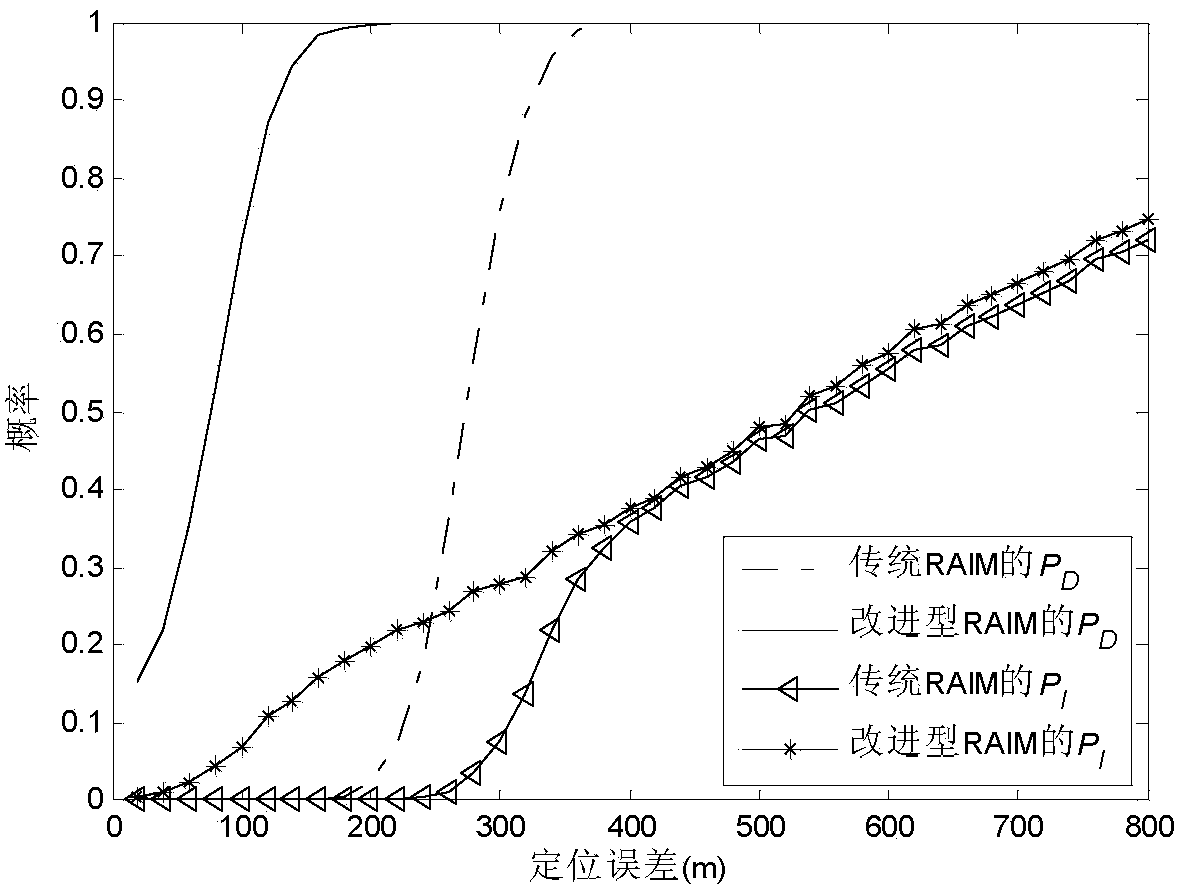
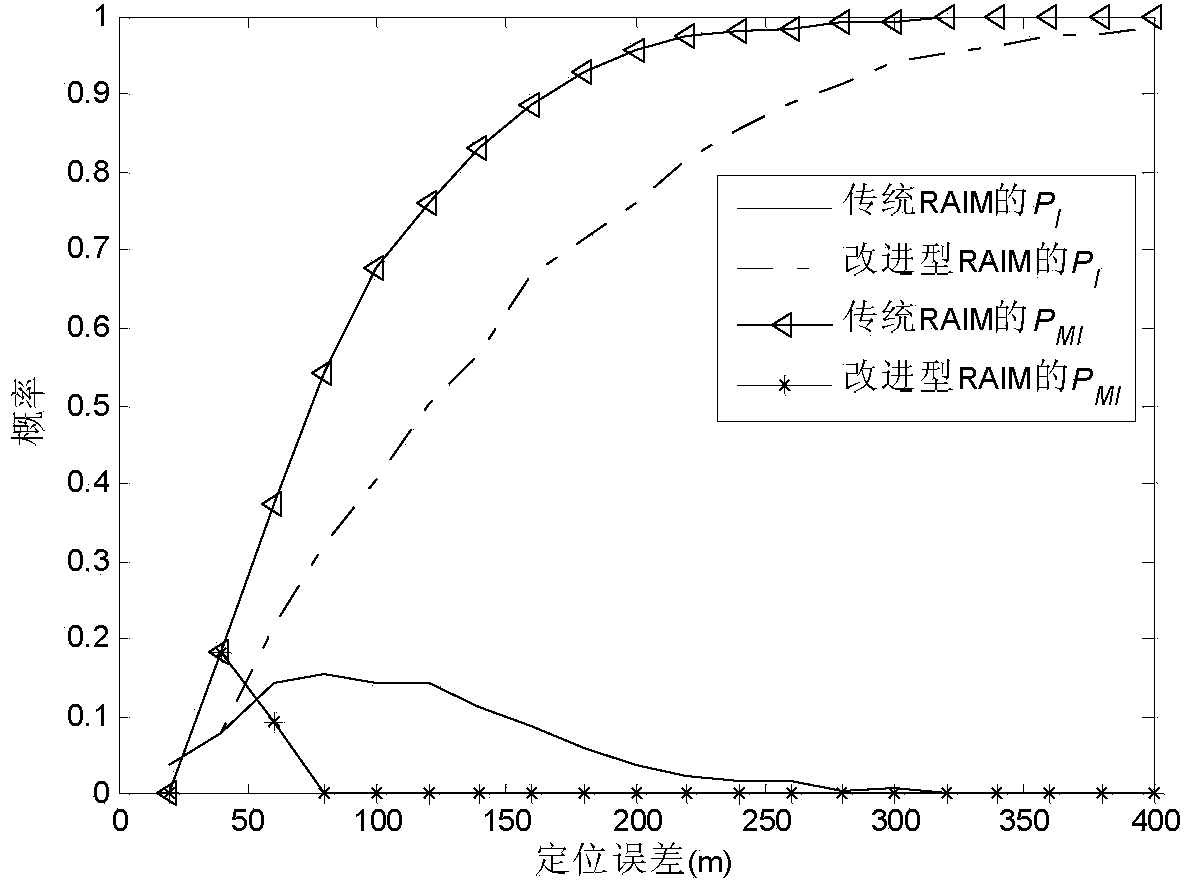
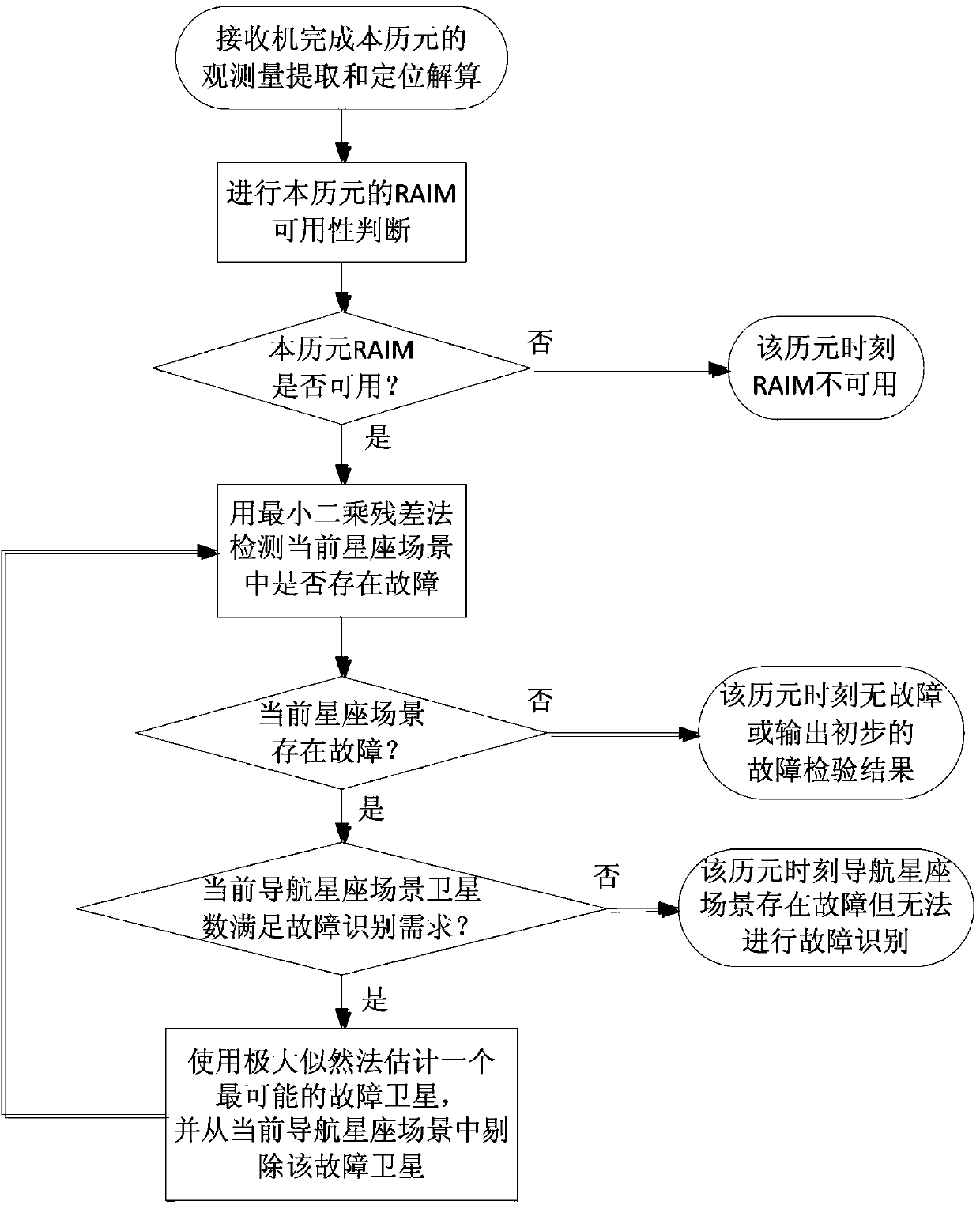
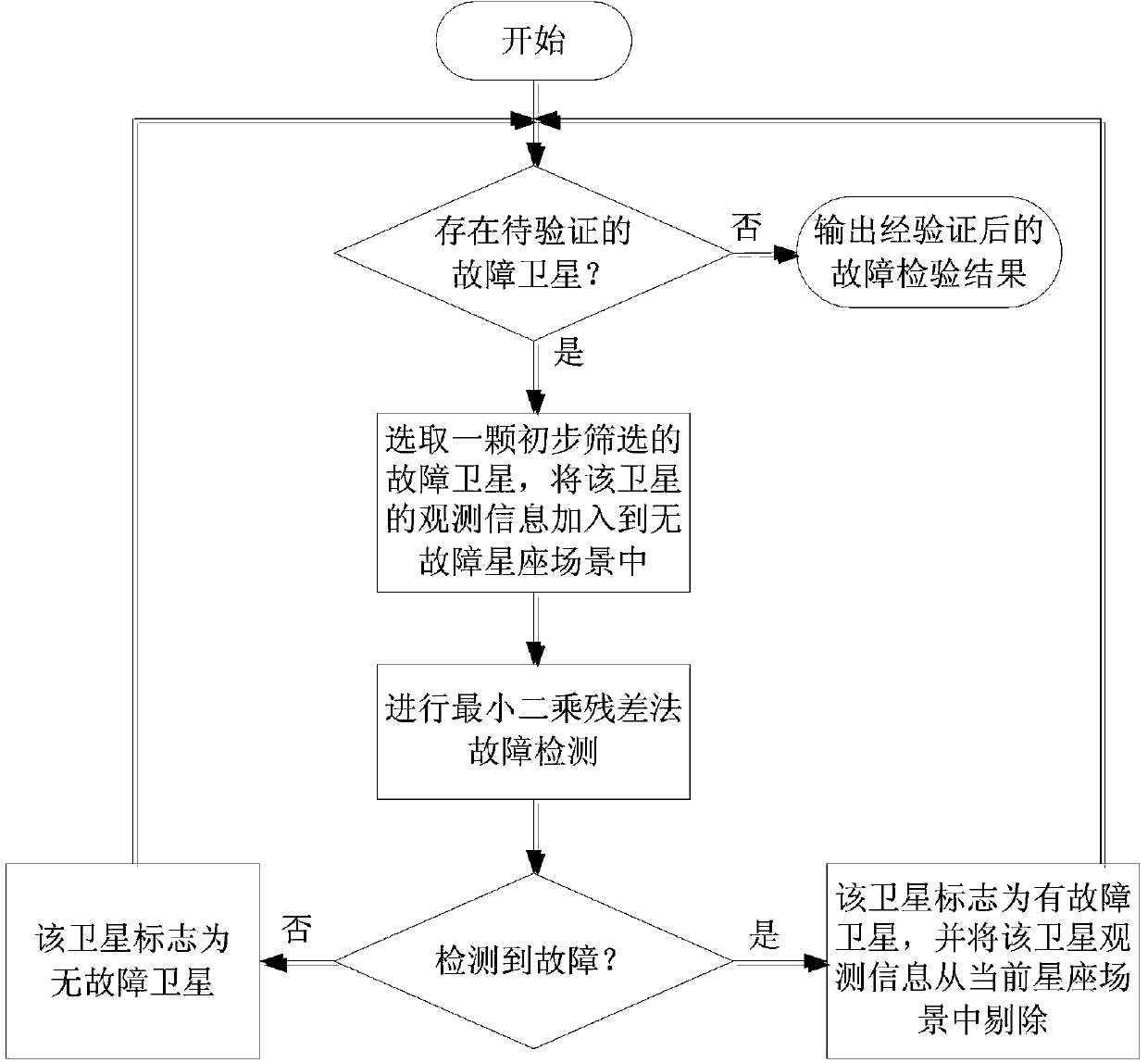
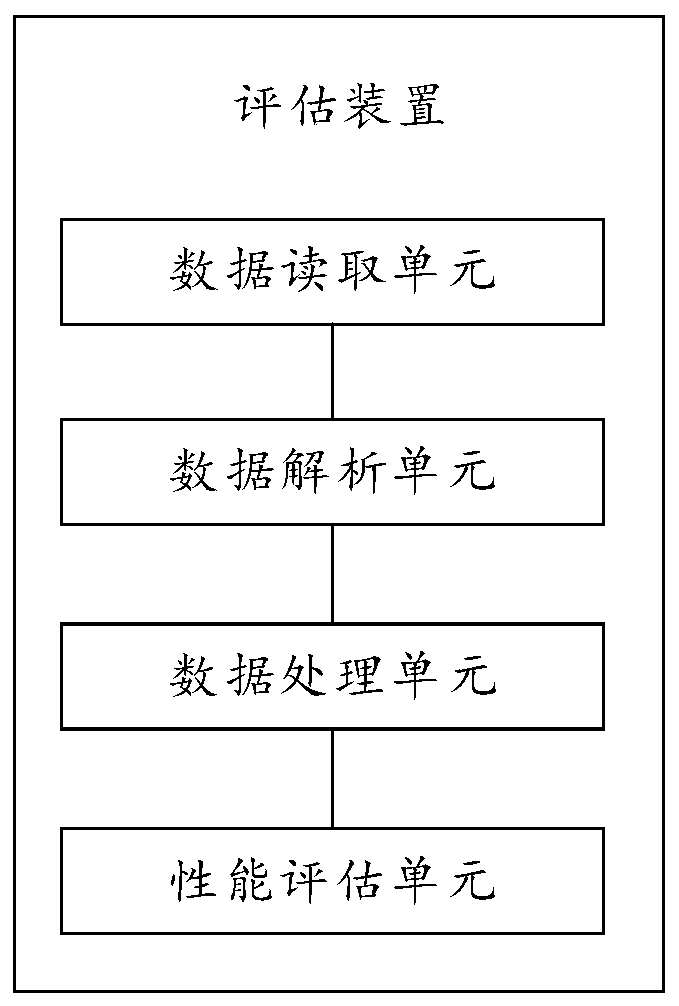
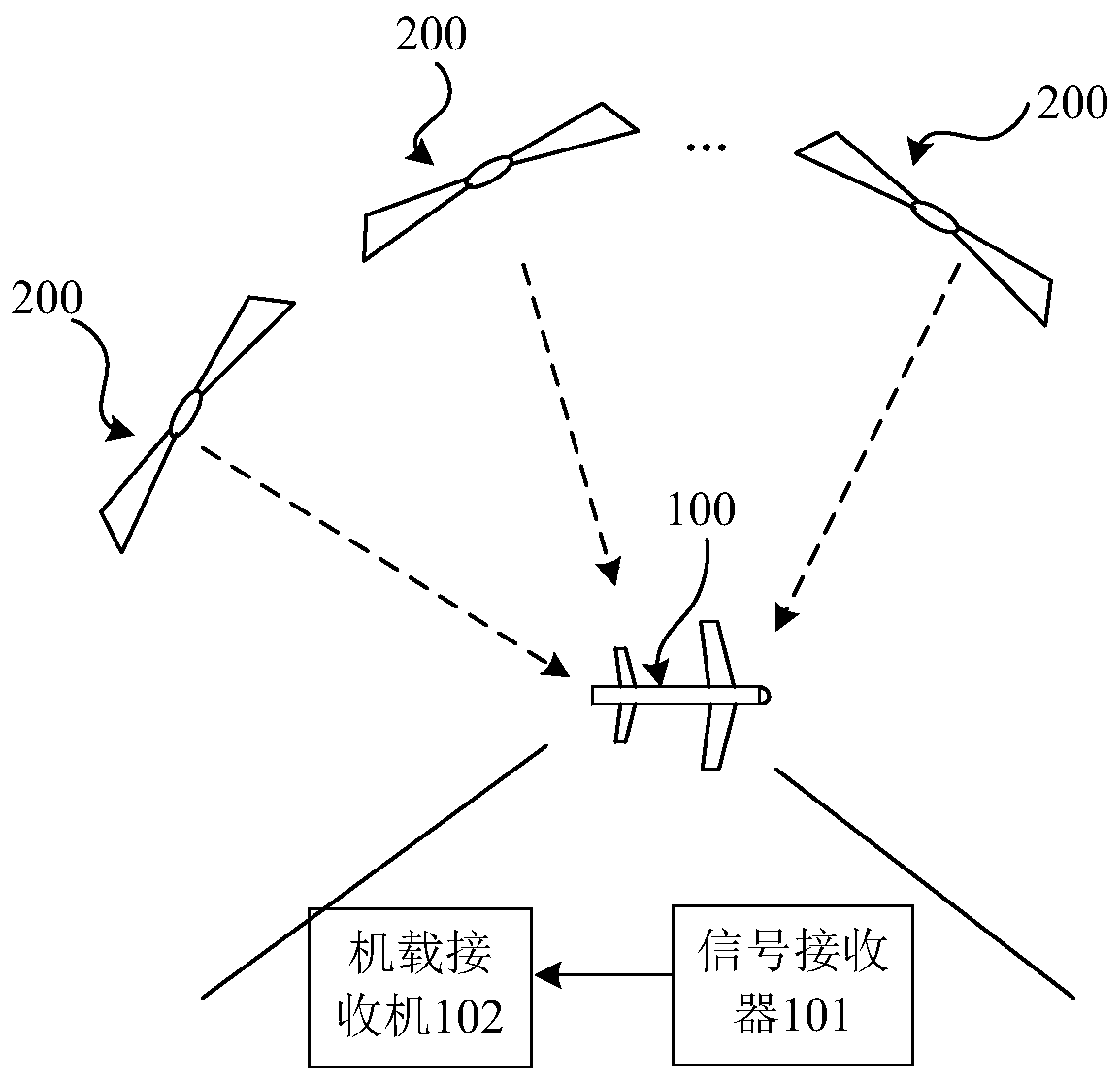
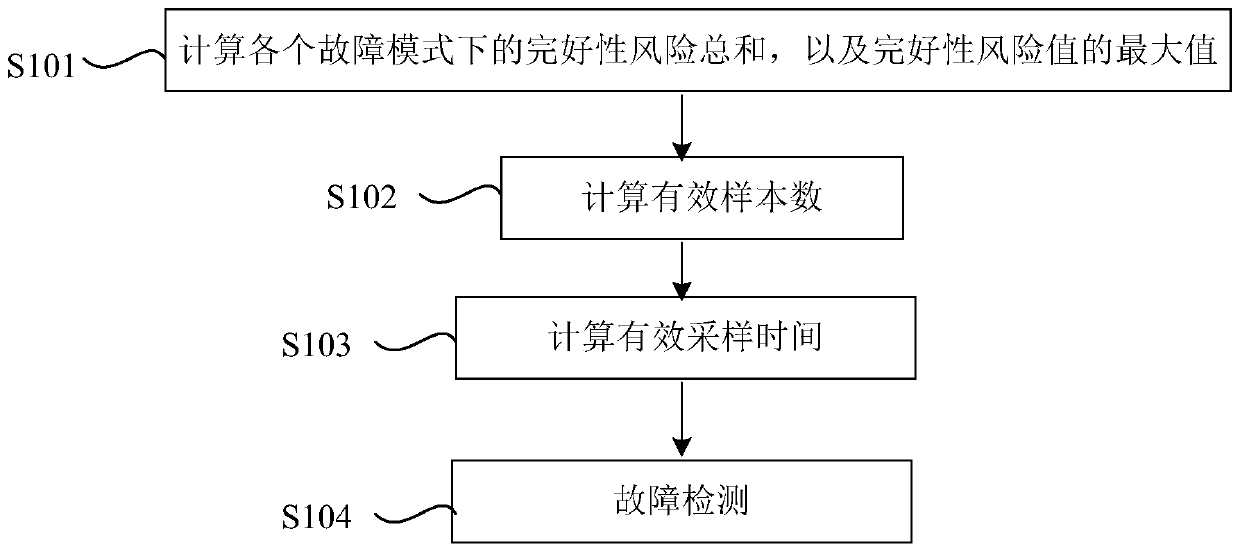
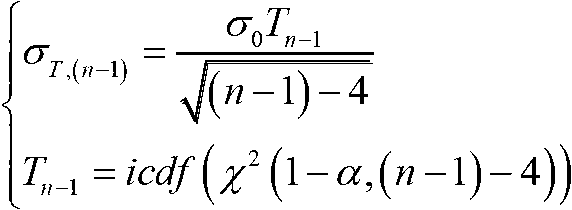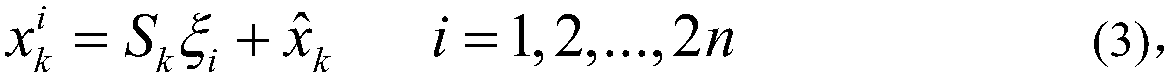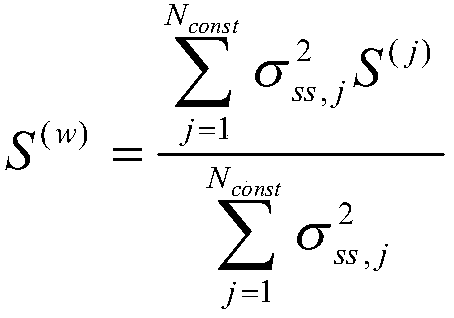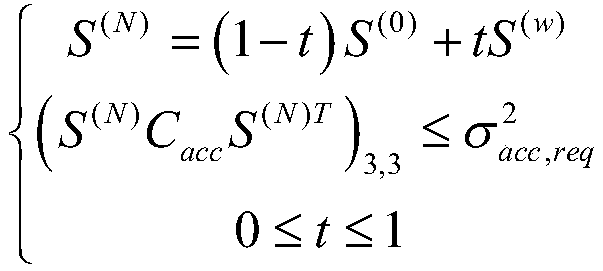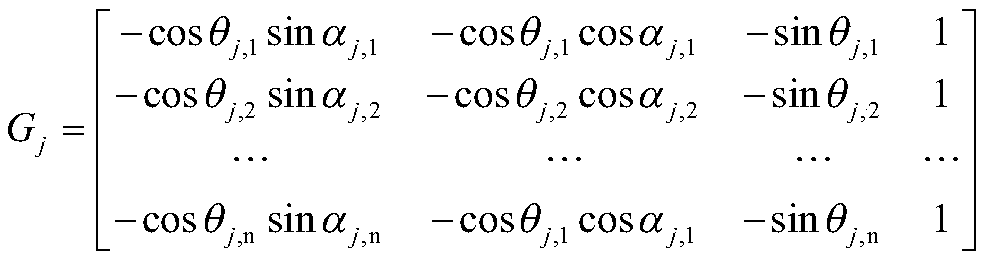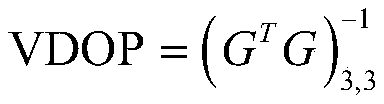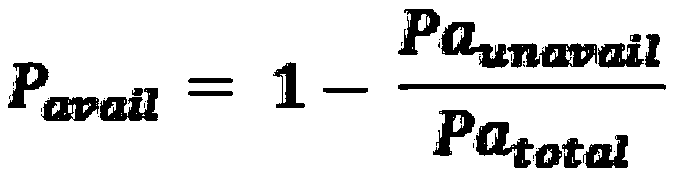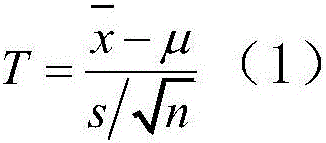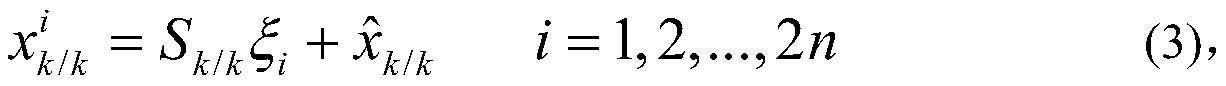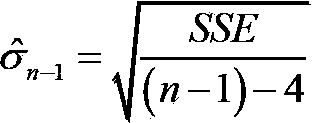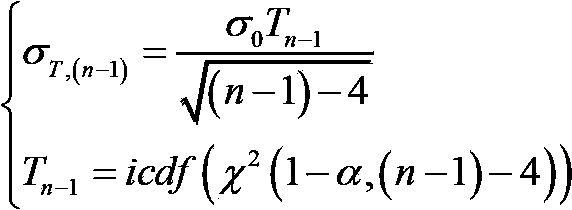Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40 results about "Receiver autonomous integrity monitoring" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
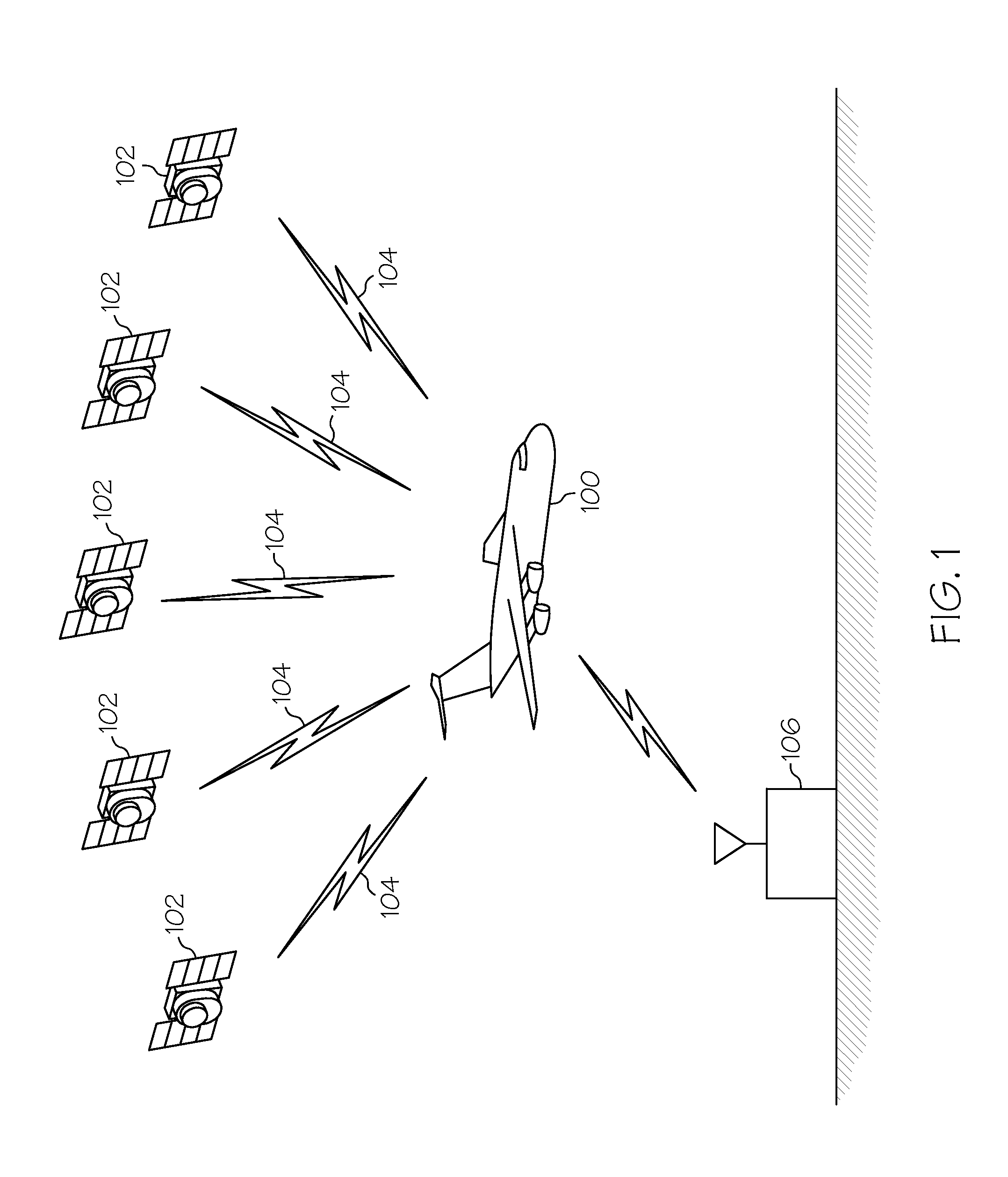
Receiver autonomous integrity monitoring (RAIM) is a technology developed to assess the integrity of global positioning system (GPS) signals in a GPS receiver system. It is of special importance in safety-critical GPS applications, such as in aviation or marine navigation.
GNSS navigation solution integrity in non-controlled environments
ActiveUS20100033370A1Efficient methodImprove navigation accuracyPosition fixationNavigation instrumentsNoise levelMarine navigation
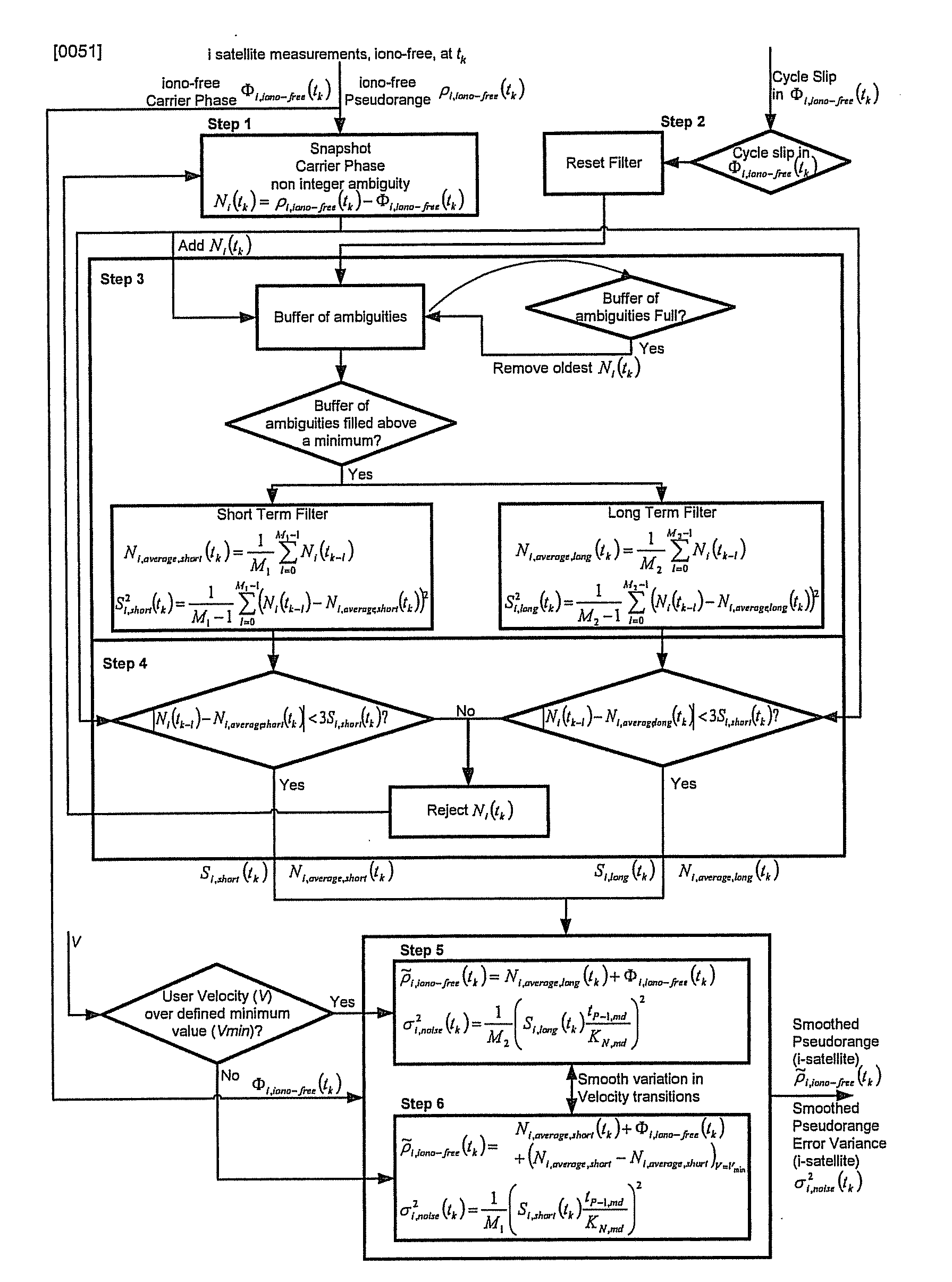
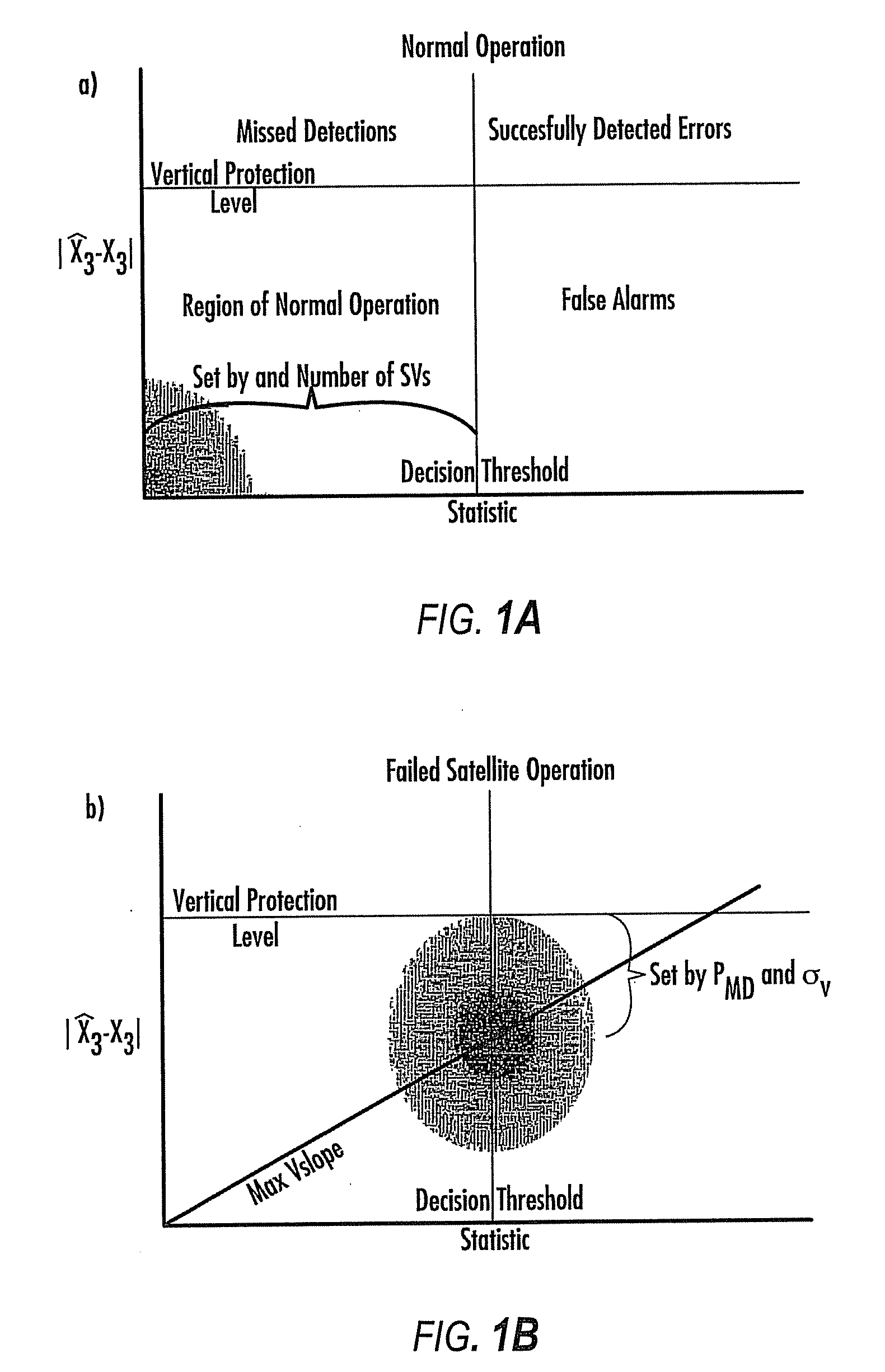
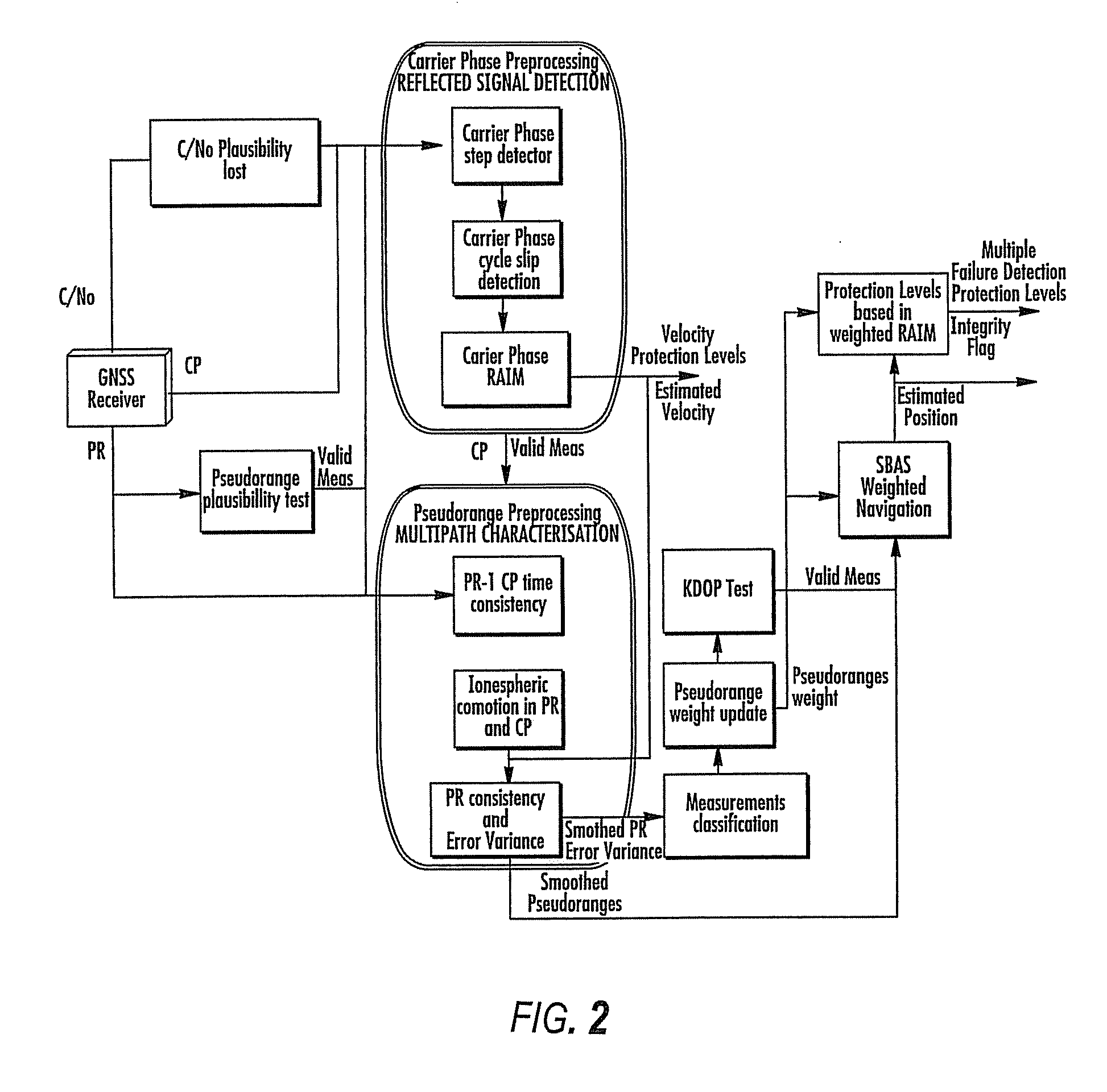
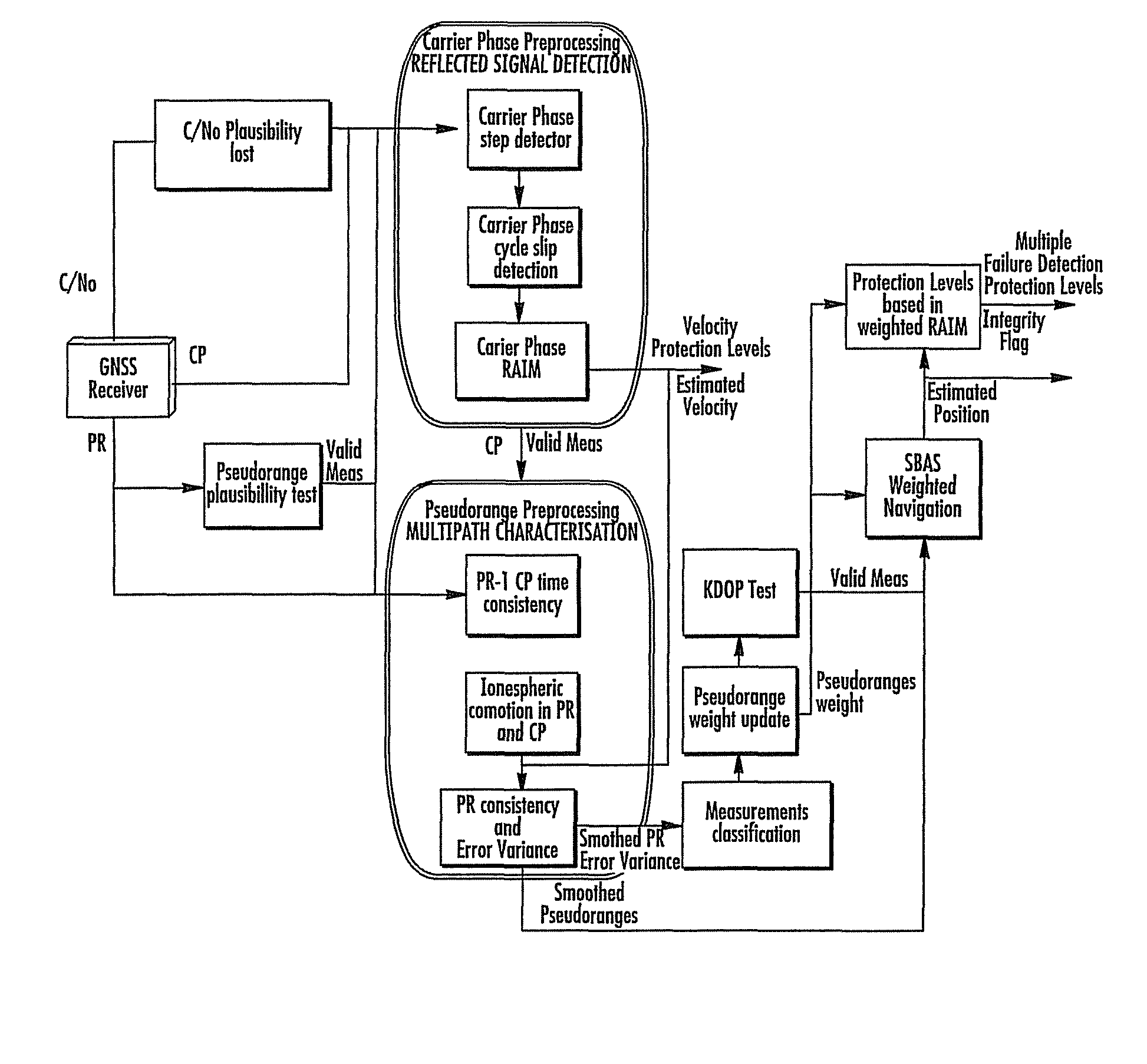
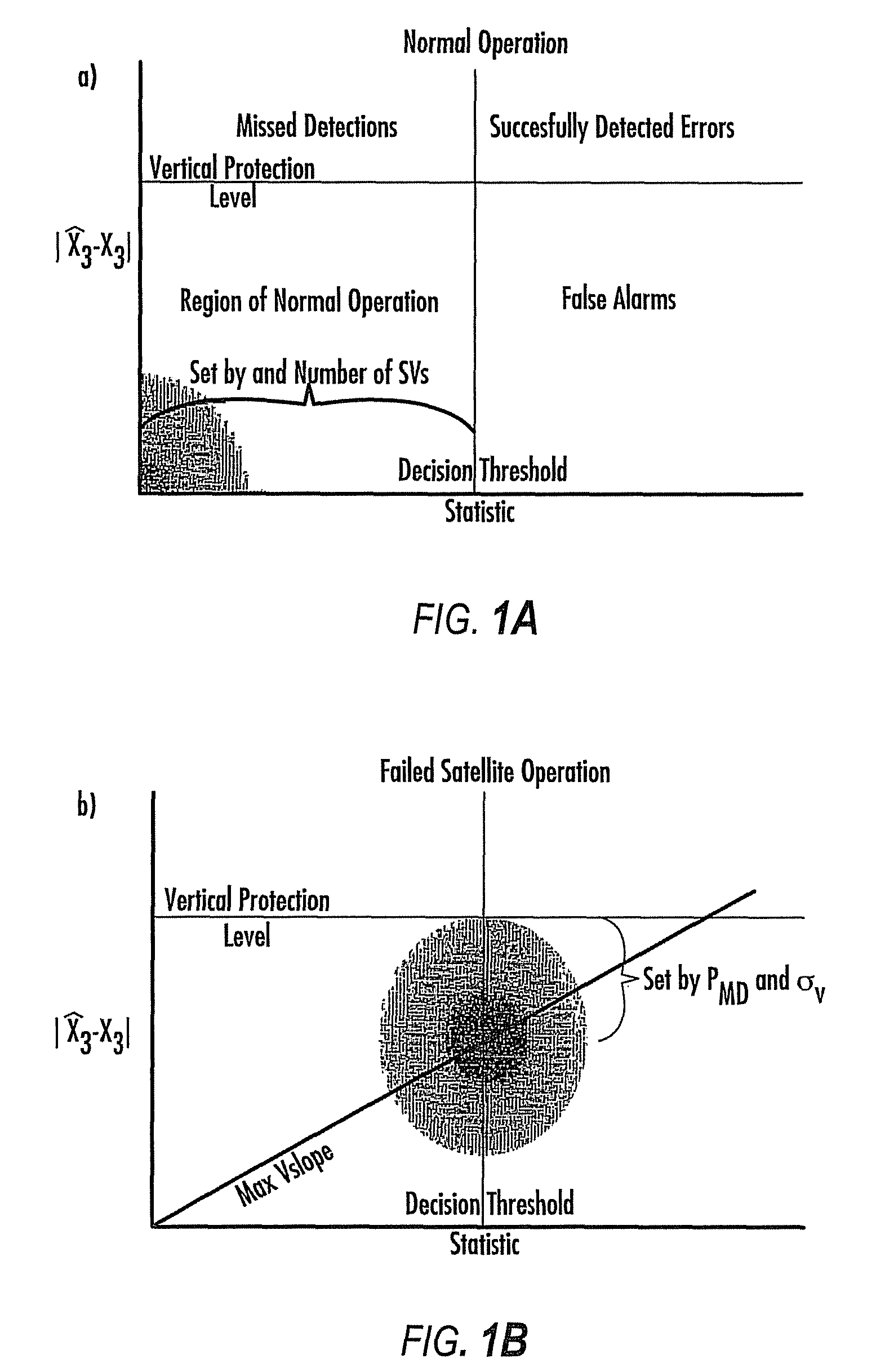
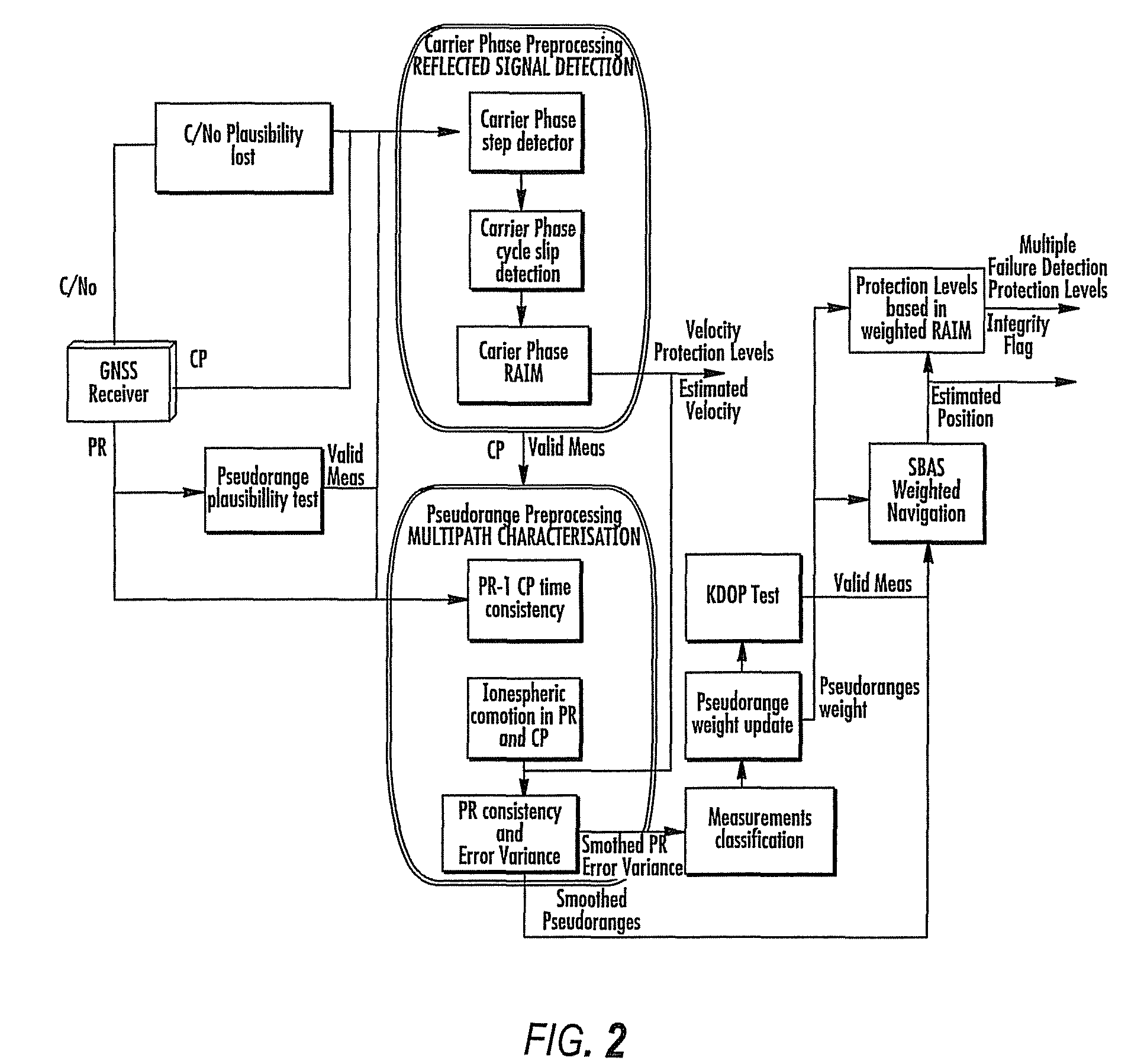
Disclosed is a method for providing a Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) navigation position solution with guaranteed integrity in non-controlled environments, the method including processing a (GNSS) signal including multiple satellites generating at least one signal to obtain carrier phase and pseudorange measurements; pre-processing the measurements to detect and characterize local errors in the measurements, wherein the local errors cannot be ascertained a priori, the characterization including providing error bounds estimated by measuring the carrier phase and pseudoranges measurements, thereby providing a set of measurements rejections when the characterization is not possible; and using the estimated error bounds, together with error bounds provided by the GNSS signal concerning satellite and ionospheric errors, to build in each measurement an estimated noise level in the measurements as input to a weighted Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring (RAIM) algorithm in order to compute position coordinates and associated protection levels in the non-controlled environments.
Owner:GMV AEROSPACE & DEFENCE
New method for RAIM (receiver autonomous integrity monitoring) based on satellite selecting algorithm in multimode satellite navigation system
InactiveCN103592658AReduce operational complexityHigh positioning accuracySatellite radio beaconingLoop bandwidthClock correction
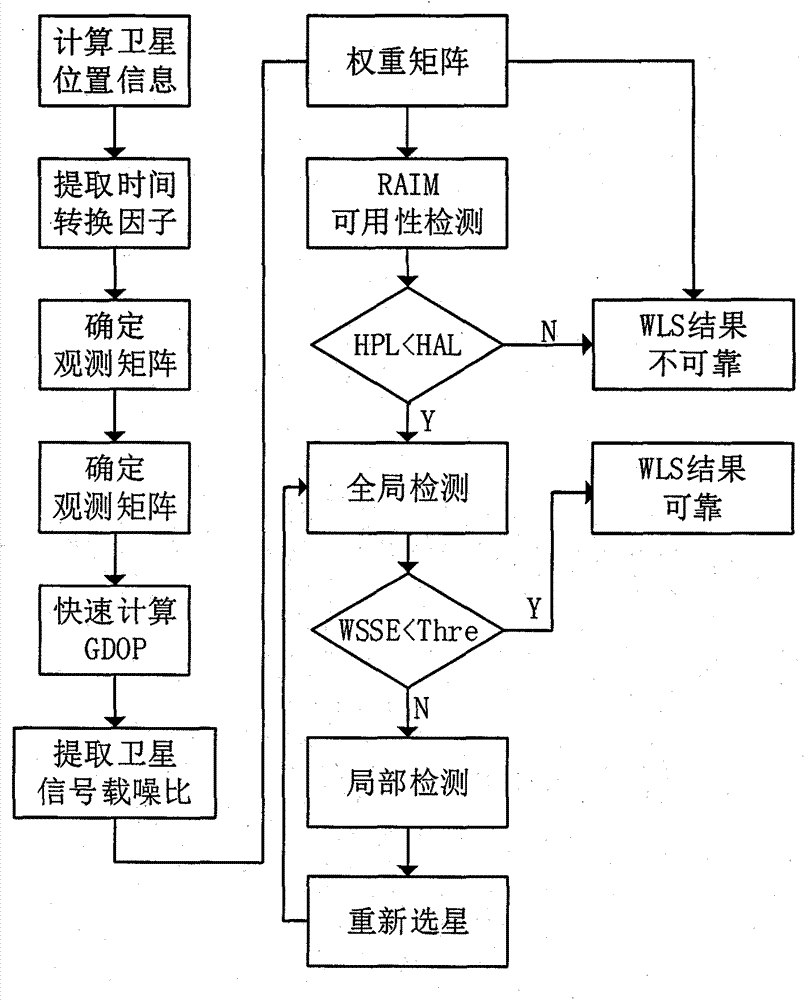
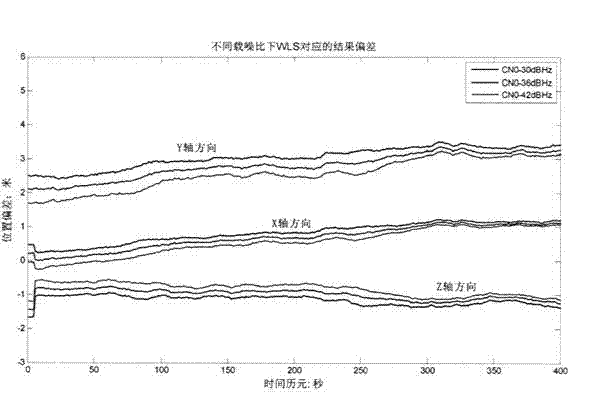
The invention discloses a new method for RAIM (receiver autonomous integrity monitoring) based on a satellite selecting algorithm in a multimode satellite navigation system. The method comprises the steps of first determining space position information of satellites according to a navigation message and eliminating satellites with a small elevation angle according to a shielding angle; determining an observation matrix including only one clock correction item according to clock correction conversion factors in the navigation message; selecting p satellites from N visible satellites so as to be used for positioning calculation of a receiver, acquiring a satellite combination, which enables the GDOP (geometric dilution of precision) to be minimum, through the satellite selecting algorithm to act as calculating satellites, and determining a weight matrix in WLS (weighted least squares) according to parameters such as the carrier-to-noise ratio, the loop bandwidth, pre-check integral time and the like of satellite signals; carrying out RAIM availability detection according to a false alarm rate and a missed alarm rate which are preset by the receiver, and calculating a pseudo-range residual error threshold value after positioning according to the false alarm rate and a degree of freedom in Chi-squared distribution; carrying out global detection at first, then carrying out local monitoring in a circumstance that a fault satellite exists, determining calculation satellites again through satellite selection, and finally carrying out positioning calculation through selecting satellite combinations within the threshold value. The method disclosed by the invention is simple, high in fault recognition rate, not only applicable to multi-mode and multi-fault satellite navigation systems, but also applicable to single-mode and multi-fault satellite navigation systems, thereby providing new ideas for carrying out RAIM by a modern GNSS (global navigation satellite system).
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method for receiver autonomous integrity monitoring and fault detection and elimination
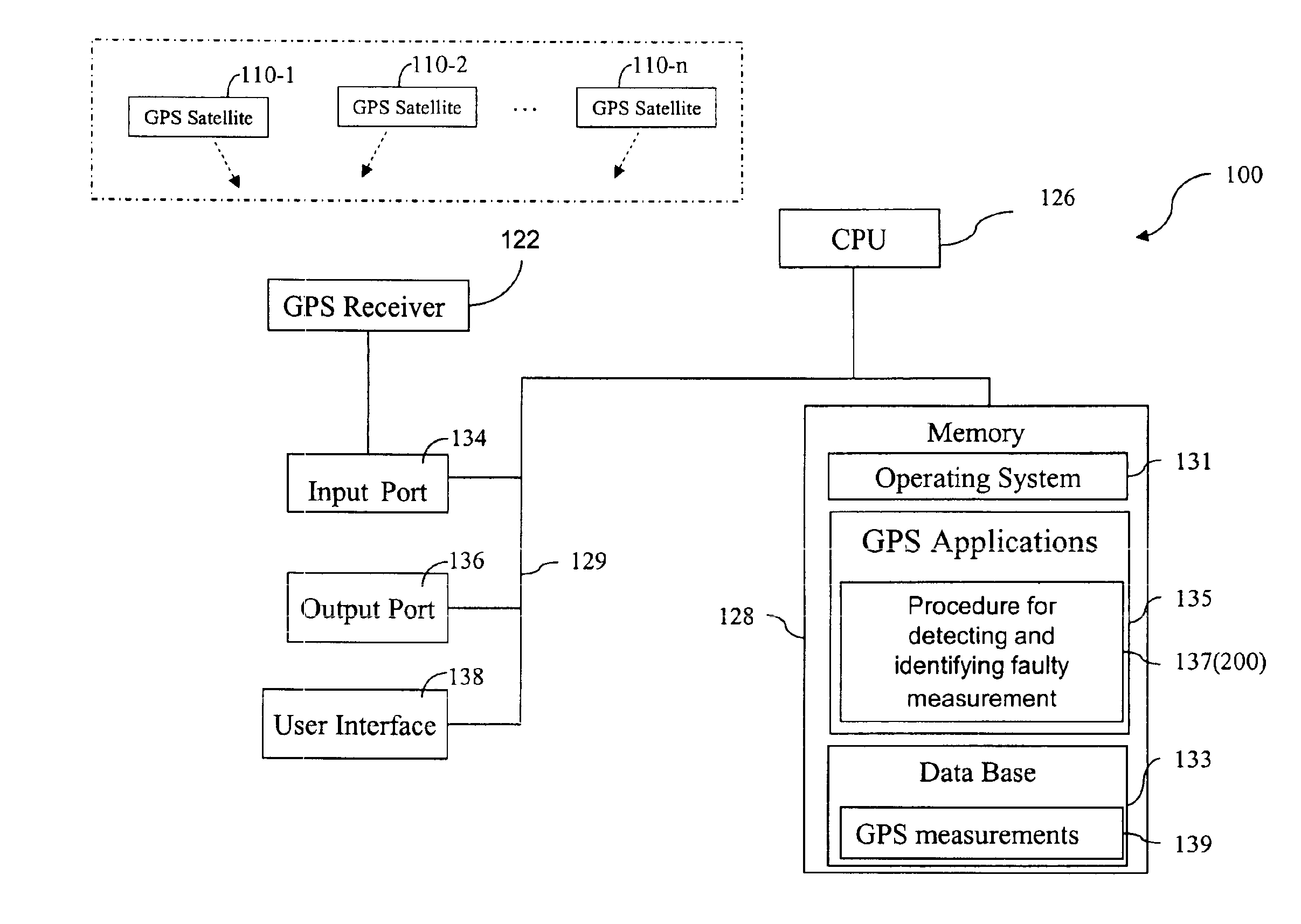
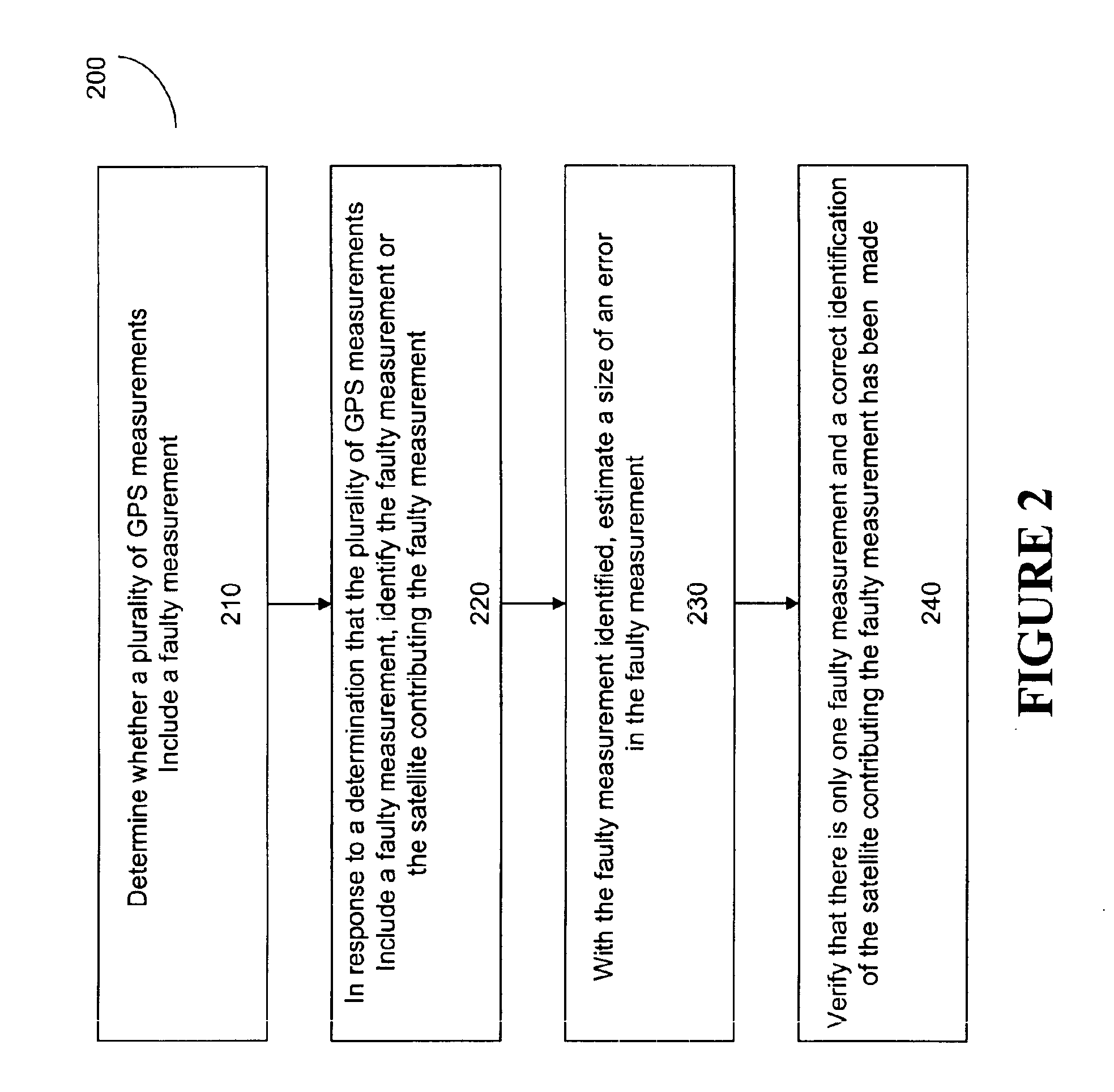
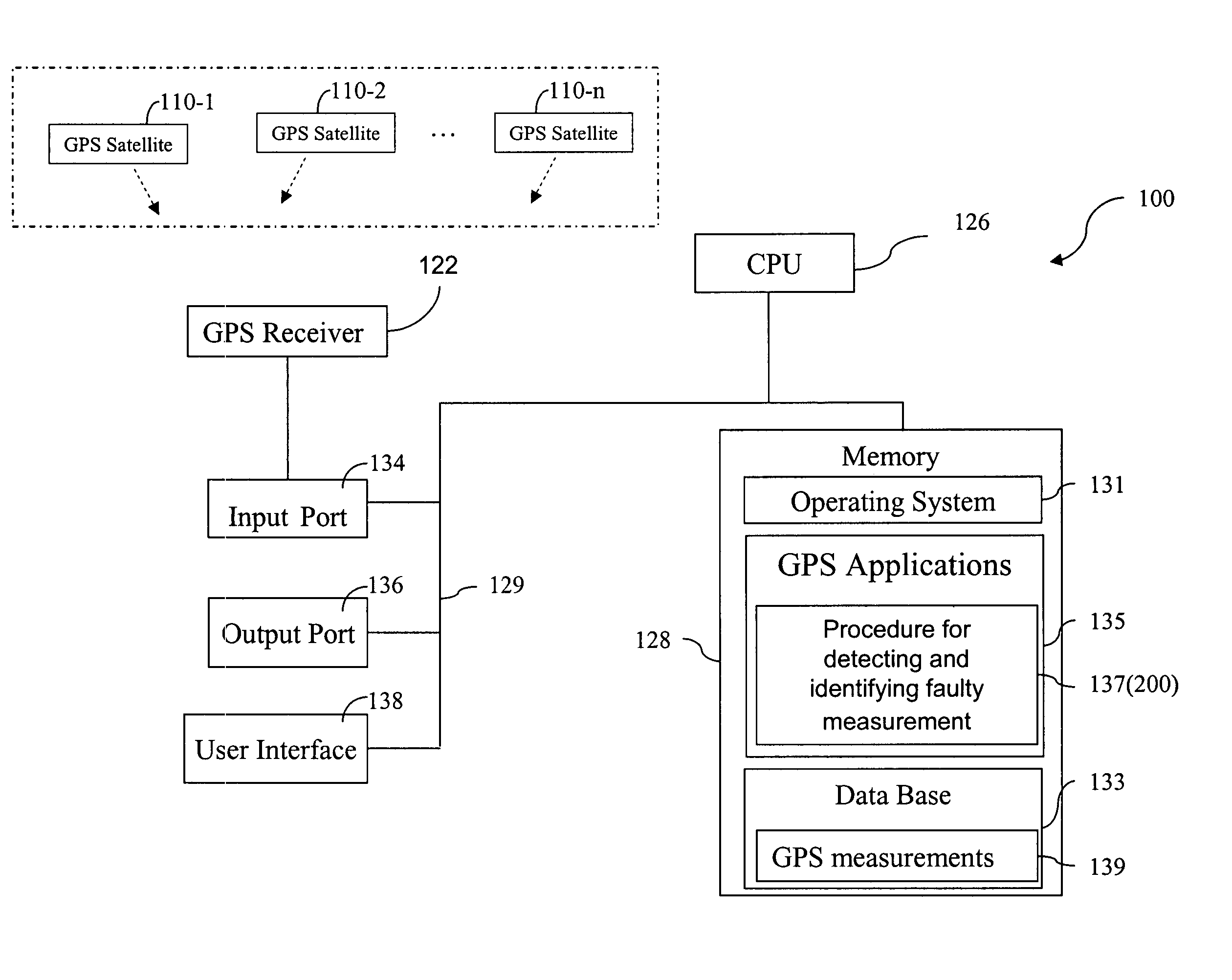
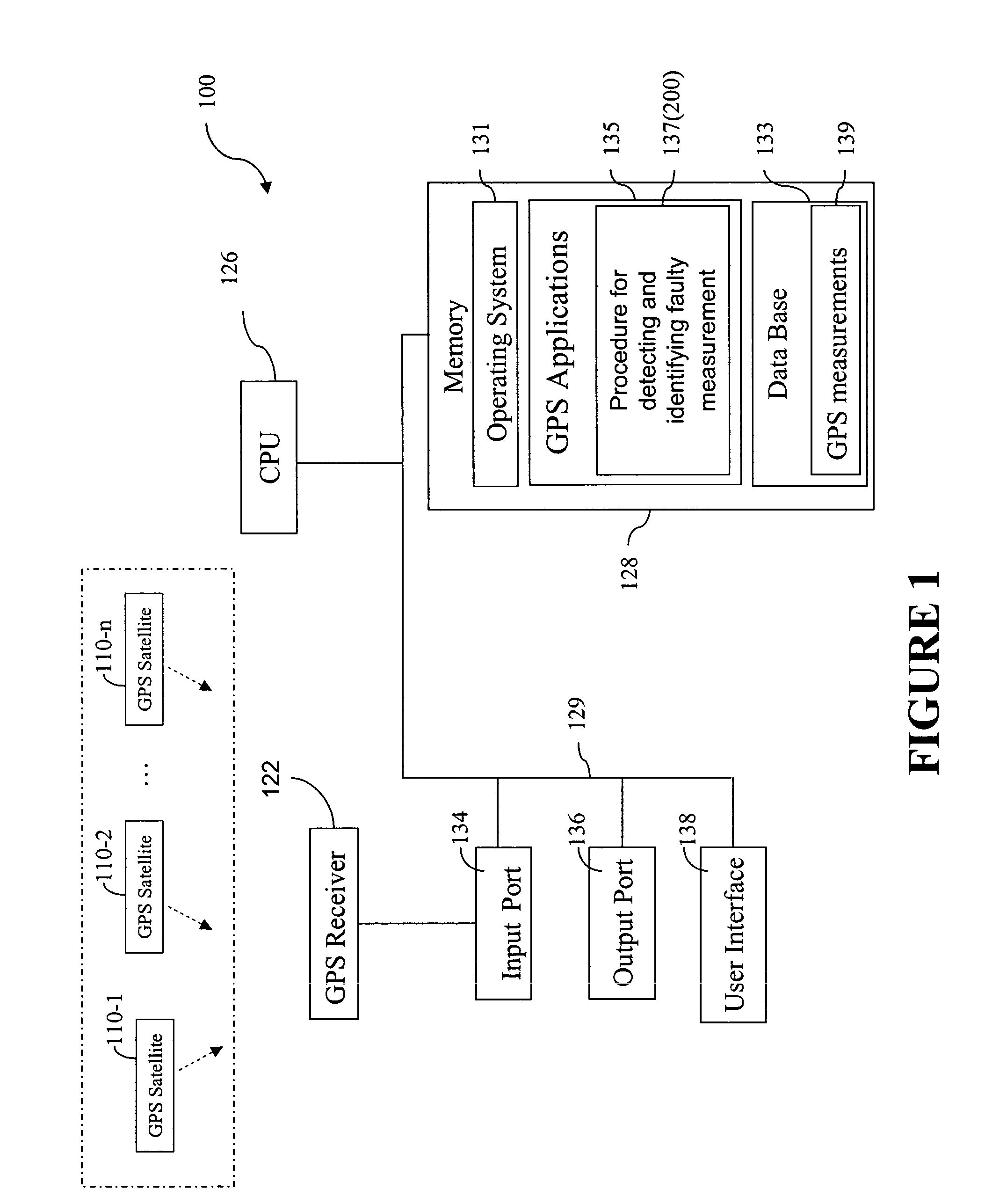
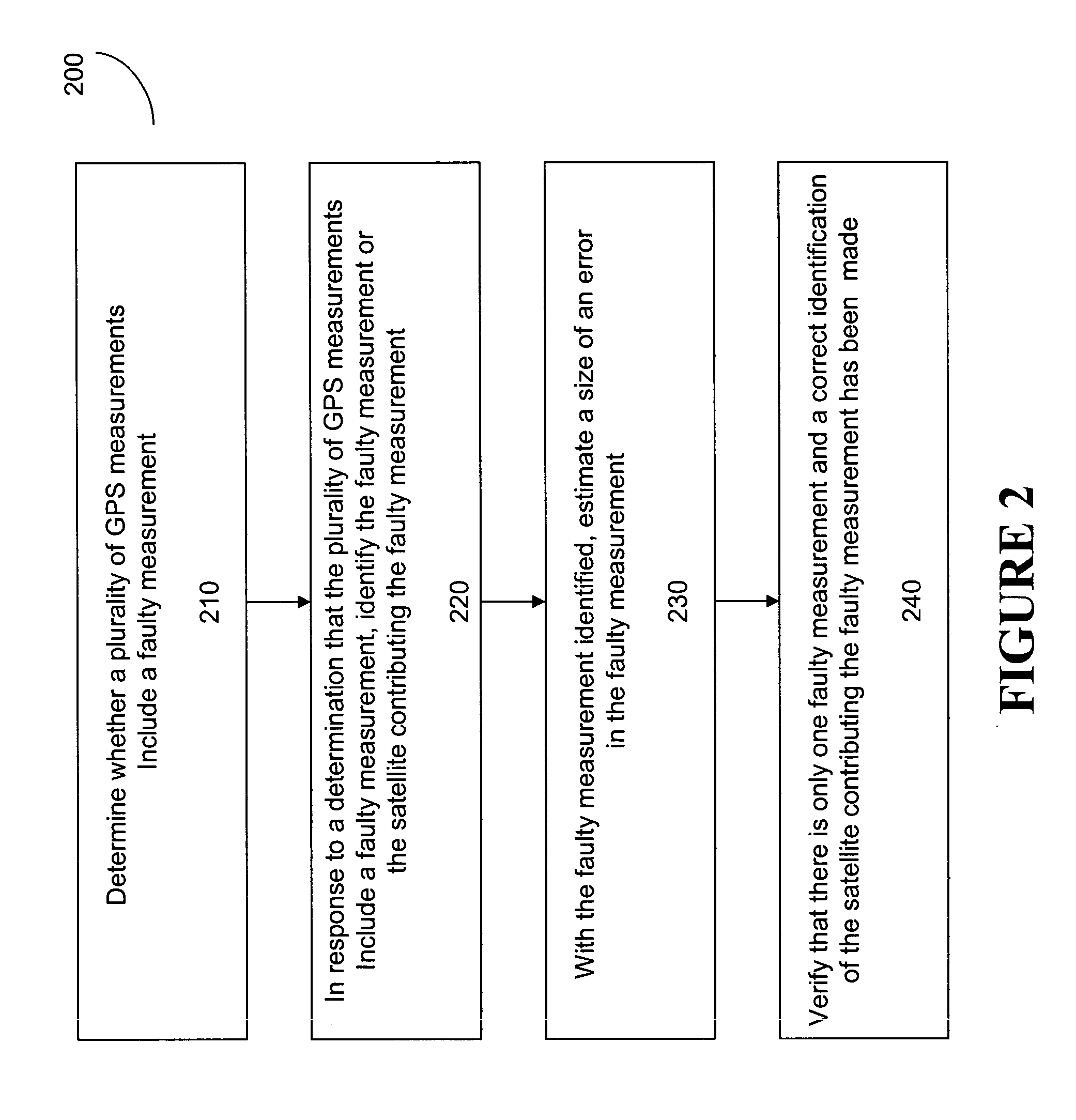
A method for detecting and identifying a faulty measurement among a plurality of GPS measurements, obtained by a GPS receiver with respect to a plurality of satellites in view of the GPS receiver, determines whether the plurality of GPS measurements include a faulty measurement. In response to a determination that the plurality of GPS measurements include a faulty measurement, the method identifies a satellite contributing the faulty measurement by computing a correlation value associated with each of the plurality of satellites, and selecting a satellite associated with a highest correlation value as the satellite contributing the faulty measurement.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Method of multiple satellite measurement failure detection and isolation for GNSS
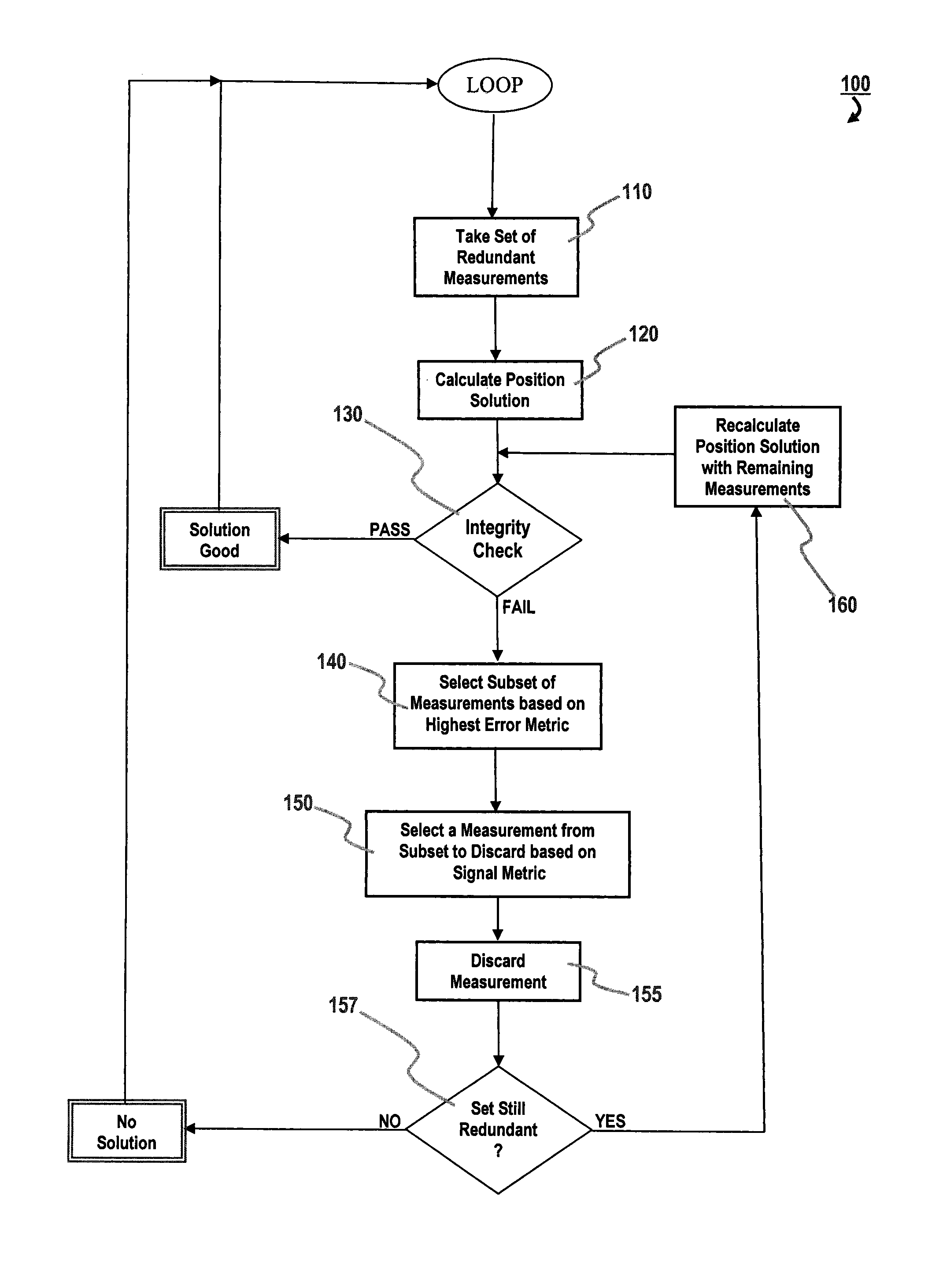
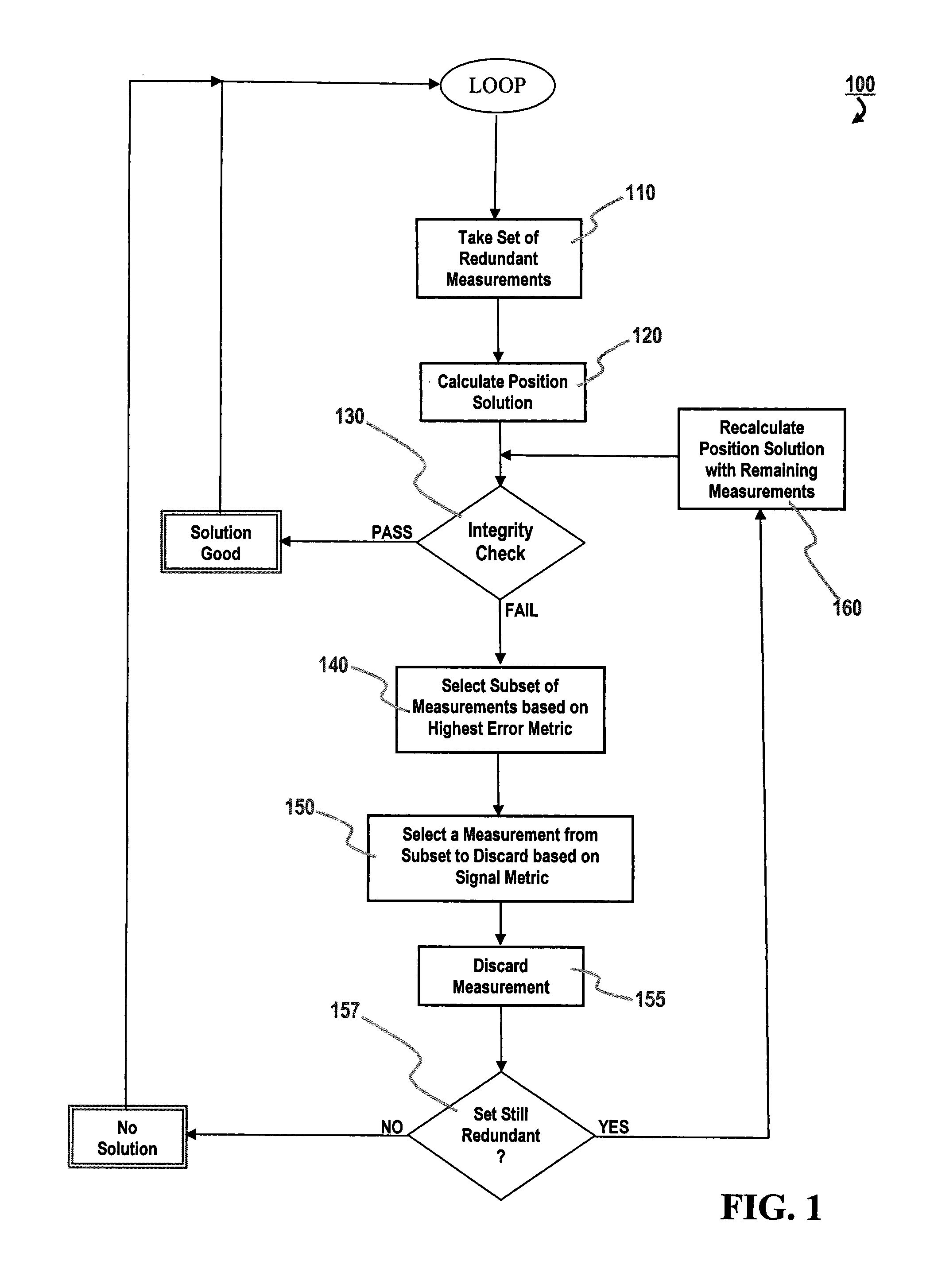
Methods for reducing the resources needed to detect and identify faulty pseudorange measurements in a GNSS receiver are described. In a Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring (RAIM) method, a position solution is calculated using a weighted least squares method on measurements from satellites of one or more GNSS constellations. A test statistic is calculated from residuals and a threshold is calculated based on a probability function. If the test statistic is greater than or equal to the threshold, a subset is selected from the set of pseudorange measurements using a metric indicative of possible measurement error. A measurement is selected from the subset using a metric indicative of signal strength or some other metric and discarded from the set of pseudorange measurements. If the number of measurements remaining in the set of pseudorange measurements is greater than five, the method loops back to the step of calculating a position solution.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Parity vector method-based double-satellite failure recognition method
InactiveCN102901971ASolve the problem of fault offset offsetRealize detection and identificationSatellite radio beaconingRemote sensingReceiver autonomous integrity monitoring
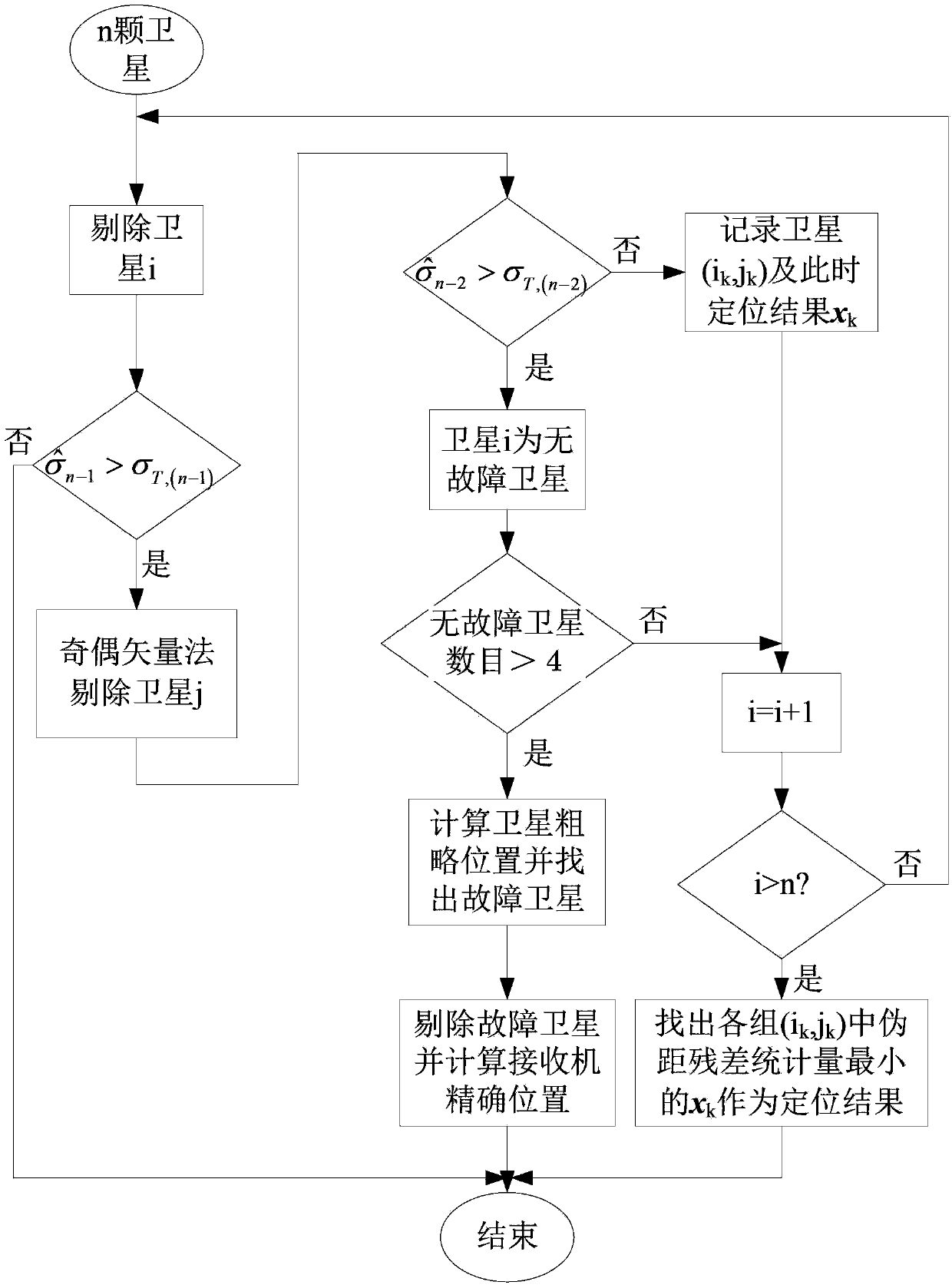
The invention relates to global satellite navigation system receiver autonomous integrity monitoring technology and discloses a parity vector method-based double-satellite failure recognition method, aiming at the problems of false positives and false negatives caused by fault deviation offsetting when the parity vector method is used for recognizing two fault satellites. According to the technical scheme, the parity vector method is used for recognizing one fault satellite; with the fault satellite as the basis, four fault-free satellites are found out, and the information of the fault-free satellites is used for roughly locating, so that the fault satellites can be recognized; the recognized fault satellites are removed, and then the position resolution is carried out again, so that the locating accuracy is improved; therefore, the problems of false positives or false negatives caused by fault deviation offsetting can be avoided. The method solves the problem of the fault deviation offsetting caused by parity vector residual error and realizes the detection and the recognition for a plurality of fault satellites. After the method is used for detecting and recognizing satellite failure, the locating accuracy is improved. The method is mainly used for monitoring the autonomous integrity of a global satellite navigation system receiver.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Receiver autonomous integrity monitoring (RAIM) method used for satellite navigation system
ActiveCN101806903AEnable autonomous integrity monitoringSolve difficult-to-identify problemsSatellite radio beaconingSingle faultMonitoring methods
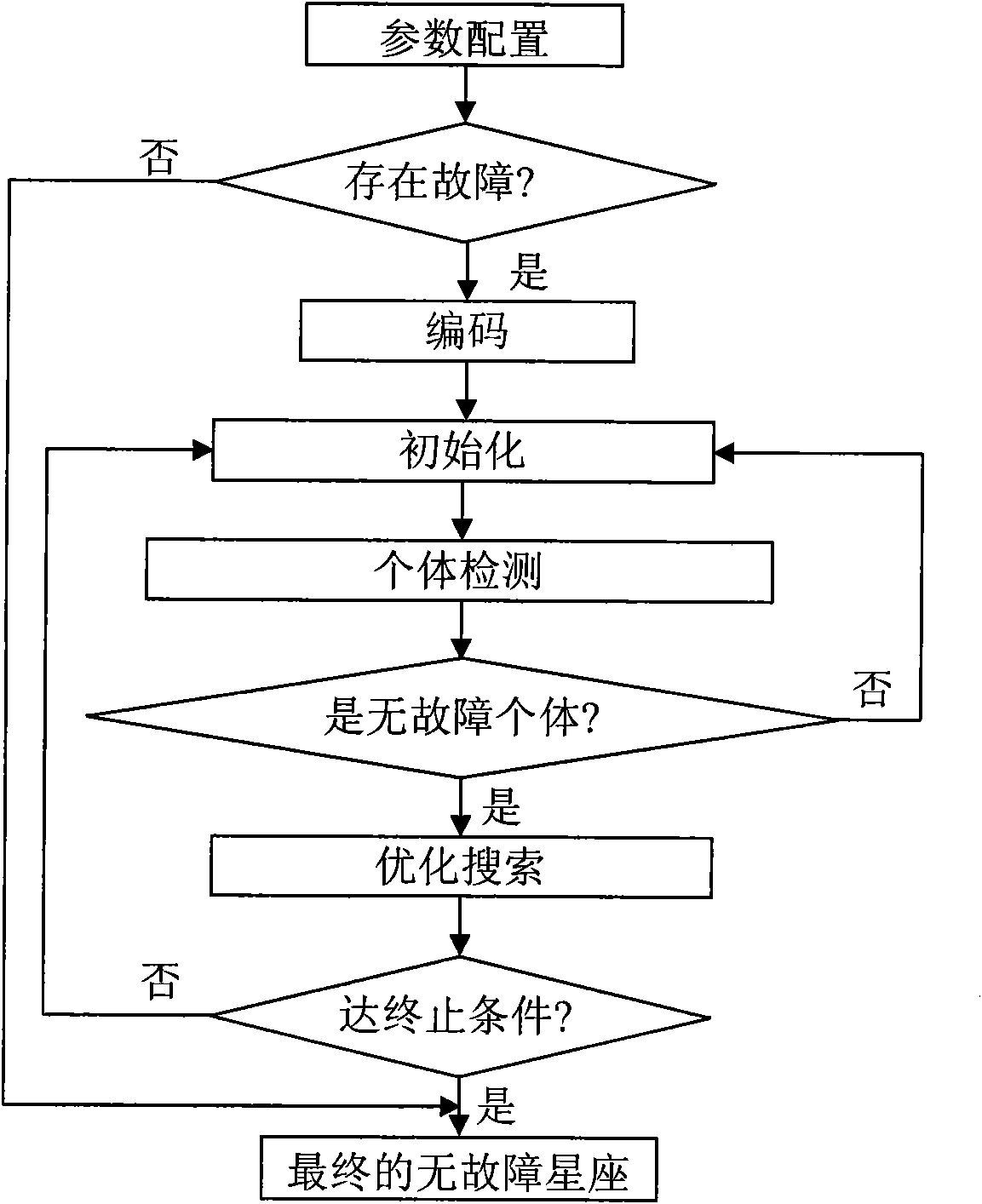
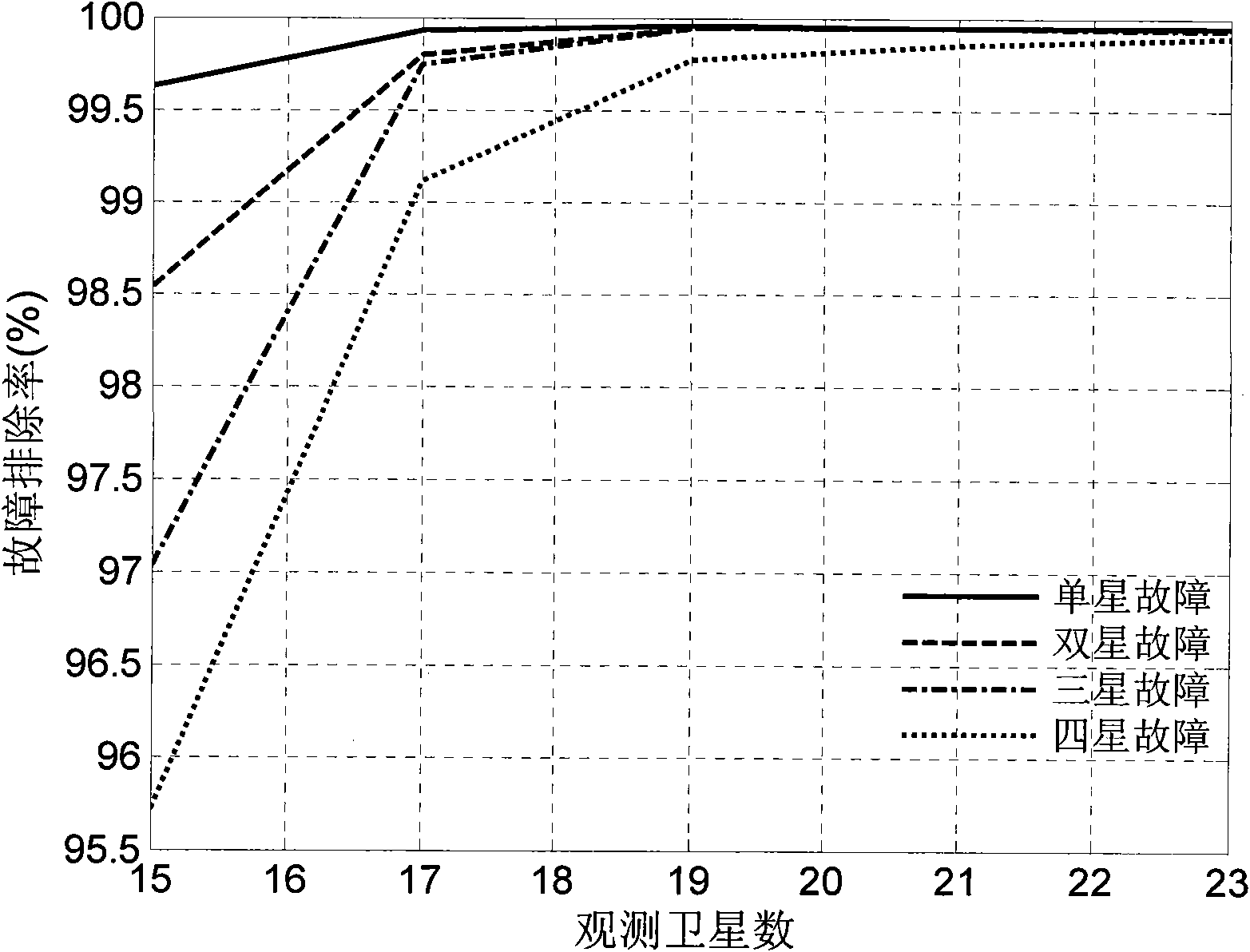
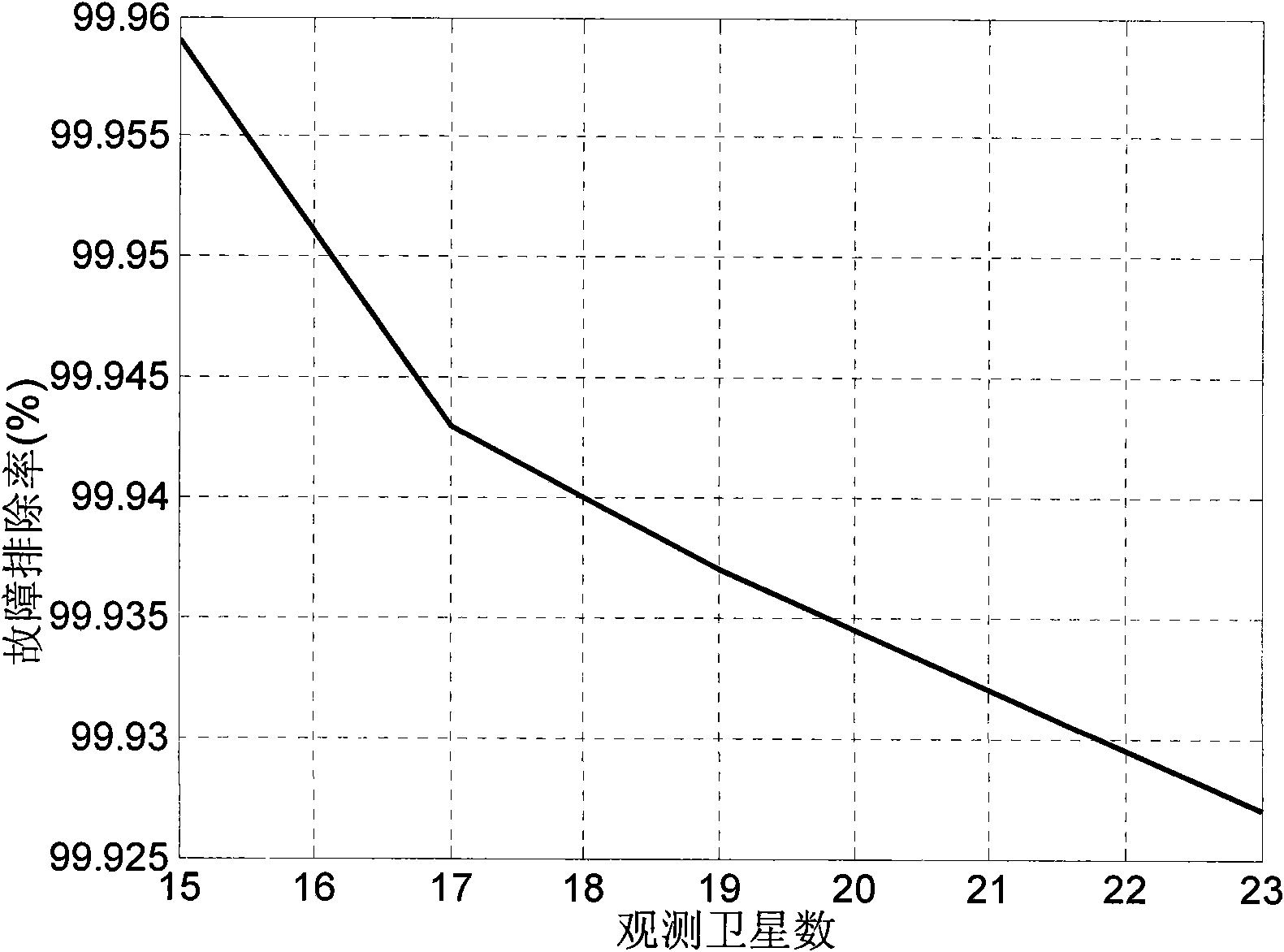
The invention discloses a receiver autonomous integrity monitoring method used for a satellite navigation system, which is an RAIM method based on multi-satellite fault detection and removal and achieve the fault removal goal by a mode of acquiring constellations comprising the most fault-free satellites. In the method, fault-free individuals are formed by adopting coding, initialization and individual detection; then an individual comprising the most fault-free satellites is obtained by optimal search, and the individual is used as an initial result; when terminal condition is satisfied, the individual is the final result of RAIM. The method has simple realization, high fault removal efficiency and good robustness, not only can carry out single-fault detection and removal but also can carry out multi-fault detection and removal, is not only suitable for single system but also is suitable for multisystem and effectively achieve the goal of carrying out multi-satellite fault detection and removal in the RAIM method.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
GNSS navigation solution integrity in non-controlled environments
ActiveUS8131463B2Improve navigation accuracyPosition fixationNavigation instrumentsNoise levelErrors and residuals
Disclosed is a method for providing a Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) navigation position solution with guaranteed integrity in non-controlled environments, the method including processing a (GNSS) signal including multiple satellites generating at least one signal to obtain carrier phase and pseudorange measurements; pre-processing the measurements to detect and characterize local errors in the measurements, wherein the local errors cannot be ascertained a priori, the characterization including providing error bounds estimated by measuring the carrier phase and pseudoranges measurements, thereby providing a set of measurements rejections when the characterization is not possible; and using the estimated error bounds, together with error bounds provided by the GNSS signal concerning satellite and ionospheric errors, to build in each measurement an estimated noise level in the measurements as input to a weighted Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring (RAIM) algorithm in order to compute position coordinates and associated protection levels in the non-controlled environments.
Owner:GMV AEROSPACE & DEFENCE
Method for monitoring autonomous integrity of GNSS receiver
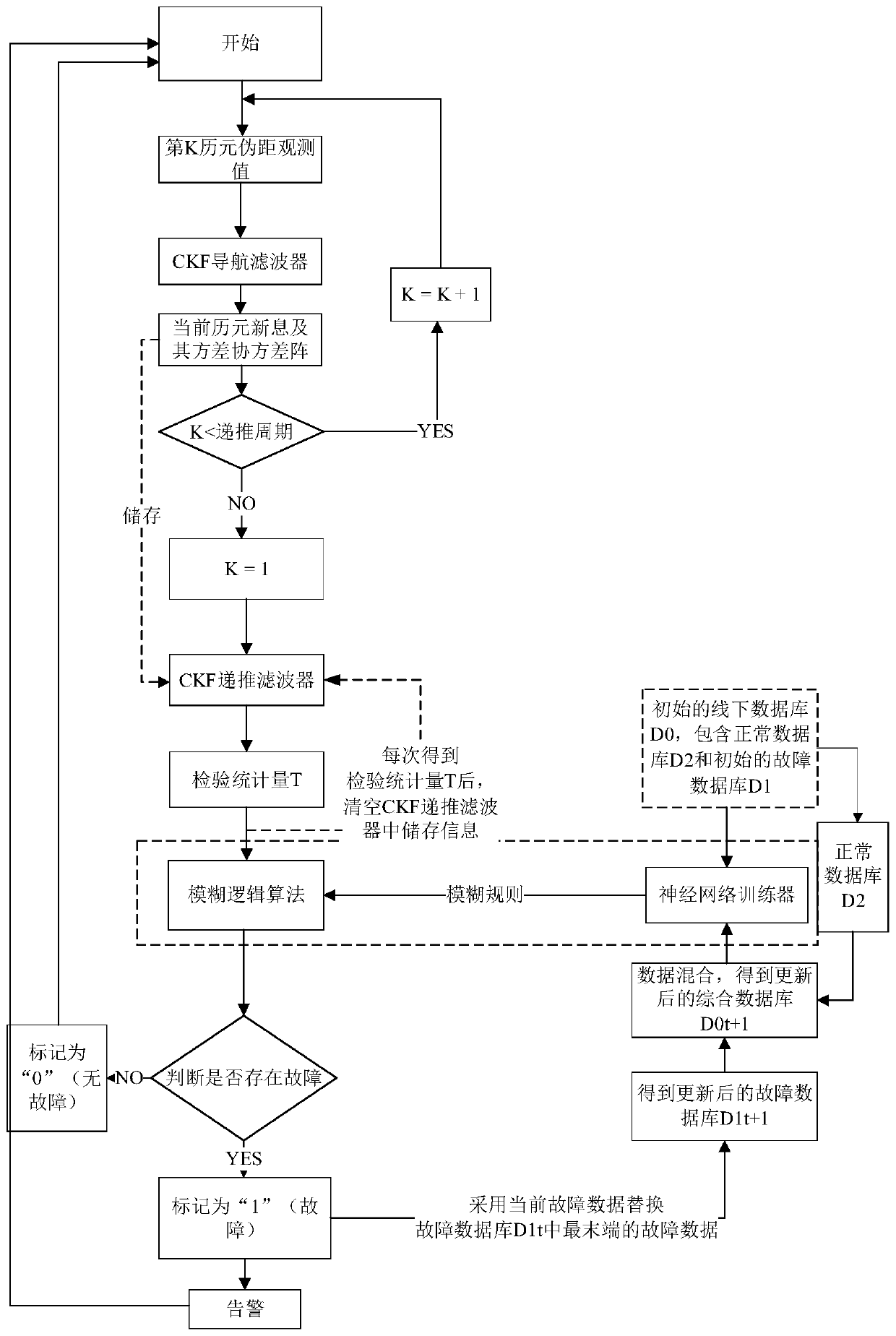
ActiveCN109490916AAdapt to the requirements of comprehensive fault detectionAvoid first-order approximationsSatellite radio beaconingLearning ruleCovariance matrix
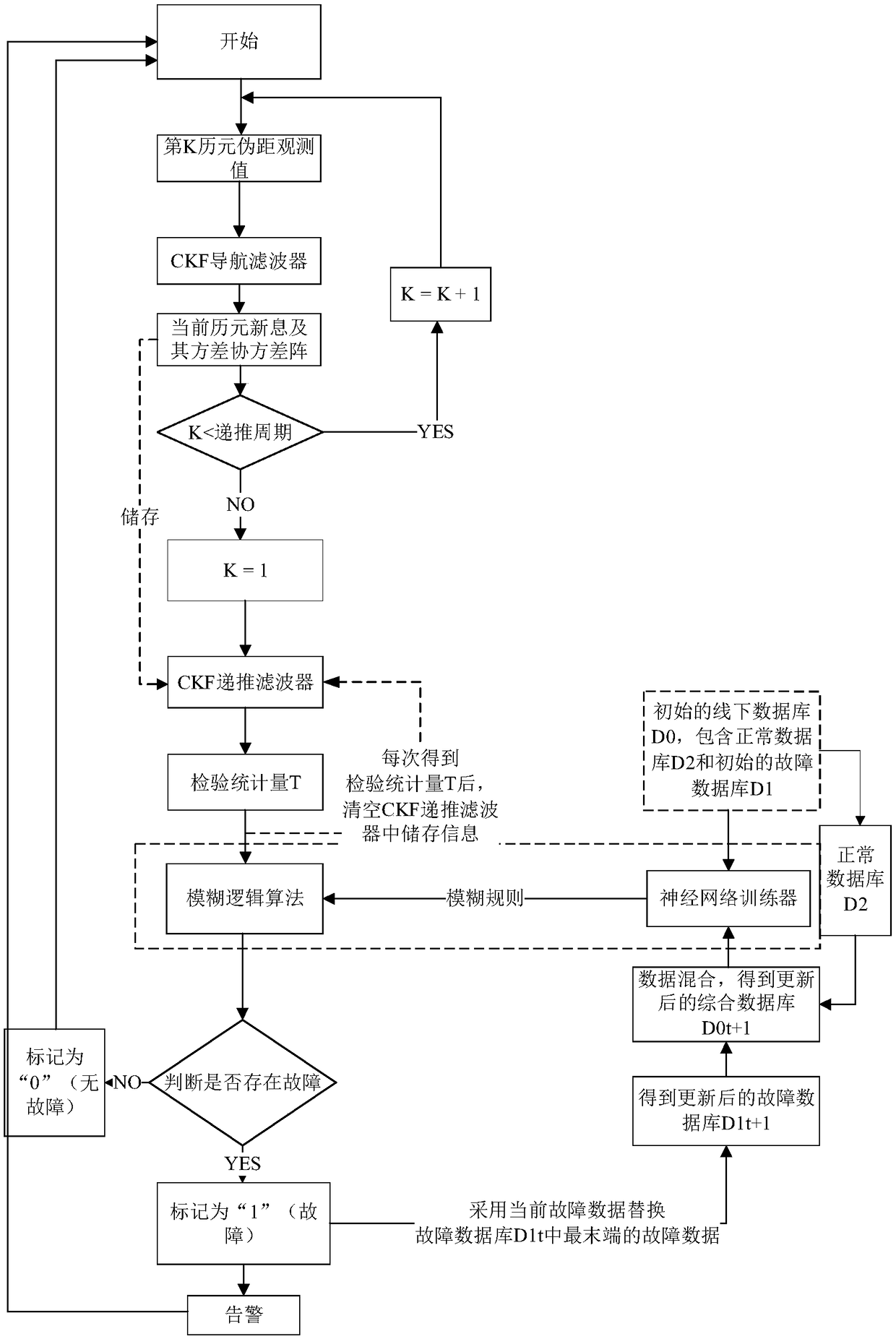
The invention discloses a method for monitoring autonomous integrity of a GNSS receiver, relates to a receiver autonomous integrity monitoring technology, and belongs to the technical field of measurement and test. The method adopts a CKF-based and innovation extrapolation method to achieve monitoring of the autonomous integrity of the GNSS receiver, and innovation generated in an innovation extrapolation process and a variance-covariance matrix thereof construct test statistic of each extrapolation moment, micro slowly-changing pseudo-range deviation can be tested; a machine learning algorithm is adopted to judge and classify the test statistic of the each extrapolation moment, and dynamically updates a fault database used for generating a machine learning rule at the same time; on-line learning of judgment rules of unmodeled fault types has the advantages of being less in calculation amount, proper in precision, suitable for nonlinear systems and capable of monitoring the micro slowly-changing pseudo-range deviation with high confidence degree.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS +1
Method for receiver autonomous integrity monitoring and fault detection and elimination
A method for detecting and identifying a faulty measurement among a plurality of GPS measurements, obtained by a GPS receiver with respect to a plurality of satellites in view of the GPS receiver, determines whether the plurality of GPS measurements include a faulty measurement. In response to a determination that the plurality of GPS measurements include a faulty measurement, the method identifies a satellite contributing the faulty measurement by computing a correlation value associated with each of the plurality of satellites, and selecting a satellite associated with a highest correlation value as the satellite contributing the faulty measurement.
Owner:DEERE & CO
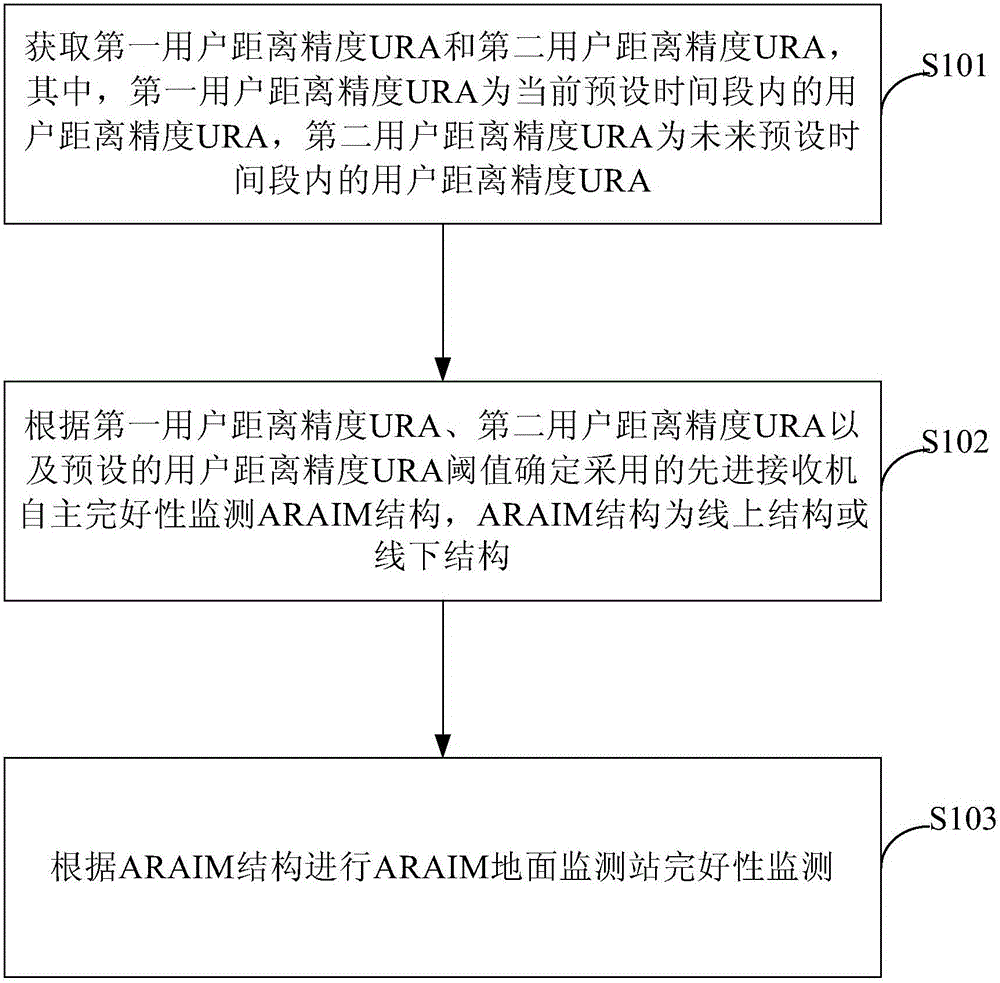
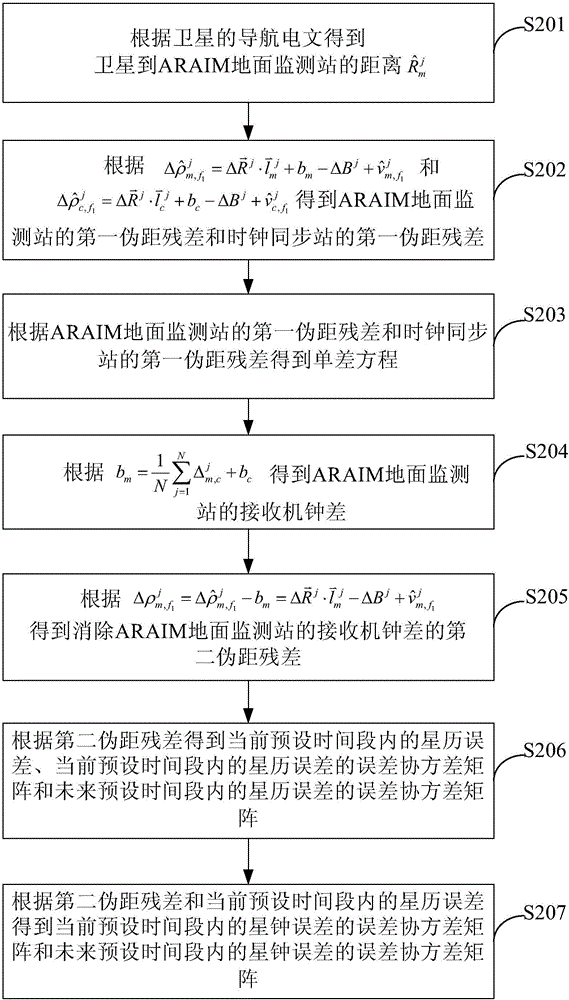
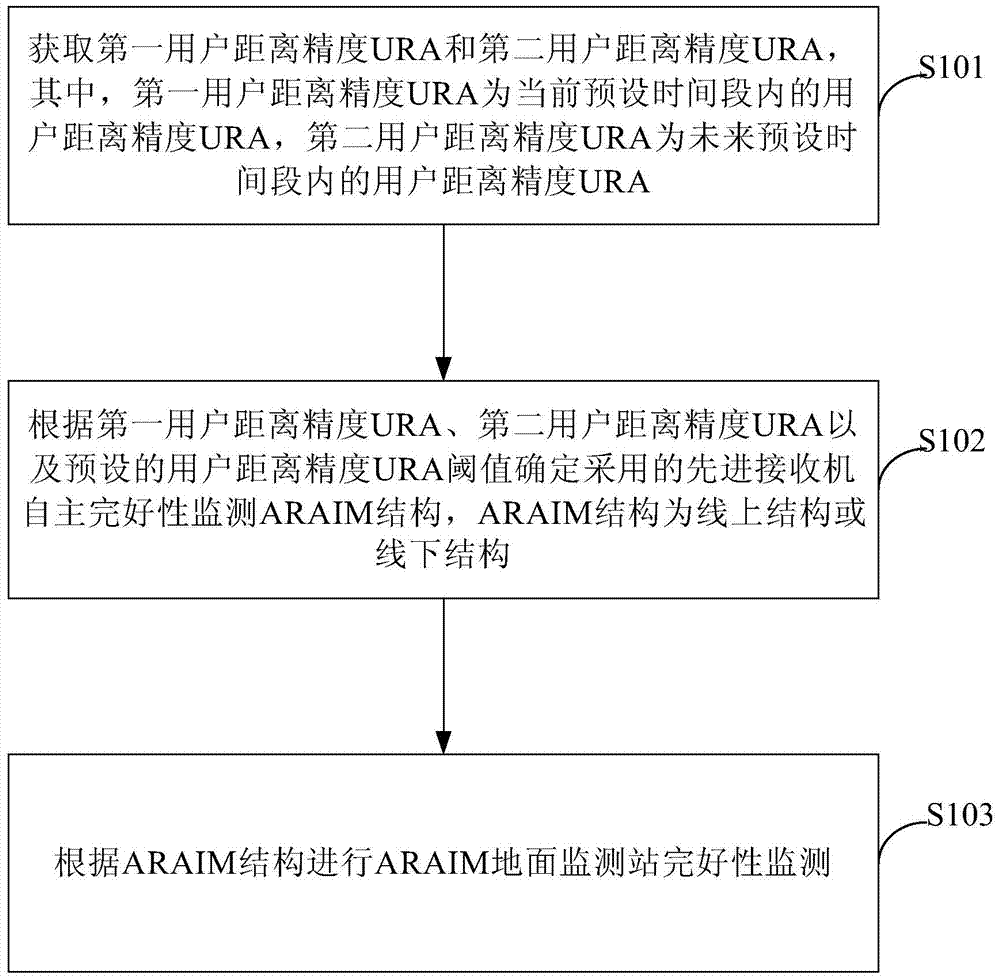
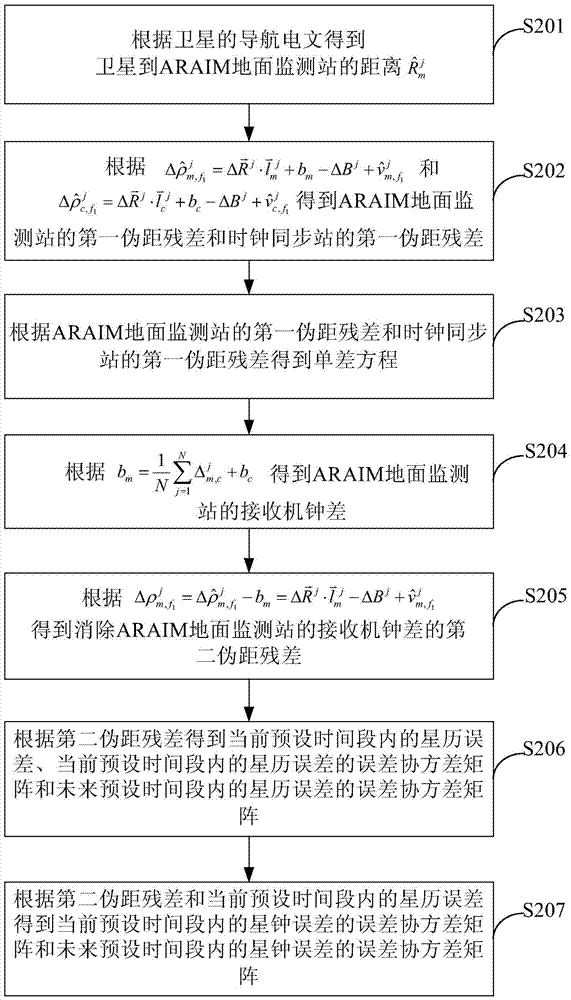
ARAIM ground monitoring station integrity monitoring method and ARAIM ground monitoring station integrity monitoring device
ActiveCN105116423AImprove usabilityMeet precision requirementsSatellite radio beaconingUsabilityComputer science
The invention provides an ARAIM ground monitoring station integrity monitoring method and an ARAIM ground monitoring station integrity monitoring device. The ARAIM ground monitoring station integrity monitoring method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: acquiring first user range accuracy URA and second user range accuracy URA, wherein the first user range accuracy URA is the user range accuracy URA in a current preset period of time, and the second user range accuracy URA is the user range accuracy URA in a future preset period of time; determining an adopted advanced receiver autonomous integrity monitoring ARAIM structure according to the first user range accuracy URA, the second user range accuracy URA and a preset user range accuracy URA threshold, wherein the ARAIM structure is an online or offline structure; and performing ARAIM ground monitoring station integrity monitoring according to the ARAIM structure. The ARAIM ground monitoring station integrity monitoring method and the ARAIM ground monitoring station integrity monitoring device provided by the invention can meet the requirement of most areas for accuracy and integrity. The application rang is expanded, and the usability of LPV-200 is improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
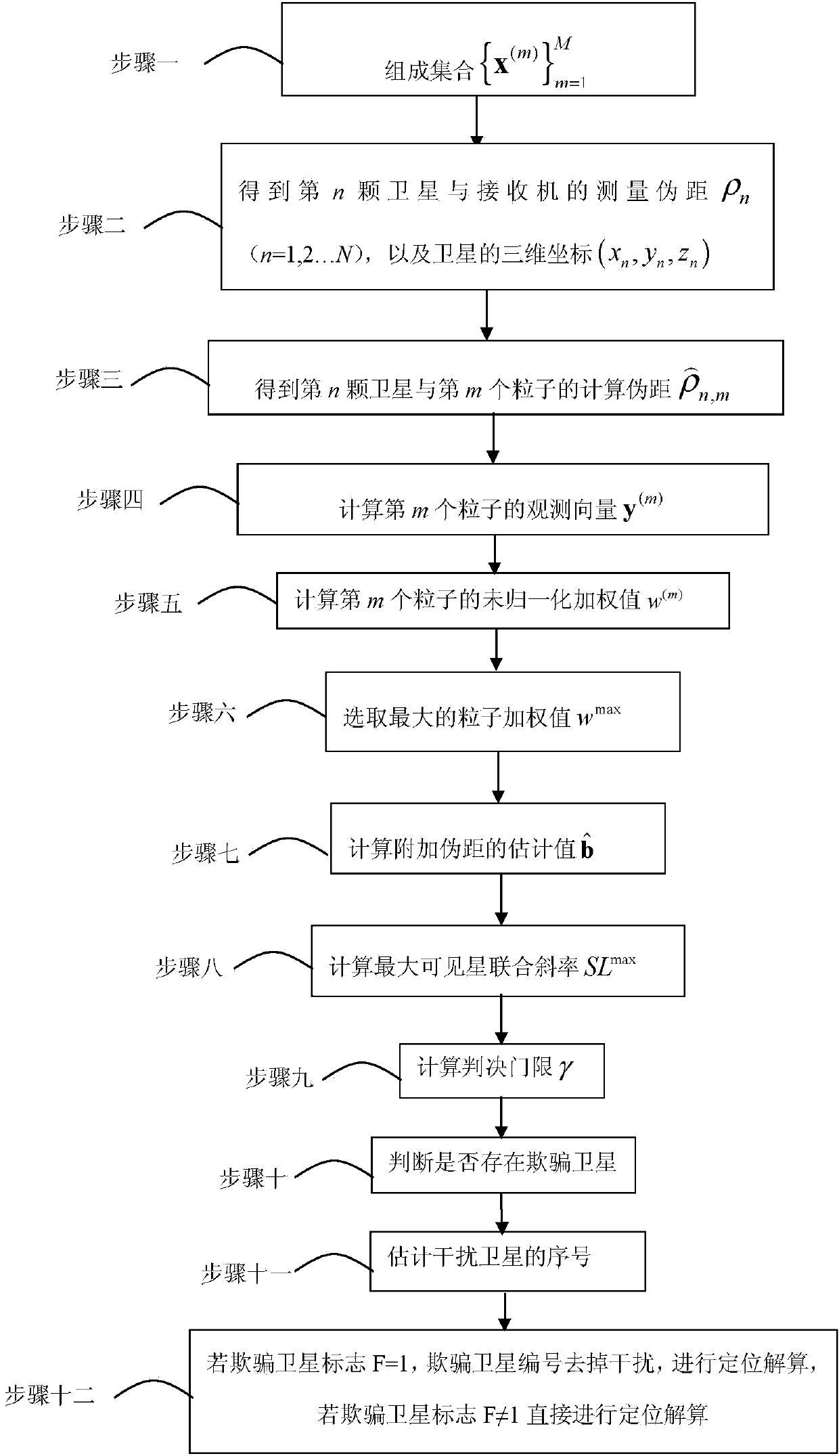
Particle filter-based improved RAIM (Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring) anti-deception jamming method
ActiveCN103983986AEasy to detectAchieving identifiabilitySatellite radio beaconingComputational physicsReceiver autonomous integrity monitoring
The invention discloses a particle filter-based improved RAIM (Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring) anti-deception jamming method. The invention relates to an improved RAIM anti-deception jamming method. For solving the problems of measurement failure of a single satellite, positioning misleading of a receiver by a control resolving flow, and neglecting of dependency and similarity among remaining vectors by RAIM, the invention provides a particle filter-based improved RAIM anti-deception jamming method. The particle filter-based improved RAIM anti-deception jamming method comprises the following steps: 1, forming a formula described in the specification; 2, obtaining a Rho n and three-dimensional coordinates of the satellite; 3, calculating a parameter described in the specification; 4, calculating y (m); 5, calculating w (m); 6, selecting wmax; 7, calculating a parameter described in the specification; 8, calculating a maximal visible satellite SLmax; 9, calculating a judgment threshold gamma; 10, judging the existence of a deception satellite; 11, estimating a sequence number of the deception satellite; and 12, if the mark F of the deception satellite is equal to 1, removing jamming, carrying out positioning resolving, and if F is not equal to 1, carrying out positioning resolving. The particle filter-based improved RAIM anti-deception jamming method is applied to the field of improved RAIM anti-deception jamming.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for detecting and identifying satellite navigation RAIM (Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring) multi-satellite faults
ActiveCN104199051AReduce false alarm rateImprove detection rateSatellite radio beaconingEstimation methodsGround station
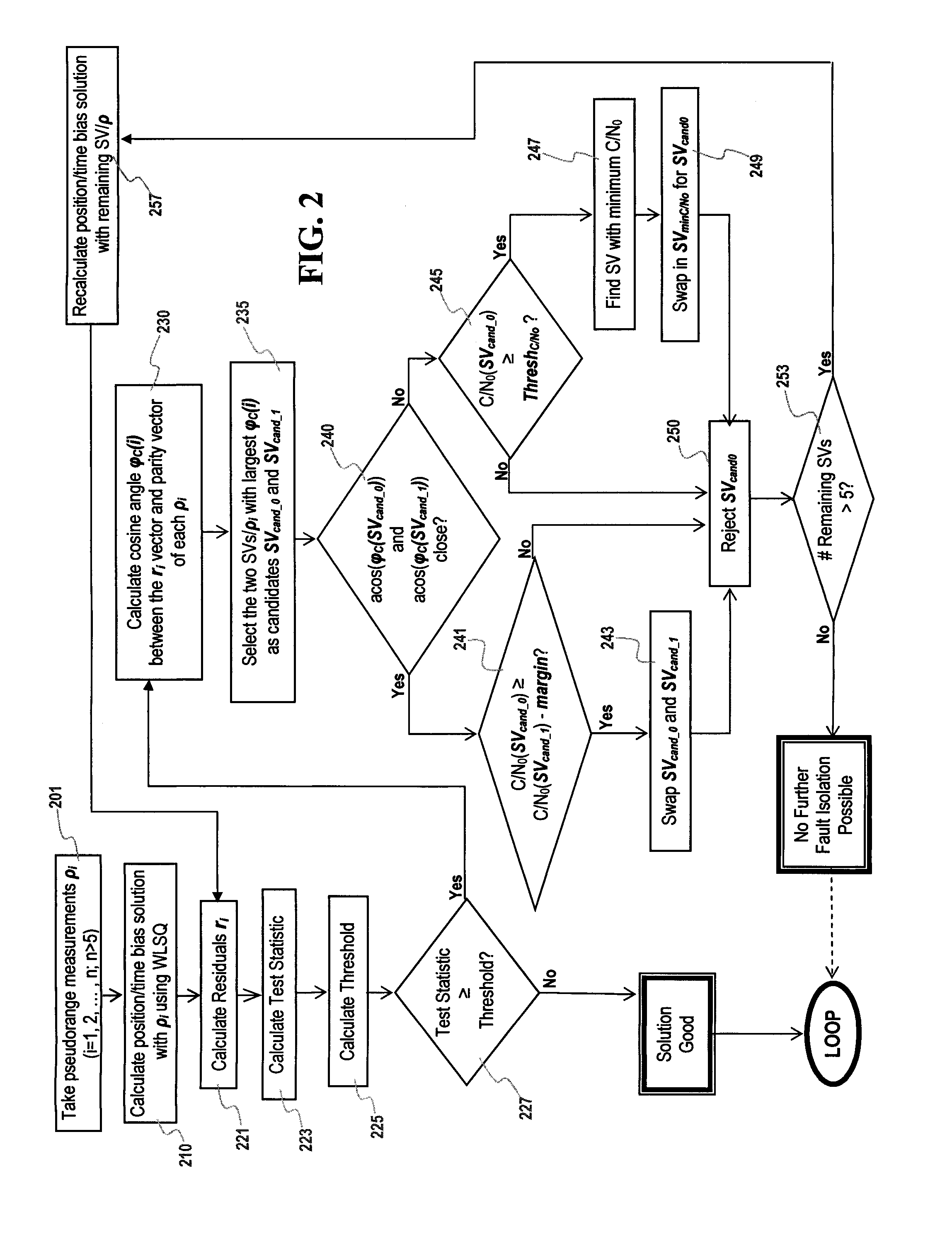
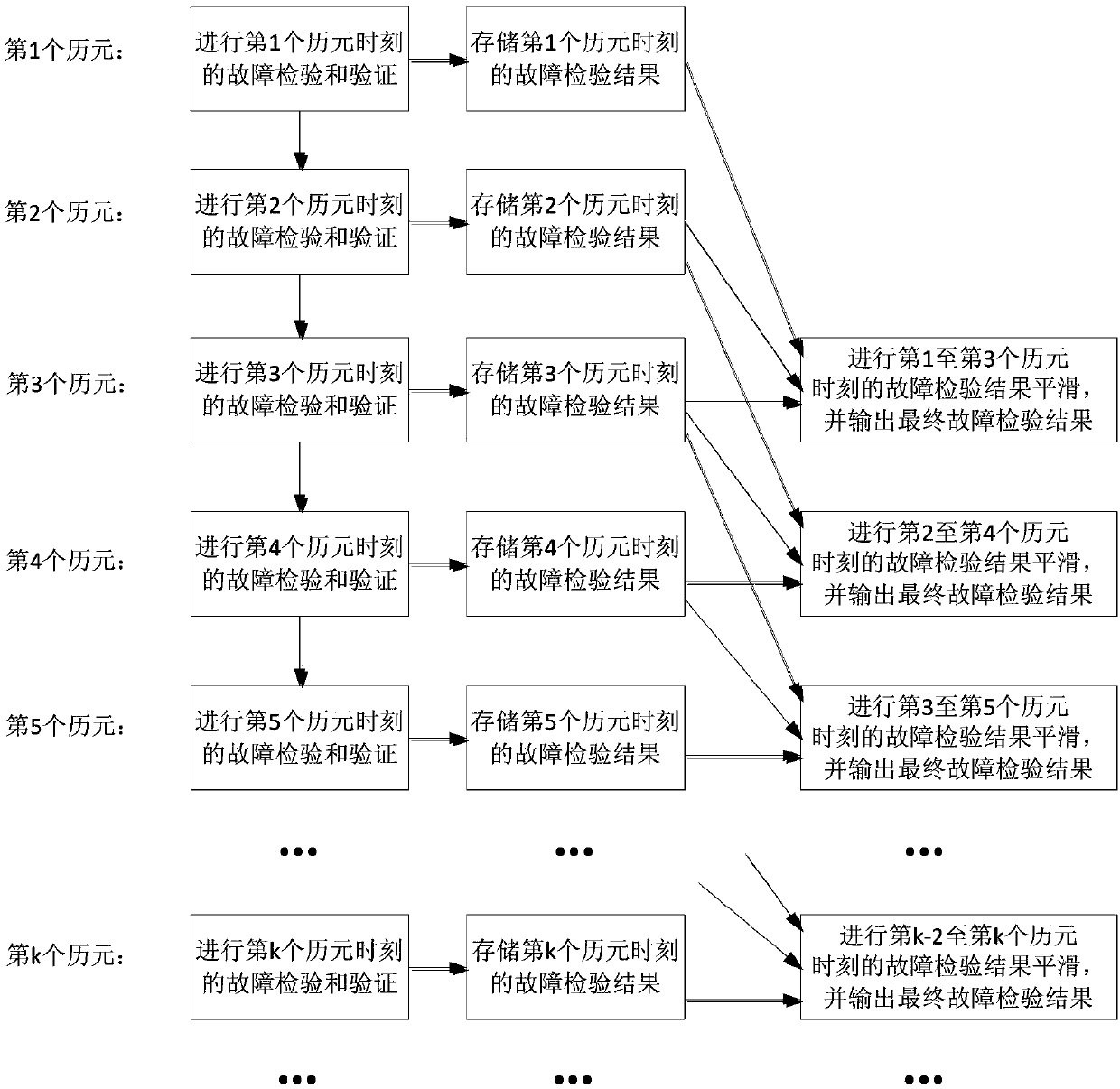
The invention discloses a method for detecting and identifying satellite navigation RAIM (Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring) multi-satellite faults, and relates to a method for detecting and identifying the RAIM starry faults on the basis of the least squares residual error method and the maximum likelihood estimation method, wherein the method has the advantages that the false alarm probability is low, the detection probability is high, and the computational load is relatively low. The method provided by the invention mainly comprises the following three aspects: firstly, using the least squares residual error method and the maximum likelihood estimation method to detect and identify multiple fault satellites in single step and by stages, removing one by one, and acquiring the fault-free satellite constellation; secondly, adopting the fault-free satellite constellation to conduct preliminary screening on the fault satellites and conduct identification one by one, and removing all of the false fault satellites; thirdly, adopting the multi-epoch fault detection result smoothing method to further improve the fault detection probability and reduce the false alarm probability. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the detection probability is high, the false alarm probability is relatively low, and the computational load is less, therefore, the method applies to the application of user computers and ground station equipment.
Owner:NO 54 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP
Prediction method and prediction system for receiver autonomous integrity monitoring
InactiveCN105044738AAccurate calculation of horizontal protection valueAccurately capture autonomous integrity monitoring resultsSatellite radio beaconingTerrainObservational error
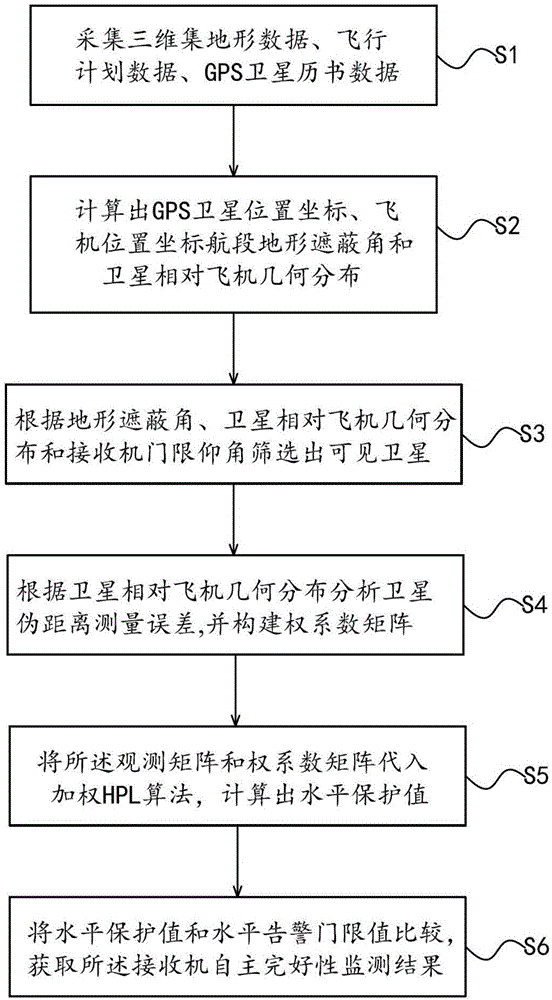
The invention relates to a prediction method and prediction system for receiver autonomous integrity monitoring (RAIM). The method includes the following steps of: acquiring three-dimensional terrain data, flight plan data and GPS satellite ephemeris data; calculating GPS satellite position coordinates, plane coordinates, leg terrain shielding angles and the geometric distribution of satellites relative to a plane at a certain moment in the flight plan data; screening visible satellites according to the terrain shielding angles, the geometric distribution of the satellites relative to the plane and receiver threshold elevations; analyzing satellite pseudo distance measurement errors, and constructing a weight coefficient matrix; calculating a horizontal protection value according to a weighted horizontal protection value (HPL) algorithm; and comparing the horizontal protection value with a horizontal alarm threshold value, and obtaining receiver autonomous integrity monitoring results. According to the prediction method, in a visible satellite screening process, a terrain shielding angle screening step is additionally adopted, and therefore, the accuracy and reliability of the prediction of the receiver autonomous integrity monitoring (RAIM) can be improved.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION FLIGHT UNIV OF CHINA
Method for realizing single-mode RAIM (Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring) under small number of visible satellites based on assistance of clock correction
InactiveCN103592657AHigh precisionEasy to implementSatellite radio beaconingClock rateClock correction
The invention discloses a method for realizing single-mode RAIM (Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring) under a small number of visible satellites based on assistance of clock correction, which is a method for realizing single-mode RAIM under the condition that the number of the visible satellites is small in loop tracking. Clock correction prediction is carried out through a Newton interpolation model under the premise that the clock frequency of a receiver is stable, and detection and elimination of a fault satellite can be carried out under the condition that the number of the visible satellites is five, thereby improving the positioning precision, the continuity and the stability of the receiver. The method comprises the steps of: first, determining weight factor in weighted least squares through parameters such as a carrier-to-noise ratio and the like of satellite signals; then, carrying out RAIM availability detection through a false alarm rate, a missed alarm rate, an observation equation and a weight matrix, determining a detection threshold value by using a tolerant false alarm rate in a non-precision condition, and carrying out clock correction prediction for the receiver through the Newton interpolation model so as to realize detection and elimination of the fault satellite, and finally, carrying out analysis and comparison on a dilution of precision (DOP) after a clock correction auxiliary equation is added. The method disclosed by the invention can realize detection and elimination of the fault satellite under the condition that only one redundant satellite exists, reduces the space dilution of precision through the clock correction auxiliary model, and improving the positioning accuracy of the receiver and the system robustness.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
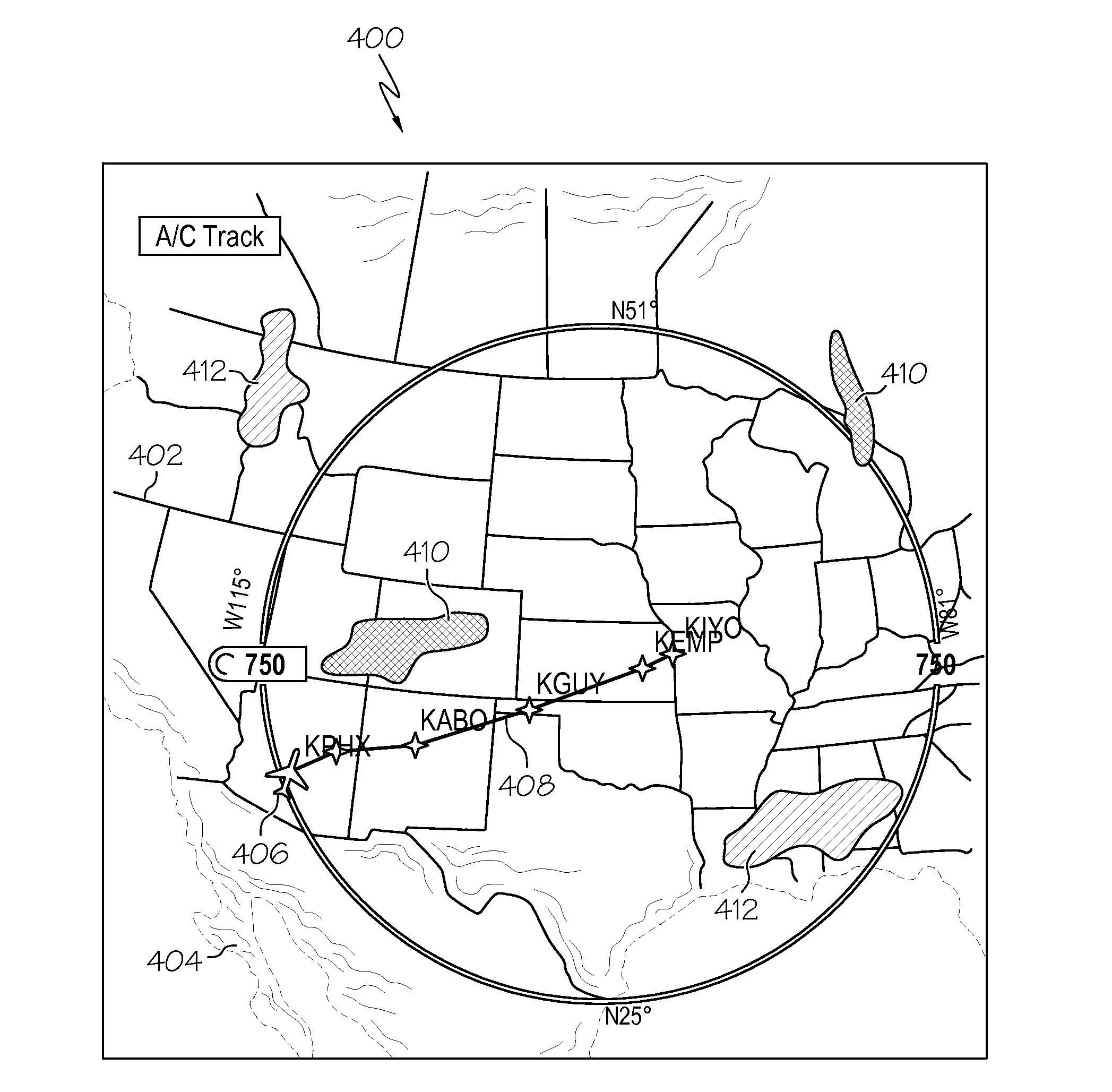
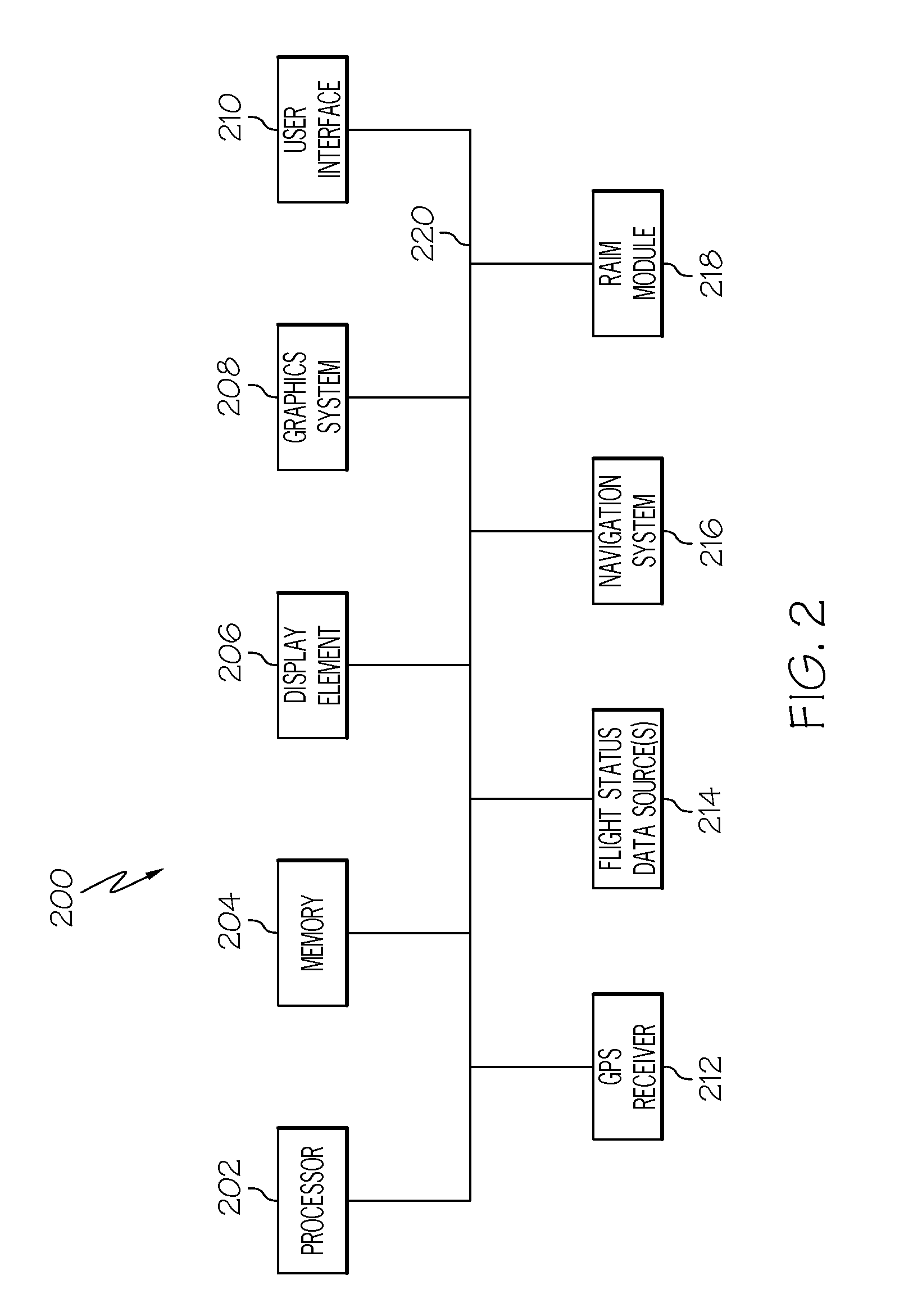
Graphical presentation of receiver autonomous integrity monitoring outage regions on an aircraft display
InactiveUS20130138338A1Well formedRoad vehicles traffic controlNavigation instrumentsGraphicsGeographic site
A system and related methods of displaying receiver autonomous integrity monitoring (RAIM) information on a display element of an aircraft are provided. The method obtains geographic position data for the aircraft, accesses lateral map data corresponding to the geographic position data, obtains RAIM outage data, and renders a dynamic lateral map on the display element. The map is rendered in accordance with the geographic position data, the lateral map data, and the RAIM outage data, and the map includes a graphical representation of a map and a graphical representation of a RAIM outage region.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
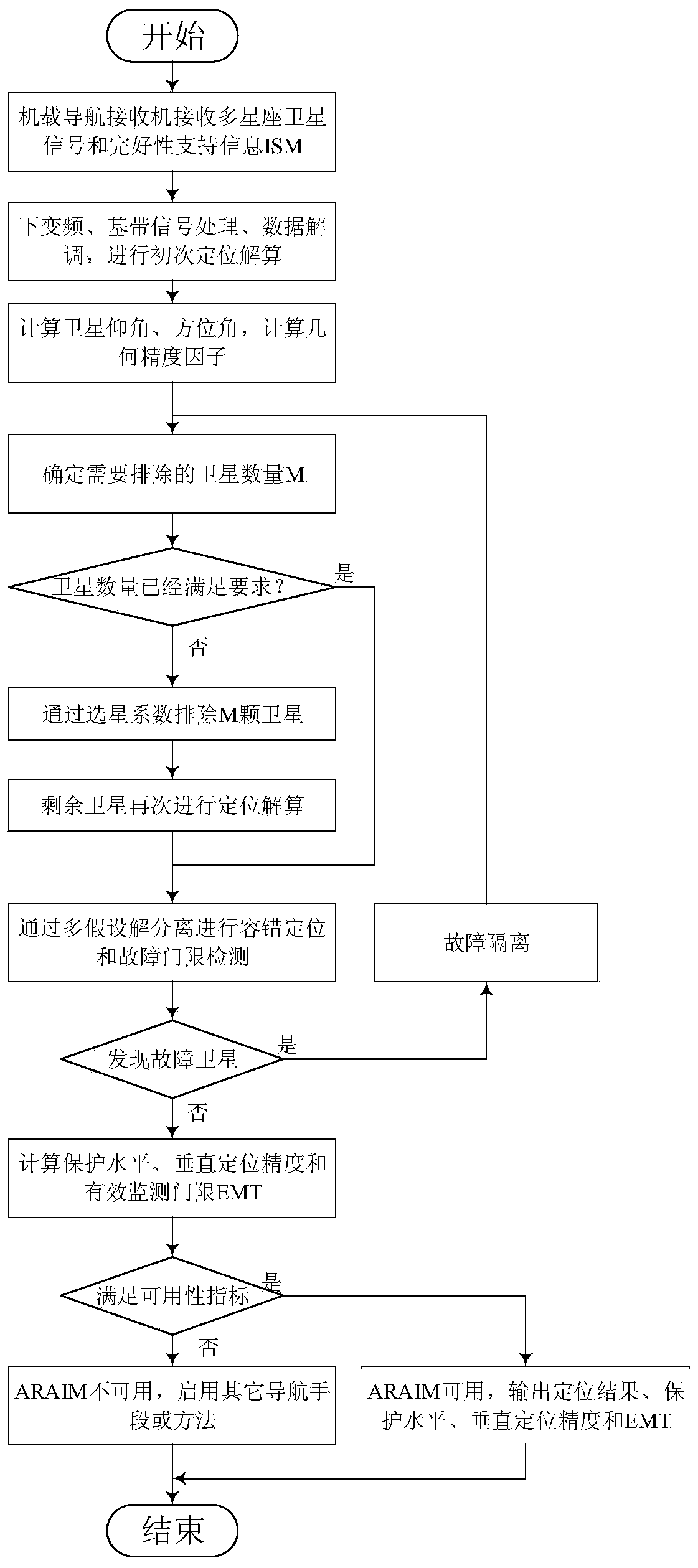
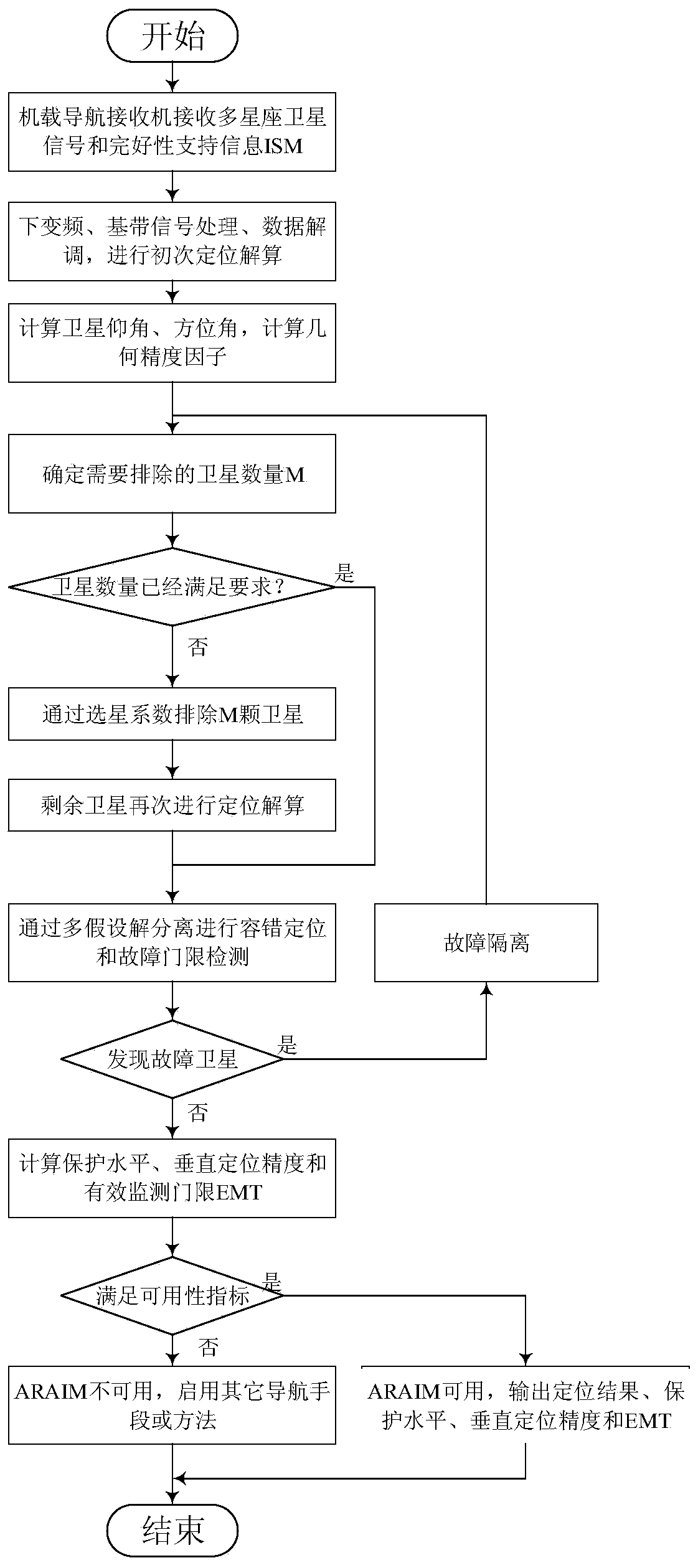
Satellite selection optimized advanced receiver autonomous integrity monitoring method
ActiveCN110007317AImprove usabilitySimplify handling complexitySatellite radio beaconingComputation complexityHypothesis
The invention discloses a satellite selection optimized advanced receiver autonomous integrity monitoring method, and belongs to the technical field of satellite navigation. Advanced receiver autonomous integrity monitoring is a receiver end fault diagnosis and integrity monitoring technology based on a multi-constellation satellite navigation system, ARAIM provides a more strict integrity level by receiving the observed quantity of a multi-constellation satellite, however, due to participation of too many satellites, a fault mode needing to be monitored is increased, and the protection levelis expanded; in addition, the satellite with the large prior fault probability can increase the fault probability. And the ARAIM availability is easily reduced under the condition. According to the ARAIM method based on satellite selection optimization provided by the invention, the space satellite constellation is optimized according to the geometric accuracy factor of the constellation, the fault prior probability of the satellite and the like, the ARAIM availability is improved, and the calculation complexity is simplified. The method is suitable for autonomous integrity monitoring application of the satellite navigation receiver, and the same idea is suitable for other signal systems adopting multi-hypothesis solution separation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
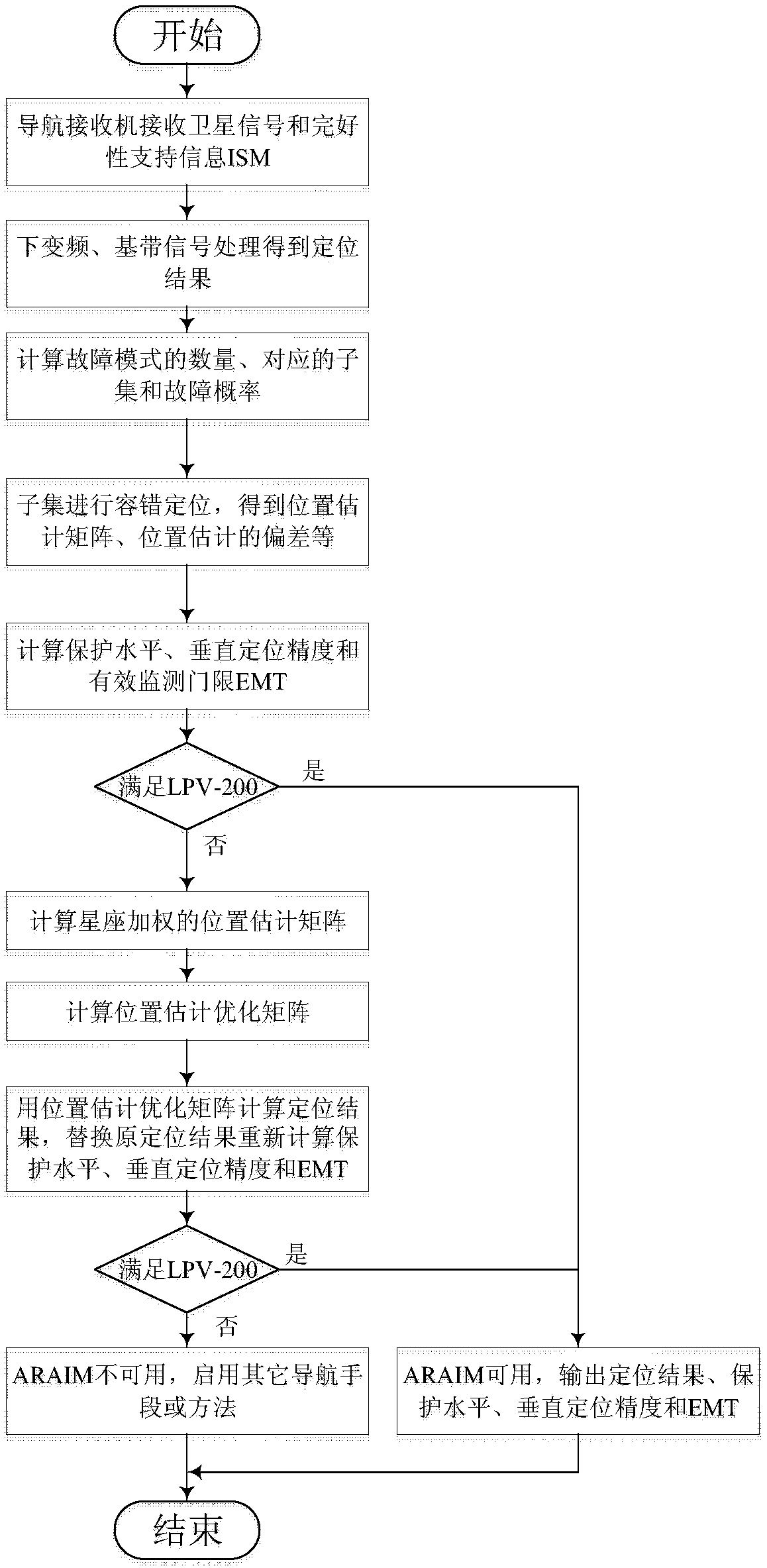
Position estimation optimization method for advanced receiver autonomous integrity monitoring
ActiveCN108761498AReduce variance in positioning accuracyImprove usabilitySatellite radio beaconingComputation complexityMultiple hypothesis
The invention discloses a position estimation optimization method for advanced receiver autonomous integrity monitoring. The invention puts forwards an optimization method for position estimation in allusion to the availability of advanced receiver autonomous integrity monitoring. When a positioning result obtained according to the traditional method in ARAIM (Advanced Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring) does not satisfy an available criterion, a constellation weighted positioning result is adopted to replace the original positioning result within an allowable range of the positioning precision, and the protection level and effective monitoring threshold are recalculated. The method can reduce the difference in positioning precision of different constellations and improve the availability of ARAIM. The method has the characteristics of low computation complexity and good compatibility. The method is suitable for autonomous integrity monitoring of satellite navigation receivers, and the same idea is applicable to other signal systems adopting multiple hypothesis solution separation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
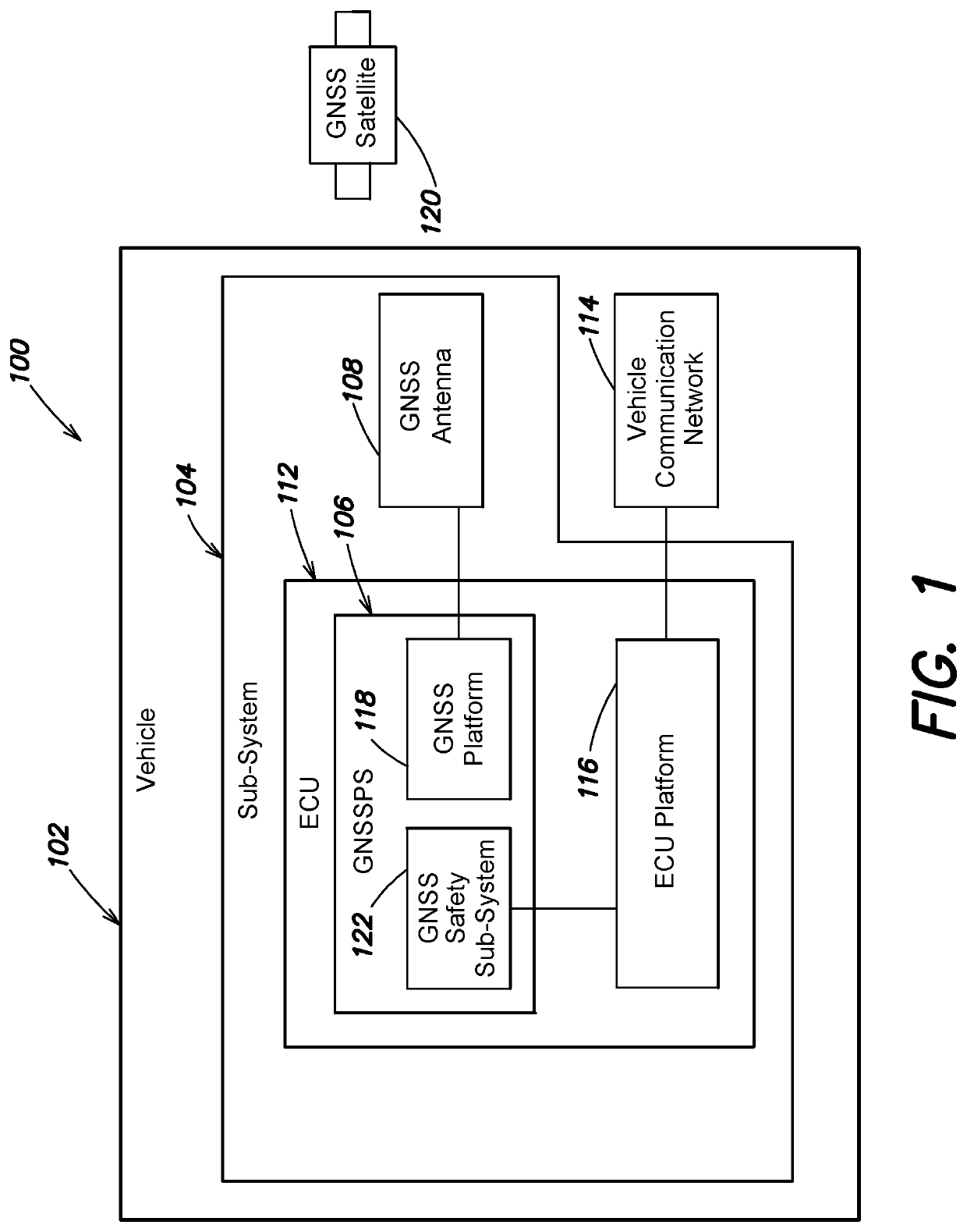
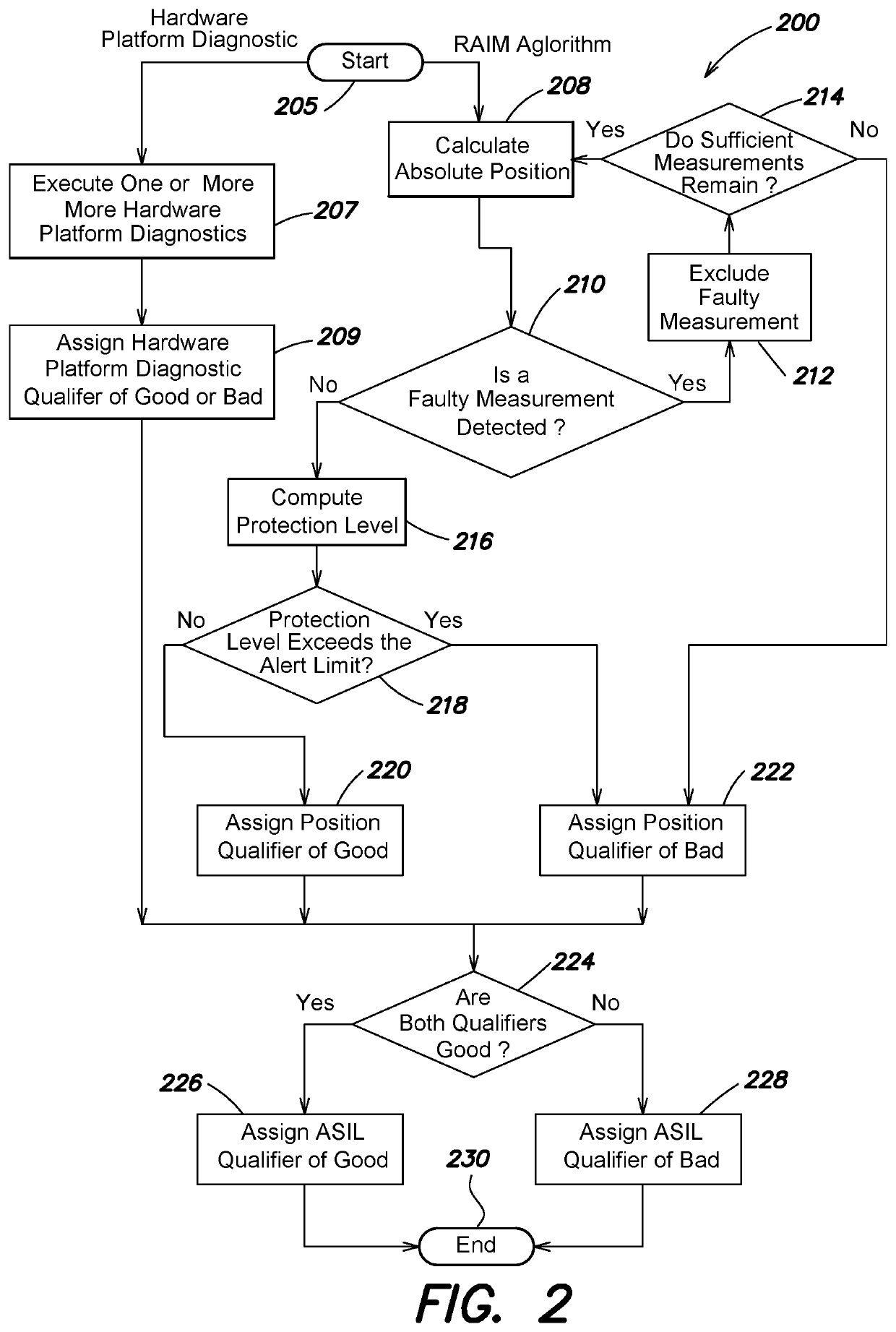
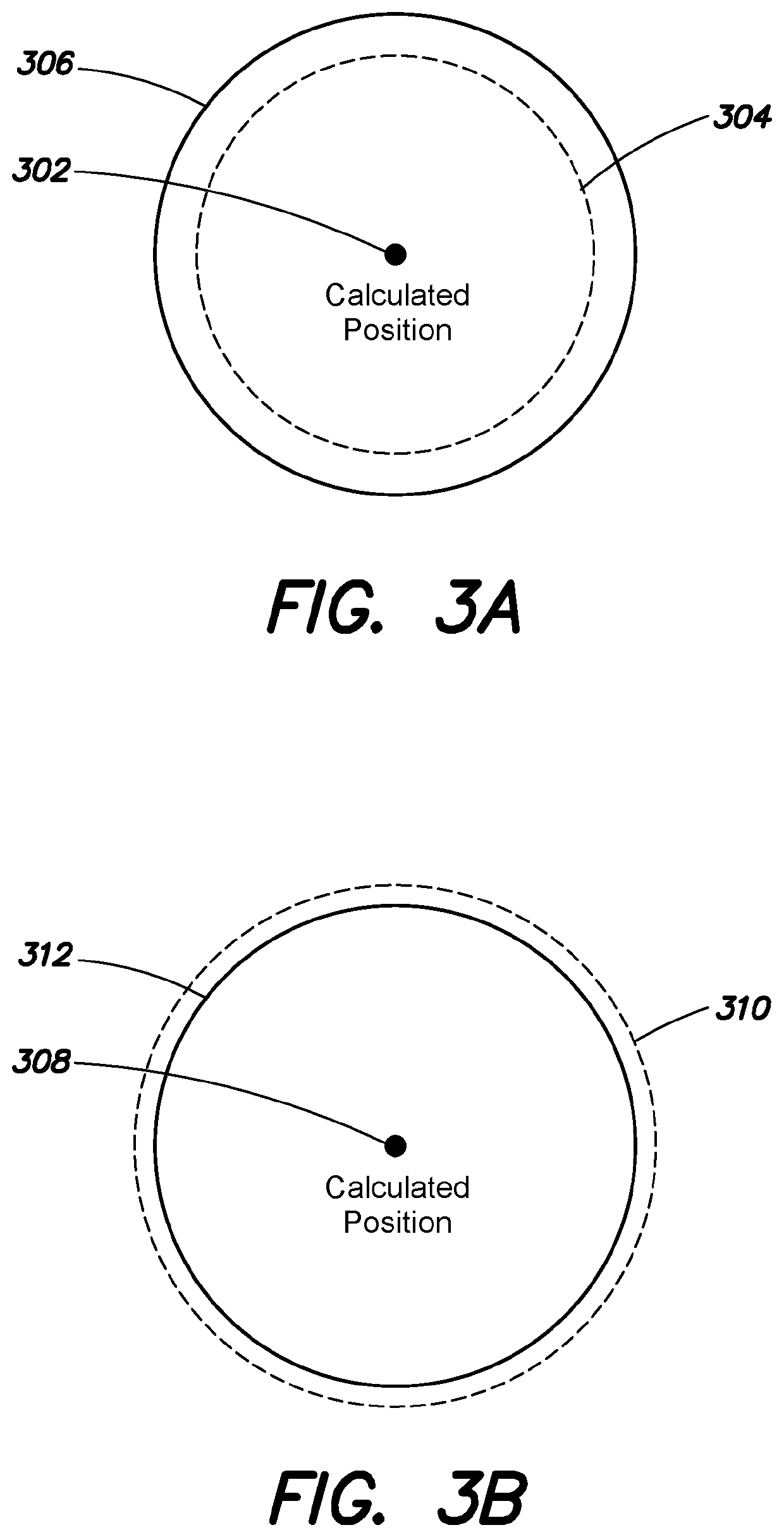
System and method to provide an asil qualifier for GNSS position and related values
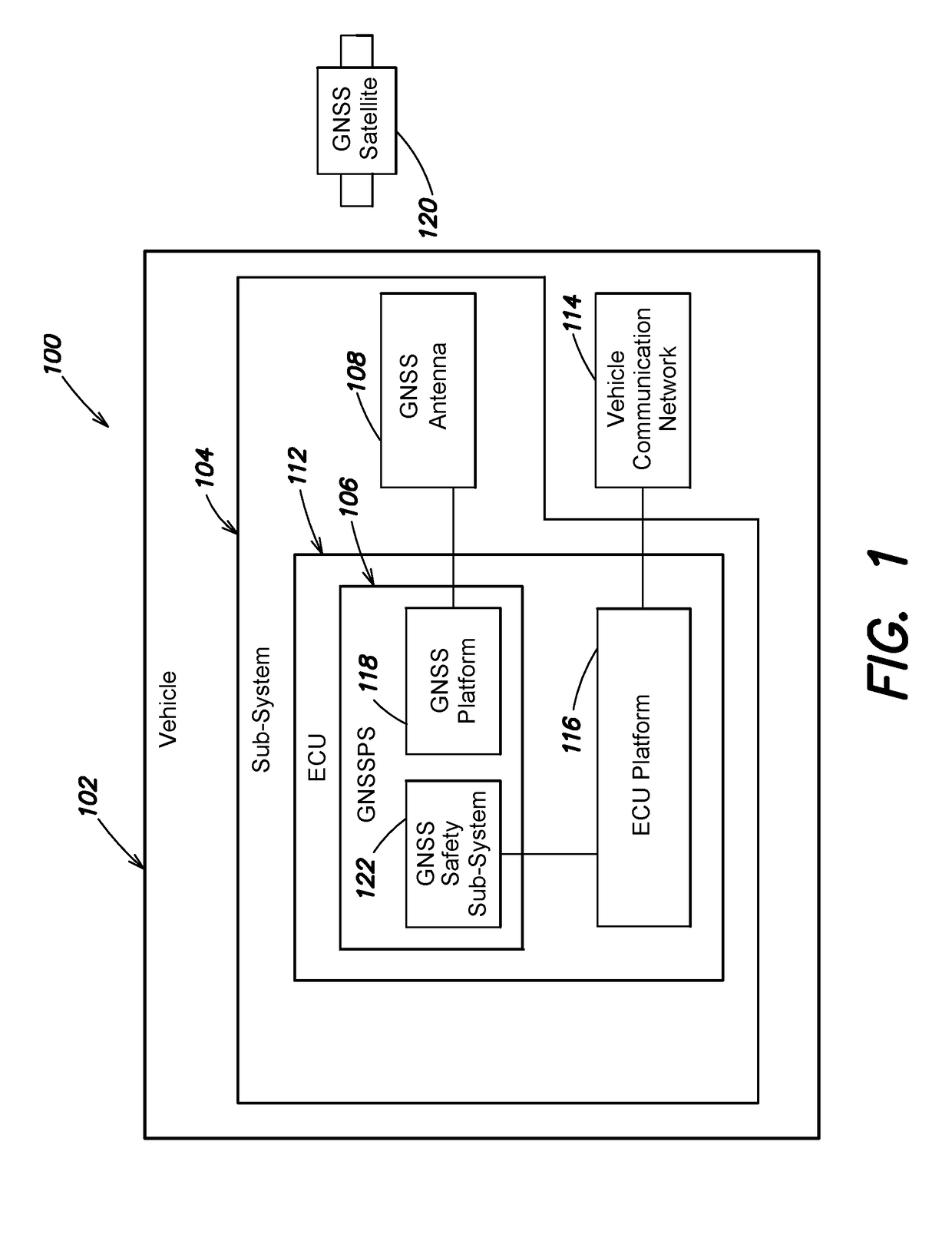
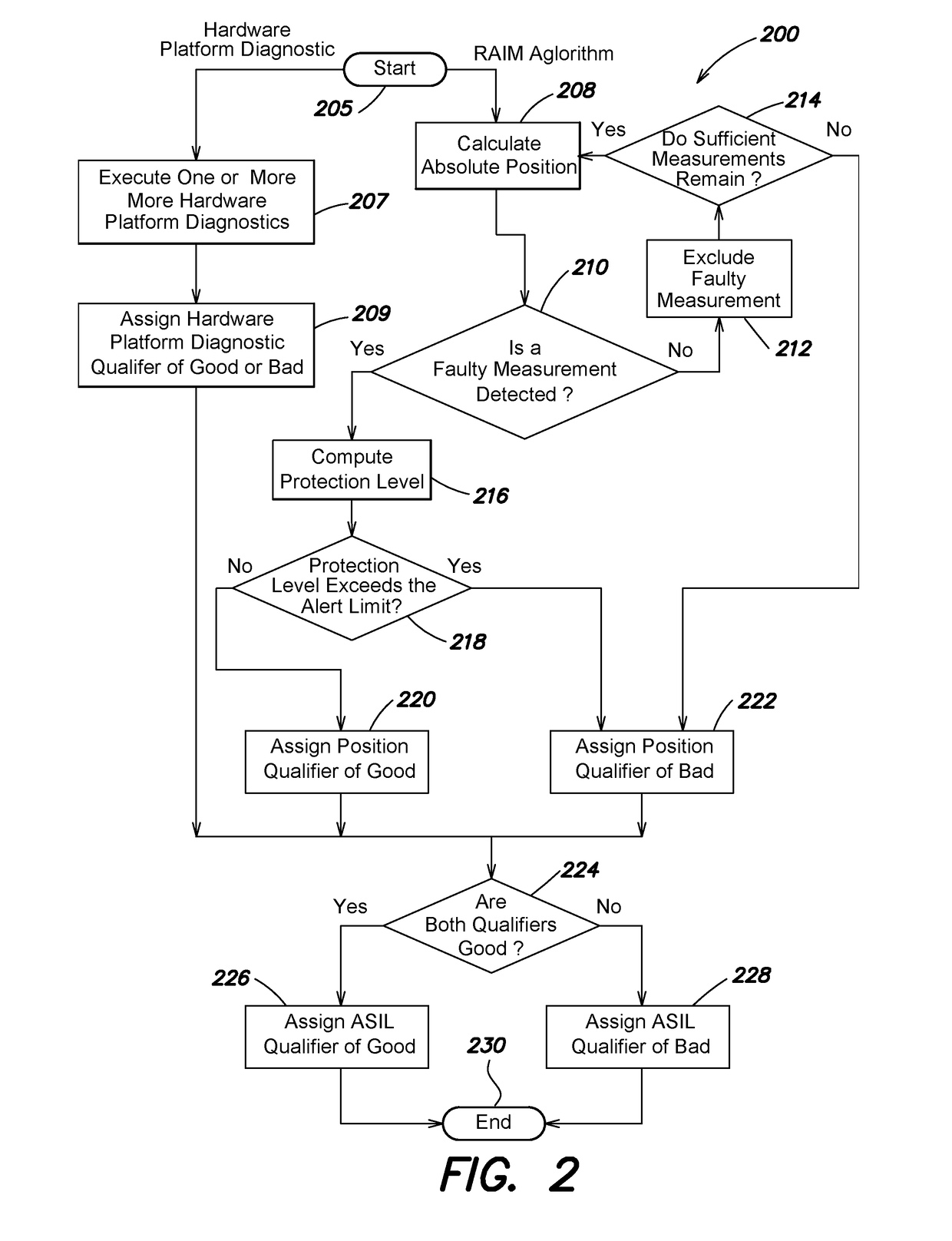
A system and method provides an Automotive Safety Integrity Level (ASIL) qualifier for Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) position and related values. Specifically, hardware platform diagnostics are executed on one or more platforms associated with a GNSS Position Sensor (GNSSPS) that calculates / obtains position and / or related values. Also, a Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring (RAIM) algorithm is executed on the calculated / obtained position and / or related values. If the results both produce a “good” qualifier, the position and / or related values is assigned an ASIL qualifier of “good” and may be utilized by an ASIL rated system. If either of the qualifiers is a “bad” qualifier, the position and / or related values is assigned an ASIL qualifier of “bad” and cannot be utilized by the ASIL rated system. In addition, the inventive system and method may compute a probability associated with an integrity violation of the RAIM algorithm which may consider the probability of hardware failure.
Owner:NOVATEL INC
Dynamic constellation selection method for advanced receiver autonomous integrity monitoring
ActiveCN110196434AImprove usabilityReduce complexitySatellite radio beaconingHigh level techniquesComputation complexitySignaling system
The invention, which belongs to the technical field of satellite navigation, discloses a dynamic constellation selection method for advanced receiver autonomous integrity monitoring. The advanced receiver autonomous integrity monitoring (ARAIM) is a receiver-side fault diagnosis and integrity monitoring technology of a multi-constellation satellite navigation system. The invention puts forward a dynamic constellation selection method so as to solve a problem of ARAIM global availability reduction directly caused by fault subset positioning difference increasing due to the space constellation geometrical configuration differences of different satellite navigation systems. The geometric configurations of different constellations are evaluated and ranked; and two systems with the optimal space constellations are selected to carry out positioning solution and integrity monitoring. With the disclosed method, the influence on the ARAIM availability by the spatial configuration differences ofdifferent systems can be reduced effectively; the ARAIM availability is improved; the computational complexity is reduced; and the computational efficiency of integrity monitoring is improved. The method is suitable for autonomous integrity monitoring application of the satellite navigation receiver and the same concept is suitable for fault diagnosis and integrity monitoring of other signal systems.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
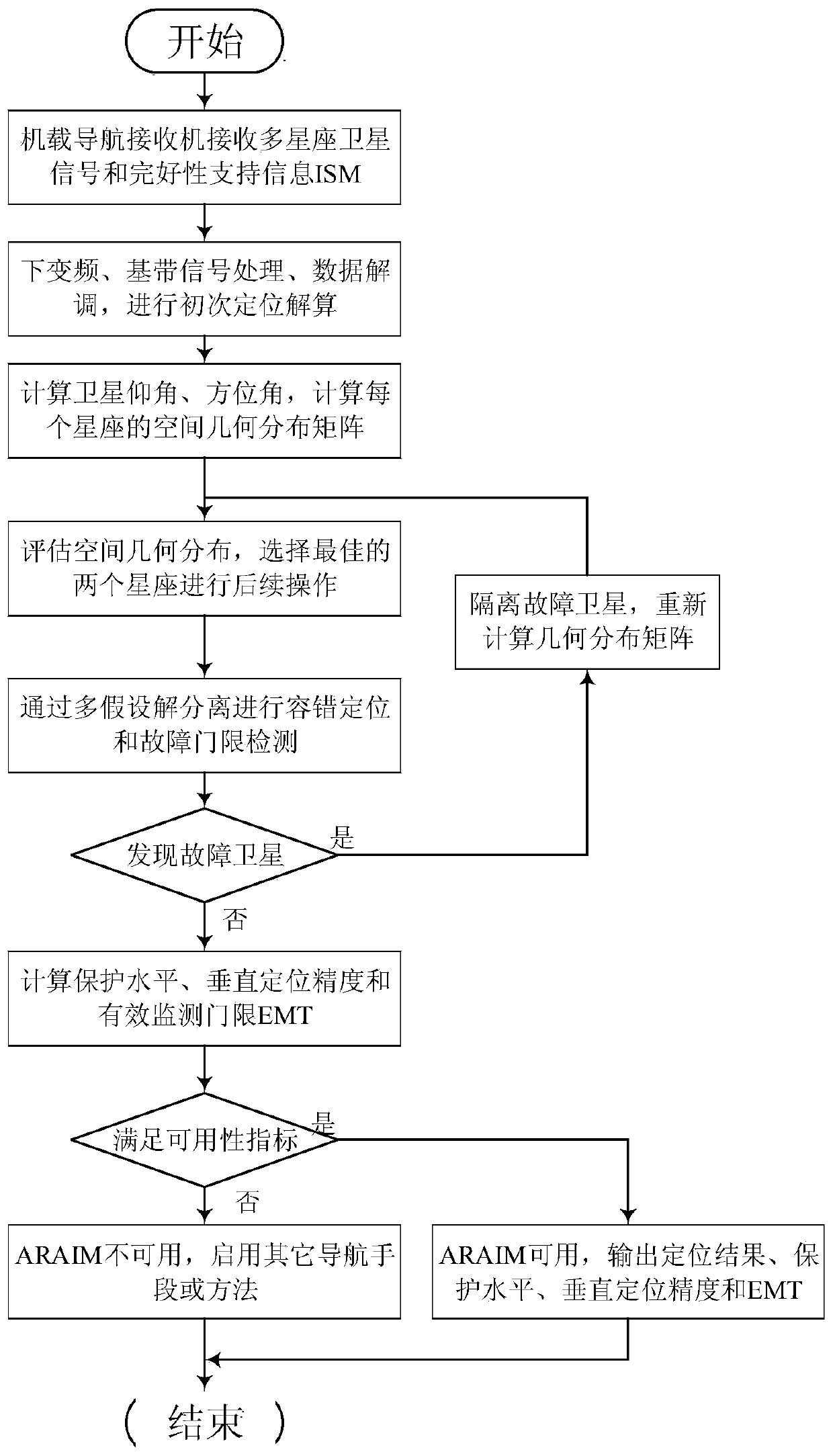
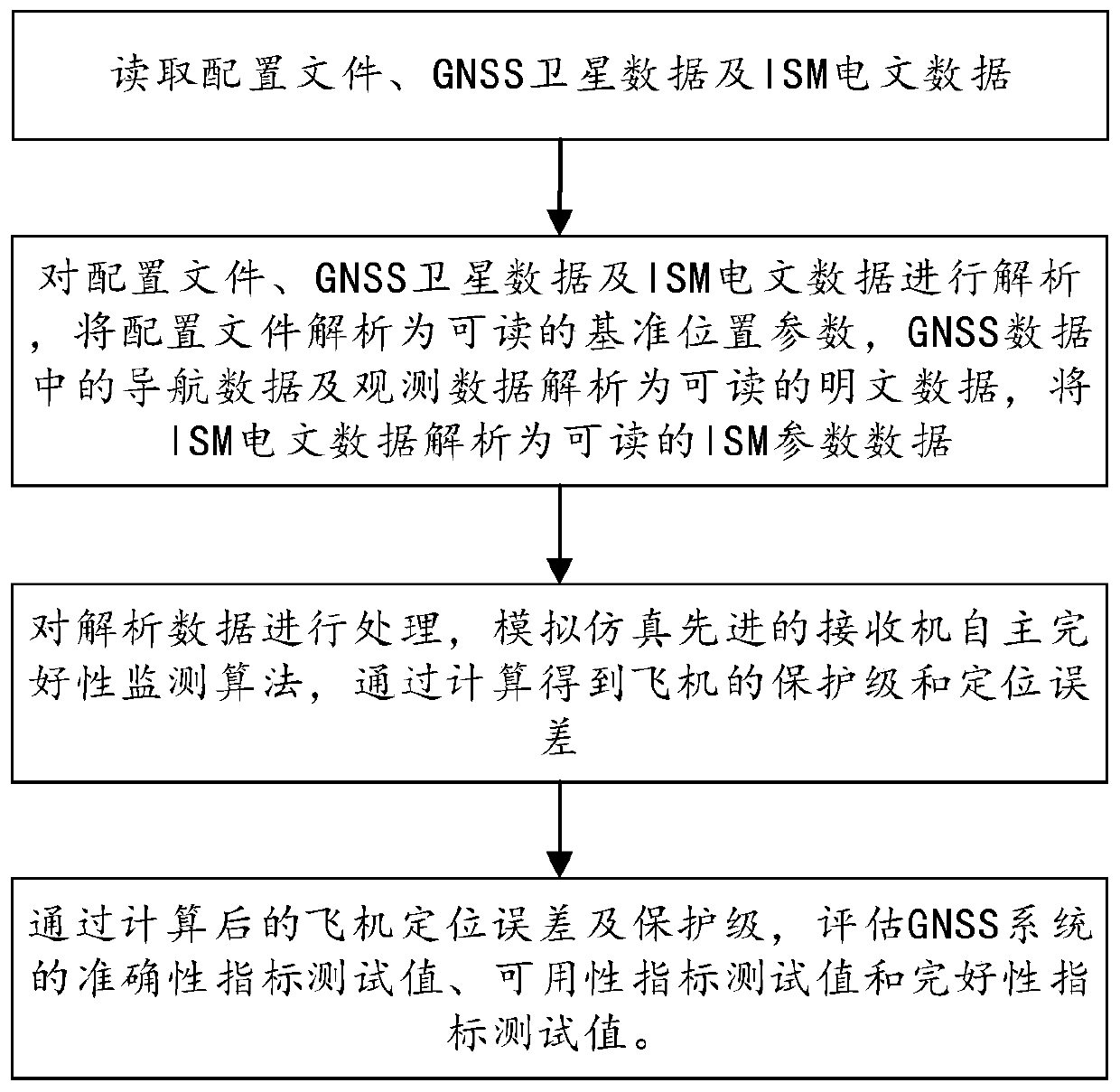
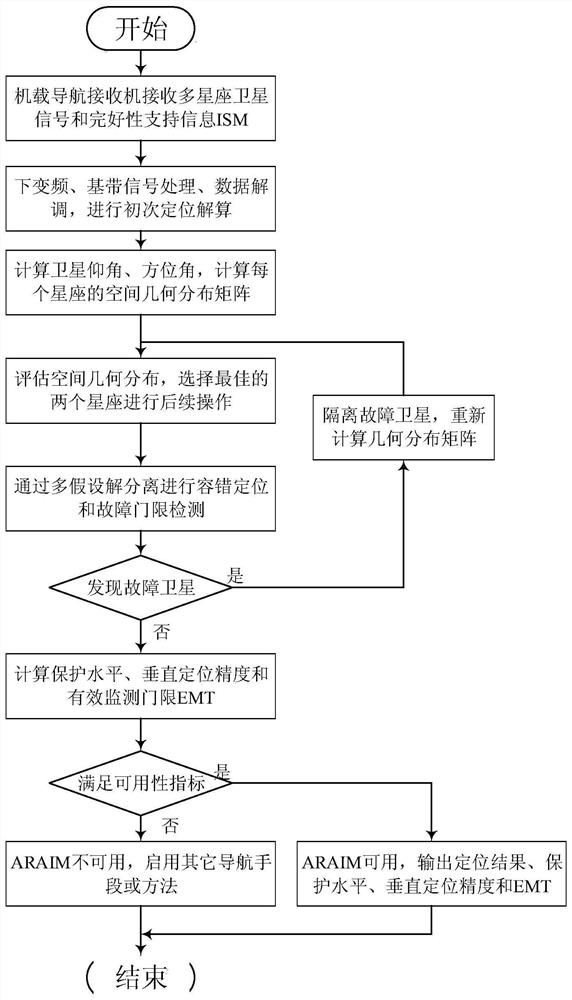
Advanced receiver autonomous integrity monitoring simulation evaluation method and device
ActiveCN110988930ASimulation evaluation process is simpleEasy to implementSatellite radio beaconingSatellite dataSquitter
The invention provides an advanced receiver autonomous integrity monitoring simulation evaluation method and device. The method comprises the following steps of: reading a configuration file, GNSS satellite data and ISM message data; through the analyzed GNSS satellite data and ISM message parameters, simulating an advanced receiver autonomous integrity monitoring (ARAIM) algorithm, and performingcalculation to obtain the protection level and positioning error of an aircraft; and evaluating an accuracy index test value, an availability index test value and an integrity index test value of theGNSS system according to the calculation result. The advanced receiver autonomous integrity monitoring simulation evaluation method is completely and systematically established, the ARAIM does not have an existing standard, an ARAIM standard environment is simulated for monitoring, and the whole simulation evaluation process is simple and easy to execute.
Owner:NO 20 RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP +1
ARAIM (Advanced Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring) fault detection method based on pseudo-range measurement characteristic value extraction
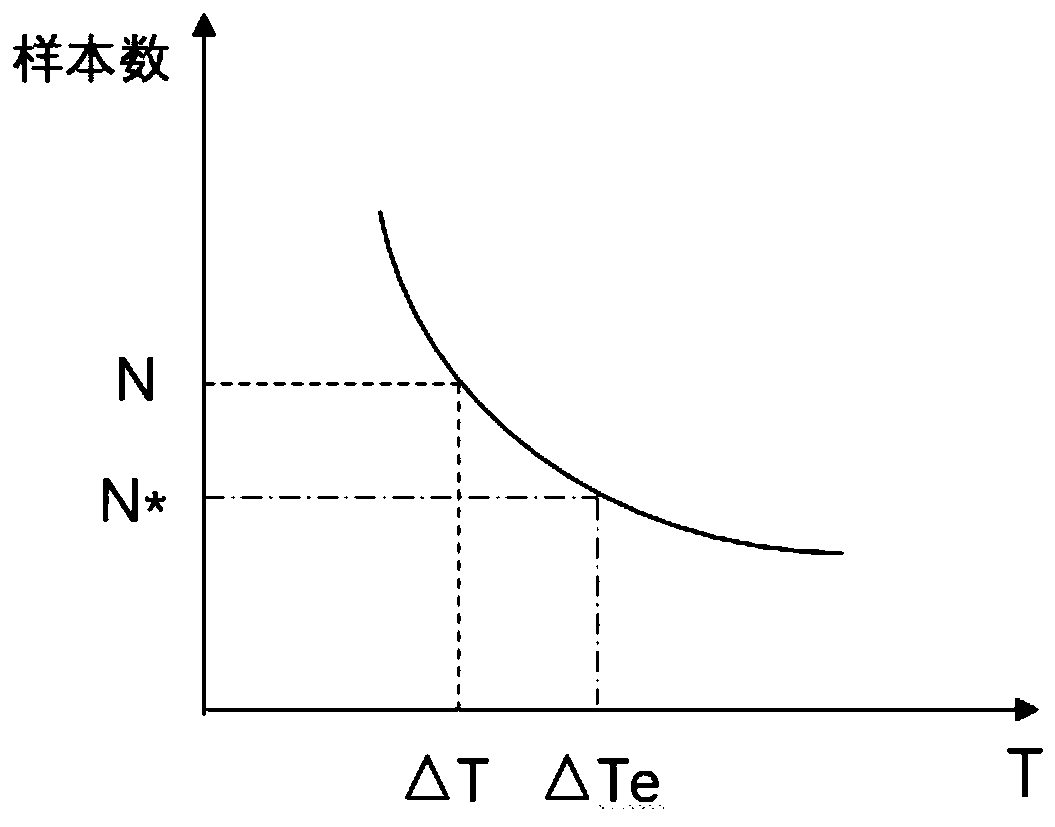
ActiveCN110068840AReduce data processingReduce the burden onSatellite radio beaconingComplex mathematical operationsSample numberReceiver autonomous integrity monitoring
The invention provides an ARAIM (Advanced Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring) fault detection method based on pseudo-range measurement characteristic value extraction. The method comprises the steps of computing integrity risk sum in each fault mode and the maximum value of integrity risk values in each fault mode; computing the number of fault modes through utilization of specific values between the integrity risk sum in each fault mode and an integrity risk of the maximum fault and taking the sample number of corresponding pseudo-range measurement values as the effective sample number;taking the specific value between certain time period T and the effective sample number as effective sample time; sampling pseudo-range measurement value samples collected by a receiver according tothe effective sampling time, thereby obtaining an effective pseudo-range measurement set; computing detection statistics through utilization of the effective pseudo-range measurement set, and carryingout integrity fault detection. According to the method, data processing quantity of an airborne receiver is reduced, load of the airborne receiver is reduced, and algorithm timeliness is improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method and device for optimizing protection level of advanced receiver autonomous integrity monitoring
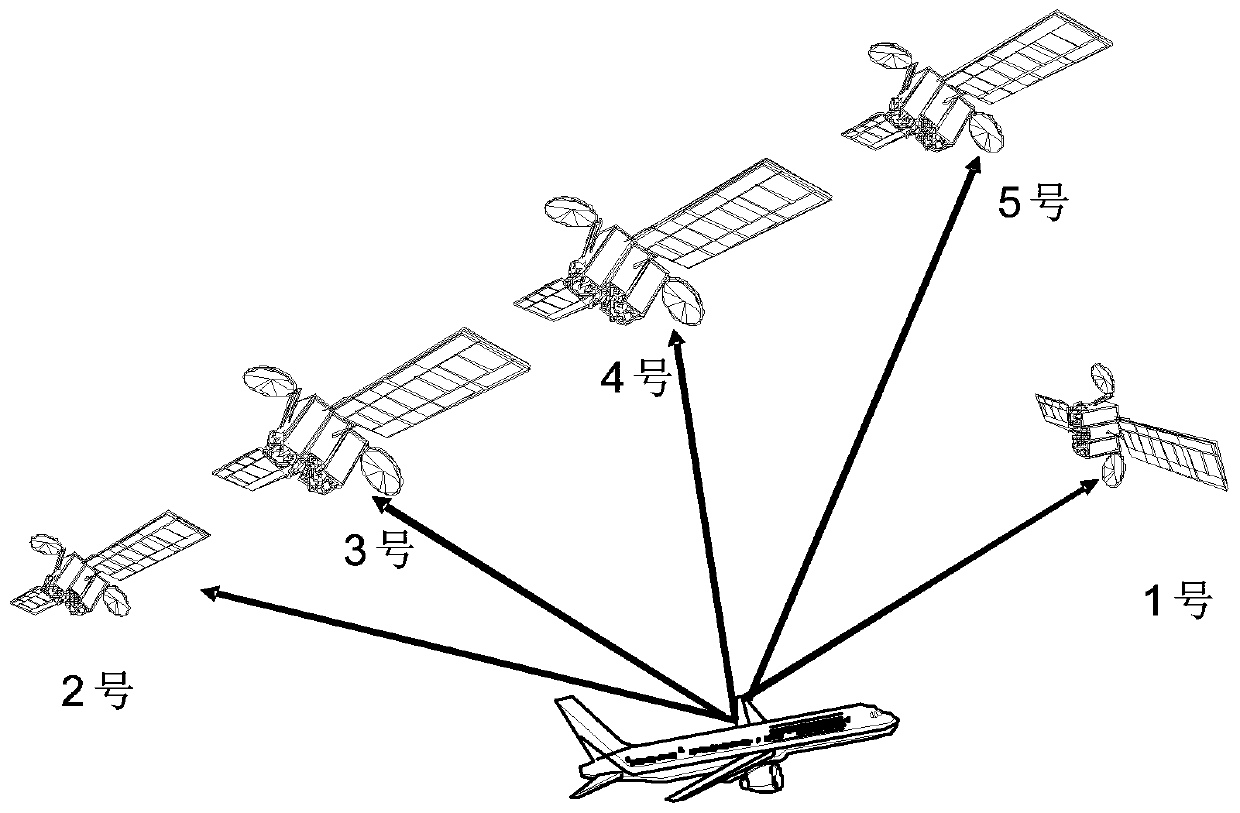
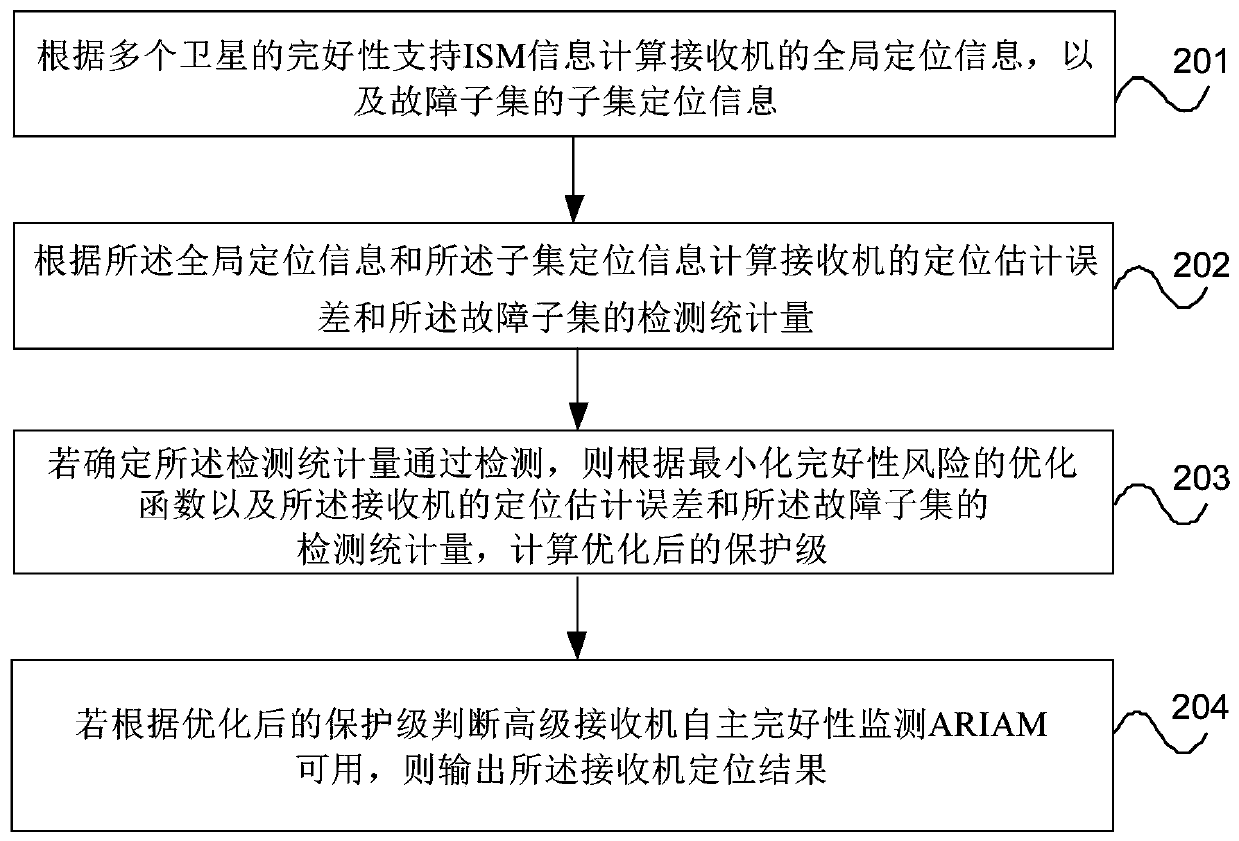
ActiveCN110687557AEnsure flight safetyReduce integrity riskSatellite radio beaconingReliability engineeringReceiver autonomous integrity monitoring
The invention provides a method and device for optimizing the protection level of advanced receiver autonomous integrity monitoring. The method comprises the steps of calculating global positioning information of a receiver and subset positioning information of a fault subset according to ISM information of a plurality of satellites; calculating the distribution of positioning estimation errors ofthe receiver and the distribution of detection statistics of the fault subset according to the global positioning information and the subset positioning information; if it is determined that the detection statistics pass the detection, calculating the optimized protection level according to an optimization function for minimizing the integrity risk, the distribution of the positioning estimationerrors and the distribution of the detection statistics; and if the ARIAM is judged to be available according to the optimized protection level, outputting a positioning result of the receiver. According to the method provided by the embodiment of the invention, whether different fault subsets pass detection or not is determined under unbalanced satellite geometric distribution, the integrity target under each satellite fault hypothesis is established, and the integrity risk caused by fault missing detection is reduced by taking the minimum integrity risk as the target.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Inertial information-assistant RAIM (Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring) detection method
InactiveCN106483533AImprove stabilityImprove reliabilitySatellite radio beaconingInformation processingLeast squares
The invention belongs to the field of satellite navigation receiver information processing, and particularly relates to an inertial information-assistant RAIM (Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring) detection method, so as to solve the problems of satellite receiver positioning stability and reliability. The method mainly comprises steps: satellite capturing, tracking and synchronizing are carried out; parameters of the satellite after frame synchronization are taken; the satellite position velocity is calculated; least square solution is carried out; a least square pseudo range residual vector and the root mean square are calculated; the pseudo range residual between the receiver and the satellite is calculated; the obtained pseudo range residuals of satellites are ranked from large to small, and each four points serves as a combination from front to behind to calculate the root mean square of one pseudo range residual; a combination with the minimum root mean square of the pseudo range residual is found out; and the pseudo range residual of each satellite and a mean value are compared, and the satellite whose pseudo range residual is larger than a fault recognition threshold value is judged to be a failed satellite. Due to the method of the invention, channel tracking or satellite failure can be effectively detected in a condition with five satellites in a single system, and a failed satellite can be recognized.
Owner:BEIJING AUTOMATION CONTROL EQUIP INST
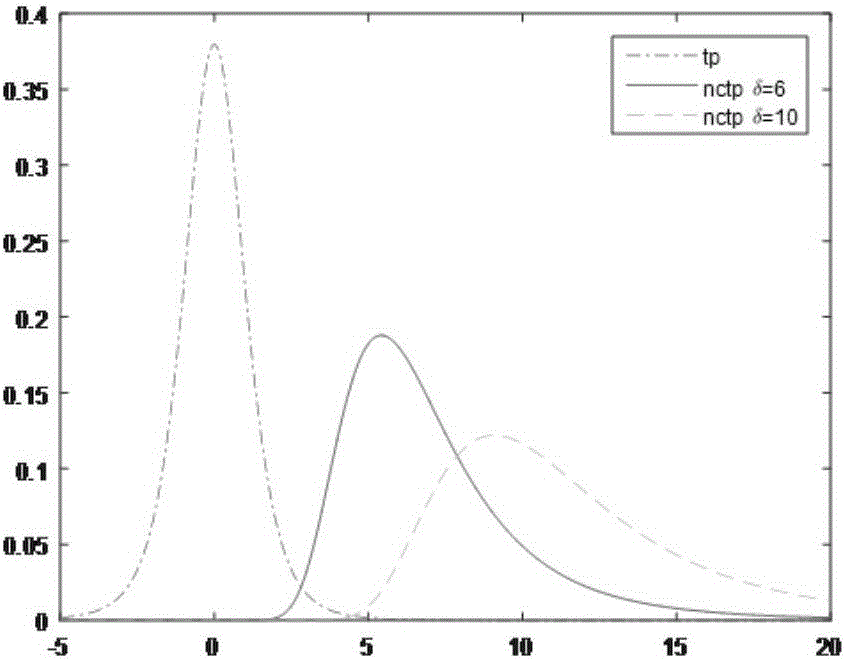
Receiver autonomous integrity monitoring and troubleshooting method based on student's t-distribution
The embodiment of the invention provides a receiver autonomous integrity monitoring and troubleshooting method based on student's t-distribution. The method comprises the steps of respectively calculating by adopting a student's t-distribution algorithm according to a plurality of satellite sets in an RAIM (Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring) operation period to acquire a plurality of parity vectors, calculating a parity vector sample mean x-bar and a sample variance S of (m+1) sampling in a plurality of parity vector sets Samp1, calculating a test statistic T, comparing the test statistic T with a preset threshold TD, and determining whether there is a satellite with pseudo-range deviation in the satellite sets or not according to a comparison result; and if the satellite sets are determined to have no satellite with pseudo-range deviation, outputting a satellite set Setj without a deviation trouble, calculating a horizontal protection level HPL of the satellite set Setj without a deviation trouble, and determining whether a positioning result of the satellite set Setj without a deviation trouble meets performance requirements or not. The method provided by the invention makes full use of information between redundant receivers, and various system troubles including receiver noises can be monitored.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAYS CORPORATION +1
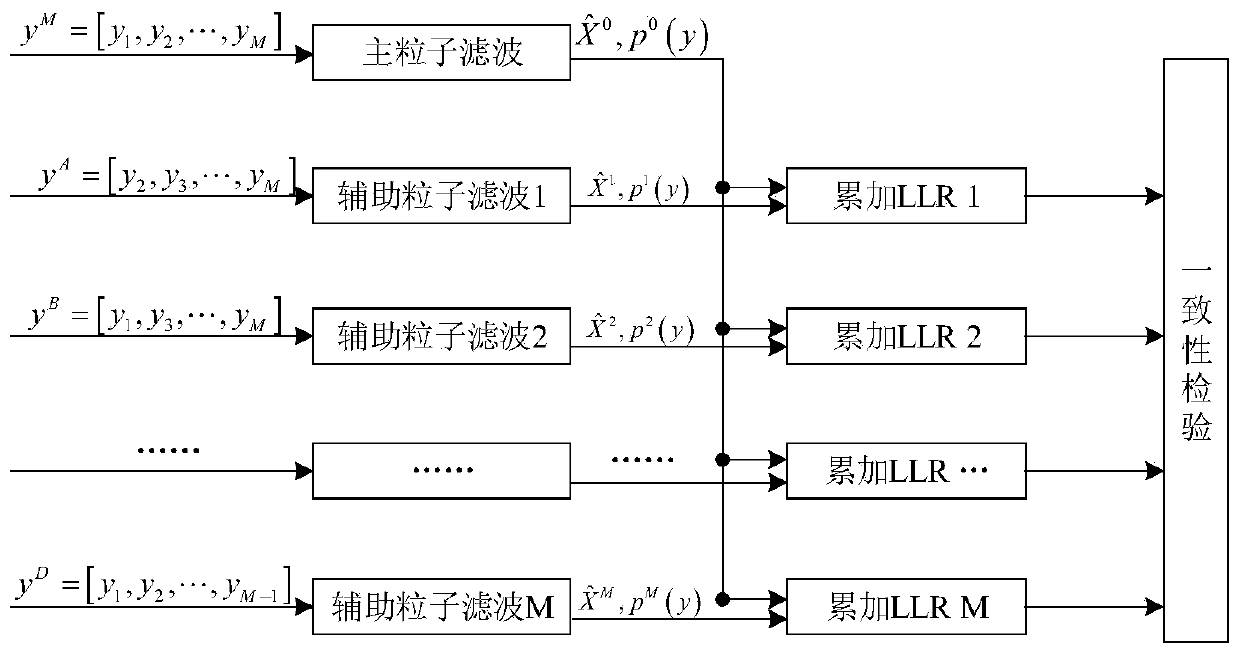
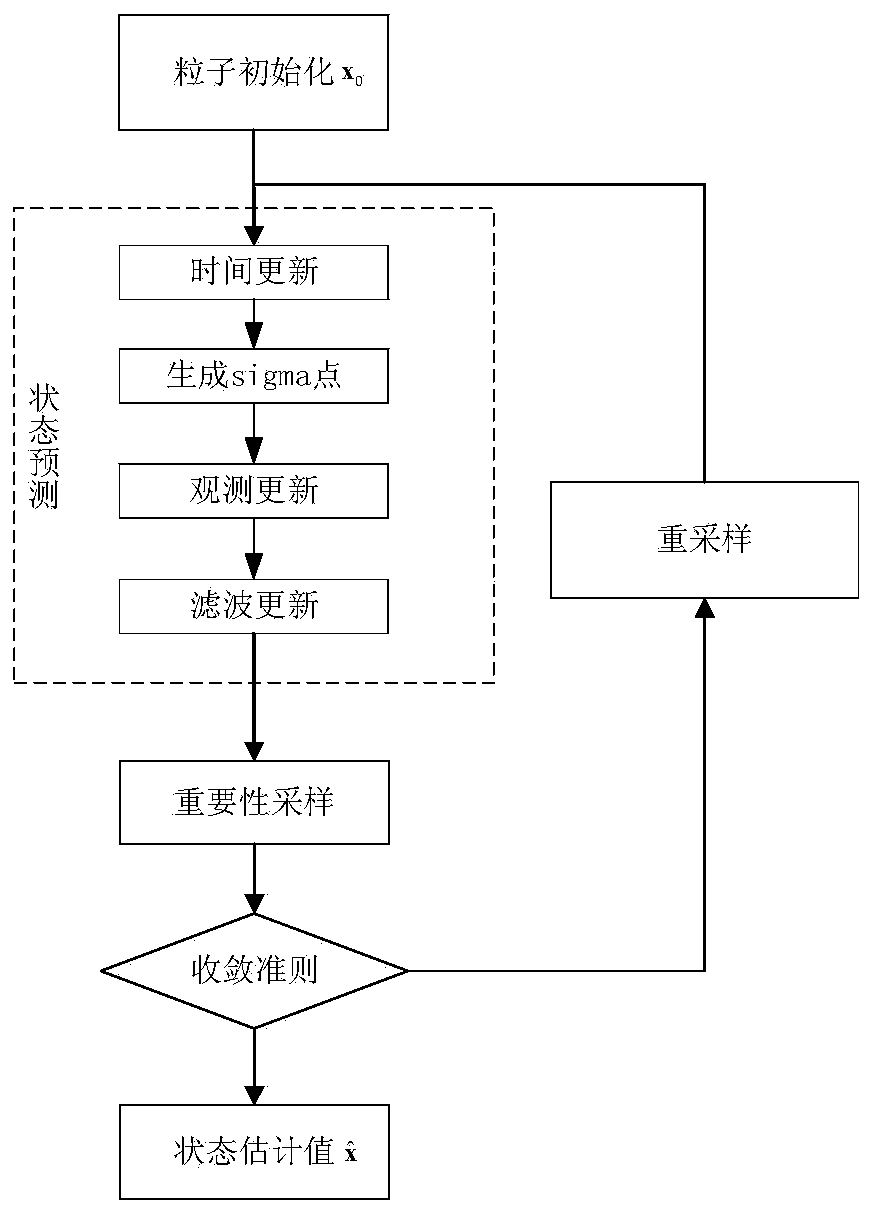
RAIM method based on improved unscented Kalman particle filtering
InactiveCN110967706AGuaranteed adaptabilityPrevent degradationSatellite radio beaconingState predictionEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of global satellite navigation detection, and particularly relates to an RAIM method based on improved unscented Kalman particle filtering. Compared with the prior art, according to the invention, receiver autonomous integrity monitoring can be effectively carried out in a non-Gaussian observation noise environment; improved unscented Kalman filtering is introduced into a particle filtering method; more reasonable state prediction and suggested density calculation in particle filtering are realized by improving unscented Kalman filtering; the particle filter receiver autonomous integrity monitoring method can effectively avoid a particle degradation phenomenon, guarantees the adaptability of the particle filter receiver autonomous integrity monitoring method to a non-Gaussian observation noise environment, also reduces the calculation amount caused by the introduction of unscented Kalman particle filtering, and guarantees the algorithm operation efficiency. Therefore, according to the scheme, the problem of particle filtering degradation is solved, meanwhile, the adaptability of the method to non-Gaussian observation noise is guaranteed,and the calculated amount caused by improvement of unscented Kalman filtering is also reduced.
Owner:北京京航计算通讯研究所
A Dynamic Constellation Selection Method for Advanced Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring
ActiveCN110196434BImprove usabilityReduce complexitySatellite radio beaconingHigh level techniquesComputation complexityNavigation system
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
System and method to provide an ASIL qualifier for GNSS position and related values
A system and method provides an Automotive Safety Integrity Level (ASIL) qualifier for Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) position and related values. Specifically, hardware platform diagnostics are executed on one or more platforms associated with a GNSS Position Sensor (GNSSPS) that calculates / obtains position and / or related values. Also, a Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring (RAIM) algorithm is executed on the calculated / obtained position and / or related values. If the results both produce a “good” qualifier, the position and / or related values is assigned an ASIL qualifier of “good” and may be utilized by an ASIL rated system. If either of the qualifiers is a “bad” qualifier, the position and / or related values is assigned an ASIL qualifier of “bad” and cannot be utilized by the ASIL rated system. In addition, the inventive system and method may compute a probability associated with an integrity violation of the RAIM algorithm which may consider the probability of hardware failure.
Owner:NOVATEL INC
Integrity monitoring method and device for araim ground monitoring station
ActiveCN105116423BImprove usabilityMeet precision requirementsSatellite radio beaconingUsabilityMonitoring methods
The invention provides an ARAIM ground monitoring station integrity monitoring method and an ARAIM ground monitoring station integrity monitoring device. The ARAIM ground monitoring station integrity monitoring method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: acquiring first user range accuracy URA and second user range accuracy URA, wherein the first user range accuracy URA is the user range accuracy URA in a current preset period of time, and the second user range accuracy URA is the user range accuracy URA in a future preset period of time; determining an adopted advanced receiver autonomous integrity monitoring ARAIM structure according to the first user range accuracy URA, the second user range accuracy URA and a preset user range accuracy URA threshold, wherein the ARAIM structure is an online or offline structure; and performing ARAIM ground monitoring station integrity monitoring according to the ARAIM structure. The ARAIM ground monitoring station integrity monitoring method and the ARAIM ground monitoring station integrity monitoring device provided by the invention can meet the requirement of most areas for accuracy and integrity. The application rang is expanded, and the usability of LPV-200 is improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
A method for autonomous integrity monitoring of gnss receivers
ActiveCN109490916BAdapt to the requirements of comprehensive fault detectionAvoid first-order approximationsSatellite radio beaconingCovariance matrixReliability engineering
The invention discloses a method for monitoring autonomous integrity of a GNSS receiver, relates to a receiver autonomous integrity monitoring technology, and belongs to the technical field of measurement and test. The method adopts a CKF-based and innovation extrapolation method to achieve monitoring of the autonomous integrity of the GNSS receiver, and innovation generated in an innovation extrapolation process and a variance-covariance matrix thereof construct test statistic of each extrapolation moment, micro slowly-changing pseudo-range deviation can be tested; a machine learning algorithm is adopted to judge and classify the test statistic of the each extrapolation moment, and dynamically updates a fault database used for generating a machine learning rule at the same time; on-line learning of judgment rules of unmodeled fault types has the advantages of being less in calculation amount, proper in precision, suitable for nonlinear systems and capable of monitoring the micro slowly-changing pseudo-range deviation with high confidence degree.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS +1
Parity vector method-based double-satellite failure recognition method
InactiveCN102901971BSolve the problem of fault offset offsetRealize detection and identificationSatellite radio beaconingRemote sensingReceiver autonomous integrity monitoring
The invention relates to global satellite navigation system receiver autonomous integrity monitoring technology and discloses a parity vector method-based double-satellite failure recognition method, aiming at the problems of false positives and false negatives caused by fault deviation offsetting when the parity vector method is used for recognizing two fault satellites. According to the technical scheme, the parity vector method is used for recognizing one fault satellite; with the fault satellite as the basis, four fault-free satellites are found out, and the information of the fault-free satellites is used for roughly locating, so that the fault satellites can be recognized; the recognized fault satellites are removed, and then the position resolution is carried out again, so that the locating accuracy is improved; therefore, the problems of false positives or false negatives caused by fault deviation offsetting can be avoided. The method solves the problem of the fault deviation offsetting caused by parity vector residual error and realizes the detection and the recognition for a plurality of fault satellites. After the method is used for detecting and recognizing satellite failure, the locating accuracy is improved. The method is mainly used for monitoring the autonomous integrity of a global satellite navigation system receiver.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com