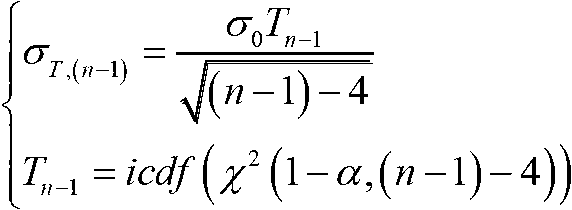Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
234 results about "Position resolution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Position Resolution. The position resolution of a PSD is the minimum detectable displacement of a spot of light on the detector surface. The position resolution of On-Trak PSDs are proven better than one part in a million. Resolution dependent on:
Method and apparatus for direct frame switching using frame contained destination information
InactiveUS20050027881A1Digital computer detailsData switching by path configurationImage resolutionEmbedded system
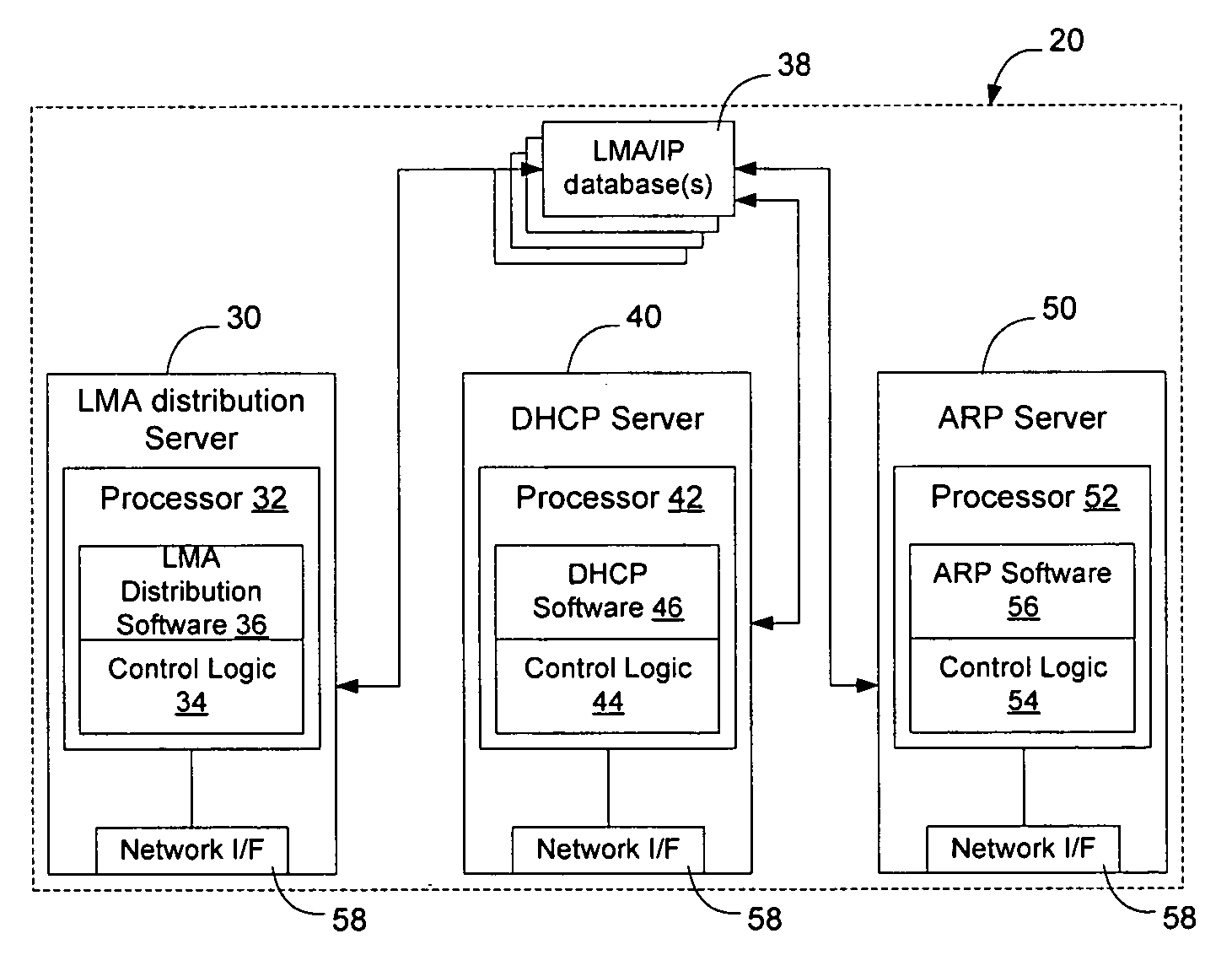
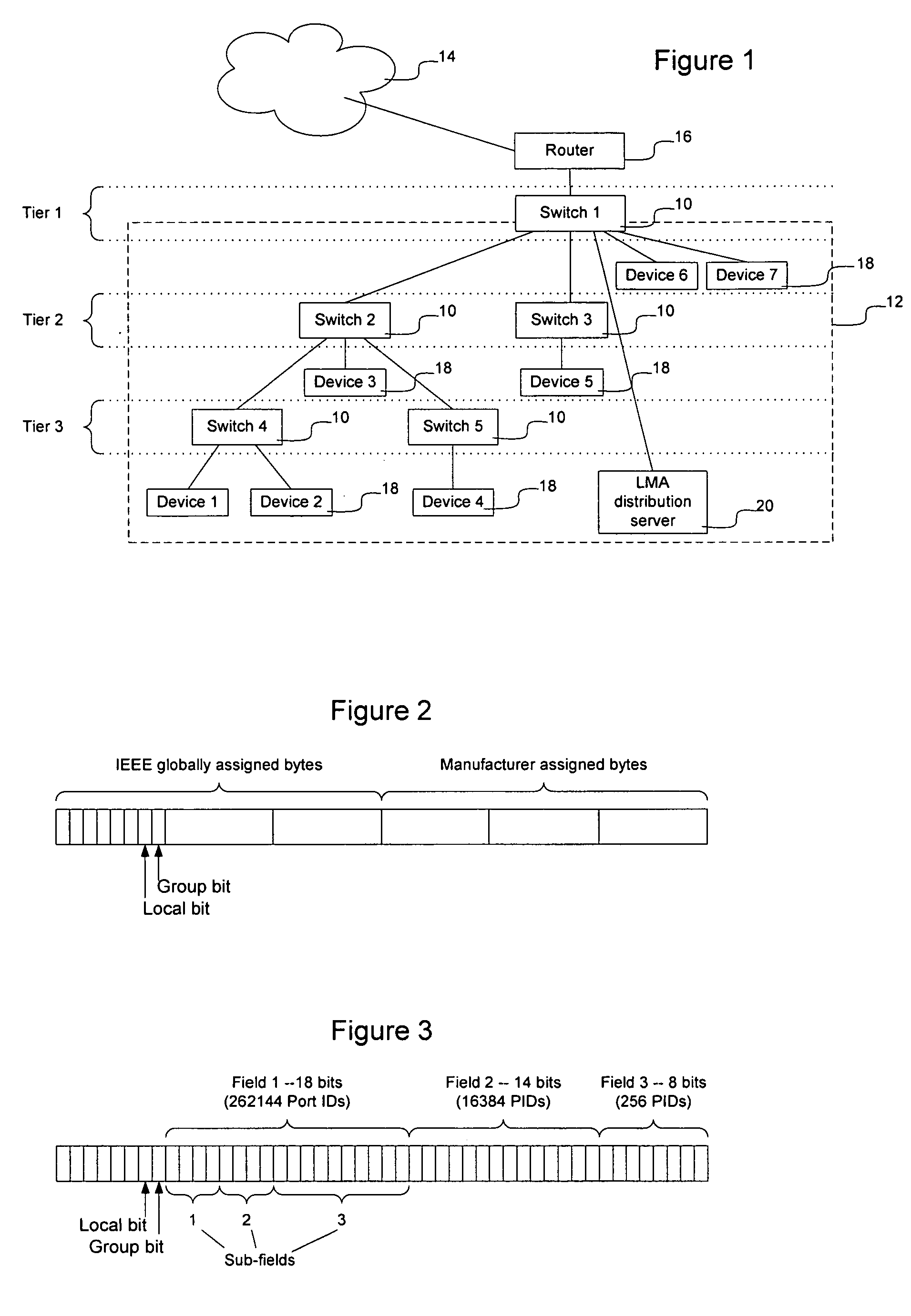
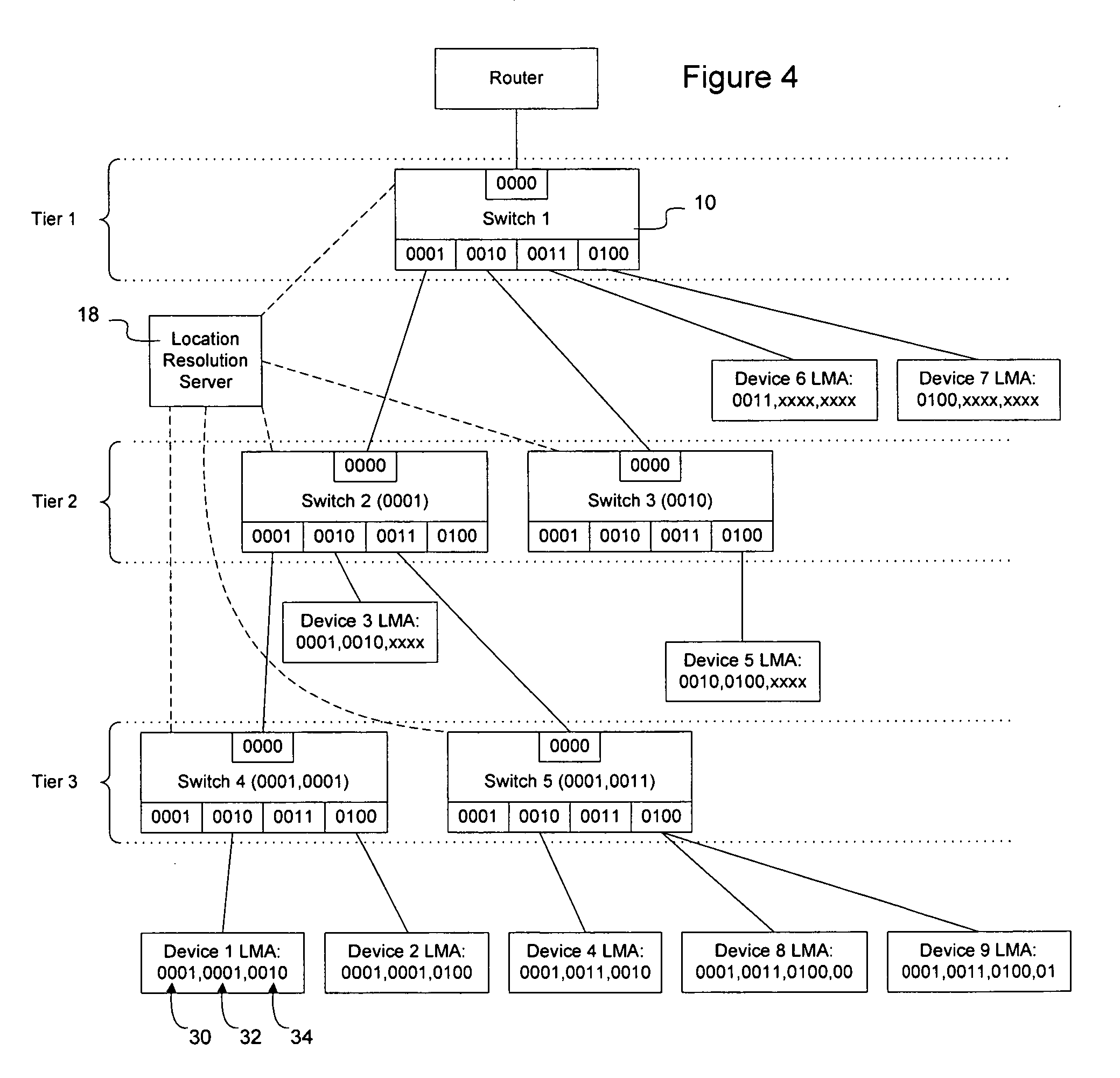
Frame contained destination information may be used by a switch to identify an appropriate output port for a given frame without performing a table access operation. This reduces the processing requirements of the switch to enable the switch to handle frames more efficiently. The frame contained destination information may be contained in the frame's local destination MAC addresses (DA) such that a portion of the DA directly indicates, for each switch that handles the frame, an output port for that switch. Different portions of the DA may be used by different switches, depending on where they are in the network hierarchy. Large switches may also use sub-fields within their allocated portion in the DA to identify internal switching components. A location resolution server may be provided to store and distribute IP and MAC addresses and respond to local ARP requests on the local domain.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Short range spread-spectrum radiolocation system and method
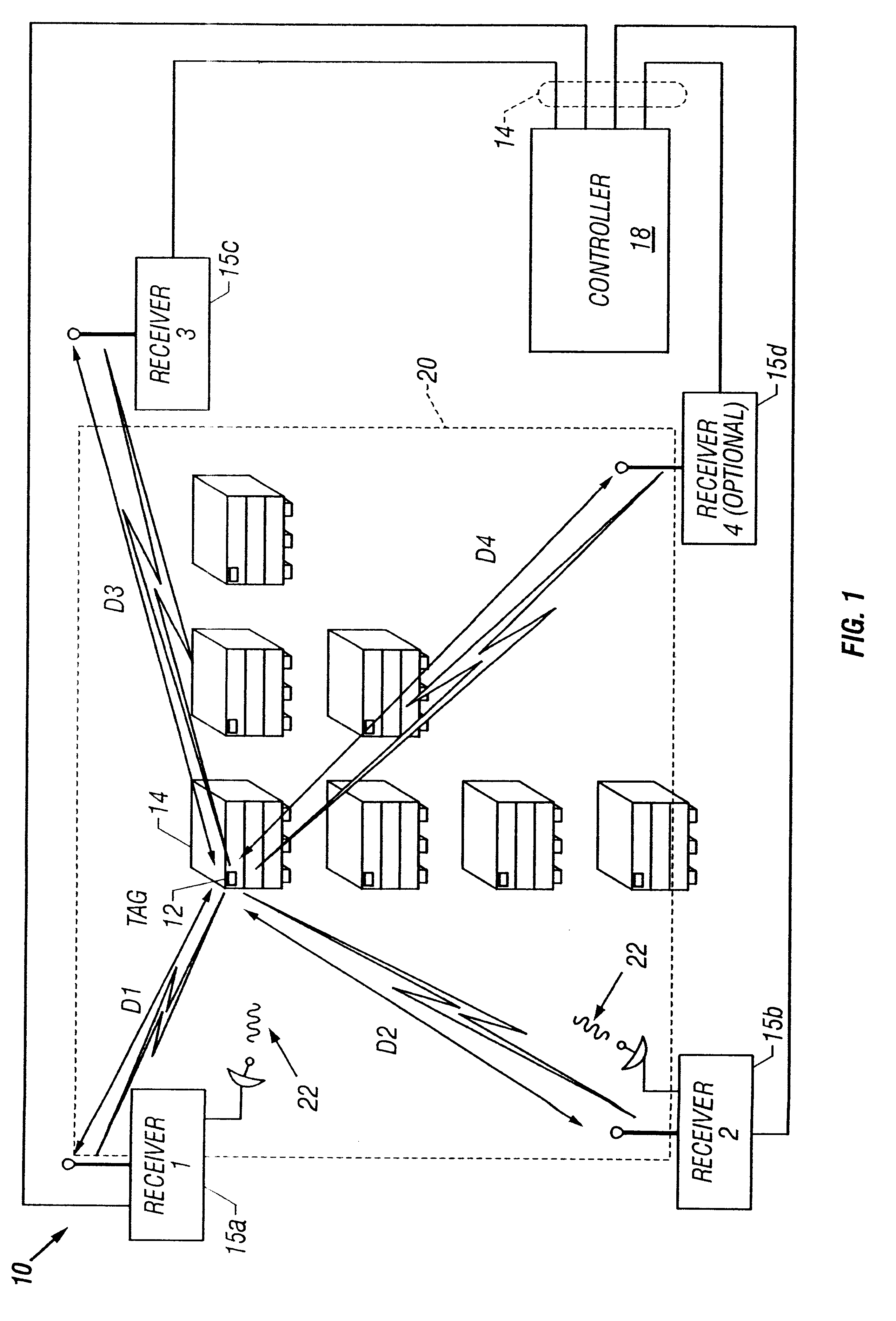
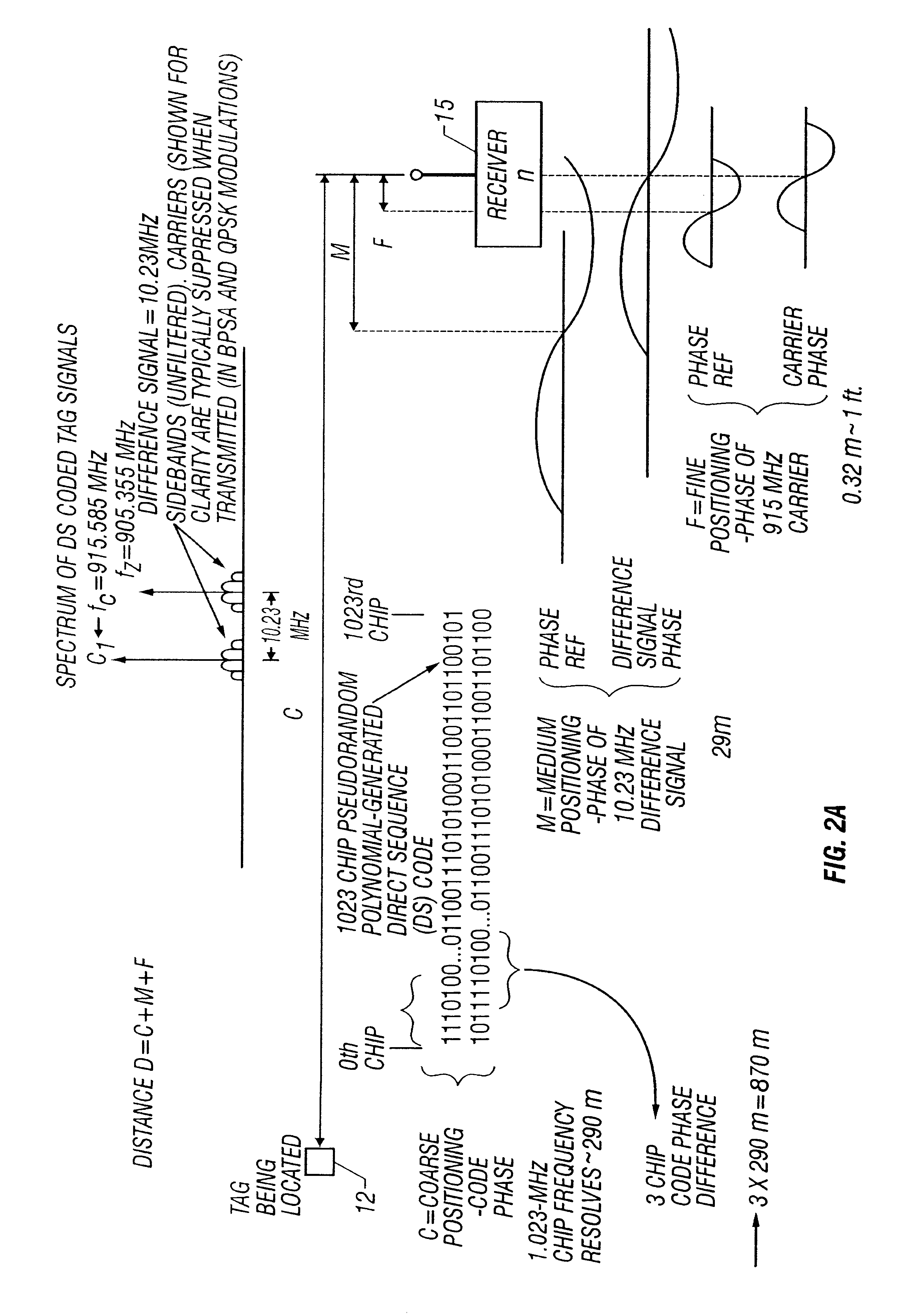
InactiveUS6556942B1Sufficient gross rangingLow costDirection finders using radio wavesBeacon systems using radio wavesData setTriangulation
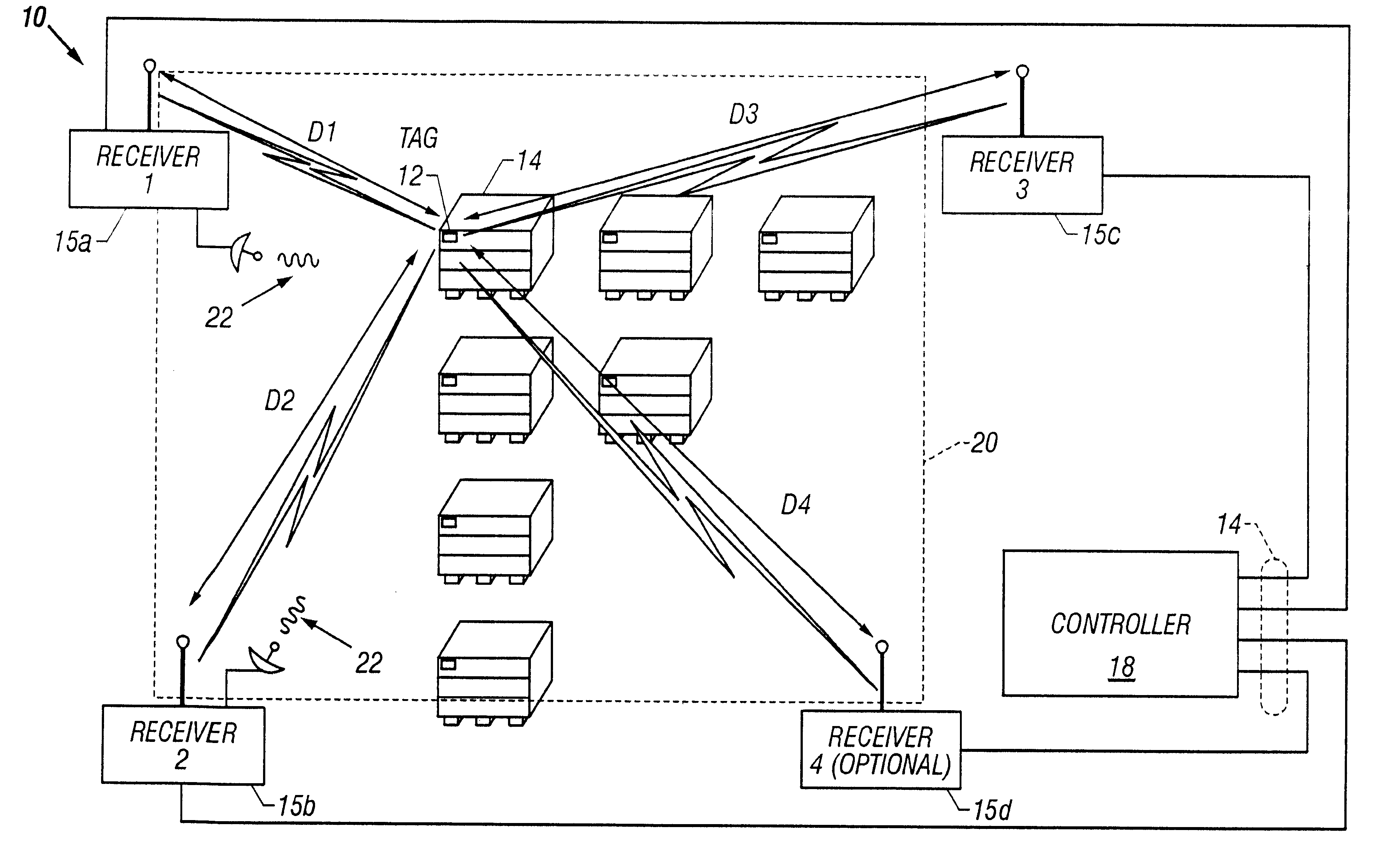
A short range radiolocation system and associated methods that allow the location of an item, such as equipment, containers, pallets, vehicles, or personnel, within a defined area. A small, battery powered, self-contained tag is provided to an item to be located. The tag includes a spread-spectrum transmitter that transmits a spread-spectrum code and identification information. A plurality of receivers positioned about the area receive signals from a transmitting tag. The position of the tag, and hence the item, is located by triangulation. The system employs three different ranging techniques for providing coarse, intermediate, and fine spatial position resolution. Coarse positioning information is provided by use of direct-sequence code phase transmitted as a spread-spectrum signal. Intermediate positioning information is provided by the use of a difference signal transmitted with the direct-sequence spread-spectrum code. Fine positioning information is provided by use of carrier phase measurements. An algorithm is employed to combine the three data sets to provide accurate location measurements.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Method and apparatus for integrating wireless communication and asset location
ActiveUS7411921B2Minimizing of activityMinimizing disruptionMemory record carrier reading problemsNetwork topologiesCommunications systemImage resolution
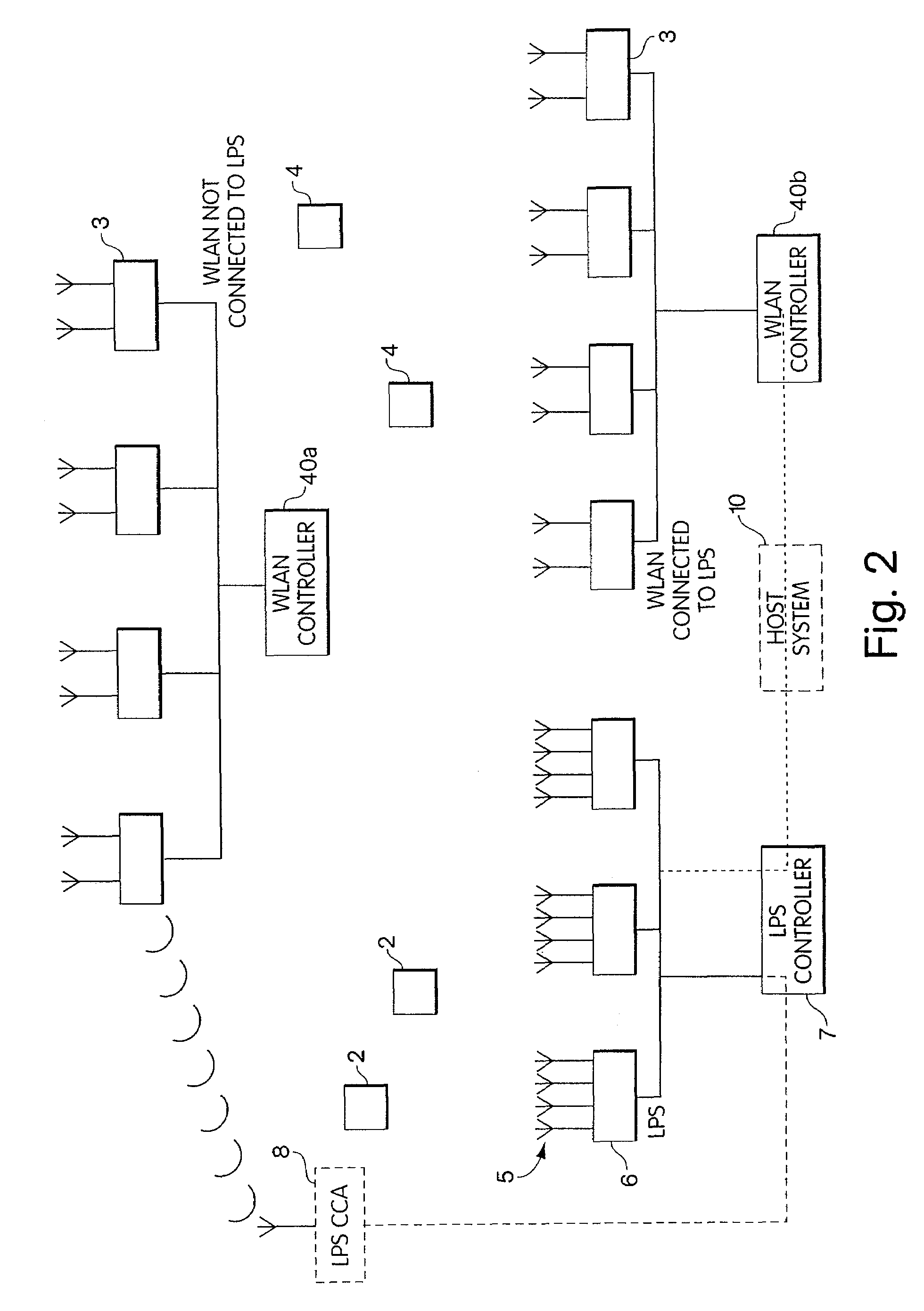
A method and apparatus to identify tags in a wireless tag identification system. Operation of the wireless tag identification system may be controlled to minimize interference or otherwise improve interoperation with a wireless communication system, such as a wireless local area network (WLAN). For example, the timing and / or power of wireless signals produced by the wireless tag identification system can be controlled to provide sufficient space to the wireless communication system to operate properly. The systems may be tightly integrated, e.g., so that tags may be identified by responding to wireless communications traffic as opposed to special purpose tag search signals. The wireless communications traffic may be modified to enhance tag location resolution.
Owner:RF TECH
Position-tracking system
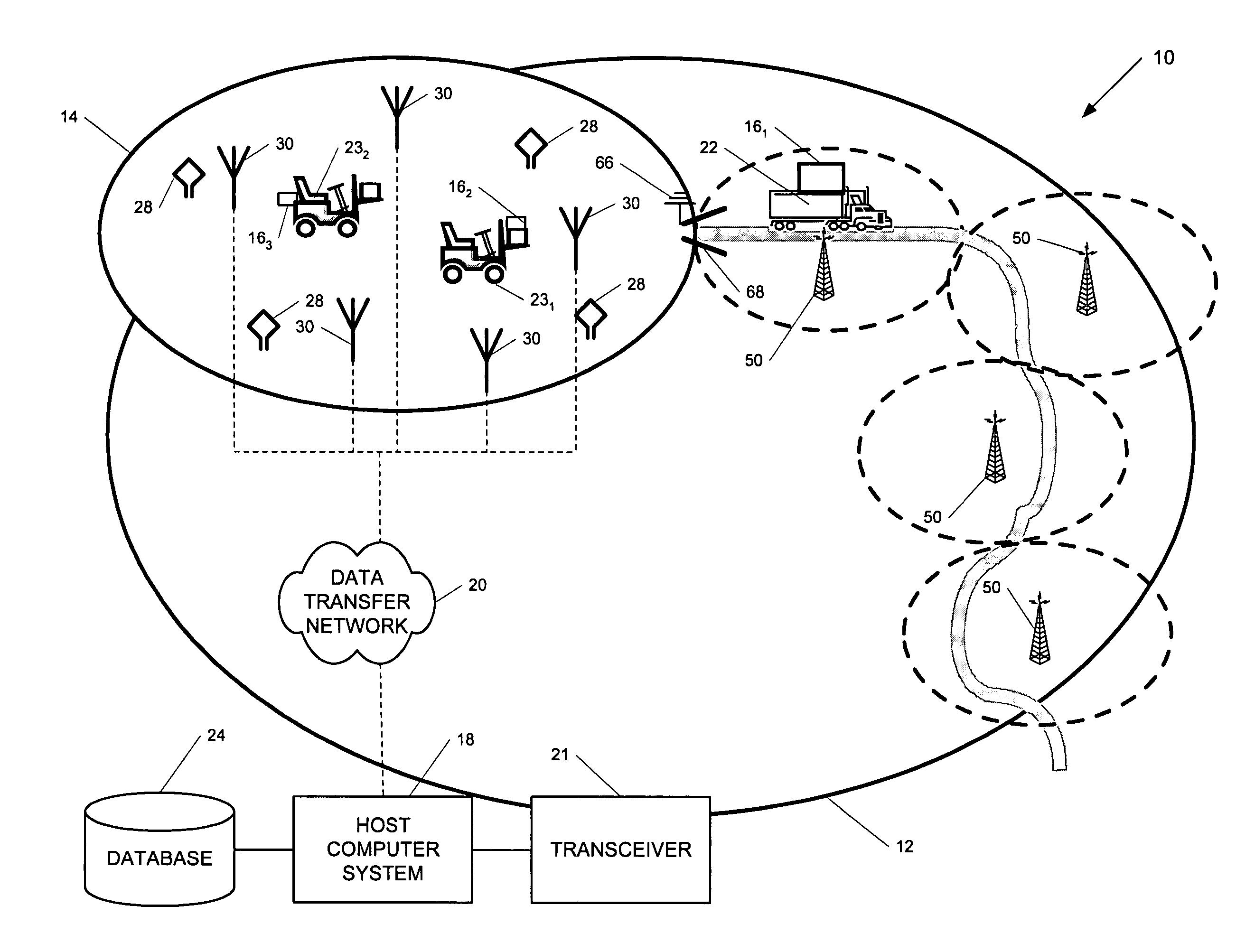
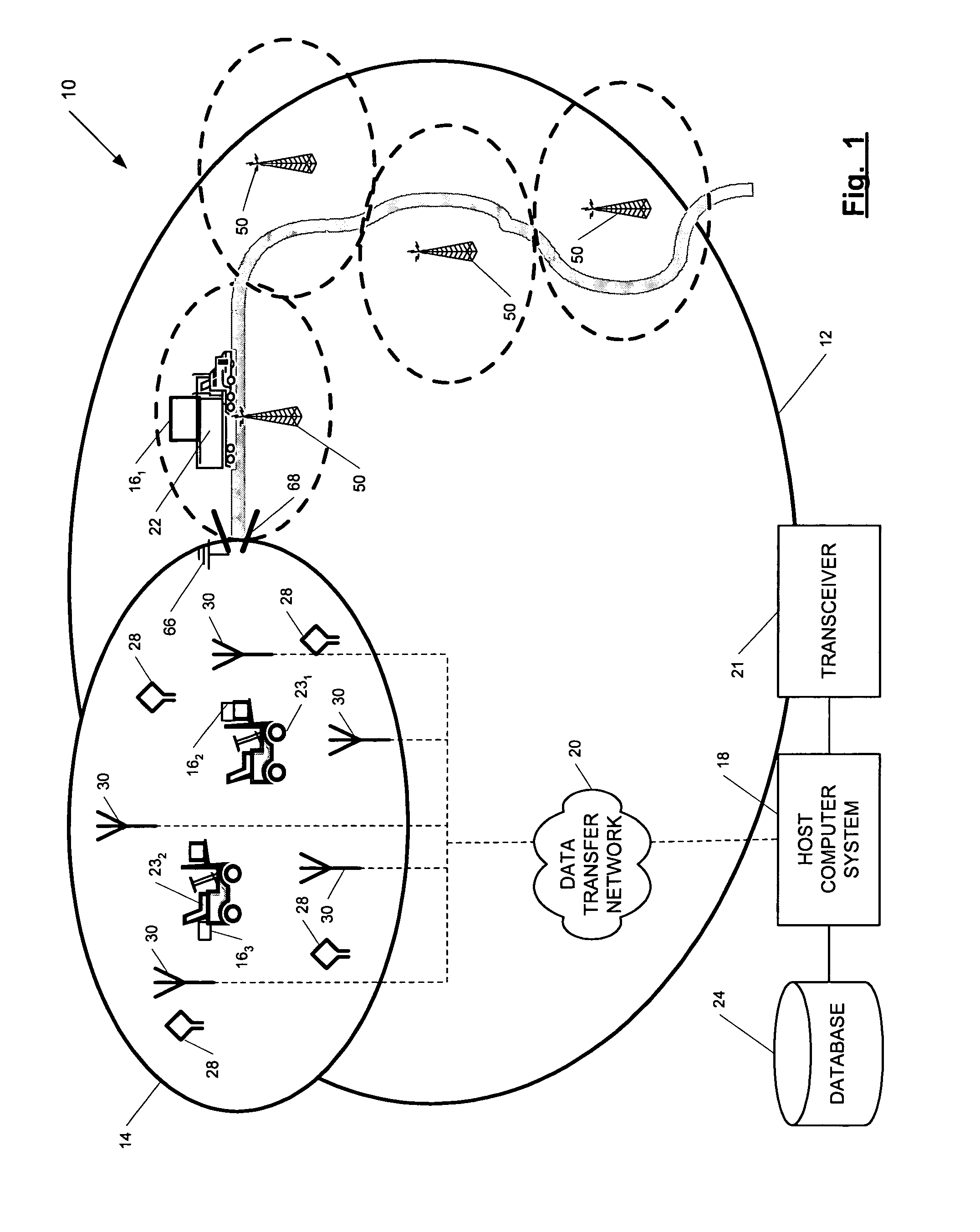
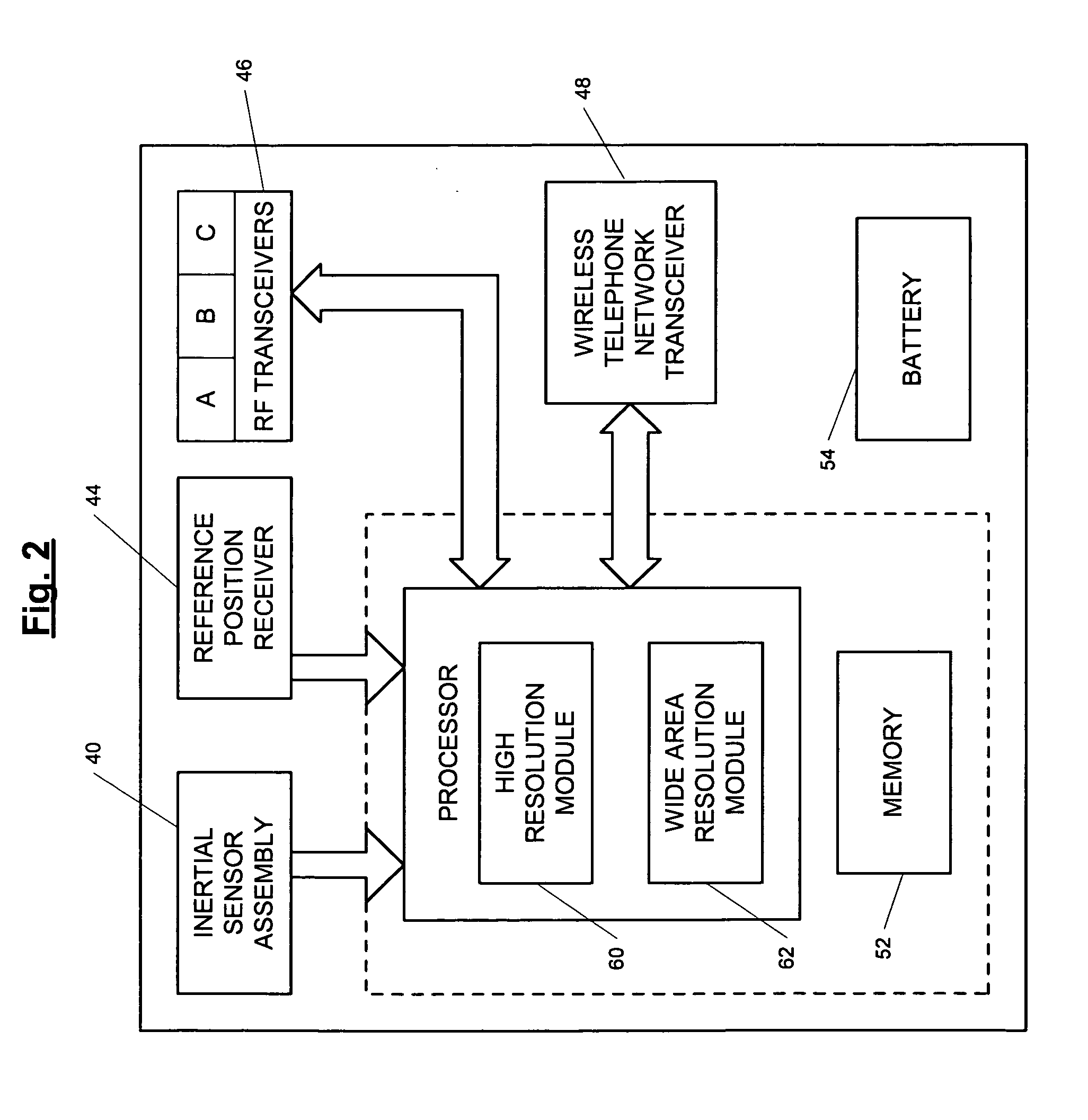
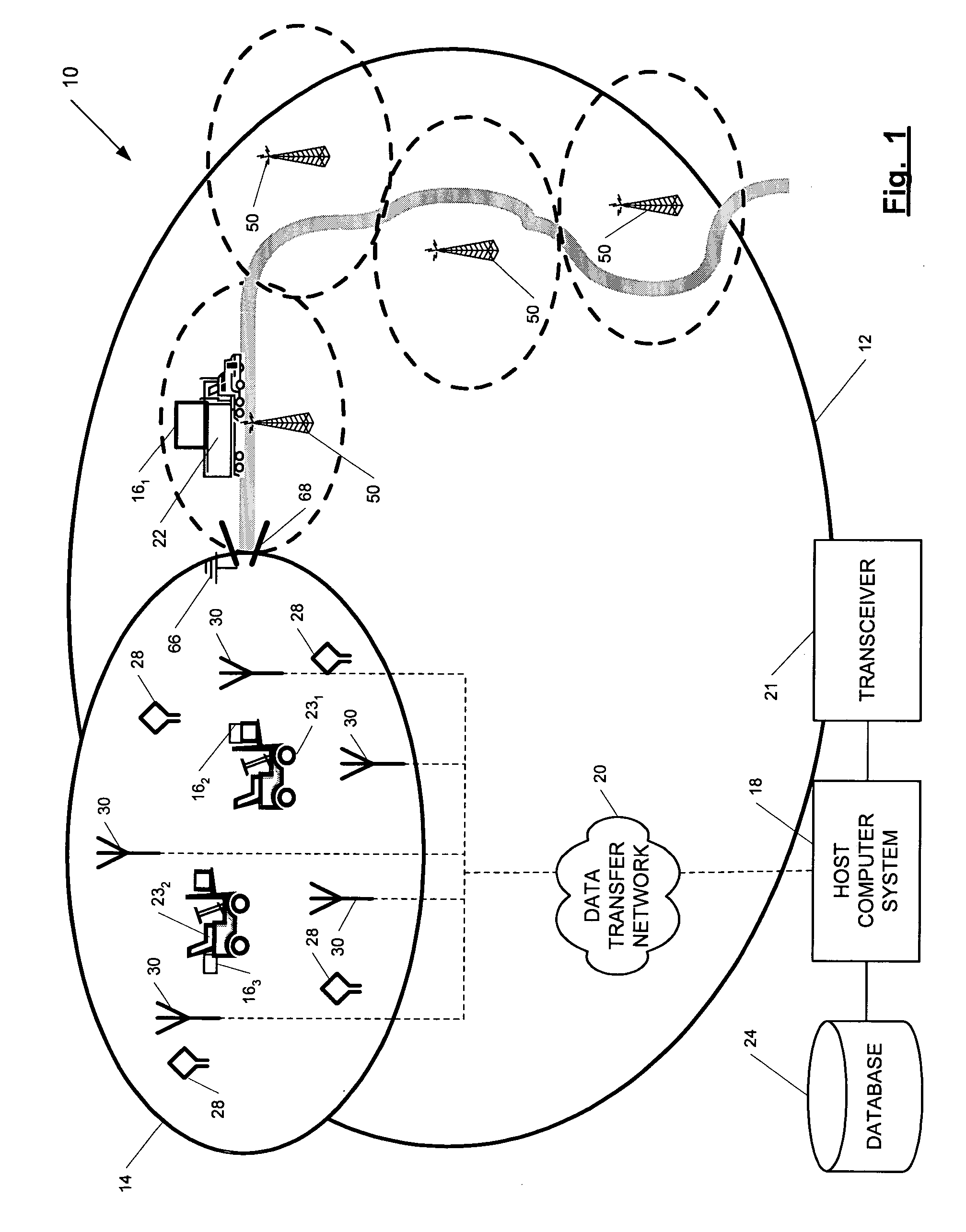
ActiveUS7236091B2High position resolutionImprove accuracyRoad vehicles traffic controlElectric/electromagnetic visible signallingObject basedTransceiver
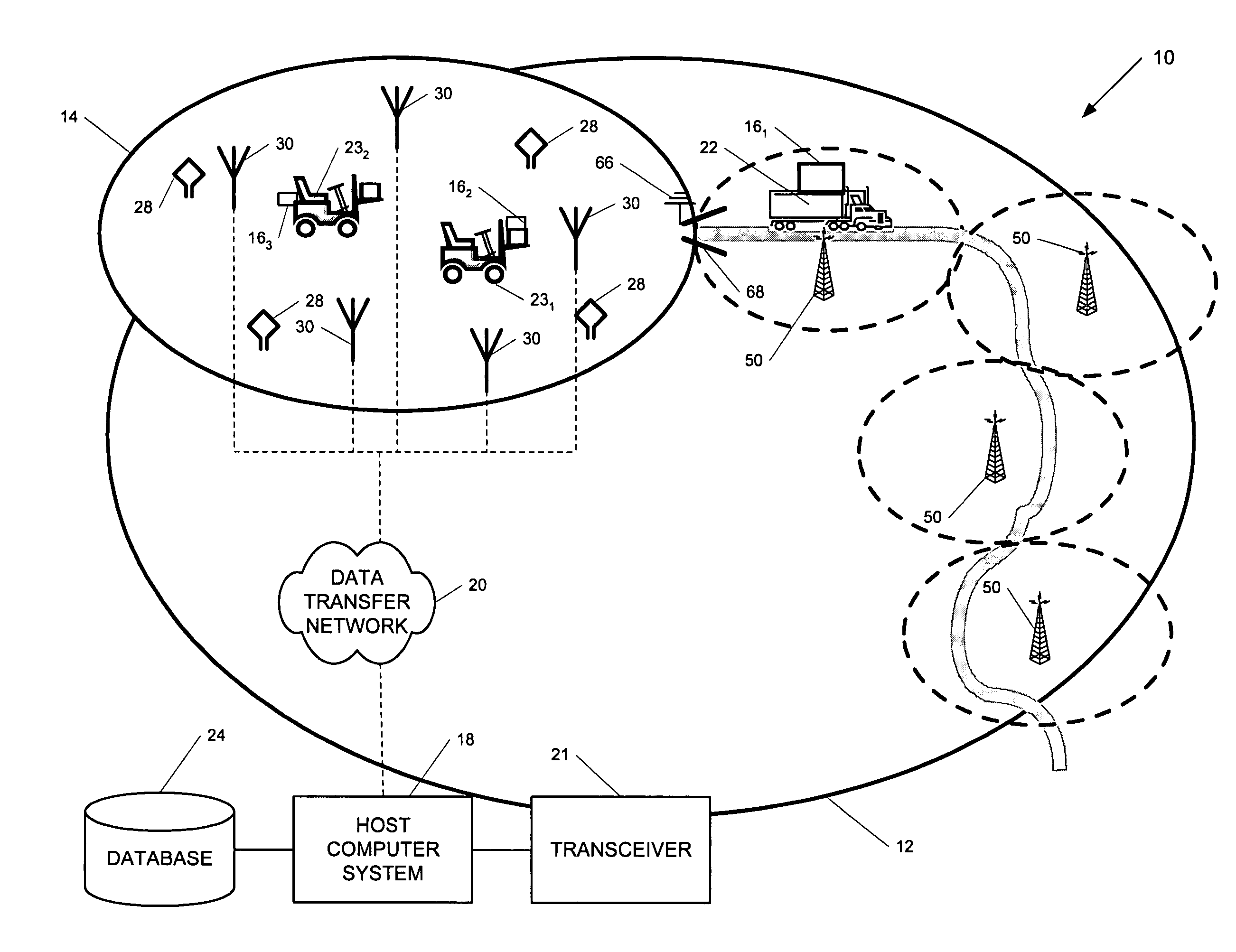
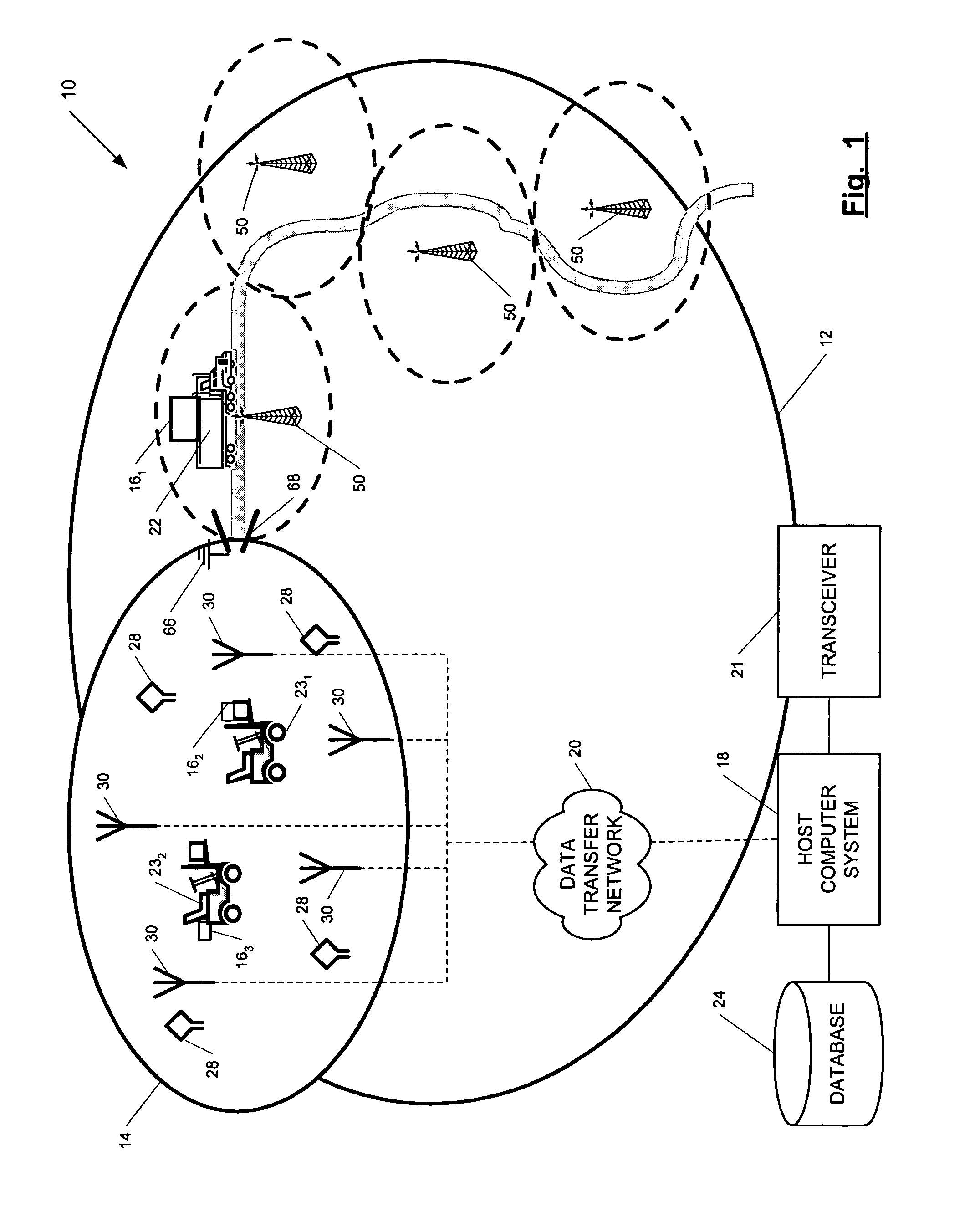
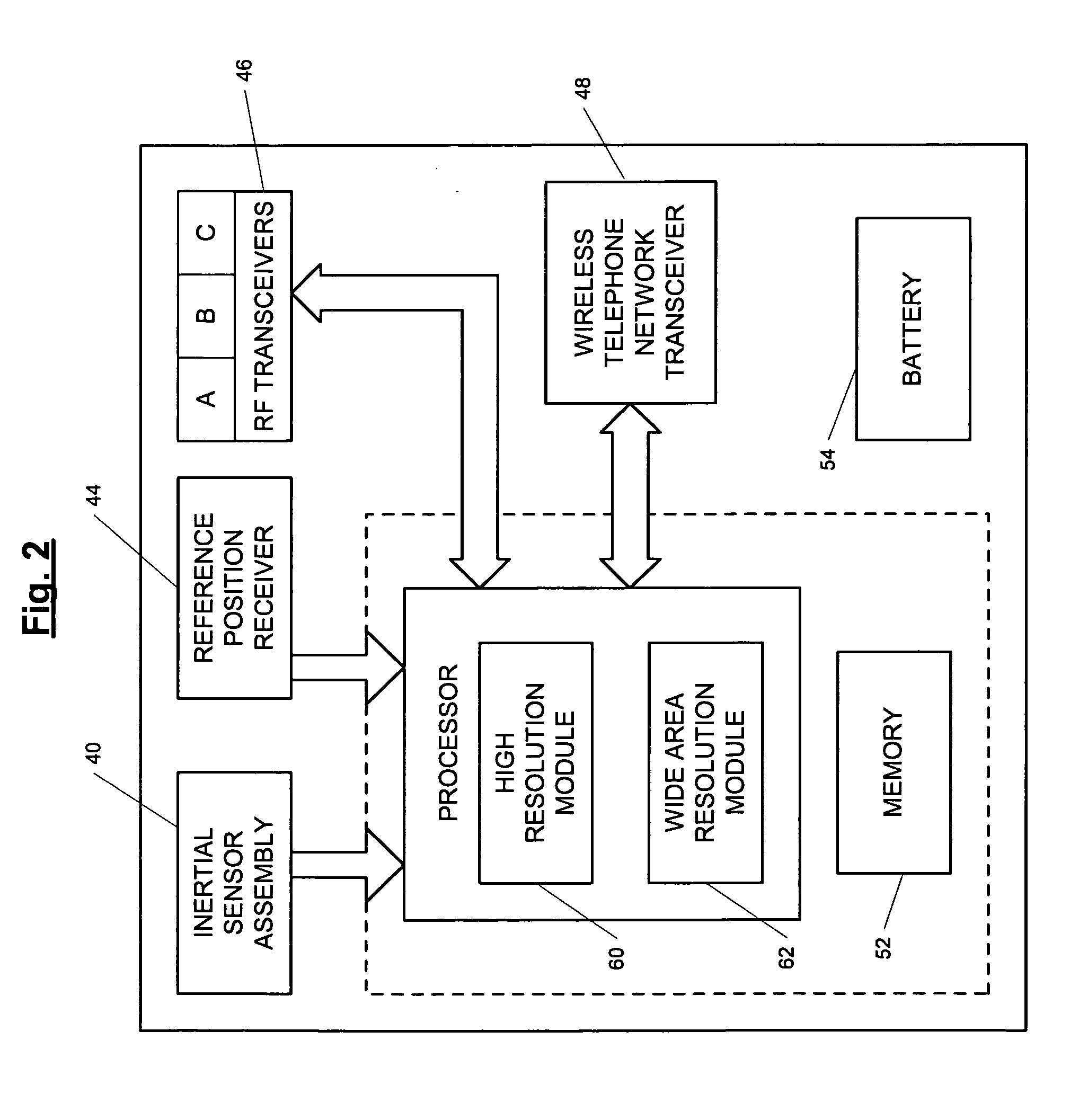
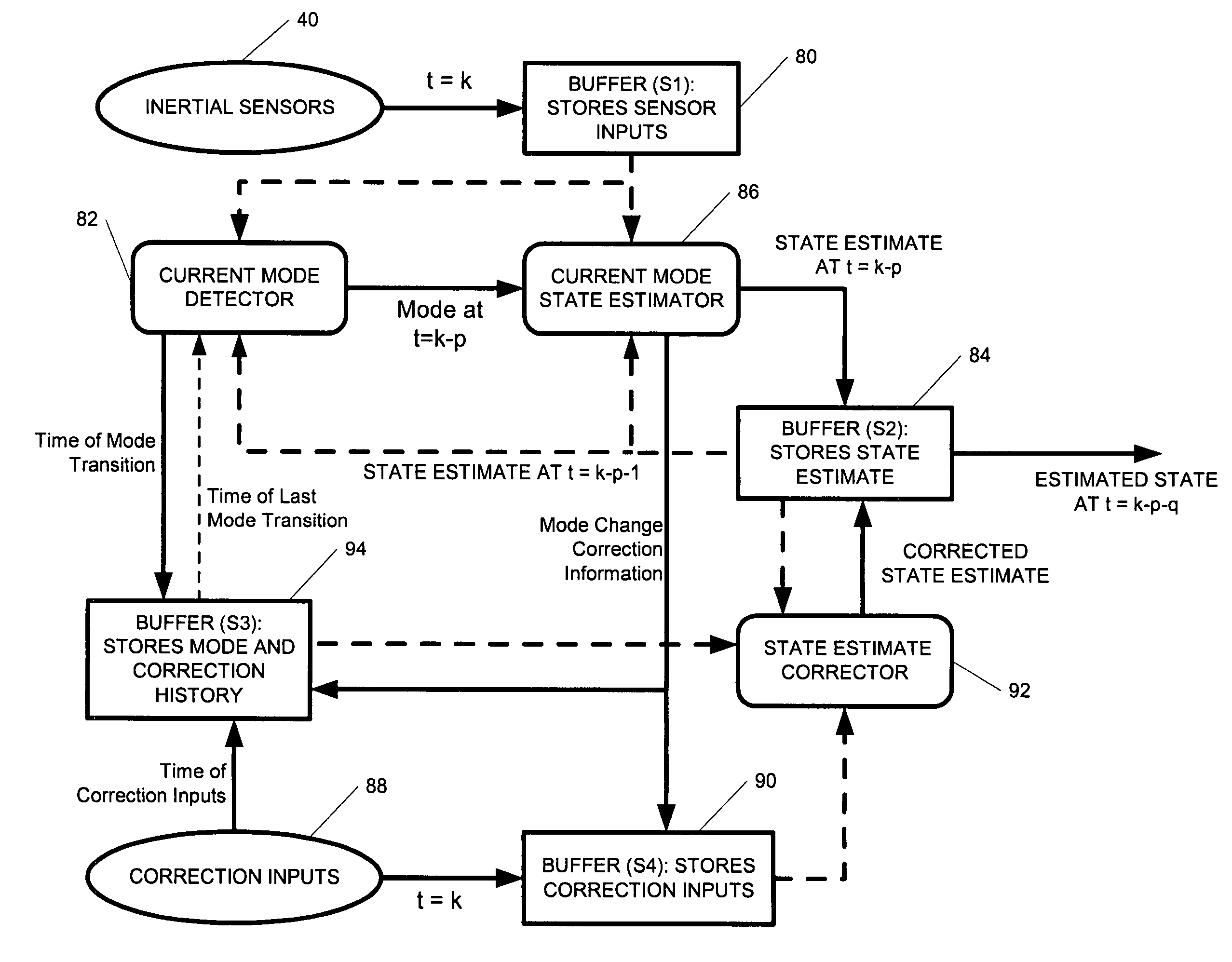
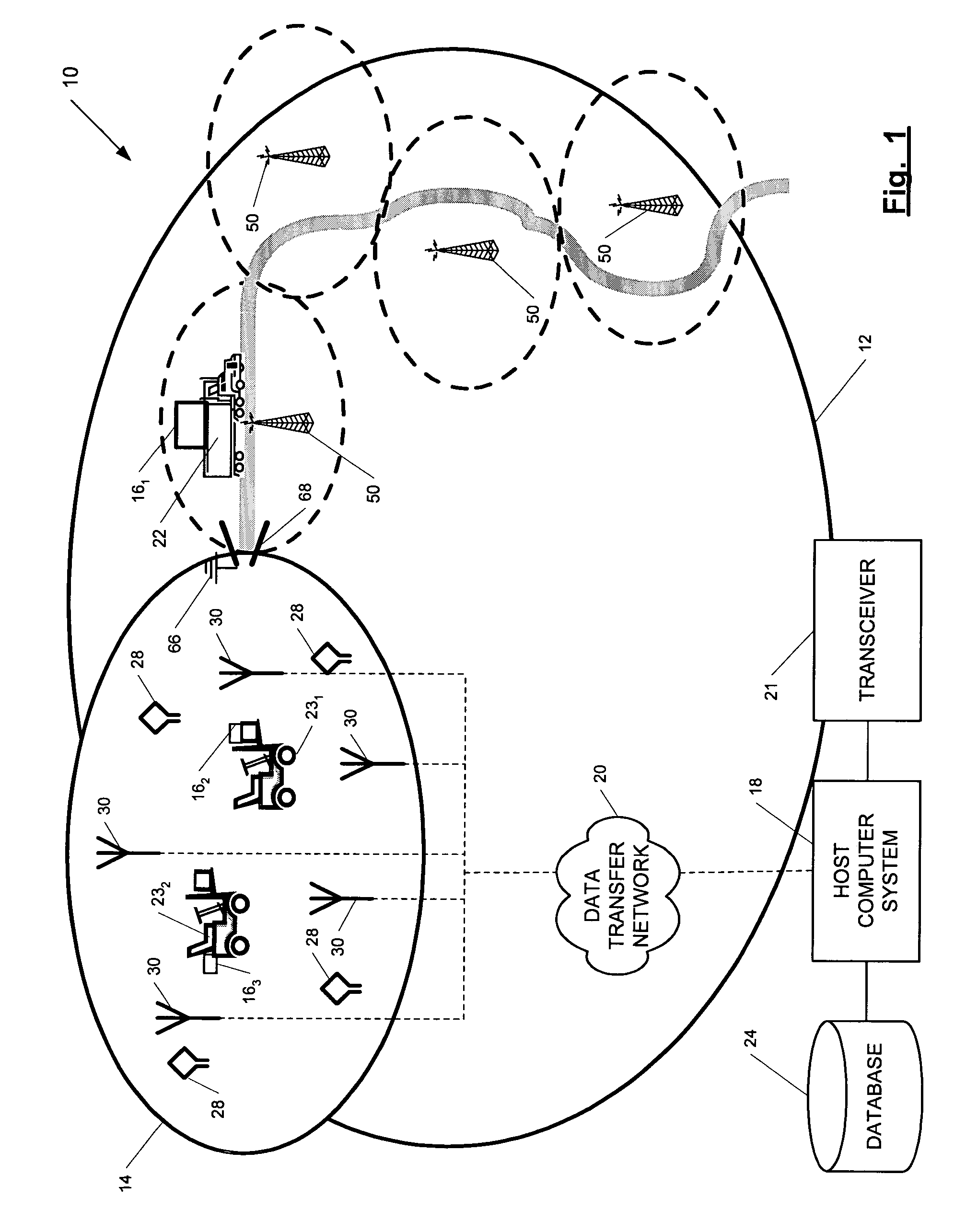
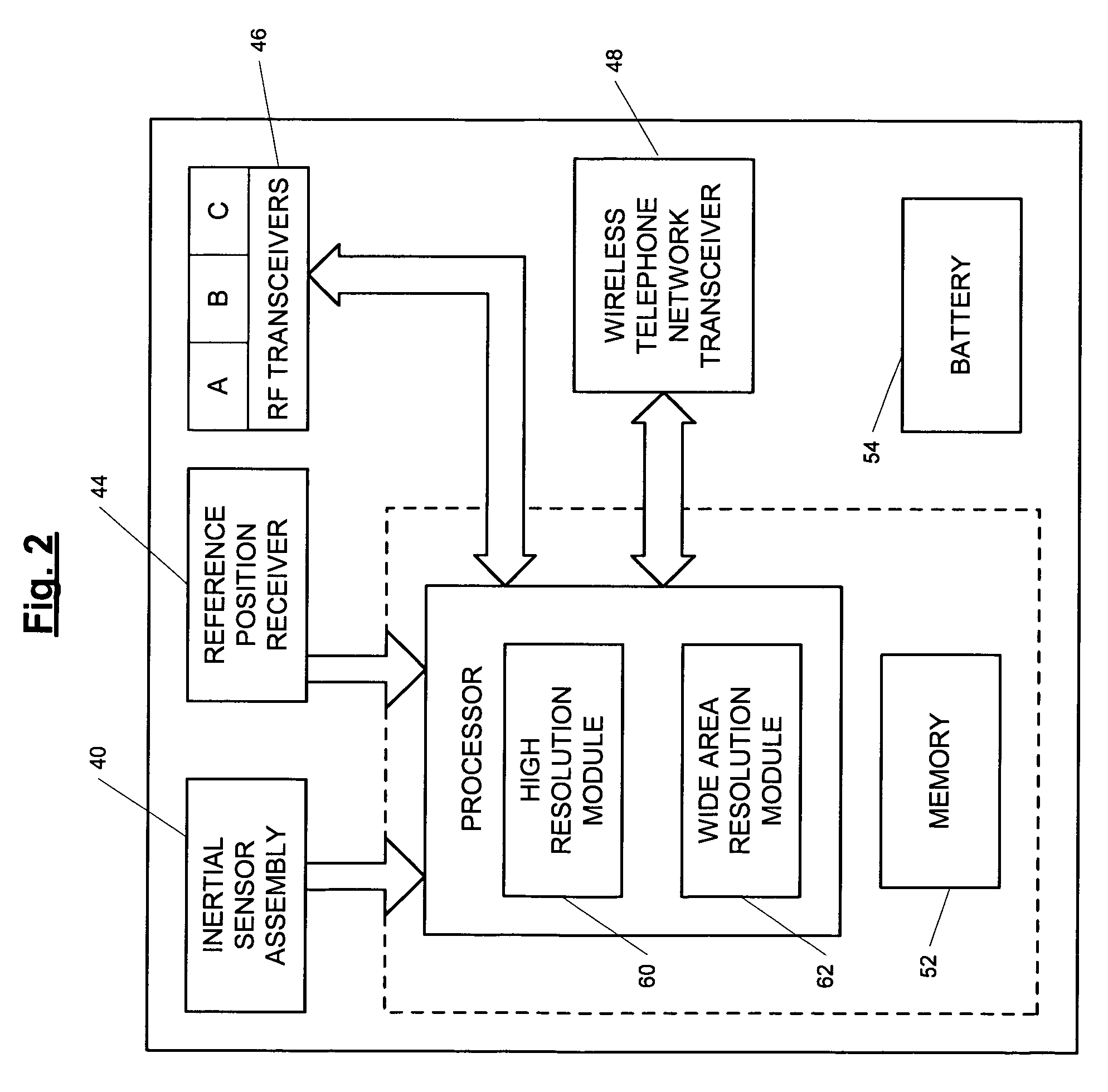
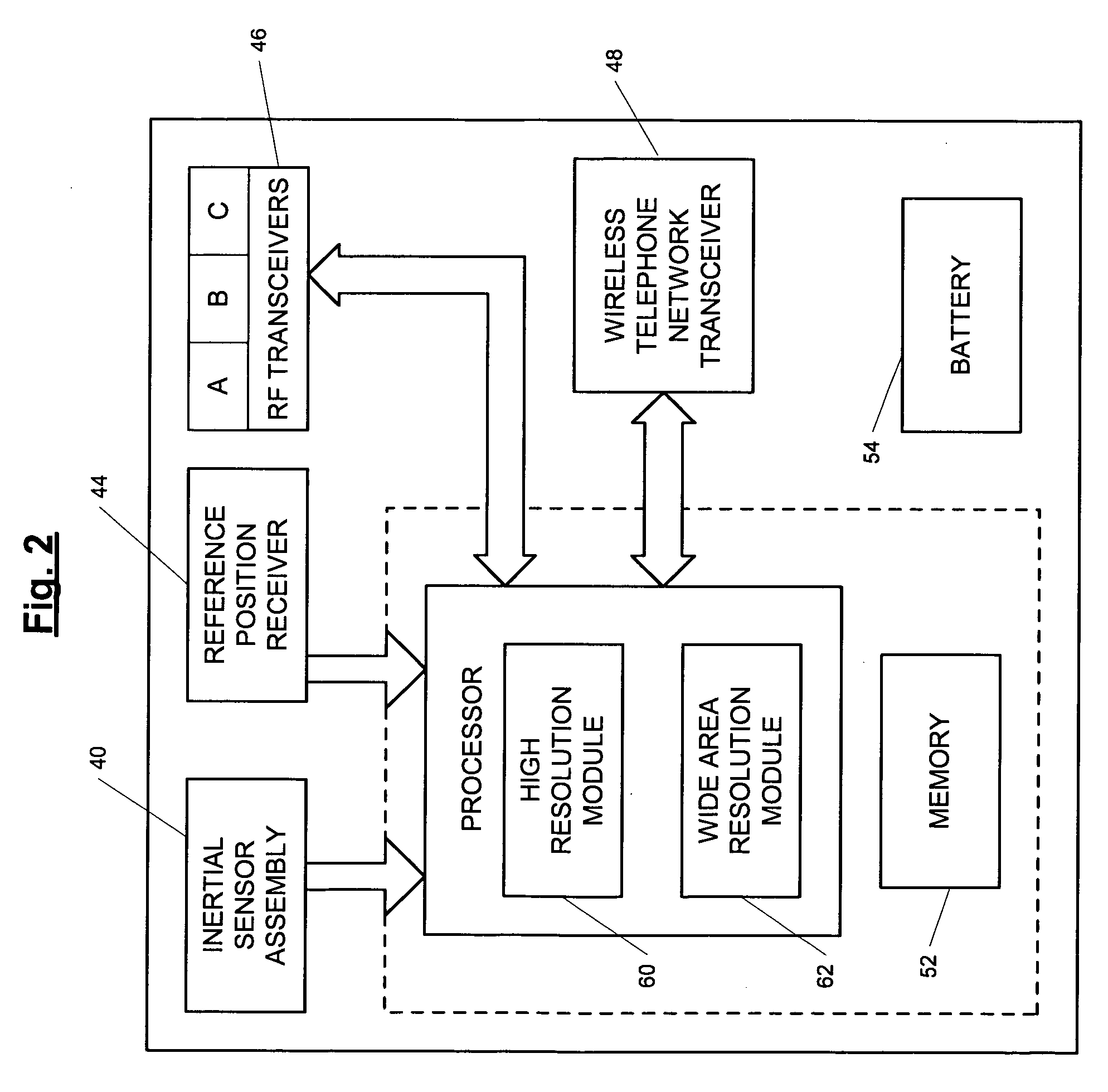
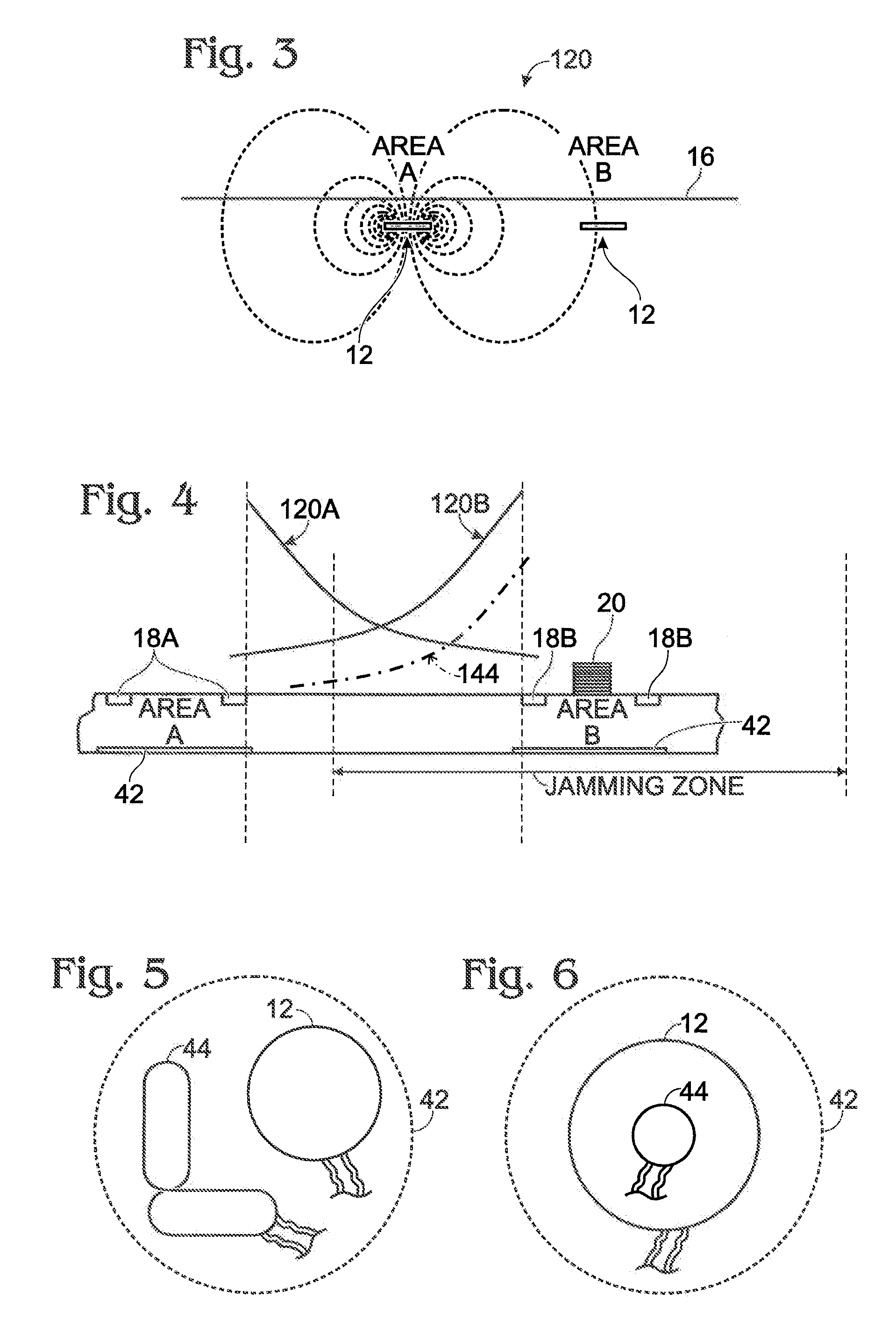
A position-tracking system for tracking the position of an object is disclosed. According to various embodiments, the tracking system includes a tracking device that is connected to or otherwise affixed to the object to be tracked. The tracking device may include, among other things, an inertial sensor assembly, radio transceivers and a processor. The position tracking system may also include a host processing system that is in communication with the tracking device. The position tracking system may provide variable-resolution position information based on the environment in which the object is moving. In a “wide resolution” area, the system may compute a general position for the object based on a wireless telephone network Cell-ID / map correlation architecture. In a high-resolution area, greater position resolution may be realized from the combination of a wireless aiding system and inputs from the inertial sensors. In the high-resolution mode, the system may exploit distinct patterns of motion that can be identified as motion “signatures” that are characteristic of certain types of motion. Kinematic (or object movement) models may be constructed based on these motion signatures and the position tracking system may estimate the state of the object based on the kinematic model for the current mode of the object. Adaptive and cascaded Kalman filtering may be employed in the analysis to more accurately estimate the position and velocity of the object based on the motion pattern identified.
Owner:PINC SOLUTIONS
Position-tracking device for position-tracking system
ActiveUS7245215B2High position resolutionImprove accuracyInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlTransceiverObject based
A position-tracking system for tracking the position of an object is disclosed. According to various embodiments, the tracking system includes a tracking device that is connected to or otherwise affixed to the object to be tracked. The tracking device may include, among other things, an inertial sensor assembly, radio transceivers and a processor. The position tracking system may also include a host processing system that is in communication with the tracking device. The position tracking system may provide variable-resolution position information based on the environment in which the object is moving. In a “wide resolution” area, the system may compute a general position for the object based on a wireless telephone network Cell-ID / map correlation architecture. In a high-resolution area, greater position resolution may be realized from the combination of a wireless aiding system and inputs from the inertial sensors. In the high-resolution mode, the system may exploit distinct patterns of motion that can be identified as motion “signatures” that are characteristic of certain types of motion. Kinematic (or object movement) models may be constructed based on these motion signatures and the position tracking system may estimate the state of the object based on the kinematic model for the current mode of the object. Adaptive and cascaded Kalman filtering may be employed in the analysis to more accurately estimate the position and velocity of the object based on the motion pattern identified.
Owner:PINC SOLUTIONS
System and method for locating a mobile subscriber terminal when roaming
InactiveUS20120253957A1Reduce in quantityPoint-of-sale network systemsTransmissionTelecommunicationsComputer terminal
The location of a mobile subscriber roaming outside a home network may be used to authorize a transaction initiated by the mobile subscriber or to authenticate the mobile subscriber when signing into secure accounts. The location of the mobile subscriber is determined by providing a unique mobile subscriber identifier, such as the MSISDN, to an application that communicates with the home network and the roaming network. By communicating with the roaming network, the application can determine the current location of the roaming mobile subscriber terminal with location resolution down to the specific cell in which the mobile subscriber terminal is located. The location of the mobile subscriber terminal may be saved locally in a database associated with an authorization entity, thereby advantageously reducing the number of location look-ups requested by the authorization entity.
Owner:ZUMIGO
Method for the continuous real time tracking of the position of at least one mobile object as well as an associated device
ActiveUS7139582B2Reduce cross-correlationMaximize accuracyDirection finders using radio wavesGymnastic exercisingBurst transmissionTemporal resolution
In a method for the continuous real time tracking of the position of at least one mobile object in a defined multidimensional space, at least one mobile transmitter module is attached to at least one mobile object and the signals from the at least one module are received by a stationary receiving and signal processing network and then centrally processed. The signals emitted by each transmitter module are electromagnetic waves sent within a frequency band range using time division multiplexing techniques. Due to the fact that the frequency band is used as a single channel for the purpose of maximizing the accuracy with which a position is detected, and due also to the fact that the communication process between the transmitters and the receivers is based on the principle of pseudo-random time division multiplexing using burst transmissions of low cross correlation with non synchronized pseudo-random patterns, there is created a method for the continuous tracking of the position of one or more mobile objects at any time and in any place which is of very high positional resolution and has a temporal resolution of just a few milliseconds.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Position-tracing system
ActiveUS20060187028A1Improve accuracyHigh position resolutionInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlTransceiverObject based
A position-tracking system for tracking the position of an object is disclosed. According to various embodiments, the tracking system includes a tracking device that is connected to or otherwise affixed to the object to be tracked. The tracking device may include, among other things, an inertial sensor assembly, radio transceivers and a processor. The position tracking system may also include a host processing system that is in communication with the tracking device. The position tracking system may provide variable-resolution position information based on the environment in which the object is moving. In a “wide resolution” area, the system may compute a general position for the object based on a wireless telephone network Cell-ID / map correlation architecture. In a high-resolution area, greater position resolution may be realized from the combination of a wireless aiding system and inputs from the inertial sensors. In the high-resolution mode, the system may exploit distinct patterns of motion that can be identified as motion “signatures” that are characteristic of certain types of motion. Kinematic (or object movement) models may be constructed based on these motion signatures and the position tracking system may estimate the state of the object based on the kinematic model for the current mode of the object. Adaptive and cascaded Kalman filtering may be employed in the analysis to more accurately estimate the position and velocity of the object based on the motion pattern identified.
Owner:PINC SOLUTIONS
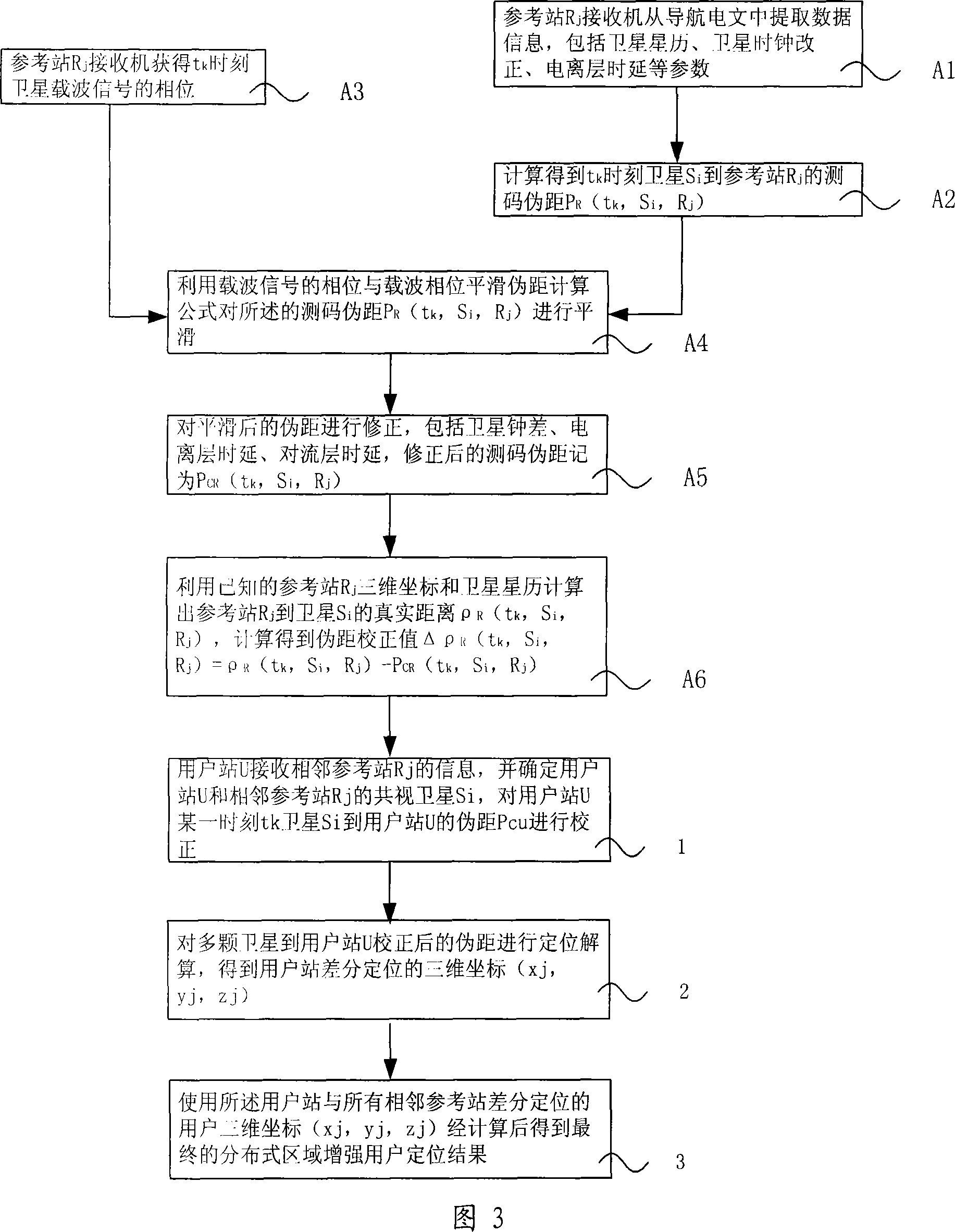
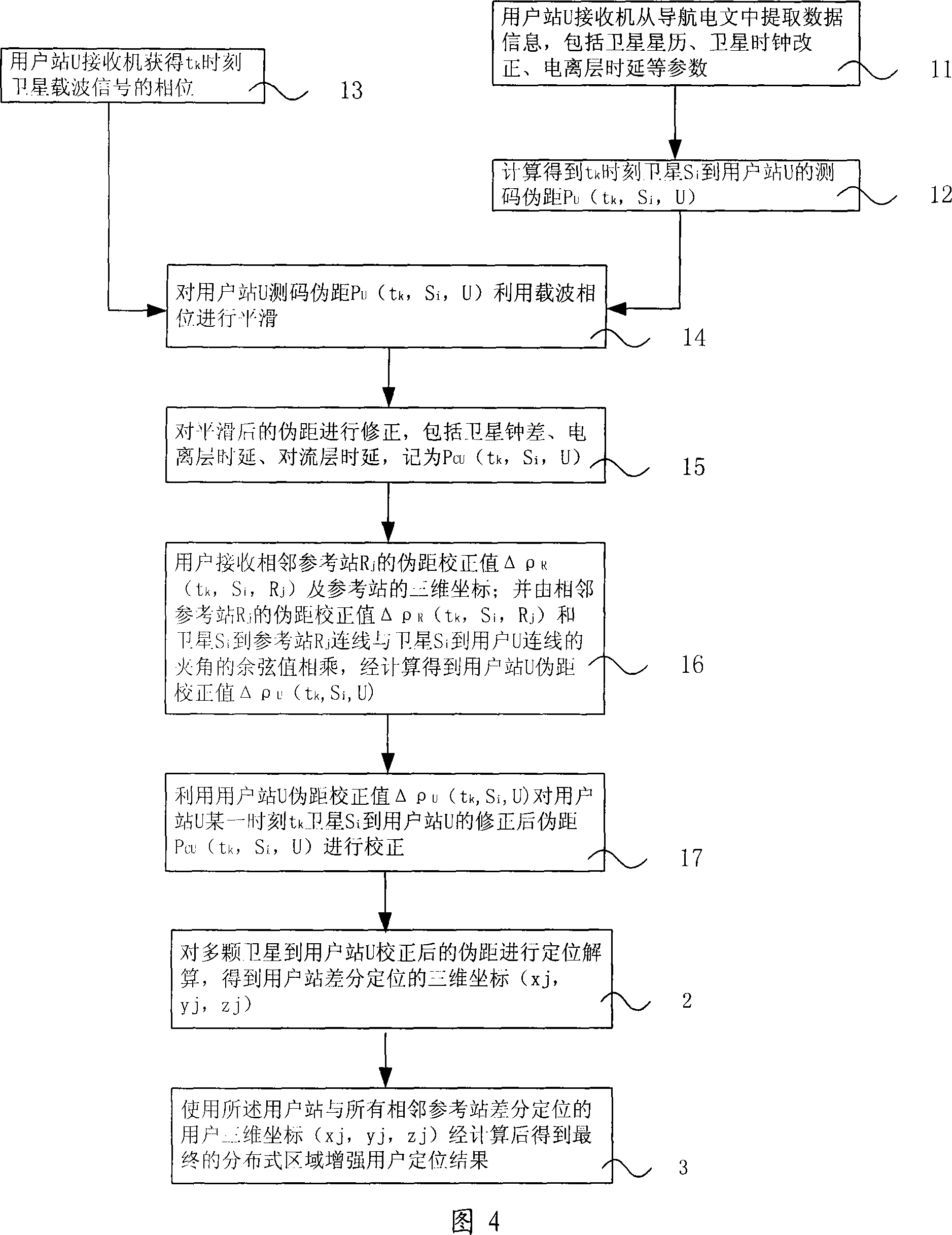
Locating method for satellite navigation reinforcing system
InactiveCN101109805AOvercome precisionOvercome distancePosition fixationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTroposphereIonosphere
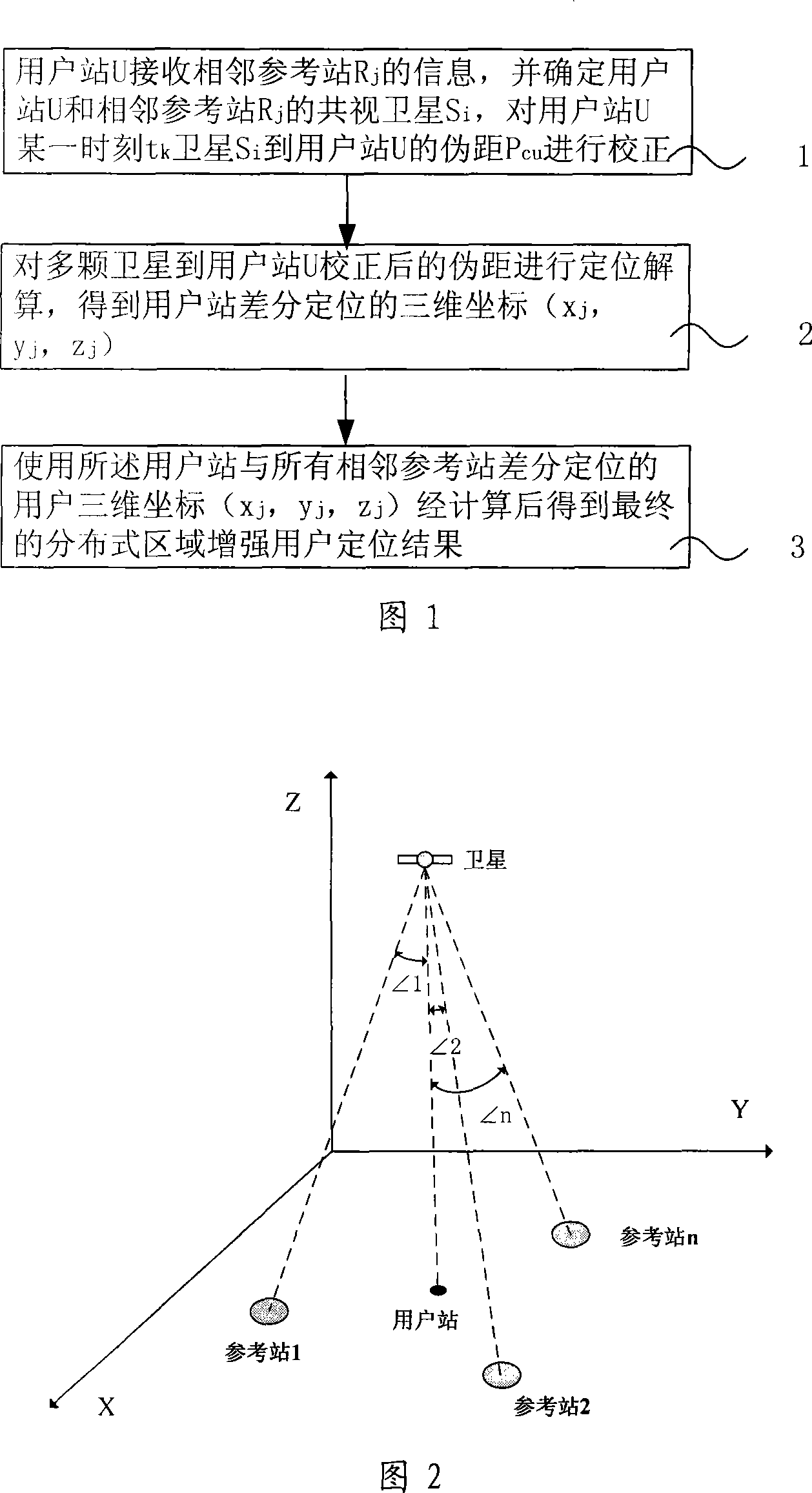
The invention relates to a positioning method for a satellite navigation enhancing system comprising such procedures as, a user station receives info from an adjacent reference station, and determines the mutually-visual satellite of the user station and the adjacent reference station, and calibrates the pseudo distance from a satellite to the user station in a time period; a reference station adjacent to the user station is used to carry out positioning resolution of the calculated pseudo distance from a plurality of satellites to the user station, so as to get the 3D coordinates of the differential positioning of the user station; the positioning result of the user is enhanced by using the final distributed area got by weighted average calculation of 3D coordinates of differential positioning of the user station and all adjacent reference stations. The invention enhances the positioning accuracy for a user by using the enhancing info from a plurality of local areas in a foundation enhancement covered area in respect to the shortcoming that the positioning accuracy is greatly reduced when the user is far from the ground station and a big difference exists between the delay error of the ground station and that of the ionized stratum and the troposphere of the user.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Road information providing system and road information providing apparatus and road information generating method
InactiveUS20050171649A1Flexible supportInstruments for road network navigationArrangements for variable traffic instructionsImage resolutionDecodes
An object of the invention is to provide a traffic information provision system which can arbitrarily set a position resolution and a traffic representation resolution and flexibly support a traffic information prediction service. The traffic information provision system of the invention quantizes the state quantity of traffic information changing along a road, converts said quantized state quantity to a value having statistical deviation, performs encoding of said value, and provides the encoded value to traffic information utilization apparatus such as a car navigation system. The traffic information utilization apparatus decodes said encoded state quantity to reproduce the traffic information on said road.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Scintillation crystal array detecting device
InactiveCN101644780AReduce the numberLow costX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentImage resolutionLight guide
The invention relates to a scintillation crystal array detecting device, which comprises a crystal array, M*N light guides, an optical fiber splitter unit, an optical fiber merging unit and an opticalfiber signal reading unit, wherein the crystal array comprises M*N crystals for generating fluorescence photons, M represents the number of rows, and N represents the number of columns; each light guide is connected with the surface of a crystal to collect and transmit the fluorescence photons generated by the crystal; the optical fiber splitter unit is used for splitting fluorescence photons transmitted by each light guide into two paths of optical fibers which are a row transmission optical fiber and a column transmission optical fiber to transmit the fluorescence photons; the optical fibermerging unit is used for fusing row transmission optical fibers corresponding to light guides connected with the same row of crystals into a row optical fiber and fusing column transmission optical fibers corresponding to light guides connected with the same column of crystals into a column optical fiber; and the optical fiber signal reading unit is connected with the row optical fibers and the column optical fibers to recognize the numbers of the rows in which the row optical fibers transmitting the fluorescence photons are and the numbers of the columns in which the column optical fibers transmitting the fluorescence photons are to further determine the position of scintillation crystals and detect the total quantity and energy of received fluorescence photons. The device is reduced incost, volume and weight and has high position resolution and fluorescence collection efficiency.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Large-array underwater wideband spread spectrum beacon navigational positioning system and method based on time synchronization
The invention discloses a large-array underwater wideband spread spectrum beacon navigational positioning system and method based on time synchronization, and time synchronization is carried out on a positioning array buoy and a sound beacon through a high-accuracy time synchronization technology. The sound beacon subjected to strict time synchronization emits spread spectrum water sound signals in a timing mode. After the positioning array buoy receives the spread spectrum signals, the position of the sound beacon is obtained through signal resolution, distance calculation and position resolution. The position of the sound beacon is obtained after the coordinates are worked out, the movement track of the sound beacon can be drawn out through continuous response, resolving and positioning, and accurate positioning and navigation of underwater equipment are achieved.
Owner:江苏中海达海洋信息技术有限公司
Speed detection method and apparatus of moving body
The invention provides a speed detecting method of a moving body and a device thereof. In the lift using terminal floor reduction device, the device is able to obtain the necessary overspeed detecting response time near the terminal floor by the speed detector equipped in the lift car without using the linear coder having high position resolving capability. The position differential value from the linear coder and the acceleration integral quantity from the acceleration sensor are combined into speed value to carry out the overspeed judgment. The acceleration integral quantity is reset and differed at pulse edge of the linear coder. The necessary response time detecting the overspeed near the terminal floor is improved, and the speed needed by the terminal floor reduction device is accurately processed.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Collection of secondary electrons through the objective lens of a scanning electron microscope
InactiveUS6946654B2Enhanced signalReduce acquisition timeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesImage resolutionLight beam
A high resolution scanning electron microscope collects secondary Auger electrons through its objective lens to sensitively determine the chemical make-up with extremely fine positional resolution. The system uses a magnetic high resolution objective lens, such as a snorkel lens or a dual pole magnetic lens which provides an outstanding primary electron beam performance. The Auger electrons are deflected from the path of the primary beam by a transfer spherical capacitor. The primary beam is shielded, by a tube or plates, as it traverses the spherical capacitor to prevent aberration of the primary beam and the external wall of the shield maintains a potential gradient related to that of the spherical capacitor to reduce aberration of the primary electron beam. The coaxial configuration of the primary electron beam and the collected secondary electron beam allows the Auger image to coincide with the SEM view.
Owner:FEI CO
Position-tracking device for position-tracking system
ActiveUS20060176174A1Improve accuracyHigh position resolutionInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlTransceiverObject based
A position-tracking system for tracking the position of an object is disclosed. According to various embodiments, the tracking system includes a tracking device that is connected to or otherwise affixed to the object to be tracked. The tracking device may include, among other things, an inertial sensor assembly, radio transceivers and a processor. The position tracking system may also include a host processing system that is in communication with the tracking device. The position tracking system may provide variable-resolution position information based on the environment in which the object is moving. In a “wide resolution” area, the system may compute a general position for the object based on a wireless telephone network Cell-ID / map correlation architecture. In a high-resolution area, greater position resolution may be realized from the combination of a wireless aiding system and inputs from the inertial sensors. In the high-resolution mode, the system may exploit distinct patterns of motion that can be identified as motion “signatures” that are characteristic of certain types of motion. Kinematic (or object movement) models may be constructed based on these motion signatures and the position tracking system may estimate the state of the object based on the kinematic model for the current mode of the object. Adaptive and cascaded Kalman filtering may be employed in the analysis to more accurately estimate the position and velocity of the object based on the motion pattern identified.
Owner:PINC SOLUTIONS
Method and Apparatus for the Identification and Position Measurement of Chips on a Gaming Surface
ActiveUS20090221364A1Precise positioningBoard gamesSubscribers indirect connectionEngineeringInductance
The present invention is directed to a method for determining a position of each of a plurality of gaming chips on a gaming surface. Each of the plurality of gaming chips includes an inductively coupled RFID tag disposed therein. The gaming surface includes a first area and at least one second area disposed adjacent to the first area. The method includes transmitting a near-field inductively coupled interrogation signal to the plurality of gaming chips. A near-field inductively coupled response signal is received from at least a portion of the plurality of gaming chips. A position resolution action is performed in conjunction with either the step of transmitting or the step of receiving. Each of the plurality of gaming chips are associated with either the first area or the at least one second area in accordance with the step of performing a position resolution action.
Owner:TECHNOLOGY CAPITAL LLC
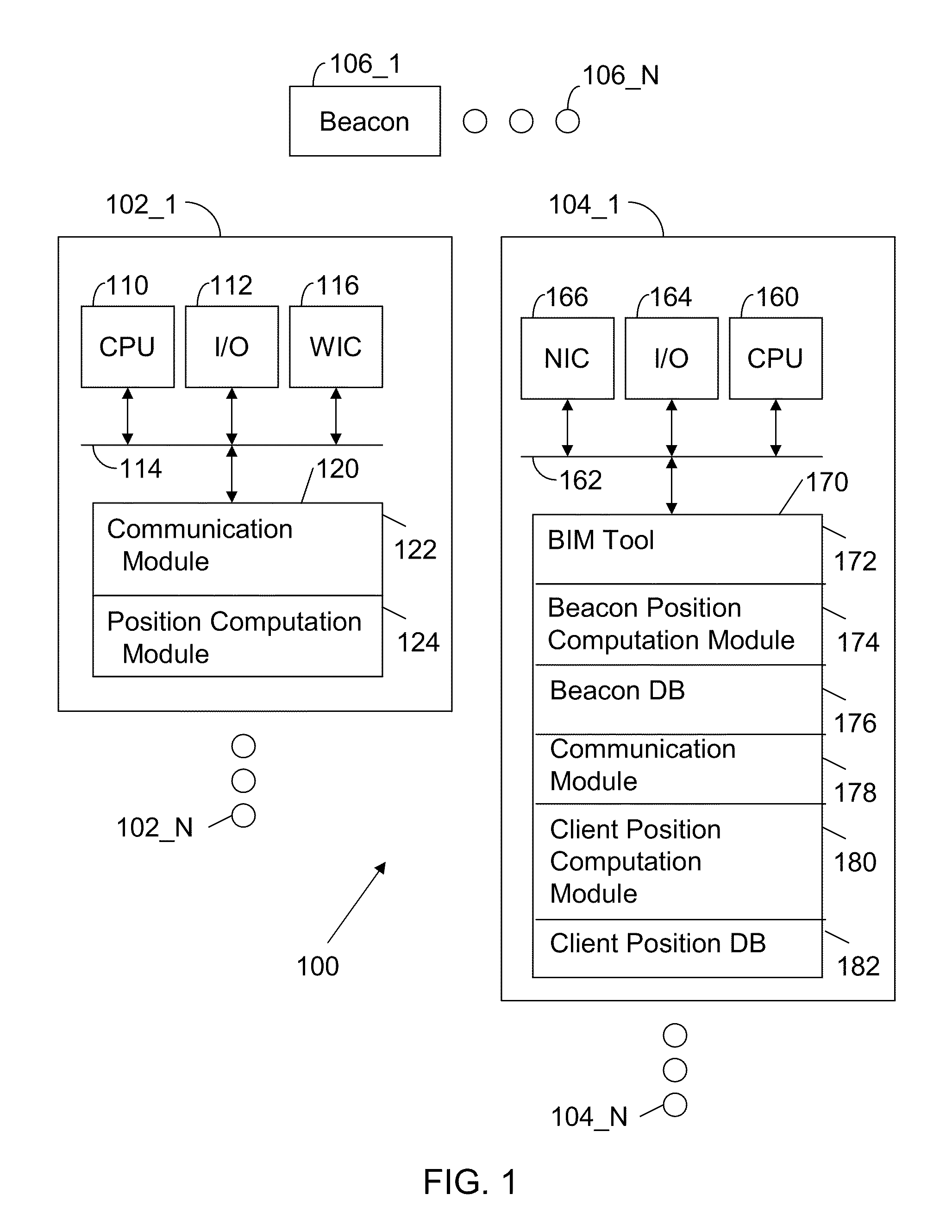
Apparatus and Method for Constructing and Utilizing a Beacon Location Database
ActiveUS20110068981A1Direction finders using radio wavesBeacon systems using radio wavesImage resolutionComputer science
A method to support client device position discovery within a building includes ascribing building position coordinates to beacons within the building. The building position coordinates are converted to physical position coordinates. The physical position coordinates are augmented with at least one additional parameter that supports position resolution. A client device communicates with accessed beacons positioned within the building. A beacon location database characterizing the physical locations of the accessed beacons is also accessed. The physical location of the client device is computed based upon the physical locations of the accessed beacons.
Owner:TEECOM
Parity vector method-based double-satellite failure recognition method
InactiveCN102901971ASolve the problem of fault offset offsetRealize detection and identificationSatellite radio beaconingRemote sensingReceiver autonomous integrity monitoring
The invention relates to global satellite navigation system receiver autonomous integrity monitoring technology and discloses a parity vector method-based double-satellite failure recognition method, aiming at the problems of false positives and false negatives caused by fault deviation offsetting when the parity vector method is used for recognizing two fault satellites. According to the technical scheme, the parity vector method is used for recognizing one fault satellite; with the fault satellite as the basis, four fault-free satellites are found out, and the information of the fault-free satellites is used for roughly locating, so that the fault satellites can be recognized; the recognized fault satellites are removed, and then the position resolution is carried out again, so that the locating accuracy is improved; therefore, the problems of false positives or false negatives caused by fault deviation offsetting can be avoided. The method solves the problem of the fault deviation offsetting caused by parity vector residual error and realizes the detection and the recognition for a plurality of fault satellites. After the method is used for detecting and recognizing satellite failure, the locating accuracy is improved. The method is mainly used for monitoring the autonomous integrity of a global satellite navigation system receiver.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
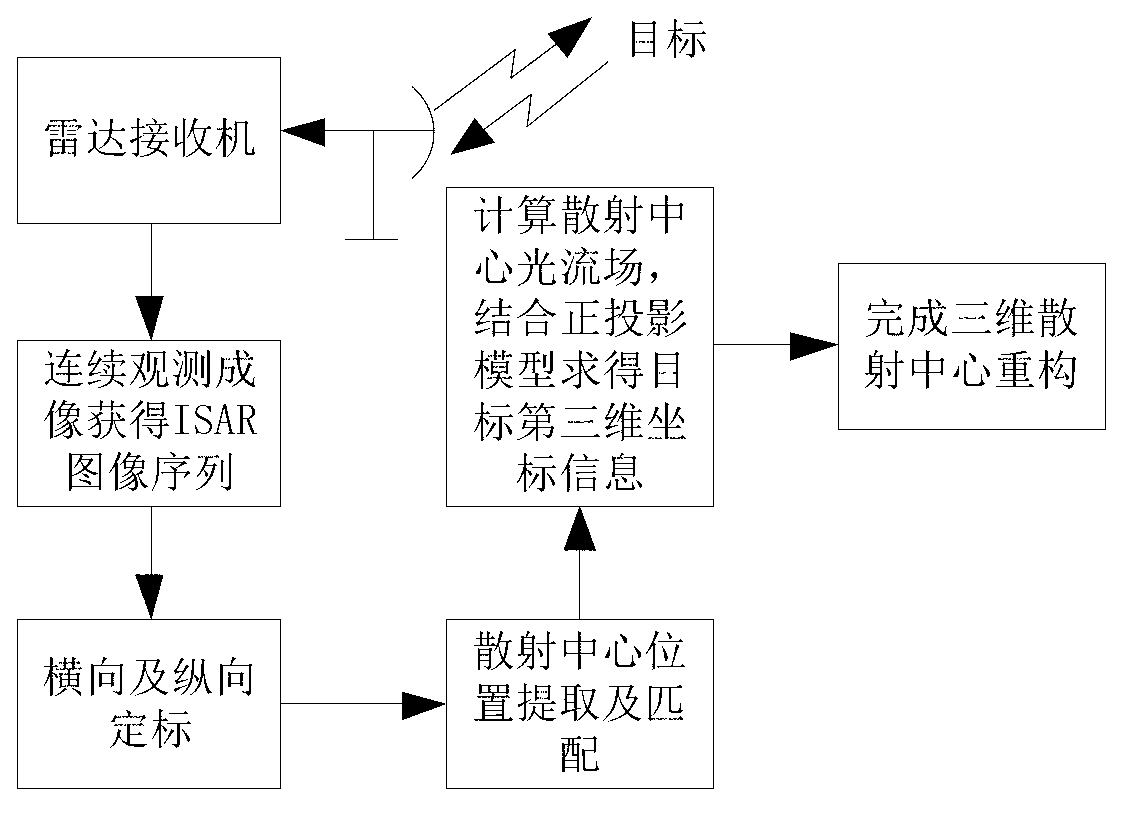
Method for reconstructing target three-dimensional scattering center of inverse synthetic aperture radar
InactiveCN103217674AResolve mismatchSmall amount of calculationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInterferometric synthetic aperture radarInverse synthetic aperture radar
The invention provides a method for reconstructing target three-dimensional scattering center inverse synthetic aperture radar. The method for reconstructing the target three-dimensional scattering center of the inverse synthetic aperture radar comprises the following steps: conducting continuous image formation on echo data after motion compensation so as to obtain an ISAR two-dimensional image sequence; respectively conducting horizontal scaling and vertical scaling on the information storage and retrieval (ISAR) two-dimensional image sequence so as to obtain a position coordinate of the scattering center; and respectively extracting a position coordinate of the scattering center in an ISAR two-dimensional image of each frame, calculating a displacement velocity field of every two adjacent frames of the scattering center of the ISAR two-dimensional image, combining projection equation and target motion equation of an orthographic projection model so as to obtain estimated values of a third dimension coordinate by combining a projection equation and a target motion equation of an orthographic projection model, and averaging multiple estimated values to obtain the final third dimension coordinate. Therefore, reconstruction of the target three-dimensional scattering center is completed directly. The method for reconstructing the target three-dimensional scattering center of the inverse synthetic aperture radar does not need cost of extra system hardware, can distinguish scattering centers with different heights in the same distance and position resolution unit, does not need to utilize prior information such as observation perspective of the radar, and has relatively small calculating amount.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Two-dimensional touch panel
ActiveUS8842091B2Reduce processing stepsPrecise positioningTransmission systemsInput/output processes for data processingCapacitanceImage resolution
A capacitive touch panel is provided capable of detecting multiple simultaneous touches. The touch panel delivers sets of capacitance signal values to a processor which computes the coordinates of single or multiple touch locations on the touch panel. The processing of each set is performed by (i) identifying the sensing element having the largest capacitance signal value; (ii) defining a region around that sensing element; and (iii) repeating the process iteratively, wherein each subsequent identifying step excludes signals that lie in previously defined regions. A multi-touch sensor is thus provided in which the signal processing is based on successive definition of regions or sub-blocks in the touch: panel. The touch location in each region can be determined more accurately by then applying interpolation between the adjacent signal values. This allows for position resolution at a finer scale than that defined by the touch panel's electrode patterning.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
Straight-line suppersonic motor based on vibration in rectangular piezoelectric ceramic thin plate
InactiveCN1327301APiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesLinear motionImage resolution
The miniature linear supersonic motor consists of pedestal, back cover plate, upper cover plate, rectangular piezoelectric ceramic sheet, protuberant object, active cell, ball mat, rubber jacket, prestressed sheet spring, prestressed mat, prestressed screw and nut. The supersonic motor has simple structure, small volume, high mechnoelectrical conversion rate, and high position resolution. It outputs well controlled linear motion directly and it is suitable for driving and control for small and precise linear motion.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method and apparatus to digitize pulse shapes from radiation detectors
ActiveUS10027340B1Improve scalabilityReduce data volumeElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue/digital/analogue conversionData acquisitionDetector array
A field programmable gate array based multi-channel flash ADC unit combined with a high speed multi-lane data communications channel / Ethernet-like modular intercommunication providing a complete but easily expandable high-speed data acquisition system. This apparatus and method permits high-speed pulse-shape digitalization allowing position resolution imaging of particles having a range of energies and is scalable to achieve the efficient capture of coincident data from large electromagnetic detector arrays.
Owner:JEFFERSON SCI ASSOCS LLC
Method and device for fast raster beam scanning in intensity-modulated ion beam therapy
InactiveUS20160030769A1Continuous motionX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyTreatment implementationDose profile
A method and device are designed to deliver intensity-modulated ion beam therapy radiation doses closely conforming to tumors of arbitrary shape, via a series of two-dimensional (2-D) continuous raster scans of a pencil beam, wherein each scan takes no more than about 100 milliseconds to complete. The device includes a fast scanning nozzle for the exit of an ion beam delivery gantry. The fast scanning nozzle has a fast combined-function X-Y steering magnet, and is coupled to a rastering control system capable of adjusting the length of each scan line, continuously varying the beam intensity along each scan line, and executing multiple rescans of a tumor depth layer within a single patient breathing cycle. An in-beam absolute dose and dose profile monitoring system is capable of millimeter-scale position resolution and millisecond-scale feedback to the control system to ensure the safety and efficacy of the treatment implementation.
Owner:PHENIX MEDICAL
Three-degree-of-freedom translation force feedback hand controller
The invention discloses a three-degree-of-freedom translation force feedback hand controller. The device is improved based on a plane five-rod mechanism, and one-degree-of-freedom motion is added to the two-degree-of-freedom motion vertical to the plane. The device mainly comprises a base, a positioning support, a plane motion part, a vertical motion part, a drive motor, a counterweight and a force sensor. In accordance with the design requirements for a force sense interaction device, the three-degree-of-freedom translation device is subjected to kinematics analysis, work space design, position resolution analysis and the like. Compared with a traditional hand controller, a six-dimensional force / torque sensor is mounted at the tail end of the device, an accurate force sense feedback effect is realized, and the resolution of the feedback force is higher; moreover, the work space is larger, and the rigidity is higher. The three-degree-of-freedom translation force feedback hand controller disclosed by the invention has simple structure and high accuracy; the control method is simple and effective; the hand controller is convenient to operate and has broad application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Explosives detection by directional fast neutron beams scan with associated particles
ActiveUS7420175B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsOperation modeNeutron yield
This invention is related to equipment and techniques for fast neutron activation analysis of explosives and / or other warfare agent. The techniques are based on 14 MeV fast neutrons from D-T fusion reaction, the kinematics of the nuclear reaction and fast coincidence between α-particles of the D-T reaction and γ-quanta from fast neutron induced reactions. A fast neutron generator with effective target cooling and different operation modes provides high neutron yield, long life, and simple maintenance of the equipment and good geometric resolution of the directional neutron beam. High positional resolution of the directionally scanning neutron beam, high time resolution of the coincidence and high neutron yield provide the real time robust screen of explosives with high speed and / or high sensitivity, flexibility for big and small items and overall high probability of detection (PD) and low probability of false alarms (PFA). The remote video scan device also has zooming capability to change solid angle.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
Focus detector arrangement for generating phase-contrast X-ray images and method for this
ActiveCN101011250AHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionHandling using diaphragms/collimetersSoft x rayPhase grating
A focus-detector arrangement and an X-ray apparatus for generating projective or tomographic phase contrast recordings of a subject are disclosed. In at least one embodiment, the focus-detector arrangement includes a radiation source with a focus, arranged on a first side of the subject, for generating a fan-shaped or conical beam of rays; at least one X-ray optical grating arranged in the beam path, with at least one phase grating arranged on the opposite second side of the subject in the beam path generating an interference pattern of the X-radiation preferably, in a particular energy range; and an analysis-detector system which detects at least the interference pattern generated by the phase grating in respect of its phase shift with position resolution. According to at least one embodiment of the invention, at least one X-ray optical grating including bars which are free from overhangs form shadows in the beam path of the fan-shaped or conical beam of rays.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
Method for synchronizing radio navigation system with direct sequence spread-spectrum and frequency hopping system
InactiveCN101706566AImprove anti-interference abilityImprove confidentialityBeacon systems using radio wavesLow noiseAudio power amplifier
The invention provides a method for synchronizing a radio navigation system of a direct sequence spread-spectrum and frequency hopping system, which comprises the steps that: an antenna (1) receives a radio signal and transmits the radio signal to a low-noise amplifier (2); the low-noise amplifier (2) performs low-noise amplification on the signal and transmits the amplified signal to a radio frequency processing module (3), the radio frequency processing module (3) performs filtering and automatic gain control (AGC) on the signal and then transmits the processed signal to a direct sequence spread-spectrum and frequency hopping synchronizing module (4); the direct sequence spread-spectrum and frequency hopping synchronizing module (4) realizes the synchronization of a frequency hopping sequence and a direct sequence spread-spectrum sequence; and a subsequent processing module (5) performs subsequent operations which are observed vector extraction, information demodulation and position resolution respectively according to synchronization information provided by the direct sequence spread-spectrum and frequency hopping module (4). The method effectively improves performance of capturing and tracking direct sequence spread-spectrum and frequency hopping signals, can quickly capture and stably track the direct sequence spread-spectrum sequence and the frequency hopping sequence which are relatively longer, and compared with the conventional method for synchronizing frequency hopping first and then synchronizing direct sequence spread-spectrum, is higher in synchronization speed, higher in synchronization accuracy and more ensured in privacy.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
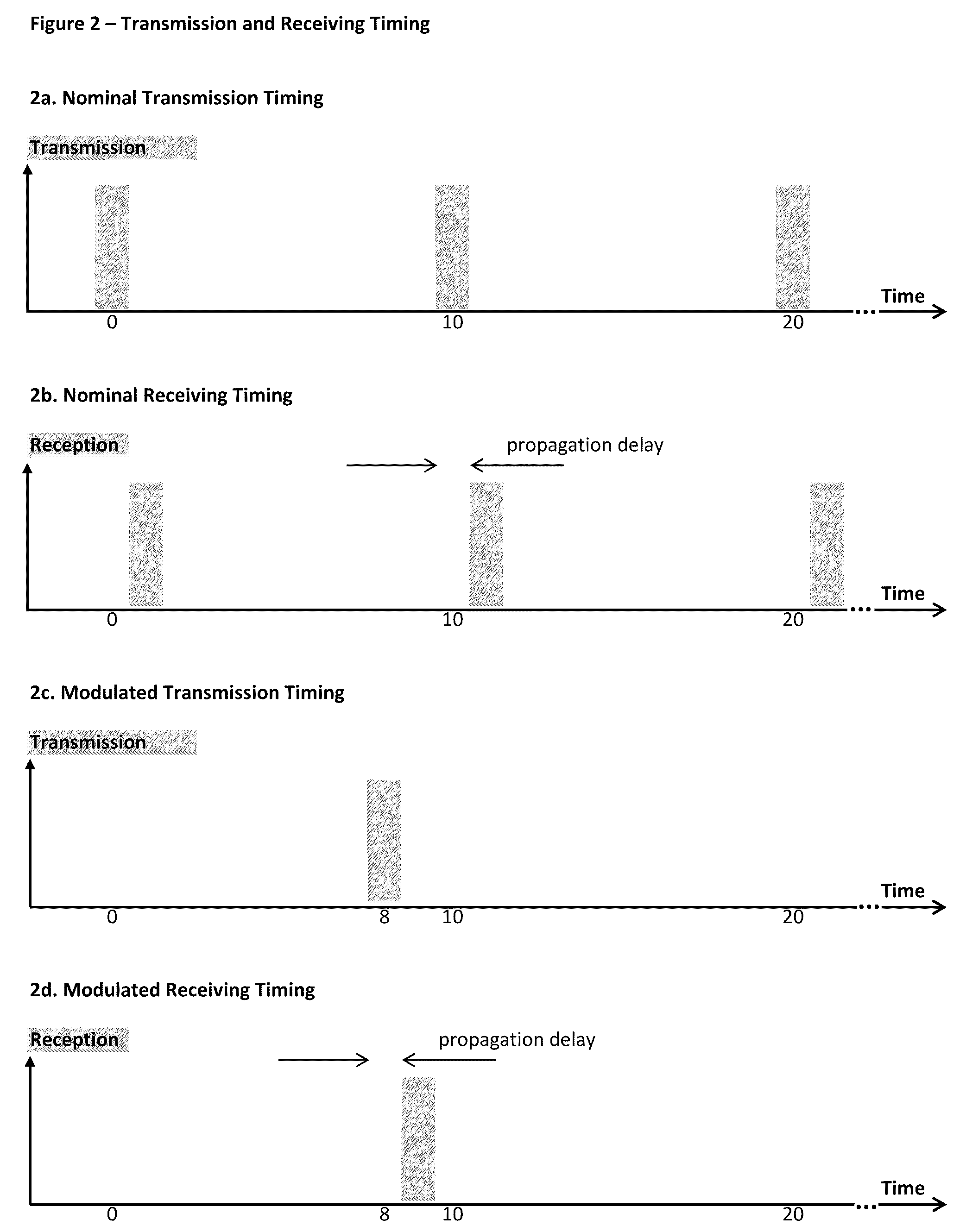
Modulating transmission timing for data communications
ActiveUS7693216B1Accurately synchronously determiningSimple taskPosition fixationFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationPropagation delayBurst transmission
A modulation method, applicable for augmentation of present art modulated signals. The method, for communicating data from a transmitter to a receiver, is based on periodical burst transmissions, set at a nominal timing, of signals which are either pure carriers or already modulated by data (e.g. ASK, FSK, PSK). Knowing the transmission timing and assessing the propagation delay, the receiver can estimate the nominal reception timing of these periodical transmissions. Modifying the nominal timing of a transmission, by a specific time period, is used to communicate a symbol between the transmitter and the receiver, according to a predefined encoding table which associates between a symbol and a unique time period. According to one embodiment of the invention, the transmitter is a distress radio beacon, configured to report its position upon activation, in periodical data burst transmissions, to ground stations through satellites. The present method is used to augment this report, complying with the present beacon specifications, yet providing a finer resolution of the reported coordinates. According to one embodiment, the position resolution is improved approximately from 125 to 8 meters.
Owner:MOBIT TELECOM
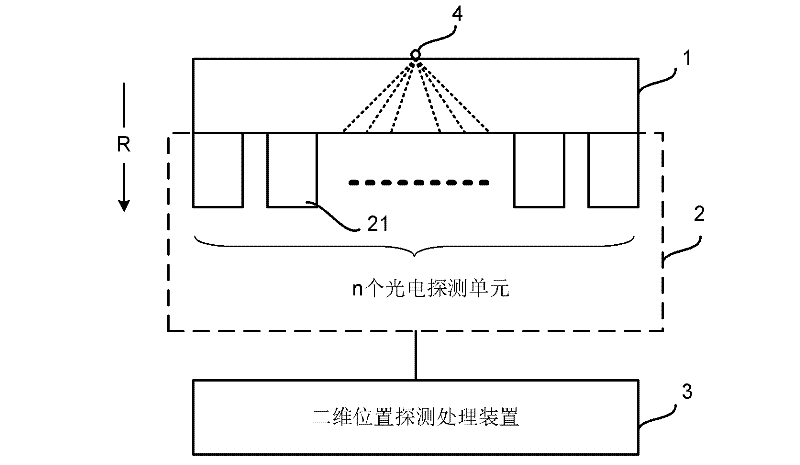
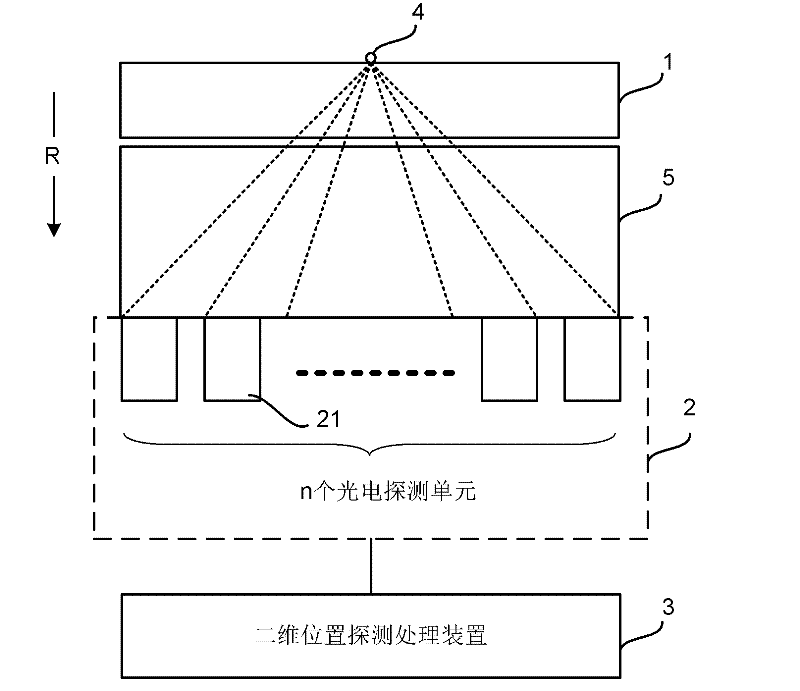
Two-dimensional position detection system based on scintillator
ActiveCN102288982AHigh position resolutionReduce complexityX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentImage resolutionX-ray
The invention discloses a scintillator-based two-dimensional position detection system, which comprises a whole continuous scintillator, a photoelectric detection device and a two-dimensional position detection processing device, wherein the scintillator is used for receiving ray particles (such as X rays, alpha rays, gamma rays, beta rays, neutrons and the like), interacts with the ray particles to generate light signals and makes the light signals be scattered in the propagation process; the photoelectric detection device comprises n (a natural number more than 1) photoelectric detection units, and each photoelectric detection unit is used for detecting the light signals transmitted by the scintillator respectively and converting the light signals into electric signals; and the two-dimensional position detection processing device is connected with the photoelectric detection device, and is used for determining the distribution center of the light signals transmitted by the scintillator according to the electric signals converted by each photoelectric detection unit in the photoelectric detection device, and determining the distribution center of the light signals as the position of the ray particles which are shot to the scintillator. The scintillator-based two-dimensional position detection system provided by the invention can improve position resolution and reduce the complexity of two-dimensional position detection.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Sensorless rotor position identification system and method for brushless direct current motor
ActiveCN105680742AImprove control efficiencyImprove controlElectronic commutatorsFlux linkageVIT signals
The invention relates to a sensorless rotor position identification system and method for a brushless direct current motor. According to the method, a motor is firstly started by a 'two-step' method; a control system is switched into a motor self-synchronization operation state within a proper rotating speed range; a controller reads a commutation signal and controls a corresponding switch tube to be on or off according to a high-low level change signal generated by a line counter electromotive force zero-crossing point; an interval in which an existing rotor flux is located is further judged according to the signal; three-phase line counter electromotive force is reconstructed according to voltage and current signals obtained by a sensor; two-phase voltage components under an alpha-beta coordinate are obtained through coordinate transformation; arc tangent values are determined; and the arc tangent values and the interval are corrected by each other, so that a transient rotor flux position can be obtained. The hardware system is simplified; the estimation accuracy is improved; the system reliability is strengthened; the sensorless rotor position identification system and method are easy to debug and flexible to implement; and the disadvantage of low rotor position resolution of a brushless direct current motor square wave drive technology is compensated.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com