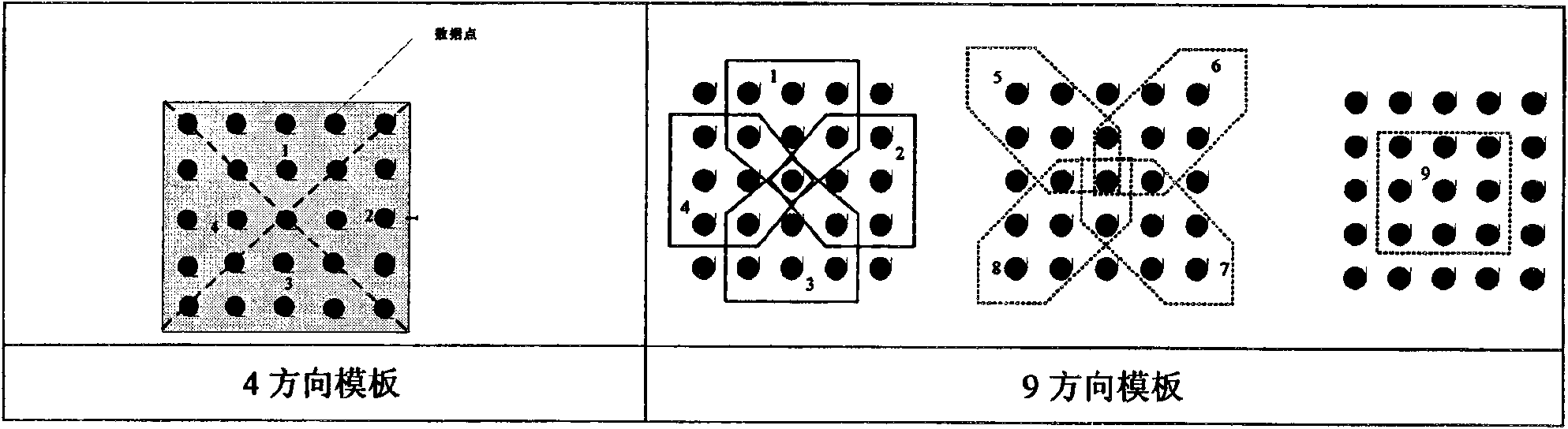
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
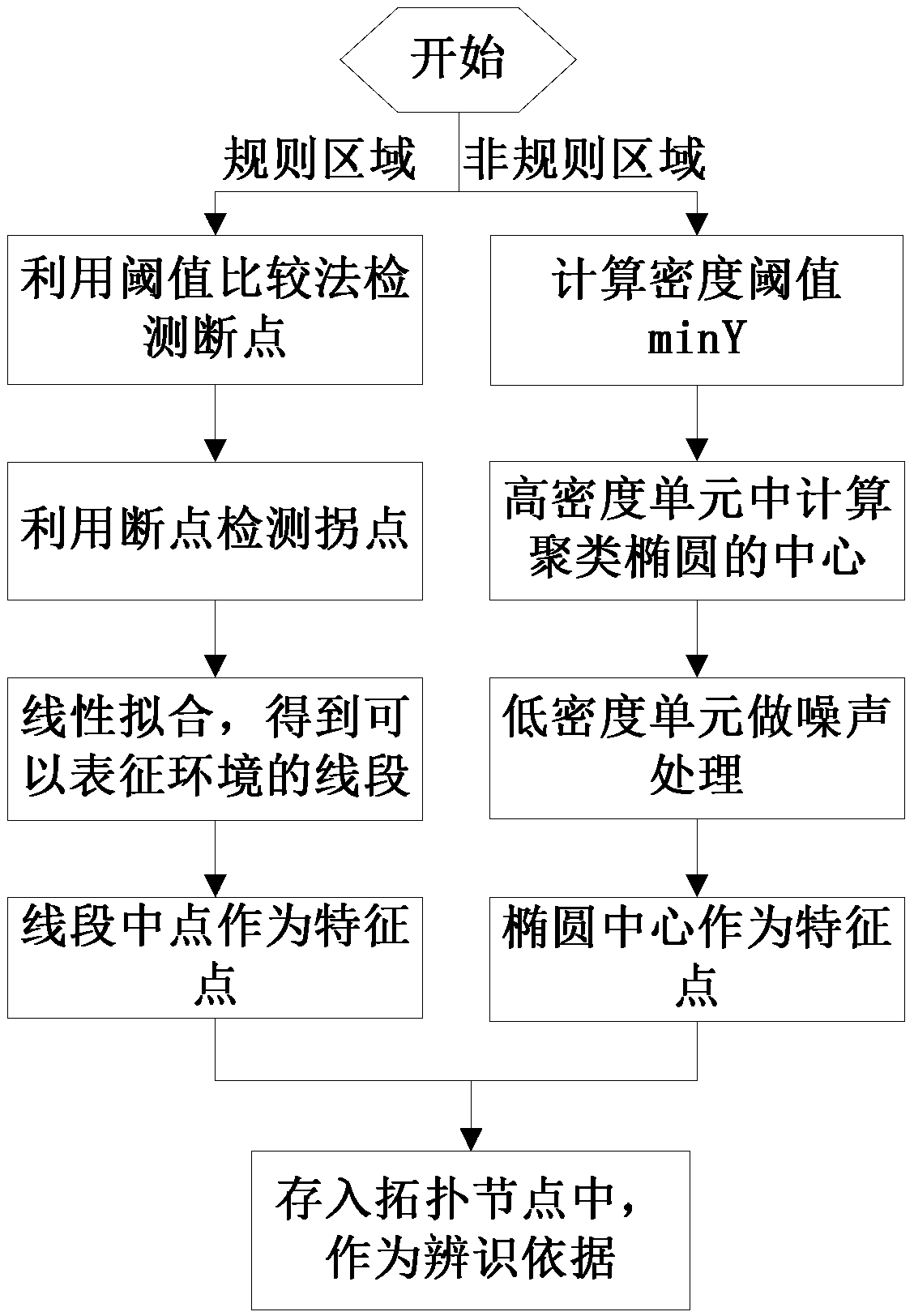
3172 results about "Laser sensor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
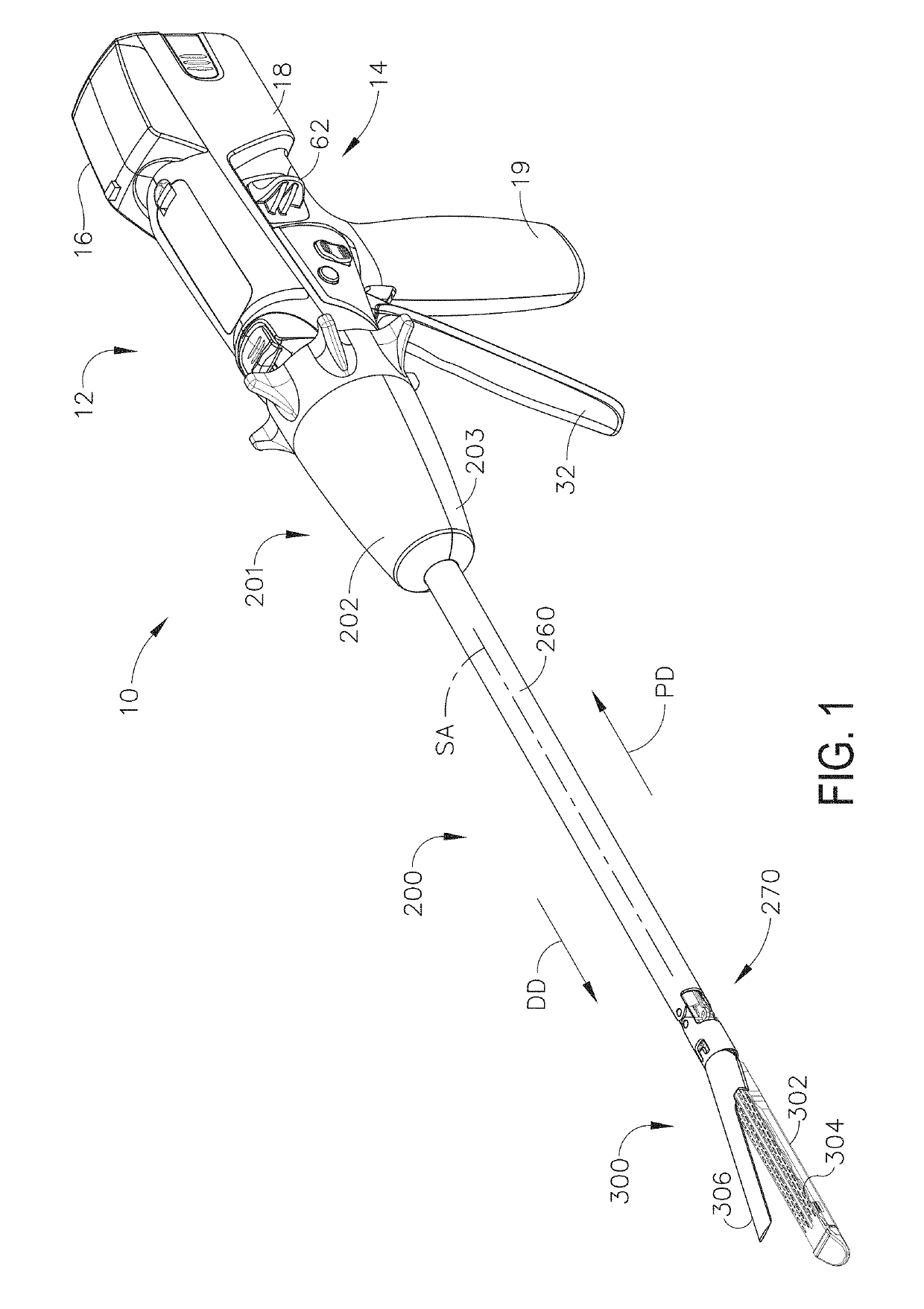
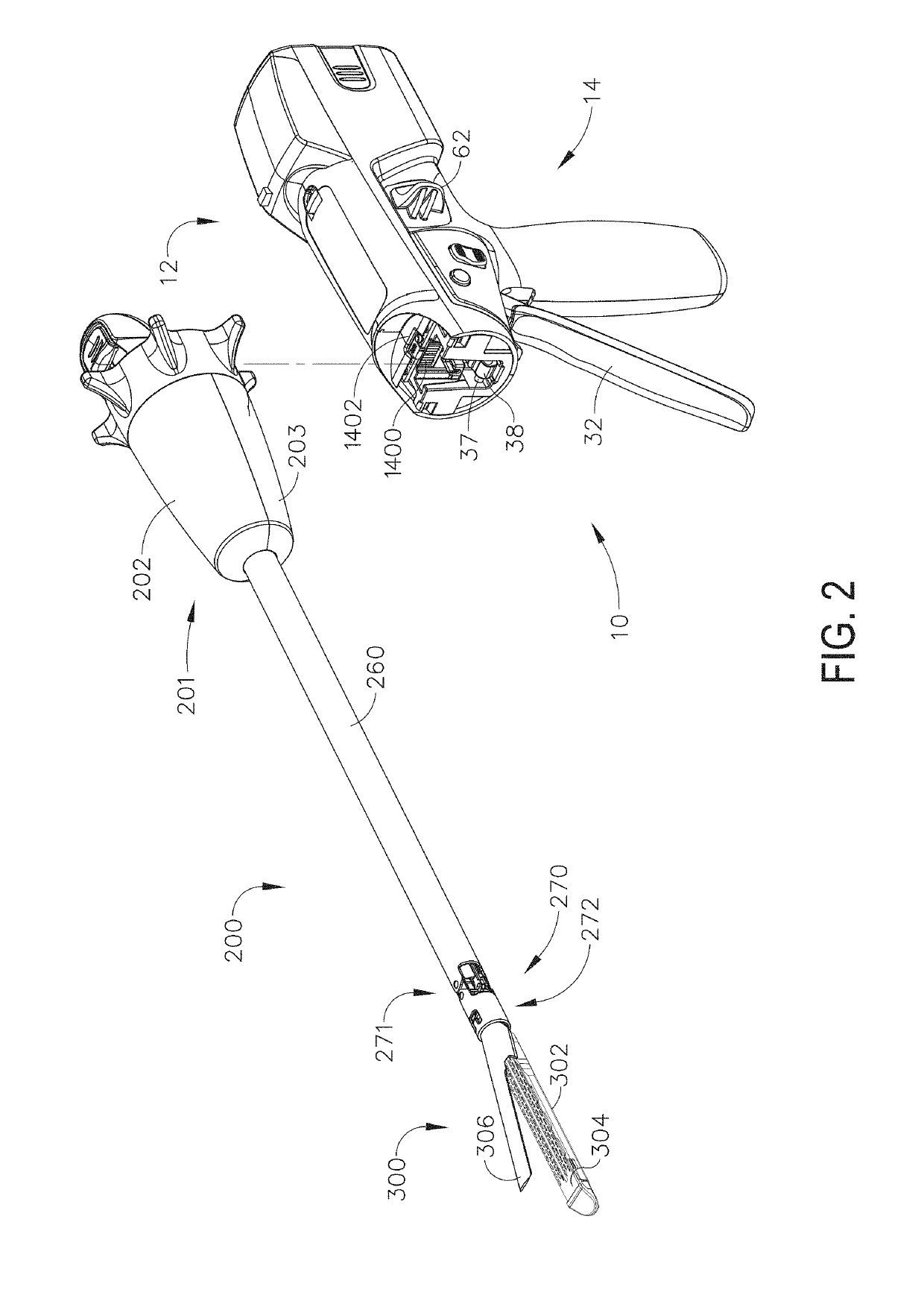
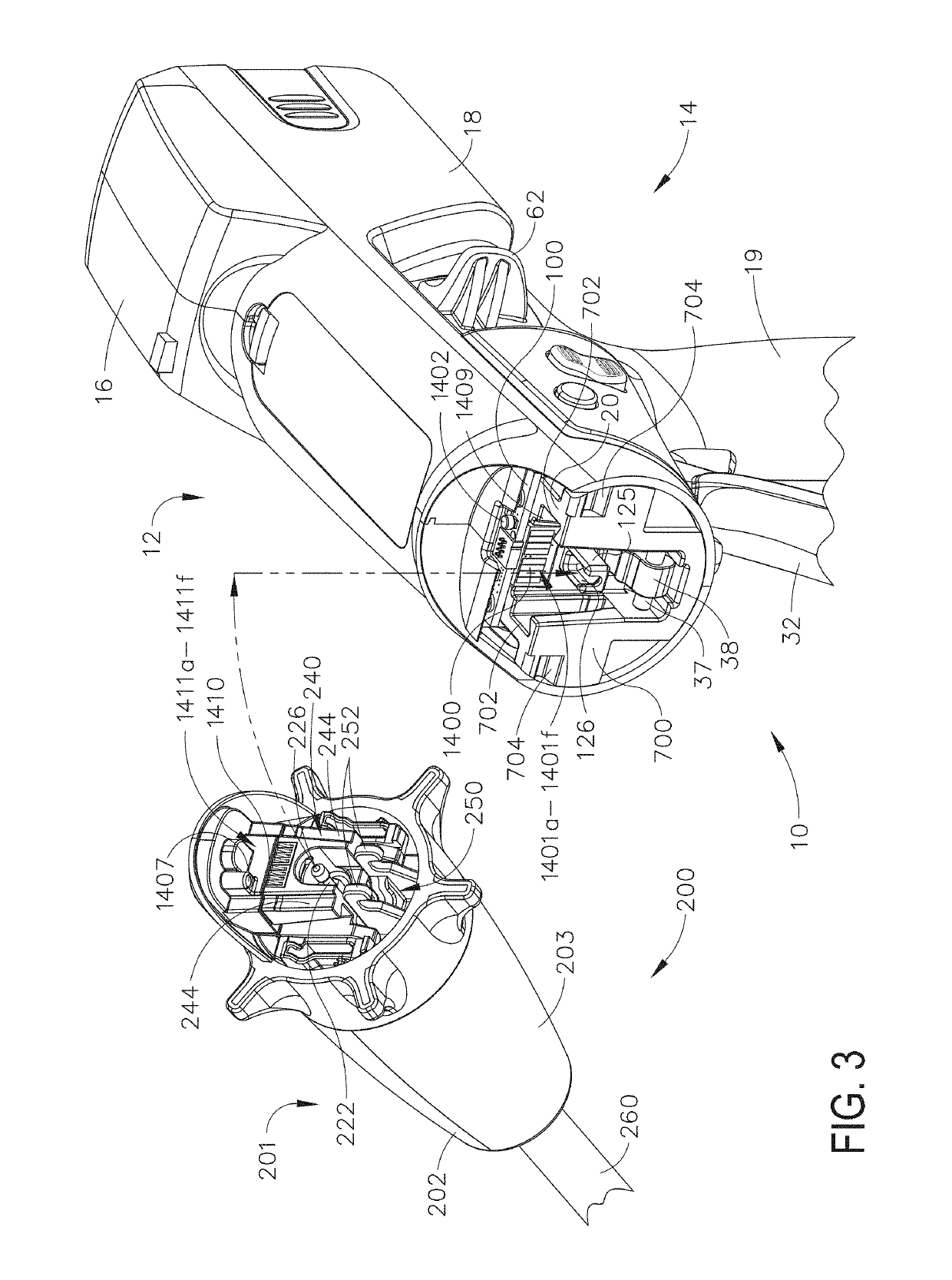
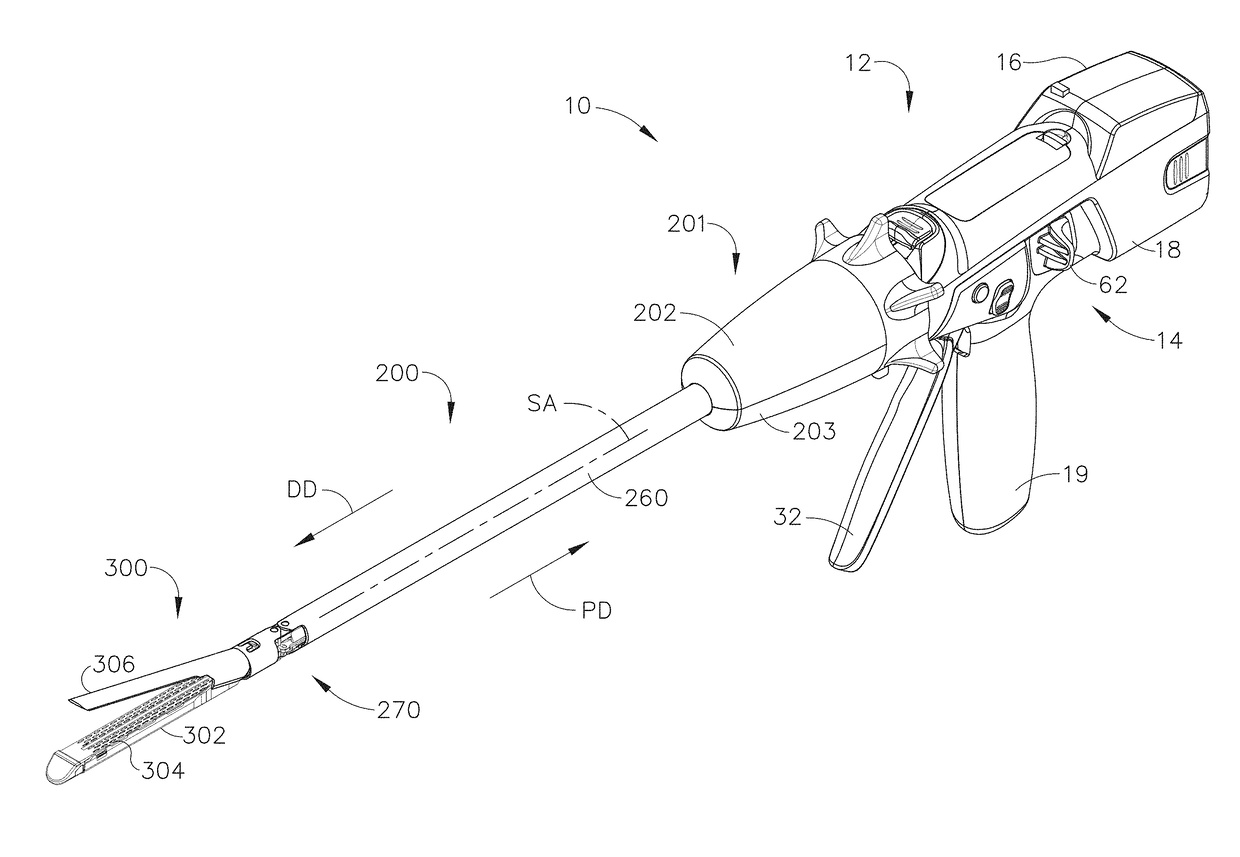
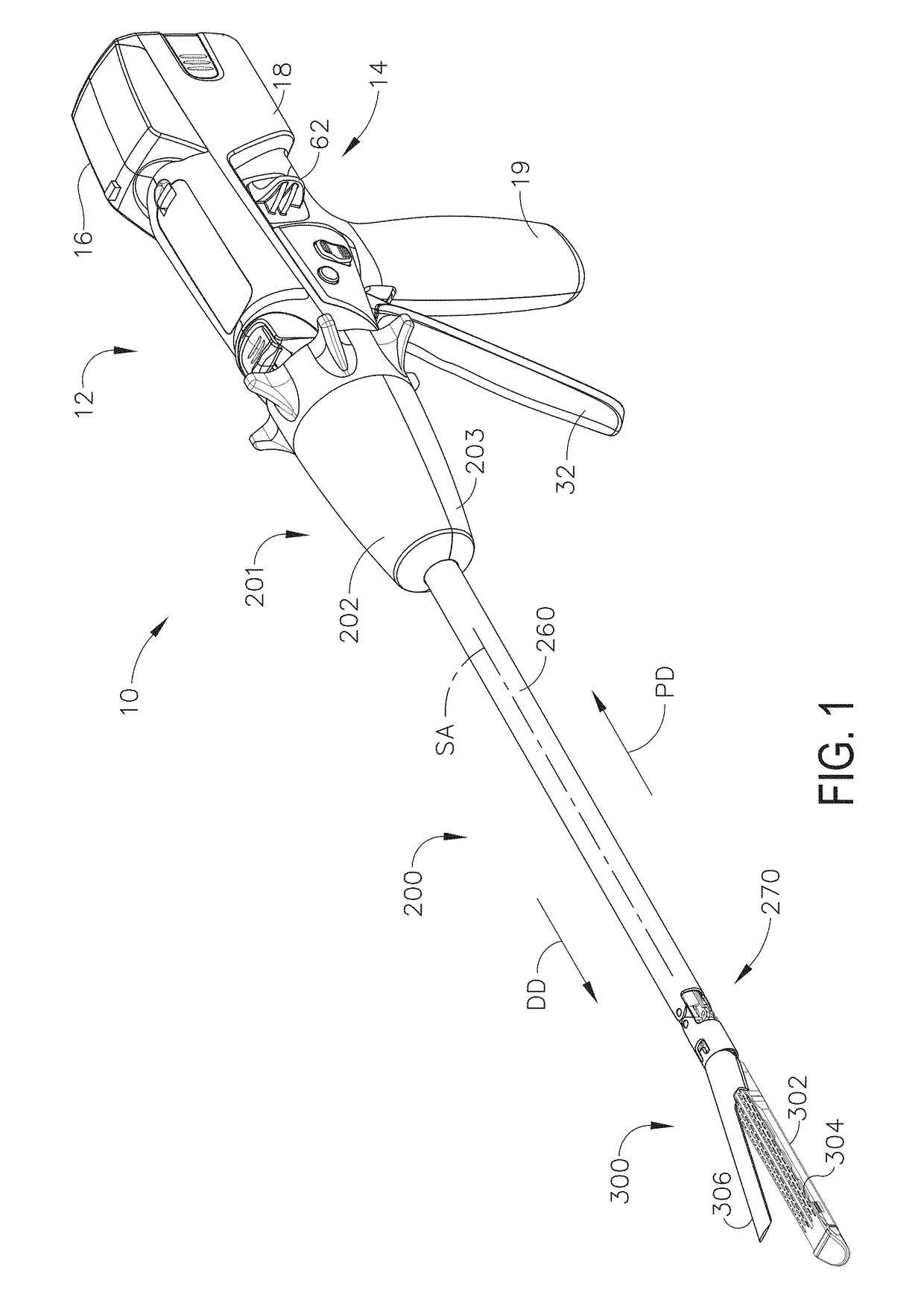
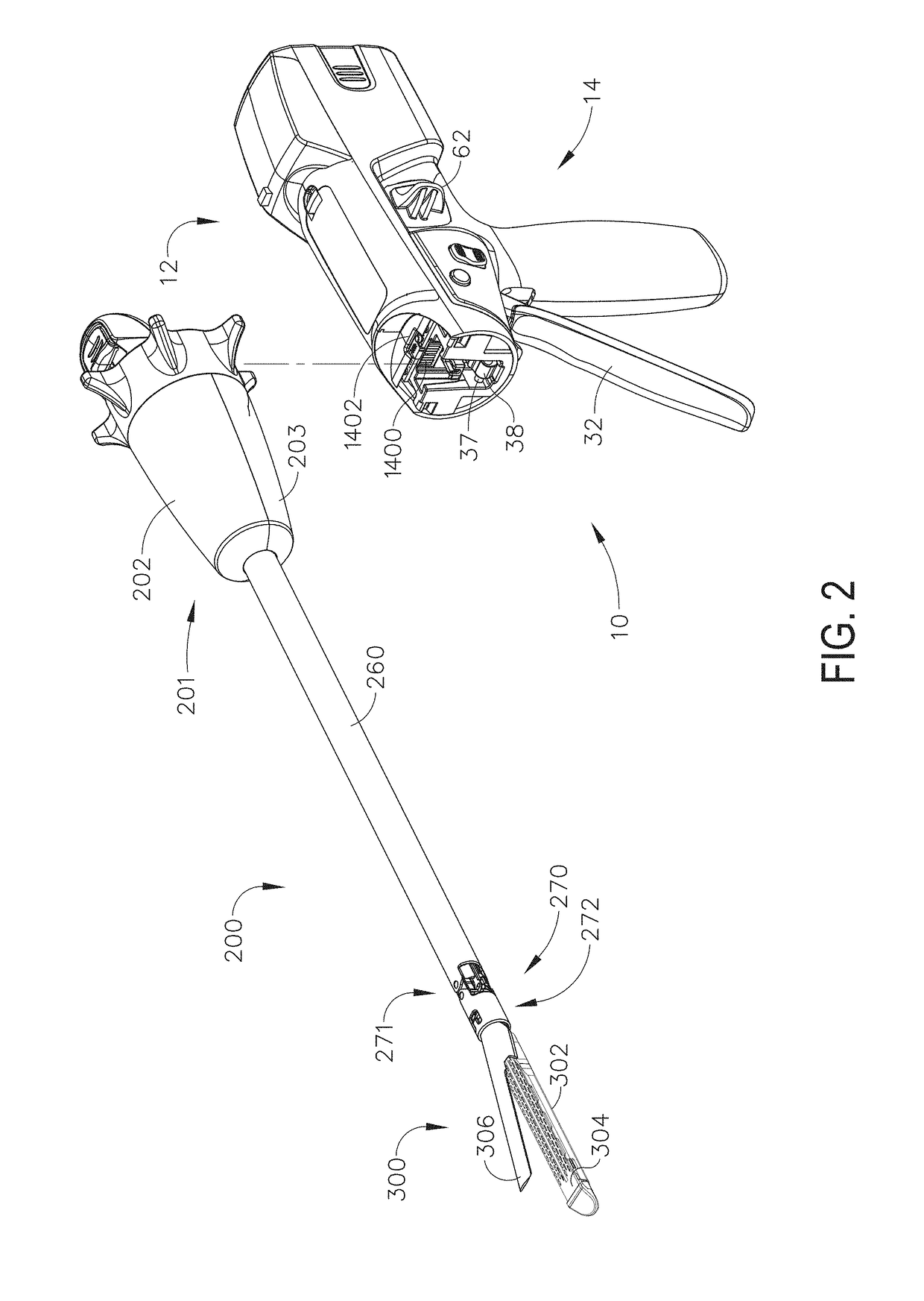
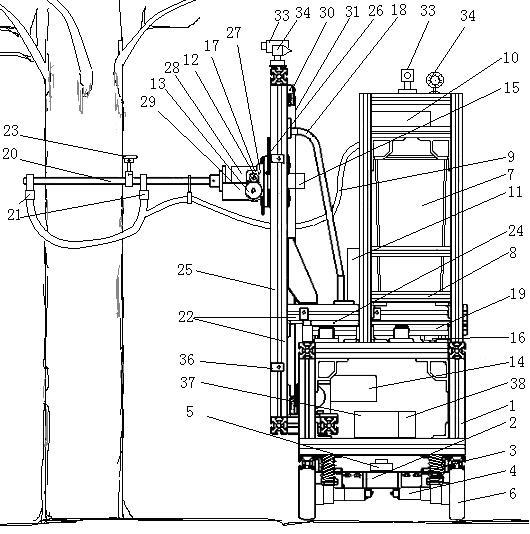
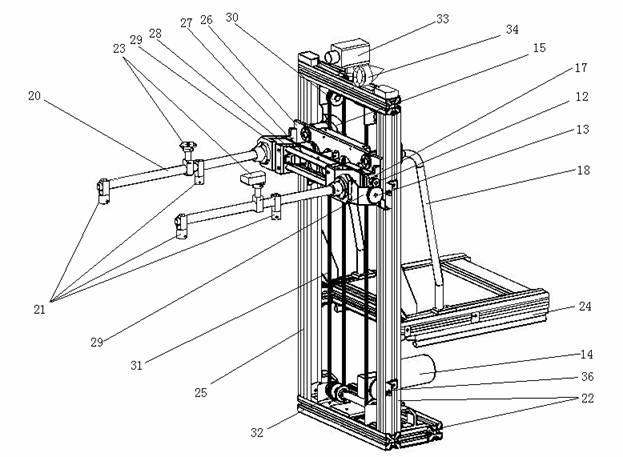
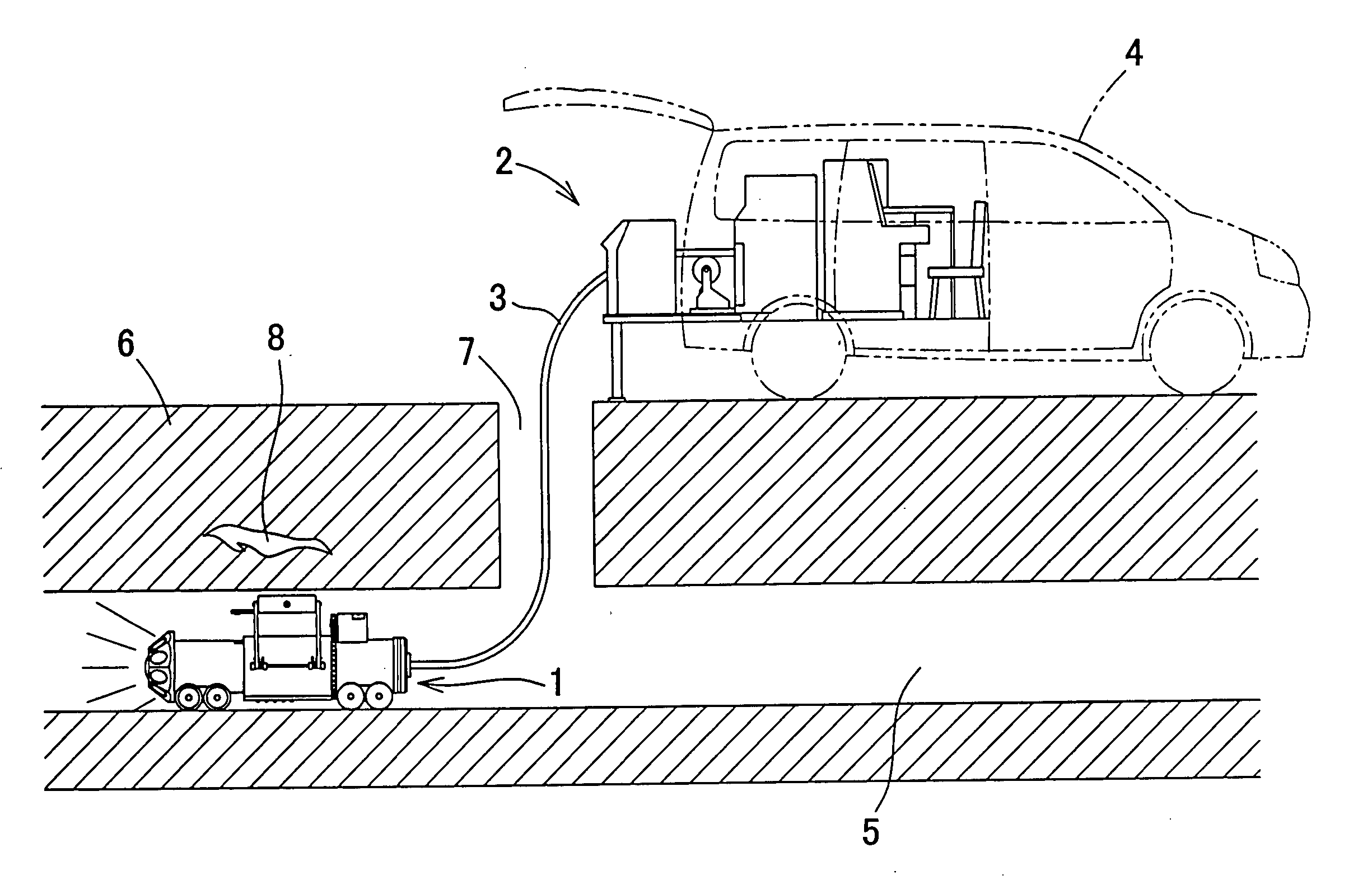
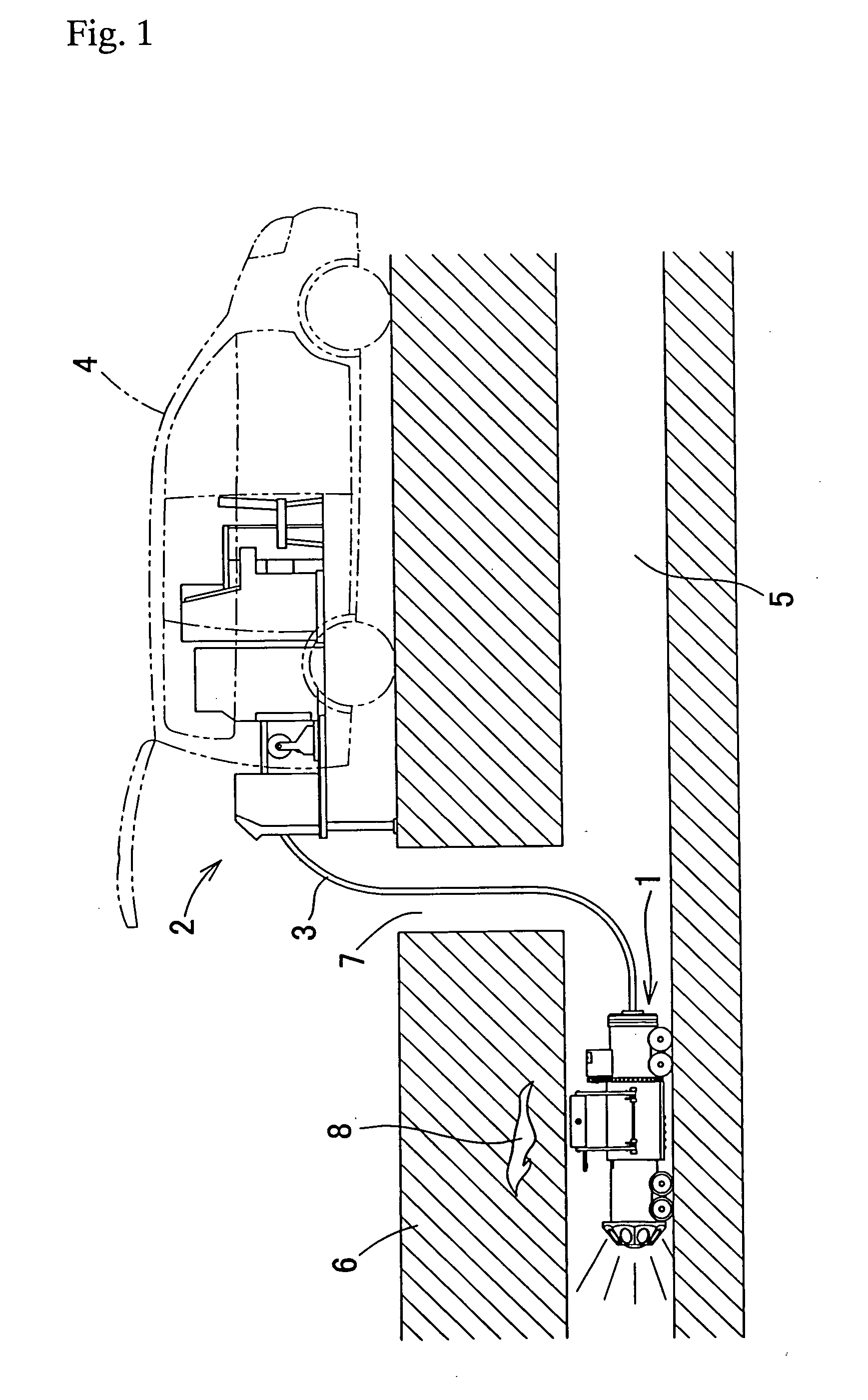
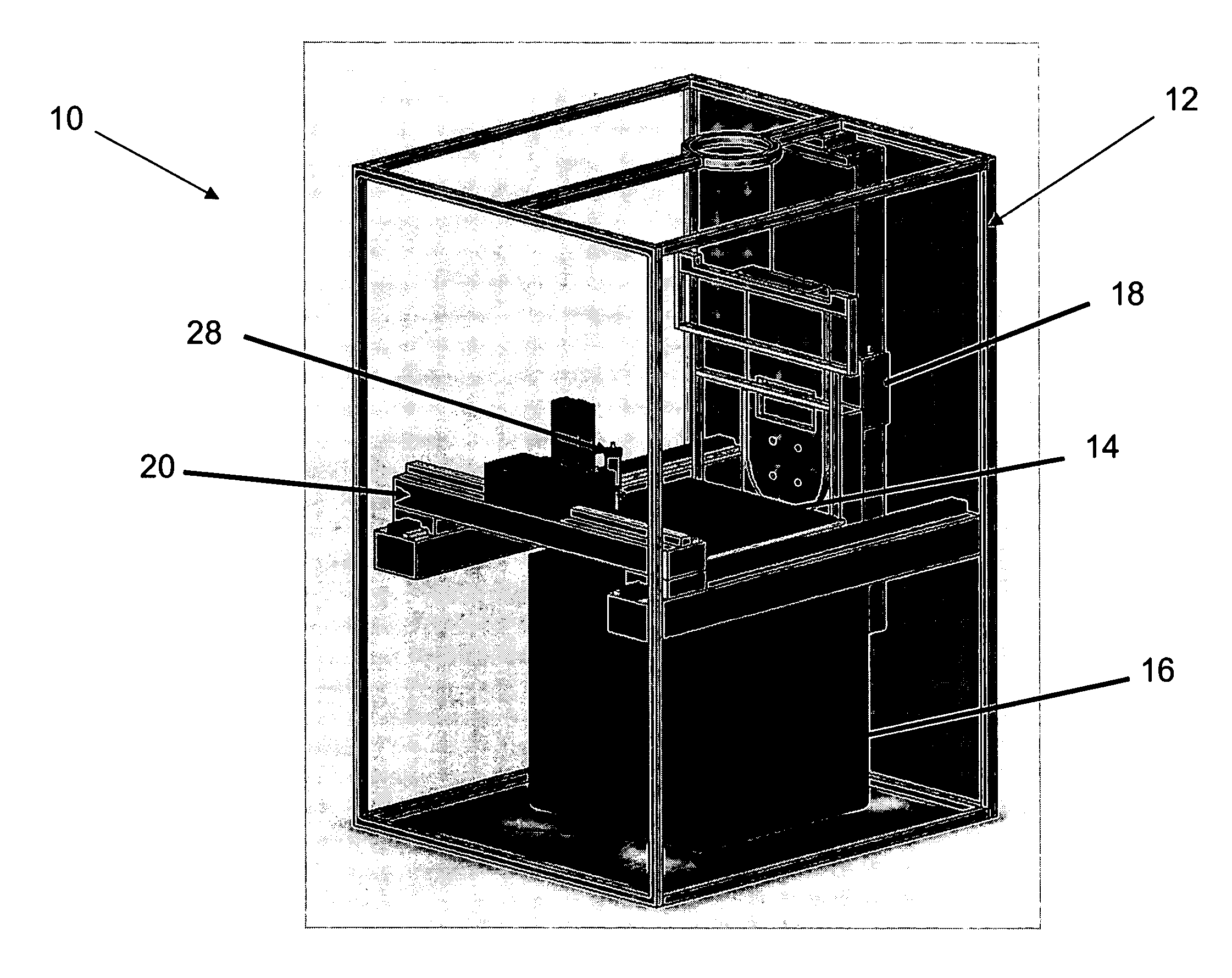
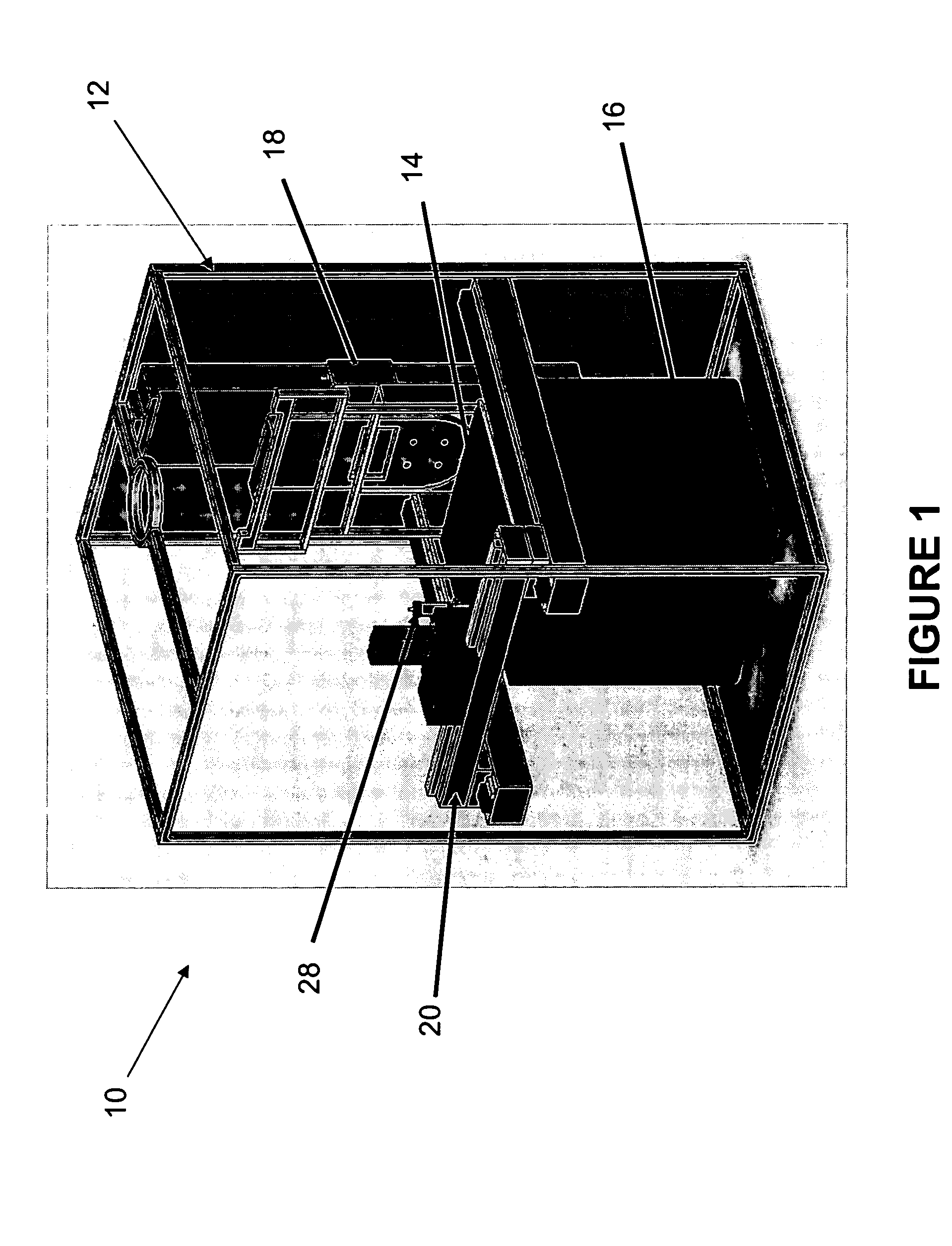
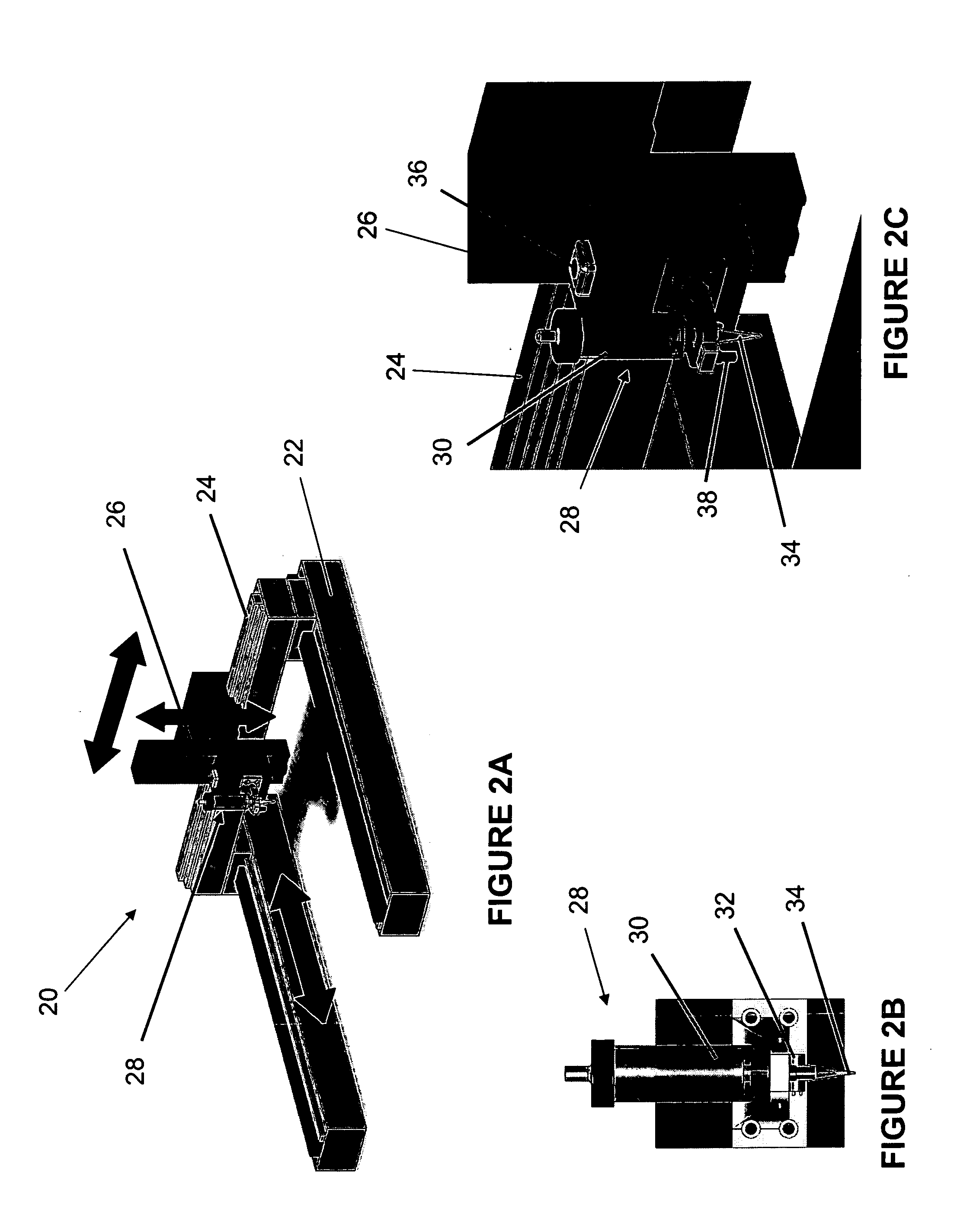
Surgical instrument with detection sensors
Aspects of the present disclosure are presented for a surgical instrument having one or more sensors at or a near an end effector and configured to aide in the detection of tissues and other materials and structures at a surgical site. The detections may then be used to aide in the placement of the end effector and to confirm which objects to operate on, or alternatively, to avoid. Examples of sensors include laser sensors used to employ Doppler shift principles to detect movement of objects at the surgical site, such as blood cells; resistance sensors to detect the presence of metal; monochromatic light sources that allow for different levels of absorption from different types of substances present at the surgical site, and near infrared spectrometers with small form factors.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Surgical instrument with detection sensors
ActiveUS20170296178A1Diagnostics using lightDiagnostics using pressureSmall form factorSurgical site
Aspects of the present disclosure are presented for a surgical instrument having one or more sensors at or a near an end effector and configured to aide in the detection of tissues and other materials and structures at a surgical site. The detections may then be used to aide in the placement of the end effector and to confirm which objects to operate on, or alternatively, to avoid. Examples of sensors include laser sensors used to employ Doppler shift principles to detect movement of objects at the surgical site, such as blood cells; resistance sensors to detect the presence of metal; monochromatic light sources that allow for different levels of absorption from different types of substances present at the surgical site, and near infrared spectrometers with small form factors.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
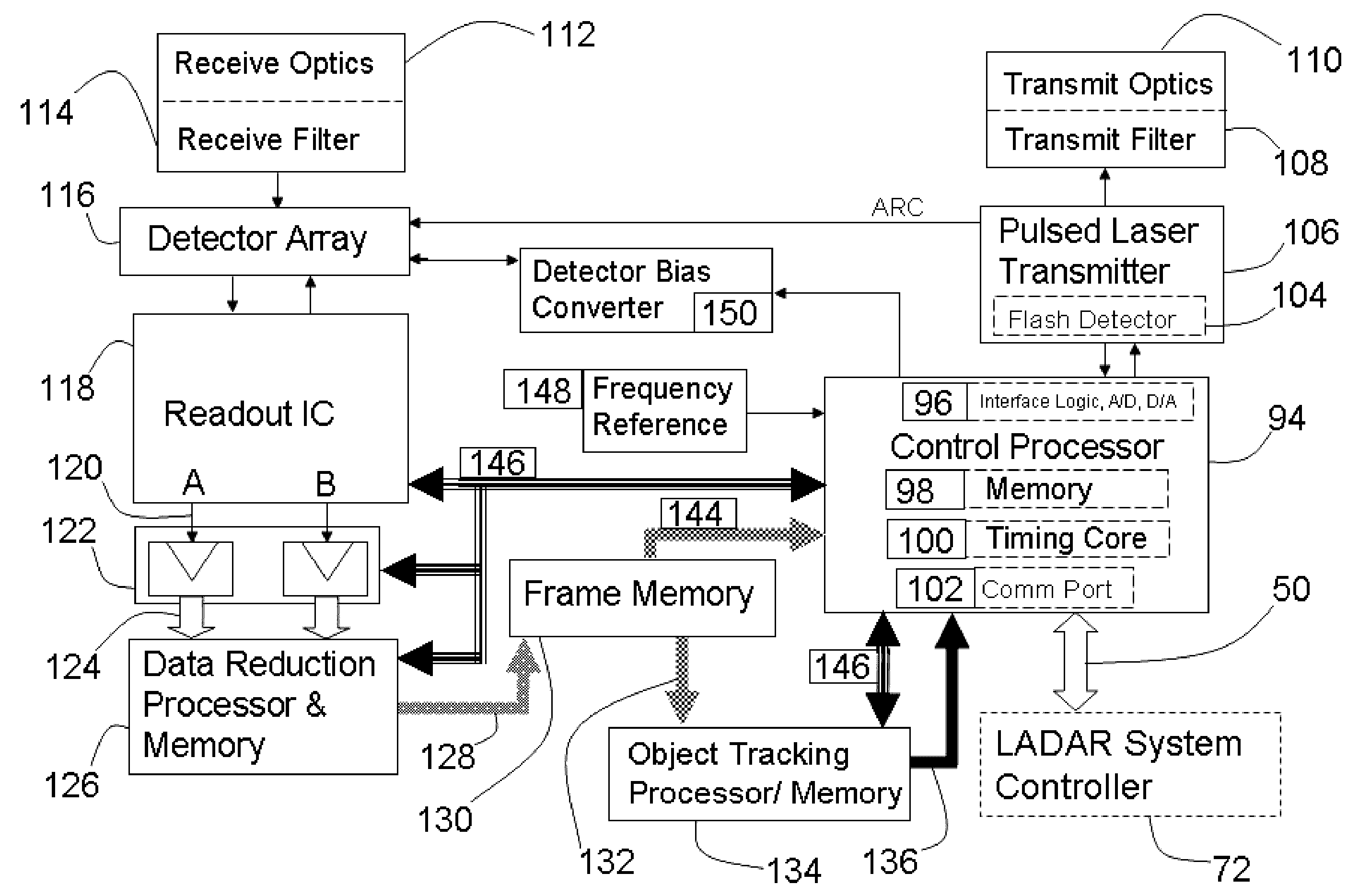
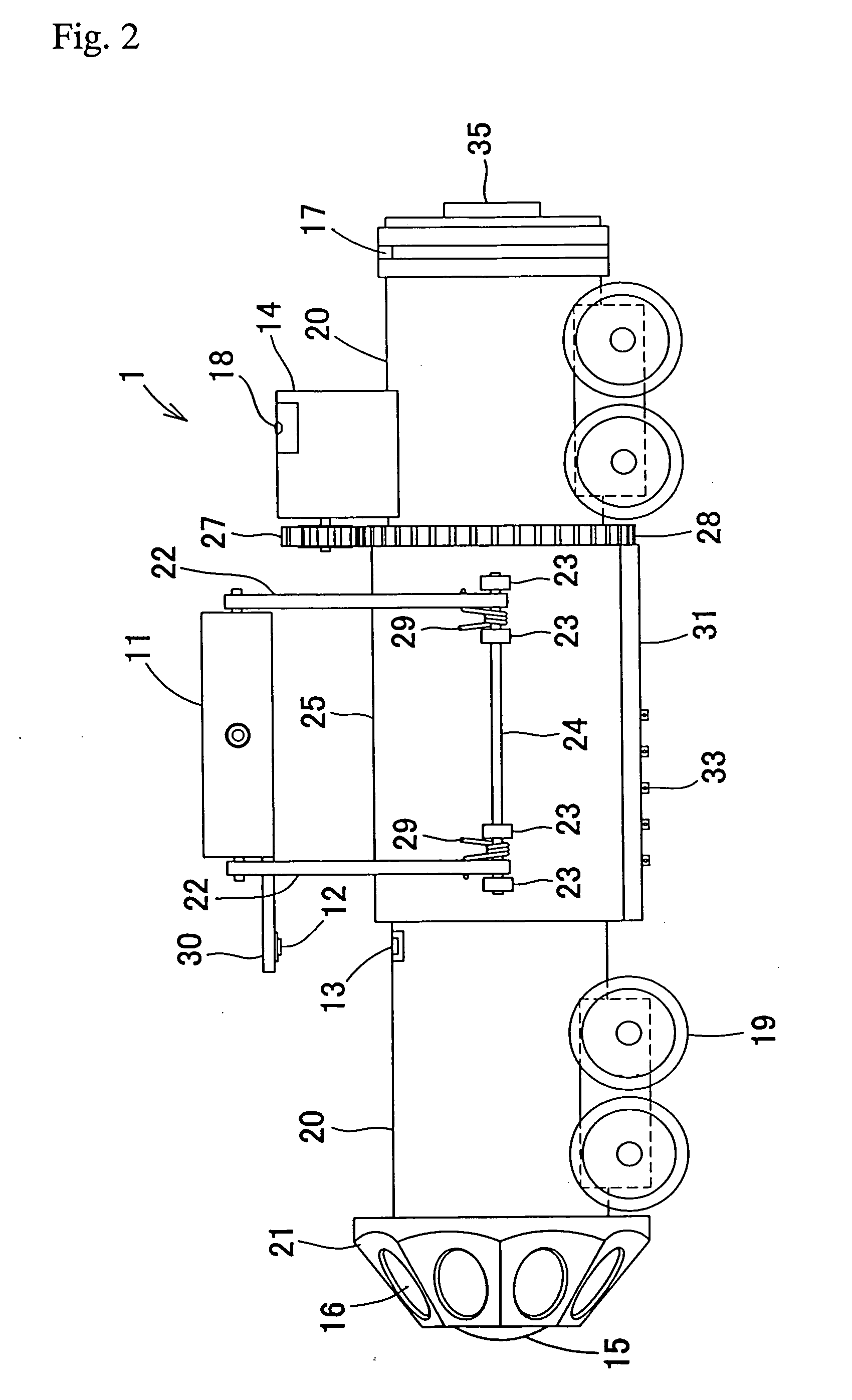
Ladar sensor for a dense environment
ActiveUS20160003946A1Optical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationDiscriminatorFloating point
A multi-ladar sensor system is proposed for operating in dense environments where many ladar sensors are transmitting and receiving burst mode light in the same space, as may be typical of an automotive application. The system makes use of several techniques to reduce mutual interference between independently operating ladar sensors. In one embodiment, the individual ladar sensors are each assigned a wavelength of operation, and an optical receive filter for blocking the light transmitted at other wavelengths, an example of wavelength division multiplexing (WDM). Each ladar sensor, or platform, may also be assigned a pulse width selected from a list, and may use a pulse width discriminator circuit to separate pulses of interest from the clutter of other transmitters. Higher level coding, involving pulse sequences and code sequence correlation, may be implemented in a system of code division multiplexing, CDM. A digital processor optimized to execute mathematical operations is described which has a hardware implemented floating point divider, allowing for real time processing of received ladar pulses, and sequences of pulses.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTONOMOUS MOBILITY US LLC
LADAR sensor for a dense environment
A multi-ladar sensor system is proposed for operating in dense environments where many ladar sensors are transmitting and receiving burst mode light in the same space, as may be typical of an automotive application. The system makes use of several techniques to reduce mutual interference between independently operating ladar sensors. In one embodiment, the individual ladar sensors are each assigned a wavelength of operation, and an optical receive filter for blocking the light transmitted at other wavelengths, an example of wavelength division multiplexing (WDM). Each ladar sensor, or platform, may also be assigned a pulse width selected from a list, and may use a pulse width discriminator circuit to separate pulses of interest from the clutter of other transmitters. Higher level coding, involving pulse sequences and code sequence correlation, may be implemented in a system of code division multiplexing, CDM. A digital processor optimized to execute mathematical operations is described which has a hardware implemented floating point divider, allowing for real time processing of received ladar pulses, and sequences of pulses.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTONOMOUS MOBILITY US LLC
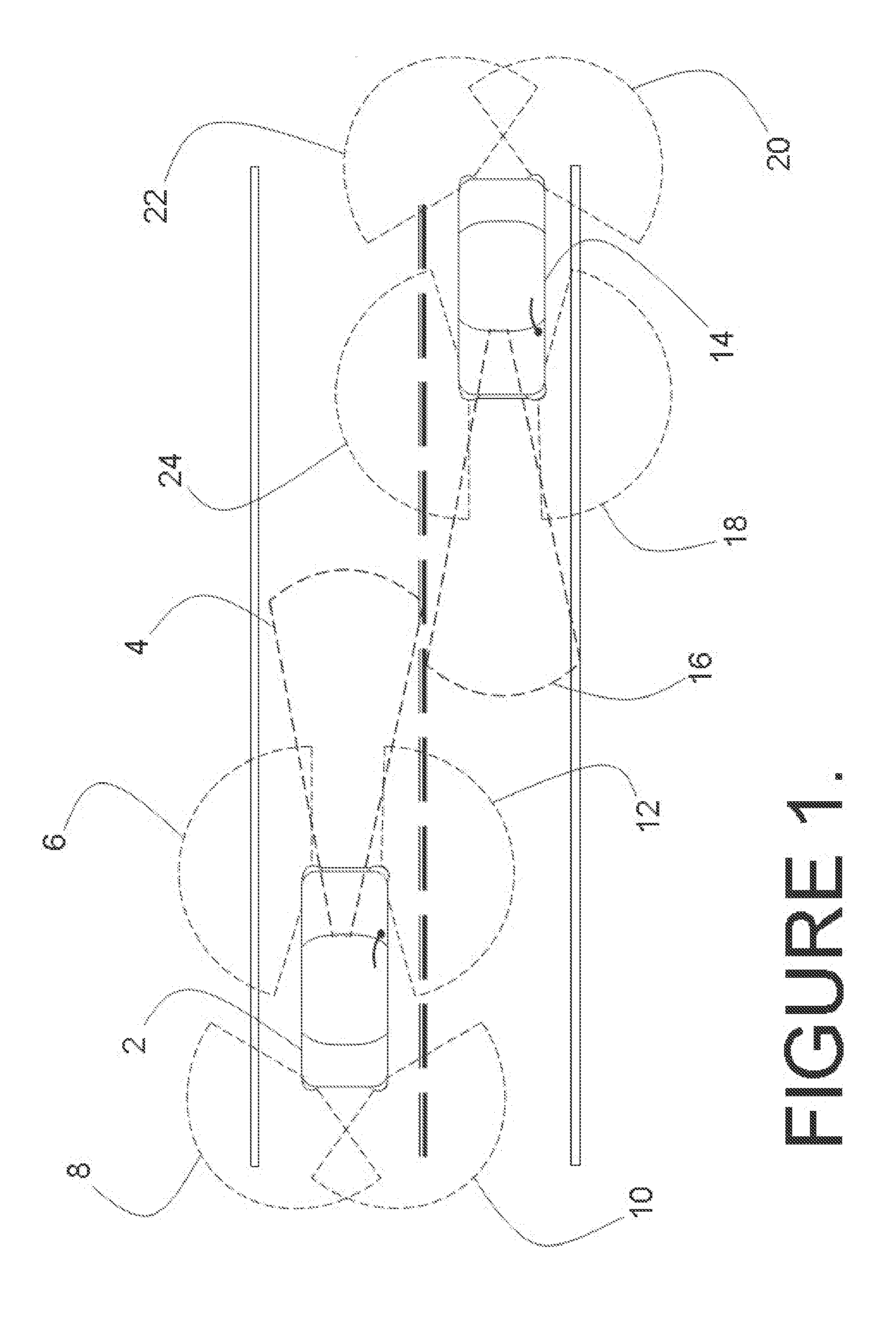
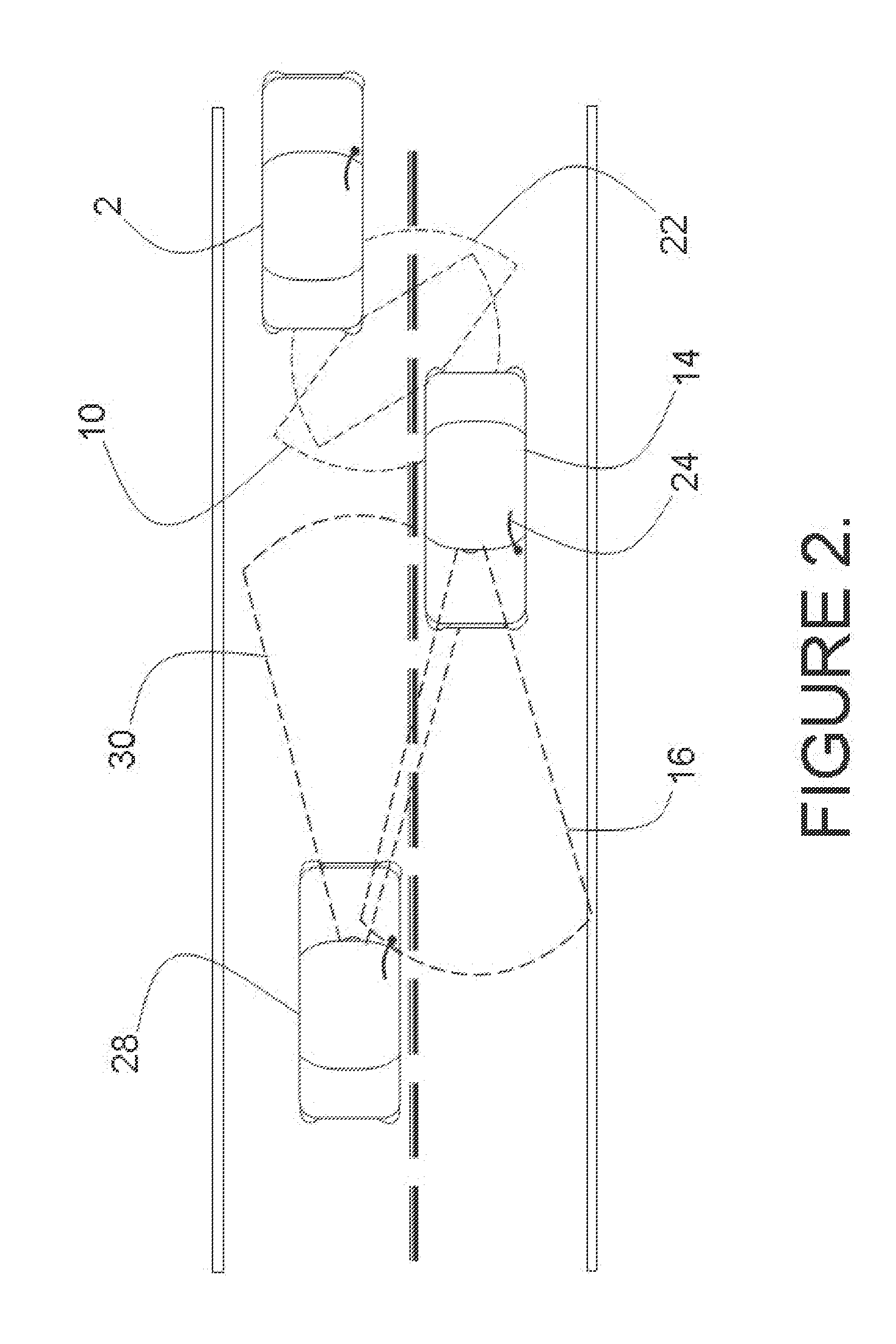
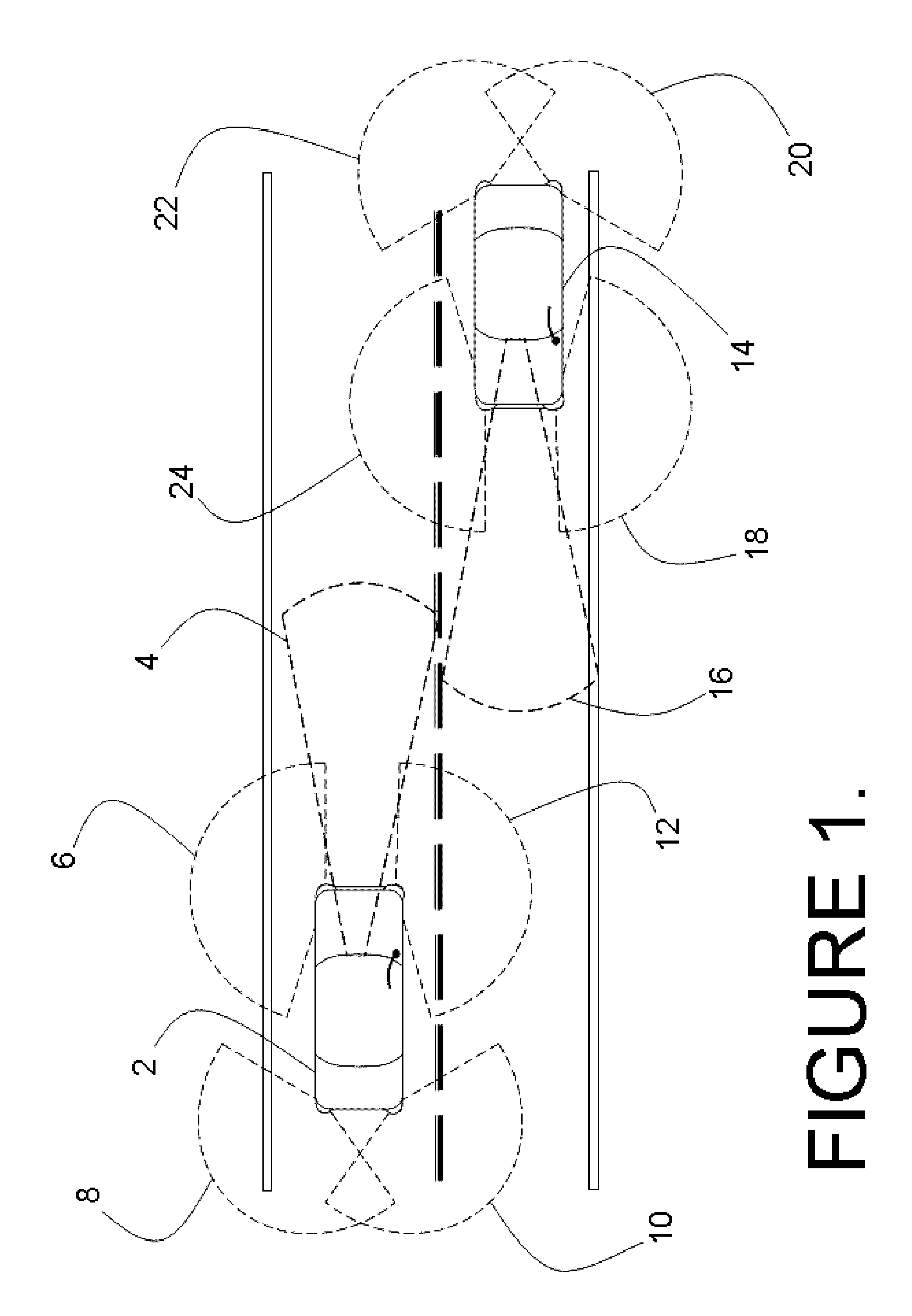
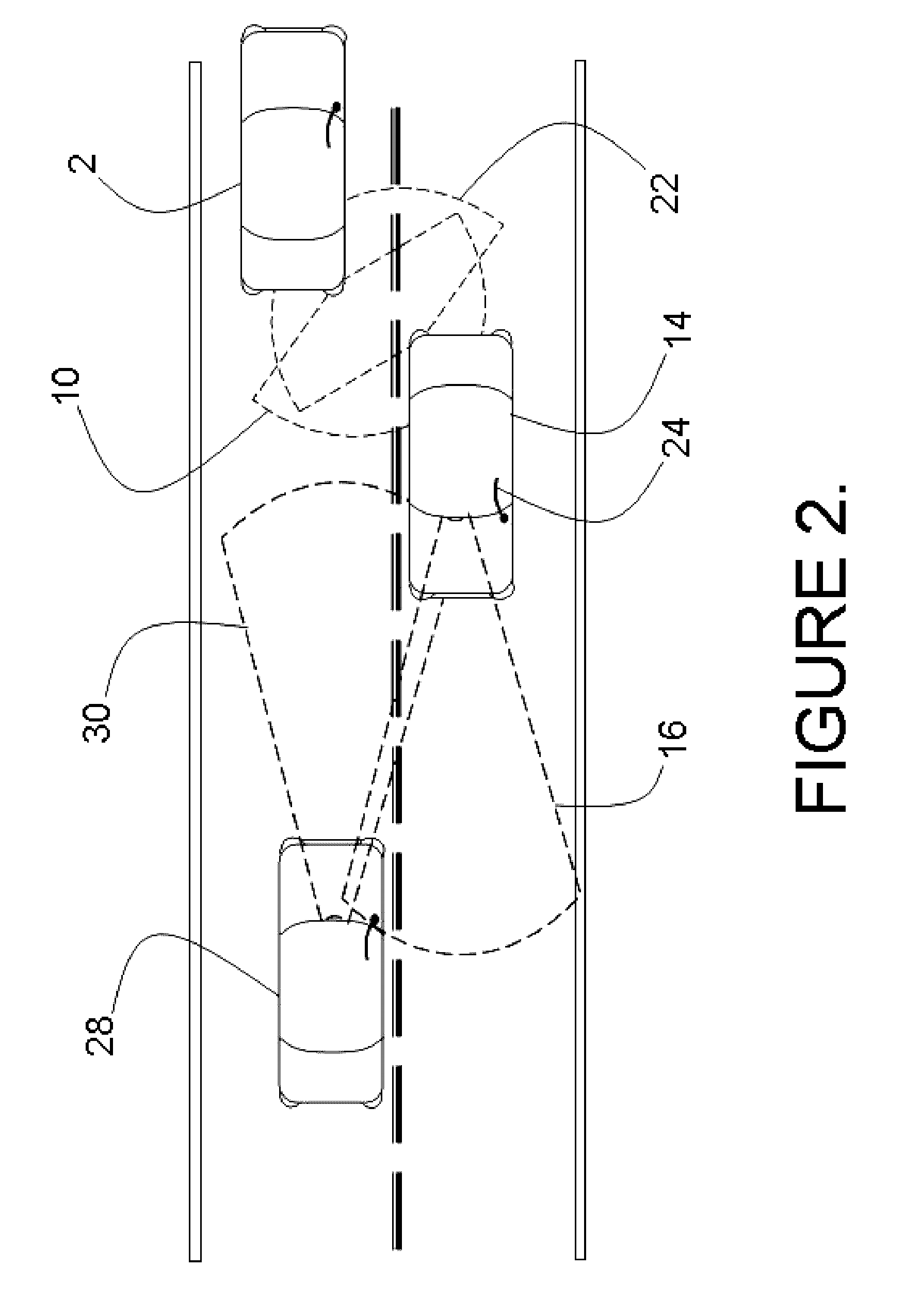
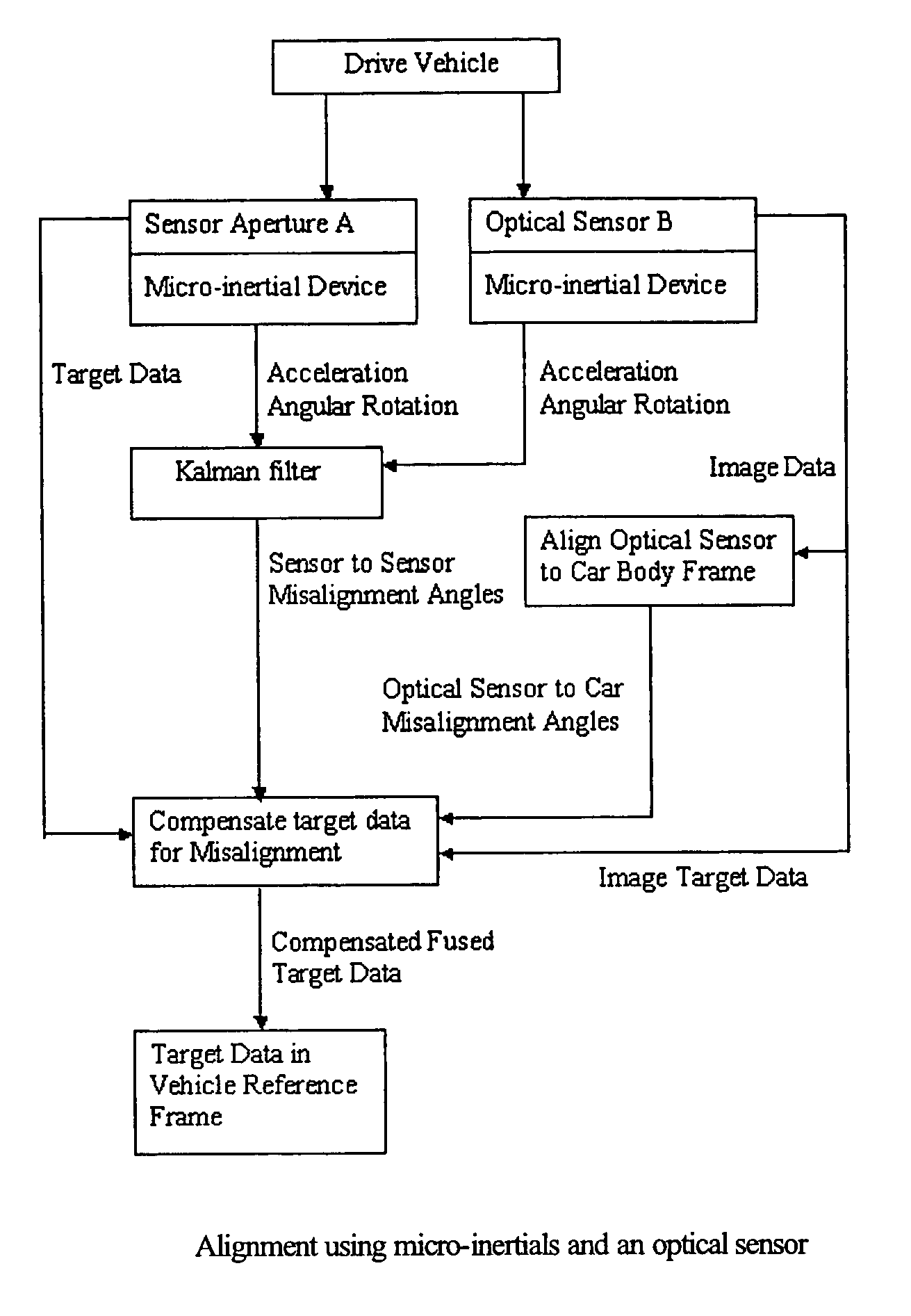
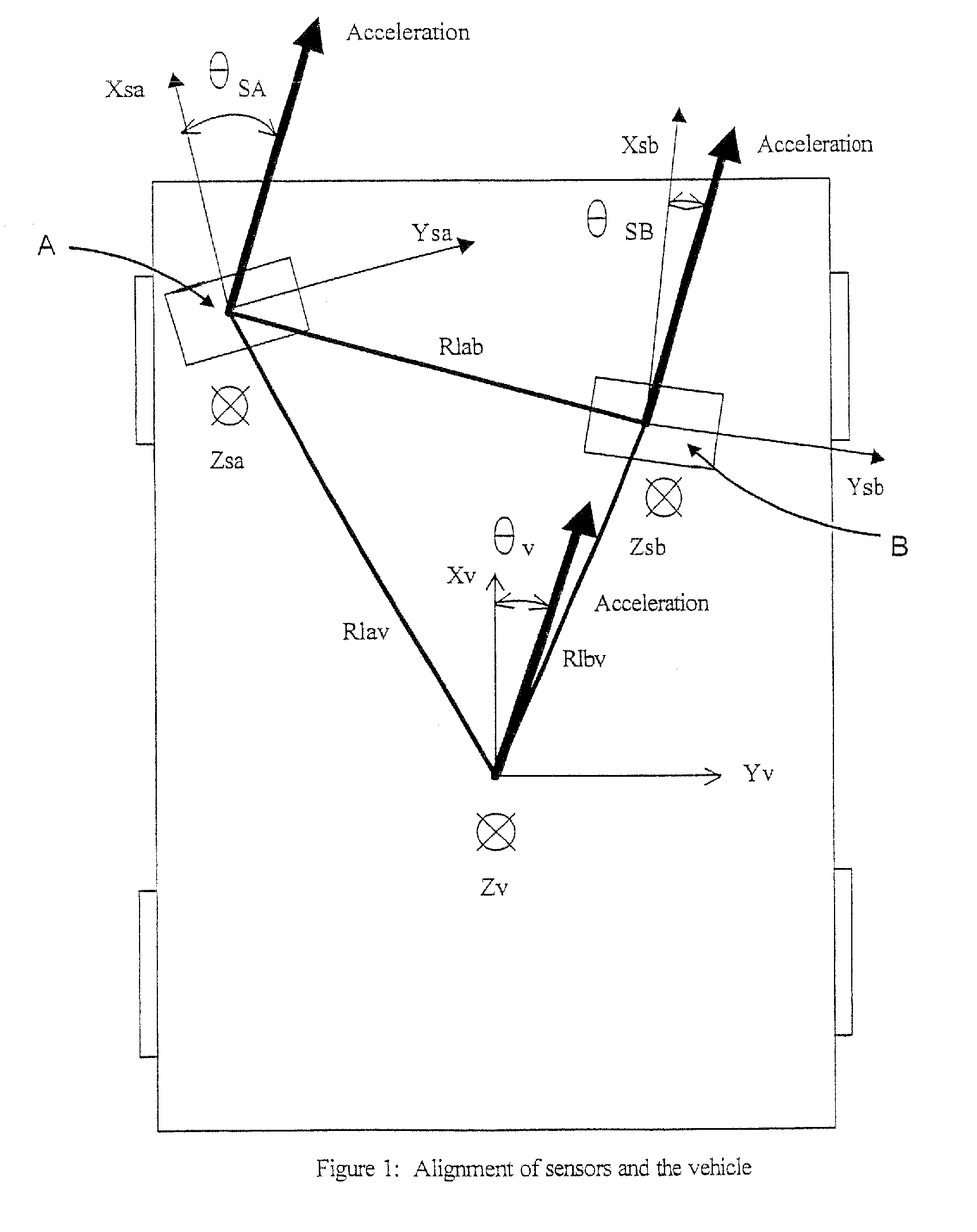
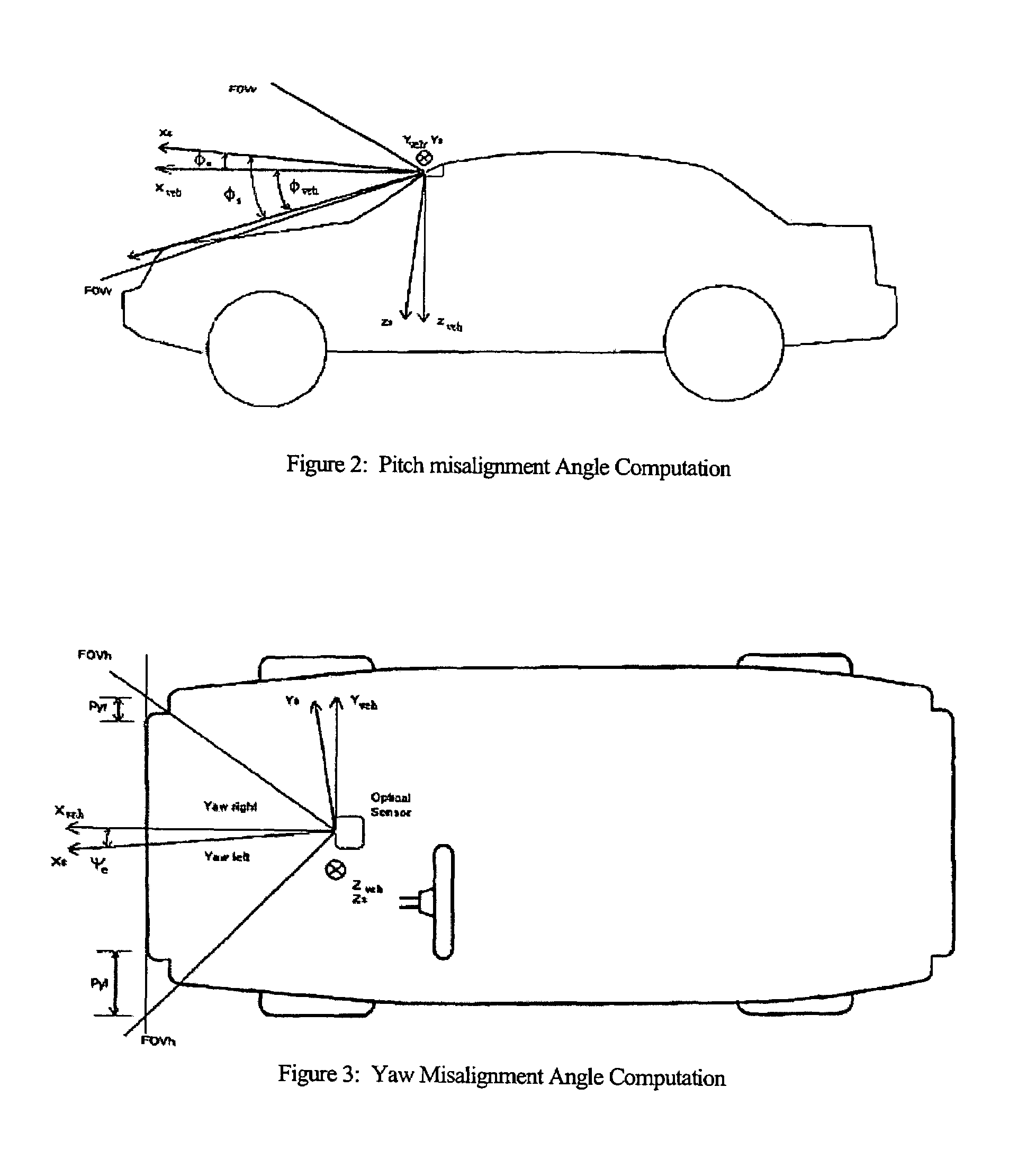
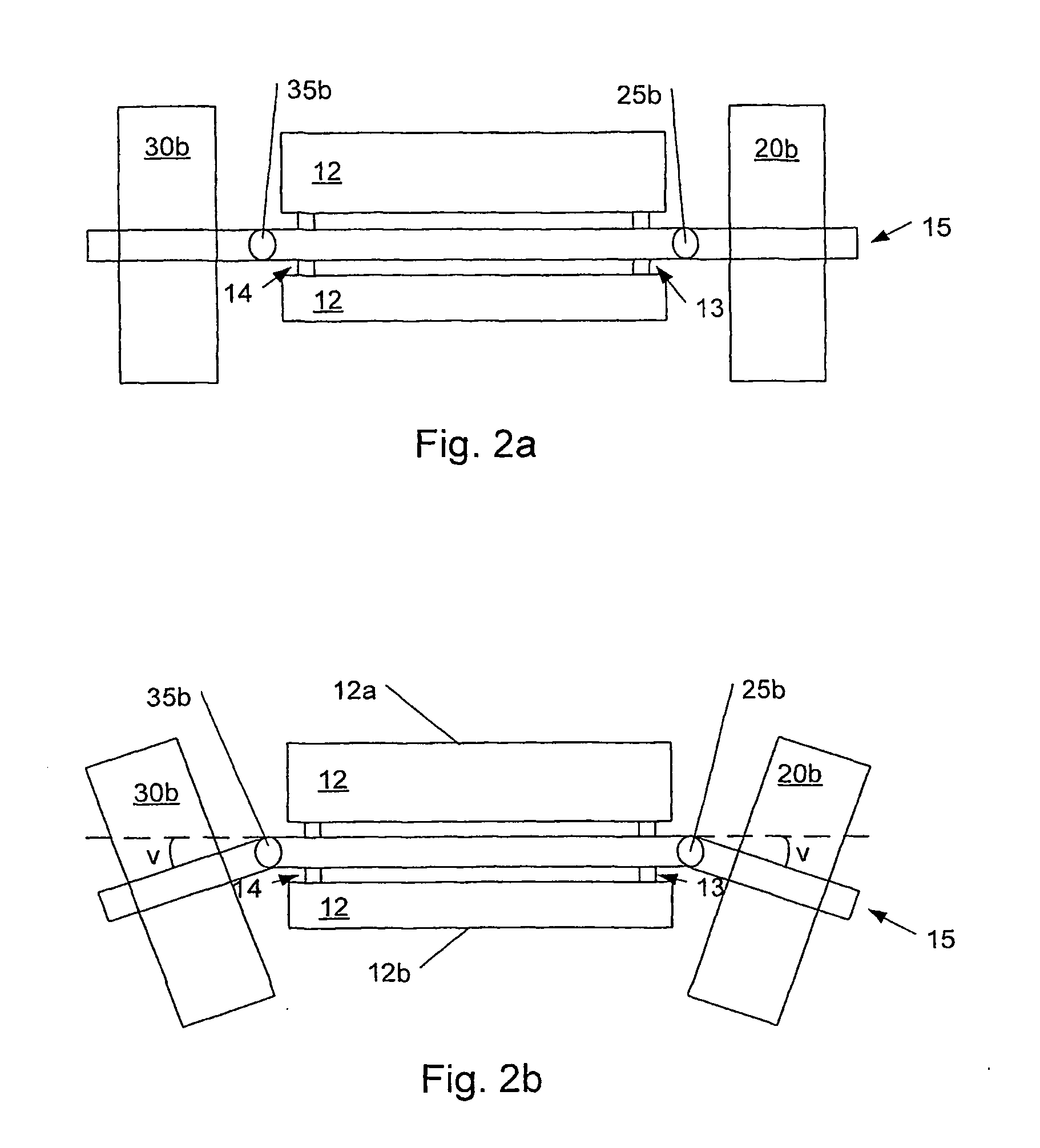
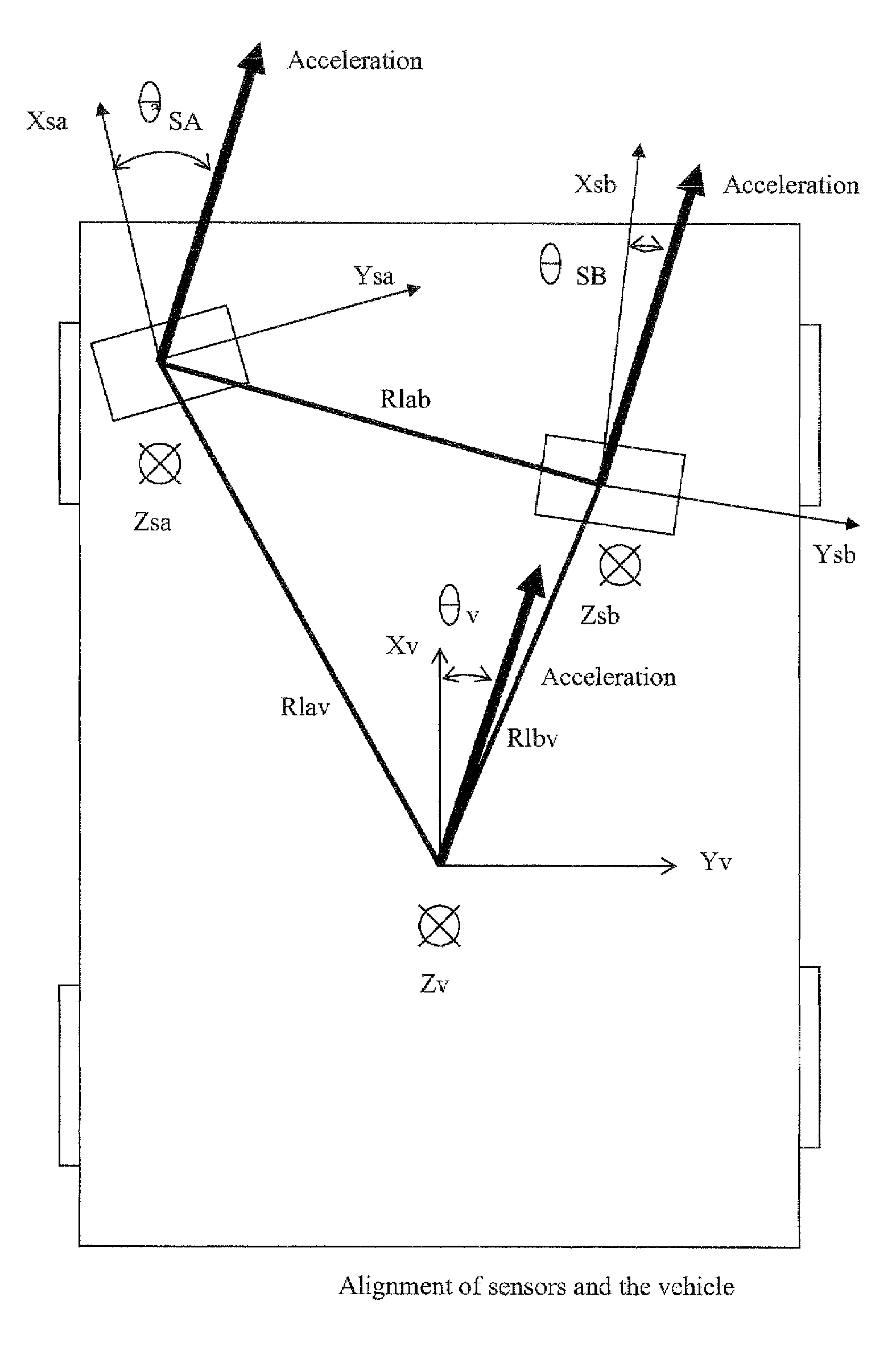
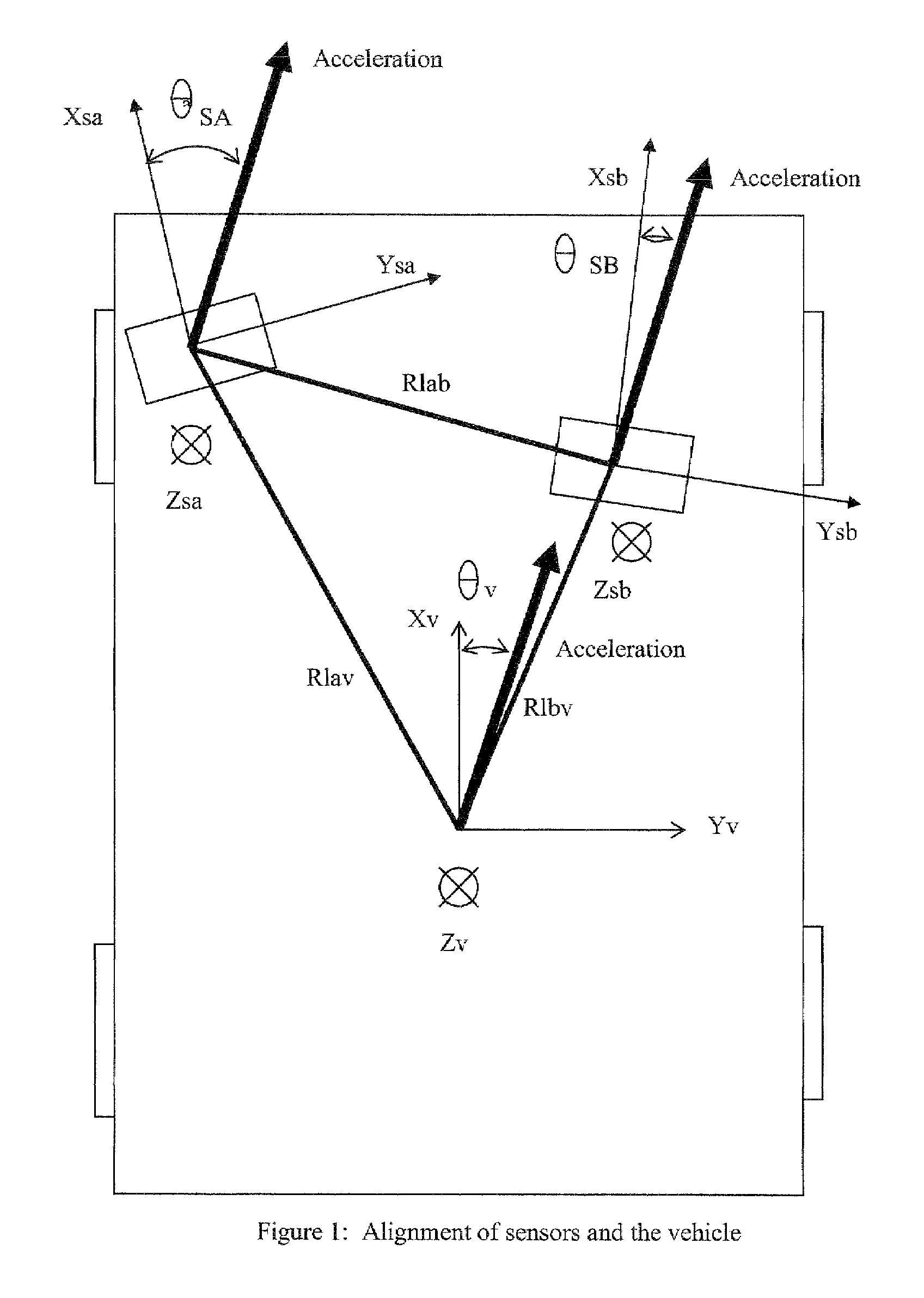
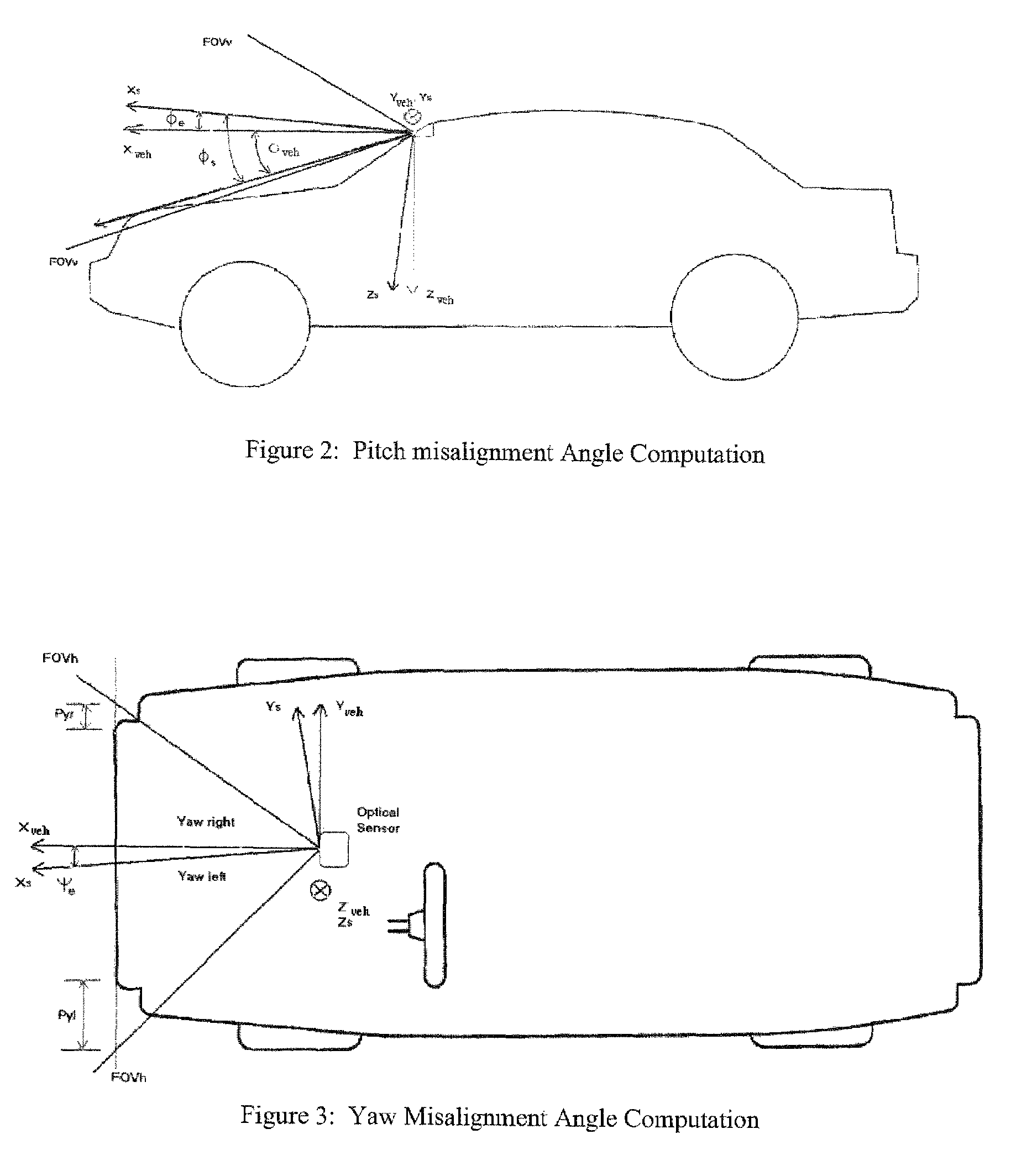
System and method for aligning sensors on a vehicle
ActiveUS7337650B1Acceleration measurement using interia forcesTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesRadarEngineering
A vehicle sensor system consisting of video, radar, ultrasonic or laser sensors, oriented to obtain a 360 degree view around the vehicle for the purpose of developing a situation or scene awareness. The sensors may or may not have overlapping field of views, or support the same applications, but data will be shared by all. Orientation of the sensor to the vehicle body coordinates is critical in order to accurately assess threat and respond. This system describes methods based on measuring force and rotation on each sensor and computing a dynamic alignment to first each other, then second to the vehicle.
Owner:AUTOBRILLIANCE LLC +1
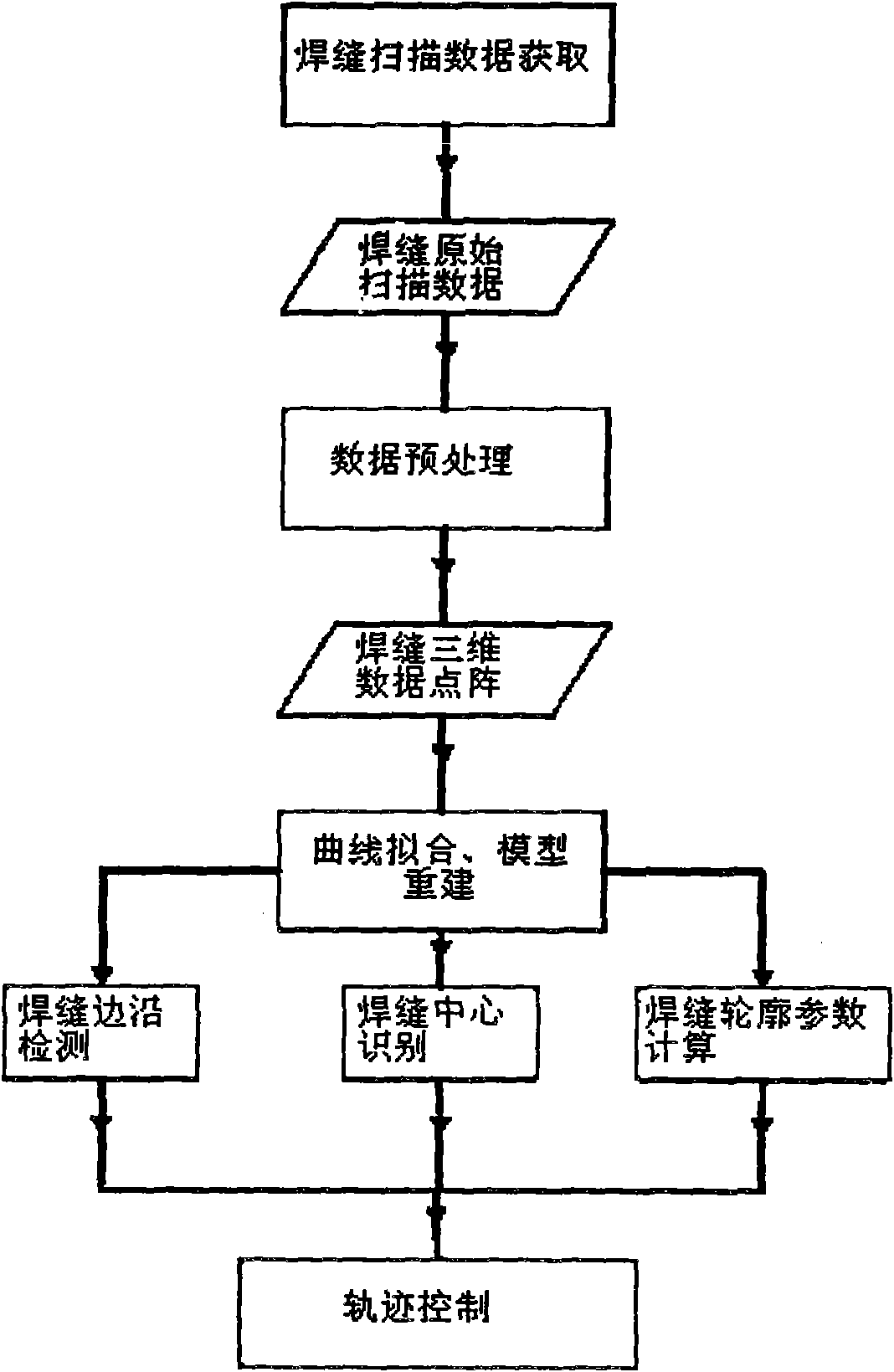
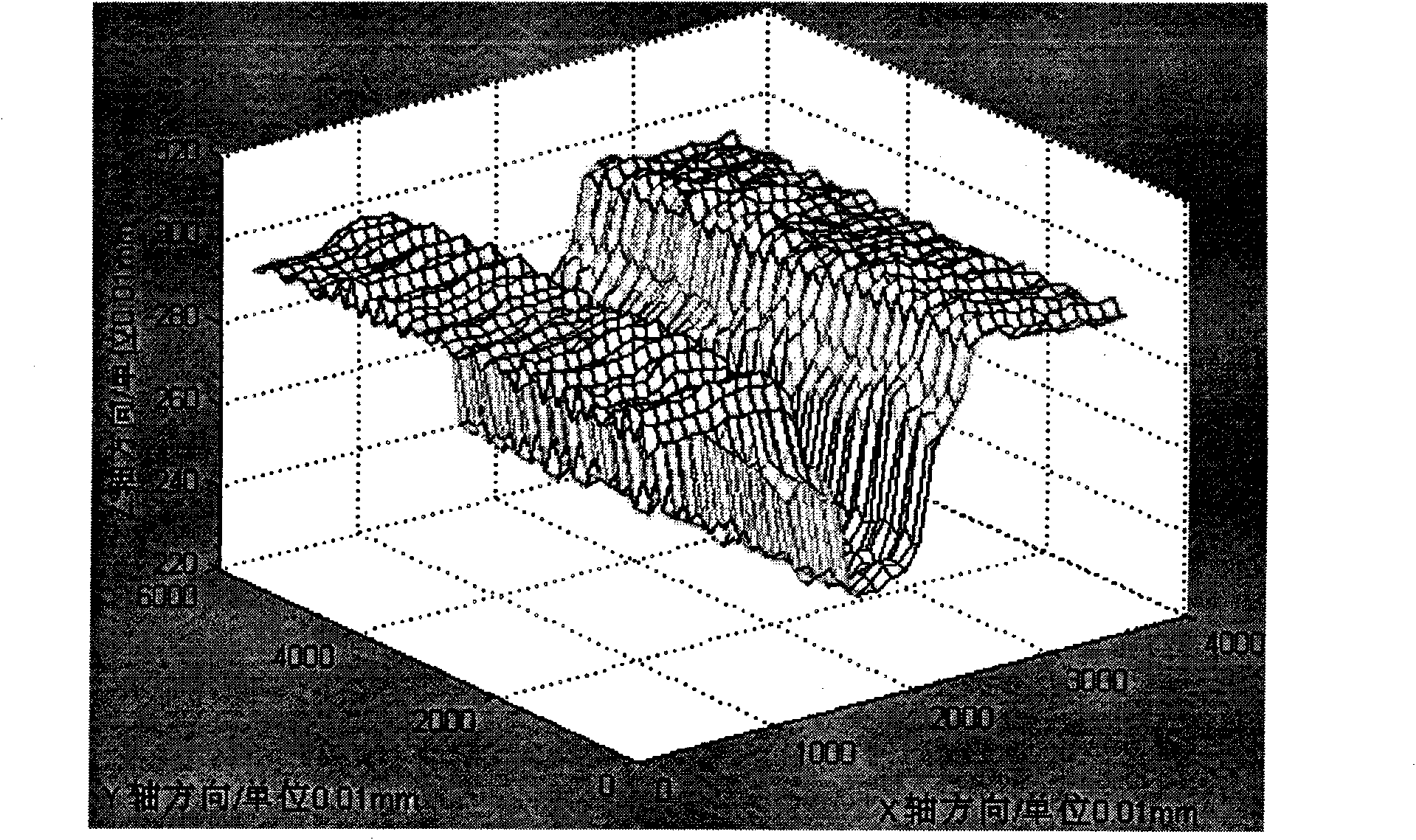
Welding track detection and control method of plate butt weld based on laser ranging
InactiveCN101559512ATo achieve the purpose of seam trackingTo achieve the purpose of trackingArc welding apparatusNumerical controlLaser rangingField tests
The invention relates to a welding track detection and control method of plate butt weld based on laser ranging, including the following steps: A. track detection is carried out; B. track identification and extraction are carried out; C. track control is carried out; D. the relative position relation between a welding gun and a welding seam is adjusted at last by performing mechanism actions. In the invention, the information of welding seam profile is obtained by transverse scanning of a laser sensor, and welding seam is rebuilt after effective wave filtering treatment to realize three-dimensional detection of the welding seam; simultaneously, the welding track curve is obtained by fit while detecting welding seam by using dynamic B spline fit algorithm, and the track control is carried out in combination with constant speed B spline track interpolation algorithm, thereby fundamentally solving the problem of track detection and control in automatic welding of plate butt weld. By using the method in the invention, the field test welding has welding profile identification precision of 0.15mm and welding track identification precision of 0.2mm, and the welding speed is more than four times of common manual welding.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Service mobile robot navigation method in dynamic environment
InactiveCN103558856AEnsure predictabilityImprove securityPosition/course control in two dimensionsLocation trackingLaser sensor
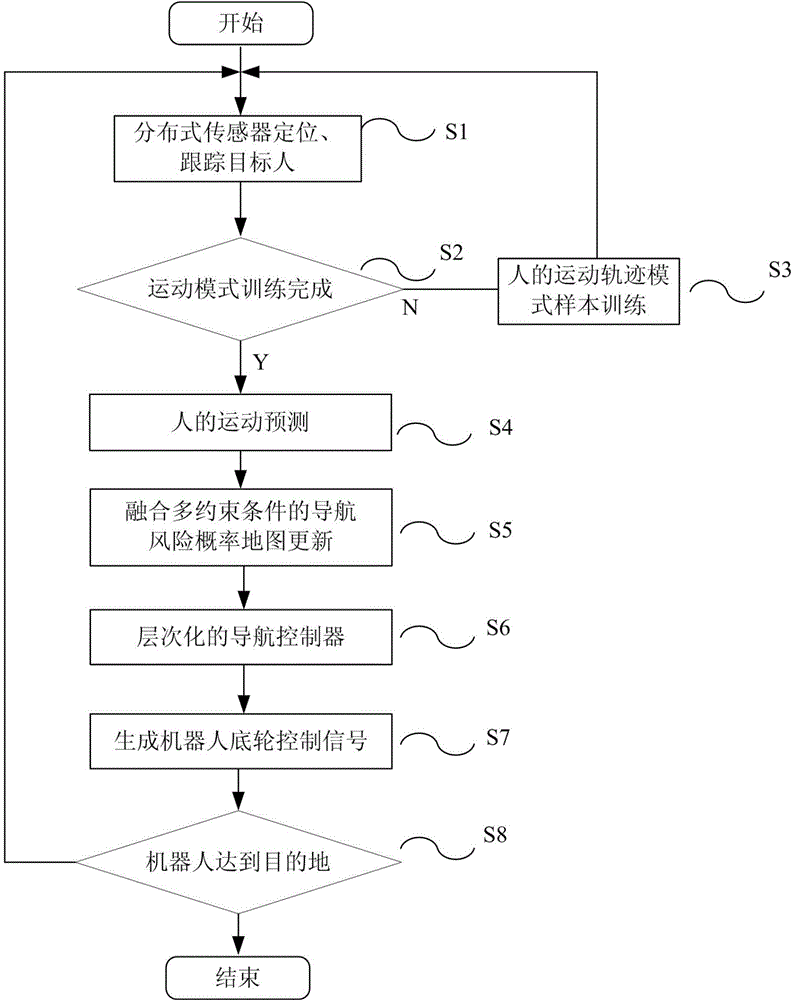
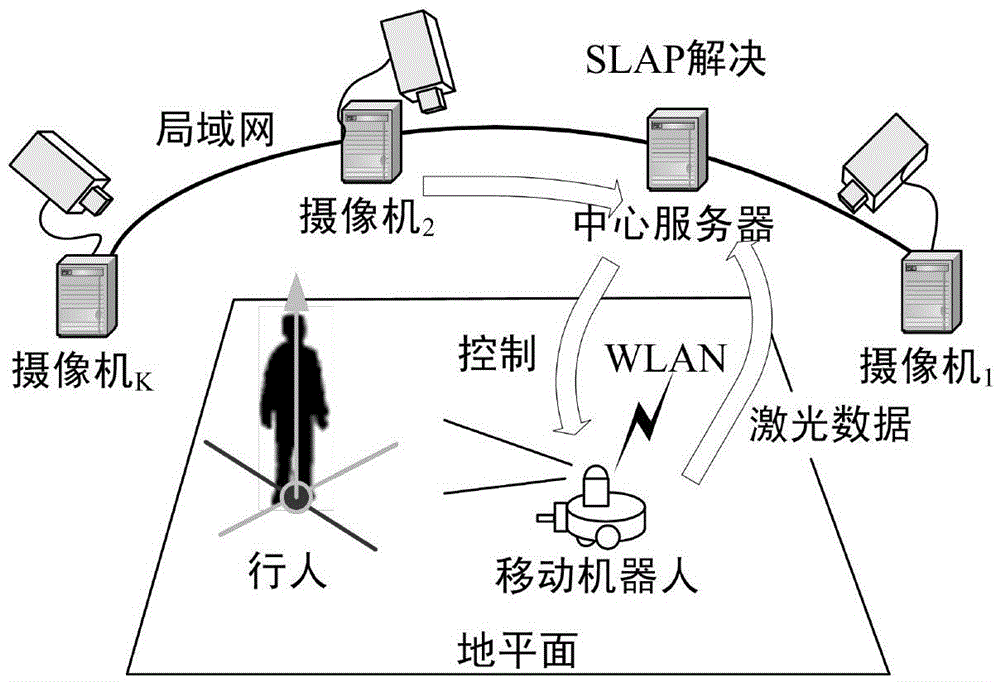
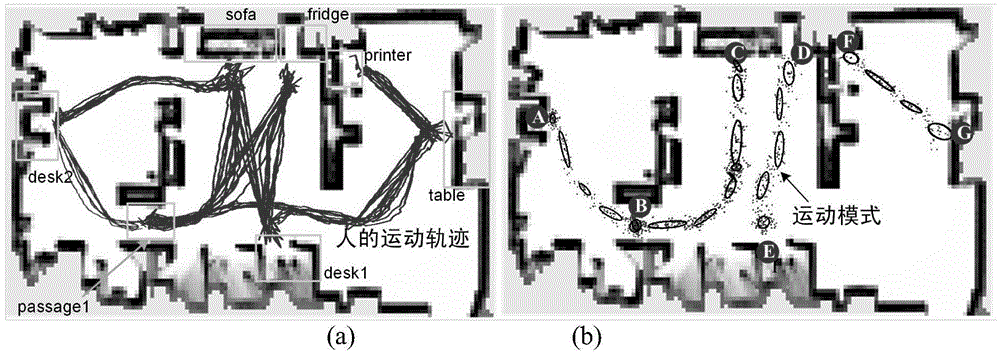
The invention relates to the technical field of mobile robot autonomous navigation and discloses a service mobile robot navigation method in a dynamic environment. The service mobile robot navigation method in the dynamic environment includes the following steps that firstly, position tracking of people can be achieved by utilizing multiple global cameras and robot vehicle-mounted laser sensors in an indoor environment; secondly, the moving mode of people under a specific indoor environment site is trained according to collected samples, and the moving trend of people is predicated; thirdly, a current position and a predicated position of people are merged with an environment static obstacle raster map, and a navigation risk probability map is generated; fourthly, a robot navigation movement controller of a global route planning-local obstacle avoidance control gradational structure is adopted to control robot navigation behavior, and safe and efficient navigation behavior of a robot under a complex dynamic environment where the robot coexists with people is ensured through controlling.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
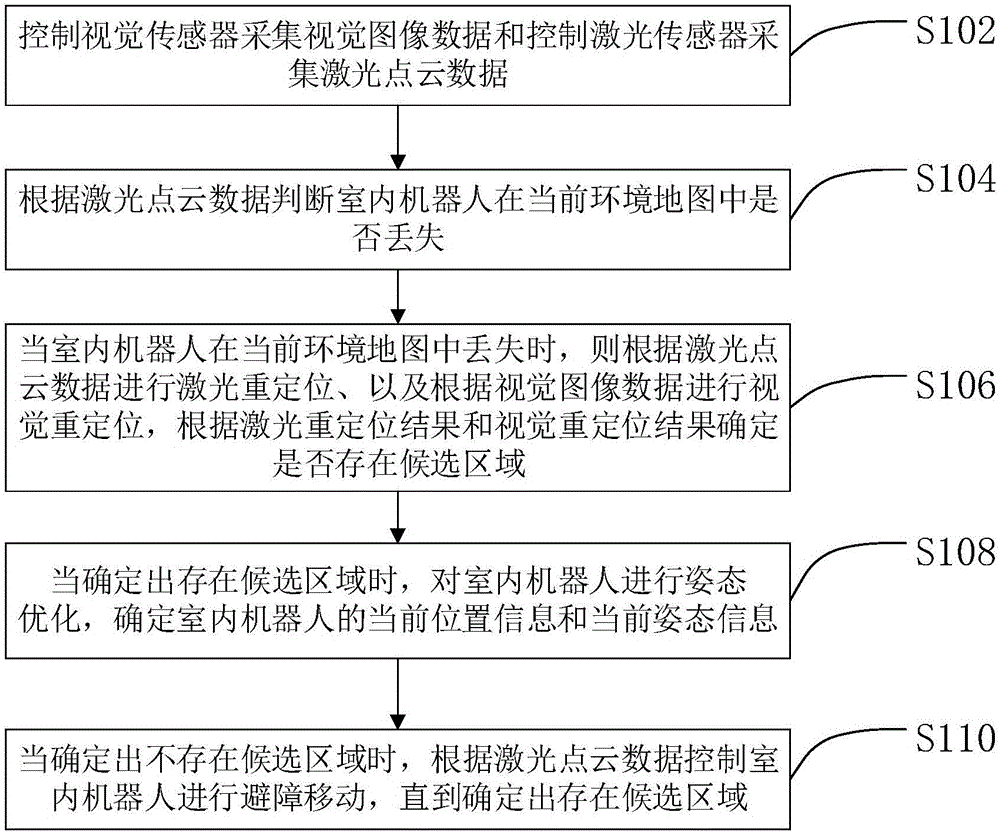
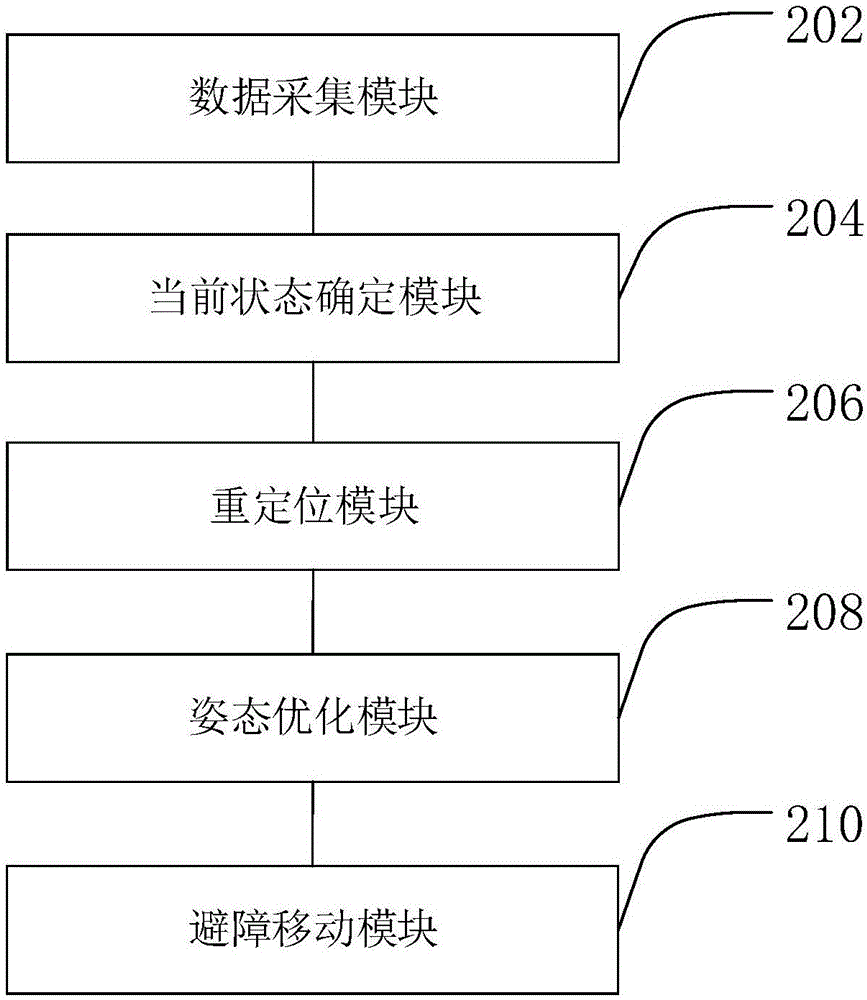
Relocating method and apparatus of indoor robot
ActiveCN106092104AImprove accuracyAccurate Autonomous NavigationNavigational calculation instrumentsLaser sensorCloud data
The invention provides a relocating method and apparatus of an indoor robot. The method comprises the following steps: controlling a visual sensor to acquire visual image data, and controlling a laser sensor to acquire laser dot cloud data; judging whether the robot is lost in a current environmental map according to the laser dot cloud data; if yes, laser relocating the robot according to the laser dot cloud data, visually relocating the robot according to the visual image data, and determining whether a candidate area exists or not according to a laser relocating result and a visual relocating result; when the candidate area exists, carrying out the posture optimization for the robot, and determining current position information and current posture information of the robot; and when the candidate area does not exist, controlling the robot to make obstacle avoidance motion according to the laser dot cloud data until the candidate area is determined. The robot is relocated by adopting a way of combining the laser sensor and the visual sensor, so that the relocating accuracy of the robot is improved, and the robot can be accurately and autonomously navigated.
Owner:SHENZHEN WEIFU ROBOT TECH CO LTD
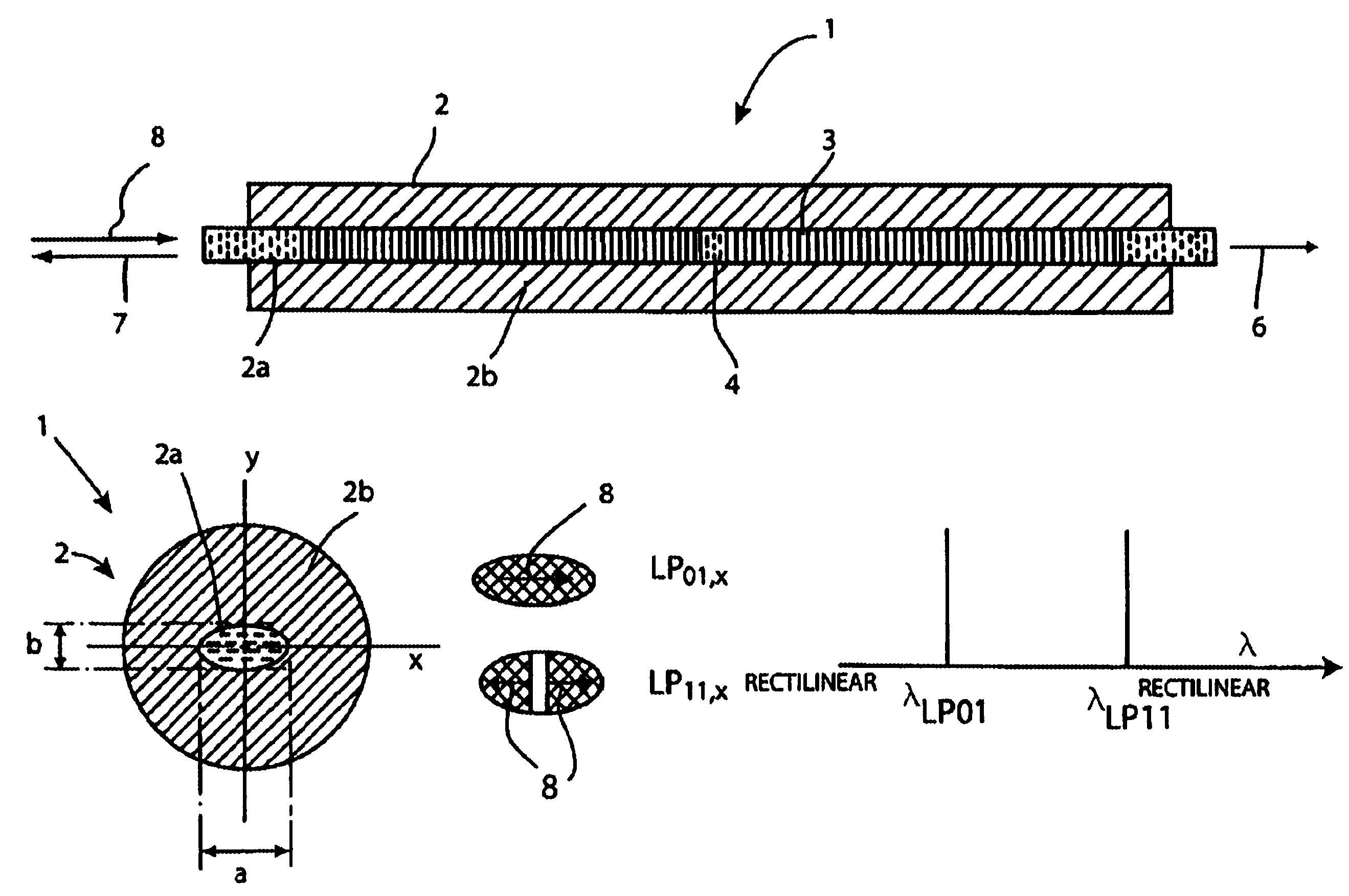
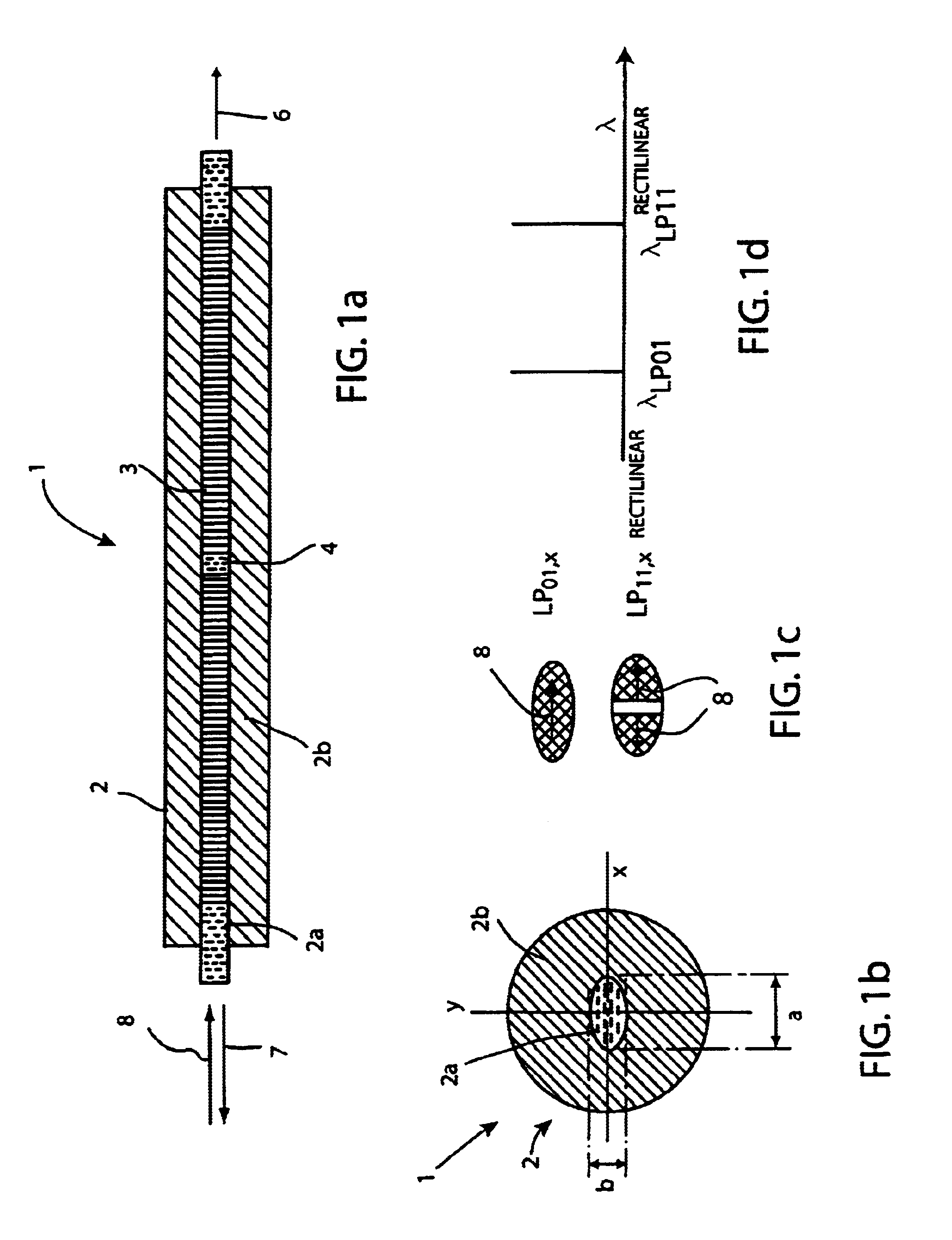
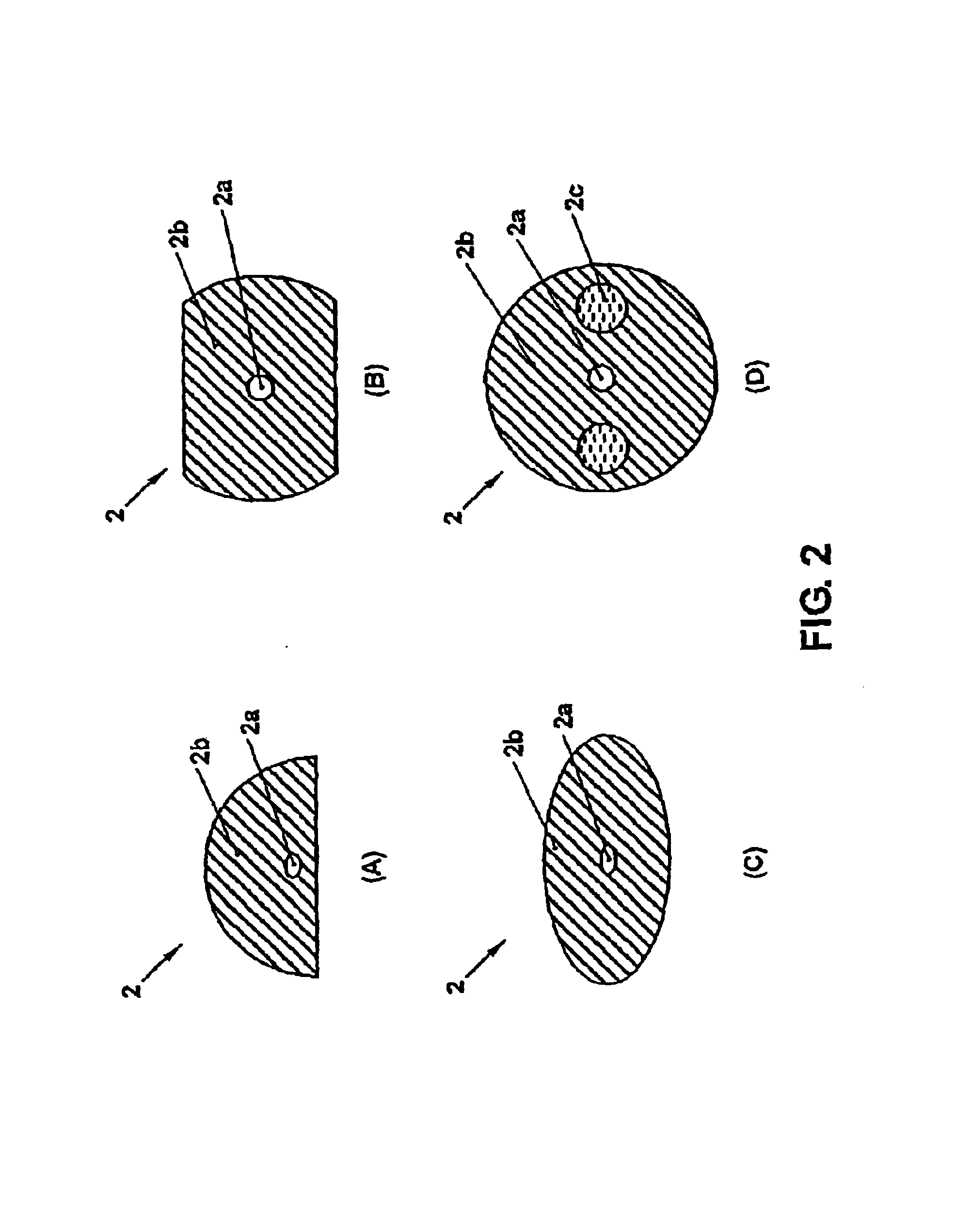
Anisotropic distributed feedback fiber laser sensor
The invention relates to a DFB fiber laser sensor (1). A measurement quantity makes it possible to induce a linear birefringence between mode pairs of the laser-amplifying fiber (2) and to measure an associated beat frequency (Δν1, Δν2, Δν3). According to the invention, the laser-amplifying fiber (2) has a nonrotationally symmetrical structure, so that it is possible to detect isotropic pressures p, acoustic waves or chemical substances that can be added radially to the laser-amplifying fiber (2). In a second aspect of the invention, an emission wavelength range and parameters (a, b, ΔN) of the laser-amplifying fiber (2) and also a grating period L of the fiber Bragg grating resonator (3) are coordinated with one another such that at least two different spatial modes (LP01, LP11even, LP11odd, LP21even) are propagatable and it is possible to measure beat frequencies (Δν1, Δν2, Δν3) between oscillatory longitudinal laser modes assigned to them. Exemplary embodiments relate to: rotationally asymmetrical fiber types, a choice of special spatial modes (LP11odd, LP21even) and / or multiple fiber Bragg gratings (3) for reducing the beat frequencies (Δν1, Δν2, Δν3) below 100 GHz; and elimination of temperature influences e.g. by the detection of a plurality of beat frequencies (Δνa, Δνb, Δνc, Δνd) between different pairs of spatial modes (LP01, LP11even, LP11odd, LP21even) and / or polarization modes (X, Y).
Owner:GE OIL & GAS UK LTD
Method for collaborative mapping and locating of multiple robots for large-scale environment
InactiveCN106272423AEliminate Motion Accumulation ErrorsPrecise positioningProgramme-controlled manipulatorAlgorithmMultirobot systems
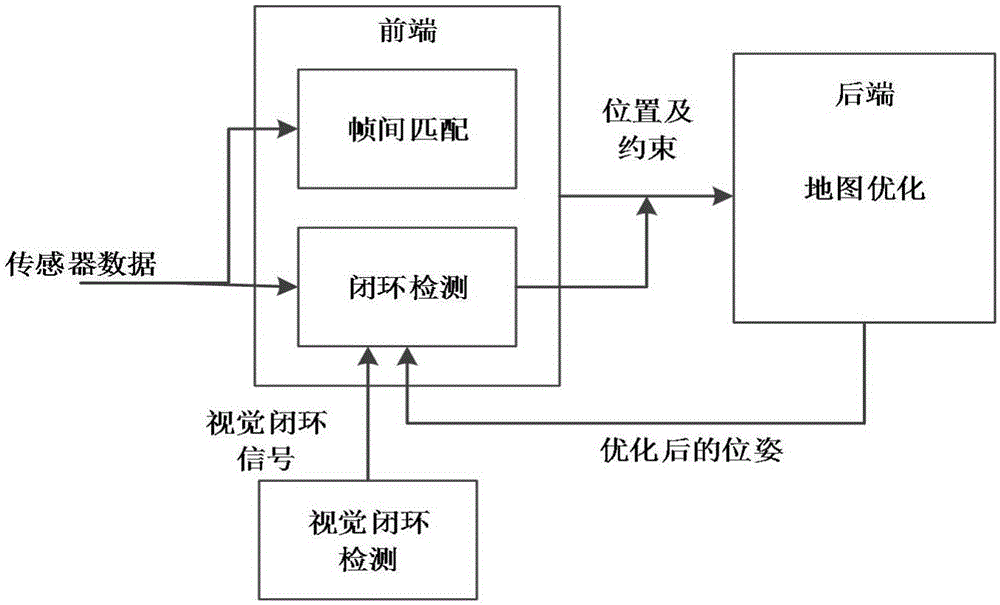
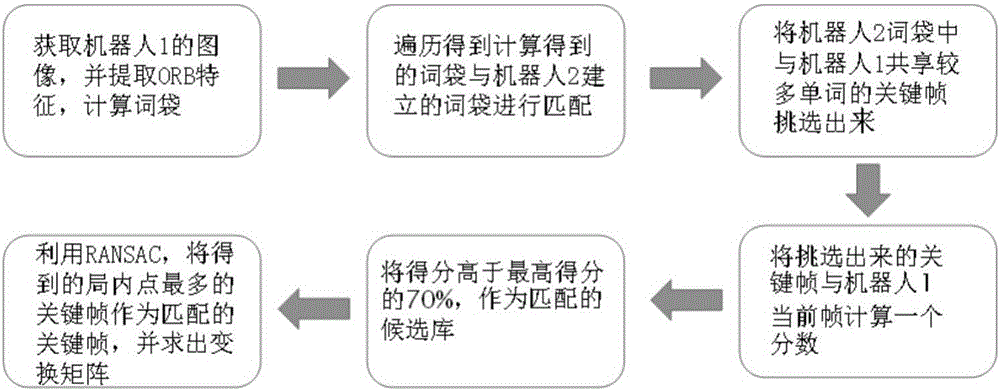
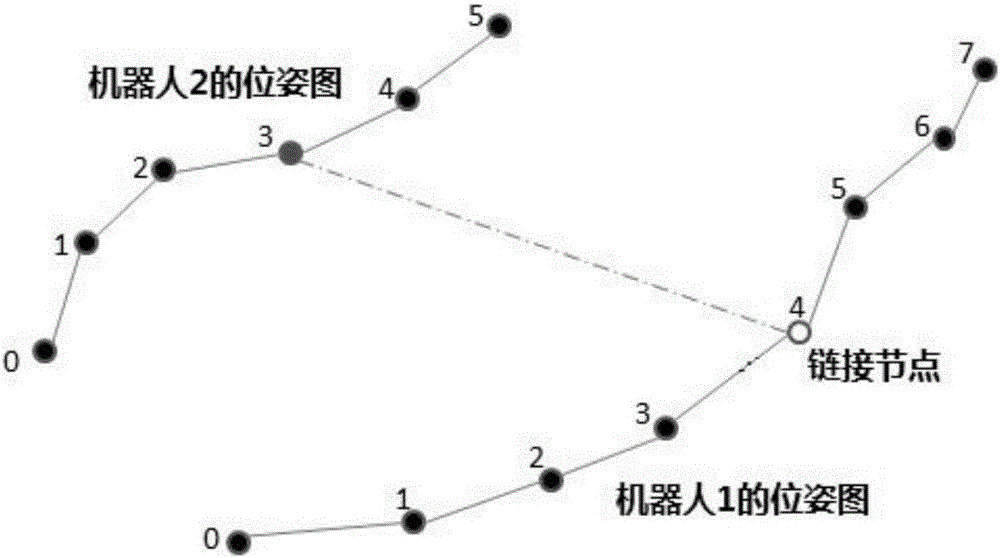
The invention provides a method for collaborative mapping and locating of multiple robots for a large-scale environment. The method comprises a single-robot laser SLAM algorithm based on a visual detection closed loop, a multi-robot pose constraint estimation algorithm and a multi-robot map fusion algorithm, wherein according to the single-robot laser SLAM algorithm based on the visual detection closed loop, a visual sensor is adopted for assisting a laser sensor in achieving the SLAM algorithm with the more stable roughness. Simultaneous locating and mapping of the multiple robots are achieved through the laser sensor and the visual sensor. The closed loop is detected by obtaining the visual characteristic of the roughness through a camera, and the problem about closed loop detection caused by the robot motion accelerative error is solved effectively; meanwhile through a multi-robot system, simultaneous locating and mapping in the large regional environment are completed efficiently, and the defect that the efficiency is low by means of a single robot is overcome. By the adoption of the method, the precise robot location and map creation of the environment are achieved in the large-scale environment, and the method is also suitable for small-scale environments.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Intelligent tree trunk white paining robot
InactiveCN102151634AImprove work efficiencyQuality improvementLiquid spraying apparatusPlant protectionProgrammable logic controllerTree trunk
The invention discloses an intelligent tree trunk white painting robot and belongs to the related fields of urban and garden greening equipment. The intelligent tree trunk white painting robot comprises a machine frame system, a robot traveling system, a lime slurry supply system, an automatic white painting execution system and a real-time detection system. Adopting a spray painting mode for white painting of tree trunks, the robot can automatically walk along a side pavement and quickly and efficiently spray lime solution onto trees along the side pavement. In a real-time detection system, a digital compass, a laser sensor and a vision system are adopted to realize the semi-automatic searching of tree trunks and tree trunk automatic positioning, an ultrasonic transducer is adopted to realize automatic obstacle avoidance, and the whole-process real-time monitoring with a personal computer (PC) and a programmable logic controller (PLC) is realized. When the intelligent tree trunk white painting robot is used, coating is saved and the painting effect is optimized; and the robot automatically performs white painting of trees along the side pavement, the working efficiency is improved, labor force is saved, and the goals of intelligent control and green environmental sanitation are fulfilled.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
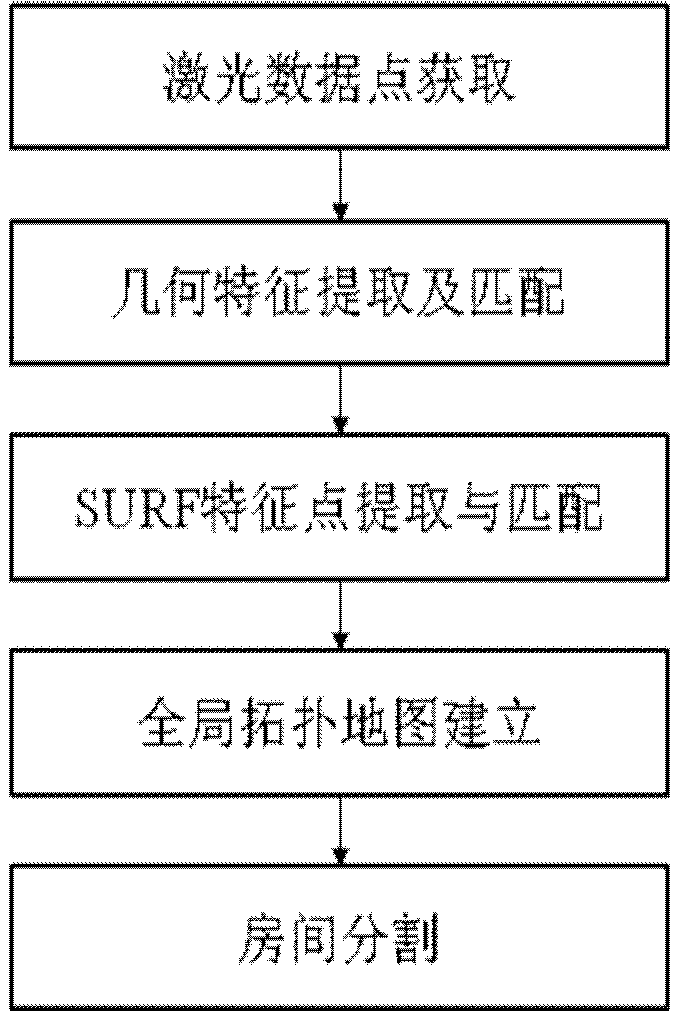
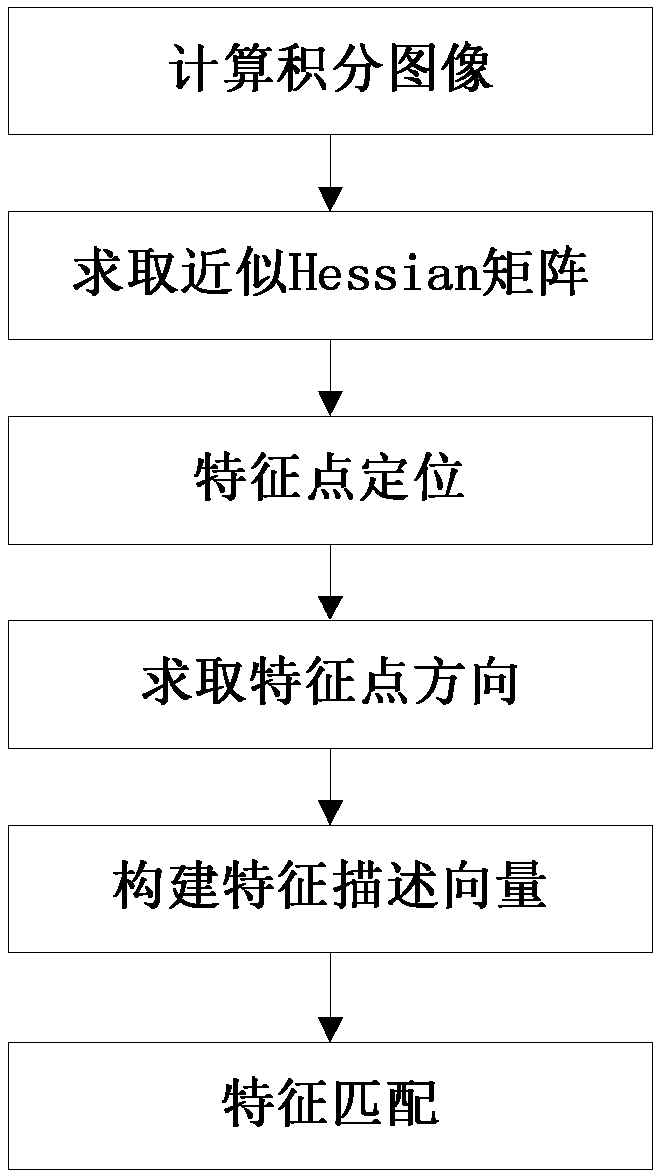
Mobile robot cascading type map creating method based on mixed characteristics
InactiveCN103268729AFix the defect createdRich room informationImage enhancementImage analysisTopological graphLaser data
The invention belongs to the field of intelligent mobile robots and discloses a mobile robot cascading type map creating method based on mixed characteristics. The mobile robot cascading type map creating method based on the mixed characteristics overcomes the defect of the creation of a signal map and solves the problem that a large amount of service information can not be supplied by single map creation. The method comprises the steps of acquiring laser data points, extracting geometrical characteristics and conducting characteristic matching, extracting SURF characteristic points and conducting matching, establishing a cascading type map and segregating a room. According to the mobile robot cascading type map creating method based on the mixed characteristics, a laser optical sensor is used for acquiring environmental data and extracting the geometrical characteristics, meanwhile, a visual sensor is used for extracting SURF characteristics, an overall topological graph is created, an undirected weighted graph is structured to achieve segmentation of the room, the defects that in a traditional topological map, geometric environment information contained in topological nodes is less and precise location cannot be achieved are effectively overcome, and abundant room information can be provided. The mobile robot cascading type map creating method based on the mixed characteristics is suitable for the field of service robots and other fields related to mobile robot map creation.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
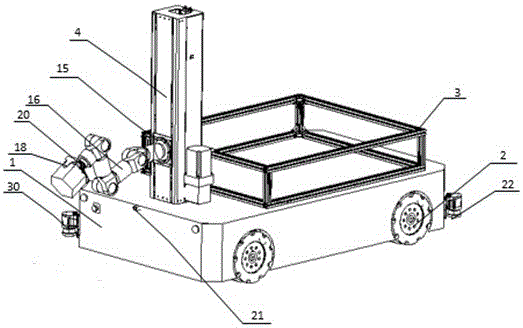
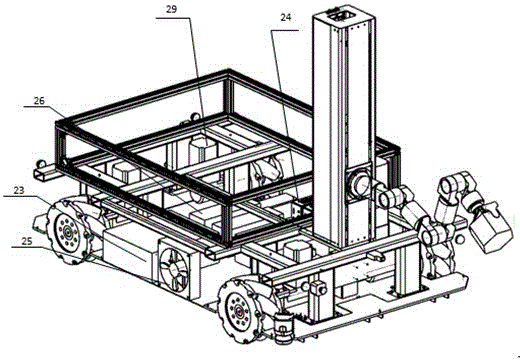
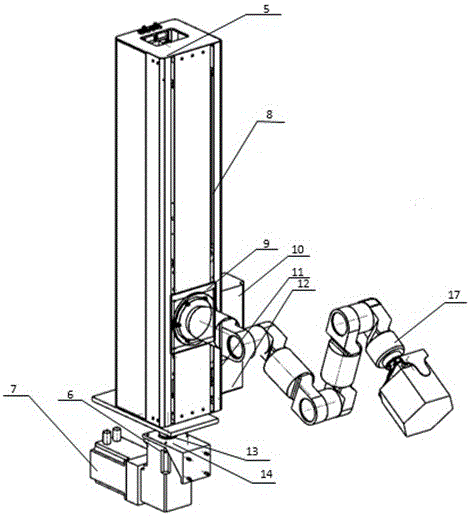
Omni-directional mobile transfer robot
InactiveCN106272415AImprove automationImprove completenessProgramme-controlled manipulatorControl systemSimulation
The invention discloses an omni-directional mobile transfer robot. The omni-directional mobile transfer robot comprises a mobile chassis, a carrying rack, a rotating mechanism, a lifting mechanism, a manipulator, a visual system, a laser sensor, a control system and a charging system. The mobile chassis is provided with Mecanum wheels for realizing omni-directional moving. The lifting mechanism can adjust the height of the manipulator. Rotational motion of a stand column at any angle can be realized through the rotating mechanism. Moreover, through cooperation of the manipulator having seven degrees of freedom, the working range is larger. Precision guidance can be realized through the laser sensor and the visual system. Operation is convenient. Motion is fast. The omni-directional mobile transfer robot is used for replacing manual operation, the working strength is reduced, and the production efficiency is improved. The omni-directional mobile transfer robot has high flexibility.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
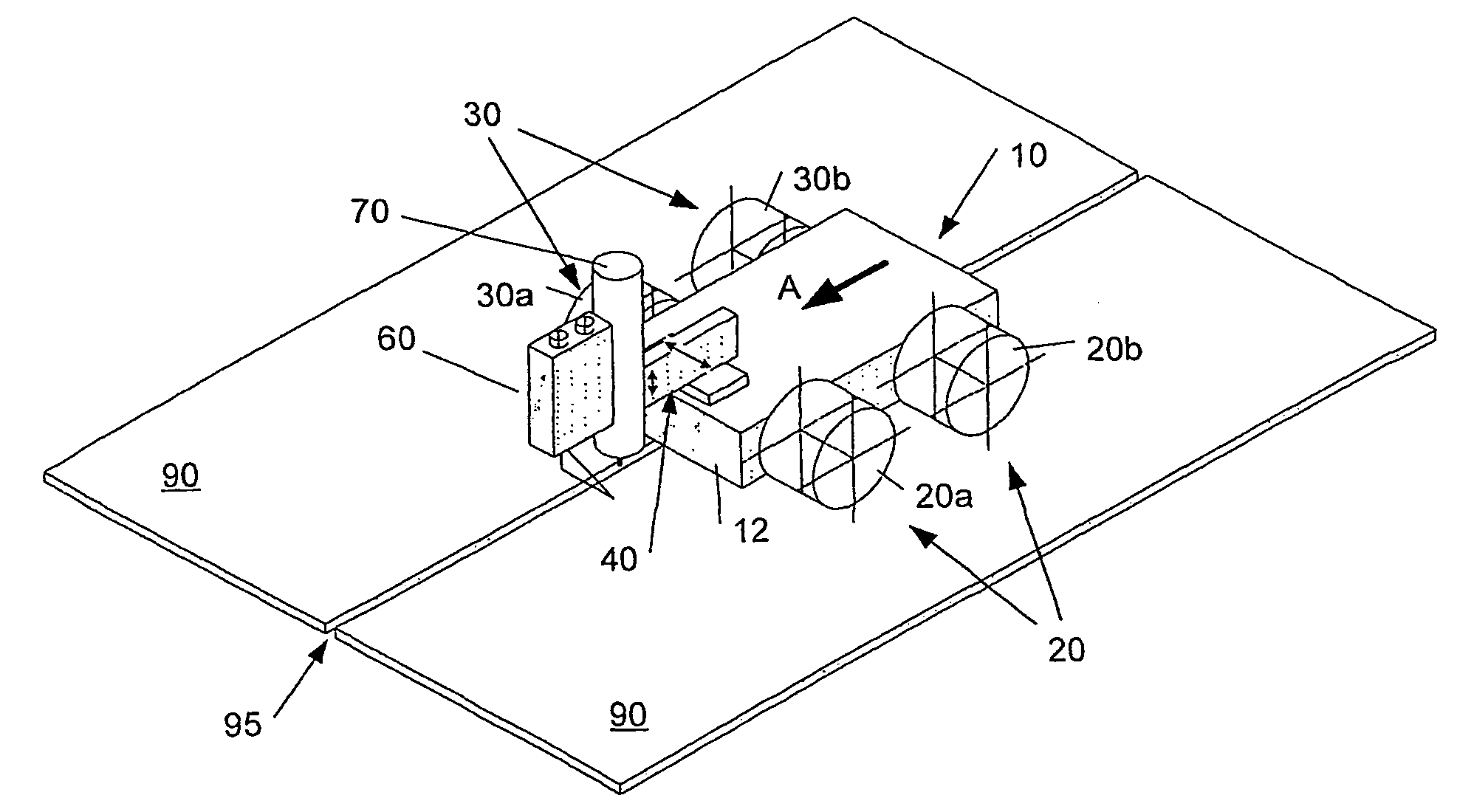
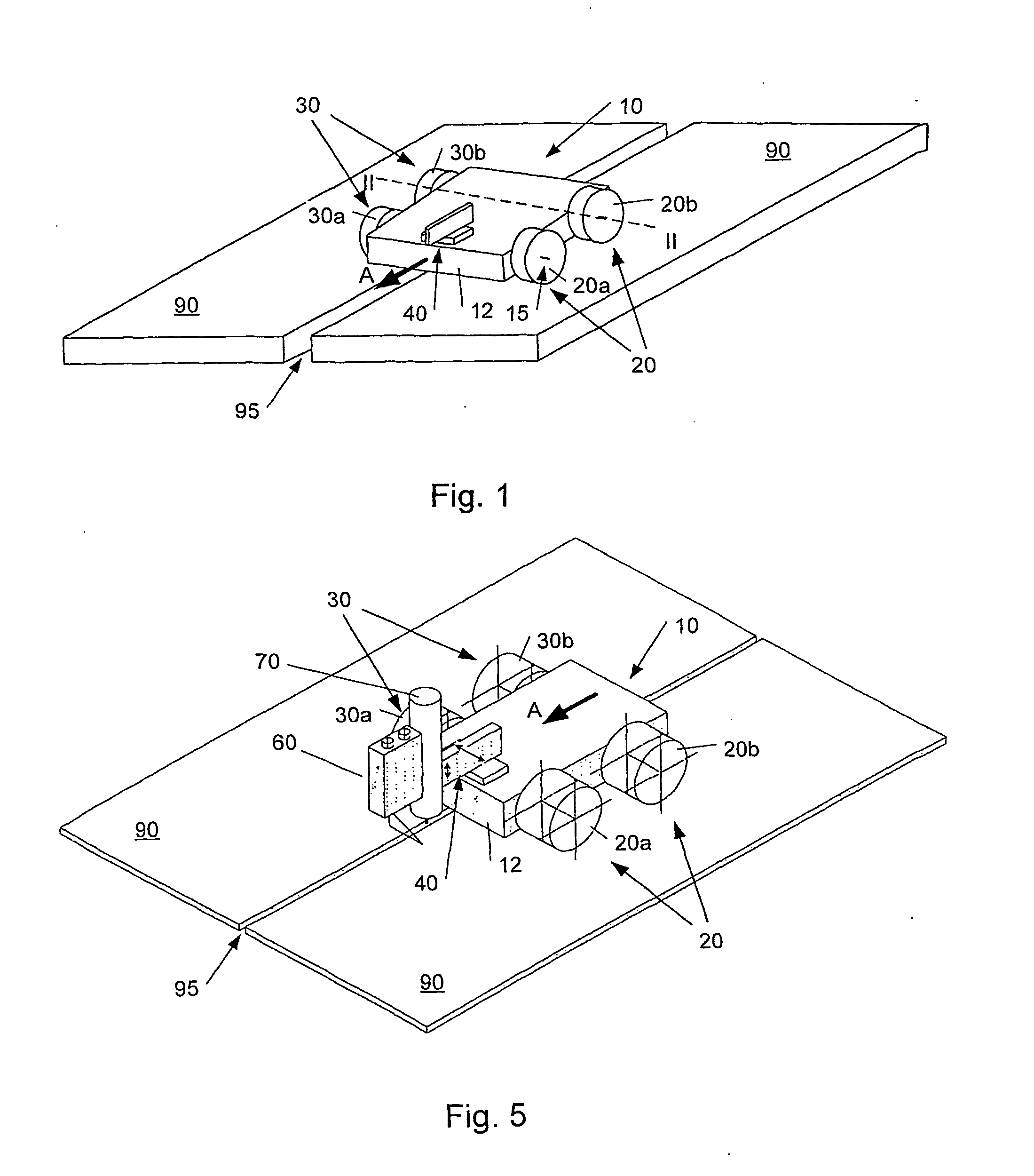
Rail Sensing Apparatus Method
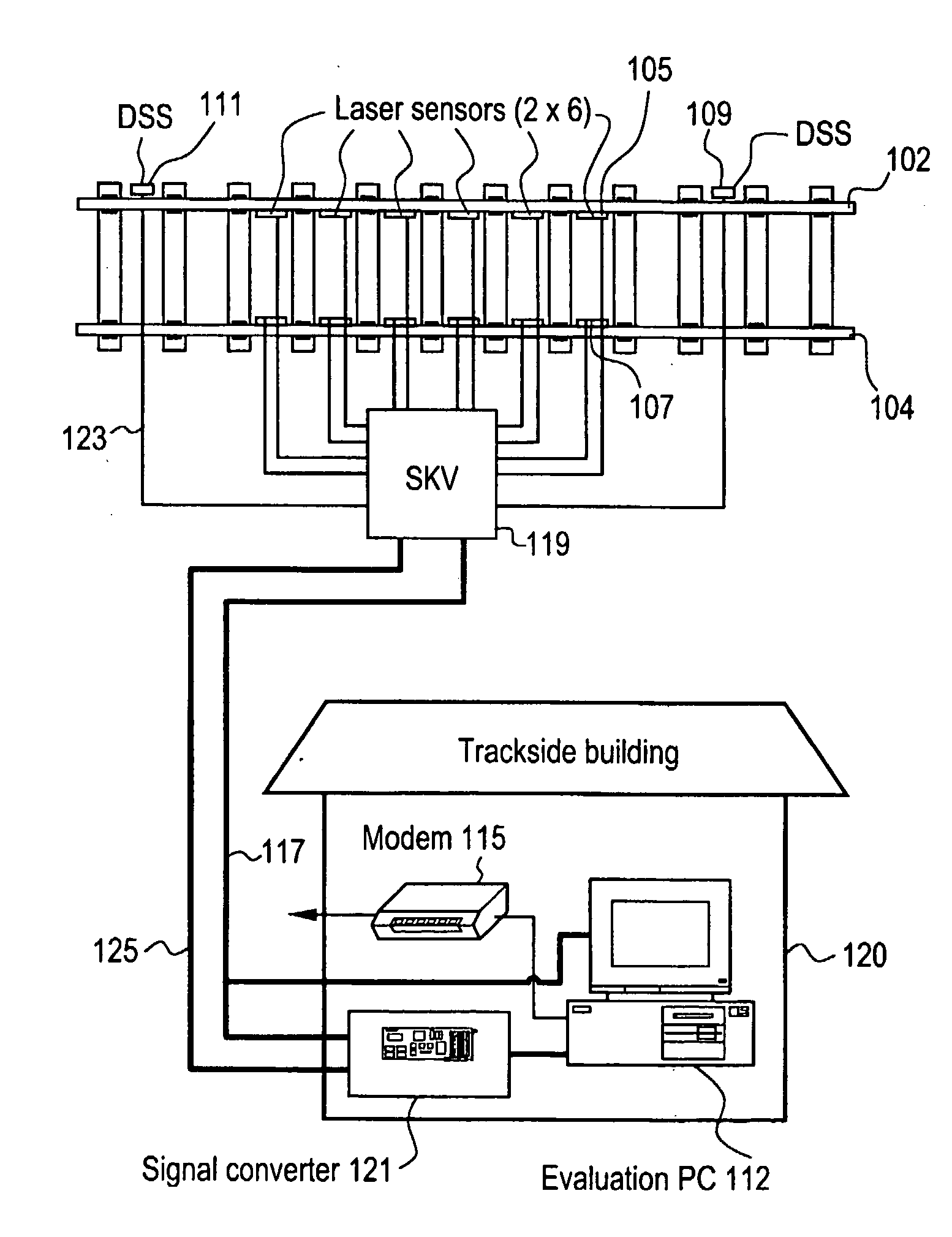
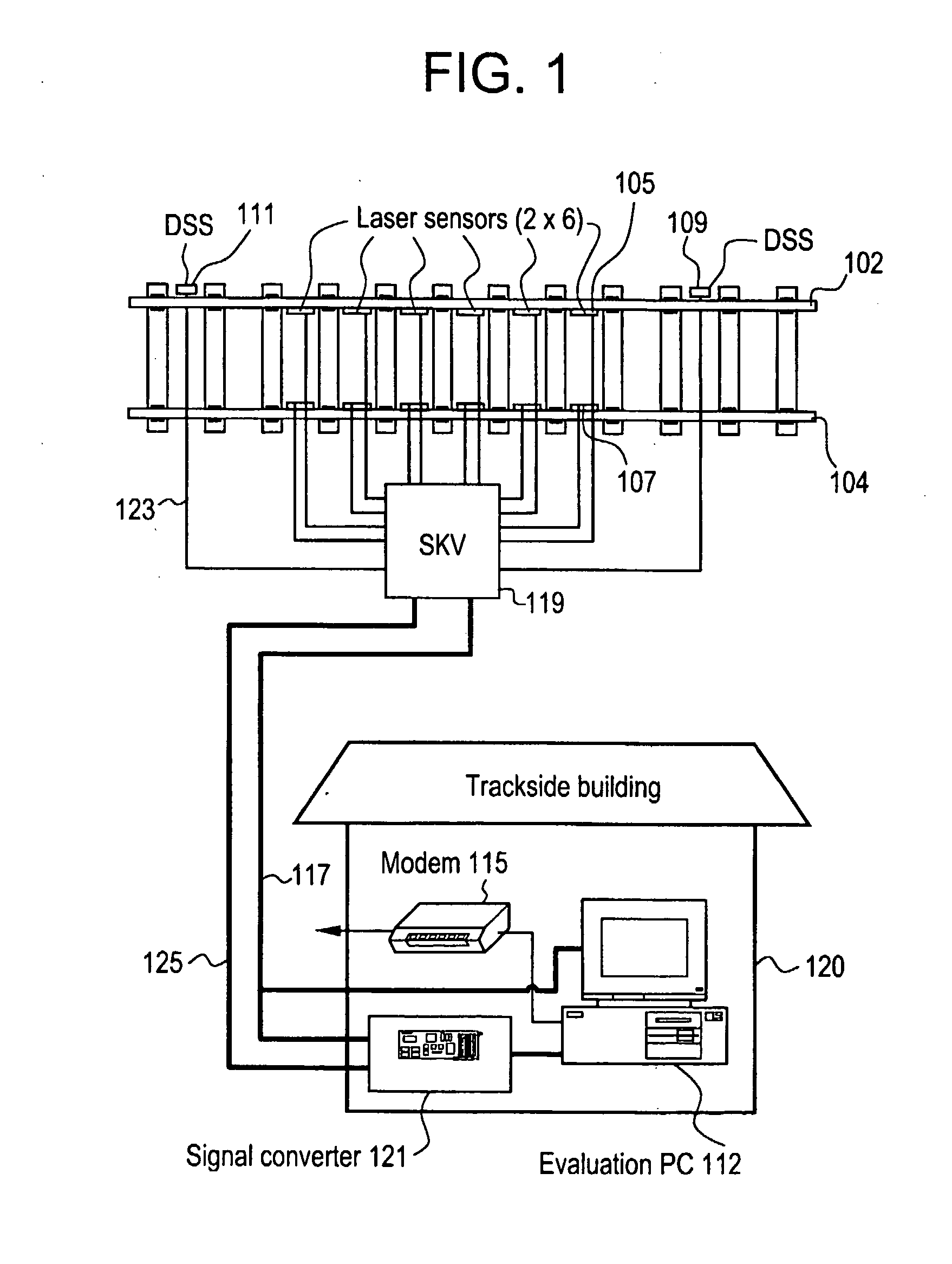
ActiveUS20080304065A1Measure directlyMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansBogieLaser sensor
A rail sensing and analysis system utilizes a laser sensor 105, 107 to detect displacement of a rail 102, 104 resulting from loads imposed by a passing rail vehicle. Vertical and / or lateral displacements / loads may be sensed. Signatures in the resulting signals are indicative of useful information about the rail vehicle; such as wheel condition, bearing condition, truck condition, degree of bogie hunting, total load, load distribution, etc. The ratio of Lateral over Vertical force (L / V) may be used as an evaluation criterion.
Owner:PROGRESS RAIL SERVICES
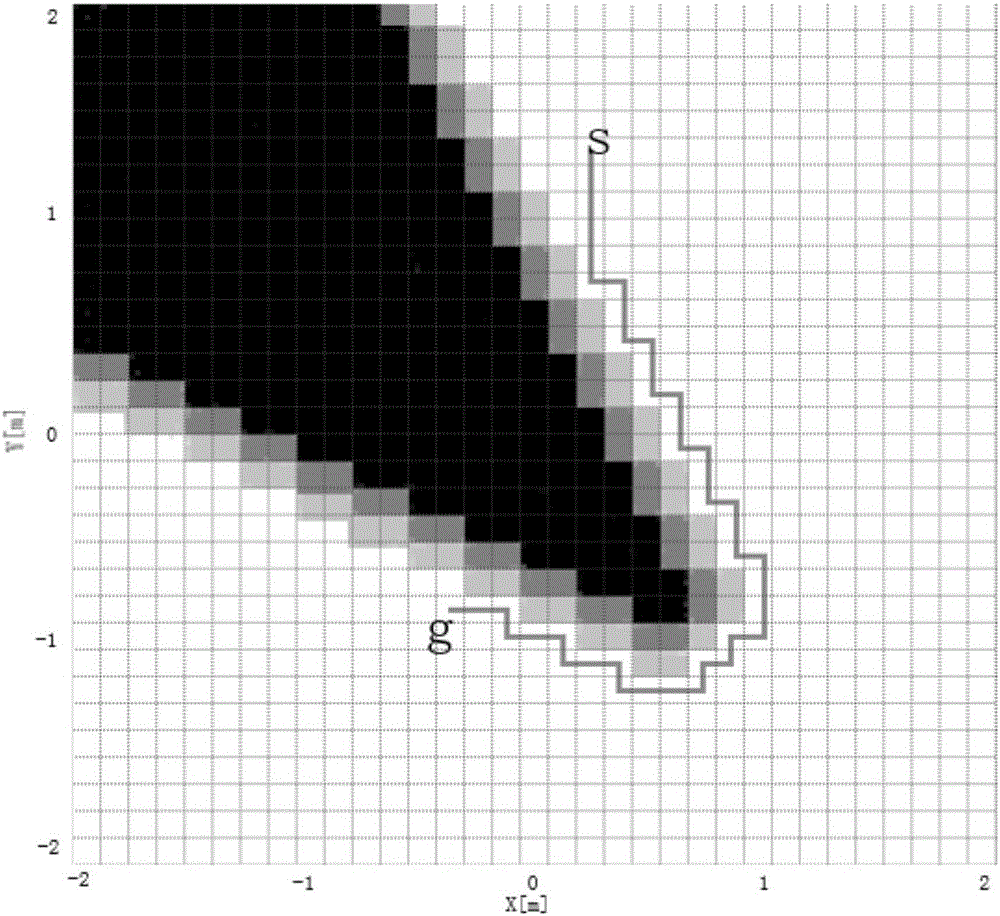
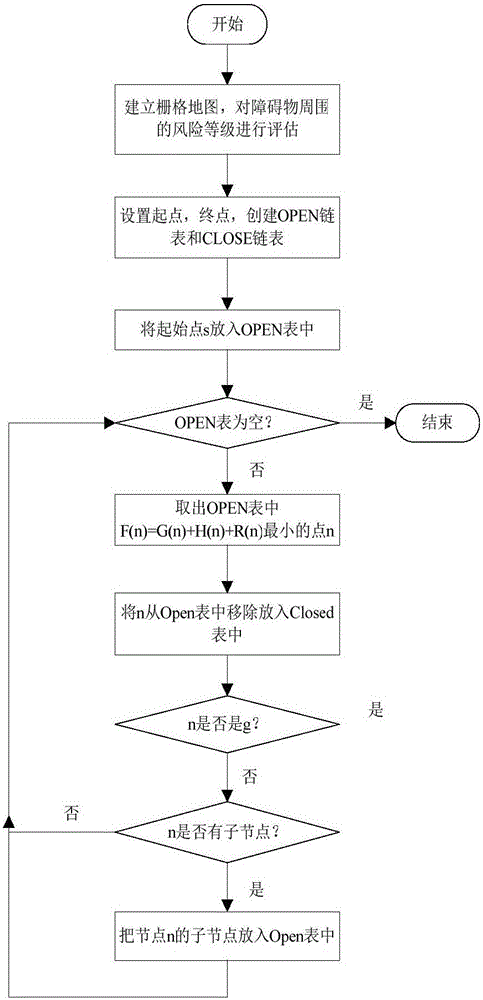
AGV path tracking and obstacle avoiding coordination method based on A* extraction guide point
The invention discloses an AGV path tracking and obstacle avoiding coordination method based on an A* extraction guide point, and relates to the field of mobile robot navigation. The method can achieve the coordination of path tracking and obstacle avoiding. The method comprises the steps: planning a safe global path; building an initial grid map according to the environment information; carrying out the evaluation of the risk level of surrounding nodes of an obstacle avoiding object through a risk evaluation function R(n); obtaining a new safety grid map with a risk region; extracting a key path point from the global path obtained through planning. For the path tracking and obstacle avoiding coordination, the method employs a dynamic window based on a laser sensor for obstacle avoiding, takes the key path point as the guide point, carries out the updating of the guide point, and achieves the coordination of the path tracking and obstacle avoiding.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
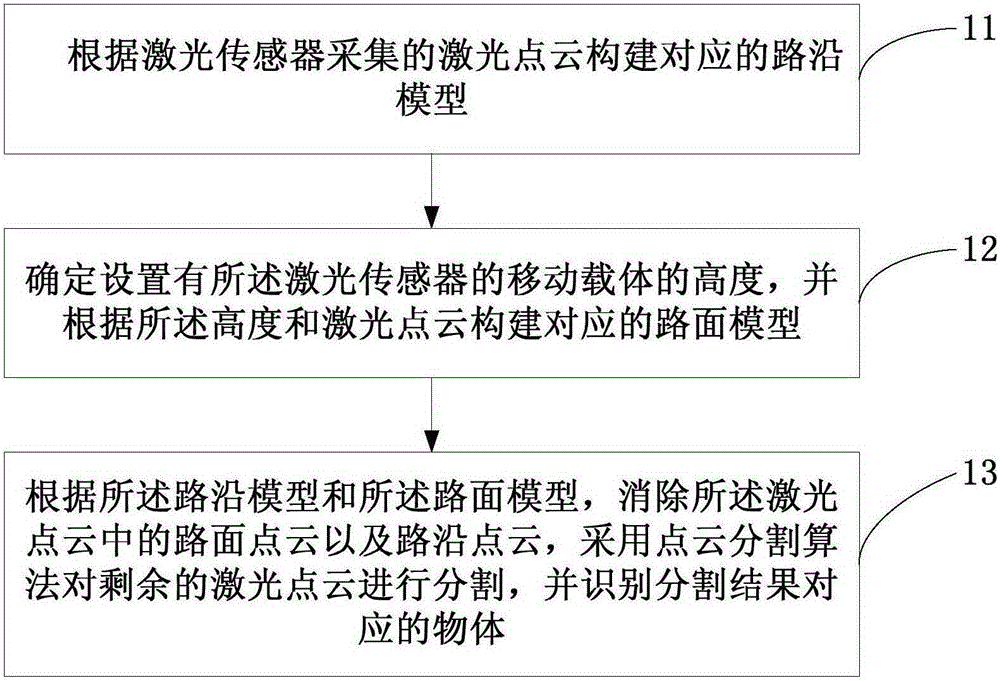
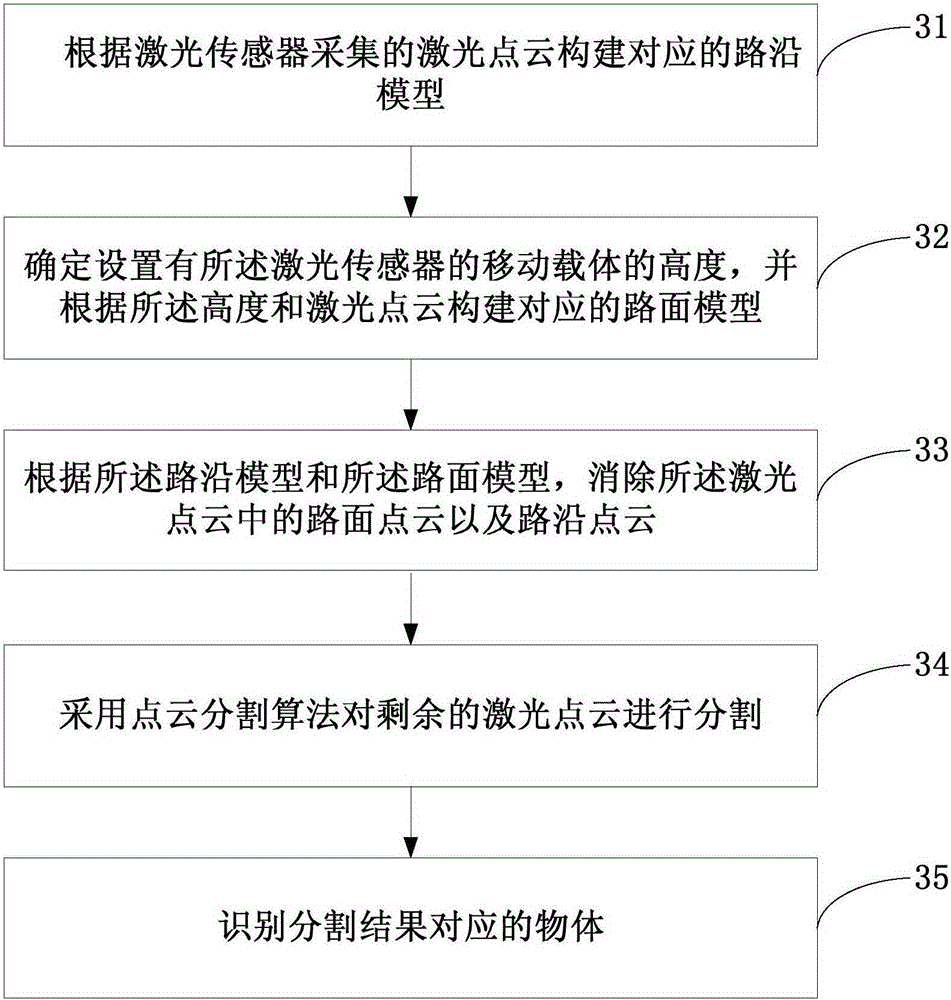
Laser-point-cloud-based urban road identification method and apparatus
ActiveCN105184852AImprove build efficiencyImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisEngineeringRoad surface
The embodiment of the invention discloses a laser-point-cloud-based urban road identification method and apparatus. The method comprises: a corresponding road edge model is constructed according to laser point clouds collected by a laser sensor; a height of a mobile carrier with the laser sensor is determined and a corresponding road surface model is constructed based on the height and the laser point; and according to the road edge model and the road surface model, a road surface point cloud and a road edge point cloud in the laser point cloud are eliminated, the rest of laser point clouds are segmented by using a point cloud segmentation algorithm, and an object corresponding to the a segmentation result is identified. The height of the mobile carrier is estimated based on the laser point cloud and the road surface model corresponding to the laser point cloud is constructed by using the height, so that the construction efficiency and accuracy of the road surface model are improved. Therefore, the identification efficiency and accuracy of the corresponding object are improved.
Owner:BAIDU ONLINE NETWORK TECH (BEIJIBG) CO LTD
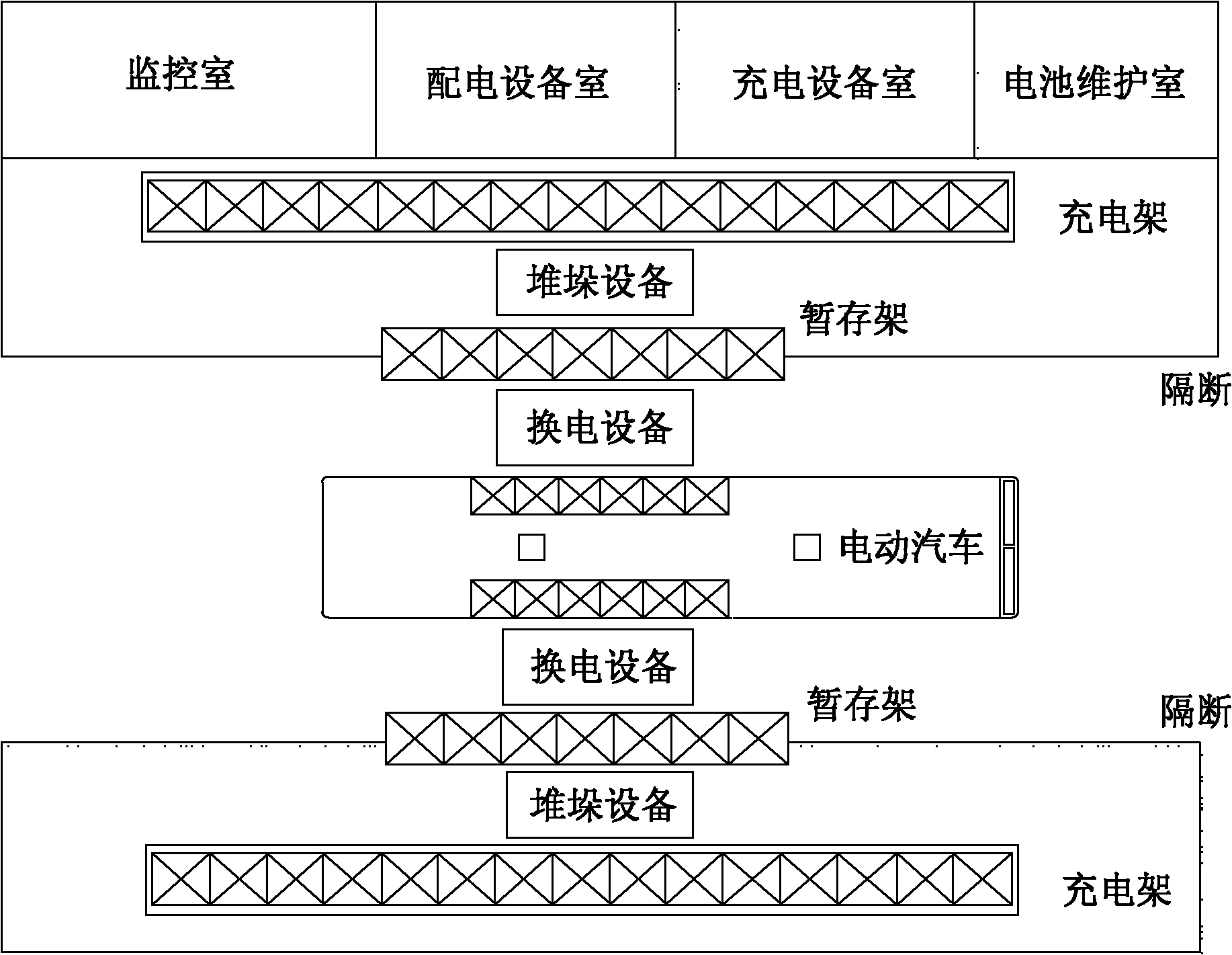
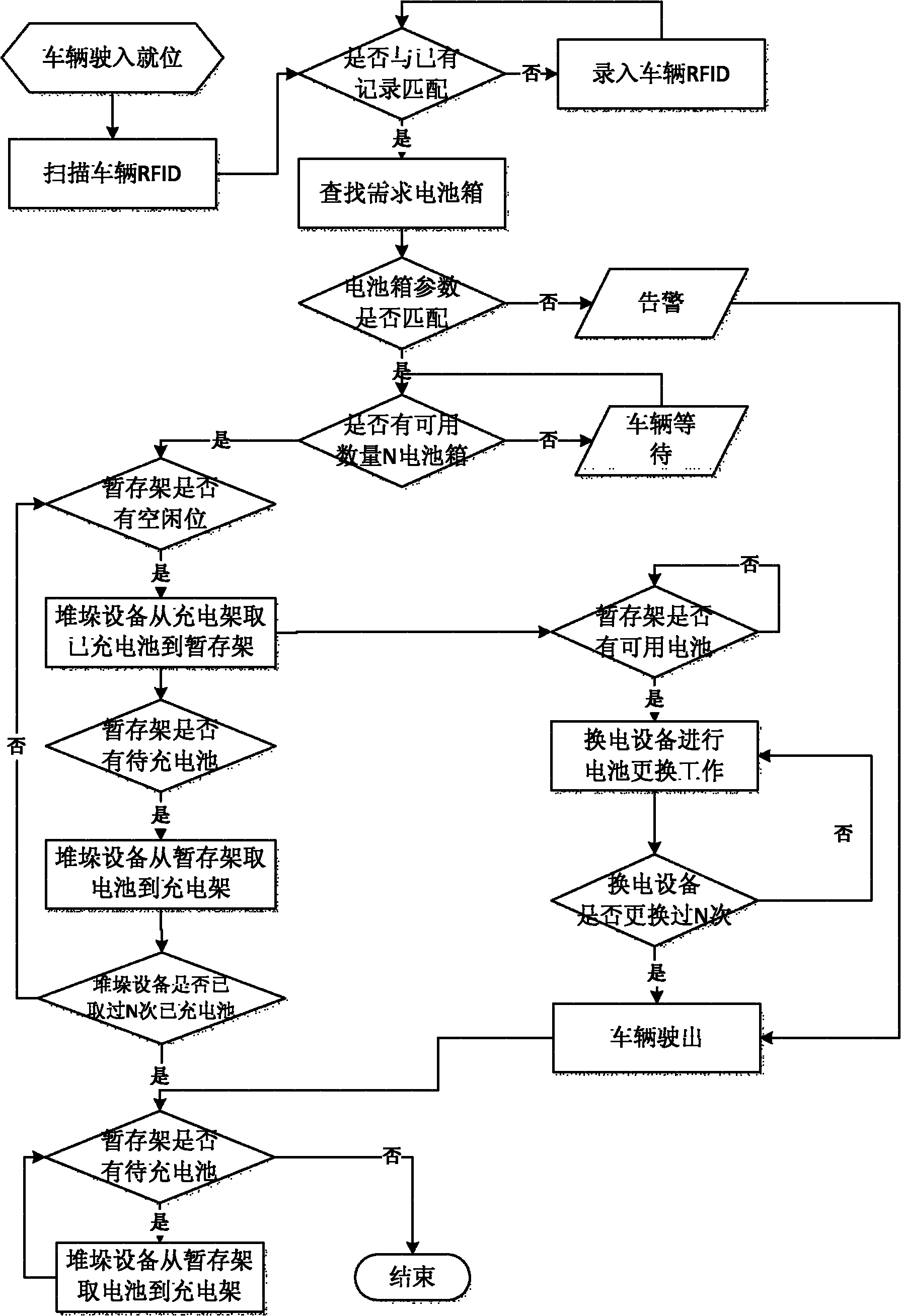
Battery replacing system and battery replacing method of electromobile battery replacing station
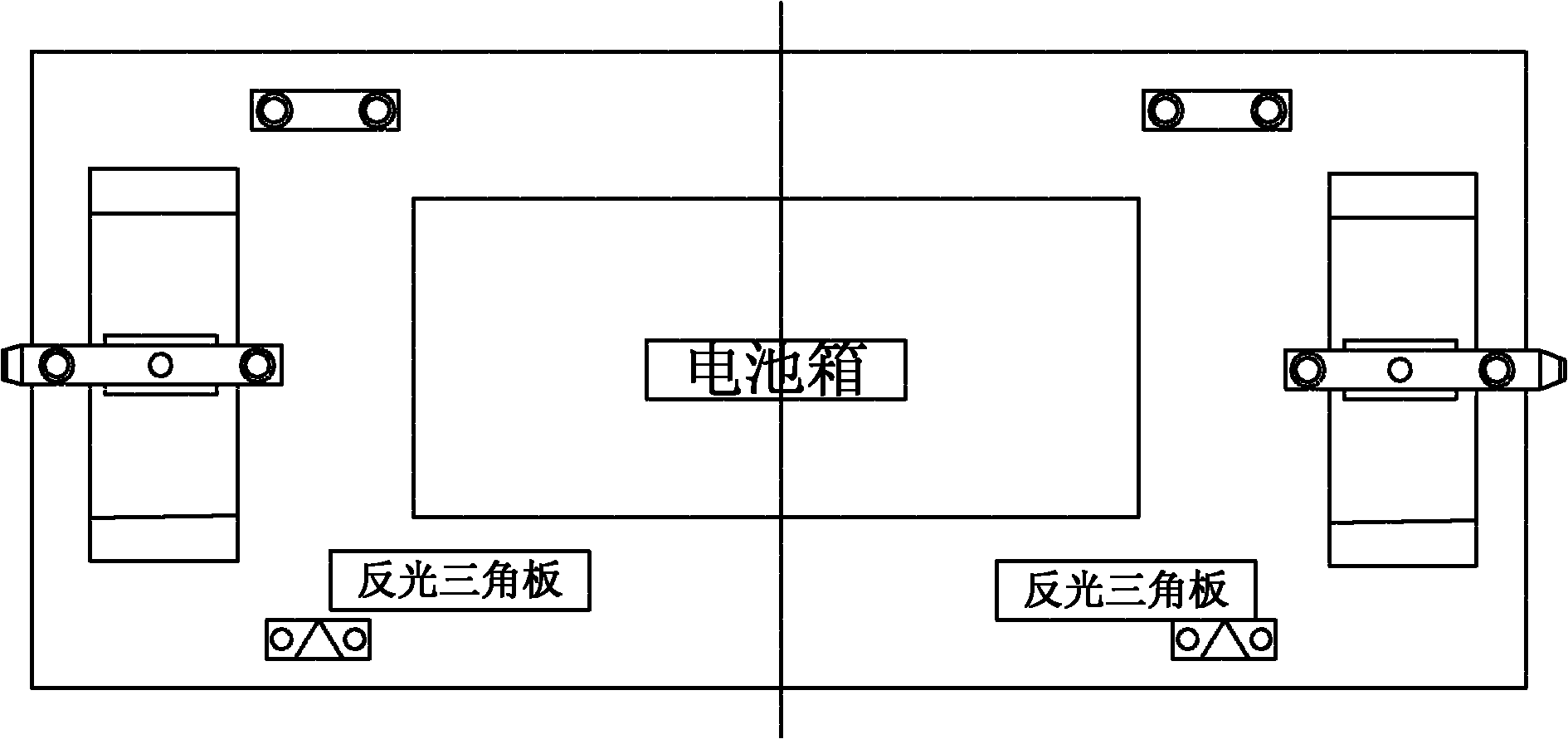
ActiveCN102152776AImprove replacement efficiencyIncrease in sizeCharging stationsElectric propulsion mountingElectricityElectrical battery
The invention discloses a battery replacing system of an electromobile battery replacing station. The battery replacing system comprises a charging rack, stacking equipment, a temporary storage rack, electric-switching equipment and a charger system. The battery replacing system is characterized in that: the stacking equipment is used for carrying batteries between the charging rack and the temporary storage rack; the electric-switching equipment is used for carrying the batteries between the temporary storage rack and the electomobile; the stacking equipment has translation, hoisting and loading / unloading functions and is used for carrying the batteries between the charging rack and the temporary storage rack; and the electric-switching equipment has translation, hoisting, rotating, inclination angle adjustment and loading / unloading functions, and is used for carrying the batteries between the temporary storage rack and an electromobile. Accurate positioning of a battery box by the electric-switching equipment is realized in a way that a self-carried laser transducer scans a light-reflecting triangular panel arranged on an electromobile battery box frame. Due to the different designs of the charging rack and the temporary storage rack, the stacking equipment and the electric-switching equipment coordinately work together, and then the electromobile battery replacing efficiency is effectively improved.
Owner:NARI TECH CO LTD +4
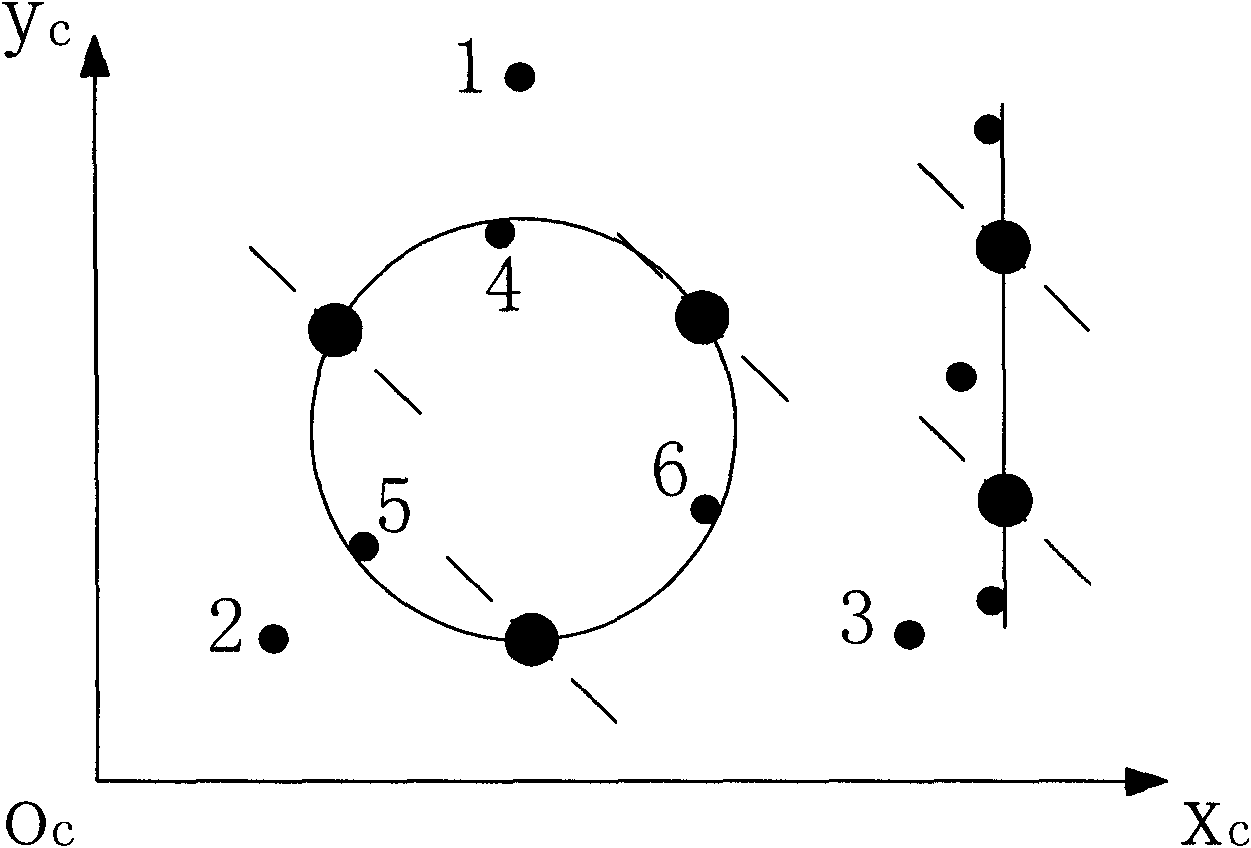
Three-dimension laser sensor and two-dimension laser sensor combined calibration method
ActiveCN103257342AImprove efficiencyHigh precisionWave based measurement systemsLaser rangingPoint cloud
The invention discloses a three-dimension laser sensor and two-dimension laser sensor combined calibration method. Distance measuring mutation characteristics produced when two-dimension laser is used for scanning a calibration plate with clearance in the middle. Mapping relevance between a data matrix of a straight line, where the clearance is located, in a laser sensor local coordinate system and a data matrix of the straight line, where the clearance is located, in an unmanned intelligent cart coordinate system is utilized to rectify rotating gestures of laser sensors. On the basis of the rectification, point cloud data of a protruding rectangular object in a level scene is further extracted, and horizontal moving rectification is conducted according to an ICP iterative optimization algorithm. Consequently, combined calibration of a three-dimension laser distance detection sensor and a plurality of two-dimension laser distance detection sensors is achieved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Movable laser cladding and repairing system
ActiveCN103074625AAchieve claddingAchieve fixMetallic material coating processesLaser scanningLaser sensor
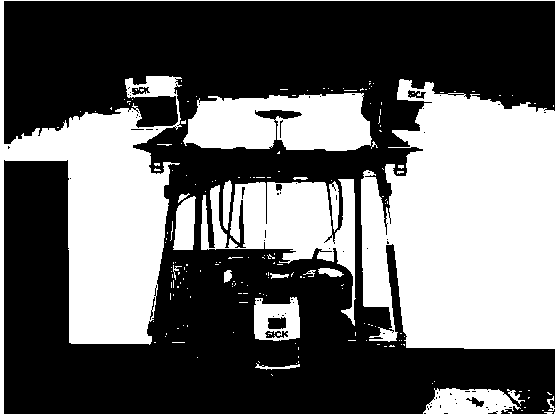
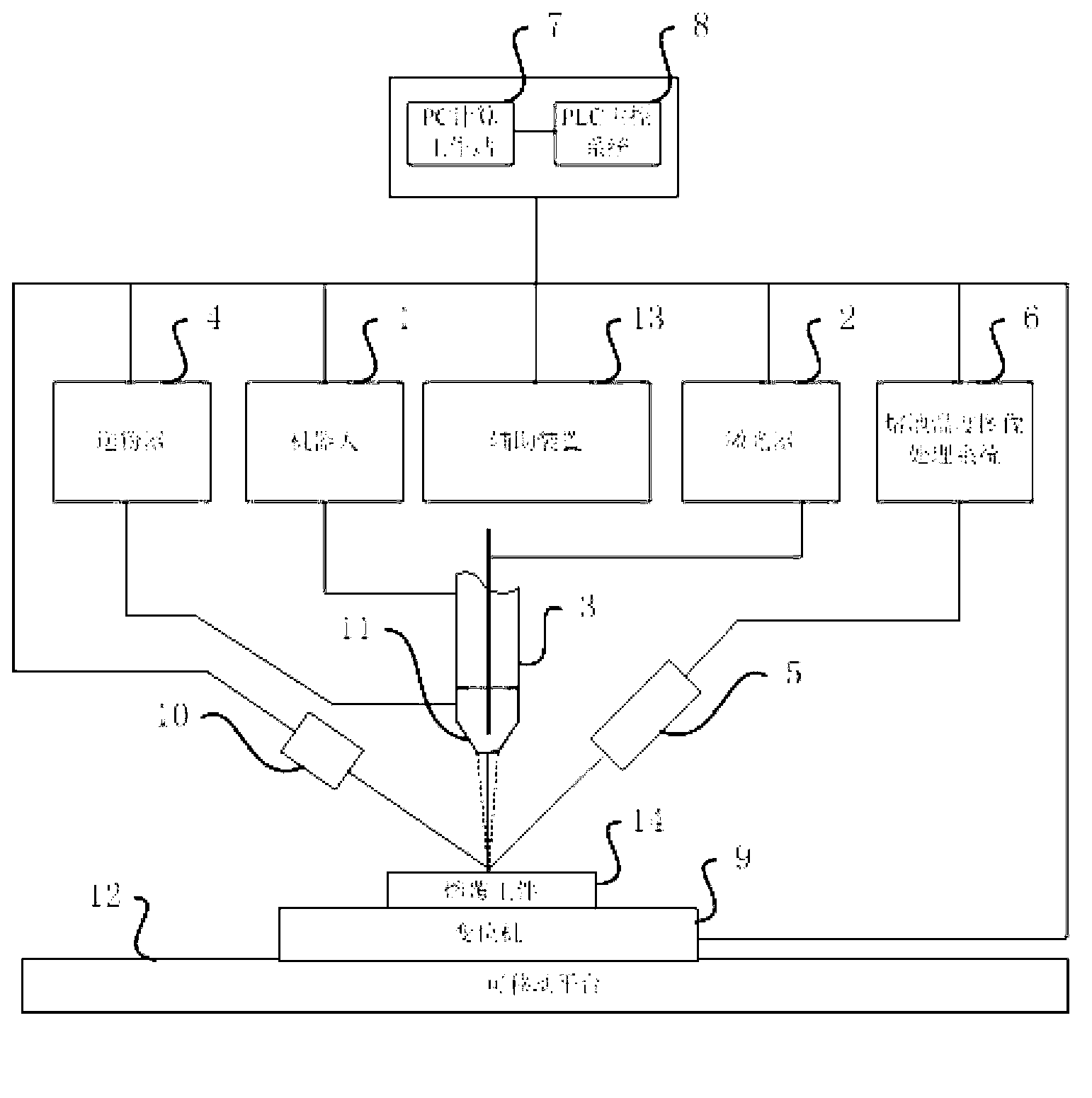
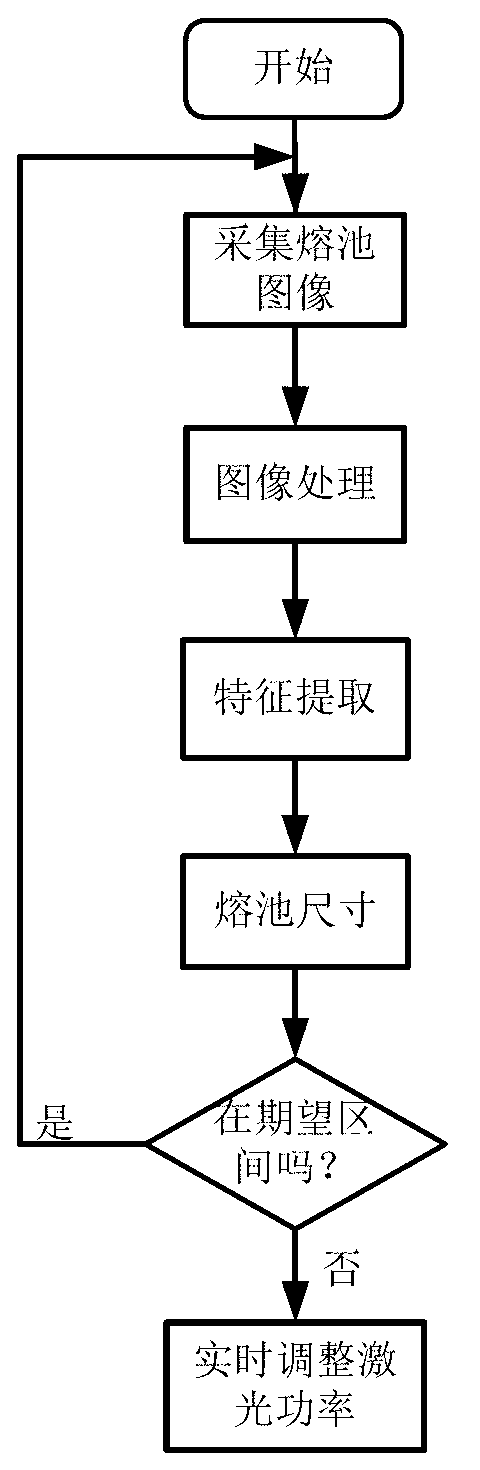
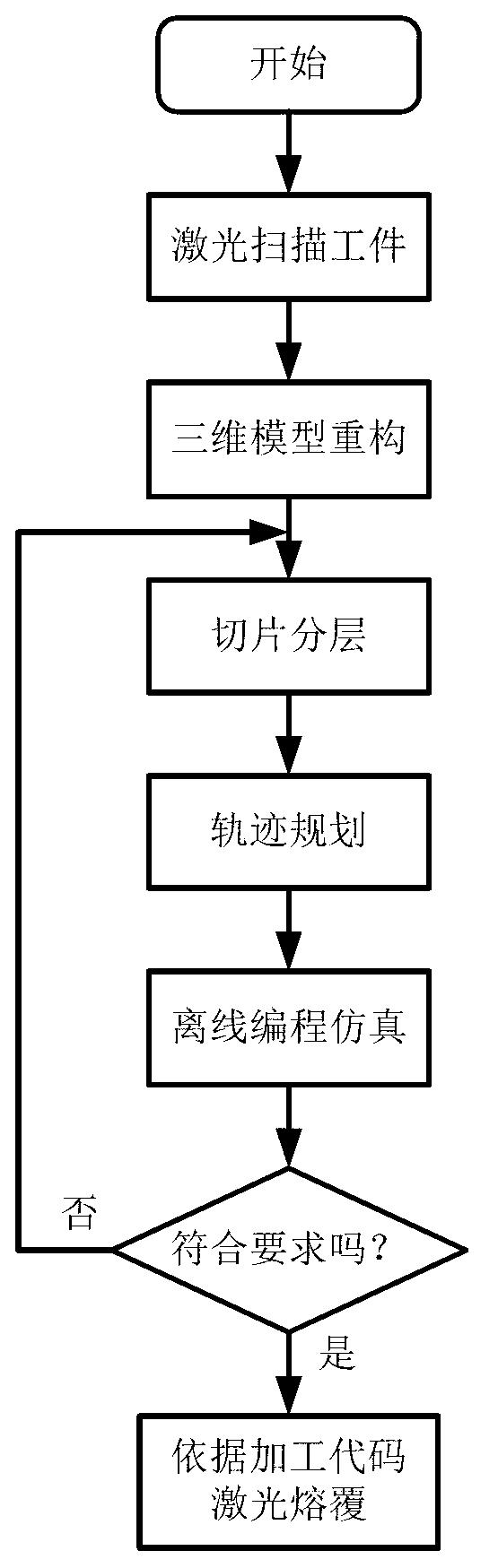
The invention provides a movable laser cladding and repairing system in the field of laser cladding and repairing. The movable laser cladding and repairing system comprises a movable platform, wherein a laser, a robot, a position changing machine, a powder feeder, an image processing system, a control system (comprises a PLC (programmable logic controller) main control system, a PC (personal computer) computing workstation), a video camera, a three-dimensional laser scanning sensor, a laser processing head and a coaxial powder feeding head are fixedly arranged on the movable platform. The movable laser cladding and repairing system takes the robot as a moving body, controls the clad pool size, the temperature and other information by using an image acquiring and processing system, and scans a workpiece to slice, stratify and automatically clad a three-dimensional workpiece model based on the three-dimensional laser sensor; the movable laser cladding and repairing system is convenient and flexible, simplifies a repairing process, achieves precision and self-adaptive control of a cladding process, effectively improves the cladding quality, and facilitates field application of a large component through the movable platform.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
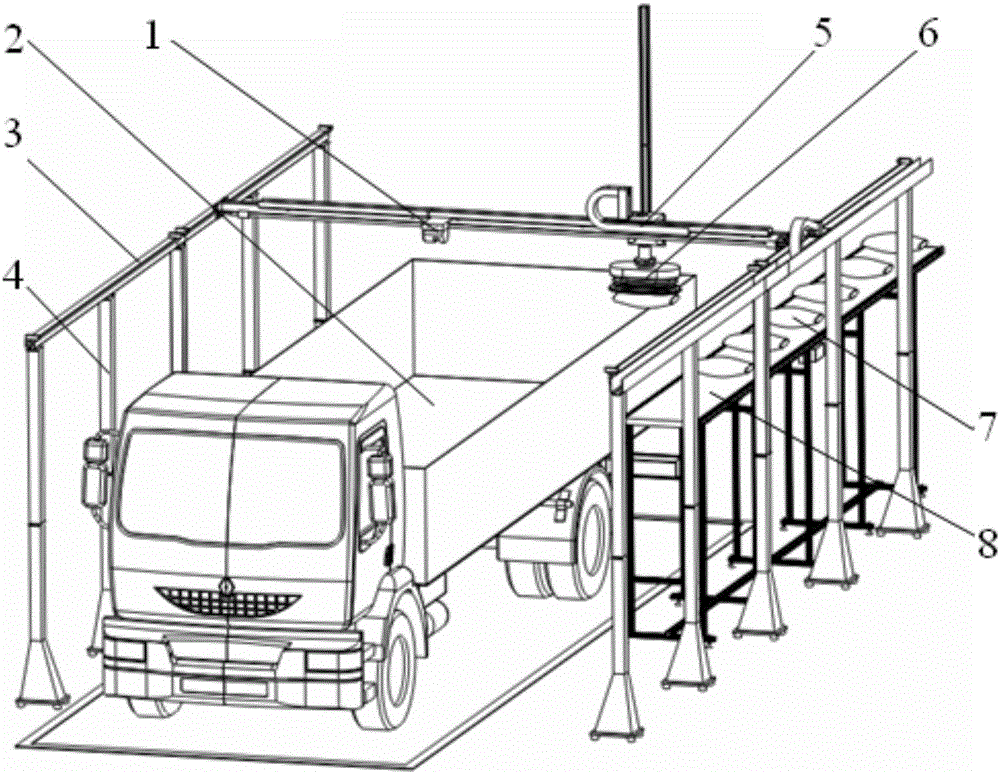
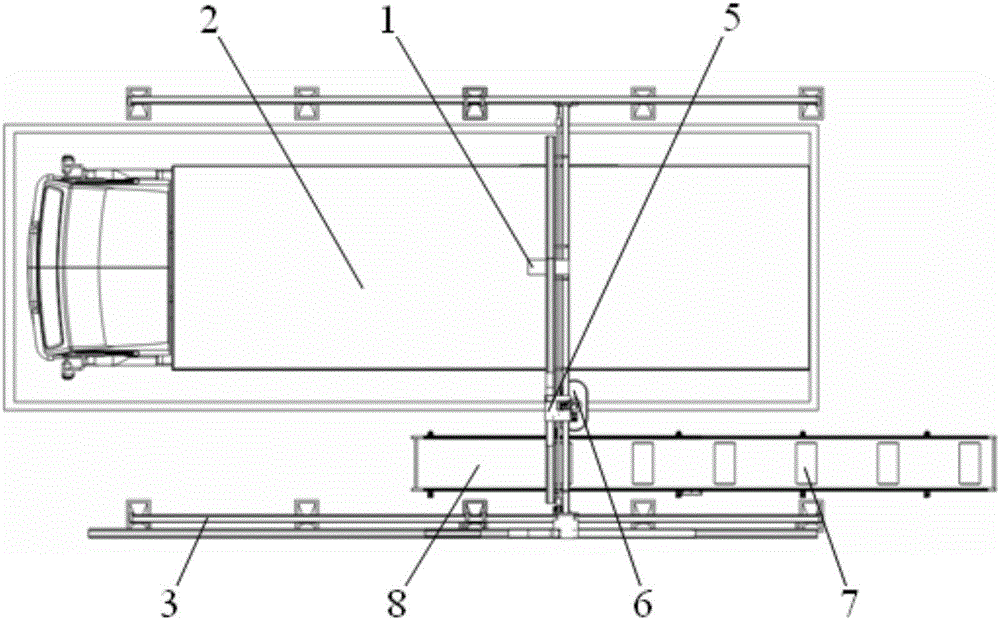
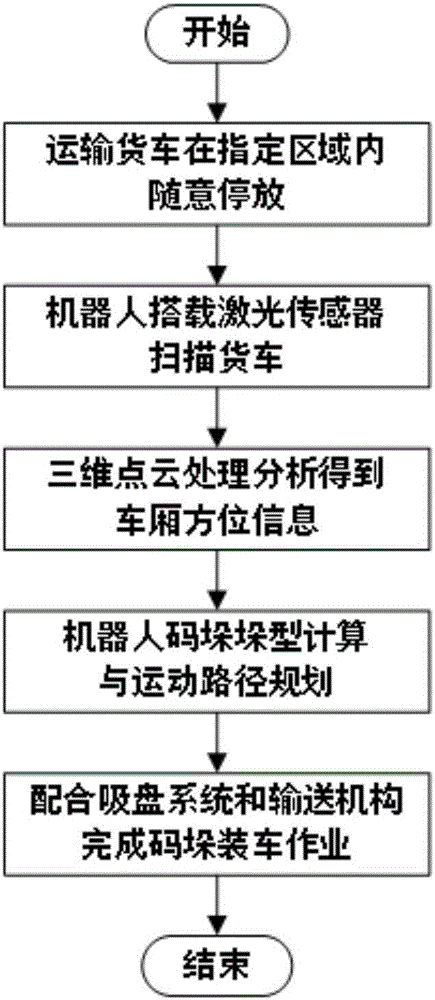
Automatic stacking and truck-loading system and truck-loading method thereof
InactiveCN106429483AReduce labor intensityReduce complexityStacking articlesDe-stacking articlesTruckLaser sensor
The invention discloses an automatic stacking and truck-loading system. According to the technical scheme of the automatic stacking and truck-loading system, goods (7) are loaded onto and unloaded from a transportation truck (2) through a robot, and the robot is a four-axis gantry type robot (5); a sucking disc device (6) used for delivering the goods (7) is arranged on the four-axis gantry type robot (5); and the four-axis gantry type robot (5) is further provided with a laser sensor (1). The invention further discloses a truck-loading method of the truck-loading system. By means of the automatic stacking and truck-loading system and the truck-loading method thereof, the goods stacking and truck-loading technology based on the laser sensor is adopted; real full automatization of the whole process including positioning inspection of the transportation truck and goods stacking and truck-loading is achieved; intelligentized positioning of a compartment of the truck is achieved, and scientific planning can be conducted on the stacking process; human cost and labor intensity of operators are lowered, and safety and reliability of truck-loading operation are enhanced; and meanwhile, equipment cost is lowered.
Owner:WUHU HIT ROBOT TECH RES INST
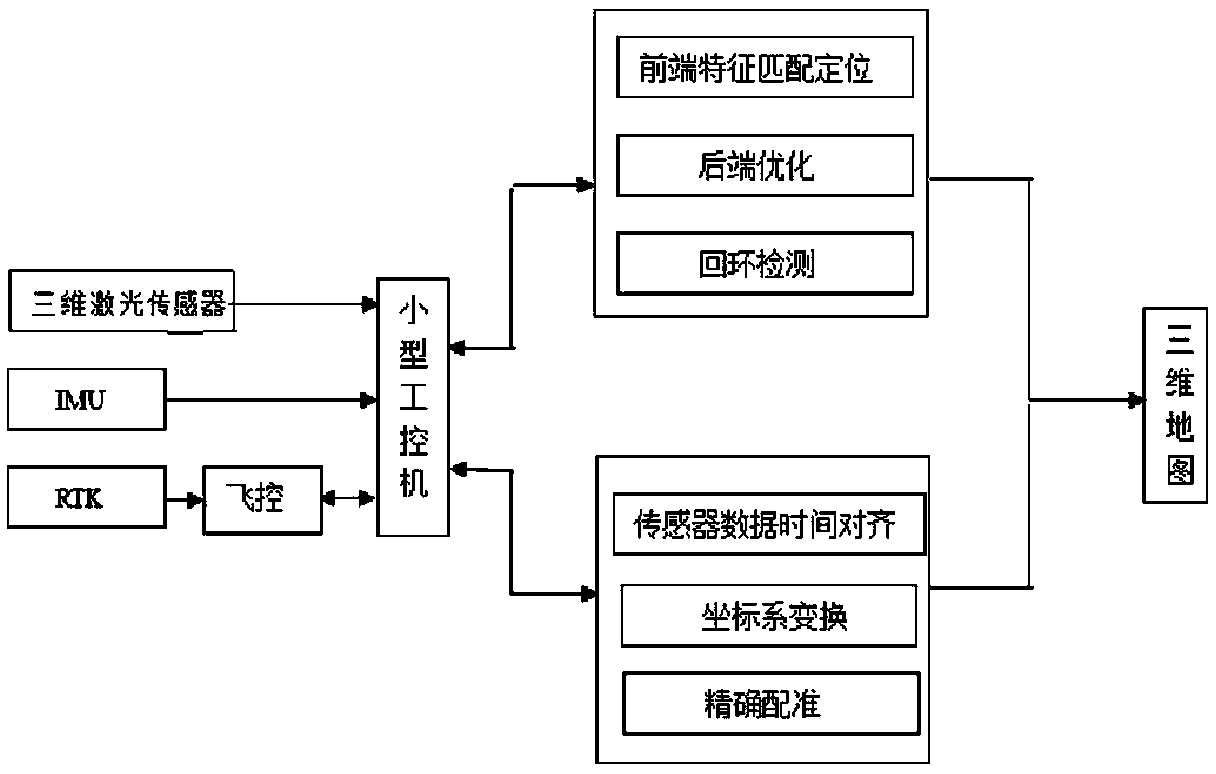
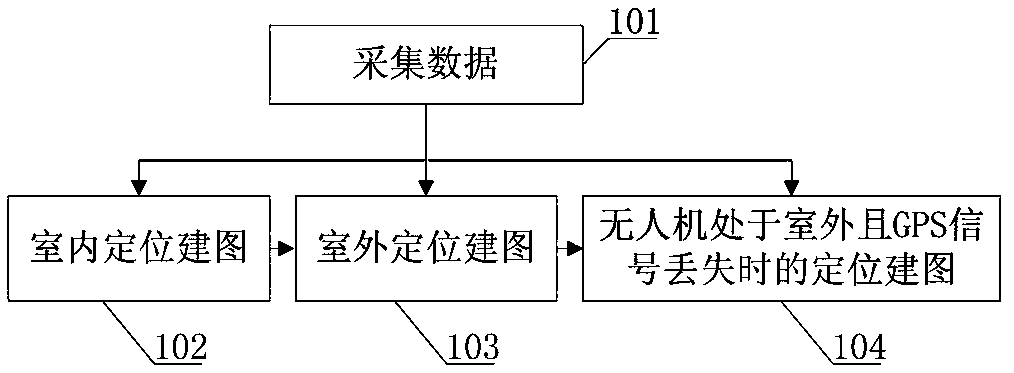
Multi-scene drone locating mapping method based on three-dimensional laser radar
The invention provides a multi-scene drone locating and three-dimensional map mapping method based on a three-dimensional laser radar. In an indoor environment, when no GPS signal exists, a SLAM algorithm based on a three-dimensional laser sensor is built; in an outdoor environment, position information provided by RTK is mainly relied on to build the three-dimensional map, and after RTK loses theGPS signal, SLAM assists in locating. An indoor and outdoor three-dimensional map is quickly built, a convenient and efficient method is provided for obtaining the three-dimensional environment map,and the efficiency of building the three-dimensional environment map in the indoor environment and the outdoor environment is improved to a great extent; on the theoretical basis of mapping optimization of the SLAM algorithm, a drone platform SLAM algorithm is built based on the three-dimensional laser sensor, the three-dimensional environment map is built in the environment without the GPS signal, the problems of indoor locating and indoor and outdoor locating merging of a drone are solved, requirements of multi-scene drone locating are met, on the basis of obtaining high-precision attitude information, laser data is merged, and the three-dimensional map is built.
Owner:江苏中科智能科学技术应用研究院
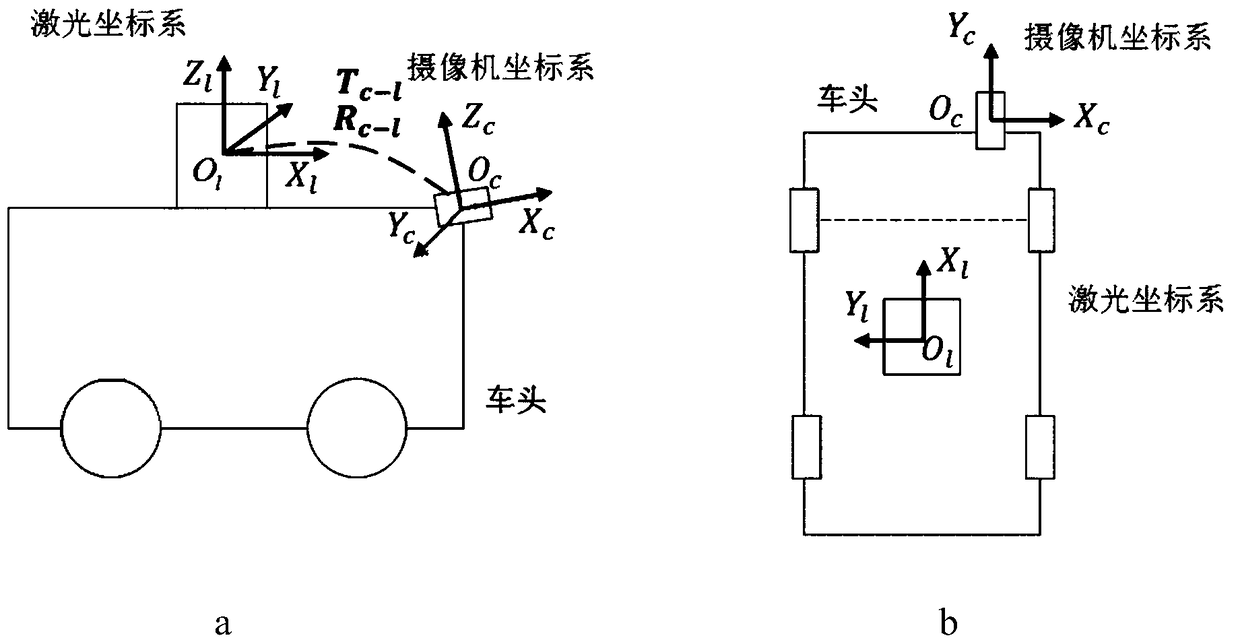
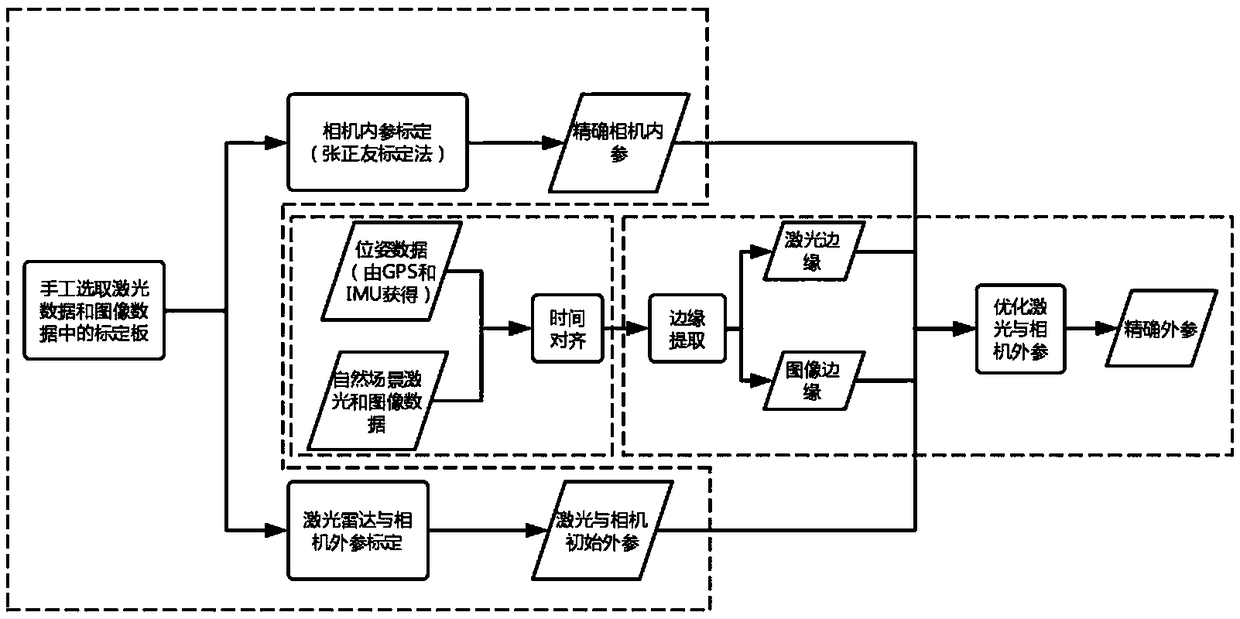
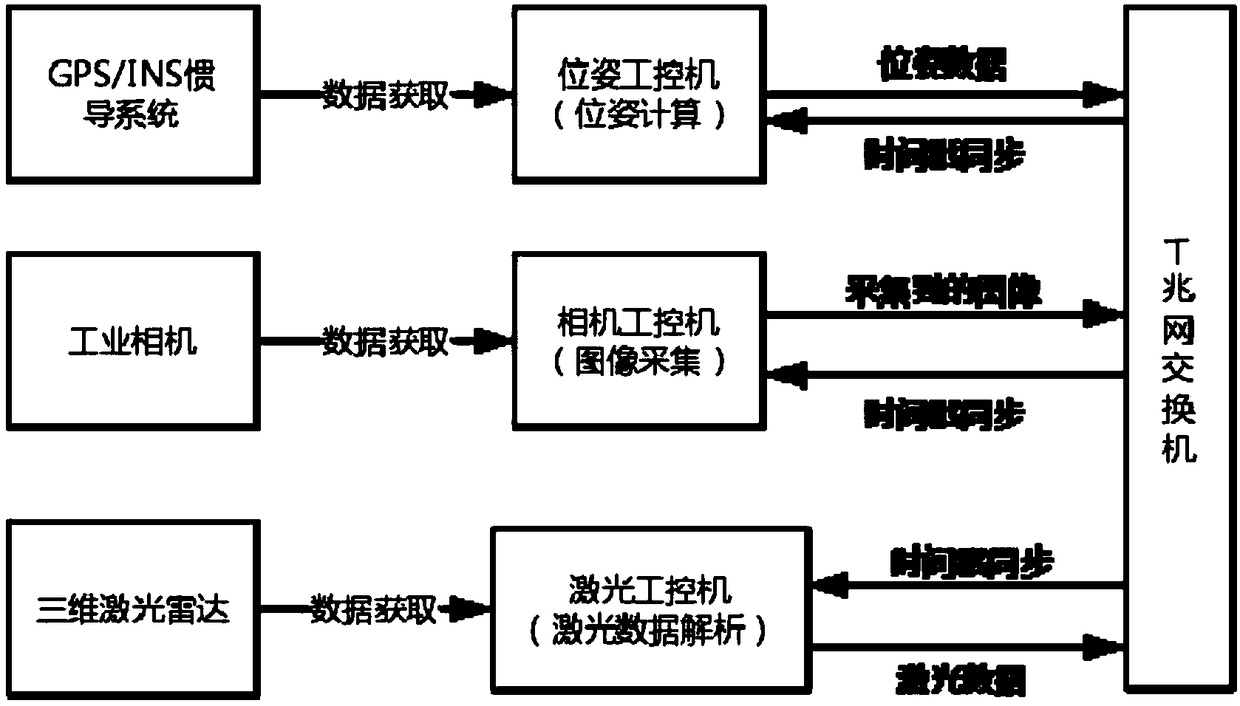
Intelligent vehicle laser sensor and online camera calibration method
ActiveCN109270534AAchieve high-precision calibrationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionLaser dataTime alignment
The invention discloses an intelligent vehicle laser sensor and an online camera calibration method. Laser data and image data are accurately calibrated via the steps of camera calibration, offline calibration of a three-dimensional laser sensor and an image sensor, time alignment of laser data and image data, and online alignment of the laser sensor and the image sensor. The calibration system can be applied to multiple different road conditions and scene, to achieve online high precision calibration of laser and an image. After the laser and the image are calibrated, the information of the two sensors can be used for comprehensively analyzing a barrier and making an accurate decision, so that the method has is significant in sensing technology of an intelligent vehicle. Therefore, the technology can be widely applied to the fields of driverless vehicle visual navigation and intelligent vehicle visual assistance driving.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Device and method for inspecting inside of underground pipe line and method of inspecting concrete on inside of underground pipe line for deterioration
InactiveUS20050115337A1Reliably determinedAccurate measurementHollow article cleaningStructural/machines measurementFisheye lensGyroscope
A device for inspecting the inside of an underground pipe line which makes it possible to search for cavities on the outside of the underground pipe over the entire internal peripheral surface of the underground pipe, that is, not only upward of the underground pipe, but also toward both sides and downward thereof, to obtain detailed images of the inner peripheral surface of the pipe line without using a complex mechanism, and to display patterns of cracks and irregularities on the inner peripheral surface of the underground pipe by three-dimensional convergence images. The device comprises a pipe line internal self-propelled vehicle and an on-ground control unit, and the pipe line internal self-propelled vehicle is provided with a radar antenna, a camera equipped with a fisheye lens, a gyro, a laser sensor, and an infrared encoder.
Owner:BURN AM
Non-contact image measuring system
The invention discloses a non-contact image measuring system, which comprises a worktable, a three-dimensionally movable camera, a laser displacement sensor and a triaxial grating bar and grating data acquisition card, wherein the camera and the laser sensor are connected with a Z-axis guide rail via a connection beam and vertically correspond to the worktable; and a servo motor can drive a slide block to move so as to enable the camera to vertically move up and down. The invention acquires images in the XY plane via the camera for plane survey, the height of each positioning point near the measured pixel is measured via the laser displacement sensor in the Z direction to work out the average value, and the distance of the camera needing to be moved when being focused is determined according to the average value, so the system can simply and quickly detect complex workpieces, increases the measurement efficiency, expands the scope of measurement and meets the measurement requirements on the images.
Owner:CHONGQING JIANSHE IND GRP
Carriage for Automating Welding, Brazing, Cutting and Surface Treatment Processes
InactiveUS20100176106A1Easy to weldEliminate needWelding/cutting auxillary devicesArc welding apparatusLaser sensorEngineering
This invention relates to a welding carriage operable to drive across a surface of a work piece having a joint to be welded. The welding carriage comprises a number of wheels, where each wheel is pivotal around an axle and where each wheel is a magnetic wheel; the welding carriage further comprises means for supporting a welding device wherein at least one of the wheels can be flexed inwardly or outwardly so that the welding carriage can travel over curved surfaces. The welding carriage can travel over magnetizable surfaces having any direction, e.g. orientation in space. The welding carriage can carry a laser sensor arrangement arranged to detect the position as well as the direction of a joint to be welded, so that the welding carriage is applicable for performing fully automated welding.
Owner:FORCE TECH
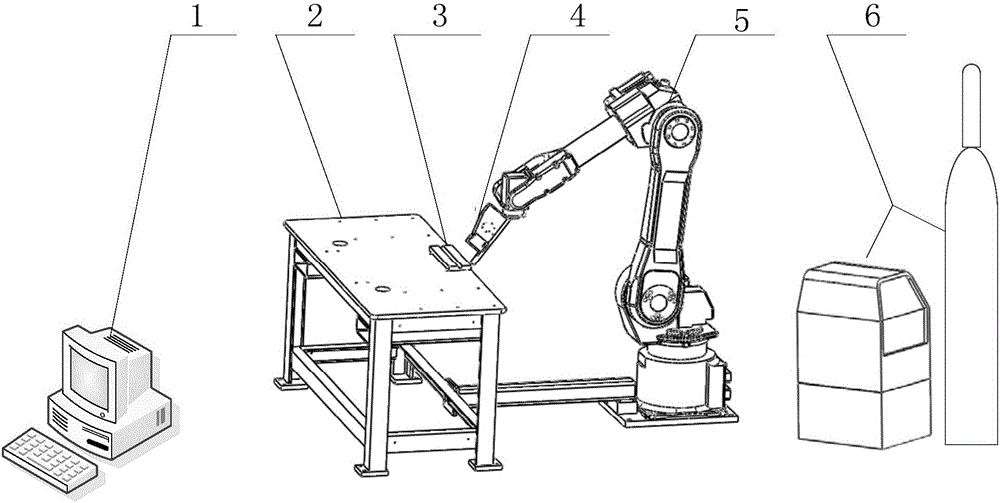
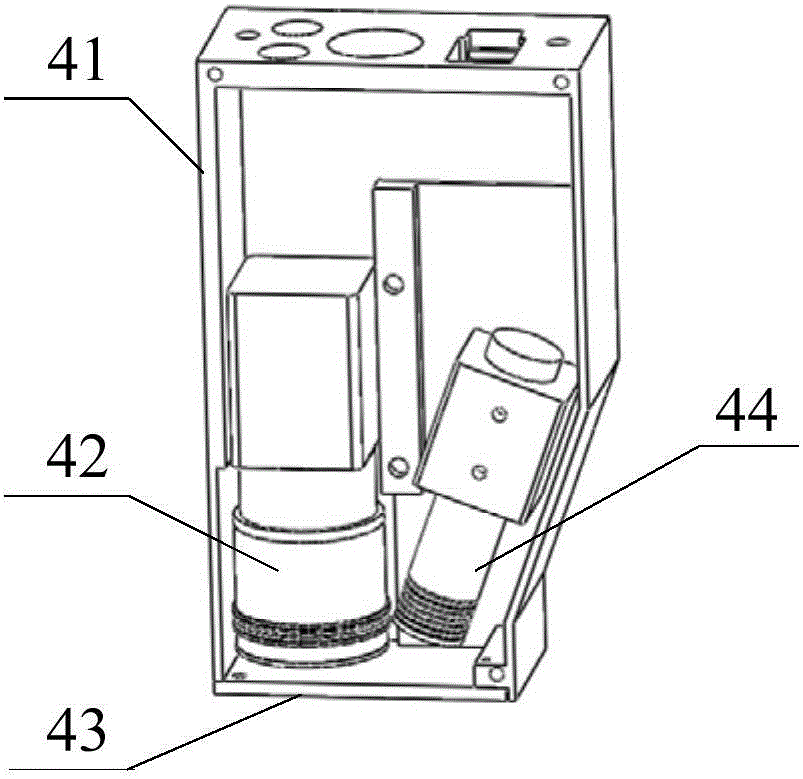
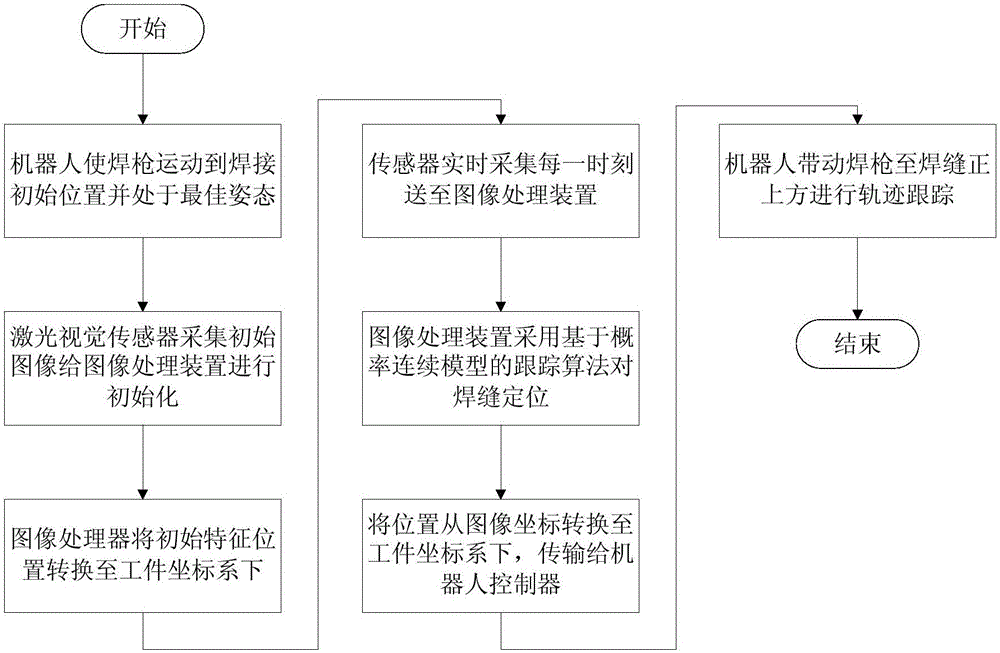
Laser vision guided automatic welding track tracking system and method
InactiveCN106312397ASimple structureImprove data processing efficiencyWelding/cutting auxillary devicesArc welding apparatusImaging processingLight irradiation
The invention discloses a laser vision guided automatic welding track tracking system which comprises an embedded type industrial personal computer with an image processing device, a laser vision sensor, a welding robot, matched welding equipment and a workpiece clamping workbench; the laser vision sensor is installed on a welding gun in an advanced parallel manner in the welding direction through a laser sensor fixing element; the welding gun is installed on a tail end flange disc of the welding robot through a welding gun fixing element; and the embedded type industrial personal computer is connected with the laser vision sensor through a circuit. The invention also discloses a laser vision guided automatic welding track tracking method. With adoption of the laser vision guided automatic welding track tracking system and method, without the process of teaching in advance, the welding production efficiency and the adaptive ability are improved through real-time detection and tracking; and meanwhile, the problem of tracking lag caused by advanced detection is prevented, and the problem that when a sensor is too near the welding gun, large noise of coupling feature images is caused by factors including strong arc light irradiation, high temperature and smoke dusts, thus the real time and the tracking accuracy of the system are restricted is solved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Methods and systems for integrating fluid dispensing technology with stereolithography
InactiveUS20060225834A1Increased micro-fabricationEfficient and effectiveAdhesive processesMechanical working/deformationMulti materialLaser sensor
An integrated system and method of integrating fluid dispensing technologies (e.g., direct-write (DW)) with rapid prototyping (RP) technologies (e.g., stereolithography (SL)) without part registration comprising: an SL apparatus and a fluid dispensing apparatus further comprising a translation mechanism adapted to translate the fluid dispensing apparatus along the Z-, Y- and Z-axes. The fluid dispensing apparatus comprises: a pressurized fluid container; a valve mechanism adapted to control the flow of fluid from the pressurized fluid container; and a dispensing nozzle adapted to deposit the fluid in a desired location. To aid in calibration, the integrated system includes a laser sensor and a mechanical switch. The method further comprises building a second part layer on top of the fluid deposits and optionally accommodating multi-layered circuitry by incorporating a connector trace. Thus, the present invention is capable of efficiently building single and multi-material SL fabricated parts embedded with complex three-dimensional circuitry using DW.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC +1
Measuring method for amount of grain reserve in grain depot
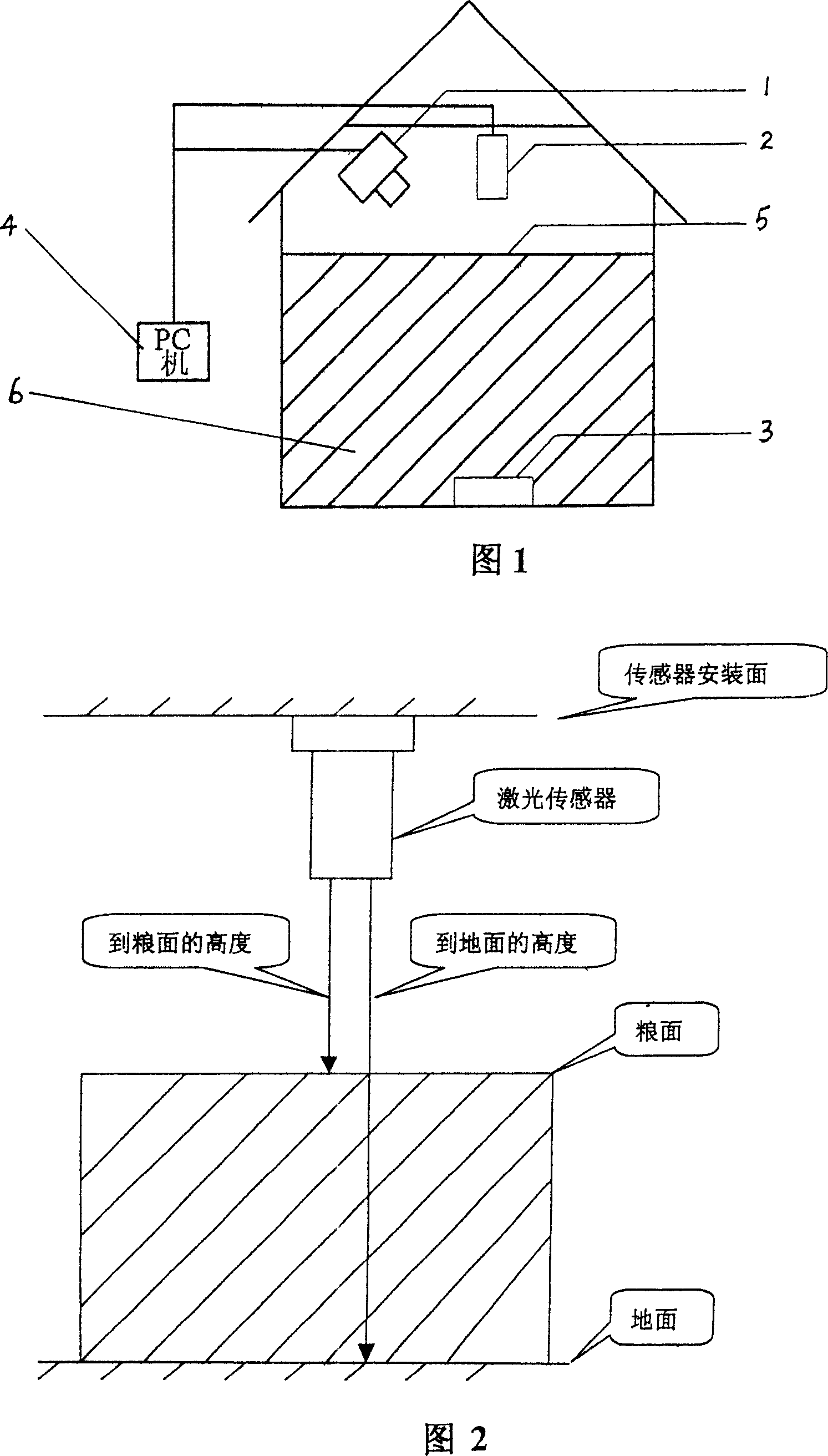
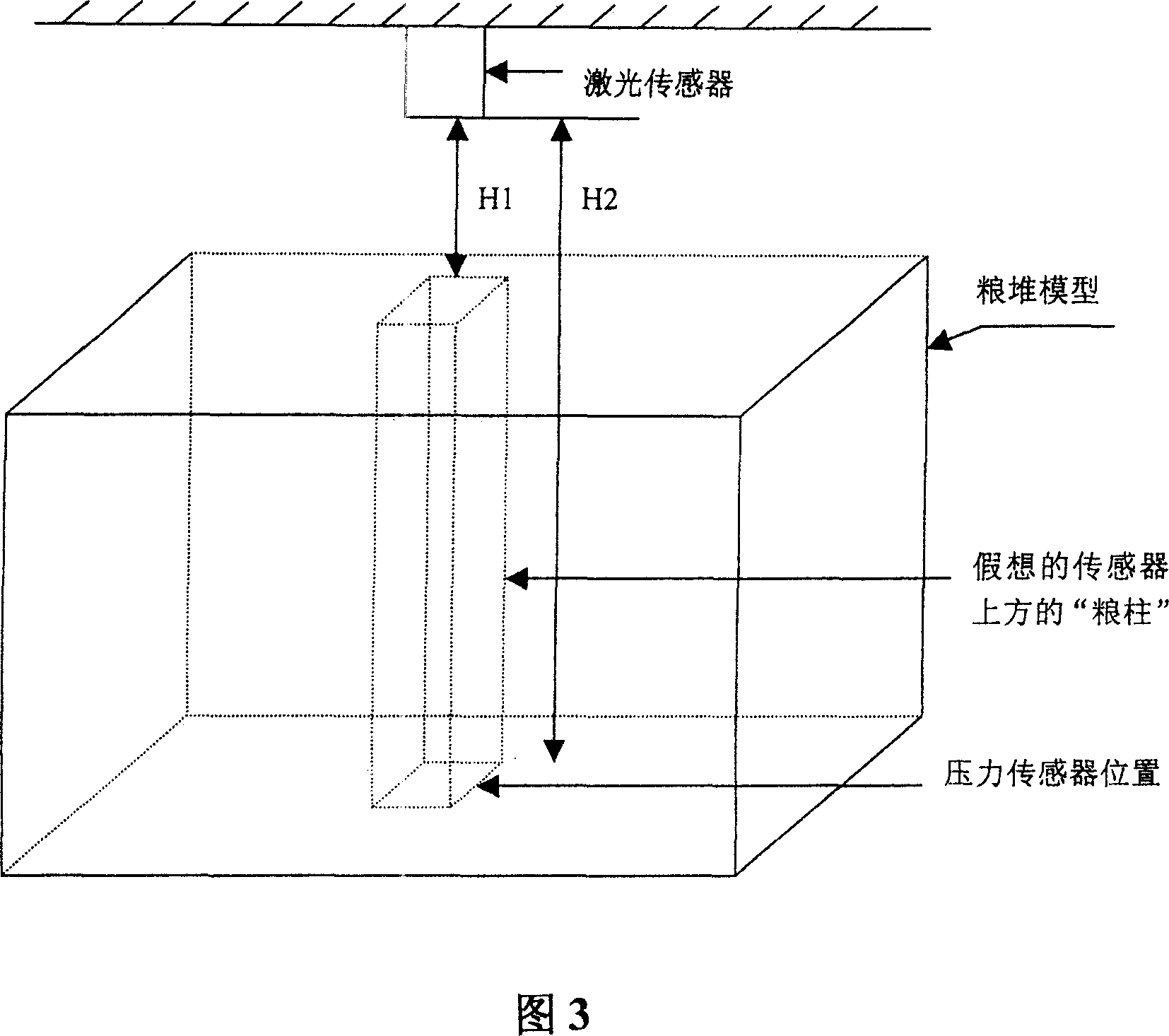
InactiveCN1963377AThe measurements are trueAccurate measurementElectric signal transmission systemsVolume measurement apparatus/methodsVolume measurementsStorage management
This invention relates to one food storage volume measurement method, which comprises the following steps: using laser sensor to measure its volume and starting cameral head for shot stored into PC database; correcting according to the volume by laser sensor; measuring food storage intensity by use of pressure sensor to weight sensor above column weight and measuring sensor food column height through laser sensor; computing food column intensity according to the weight, height and pressure area; computing food storage total weight according to the intensity and volume.
Owner:朱阳明
System and method for aligning sensors on a vehicle
A vehicle sensor system consisting of video, radar, ultrasonic or laser sensors, oriented to obtain a 360 degree view around the vehicle for the purpose of developing a situation or scene awareness. The sensors may or may not have overlapping field of views, or support the same applications, but data will be shared by all. Orientation of the sensor to the vehicle body coordinates is critical in order to accurately assess threat and respond. This system describes methods based on measuring force and rotation on each sensor and computing a dynamic alignment to first each other, then second to the vehicle.
Owner:AUTOBRILLIANCE LLC +1
Mobile robot indoor route planning method based on array map
Provided is a mobile robot indoor route planning method based on an array map. A map expression method involves a geographic map, a point cloud map, a topological map, a grid map and the like. The grid map divides the environment into a series of grids, wherein a probable value is given to each grid to express the occupation probability of the grid. On the basis of the concept of the grid map, the special situation of the grid map is used, an appropriate change is made in the map establishing process, and the concept of the array map is put forward. On the basis of the array map, route planning is conducted through an A* algorithm; meanwhile, in the robot moving process, real-time data is obtained according to a carried laser sensor, and the array map is dynamically upgraded.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com