Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
86 results about "Wall motion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Regional wall motion abnormality means that the motion of a region of the heart muscle is abnormal. It is a term commonly used in echocardiography. Echocardiography is ultrasound imaging of the heart.
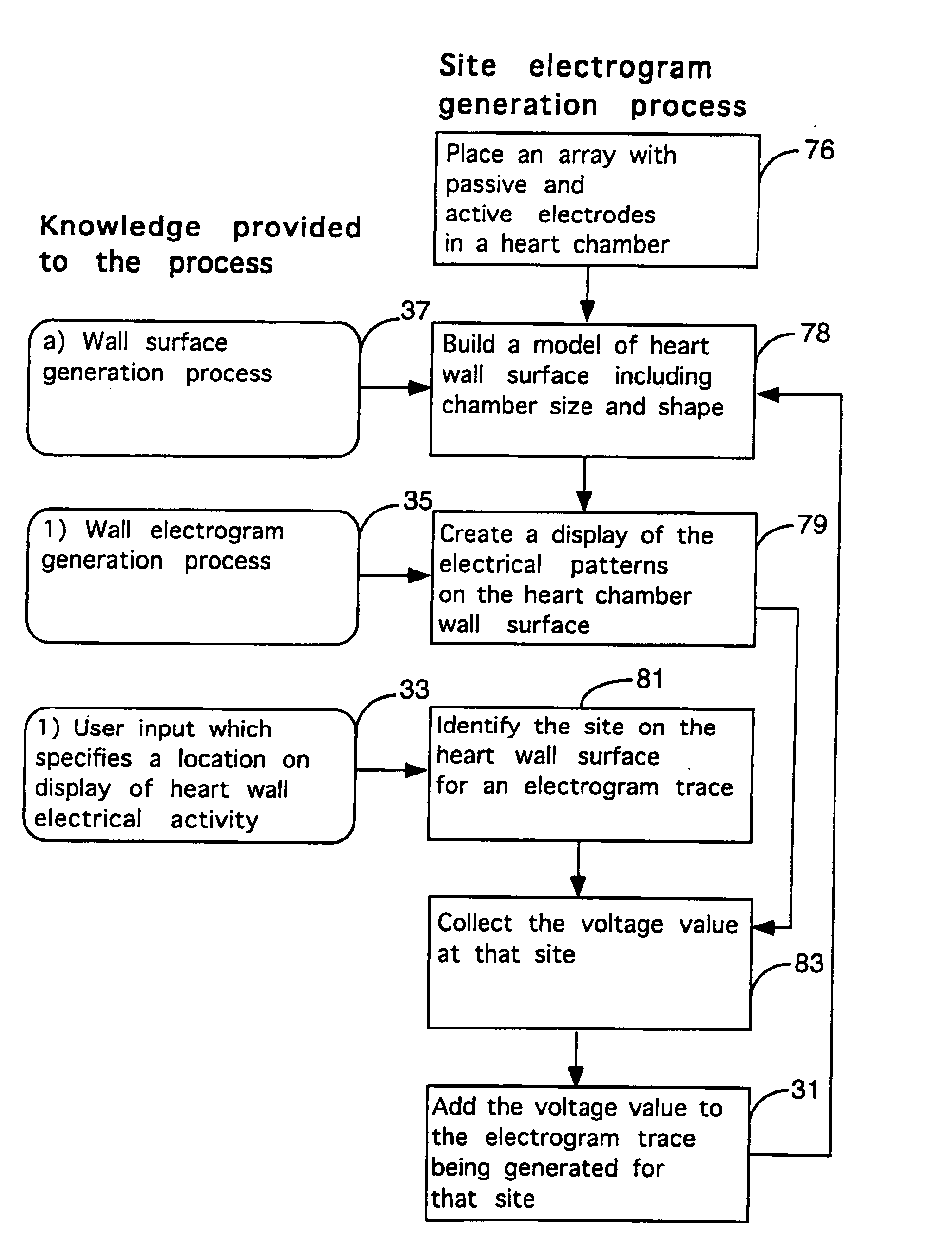
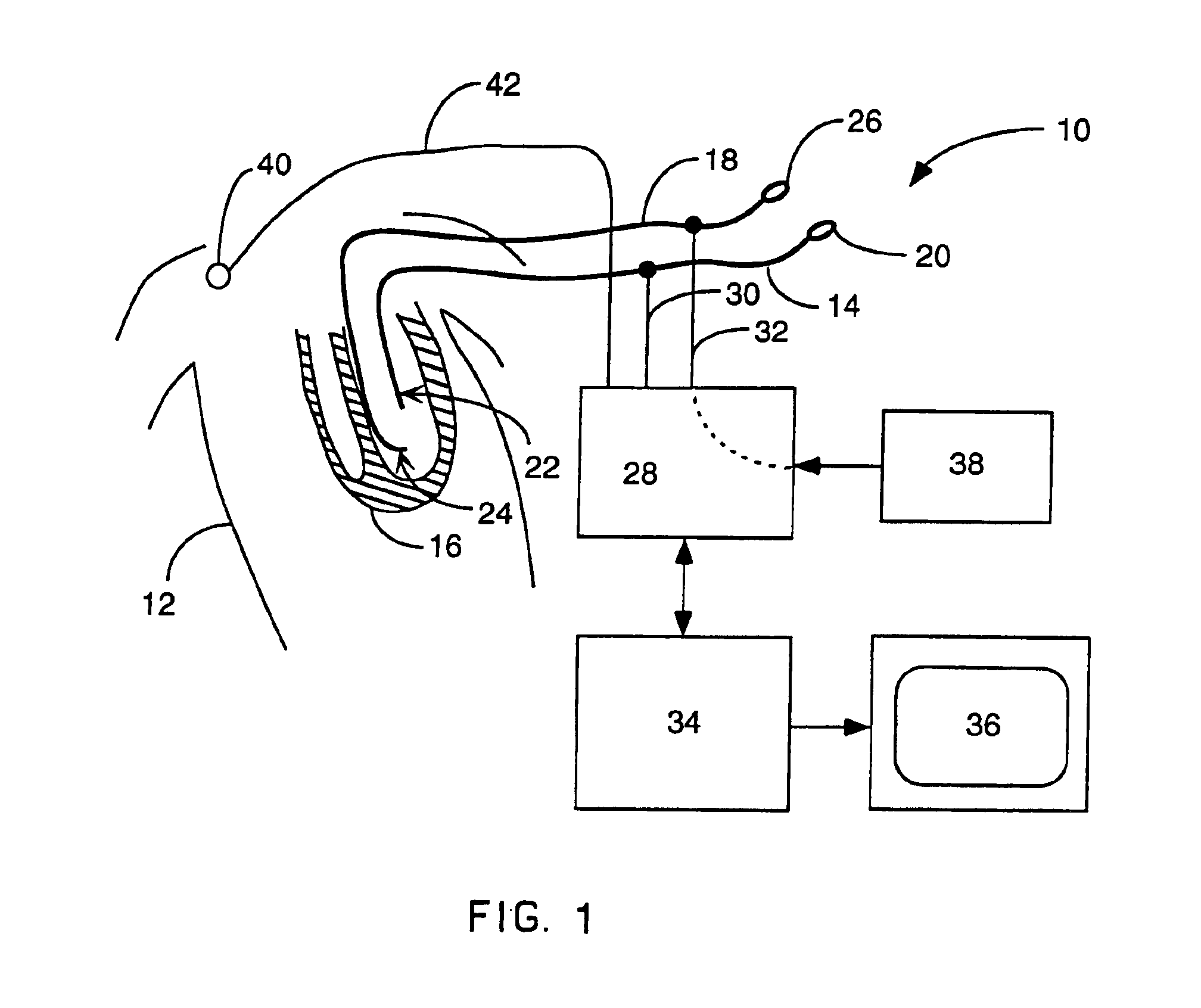
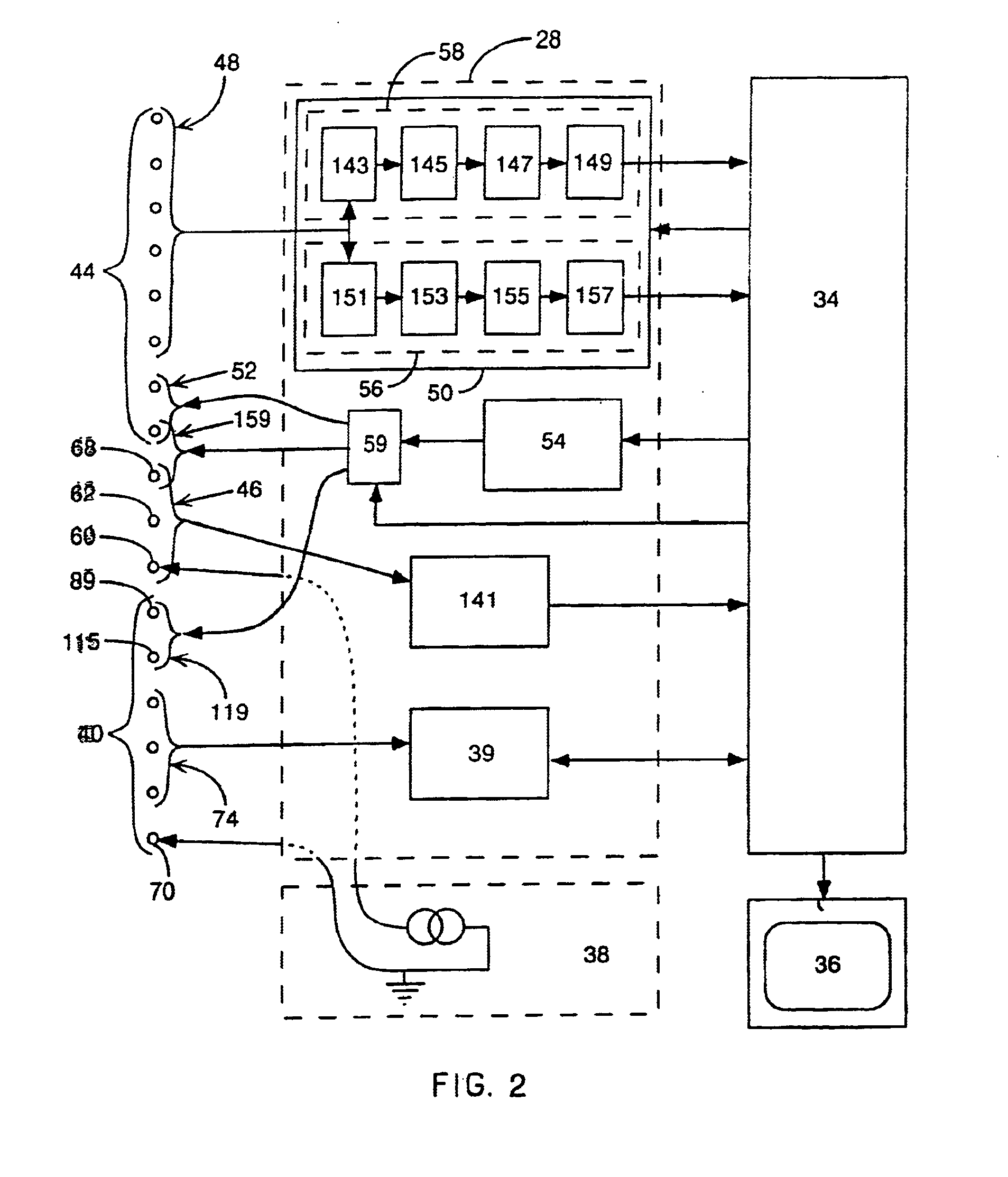
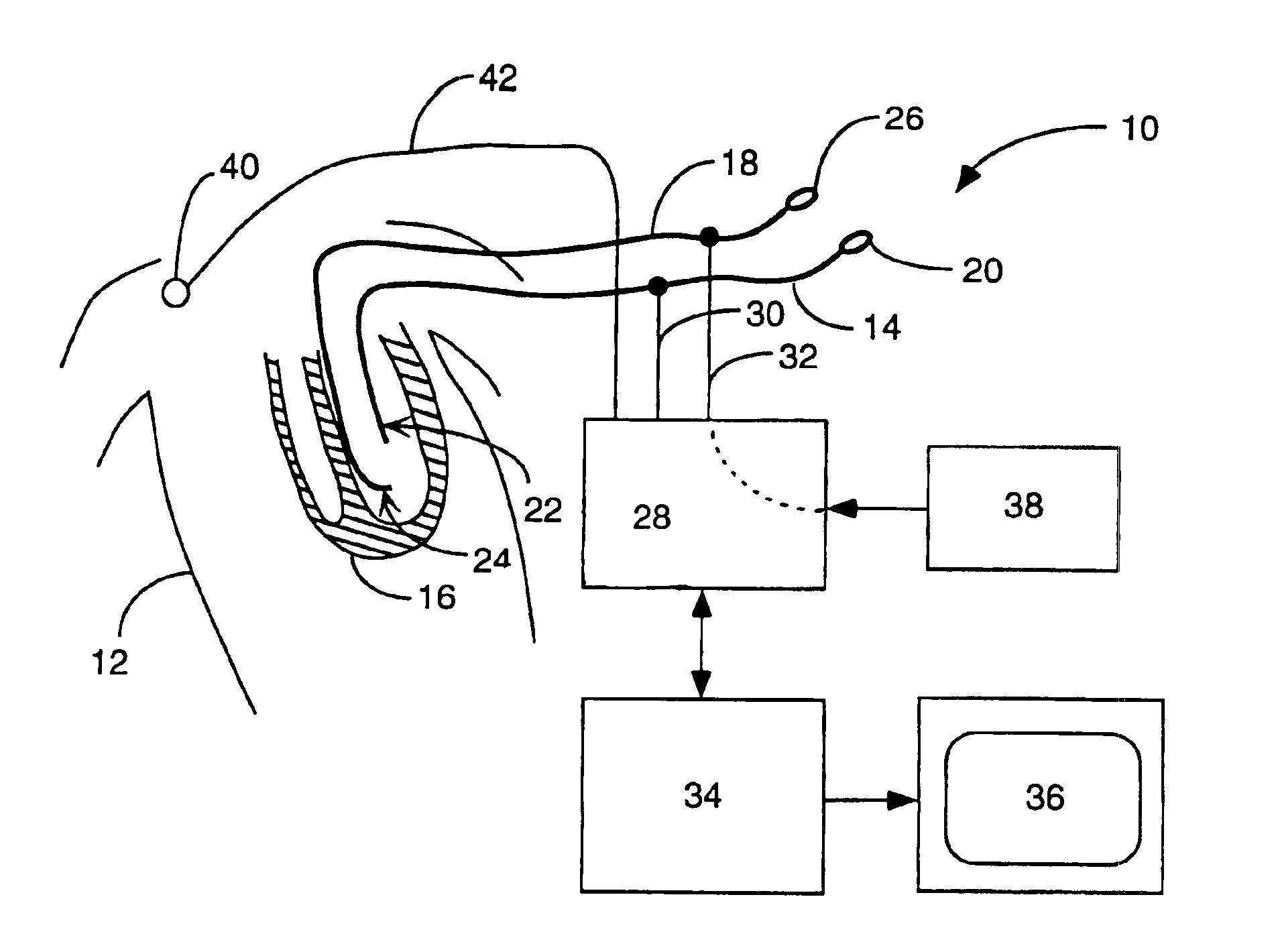
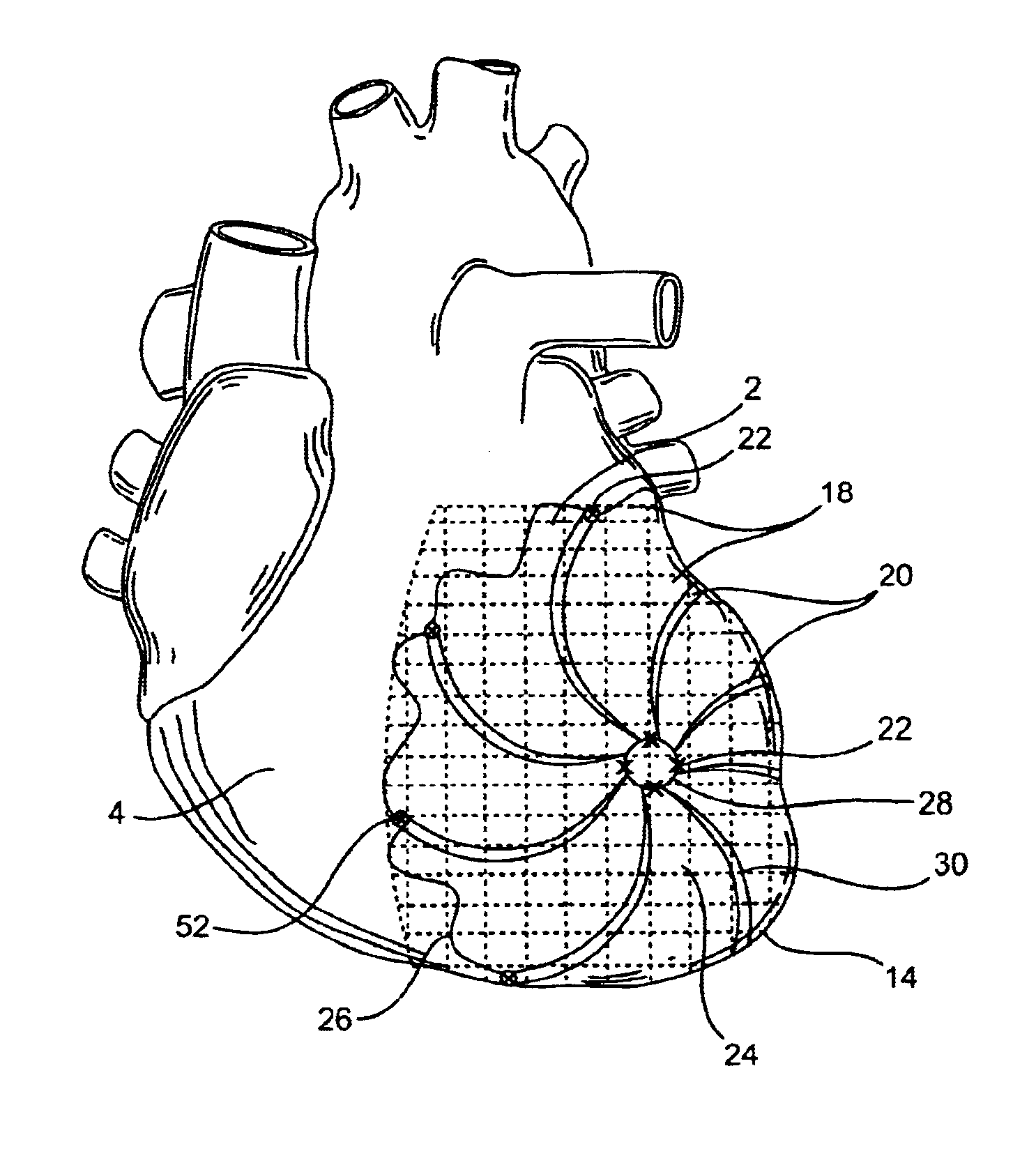
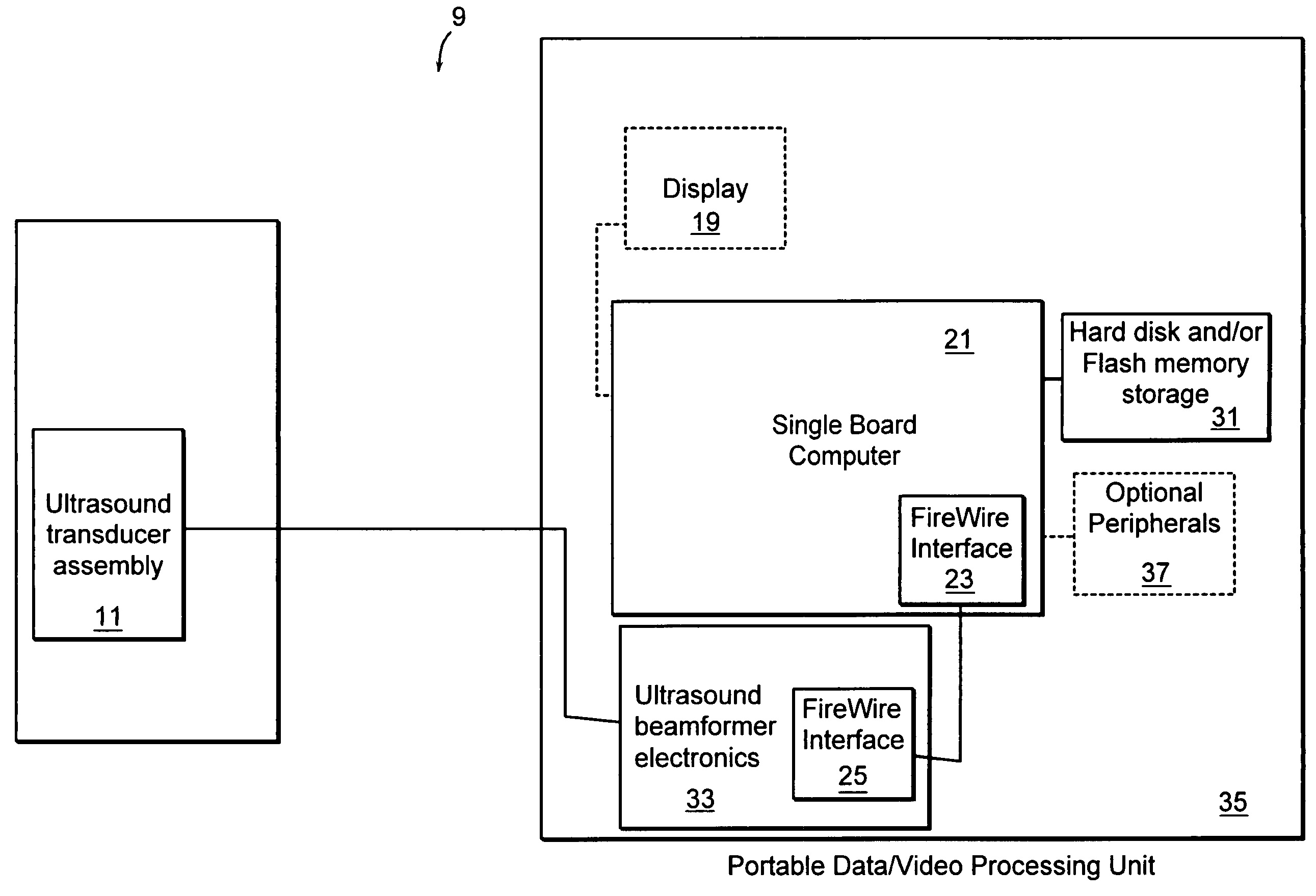
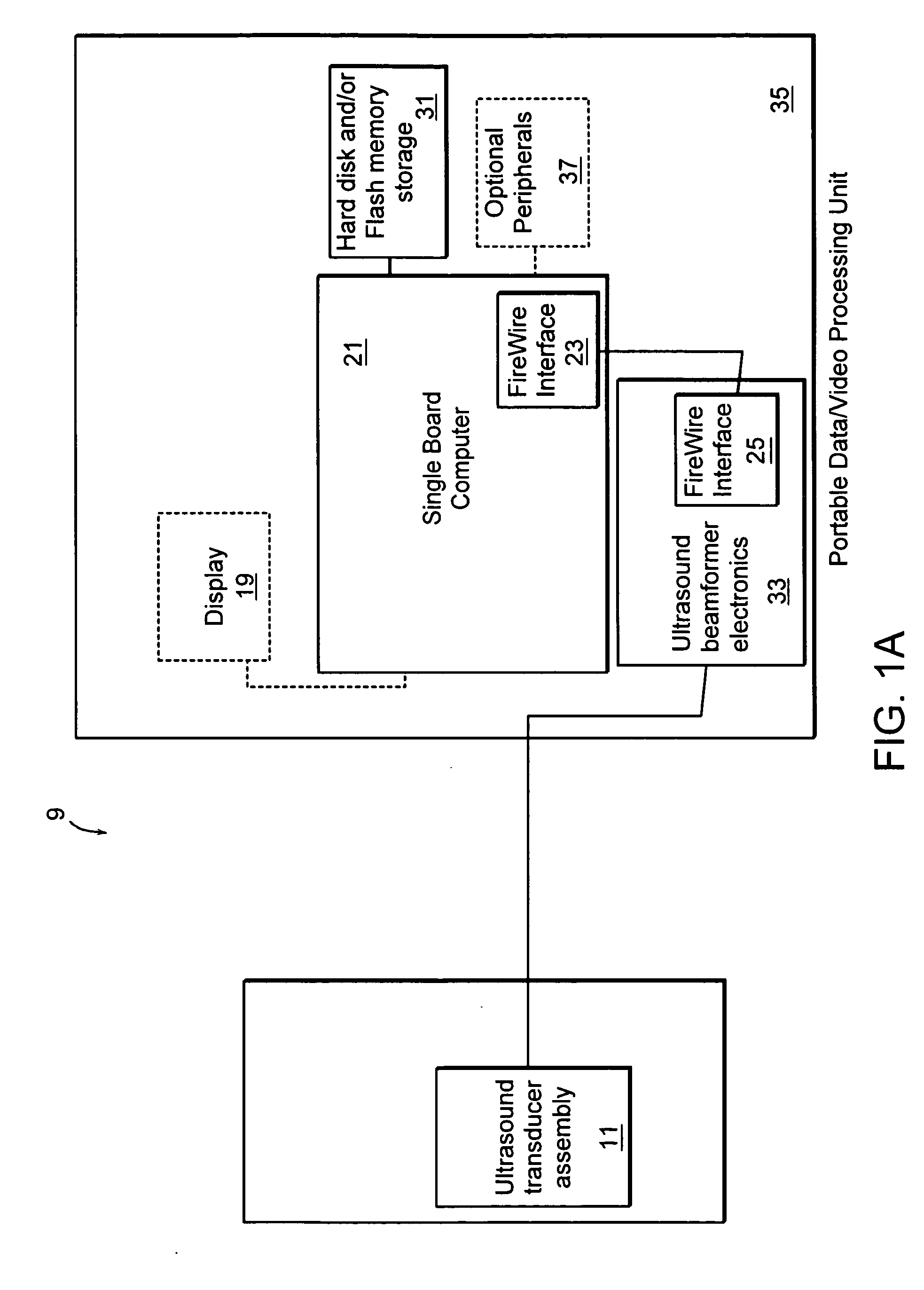
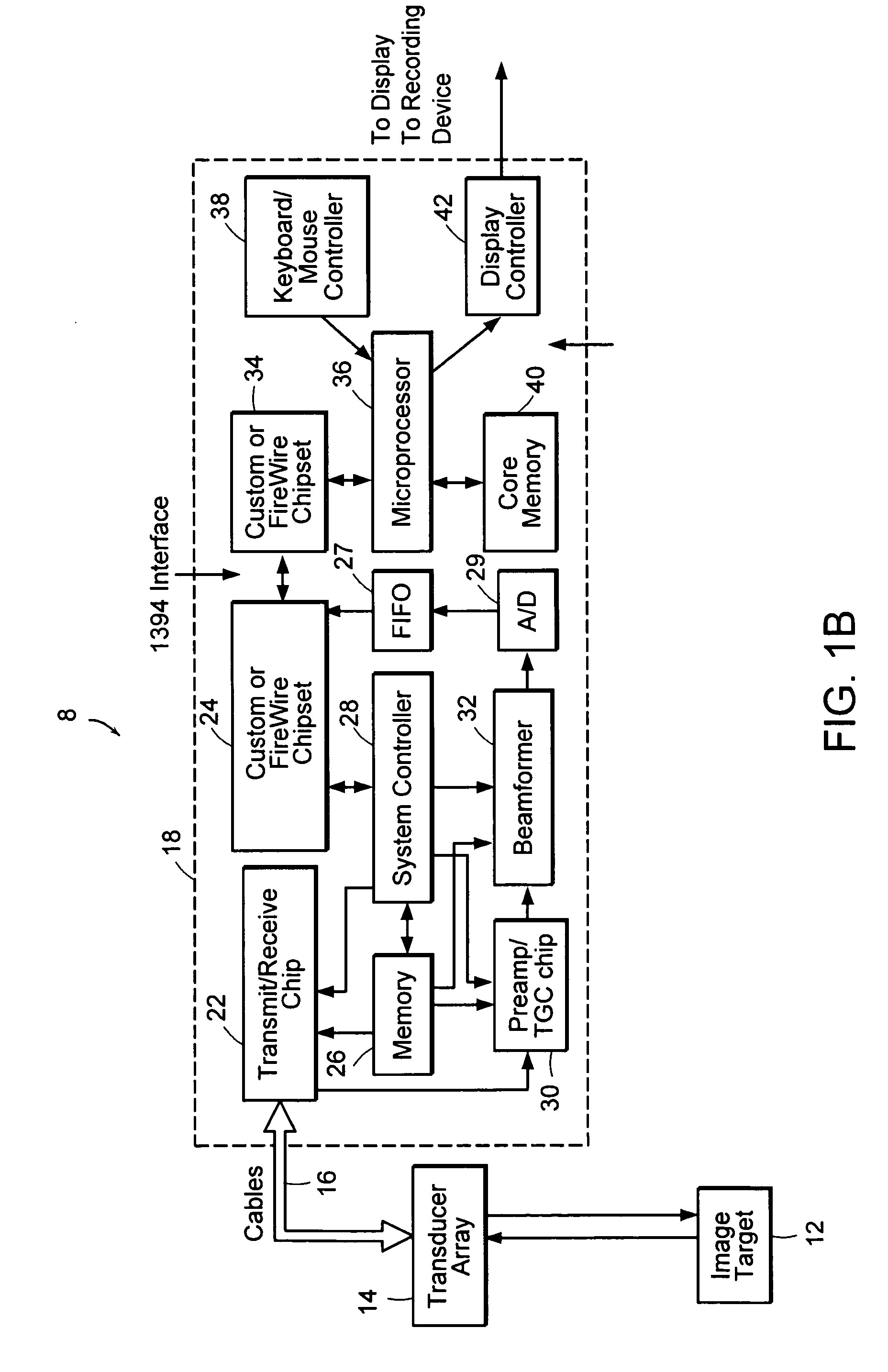
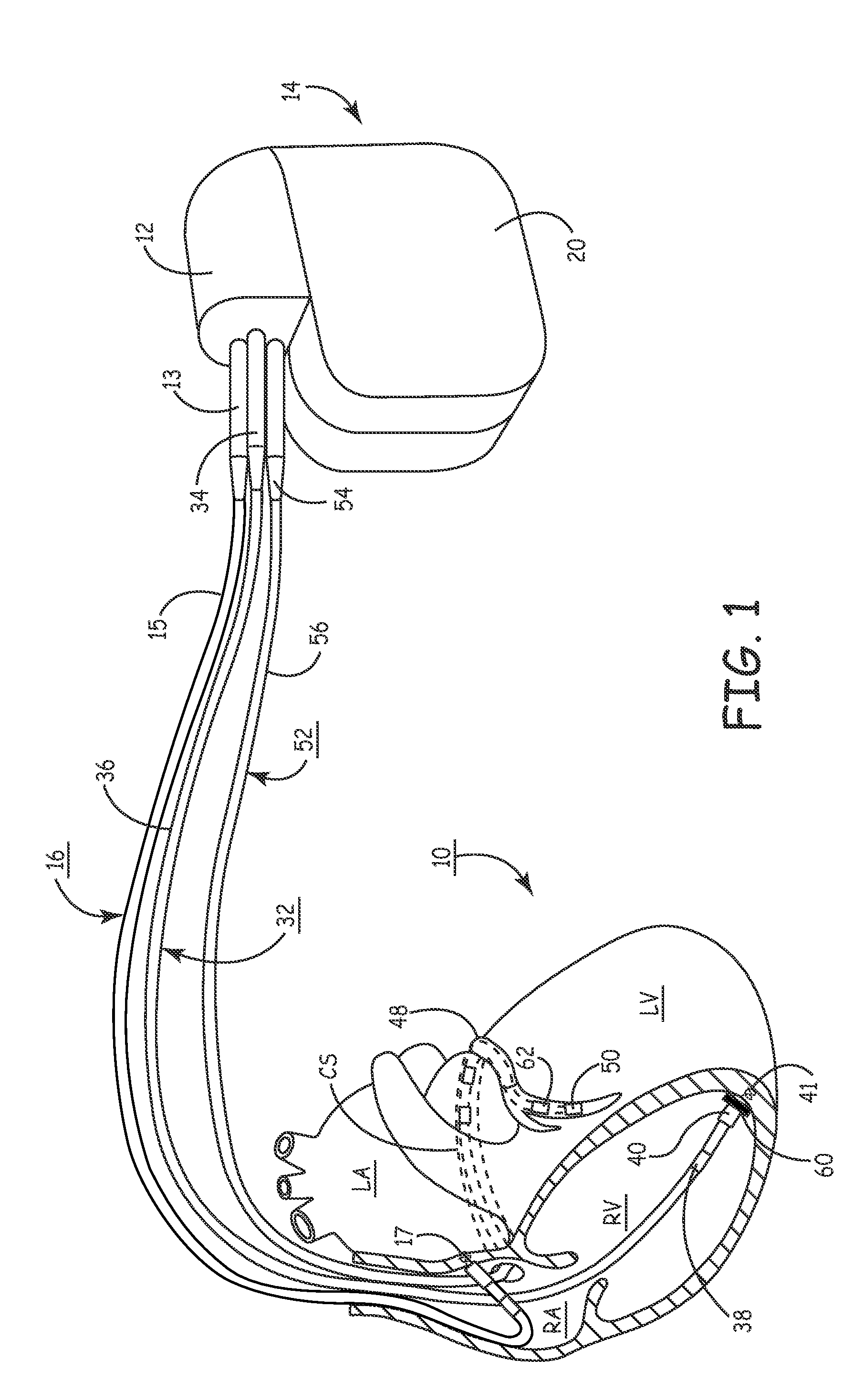
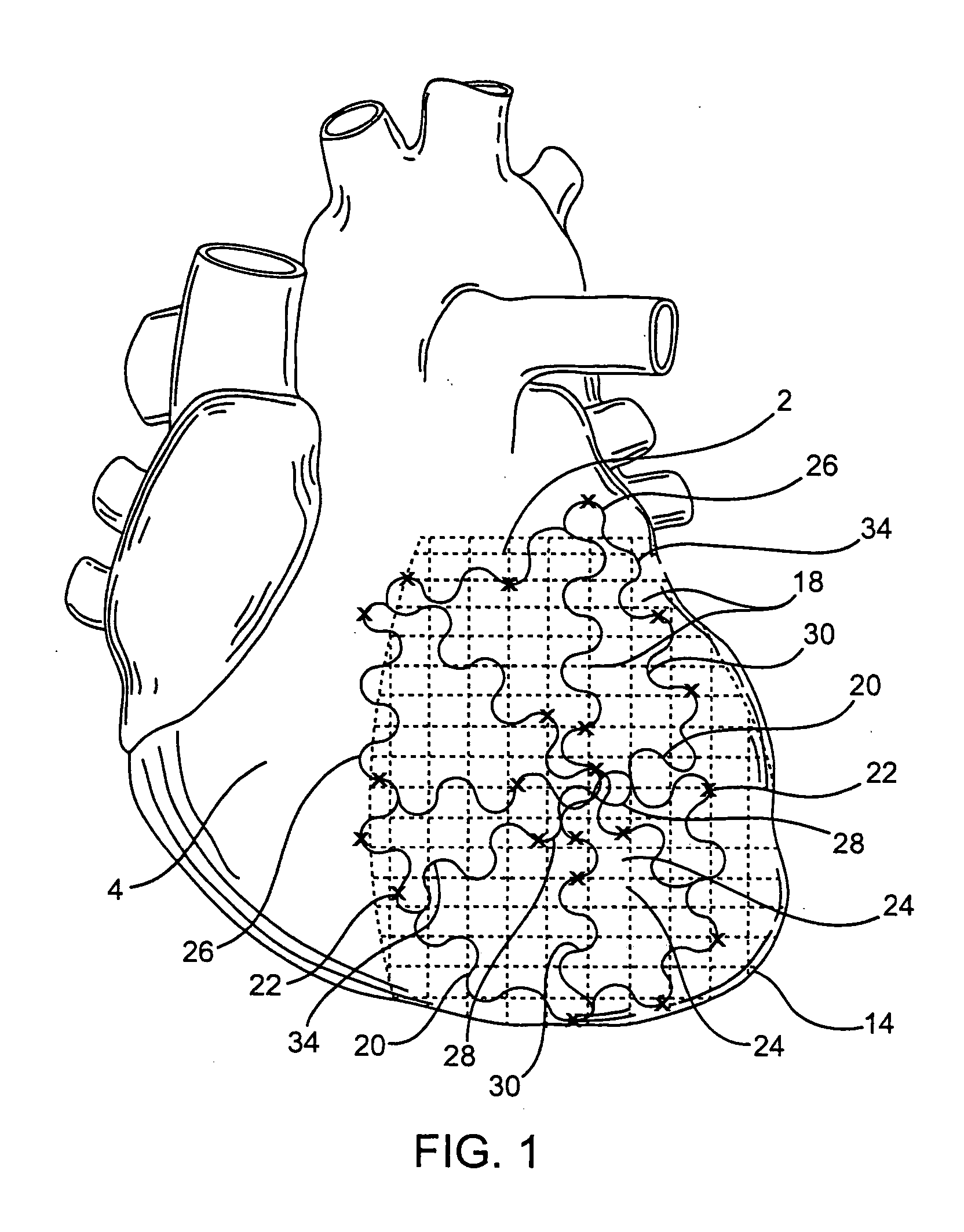
Method for mapping heart electrophysiology
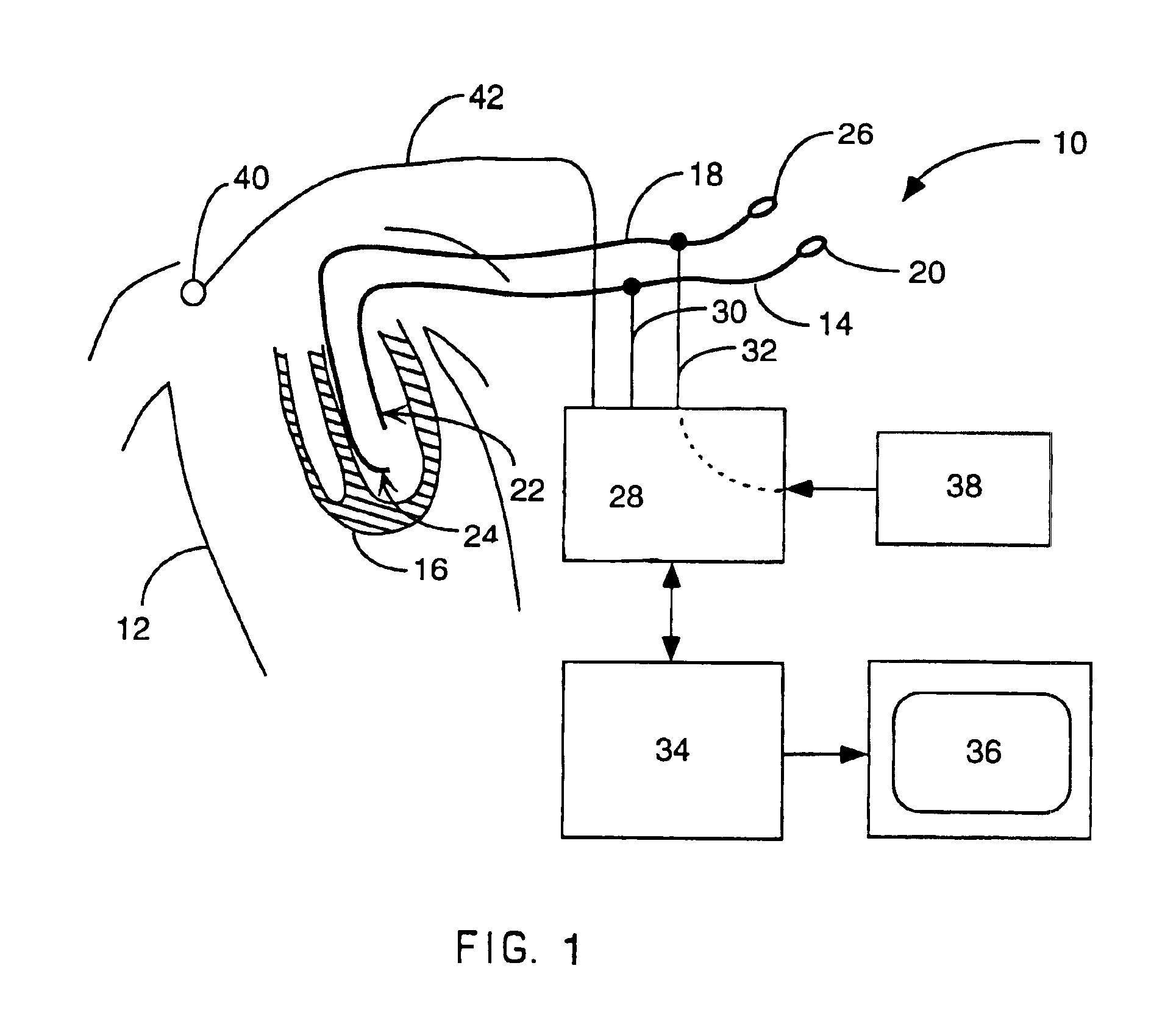
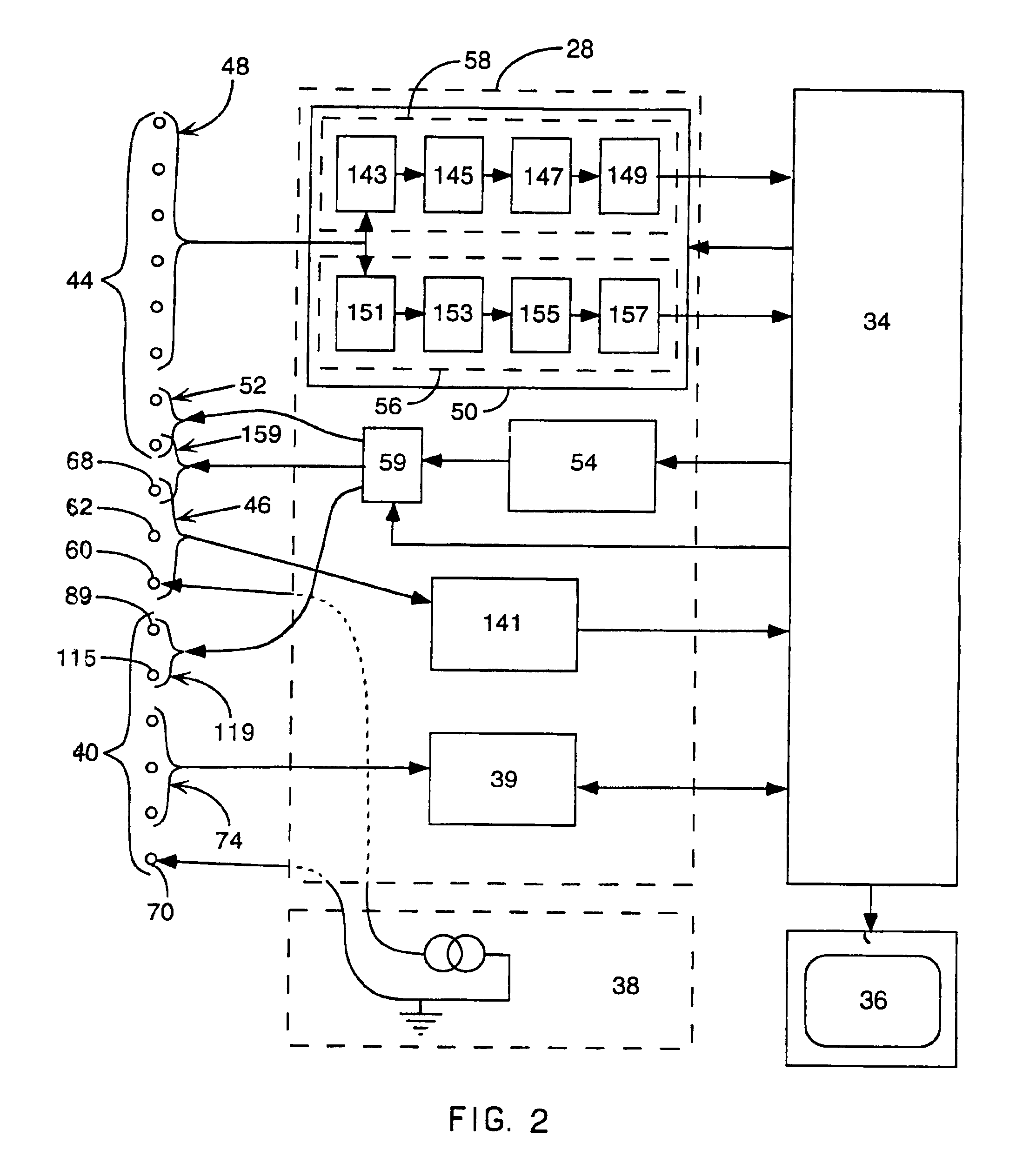
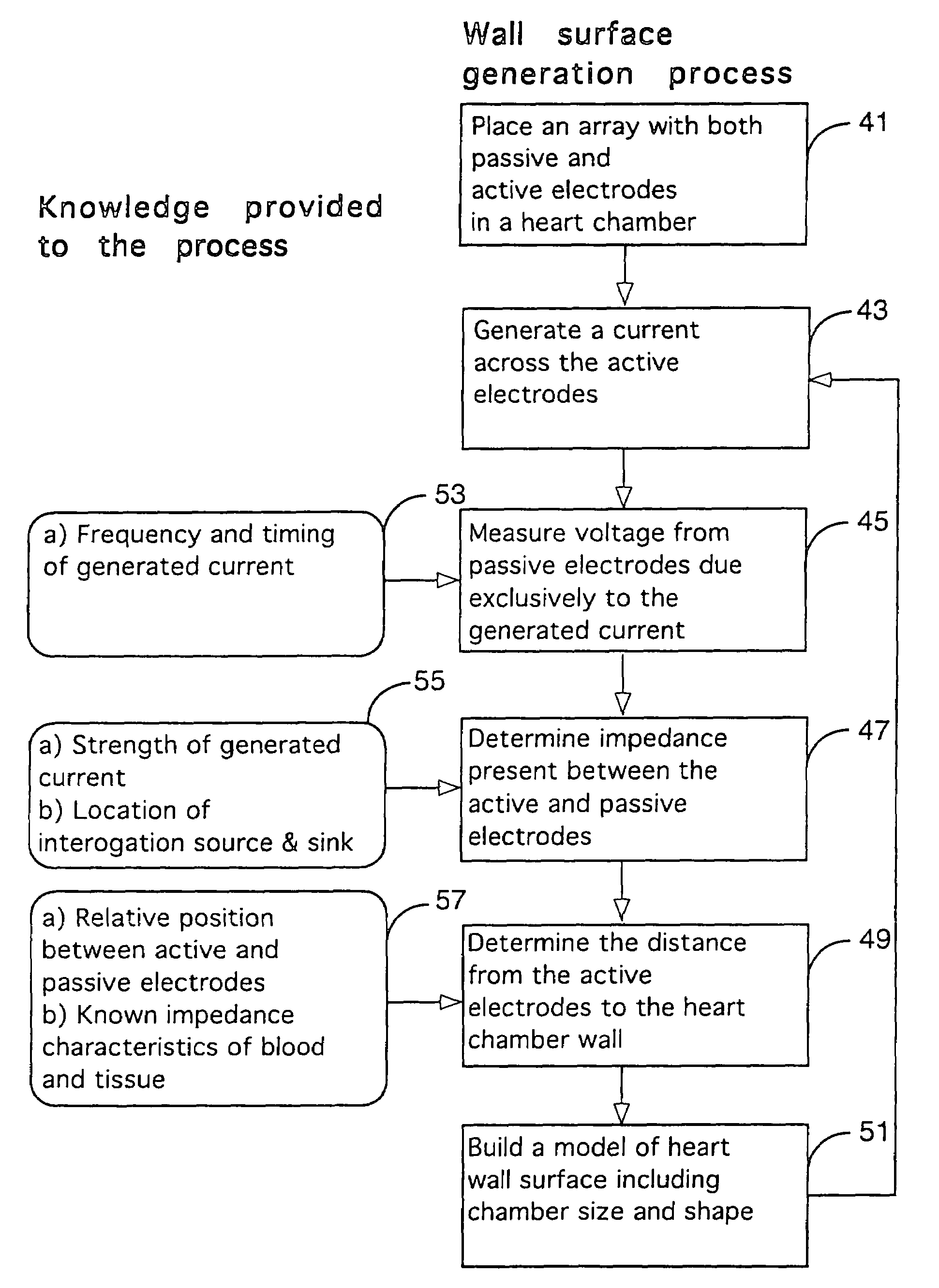
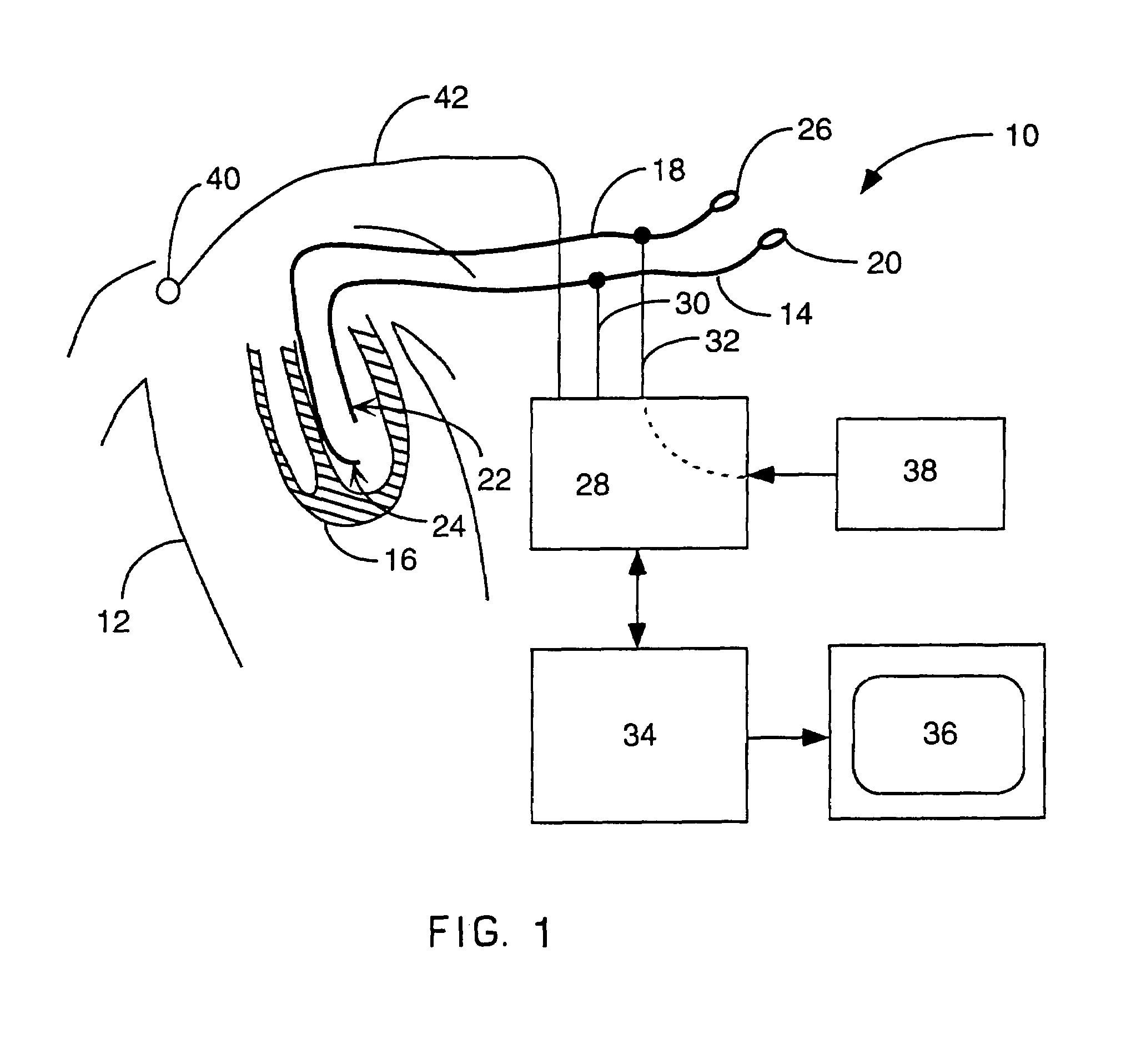
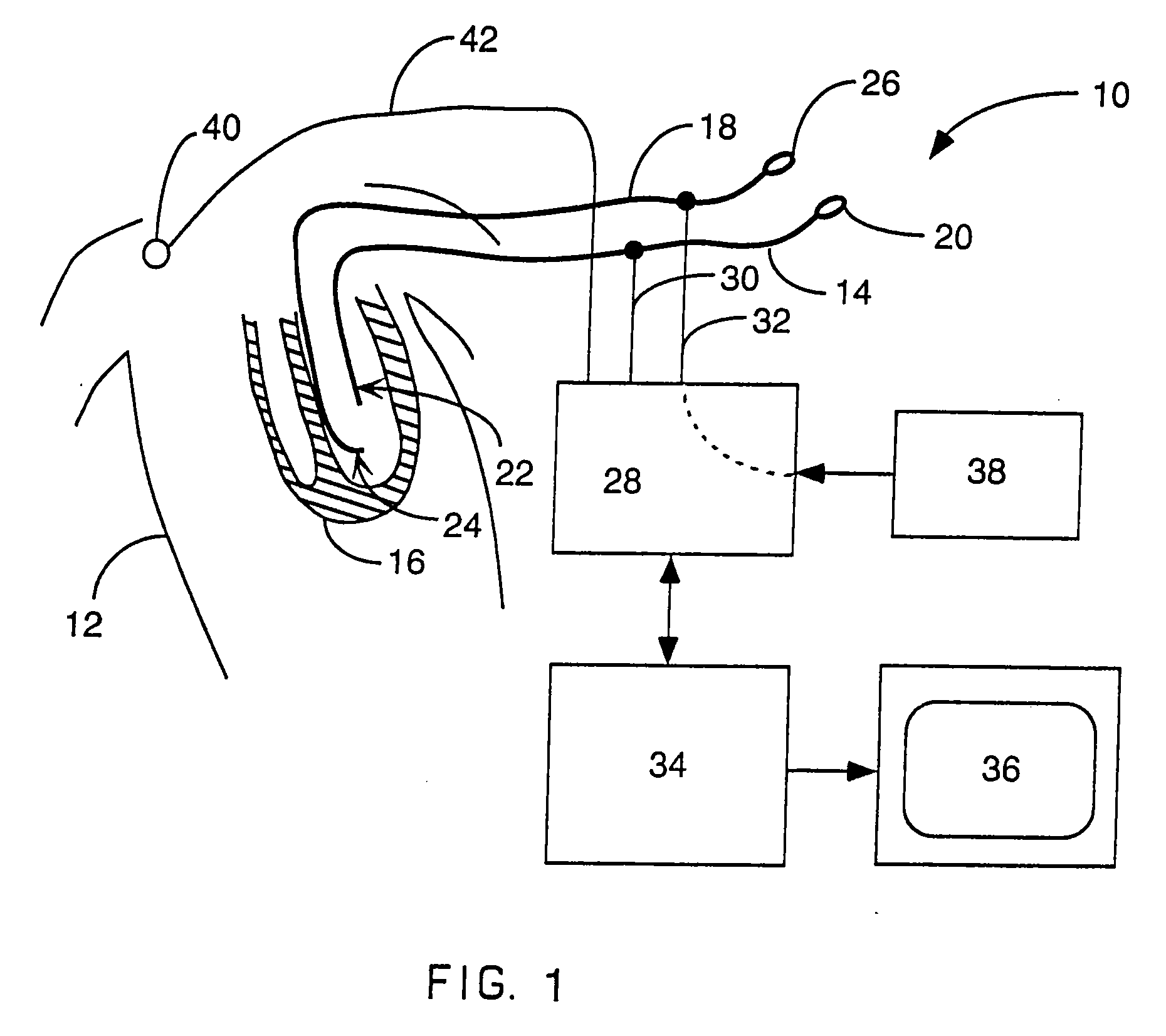
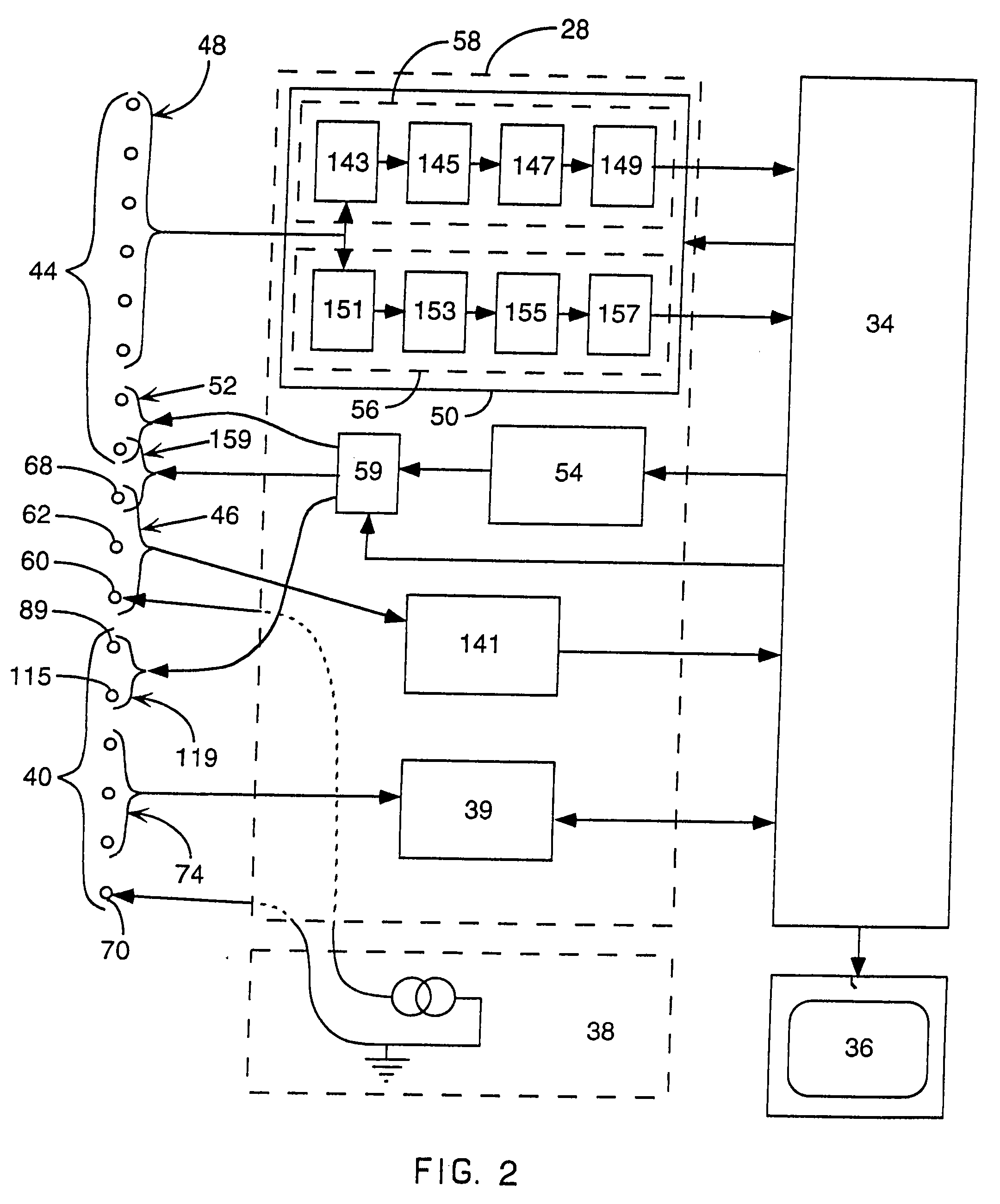
A mapping catheter is positioned in a heart chamber, and active electrode sites are activated to impose an electric field within the chamber. The blood volume and wall motion modulates the electric field, which is detected by passive electrode sites on the preferred catheter. Electrophysiology measurements, as well as geometry measurements, are taken from the passive electrodes and used to display a map of intrinsic heart activity.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
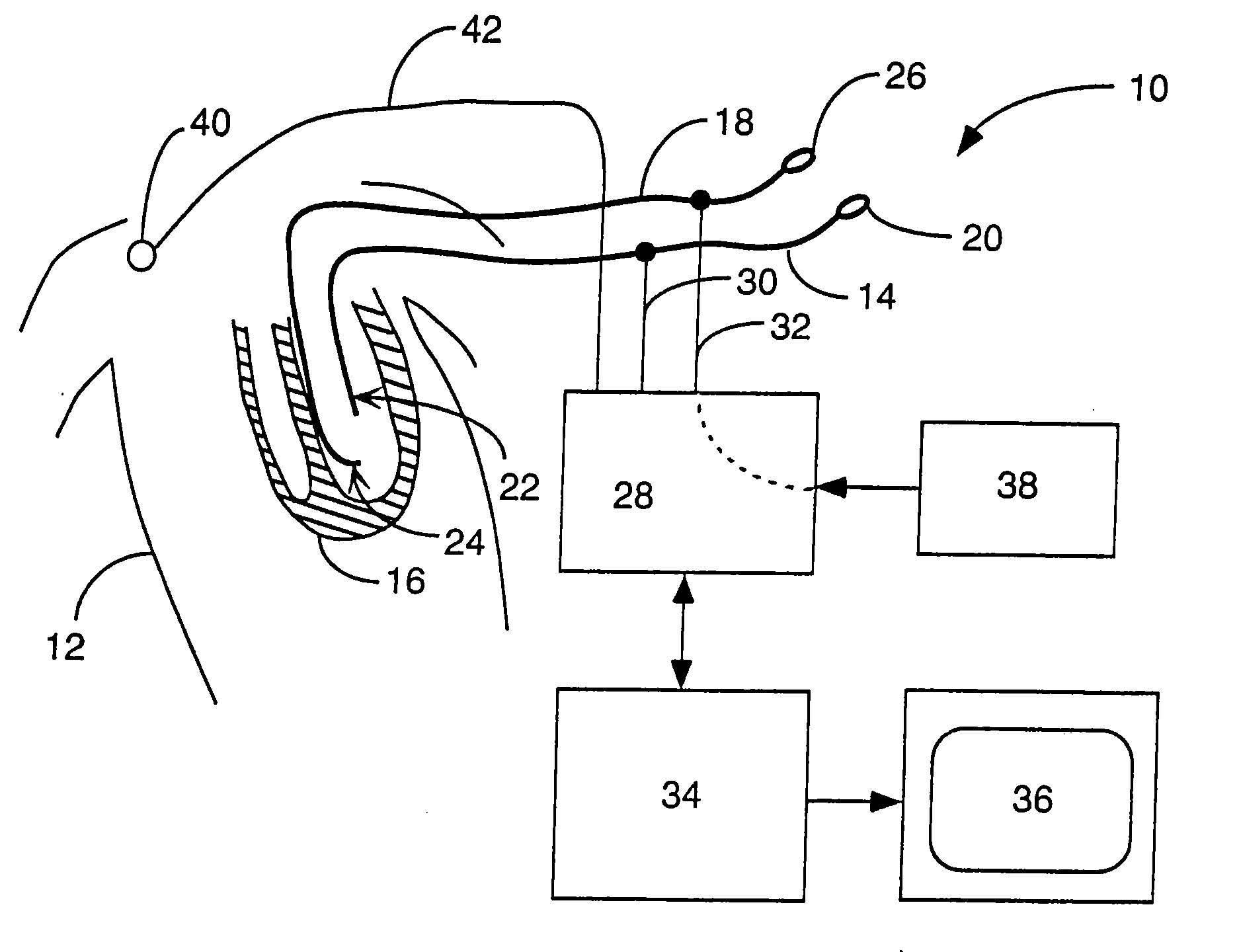
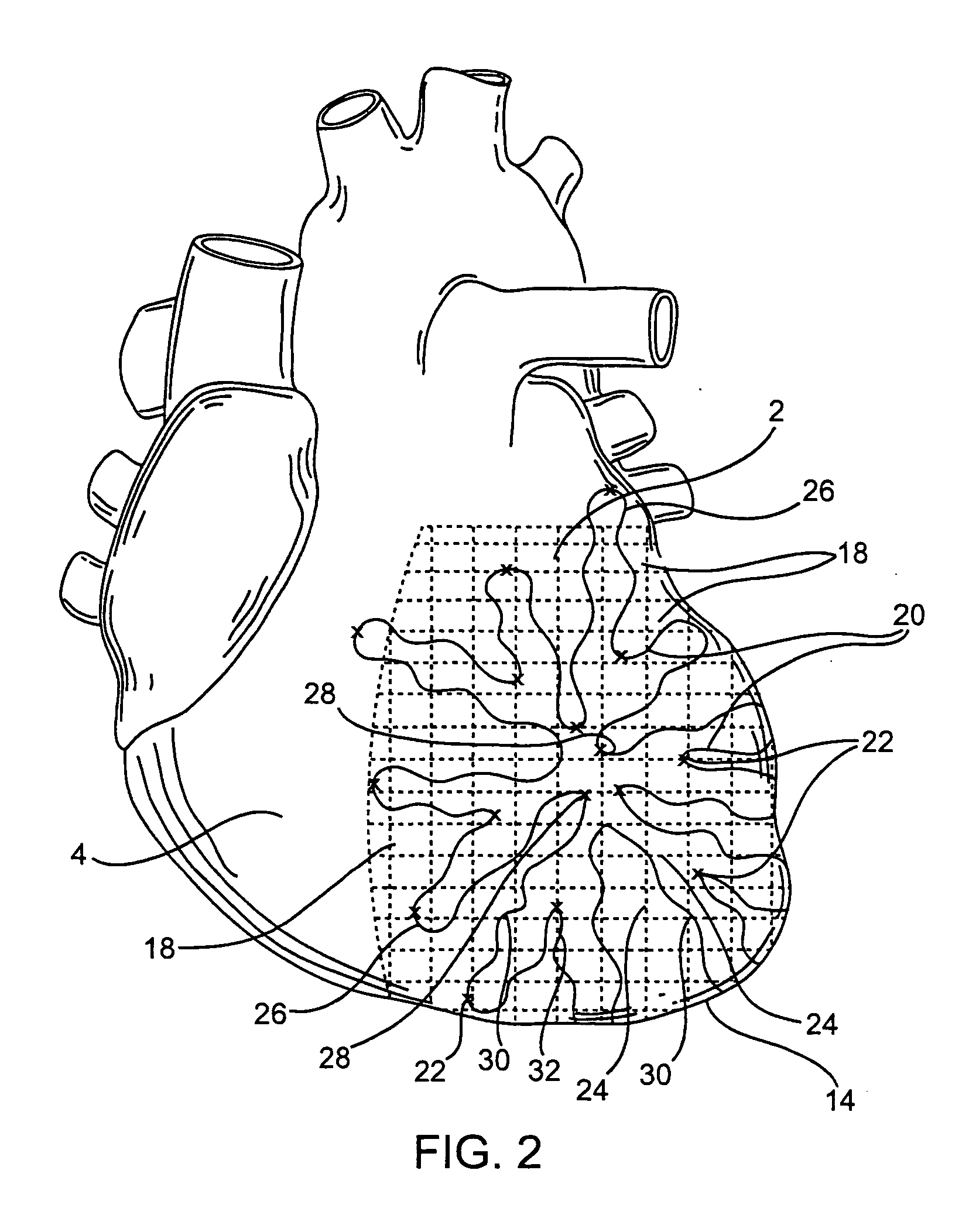
Interface system for endocardial mapping catheter
A mapping catheter is positioned in a heart chamber, and active electrode sites are activated to impose an electric field within the chamber. The blood volume and wall motion modulates the electric field, which is detected by passive electrode sites on the preferred catheter. Electrophysiology measurements, as well as geometry measurements, are taken from the passive electrodes and used to display a map of intrinsic heart activity.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Method for measuring heart electrophysiology
A mapping catheter is positioned in a heart chamber, and active electrode sites are activated to impose an electric field within the chamber. The blood volume and wall motion modulates the electric field, which is detected by passive electrode sites on the preferred catheter. Electrophysiology measurements, as well as geometry measurements, are taken from the passive electrodes and used to display a map of intrinsic heart activity.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
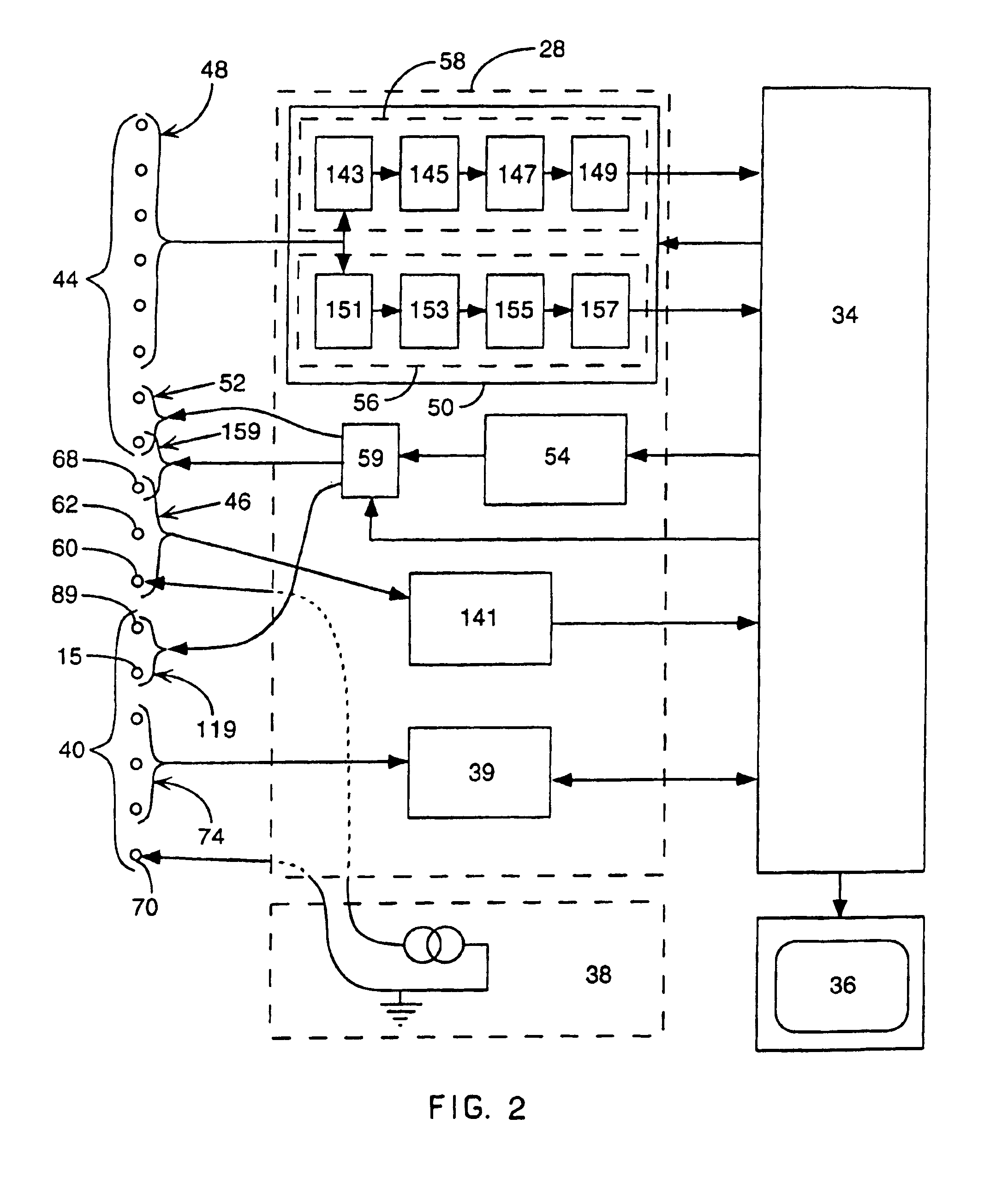
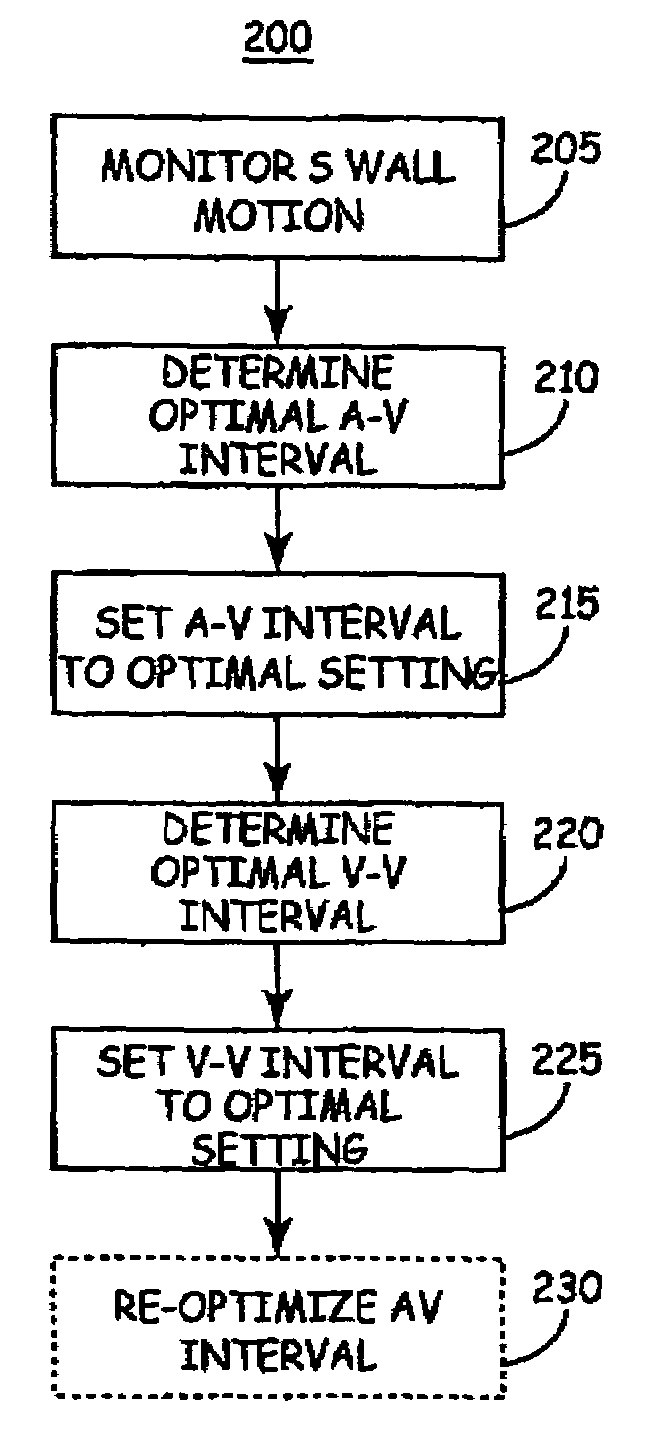
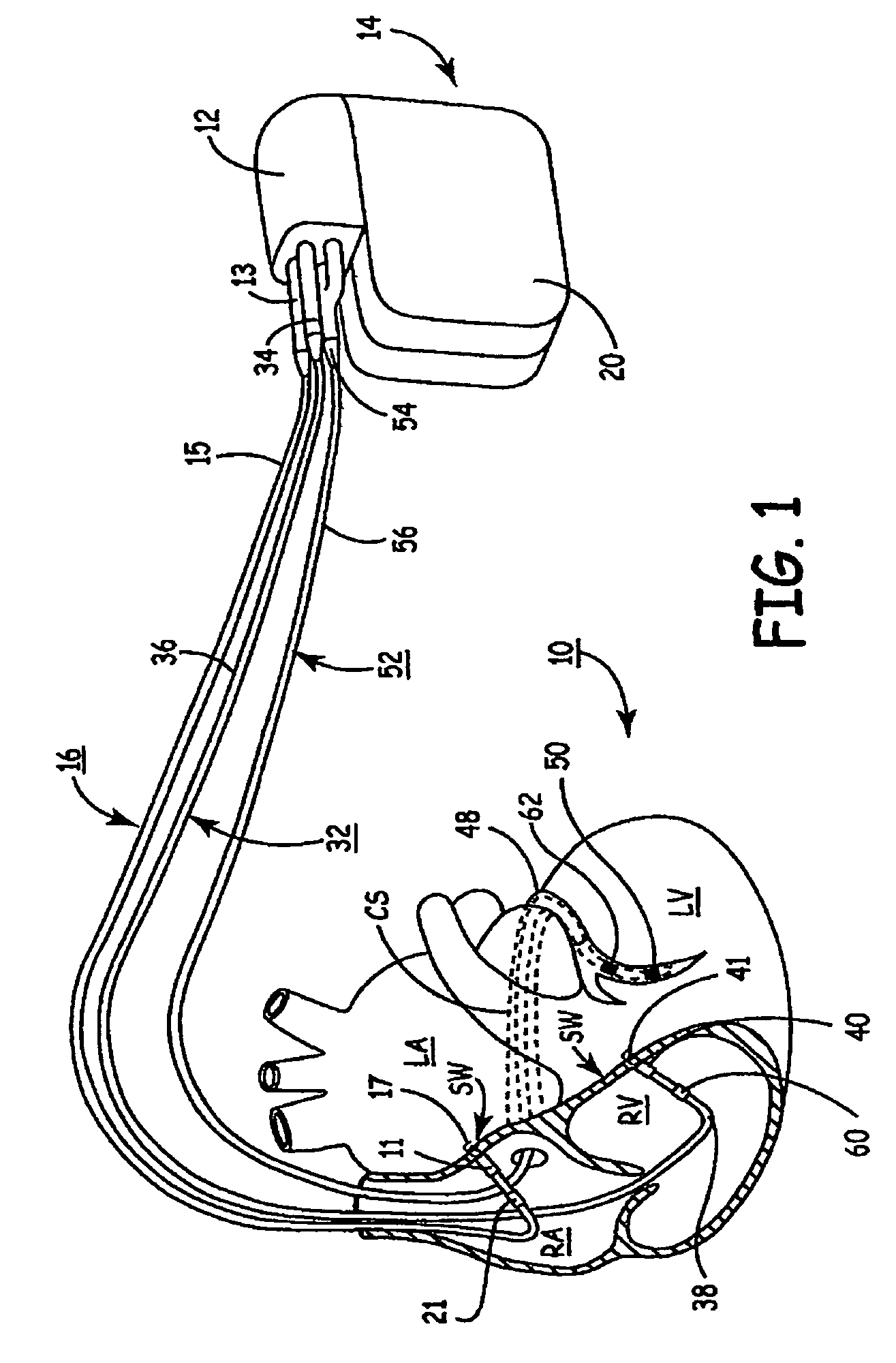
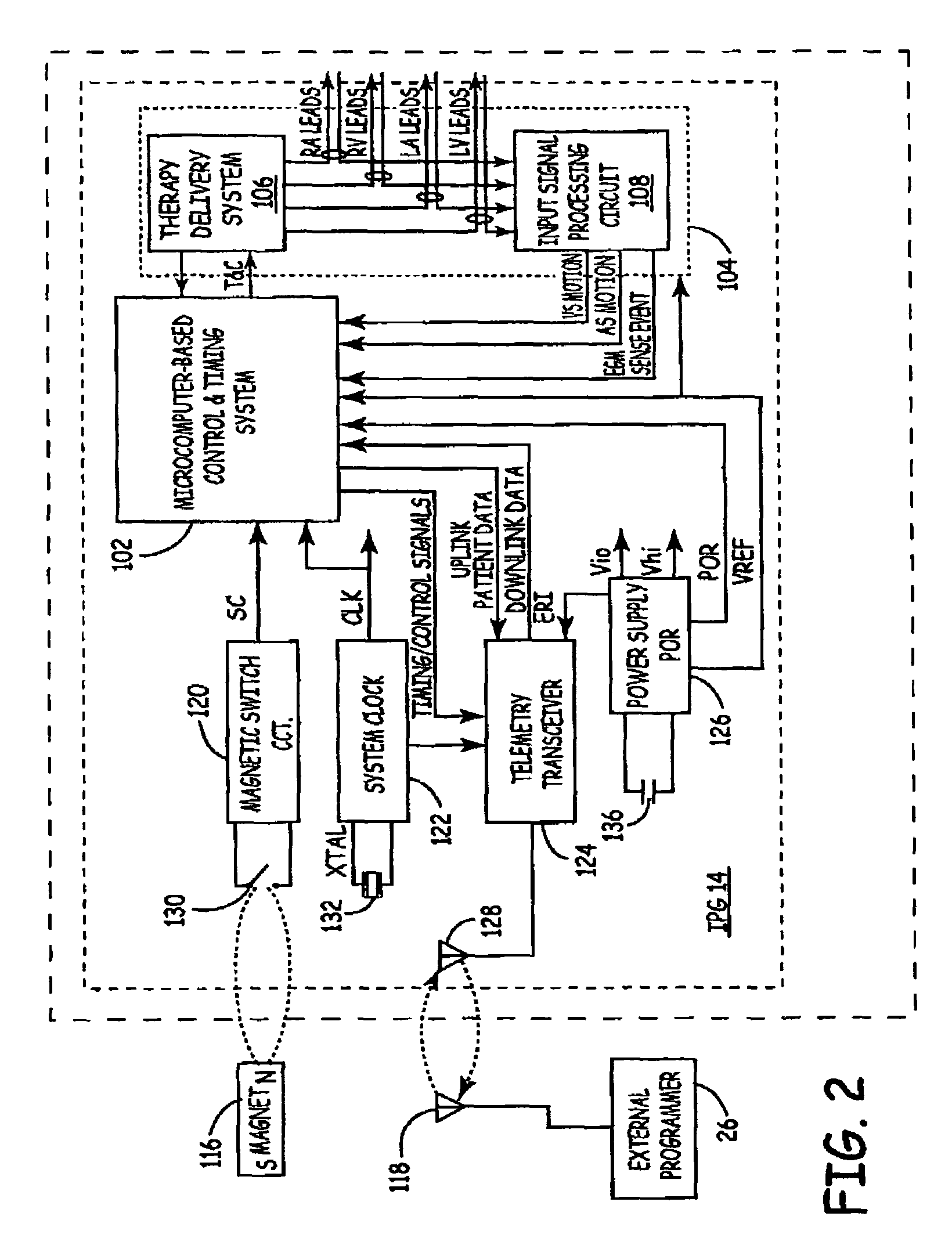
Method of optimizing cardiac resynchronization therapy using sensor signals of septal wall motion
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
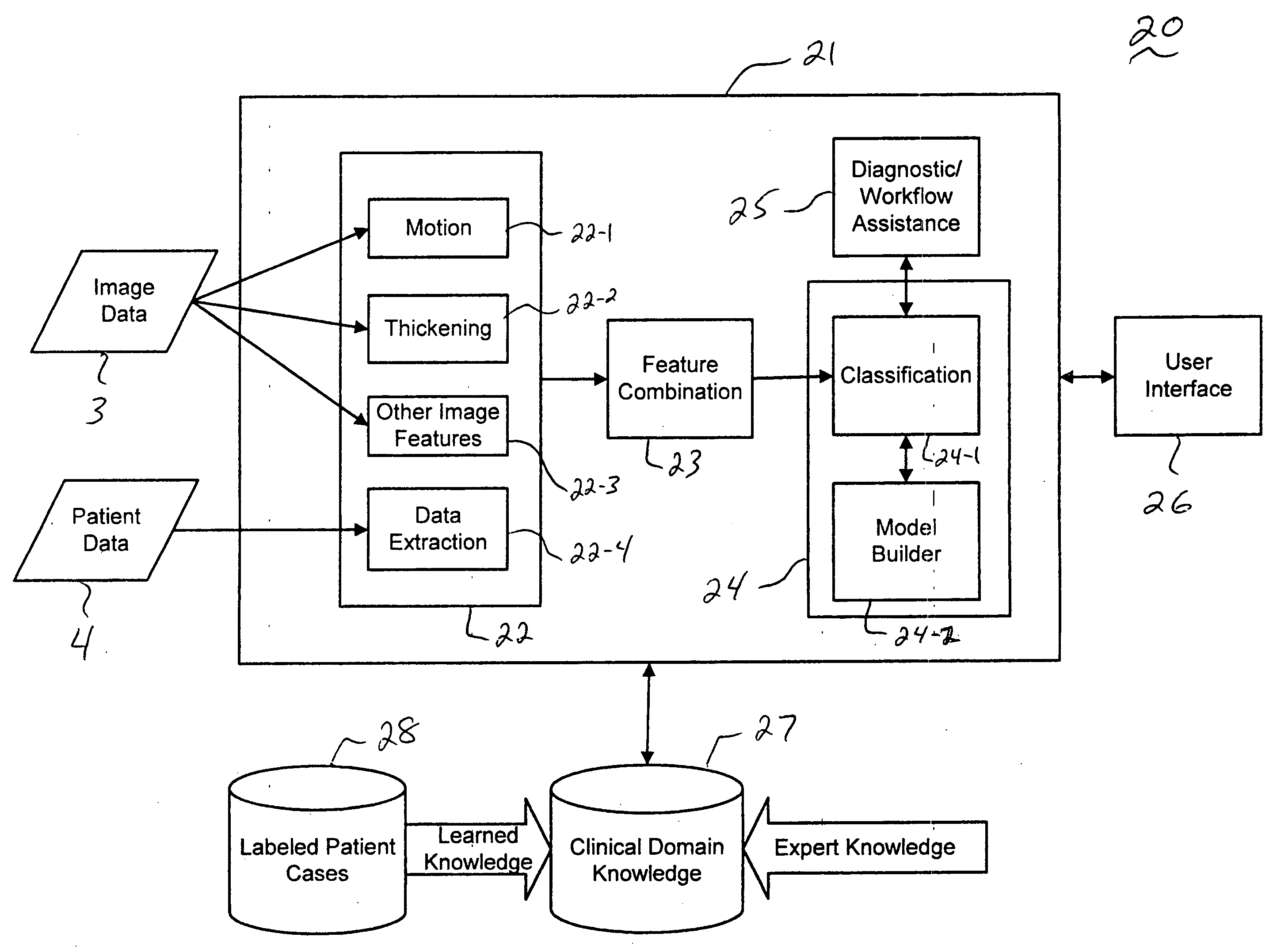
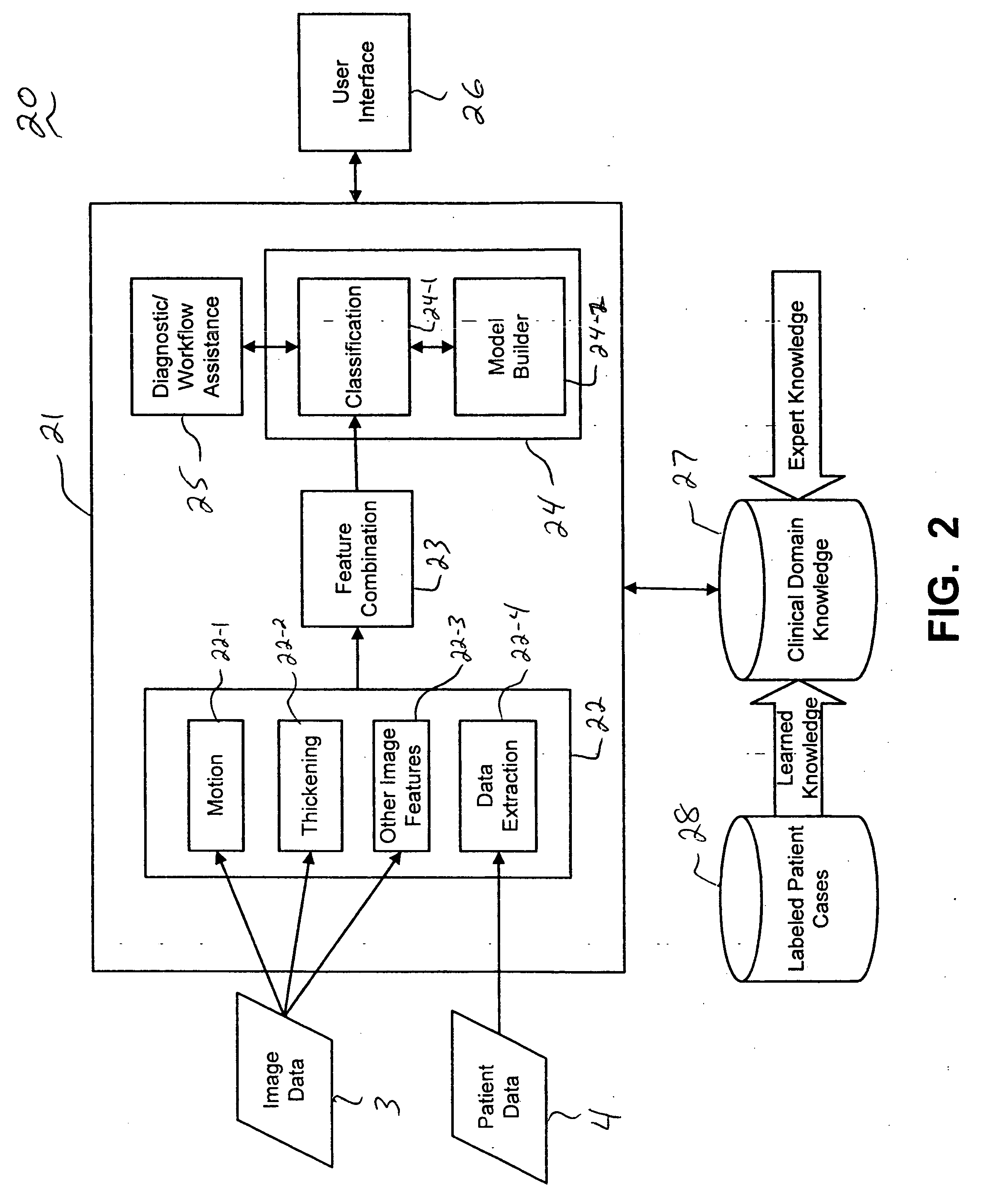
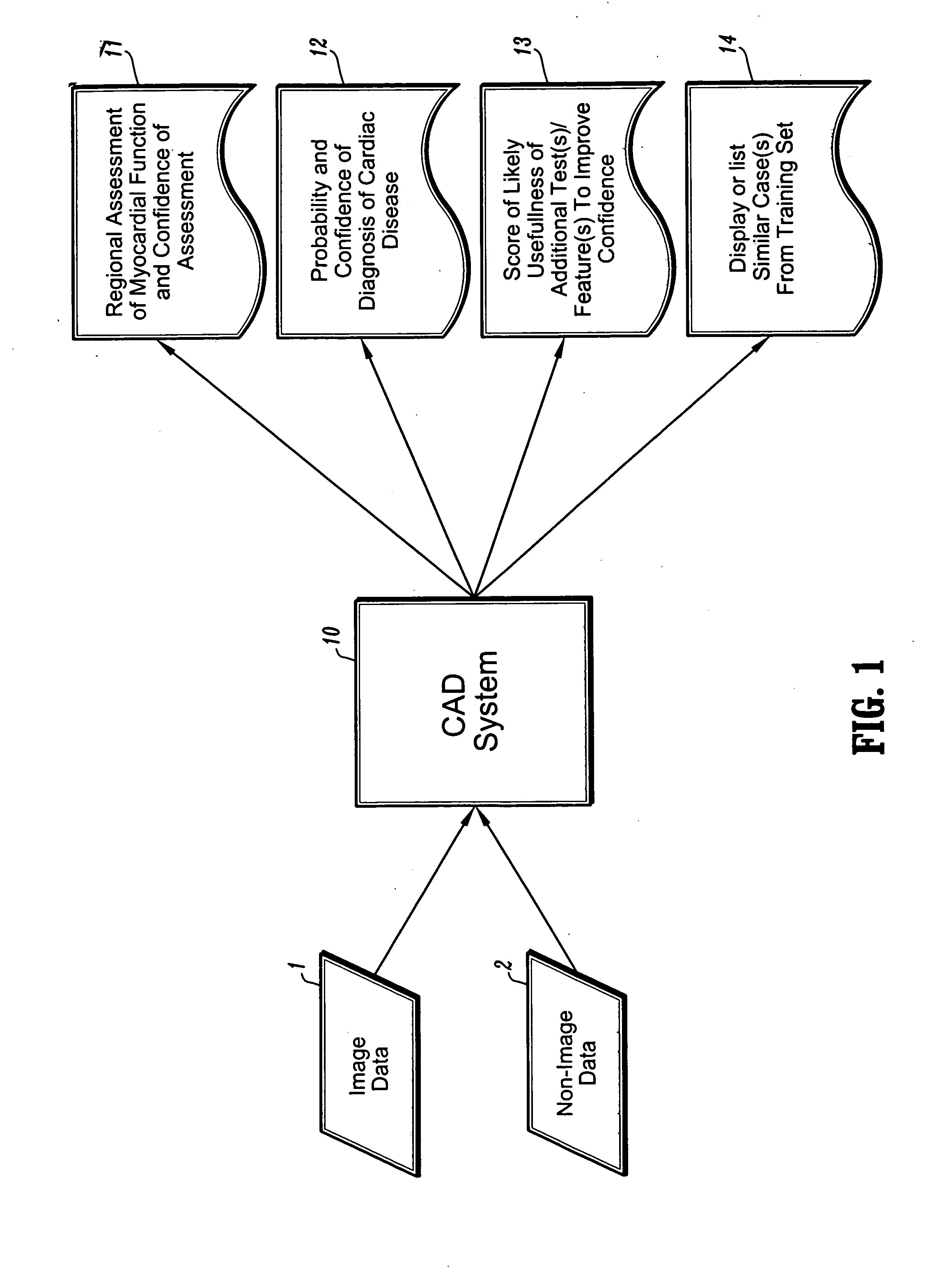
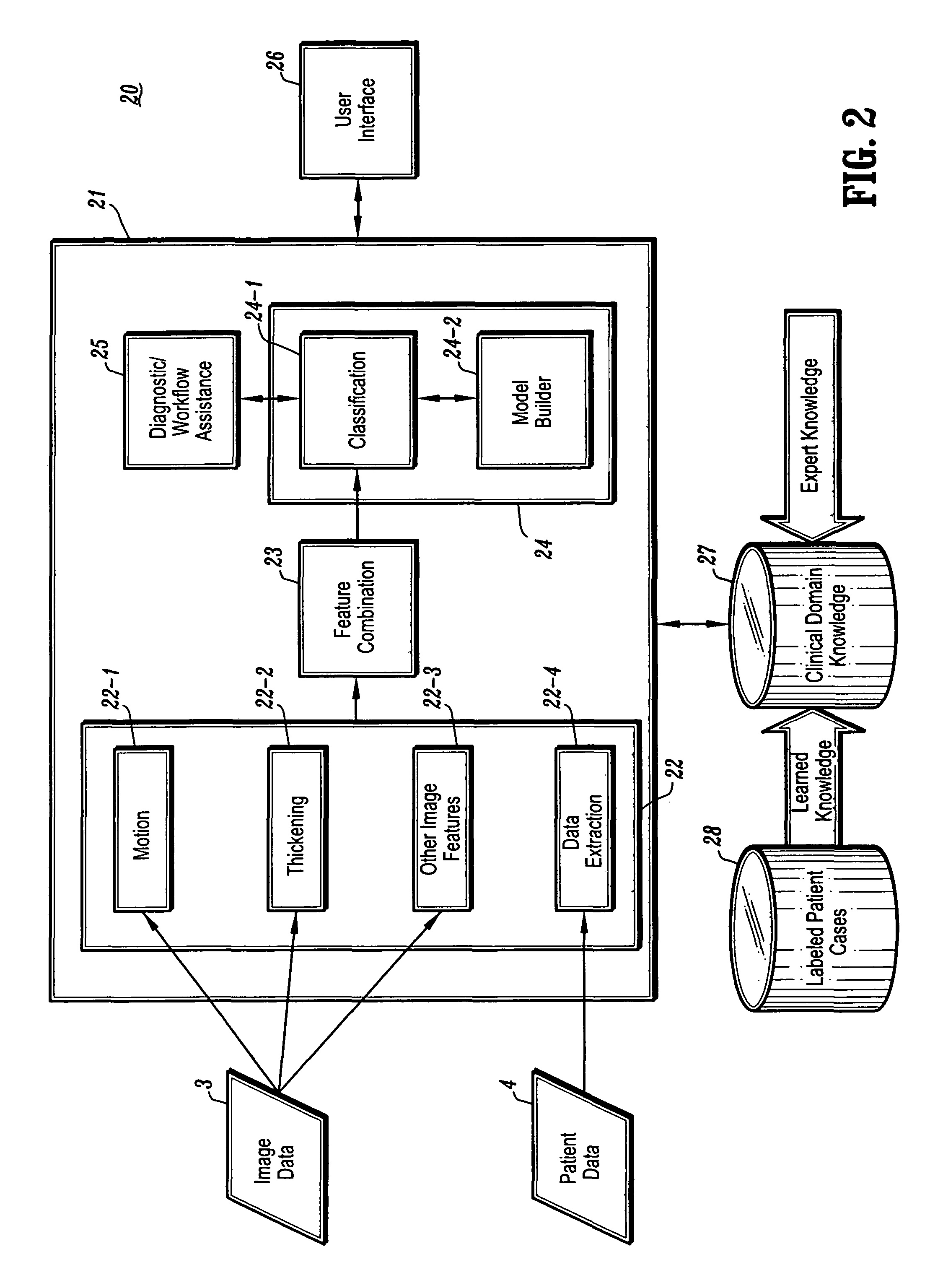
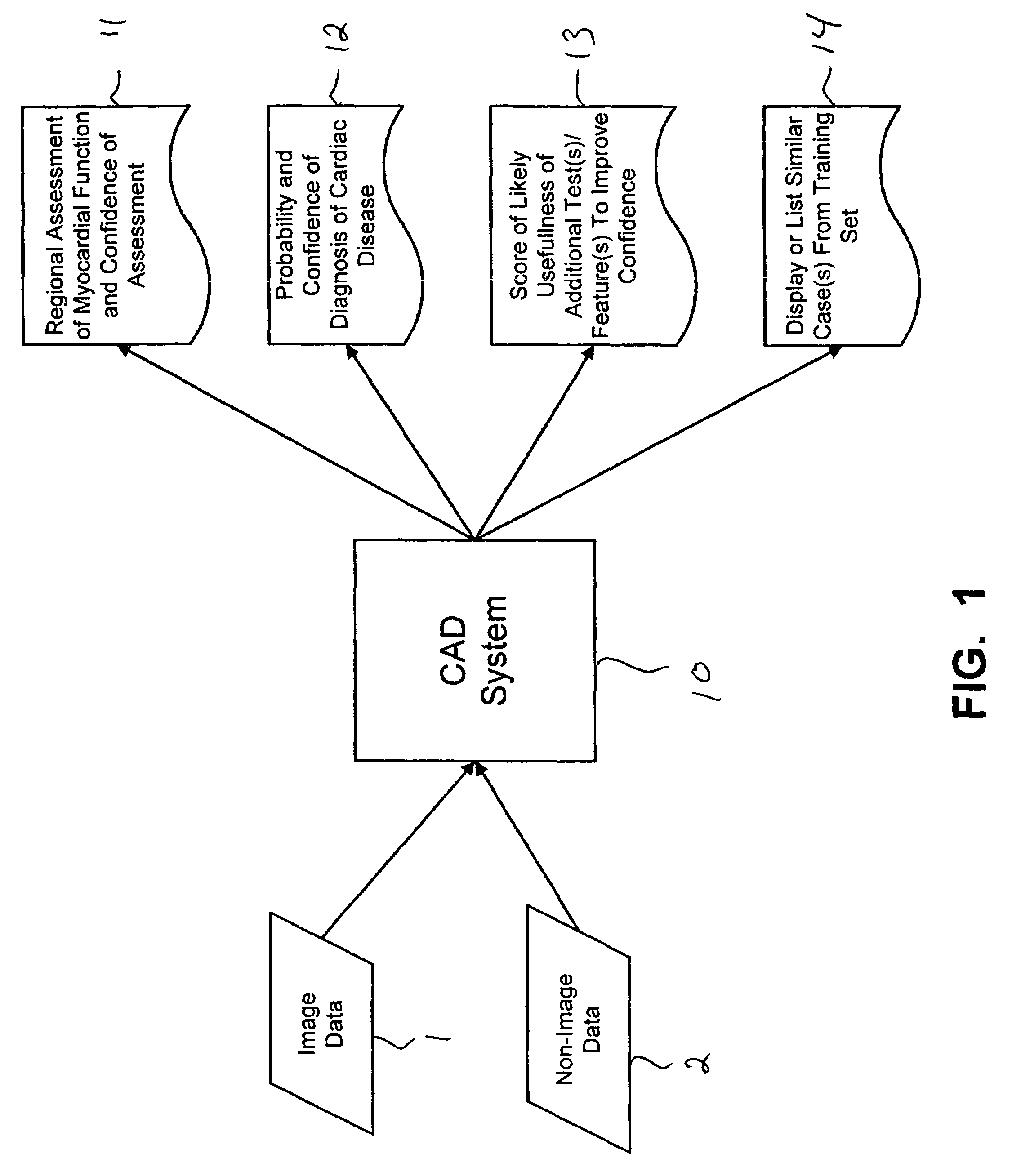
Systems and methods for providing automated regional myocardial assessment for cardiac imaging
ActiveUS20050059876A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementMedical recordAcquired characteristic
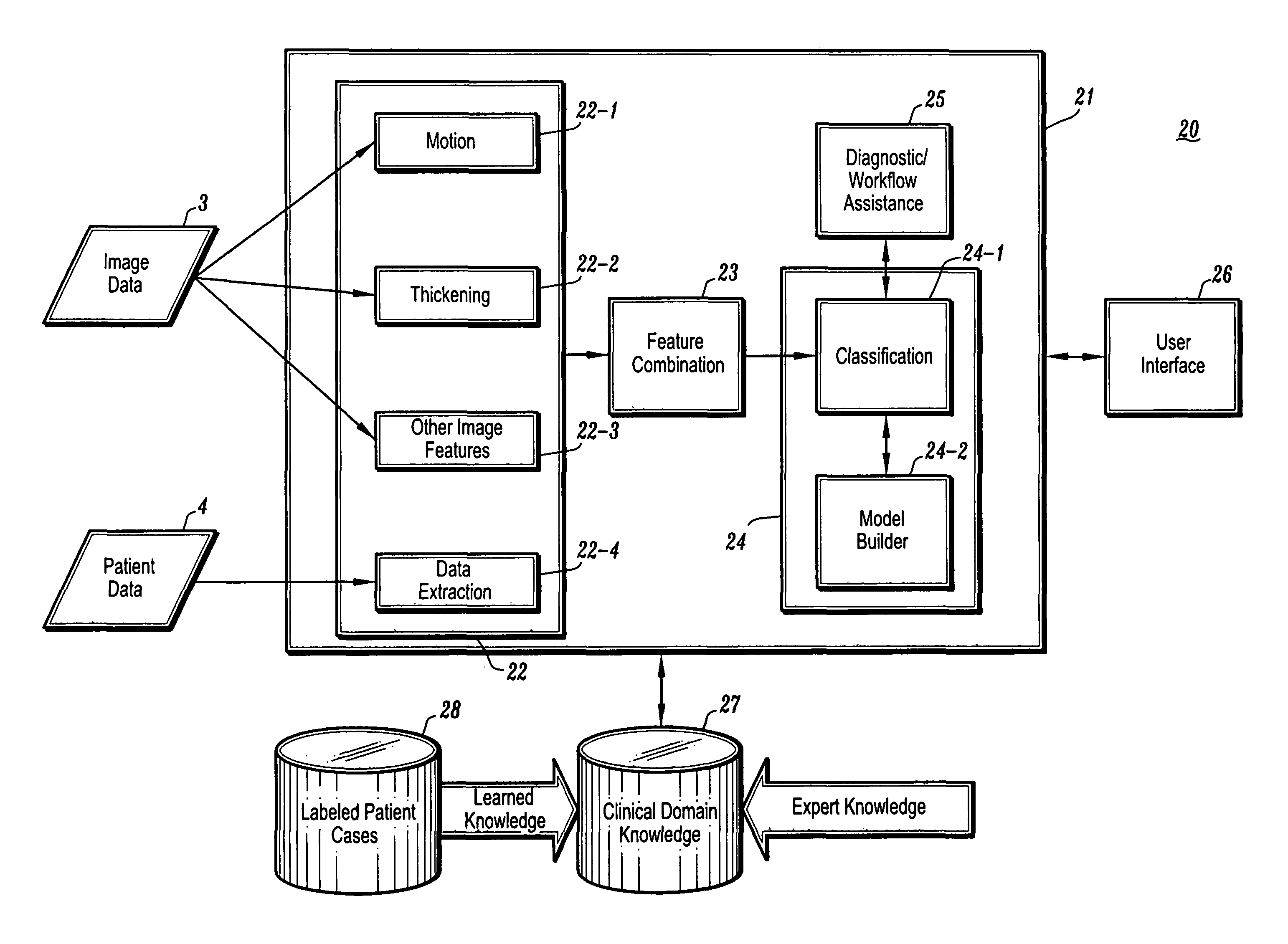
Systems and methods are provided for automated assessment of regional myocardial function using wall motion analysis methods that analyze various features / parameters of patient information (image data and non-image data) obtained from medical records of a patient. For example, a method for providing automatic diagnostic support for cardiac imaging generally comprises obtaining image data of a heart of a patient, obtaining features from the image data of the heart, which are related to motion of the myocardium of the heart, and automatically assessing regional myocardial function of one or more regions of a myocardial wall using the obtained features.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
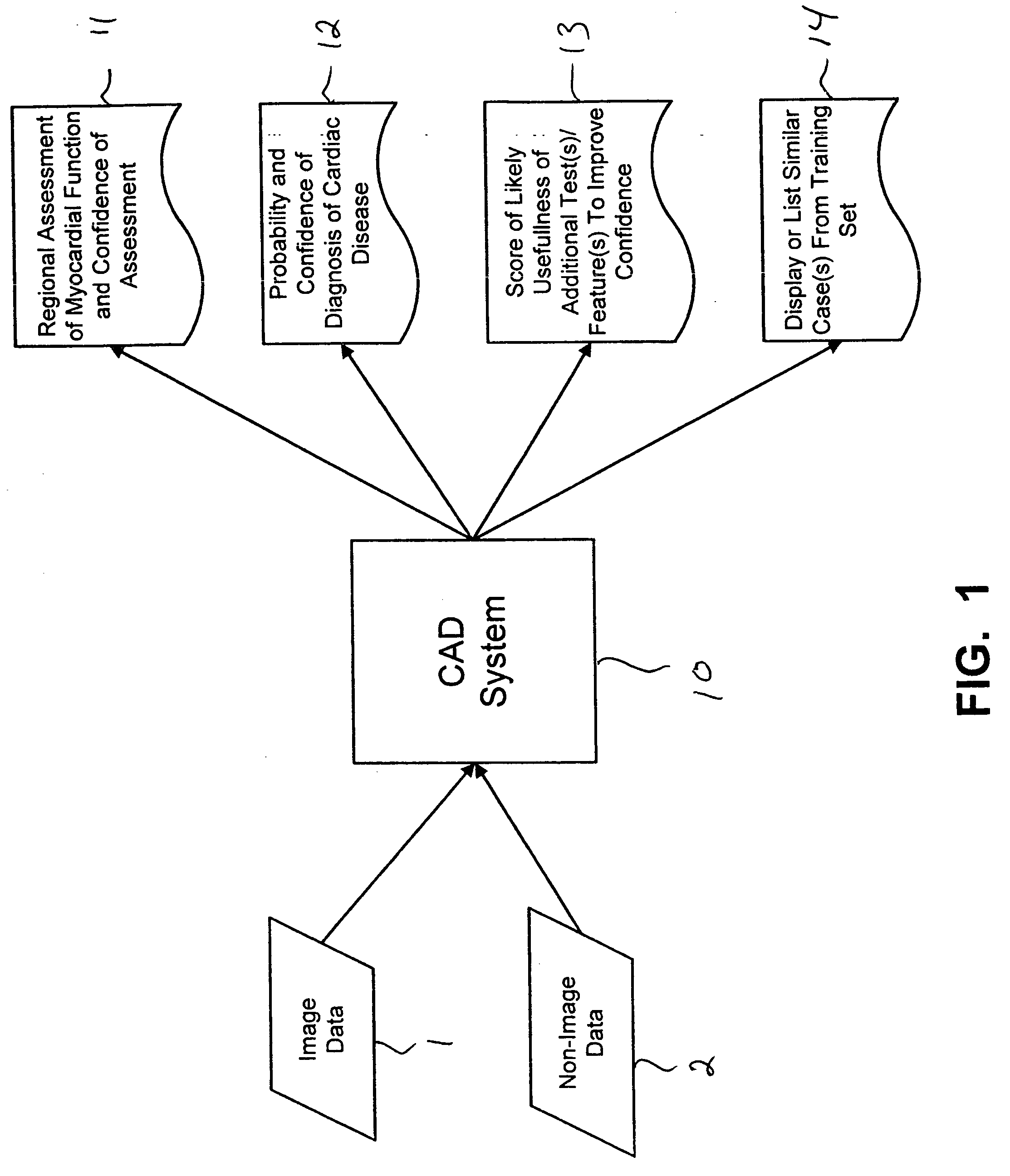
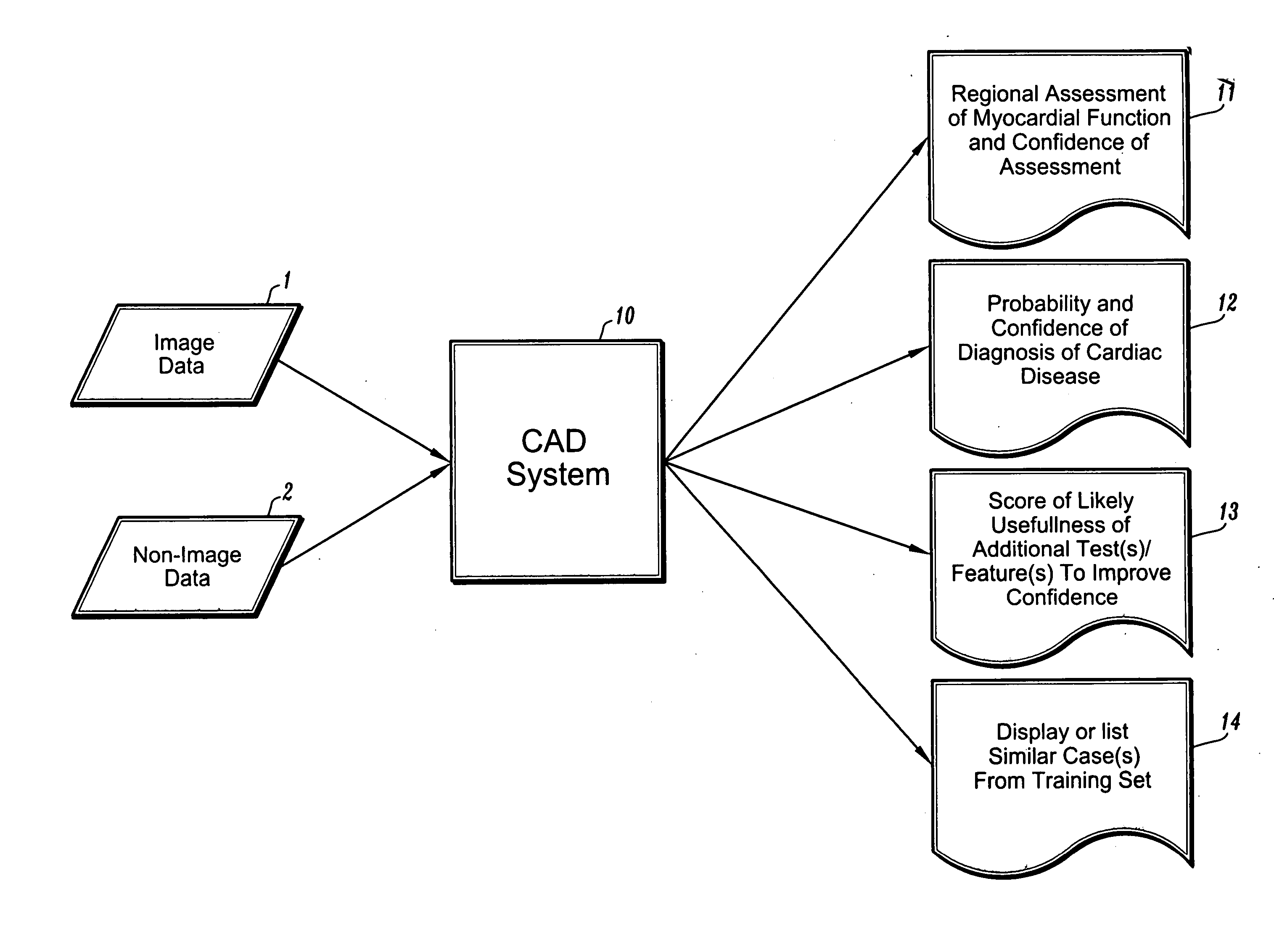
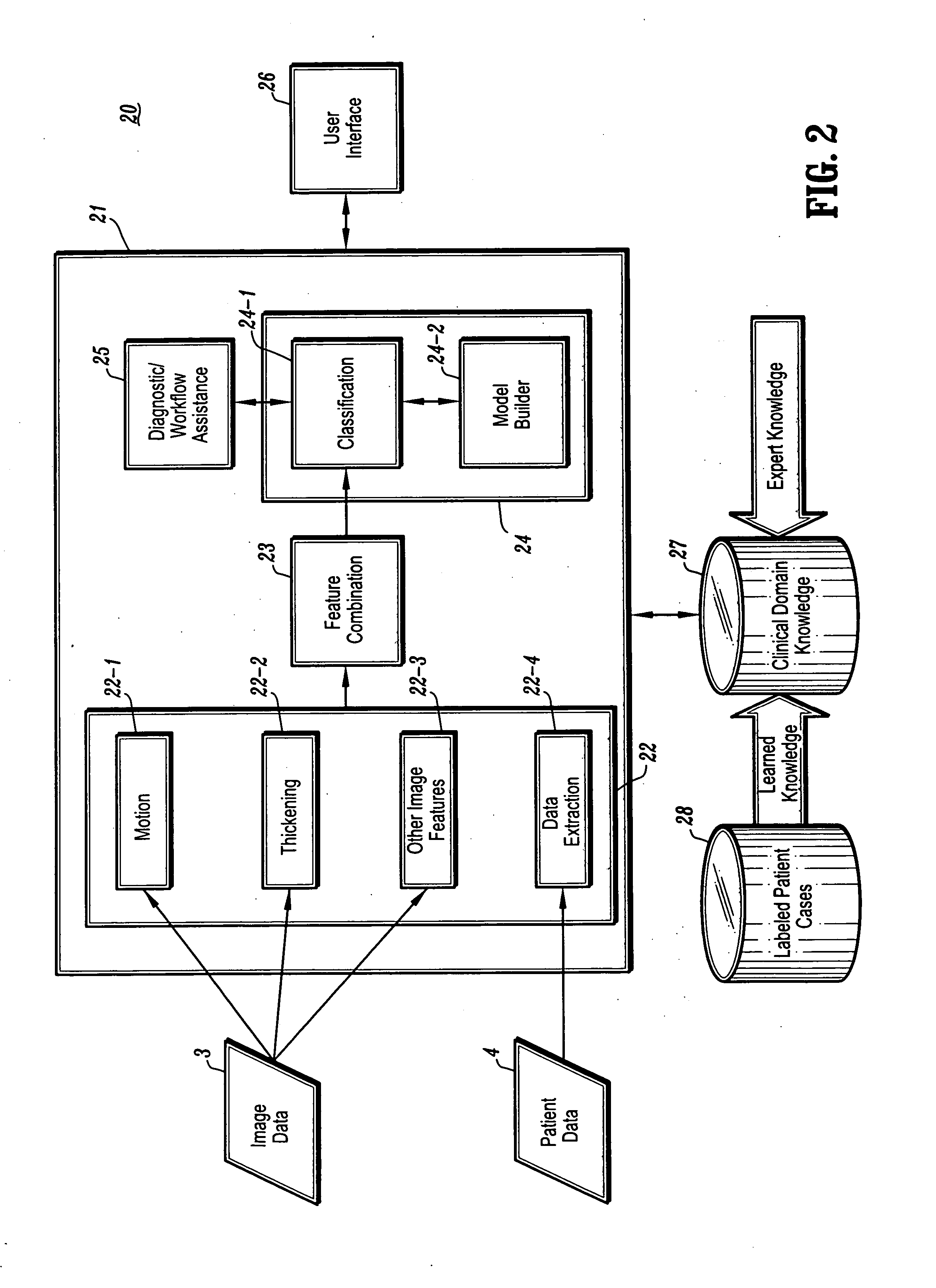
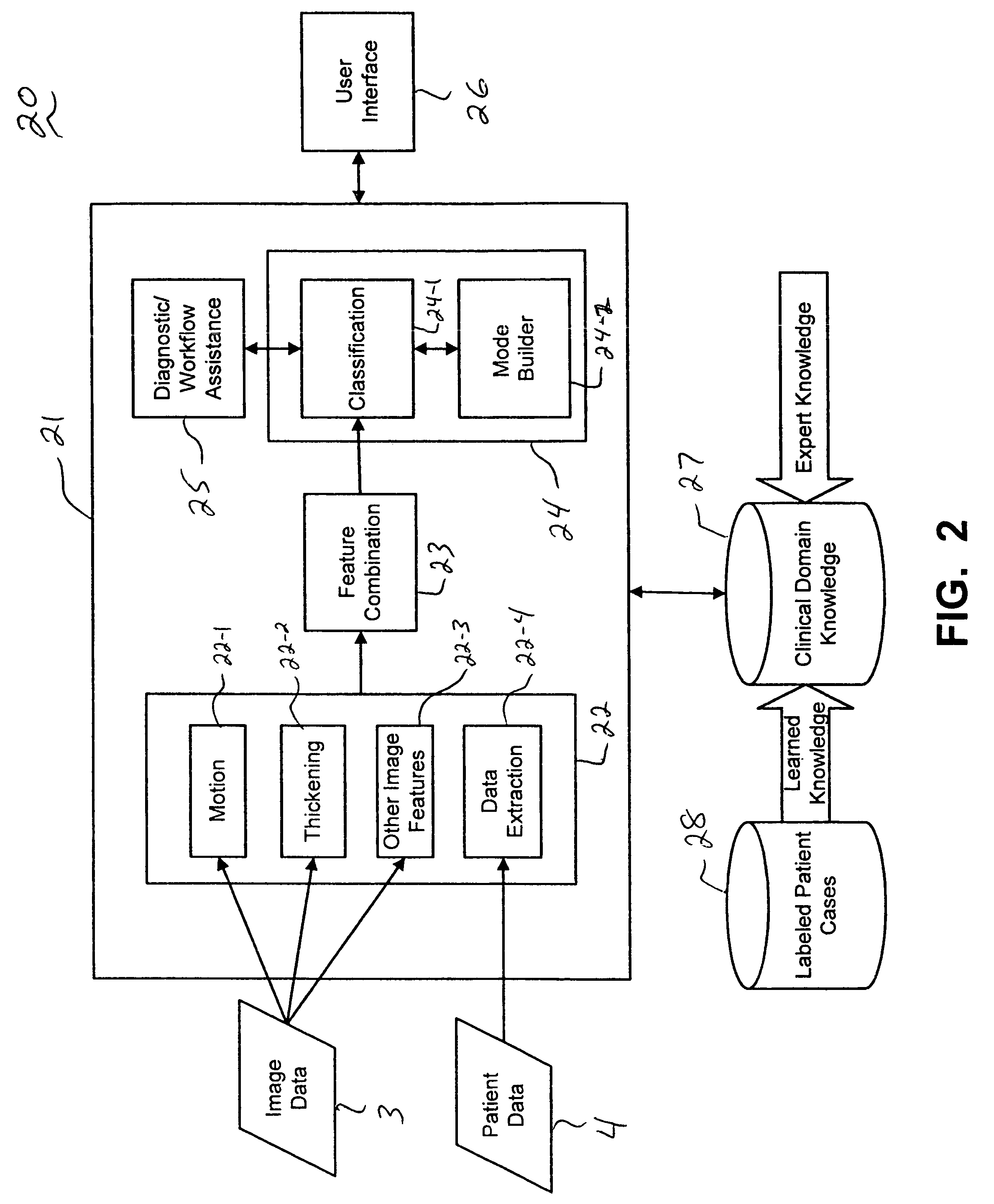
Systems and methods for automated diagnosis and decision support for heart related diseases and conditions
InactiveUS20050020903A1Character and pattern recognitionMedical automated diagnosisCoronary artery diseasePatient data
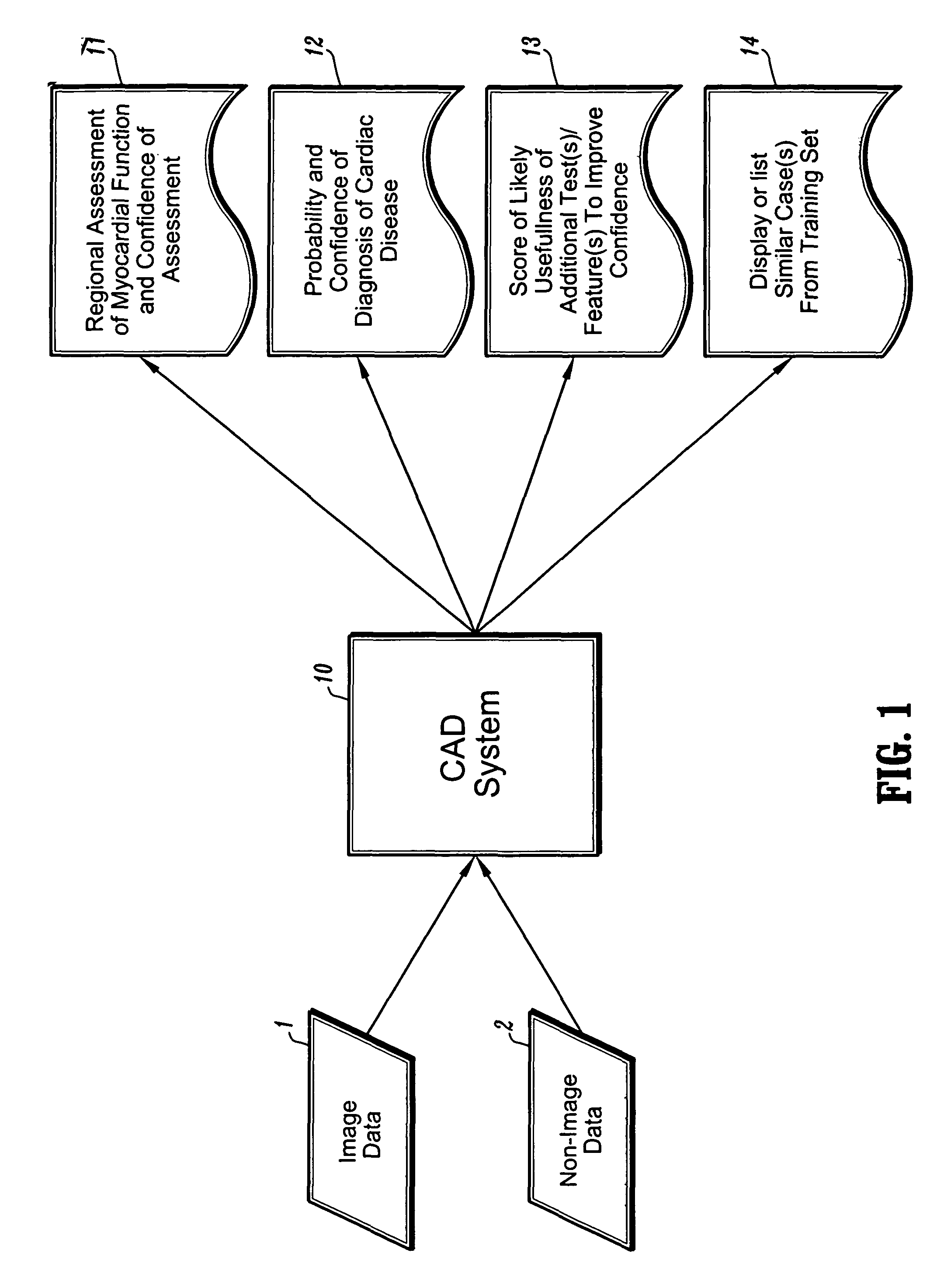
CAD (computer-aided diagnosis) systems and applications for cardiac imaging are provided, which implement methods to automatically extract and analyze features from a collection of patient information (including image data and / or non-image data) of a subject patient, to provide decision support for various aspects of physician workflow including, for example, automated assessment of regional myocardial function through wall motion analysis, automated diagnosis of heart diseases and conditions such as cardiomyopathy, coronary artery disease and other heart-related medical conditions, and other automated decision support functions. The CAD systems implement machine-learning techniques that use a set of training data obtained (learned) from a database of labeled patient cases in one or more relevant clinical domains and / or expert interpretations of such data to enable the CAD systems to “learn” to analyze patient data and make proper diagnostic assessments and decisions for assisting physician workflow.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC +1
Heart support to prevent ventricular remodeling
InactiveUS6887192B1Reducing end-diastolic diameterRelieve stressHeart valvesControl devicesSystoleCardiac functioning
This is a support device that prevents, reduces, and delays remodeling of diseased cardiac tissue, and also decreases the impact of such remodeling on collateral tissue is disclosed. The invention further reinforces abnormal tissue regions to prevent over-expansion of the tissue due to increased afterload and excessive wall tension. As a result, the support device prevents phenomenon such as systolic stretch from occurring and propagating. The support structure maintains and restores diastolic compliance, wall motion, and ejection fraction to preserve heart functionality. As such, the support device prevents and treats cardiomyopathy and congestive heart failure.
Owner:CONVERGE MEDICAL
Electrophysiology Therapy Catheter
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Systems and methods for automated diagnosis and decision support for heart related diseases and conditions
InactiveUS7912528B2Medical automated diagnosisCharacter and pattern recognitionCoronary artery diseasePatient data
CAD (computer-aided diagnosis) systems and applications for cardiac imaging are provided, which implement methods to automatically extract and analyze features from a collection of patient information (including image data and / or non-image data) of a subject patient, to provide decision support for various aspects of physician workflow including, for example, automated assessment of regional myocardial function through wall motion analysis, automated diagnosis of heart diseases and conditions such as cardiomyopathy, coronary artery disease and other heart-related medical conditions, and other automated decision support functions. The CAD systems implement machine-learning techniques that use a set of training data obtained (learned) from a database of labeled patient cases in one or more relevant clinical domains and / or expert interpretations of such data to enable the CAD systems to “learn” to analyze patient data and make proper diagnostic assessments and decisions for assisting physician workflow.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC +1
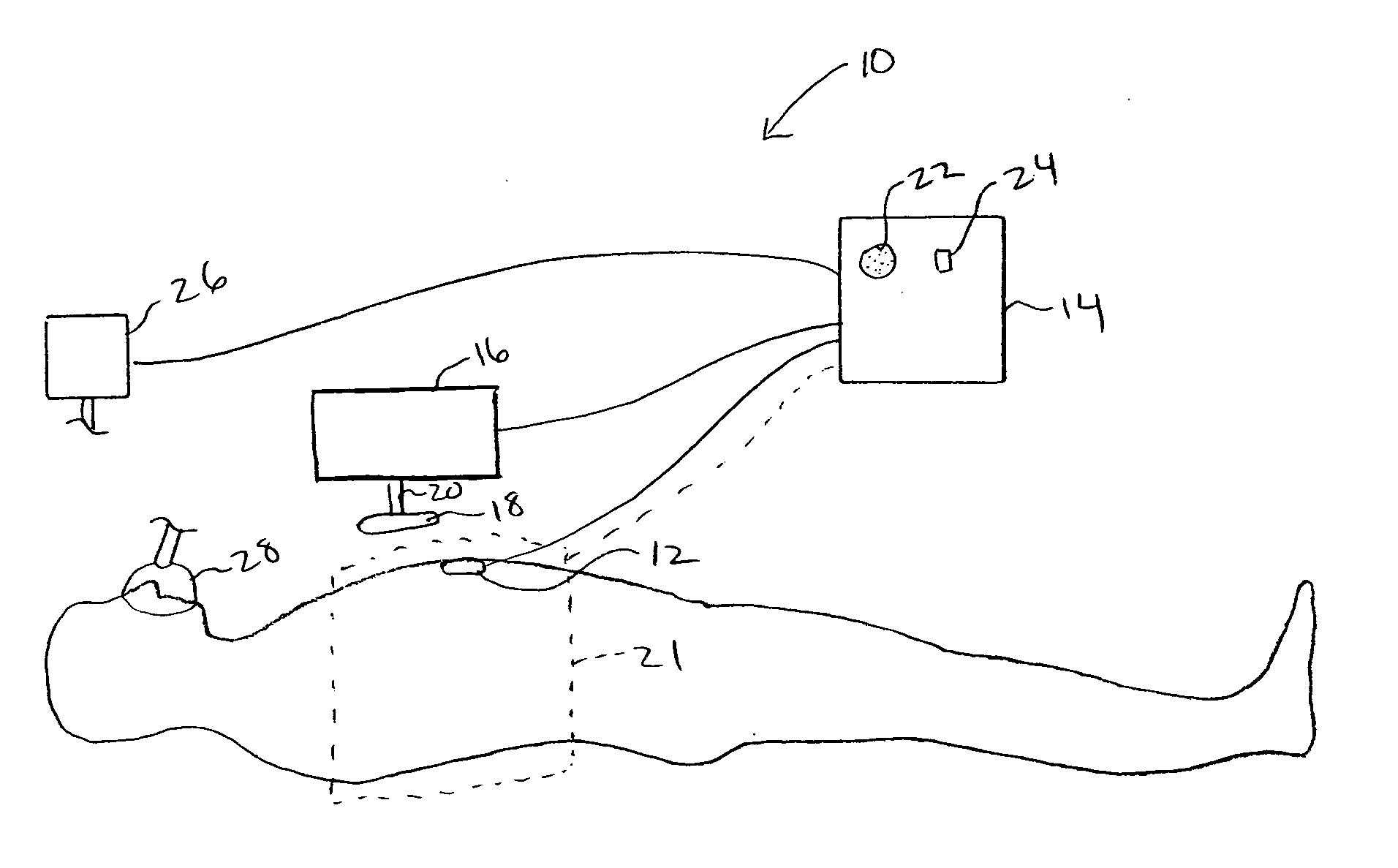
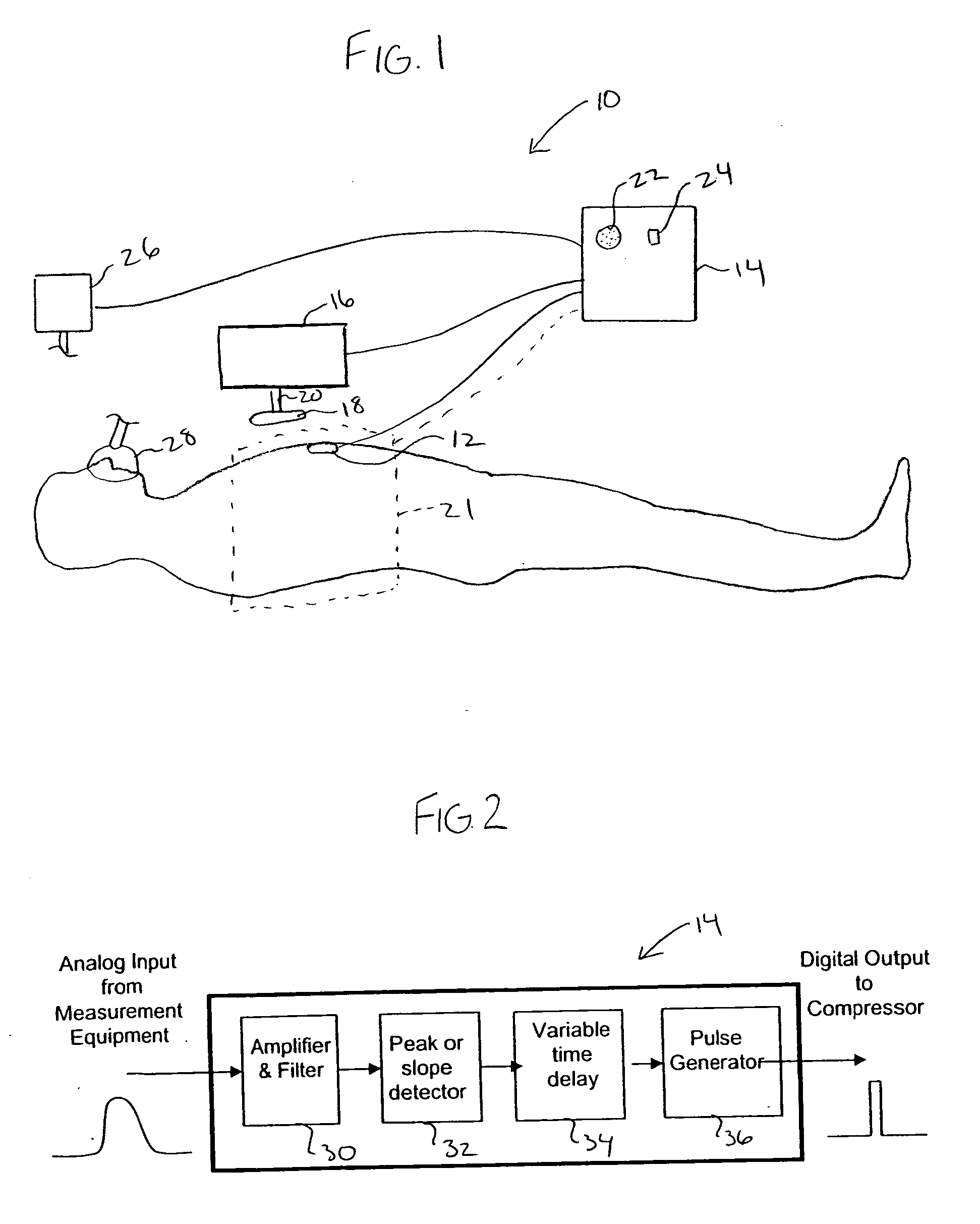
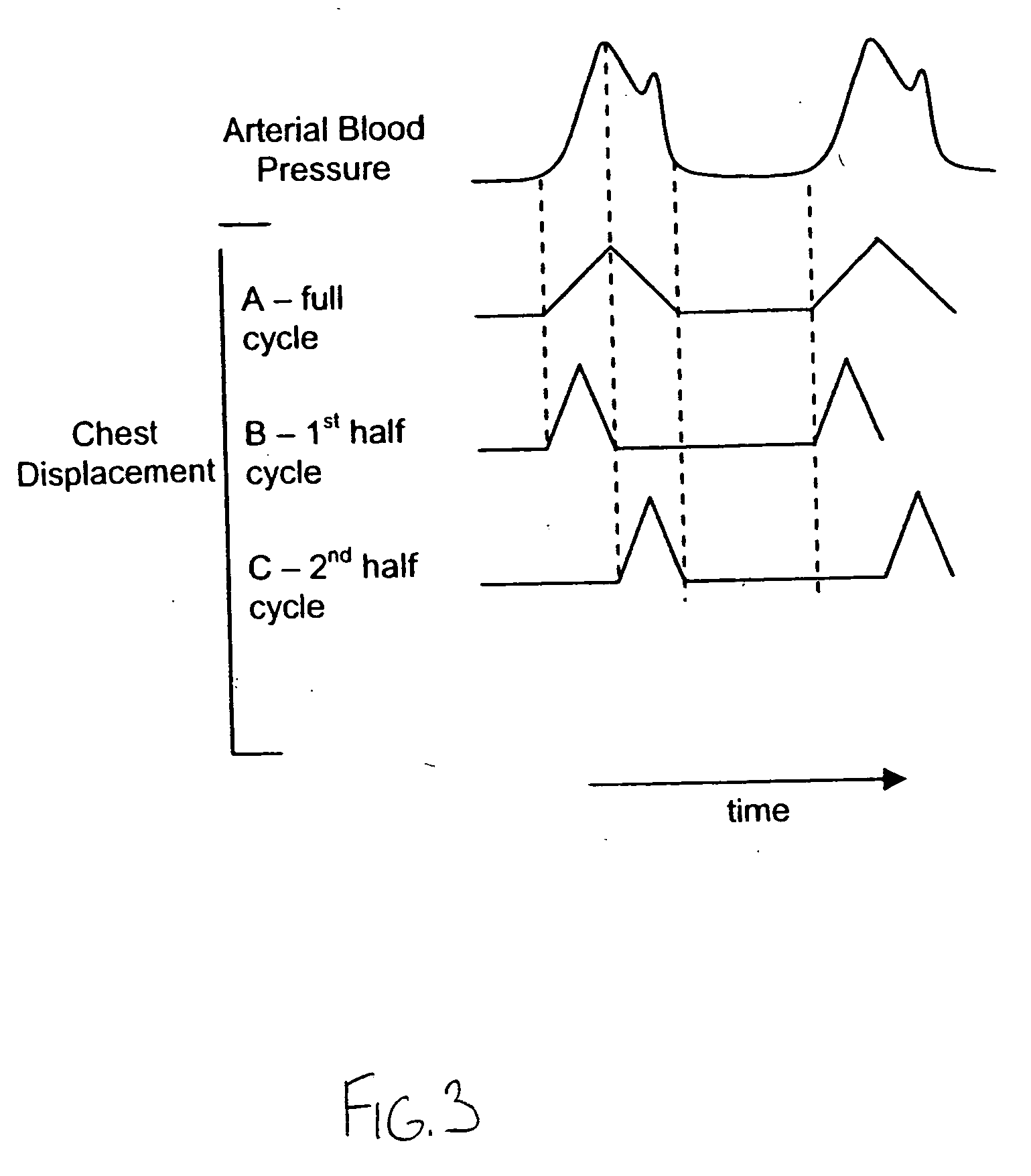
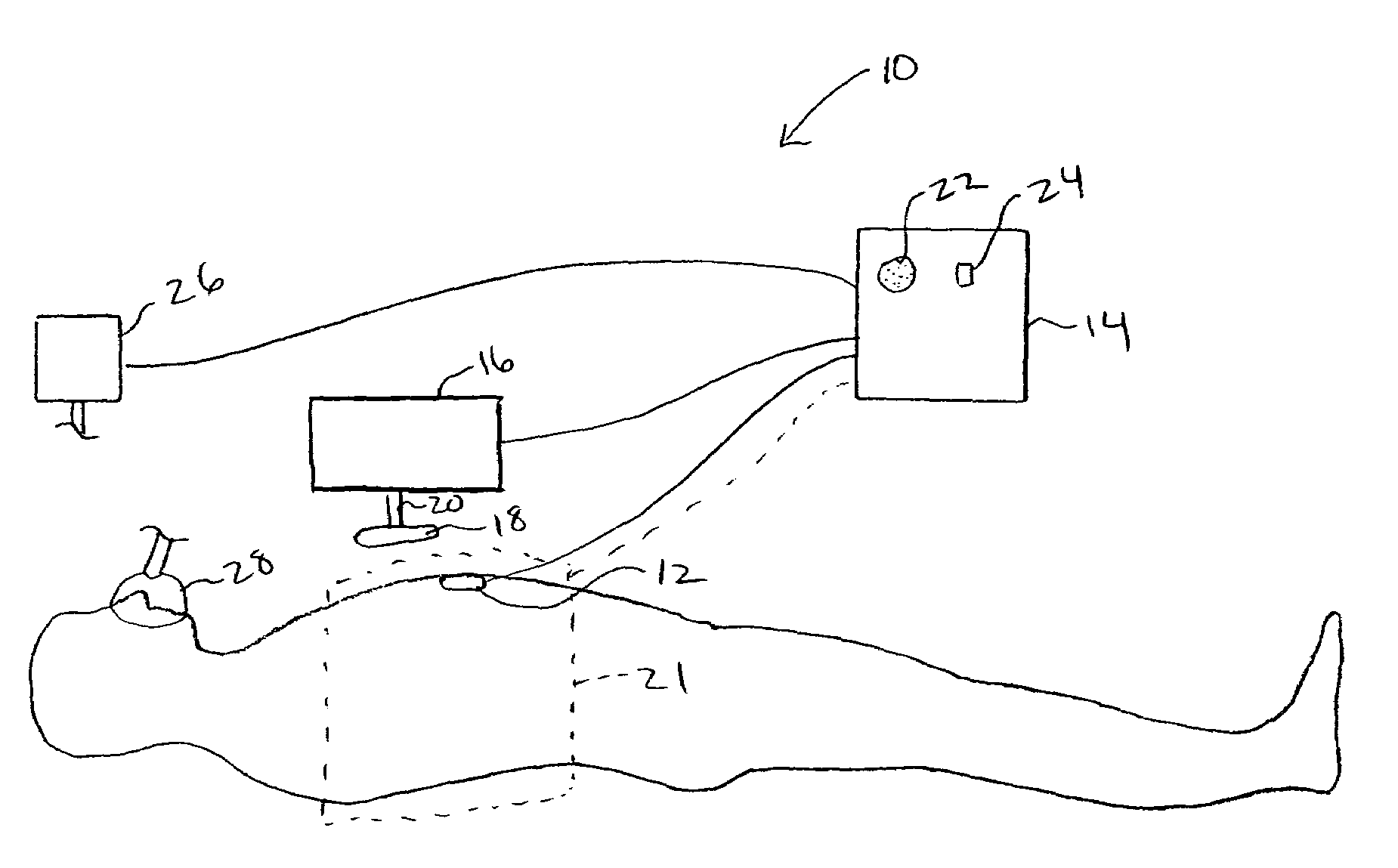
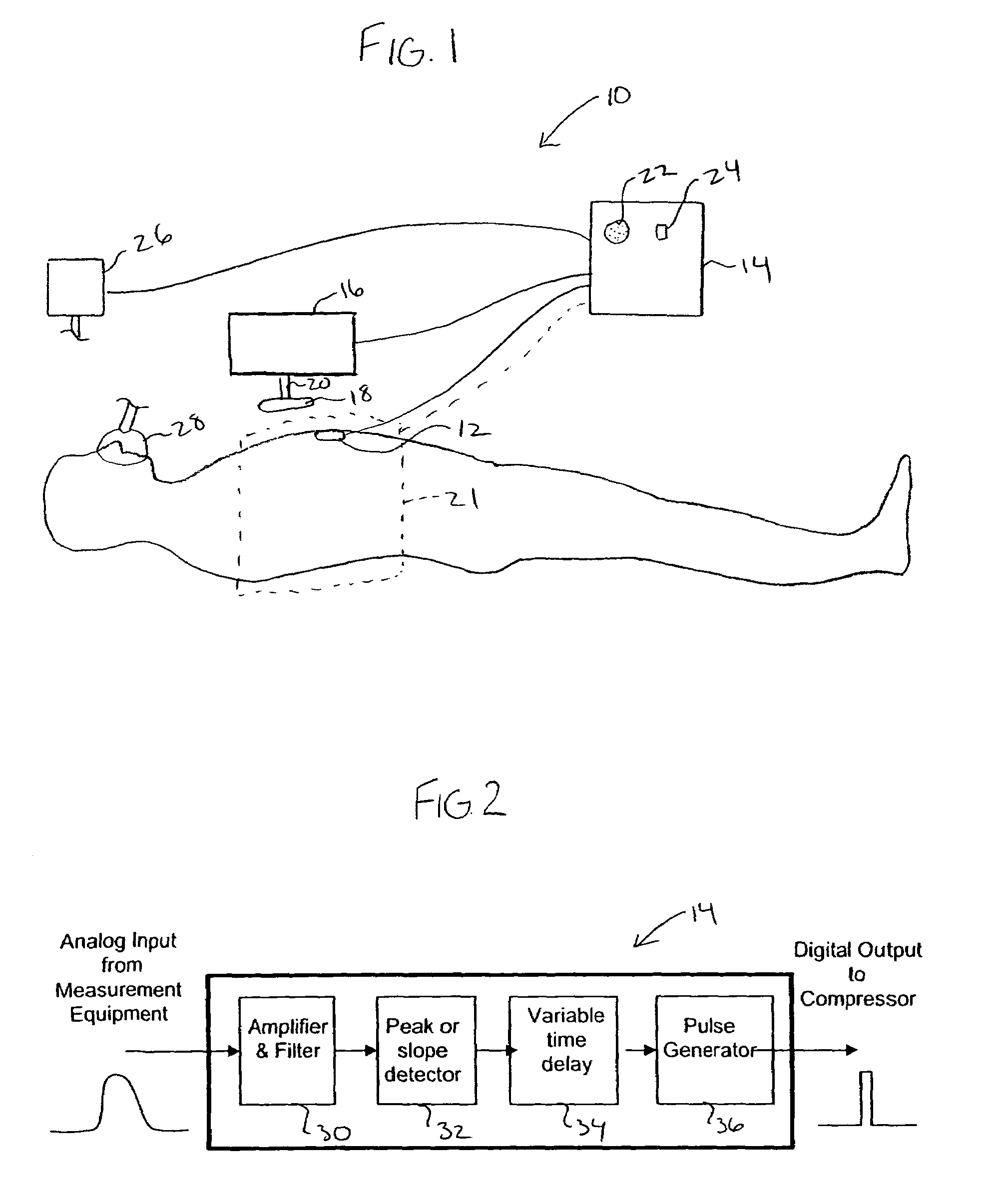
Non-invasive device for synchronizing chest compression and ventilation parameters to residual myocardial activity during cardiopulmonary resuscitation
ActiveUS20060089574A1Promote recoveryDecreased cardiac outputRespiratorsElectrotherapyPulseless electrical activityLeft ventricular size
In one embodiment, a method for improving the cardiac output of a patient who is suffering from pulseless electrical activity or shock and yet still displays some myocardial wall motion comprises sensing myocardial activity to determine the presence of residual left ventricular pump function having a contraction or ejection phase and a filling or relaxation phase. In such cases, a compressive force is repeatedly applied to the chest based on the sensed myocardial activity such that the compressive force is applied during at least some of the ejection phases and is ceased during at least some of the relaxation phases to permit residual cardiac filling, thereby enhancing cardiac output and organ perfusion. Also incorporated may be a logic circuit capable of utilizing multiple sensing modalities and optimizing the synchronization pattern between multiple phasic therapeutic modalities and myocardial residual mechanical function.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
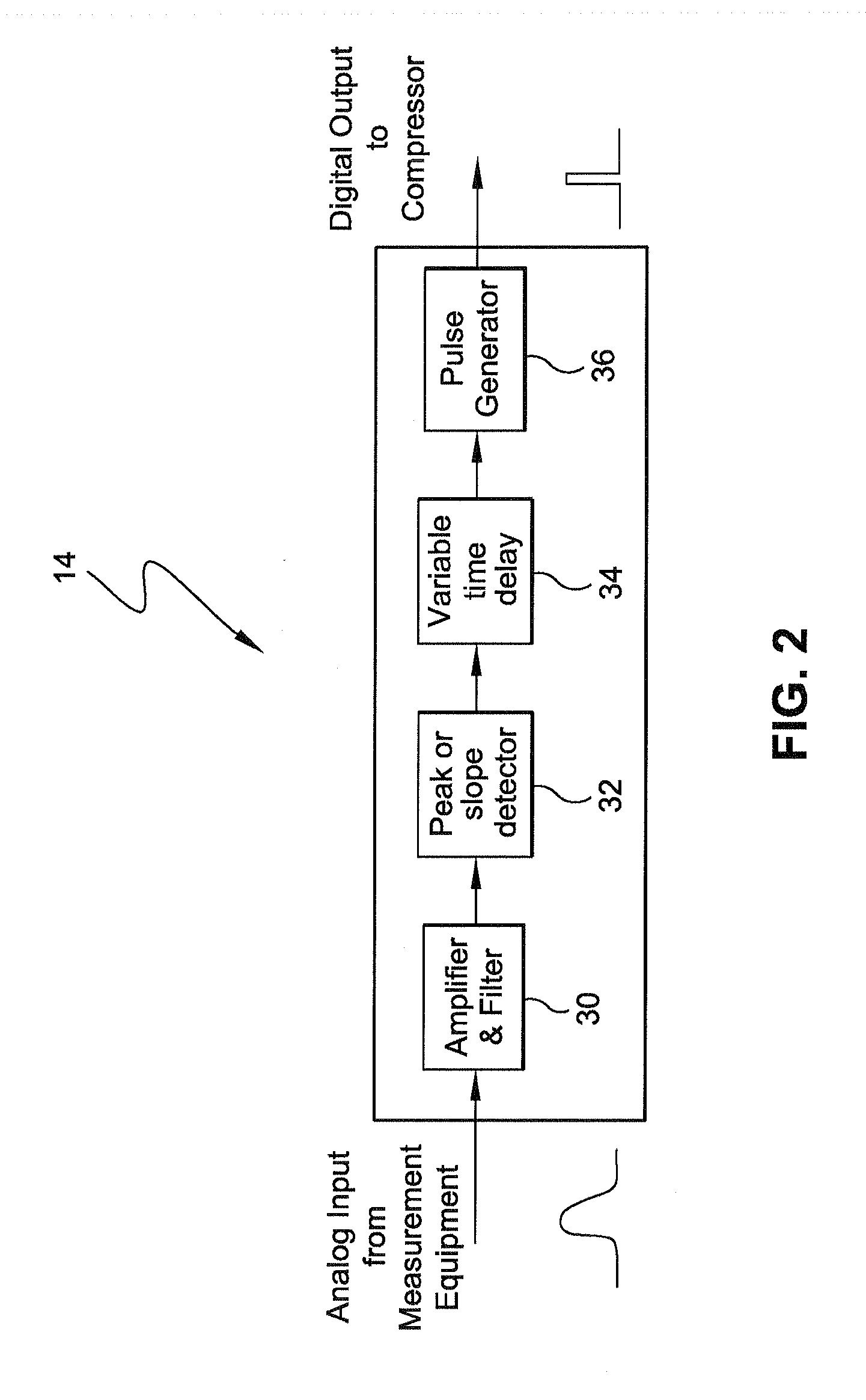
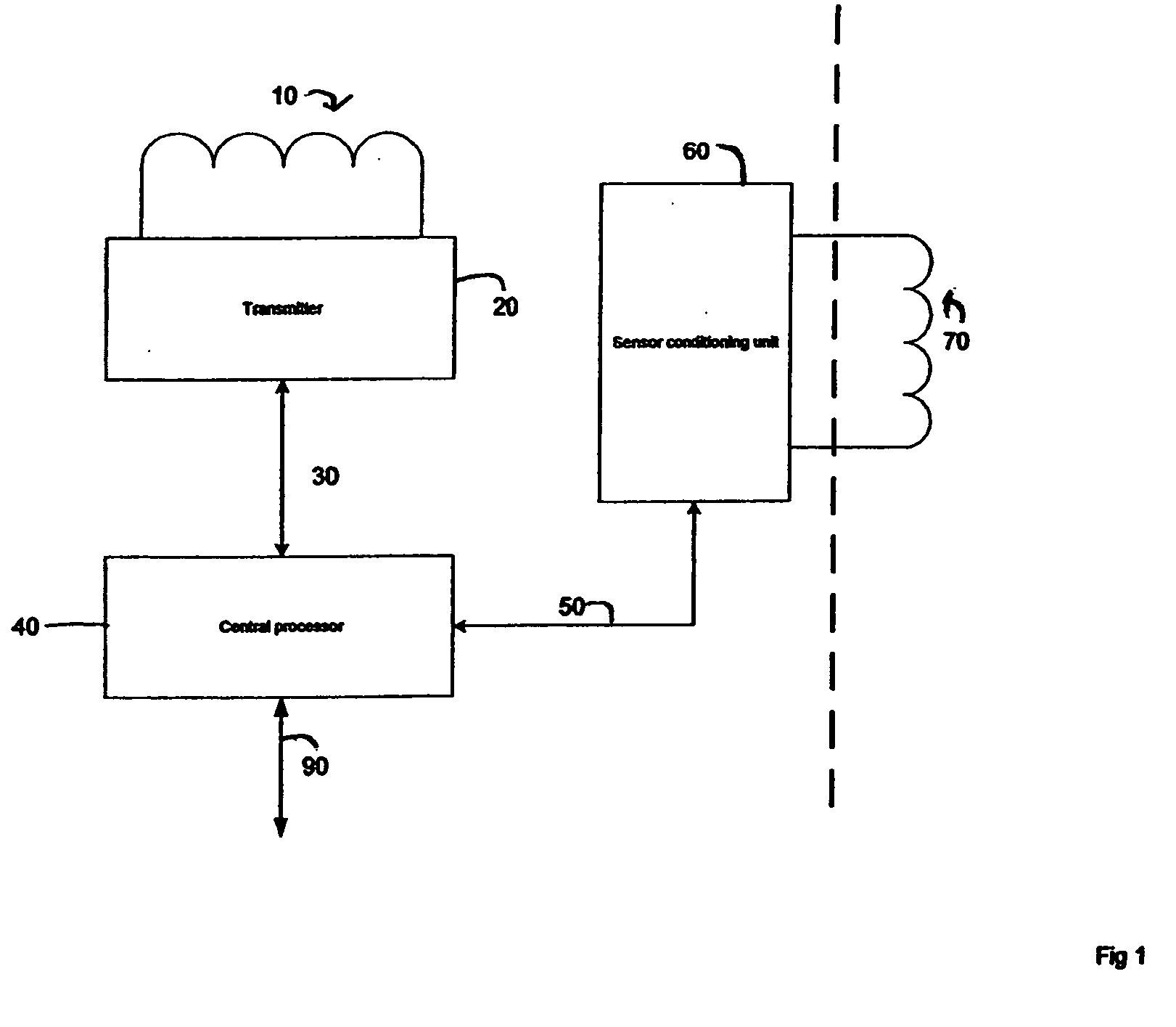
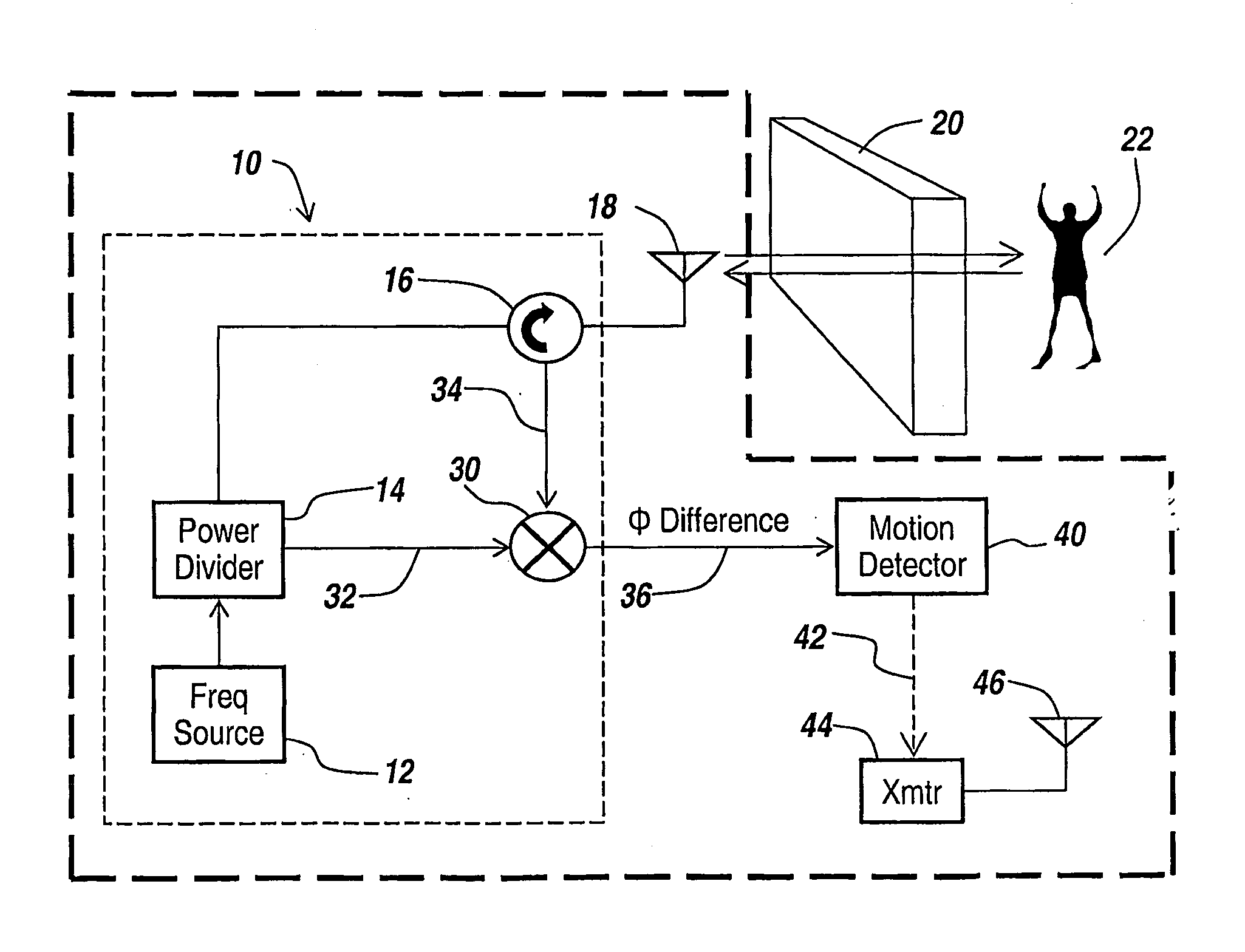
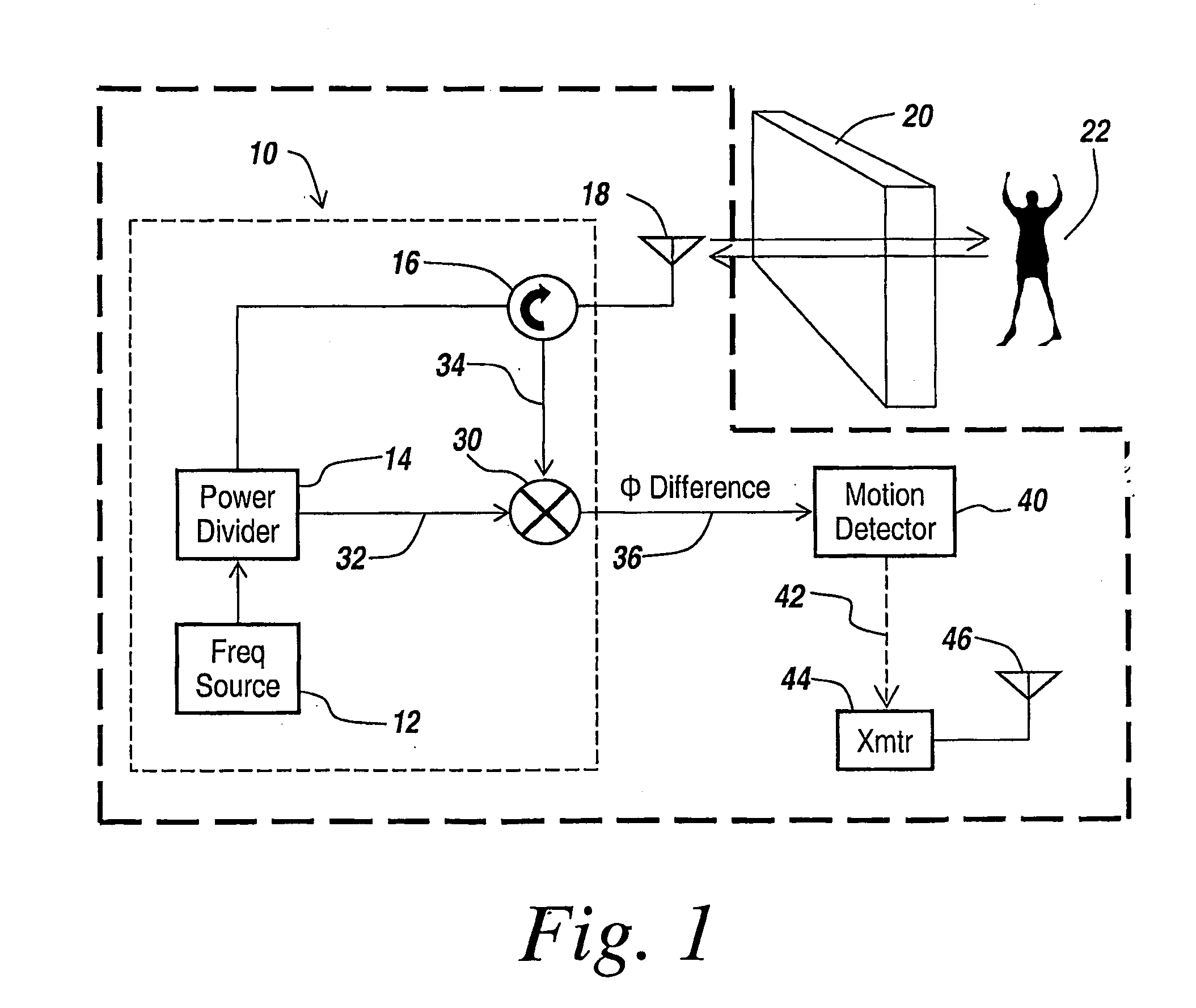
Method and apparatus for through-the-wall motion detection utilizing cw radar
InactiveUS20070024488A1Easy to detectReduce the required powerRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPhase differenceClassical mechanics
A CW radar (10) is used to detect motion of objects (22) behind a wall (20) by projecting a radar beam through the wall and by measuring the returns from the objects behind the wall, with a change in the phase difference between the transmitted and received CW signals providing an indication of motion behind the wall and thus the presence of an individual.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Wall motion analyzer
InactiveUS20050228276A1Used to determineOrgan movement/changes detectionCatheterCardiac wallReference image
A system and method for real-time quantitative analysis of heart wall motion is provided. A Doppler imaging system is used to monitor the movement of a heart, or other organ. A B-mode reference image of the target organ is made and then a region-of-interest is defined through the use of a gate. Then pulsed wave spectral tissue Doppler data of the region-of-interest is formed and used to determine the velocity of a region of the target organ. The system may be used for determining appropriate biventricular pacemaker settings for patients suffering from heart disease.
Owner:TERATECH CORP
System and method for infrasonic cardiac monitoring
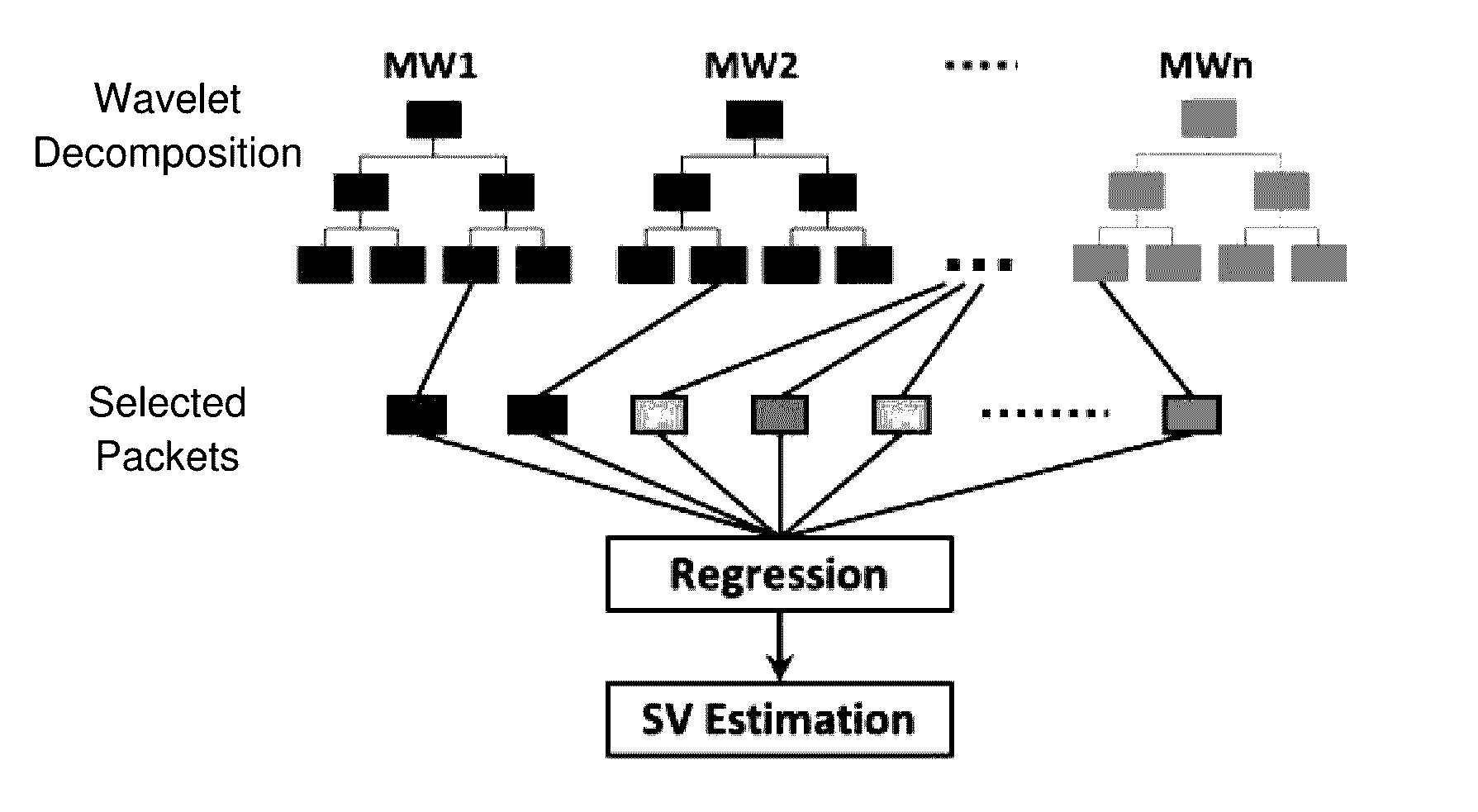
ActiveUS20160361041A1With balanceHigh and good performanceBlood flow measurement devicesHealth-index calculationVentricular contractionCardiac monitoring
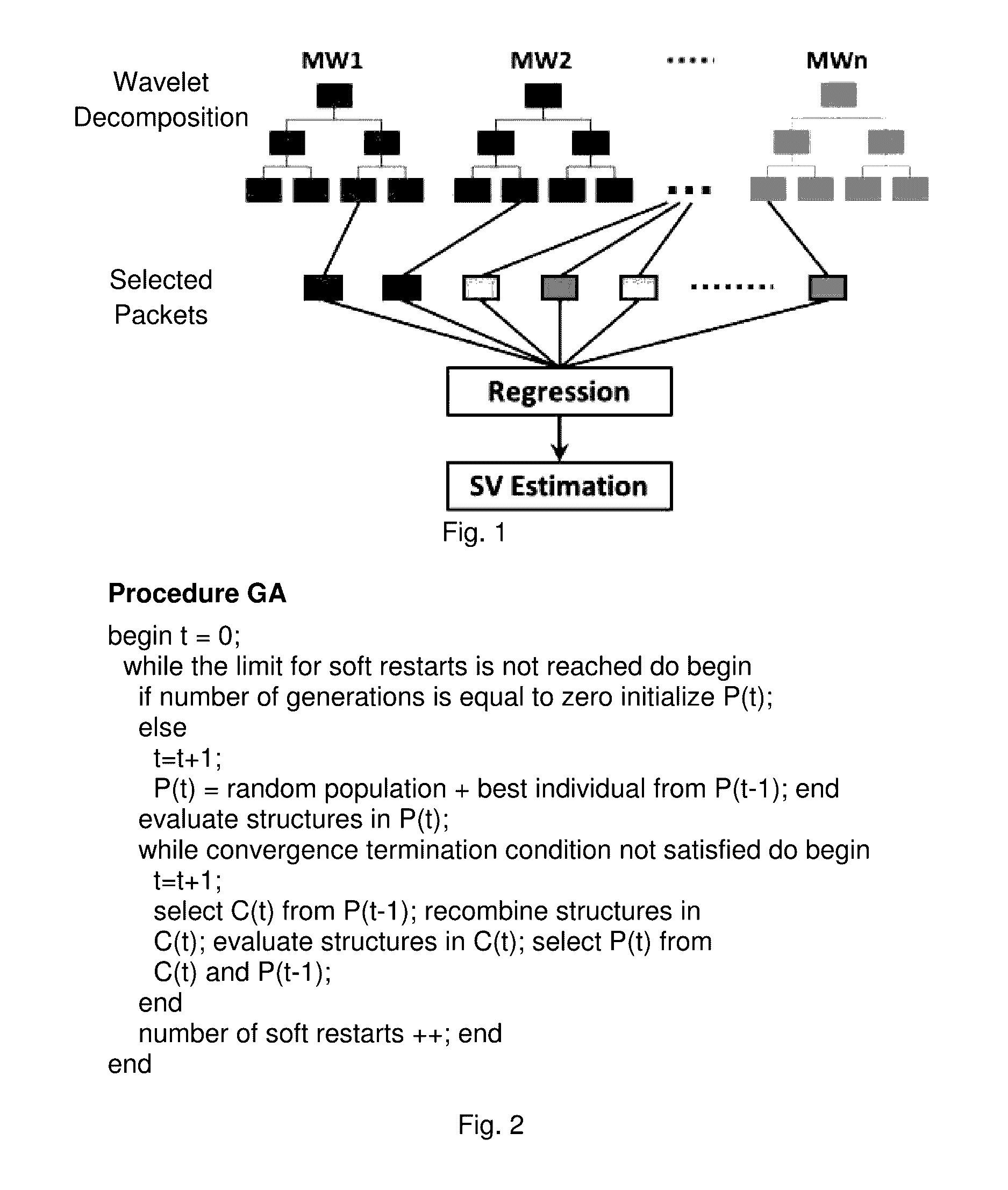
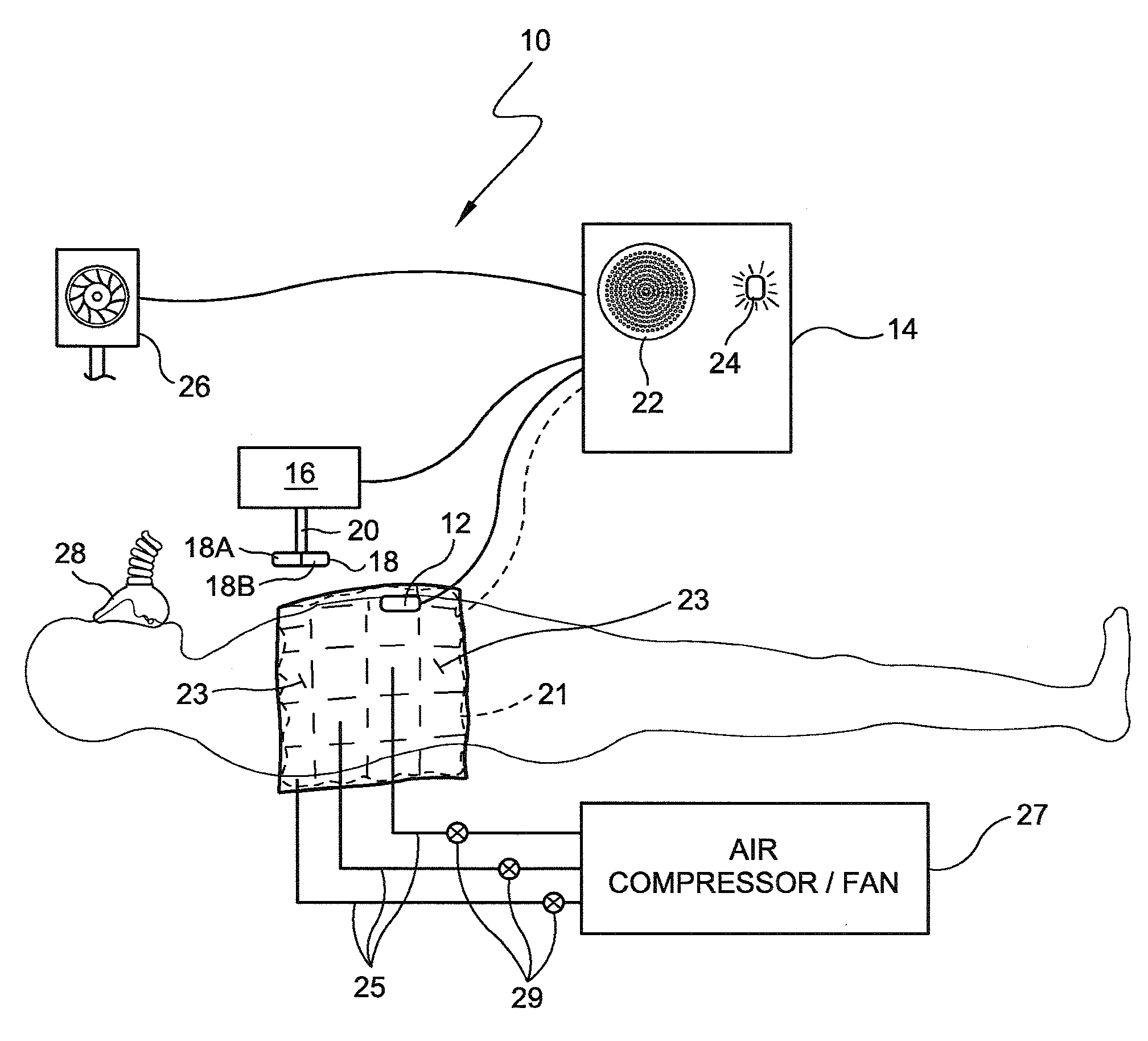
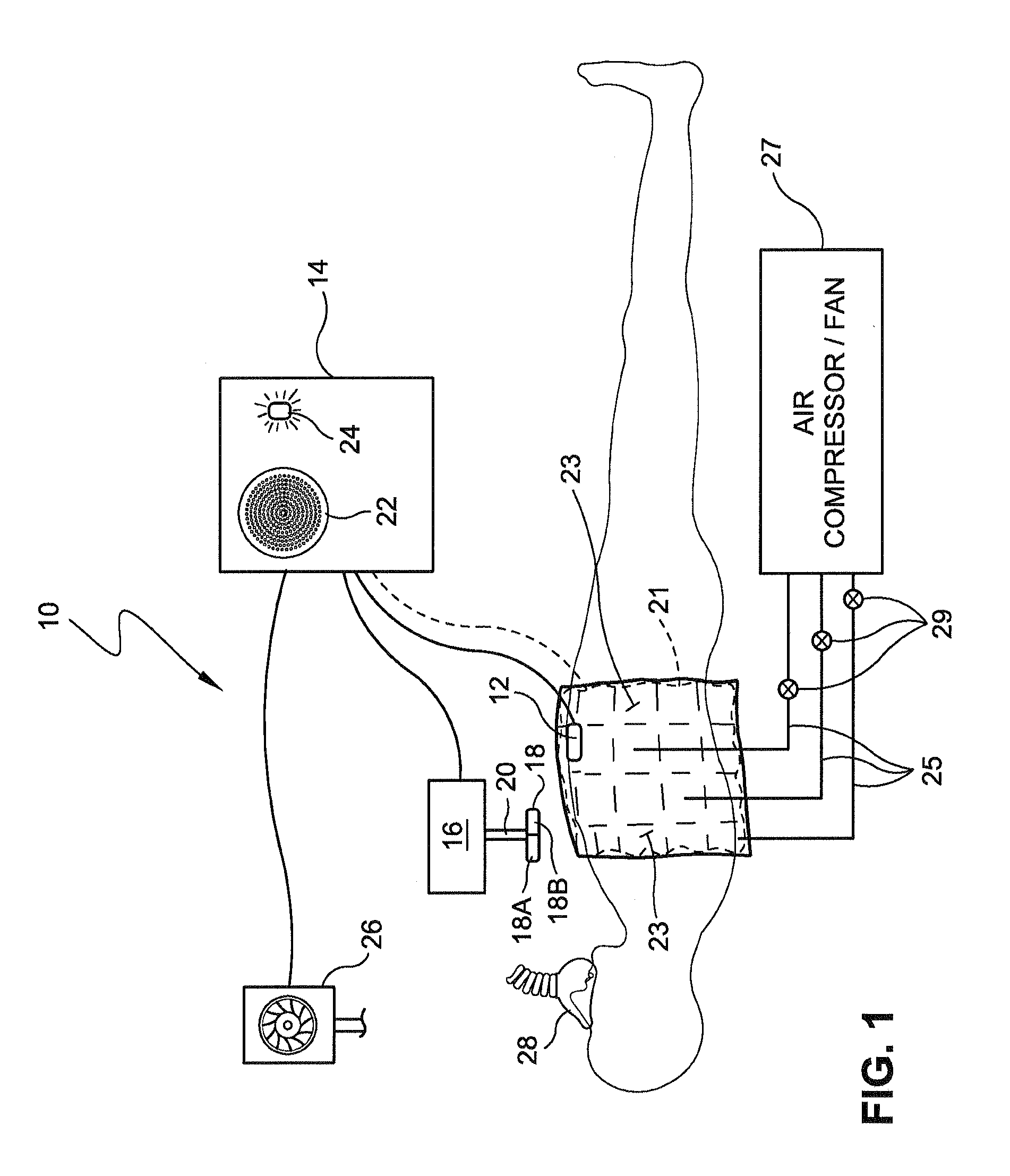
Cardiac Output (CO) has traditionally been difficult, dangerous, and expensive to obtain. Surrogate measures such as pulse rate and blood pressure have therefore been used to permit an estimate of CO. MEMS technology, evolutionary computation, and time-frequency signal analysis techniques provide a technology to non-invasively estimate CO, based on precordial (chest wall) motions. The technology detects a ventricular contraction time point, and stroke volume, from chest wall motion measurements. As CO is the product of heart rate and stroke volume, these algorithms permit continuous, beat to beat CO assessment. Nontraditional Wavelet analysis can be used to extract features from chest acceleration. A learning tool is preferable to define the packets which best correlate to contraction time and stroke volume.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Non-invasive device for synchronizing chest compression and ventilation parameters to residual myocardial activity during cardiopulmonary resuscitation
ActiveUS20120016179A1Promote recoveryDecreased cardiac outputRespiratorsElectrocardiographyCardiac arrest- pulseless electrical activityDiagnostic Radiology Modality
A method for improving the cardiac output of a patient who is suffering from pulseless electrical activity or shock and yet still displays some myocardial wall motion including sensing myocardial activity to determine the presence of residual left ventricular pump function having a contraction or ejection phase and a filling or relaxation phase. In such cases, a compressive force is repeatedly applied to the chest based on the sensed myocardial activity such that the compressive force is applied during at least some of the ejection phases and is ceased during at least some of the relaxation phases to permit residual cardiac filling, thereby enhancing cardiac output and organ perfusion. Also incorporated may be a logic circuit capable of utilizing multiple sensing modalities and optimizing the synchronization pattern between multiple phasic therapeutic modalities and myocardial residual mechanical function.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
Ultrasonic image processing apparatus and ultrasonic image processing method
ActiveUS20080267482A1Quick and Accurate AcquisitionOrgan movement/changes detectionCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingProjection image
Three slices, i.e., Basal, Mid, and Apical slices, which correspond to clinically useful ASE segmentation are designated, and the positions of the three slices are tracked through at least one cardiac cycle by performing three-dimensional speckle tracking in the remaining time phases. Three C-mode projection images concerning the tracked positions are reconstructed. In addition, arbitrary myocardial wall motion parameters at the tracked positions are computed and displayed upon being superimposed on C-mode images or projected / displayed on a polar map. As a C-mode projection image method, one of the following techniques can be used detecting and projecting only movement components perpendicular to slices determined in an initial time phase, detecting and projecting average movement components of the respective walls, and tracking and projecting each myocardial position. The obtained C-mode images are simultaneously displayed together with markers indicating the positions of long-axis images and C-mode images.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
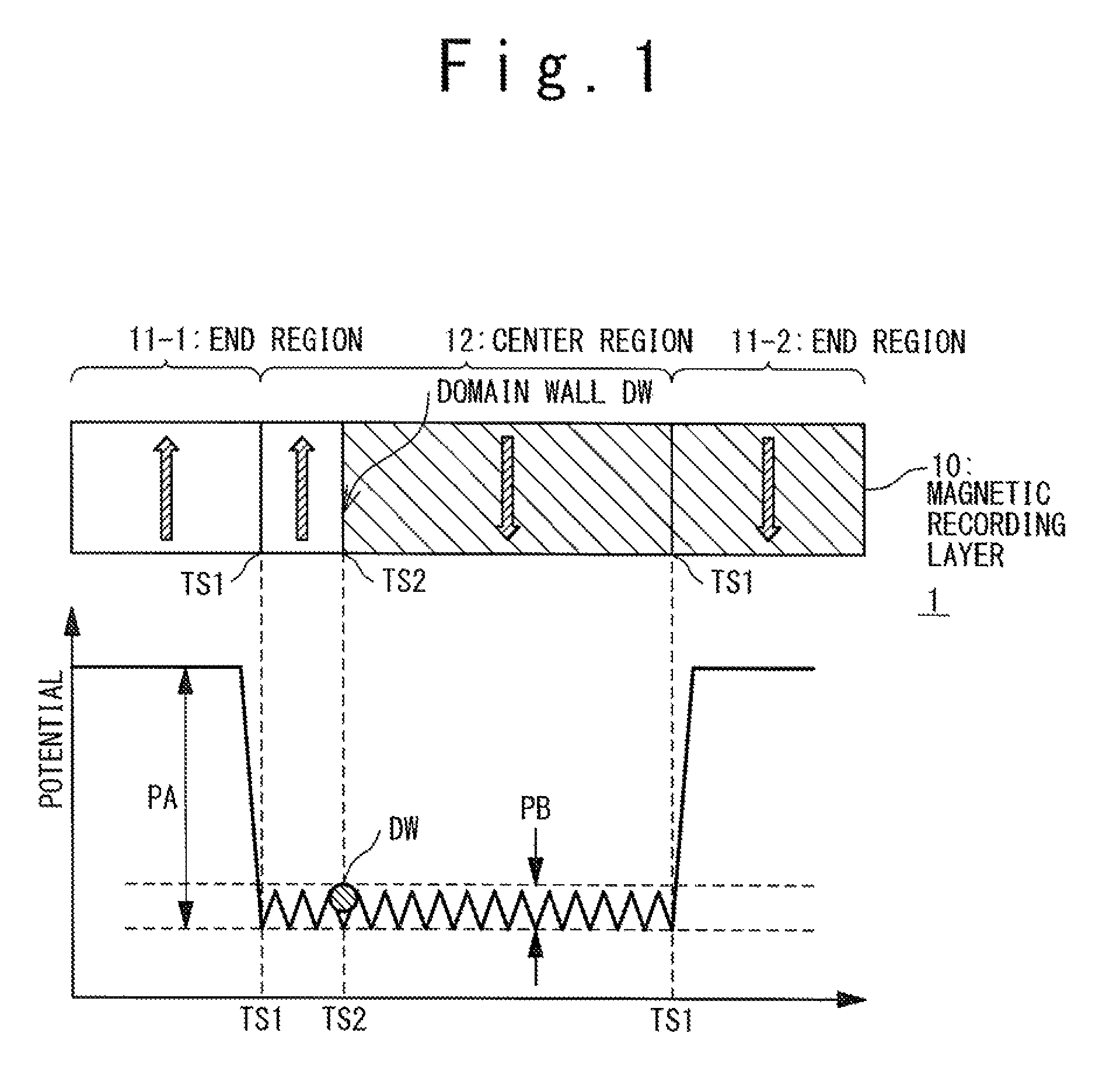
Domain wall motion element and magnetic random access memory
ActiveUS20110129691A1NanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsStatic random-access memoryRandom access memory
A domain wall motion element has a magnetic recording layer 10 that is formed of a ferromagnetic film and has a domain wall DW. The magnetic recording layer 10 has: a pair of end regions 11-1 and 11-2 whose magnetization directions are fixed; and a center region 12 sandwiched between the pair of end regions 11-1 and 11-2, in which the domain wall. DW moves. A first trapping site TS1 by which the domain wall DW is trapped is formed at a boundary between the end region 11-1, 11-2 and the center region 12. Furthermore, at least one second trapping site TS2 by which the domain wall DW is trapped is formed within the center region 12.
Owner:NEC CORP
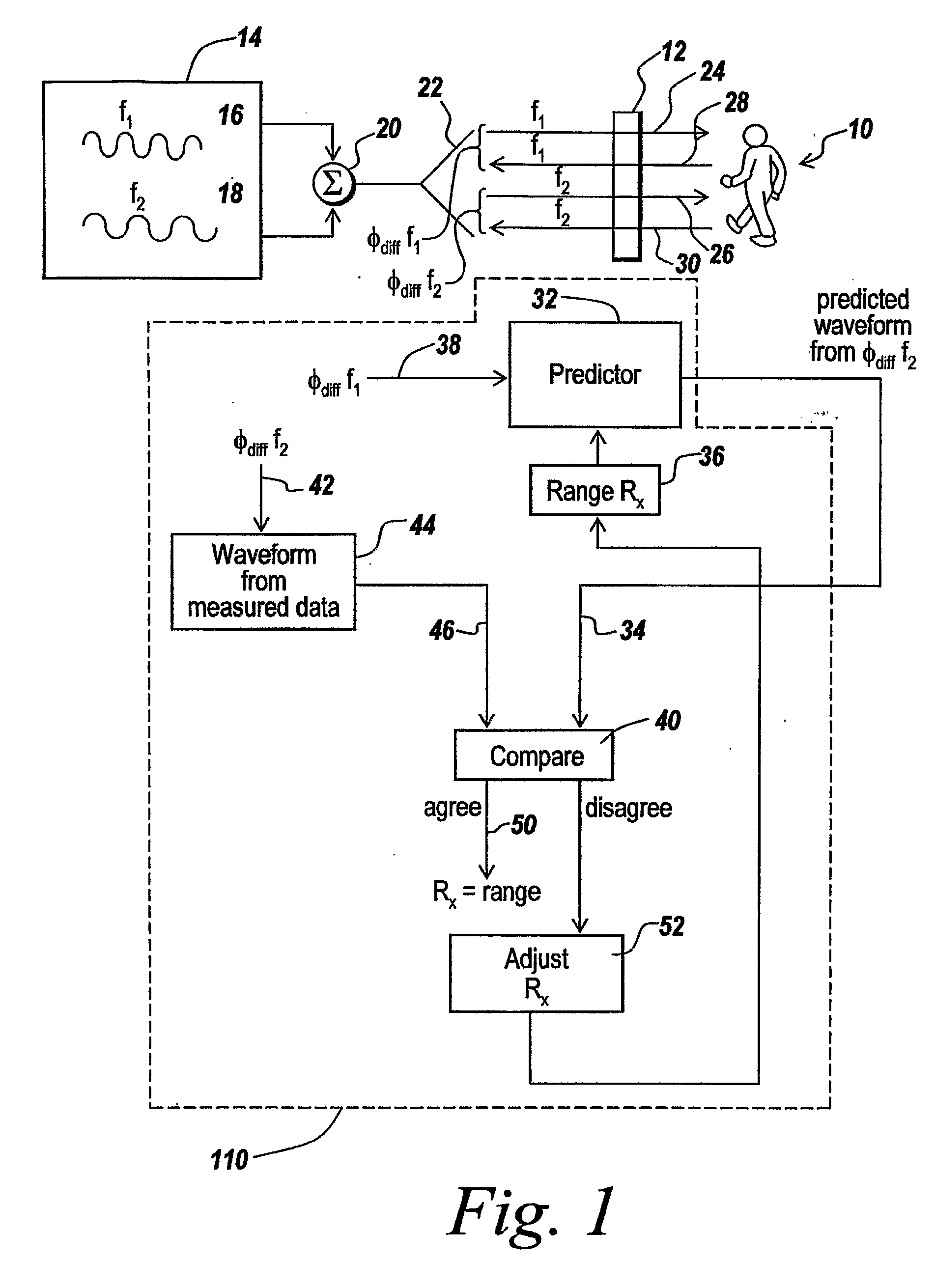
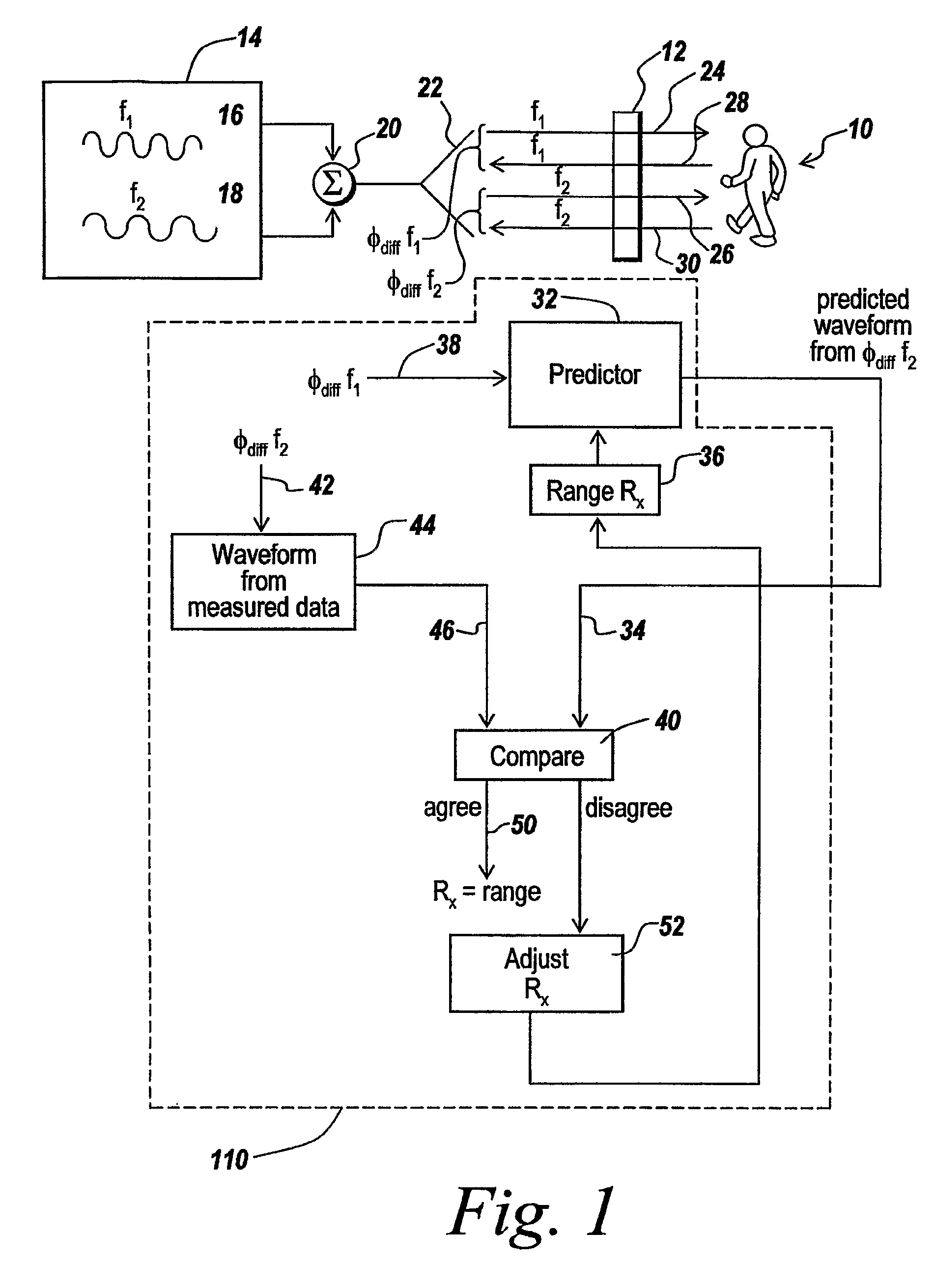
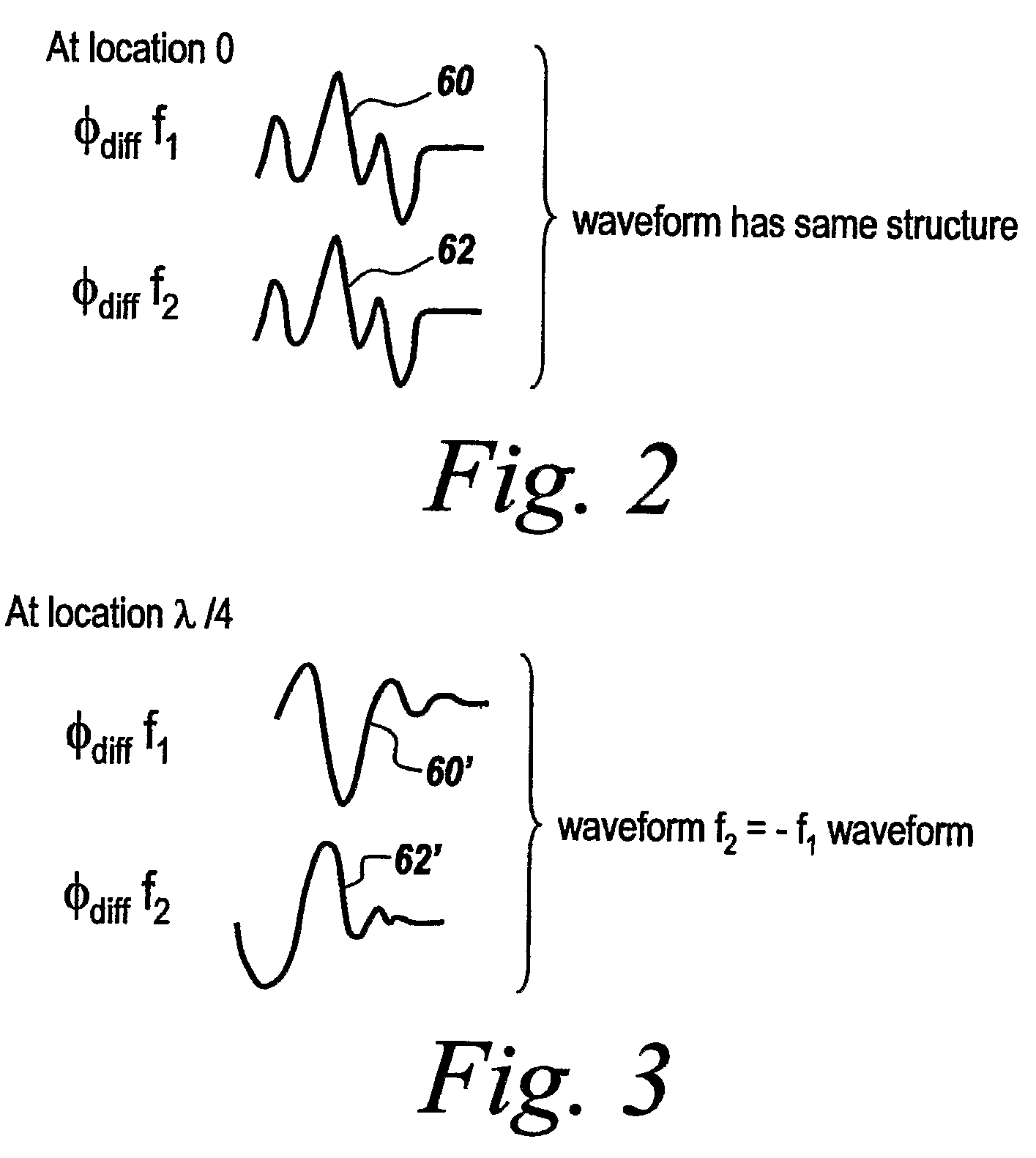
Multiple frequency through-the-wall motion detection and ranging using a difference-based estimation technique
InactiveUS20070024487A1Easy to carryLow costRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPartition of unityPhase difference
A multi-tone CW radar (14) is used to project signals from an antenna (22) and to receive returns with the same antenna. The phase differences between the outgoing signals and the returns are analyzed to determine the existence of motion and the range to a moving object (10). A model is made which has range as its major parameter. A waveform associated with the phase difference between outgoing signals and returns for one of the tones is compared to templates produced by the model to determine which has a range that most closely matches. By varying the range parameters, when a match is detected the range to the object can be obtained even if its motion is pseudorandom. If the range is measured with multiple units it is possible to measure the location of the object. This can be done assuming a grid and algorithmically combining the ranges from the units.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Systems and methods for providing automated regional myocardial assessment for cardiac imaging
ActiveUS7693315B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementMedical recordAcquired characteristic
Systems and methods are provided for automated assessment of regional myocardial function using wall motion analysis methods that analyze various features / parameters of patient information (image data and non-image data) obtained from medical records of a patient. For example, a method for providing automatic diagnostic support for cardiac imaging generally comprises obtaining image data of a heart of a patient, obtaining features from the image data of the heart, which are related to motion of the myocardium of the heart, and automatically assessing regional myocardial function of one or more regions of a myocardial wall using the obtained features.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
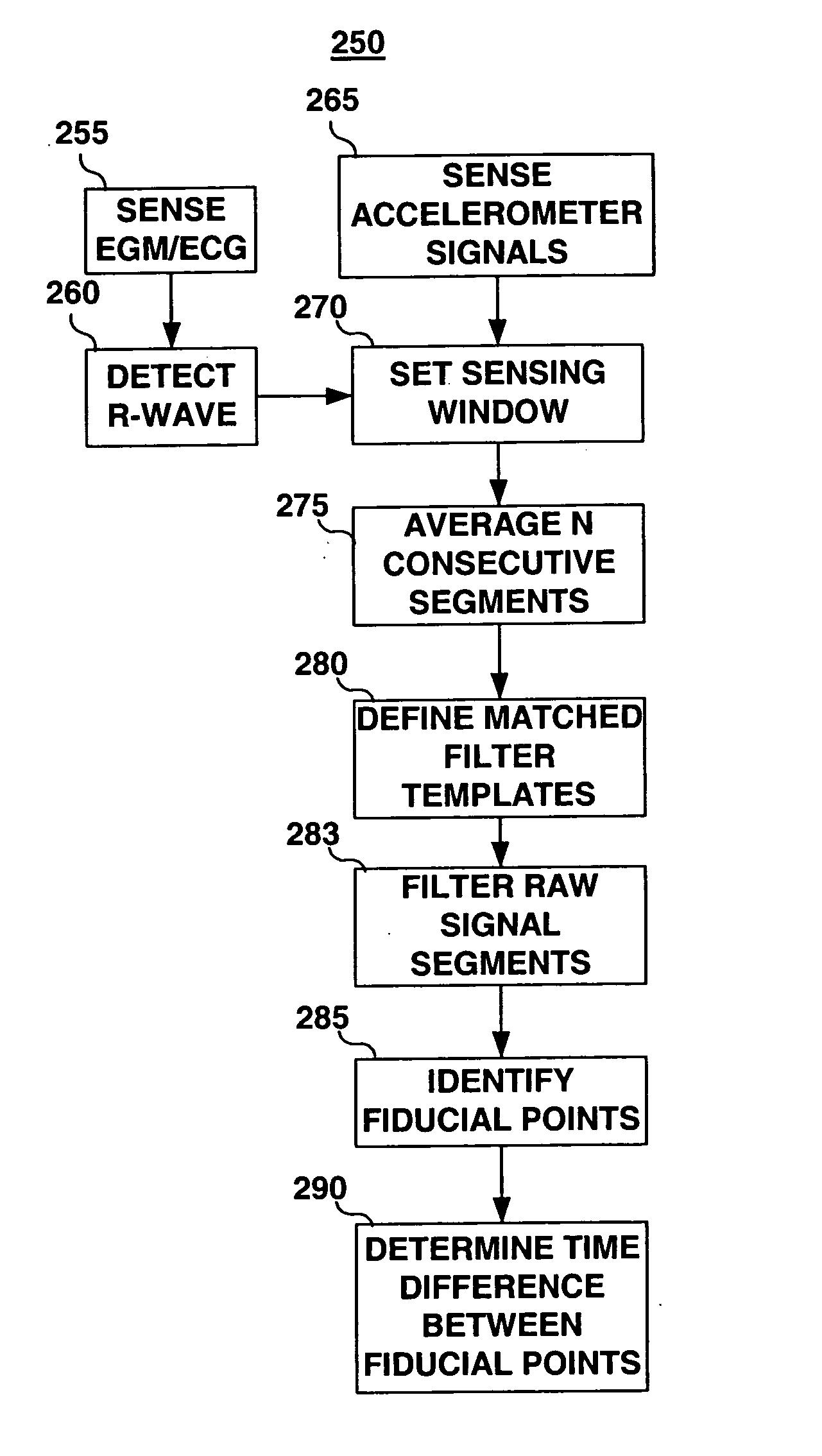
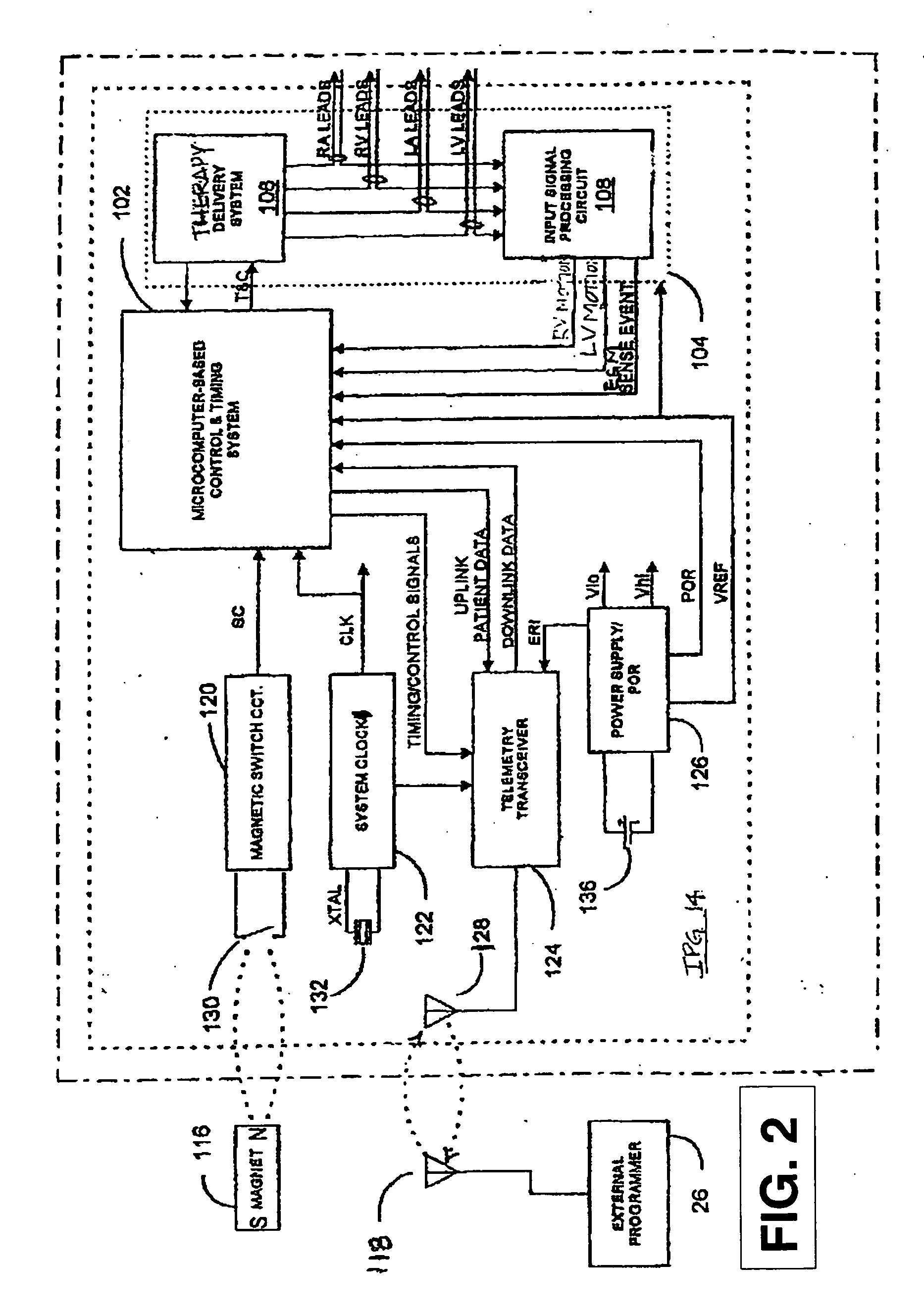
Real-time optimization of right to left ventricular timing sequence in bi-ventricular pacing of heart failure patients
ActiveUS7203541B2Improve performanceHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringAccelerometerWall motion
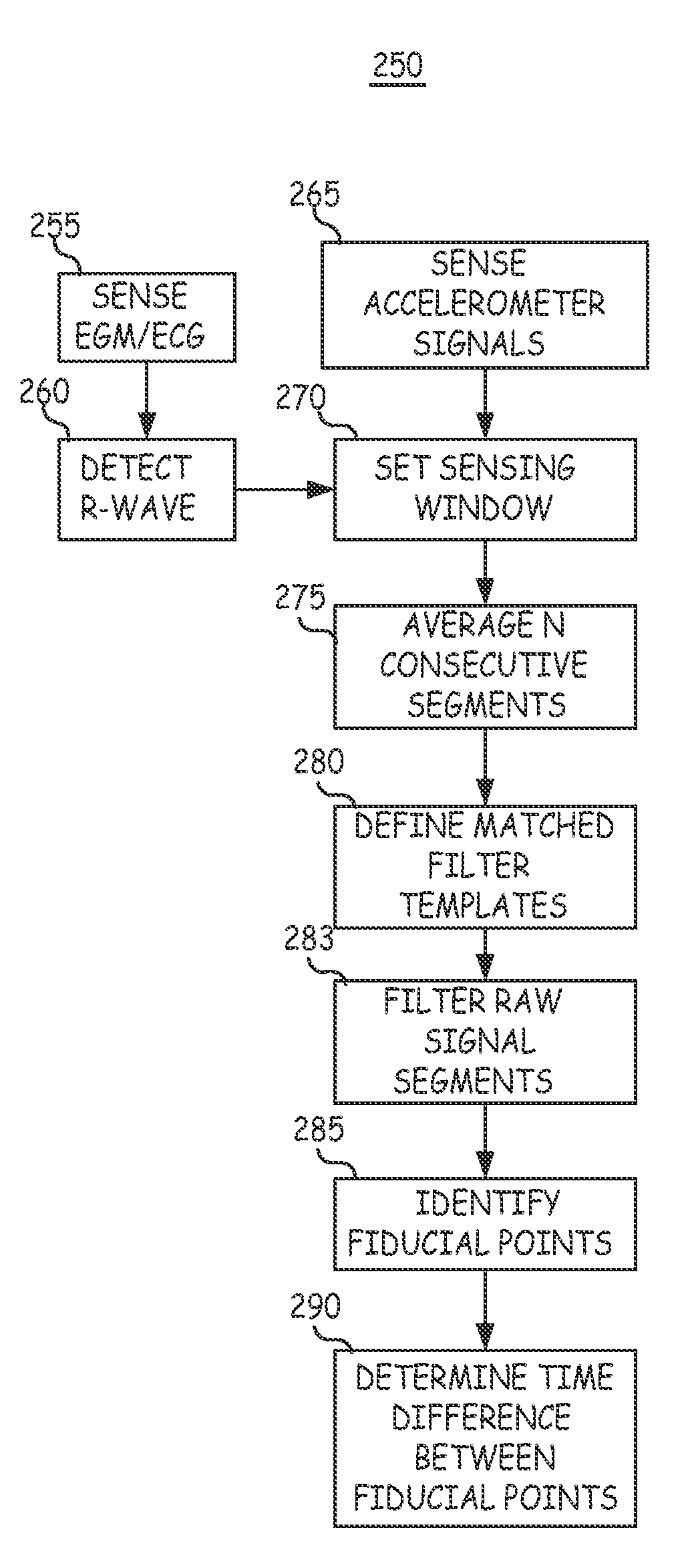
A system and automated method for assessing ventricular synchrony in ambulatory patients is provided including at least one mechanical sensor (e.g., accelerometer, tensiometric sensor, force transducer, and the like) operatively coupled to a first myocardial location in order to measure a wall motion signal of a first chamber, and a second mechanical sensor operatively coupled to a second myocardial location in order to measure a wall motion signal of a second chamber. The wall motion signals are processed in order to identify the time at which a fiducial (e.g., an inflection point, a threshold crossing, a maximum amplitude, etc.) occurs for each respective signal. The temporal separation between the fiducial points on each respective signal is measured as a metric of ventricular synchrony and can be optionally utilized to adjust pacing therapy timing to improve synchrony.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method for detecting contact with the wall of a region of interest
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL INT HLDG SARL
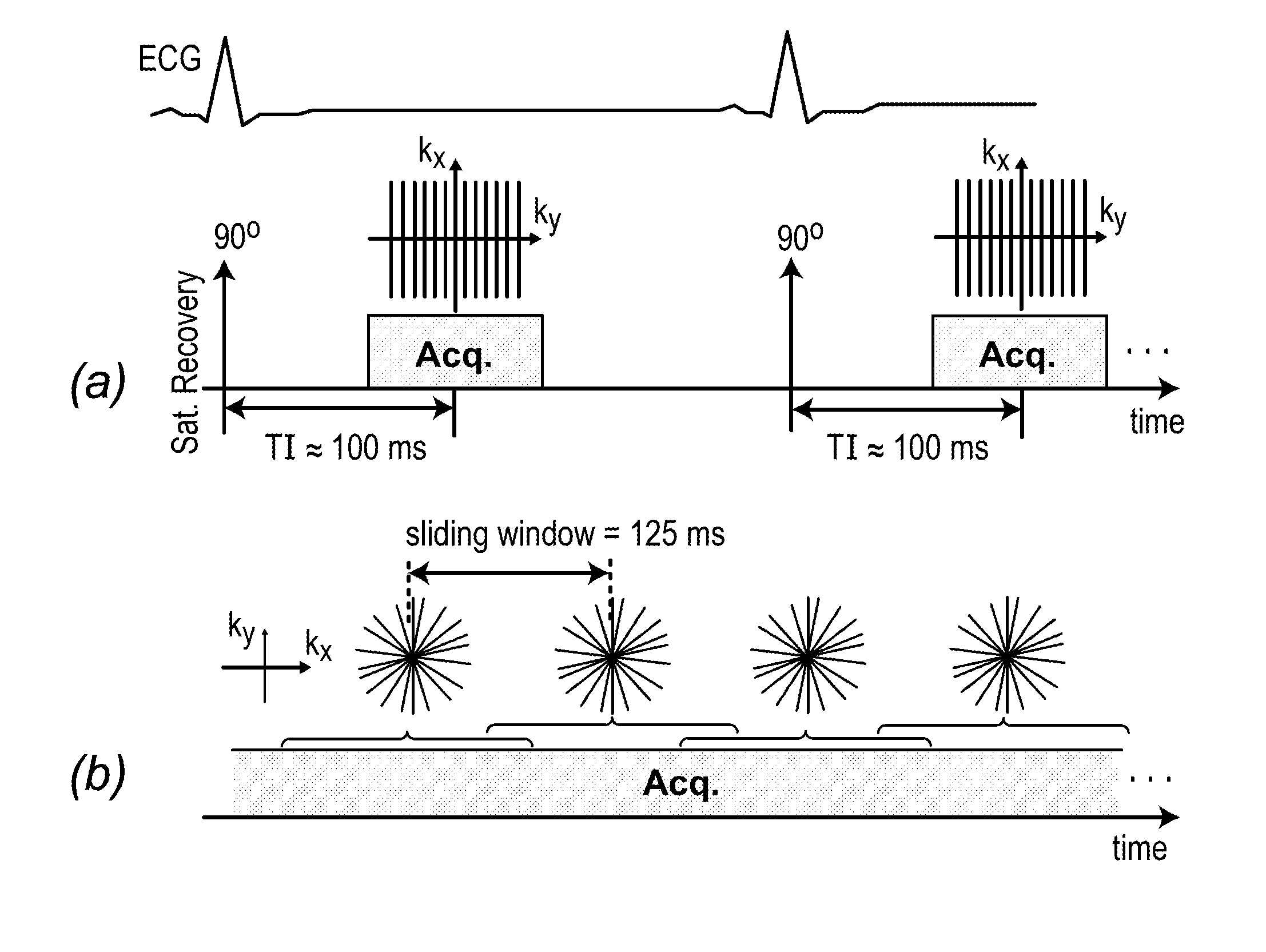
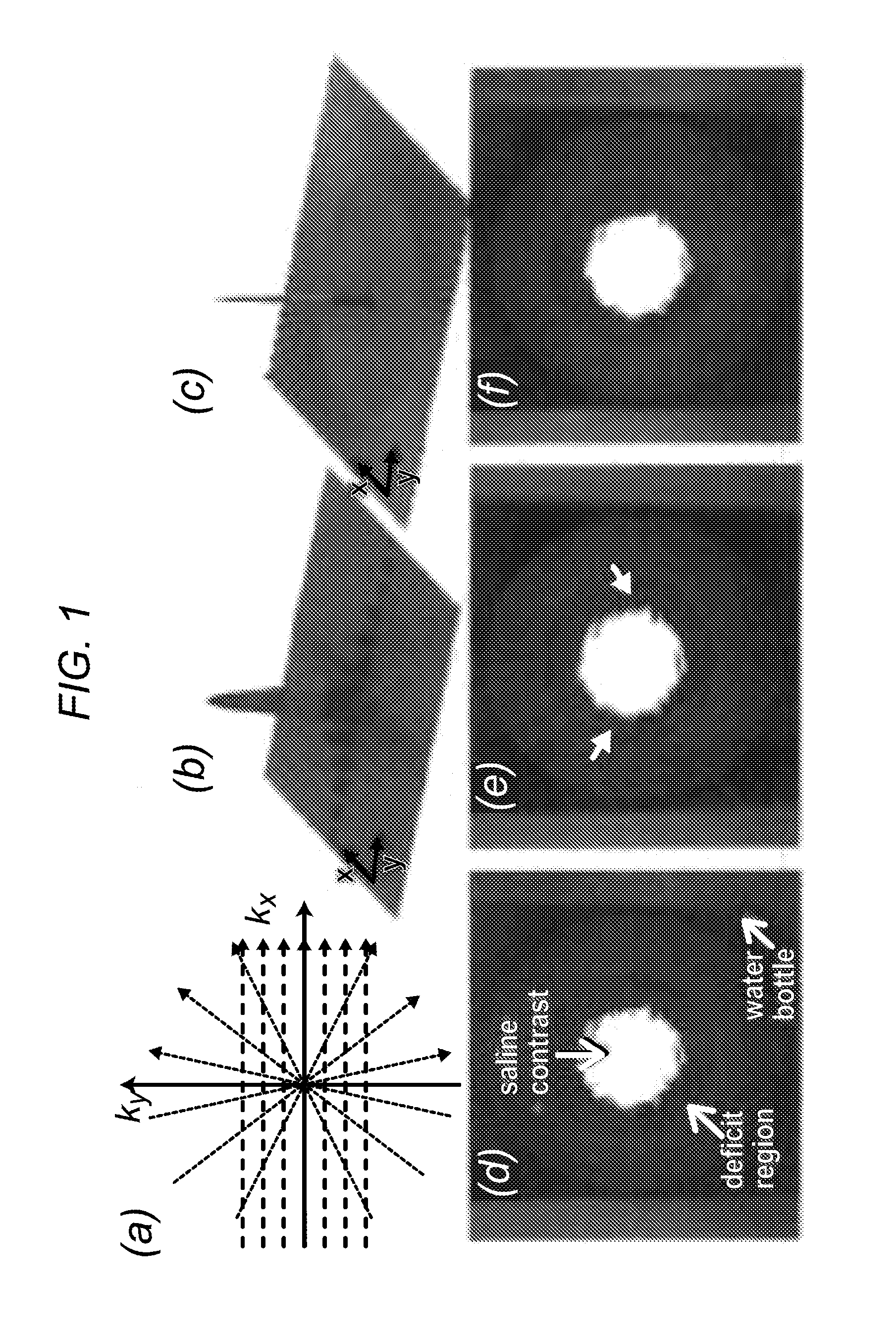
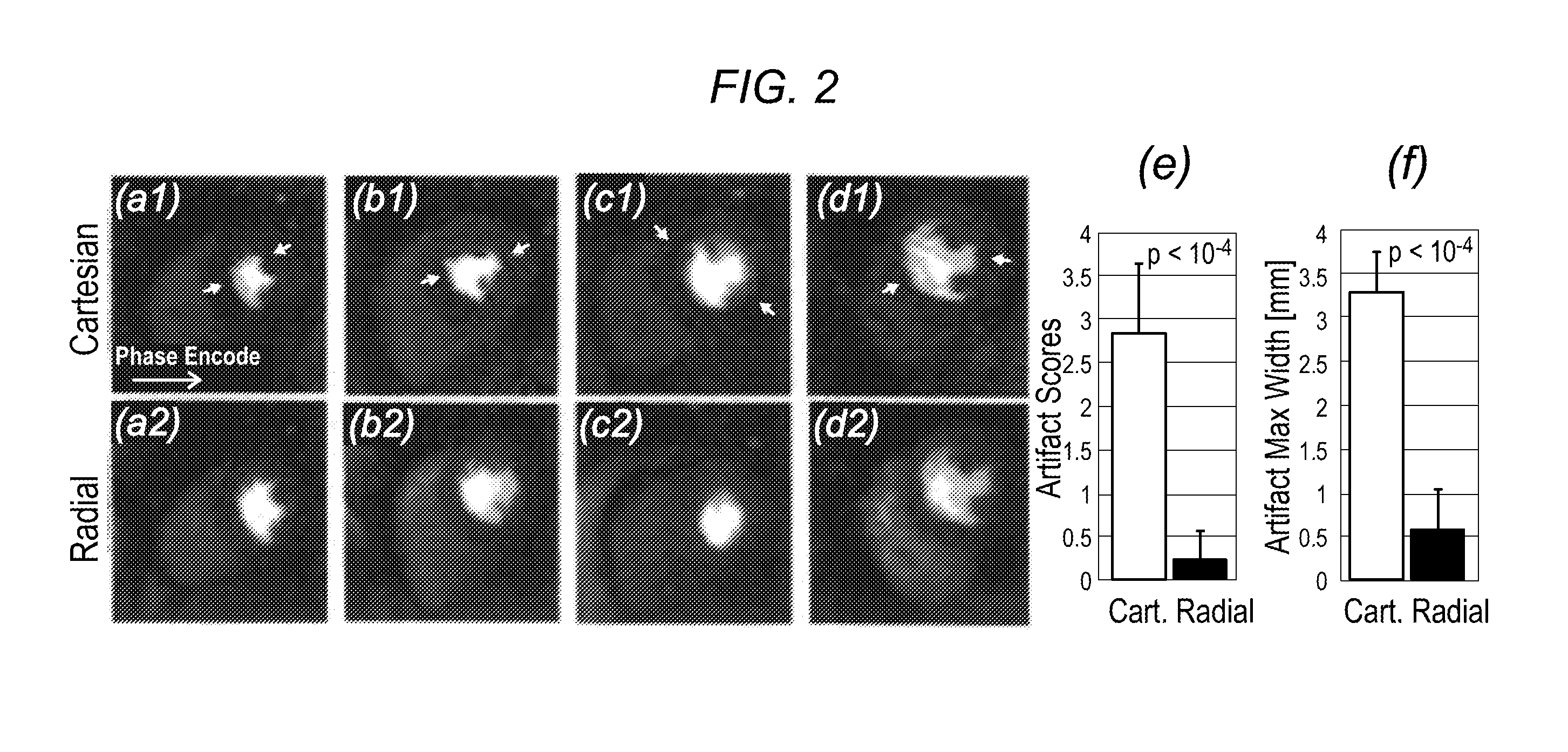
Systems and methods for myocardial perfusion MRI without the need for ECG gating and additional systems and methods for improved cardiac imaging
In some embodiments, the present application discloses systems and methods for cardiac MRI that allow for continuous un-interrupted acquisition without any ECG / cardiac gating or synchronization that achieves the required image contrast for imaging perfusion defects. The invention also teaches an accelerated image reconstruction technique that is tailored to the data acquisition scheme and minimizes or eliminates dark-rim image artifacts. The invention further enables concurrent imaging of perfusion and myocardial wall motion (cardiac function), which can eliminate the need for separate assessment of cardiac function (hence shortening exam time), and / or provide complementary diagnostic information in CAD patients.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Real-time optimization of right to left ventricular timing sequence in bi-ventircular pacing of heart failure patients
ActiveUS20050203579A1Improved hemodynamic performanceImprove performancePerson identificationHeart stimulatorsAccelerometerCardiac muscle
A system and automated method for assessing ventricular synchrony in ambulatory patients is provided including at least one mechanical sensor (e.g., accelerometer, tensiometric sensor, force transducer, and the like) operatively coupled to a first myocardial location in order to measure a wall motion signal of a first chamber, and a second mechanical sensor operatively coupled to a second myocardial location in order to measure a wall motion signal of a second chamber. The wall motion signals are processed in order to identify the time at which a fiducial (e.g., an inflection point, a threshold crossing, a maximum amplitude, etc.) occurs for each respective signal. The temporal separation between the fiducial points on each respective signal is measured as a metric of ventricular synchrony and can be optionally utilized to adjust pacing therapy timing to improve synchrony.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Multiple frequency through-the-wall motion detection and ranging using a difference-based estimation technique
InactiveUS7460052B2High resolutionEasy to separateRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPartition of unityPhase difference
A multi-tone CW radar (14) is used to project signals from an antenna (22) and to receive returns with the same antenna. The phase differences between the outgoing signals and the returns are analyzed to determine the existence of motion and the range to a moving object (10). A model is made which has range as its major parameter. A waveform associated with the phase difference between outgoing signals and returns for one of the tones is compared to templates produced by the model to determine which has a range that most closely matches. By varying the range parameters, when a match is detected the range to the object can be obtained even if its motion is pseudorandom. If the range is measured with multiple units it is possible to measure the location of the object. This can be done assuming a grid and algorithmically combining the ranges from the units.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTEGRATION INC
Multi-Electrode Mapping Catheter
ActiveUS20160073960A1Eliminate needIncrease valueGuide needlesElectrocardiographyElectrical conductorHeart chamber
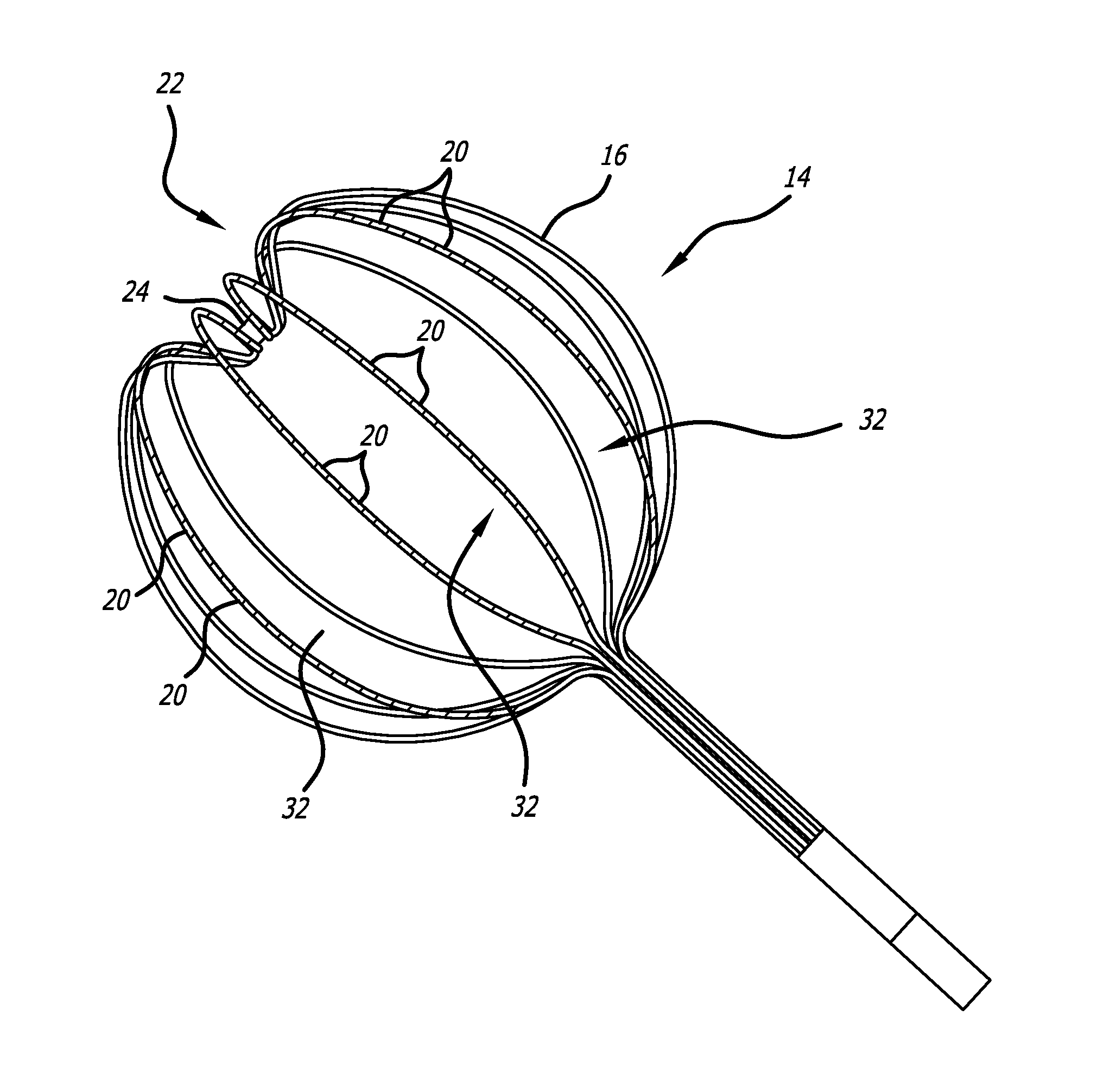
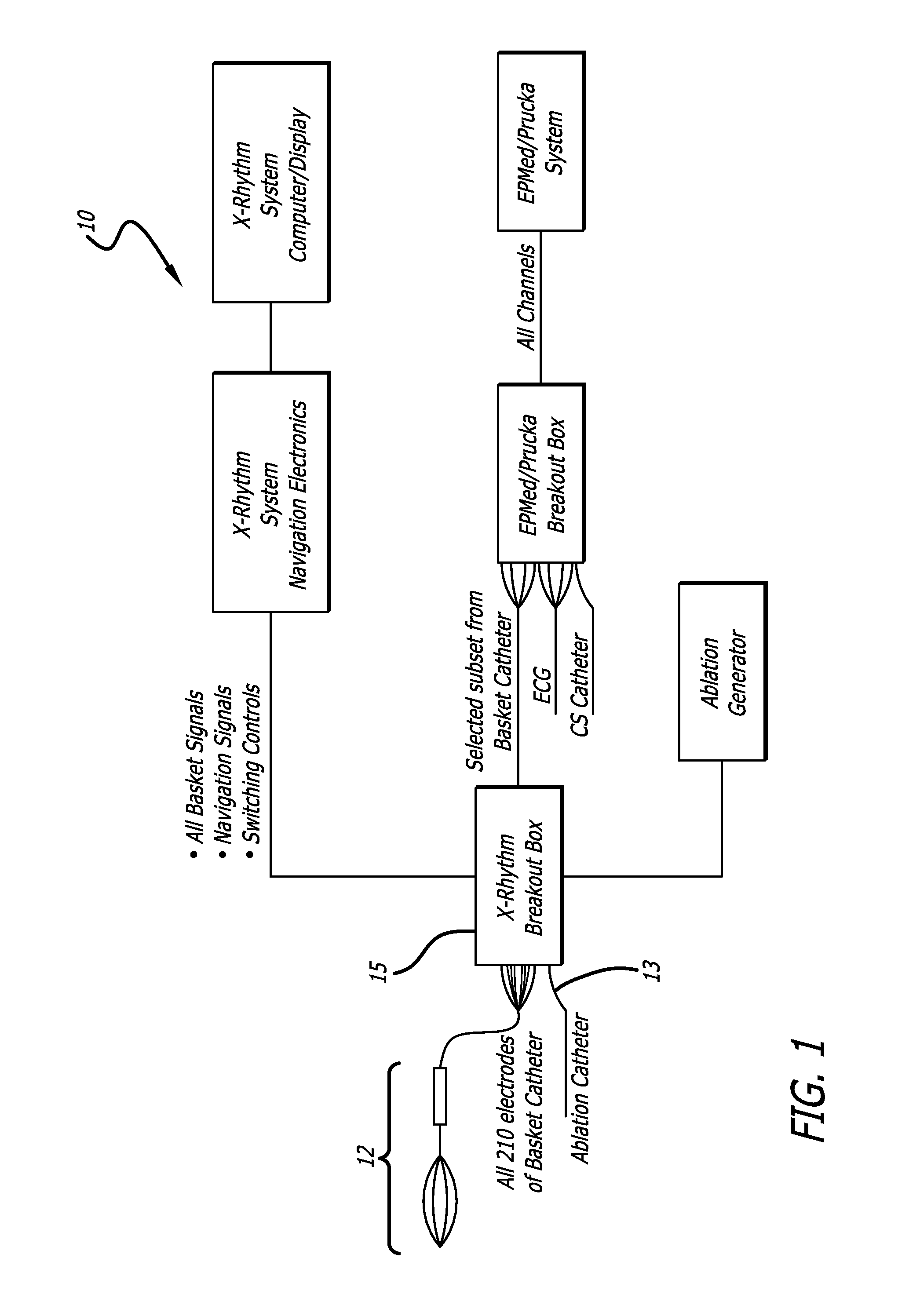
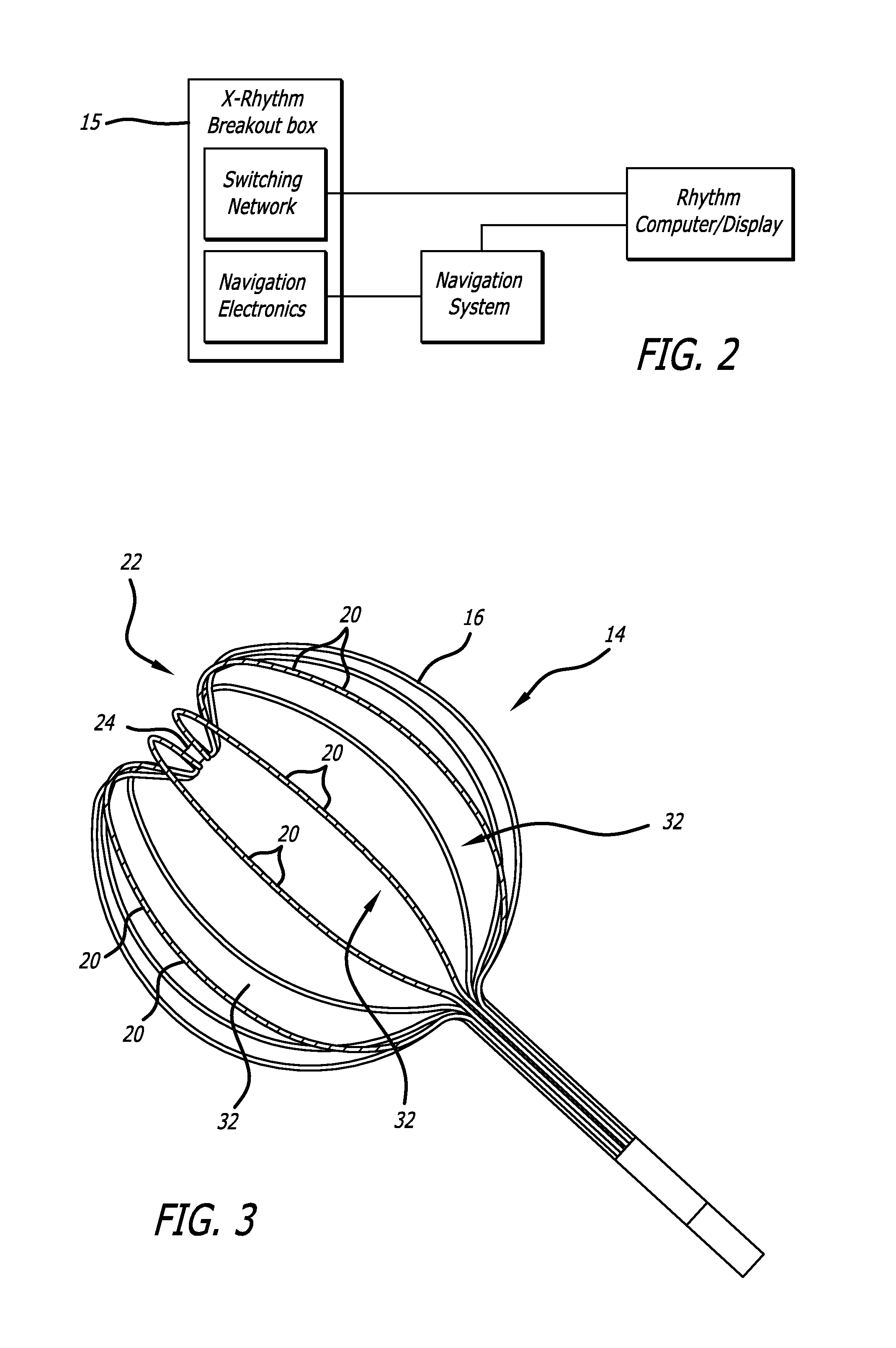
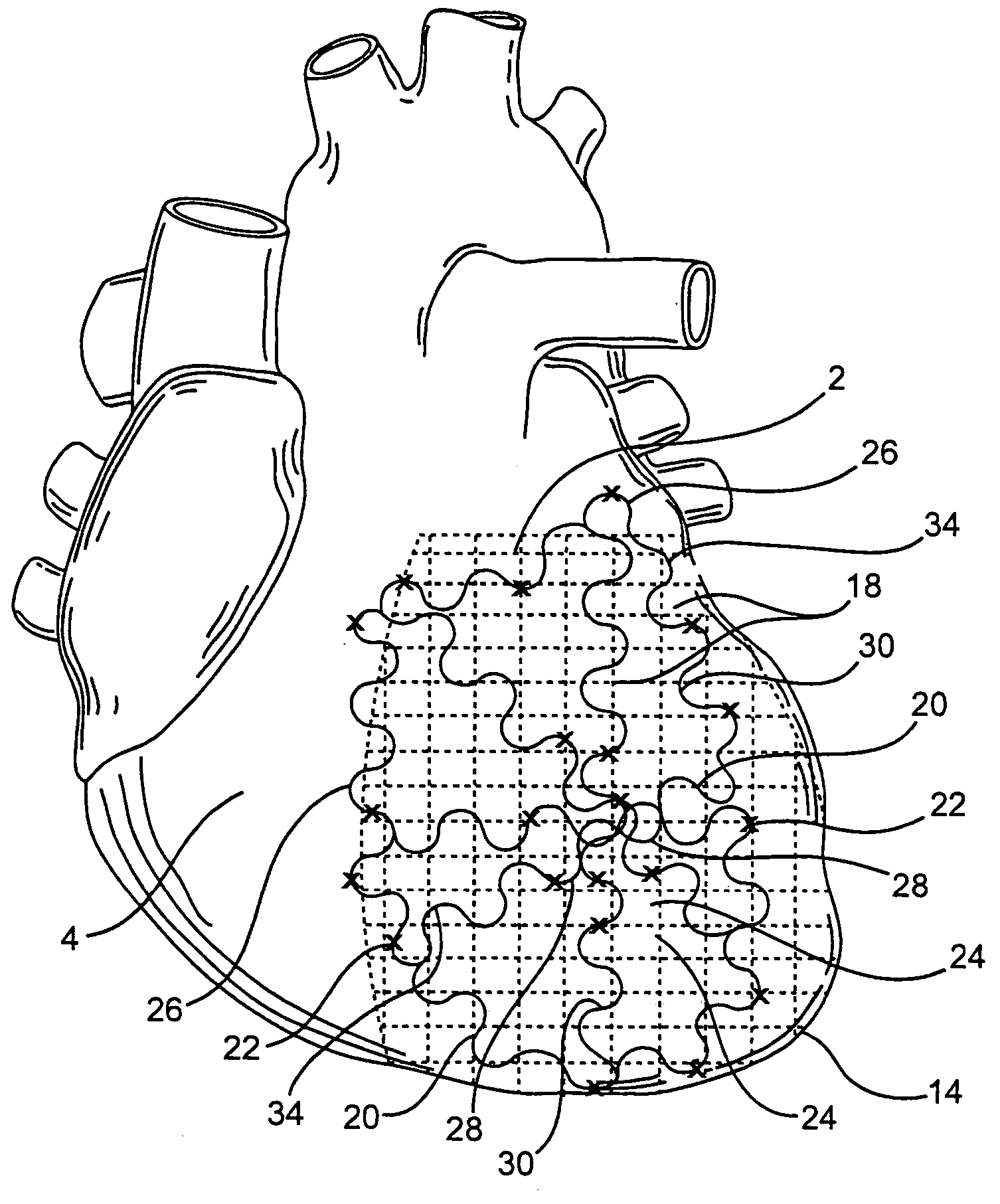
A multi-electrode mapping catheter for endocardial contact mapping of a heart chamber includes an expandable basket movable between a contracted configuration and a pre-shaped deployed configuration, the expandable basket including a plurality of flexible splines. Each spline includes a flex circuit and an electrode for mapping. A catheter shaft extending from the basket includes a lumen formed therethrough for receiving an ablation catheter for placement within the expandable basket. Each flex circuit includes a conductor that directly connects the proximal end of the catheter shaft to an electrode as a single continuous piece. In another embodiment, a shaft flex circuit extends along the length of the shaft and is electrically connected to a basket flex circuit. The expandable basket maintains the electrodes in direct contact with the wall of the heart while accommodating wall motion of the beating heart during mapping and can continually map while ablating.
Owner:X RHYTHM
System and method for segmenting m-mode ultrasound images showing blood vessel wall motion over time
ActiveUS20110044522A1Existing techniqueHigh resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisSonificationComputer module
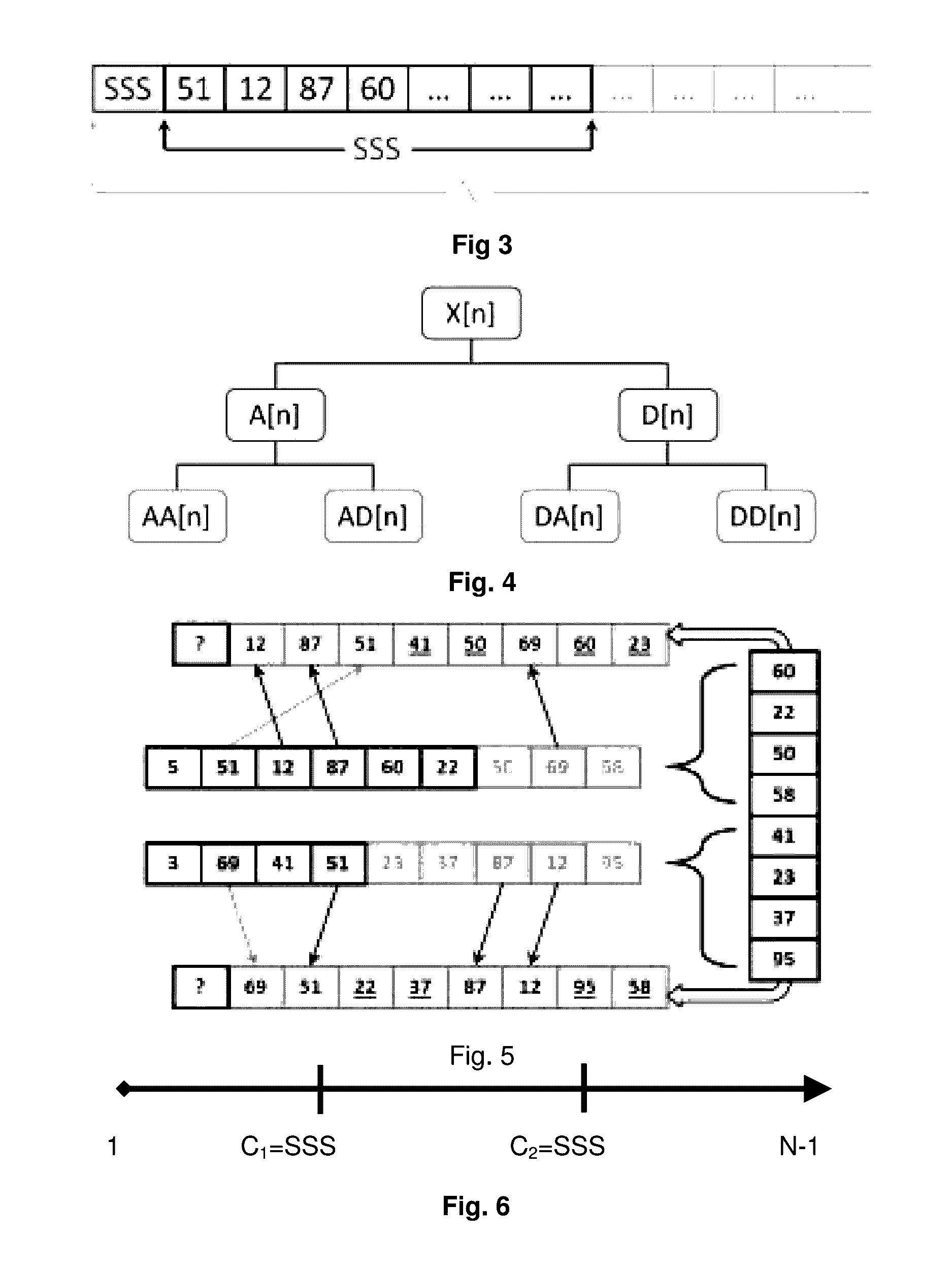
The present invention uses a microprocessor, a memory storage device, and a segmentation program comprising a plurality of program modules containing computer-readable instructions that cause the microprocessor to measure the spatial offsets between all pairs of scans in an m-mode image of a blood vessel with a cross-correlation function, convert the spatial offsets to a relative wall motion waveform through a global optimization procedure, and then translate the relative wall motion waveform to an absolute wall motion waveform by interpolation over the m-mode image. The resulting detailed absolute wall distension waveform may be beneficially rendered (e.g., superimposed) on the m-mode ultrasound image for display (e.g., on a printer and / or video monitor) and diagnostic purposes, and has enormous potential for enhancing existing techniques for identifying and studying vascular biomarkers, such as vessel wall strain and compliance.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Heart support to prevent ventricular remodeling
InactiveUS20050113635A1Reducing end-diastolic diameterRelieve stressHeart valvesControl devicesSystoleCardiac functioning
This is a support device that prevents, reduces, and delays remodeling of diseased cardiac tissue, and also decreases the impact of such remodeling on collateral tissue is disclosed. The invention further reinforces abnormal tissue regions to prevent over-expansion of the tissue due to increased afterload and excessive wall tension. As a result, the support device prevents phenomenon such as systolic stretch from occurring and propagating. The support structure maintains and restores diastolic compliance, wall motion, and ejection fraction to preserve heart functionality. As such, the support device prevents and treats cardiomyopathy and congestive heart failure.
Owner:CONVERGE MEDICAL
Non-invasive device for synchronizing chest compression and ventilation parameters to residual myocardial activity during cardiopulmonary resuscitation
ActiveUS7645247B2Promote recoveryReduce outputRespiratorsElectrotherapyLeft ventricular sizeNon invasive
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
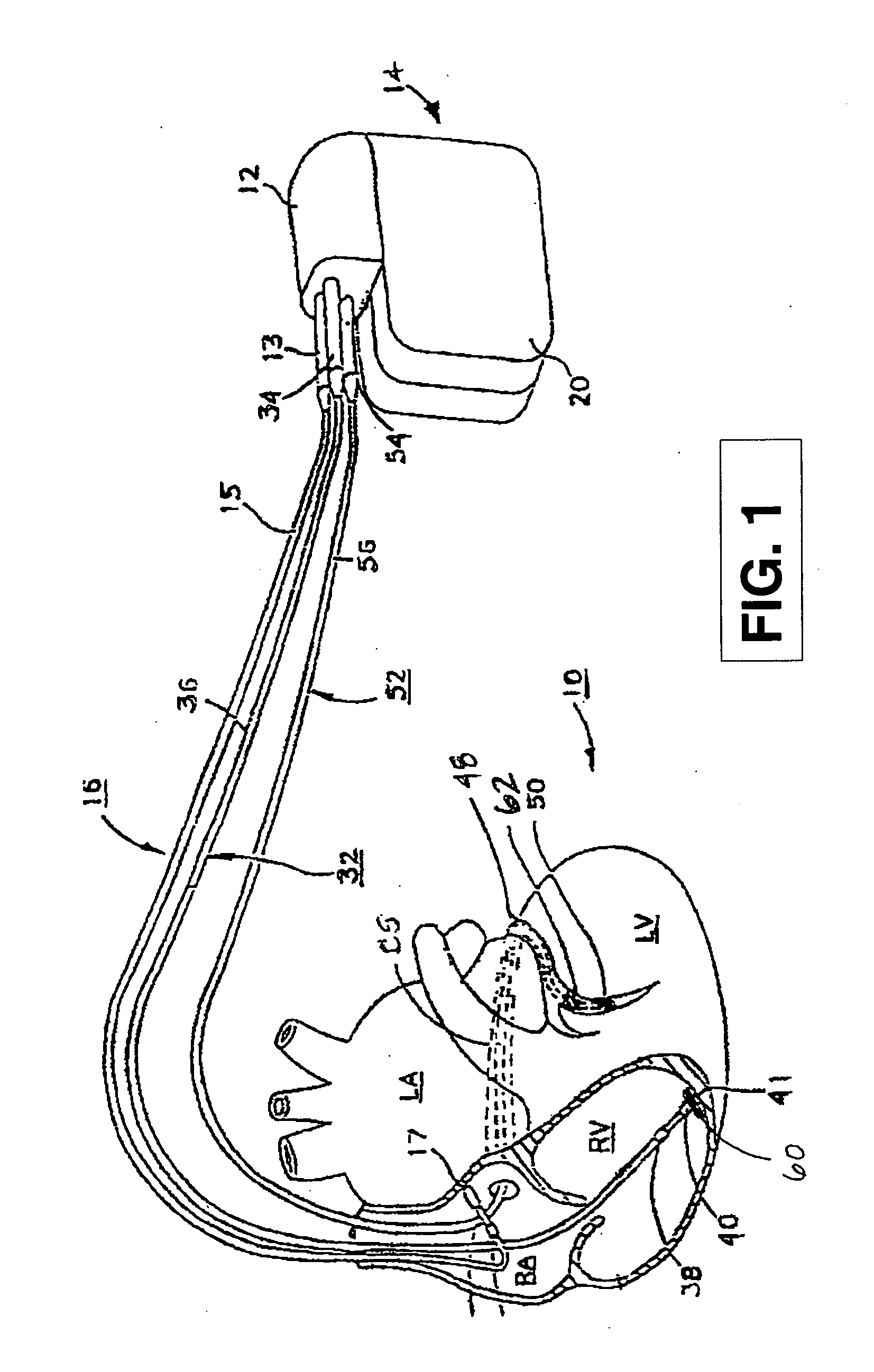
Lead Tracking Of Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD) And Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) Devices
InactiveUS20090105779A1Eliminate fragile wiringImprove reliabilityTransvascular endocardial electrodesSurgical navigation systemsHome environment3d tracking
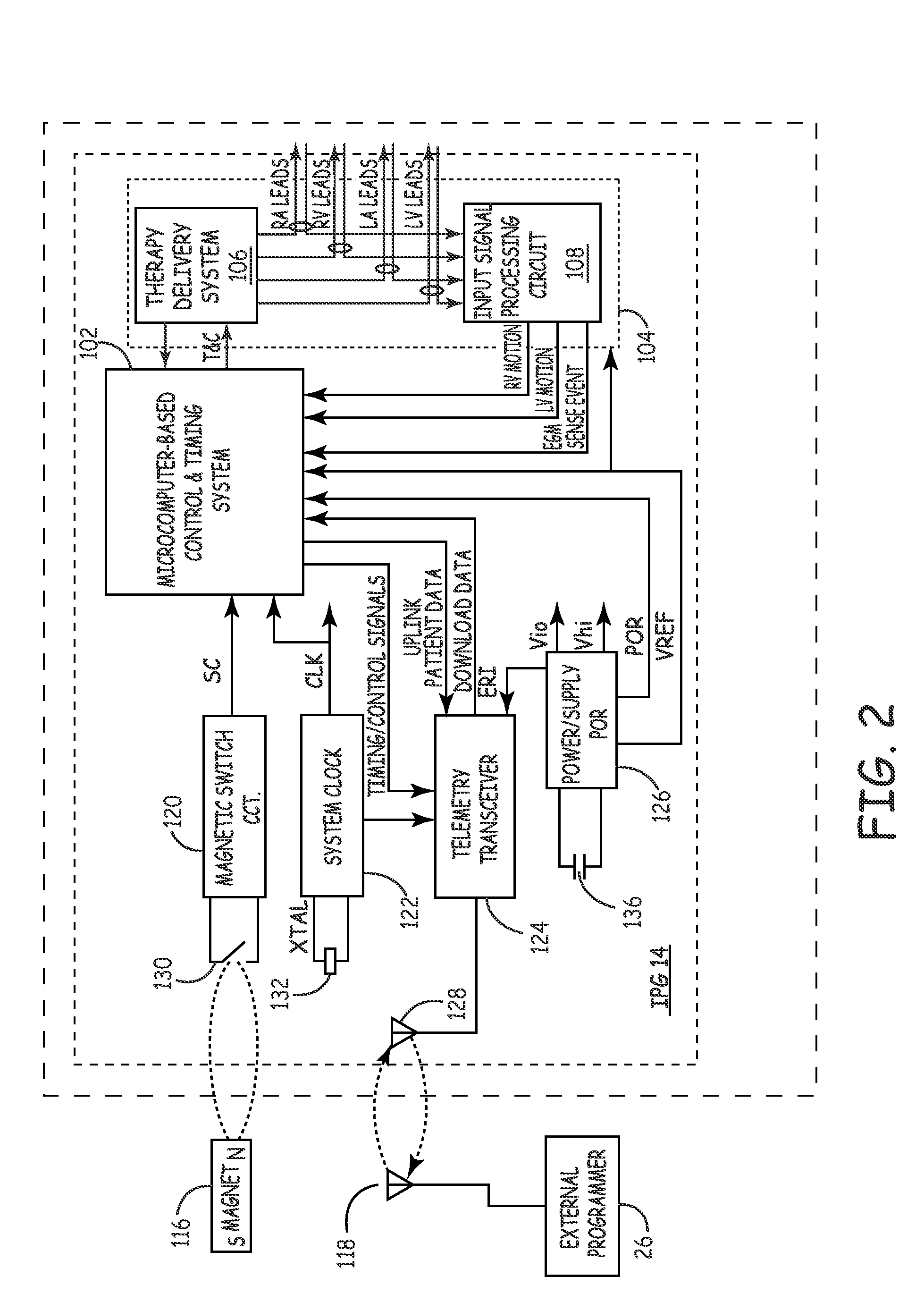
Lead Tracking of Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator and Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Devices improve upon the process of implantation of ICD-CRT devices, placing their leads, and improving the information fed back to the device and / or clinician. Tracking of the placement of the leads during implantation is accomplished along with monitoring the leads once implanted. Benefits include reducing the risk and complication rate, simplifying implantation procedure, and enabling the extraction of vital data not previously available. Leads are tracked to at least minimize the need to use fluoroscopy. Three dimensional tracking (10) is employed to facilitate obtaining of data that allows the surgeon to better visualize lead insertion and placement. Placement of the leads during a procedure requires use of an external tracking component along with means and method for tracking the implantable leads. Transmitting antennas (10, 110) are provided, equal in number to the number of degrees of freedom of tracking required. A link (50) between the sensor (70) and the computation unit (40) can be wired or wireless. Once leads are implanted, heart wall motion must be monitored via the tracking of the leads within a clinical or home environment. Such tracking of the leads may be accomplished in real time.
Owner:ASCENSION TECH
Through-the-wall motion detector with improved antenna
InactiveUS20090033539A1Eliminate the effects ofPrevent receiver swampingAntenna arraysAntenna supports/mountingsRadarRefractive index
A flat panel antenna used at a wall in a through-the-wall CW radar application is spaced from the wall by a half wavelength to eliminate the effects of energy reflected by the wall back to the antenna. In one embodiment, a ½-wavelength dielectric absorbing material insert is placed adjacent the flat panel antenna, which allows the flat panel antenna to be pressed against the wall for antenna stabilization, with the index of refraction of the material desirably being 3.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Domain wall motion element and magnetic random access memory
A domain wall motion element has a magnetic recording layer 10 that is formed of a ferromagnetic film and has a domain wall DW. The magnetic recording layer 10 has: a pair of end regions 11-1 and 11-2 whose magnetization directions are fixed; and a center region 12 sandwiched between the pair of end regions 11-1 and 11-2, in which the domain wall. DW moves. A first trapping site TS1 by which the domain wall DW is trapped is formed at a boundary between the end region 11-1, 11-2 and the center region 12. Furthermore, at least one second trapping site TS2 by which the domain wall DW is trapped is formed within the center region 12.
Owner:NEC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com