Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
249 results about "Helical scan" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
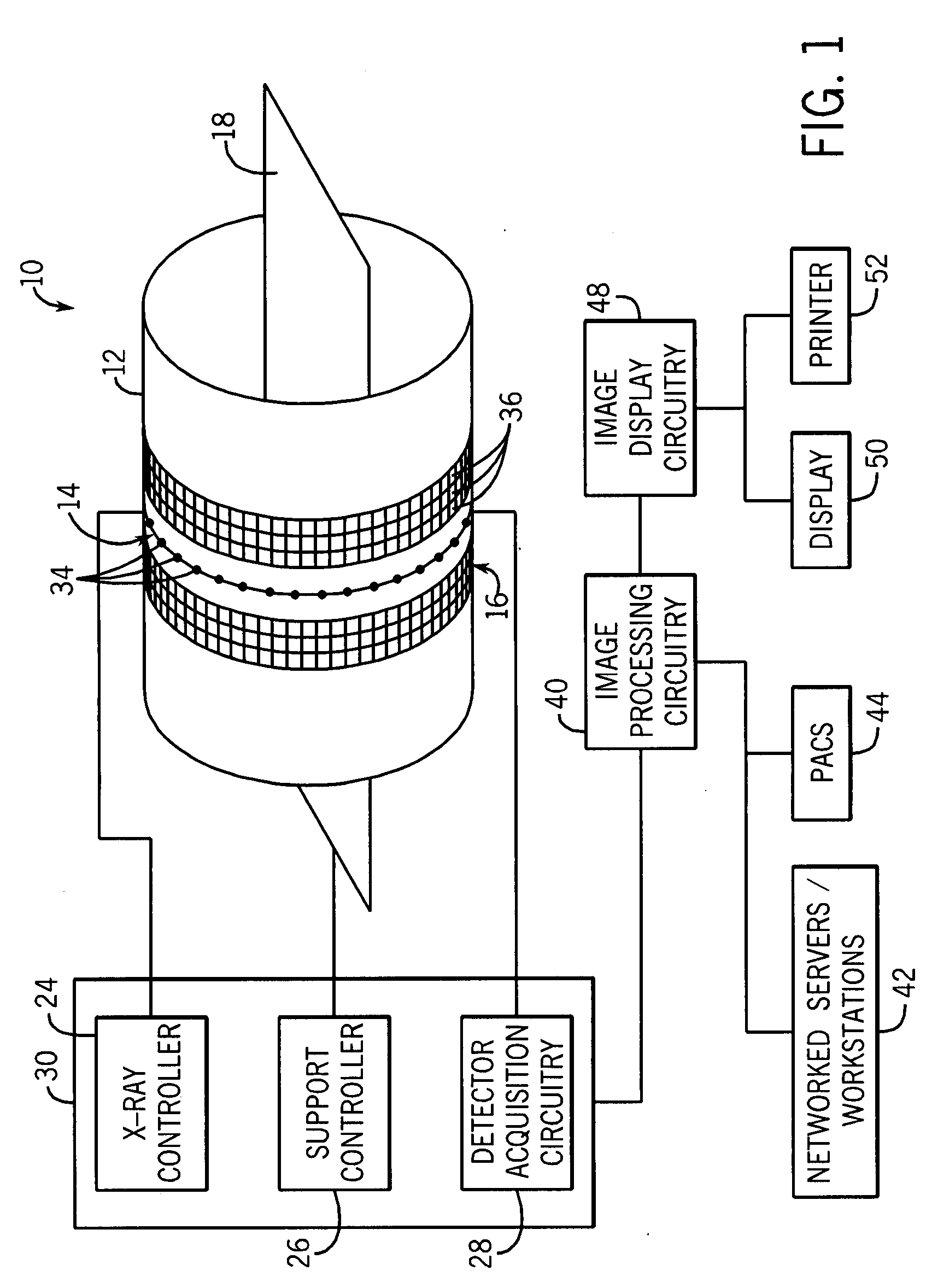
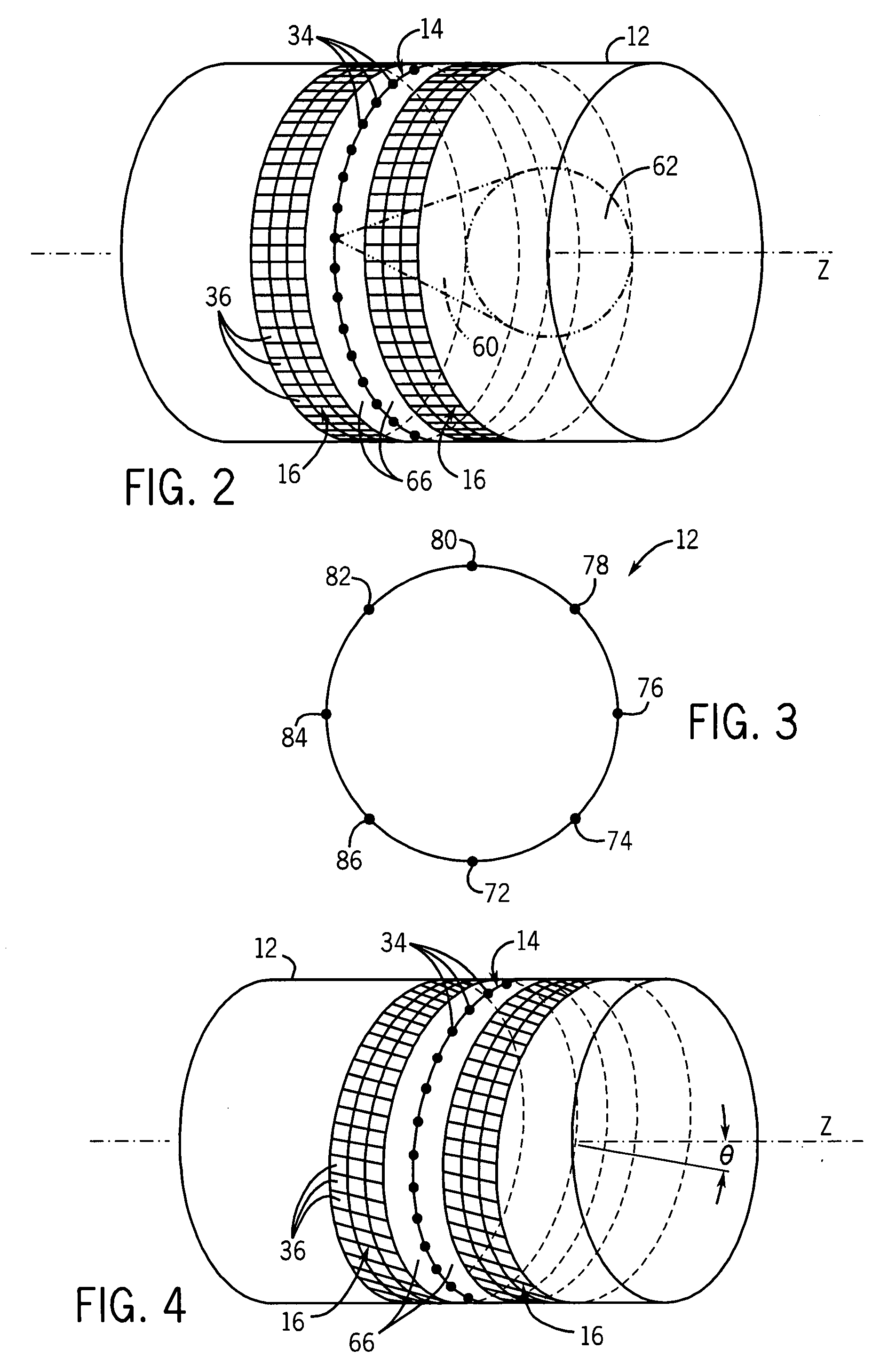
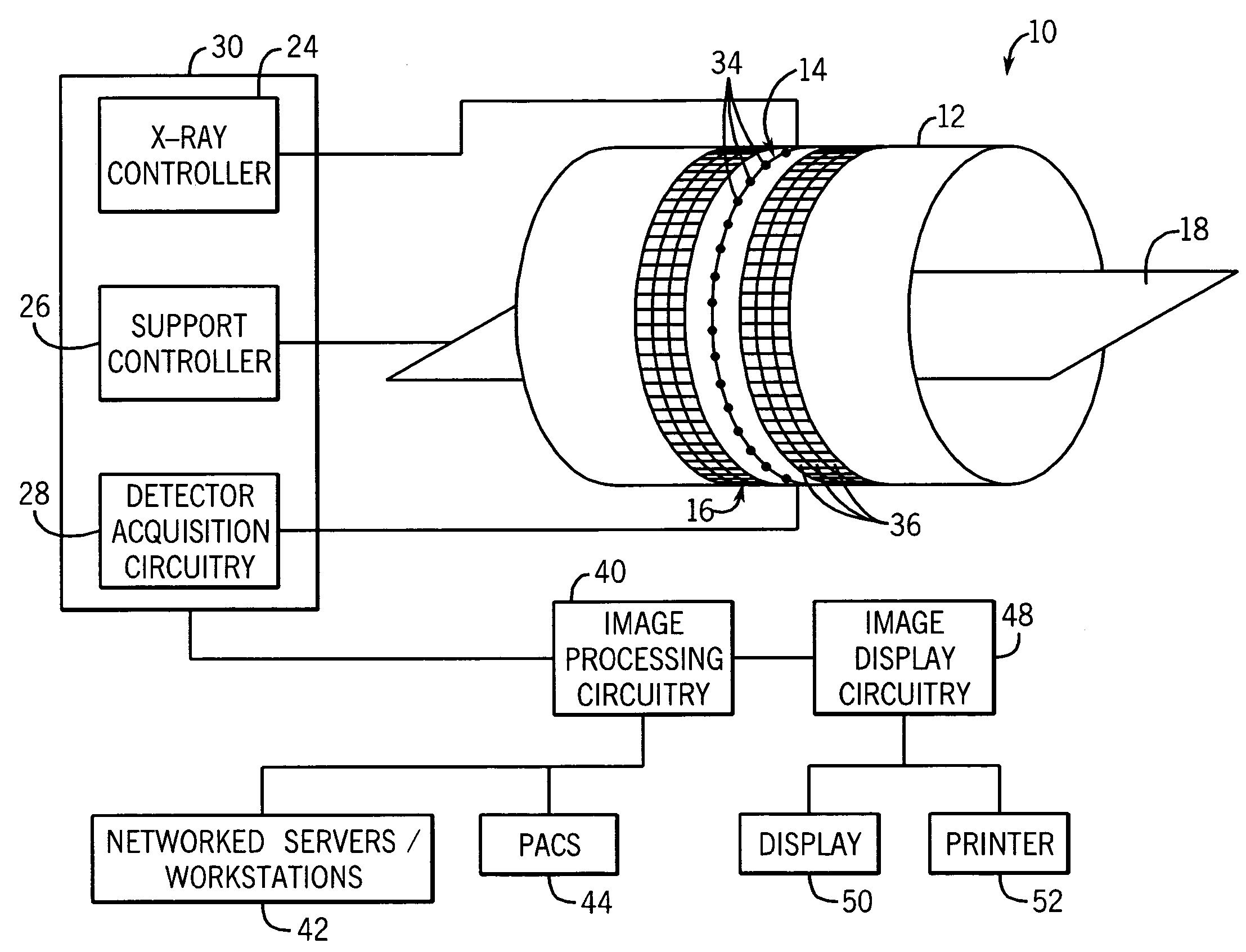
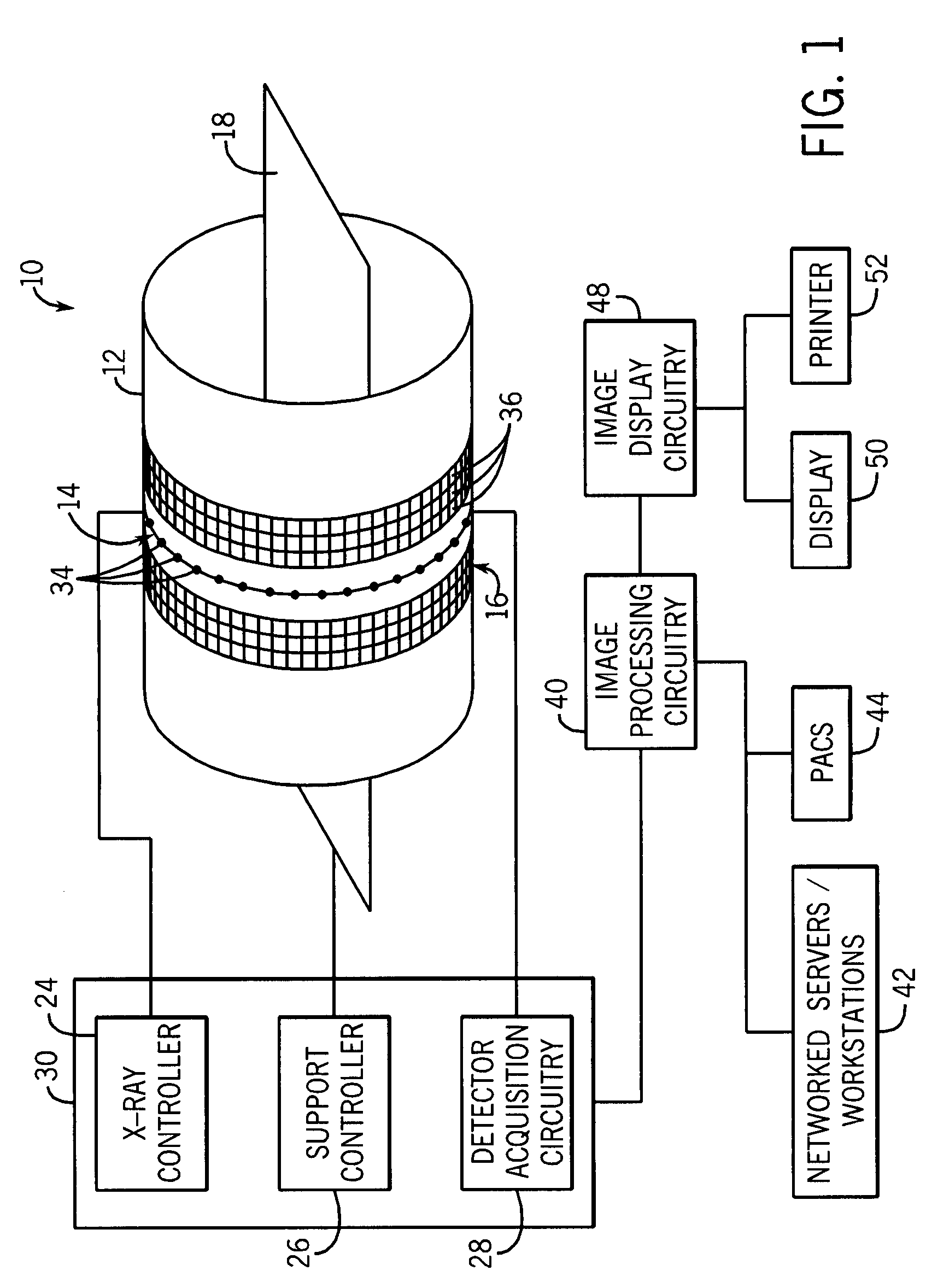
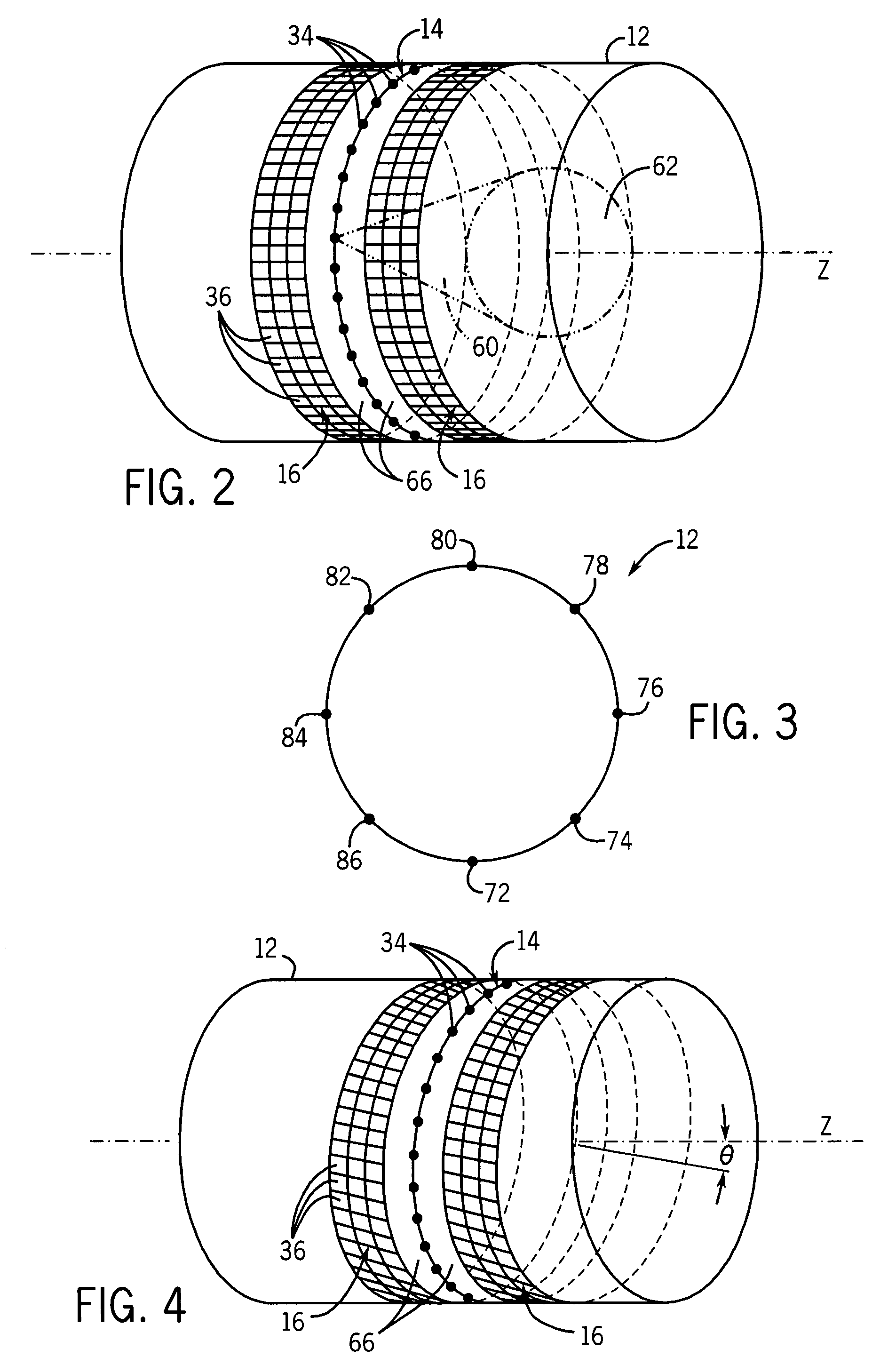
Helical scan is a method of recording high-frequency signals on magnetic tape. It is used in open-reel video tape recorders, video cassette recorders, digital audio tape recorders, and some computer tape drives.
CT extremity scanner
ActiveUS7388941B2Easy to useRadiation/particle handlingComputerised tomographsHelical scanCt scanners
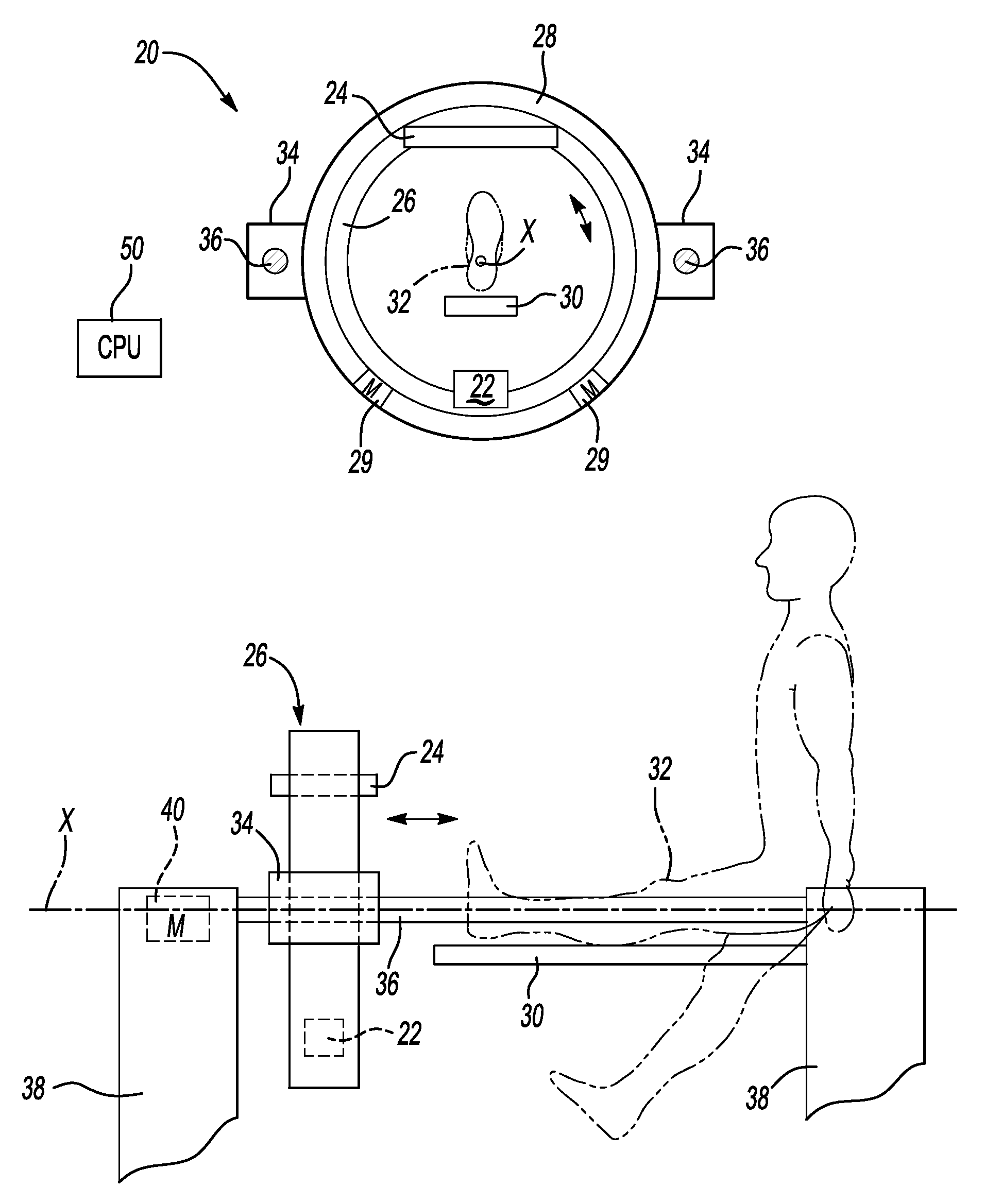
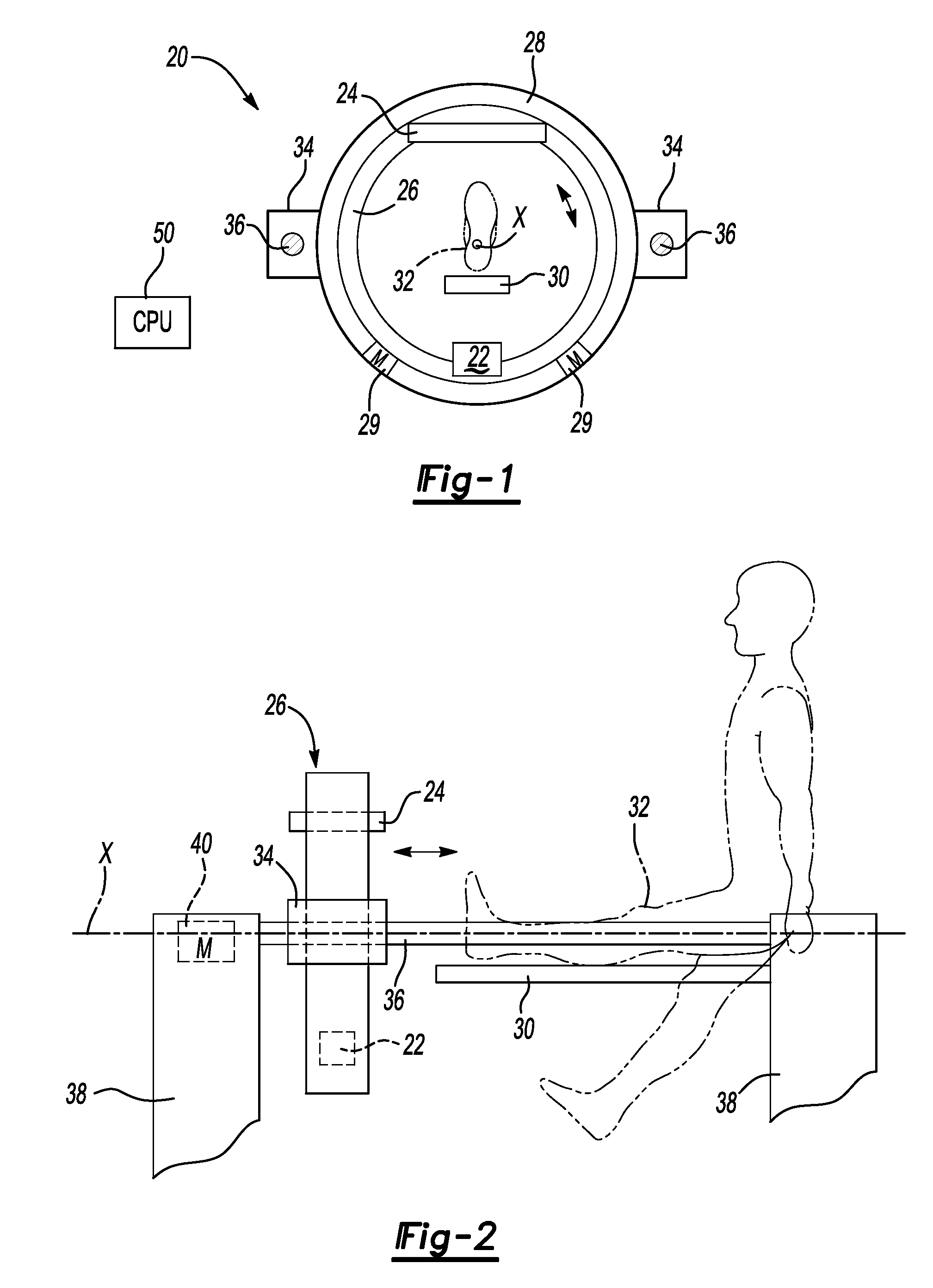
A CT scanner according to the present invention is particularly adapted for scanning the extremities of a patient. The CT scanner includes an x-ray source and x-ray detector mounted for rotation and translation along an axis parallel to a table for supporting the patient's extremity. The source and detector are mounted opposite one another on an inner circumference of an inner ring. The inner ring is rotatable about the axis within an outer ring mounted on at least one carriage. The carriage is movable parallel to the axis. During scanning, the inner ring rotates within the outer ring while the rings and carriage move along the axis, thereby producing a helical scan of the extremity.
Owner:XORAN TECH
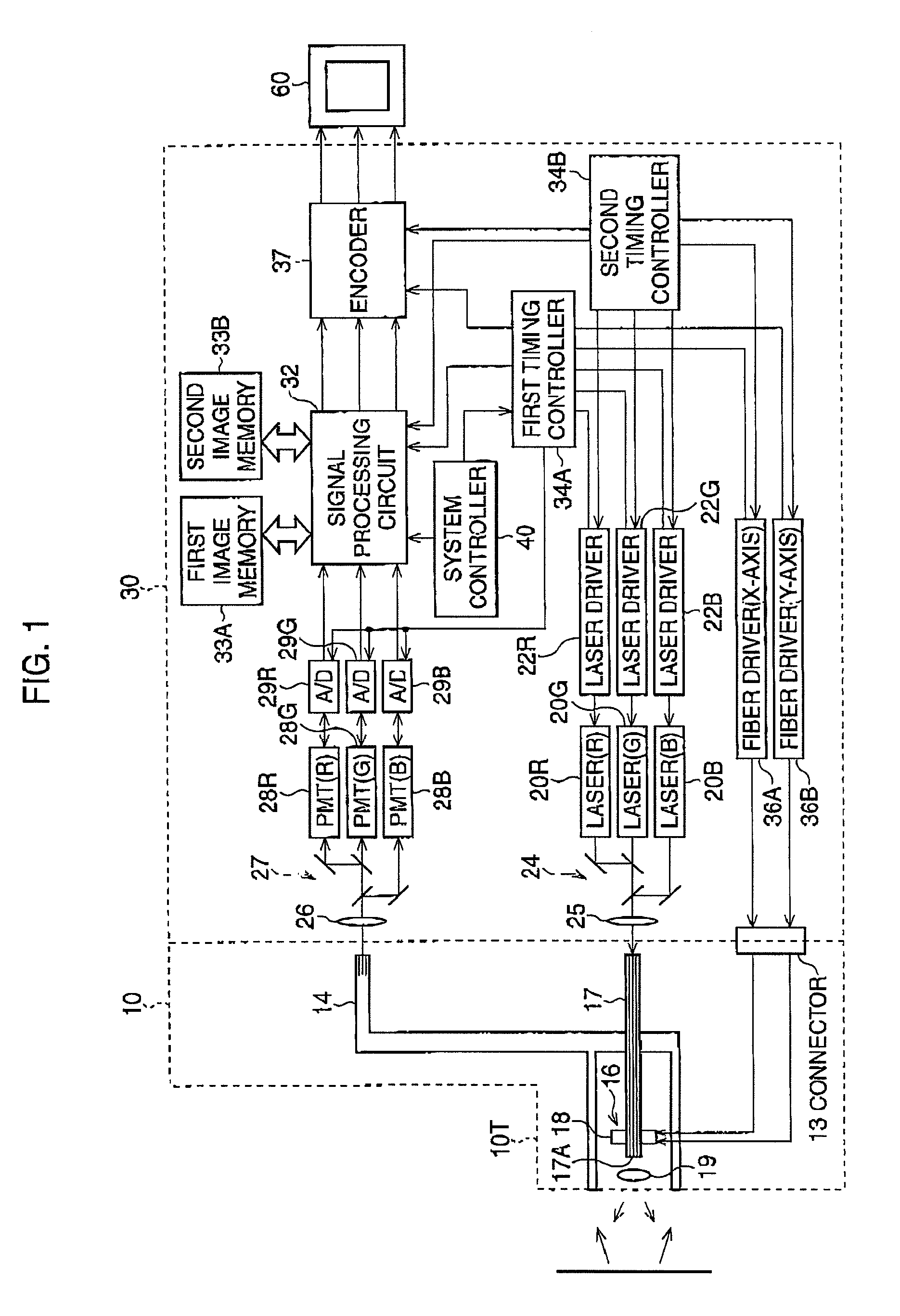
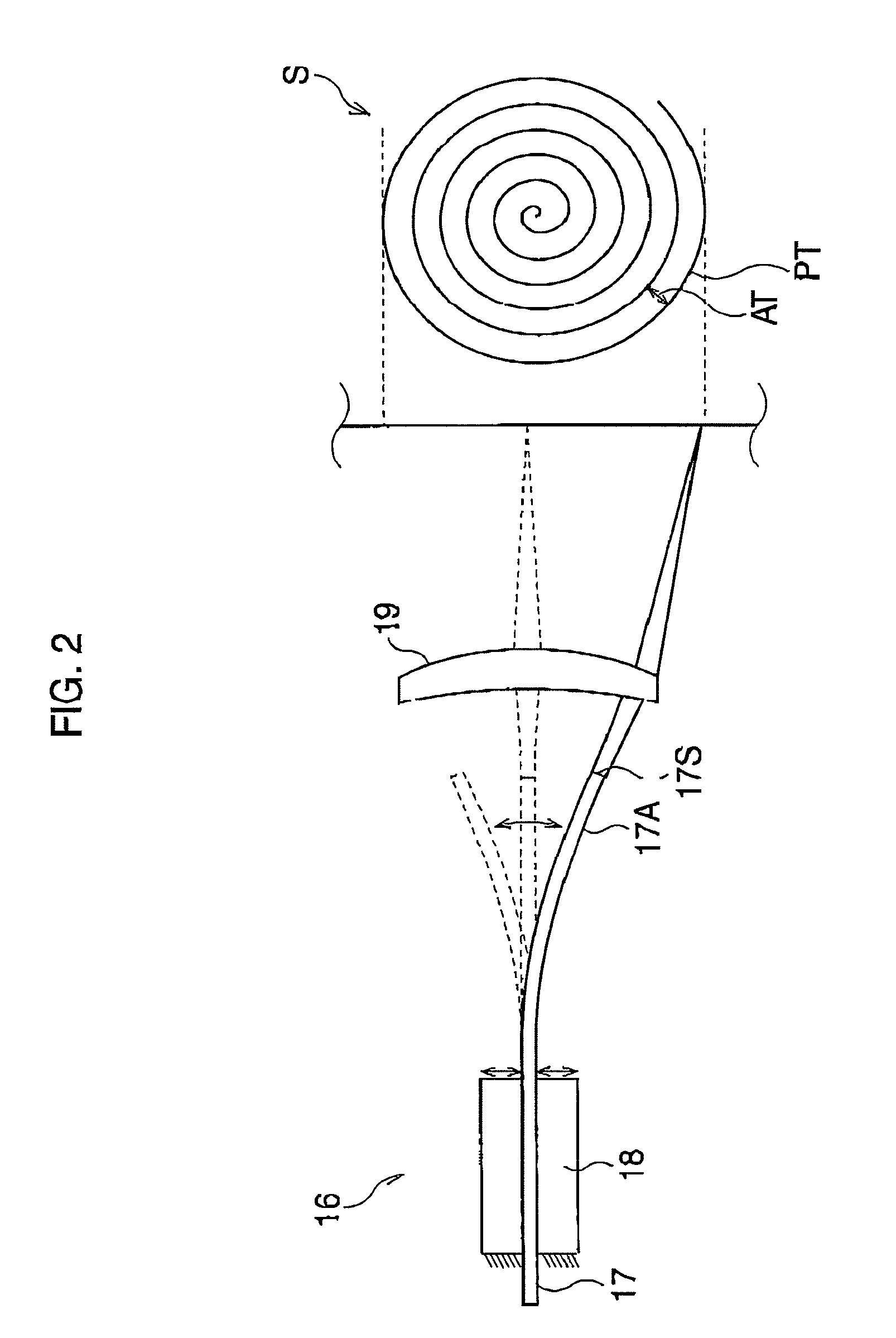
Endoscope system with scanning function
An endoscope system has an optical fiber configured to transmit illumination light emitted from a light source to the tip portion of a scope; a scanner configured to spirally scan a target area with illumination light by vibrating the tip portion of said optical fiber; and an image generator configured to generate image data from image-pixel signals obtained from the light reflected from the target area. Then, the scanner scans the illumination light in a circular motion midway through a spiral scanning procedure.
Owner:HOYA CORP
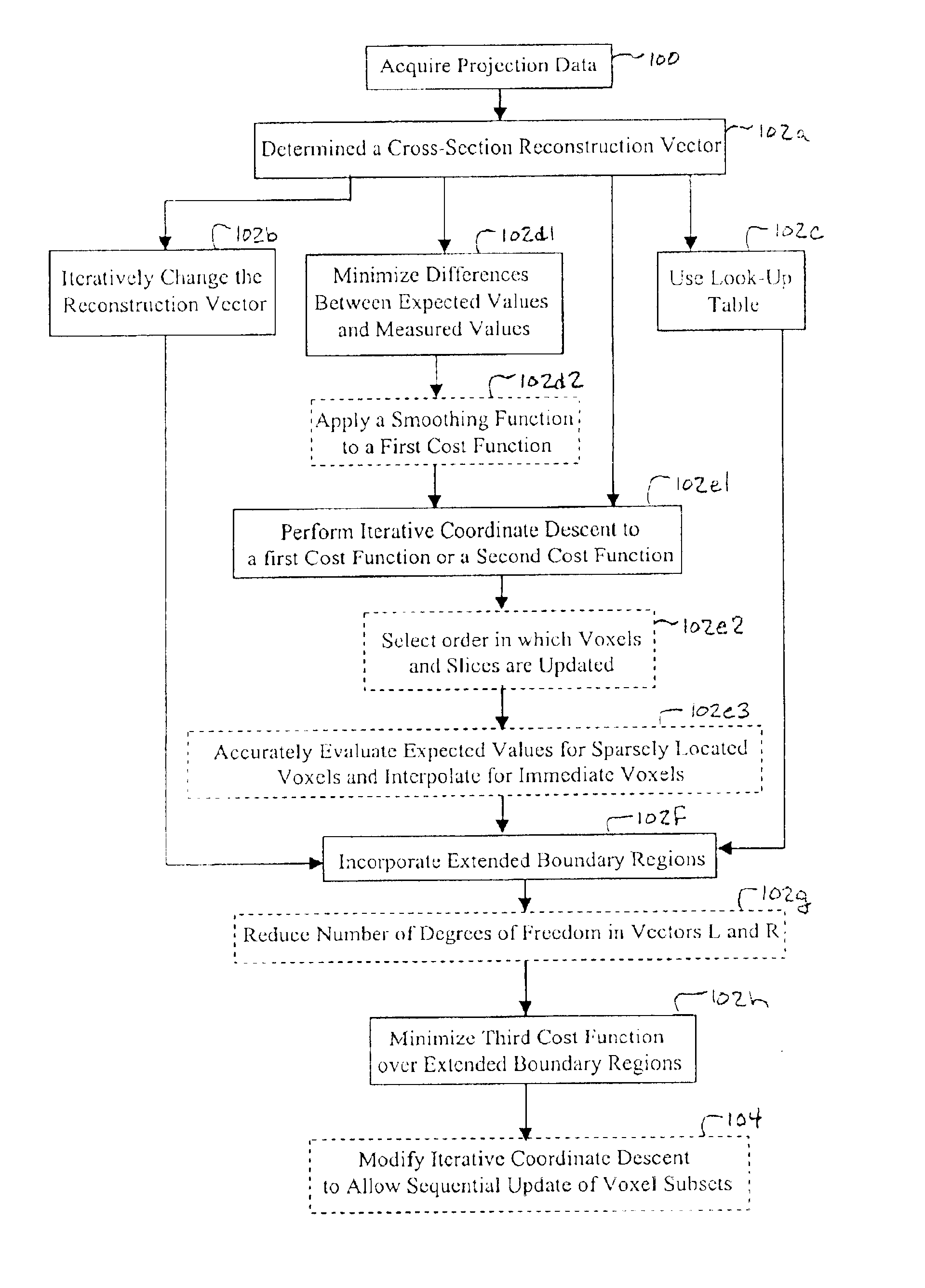
Iterative reconstruction methods for multi-slice computed tomography
InactiveUS6907102B1Avoid warpingError minimizationReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHelical scanMulti slice
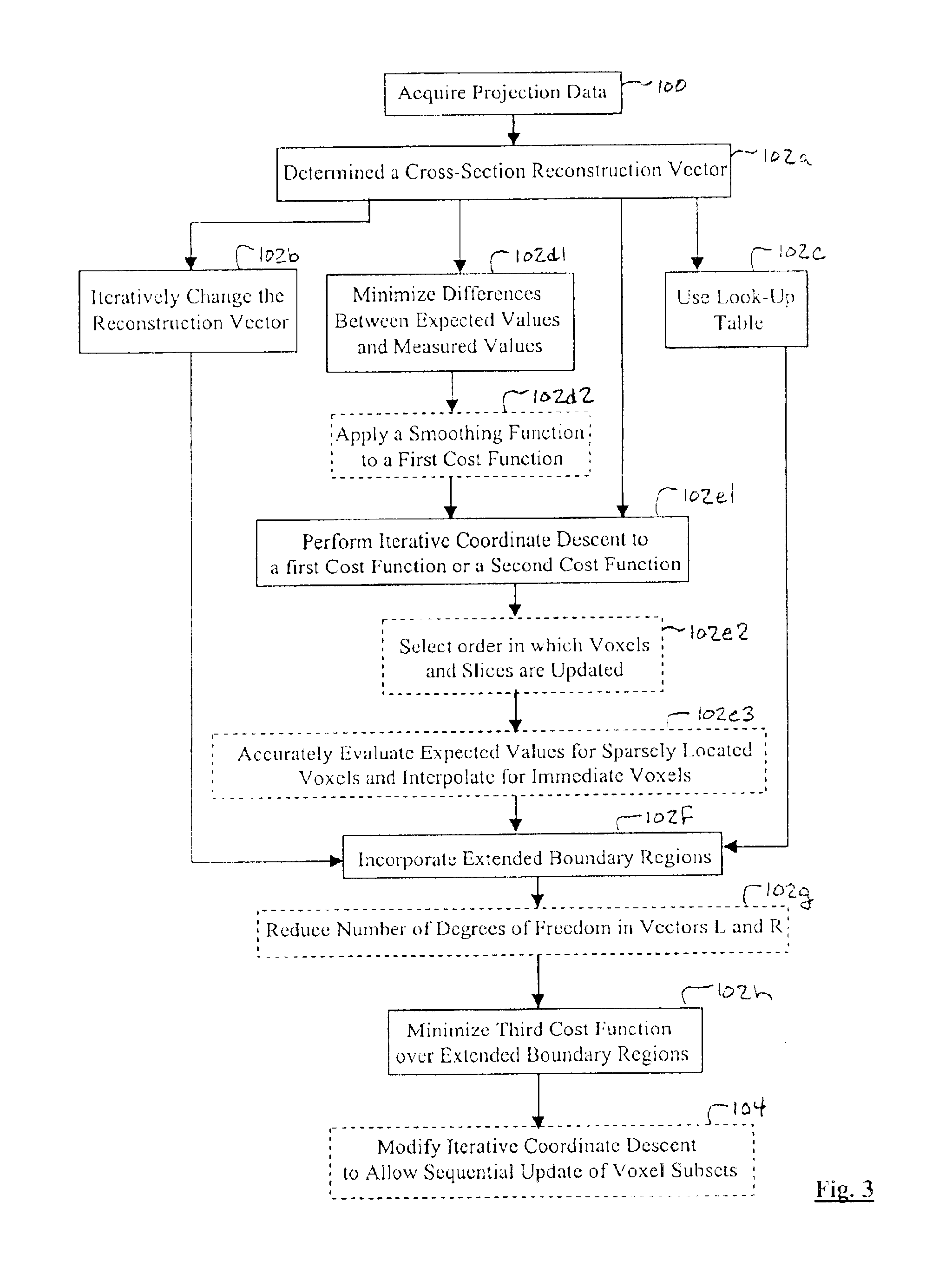
A multi-slice computed tomography imaging system is provided including a source that generates an x-ray beam and a detector array that receives the x-ray beam and generates projection data. A translatable table has an object thereon and is operable to translate in relation to the source and the detector array. The source and the detector array rotate about the translatable table to helically scan the object. An image reconstructor is electrically coupled to the detector array and reconstructs an image in response to the projection data using a computed tomography modeled iterative reconstruction technique. The iterative reconstruction technique includes determining a cross-section reconstruction vector, which approximately matches the projection data via a computed tomography model. Methods for performing the same are also provided including accounting for extended boundary regions.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC +2
Display stand including means for dispensing and collecting helical cable
InactiveUS20090173868A1Stop theftAvoid accidental removalStands/trestlesKitchen equipmentHelical scanDisplay device
A display stand for displaying an article of merchandise includes a base defining an outer periphery and means for dispensing and collecting a helical cable attached to the article of merchandise. The means for dispensing and collecting supports and guides the helical cable along the outer periphery of the base between a retracted length and an extracted length. The dispensing and collecting means may include at least one wheel disposed on the outer periphery of the base. The dispensing and collecting means may include at least one roller disposed on the outer periphery of the base. The dispensing and collecting means may include a low-friction surface disposed on the outer periphery of the base. The dispensing and collecting means may include a scalloped surface disposed on the outer periphery of the base. The display stand may further include a collection tube for delivering the helical cable to the article.
Owner:INVUE SECURITY PROD INC
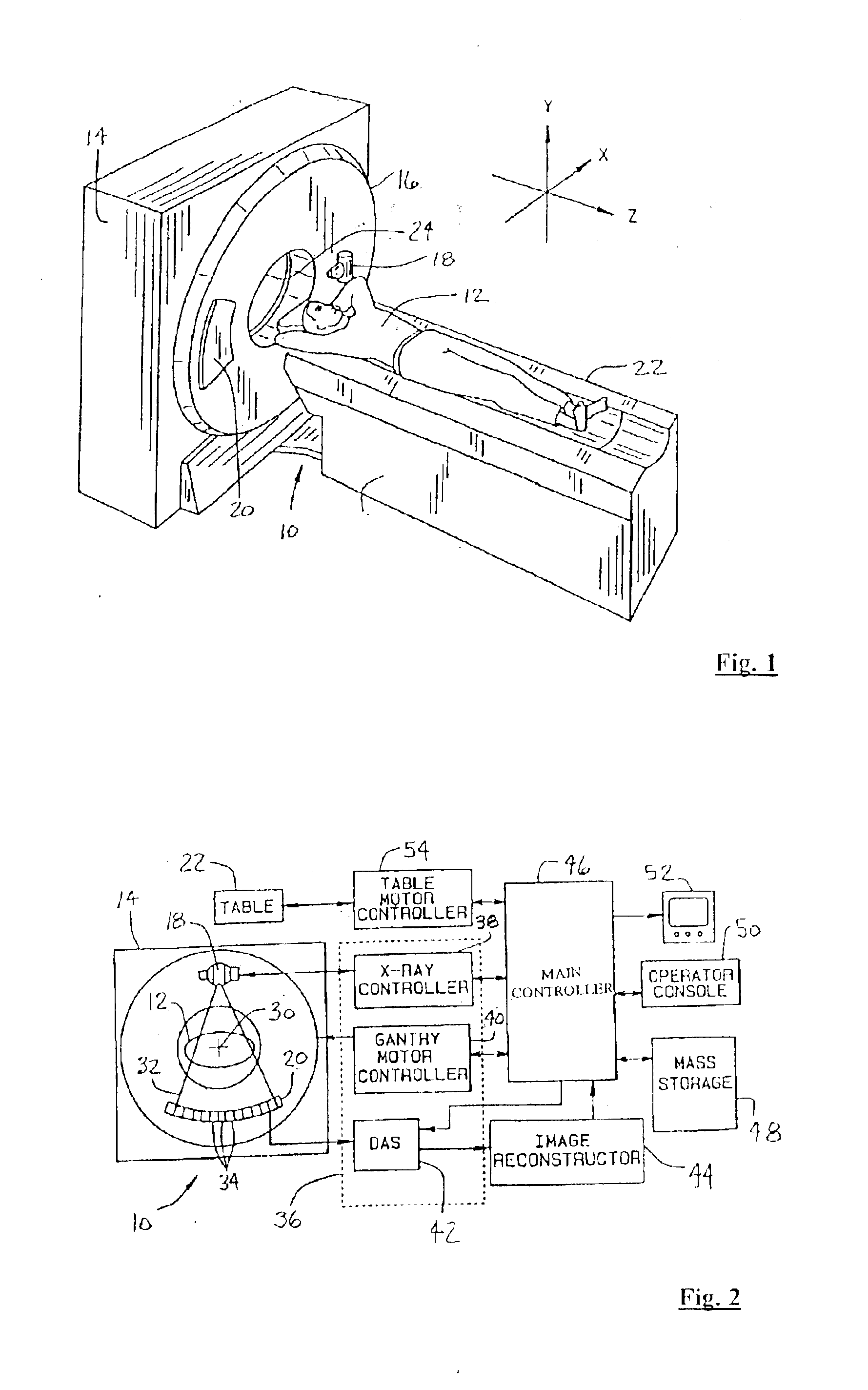
X-ray computed tomographic imaging apparatus
InactiveUS6990170B2Prevent irradiationAvoid omissionsReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHelical scanData reconstruction
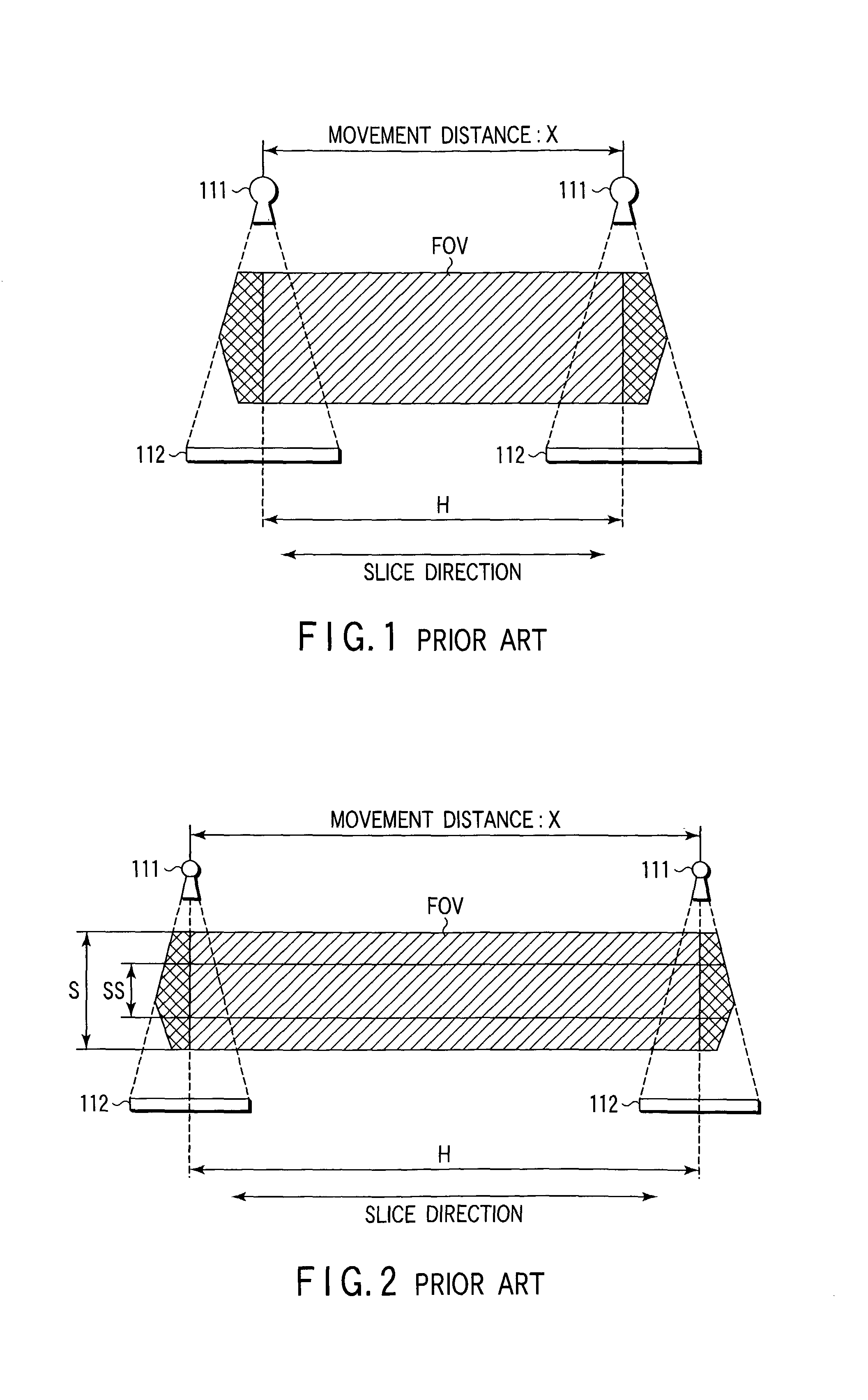
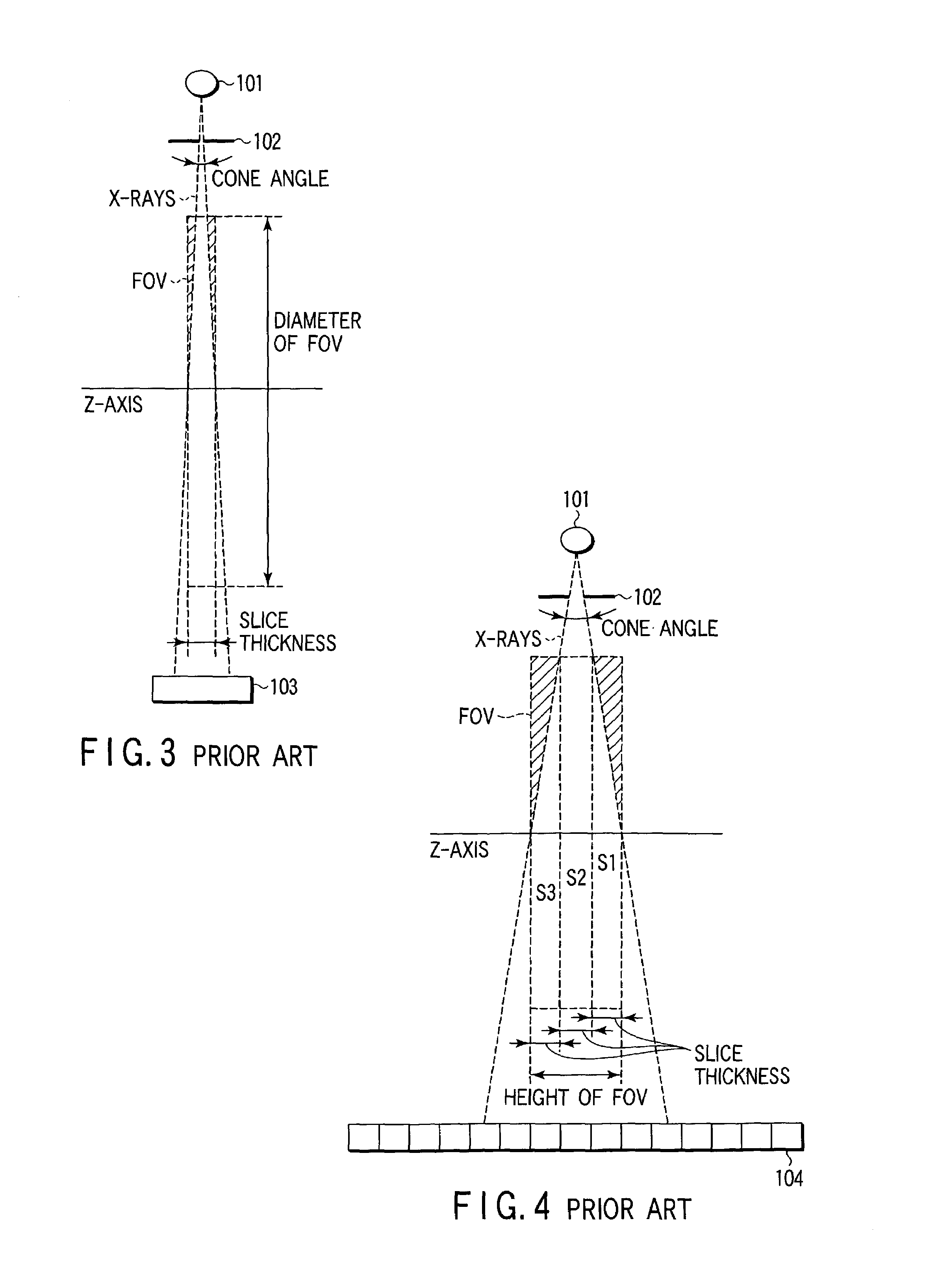
An X-ray computed tomography apparatus includes a cone beam X-ray tube, an X-ray detector, a rotating mechanism for supporting the X-ray tube and X-ray detector, a moving mechanism for moving the object in the slice direction, a control unit for controlling the rotating mechanism and moving mechanism to execute helical scan operation and move relative to the object, an input device for setting a substantially cylindrical reconstruction area, and an image reconstructing unit for reconstructing image data within the set reconstruction area based on the output of the detector. The apparatus also includes a movement distance determining unit for determining the movement distance of the X-ray tube and X-ray detector relative to the object on the basis of the radius of the set reconstruction area as well as its height.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
Virtual spherical anode computed tomography
InactiveUS7333588B2Improved volumetric acquisitionIncrease flexibilityRadiation/particle handlingComputerised tomographsIn planeHelical scan
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Stand-up CT scanner
ActiveUS7224764B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingHelical scanCt scanners
A CT scanner according to the present invention is particularly useful for scanning the spine and extremities, such as knees, and ankles, especially while the patient is in an upright position. The CT scanner generally includes a source and detector that are rotatable about a generally upright axis. The source and detector are also moved along the upright axis during rotation to perform a helical scan. The source and detector are mounted to an inner ring, which is rotatably mounted within an outer ring. The outer ring is fixedly mounted to a carriage that is movable along an upright rail.
Owner:XORAN TECH
Stand-up CT scanner
ActiveUS20050053186A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingHelical scanCt scanners
A CT scanner according to the present invention is particularly useful for scanning the spine and extremities, such as knees, and ankles, especially while the patient is in an upright position. The CT scanner generally includes a source and detector that are rotatable about a generally upright axis. The source and detector are also moved along the upright axis during rotation to perform a helical scan. The source and detector are mounted to an inner ring, which is rotatably mounted within an outer ring. The outer ring is fixedly mounted to a carriage that is movable along an upright rail.
Owner:XORAN TECH
Method for operating a computed tomography apparatus having a diaphragm at the radiation detector
InactiveUS7170975B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diaphragms/collimetersHelical scanProximate
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
CT extremity scanner
ActiveUS20050053185A1Easy to useRadiation/particle handlingComputerised tomographsHelical scanCt scanners
A CT scanner according to the present invention is particularly adapted for scanning the extremities of a patient. The CT scanner includes an x-ray source and x-ray detector mounted for rotation and translation along an axis parallel to a table for supporting the patient's extremity. The source and detector are mounted opposite one another on an inner circumference of an inner ring. The inner ring is rotatable about the axis within an outer ring mounted on at least one carriage. The carriage is movable parallel to the axis. During scanning, the inner ring rotates within the outer ring while the rings and carriage move along the axis, thereby producing a helical scan of the extremity.
Owner:XORAN TECH
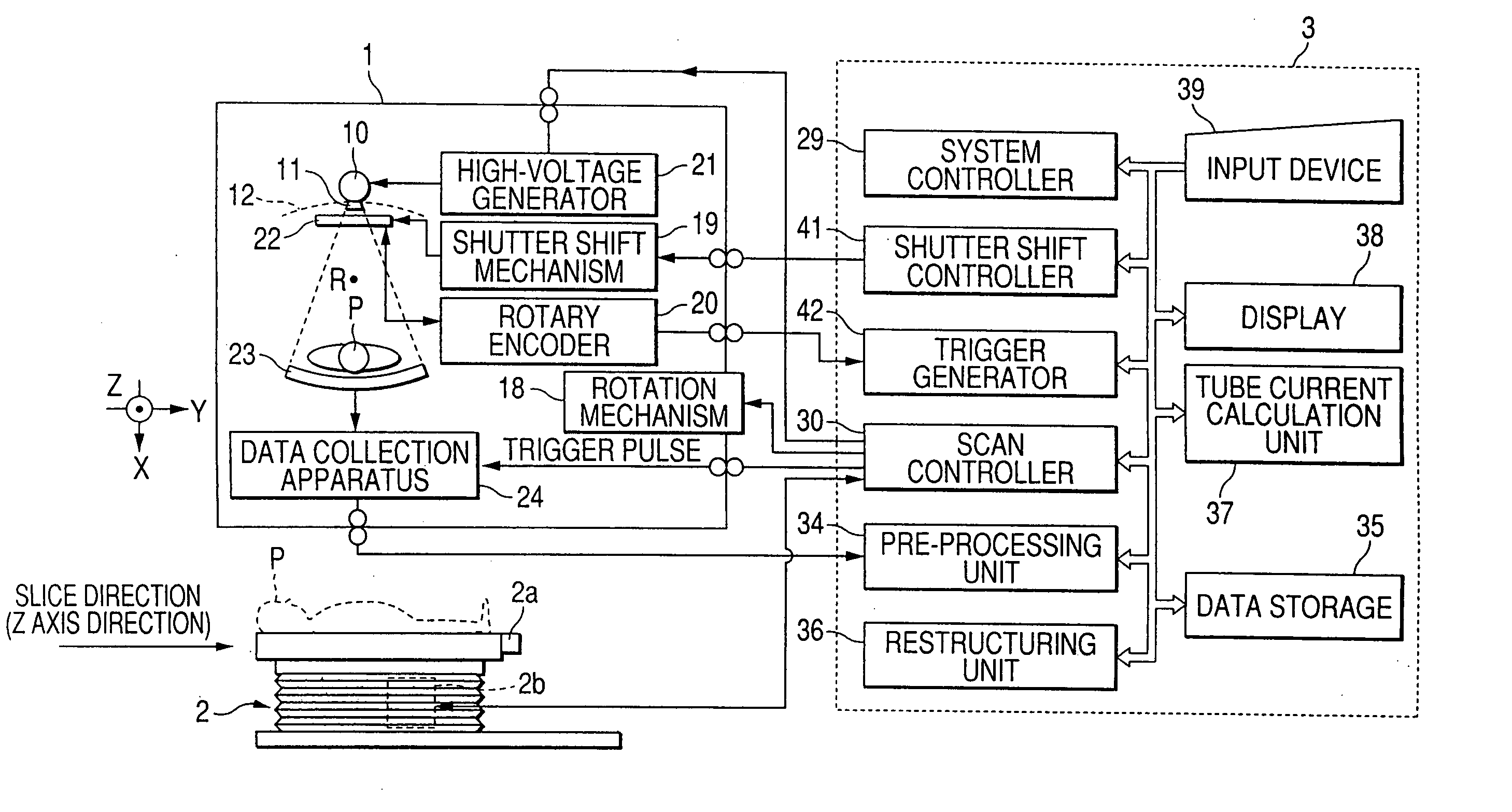
Scan parameter setting method for shuttle mode helical scan and X-ray CT apparatus
InactiveUS20060262896A1Efficiently and intelligibly settingReduce exposureMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingGraphicsHelical scan
A scout image of a subject is displayed. An operator designates at least one range in a body-axis direction, of the scout image. Further, the operator graphically inputs or key-inputs and sets imaging condition parameters such as a helical pitch, a noise index and the like for a shuttle mode helical scan with being made independent every ranges. Thus, conditions such as helical pitch and noise index for the shuttle mode helical scan can efficiently and intelligibly be set independently for each region or organ, and hence the control / optimization of imaging conditions is enabled.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Acquisition and reconstruction of projection data using a stationary CT geometry
ActiveUS20080056437A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingHelical scanDistributed source
Systems and methods are provided for acquiring and reconstructing projection data using a computed tomography (CT) system having stationary distributed X-ray sources and detector arrays. In one embodiment, a non-sequential activation of X-ray source locations on an annular source is employed to acquire projection data. In another embodiment, a distributed source is tilted relative to an axis of the scanner to acquire the projection data. In a further embodiment, a plurality of X-ray source locations on an annular source are activated such that the aggregated signals correspond to two or more sets of spatially interleaved helical scan data.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Apparatus and method for controlling start and stop operations of a computed tomography imaging system
ActiveUS20070230657A1Prevent movementRadiation/particle handlingX-ray apparatusHelical scanCt scanners
An apparatus and method for scanning an object with a helical CT scanner, the method comprising: acquiring an amount of data corresponding to the object that is scanned by the CT scanner, wherein the amount of data is generated by an x-ray source that projects a fan beam of x-rays toward a detector array on an opposite side of a gantry of the CT scanner, the fan beam being generated at multiple x-ray source positions as the x-ray source is rotated about the object as the object passes through an opening in the gantry disposed about a conveyor for moving the object through the opening; monitoring a position of the conveyor as the object passes through the opening in the gantry; determining if the conveyor has been stationary for more than one rotation of the gantry and discarding redundant data after one rotation, optionally turning off the x-ray tube if the conveyor has been stationary for more than one gantry rotation, and if so preventing the conveyor from moving again until the tube is turned on and is stable, inputting the position of the conveyor at each x-ray source position into a reconstruction algorithm; and presenting an image of the object.
Owner:MORPHO DETECTION INC
X-ray CT apparatus
InactiveUS20070053480A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingHelical scanX-ray
This invention provides an X-ray CT capable of presenting information of exposure to the operator by displaying X-ray dose information of each of regions of interest to be scanned by an X-ray CT apparatus, thereby encouraging reduction in exposure and optimization. X-ray dose information of each region to be scanned by a conventional scan (axial scan), a cine scan, a helical scan, or a variable-pitch helical scan of an X-ray CT apparatus is displayed so that the operator can recognize the X-ray dose information before acquisition of an image of a subject. The X-ray dose information can be predicated with higher precision and displayed by using a dose prediction value obtained by an interpolation value and an extrapolation value of the first or higher order on at least three or more kinds of phantom measurement values, not a simple prediction value such as a zero-th order interpolation value or a zero-th order extrapolation value obtained by using measurement values of two kinds of phantoms like in the present CTDI display.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Apparatus and methods for computed tomography imaging
ActiveUS20110110486A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingHelical scanComputed tomography
Apparatus and methods for computed tomography (CT) imaging are provided. One method includes providing a patient table to move along an examination axis of a rotating gantry of a CT imaging system having at least one imaging detector. The imaging detector includes a pixelated detector array. The method further includes configuring the CT imaging system to perform an overlapping helical CT scan by controlling a speed of the moving patient table along the examination axis through a field of view (FOV) of the at least one imaging detector of the rotating gantry.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Collimator control method and X-ray CT apparatus
InactiveUS20060039536A1Reduce exposureEasy to controlMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diaphragms/collimetersHelical scanBody axis
A collimator control method for an X-ray CT apparatus includes changing an aperture of the collimator according to a position of a helical scan on the body axis of the subject in the progress of the helical scan.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Acquisition and reconstruction of projection data using a stationary CT geometry
ActiveUS7706499B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingHelical scanDistributed source
Systems and methods are provided for acquiring and reconstructing projection data using a computed tomography (CT) system having stationary distributed X-ray sources and detector arrays. In one embodiment, a non-sequential activation of X-ray source locations on an annular source is employed to acquire projection data. In another embodiment, a distributed source is tilted relative to an axis of the scanner to acquire the projection data. In a further embodiment, a plurality of X-ray source locations on an annular source are activated such that the aggregated signals correspond to two or more sets of spatially interleaved helical scan data.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods and apparatus for dynamical helical scanned image production
Some configurations of the present invention thus provide a method for producing images of an object. The method includes dynamically helically scanning an object on a moving table utilizing a scanning imaging system. During the scan, projection views of the object are acquired and stored together with corresponding table locations. A plane for reconstruction of an image of the object is selected. The stored table locations are used to determine geometric variables applicable to the stored projection views; and the stored projection views are filtered and backprojected utilizing the geometrical variables to reconstruct an image of the object at the reconstruction plane.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
X-ray CT apparatus
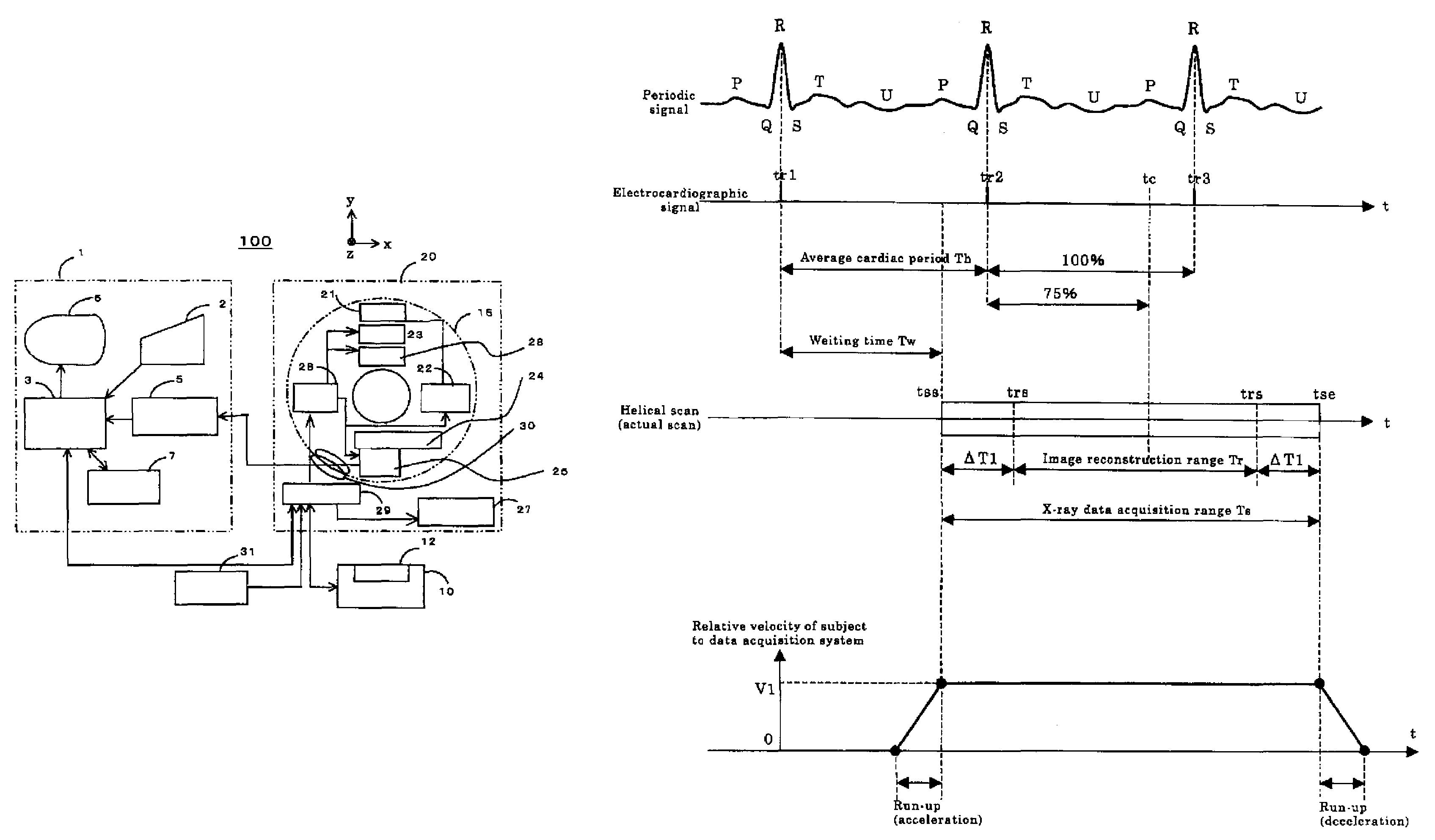
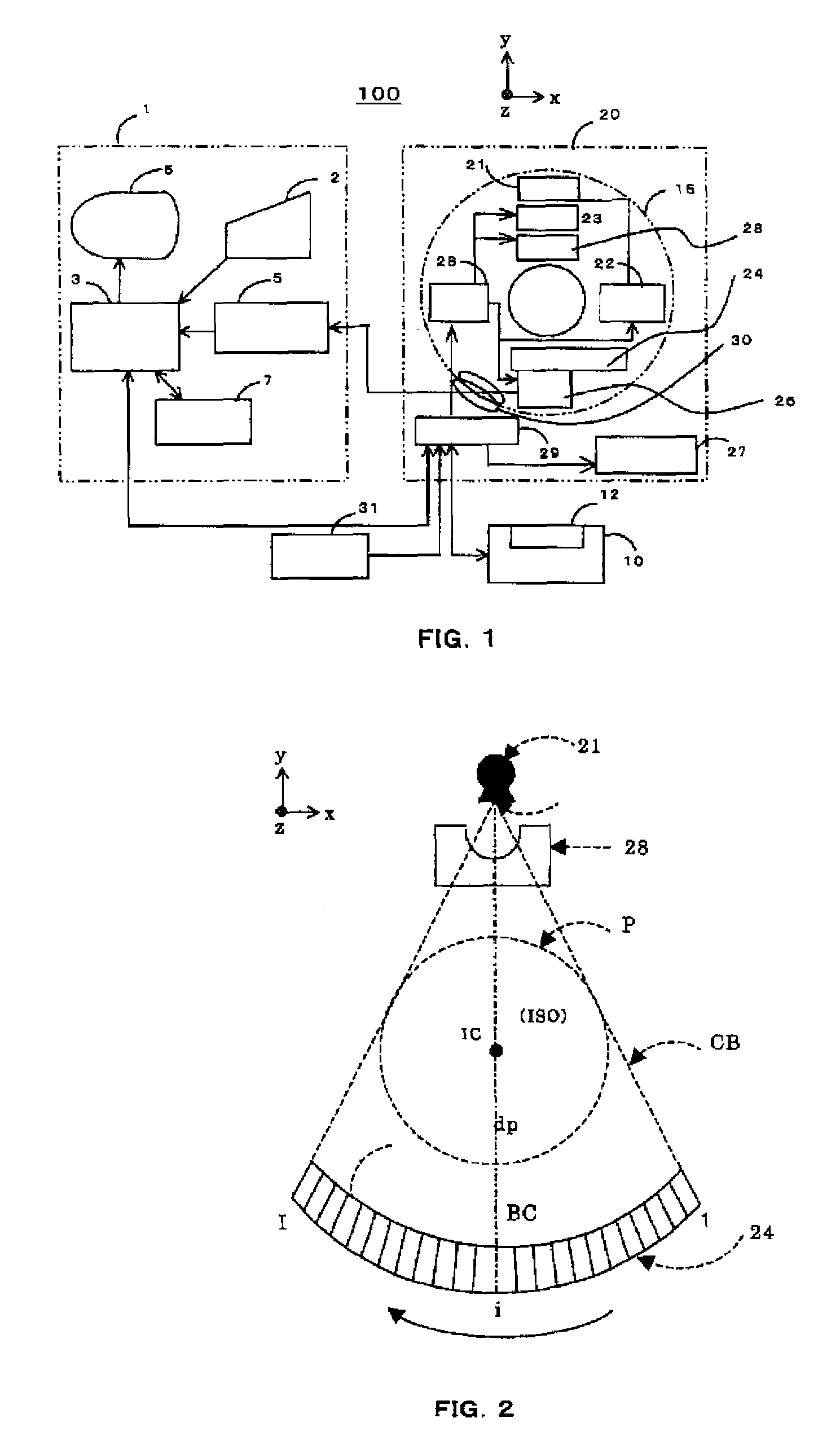
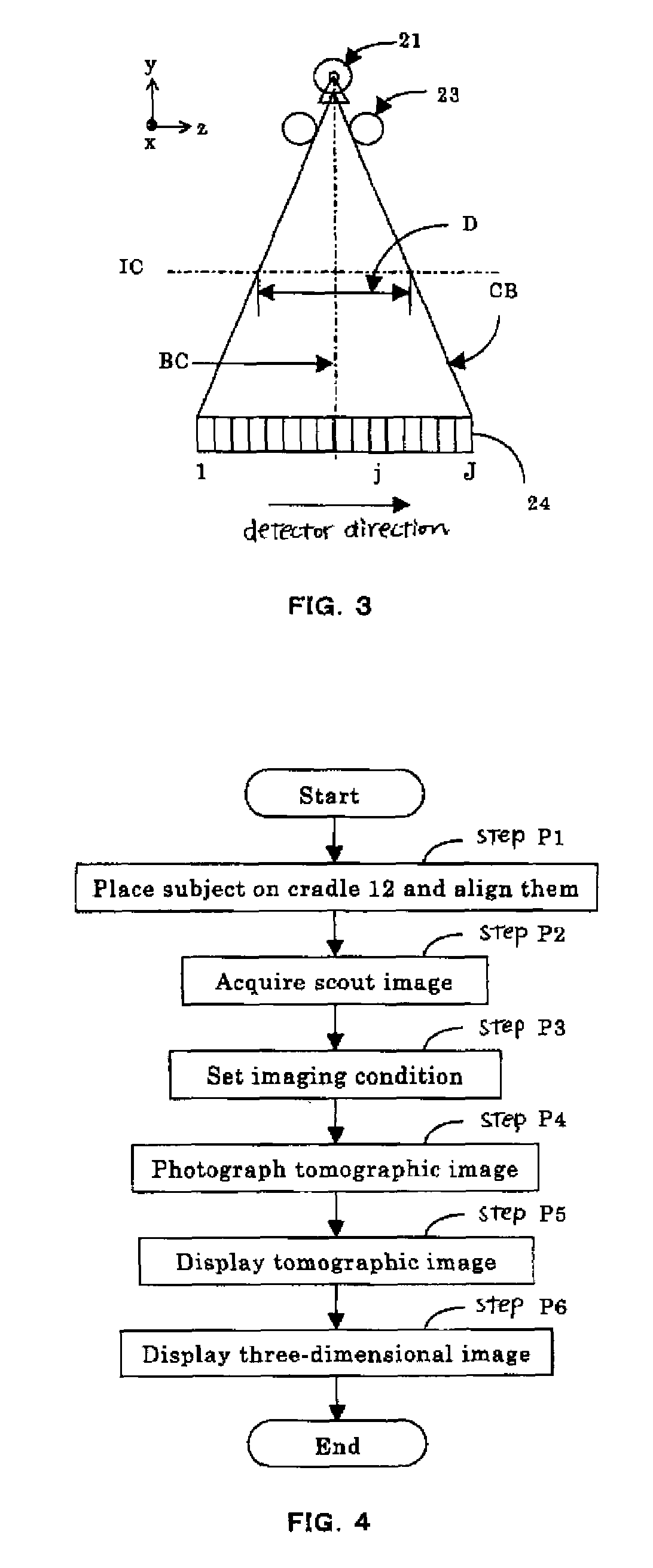
ActiveUS7522696B2Increase speedImprove image qualityElectrocardiographyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSoft x rayHelical scan
An X-ray CT apparatus includes an X-ray data acquisition device for acquiring X-ray projection data transmitted through a subject lying between an X-ray generator and an X-ray detector having a two-dimensional detection plane and detecting X rays in opposition to the X-ray generator, while the X-ray generator and the X-ray detector are being rotated about a center of rotation lying there between; an image reconstructing device for image-reconstructing the acquired projection data; an image display device for displaying the image-reconstructed tomographic image; and an imaging condition setting device for setting various kinds of imaging conditions for tomographic image, wherein the X-ray data acquisition device acquires X-ray projection data in sync with an external sync signal by a helical scan with a predetermined range of the subject with a helical pitch set to 1 or more.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Scan control method and X-ray CT apparatus
InactiveUS7313216B2Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHelical scanX-ray
A scan control method for an X-ray CT apparatus wherein a subject with a contrast agent injected therein is helically scanned with an X-ray beam and image reconstruction is performed based on projection data obtained through an X-ray detector. The method includes controlling a velocity of a helical scan following motion of the contrast agent in the subject.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Scan control method and X-ray CT apparatus
InactiveUS20060034419A1Sharp contrastReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHelical scanX-ray
A scan control method for an X-ray CT apparatus wherein a subject with a contrast agent injected therein is helically scanned with an X-ray beam and image reconstruction is performed based on projection data obtained through an X-ray detector. The method includes controlling a velocity of a helical scan following motion of the contrast agent in the subject.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Computed tomography (CT) iteration reconstruction method for asymmetrical detector
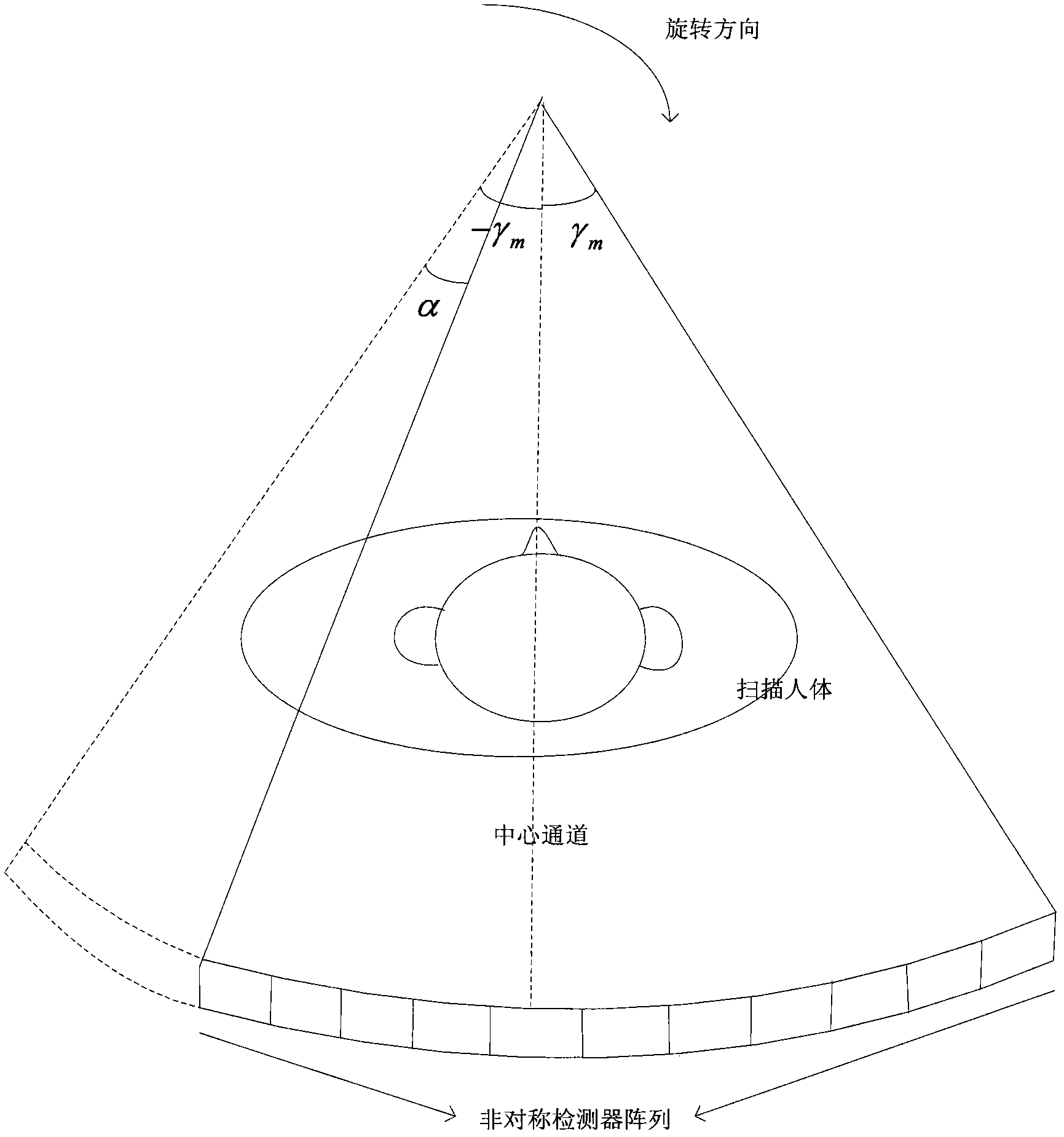
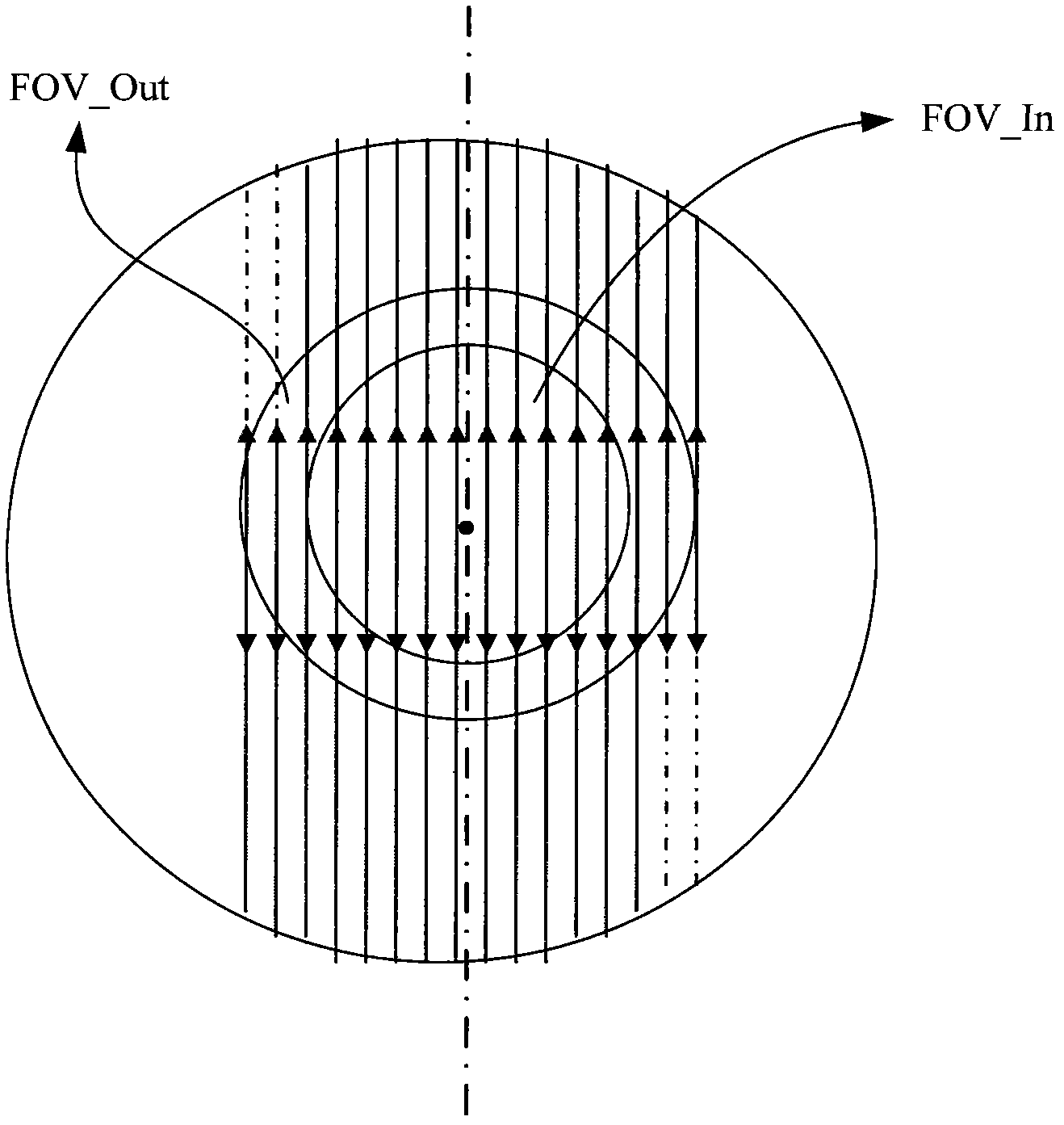
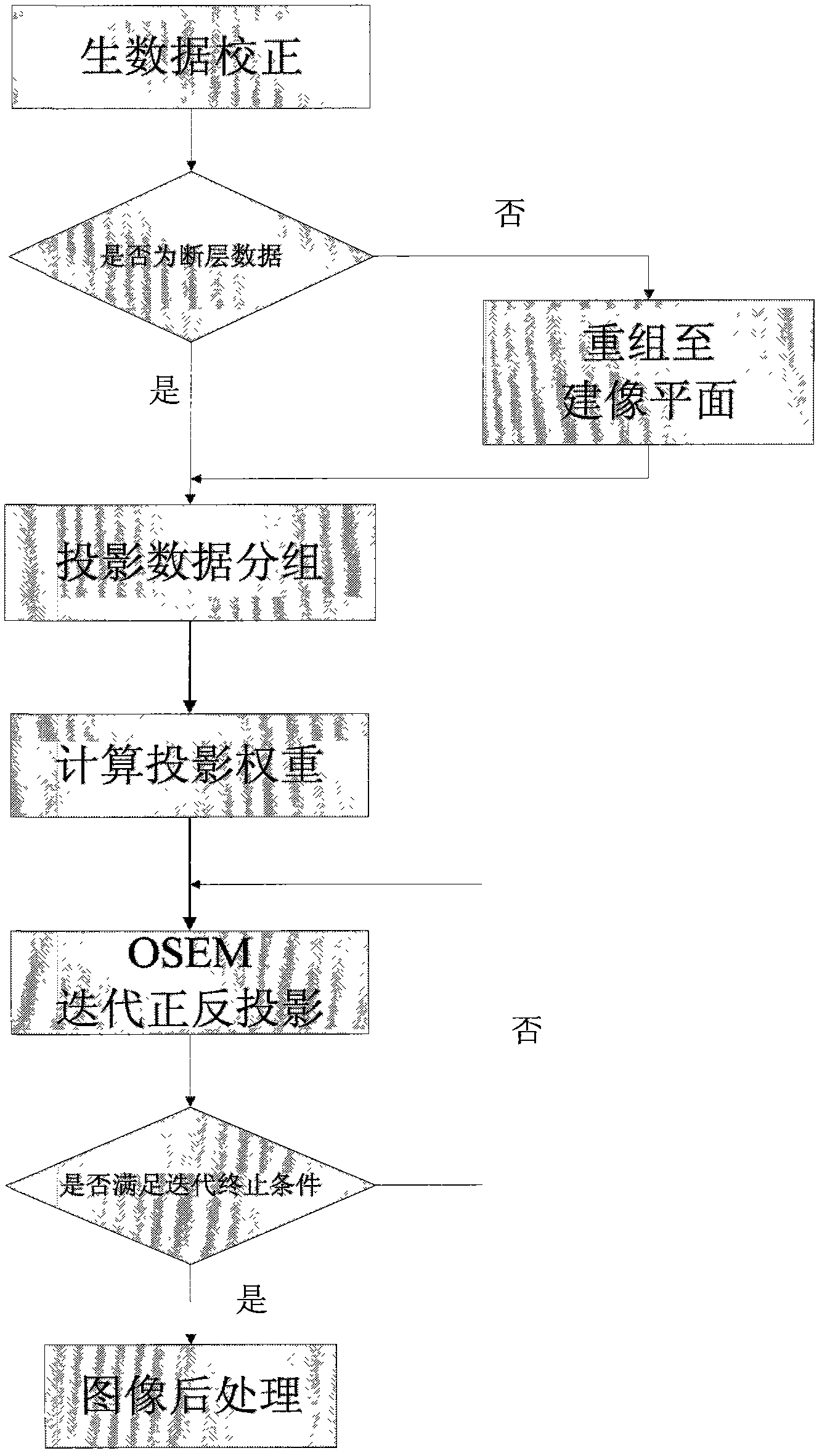
InactiveCN102376097AReduce artifactsSuppression of noise level differences2D-image generationComputerised tomographsHelical scanNoise level
The invention relates to a computed tomography (CT) iteration reconstruction method for an asymmetrical detector. The CT iteration reconstruction method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: performing air correction, nonlinear correction, crosstalk correction, defocus correction and calibration correction on raw data acquired by a computed tomography scanner to obtain projection data; judging whether the projection data is CT scan data or helical scan data, and if the projection data is the CT scan data, grouping the CT scan data; calculating a projection weight to obtain a weight matrix; performing ordered subset expectation maximization (OSEM) iteration orthographic and back projection according to the weight matrix; judging whether iteration ending conditions are met, if so, ending the iteration orthographic and back projection to obtain an initial CT image; and performing postprocessing on the initial CT image to obtain the reconstructed CT image. By the method, the iteration back projection reconstruction is carried out by directly using incomplete projection data, artifact can be relived, noise level difference caused by data inconsistency due to interpolation is inhibited, and the CT iteration reconstruction method is mainly suitable for less-than-four-row CT detectors.
Owner:PHILIPS & NEUSOFT MEDICAL SYST
Methods and apparatus for helical reconstruction for multislice CT scan
InactiveUS6980681B1Improved sampling patternEasy to useReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis by optical meansHelical scanUltrasound attenuation
One embodiment of the present invention is a method for imaging an object with a computed tomographic (CT) imaging system that includes steps of helically scanning the object with a multi-slice CT imaging system to acquire attenuation measurements of the object, the measurements including more than two conjugate samples for estimation of a projection at a plane of reconstruction of the object; and filtering and backprojecting the attenuation measurements of the object, including the more than two conjugate samples, to reconstruct at least one image slice of the object. An improved sampling pattern and better use of the attenuation samples obtained during a scan is thus provided.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC +1
Multi plate screw press sludge dewatering machine
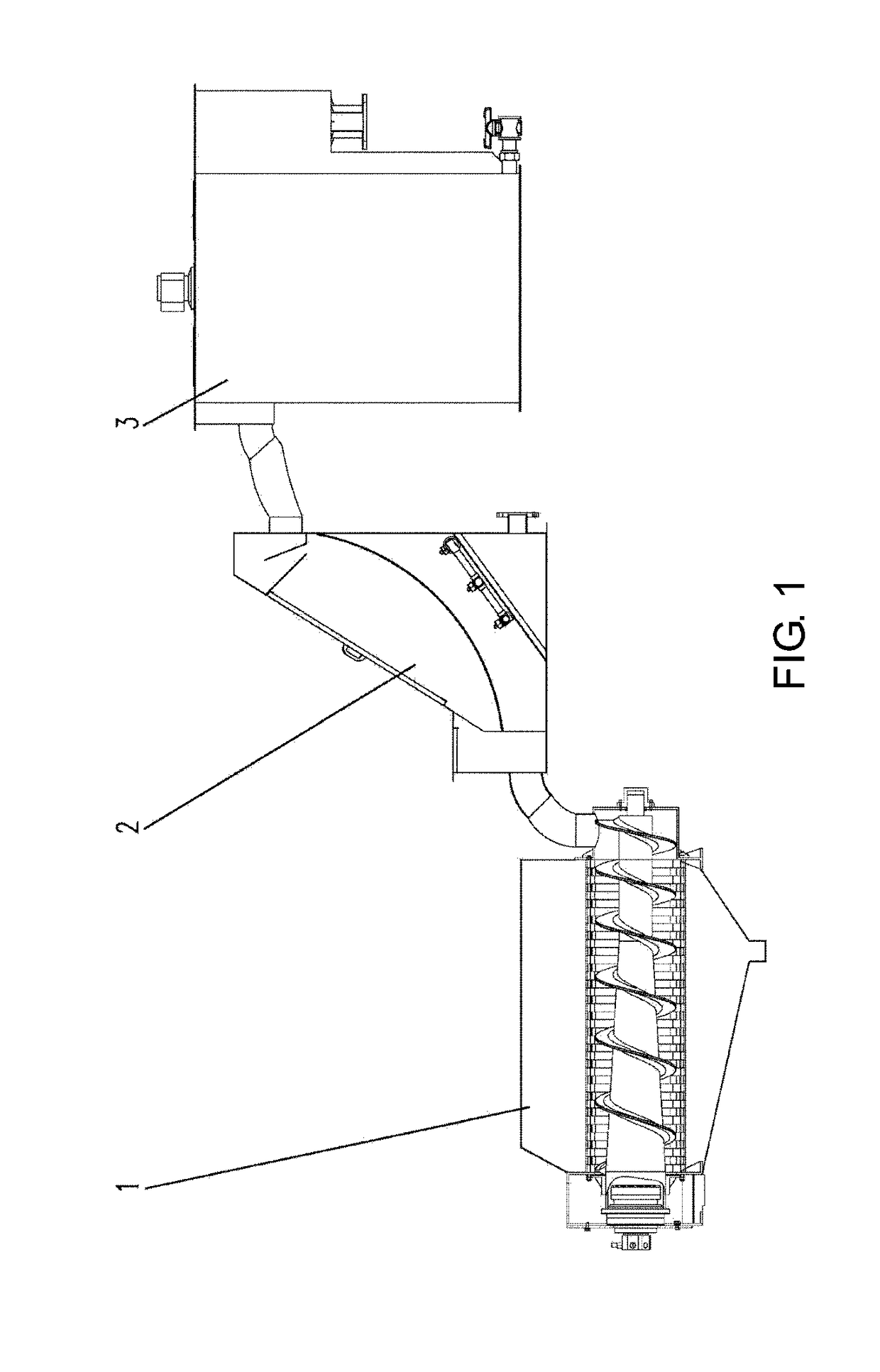
ActiveUS20180346362A1Convenience to workReduced footprintSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningSpecific water treatment objectivesHelical scanHelical blade
The present invention provides a multi plate screw press sludge dewatering machine and a helical shaft thereof. The multi plate screw press sludge dewatering machine includes fixed rings, movable rings, the helical shaft, a sludge inlet tank and a sludge discharging tank; the helical shaft adopts a variable diameter variable pitch helical shaft, a lead angle arrangement sequence of a helical blade of the whole helical shaft is gradual reduction from the sludge discharging tank to the sludge inlet tank, and the lead angle arrangement sequence is gradually reduced from 16°-22° to 6°-14°; a pitch of the helical shaft is gradually increased along a direction from the sludge inlet tank to the sludge discharging tank; a diameter of a shaft body of the helical shaft is gradually increased along with a direction of the sludge discharging tank from a ⅓ position of a shaft length; and blockage prevention plates are arranged on two sides of the bottom of the helical blade. The helical shaft in the present invention is specially designed, so that the pitch is more reasonable, a helical angle is gentler, frictional resistance when sludge passes through the helical shaft may be effectively reduced, and phenomena of shaft blockage and shaft sticking of the sludge may be reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI TECHASE ENVIRONMENT PROTECTION
Injection mold for making helical fan
The invention discloses an injection mold for making a helical fan, comprising a movable mold base plate, square iron, a supporting plate, a movable mold plate, a fixed mold plate, a front inner mold, a helical mold core, a split type inclined bearing, a slide block, a scraping machine, an inclined guide pillar, a water gap push plate, a fixed mold base plate, a positioning ring, a bottom needle plate, a surface needle plate, an ejector sleeve and an ejector sleeve needle. According to the invention, the structure is simple, the cost is reduced, the structure comprises the slide block and the helical mold core, the helical mold core allows the ejector sleeve to extrude a mold product by rotating the split type inclined bearing, thus the complicated demolding problem becomes simple, and the quality of the product is guaranteed.
Owner:南通海睿知新信息科技有限公司
Methods and apparatus for dynamical helical scanned image production
The present invention provides a method for producing images of an object. The method includes dynamically helically scanning an object on a moving table utilizing a scanning imaging system. During the scan, projection views of the object are acquired and stored together with corresponding table locations. A plane for reconstruction of an image of the object is selected. The stored table locations are used to determine geometric variables applicable to the stored projection views; and the stored projection views are filtered and backprojected utilizing the geometrical variables to reconstruct an image of the object at the reconstruction plane.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Electron beam computed tomographic scanner system with helical or tilted target, collimator and detector components to eliminate cone beam error and to scan continuously moving objects
InactiveUS7020232B2Reduce system costReduce computational overheadReconstruction from projectionHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionHelical scanMulti slice
A scanning electron beam computed tomographic system eliminates axial offset between target and detector by disposing the target, collimator, and detector such that active portions of the target and detector are always diametrically opposite each other. This result is achieved by providing a helical target, collimator, and detector, or by providing planar target, collimator, and detector components that are inclined relative to the vertical axis such that active portions of the target and detector are always diametrically opposite each other. Either configuration eliminates cone beam error and the necessity to correct for same. Further, the system can provide multi-slice scanning of an object that is in constant motion at a critical velocity, without having to interpolate data. Conventional helical scanning may still be undertaken. Detector elements can be disposed axially to improve signal / noise ratio and to produce a cone beam cancellation effect.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
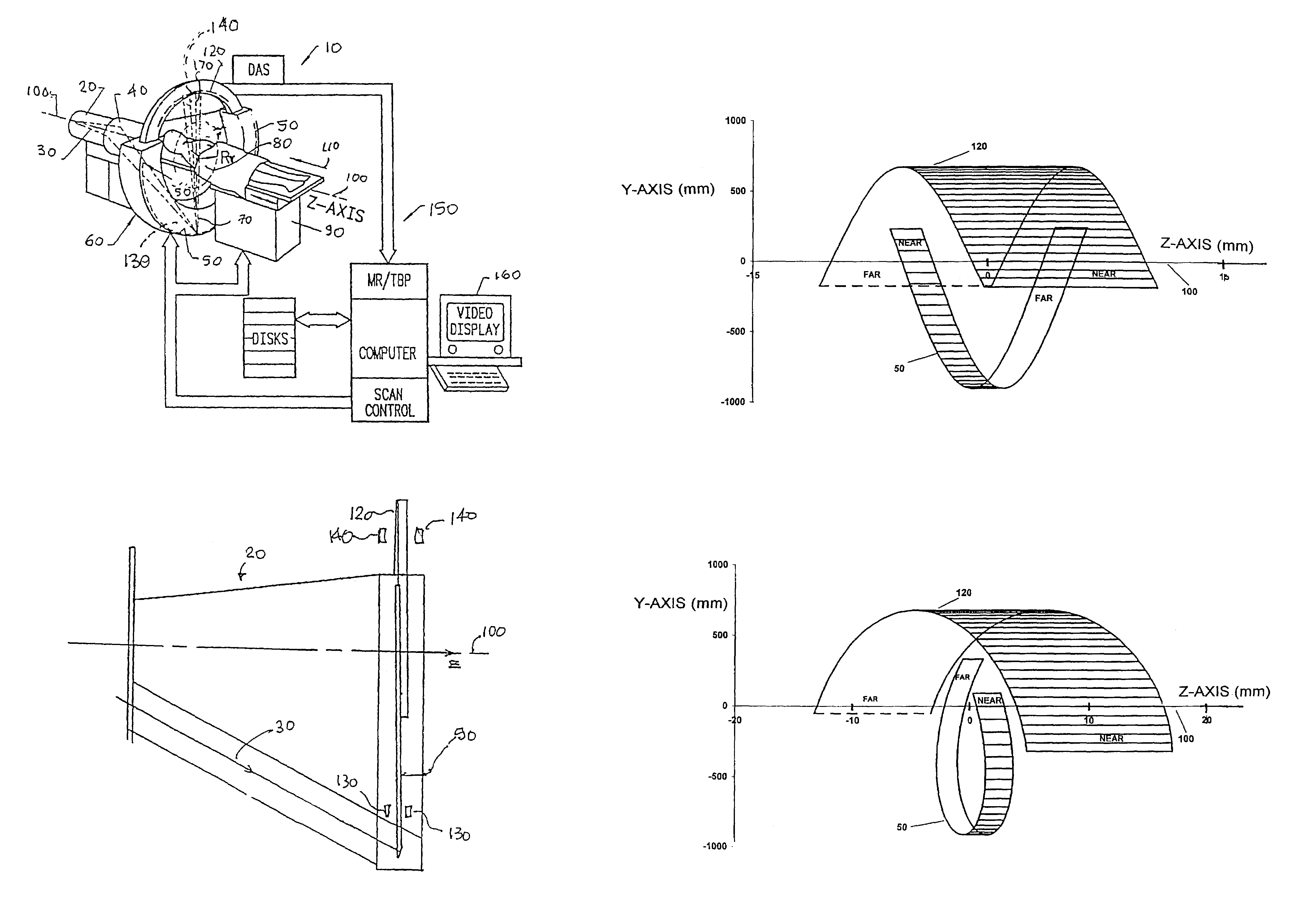
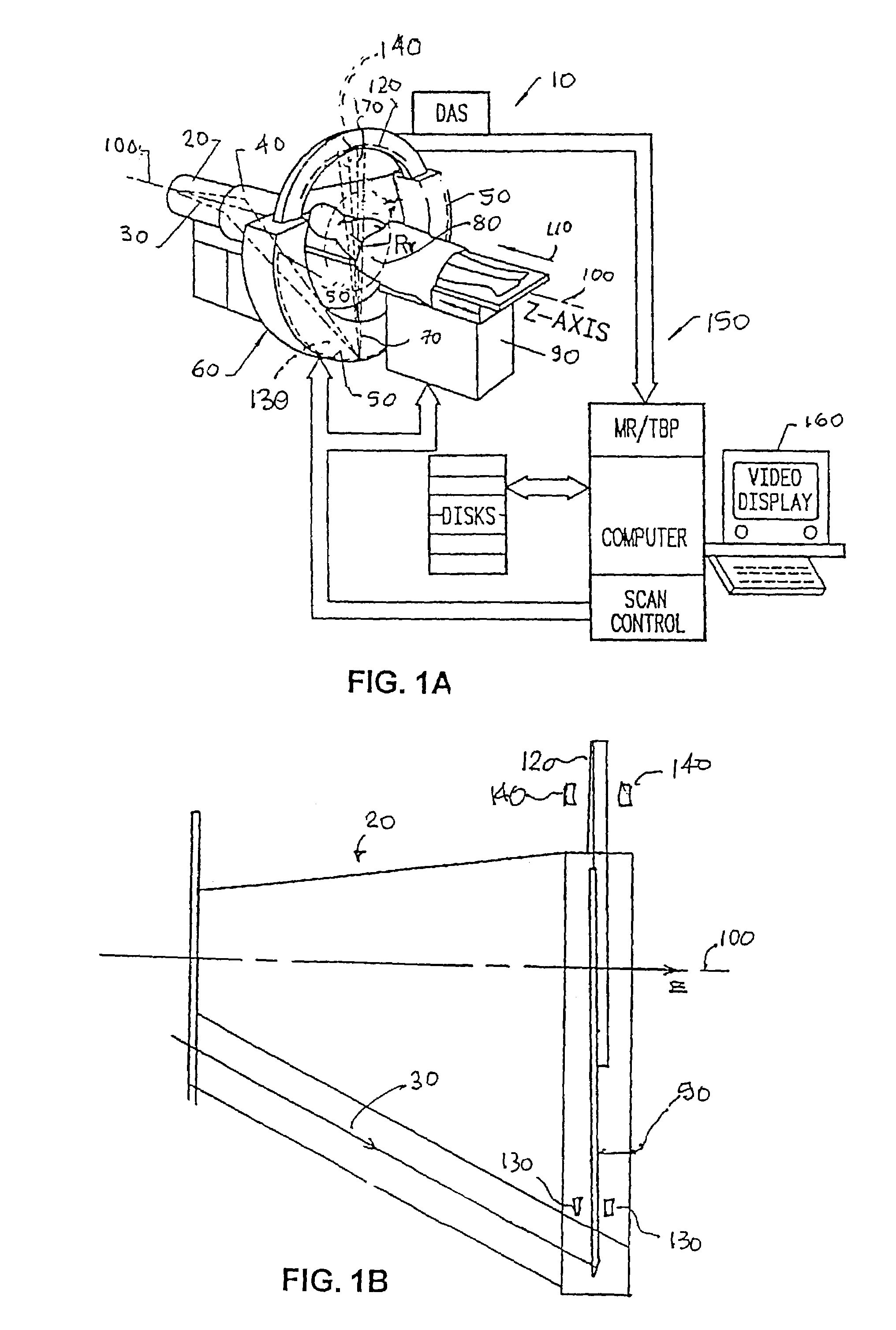
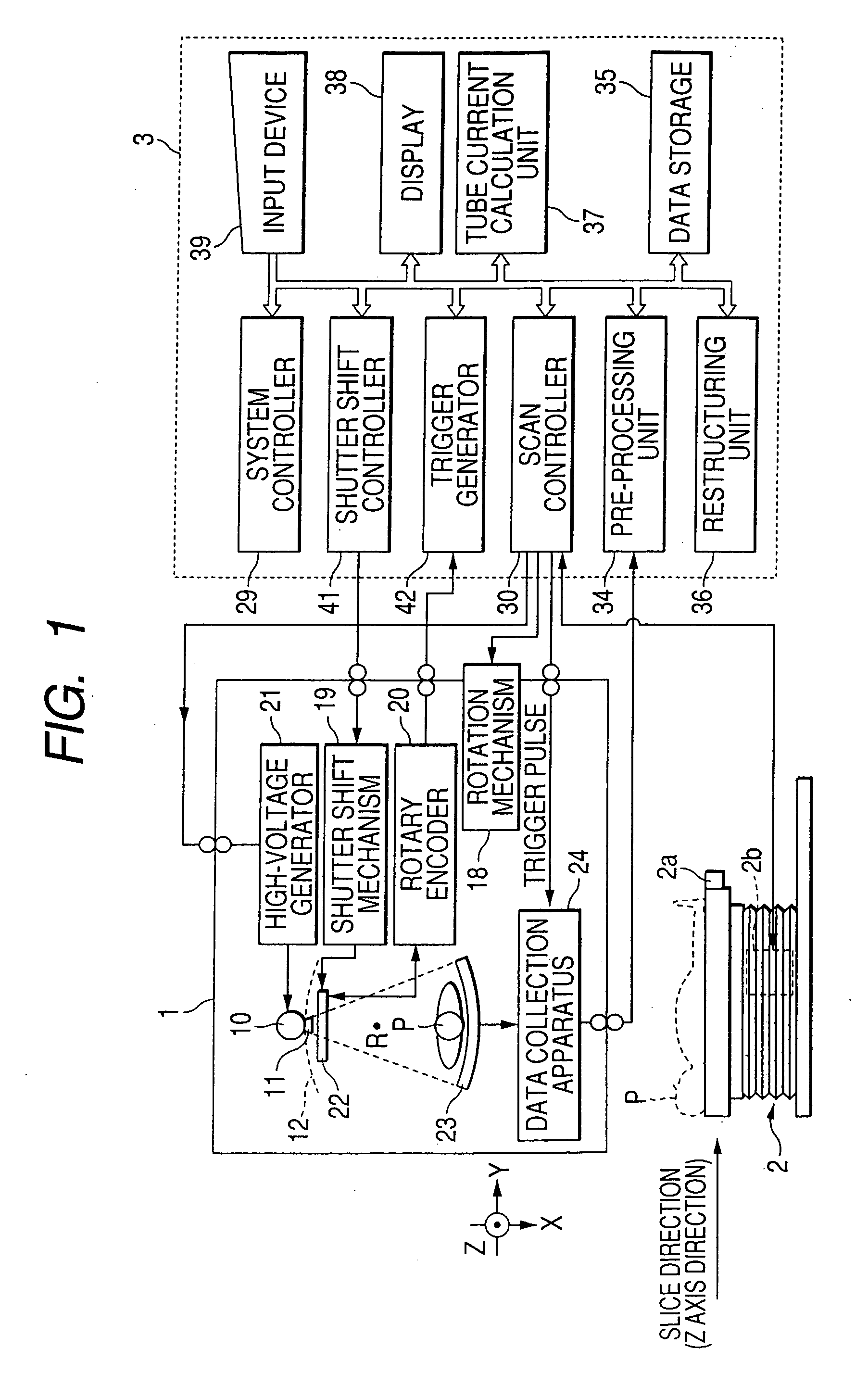
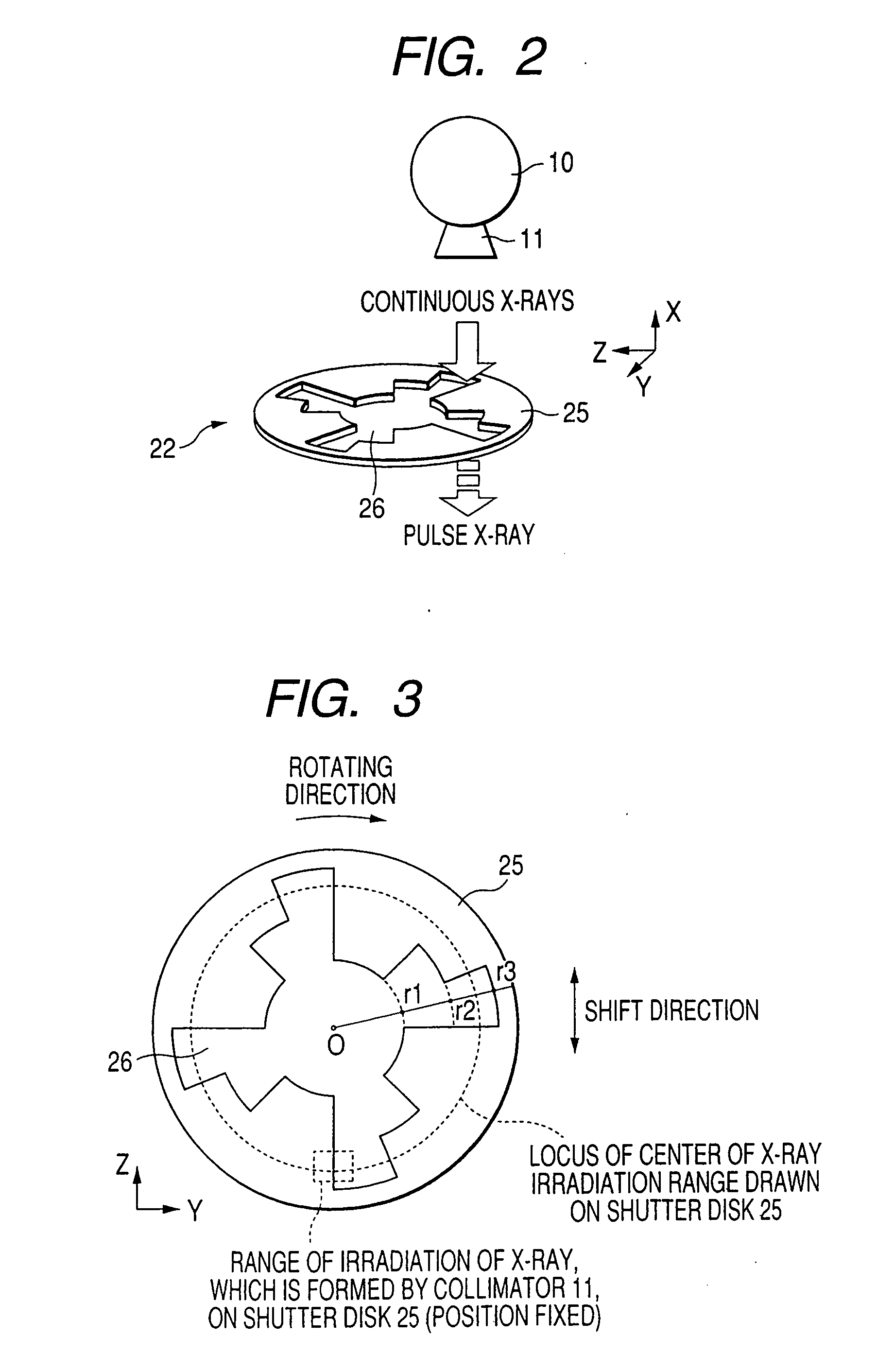
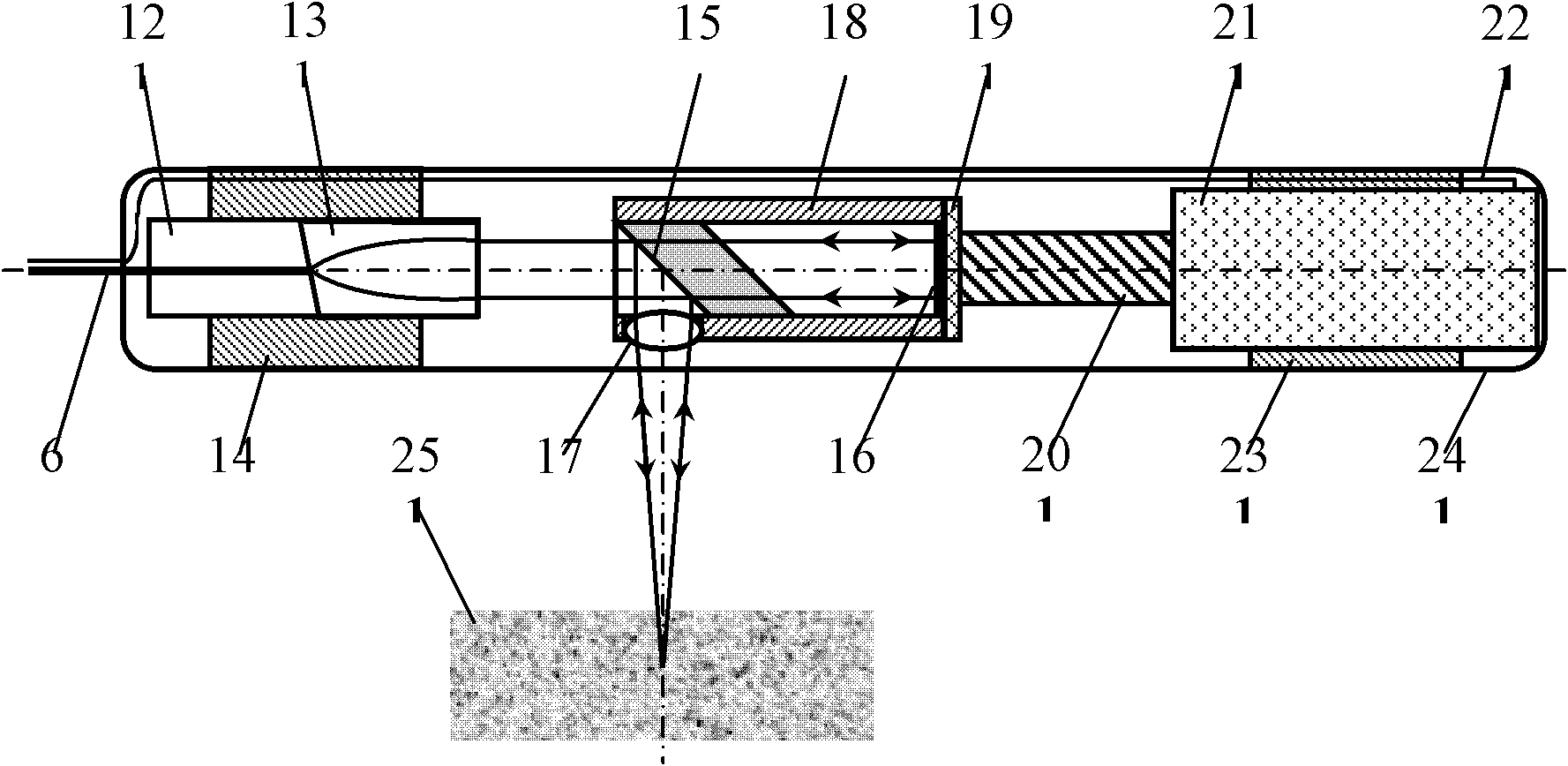
X-ray computer tomography apparatus
InactiveUS20060008048A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diaphragms/collimetersHelical scanX-ray
An X-ray computer tomography apparatus includes an X-ray tube, an X-ray detector, a data collection apparatus that collects X-ray signals from the X-ray detector repeatedly, a shutter mechanism that is arranged between the X-ray tube and a subject in order to convert an X-ray into a pulse-like X-ray and is constituted such that a ratio of a shutter open period and a shutter close period is variable, a restructuring unit that restructures image data on the basis of the collected X-ray signals, and a control unit that controls the shutter mechanism in order to change the ratio of a shutter open period and a shutter close period during a helical scan.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
X-ray CT imaging method and x-ray CT system
InactiveUS20050008116A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingHelical scanX-ray
An object of the present invention is to utilize a distance, which is linearly moved for acceleration or deceleration, out of an overall distance linearly moved during a helical scan for the purpose of image reconstruction. Projection data is acquired even during acceleration or deceleration of linear movement made for a helical scan. The acquired projection data is utilized for image reconstruction. Moreover, during the acceleration of linear movement, while a tube current is being increased, projection data is acquired. During the deceleration of linear movement, while the tube current is being decreased, projection data is acquired.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
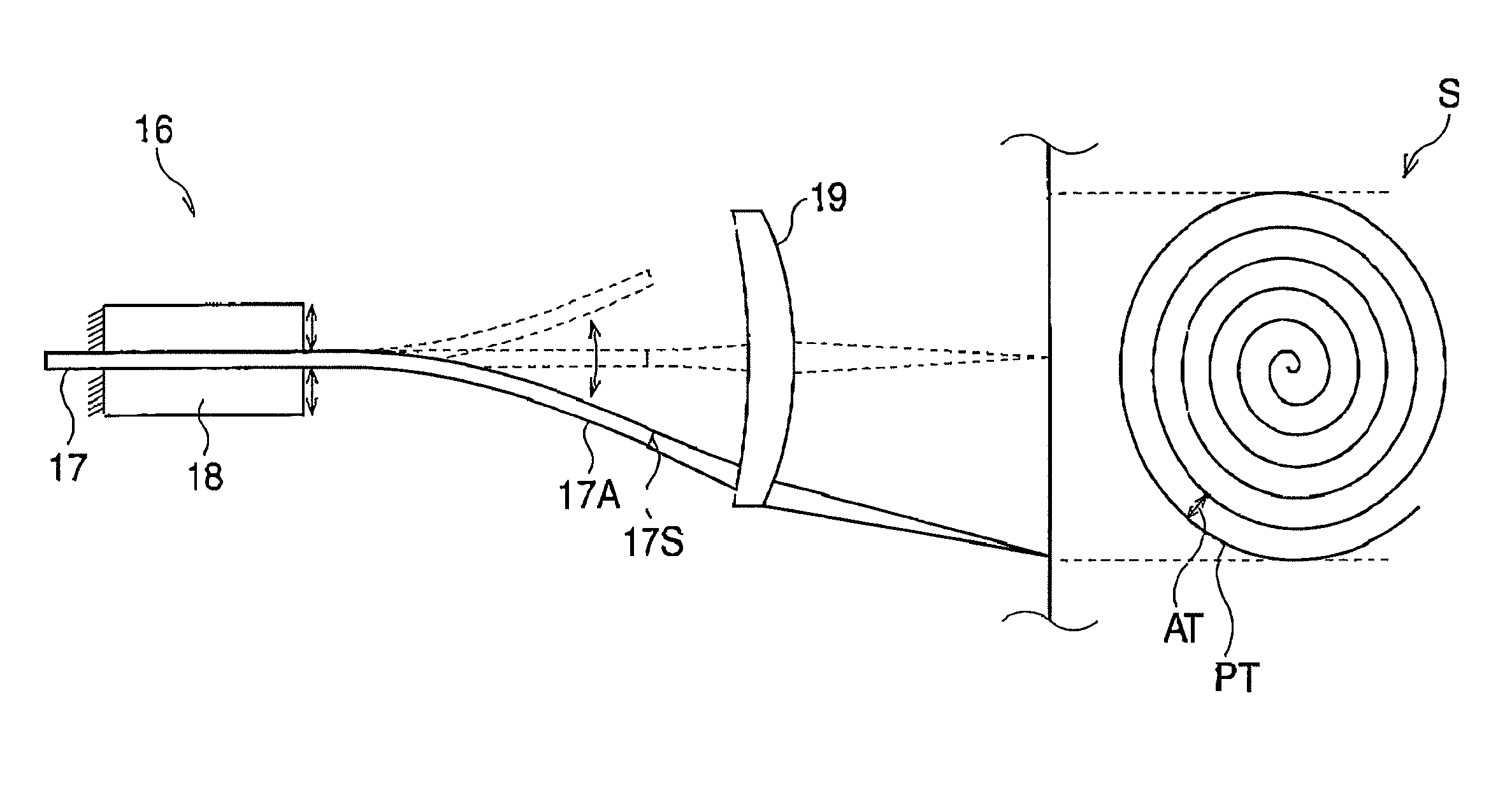
Helical scanning common path interference type endoscopic frequency-swept OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography) real-time imaging method and helical scanning common path interference type endoscopic frequency-swept OCT real-time imaging system
ActiveCN102525382AAvoid Image Quality DegradationRealize plug and playEndoscopesDigital signal processingPhysics
The invention relates to a helical scanning common path interference type endoscopic frequency-swept optical coherence tomography (OCT) real-time imaging method and a helical scanning common path interference type endoscopic frequency-swept OCT real-time imaging system. A light splitter and a reference lens are arranged in a probe, so that the whole system is formed into a common path interference structure, a micromotor mounted in the probe is used for carrying out the smooth helical scanning of a focused illuminating light beam, and the frequency-swept OCT technology which does not require mechanical scanning movement along the depth direction of a sample is adopted to achieve the purpose of fast imaging; and finally, a series of digital signal processing is carried out on the acquired interference signals to obtain the three-dimensional image of the detected sample. The invention is characterized in that: the system is not sensitive to various interferences, the probe is plug-and-play, three-dimensional imaging is real-time, image distortion is little, and the omission of pathological changes is reduced.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com