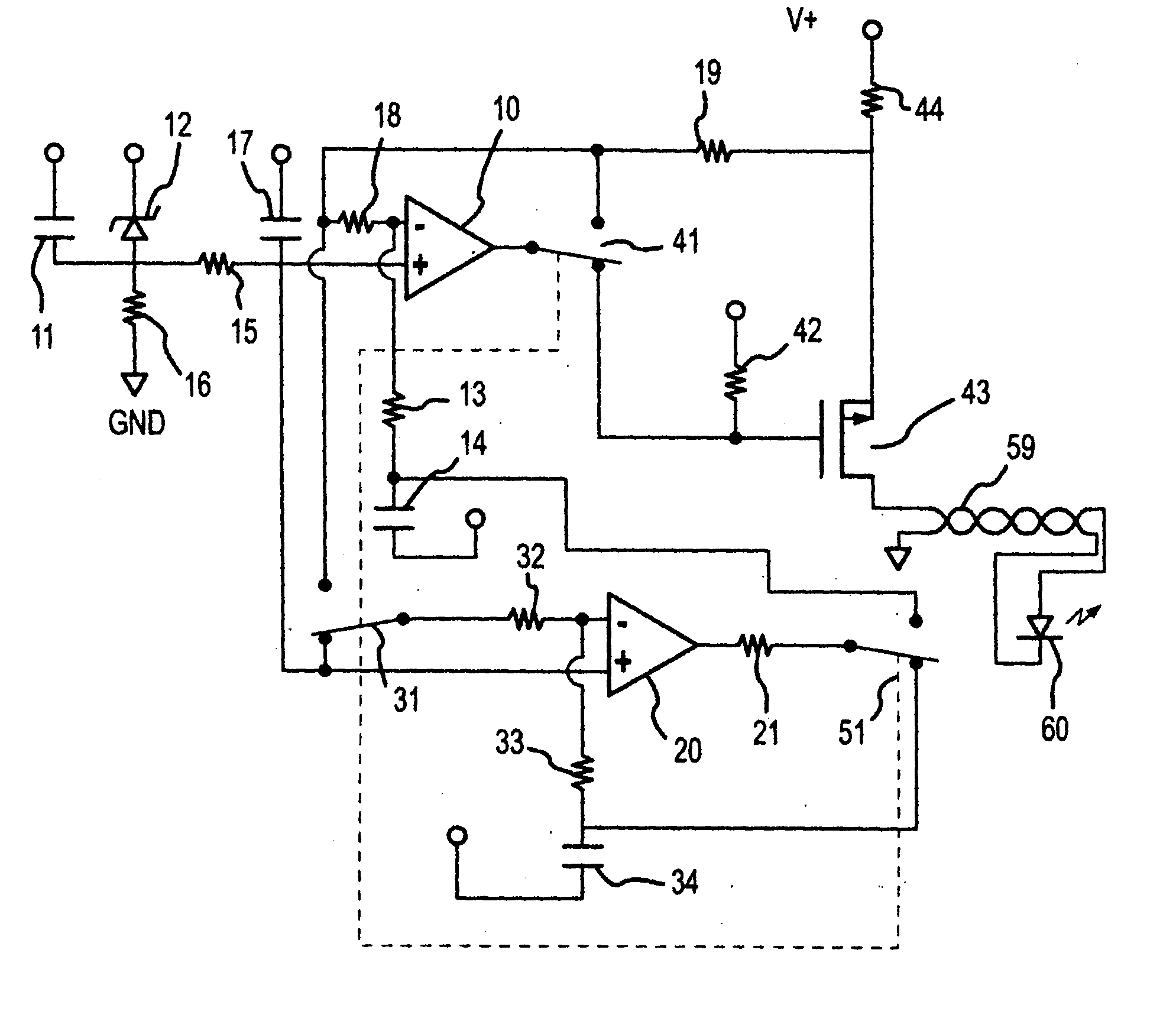
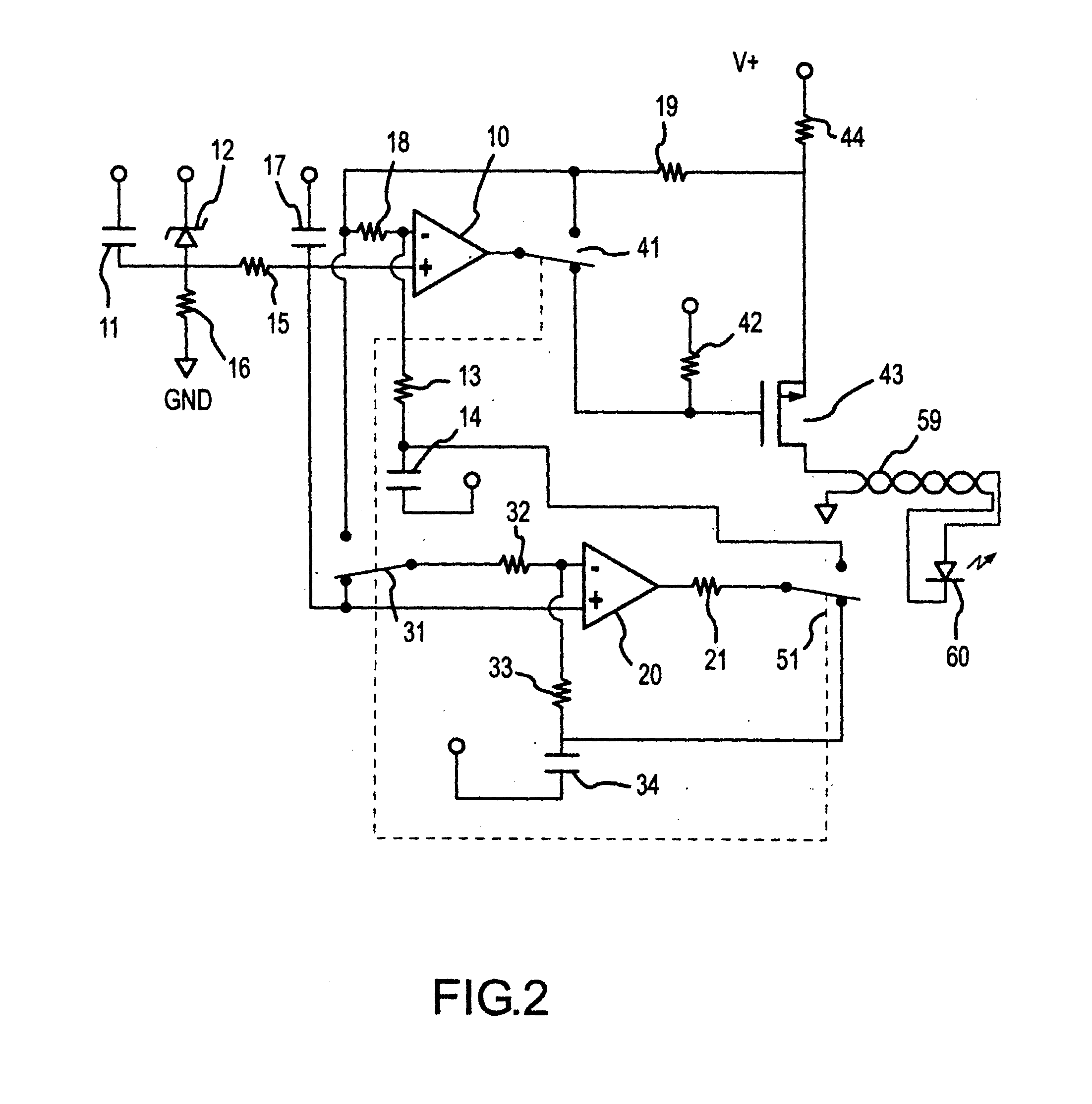
Oximeter with nulled op-amp current feedback
InactiveUS6720734B2Eliminating low frequency driftEasy to detectElectric light circuit arrangementDiagnostic recording/measuringDriving currentLight flashes
A method of producing a diode drive current in an oximeter includes sensing at least a part of a current passing through the diode and converting the sensed current to a sensed voltage, inputting the sensed voltage to a feedback amplifier for stabilizing the current passing through the diode, and eliminating an offset voltage across inputs of the feedback amplifier. A pulse oximeter includes a diode for emitting light flashes, a feedback amplifier having inputs, a feedback capacitor, and an output, the feedback amplifier stabilizing a current passing through the diode, a nulling amplifier having inputs, a nulling capacitor, and an output, the nulling amplifier charging and discharging the feedback capacitor until the inputs of the feedback amplifier are at a same voltage. The operation may include synchronizing an elimination of input offset voltages of the feedback and nulling amplifiers with on or off state of diode current.
Owner:DATEX OHMEDA
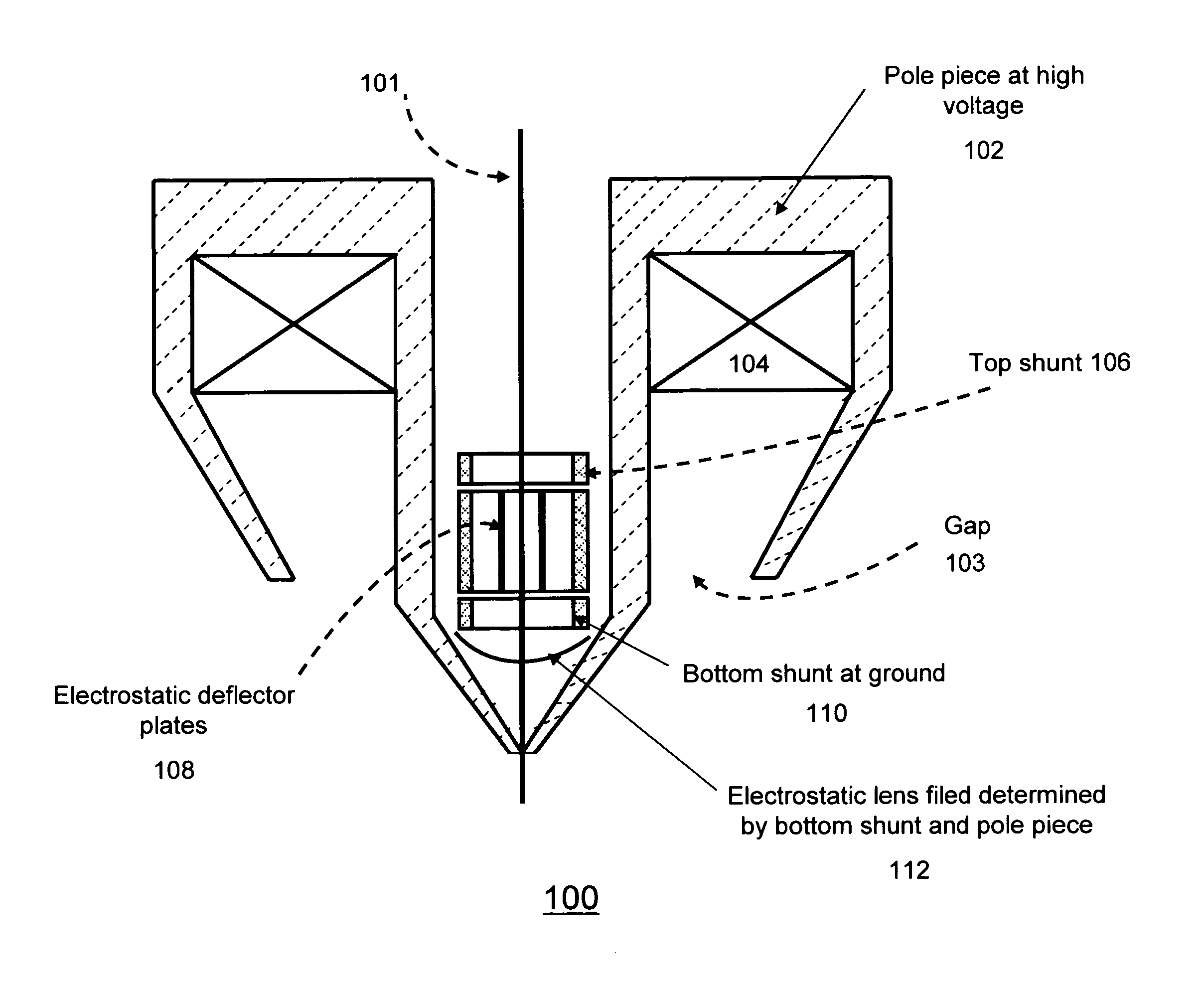
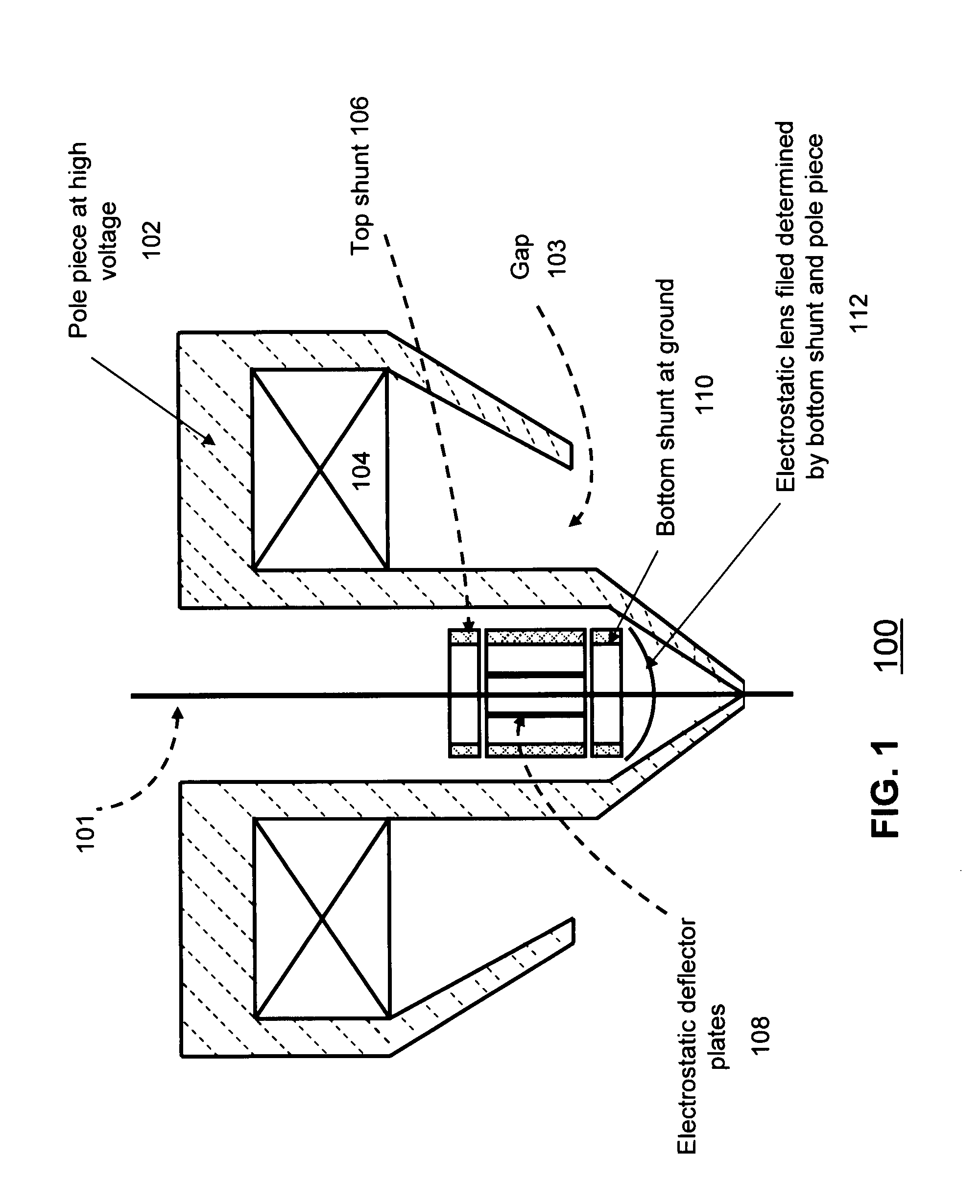
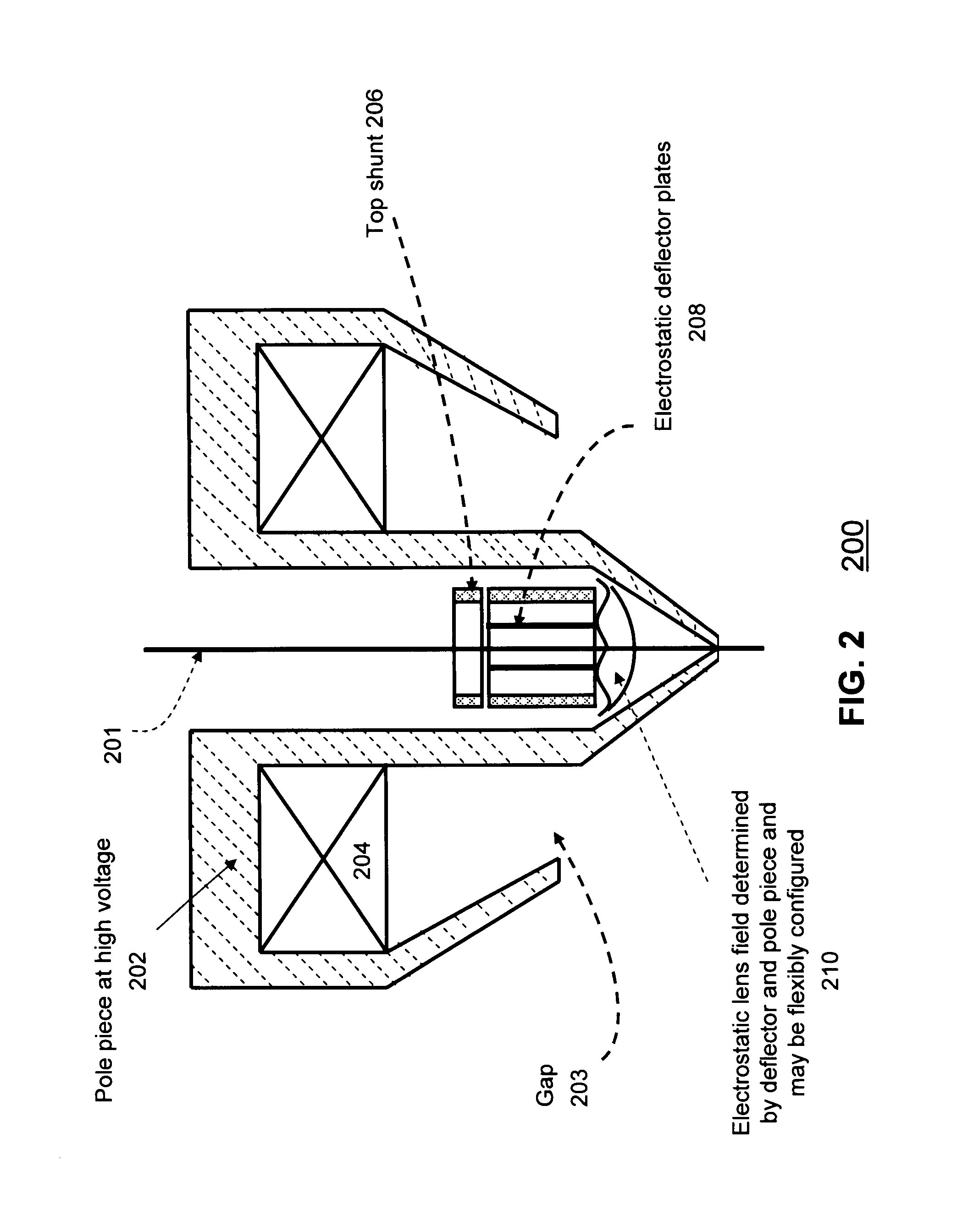
Objective lens with deflector plates immersed in electrostatic lens field
InactiveUS8698093B1Stability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMagnetic polesPole piece
One embodiment relates to an objective lens utilizing magnetic and electrostatic fields which is configured to focus a primary electron beam onto a surface of a target substrate. The objective lens includes a magnetic pole piece and an electrostatic deflector configured within the pole piece. An electrostatic lens field is determined by the pole piece and the electrostatic deflector, and the electrostatic lens field is configured by adjusting offset voltages applied to plates of the electrostatic deflector. Other embodiments, aspects and features are also disclosed.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
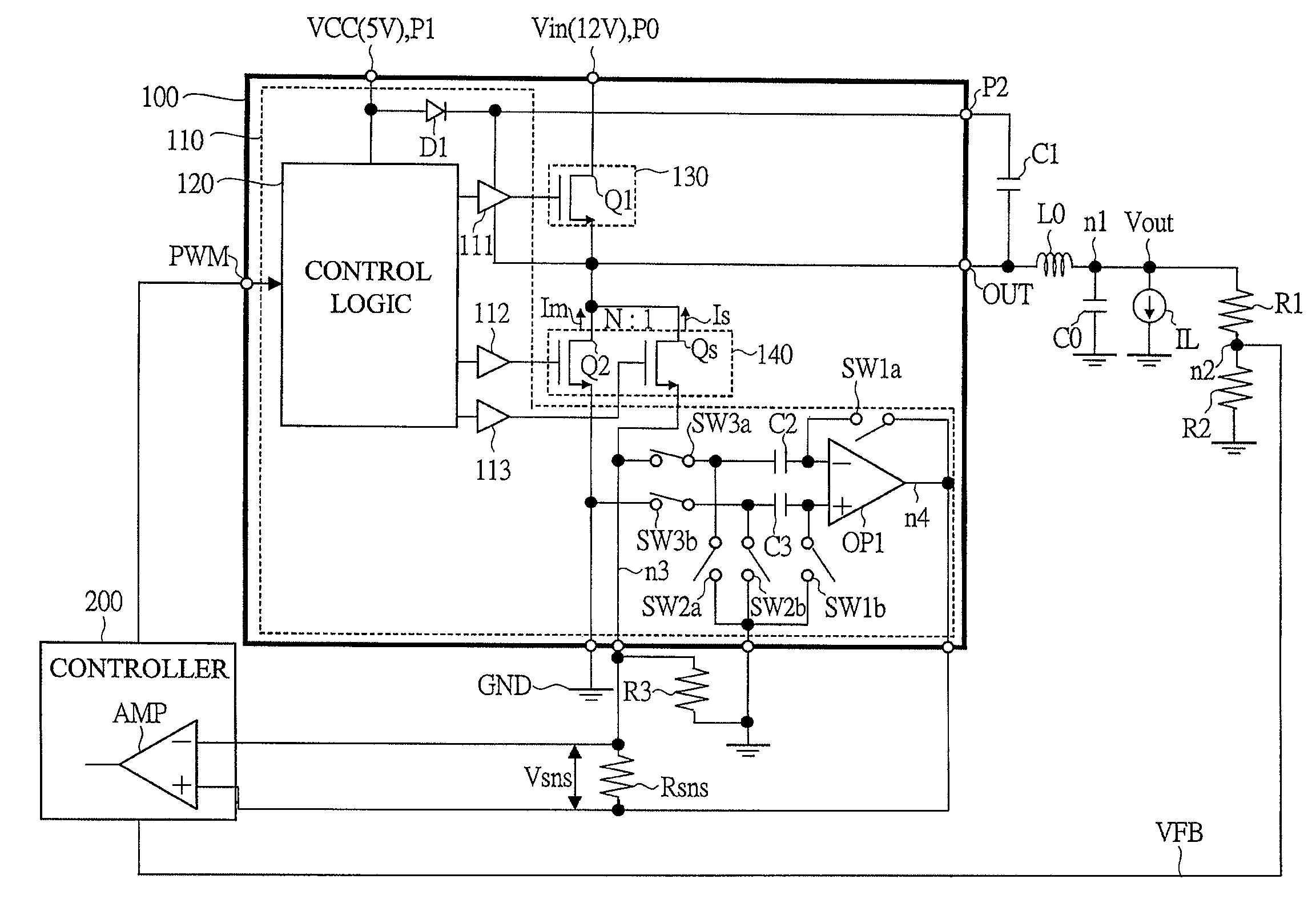
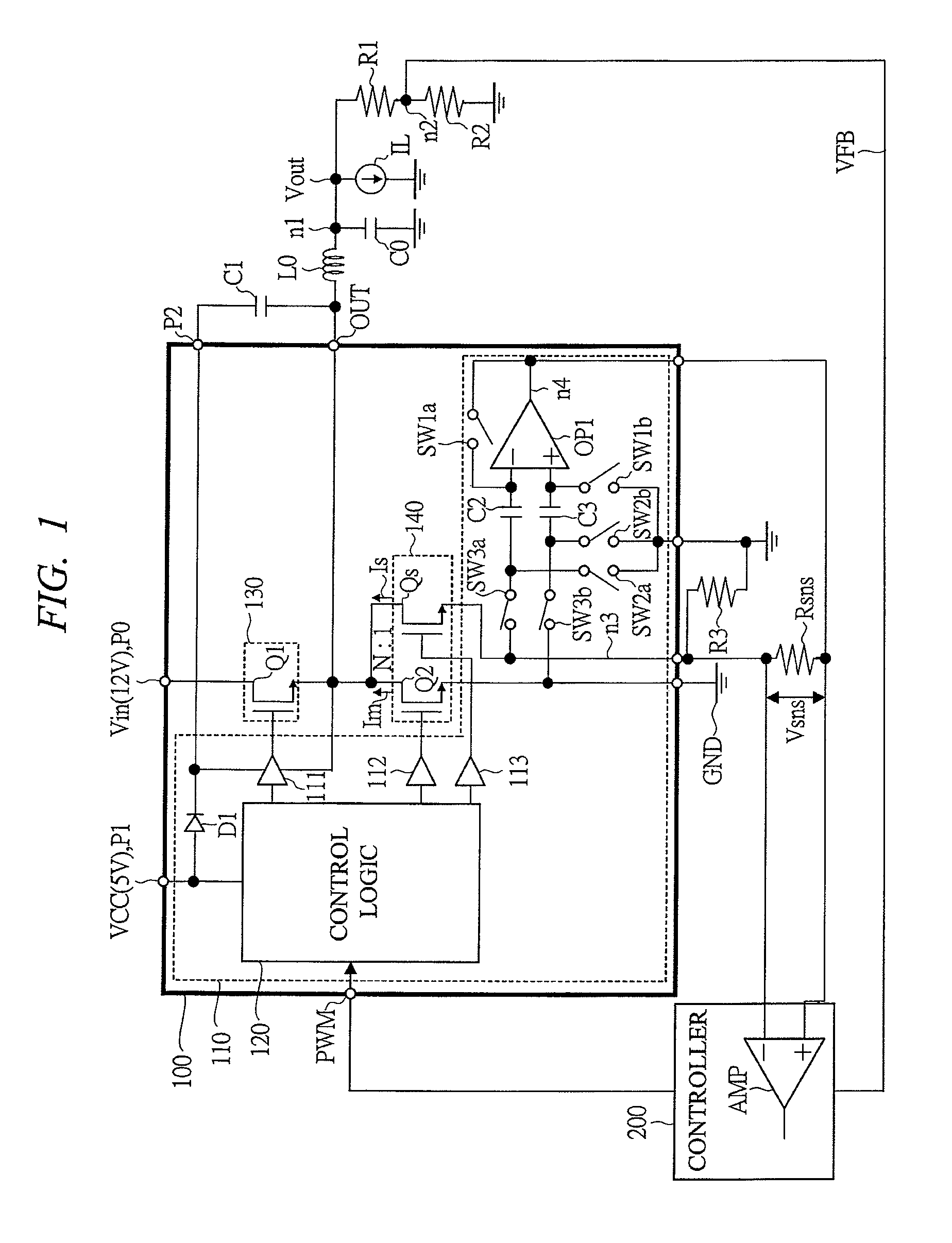
Switching power supply
InactiveUS7385380B2Highly precise and high speed current controlCurrent detectionDc-dc conversionPulse techniqueAudio power amplifierEngineering
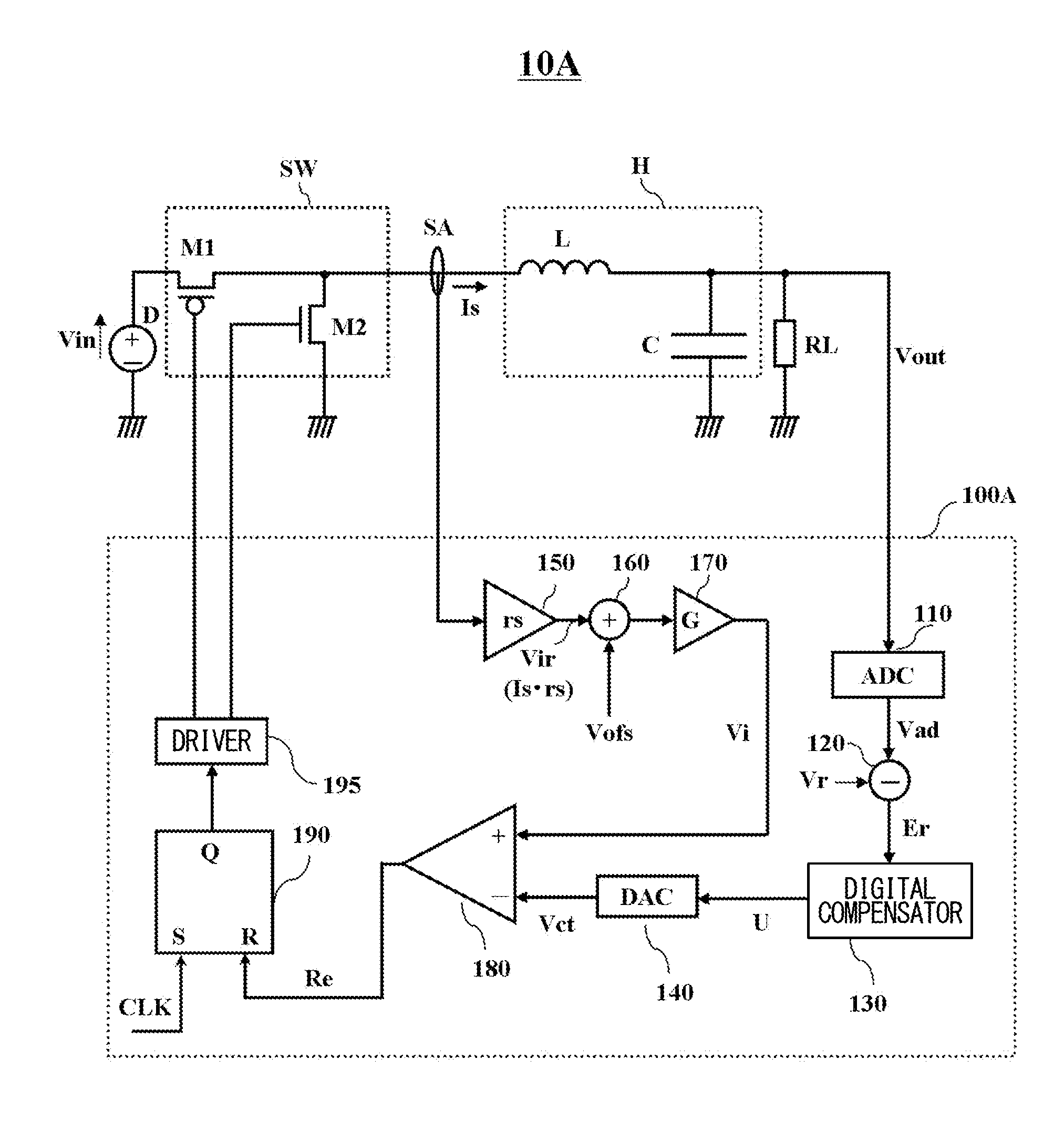
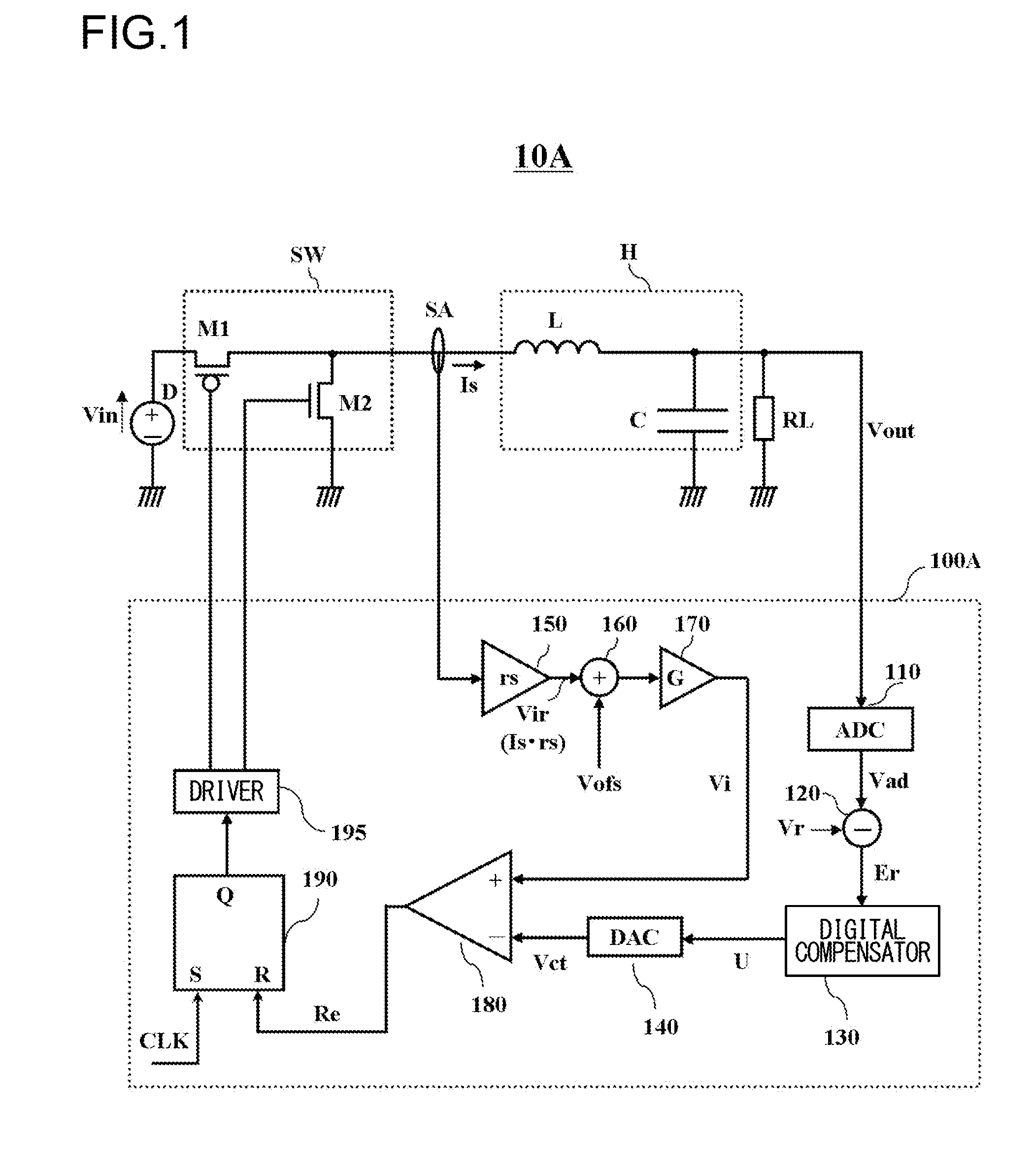
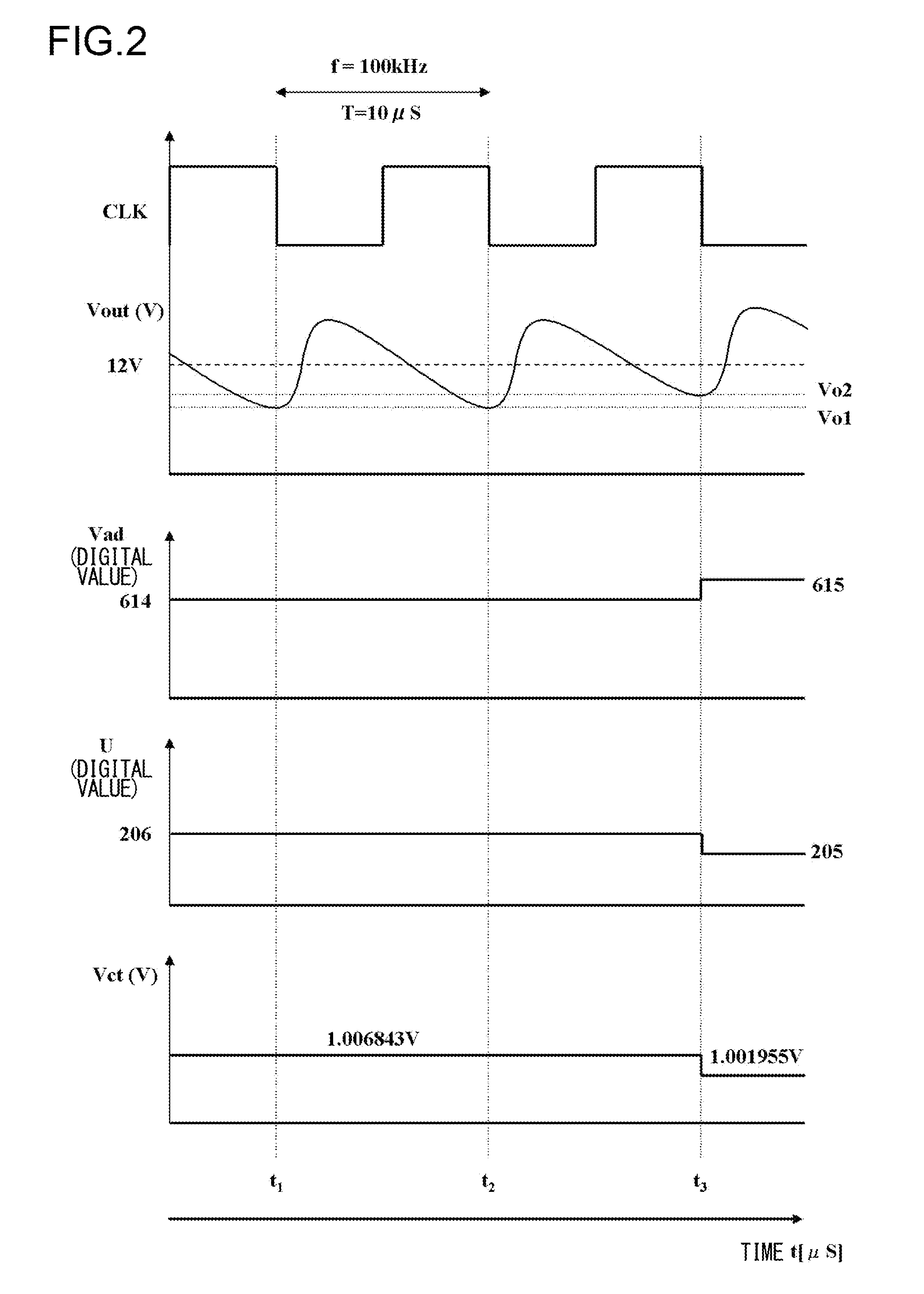
In a switching power supply apparatus for performing a switching control of a power MOS transistor that flows current to a coil and converting input voltage into output voltage, even if there occurs offset voltage in a current sensing operational amplifier, source potential of a current sensing MOS transistor is precisely kept at source potential of a low side power MOS transistor. For example, an offset cancel capacitor is arranged at an inverting input terminal of the current sensing operational amplifier, and voltage in the direction to offset the offset voltage occurring in the operational amplifier is charged to this capacitor.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
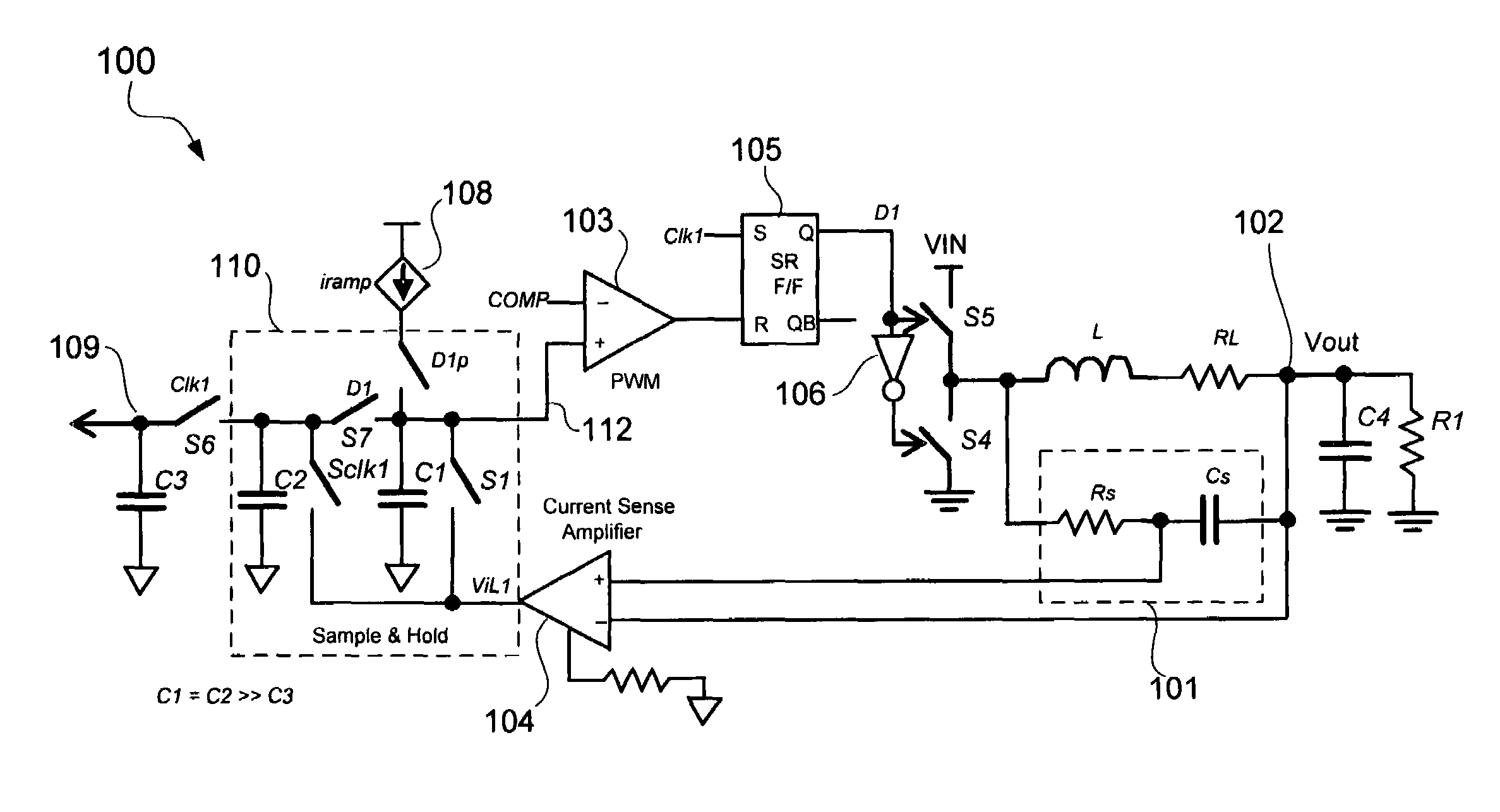
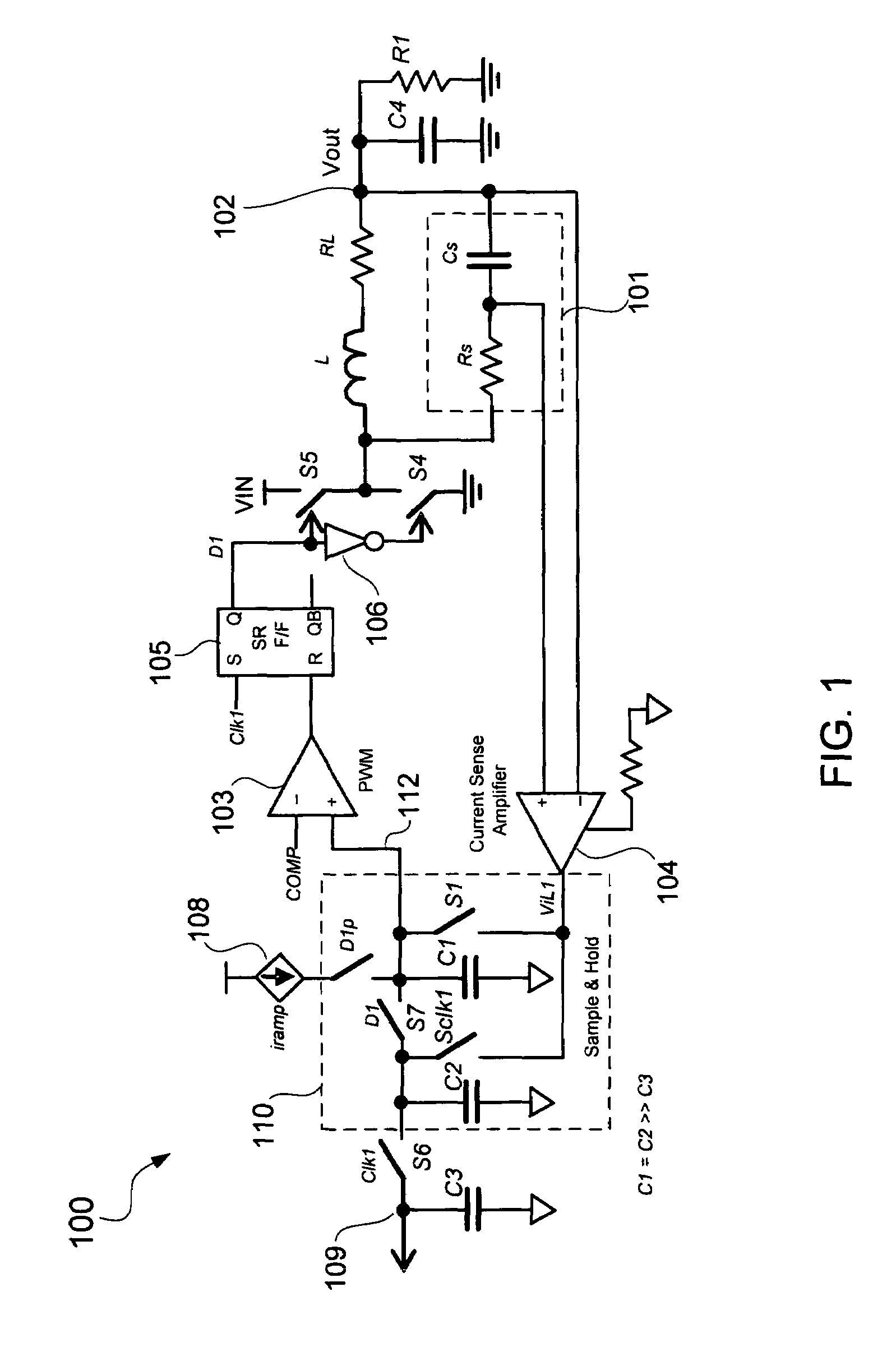
Sample and hold technique for generating an average of sensed inductor current in voltage regulators
A sample and hold inductor current sense configuration senses inductor current flowing through an output inductor of a voltage regulator and generates an average of the sensed inductor current. The average of the sensed inductor current may be generated from samples of peaks and valleys of the sensed inductor current. For example, the peak of the sensed inductor current may be stored in a first capacitor and the valley of the sensed inductor current may be stored in a second capacitor. The first and second capacitors may be coupled together to generate the average of the sensed inductor current. The average of the sensed inductor current may be provided to a droop control circuit to control droop of an output voltage of the voltage regulator. An input offset voltage of a current sense amplifier sensing the inductor current may be calibrated between samplings of the sensed inductor current.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
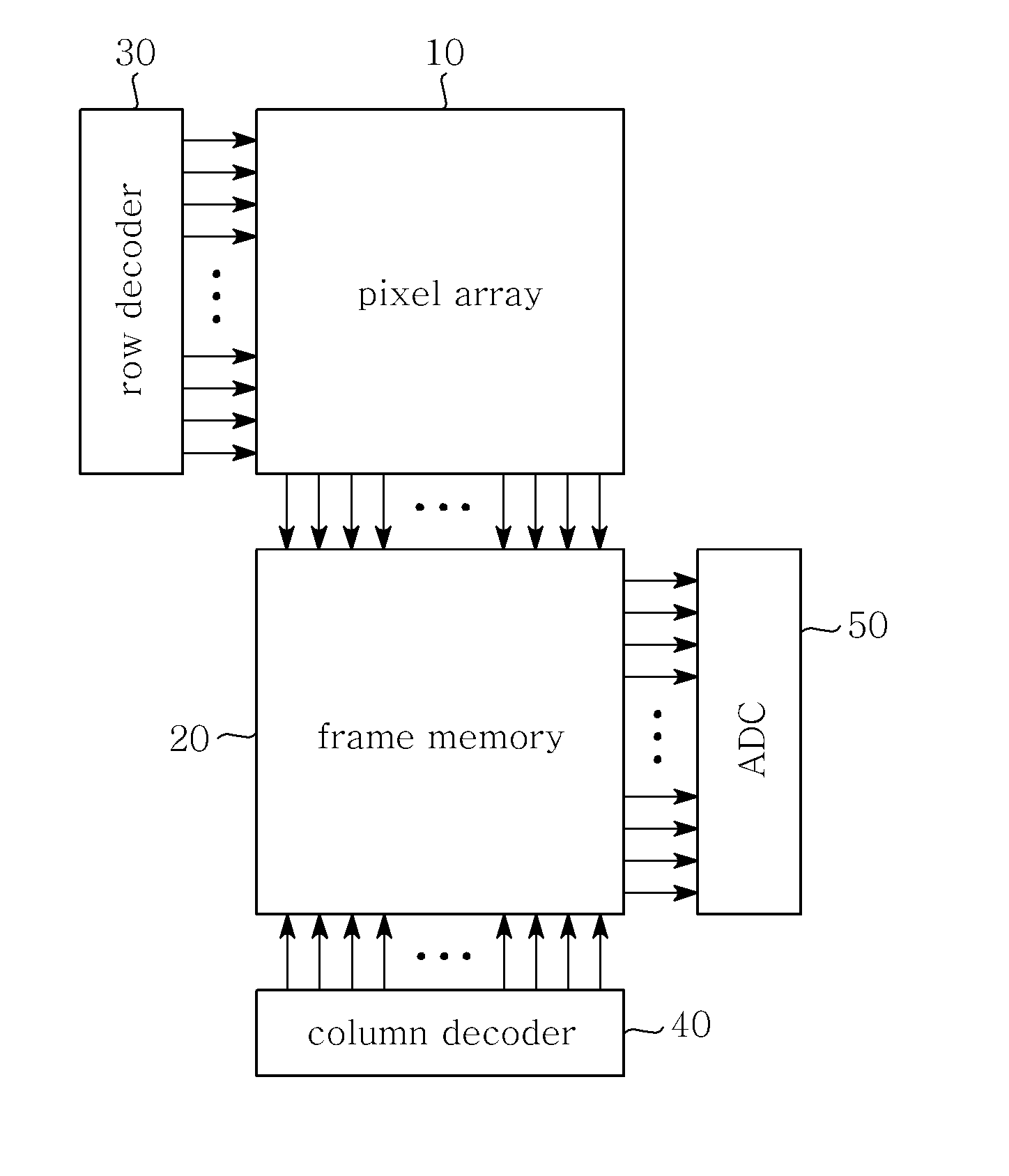
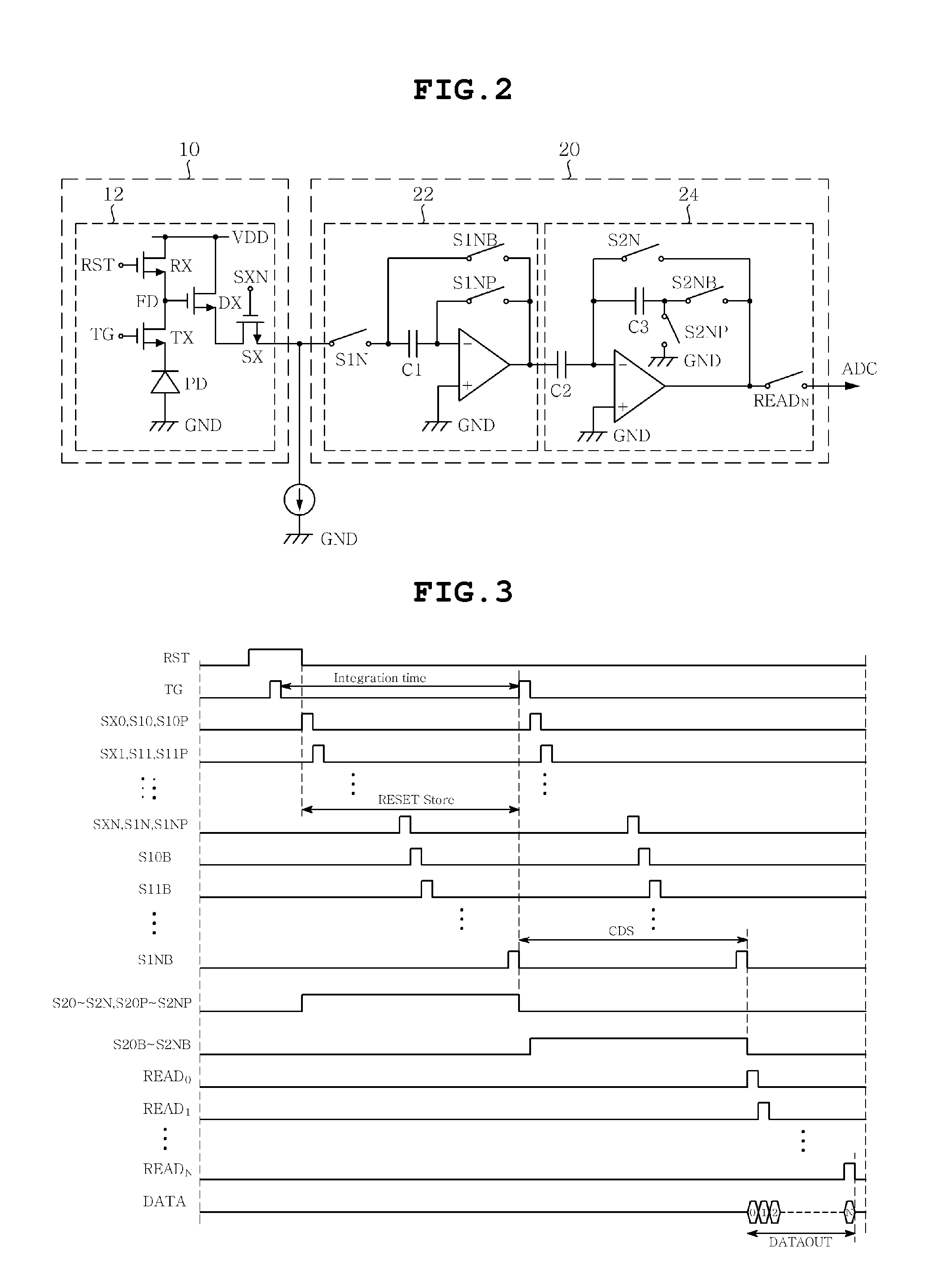
CMOS image sensor
InactiveUS20110194007A1Avoid chargingAvoid noiseTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsEngineeringAnalog signal
Disclosed herein is a Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) image sensor. The CMOS image sensor includes a pixel array, a frame memory, and an analog-to-digital converter. The pixel array includes N unit pixels for converting optical signals, caused by light, into electric signals. The frame memory eliminates offset voltage included in reset voltage and signal voltage transmitted from the pixel array and internal offset voltage, and performs Correlated Double Sampling (CDS) on the reset voltage and the signal voltage. The analog-to-digital converter converts an analog signal, transmitted from the frame memory, into a digital signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD +1
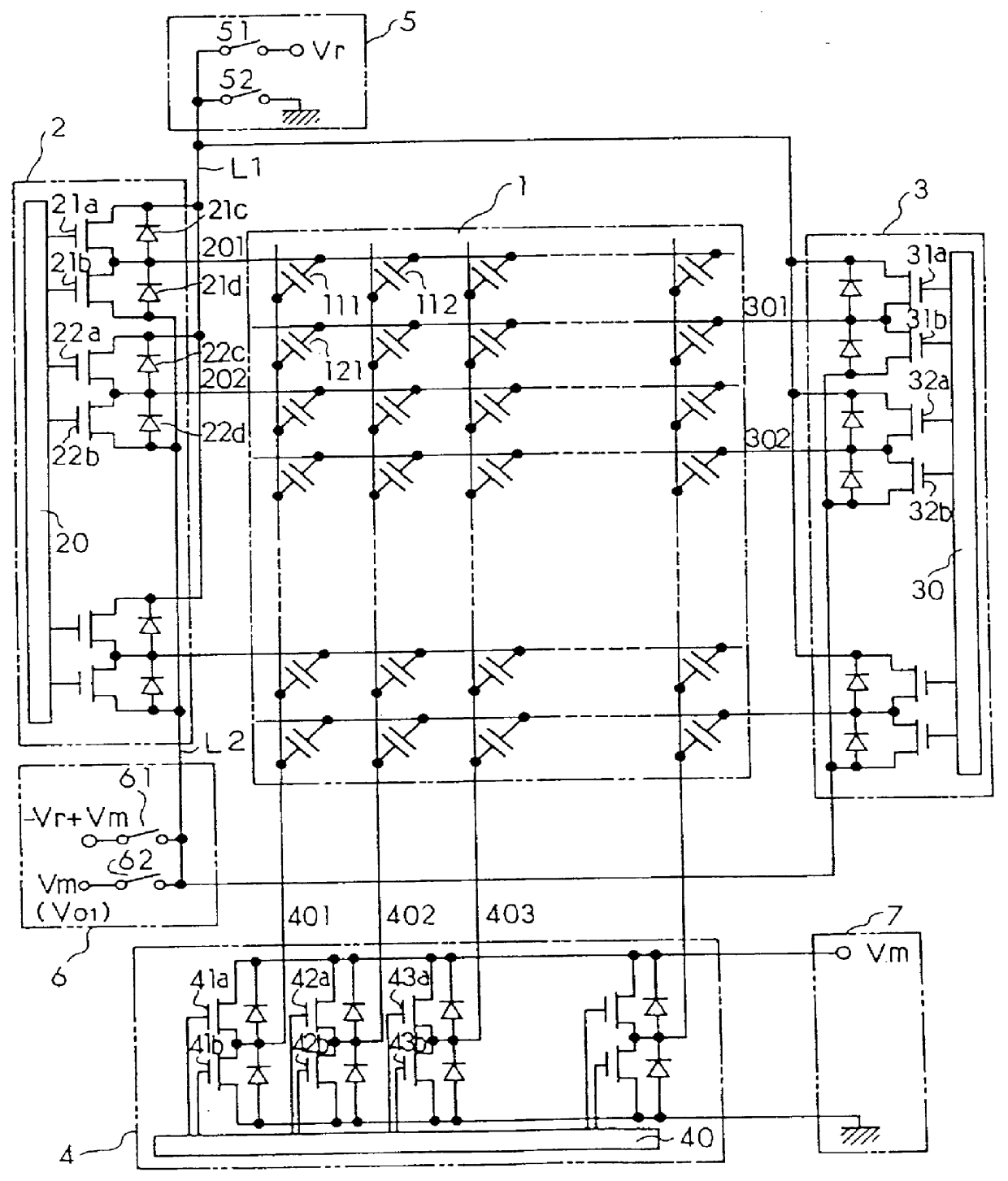
Electroluminescent display device
InactiveUS6064158ACathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingElectricityAC - Alternating current
A scan driver IC for an EL element in an EL display device supplies, in a positive field, a positive polarity scan voltage and an offset voltage which is higher than ground to scan side driver ICs from voltage supply circuits, and the scan side driver ICs set voltage of scan electrodes to be the offset voltage in the positive field, together with outputting the positive polarity scan voltage to the scan electrodes during electroluminescence timing. Consequently, a voltage of Vr-Vm is applied to the scan side driver ICs, and so the breakdown voltage can be lowered by an amount corresponding to the offset voltage Vm. Circuits for providing such voltages, for providing alternating current drive voltages, and for reducing power consumption of the drive circuits are also disclosed.
Owner:DENSO CORP
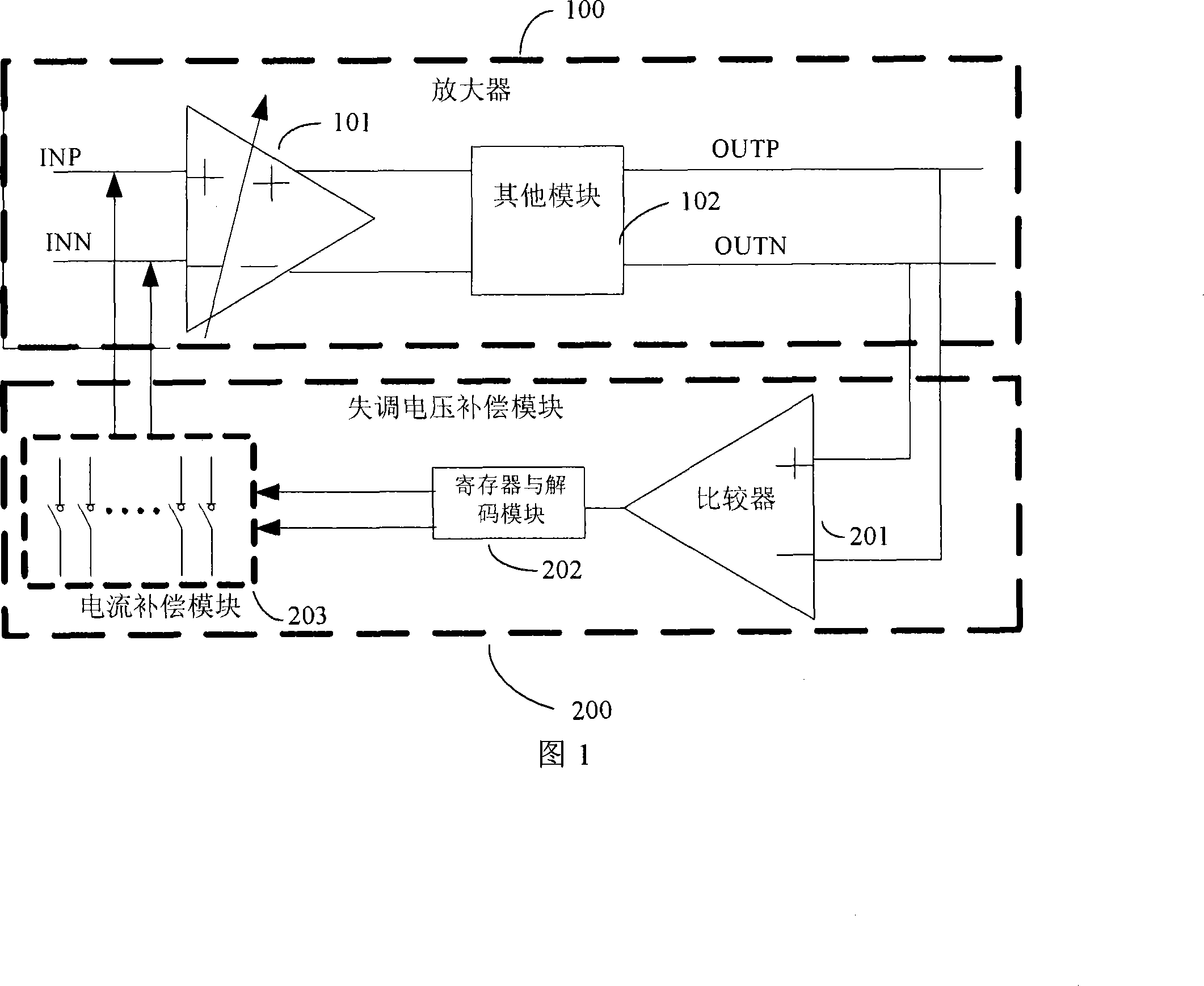
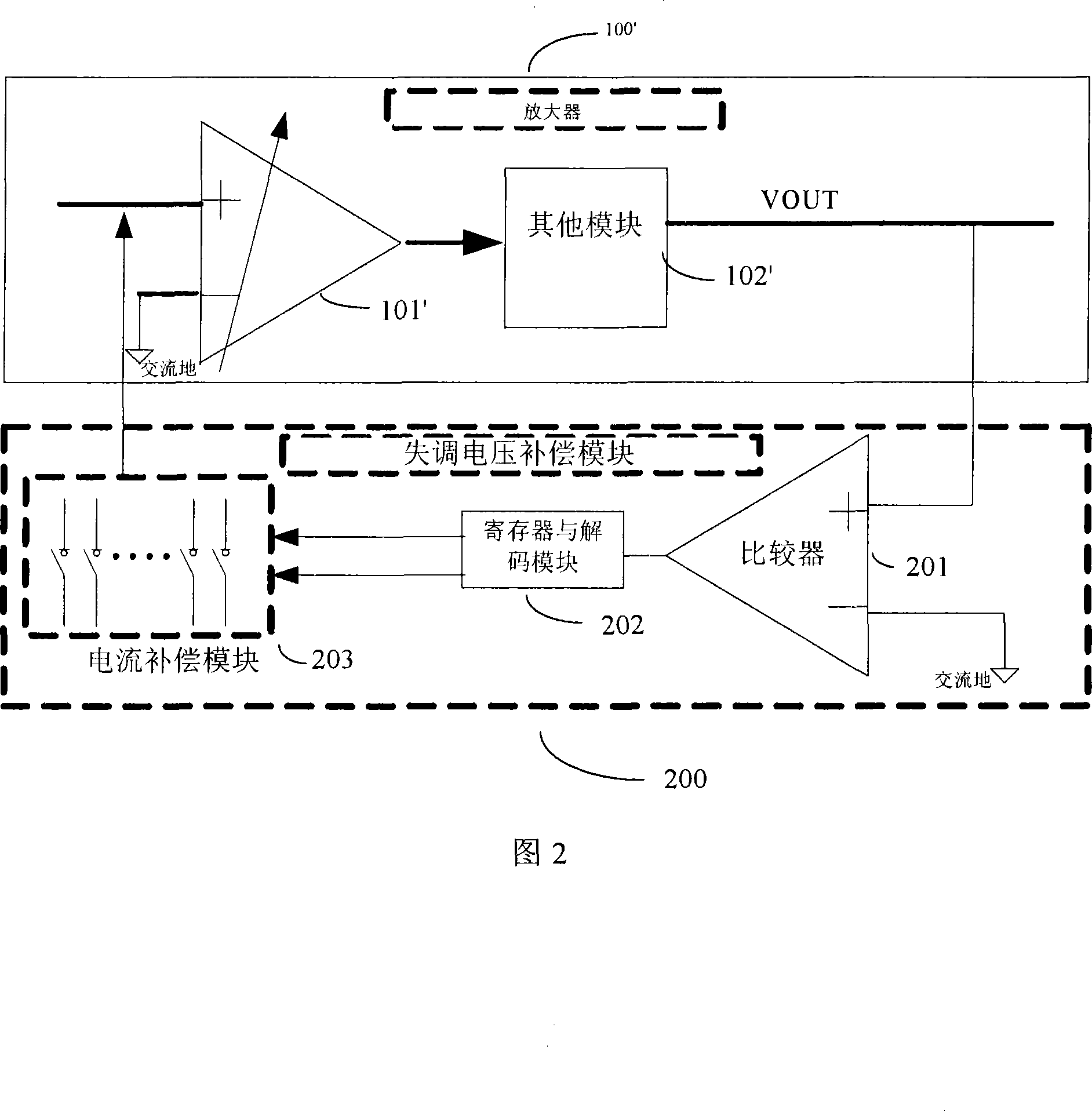
A compensatory method and device for DC offset voltage of amplifier
InactiveCN101217263ASmall scaleSimple structureDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesAudio power amplifierSwitching frequency
The invention provides a compensating method of the switching frequency of a amplifier which comprises the following steps: two output end polarities is compared in the state in which the amplifier has no signal outputting; the inputting end current of the amplifier is adjusted according to the electrode; repeated circle is carried out until achieving the requirement of stopping the cycle. The invention also provides a compensating device of the DC offset voltage of the amplifier which comprises a comparator, a register, a decoding module and a current compensation module. The invention has the advantages of simple structure, low cost, small power-consumption. Meanwhile, the invention is used both for a signal amplifier and an amplifier system, which can limit the imbalance voltage to be in small scope.
Owner:APEXONE MICROELECTRONICS
Circuit and method for compensating for offset voltage
InactiveUS7227389B2Variation in characteristicMultiple input and output pulse circuitsPulse automatic controlPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A circuit for compensating for an offset voltage in a PhotoDetector Integrated Circuit (PDIC). The circuit includes a temperature detection unit, a current transfer unit and a current adjustment unit. The temperature detection unit generates a current that varies with variation in surrounding temperature. The current transfer unit transfers the generated current. The current adjustment unit adjusts the current transferred from the current transfer unit at a predetermined ratio and outputs the adjusted current.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Display panel and driving method of display panel
ActiveUS20180301080A1Convenient lightingImprove uniformityStatic indicating devicesEngineeringControl circuit
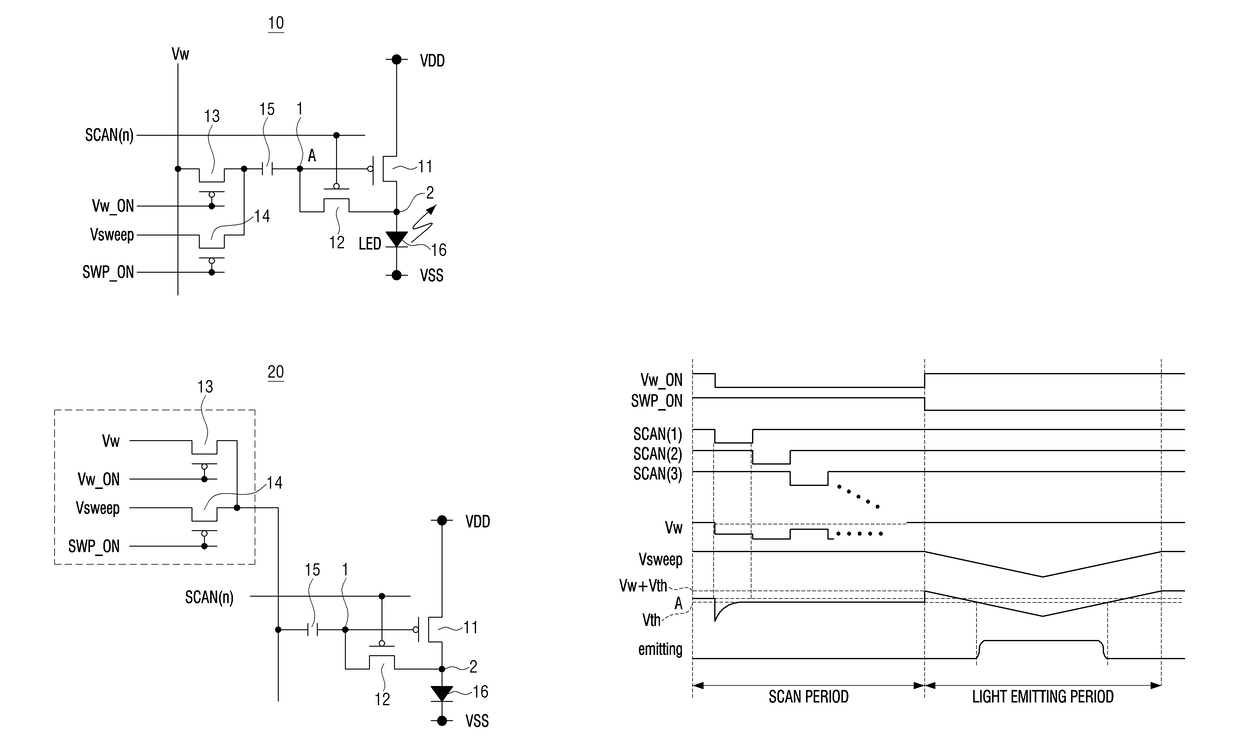
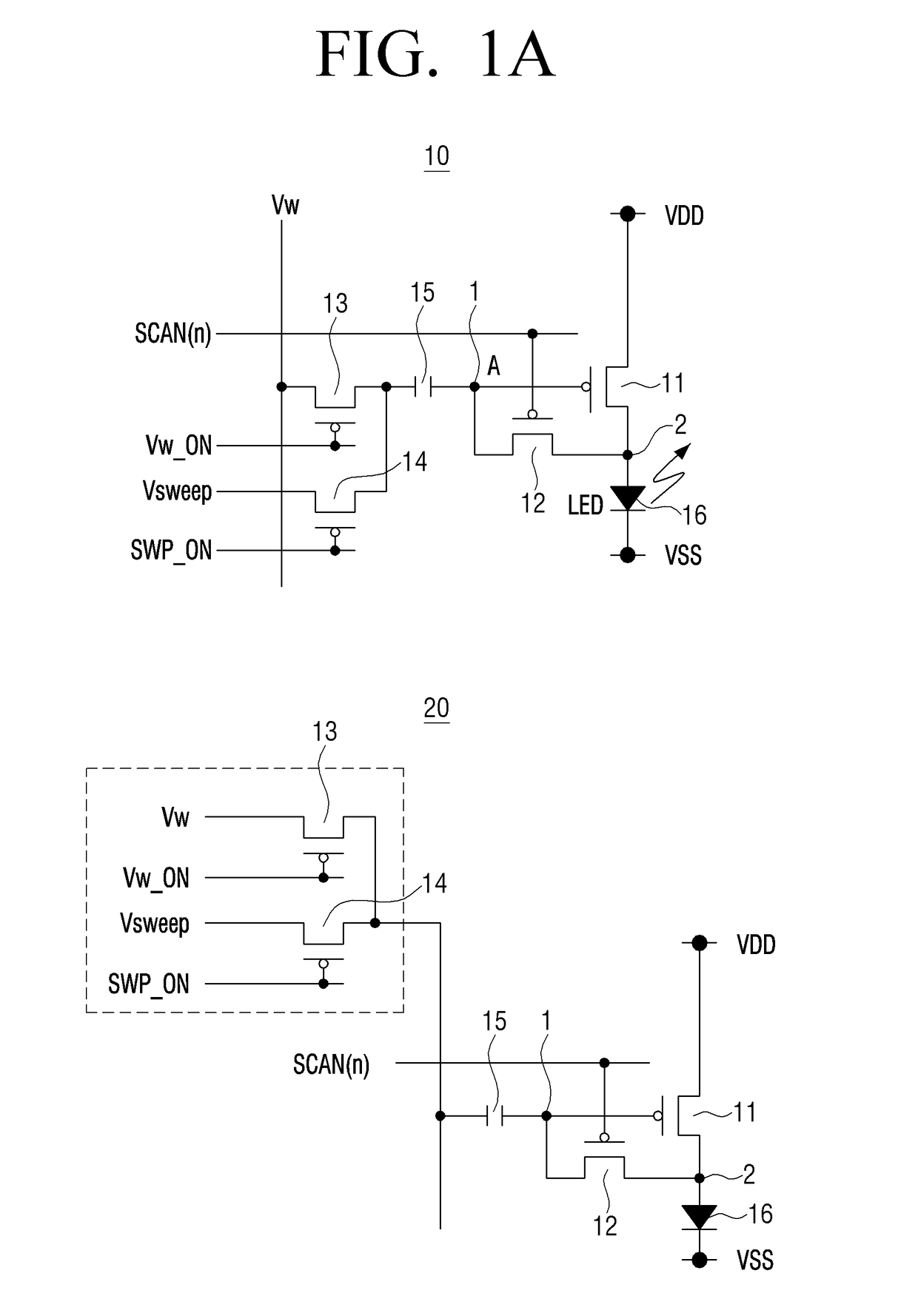
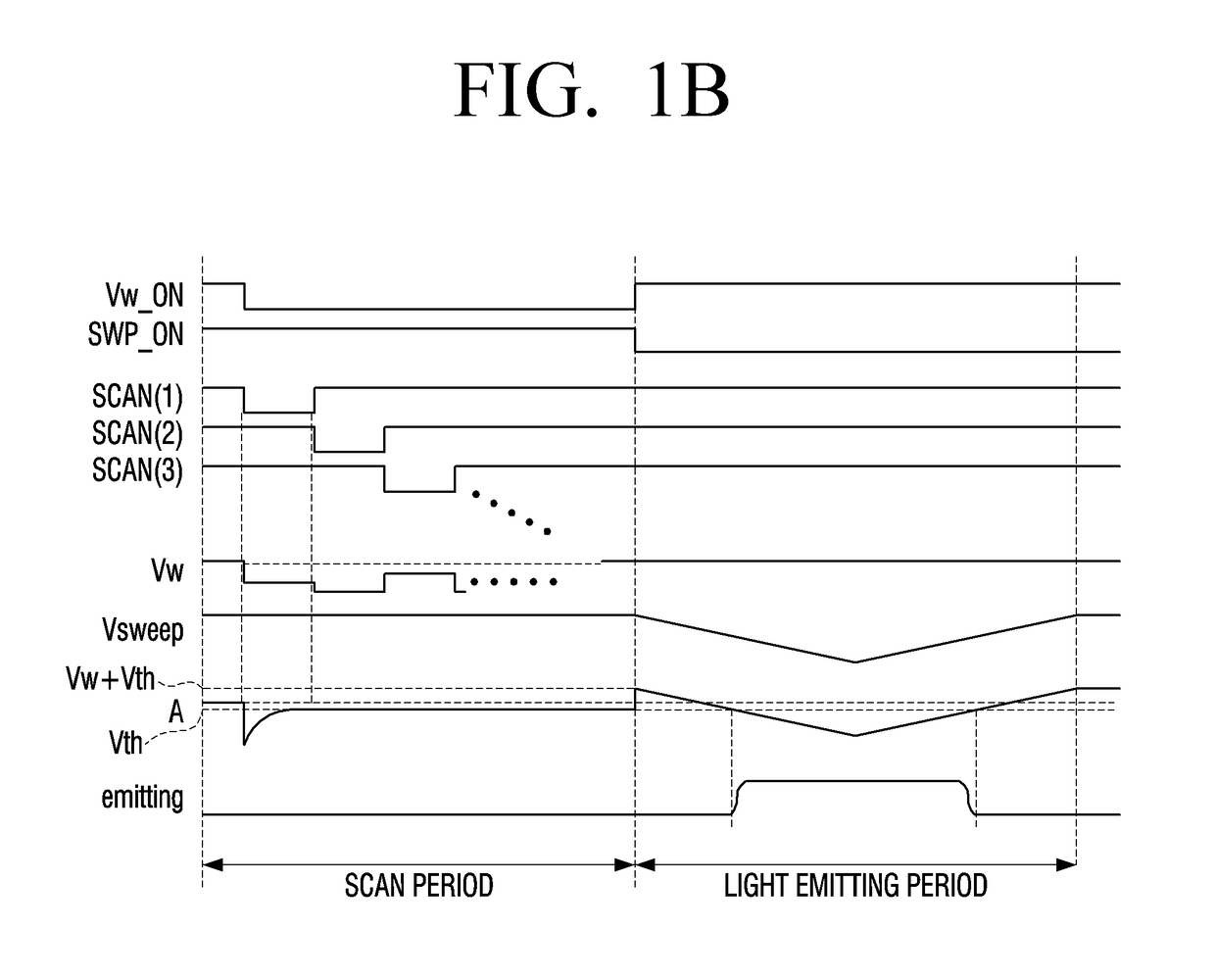
A display panel including a plurality of pixel circuits is provided. Each of the plurality of pixel circuits includes a light emitting unit including a light emitting element; a control circuit configured to control a light emitting duration of the light emitting element based on an input end voltage; a first switching element connected between an input end and an output end of the control circuit; and a signal input unit including a second switching element and configured to transmit an input signal to the input end of the control circuit. The first switching elements of each of the plurality of pixel circuits are configured to simultaneously turn on or off.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Automatic gain control circuit with high linearity and monotonically correlated offset voltage
InactiveUS6538507B2Easily and reduced and eliminatedLow absolute gain toleranceAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAutomatic controlAudio power amplifier
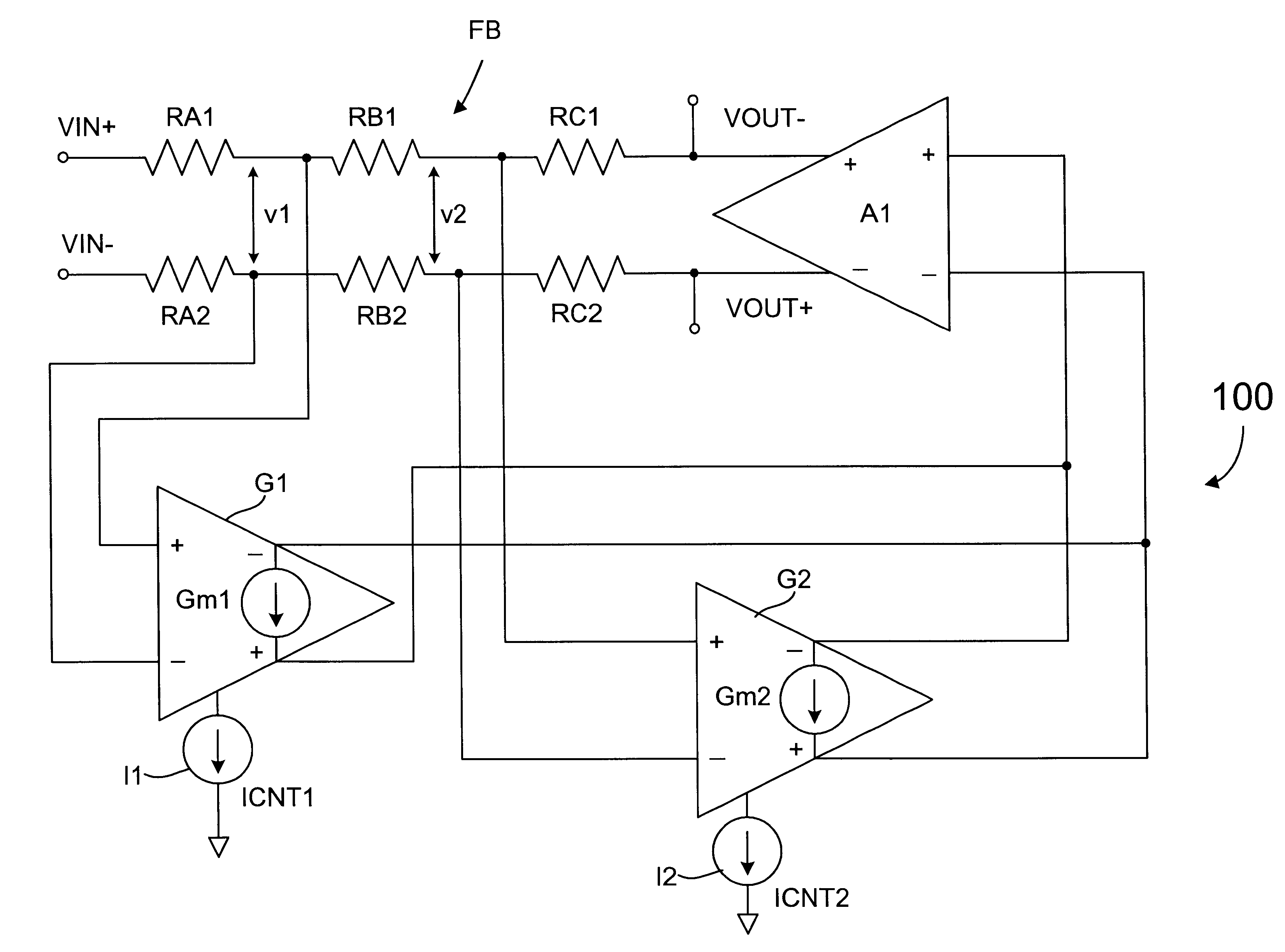
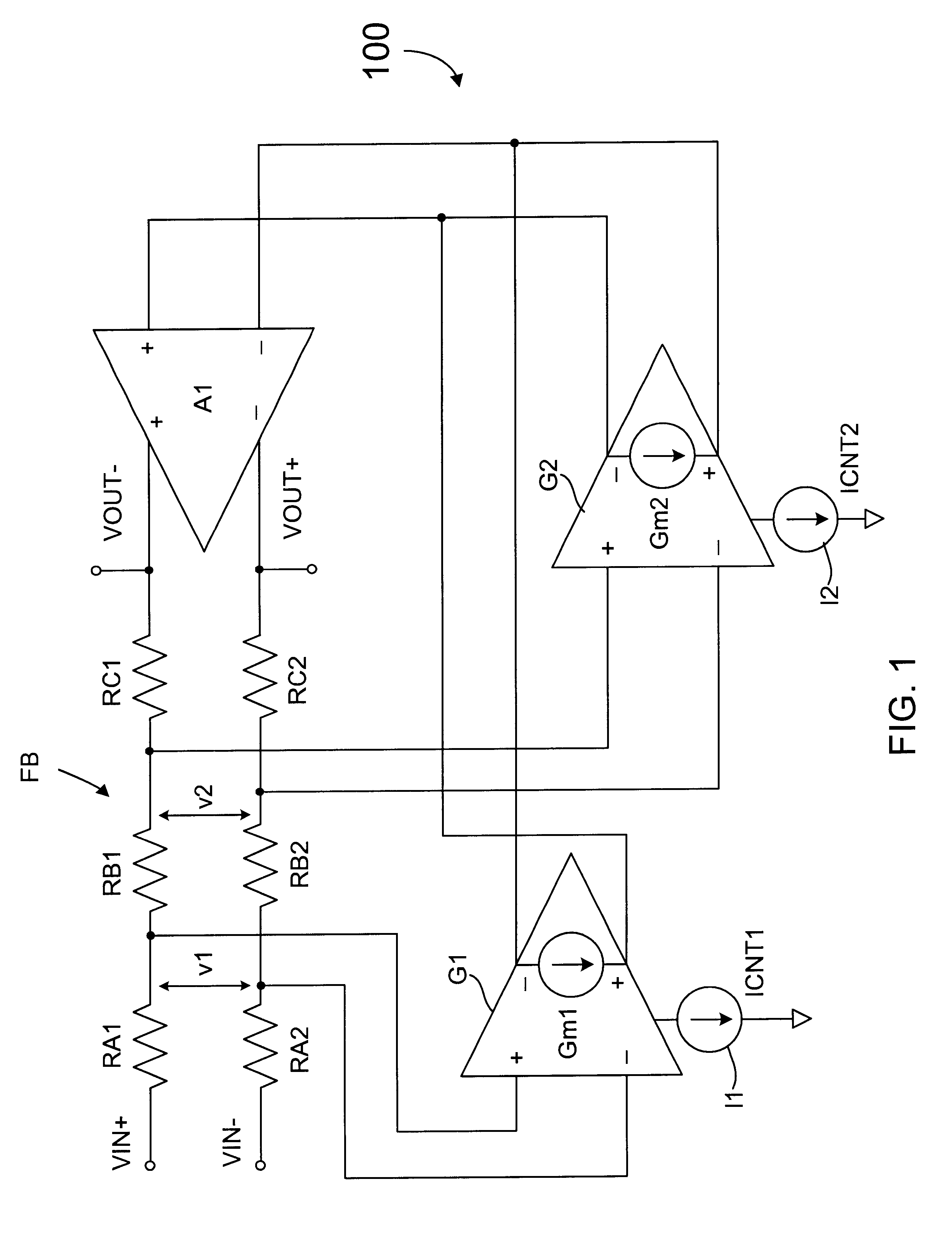
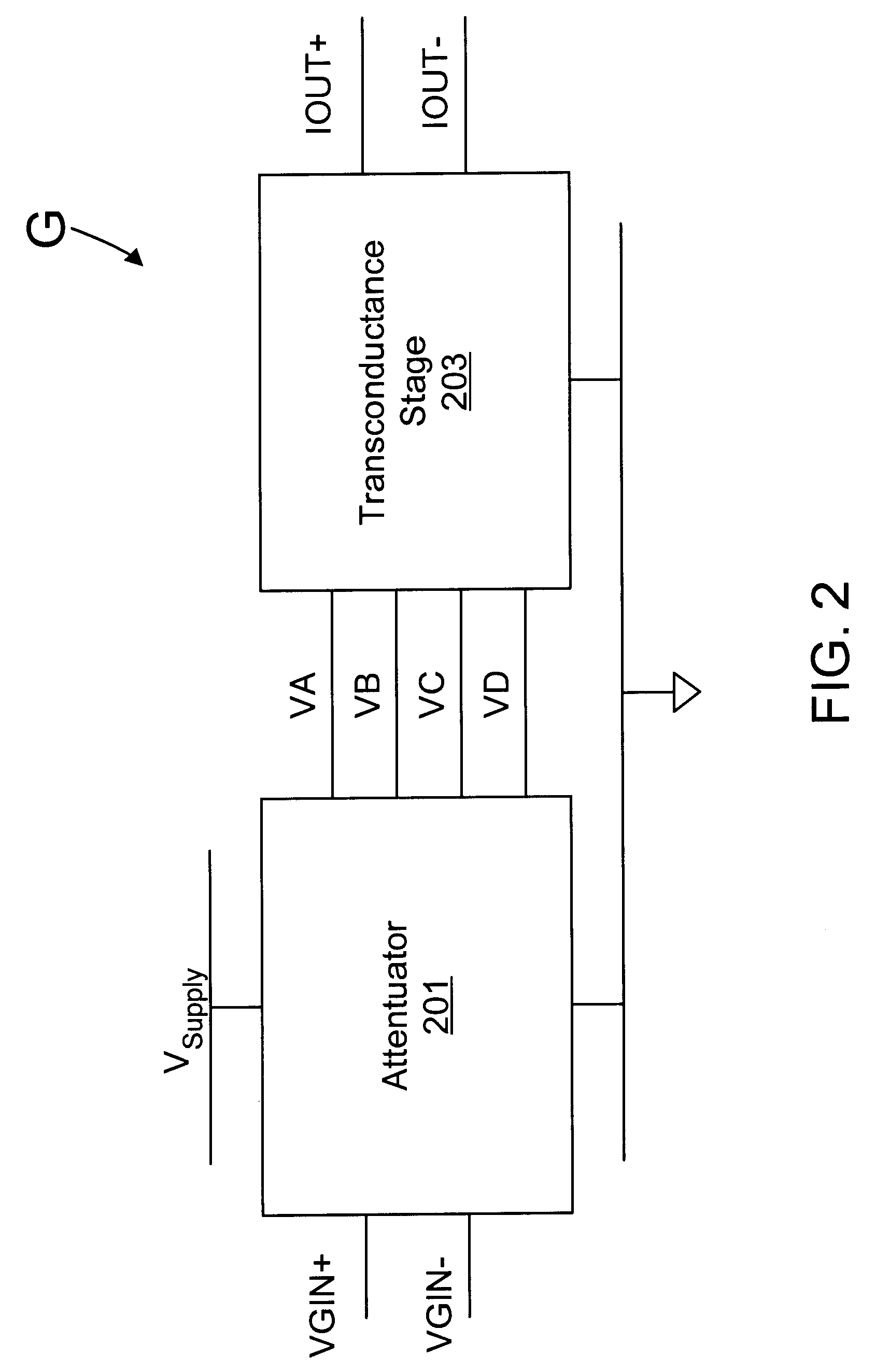
An automatic gain control (AGC) circuit including a high gain amplifier, a feedback network and two transconductance amplifiers. The feedback network has a first end that receives an input signal of the AGC circuit, a second end coupled to the output of the high gain amplifier and two intermediate nodes. Each transconductance amplifier has an input coupled to a respective intermediate node of the feedback network and an output coupled to the input of the high gain amplifier. The transconductance amplifiers collectively control a position of a virtual ground within the feedback network to control gain of the AGC circuit. The transconductance amplifiers each include an attenuator and a transconductance stage coupled between the feedback network and the high gain amplifier and are configured to operate linearly across a relatively wide input voltage range. The input offset voltage of the AGC circuit varies monotonically with gain of the AGC circuit.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
Magnetic sensor circuit, semiconductor device, and magnetic sensor device
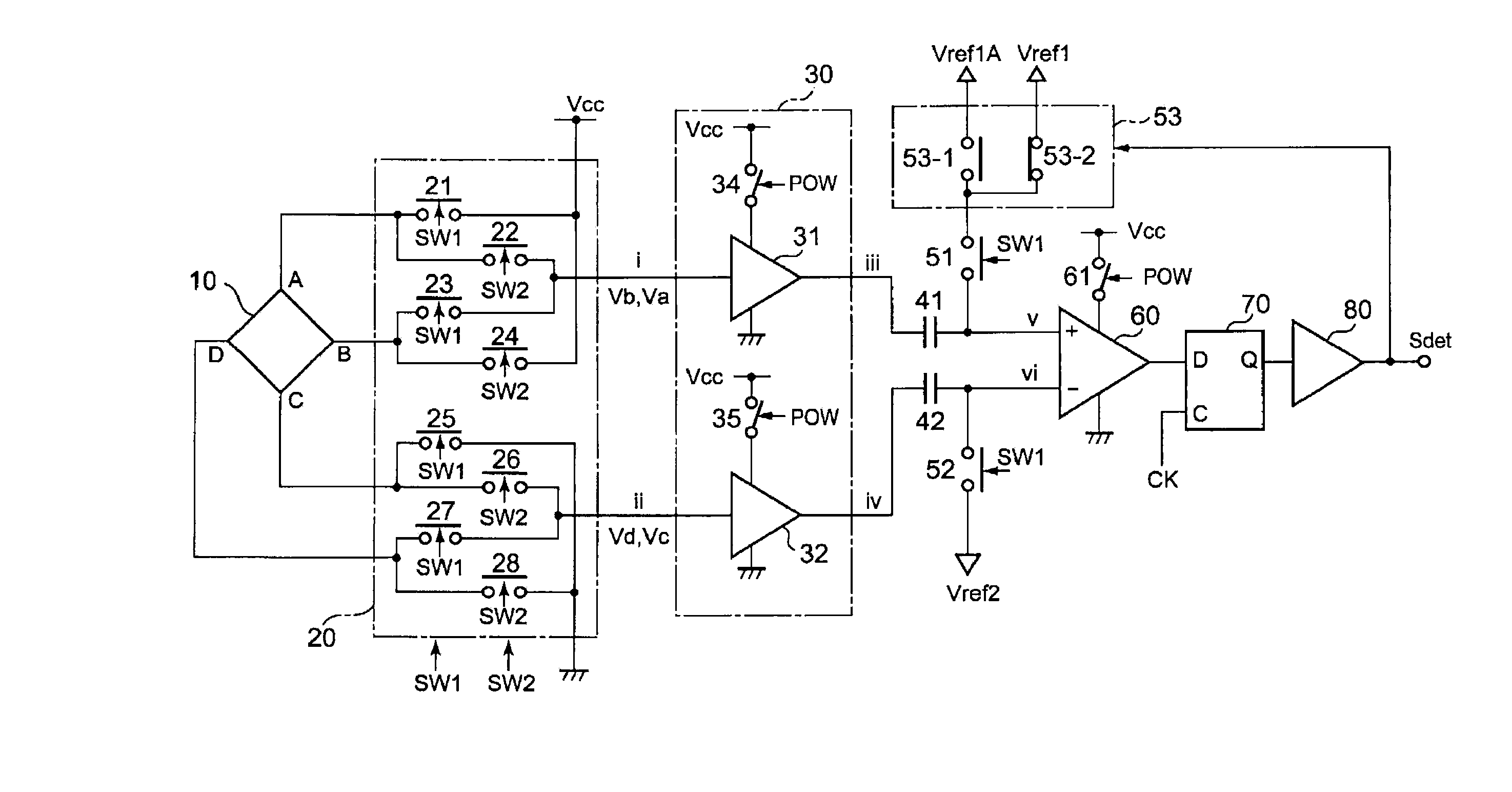
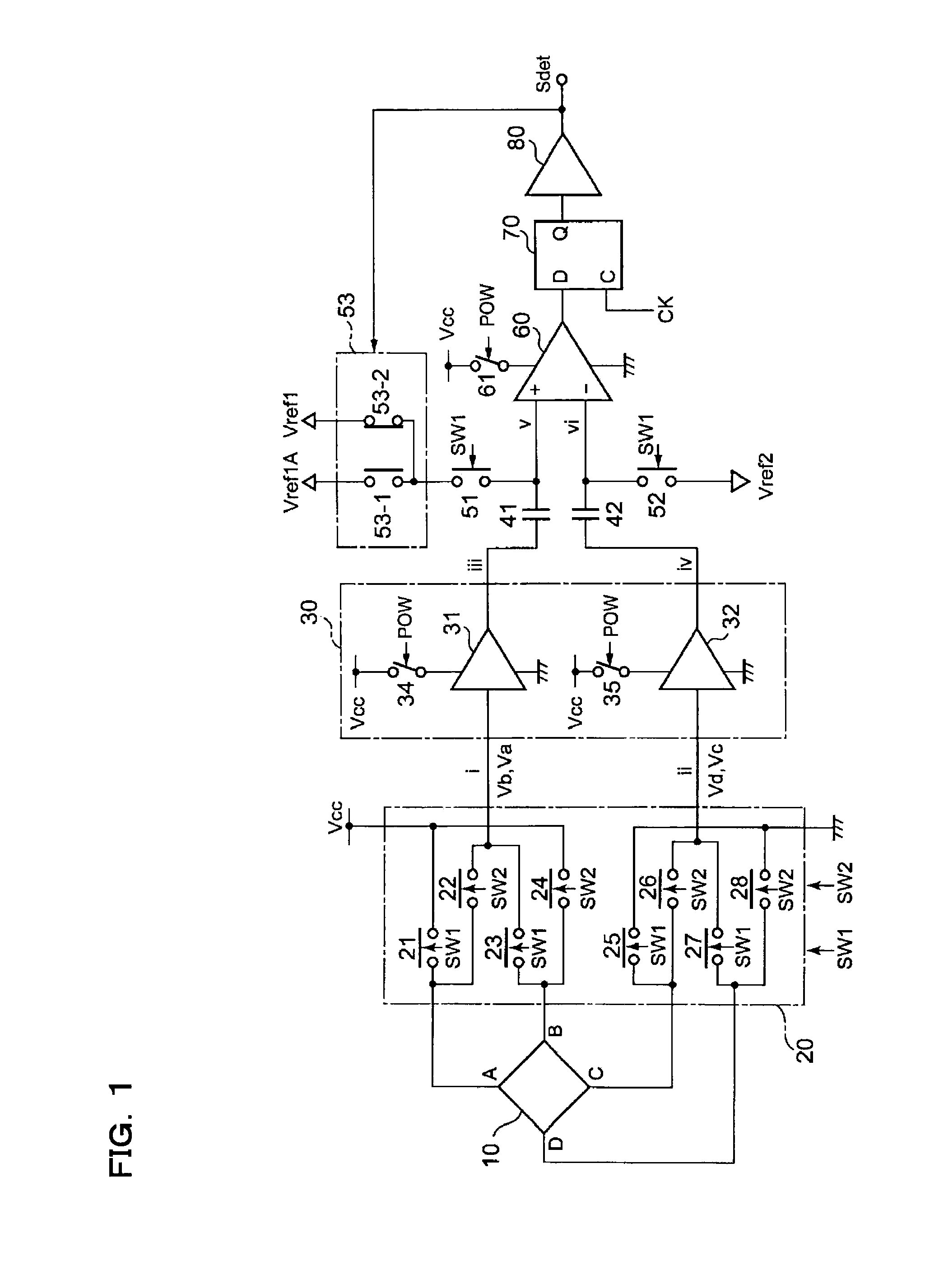
A magnetic sensor circuit has Hall devices 10X and 10Y, selection switch circuits 20X and 20Y, amplifier units 30X ad 30Y, a comparison unit 60, capacitors 41X, 42X, 41Y, and 42Y, and switch circuits 51 and 52. The Hall voltages obtained from the Hall devices 10X and 10Y are outputted in either of a first and a second states switched by the selection switch circuits 20X and 20Y. The amplifier units 30X ad 30Y each operate differentially and, if the difference between their outputs is greater than a set hysteresis width, the output logic of a detection signal Sdet is shifted. This configuration helps reduce the influence of device offset voltages in the Hall devices, and also helps reduce the influence of input offset voltages arising in the amplifiers.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Amplifier with accurate built-in threshold
InactiveUS7057444B2Electronic switchingDifferential amplifiersVoltage generatorAudio power amplifier
Various embodiments of a voltage level detector implemented as an integrated circuit whose trip point is approximately constant over variations in temperature as well as variations in transistor fabrication parameters are disclosed along with a differential amplifier whose input offset voltage is highly immune to said variations. In one embodiment, a voltage generator supplies a composite voltage to the gate of the tail current transistor of the voltage level detector or differential amplifier. The first component of the voltage is approximately equal to the threshold voltage of NMOS transistors comprised in the device over variations in operating temperature as well as variations in transistor fabrication parameters while the second component is approximately constant with respect to said variations. When applied to the gate of the tail current transistor, the first component may turn the transistor on in spite of the above-mentioned parametric variations.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Method and circuit for automatically correcting offset voltage
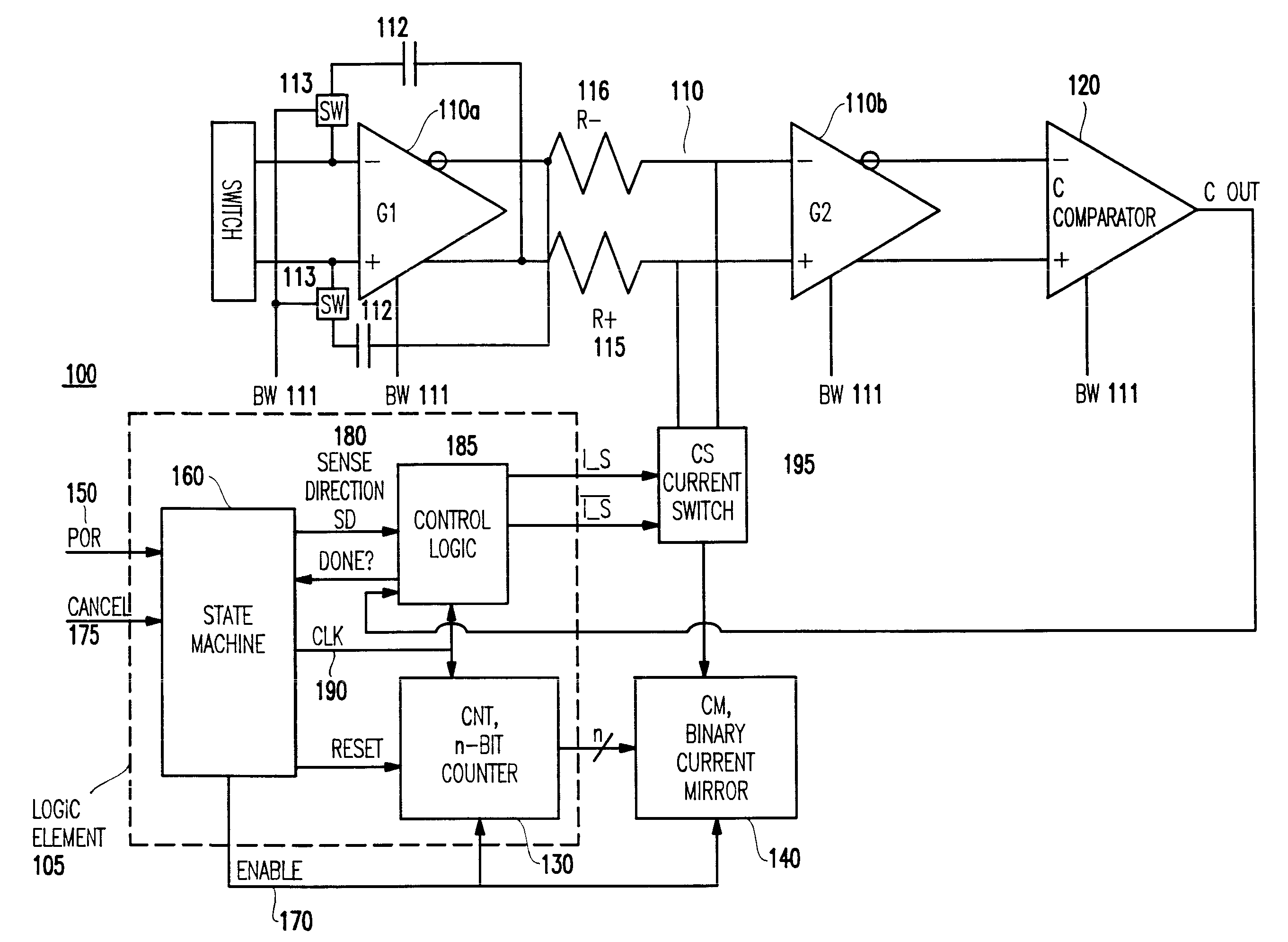
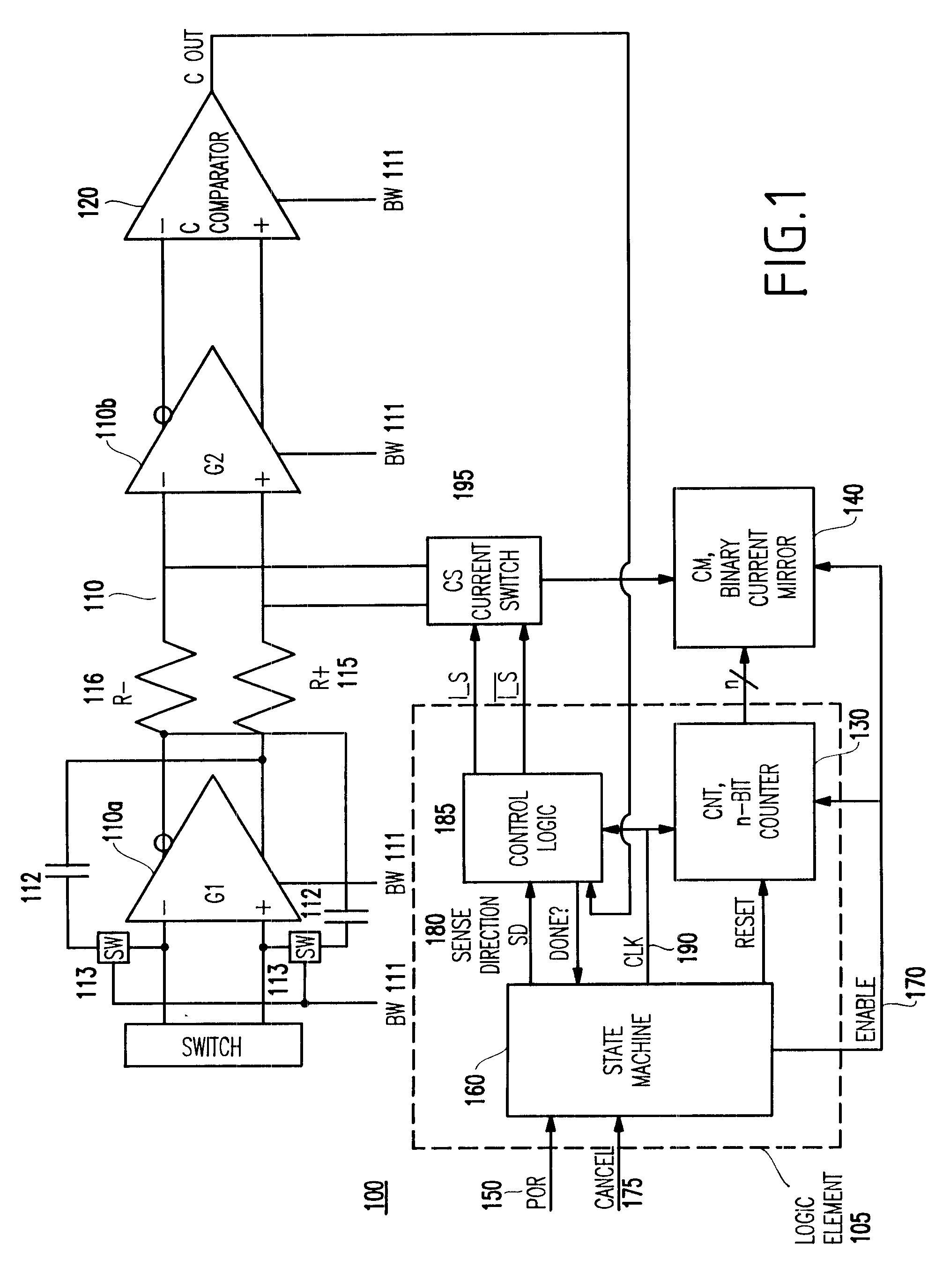
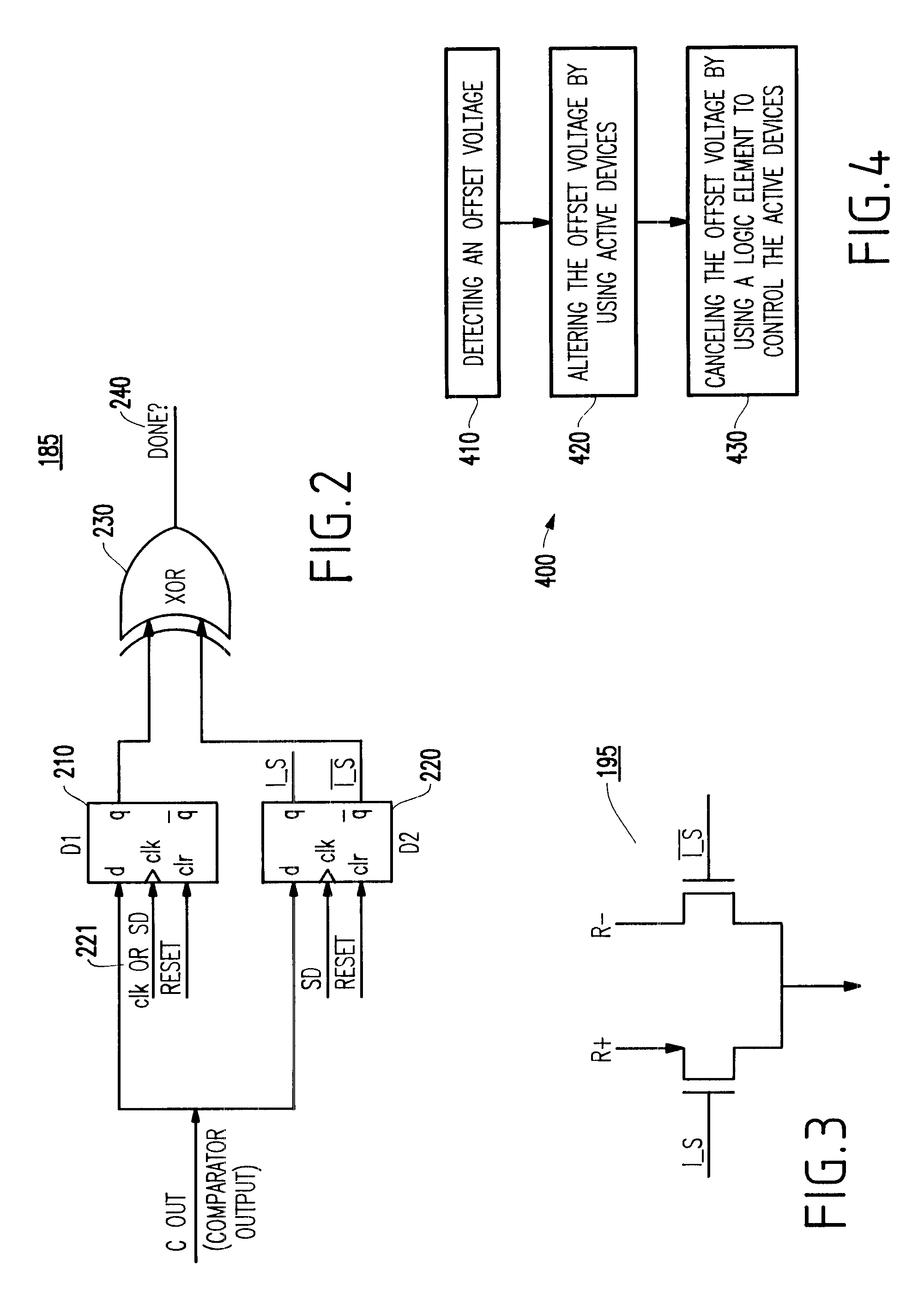
InactiveUS6507241B1Robust offset correctionInexpensive and robustPulse automatic controlAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyEngineeringCurrent switch
A circuit (and method) for correcting offset voltage in high-gain differential amplifier chains includes a detector element for detecting an offset voltage and a current mirror for generating an offset correction voltage. The circuit further has a current switch which outputs the offset correction voltage into the correct arm of the amplifier chain and a logic element which clocks the circuit, inputs a signal from the detector element and outputs a signal to the current switch.
Owner:IBM CORP
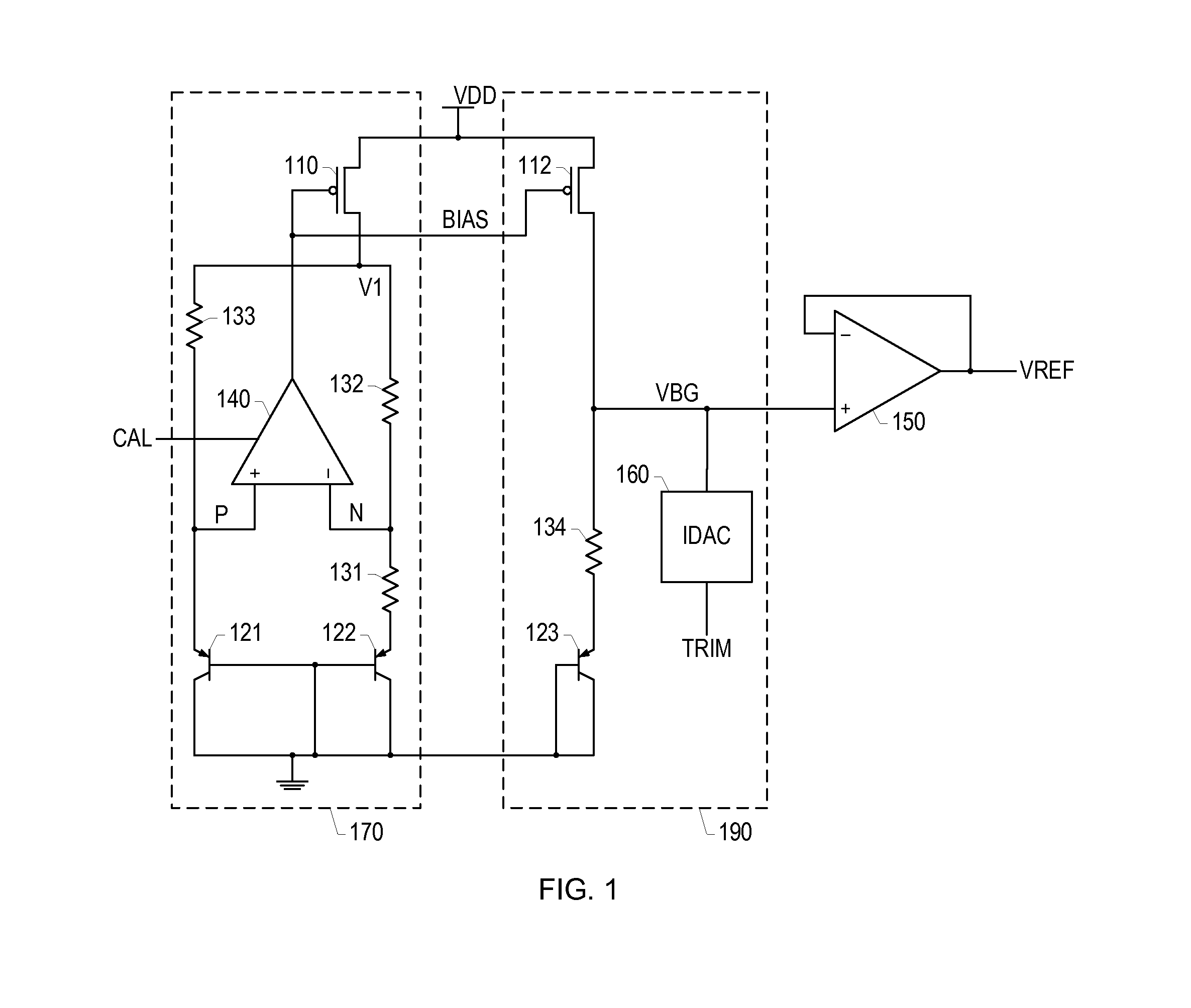
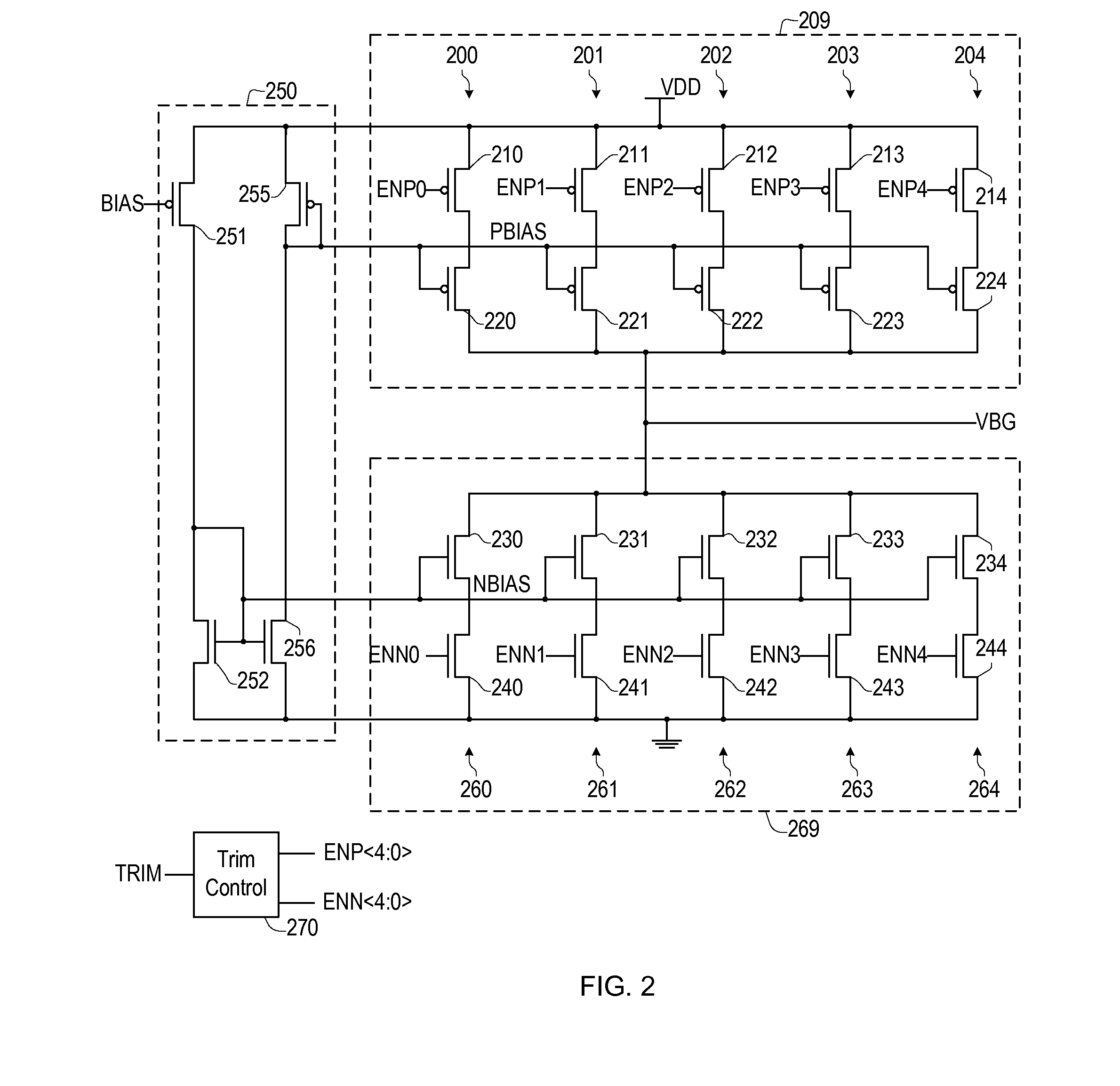
Band-gap reference voltage producing circuit
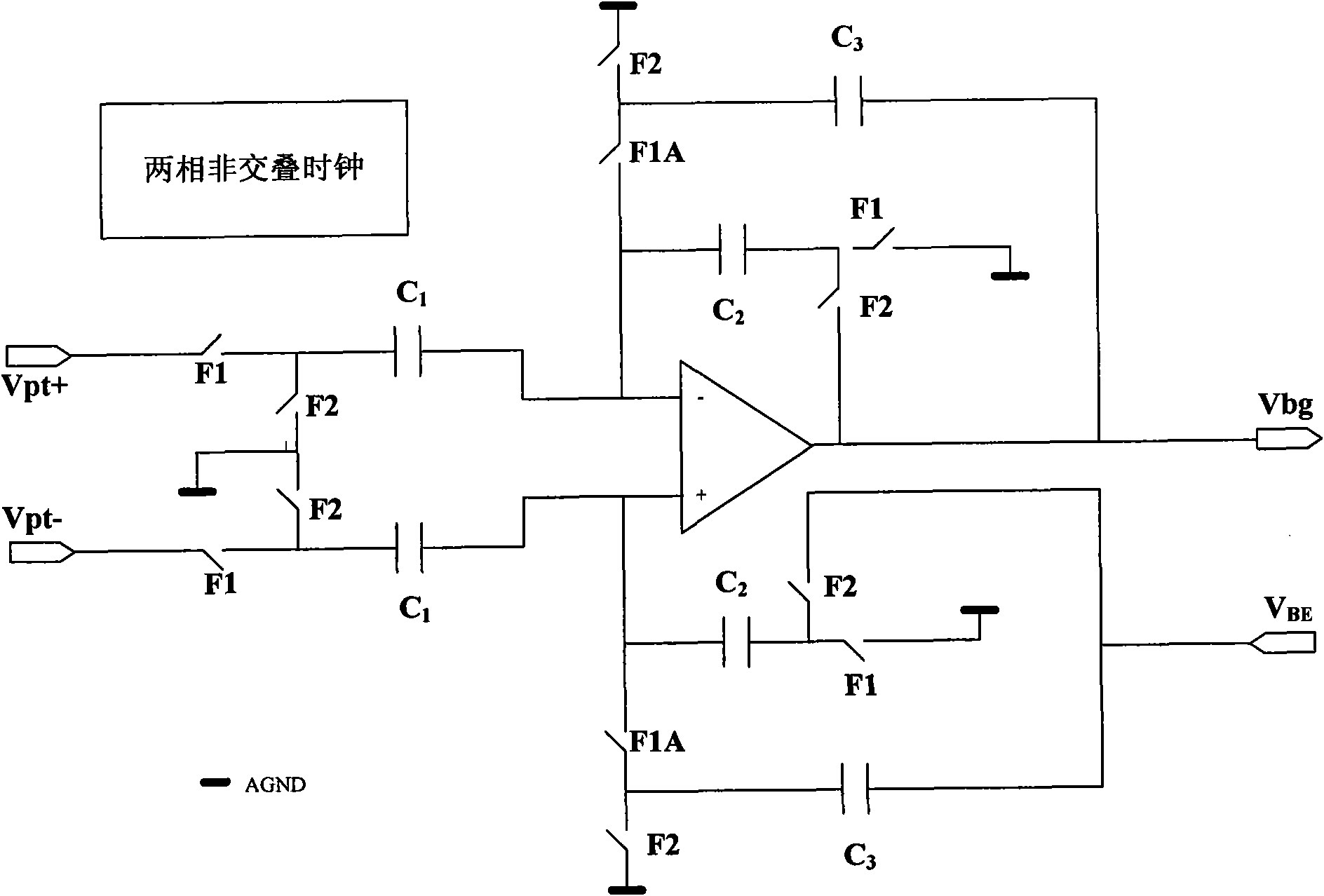
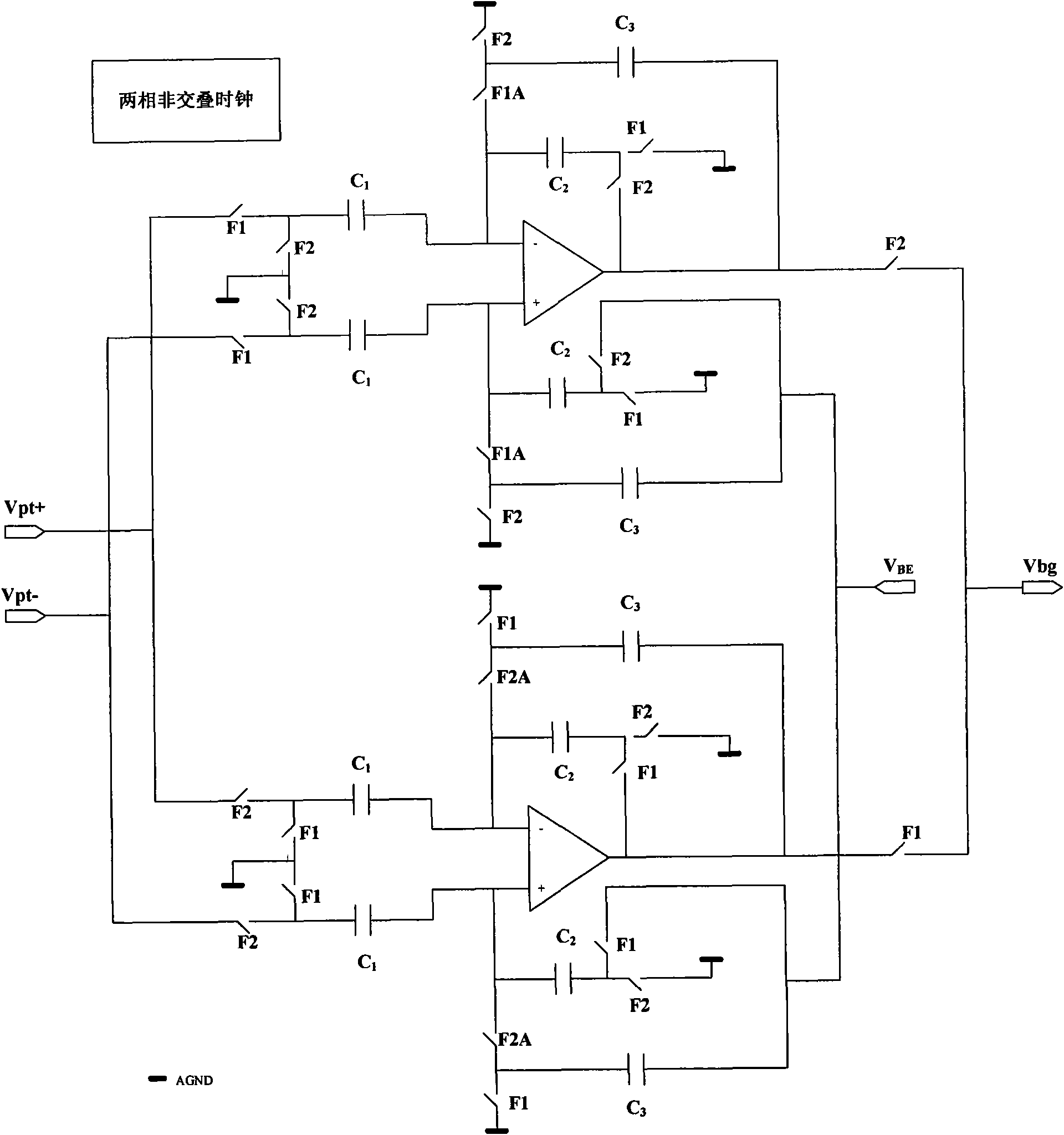
The invention provides a novel high-precision full-period output switch capacitor band-gap voltage producing circuit for meeting the demand of a high-precision increment ADC to the precision of a reference voltage. A dual-rotary single-switch capacitor operation amplifier structure is used by the circuit structure to eliminate the influence of the operation amplifier input offset voltage as well as reduce the limited gain error of the operation amplifier; the invention further comprises two same switch capacitor band-gap reference producing circuits with complementary clock periods; and meanwhile, a gating switch is connected in series with each output end, thereby, realizing the full-period band-gap reference voltage output.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES INST OF MICROELECTRONICS SHRIME PEKING UNIV
Circuit and method for correcting offset voltage of comparator
ActiveCN103036538AHigh precisionHigh speedMultiple input and output pulse circuitsElectric variable regulationVoltage generatorComputer module
The invention discloses a circuit and a method for correcting offset voltage of a comparator. The circuit for correcting the offset voltage of the comparator comprises the comparator, an output latch, a selecting module, a first substrate voltage generator and a second substrate voltage generator, wherein two input ends of the comparator are connected with working voltage or common mode level (VCM), a normal phase output end of the comparator is connected with the selecting module or a first output end (VOUT+) of the circuit of correcting the offset voltage of the comparator through the output latch, a reversal phase output end of the comparator is connected with the selecting module or a second output end (VOUT-) of the circuit of correcting the offset voltage of the comparator through the output latch, an input end of the first substrate voltage generator and an input end of the second substrate voltage generator are both connected with the selecting module, an output end of the first substrate voltage generator outputs a first variable voltage (VB+) to a metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) of a normal phase input end of the comparator and an output end of the second substrate voltage generator outputs a second variable voltage (VB+) to a metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) of a reversal phase input end of the comparator. The circuit for correcting the offset the voltage of the comparator and the method for correcting the offset voltage of the comparator has the advantages of being capable of rapidly achieving large-scale and high-precision correct because digital correction is applied and simultaneously correcting the substrate voltage of two input pipes, and more flexible.
Owner:NATIONZ TECH INC
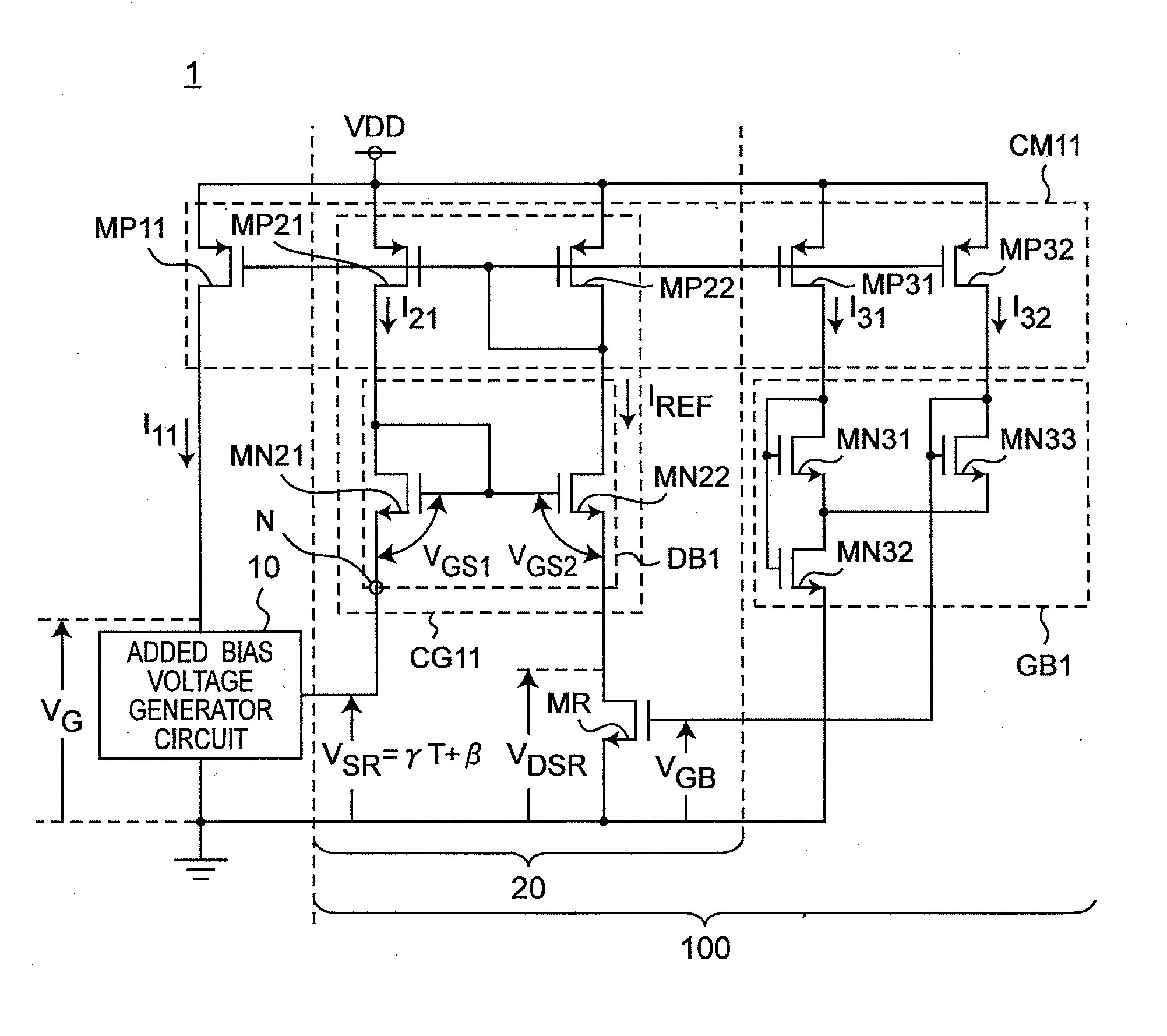
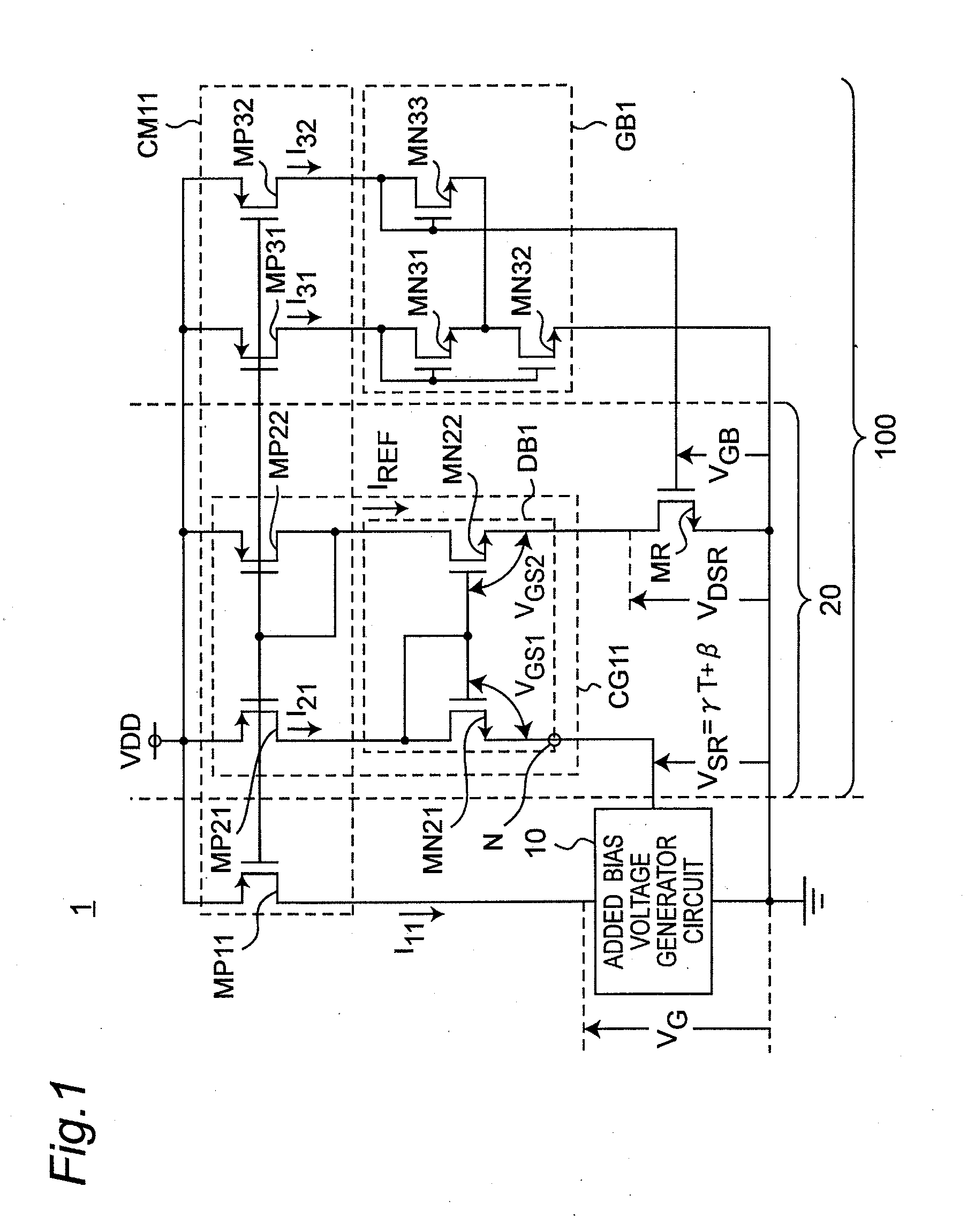
Reference current source circuit including added bias voltage generator circuit
InactiveUS20120025801A1Reduce circuit areaSuppress inclinationElectric variable regulationVoltage generatorLinear region
A MOS resistor generates an output current based on a voltage induced across a drain and a source thereof. A gate bias voltage generator circuit generates a gate bias voltage so as to operate the MOS resistor in a strong-inversion linear region, and applies the gate bias voltage to a gate of the MOS resistor. A drain bias voltage generator circuit generates a drain bias voltage, and applies the drain bias voltage to the drain of the MOS resistor. An added bias voltage generator circuit generates an added bias voltage, which has a predetermined temperature coefficient and includes a predetermined offset voltage, so that the output current becomes constant against temperature changes. The drain bias voltage generator circuit adds the added bias voltage to the drain bias voltage, and applies a voltage of adding results to the drain of the MOS resistor as the drain bias voltage.
Owner:SEMICON TECH ACADEMIC RES CENT
Chopped wave band-gap reference circuit
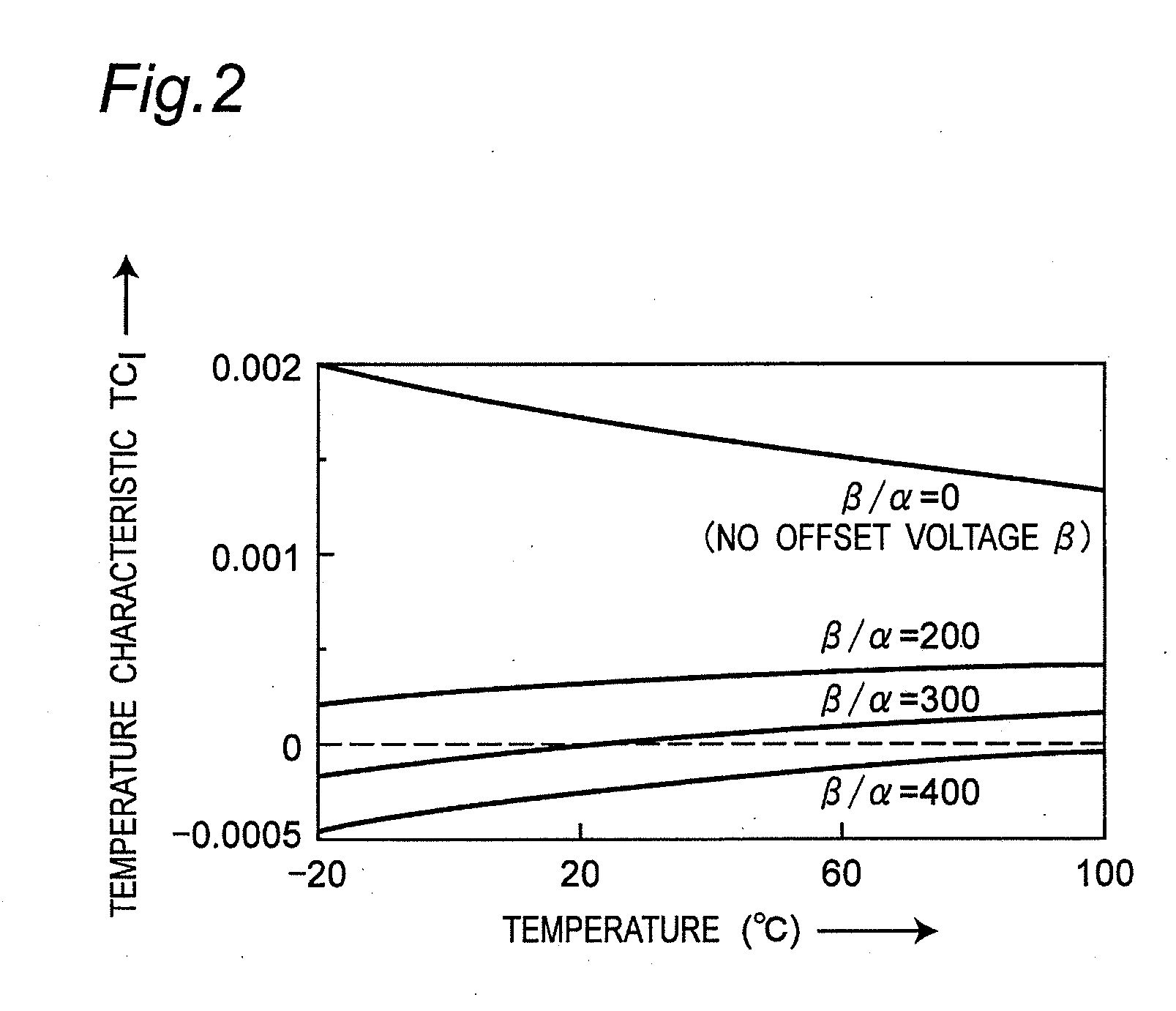
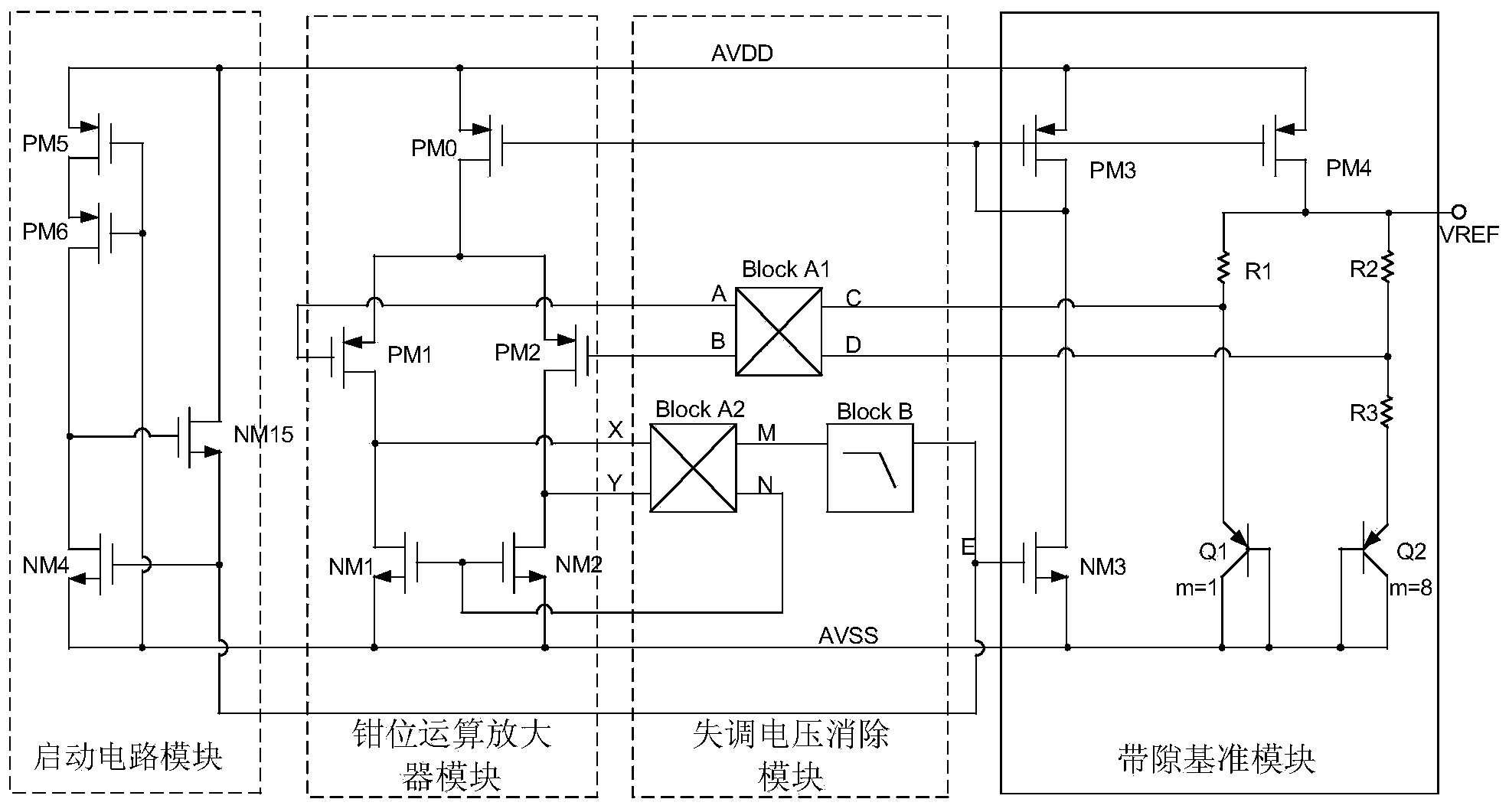
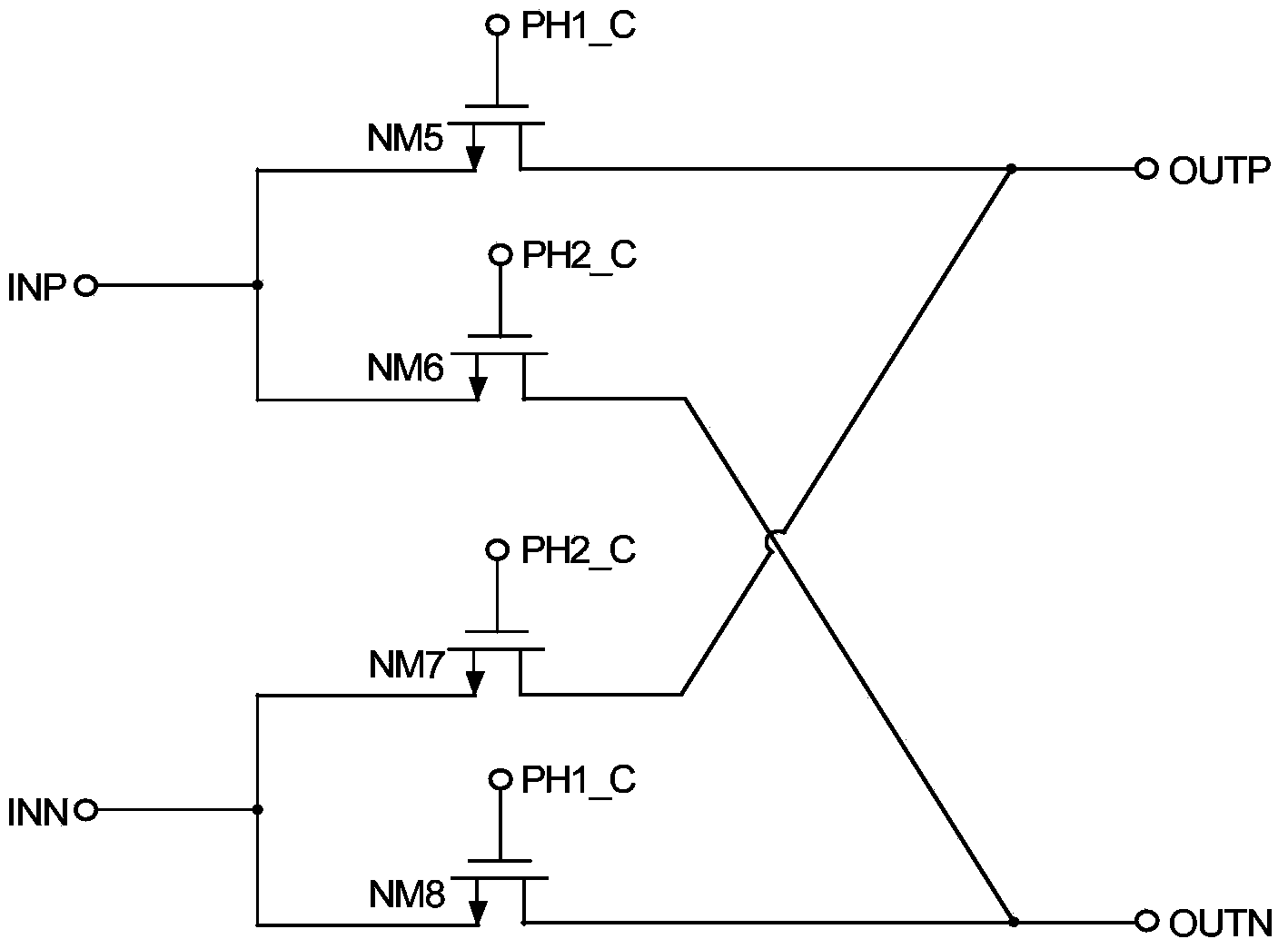
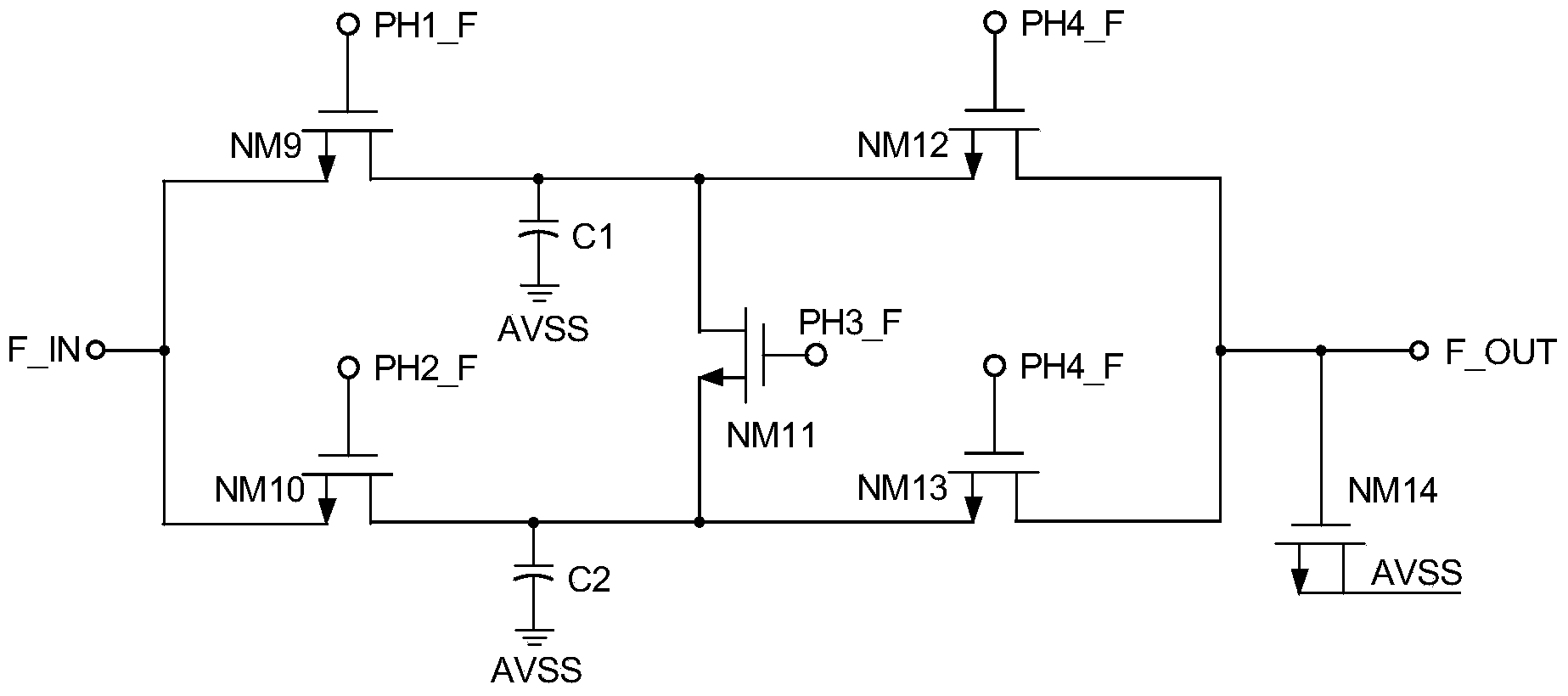
ActiveCN103869867ACancel offset voltageHigh precisionElectric variable regulationInput offset voltageWave band
The invention provides a chopped wave band-gap reference circuit which comprises a starting circuit module, a clamping operational amplifier module, an offset voltage eliminating module and a band-gap reference module, wherein the starting circuit module is used for supplying a starting voltage to the band-gap reference module and is closed after the band-gap reference module is started; the clamping operational amplifier module is used for clamping voltages at two nodes of the band-gap reference module; the offset voltage eliminating module is used for eliminating an offset voltage of the clamping operational amplifier module; the band-gap reference module is used for generating the voltage which does not change following the temperature; the clamping operational amplifier module comprises a first chopped wave circuit, a second chopped wave circuit and a filtering circuit for a switch capacitor. A chopped wave technique is adopted by the chopped wave band-gap reference circuit for eliminating the offset voltage and acquiring a high-precision output voltage. The switch capacitor instead of a traditional RC technique is adopted by a filter, so that the area of the filter is reduced, the chip cost is lowered, and the integration degree is increased.
Owner:VERISILICON MICROELECTRONICS SHANGHAI +3
Semiconductor device and learning method thereof
InactiveUS6844582B2High reliability in learningOperation speed satisfactoryTransistorElectric analogue storesNeural network systemBinary multiplier
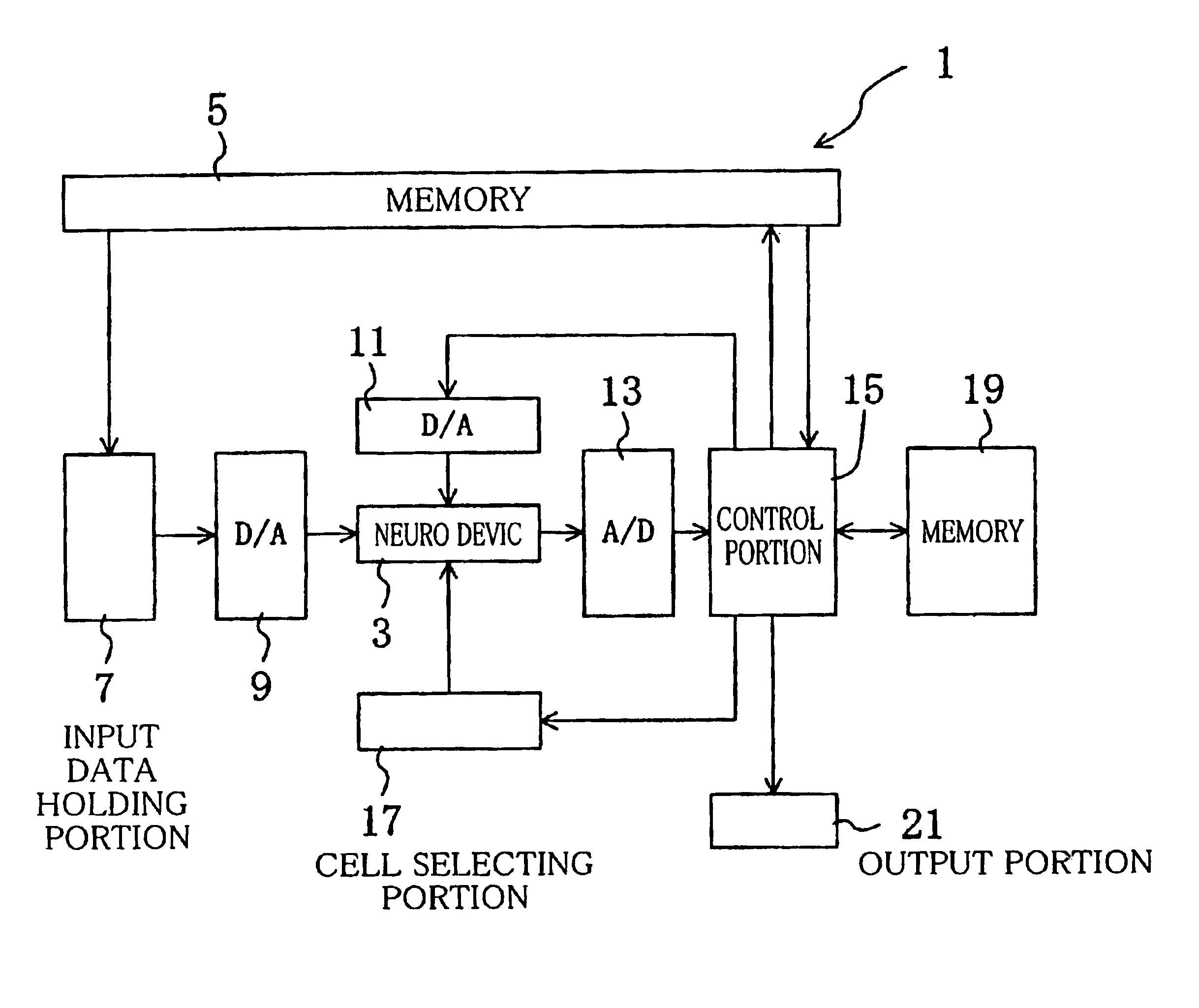
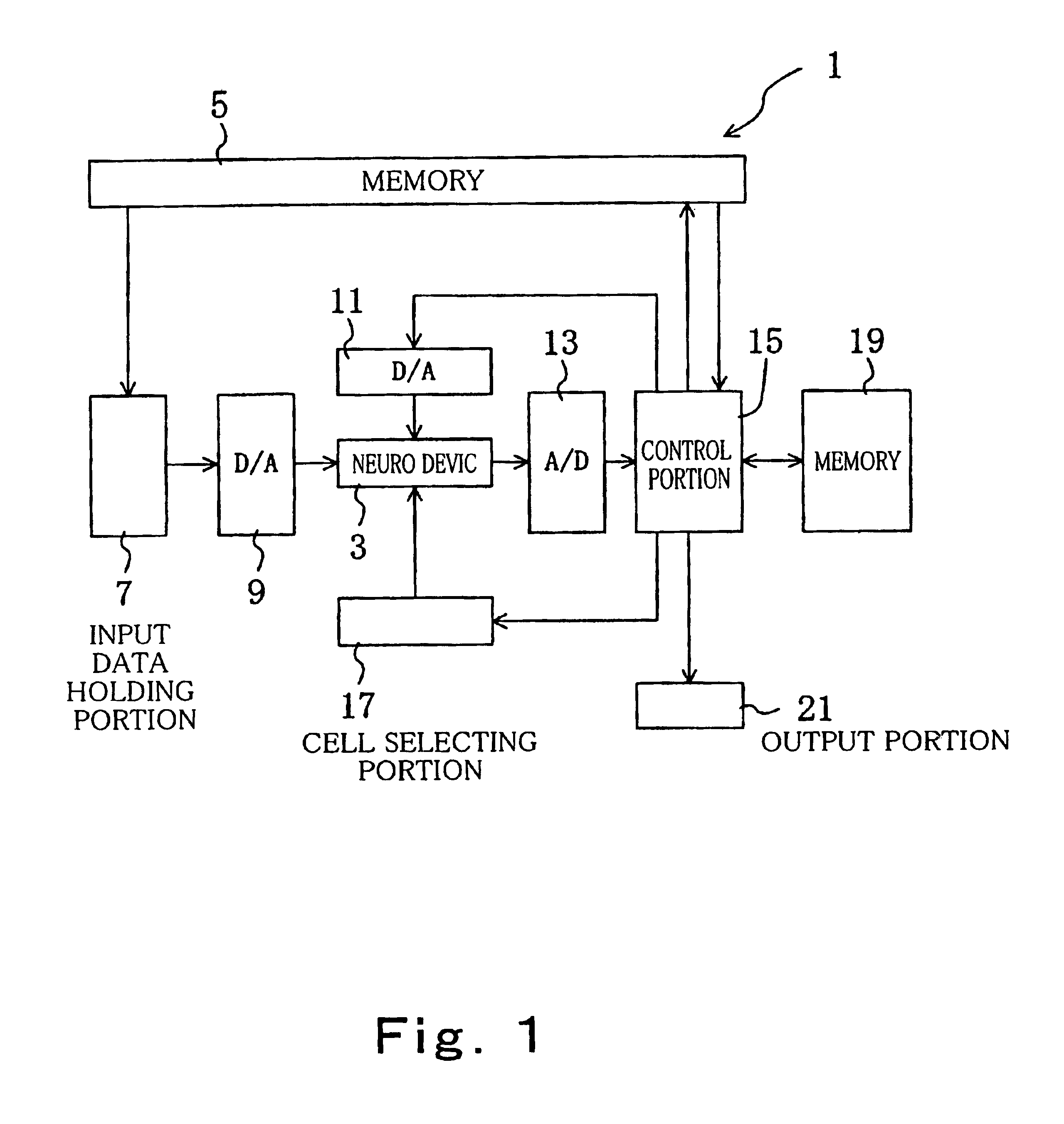
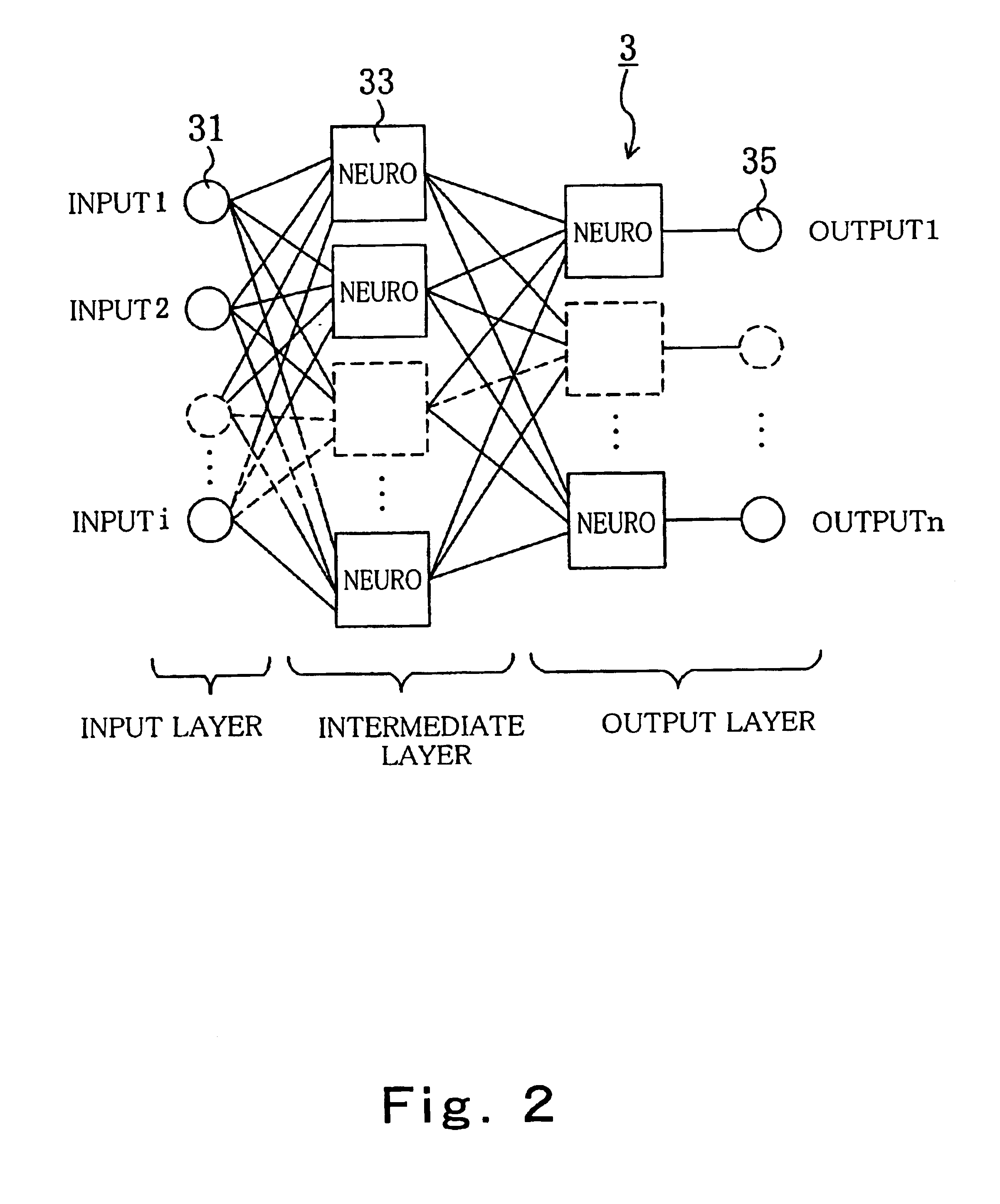
A learning method of a semiconductor device of the present invention comprises a neuro device having a multiplier as a synapse in which a weight varies according to an input weight voltage, and functioning as a neural network system that processes analog data, comprising a step A of inputting predetermined input data to the neuro device and calculating an error between a target value of an output of the neuro device with respect to the input data and an actual output, a step B of calculating variation amount in the error by varying a weight of the multiplier thereafter, and a step C of varying the weight of the multiplier based on the variation amount in the error, wherein in the steps B and C, after inputting a reset voltage for setting the weight to a substantially constant value to the multiplier as the weight voltage, the weight is varied by inputting the weight voltage corresponding to the weight to be varied.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
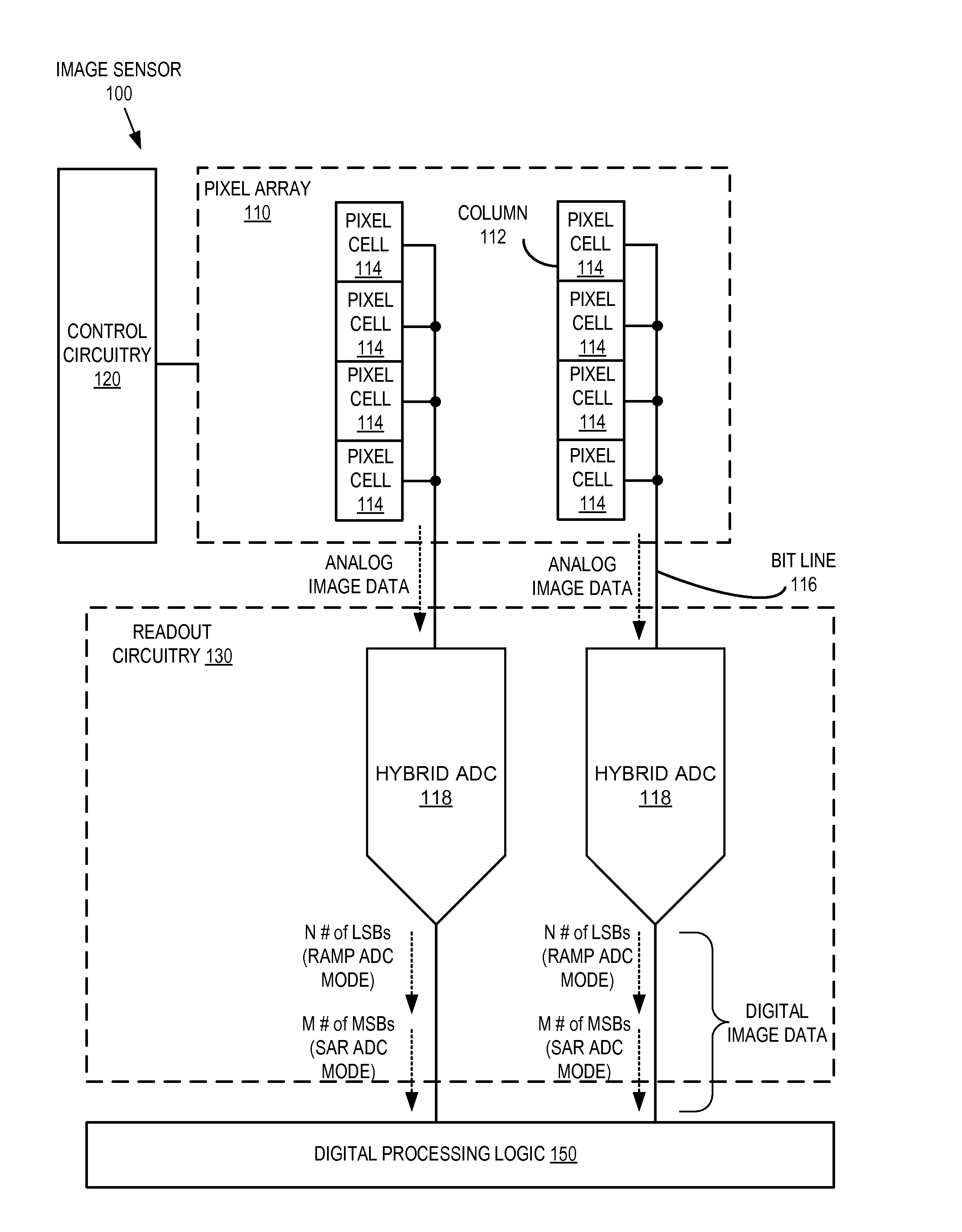
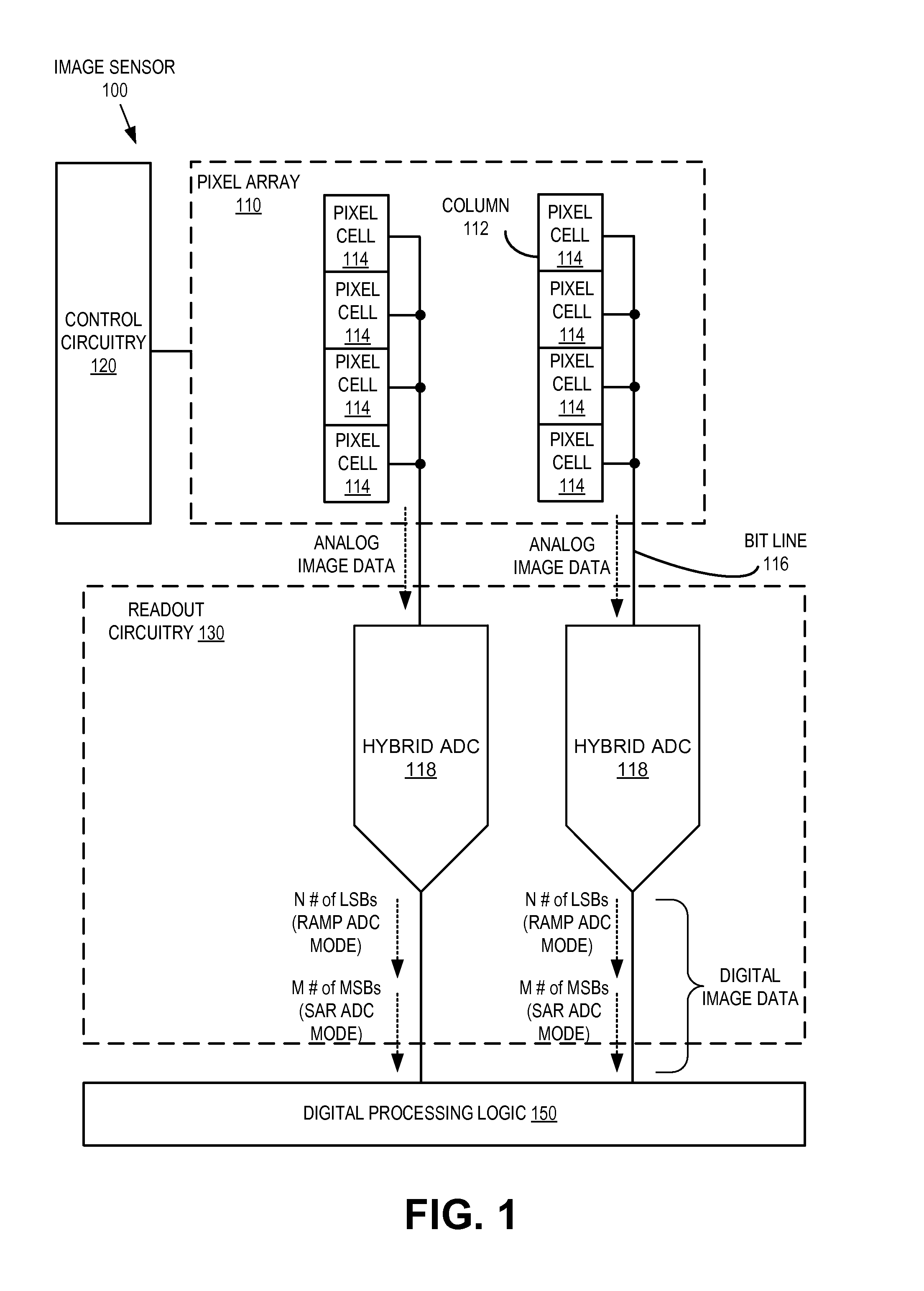
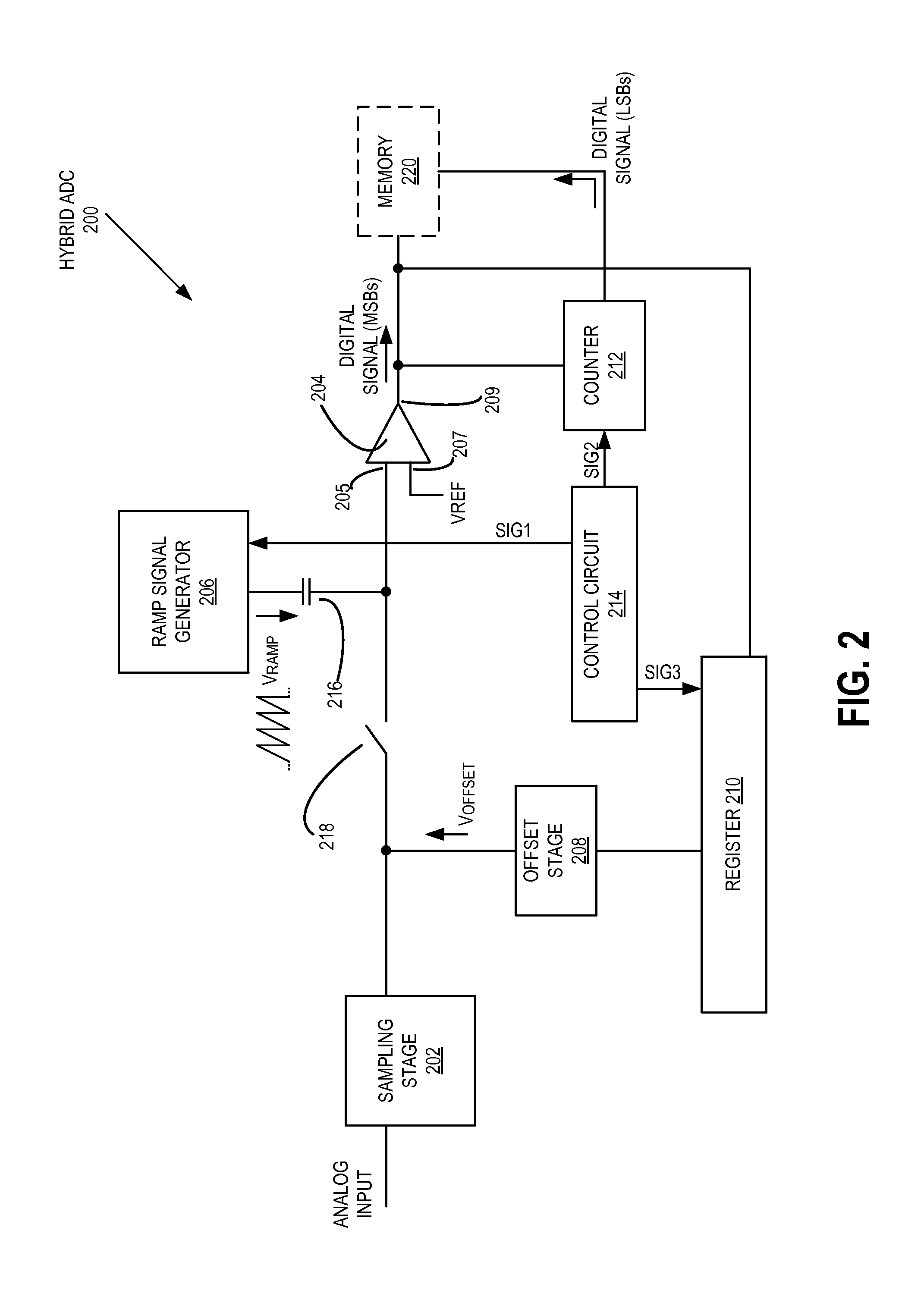
Hybrid analog-to-digital converter having multiple ADC modes
ActiveUS20140008515A1Electric signal transmission systemsSolid-state devicesProcessor registerEngineering
A hybrid ADC having a successive approximation register (SAR) ADC mode for generating a bit of a digital signal and a ramp ADC mode for generating an additional bit of the digital signal is disclosed. When in the SAR ADC mode, a control circuit is configured to disable a ramp signal generator; disable a counter; and enable a register to control an offset stage to set the magnitude of an offset voltage that is provided to an input of a comparator of the ADC. When in the ramp ADC mode, the control circuit is configured to enable the ramp signal generator to provide a ramp signal to the input of the comparator; enable the counter to begin providing the digital count in response to the output of the comparator; and disable the register so that the offset stage is not providing the offset voltage.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
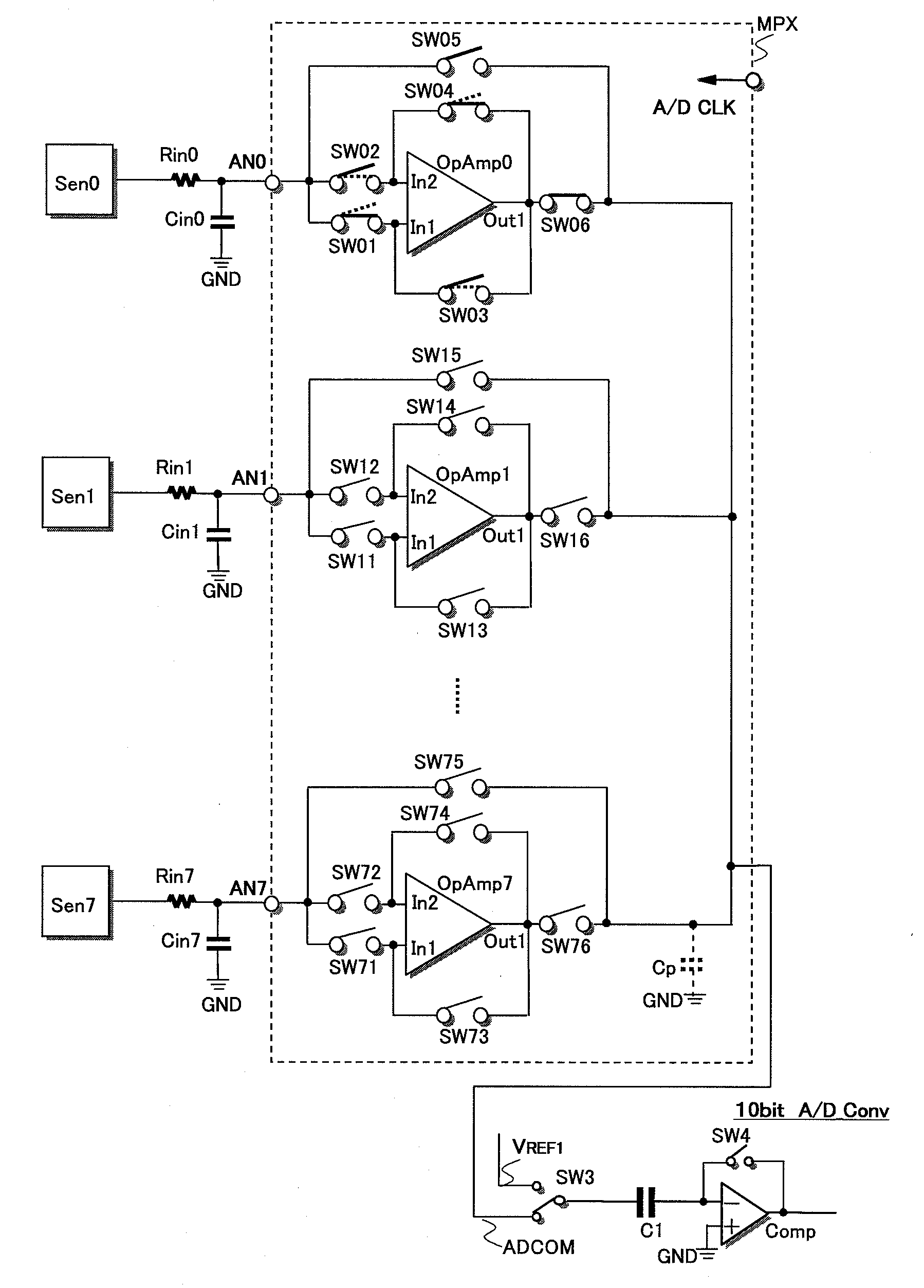
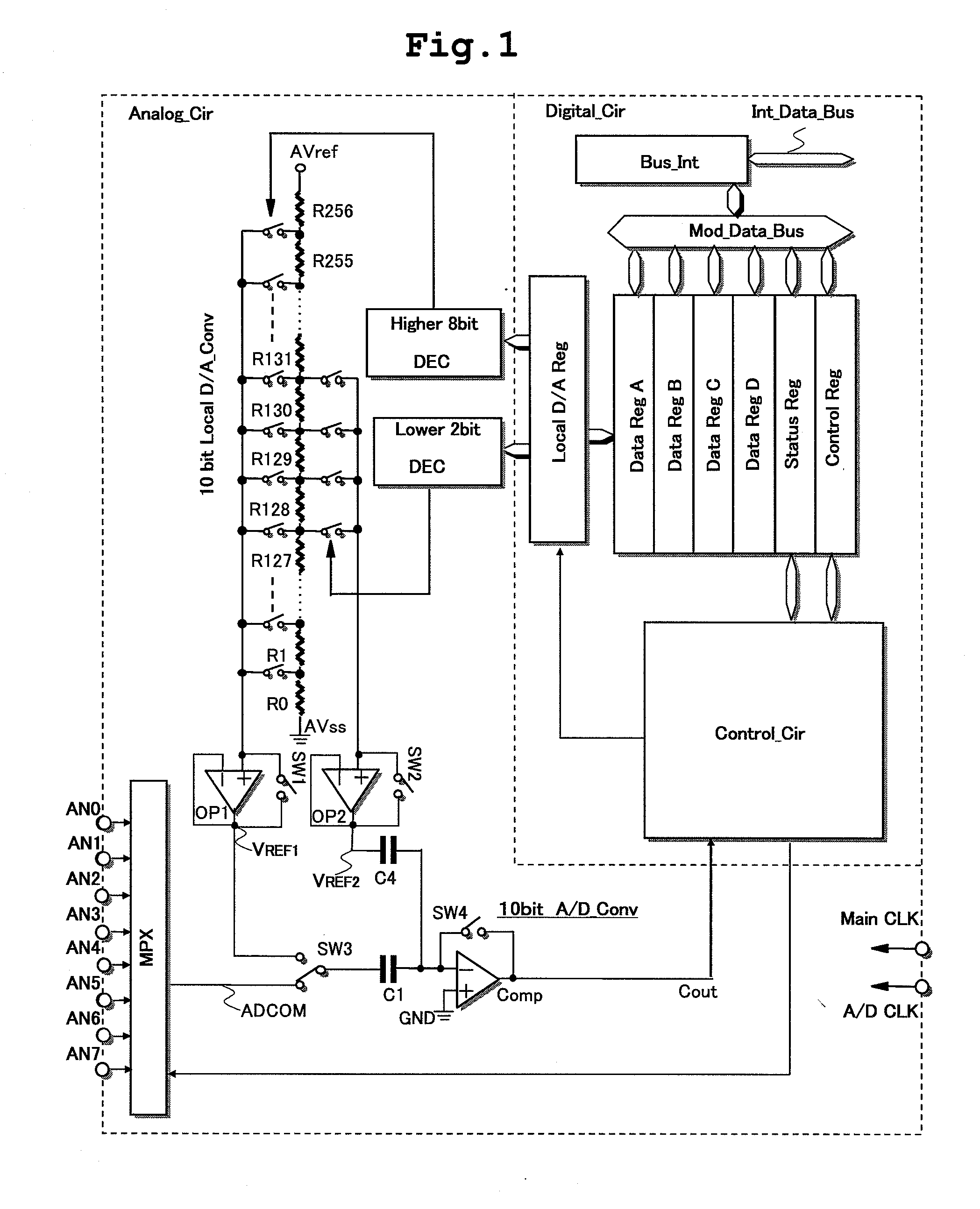
Semiconductor integrated circuit
ActiveUS20090140802A1Reduce impactReduce the voltage levelElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionSample ModeAudio power amplifier
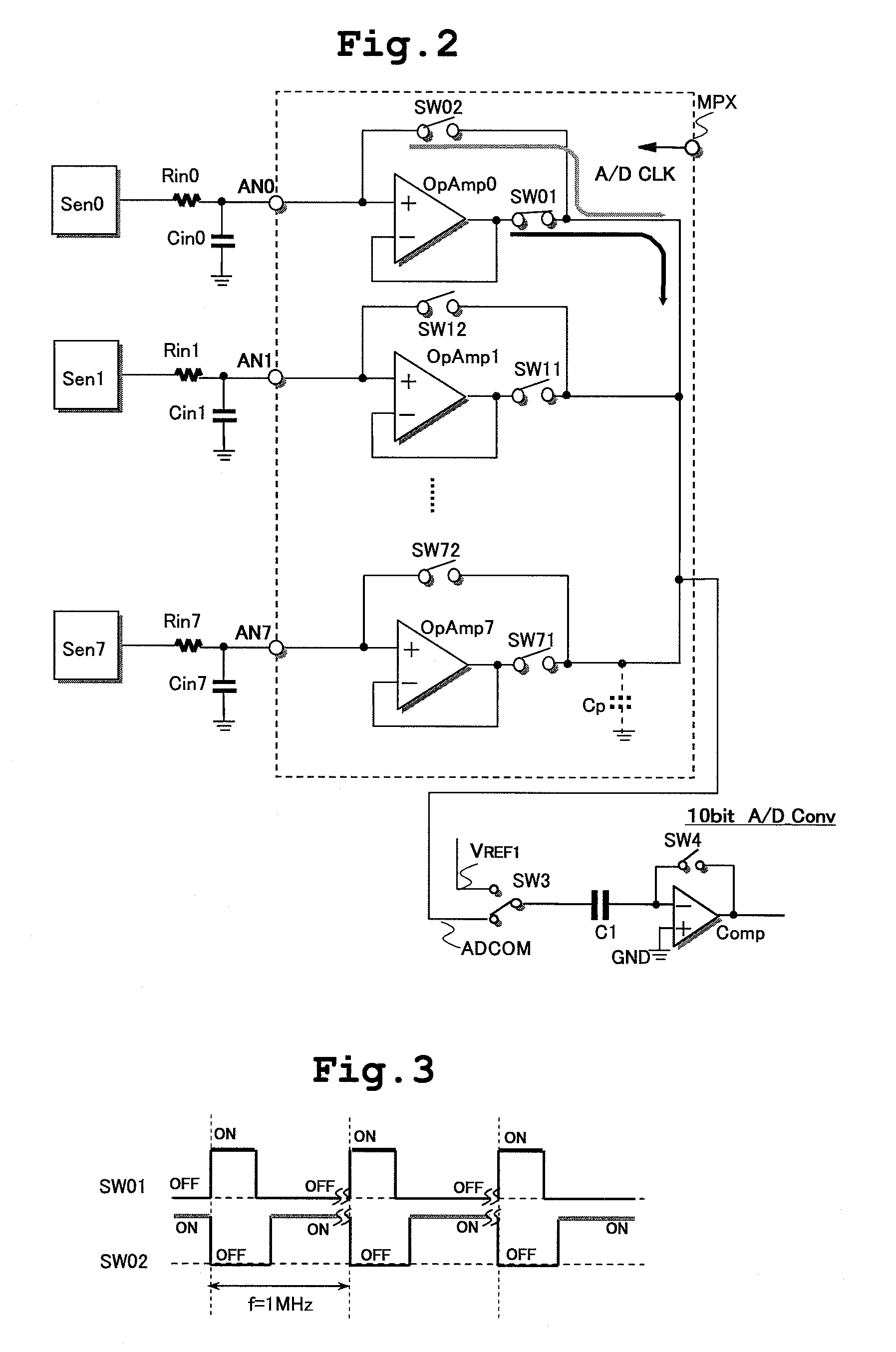
The present invention is directed to reduce offset error voltage in a signal source impedance of analog input signal voltage supplied to an input terminal due to input offset voltage of an operational amplifier in a sampling circuit or a multiplexer coupled to an input terminal of an A / D converter. A semiconductor integrated circuit has an A / D converter and a sampling circuit. The sampling circuit samples an analog input signal in first and second sample modes. The A / D converter converts the sampled analog signal to a digital signal in a conversion mode. By switching of an internal circuit of an operational amplifier between the first and second sample modes, the functions of a non-inverting input terminal (+) and an inverting input terminal (−) realized by first and second input terminals are switched. Synchronously with the switching, supply of an analog signal to the non-inverting input terminal by input switches is also switched.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Switching power supply control circuit
ActiveUS20150035510A1Facilitate detection valueReduce oscillationDc-dc conversionPower supply arrangements for electric/magnetic computingPower flowConversion coefficients
A switching power supply control circuit has a switching element, a smoothing circuit, and a switching control circuit configured to control the switching element. The switching control circuit includes I-V converter configured to multiply an output current flowing into the switching element by a predetermined conversion coefficient and generating an I-V conversion voltage, an amplifier configured to amplify the sum of the I-V conversion voltage and an offset voltage and generating a current detection signal, a first DAC configured to convert a digital compensation value computed from an output voltage of the smoothing circuit to an analog converted value, a first analog comparator configured to compare the current detection signal with the analog converted value and generating a first comparison result signal, and a driver configured to control the switching element on the basis of the first comparison result signal.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
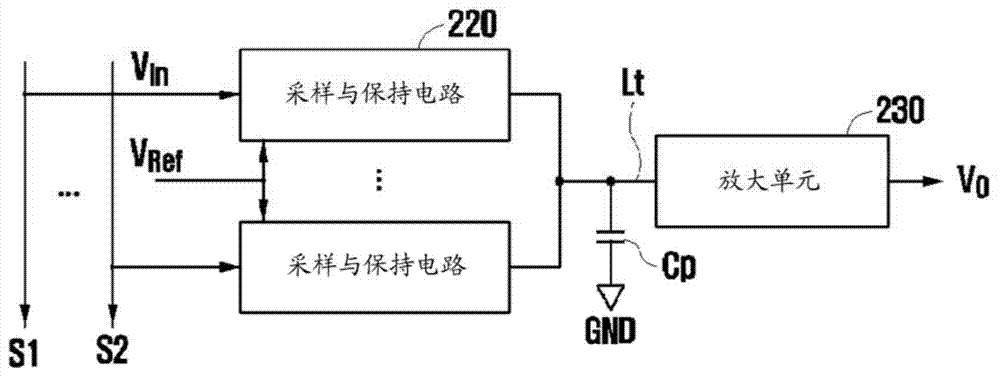
Sample and hold circuit and a/d converter apparatus
A sample and hold circuit includes an operational amplifier; a sampling capacitor configured to sample input voltages at a plurality of different timings; an adding / subtracting unit configured to perform an adding or subtracting operation of the input voltages sampled by the sampling capacitor; and an offset voltage removing unit configured to remove an input offset voltage component of the operational amplifier from a voltage obtained by the adding or subtracting operation. The operational amplifier is configured to produce an output by holding the voltage from which the input offset voltage component of the operational amplifier has been removed by the offset voltage removing unit.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
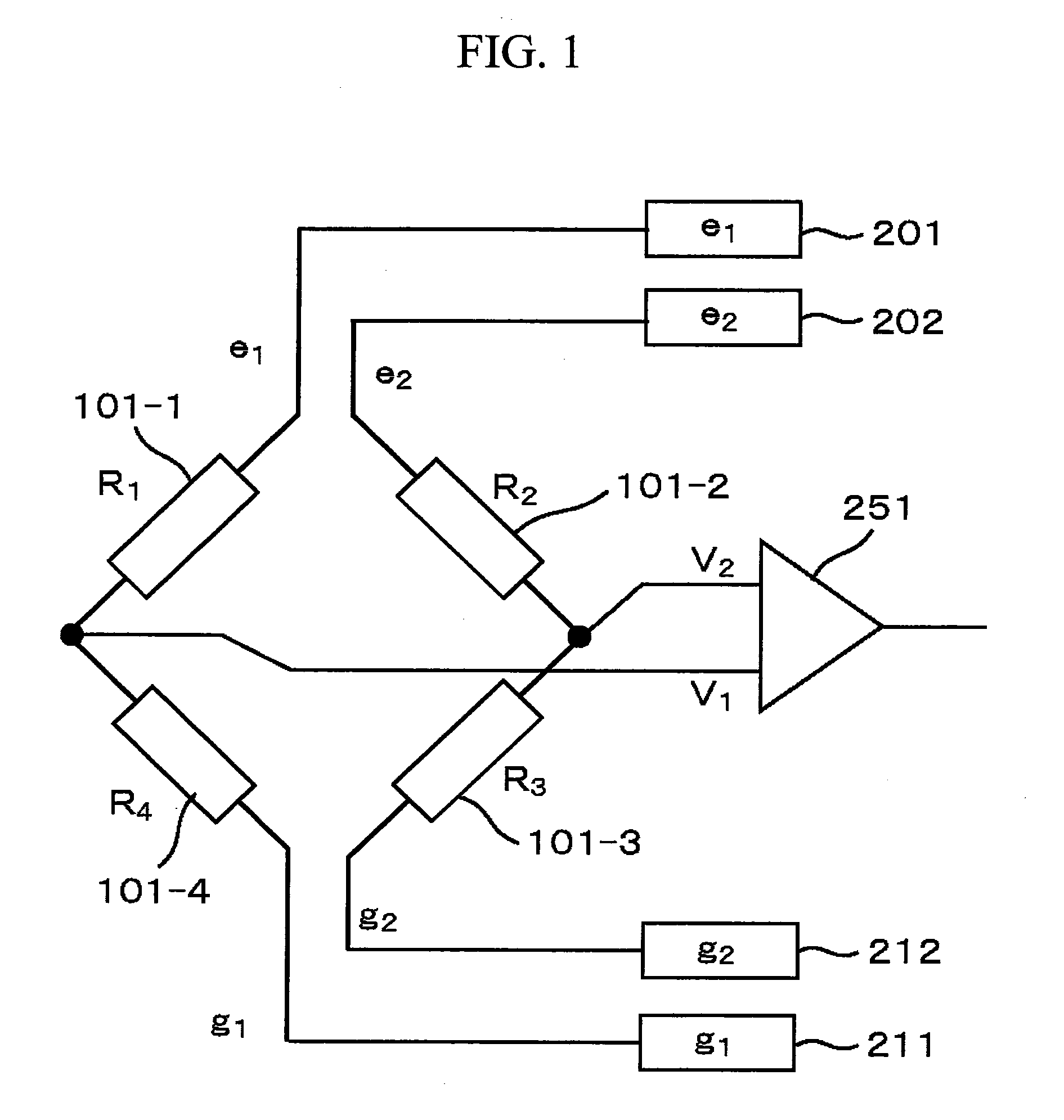
Magnetic Field Detection Apparatus and Measurement Apparatus
ActiveUS20100219822A1Accurate measurementEliminate Offset VoltageRecording apparatusMeasurement arrangements for variableMeasurement deviceMagnetic reluctance
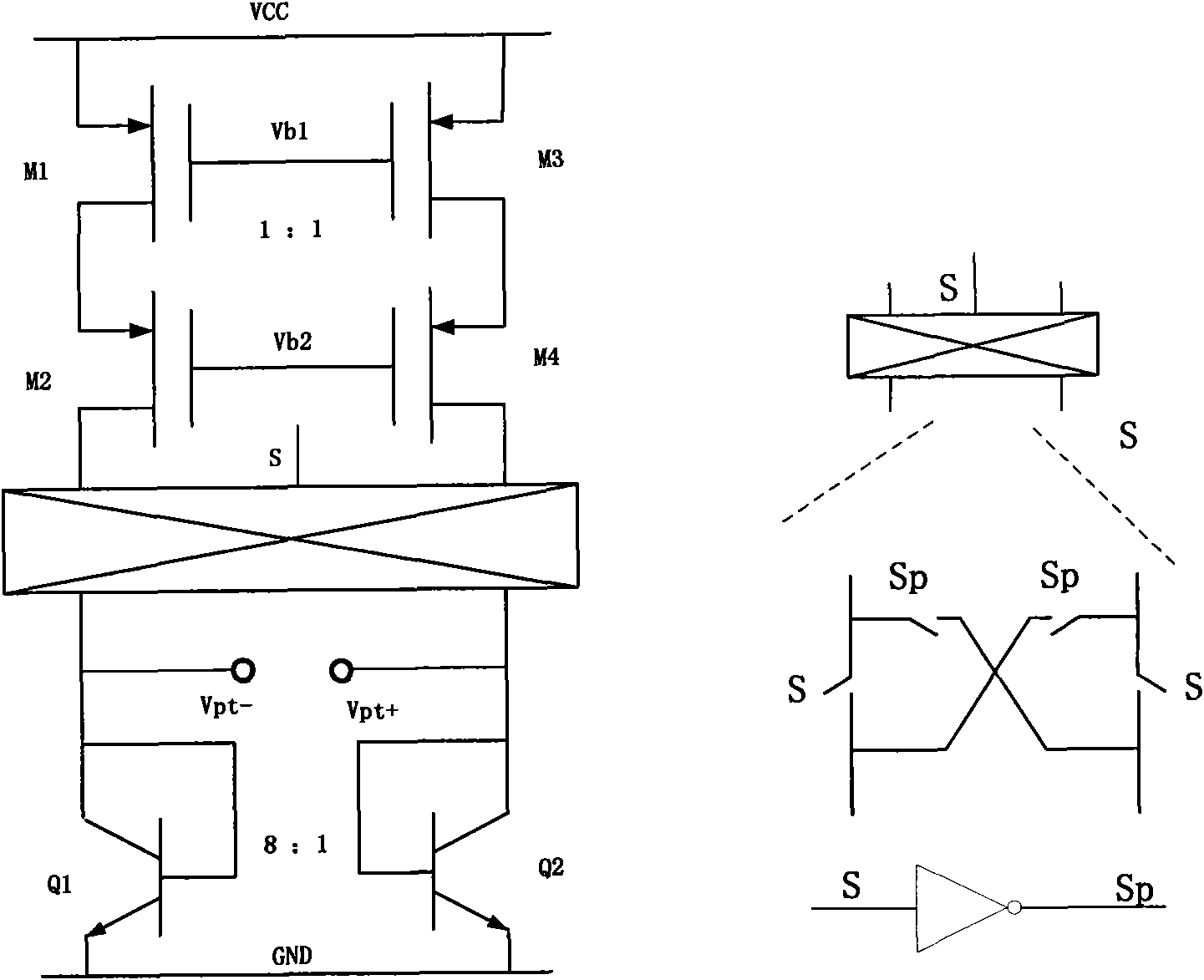
There has been a problem that a bridge circuit using magneto-resistive elements or transducer elements could output a signal including an offset voltage, which could result in lower measurement accuracy. In order to solve such a problem, half-bridges each having magneto-resistive elements or transducer elements are excited with different excitation voltages so that the offset voltage is eliminated and the measurement accuracy is improved.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
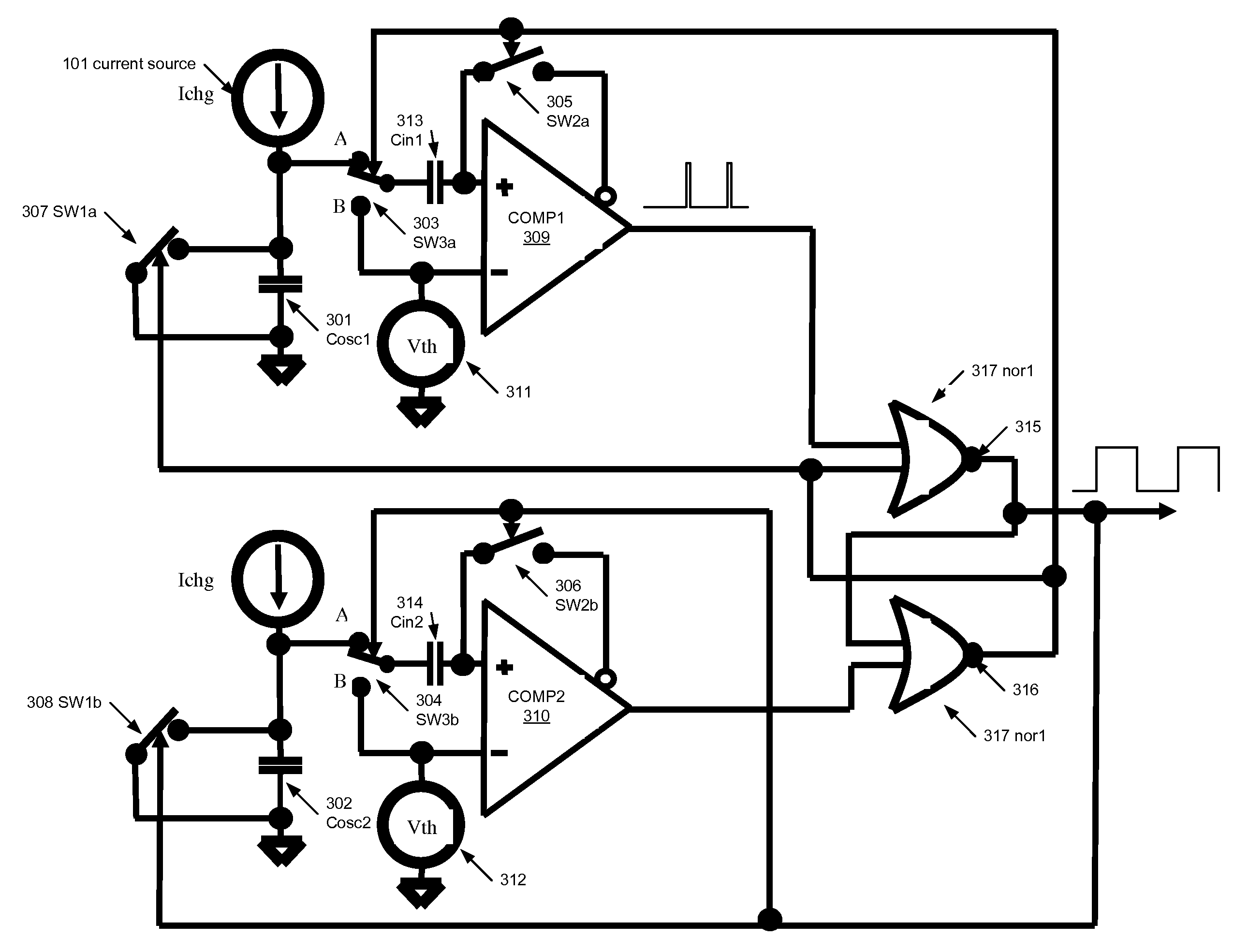
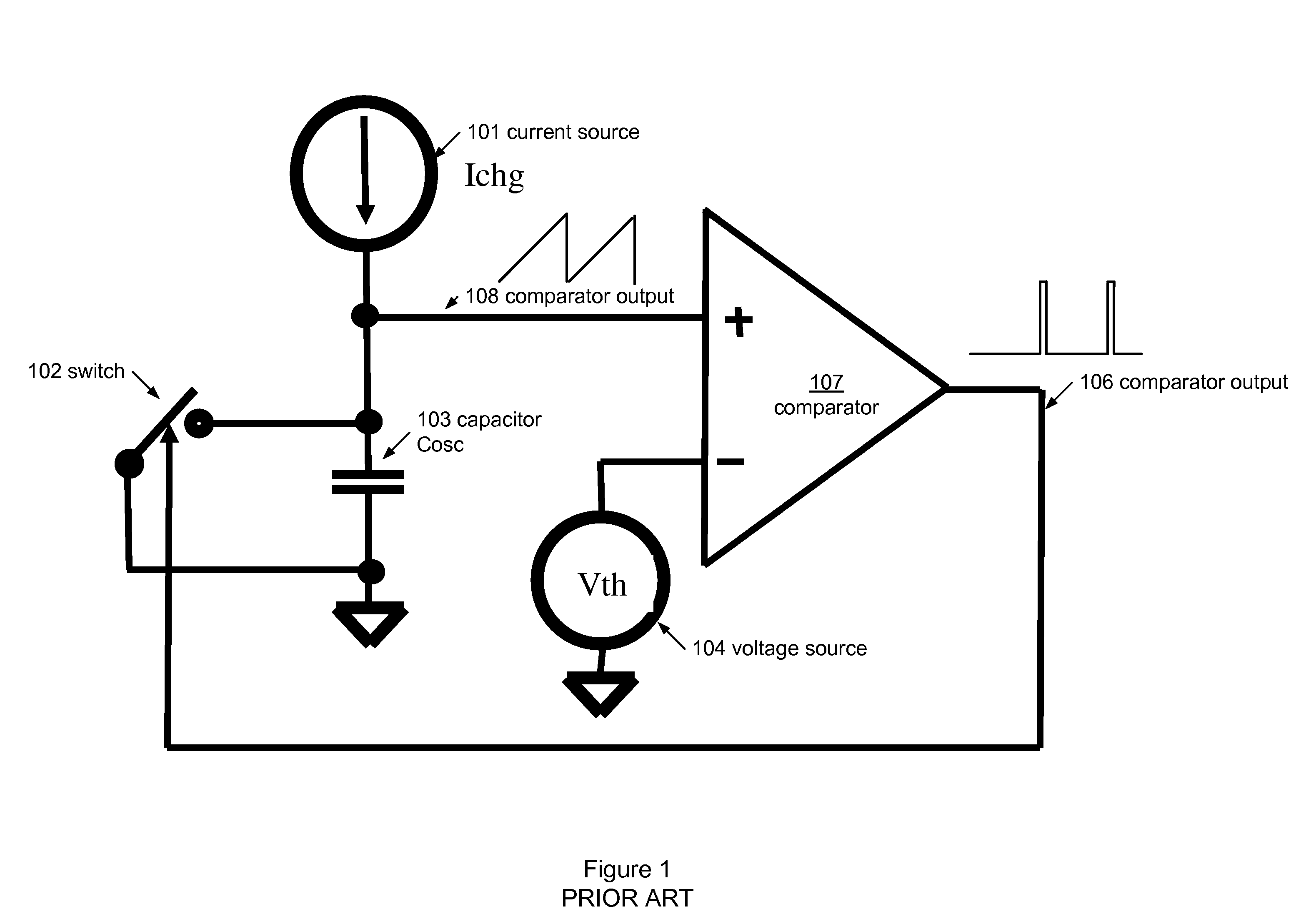
System and method for oscillator noise cancellation
InactiveUS7474163B1Reduce impactGenerator stabilizationElectric pulse generator circuitsSecondary stageEngineering
The invention relates to an electronic circuit comprising a first comparator having a first input offset voltage, wherein the first comparator is operatively coupled to a first sampling capacitor, a second comparator having a second input offset voltage, wherein the second comparator is operatively coupled to a second sampling capacitor, and a control circuit operatively coupled to the first comparator and the second comparator for generating alternate cycles having a first phase and a second phase, wherein a first sampled offset voltage is stored in the first sampling capacitor during the first phase of the alternate cycles, wherein the first sampled offset voltage is subtracted from the first input offset voltage during the second phase of the alternate cycles, wherein a second sampled offset voltage is stored in the second sampling capacitor during the second phase of the alternate cycles, and wherein the second sampled offset voltage is subtracted from the second input offset voltage during the first phase of the alternate cycles.
Owner:SENSOR PLATFORMS
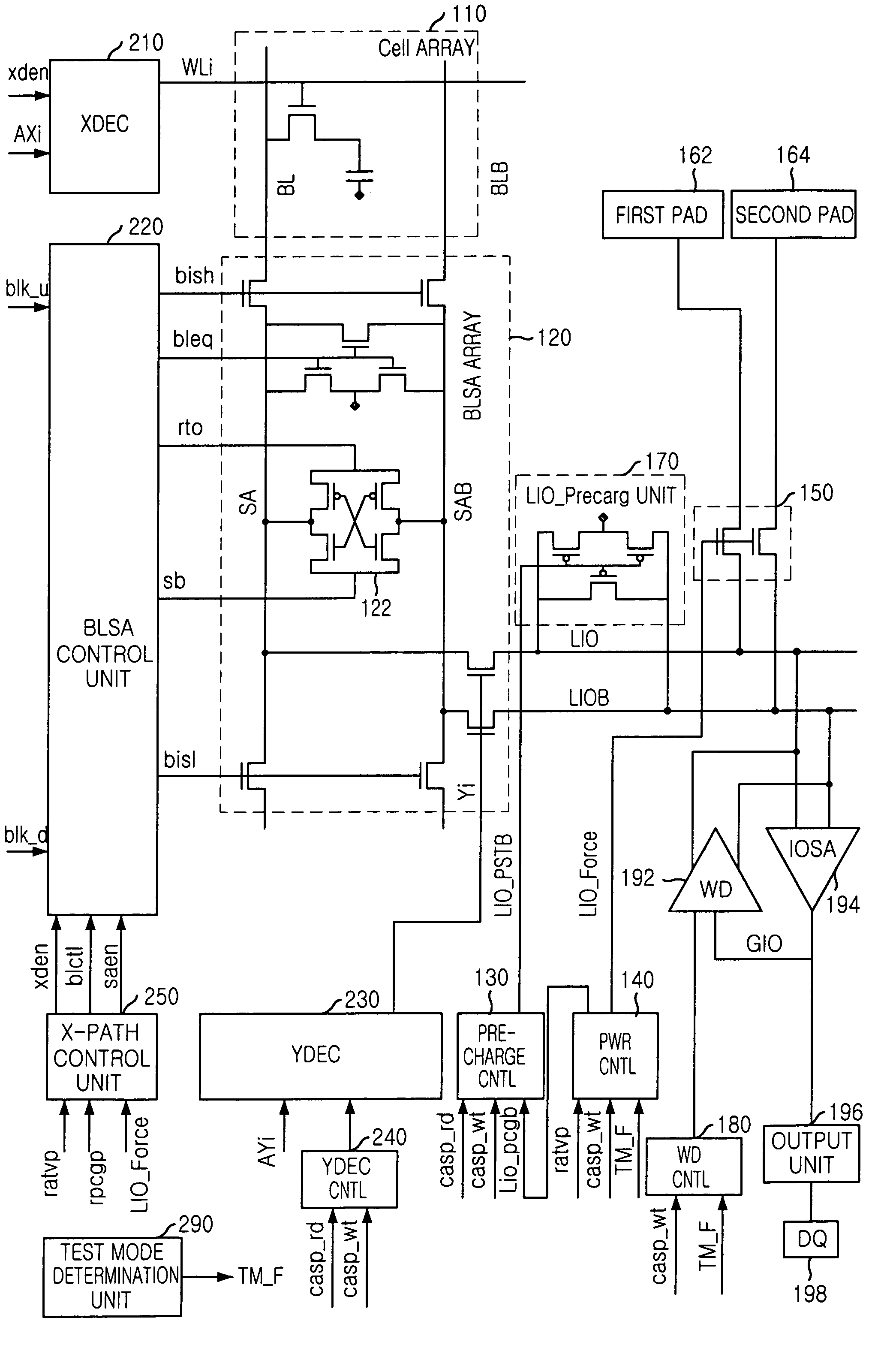
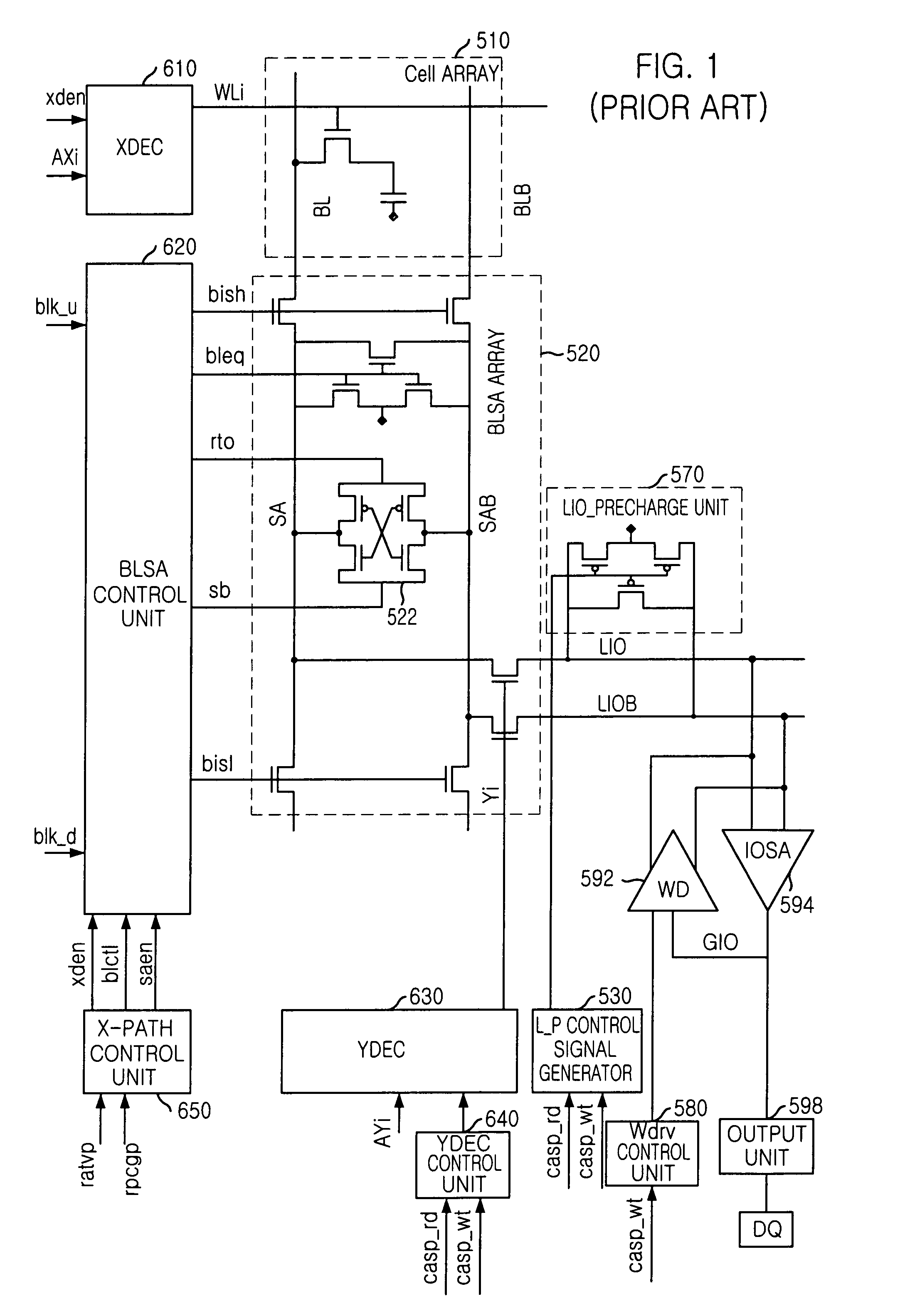
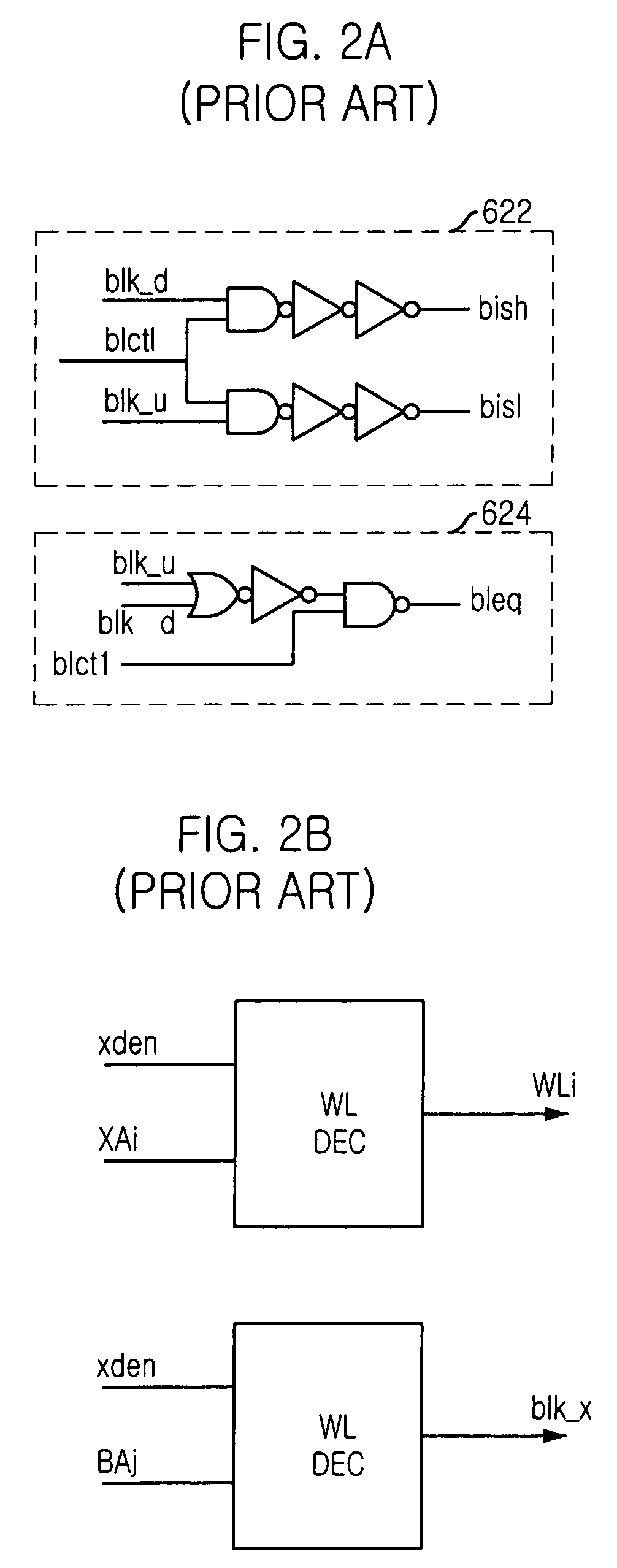
Method for measuring offset voltage of sense amplifier and semiconductor employing the method
A semiconductor memory device precisely measures the offset voltage of a bit line sense amplifier. The semiconductor memory device of the invention includes: a bit line sense amplifier for amplifying a voltage difference between a bit line and an inversion bit line, which carry data written on a memory cell when the data is read; a data input / output line and an inversion data input / output line within a core region coupled to the bit line and the inversion bit line via one or more switches; a first external voltage supply pad connected to the data input / output line; a second external voltage supply pad connected to the inversion data input / output line; and an external voltage supply controller for switching a connection of the data input / output line and the first external voltage supply pad and a connection of the inversion data input / output line and the second external voltage supply pad.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Dynamic comparator
ActiveCN102647189ALower Input Offset VoltageMeet the needs of the designAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsEngineeringComparator
The invention provides a dynamic comparator. The dynamic comparator comprises a pre-amplification circuit, a dynamic latch circuit and an output-stage circuit which are connected in sequence, wherein the pre-amplification circuit comprises a first-stage amplification unit adopting an input detuning storage technology and a second-stage amplification unit adopting an output detuning storage technology; the dynamic latch circuit is used for amplifying the output signal of the pre-amplification circuit, and transforming the amplified signal into a digital logical output level; the output-stage circuit is used for outputting the digital logical output level at a latched phase, and outputting logic zero at a rest phase. The dynamic comparator provided by the invention adopts a detuning canceling technology and a structure isolating kickback noise in the pre-amplification circuit, thus effectively reducing the input detuning voltage, and greatly meeting the demands for design of high speed and high precision analog-digital convertors.
Owner:昆山启达微电子有限公司
Precision bandgap reference
InactiveUS20160266598A1Electric variable regulationElectrical resistance and conductanceAudio power amplifier
Systems and methods for producing reference voltages are disclosed. An example bandgap reference circuit includes a core bandgap module that produces a bias control for biasing the gate of a transistor to produce a proportional to absolute temperature current. The core bandgap module may use an operational amplifier that uses auto-calibration to reduce its input offset voltage. A trimming module uses the bias control to produce a proportional to absolute temperature current that is combined with a trim current and supplied to a resistor and diode to produce a trimmed bandgap voltage. The trimmed bandgap voltage is buffered to produce a reference voltage output. The trim current may be set based on a room temperature measurement of the reference voltage output.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
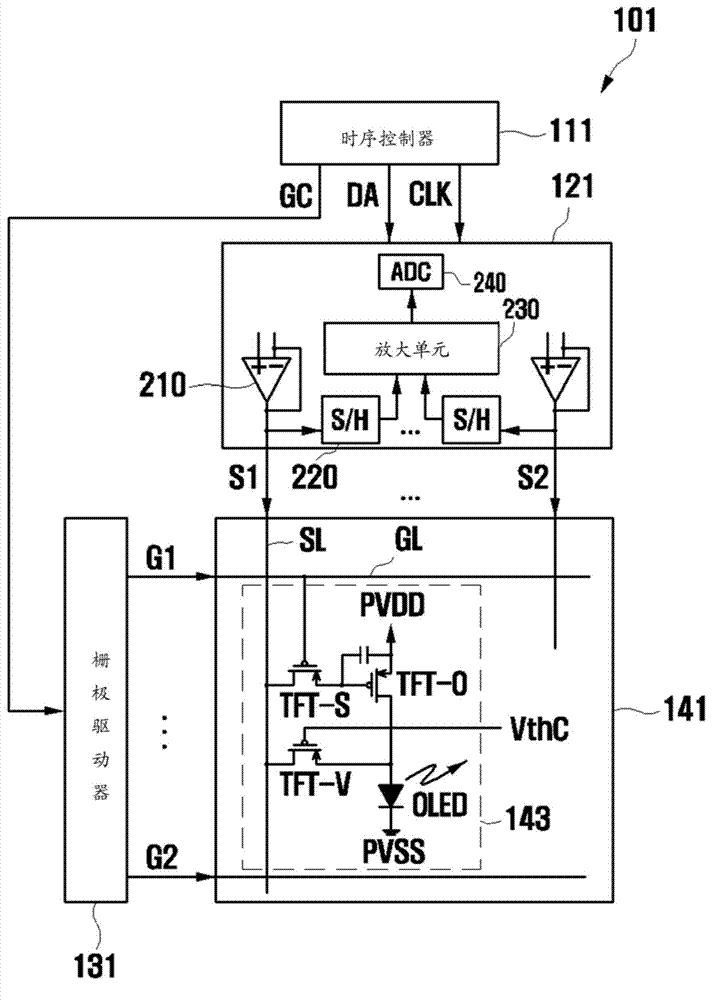
Source driver of display device
ActiveCN104517566AControl Offset VoltageAvoid differencesStatic indicating devicesParasitic capacitorAudio power amplifier
A source driver may include: a transmission line configured to transmit an output signal of a sample and hold circuit which stores pixel information of an organic light emitting diode (OLED) cell; an amplifier is formed a first offset voltage at an input terminal by a parasitic capacitor of the transmission line; and an offset voltage storage unit configured to store the first offset voltage outputted from the amplifier as a second offset voltage while the transmission of the output signal of the sample and hold circuit through the transmission line is turned off, and offset the first offset voltage by providing the second offset voltage to the input terminal of the amplifier when the output signal of the sample and hold circuit is transmitted through the transmission line.
Owner:SILICON WORKS CO LTD
Low ripple wave boosting type charge pump
InactiveCN101694961ASmall rippleApparatus without intermediate ac conversionAudio power amplifierContinuous feedback
The invention discloses a low ripple wave boosting type charge pump which comprises a single-capacitor voltage doubling circuit, wherein a continuous feedback circuit is arranged between the output voltage and the input voltage of the single-capacitor voltage doubling circuit; the continuous feedback circuit comprises an output voltage sampling branch circuit, an operation amplifier and an adjusting pipe which are sequentially connected; the detecting voltage and the reference voltage of the output voltage sampling branch circuit are respectively connected to both input ends of the operation amplifier, the output end of the operation amplifier is connected to the input end of the adjusting pipe, and a feedback mechanism of the continuous feedback circuit finally stabilizes the output voltage to a preset value. The continuous feedback mechanism comprising the output voltage sampling branch circuit, the operation amplifier and an active adjusting pipe is added; on one hand, when the factor of input voltage or temperature, and the like is changed, the stability of the output voltage is maintained by feedback; on the other hand, a ripple wave of the output voltage does not comprise the unideal factor of offset voltage, and the like due to the continuity of the feedback, thereby having a lower ripple wave.
Owner:IPGOAL MICROELECTRONICS (SICHUAN) CO LTD
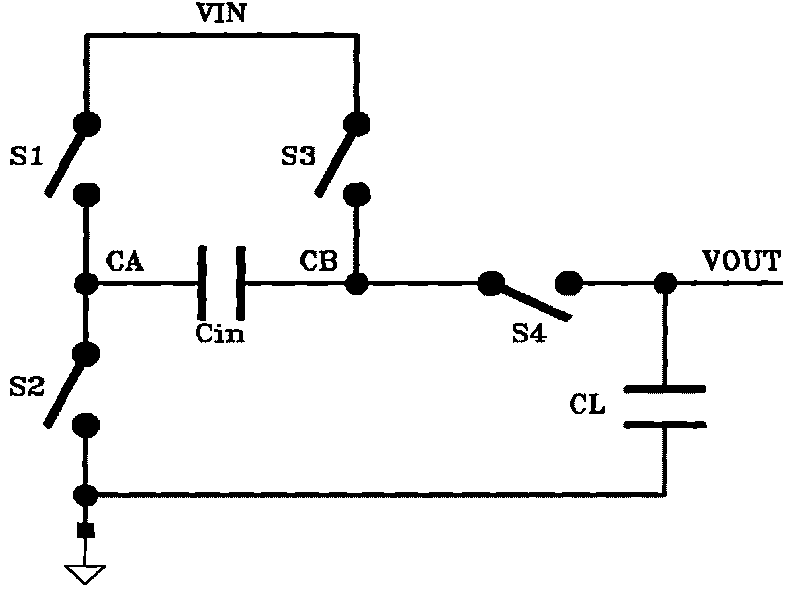
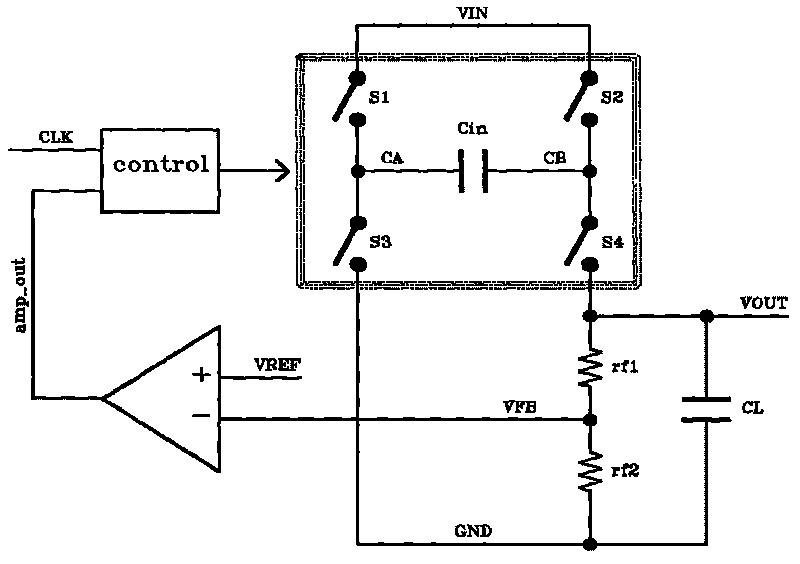
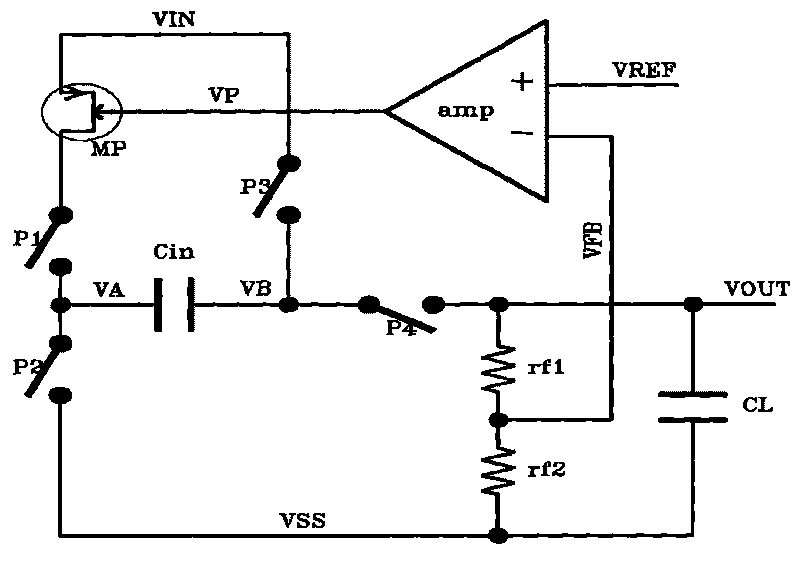
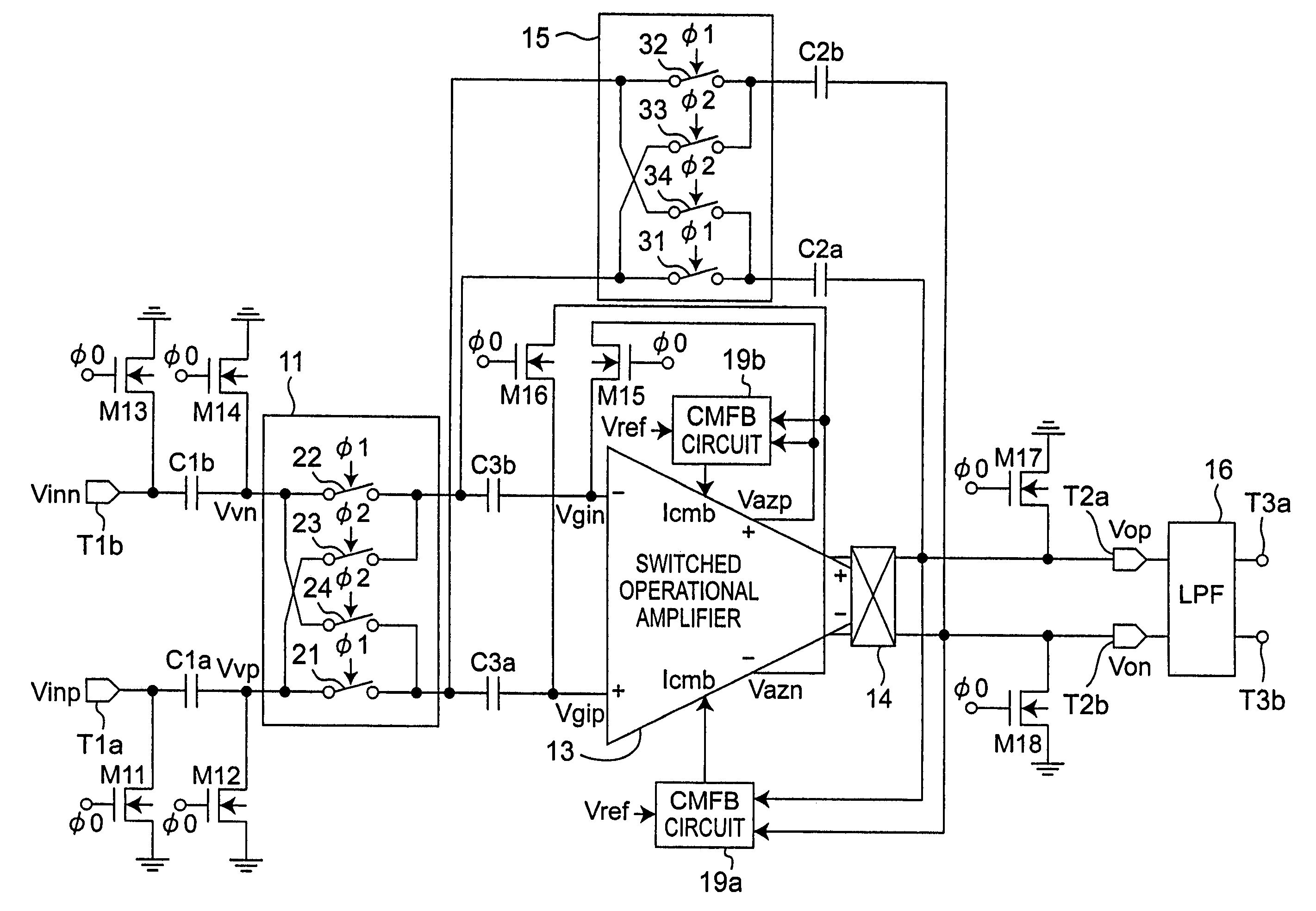
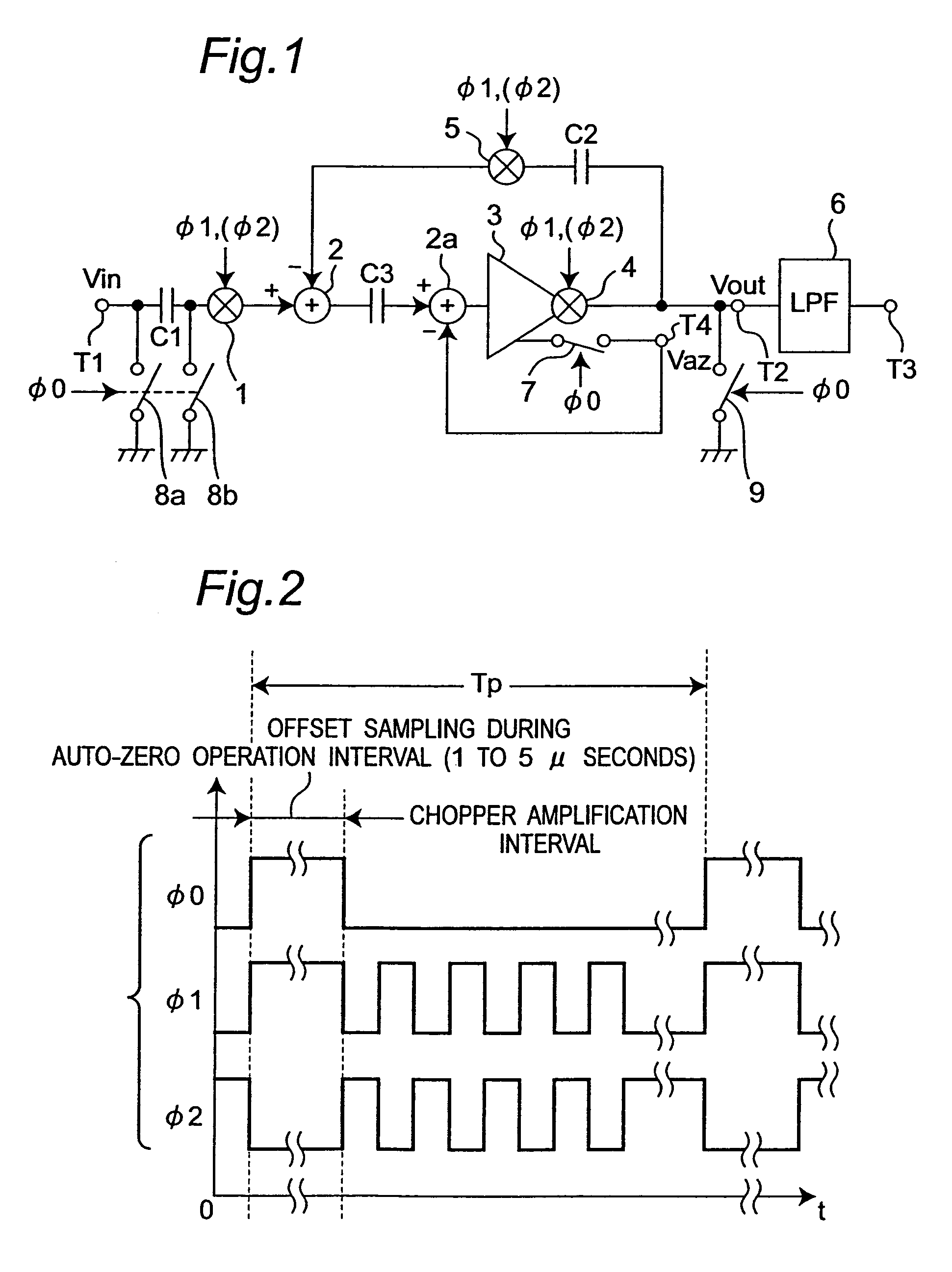
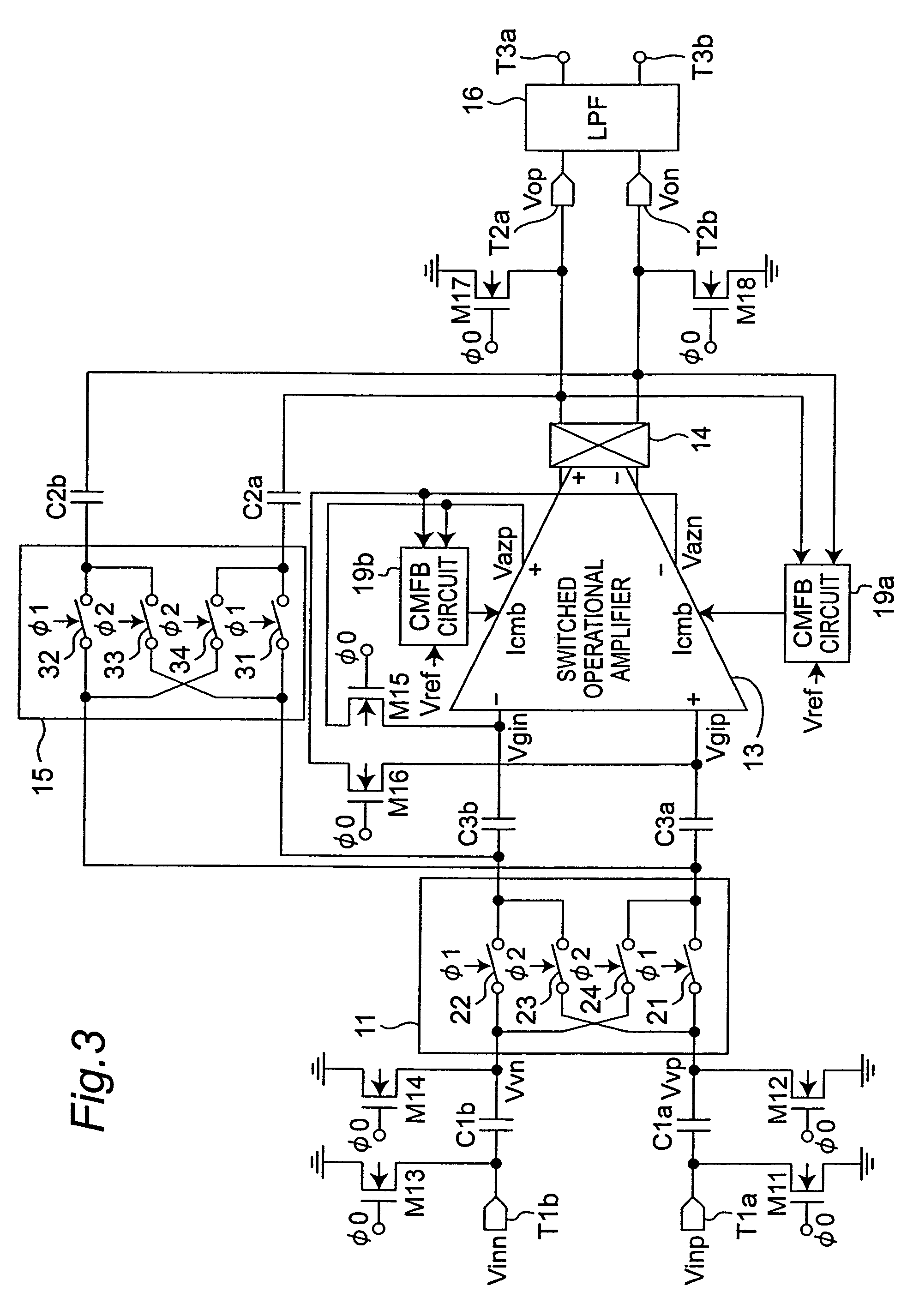
Feedback amplifier circuit operable at low voltage by utilizing switched operational amplifier and chopper modulator
InactiveUS7589587B2Easy to set upExclude influenceAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyDifferential amplifiersAudio power amplifierLow voltage
In a feedback amplifier circuit, a first switching device executes an auto-zero operation by inputting a signal outputted from an amplifier to an input terminal of the amplifier during an auto-zero operation interval prior to an amplification interval. A first capacitor accumulates and holds an offset voltage at the output terminal of the amplifier during the auto-zero operation interval, and cancels an offset voltage at the input terminal of the amplifier by an accumulated and held offset voltage during an amplification interval subsequent to the auto-zero operation interval. A second switching device grounds the feedback point of the feedback circuit during the auto-zero operation interval. A second capacitor blocks a DC voltage, and accumulates and holds an offset voltage at an output terminal of the amplifier, and cancels an offset voltage at an input terminal of the amplifier by the accumulated and held offset voltage during an amplification interval.
Owner:SEMICON TECH ACADEMIC RES CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com