Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
484 results about "Air navigation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The basic principles of air navigation are identical to general navigation, which includes the process of planning, recording, and controlling the movement of a craft from one place to another. Successful air navigation involves piloting an aircraft from place to place without getting lost, not breaking the laws applying to aircraft, or endangering the safety of those on board or on the ground. Air navigation differs from the navigation of surface craft in several ways; Aircraft travel at relatively high speeds, leaving less time to calculate their position en route. Aircraft normally cannot stop in mid-air to ascertain their position at leisure. Aircraft are safety-limited by the amount of fuel they can carry; a surface vehicle can usually get lost, run out of fuel, then simply await rescue. There is no in-flight rescue for most aircraft. Additionally, collisions with obstructions are usually fatal. Therefore, constant awareness of position is critical for aircraft pilots.
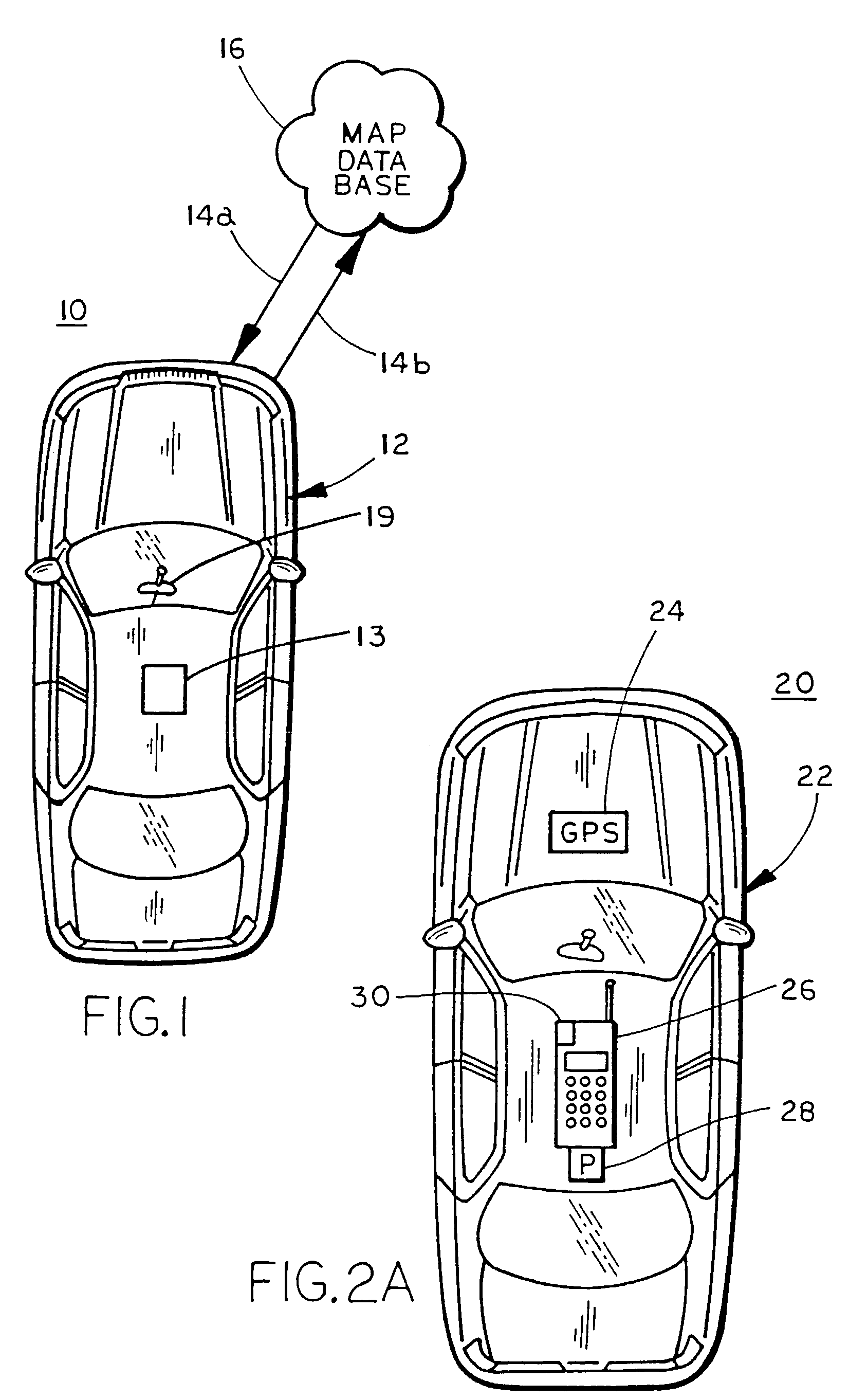
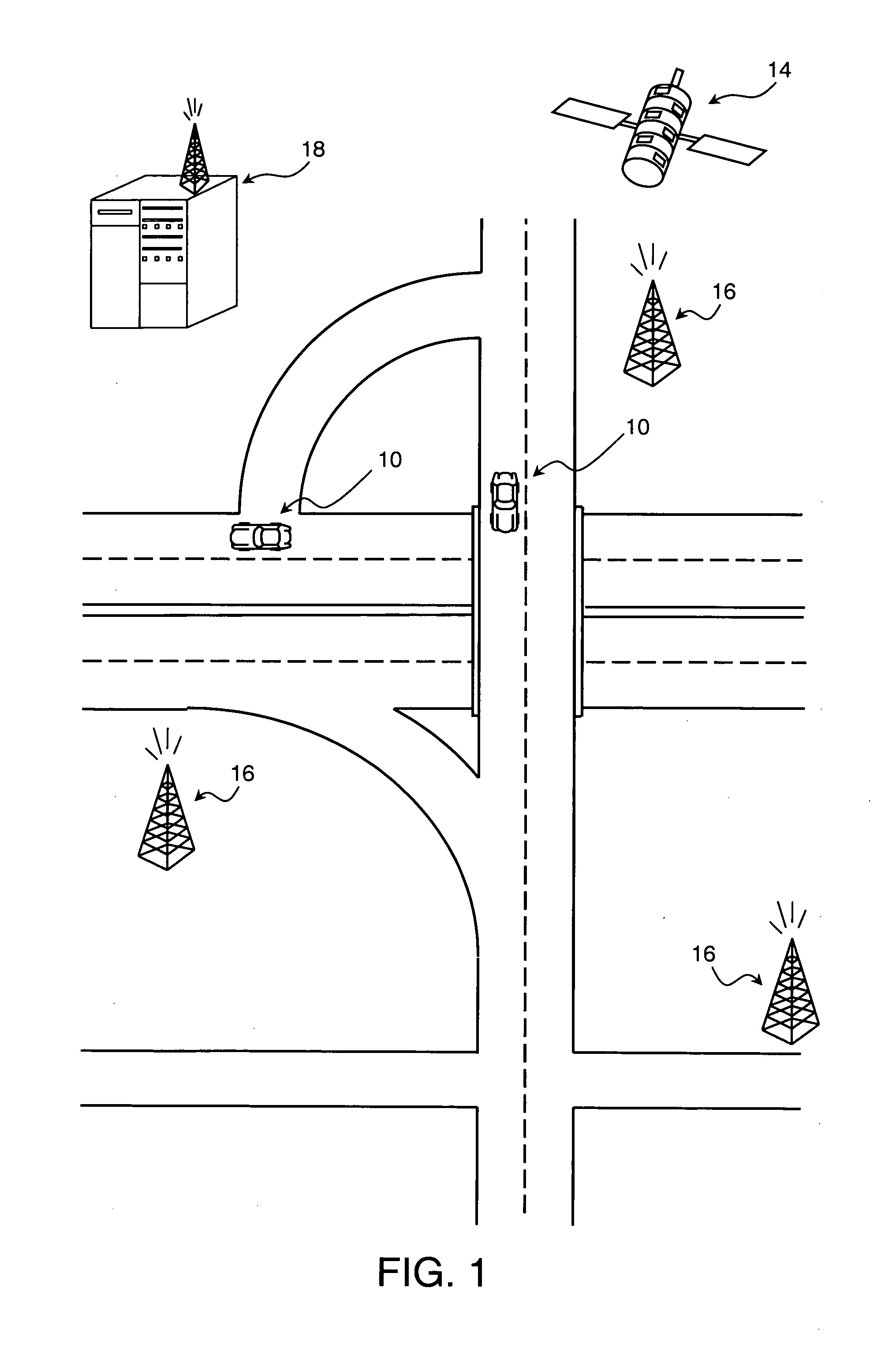
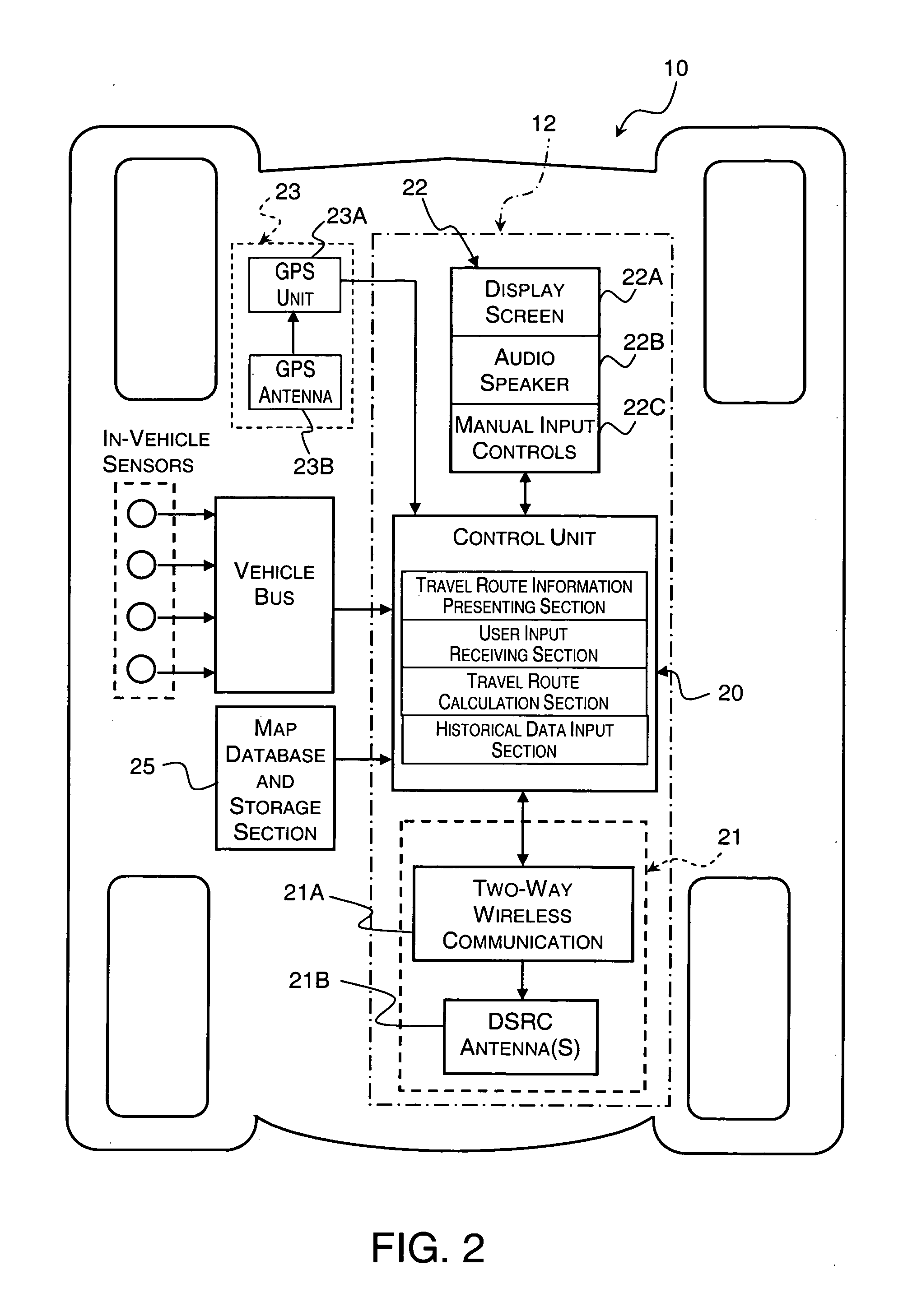
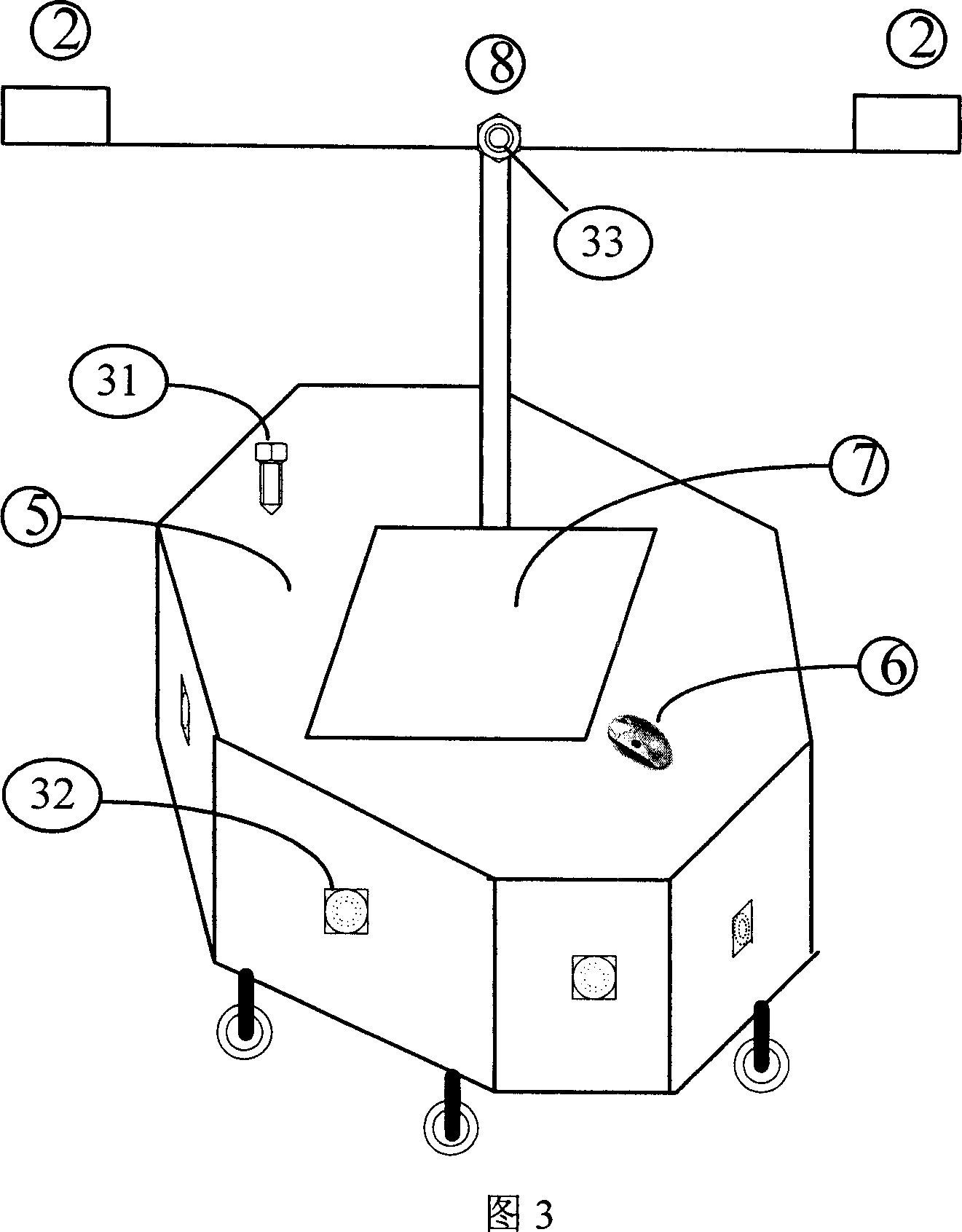
Dynamic navigation system
InactiveUS20050033511A1Increase speedImprove clarityInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlNavigation systemComputer science
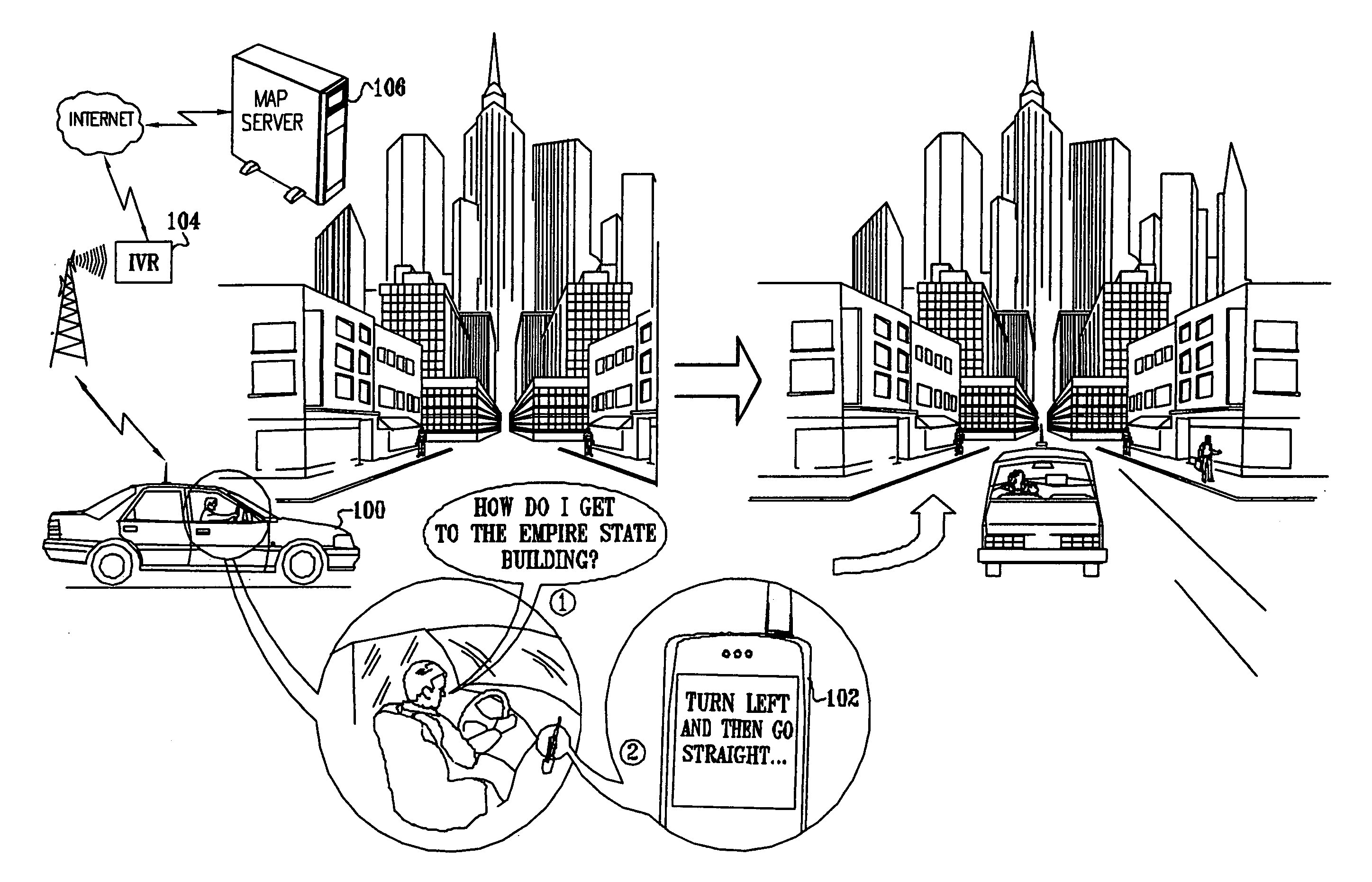
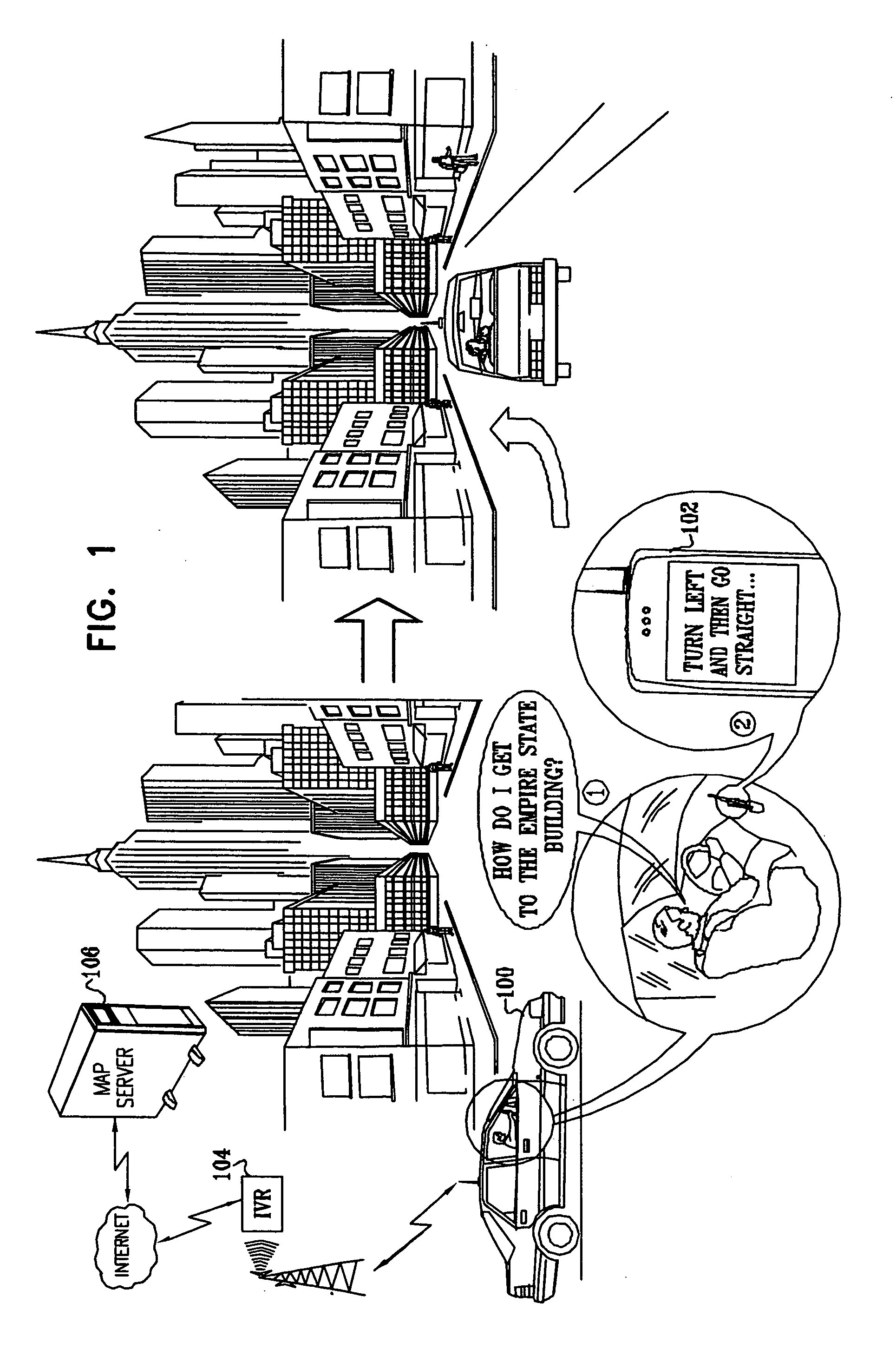
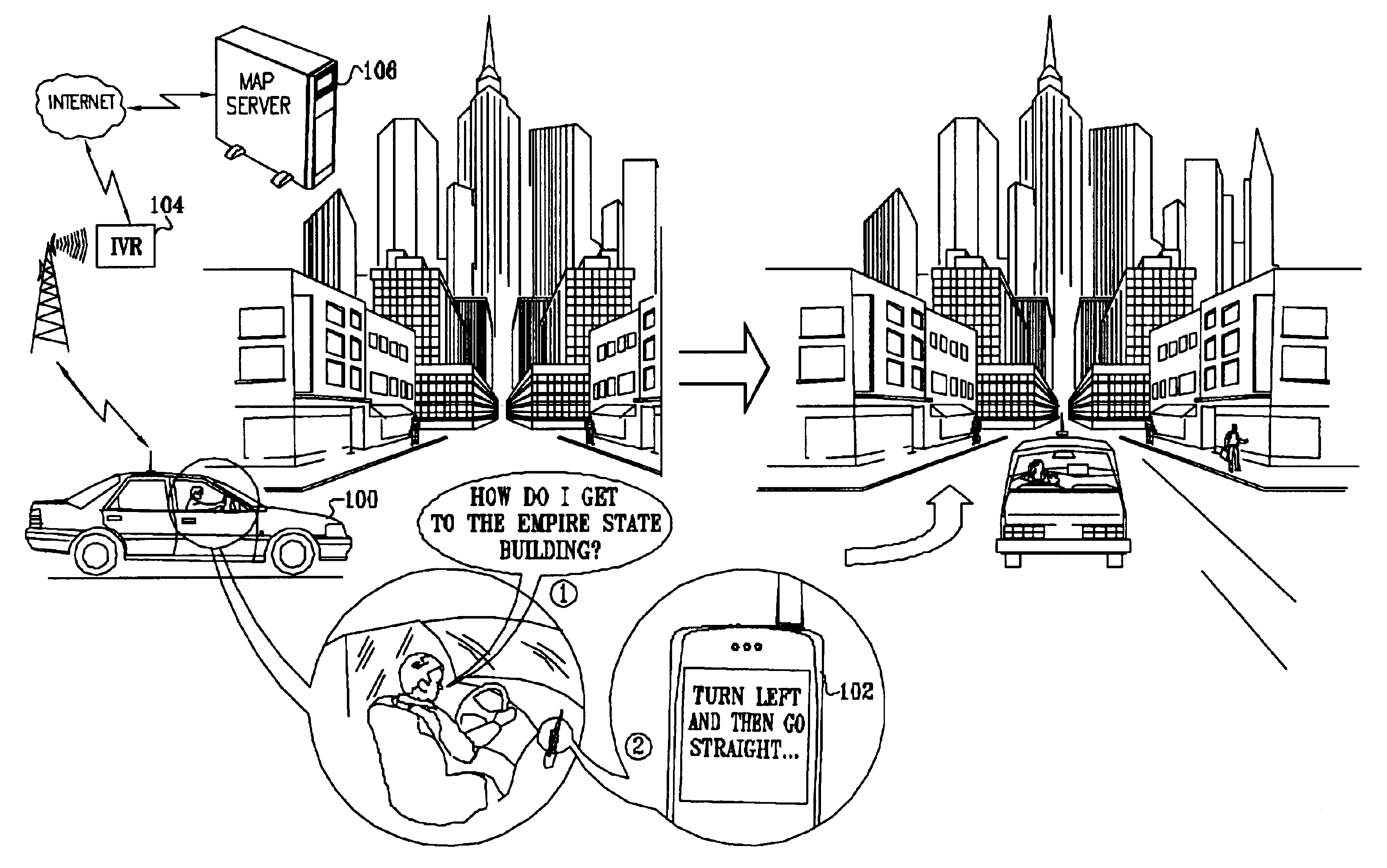
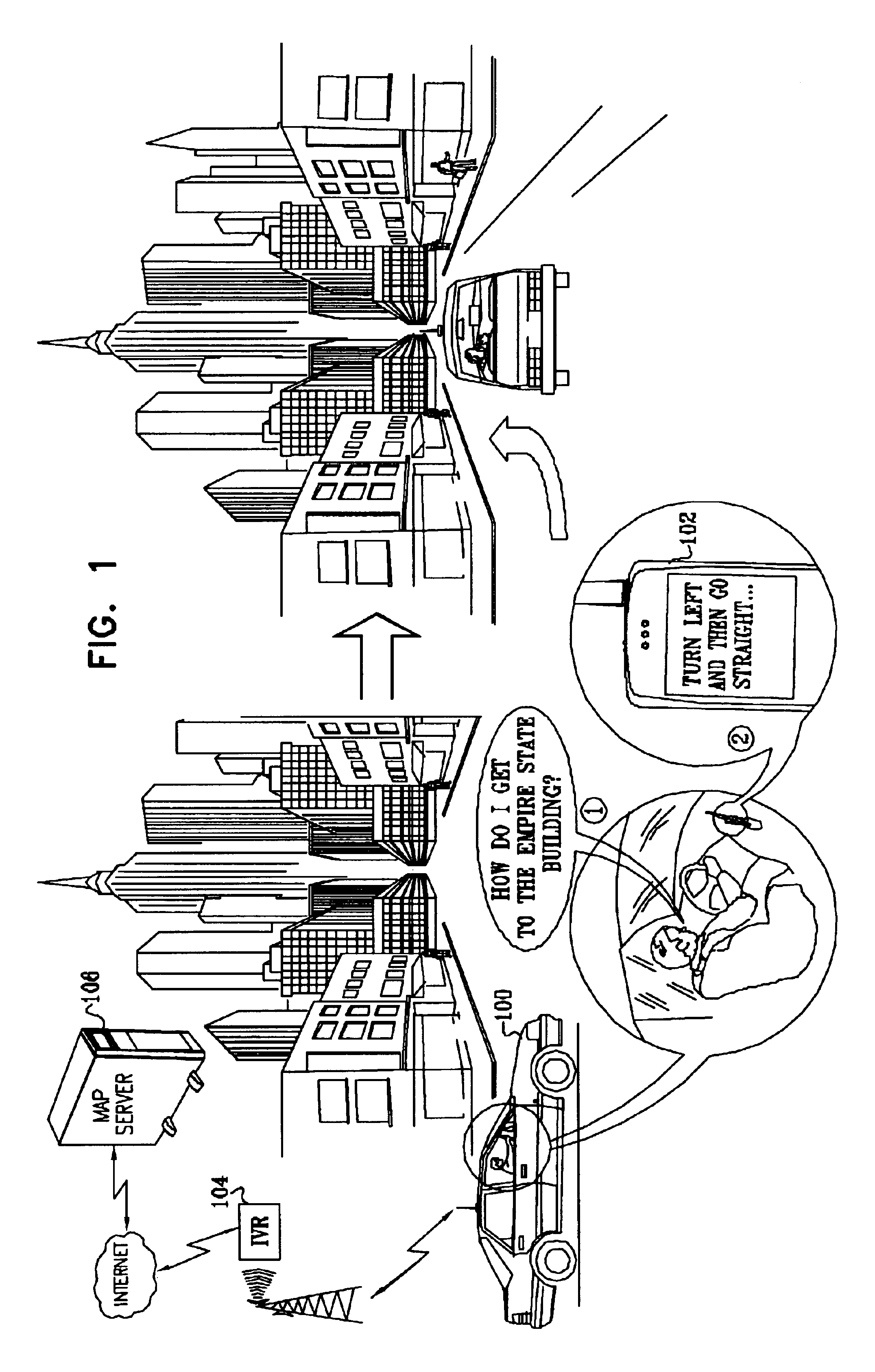
A method for navigation includes storing map data on a server, the map data including vector information delineating roads in a map. A portion of the vector information corresponding to an area in which a user of a mobile client device is traveling is downloaded from the server to the client device. Approximate position coordinates of the user are found using a location providing device associated with the client device and are corrected in the client device, using the downloaded vector information, so as to determine a location of the user on one of the roads in the map. A navigation aid is provided to the user of the client device based on the determined location.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
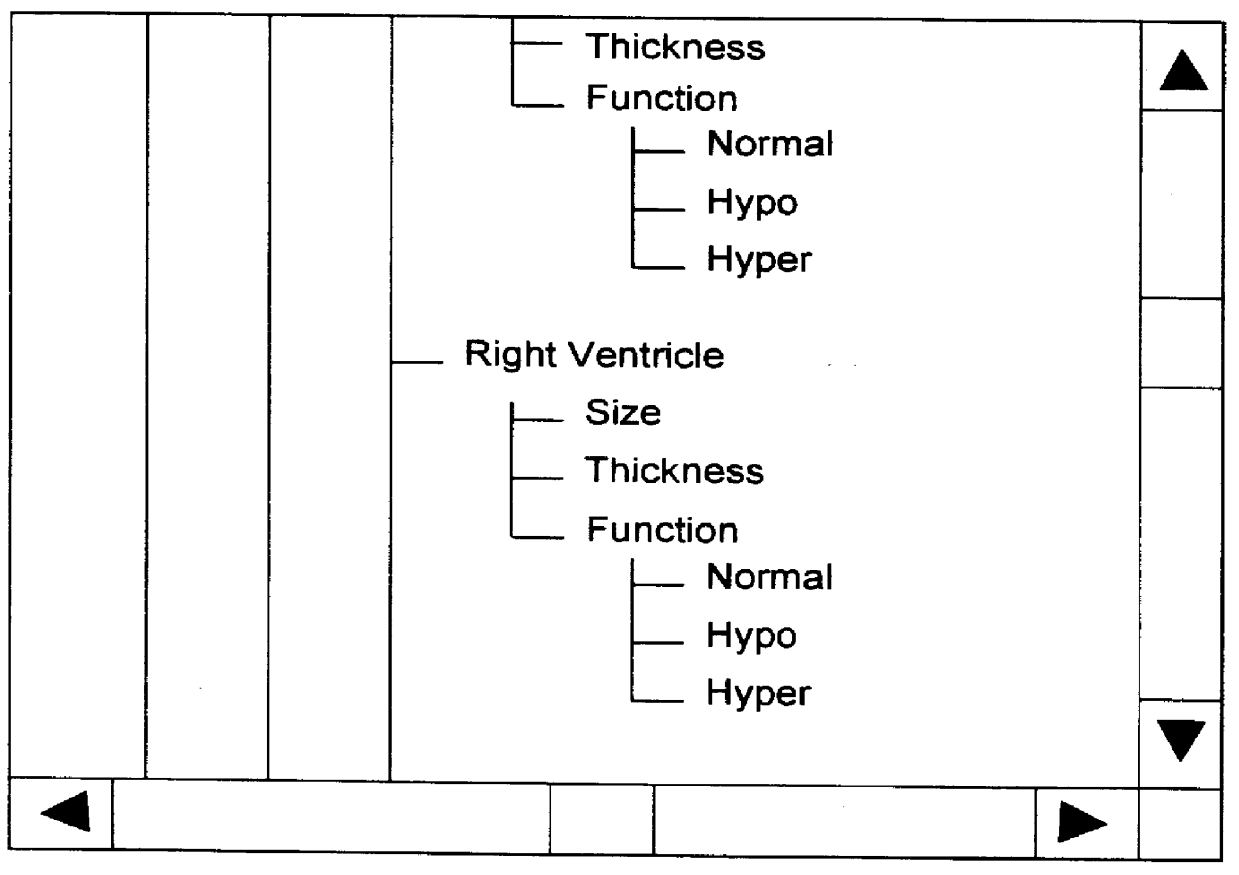
Method and system for navigation and data entry in heirarchically-organized database views
InactiveUS6154750AIncrease entryIncrease updateData processing applicationsOther databases browsing/visualisationDisplay deviceComputer science
A method and system for navigating hierarchical database views that supports the efficient entry, review, and updating of data using a navigation display that is clear and efficient-yet compact in terms of the screen area used. At any point in the navigation process, the navigation display consists of buttons corresponding to the nodes that lie along the path to the last node visited (the set of previously made choices) and the children of this node (the set of current choices). Unselected and unselectable choices are culled and do not clutter the display. The user navigates up and down the hierarchy and enters data by selecting these buttons. An important feature of the invention is support for multiple instances of database subhierarchies within this navigation process and display. In addition, multiple nodes can be composed to form a single database entry, thereby reducing the size and complexity of the hierarchical database views. Finally, database views that are directed acyclic graphs are also supported-including both serial and parallel traversal techniques.
Owner:ASCEND HIT LLC
Vehicle-based navigation system with smart map filtering, portable unit home-base registration and multiple navigation system preferential use
InactiveUS7151997B2Instruments for road network navigationDirection finders using radio wavesImage resolutionGeolocation
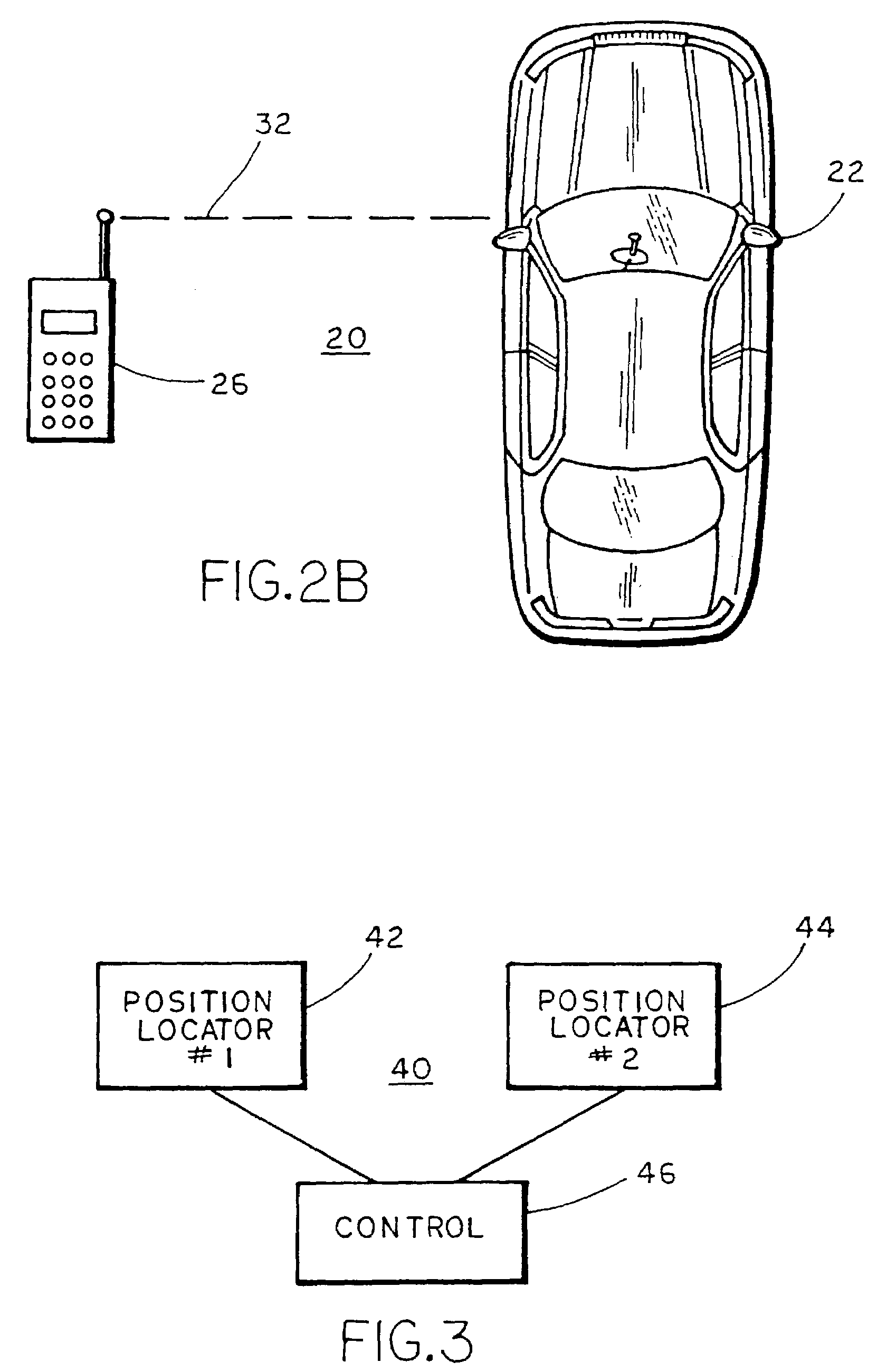
A vehicle-based navigation system is described including a position locator that establishes the geographic position of the vehicle and a map database located external to and remote from the vehicle. The system determines at least one of a vehicle parameter and a personal parameter, and transfers data from the remote map database to the vehicle and displays the data in the vehicle at a resolution that is a function of at least one of a vehicle parameter and a personal parameter.
Owner:MAGNA MIRRORS OF AMERICA INC
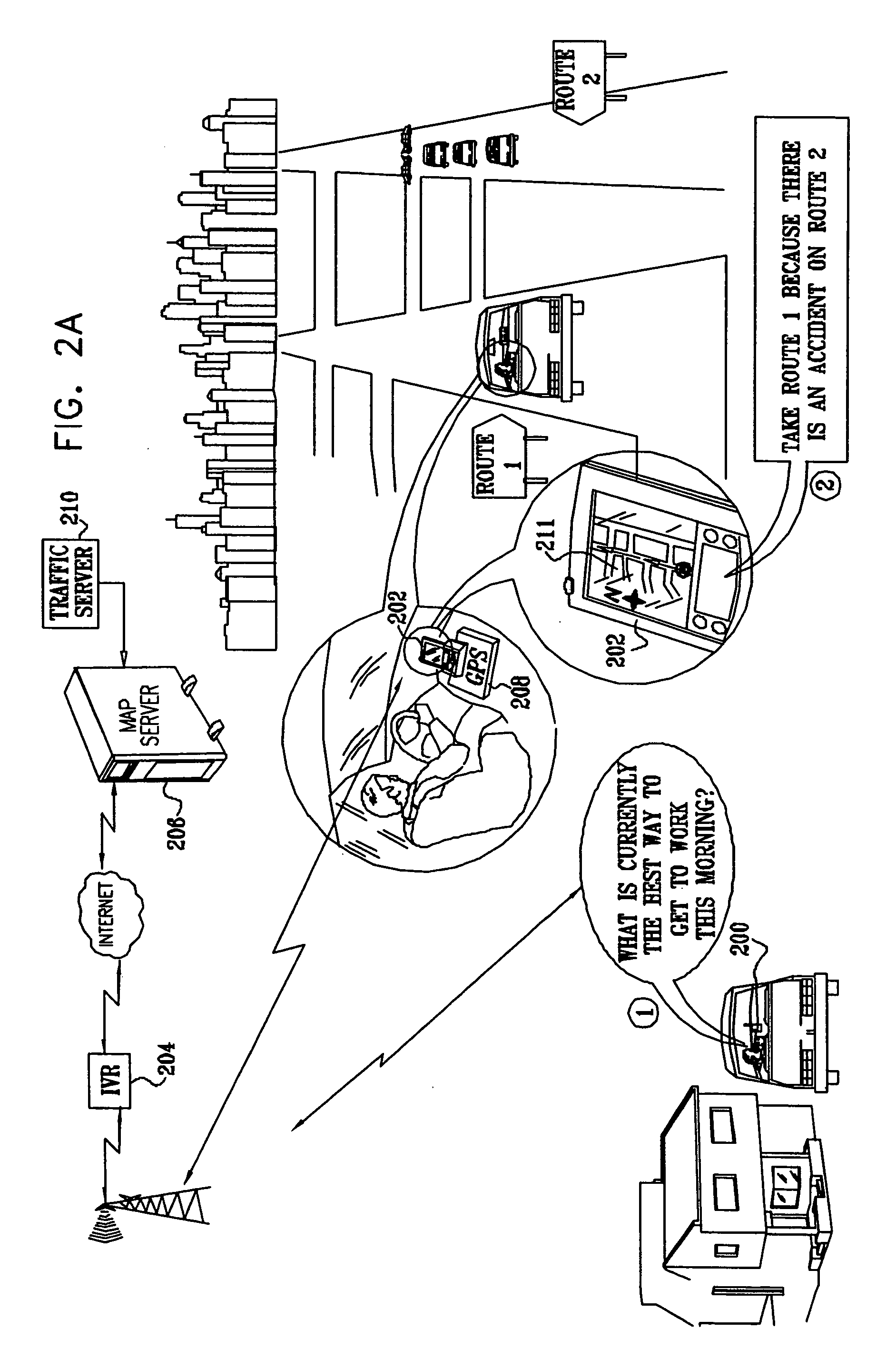
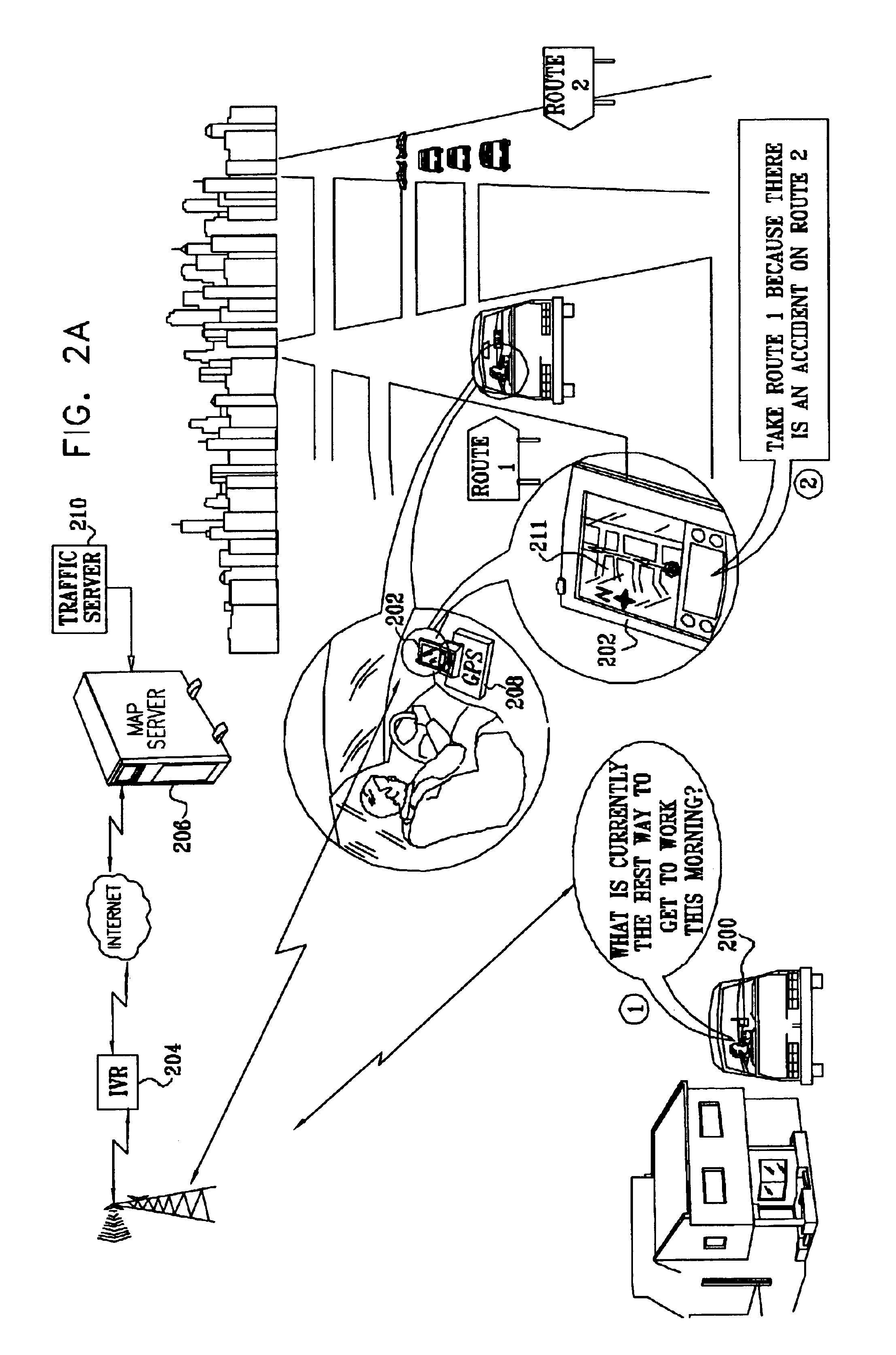
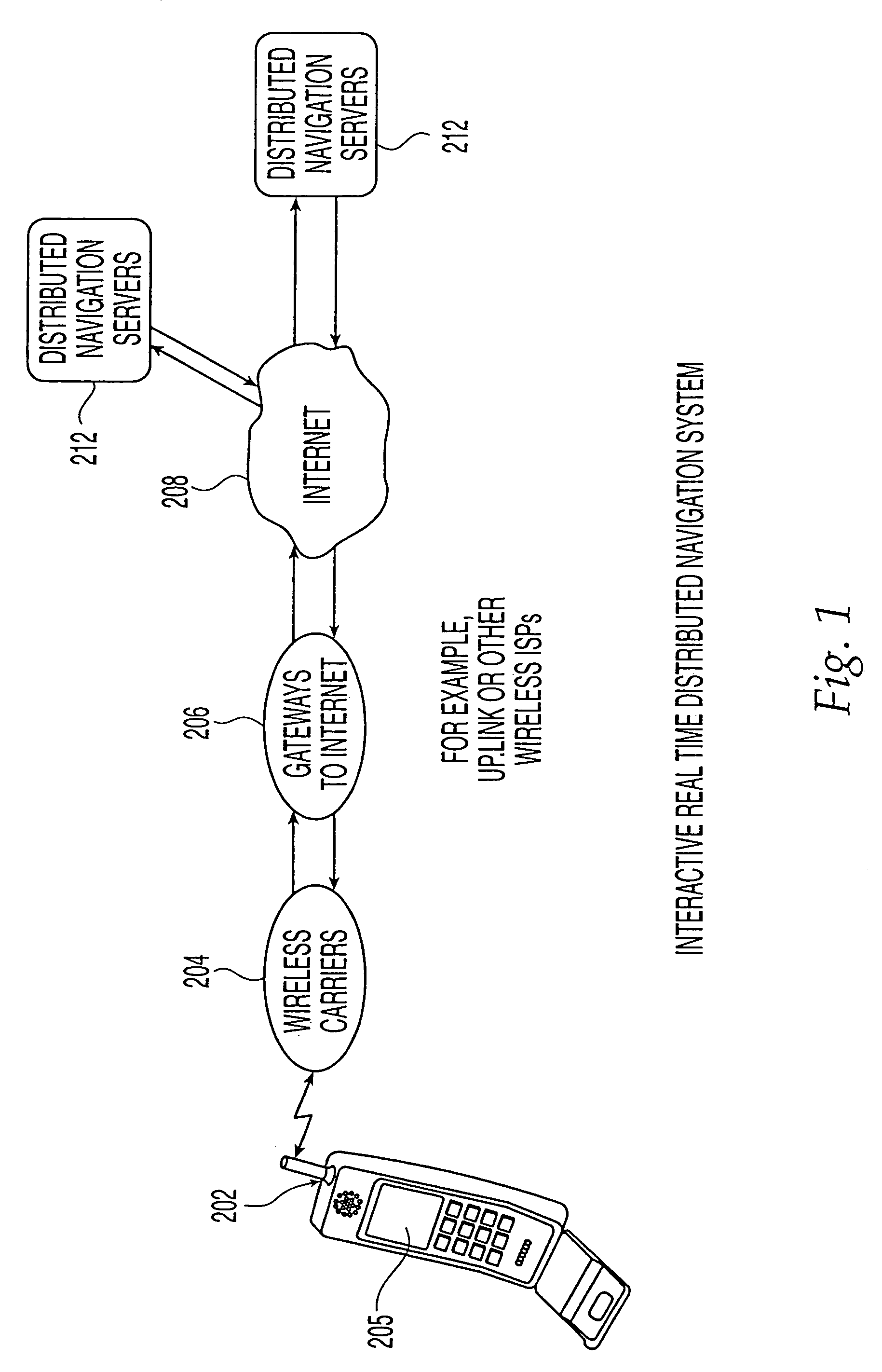
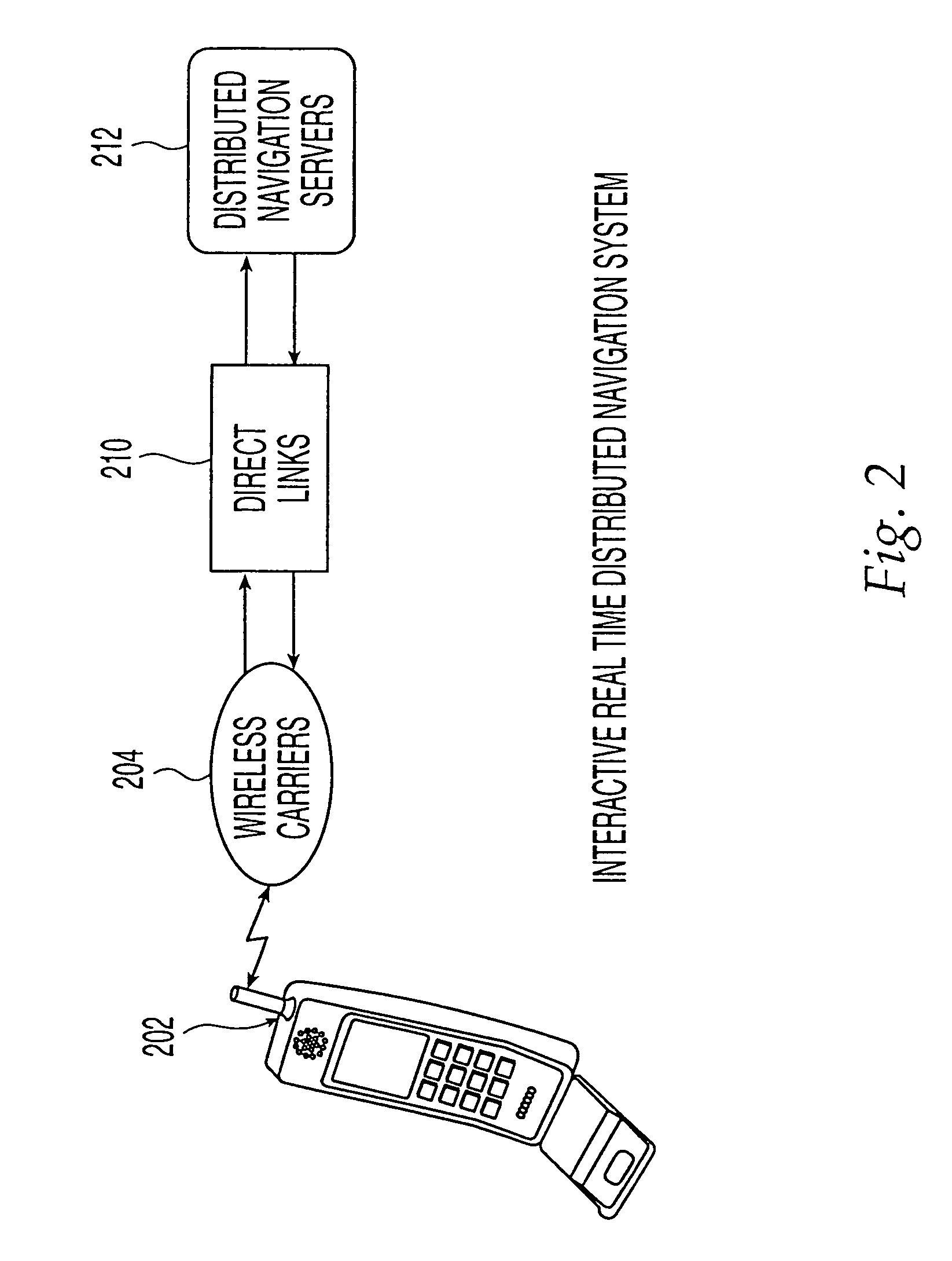
Method and system for real-time navigation using mobile telephones
InactiveUS6654683B2Reduce server trafficReduce traffic problemsInstruments for road network navigationControl with pedestrian guidance indicatorReal time navigationAmbiguity
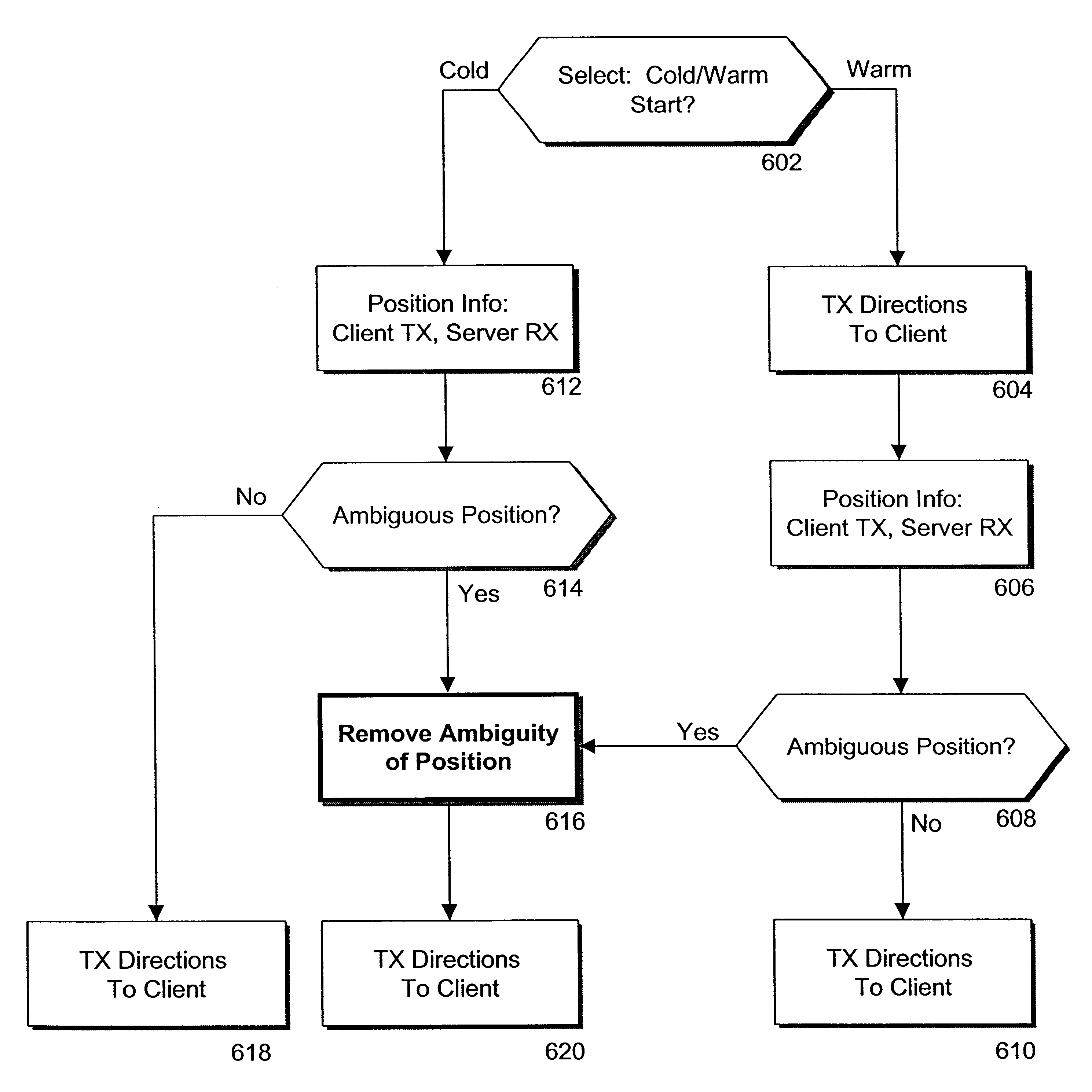
In an Interactive Real-Time Distributed Navigation system a method and system is disclosed for implementing a warm start / cold start option. Through selection of the warm start option, an interactive session for providing navigational directions to a user is more quickly established because a user's position is assumed not to be ambiguous. A method of the invention verifies this assumption. Through selection of the cold start option, the method of the invention seeks to remove ambiguity in a user's position before providing navigational directions. If, however, a user's position is not ambiguous, the method of the invention reverts to a warm start condition to immediately transmit navigational directions to the user.
Owner:JIN HAIPING +5
Dynamic navigation system
InactiveUS6917878B2Enhanced speed and clarityDownloaded rapidly and efficientlyInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlNavigation systemComputer science
A method for navigation includes storing map data on a server, the map data including vector information delineating roads in a map. A portion of the vector information corresponding to an area in which a user of a mobile client device is traveling is downloaded from the server to the client device. Approximate position coordinates of the user are found using a location providing device associated with the client device and are corrected in the client device, using the downloaded vector information, so as to determine a location of the user on one of the roads in the map. A navigation aid is provided to the user of the client device based on the determined location.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Real-time navigation system for mobile environment
InactiveUS7389179B2Conveniently and efficiently provideInstruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsReal time navigationMobile context
A system and method for providing navigational information to a user connected in real-time, such as through a wireless telephone, PDA, or other device. The system provides navigational information to the user in the form most useful to the user, such as according to landmarks, or the number of blocks until the next action. The system also provides directions to points of interest along the user's route. Further, the system allows the user to suspend and resume a session. Also, the system varies the sampling rate at which the user's location is examined, to enhance efficiency and convenience.
Owner:TELENAV INC
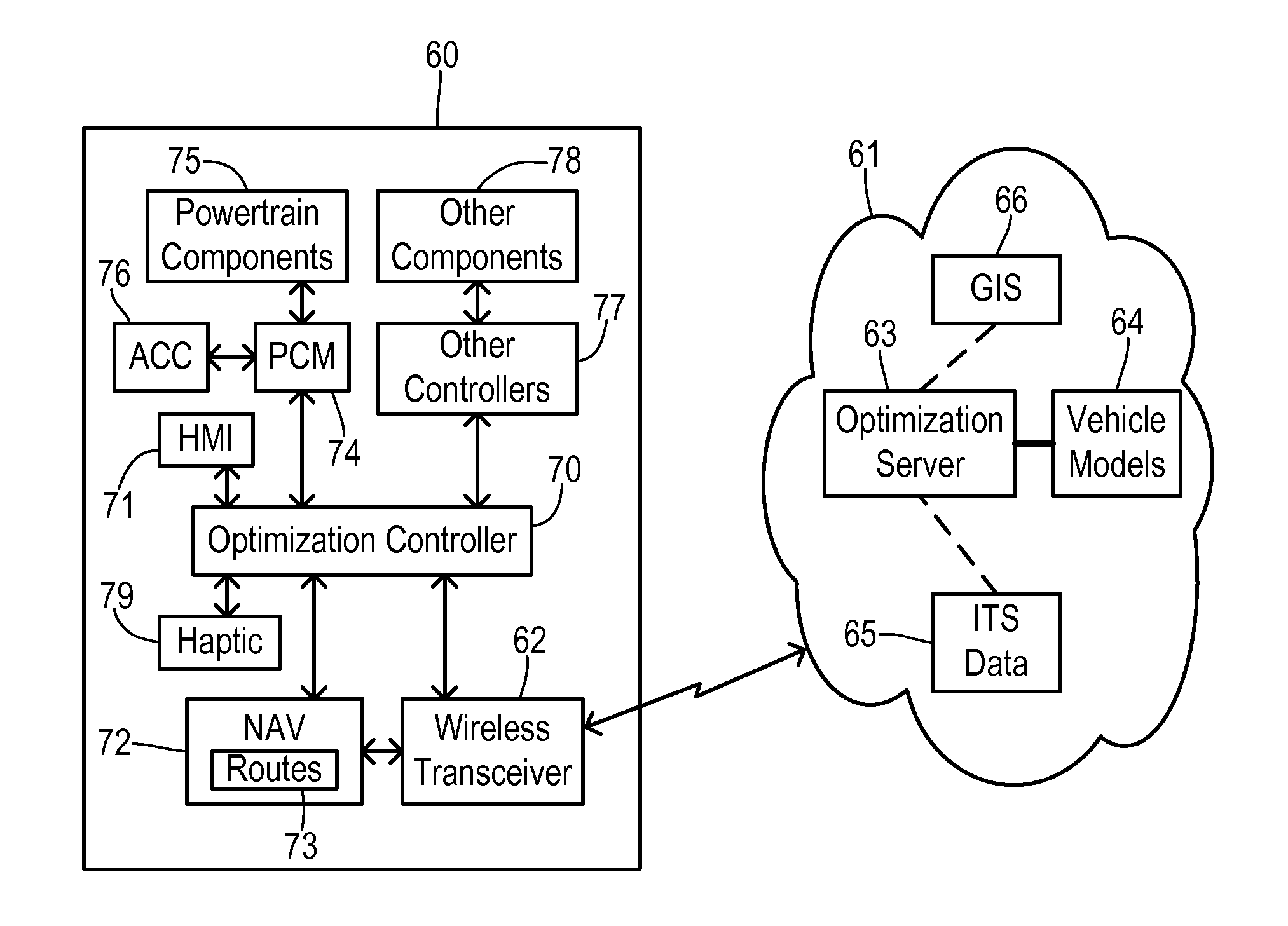
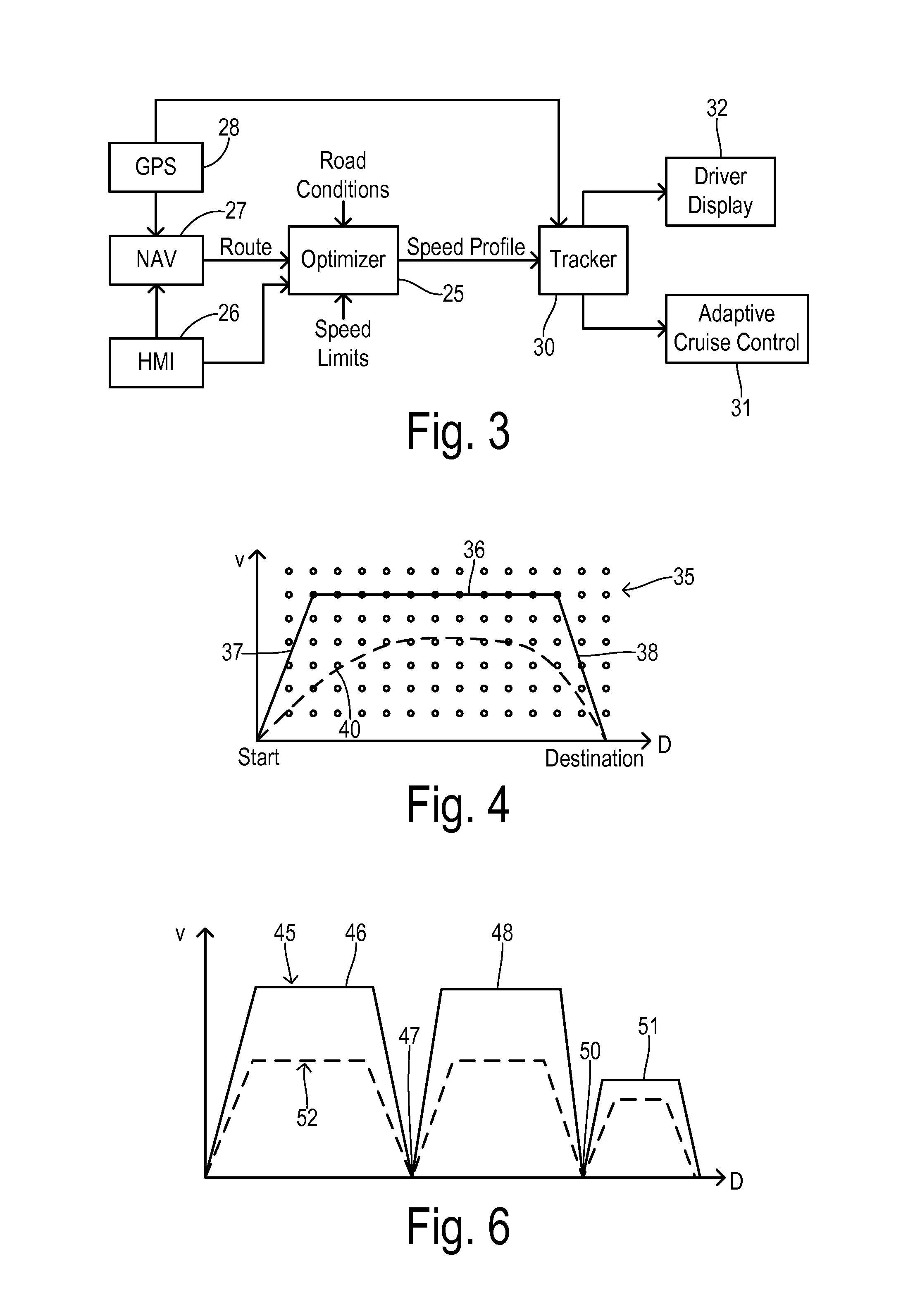
Route navigation with optimal speed profile
ActiveUS20140277835A1Reduce energy consumptionImprove carrying capacityInstruments for road network navigationVehicle fittingsEngineeringEnergy expenditure
Energy consumption of a vehicle is optimized while traveling a route assembled of road segments between a first position and a destination. A speed profile generator is located at least partially off of the vehicle and uses an energy consumption model of the vehicle together with road grade data corresponding to the route to calculate an optimal speed profile. The speed profile specifies target speeds for respective locations on the route for traversing the route with an optimized energy consumption. The speed profile generator compares energy consumption for a plurality of feasible speed profile trajectories between a maximum trajectory and a minimum trajectory in order to identify the optimal speed profile. A speed updater is responsive to a current position of the vehicle and the optimal speed profile to initiate the target speed for the current position.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
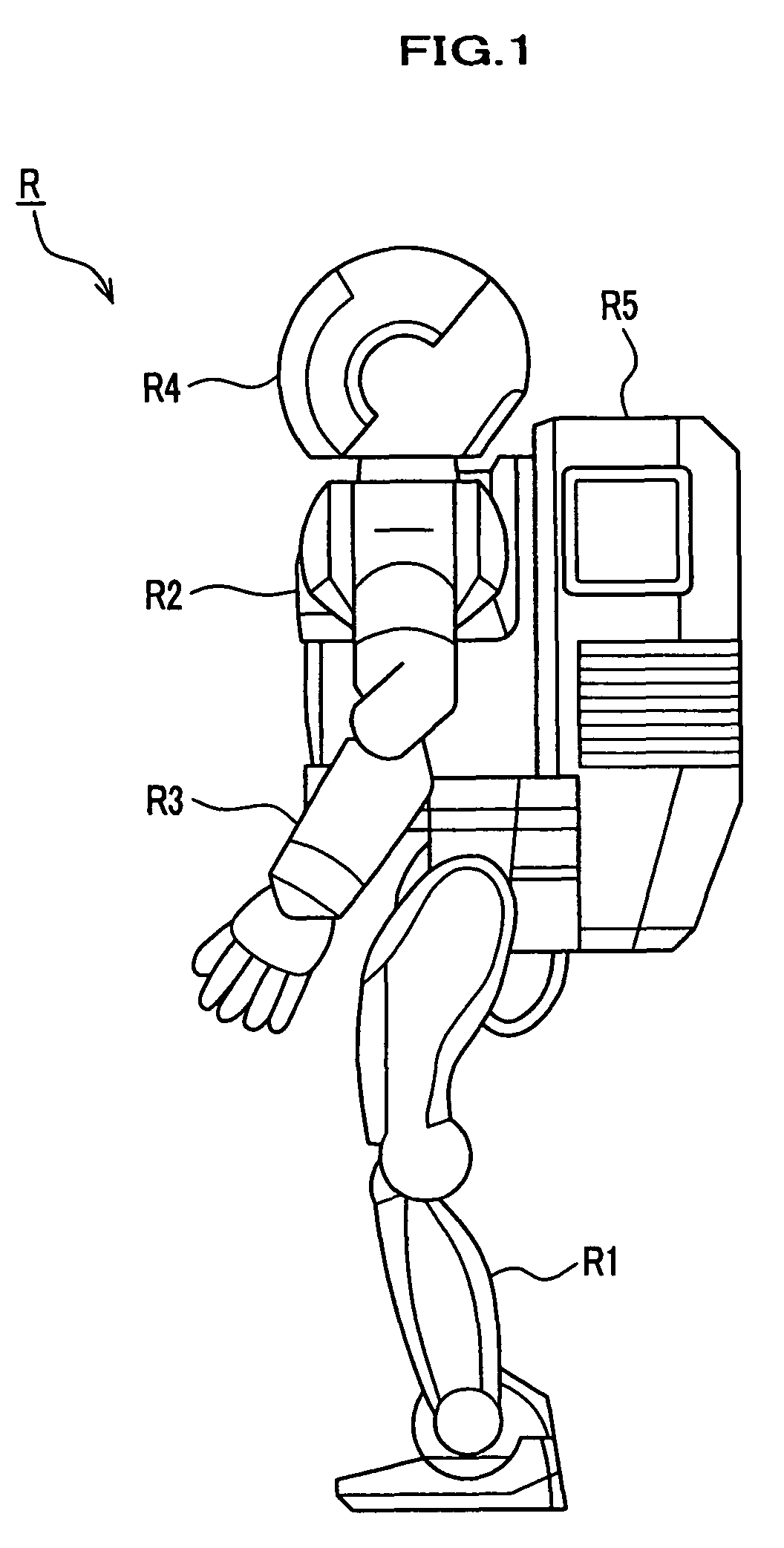
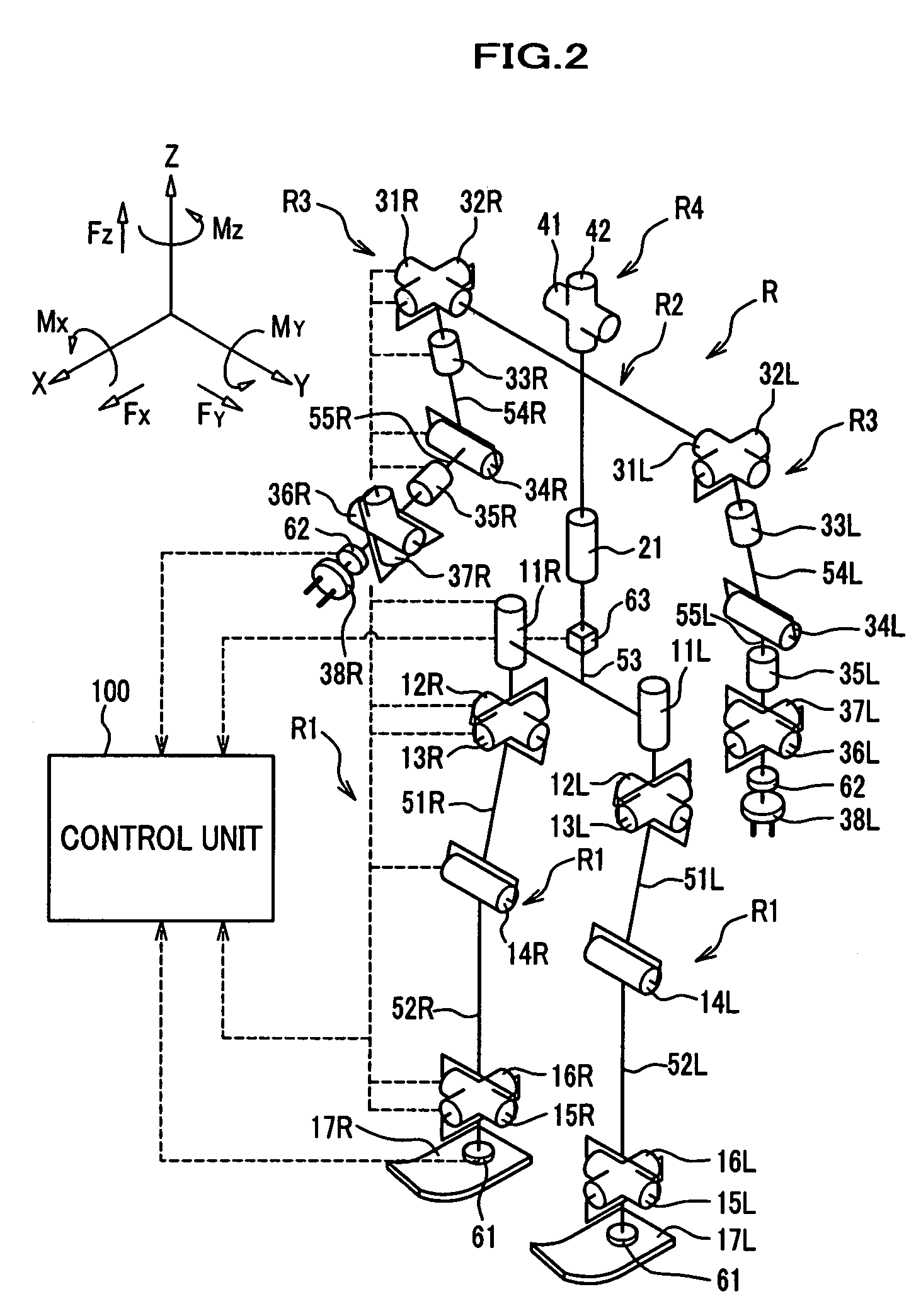
User-assisted robot navigation system
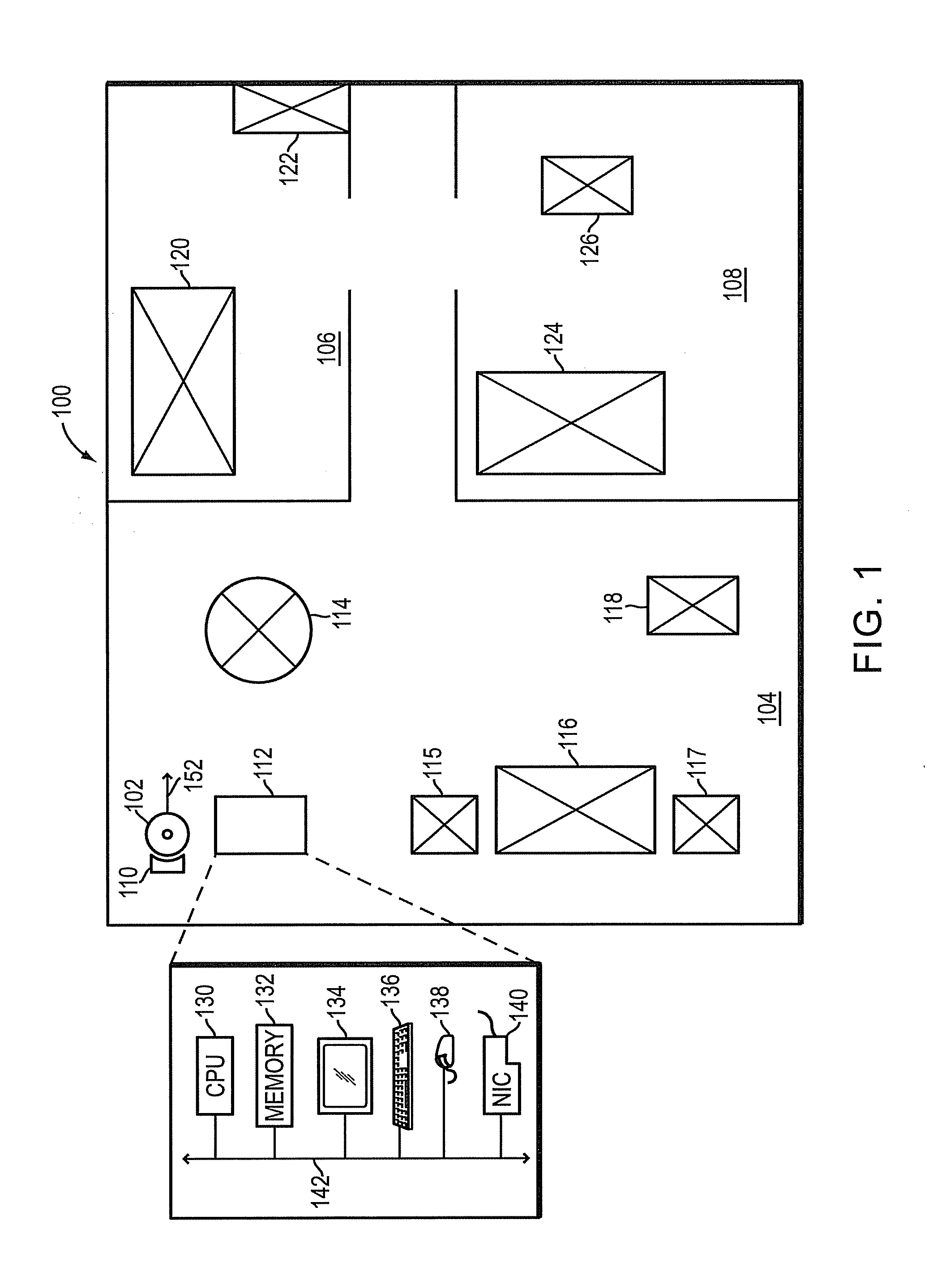
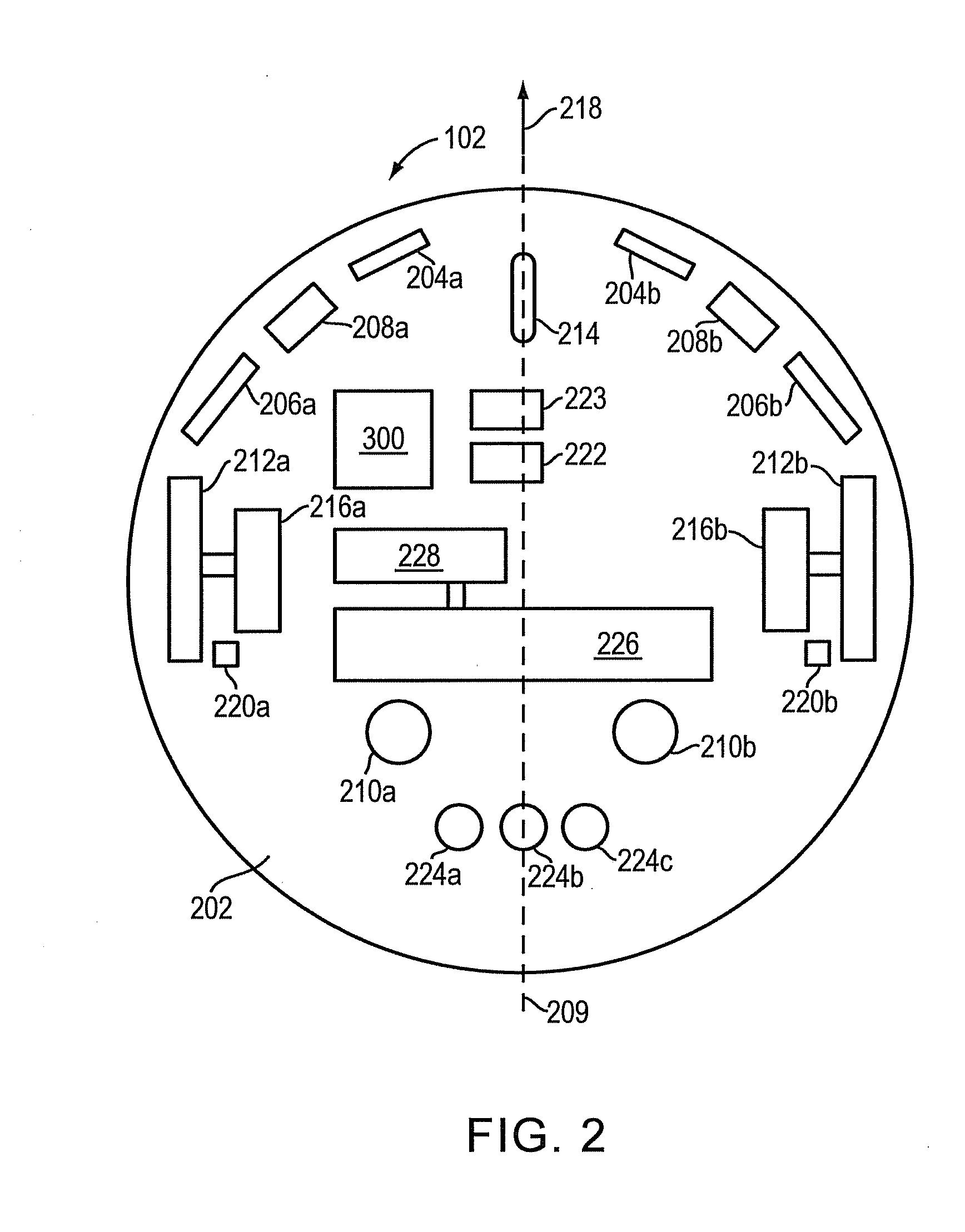
ActiveUS8364309B1Save spaceEfficiently navigateArtificial lifeVehicle position/course/altitude controlSimulationWorkstation
A system and method in which a user and a mobile robot cooperate to create a plan for use by the robot in navigating a space. The robot may include a tracking unit that detects the distance traveled and direction from a starting or home location and orientation. The robot also includes a navigation module that controls the movement of the robot based on a navigation plan received from a robot control utility residing at a workstation operated by the user. The robot further includes a position error correction engine that is configured to correct for position errors that may occur as the robot traverses the space. The position error correction engine receives data from one or more robot sensors that detect structures disposed below the surface over which the robot travels. As the robot encounters obstacles in the space, it enters them on the floor plan. The user then reviews the information added by the robot to the floor plan and accepts, rejects or modifies that information in order to create the navigation plan.
Owner:BAILEY BENDRIX L
Traffic navigation system
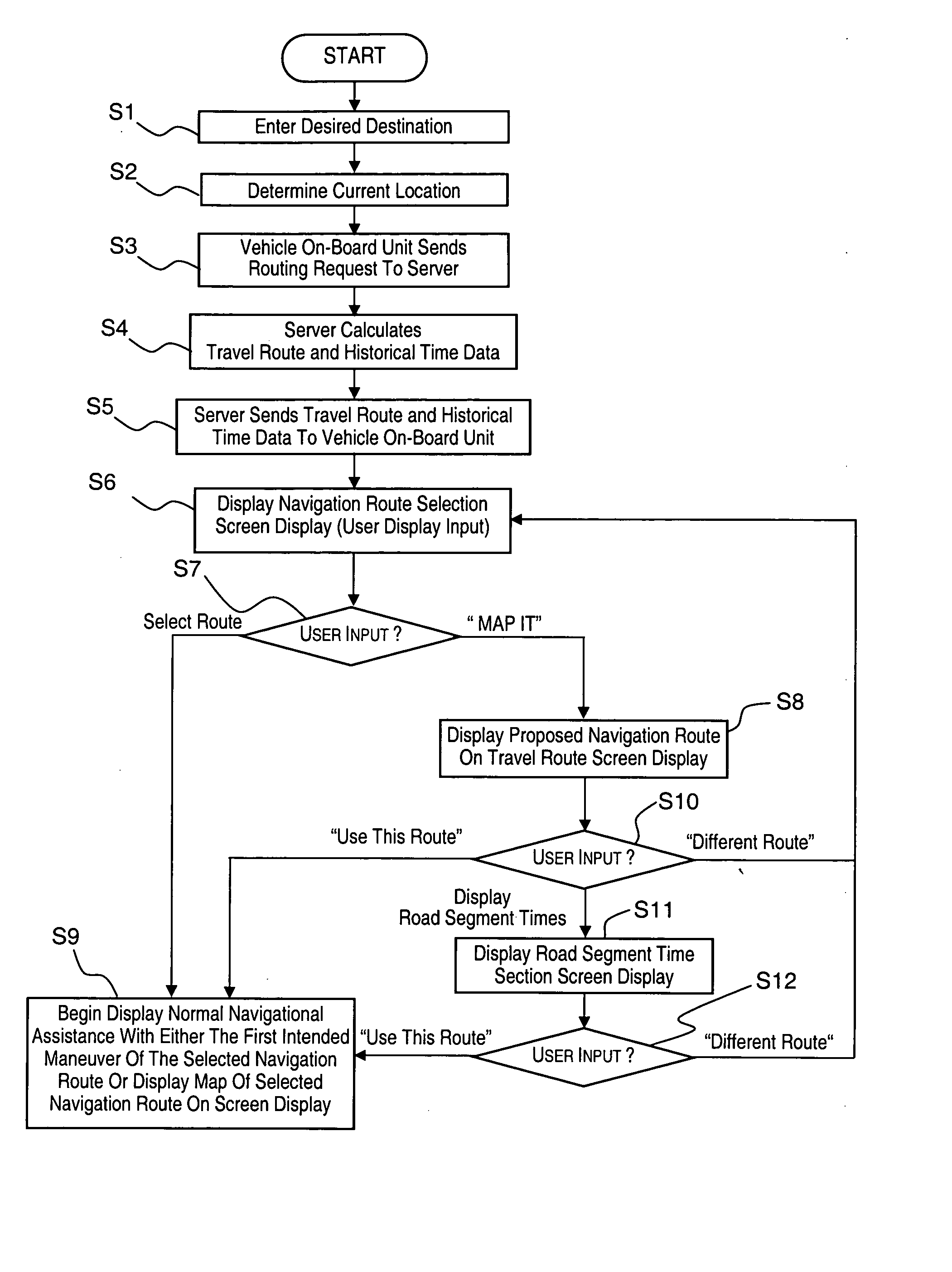
ActiveUS20080027636A1Accurately reportInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlAir navigationTime information
A vehicle navigation system is provided with a destination input section, a travel route information section, a historical data input section and an expected travel time reporting section. The travel destination input section is provided for entering a destination point. The travel route information section provides at least one potential travel route to the destination point. The historical data input section provides historical time information based on a plurality of actual motorist travel times to navigate various travel routes. The expected travel time reporting section reports to a user an expected travel times based on the historical time information for a potential travel route.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
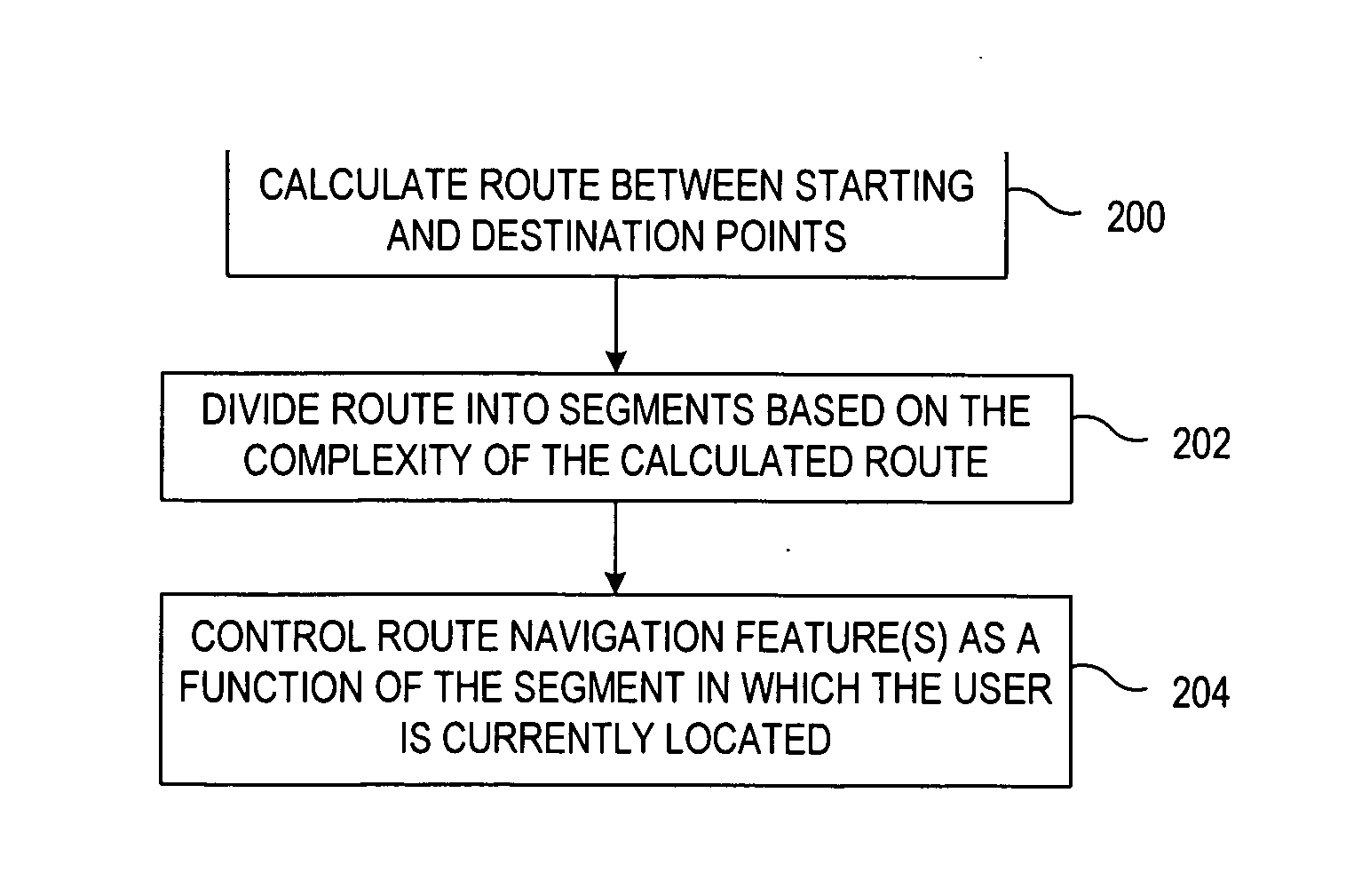
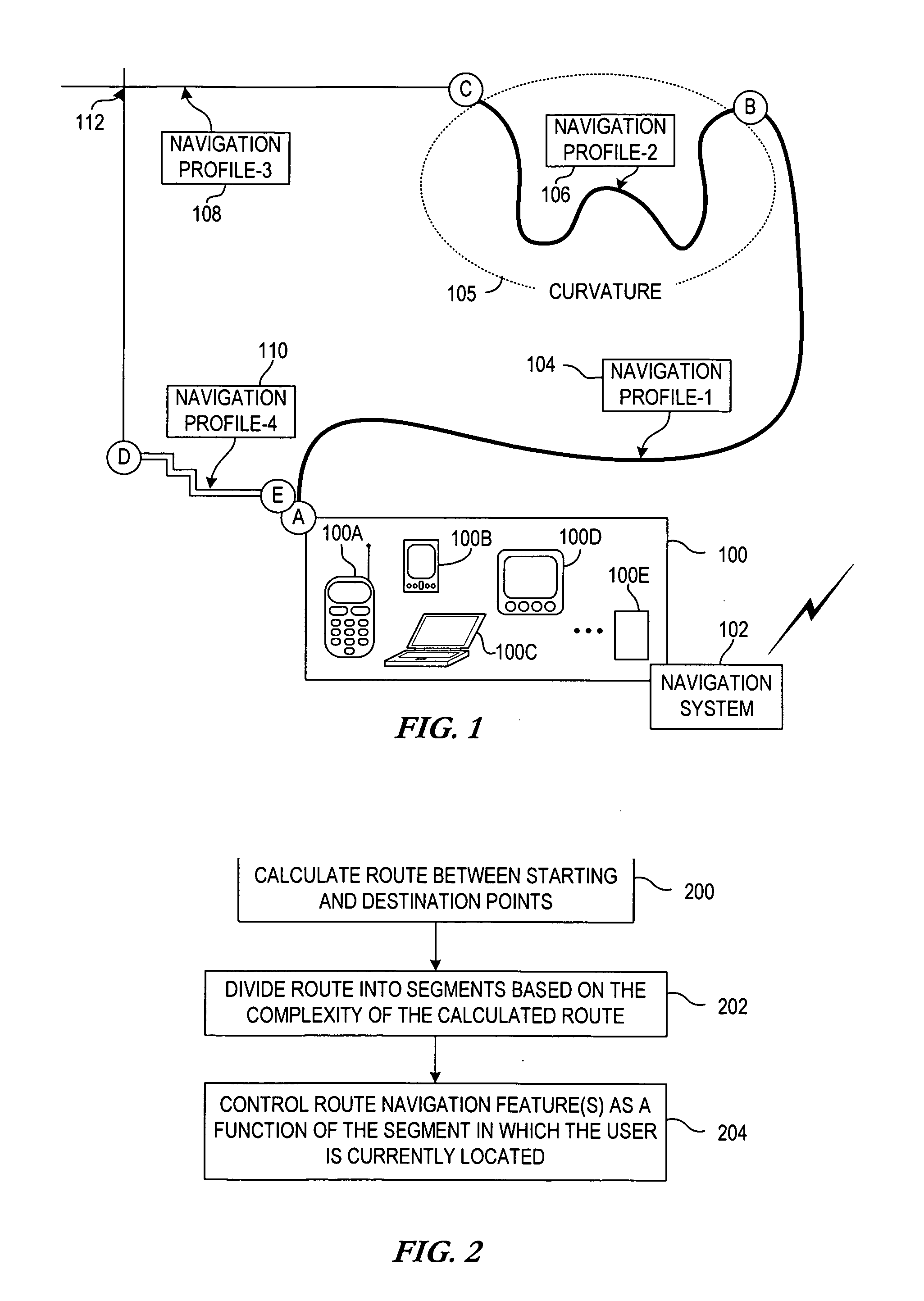
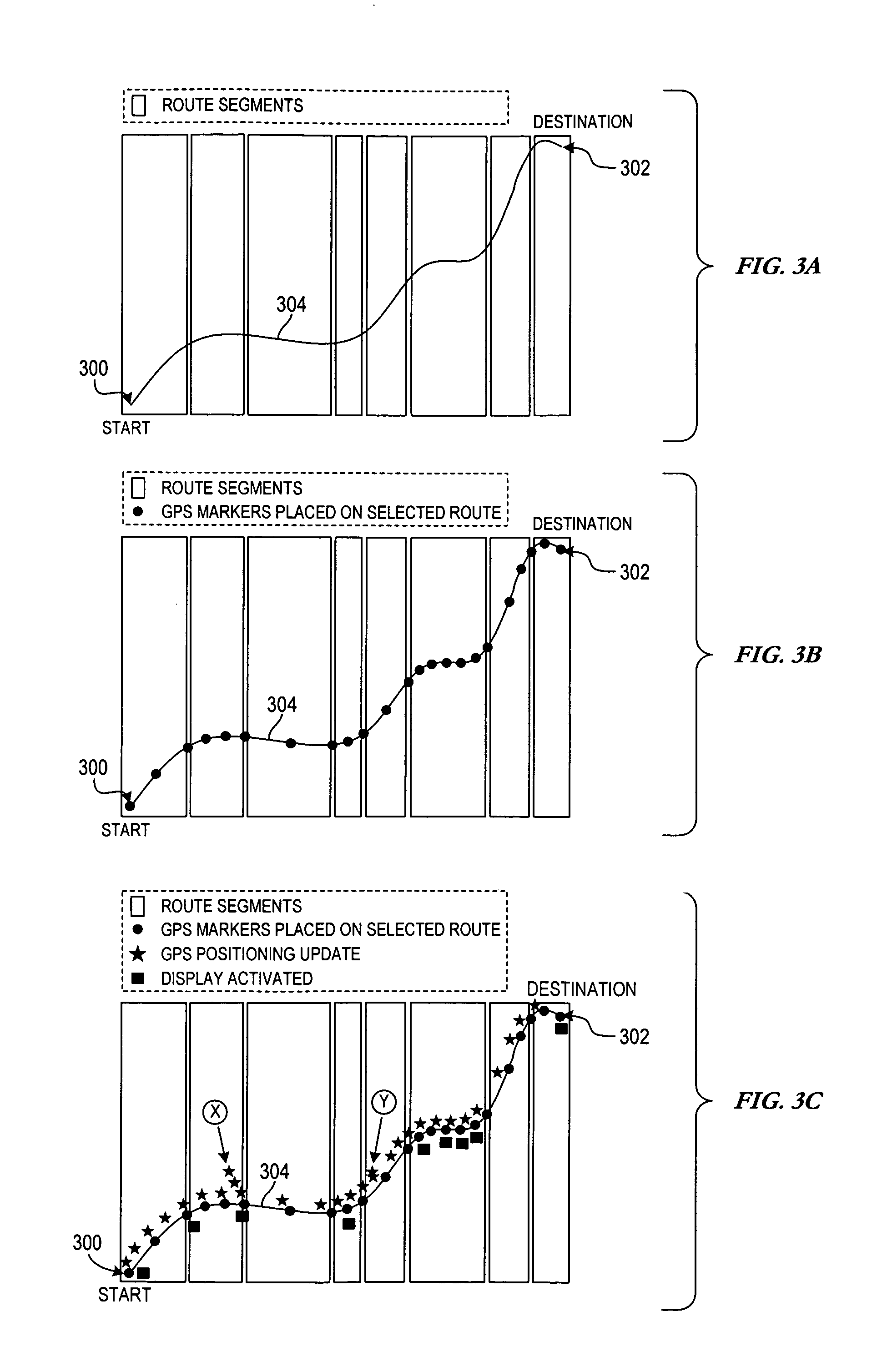
Apparatuses and methods for managing route navigation via mobile devices
ActiveUS20090164115A1Low costImproving navigational usabilityInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlMobile deviceMarine navigation
Apparatuses and methods for managing route navigation via mobile devices. A route is calculated between a starting point and a destination point. The route is divided into multiple segments based on the complexity of the calculated route, and navigation features are controlled as a function of the segment that corresponds to the user's current location. The user may opt to identify one or more segments, or one or more route portions independent of whether or not segmentation has occurred, in order to specify a portion(s) of the route where navigation support is not needed.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Navigating and steady aiming method of navigation / steady aiming integrated system
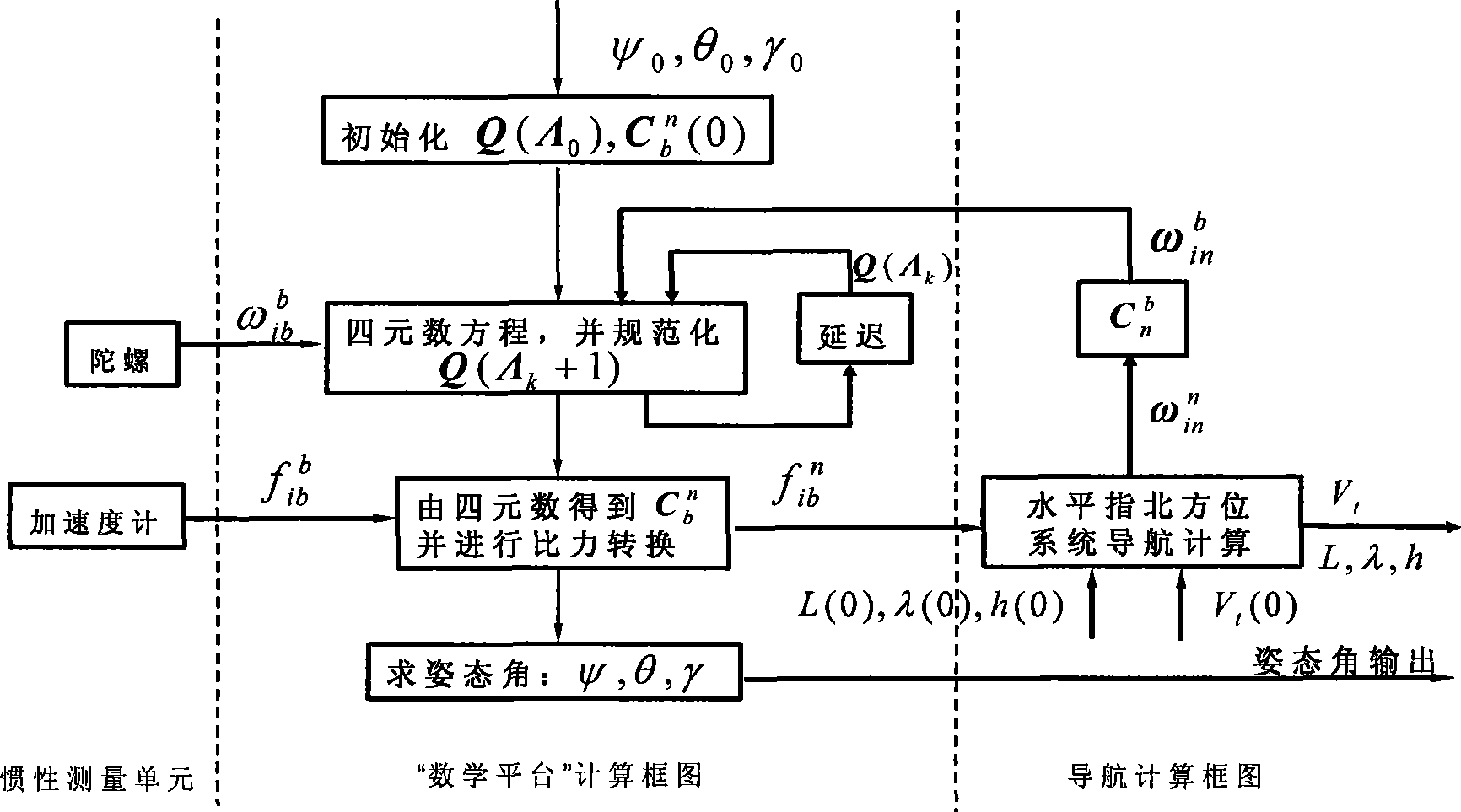
The invention relates to a navigating and stabilized sighting method of a navigation / stabilized sight all-in-one system, belonging to the inertial guidance field. The navigating method realizes stance and positioning on a load by an inertial measuring unit which is arranged on an electro-optical stabilized sighting platform. The method comprises the steps as follows: collecting the signal of the inertial measuring unit; fast and accurately initial aligning below the stabilized sighting platform; an inertial navigation algorithm based on vehicle-bone stabilized sighting platform; resolving heading attitude and analyzing the error thereof; analyzing the error of an inertial guidance system and an inertial part, modeling and compensating; and inertial guidance / milemeter / GPS multi-information fault-tolerance combined navigation. The navigation method overcomes the defects in the prior art that stabilized sighting and the navigation system can not work simultaneously and the all-in-one system can not provide full navigation information, can provide real-time, accurate and complete navigation heading attitude information and navigation positioning information for carriers (like a chariot), and can improve the battlefield viability and the comprehensive hosting ability.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
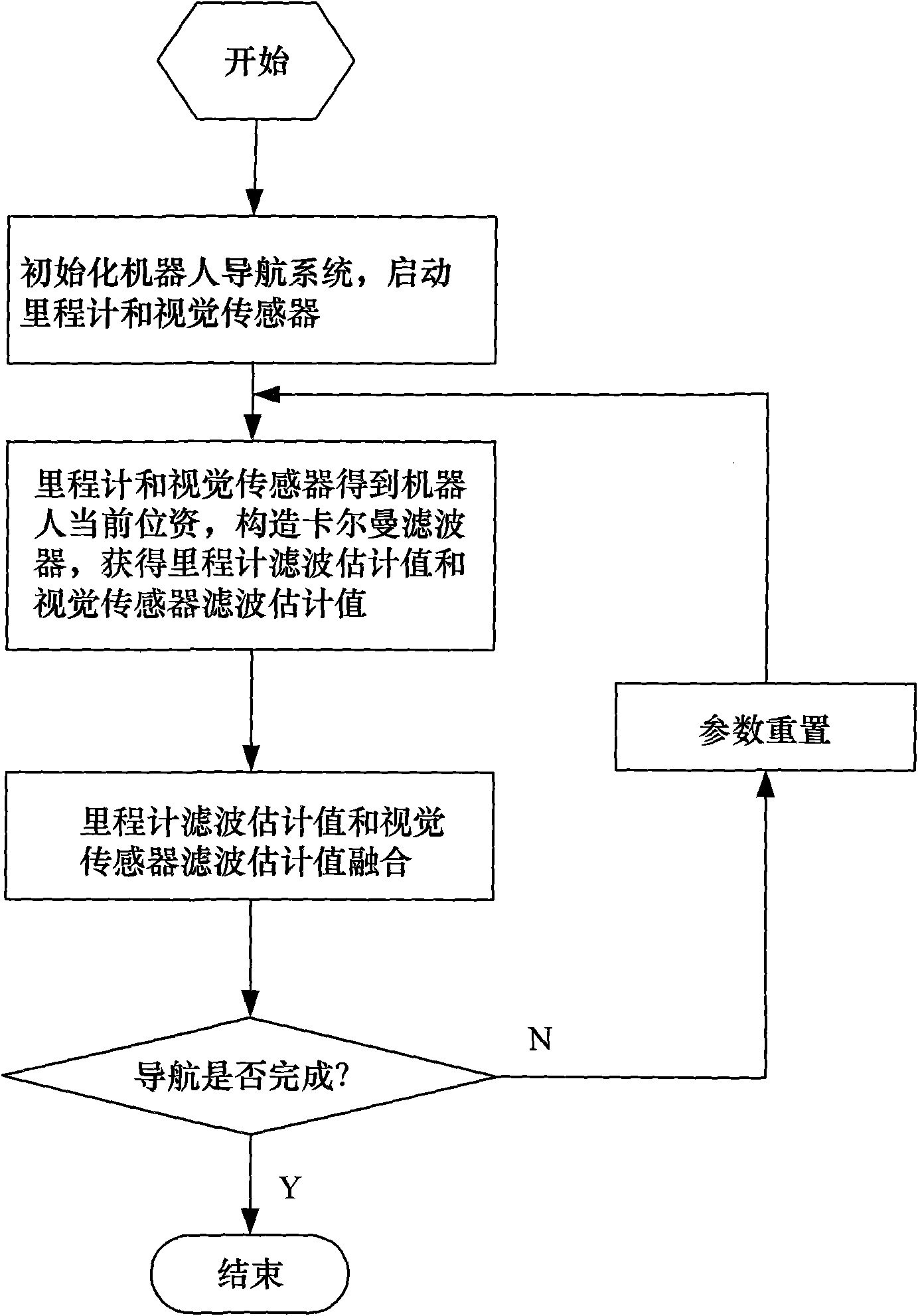
Indoor movable robot real-time navigation method based on visual information correction
InactiveCN101576384AEnsure real-time requirementsImprove accuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsFiltrationVision based
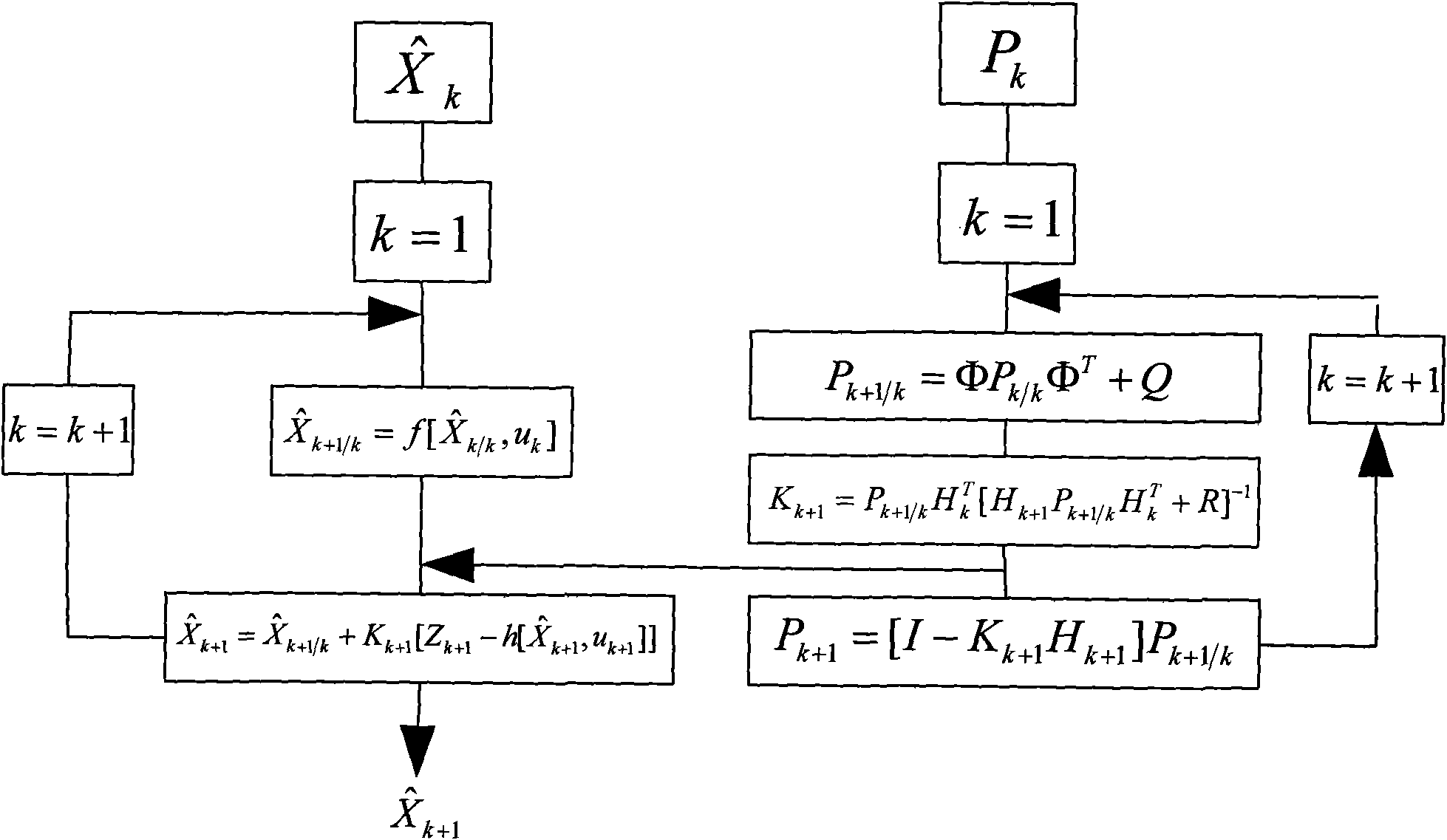
The invention discloses an indoor movable robot real-time navigation method based on visual information correction, comprising the following steps of: (1) initializing a robot navigation system, and starting a mile meter and a visual sensor; (2) obtaining the current position of a robot by the mile meter and the visual sensor and forming a kalman filter so as to obtain a mile meter filtration estimation value and a visual sensor filtration estimation value; (3) fusing the mile meter filtration estimation value and the visual sensor filtration estimation value; and (4) resetting parameters. The invention sufficiently utilizes the respective advantages of visual information and mile meter information and combines the precision of the visual information and the real-time property of the mile meter information; the invention utilizes the mile meter self information to carry out the recurrence computation to obtain navigation data at most of the time, thereby ensuring the real-time requirement of the navigation system; in addition, the invention also utilizes the visual information to correct the accumulated errors generated in the dead reckoning of the mile meter, thereby greatly enhancing the accuracy of the navigation system.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
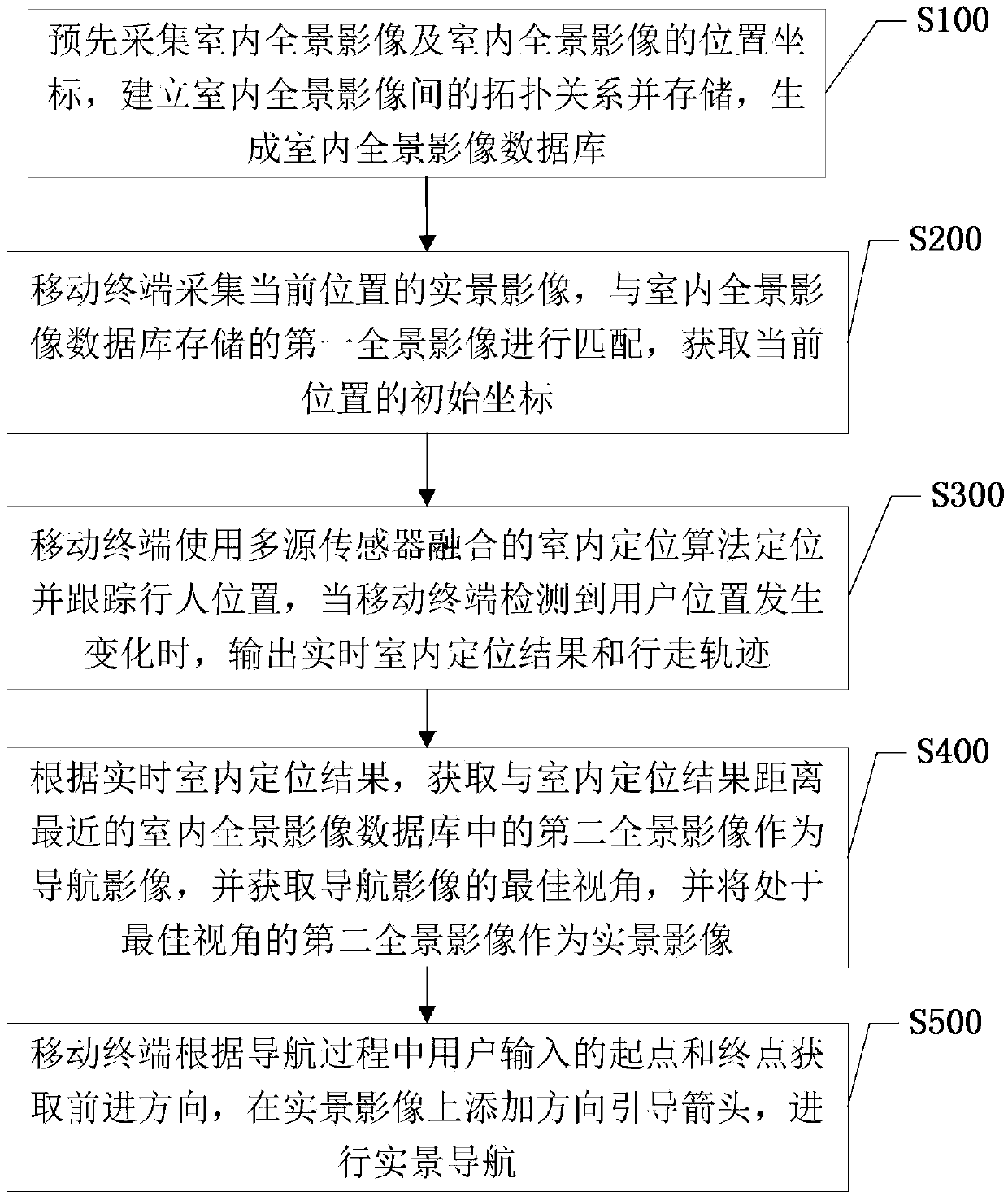
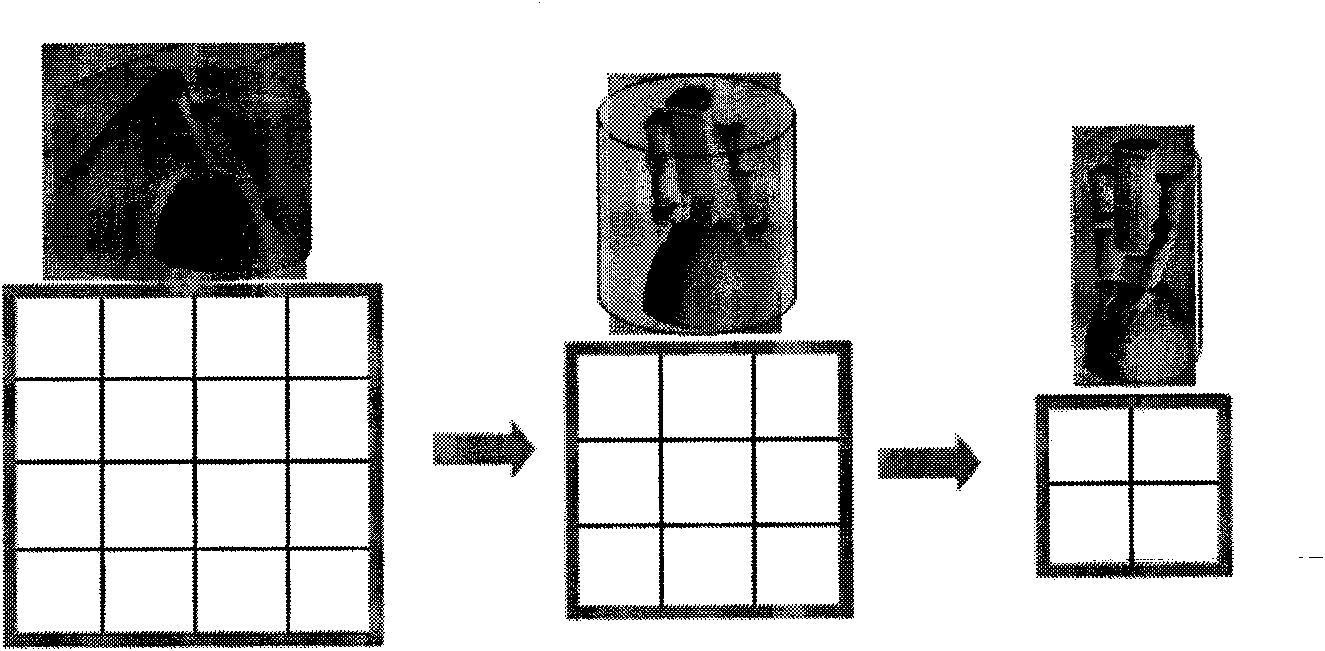
Indoor live-action navigation method and system
The invention discloses an indoor live-action navigation method and system. The method comprises the steps that a mobile terminal collects live-action images of the current position, the live-action images are matched with a first live-action image stored in an indoor live-action image database, and an initial coordinate of the current position is obtained; the position of a pedestrian is positioned and tracked in real time through a multi-source sensor fused position algorithm, and when the mobile terminal detects that the position of a user changes, a real-time position result and a walking trajectory are output; a second live-action image, closest to the indoor position result, in the indoor live-action image database is obtained according to the real-time indoor position result; the mobile terminal obtains a starting point and an ending point which are input by the user in the navigation process, a forward direction is obtained, a direction guided arrow is added on the second live-action image, and live-action navigation is conducted. By means of the indoor live-action navigation method and system, according to the position where the pedestrian is located, the live-action navigation images can be pushed automatically, the best navigation image visual angle can be judged automatically, and route guidance information such as the arrow is overlapped on the navigation images.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Service robot autonomous navigation method based on deformable topological map
InactiveCN101619985ARealize autonomous navigationReduce labor intensityInstruments for road network navigationPhysiognomyService robot
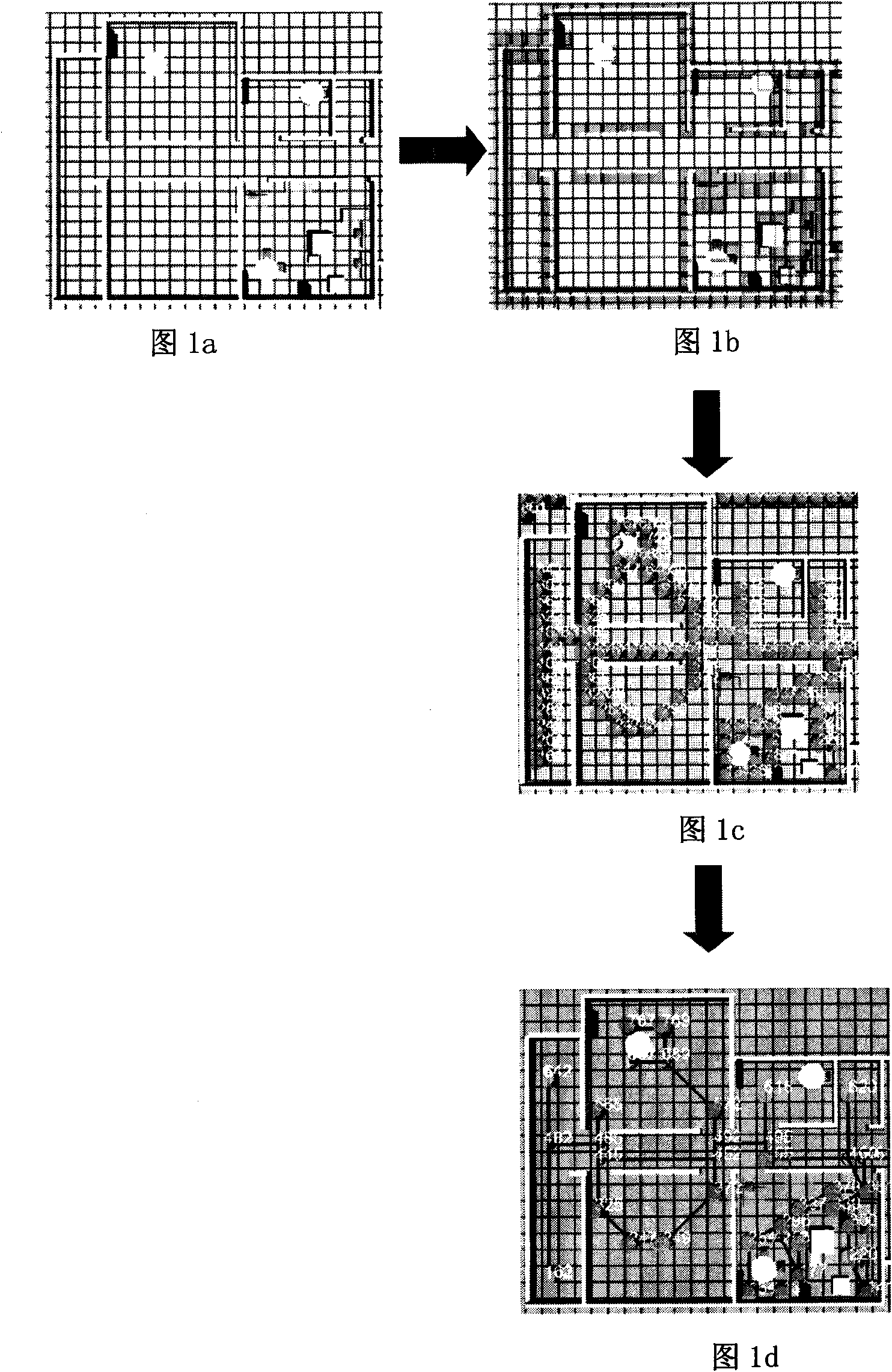
The invention relates to a service robot autonomous navigation method based on a deformable topological map in the technical field of robot navigation, which comprises the following steps: collecting the geography and physiognomy condition of an indoor and outdoor environment in which a robot is located in real time by a SLAM technology; extracting environmental characteristics; creating a topological map of collected information and establishing the needed different sizes of a topological point according to the posture change of the service robot in the foundation; taking the sizes as input amount to reconstruct the topological map; and generating a topological point self-adapting topological map conforming to the posture change of the mobile robot.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Integrated navigation system applied to pilotless aircraft
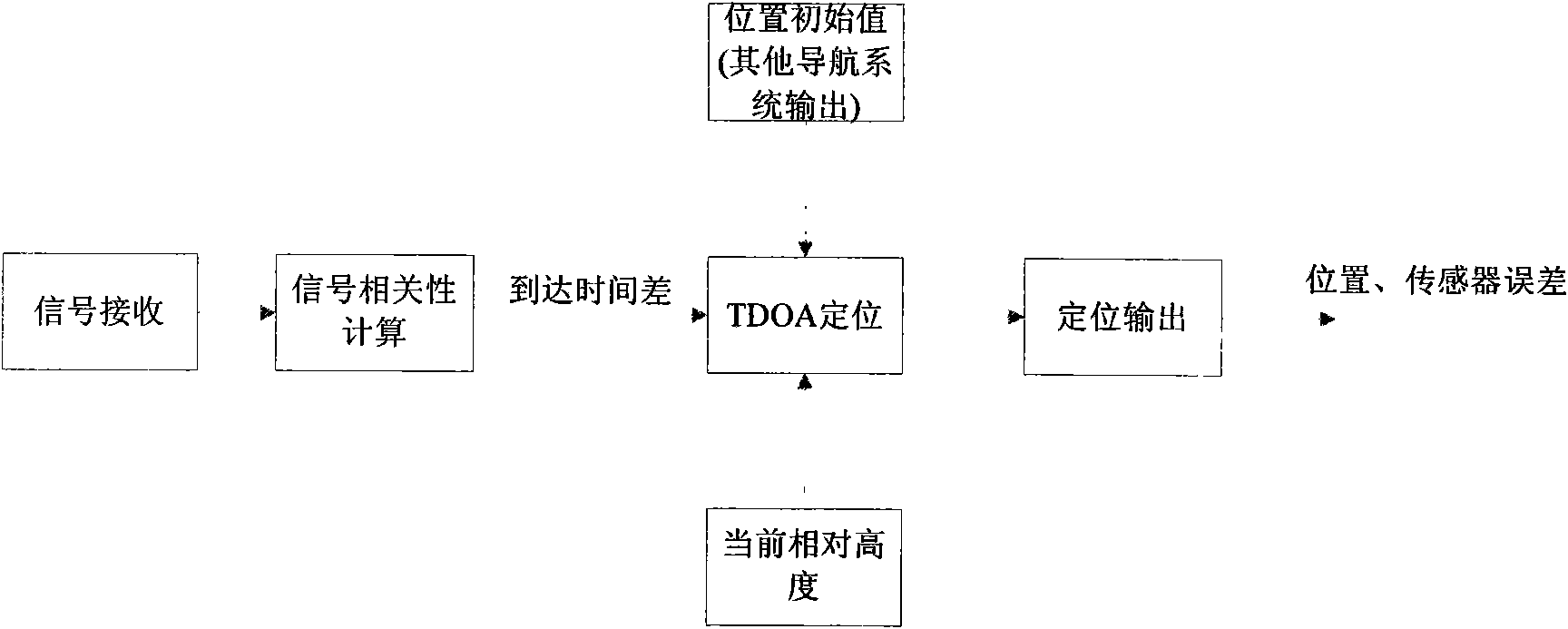
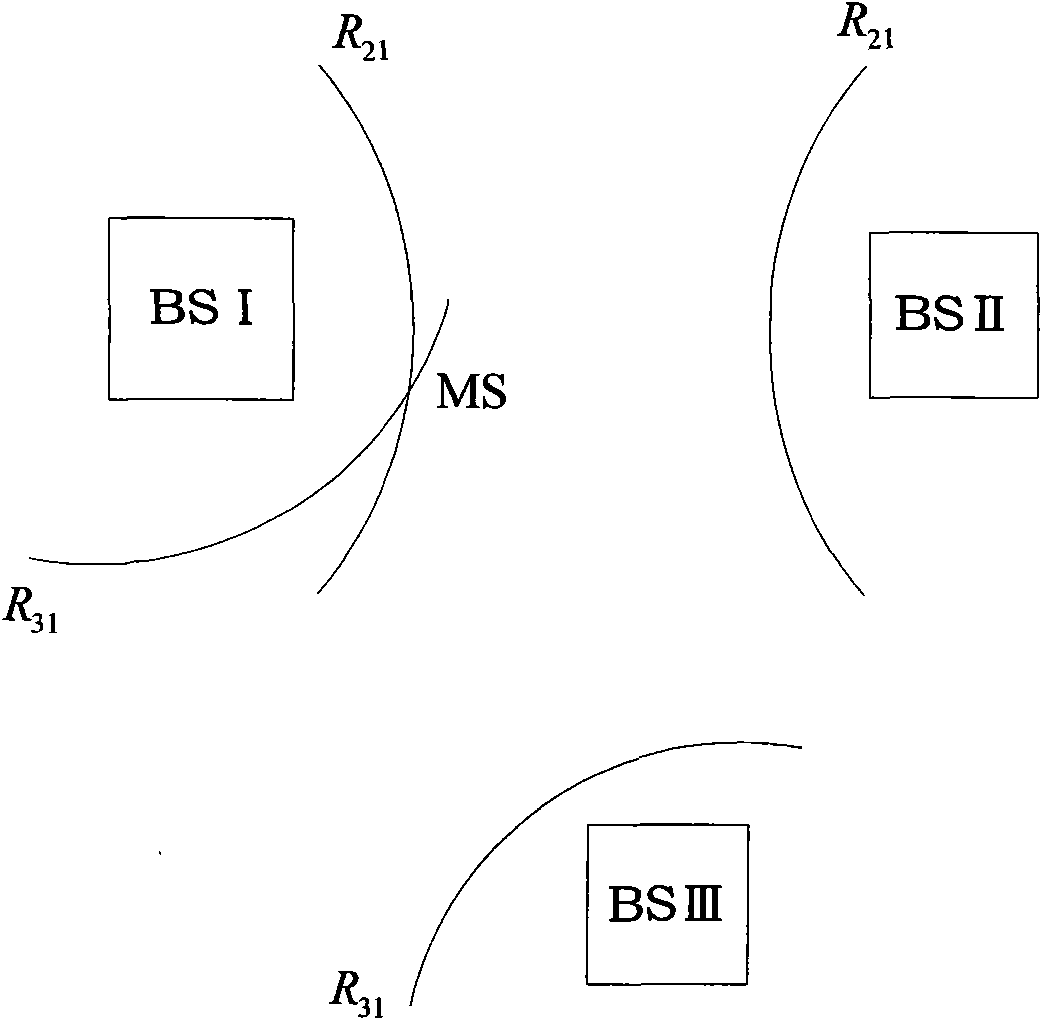
InactiveCN101598557AImprove practicalityReduce mistakesInstruments for comonautical navigationAngular velocityNavigation system
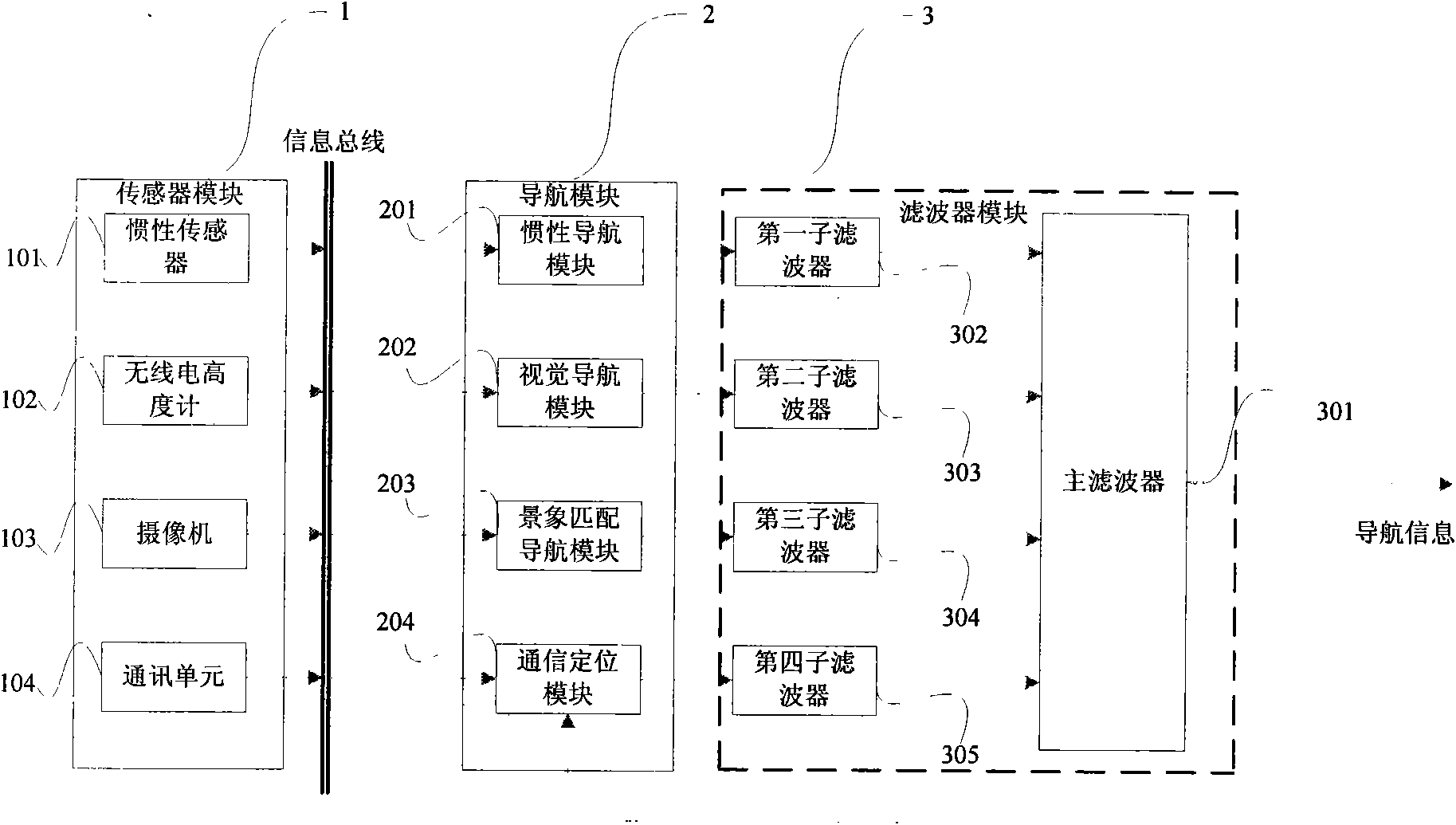
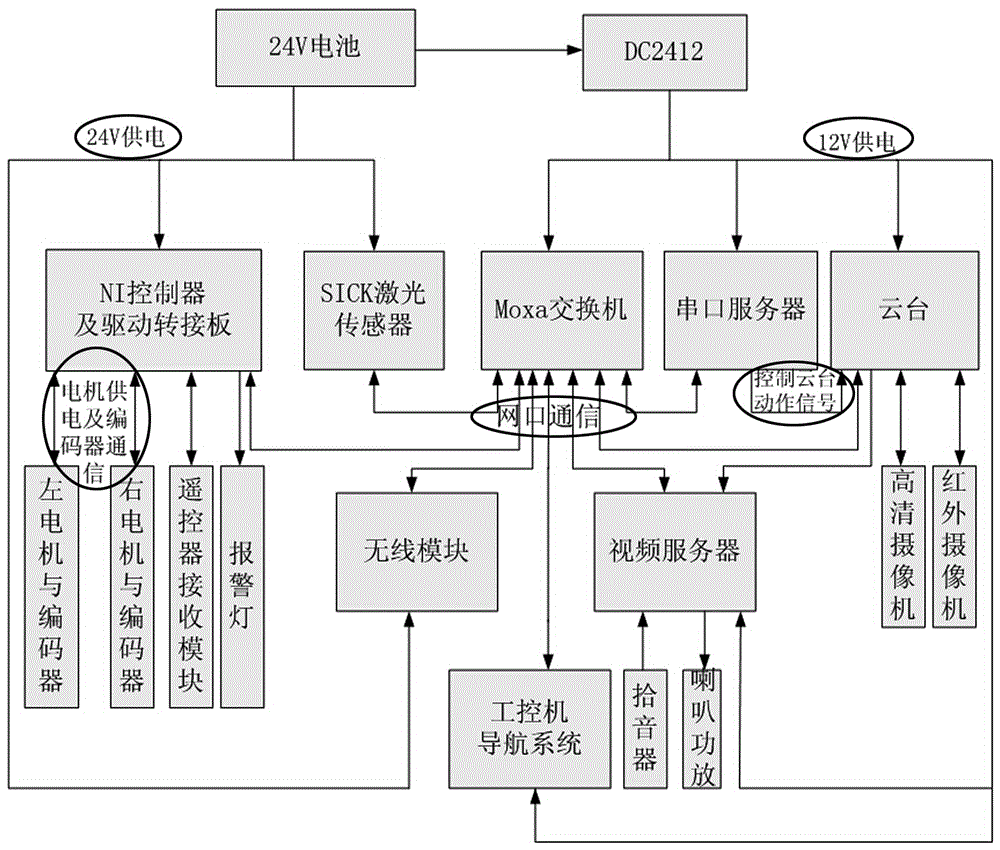
The invention discloses an integrated navigation system applied to a pilotless aircraft, which adopts a sensor comprising an inertial sensor, a radio altimeter, a communication module, a camera and the like, wherein the inertial sensor is used for acquiring motion acceleration and angular velocity of a carrier, and providing the motion acceleration and the angular velocity for an inertial navigation system and a vision navigation system in the unknown environment for setting up a system equation, thus further providing the current location information and matched trigger signals for scene matching navigation. The method integrates four combination ways which are inertial navigation, cellular wireless location navigation, vision navigation in the unknown environment and the scene matching navigation, and the four combination ways form each subsystem of the integrated navigation system and can be independently used for estimating the state of the aircraft; then, fault diagnosis and fusion estimation are carried out on the data output by the subsystems by a main filter, so that the accurate estimation of the state of the aircraft is obtained.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Robot navigation method and robot navigation system based on color coding identifiers
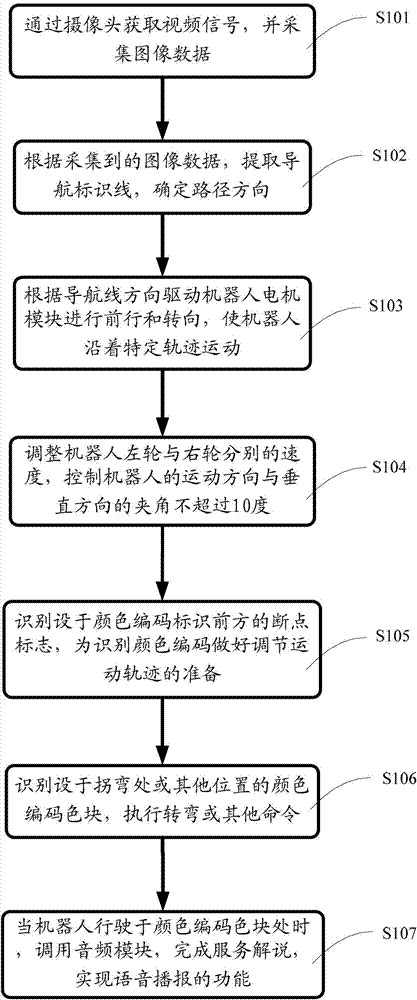
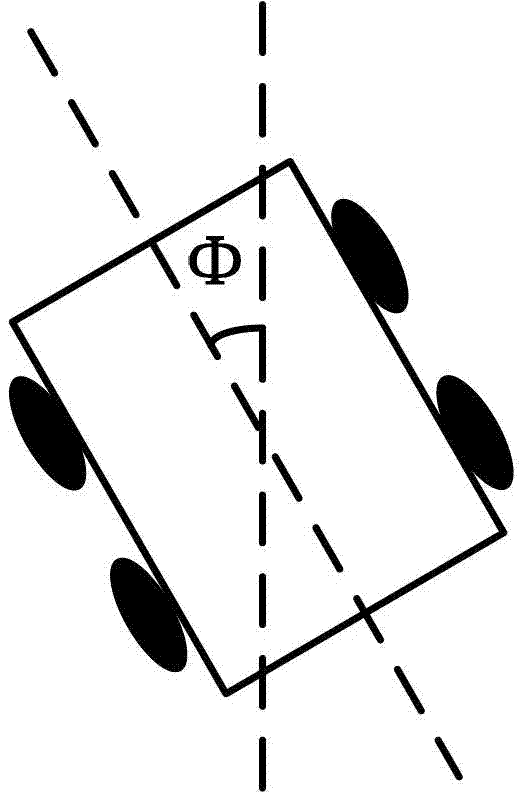
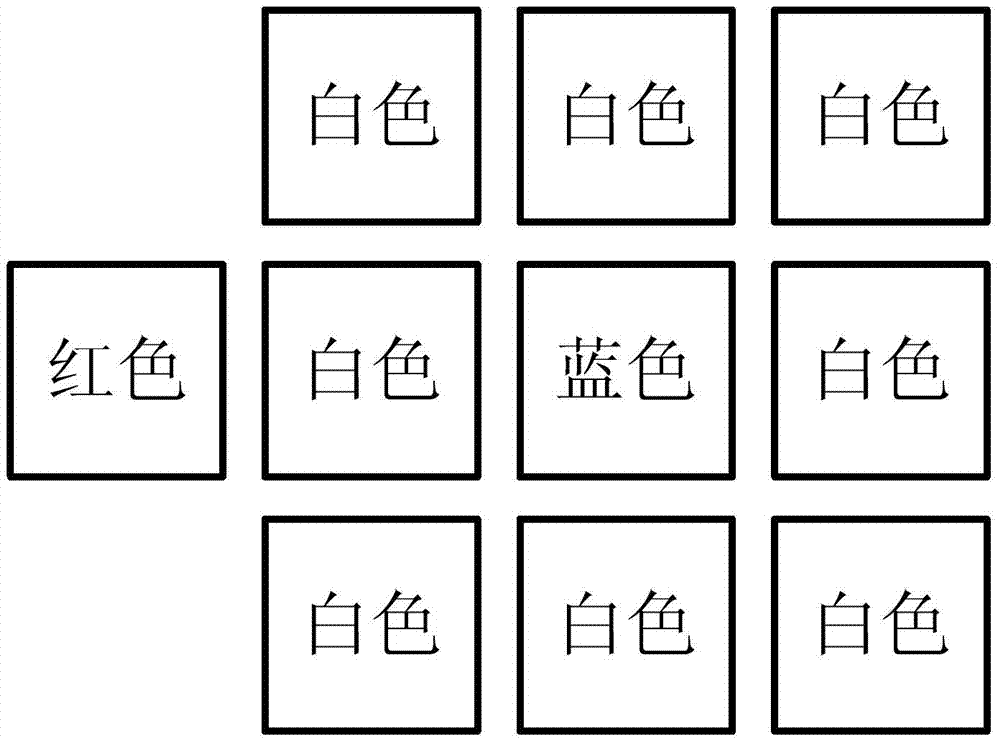
InactiveCN102789234AThe principle is simpleImprove scalabilityInstruments for road network navigationPosition/course control in two dimensionsPattern recognitionOperand
The invention discloses a robot navigation method based on color coding identifiers, which comprises the following steps of: extracting a navigation identification line according to the acquired image data, and determining the path direction; identifying a breakpoint mark in front of the color coding identifier, and preparing to regulate the movement trail for the color coding identifier; and identifying a color coding block around a corner or other positions, and executing turning or other command. The invention further discloses a robot navigation system based on the color coding identifiers. The robot navigation system has a simple principle, strong expandability and good visual perception, and can complete the positioning and navigating tasks of an indoor service robot; the robot navigation system can be combined with other navigation systems, so the stability and practicability of the navigation system are improved; and the problems of weaker applicability to complicated environments, error navigation accumulation, large operand, mutual interfered sensors and the like in the current robot navigation field can be effectively solved.
Owner:GUANGDONG SCI CENT
Traffic navigation system and method based on big data
The invention discloses a traffic navigation system and method based on big data. The system comprises a traffic flow information acquisition module, a traffic flow analysis module, a navigation path planning module and a navigation terminal, wherein the traffic flow information acquisition module acquires traffic flow information and transmits the traffic flow information to the traffic flow analysis module; the traffic flow analysis module analyzes real-time traffic flow data, generates real-time jam state information of a whole road network, analyzes historical traffic flow data and vehicle travel plans, and generates and predicts future jam state information; the navigation path planning module receives the vehicle travel plans and vehicle information uploaded by the navigation terminal, and transmits the vehicle travel plans to the traffic flow analysis module; the navigation path planning module obtains the real-time jam state information of the whole road network and the future jam state information generated by the traffic flow analysis module, and plans a travel path for a travel vehicle in combination with the vehicle information; and the navigation terminal shows the planned travel path to a user for selection, and performs voice navigation according to a path selected by the user.
Owner:CHENGDU SEFON SOFTWARE CO LTD
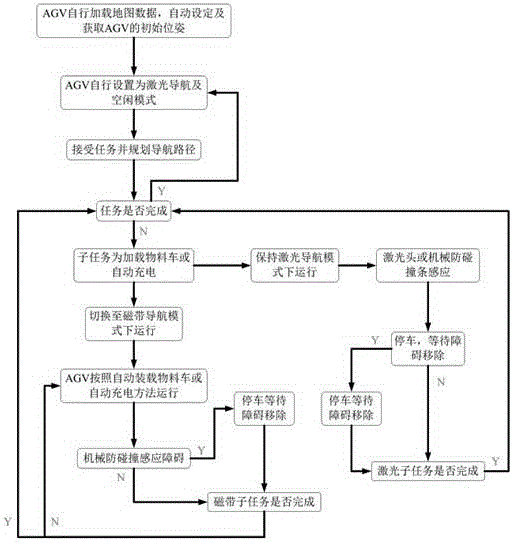
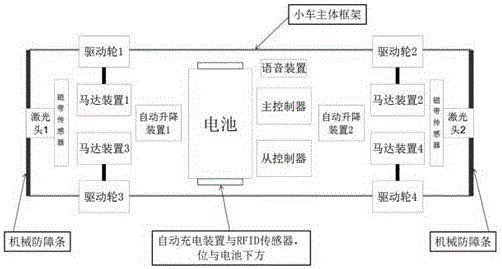
AGV laser tape hybrid navigation system
ActiveCN105045268AFlexible shippingEasy to modifyPosition/course control in two dimensionsControl systemMagnetic tape
The invention discloses an AGV laser tape hybrid navigation system. The system comprises an AGV upper control system and an AGV dolly. The AGV upper control system adopts a mode of combining tape navigation and laser navigation to realize system navigation. A specific structure of the system comprises a laser navigation module, a laser tape hybrid accuracy positioning material module and an automatic charging module. By using the system of the invention, the material can be flexibly transported in a factory; simultaneously, advantages of a flexible laser navigation path and accurate tape navigation positioning are possessed; and a requirement to complexities of the structure, a navigation control algorithm and a task scheduling algorithm is reduced. Cost is low, control is stable and reliable, the structure is simple, a full limitation path requirement is not needed, a navigation path can be conveniently modified and a loading and unloading area and a power supply area possess high positioning precision.
Owner:SHENZHEN ZHUMANG TECH CORP
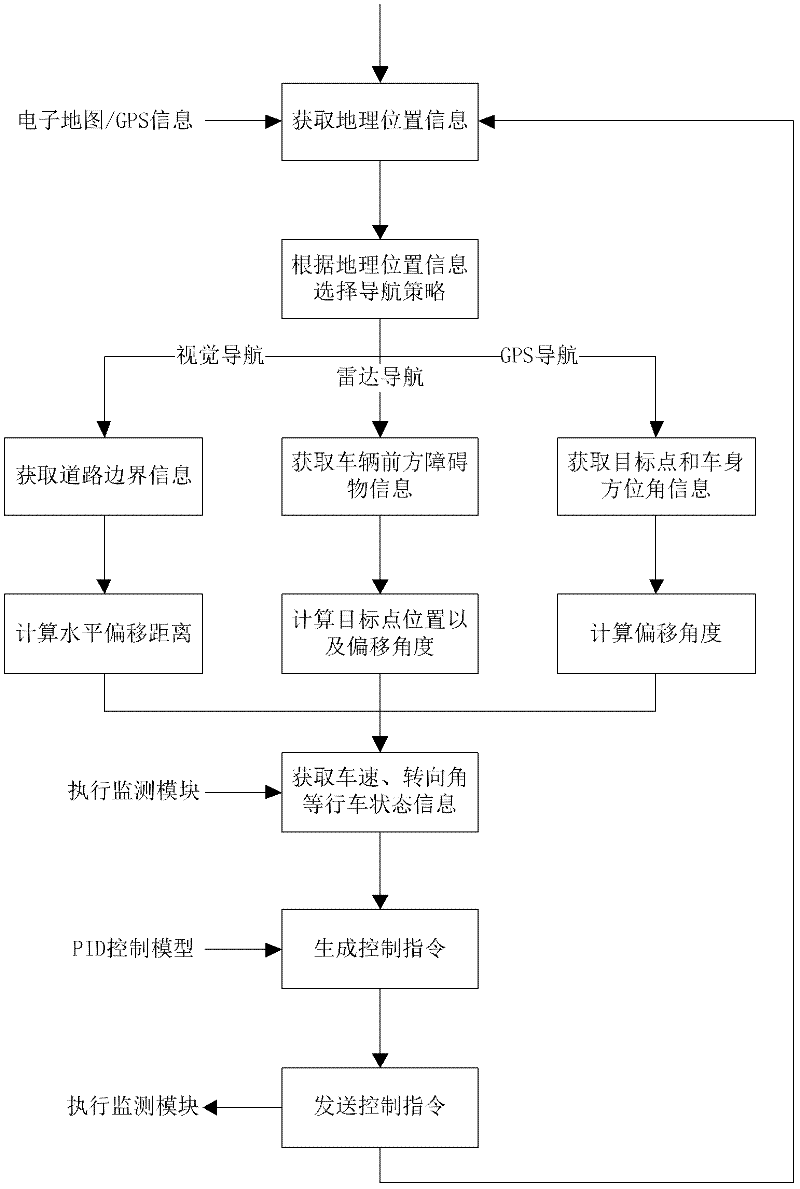
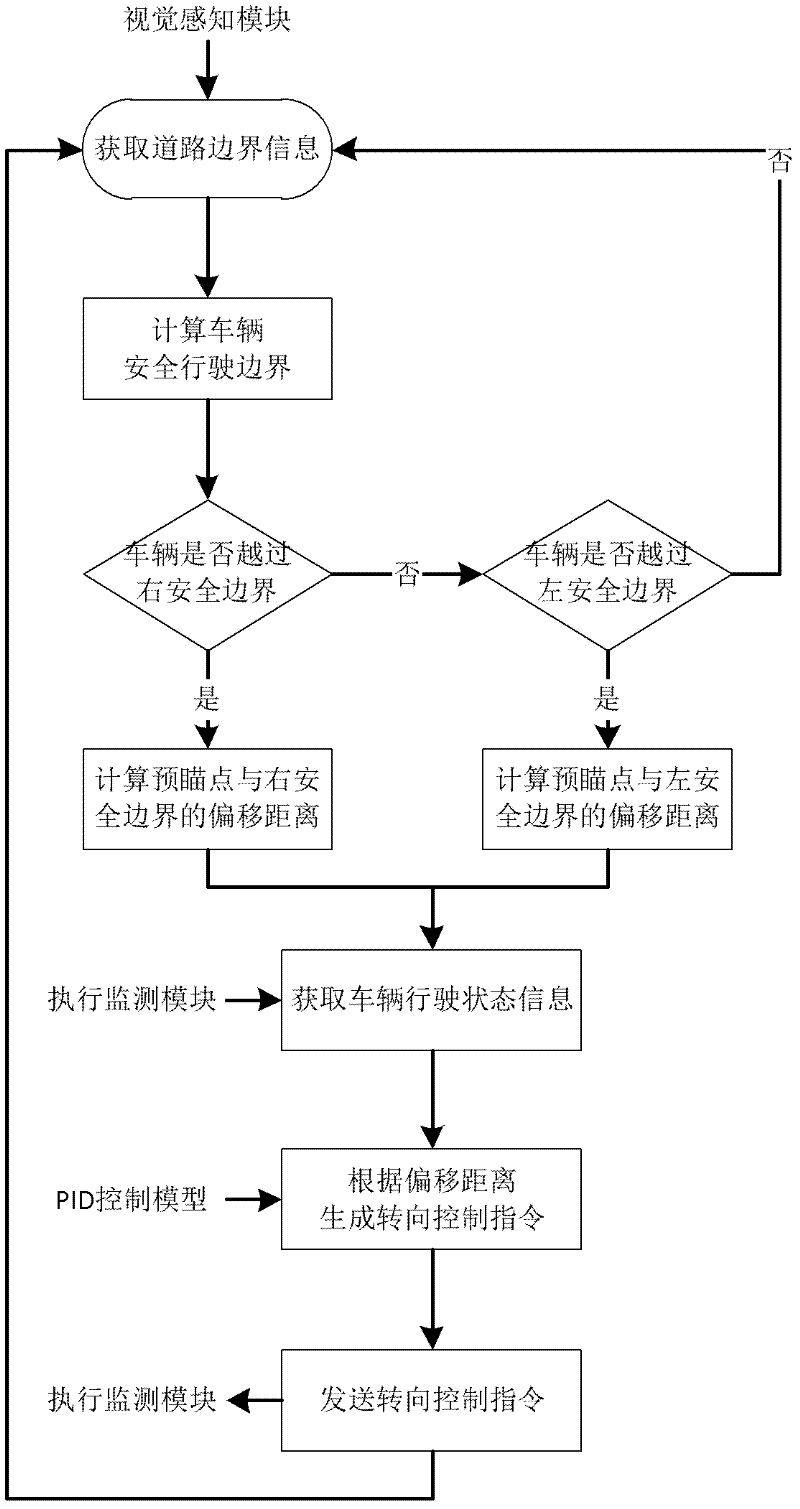
Navigation method of pilotless automobile
InactiveCN102393744AAchieving Robust ControlStability Navigation ControlPosition/course control in two dimensionsGeolocationGps navigation
A navigation method of pilotless automobile is disclosed. The method comprises the following steps: (1) integrating three kinds of navigation strategies: vision navigation, radar navigation and GPS navigation; (2) calculating current geographical location information of an automobile according to an electronic map and a GPS signal; (3) selecting the navigation strategy according to the current geographical location information of an automobile: a priority of the vision navigation strategy is the highest, and if road boundary information perceived and identified by a vision navigation module corresponding to the vision navigation strategy is inaccurate and instable, the radar navigation strategy is the priority; if obstacle information identified by a laser radar detection module corresponding to the radar navigation strategy is inaccurate and instable, the GPS navigation strategy is selected. By using the method of the invention, a principle is simple; an applicable scope is wide; navigation precision is high; controllability and reliability are good. The method has many other advantages.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Secure control of unmanned vehicles
InactiveUS20180253092A1Unmanned aerial vehiclesRemote controlled aircraftControl communicationsUncrewed vehicle
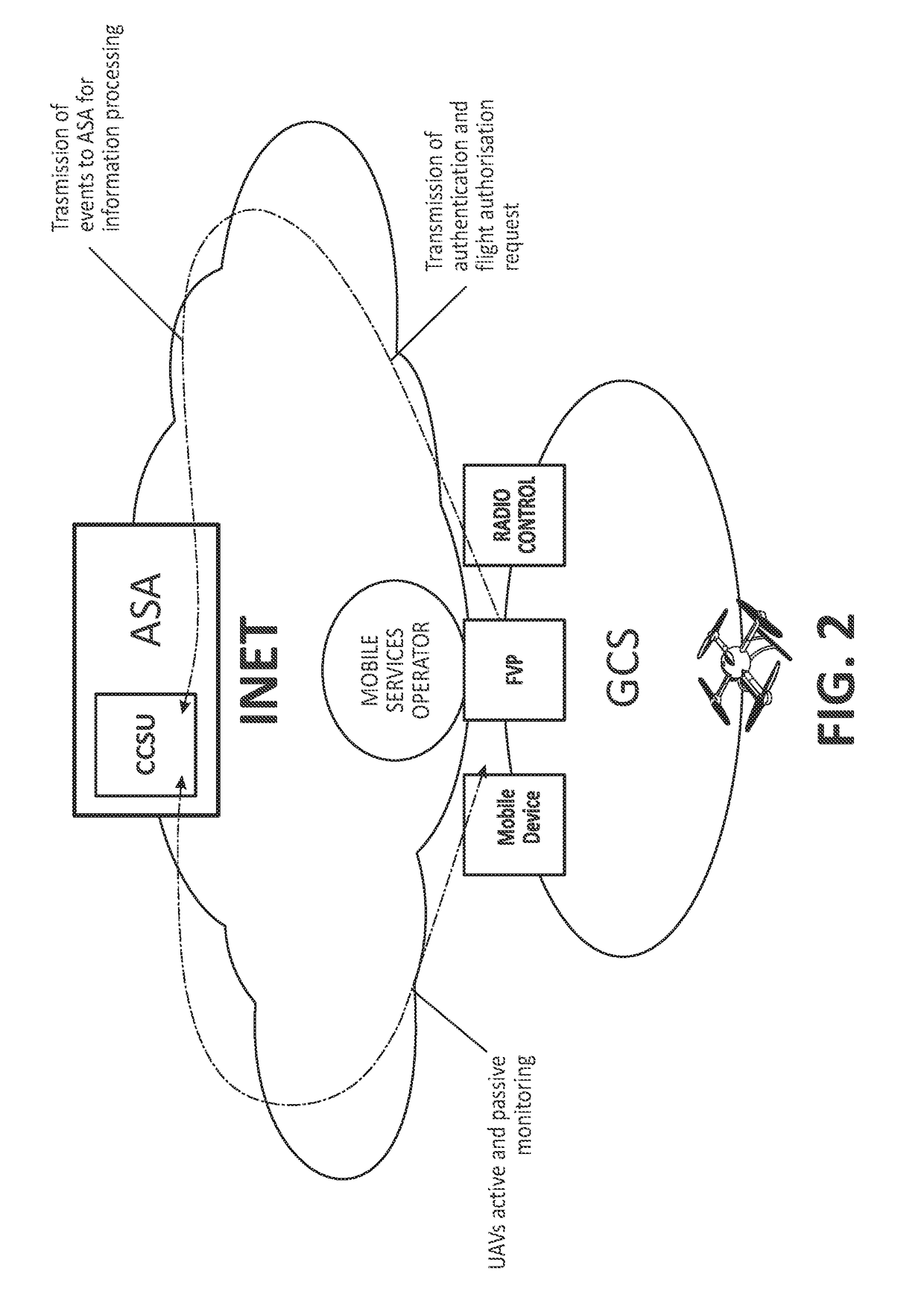
The present invention provides a method, system and devices to establish safe mechanisms for controlling aerial navigation of Unmanned Vehicles (for example. unmanned aerial vehicles, UAVs). Safety in the aerial navigation of the UAVs is increased, through authentication, authorization and monitoring mechanisms that address current technical vulnerabilities, especially in UAV control communications and in the information generated by the UAV, creating links between the pilot of the UAV, the UAV and aviation safety control / regulation (ASAs) bodies.
Owner:TECTECO SECURITY SYST
Coded marker navigation system and method
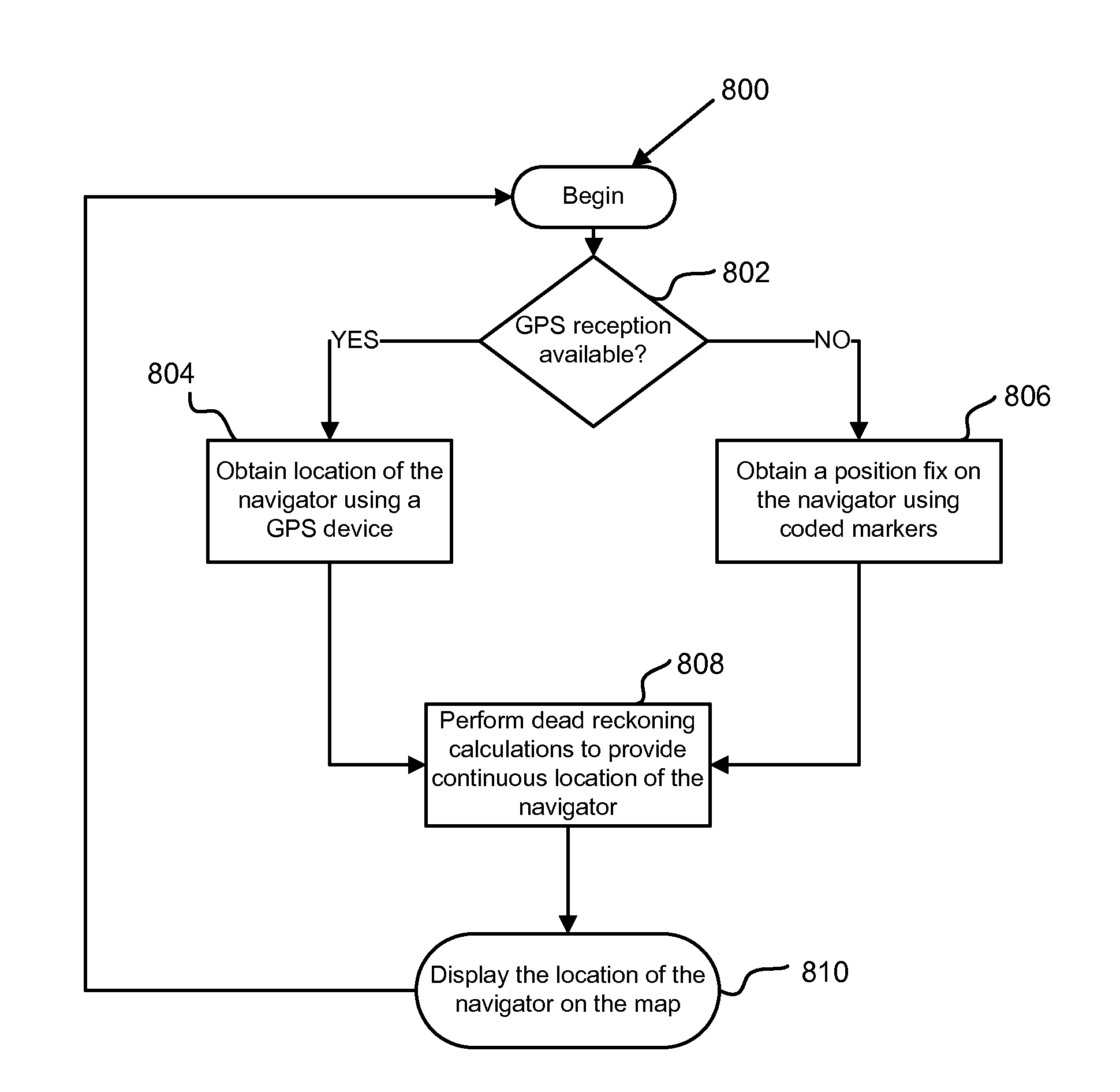
ActiveUS20120197519A1Navigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsNavigation systemMarine navigation
A navigation system and method for determining a location of a navigator in a navigation environment using coded markers located within the navigation environment. In one example, the navigation system includes a camera apparatus configured to obtain an image of a scene containing images of at least one coded marker in a navigation environment, video analytics configured to read the at least one coded marker, and a processor coupled to the video analytics and configured to determine a position fix of a navigator based on a known location of the at least one coded marker.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Robot navigation system and navigation method
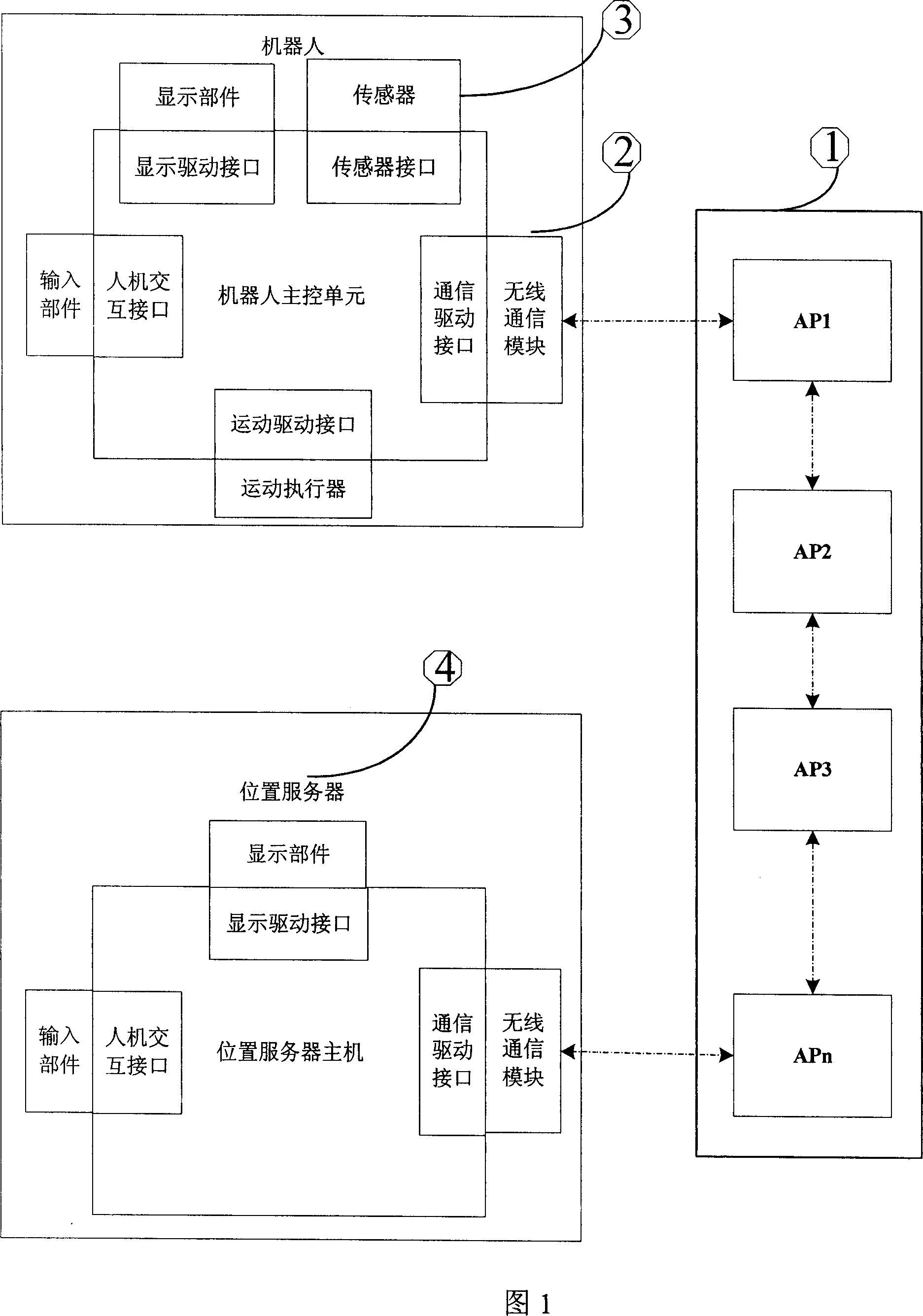
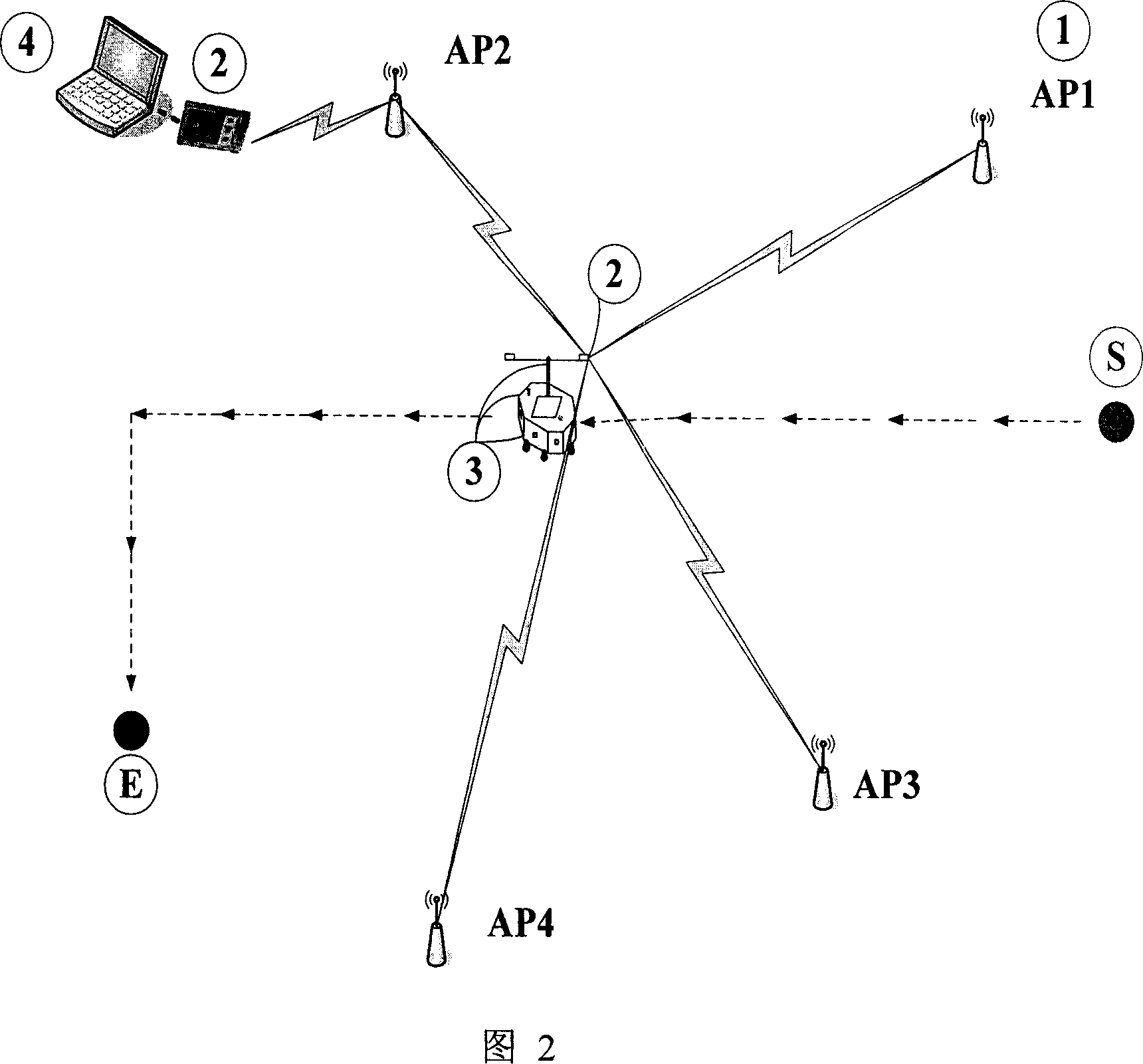
InactiveCN101126808AAchieving Radio Signal StrengthAvoid re-entryNavigation instrumentsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRelevant informationEnvironment effect
The utility model discloses a robot navigation system and a navigation method. The robot navigation system comprises a navigation network which is formed by a plurality of wireless access points, a wireless communication module which is used for transferring data and collecting the intensity sequence communicated with the wireless access points, a sensor which is used for checking that the robot meets barriers or not, and a position server which is used for storing the referenced intensity sequence and running the intricate position arithmetic, and is characterized in that the position server is connected with the wireless communication module and interacts with the navigation network. The navigation method is characterized in that the robot judges the next target position until reaches the destination by comparing the intensity sequence collected in real time with stored reference intensity sequence of the position points; when the robot meets barriers, the robot records and demarcates the intensity sequence of the position in order to avoid entering the position again, therefore achieving intellectual learning; the robot can upload the correlative information to the position server and achieve the assistant navigation position by the help of the database of the position server and the position arithmetic. The utility model is not likely to be affected by the environment and also has the advantages of low cost of maintenance.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
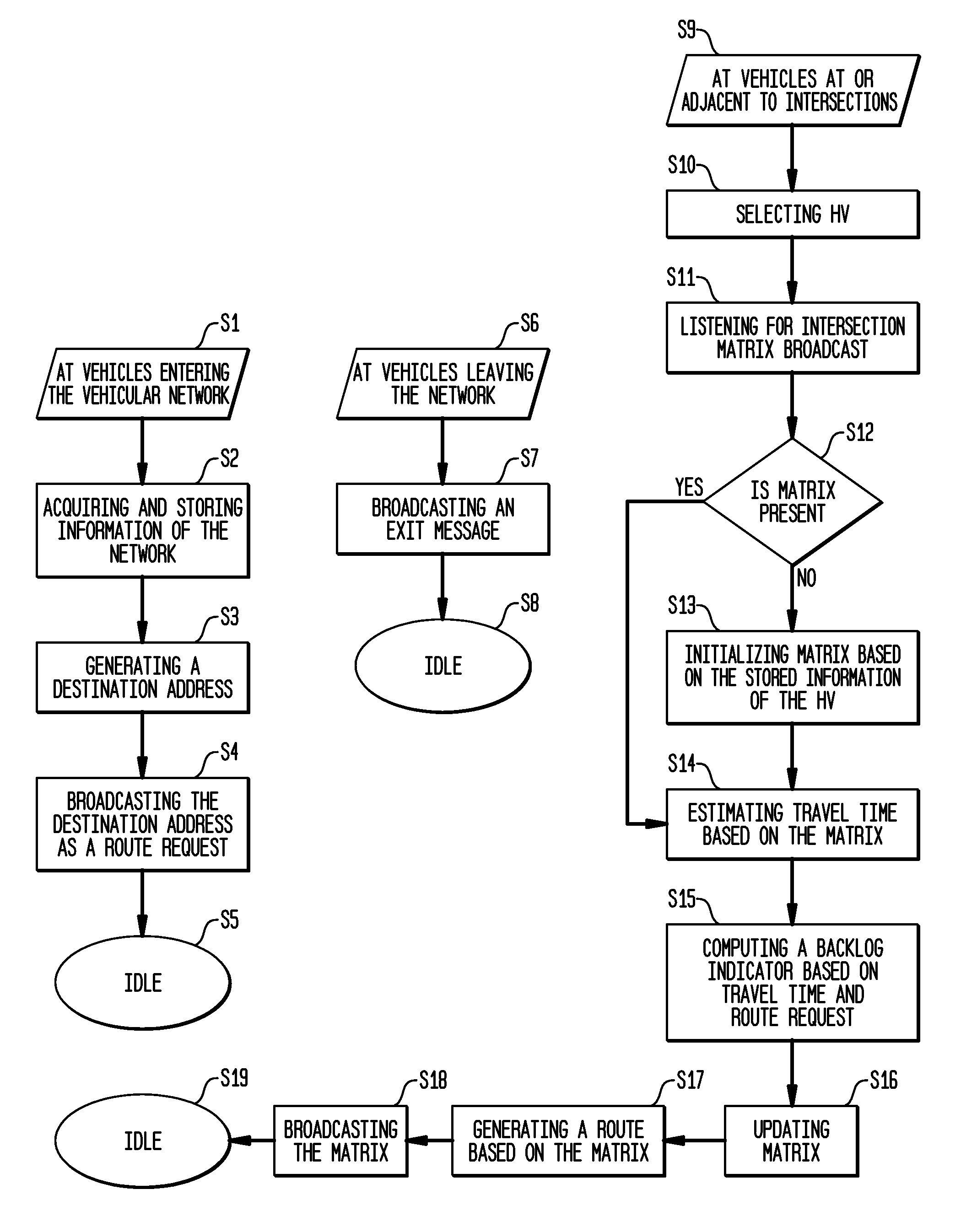
Distributed traffic navigation using vehicular communication
ActiveUS8589073B2Analogue computers for vehiclesInstruments for road network navigationBroadcastingMarine navigation
A method for distributed traffic navigation in a vehicular network is presented. At each vehicle entering the network, information associated with the vehicular network is acquired and stored, and destination addresses are broadcasted as route requests. At each vehicle in the network, the stored information is updated through vehicle to vehicle communication. At each junction, a header vehicle is selected for listening for broadcasts to determine the presence of a matrix. If the matrix is not present, the matrix is initialized based on the stored information of the header vehicle. The header vehicle further estimates travel time on the road segments based on the matrix, calculates a backlog indicator based on the segment travel time and the route requests. The header vehicle further updates the matrix and generates a route based on the matrix. The matrix is broadcasted from the header vehicle.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC
A method and system for automatically detecting and mapping points-of-interest and real-time navigation using the same
InactiveUS20180301031A1Shorten the timeEliminate needImage enhancementInstruments for road network navigationParking areaReal time navigation
The present invention relates to a system and method for automatically detecting and mapping points-of-interest (POI) such as parking spaces, and accordingly locating and directing drivers to available parking spaces as close as possible to desired POI and locations. The system is completely autonomous and independent and it uses a Parking Space Detection module that employs machine learning and computer vision techniques for learning the surface of the parking area, the unoccupied life span of a parking space, the occupancy life span of the parking space, detection of suspicious vehicles in terms of parking searcher to independently predict in which available parking space they may parked, and accordingly to navigate in real-time a user to a parking space that has the highest probability to remain free on arrival of that user.
Owner:PARKAM ISRAEL
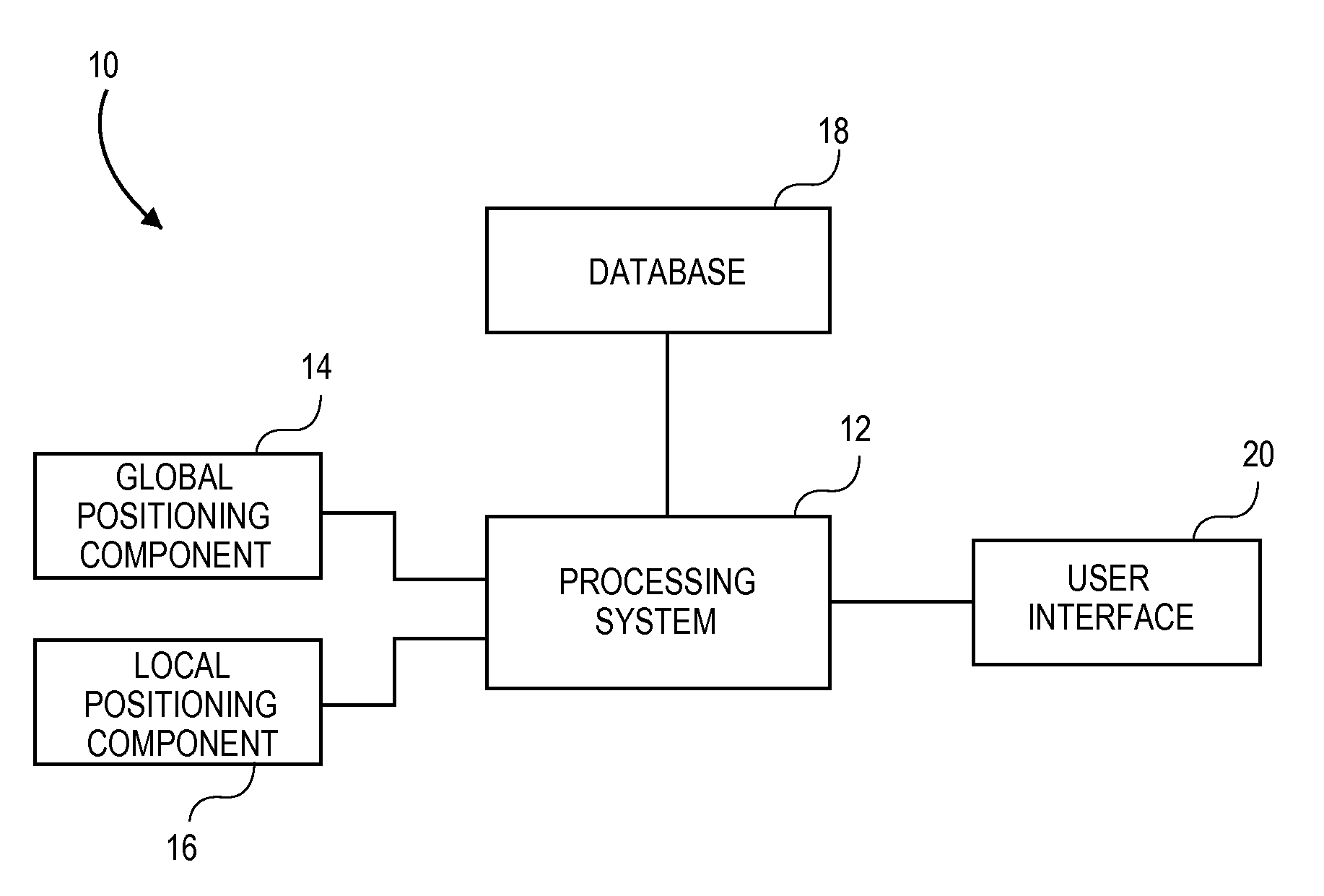
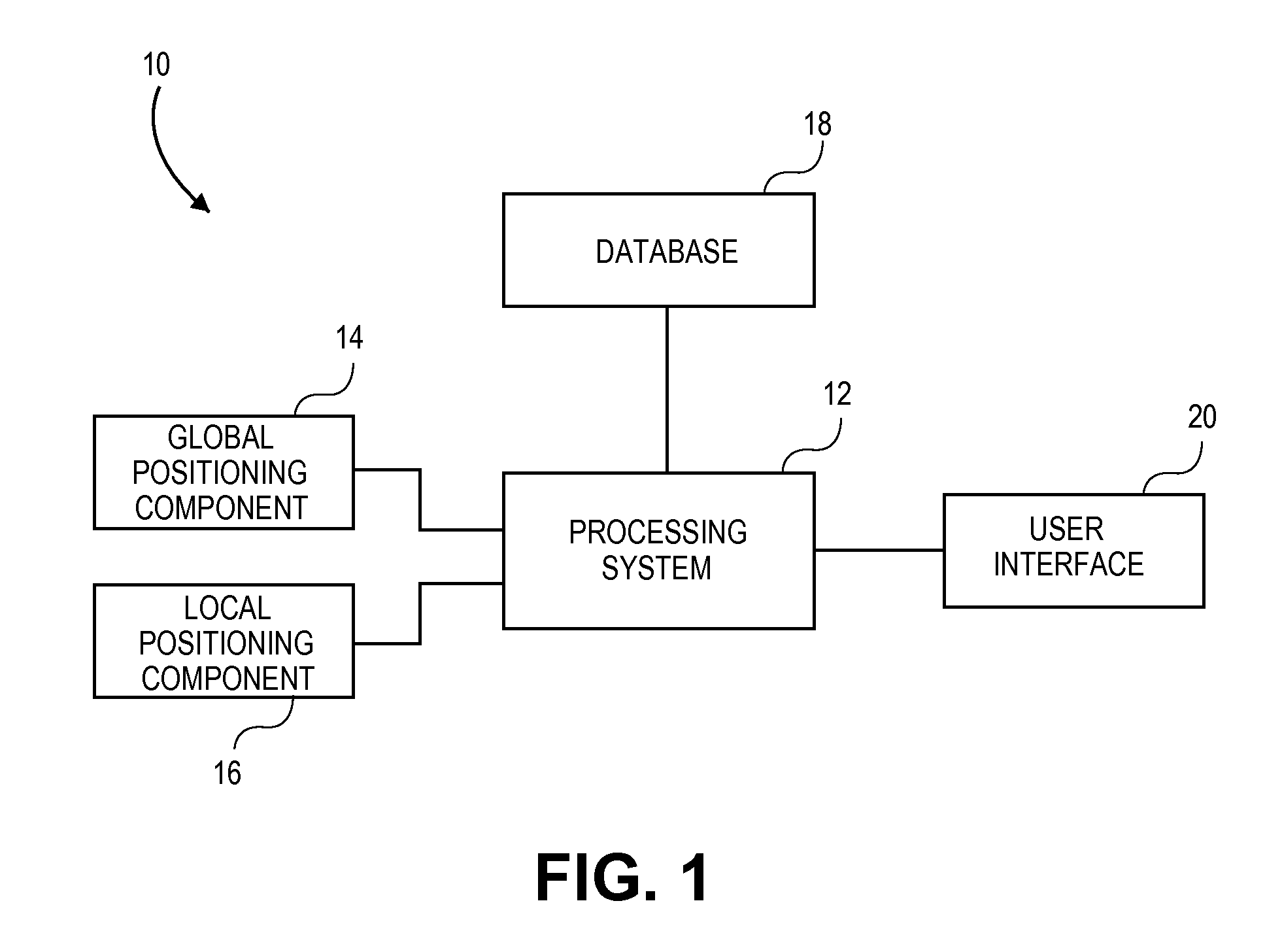
System and method of assisted aerial navigation
ActiveUS8035547B1Enhanced Situational AwarenessAnalogue computers for trafficRoad vehicles traffic controlVirtual targetAviation
A system and method of providing aerial navigation. Techniques are described for receiving global positioning system data, receiving local positioning system data such as instrument landing system data, generating a virtual target flight path using the global positioning system data and the local positioning system data, and presenting a virtual target flight path indicator corresponding to the virtual target flight path. In one implementation, the system includes a user interface, a global positioning component, a local positioning component, and a processing system.
Owner:GARMIN INT
Previewing points of interest in navigation system
InactiveUS7133775B2Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlNavigation systemMinutiae
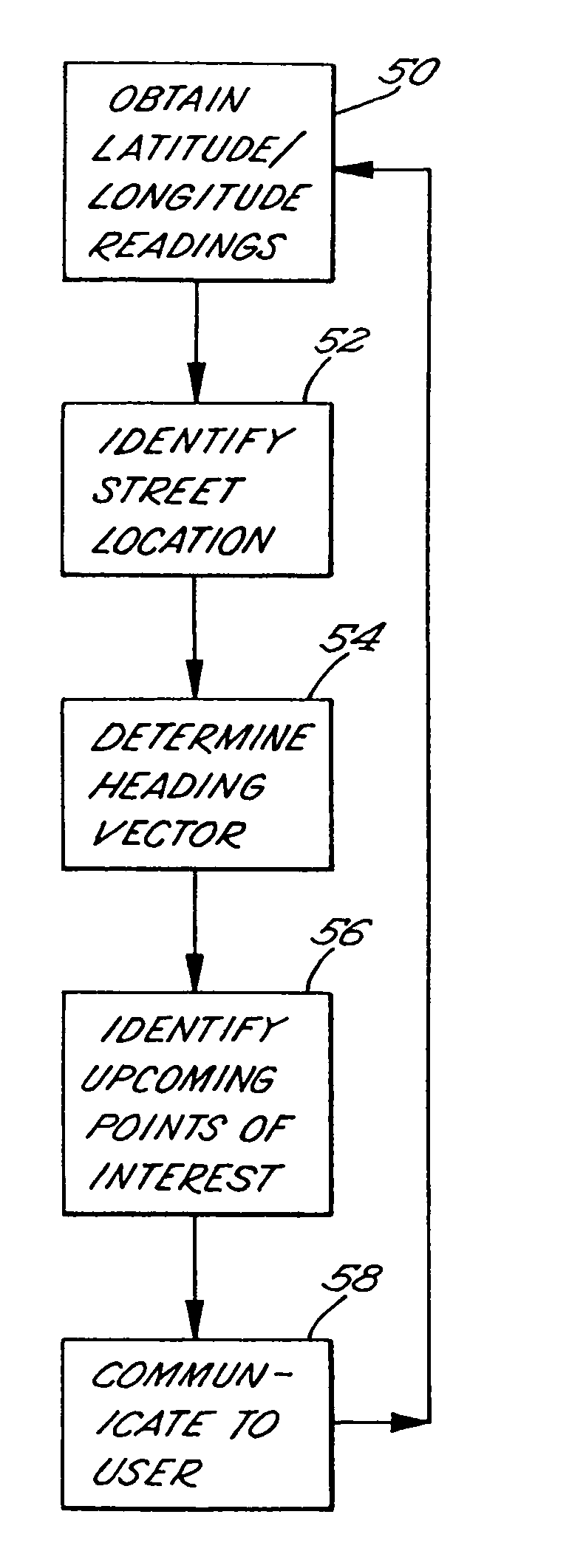
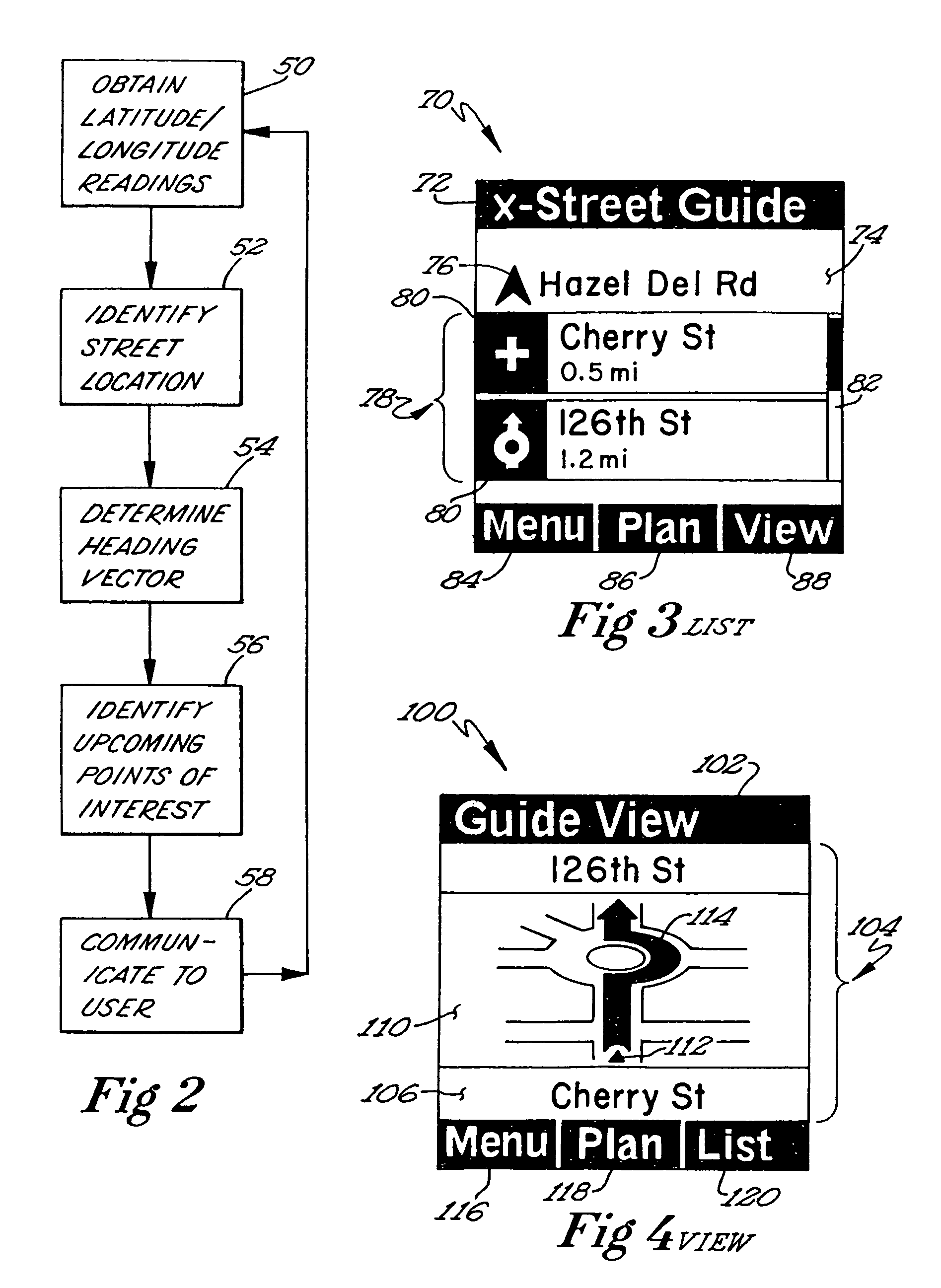
A vehicle navigation system provides information relating to a list of intersections or other points of interest located ahead of a vehicle relative to a heading vector of the vehicle. The vehicle navigation system uses information about the current location of the vehicle and the heading vector in connection with a navigation database to identify a list of the intersections or other points of interest along the current street. The vehicle navigation system presents this information to an occupant of the vehicle. As the vehicle progresses and makes turn maneuvers, the navigation system updates the list of intersections or other points of interest that the vehicle is approaching. The occupant can receive information regarding points of interest without needing to enter a planned destination beforehand. In addition, the occupant can determine the location of the vehicle relative to the surrounding area without the clutter of irrelevant map details.
Owner:VALUE STREET CONSULTING GRP
Laser navigation system applicable to intelligent inspection robot of transformer substation
InactiveCN105698807AReduce development costsReliable and efficient completion of inspection workInstruments for road network navigationPosition/course control in three dimensionsTransformerRobot position
The invention discloses a laser navigation system applicable to an intelligent inspection robot of a transformer substation, overcoming the problem in the prior art that navigation control positioning precision of the robot still needs to be improved. The laser navigation system comprises the following steps: step 1, configuring the robot; step 2, establishing an environment map; step 3, carrying out a laser navigation positioning test; and step 4, executing tasks at stopping points. In the step 3, a move_base packet in the laser navigation positioning test is used for doing a path plan on the map by utilizing robot position information and real-time obstacle information sensed by a laser sensor, and issuing planning speed information to a movement controller on the bottom layer, so that the robot safely arrives at an appointed target position. The invention provides the laser navigation type intelligent inspection robot of the transformer substation, which is not interfered by a strong electromagnetic field in a transformer substation environment, and is reliable to operate, accurate in navigation positioning, easy to realize and low in development cost.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU JINHUI COMP SYST ENG
Robot navigation system avoiding obstacles and setting areas as movable according to circular distance from points on surface of obstacles
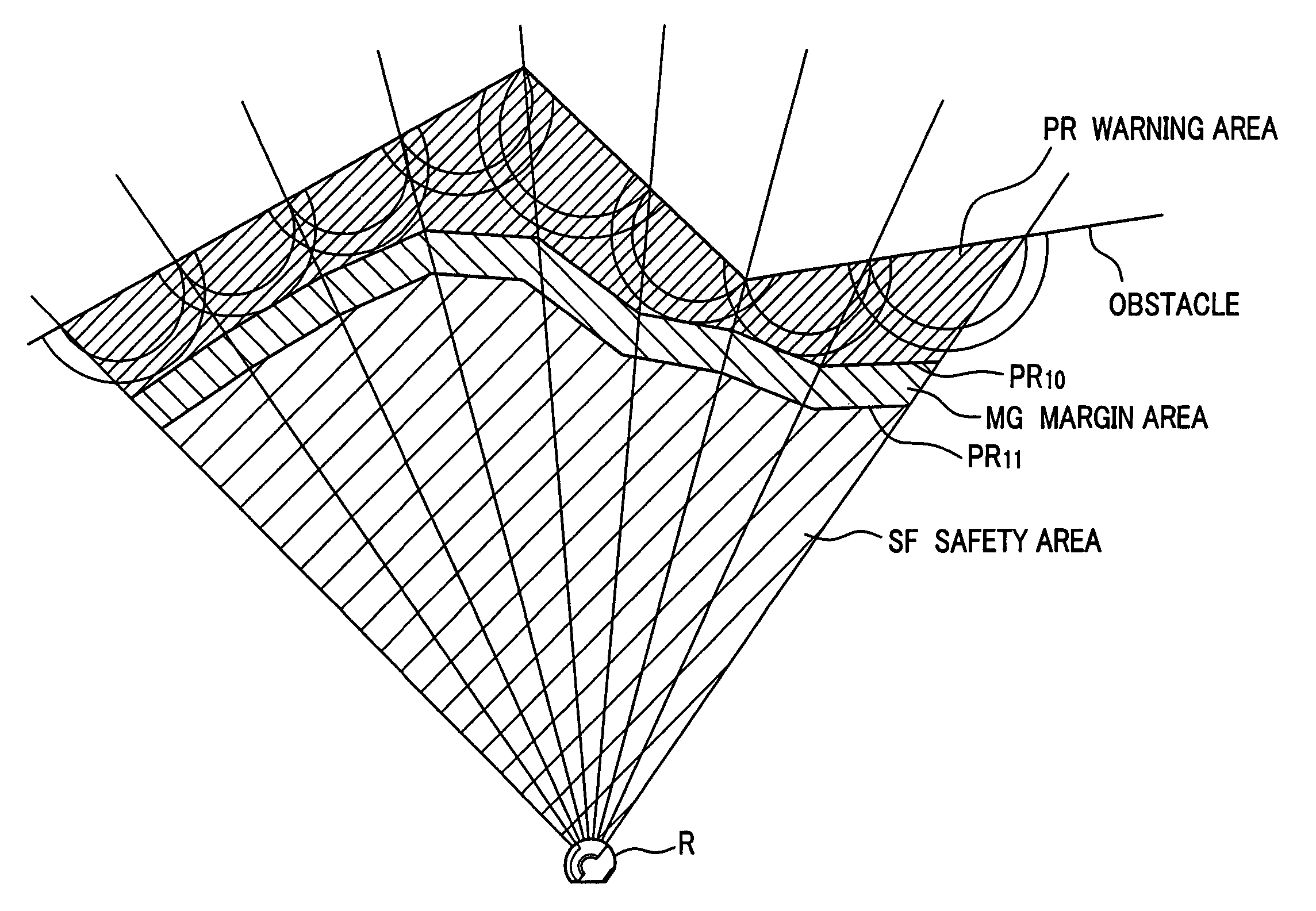
InactiveUS7873448B2Safe and smoothSmooth mobile operationImage analysisComputer controlNavigation systemSpeech sound
The content of the voice designation of a designator is recognized by a voice recognition part 130 at the time of controlling a robot, and the content of the indication of gesture or the like is recognized by an image recognition part 120. A movement destination and a map around the specific position designated are referred from a map data base 150 registering the position of an obstacle and the current position estimated by a self-position estimation part 140. After movement ease is decided by a movement ease decision part 112, the behavior is decided. When movement designation is given to the robot, correspondence according to a situation can be performed.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Fleet navigation system, piloting navigation apparatus, sub-navigation apparatus and navigation thereof
ActiveCN101408433AReduce navigation costsInstruments for road network navigationNavigation functionNavigation system
The invention relates to a navigation technology. Aiming at the defect of over high cost in the existing motorcade navigation proposal, the technology provides a motorcade navigation system, a piloting navigation device, an accessory navigation device and a navigation method thereof. the motorcade navigation system comprises a piloting navigation device for receiving the information of a starting place and a destination and generating and sending out a navigation route; receiving satellite navigation signals, calculating and sending out the current position coordinates; the accessory navigation device is used for receiving and displaying the navigation route sent by the piloting navigation device; receiving the current position coordinates sent by the piloting navigation device, thus displaying the current position of the piloting navigation device. The invention further provides the piloting navigation device, the accessory navigation device and the navigation method thereof. The piloting navigation device sends the optimal route to the accessory navigation device, thus leading the accessory navigation device to be only in need of being configured with mobile communication function and displaying function without configuring the navigation device with full function for each automobile in a motorcade, thus reducing the navigation cost of the whole motorcade.
Owner:CARELAND TECH SHENZHEN
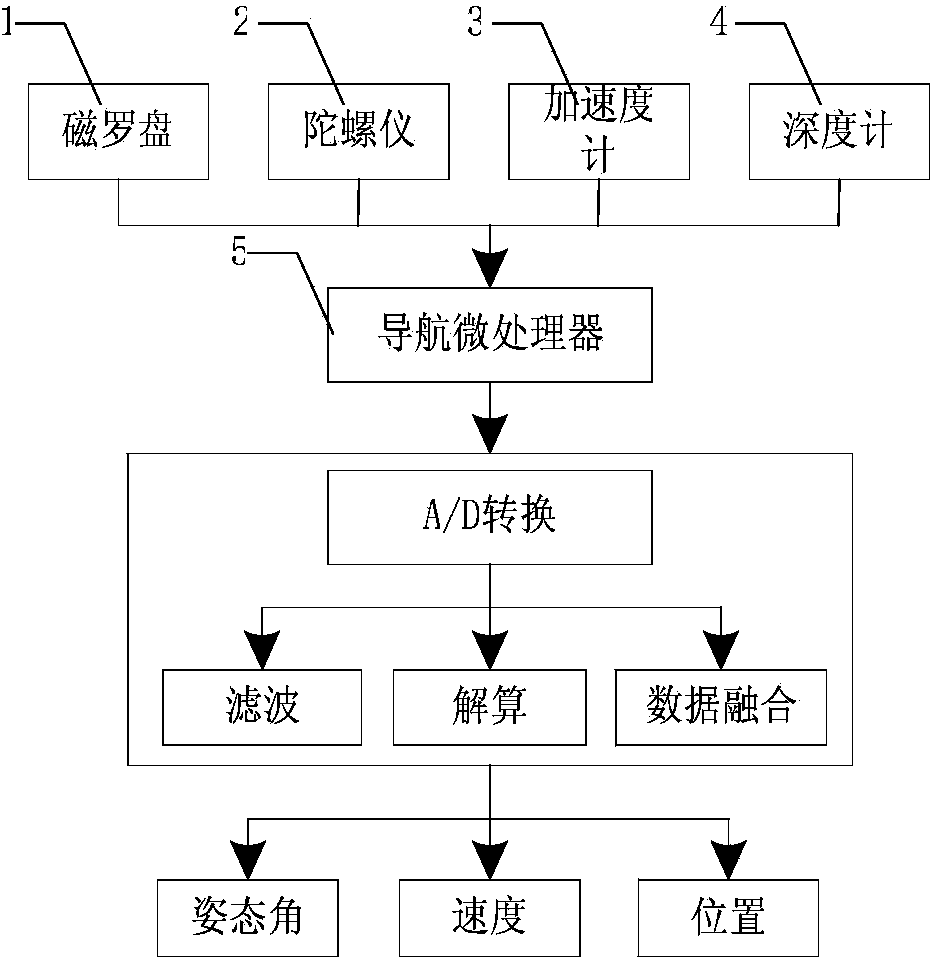
Real-time navigation system and real-time navigation method for underwater structure detection robot
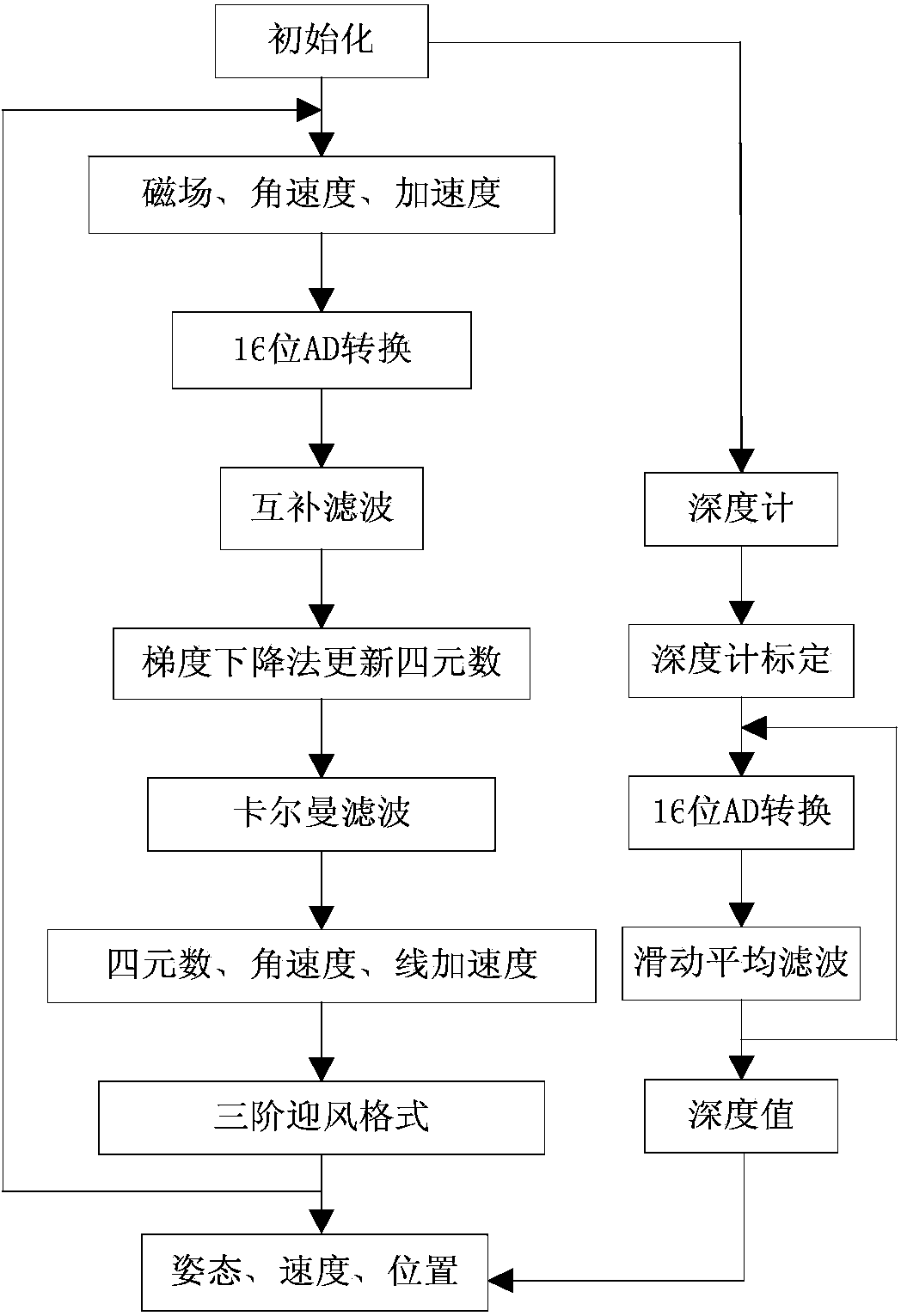
ActiveCN104197927AAvoid divergenceReduce Attitude DriftNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsMoving averageAccelerometer
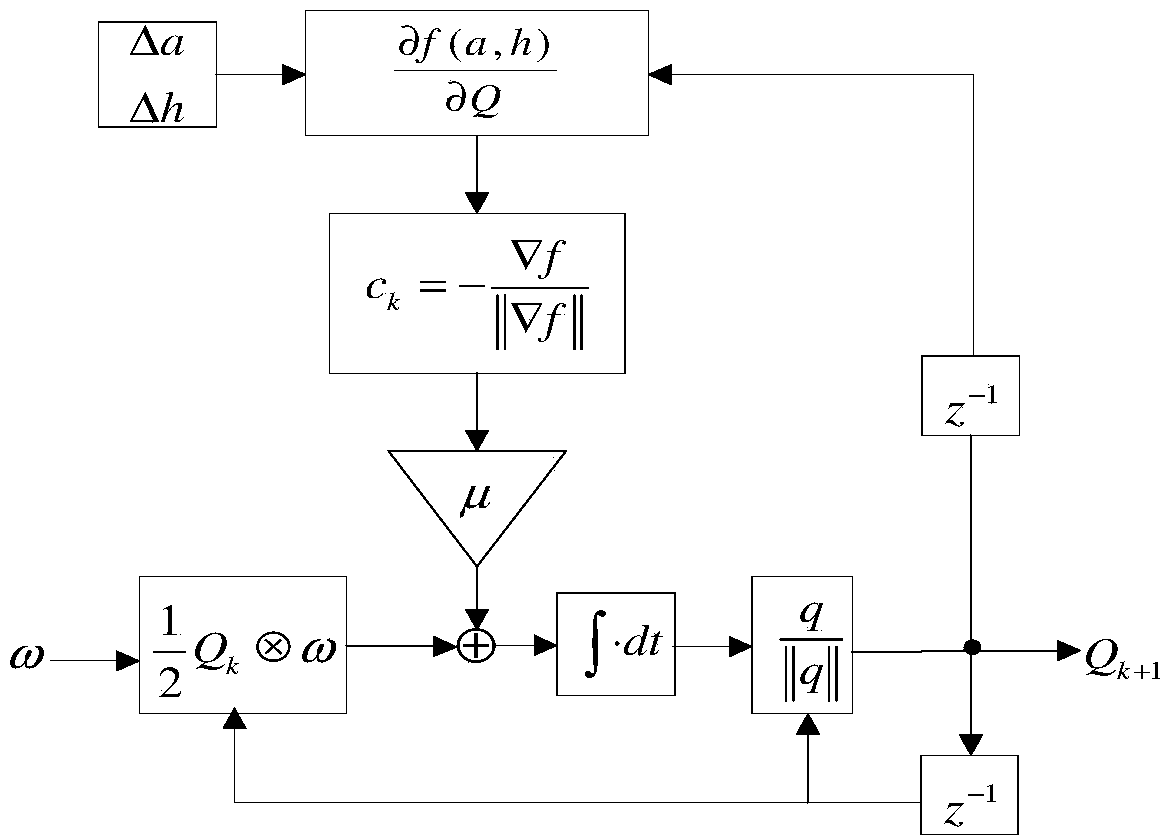
The invention discloses a real-time navigation system and a real-time navigation method for an underwater structure detection robot. The navigation system comprises a magnetic compass, a gyroscope, an accelerometer, a depth meter and a navigation microprocessor, wherein the magnetic compass, the gyroscope, the accelerometer and the depth meter are used for respectively collecting magnetic field intensity, an angular speed, a linear speed and submerged depth data and transmitting the magnetic field intensity, the angular speed, the linear speed and the submerged depth data to the navigation microprocessor; the navigation microprocessor is used for calculating attitude and position of the underwater robot according to the collected data. The navigation method comprises an attitude algorithm, a speed algorithm and a depth algorithm; according to the attitude algorithm, a complementary filtering method, a quaternion gradient descent method and a Kalman algorithm are combined for obtaining an attitude matrix and an attitude angle; the speed algorithm is used for calculating the speed and the position of the robot by using a three-order upwind scheme with rotary compensation; the depth algorithm is used for processing the data of the depth meter by using a moving average filter algorithm so as to obtain the submerged depth. By virtue of the real-time navigation system for the underwater structure detection robot and the method thereof, the navigation cost is reduced and a relatively good navigation precision is achieved.
Owner:CETC NINGBO MARINE ELECTRONICS RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com