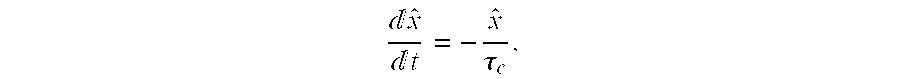Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
292 results about "Radio navigation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Radio navigation or radionavigation is the application of radio frequencies to determine a position of an object on the Earth. Like radiolocation, it is a type of radiodetermination.
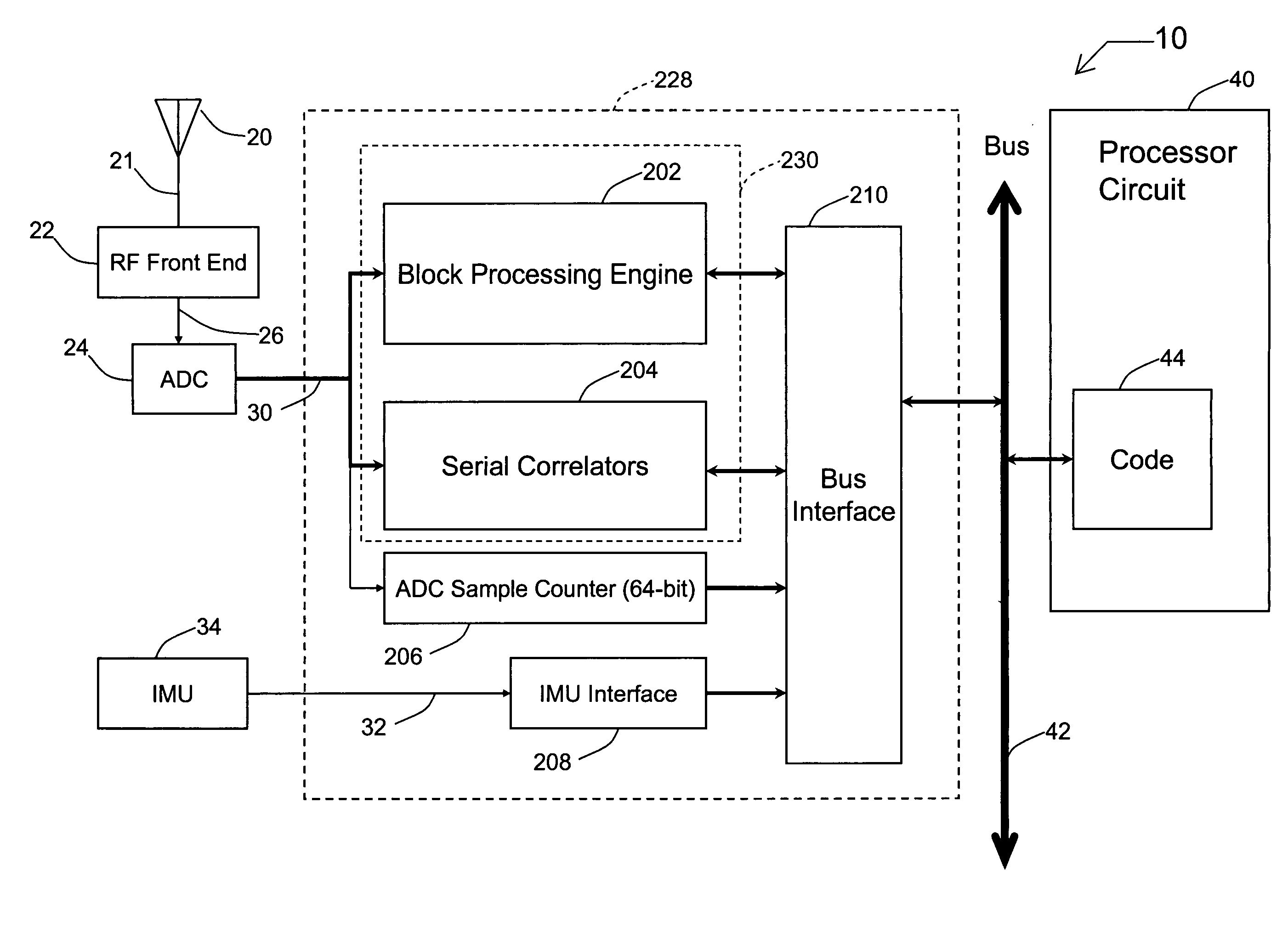
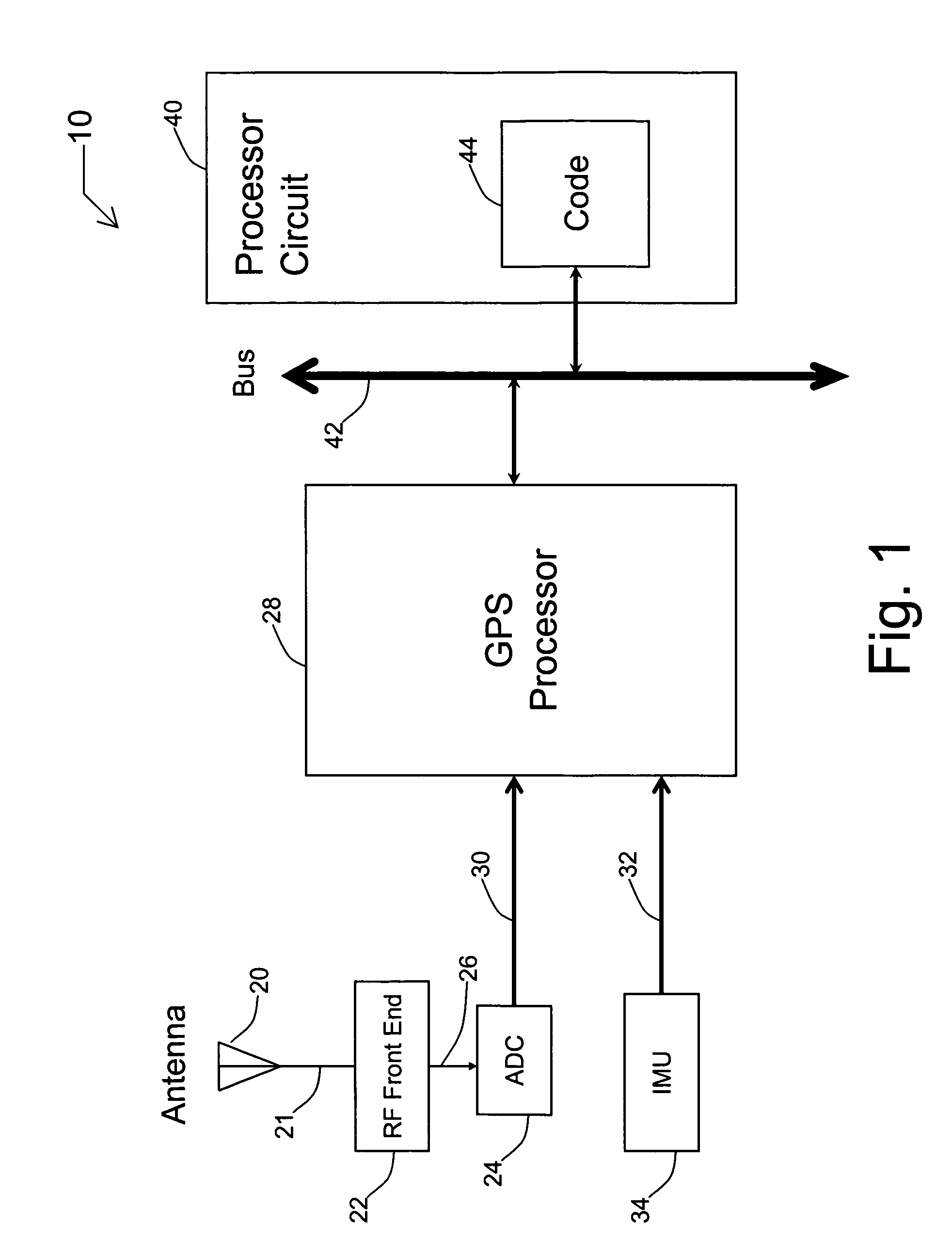
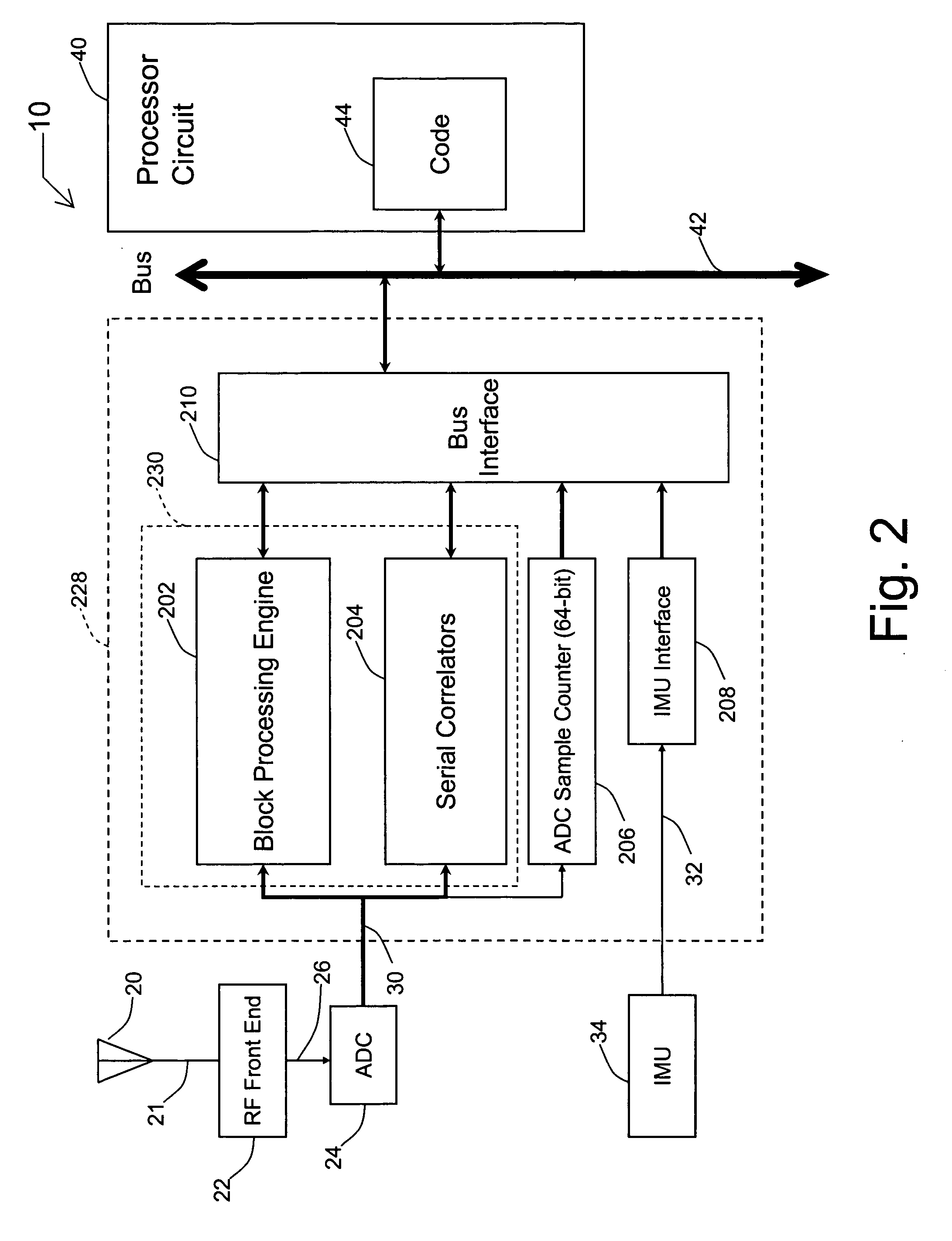
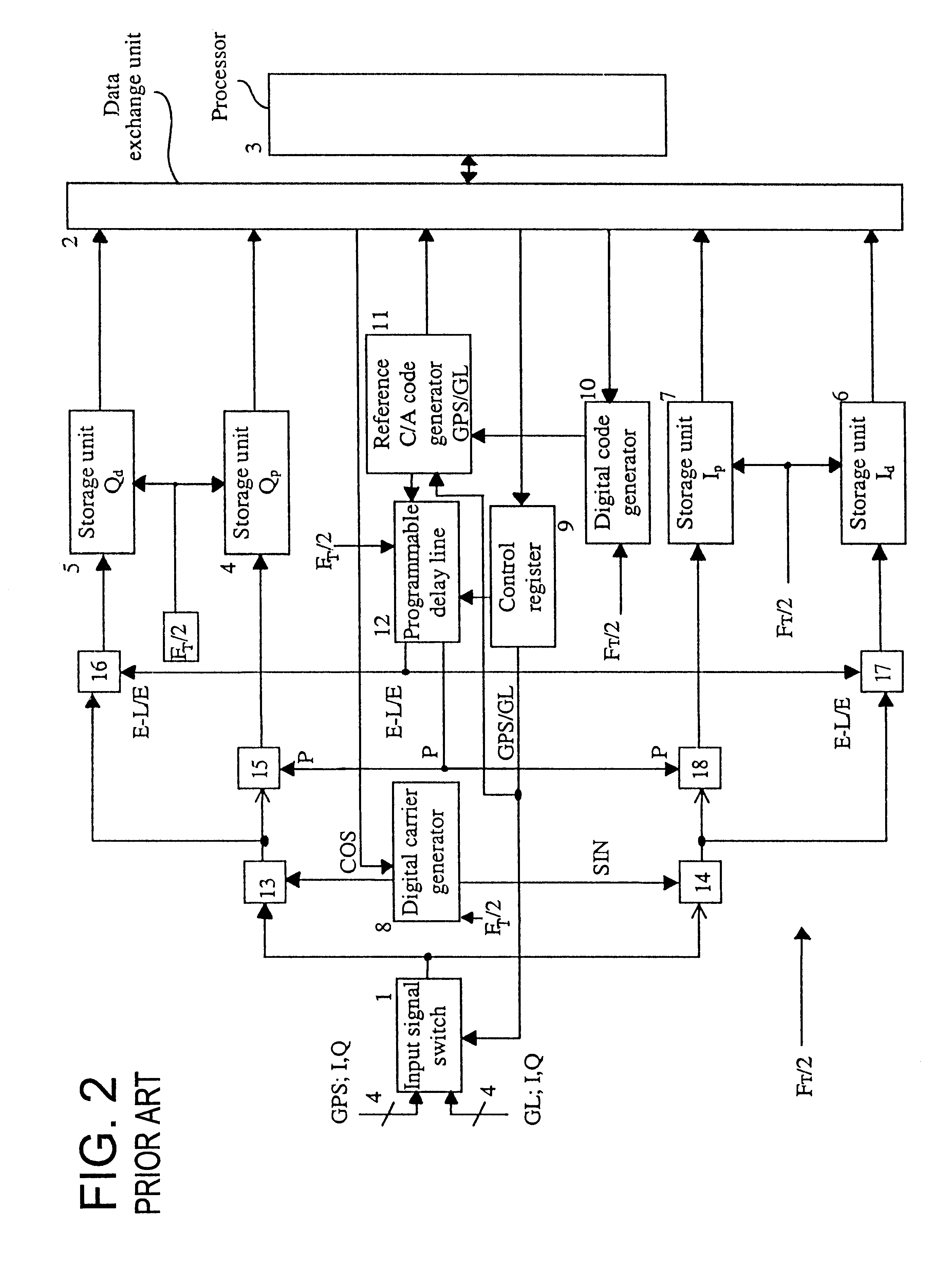
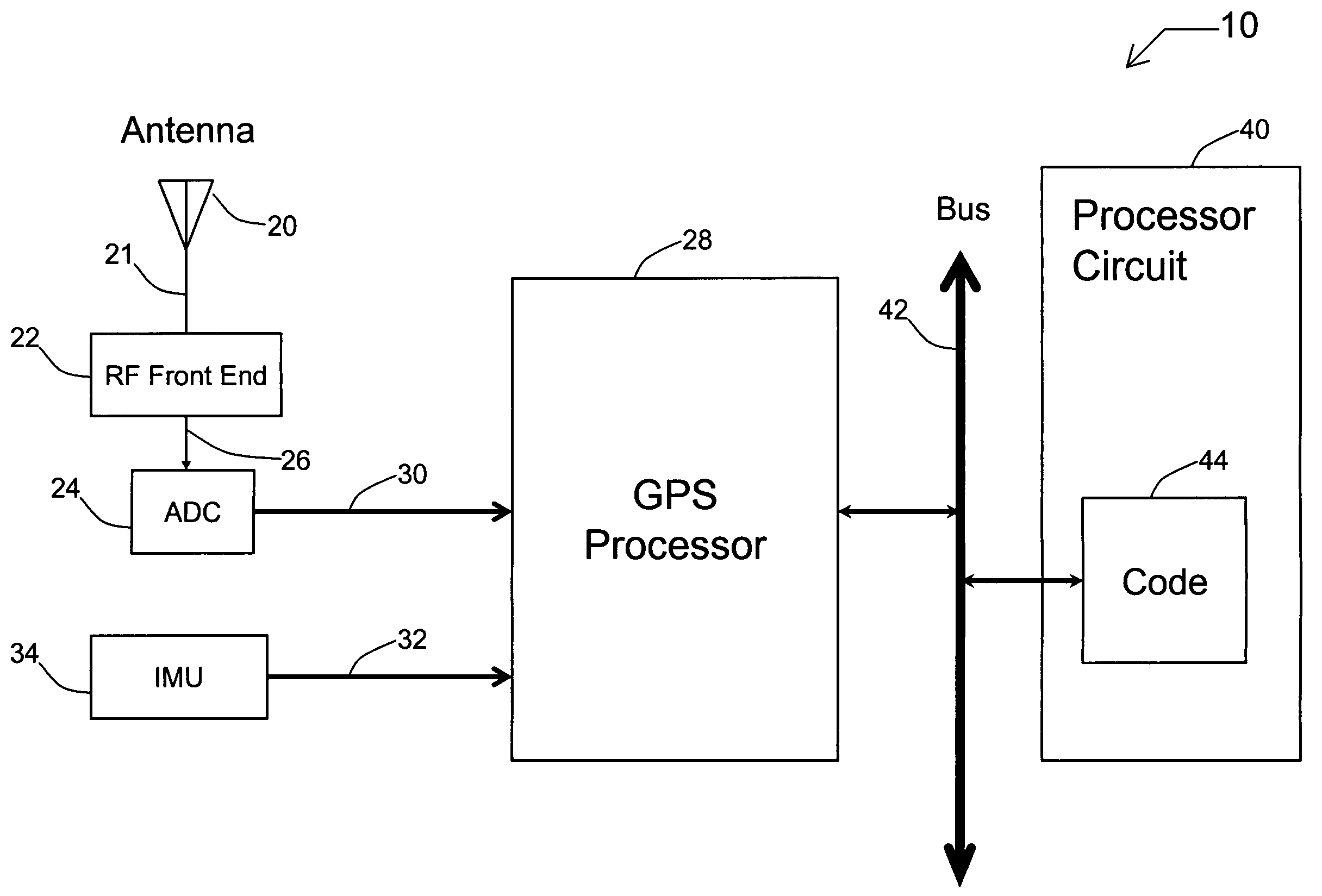
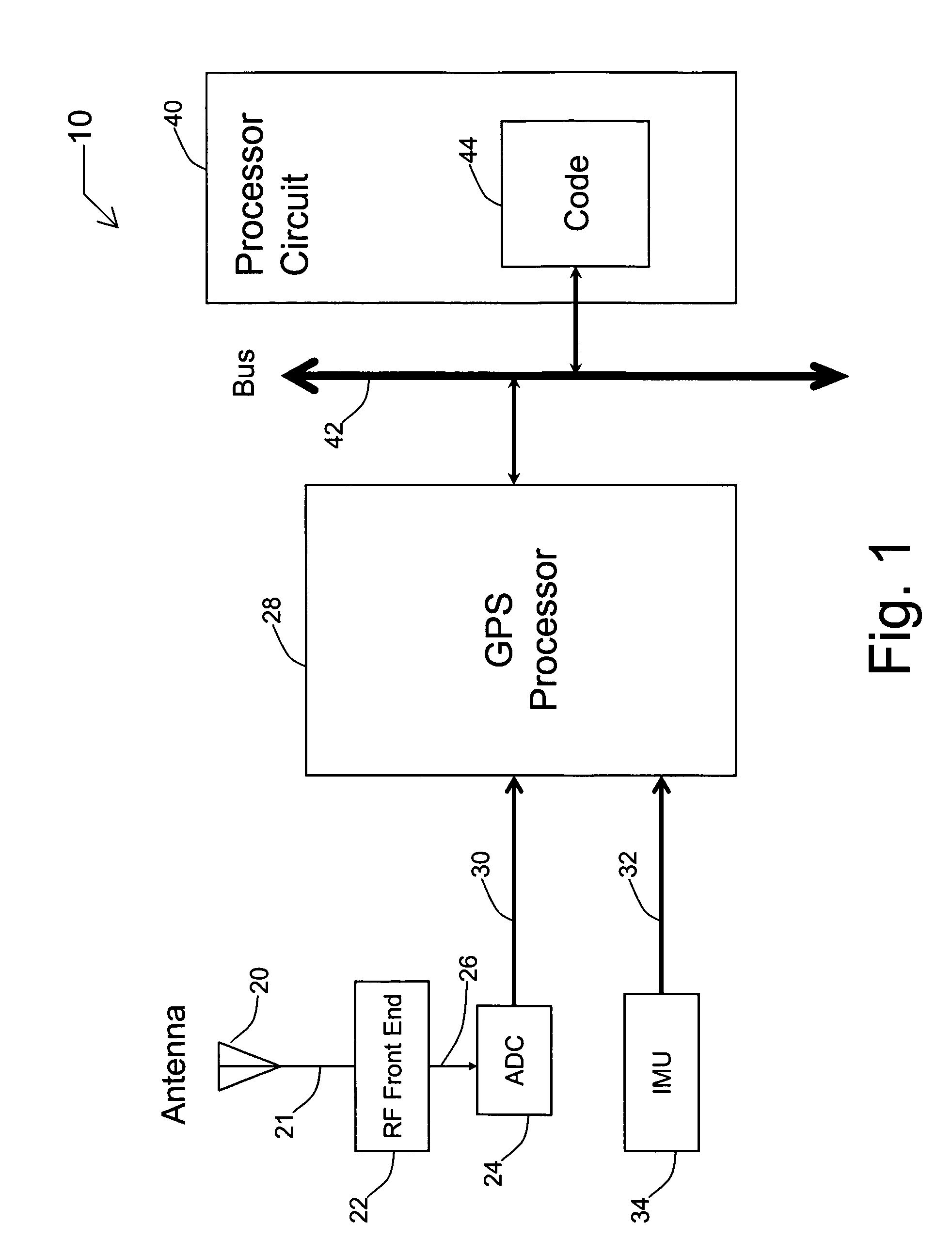
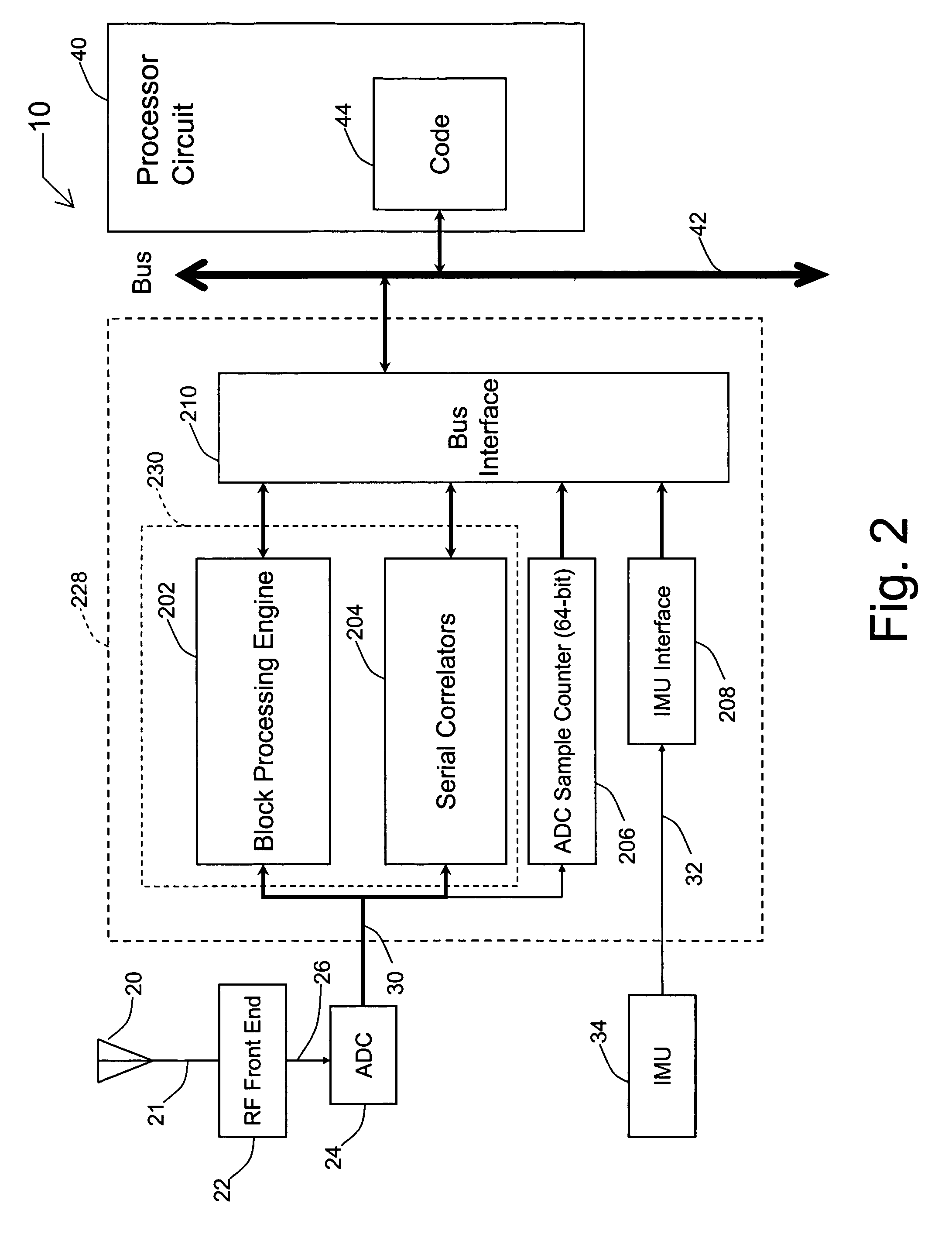
Systems and methods for acquisition and tracking of low CNR GPS signals
A receiver for continuous carrier phase tracking of low carrier-to-noise ratio (“CNR”) signals from a plurality of radio navigation satellites while the receiver is mobile. The receiver may have: a radio frequency (RF) front-end that provides satellite data corresponding to signals received from the plurality of radio navigation satellites; an inertial measurement unit (IMU) that provides inertial data; and a processor circuit in circuit communication with the RF front end and the IMU, the processor circuit being capable of using satellite data from the RF front-end and inertial data from the IMU to perform continuous carrier phase tracking of low CNR radio navigation satellite signals having a CNR of about 20 dB-Hz, while the receiver is mobile. The receiver may be a GPS receiver for continuous carrier phase tracking of low-CNR GPS signals.
Owner:OHIO UNIV
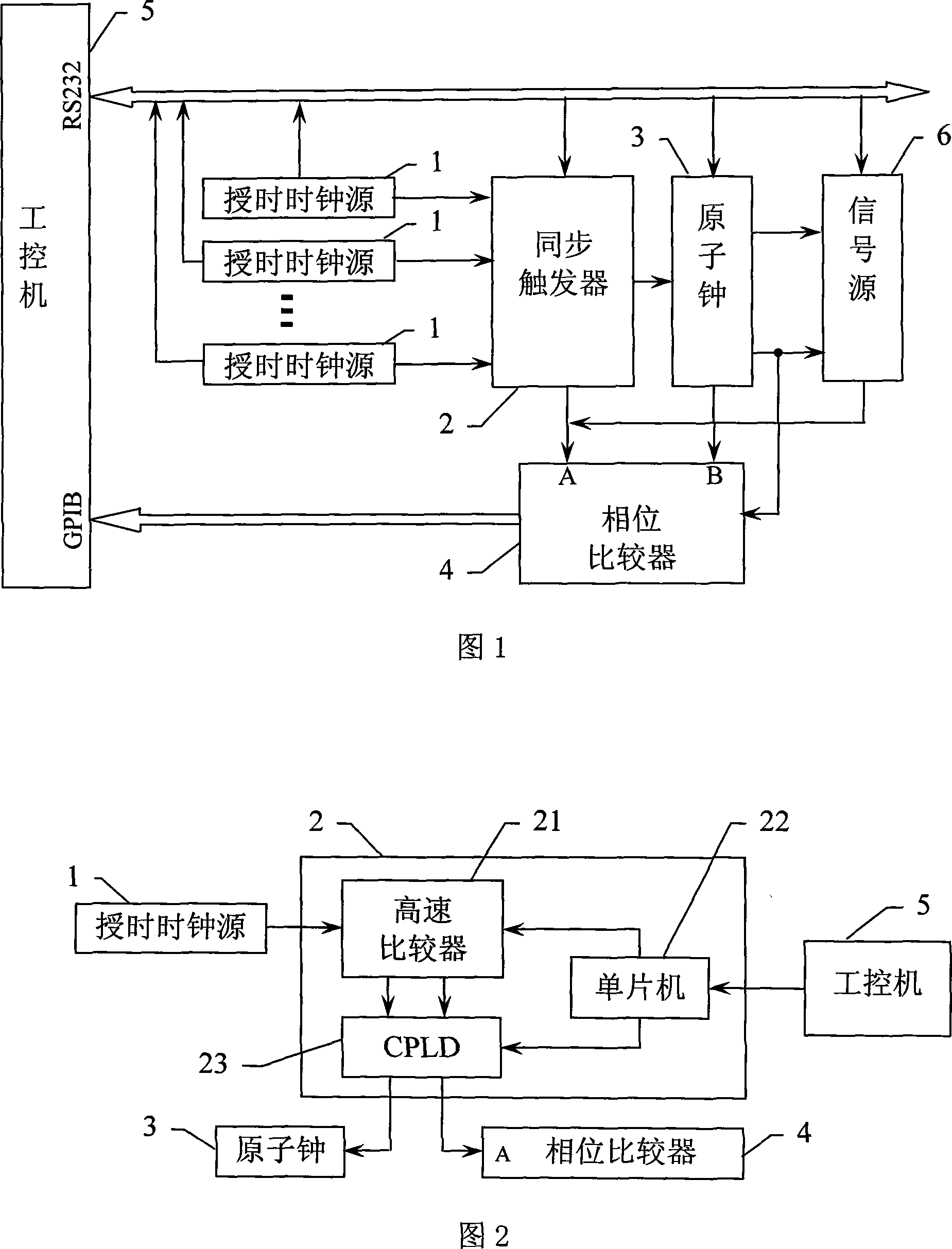
High-precision time synchronizing apparatus
InactiveCN101231337AReal time monitoringReal-time adjustmentPulse automatic controlSynchronous motors for clocksMonitoring statusPhase difference
The invention relates to a time synchronization device in a radio navigation system, in particular to a high-precision time synchronization device, which solves the problems in the prior time synchronization device including long-time synchronization adjustment and inability of real-time monitoring and adjustment of clock signal. In the device of the invention, an industrial computer obtains phase difference signal output from a phase comparator via a GPIB bus, and respectively transmits a control signal to a synchronizer trigger, an atomic clock and a signal source via a RS232 serial communication bus; and the industrial computer further controls the operating state and the switching thereof. The operating state includes time synchronization state: the phase comparator obtains the phase difference of signals output from the synchronizer trigger and the atomic clock, and the industrial computer adjusts the signal output from the atomic clock to synchronize with the signal output from the synchronizer trigger; and monitoring state: the phase comparator obtains the phase difference of signals output from the atomic clock and the signal source, and the industrial computer adjusts the signal output from the signal source to synchronize with the signal output from the atomic clock.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Precise tracking and measuring method of high dynamic signal of air fleet link
InactiveCN101776752ASolve the defect of poor precisionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDigital signal processingAviation
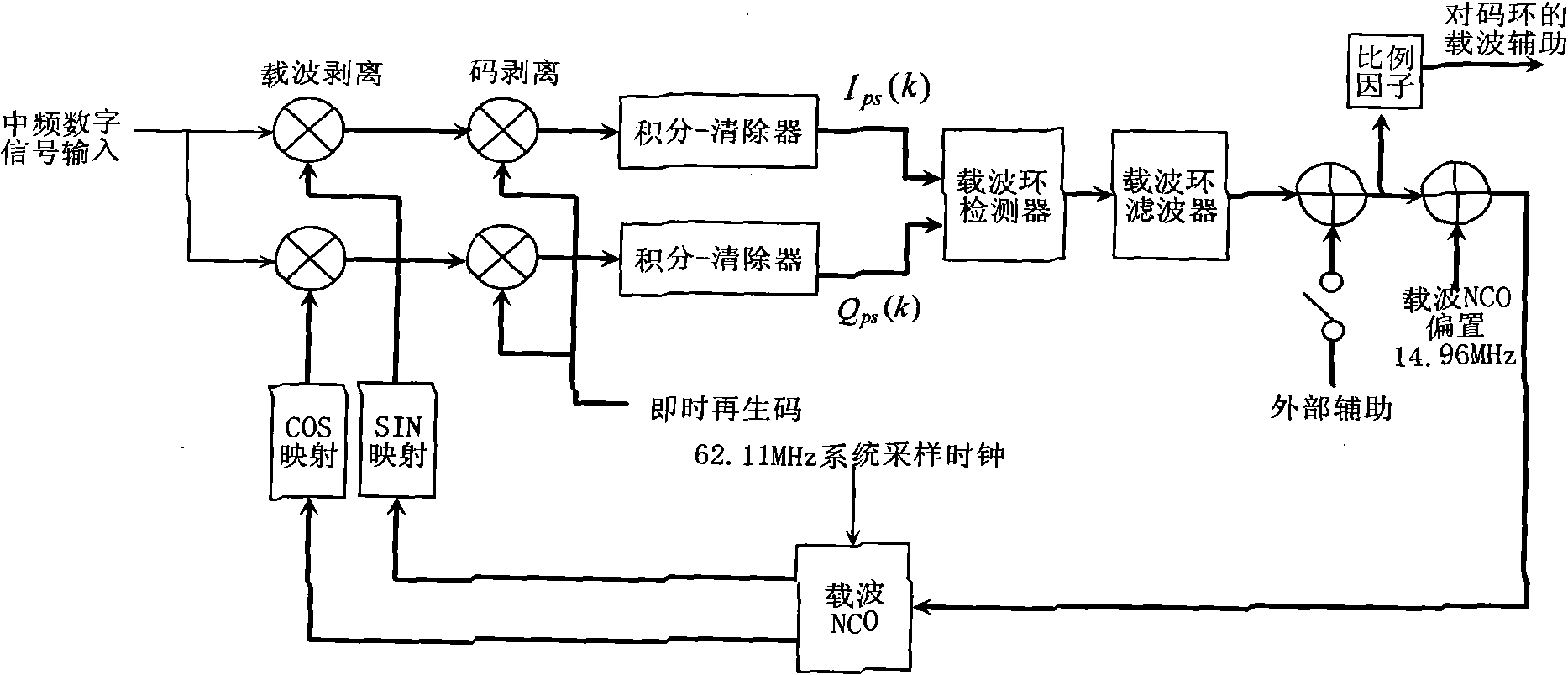
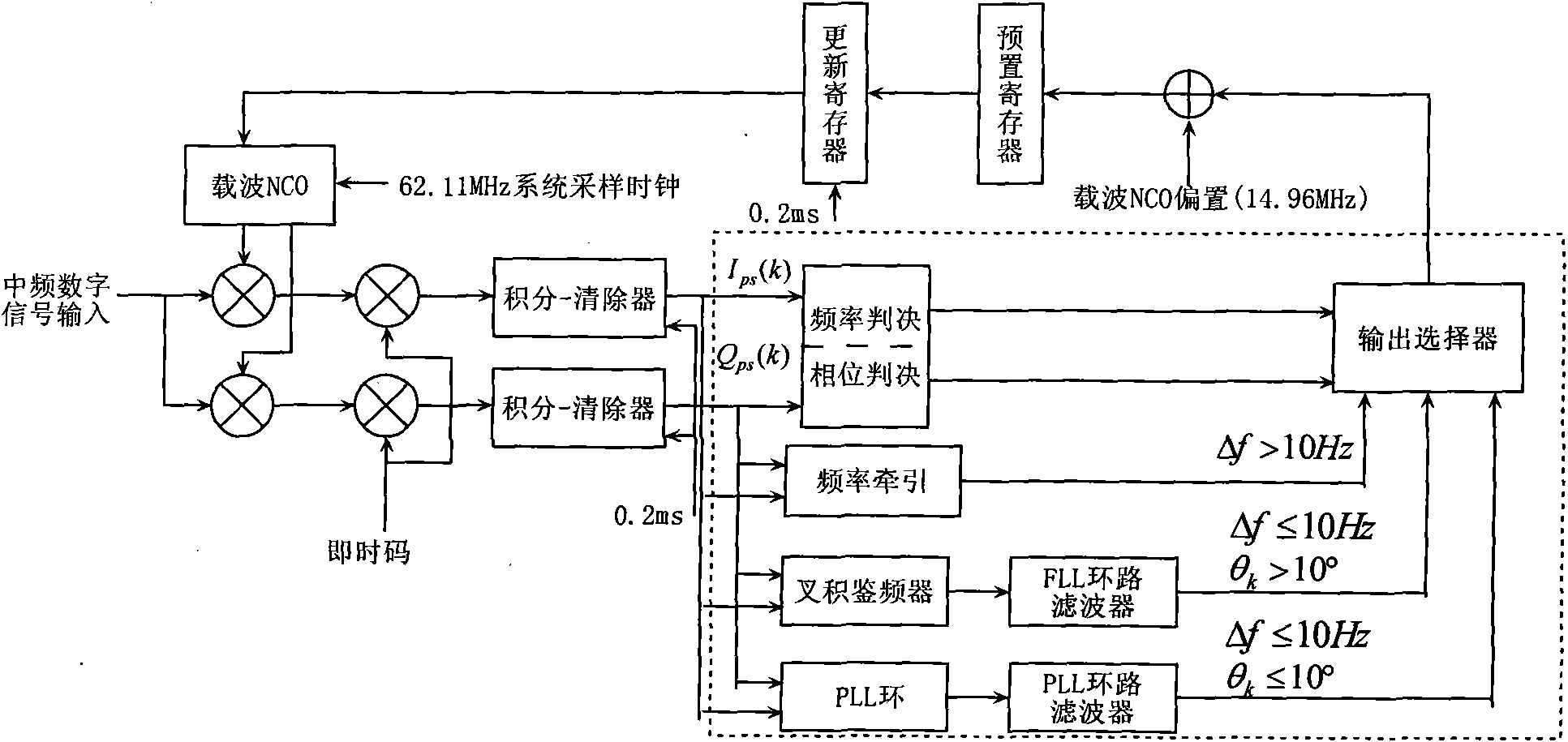
The invention relates to a precise tracking and measuring method of a high dynamic signal of an air fleet link, belonging to the technical field of aeronautical data links and radio navigation, and aiming at providing a precise tracking and measuring method of the high dynamic signal the an air fleet link and an implementation structure to solve the problems in the prior art. The invention provides a system framework of the precise tracking and measuring method of the high dynamic signal of the air fleet link, which can be implemented on a digital signal processor (DSP) and a FPGA (field programmable gate array) of a circuit board, and overcomes the defects of the unfavorable precision of a traditional high dynamic receiver by utilizing a double-loop structure of a frequency tracking loop of carrier tracking and a phase locking loop as well as a code phase locking loop to realize the high precise tracking under a high dynamic condition. The method can be widely applied to satellite navigation receivers, range measurement systems and communication systems based on a quiescent carrier modulation direct sequence spread spectrum system.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
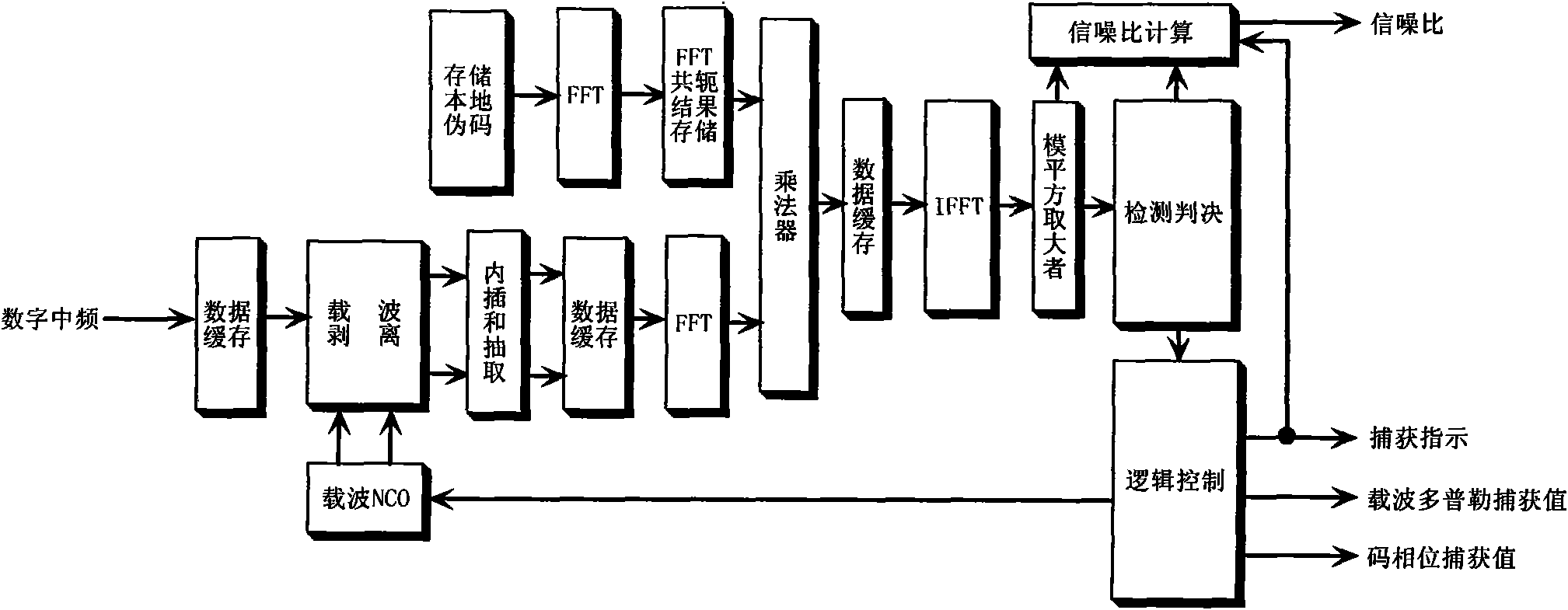
Method and device for fast correlation calculation
ActiveUS20090259707A1Shorten the construction periodReduce in quantityComputation using non-contact making devicesSatellite radio beaconingAnalog signalRadio navigation
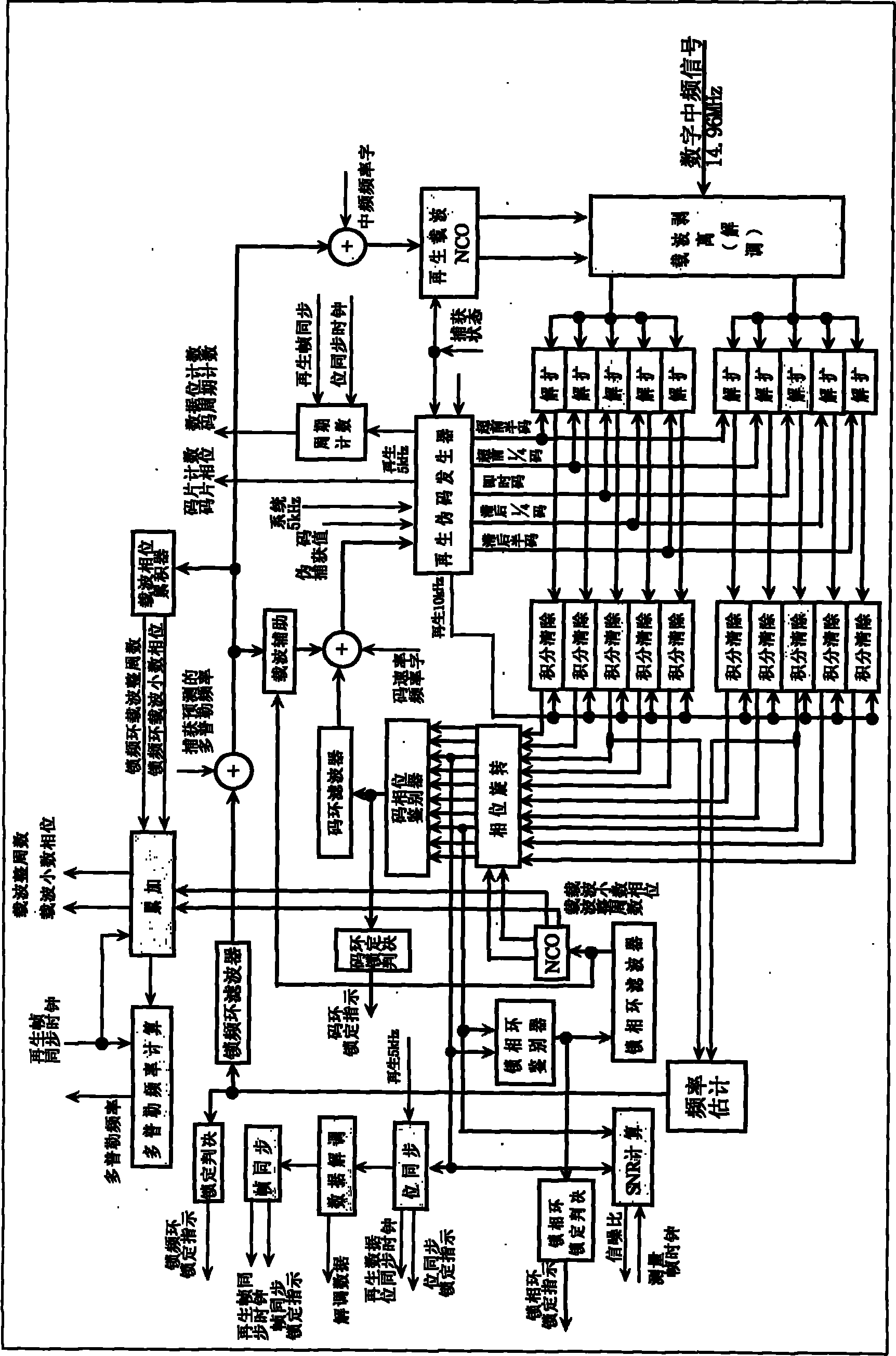
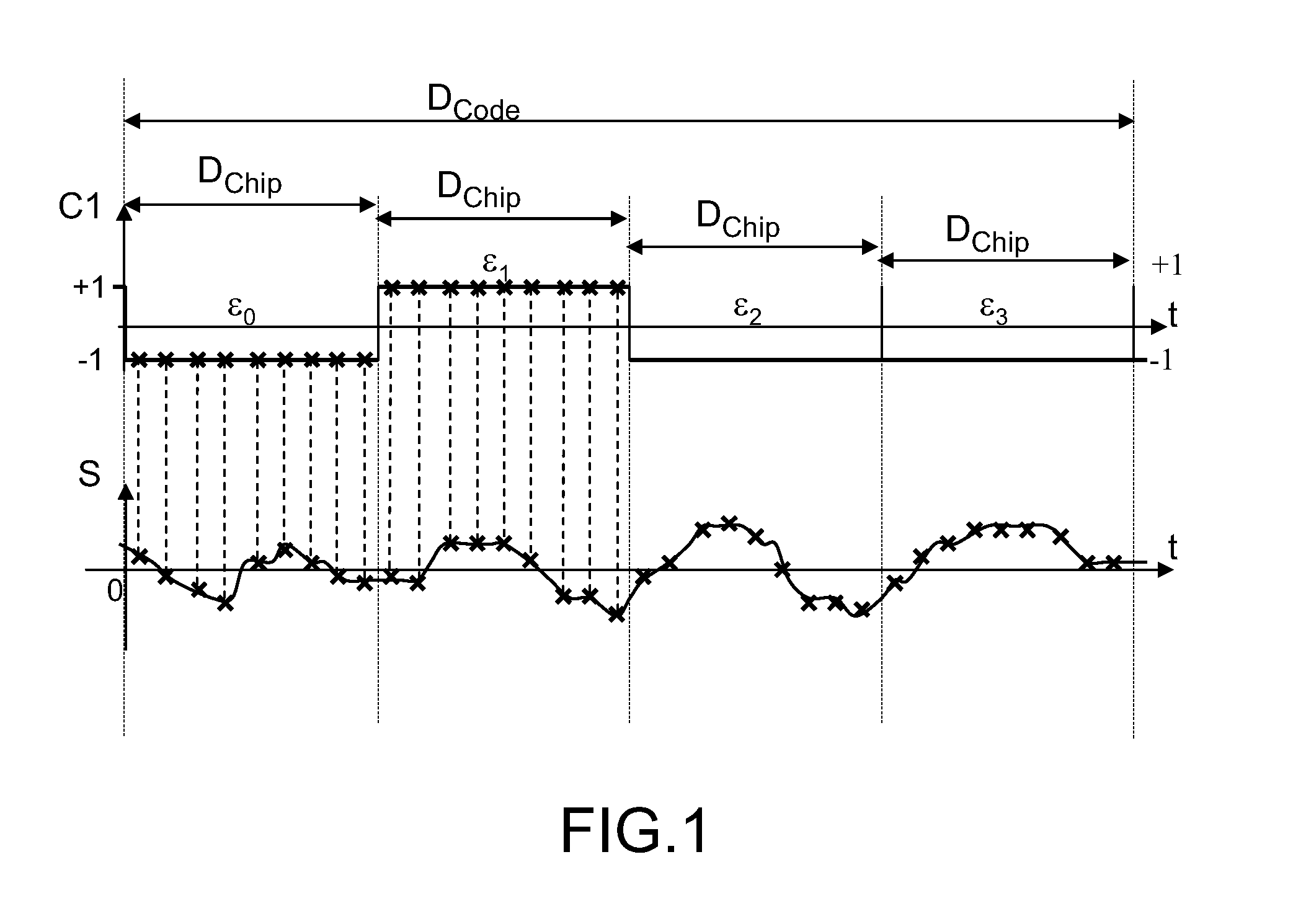
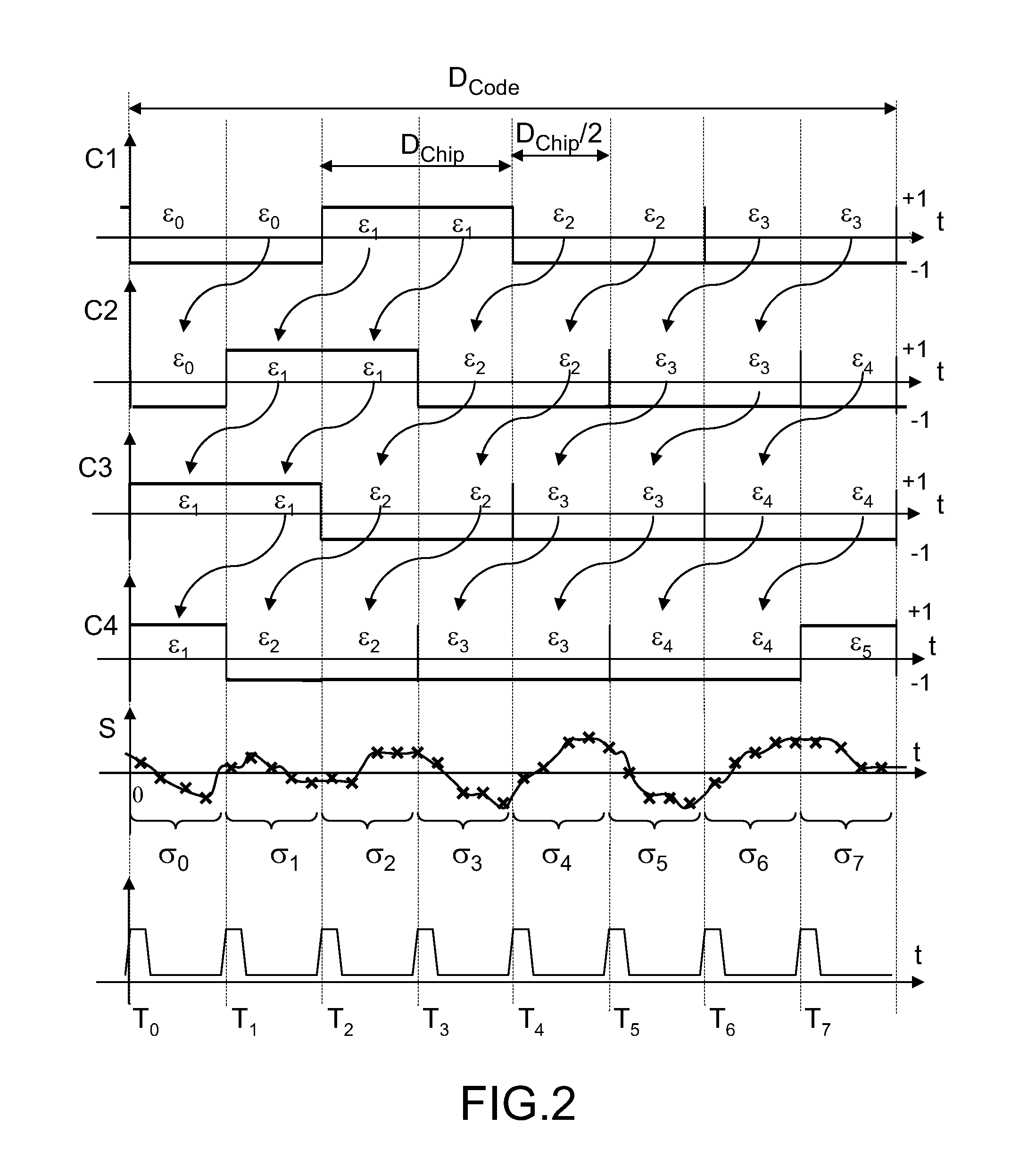
The field of the invention is that of the reception of a radionavigation signal originating from a satellite positioning system such as the GPS system. The present invention concerns a method for calculating correlations between a first sequence and a second sequence, said first sequence and said second sequence having a duration DCode, the first sequence being extracted from a digital signal comprising a code, said code comprising elementary time divisions, called chips, of mean duration Dchip, said chips being synchronized with pulses delivered by an NCO oscillator at the mean frequency 2 / Dchip, the second sequence resulting from a sampling at a frequency Fe of an analog signal, the frequency Fe being greater than 2 / Dchip. According to the invention, the method comprises a step of aggregating samples of the second sequence, over consecutive integration intervals of duration equal on average to Dchip / 2, starting at each pulse of the NCO oscillator, so as to determine results of elementary aggregates.
Owner:THALES SA
Aircraft flight risk measuring system and method of operation
ActiveUS6940426B1Improve flight safetyAnalogue computers for trafficComputations using stochastic pulse trainsOn boardAircraft flight mechanics
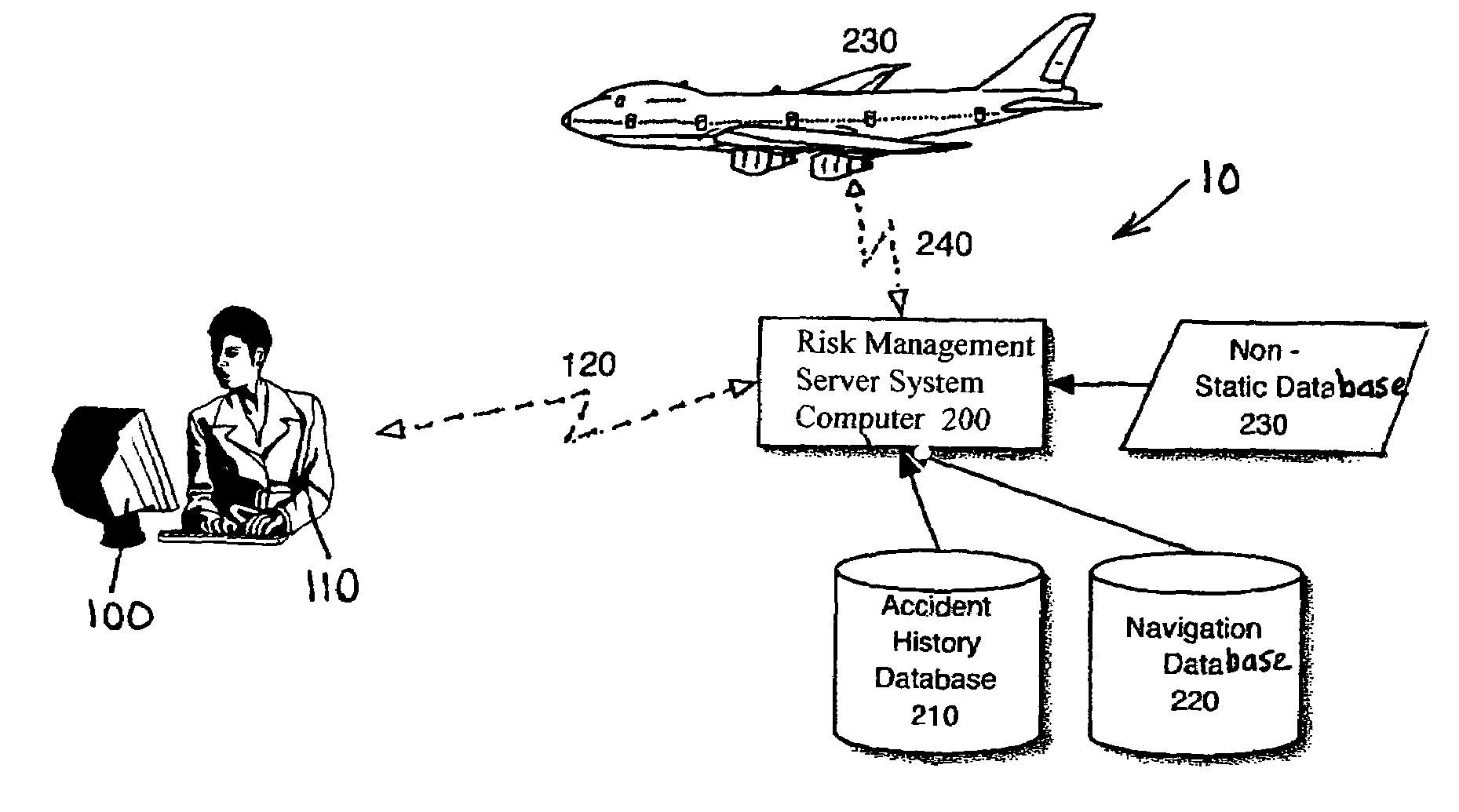
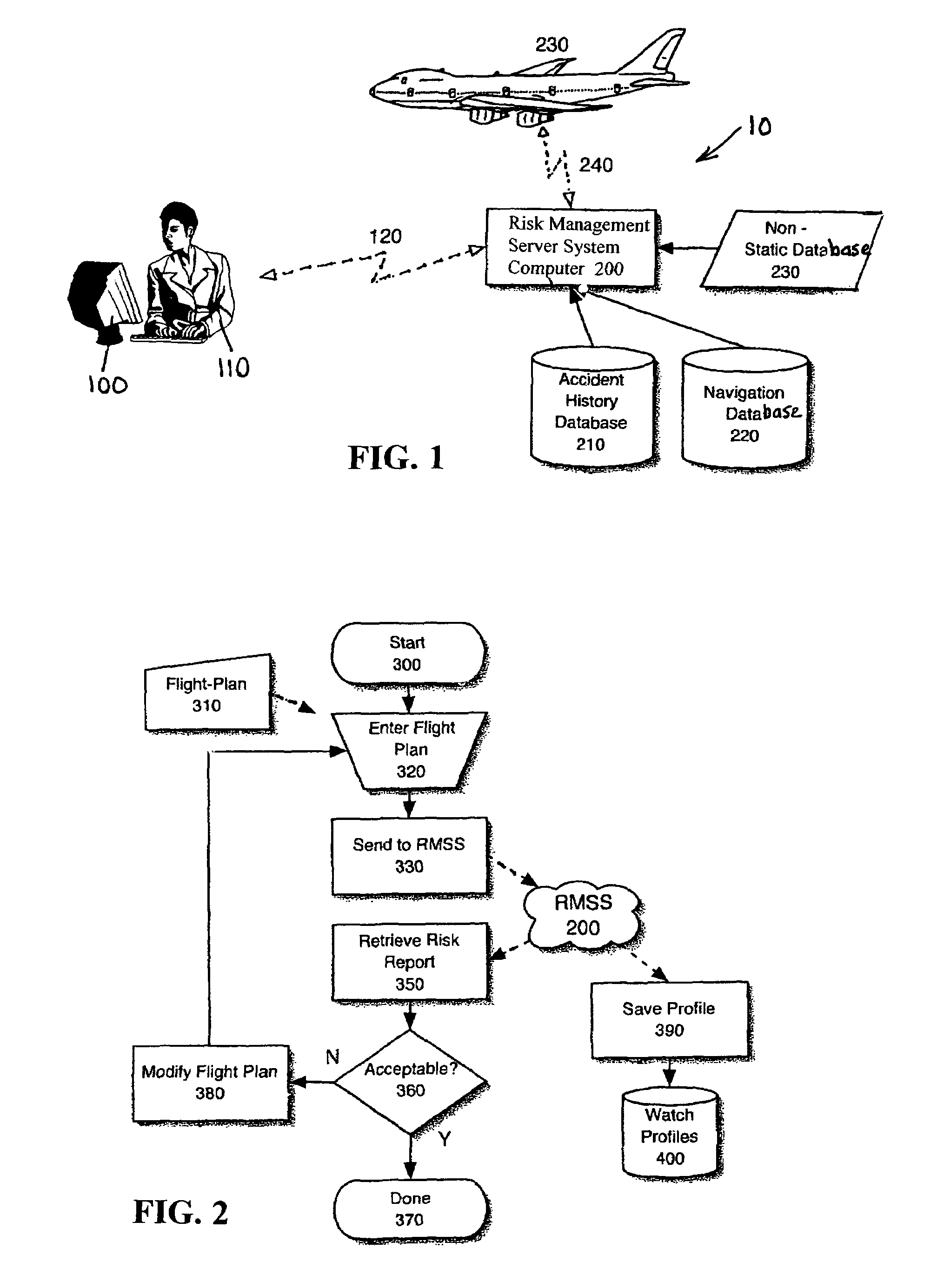
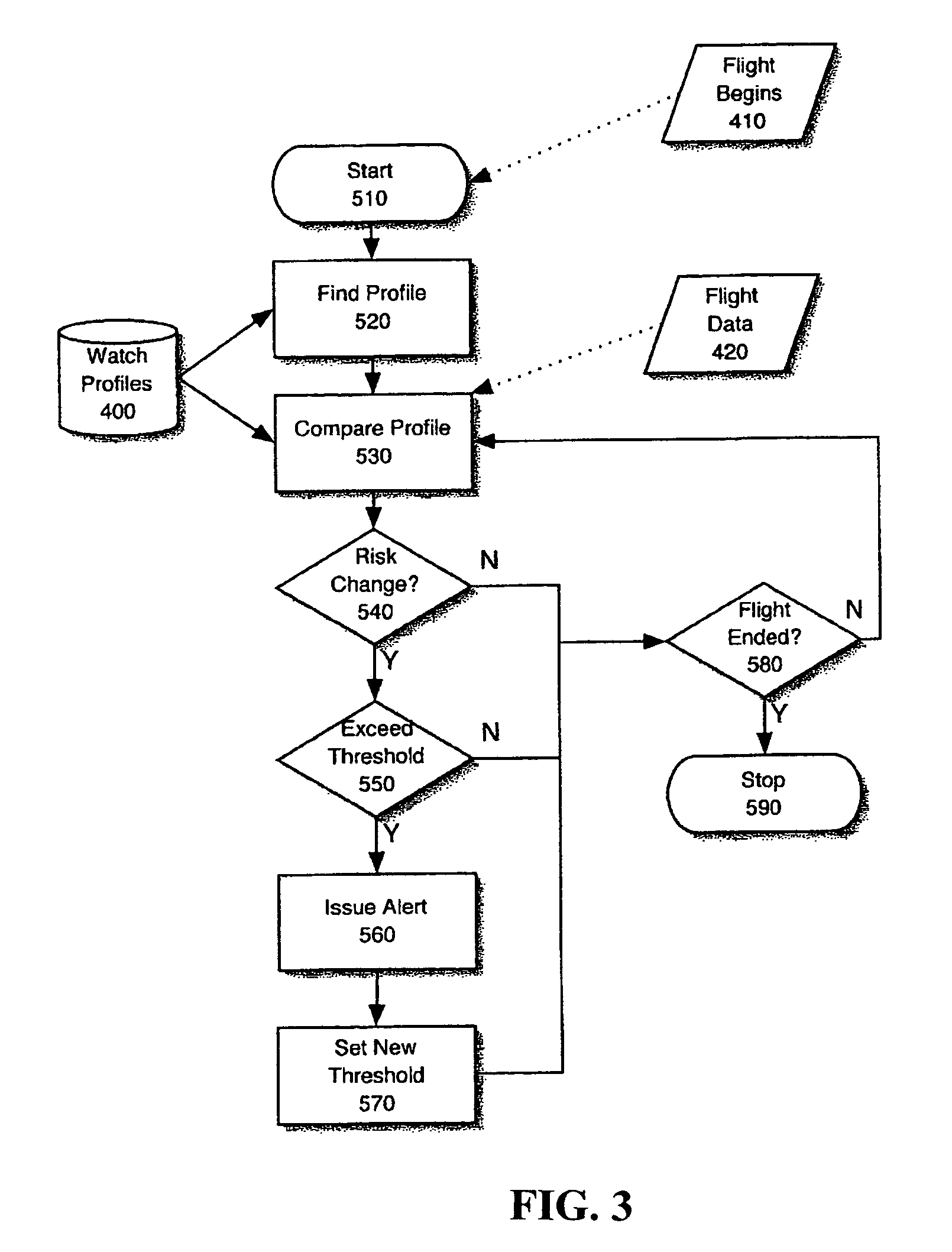
An aircraft flight risk measuring system for analyzing risks related to a flight of an aircraft. A user of the risk measuring system can be a flight dispatcher, an owner / operator, a pilot and other interested parties. The risk measuring system includes a risk management server system computer. The system computer has a two-way communication with a user computer operated by the user. An accident history database is connected to the system computer for providing accident reports related to the aircraft and other accident data. Also, a navigation database is connected to said system computer for providing airspace data, radio navigation aids, preferred routes, elevation data, geographic data and information related to a destination airport. Further, a non-static database is connected to the system computer for providing live information related to weather forecasts and data related to the aircraft's flight. As an option, a two-way communication between said system computer and an aircraft computer on board the aircraft can be included. The two-way communication used for receiving and transmitting encoded data from the aircraft when the flight is in progress.
Owner:AUCTNYC 3
Three-dimensional visual navigation method based on multi-sensor information fusion
ActiveCN101833104AEfficient detectionEffective intelligence analysisSatellite radio beaconing3D modellingNavigation systemRadio navigation
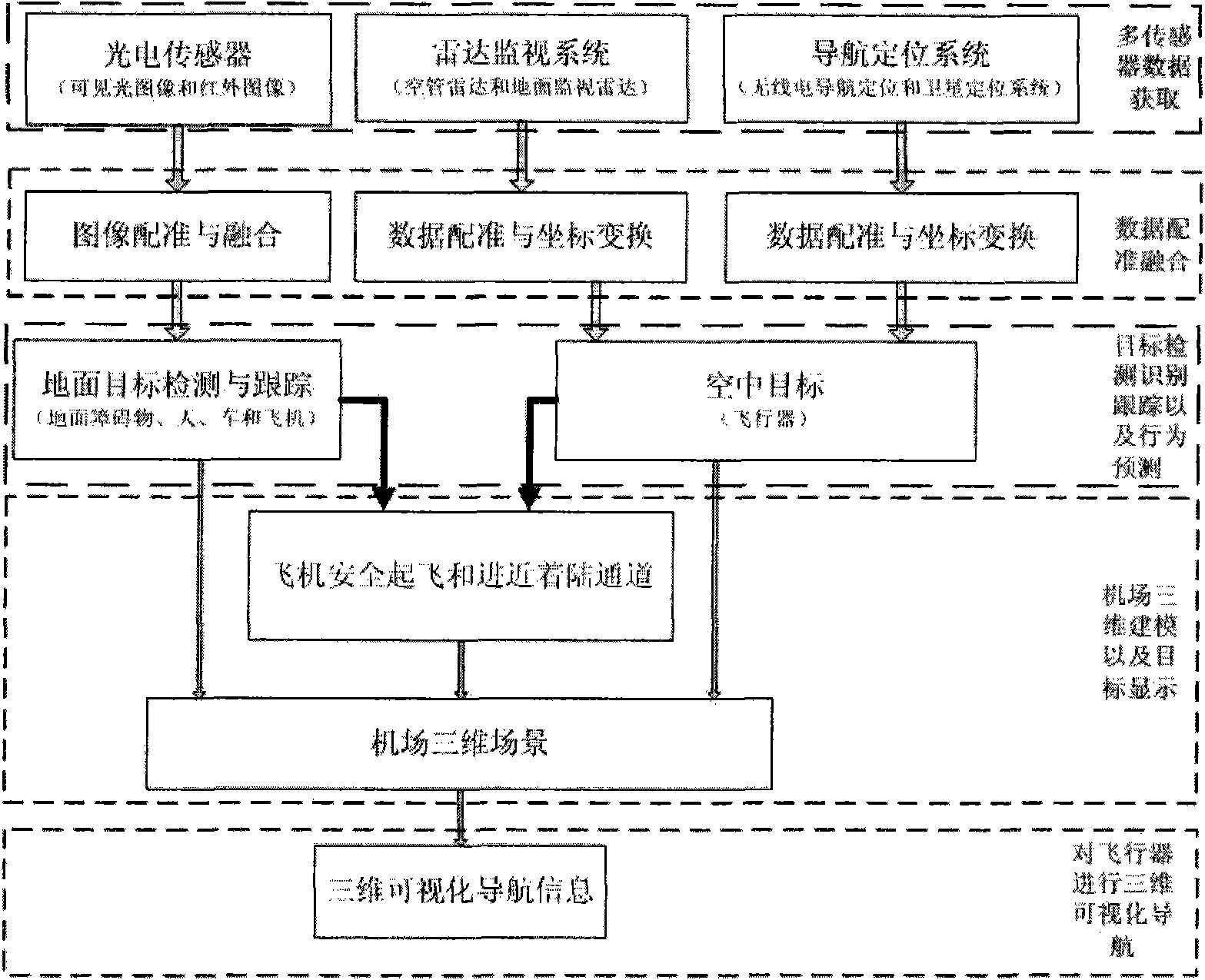
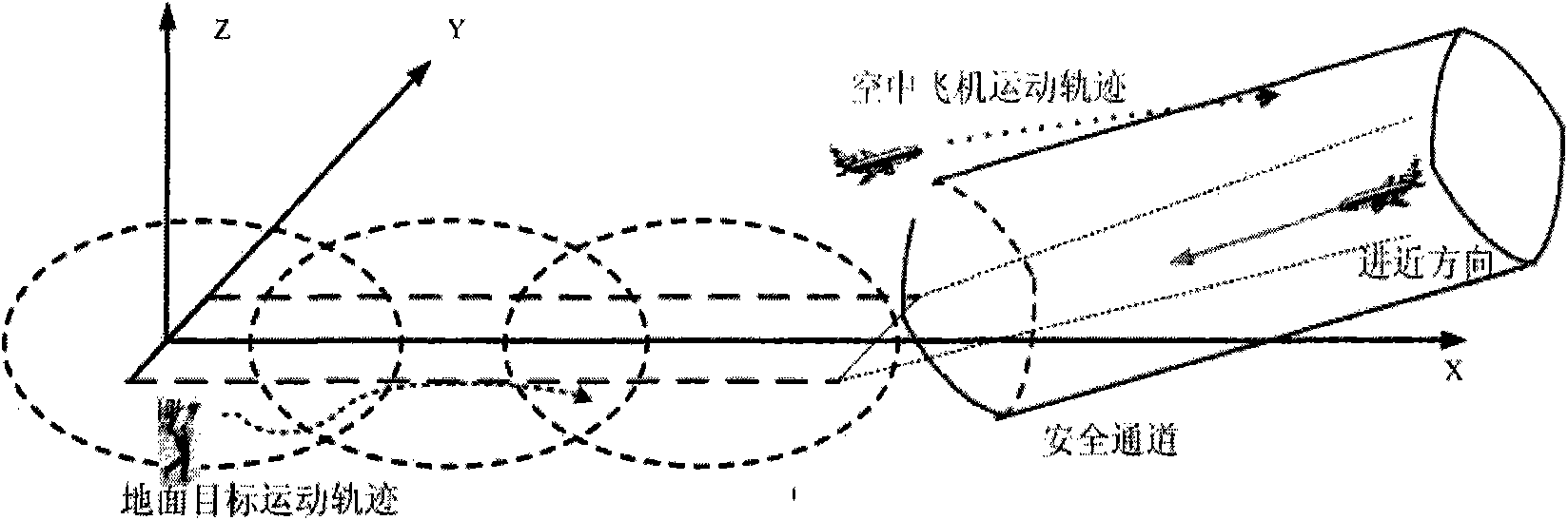
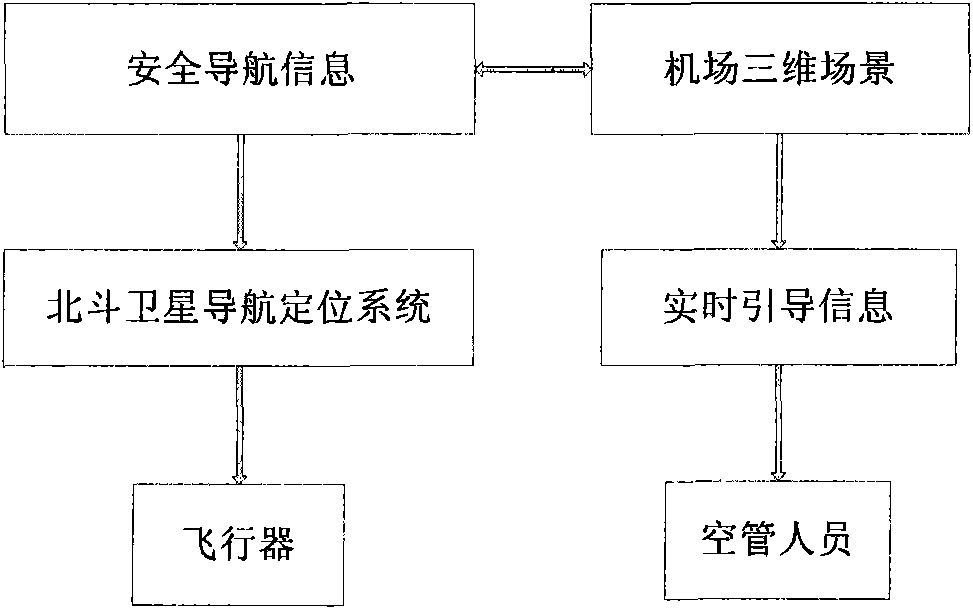
The invention relates to a three-dimensional (3D) visual navigation method based on multi-sensor information fusion. The multi-sensor data registration and fusion are finished based on acquiring multi-sensor data by means of a photoelectric sensor (infrared and visible lights), an airport radar monitor system (air traffic control radar and ground surveillance radar) and navigation positioning systems (radio navigation positioning system and global positioning system); and the detection, identification, track and behavior prediction are carried out on the targets (obstacles, humans, vehicles and planes) in the air or on the ground; the plane safety take-off and straight-in approach optimization information is automatically generated according to the target information in the air or on the ground; the target information and the plane safety take-off and straight-in approach optimization information are fused and displayed in an airport 3D scene to form a 3D visual navigation; and the system can automatically generate the 3D visual navigation information and transmits the navigation information to the aircraft via the GPS to realize the 3D visual navigation on the aircraft. The realization of the method comprises the following specific steps of: firstly, acquiring the multi-sensor data; secondly, registering and fusing the multi-sensor data; thirdly, detecting, identifying and tracking the targets in the air or on the ground by utilizing the fused data, and predicting the behavior of the targets; fourthly, establishing a 3D model of the airport, and fusing the targets and the behavior prediction data thereof and displaying the data in the airport 3D scene to form a 3D visual navigation system; and finally, carrying out the 3D visual navigation on the aircraft by means of the 3D visual navigation system to realize the safe take-off or approach of the aircraft.
Owner:内蒙古盛邦北斗卫星信息服务有限公司
Networking topologic structure of fleet formation and design method for combined multi-address system
InactiveCN101795221AMeet the real-time sharing needs of the whole networkImprove reliabilityError preventionStar/tree networksDigital signal processingCross-link
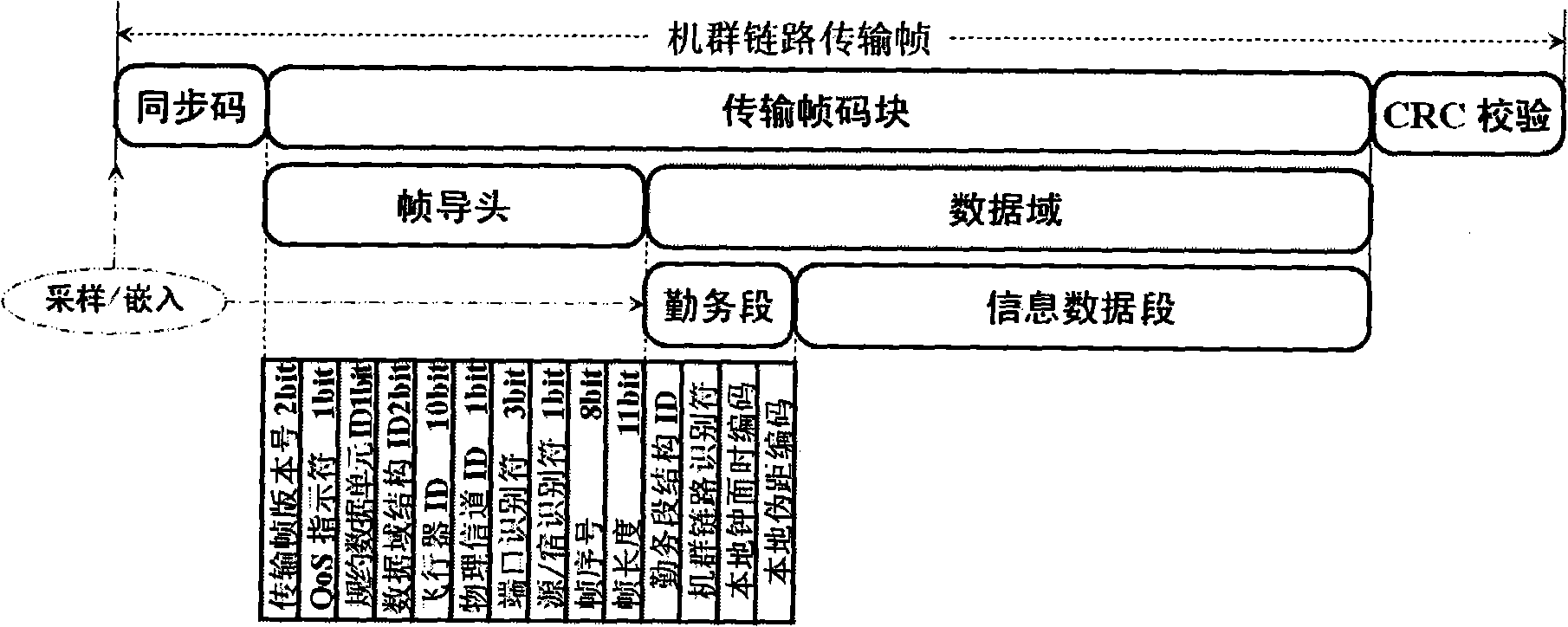
The invention relates to a networking topologic structure of fleet formation and a design method for a combined multi-address system, belonging to the technical field of the aviation data link, radio navigation and aircraft automation. The invention provides a multi-address system and a networking topologic structure for networking communication and measurement of fleet formation, meets the passive detection and location and the cooperative attack task of the fleet formation to the moving-target. The invention provides the networking topologic structure which can realize the combined multi-address system and support the fleet formation on a DSP (Digital Signal Processor), an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) apparatus and a radio frequency channel on an intermediate-frequency signal processing circuit board of a fleet link terminal. The invention provides two novel multi-address access systems of communication topologic configuration, namely the CDMA Code Division Multiple Access) / FDAM combined multi-address communication system of the fleet formation based on cross-link networking topology and a graded hierarchical multi-address communication system of the fleet formation based on tree topology. The former can support a single-hop access mode of total network coverage and the latter provides a multiple-hop access mode of total network coverage.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
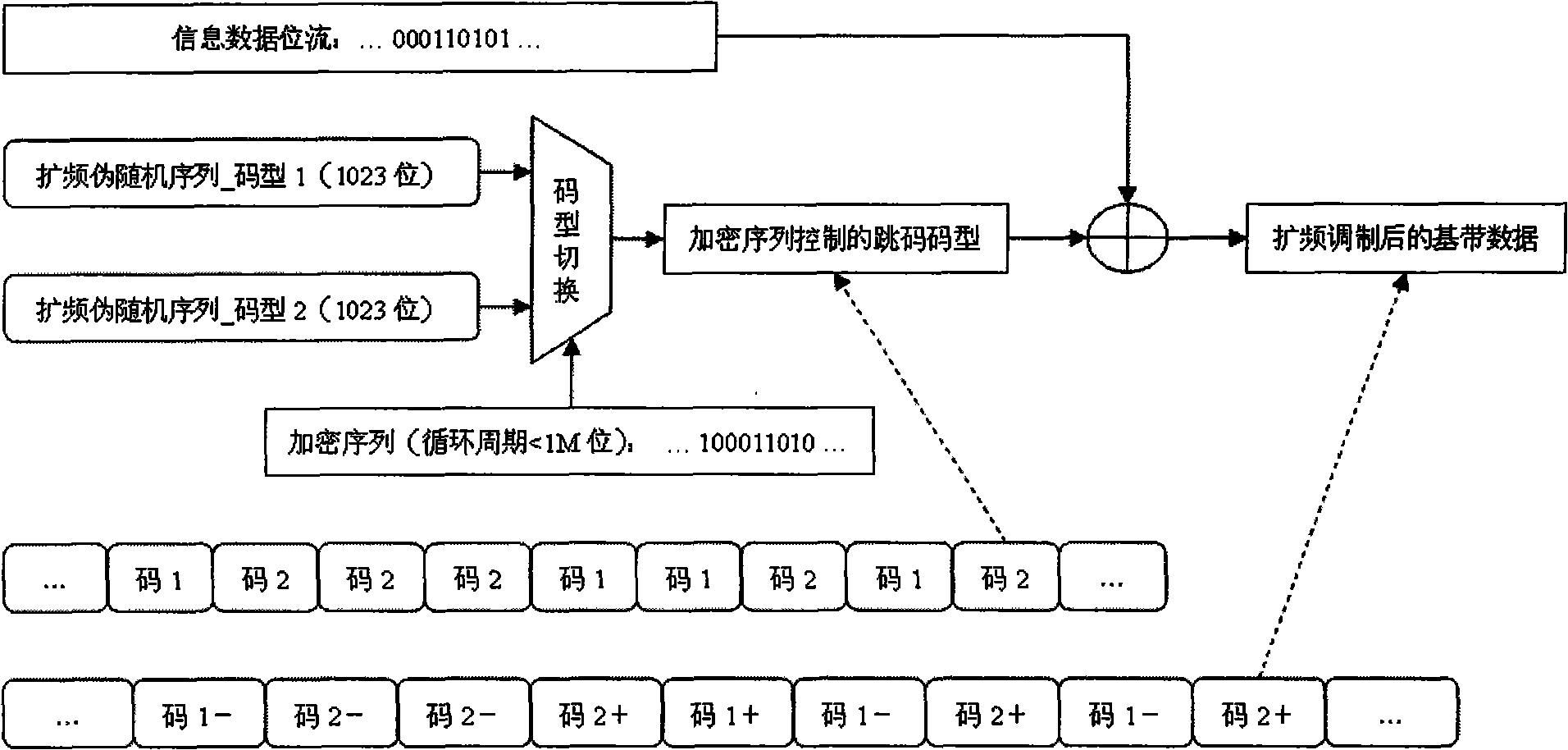
Generation and capture system of encrypted frame hopping spread spectrum signal of air fleet link
InactiveCN101777933AEnhanced anonymityImprove anti-interference abilityTransmissionDigital signal processingCarrier signal
The invention relates to a generation and capture system of an encrypted frame hopping spread spectrum signal of an air fleet link, belonging to the technical field of aeronautical data link and radio navigation. The invention discloses a system framework of an encrypted frame hopping spread spectrum signal generation and capture method which can be implemented on a digital signal processor (DSP)and a FPGA (field programmable gate array) of a circuit board, and provides a baseband signal generation algorithm of an encrypted frame hopping spread spectrum system to replace a traditional long periodic sequence spread spectrum code and a compound pseudo code by absorbing the advantages of the easy capture of the compound pseudo code and the difficult breaking of the long periodic sequence spread spectrum code; and meanwhile, the invention provides two advanced and high-performance encrypted frame hopping spread spectrum signal capture algorithms, i.e. a frequency domain parallel capture method of the encrypted frame hopping spread spectrum signal of based on a FFT (fast fourier transform algorithm) and a direct capture method of the encrypted frame hopping spread spectrum signal based on a matching filter and the FFT. The invention solves the problem of difficult capture of the traditional long periodic sequence spread spectrum code. The method can be widely applied to satellite navigation receivers, range measurement systems and communication systems based on a quiescent carrier modulation direct sequence spread spectrum system.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
Multifunction printed-circuit antenna
InactiveUS6198439B1Efficient connectionSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsDielectric substrateGround plane
The multifunction printed-circuit antenna is designed for the reception of radioelectric waves sent by the GPS, GLONASS and MLS radio navigation systems. It comprises first, second and third circular patches that are parallel to one another and superimposed in this order above one and the same ground plane that is parallel to them, the centers of the patches being aligned on one and the same axis z'z perpendicular to the plane of the three patches, the patches being separated from one another by thicknesses of a substrate-forming dielectric material for each of the patches. The first and second patches form, with the ground plane, the antenna structure for the reception of the GPS, GLONASS waves. The MLS antenna reception structure is formed by the third and second patches. The second patch also serves as a ground plane for the MLS antenna structure. The third patch of the MLS structure has a diameter smaller than that of the first and second patches of the GPS, GLONASS structure, and the surface dimensions of the dielectric substrate between the third and second patches are smaller than those of the first and second patches. Application to GPS / GLONASS, MLS antennas.
Owner:THOMSON CSF SA
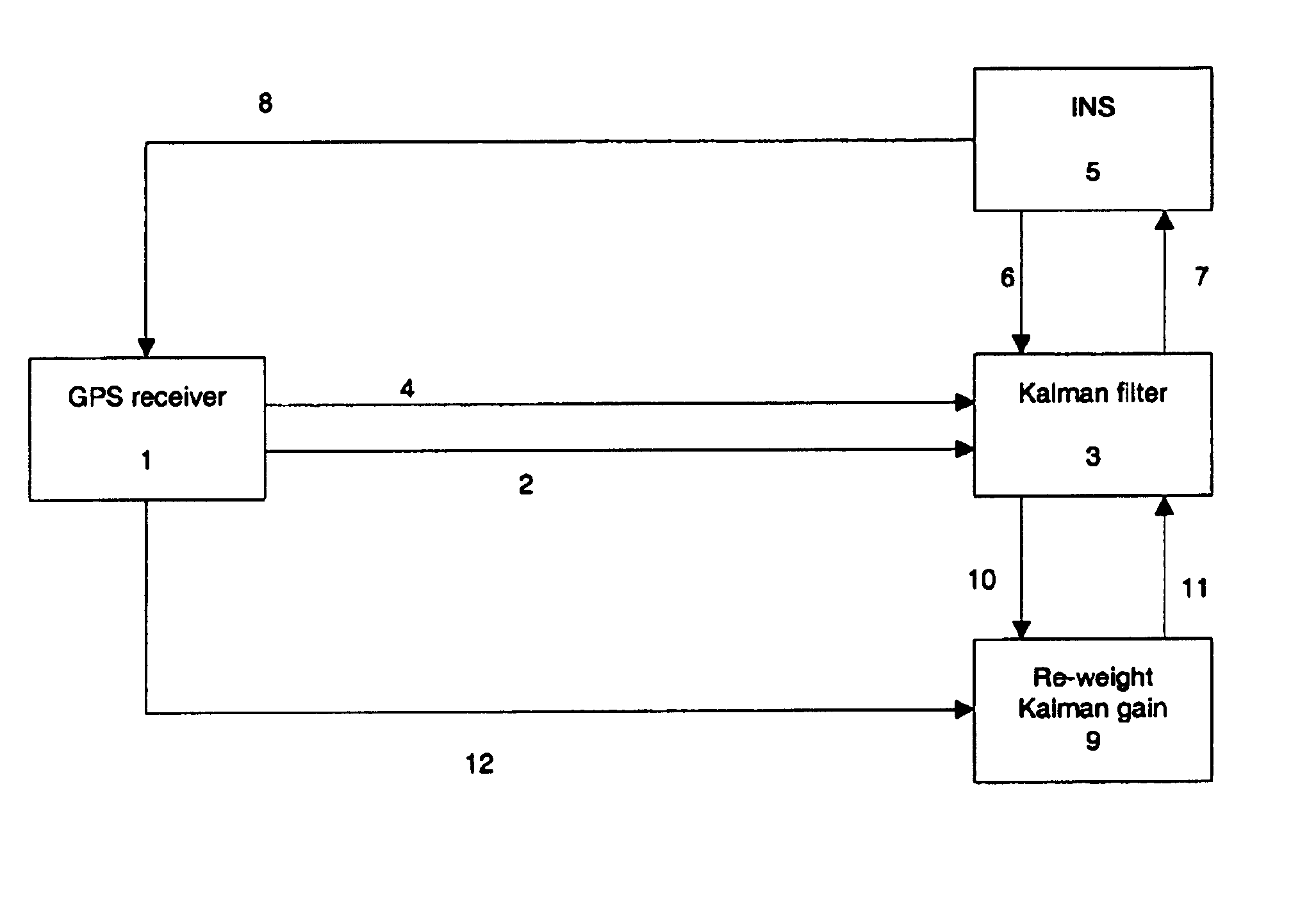
Adaptive GPS and INS integration system
InactiveUS6900760B2Increase weightImprove accuracyInstruments for road network navigationPosition fixationSatellite radioLoop bandwidth
This invention relates to the field of Inertial Navigation Systems (INS) and satellite navigation systems such as the Global Positioning System (GPS) and in particular relates to methods of integrating GPS and INS data in order to provide more accurate navigation solutions. The invention provides a method of improving the accuracy of a tightly coupled integrated INS and satellite radio navigation system in cases where the satellite navigation receiver has adaptive tracking loop bandwidths.
Owner:QINETIQ LTD
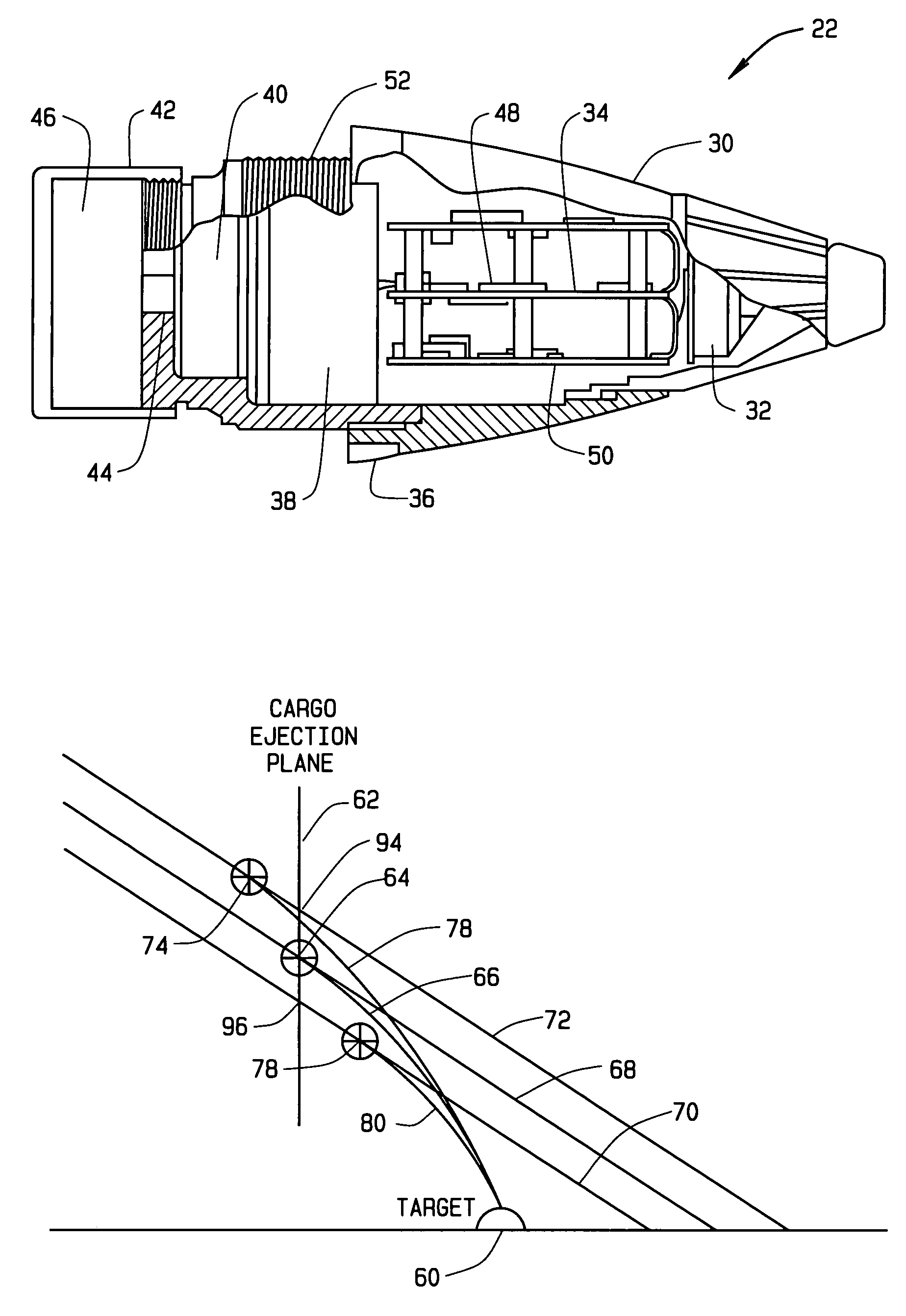
Accuracy fuze for airburst cargo delivery projectiles
InactiveUS7121210B2Low costReduce in quantityAmmunition projectilesProximity fuzesRadio navigationFuze
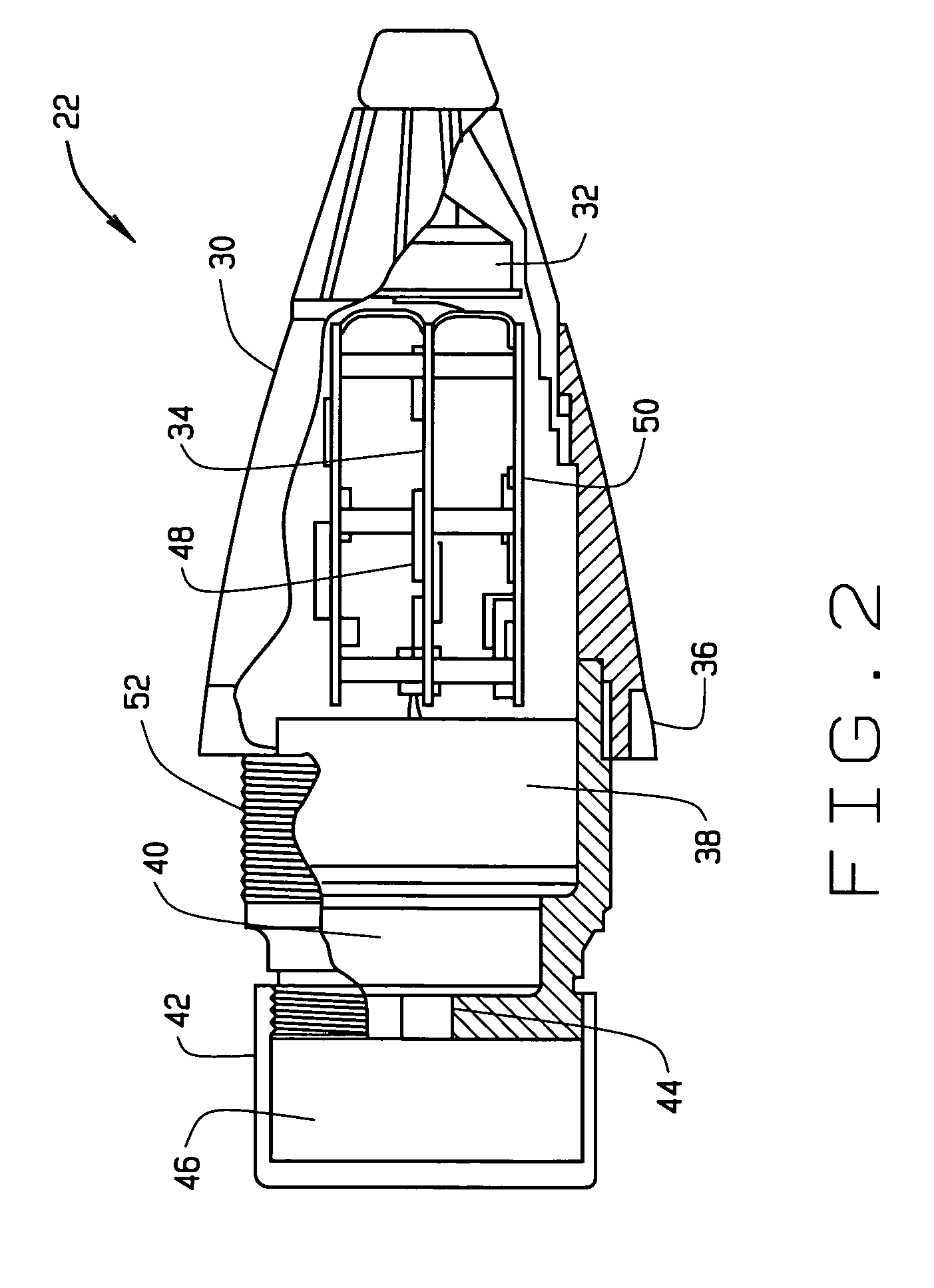
In one aspect, an artillery projectile apparatus is provided that includes a carrier projectile containing a payload, and a fuze disposed at an ogive of the projectile and which is configured to eject the payload when the fuze is detonated. The fuze includes a receiver configured to receive location information from a radionavigation source and a processor configured to acquire position data from the receiver. The processor is also configured to estimate a projectile flight path using the position data, to determine intercept parameters of the artillery projectile relative to an ejection plane of its payload cargo, and to adjust an ejection event initiation command time of the payload in accordance with the determined intercept parameters. In some configurations, the present invention dramatically decreases range errors typically associated with delivering artillery payloads to specific targets.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
Method for determining the co-ordinates of a satellite
InactiveUS6567712B1Navigational calculation instrumentsInstruments for comonautical navigationSatellite radioNODAL
The invention relates to the field of radio navigation and, more specifically, it relates to methods of determining the current values of the orbital position of the artificial satellite of the Earth which is used in a satellite radio navigation system (SRNS), by the ephemeredes and can be used when performing the radio navigation measurements in the equipment of the consumers of the SRNS signals. The variants of a fast method for determining the coordinates of the satellite are proposed, which consist in that the satellite coordinates are determined at preset points of the orbit spaced from each other by a selected time interval, and further determining the velocities of the satellite at the nodal points, while at the points between the nodal points the satellite coordinate are determined in the geocentric inertial system of coordinates are in a system the Greenwich geocentric coordinates using special formulas or the Taylor polynomial of the second or third order, and determining these at the nodal points using the six-order Taylor polynomial.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
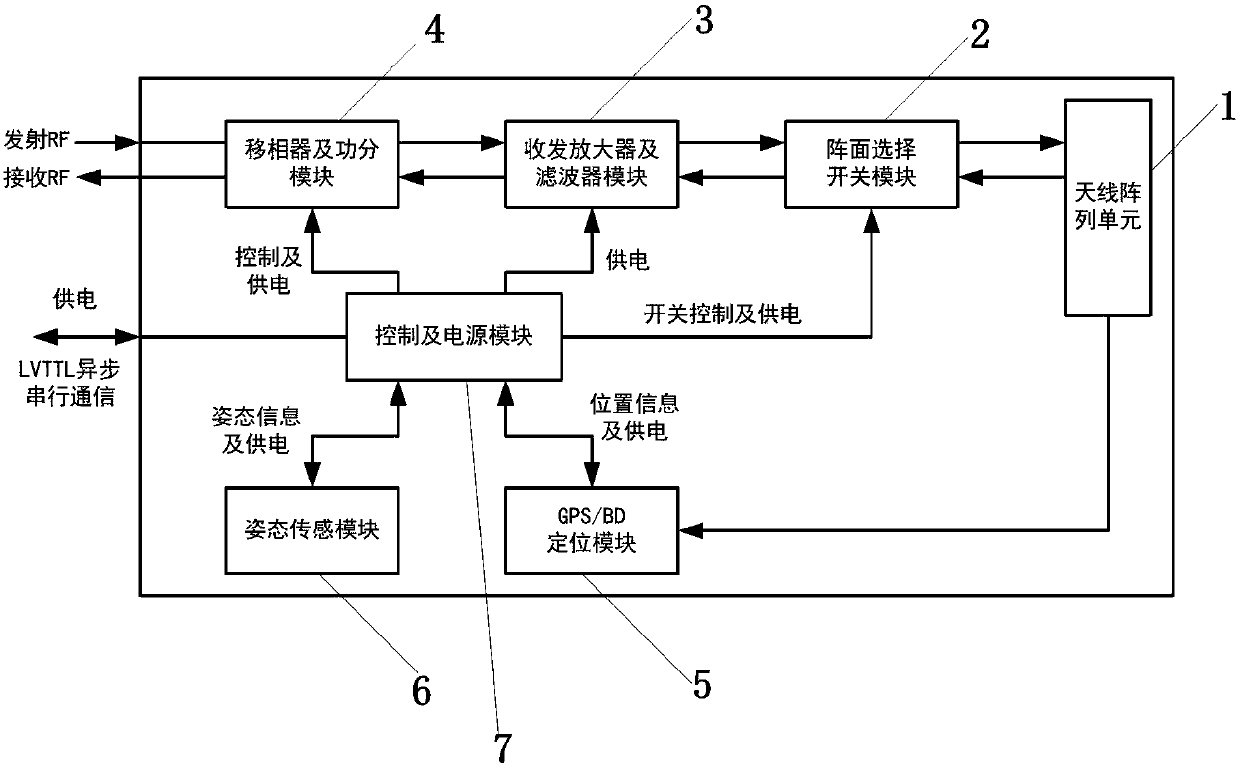
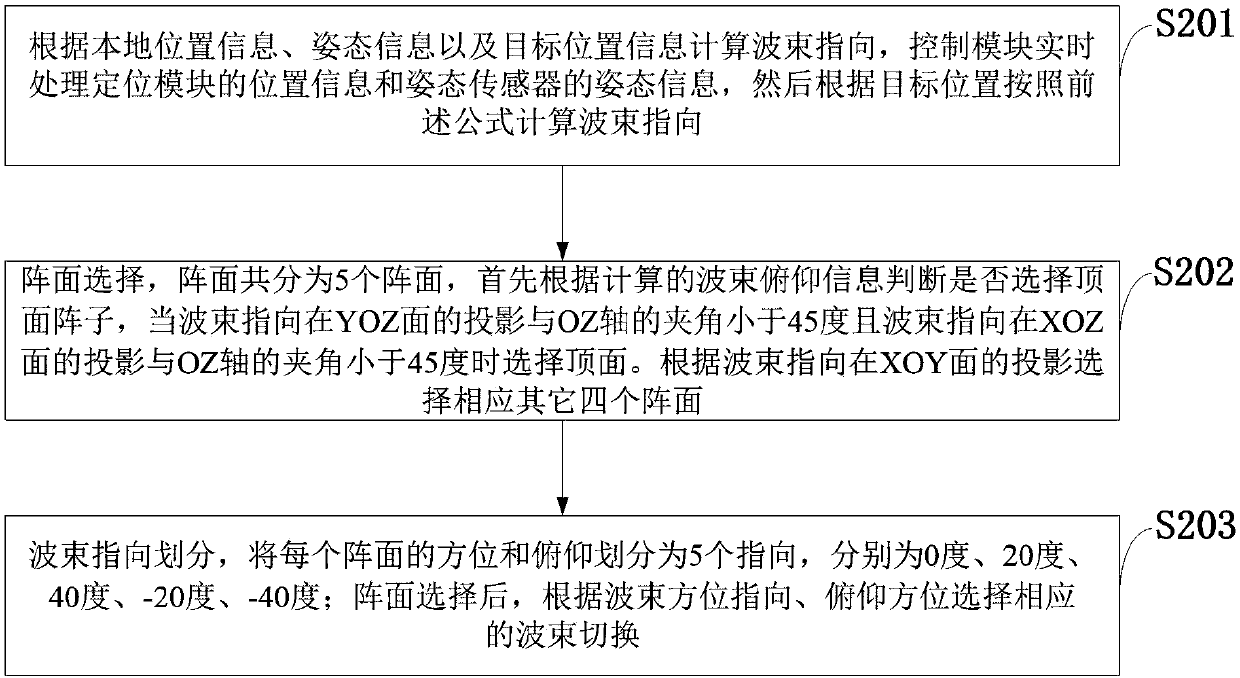
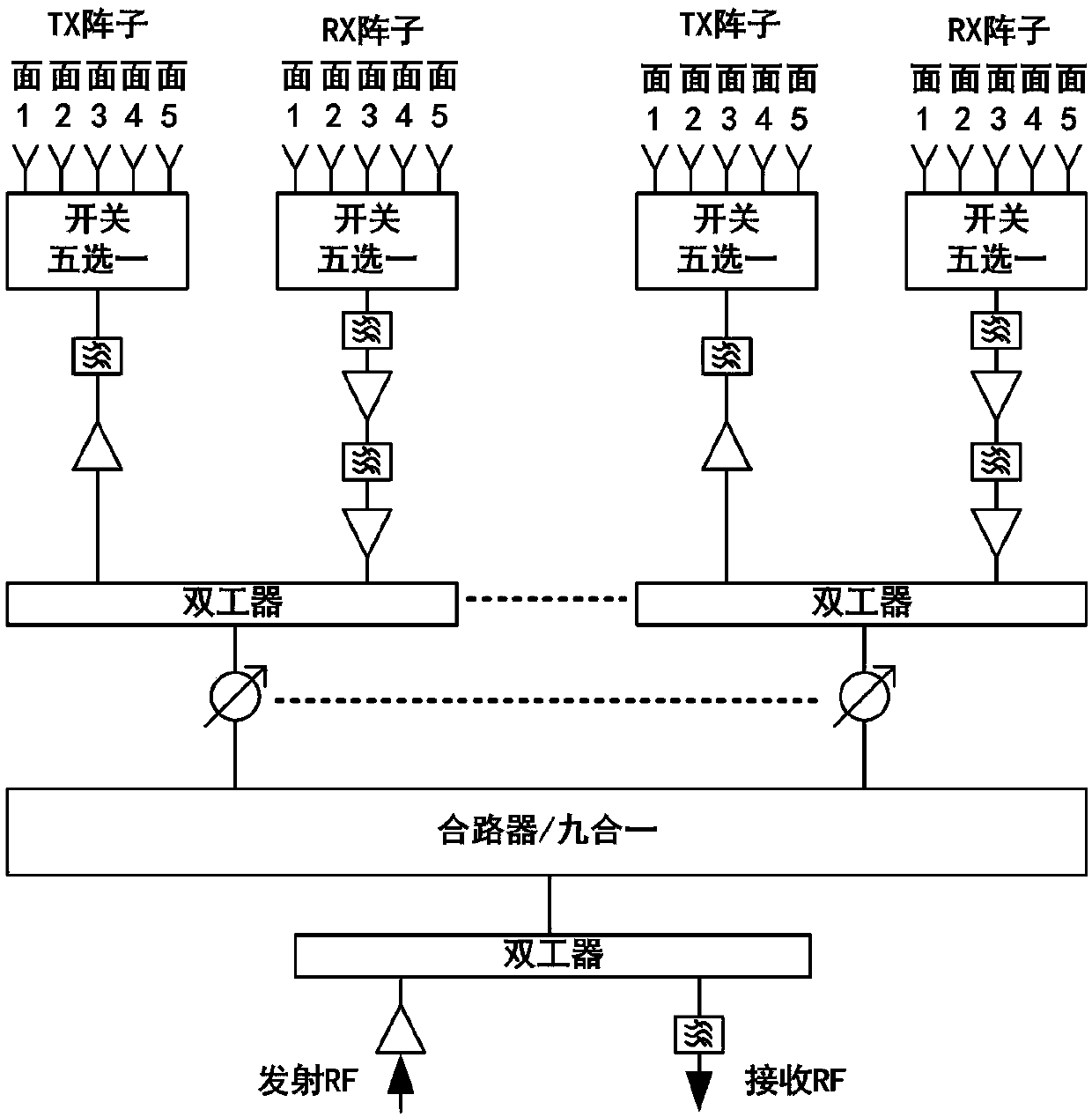
Antenna control system and method of phased array radar
ActiveCN108539418APointing accuratelyReduced number of RF transceiver channelsDifferential interacting antenna combinationsAutomatic controlTime delays
The invention discloses an antenna control system and method of a phased array radar, and belongs to the technical fields of radio orientation, radio navigation, radio wave range finding or velocity measurement, positioning or existence detection via reflection or re-radiation of radio waves, and similar devices with other waves. The system comprises an antenna array module, an array plane selector switch module, a transmitting-receiving amplifier and filter module, a phase shifter and power divider module, a GPS / BD positioning module, an attitude sensor module, a control and power supply module and a wave beam oriented automatic control module. The system and method can satisfy the requirements of minimization, low power consumption, high radiation efficiency and high isolation degree. Compared with a traditional phased array configuration system, the number of RF transmitting-receiving channels is reduced to 1 / 5, the power consumption is reduced to 1 / 5 correspondingly, a switch linephase shifter is used, the phase delay within the work bandwidth satisfies the time delay characteristic of a signal space, and different frequency points are directed accurately; all machinery related equipment is omitted; and the total power consumption is reduced greatly.
Owner:西安欣创电子技术有限公司
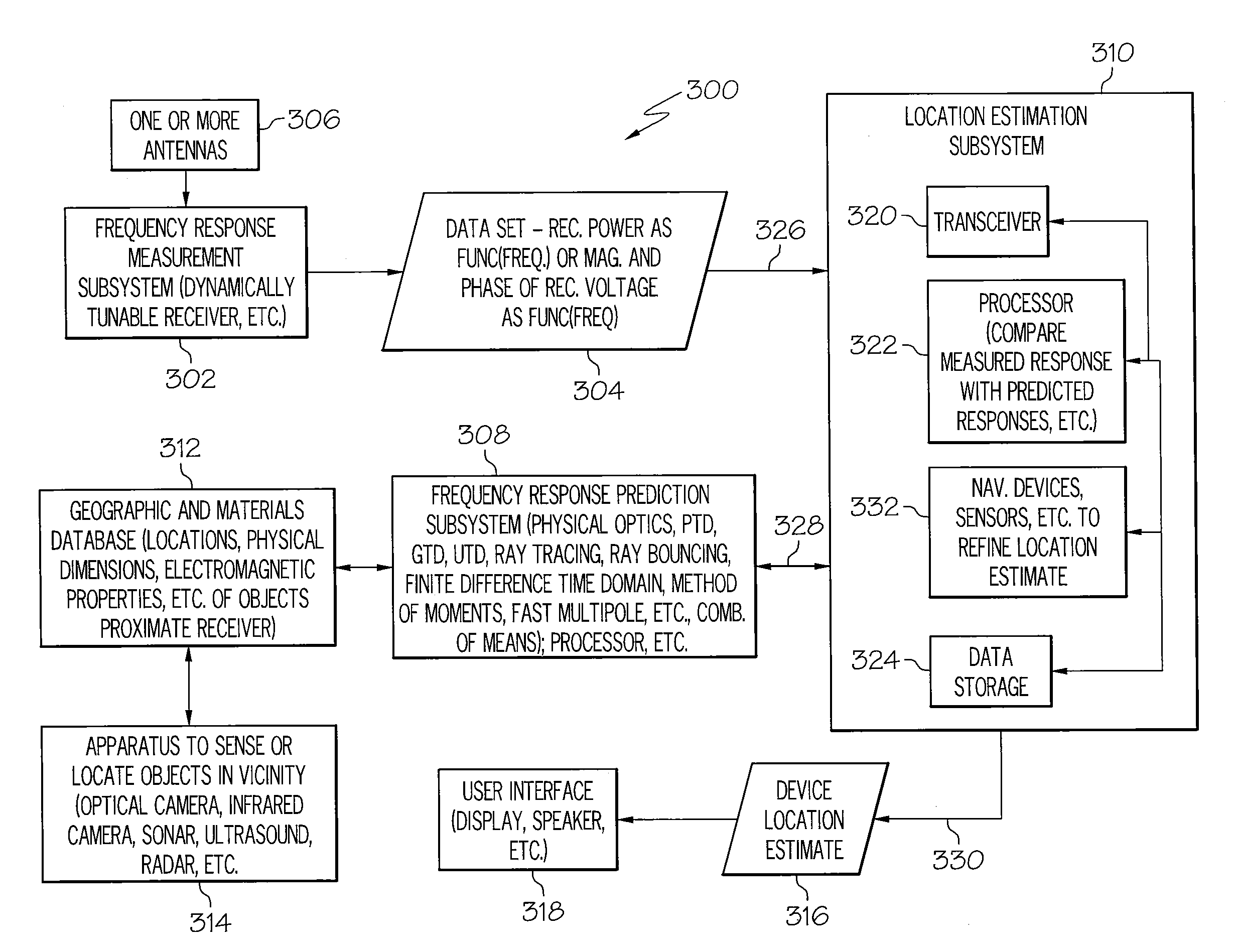
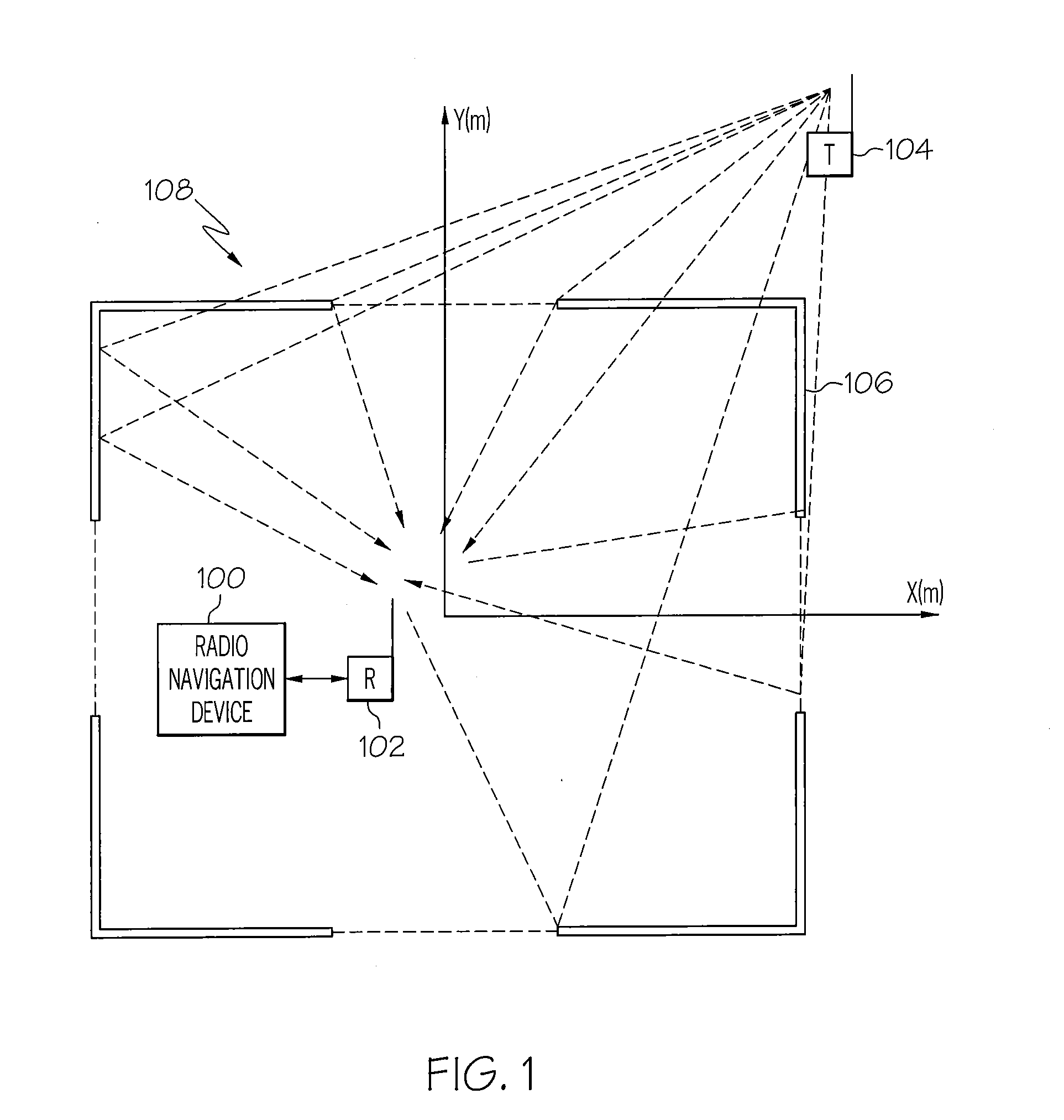
Radio frequency navigation using frequency response matching
InactiveUS20080143605A1Direction finders using radio wavesPosition fixationEngineeringFrequency matching
A method for radio navigation may include predicting a frequency response for each of a multiplicity of possible device locations. The method may also include measuring a frequency response at an actual device location. The method may further include matching the measured frequency response to one of the predicted frequency responses to determine an estimated device location, wherein the estimated device location corresponds to the possible device location associated with the one predicted frequency response that most closely matches the measured frequency response.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
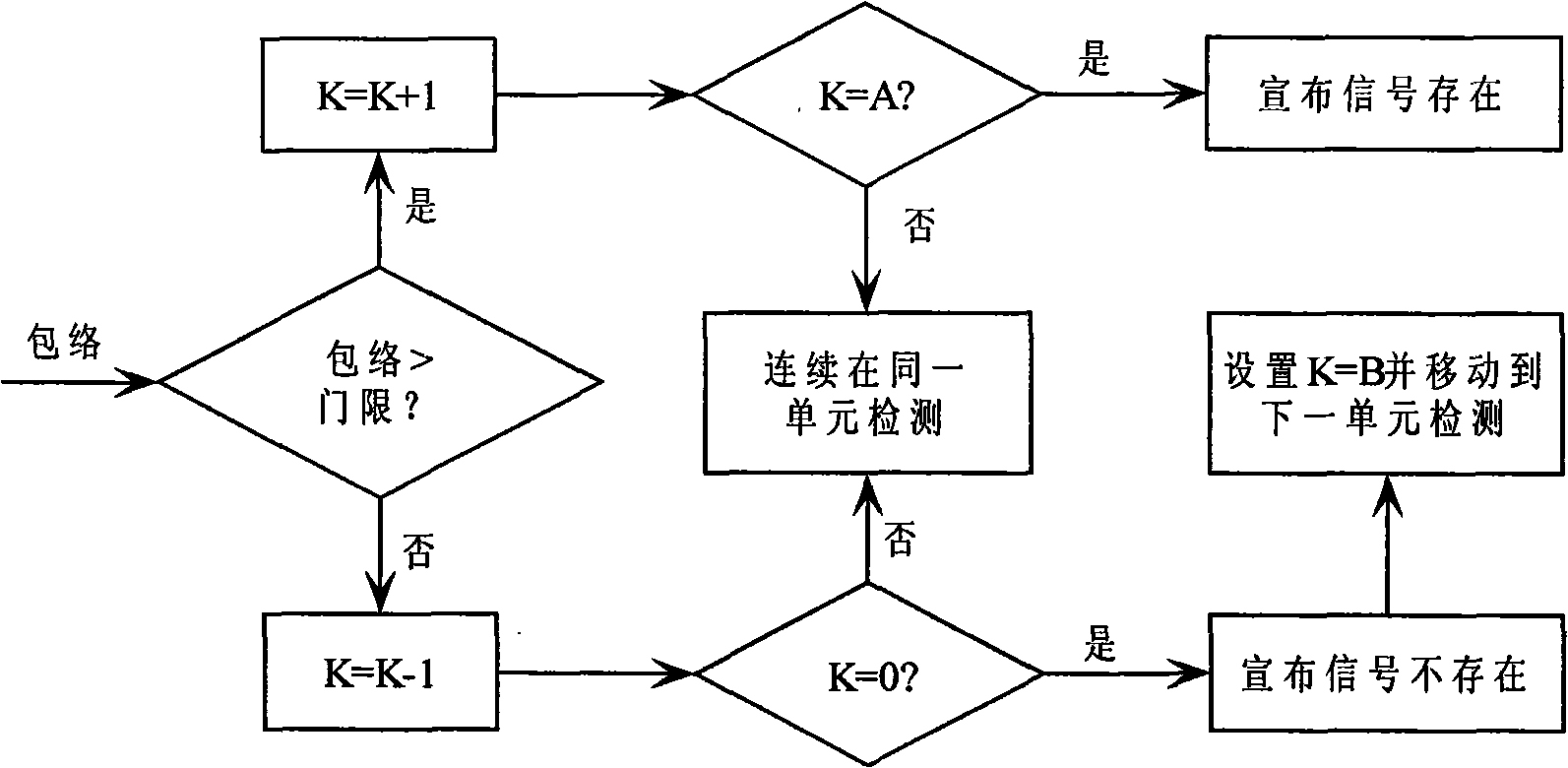
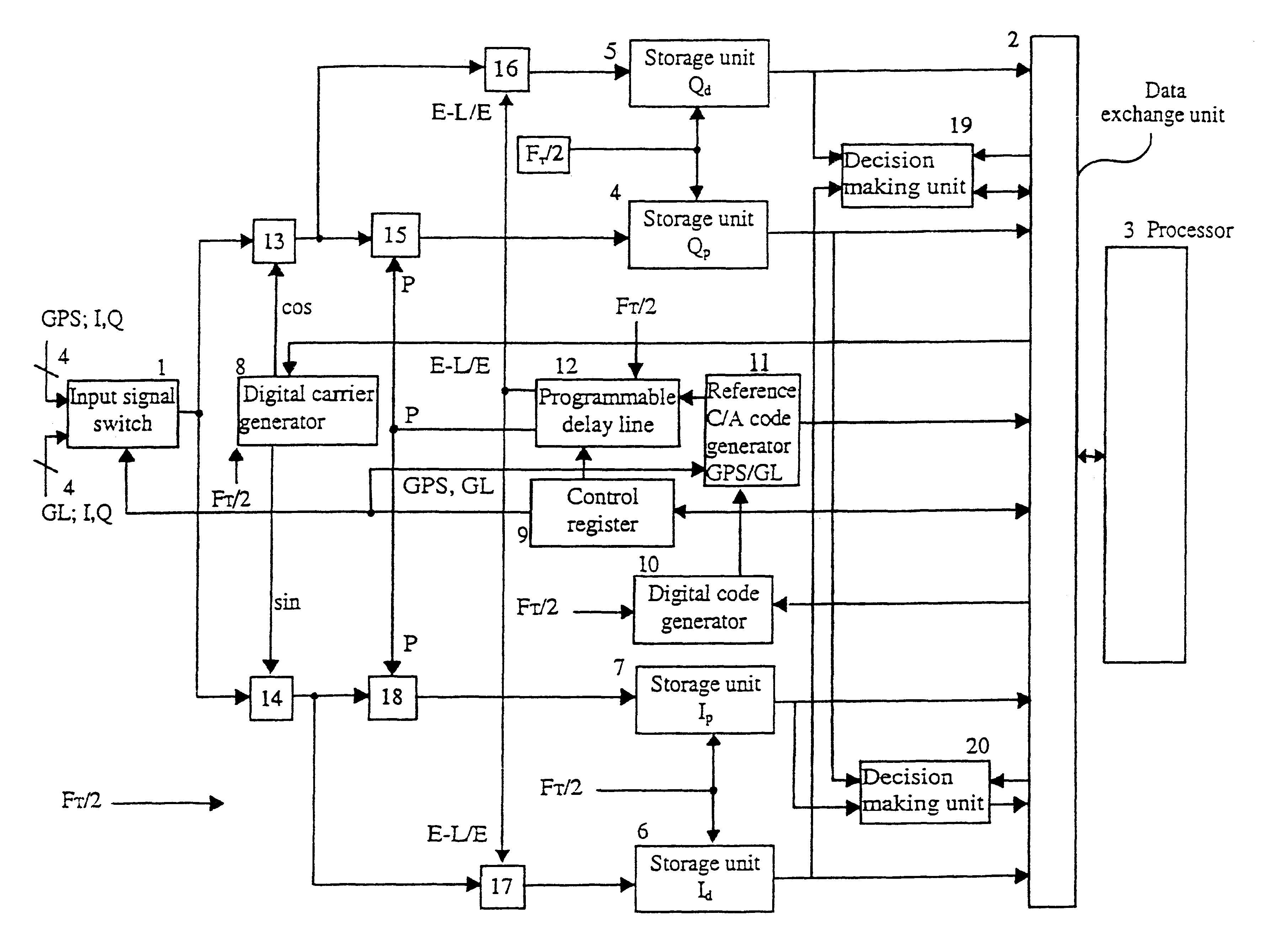
Digital correlator for a receptor of signals from satellite radio-navigation systems
Digital correlator of a receiver for reception of signals of satellite radio navigation systems which has one or more decision making unit(s) generating detection signals indicative of a strength of the received signals of satellite radio navigation systems, whereby a fast search is performed for detection of strong signals, and a slow search is performed only when signals were not detected during the fast search.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Track detecting system and method based on integrated navigation
InactiveCN105857340AEliminate measurement accuracy divergence issuesSolve the problem of measurement accuracy divergenceRailway auxillary equipmentRailway profile gaugesEngineeringRadio navigation
The invention discloses a track detecting system and method based on integrated navigation. The track detecting system and method accurately and rapidly detect a railway track. A wireless navigation base station is established in a GNSS signal shielding zone; an integrated navigation device receiving GNSS and / or wireless navigation signals is integrated into track detecting equipment; position drifting and posture drifting of a gyro sensor are eliminated through GNSS and / or wireless navigation, positioning and track plotting, and therefore the divergence problem of track detecting accuracy is solved; and a self-adaption smoothing compiling high-pass filter is adopted for eliminating influences such as changes of the slowly-changing track elevation with an extremely low frequency and a large value, changes of the filter-out gradient and superelevation on a curve of the gyro sensor; and the system integrates a displacement sensor, an inclination sensor, the gyro sensor and the like of the track detecting equipment, a mileage counter and the added integrated navigation device, a data fusion technology is adopted, track internal geometric parameters, coordinates, elevations and 150-300 m base length irregularity are independently detected, and the detecting speed is higher than 4 km / h, so that the bottleneck problems of track detecting in operation maintenance of high-speed and common-speed railways are solved.
Owner:郑君伟
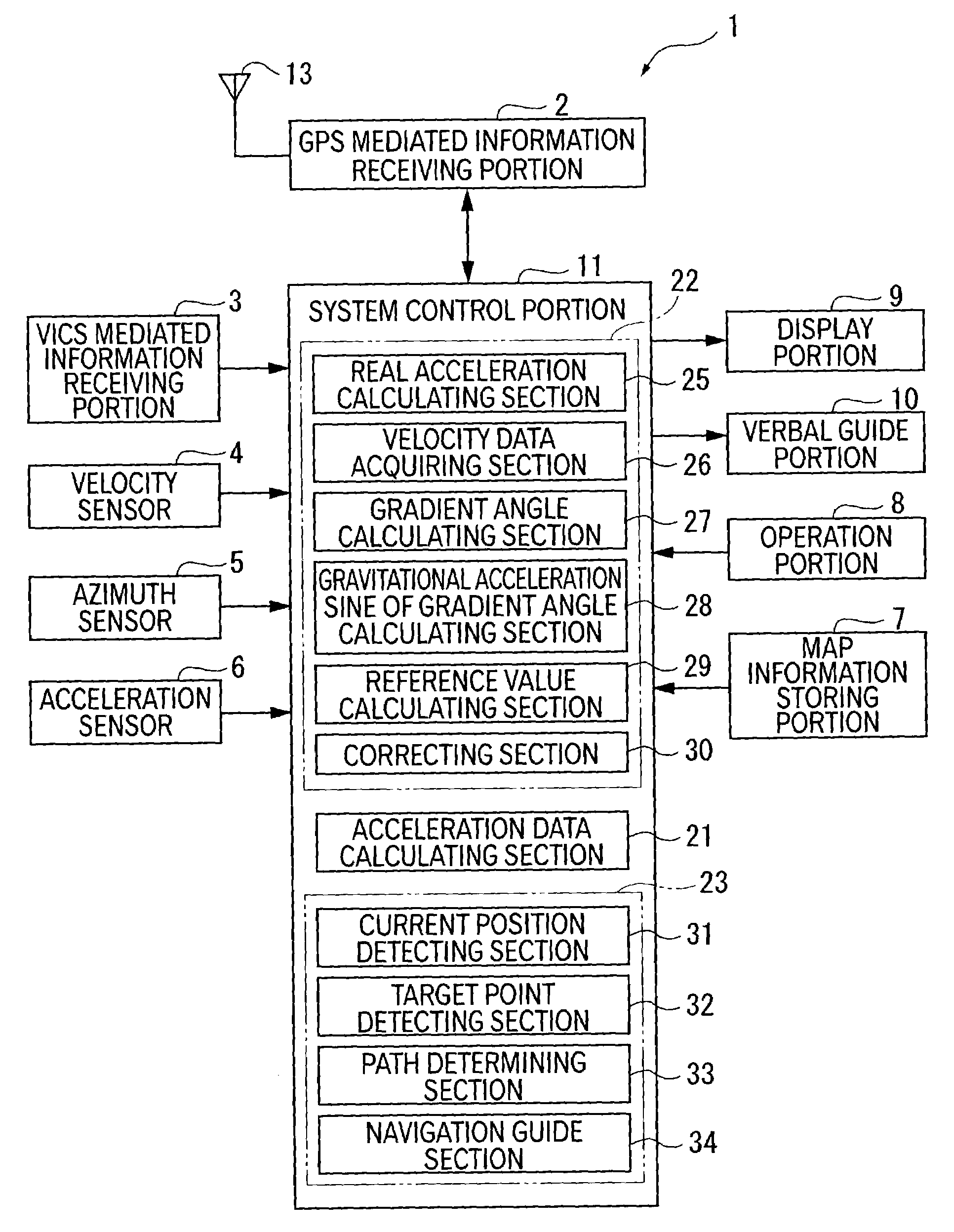
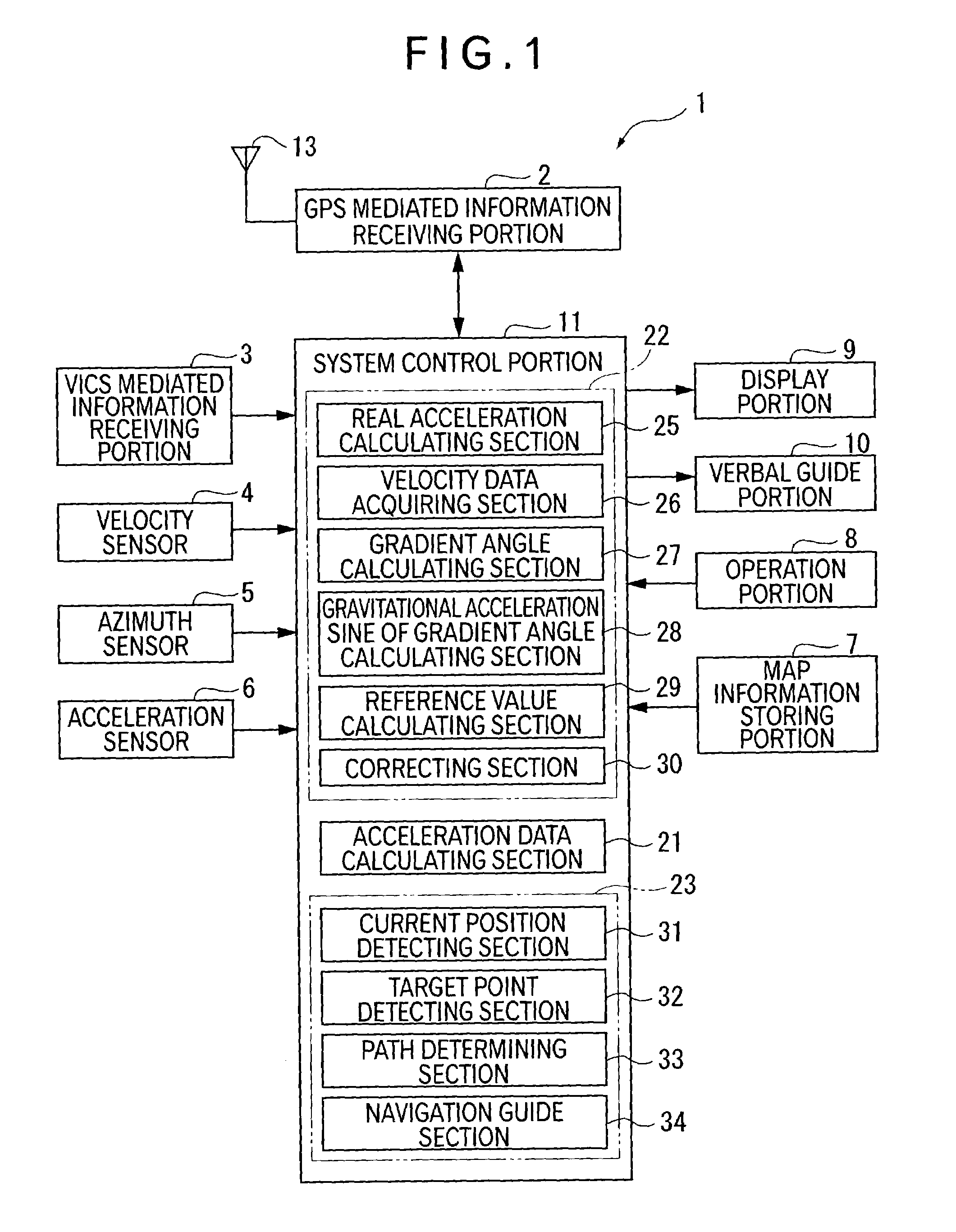
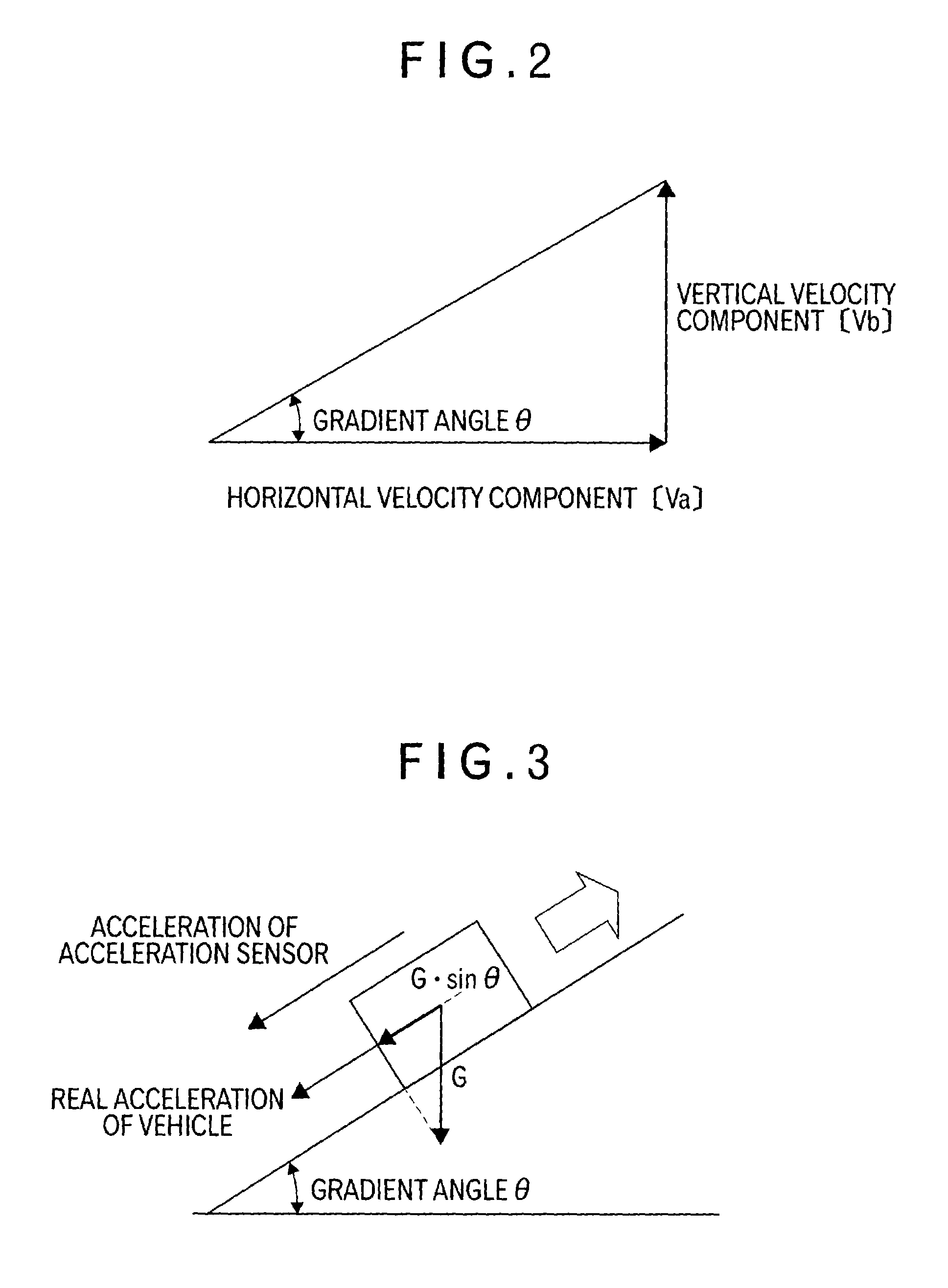
Correction device for correcting acceleration data, method therefor, program therefor, recording medium containing the program and navigation guide device
InactiveUS6959240B2Easy to getAccurate guideAnalogue computers for trafficRoad vehicles traffic controlRadio navigationHorizontal and vertical
A correction device determines, by calculation, a real acceleration based on output from a velocity sensor 4. GPS mediated signal receiving portion 2 receives radio navigation waves from plural GPS satellites. The device detects a frequency change of the radio waves evoked as a result of Doppler effect, acquires horizontal and vertical velocity components based on the frequency change, and determines, by calculation, a gradient angle. Then, the device determines, by calculation, the gravitational acceleration sine of the gradient angle (G. sin θ). The device adds the real acceleration and the gravitational acceleration sine of the gradient angle (G. sin θ) to provide a theoretical acceleration of the acceleration sensor. The device divides the theoretical acceleration of the acceleration sensor with the sensitivity of the acceleration sensor 6, and subtracts the result from output from the acceleration sensor 6, to provide a right offset value. Then, the sequentially obtained offset values are averaged to give an updated offset value. This process makes it possible to readily obtain a right offset value even during the driving of the mobile body.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
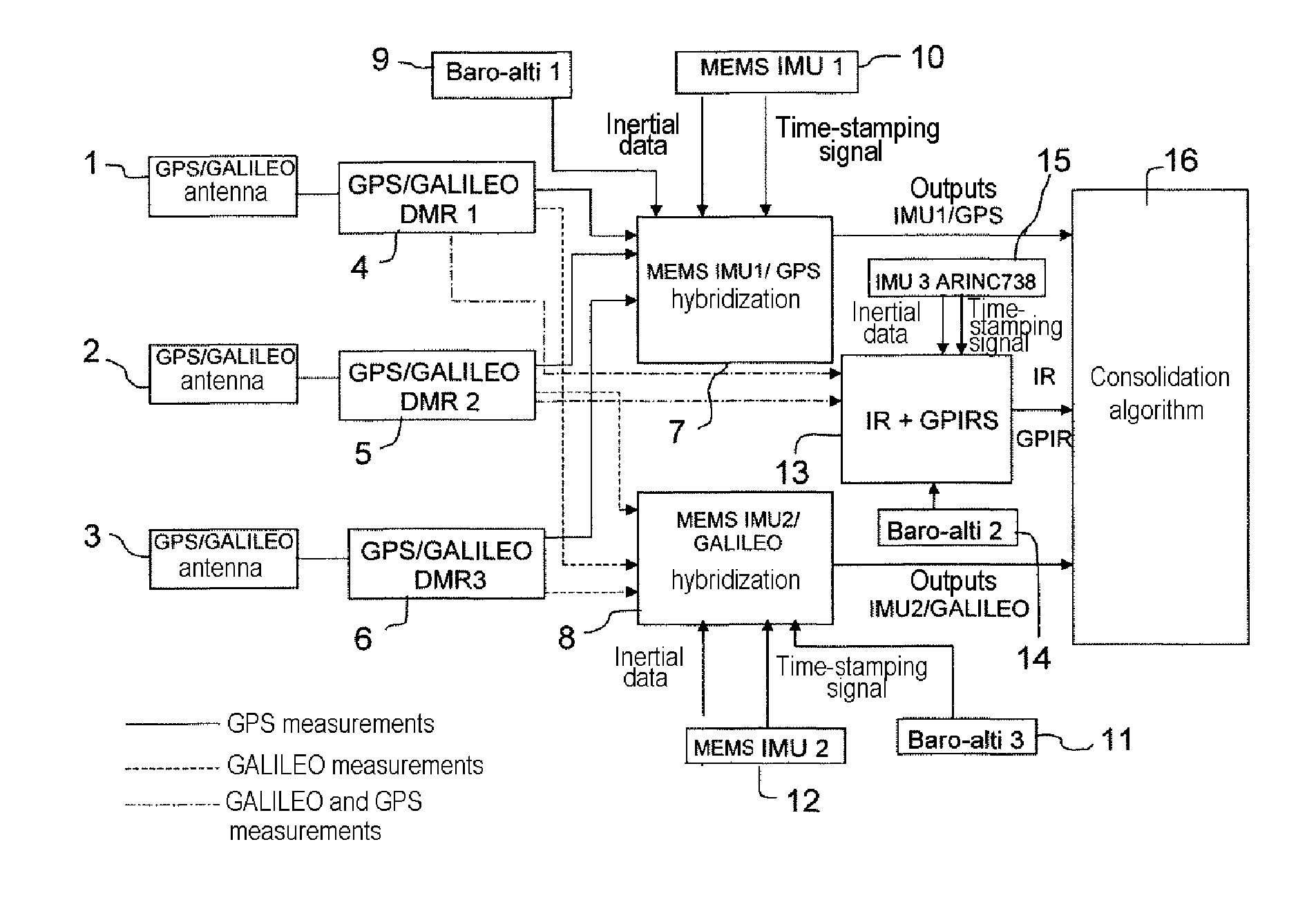
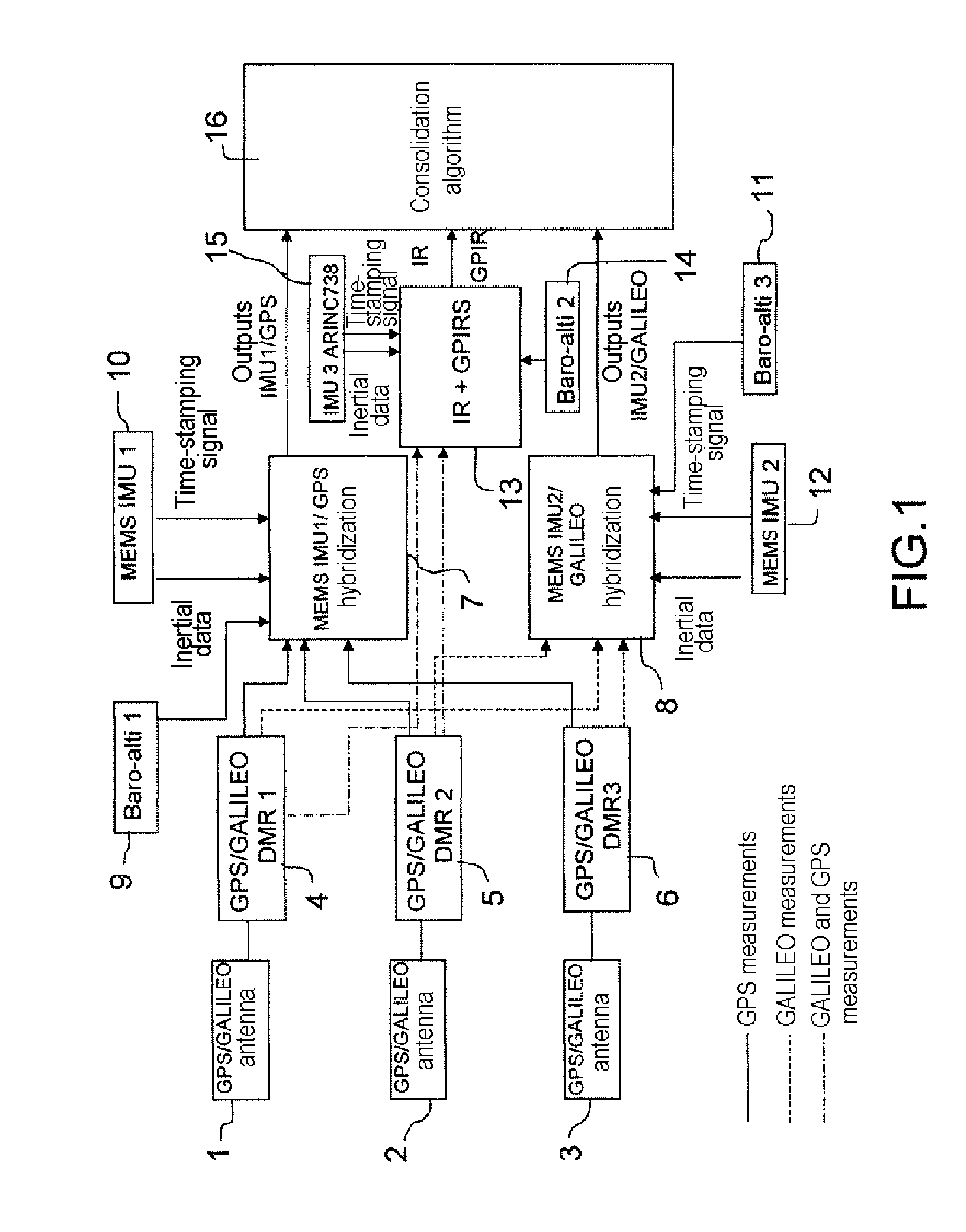
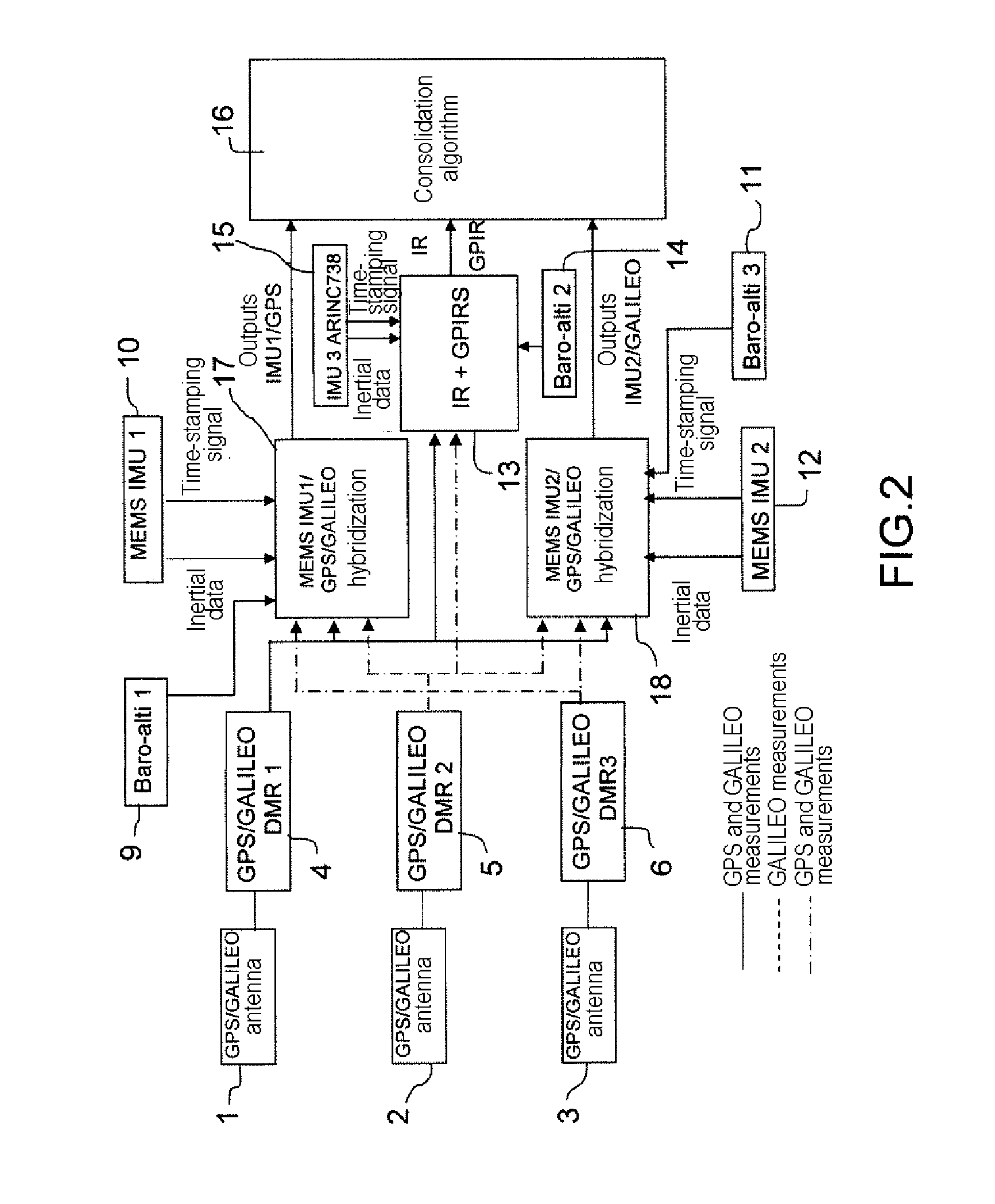
Air navigation device with inertial sensor units, radio navigation receivers, and air navigation technique using such elements
InactiveUS20120004846A1Improve mean time between failuresEasy to operatePosition fixationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsEngineeringRadio navigation
The present invention relates to an air navigation device with inertial sensor units and radio navigation receivers, and is characterized in that its radio navigation receivers are multiple-constellation receivers and in that their output data are hybridized with the data from the inertial sensor units. According to another feature of the invention, at least some of the inertial sensor units are of MEMS type.
Owner:THALES SA
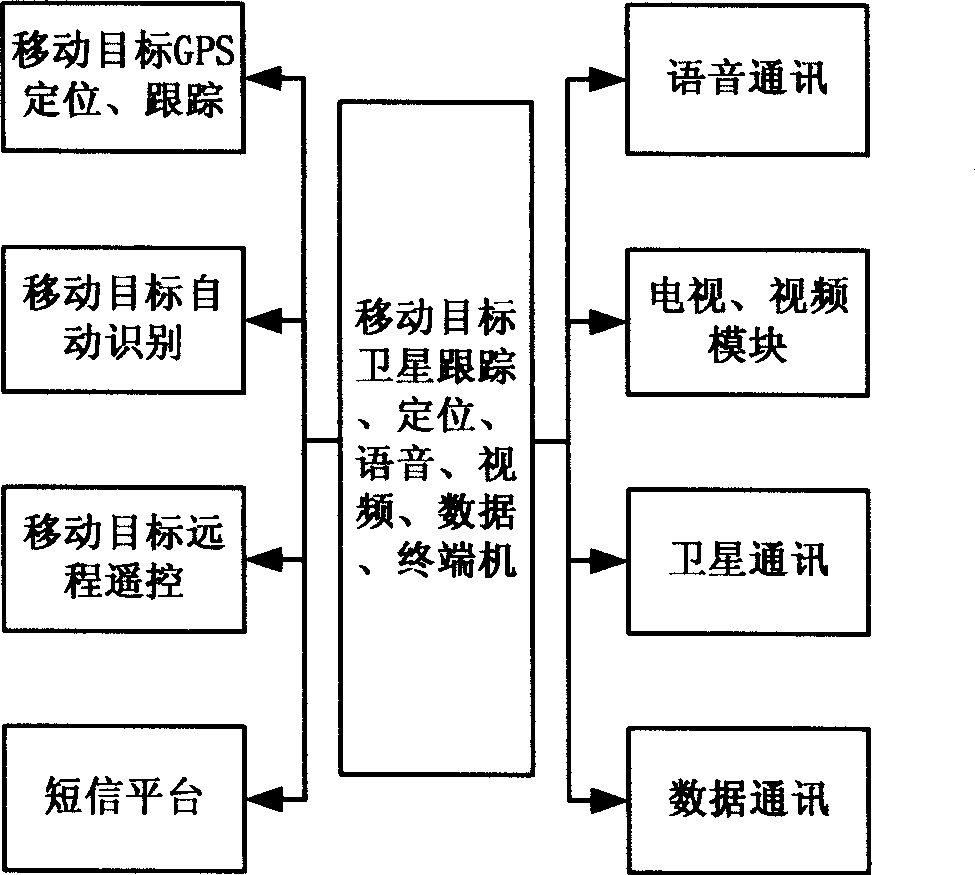
Mobile target satellite tracking localization, recognition, voice video and data transmission terminal
InactiveCN101414866ABest sailing timeIntuitive Collision Avoidance InformationBeacon systems using radio wavesRadio transmissionData informationRadio navigation
The invention discloses a realizing method of a terminal for tracking and positioning, identification, voice video and data transmission of a moving target satellite, in particular to an integrated navigation information system used for completing integrated ship-handling tasks on the basis of an electronic chart. The invention can integrate reckoned ship-position information, satellite positioning and radio navigation system data, chart information, voice information, video information, data information and radar information for processing and display; and the processed result is returned to various control equipment to control or prompt navigating staffs by medias such as images, voices, languages and the like. The invention not only can complete the operations which are carried out on the traditional paper chart and comprise design of intended route, calculation of distance and orientation, reckoning of position modification, positioning calculation, track indication and the like, but also can solve new problems that when the ship enters a danger area, alarming is carried out automatically, the ship avoids rock and prevents shallowness, the superimposing of the electronic chart and the radar images is used for providing more intuitive shockproof information and the chart is modified automatically. The invention can complete the construction of the platforms of the whole set of system.
Owner:中卫视讯卫星科技(北京)有限公司
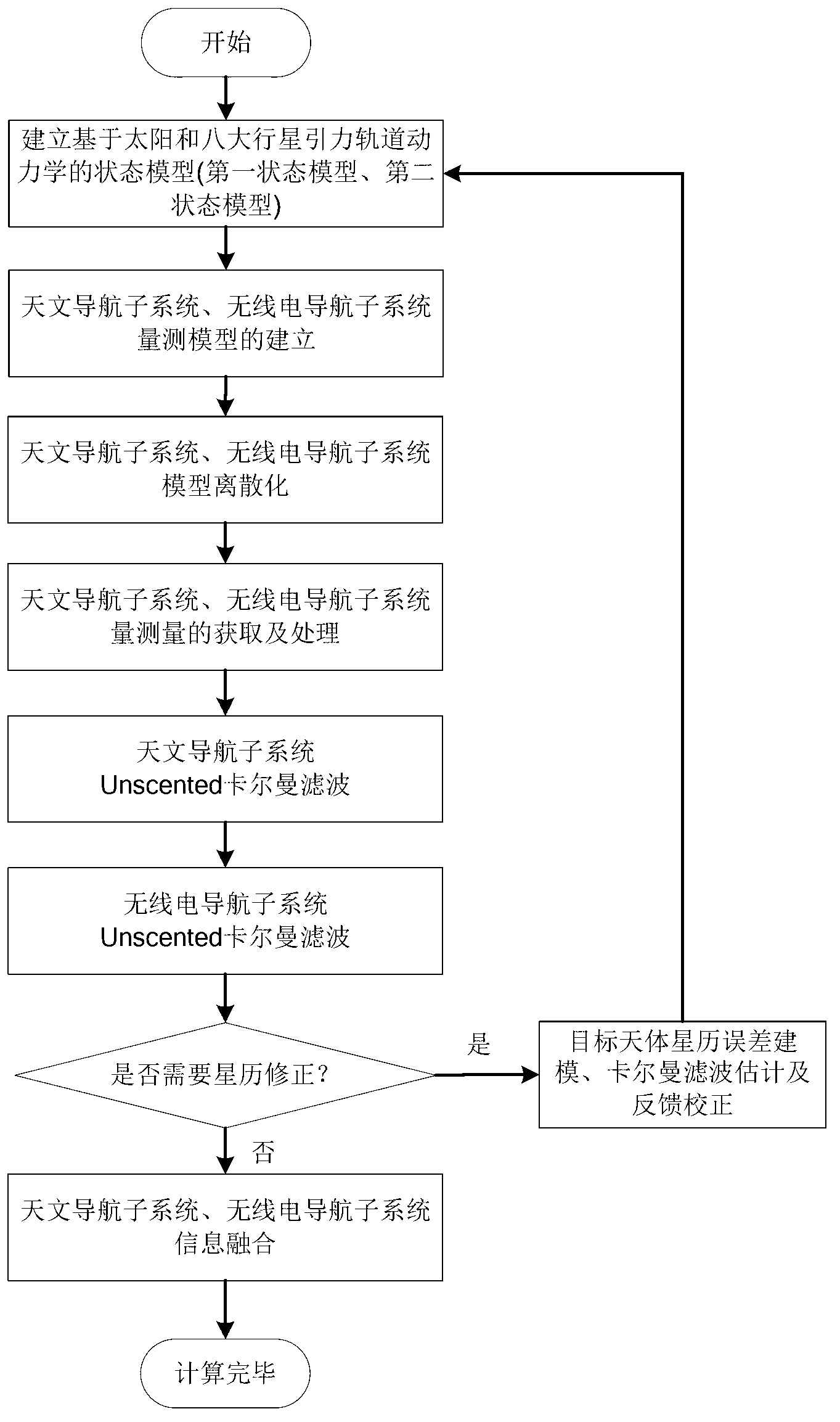
Deep space detector astronomy/radio combination navigation method based on ephemeris correction
ActiveCN103063217AAchieving High-Precision EstimationLittle impact on accuracyInstruments for comonautical navigationNavigation systemSpaceflight
The invention relates to a deep space detector astronomy / radio combination navigation method based on ephemeris correction. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a Mars detector state model and astronomy astronomy navigation and radio navigation subsystem measurement models, acquiring the measured values of astronomy and radio navigation subsystems, and carrying out filtering estimation to obtain the position of the detector in an inertia coordinate system treating a target heavenly body as a center and the speed of the detector; and establishing the ephemeris error state model and the measurement model of the target heavenly body based on the position and the speed, obtaining the ephemeris error measurement value of the target heavenly body according to the estimation states of the two astronomy and radio navigation subsystems, utilizing a Kalman filtering method estimate the ephemeris error of the target heavenly body, feeding back to a navigation system model, and carrying out information fusion. The deep space detector astronomy / radio combination navigation method belongs to the technical field of spaceflight and navigation, can realize the online estimation of the heavenly body ephemeris error and the correction of the navigation system model error, and is suitable for the capture segment of a detector.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Radio guidance antenna, data communication method, and non-contact data communication apparatus
InactiveUS7342548B2Valid conversionImprove performanceResonant long antennasAntenna supports/mountingsElectrical conductorRadio navigation
A radio guidance antenna in which the sum of mutual inductances of antennas is minimized. The radio guidance antenna includes a first antenna which is divided into upper and lower half regions by antenna conductors, and a second antenna which is composed of an antenna conductor and formed on the same plane as or a plane parallel to a plane of the first antenna. The second antenna is not connected to the first antenna at any points where it intersects the first antenna, but rather is inductively coupled to the upper and lower halves of the first antenna through mutual inductance regions. The first antenna is supplied with electric power from a first feeding point, and the second antenna is supplied with electric power from a second feeding point. The invention also includes a data communication method and a non-contact data communication apparatus which make use of the radio guidance antenna.
Owner:ORMON CORP
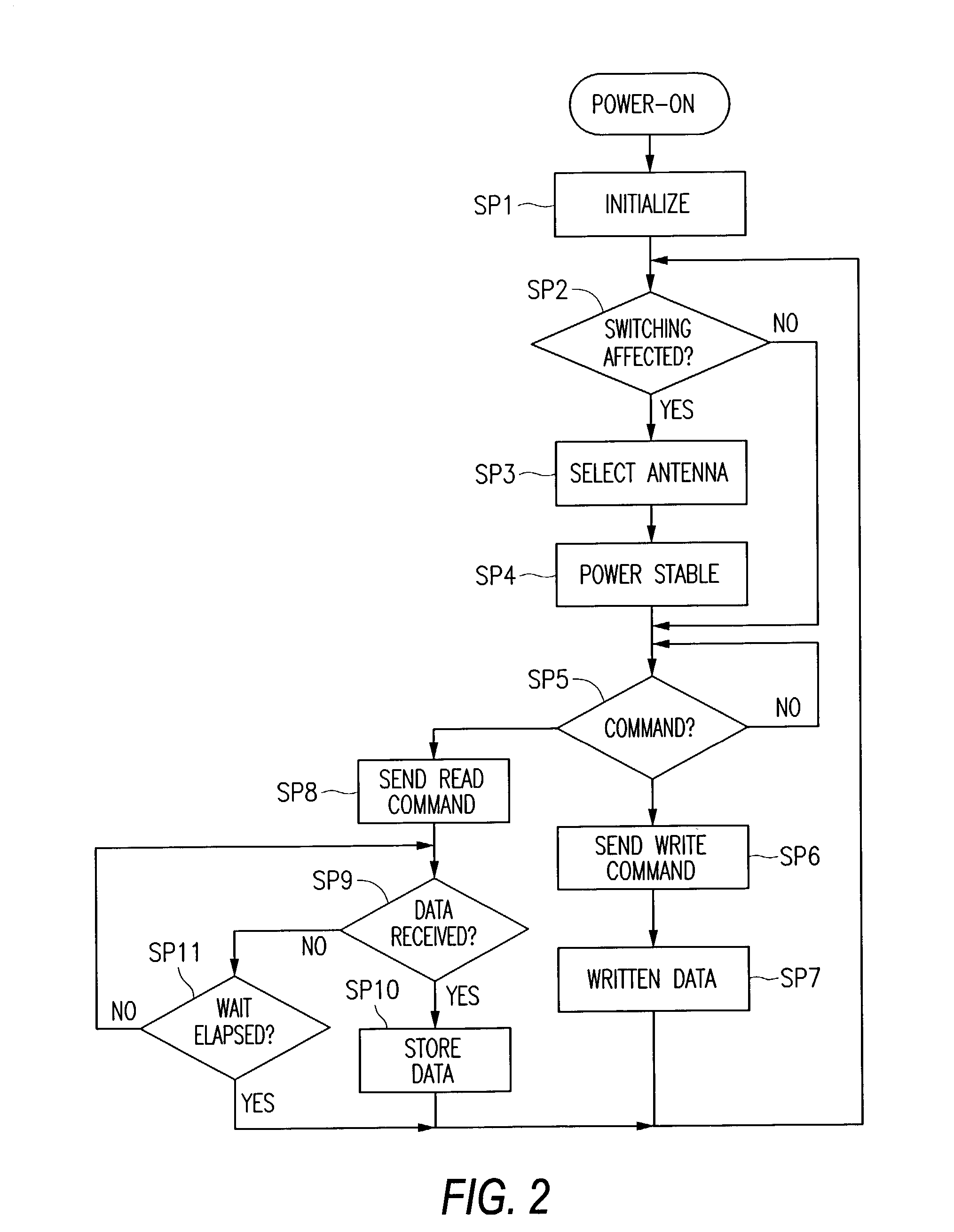
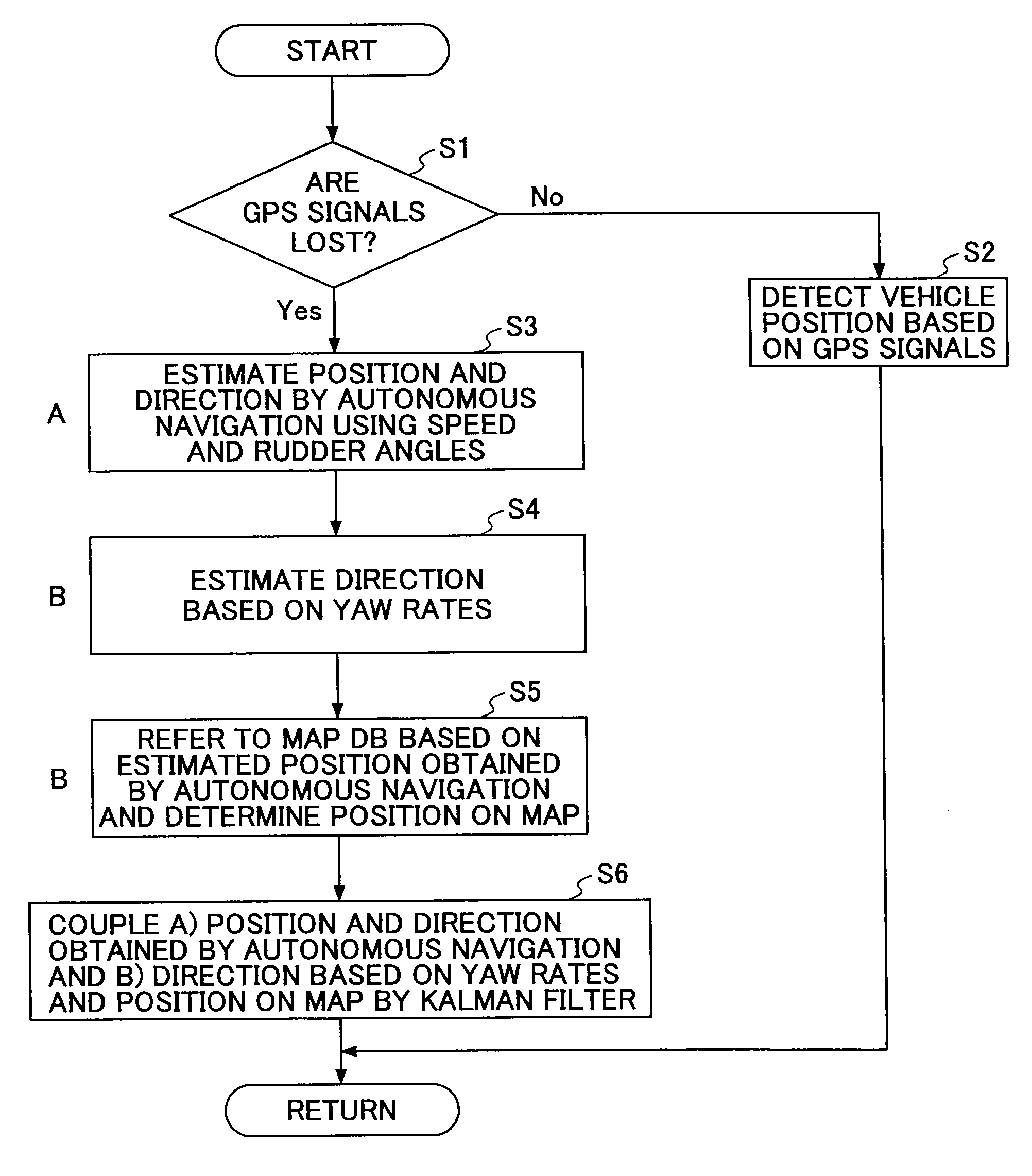
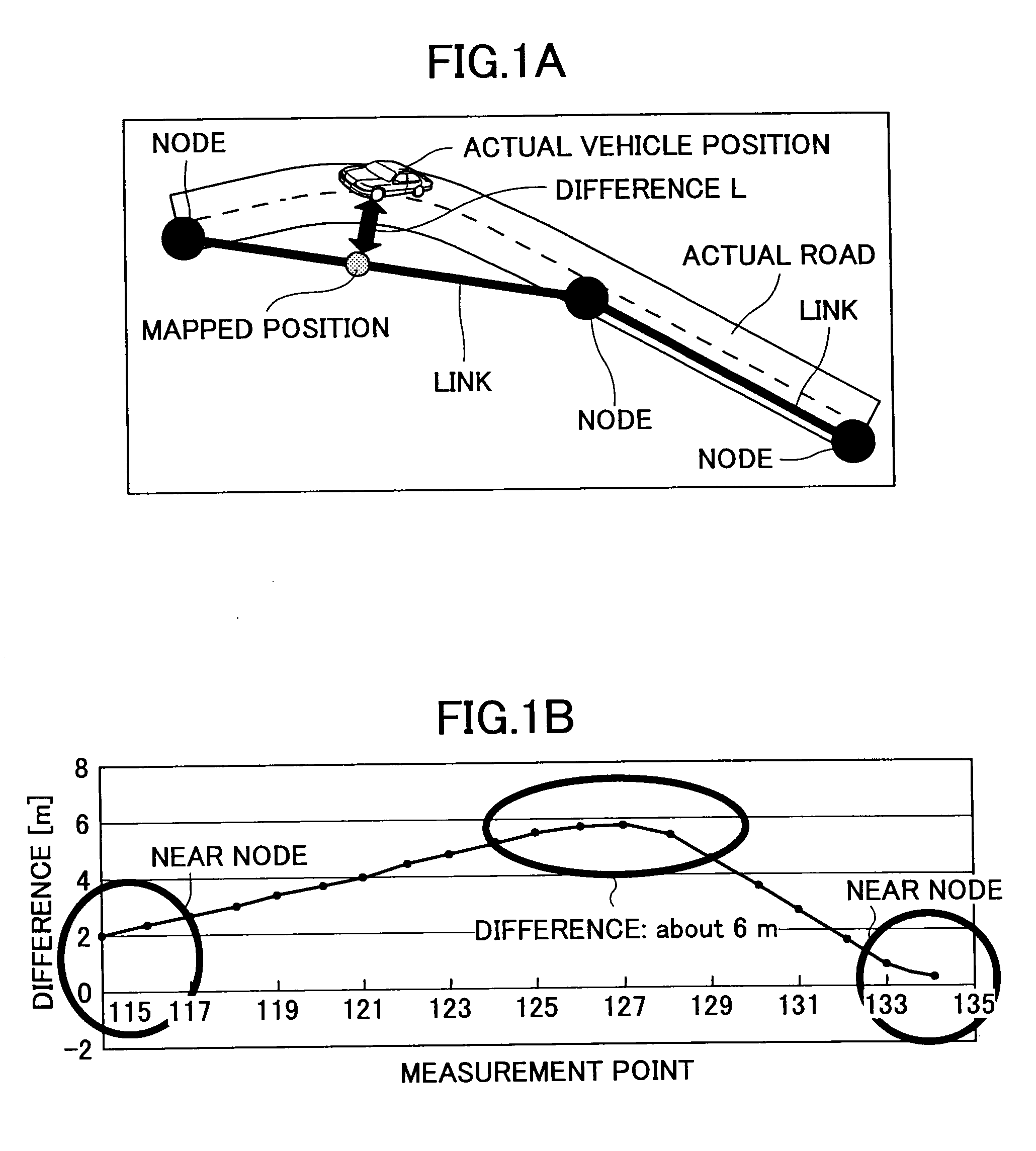
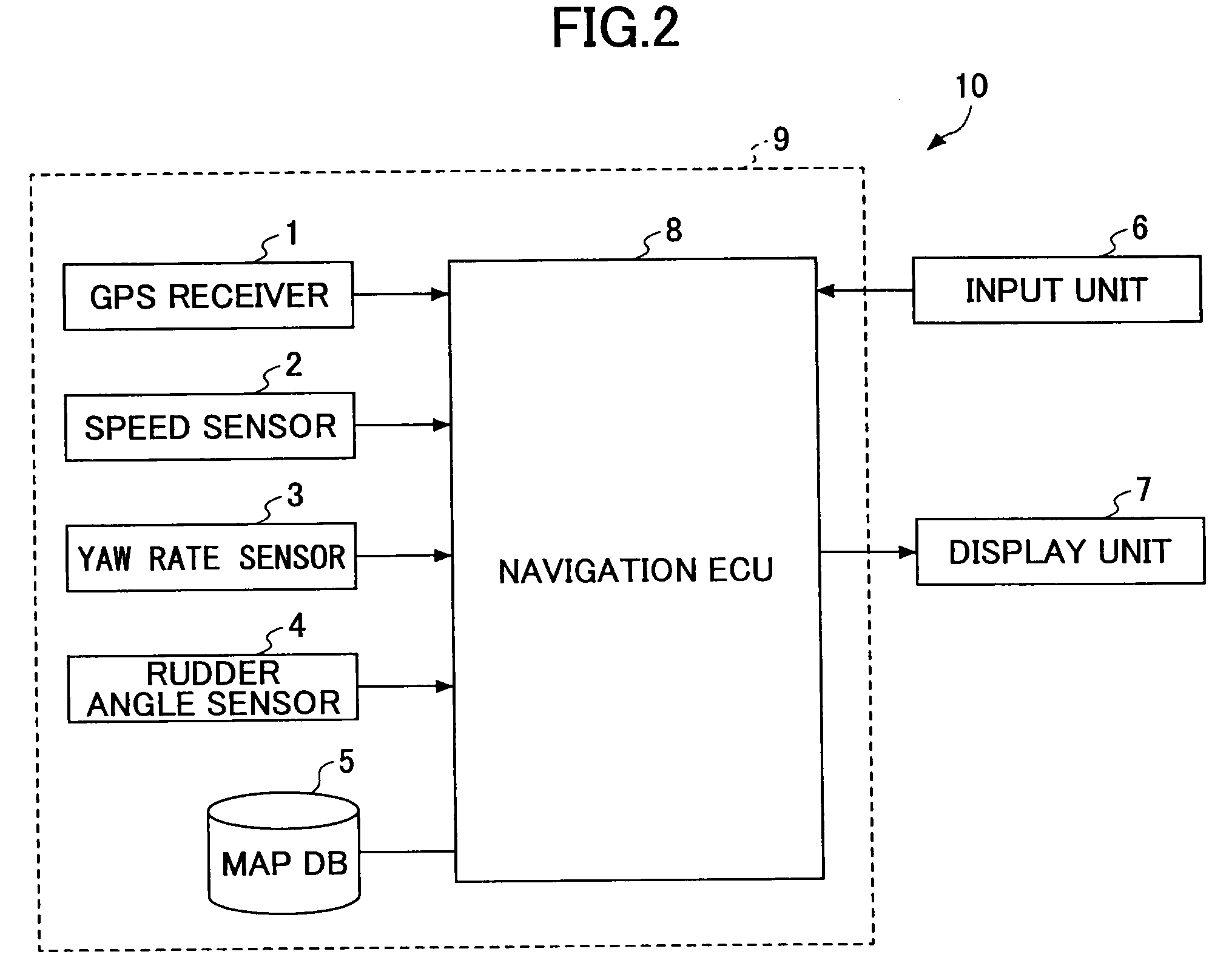
Positioning Device, and Navigation System
ActiveUS20080228395A1Precise positioningInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlLocation detectionKaiman filter
A positioning device that detects a position of a mobile body with a radio navigation positioning unit includes: first and second autonomous sensors obtaining behavioral information on the mobile body; a position detecting unit obtaining an estimated position and an estimated direction by updating a detection result based on the behavioral information from the first autonomous sensor; a map data positioning unit that refers to a map data storage unit based on the estimated position and obtains a map data linked position at a predetermined distance away from a link; a direction detecting unit obtaining a cumulative estimated direction by updating the detection result based on the behavioral information from the second autonomous sensor; and a most probable position estimating unit estimating the position of the mobile body from the estimated positions and directions using the Kalman filter.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
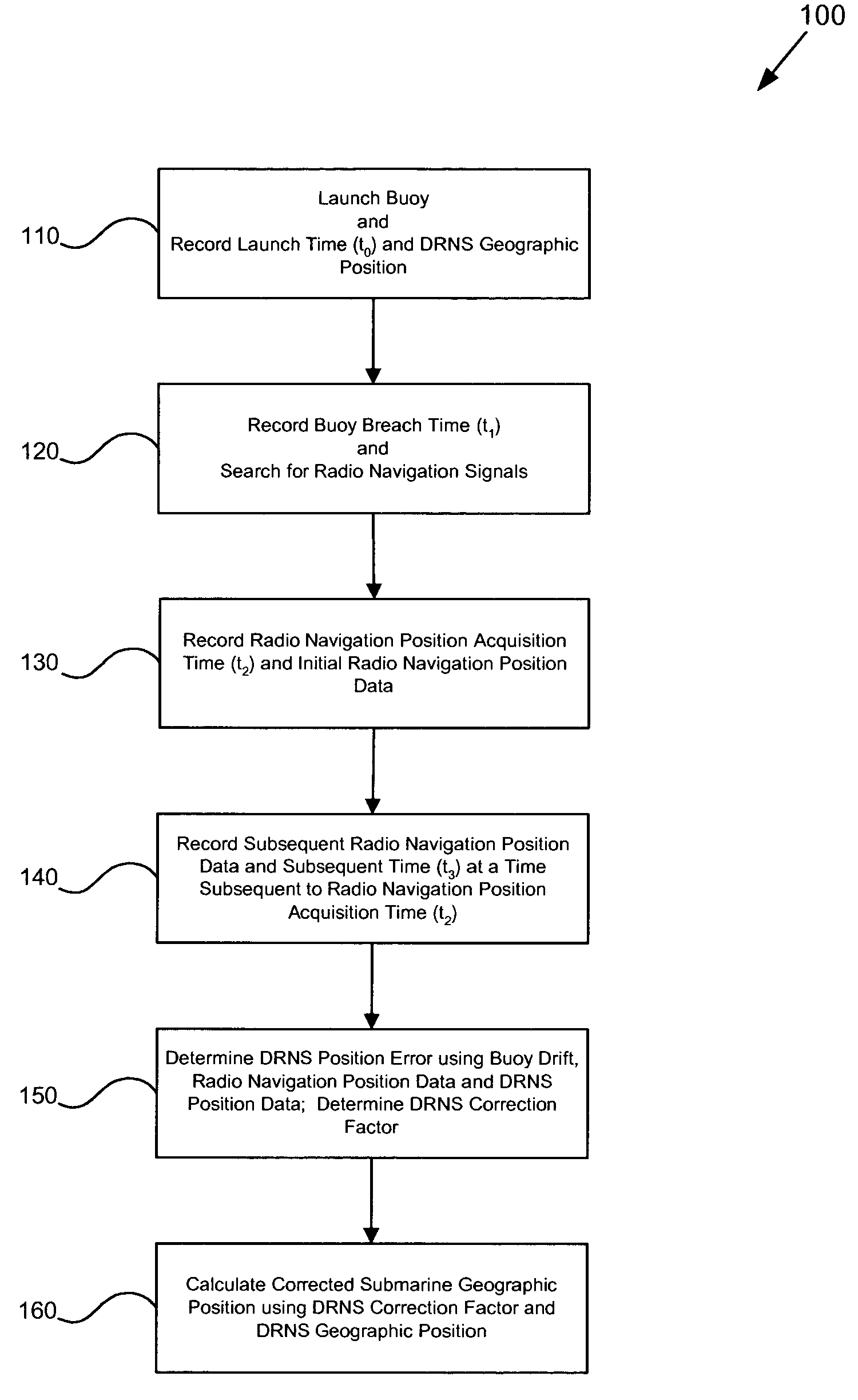
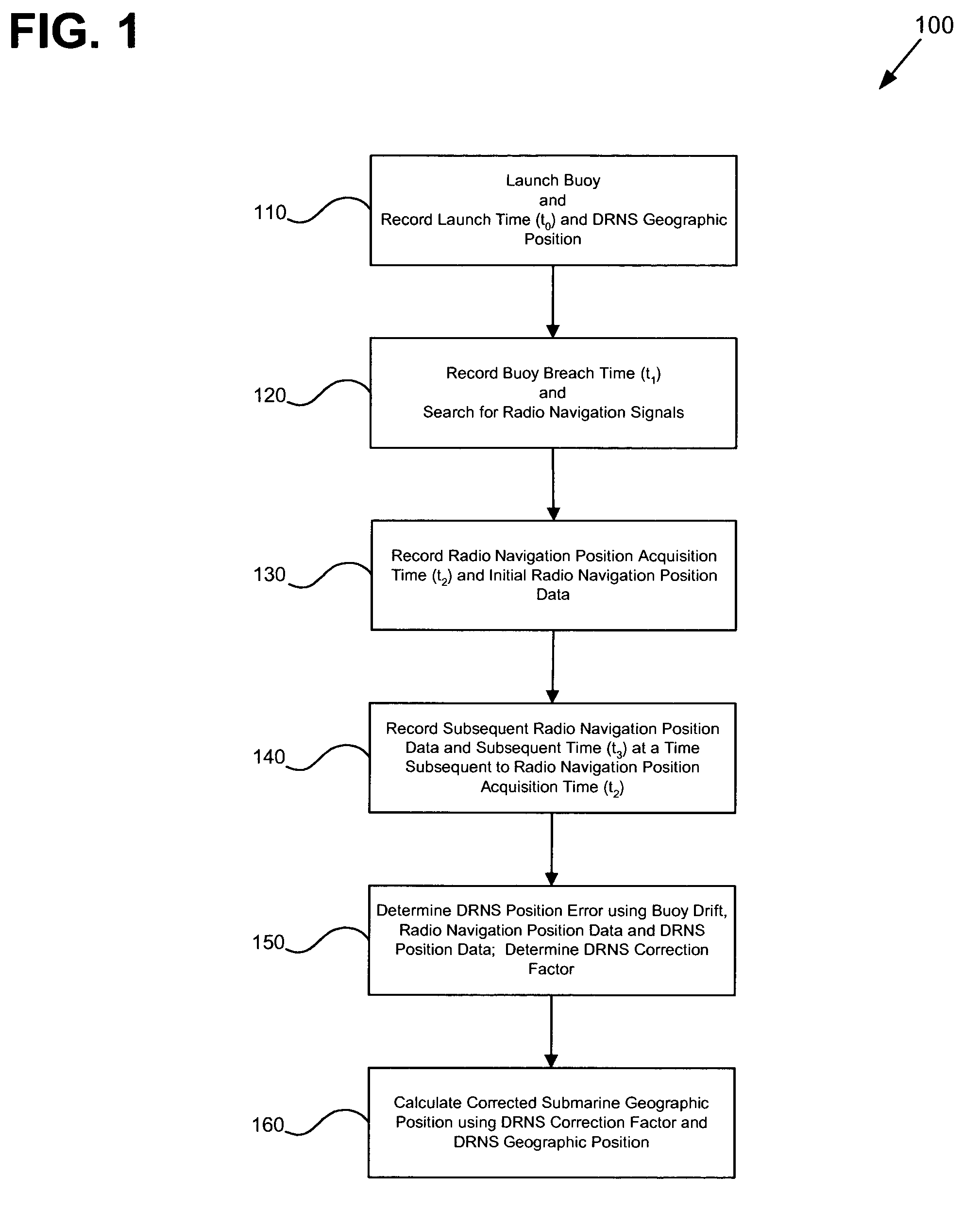
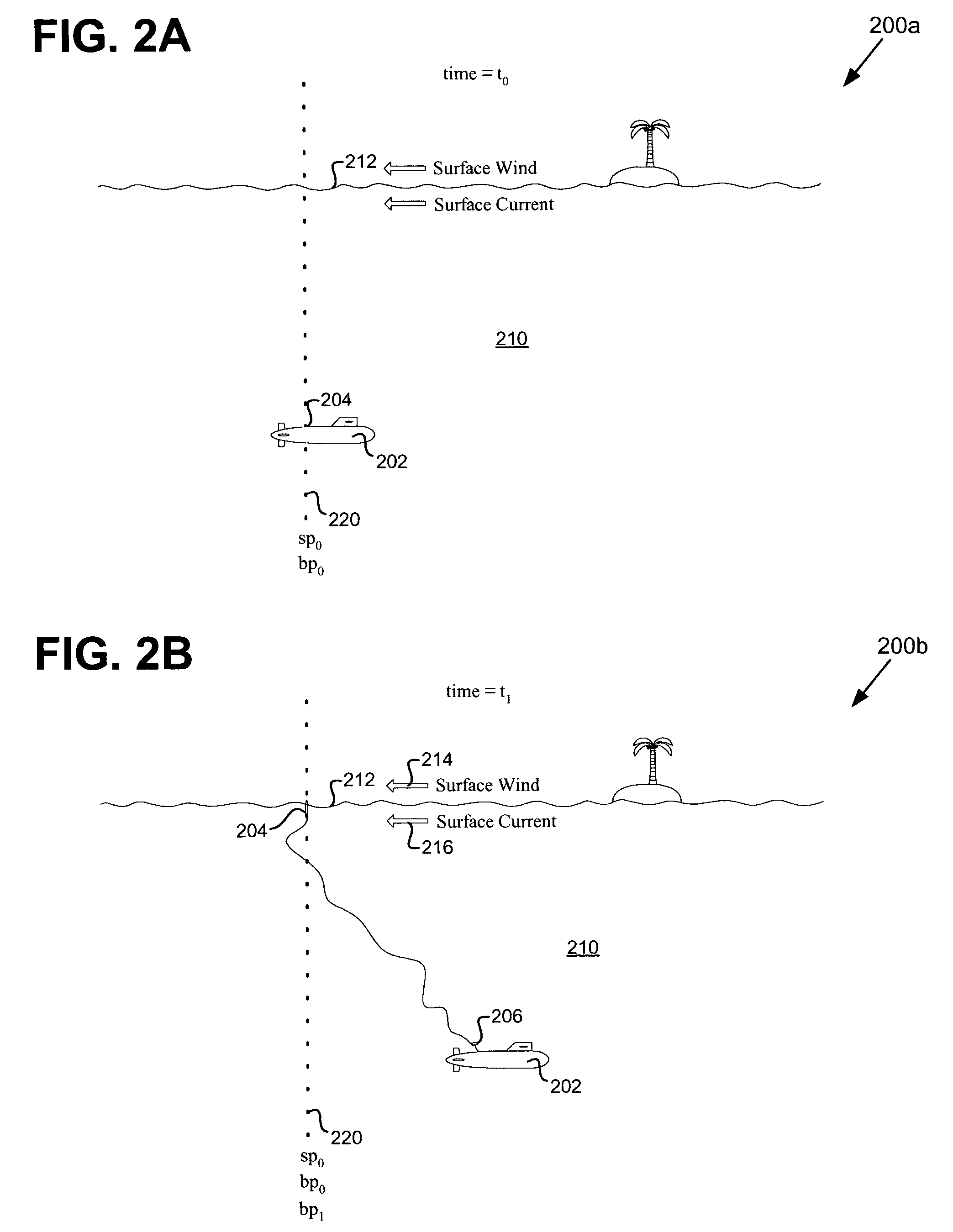
Submarine launched expendable radio navigation buoy system
InactiveUS6961657B1Improve accuracyInaccuracy can be correctedSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionPosition fixationOcean bottomAcquisition time
A submarine launched expendable radio navigation system (SSXRN) buoy method and apparatus. According to one embodiment, a method for determining a submarine geographic position using a SSXRN buoy system is disclosed. The method comprising launching a radio navigation-enabled buoy and recording a launch time and DRNS submarine position. The method further comprises recording a buoy breach time and searching for radio navigation RF signals. Then, recording a radio navigation position acquisition time and an initial radio navigation position. Further, recording a subsequent radio navigation position data and a subsequent time. Moreover, determining a DRNS correction factor using a DRNS position error, a buoy drift, radio navigation position data and DRNS position data. In addition, estimating the submarine geographic position using the DRNS correction factor and a DRNS geographic position. In another embodiment, a SSXRN buoy system is disclosed.
Owner:NAVY SEC OF THE UNITED STATES
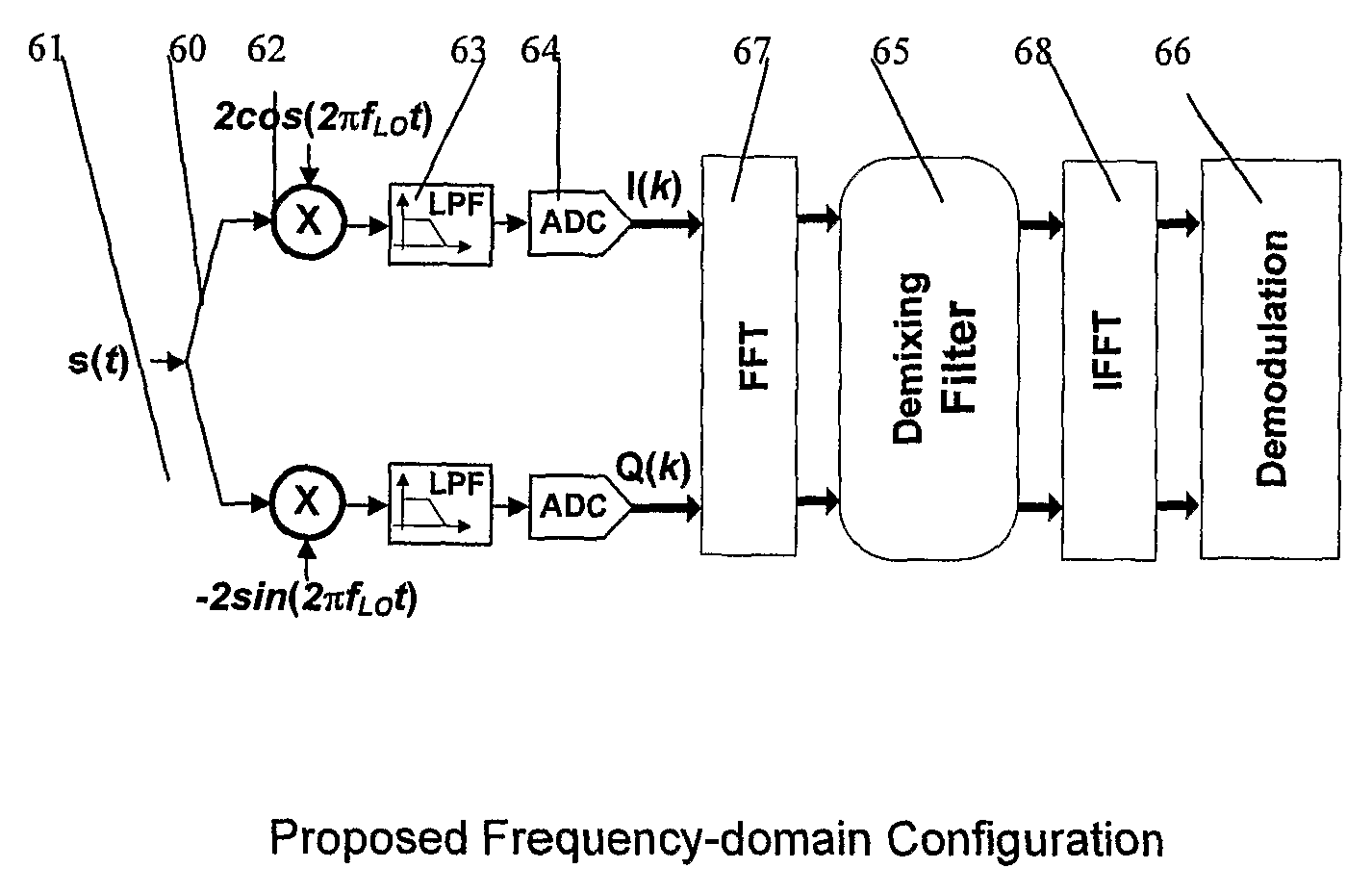
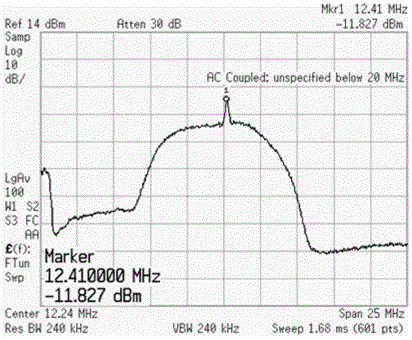
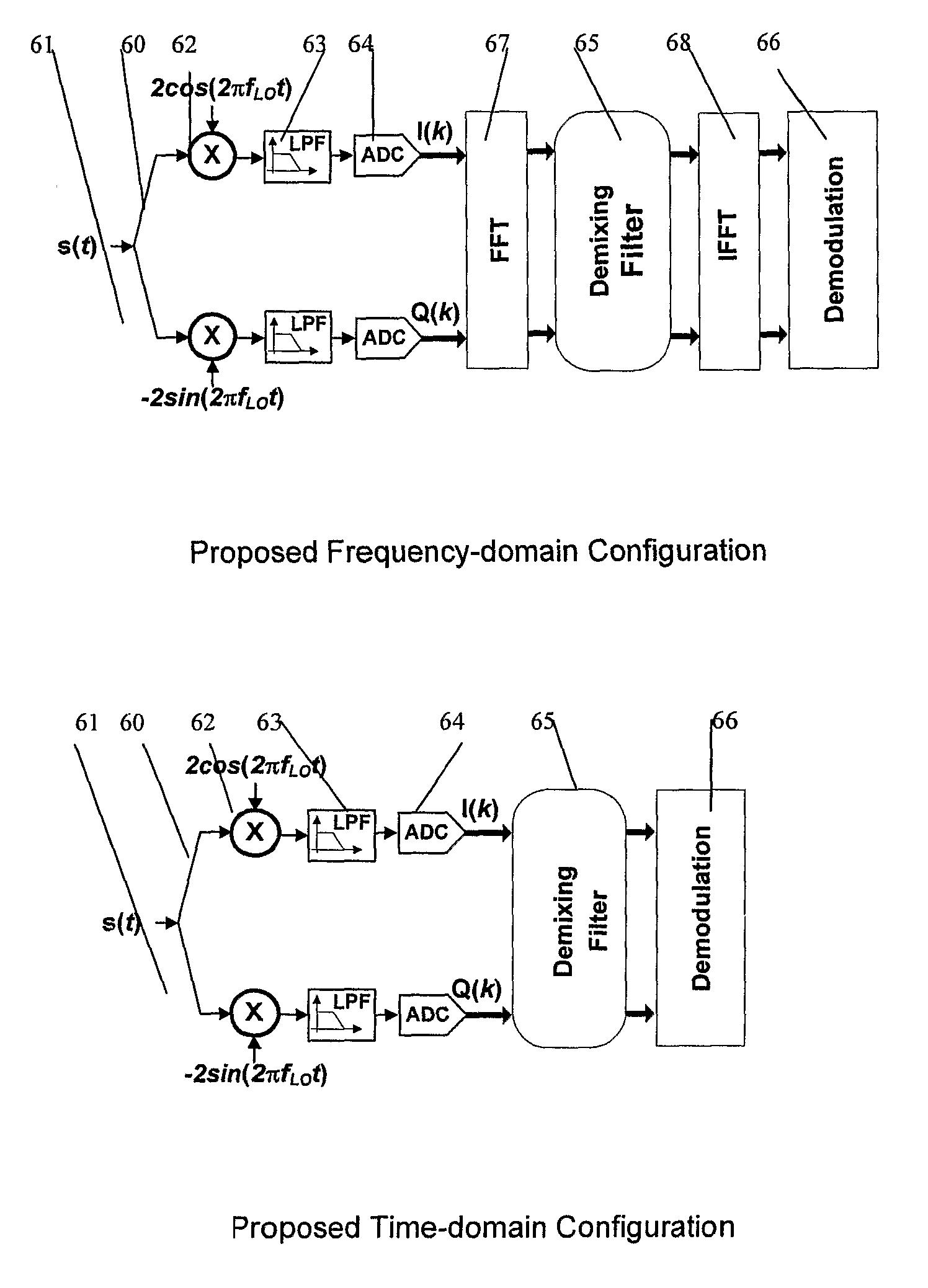
Satellite radio navigation receiver
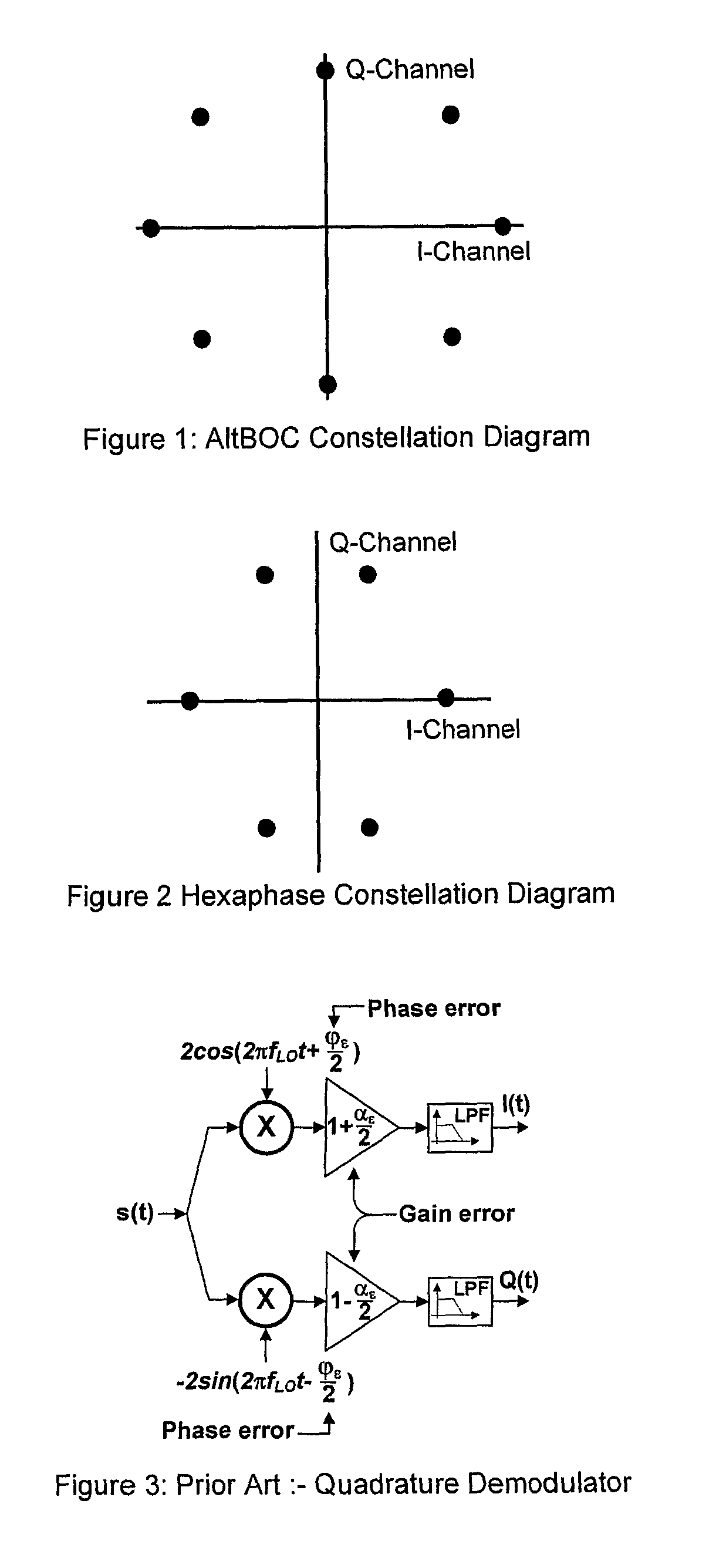
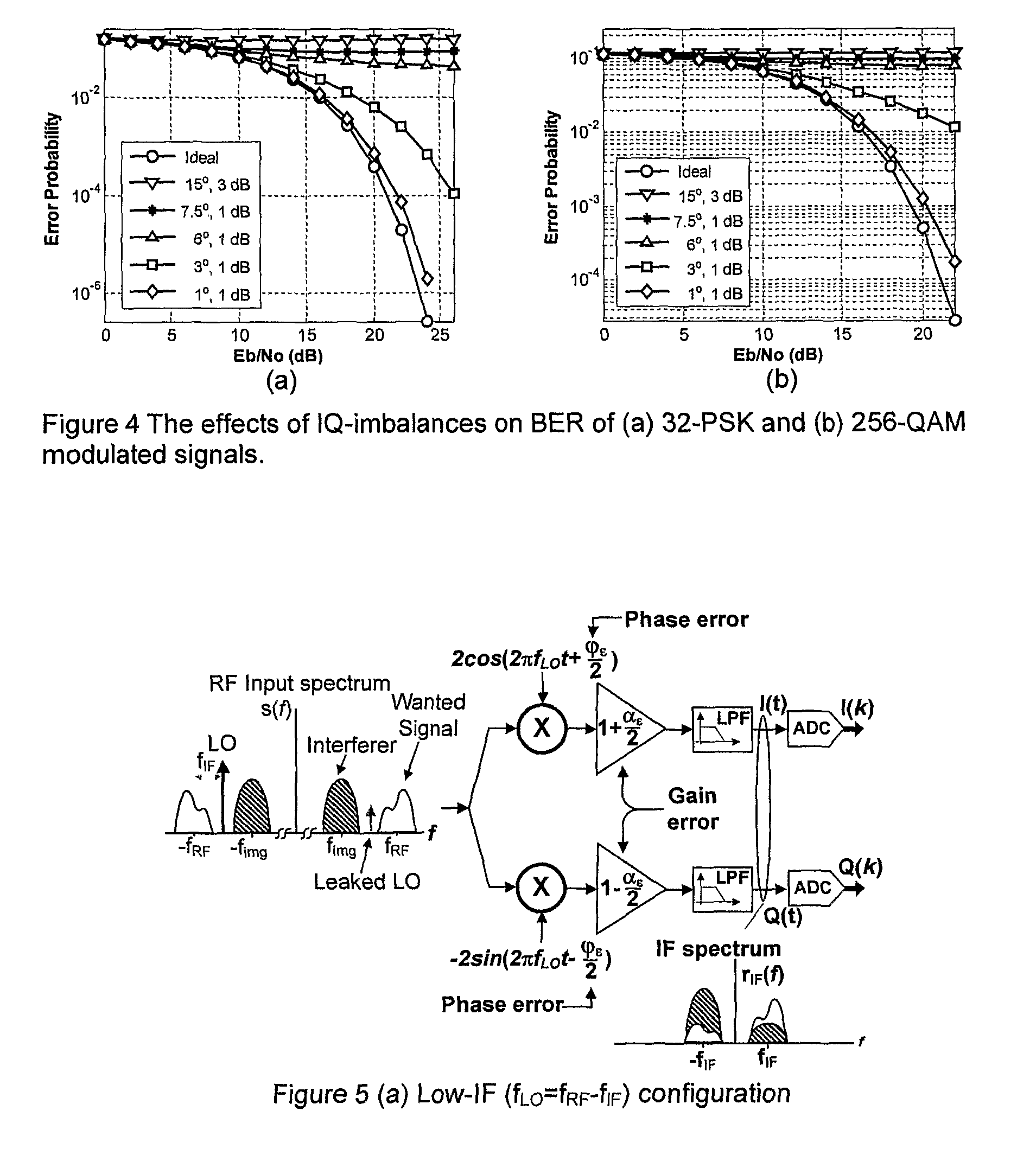
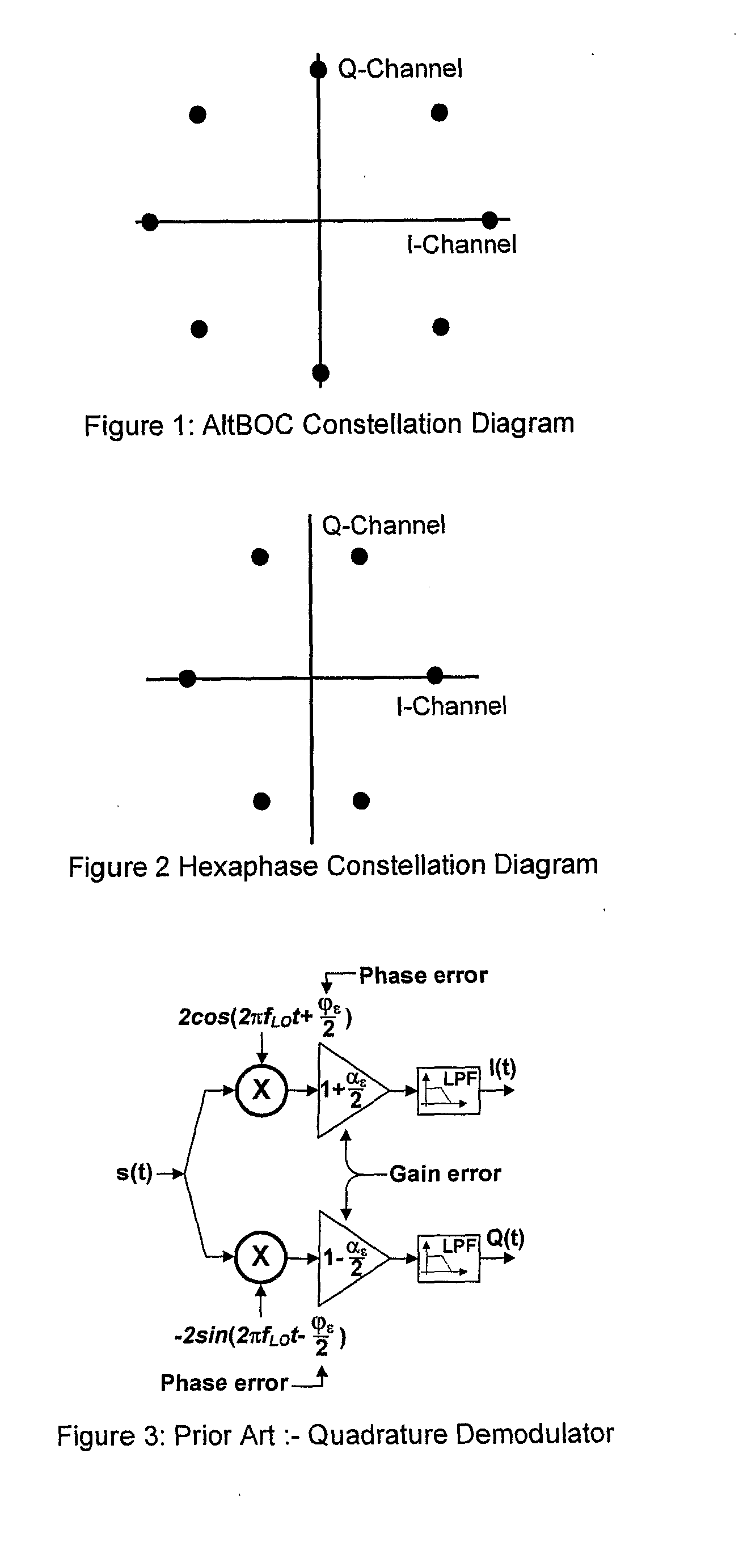
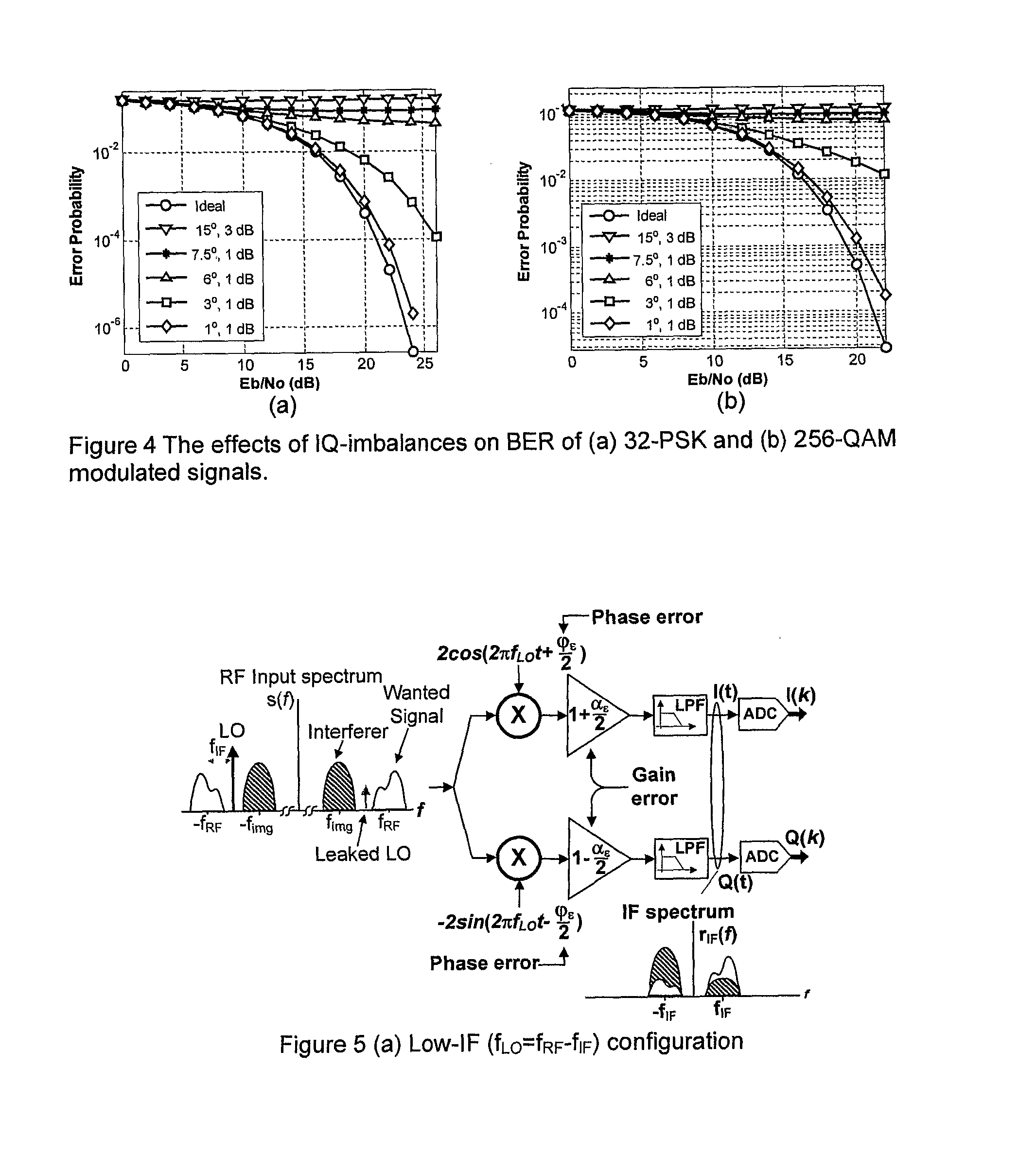
InactiveUS7839314B2Reduce RF impairmentEasy to integrateElectric signal transmission systemsEqual length code transmitterSatellite radioTime domain
In a satellite radio navigation receiver receiving a transmitted radio navigation signal, a method of removing I / Q-mismatches in the received signal, comprising: resolving the received signal into I and Q signal component, and providing them as inputs to a demixing stage which removes unwanted signals, the demixing stage including first and second cross-coupled adaptive filters, whose coefficients are updated by the outputs of the demixing stage, the outputs of the demixing stage representing an IQ mismatch corrected signal. The coefficients are updated only by the polarity values of the outputs, resulting in great simplification. The receiver may be a zero-IF or low-IF receiver, and may operate on time domain or frequency domain signals.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WESTMINSTER
Radio navigation emulating GPS system
InactiveUS6901331B1Eliminate errorsAccurately determineBeacon systems using radio wavesPosition fixationLongitudeRadio navigation
The present invention provides a radio navigation emulating GPS device. In one embodiment, the radio navigation emulating GPS device receives an identifier associated with a conventional radio navaid. The present radio navigation emulating GPS device then retrieves latitude and longitude information corresponding to the received conventional radio navaid from a database. A satellite based position information system generates position information for the aircraft on which the present radio navigation emulating GPS device is disposed. The present radio navigation emulating GPS device then generates navigation information for the aircraft using the retrieved latitude and longitude information and the satellite based position information for the aircraft. The present radio navigation emulating GPS device then presents the navigation information in a manner which emulates the presentation of navigation information generated by a conventional radio navigation device. The entire emulation process is transparent to the user of the present radio navigation emulating GPS device.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
Radioelectronic unit
InactiveUS6437991B1Cross-talk/noise/interference reductionPrinted electric component incorporationSatellite radioElectrical conductor
The invention relates to electronics and can be used in construction of electronic units performing the reception and processing of signals of the satellite radio navigation systems (SRNS). The essence of the invention is that in an electronic unit comprising a multilayer printed-circuit card, the conductors intended for screening the corresponding linking signal conductor are disposed at both its external surfaces and are connected with the ground planes by means of metallized holes of interface connections made at least at the beginning and end of each screening wire to form a closed electric circuit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Systems and methods for acquisition and tracking of low CNR GPS signals
A receiver for continuous carrier phase tracking of low carrier-to-noise ratio (“CNR”) signals from a plurality of radio navigation satellites while the receiver is mobile. The receiver may have: a radio frequency (RF) front-end that provides satellite data corresponding to signals received from the plurality of radio navigation satellites; an inertial measurement unit (IMU) that provides inertial data; and a processor circuit in circuit communication with the RF front end and the IMU, the processor circuit being capable of using satellite data from the RF front-end and inertial data from the IMU to perform continuous carrier phase tracking of low CNR radio navigation satellite signals having a CNR of about 20 dB-Hz, while the receiver is mobile. The receiver may be a GPS receiver for continuous carrier phase tracking of low-CNR GPS signals.
Owner:OHIO UNIV
Digital television multimedia broadcast transmission system exciter
InactiveCN101163246ASimple structureTelevision system detailsColor television detailsProcess moduleCarrier signal
Based on a new processing structure, the invention discloses a transfer system stimulator of digital television multimedia broadcasting which can implement signal process under per carrier modulation and multi carrier modes. The stimulator consists of a nonlinear pre-correction process module and a modulator, wherein, the modulator comprises a code current process module, a baseband digital modulation module, a digital-analogy switch module, a local oscillation generator, a phase shifter, a mixer, a combiner, a filter, a controller, and a controlling interface. The invention realizes the single frequency network combination of digital multimedia broadcasting transfer system, and accords with the requirements of CNS GB20600-2006 ground digital multimedia broadcasting (DTMB). Besides, the invention can be used to a plurality of other digital television multimedia broadcasting transfer system, with important applications in military and civil use such as deep sky detection, multimedia communication, radio navigation, etc.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Anti-4G (fourth generation)-interference Beidou GPS (global positioning system) multi-mode receiving-dispatching integration navigation communication module
ActiveCN104483685APrevent external radiationGuarantee authenticitySatellite radio beaconingIntermediate frequencyLow-pass filter
The invention discloses an anti-4G (fourth generation)-interference Beidou GPS (global positioning system) multi-mode receiving-dispatching integration navigation communication module, which comprises a Beidou first-generation RDSS (radio determination satellite service) unit, a Beidou second-generation RNSS (radio navigation satellite service) / GPS unit, a power supply processing unit, a connector and a metal box body, wherein the Beidou first-generation RDSS unit and the Beidou second-generation RNSS / GPS unit are both loaded on a PCB (printed circuit board); the power supply processing unit supplies power to the Beidou first-generation RDSS unit and the Beidou second-generation RNSS / GPS unit; a receiving-dispatching processing channel adopts an anti-4G-intererence receiving-dispatching circuit and comprises a low-noise amplifier (LNA), a first-level frequency Mixer1, a first low pass filter (LPF), a second-level frequency Mixer2, a band-pass filter (BPF), a variable gain amplifier (VGA) and a second LPF, wherein all components are successively connected; the signal output end of the second LPF is connected with a baseband processing module; a radio frequency signal IF1OUT output from the first-level frequency mixer1 is input into a first intermediate frequency surface acoustic wave filter IF1SAW; the IF1SAW outputs a frequency radio signal IF1IN to the input end of the first LPF. According to the module, the problem of receiving interference on the Beidou first-generation RDSS by a 4G signal is solved.
Owner:BONA RAINFIELD ELECTRONICS
Satellite Radio Navigation Receiver
InactiveUS20090058705A1Reduce RF impairmentEasy to integrateElectric signal transmission systemsEqual length code transmitterTime domainSatellite radio
In a satellite radio navigation receiver receiving a transmitted radio navigation signal, a method of removing I / Q-mismatches in the received signal, comprising: resolving the received signal into I and Q signal component, and providing them as inputs to a demixing stage which removes unwanted signals, the demixing stage including first and second cross-coupled adaptive filters, whose coefficients are updated by the outputs of the demixing stage, the outputs of the demixing stage representing an IQ mismatch corrected signal. The coefficients are updated only by the polarity values of the outputs, resulting in great simplification. The receiver may be a zero-IF or low-IF receiver, and may operate on time domain or frequency domain signals.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WESTMINSTER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com